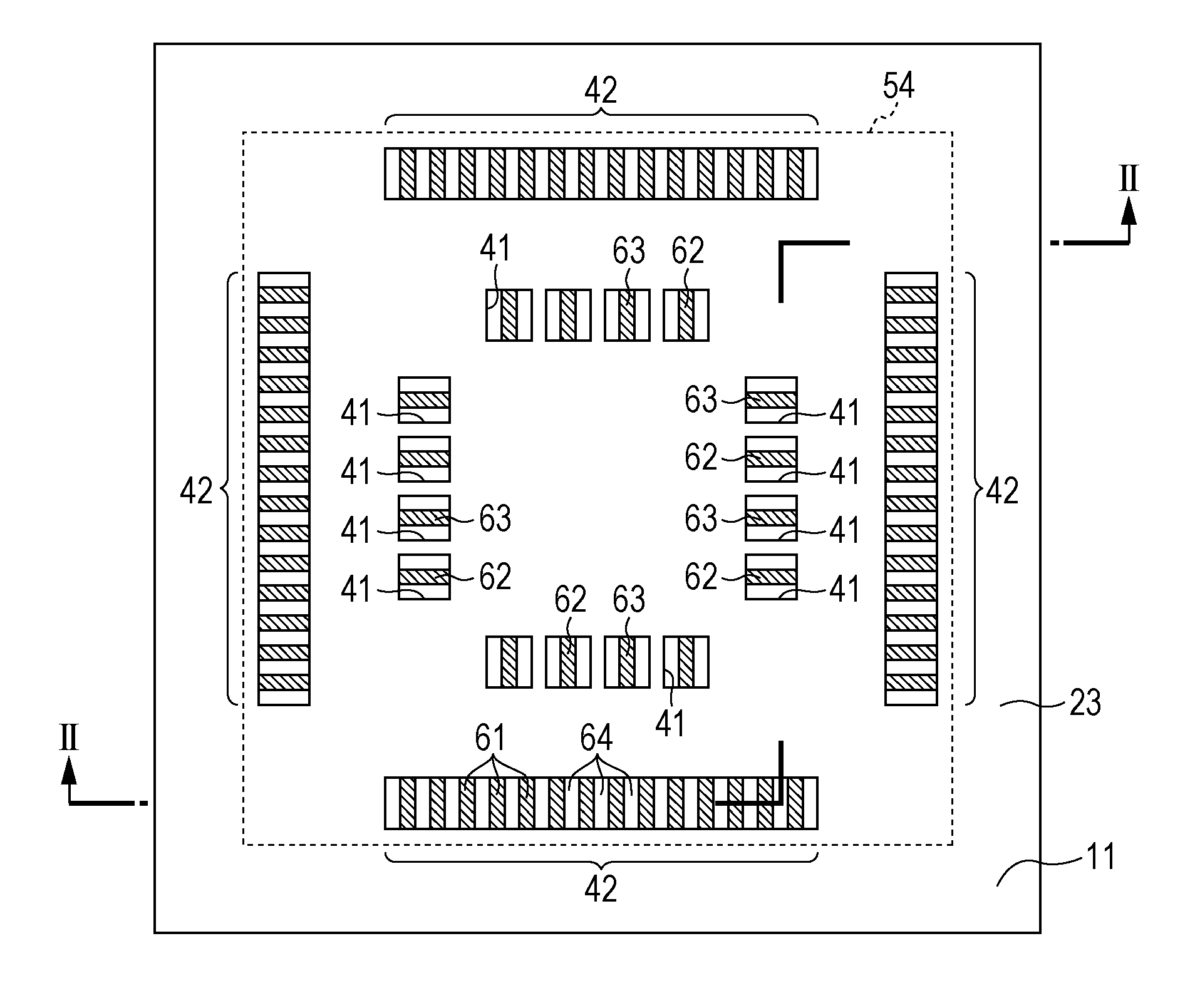
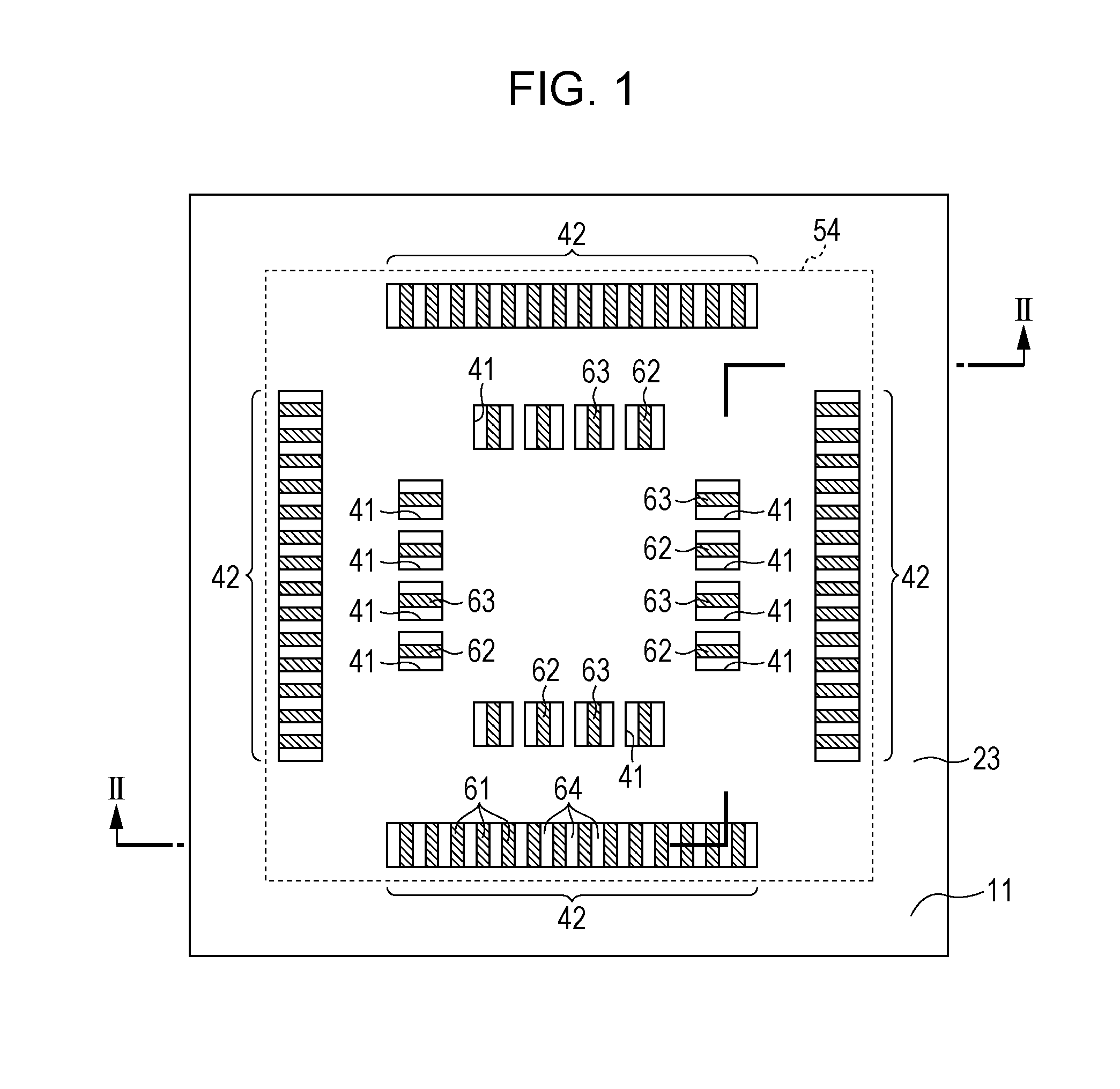
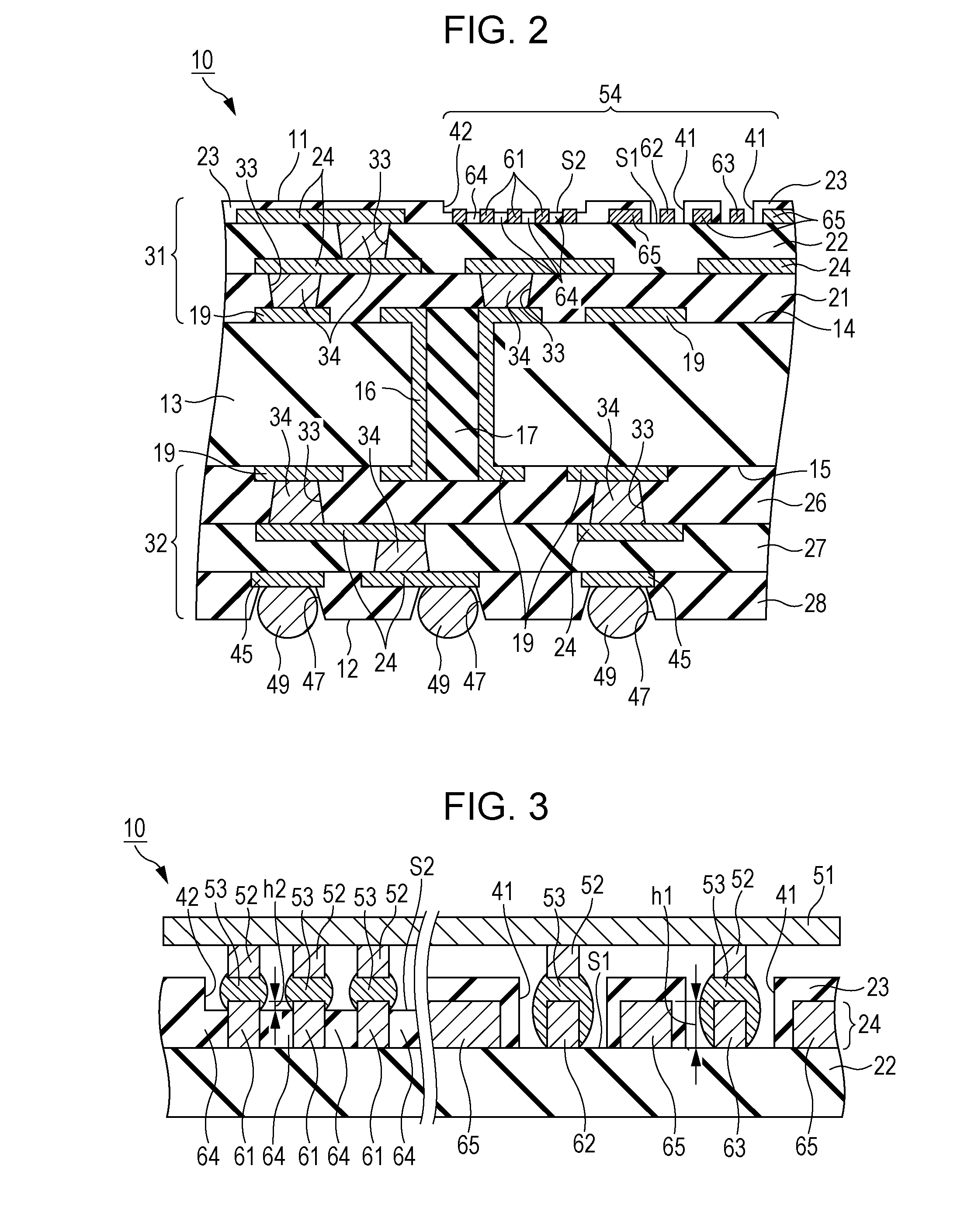
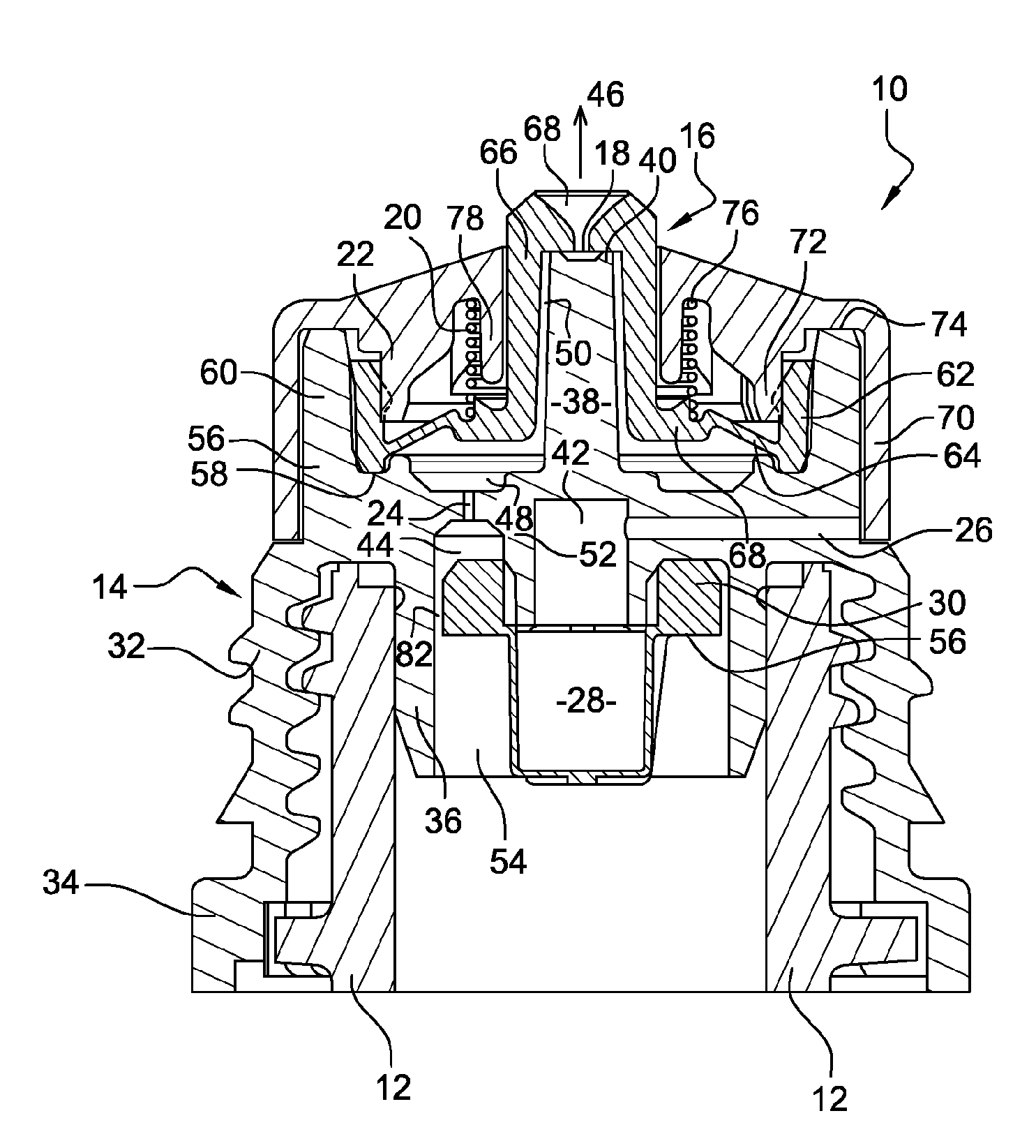
Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Reliably flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
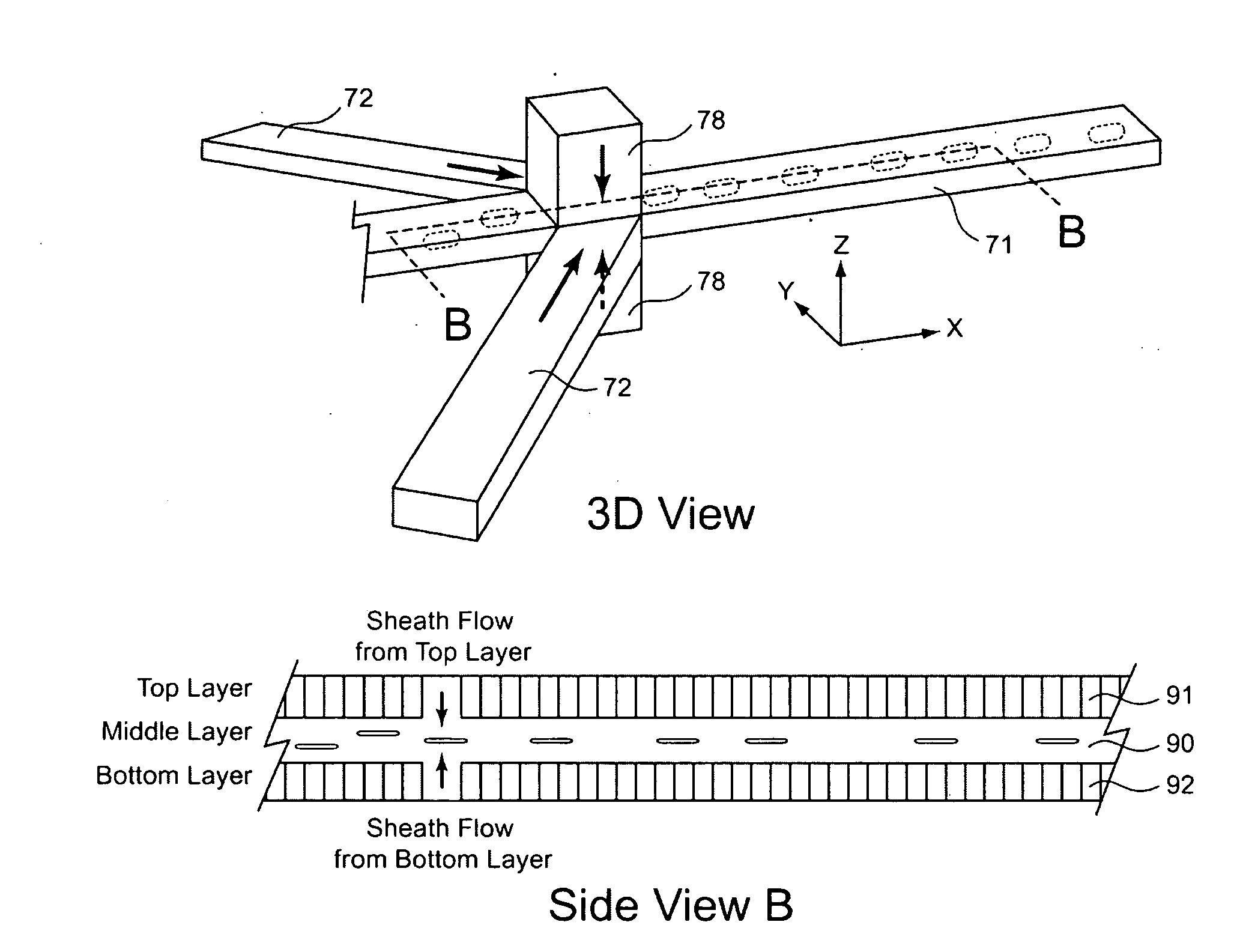
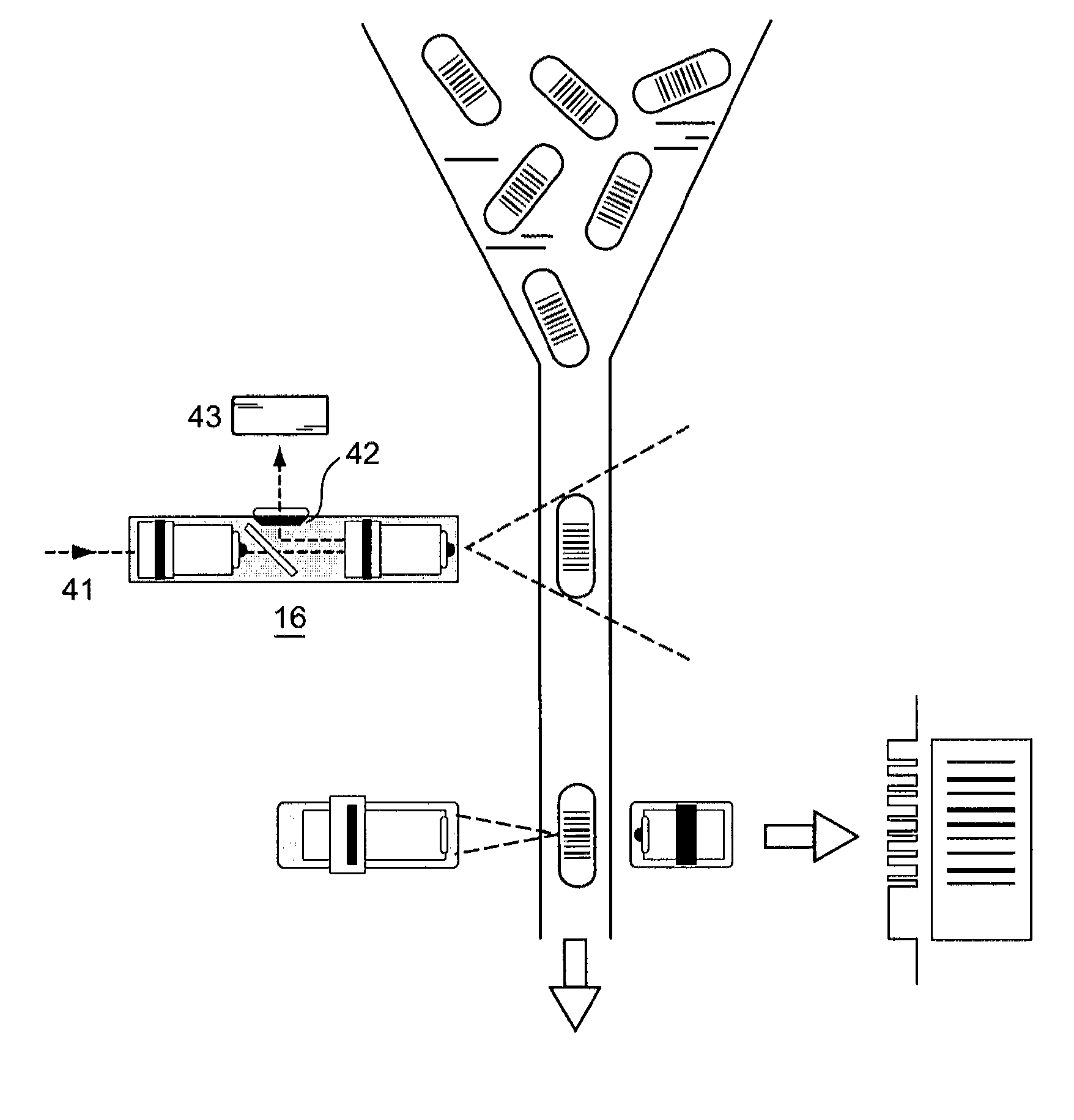
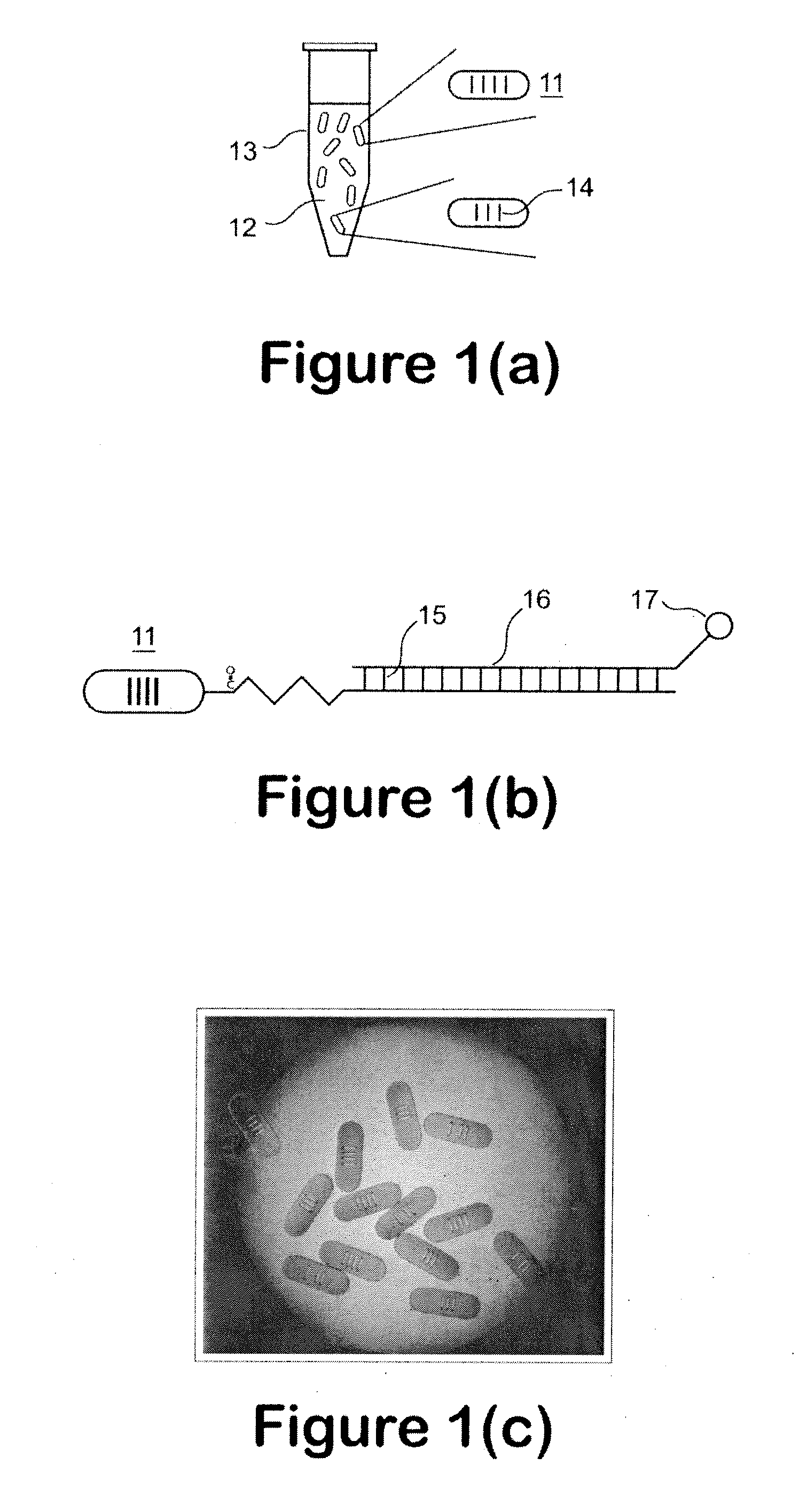
Hydrodynamic focusing for analyzing rectangular microbeads
InactiveUS20090201504A1Improve liquidityNo cloggingVolume/mass flow measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBarcodeEngineering
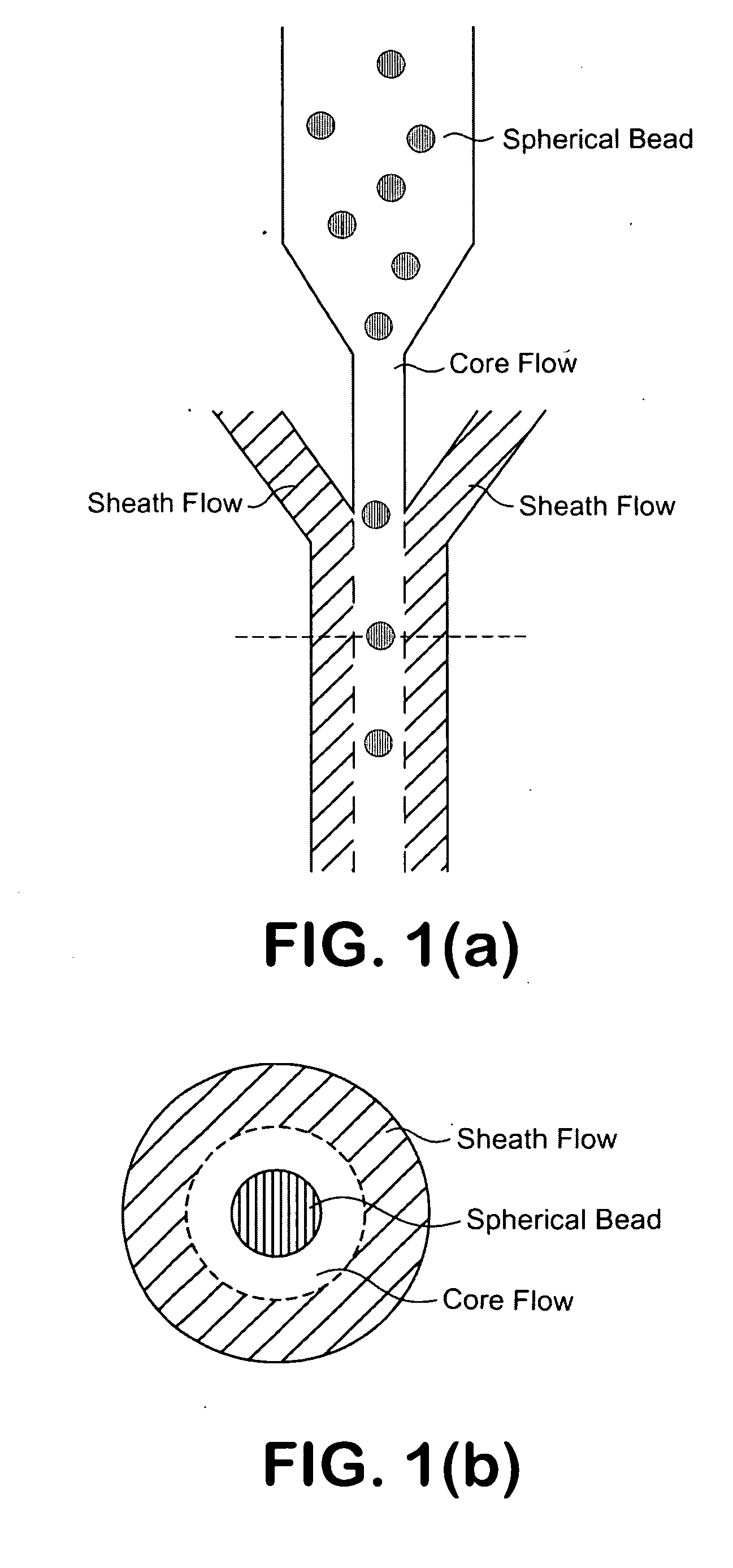
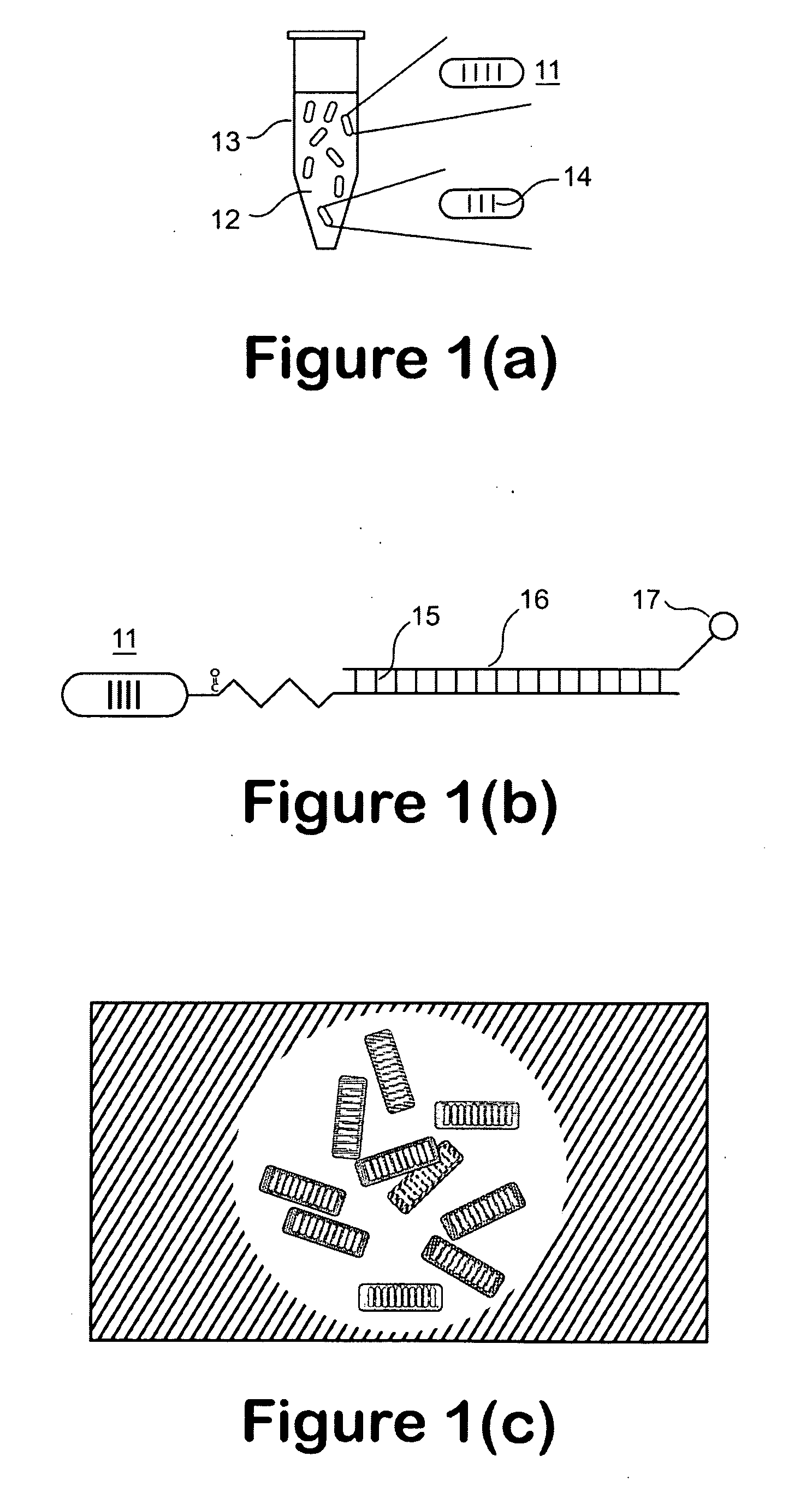
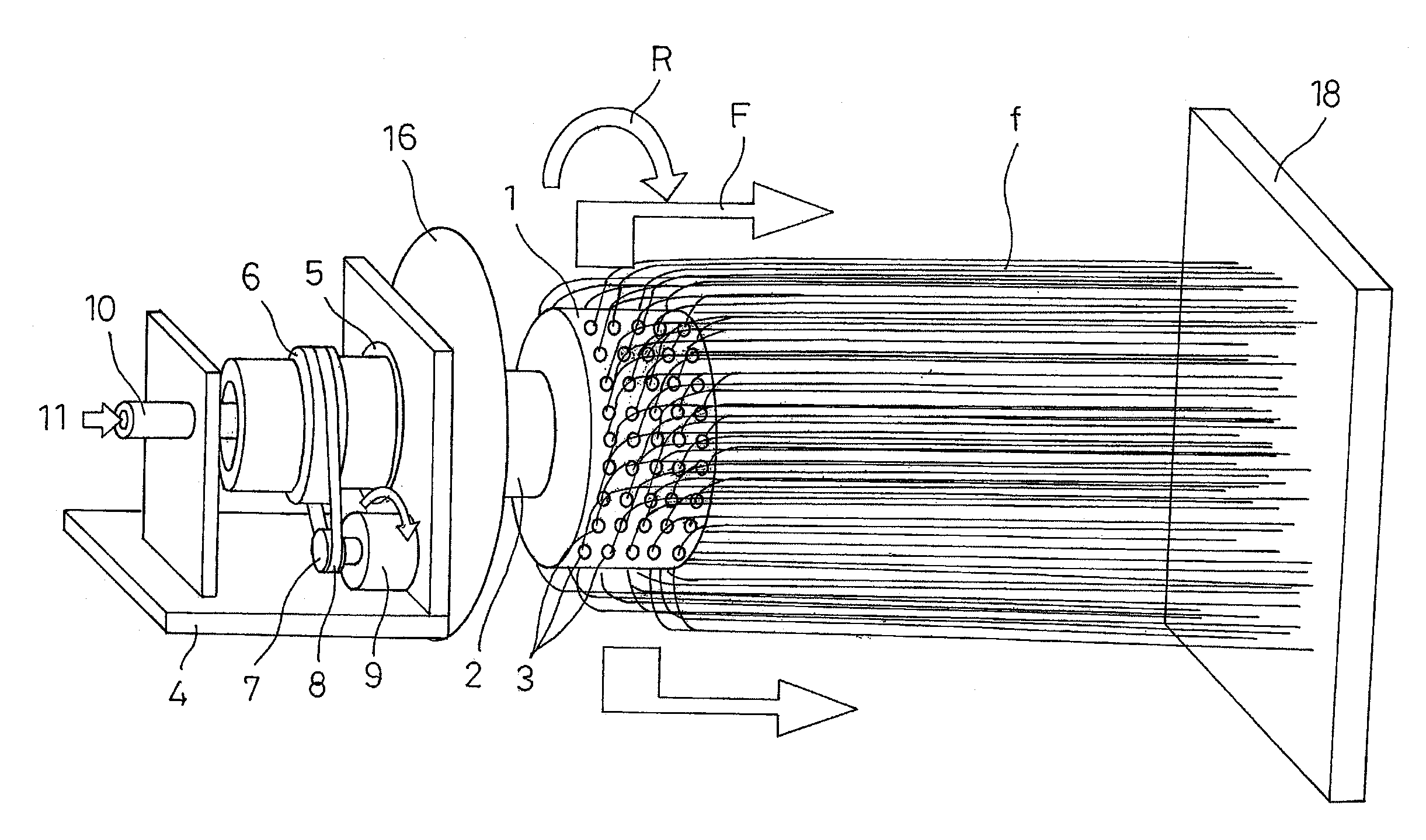
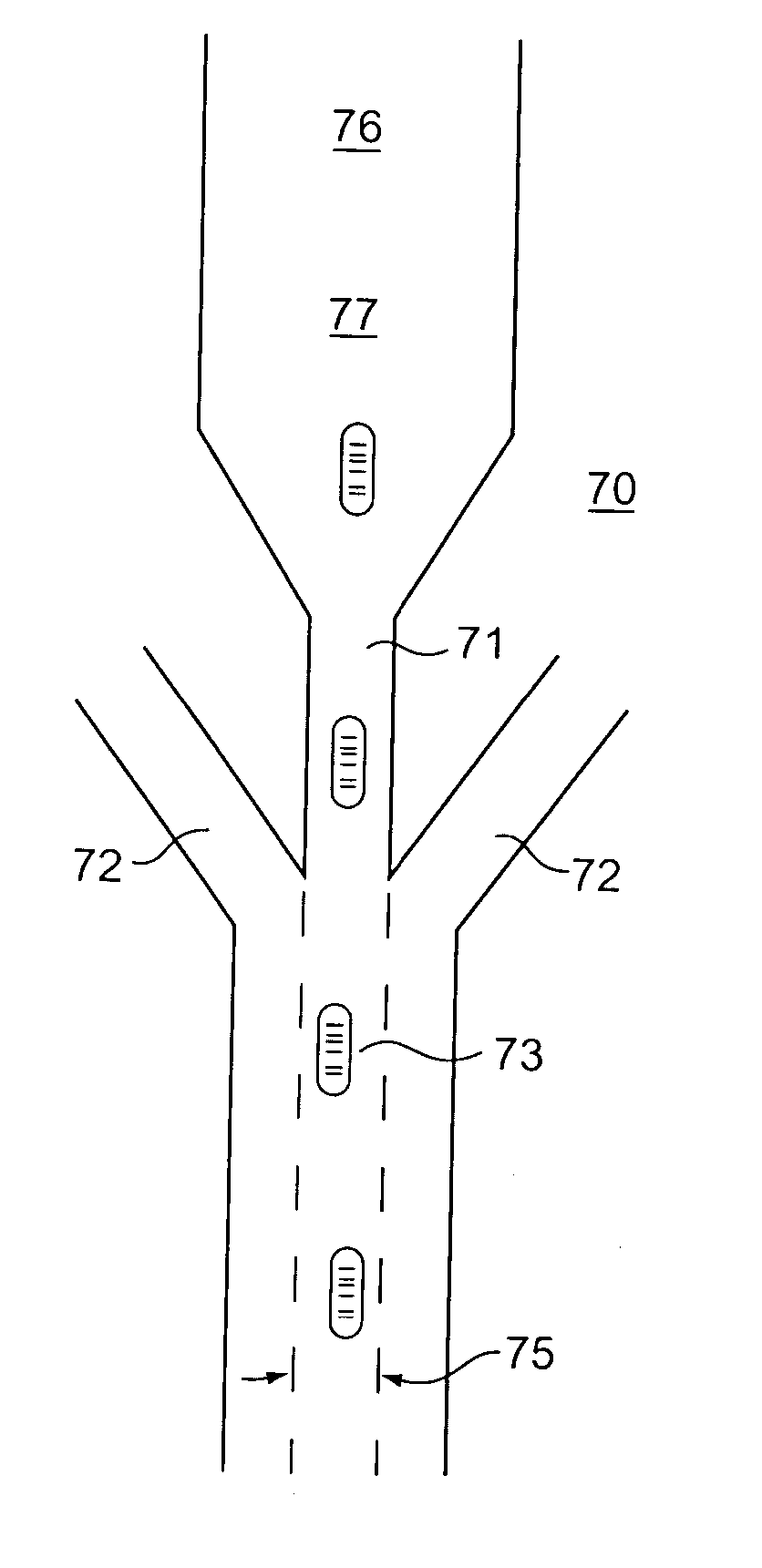
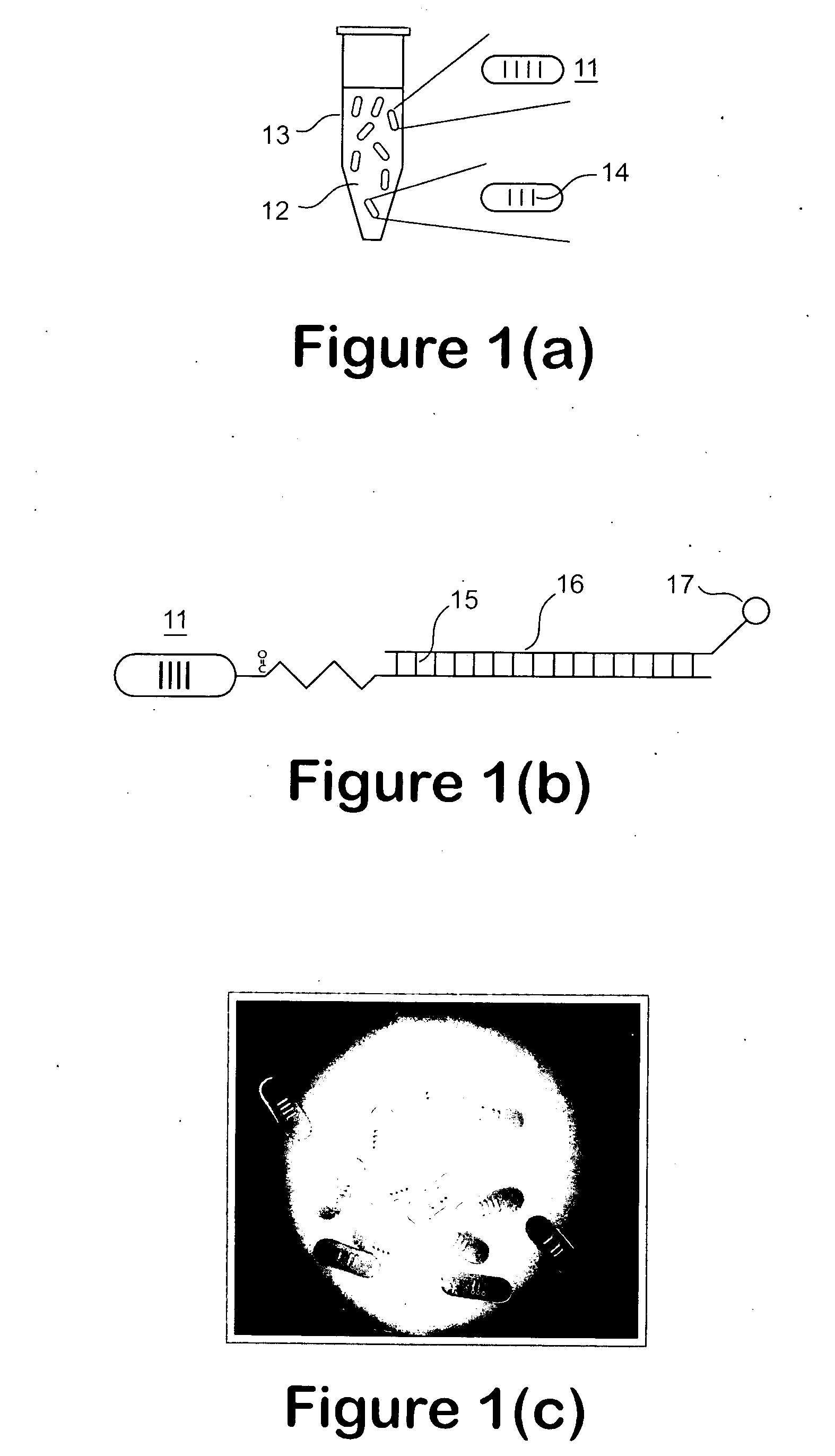
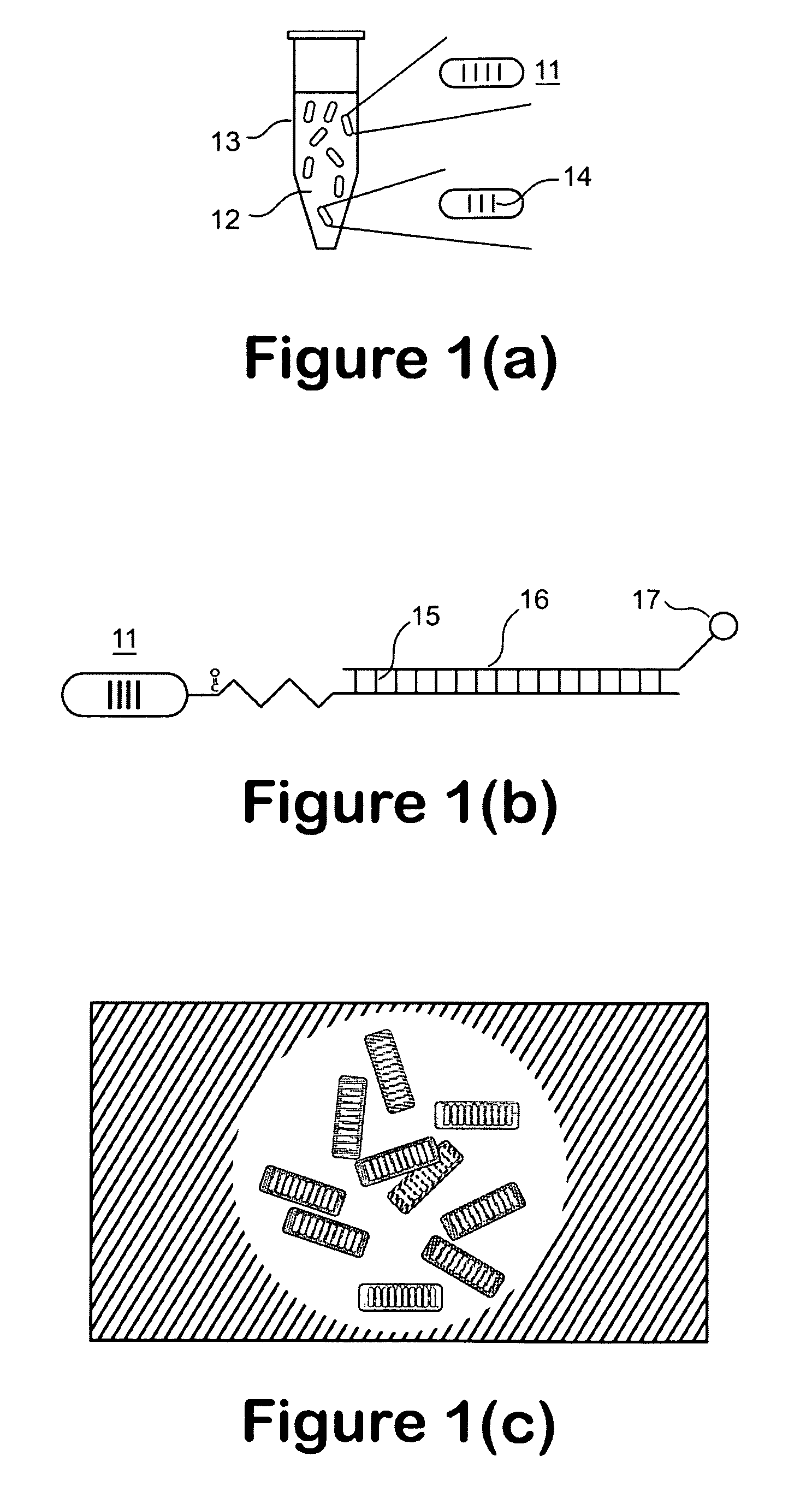
A microfluidic apparatus having a one-dimensional or two-dimensional hydrodynamic flow system to control stable and proper digitally coded bead orientation through the optical detection area of a bioanalysis system. The hydrodynamic system include one core flow, which carries the rectangular barcode beads, and sheath flows, on the sides of or about or around the outer periphery of the core flow, pull the core flow into a proper orientation. The sheath flows, at much higher flow speed but lower volume flow rate, can be pushed or pulled by vacuum, gravity, or pressure. By this method, the coded bead will align themselves in line and flow reliably, without wobbling or flipping, in the core flow channel through the detection zone. By adjusting the relative flow rate of core flow and sheath flows, the coded beads flow reliably in the flow system, thus it can be decoded and detected by an optical system accurately.
Owner:MAXWELL SENSORS
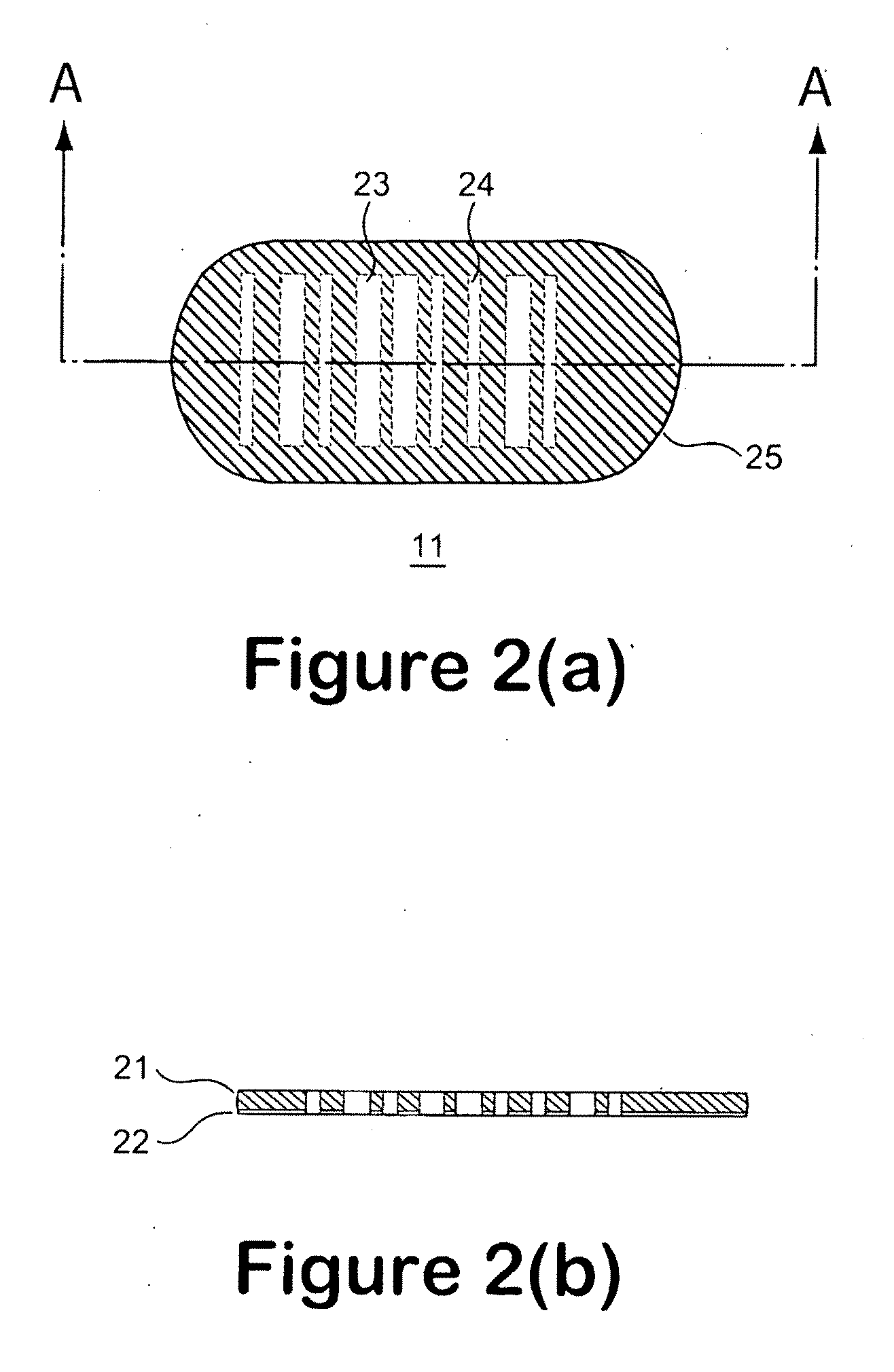
Apparatus and method for digital magnetic beads analysis
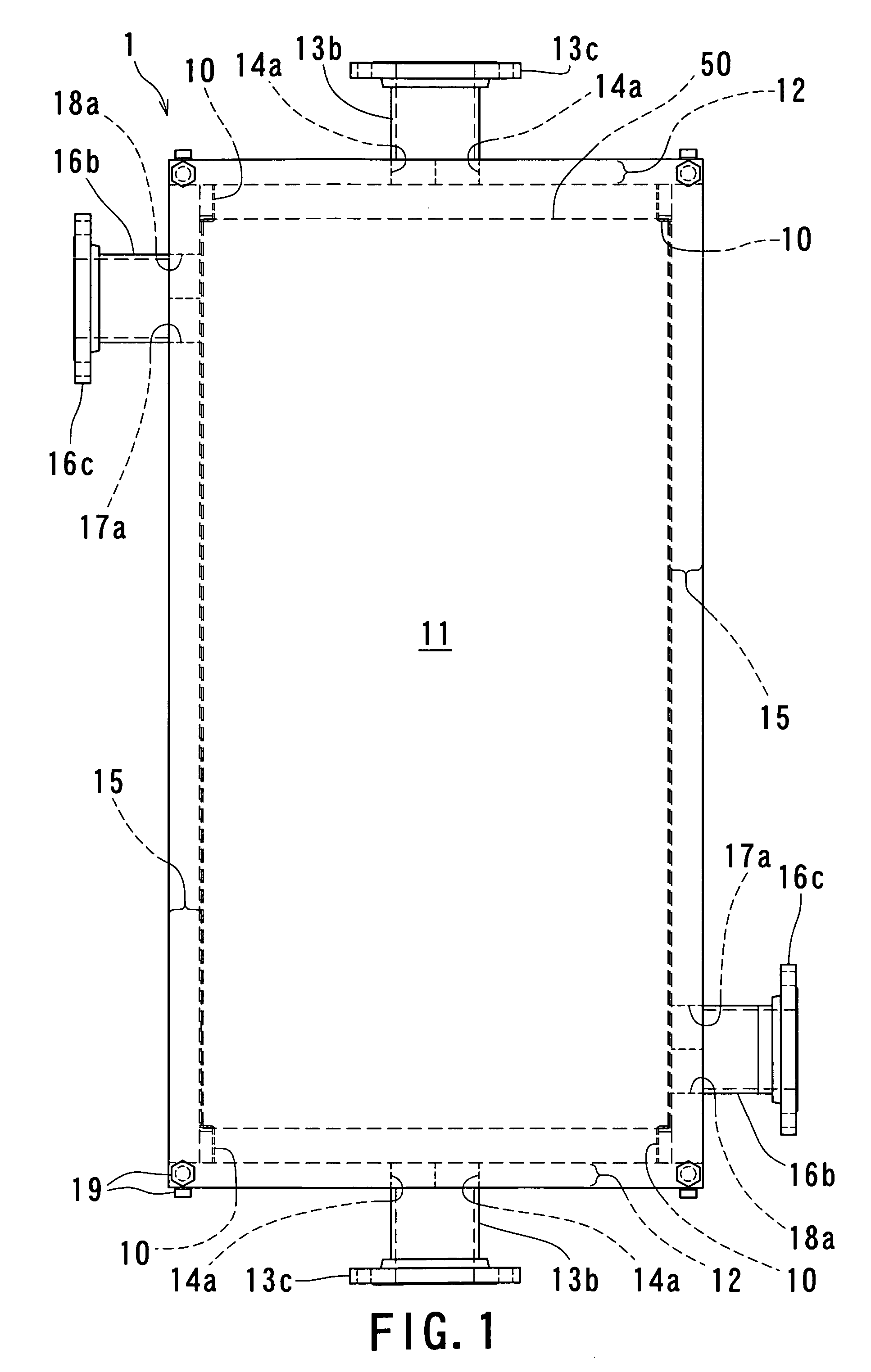
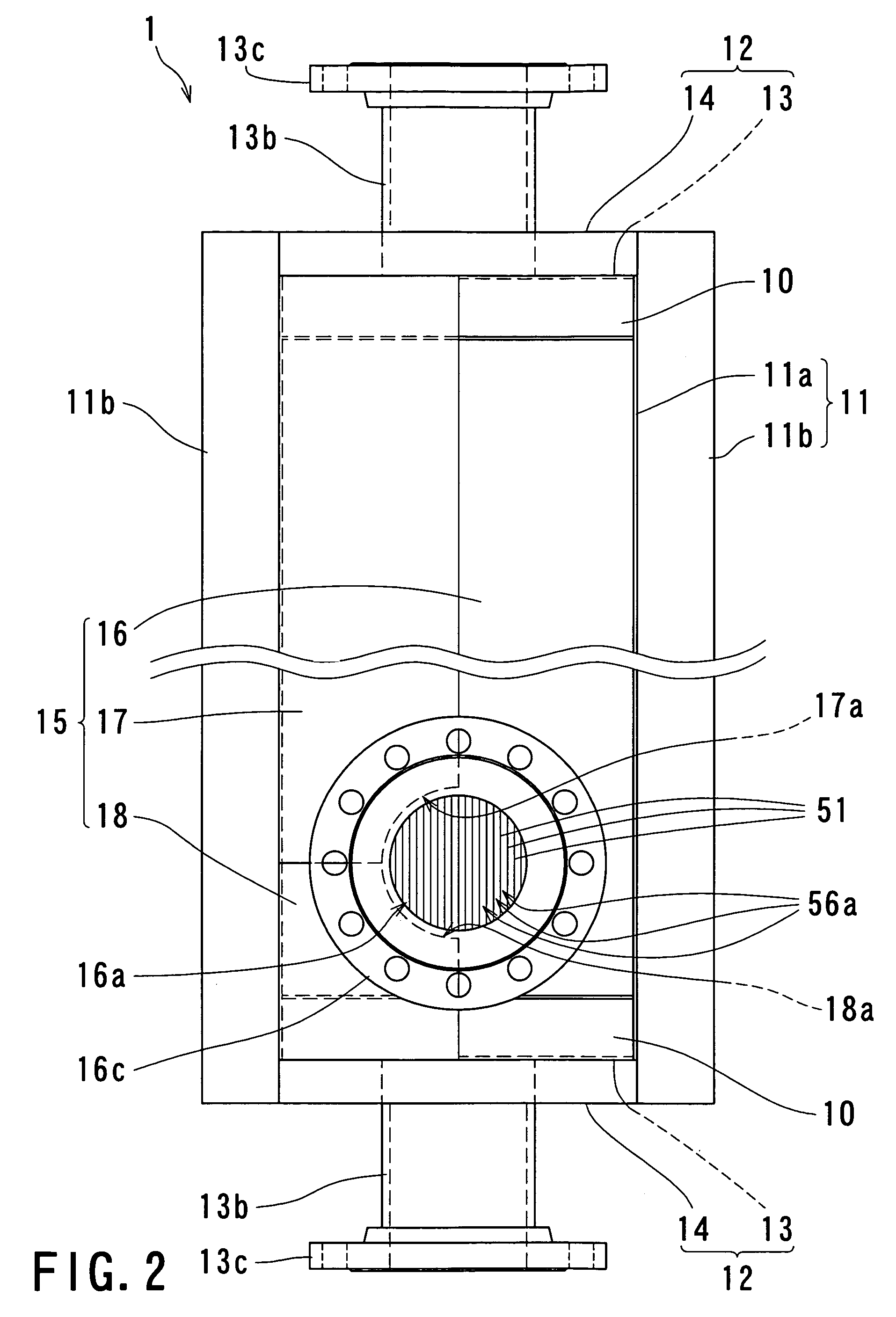
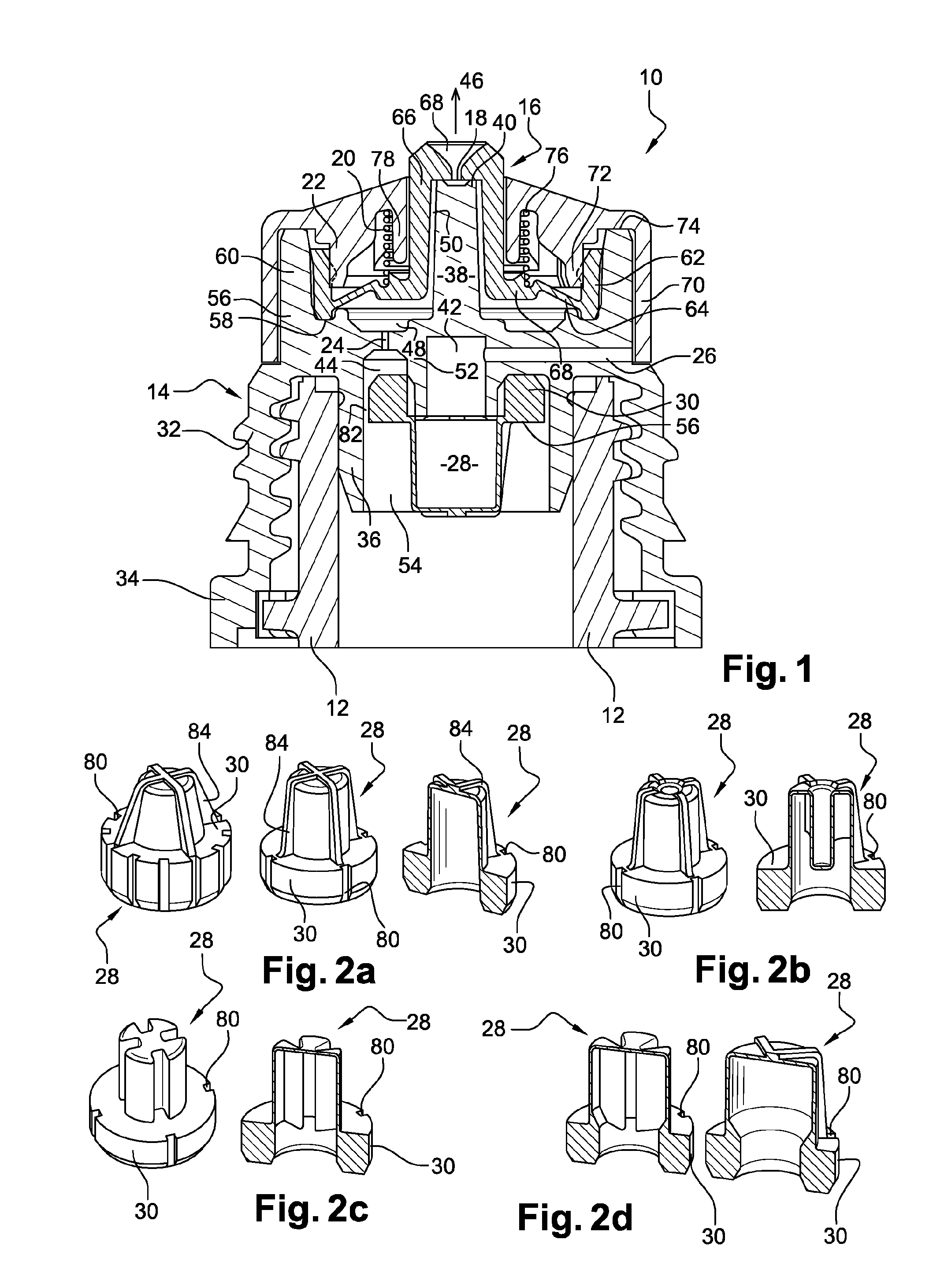
ActiveUS20080234144A1Reliably flowAccurate detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTransmitted lightStandard form
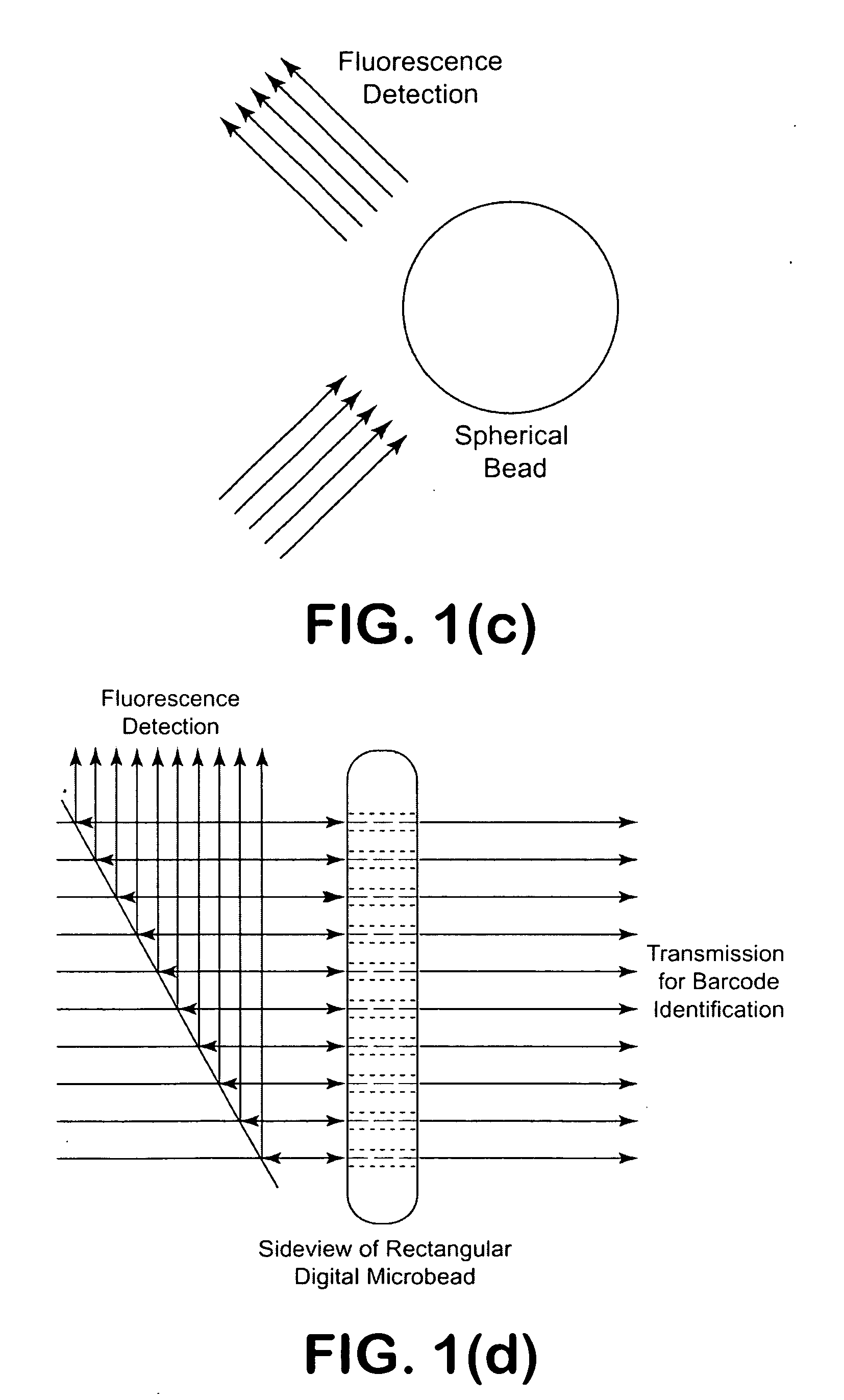
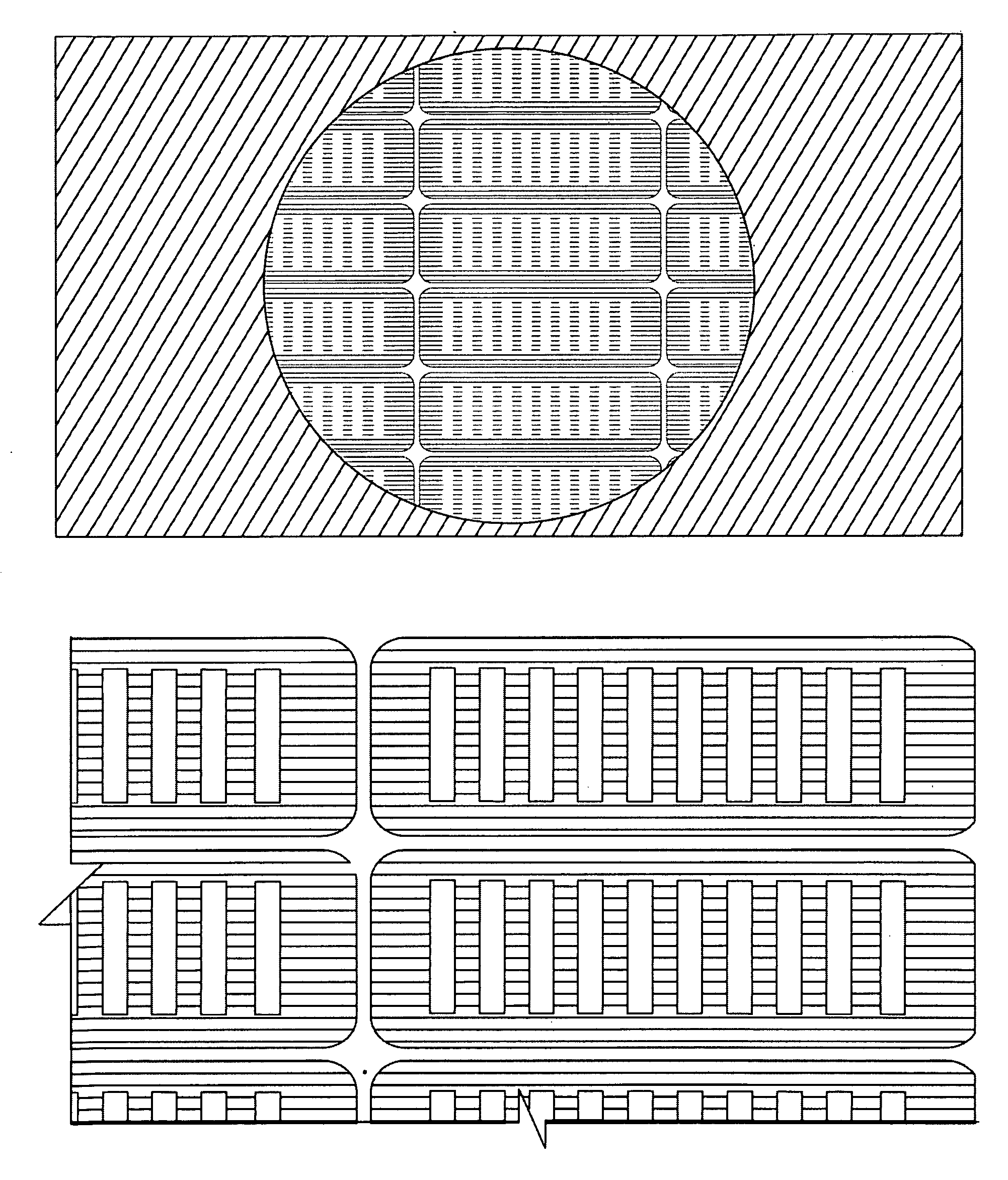
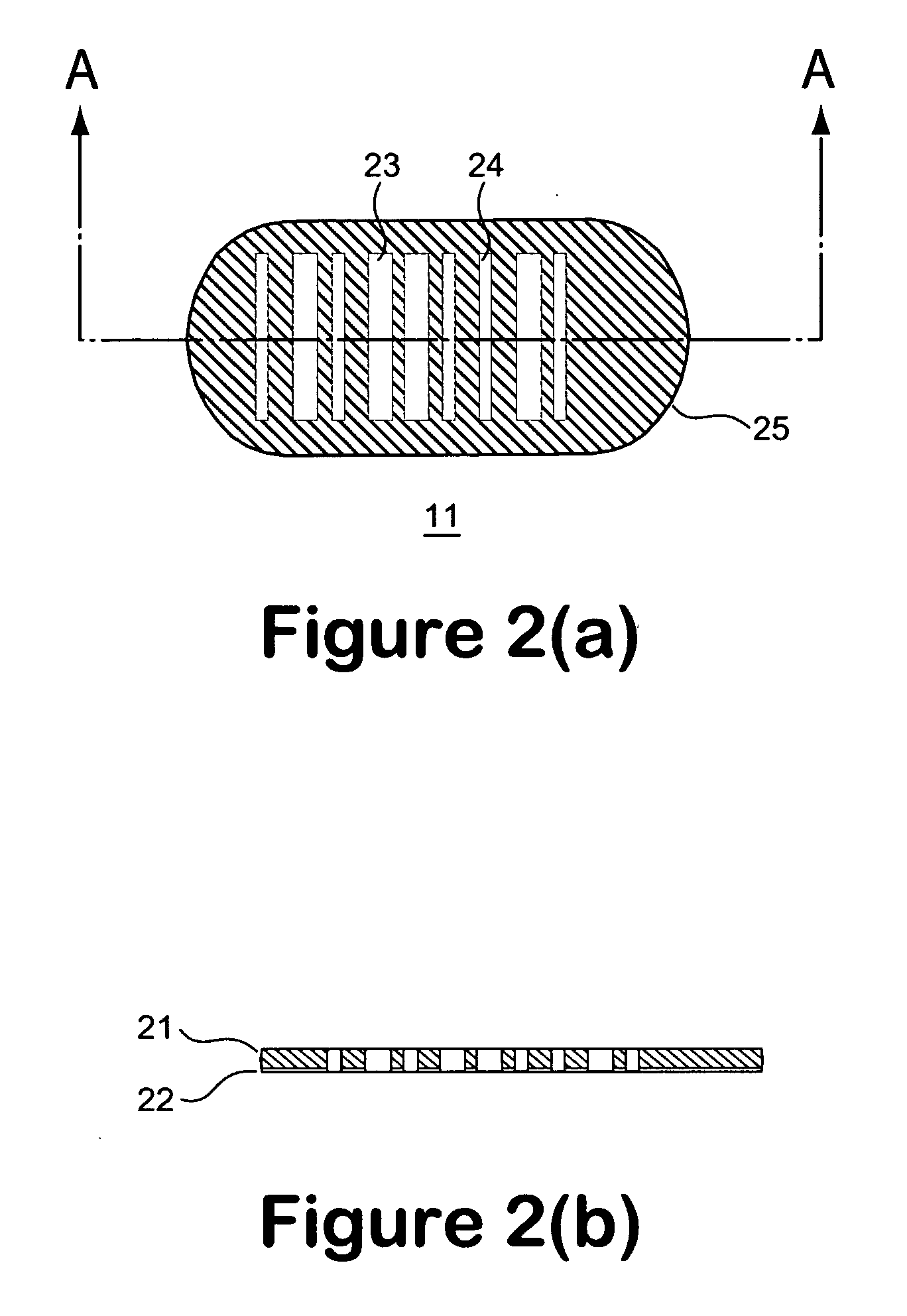
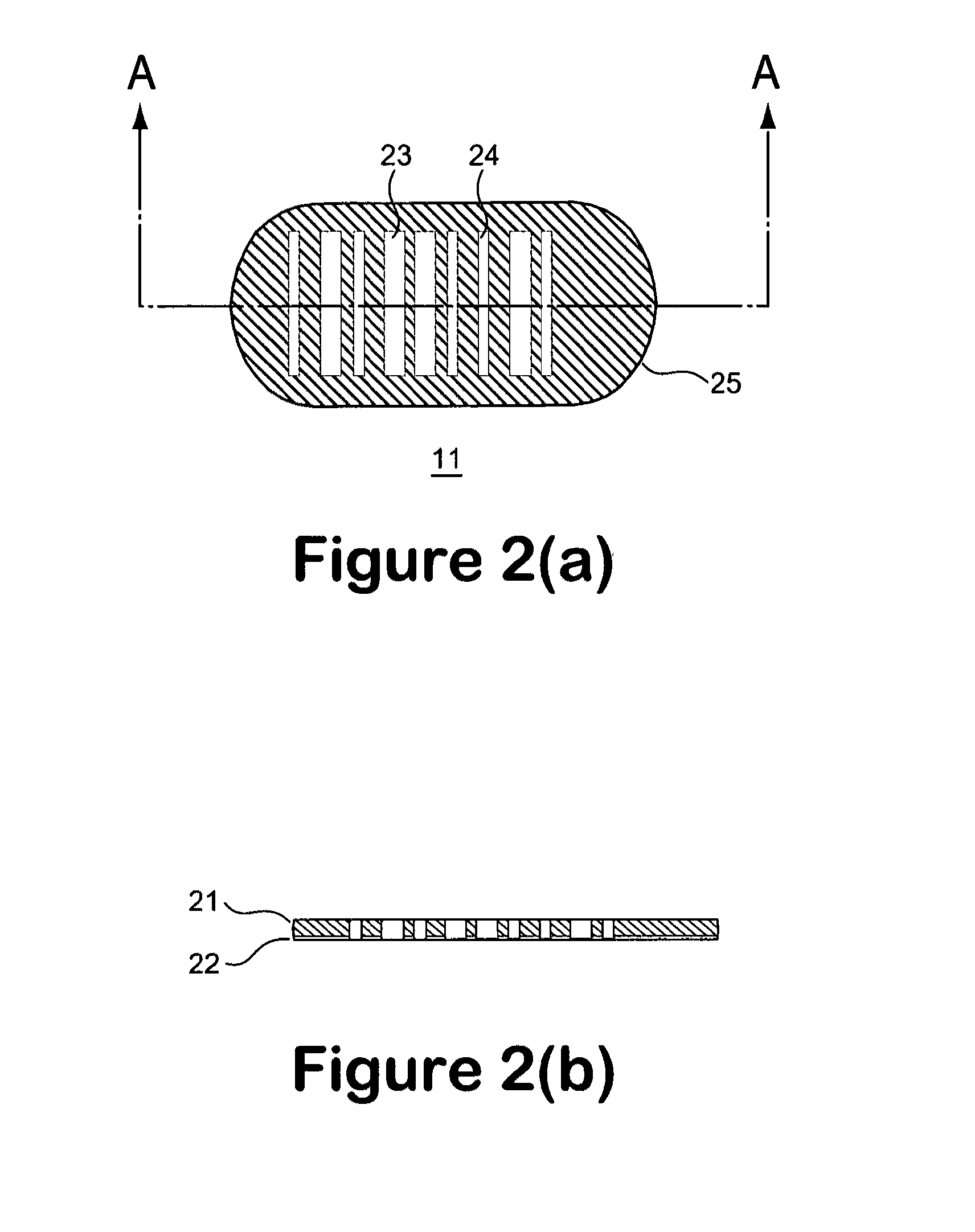
A micro bead having a digitally coded structure that is partially transmissive and opaque to light. The pattern of transmitted light is determined by to decode the bead. The coded bead may be structured a series of alternating light transmissive and opaque sections, with relative positions, widths and spacing resembling a 1D or 2D bar code image. To decode the image, the alternating transmissive and opaque sections of the body are scanned in analogous fashion to bar code scanning. The coded bead may be coated or immobilized with a capture or probe to effect a desired bioassay. The coded bead may include a paramagnetic material. A bioanalysis system conducts high throughput bioanalysis using the coded bead, including a reaction detection zone and a decoding zone. Alternative method for barcode determination is based on barcode pattern image processes. Microbeads can also be settled down to the bottom of the well in a microplate, so the barcode can be decoded by image processed directly. Therefore, multiple-analyte tests can be performed in one single well. Microplate is a standard format; each plate can have 96, 384, or 1536 patient samples. The bead image is taken with a conventional microscope and optical detector from the bottom of an optically clear microplate, and barcode pattern can be decoded by image software. Therefore, the whole bead experiment can be performed in the microplate without taking the beads out.
Owner:APPLIED BIOCODE
Battery container unit
InactiveUS20090061305A1Improve cooling effectMiniaturization possibleSecondary cellsCell component detailsCooling mediumElectrical and Electronics engineering
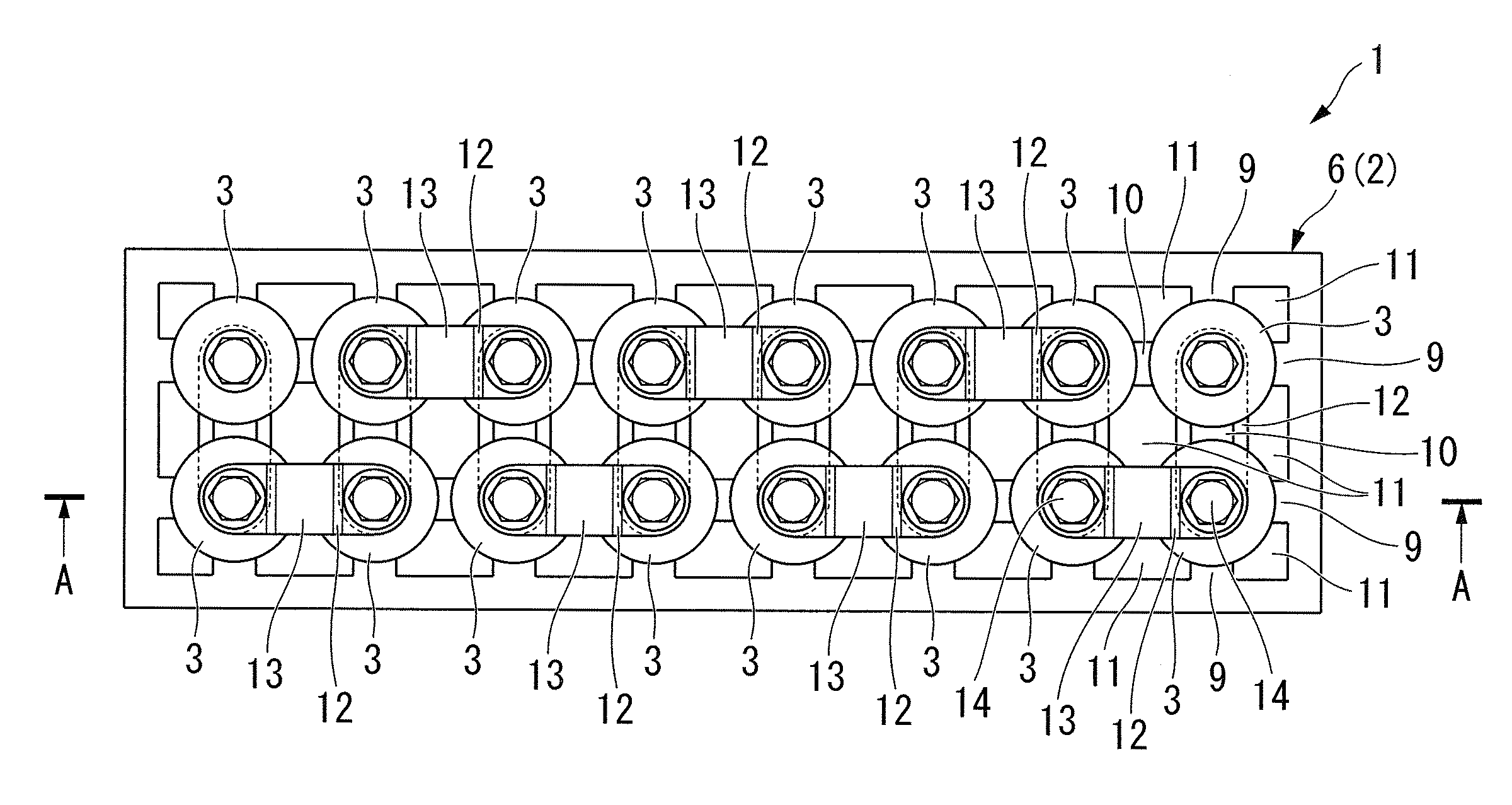
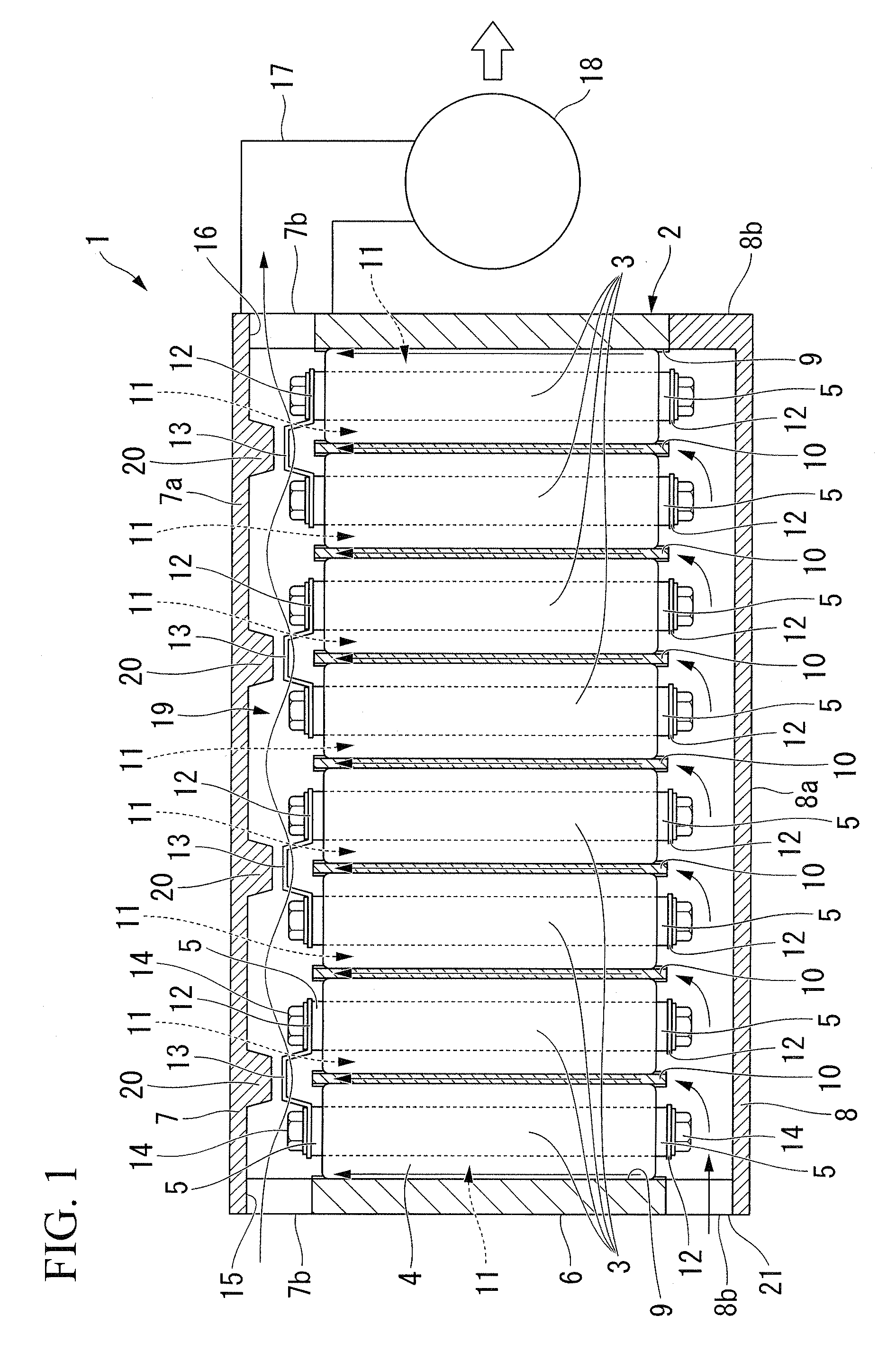
A battery container unit including: an enclosure; and a plurality of battery modules of cylindrical shape, wherein each adjacent pair of the electrode terminals is serially connected by a conductive linking member, the plurality of battery modules are provided in matrix form within the enclosure by a support member, a first cooling medium flow path is provided which linearly flows a cooling medium along in parallel with the electrode terminals and the conductive linking members of the plurality of battery modules in a region within the enclosure near an end in the axial direction of the plurality of battery modules, and a second cooling medium flow path is provided in a gap along the axial direction of the battery modules, between adjacent battery modules within the enclosure, which flows the cooling medium toward the first cooling medium flow path.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for producing nanofibers and polymer web
ActiveUS20100072674A1Efficient and stable productionEnsure efficient flowElectric discharge heatingFilament/thread formingProduction rateNanofiber
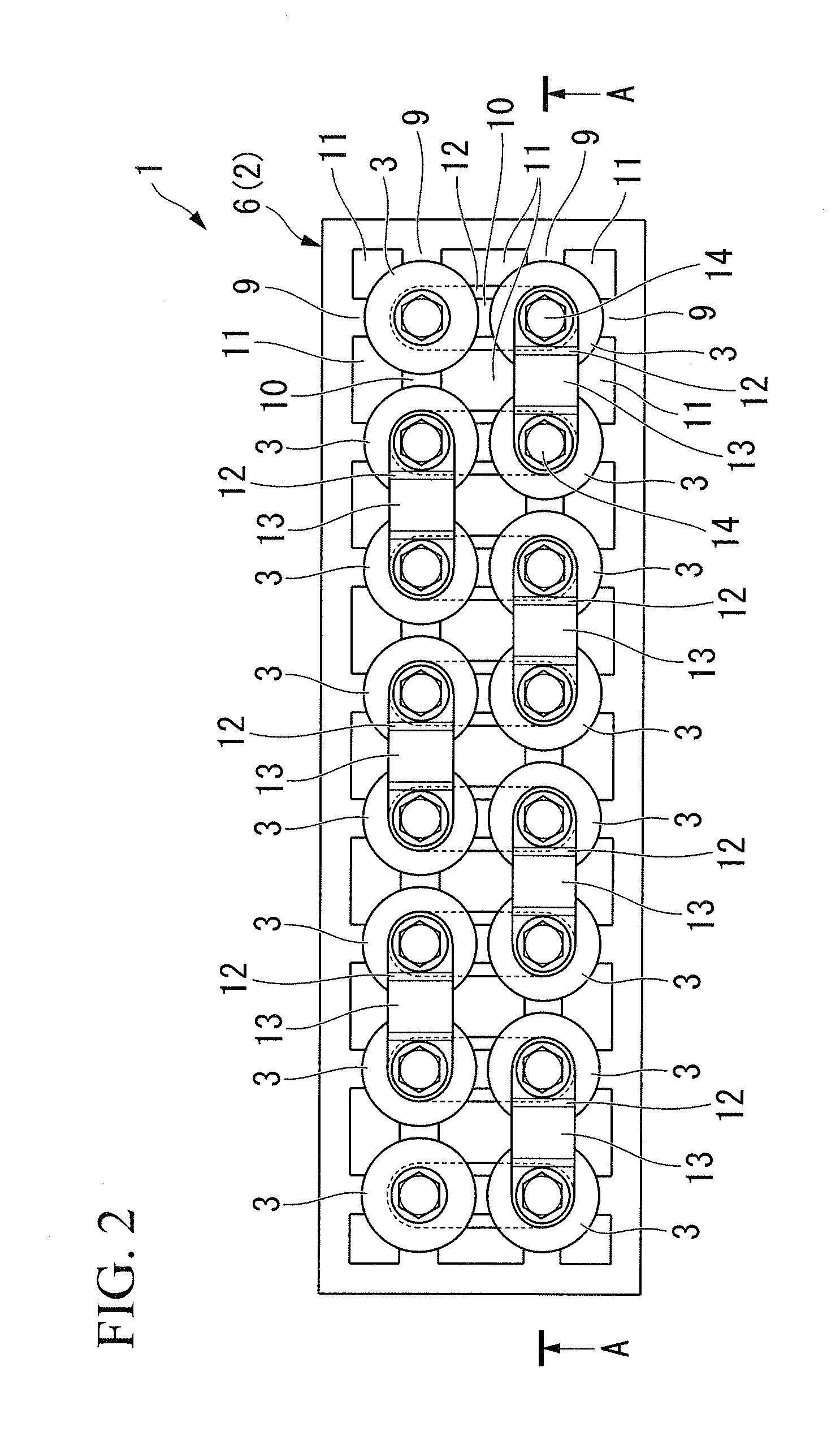
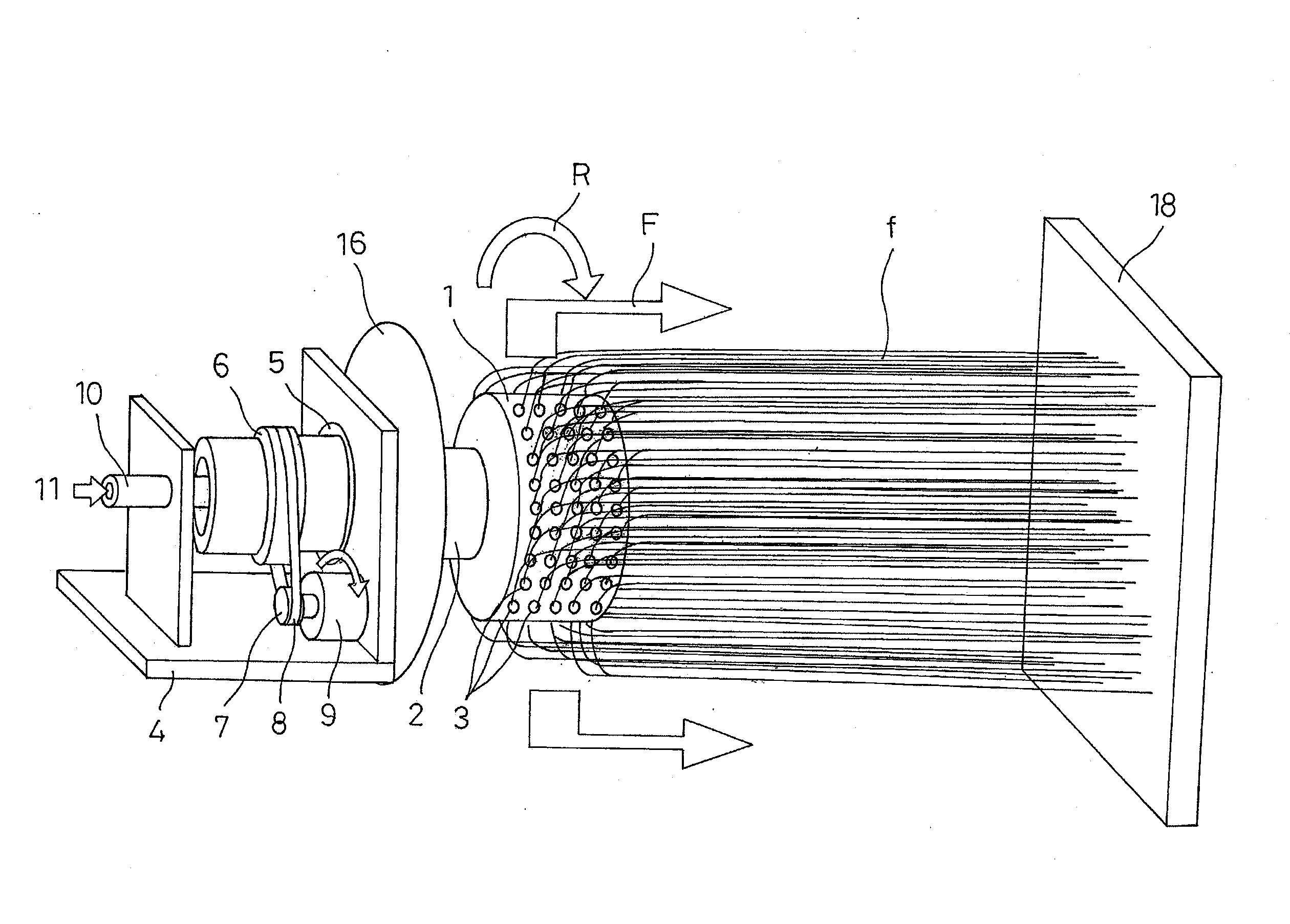
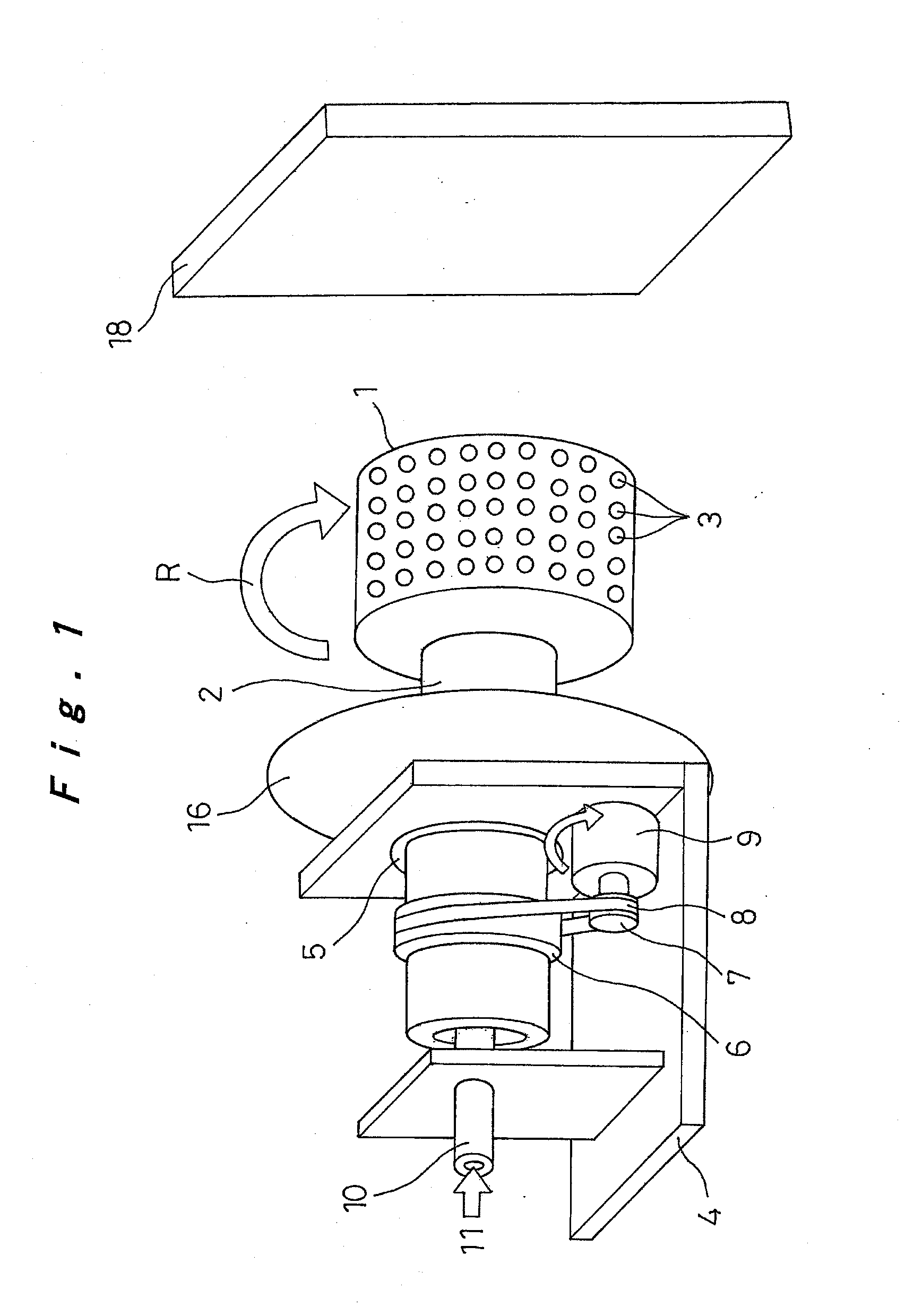
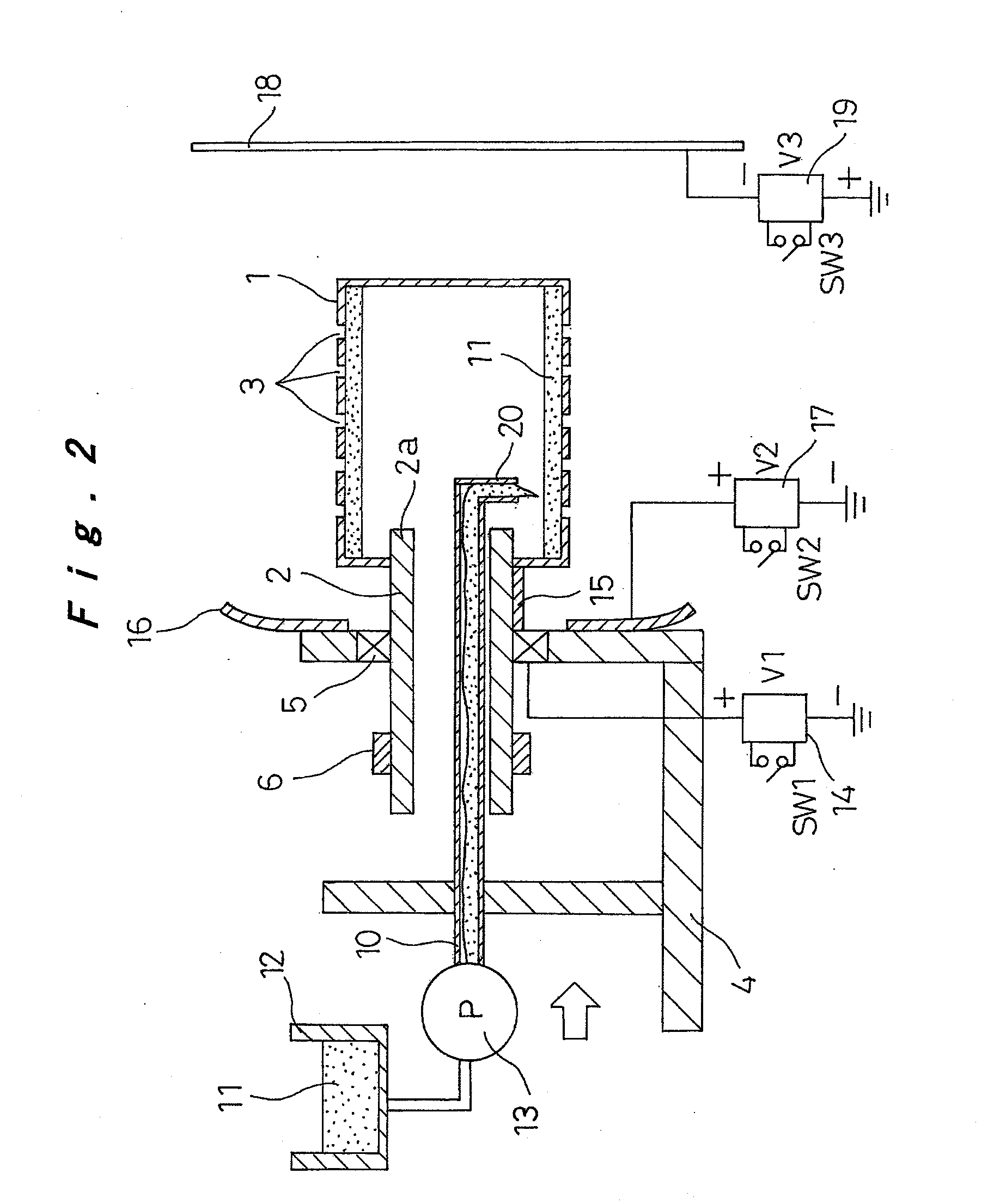
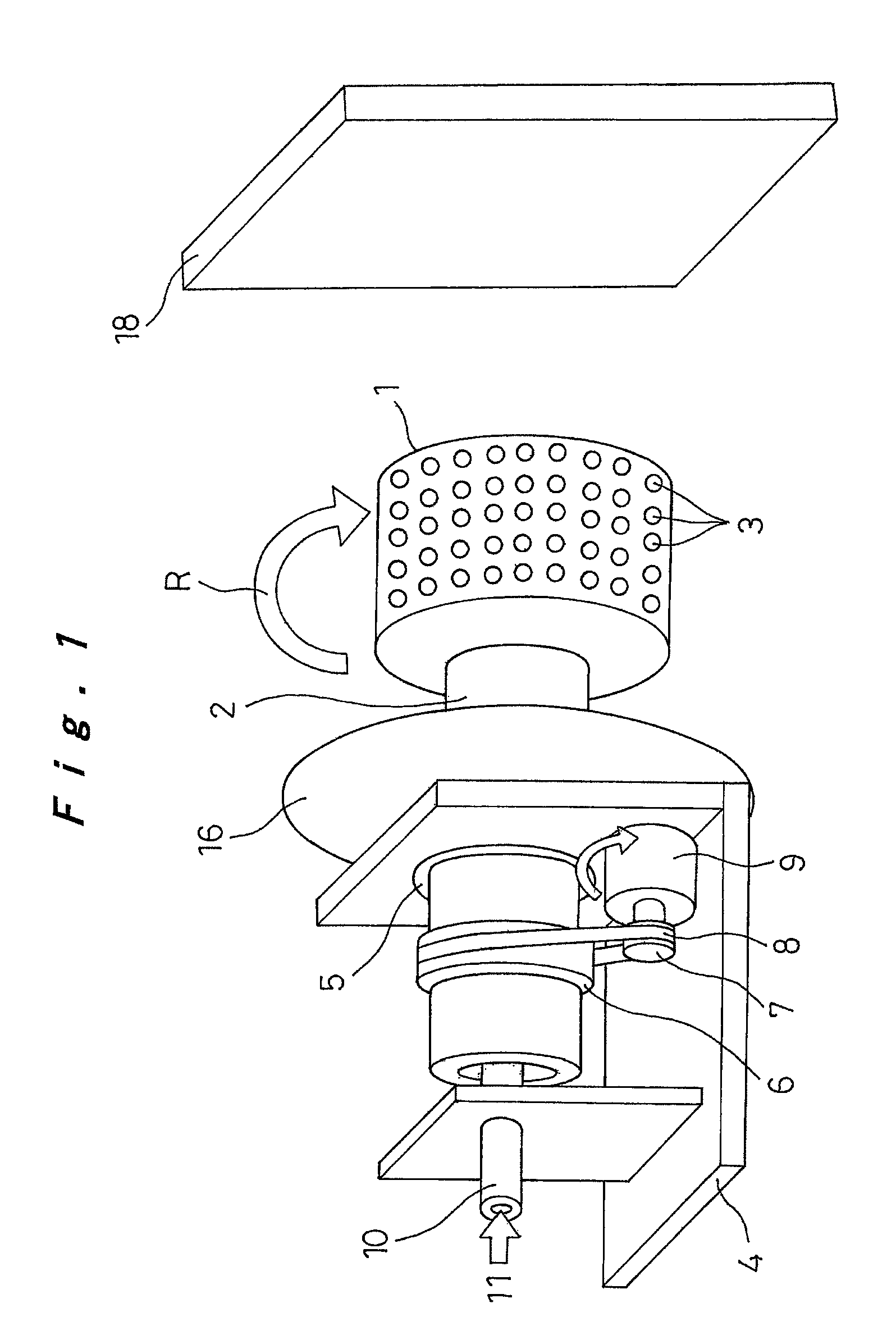
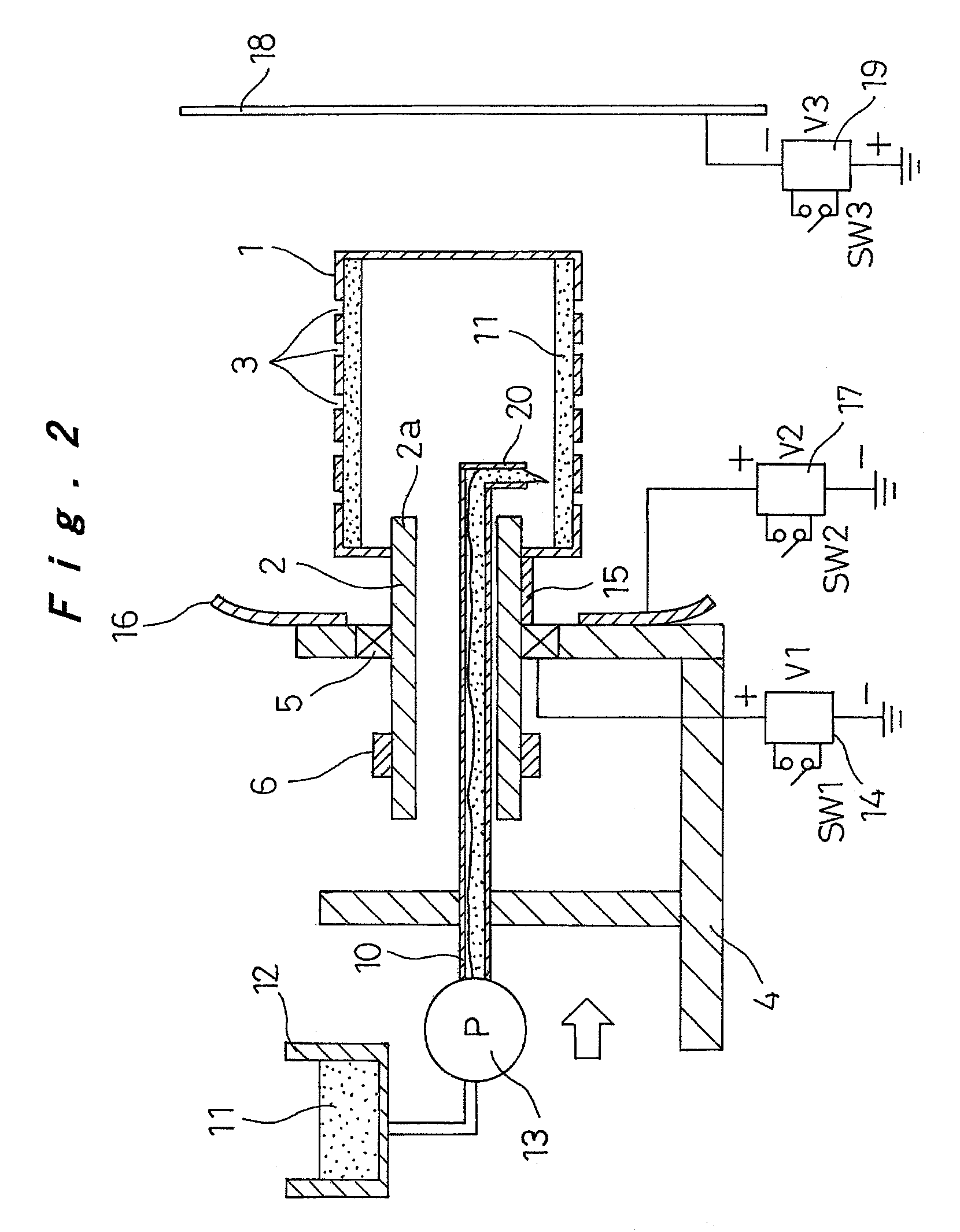
Nanofibers are formed from a polymer material by rotating a conductive rotating container having a plurality of small holes while supplying a polymer solution formed by dissolving a polymer material in a solvent into the rotating container, charging the polymer solution discharged from the small holes of the rotating container by charging means, and drawing the discharged filamentous polymer solution by centrifugal force and an electrostatic explosion resulting from evaporation of the solvent. The nanofibers from this production step are oriented and made to flow from one side toward the other side in a shaft center direction of the rotating container by a reflecting electrode and / or blowing means, or those nanofibers are deposited, to produce a polymer web. The nanofibers and the polymer web using these nanofibers can be produced uniformly by a simple configuration with good productivity.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fuel cell and fuel cell stack
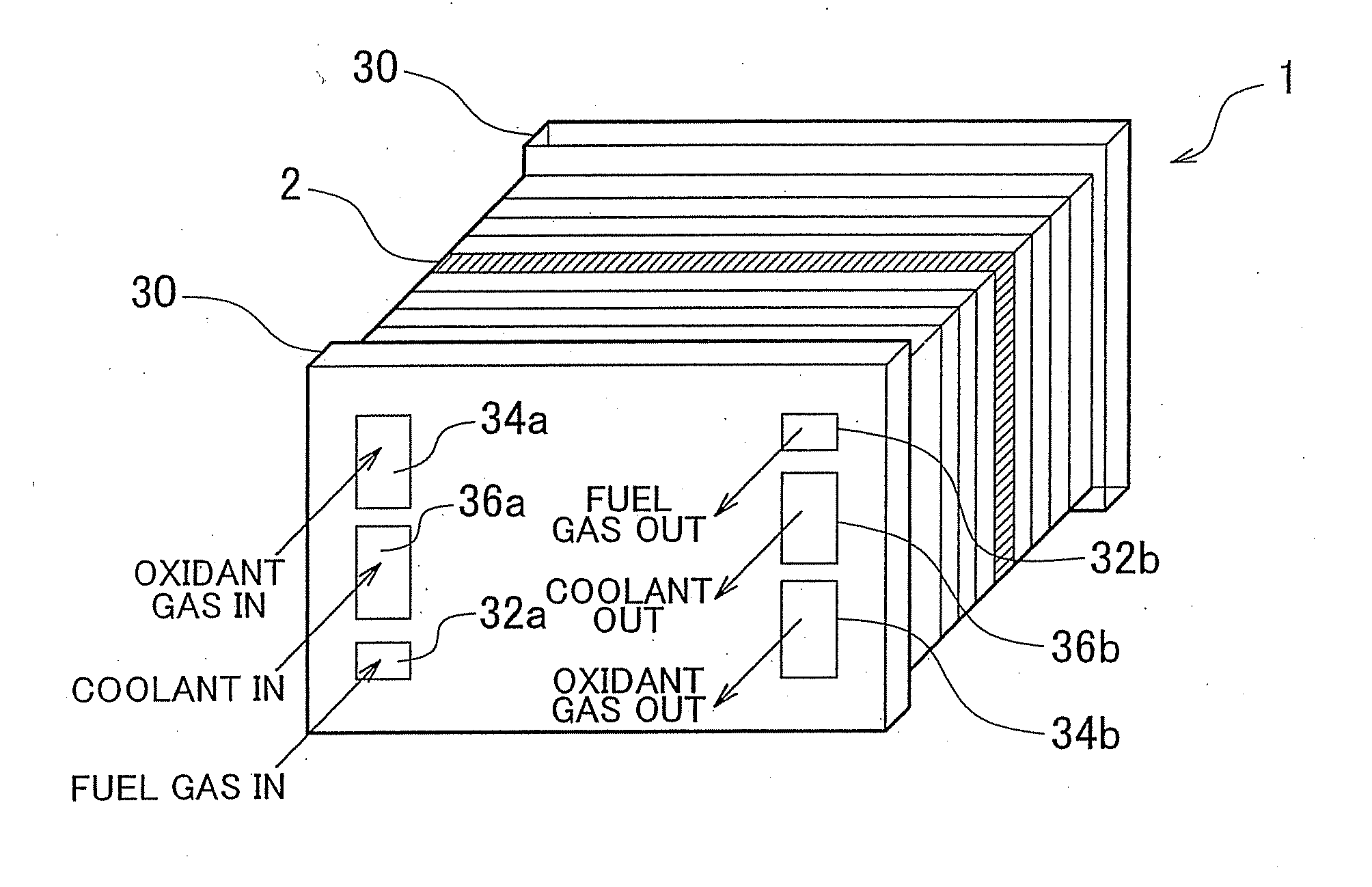
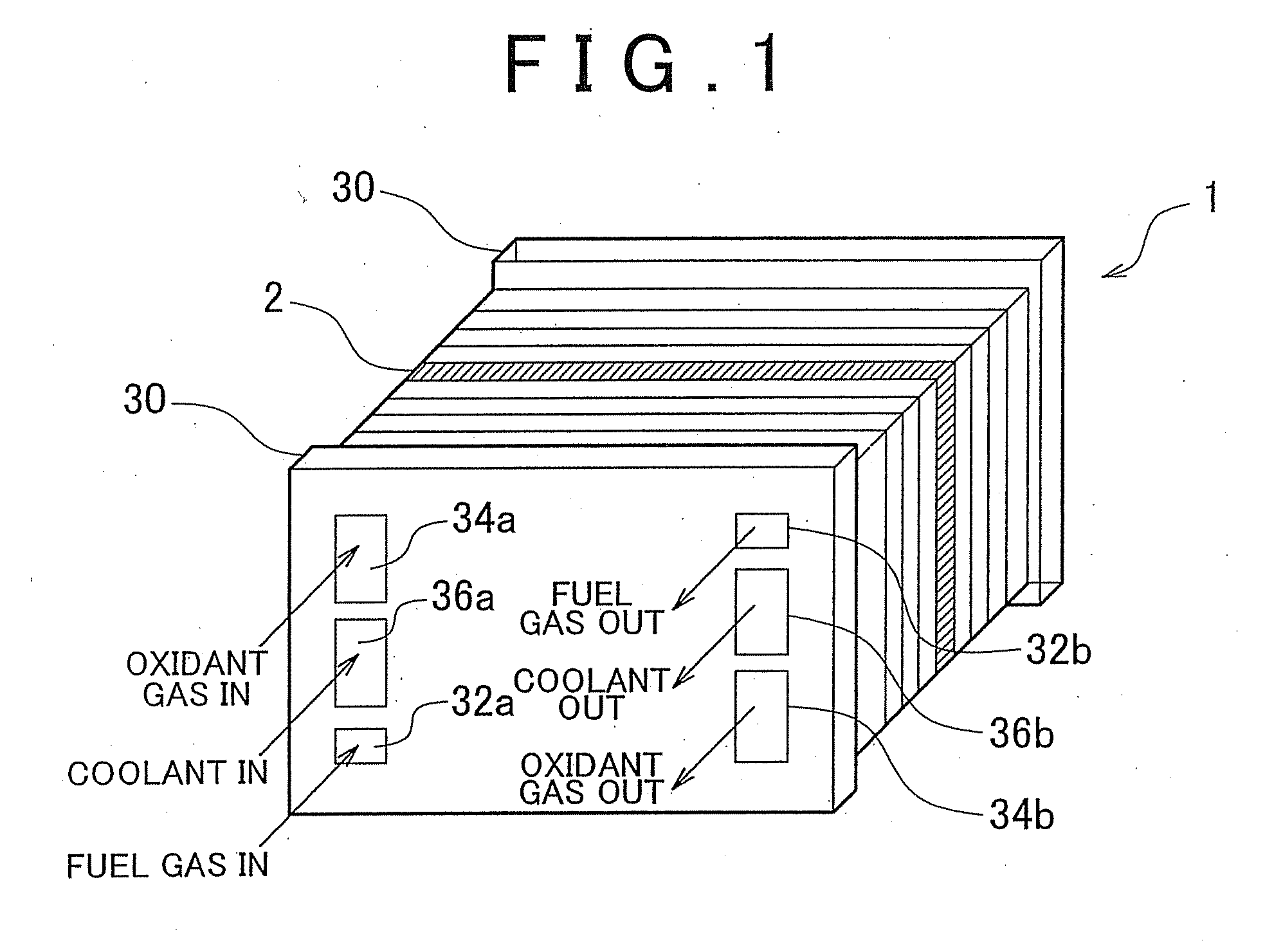
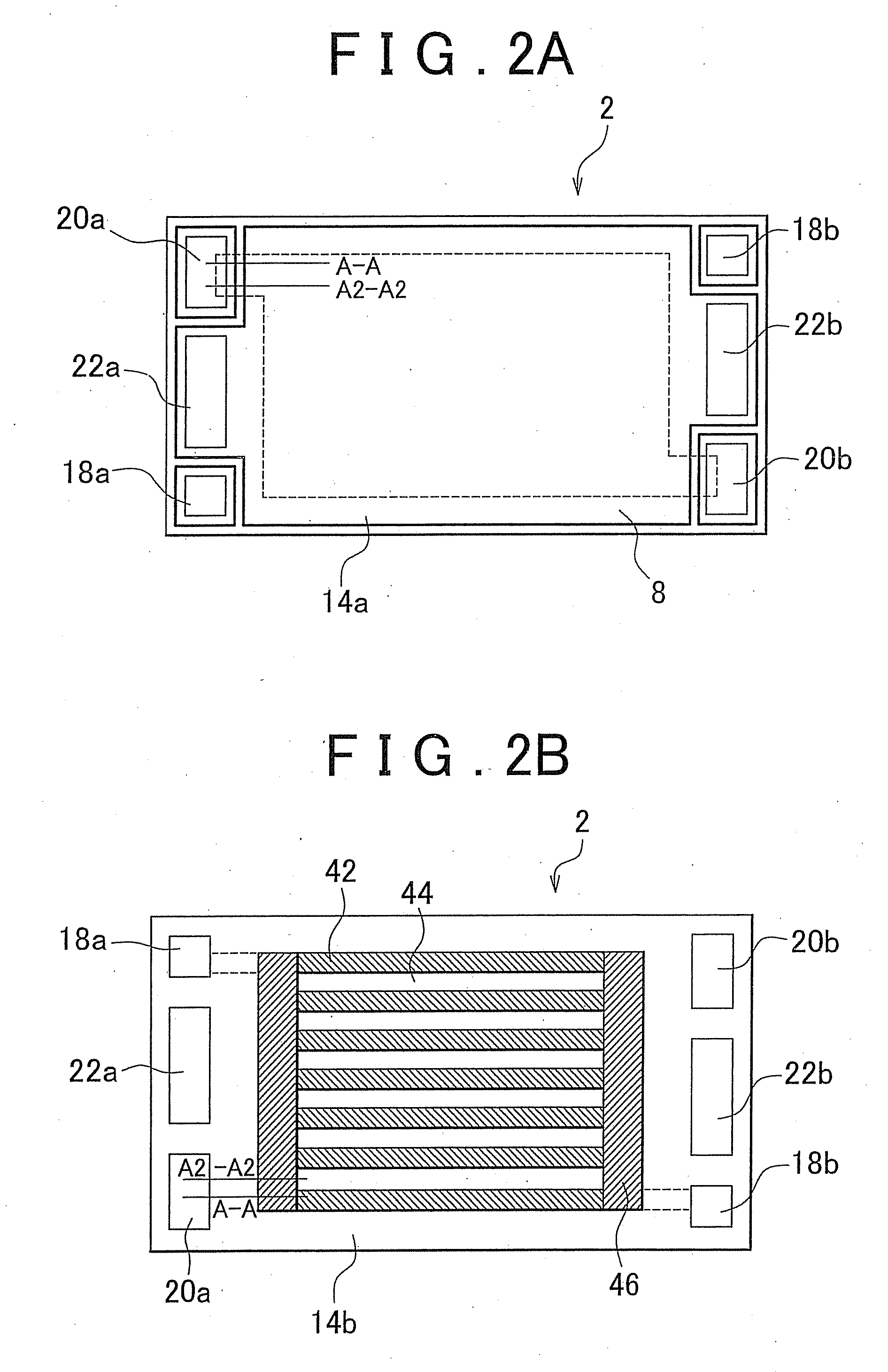
ActiveUS20130260281A1Increase power generation capacitySmall sizeFuel cell shape/formFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsFuel gas
A fuel cell (2) includes: a membrane electrode assembly (6) having an electrolyte membrane (3), an anode (5) disposed on one side of the electrolyte membrane, and a cathode (4) disposed on the other side thereof; a porous passage (8) that is disposed on at least one side of the membrane electrode assembly (6), and through which a fuel gas is supplied to the anode (5) or an oxidant gas is supplied to the cathode (4); and a manifold portion (20a), through which the fuel gas or the oxidant gas is supplied to the porous passage (8), and that is provided so as to pass through the fuel cell (2) in a stacking direction, in which the electrolyte membrane (3), the anode (5), the cathode (4), and the porous passage (8) are stacked, wherein a manifold portion-side end portion of the porous passage (8) has a gas inlet at at least one of stacking surfaces of the porous passage (8) that face in the stacking direction.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
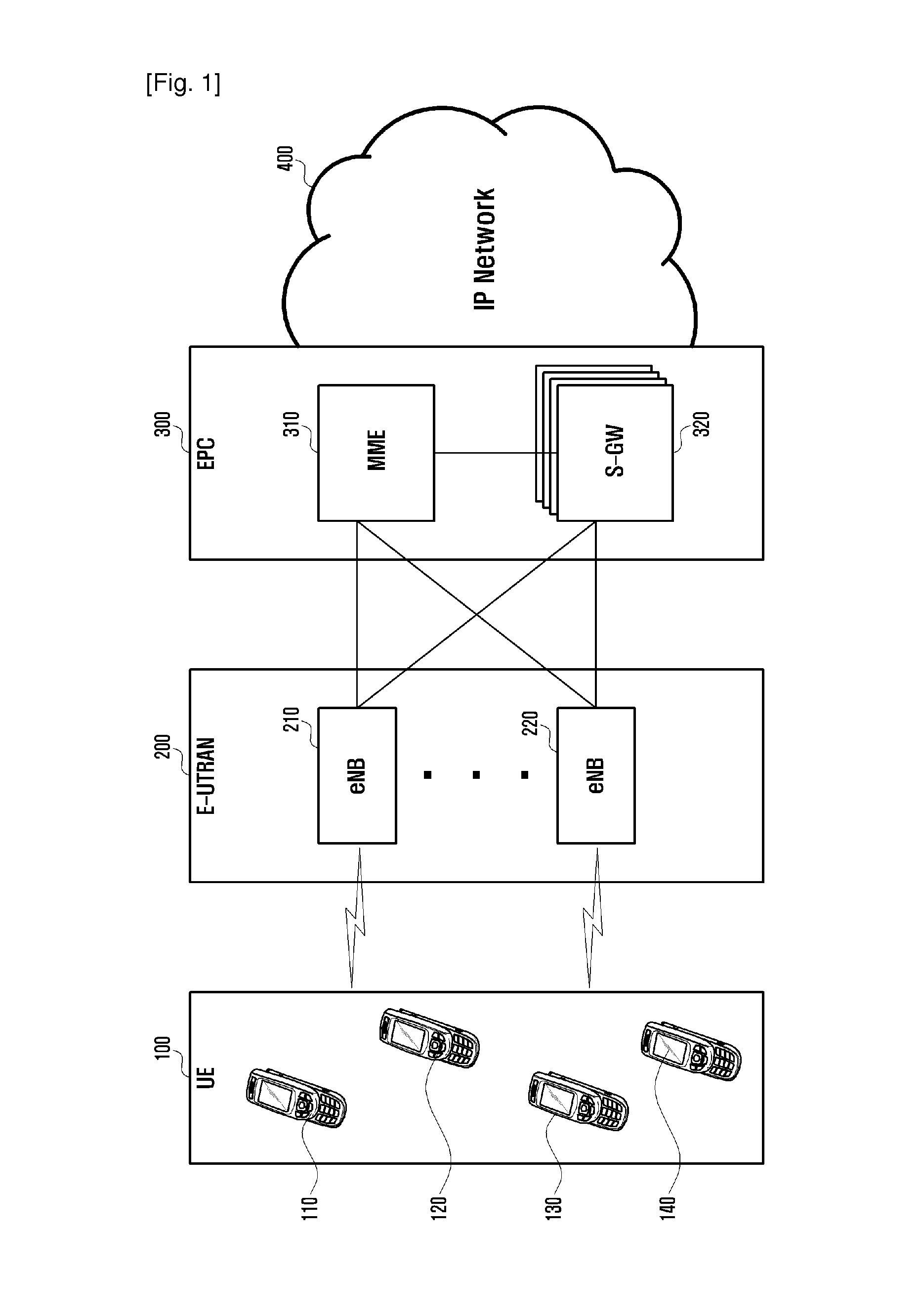
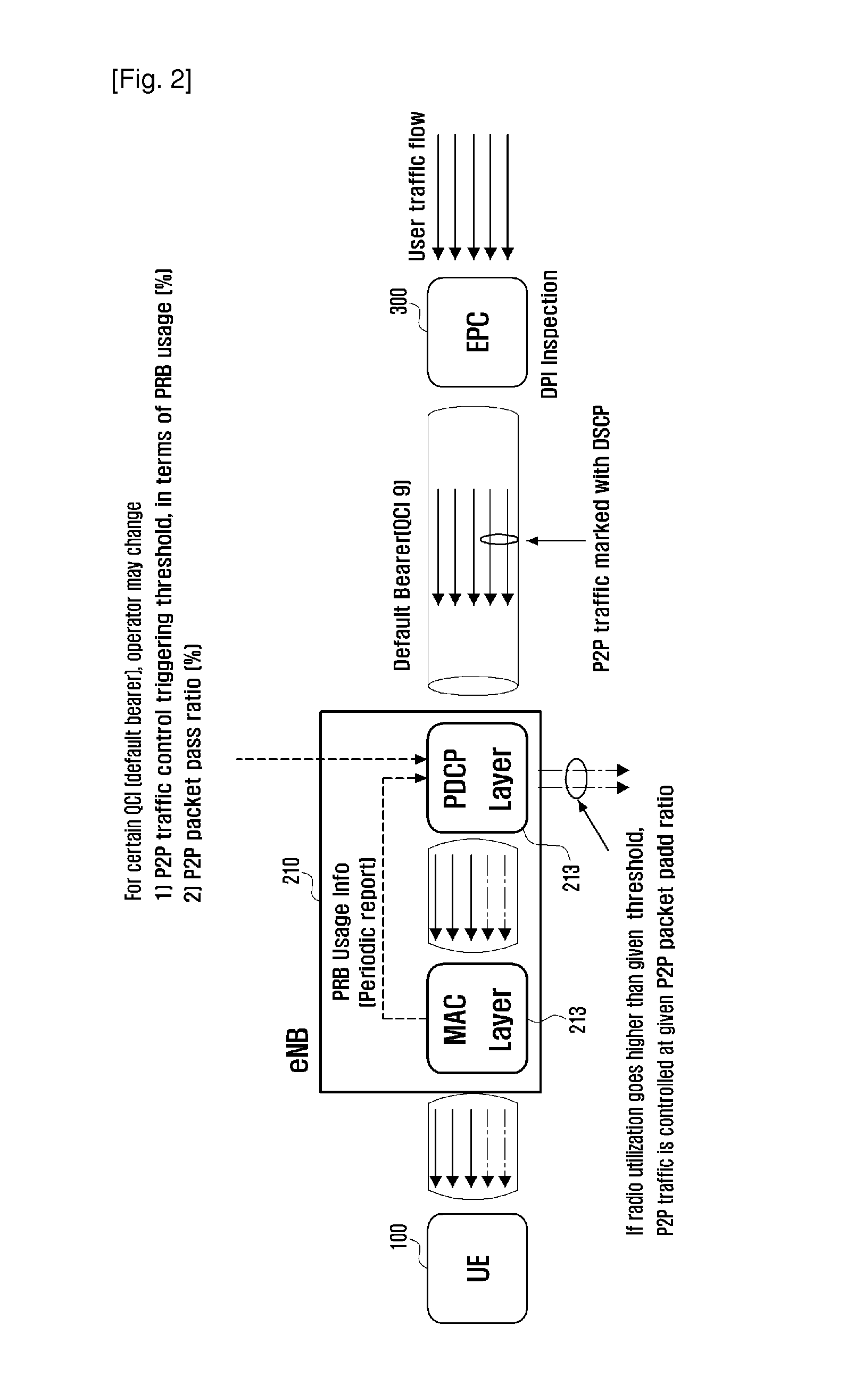
Wireless communication system and traffic control method thereof
InactiveUS20140321288A1Reduce network loadControlling traffic efficientlyError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemControl data
A data traffic control method and system is provided for controlling data transmission amount efficiently in a Long Term Evolution (LTE) system. The traffic control method of the present invention includes monitoring to detect overload of traffic by checking radio resource usage periodically; checking, when traffic overload is detected, a non-controlled packet ratio; and determining whether to control the traffic depending on the non-controlled packet ratio.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
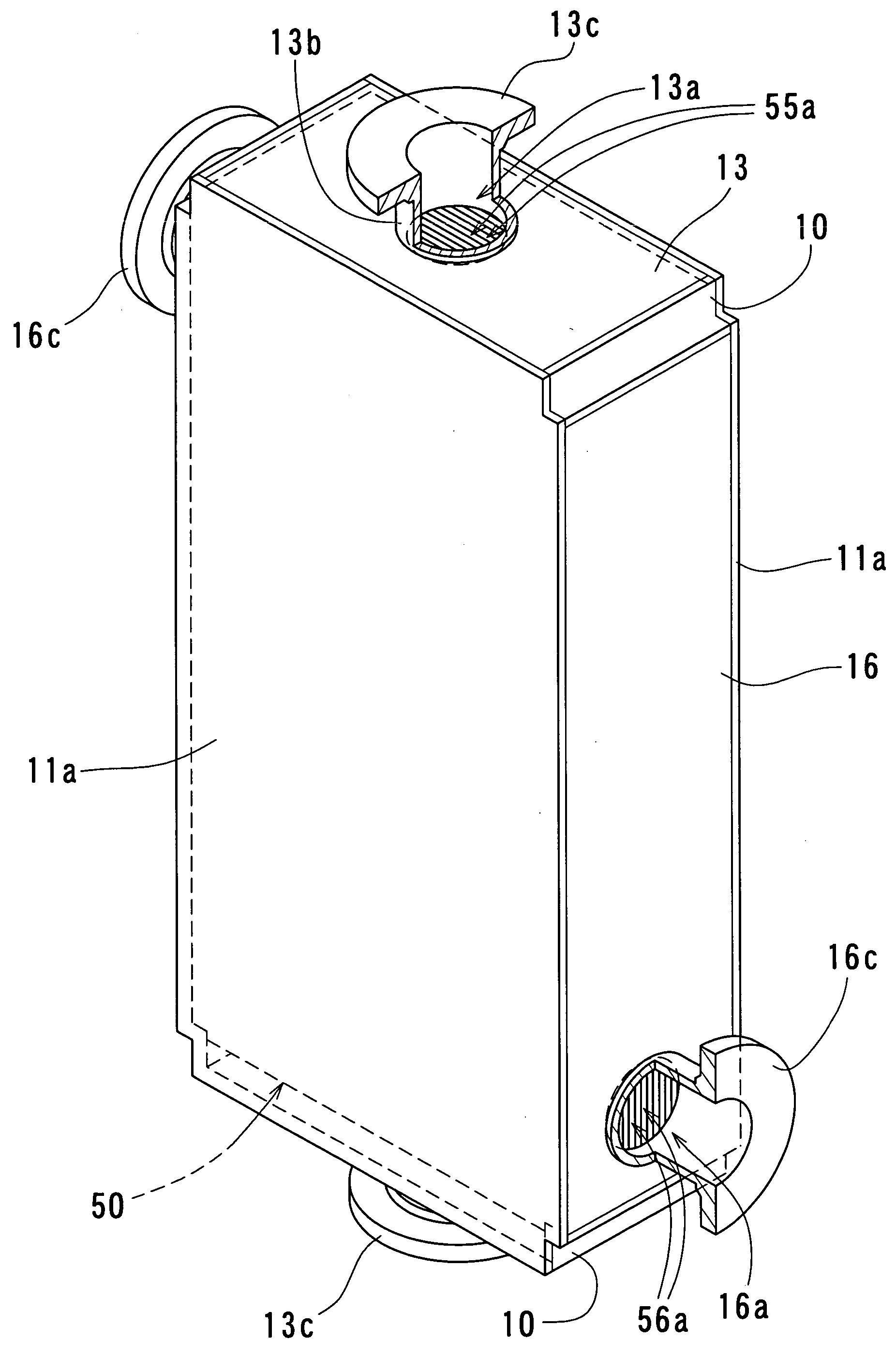
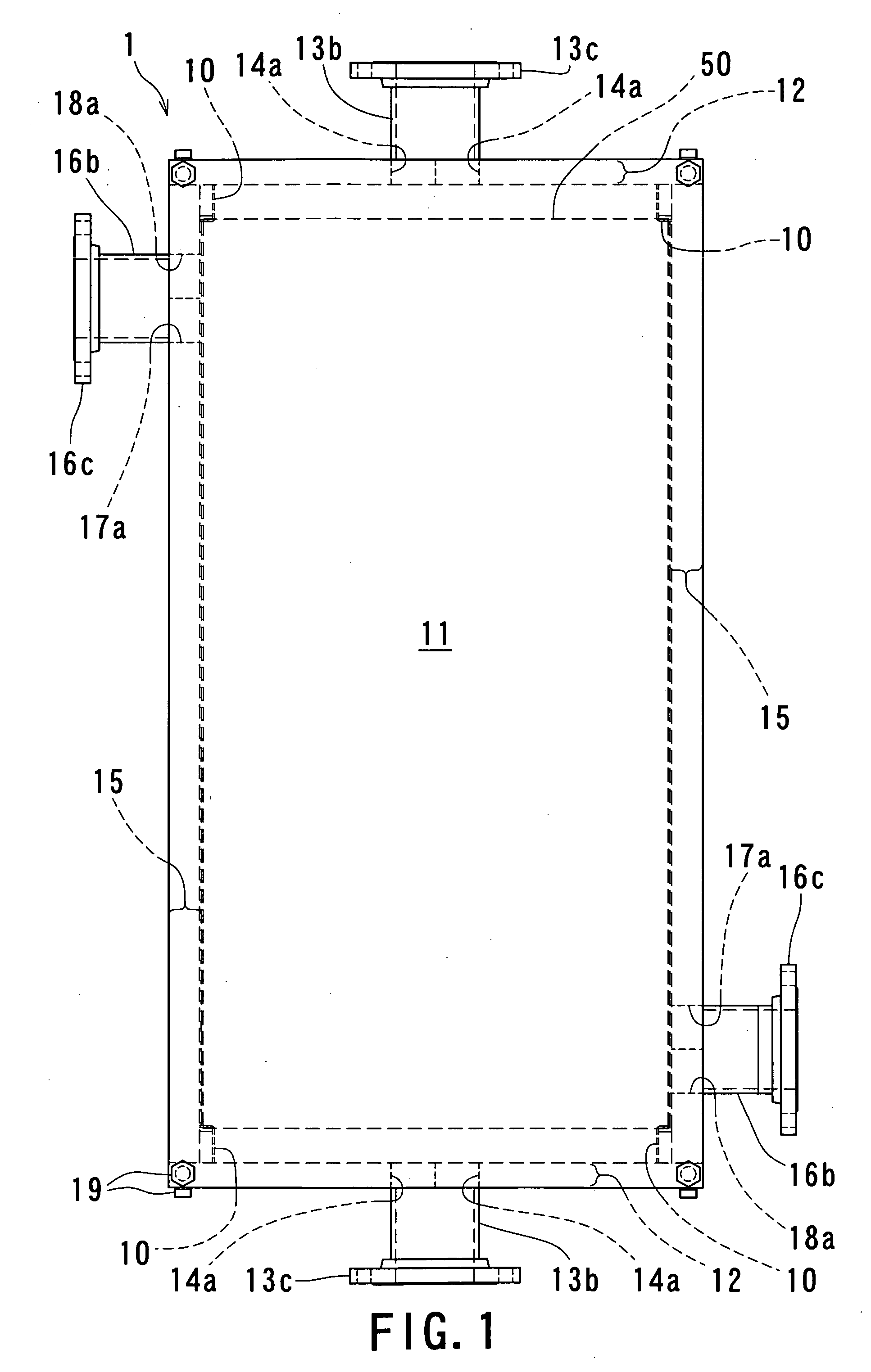
Outer shell structure for a heat exchanger
InactiveUS20060201660A1Good heat exchange efficiencySmall sizeReinforcing meansSurgical furnitureEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:XENESYS
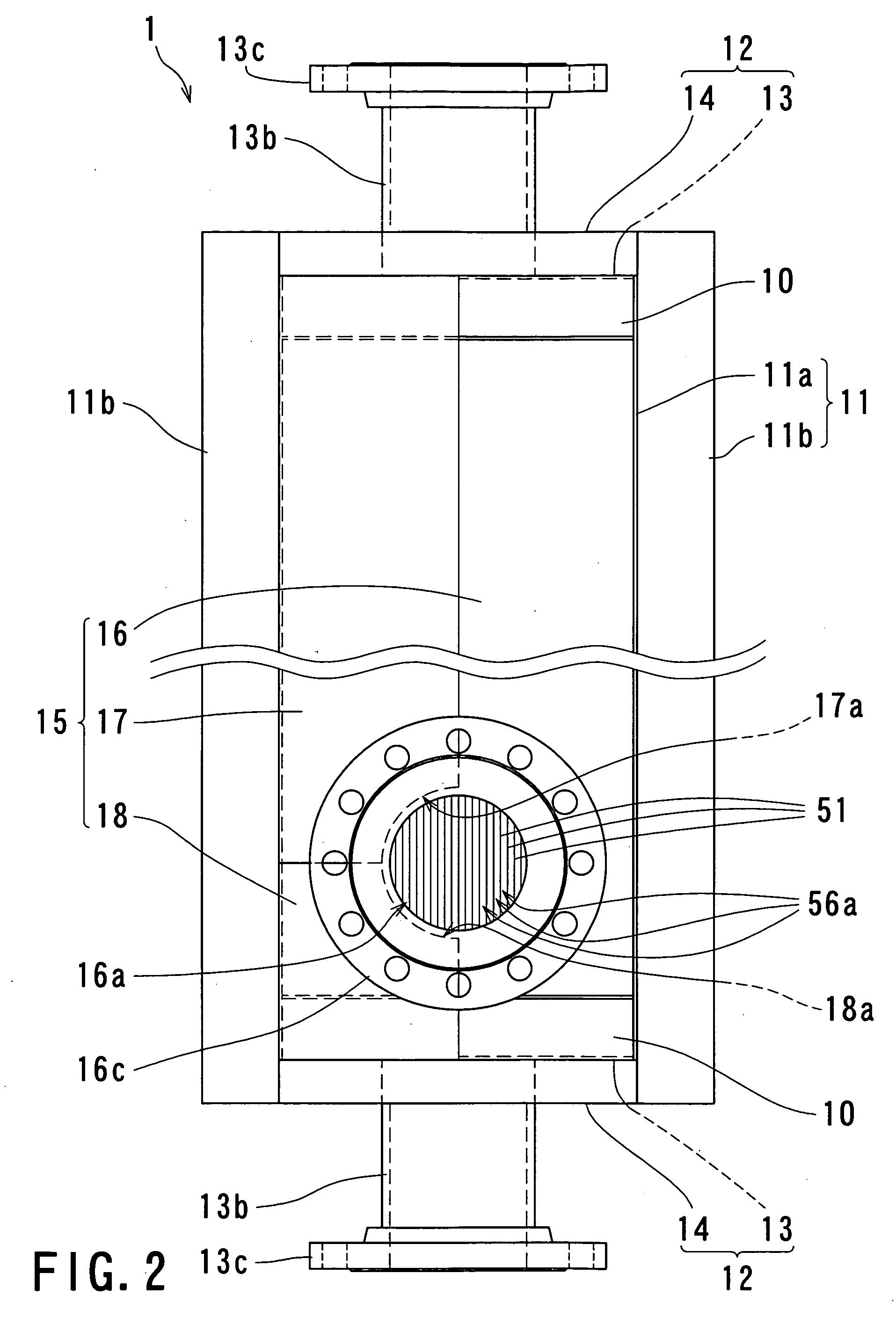
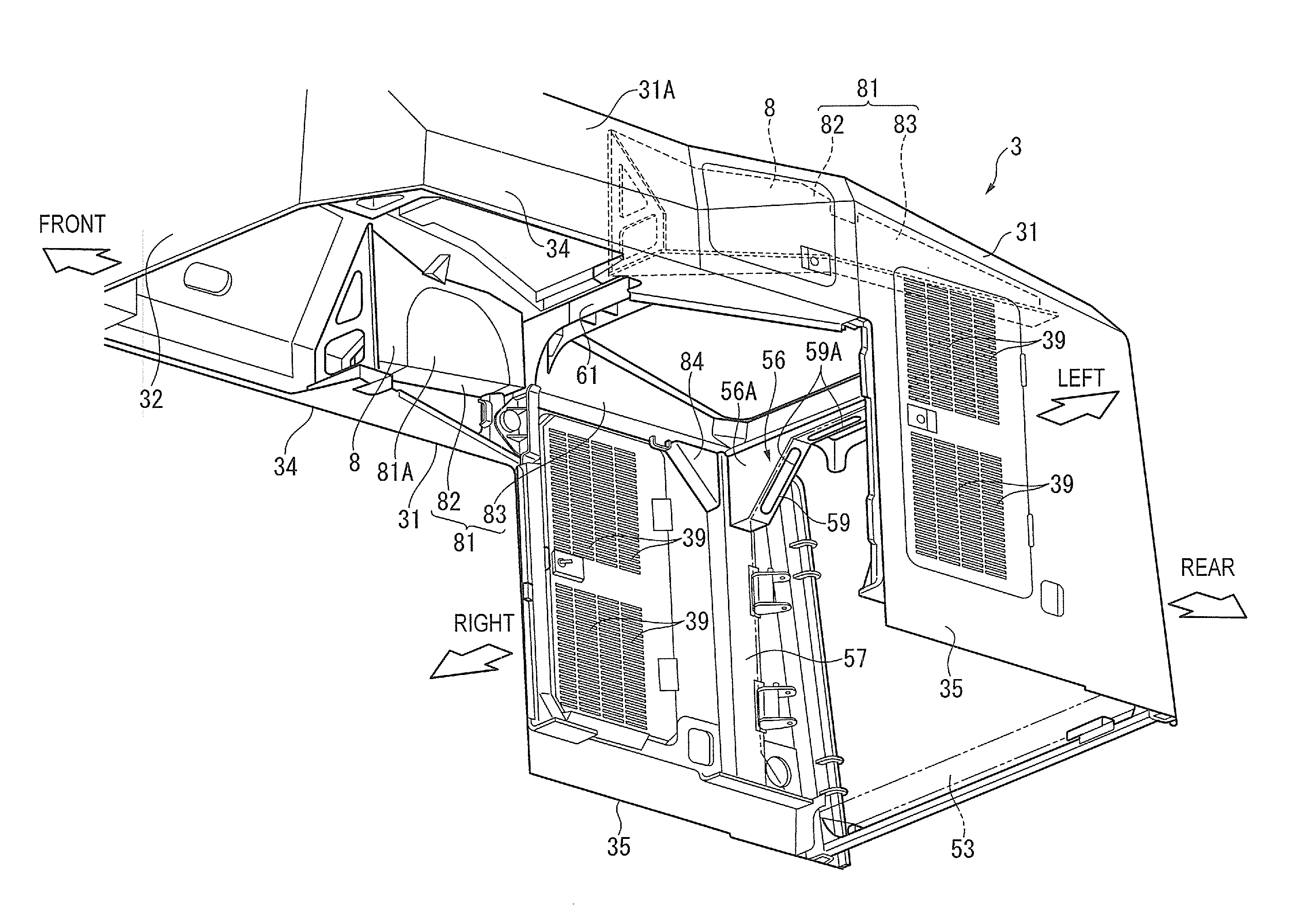
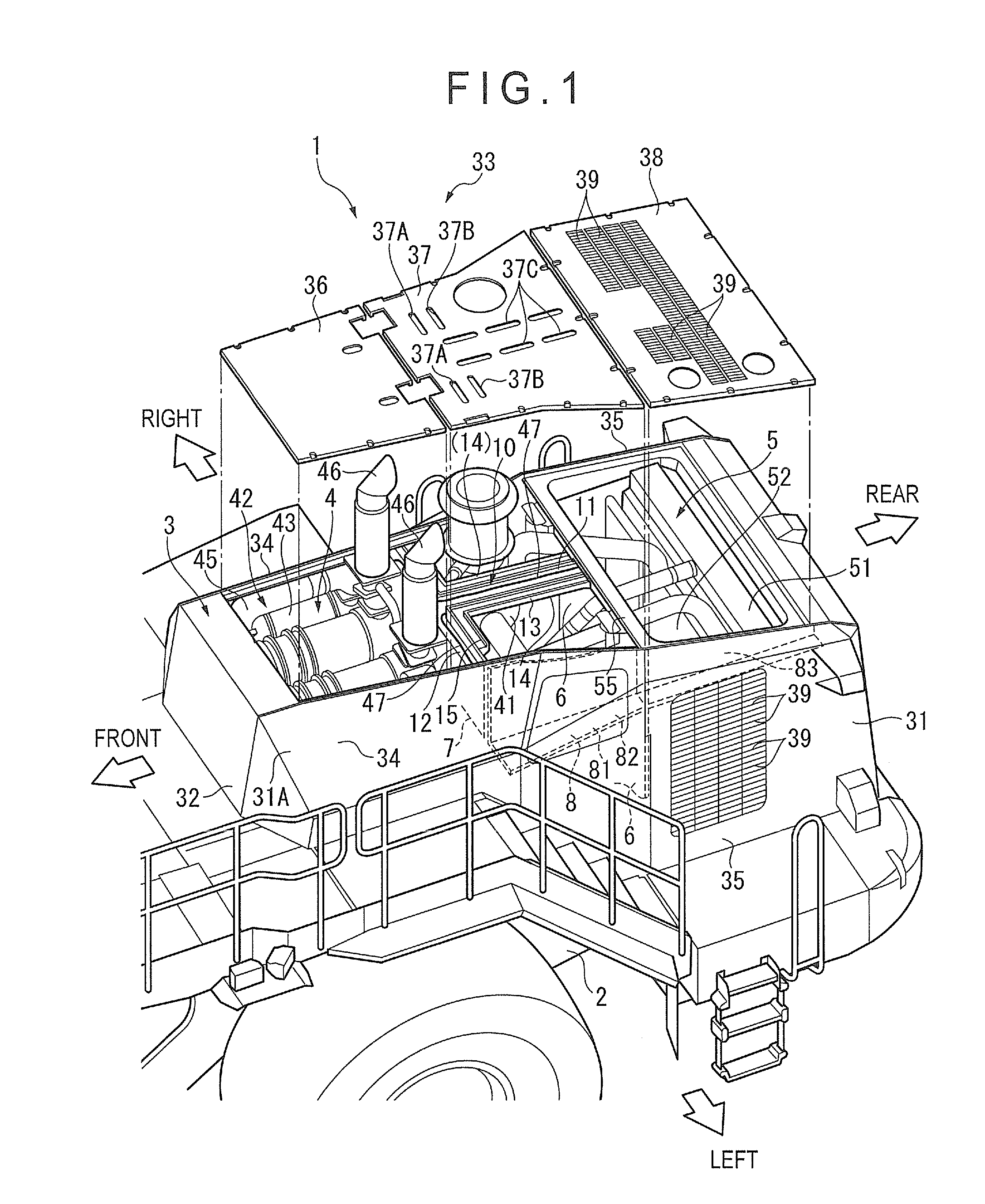
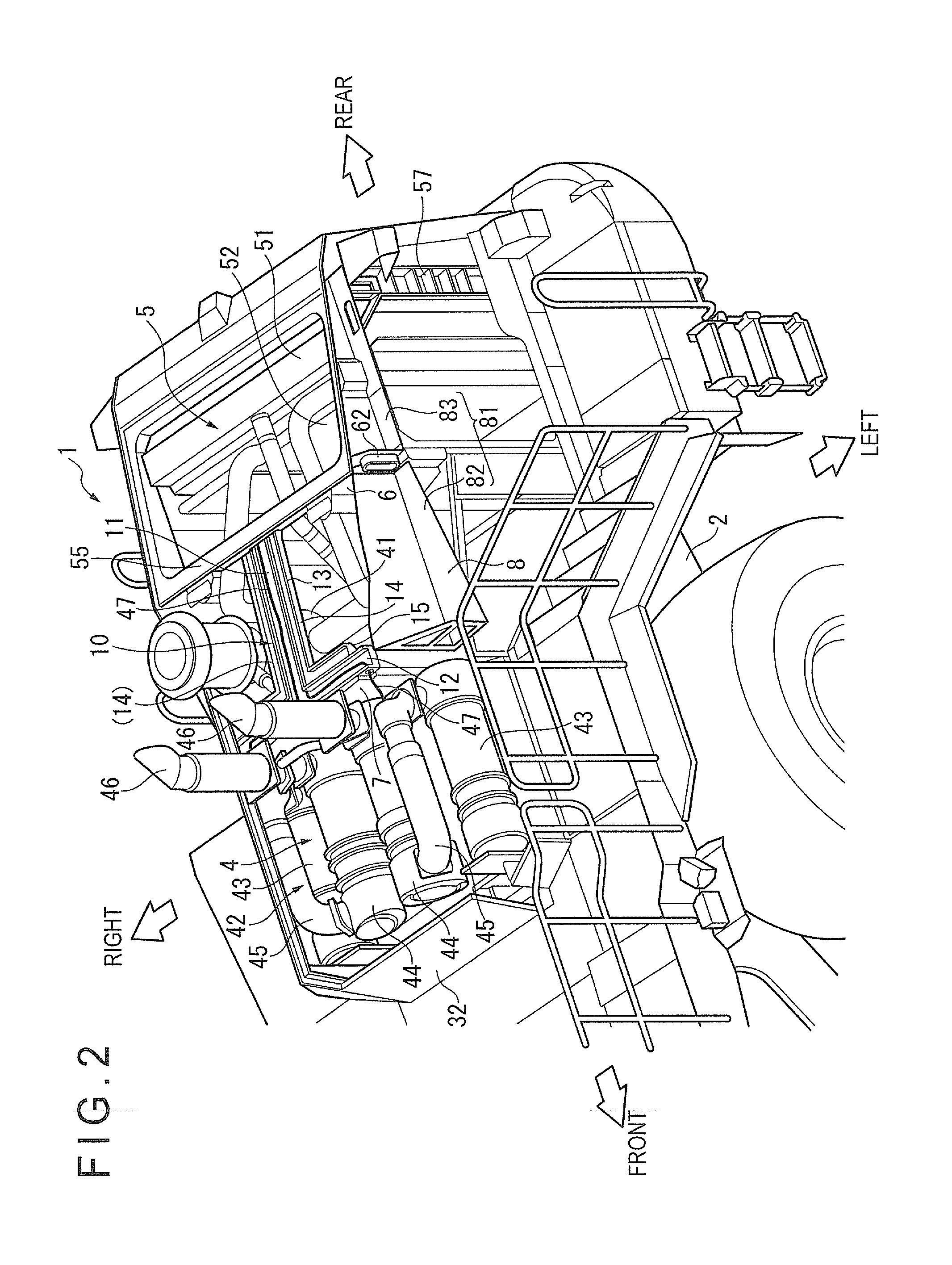
Cooling structure for urea aqueous solution conduit
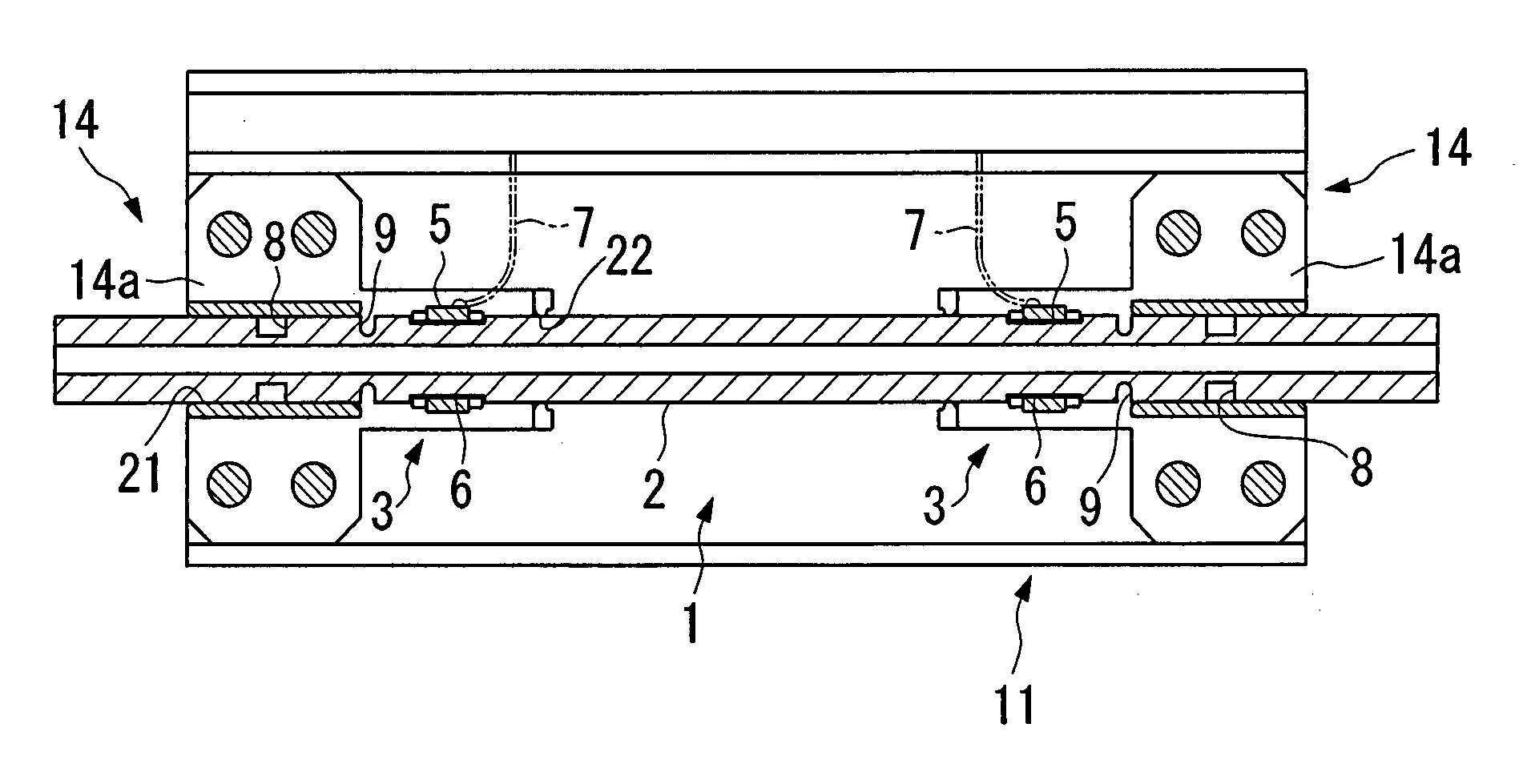
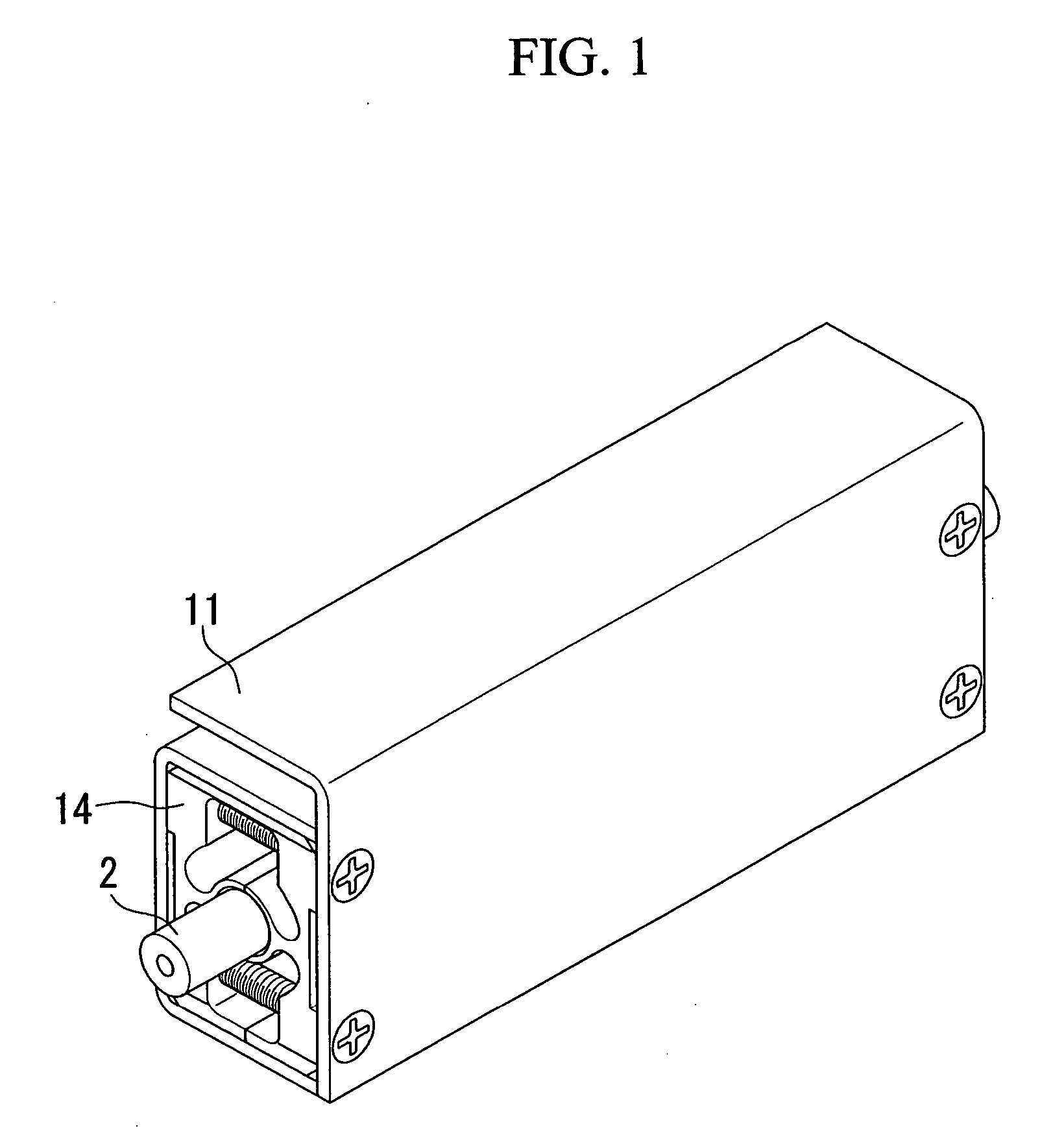
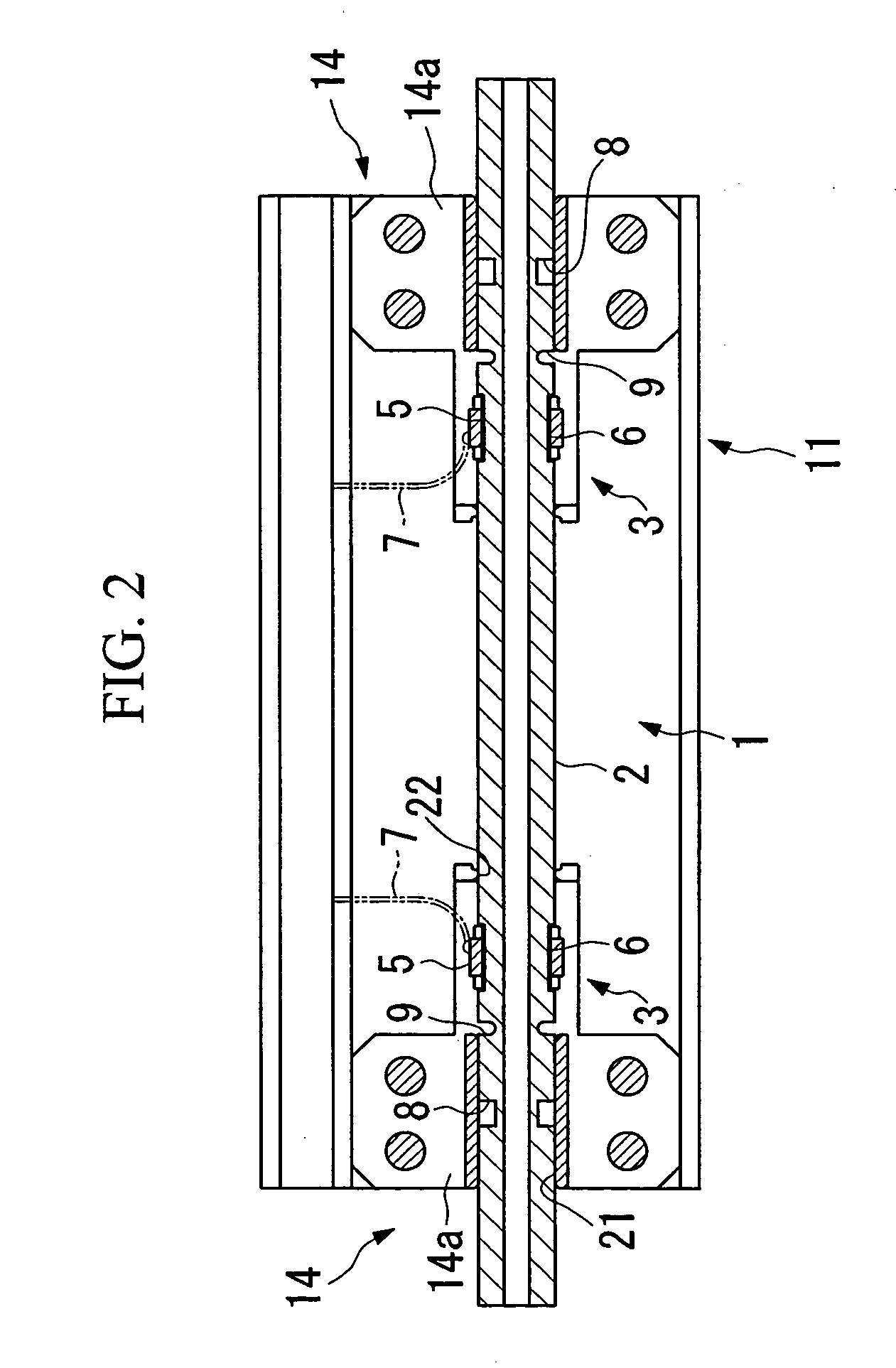
ActiveUS20150176451A1Reliably flowAvoid simple structuresInternal combustion piston enginesAir coolingExhaust fumesAmmonia
In a working vehicle, an exhaust gas aftertreatment device is provided in an engine compartment that is adjacent to a cooling fan through which cooling air is supplied to a heat exchanger. The exhaust gas aftertreatment device includes a selective catalytic reduction device in which ammonia obtained from a urea aqueous solution is used as a reduction-causing agent. A urea aqueous solution pipe through which the urea aqueous solution is supplied is laid to the selective catalytic reduction device through the engine compartment. In the engine compartment, a pipeline-forming member having pipelines in which the urea aqueous solution pipe is installed. The cooling air sucked by a cooling fan flows into the pipelines.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
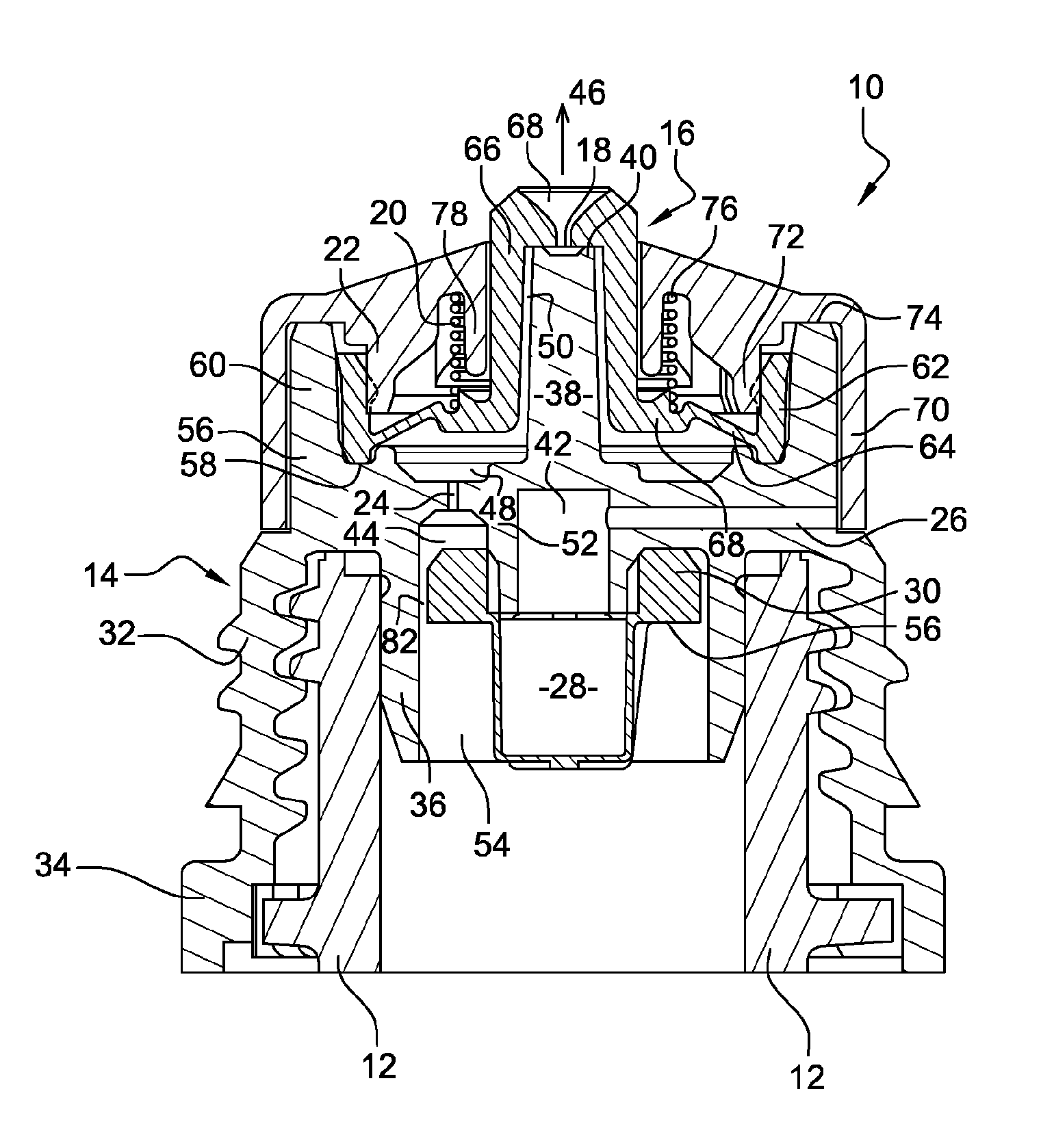
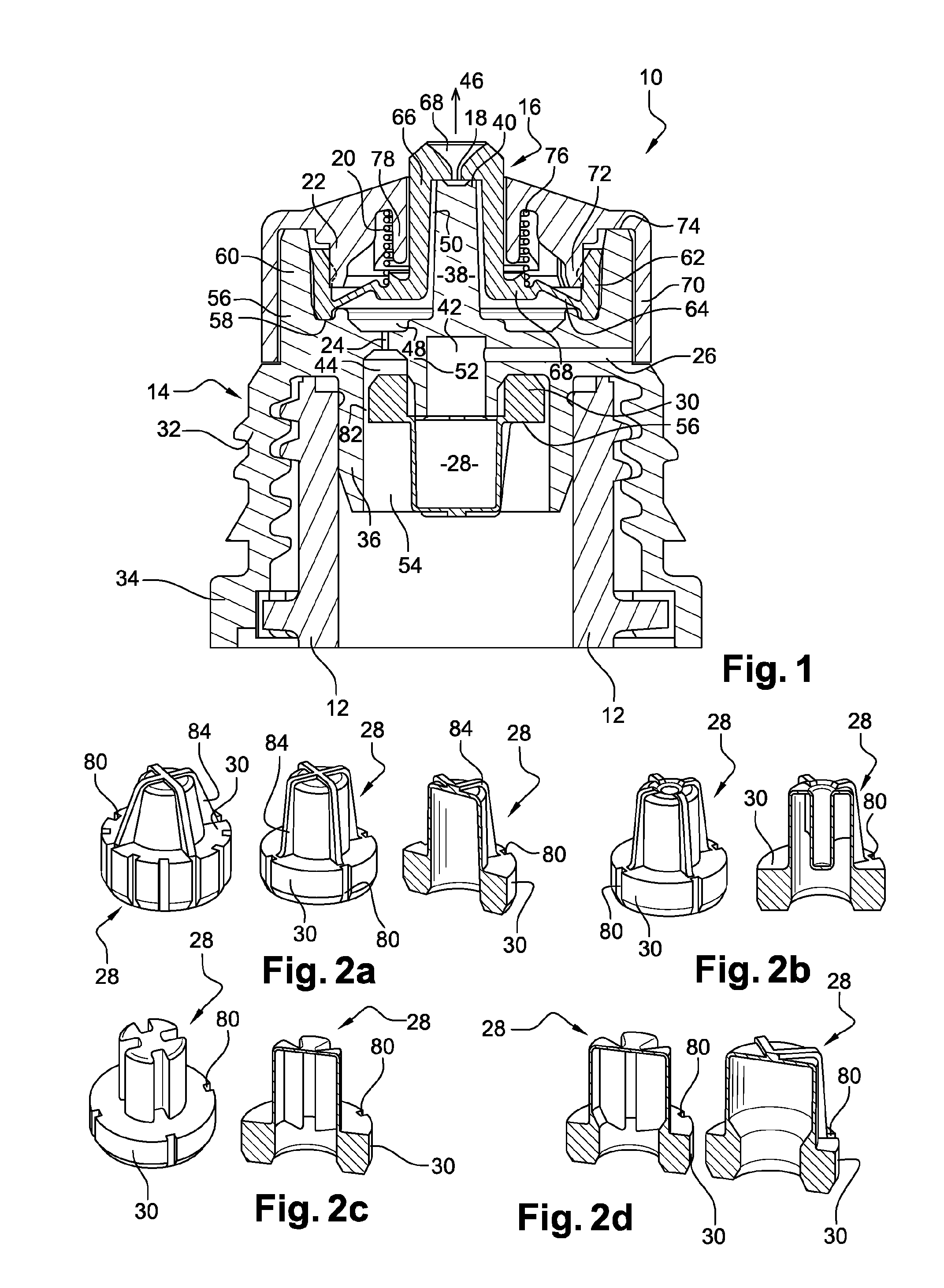
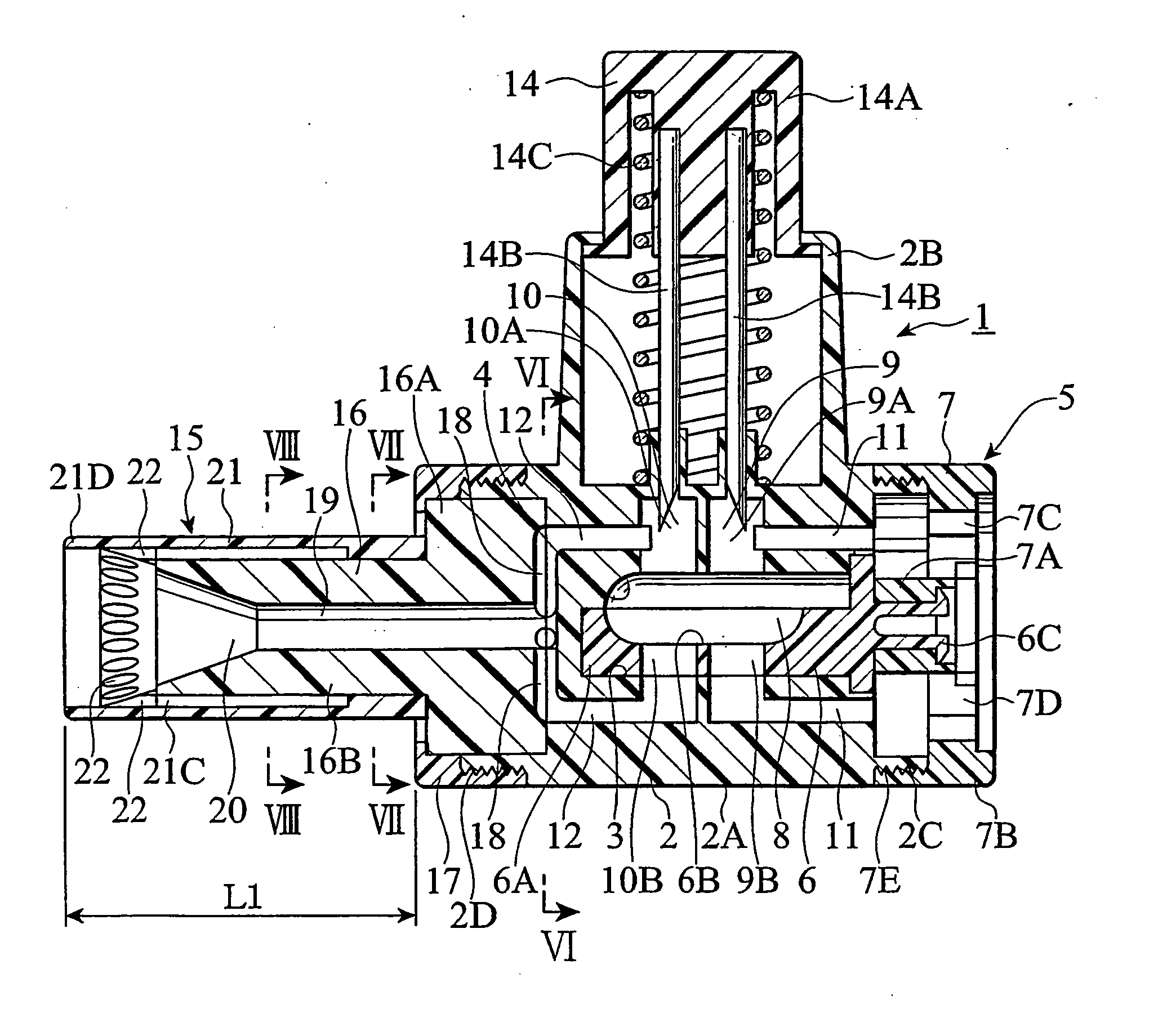
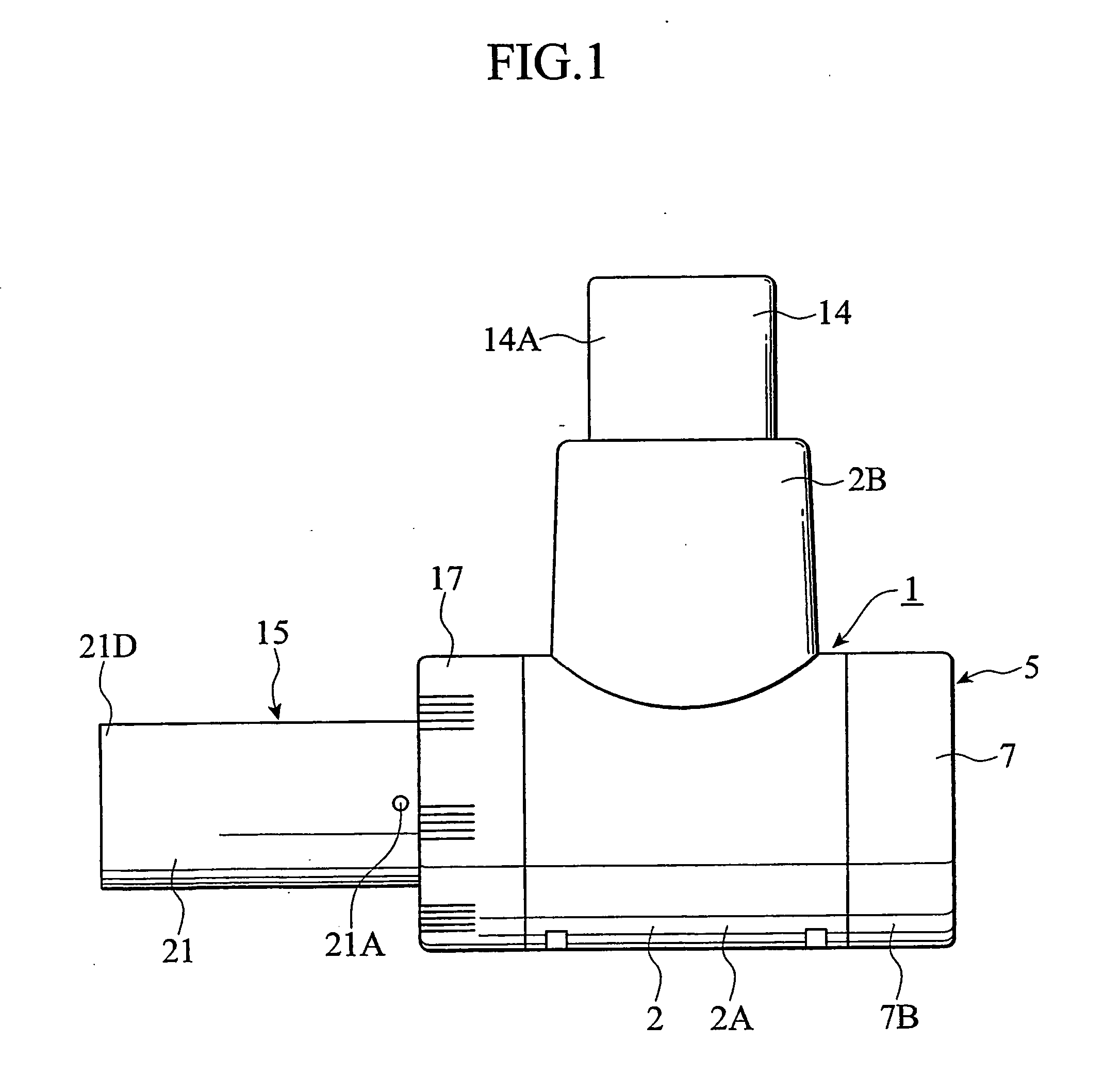
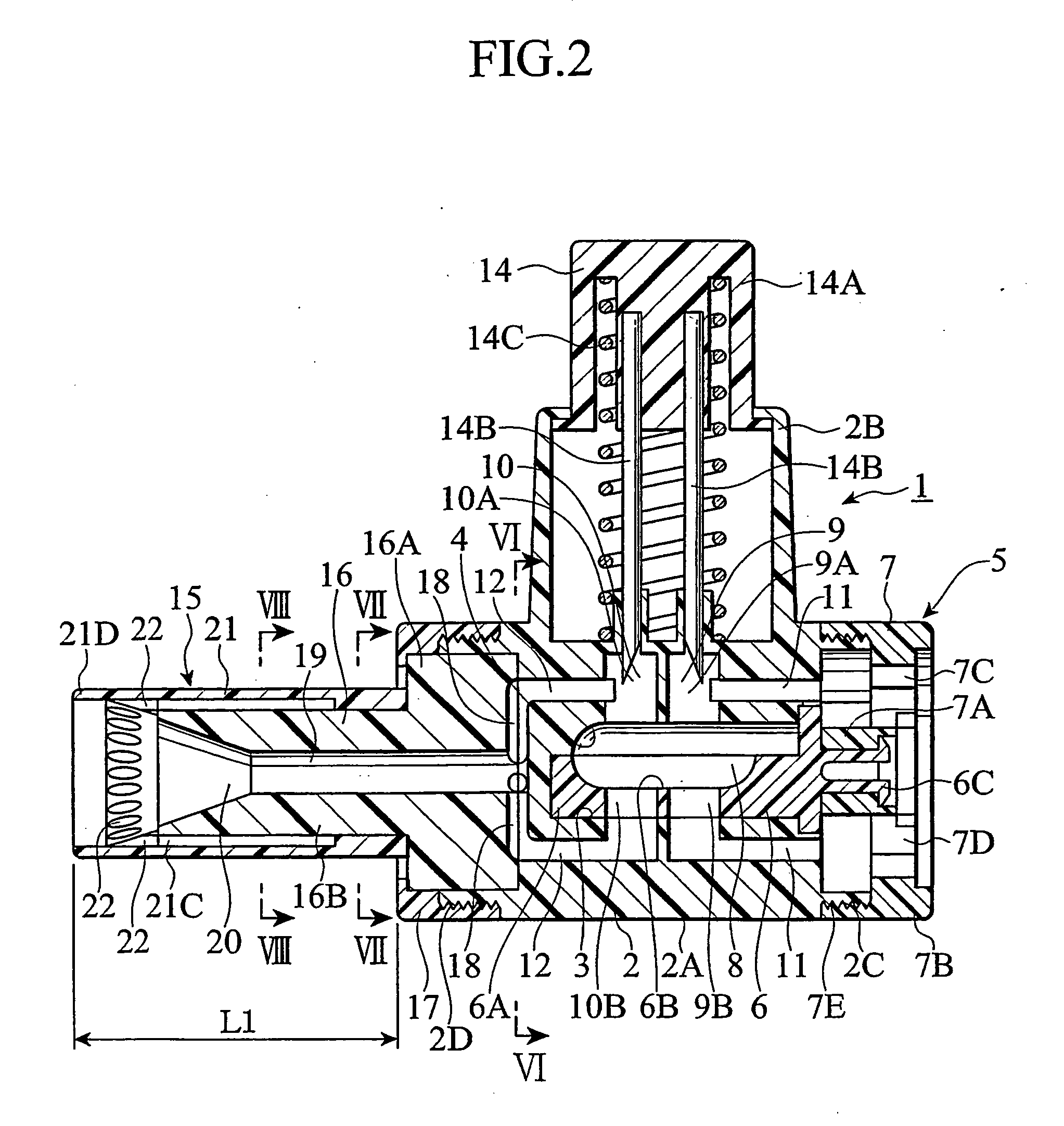
Contact terminal having a plunger pin
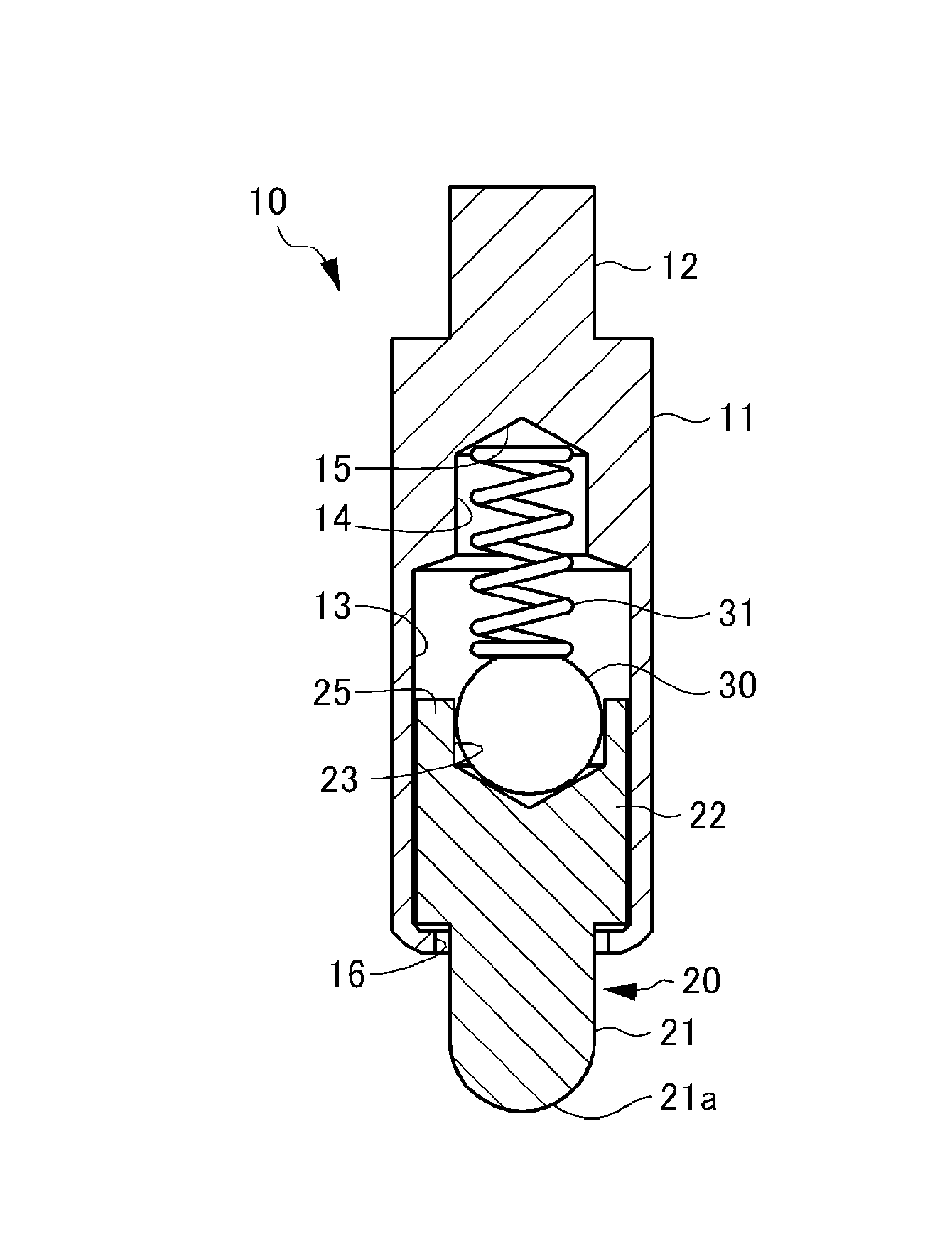
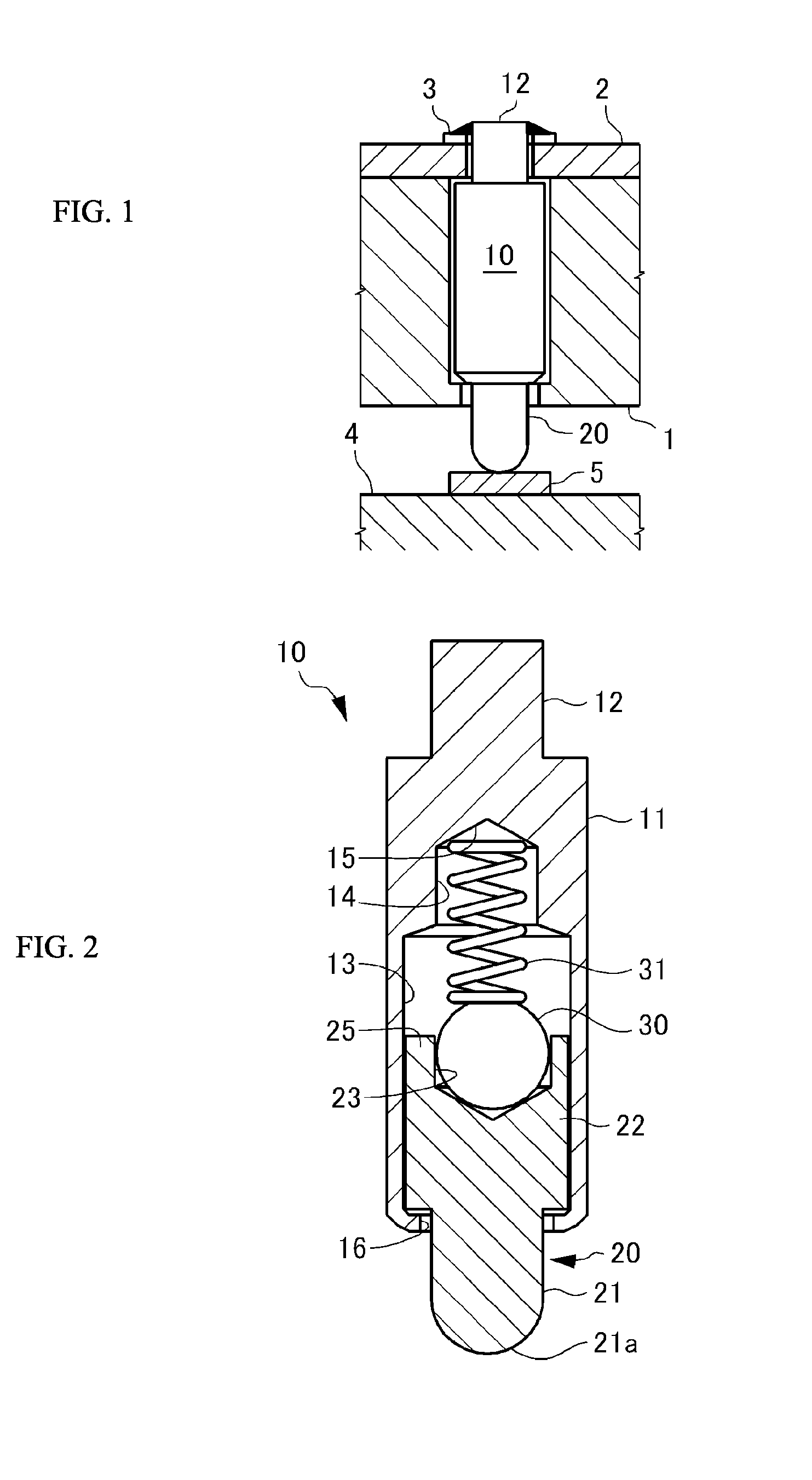
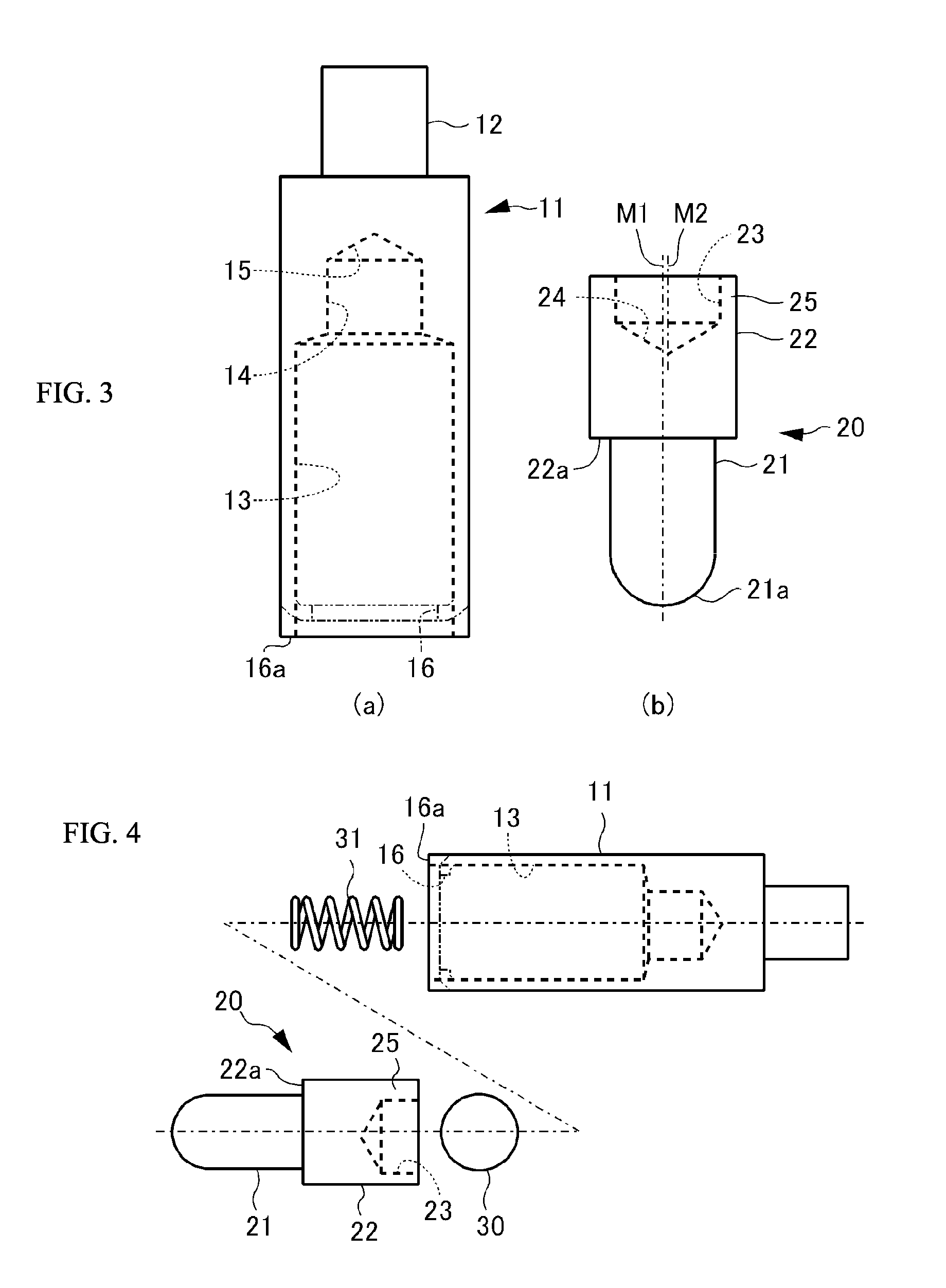
InactiveUS8926376B2Reliably flowSmall diameterElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingCoil springEngineering
A contact terminal having a main body case and a plunger pin received in an elongate hole formed in the main body case is provided. The plunger pin is a round bar provided with a step and includes a small diameter portion including the protrusion end portion and a large diameter portion that slides on a surface of the hole to freely move in a longitudinal direction thereof. A cut space is formed to extend from an end of the large diameter portion so as to leave at least a part of a side surface portion of the large diameter portion and the cut space receives an insulation ball including at least an insulation surface. A coil spring is arranged between the hole and the insulation ball to press the protrusion end portion of the plunger pin such that the protrusion end portion protrudes from the main body case.
Owner:SHIMANO MFG
Method and apparatus for producing nanofibers and polymer web
ActiveUS8110136B2Efficient and stable productionEnsure efficient flowElectric discharge heatingPhysical treatmentProduction rateEvaporation
Nanofibers are formed from a polymer material by rotating a conductive rotating container having a plurality of small holes while supplying a polymer solution formed by dissolving a polymer material in a solvent into the rotating container, charging the polymer solution discharged from the small holes of the rotating container by charging means, and drawing the discharged filamentous polymer solution by centrifugal force and an electrostatic explosion resulting from evaporation of the solvent. The nanofibers from this production step are oriented and made to flow from one side toward the other side in a shaft center direction of the rotating container by a reflecting electrode and / or blowing means, or those nanofibers are deposited, to produce a polymer web. The nanofibers and the polymer web using these nanofibers can be produced uniformly by a simple configuration with good productivity.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
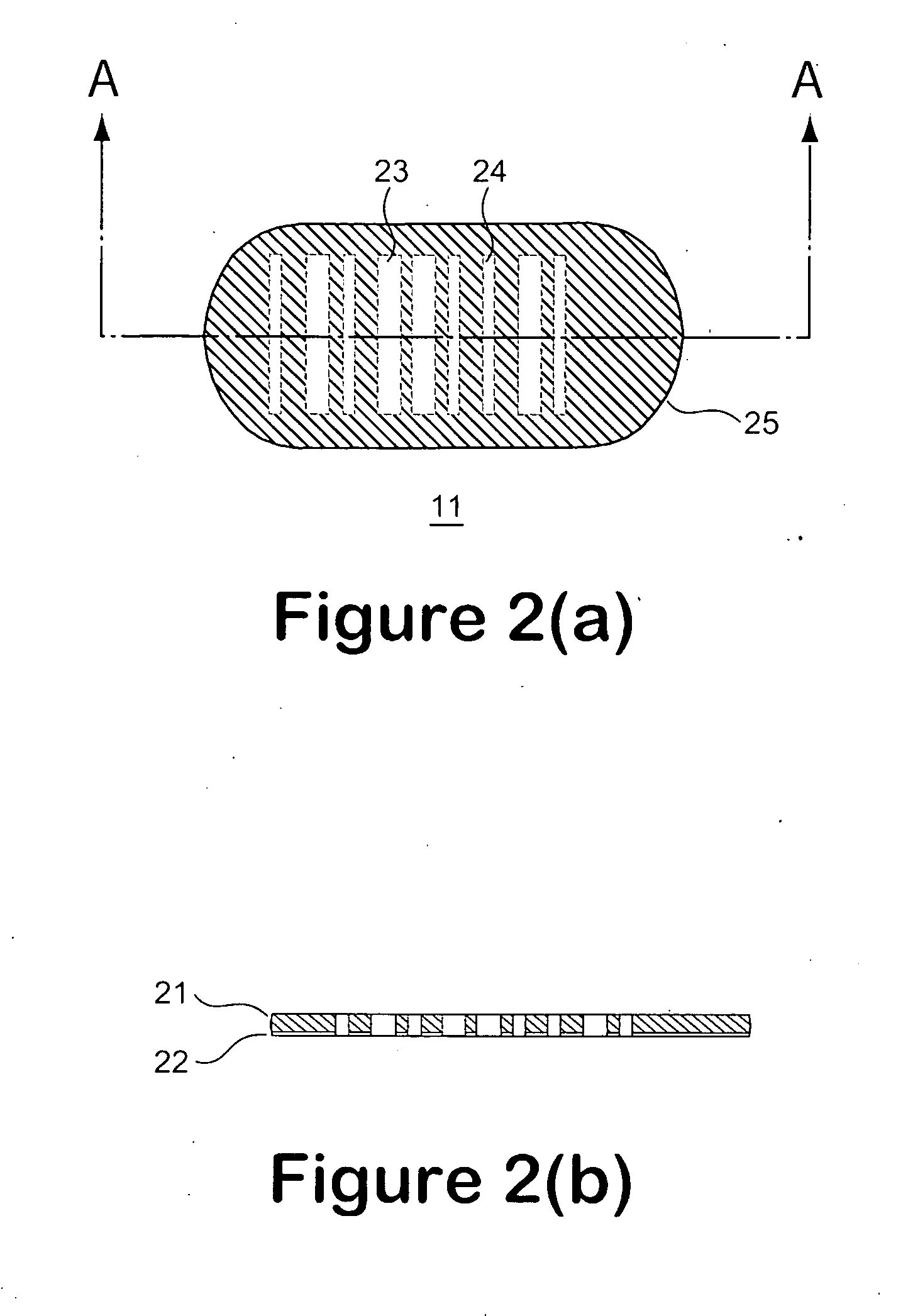
Light transmitted assay beads
ActiveUS20070099218A1Increase contrastImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechBarcodeTransmitted light
A micro bead having a digitally coded structure that is partially transmissive and opaque to light. The pattern of transmitted light is determined by to decode the bead. The coded bead may be structured a series of alternating light transmissive and opaque sections, with relative positions, widths and spacing resembling a 1D or 2D bar code image. To decode the image, the alternating transmissive and opaque sections of the body are scanned in analogous fashion to bar code scanning. The coded bead may be coated or immobilized with a capture or probe to effect a desired bioassay. The coded bead may include a paramagnetic material. A bioanalysis system conducts high throughput bioanalysis using the coded bead, including a reaction detection zone and a decoding zone.
Owner:APPLIED BIOCODE
Device for dispensing liquid in the form of drops
ActiveUS8986266B2Easy to checkReliably flowSpray nozzlesMedical devicesMechanical engineeringPolymer
Owner:NEMERA LA VERPILLIERE SAS
Apparatus and method for digital magnetic beads analysis
ActiveUS8232092B2Increase contrastImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic beadMechanical engineering
A micro bead having a digitally coded structure that is partially transmissive and opaque to light. The pattern of transmitted light is determined by to decode the bead. The coded bead may be structured a series of alternating light transmissive and opaque sections, with relative positions, widths and spacing resembling a 1D or 2D bar code image. To decode the image, the alternating transmissive and opaque sections of the body are scanned in analogous fashion to bar code scanning. The coded bead may be coated or immobilized with a capture or probe to effect a desired bioassay. The coded bead may include a paramagnetic material. A bioanalysis system conducts high throughput bioanalysis using the coded bead, including a reaction detection zone and a decoding zone. Alternative method for barcode determination is based on barcode pattern image processes. Microbeads can also be settled down to the bottom of the well in a microplate, so the barcode can be decoded by image processed directly. Therefore, multiple-analyte tests can be performed in one single well. Microplate is a standard format; each plate can have 96, 384, or 1536 patient samples. The bead image is taken with a conventional microscope and optical detector from the bottom of an optically clear microplate, and barcode pattern can be decoded by image software. Therefore, the whole bead experiment can be performed in the microplate without taking the beads out.
Owner:APPLIED BIOCODE
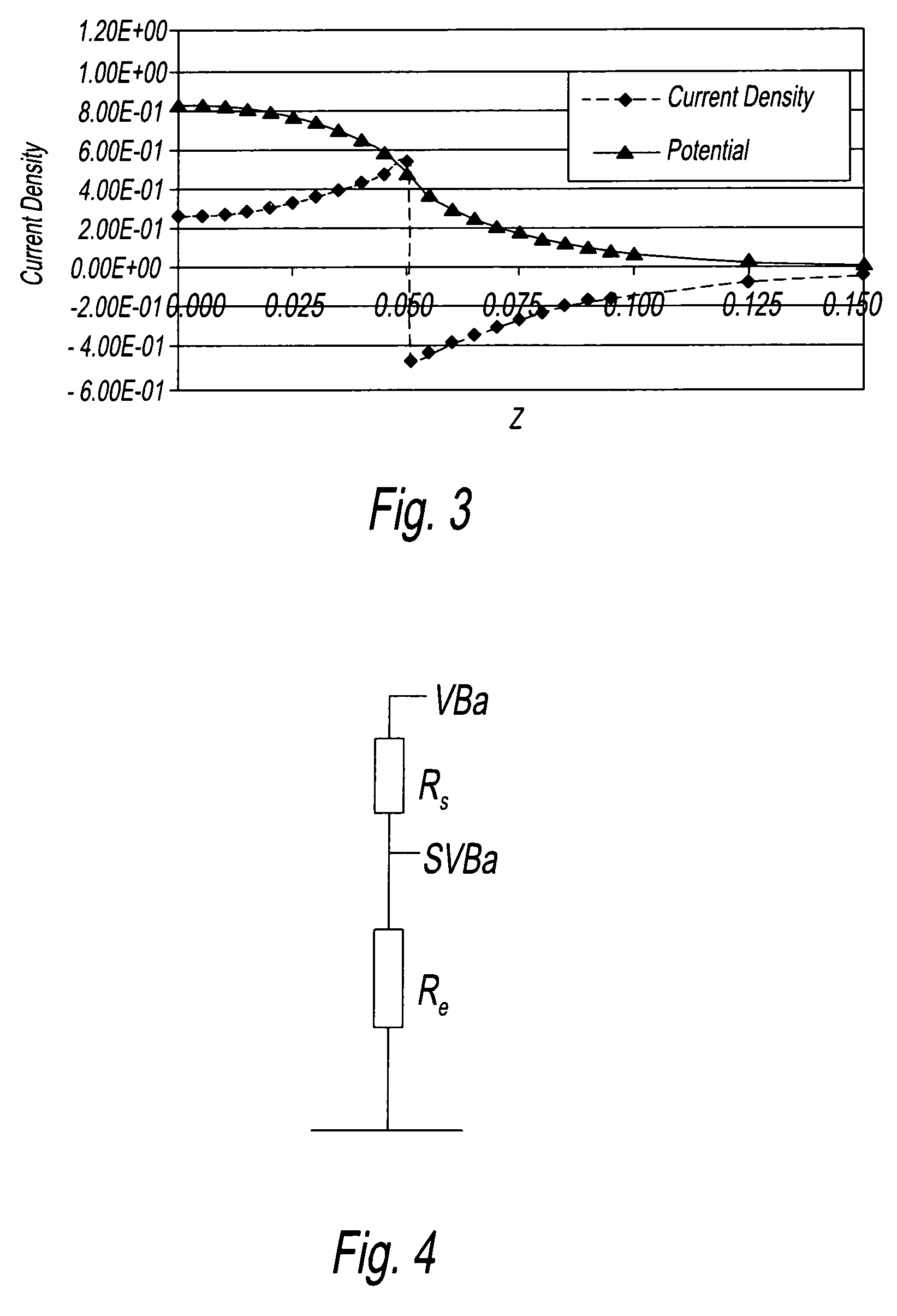
Electromagnetic flow meter for low conductivity fluids
InactiveUS7117749B2Decrease effective electrode impedanceIncrease the lengthVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersOrganic solventTurpentine
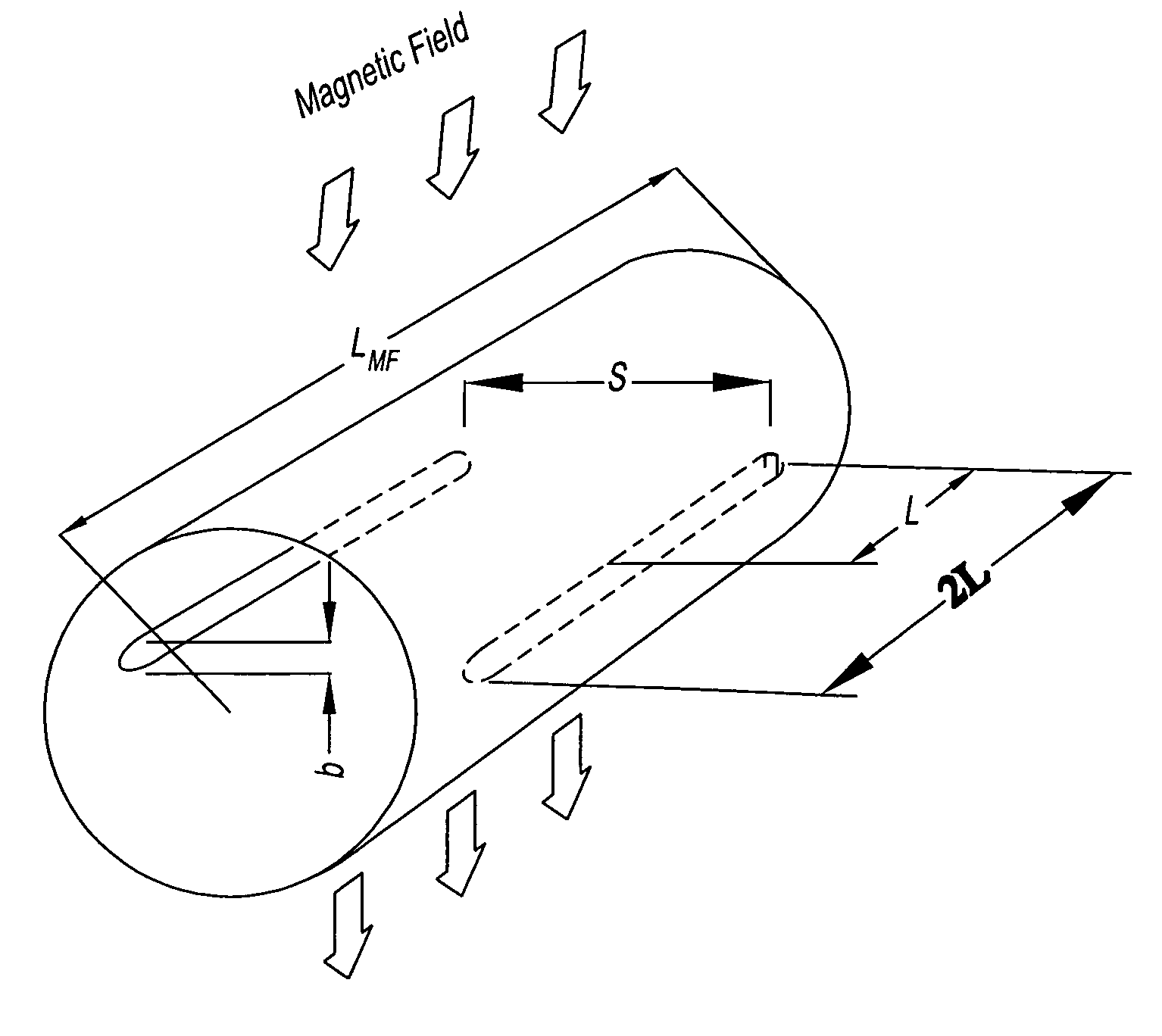
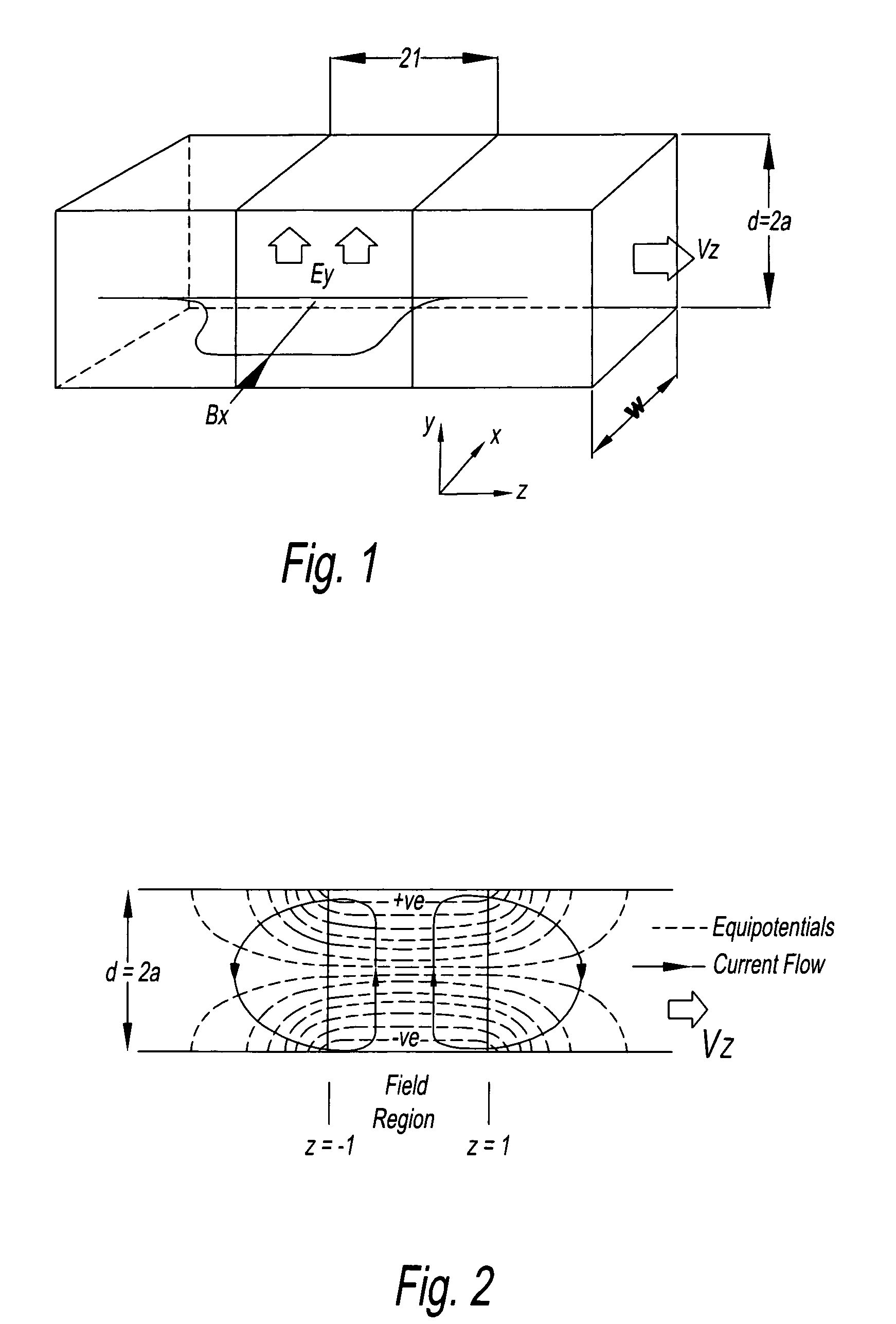
An electromagnetic flow meter is disclosed which can be used to measure flow in low conductivity fluids, for example alcohol, turpentine, oil or other organic solvents. In one embodiment, the electromagnetic flow meter includes an elongate flow conduit having a direction of elongation corresponding to a direction of fluid flow, magnetic field generating means for generating a magnetic field across the flow conduit and potential sensing electrodes for sensing a potential generated by the magnetic field in a fluid flowing through the conduit. Both the field generating means and the potential sensing electrodes of the flow meter are elongate in the direction of flow.
Owner:STONEFIELD WORKS
Light Transmitted Assay Beads
InactiveUS20100210477A1Increase contrastImprove efficiencyNanotechPeptide librariesBarcodeTransmitted light
A micro bead having a digitally coded structure that is partially transmissive and opaque to light. The pattern of transmitted light is determined by to decode the bead. The coded bead may be structured a series of alternating light transmissive and opaque sections, with relative positions, widths and spacing resembling a 1D or 2D bar code image. To decode the image, the alternating transmissive and opaque sections of the body are scanned in analogous fashion to bar code scanning. The coded bead may be coated or immobilized with a capture or probe to effect a desired bioassay. The coded bead may include a paramagnetic material. A bioanalysis system conducts high throughput bioanalysis using the coded bead, including a reaction detection zone and a decoding zone.
Owner:APPLIED BIOCODE
Outer shell structure for a heat exchanger
InactiveUS7740056B2Reduce in quantityReliably flowReinforcing meansSurgical furnitureEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:XENESYS
Inhalation type medication apparatus
InactiveUS20060231096A1Relief discomfortInhale comfortablyRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsBiomedical engineeringOral cavity
A mouthpiece 15 is configured to be provided with a plurality of air nozzles 22 which are positioned around an admission port, and from which the air to enclose the surroundings of medicine powder flow discharged from the admission port 20 is blown off. Accordingly, when the breath is inhaled while an outer body 21 of the mouthpiece 15 is being held in the mouth, the air to be blown off from the air nozzles 22 forms an air curtain 24 to enclose the surroundings of the medicine powder flow 23 discharged from the admission port 20. Thereby, medicine powder included in the medicine powder flow 23 is prevented, by the air curtain 24, from adhering to the surface of the tongue, the internal surface of the oral cavity and the like. Thus, the medicine powder can be inhaled comfortably while unnecessary taste of the medicine powder such as sweetness, saltiness, sourness, bitterness and the like, is not being sensed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Liquid ejecting apparatus
InactiveUS20110199440A1Avoid it happening againOccurrence of ejection failures can be preferably preventedPrintingEngineeringStreamflow
A liquid ejecting apparatus includes, a plurality of liquid ejecting sections ejecting liquid, and a liquid supplying flow path. In the device, an upstream side of the liquid supplying flow path is coupled to the liquid supplying source while a downstream side of the liquid supplying flow path branches into a plurality of flow paths at a branch point and each of the plurality of flow paths is coupled to one of the liquid ejecting sections. In the liquid supplying flow path, an average flow path resistance value of a flow path upstream of the branch point serving as a reference is smaller than an average flow path resistance value of a flow path having the smallest average flow path resistance value among average flow path resistance values of flow paths downstream of the branch point serving as the reference.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Imaging system with anesthesia system
InactiveUS20070089742A1Reducing flow rate fluctuationReliably flowRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsHigh pressureOxygen
The present invention provides improved anesthesia delivery systems that consistently and reliably deliver anesthesia gas to multiple gas outlets. The systems are particularly useful for anesthetizing multiple mammals and living specimens to be imaged by a low-light level imaging system. The anesthesia delivery systems are suitable for use with conventional oxygen sources, and convert the high pressures associated with a conventional oxygen source to lower pressures suitable for use with small mammals and suitable for combination with an anesthesia gas at low flow rates. The systems include an anesthesia gas source that combines anesthesia gas with the oxygen. The combination of anesthesia gas and oxygen is supplied to one or more multiple outlets.
Owner:XENOGEN CORP
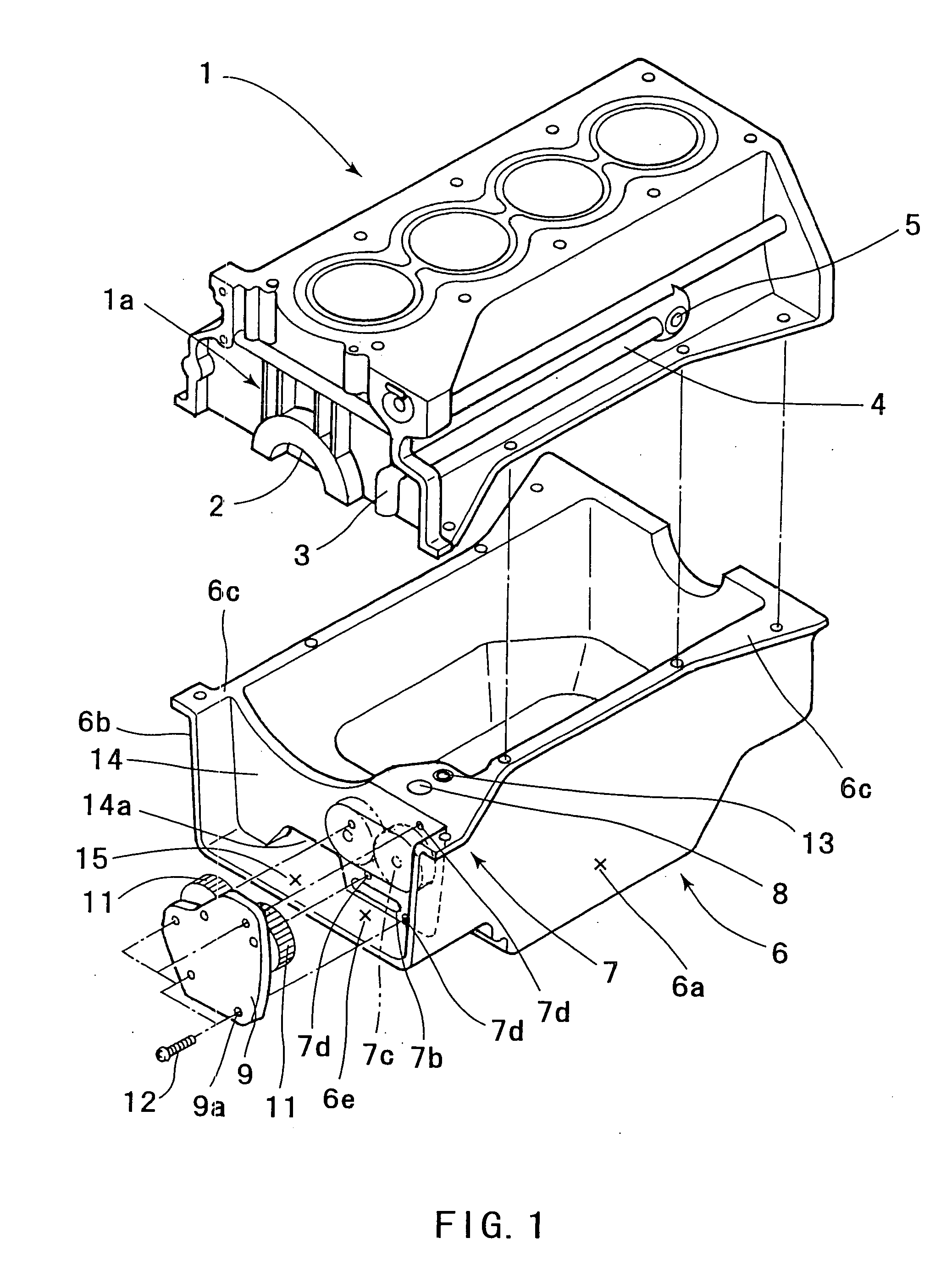
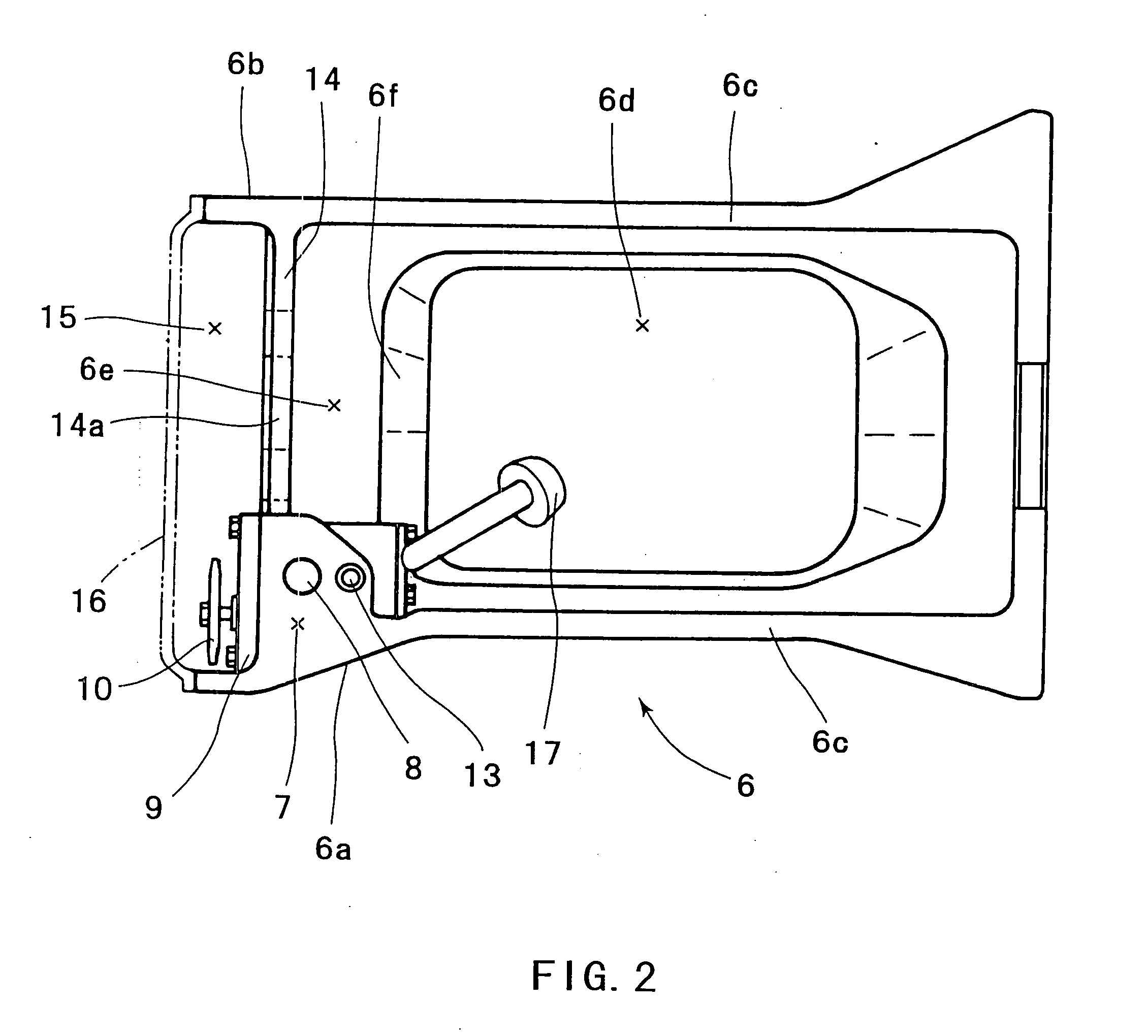
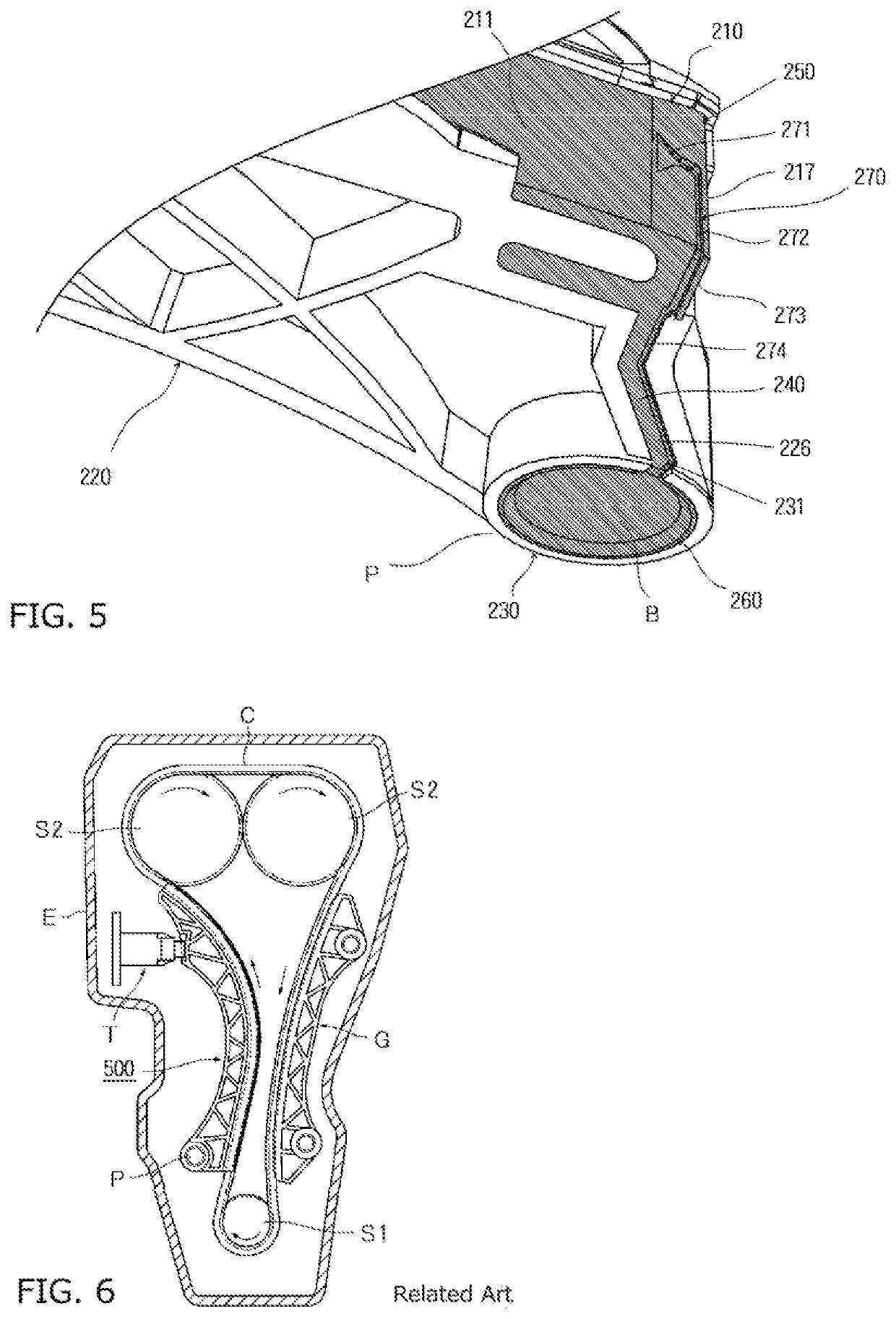
Oil pan structure
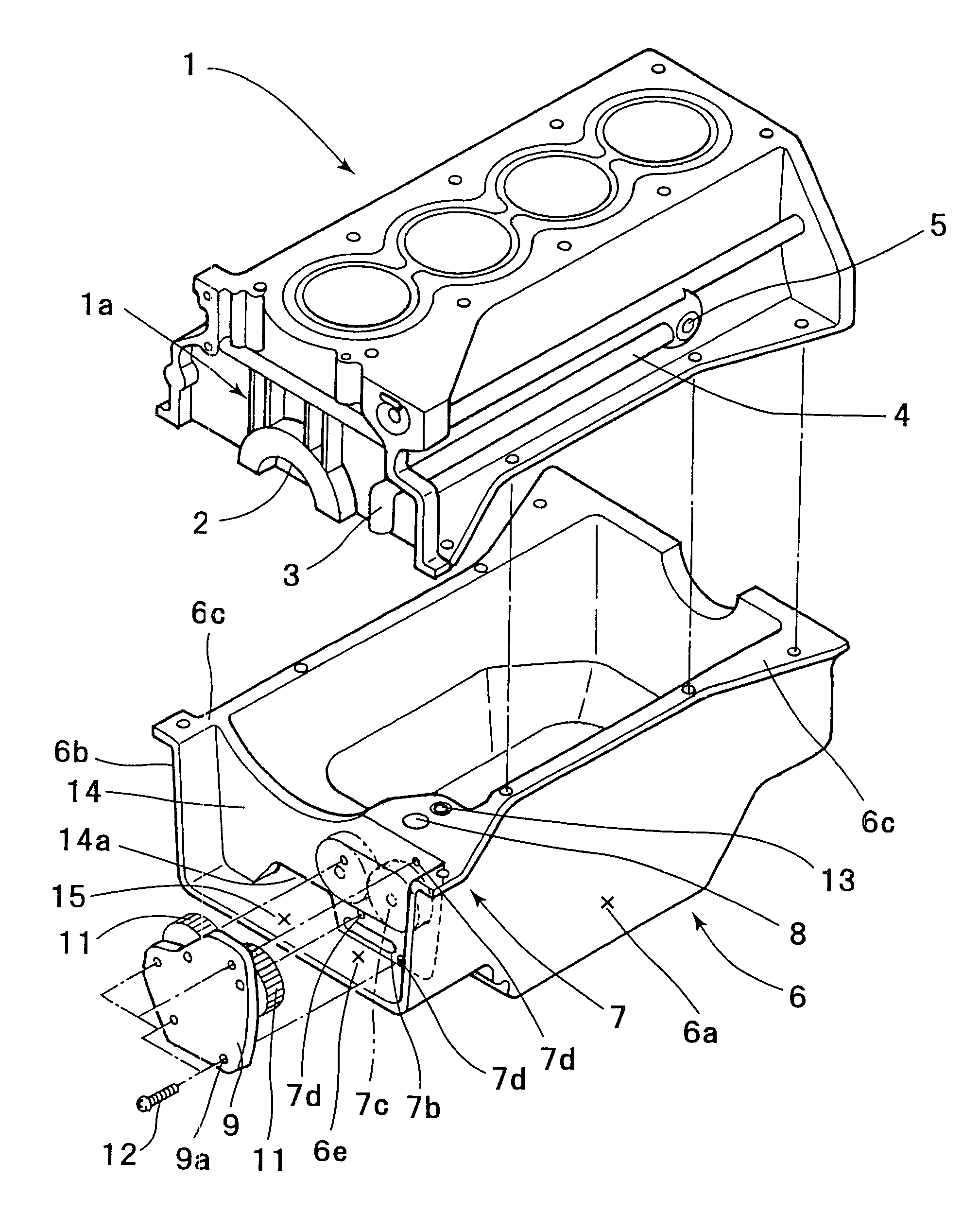
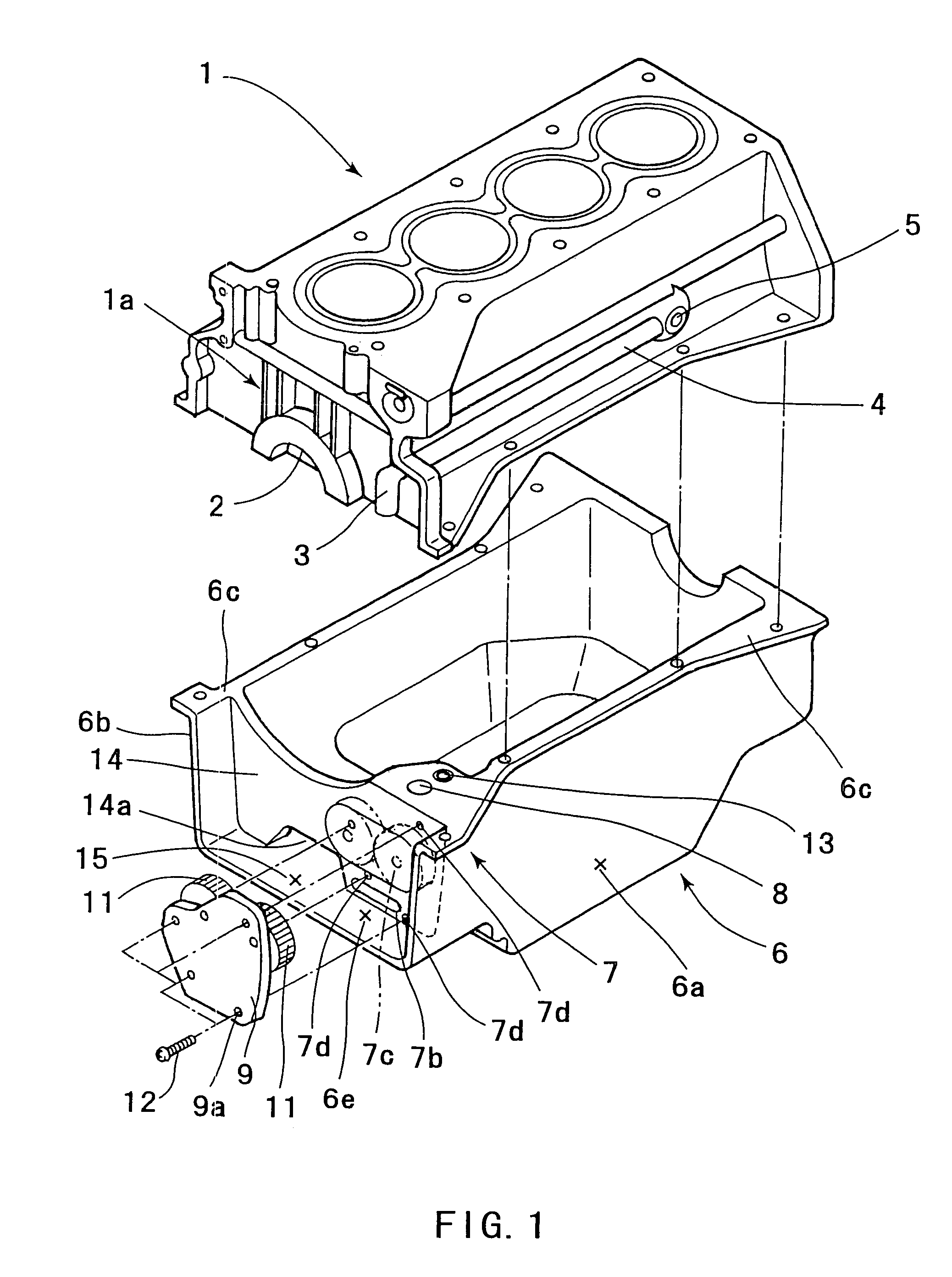
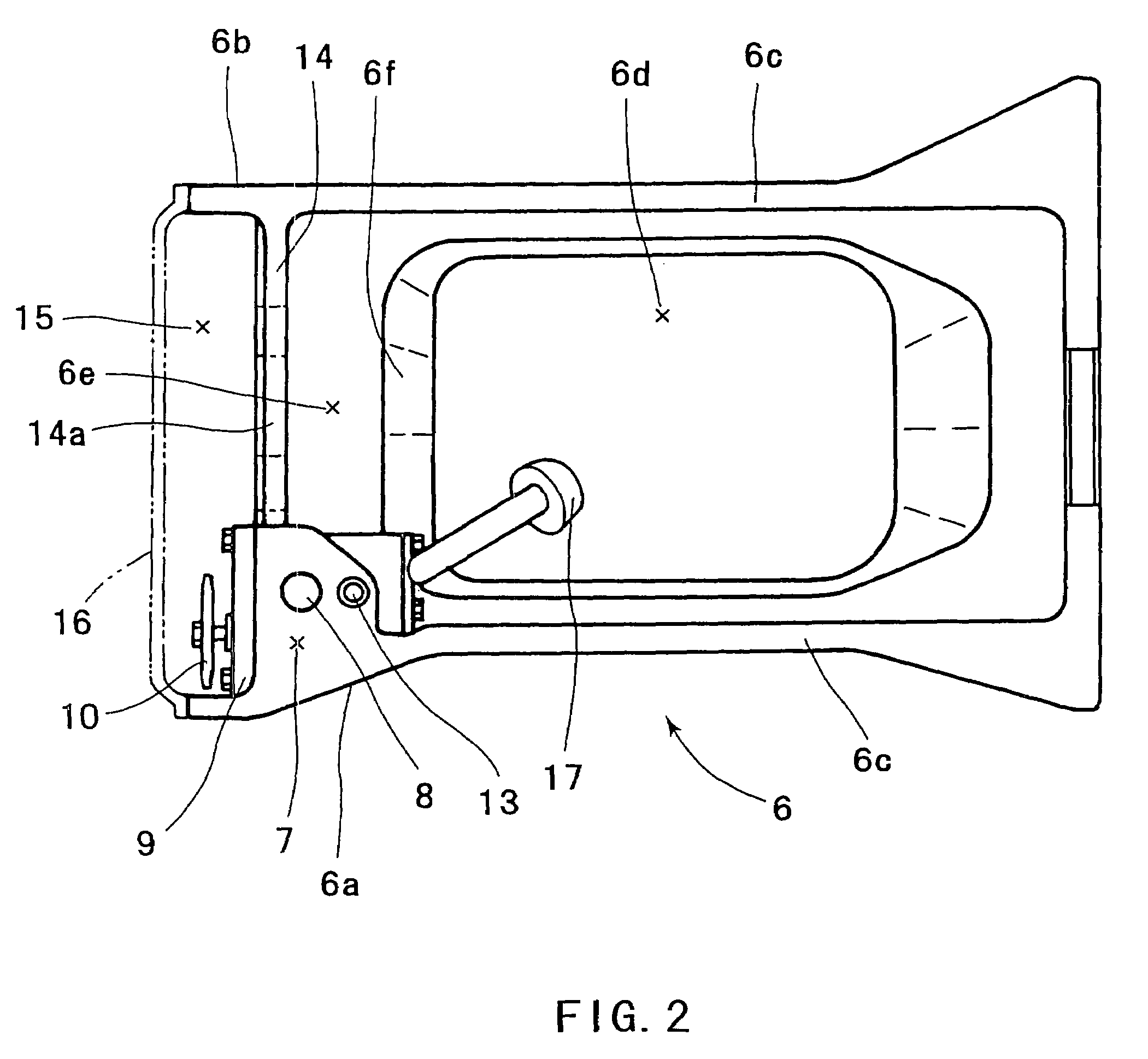
ActiveUS20050081815A1Reliably flowImprove production efficiencyCasingsLubrication of auxillariesMarine engineeringCylinder block
An oil pan (6) is mounted to a lower surface of a cylinder block (1) in order to reserve an oil. An oil pump housing (7) is cast integrally with the inner side of the right side surface (6a) of the oil pan (6). A rib (14) is formed in order to connect the right side surface (6a) and a left side surface (6b) of the oil pan (6).
Owner:AICHI MASCH IND CO LTD +1
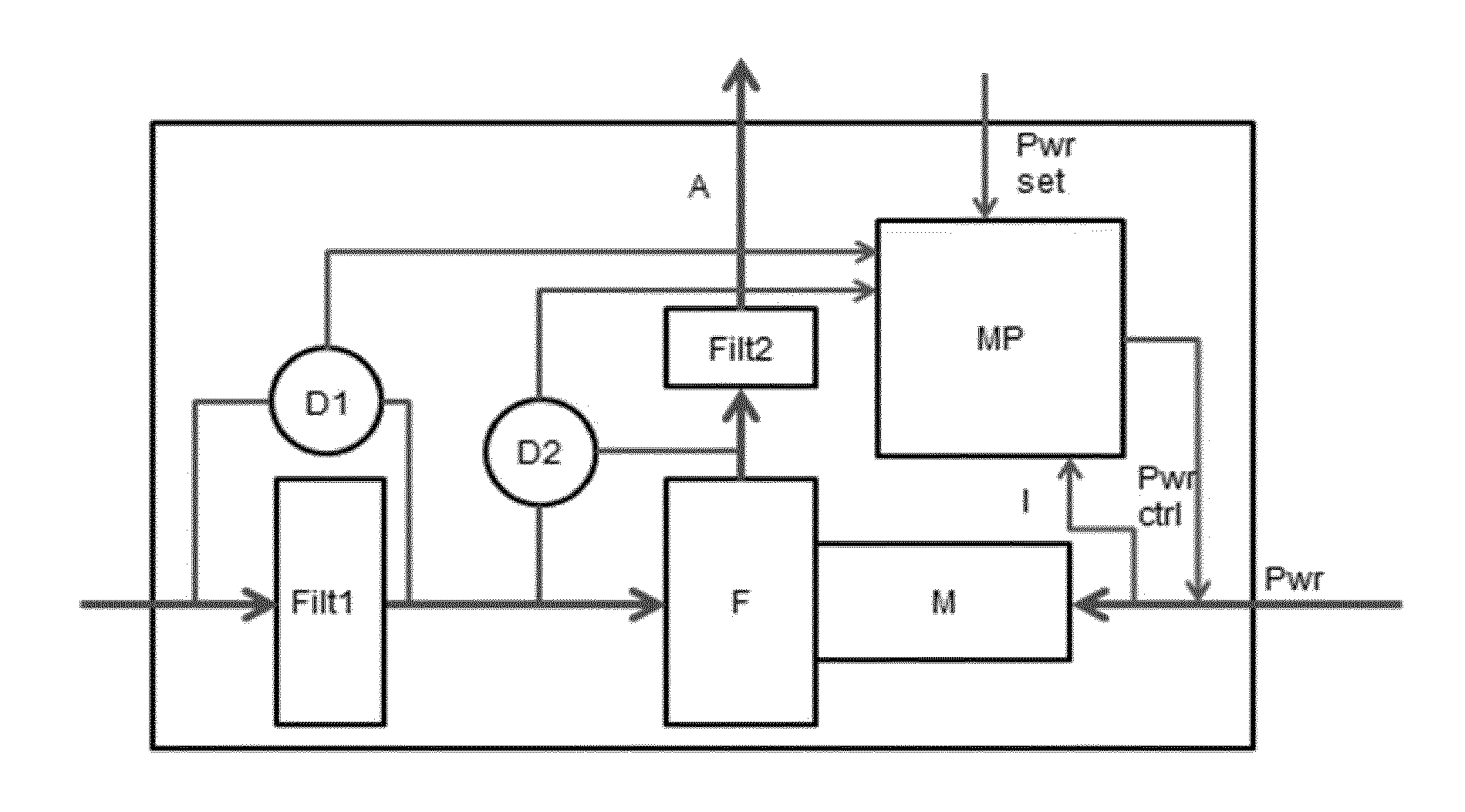
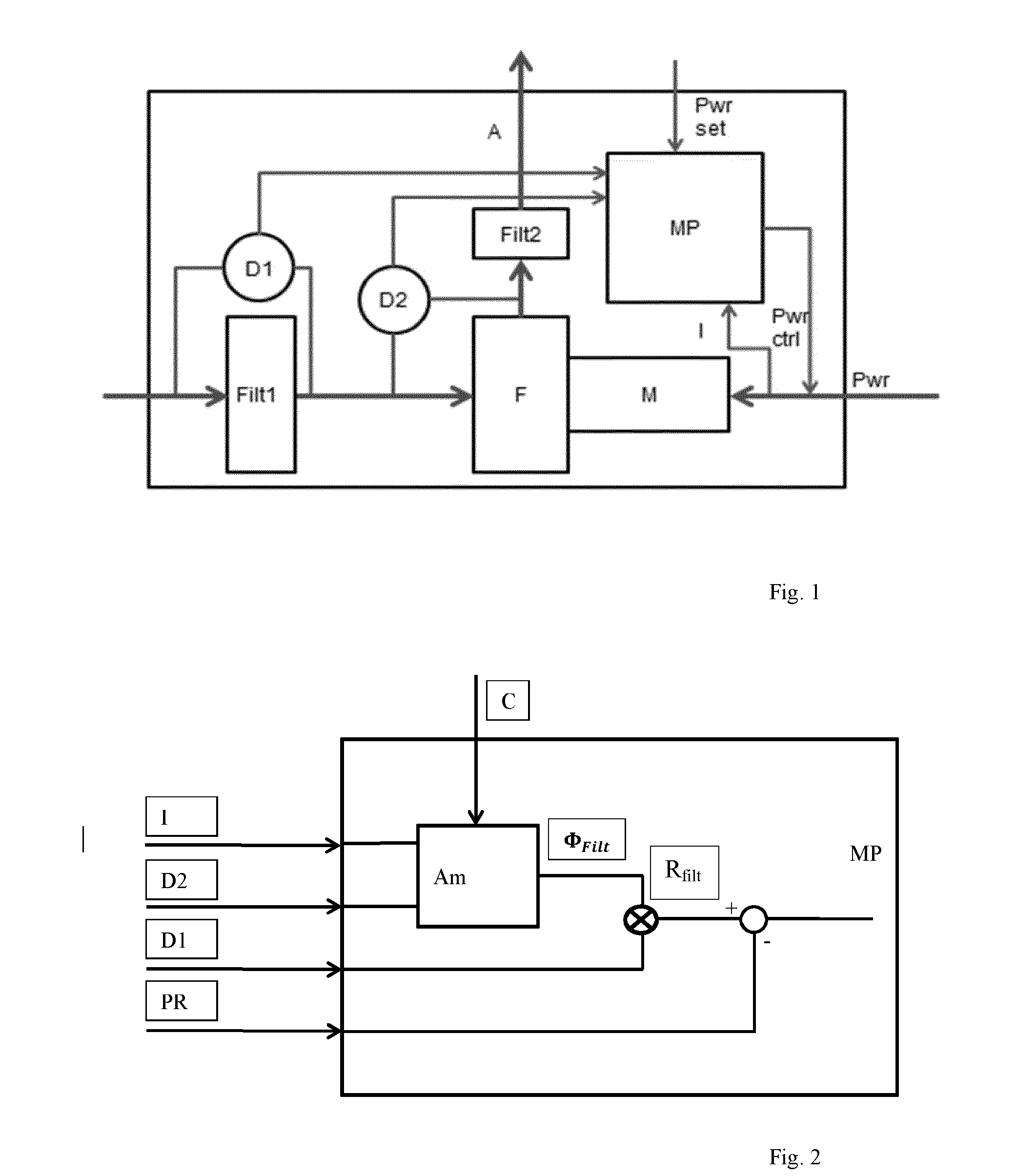
Air filter monitoring
ActiveUS20160256026A1Reliable flow predictionReliably flowSuction filtersPermeability/surface area analysisPower flowAir filter
In a method of monitoring pollution of an air filter (Filt1) in a device in which an air flow (A) generated by a fan (F) engaged by a motor (M) passes the air filter (Filt1), the pollution is determined using data representative of a pressure difference (D2) over the fan (F), a pressure difference (D1) over the air filter, and a motor current (I) to the motor (M). The method comprises the steps of: estimating a flow through the air filter from data representative of the pressure difference (D2) over the fan (F), and the motor current (I) to the motor (M), estimating a filter resistance of the air filter from data representative of the flow through the air filter, and the pressure difference (D1) over the air filter, and estimating the pollution of the air filter from data representative of the filter resistance of the air filter.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Radiation image capturing apparatus
ActiveUS20090080620A1Cool evenlyReliably flowX-ray tube electrodesMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsImage capture
A radiation image capturing apparatus includes a cooling mechanism for causing cooling medium to flow from a rear surface side to a radiation detector to a front surface side of radiation detector through a narrow space formed between an end of the radiation detector and a casing for housing the radiation detector. It is therefore possible to cool the narrow space, as well as regions in the vicinity of the narrow space, with the cooling medium and to discharge the cooling medium from the front surface side of the radiation detector.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Circuit board
ActiveUS20160095216A1Improve power efficiencyReduce riskFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectronic componentFlip chip
A circuit board is provided that includes an outermost conductor layer including a plurality of terminals for flip-chip bonding and an outermost resin insulating layer defining a first opening and a second opening in an electronic-component mounting region. One of a power supply terminal and a ground terminal is exposed in the first opening. A plurality of signal terminals are exposed in the second opening. The resin insulating layer includes a reinforcing portion that defines an inner bottom surface of the second opening. A height of a portion of the terminal exposed in the first opening, the portion projecting from an inner bottom surface of the first opening, is greater than a height of portions of the terminals exposed in the second opening, the portions projecting from the inner bottom surface of the second opening.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Device for dispensing liquid in the form of drops
ActiveUS20120296291A1Precise positioningEasily avoidedMedical devicesSpray nozzlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:NEMERA LA VERPILLIERE SAS
In-wheel motor drive assembly
InactiveUS20140232175A1Effective lubricationReliably flowSpeed controllerElectric devicesMotor driveGear wheel
An in-wheel motor drive assembly includes a motor case defining a motor chamber and a reduction mechanism chamber provided on one side of and isolated from the motor chamber by a partition wall. An electric motor is mounted in the motor chamber. A planetary gear reduction mechanism is mounted in the reduction mechanism chamber, and reduces the rotation of the electric motor and outputs the reduced rotation to a hub ring. The reduction mechanism is lubricated by lubricating oil stored in the reduction mechanism chamber. A tapered oil guide surface is formed at the center of the inner surface of the partition wall facing the reduction mechanism chamber. The oil guide surface guides lubricating oil splashed up by the rotating reduction mechanism and flowing down along the inner surface of the partition wall, onto the rotor shaft of the electric motor, thereby lubricating bearings mounted on the rotor shaft.
Owner:NTN CORP
Oil pan structure
ActiveUS7040275B2Reduce weightImprove rigidityCasingsLubrication of auxillariesMarine engineeringEngineering
An oil pan (6) is mounted to a lower surface of a cylinder block (1) in order to reserve an oil. An oil pump housing (7) is cast integrally with the inner side of the right side surface (6a) of the oil pan (6). A rib (14) is formed in order to connect the right side surface (6a) and a left side surface (6b) of the oil pan (6).
Owner:AICHI MASCH IND CO LTD +1
Adhesive dispensing device having optimized reservoir and capacitive level sensor
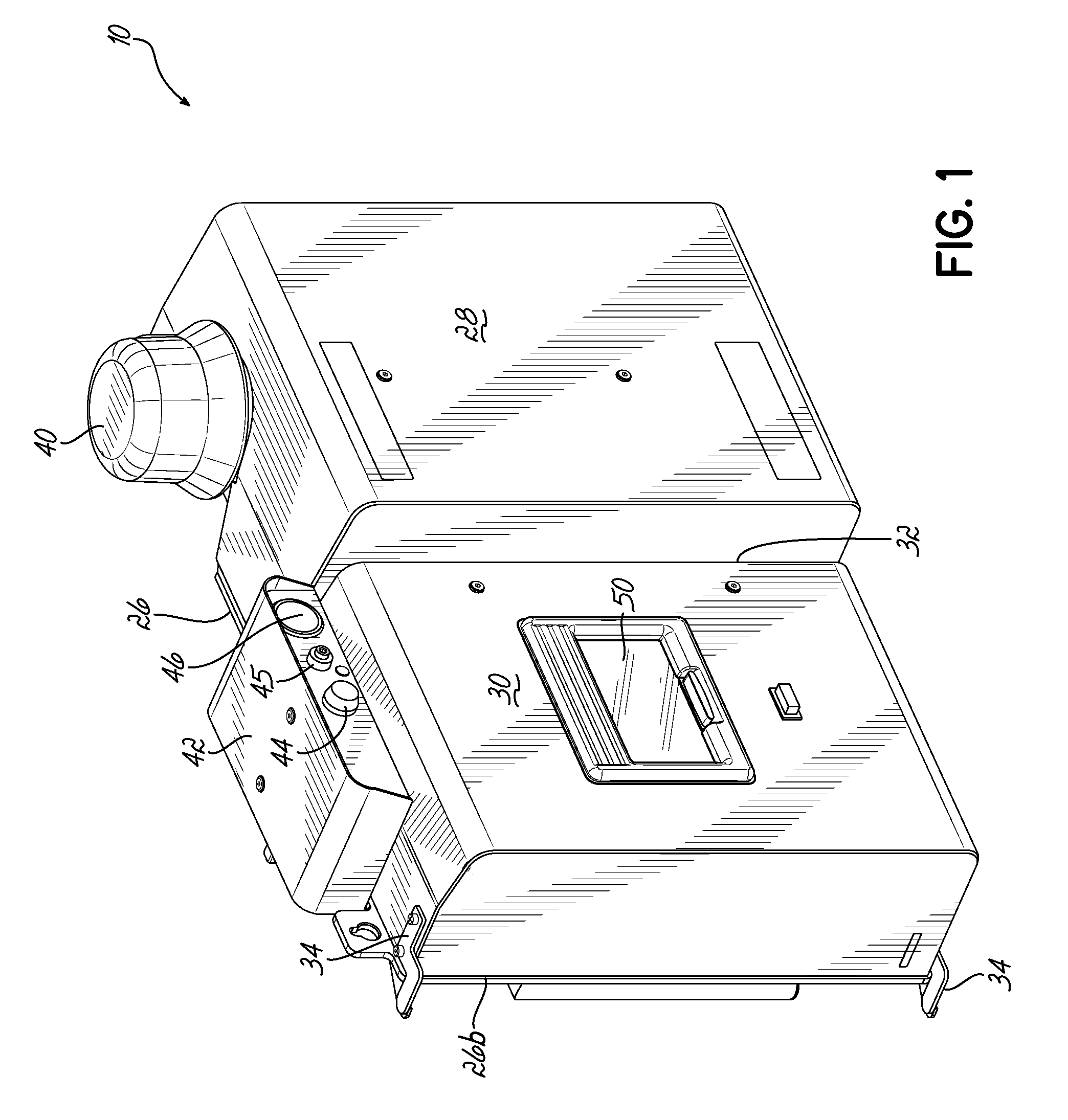
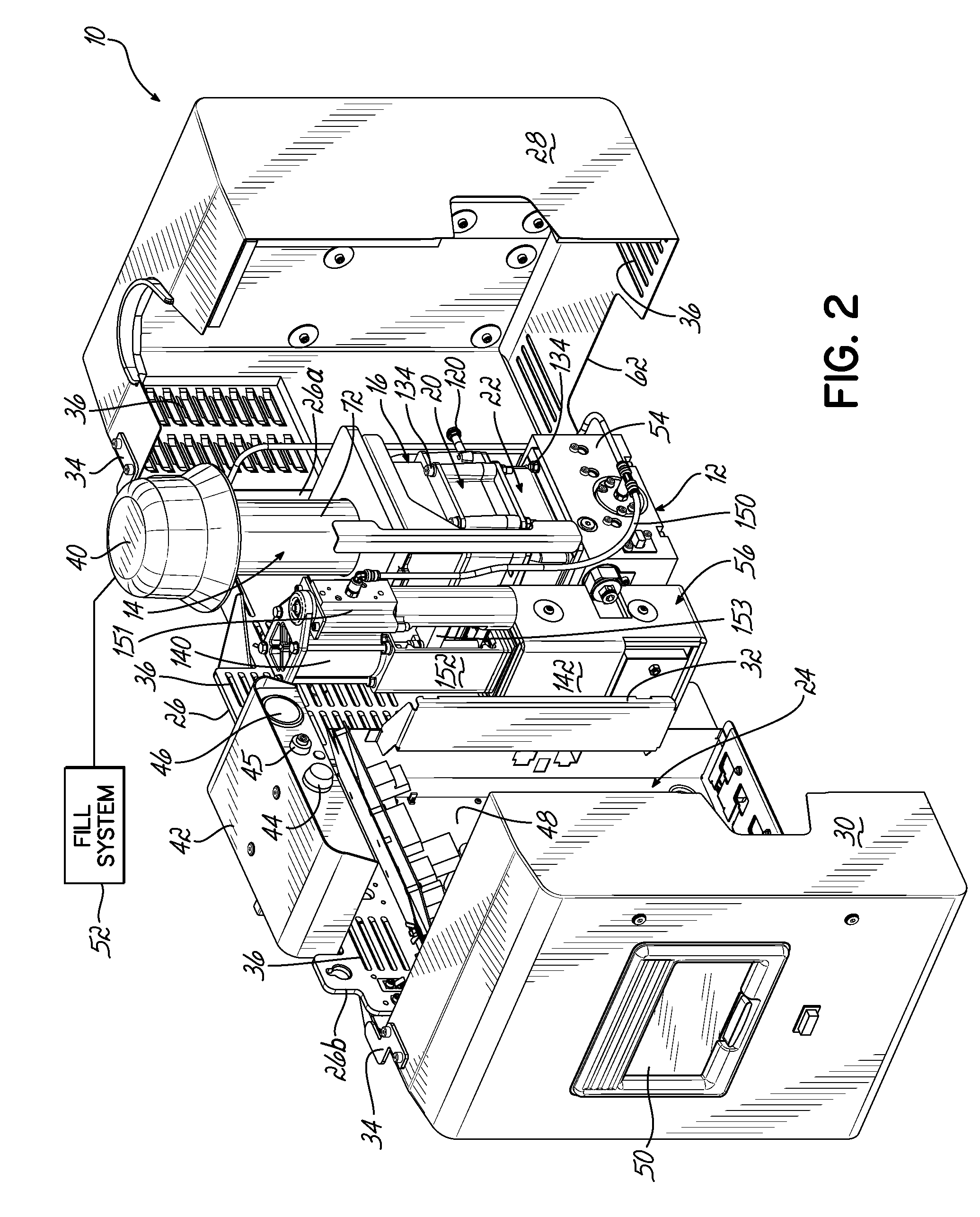
An adhesive dispensing device includes a heater unit for melting adhesive, a fill system communicating with a receiving space for feeding the heater unit, and a reservoir for receiving melted adhesive from the heater unit. The dispensing device also includes a capacitive level sensor located along a sidewall of the receiving space such that the level of adhesive in the receiving space can be detected by sensing the difference in dielectric capacitance where the adhesive is located compared to where air acts as the dielectric. The size of the driven electrode produces a broader sensing window capable of generating multiple control signals corresponding to different fill levels of adhesive. The receiving space and reservoir are minimized in size so that adhesive is not held at elevated temperatures long enough to char or degrade.
Owner:NORDSON CORP
Tensioner lever
ActiveUS20200362944A1Reduce friction lossIncreased durabilityGearingGearing detailsSlider bearingEngineering
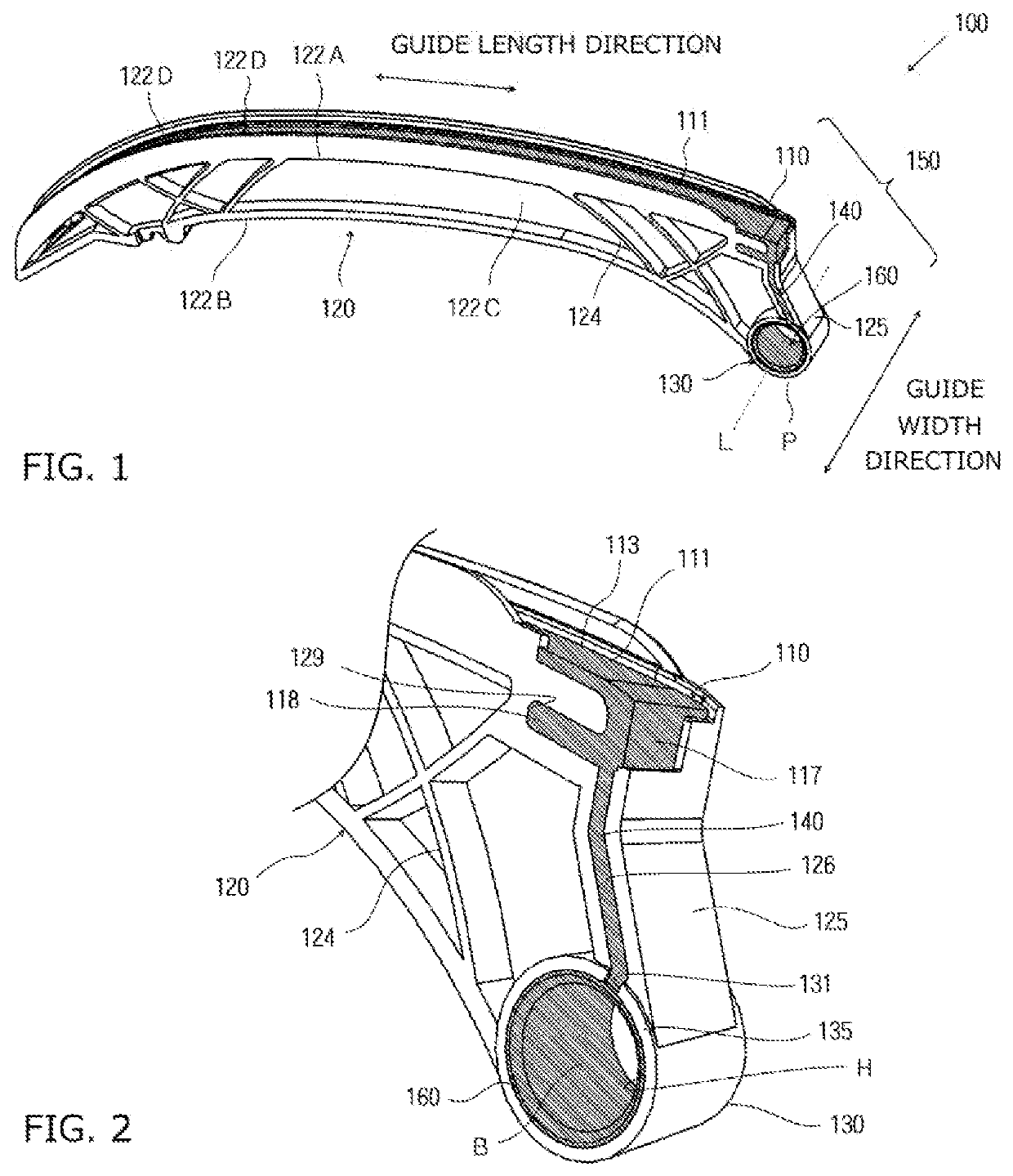
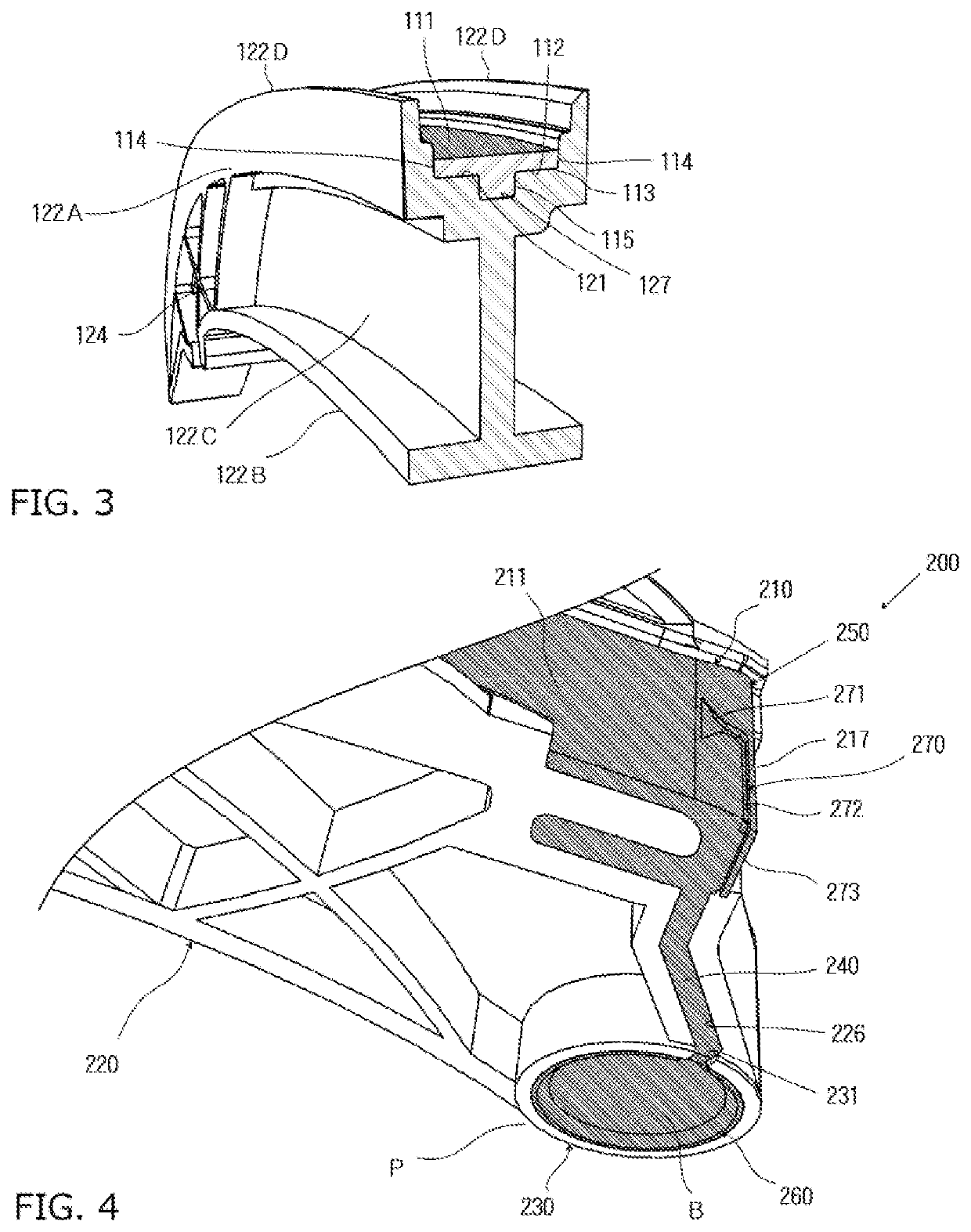
The problem to be solved is to provide a tensioner lever that inhibits friction-induced wear or seizure on a surface of a pivoting support boss contacting a shoulder bolt so that high durability is achieved, and that is easily producible and enables cost reduction. As a solution to the problem noted above, the tensioner lever includes a shoe having a traveling surface, a lever body, and a pivotal support boss provided at a proximal end of the lever body to allow a distal end thereof to swing. The shoe and the lever body are integrally formed and assembled together by double injection molding. The lever body includes a slide bearing member, and a connecting part that connects the slide bearing member and the shoe. The slide bearing member, the connecting part, and the shoe are made of the same synthetic resin, and configured as a continuous one-piece component.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
Device and method of classifying emulsion and method of demulsifying emulsion
InactiveUS20060113239A1Easy to classifyReliably flowSolid separationLoose filtering material filtersEmulsionEngineering
A classifying apparatus (1) has a flow path (structure) through which an emulsion flows. The flow path is provided between at least two plates (upper plate (2), lower plate (4)) that are separated by a distance smaller than the largest diameter of a liquid droplet included in the emulsion. Emulsion is fed from a supply port (5) provided in the upper plate (2) and can be classified by passing it in the flow path.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Ultrasonic flow meter
ActiveUS20050011280A1Prevent mixture of noiseReduce noiseVolume/mass flow measurementPropagation timeEngineering
The present invention proposes an ultrasonic flow meter, comprising a conduit for measurement in which a liquid flows therein, and a pair of measurement sections which are provided in said conduit for measurement and are spaced apart by a certain interval along its longitudinal direction, and which obtains the flow velocity of said flowing liquid from the difference in the propagation time periods of ultrasonic in the two opposite directions between these measurement sections, and thereby measures the flow rate thereof; wherein a pair of fixing portions are provided which respectively support said conduit for measurement at the exterior side and also at the interior side in the longitudinal direction of said measurement sections.
Owner:SURPASS IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com