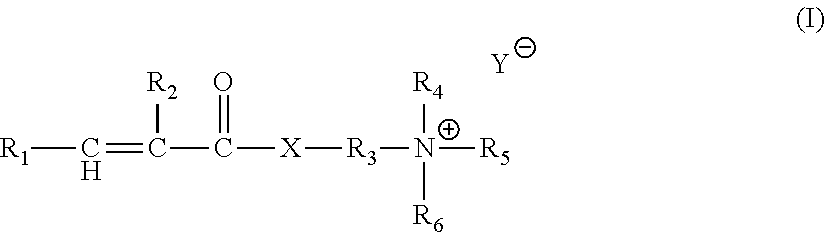Patents
Literature
99results about How to "No additional benefit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
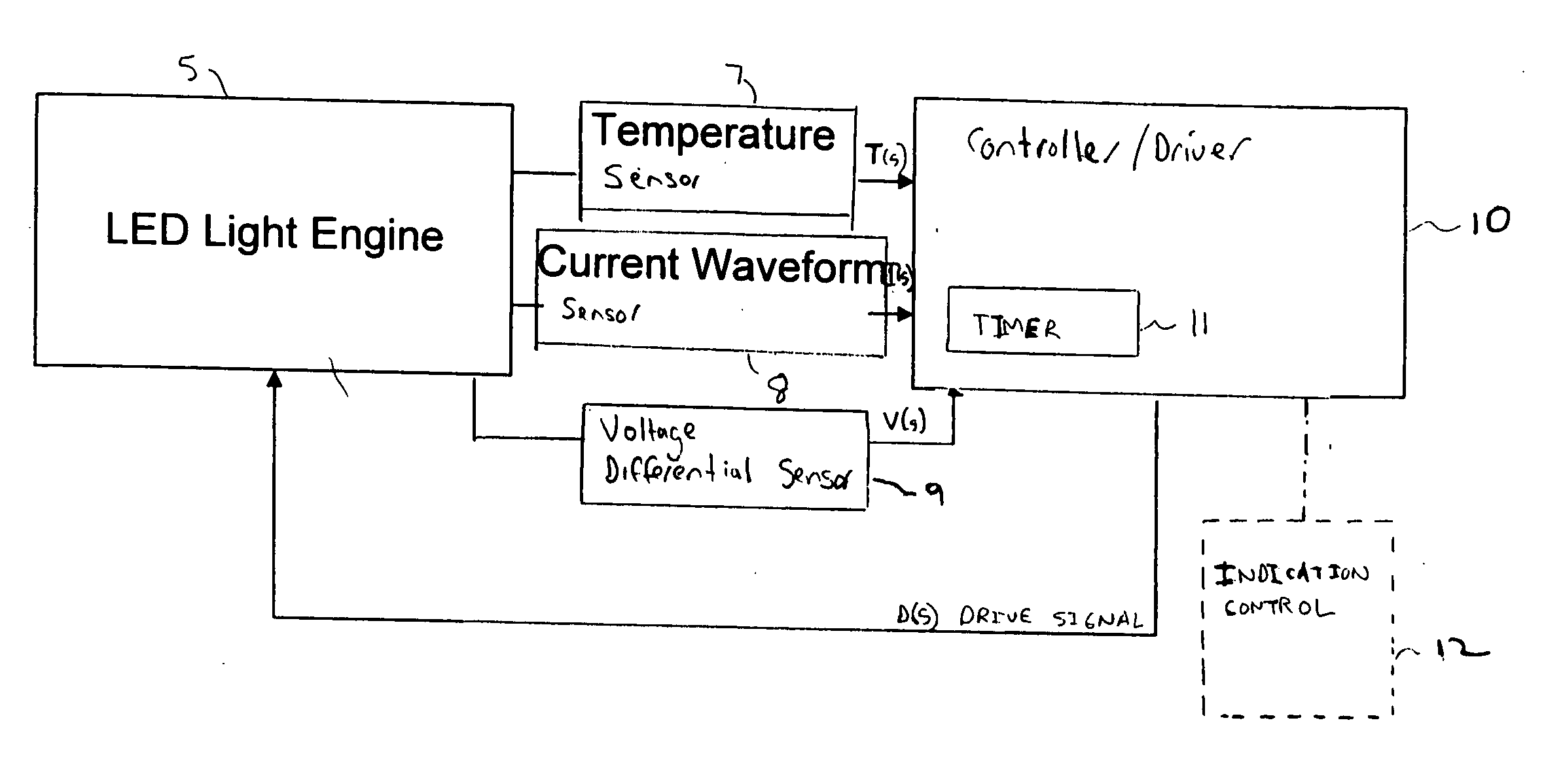
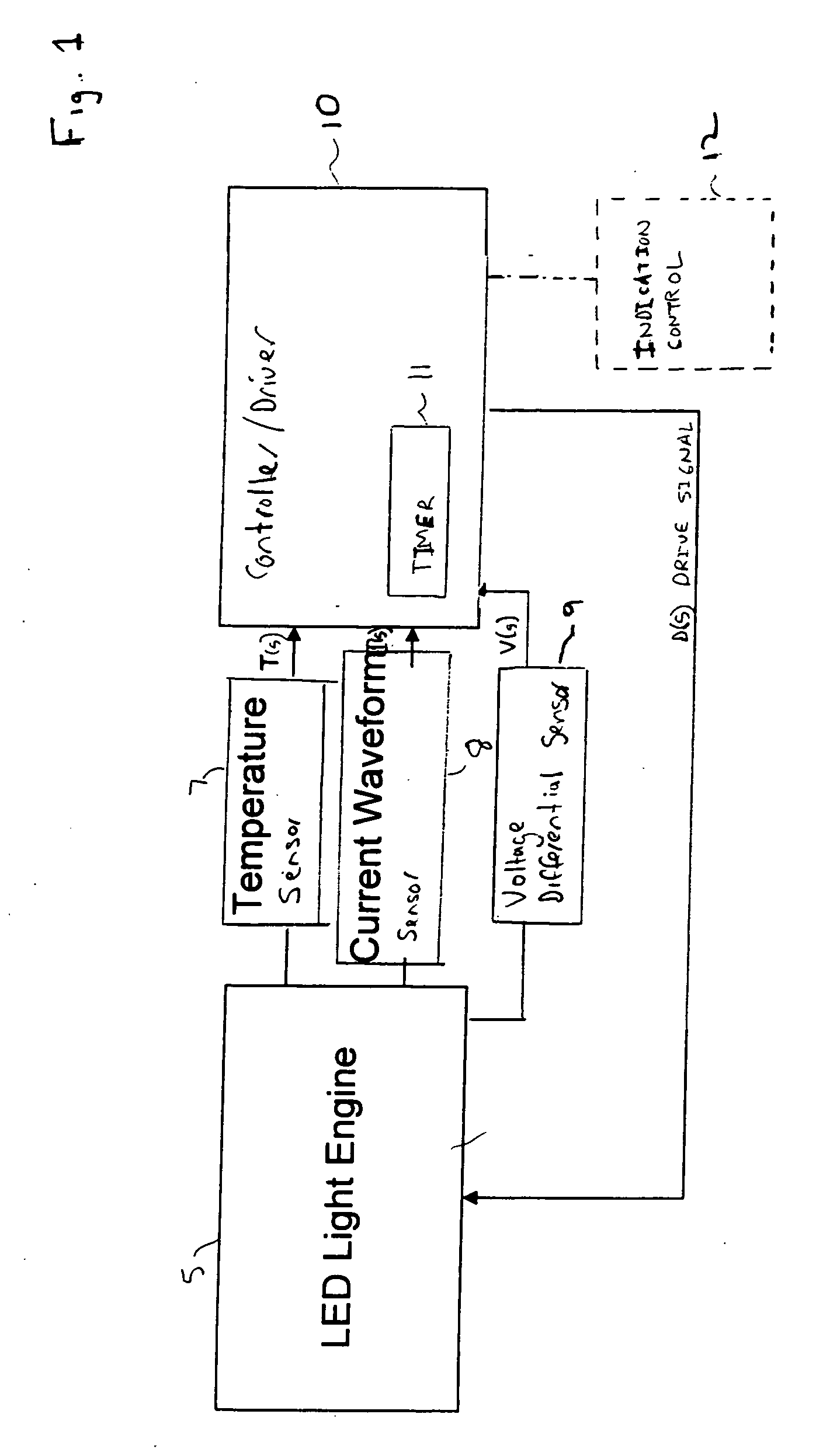
Intelligent drive circuit for a light emitting diode (LED) light engine
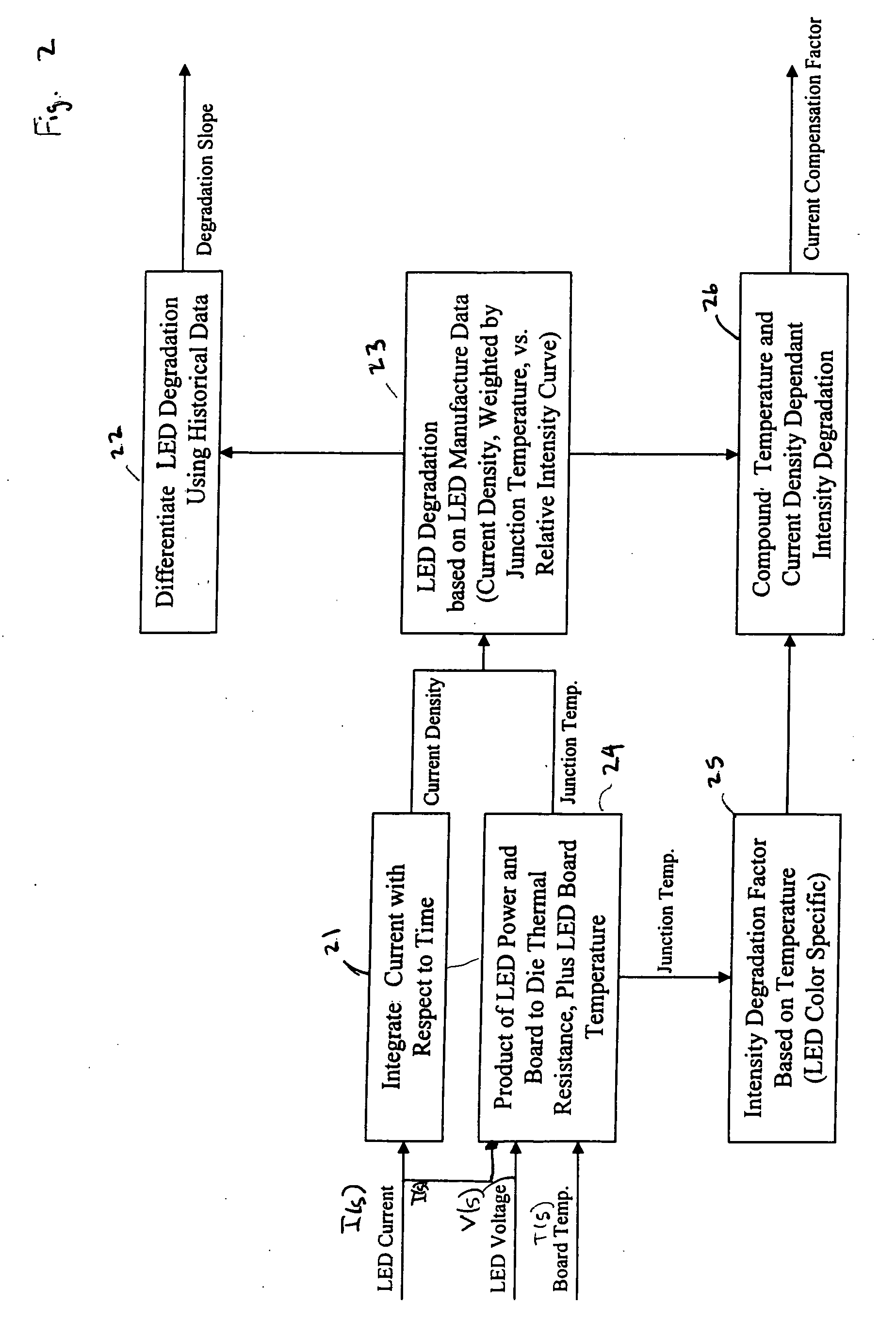
ActiveUS20060028155A1Increased operating lifeMore energy efficientElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementDriving currentDriver circuit
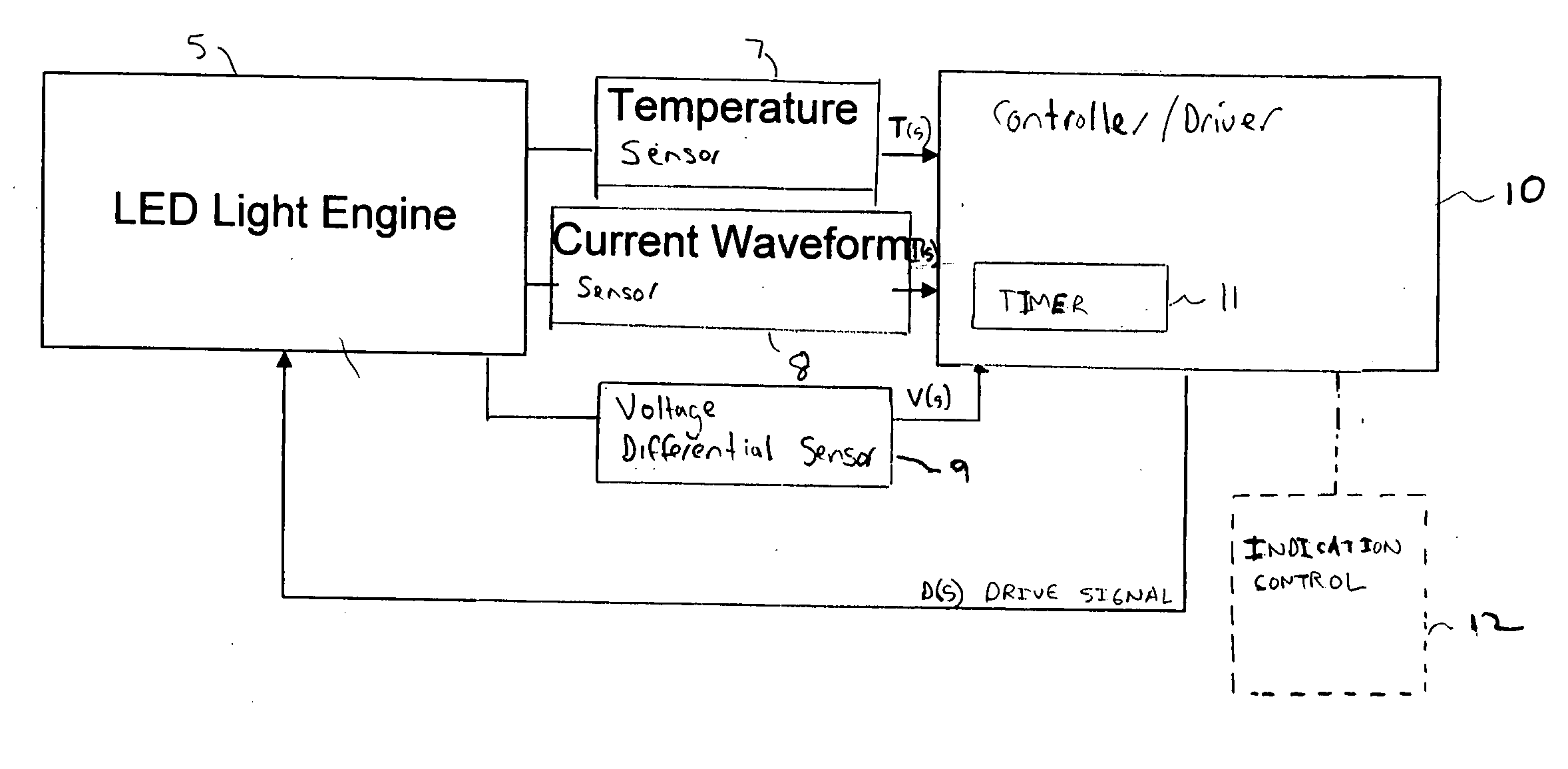
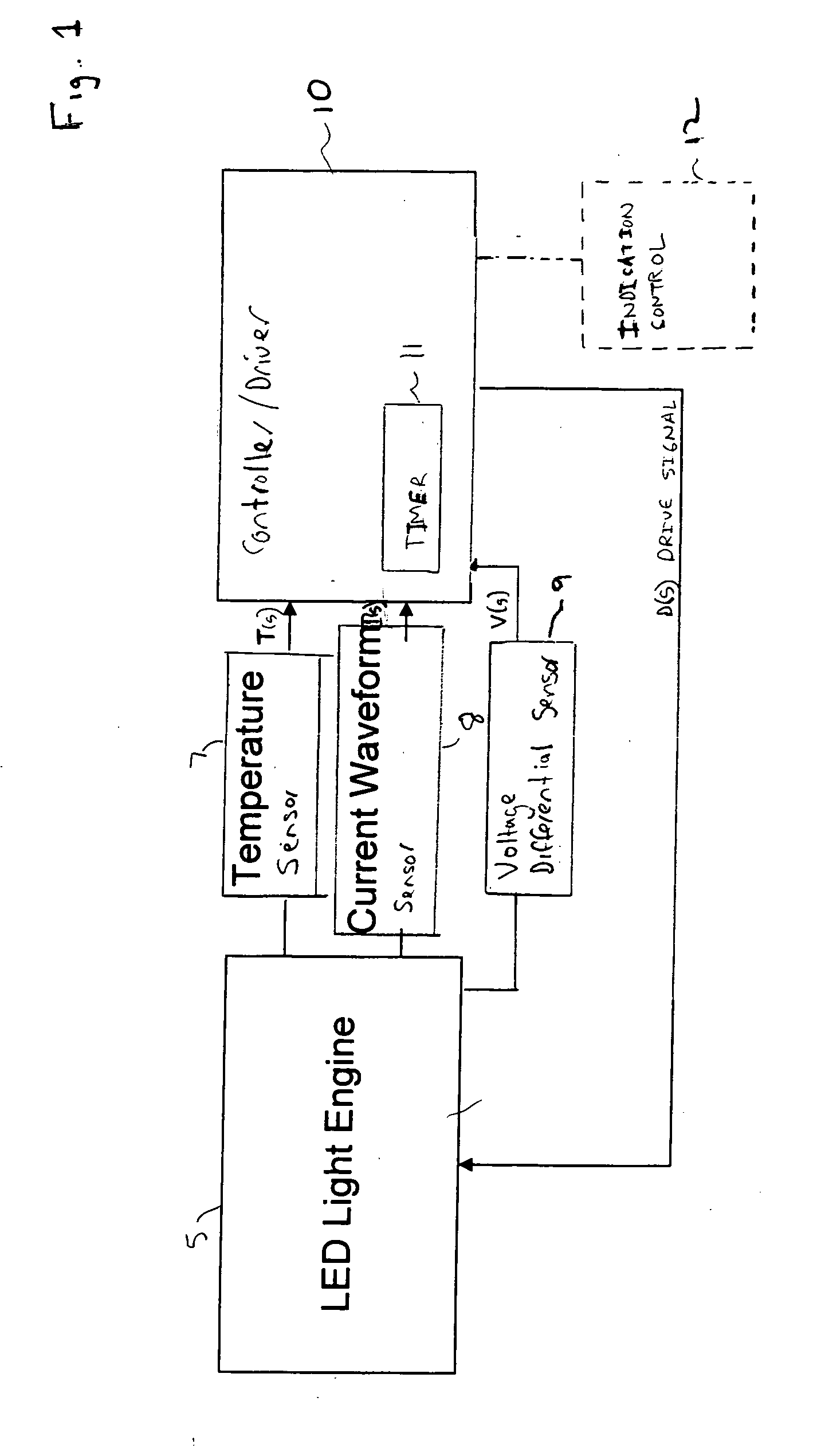
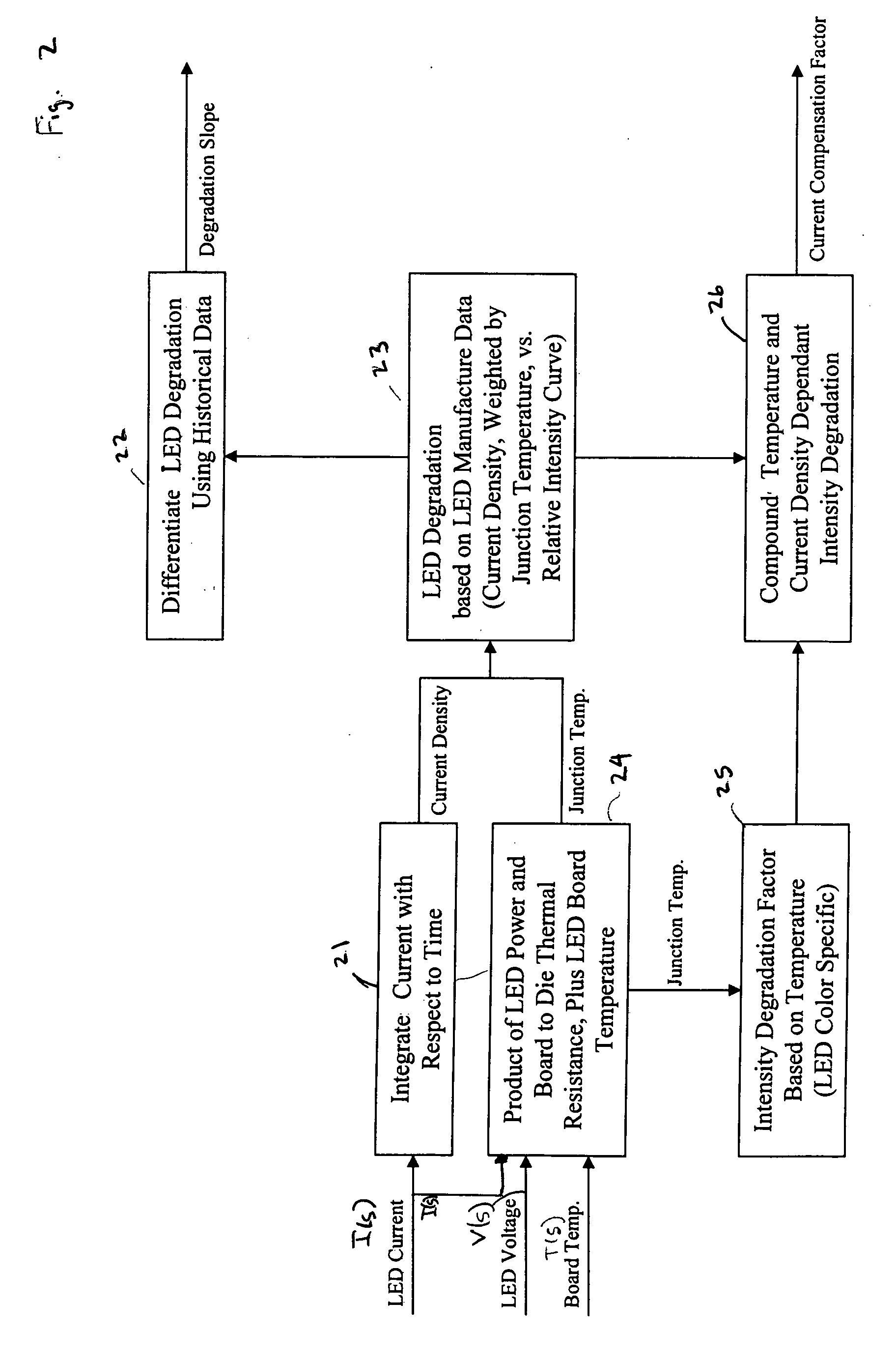
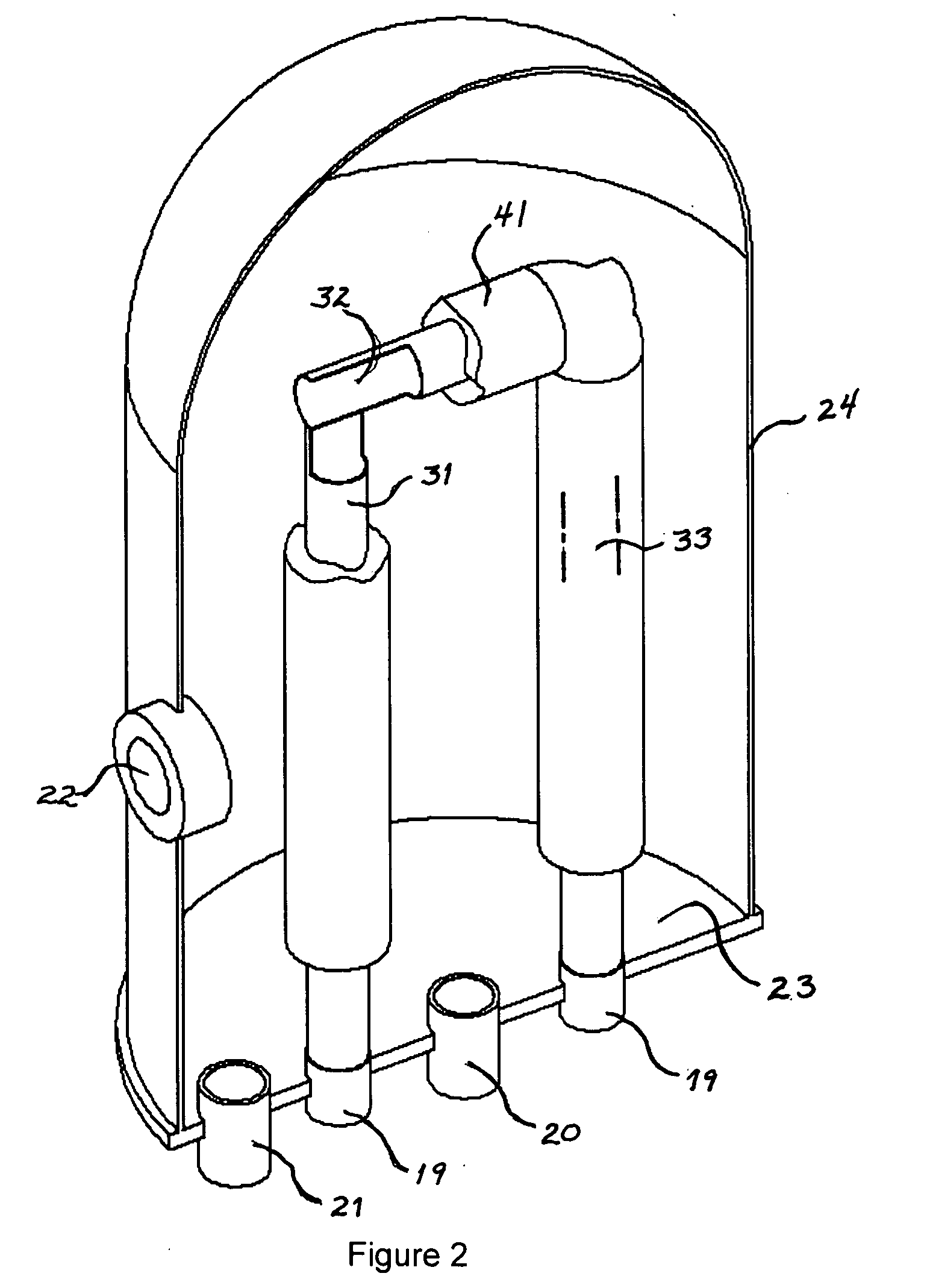
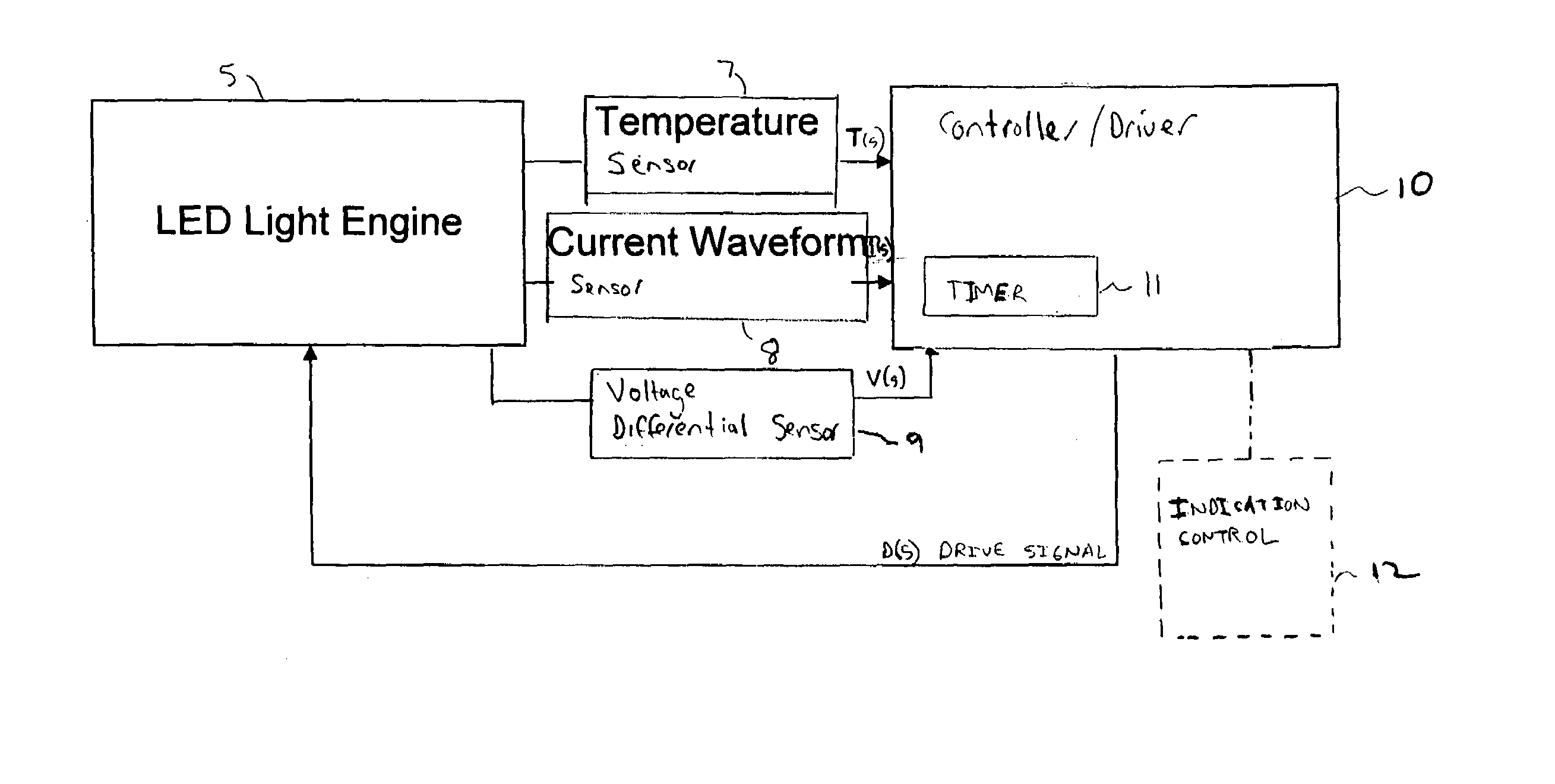
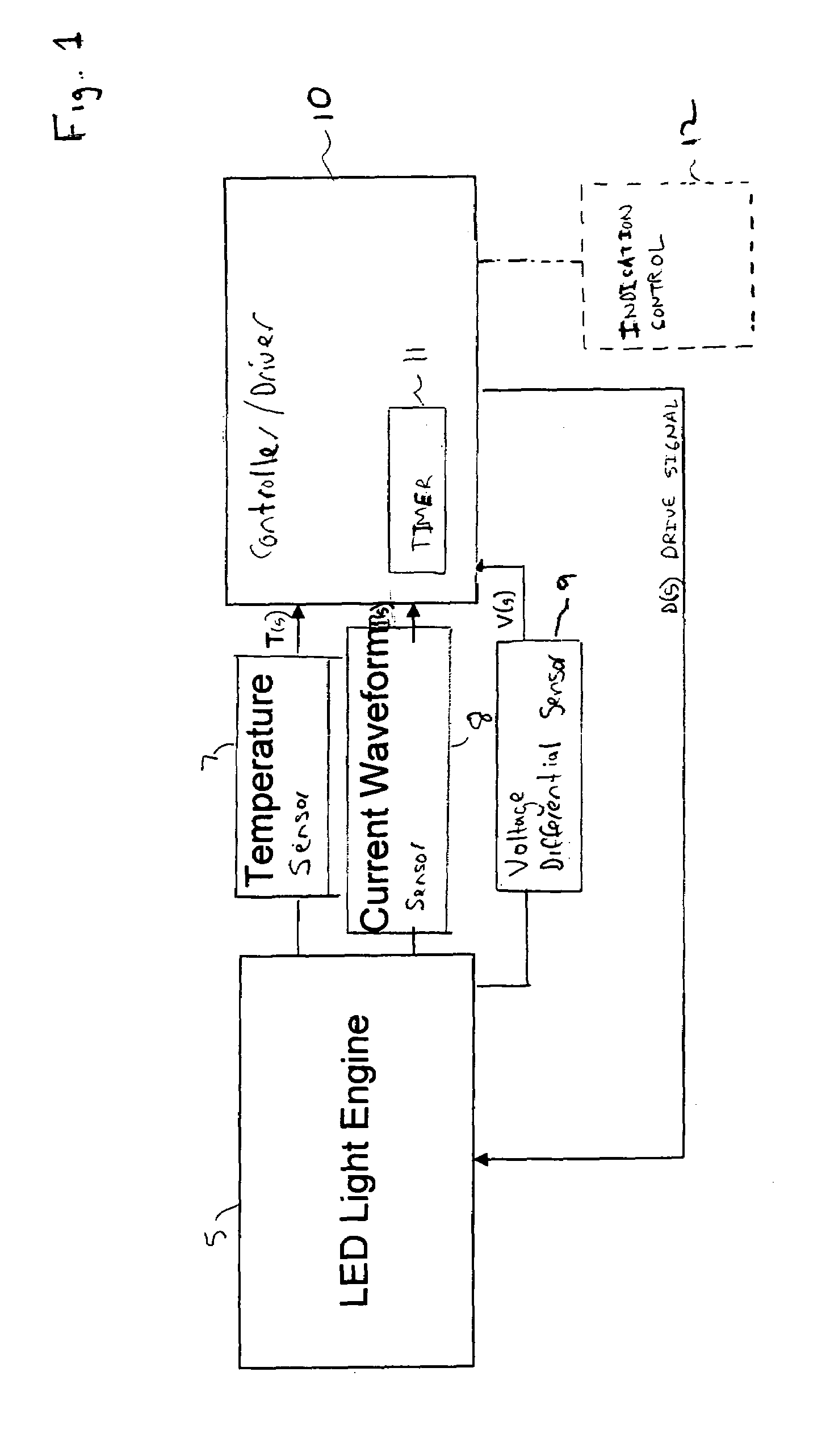
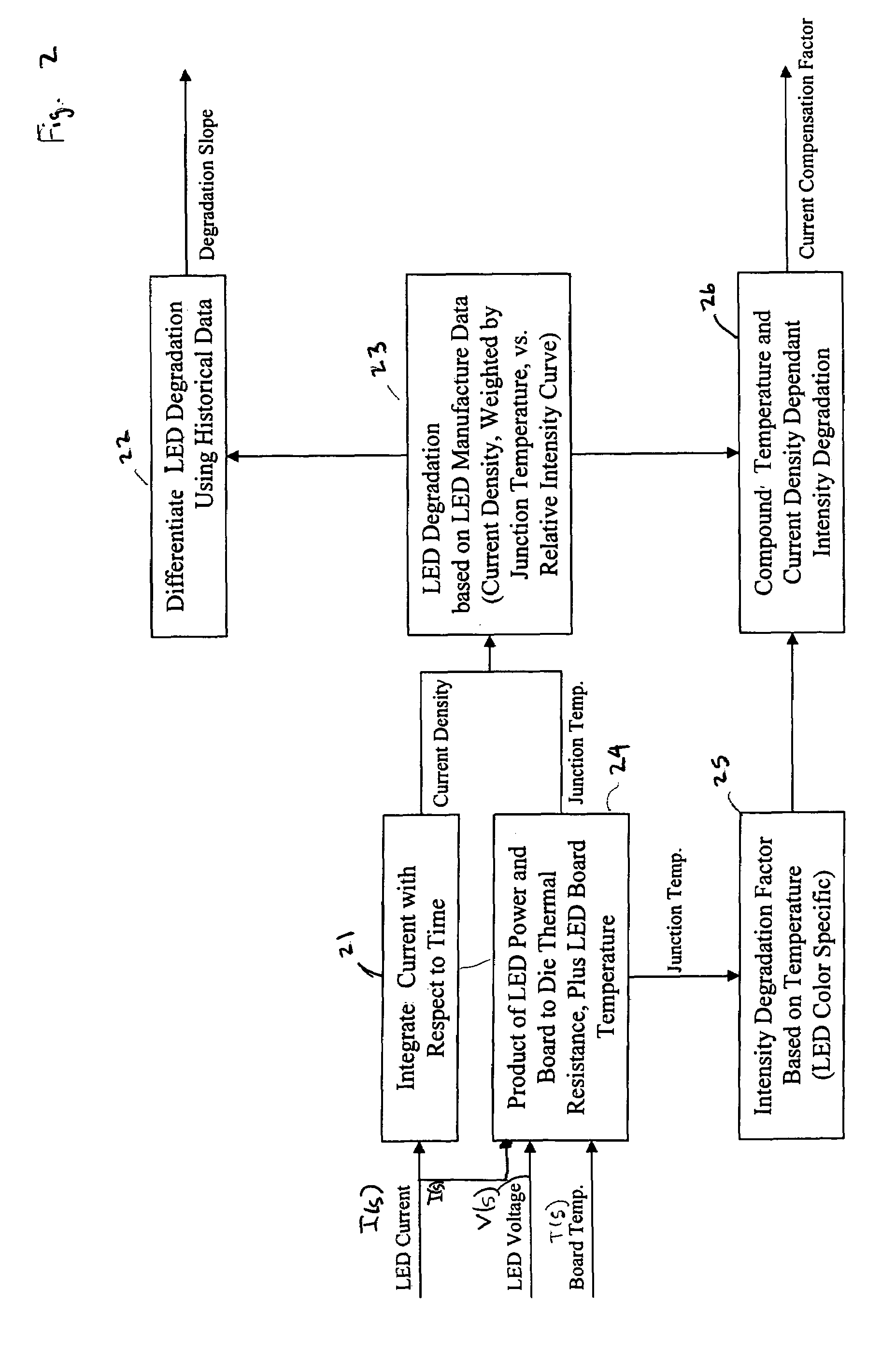
A controller for controlling a light emitting diode (LED) light engine. The controller includes a temperature sensor configured to sensor temperature at the LED light engine. A current sensor senses a drive current of the LED light engine. A voltage differential sensor senses a voltage differential across LEDs of the LED light engine. A timer monitors a time of operation of the LED light engine. Further, a control device controls the drive current to the LED light engine based on the sensed temperature, the sensed drive current, the sensed voltage differential, and the monitored time of operation. Further, the control device outputs an indication of intensity degradation of an LED, and if the intensity degradation exceeds a predetermined threshold the control can output an indication of such to a user, so that the user can be apprised that the LED needs to be changed.
Owner:DIALIGHT CORP
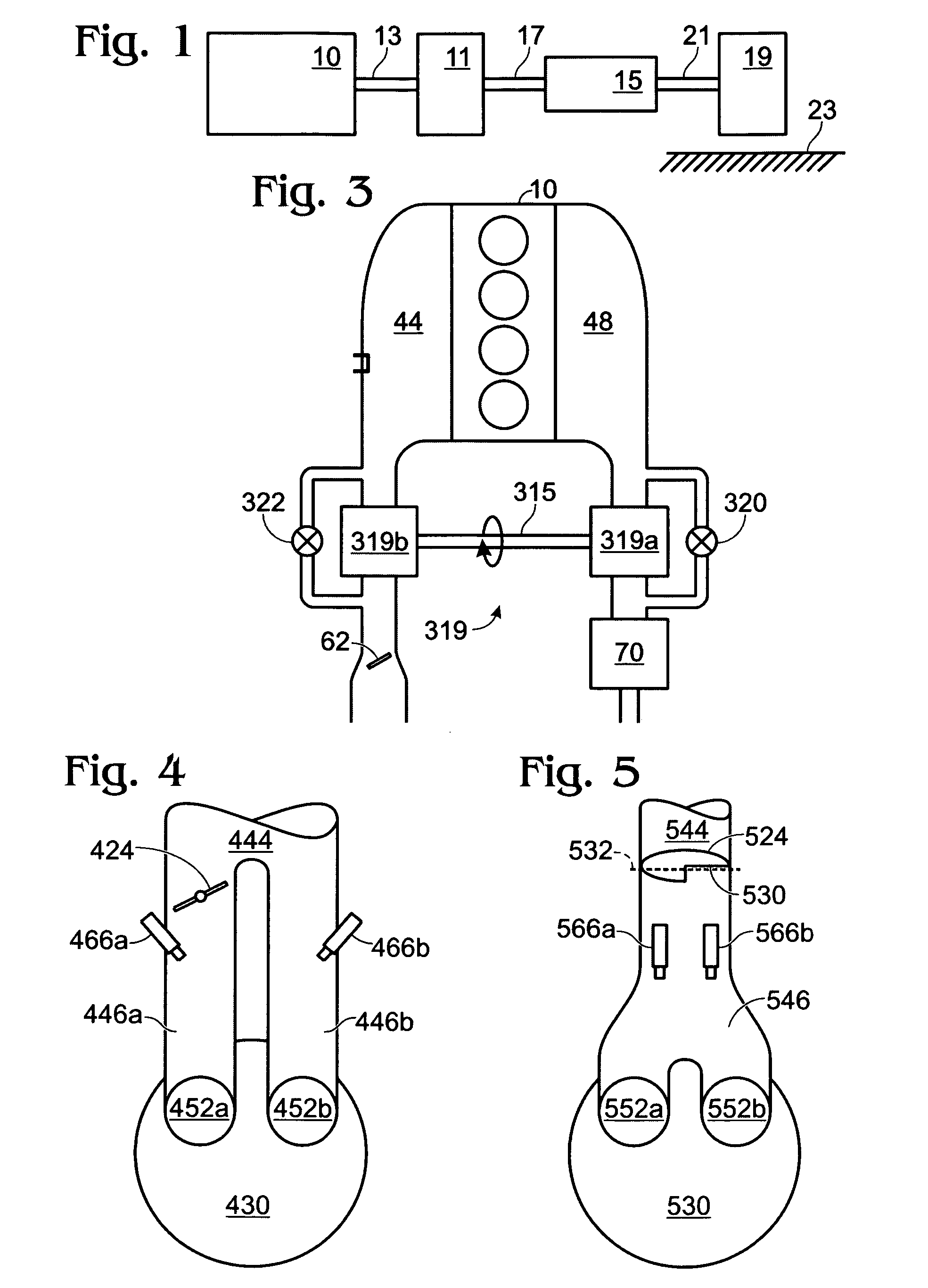
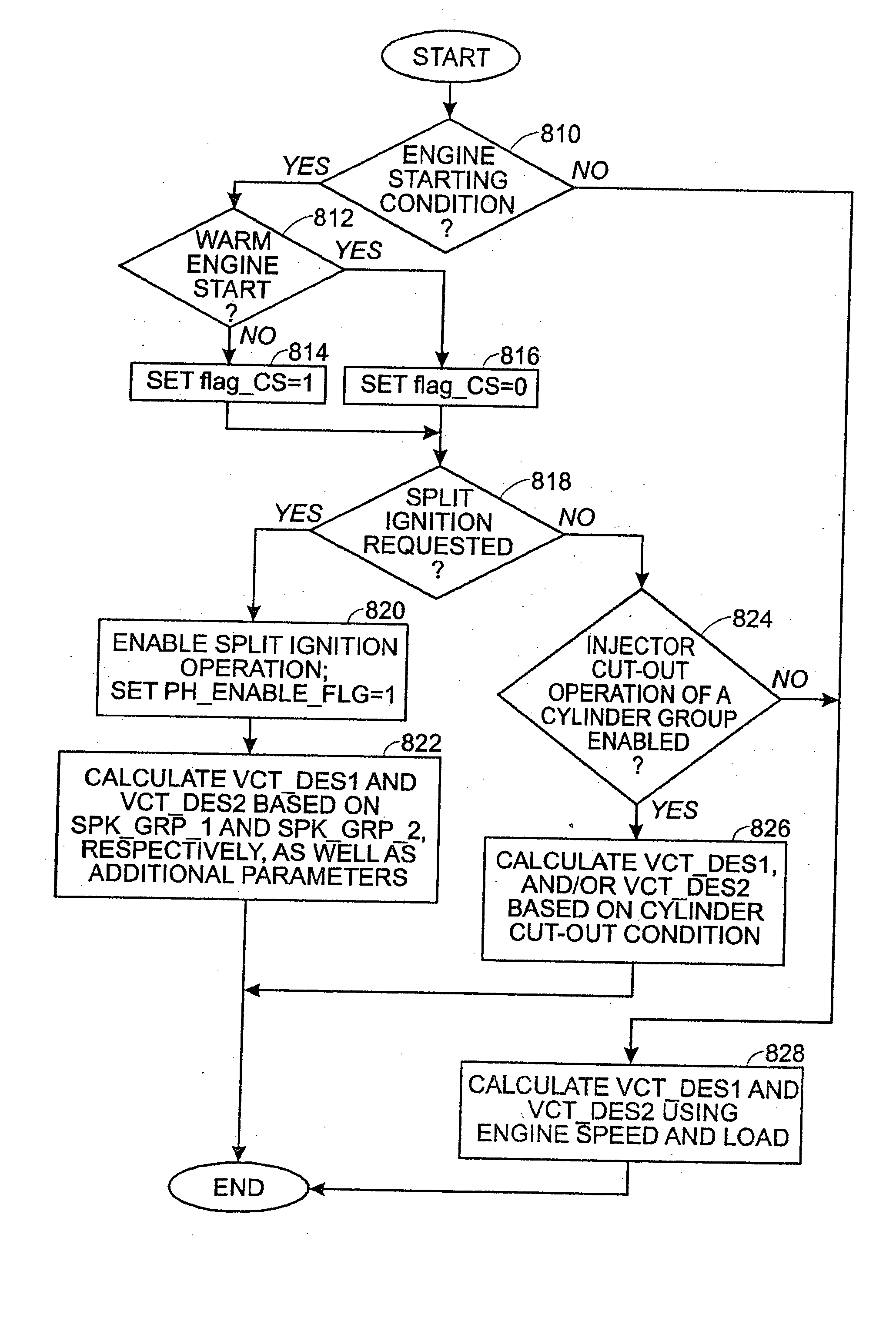
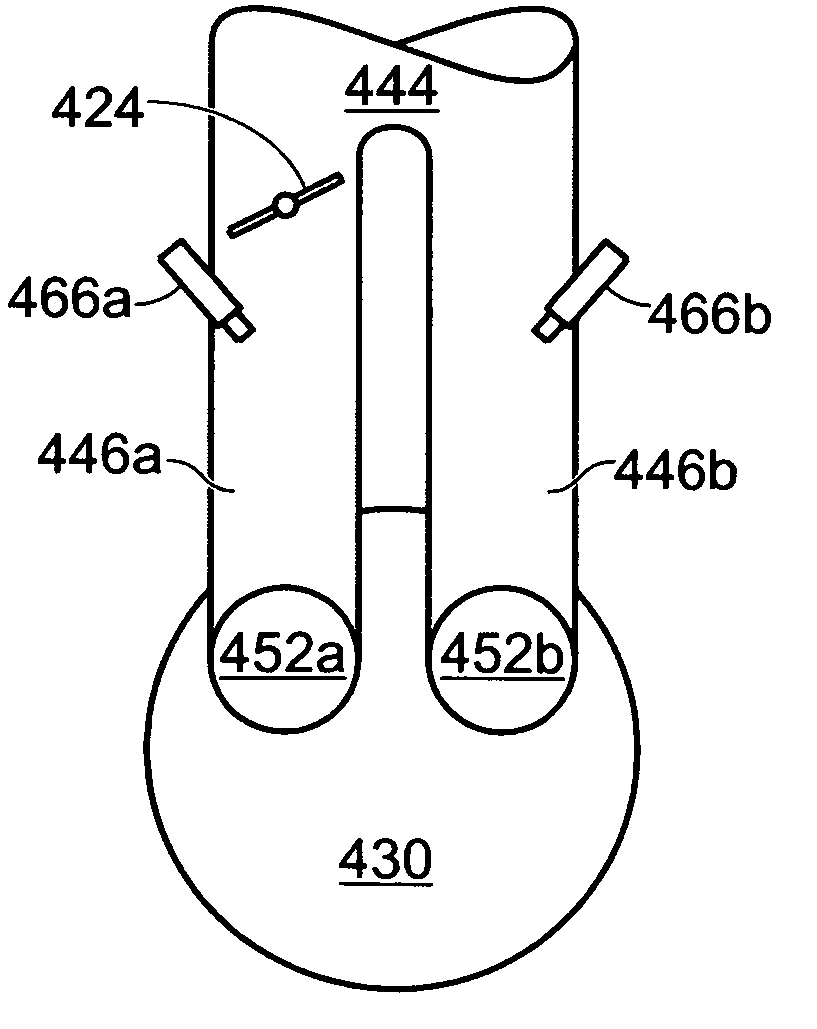
Method for controlling injection timing of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7278396B2Reduce mixEmission reductionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineIgnition timing
A method to control injection timing for an internal combustion engine having a plurality of injectors in at least a cylinder, the method comprising of injecting a first fuel amount to at least a cylinder of an internal combustion engine from a first injector, injecting a second fuel amount fuel to said cylinder from a second injector, and adjusting the timing between starting or ending injection of said first fuel amount, and starting or ending of said second fuel amount in response to an operating condition of said engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
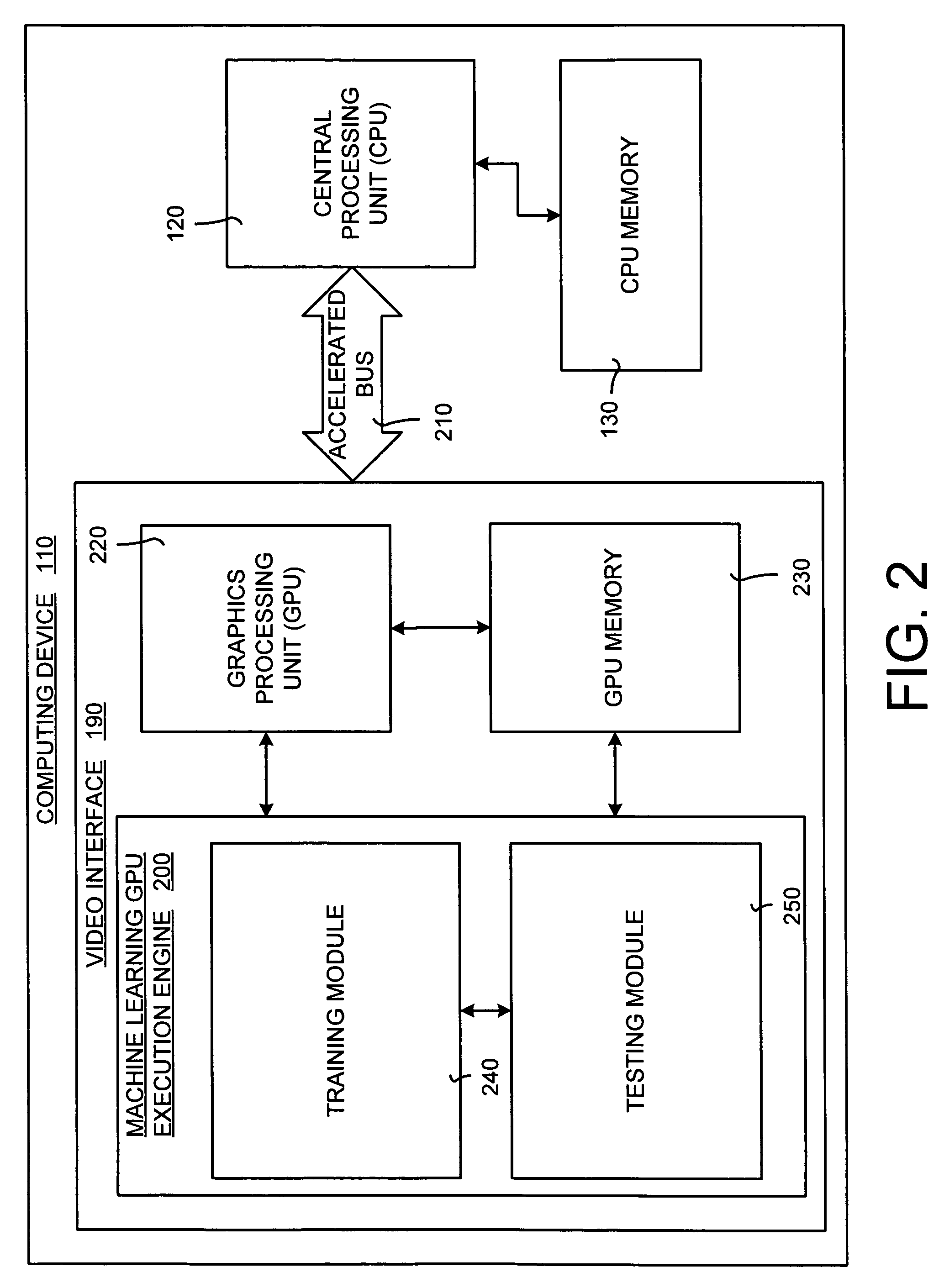
System and method for accelerating and optimizing the processing of machine learning techniques using a graphics processing unit
ActiveUS7219085B2Alleviates computational limitationMore computationCharacter and pattern recognitionKnowledge representationGraphicsTheoretical computer science
A system and method for processing machine learning techniques (such as neural networks) and other non-graphics applications using a graphics processing unit (GPU) to accelerate and optimize the processing. The system and method transfers an architecture that can be used for a wide variety of machine learning techniques from the CPU to the GPU. The transfer of processing to the GPU is accomplished using several novel techniques that overcome the limitations and work well within the framework of the GPU architecture. With these limitations overcome, machine learning techniques are particularly well suited for processing on the GPU because the GPU is typically much more powerful than the typical CPU. Moreover, similar to graphics processing, processing of machine learning techniques involves problems with solving non-trivial solutions and large amounts of data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
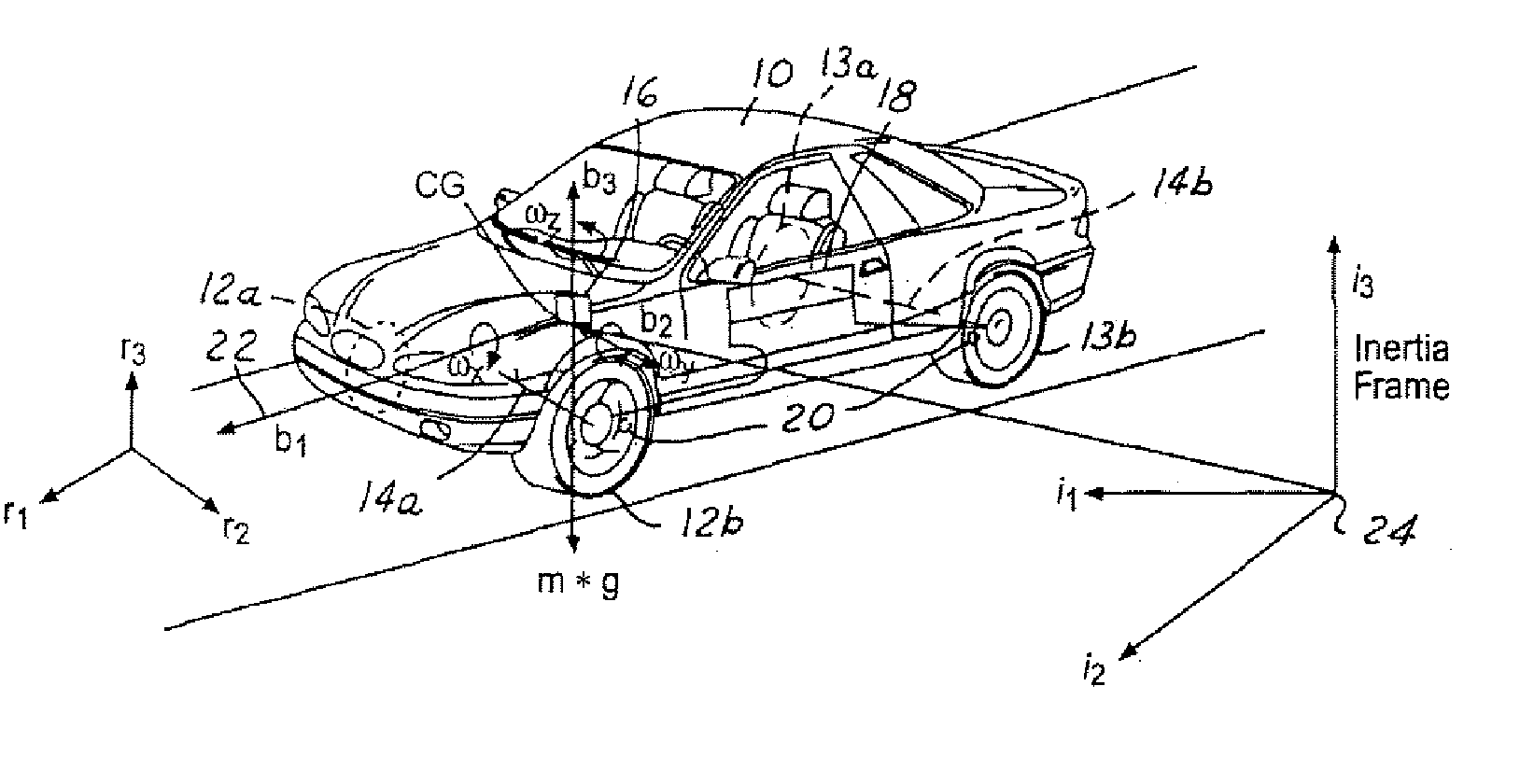
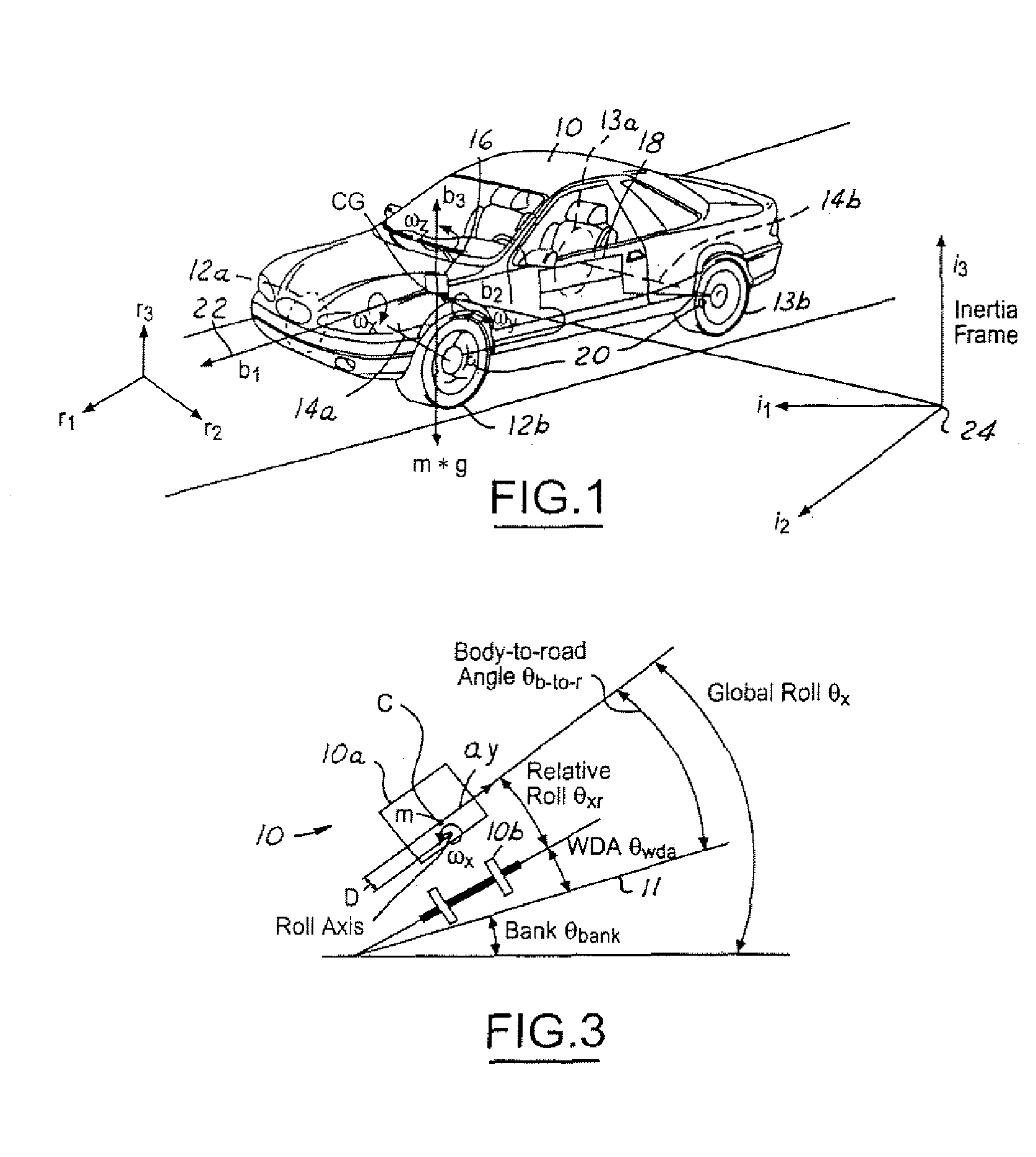
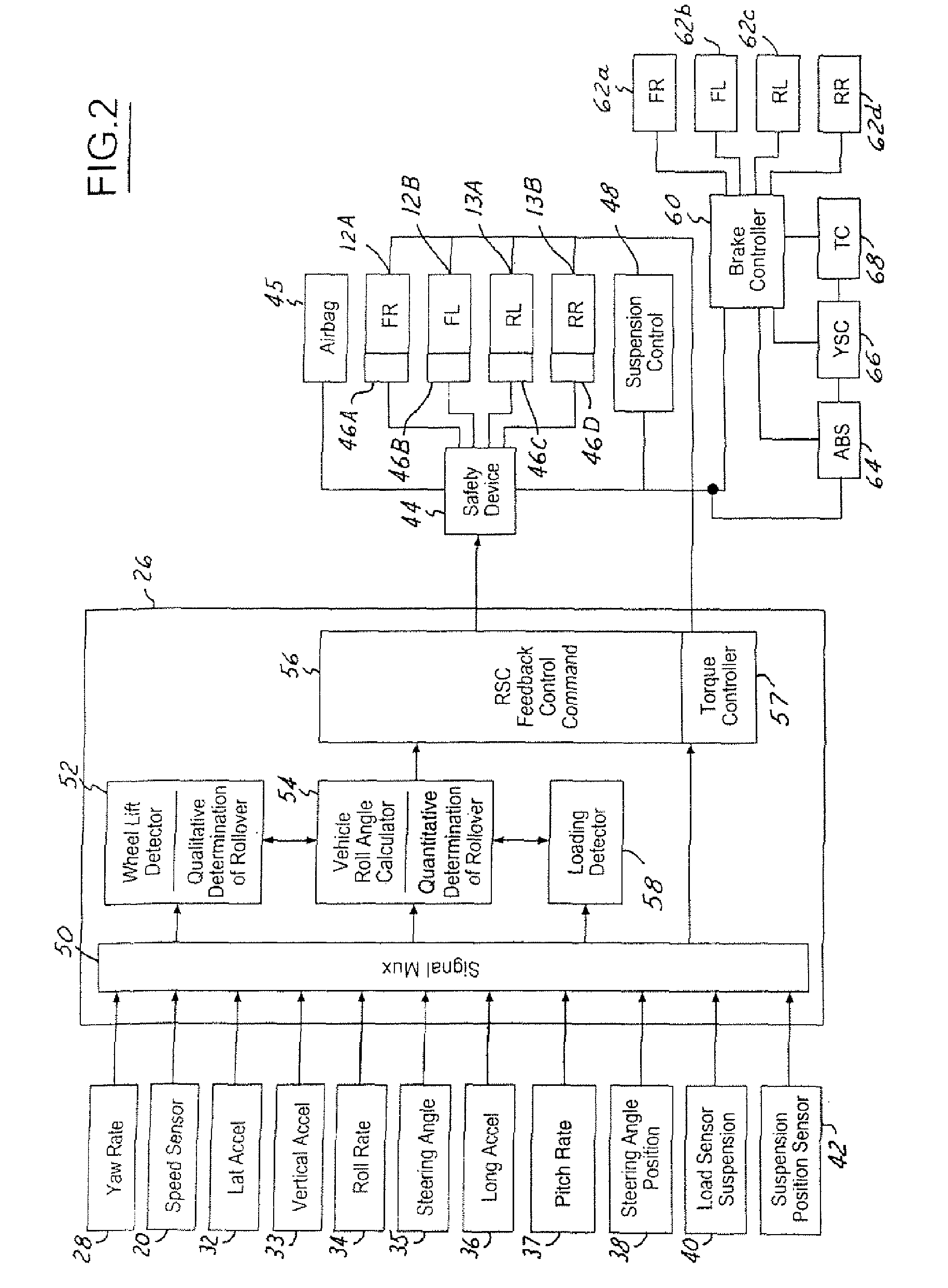
Roll stability control using four-wheel drive
ActiveUS20060074530A1Increase driving torque of drivenSimple torque controlHand manipulated computer devicesDigital data processing detailsRolloverControl system
A control system (18) and method for controlling an automotive vehicle (10) includes a number of sensors that are used to generate a potential rollover signal. In response to the potential rollover, active differentials (112, 114, 116) may be used alone or in addition to braking to prevent the vehicle from rolling over.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
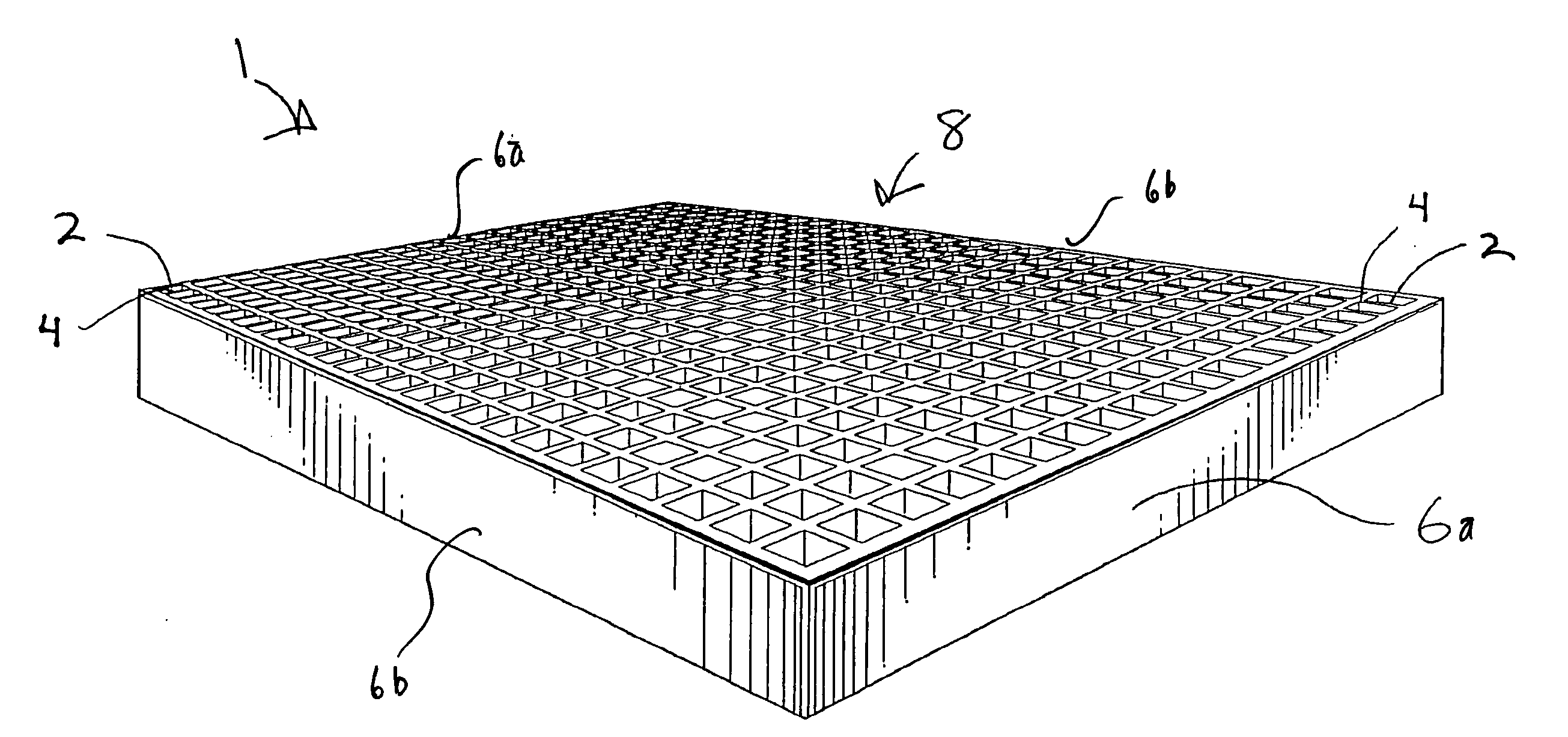
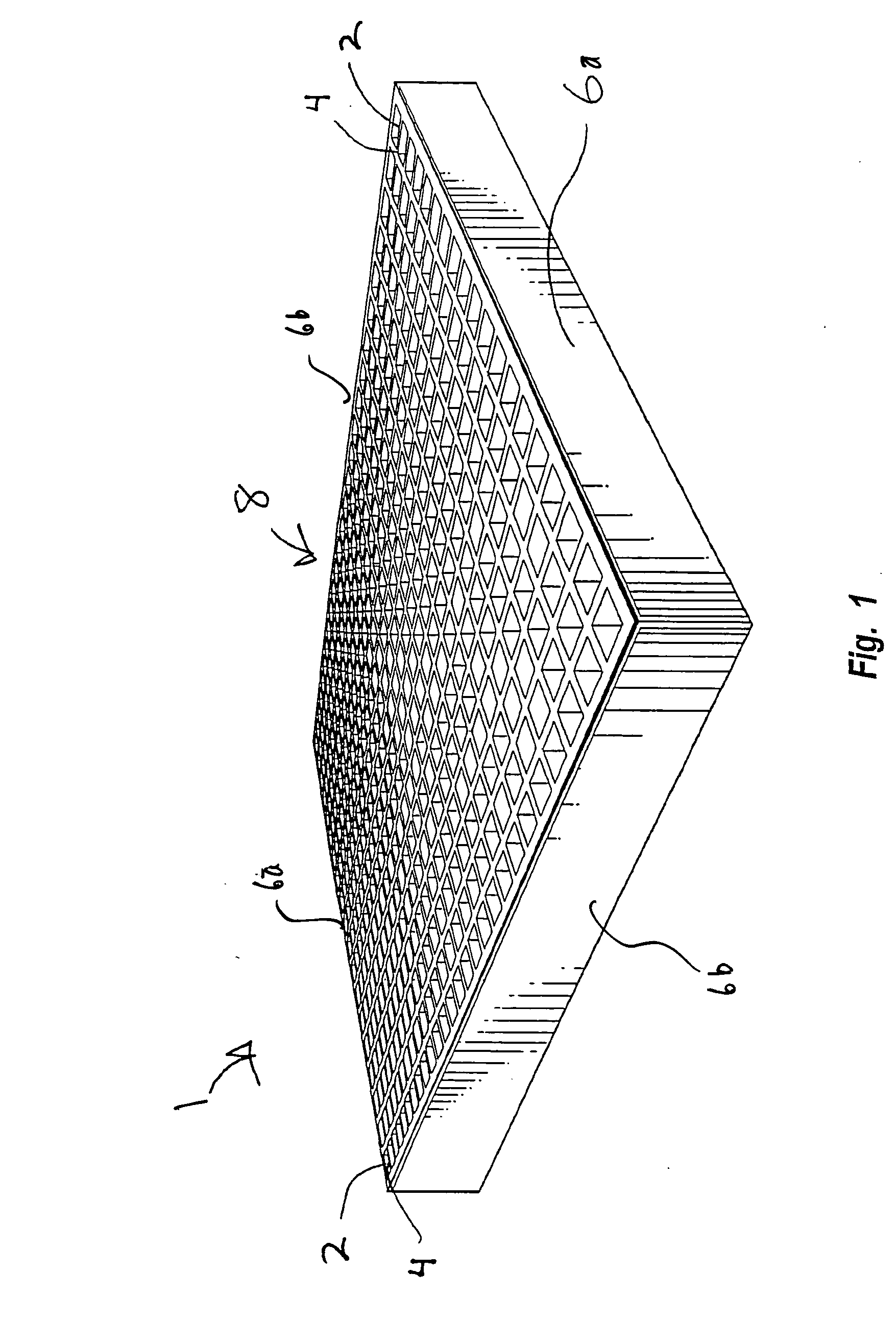
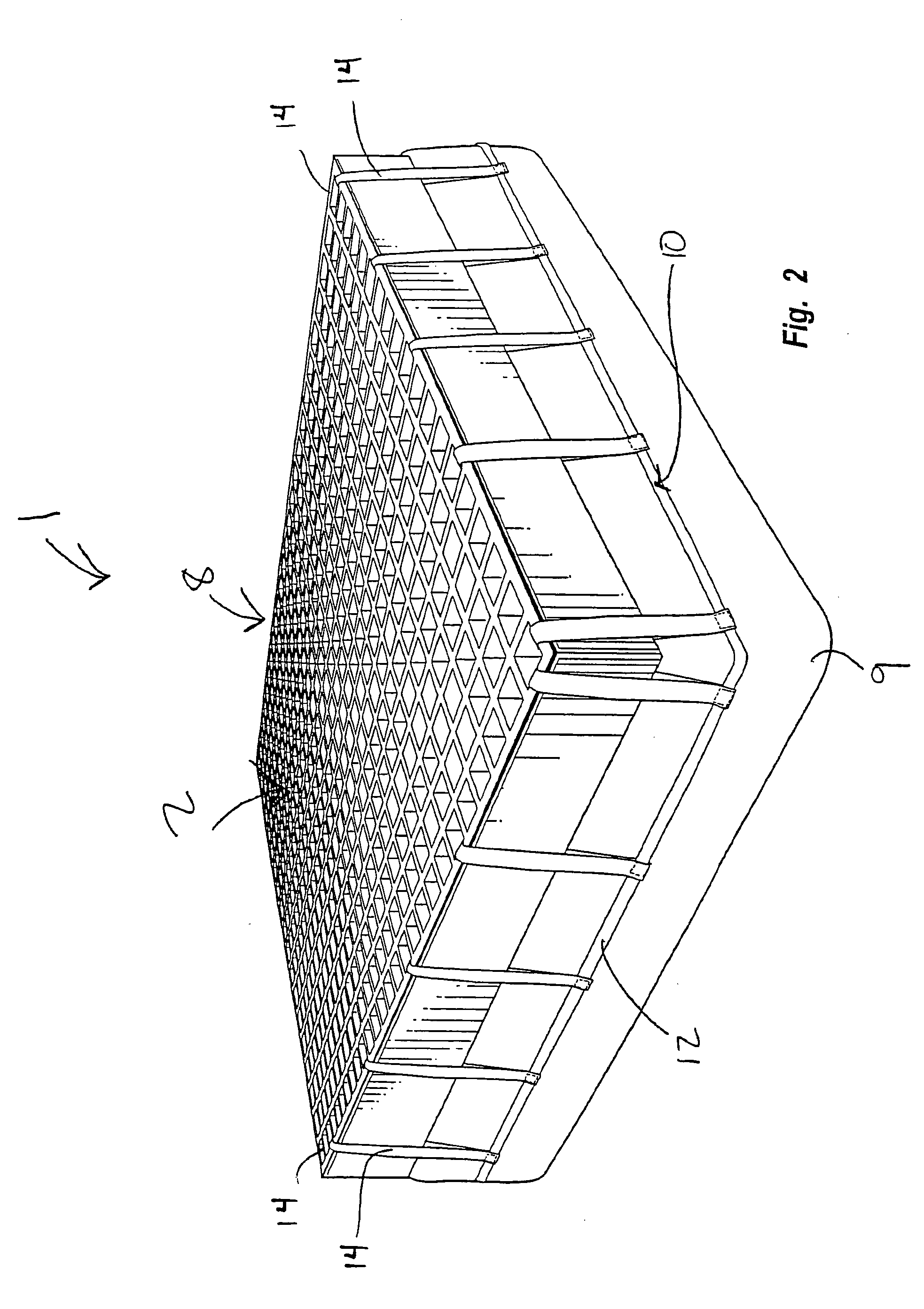
Cushioned apparatus
InactiveUS20050223667A1Easy to optimizeEliminate pointStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesCushioningThermoplastic
The present invention relates to cushioning apparatus having a plurality of intersecting columns, the columns being formed from a thermoplastic, silicone, two-part, or other gel material. The cushioning apparatus are extremely strong and durable yet provide an improved cushioning apparatus. The intersecting columnar configuration of the cushioning apparatus allow for weight to be shared with neighboring column walls. When force is exerted on the columns, the column walls are designed to buckle in the areas of greatest pressure. The column buckling diffuses energy from the areas of highest pressure effectively eliminating pressure points. As the polymer gel collapses within the column walls, the column walls essentially collapse at least partially in a lateral direction allowing pressure to flow away from the areas of greatest pressure to areas of lesser pressure. This provides an improved cushioning surface on which a user can sit, sleep, or other types of cushioning can be provided.
Owner:MCCANN BARRY +1
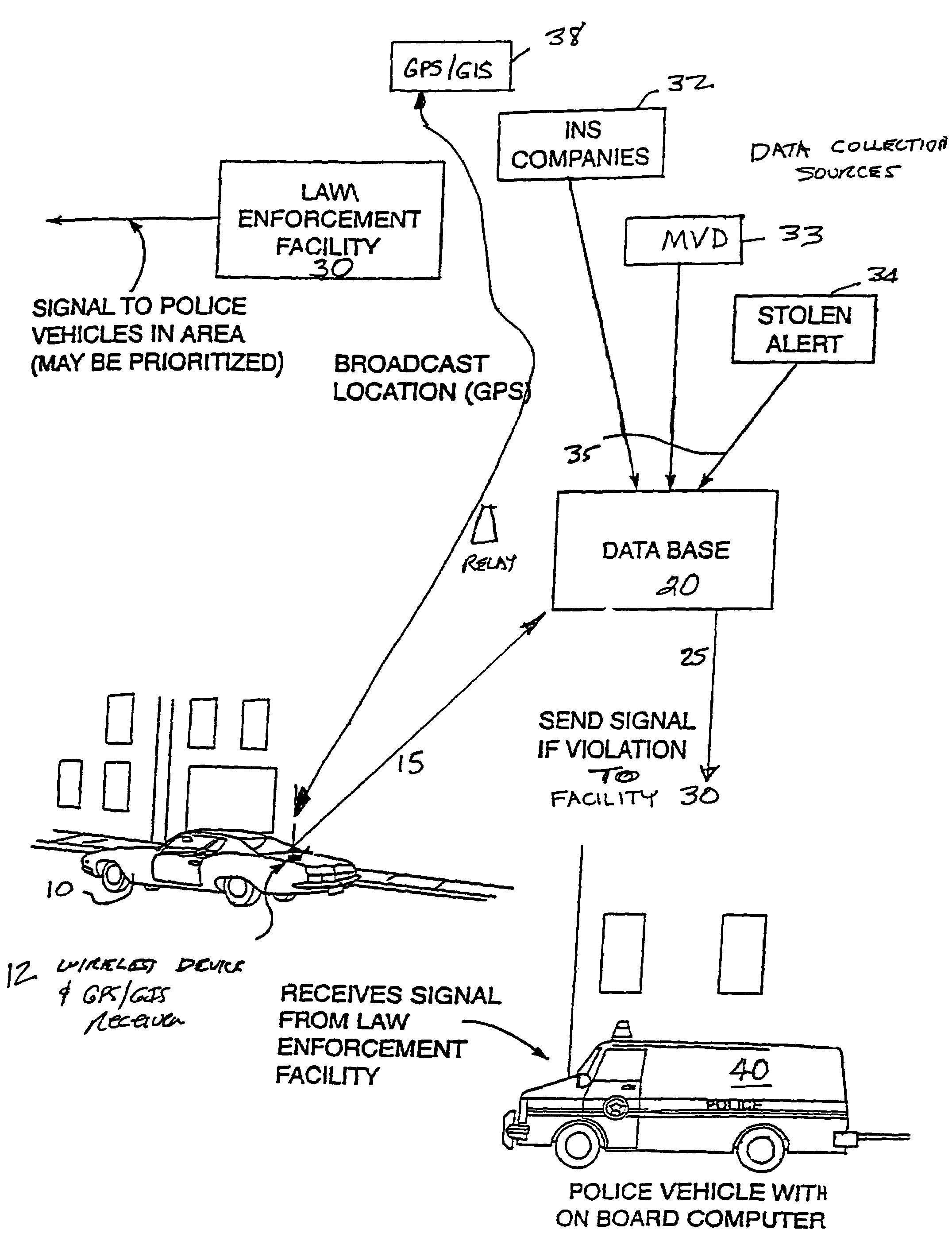
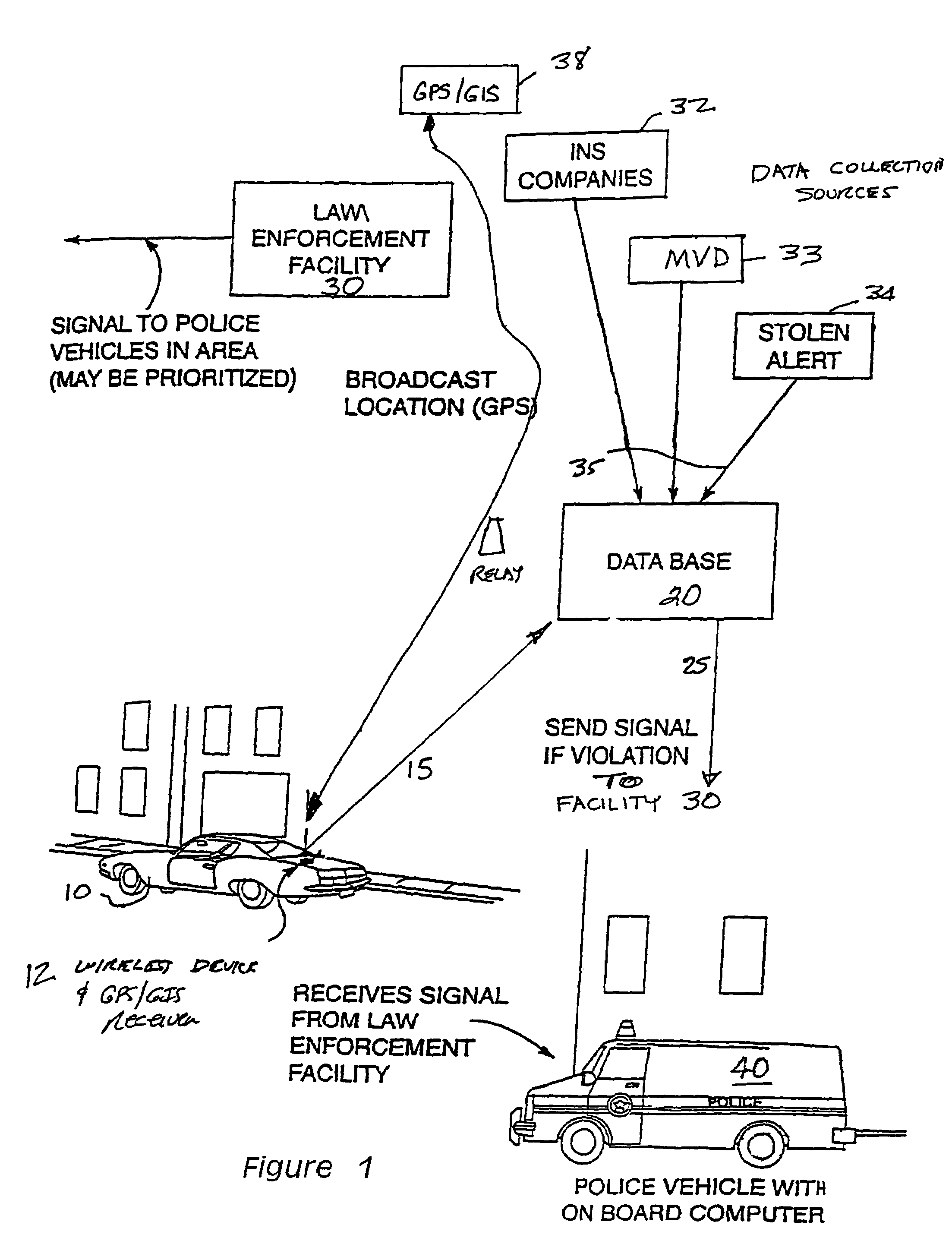
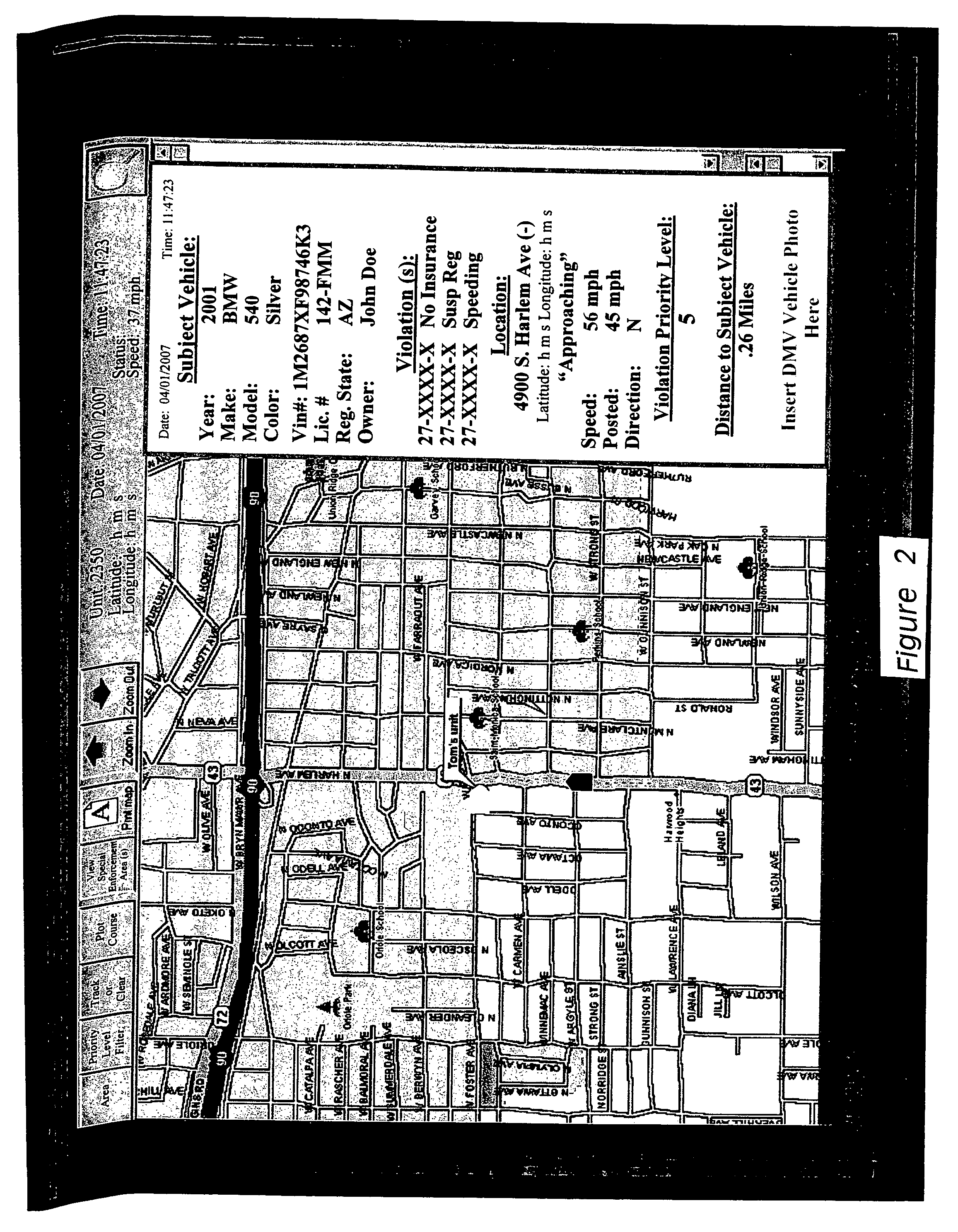
Vehicle tracking and monitoring system
InactiveUS7701363B1Increase enforcementReduce violationAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficDatabase maintenanceTraffic enforcement
Owner:ZLOJUTRO MILAN
Increased polysilicon deposition in a CVD reactor
ActiveUS20070251455A1Reduce voltageShorten the timeSilicon compoundsChemical vapor deposition coatingProduction rateGas phase
A method and process for the production of bulk polysilicon by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) where conventional silicon “slim rods” commonly used in Siemens-type reactors are replaced with shaped silicon filaments of similar electrical properties but larger surface areas, such as silicon tubes, ribbons, and other shaped cross sections. Silicon containing gases, such as chlorosilane or silane, are decomposed and form a silicon deposit on the hot surfaces of the filaments The larger starting surface areas of these filaments ensures a higher production rate without changing the reactor size, and without increasing the number and length of the filaments. Existing reactors need only the adaptation or replacement of filament supports to use the new filaments. The filaments are grown from silicon melt by Edge-defined, Film-fed Growth (EFG) method. This also enables the doping of the filaments and simplification of power supplies for new reactors.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIAL SOLUTIONS LLC
Intelligent drive circuit for a light emitting diode (LED) light engine
ActiveUS7132805B2Energy consumptionPromote degradationLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitDriving current
A controller for controlling a light emitting diode (LED) light engine. The controller includes a temperature sensor configured to sensor temperature at the LED light engine. A current sensor senses a drive current of the LED light engine. A voltage differential sensor senses a voltage differential across LEDs of the LED light engine. A timer monitors a time of operation of the LED light engine. Further, a control device controls the drive current to the LED light engine based on the sensed temperature, the sensed drive current, the sensed voltage differential, and the monitored time of operation. Further, the control device outputs an indication of intensity degradation of an LED, and if the intensity degradation exceeds a predetermined threshold the control can output an indication of such to a user, so that the user can be apprised that the LED needs to be changed.
Owner:DIALIGHT CORP
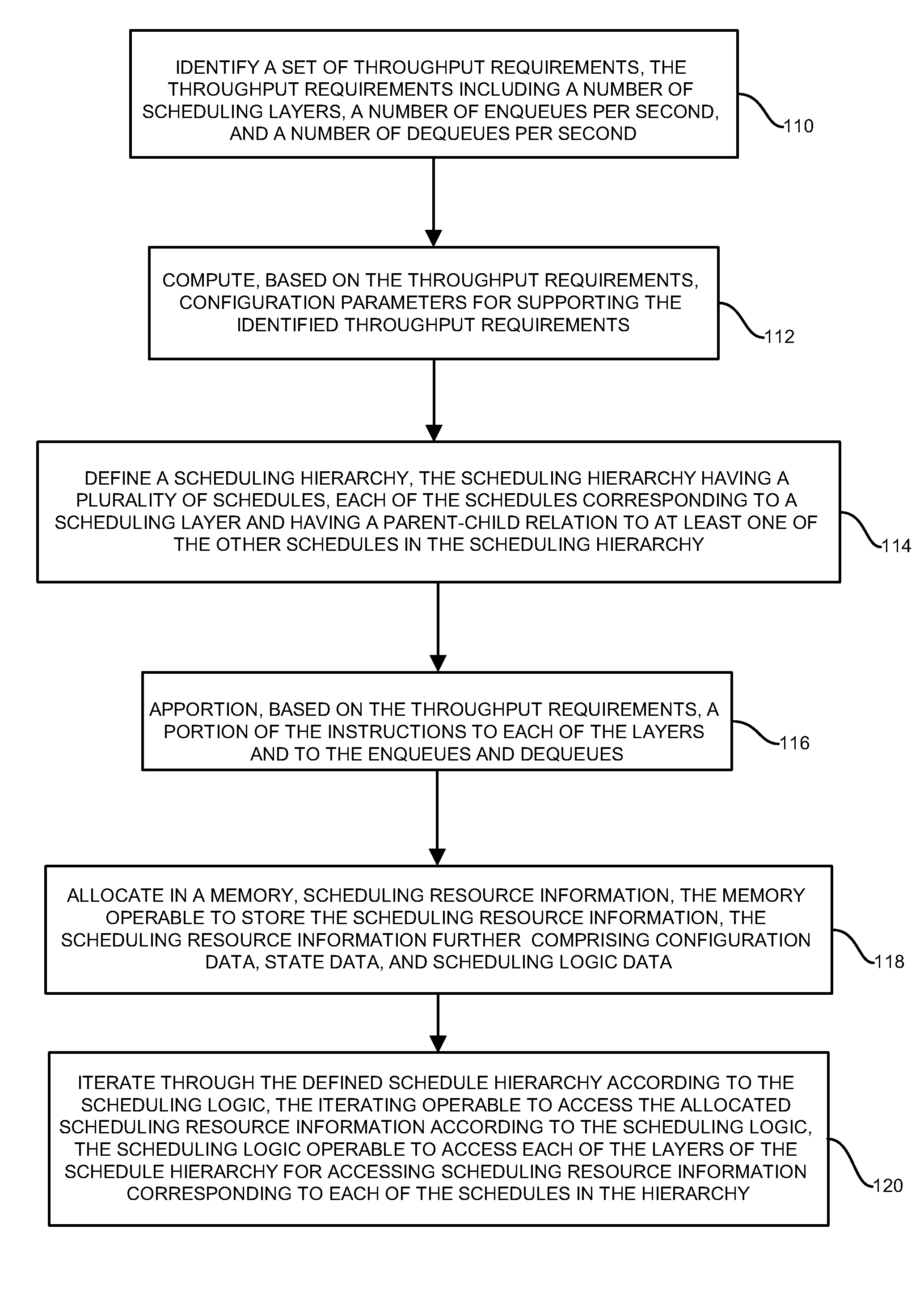
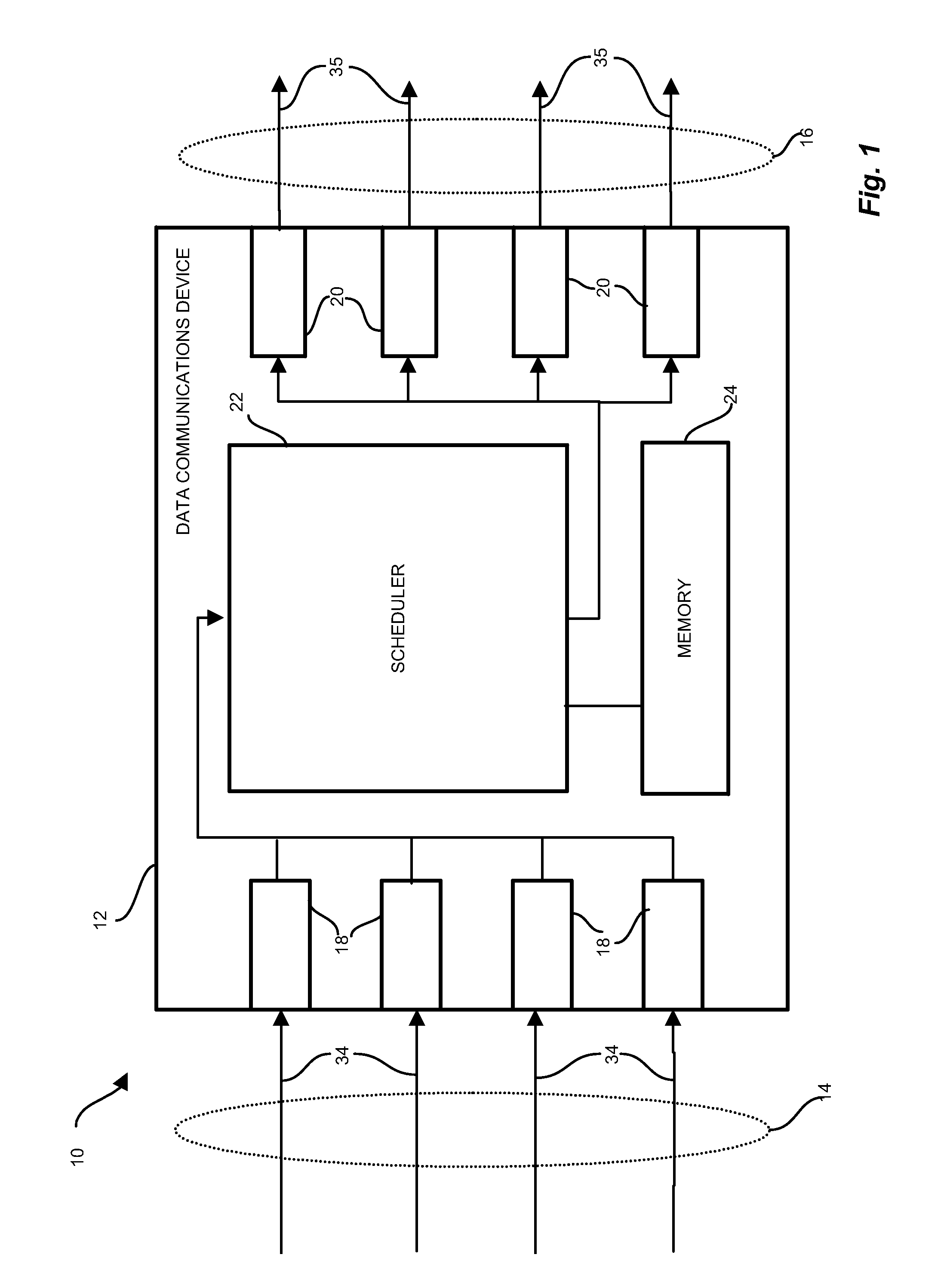
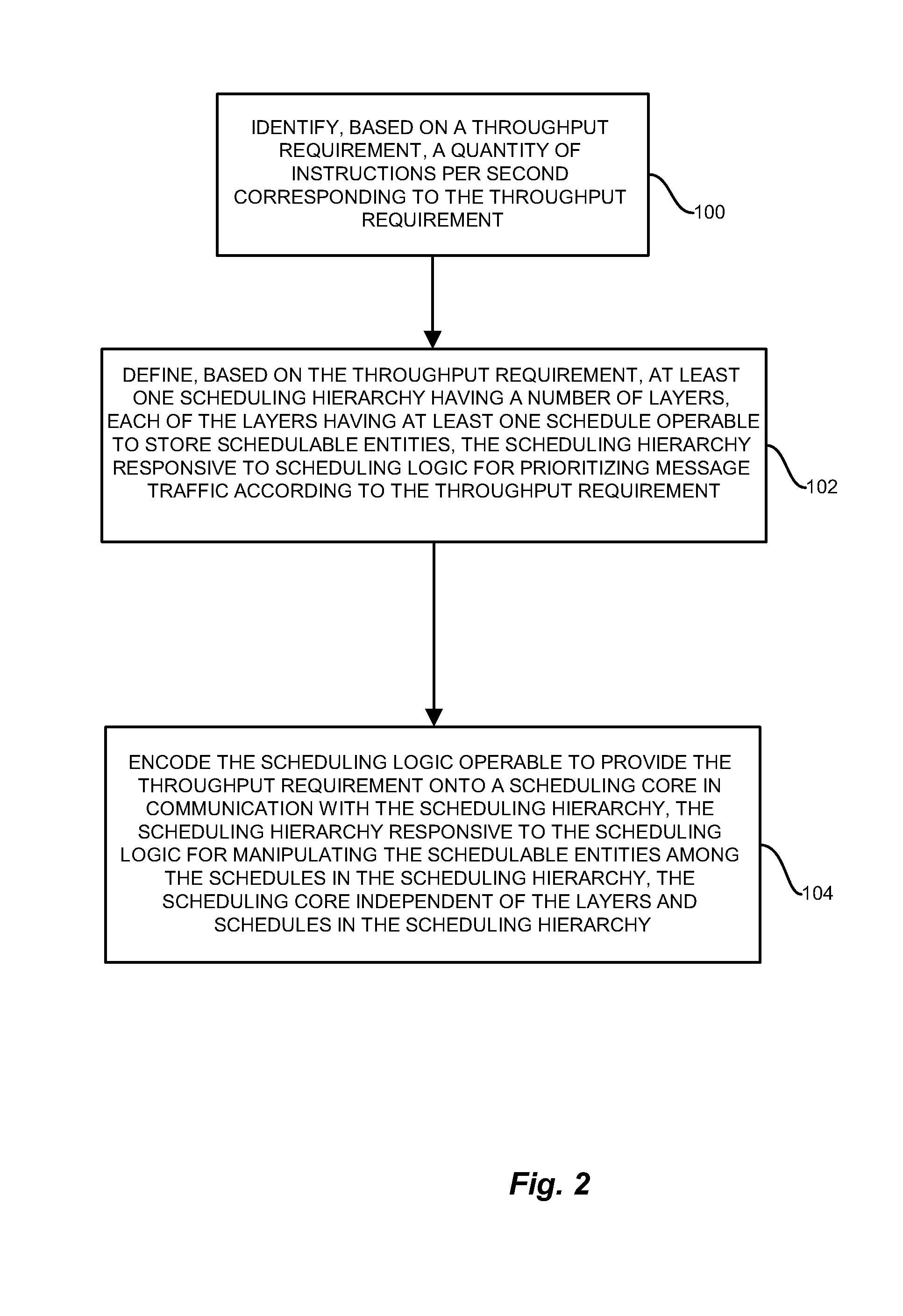
Iterative architecture for hierarchical scheduling
InactiveUS7321940B1Easy to traverseIncrease demandMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksGranularityComputer science
Conventional schedulers employ designs allocating specific processor and memory resources, such as memory for configuration data, state data, and scheduling engine processor resources for specific aspects of the scheduler, such as layers of the scheduling hierarchy, each of which consumes dedicated processor and memory resources. A generic, iterative scheduling engine, applicable to an arbitrary scheduling hierarchy structure having a variable number of hierarchy layers, receives a scheduling hierarchy structure having a predetermined number of layers, and allocates scheduling resources such as instructions and memory, according to scheduling logic, in response to design constraints and processing considerations. The resulting scheduling logic processes the scheduling hierarchy in iterative manner which allocates the available resources among the layers of the hierarchy, such that the scheduler achieves throughput requirements corresponding to enqueue and dequeue events with consideration to the number of layers in the scheduling hierarchy and the corresponding granularity of queuing.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Applying motion sensor data to wheel imbalance detection, tire pressure monitoring, and/or tread depth measurement
ActiveUS20180003593A1Improve securityReduce fuel consumptionVibration measurement in solidsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMobile vehicleAccelerometer
A computer-based method to facilitate detecting wheel imbalance, a tire pressure problem, or excessive tread wear on tires of a moving vehicle is disclosed. The method includes collecting (e.g., from an accelerometer of a mobile personal computing device) data that represents vibration that results, at least in part, from the vehicle's motion, and determining, with a computer-based processor, whether the moving vehicle has wheel imbalance, a tire pressure problem, and / or excessive tire tread wear based at least in part on the vibration data produced by the accelerometer (and, possibly other data), where the mobile personal computing device and the accelerometer are moving with the vehicle when the data is being collected.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
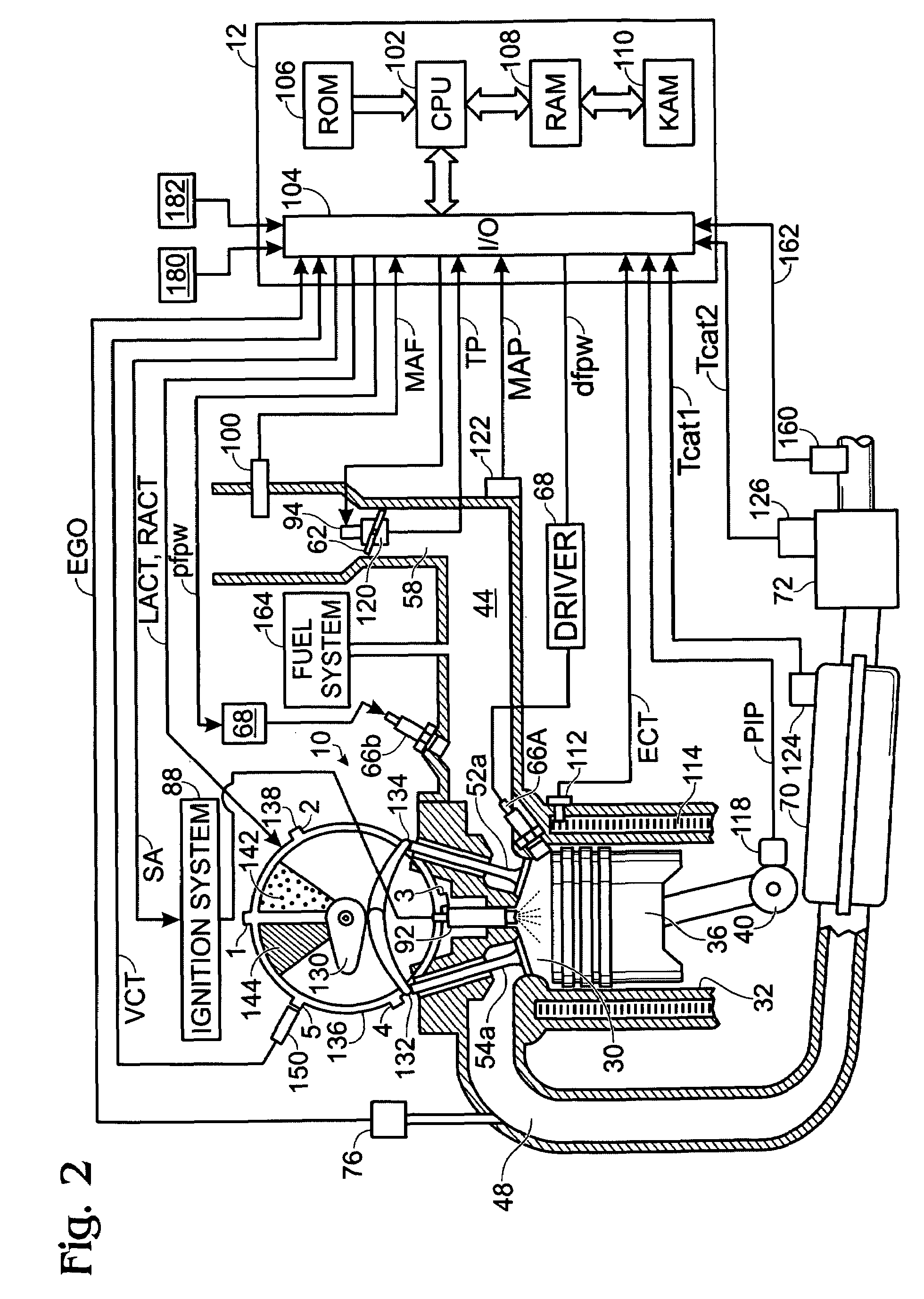
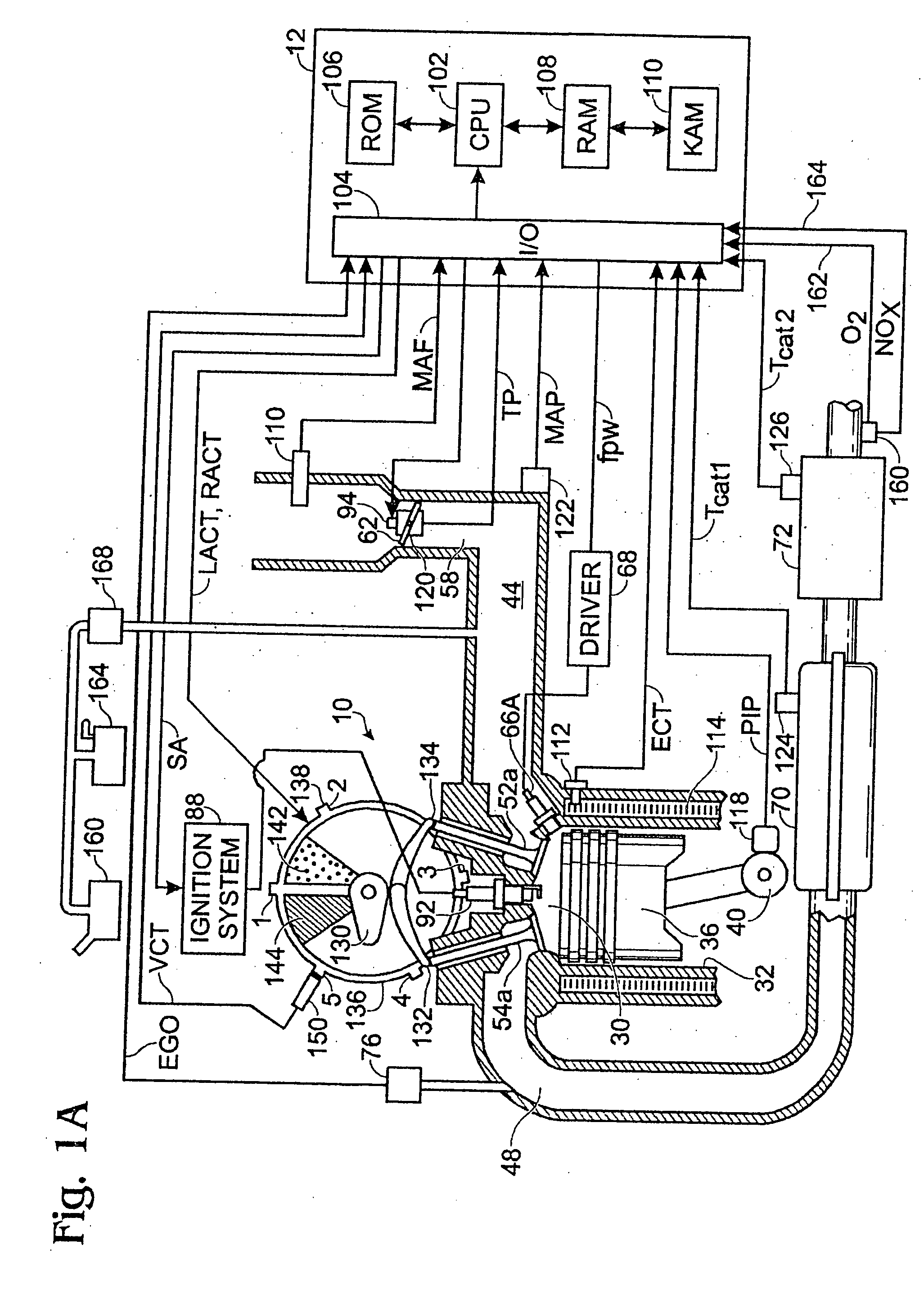
Engine system and method for injector cut-out operation with improved exhaust heating
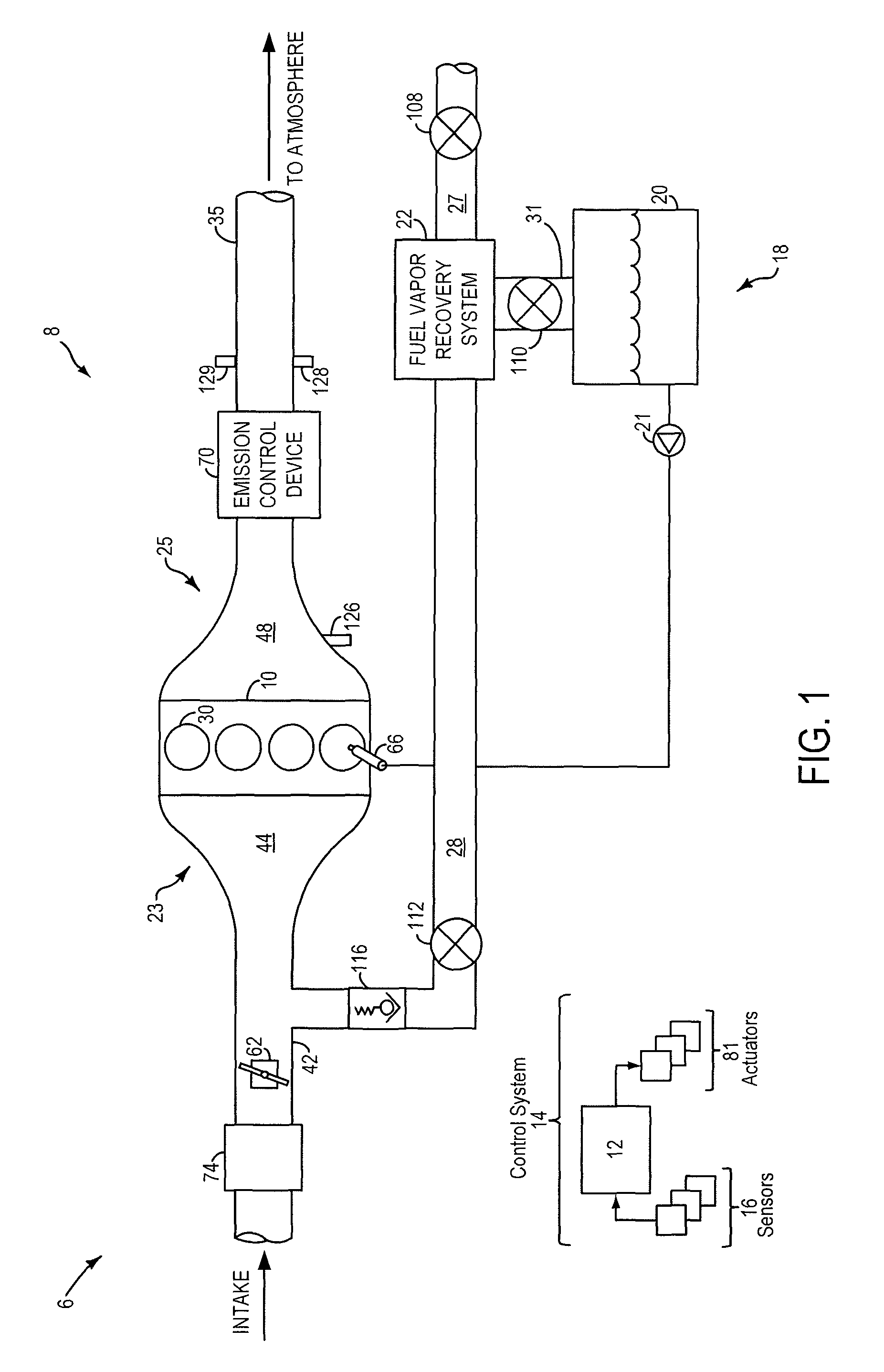
InactiveUS20040237514A1Improve fuel economyNo additional benefitElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelSystems designAir–fuel ratio
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
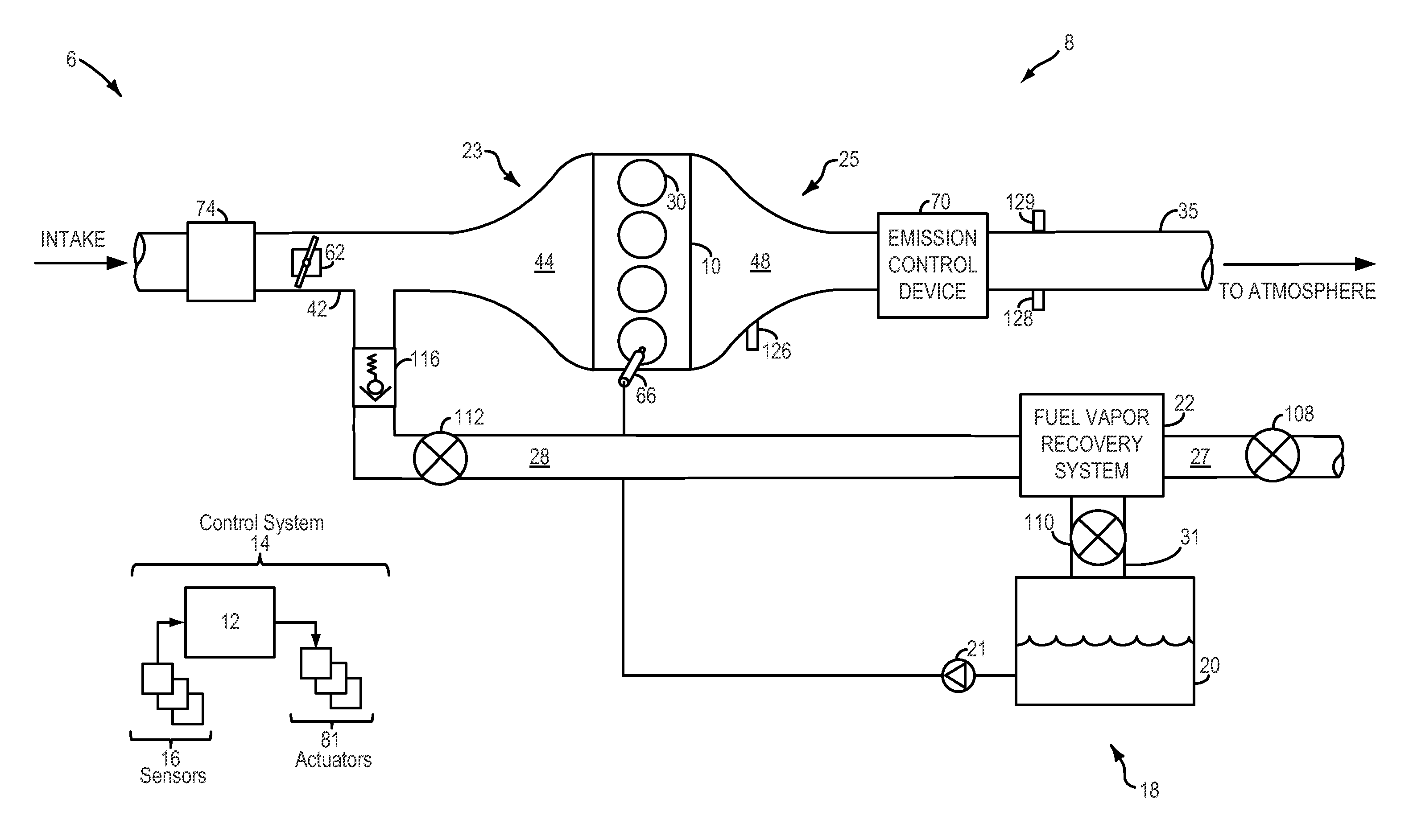
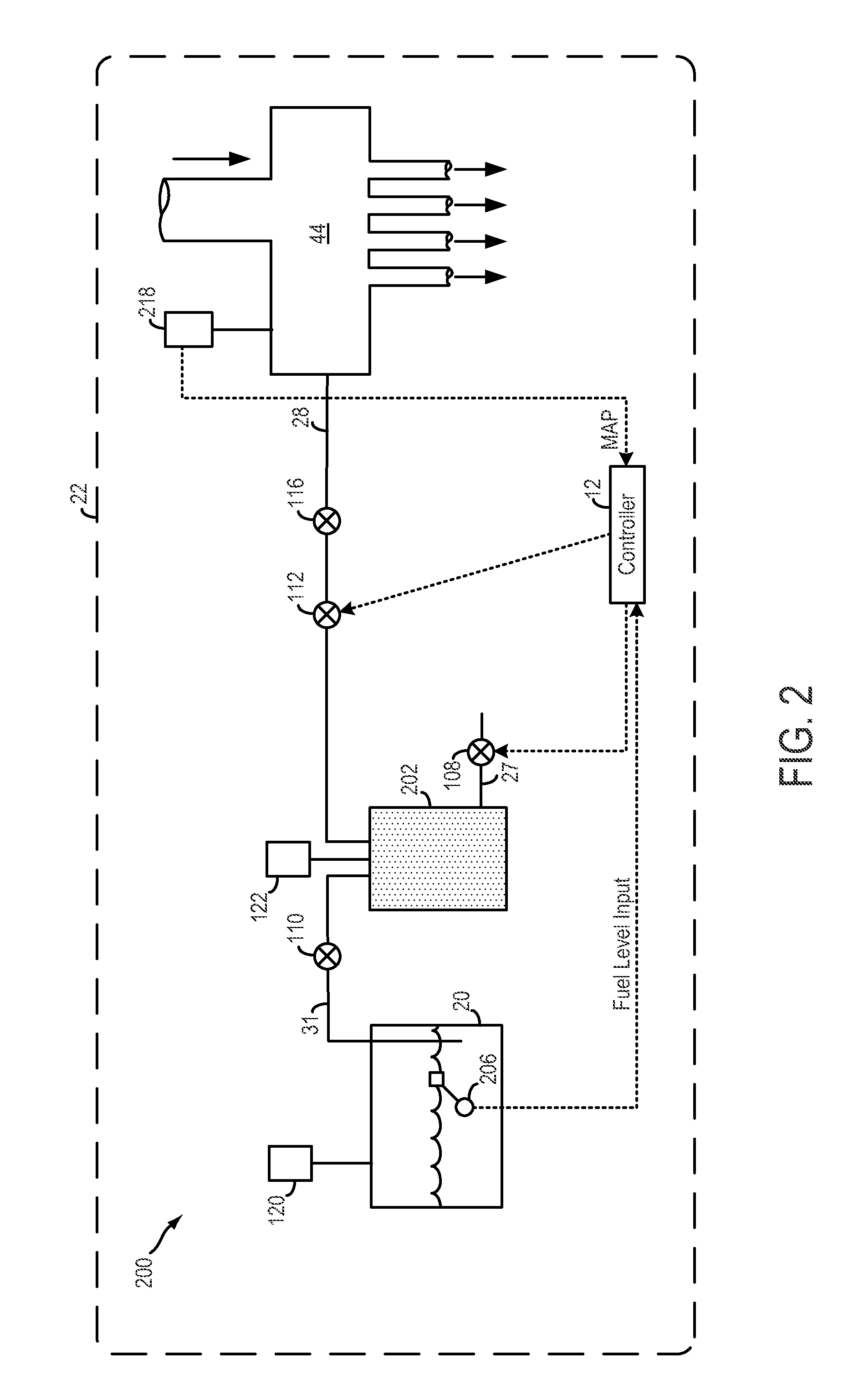
Method and system for fuel vapor control
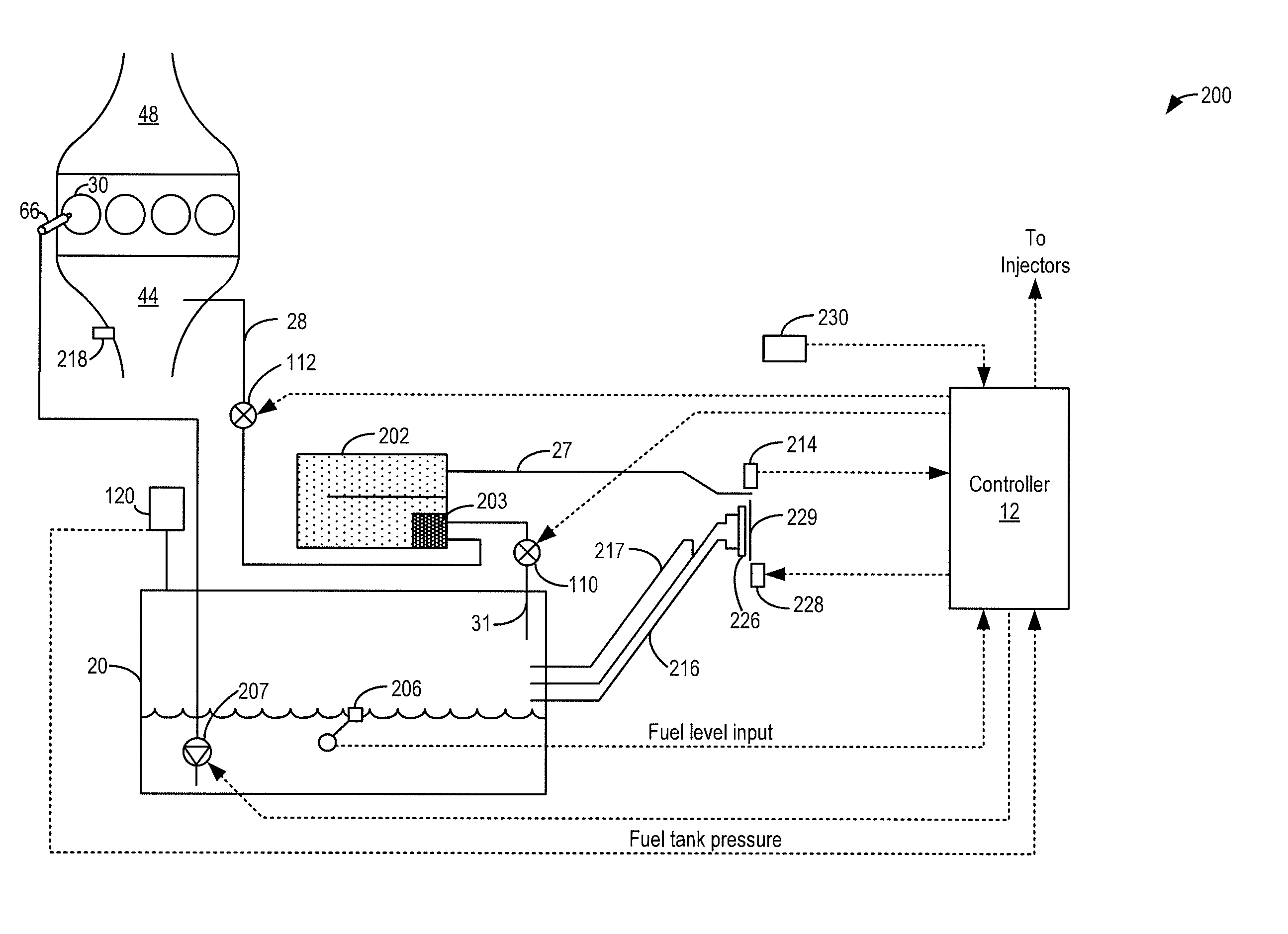
ActiveUS20120211087A1Shorten operation timeEnable fuel economyInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlIsolation valveFuel vapor
Methods and systems are provided for monitoring a fuel vapor recovery system including a fuel tank isolation valve coupled between a fuel tank and a canister. During selected conditions, the valve is modulated and pressure pulsations in the fuel vapor recovery system are monitored. Valve degradation is identified based on correlations between the valve modulation and the resultant pressure pulsations.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for controlling injection timing of an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20070119420A1Improve fuel mixingImprove engine emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineInjector
A method to control injection timing for an internal combustion engine having a plurality of injectors in at least a cylinder, the method comprising of injecting a first fuel amount to at least a cylinder of an internal combustion engine from a first injector, injecting a second fuel amount fuel to said cylinder from a second injector, and adjusting the timing between starting or ending injection of said first fuel amount, and starting or ending of said second fuel amount in response to an operating condition of said engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
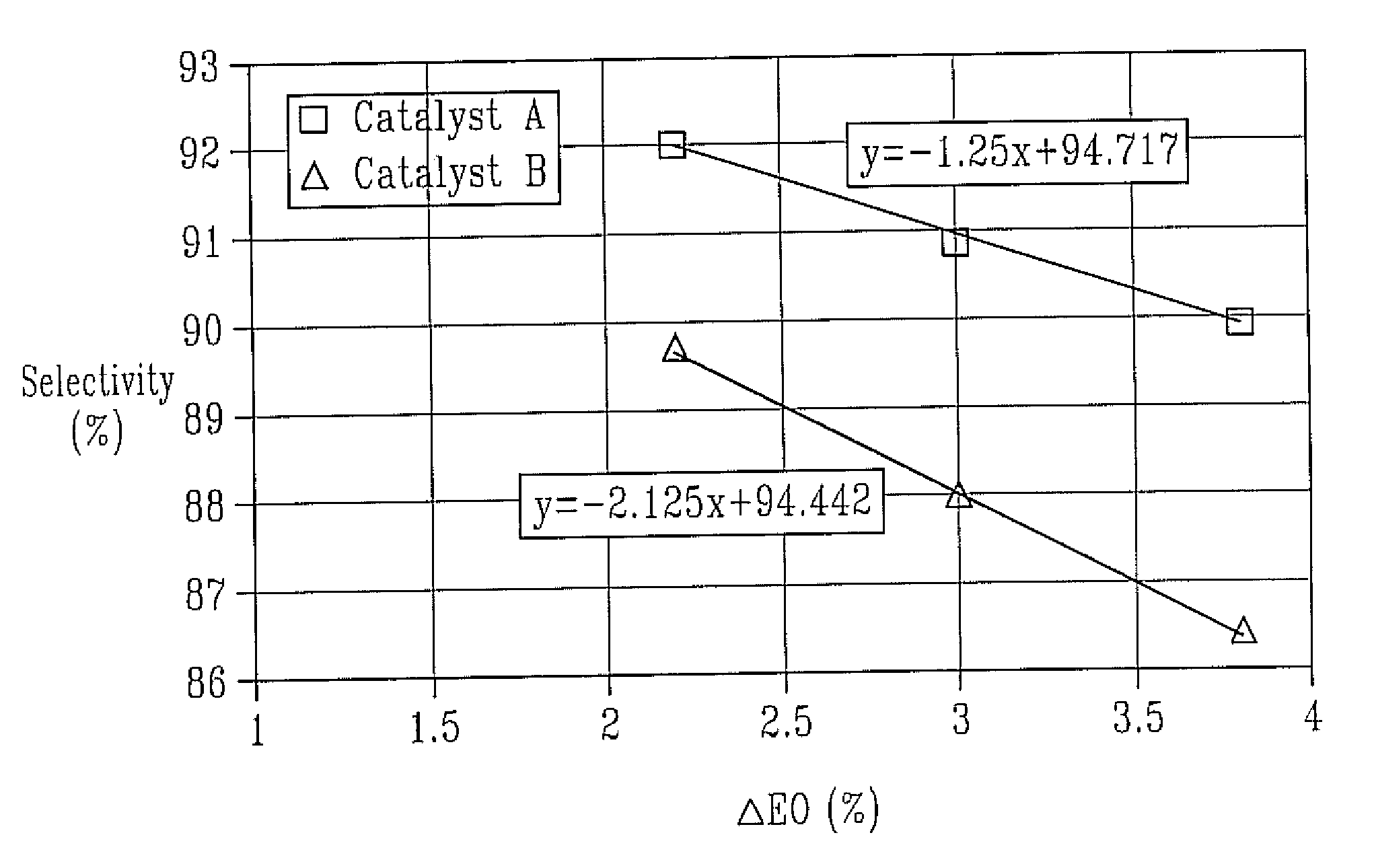
Process for production of an olefin oxide
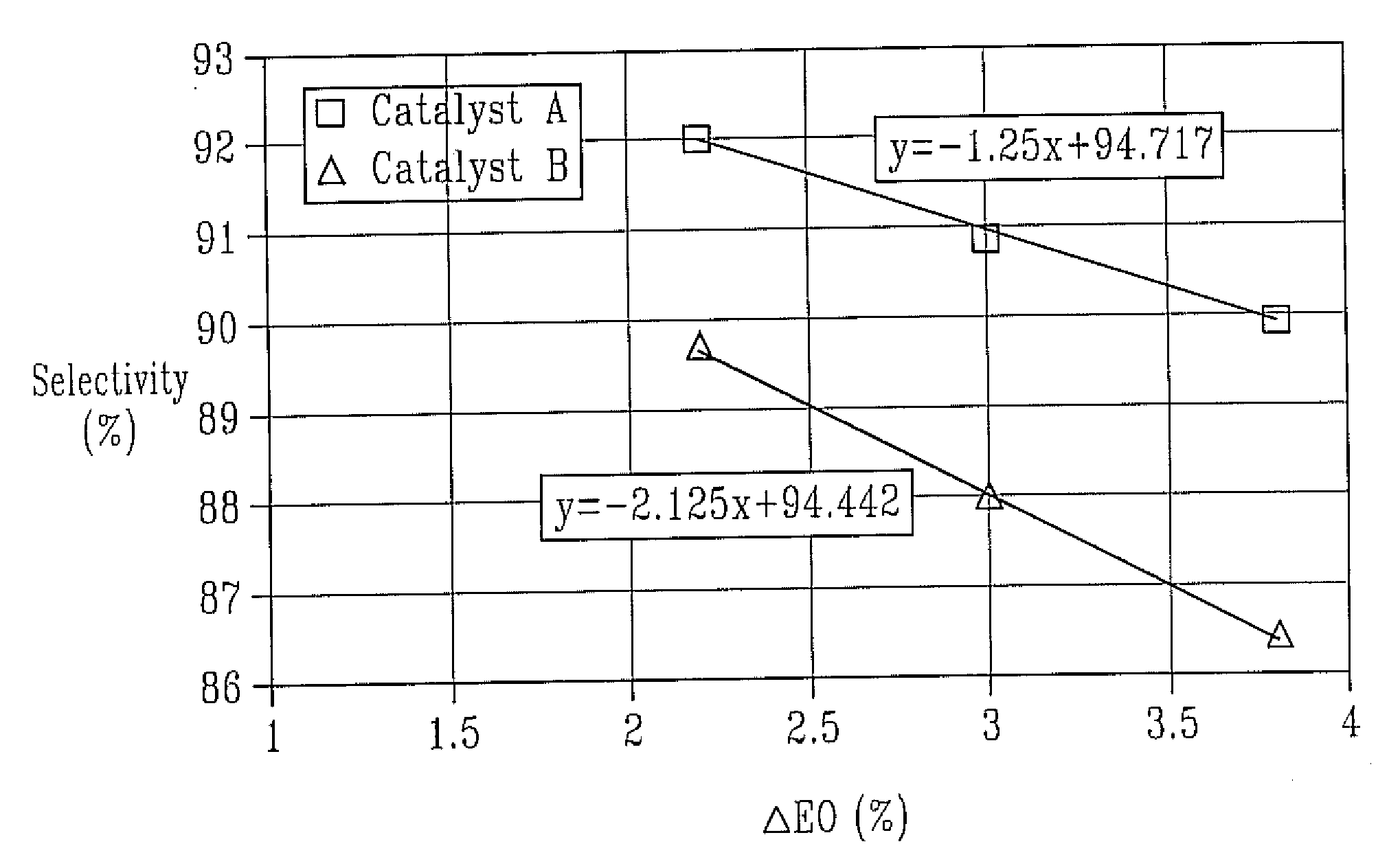
ActiveUS7507845B1Loss in selectivityImprove productivityOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsRheniumProduction rate
The invention relates to a process for the epoxidation of an olefin, wherein the concentration of the olefin oxide in the outlet is greater than about 2.2% by volume. More particularly, the invention relates to a process for the epoxidation of ethylene by contacting a feed including at least ethylene and oxygen with an improved epoxidation catalyst. The catalyst which has improved selectivity in the epoxidation process at high productivities, includes a solid support having a surface, which has a first mode of pores that have a diameter ranging from about 0.01 μm to about 5 μm and having a differential pore volume peak in the range from about 0.01 μm to about 5 μm. The surface also has a second mode of pores, which is different from the first mode of pores, having a diameter ranging from about 1 μm to about 20 μm and have a differential pore volume peak in the range from about 1 μm to about 20 μm. On the bimodal pore surface is a catalytically effective amount of silver or a silver-containing compound, a promoting amount of rhenium or a rhenium-containing compound, and a promoting amount of one or more alkali metals or alkali-metal-containing compounds.
Owner:SD LIZENZVERWGMBH
Preservative compositions
InactiveUS20080234173A1No additional benefitPromote microbial growthCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsEthyl cinnamateBenzaldehyde
The present Invention relates to a preservative composition comprising:a mixture of two to ten of well characterized fragrance raw materials with a cosmetic function, of which at least two are selected from: allyl caproate, benzyl acetate, benzaldehyde, dihydrolsojasmonate, ethyl phenethylacetal, ethyl cinnamate, ethyl methyl phenyl glycidate, ethyl vanillin, 2-heptylcyclopentanone, geranyl acetate, heliotropine, cis-hex-3-en-1-ol, ethylene brassylate, nonalactone gamma, camphylcyclohexanol, undecalactone gamma, 2-t-butylcyclohexylacetate, pentyl salicylate, 2-phenylethanol and 2-phenylethyl acetate; and are contained in at least 20% by weight of said mixture;at least one preservative; and a sequestrant.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Cluster ion implantation for defect engineering
InactiveUS20080299749A1Easily annealed outEffective controlElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolecular clusterCrystallographic defect
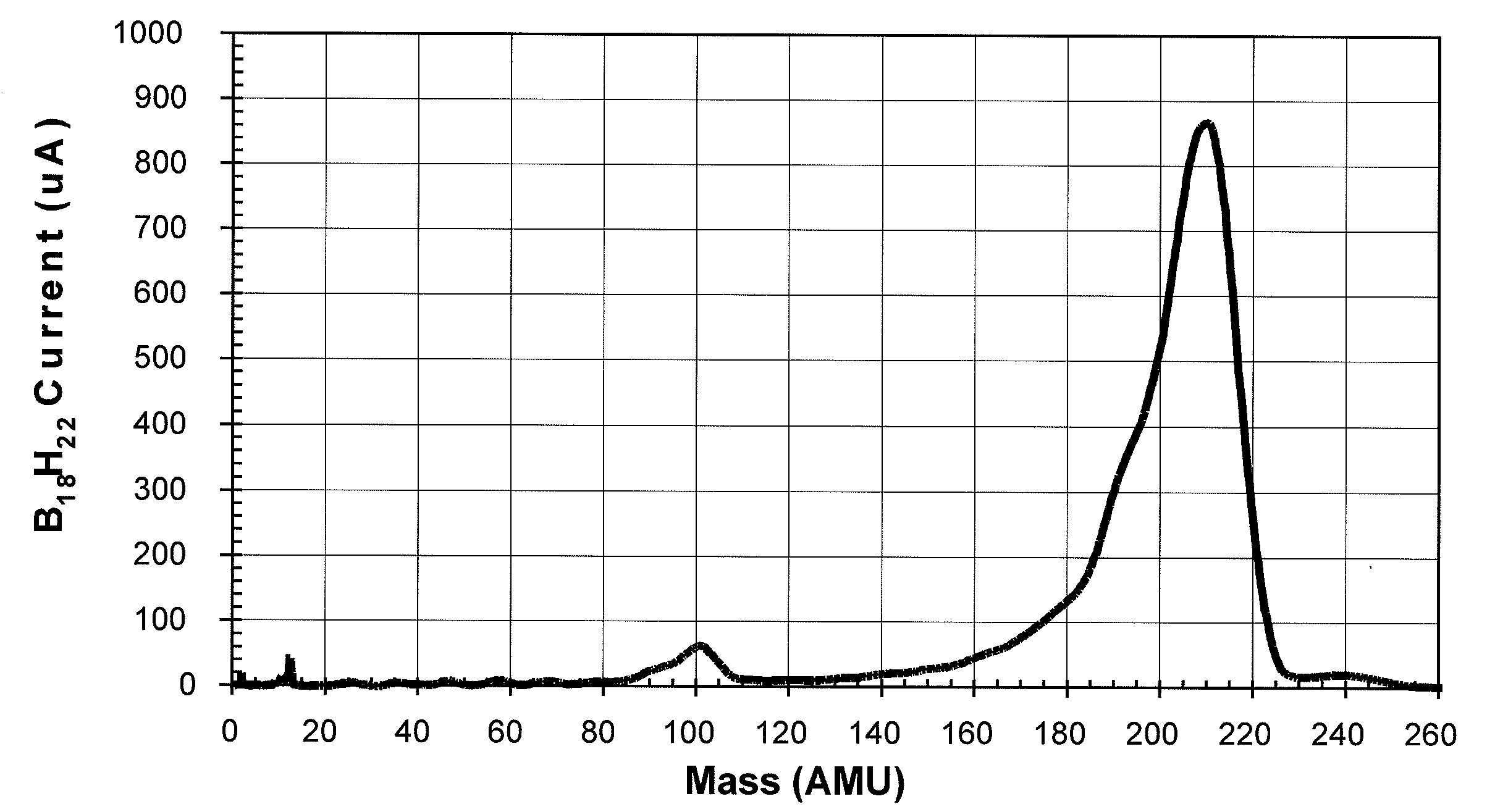
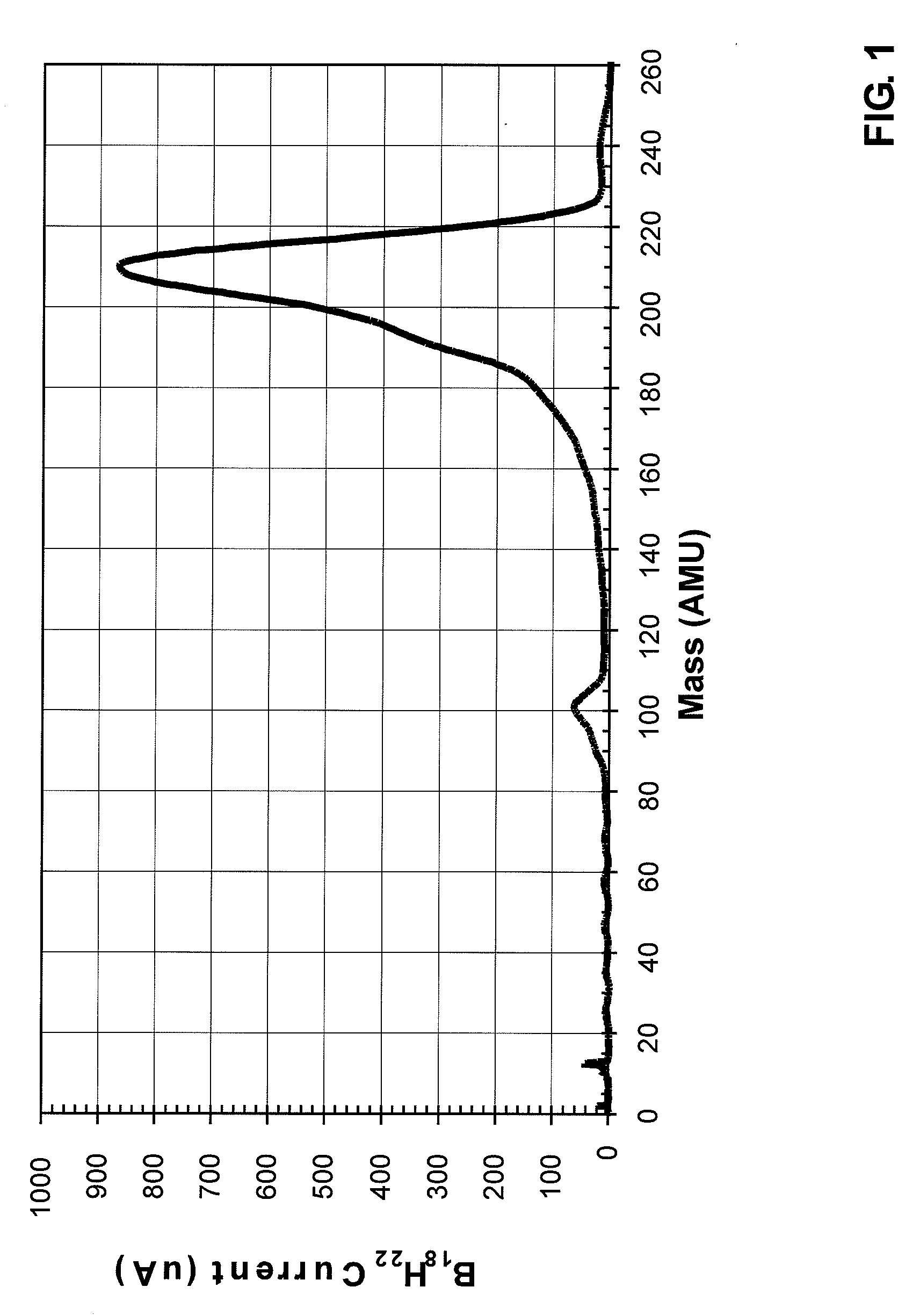
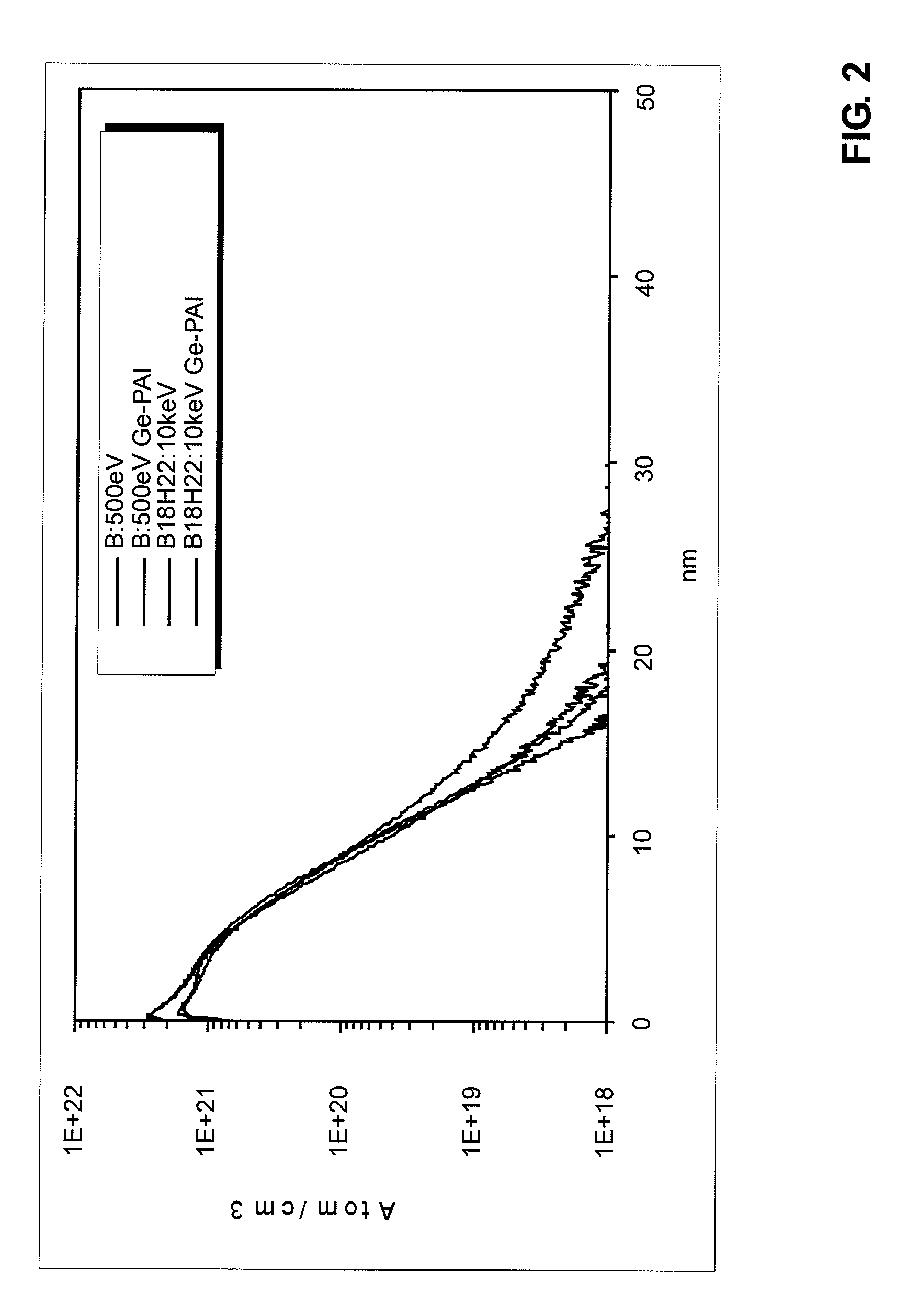
A method of semiconductor manufacturing is disclosed in which doping is accomplished by the implantation of ion beams formed from ionized molecules, and more particularly to a method in which molecular and cluster dopant ions are implanted into a substrate with and without a co-implant of non-dopant cluster ion, such as a carbon cluster ion, wherein the dopant ion is implanted into the amorphous layer created by the co-implant in order to reduce defects in the crystalline structure, thus reducing the leakage current and improving performance of the semiconductor junctions. Dopant ion compounds of the form AnHx+ and AnRzHx+ are used in order to minimize crystal defects as a result of ion implantation. These compounds include co-implants of carbon clusters with implants of monomer or cluster dopants or simply implanting cluster dopants. In particular, the invention described herein consists of a method of implanting semiconductor wafers implanting semiconductor wafers with carbon clusters followed by implants of boron, phosphorus, or arsenic, or followed with implants of dopant clusters of boron, phosphorus, or arsenic. The molecular cluster ions have the chemical form AnHx+ or AnRzHx+, where A designates the dopant or the carbon atoms, n and x are integers with n greater than or equal to 4, and x greater than or equal to 0, and R is a molecule which contains atoms which, when implanted, are not injurious to the implantation process (for example, Si, Ge, F, H or C). These ions are produced from chemical compounds of the form AbLzHm, where the chemical formula of Lz contains R, and b may be a different integer from n and m may be an integer different from x and z is an integer greater than or equal to zero.
Owner:SEMEQUIP
Treatment compositions
InactiveUS20160024427A1No additional benefitCationic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsMedicineEngineering
The present invention relates to treatment compositions containing polymer systems that provide stability and benefit agent deposition as well as methods of making and using same. Such treatment compositions may be used for example as through the wash and / or through the rinse fabric enhancers as well as unit dose treatment compositions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Intelligent drive circuit for a light emitting diode (LED) light engine
InactiveUS20070040518A1Energy consumptionPromote degradationElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitDriving current
Owner:DIALIGHT CORP
Sun protective fabric
InactiveUS6025284AReduce ultraviolet radiation transmissionLow production costGarment special featuresSynthetic fibresWrinkle skinPolyester
Wrinkled fabrics comprising ultraviolet absorbers are disclosed which provide improvements in ultraviolet transmission, wearer comfort, and cost over those of the prior art. The preferred fabric is polyester and the preferred UV absorbers are chlorobenzotriazoles. The polyester is wrinkled permanently so as to provide an extra barrier to ultraviolet radiation from solely utilizing UV absorbers alone. This wrinkled product is also more comfortable to a wearer, particularly in warm weather or hotter climates. Other non-apparel uses are also contemplated including tents, awnings, and crowd covers. A method of making such a fabric is also disclosed comprising stuffing a jet dyeing machine with a more than normal load amount of fabric and eventually heat setting such resultant wrinkles into the finished product.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO +1
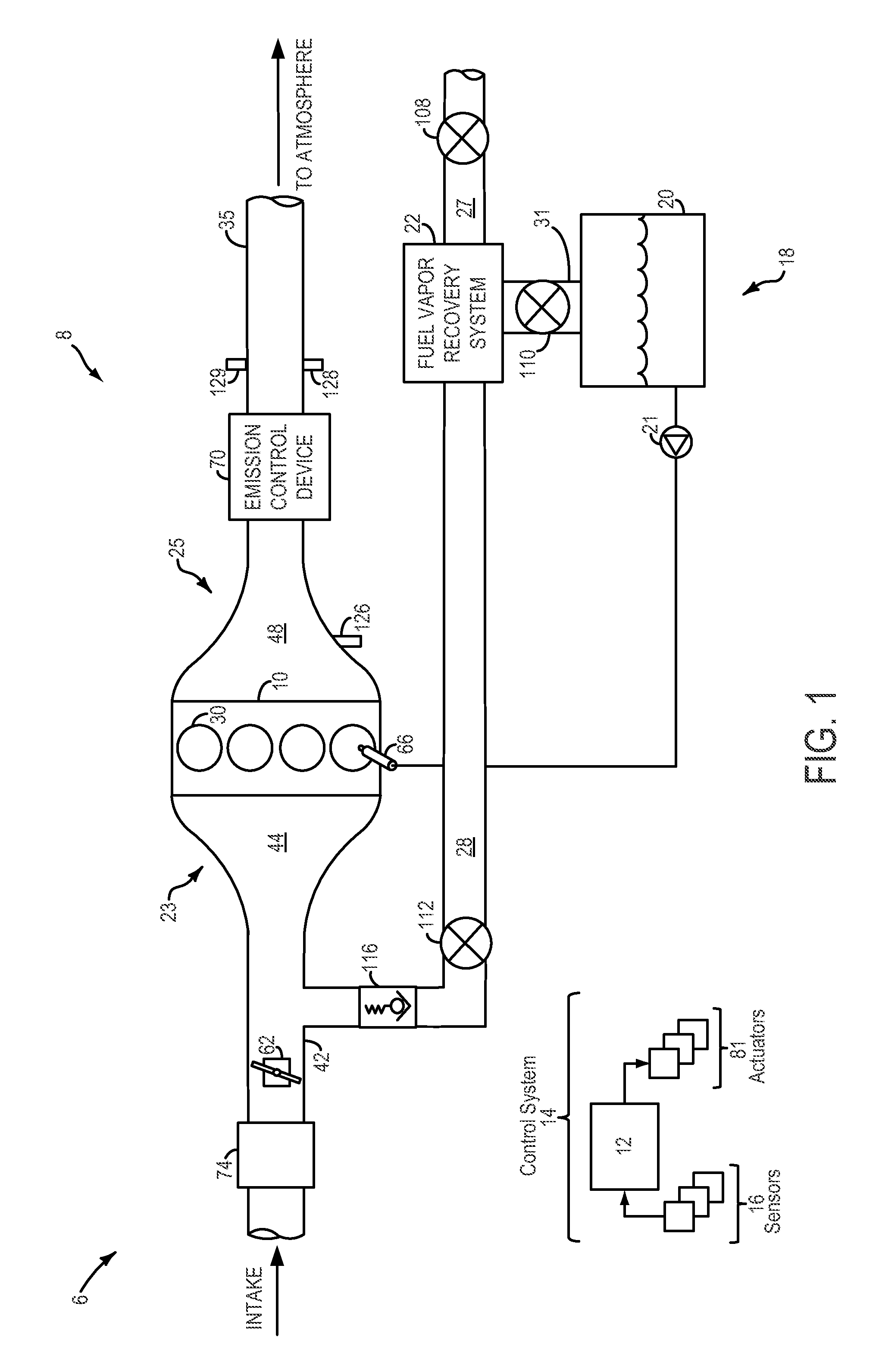
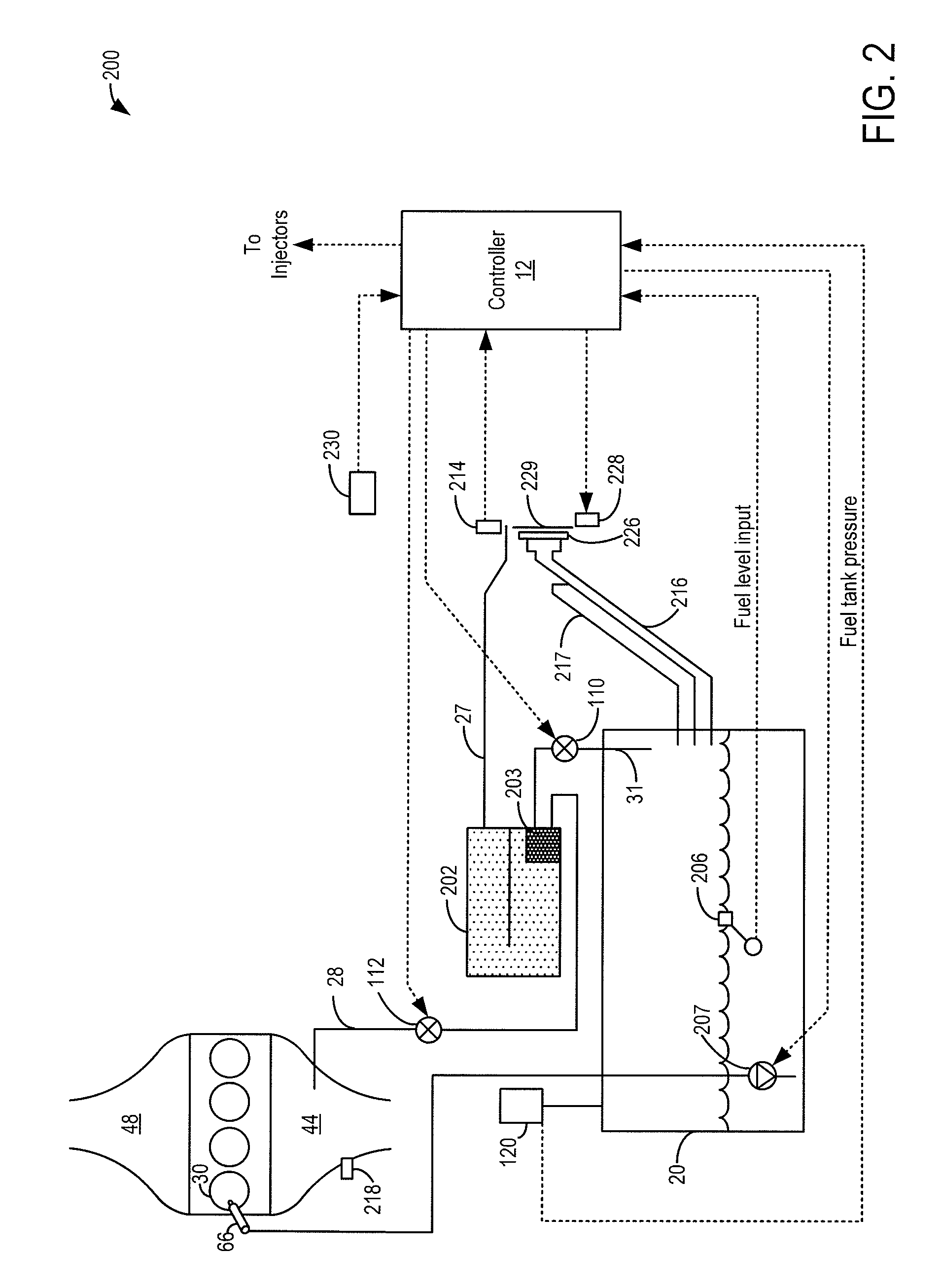
Method and system for fuel vapor control
ActiveUS8434461B2Shorten operation timeEnable fuel economyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelMachines/enginesIsolation valveFuel vapor
Methods and systems are provided for operating a fuel vapor recovery system having a fuel tank isolation valve coupled between a fuel tank and a canister. Fuel vapors are purged from the fuel tank to a canister buffer over a plurality of purge pulses. The pulses are adjusted based on the buffer capacity, a purge flow rate, and a fuel tank pressure to improve control of canister loading and reduce air-to-fuel ratio disturbances.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Rinse-Off Conditioning Composition Comprising a Near-Terminal Branched Alcohol
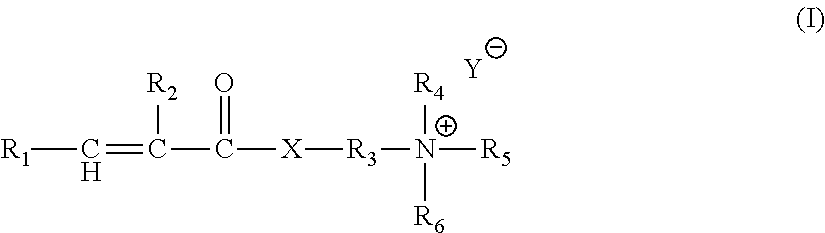
InactiveUS20120014901A1Increase depositionNo additional benefitCosmetic preparationsCationic surface-active compoundsAlcoholSURFACTANT BLEND
A rinse-off conditioning composition comprising: (a) near-terminal branched alcohol according to Formula I; (b) a cationic surfactant; (c) a terminal aminosilicone; wherein the near-terminal branched alcohol and the cationic surfactant are comprised in a lamellar gel matrix.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
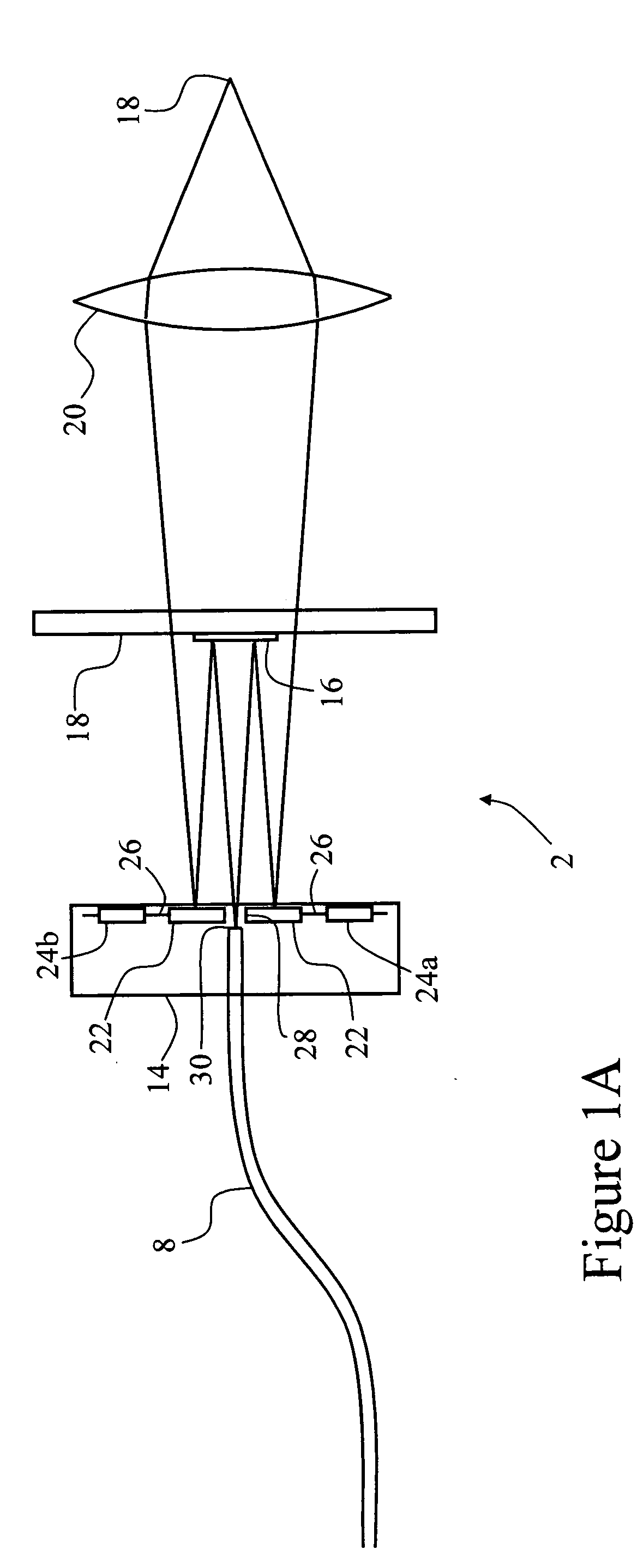
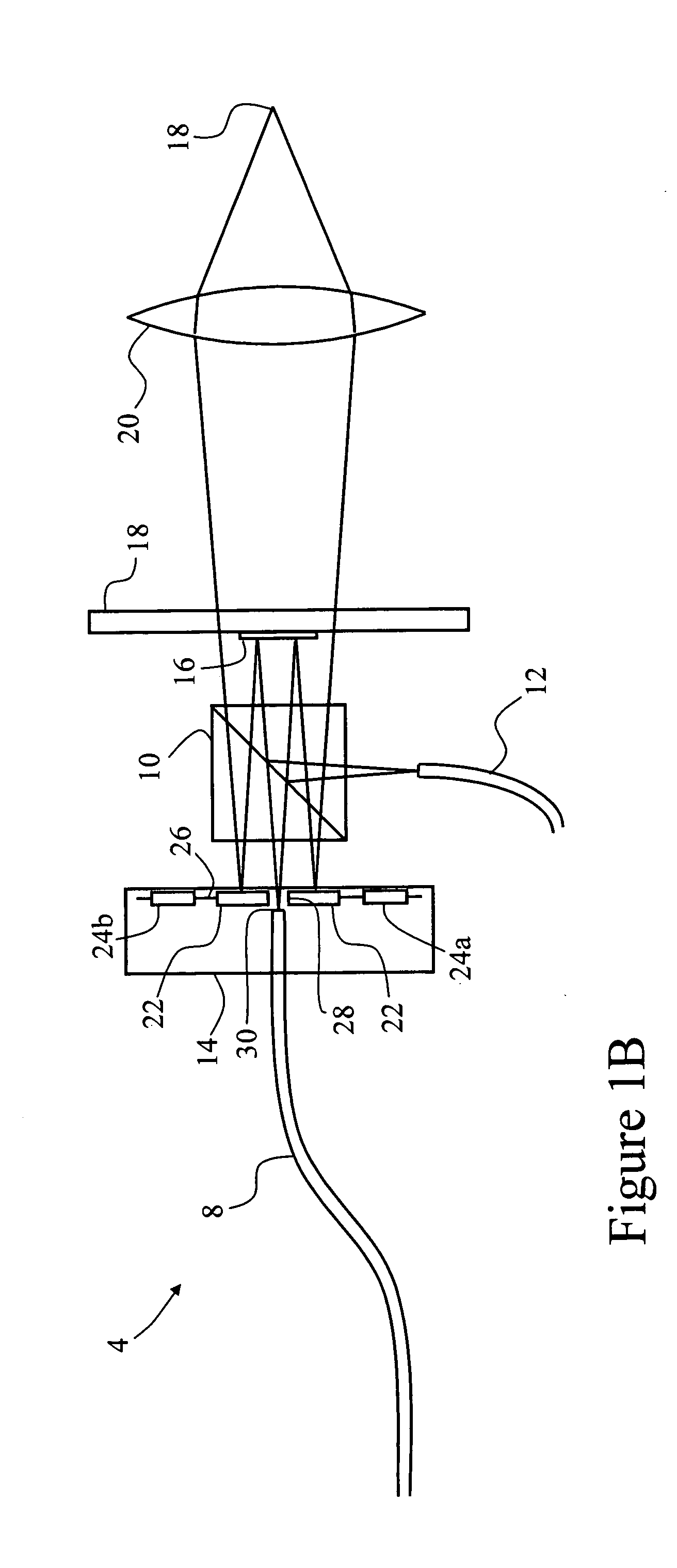
Light scanning device
InactiveUS20050162722A1Reduce vibrationReduce transmissionMicroscopesTelescopesOptoelectronicsLight scanning
The invention provides a light scanning device for scanning light from a light source, the light scanning device having: a pivotably mounted mirror for receiving light from the light source; a counterbalance; and a drive for oscillatorily pivoting the mirror and the counterbalance simultaneously in opposite directions to reduce uncoupled forces.
Owner:OPTISCAN +1
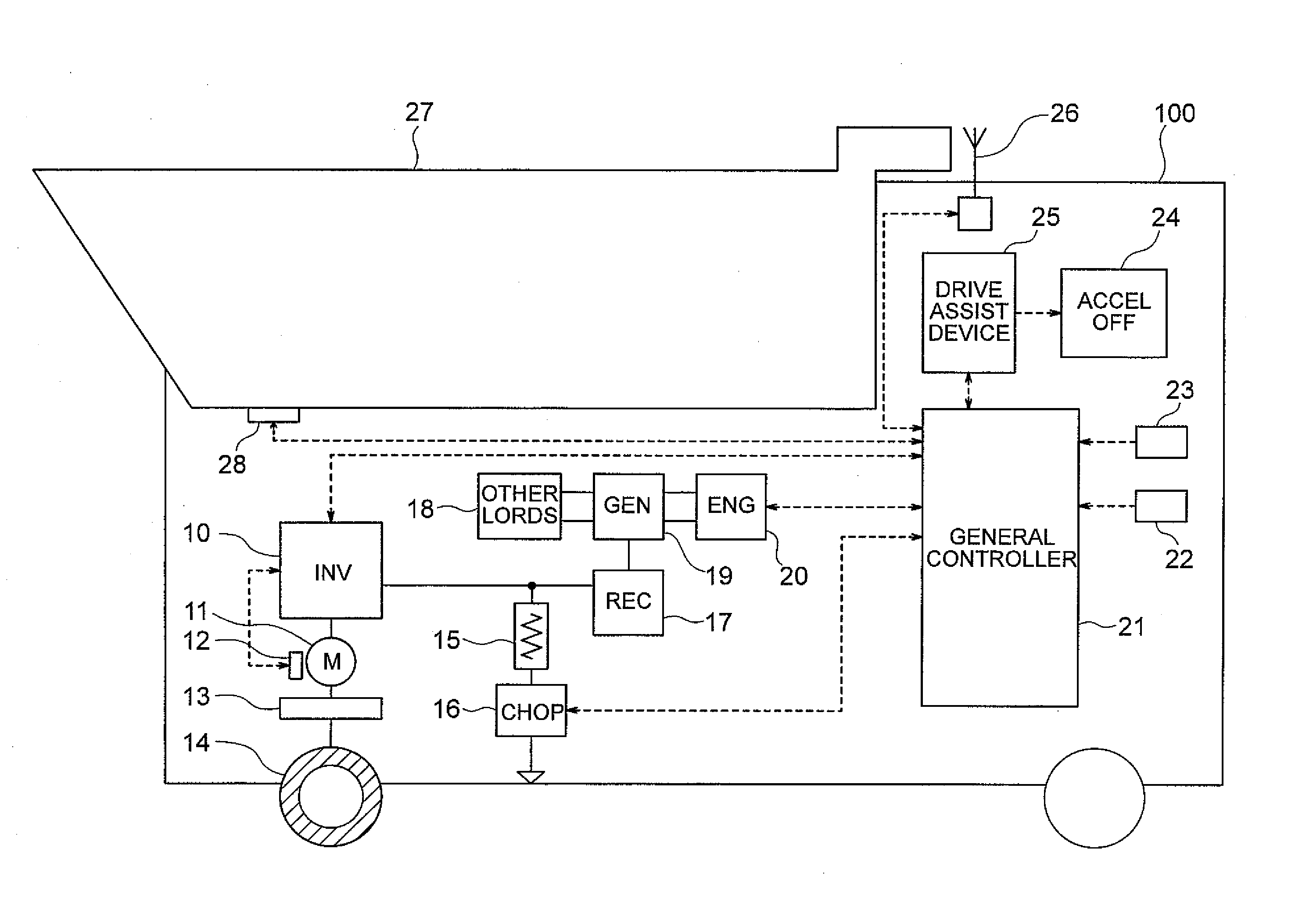
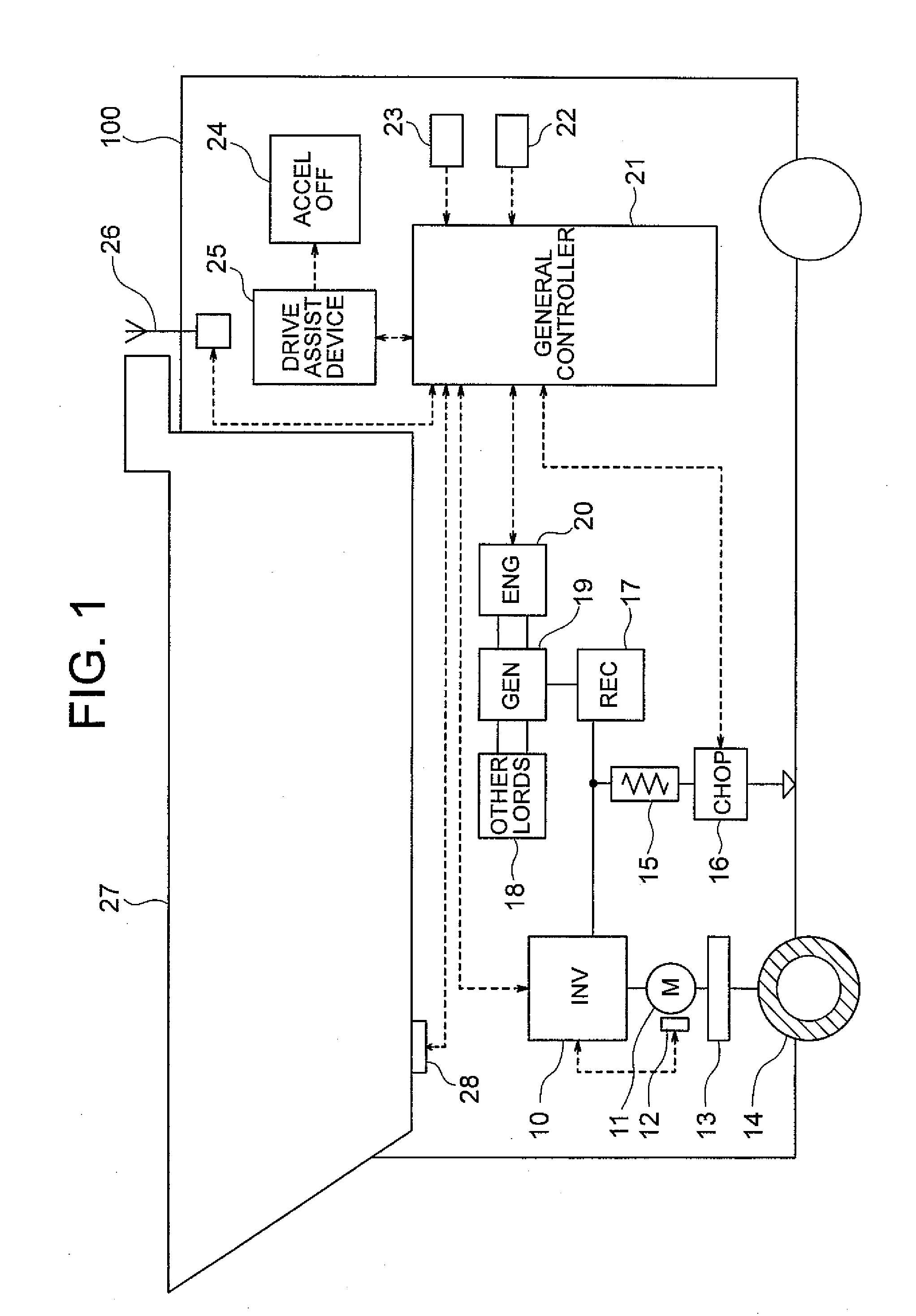
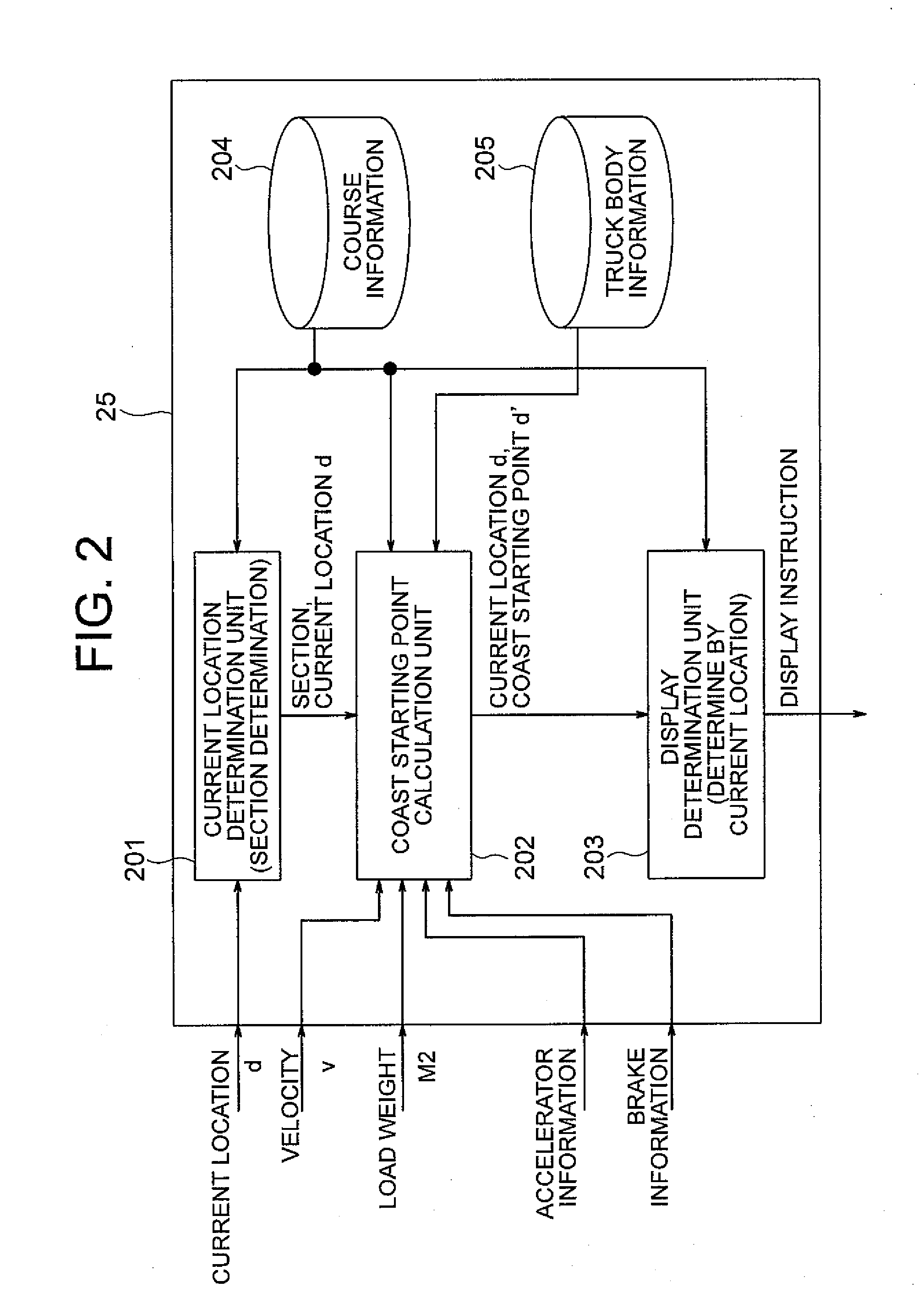
Drive assist device and method for motor driven truck
InactiveUS20100256848A1Reduce fuel consumptionReduce probabilityDigital data processing detailsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingDriver/operatorMotor drive
A drive assist device for a diesel-electric driven truck is provided to guide and assist a driver in starting to coast so that appropriate coasting deceleration suitable for load weight is realized. The drive assist device includes a course information database that stores information about a course, a truck body information database that stores information about the truck body, a current location determination unit that calculates current location information, a coast initiation timing calculation unit that calculates timing of coasting based on a current location and velocity of the truck and a target velocity at a predetermined point ahead of the truck, those of which being obtained from the databases and input information, the timing of coasting being used to achieve the target velocity at the predetermined point and a guidance unit that informs a truck driver of the timing of coasting according to an output of the calculation unit.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
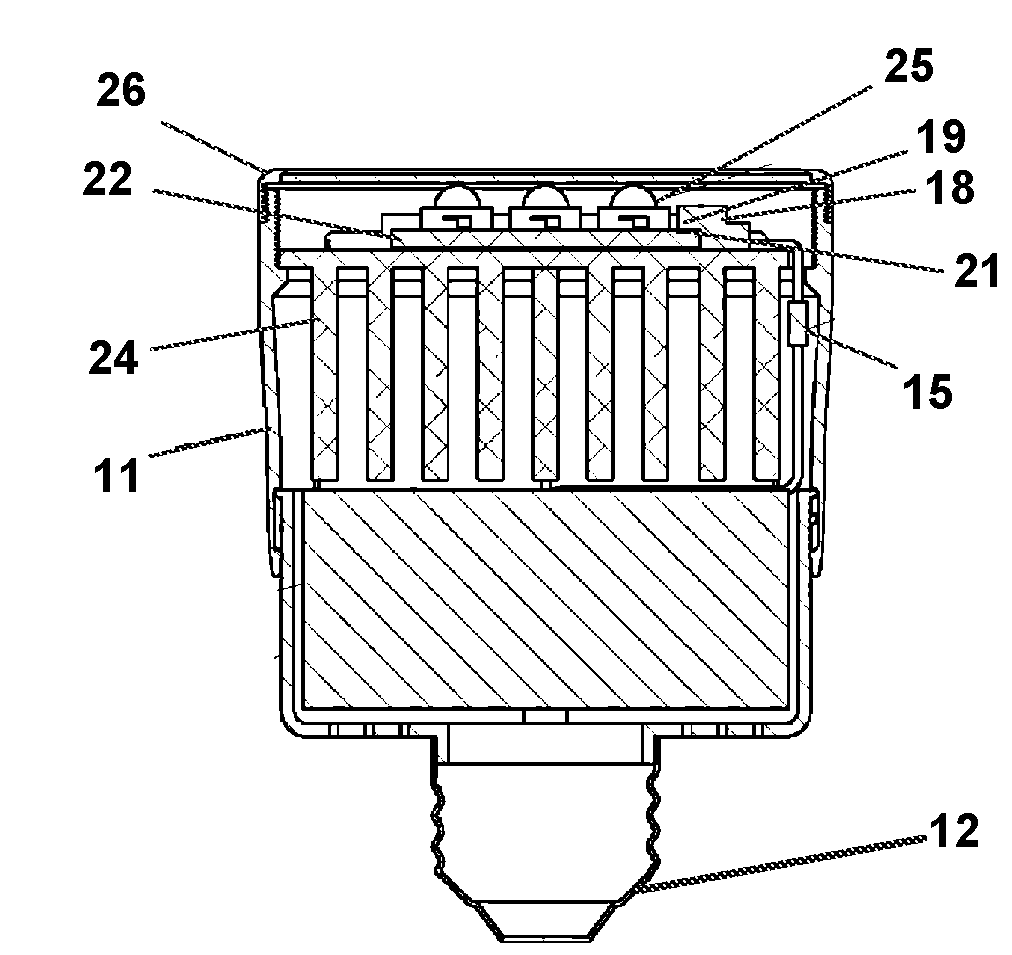
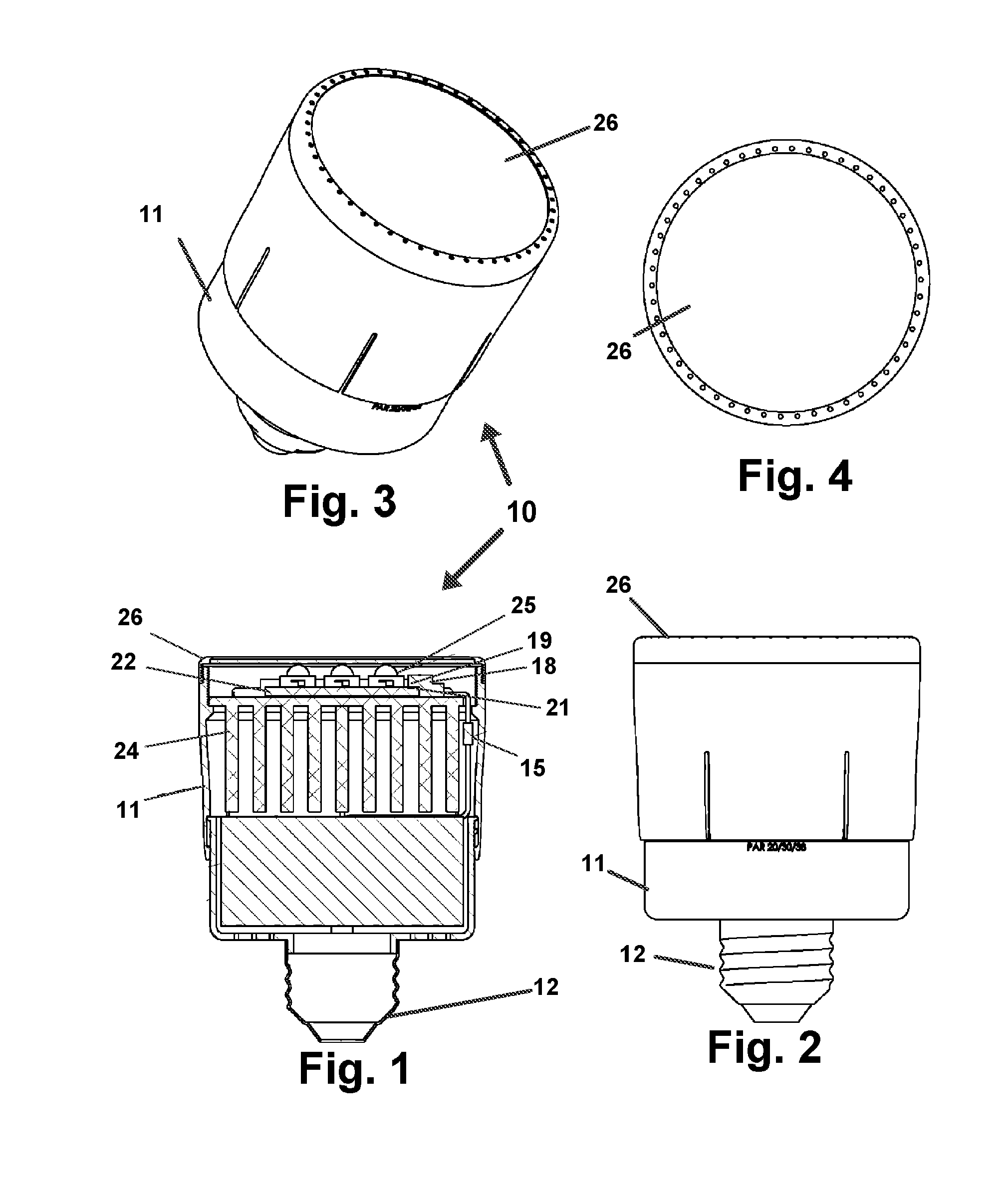
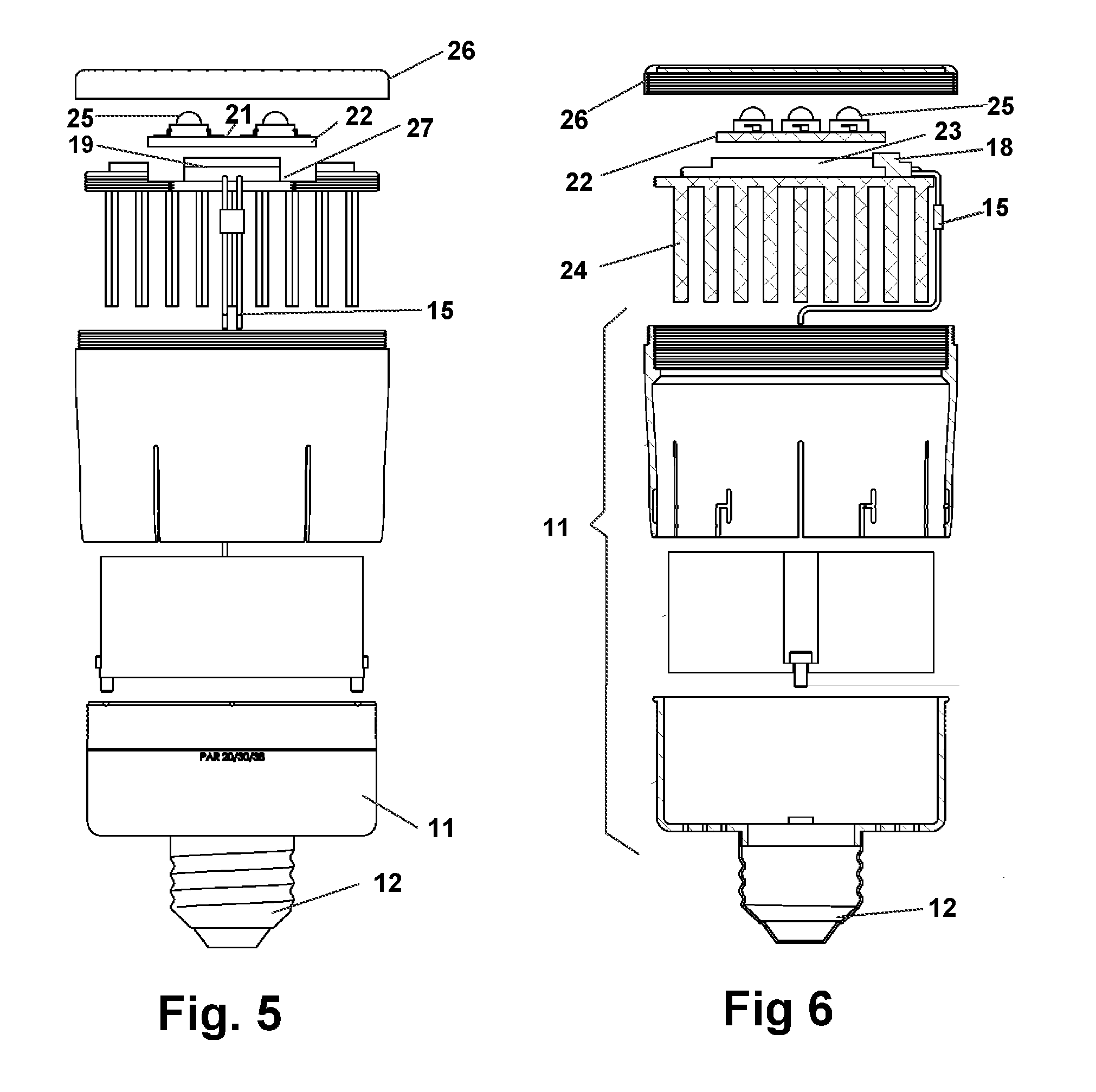
Modular LED light system and method
InactiveUS20100177515A1Rapid and easy deploymentSafer configurationLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceLighting systemEngineering
A modular device and system for formation of an LED based light bulb. The formed bulb is assembled from interchangeable components which adapted it for engagement to any of a plurality of conventional bulb light fixture connectors. Diffusors and hoods are also attachable to change the diffusion and focus of light emitted from the formed bulb. A plurality of different circuit boards may be engaged to a socket positioned on a heat sink to increase or decrease emitted light. The socket will only electrically engage the circuit board if the heat sink will dissipate the anticipated heat generated by the circuit board.
Owner:SHOUSHTARI HAMID
Respiratory disease treatment
InactiveUS8236786B2Anti-inflammatory effect of the compound to be achieved more efficientlyNo additional benefitBiocidePowder deliveryEnantiomerInhalation
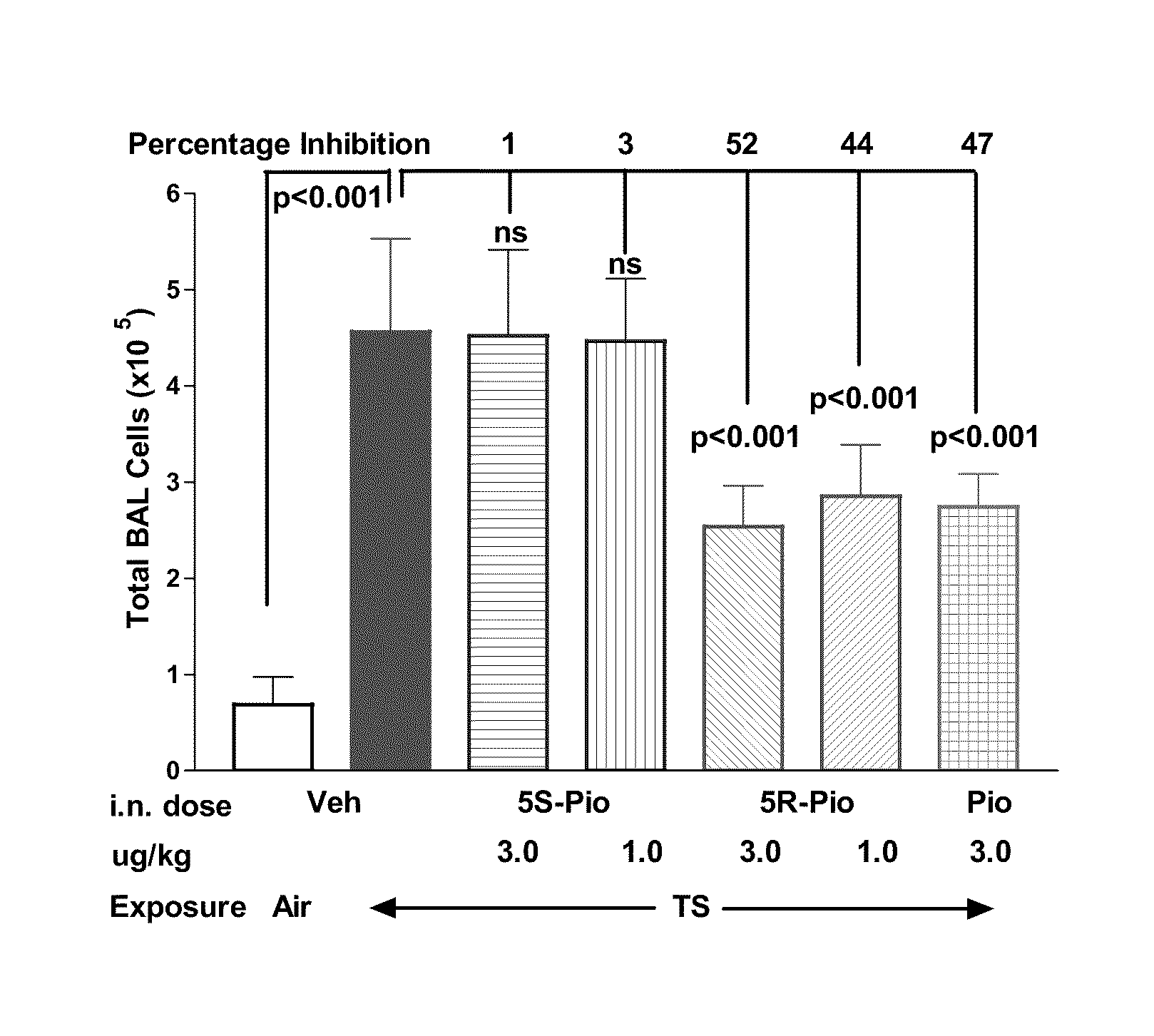
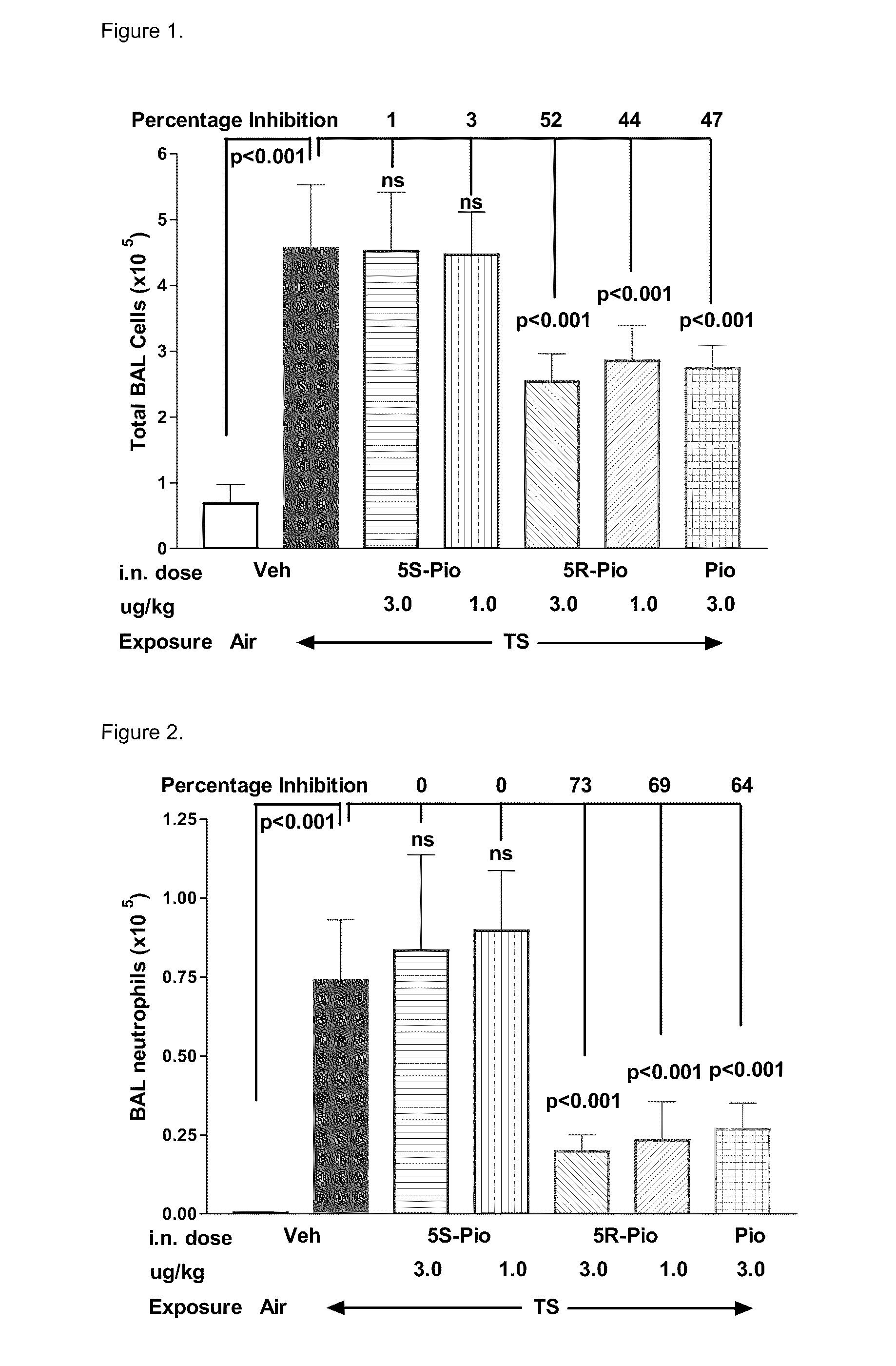
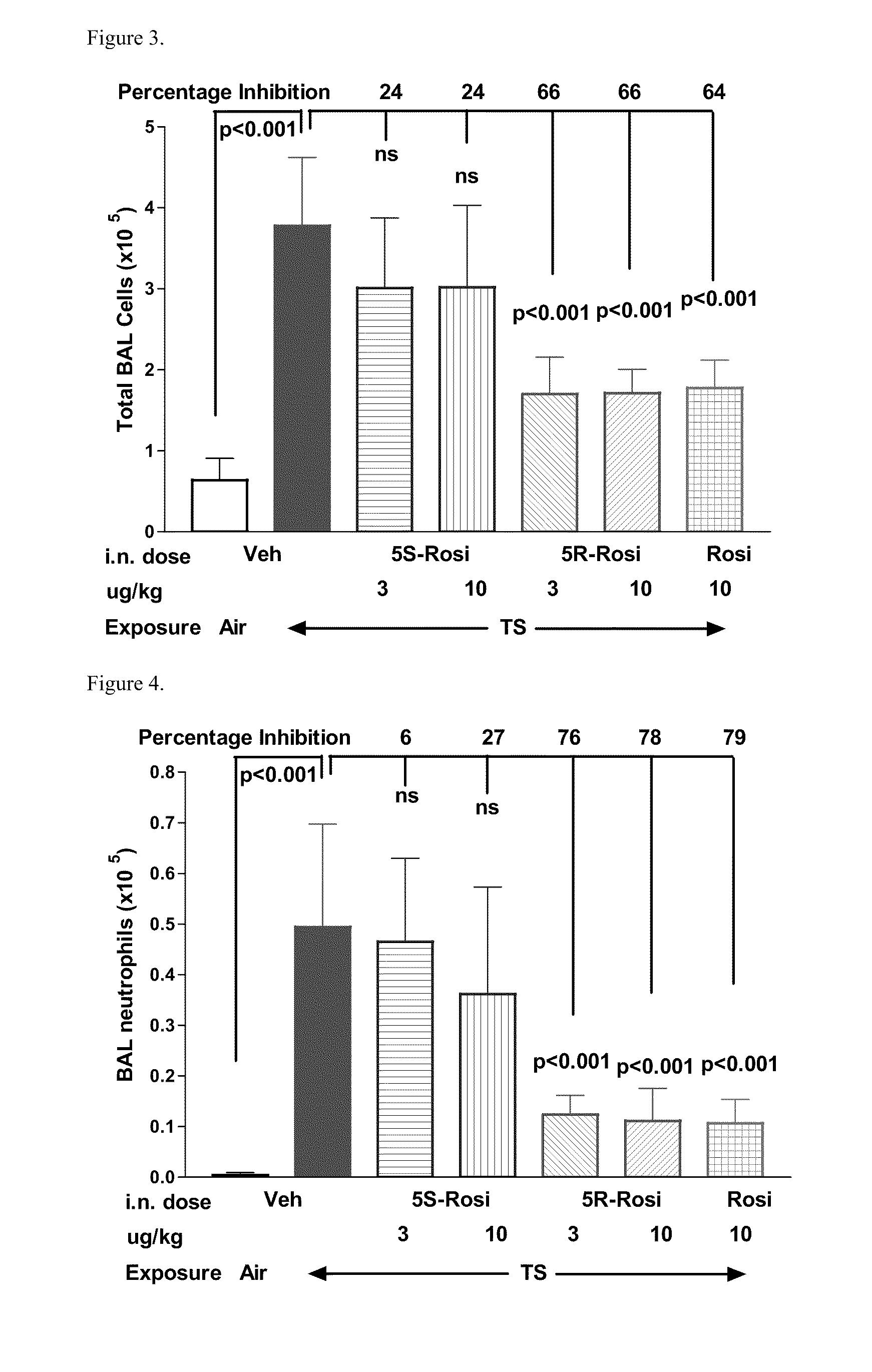
There is provided a pharmaceutical composition that is adapted for pulmonary administration by inhalation, which composition comprises a glitazone, such as pioglitazone or rosiglitazone, and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and / or excipients, and wherein the glitazone content of the composition consists of at least 95% by weight of the 5R enantiomer and less than 5% by weight of the 5S enantiomer. There is also provided a use and kit.
Owner:PULMAGEN THERAPEUTICS INFLAMMATION LTD
Treatment compositions
InactiveUS20160024428A1No additional benefitCationic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsBiomedical engineeringPolymer
The present invention relates to treatment compositions containing polymer systems that provide stability and benefit agent deposition as well as methods of making and using same. Such treatment compositions may be used for example as through the wash and / or through the rinse fabric enhancers as well as unit dose treatment compositions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method of manufacturing light emitting device, and light emitting device
ActiveUS20150155447A1Good light sourceImprove light extraction efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescencePhosphor
A method for manufacturing a light emitting device, having; a die bonding step of mounting a light emitting element on a board; a phosphor layer formation step of forming a phosphor layer that contains a phosphor by spraying on surfaces of the board and the light emitting element after the die bonding step; and a cover layer formation step of forming a cover layer that contains at least one type of light reflecting material and light blocking material on a surface of the phosphor layer over the board.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Aircraft engine fuel system
ActiveUS20150100220A1Optimising engine efficiencyNo additional benefitAnalogue computers for vehiclesEfficient propulsion technologiesCombustionEngineering
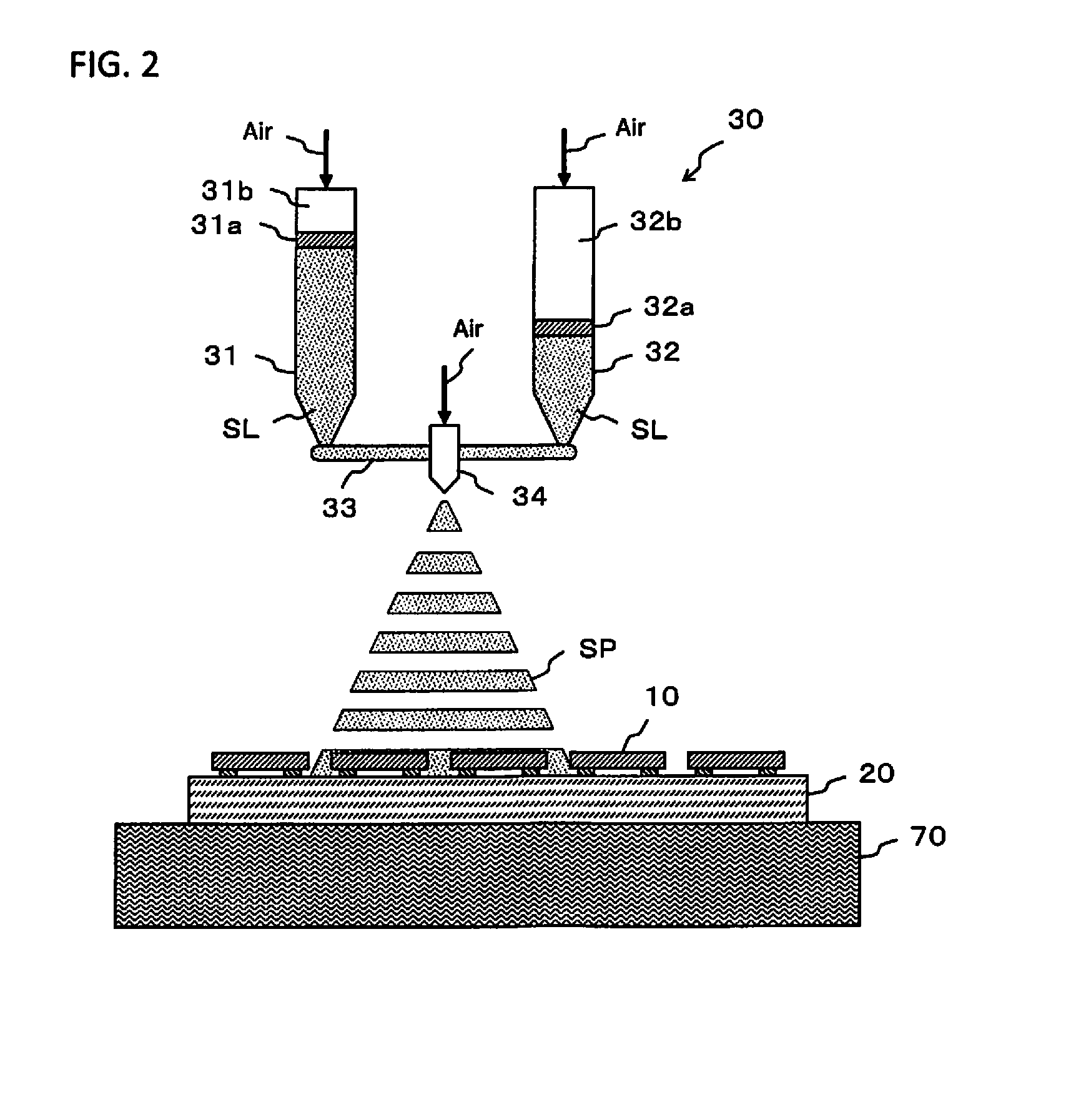
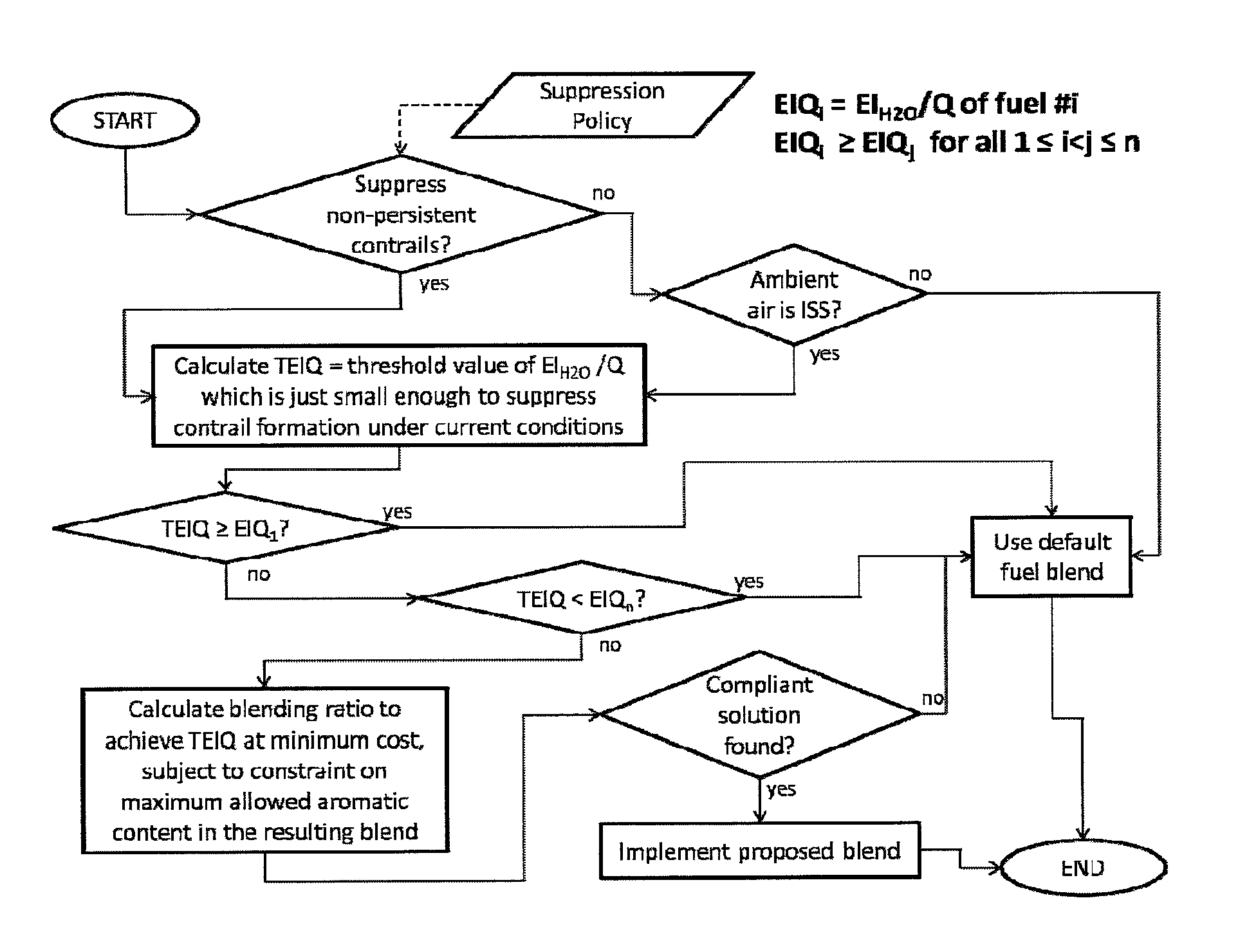
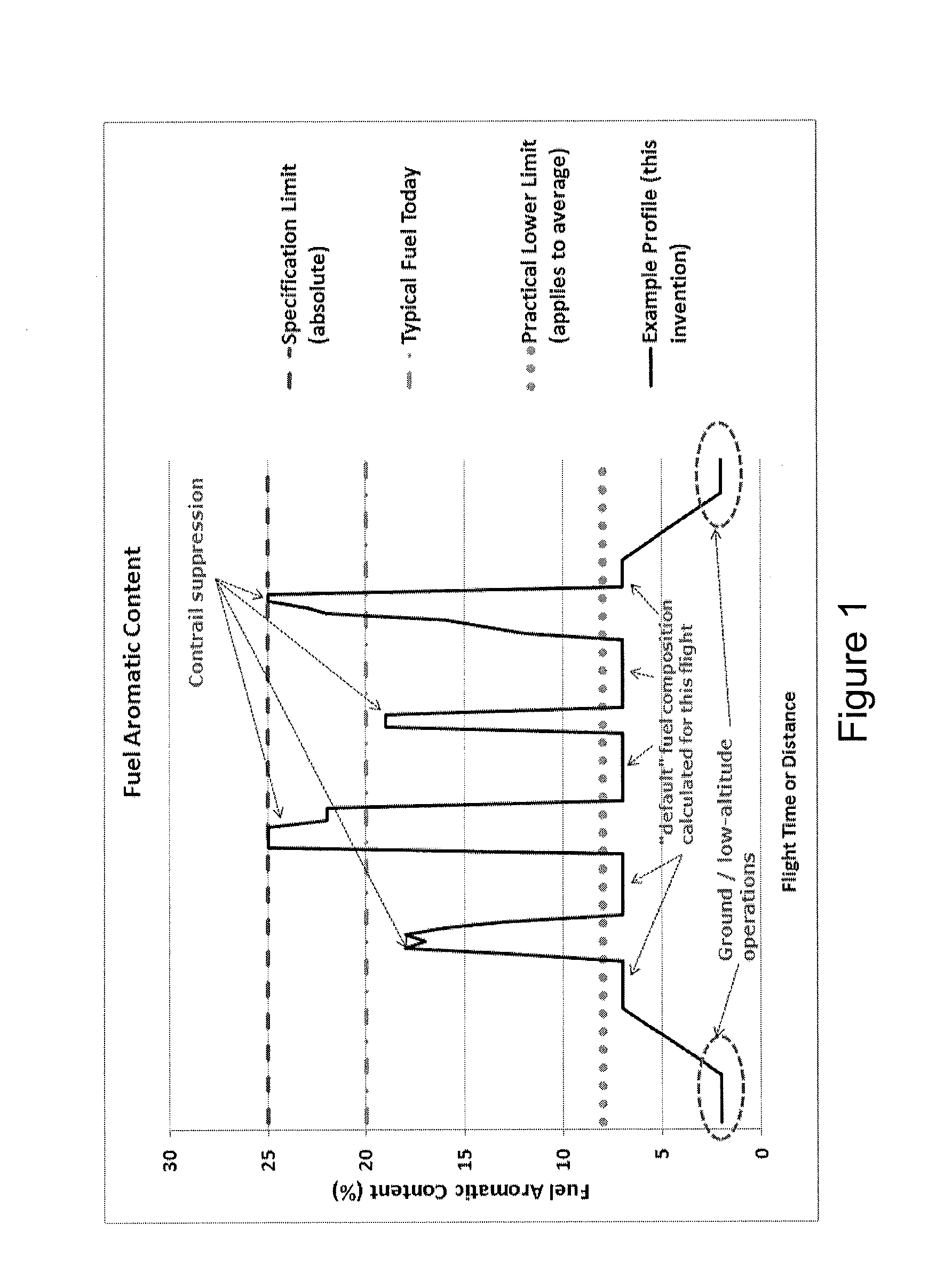
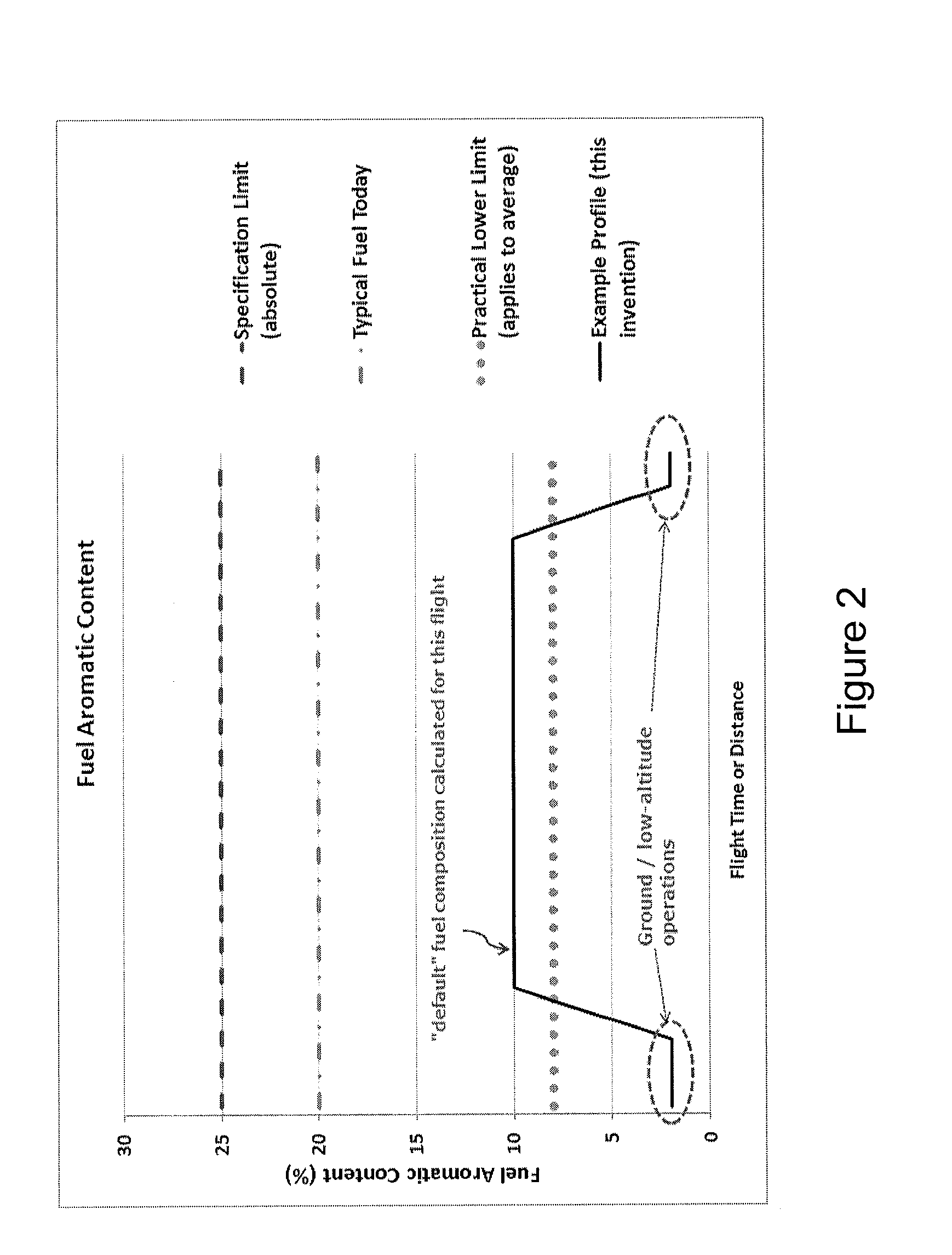
This invention concerns a method of delivering fuel to an aircraft engine 60, which involves providing a plurality of distinct fuel sources 20, 22, a first fuel source 20 comprising a first fuel having a first aromatic content and a second fuel source 22 comprising a second fuel having a second aromatic content. One or more ambient atmospheric condition is determined for at least a portion of a flight path of the aircraft, said condition being indicative of a likelihood of contrail 135 formation by the engine 60. A desirous fuel composition for combustion by the engine is determined based upon the one or more ambient atmospheric condition and a ratio of the first and second fuels from said respective fuel sources is selected according to said desirous fuel composition. The selected ratio of the first and second fuels is delivered to the aircraft engine 60.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Method and system for limiting use of electronic equipment
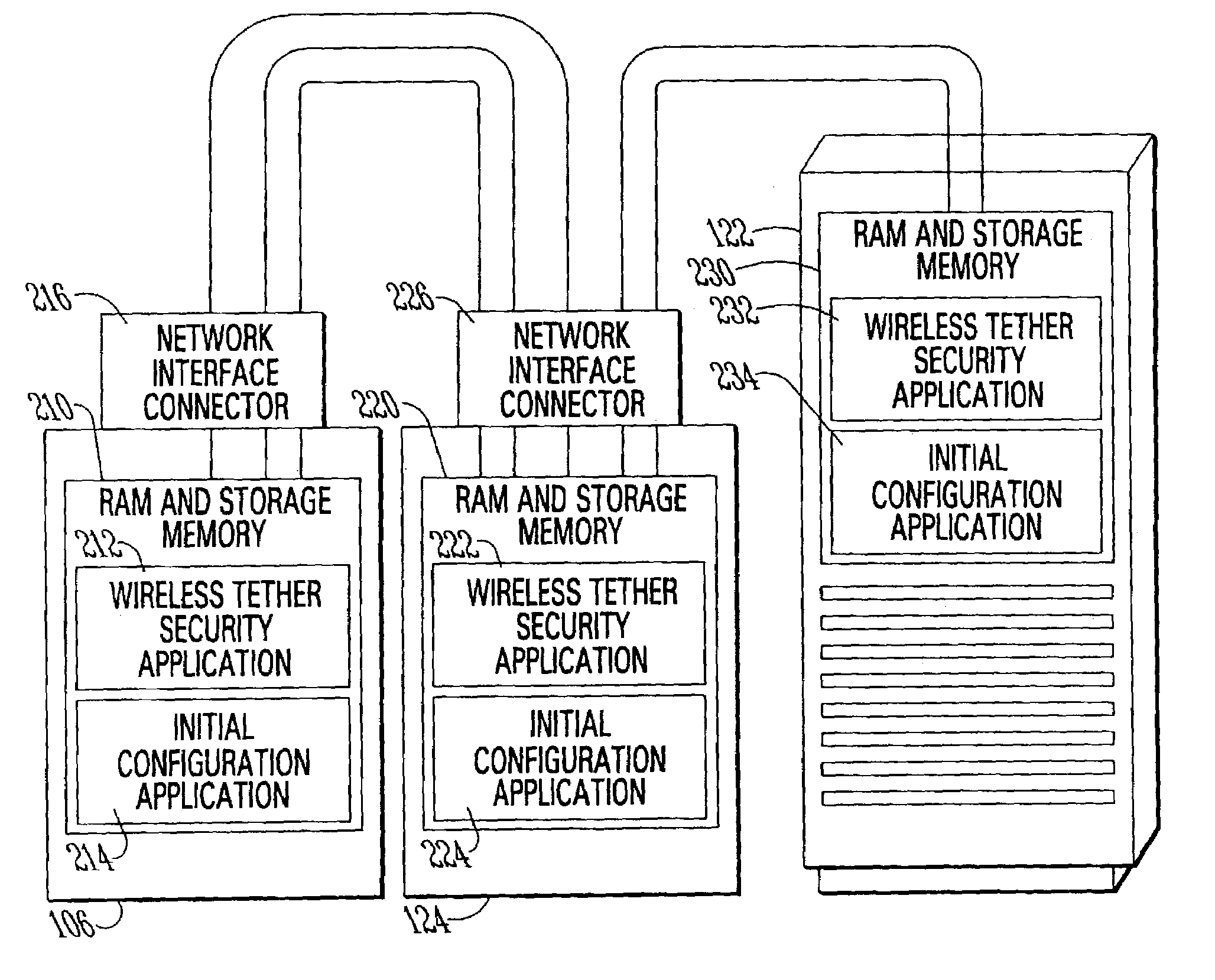
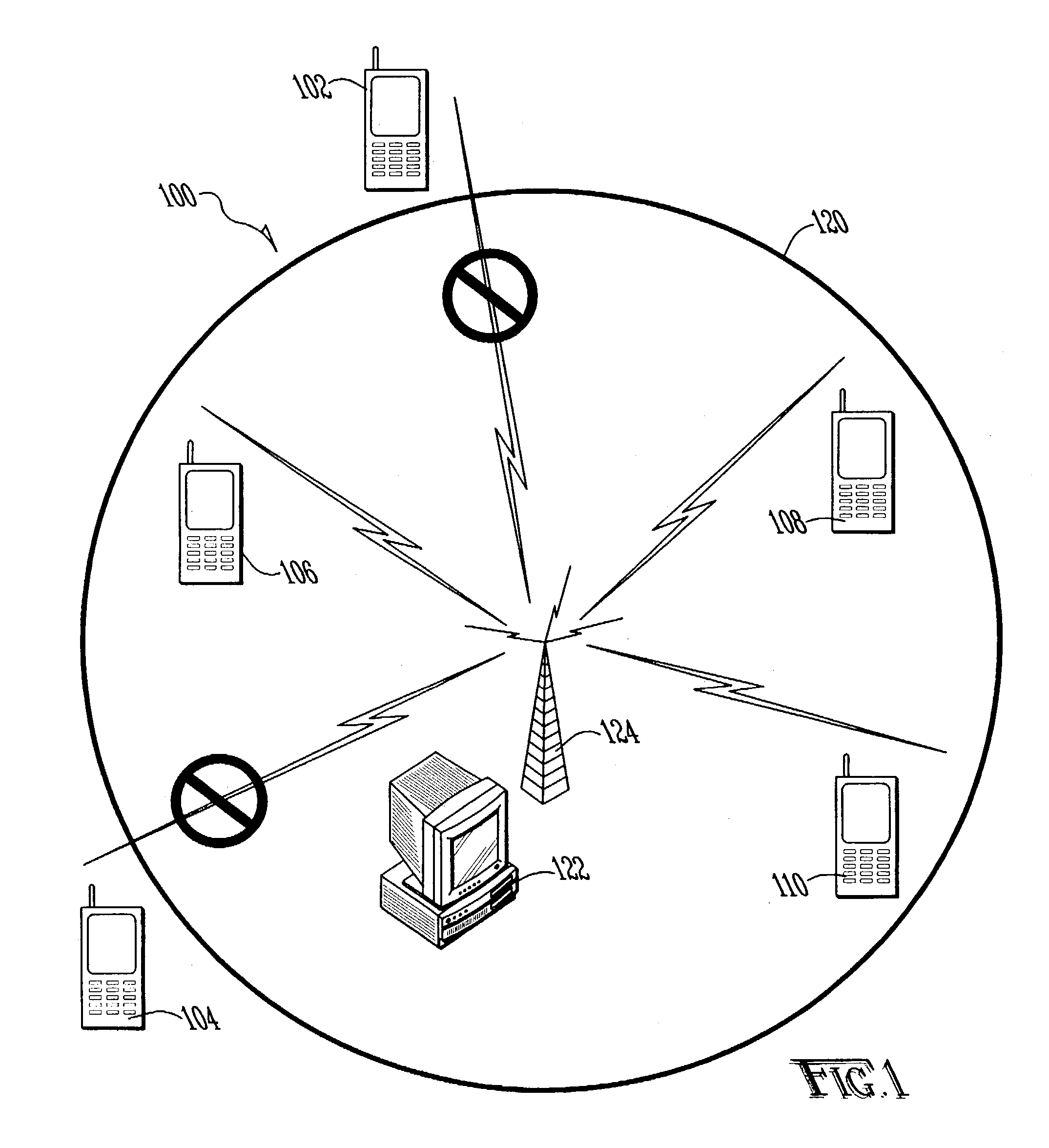
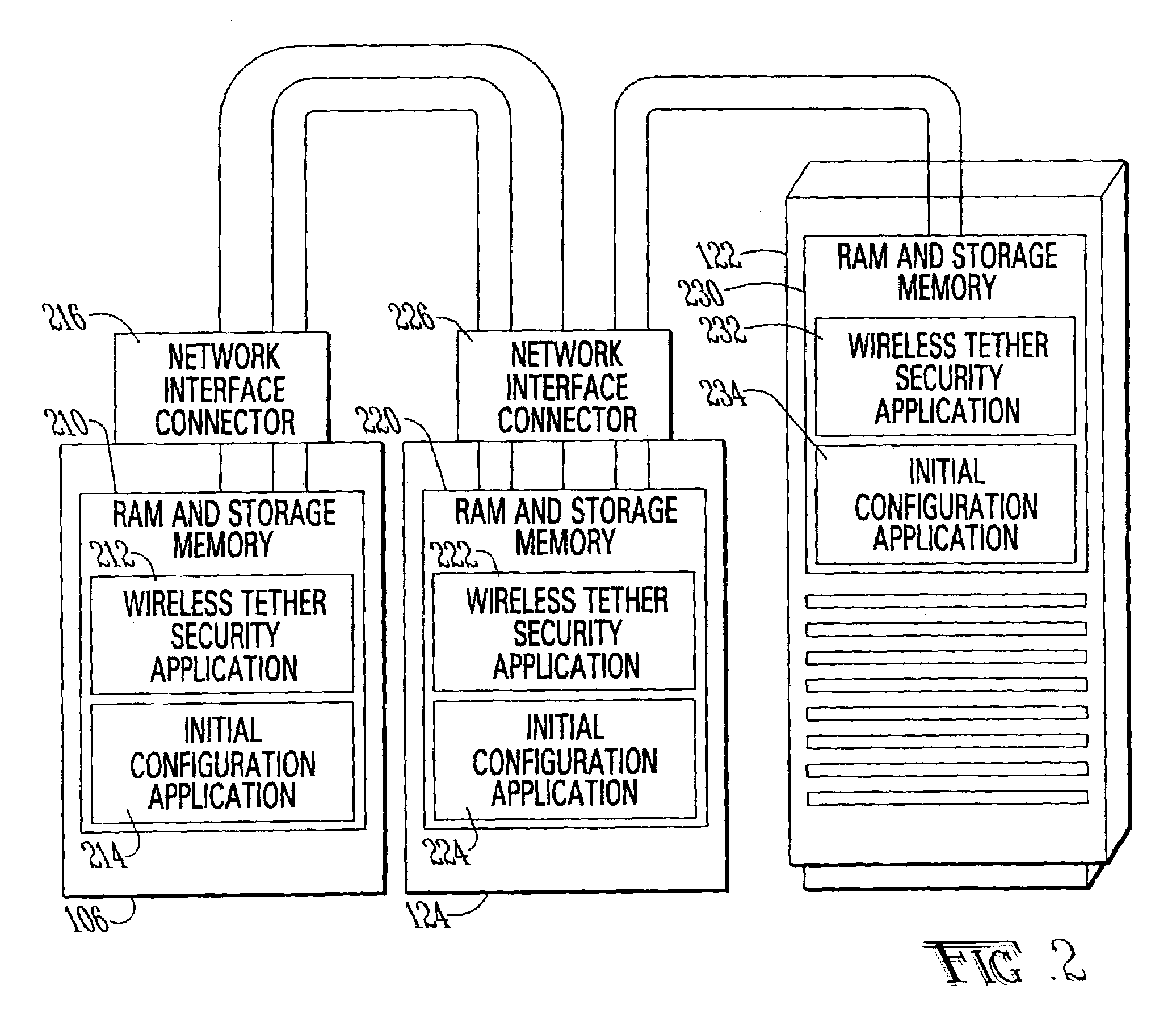
ActiveUS7034659B2Improve securityLow efficiencyElectric signal transmission systemsVolume/mass flow measurementElectron device
A system and method for securing electronic devices with a non-physical tether which automatically disables operation of the device when the device fails to confirm its location within a predetermined area and / or connection to a predetermined network.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
Process for production of an olefin oxide
ActiveUS20090062557A1Loss in selectivityImprove productivityOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsRheniumProduction rate
The invention relates to a process for the epoxidation of an olefin, wherein the concentration of the olefin oxide in the outlet is greater than about 2.2% by volume. More particularly, the invention relates to a process for the epoxidation of ethylene by contacting a feed including at least ethylene and oxygen with an improved epoxidation catalyst. The catalyst which has improved selectivity in the epoxidation process at high productivities, includes a solid support having a surface, which has a first mode of pores that have a diameter ranging from about 0.01 μm to about 5 μm and having a differential pore volume peak in the range from about 0.01 μm to about 5 μm. The surface also has a second mode of pores, which is different from the first mode of pores, having a diameter ranging from about 1 μm to about 20 μm and have a differential pore volume peak in the range from about 1 μm to about 20 μm. On the bimodal pore surface is a catalytically effective amount of silver or a silver-containing compound, a promoting amount of rhenium or a rhenium-containing compound, and a promoting amount of one or more alkali metals or alkali-metal-containing compounds.
Owner:SD LIZENZVERWGMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com