Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Cleaning time is short" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
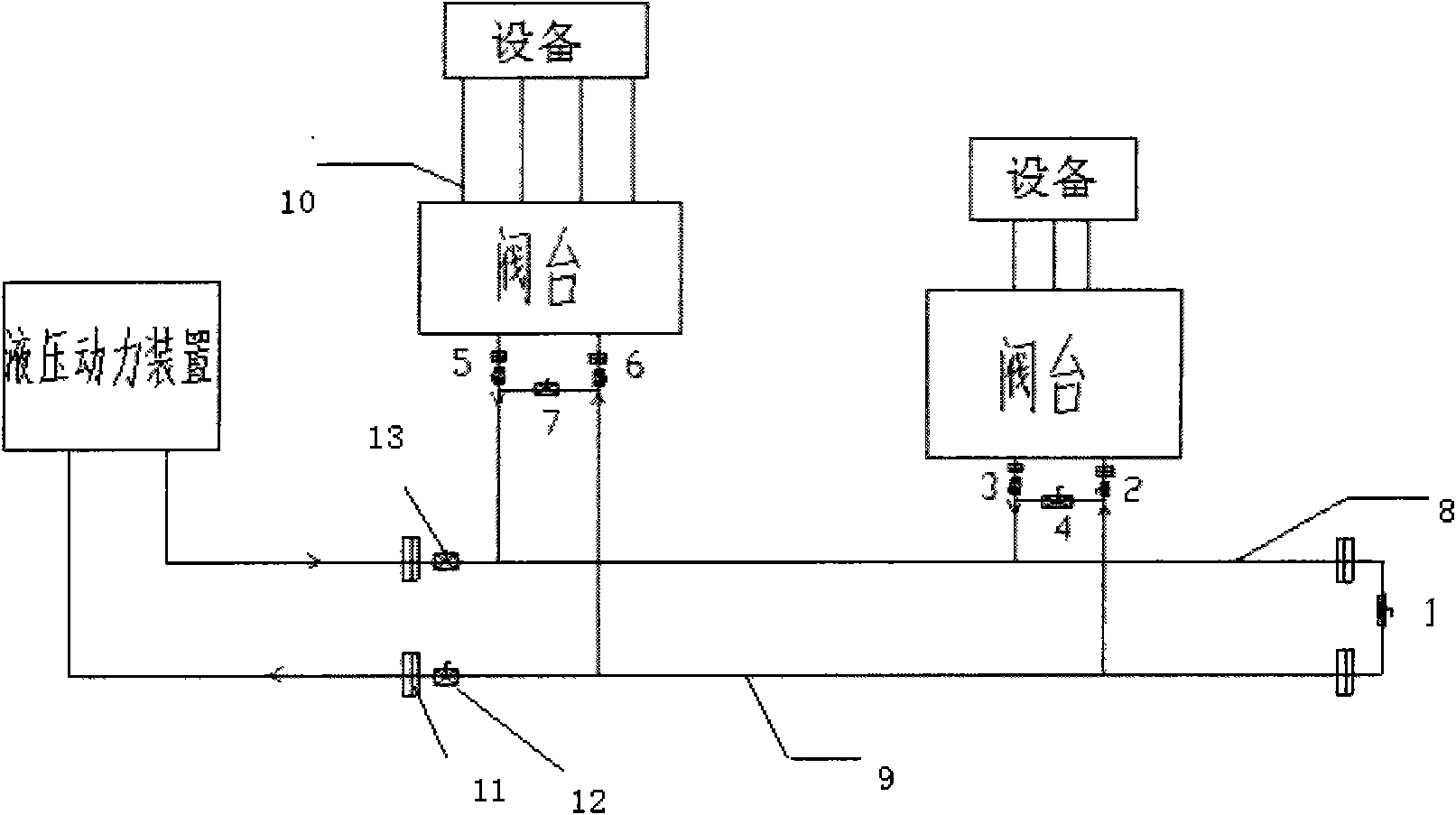
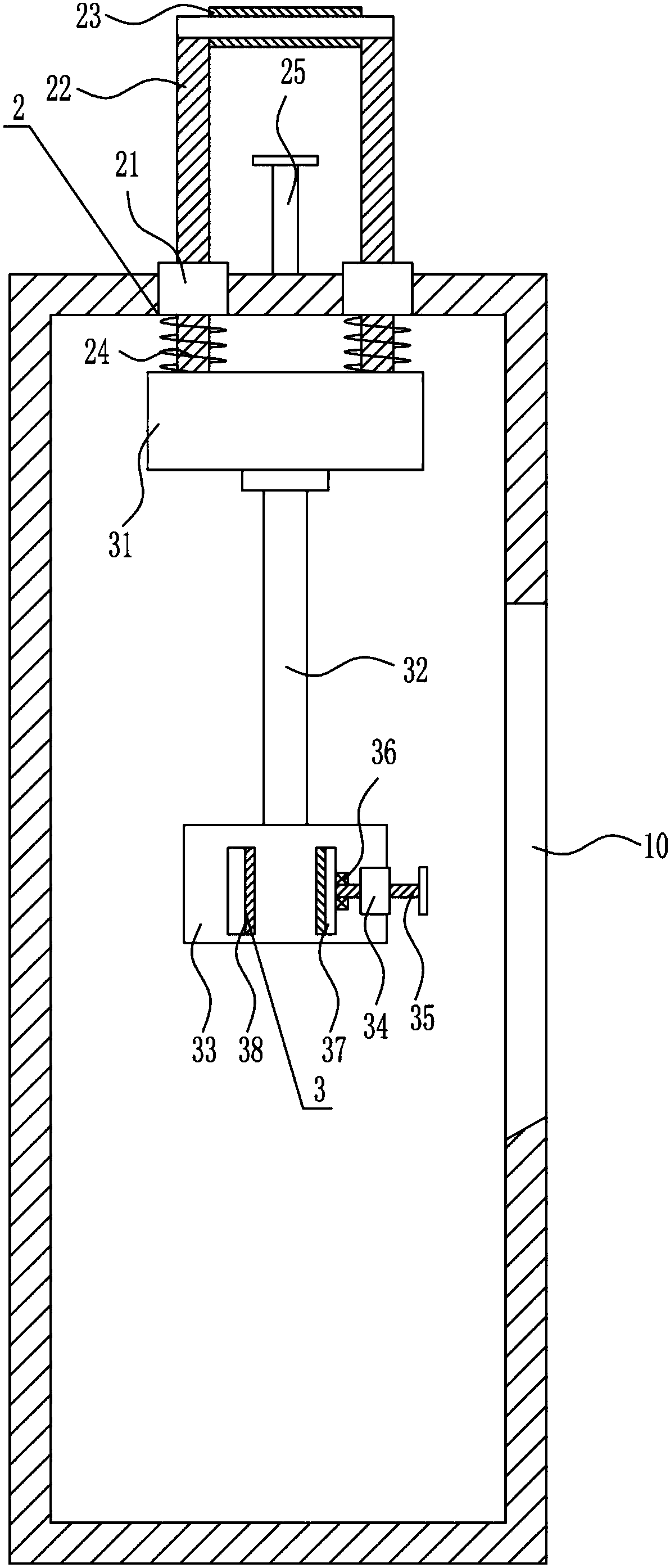
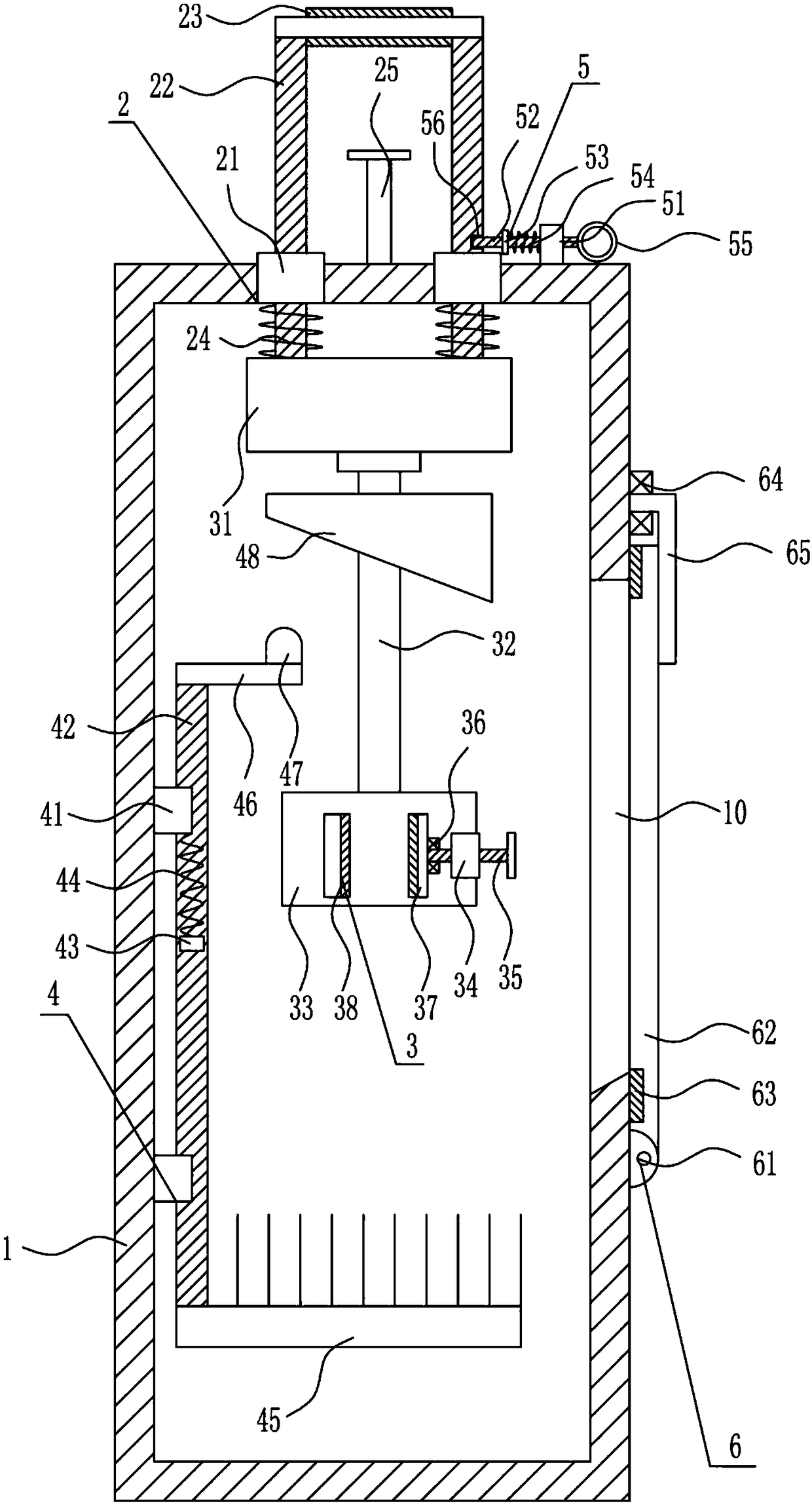
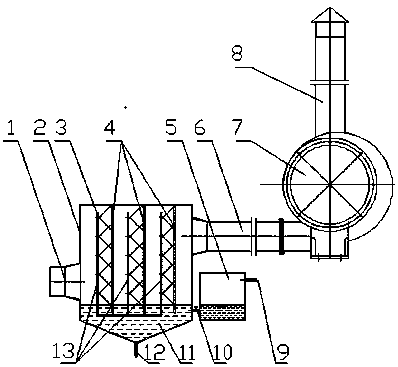
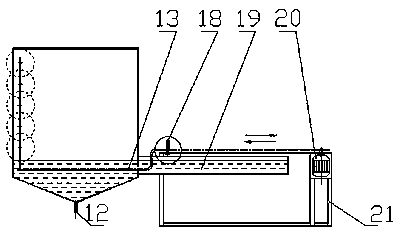
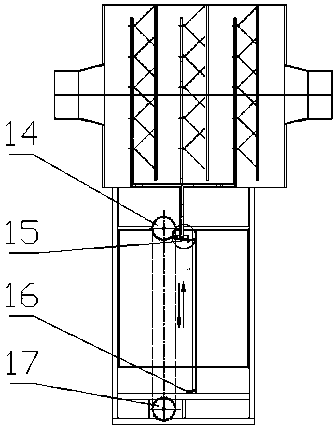
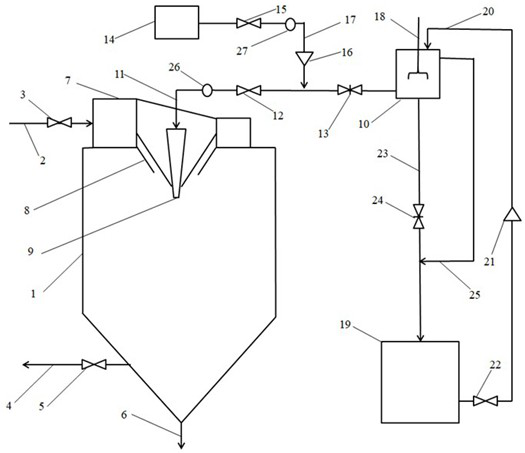
Pipeline cleaning method
ActiveCN101637768AWashed away wellCleaning time is shortHollow article cleaningIsolation valveEngineering
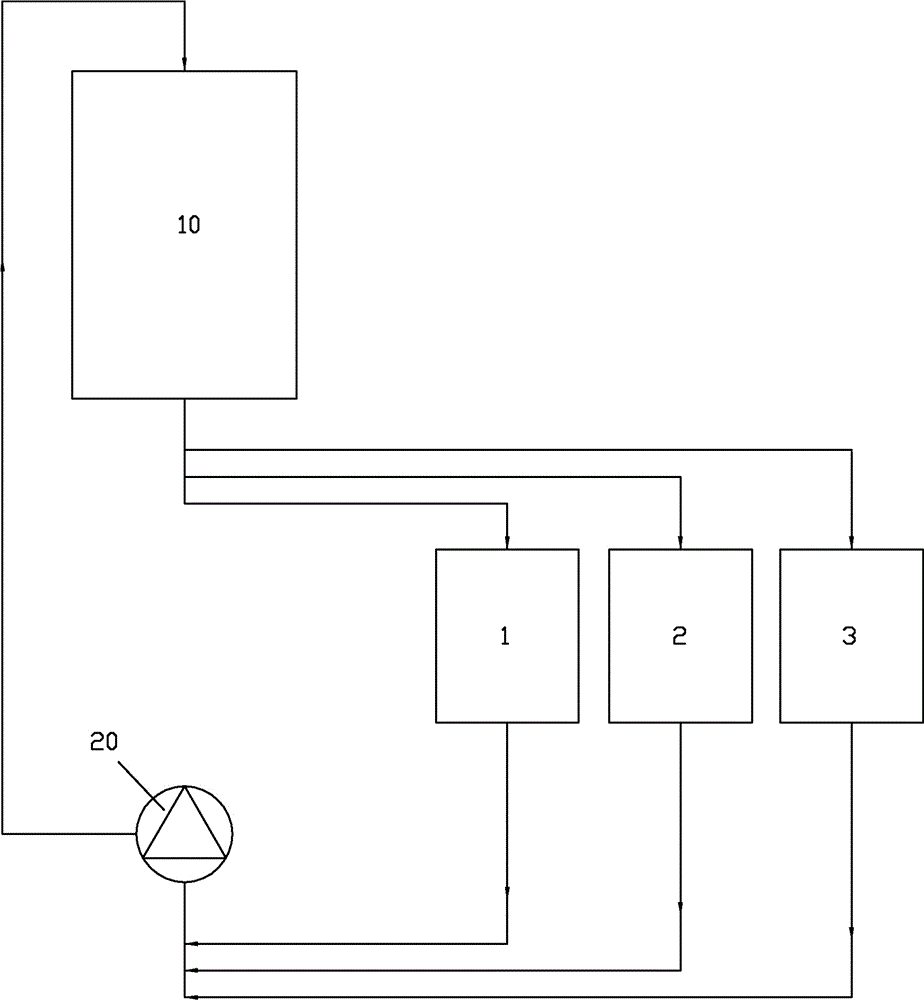
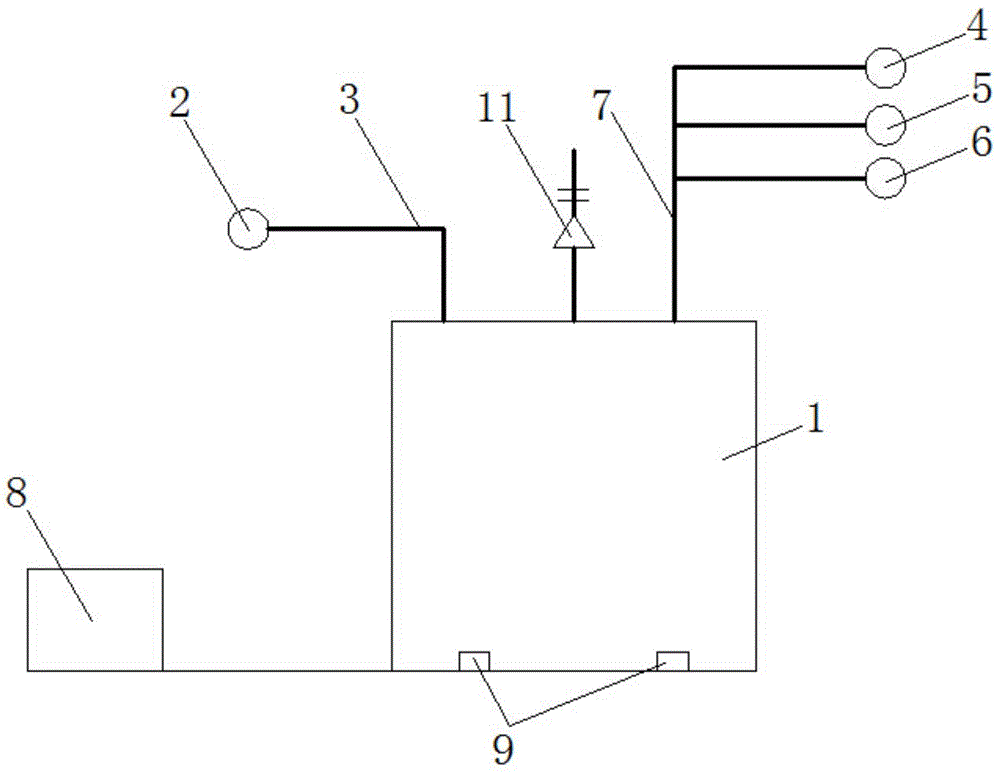
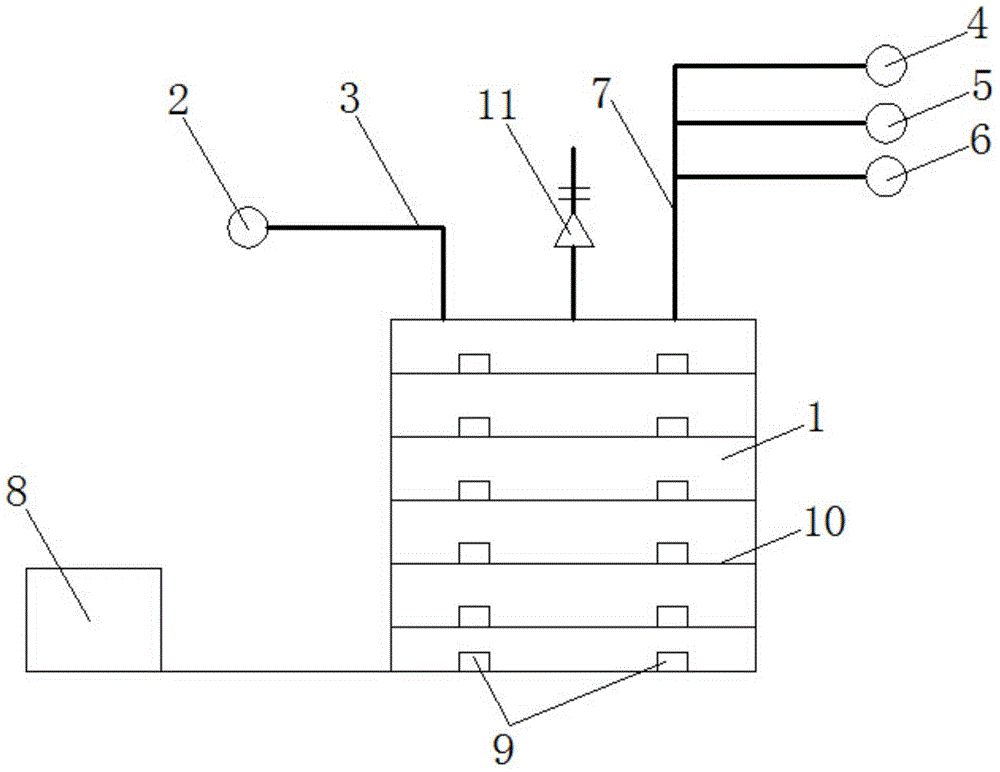
The invention relates to a pipeline cleaning method, which uses cleaning oil as medium and uses a pump to clean forcibly and circularly. The pipeline cleaning method comprises the following steps: 1)steps of processing and installing the pipeline: respectively installing a separating valve at a main pipeline, a branch pipeline and connecting part of bypass pipelines; 2) steps of installing a temporary cleaning device and disassembling the branch pipeline; 3) step of primary cleaning; 4) step of restoring the normal pipelines; and 5) step of secondary cleaning. Compared with the traditional construction process, the construction technique increases a control valve on the original basis, increases the step of reverse cleaning, uses the control of the bypass valve, has circular and thoroughcleaning, high cleanness, short time and low cost, avoids the defects that the dead angles are formed in cleaning and the like and has better technical effect and promotion value.
Owner:CHINA HUAYE GROUP
Cleaning method and device for engine
ActiveCN108856136ASmoothly intoEasy to focus on cleaningDrying gas arrangementsMachines/enginesCombustion chamberTransformer
The invention discloses a cleaning method and device for an engine. The cleaning method comprises the steps for cleaning a combustion chamber of the engine, specifically, an appropriate number of cleaning agents are added into the combustion chamber; ultrasonic waves are transmitted to the cleaning agents through an energy-concentrating-type ultrasonic amplitude transformer, so that the cleaning agents vibrate, and then carbon deposits on the inner wall of the combustion chamber fall off; the cleaning agents and the fallen-off carbon deposits are sucked out of the combustion chamber through amaterial suction pipe; and the fallen-off carbon deposits remaining in the combustion chamber are blown out through a blower gun, and the combustion chamber is blow-dried. The invention further discloses the ultrasonic cleaning device for the engine. The ultrasonic cleaning device comprises the energy-concentrating-type ultrasonic amplitude transformer matched with the combustion chamber of the engine and provided with a specific structure. According to the technical scheme, the cleaning agents do not need to be heated up and do not need have the high PH value, then the car engine can be effectively cleaned, and corrosion of cleaning liquid to the car engine can further be effectively avoided.
Owner:艾斯格林科技深圳有限公司
Chopstick cleaning assembly and bowl washing machine
ActiveCN106562748AImprove cleaning efficiencyCleaning time is shortTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
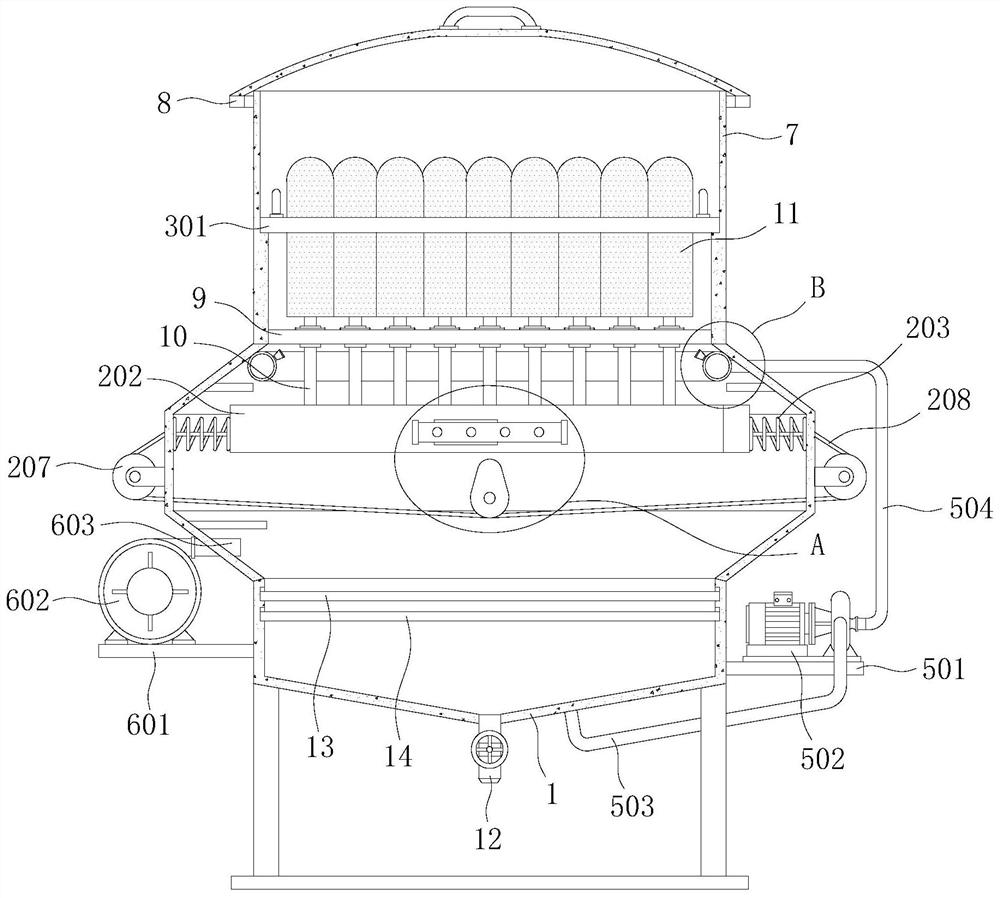
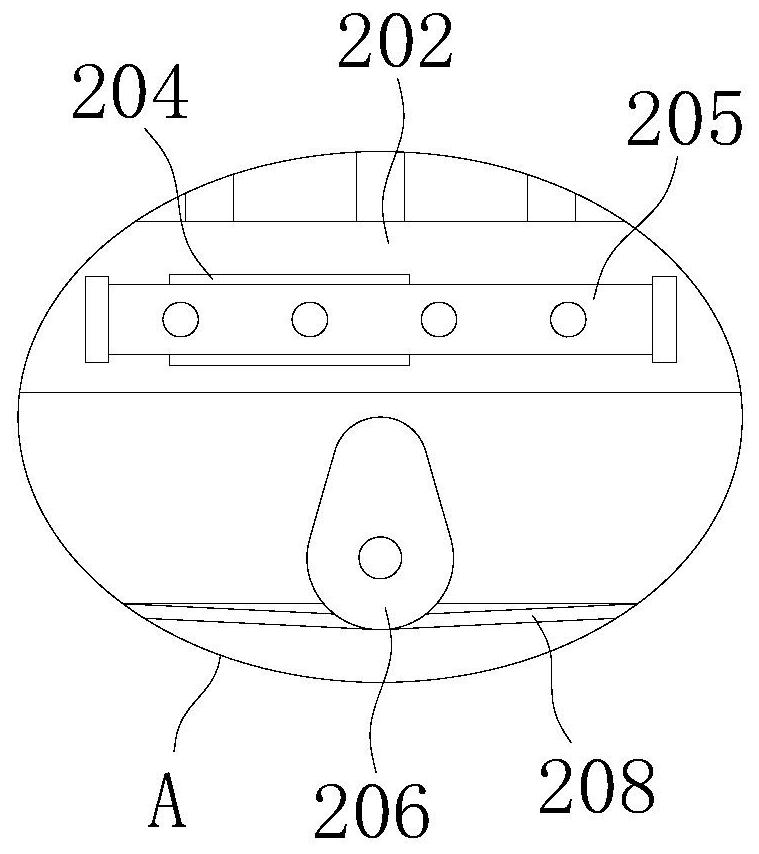
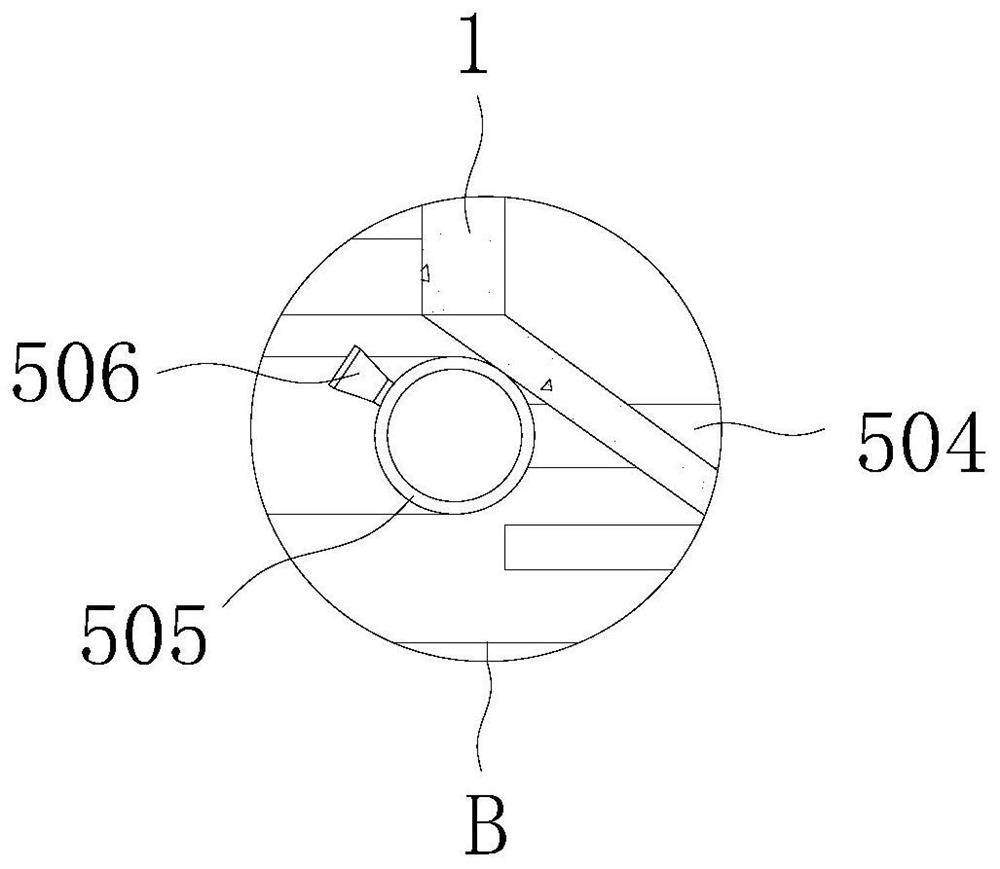
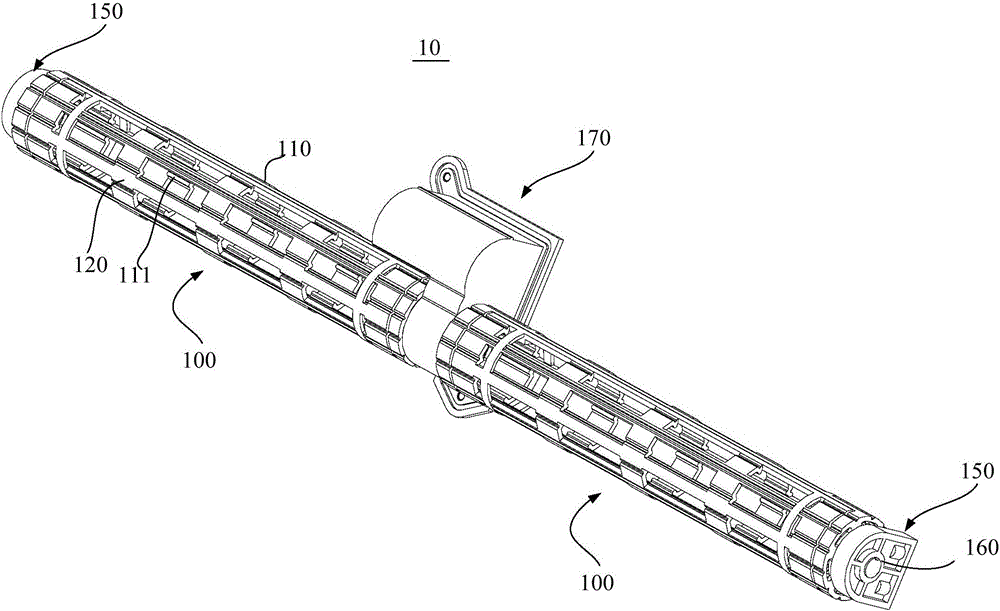
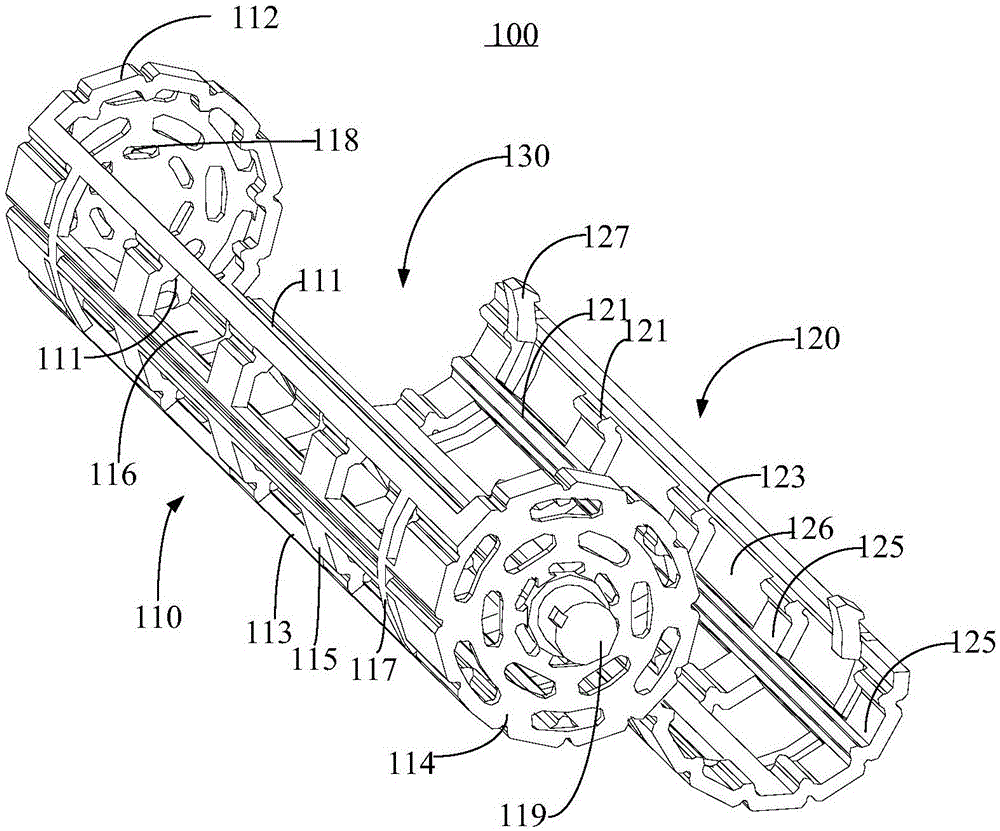
The invention relates to a chopstick cleaning assembly and a bowl washing machine. The chopstick cleaning assembly comprises a tubular cleaning structure and a tubular accommodating structure, wherein the tubular cleaning structure comprises a rotating shaft and a tubular carrying part; the tubular carrying part is fixedly connected with the rotating shaft, and comprises a plurality of chopstick accommodating elements arranged at intervals; the tubular accommodating structure forms a tubular accommodating space so as to accommodate the tubular cleaning structure; the tubular cleaning structure is rotatablely arranged in the tubular accommodating space and is coaxial with the tubular accommodating structure; a chopstick inlet extending in a direction being parallel to the rotating shaft is arranged on the top of the tubular accommodating structure; and the chopstick accommodating elements and the tubular accommodating structure form a space for accommodating chopsticks. The chopstick cleaning assembly and the bowl washing machine provided by the invention have the advantages that the cleaning efficiency is high; and the cleaning time is short, so that the water and the electric energy can be saved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Automatic water cleaning system for air purification devices
ActiveCN104930678ACleaning time is shortReduce consumptionMechanical apparatusDispersed particle filtrationElectricityMotor drive
The invention discloses an automatic water cleaning system for air purification devices. The automatic water cleaning system comprises a water tank portion and a sliding way portion; the water tank portion comprises a water tank, a water pump, a water inlet pipe, a water outlet pipe and a water spraying pipe; the water pump is arranged on the water outlet pipe outside the water tank, and the water spraying pipe is connected with the water outlet pipe; a water spraying nozzle is formed in the water spraying pipe; and the sliding way portion comprises a sliding way, a motor, an electromagnetic valve, a sliding block and a transmission shaft; the sliding block is arranged on the sliding way in a sliding manner, and the water spraying pipe is detachably arranged on the sliding block; the electromagnetic valve is arranged on the water spraying pipe, and the transmission shaft is arranged at the top end of the sliding way; and the motor drives the sliding block to move in a reciprocating manner in the vertical direction through the transmission shaft. The automatic water cleaning system has the advantages and beneficial effects that in the water cleaning process, the cleaning consumed time is short, and according to actual needs, the cleaning amount can be adjusted; cleaning is thorough and rapid, and the water consumption amount of water and electricity is reduced; the automatic water cleaning system can adapt to automatic cleaning of air purification devices such as a coarse efficient air purification device, a medium efficient air purification device and a sub efficient air purification device; manual participation is not needed, and through presetting, cleaning is operated through a control system.
Owner:TIANJIN RAILWAY SIGNAL
Bottle washing machine with draining and drying functions for rheumatalgia medicinal liquor packaging bottles
ActiveCN112570397AImprove cleaning efficiencyCleaning time is shortDrying solid materials without heatHollow article cleaningEngineeringProcess engineering
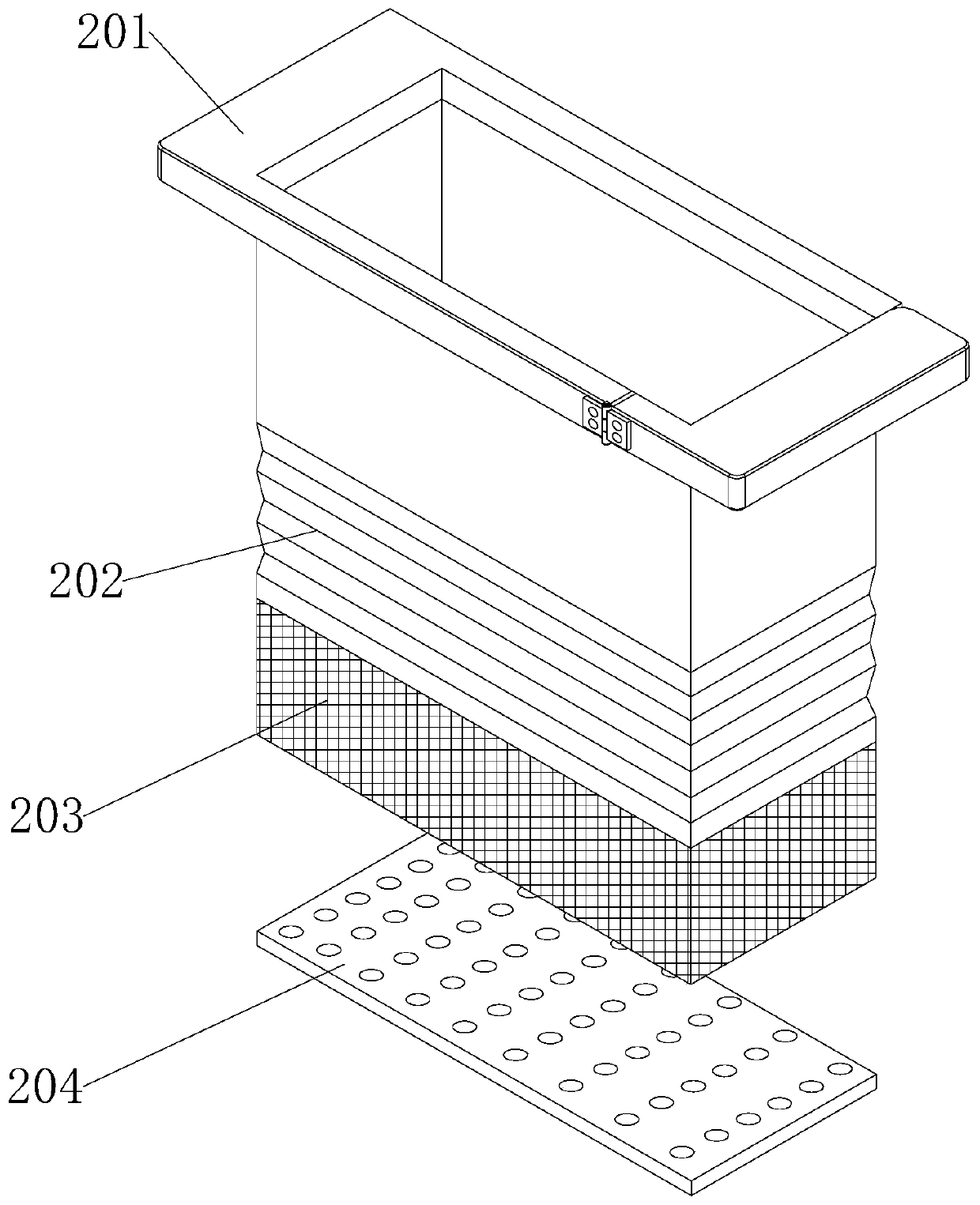
The invention discloses a bottle washing machine with draining and drying functions for rheumatalgia medicinal liquor packaging bottles, and relates to the technical field of medicinal liquor packaging. The bottle washing machine with the draining and drying functions for the rheumatalgia medicinal liquor packaging bottles comprises a washing box, a transmission mechanism, a fixing mechanism, a driving mechanism, a washing mechanism and a drying mechanism are arranged on the washing box, a processing box is fixedly installed at an opening in the top of the washing box, and a fixing plate is fixedly installed on the inner wall of the processing box; and a plurality of sets of sleeve rods are rotationally installed on the fixing plate, and cleaning brushes are fixedly installed on the outerwalls of the sections, located above the fixing plate, of the sleeve rods. According to the bottle washing machine with the draining and drying functions for the rheumatalgia medicinal liquor packaging bottles, the multiple sets of medicinal liquor bottles can be cleaned and brushed at the same time, the cleaning time is shortened, the cleaning efficiency of the machine is improved, it can be guaranteed that all sets of medicinal liquor bottles do not collide with one another during cleaning, and a user can conveniently take out the multiple sets of medicinal liquor bottles at the same time after cleaning.
Owner:江西众源药业有限公司
Punch filling pile bottom cleaning method
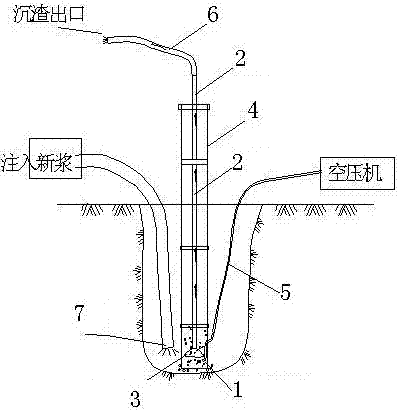
The invention relates to pile foundation construction, and discloses a punch filling pile bottom cleaning method. The method comprises the steps that two sections of connected bent pipes are welded tothe interior and the exterior of a section of concrete pouring guide pipe correspondingly to form a bottom section guide pipe; a circular horn mouth metal cover is welded to the end of a steel pipe,another section of concrete pouring guide pipe is taken, a steel plate is welded to the top of the section of concrete pouring guide pipe, a hole is formed after sealing, and the section of concrete pouring guide pipe is used as a first section guide pipe; after pile hole completion, a hose is connected to the ventilation bent pipes of the bottom section guide pipe and stretched to an air compressor, and the bottom section guide pipe is connected with a standard guide pipe to be installed into a filling pile hole; the steel pipe is installed into the concrete pouring guide pipe to the bottom of the hole; the first section guide pipe is installed to the portion, in the pile hole, of the guide pipe, and the steel pipe in the pipe just penetrates through the hole in the top of the first section guide pipe, and a hose is connected to the top of the steel pipe and stretched into a slag discharge pool; a new pulp pipe is directly connected into the bottom of the pile hole, new pulp is injected, the air compressor is started to increase pressure and refill air to push sediment and chippings at the bottom of the hole into the portion, with the metal cover, of the steel pipe, and the sediment and the chippings are pressed out of the pile hole along with the steel pipe. The sedimentation at the bottom of the hole can be thoroughly removed.
Owner:CHINA MCC20 GRP CORP
Cleaning equipment of cosmetic brush
The invention relates to cleaning equipment, and particularly relates to cleaning equipment of a cosmetic brush. The invention aims to solve the technical problem and provide the cleaning equipment ofthe cosmetic brush. The cleaning equipment has the advantages of high cleaning neatness, simpleness and easiness in operation and short cleaning time. In order to solve the above-mentioned technicalproblem, the cleaning equipment of the cosmetic brush, provided by the invention, comprises a cleaning box and the like, wherein a moving mechanism is mounted at the top of the cleaning box, a rotarycleaning mechanism is mounted on the moving mechanism, and a through hole is formed in the middle part of the right side of the cleaning box. According to the cleaning equipment of the cosmetic brush,the cosmetic brush is fully washed through the matching of the moving mechanism and the rotary cleaning mechanism; meanwhile, through optimization by using a deep cleaning mechanism and a fixing mechanism, the effects of high cleaning neatness, simpleness and easiness in operation and short cleaning time are achieved.
Owner:江西昂奈雅实业有限公司
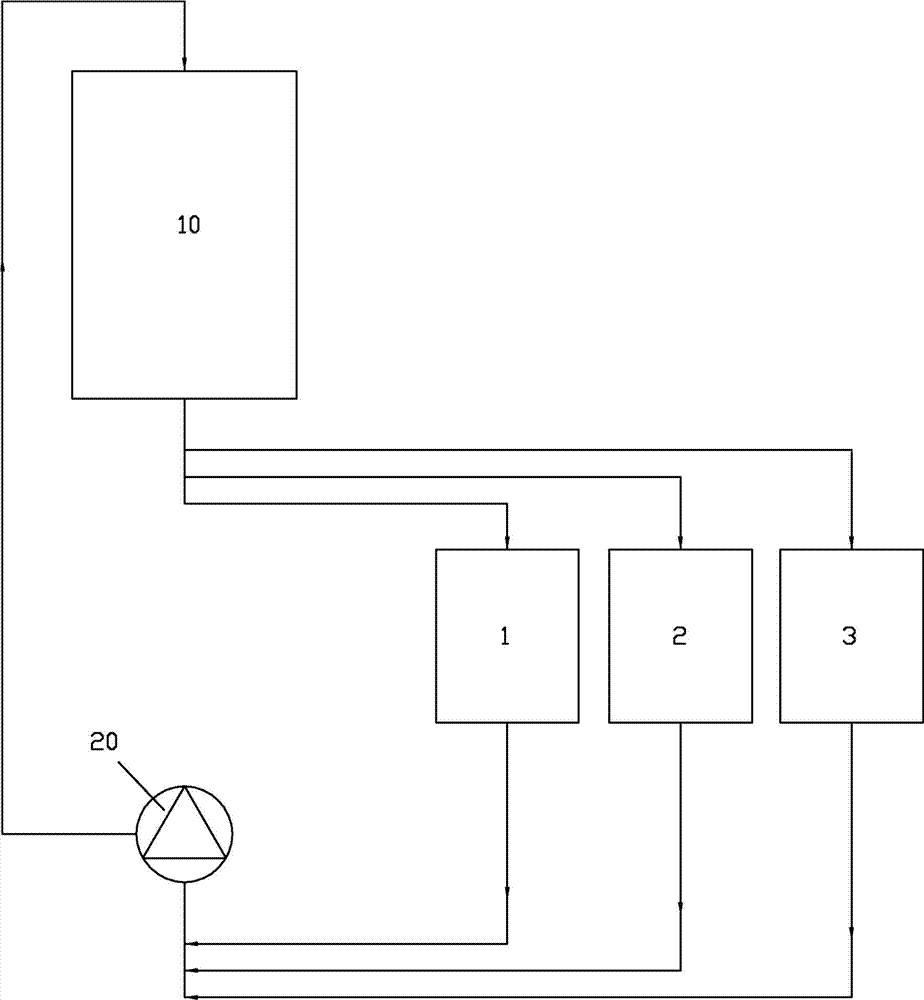
Graphite heat exchanger efficient washing method for silicon steel pickling line
ActiveCN104511455ASolve the blockageSolve pollutionHollow article cleaningCleaning using liquidsMetasilicateSludge
Disclosed is a graphite heat exchanger efficient washing method for a silicon steel pickling line. The graphite heat exchanger efficient washing method for the silicon steel pickling line includes following steps: 1) preparing hydrofluoric acid 0.1-0.4wt% in concentration, and placing the hydrofluoric acid in a 1# cleaning fluid tank; preparing ammonia water 0.8-1.2wt% in concentration, and placing the ammonia water in a 2# cleaning fluid tank; preparing a sodium hydroxide solution 10-15wt% in concentration, heating the sodium hydroxide solution so as to raise temperature of the sodium hydroxide solution to 65-80 degree centigrade, adding an amino carboxylic metal chelating agent, and then placing the sodium hydroxide solution in a 3# cleaning fluid tank; 2) disconnecting a graphite heat exchanger acid inlet and outlet pipeline, and using a pipeline to connect a heat exchanger inlet and outlet pipeline with the 1# cleaning fluid tank; 3) starting a cleaning pump, enabling the hydrofluoric acid to enter a heat exchanger and circulate in the heat exchanger for 30-60s; 4) using another pipeline to connect the heat exchanger with the 2# cleaning fluid tank; 5) starting a cleaning pump, and enabling the ammonia water to enter the heat exchanger and circulate in the heat exchanger for 10-15min; 6) using another pipeline to connect the heat exchanger with the 3# cleaning fluid tank; 7) starting the cleaning pump, and enabling sodium hydroxide to enter the heat exchanger and circulate for 3-5h. The graphite heat exchanger efficient washing method for the silicon steel pickling line not only can thoroughly remove stubborn dirt such as silicon sludge and ferric metasilicate, but also does not need to disassemble the heat exchanger, and thereby prevents integrity of the heat exchanger from being destroyed, and furthermore is short in cleaning time, and causes small influences on environment.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
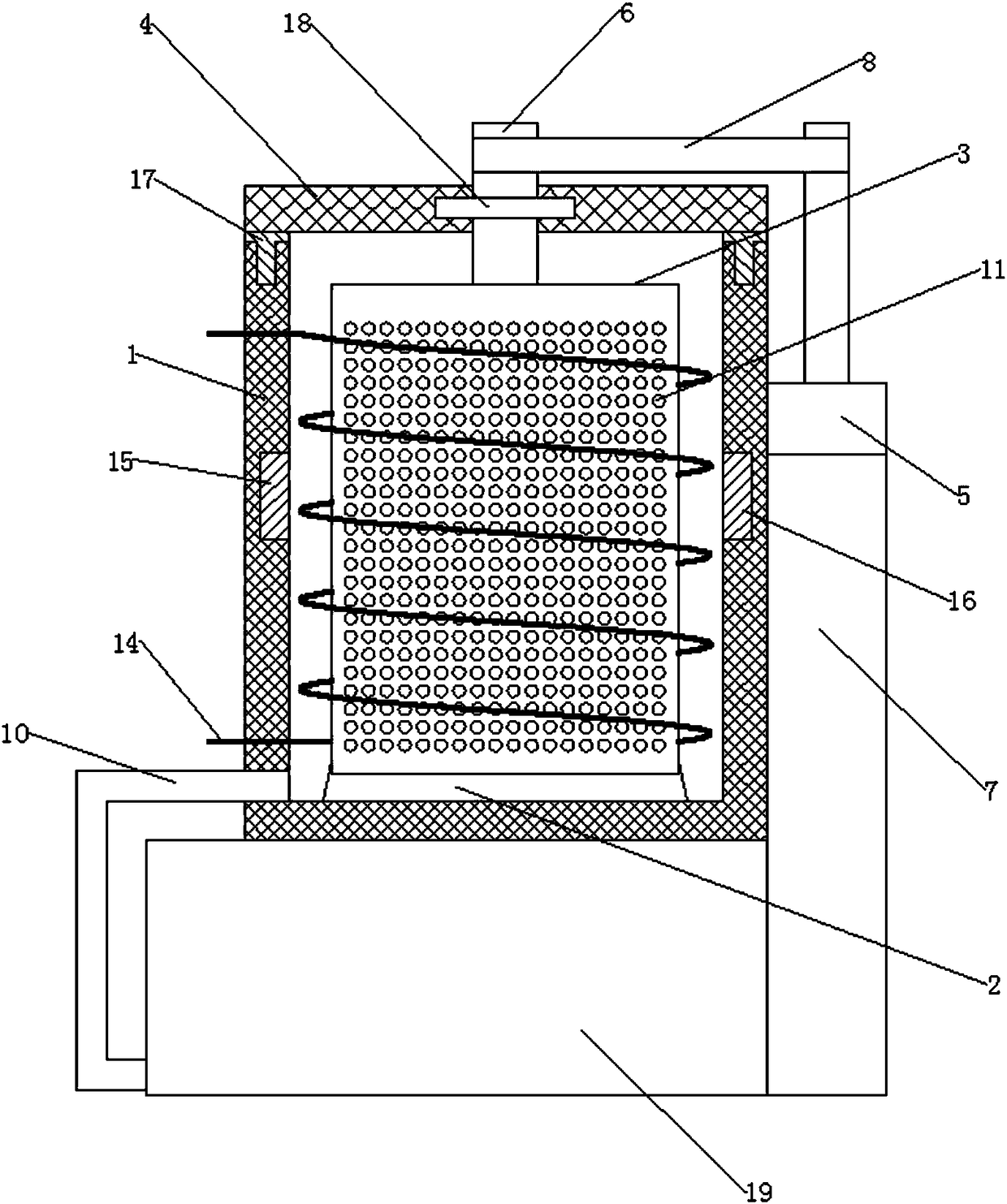
Electric field purification component cleaning device
PendingCN108543761AIncrease the heating areaShorten the timeCleaning using liquidsUltrasonic assistedWastewater
The invention relates to an electric field purification component cleaning device. The electric field purification component cleaning device comprises an outer barrel, a rotating support base, an inner barrel coaxial with the outer barrel and a heater disposed between the inner barrel and the outer barrel, wherein the heater is used for heating cleaning water in the device. A clamp for holding anobject to be cleaned is also fixedly mounted on the rotating support base. By combining the inner barrel and the outer barrel, an electro-discharge component and a dust collecting assembly are cleaned, the probability and intensity of the contact between the cleaning water, a detergent in the water and the object to be cleaned are improved, the cleaning efficiency is improved, and the heating timeis shortened so that the cleaning time is shortened. Ultrasonic assist during heating is beneficial to removing stains from the object to be cleaned. The arrangement of the fixing clamp ensures the static state of the object to be cleaned in the device, and the object to be cleaned is prevented from being damaged by collision with the rotating inner barrel. The design of a top cover facilitates loading and fetching of the object to be cleaned, the adverse effect cause by shaking of the device on operation of a motor is avoided, and cleaning wastewater is filtered to avoid environmental pollution.
Owner:广东拓鑫电器制造有限公司
Bracket cleaning device for production of LED lamps
InactiveCN111375593AImprove impact performanceIncrease impactCleaning using liquidsWater flowStructural engineering
The invention discloses a bracket cleaning device for production of LED lamps. The bracket cleaning device for production of the LED lamps comprises a cleaning box, water-flow rotating drums, a lifting box and a movable coaming; the lower end face of the cleaning box is fixedly connected with a driving box; two water-flow rotating drums are arranged on the inner wall of the driving box; the upperend face of the cleaning box is fixedly connected with four lifting air cylinders; the cleaning box is movably connected to a lifting box through the four lifting air cylinders; and the lower end faceof the lifting box is fixedly connected with a flexible connecting frame. By starting the two water-flow rotating drums, the falling time of dirt on the outer wall of the bracket is shortened, time consumed by cleaning is reduced and the cleaning efficiency is improved. After the bracket is cleaned, a clamping head is disconnected with a fixed block by pressing a control block, so that the movable coaming is unlocked and can rotate along a hinge. The lifting box can incline towards the right side by lifting the two lifting air cylinders on the left side, so that the bracket in the lifting boxfalls into a bracket storage box under the action of gravity and the bracket can be taken out conveniently.
Owner:漳浦县中诺生物科技有限公司
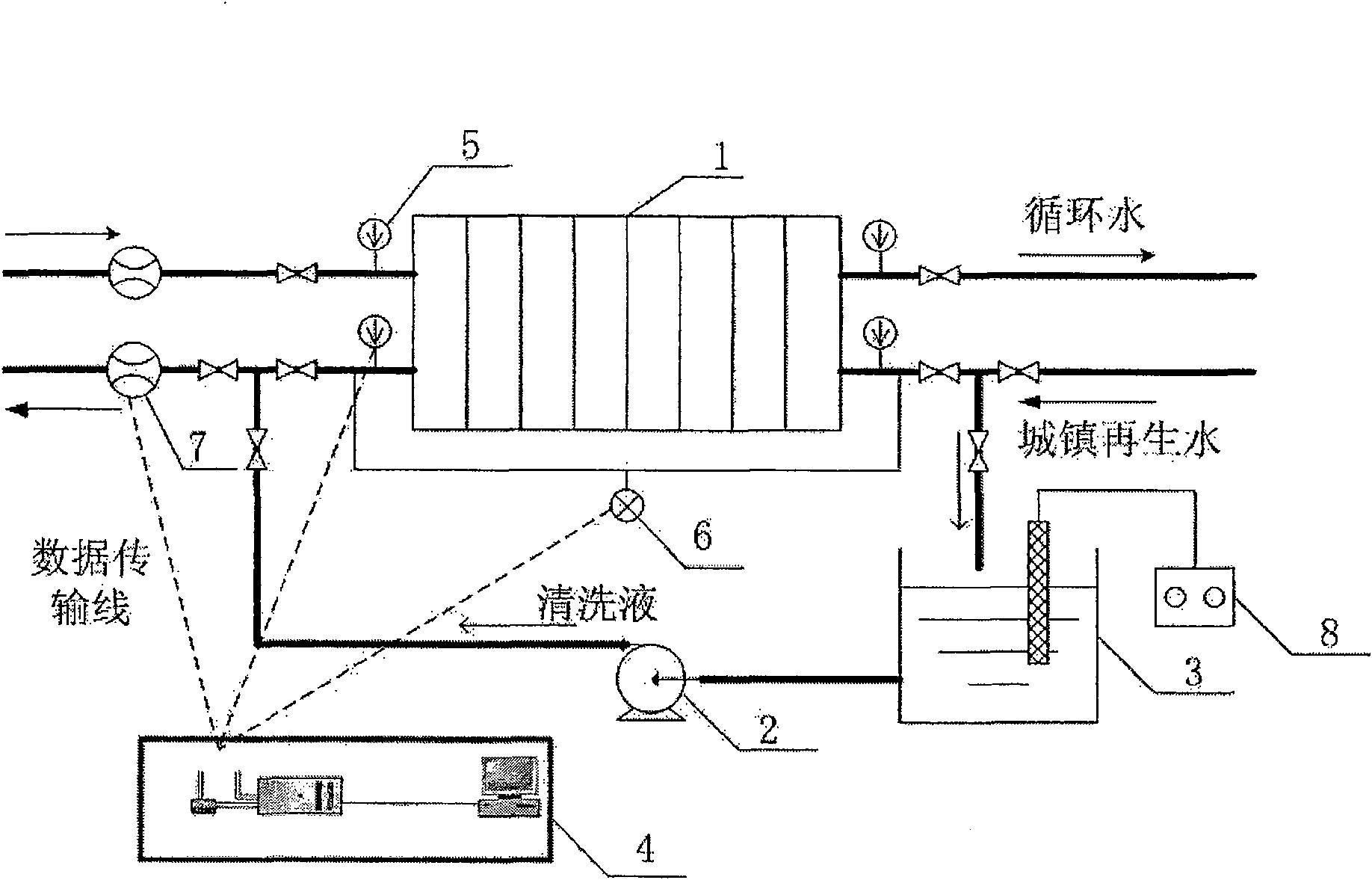
In-position cleaning method for town regenerated water plate type heat exchanger
ActiveCN100582640CRestoring flow heat transfer performanceIncrease peel rateFlush cleaningStationary plate conduit assembliesOrganic acidParticulates
The invention relates to an onsite cleaning method used for a town recycled-water plate heat exchanger. The cleaning method has two steps: the cleaning of a first step adopts an oxidizing bactericide, a carboxyl group chelate agent and a dispersant, aiming at removing surface substances of dirt on the heat exchanging wall face with an effect of killing microorganisms in dirt and removing dirt and also with the effect of leading Ca<2+>, Mg<2+>, Fe<2+> and Fe<3+> in dirt to be converted into dissolving chelate matter and distributing a large quantity of dirt components into particulates to be stably suspended in water; the cleaning of the second step adopts an organic acid dirt-rust removing agent, the oxidizing bactericide and the carboxyl group chelate agent and the dispersant, aiming at removing the bottom substances of the dirt on the heat exchanging wall face with the effect of removing organic dirt and rest microorganism films. The cleaning method proposed by the invention can be applied in the town recycled-water plate heat exchanger made of 304, 316 or further anti-corrosion stainless steel materials, with low corrosion rate, quick dirt removing speed and better effect. The plate heat exchanger can be safely and economically operated for a long period.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
Chopstick washing assembly and dish-washing machine
ActiveCN106388746AImprove cleaning efficiencyCleaning time is shortTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsHome appliance efficiency improvementBarrel ShapedEngineering
The invention relates to a chopstick washing assembly and a dish-washing machine. The chopstick washing assembly comprises a power device, a barrel-shaped chopstick box with a porous net-shaped structure and a chopstick box support. The barrel-shaped chopstick box is mounted between the power device and the chopstick box support; and the barrel-shaped chopstick box rotates under the driving of the power device. The barrel-shaped chopstick box comprises a chopstick box main body and a chopstick box cover body which is mounted on the chopstick box main body in an openable manner. A containing and washing space for containing chopsticks to be washed is commonly formed by the chopstick box main body and the chopstick box cover body. A plurality of first convex strips, which extend along the axial direction of the barrel-shaped chopstick box, are arranged on an inner surface of the chopstick box main body. According to the chopstick washing assembly and the dish-washing machine, provided by the invention, the washing efficiency is high and the time for washing is short, so that water and electric energy are saved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Silicon scale cleaning agent, and preparation method and application thereof
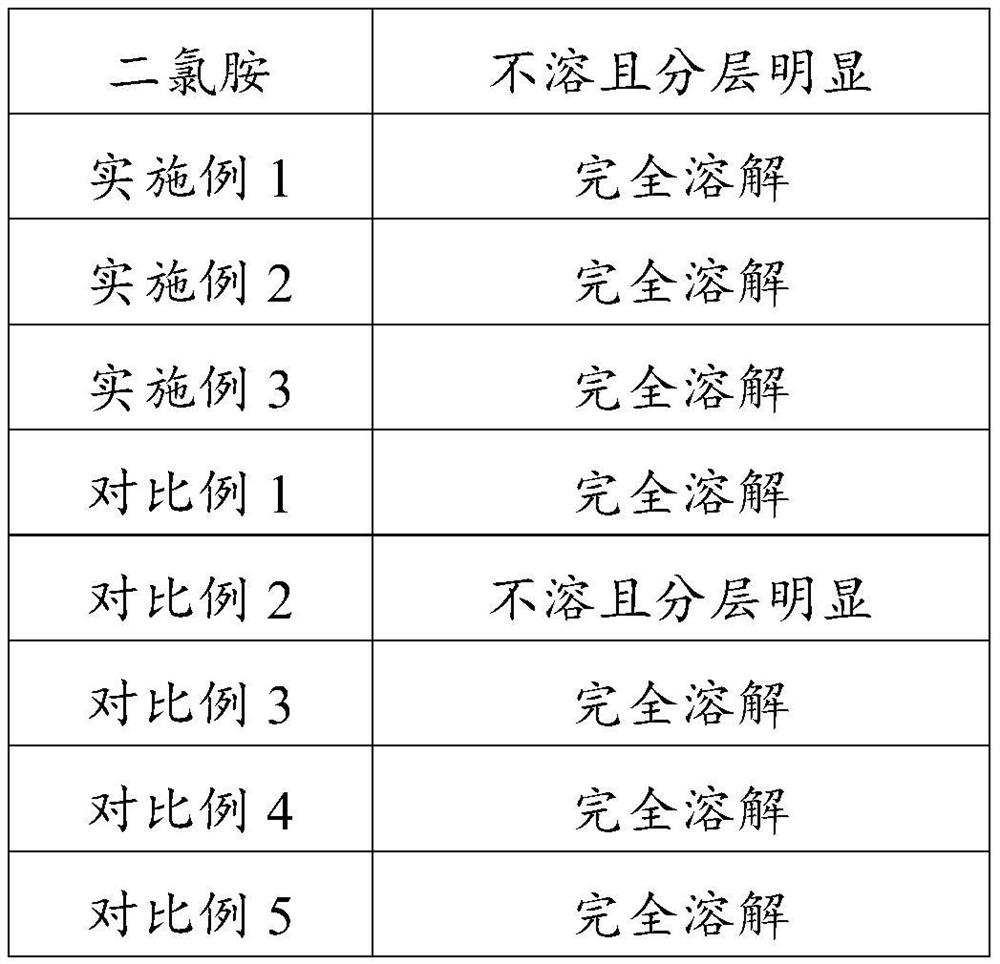
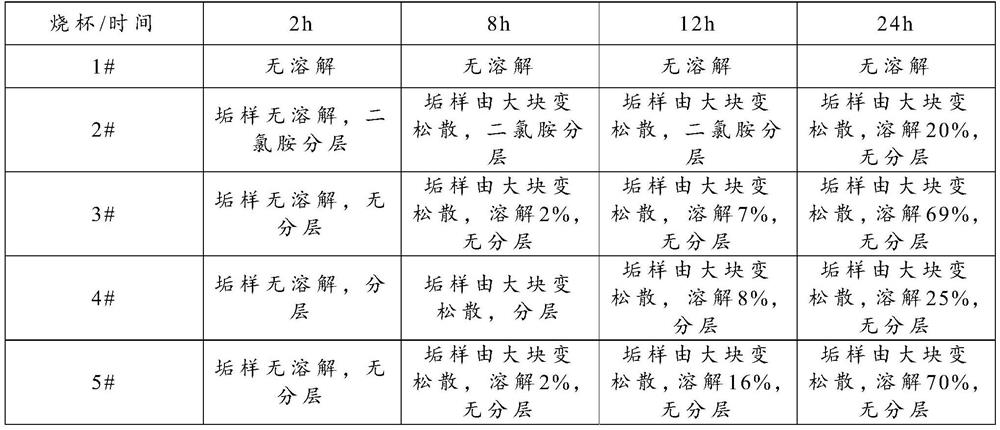
ActiveCN113244776AEasy to cleanCleaning time is shortSemi-permeable membranesEnergy based wastewater treatmentAlcoholActive agent
The invention provides a silicon scale cleaning agent, and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of cleaning agents. According to the technical scheme, the cleaning agent comprises, by weight, 20-30% of dichloramine, 5-10% of an alcohol compound, 2-5% of citric acid, 0.1-1% of a surfactant, and the balance of deionized water. The cleaning agent can be applied to reverse osmosis membrane cleaning.
Owner:威海翔泽新材料科技有限公司
Household dishwasher
InactiveCN106901670AImprove drying efficiencyImprove corrosion resistanceTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsEngineeringWater consumption
The invention discloses a household dishwasher. The dishwasher comprises a case and an air-tight door, the case is movably connected with the air-tight door, a time regulation knob is arranged on the surface of the case, a water tank is arranged at the lower portion of the case, a return pipe and a water pump are arranged on the top of the water tank, the return pipe is connected with the water tank in a detachable mode, an inner cavity is formed in the top of the case, the top of the inner cavity is provided with an air inlet pipe, an exhaust fan is arranged on the top of the air inlet pipe, a heating element is arranged inside the air inlet pipe, the air inlet pipe is fixedly connected with the heating element, a dish rack is arranged in the middle of the inner cavity, and the inner surface of the bottom of the dish rack is provided with a noise shielding part; the domestic dishwasher has the advantages of being small in water consumption for cleaning and high in drying efficiency.
Owner:王玉廷
Flushing-scrubbing type tableware washing machine
PendingCN107865632ACleaning time is shortEnough operating spaceKitchenware cleanersWater useTap water
The invention discloses a flushing-scrubbing type tableware washing machine, and relates to a tableware cleaning tool, associated to the field of energy saving and consumption reducing. The washing machine is composed of a valve body assembly, a soft rubber splash shield, a scrubbing cloth cover and a water supply three-way valve. Under the action force of running water pressure, the organic combination of scrubbing and flushing is achieved, and a conventional flushing mode from outside to inside is changed into a water consuming mode from inside to outside. With the adoption of a design solution that the self-closed micro interacting regulating valve is organically combined with the splash shield and the scrubbing cloth cover, a water consuming quantity can be conveniently regulated and controlled at any time; adhering flushing-scrubbing cleaning is conducted on tableware, so that time and labor are saved; and when a cleaning operation is stopped, a water valve is automatically turnedoff, so that the invalid loss of water resource is prevented. A main body structure of the flushing device (the washing machine) is compression-molded, and a compulsory measure that the aperture of awater outlet is diminished is also adopted by the flushing device, so that water discharge is controlled; and the three-way ball valve is added on the basis of an original faucet of a user, so that awater source is provided; therefore, the washing machine is a novel practical tool for tableware cleaning in home kitchens, small restaurants and small dining halls.
Owner:廖洪模
Method for removing dust thionazin in petroleum smelting chimney
InactiveCN108744834AHas the function of spraying and dust removalImprove cleaning efficiencyCombination devicesWater sourceHigh pressure water
The invention discloses a method for removing dust thionazin in a petroleum smelting chimney. The method is characterized in that high pressure water flow has the effects of spraying, removing dust, improving the dust removal efficiency and relieving environment contamination, and the method is applicable to dust and waste gas environment-friendly processing industries; a speed reduction motor (20) is started, a first chain wheel is driven to rotate clockwise, meanwhile, a chain drives a second chain wheel to rotate synchronously, a connecting plate (23) fixed to a chain (24) drives a high pressure water draining pipe (13) to move backwards, when a limiting block touches a limiting switch B, the speed reduction motor rotates anticlockwise, and the high pressure water draining pipe (13) isdriven to move forwards; when a limiting switch A is touched, the speed reduction motor (20) rotates clockwise, and so on; accordingly, the high pressure water draining pipe (13) is driven to move forwards and backwards, and the whole board of a filter net (4) is flushed; after a power source of the speed reduction motor is turned off and a high pressure water source is closed, the high-pressure flushing function is disabled.
Owner:QINGYANG ENERGY CHEM GRP WODE PETROLEUM TECH
Cleaning sterilization process and cleaning sterilization equipment
PendingCN111715583AExtended service lifeReduce dead angleHollow article cleaningLavatory sanitoryFilter systemProcess engineering
The invention provides a cleaning sterilization process and cleaning sterilization equipment, and relates to the technical field of medical collagen solution production. The cleaning and sterilizationprocess, and the cleaning and sterilization equipment are used in a sterilization filtering system. The cleaning sterilization process includes the steps that a sterilization step is carried out, specifically, before a filtering operation is performed, close a communicating position of a communication path and a preparation device is closed, and steam sterilization is carried out on the communication path and a filter system; a cleaning step includes a second acid cleaning step or a lye cleaning step and a second water cleaning step which are sequentially executed after the filtering operation, wherein the second acid cleaning step or the lye cleaning step includes using acid or lye to clean a containing device, the communication path and the filtering system; and the second water cleaning step includes using water for injection to clean the containing device, the communicating path and the filtering system. The cleaning sterilization process ensures the cleanliness of the equipment and the sterility of a filtrate obtained during the continuous filtering operation through steam sterilization, acid washing or alkali washing and water washing.
Owner:康膝生物医疗(深圳)有限公司
A kind of graphite heat exchanger cleaning method for silicon steel pickling line
ActiveCN104511455BPlay a cleaning effectHandle less stressHollow article cleaningCleaning using liquidsSludgeMetasilicate
Disclosed is a graphite heat exchanger efficient washing method for a silicon steel pickling line. The graphite heat exchanger efficient washing method for the silicon steel pickling line includes following steps: 1) preparing hydrofluoric acid 0.1-0.4wt% in concentration, and placing the hydrofluoric acid in a 1# cleaning fluid tank; preparing ammonia water 0.8-1.2wt% in concentration, and placing the ammonia water in a 2# cleaning fluid tank; preparing a sodium hydroxide solution 10-15wt% in concentration, heating the sodium hydroxide solution so as to raise temperature of the sodium hydroxide solution to 65-80 degree centigrade, adding an amino carboxylic metal chelating agent, and then placing the sodium hydroxide solution in a 3# cleaning fluid tank; 2) disconnecting a graphite heat exchanger acid inlet and outlet pipeline, and using a pipeline to connect a heat exchanger inlet and outlet pipeline with the 1# cleaning fluid tank; 3) starting a cleaning pump, enabling the hydrofluoric acid to enter a heat exchanger and circulate in the heat exchanger for 30-60s; 4) using another pipeline to connect the heat exchanger with the 2# cleaning fluid tank; 5) starting a cleaning pump, and enabling the ammonia water to enter the heat exchanger and circulate in the heat exchanger for 10-15min; 6) using another pipeline to connect the heat exchanger with the 3# cleaning fluid tank; 7) starting the cleaning pump, and enabling sodium hydroxide to enter the heat exchanger and circulate for 3-5h. The graphite heat exchanger efficient washing method for the silicon steel pickling line not only can thoroughly remove stubborn dirt such as silicon sludge and ferric metasilicate, but also does not need to disassemble the heat exchanger, and thereby prevents integrity of the heat exchanger from being destroyed, and furthermore is short in cleaning time, and causes small influences on environment.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A megasonic cleaning machine for wafer processing
ActiveCN114392978BEasy to cleanAvoids the problem of re-sinking to the top surface of the waferCleaning using liquidsMegasonic cleaningLiquid storage tank
The invention discloses a megasonic cleaning machine for wafer processing, comprising a base and a cleaning bin, the top outer side of the base is fixedly installed with the bottom outer side of the cleaning bin, and a cleaning liquid storage tank is fixedly installed inside the base. The invention utilizes fluid mechanics to make the cleaning liquid form two liquid eddy currents on the upper and lower surfaces of the wafer, so that the impurity particles on the wafer surface will be pushed away from the wafer surface by the eddy current of the cleaning liquid, and then move away from the wafer due to the action of inertia and eddy current thrust. The round surface avoids the problem that the impurity particles floating in the cleaning solution will sink to the upper surface of the wafer again due to the oscillation of the super / megasonic wave, which greatly improves the cleaning effect of the wafer, and does not need to flip the wafer again. By performing secondary cleaning, the cleaning time of a single wafer is doubled, which improves the wafer cleaning efficiency. At the same time, it constitutes a cleaning solution recycling system, which reduces the cleaning solution consumption and wafer cleaning costs.
Owner:ZHICHENG SEMICON EQUIP TECH (KUNSHAN) CO LTD
Equipment for performing surface treatment on graphene workpieces as well as treatment method of equipment
InactiveCN104576457AThe equipment is easy to operateCleaning time is shortSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical controlMetal substrate
The invention discloses equipment for performing surface treatment on graphene workpieces as well as a treatment method of the equipment. The equipment comprises a vacuum chamber, a vacuum pump, a pumping pipeline, an air charging device, an air charging pipeline, an electrical control device and at least one pair of electrodes, wherein a balance valve is arranged on the vacuum chamber; the vacuum pump is communicated with the vacuum chamber through the pumping pipeline; the air charging device is communicated with the vacuum chamber through the air charging pipeline; the electrodes are arranged in the vacuum chamber and connected with the electrical control device. The equipment is simple to operate, short time is consumed for cleaning, the production efficiency is high, the graphene workpieces can be cleaned in a large-scale manner, foreign matters are not left on the outer surfaces of the cleaned graphene workpieces, and previous preparation is provided for follow-up oxidation corrosion or electrochemical stripping of a metal substrate.
Owner:2D CARBON CHANGZHOU TECH INC
Cleaning device and cleaning method
PendingCN111250480AEasy to cleanImprove operational convenienceElectrostatic cleaningMechanical engineeringSemiconductor
The invention provides a cleaning device and a cleaning method. The cleaning device comprises an electrostatic precipitator and a driving component, wherein the electrostatic precipitator comprises adust collection electrode and a corona electrode; the driving component at least comprises two telescopic units and a rotating unit; the telescopic units are connected with the electrostatic precipitator, and displacement of the electrostatic precipitator is controlled through the telescopic units; the rotating unit is connected with the telescopic units and located between the telescopic units; and the direction of the telescopic units is controlled through the rotating unit. According to the cleaning device and the cleaning method provided by the invention, the position of the electrostaticprecipitator is regulated through the driving component in the cleaning device, and operation convenience is improved; the electrostatic precipitator is used for electrostatic precipitation; accordingly, the cleaning device in semiconductor equipment can effectively clean particles suspended in the air and is short in cleaning time, high in cleaning efficiency and good in cleaning effect; and external particles cannot be introduced into the semiconductor equipment in the cleaning process, resources can be saved, and the yield of products can be increased.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
A zero-discharge system and method for desulfurization wastewater that is easy to clean
ActiveCN113443671BGuaranteed cleaning effectSave waterSpecific water treatment objectivesWaste water treatment from gaseous effluentsFlue gasWastewater
Owner:DATANG ENVIRONMENT IND GRP
A cosmetic brush cleaning device
The invention relates to cleaning equipment, and particularly relates to cleaning equipment of a cosmetic brush. The invention aims to solve the technical problem and provide the cleaning equipment ofthe cosmetic brush. The cleaning equipment has the advantages of high cleaning neatness, simpleness and easiness in operation and short cleaning time. In order to solve the above-mentioned technicalproblem, the cleaning equipment of the cosmetic brush, provided by the invention, comprises a cleaning box and the like, wherein a moving mechanism is mounted at the top of the cleaning box, a rotarycleaning mechanism is mounted on the moving mechanism, and a through hole is formed in the middle part of the right side of the cleaning box. According to the cleaning equipment of the cosmetic brush,the cosmetic brush is fully washed through the matching of the moving mechanism and the rotary cleaning mechanism; meanwhile, through optimization by using a deep cleaning mechanism and a fixing mechanism, the effects of high cleaning neatness, simpleness and easiness in operation and short cleaning time are achieved.
Owner:江西昂奈雅实业有限公司
Cleaning agent for metal slurry cylinder of 3D printer and preparation method of cleaning agent
InactiveCN112961737AHigh activityModerate viscosityInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsComputer printingActive agent
The invention particularly relates to a cleaning agent for a metal slurry cylinder of a 3D printer and a preparation method of the cleaning agent, and belongs to the technical field of special cleaning agents. The cleaning agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 50-75 parts of a sodium lignin sulfonate solution, 5-15 parts of a surfactant, 10-30 parts of a thickening agent and 5-15 parts of a builder. Through the synergistic effect of the components, the prepared cleaning agent has the technical effects of high activity, moderate viscosity, high cleaning speed, high efficiency and no corrosion to equipment, and specifically, the cleaning agent is more stable in flowing, higher in cleaning efficiency and shorter in cleaning time in the using process; and the cleaning agent is basically free of residues, has no corrosion effect on equipment, does not need to be heated in the cleaning process, and meanwhile, the raw materials of the cleaning agent are cheap and easy-to-obtain articles in the market, so that the cost of the cleaning agent is relatively low.
Owner:EZHOU INST OF IND TECH HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Engine cleaning method and cleaning device
ActiveCN108856136BSmoothly intoEasy to focus on cleaningDrying gas arrangementsMachines/enginesCombustion chamberProcess engineering
Owner:艾斯格林科技深圳有限公司
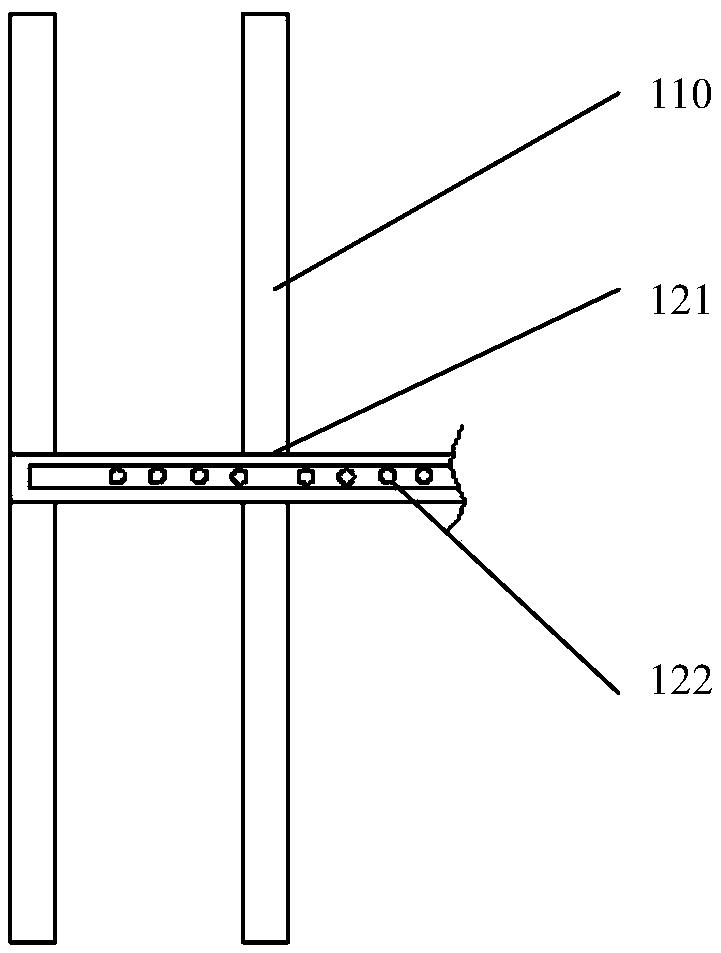
Illuminatable hand-held steel anchor pipe inner wall cleaning device
The invention provides an illuminable hand-held steel anchor pipe inner wall cleaning device and relates to the field of auxiliary tools of power transmission line hardware. The illuminable hand-heldsteel anchor pipe inner wall cleaning device comprises a brush body, a hand-held pneumatic oil gun and a lighting assembly. The brush body comprises bristles and a bristle fixing steel tube. The hand-held pneumatic oil gun comprises an oil outlet hard pipe. The oil outlet hard pipe is sleeved with the bristle fixing steel tube. The lighting assembly comprises a light emitting piece, an extension piece and a power supply piece. The power supply piece is fixed on the bristle fixing steel tube and is arranged close to an outlet of the hand-held pneumatic oil gun. According to the illuminable hand-held steel anchor pipe inner wall cleaning device, the technical problems that the inner wall of a steel anchor pipe is difficult to clean on a construction site, the cleaning time is long, the speedis low, the cleaning effect is not good, and the inner wall of the steel anchor pipe is difficult to clean when the light is not good in the prior art are relieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
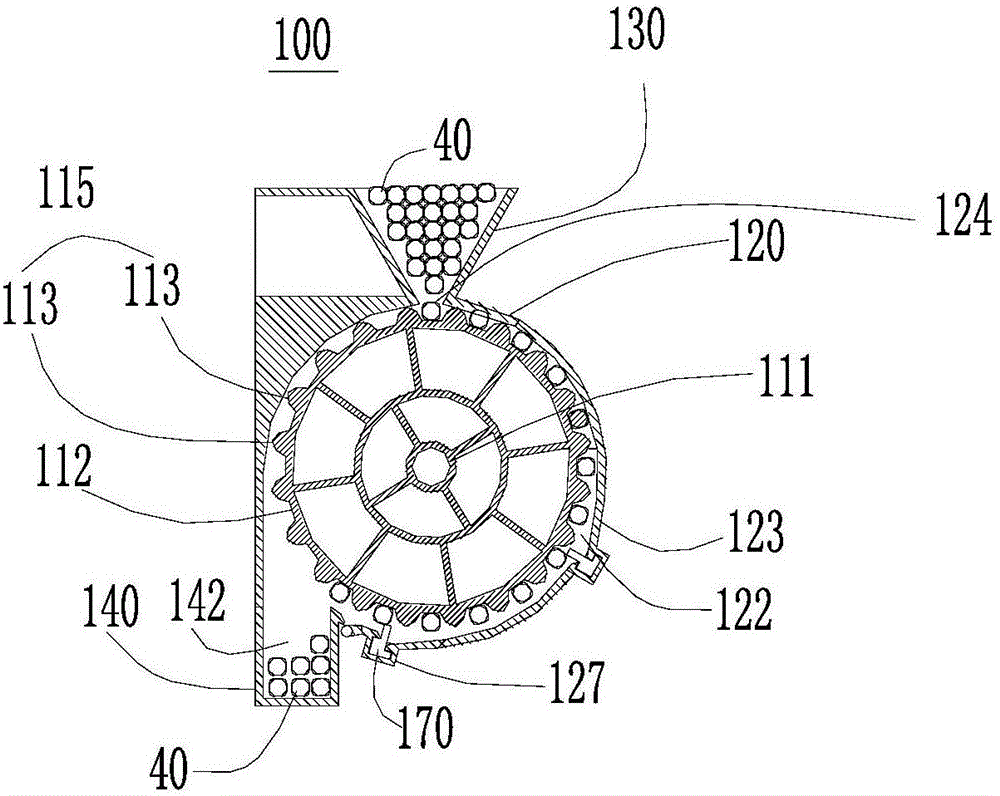
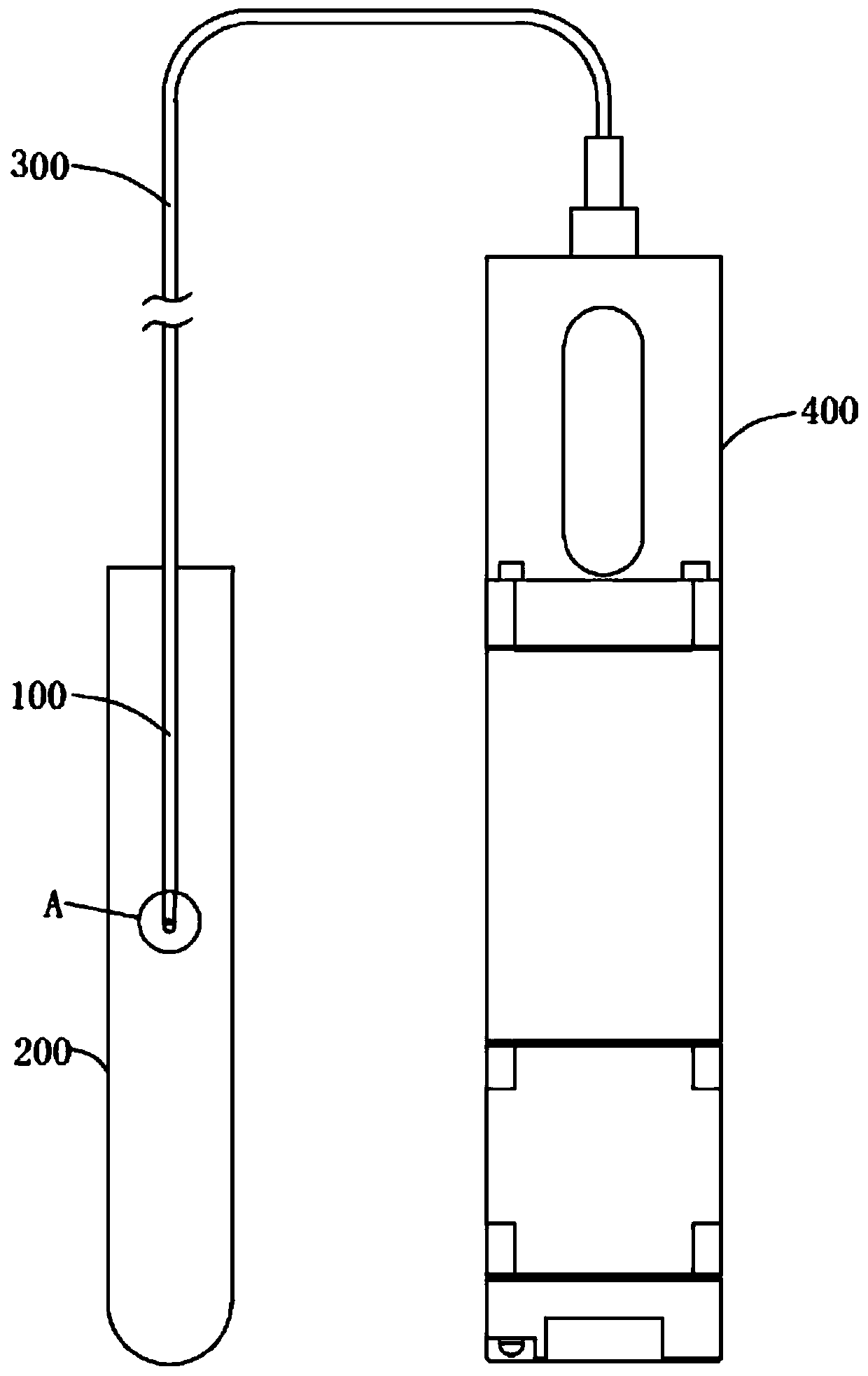
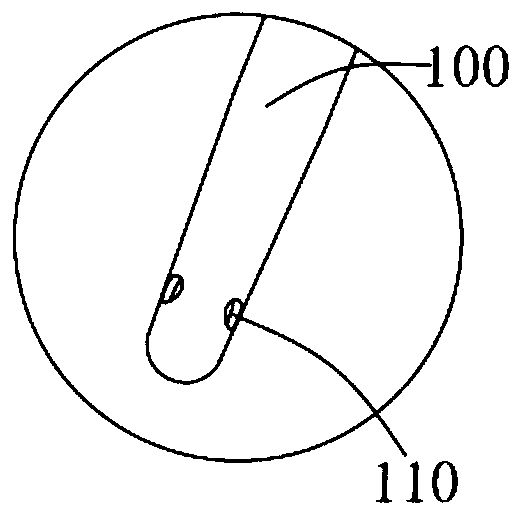
Sample tube cleaning device and solid-phase extraction equipment
PendingCN110918574AQuick washCleaning time is shortHollow article cleaningSolid sorbent liquid separationPhysical chemistryEngineering
The invention provides a sample tube cleaning device and solid-phase extraction equipment, and relates to the technical field of solid-phase extraction devices. The sample tube cleaning device comprises a sampling probe and a liquid pump, wherein one end of the sampling probe communicates with a liquid outlet of the liquid pump; and a cleaning hole is formed in the other end of the sampling probe.When the sample tube cleaning device is in use, one end, provided with the cleaning hole, of the sampling probe stretches into a sample tube, and the cleaning hole is opposite to the side wall or thebottom wall of the sample tube; and when the liquid pump works, a reagent for cleaning is pumped into the sampling probe and is ejected from the inside of the cleaning hole so as to wash the inner wall of the sample tube. The pressure of the reagent ejected from the inside of the cleaning hole is high, so that a sample on the inner wall of the sample tube is helped to be quickly cleaned thoroughly, the cleaning time is effectively reduced, and the cleaning efficiency is improved.
Owner:苏州新仪科学仪器有限公司
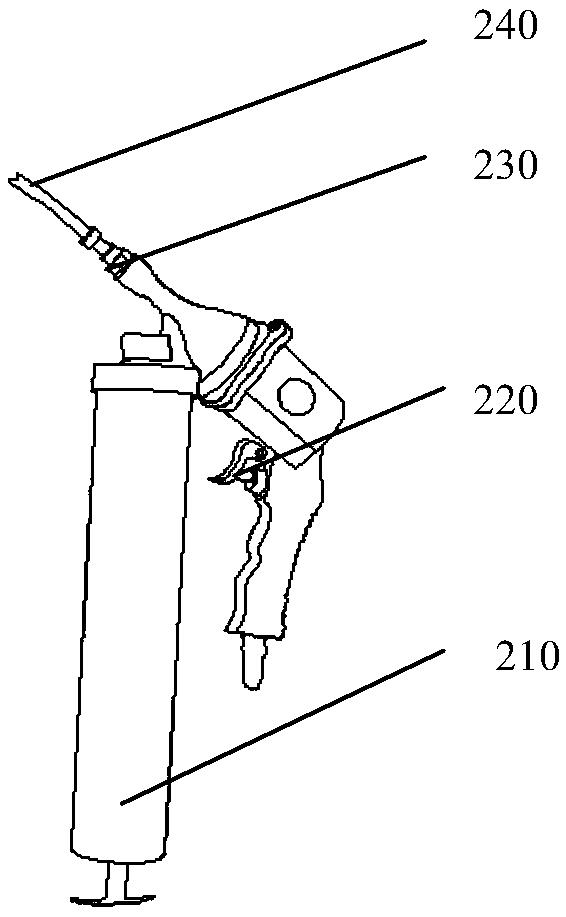
Portable hand-held steel anchor pipe inner wall cleaning device
PendingCN109013581AReduce usageEasy to useHollow article cleaningLiquid spraying apparatusBristleHand held
The invention provides a portable hand-held steel anchor pipe inner wall cleaning device, which relates to the auxiliary tooling field of transmission line fittings. The portable hand-held steel anchor pipe inner wall cleaning device comprises a brush body, a hand-held pneumatic oil gun and a sheath. The brush body comprises brush bristles and a brush bristle fixing steel pipe; one end of the bristle fixing steel pipe is a closed end, and one side close to the closed end is provided with a plurality of bristle fixing holes and a plurality of oil outlet holes; the hand-held pneumatic oil gun comprises an oil outlet hard pipe which is sleeved inside the bristle fixing steel pipe; the sheath detachably sleeves the outside of the brush body; the side wall of the sheath is provided with a graduation part. The portable hand-held steel anchor pipe inner wall cleaning device of the present invention alleviates the technical problems in the prior art that the inner wall of the steel anchor pipeis difficult to clean at the construction site, the cleaning time is long, the cleaning speed is slow, a large barrel of gasoline is required to be carried, and the whole cleaning device is inconvenient to carry.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Desulfurization wastewater zero discharge system and method convenient for cleaning
ActiveCN113443671AGuaranteed cleaning effectSave waterSpecific water treatment objectivesWaste water treatment from gaseous effluentsFlue gasControl system
The invention provides a desulfurization wastewater zero discharge system and method convenient for cleaning. The system comprises an evaporation tower, a flue gas conveying system, a waste water feeding system, a cleaning system and a control system, the flue gas conveying system provides high-temperature flue gas for the evaporation tower, the waste water feeding system provides desulfurization waste water for the evaporation tower, and a waste water flow meter, a waste water adjusting valve and a waste water switching valve are arranged on a waste water feeding pipeline. The cleaning system is communicated with the waste water feeding pipeline between a waste water adjusting valve and a waste water switch valve through a cleaning water pipeline, and the cleaning water pipeline is provided with a cleaning water adjusting valve and a cleaning water booster pump. The control system starts the cleaning system according to a waste water flow signal monitored by a waste water flowmeter and controls the cleaning water adjusting valve and the cleaning water booster pump so as to adjust the flow and pressure of the cleaning water. According to the system, zero emission of desulfurization wastewater can be realized, parts and equipment such as valves and pipelines in the system are prevented from being blocked, and guarantee is provided for long-term stable operation of the system.
Owner:DATANG ENVIRONMENT IND GRP
Pipeline cleaning method
ActiveCN101637768BWashed away wellCleaning time is shortHollow article cleaningIsolation valveEngineering
The invention relates to a pipeline cleaning method, which uses cleaning oil as medium and uses a pump to clean forcibly and circularly. The pipeline cleaning method comprises the following steps: 1) steps of processing and installing the pipeline: respectively installing a separating valve at a main pipeline, a branch pipeline and connecting part of bypass pipelines; 2) steps of installing a temporary cleaning device and disassembling the branch pipeline; 3) step of primary cleaning; 4) step of restoring the normal pipelines; and 5) step of secondary cleaning. Compared with the traditional construction process, the construction technique increases a control valve on the original basis, increases the step of reverse cleaning, uses the control of the bypass valve, has circular and thoroughcleaning, high cleanness, short time and low cost, avoids the defects that the dead angles are formed in cleaning and the like and has better technical effect and promotion value.
Owner:CHINA HUAYE GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com