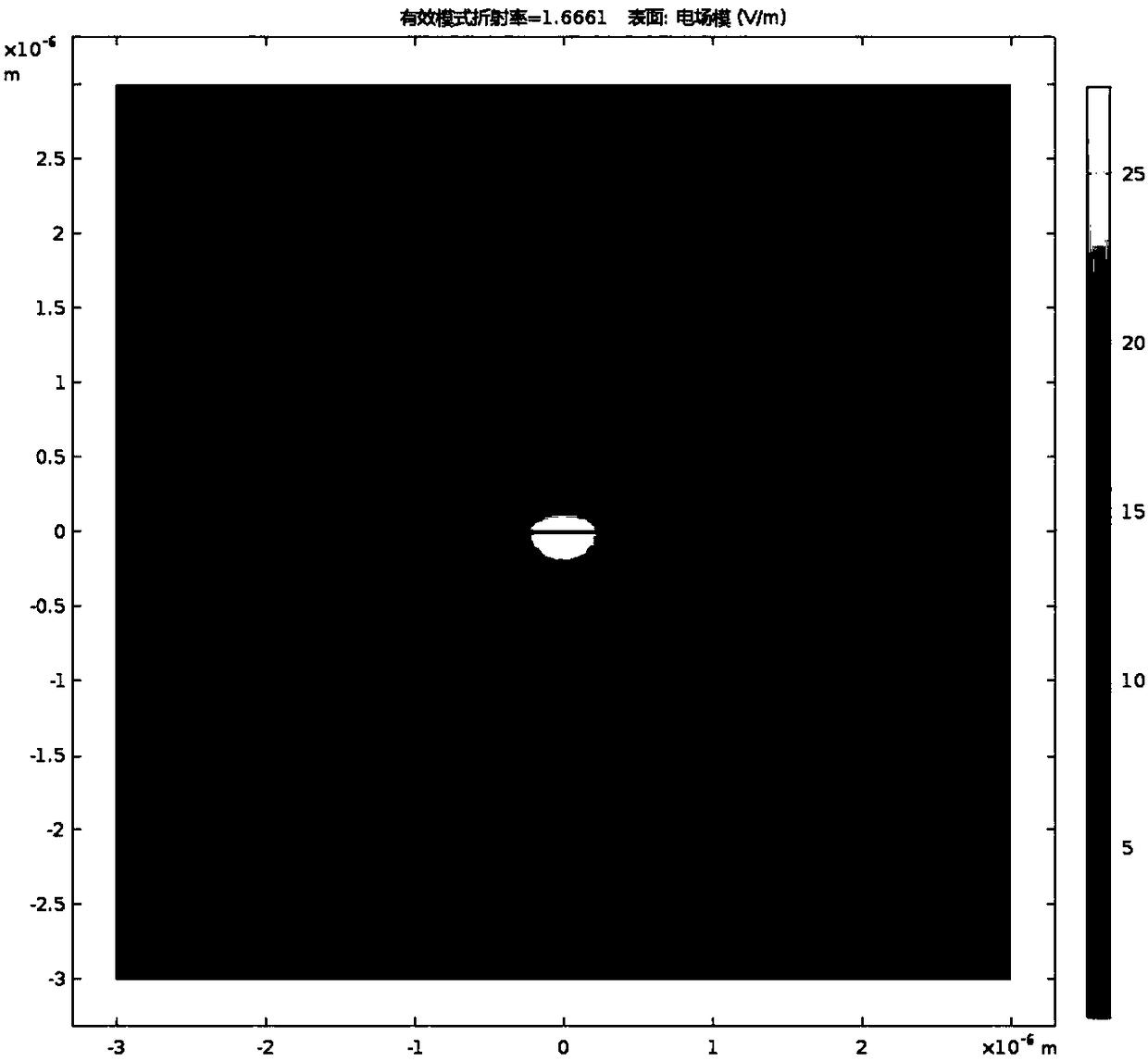
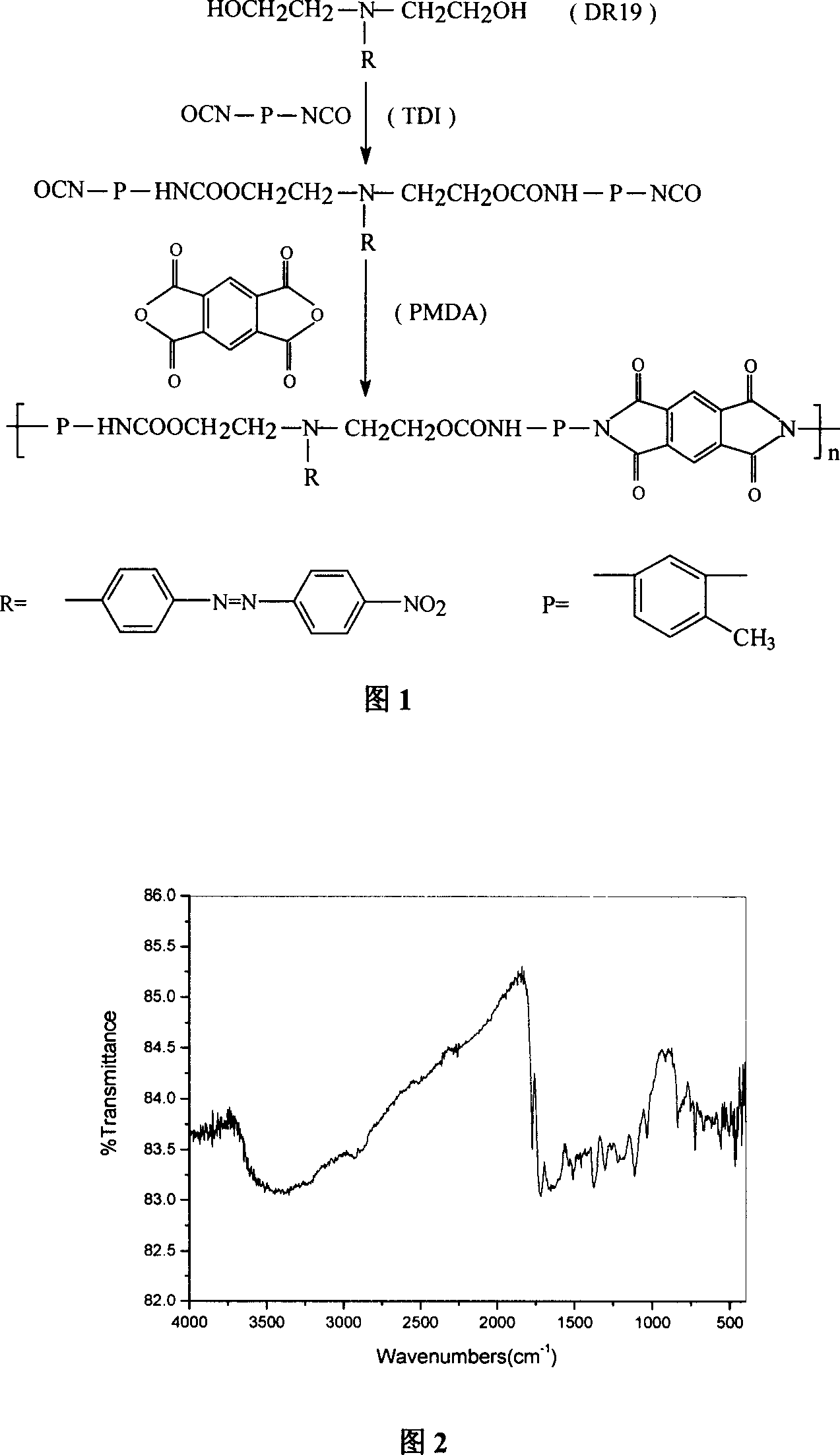
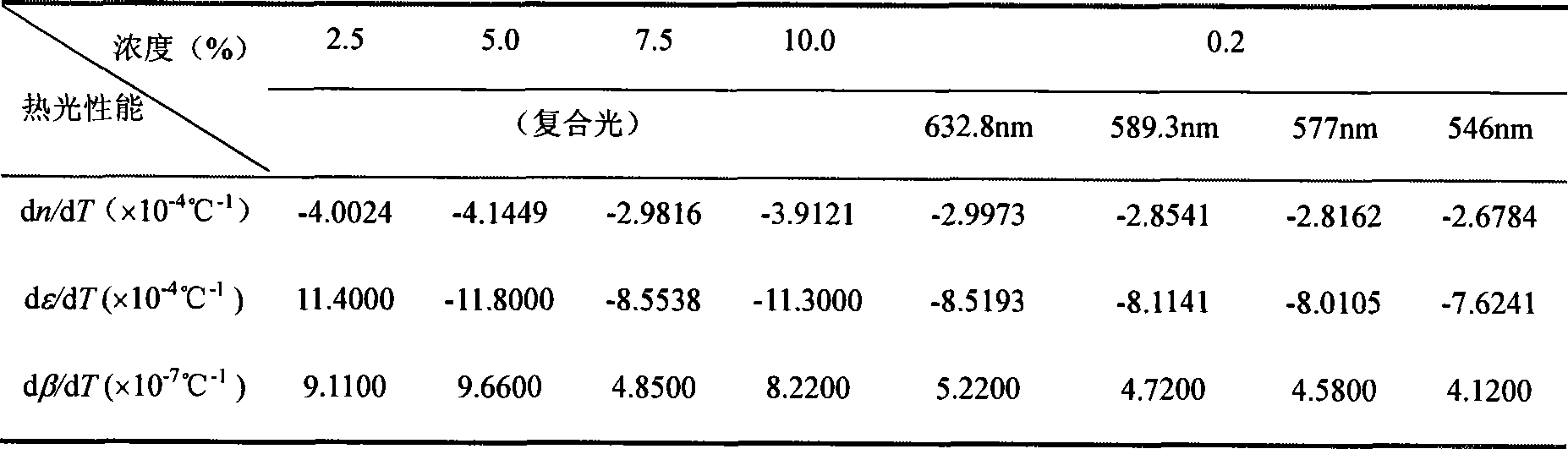
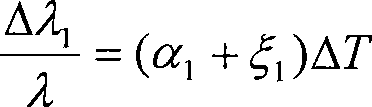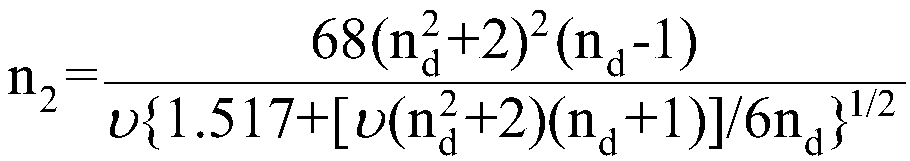Patents
Literature
108 results about "Thermo-optic coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
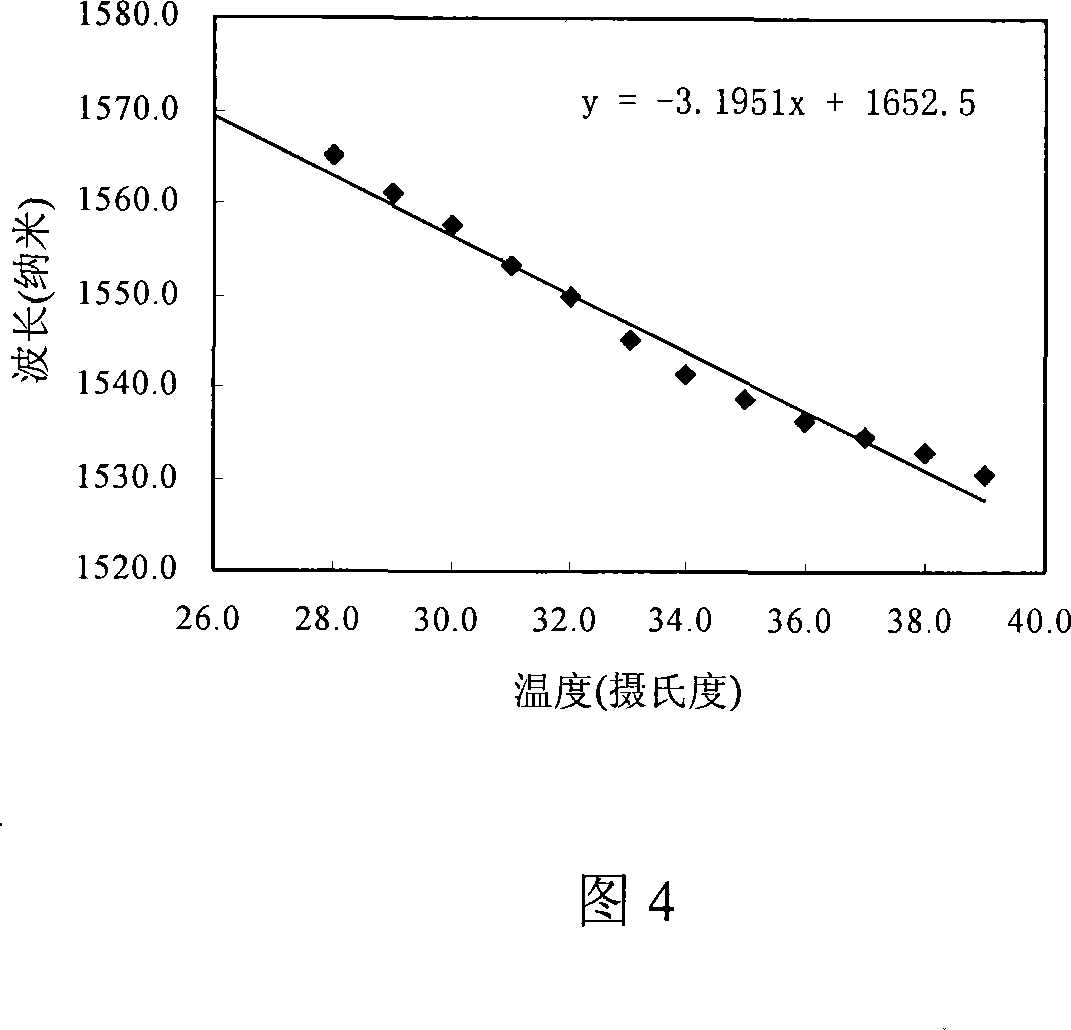
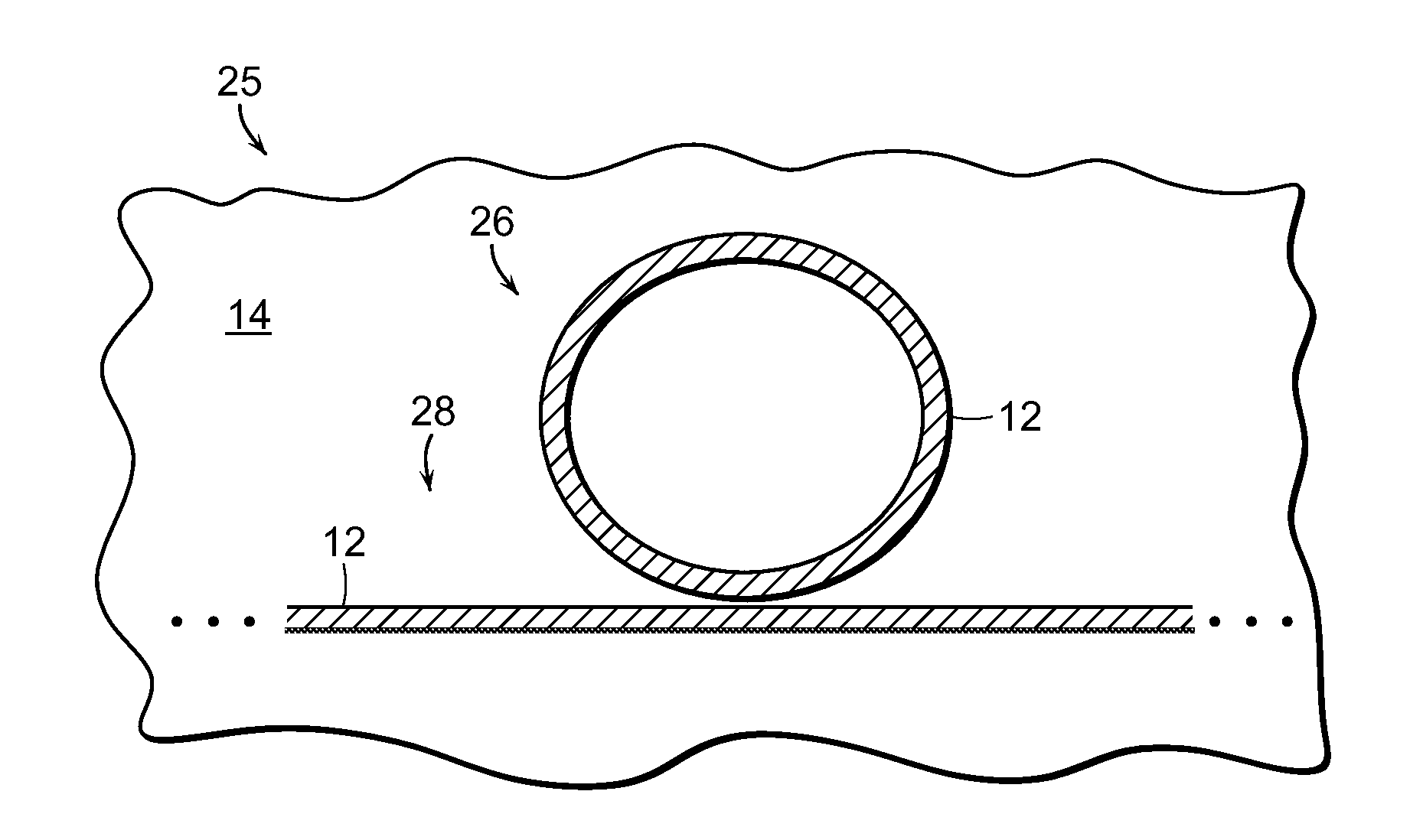
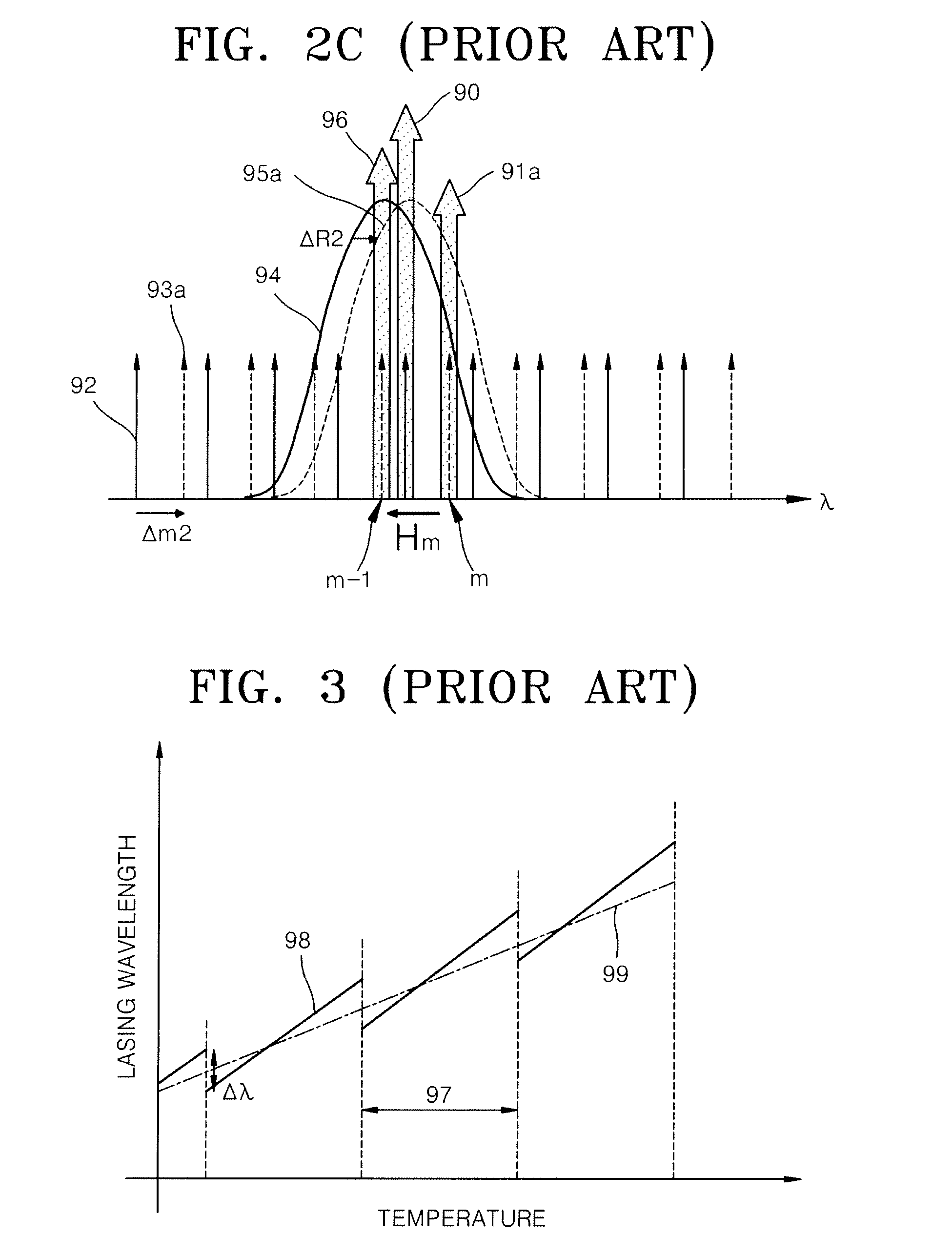
The thermo-optic coefficient of a material is the change in refractive index with response to temperature. This value itself also depends on the present temperature of the material and so has second order behaviours. At low temperatures (<400K), the relationship is linear but at higher ones it exhibits a second order polynomial behaviour.
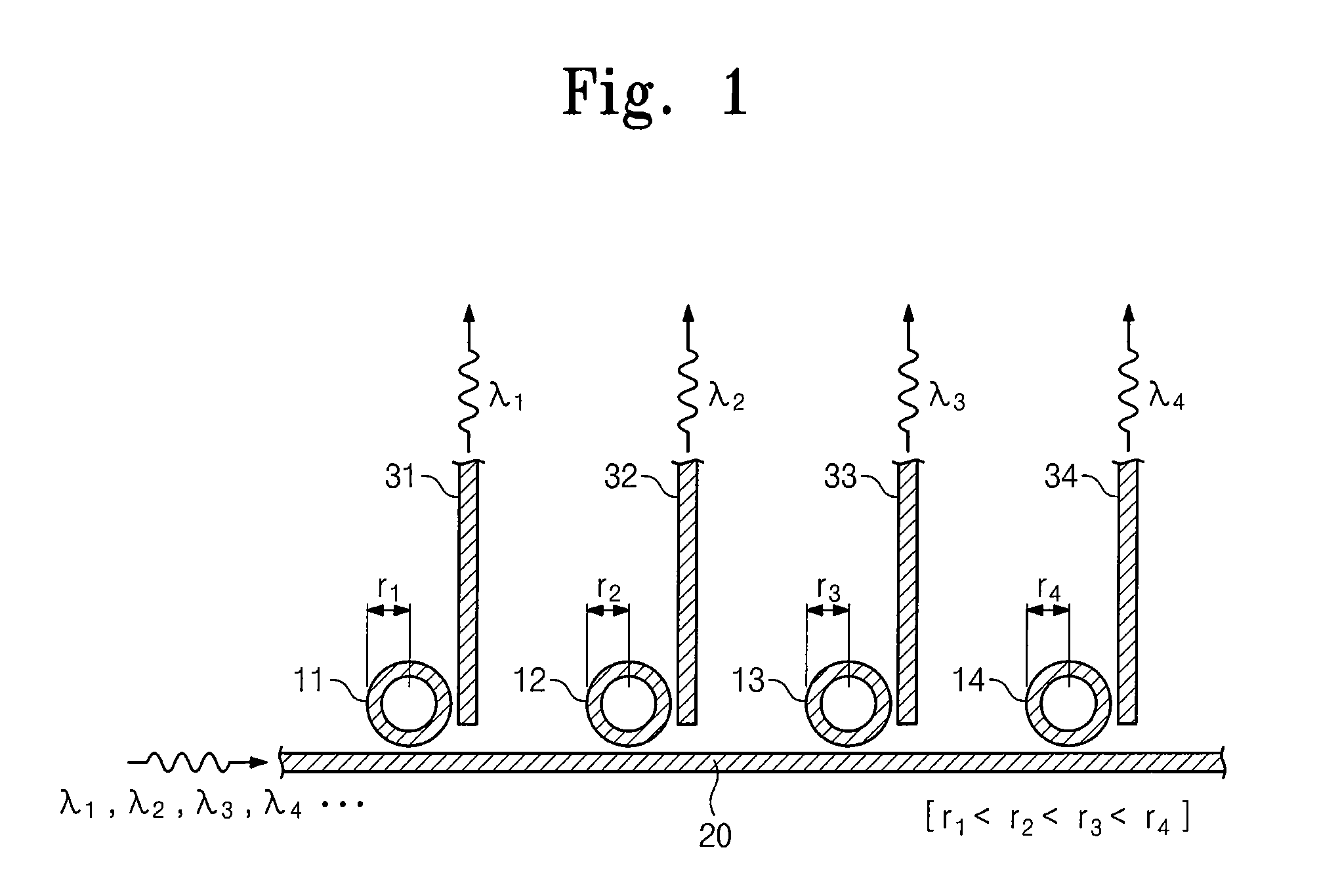
Optical fiber and optical fiber sensors
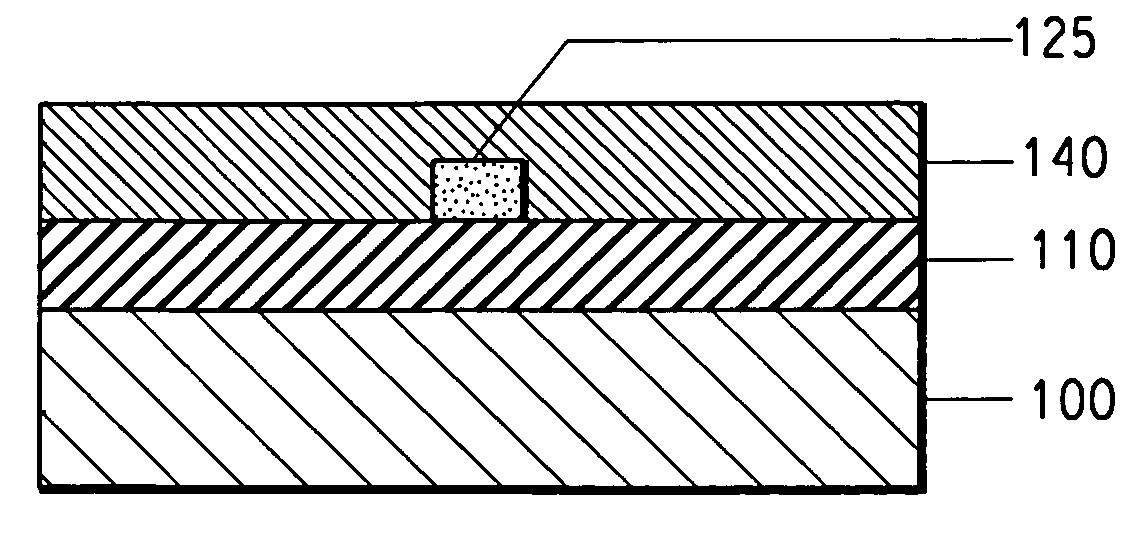
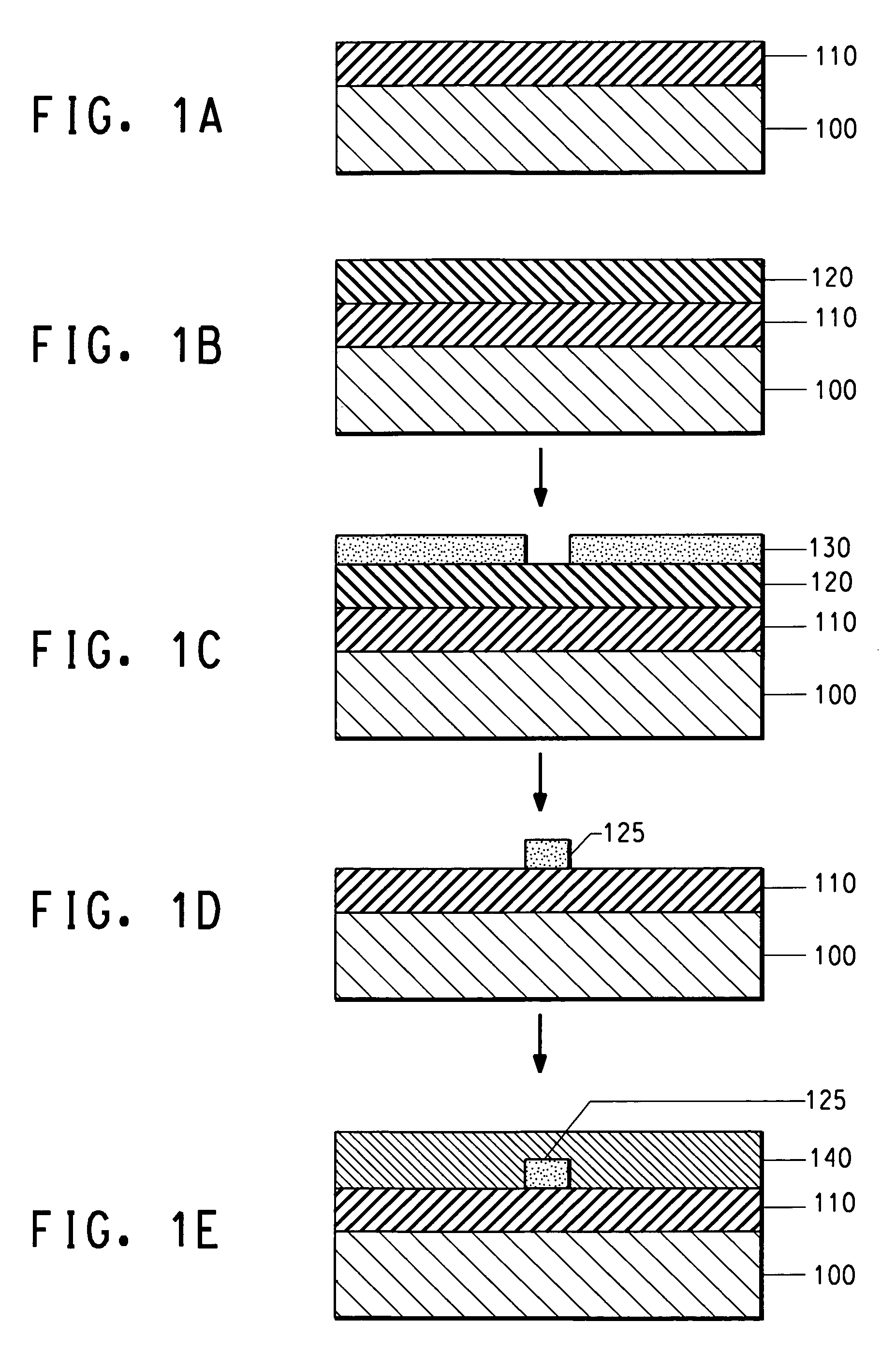
InactiveUS7027699B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical articlesGratingThermal expansion
An optical fiber device has at least two cores within the same cladding having different characteristics. The characteristics include including strain optic coefficient, thermo-optic coefficient, thermal expansion coefficient, photo-sensitivity and refractive index. One or more cores can have a Bragg grating.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
High sensitivity optical fiber temperature sensor
InactiveCN101126666ASimple structureEasy to manufactureCladded optical fibreThermometers using physical/chemical changesEpoxyOptical coefficient
The utility model discloses a high-sensitivity optical fiber temperature transmitter, which belongs to the technical field of fiber optic sensing, and comprises an aluminum or aluminum alloy pipe or box shell; wherein, a segment of multimode optical fiber is arranged hermetically in the pipe or box shell; the core of the multimode optical fiber with a diameter of 50 to 250 Mu m is made of quartz; the covering of the multimode optical fiber is formed by polyimide with a thermo-optical coefficient of minus one ten-thousandth to minus five ten-thousandth per centidegree; one end of the multimode optical fiber is connected with single model input optical fibers, and the other end is connected with single mode output optical fibers; the single mode input and output optical fibers are bonded with the ports of the pipe or box shell with epoxy resin adhesives. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, easy manufacture, and convenient use. In addition, the utility model reaches a sensitivity of minus three point nine fifteen per centidegree, which is several times or decades of times than that of the prior wavelength encoding type optical fiber temperature sensor, meanwhile has the same wavelength encoding and division multiplex as the fiber bragg grating (FBG).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Optical waveguide and optical device based on the same
InactiveUS20150192803A1Minimize power consumptionEasy to adjustOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideLength waveWaveguide
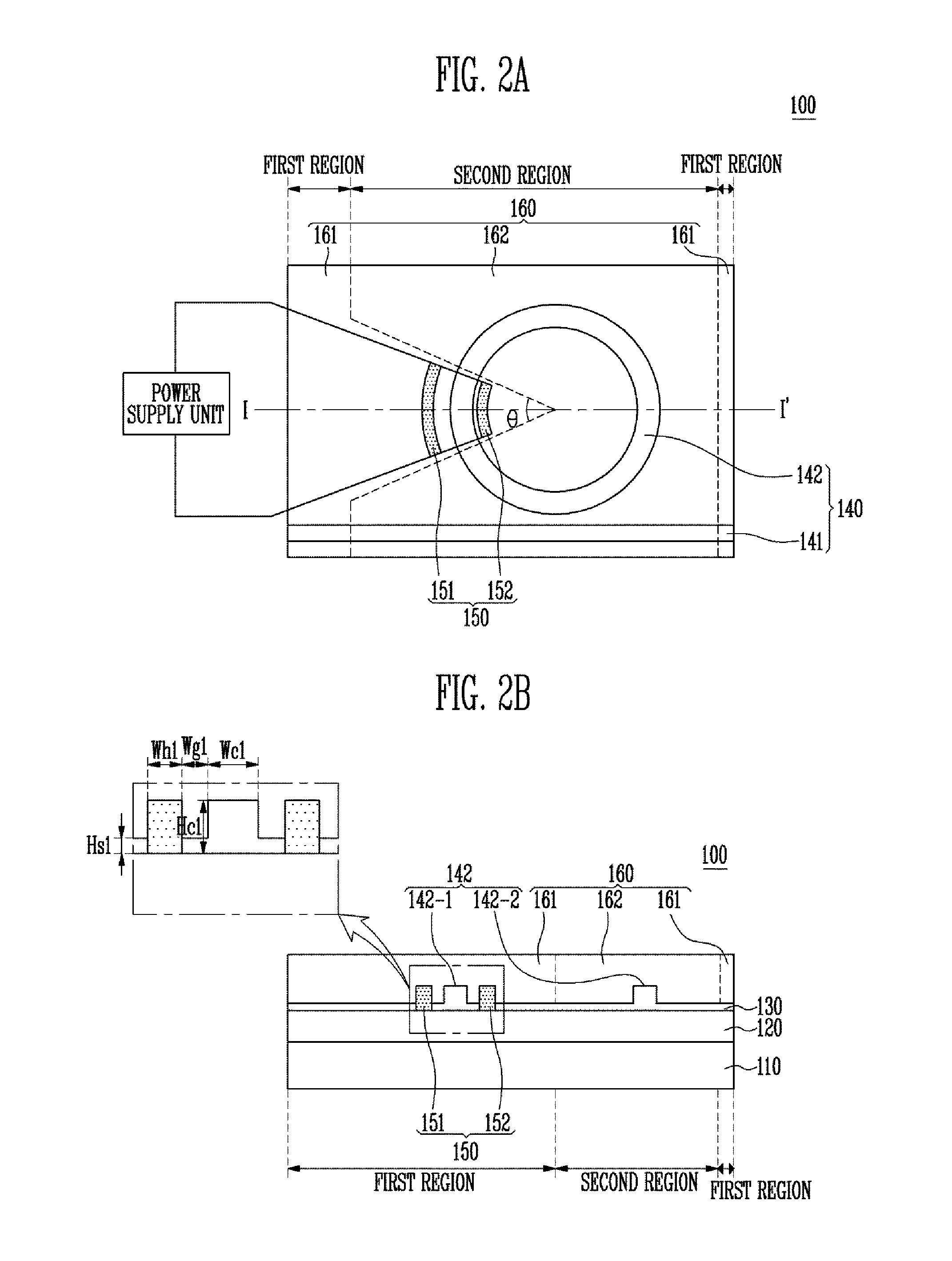
Disclosed is a technology related to an optical waveguide which is insensitive to an ambient temperature and is capable of adjusting a wavelength error due to a manufacturing processing deviation. The optical waveguide includes: a clad layer positioned on a substrate; a core layer positioned between the substrate and the clad layer, and including patterns positioned in a first region and a second region; and a wavelength adjusting unit positioned in the first region between the substrate and the clad layer, and configured to adjust a wavelength of an optical signal propagated through patterns passing through the first region based on received electric energy, in which the clad layer includes a material having a Thermo-Optic Coefficient (TOC) with an opposite sign to that of a material included in the core layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Micro-ring resonant cavity electro-optical modulator based on graphene/molybdenum disulfide heterojunction
InactiveCN105372853AImprove toleranceReduce light lossNon-linear opticsHeterojunctionResonant cavity
The invention discloses a micro-ring resonant cavity electro-optical modulator based on a graphene / molybdenum disulfide heterojunction. The micro-ring resonant cavity electro-optical modulator comprises a substrate layer, a direct-light waveguide, a micro-ring resonant cavity waveguide and a graphene covering layer. The direct-light waveguide and the micro-ring resonant cavity waveguide are embedded into the substrate layer, and a coupling space is reserved between the direct-light waveguide and the micro-ring resonant cavity waveguide. The upper surface of the micro-ring resonant cavity waveguide is covered with a part of the graphene covering layer. The graphene covering layer comprises a first graphene layer, a second graphene layer, molybdenum disulfide, a first electrode and a second electrode, wherein the first graphene layer and the second graphene layer are isolated by the molybdenum disulfide, the first graphene layer stretches outwards from one side of the micro-ring resonant cavity waveguide and is connected with the first electrode, and the second graphene layer stretches outwards from the other side of the micro-ring resonant cavity waveguide and is connected with the second electrode. The micro-ring resonant cavity electro-optical modulator has extremely low optical loss, a low thermo-optical coefficient, low insertion loss, large environment temperature tolerance, a good modulation depth and a high extinction ratio.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Athermal Photonic Waveguide With Refractive Index Tuning
ActiveUS20130243383A1Eliminate needOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guidePhotonicsLength wave
In a photonic waveguide, there is provided an undercladding layer and a waveguide core, having a cross-sectional height and width, that is disposed on the undercladding layer. The waveguide core comprises a waveguide core material having a thermo-optic coefficient. A refractive index tuning cladding layer is disposed on top of the waveguide core. The refractive index tuning cladding layer comprises a refractive index tuning cladding material having an adjustable refractive index and an absorption length at a refractive index tuning radiation wavelength. A thermo-optic coefficient compensation cladding layer is disposed on top of the refractive index tuning cladding layer. The thermo-optic coefficient compensation cladding layer comprises a thermo-optic coefficient compensation material having a thermo-optic coefficient that is of opposite sign to the thermo-optic coefficient of the waveguide core material. The thermo-optic coefficient compensation cladding layer provides at least partial compensation for the waveguide core thermo-optic coefficient.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO +1
Measuring etching rates using low coherence interferometry
InactiveUS20090065478A1Real time monitoringSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsPartial reflectionThermo-optic coefficient
Measuring thickness and the rate of change of thickness of a material having a surface while the material is being etched, comprising: illuminating the material with low coherence light, a portion of the which transmits through the material and a portion of which is reflected; etching the material surface and while etching, collecting a portion of the reflected light from each optical interface of the material with a low coherence light interferometer; calculating the thickness and rate of change of thickness of the material or part of the material according to the obtained interferometric data; and storing or displaying the resultant thickness and rate of change of thickness of the material. The present invention provides a unique way of calculating the thermo optic coefficient of a material. This method can be used simultaneously with etching the material so that changes to the etching rate can be made in real time.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Athermal external cavity laser
InactiveUS20100014545A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove combination efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionExternal cavity laserGrating
Provided is an athermal external cavity laser (ECL), whose output optical power and output wavelength can be kept regular irrespective of temperature changes without using additional temperature controlling components. The ECL comprises: a semiconductor amplifier; an optical fiber comprising a core in which a Bragg grating is formed and a cladding surrounding the core; and a thermosetting polymer that fixes the optical fiber to a ferrule and has a negative thermooptical coefficient, wherein the thickness of the cladding surrounding the core in which the Bragg grating is formed is smaller than the portion of the cladding surrounding the portion of the core where the Bragg grating is not formed, and the thermosetting polymer the negative thermooptical coefficient surrounds the cladding. The ECL does not need additional temperature controlling components and thus can be manufactured compact and at low cost, and thus can be used as a light source of a dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) system in designing economical WDM passive optical networks (PON).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
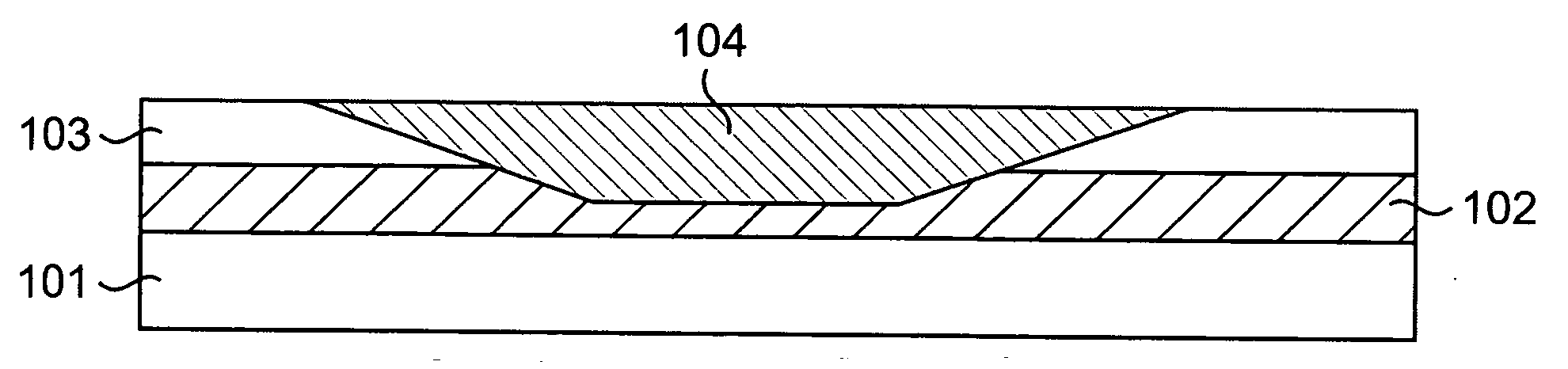
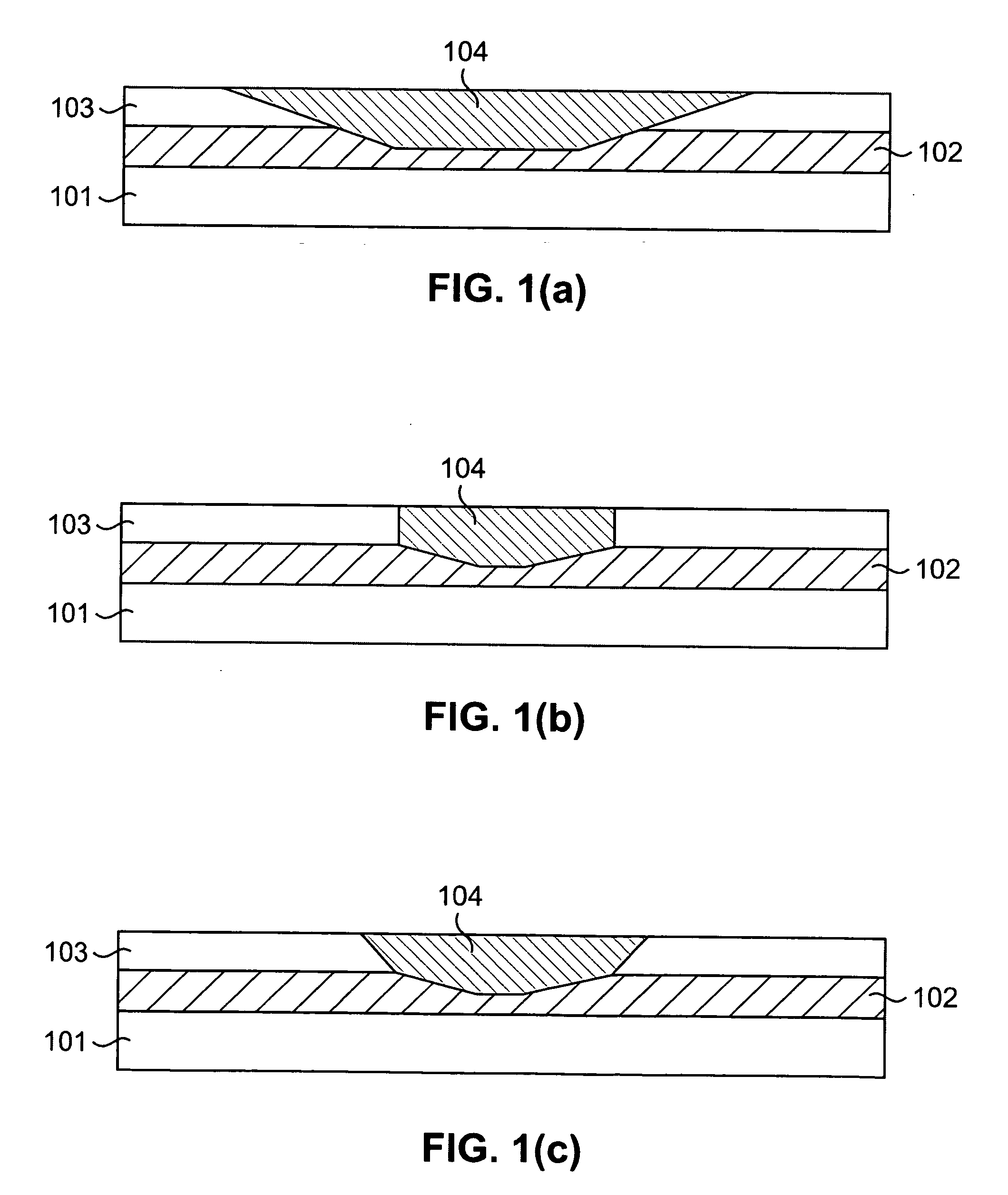
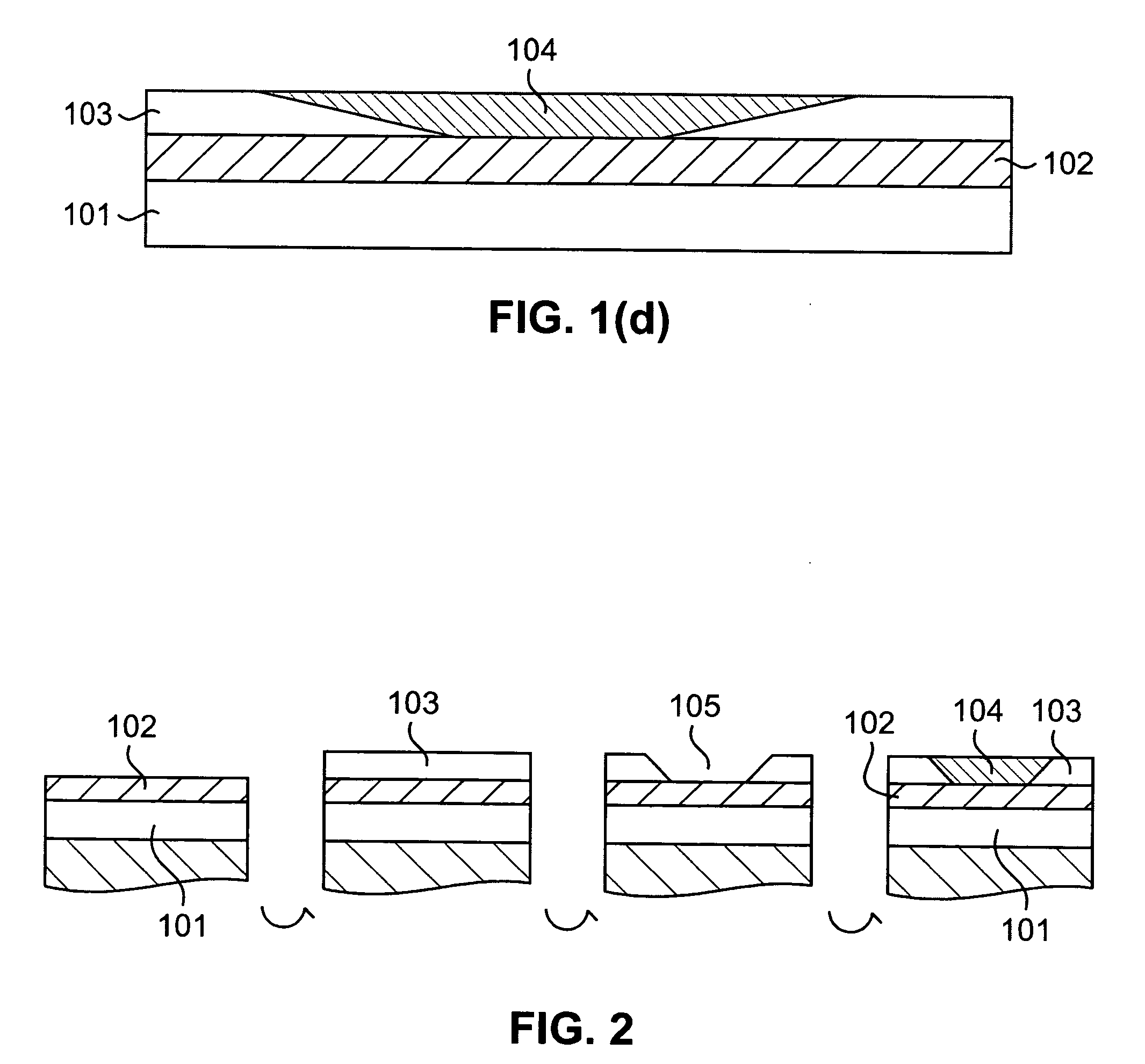
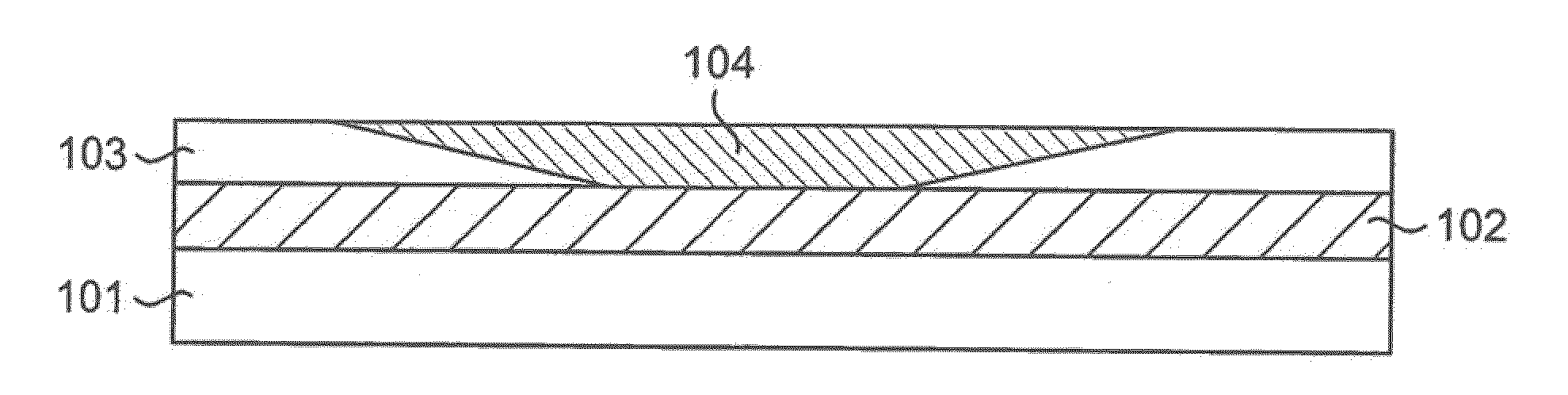
Thermal compensation of waveguides by dual material core having positive thermo-optic coefficient inner core
InactiveUS6987895B2Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideThermo-optic coefficient
A planar lightwave circuit comprises a waveguide that is thermally-compensating. The waveguide comprises a cladding and a core that comprises two regions running lengthwise through the core. One region has a negative thermo-optic coefficient; the other region has a positive thermo-optic coefficient.
Owner:INTEL CORP
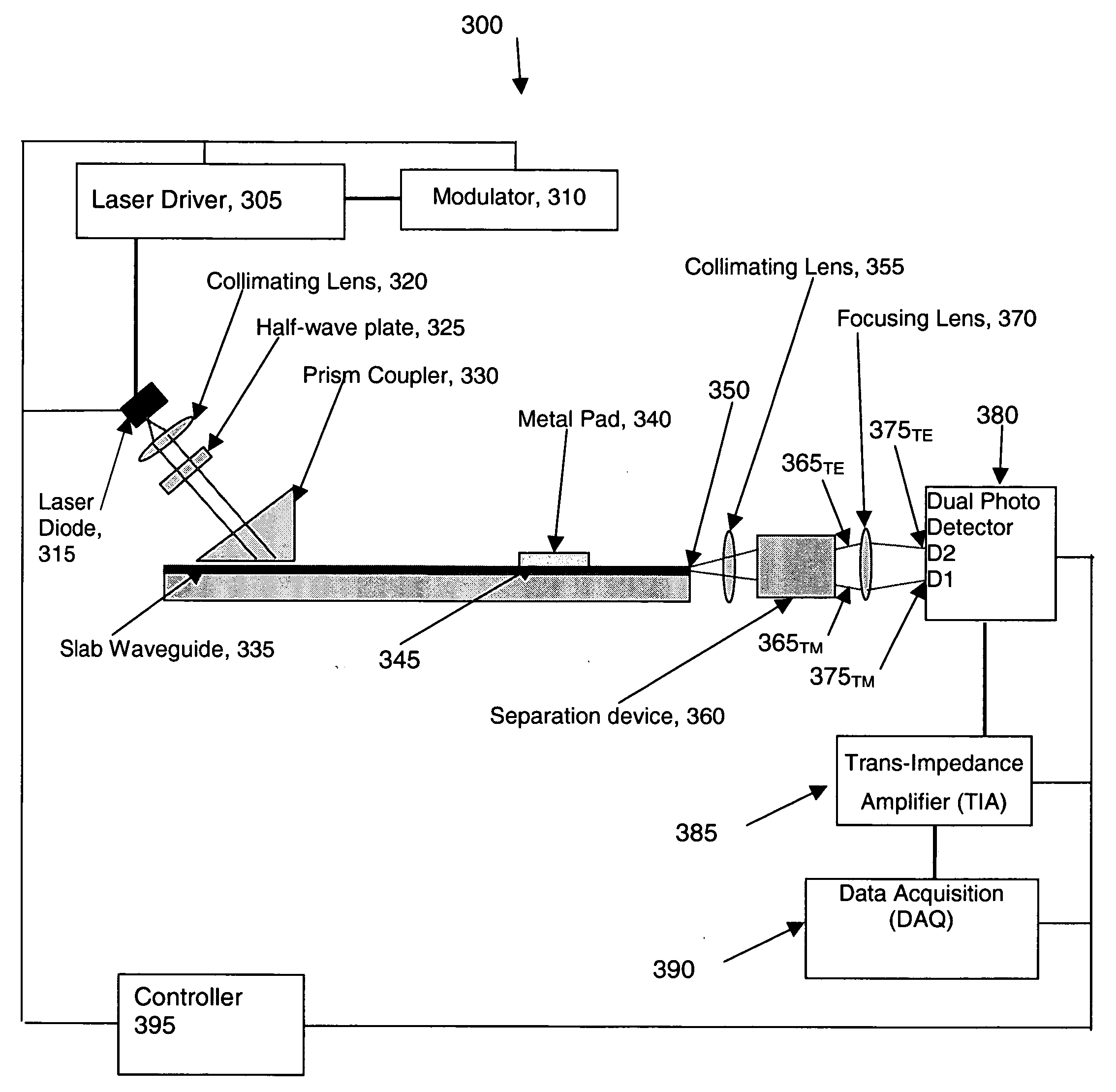
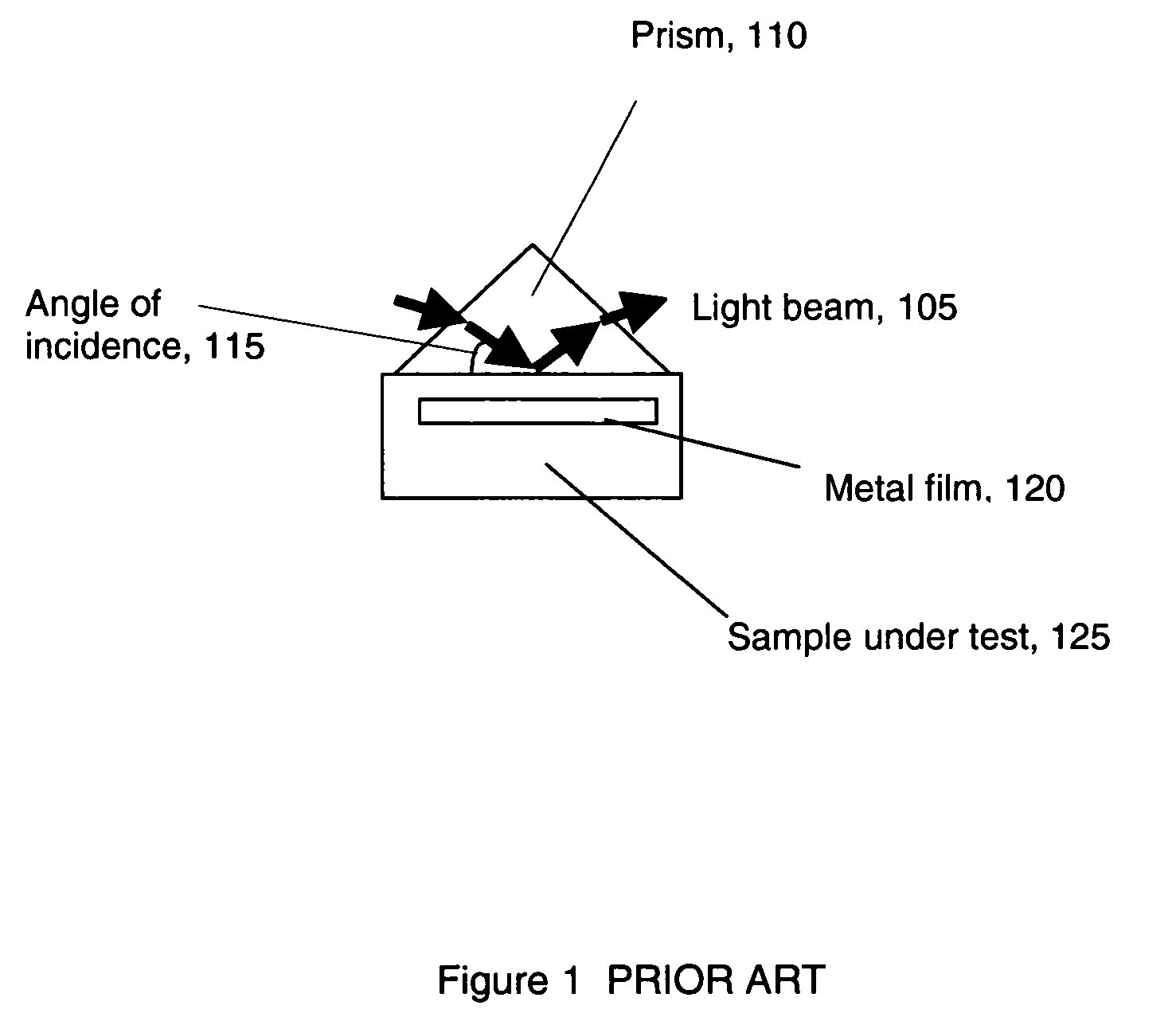
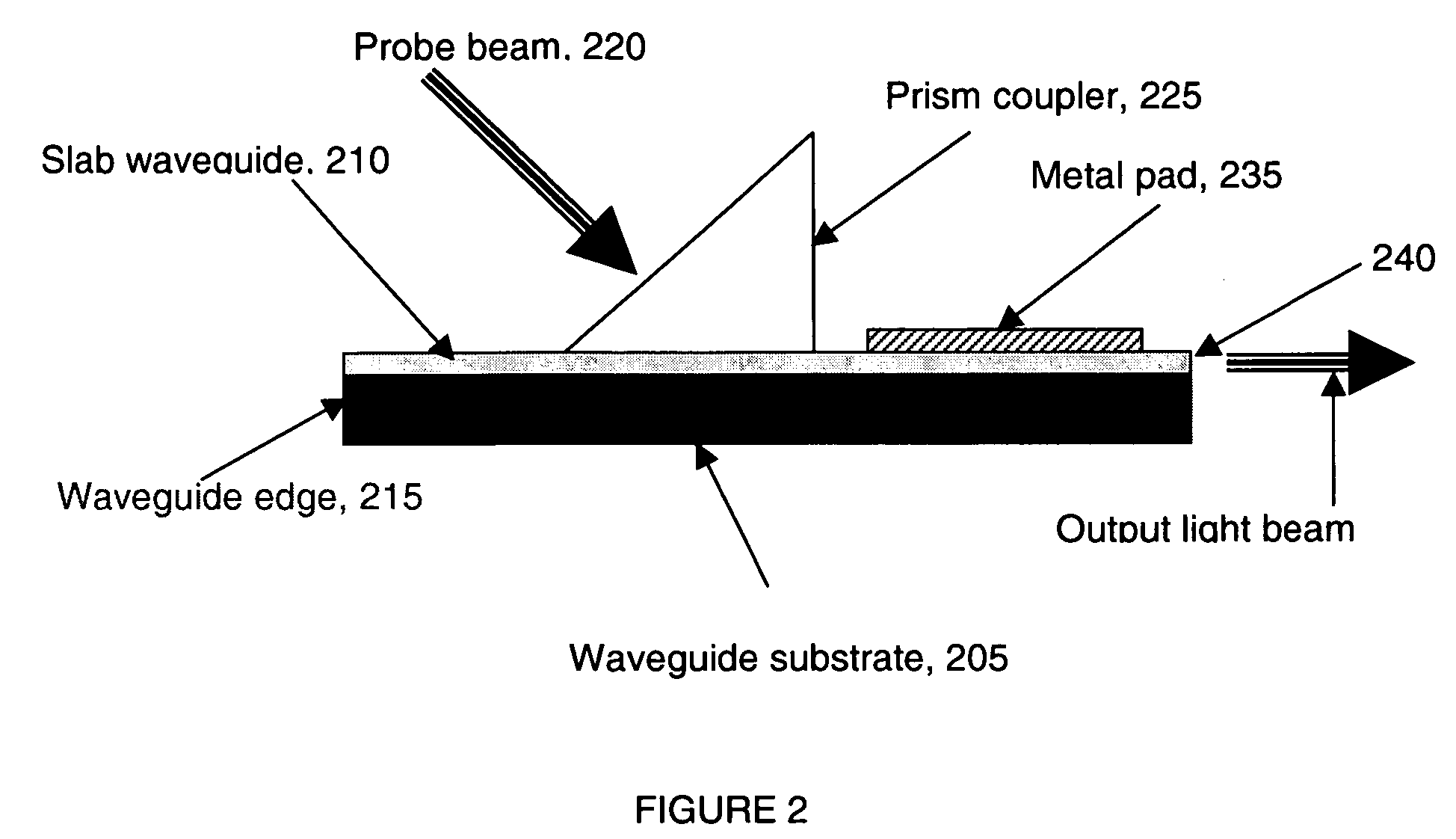
High sensitivity optical detection by temperature independent differential polarization surface plasmon resonance
Detecting an amount of change in light intensity caused by surface plasmon resonance includes coupling light having transverse magnetic and transverse electric polarization modes into a slab waveguide having a metallic film that supports the surface plasmon resonance, detecting the transverse magnetic and transverse electric polarized light as it emanates from the slab waveguide, and determining an instantaneous difference in intensities between the transverse magnetic and transverse electric polarization modes of the emanated light. A thickness of the metal film may be varied to shift a response curve of the surface plasmon resonance, and the materials of a slab waveguide substrate may be selected to have a thermo-optic coefficient that substantially matches that of a test sample under analysis.
Owner:BIO TELL
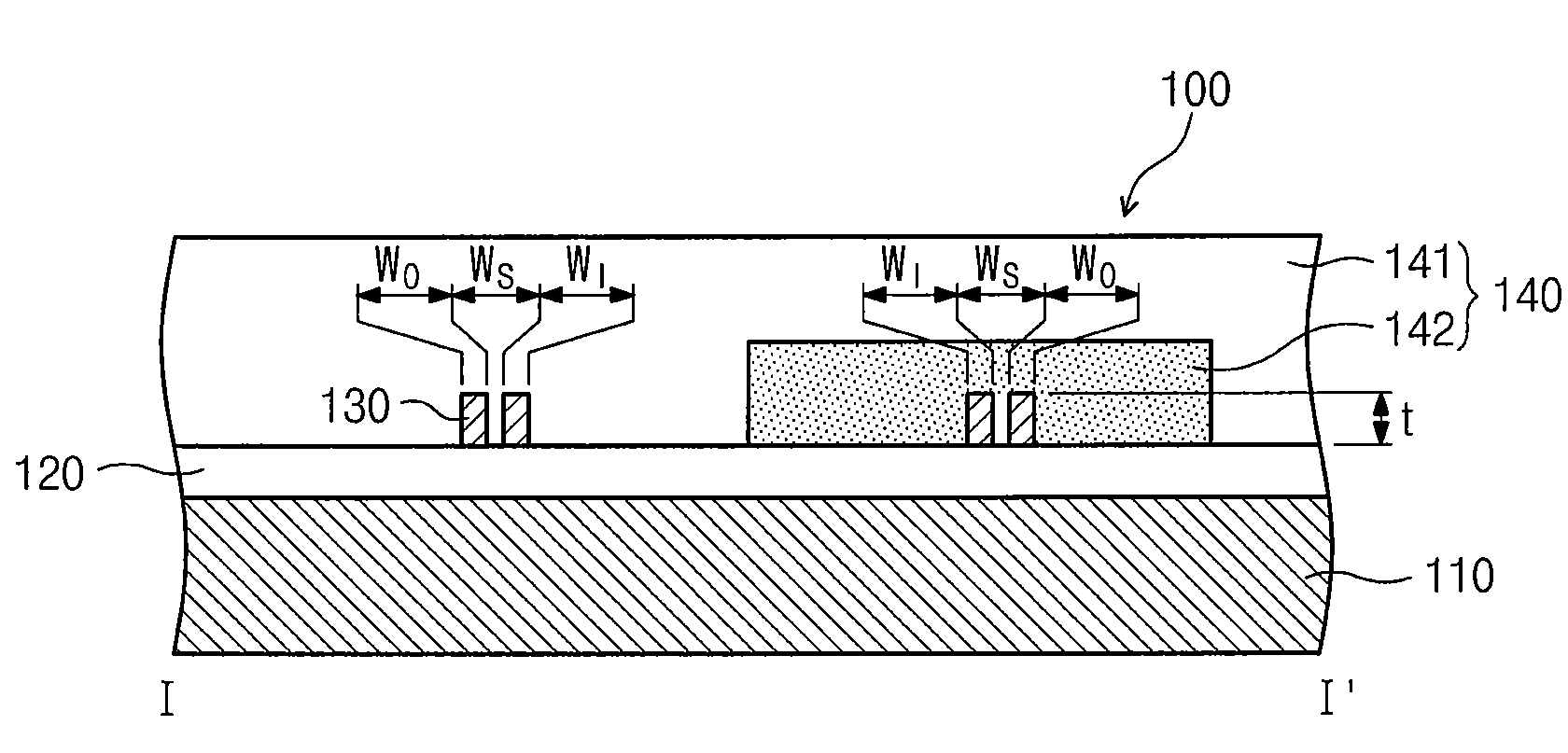
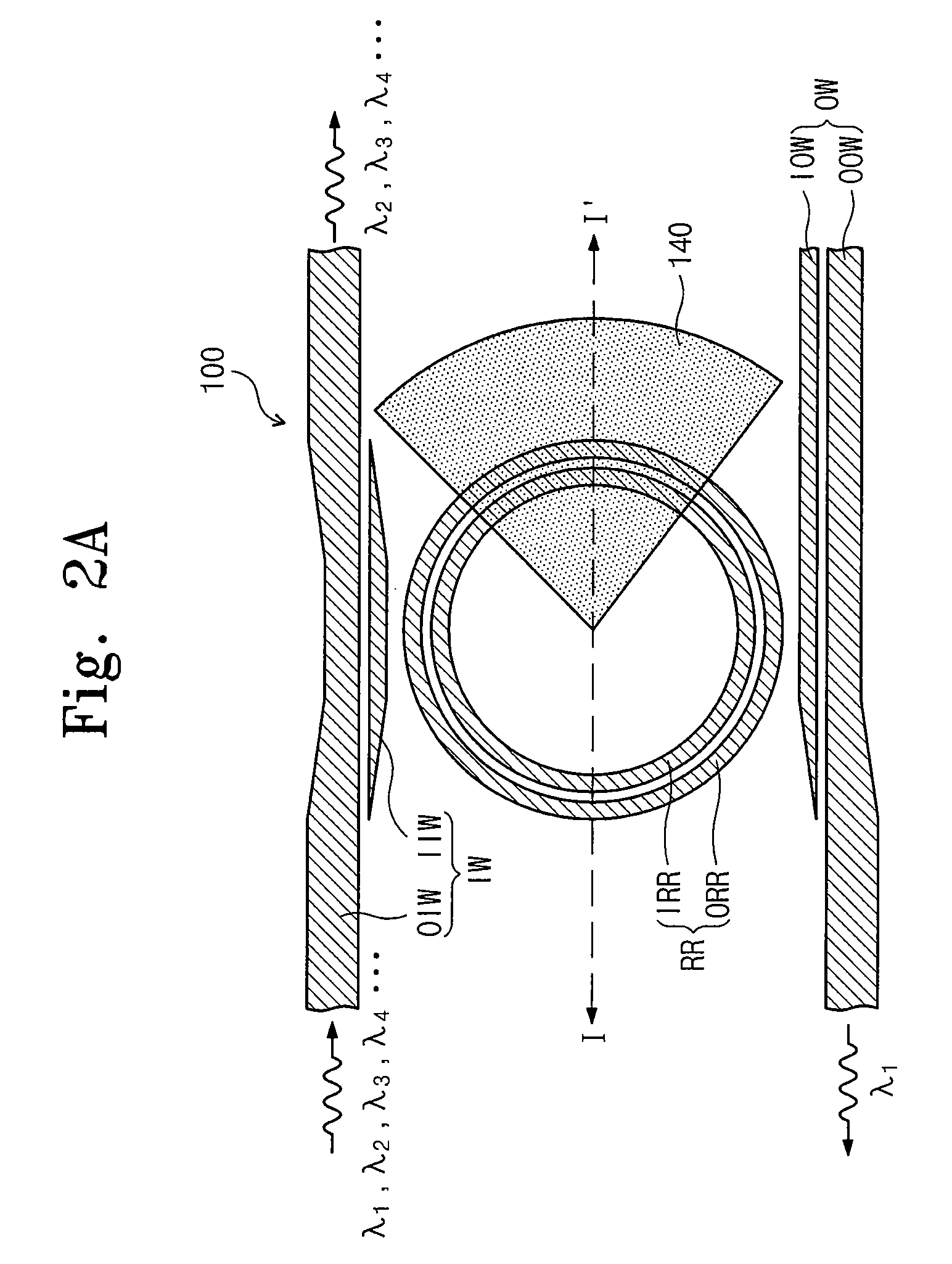
Waveguide structure
InactiveUS7693384B2Suppressing temperature-dependent wavelength shift (TDWS)Accurate pressingOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideThermo-optic coefficient
A waveguide structure is provided. The waveguide structure includes: a slot channel waveguide including first and second patterns, which are spaced apart from each other to define a slot; a first upper layer covering at least a portion of the slot channel waveguide; and a second upper layer covering the remaining portion of the slot channel waveguide. A thermo-optic coefficient (TOC) of the channel waveguide times a TOC of the second upper layer is a negative number.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Athermal photonic waveguide with refractive index tuning
ActiveUS9110221B2Eliminate needOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesPhotonicsLength wave
In a photonic waveguide, there is provided an undercladding layer and a waveguide core, having a cross-sectional height and width, that is disposed on the undercladding layer. The waveguide core comprises a waveguide core material having a thermo-optic coefficient. A refractive index tuning cladding layer is disposed on top of the waveguide core. The refractive index tuning cladding layer comprises a refractive index tuning cladding material having an adjustable refractive index and an absorption length at a refractive index tuning radiation wavelength. A thermo-optic coefficient compensation cladding layer is disposed on top of the refractive index tuning cladding layer. The thermo-optic coefficient compensation cladding layer comprises a thermo-optic coefficient compensation material having a thermo-optic coefficient that is of opposite sign to the thermo-optic coefficient of the waveguide core material. The thermo-optic coefficient compensation cladding layer provides at least partial compensation for the waveguide core thermo-optic coefficient.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO +1
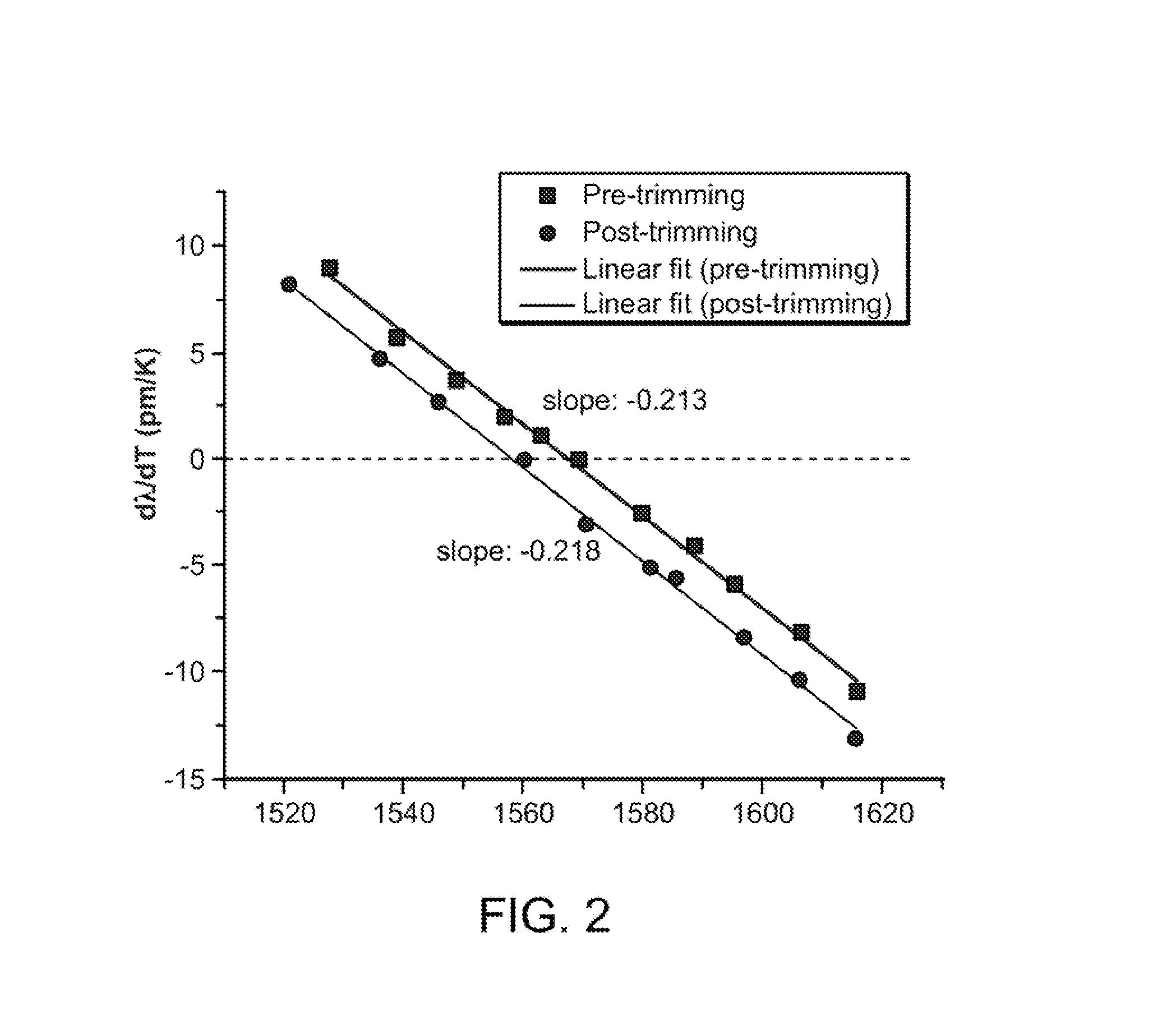
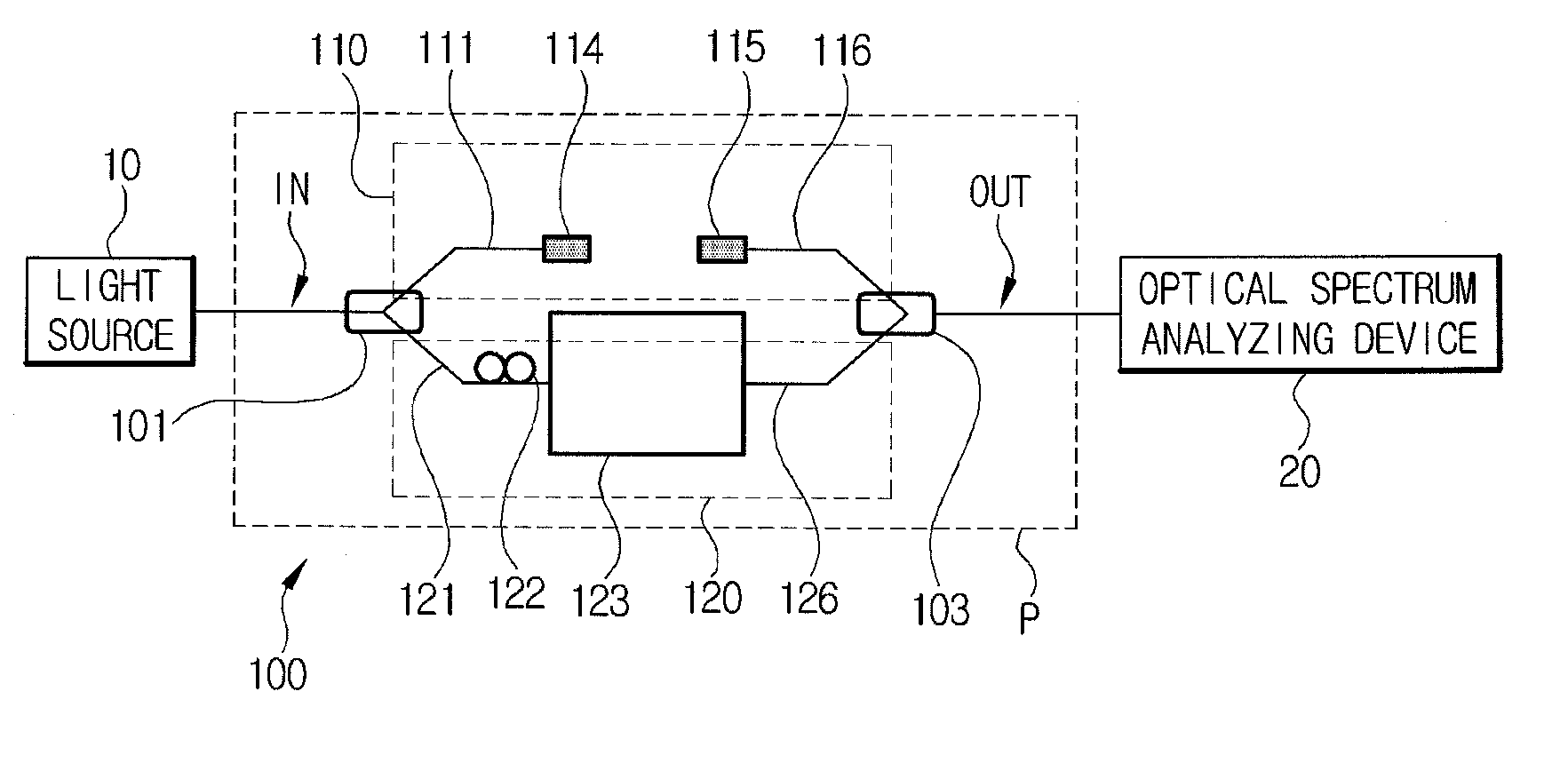
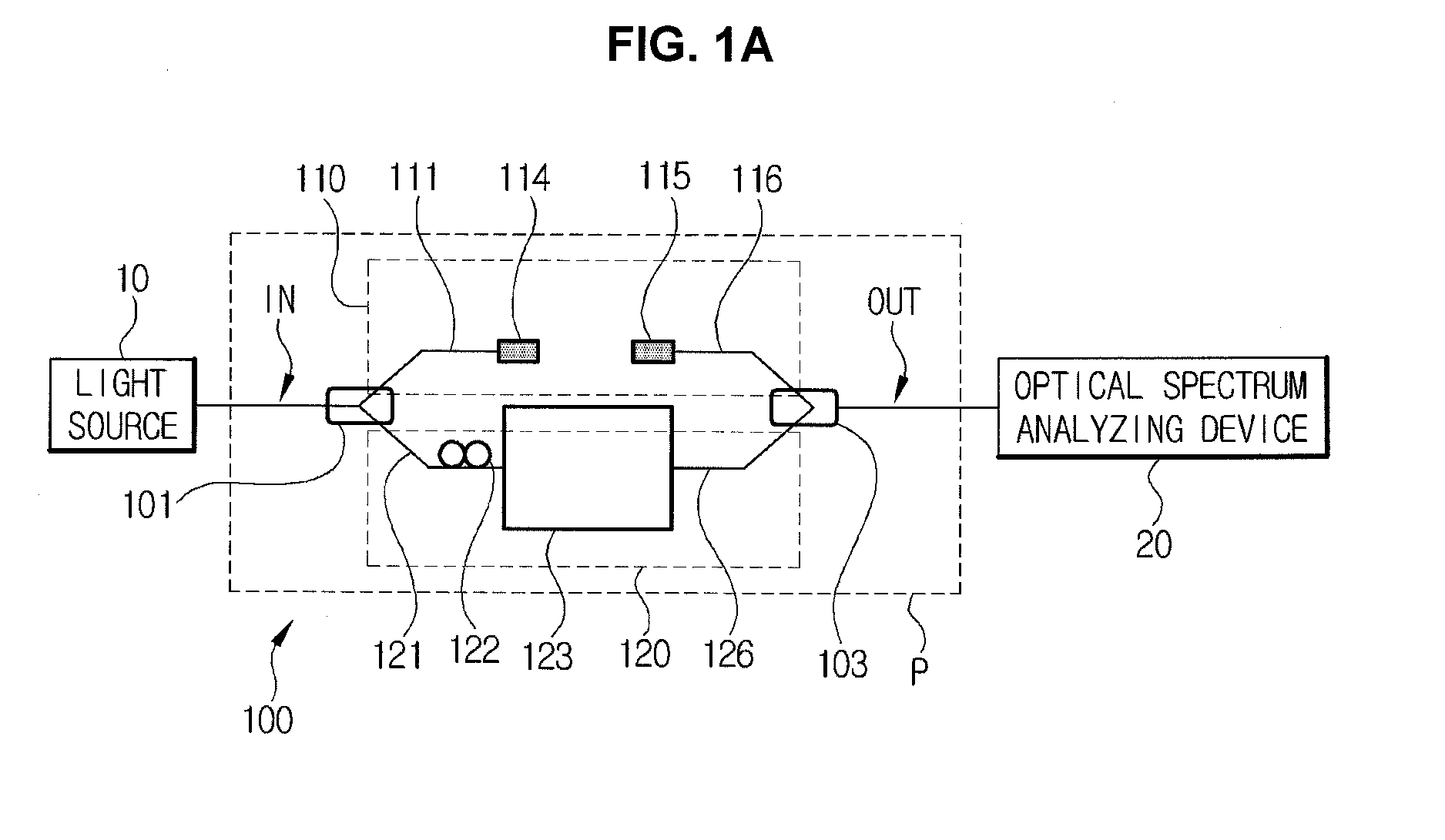
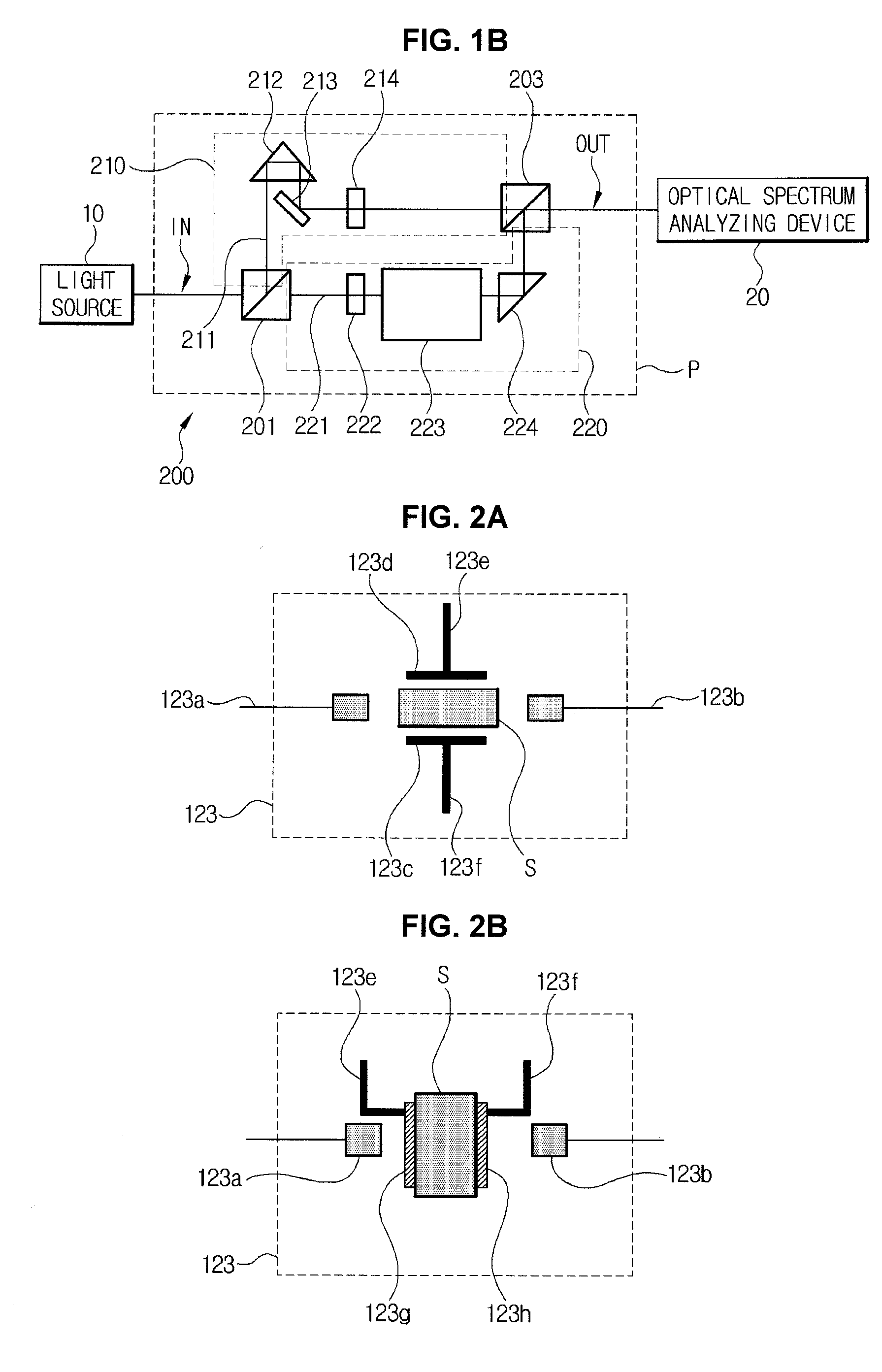
Systems for measuring electro-optic and thermo-optic coefficients by using interference fringe measurement, and methods of measuring electro-optic and thermo-optic coefficients by using the systems
InactiveUS20100290055A1Fast and accurate measurement systemThe process is fast and accurateRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryThermo-optic coefficientMulti wavelength
Measuring of an electro-optic coefficient and a thermo-optic coefficient of an optical device and an optical material, and more specifically, to measurement systems and methods of evaluating the electro-optic and thermo-optic coefficients by using interference fringe measurement techniques, wherein those optical characteristics can be precisely measured over a wide wavelength intended without using a complicated measuring equipment. The system for measuring an electro-optic coefficient includes: a light source for outputting an optical beam of multi-wavelengths, an optical interferometer including an optical beam splitter for dividing the optical beam received from the light source into two separate beams, a reference arm for receiving any one of the divided optical beams, a sample arm for receiving the other of the divided optical beams and applying a voltage to an optical sample to be measured by being connected to the optical sample, and an optical beam combiner for combining and mutually interfering optical beams that are output through the reference arm and the sample arm, and an optical spectrum analyzing device for receiving the mutually interfered optical beam from the optical interferometer and analyzing a spectrum of the mutually interfered optical beam.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
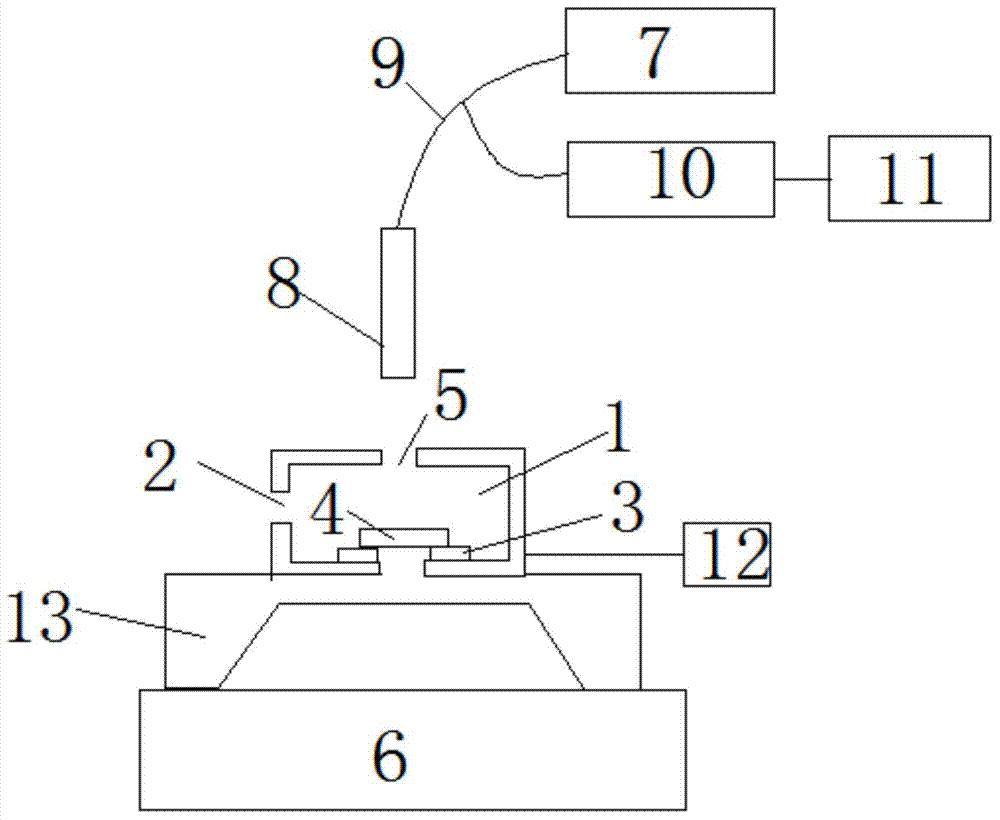
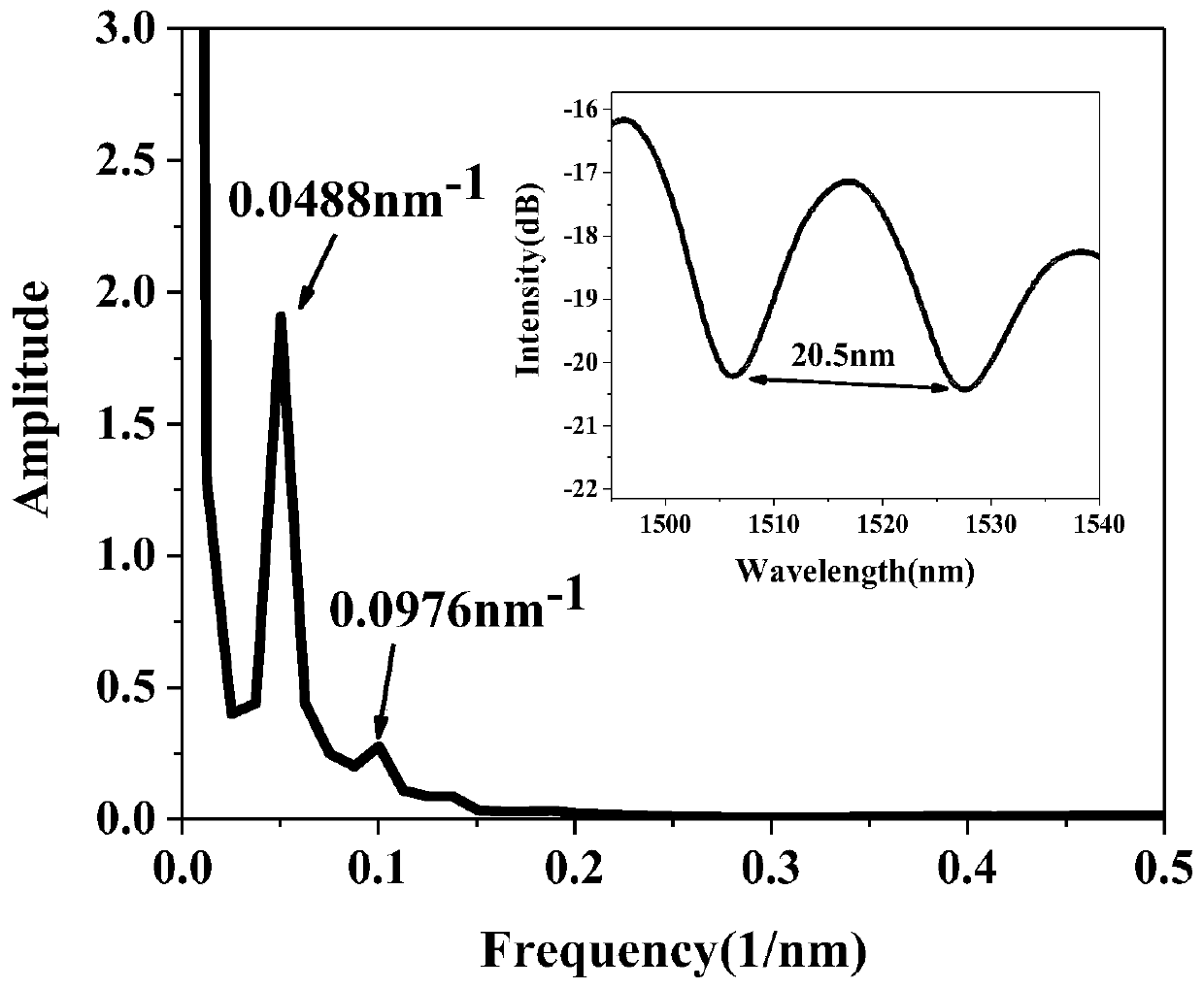
Device and method for measuring thermo-optical coefficient of thin-film material
InactiveCN104749115ASimple structureEasy to implementPhase-affecting property measurementsTransmissivity measurementsTemperature controlTransmittance
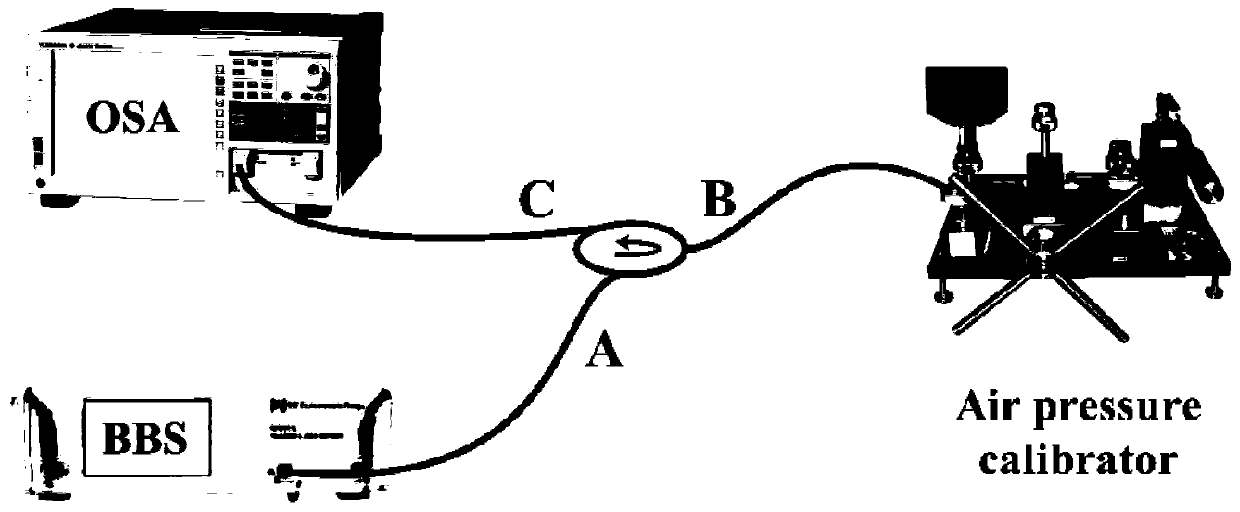
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the thermo-optical coefficient of a thin-film material, and belongs to the technical field of tests. The invention provides a device and a method capable of directly and rapidly measuring a thermo-optical coefficient. The device comprises a workbench, a light source, a Y-shaped optical fibre, a reflection frequency spectrometer and a computer, wherein the two optical fibre arms of the Y-shaped optical fibre are connected with the light source and the reflection frequency spectrometer respectively, and the reflection frequency spectrometer is connected with the computer. The device further comprises a support frame and a heating unit, wherein the heating unit is erected on the workbench through the support frame; the heating unit comprises a box; a test cavity is formed in the box; an air inlet hole and a light passing hole are formed in the box; a heating plate is placed in the test cavity; the common end of the Y-shaped optical fibre is located above the light passing hole; the light passing hole corresponds to the heating plate in position. The device further comprises a temperature controller connected with the test cavity. The device is capable of obtaining the continuous spectral lines of the optical constant and the transmissivity of a film at different temperatures without breakages to the surface of the film through non-contact measurement, high in measurement accuracy, and suitable for measuring the thermo-optical coefficient of a film material.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
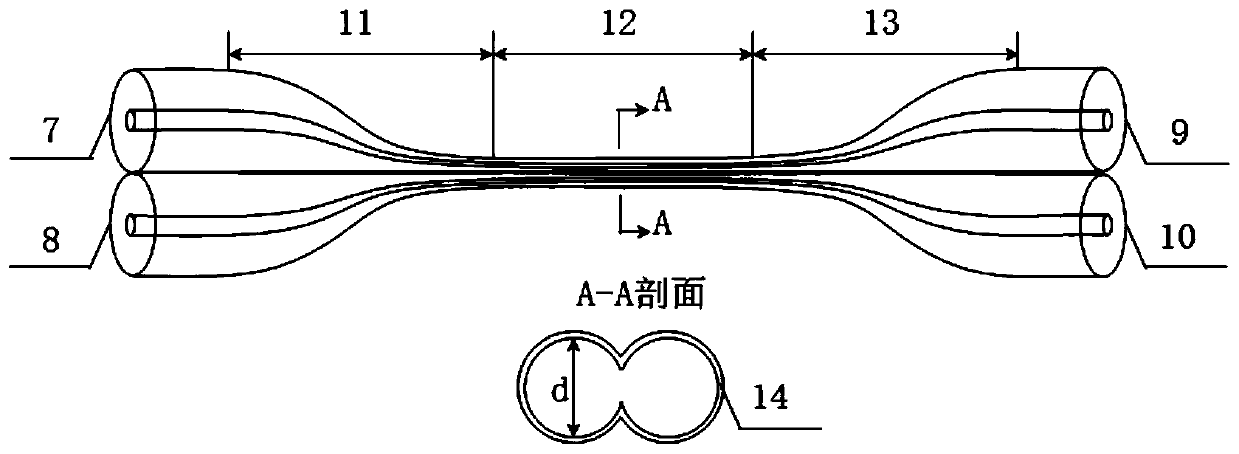
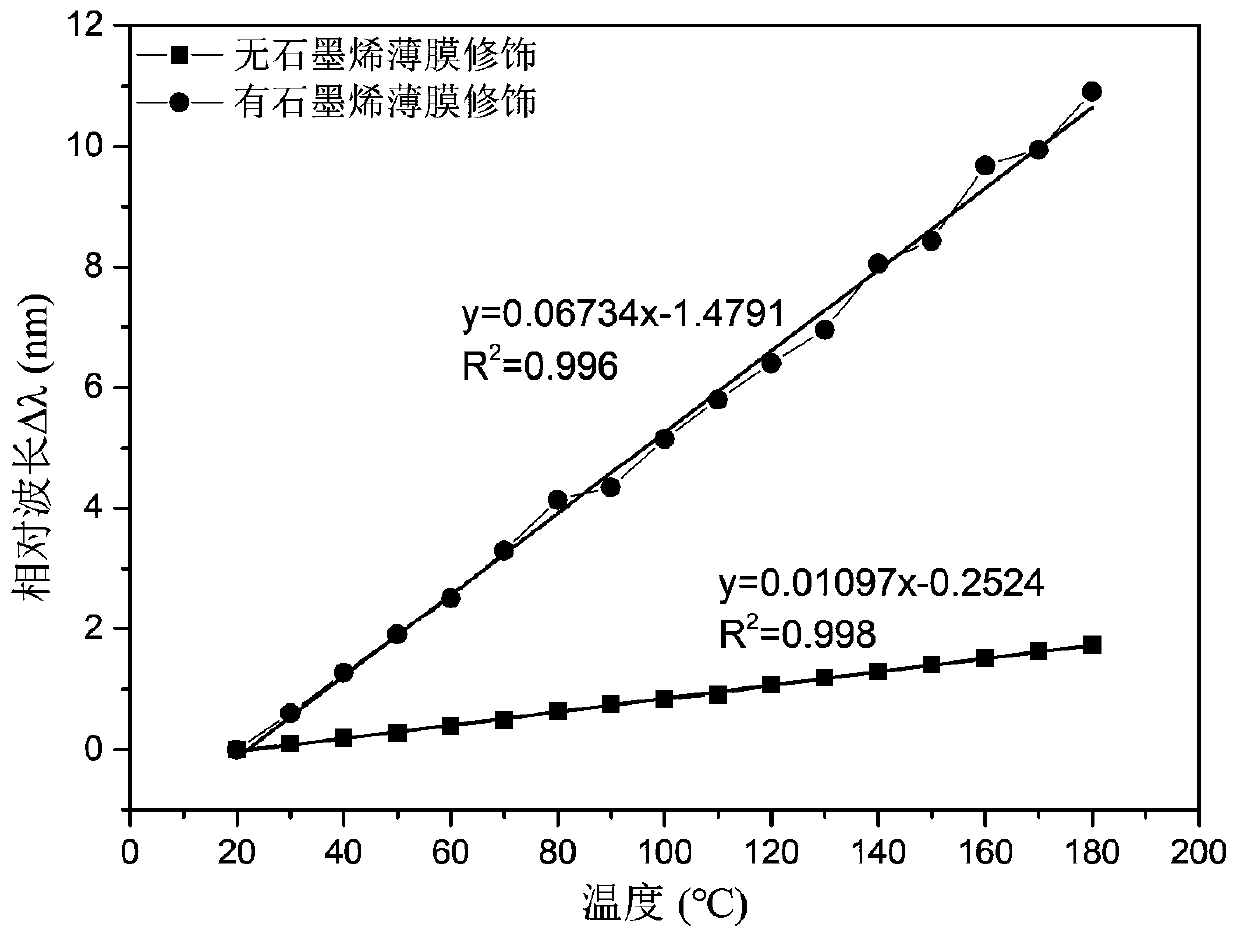
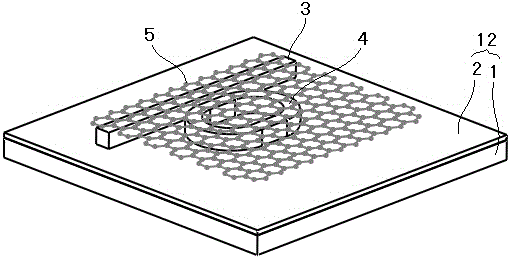
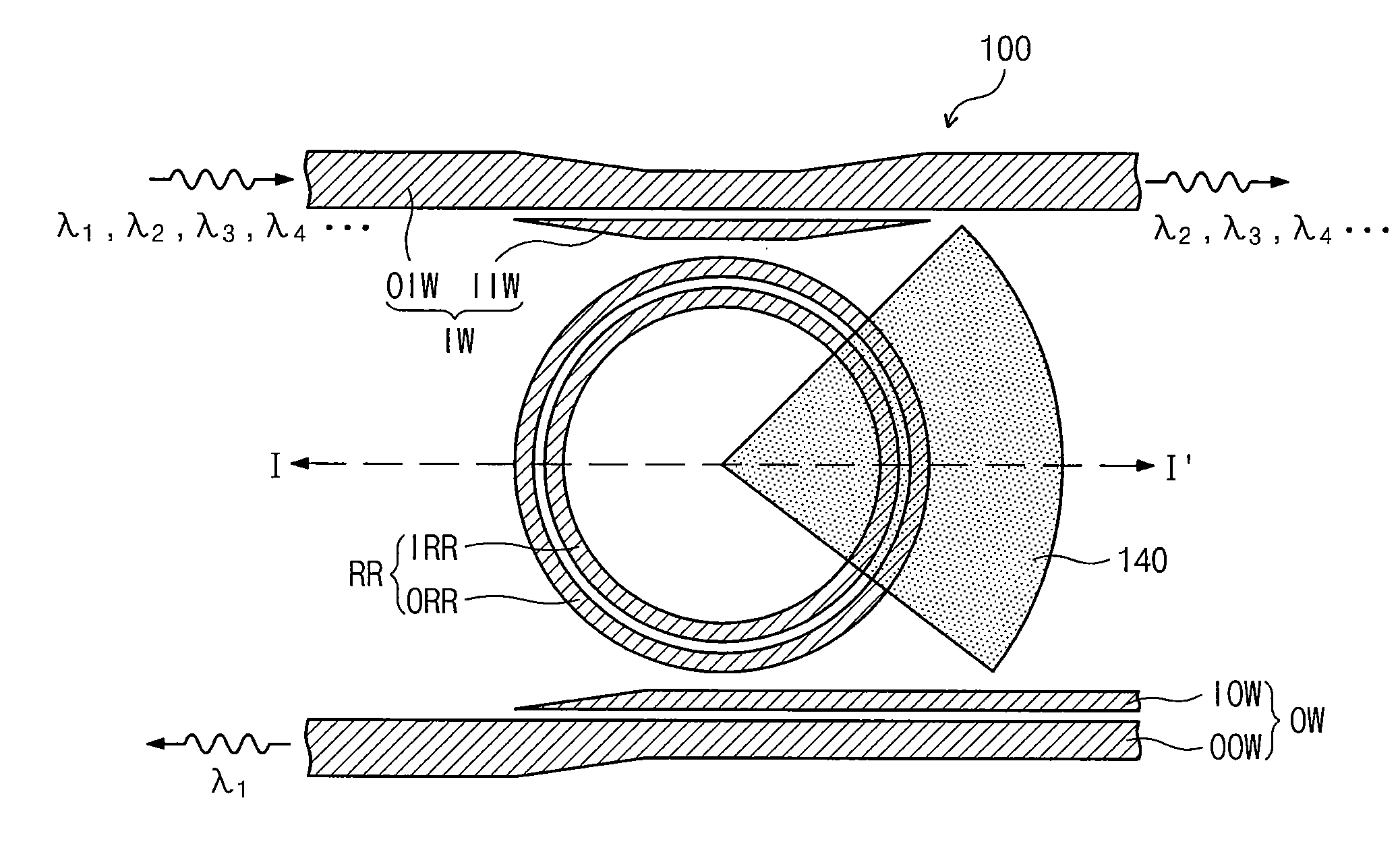
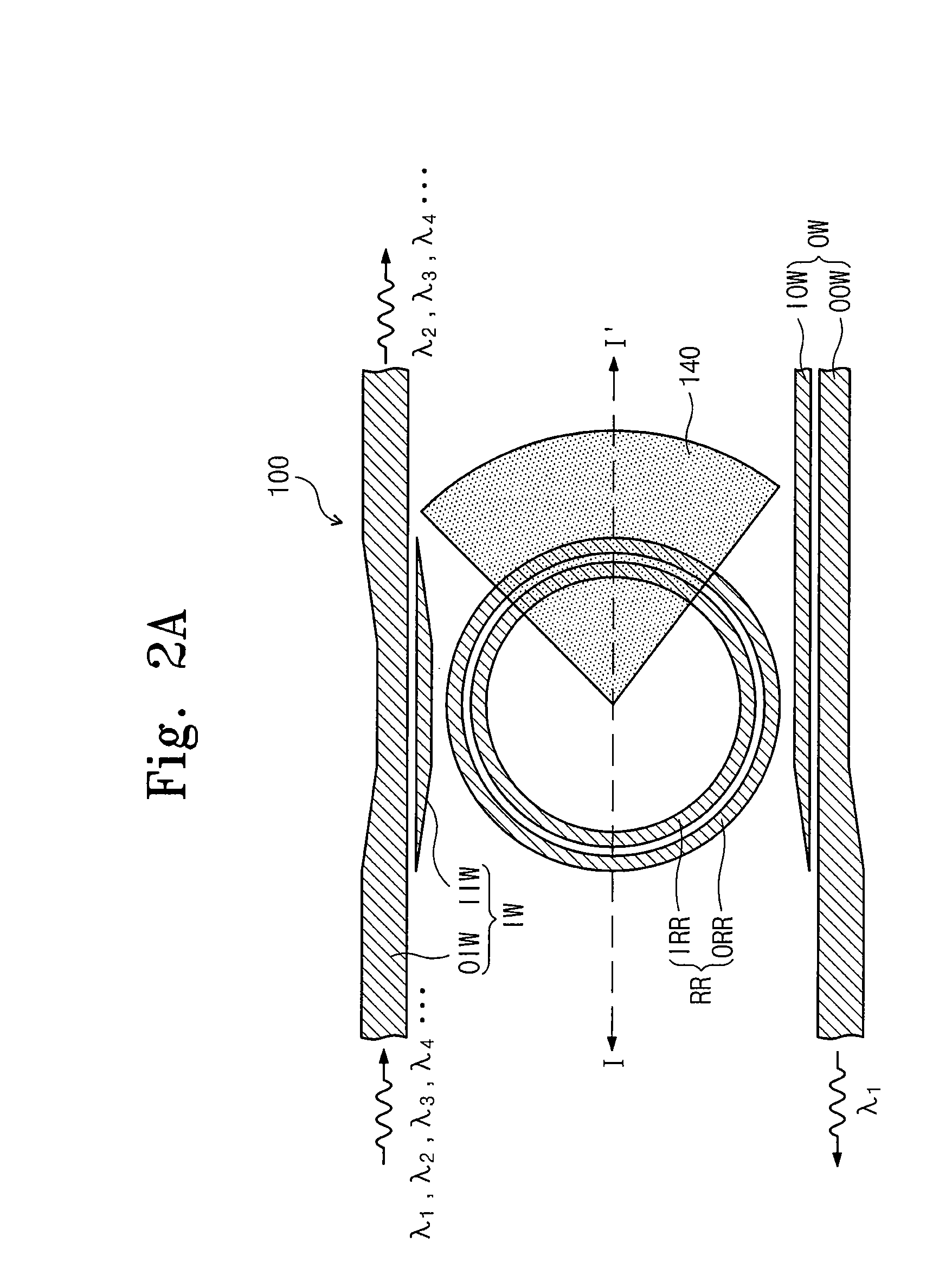
Temperature sensor based on grapheme-film-modified biconical micro-nano optical fiber coupler
ActiveCN110501091AHigh sensitivityCompensation for weak thermal light effectThermometers using physical/chemical changesCoupling light guidesMicro nanoSpectrum analyzer
The invention discloses a temperature sensor based on a grapheme-film-modified biconical micro-nano optical fiber coupler. The device comprises a super-continuous broadband light source, a graphene-modified micro-nano optical fiber coupler sensing unit and a spectrum analyzer. The graphene-modified micro-nano optical fiber coupler sensing unit is respectively connected with the super-continuous broadband light source and the spectrum analyzer through connecting optical fibers. On the basis of the electric heating high-temperature fused biconical taper method, a biconical 2*2 micro-nano opticalfiber coupler is prepared; the central lumbar vertebra uniform area of the coupler is plated with a graphene film by using a film wet transfer method; and the sensitivity of the effective refractiveindex of the coupler intermode interference to the external environment temperature is improved by utilizing the high thermo-optic coefficient and the high thermal conductivity of the graphene film, so that the high temperature measurement sensitivity is realized. Meanwhile, the involved sensor shows the excellent linearity, repeatability and stability in experiments. The temperature sensor has advantages of being compact in structure, easy to manufacture, low in cost and easy to integrate with other optical fiber systems.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Thermo-optical modulator based on graphene microring structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105044929AImprove thermal conductivityFast dynamic responseNon-linear opticsResonant cavityGraphene
The invention discloses a thermo-optical modulator based on a graphene microring structure. The thermo-optical modulator comprises insulated silicon-on-substrate as a substrate. A straight waveguide and an annular resonant chamber are adjacently arranged on the insulated silicon-on-substrate. A square graphene conducting layer is arranged above the straight waveguide and the annular resonant chamber. A first electrode layer and a second electrode layer without overlapping are arranged above the other end of the graphene conducting layer. According to the thermo-optical modulator, the graphene directly contacts with a silicon microring waveguide. Heat which is generated by the graphene is changed through controlling the voltage which is applied on the graphene, and finally light modulation in the silicon microring is realized. The thermo-optical modulator can be prepared in a relatively easy manner. Furthermore a microring resonant cavity is very sensitive. Furthermore because of a relatively large thermo-optic coefficient of the silicon, strong optical modulation can be realized. Furthermore because of an ultrahigh thermal conductivity of the graphene, dynamic response of the device is improved to a relatively large extent.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
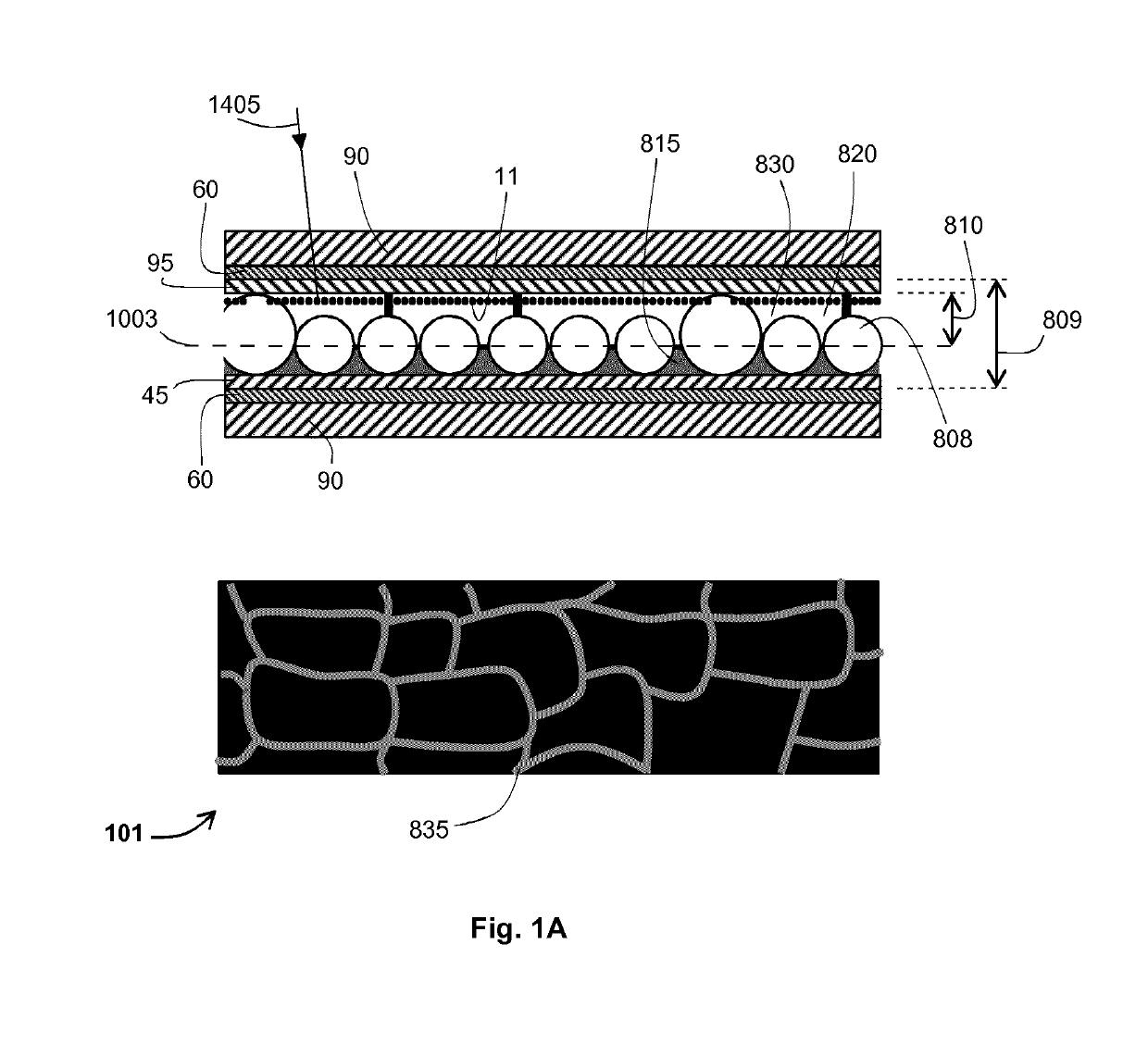
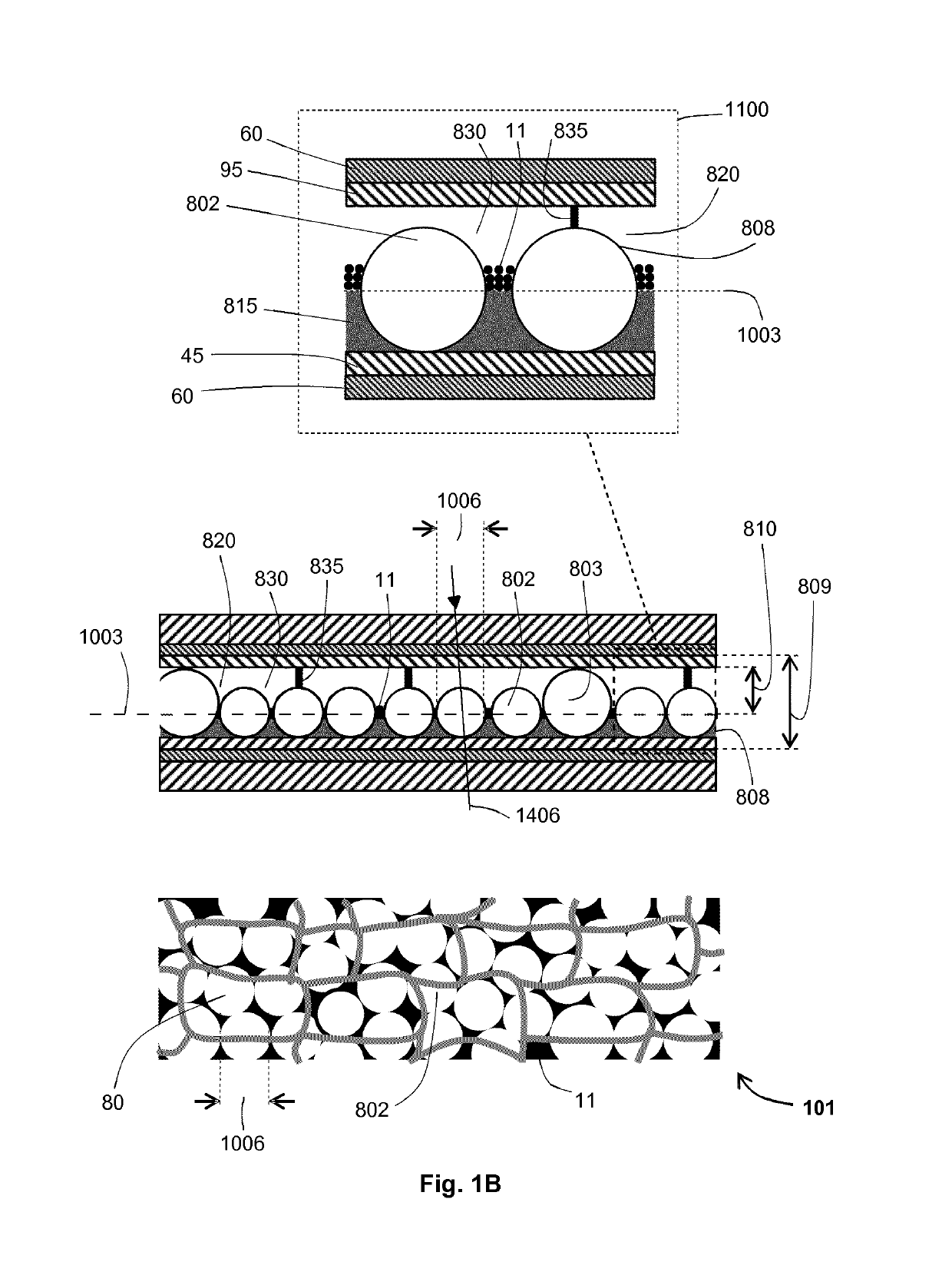
Wide operating temperature range electrophoretic device
ActiveUS20160246154A1Aromatic content is minimized and avoidedIncreasing solubility and toxicityLight protection screensNon-linear opticsElectrophoresisMean difference
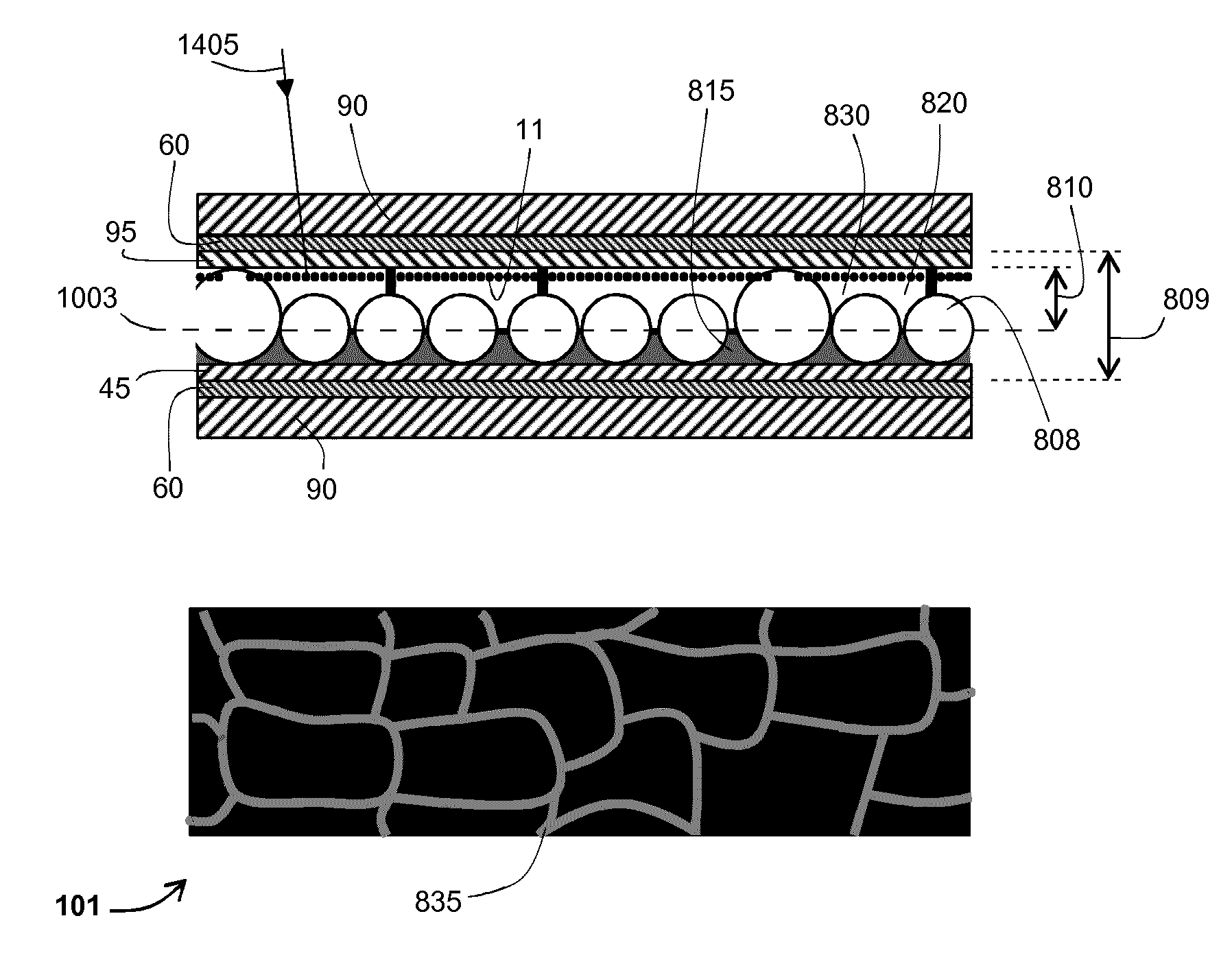
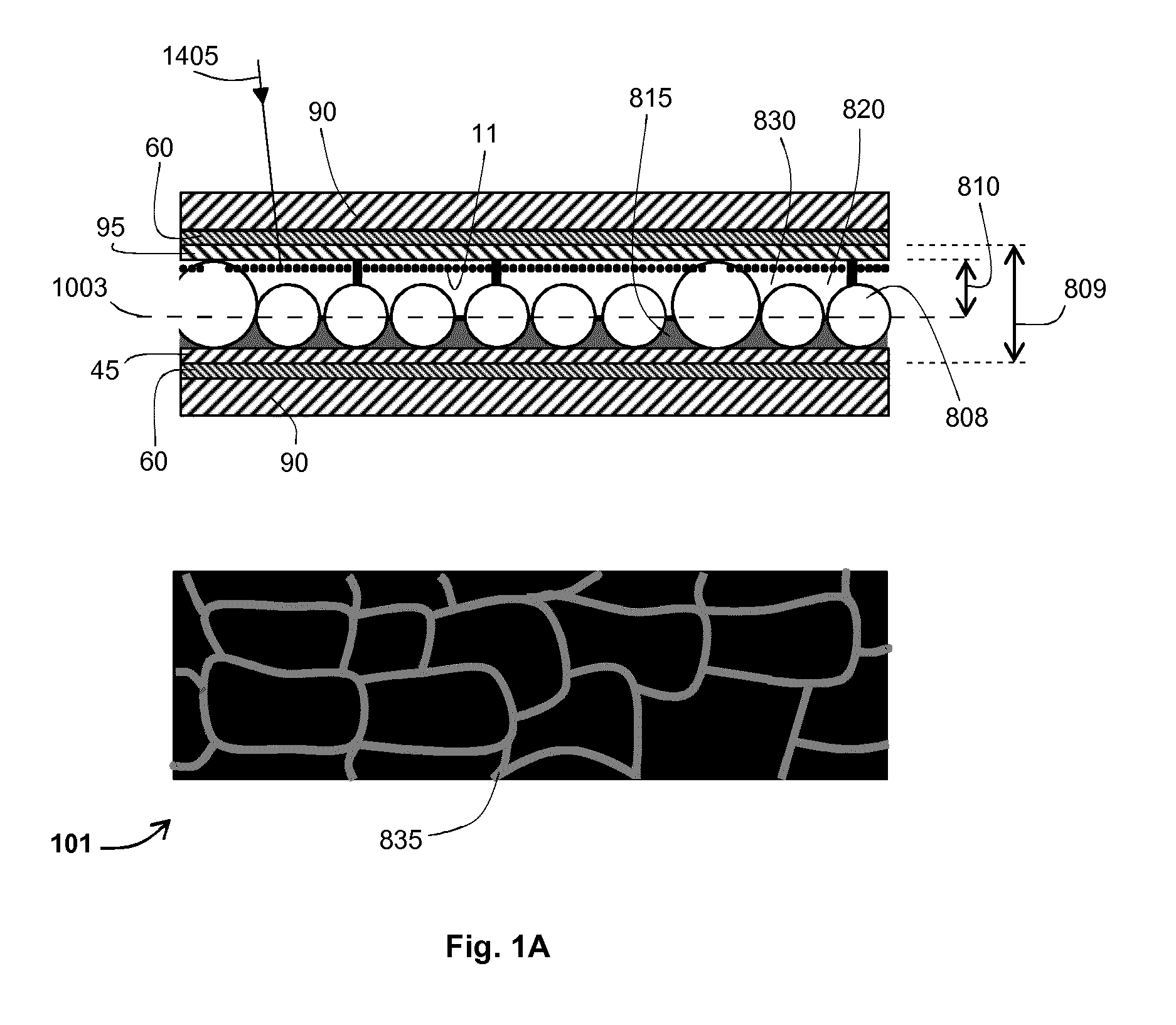
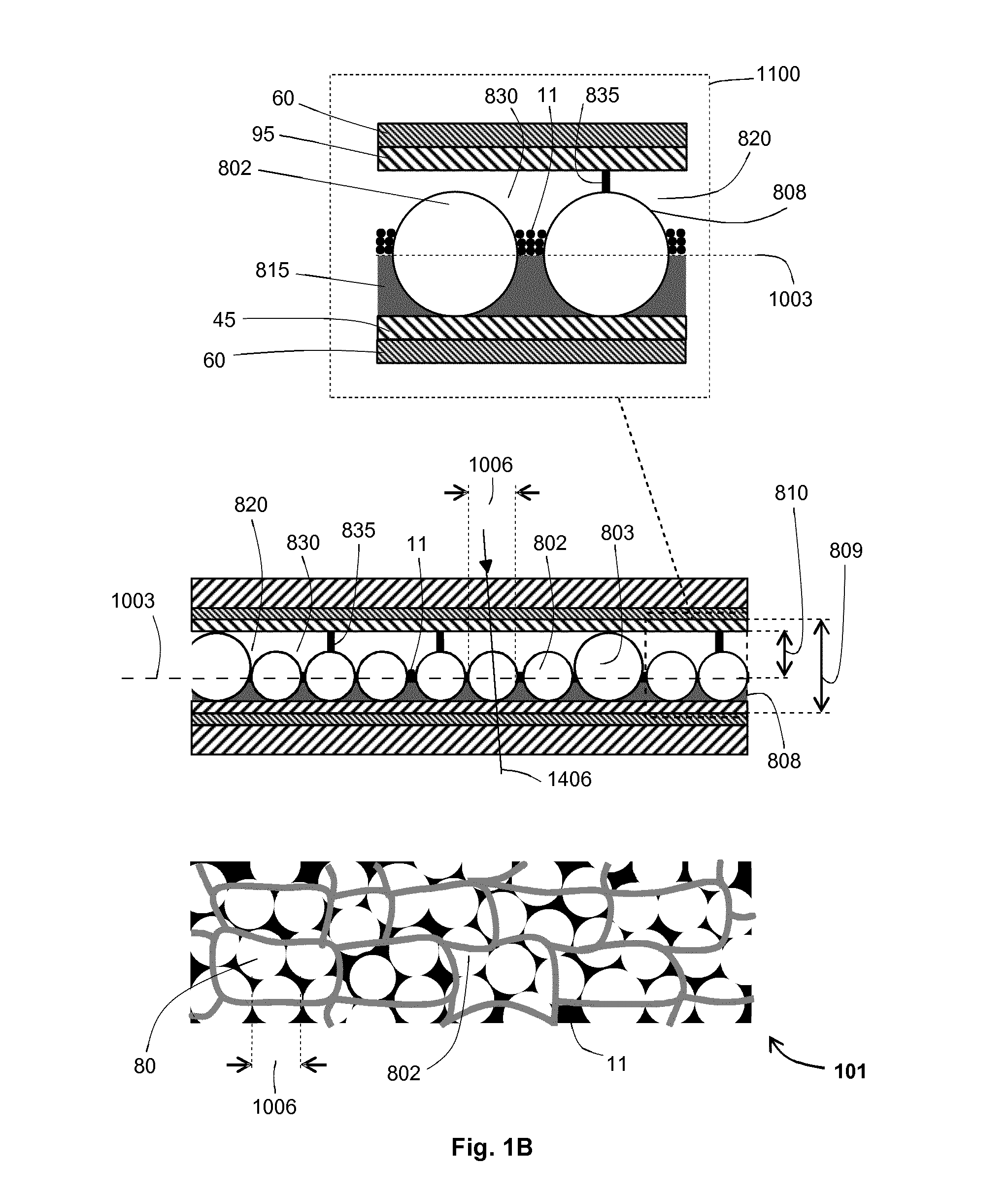
An electrophoretic device (101) comprises a first electrode (60) and a second electrode (60) spaced apart from the first electrode (60). An electrophoretic cell (809) containing an electrophoretic ink (830) and one or more optically-transparent, non-planar, solid polymer elements (808) is located between the electrodes (60). The ink (830) includes charged particles (11) of at least one type suspended in an optically-transparent suspending fluid (820). The refractive indices of the solid polymer elements (808) and the suspending fluid (820) are matched to have a difference of less than 0.0075, and for half or more of the operating temperature range of the device (0° C.-70° C.), the thermo-optic coefficients (temperature coefficient of refractive index per Kelvin) of the solid polymer elements (808) and the suspending fluid (820) are matched to have an arithmetic-mean difference of less than 0.0002 / K in magnitude.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
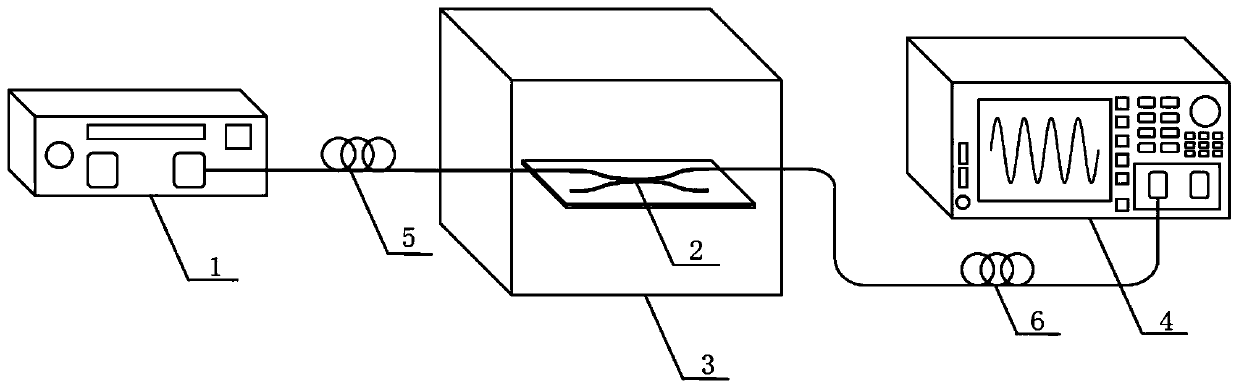
High sensitivity compact M-Z interference temperature sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106959172AHigh sensitivityObvious double beam interference effectThermometers using physical/chemical changesMicrostructure fiberOptoelectronics
The invention provides a high sensitivity compact M-Z interference temperature sensor and a manufacturing method thereof; the sensor comprises an input single-mode fiber, a microstructure fiber and an output single-mode fiber connected in sequence; the microstructure fiber is placed under a tested environment; the fiber core of the input single-mode fiber is respectively connected with the microstructure fiber core and an air hole filled with a high heat optical coefficient medium, thus using the microstructure fiber core to transmit partial the input single-mode fiber output light to the output single-mode fiber, and using the microstructure fiber air hole filled with the high heat optical coefficient medium to transmit the residual light to the output single-mode fiber; the output single-mode fiber transmits the received light to a spectral analyzer for spectral analysis, thus determining the temperature of the tested environment according to the spectral analysis result. The high heat optical coefficient medium is filled in the microstructure fiber, thus providing the high sensitivity super compact structure M-Z temperature sensor.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Temperature-drift-free on-chip integrated laser and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108123365AStable output wavelengthReduce power consumptionOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical coefficientLength wave
The invention discloses a temperature-drift-free on-chip integrated laser and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of electronic devices. The temperature-drift-free on-chipintegrated laser comprises a gain medium, a spot-size converter, an alignment mark, a temperature-drift-free hybrid integrated optical waveguide and a temperature-drift-free optical resonator, whereinthe gain medium is connected with the temperature-drift-free hybrid integrated optical waveguide through the spot-size converter; the temperature-drift-free hybrid integrated optical waveguide comprises high-refractive-index material layer formed on a low-refractive-index substrate and a negative-thermo-optical-coeffecient material layer which can compensate for a positive thermo-optical coefficient of the high-refractive-index material layer; and the temperature-drift-free optical resonator is of a resonator structure formed based on the temperature-drift-free hybrid integrated optical waveguide, and is used for stabilizing output wavelengths of the laser at different temperatures. The problem that an output wavelength of a silicon-based on-chip integrated laser changes with the temperature is solved. An additional regulation and control device does not need to be added, so that the temperature-drift-free on-chip integrated laser is low in power consumption, high in integration degree and low in preparation cost.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Method for preparing linear polyester-imides and thermal-optical property usage thereof
InactiveCN101134805AGood film-forming performancePI has a high glass transition temperatureElectronic switchingMaleic anhydrideDimethyl formamide
The present invention relates to one kind of polyurethane-imide (PUI) material and it preparation process and application. The PUI material is prepared in N, N-dimethyl formamide (DMF) solvent with TDI and DR-19 or DR-1 with active hydroxyl radical, and through pre-polymerization to form pre-polymer with non-linear chromogenic molecule and -NCO terminal, and the subsequent polycondensation reaction of the pre-polymer and maleic anhydride monomer first at 40-110 deg.c for 40 min to 4 hr and then reflux at 90-200 for 1-5 hr. The PUI material as one polymer material containing non-linear optical radical has non-linear optical property, high heat stability and great thermo-optical coefficient, and may find broad application in integrated optics, logic optics, thermo-optical switch, etc.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method and applications of hyperbranched azo polymer
InactiveCN103193967AHigh thermo-optic coefficientLow driving powerTenebresent compositionsBenzoic acidPolymer science
The invention relates to a preparation method and applications of a hyperbranched azo polymer, belonging to the organic synthesis field. The preparation method comprises the steps: firstly, performing nitroreduction and carboxyl acylation by taking p-nitrobenzoic acid as a raw material, to obtain an A2 type monomer azo-bi(benzoyl chloride) with an azobenzene structure, and then reacting the A2 type monomer azo phthaloyl dichloride with a B3 type monomer glycerol according to certain mole ratio to obtain the hyperbranched azo polymer. The materials of the obtained hyperbranched azo polymer has higher thermo-optical coefficient which is more than ten times of that of inorganic materials such as borosilicate glass, zinc silicate glass, silica glass and the like, and the material provides a possibility for developing a novel digital thermo-optical switch with low driving power.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
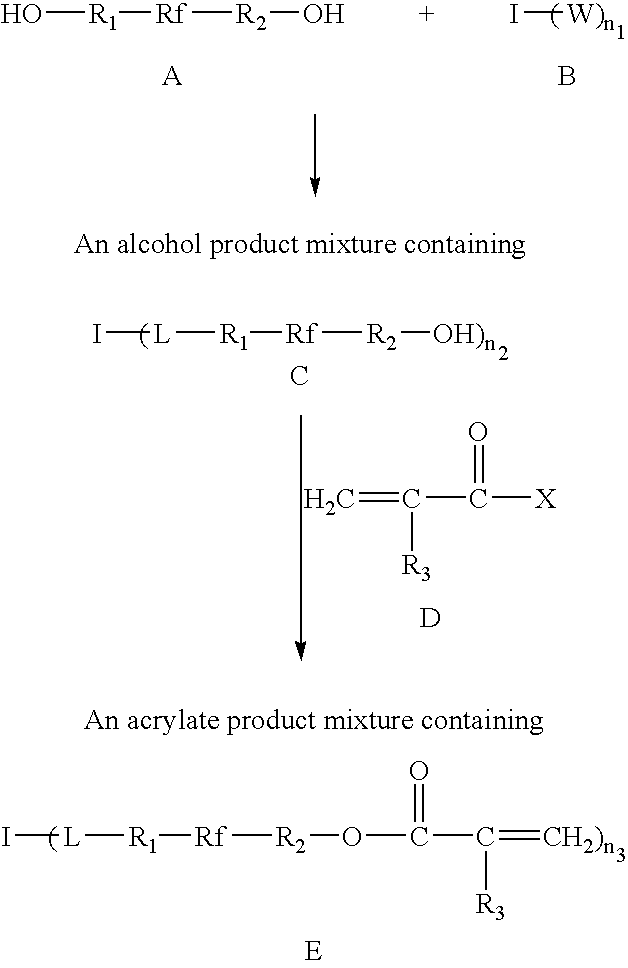
Photosensitive acrylate composition and waveguide device
InactiveUS7078445B2High photo contrastFast curingPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusAlcoholPhotoinitiator
A photosensitive composition suitable for practical waveguide devices is provided. The photosensitive composition comprises at least one multifunctional acrylate prepared from a fluorinated multifunctional alcohol and at least one photoinitiator. The said composition has high photo contrast, high curing speed, controllable refractive index, low curing shrinkage, high thermo-optic coefficient, low volatility and high viscosity. A waveguide device is formed by patterning the photosensitive composition.
Owner:ENABLENCE TECH USA
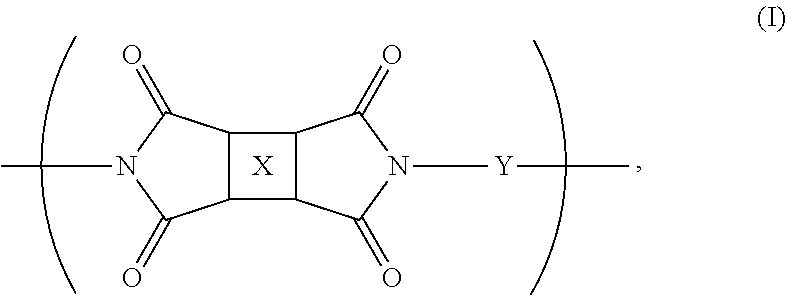
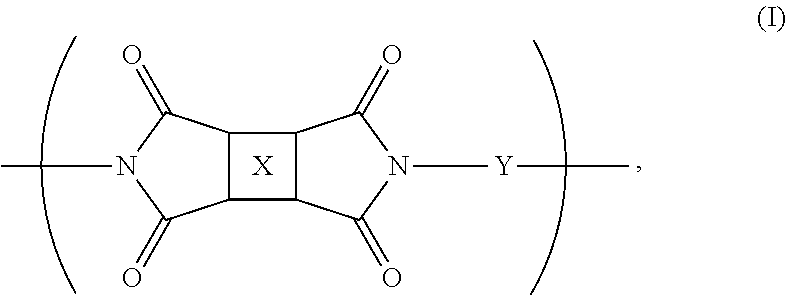
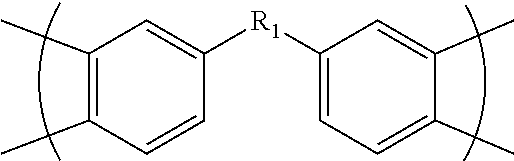
Fluorinated polyimides with fluorene cardo structure as optical materials that have low absolute thermo-optic coefficients
The present invention provides new polyimide materials suitable for use in optically transparent fiber composites, ribbon composites, and optical communications applications. The polyimide compounds include monomeric repeat units comprising a fluorinated moiety and a fluorene cardo structure. The polyimides exhibit good optical transparency and have a low absolute thermo-optic coefficient (|dn / dT|).
Owner:BREWER SCI
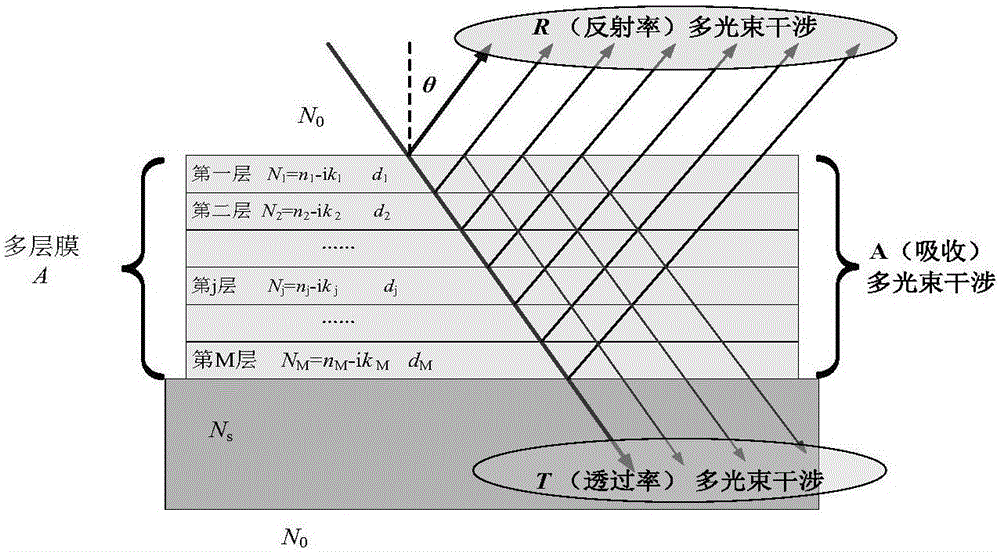
Method for calculating spectrum thermal radiance of multilayer optical film
ActiveCN106644087ASimple operabilityAvoid complex structure designRadiation pyrometryMeasuring instrumentRadiance
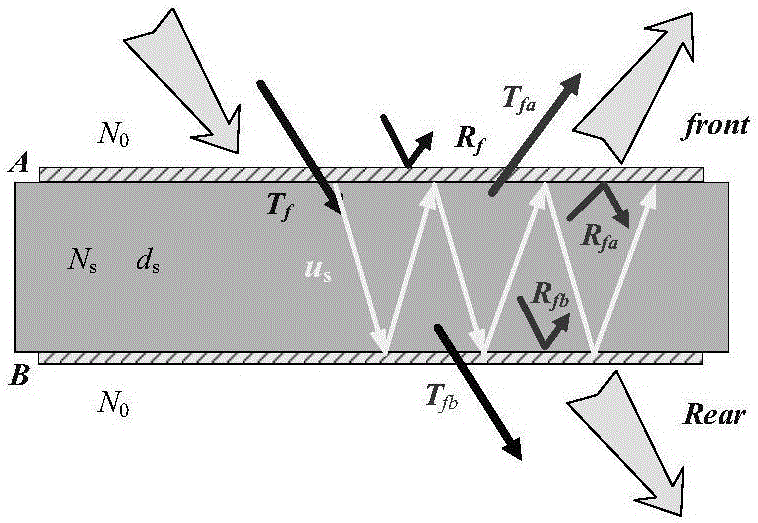
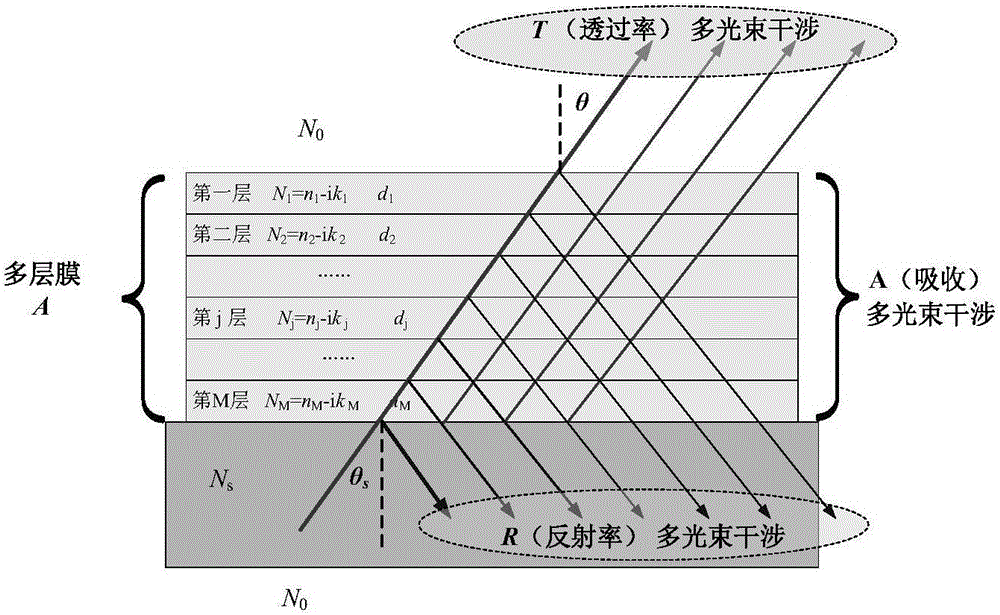
The invention belongs to the field of spectrum thermal radiance representation, and specifically relates to a method for calculating the spectrum thermal radiance of a multilayer optical film. The method is simple and feasible. For a determined multilayer film-substrate-multilayer film system structure, the method can completely express the spectrum directional radiance, directional radiance, spectrum radiance and integral spatial radiance of an optical multilayer film with only one need to determine the thermo-optical coefficients of a substrate and a film material. The method can avoid the tedious operation of direct measurement and a complex structure design of a measuring instrument, and has a certain scientific and application value.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG INST OF TECH PHYSICS
Waveguide structure
InactiveUS20090148115A1Avoid it happening againProcess stabilityOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideThermo-optic coefficient
A waveguide structure is provided. The waveguide structure includes: a slot channel waveguide including first and second patterns, which are spaced apart from each other to define a slot; a first upper layer covering at least a portion of the slot channel waveguide; and a second upper layer covering the remaining portion of the slot channel waveguide. A thermo-optic coefficient (TOC) of the channel waveguide times a TOC of the second upper layer is a negative number.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Tapered composite waveguide for athermalization
InactiveUS20080069498A1No optical lossNegligibly smallCoupling light guidesFilling materialsWaveguide
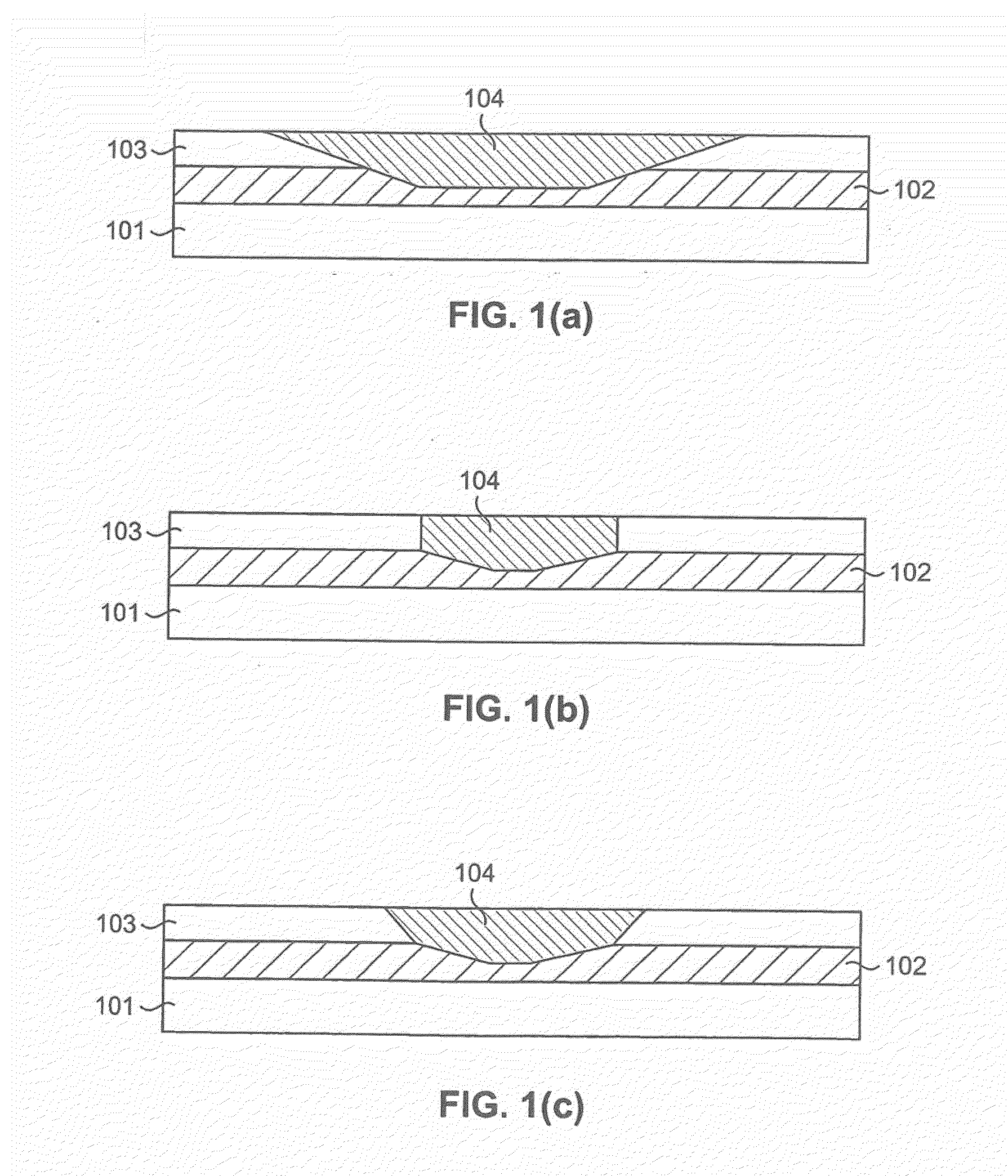
A planar waveguide circuit includes a silica-based planar optical waveguide circuit having a lower cladding, a core and an upper cladding. At least one input waveguide and one output waveguide are each coupled to the optical waveguide circuit. At least one tapered waveguide section is located in the waveguide circuit, which has an upper cladding segment that tapers down to at least the core to define a tapered recess. A filler material having a negative thermo-optic coefficient fills the tapered recess so that the optical waveguide circuit has an optical characteristic with a reduced temperature dependence.
Owner:CYOPTICS ISRAEL
Adiabatic tapered composite waveguide for athermalization
InactiveUS20100165352A1Negligibly smallLow temperature dependenceOptical articlesUsing optical meansFilling materialsSilicon dioxide
A planar waveguide circuit includes a silica-based planar optical waveguide circuit having a lower cladding, a core and an upper cladding. At least one input waveguide and one output waveguide are each coupled to the optical waveguide circuit. At least one tapered waveguide section is located in the waveguide circuit, which has an upper cladding segment that tapers down to at least the core to define a tapered recess. A filler material having a negative thermo-optic coefficient fills the tapered recess so that the optical waveguide circuit has an optical characteristic with a reduced temperature dependence.
Owner:CYOPTICS ISRAEL
Optical fiber gas pressure sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111272330AGood repeatabilityConsistent structureFluid pressure measurement by optical meansThermal dilatationFilm material
The invention discloses an optical fiber gas pressure sensor and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a gas pressure sensor and a preparation method thereof. The problems that an existing FPIoptical fiber gas sensor plugging thin film is difficult to prepare and low in structural strength, and temperature crosstalk exists due to the fact that the optical fiber and a plugging thin film material have thermo-optical coefficients and thermal expansion coefficients are solved. The optical fiber gas pressure sensor is an FPI optical fiber gas sensor; the optical fiber gas pressure sensor iscomposed of a hollow-core optical fiber, a single-mode optical fiber and a film, one end of the hollow-core optical fiber is welded with the single-mode optical fiber, and the other end of the hollow-core optical fiber is blocked by the film; and the thin film is a polydimethylsiloxane thin film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing an initial structure; 2, dipping in a PDMS liquid; 3, adjusting the thickness of the film; 4, performing curing.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Wide operating temperature range electrophoretic device
ActiveUS10324353B2Increasing solubility and toxicityGood chemical resistanceLight protection screensNon-linear opticsElectrophoresisEngineering
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Phosphate laser neodymium glass free of thermo-optic effect
ActiveCN108840564AImprove performanceReduced nonlinear index of refractionHigh power lasersPhosphate
Owner:CDGM GLASS LLC
Broadband temperature-insensitive optical waveguide device
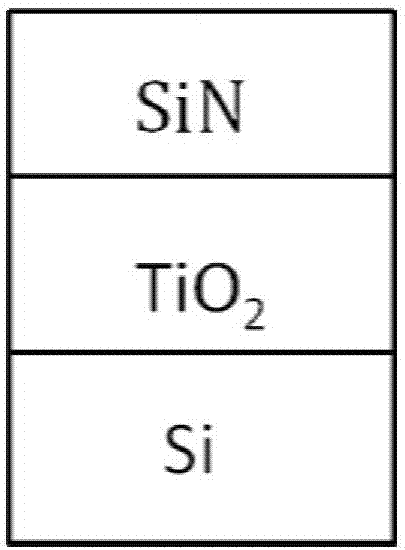
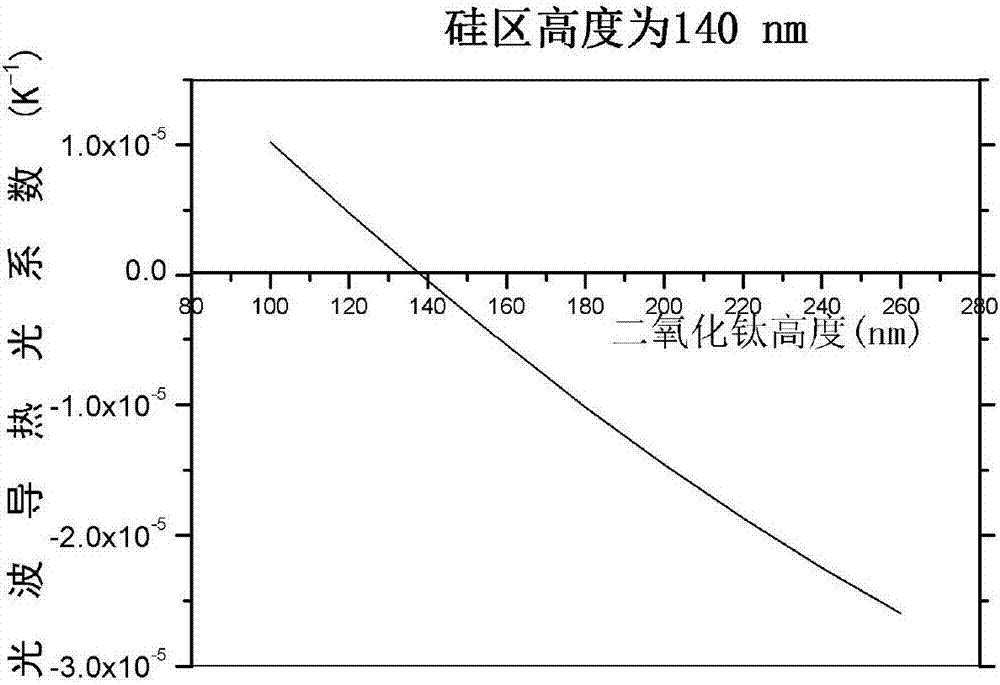
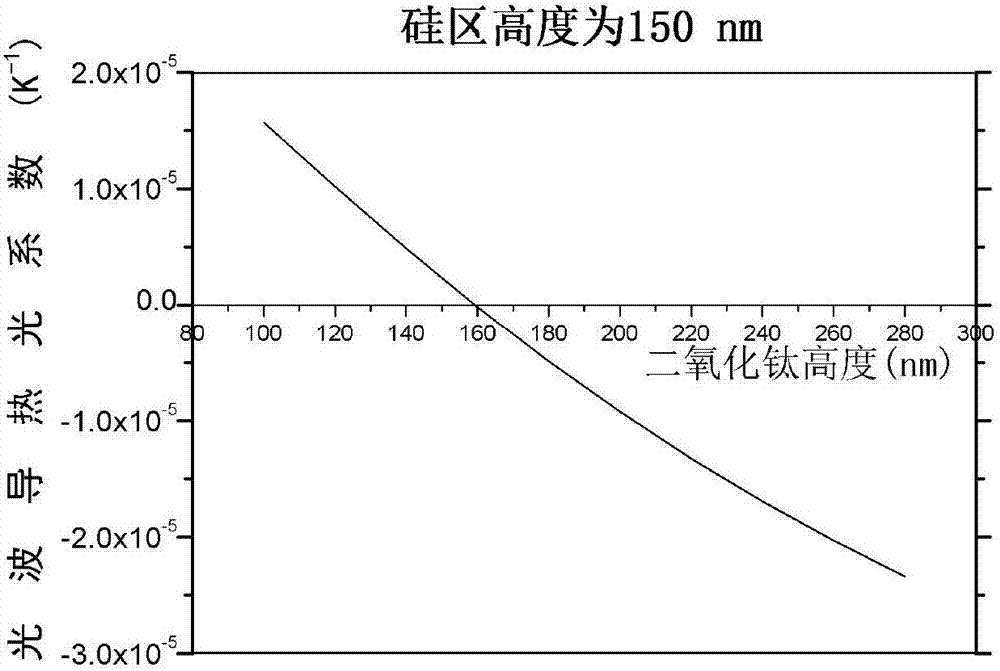
The invention discloses a broadband temperature-insensitive optical waveguide device, which comprises a core area and a cladding in mutual lamination, wherein the core area adopts silicon; the cladding adopts titanium dioxide; the other surface of the cladding is provided with a coverage layer; and the coverage layer adopts a material with a positive calorescence coefficient. The light intensity limiting factor of each structure layer in the optical waveguide is influenced by the wavelength, after the wavelength become larger, an evanescent field of the light transmitted in the optical waveguide becomes larger, and correspondingly, the light intensity limiting factor in the cladding becomes larger. Thus, corresponding to different wavelengths, the light intensity limiting factor in each layer changes, as the wavelength become larger, the total calorescence coefficient of the optical waveguide does not monotonously change along with the temperature, a curve similar to a parabolic change is formed, and temperature insensitivity in a broad wavelength range can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com