Patents
Literature
105results about "Correlation spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
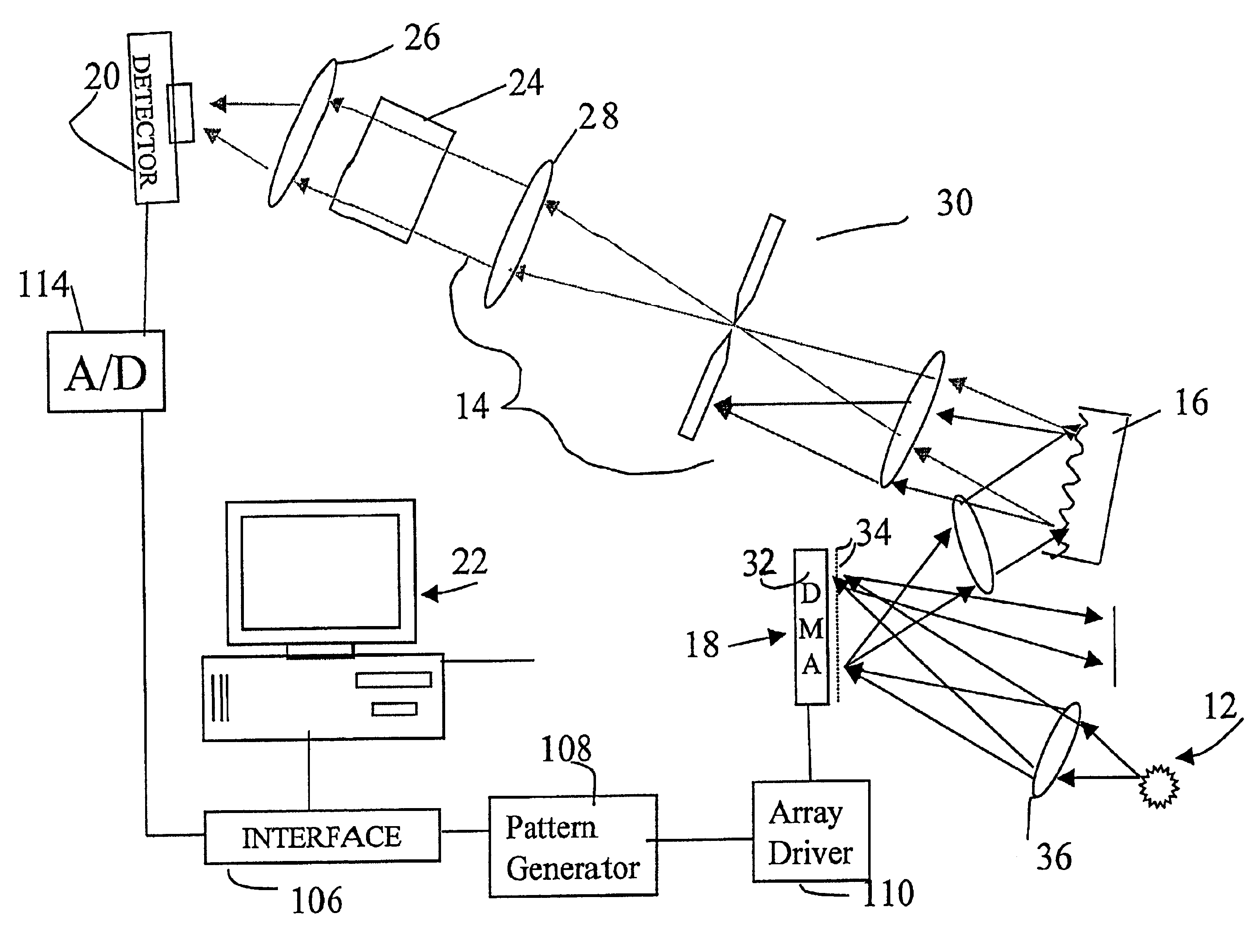
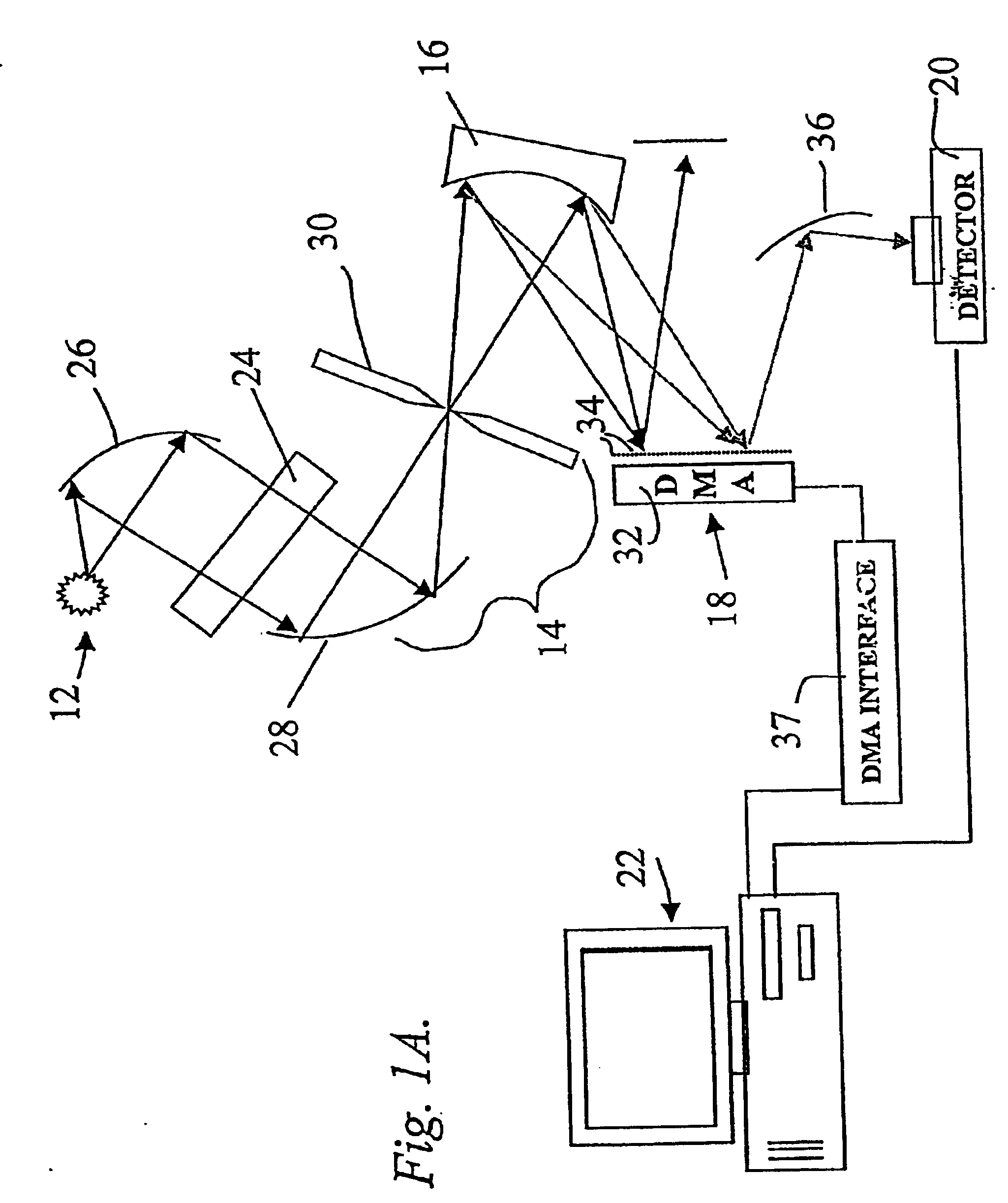
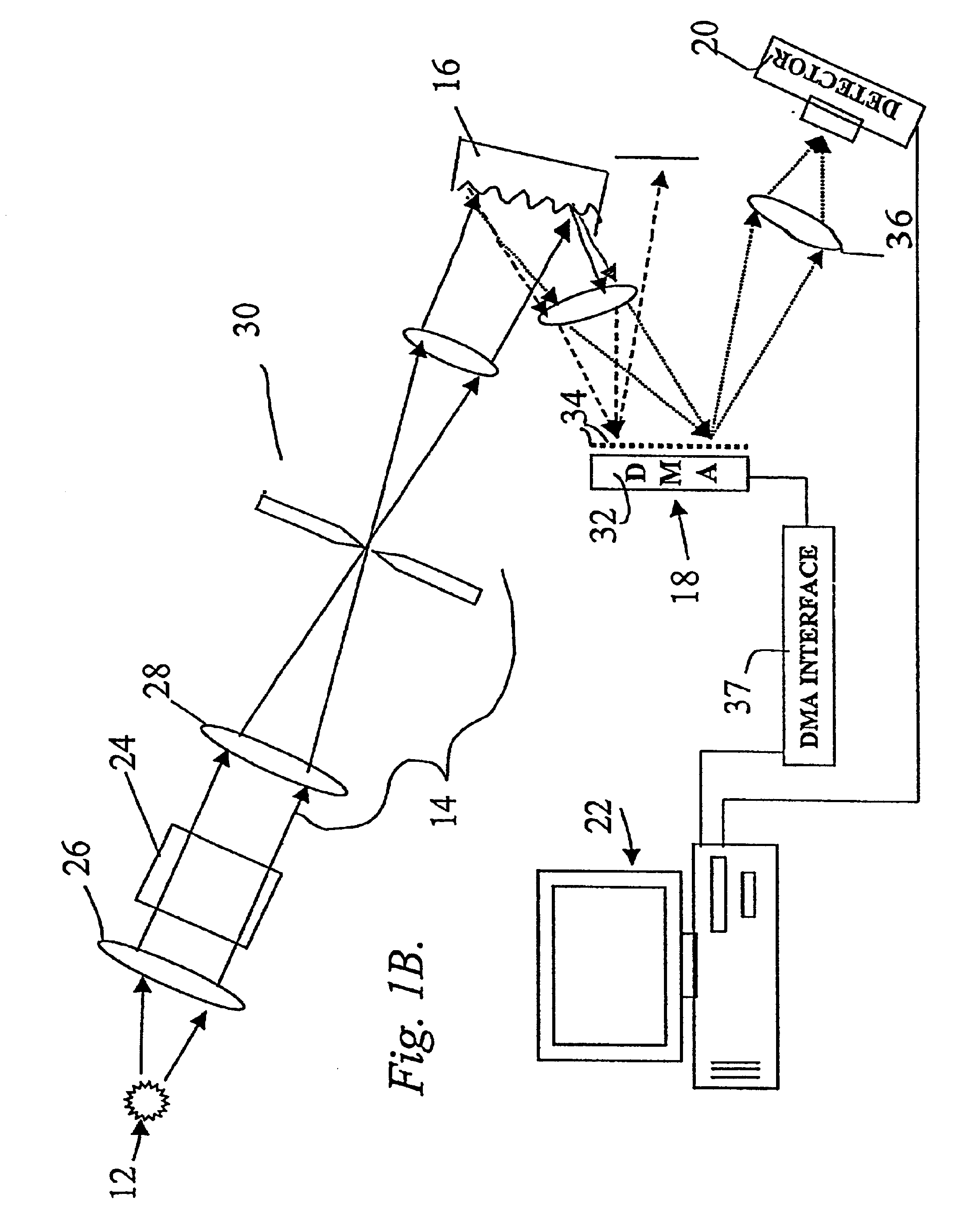
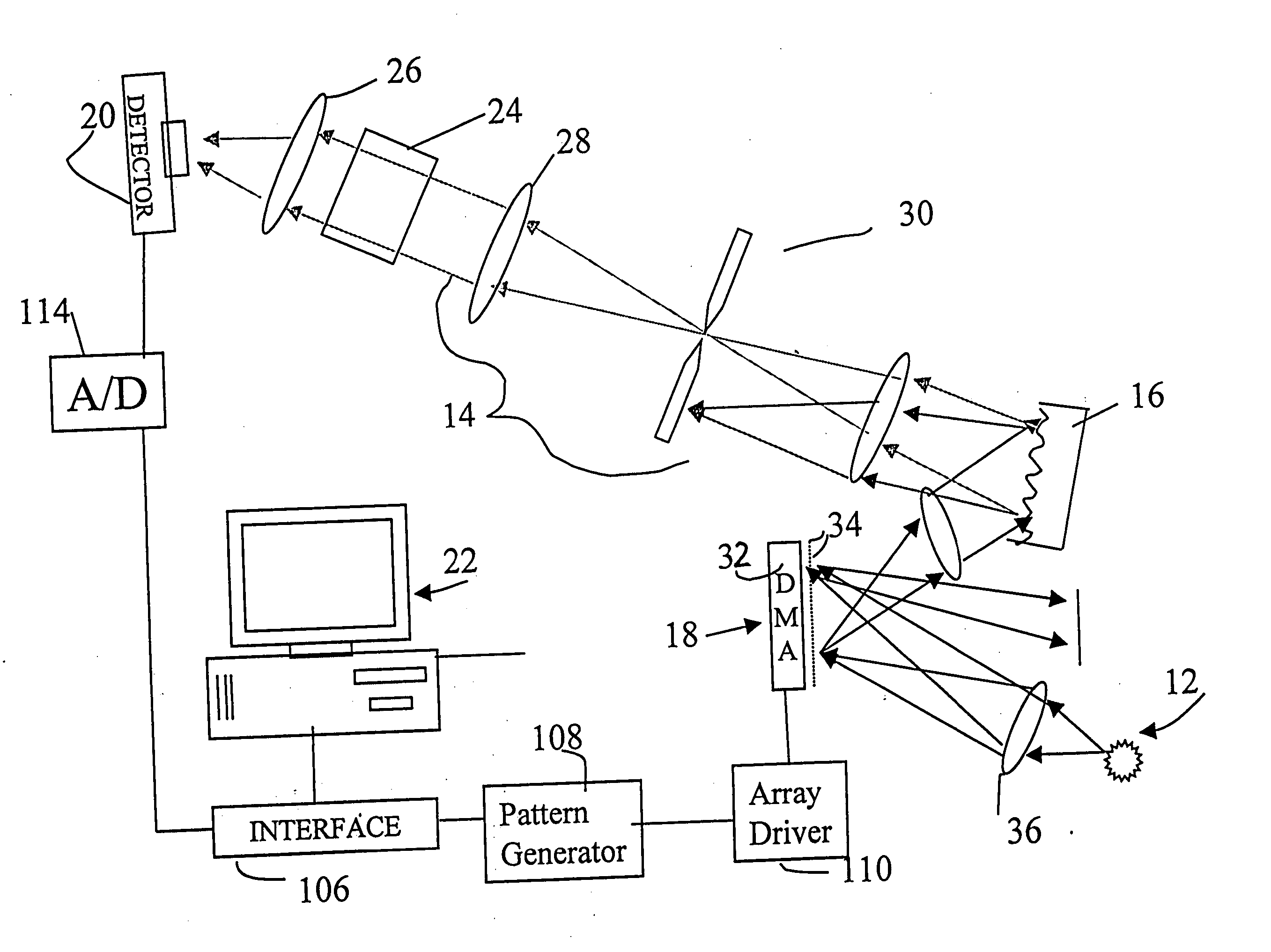
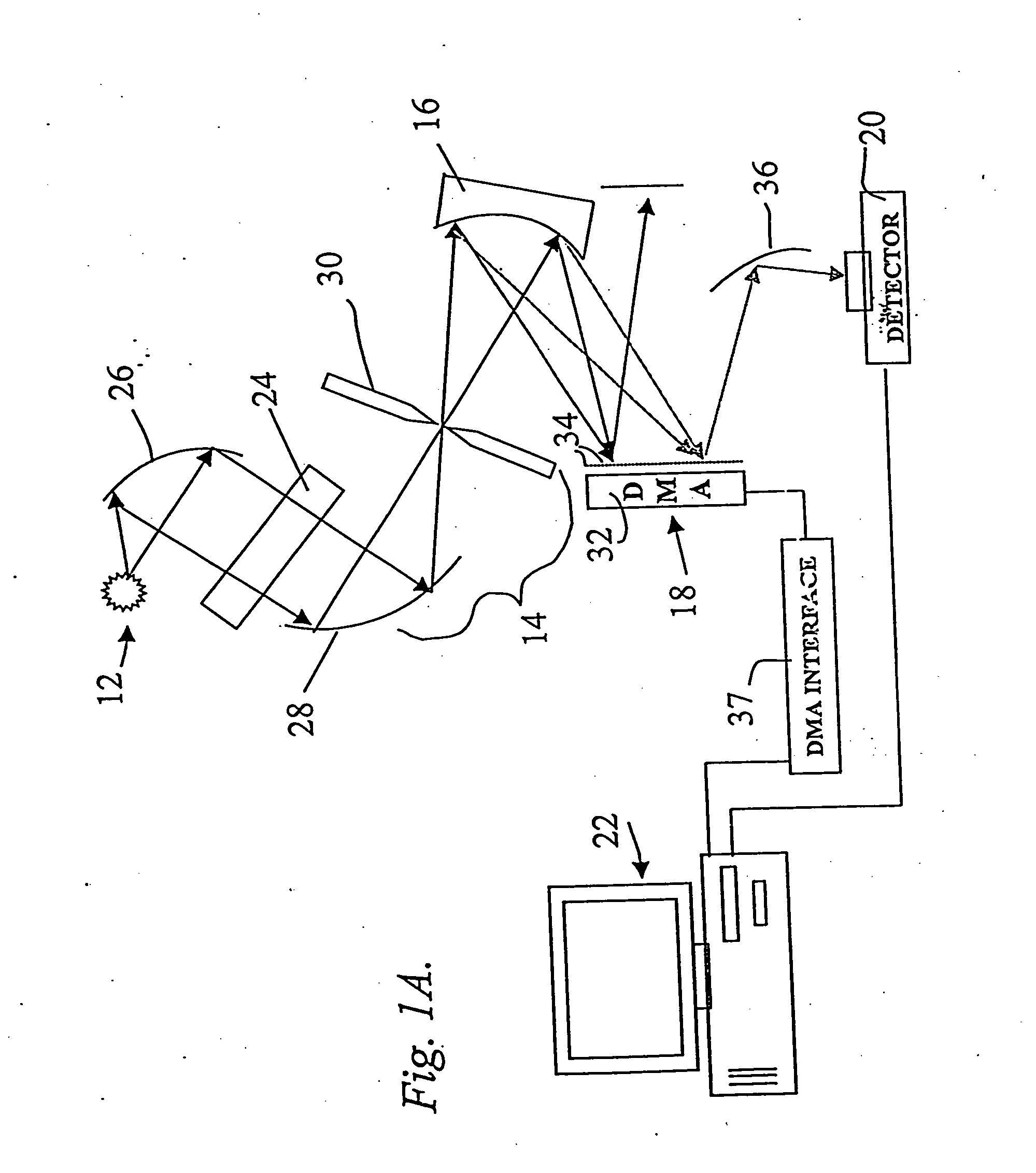
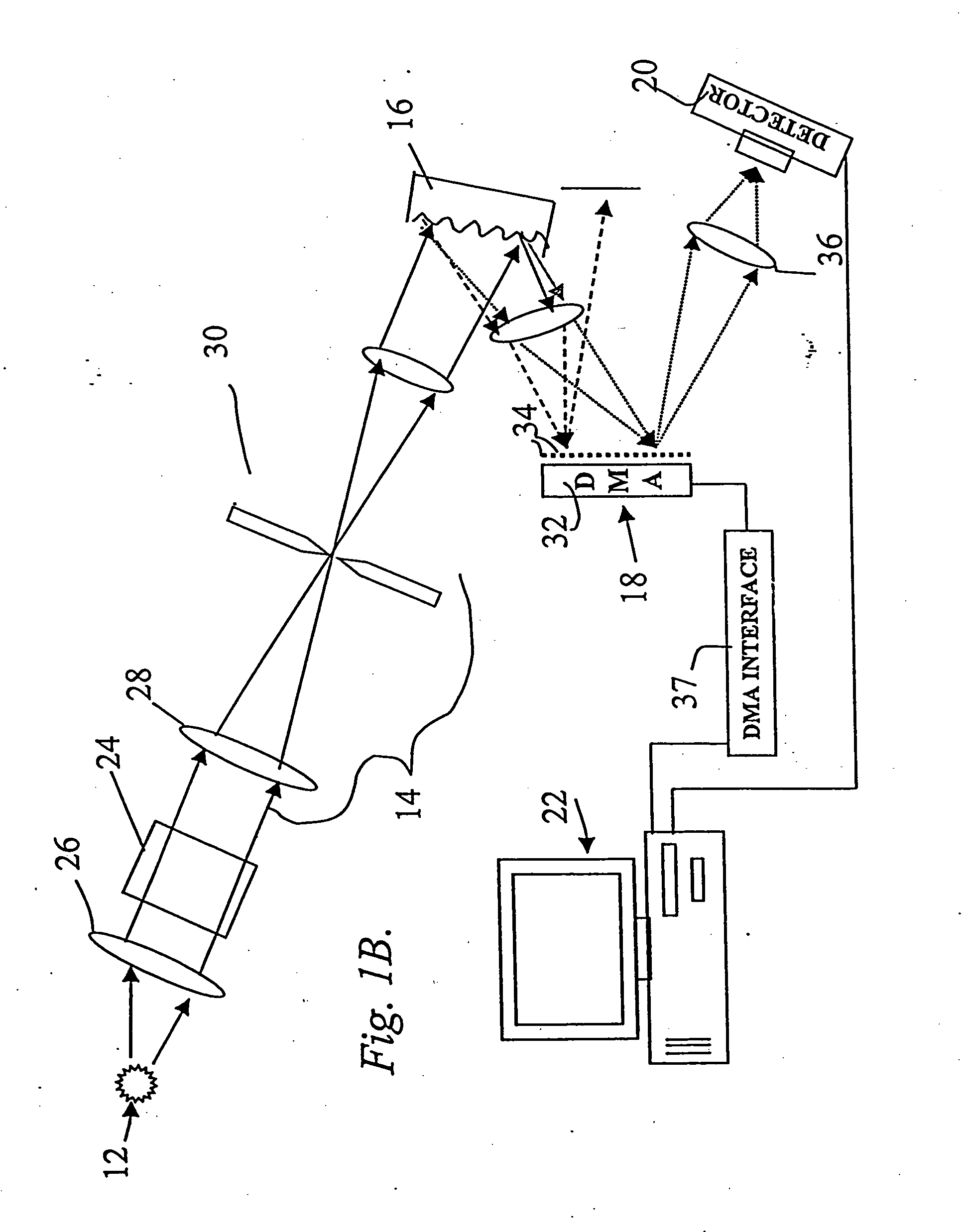
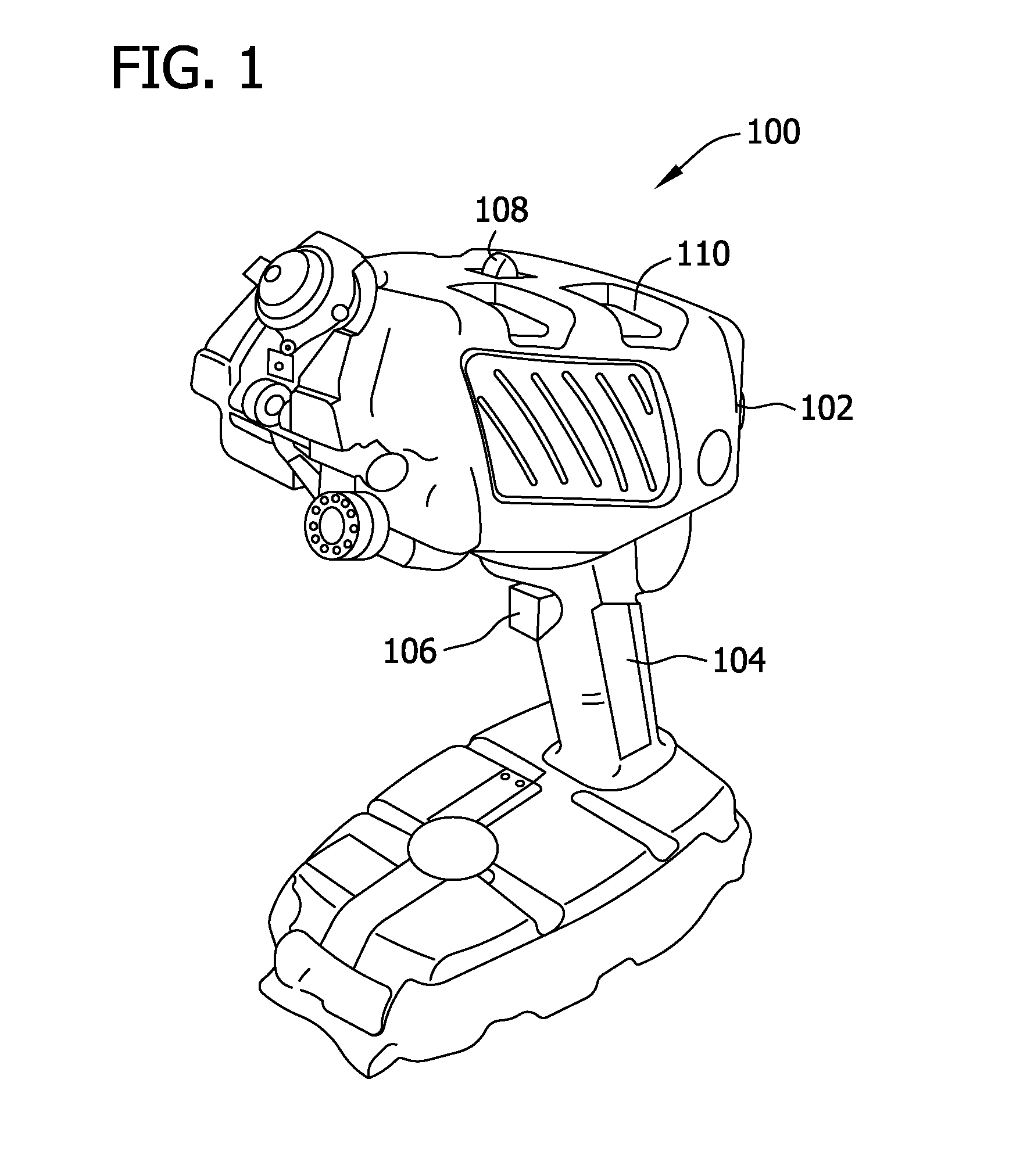
System and method for encoded spatio-spectral information processing
InactiveUS6859275B2Less sensitive to ambient noiseEasy to operateRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsInformation processingLength wave
Encoded spatio-spectral information processing is performed using a system having a radiation source, wavelength dispersion device and two-dimensional switching array, such as digital micro-mirror array (DMA). In one aspect, spectral components from a sample are dispersed in space and modulated separately by the switching array, each element of which may operate according to a predetermined encoding pattern. The encoded spectral components can then be detected and analyzed. In a different aspect, the switching array can be used to provide a controllable radiation source for illuminating a sample with radiation patterns that have predetermined characteristics and separately encoded components. Various applications are disclosed.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT SYST
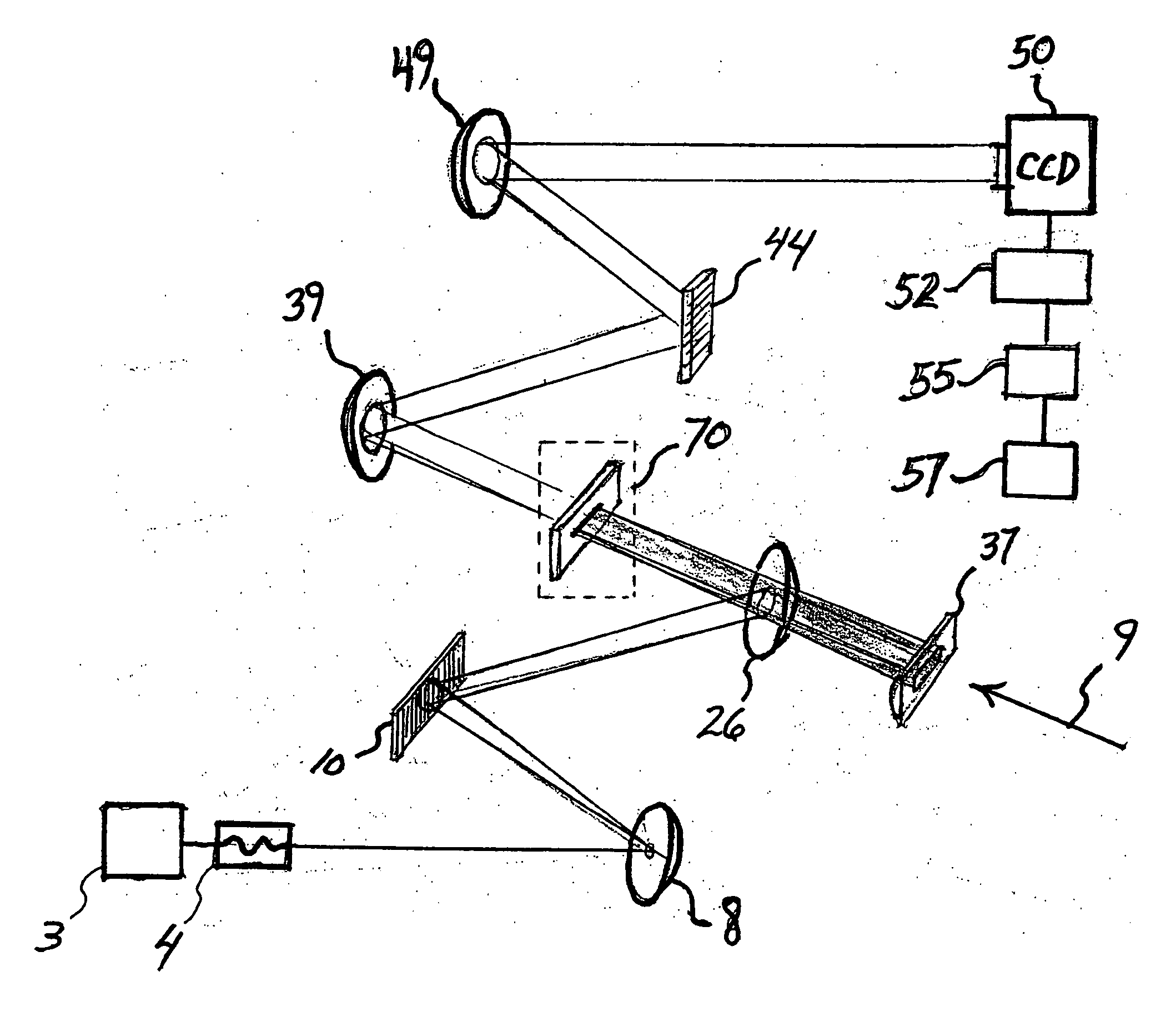
Method and apparatus for two-dimensional spectroscopy
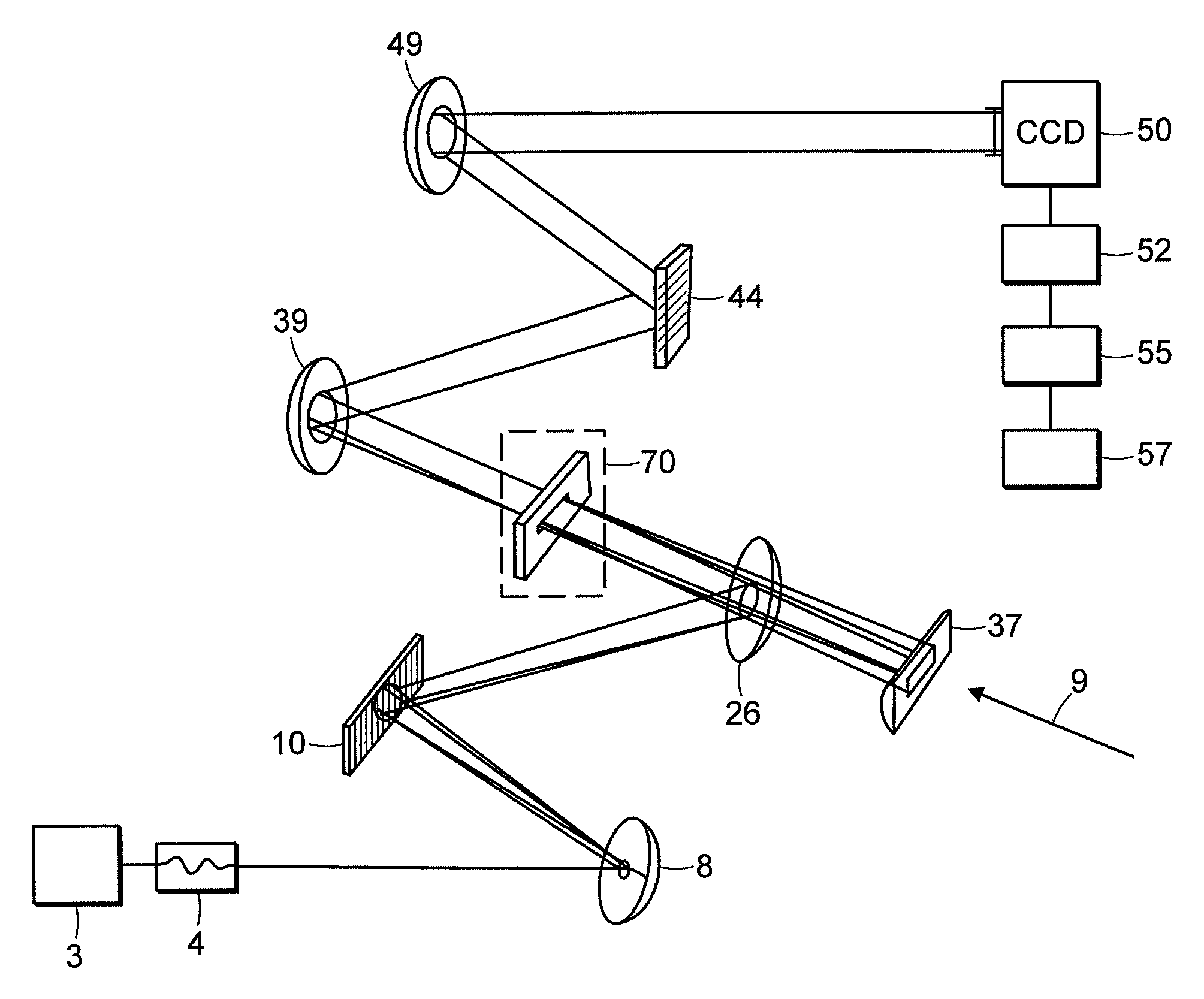
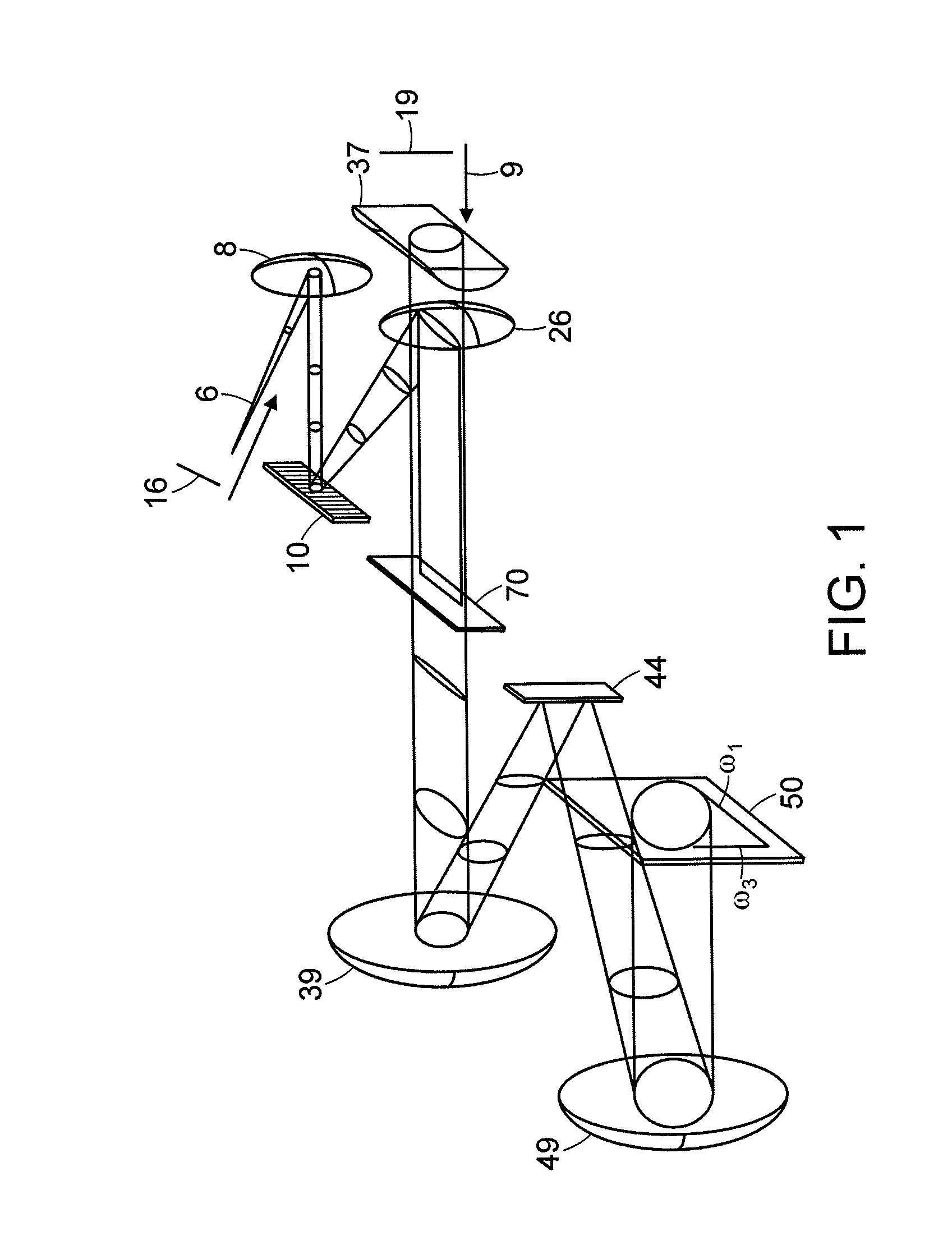
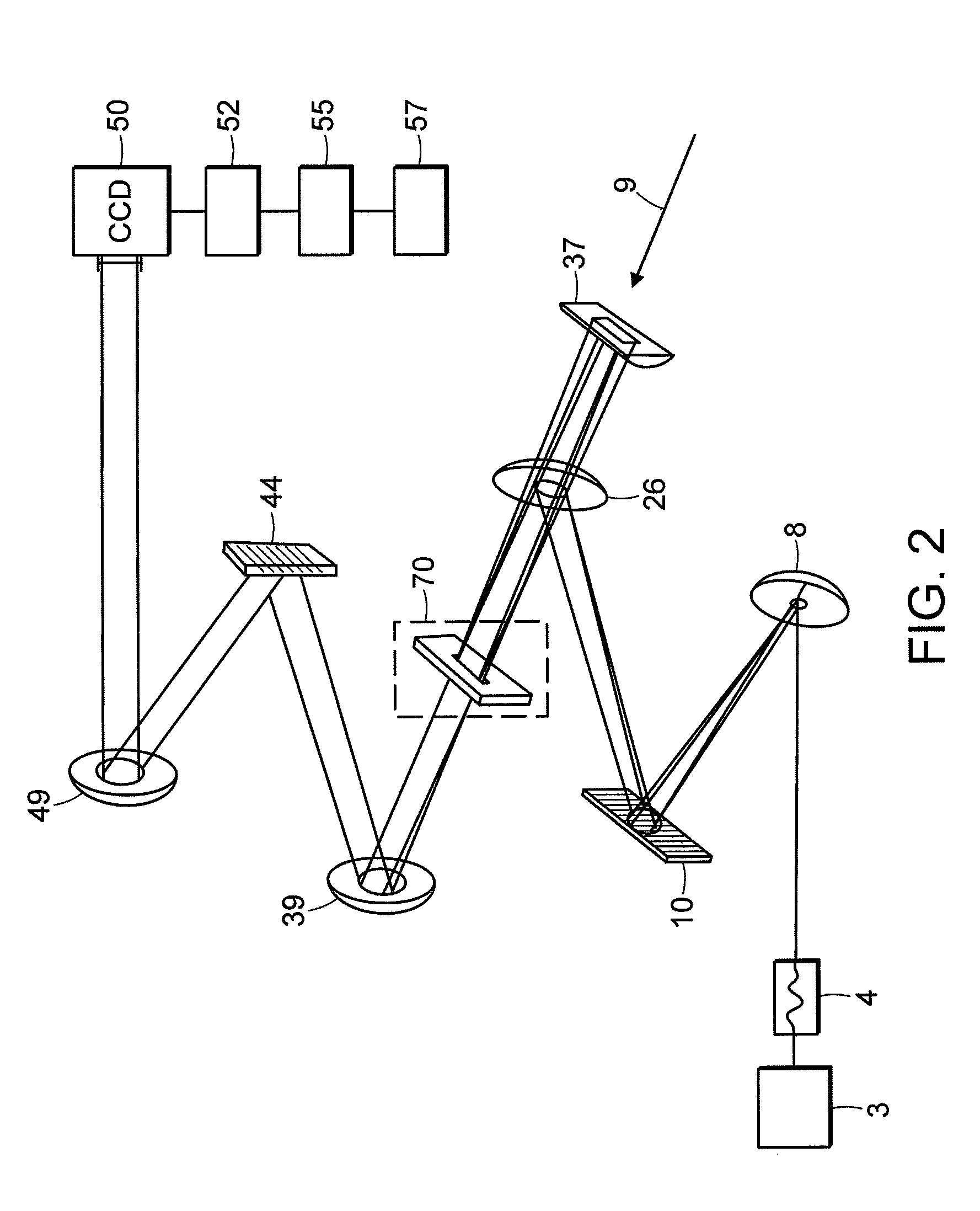
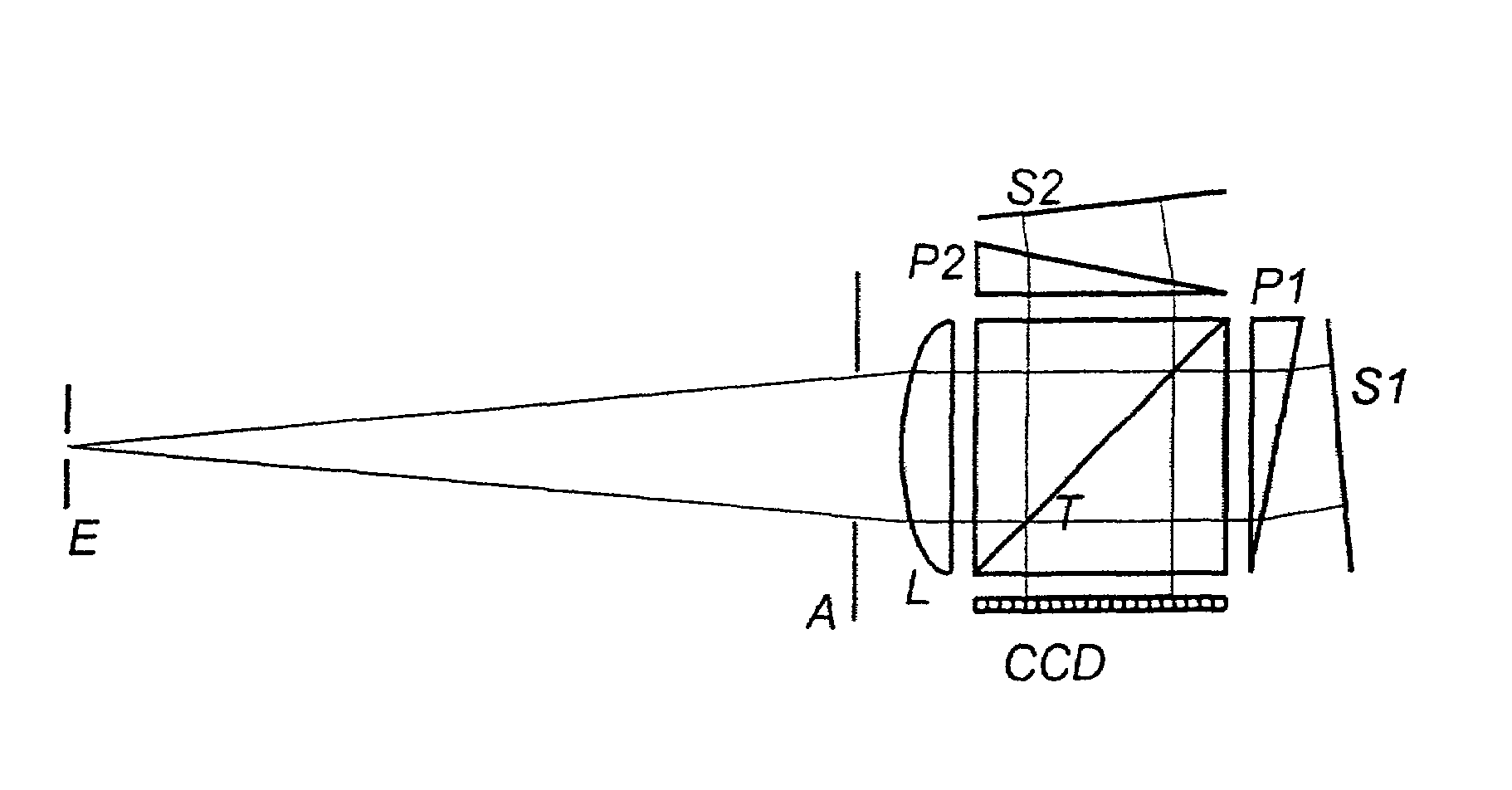
Preferred embodiments of the invention provide for methods and systems of 2D spectroscopy using ultrafast, first light and second light beams and a CCD array detector. A cylindrically-focused second light beam interrogates a target that is optically interactive with a frequency-dispersed excitation (first light) pulse, whereupon the second light beam is frequency-dispersed at right angle orientation to its line of focus, so that the horizontal dimension encodes the spatial location of the second light pulse and the first light frequency, while the vertical dimension encodes the second light frequency. Differential spectra of the first and second light pulses result in a 2D frequency-frequency surface equivalent to double-resonance spectroscopy. Because the first light frequency is spatially encoded in the sample, an entire surface can be acquired in a single interaction of the first and second light pulses.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
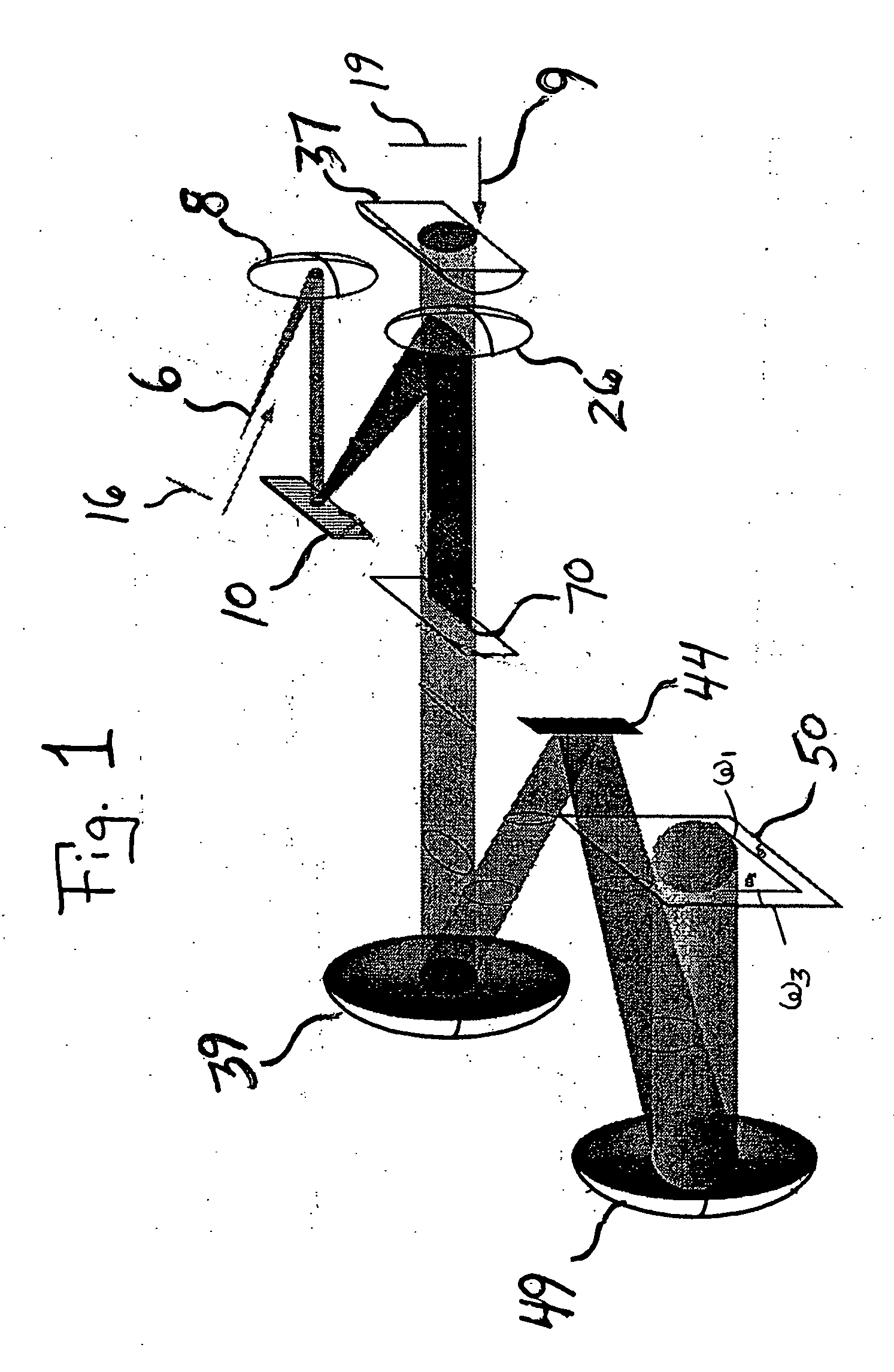
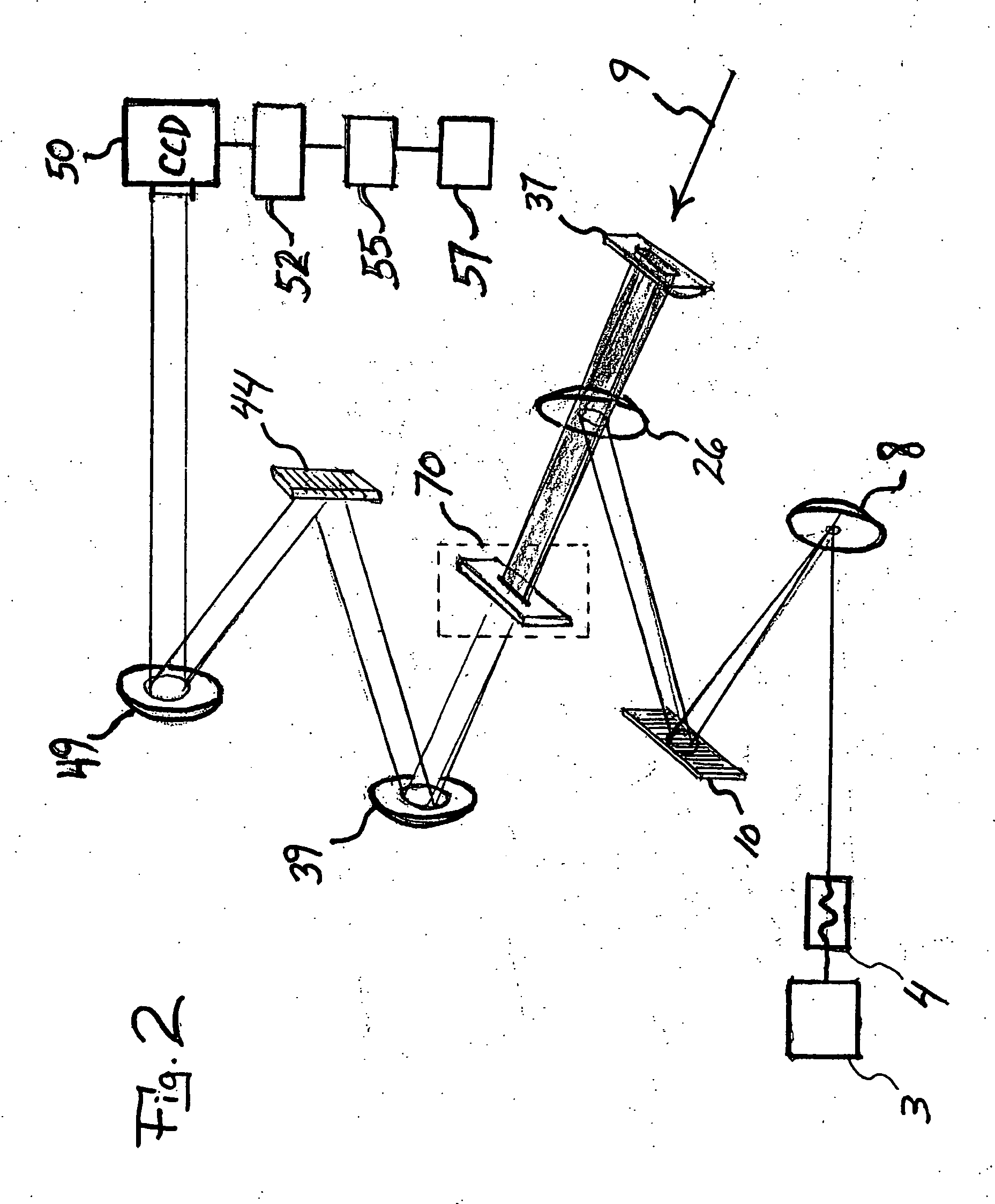
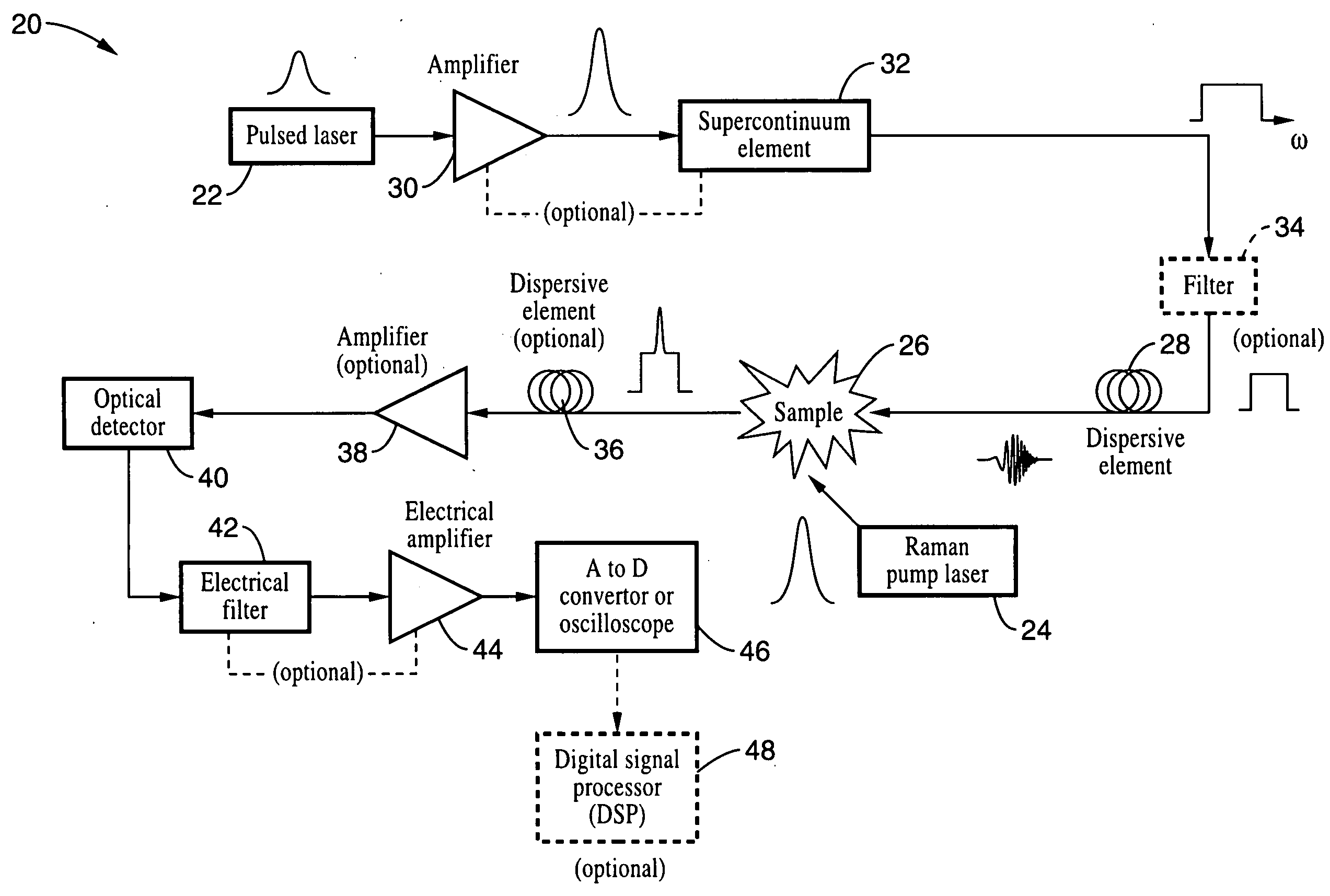
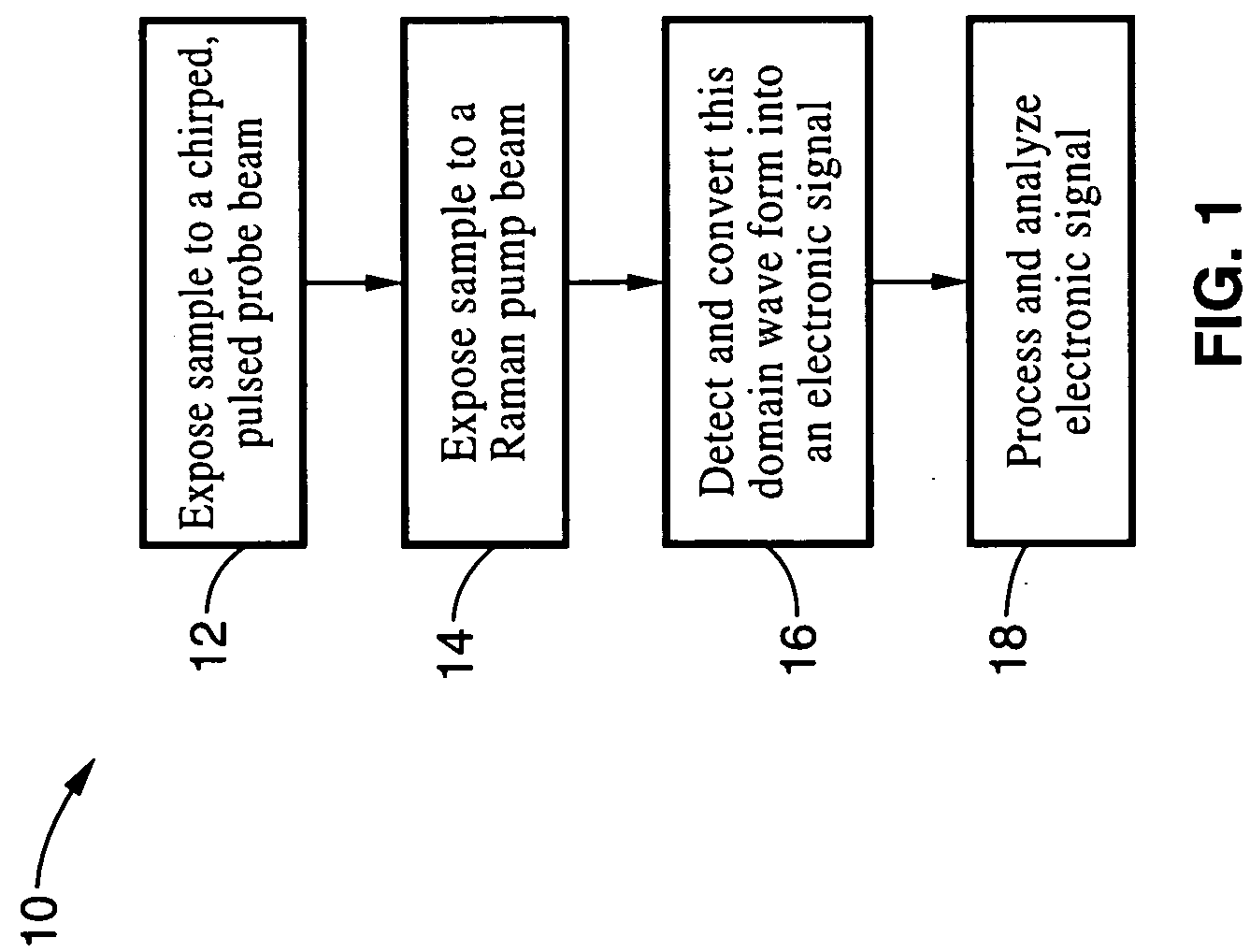
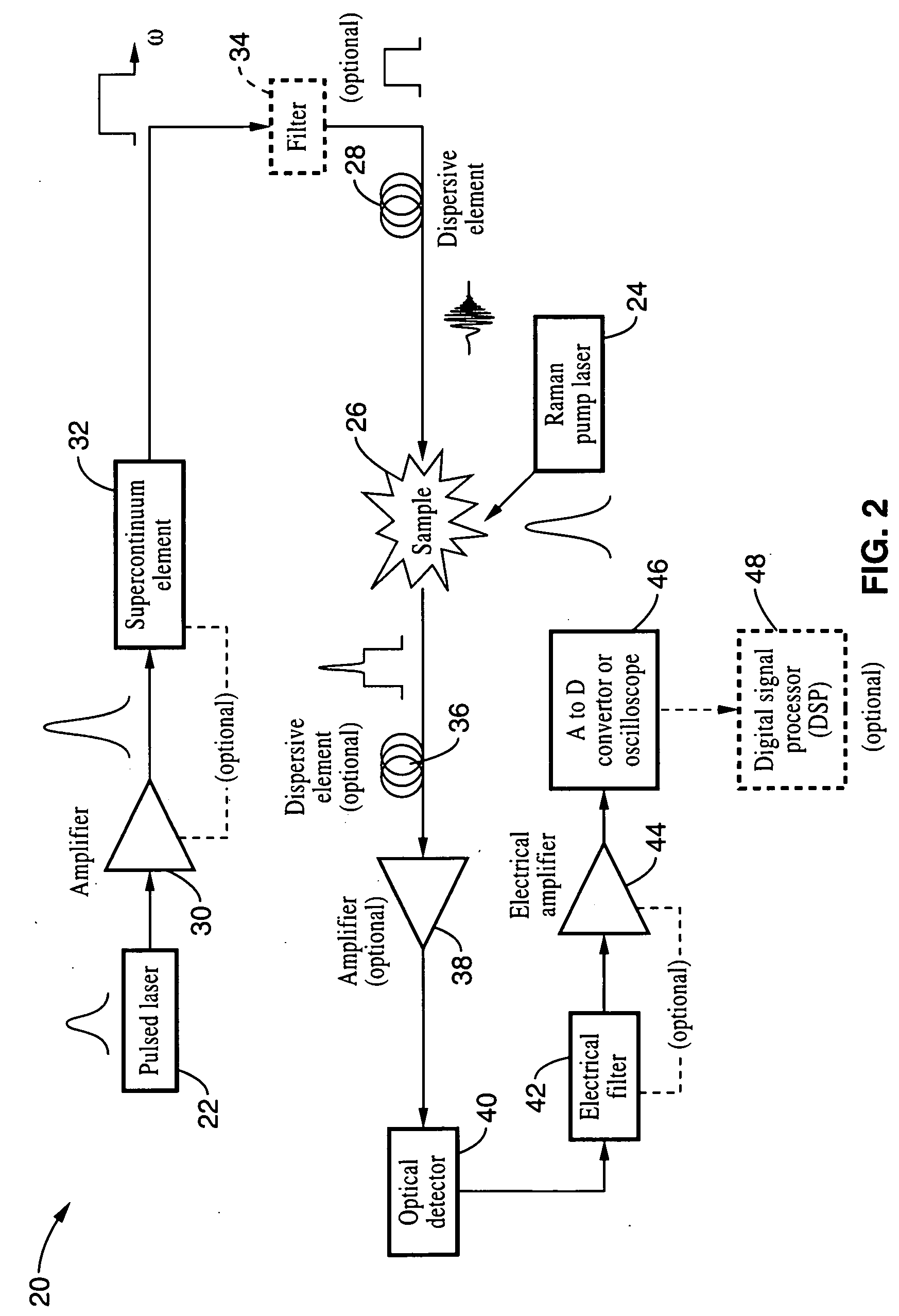
Apparatus and method for raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS20090073432A1Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySpectroscopySpectrometer
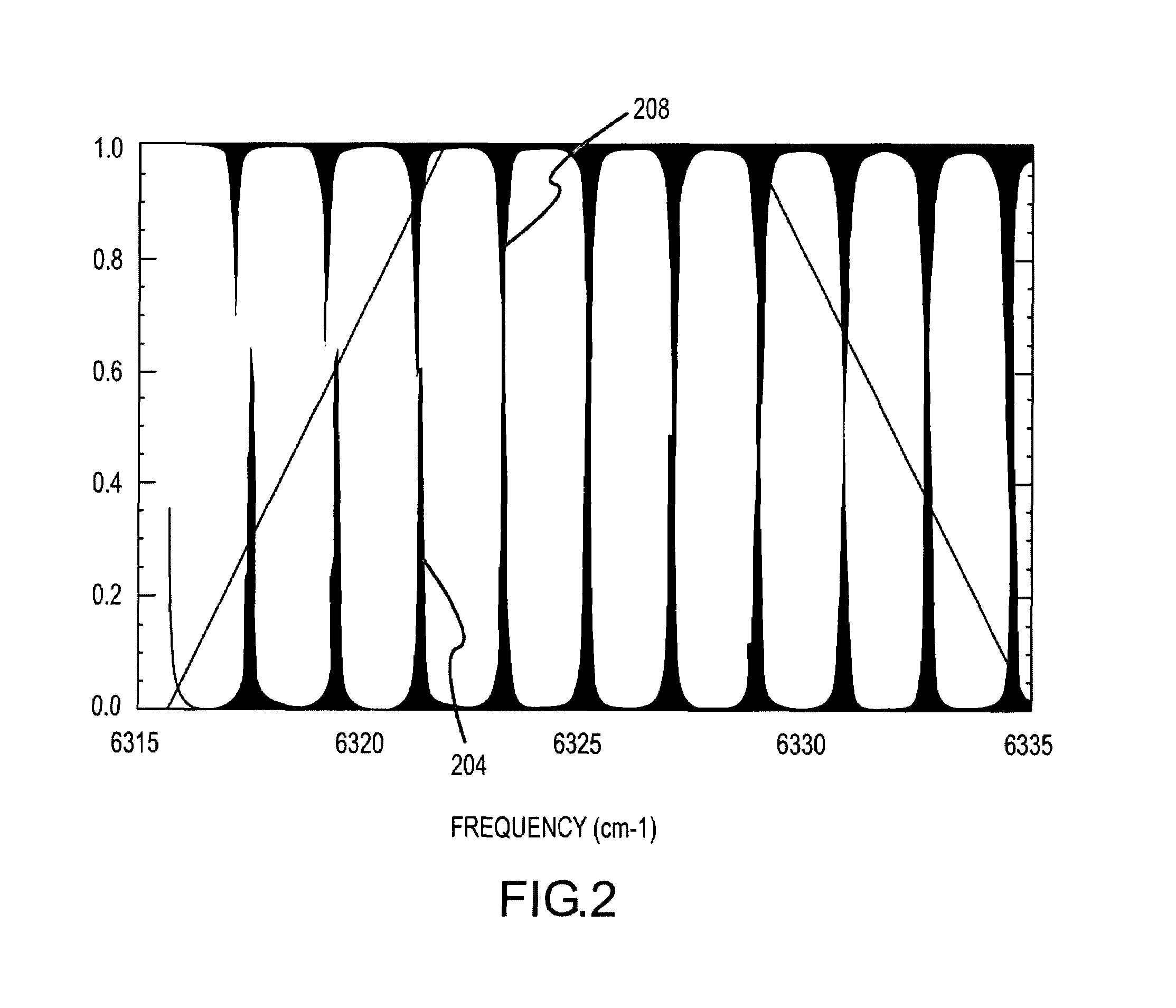
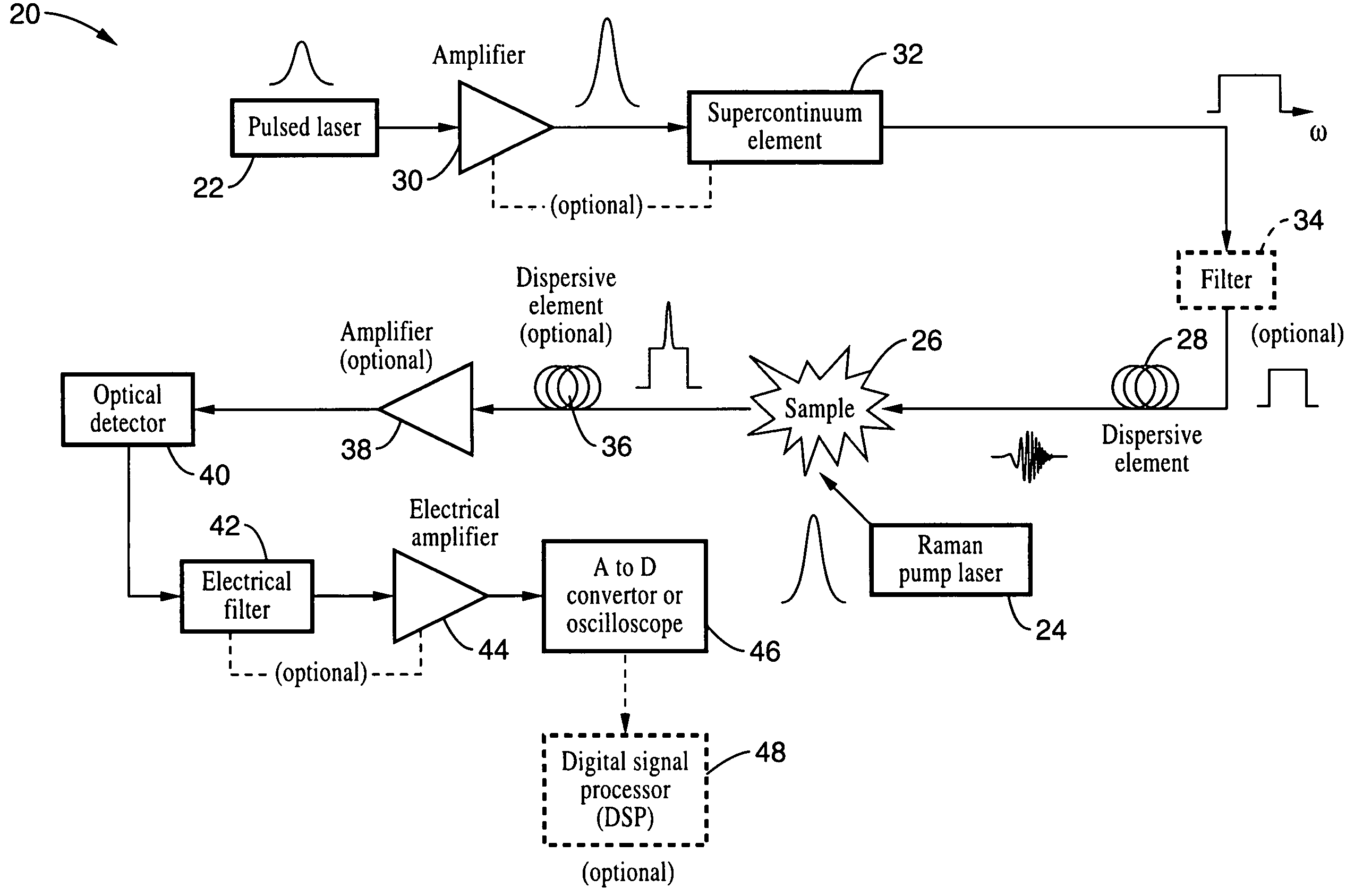
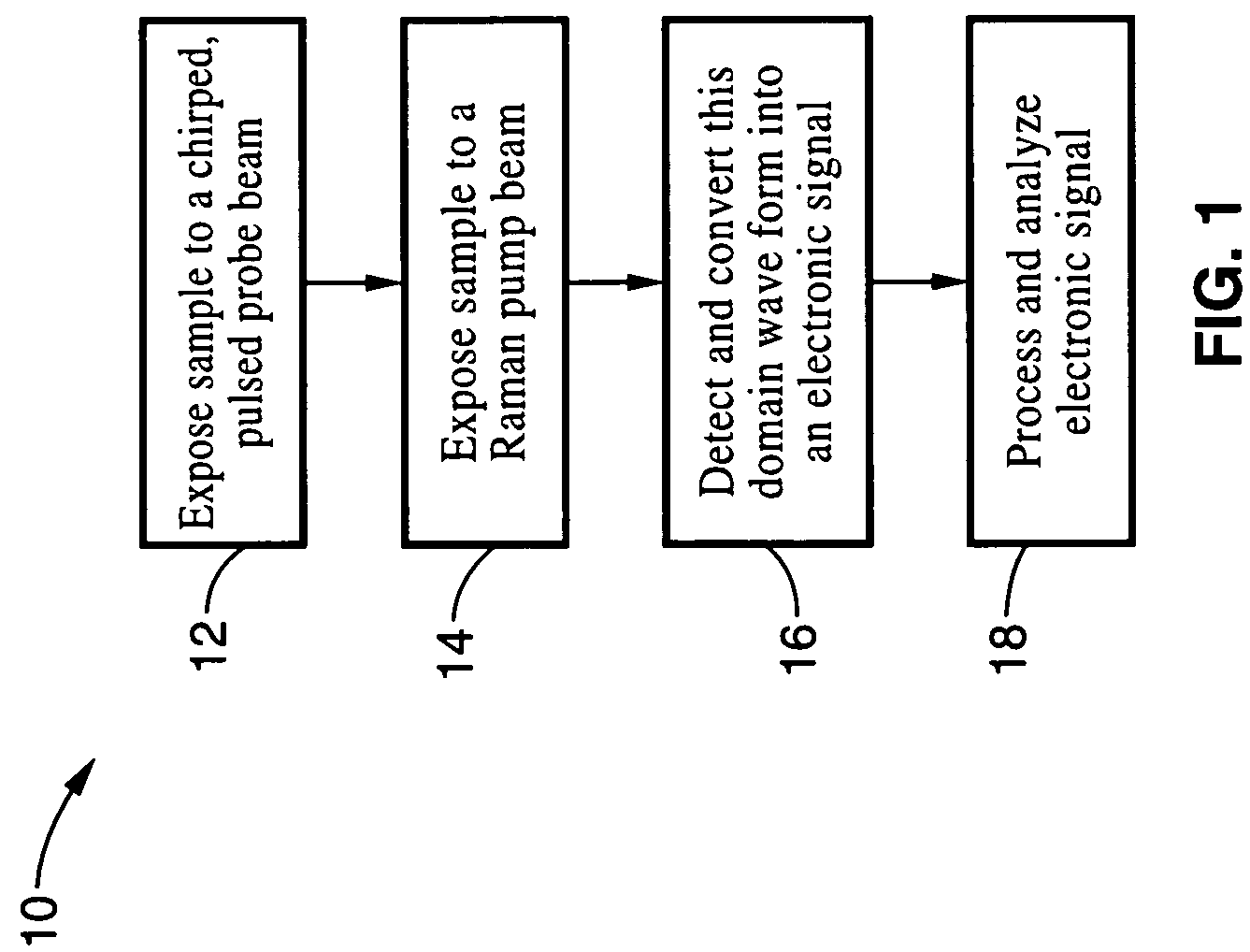
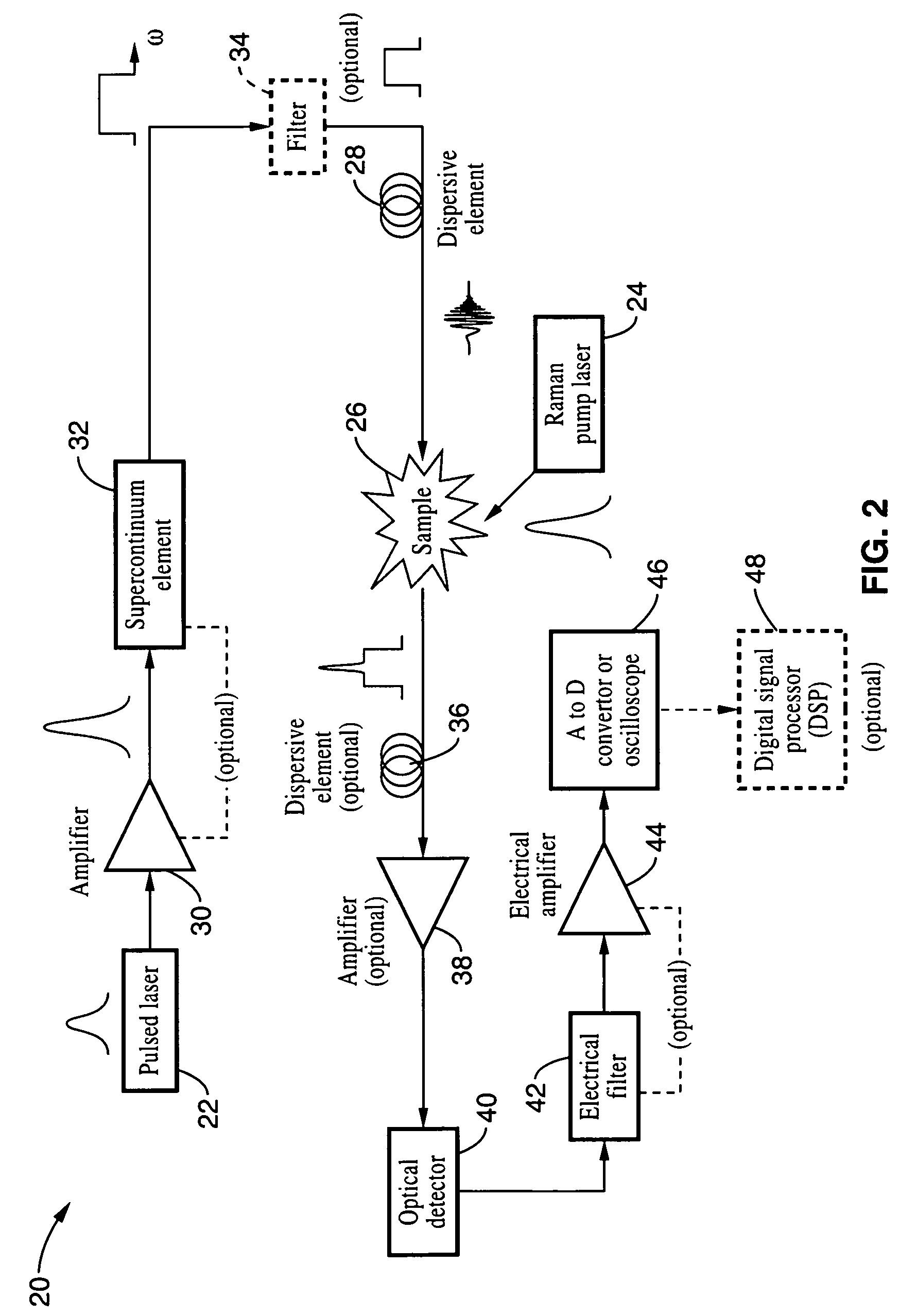
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for encoded spatio-spectral information processing
InactiveUS20050024640A1Less sensitive to ambient noiseEasy to operateRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsInformation processingFrequency spectrum
Encoded spatio-spectral information processing is performed using a system having a radiation source, wavelength dispersion device and two-dimensional switching array, such as digital micro-mirror array (DMA). In one aspect, spectral components from a sample are dispersed in space and modulated separately by the switching array, each element of which may operate according to a predetermined encoding pattern. The encoded spectral components can then be detected and analyzed. In a different aspect, the switching array can be used to provide a controllable radiation source for illuminating a sample with radiation patterns that have predetermined characteristics and separately encoded components. Various applications are disclosed.
Owner:FATELEY WILLIAM G +3
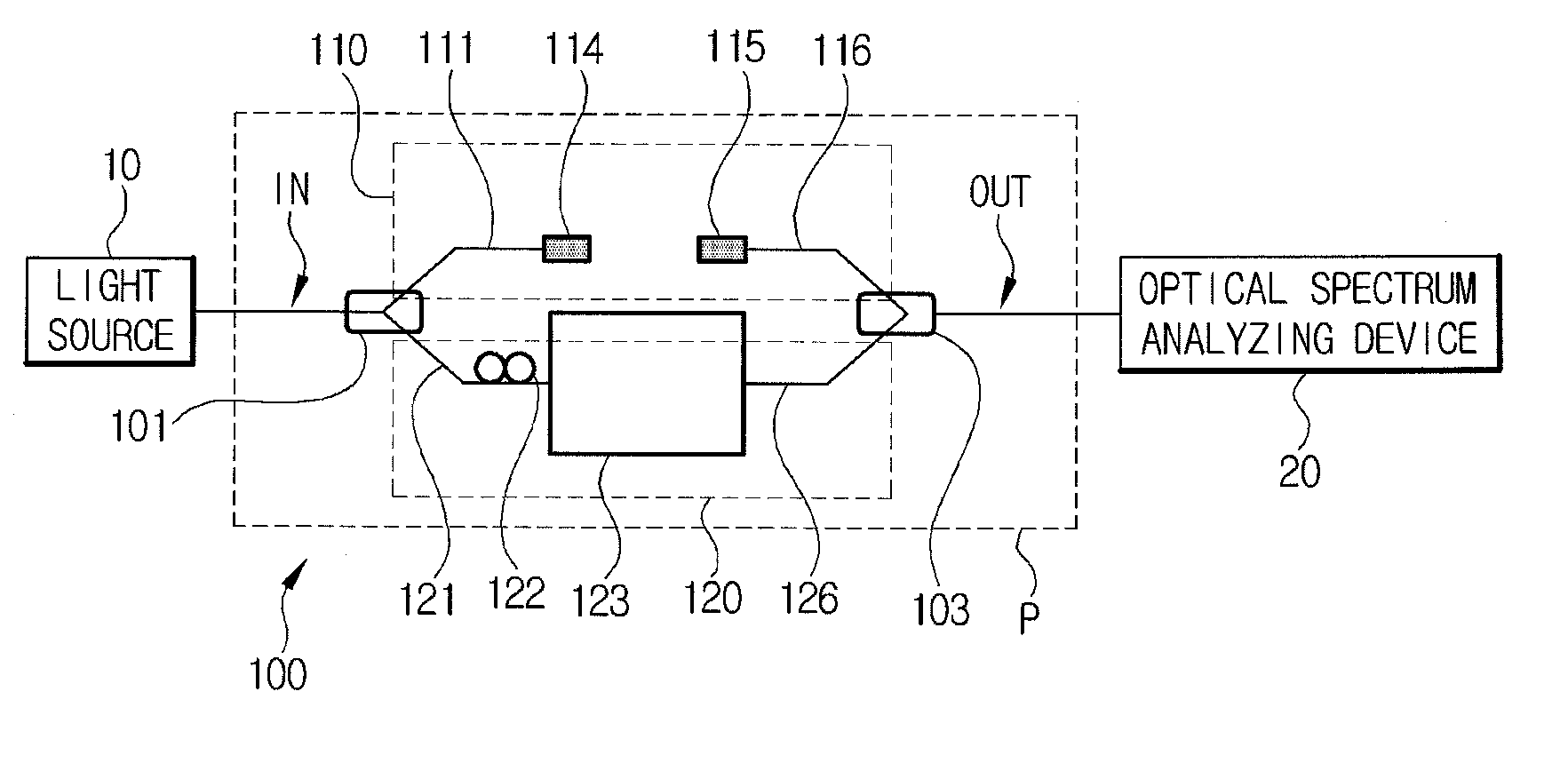
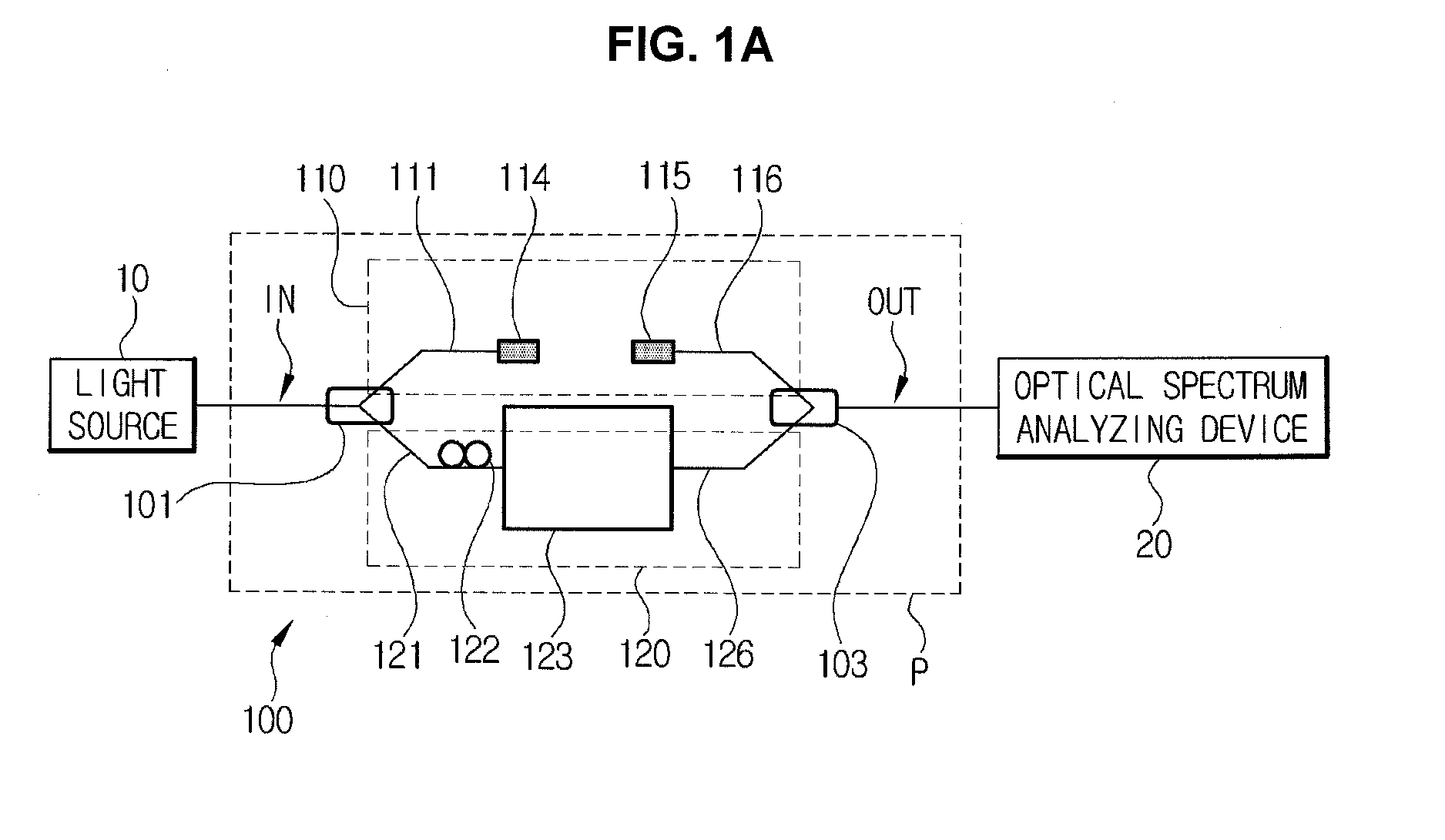
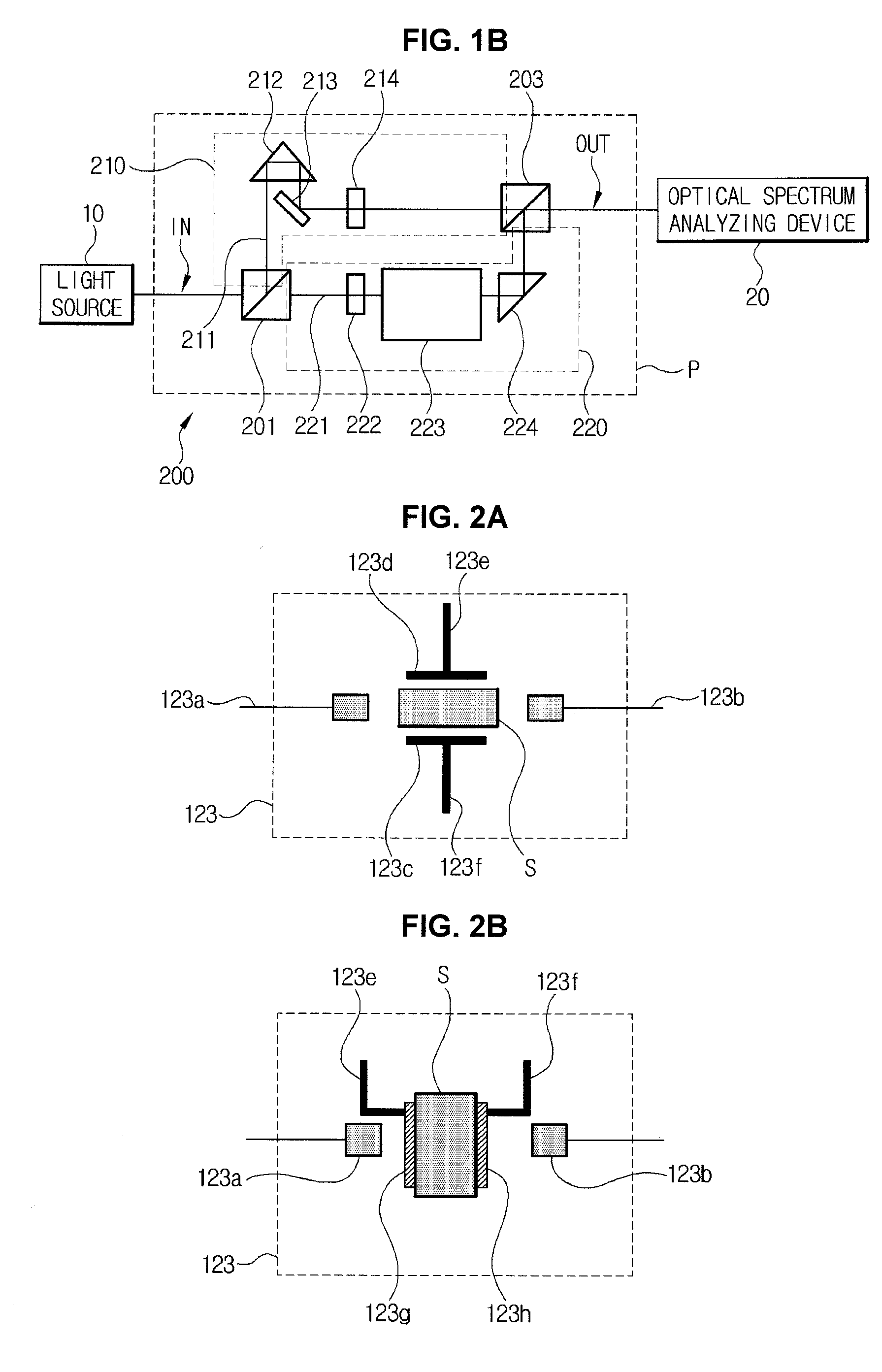
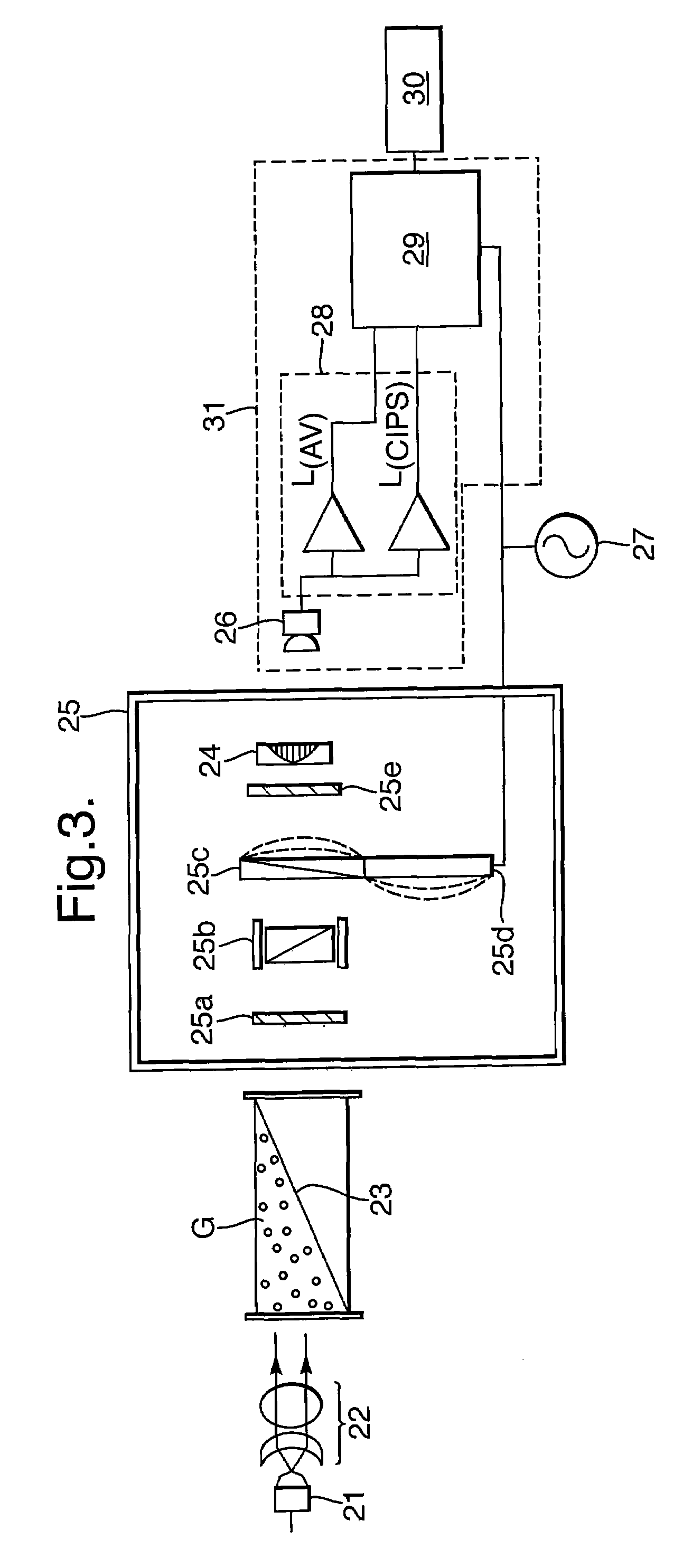
Spectrometry device and spectrometry method
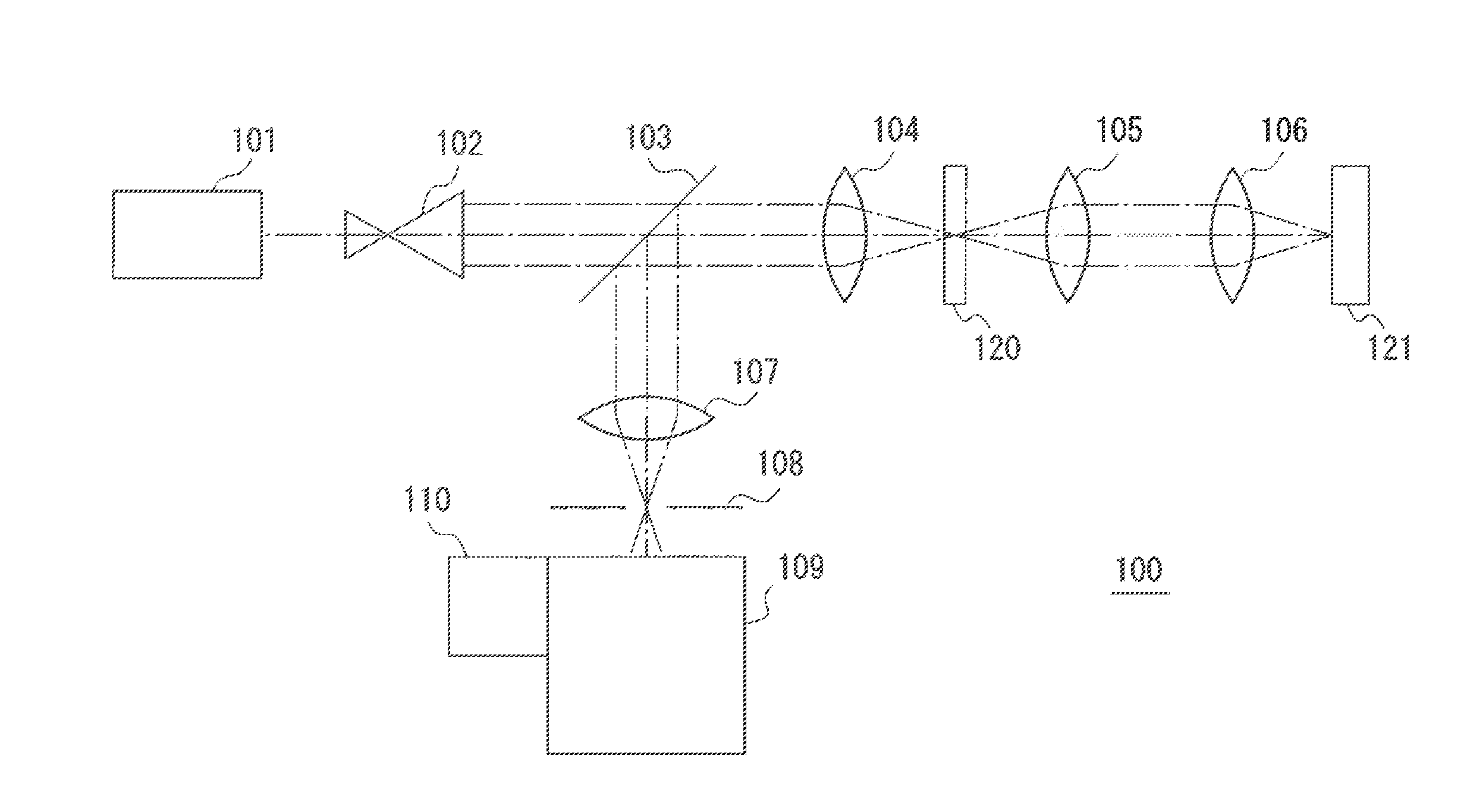
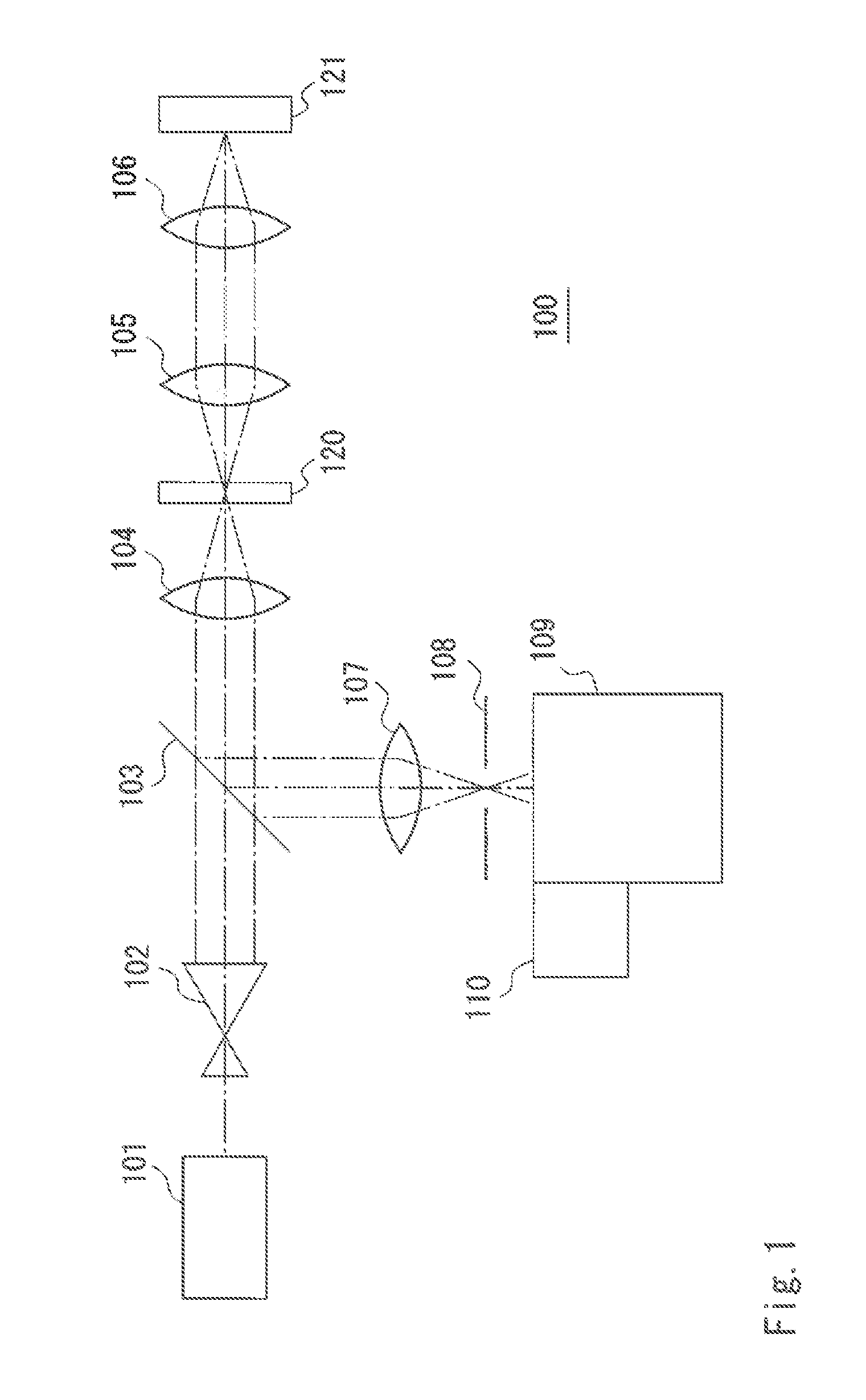
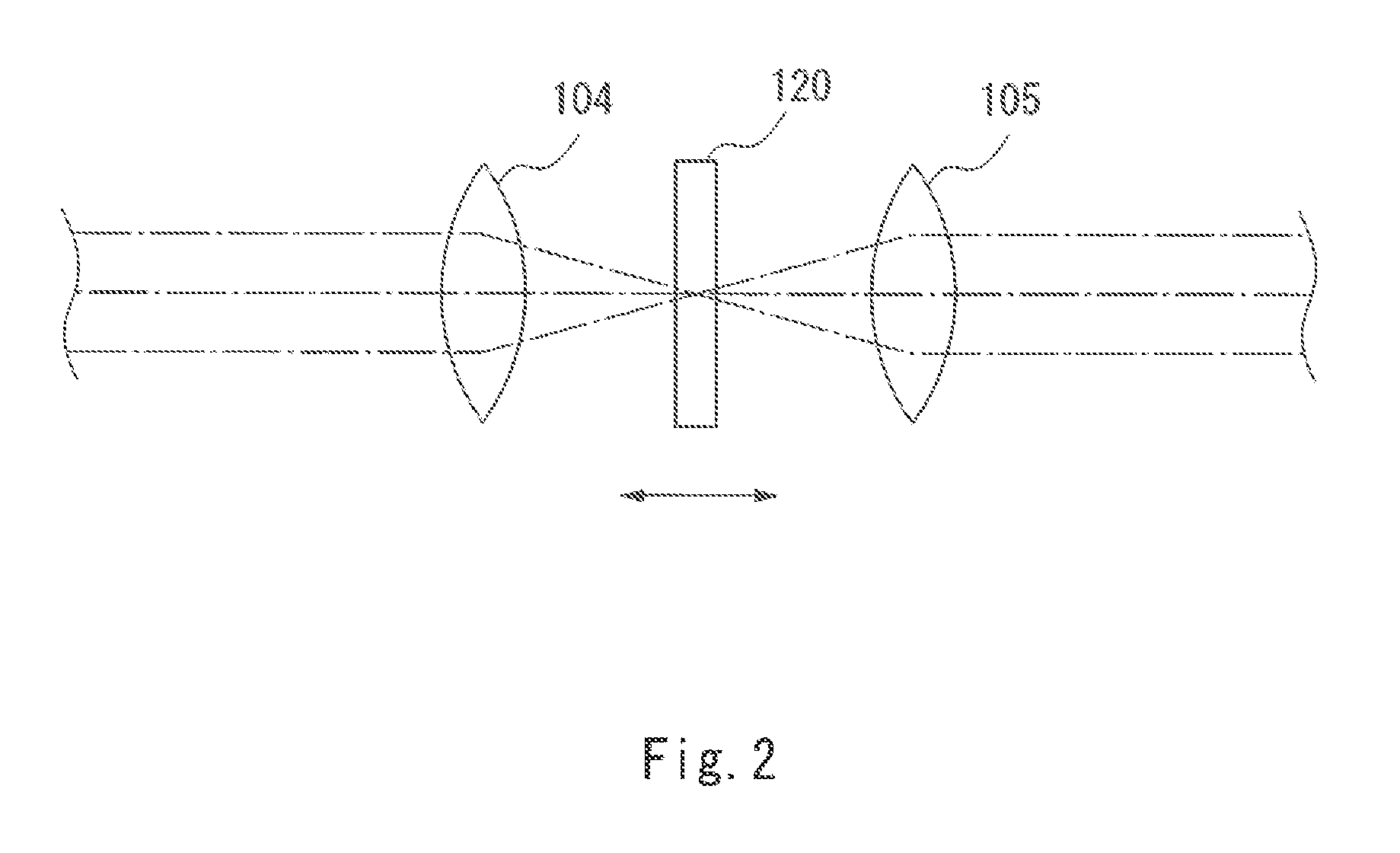
ActiveUS20130162990A1Slow performanceHigh precision measurementRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringReference sampleBeam splitter
A spectrometry device according to an aspect of the present invention is including a light source (101), a lens 104 concentrating a light beam from the light source (101) on a reference sample (120), an objective lens (106) concentrating a light beam that has passed through the first lens (104) on a measurement sample (121), a spectroscope (109) dispersing light having a different wavelength from that of the light beam generated in the measurement sample (121) and the reference sample (120) by irradiation of the light beam into a spectrum, a detector (110) detecting light that is dispersed by the spectroscope (109), and a beam splitter (103) separating an optical path of light from the reference sample (120) and the measurement sample (121) toward the spectroscope (109) from an optical path of a light beam that propagates from the light source (101) toward the measurement sample (121).
Owner:NANOPHOTON
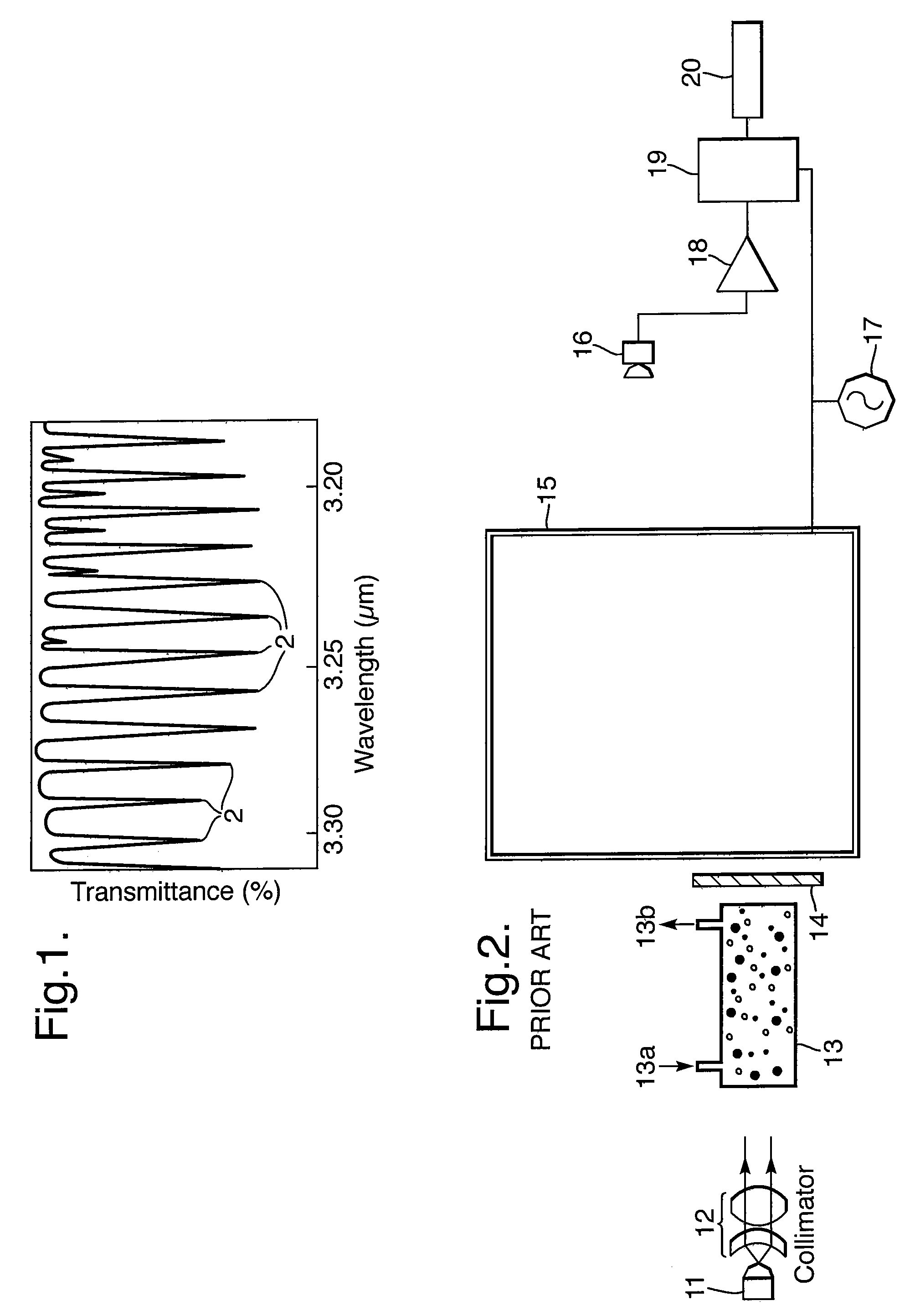
Tunable filter
InactiveUS6650810B1Simple and accurate mannerReduce signal noiseRadiation pyrometryOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFrequency spectrumLight energy
A tunable optical filter for simulating the waveband spectrums of selected substances. The filter includes an optical waveguide with a core material for transmitting light energy and a nominal core refractive index for the core material. Predetermined periodic variations are formed in the core material of the optical waveguide between the input and output ends that alter the core refractive index of the waveguide at the location of the periodic variations. Depending upon the periodic variations, the waveguide produces a predetermined reference waveband spectrum output that matches the waveband spectrum of a selected substance. A modulator is coupled to the waveguide to selectively modulate the periodic variations to intermittently shift the reference waveband spectrum output to fine tune the filter and reduce signal noise. The filter is useful as a reference cell for correlation spectroscopy, DIAL LIDAR, equipment calibration, and other uses where a predetermined or known waveband spectrum is useful or desirable.
Owner:MERCURY MISSION SYST LLC
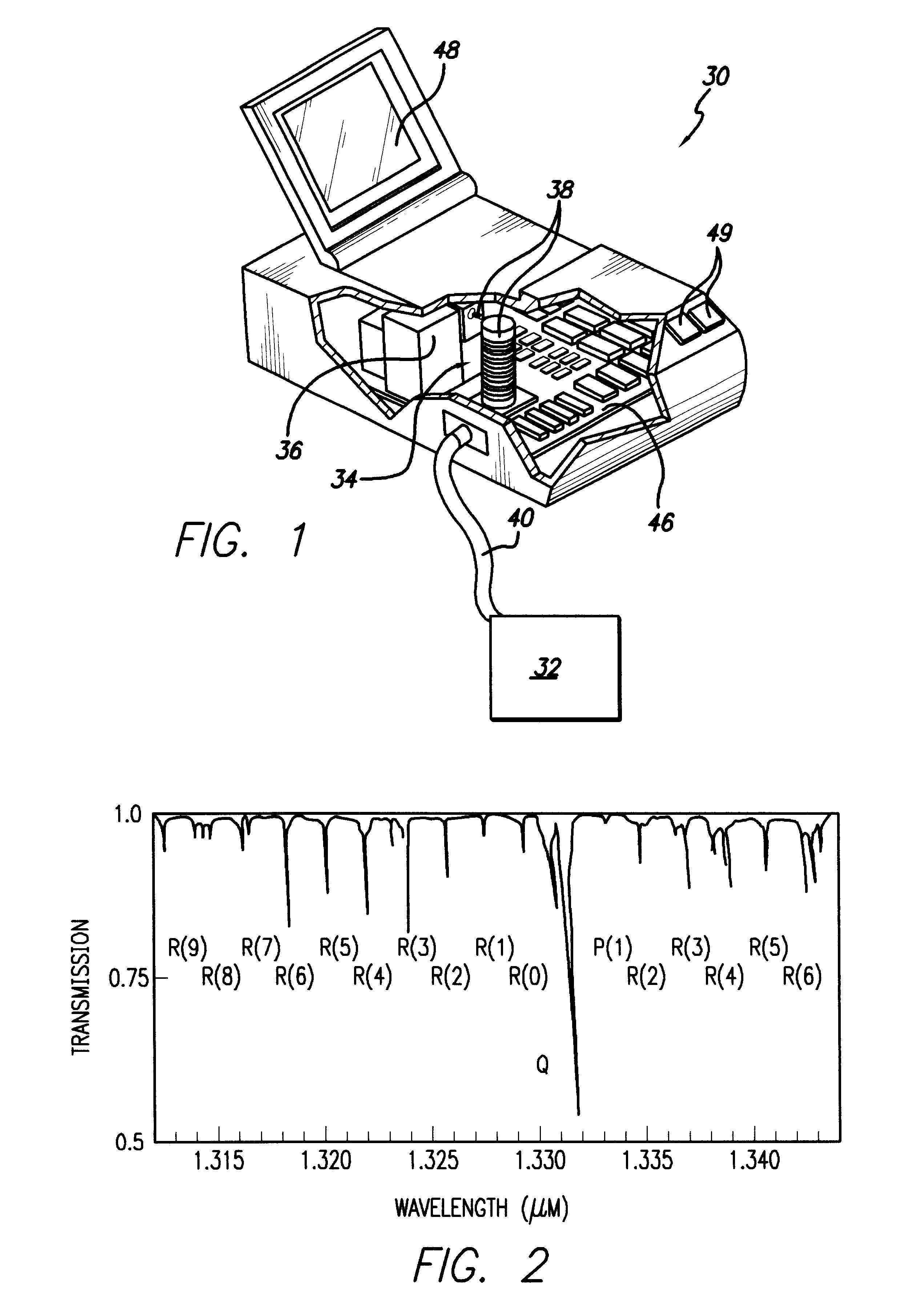
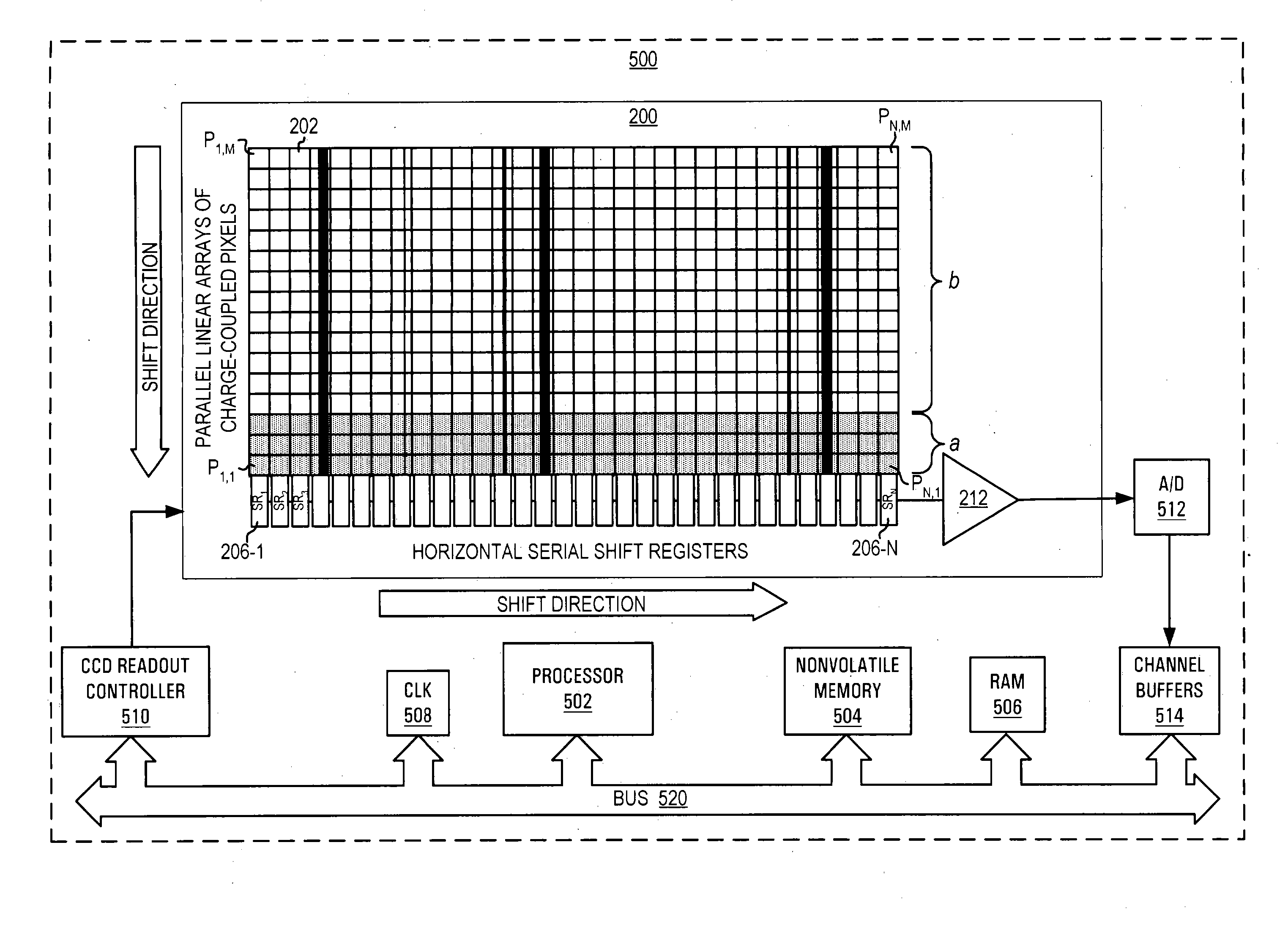
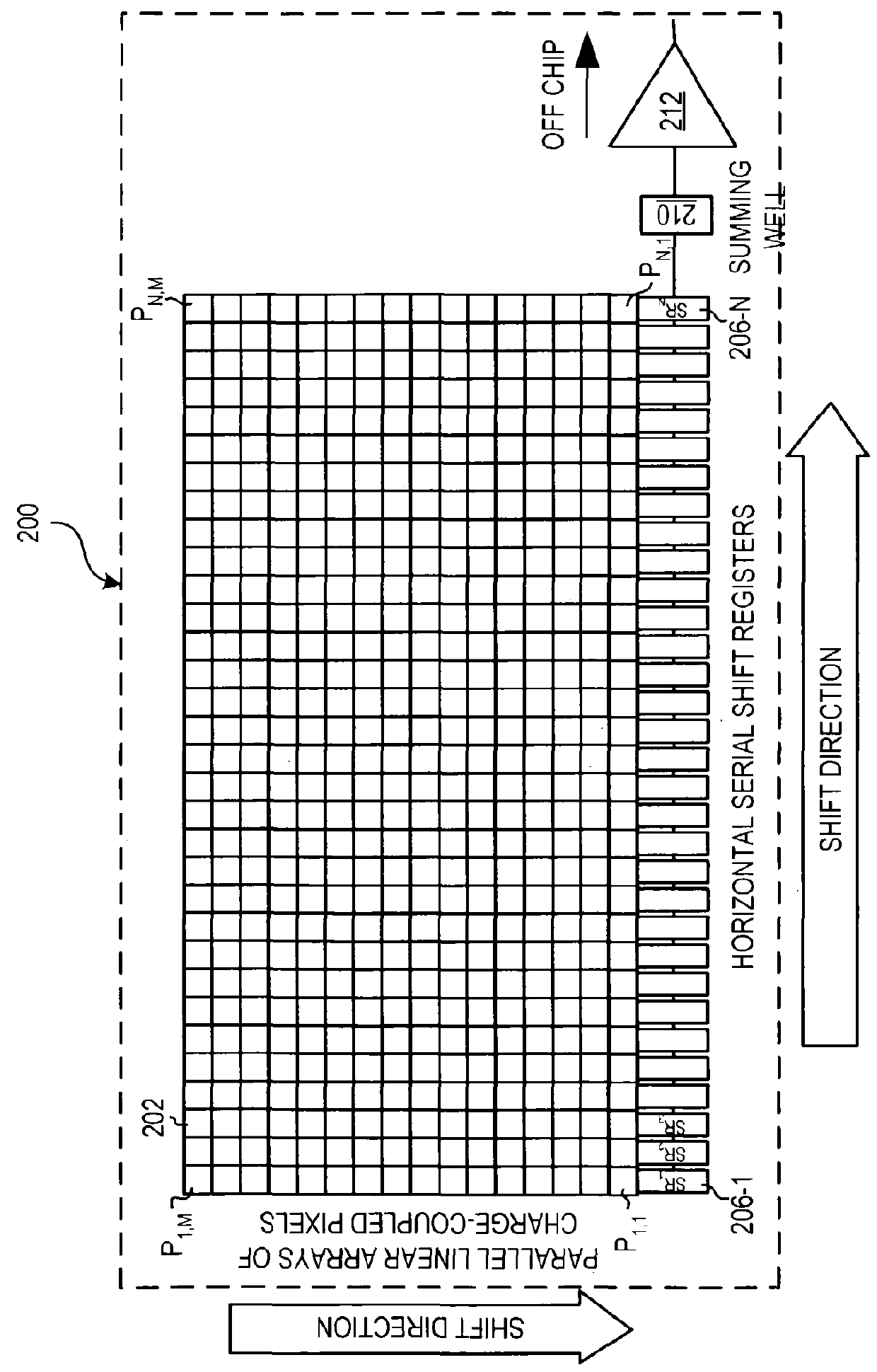
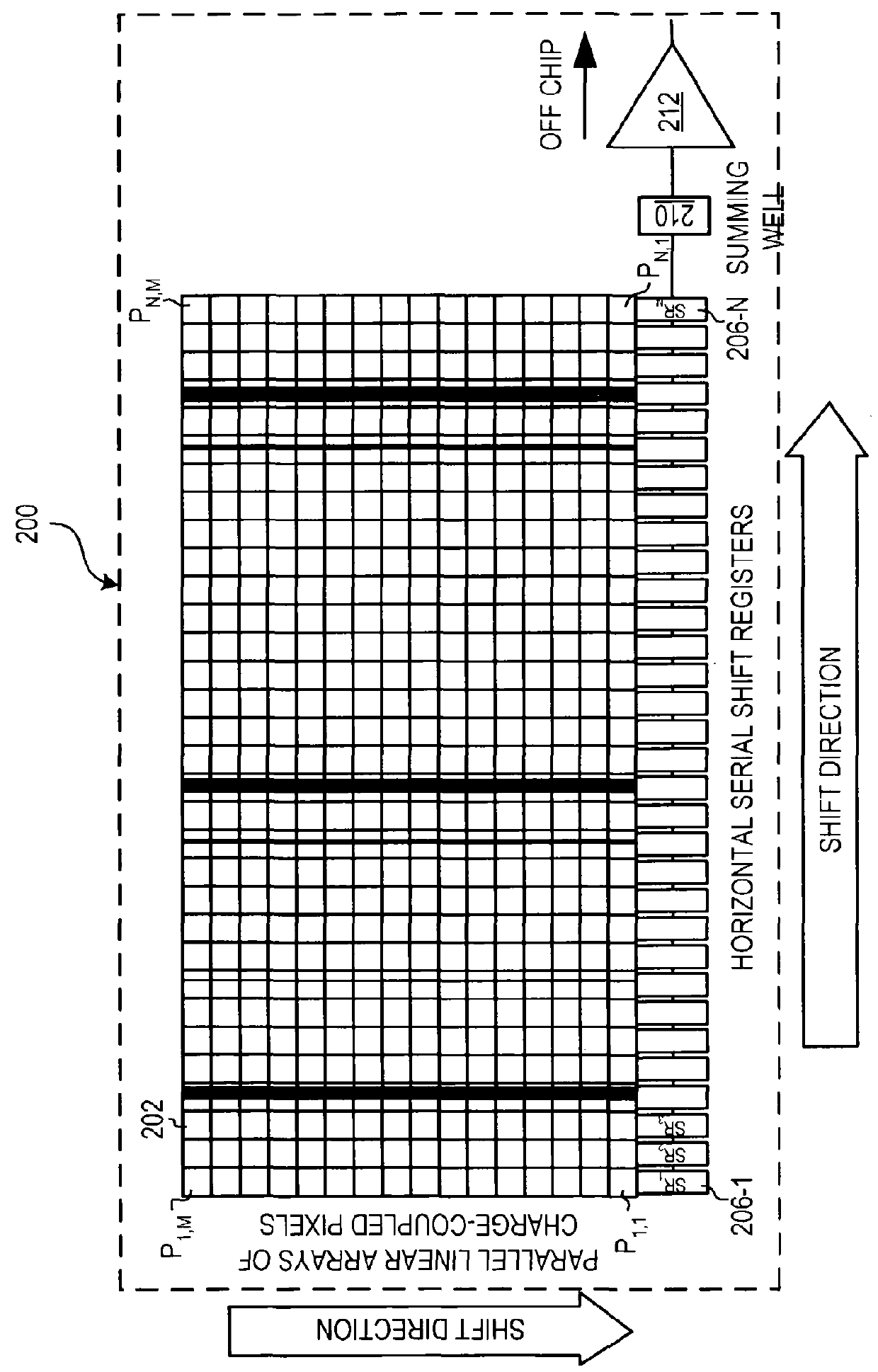
Apparatus and method for enhancing dynamic range of charge coupled device-based spectrograph
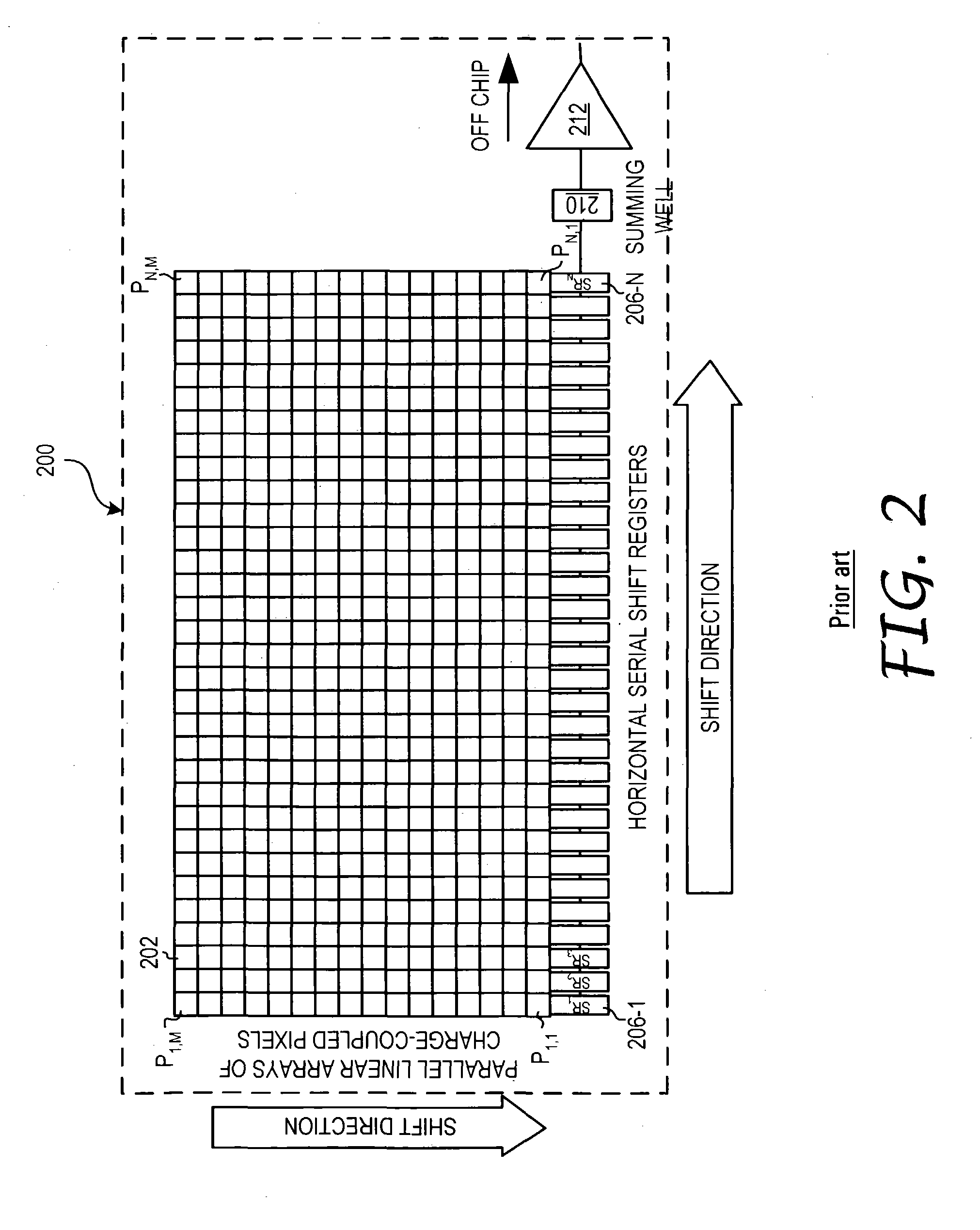
InactiveUS20050001914A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSmall amplitudeShift register
The present invention is directed to an apparatus, method and software product for enhancing the dynamic range of a CCD sensor without substantially increasing the noise. Initially, the area of a N×M pixel CCD sensor array is subdivided into two regions, a large region having (M−a) pixels in each column for outputting large-amplitude signals with low noise and a smaller region having a pixels in each column for outputting small-amplitude signals with improved dynamic range. At integration time, the CCD is read out one region's rows at a time into the horizontal shift registers by shifting the pixel charges in either a or M−a vertical shifts. The charges in the horizontal shift registers are then shifted out of the horizontal shift registers in N horizontal shifts. Next, the remaining pixels in the region of the CCD are read out into the horizontal shift registers by shifting the pixel charges in the other of a or M−a vertical shifts. Those charges are then shifted out of the horizontal shift registers in N horizontal shifts. In a spectrographic application, the data from the two regions is read out in the form of a large-amplitude channel from the larger region's rows and a small-amplitude channel from the smaller region's rows.
Owner:VERITY INSTR
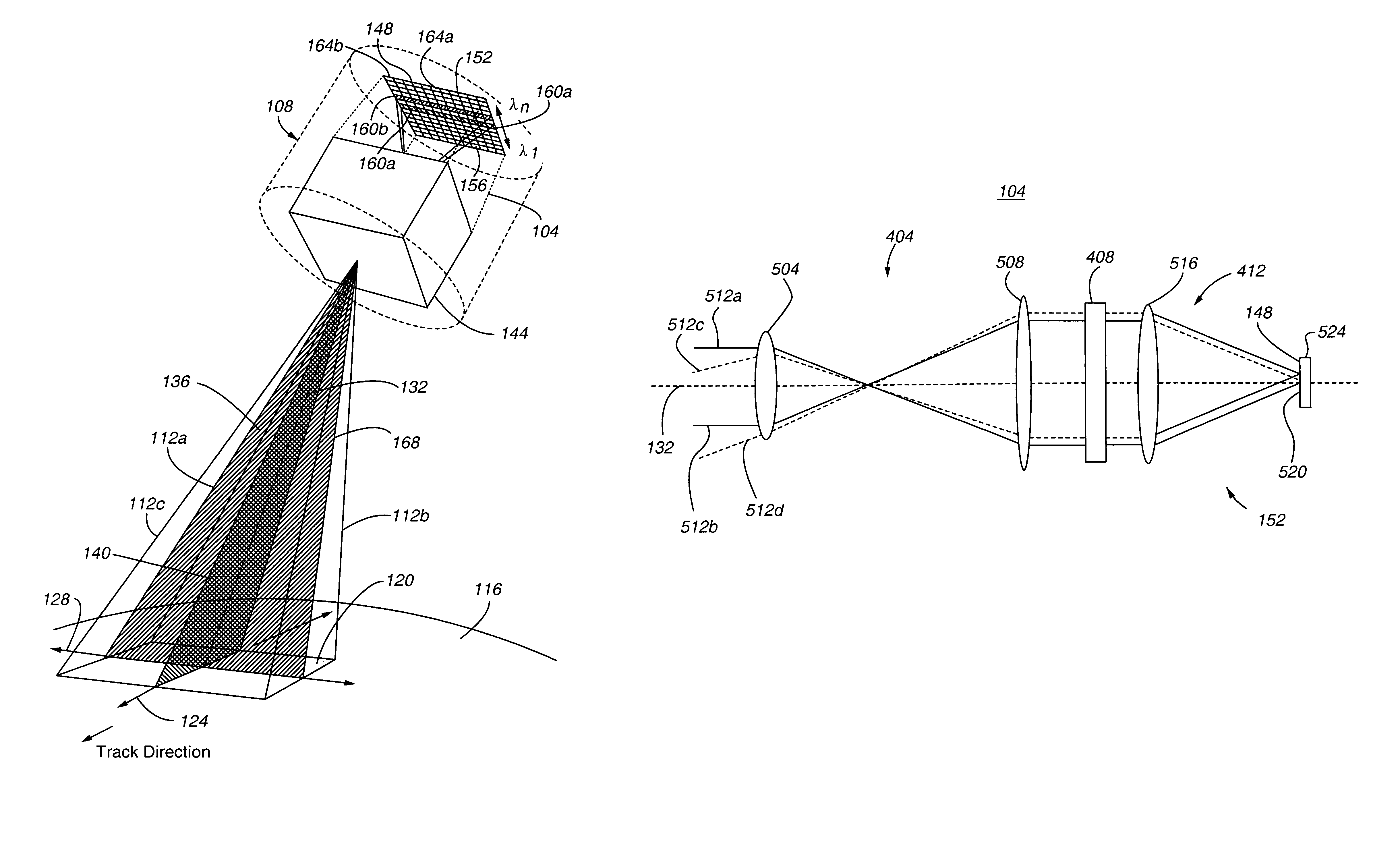
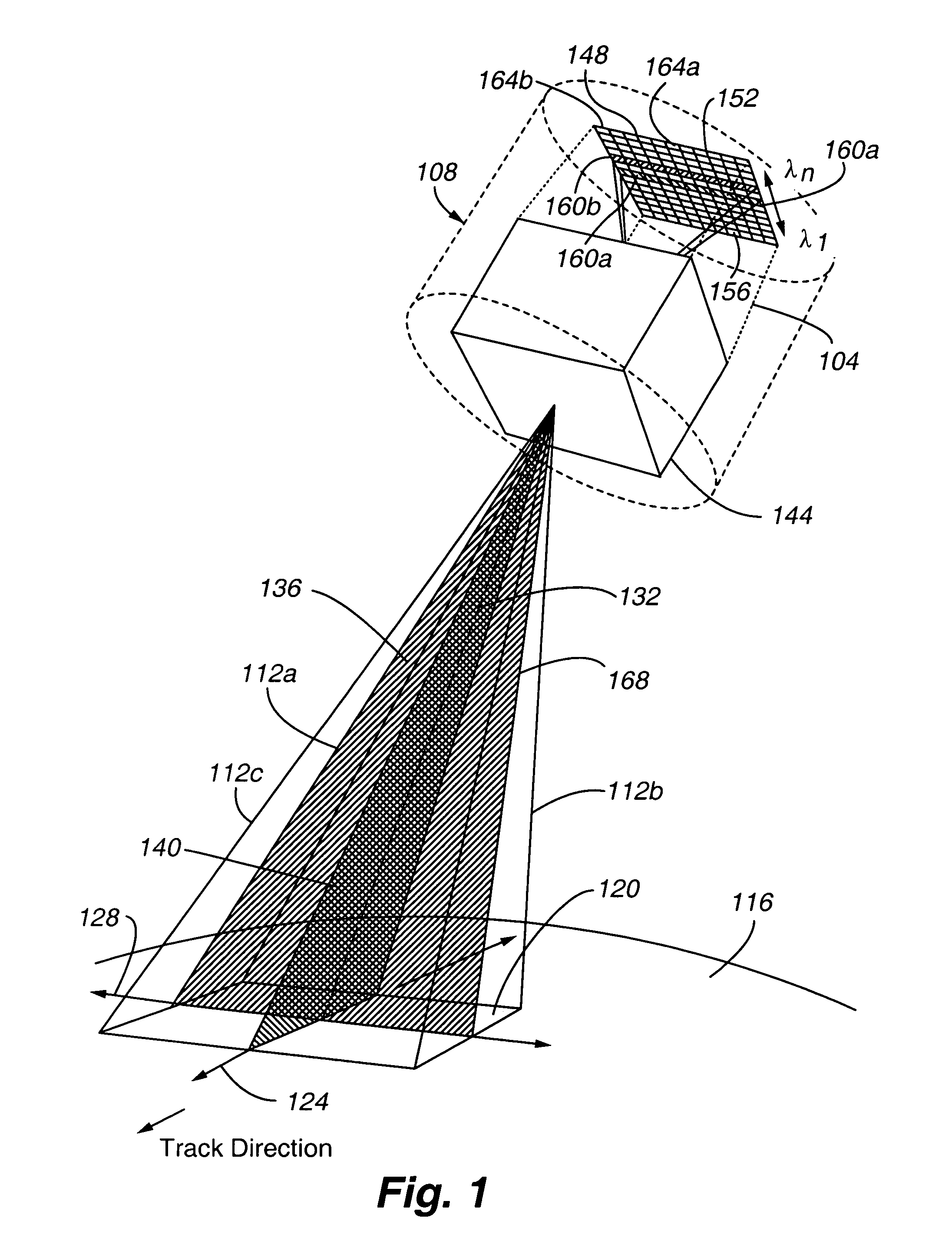
Field condensing imaging system for remote sensing of atmospheric trace gases
ActiveUS7030991B1Reliable maintenanceRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryWide fieldOptic system
A sensor system featuring a field angle compression telescope optical system for measuring atmospheric trace gases is provided. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the telescope optical system condenses the field angle of received light with respect to a cross track plane, while leaving the field angle with respect to an along-track plane uncompressed. Such an anamorphic telescope design provides a wide field of view, while allowing information regarding the altitude or height distribution of a gas to be obtained. According to another embodiment of the present invention, the field angle of received light is compressed by magnifying the received light by a value less than 1.0 in all directions.
Owner:BALL AEROSPACE & TECHNOLOGIES
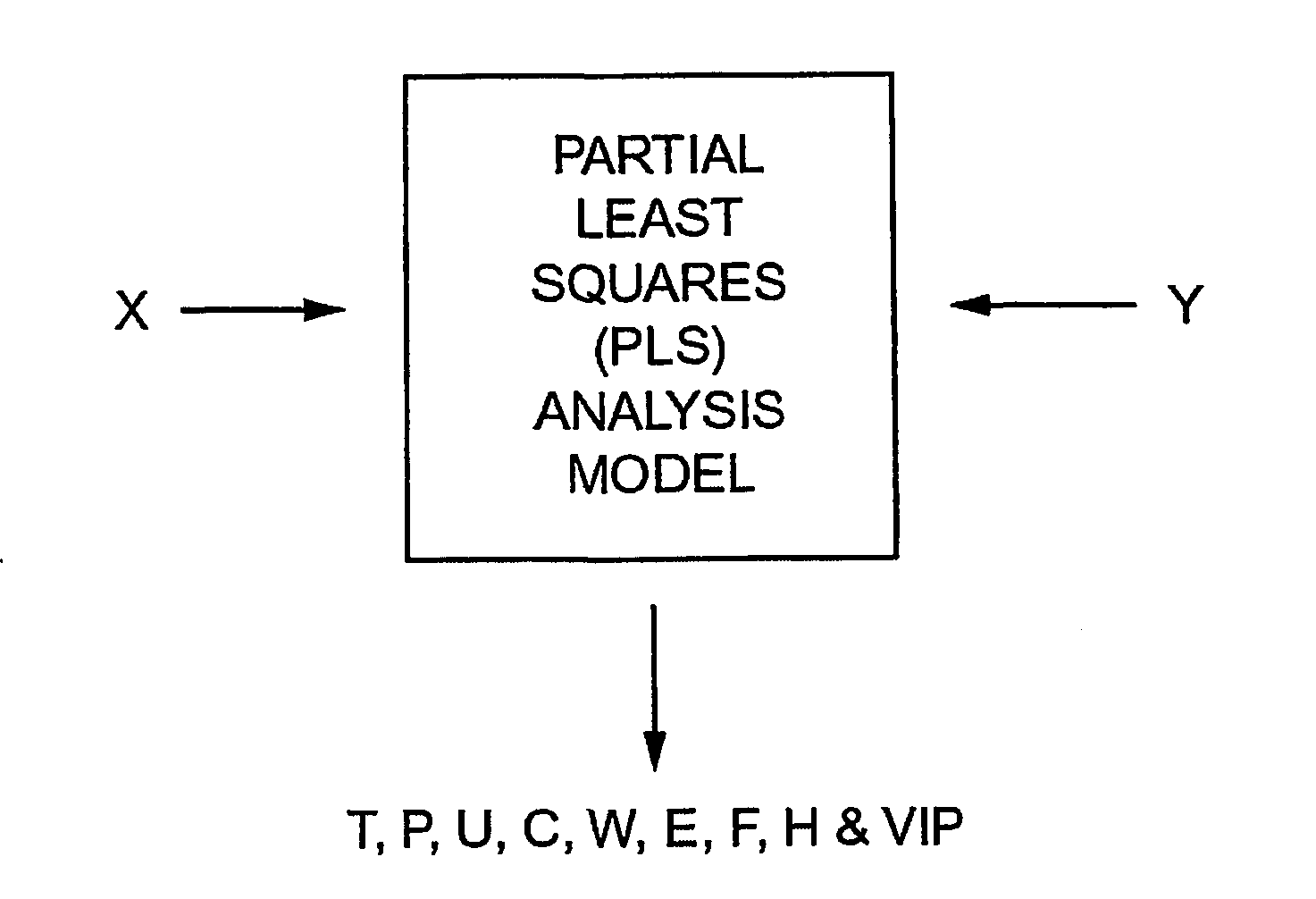
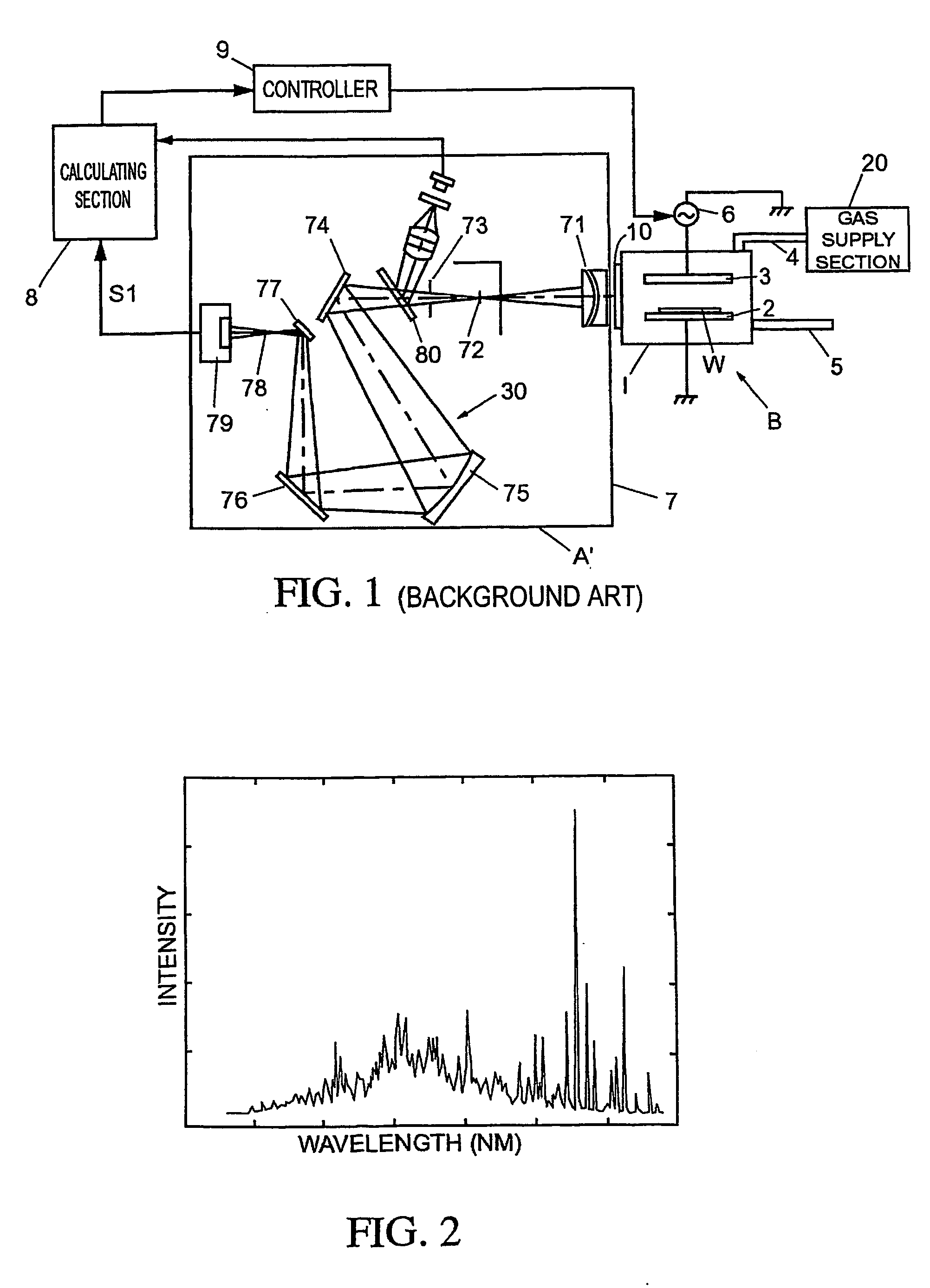
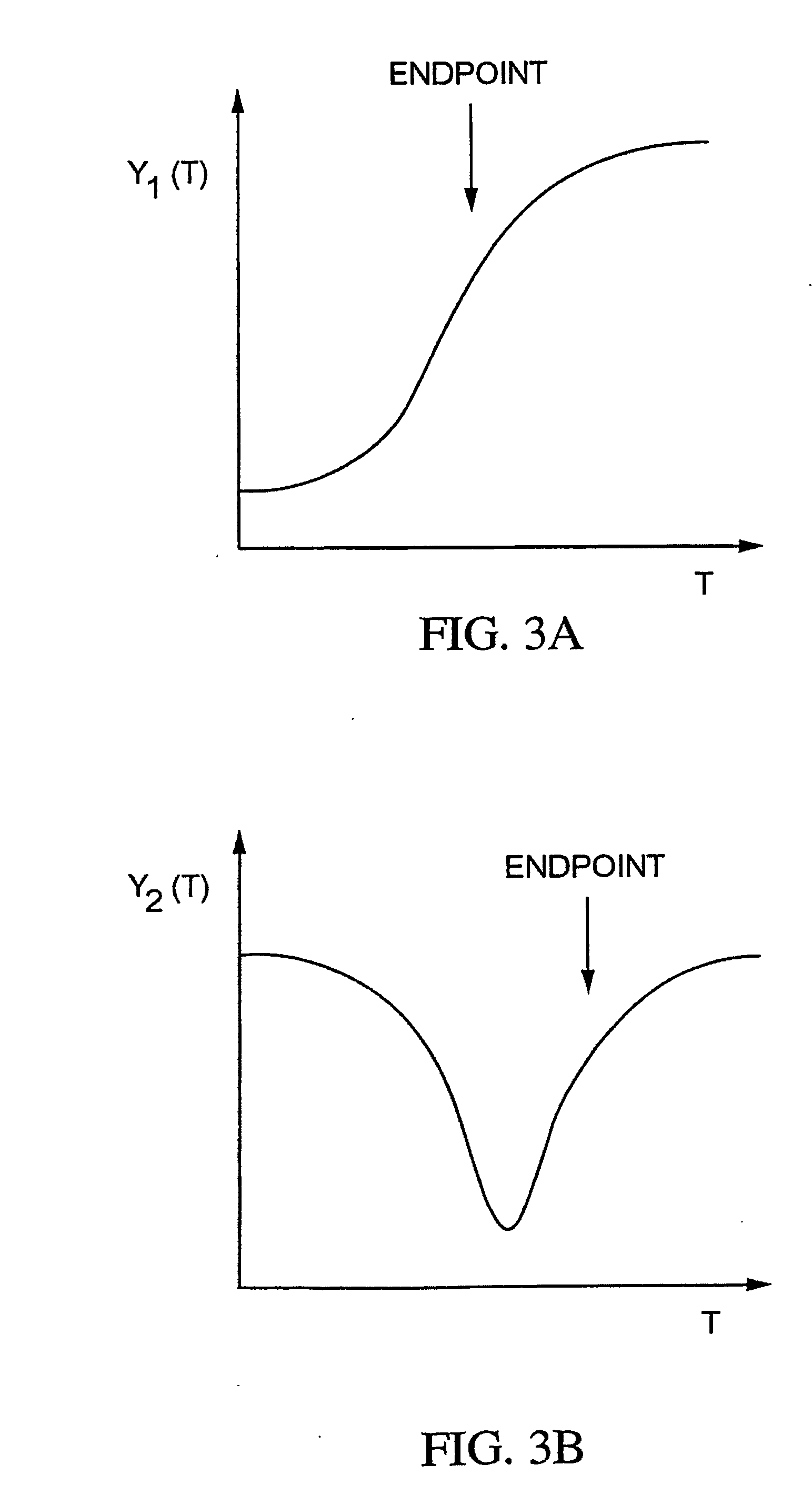
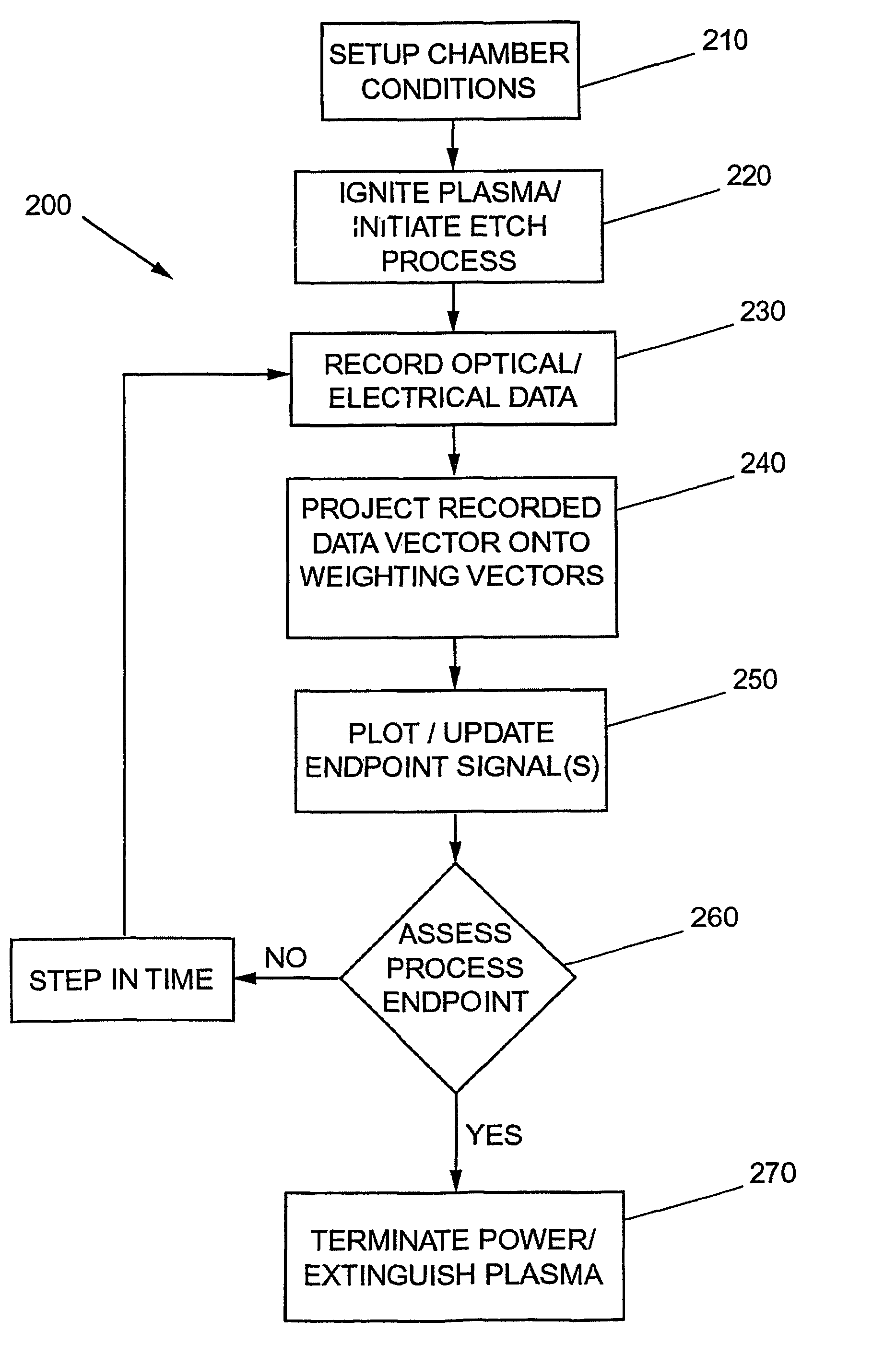
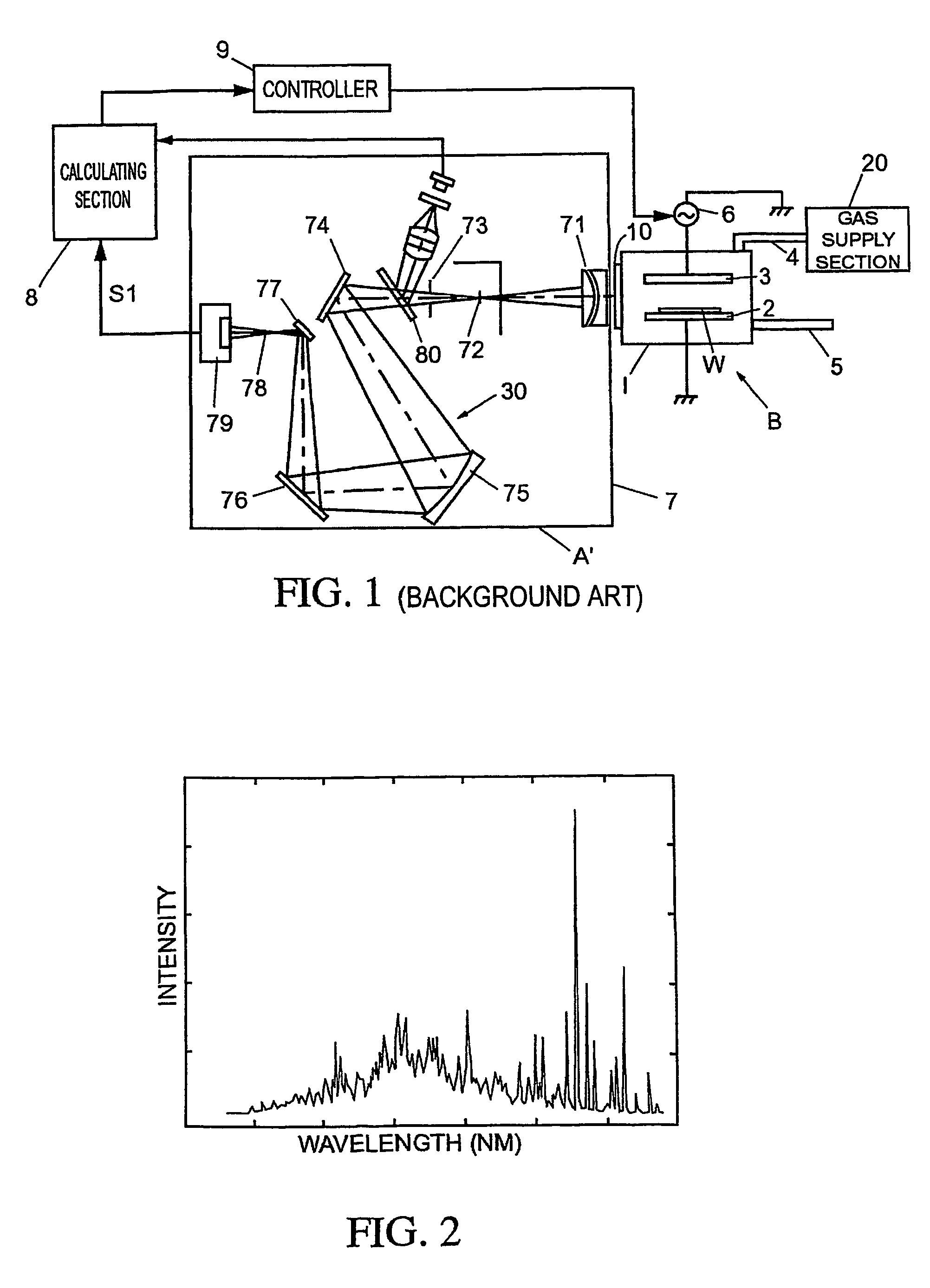
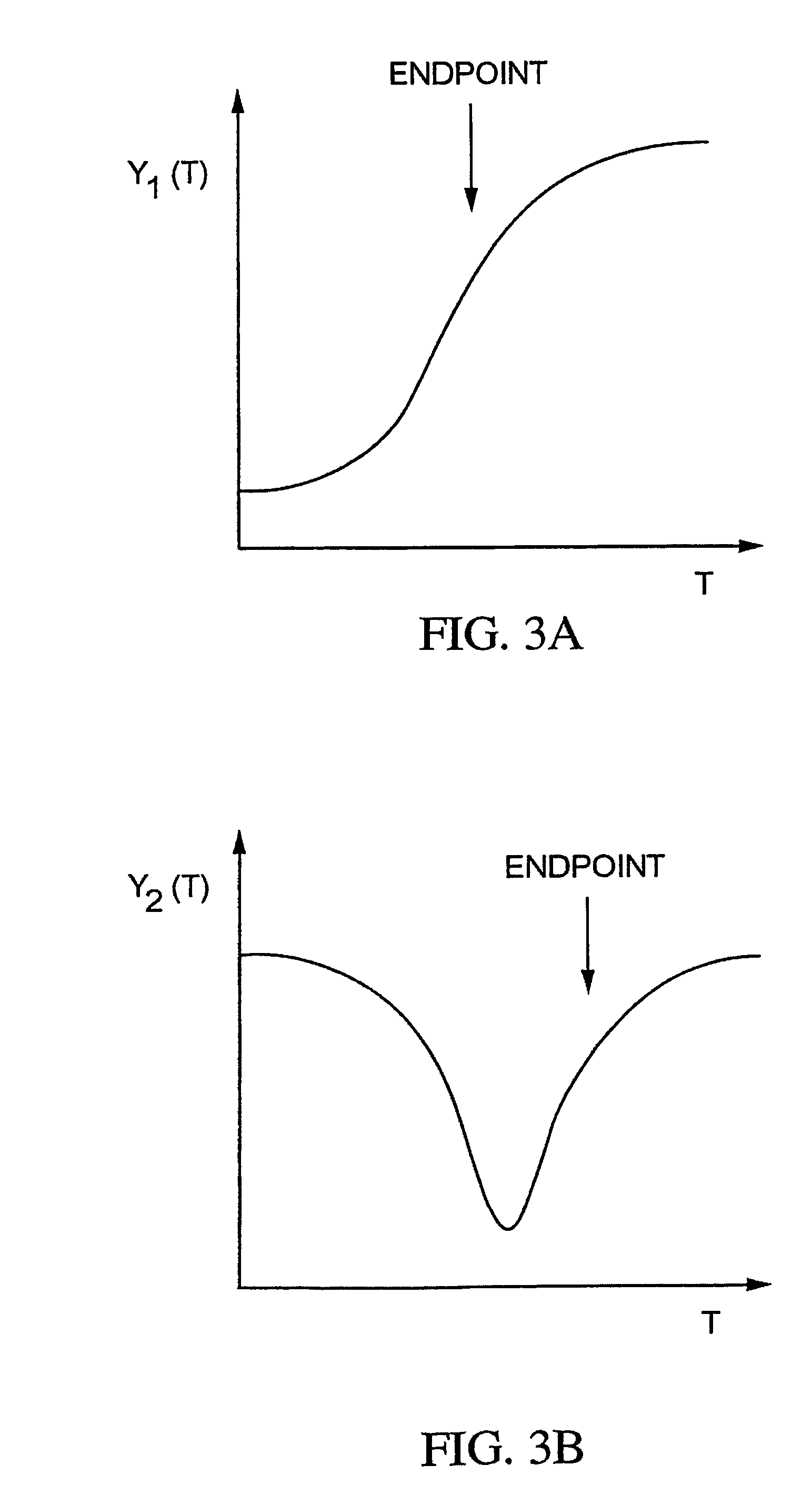
Method and apparatus for endpoint detection using partial least squares
InactiveUS20050016947A1Easy to detectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesAlgorithmLeast squares
An apparatus and method for detection of a feature etch completion within an etching reactor. The method includes determining a correlation matrix by recording first measured data regarding a first etch process over successive time intervals to form a first recorded data matrix, assembling a first endpoint signal matrix using target endpoint data for a specific etch process, performing a partial least squares analysis on the recorded data matrix and the first endpoint signal matrix to refine the recorded data matrix, and computing a correlation matrix based upon the refined recorded data matrix and the first endpoint signal matrix. The method further includes performing a second etch process to form a second recorded data matrix. The correlation matrix and the second recorded data matrix are analyzed to determine whether an endpoint of the second etch process has been achieved.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Spectrometer
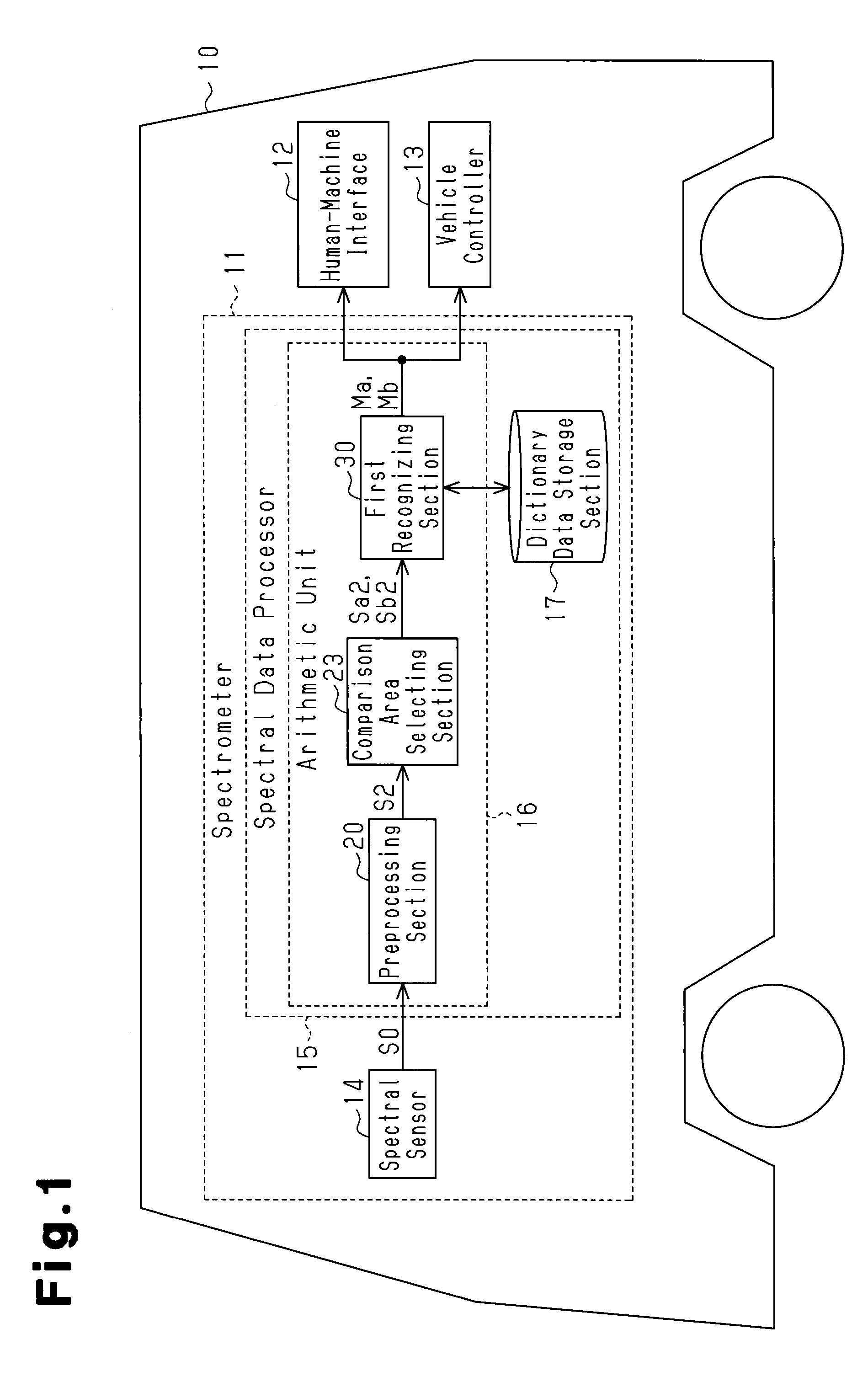
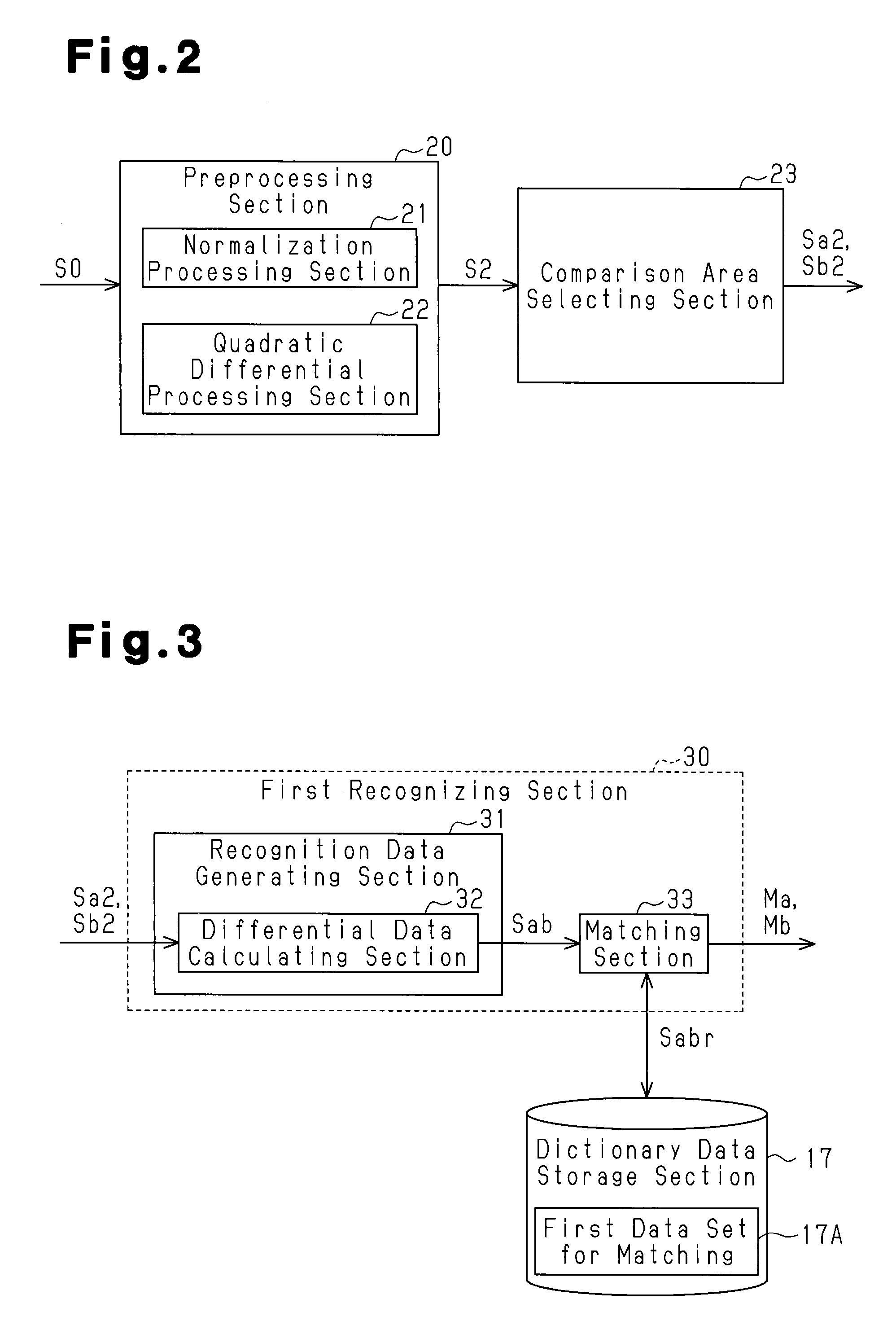
InactiveUS9234800B2Improve accuracyRemoving and reducing influence of ambient lightRadiation pyrometryAnti-collision systemsPhase correlationData set
A spectrometer recognizes a measurement target on the basis of the spectral data set of observed light detected by a spectral sensor capable of measuring wavelength information and light intensity information. The spectrometer is provided with a spectral data processor. Spectral data sets are detected at two different positions by the spectral sensor, and the processor subtracts a first spectral data set from a second spectral data set, or divides the first spectral data set by the second spectral data set to calculate one phase correlation spectral data set, which is correlated to the spectral data sets at the two different positions. The processor simultaneously identifies the measurement target corresponding to the two different positions on the basis of the correlation spectral data set.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
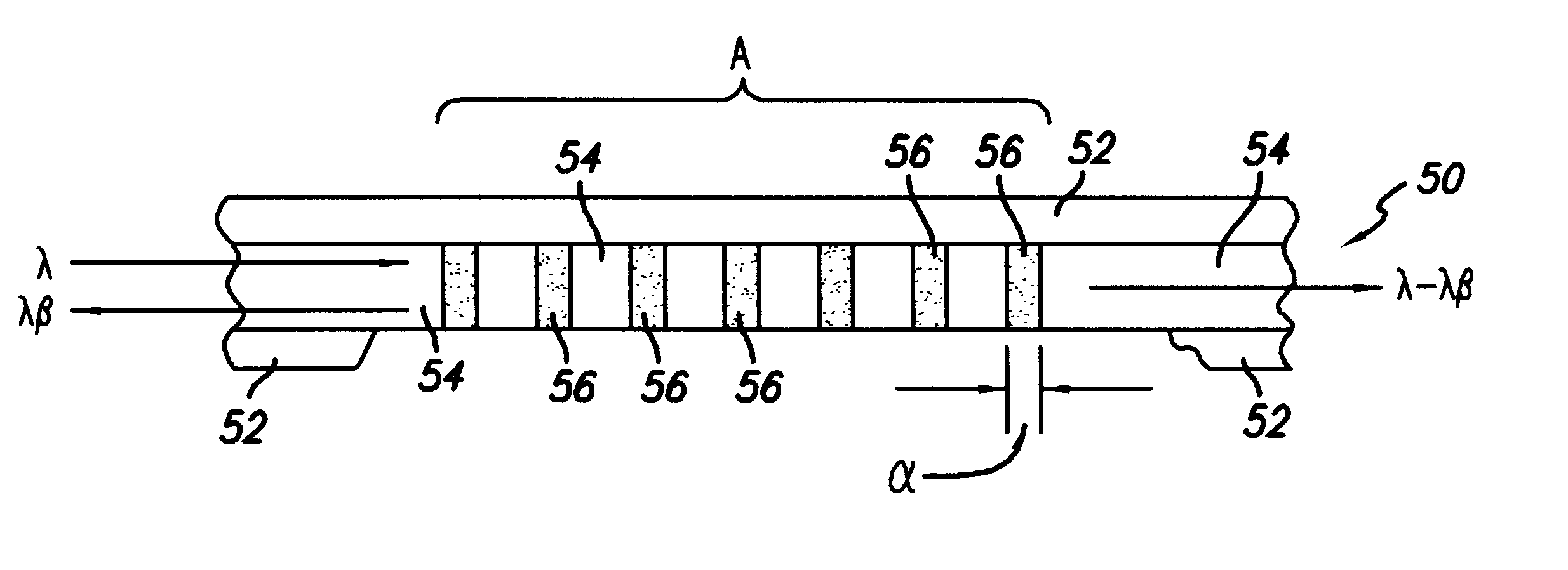
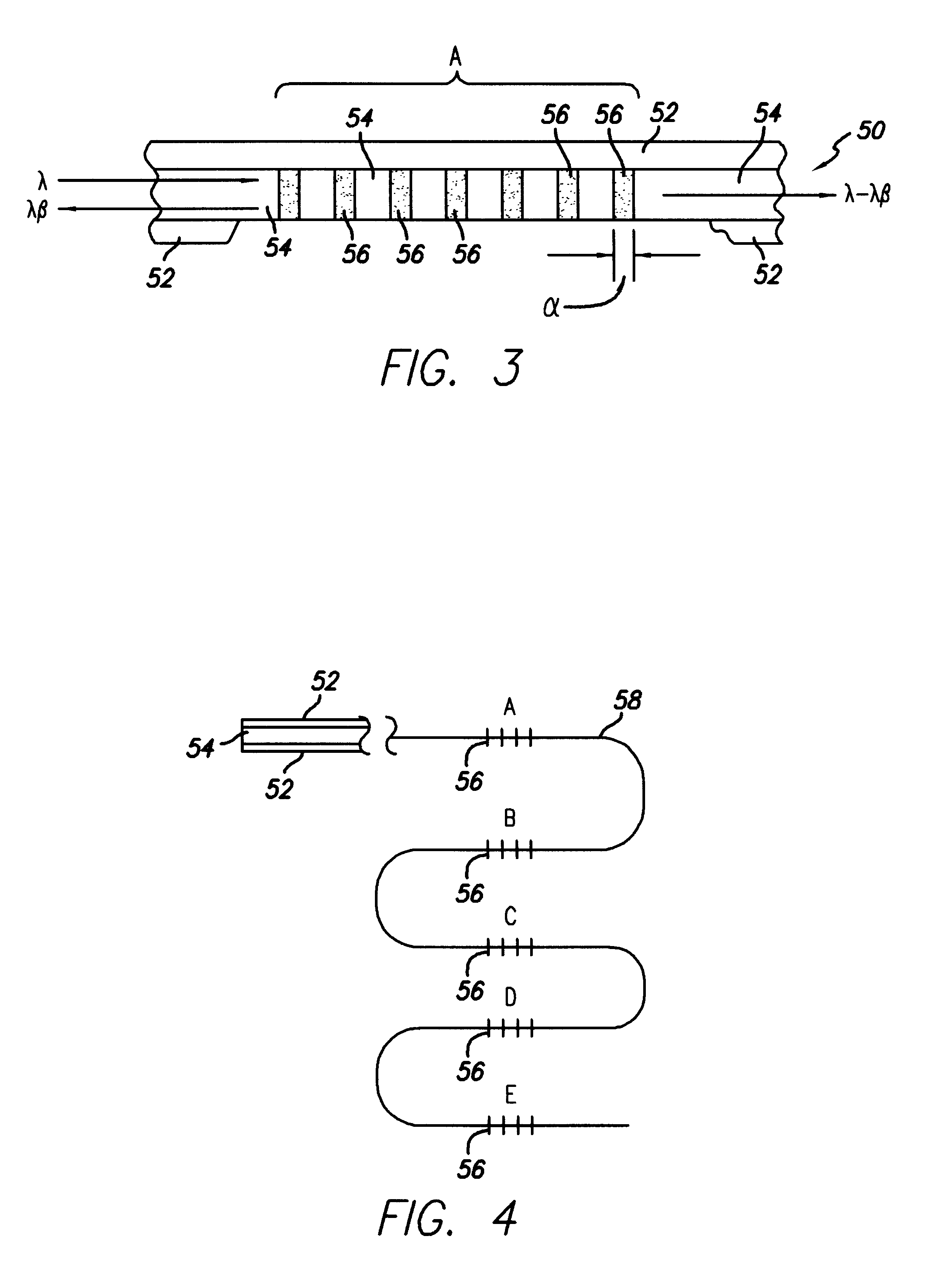
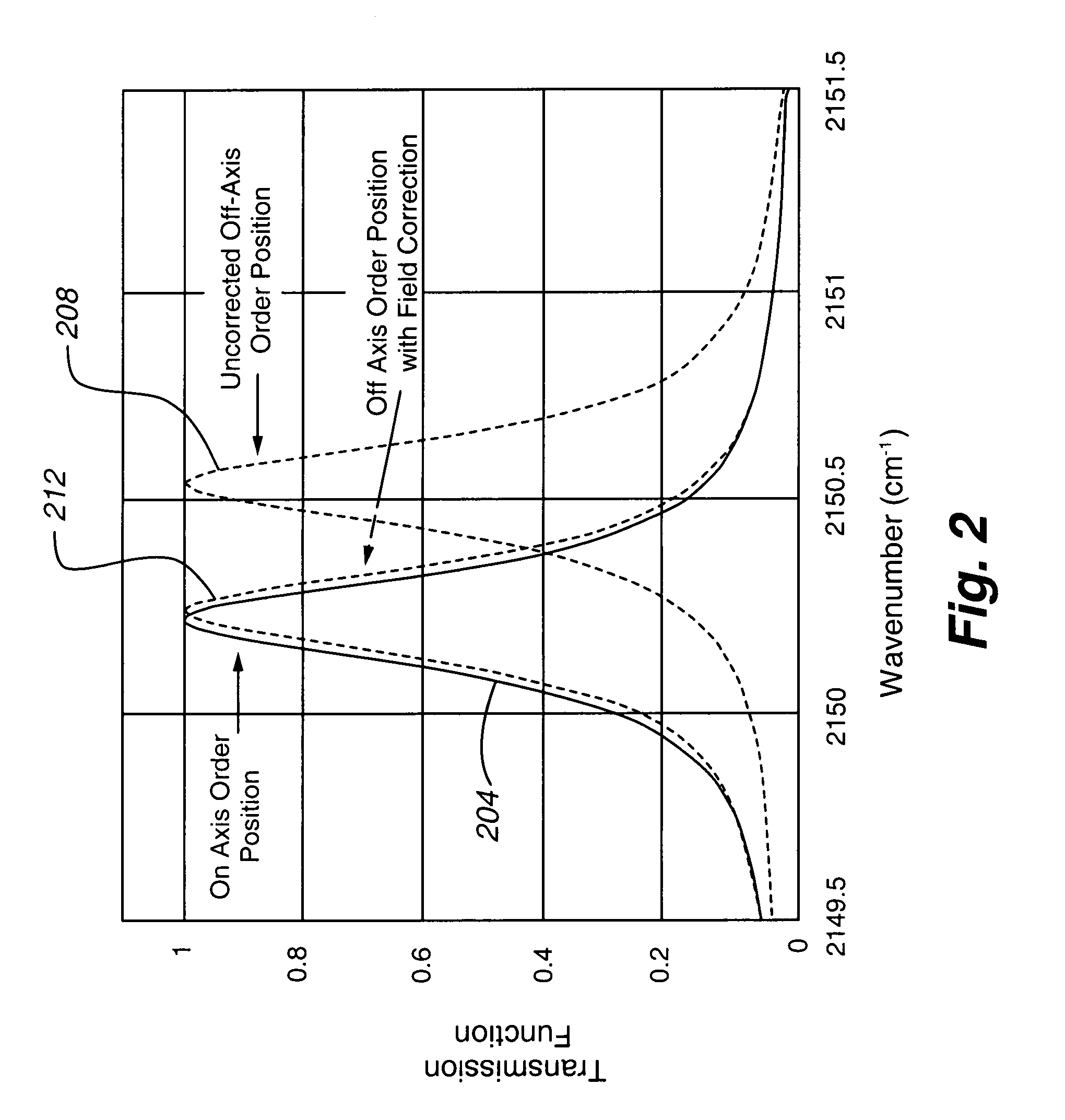
Method and apparatus for providing a gas correlation filter for remote sensing of atmospheric trace gases
InactiveUS7050215B1Accurate spacingAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyNon-linear opticsOptical cavitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A correlation filter is provided having passbands at wavelengths corresponding to the absorption spectrum of an atmospheric gas of interest. In particular, the correlation filter features narrow, non-linearly spaced passbands having center wavelengths that are correlated to the non-linearly spaced absorption lines of an atmospheric gas. A correlation filter in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention includes a compensation stack having a number of thin film layers, at least some of which have an optical thickness that is not equal to an integer multiple of one-quarter of a wavelength of an absorption line of the gas of interest. The correlation filter may be provided in association with an etalon, or may comprise a number of optical cavities. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a number of absorption lines associated with an atmospheric gas may be simultaneously viewed, providing a signal indicating the presence and quantity of such gas in the atmosphere having a high signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:BALL AEROSPACE & TECHNOLOGIES
Apparatus and method for Raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS7821633B2Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectroscopySpectrometer
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for two-dimensional spectroscopy
Preferred embodiments of the invention provide for methods and systems of 2D spectroscopy using ultrafast, first light and second light beams and a CCD array detector. A cylindrically-focused second light beam interrogates a target that is optically interactive with a frequency-dispersed excitation (first light) pulse, whereupon the second light beam is frequency-dispersed at right angle orientation to its line of focus, so that the horizontal dimension encodes the spatial location of the second light pulse and the first light frequency, while the vertical dimension encodes the second light frequency. Differential spectra of the first and second light pulses result in a 2D frequency-frequency surface equivalent to double-resonance spectroscopy. Because the first light frequency is spatially encoded in the sample, an entire surface can be acquired in a single interaction of the first and second light pulses.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Device and method for optical spectroscopy
InactiveUS7330267B1Improve accuracyImprove performanceOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryQuantum-optical spectroscopyWavefront
The invention relates to an apparatus for optical spectroscopy having means to produce an interference pattern and having a spatially resolving detector which can record the interference pattern produced. In accordance with the invention, the wavefronts of at least one of the part rays involved in the interference pattern is influenced in dependence on the wavelength by spectrally dispersive or diffractive optical elements.
Owner:CAMPUS TECH
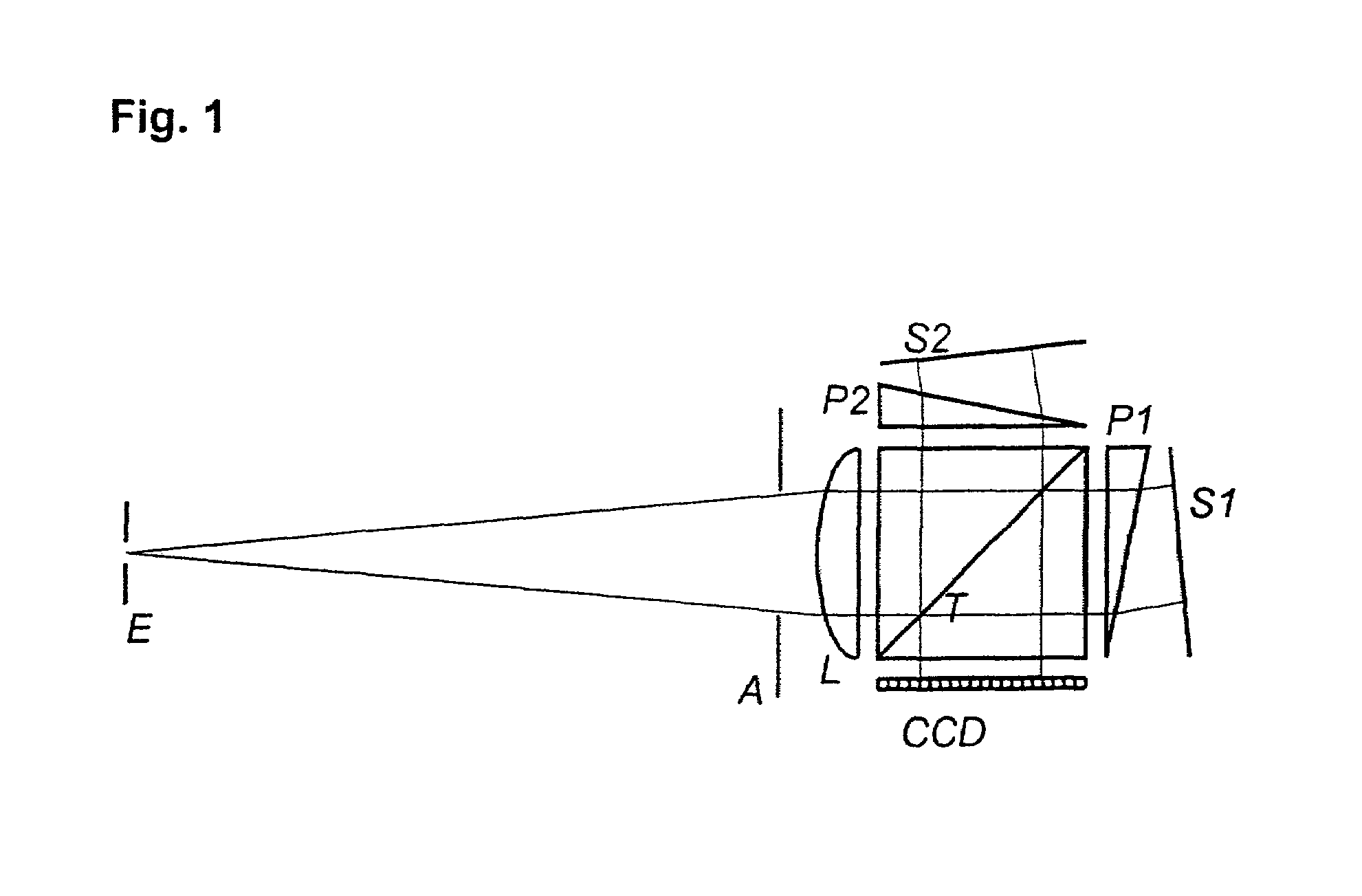
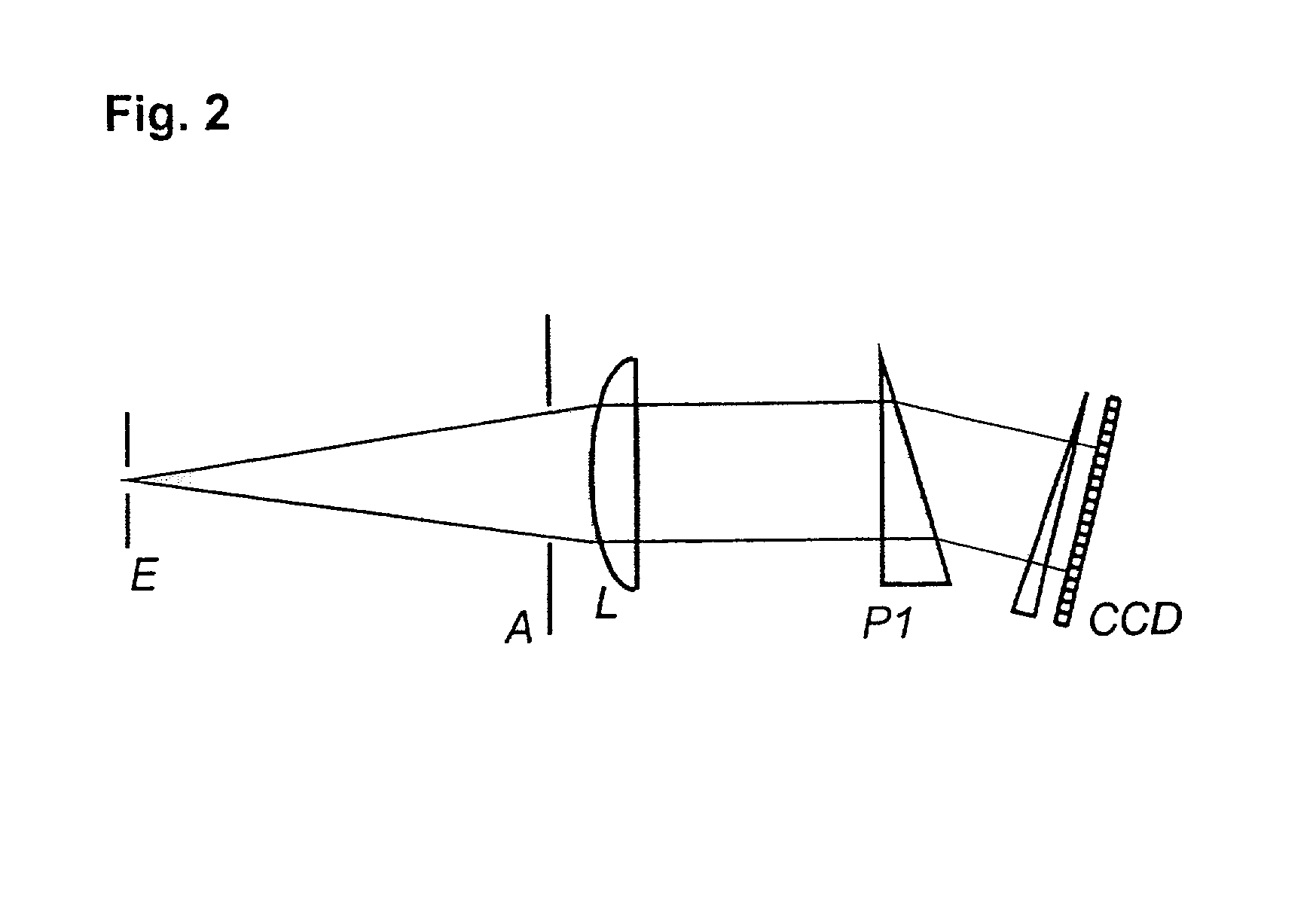
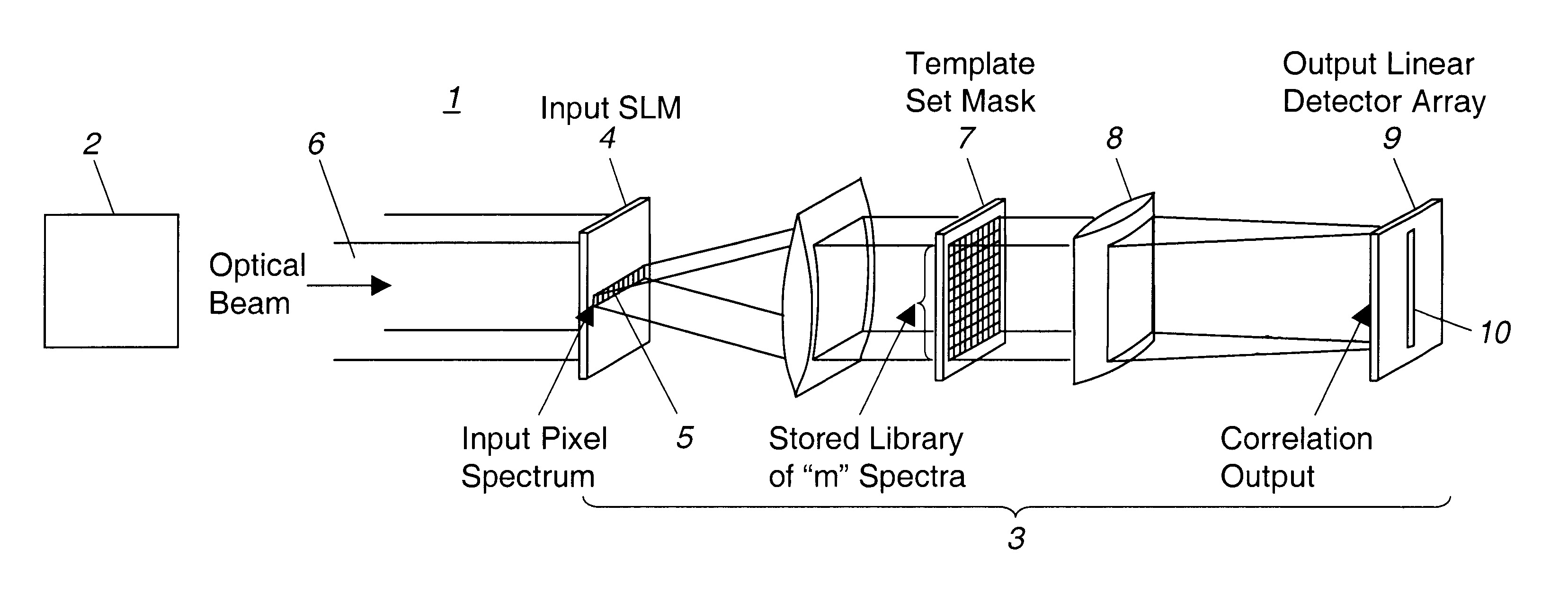
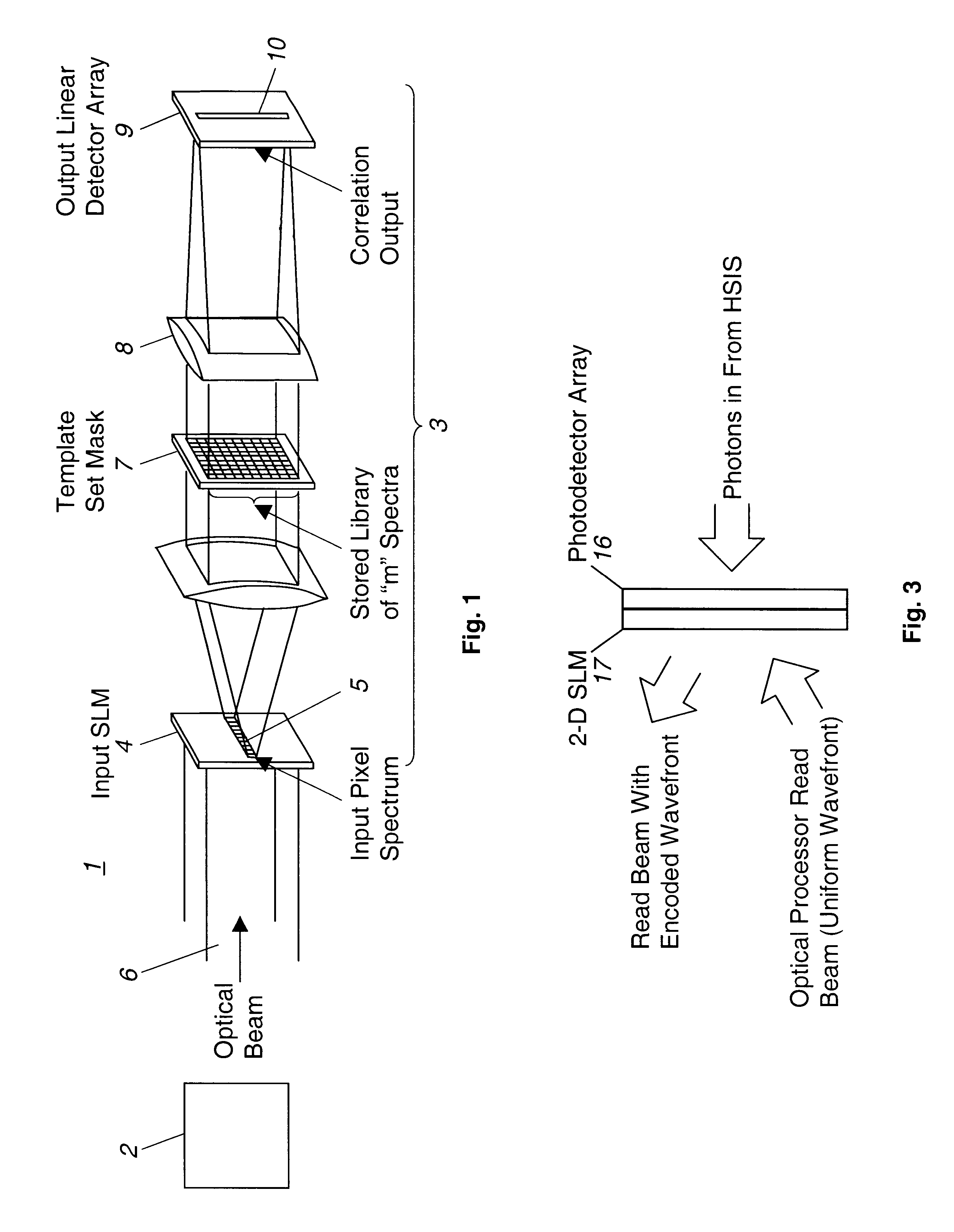
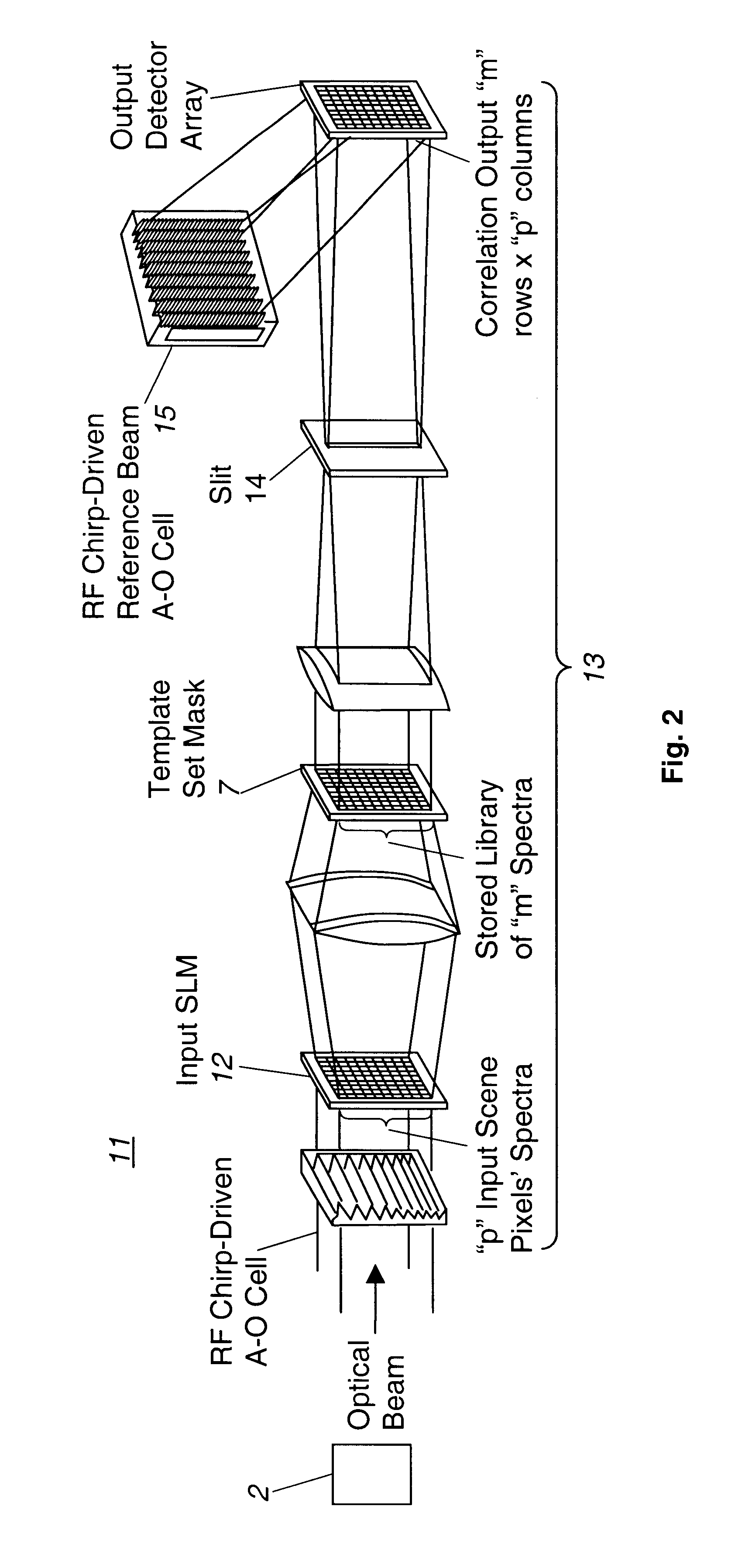
Multispectral imaging system and method
InactiveUS6480273B1Radiation pyrometryCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial light modulatorSpectral bands
A multispectral imaging system (1) and method utilize an optical processor (3) for simultaneously comparing an input wavelength spectrum observed in a single spatial pixel in a scene image from a multispectral imager (2) with a plurality of template wavelength spectra to find a correlation. The optical processor exploits the three-dimensional attributes of optical correlation to perform massively parallel correlation processing by modulating (4) respective ones of a plurality of spectral bands of the input wavelength spectrum of an incident light beam (6) with modulating elements (5) to alter at least one property of the incident light beam by a value corresponding to the observed intensity of the input spectrum in the respective spectral band. In a disclosed embodiment, the modulated beam is expanded and transited through a spatial light modulator (7) having a two-dimensional array of modulating elements. Each row of the elements of the array alter the at least one property of the incident light by values corresponding to a particular template wavelength spectrum of a plurality of template wavelength spectra of the modulator. The values corresponding to each template spectrum are the conjugates of the representative values of the modulating elements of the template spectrum of the plurality of template spectra.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
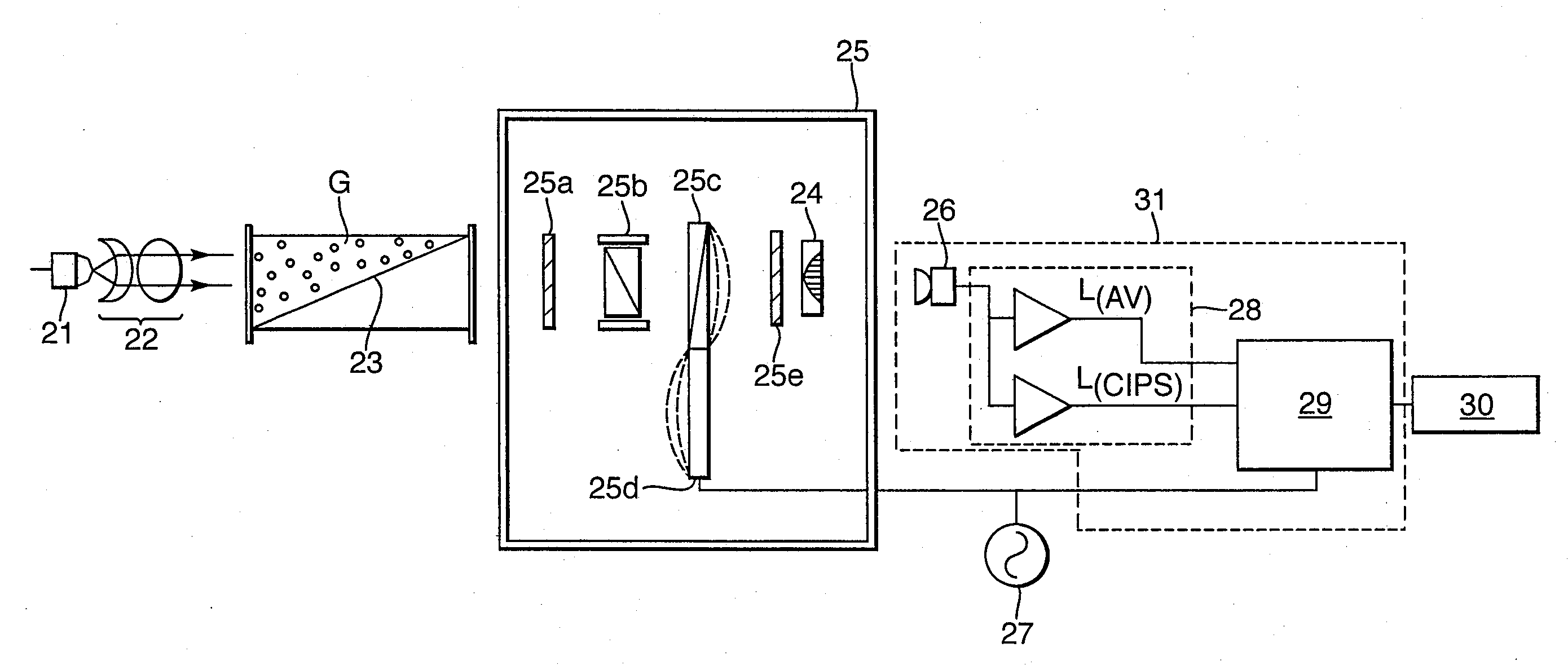
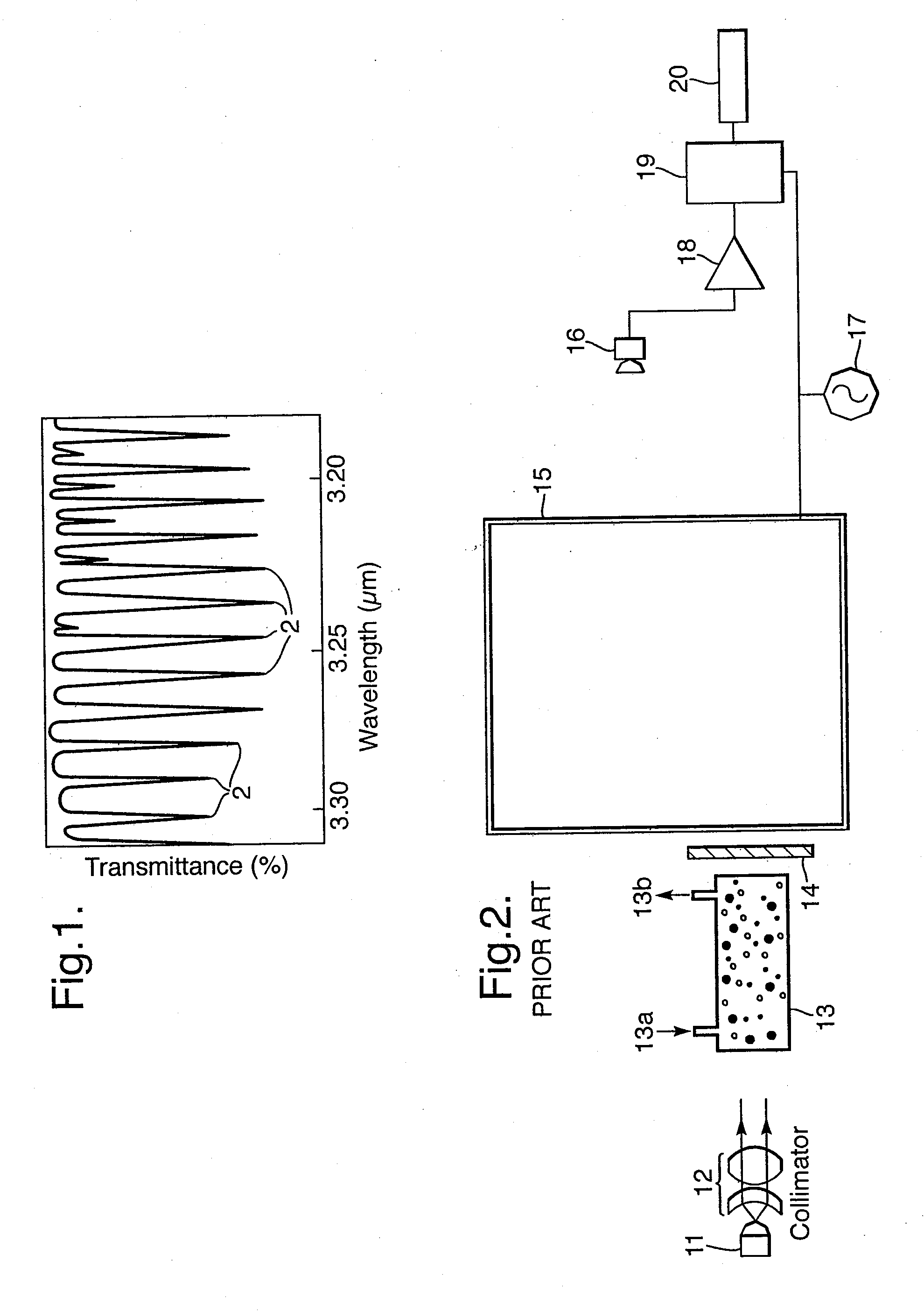
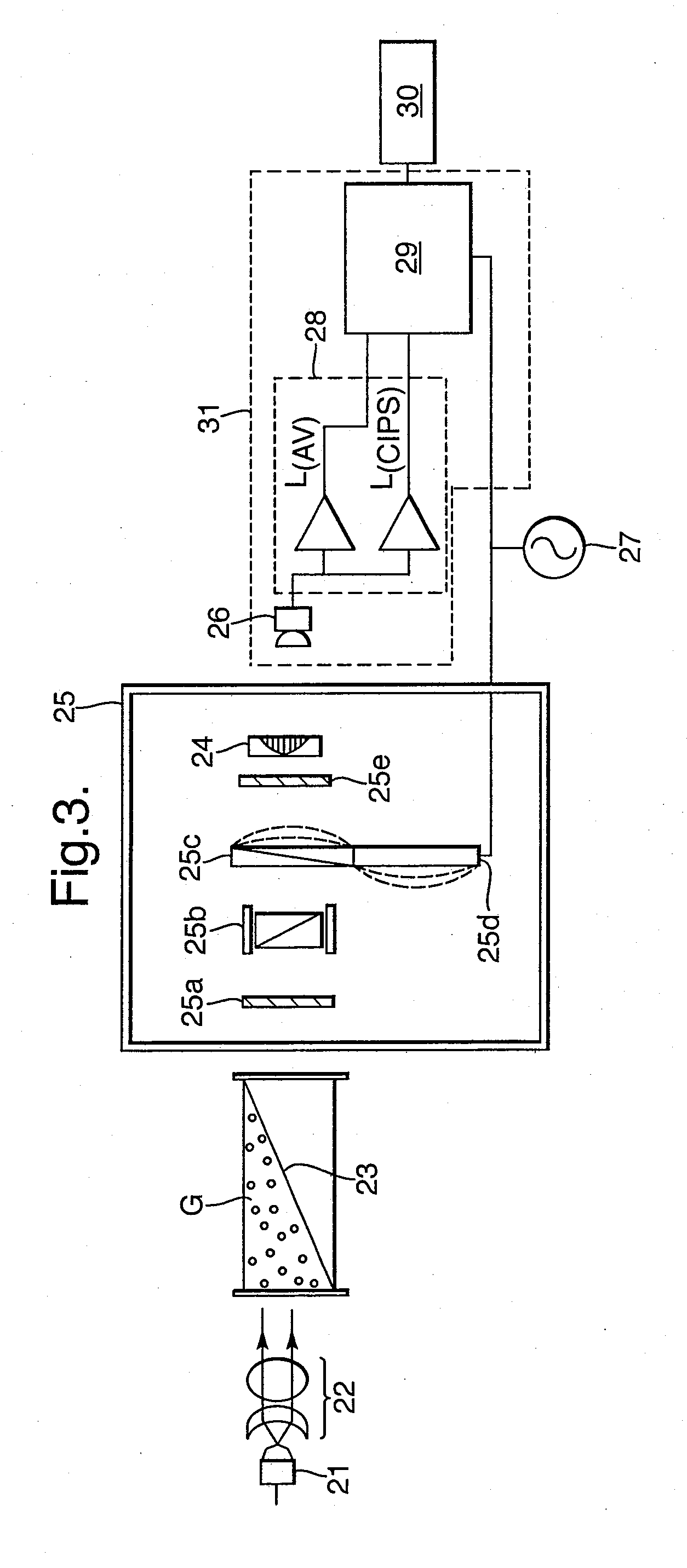
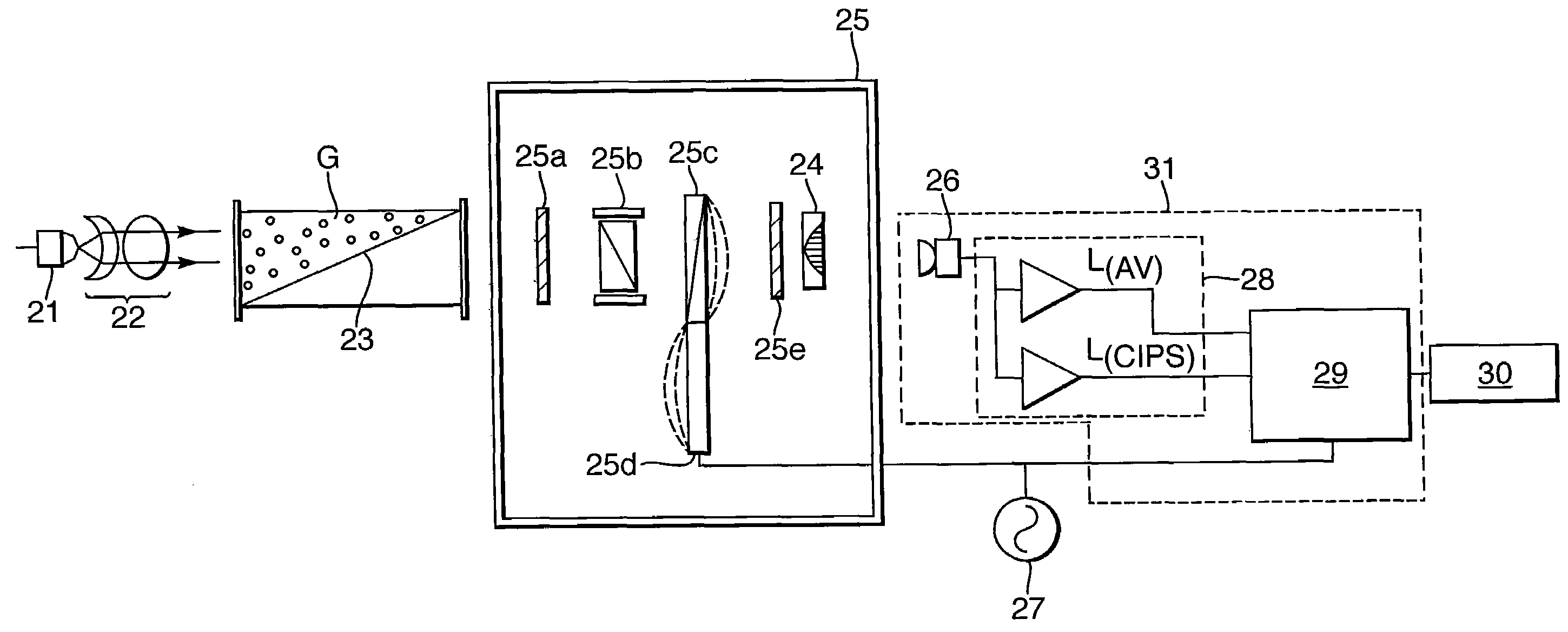
Optical Absorption Spectrometer and Method for Measuring Concentration of a Substance
InactiveUS20090257064A1High sensitivityAccurate measurementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryOptical absorption spectraSpectrometer
An optical absorption spectrometer is provided for determining the concentration of a substance within a sample. The optical absorption spectrometer comprises a first radiation source for supplying radiation to the sample to be measured; at least one cavity for containing the sample during measurement; and a detector assembly for detecting radiation transmitted along first and second optical paths through the sample, the length of the first optical path being greater than that of the second optical path.
Owner:BAH HLDG
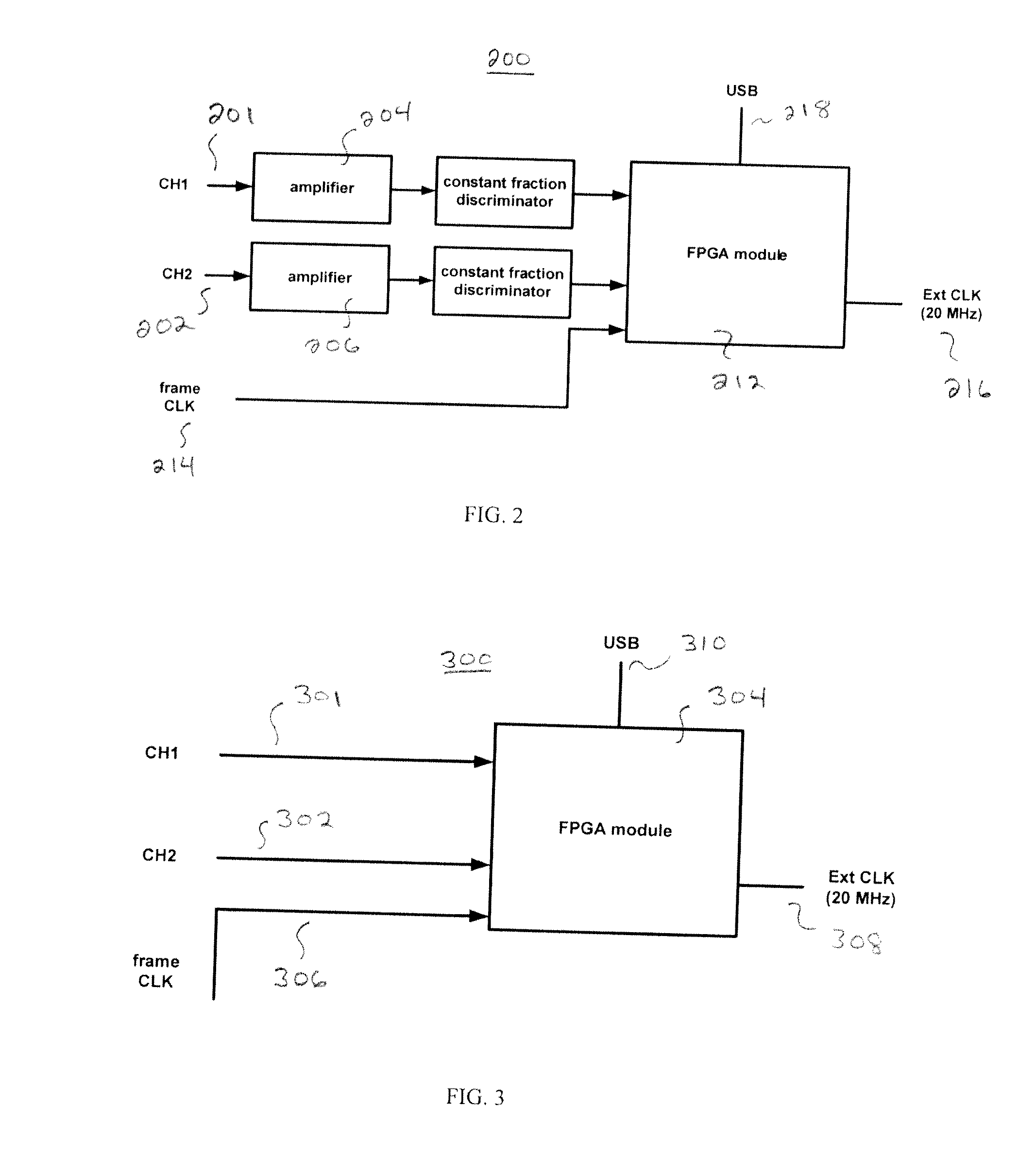
Correlation interferometric methods, devices and systems for low cost and rugged spectroscopy
ActiveCN102369421AInterferometric spectrometryPhase-affecting property measurementsSpectrographArrival time
A correlation interferometric spectroscopy devices are described that detect the spectral characteristics of a sample wherein device consists of an electromagnetic radiation source for exciting a sample with photons; and a detector adapted to detect an arrival time of a photon at the detector and further adapted to detect a delay between the arrival time of different photons. The device may further consist of an autocorrelator adapted to analyze the between the arrival of photons at the detector. The device may also be used together with other spectral detection and characterizing systems, such as Raman spectroscopy and attenuated total reflectance spectroscopy. Also provided herein are methods, systems, and kits incorporating the correlation interferometric spectroscopy device.
Owner:RARE LIGHT
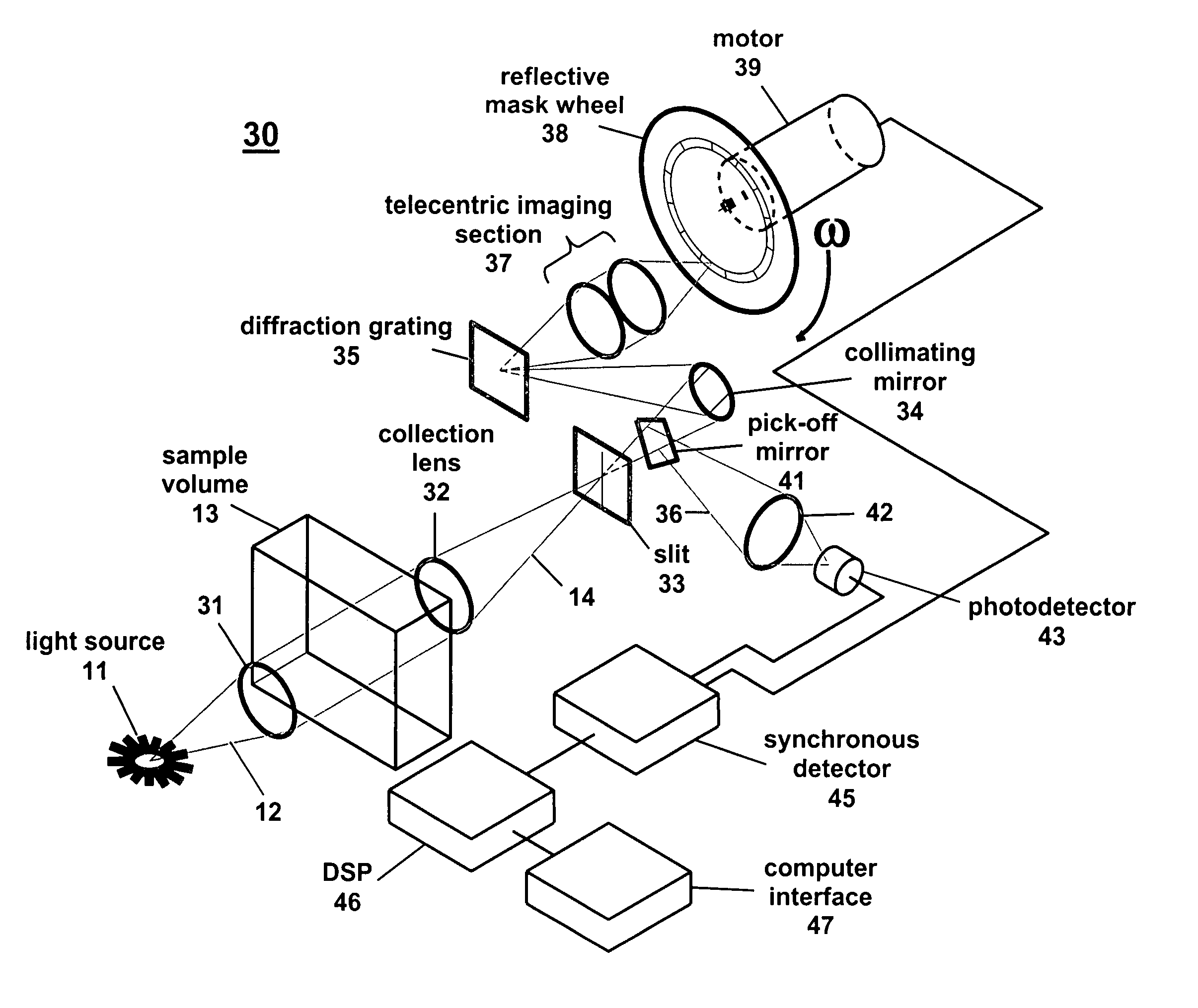
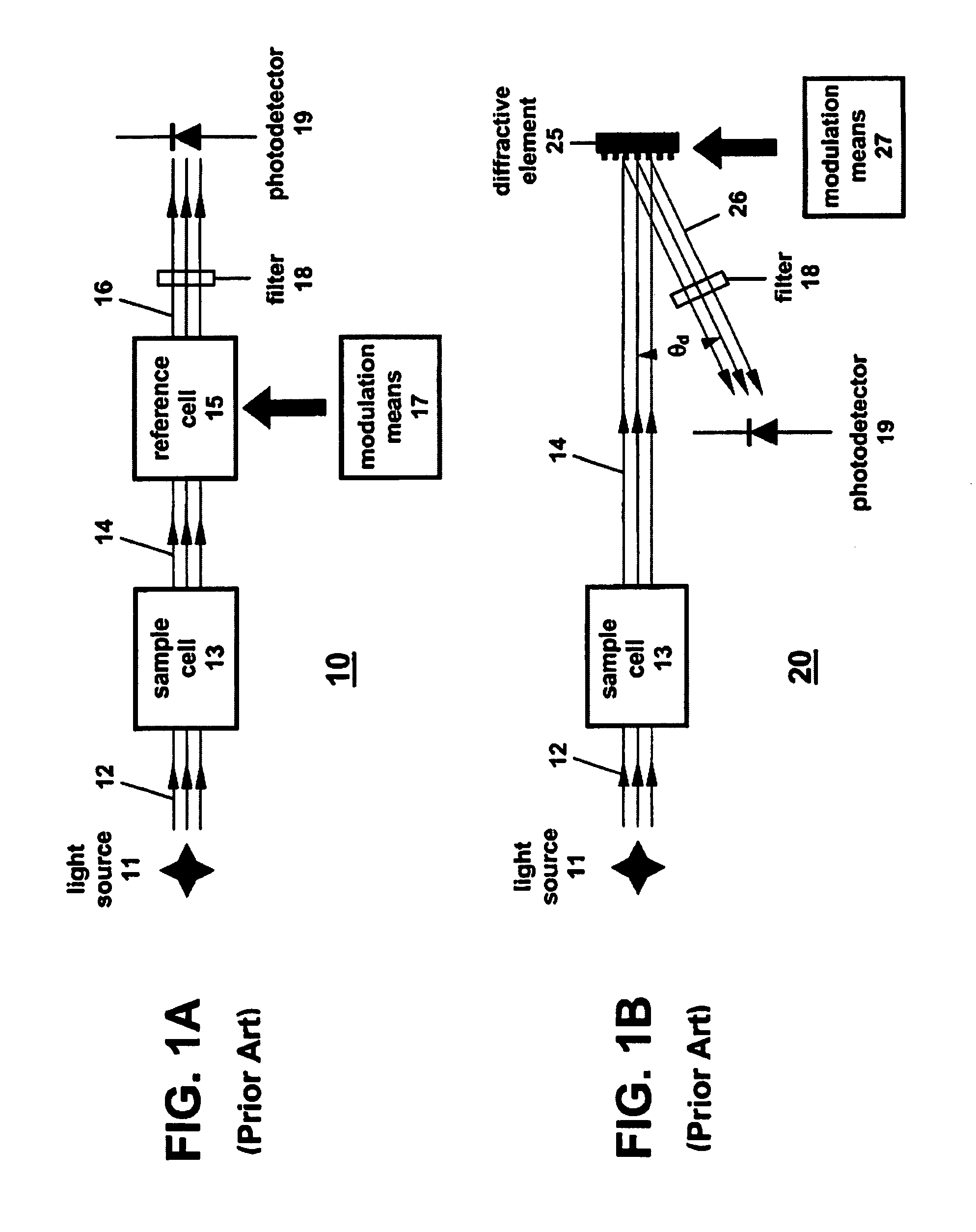
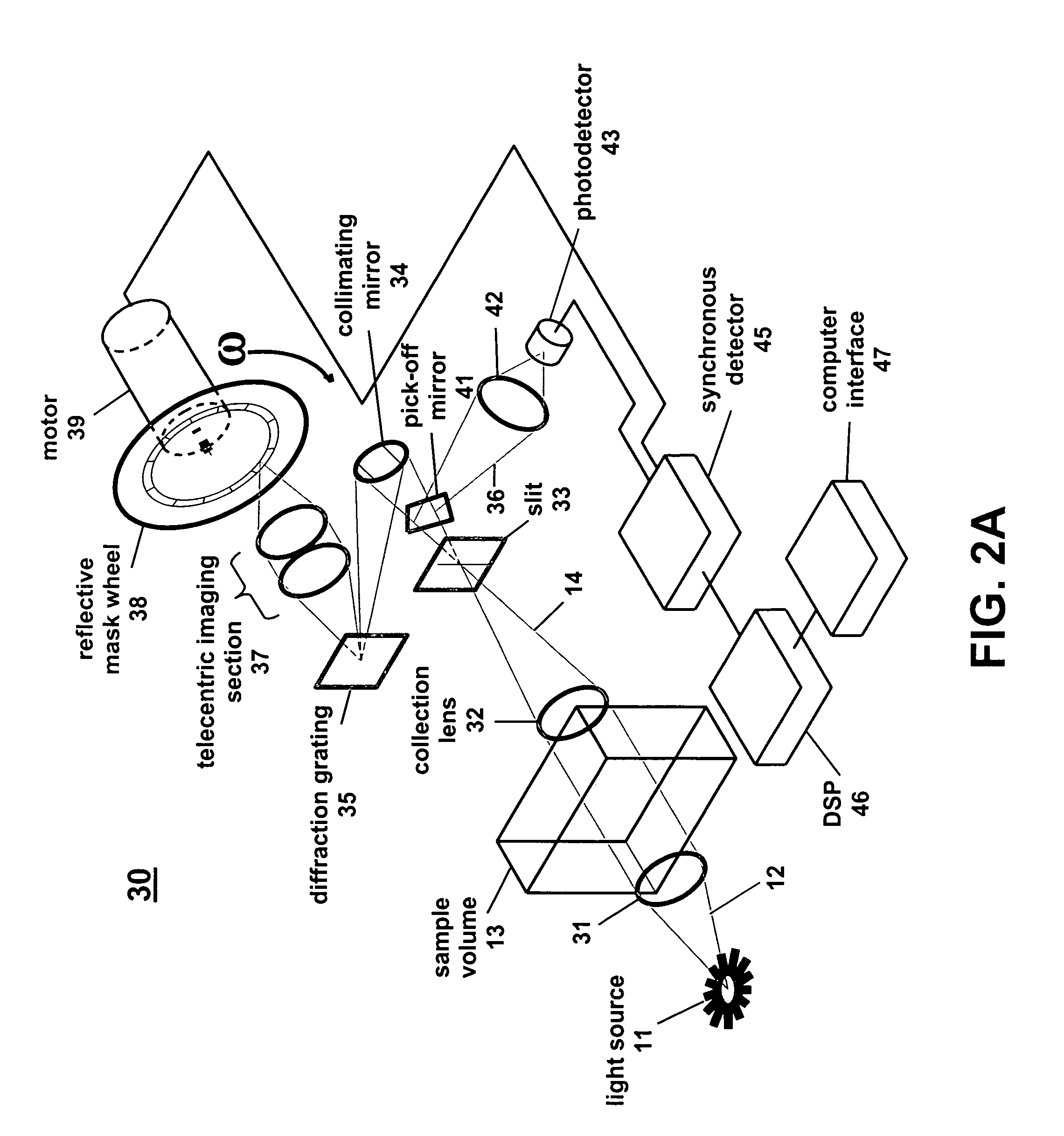
Correlation spectrometer
A correlation spectrometer can detect a large number of gaseous compounds, or chemical species, with a species-specific mask wheel. In this mode, the spectrometer is optimized for the direct measurement of individual target compounds. Additionally, the spectrometer can measure the transmission spectrum from a given sample of gas. In this mode, infrared light is passed through a gas sample and the infrared transmission signature of the gasses present is recorded and measured using Hadamard encoding techniques. The spectrometer can detect the transmission or emission spectra in any system where multiple species are present in a generally known volume.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
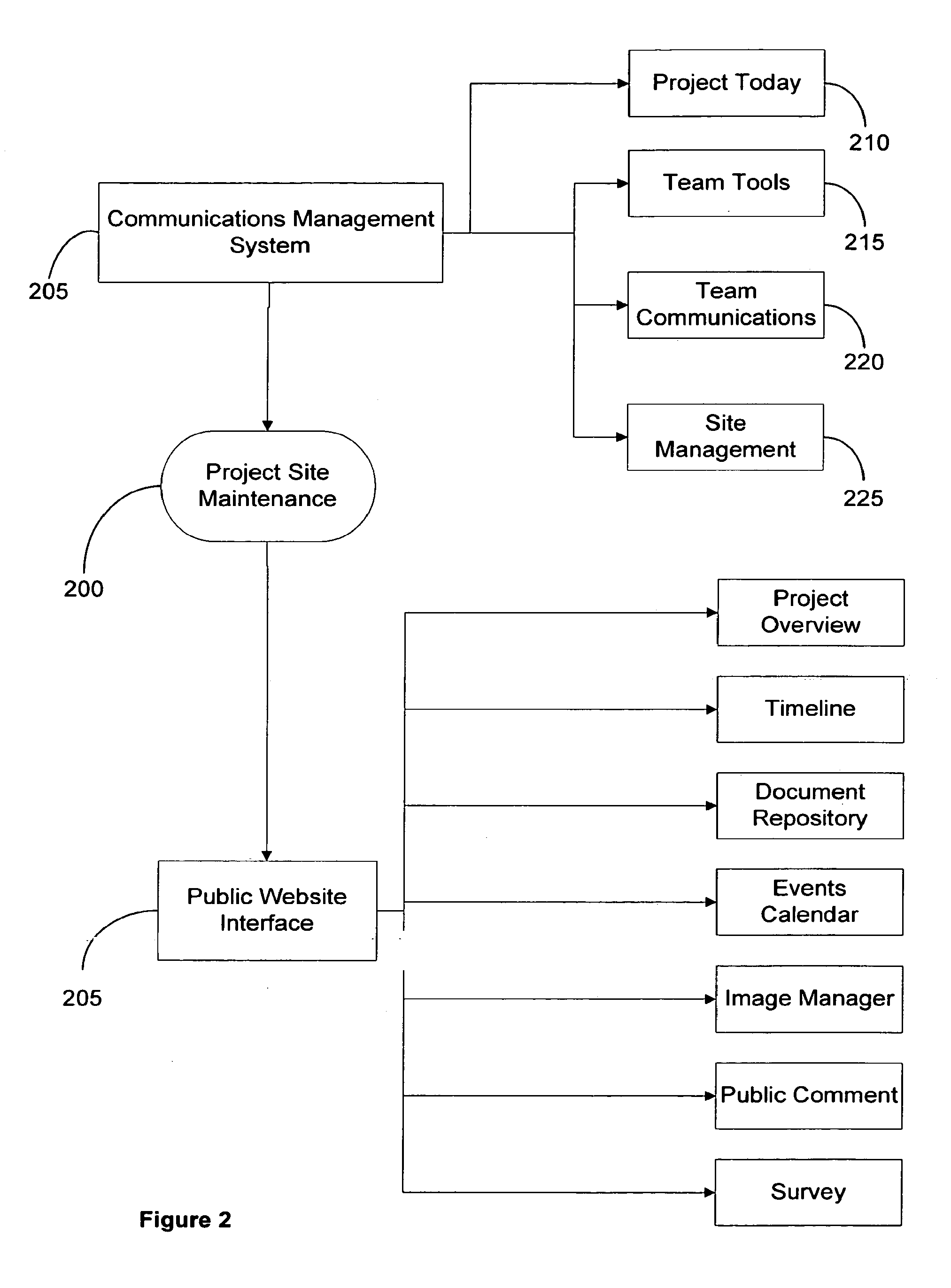
Platform for management of internet based public communications and public comment
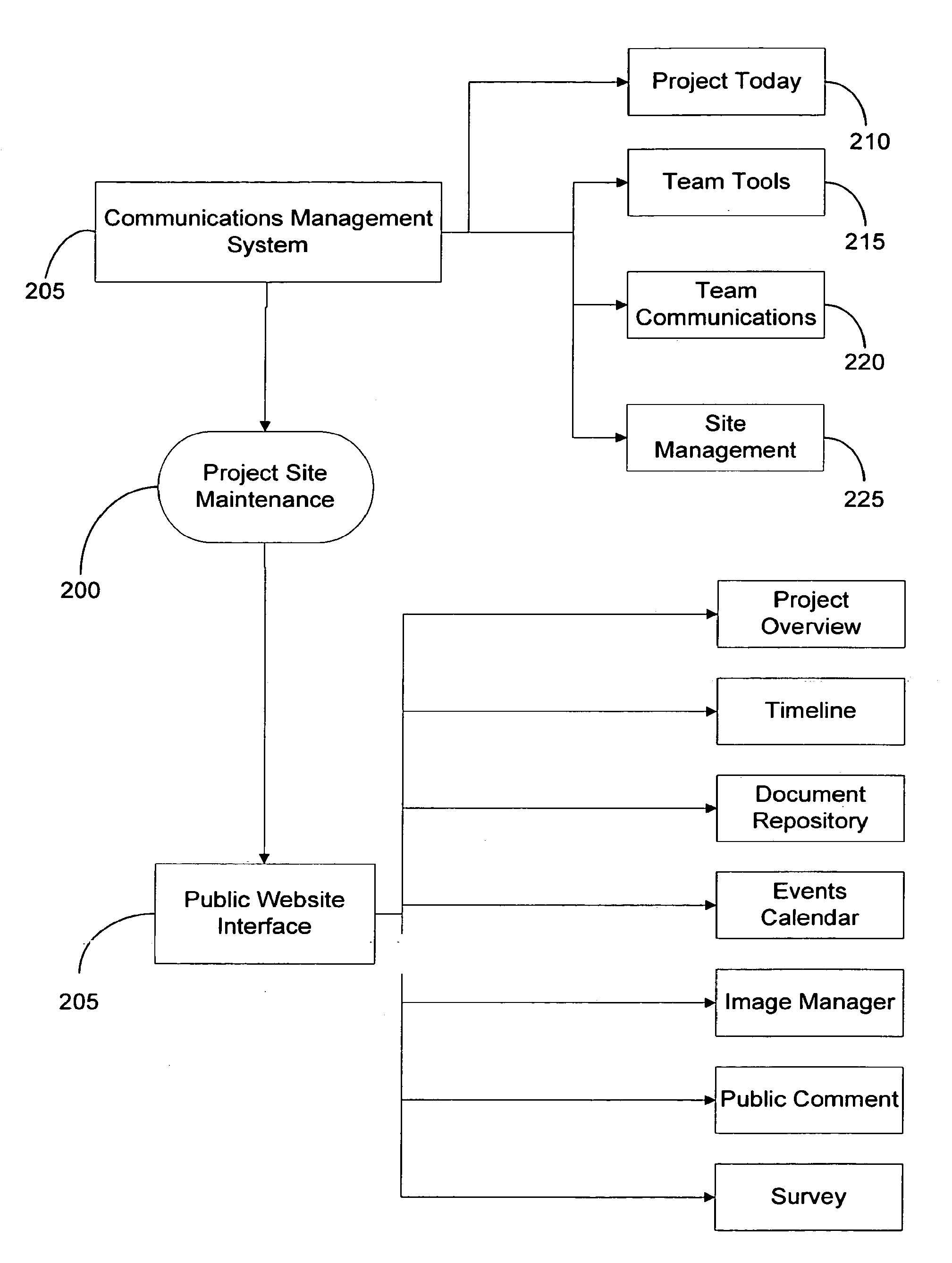
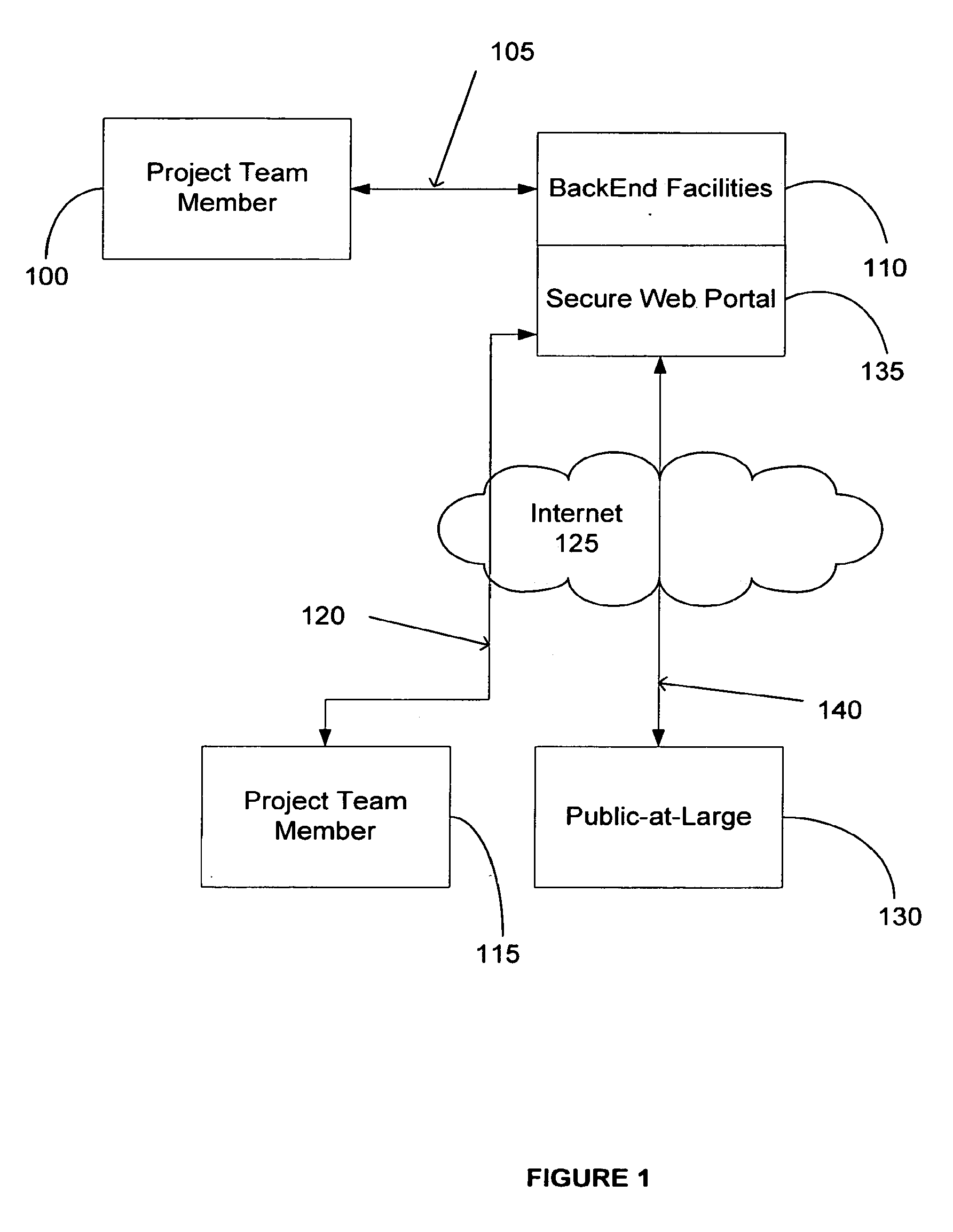
InactiveUS20090222382A1Low costEfficient use ofRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsWeb siteGraphics
An Internet-based integrated technology platform that simultaneously supports the management of Public Information Sites—Web sites used to both (1) inform the public; and (2) capture and manage public comment (including submission of images—while at the same time providing support for electronic communication for project teams that manage public involvement projects. The support includes sharing of graphic, text and collaborative tasks. The system and method allow revisions to comments and dynamic feedback in agency decision making based on comments with greater responsiveness. The system is also suited for implementing charettes with a large number of participants.
Owner:NEIGHBORHOOD AMERICA
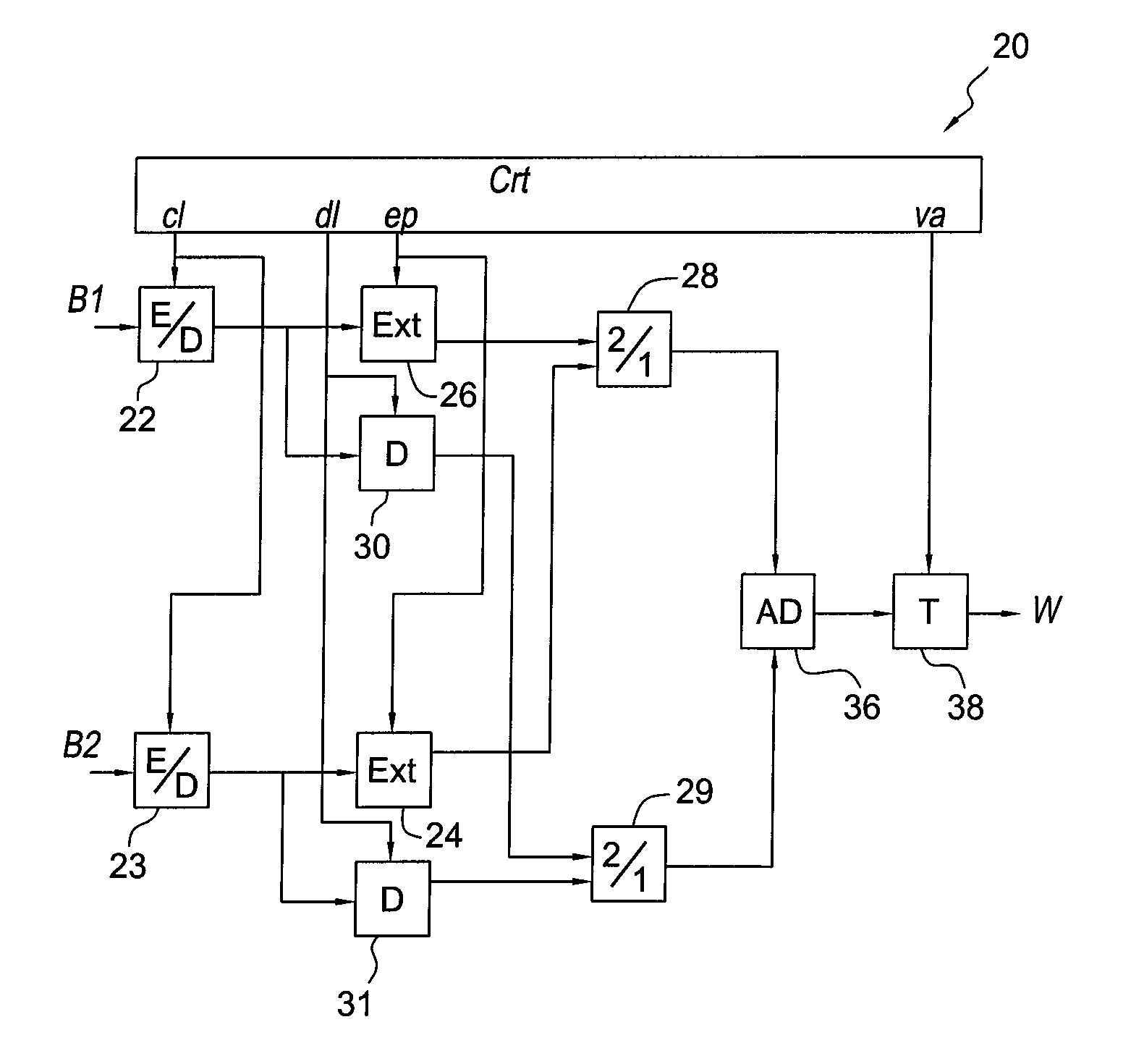
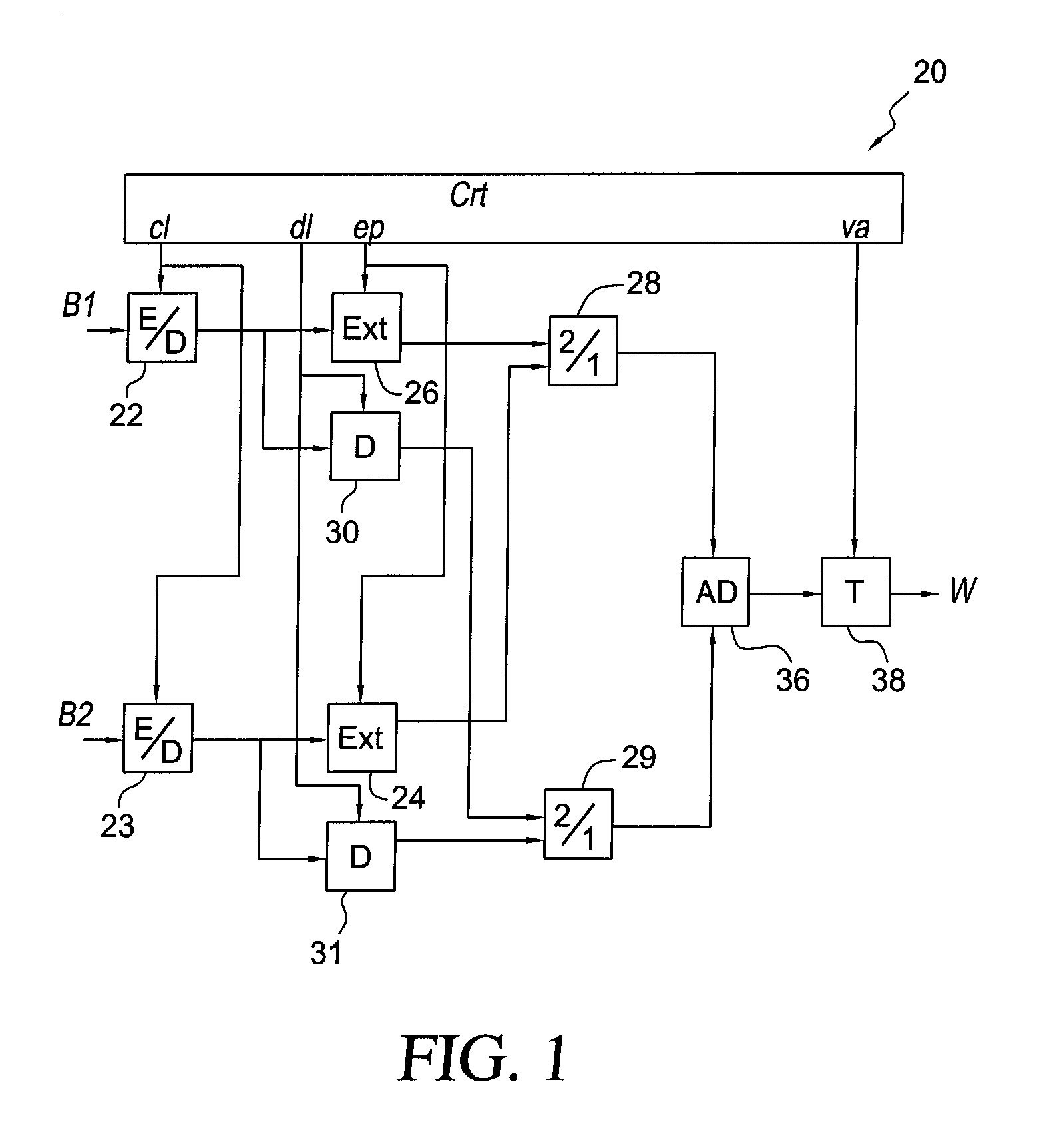
Device and method for optimally estimating the transmission spectrum by means of the simultaneous modulation of complementary sequences
InactiveUS20050245196A1Wave based measurement systemsModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumEngineering
A device and method for optimally estimating the transmission spectrum simultaneously modulates complementary sequences employing a signal transmitter, an encoder, a transmitter having a modulator; a convolver, an antenna, a receiver having a demodulator, and a decoder having an output filter. The device uses complementary sets of sequences, simultaneously transmitted to a physical means, the sum of autocorrelations of which corresponds to a Krönecker delta, allowing the extraction in reception of the spectral and temporal features of the means minimizing the effect of the noise.
Owner:DIAZ FUENTE VINCENTE
Systems for measuring electro-optic and thermo-optic coefficients by using interference fringe measurement, and methods of measuring electro-optic and thermo-optic coefficients by using the systems
InactiveUS20100290055A1Fast and accurate measurement systemThe process is fast and accurateRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryThermo-optic coefficientMulti wavelength
Measuring of an electro-optic coefficient and a thermo-optic coefficient of an optical device and an optical material, and more specifically, to measurement systems and methods of evaluating the electro-optic and thermo-optic coefficients by using interference fringe measurement techniques, wherein those optical characteristics can be precisely measured over a wide wavelength intended without using a complicated measuring equipment. The system for measuring an electro-optic coefficient includes: a light source for outputting an optical beam of multi-wavelengths, an optical interferometer including an optical beam splitter for dividing the optical beam received from the light source into two separate beams, a reference arm for receiving any one of the divided optical beams, a sample arm for receiving the other of the divided optical beams and applying a voltage to an optical sample to be measured by being connected to the optical sample, and an optical beam combiner for combining and mutually interfering optical beams that are output through the reference arm and the sample arm, and an optical spectrum analyzing device for receiving the mutually interfered optical beam from the optical interferometer and analyzing a spectrum of the mutually interfered optical beam.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
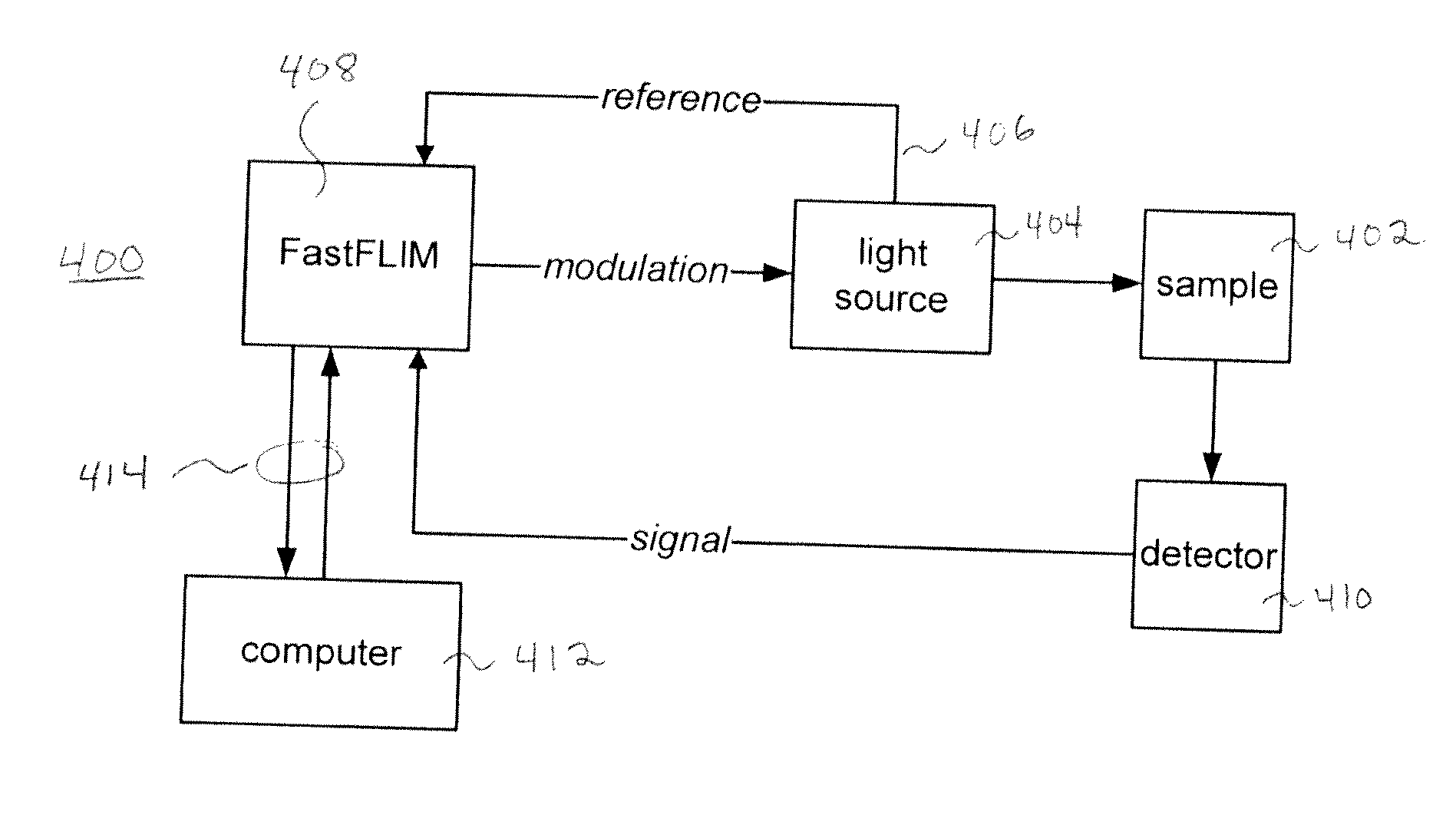
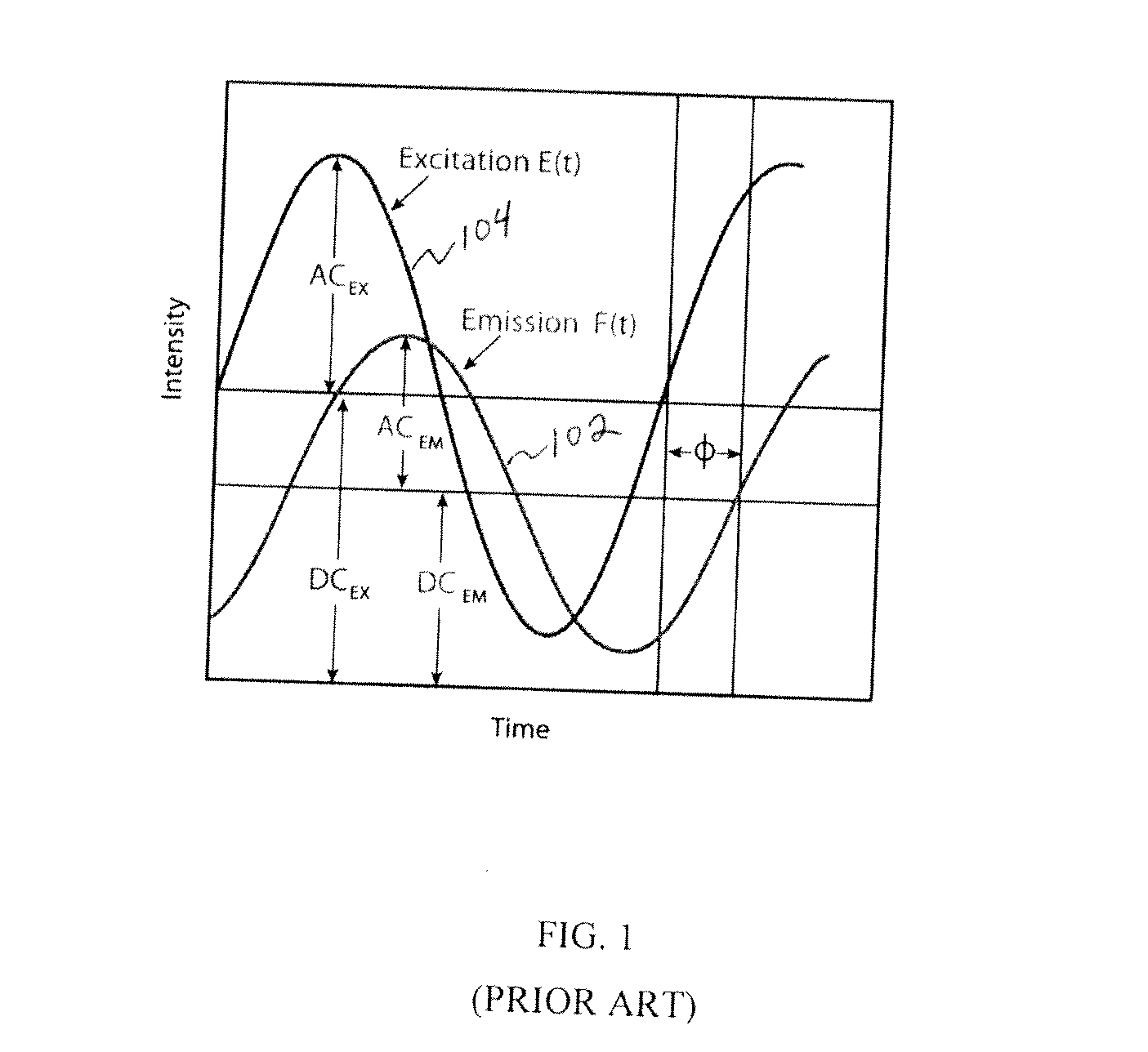
System and method for digital parallel frequency fluorometry
ActiveUS20110180726A1Small and less-expensive instrumentSimplifies amountRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotometryFluorescencePhoton detection
A system and method is provided for improved fluorescence decay time measurement. A digital heterodyning technique is disclosed in which a photon detector is sampled at a rate slightly faster than a digitally pulsed excitation signal. A resulting cross correlation frequency is low enough to be read by inexpensive electronics such as by a field programmable gate array. Phase information in the signal provides correlation with corresponding photon detections.
Owner:I S S USA
Optical absorption spectrometer and method for measuring concentration of a substance
ActiveUS7570360B1Accurate measurementReduce dependenceRadiation pyrometryAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceOptical absorption spectraSpectrometer
An optical absorption spectrometer is provided for determining the concentration of a substance within a sample. The optical absorption spectrometer comprises a first radiation source for supplying radiation to the sample to be measured; at least one cavity for containing the sample during measurement; and a detector assembly for detecting radiation transmitted along first and second optical paths through the sample, the length of the first optical path being greater than that of the second optical path.
Owner:BAH HLDG
Sensor system for multi-component fluids
InactiveUS20170205338A1Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyUltravioletChemical sensor
A small scale and low cost spectral sensing system designed primarily for multi-component fluids that provides a compact, low cost platform for analyzers or chemical sensors with limited number of optical and mechanical components featuring a light source, an optical interface with the sample, and a custom detector (multi-element). A single detector element has a specific wavelength, defined by a filter that can be used to select and measure specific chemical compounds. Multiple detector elements are combined to create a multi-channel detector capable of measuring a broad range of wavelengths from ultraviolet (UV) to near and mid-infrared wavelengths. The fabricated sensor can be configured for almost any class of material including gases, vapors, and liquids, with extension to solids. This is linked to the use of the custom detectors featuring filters tailored to specific substances in a broad spectral range from the UV to infrared.
Owner:SAAM INC
Spectroscopic analyzer and spectroscopic analysis method
InactiveUS20110307187A1Characteristic of in shortShort timeColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis methodNear infrared light
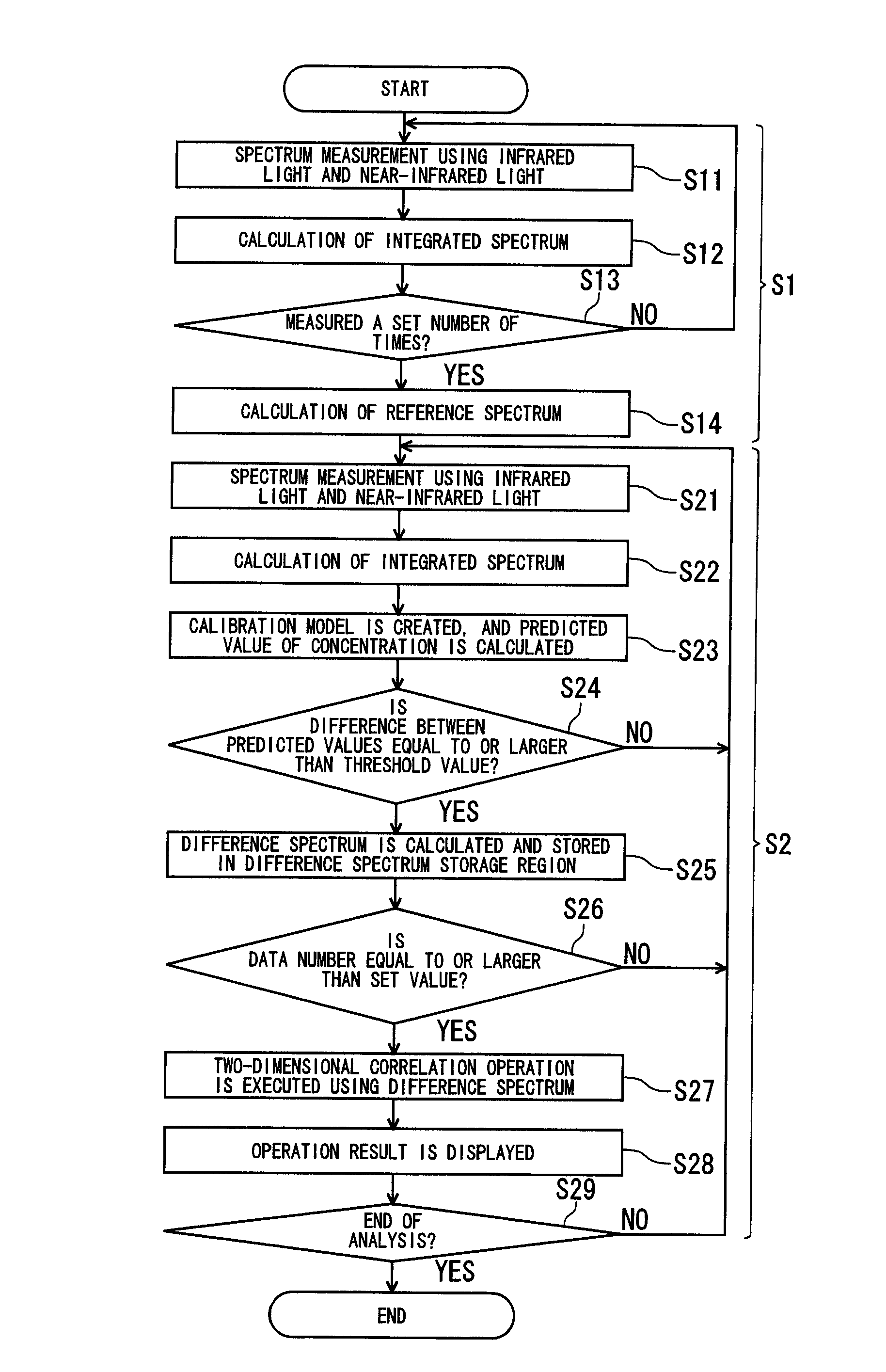
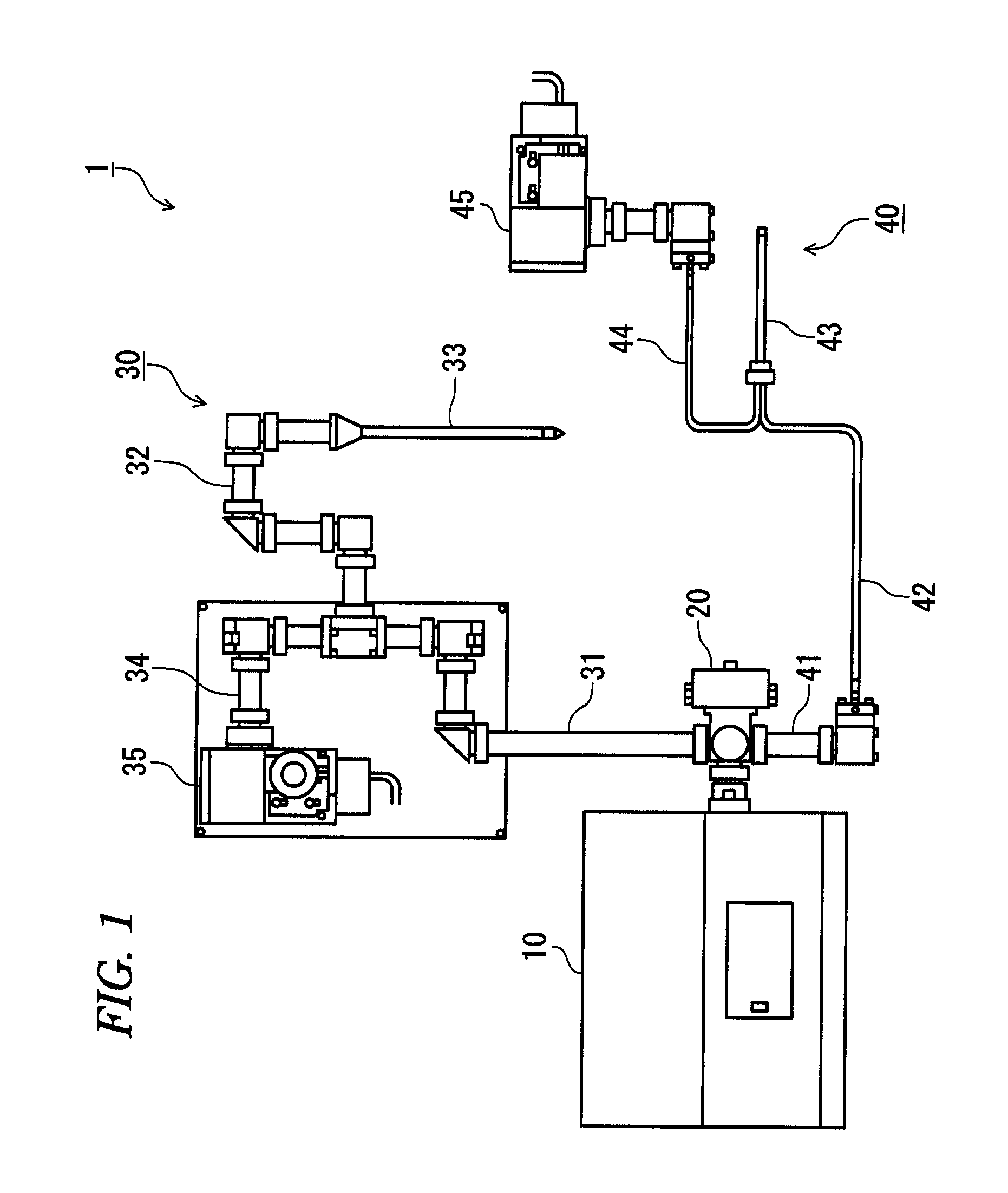
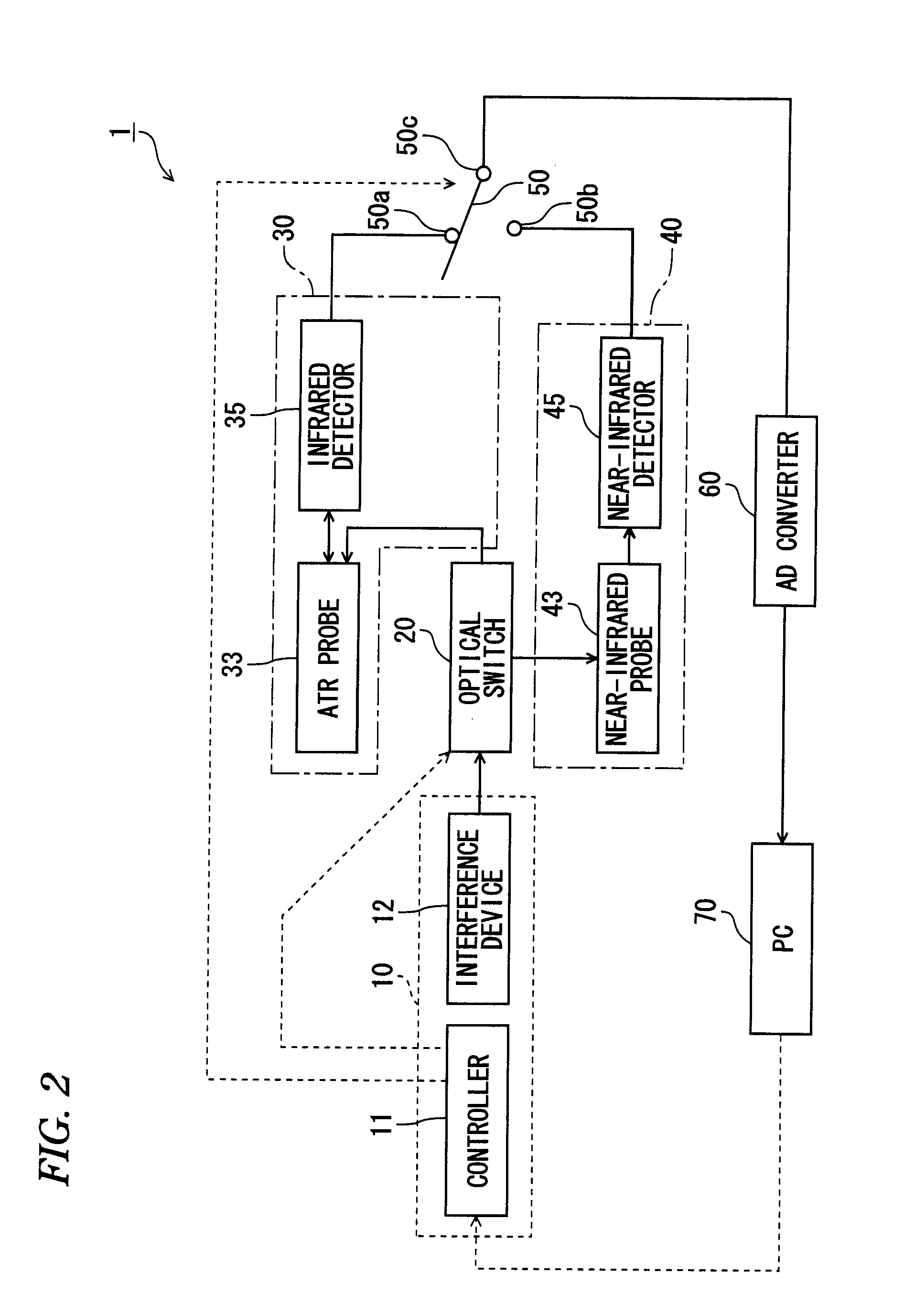
A spectroscopic analyzer includes a first measurement section which measures a spectrum of near-infrared region by irradiating a sample with near-infrared light, a second measurement section which measures a spectrum of infrared region by irradiating the sample with infrared light, and an analysis section which analyzes characteristics of the sample using the spectra measured by the first and second measurement sections. The analysis section includes a first calculation module which acquires a integrated spectrum by combining the spectrum of near-infrared region and the spectrum of infrared region, a second calculation module which calculates a difference spectrum of a reference spectrum measured in advance and the integrated spectrum, and a third calculation module which calculates correlation between the spectrum of near-infrared region and the spectrum of infrared region by performing a two-dimensional correlation operation using the difference spectrum.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Systems and methods for identifying a mixture
InactiveUS20130297254A1Molecular entity identificationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceComputer scienceSpectrometer
A spectrometer for identifying a mixture is provided. The spectrometer includes a detector configured to generate a signal based on an interaction of light with a sample of the mixture, and a memory device having a library and a correlation matrix stored therein, wherein the library includes a plurality of spectra, each spectrum associated with a respective compound, and wherein the correlation matrix includes a correlation between each possible pair of spectra in the library. The spectrometer further includes a processor coupled to the memory device and configured to determine a spectrum of the mixture based on the signal generated by the detector, calculate a correlation vector that includes a correlation between the mixture spectrum and each spectrum in the library, and identify the mixture based on the correlation matrix and the correlation vector.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Airborne/spaceborne oil spill determining system
InactiveUS20110101225A1High radiometric sensitivityRadiation pyrometryPhotometryImage resolutionRadiometer
Owner:ALAWADI FAHAD A M I
System and method for detecting number of layers of a few-layer graphene
ActiveUS20140376799A1Overcome limitationsEasy to numberTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryEngineeringMultispectral image
Provided are a system and a method for detecting a number of layers of few-layer graphene employing multispectral image reproduction process to provide rapid detection of numbers of layers of few-layer graphenes on transparent or non-transparent substrates. The application of the system and method in relevant industries expedites validation and / or verification of the number of layers of an FLG product and improves the quality control efficiency thereof.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Apparatus and method for enhancing dynamic range of charge coupled device-based spectrograph
InactiveUS9386241B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow noiseShift register
The present invention is directed to an apparatus, method and software product for enhancing the dynamic range of a CCD sensor without substantially increasing the noise. Initially, the area of a N×M pixel CCD sensor array is subdivided into two regions, a large region having (M−a) pixels in each column for outputting large-amplitude signals with low noise and a smaller region having a pixels in each column for outputting small-amplitude signals with improved dynamic range. At integration time, the CCD is read out one region's rows at a time into the horizontal shift registers by shifting the pixel charges in either a or M−a vertical shifts. The charges in the horizontal shift registers are then shifted out of the horizontal shift registers in N horizontal shifts. Next, the remaining pixels in the region of the CCD are read out into the horizontal shift registers by shifting the pixel charges in the other of a or M−a vertical shifts. Those charges are then shifted out of the horizontal shift registers in N horizontal shifts. In a spectrographic application, the data from the two regions is read out in the form of a large-amplitude channel from the larger region's rows and a small-amplitude channel from the smaller region's rows.
Owner:VERITY INSTR
Method and apparatus for endpoint detection using partial least squares
InactiveUS7297287B2Easy to detectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesAlgorithmLeast squares
An apparatus and method for detection of a feature etch completion within an etching reactor. The method includes determining a correlation matrix by recording first measured data regarding a first etch process over successive time intervals to form a first recorded data matrix, assembling a first endpoint signal matrix using target endpoint data for a specific etch process, performing a partial least squares analysis on the recorded data matrix and the first endpoint signal matrix to refine the recorded data matrix, and computing a correlation matrix based upon the refined recorded data matrix and the first endpoint signal matrix. The method further includes performing a second etch process to form a second recorded data matrix. The correlation matrix and the second recorded data matrix are analyzed to determine whether an endpoint of the second etch process has been achieved.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com