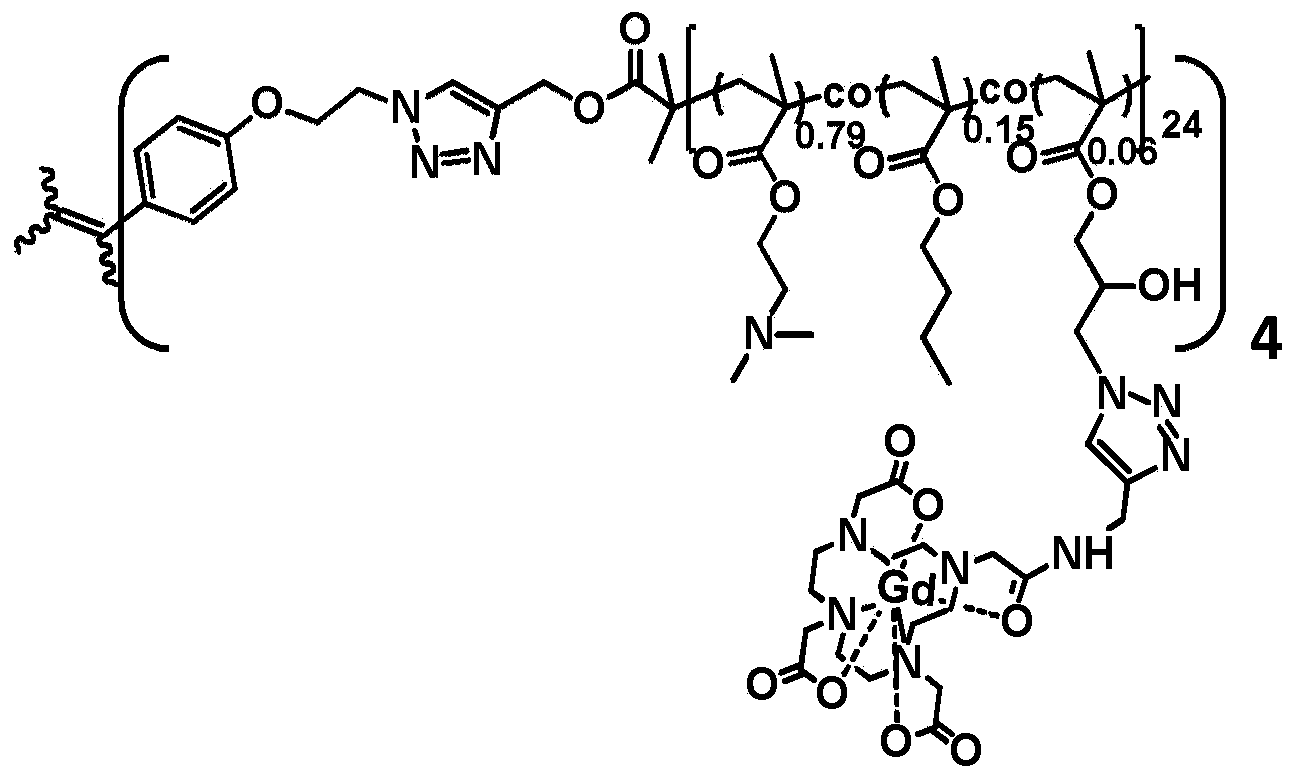
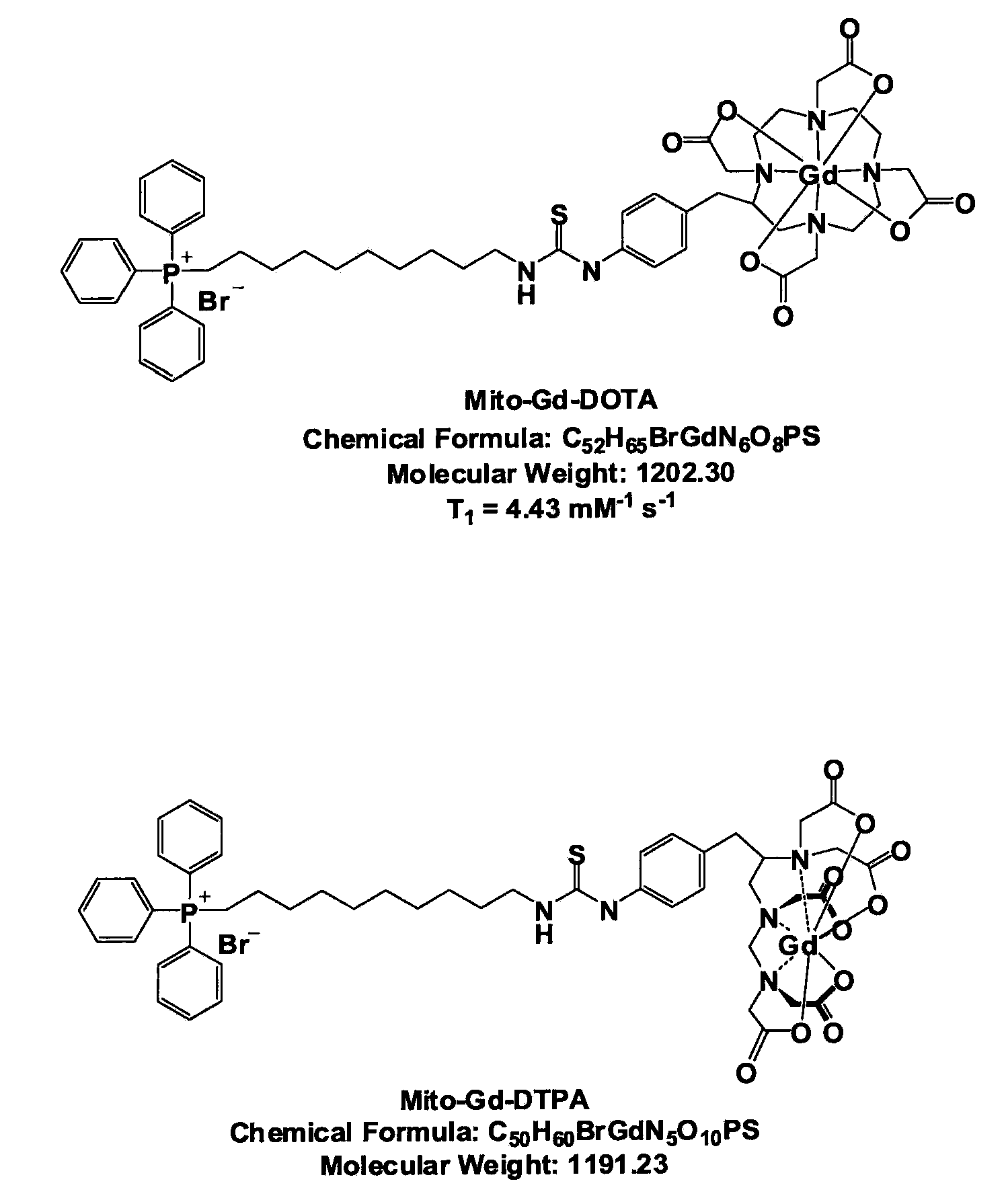
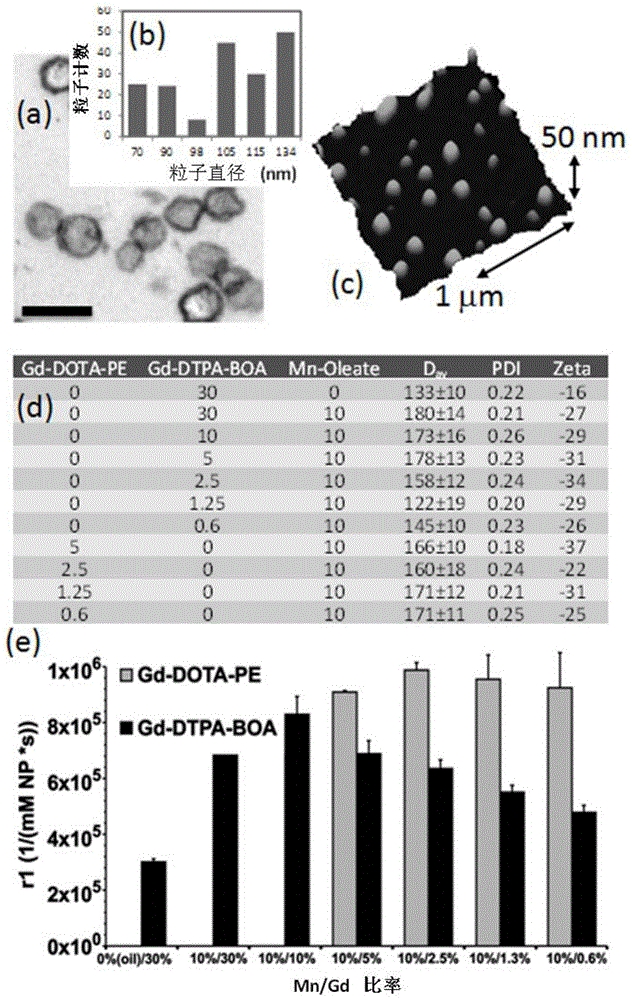
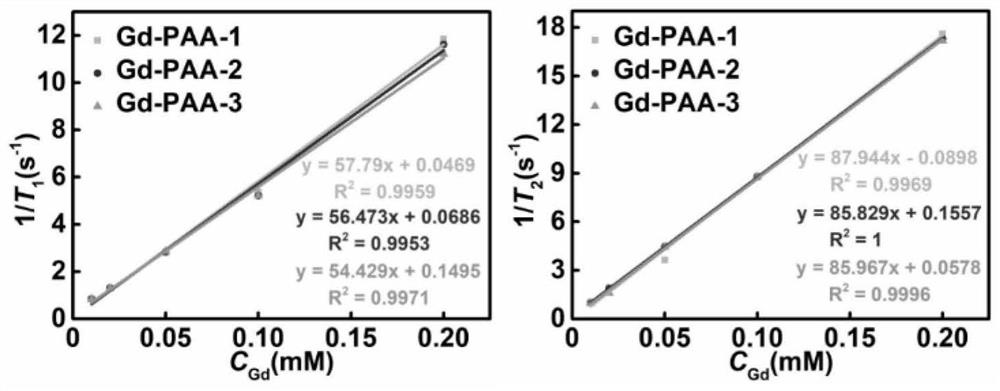
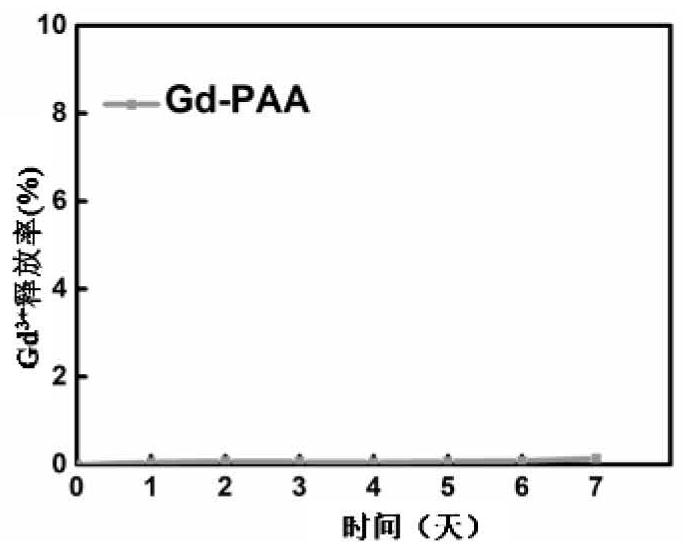
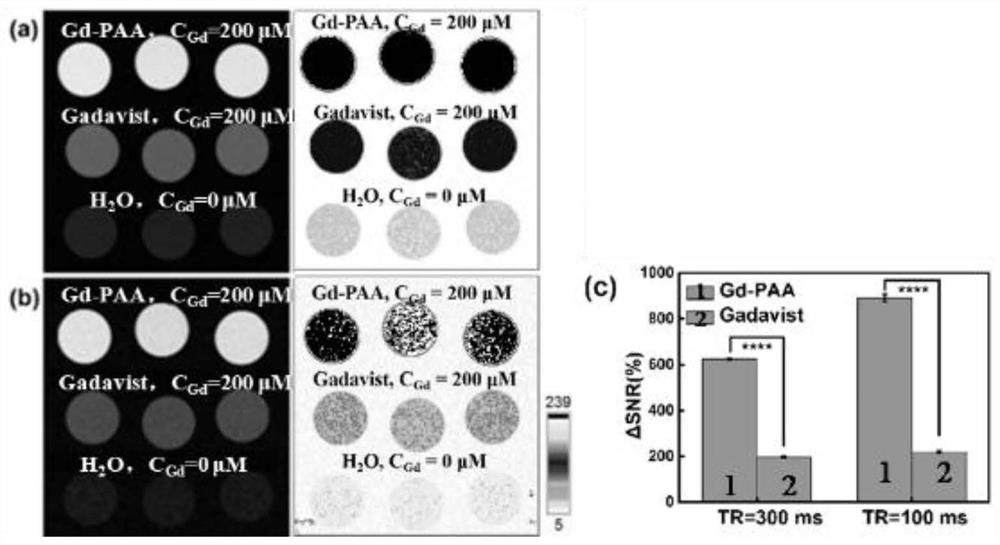
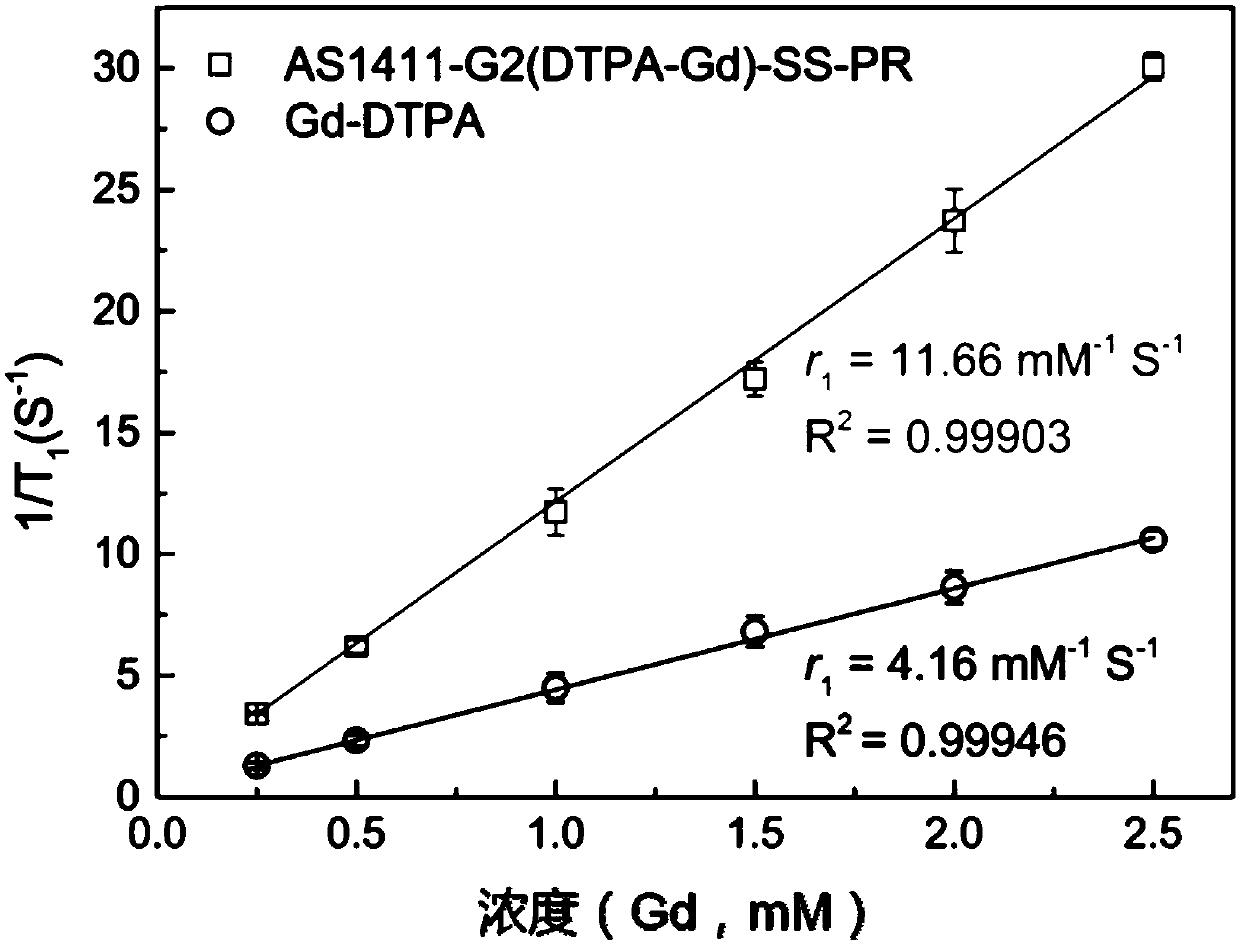
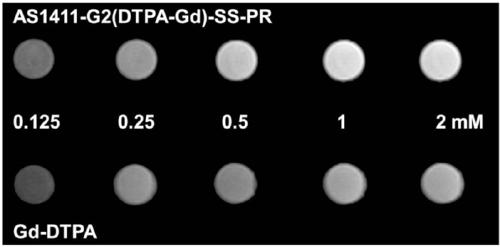
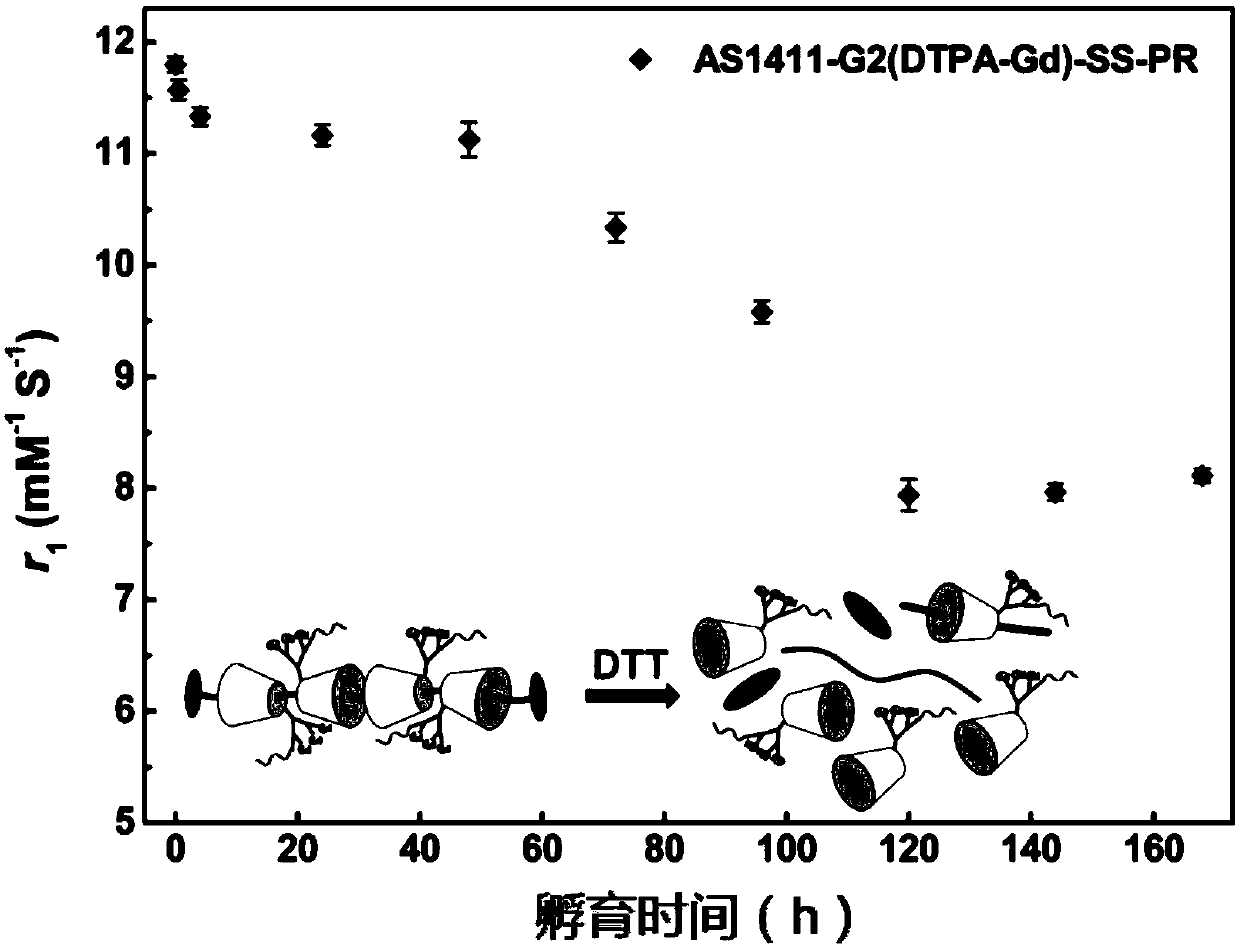
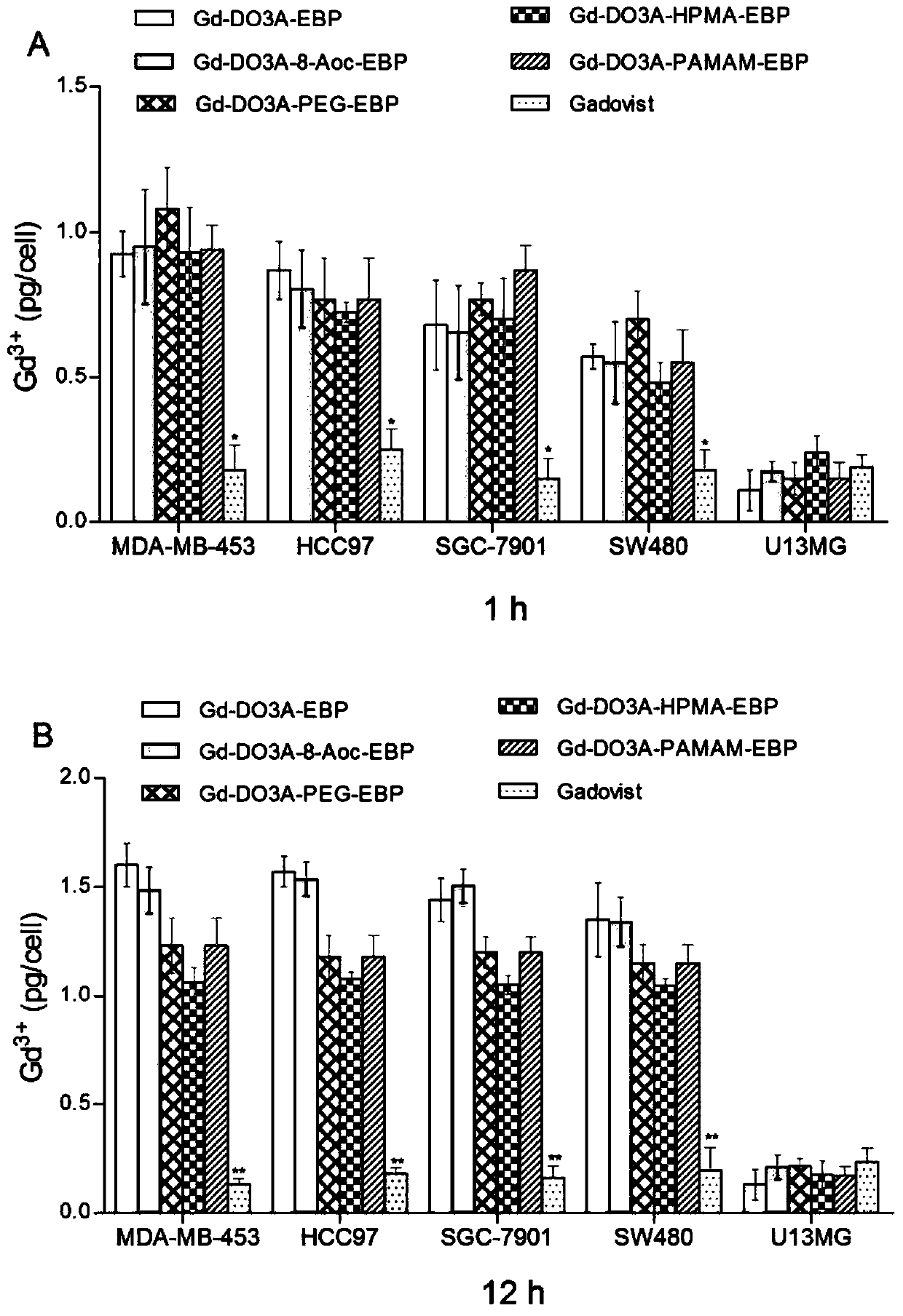
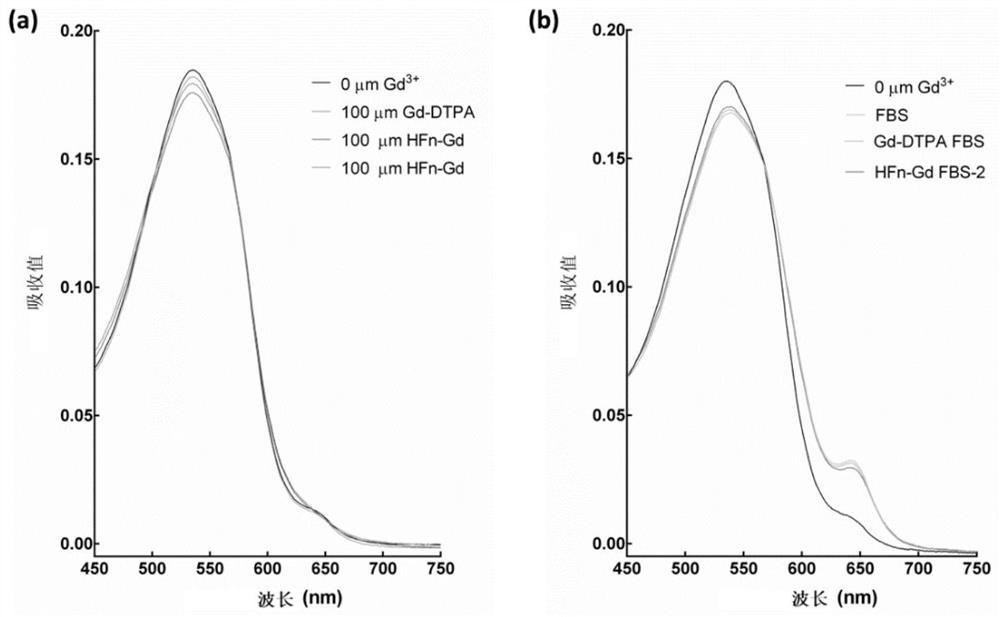
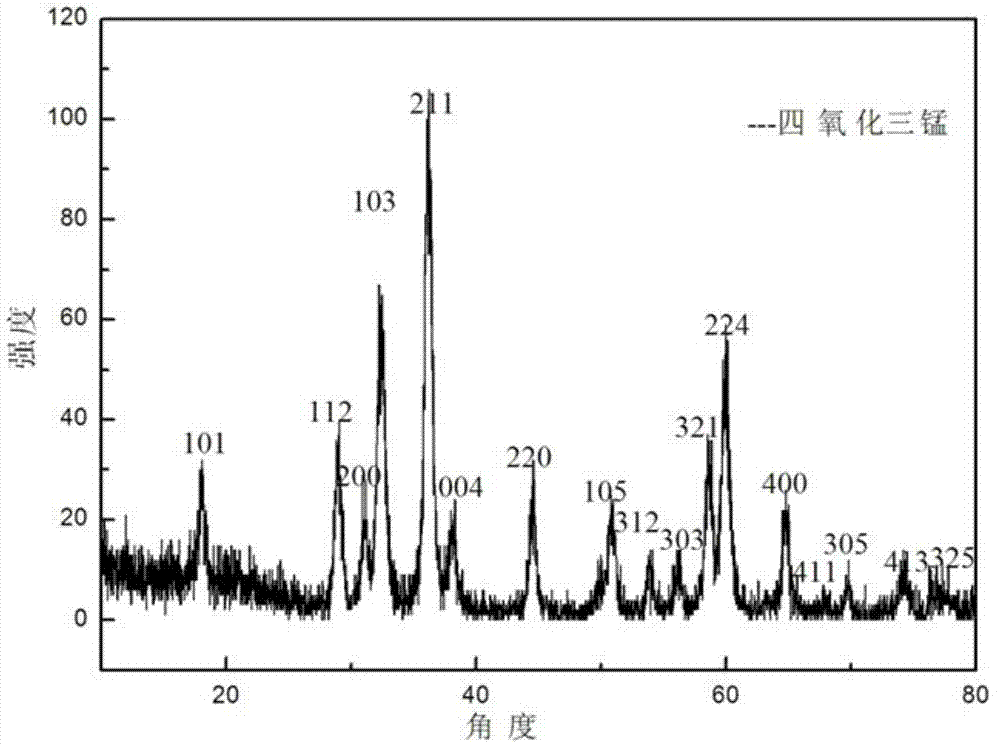
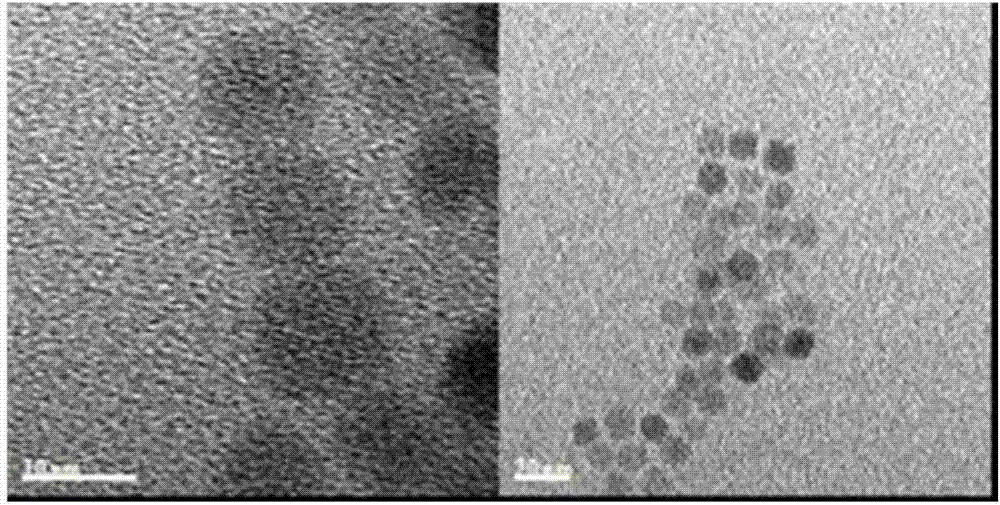
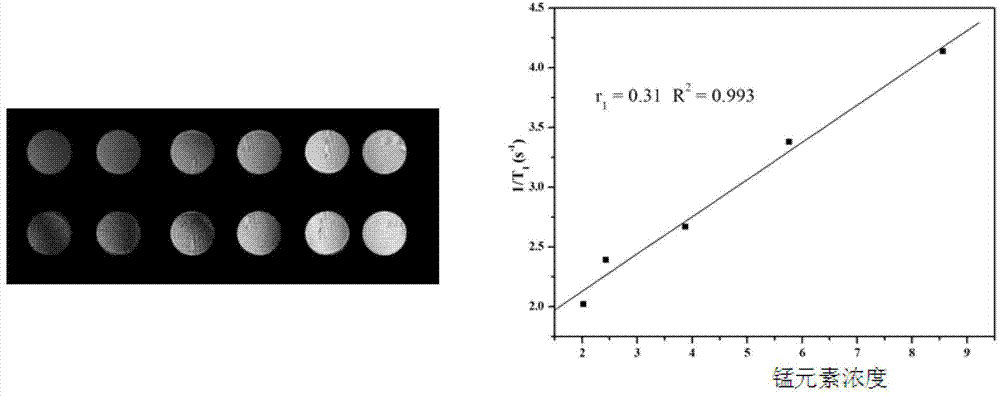
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Gadolinium-Chelate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
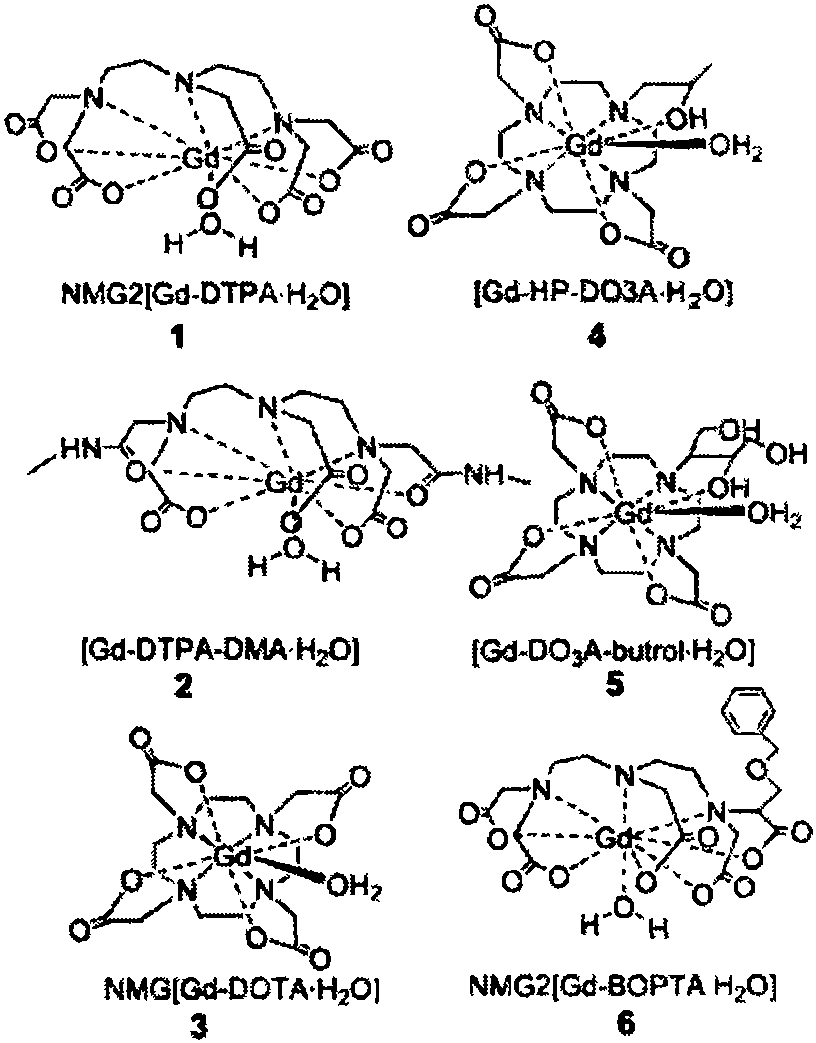
A coordination complex consisting of a gadolinium ion bound to a hexadentate organic chelating agent such as diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid. Chelates of gadolinium are frequently utilized as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents and can be used to track nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery.
Preparation method and application of star polymer
The invention relates to a novel preparation method and application of a cationic amphiphilic tetra-armed star polymer. In particular, the star polymer can be obtained through synthetic means such as atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and click chemistry. A core of the star polymer is tetraphenylethylene with the characteristic of aggregation-induced emission. A polymer linear arm is a cationic amphiphilic random copolymer with excellent antibacterial effects. A covalently labeled T1 type magnetic resonance (MR) contrast agent is an organic gadolinium chelate. By using the cationic amphiphilic tetra-armed star polymer, fluorescence / MR double quantitative detection of Gram positive and negative bacteria with negative charges on the surfaces in the environment of pure water is achieved, and meanwhile good antibacterial effects are gained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
In Vivo Mitochondrial Labeling Using Positively-Charged Nitroxide Enhanced and Gadolinium Chelate Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
InactiveUS20090214437A1Increase contrastEasy to identifyBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsIn vivoNuclear medicine
A system and method for acquiring MR imaging data from a subject includes administering positively-charged nitroxides or gadolinium chelates for in vivo mitochondrial labeling, acquiring MR imaging data from the subject, and reconstructing an image of the subject having enhanced contrast in areas including metabolic and / or mitotic activity.
Owner:MCW RES FOUND INC
Degradable dendritic macromolecule magnetic resonance contrast agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103055328AGood contrast effectHigh sensitivityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsGadolinium-ChelatePermeation
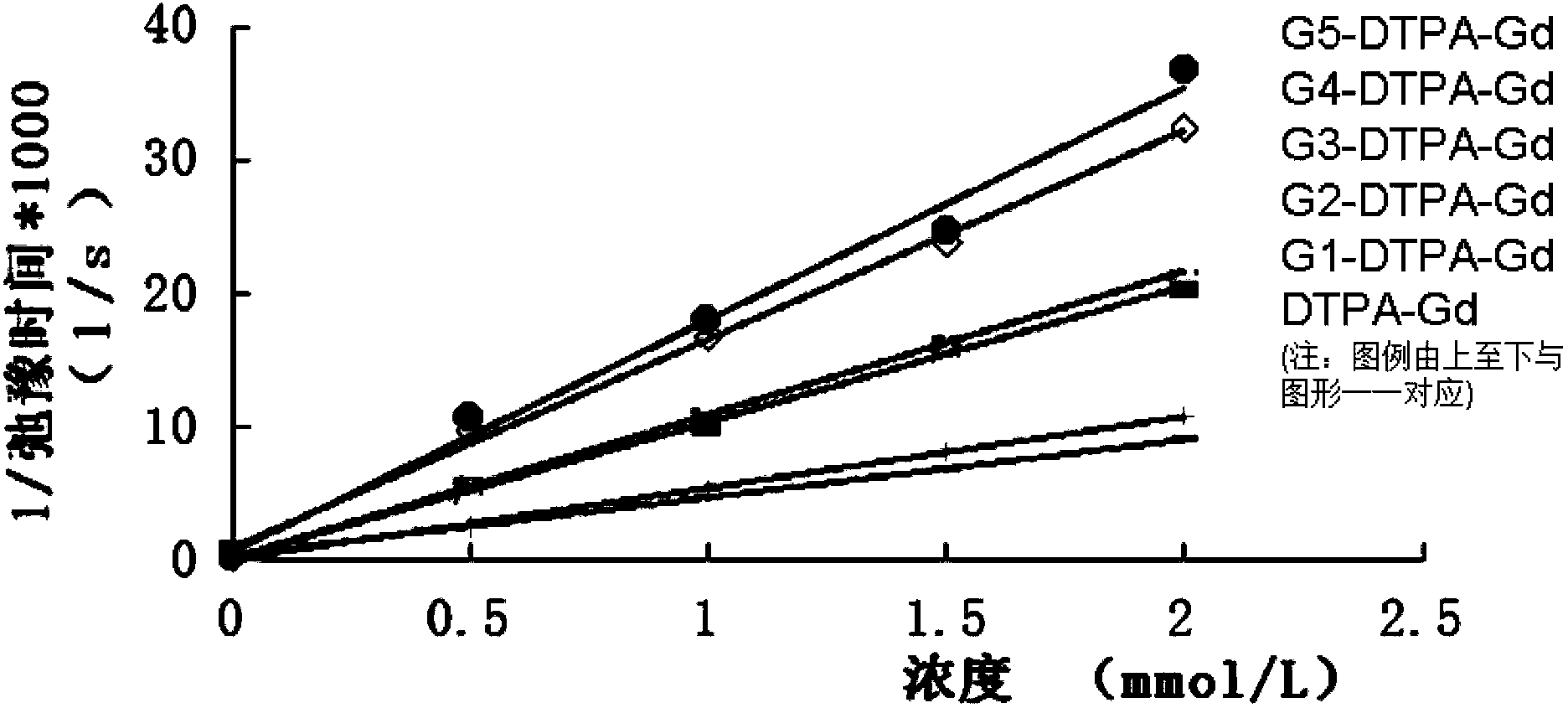
The invention discloses a degradable dendritic macromolecule magnetic resonance contrast agent and a preparation method thereof. The degradable dendritic macromolecule magnetic resonance contrast agent is characterized in that a degradable dendritic macromolecule is used as a skeleton and micromolecular gadolinium chelates are connected to the degradable dendritic macromolecule so that the degradable dendritic macromolecule magnetic resonance contrast agent is formed. The degradable dendritic macromolecule magnetic resonance contrast agent has a relaxation rate of 17.4mM<-1>.s<-1> obviously higher than a relaxation rate of the common contrast agent, has a better MRI contrast effect, can be enriched in tumor tissue by enhanced permeation and retention effects of the degradable dendritic macromolecule magnetic resonance contrast agent, and improves MRI sensitivity and an early diagnosis level of cancers. The degradable dendritic macromolecule magnetic resonance contrast agent can be hydrolyzed by internal esterase catalysis and then is gradually discharged out of a human body so that the toxicity accumulation of gadolinium in a human body is avoided. The preparation method has simple processes, can be controlled easily and is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
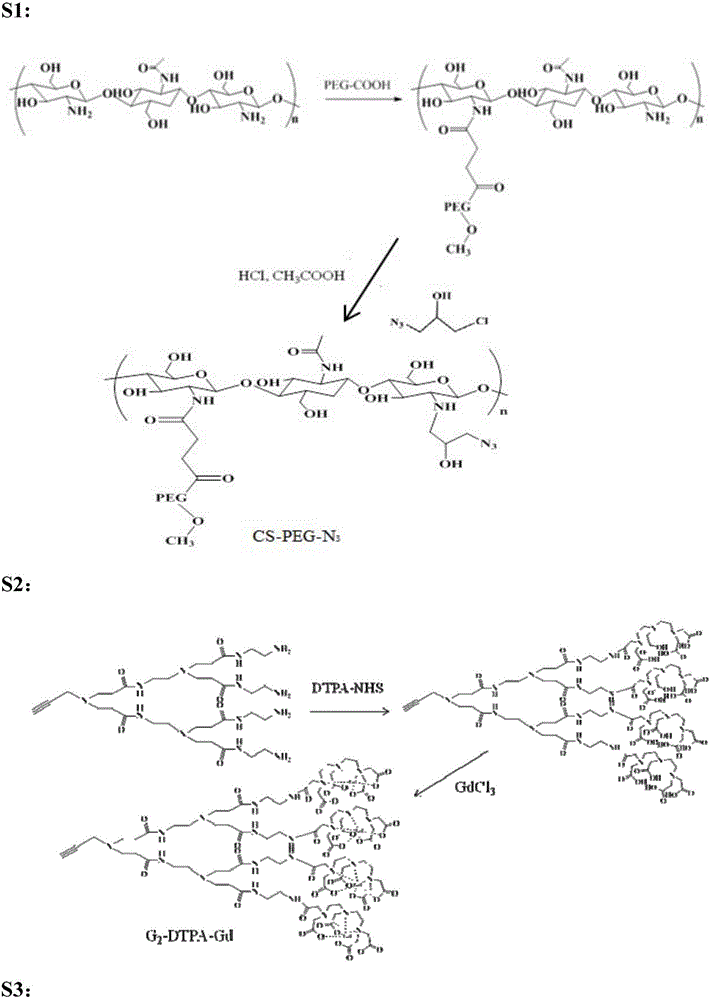
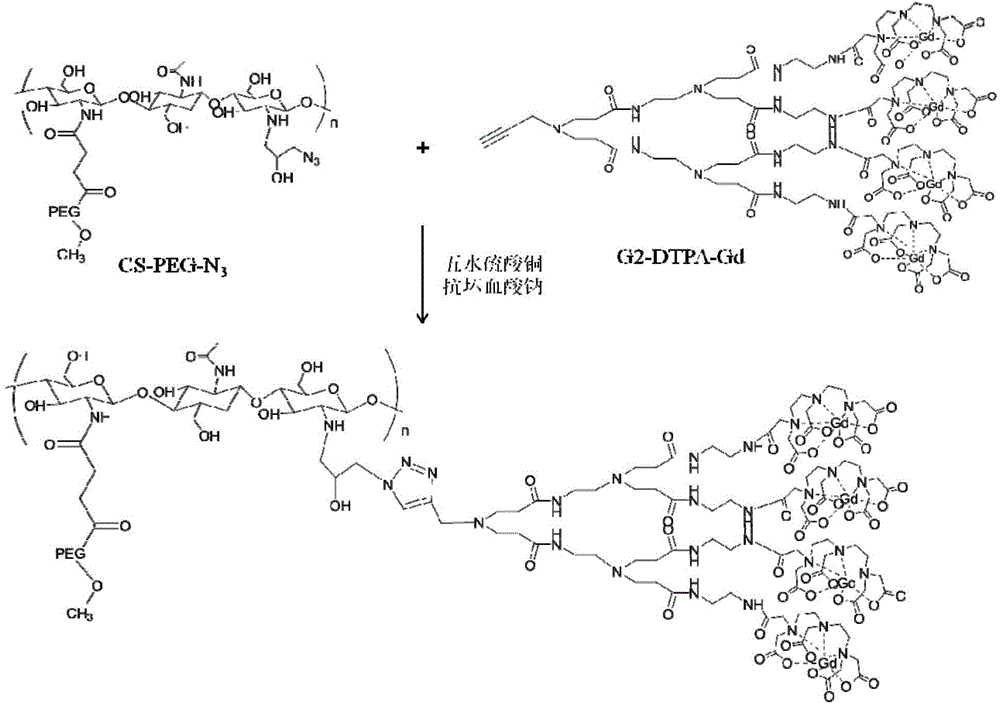
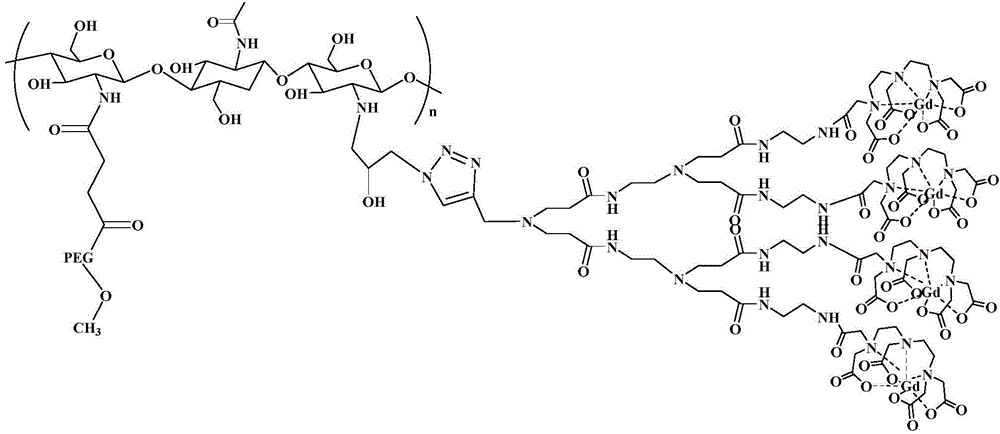
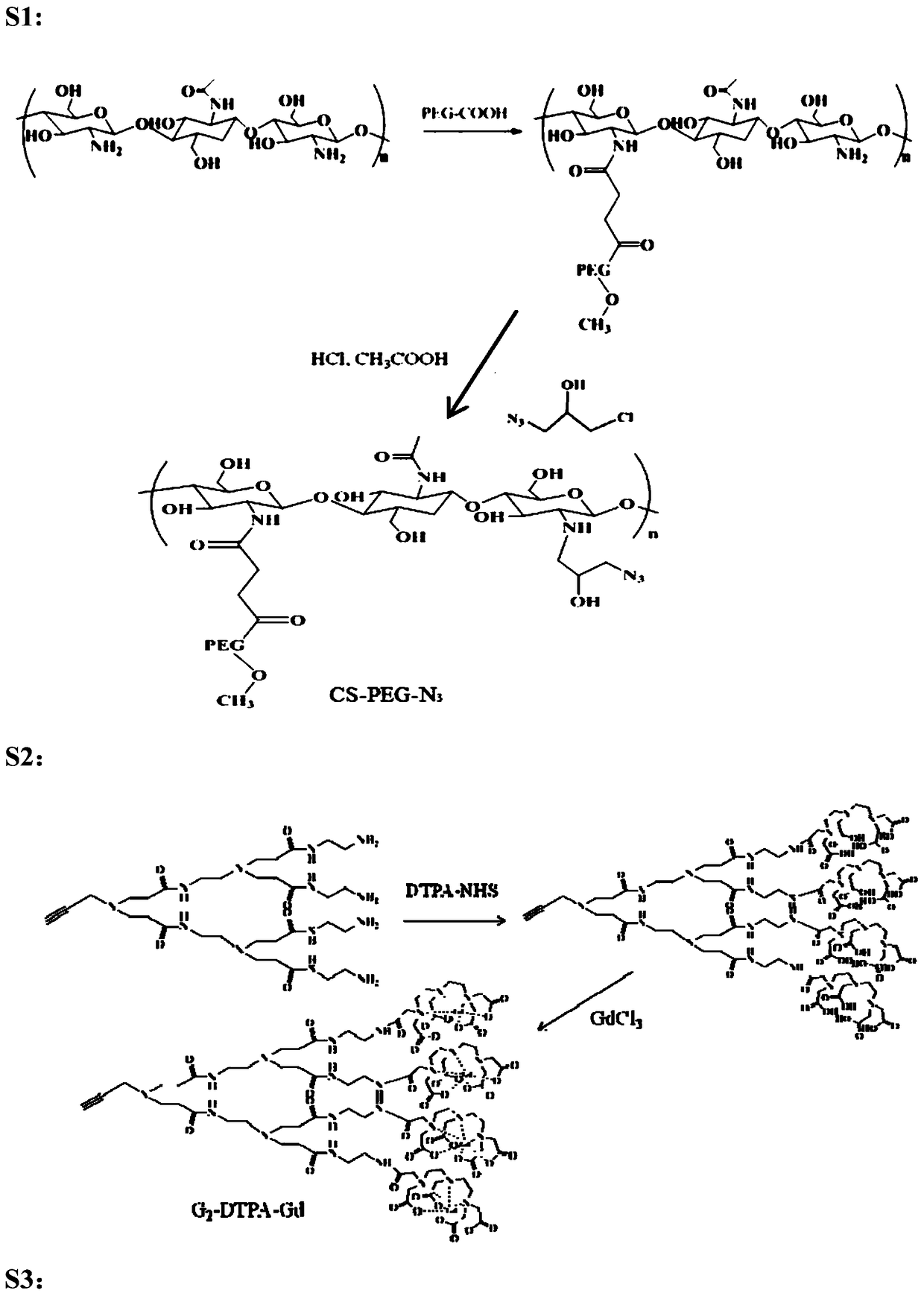
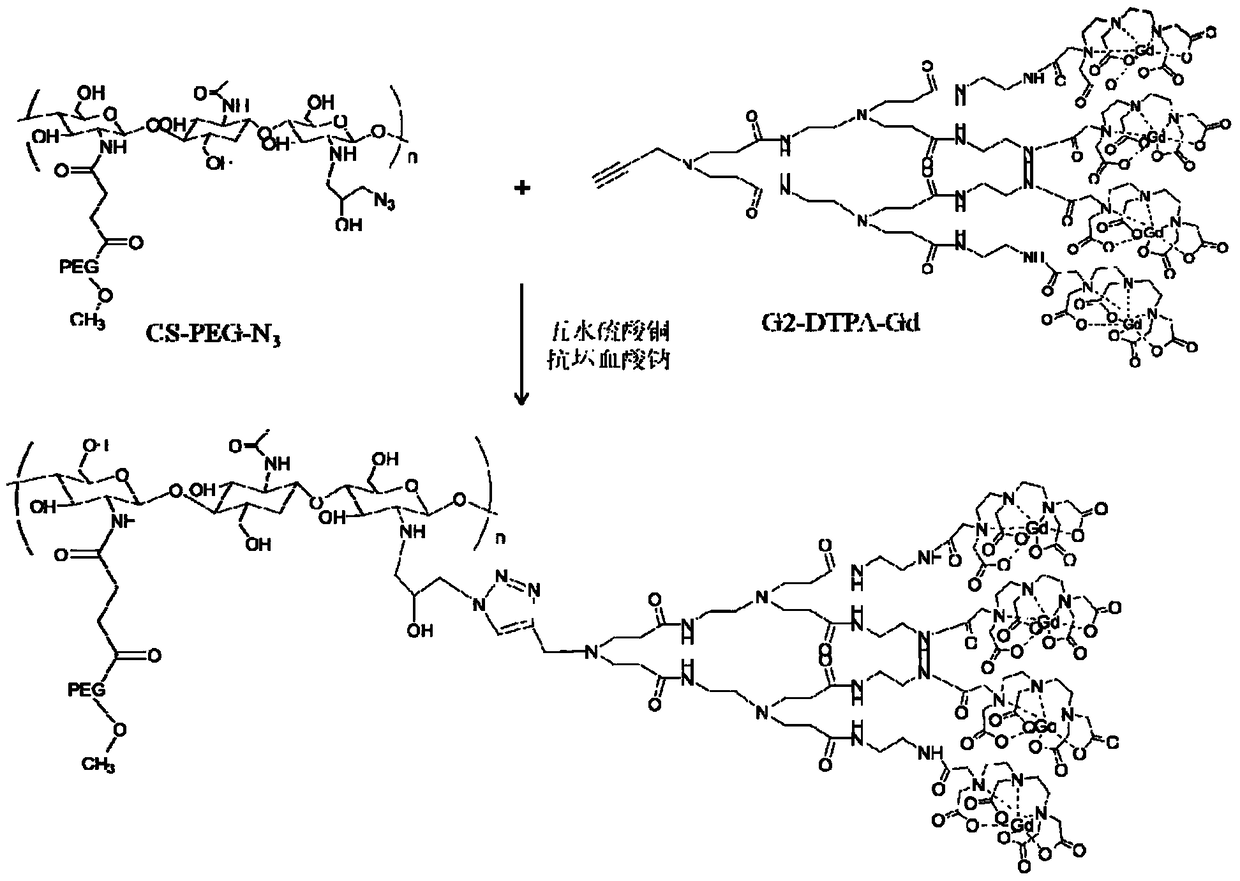
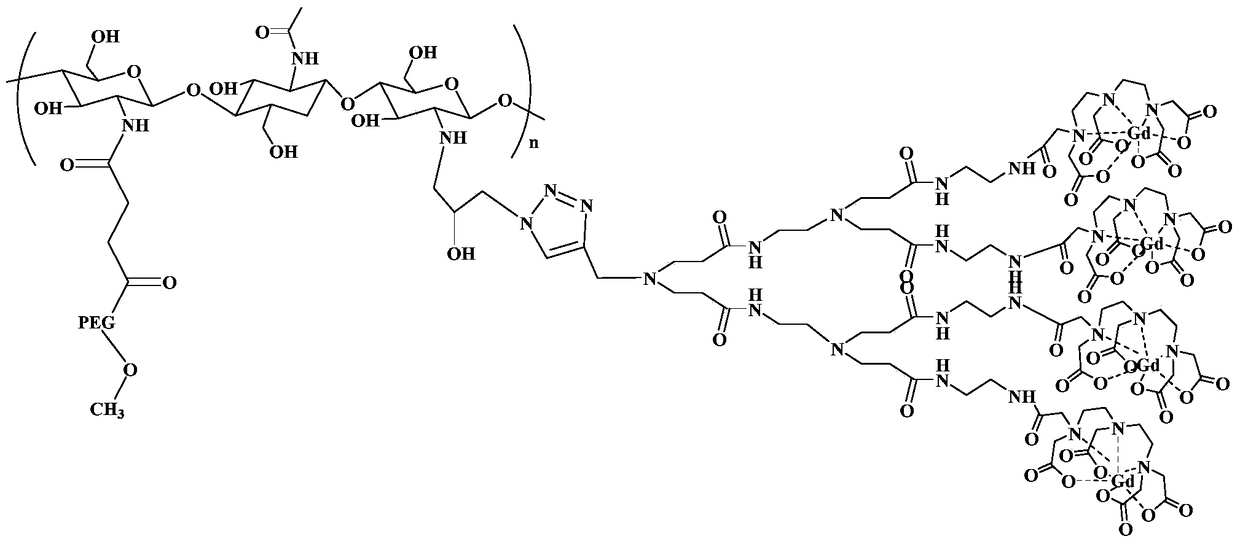
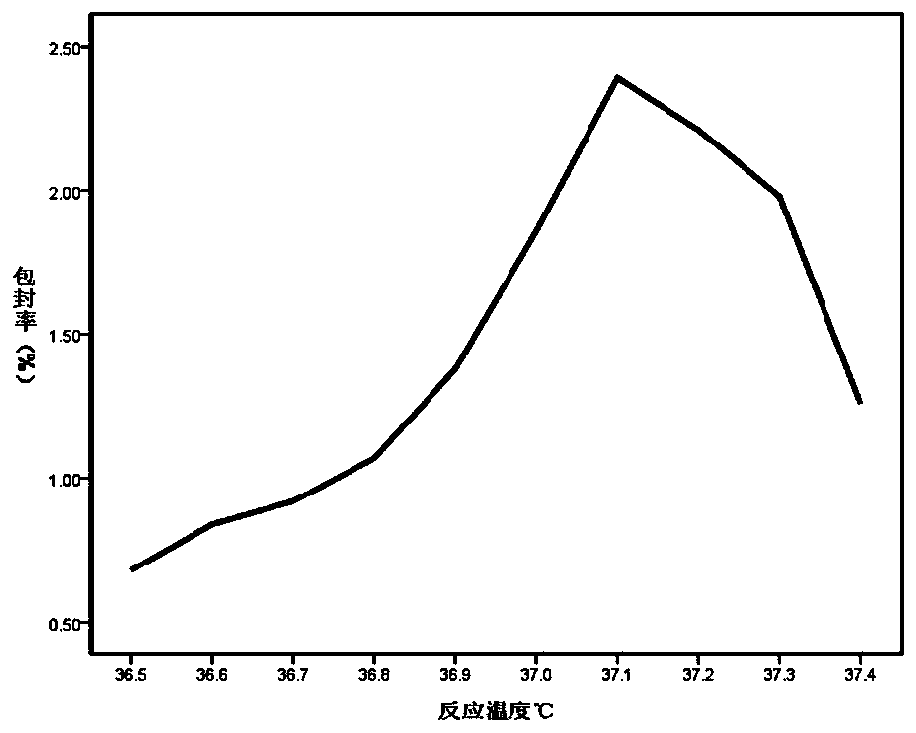
MRI contrast agent taking chitosan derivative as carrier and preparation method
ActiveCN106139166AGood biocompatibilityEasily biodegradableIn-vivo testing preparationsDendrimerMRI contrast agent
The invention discloses an MRI contrast agent taking a chitosan derivative as a carrier and a preparation method of the contrast agent. The contrast agent comprises chitosan which serves as a main body of the contrast agent and modified with polyethylene glycol and a secondary polyamide dendrimer which is mainly connected to a main chain of chitosan and provided with a gadolinium chelate. The preparation method of the contrast agent comprises the steps that chitosan modified with polyethylene glycol is provided, a chelating ligand of gadolinium is coupled to the secondary polyamide dendrimer modified with an alkynyl group, then the modified secondary polyamide dendrimer is connected to chitosan, and the contrast agent is obtained. The MRI contrast agent taking the chitosan derivative as the carrier is good in biocompatibility, easy to biologically degrade and high in relaxation rate, the preparation method is simple, the needed reaction temperature is moderate, and control is easy.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of bifunctional contrast agent based on up-conversion material and gadolinium chelate
InactiveCN103566380AHigh biosecurityGood physical and chemical stabilityNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEthyl phosphateGadolinium-Chelate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a bifunctional contrast agent based on an up-conversion material and a gadolinium chelate. The preparation method comprises following steps: preparing surface-aminated silica by utilization of the combined action of tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) and (3-aminopropyl)trimethoxysilane (APTES) and by utilization of an up-conversion nano material as a substrate; coupling a chelate to the surface-aminated silica by utilization of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) as coupling agents; and finally reacting with a gadolinium salt to obtain the gadolinium chelate, and therefore the bifunctional contrast agent combined the up-conversion material and the gadolinium chelate is obtained. The raw materials used in the preparation method have high biosecurity, and some of the raw materials are already commercial products. The preparation method has simple technology and strong operationality, and can satisfy production and applications. The bifunctional contrast agent prepared has good physical and chemical stability, luminescence performance and magnetic resonance imaging performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Manganese gadolinium heterozygous bimetallic paramagnetic nanocolloid and application in preparation of magnetic resonance imaging contrast material thereof
ActiveCN104127889AReduce loadLittle side effectsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryHigh concentrationSide effect
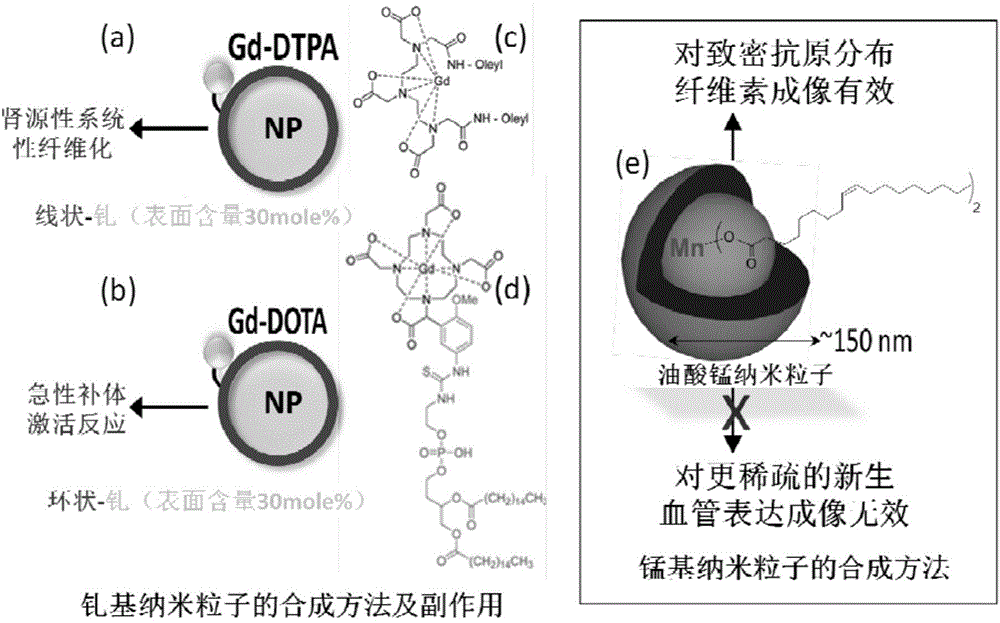
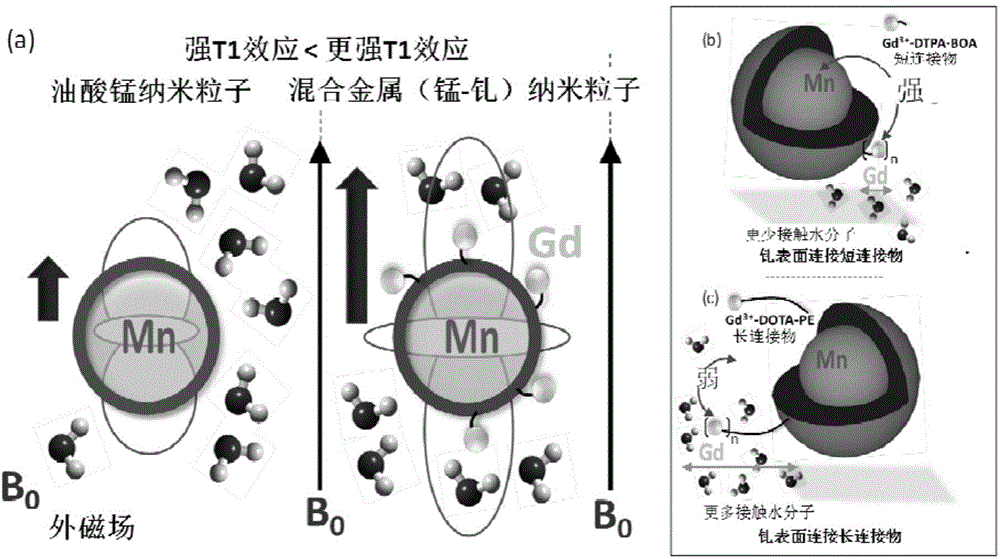
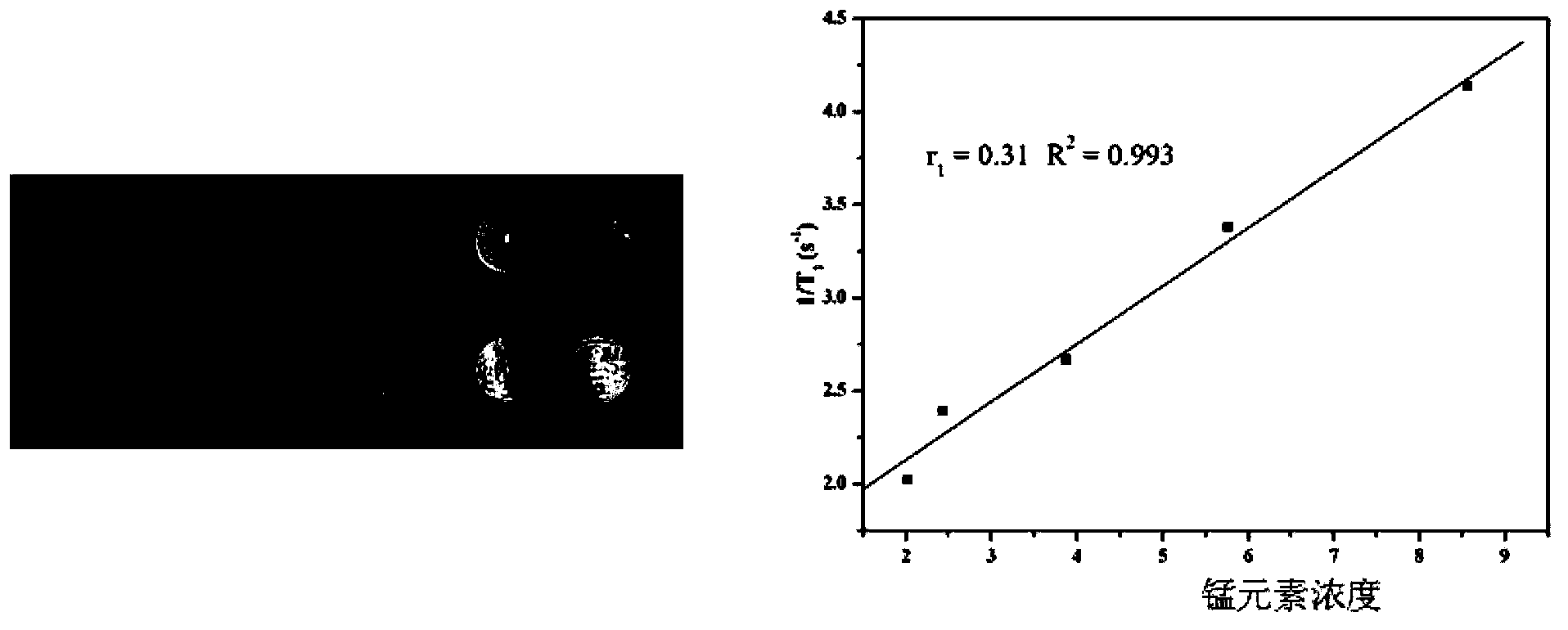
The invention discloses a manganese gadolinium heterozygous bimetallic paramagnetic nanocolloid and application in preparation of a magnetic resonance imaging contrast material thereof. The invention designs, synthesizes and evaluates a hybrid ''bimetallic'' magnetic resonance imaging nanocolloid composed of manganese element and trace gadolinium. Research shows that: the high relaxation rate of the nanocolloid provided by the invention derives from high concentration manganese oleate molecules suspending at the core of nanoparticles, and the small molecules can penetrate a phospholipid film layer to come into contact with a critical surface of water and nanoparticles. Integration of trace gadolinium chelates on the surfaces of the nanoparticles can provide an additional relaxation rate, thereby affecting the relaxation effect of surrounding protons. The manganese gadolinium heterozygous bimetallic paramagnetic nanocolloid provided by the invention can maximumly reduce gadolinium agent load, lower the side effects of gadolinium chelates and improve the biological safety, thus reaching the purpose of improving the nanoparticle r1 paramagnetic magnetic resonance contrast effect.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Gadolinium chelate as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112940157ALower ratioIncreased longitudinal relaxation rateIn-vivo testing preparationsMacromolecular drugPolyamide
The invention discloses a gadolinium chelate as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The gadolinium chelate is a complex formed by gadolinium ions and macromolecules through chelation, the macromolecules comprise a copolymer or a mixture of any one or more than two of a carboxylic acid-containing high-molecular polymer, an amino-containing high-molecular polymer, a hydroxyl-containing high-molecular polymer, a polyester high-molecular polymer, a polyether high-molecular polymer, a polyamide high-molecular polymer, protein, polypeptide and polysaccharide. The gadolinium ions and macromolecules form the gadolinium chelate through chelation, the gadolinium chelate is a water-soluble macromolecular drug, the longitudinal relaxation rate r1 can be increased, the r2 / r1 ratio can be reduced, the water solubility is good, the stability is high, meanwhile, a good imaging effect can be presented in a short time, and the MRI time is shortened.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHECI PHARM TECH CO LTD
Gadolinium-containing magnetic resonance contrast agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101979097ASmall side effectsSettle the lossEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsSide effectResonance
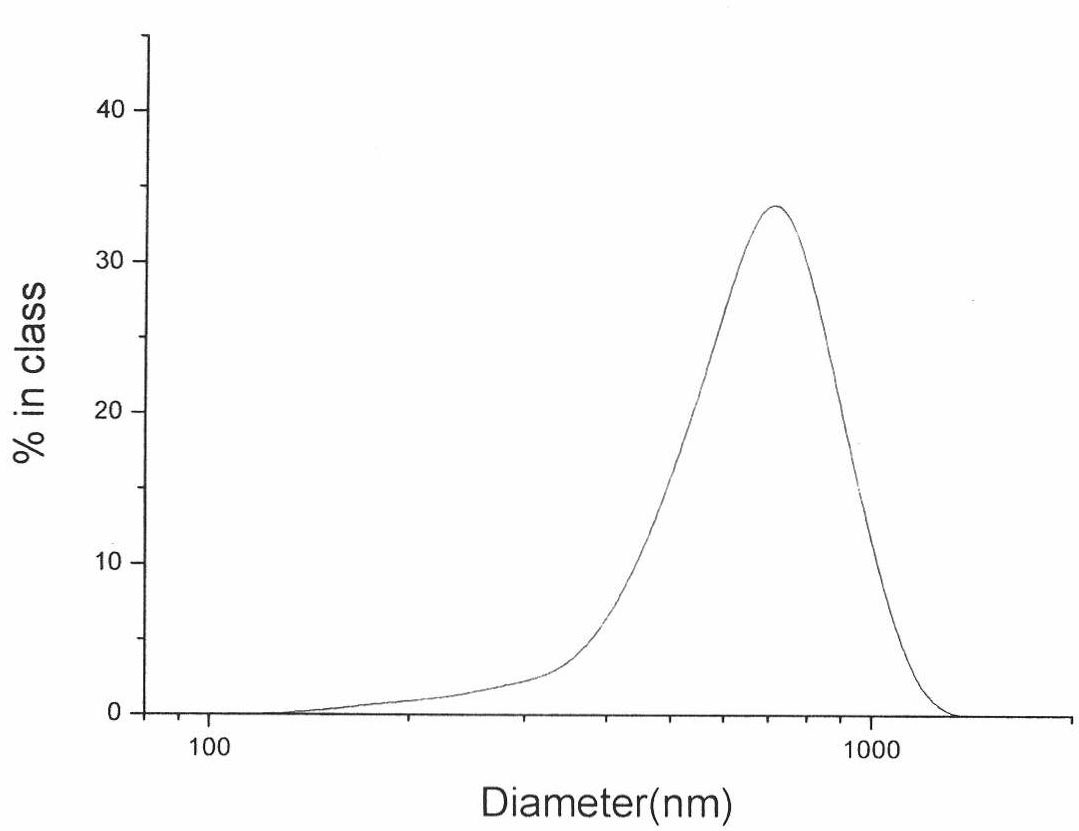
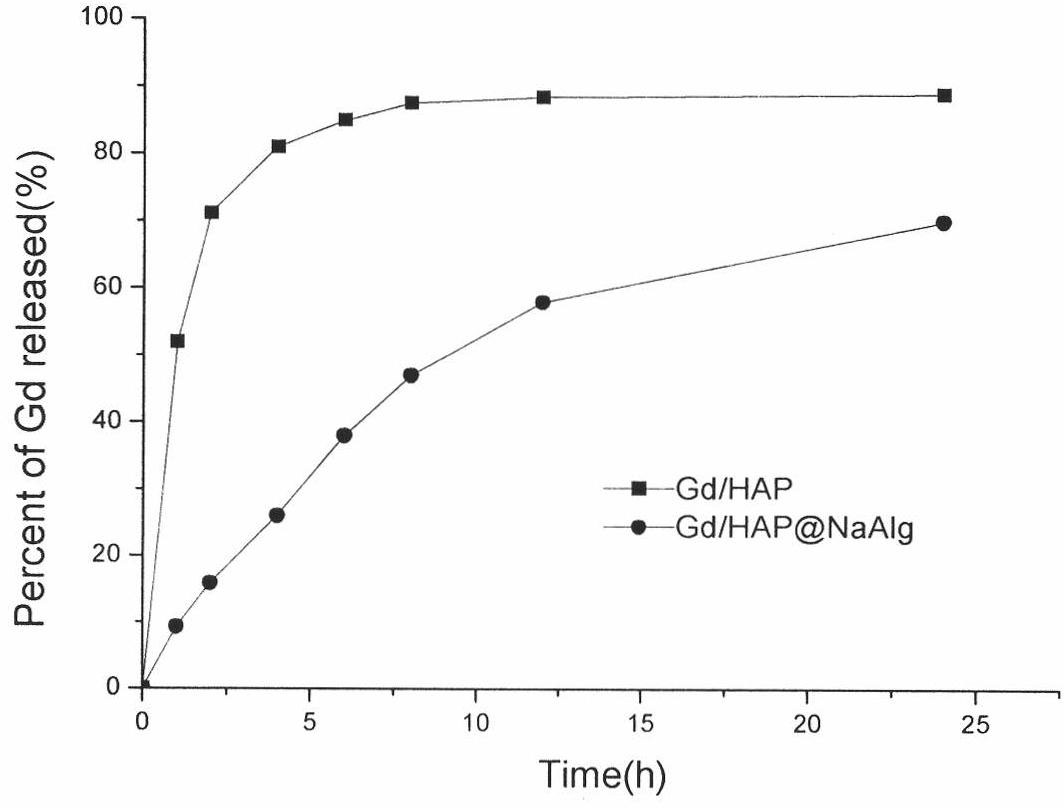
The invention relates to the field of magnetic resonance imaging, in particular to a gadolinium-containing magnetic resonance contrast agent and a preparation method thereof. The gadolinium-containing magnetic resonance contrast agent of the invention mainly comprises a gadolinium chelate, hydroxyapatite and sodium alginate, wherein the contrast agent is prepared by wrapping the gadolinium chelate-supported hydroxyapatite with the sodium alginate. The magnetic resonance contrast agent of the invention has small toxic or side effect on human body; the particle diameter of the particles is controllable (0.1 to 2.0mu m); the specificity of the liver part and the spleen part can be realized through passive targeting; and the contrast agent carries 12.5 to 20 mass percent of gadolinium chelate, has high sustained-release performance and can improve the development effect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chitosan-based MRI contrast medium and preparation method
InactiveCN105749302AGood biocompatibilityEasily biodegradableIn-vivo testing preparationsMRI contrast agentSide chain
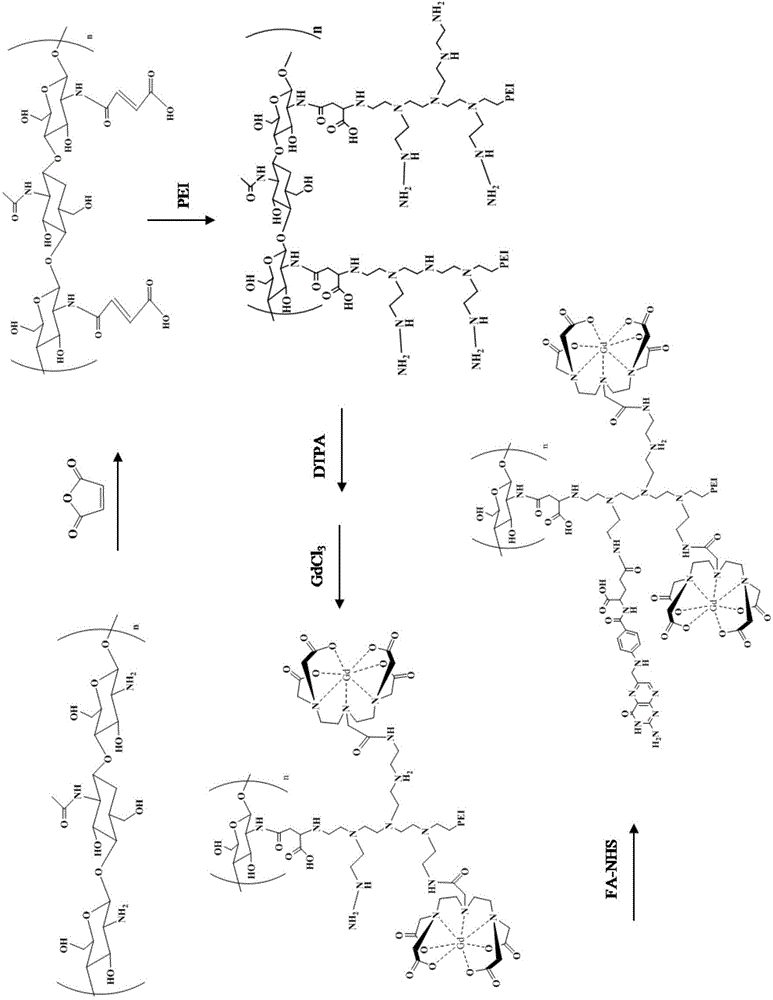
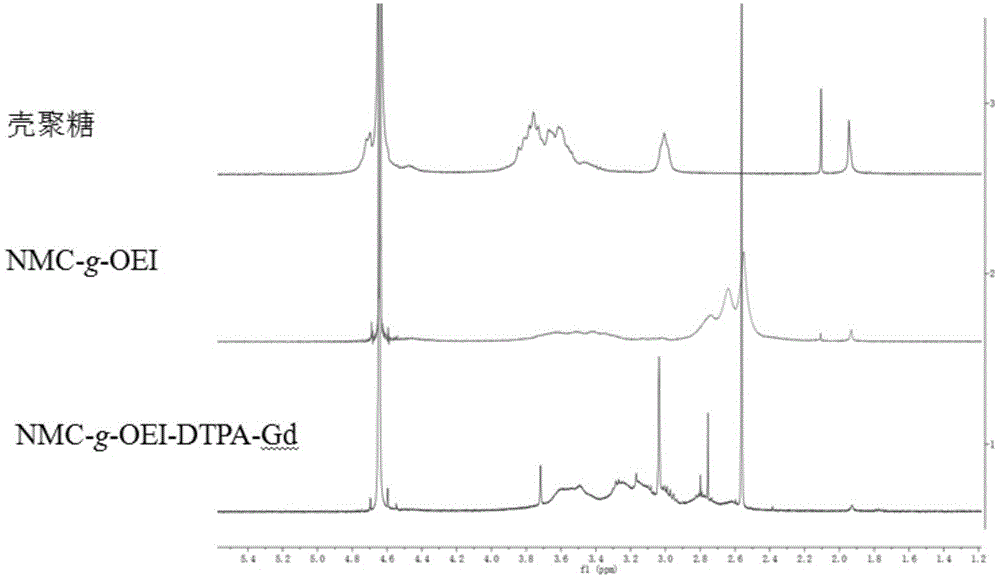
The invention discloses a chitosan-based MRI contrast medium and a preparation method. The contrast medium comprises polyethyleneimine-grafted chitosan taken as a main body of the contrast medium and a gadolinium chelate mainly connected to side chains of polyethyleneimine-grafted chitosan. Furthermore, the contrast medium also comprises a targeting group, such as folic acid, connected to side chains of polyethyleneimine-grafted chitosan. The preparation method comprises: firstly, providing polyethyleneimine-grafted chitosan, then coupling a gadolinium chelating ligand, such as diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid to polyethyleneimine-grafted chitosan, enabling the obtained product together with Gd3+ to form the gadolinium chelate, and optionally connecting the targeting group, such as folic acid to the obtained polyethyleneimine-grafted chitosan to produce the contrast medium. The chitosan-based targeting MRI contrast medium is good in biocompatibility, is easy to biologically degrade, and has a high relaxation rate. The preparation method is simple, needs medium reaction temperature, and is easy to control.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Tumor targeting gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111643684AGood biocompatibilityGood low toxicityIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetTumor targeting
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tumor targeting gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and biomedical application of the tumor targeting gadolinium-based magneticresonance imaging contrast agent. The contrast agent can be specifically bound to a transferrin receptor 1 highly expressed on the surfaces of tumor cells, and consists of genetic engineering recombinant proteins and a gadolinium chelate, and has a higher longitudinal relaxation rate than a commercial contrast agent of Magnevist (Gd-DTPA). The animal tumor model imaging effect comparison with theMagnevist is provided; the result indicates that the contrast agent provided by the invention can realize the tumor specific recognition and longer-time magnetic resonance imaging at a lower injection dose; and repeated injection is not needed. The contrast agent provided by the invention can be used through intravenous administration, and can be applied to early diagnosis of cancer, further identification of tumor metastasis and diagnosis of suspected postoperative recurrence.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
IL-13 modified gadolinium chelate containing liposome targeted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an IL-13 modified gadolinium chelate containing liposome targeted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and a preparation method and application thereof. The contrast agent is gadolinium chelate encapsulated liposome, and the surface of the liposome is modified by IL-13. The preparation method of the IL-13 modified gadolinium chelate containing liposome targeted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent comprises the steps that a liposome film is firstly prepared; then gadolinium chelate is added into a container containing the liposome film; the gadolinium chelate is wrapped by the liposome film with the assistance of ultrasonic waves to form gadolinium chelate containing multilamelar liposome; the surface of the gadolinium chelate encapsulated multilamelar liposome is modified by thiolated IL-13. The contrast agent can penetrate through a blood brain barrier to be transferred to a tumor diseased region and be specifically bound with the tumor diseased region. Therefore, the contrast agent has targeting ability, can detect a tumor focus smaller than 2 mm and can be used for early detection of tumors.
Owner:麦克斯韦磁谷科学技术(清远)有限公司
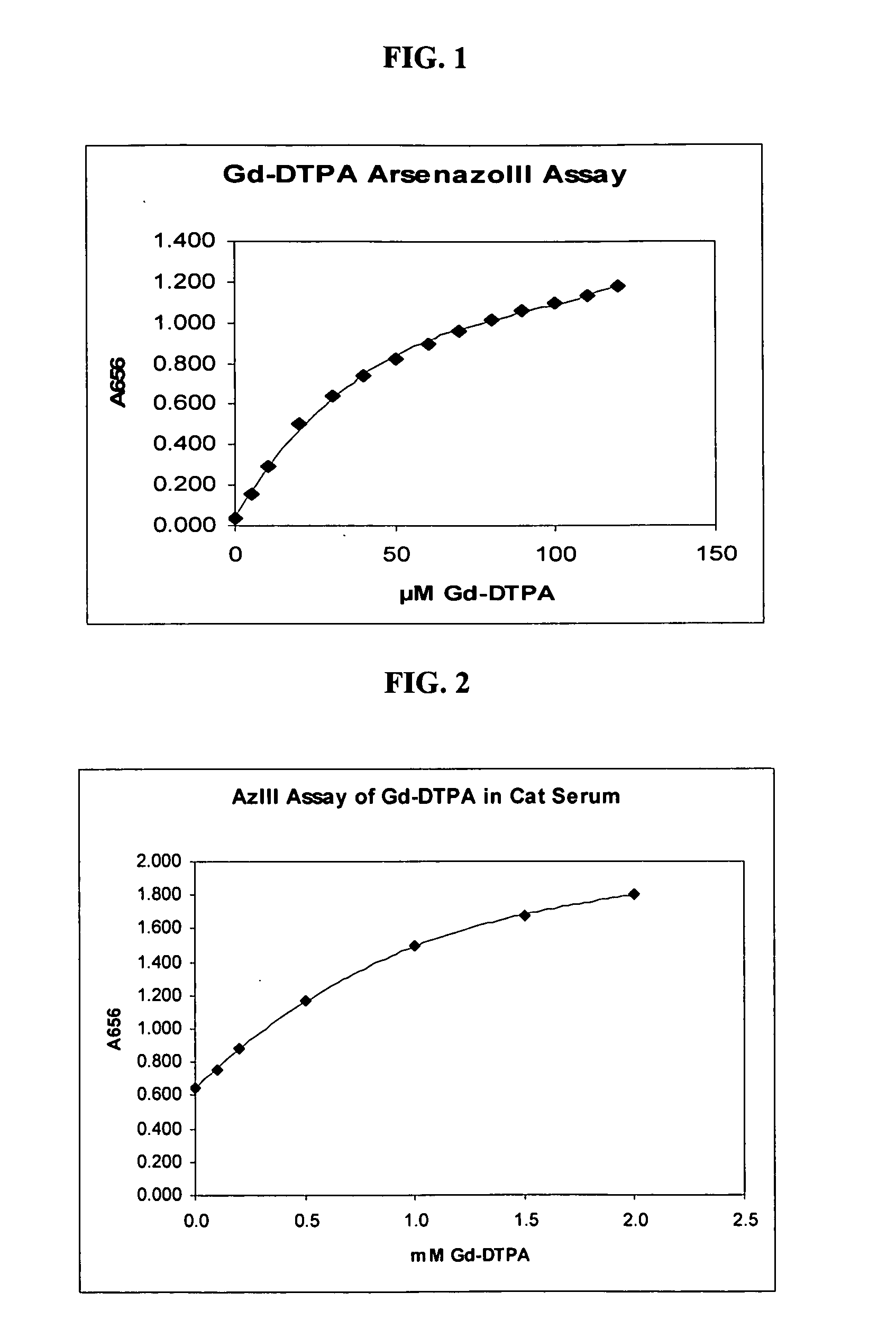
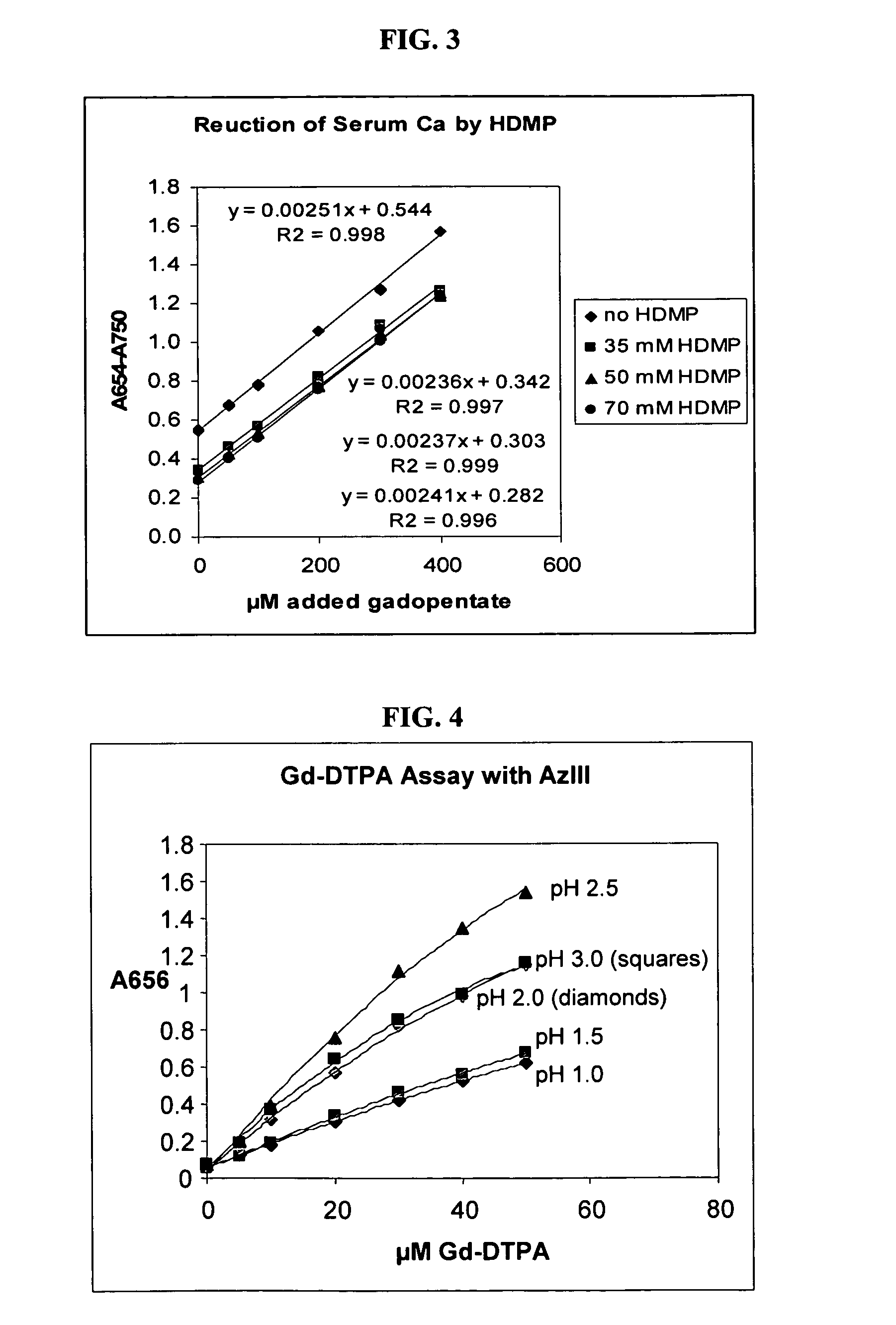
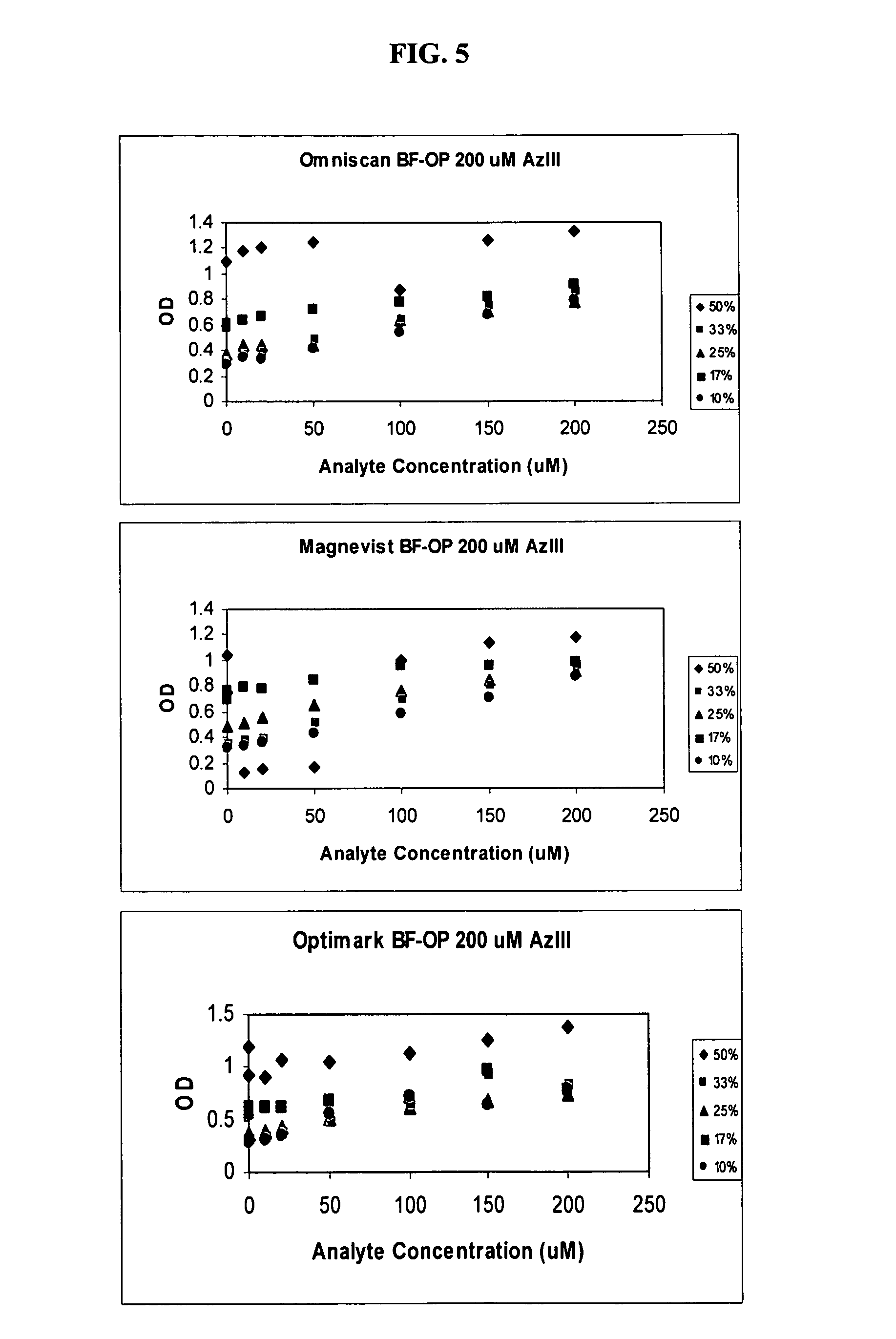
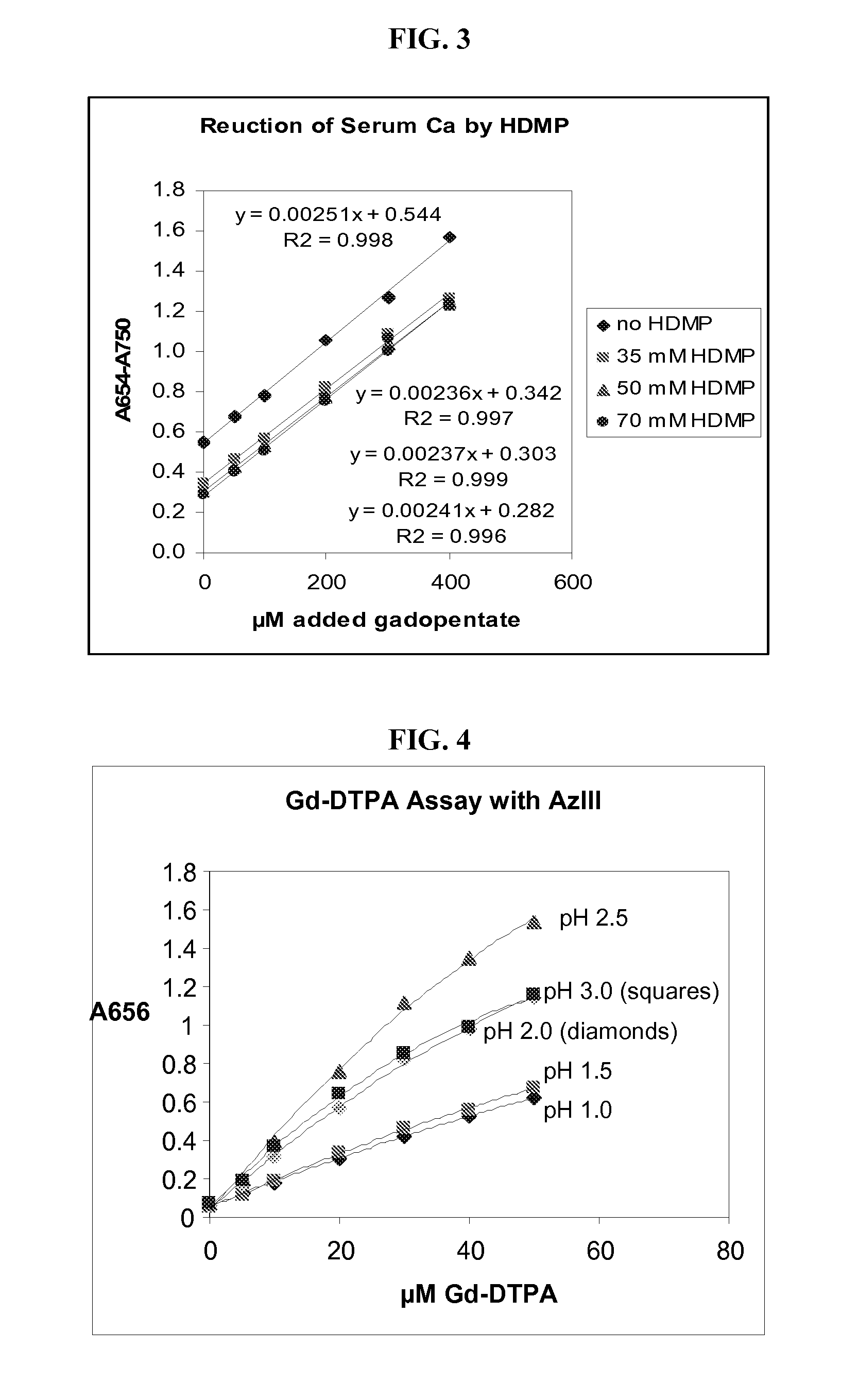
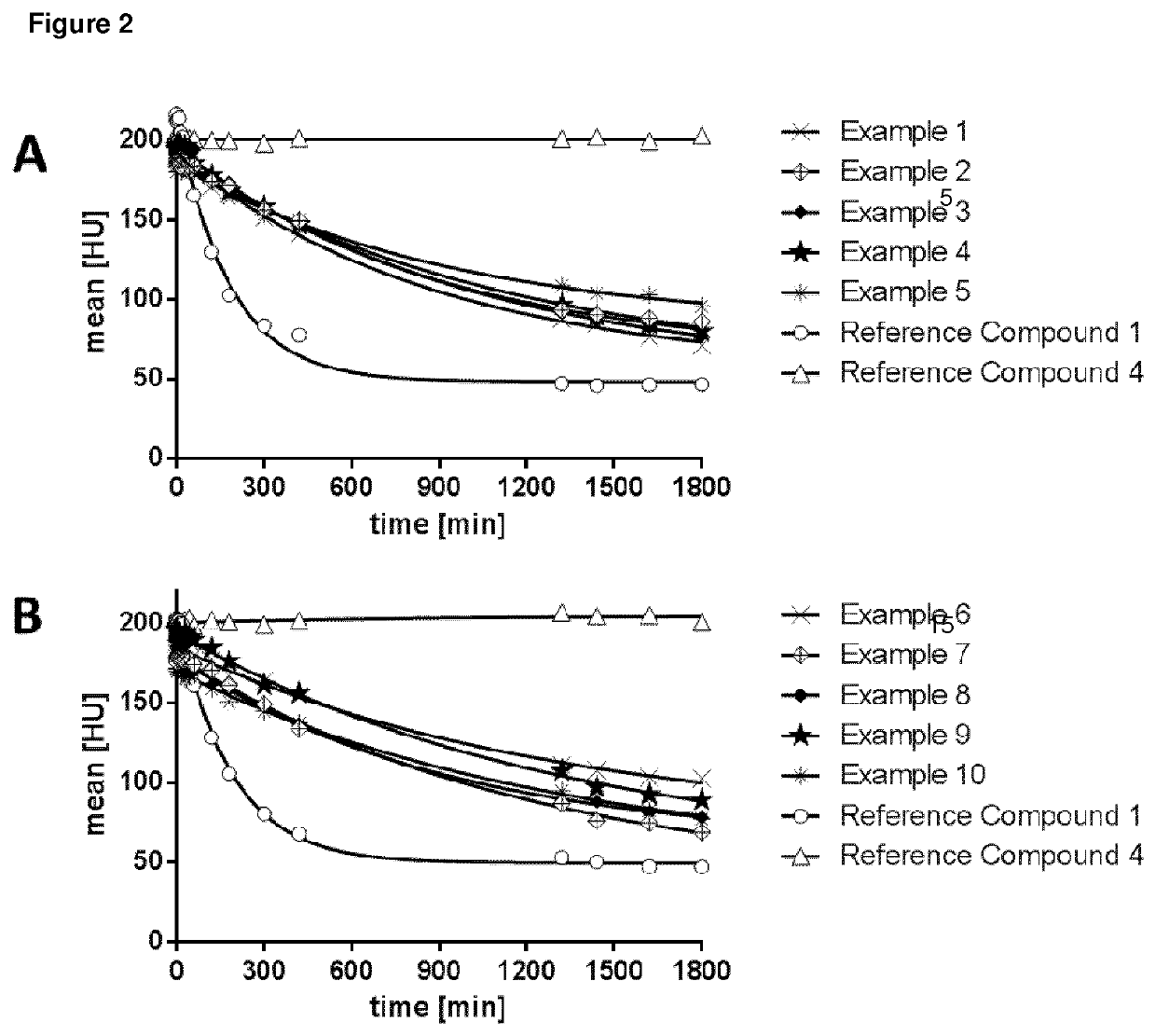
Detection of gadolinium chelates
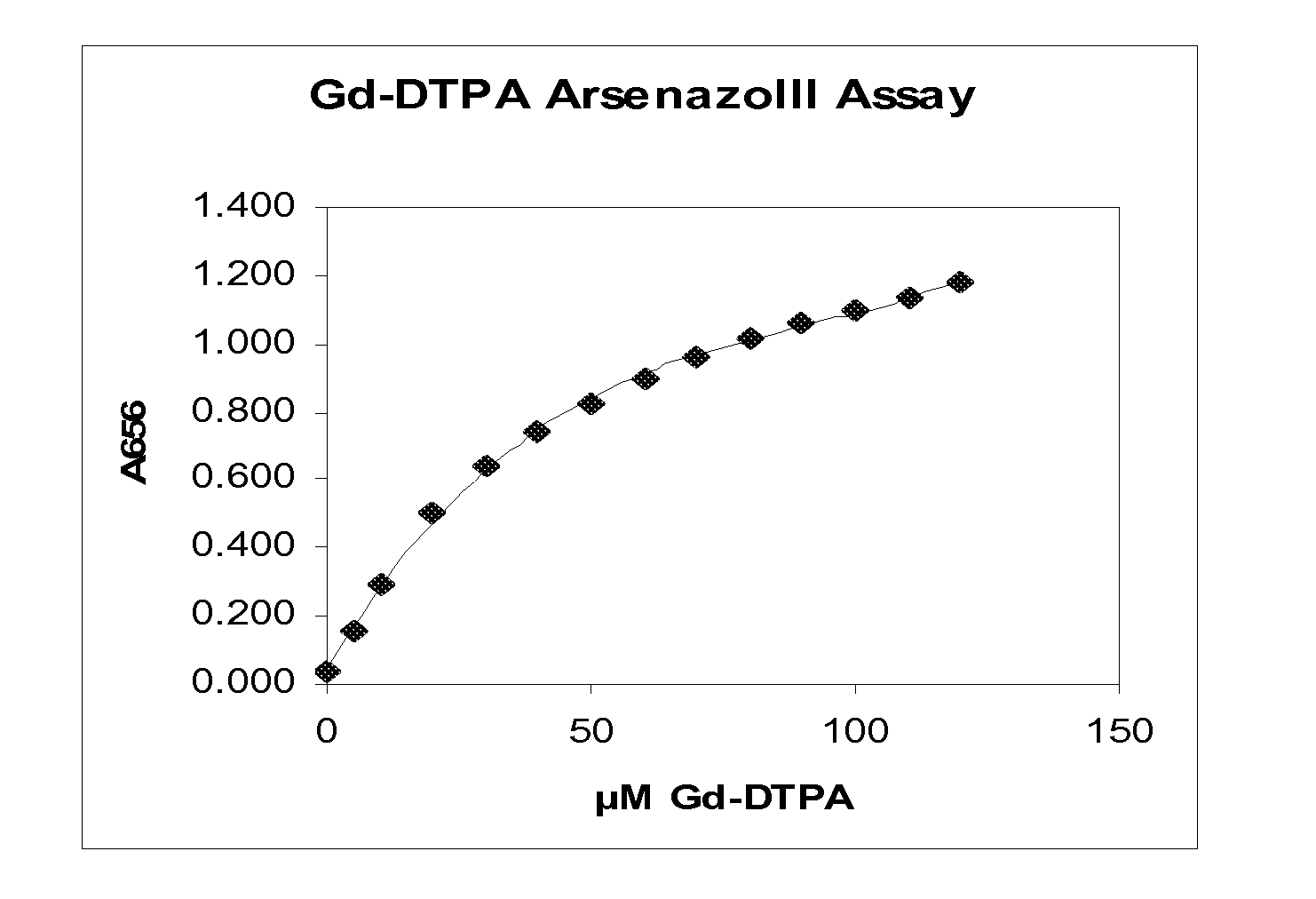
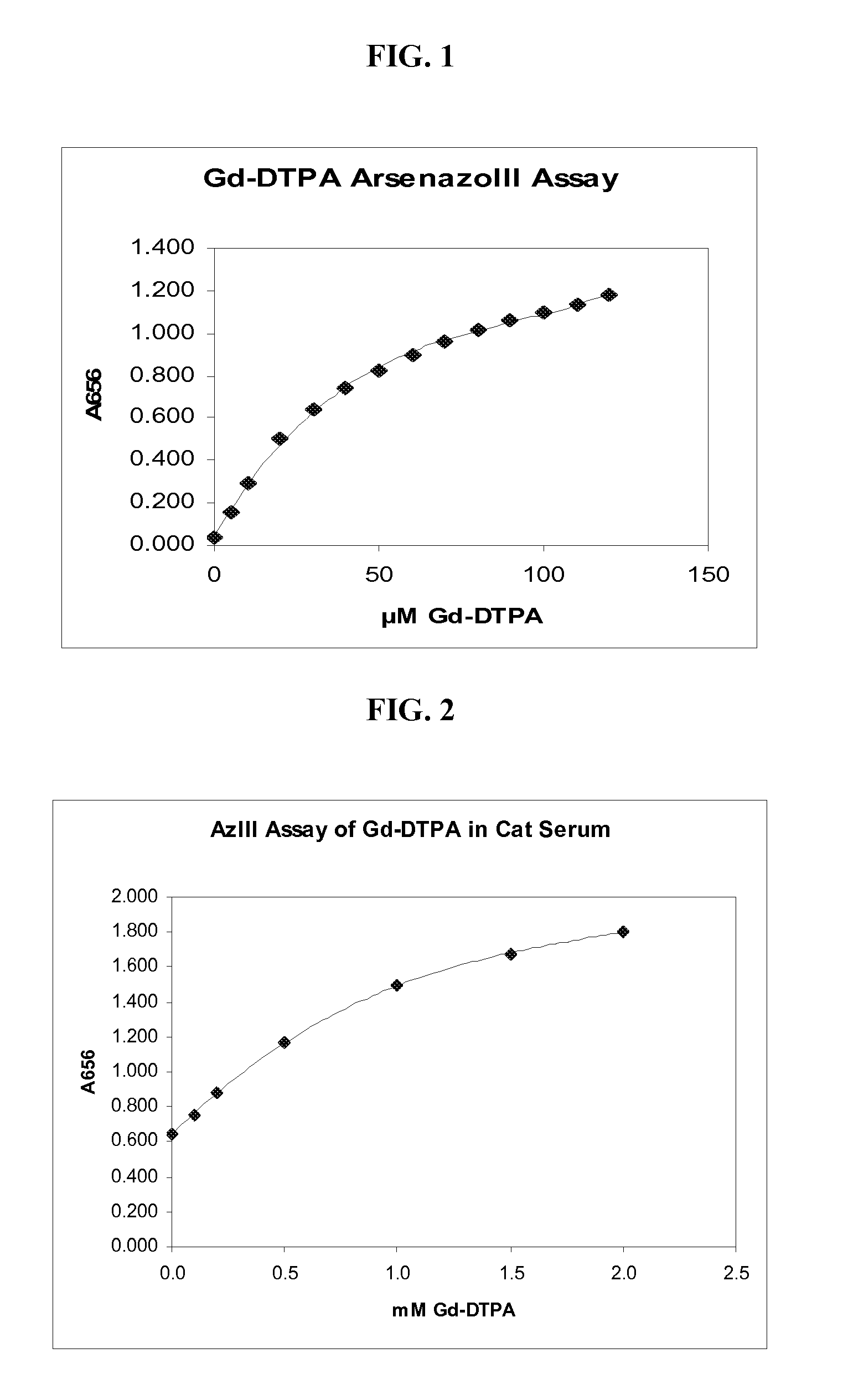
A method for determining the presence or amount of a gadolinium chelate in a biological sample. The method includes contacting a biological sample with a dye selected from arsenazo III or chlorophosphonazo at low pH, and measuring the absorbance of the sample, thereby determining the presence or amount of gadolinium in the sample. A method for determining glomerular filtration (GFR) rate in a mammal. The method includes administering to the mammal an amount of a gadolinium chelate and determining the concentration levels of the chelate in biological samples taken from the animal at plurality of intervals following administration of the chelate. The concentration levels of the chelate are correlated to GFR.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
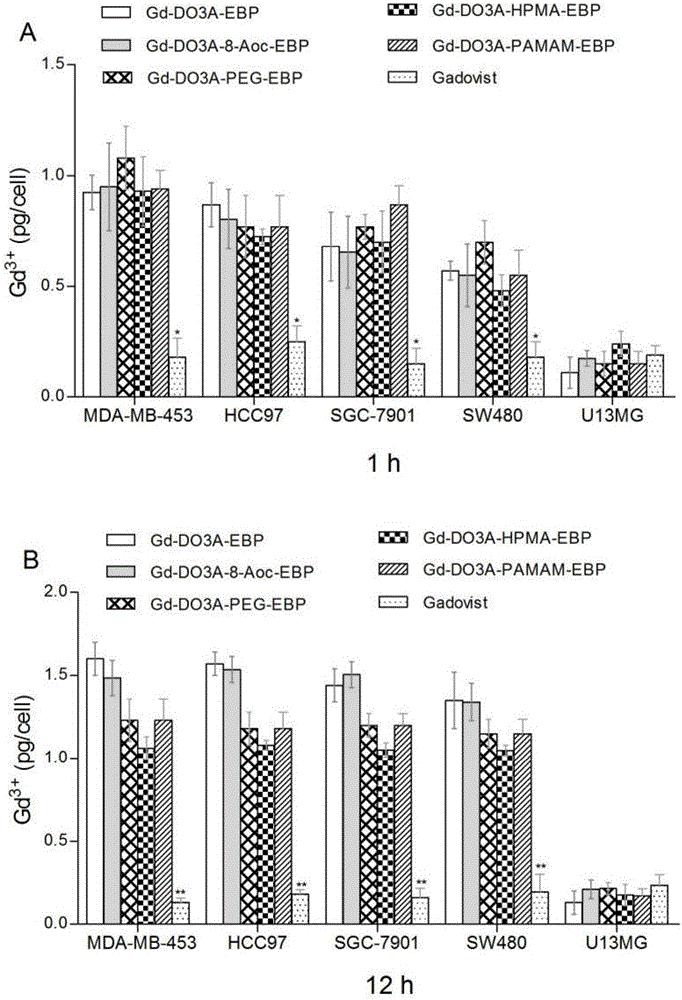
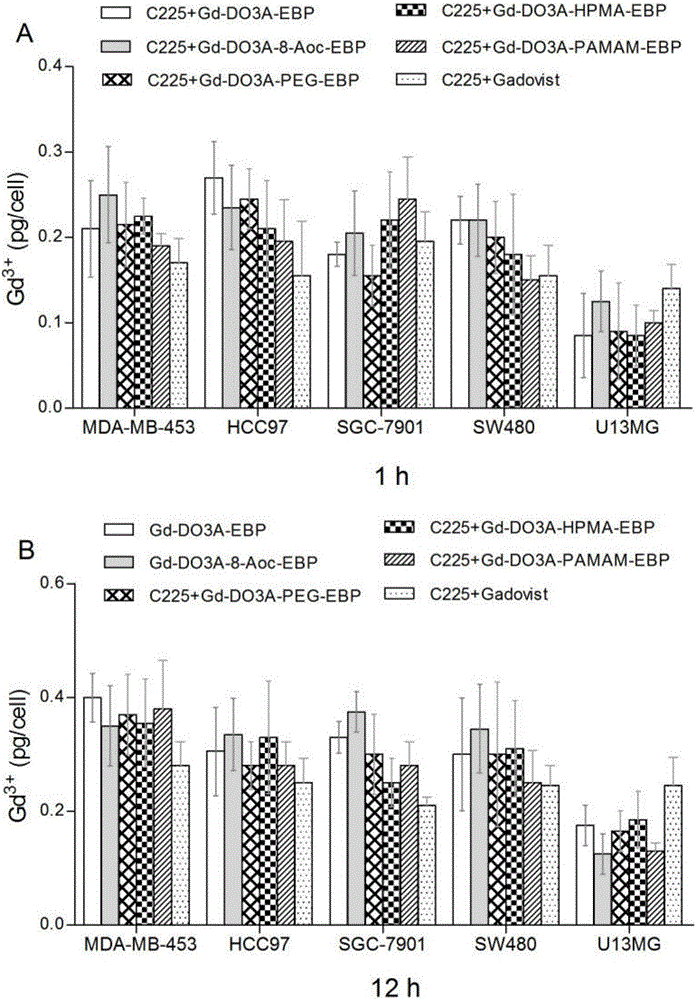
Tumor targeting MRI contrast agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105999308AImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetMRI contrast agent
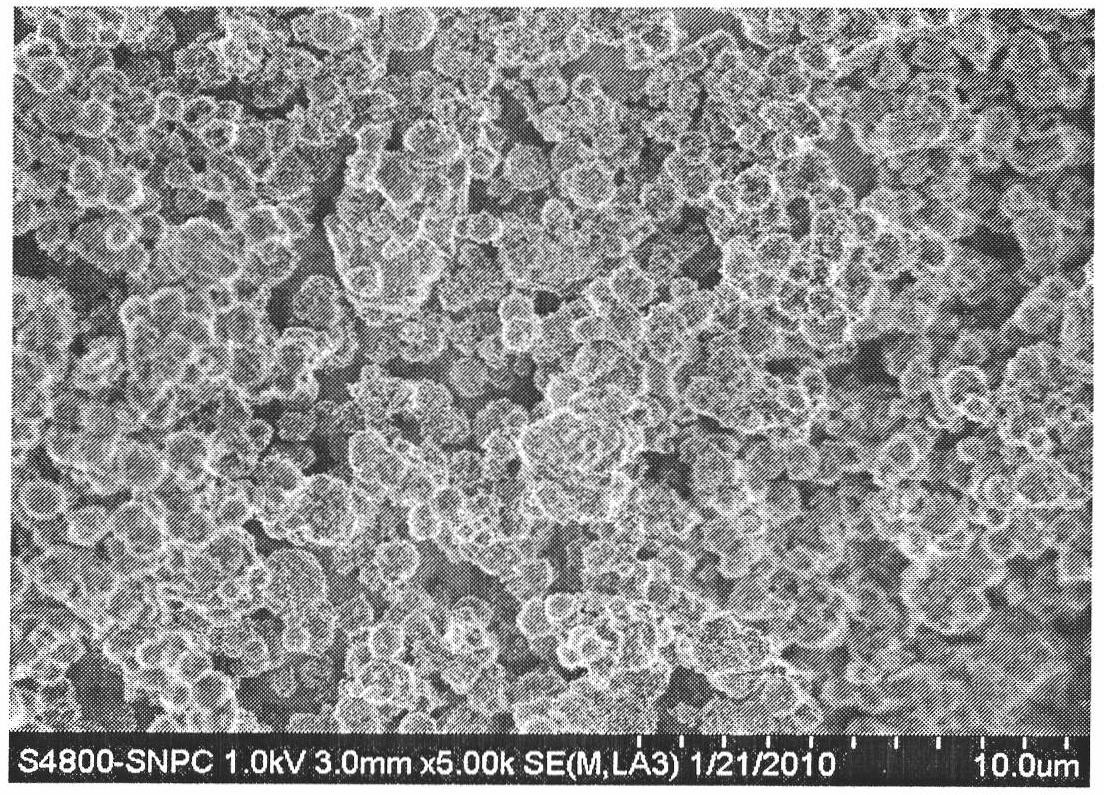
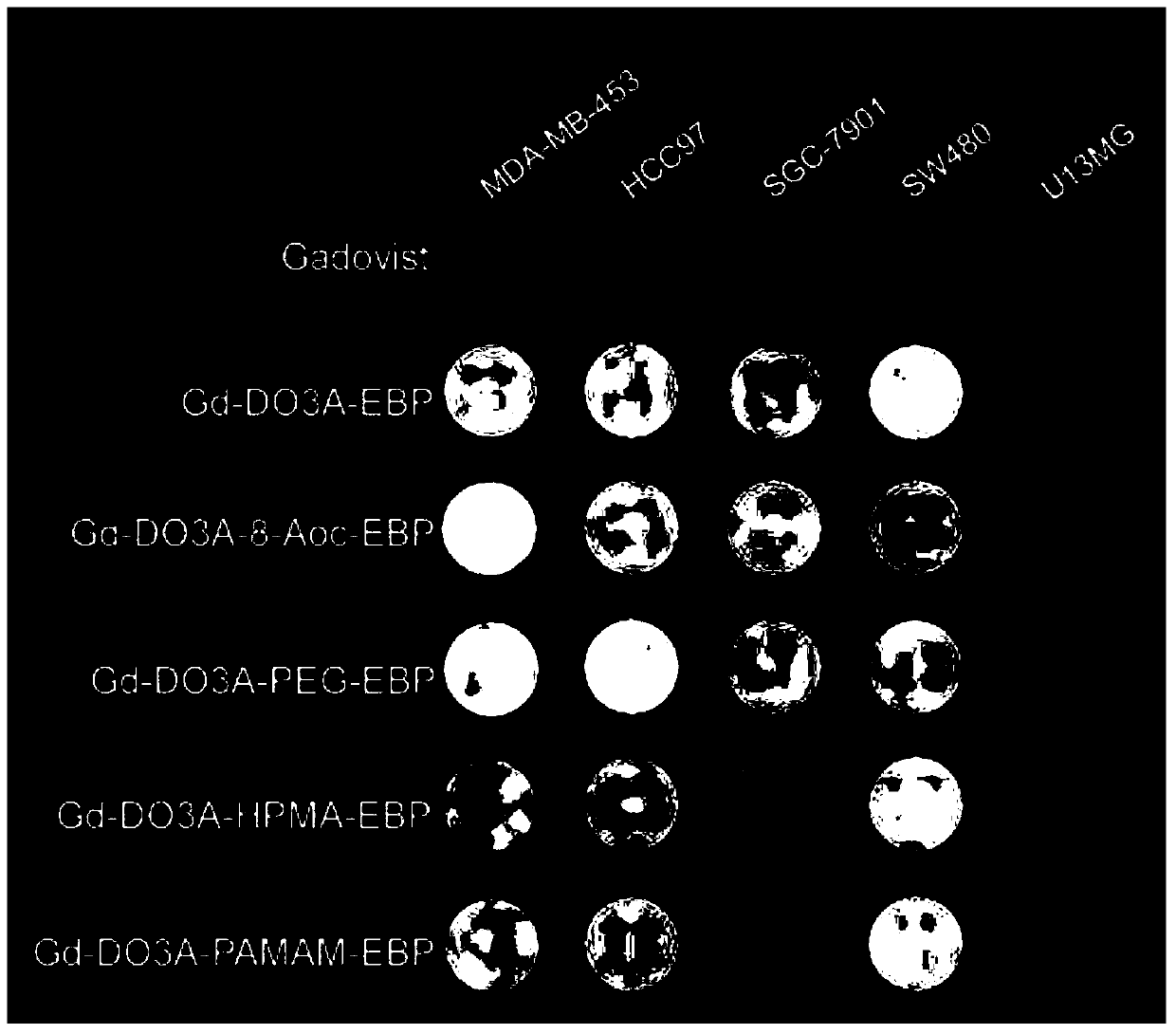
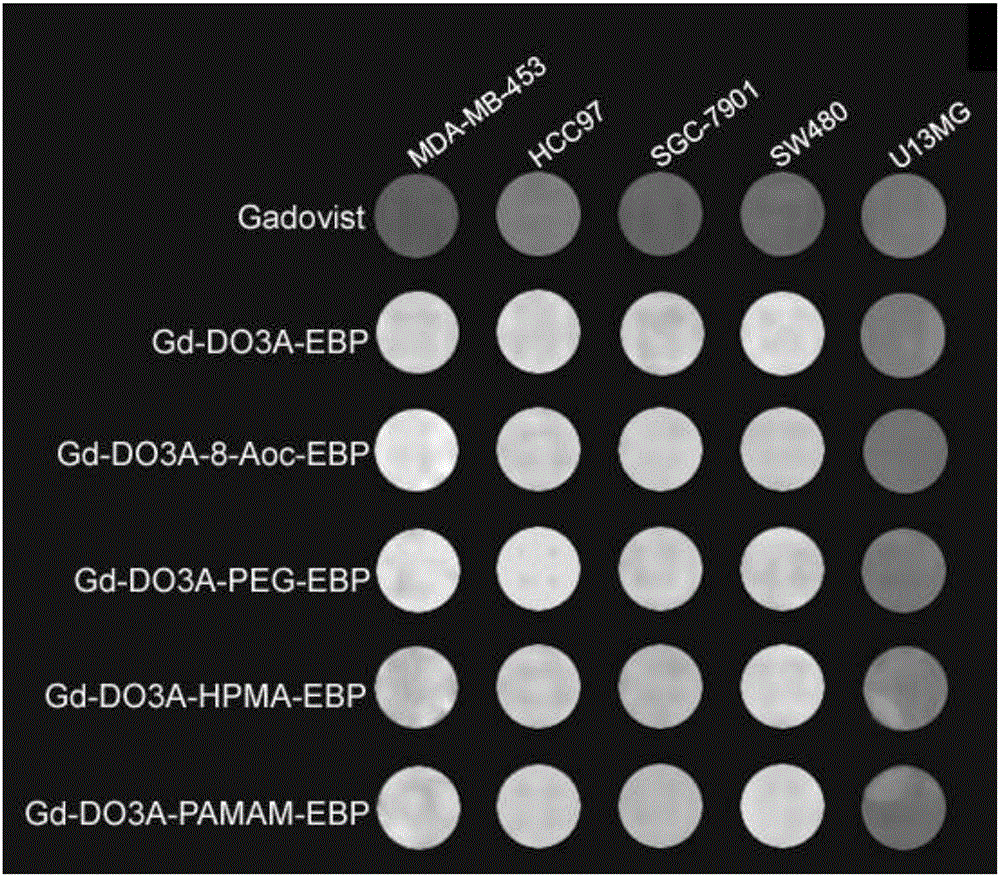
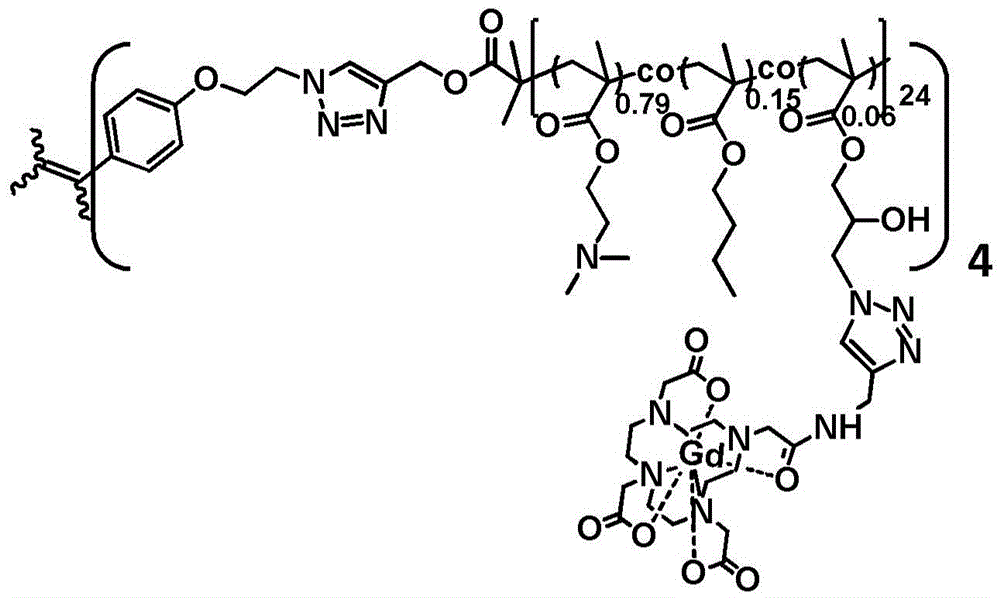
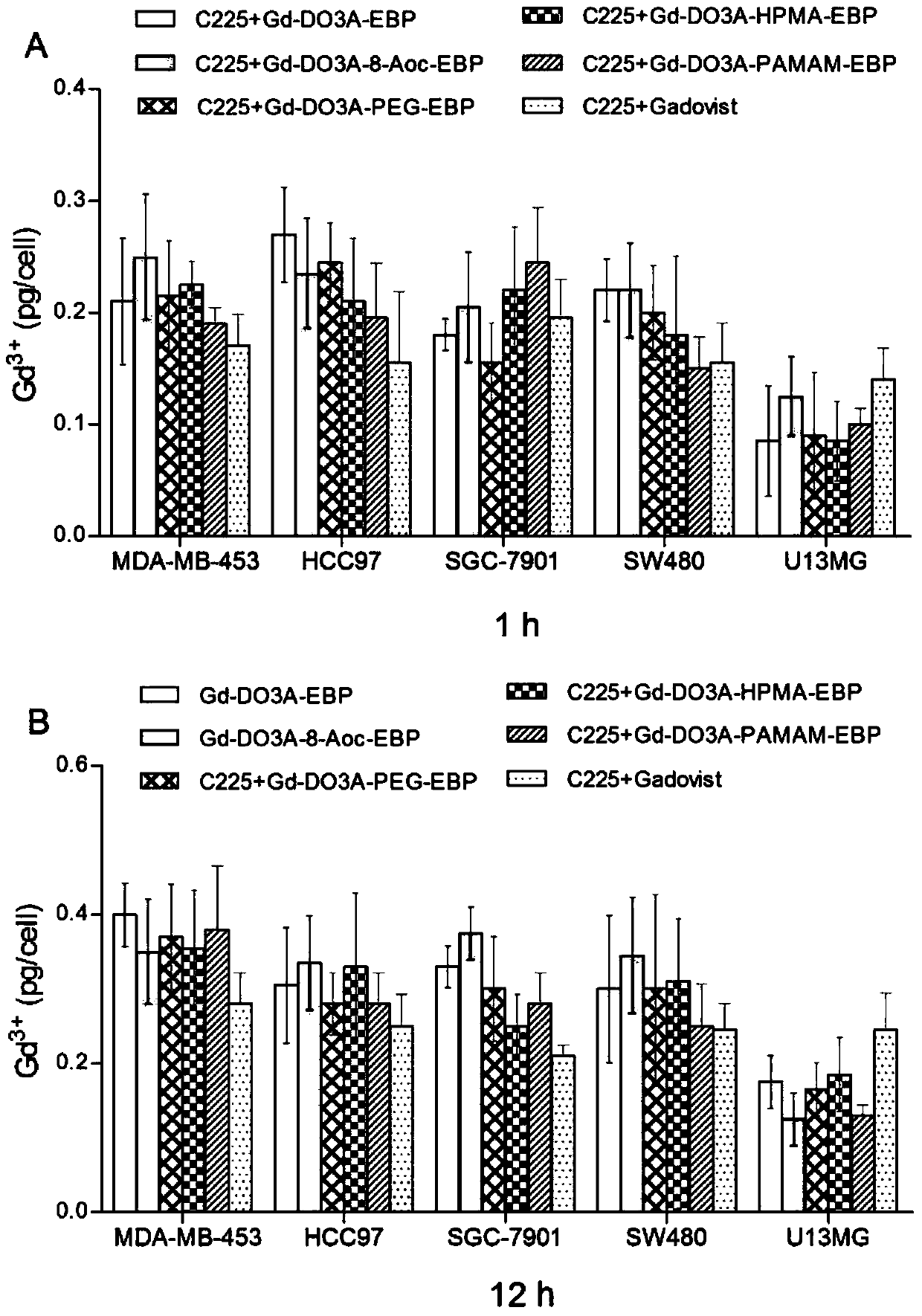
The invention provides tumor targeting MRI contrast agent and a preparation method thereof. The contrast agent is characterized by comprising a micromolecule gadolinium chelate part and a targeting carrier part, wherein the micromolecule gadolinium chelate part and the targeting carrier part are coupled through a covalent bond, the micromolecule gadolinium chelate part is Gd-DO3A, and the targeting carrier part contains EBP molecules. The contrast agent is good in relaxation enhancement ability, can be combined with EGFR of tumor cells in a targeting mode, has a strong targeting radiography effect and has strong practicability. Furthermore, the imaging time of the contrast agent in a body is prolonged, and the adding amount of the contrast agent is reduced.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
Preparation method and application of star polymer
ActiveCN103951805BDisinfectantsLuminescent compositionsPolymer scienceAtom-transfer radical-polymerization
The invention relates to a novel preparation method and application of a cationic amphiphilic tetra-armed star polymer. In particular, the star polymer can be obtained through synthetic means such as atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and click chemistry. A core of the star polymer is tetraphenylethylene with the characteristic of aggregation-induced emission. A polymer linear arm is a cationic amphiphilic random copolymer with excellent antibacterial effects. A covalently labeled T1 type magnetic resonance (MR) contrast agent is an organic gadolinium chelate. By using the cationic amphiphilic tetra-armed star polymer, fluorescence / MR double quantitative detection of Gram positive and negative bacteria with negative charges on the surfaces in the environment of pure water is achieved, and meanwhile good antibacterial effects are gained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A kind of degradable dendrimer magnetic resonance contrast agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103055328BGood contrast effectHigh sensitivityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsDendrimerGadolinium-Chelate
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Detection of Gadolinium Chelates
A method for determining the presence or amount of a gadolinium chelate in a biological sample. The method includes contacting a biological sample with a dye selected from arsenazo III or chlorophosphonazo at low pH, and measuring the absorbance of the sample, thereby determining the presence or amount of gadolinium in the sample. A method for determining glomerular filtration (GFR) rate in a mammal. The method includes administering to the mammal an amount of a gadolinium chelate and determining the concentration levels of the chelate in biological samples taken from the animal at plurality of intervals following administration of the chelate. The concentration levels of the chelate are correlated to GFR.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Gadolinium-containing chelate liposome-targeted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent modified by il-13 and its preparation method and application
The invention discloses an IL-13 modified gadolinium-containing chelate liposome targeted magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent, a preparation method and application thereof. The contrast agent is a liposome encapsulating a gadolinium chelate, and the surface of the liposome is modified with IL-13. Its preparation method is to prepare the liposome film first, then add the gadolinium chelate into the container containing the liposome film, and with the assistance of ultrasonic waves, the liposome film wraps the gadolinium chelate to form a gadolinium-containing chelate multilamellar liposomes; the surface of multilamellar liposomes encapsulating gadolinium chelates was modified with thiolated IL‑13. The contrast agent of the present invention can pass through the blood-brain barrier, deliver to tumor lesion sites and specifically bind to it. Therefore, this contrast agent is targeted, can detect tumor lesions smaller than 2mm, and can be used for early detection of tumors.
Owner:麦克斯韦磁谷科学技术(清远)有限公司
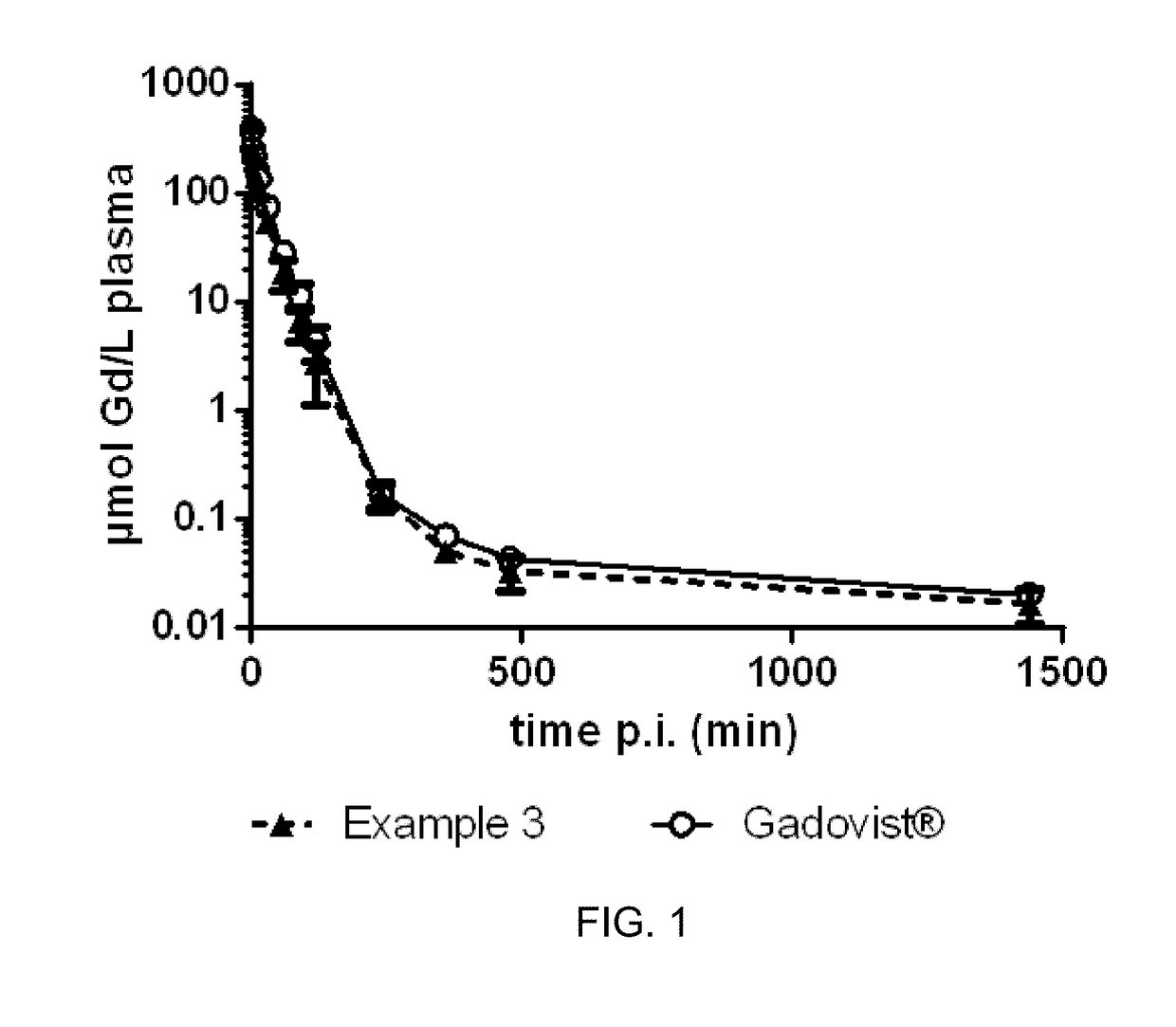
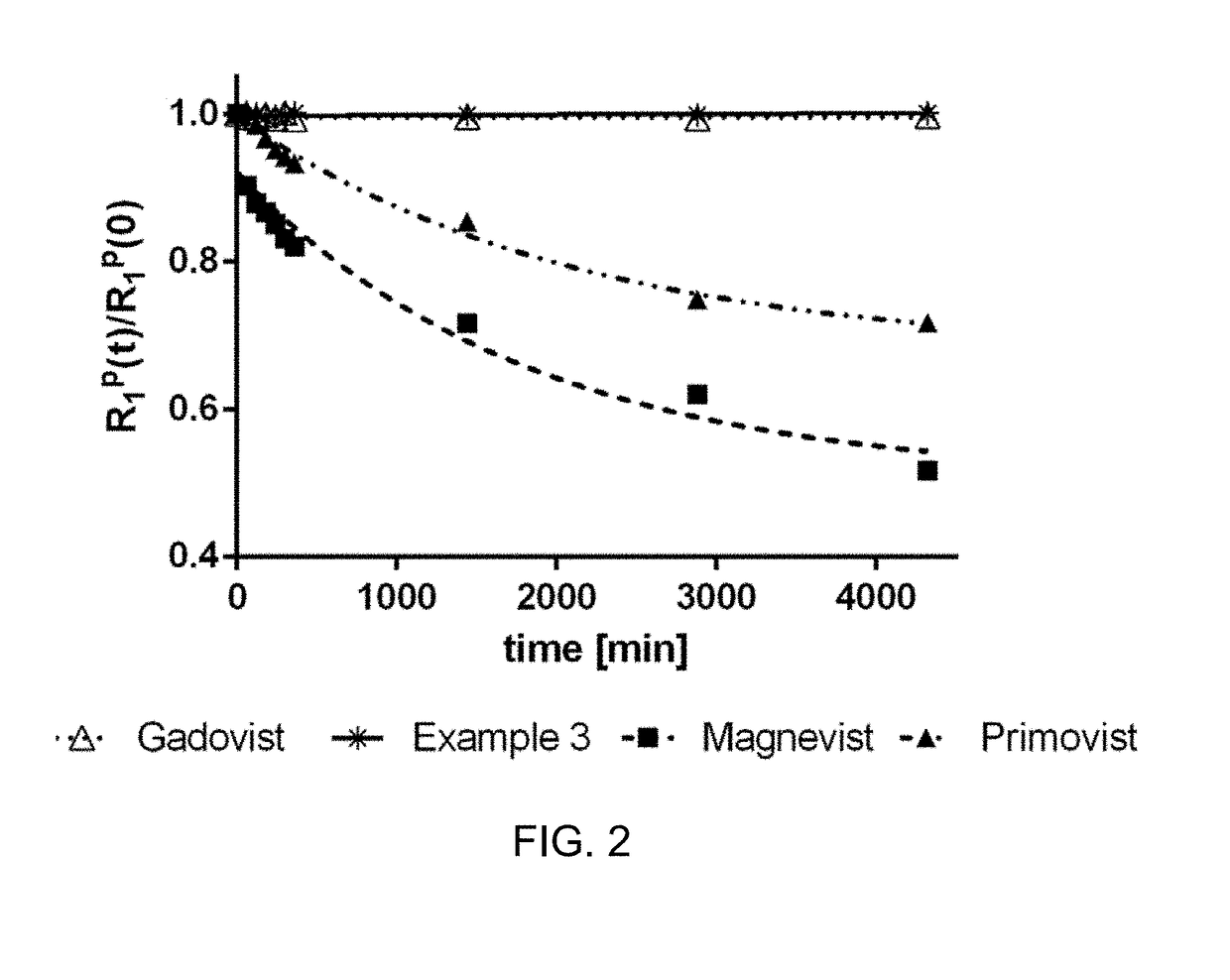
High relaxivity gadolinium chelate compounds for use in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20200283420A1High relaxation rateOrganic chemistryIn-vivo testing preparationsExtracellularMRI contrast agent
The present invention relates to a new class of high relaxivity extracellular gadolinium chelate complexes, to methods of preparing said compounds, and to the use of said compounds as MRI contrast agents.
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
High relaxivity gadolinium chelate compounds for use in magnetic resonance imaging
The present invention relates to a new class of high relaxivity extracellular gadolinium chelate complexes, to methods of preparing said compounds, and to the use of said compounds as MRI contrast agents.
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
Magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111281983AGood biocompatibilityLow toxicityNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryDendrimerEnd-group
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: reacting alpha,omega-biscystamine polyethylene glycol with alpha-cyclodextrin to form pseudopolyrotaxane; then terminating pseudopolyrotaxane with Z-tyrosine to obtain Z-tyrosine terminated polyrotaxane; then reacting the Z-tyrosine terminated polyrotaxane with propargyl carbonylimidazole to form polyrotaxane surface-modified by alkynyl groups and capable of being quickly reduced and cracked; reacting the polyrotaxane surface-modified by alkynyl groups with a lysine second-generation dendrimer with azide as an end group by means of click chemistry so as to form lysine second-generation dendrimer-grafted cleavable polyrotaxane; and bonding the lysine second-generation dendrimer-grafted cleavable polyrotaxane with a gadolinium chelate, and loading gadolinium to form the gadolinium chelate-modified lysine second-generation dendrimer-grafted cleavable polyrotaxane. The magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent is good in biocompatibility, low in toxicity and high in relaxation rate; and in addition, an AS1411 aptameris introduced as a targeting molecule to realize multivalent targeting of tumor cells and tumors with cell membrane overexpression of nucleolin, so in-vivo magnetic resonance imaging of tumors is facilitated.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
A kind of tumor-targeted MRI contrast agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105999308BImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityIn-vivo testing preparationsMRI contrast agentMoiety
The invention provides a tumor-targeted MRI contrast agent and a preparation method thereof, characterized in that: the contrast agent includes a small-molecule gadolinium chelate part and a targeting carrier part, a small-molecule gadolinium chelate part and a target Coupling to the carrier part through a covalent bond; wherein, the small molecule gadolinium chelate part is Gd-DO3A; the targeting carrier part includes EBP molecules. The contrast agent of the present invention has good relaxation enhancement ability, and can be targetedly combined with EGFR of tumor cells, not only has a strong targeted contrast effect, but also prolongs the imaging time of the contrast agent in the body, thereby reducing the contrast agent Adding dosage has strong practicality.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
High relaxivity gadolinium chelate compounds for use in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20210221798A1Organic chemistryIn-vivo testing preparationsMRI contrast agentMagnet resonance imaging
The present invention relates to a new class of high relaxivity extracellular gadolinium chelate complexes, to methods of preparing said compounds, and to the use of said compounds as MRI contrast agents.
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
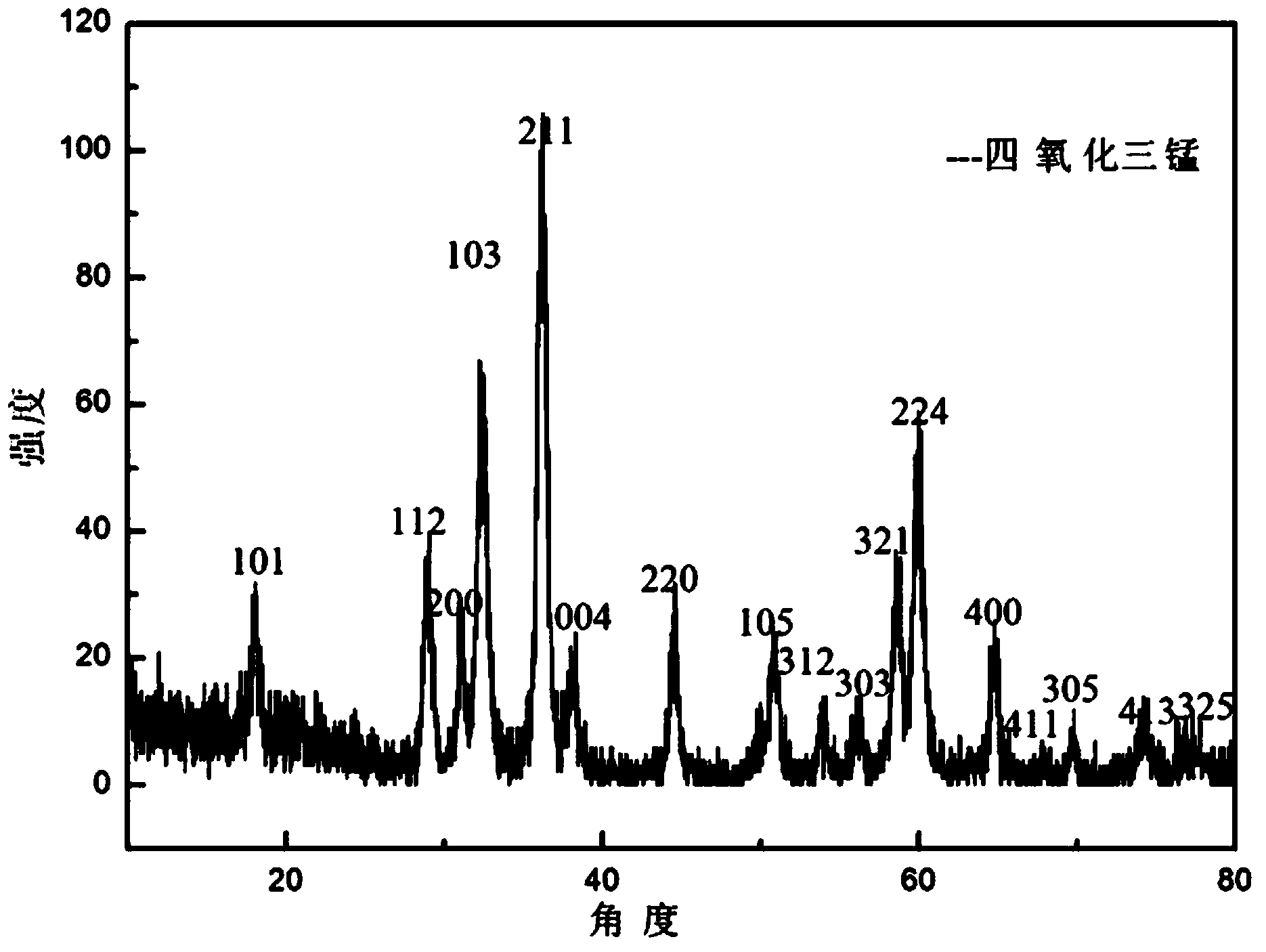
Preparation method and biological application of t1-t1 synergistic gadolinium chelated manganese tetraoxide nanoparticles
ActiveCN102923782BImprove stabilityUniform particle sizeNMR/MRI constrast preparationsSolubilityDiethylenetriamine
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Gadolinium chelate compounds for use in magnetic resonance imaging
A compound having the formula of tetragadolinium [4,10-bis(carboxylatomethyl)-7-{-3,6,12,15-tetraoxo-16-[4,7,10-tris(carboxylatomethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecan-1-yl]-9,9-bis({[{2-[4,7,10-tris(carboxylatomethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecan-1-yl]propanoyl} amino)acetyl]amino}methyl)-4,7,11,14-tetraazaheptadecan-2-yl}-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclo dodecan-1-yl]acetate wherein the stereochemistry at the chiral carbon of the four alanine substituents is selected from the group consisting of RRRR, SSSS, RSSS, RRSS, and RRRS stereoisomers, and racemic and diastereomeric mixtures of any thereof, or a tautomer, a hydrate, a solvate, or a salt thereof, or a mixture of same is described. The compounds may be used as an MRI contrast imaging agent.
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
Composition and method or recovering rare-earth elements
Disclosed is a method for recycling metal-chelates by separating the metal or metal ion from the chelate by forming a metal salt or metal precipitate apart from the chelator. In various embodiments, gadolinium-chelates, which are used as MM contrast agent and which create vial hold-up material that is otherwise discarded, are acid or solvent treated to promote separation of the gadolinium from the chelate for downstream sale or further processing.
Owner:STOCKMANN BRADLEY
MRI contrast agent with chitosan derivative as carrier and preparation method
ActiveCN106139166BGood biocompatibilityEasily biodegradableIn-vivo testing preparationsDendrimerMRI contrast agent
The invention discloses an MRI contrast agent with a chitosan derivative as a carrier and a preparation method thereof. The contrast agent comprises: polyethylene glycol-modified chitosan as the main body of the contrast agent; and a second-generation polyamidoamine dendrimer molecule mainly connected to the chitosan main chain with a gadolinium chelate; its preparation The method comprises: first providing polyethylene glycol-modified chitosan, then coupling the chelating ligand of gadolinium to the alkyne-modified second-generation polyamidoamine dendrimer, and then linking it to the chitosan, The contrast agent is obtained. The MRI contrast agent with the chitosan derivative as a carrier has good biocompatibility, is easy to biodegrade, and has a high relaxation rate. The preparation method is simple, the required reaction temperature is moderate, and it is easy to control.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Contrast agent, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111265674AGood application effectRealize one-stop comprehensive evaluationNMR/MRI constrast preparationsOn/in inorganic carrierPharmaceutical drugHematological test
The invention provides a contrast agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Erythrocyte in blood is used as a matrix, by loading the gadolinium chelate onto red blood cells by a hypotonic precipitation method, a novel electroporation method, a drug induction method and a drug induction method under a hypotonic condition, the gadolinium chelate has the advantages that the volume of the gadolinium chelate is increased, the migration of the gadolinium chelate to the outside of a blood vessel is blocked, the technical problem that an existing magnetic resonance contrast agentis easy to migrate to a gap outside the blood vessel is solved, and the contrast agent has wide application in the fields of magnetic resonance imaging and imaging.
Owner:THE FOURTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHEJIANG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
A tumor-targeted gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and its preparation method
ActiveCN111643684BGood biocompatibilityGood low toxicityIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetingEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a preparation method of a gadolinium-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent with tumor targeting and its biomedical application. The contrast agent can specifically bind to transferrin receptor 1 highly expressed on the surface of tumor cells, is composed of genetically engineered recombinant protein and gadolinium chelate, and has a higher activity than the commercial contrast agent Magnevist (Gd-DTPA). longitudinal relaxation rate. The present invention provides a comparison of the imaging effects of animal tumor models with Magnevist, indicating that the contrast agent in the present invention can achieve tumor-specific recognition and longer-term magnetic resonance imaging at a lower injection dose without repeated injections. The contrast agent in the present invention can be administered intravenously, and is applied to the early diagnosis of cancer, the further identification of tumor metastasis and the diagnosis of suspicious recurrence after operation.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and biological application of T1-T1 synergistic effect gadolinium chelate manganous-manganic oxide nano particle
ActiveCN102923782AImprove stabilityUniform particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologyNMR/MRI constrast preparationsSolubilityProton magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a preparation method and biological application of T1-T1 synergistic effect gadolinium chelate manganous-manganic oxide nano particles. The preparation method and the biological application of the T1-T1 synergistic effect gadolinium chelate manganous-manganic oxide nano particles include that firstly manganeseacetylacetonate is combined, and then oleylamine is used as a solvent, a high-temperature pyrolysis method is used to combine oil solubility manganous-manganic oxide nano particles, and then a ligand exchange method is utilized to use alendronate to be exchanged on the surfaces of the manganous-manganic oxide nano particles, so that nano particles are formed, wherein the surfaces of the nano particles are provided with a large number of amino groups. Then, the surfaces of the amino groups are connected with diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid, so that the surfaces of the nano particles are provided with a large number of carboxyl groups, and at last a chelate effect is utilized to enable the large number of carboxyl groups and gadolinium to be chelated. Therefore, gadolinium chelate manganous-manganic oxide nano particles are obtained. The preparation method is low in requirement for equipment, convenient for operated process, low in needed raw material cost, and nuisanceless in accessory products. And at last through in vitro and in vivo magnetic resonance imaging experimental testing, so that compared with independent manganese and independent gadolinium, T1 magnetic resonance imaging contrast effect is strengthened.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for contrast medium intermediate for medical diagnosis
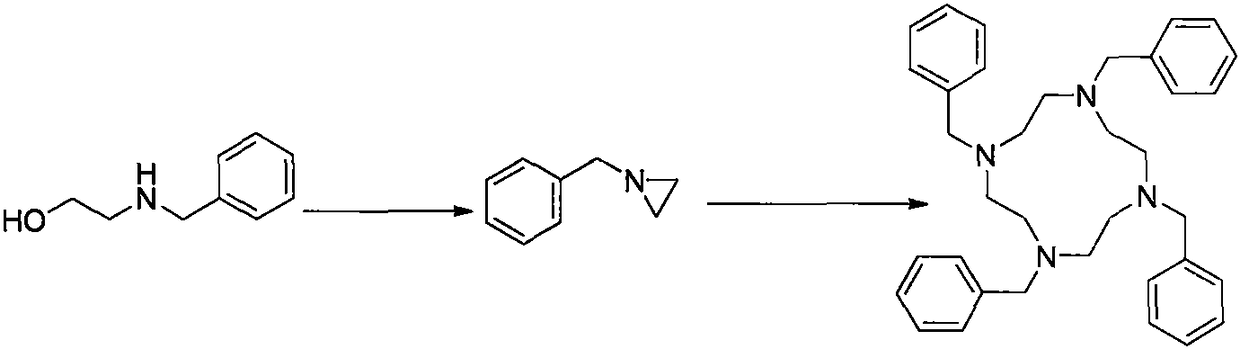
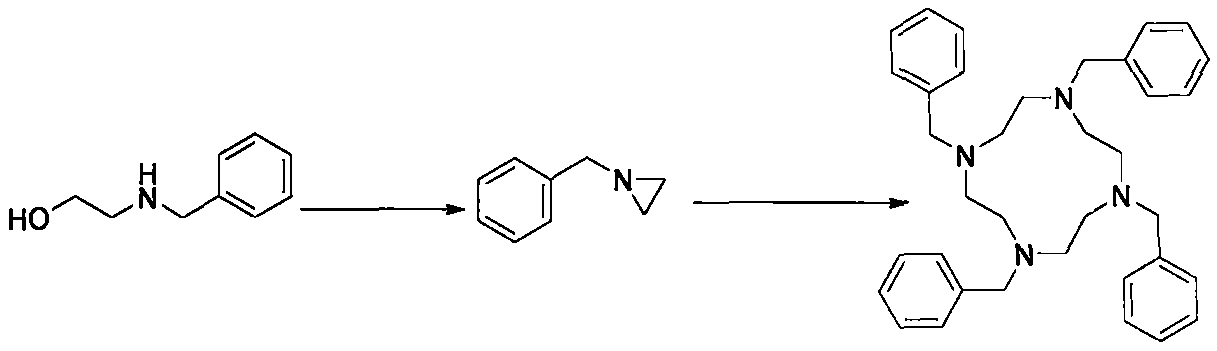
The invention discloses a preparation method for a contrast medium intermediate for medical diagnosis, and the intermediate is a key intermediate for macromolecule gadolinium chelate contrast medium.According to the method, benzylethanolamine is adopted as a starting raw material, and the product N',N'',N''',N''''-tetraazacyclododecane is obtained through backflow water diversion, sulfonation andpolymerization reaction. According to the method, methylbenzene, water and methyl alcohol are all recycled, resource saving and the environmental-friendly function are realized, the cost is saved, the product is stable in quality and high in yield, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial stable production.
Owner:XUCHANG HENGSHENG PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com