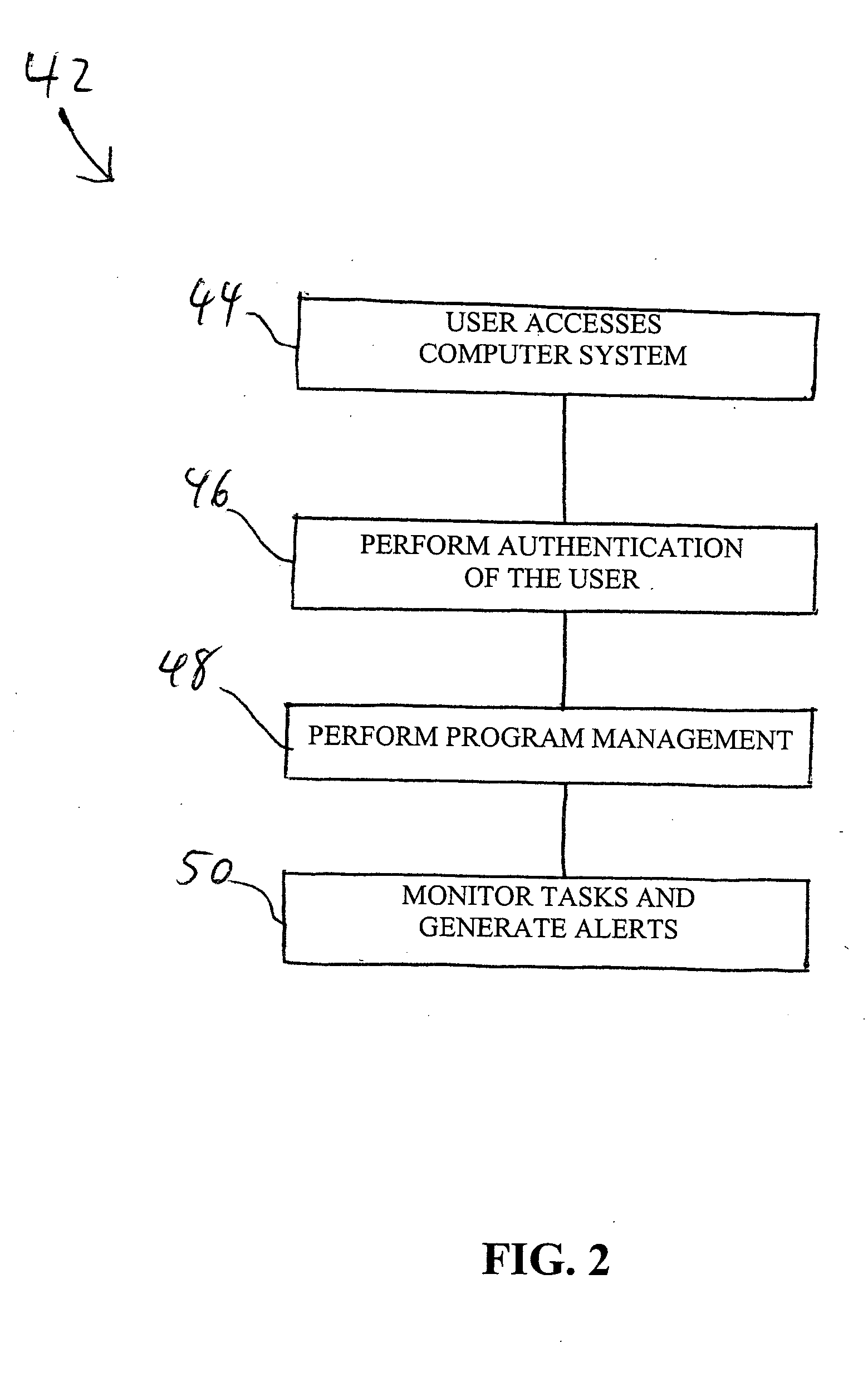
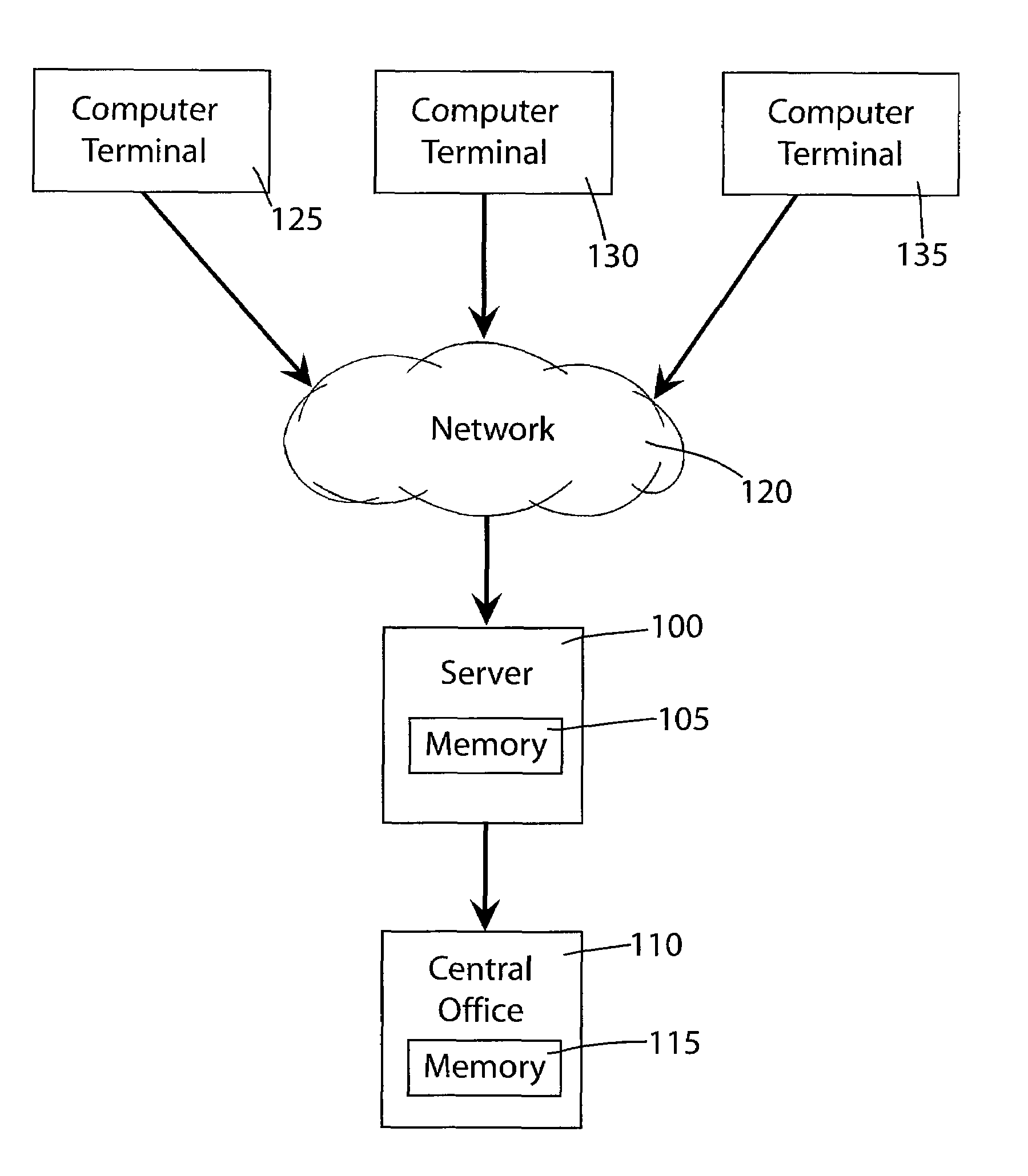
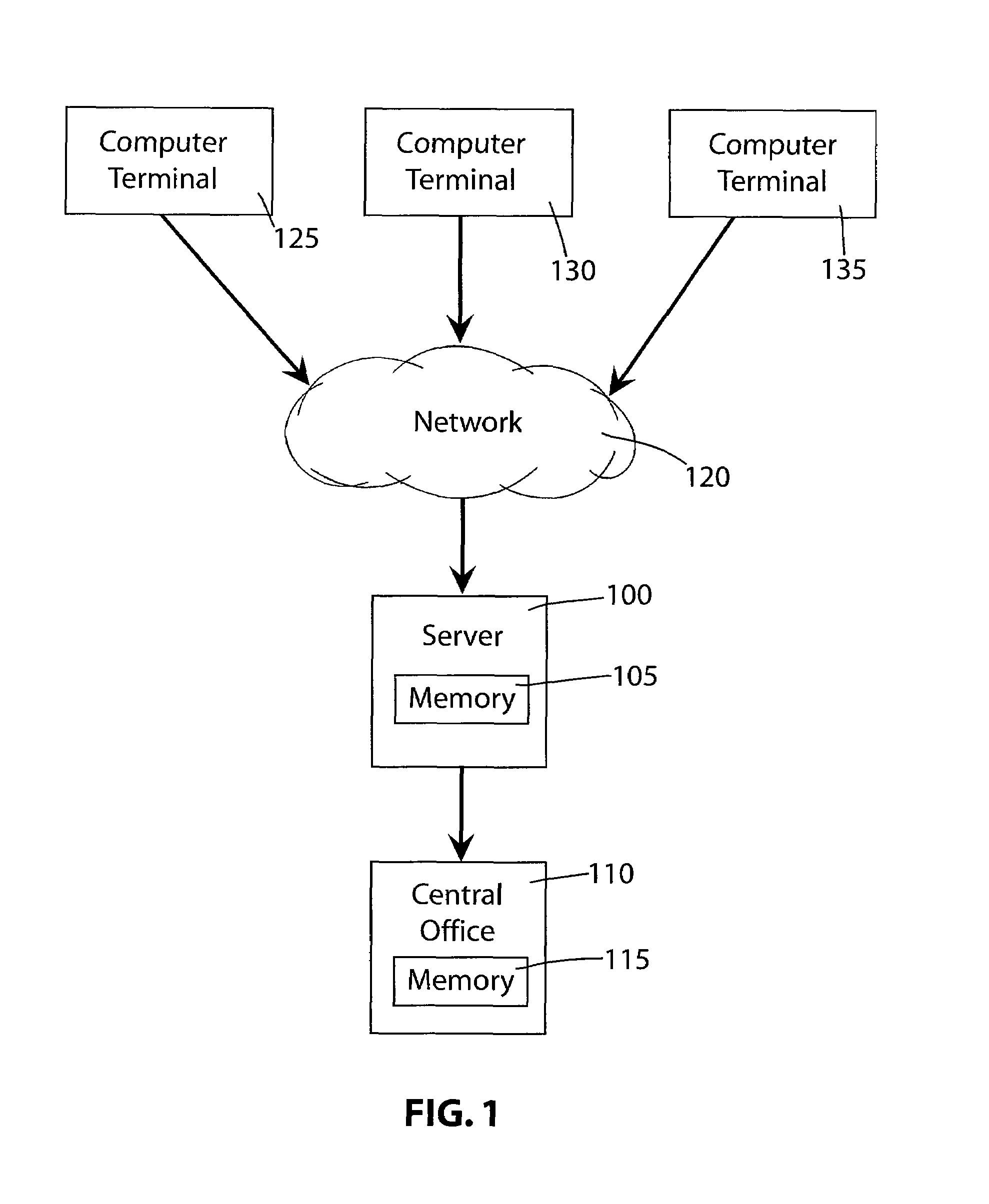
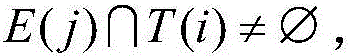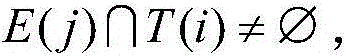Patents
Literature
327 results about "Volunteer activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Volunteering is generally considered an altruistic activity where an individual or group provides services for no financial or social gain "to benefit another person, group or organization". Volunteering is also renowned for skill development and is often intended to promote goodness or to improve human quality of life.
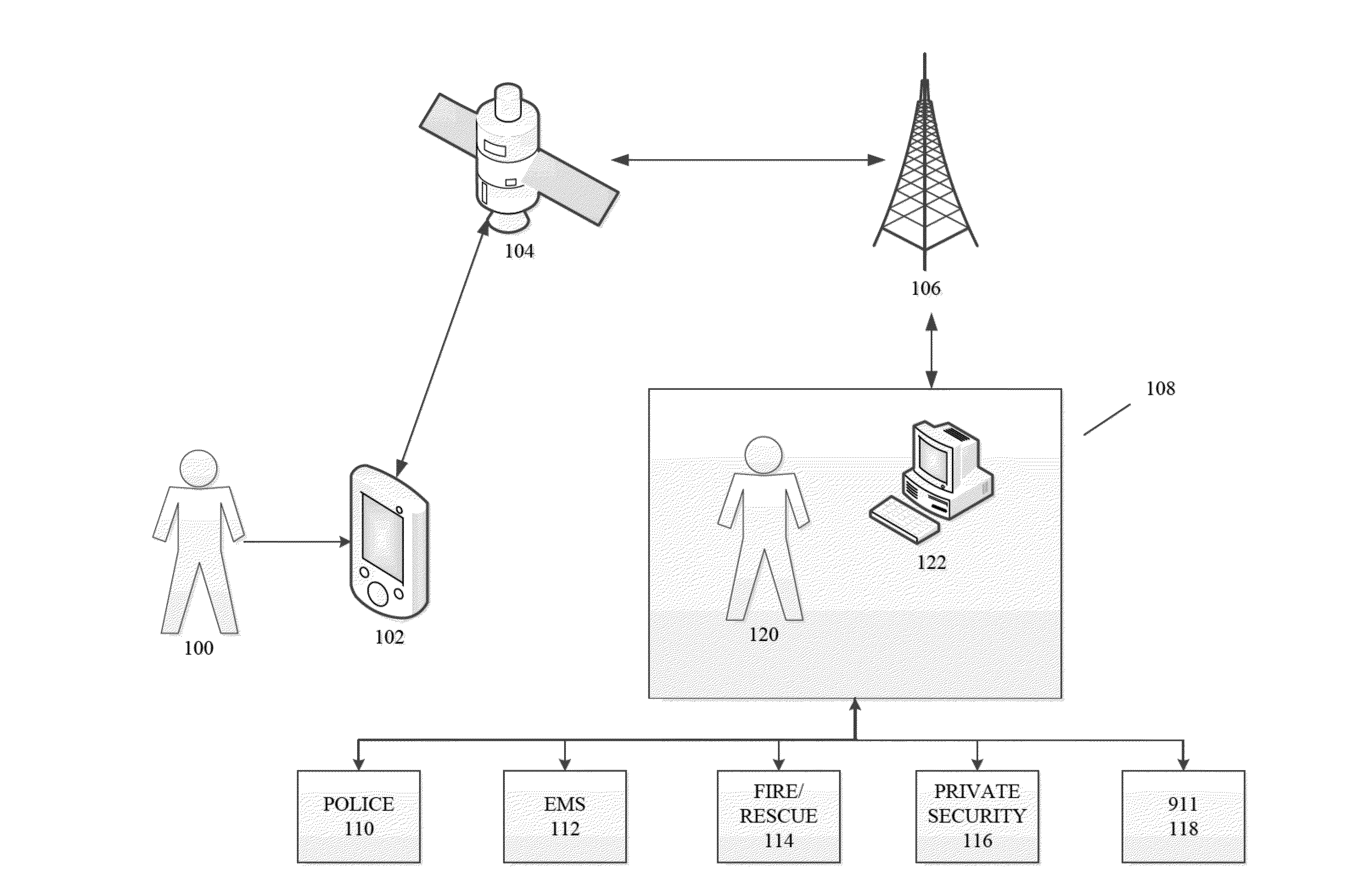
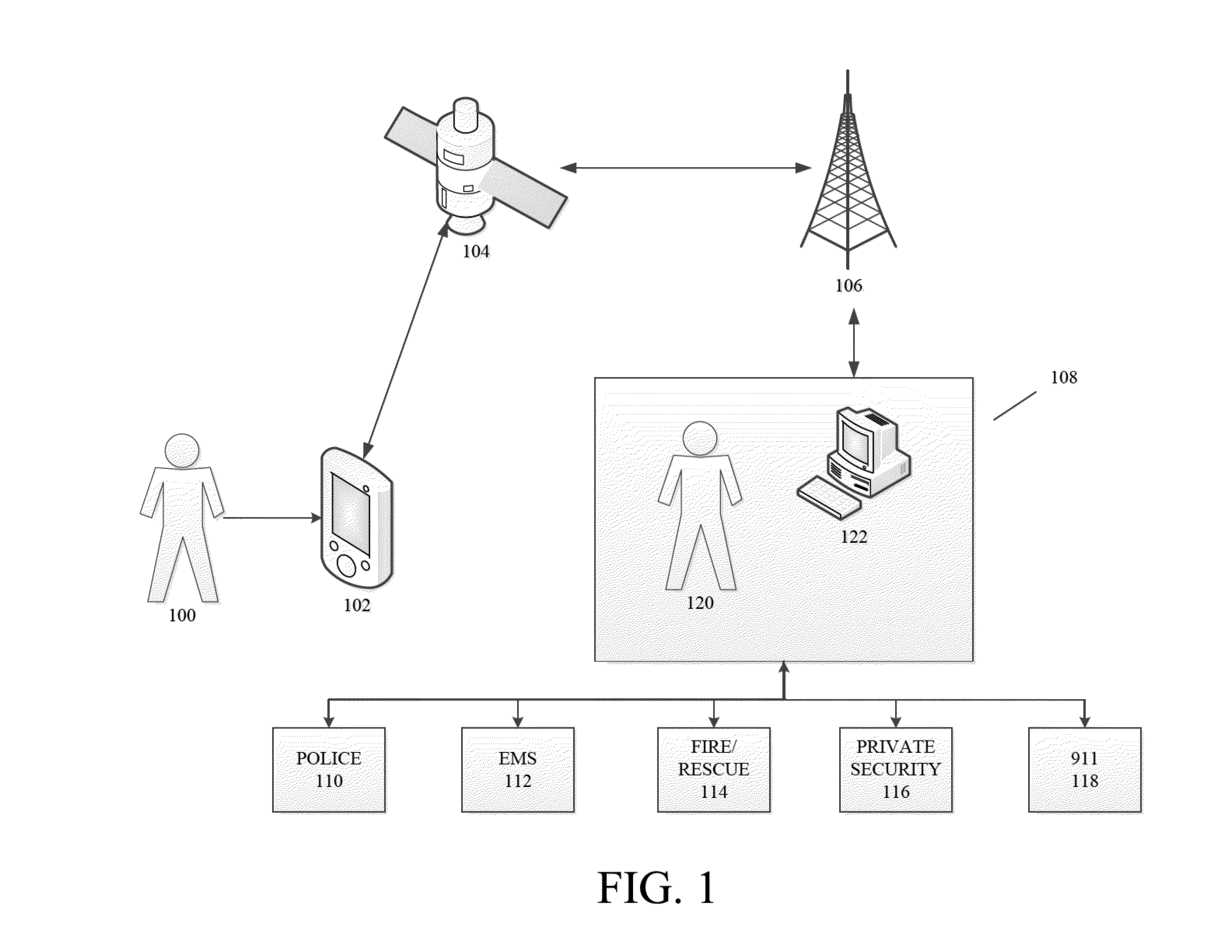
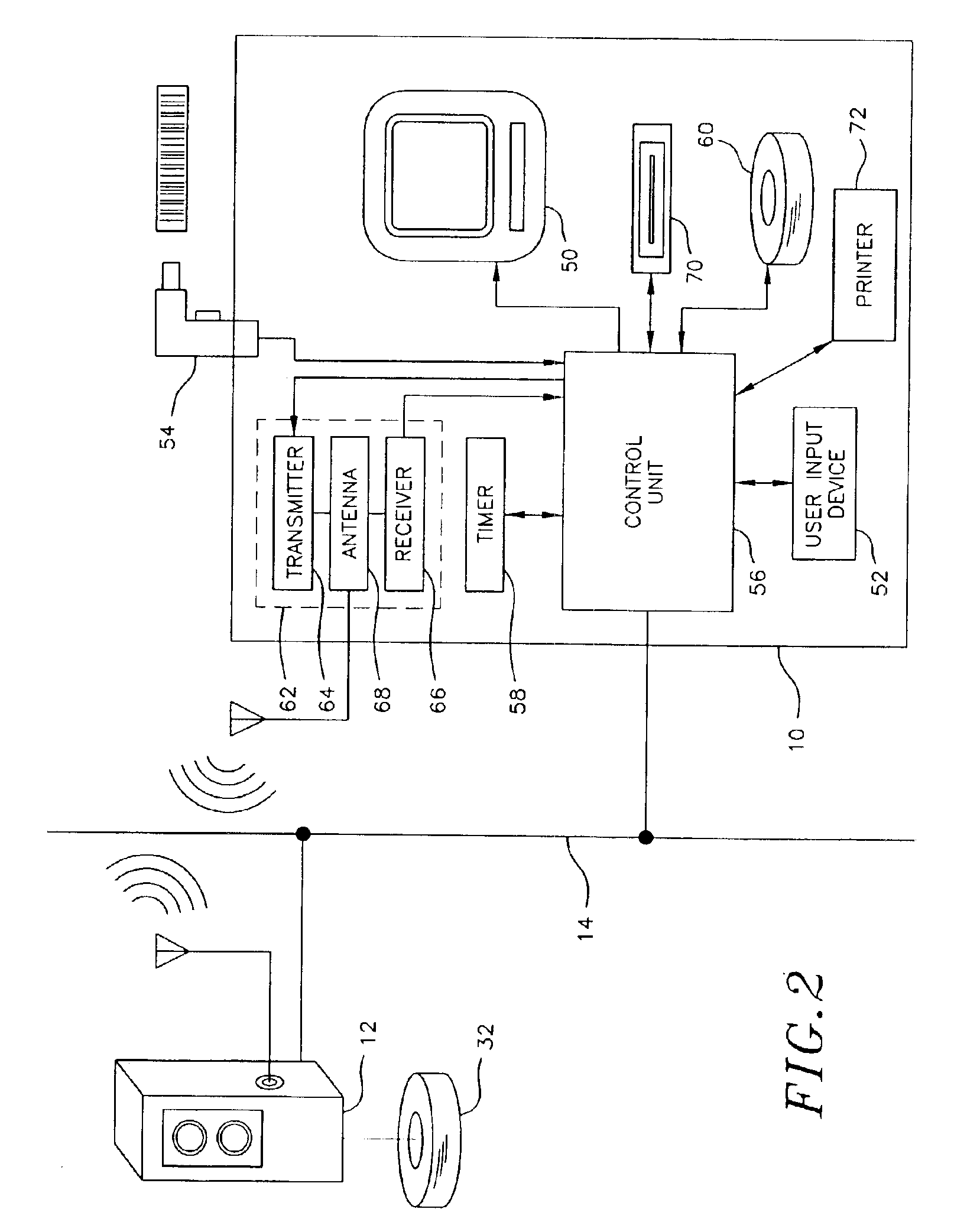
Methods and systems for requesting the aid of security volunteers using a security network
InactiveUS20140118140A1Reduce morbidityMaintain awarenessAlarmsElectric signalling detailsDividing attentionMobile device
The disclosure generally relates to providing a network of security volunteers who can opt-in to provide security services and / or a physical presence to deter, distract, delay, or prevent a potentially threatening situation. Security volunteers can receive alerts from a central monitoring center regarding nearby distress signals sent from a victim's device, and can then proceed to the location of the victim. Security volunteers can view their location and the location of the victim on a map on their mobile devices, as well as communicate with a victim's device, the central monitoring center, and other security volunteers who are responding to the scene.
Owner:AMIS DAVID
Self-scanning system with enhanced features
A self-scanning system including a mobile personal shopping terminal having enhanced features. A bar code scanner coupled to the terminal is disabled for a period of time after a scanning activity to prevent the inadvertent scanning of the same item two or multiple times. The time period varies based on the user's profile information. When a single item is nonetheless scanned two or more times, the terminal notifies the user of this fact. Usage of the terminal is also monitored to detect a user that has trouble finding an item within the retail facility. A store clerk may approach such a user and volunteer assistance. Furthermore, kiosk functions are incorporated into the terminal for providing the user information and business opportunities with the retail store. For example, the retail store may allow the user to purchase an audio piece that is being broadcast at the store using the terminal. The terminal may also be used to purchase recycled / used items that are placed for sale by individuals through the retail store.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
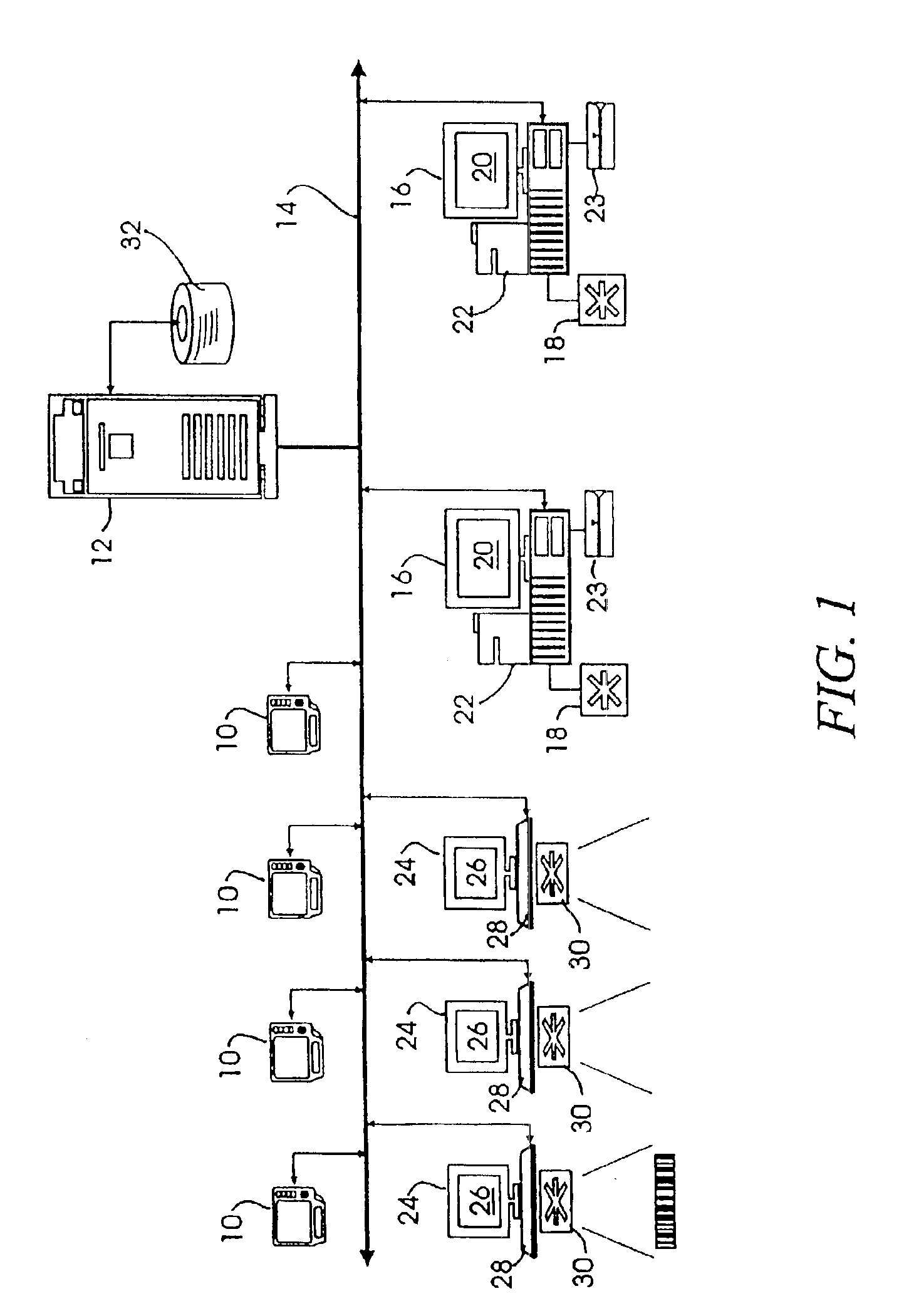
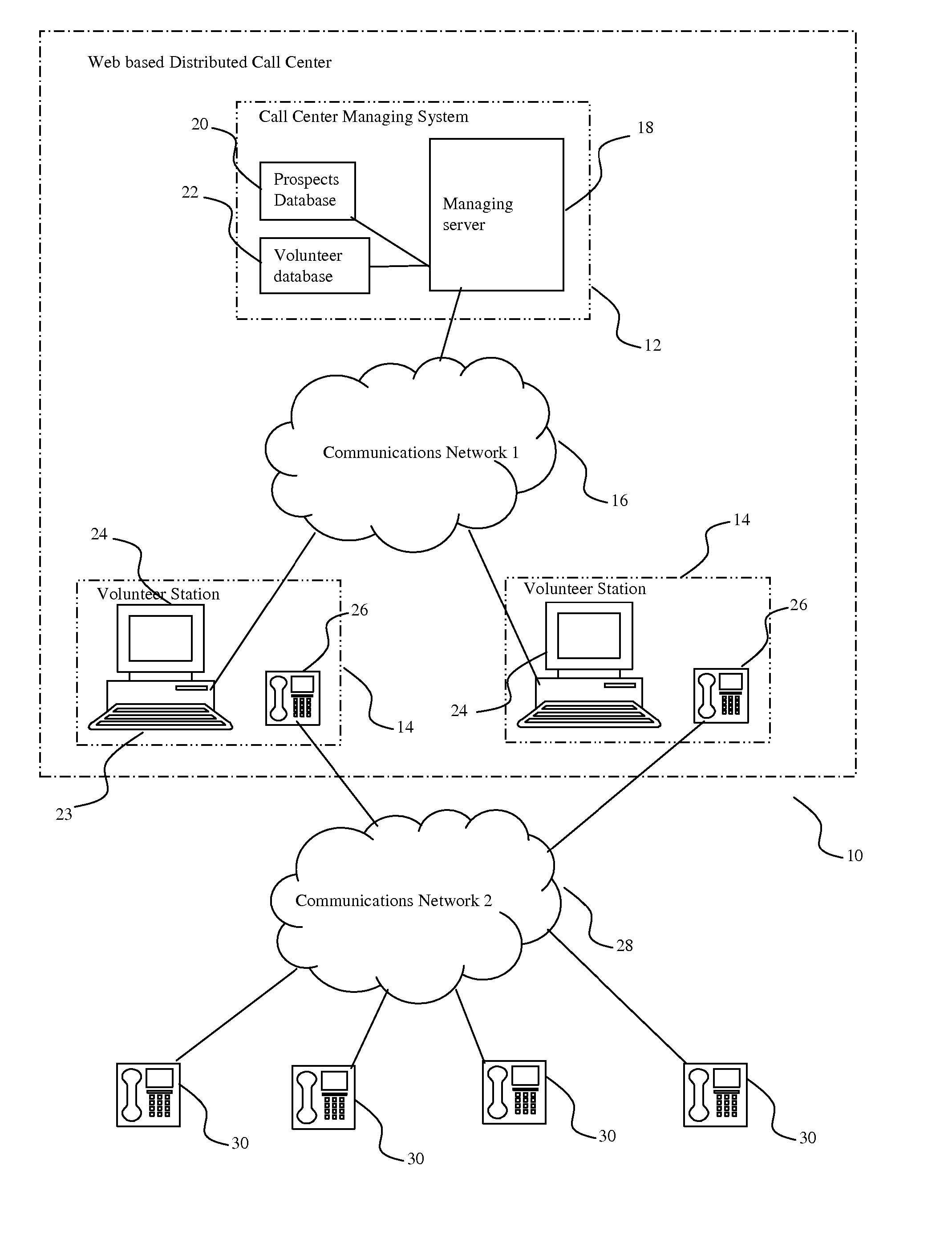
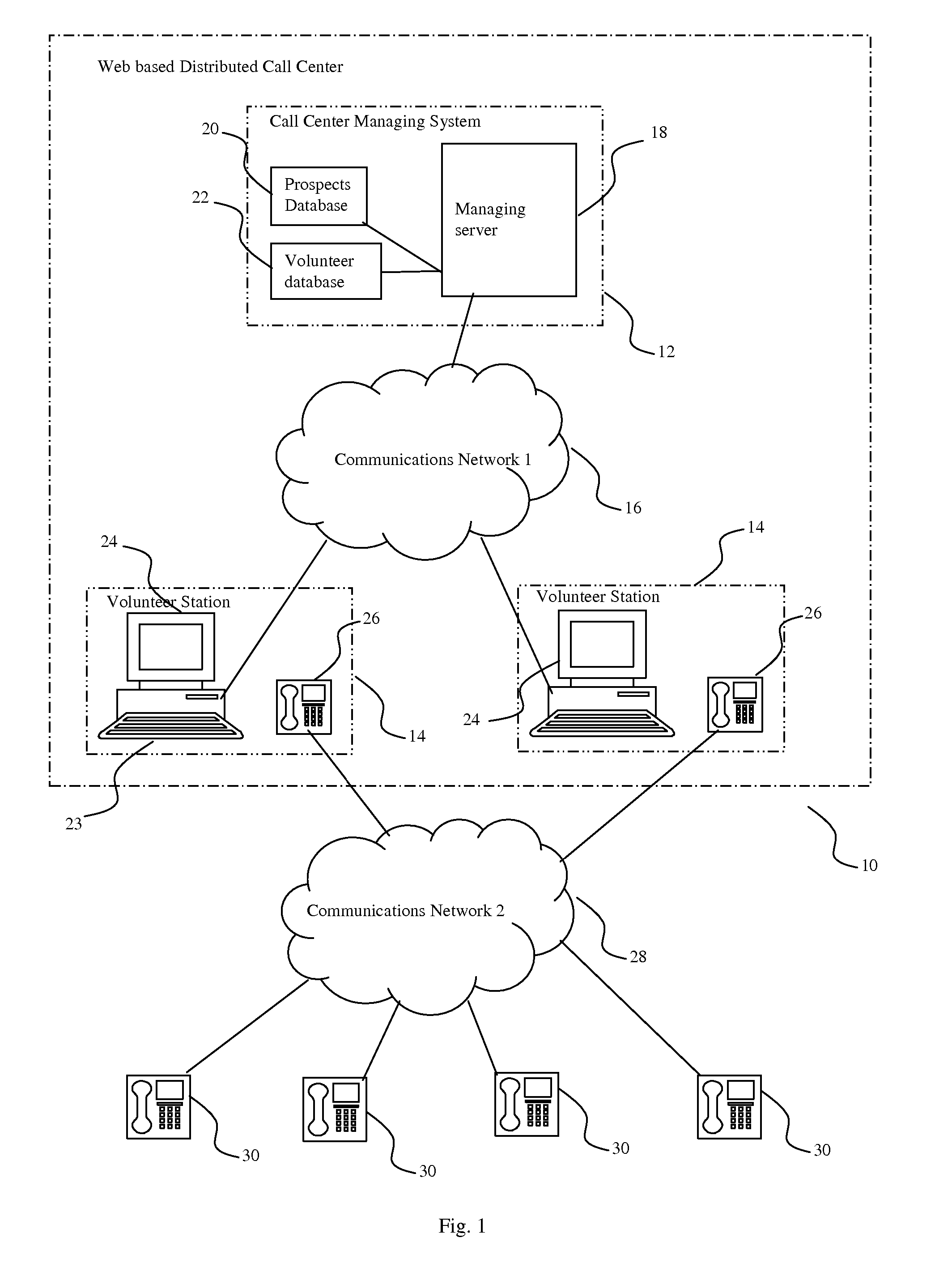
Distributed call center system and method for volunteer mobilization
InactiveUS20070274506A1Facilitate effective telephone calling campaignInterconnection arrangementsManual exchangesCommunications systemWeb browser
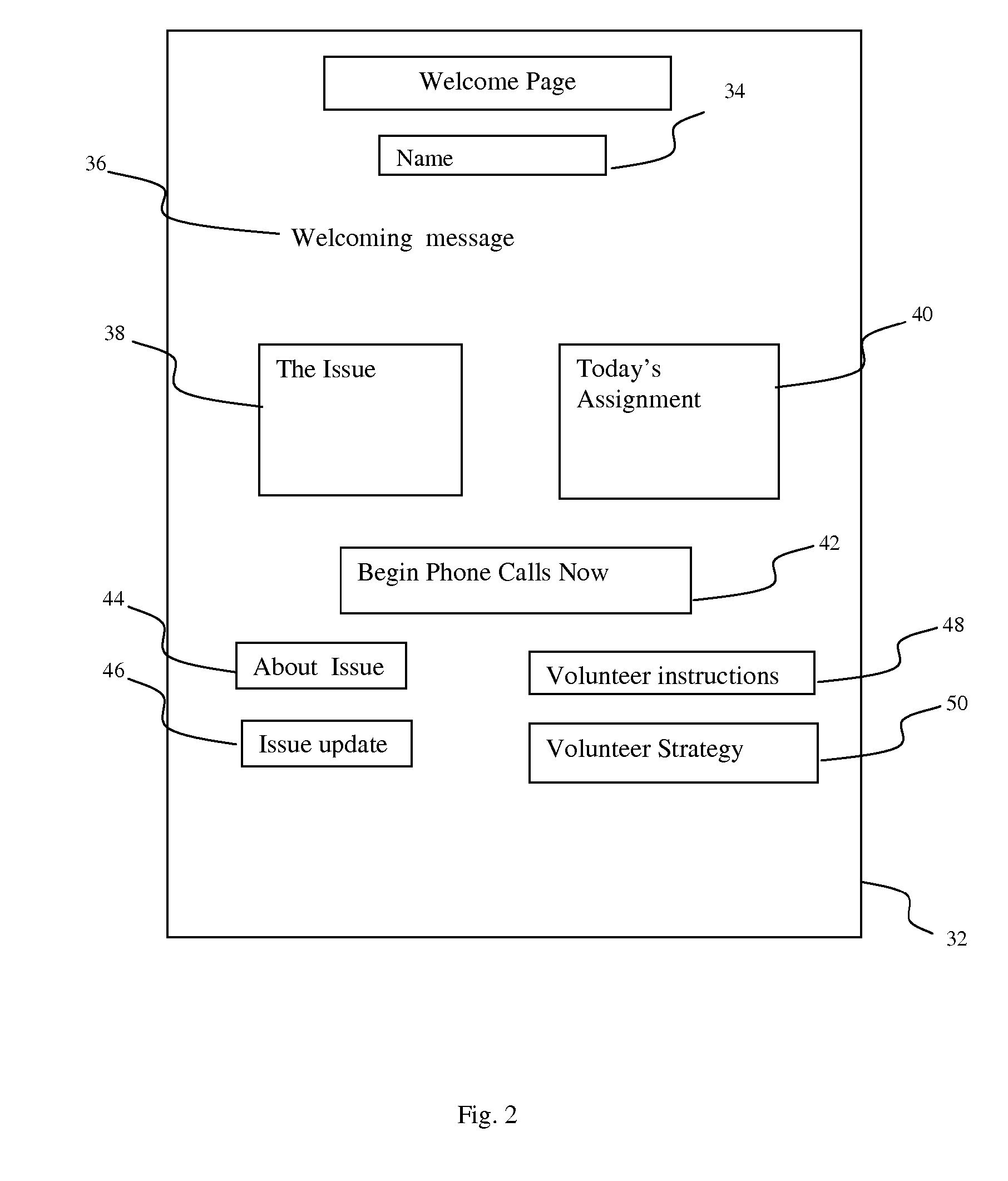
A system and method to facilitate effective telephone calling campaigns that may be conducted by geographically dispersed individuals using inexpensive communications systems, such as the Internet and a basic telephone service. The system manages lists of pre-qualified prospects divided up among a group of volunteers, including providing the volunteers with prepared scripts via web-browsers, customized to both the volunteer and the prospect and designed to solicit further information and support from the prospects. The system also processes prospect responses and oversees appropriate follow-up actions such as sending pre-prepared e-mail or direct mail packages. The system also manages and serves information and links backgrounding campaign issues, strategies and tactics and providing volunteers with technical and motivational assistance. The system of this invention is also capable of monitoring volunteer productivity and effectiveness.
Owner:PEOPLE POWER OF AMERICA
Method and apparatus for reporting road conditions
InactiveUS20070078570A1Road vehicles traffic controlDigital data processing detailsEngineeringBiological activation
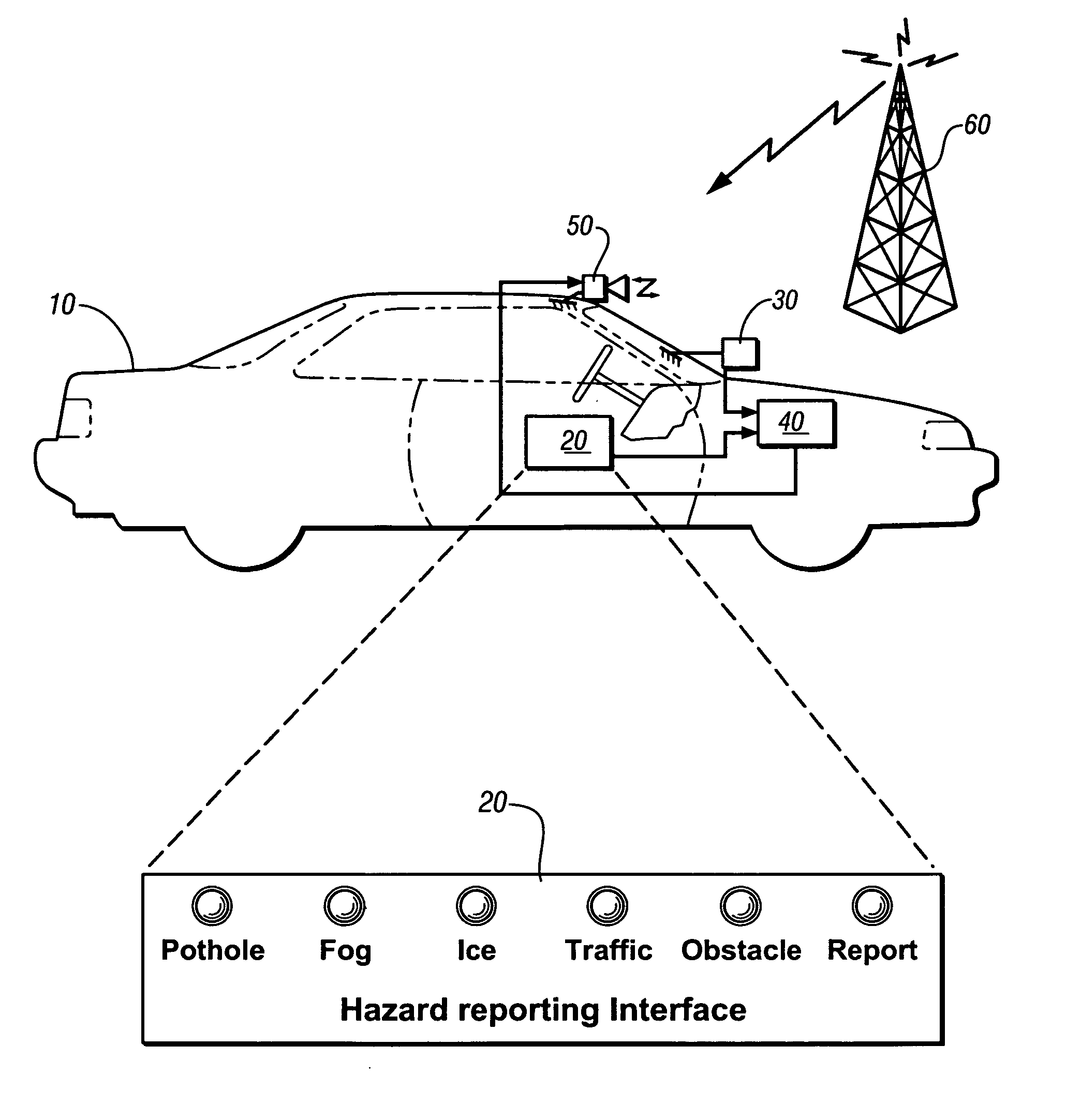
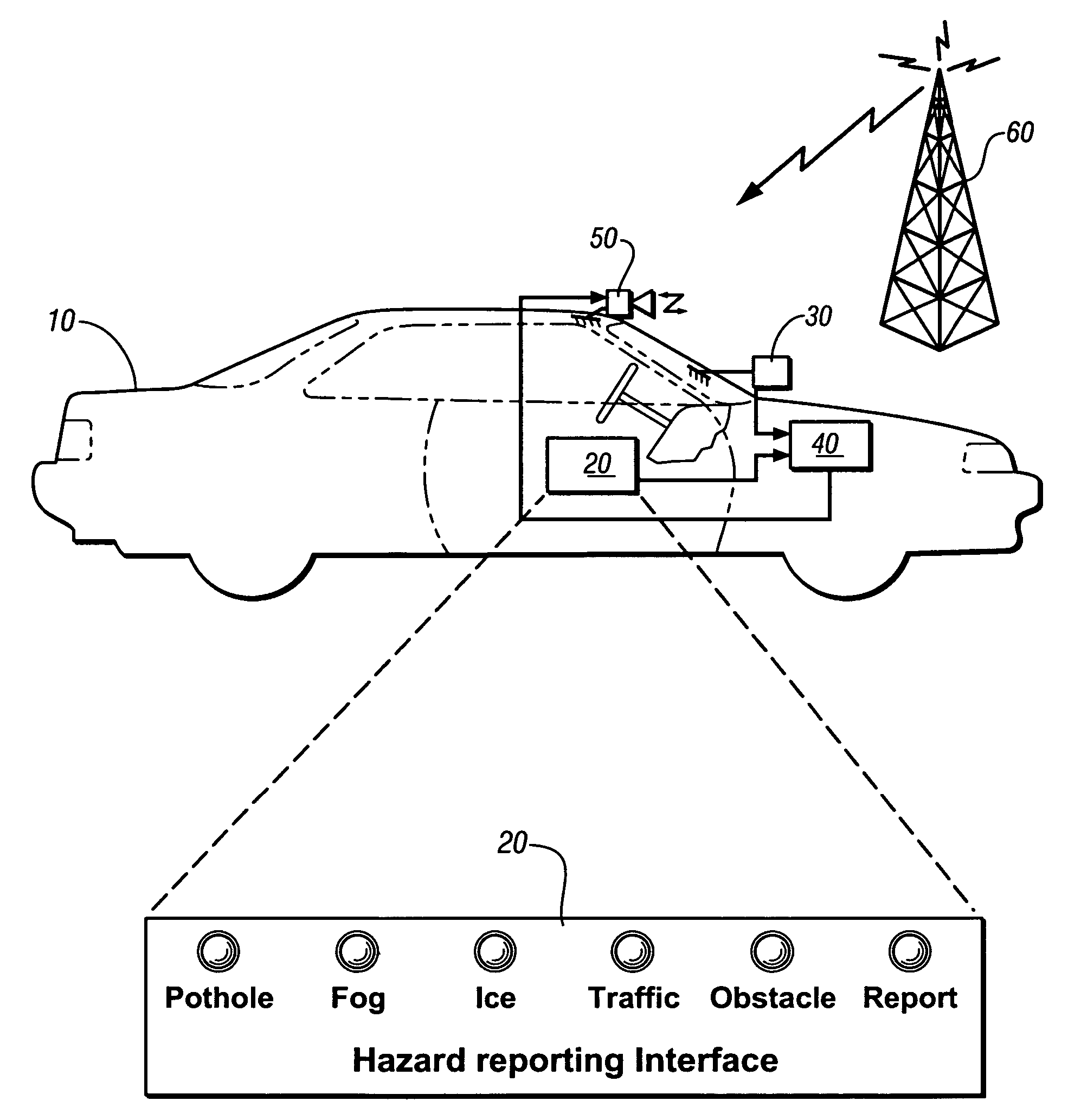
An on-vehicle system for identifying and reporting external conditions is presented. The system has an operator-selectable user interface to identify occurrence of an external condition, a global positioning system receiver; and, a wireless communications system. The unit may be used to assist in discovering localized roadway conditions that adversely affect safety and travel. The unit is placeable into a vehicle of a volunteer, is manually operated whenever a hazard is detected. Reportable hazards include potholes, obstacles or debris in the highway, snow or ice patches, fog, unusual traffic or pedestrian activity, and localized incidences, such as presence of disabled or emergency vehicles. Nature of the hazard is indicatable by manual activation of additional push buttons or other suitable devices. A GPS receiver is incorporated to estimate position, speed, and heading of the hazard. The information is encoded as a message sent to a central server.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Emergency notification system using presence, triangulation, and wireless telephony
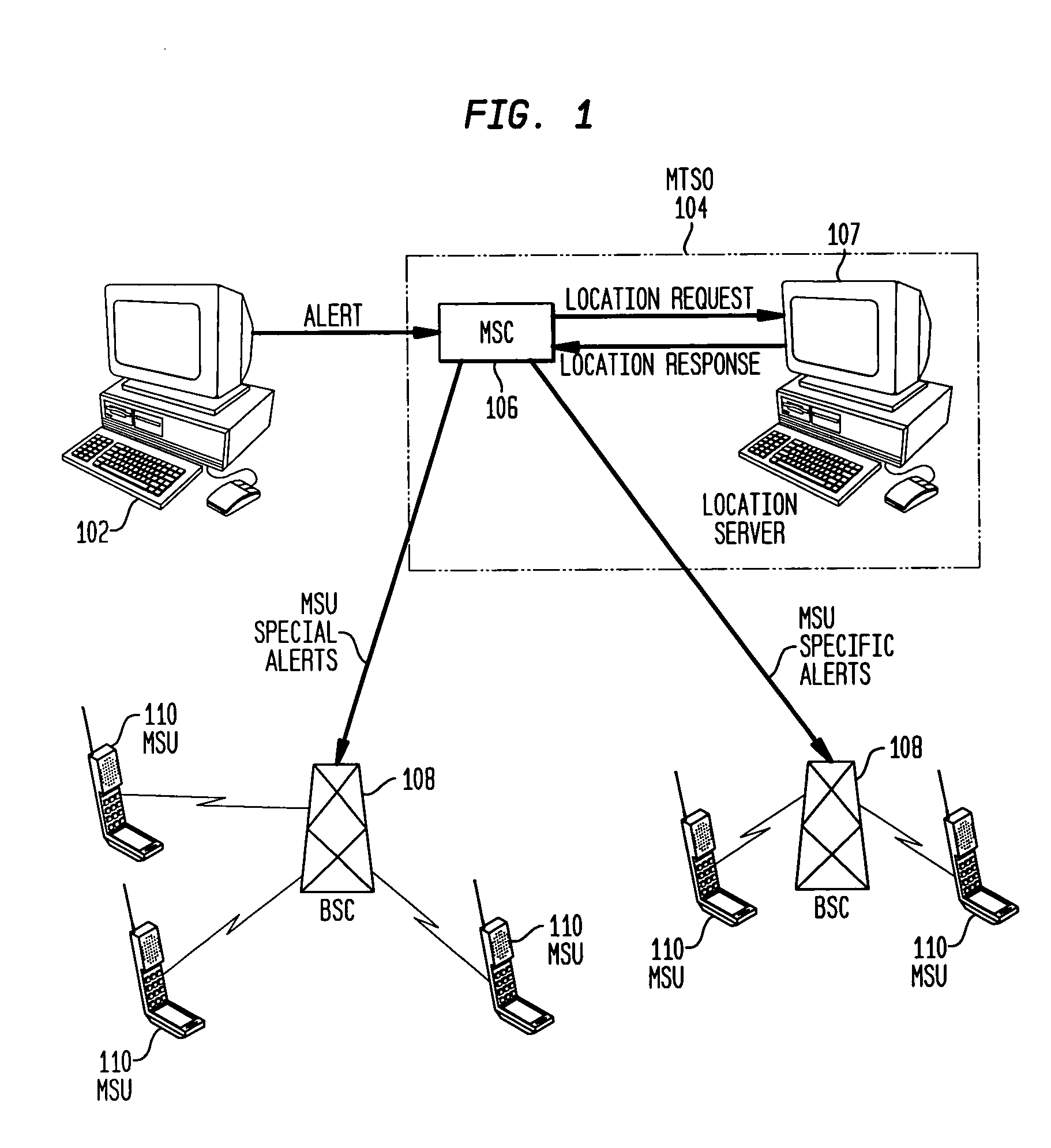
A system and method for providing alert messages to users of Mobile Subscriber Units whereby only such users who are located in the local geographical area effected by the alert receive the messages. The invention further permits limiting transmission of such alerts to only appropriate categories of message content (e.g. weather only) and classification of recipients (e.g., volunteer firemen).
Owner:AVAYA INC
Methods and reagents to detect and characterize norwalk and related viruses
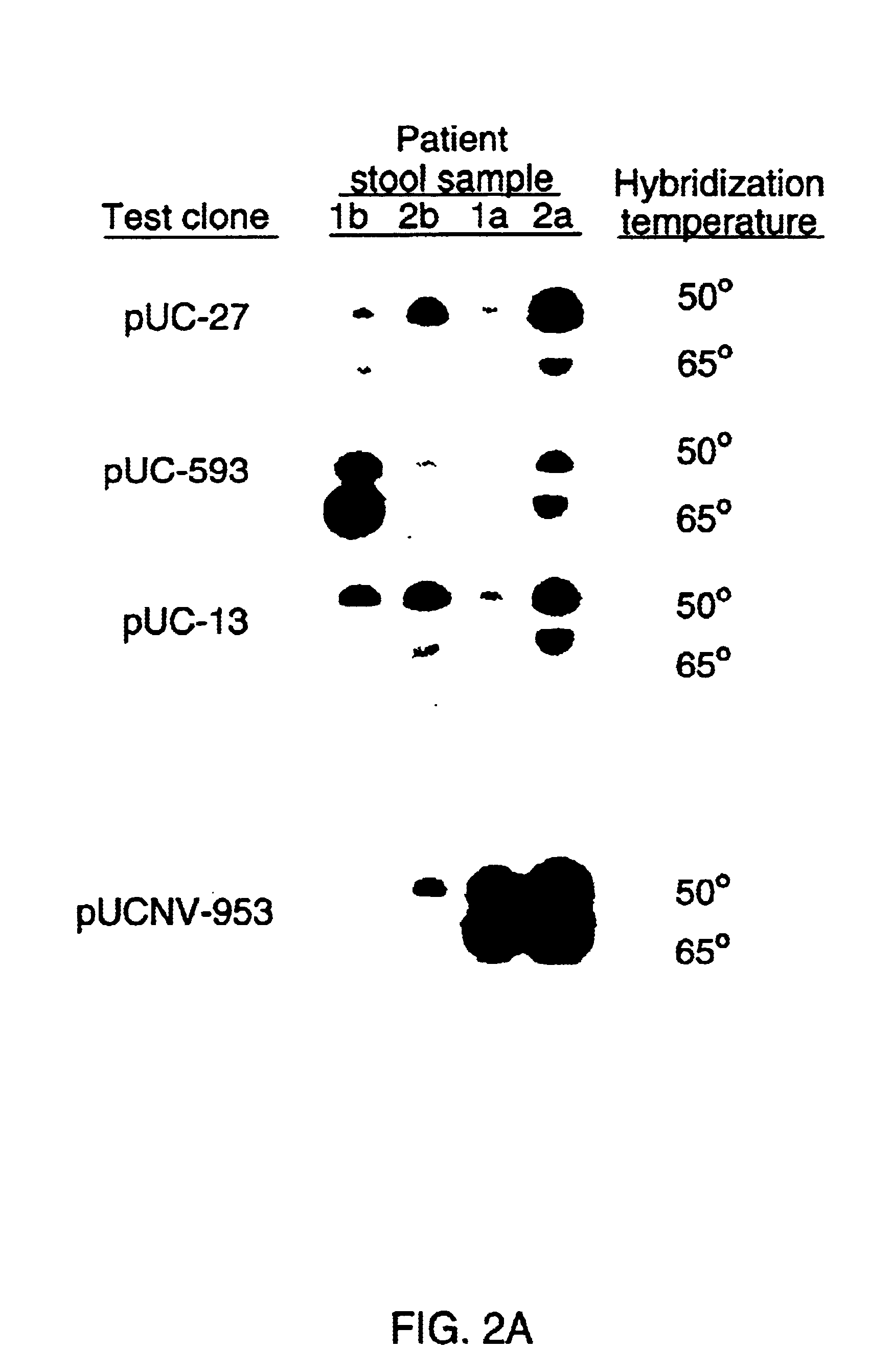
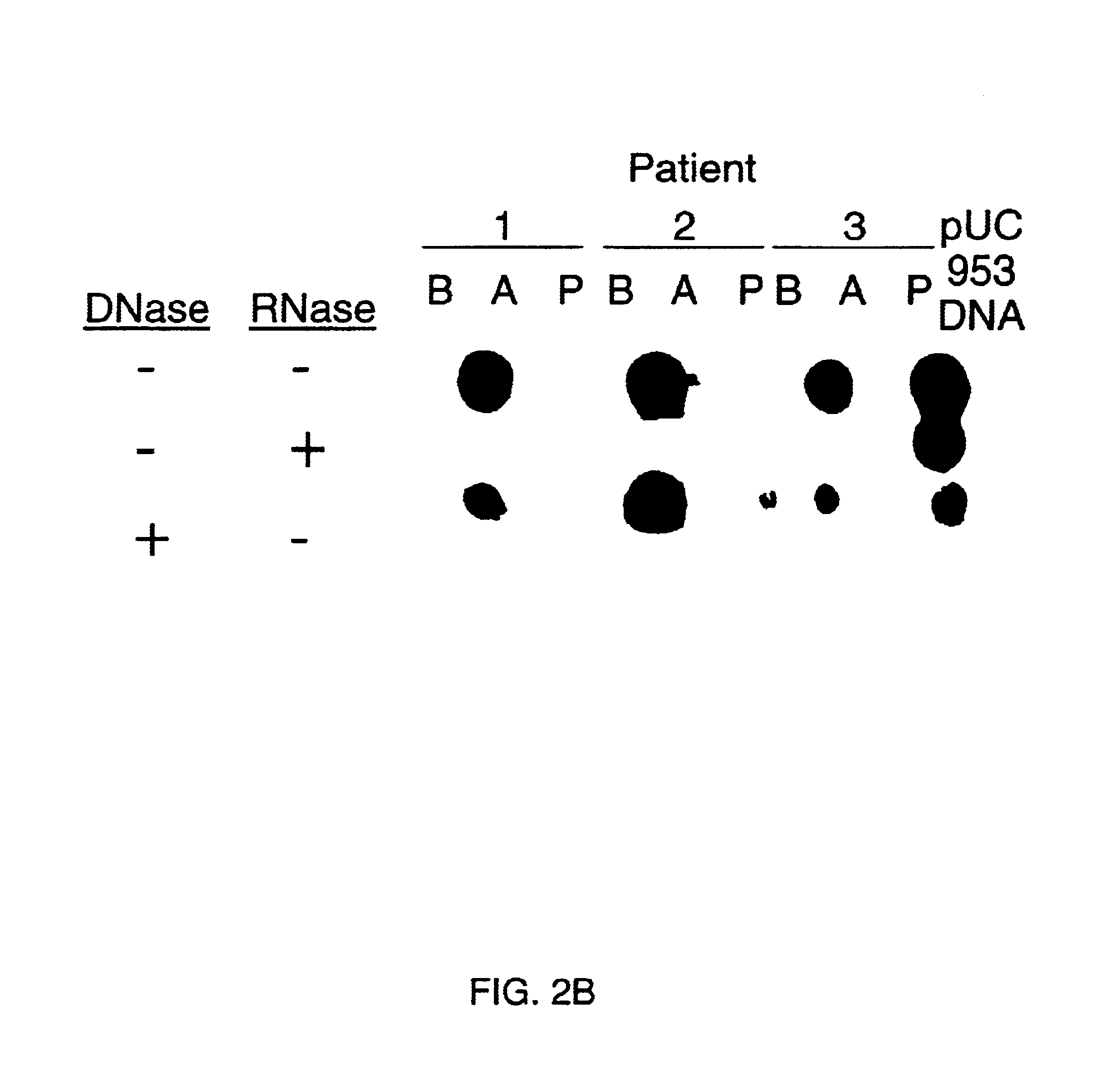
Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from nucleic acid extracted from Norwalk virus purified from stool specimens of volunteers. One clone was isolated from a cDNA library constructed in a pUC-13 vector after amplification of the cDNA. The specificity of this cDNA (pUCNV-953) was shown by hybridization assays. The cDNA reacted with post (but not pre-) infection stool samples from Norwalk volunteers and with highly purified Norwalk virus, but not with other common enteric viruses such as hepatitis A virus and rotavirus. Finally, the probe detected virus in the same fractions of CsCl gradients in which viral antigen was detected using a specific Norwalk virus radioimmunoassay, and particles were detected by immune electron microscopy. Single-stranded RNA probes derived from the DNA clone after subcloning into an in vitro transcription vector were also used to show that the Norwalk virus contains a ssRNA genome of about 8 kb in size. The original clone was also used to detect additional cDNAs which represent at least 7 kb of nucleic acid of the Norwalk genome. The availability of a Norwalk-specific cDNA and the first partial genome sequence information allow rapid cloning of the entire genome and of establishment of sensitive diagnostic assays. Such assays can be based on detection of Norwalk virus nucleic acid or Norwalk viral antigen using polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to proteins expressed from the cDNA or to synthetic peptides made based on the knowledge of the genome sequence. Assays using proteins deduced from the Norwlk virus genome and produced in expression systmes can measure antibody responses. Vaccines made by recombinant DNA technology are now feasible.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Weed and volunteer crop seed destruction
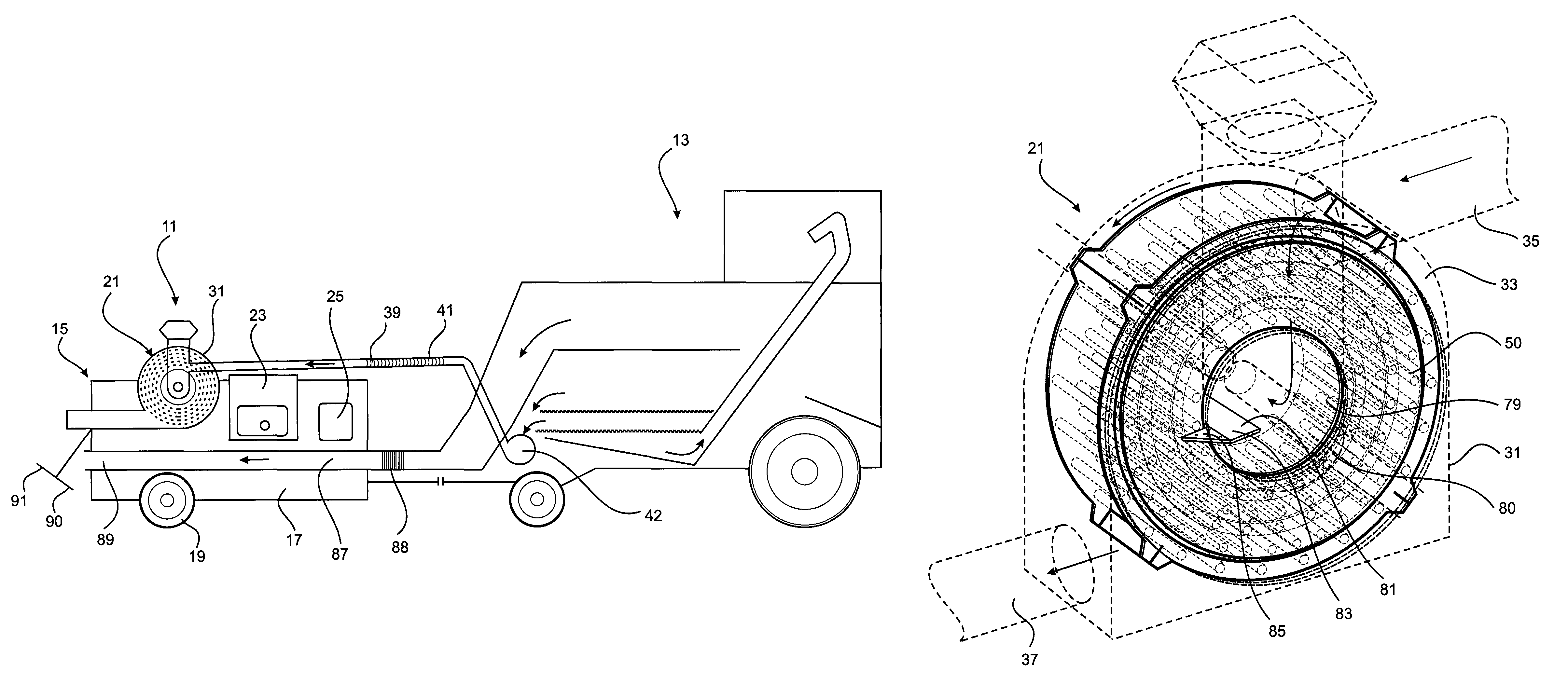
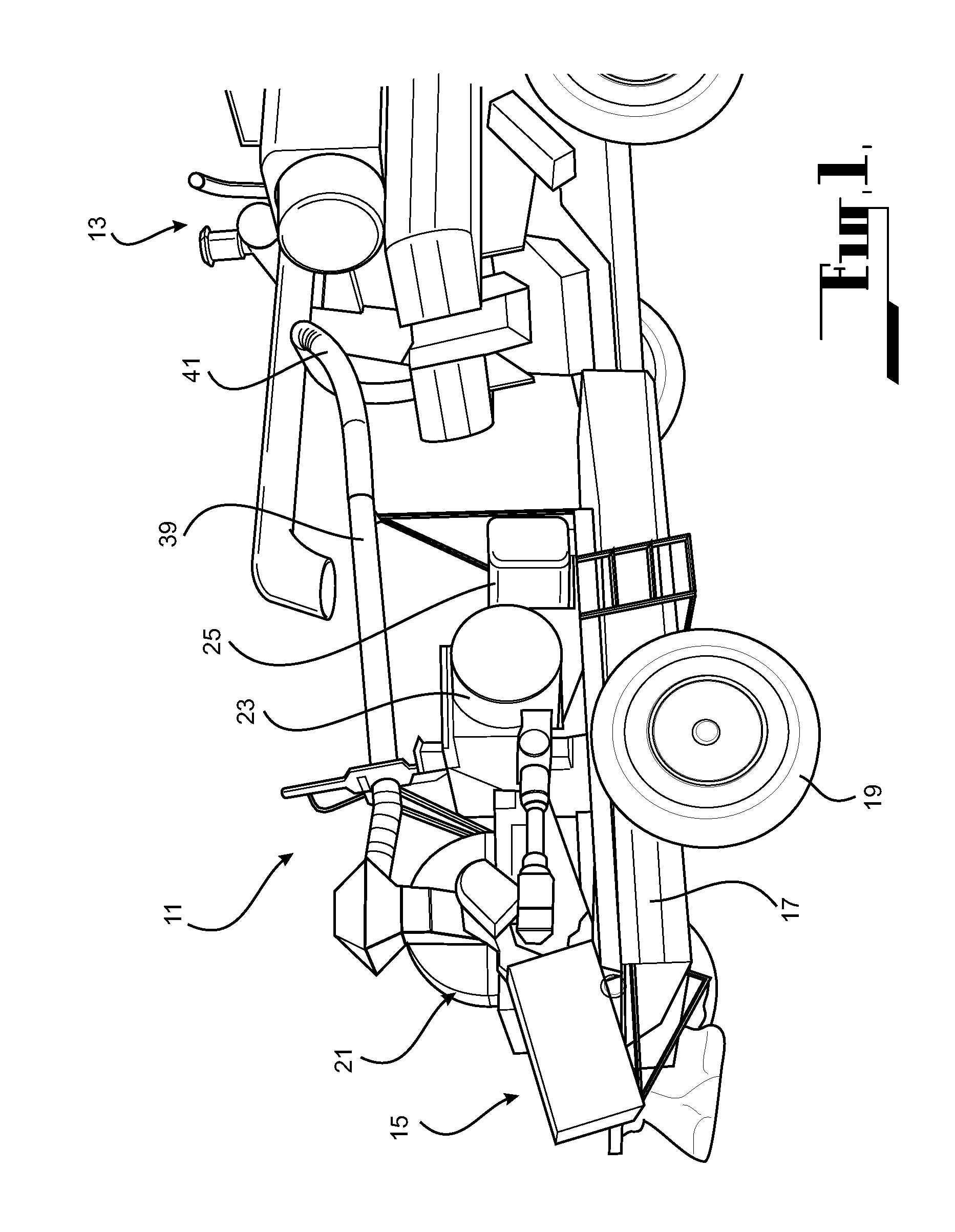
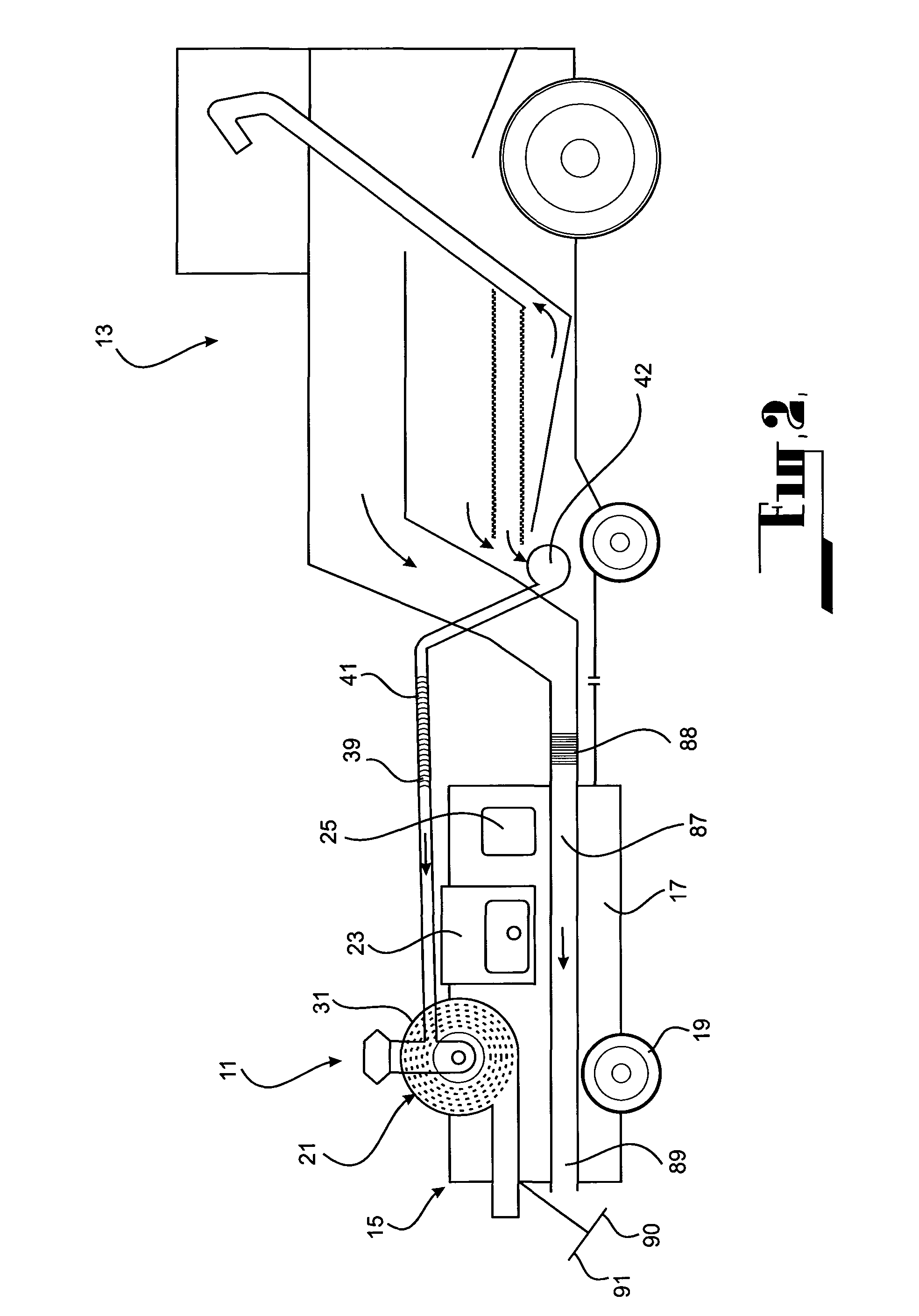
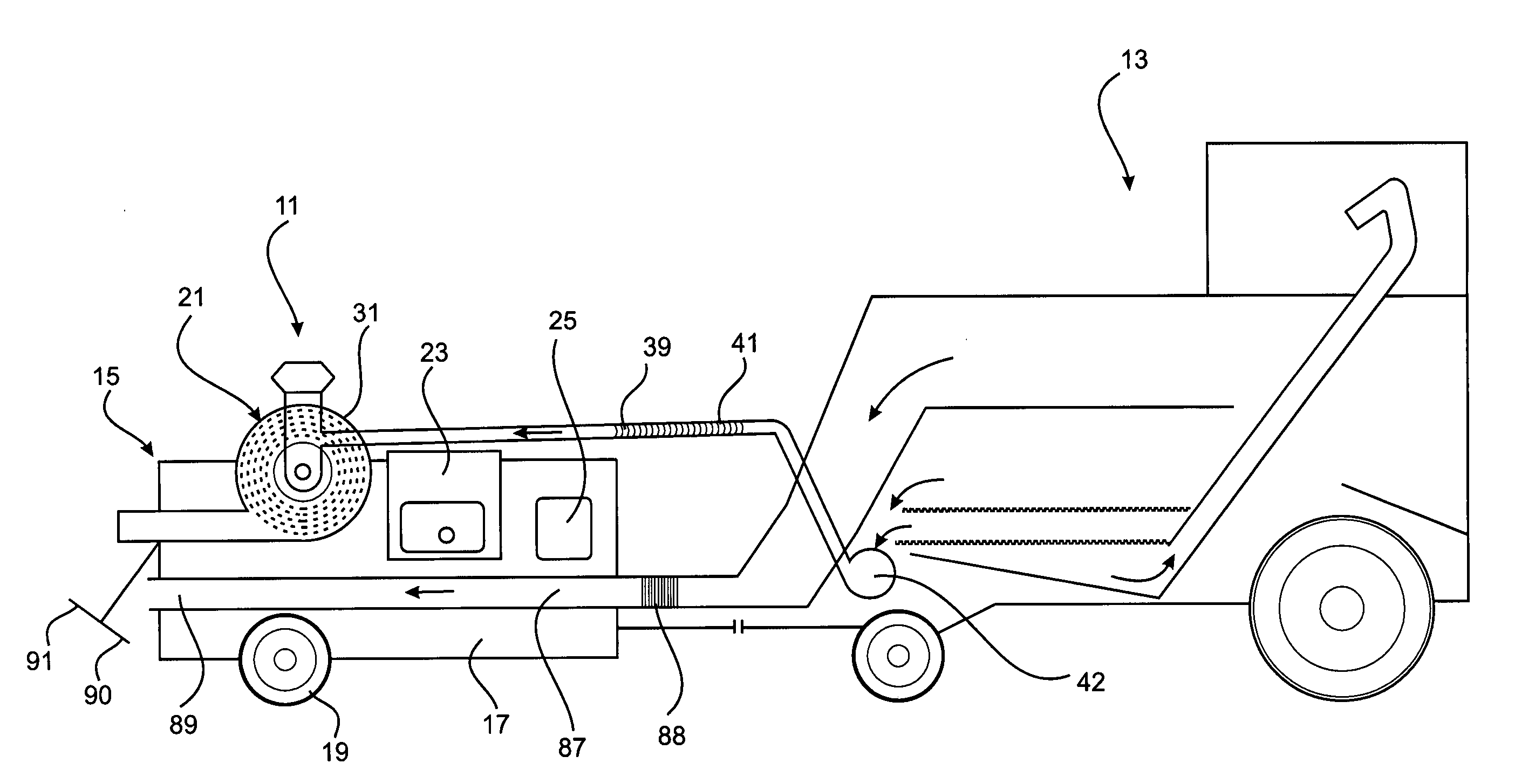
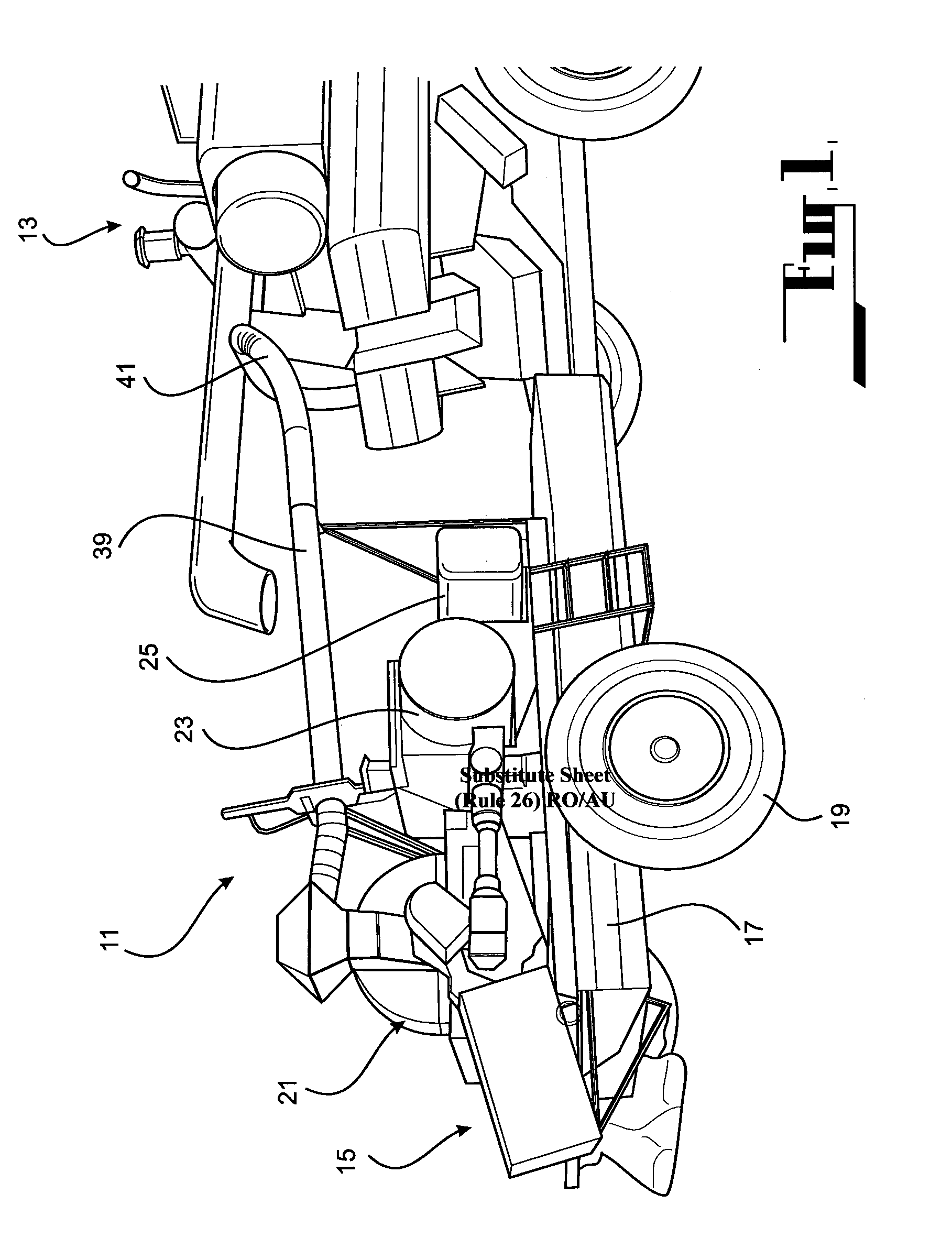
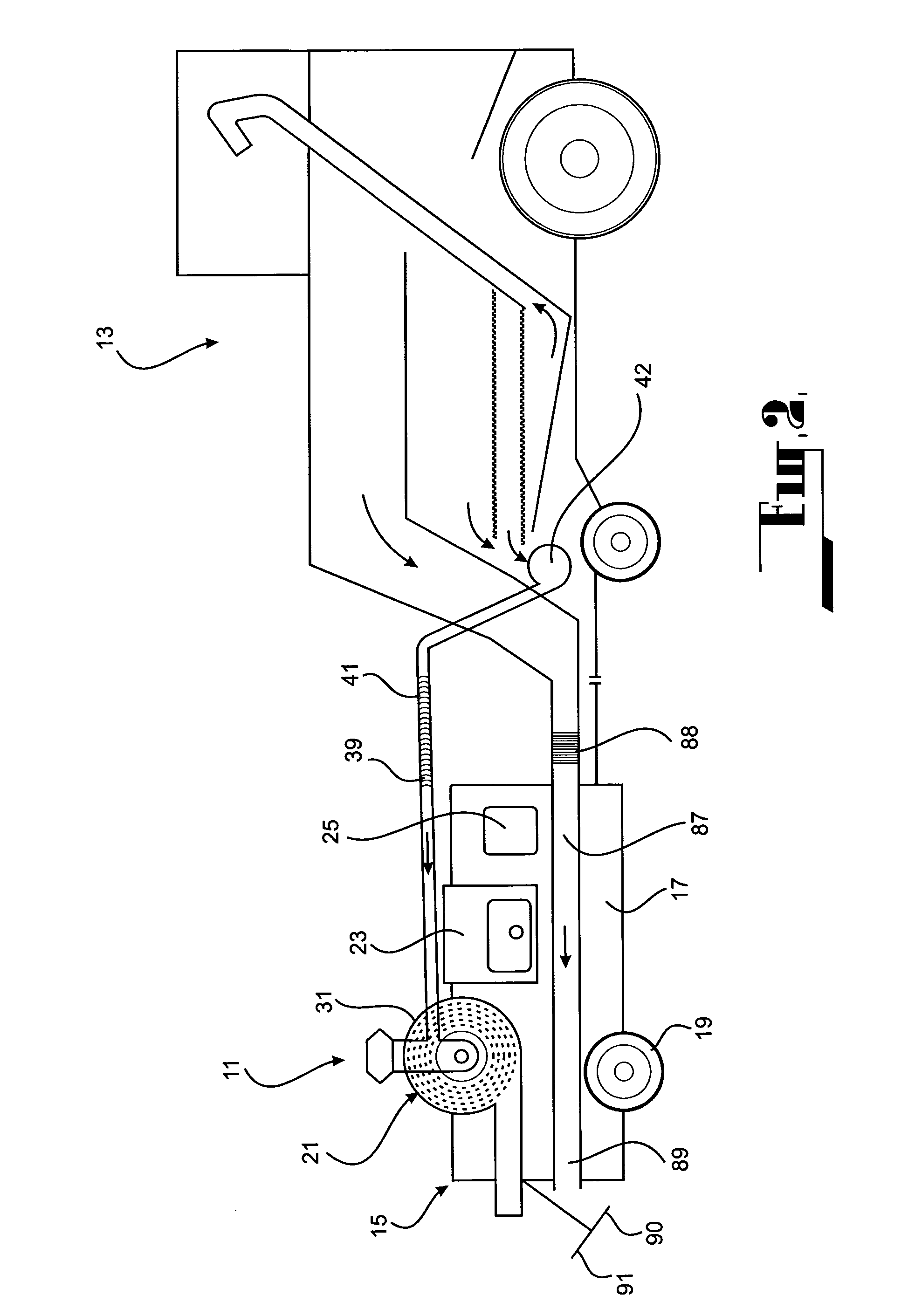
A method of harvesting crop material includes gathering the crop material and separating chaff material, and subjecting the chaff material to fragmentation in a cage mill to destroy unwanted seed material contained therein. Also provided is a mobile agricultural apparatus which travels with a harvesting machine during a harvesting operation to receive chaff material produced during the harvesting operation. At least one cage mill having rotors for fragmentation of the chaff material is included with the mobile apparatus, to destroy unwanted seed material contained therein. Such a cage mill includes at least a casing defining a milling zone, a rotor for performing milling, an inlet for introducing material for reduction into the milling zone, an outlet for removal of material from the milling zone, and an airflow through the milling zone to assist movement of the material through the milling zone from the inlet to the outlet.
Owner:GRAINS RES & DEV CORP
Weed and volunteer crop seed destruction
A method of harvesting crop material comprising gathering the crop material and separating chaff material, and subjecting the chaff material to fragmentation in a cage mill to destroy unwanted seed material contained therein. An agricultural apparatus comprising a mobile apparatus (15) adapted to travel with a harvesting machine (13) during a harvesting operation to receive chaff material produced during the harvesting operation, the mobile apparatus (15) comprising at least one cage mill (21) having a plurality of rotors (51 and 52) for fragmentation of the chaff material to destroy unwanted seed material contained therein. A mill (21) for fragmenting chaff material to destroy unwanted seed material contained therein, the mill comprising a casing defining a milling zone, a rotor means (51 and 52) within the milling zone for performing a milling operation, an inlet (35) for introducing material for reduction into the milling zone, an outlet (37) for removal of material from the milling zone, and means (67) associated with the rotor means (51 and 52) for generating an airflow through the milling zone to assist movement of the material through the milling zone from the inlet to the outlet.
Owner:GRAINS RES & DEV CORP
Method and apparatus for reporting road conditions
InactiveUS7571029B2Digital data processing detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlEngineeringBiological activation
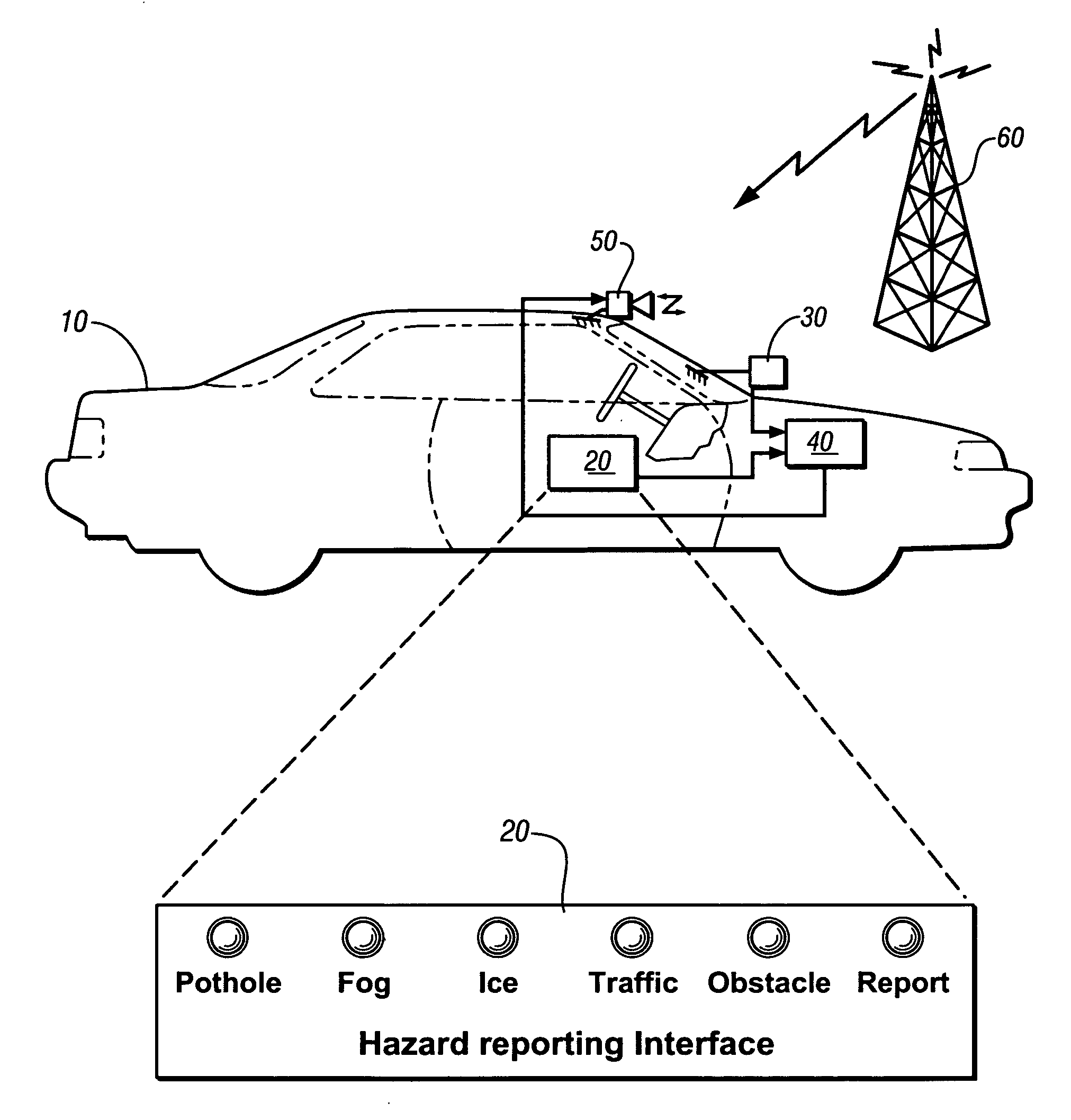
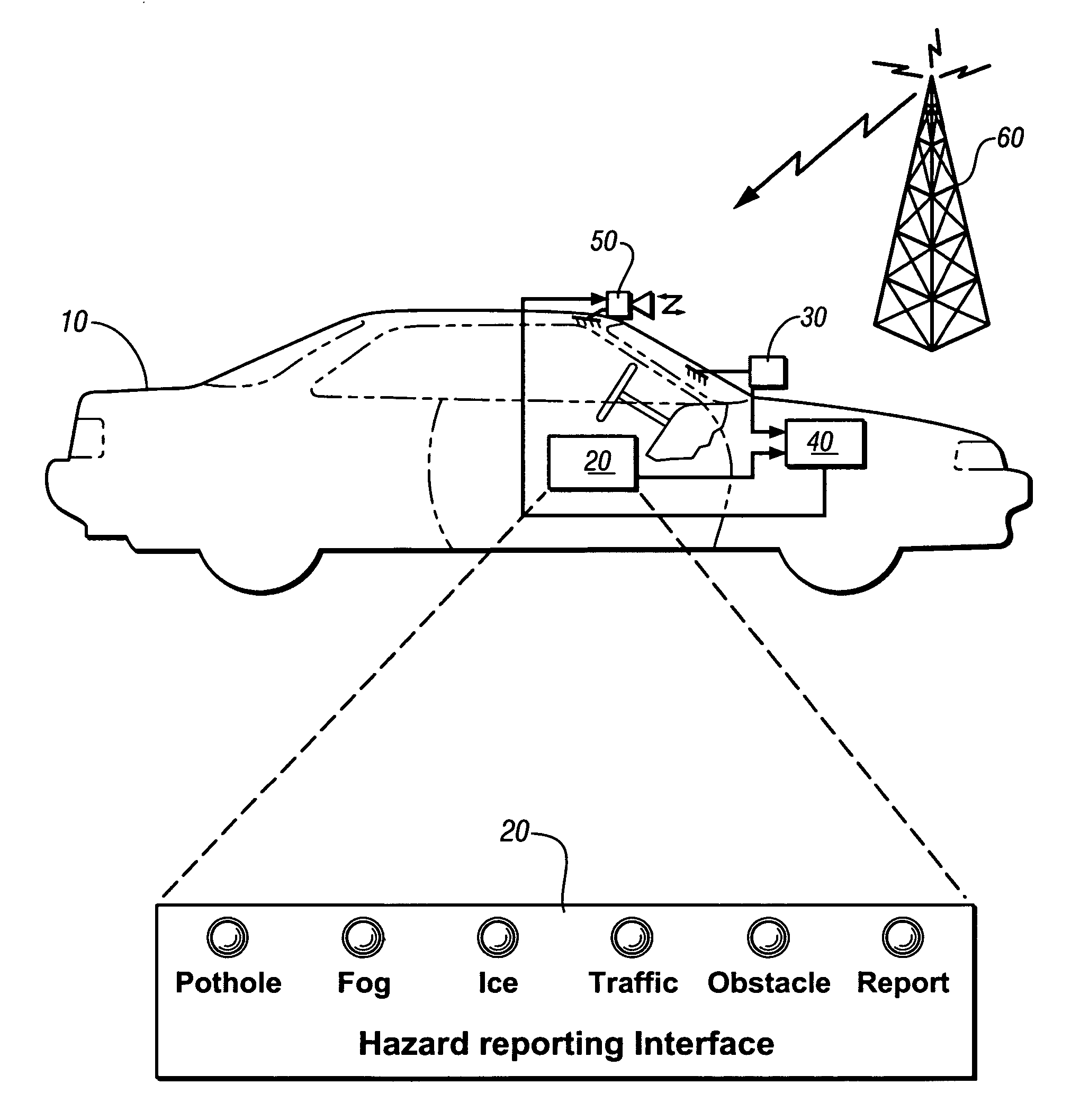
An on-vehicle system for identifying and reporting external conditions is presented. The system has an operator-selectable user interface to identify occurrence of an external condition, a global positioning system receiver; and, a wireless communications system. The unit may be used to assist in discovering localized roadway conditions that adversely affect safety and travel. The unit is placeable into a vehicle of a volunteer, is manually operated whenever a hazard is detected. Reportable hazards include potholes, obstacles or debris in the highway, snow or ice patches, fog, unusual traffic or pedestrian activity, and localized incidences, such as presence of disabled or emergency vehicles. Nature of the hazard is indicatable by manual activation of additional push buttons or other suitable devices. A GPS receiver is incorporated to estimate position, speed, and heading of the hazard. The information is encoded as a message sent to a central server.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and system for constructed response grading
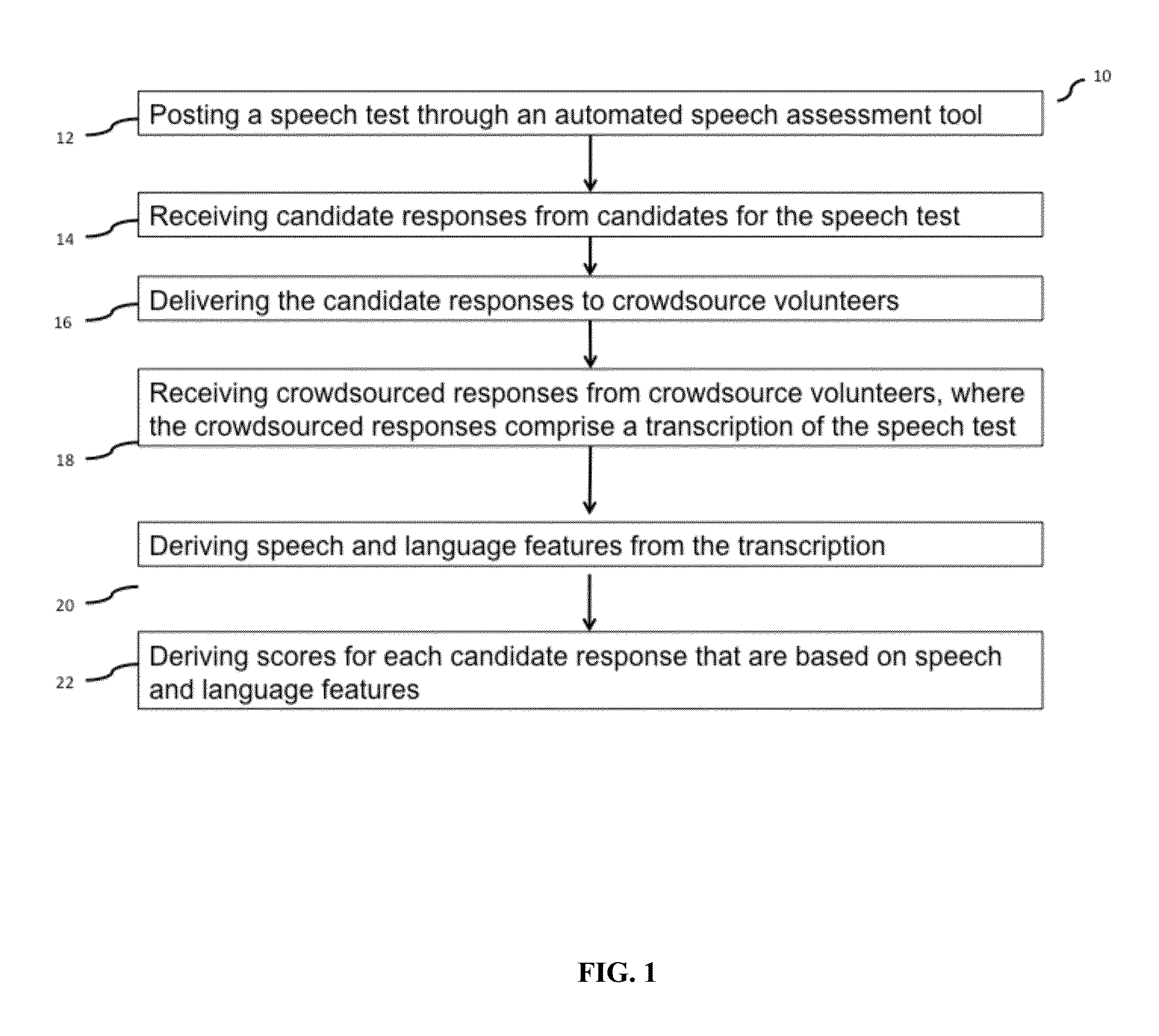
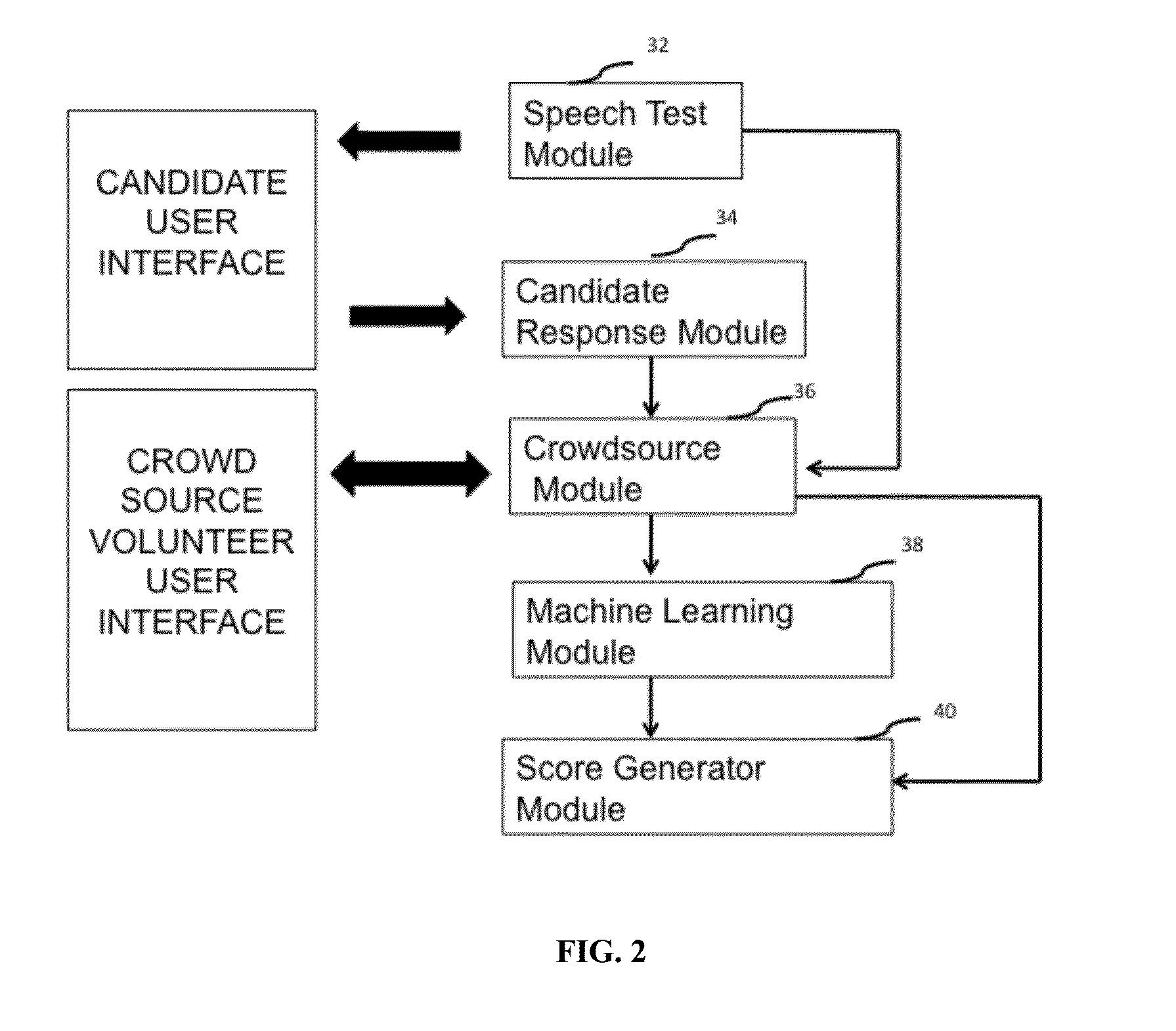
A method and system for constructive response grading for spoken language is disclosed. The method and system are computer implemented and involve a crowdsourcing step to derive evaluation features. The method includes steps for posting a speech test through an automated speech assessment tool, receiving candidate responses from candidates for the speech test; delivering the candidate responses to crowdsource volunteers; receiving crowdsourced responses from crowdsource volunteers, where the crowdsourced responses comprise a transcription of the speech test; deriving features from the transcription; and deriving a individual scores based on the features, where the individual scores are representative of pronunciation score, fluency score, content organization score and grammar score of the spoken language for each candidate.
Owner:SHL INDIA PTE LTD
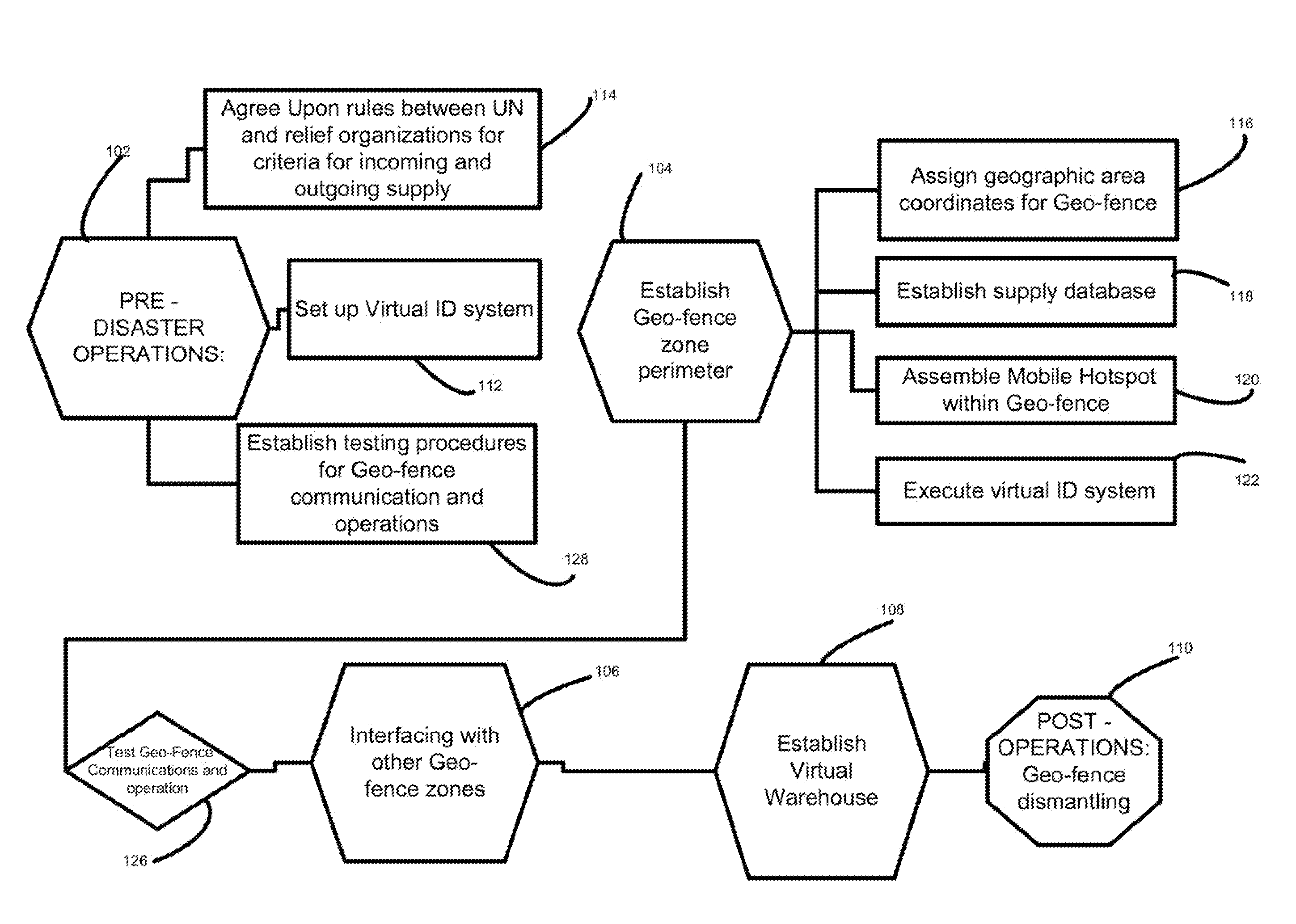
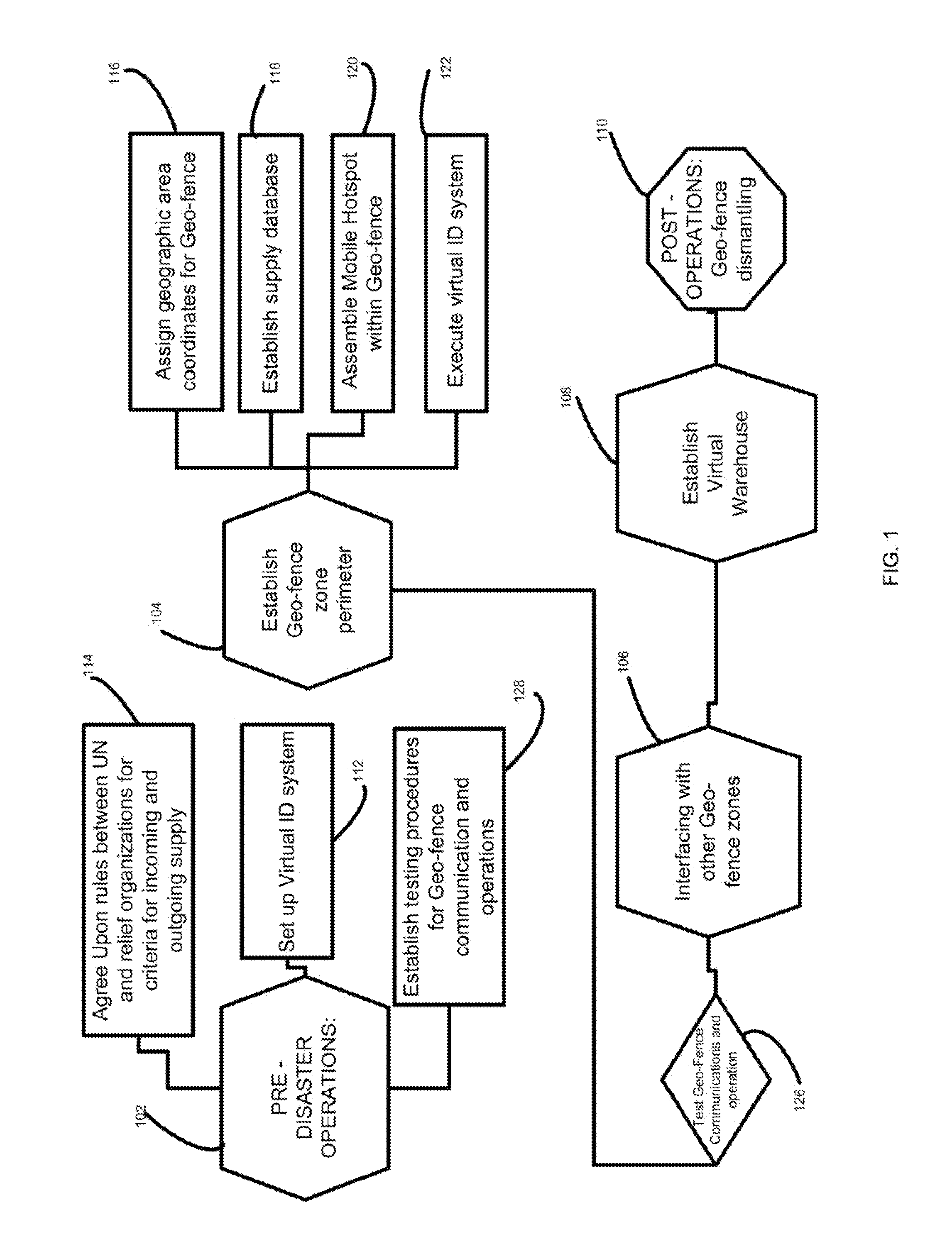
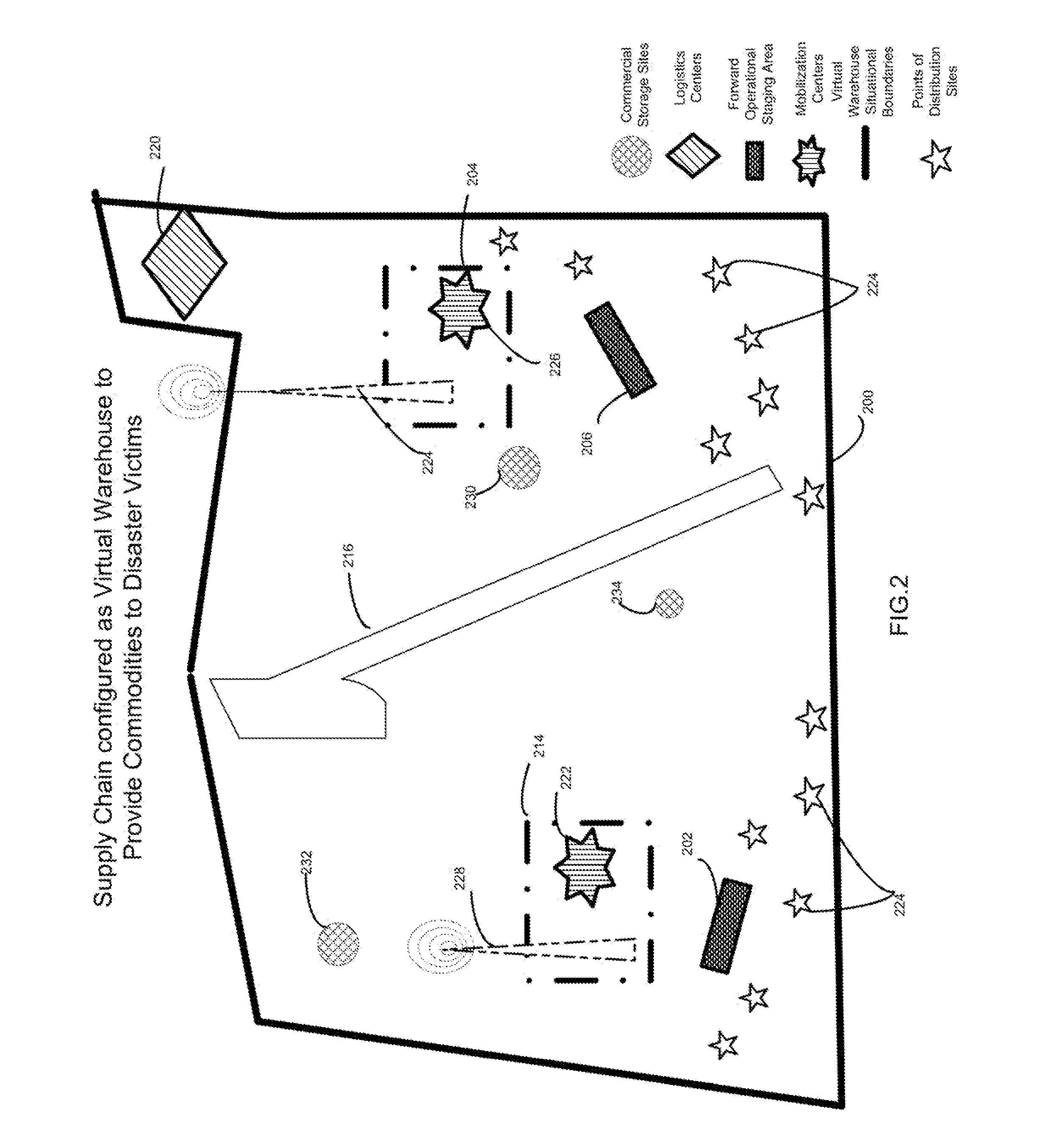
Method for establishing an impromtu geofenced area to organize and analyze shipments
A method of establishing a virtual perimeter for a real-world geographic area in which a zone is digitally customized to receive and disburse ad-hoc supplies including procedures for authorizing volunteers and other relief entities to draw supplies from the geo-fence zone utilizing wireless technology. The method of the present invention includes establishing geo-fences and communication links between the geo-fences to form a virtual warehouse. The present invention is well suited for disaster relief operations or other emergencies in which donated supplies require distribution throughout a widespread area of need.
Owner:GLOBALTRAK ACQUISITION
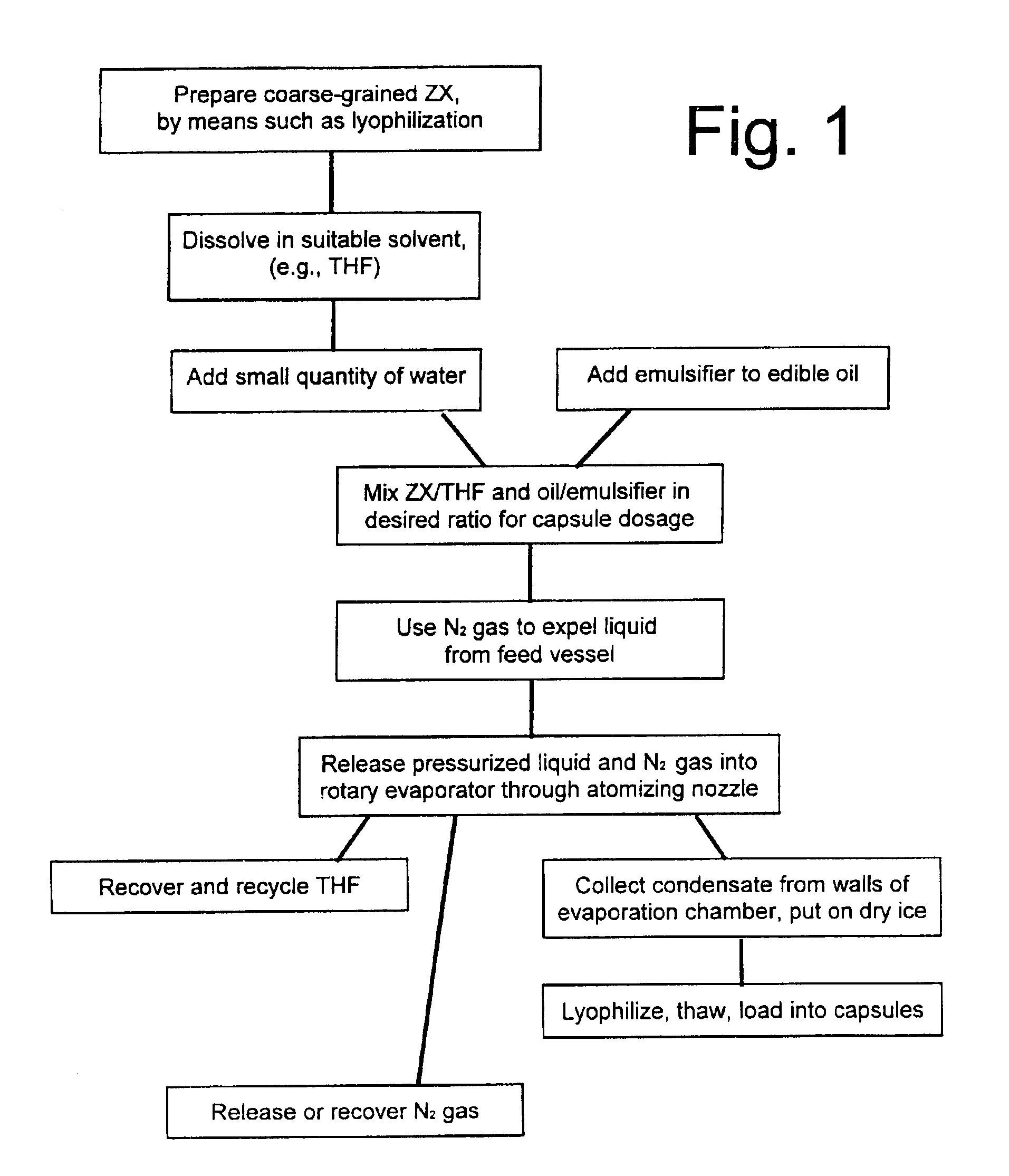
Microcrystalline zeaxanthin with high bioavailability in oily carrier formulations
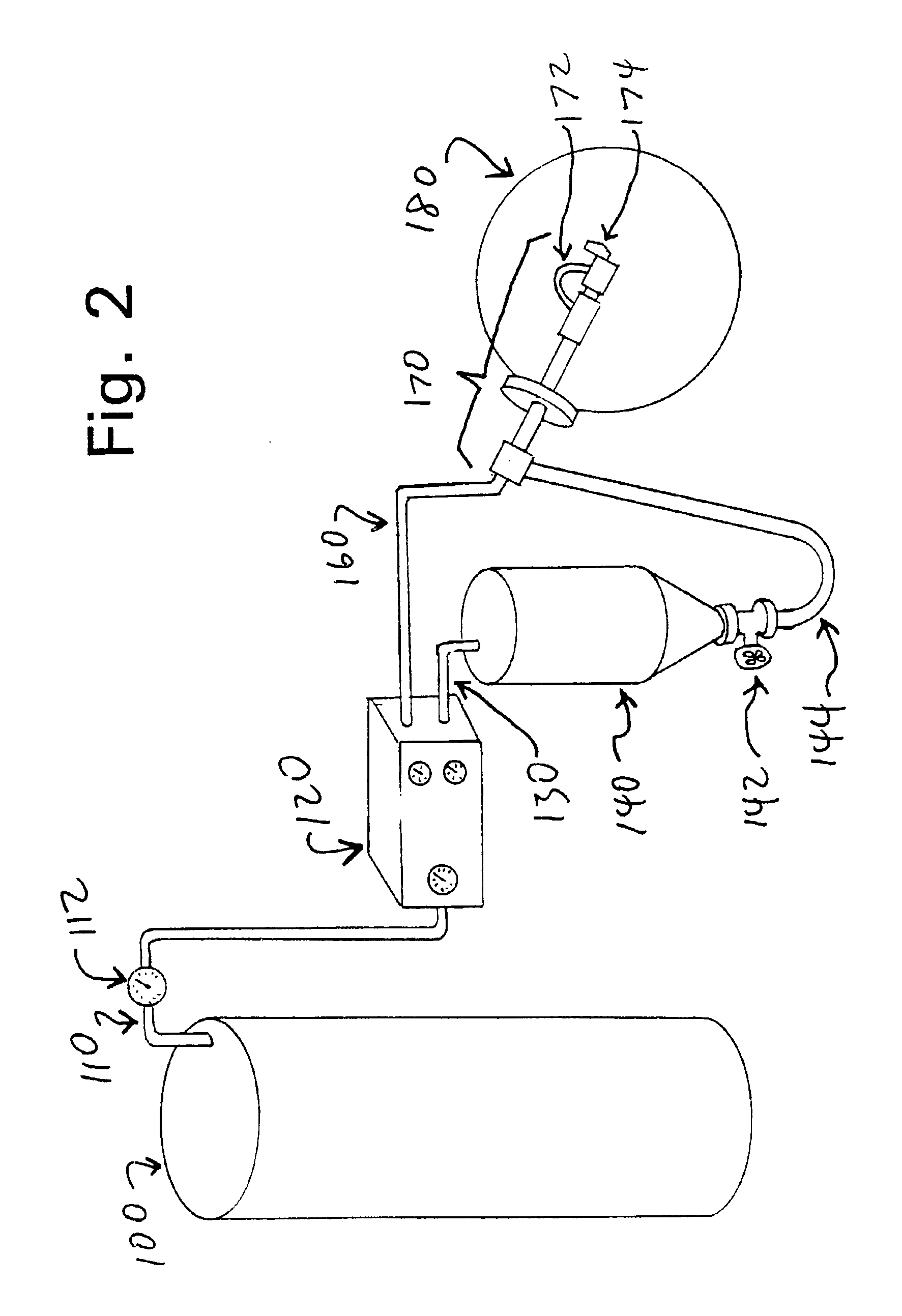
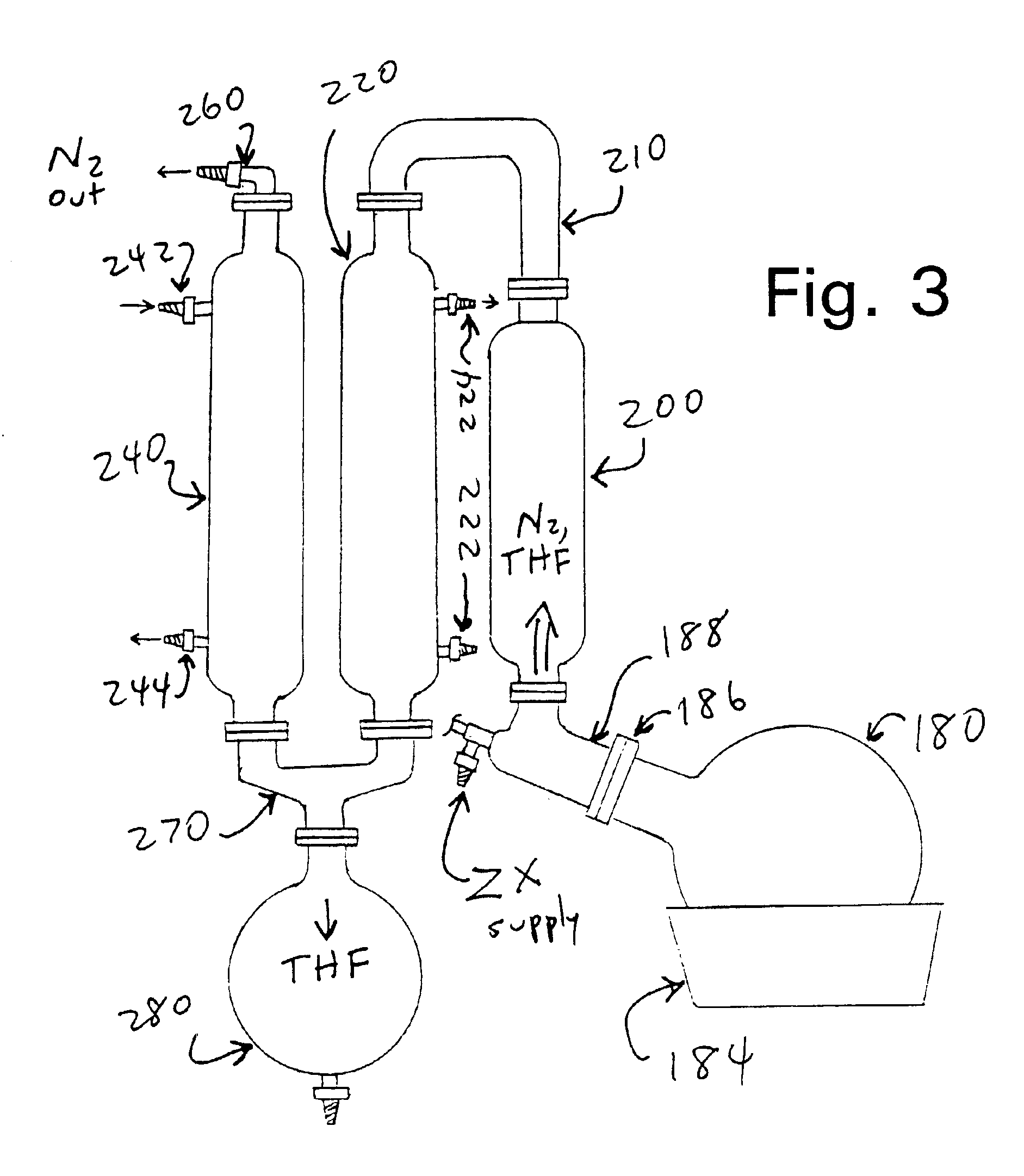
Zeaxanthin (ZX) or other medically or commercially important carotenoids can be prepared in microcrystalline form, in an oily carrier liquid, to increase their bioavailability following oral ingestion. Initial processing is carried out to prepare a “rough” or “coarse-grained” carotenoid preparation containing relatively large particles of the ZX or other carotenoid, in a suitable form such as a lyophilized stable powder. The coarse-grain preparation is dissolved in a suitable solvent such as tetrahydrofuran, and mixed with a carrier liquid comprising a digestible oil (such as a vegetable oil) and an emulsifying agent. The resulting oil-and-solvent mixture is injected, along with inert gas such as nitrogen, into a vacuum chamber, where a suitable vacuum and temperature combination is used to remove the solvent in a rapid “flash” manner which does not give the carotenoid crystals time to grow larger through accretion or aggregation. This generates a microcrystalline suspension containing very small particles of the ZX or other cartenoid, in the oily liquid carrier. This product can be further processed if desired, or it can be loaded directly into watertight capsules for oral ingestion. Tests on human volunteers have confirmed that the bioavailability of this microcrystalline form is substantially higher than prior art preparations having larger particles of the carotenoid.
Owner:ZEAVISION LLC
Caregiving social network
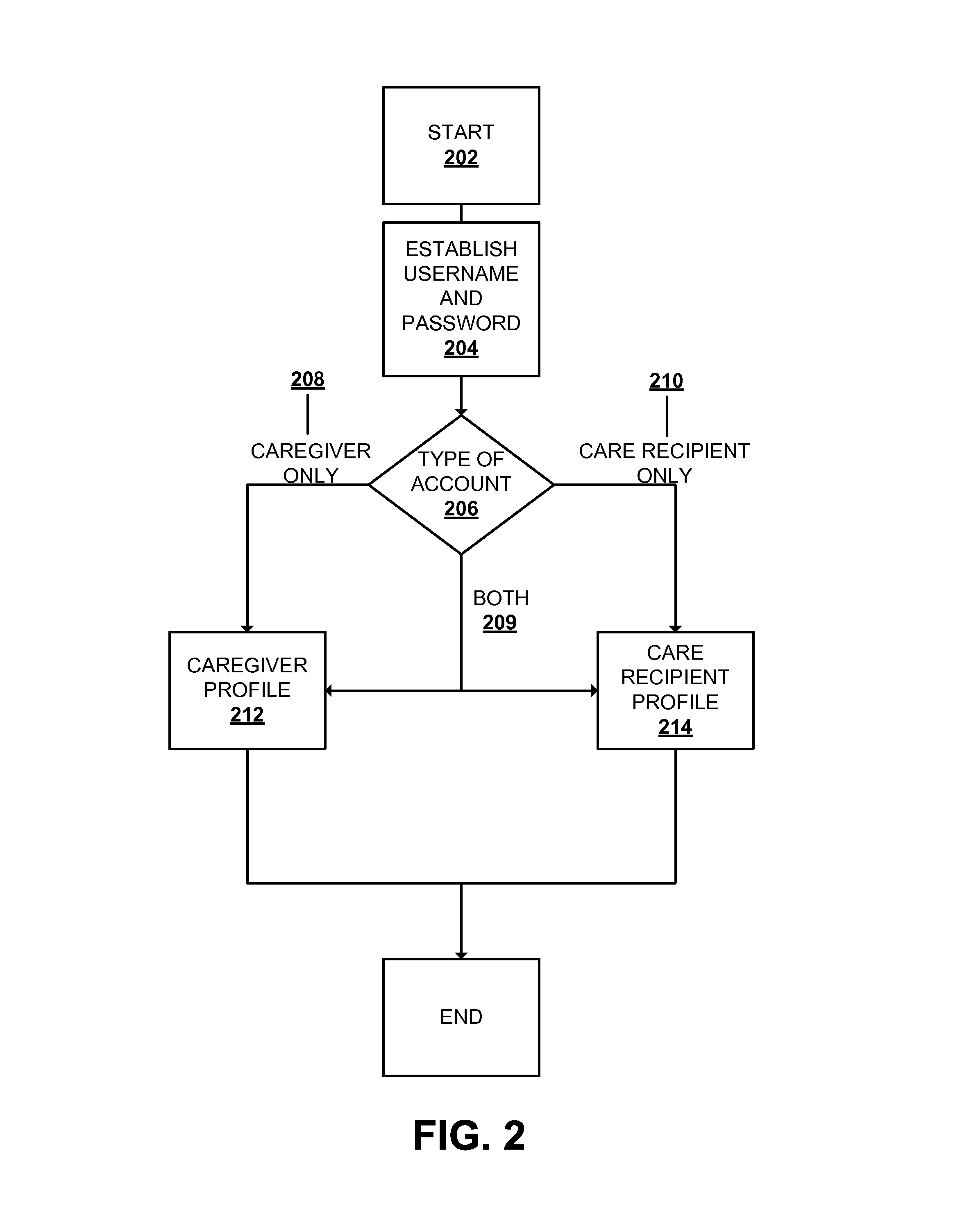
A server implements a caregiving social network dedicated to coordinating care between caregivers and care recipients. Profile information is recorded to assist in coordinating care, as well as targeting advertising and information material that is highly relevant to an individual user and his or her community. Users of the caregiving social network include seniors, disabled people, children, parents, volunteers, medical professionals, neighbors, military families, and pets. Users can maintain both a caregiver account to assist others, and a care recipient account for receiving assistance.
Owner:THE WARMAN GROUP
Automated new energy technology consulting and demand aggregation system and method
InactiveUS7512540B2Expanding outreachLow costElectric devicesSpecial tariff metersViral marketingNew energy
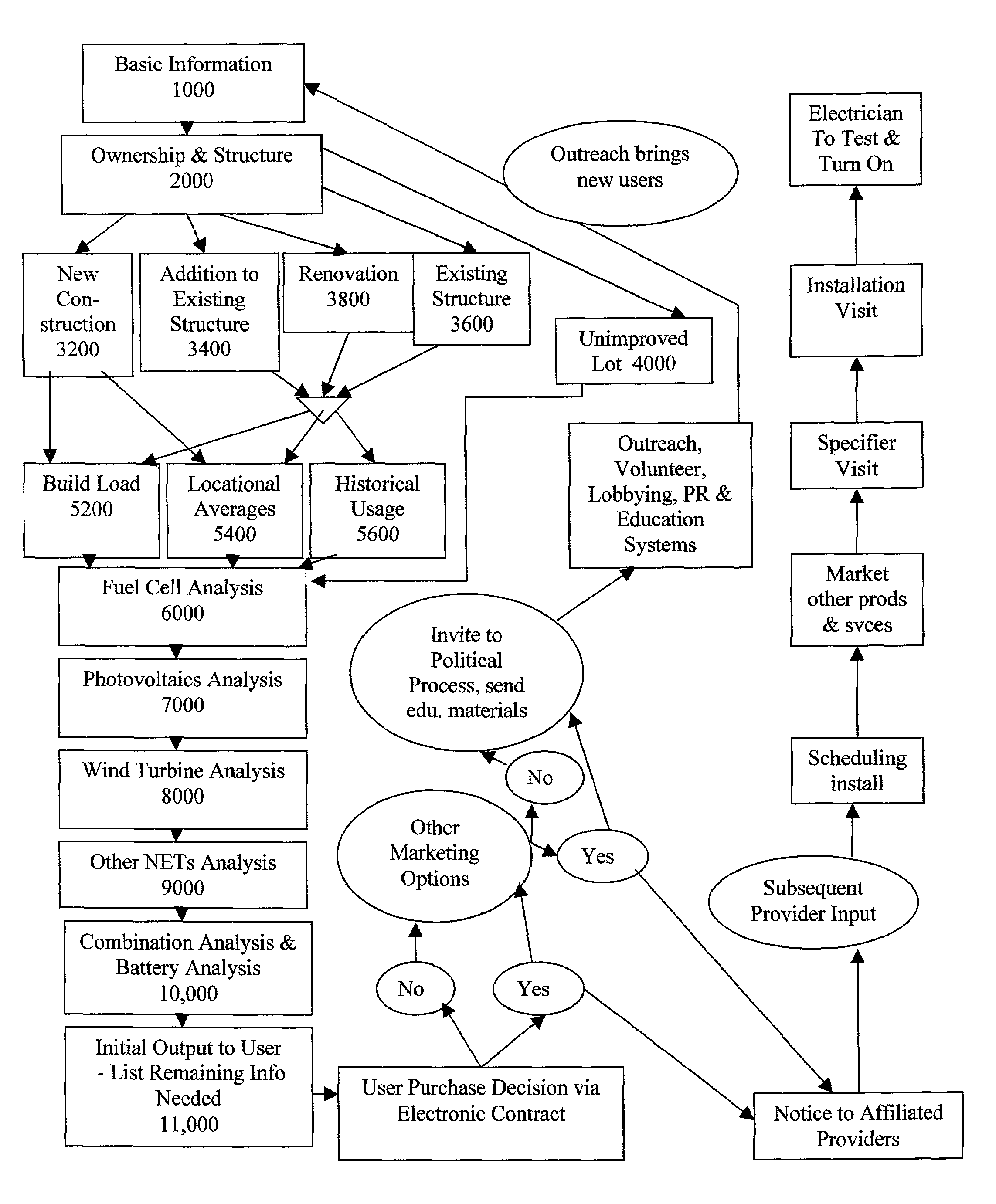
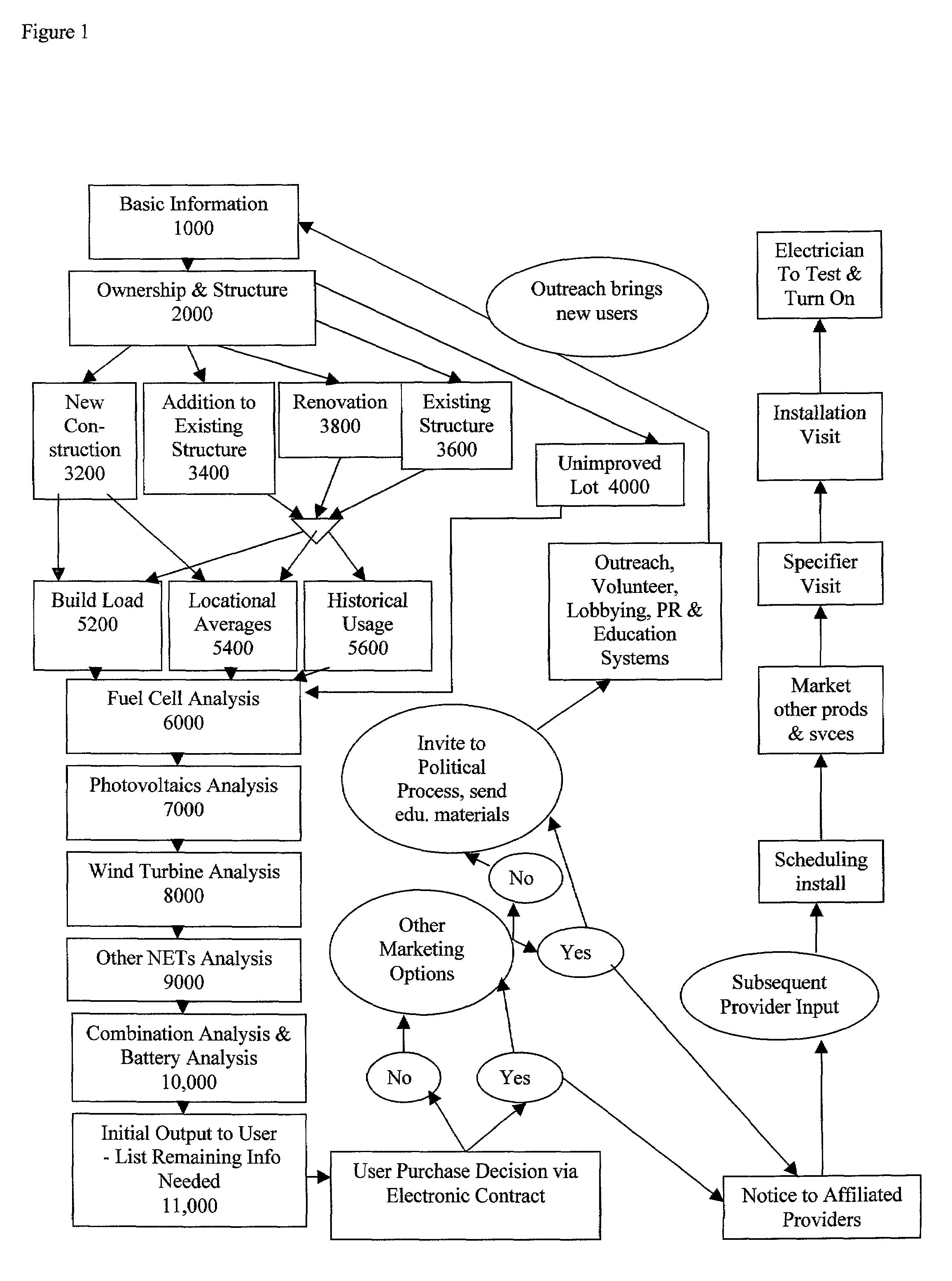
An automated energy consulting system and method is provided comprising an interactive input system linked to calculation algorithms and databases of energy-related products and services, affiliated service providers, and climate, financing and regulatory criteria. The system generates proposals of available energy-related products, services and financing options, and obtains and aggregates customer commitments to allow discounted purchasing of the components. Customers can earn referral commissions to encourage customers and volunteers to virally disseminate the access information. For customers not eligible for beneficial products and services because of regulatory deficiencies, the system automates the customer education process to encourage them to advocate politically for the changes that will make them eligible. The automation of the energy consulting and marketing process, mass customization, demand aggregation, and viral marketing reduce customer acquisition and component purchasing costs and reduce the price to consumers, creating new economically viable markets for environmentally friendly energy-related products and services.
Owner:GLUCK DANIEL S +1
Method for Crowd Sourced Multimedia Captioning for Video Content
InactiveUS20140143218A1Digital data processing detailsMetadata multimedia retrievalCrowd sourcingComputer graphics (images)
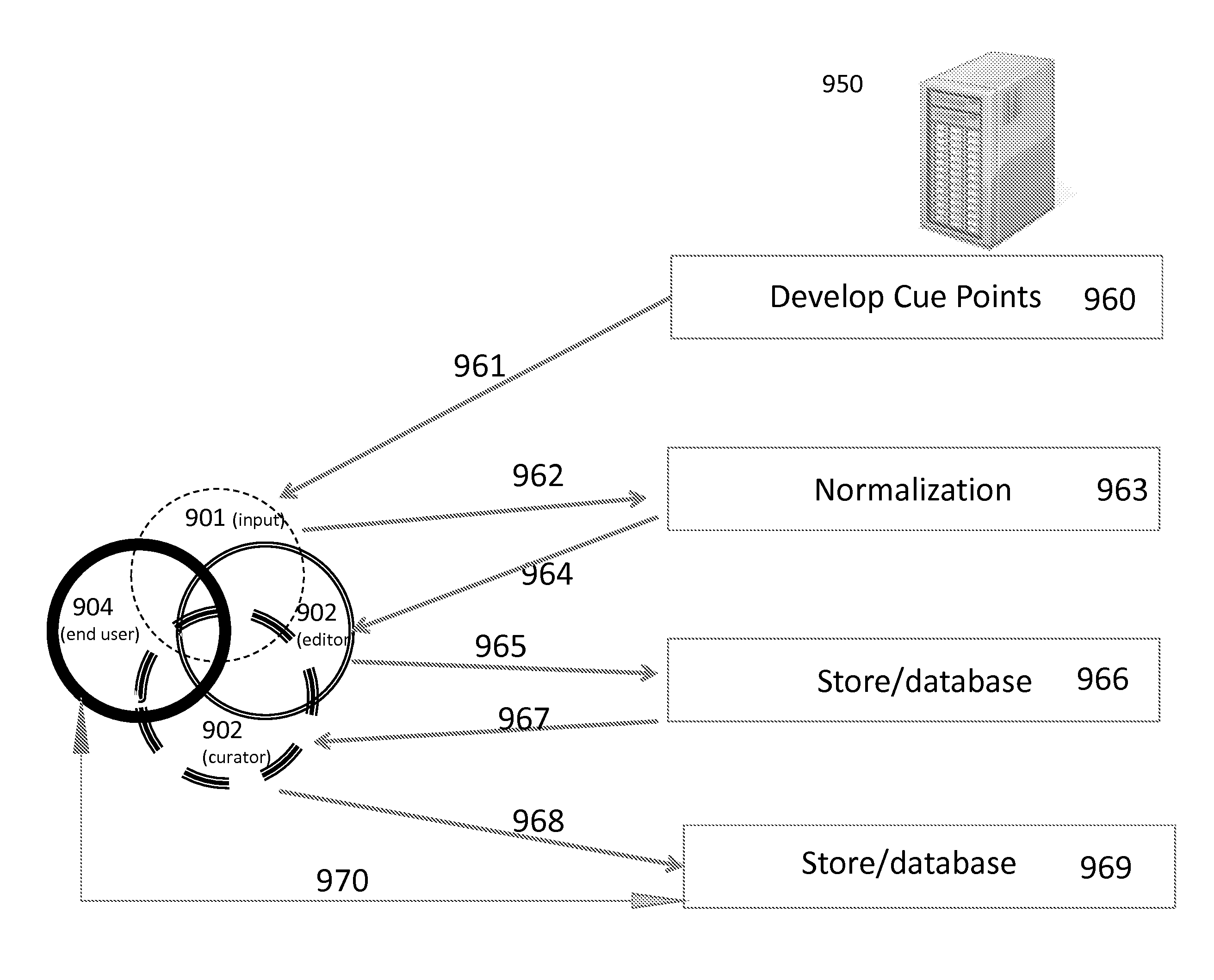
Methods and apparatus are presented for providing enhancement information associated video, for example subtitles or closed captions. Cue points are developed with respect to a video and enhancement information is aligned with the cue points such that the cue point and enhancement information may be maintained separate from the video and applied to any version of a video. Some disclosed embodiments relate to using groups of volunteers to provide and edit enhancement information in a five stage process. The volunteer groups may be operated in a crowd sourcing fashion.
Owner:APPLE INC
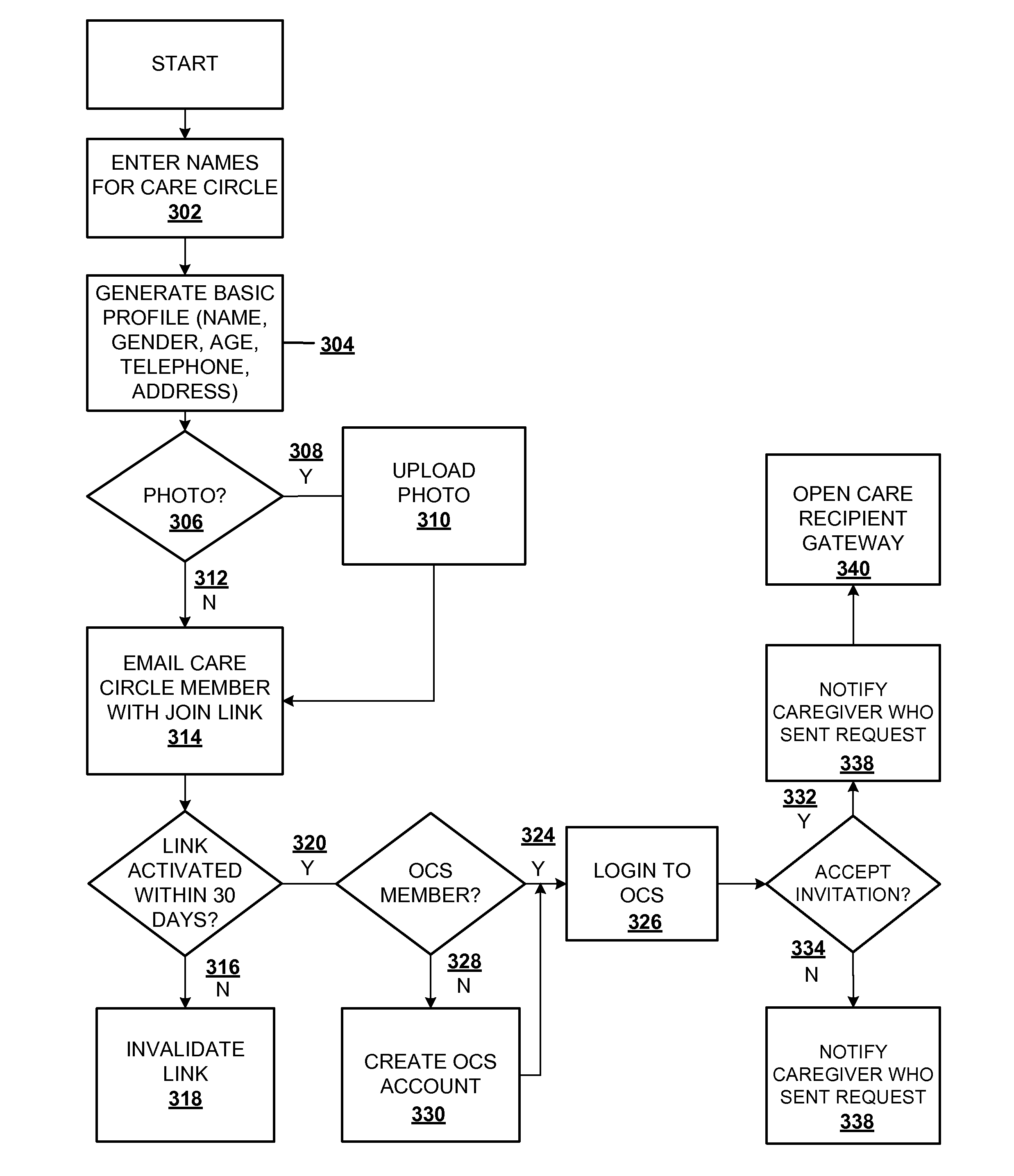
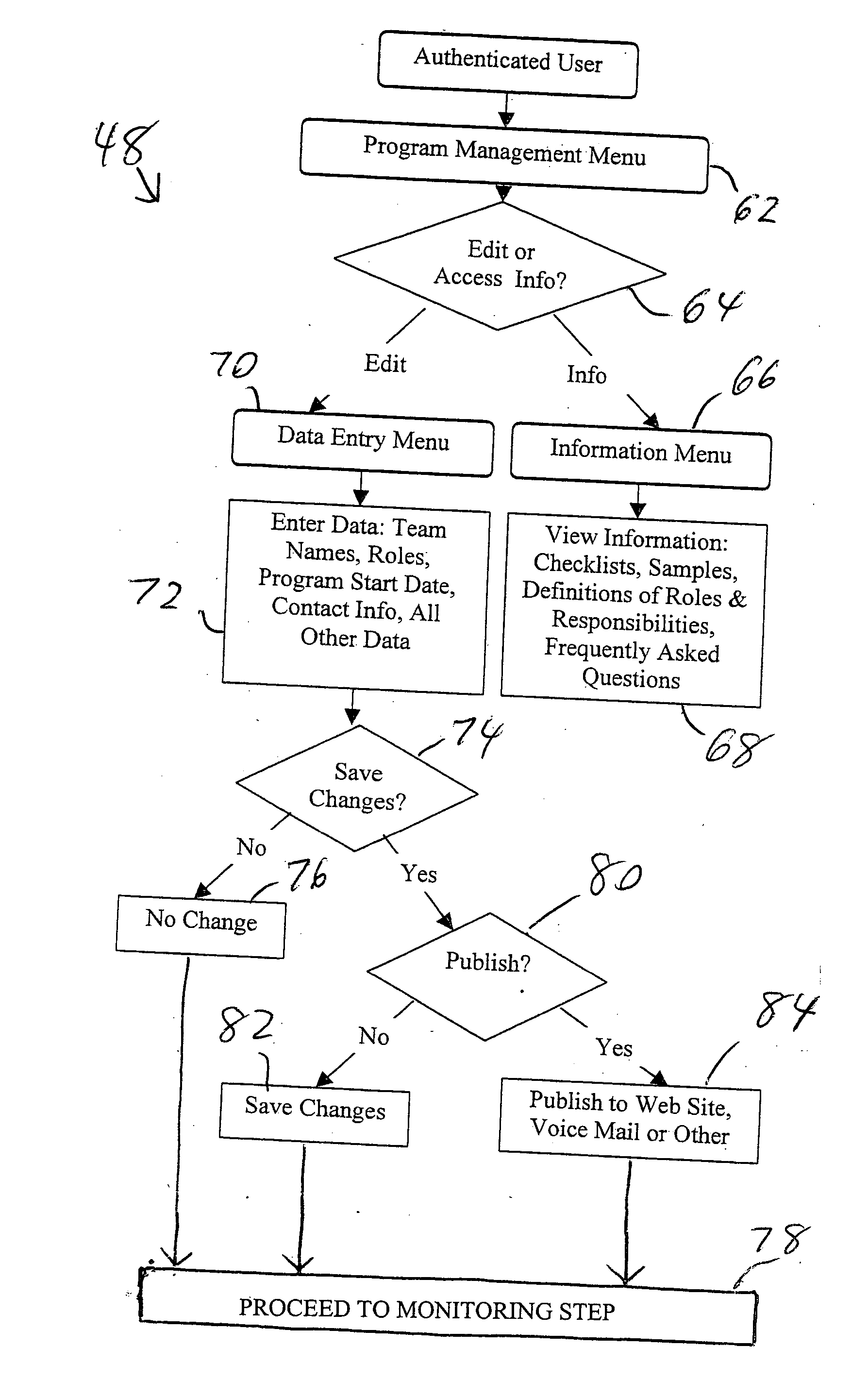
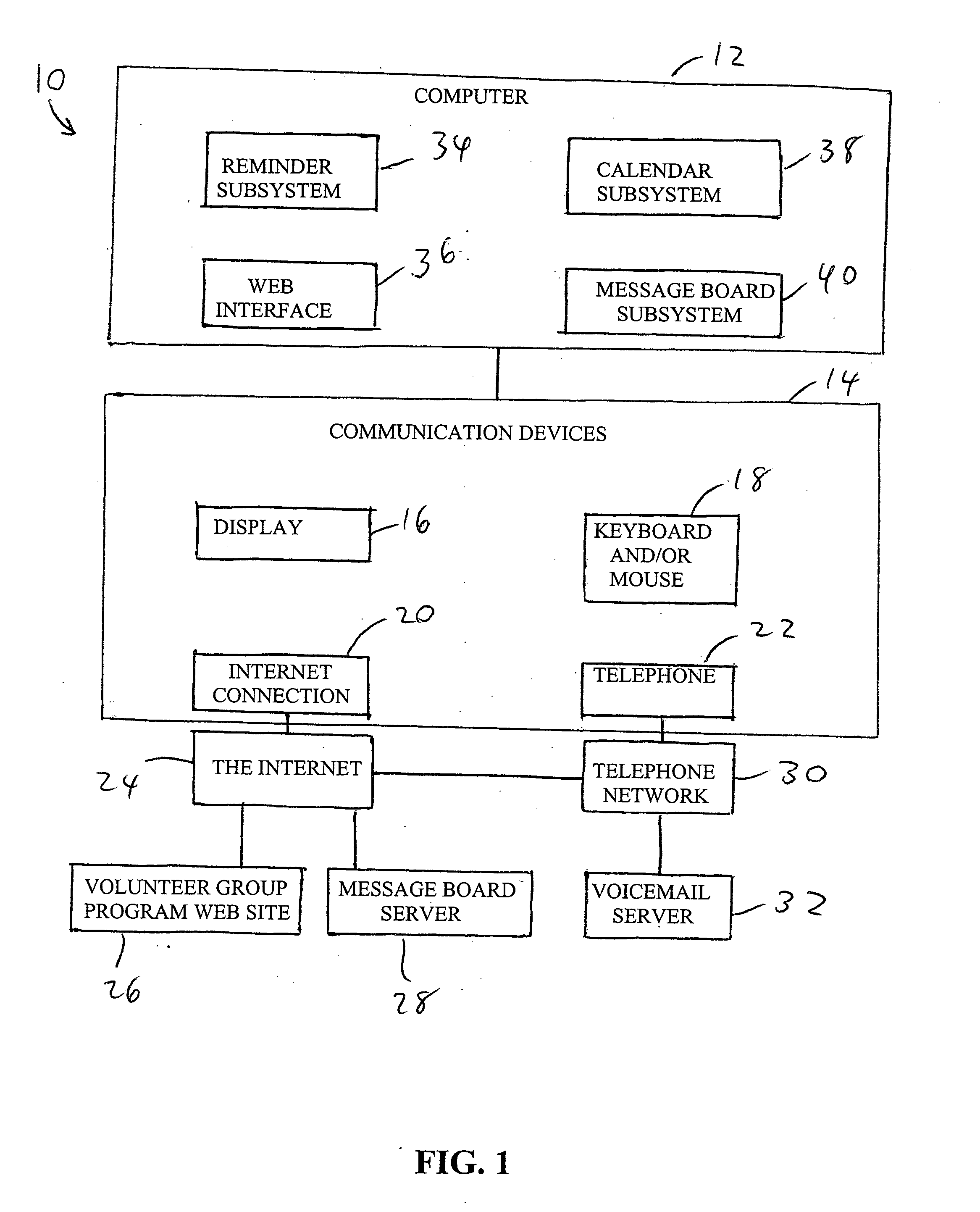
Method and system for recruiting for, organizing, and managing a volunteer group program
A method and system operate for recruiting participants, and organizing and managing a volunteer group program. The system is computer-based, and presents a menu of possible goals for the volunteer group program. Based on user input, the system generates an electronic organizational framework with specific roles, responsibilities, and sub-systems needed to achieve the stated goals. The system requests contact information for individuals who will take on specific responsibilities, along with information related to the specific preferences regarding ways to achieve program goals. The system generates an electronic operational manual for the volunteer group, along with appropriate tools for enlisting additional volunteer contributions and for managing their efforts. Tools may include a Web site, an automated telephone system, or other mechanisms for discussion, scheduling of services, and communication of program goals and status, and reminders to individual volunteers of pending tasks associated with the program.
Owner:CARE CIRCLE INT
Mobile phone user travel mode recognition method based on C4.5 decision tree
InactiveCN105101092AQuality improvementPosition fixationLocation information based serviceTravel modeTime information
The invention discloses a mobile phone user travel mode recognition method based on a C4.5 decision tree. The mobile phone user travel pattern recognition method comprises: collecting mobile phone signaling data of a volunteer, and processing the mobile phone signaling data into a travel track sequence with reference to time information and position information of the data; excavating a relationship of a travel characteristic attribute and a corresponding travel traffic mode from the travel track data of the volunteer; dividing the collected mobile phone signaling data of the volunteer into two parts according to a supervised machine learning method, which are respectively a training data set and a test data set; extracting a variety of characteristic attributes of travel behaviors from mobile phone data corresponding to the travel process of the volunteer according to the communication principle and the traffic theory; training a travel mode recognition model in combination with a real travel mode condition fed back by the volunteer via an artificial intelligence algorithm, C4.5 algorithm with supervision and learning ability to obtain a high-precision mobile phone user travel mode recognition model based on the mobile phone signaling data.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEIHUI SOFTWARE
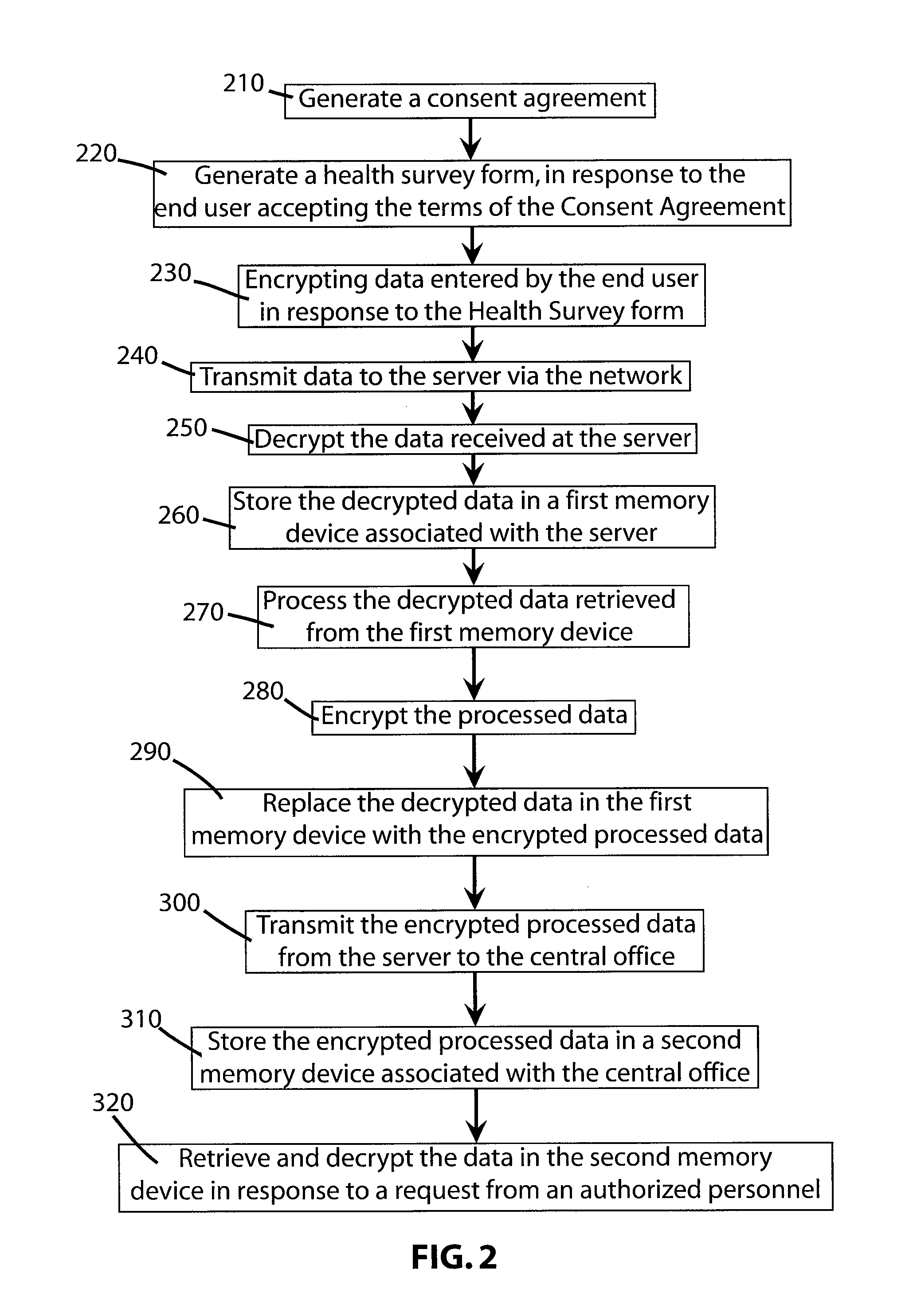
System and method for recruitment of candidates for clinical trials while maintaining security
An on-line click wrap electronic agreement that a user must agree to prior to being registered as a volunteer and considered as a potential candidate in a clinical trial or research study. The agreement authorizes the release of the end user's medical and / or personal information to representatives of the clinical trials and research studies for which the volunteer may be considered as a potential candidate. After receiving the end user's consent to the click wrap agreement an electronic survey form is generated by a secure server and displayed at the end user's computer terminal. Responses by the end user to the survey form are kept secure as much as possible while being transmitted from the computer terminal across the network to the server and while stored and accessed only by authorized personnel at the central office.
Owner:BODY HEALTH RESOURCES CORP
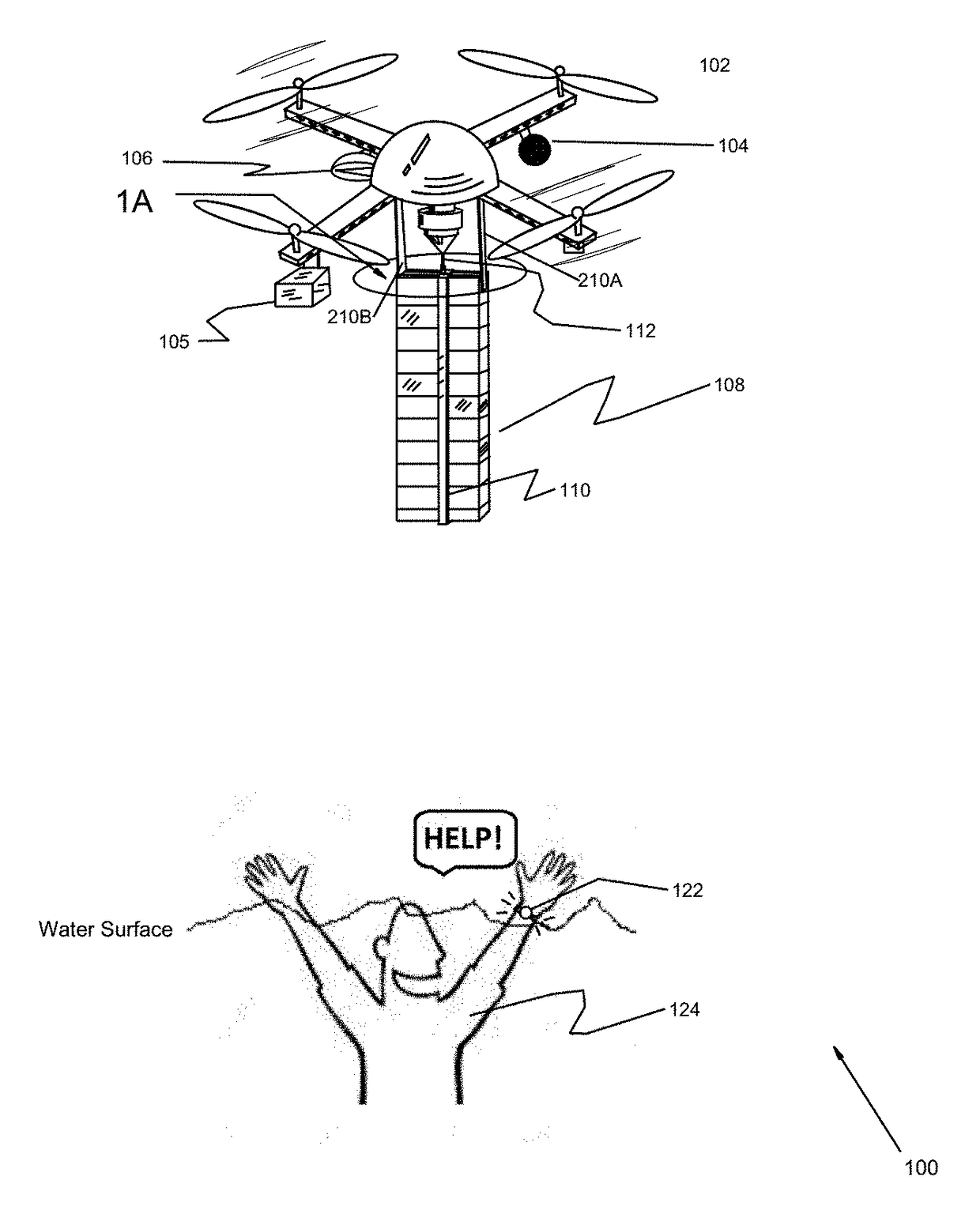
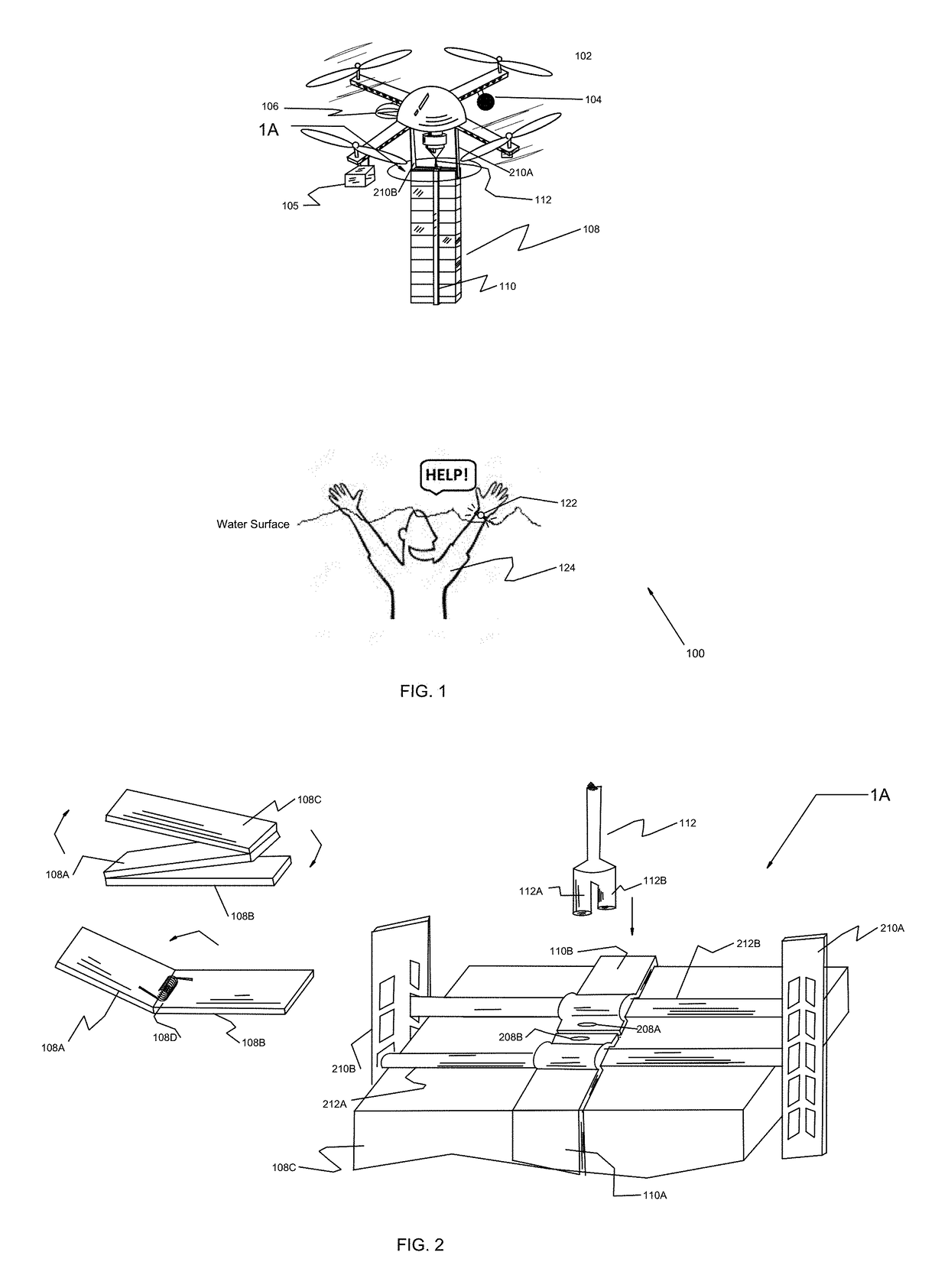
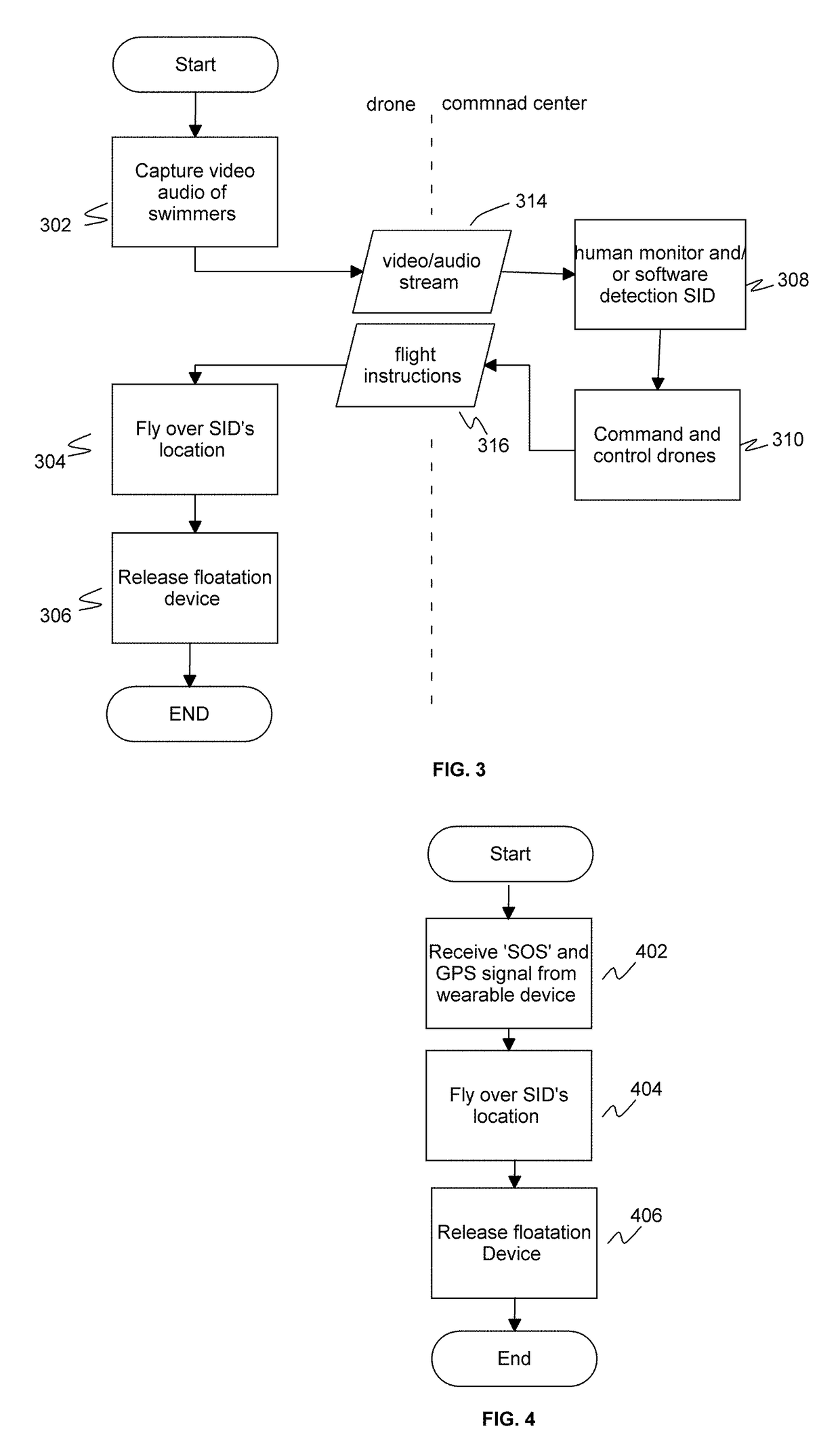
Unmanned aerial vehicle system and methods for use
Owner:TANG RUJING
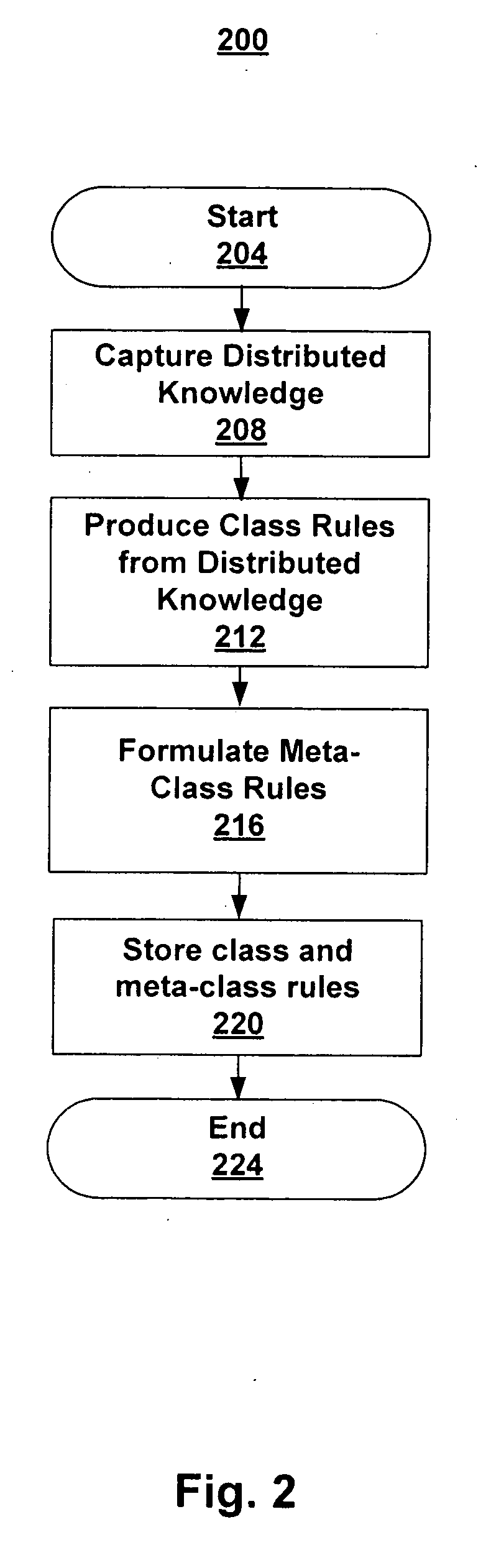
Commonsense reasoning about task instructions
A system and method enable an autonomous machine such as an indoor humanoid robot to systematically process user commands and respond to situations. The method captures distributed knowledge from human volunteers, referred to as “commonsense knowledge.” The commonsense knowledge comprises classes such as steps for tasks, responses to situations, and locations and uses of objects. Filtering refines the commonsense knowledge into useful class rules. A second level of rules referred to as meta-rules performs reasoning by responding to user commands or observed situations, orchestrating the class rules and generating a sequence of task steps. A task sequencer processes the generated task steps and drives the mechanical systems of the autonomous machine.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
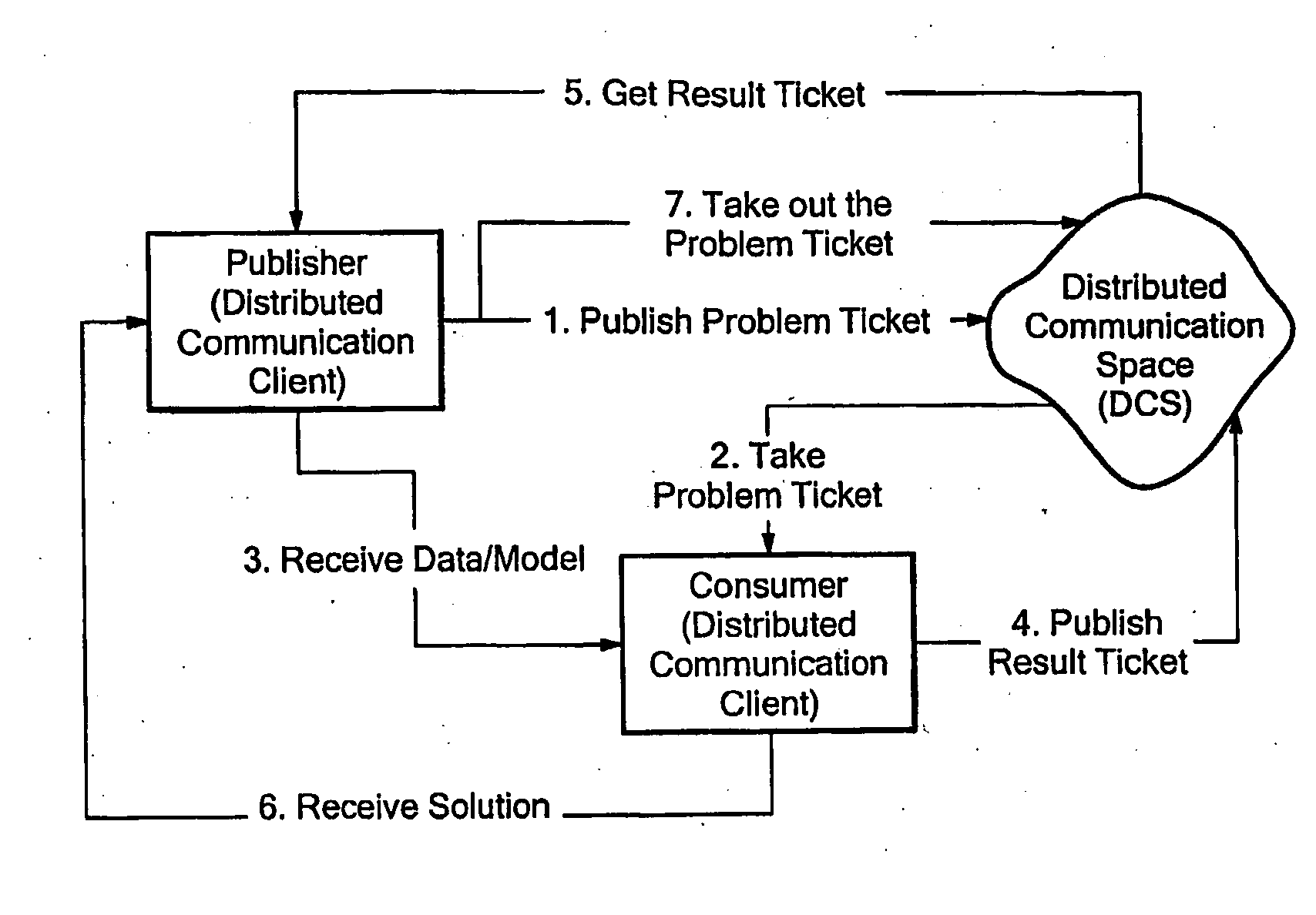
Peer-to-Peer Distributed Computational System and Method
InactiveUS20080196087A1Efficient processingQuick implementationResource allocationError detection/correctionVirtual spaceDistributed computing
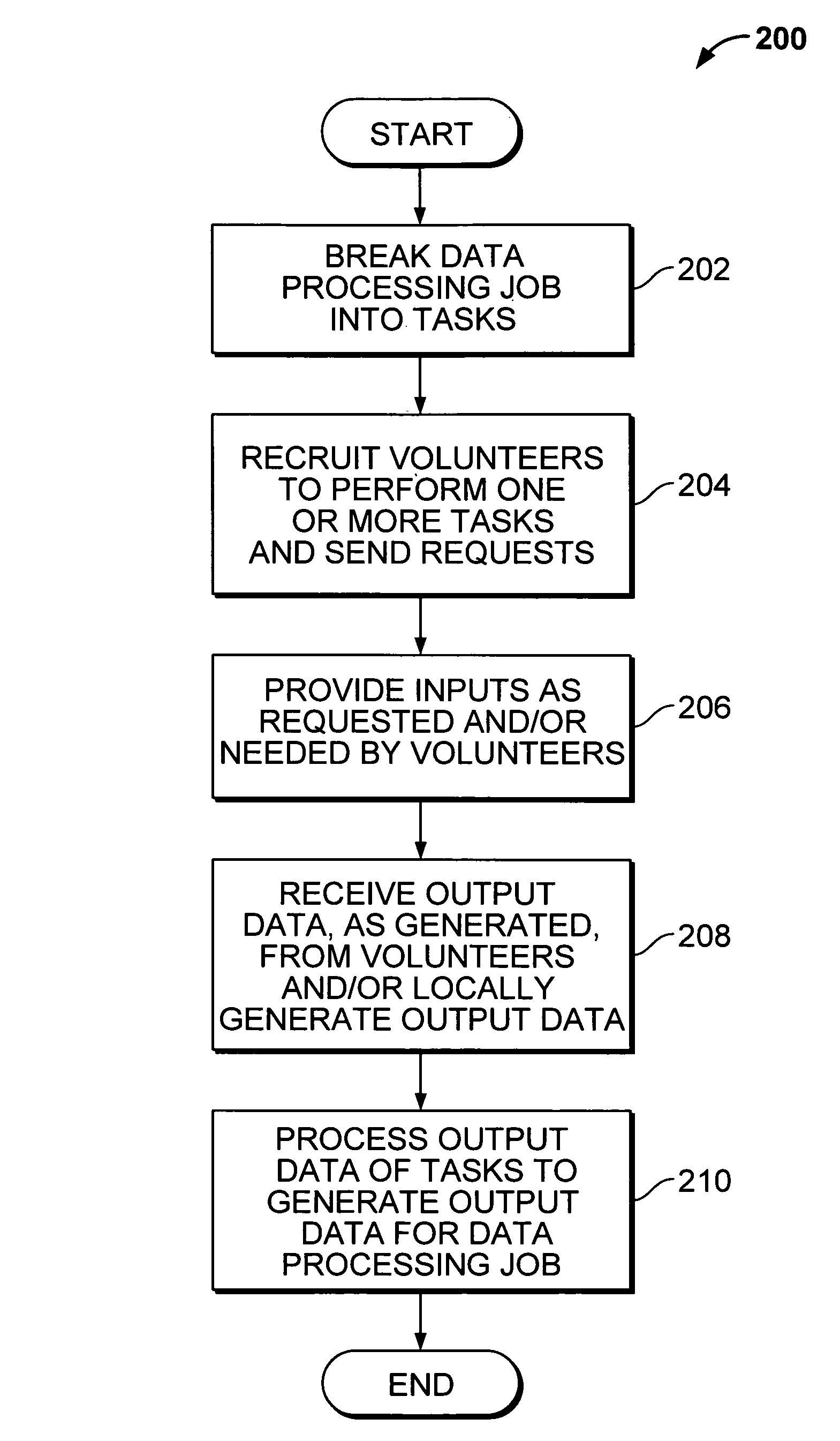
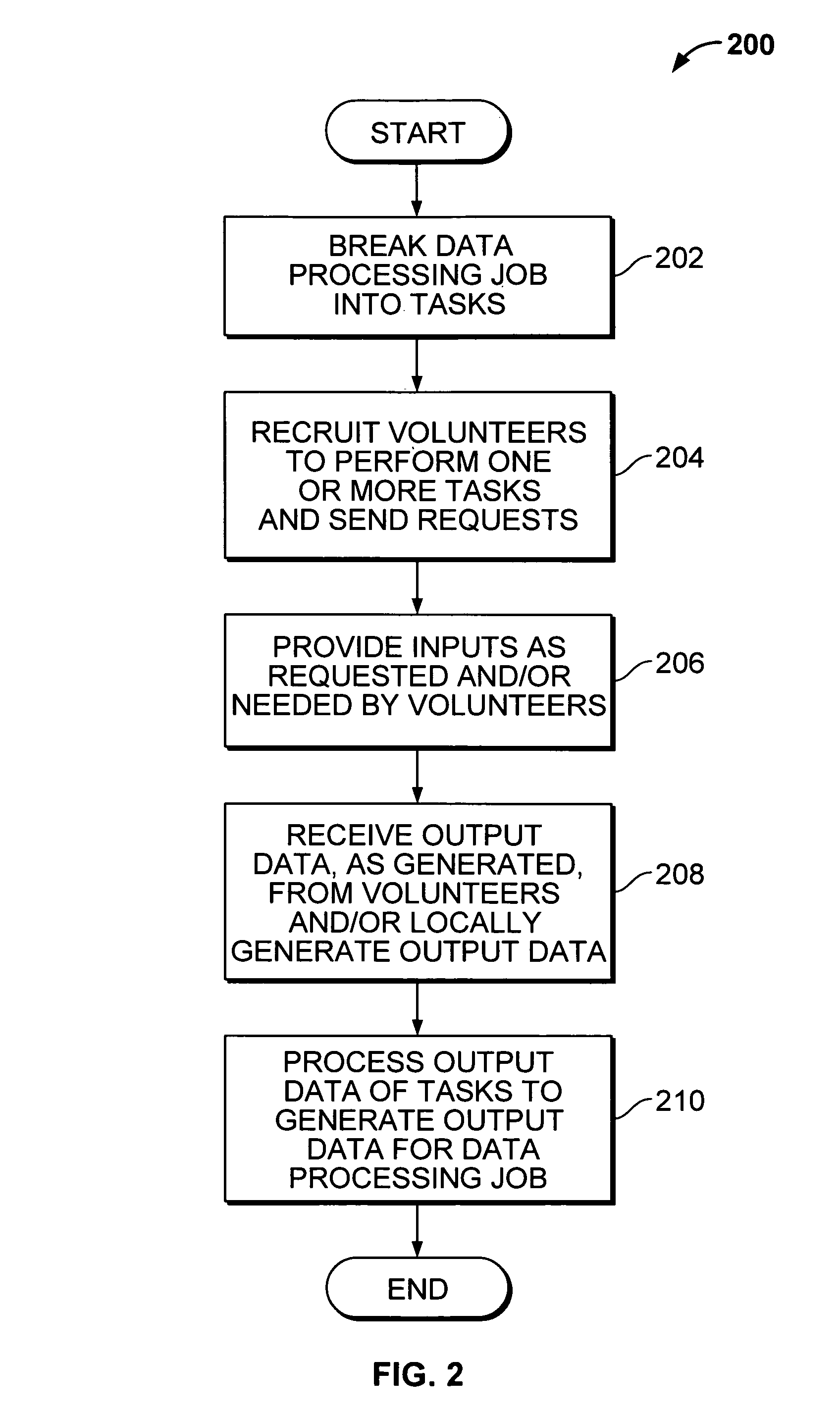
A distributed computing system operates in a peer to peer (P2P) network to take advantage of idle or unused resources. The system facilitates the reception of a problem definition that can be picked up for processing by any peer in the network community on an anonymous basis. The peers in the network community are volunteers, and return solutions to a virtual space to be picked up by the entity proposing the problem. The problem and solution specifications are stored in circular first in first out queues, so that a number of solutions can be provided to any given problem definition.
Owner:TEEZNAR CORP
Mirrored file system
InactiveUS7797670B2Error detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsData processing systemFile system
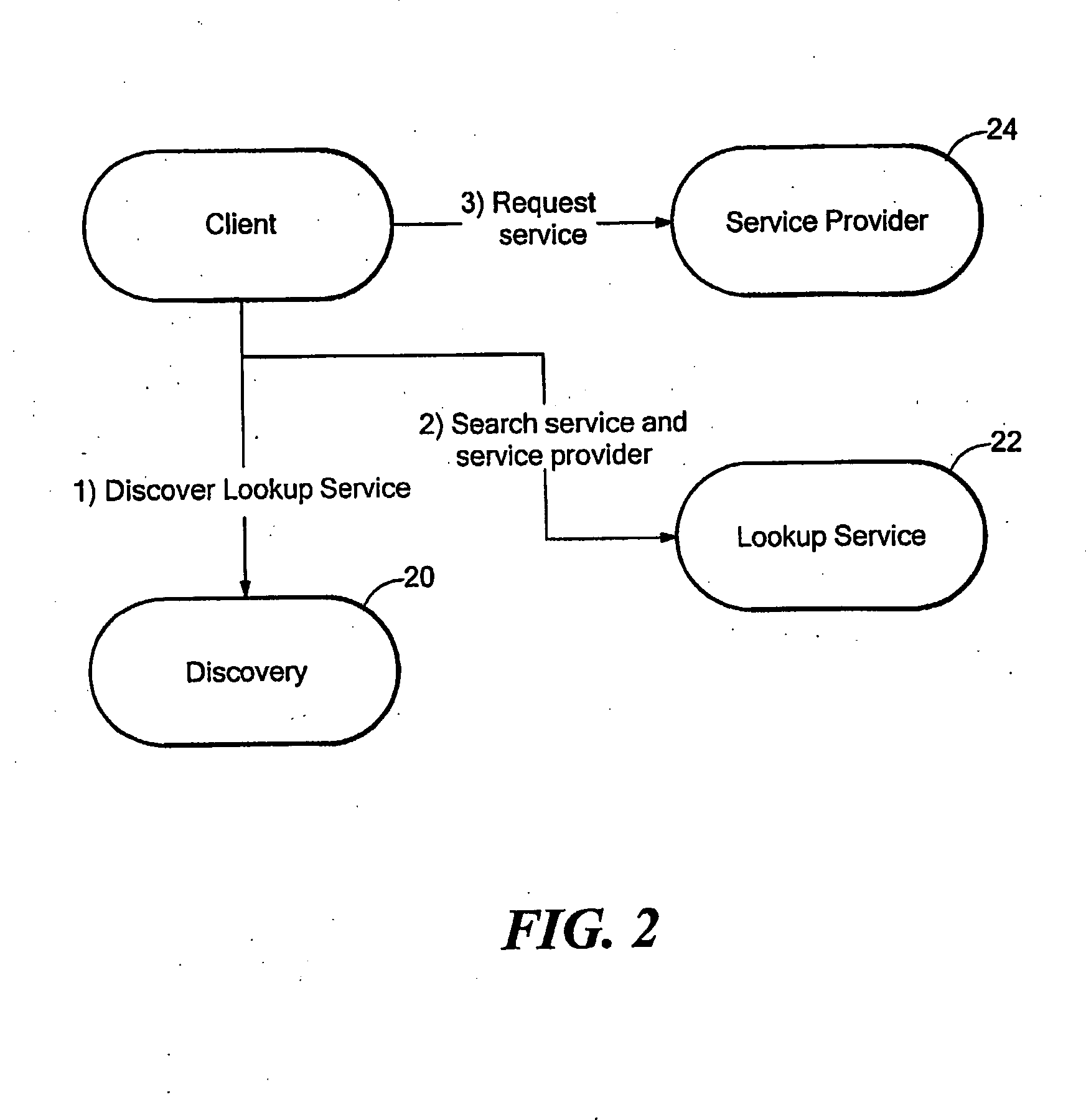
Mounting and populating a mirrored version of at least a portion of a file system of a recruiter machine at a volunteer machine performing one or more data processing tasks for the recruiter machine is disclosed. In some embodiments, an input stored in such a dedicated file system for the recruiter machine at the volunteer machine may be locally retrieved and reused, if still consistent with a corresponding input stored in a file system at the recruiter machine, when performing a data processing task for the recruiter machine at the volunteer machine. In some embodiments, if an input required by the volunteer machine to perform a data processing task for the recruiter machine is not cached in such a dedicated file system for the recruiter machine at the volunteer machine in a state that is consistent with a corresponding input stored in a file system at the recruiter machine, the input is obtained from the recruiter machine.
Owner:APPLE INC
Wireless positioning method for mobile phone terminal
ActiveCN106454747AImprove positioning accuracySolve the problem of large positioning errorsPosition fixationWireless commuication servicesCurve fittingWireless data
The invention belongs to the field of wireless data communication and specifically discloses a wireless positioning method for a mobile phone terminal. The method comprises the following steps of step 1.sorting signal strengths from small to large and solving a percentage probability P(R), a median, a mode and a mean value which are corresponding to each signal strength distribution; step 2.carrying out curve fitting on the signal strength probability distributions and carrying out peak detection on a fitted curve, if two or more of peak values exist, taking the maximum peak value in the curve fitting as a signal strength characteristic value; step 3.if only one peak value exists, carrying out step 4, if two peak values exist, taking the right peak value and carrying out step 8; and step 4.computing a coefficient of skew Cs of the probability distribution. The wireless positioning method for the mobile phone terminal is provided for the technical problem that the limitation is great when a volunteer works and carries out fingerprint positioning on the mean value of RSSI signal characteristic values due to complexity and dynamics of the indoor environment.
Owner:重庆市志愿服务工作指导中心
Dynamic vehicle disaster relief
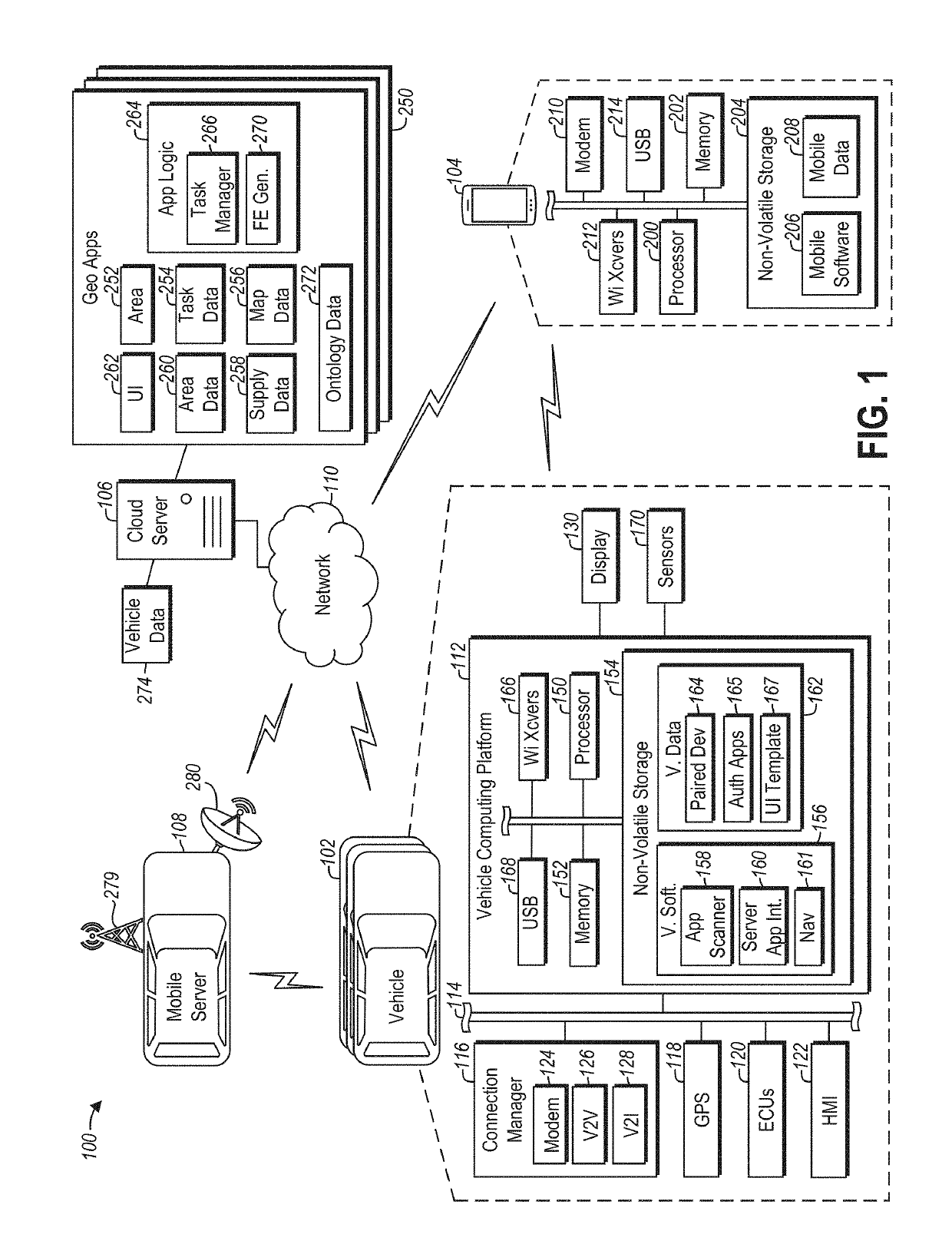
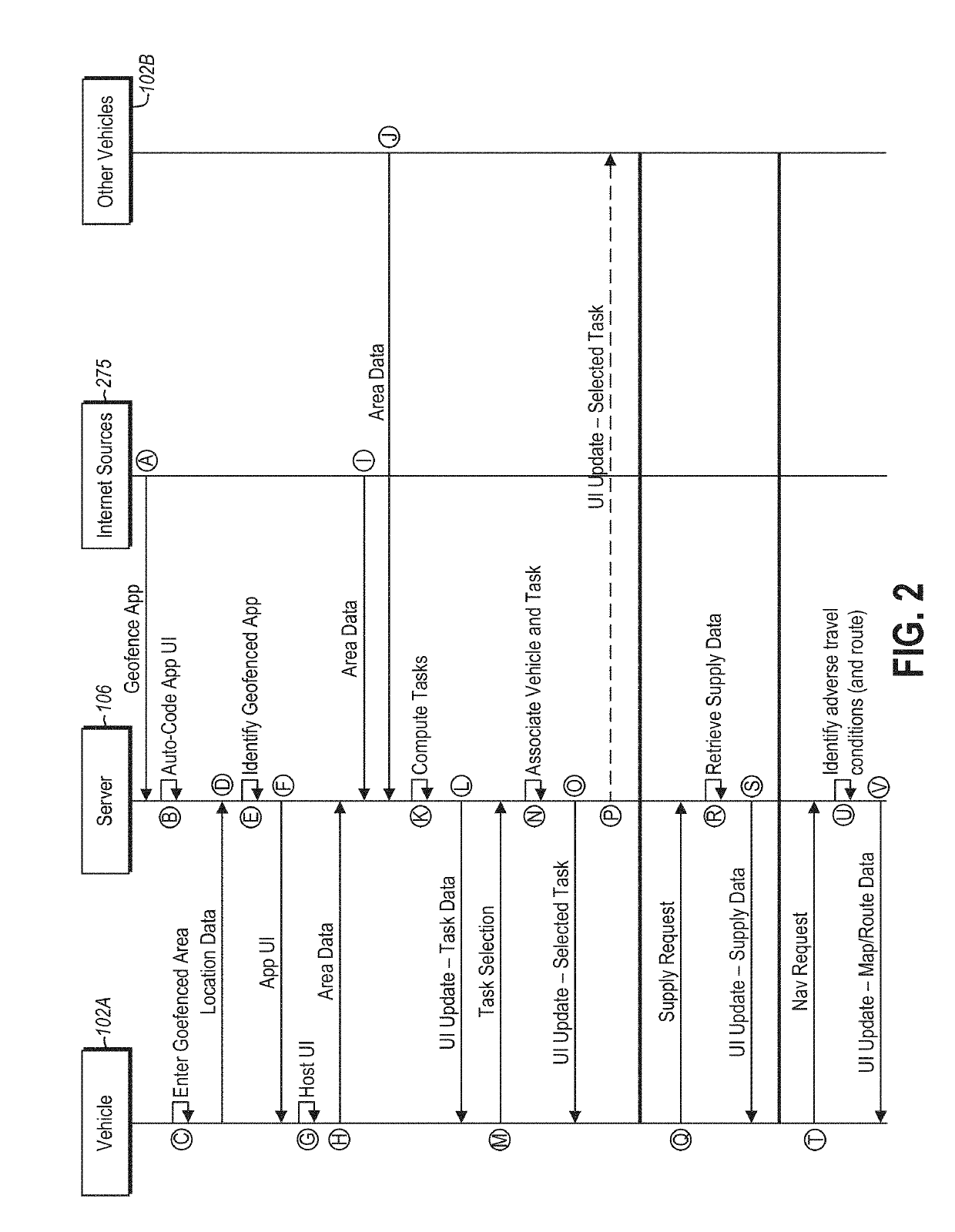
ActiveUS20190342739A1Instruments for road network navigationData processing applicationsUser interfaceGeo-fence
Systems and methods for dynamic vehicle disaster relief include a vehicle that, responsive to entering a geofenced area including a disaster, communicates the vehicle is within the geofenced area to a server. The vehicle installs a user interface received from the server responsive to the communication. The user interface is for a geofenced application associated with the geofenced area and executing on the server. The vehicle then communicates a volunteer commit message from the user interface to the geofenced application on the server.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Arginine ibuprofen tablet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101390844AFast-acting antipyreticFast-acting analgesiaOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticMedicineArginine
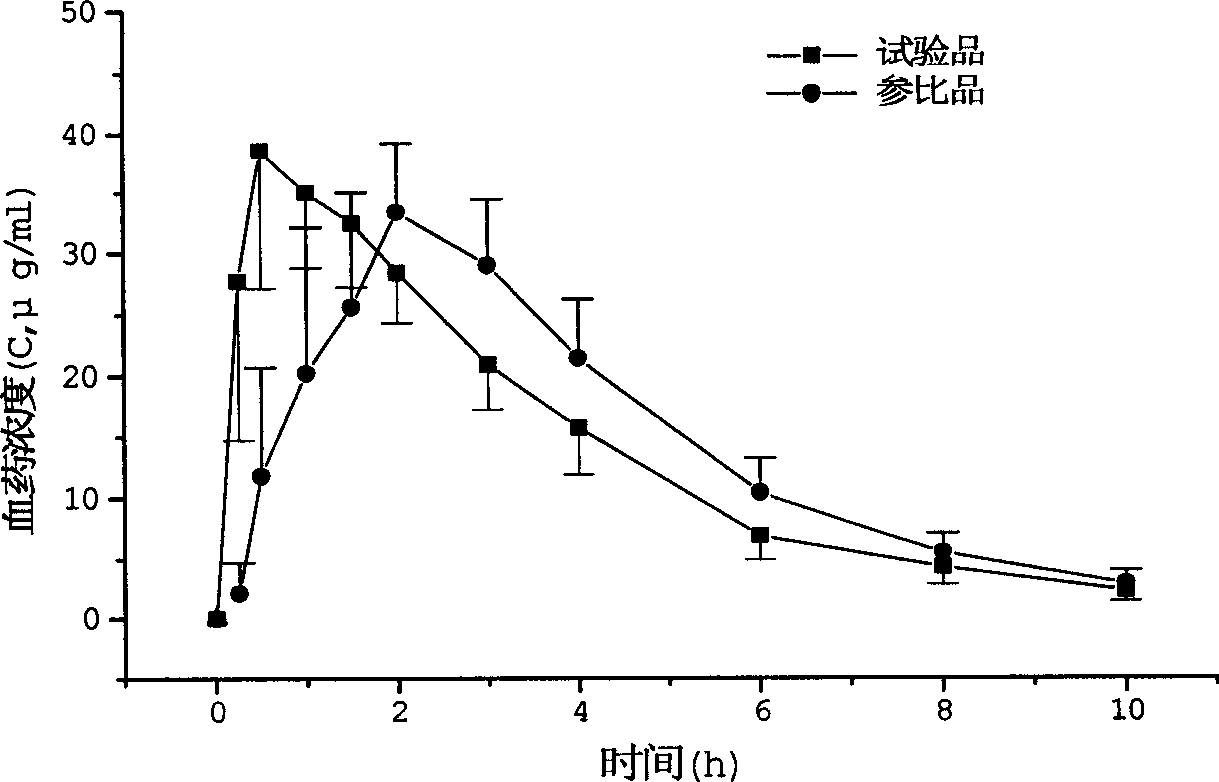
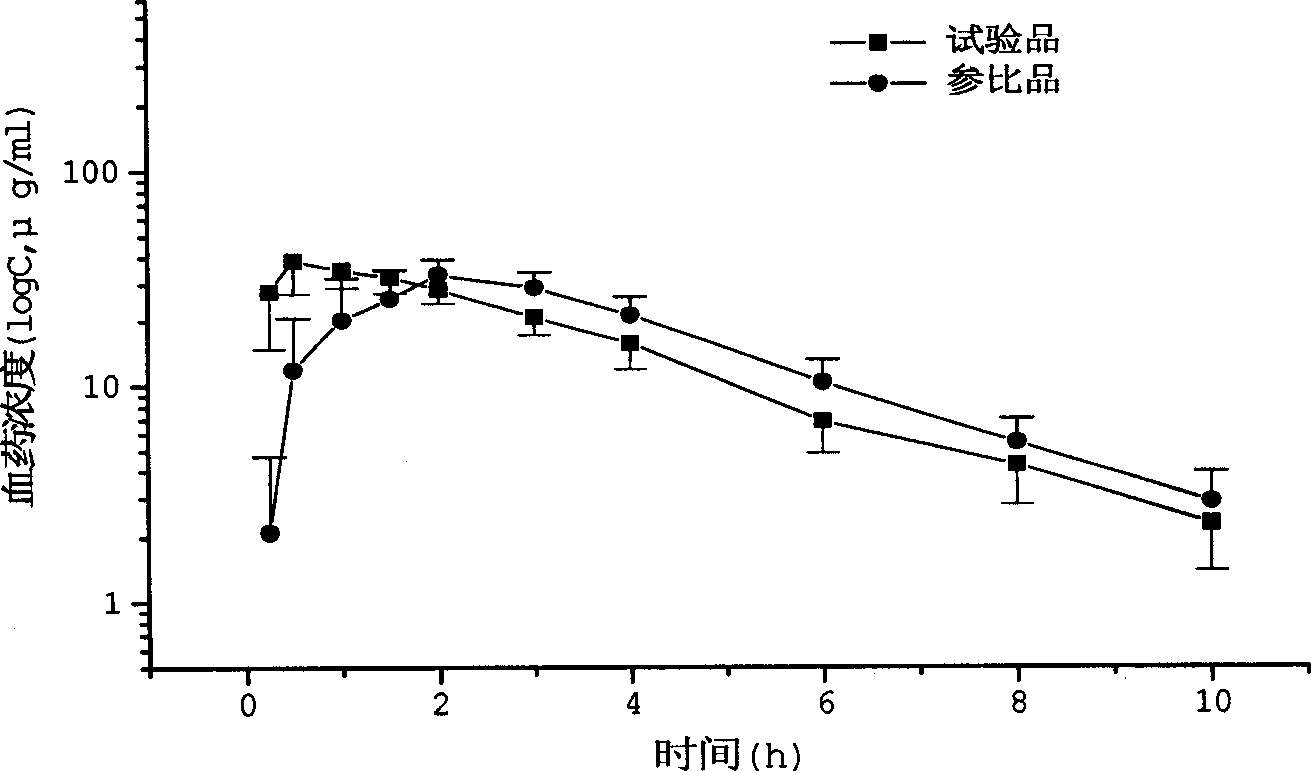
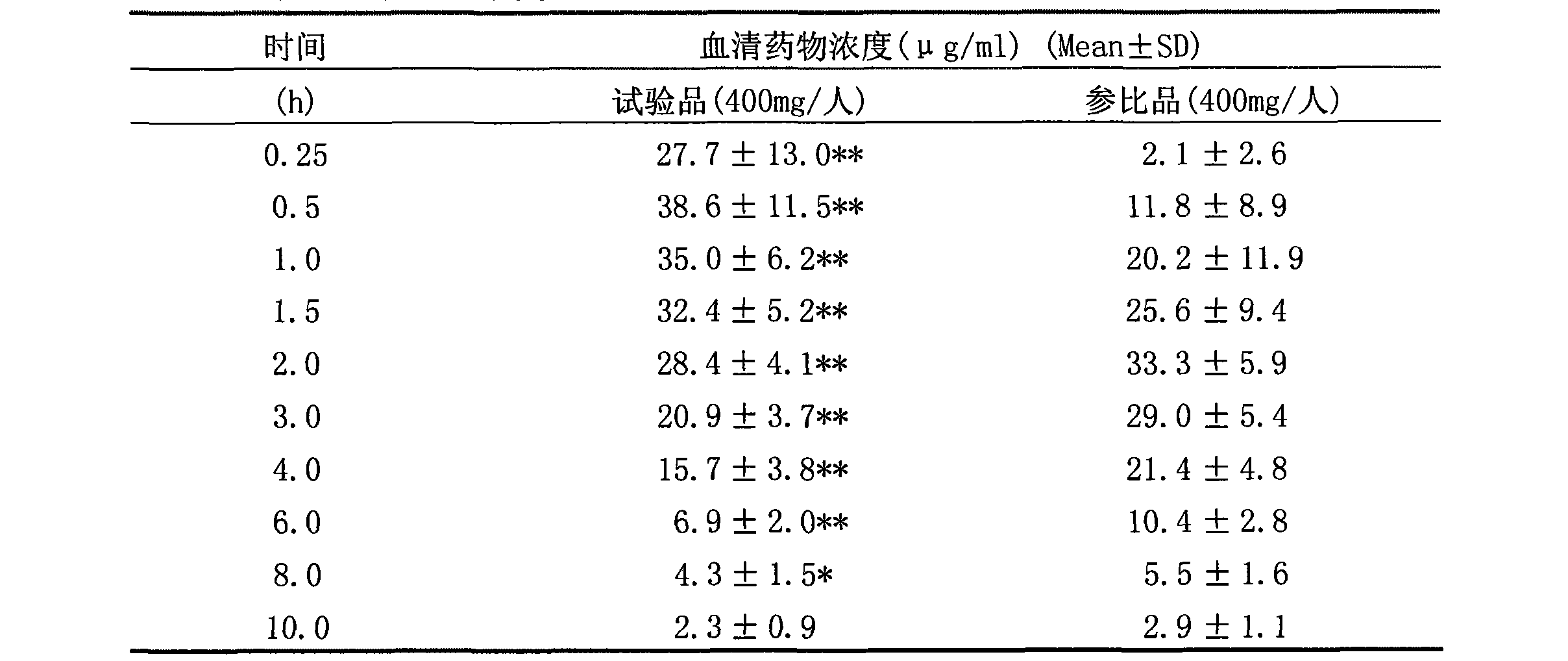
The invention relates to an arginine ibuprofen tablet which is antipyretic and analgesic, and a preparation method. The arginine ibuprofen tablet contains arginine ibuprofen and auxiliary material by weight proportion: 30%-90% of arginine ibuprofen, 10%-70% of auxiliary material and 0-10% of coating material. The preparation method adopts raw material direction compression or granule preparation; the prepared tablet can be coated or not be coated. The arginine ibuprofen tablet has short response time. As indicated in dissolution test, the dissolution rate is more than 95% in 20 minutes. 20 male volunteers take two preparations of arginine ibuprofen tablets (equal to 400 mg of ibuprofen) and ibuprofen tablets (400mg) for relative bioavailability research; the peak time of arginine ibuprofen tablet is 0.5h and the peak time of ibuprofen tablet is 2.0h. The test indicates that the arginine ibuprofen tablet has quick absorption and short peak time. Besides, the arginine ibuprofen tablet overcomes the pungent taste of arginine ibuprofen syrup and granules and can be taken by patients conveniently, so as to have the advantages of convenient carrying and low cost.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Tools and methods for determining relationship values
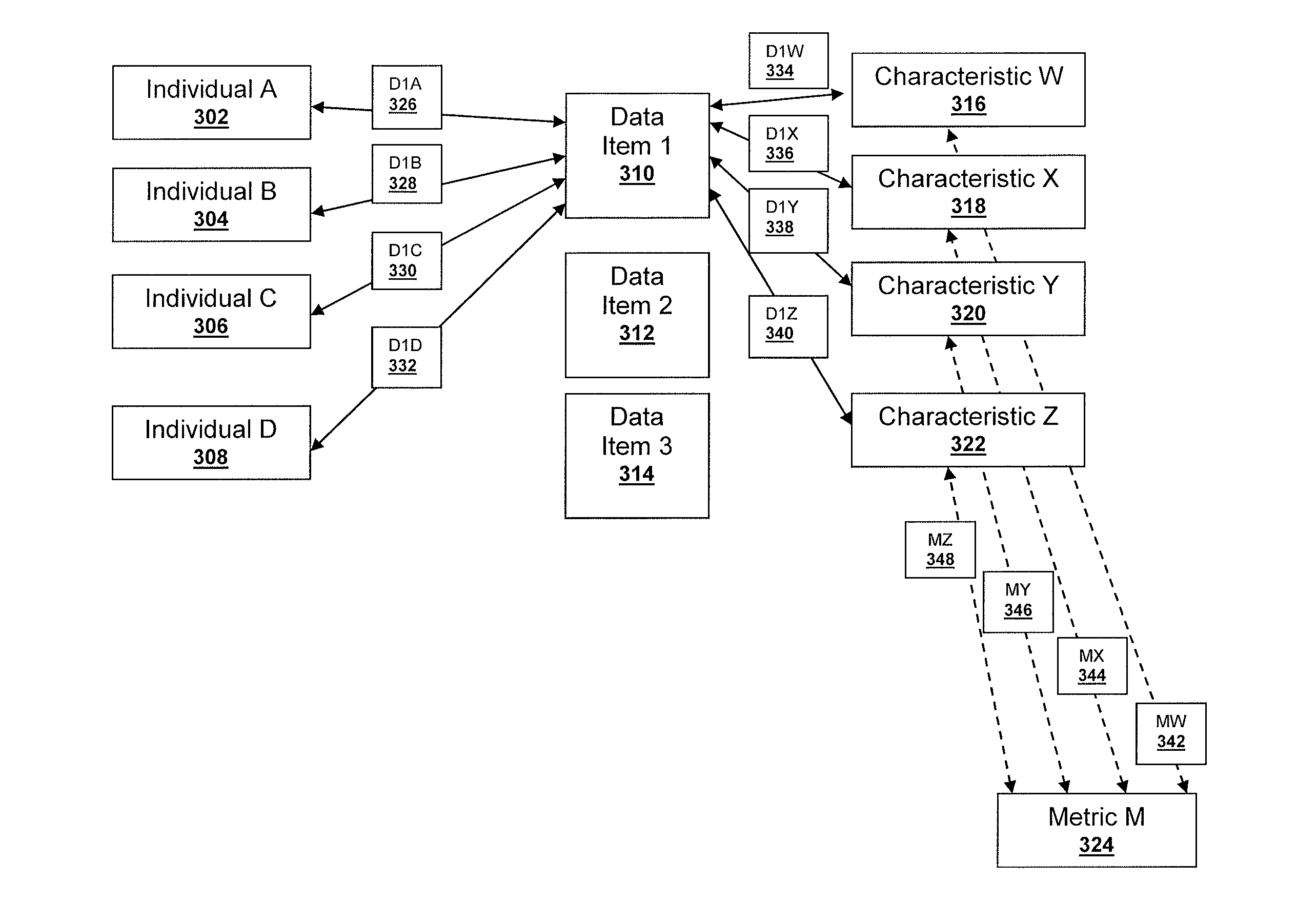
System, apparatus, and methods for profiling constituents of an organization. These constituents may include donors, volunteers, supporters, advocates, stakeholders, affiliates, customers, employees, managers, executives, advisors, regulators, vendors, suppliers, partners, contractors, beneficiaries, friends, followers, or fans of any organization. In one implementation, the relationship of constituents to an organization is determined. The system, apparatus, and methods may store characteristics describing constituents generally, along with metrics relevant to an organization; receive a plurality of data items; extract information associated with the constituents from the data items; determine a number of relationships between the data items, constituents, metric, and characteristics; and use the relationships to determine an overall relationship between the constituents and the organization, based on the data and characteristics. In addition, related groups of characteristics may be identified. Similarly, the relationships between any constituent, organization, metric, sub-metric, group of characteristics, data item, data source, characteristic, or groups thereof may also be determined.
Owner:TREISER ADAM
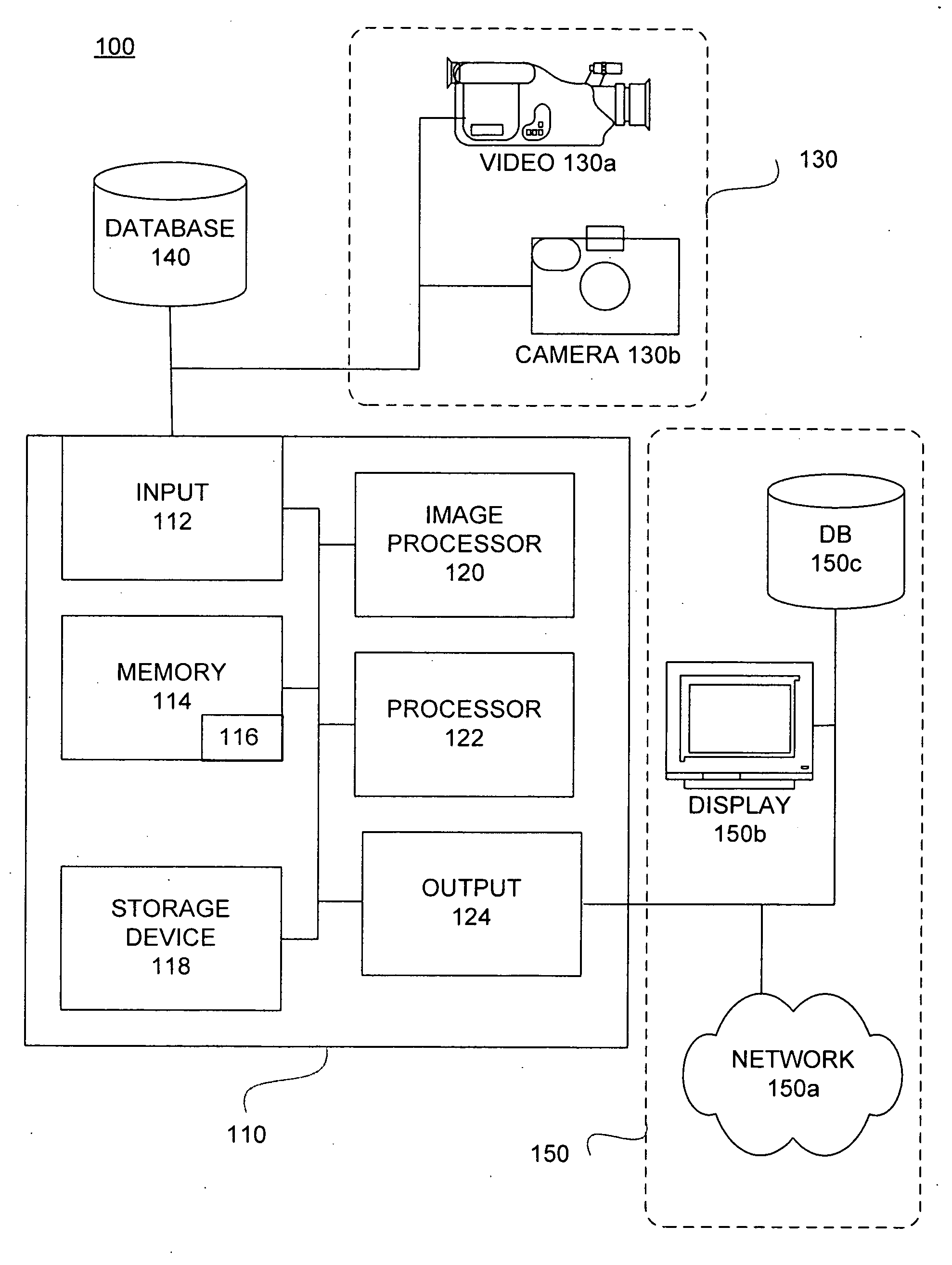
Remote non-invasive biofeedback diagnostic system based on patient image
InactiveUS6921365B2Accurate diagnosisImprove intuitionElectroencephalographySurgeryDiseaseComputer monitor
A non-invasive remote diagnostic system includes a central processing unit (CPU) adapted to feed an image of a patient such as a digital photograph to be displayed to an operator by a first computer monitor. A second computer monitor is displaying a realistic outline of a target area of diagnostic interest such as an outline of a human organ or a particular portion thereof. These two monitors together with a CPU are adapted to induce a state of heightened consciousness and intuition of a system operator. A detecting / evaluating unit is sensing non-invasively the operator's biofeedback response while the operator is exposed to the images. The biofeedback response is converted to an electrical signal and is fed back into the CPU to compare against a predetermined database of similar signals obtained from volunteers with known diseases. The biofeedback signal allows a non-invasive remote diagnosis of a patient's state of health.
Owner:CLINICTECH
Chinese medicine extracting liquid eye plaster and preparation thereof
ActiveCN101264131ARelieve eye fatigueVisual fatigue hasSenses disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsAcute toxicity testingIrritation
The invention relates to eye mask for healthcare product for eyes and the preparation method, which is characterized in that: the eye mask comprises non woven fabric adding medical solution; following raw material of weight are added into each 1000 ml of medical liquor: ginsenoside 2 to 3g, lucid ganoderma and spores powder 0.08 to 0.12g, pearl 2 to 3g, puerarin 0.4 to 0.6g, wild chrysanthemum flower 18 to 25g, mint 15 to 18g, musk 0.06 to 0.08g and borneol 0.2 to 0.6g. Through test of Health Supervision Test Center of Jilin Province: acute toxicity experiment of mouse skin shows that the eye mask does not have toxin; acute eye irritation experiment of rabbit shows the does not have irritation; test of 40 tested volunteers with fatigable eyesight shows that the eye mask has the function of relieving fatigue of eyesight.
Owner:力神药业(吉林)有限公司
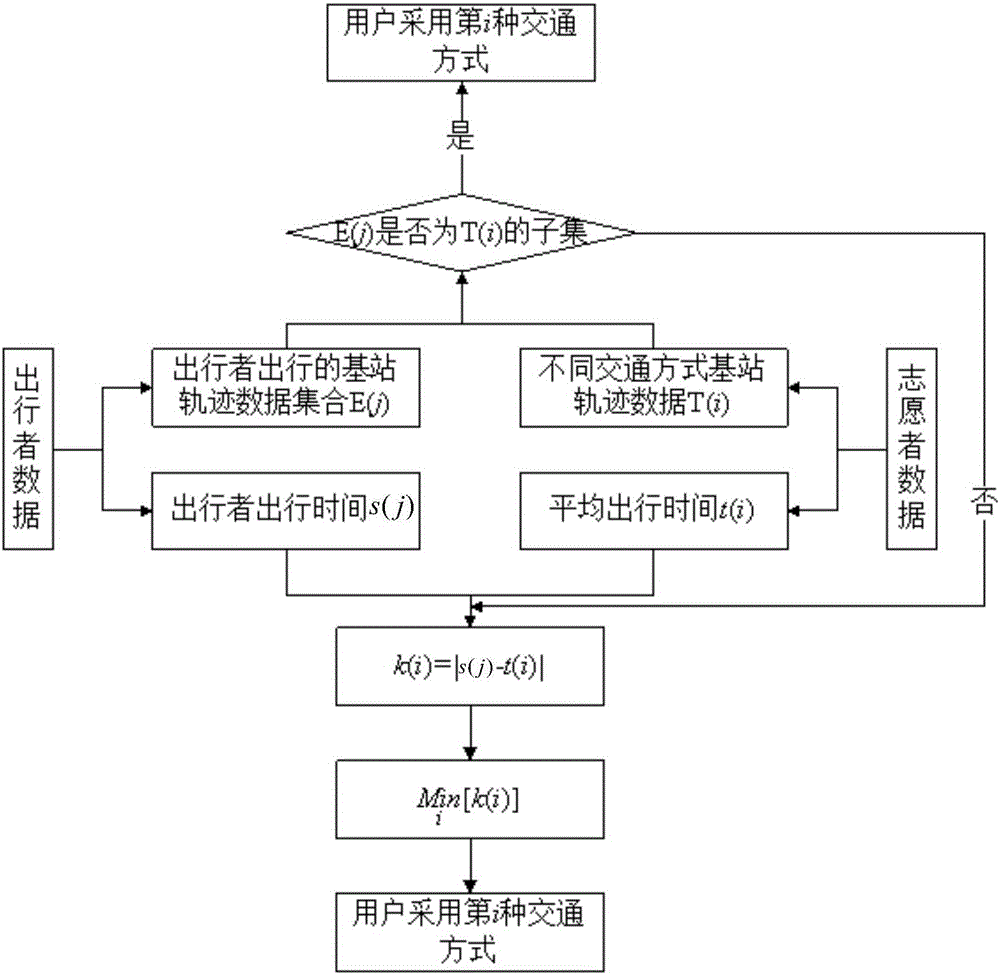
Method for classifying long-distance travel transportation types based on data of mobile phones
ActiveCN106448173AMake up for the lack of high costHigh precisionDetection of traffic movementComputer scienceMobile phone
The invention discloses a method for classifying long-distance travel transportation types based on data of mobile phones. The method comprises the following steps of 1, determining a common class I travel transportation type between a city A and a city B, and obtaining travel information of a volunteer and signaling data of the mobile phone; 2, obtaining a complete track point set T(i) and travel time t(i) of each type of travel path in the class I travel transportation type; 3, extracting a traveler set C between the two cities; 4, obtaining a track point set E(j) of each traveler in the set C; (5) obtaining a travel user set D between the city A and the city B; 6, judging the relationship between the track point set E(j) of each traveler in the set D and the set T(i); under the conditions of formula shown in the attached figure, and unique i value, judging that the j-th traveler adopts the class i transportation type; 7, under the conditions of formula shown in the attached figure, and non-unique i value, calculating the travel time s(j) of the j-th traveler, selecting the travel time, which is most approximate to the travel time s(j), of the corresponding transportation type from the possible value of i value, and using as the transportation type of the j-th traveler. The method has the advantage that the transportation type of the traveler crossing the cities can be accurately identified.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Polypeptide compound for removing wrinkles in eyes and preparation method of polypeptide compound
ActiveCN105232352AAvoid formingSpeed up circulationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWrinkle skinDipeptide
The invention provides a polypeptide compound for removing wrinkles in eyes. The polypeptide compound, in percentage by mass, consists of the following components: 0.02-0.035% of acetyl hexapeptide-3, 0.001-0.01% of palmitoyl pentapeptide-3, 0.025-0.035% of palmitoyl tetrapeptide-7, 0.025-0.035% of tripeptide, 0.08-0.12% of dipeptide-2, 0.1-0.2% of acetyl tetrapeptide-5, 4-6% of glycerol, 0.2-0.4% of sodium hyaluronate, 0.3-0.5% of 1,2-hexanediol and the balance of purified water. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a preparation method of the compound. The polypeptide compound for removing wrinkles in eyes provided by the invention, applied to volunteers, is capable of taking a significant effect of relieving wrinkles in eyes, so that the average quantity of the wrinkles in eyes is reduced, the depth of the wrinkles in eyes is reduced, the smoothness of eye skin is enhanced, the coverage area of the wrinkles in eyes is reduced and the phenomenon of the wrinkles in eyes is significantly improved.
Owner:卡丝生物(广东)科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com