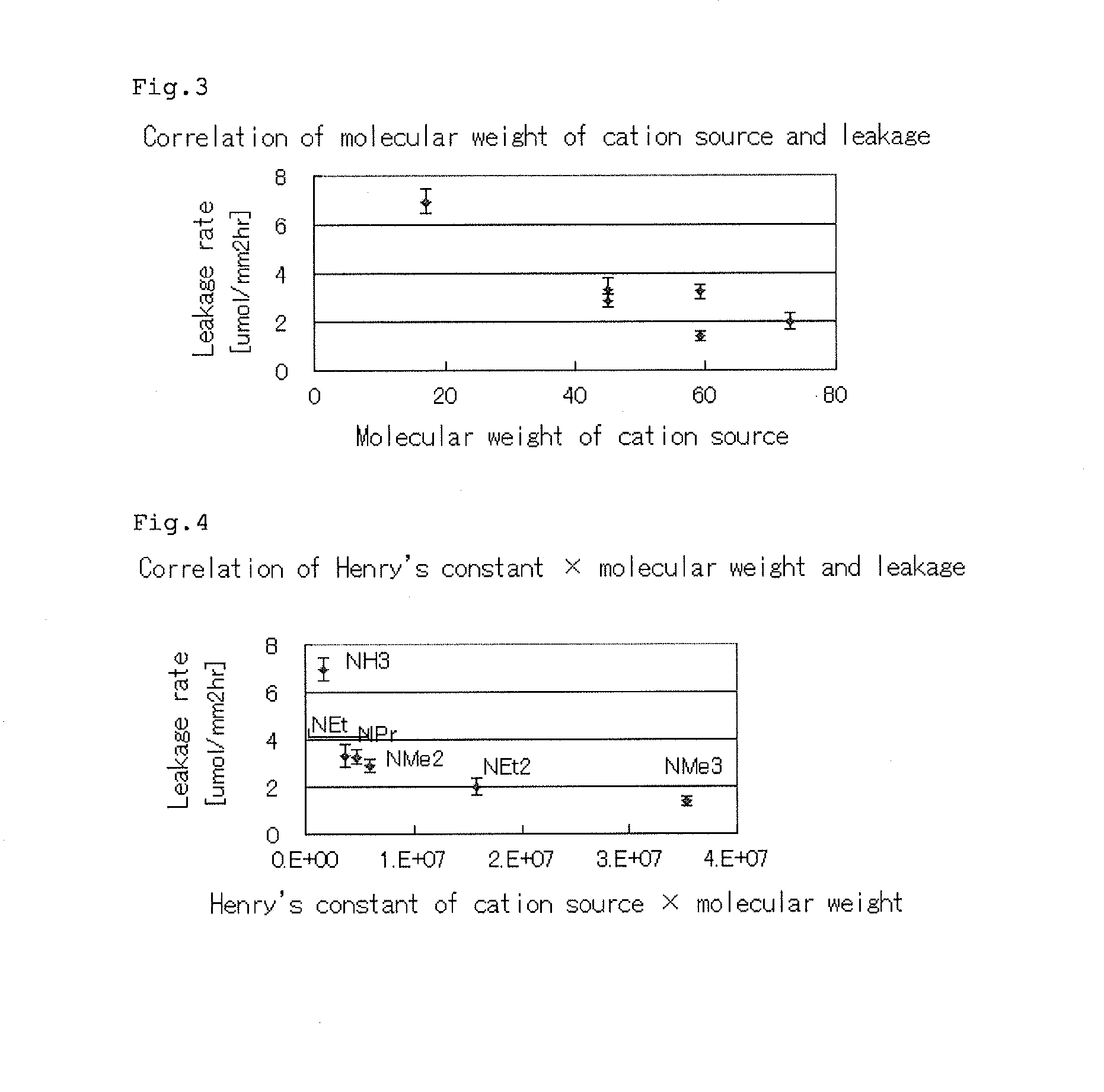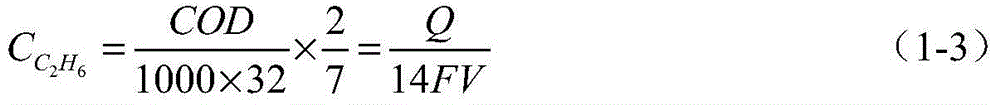Patents
Literature
30 results about "Henry's law" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physical chemistry, Henry's law is a gas law that states that the amount of dissolved gas in a liquid is proportional to its partial pressure above the liquid. The proportionality factor is called Henry's law constant. It was formulated by the English chemist William Henry, who studied the topic in the early 19th century. In his publication about the number of gases absorbed by water, he described the results of his experiments...
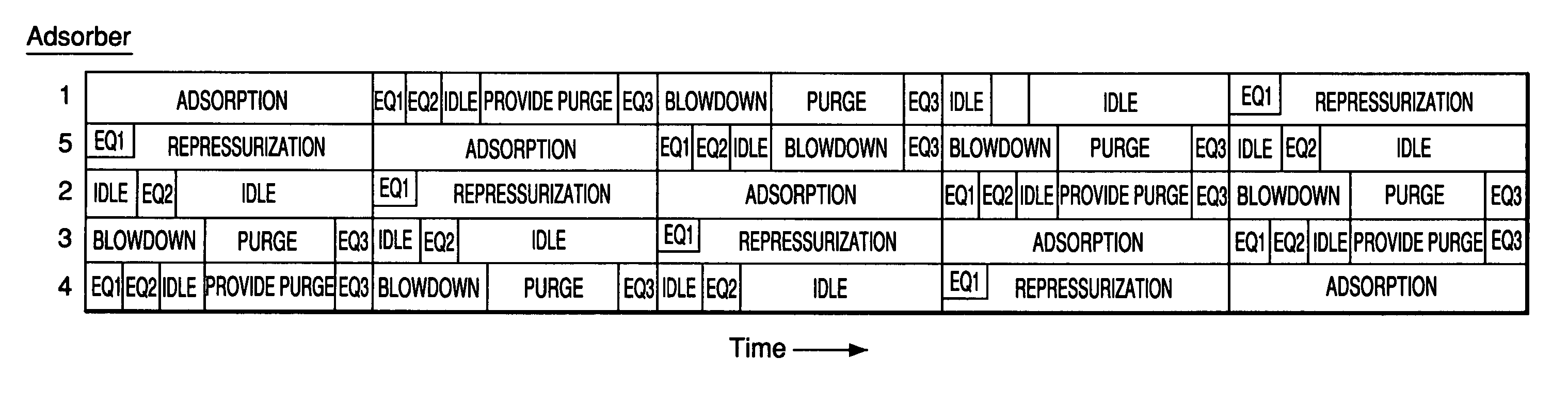
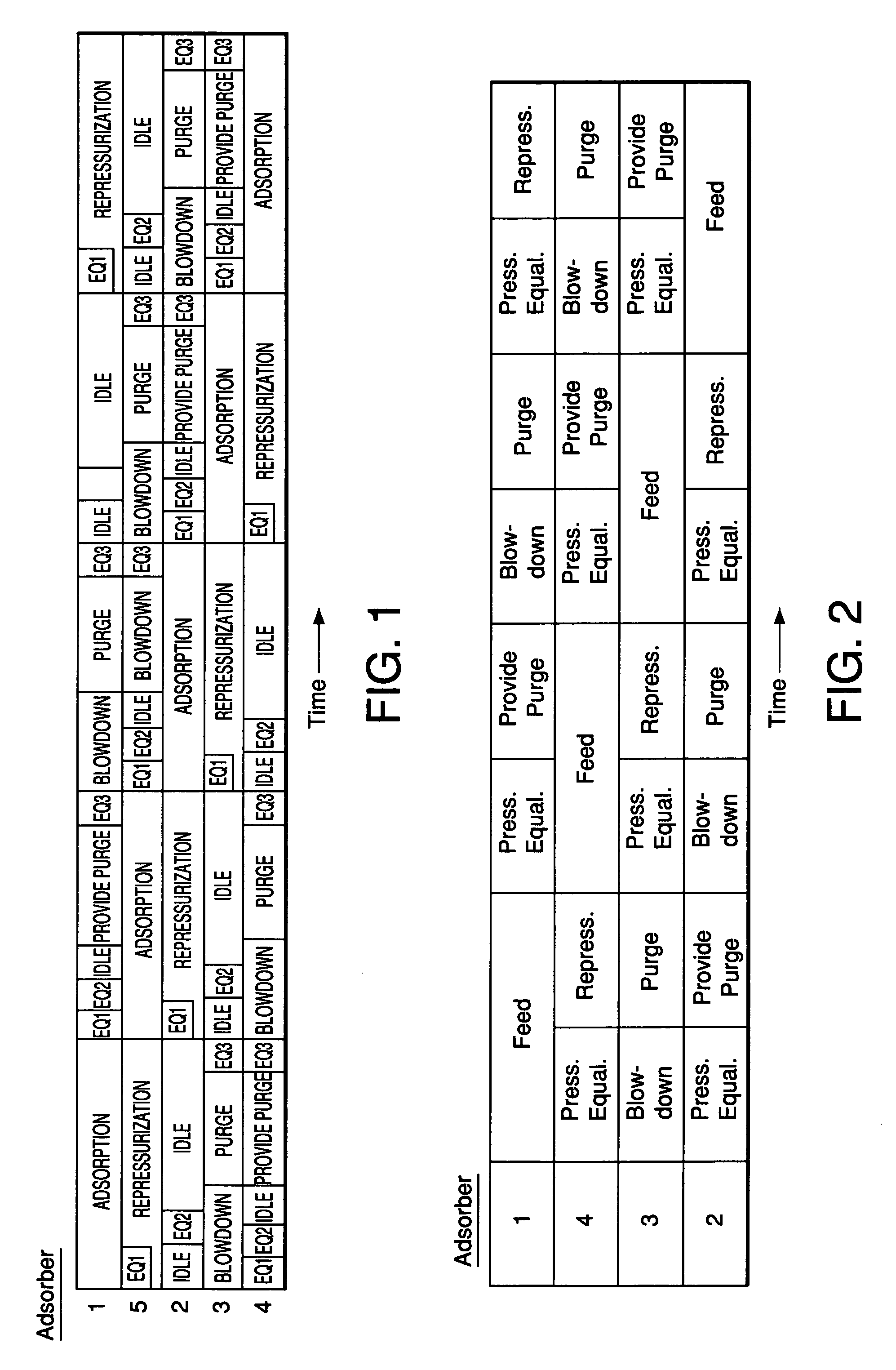
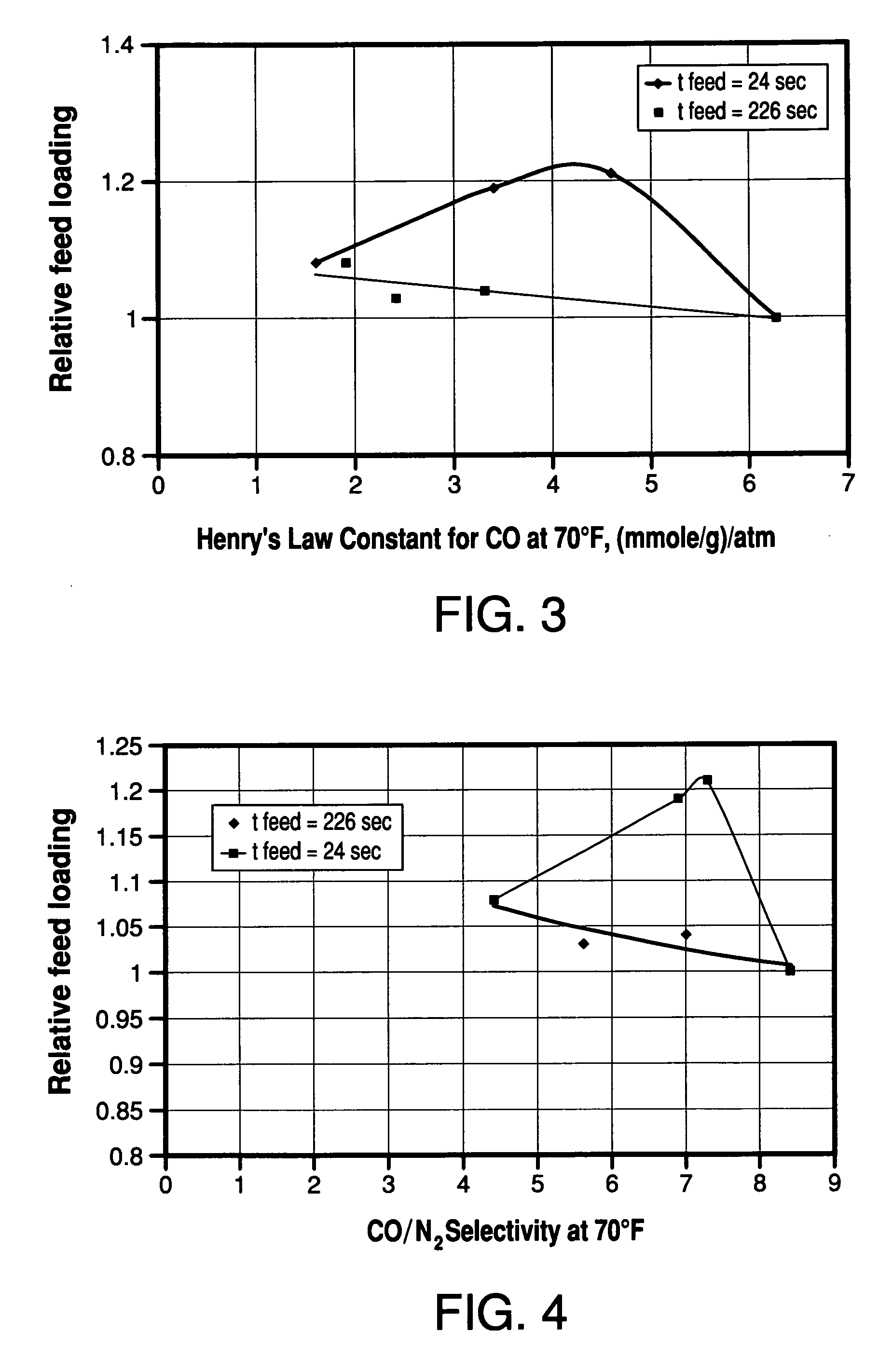
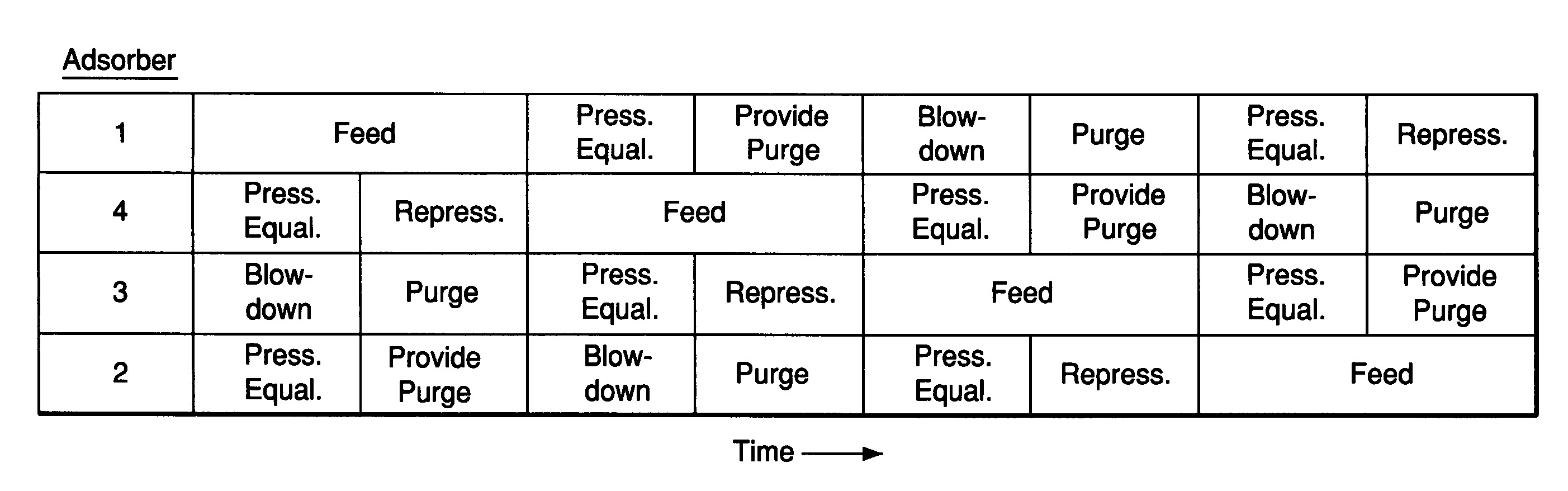
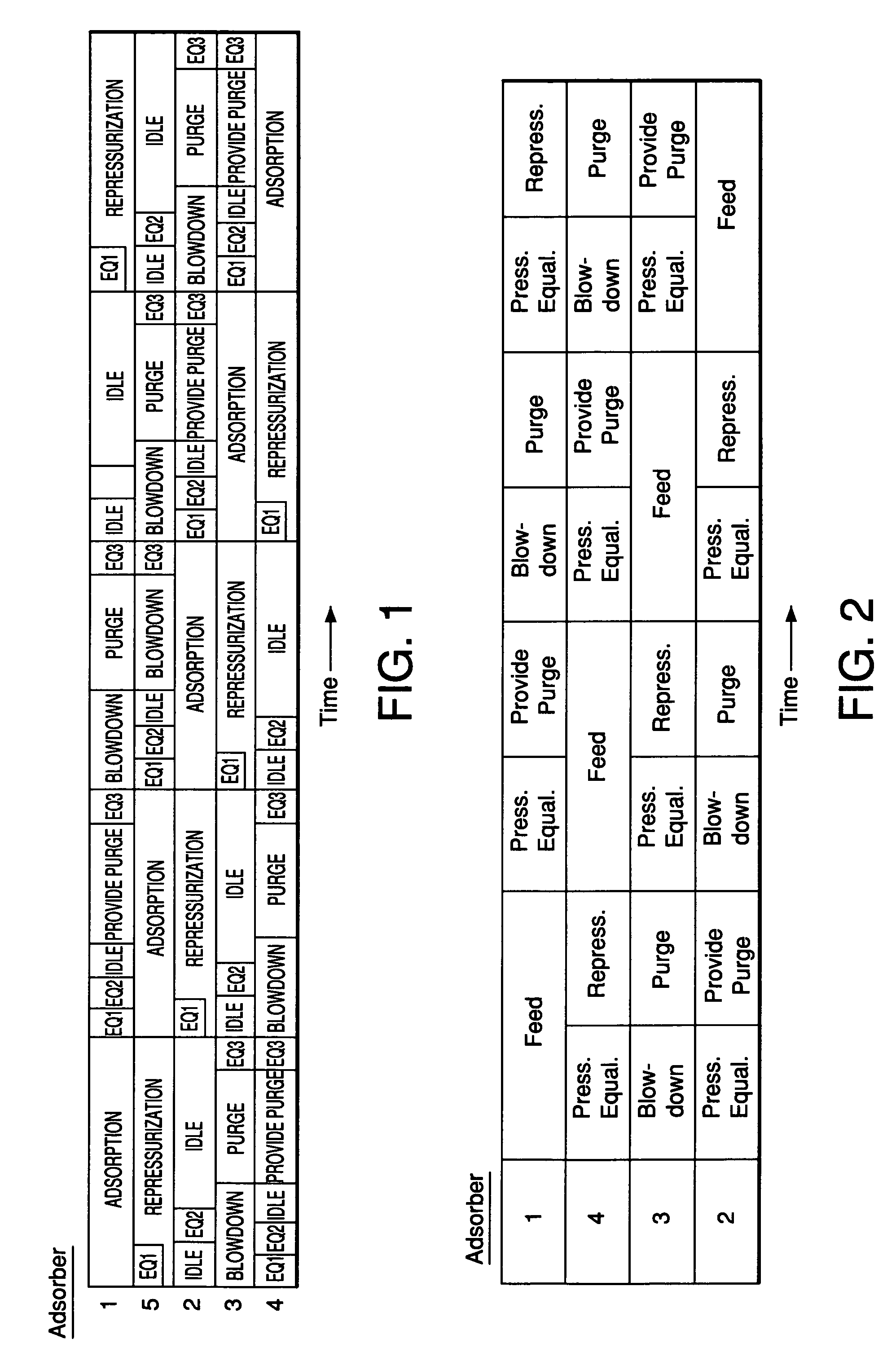
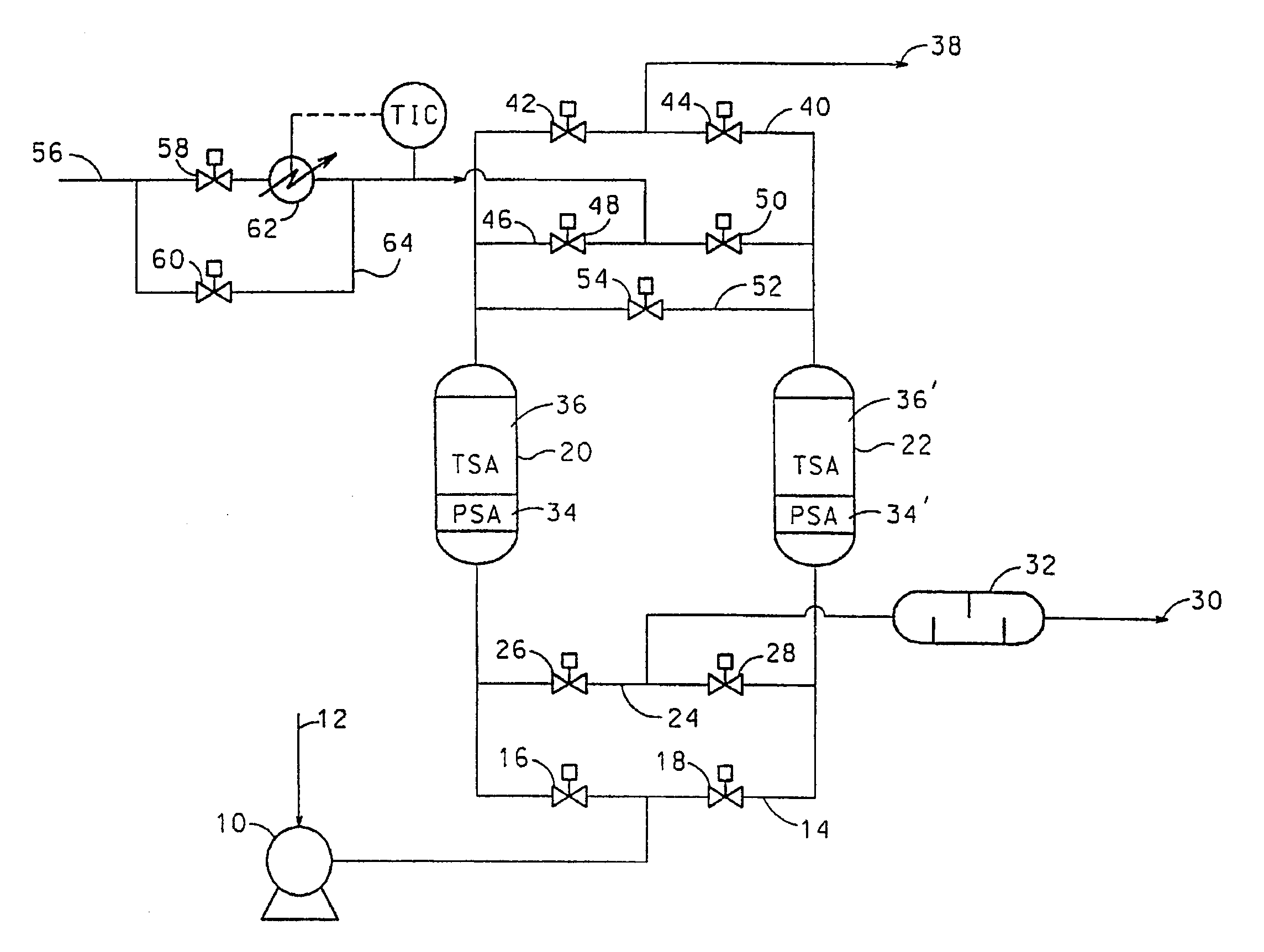
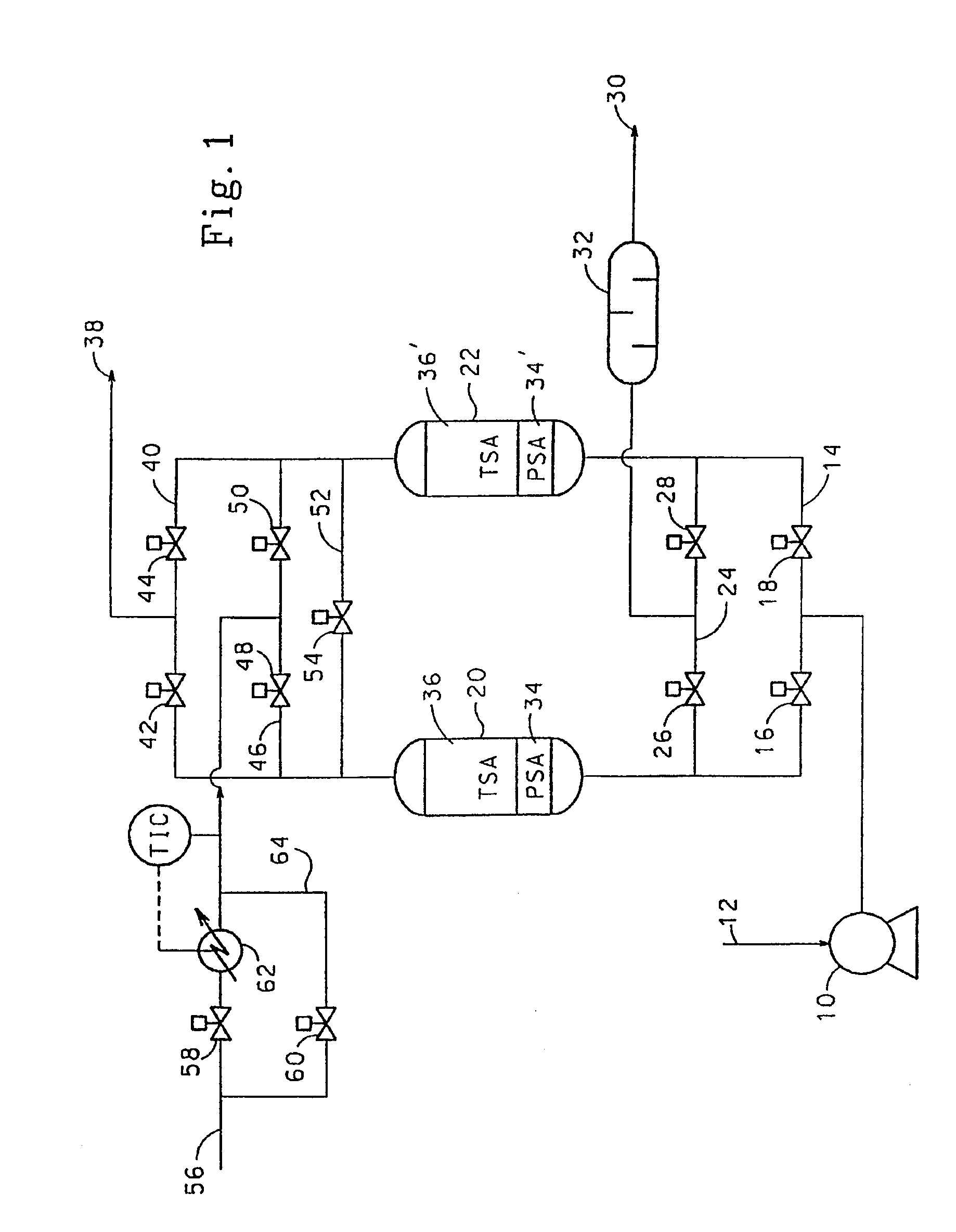
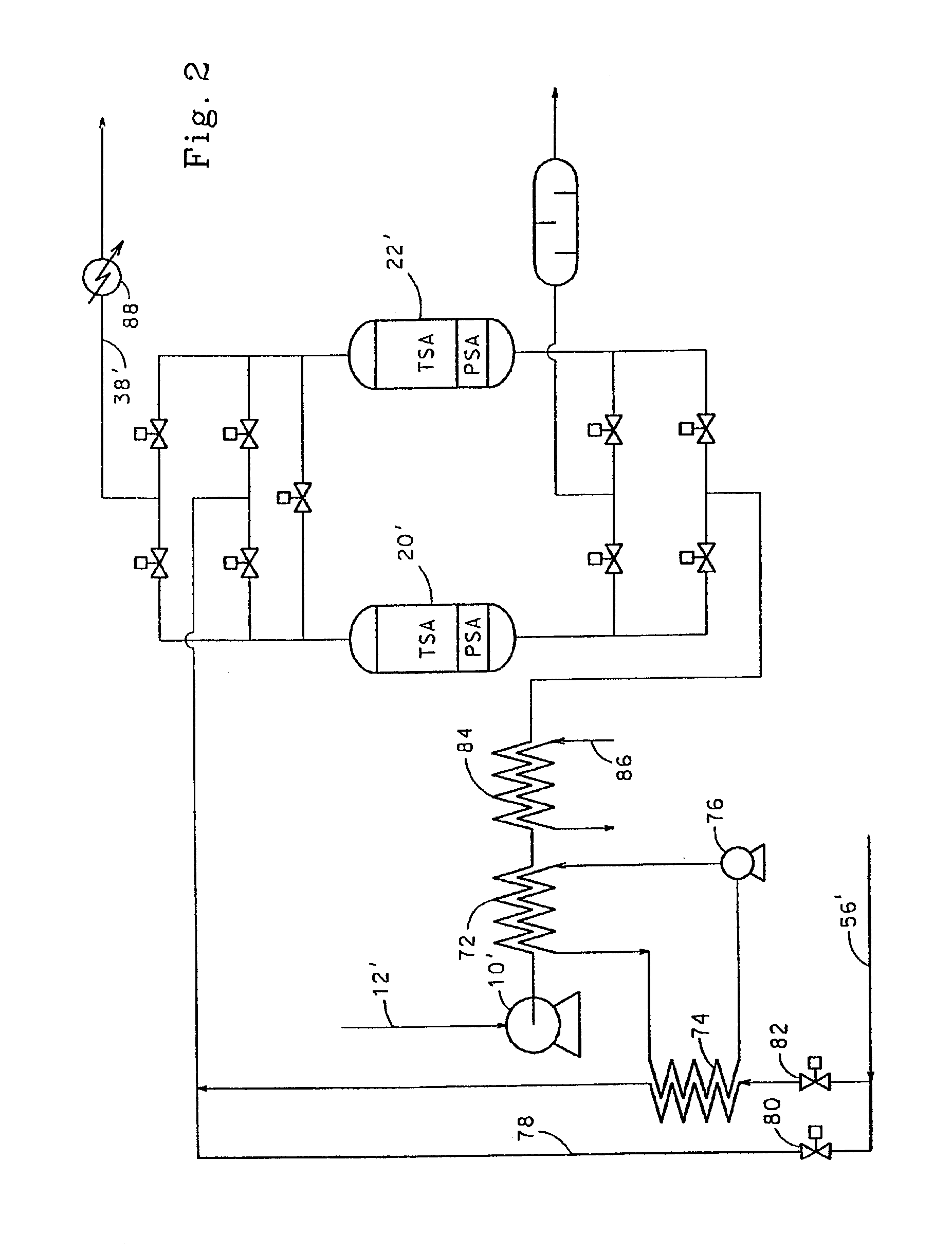
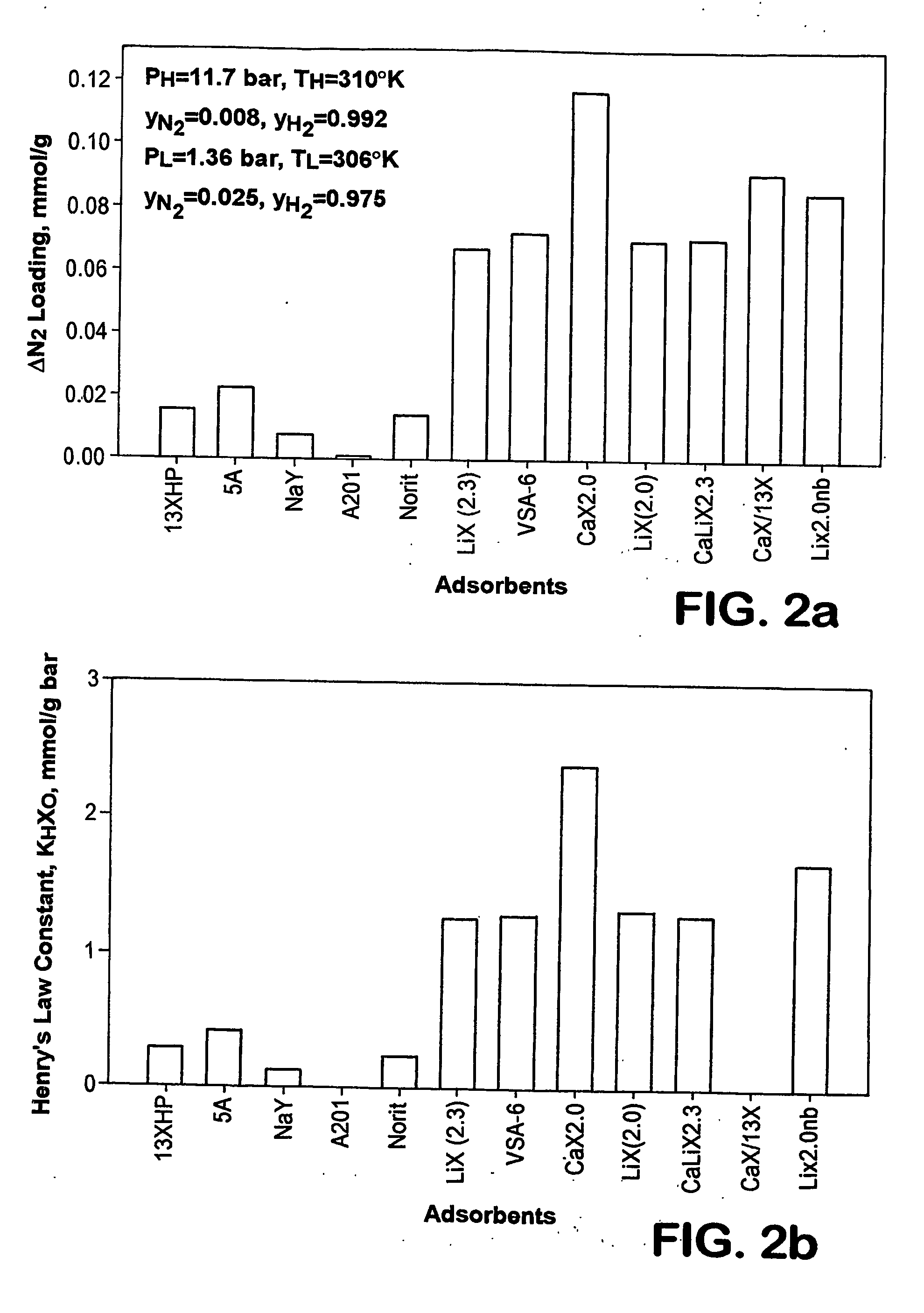
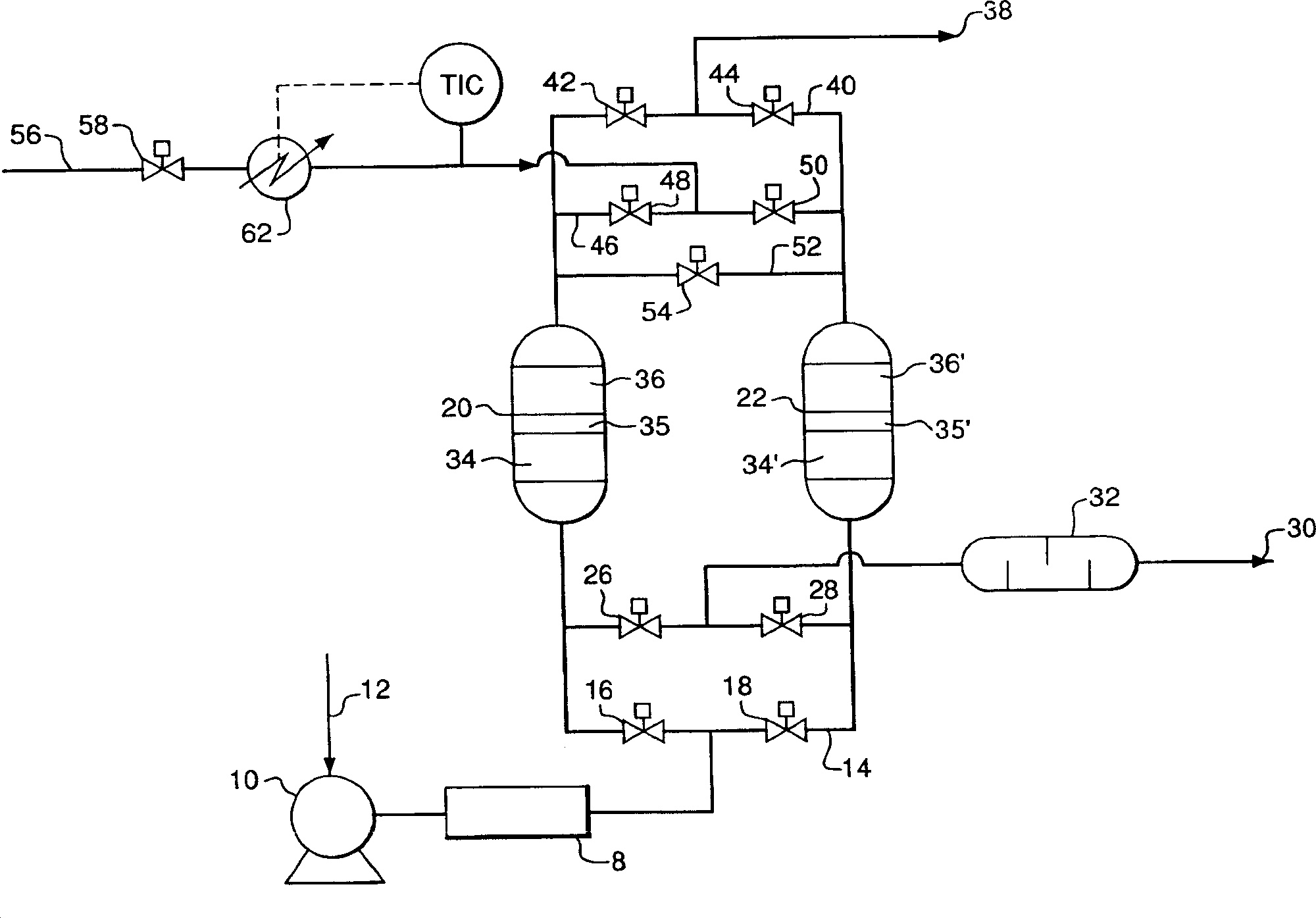
Adsorbents for rapid cycle pressure swing adsorption processes
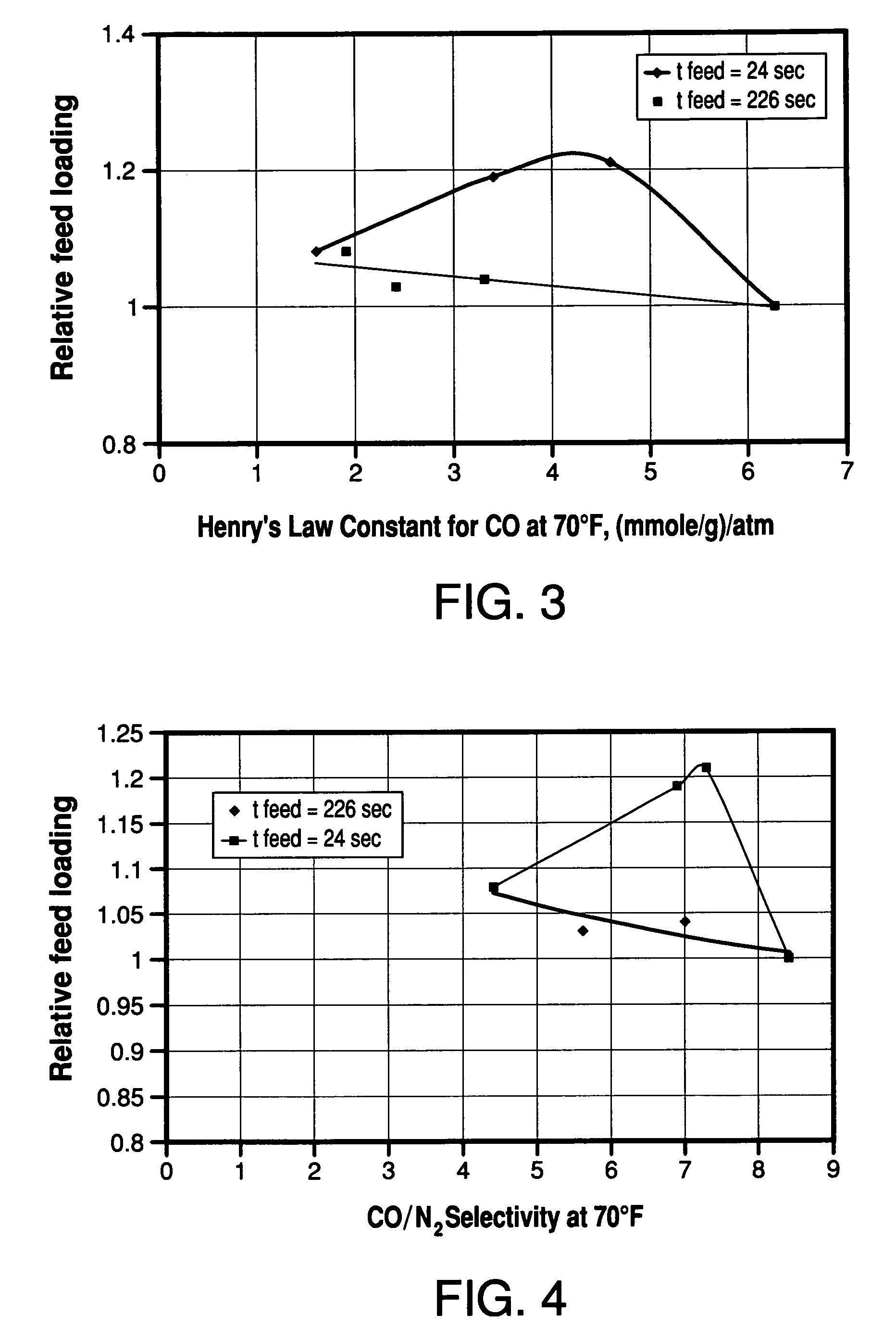
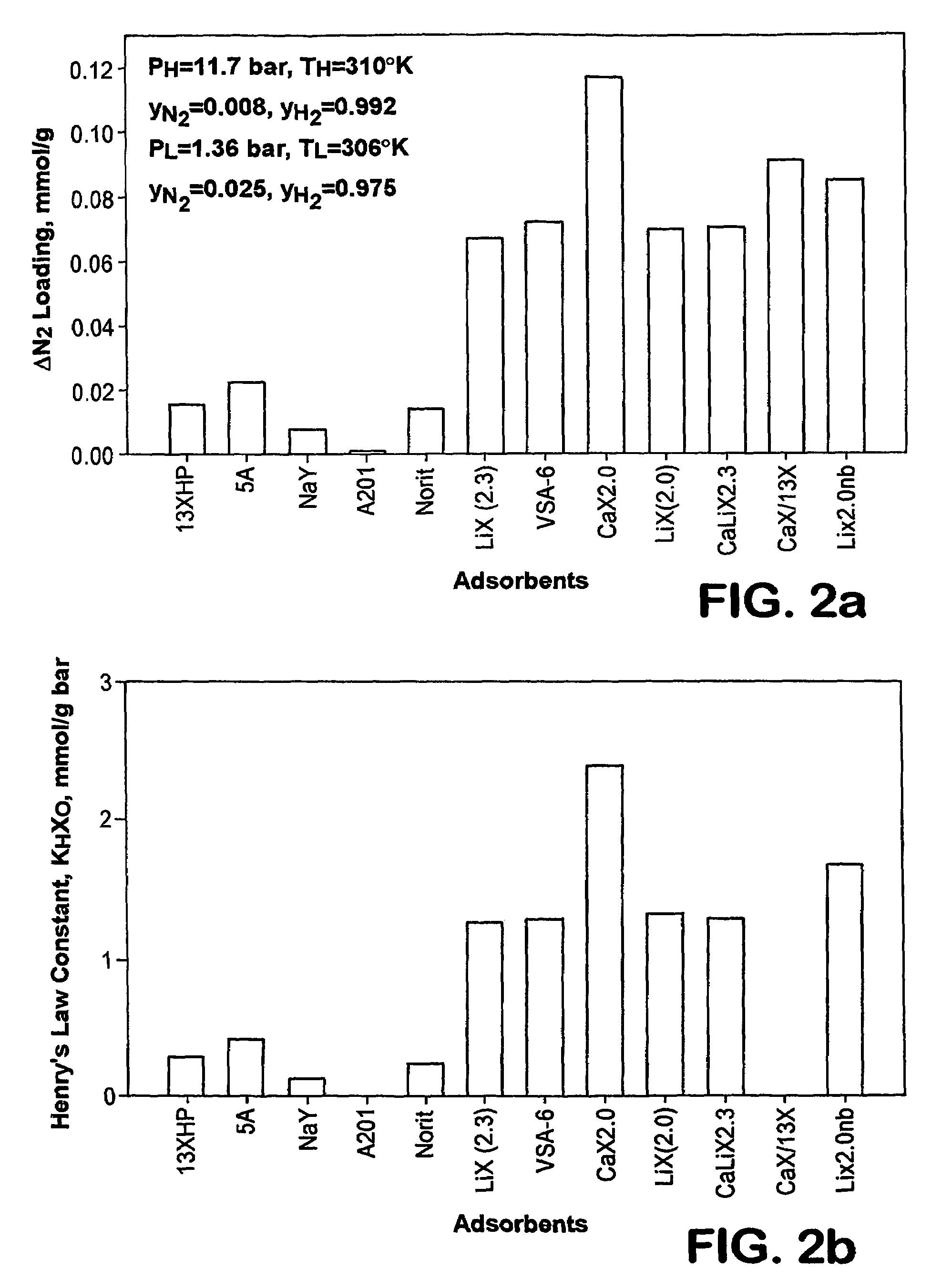
Method for the separation of a gas mixture comprising providing a PSA system with at least one adsorber vessel containing adsorbent material that is selective for the adsorption of carbon monoxide and nitrogen, passing a feed gas mixture containing at least hydrogen and carbon monoxide and optionally containing nitrogen through the adsorbent material in a feed step and withdrawing a purified hydrogen product from the adsorber vessel, wherein the feed step has a duration or feed time period of about 30 seconds or less. The adsorbent material is characterized by any of (1) a Henry's law constant for carbon monoxide between about 2.5 and about 5.5 (mmole / g) / atm; (2) a carbon monoxide heat of adsorption between about 6.0 and about 7.5 kcal / gmole; (3) a Henry's law constant for nitrogen greater than about 1.5 (mmole / g) / atm; and (4) a selectivity of carbon monoxide to nitrogen between about 5.0 and about 8.0.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Adsorbents for rapid cycle pressure swing adsorption processes
Method for the separation of a gas mixture comprising providing a PSA system with at least one adsorber vessel containing adsorbent material that is selective for the adsorption of carbon monoxide and nitrogen, passing a feed gas mixture containing at least hydrogen and carbon monoxide and optionally containing nitrogen through the adsorbent material in a feed step and withdrawing a purified hydrogen product from the adsorber vessel, wherein the feed step has a duration or feed time period of about 30 seconds or less. The adsorbent material is characterized by any of (1) a Henry's law constant for carbon monoxide between about 2.5 and about 5.5 (mmole / g) / atm; (2) a carbon monoxide heat of adsorption between about 6.0 and about 7.5 kcal / gmole; (3) a Henry's law constant for nitrogen greater than about 1.5 (mmole / g) / atm; and (4) a selectivity of carbon monoxide to nitrogen between about 5.0 and about 8.0.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
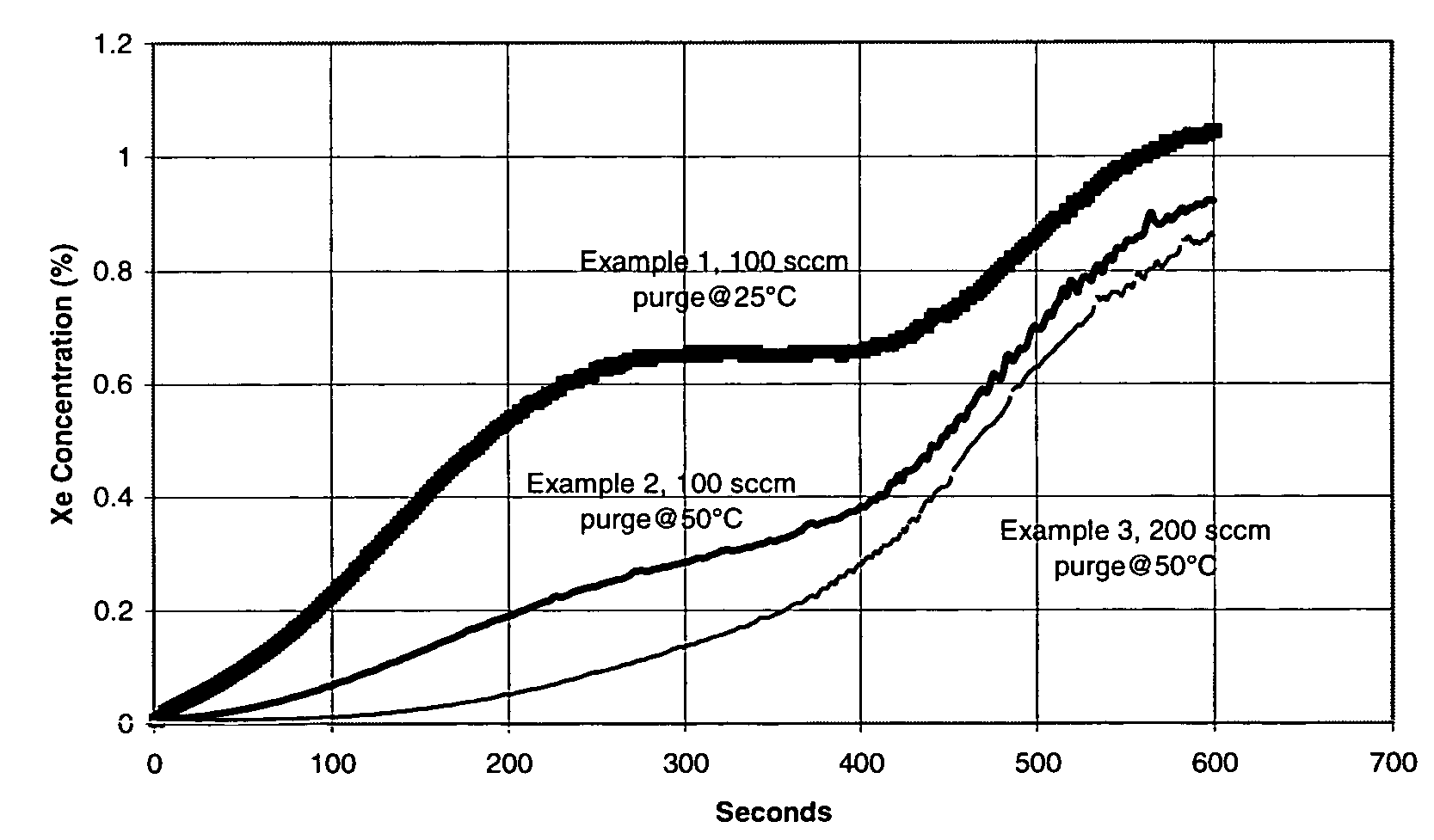
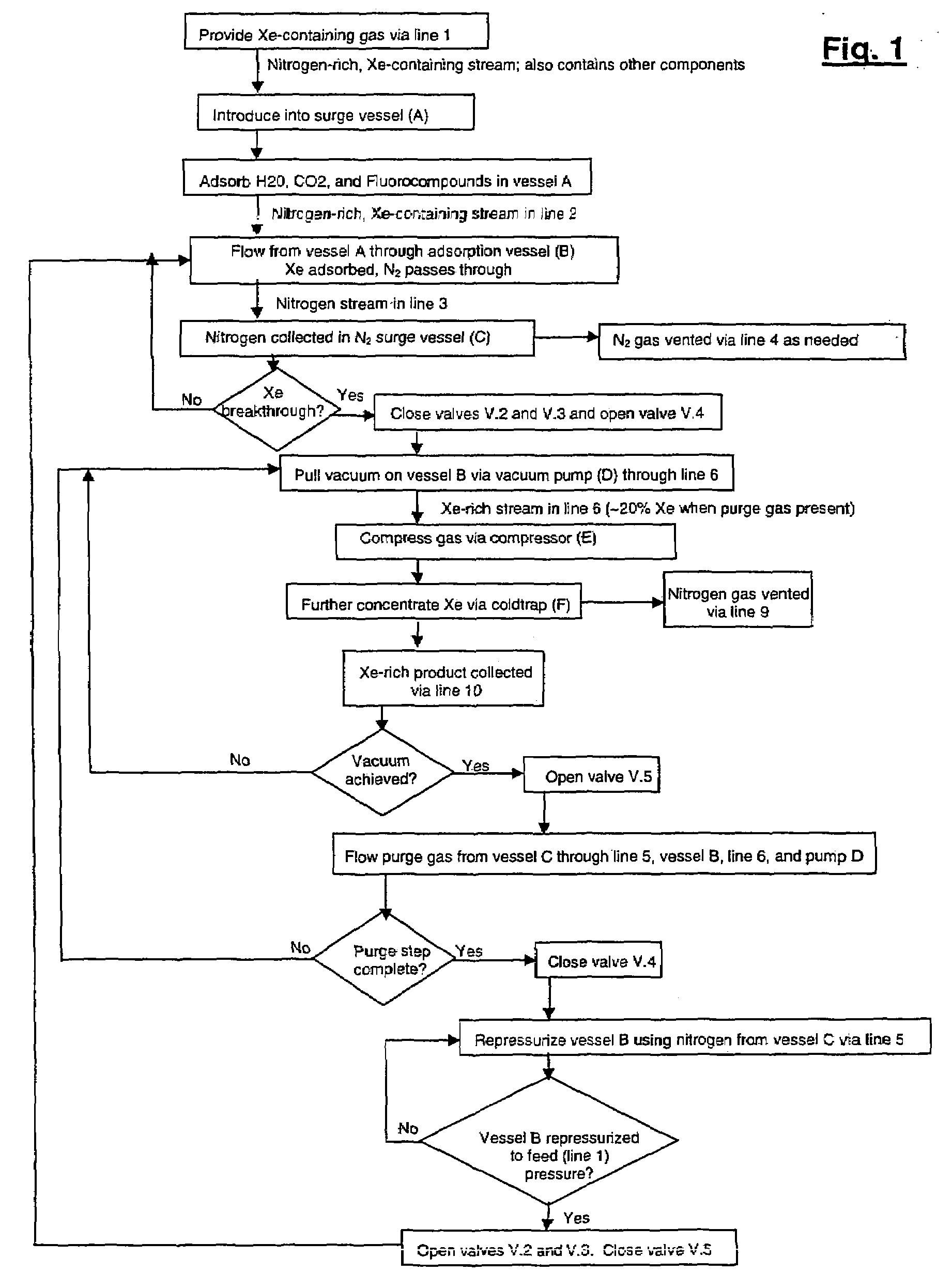
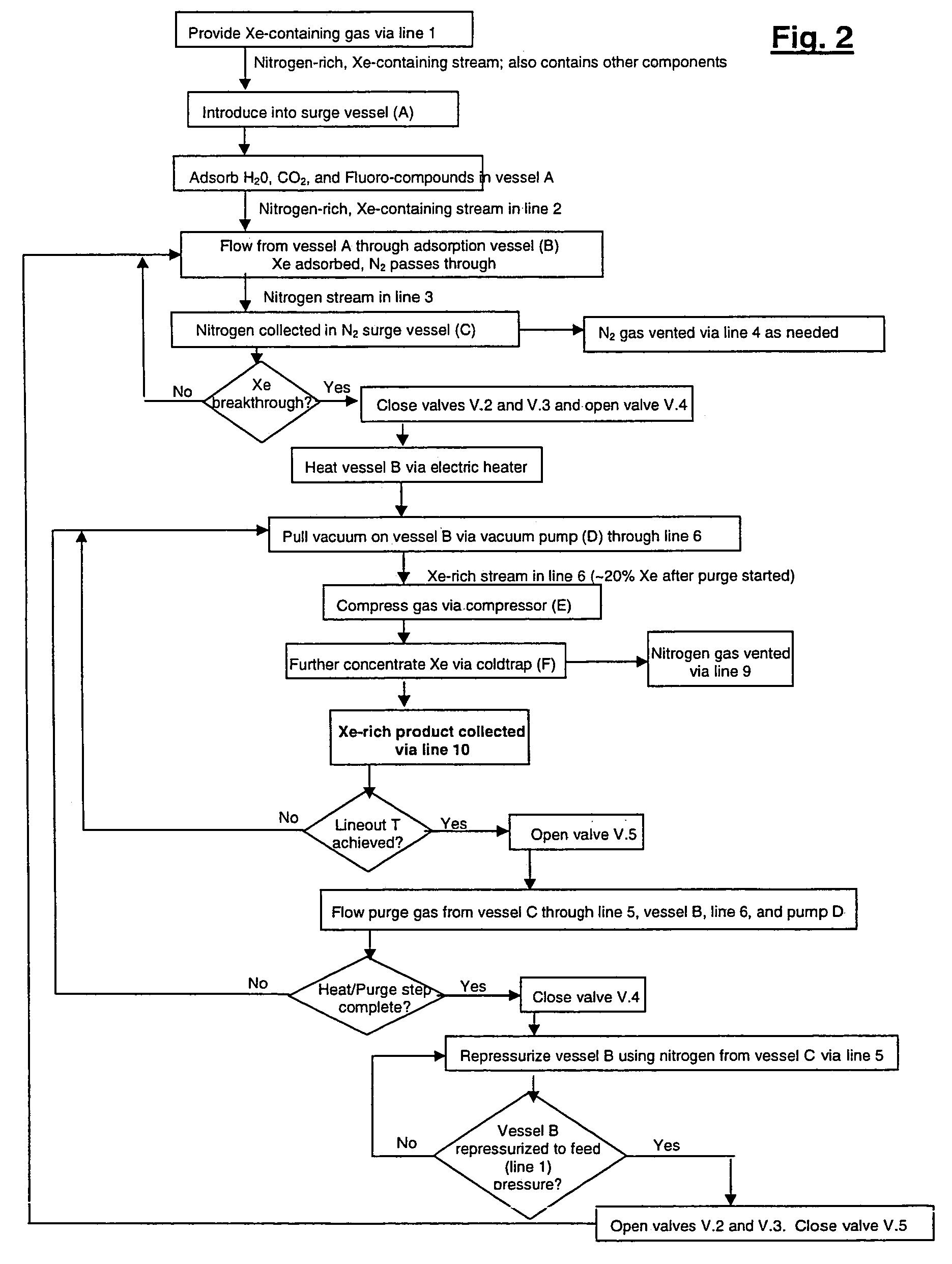
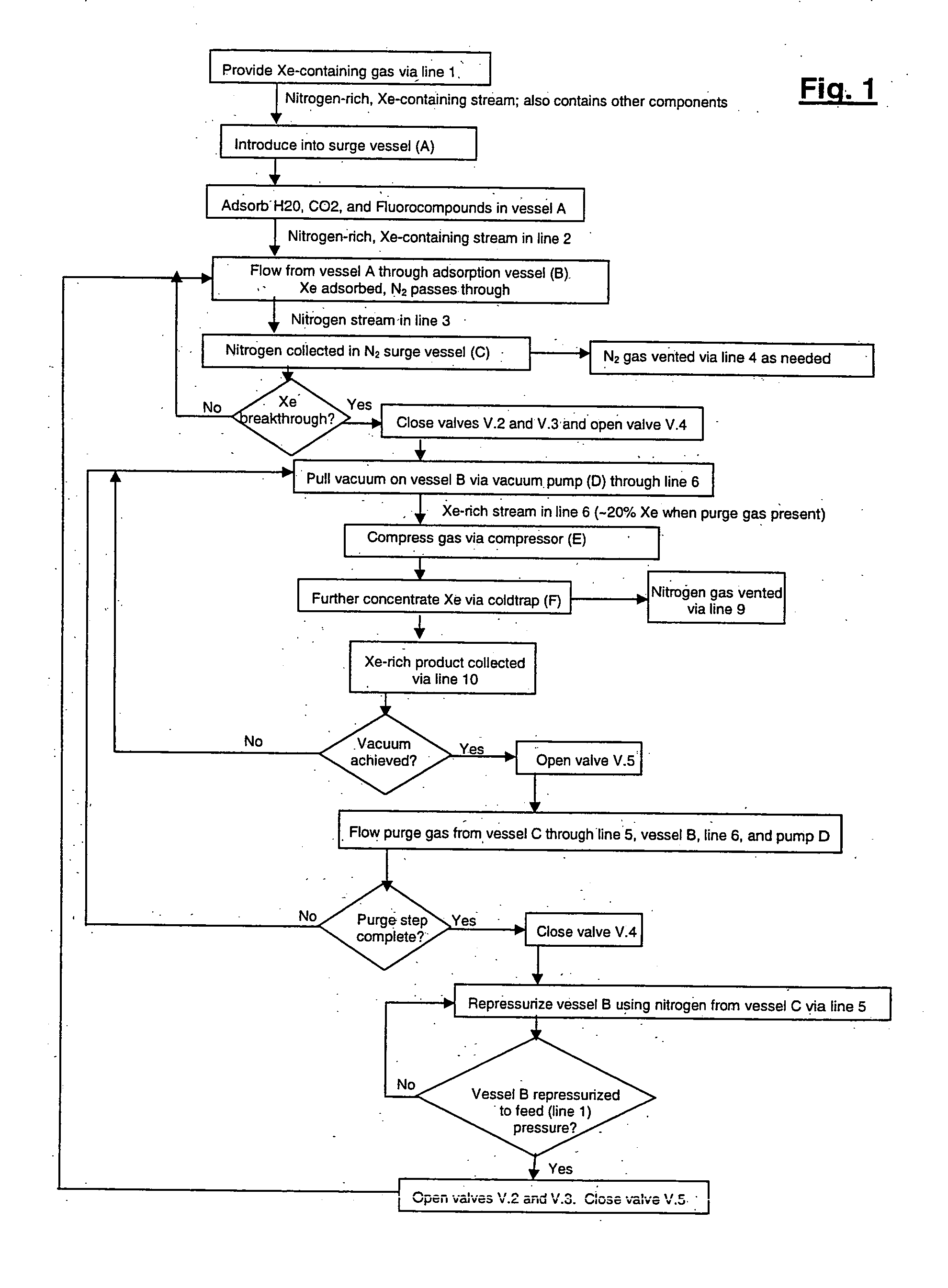
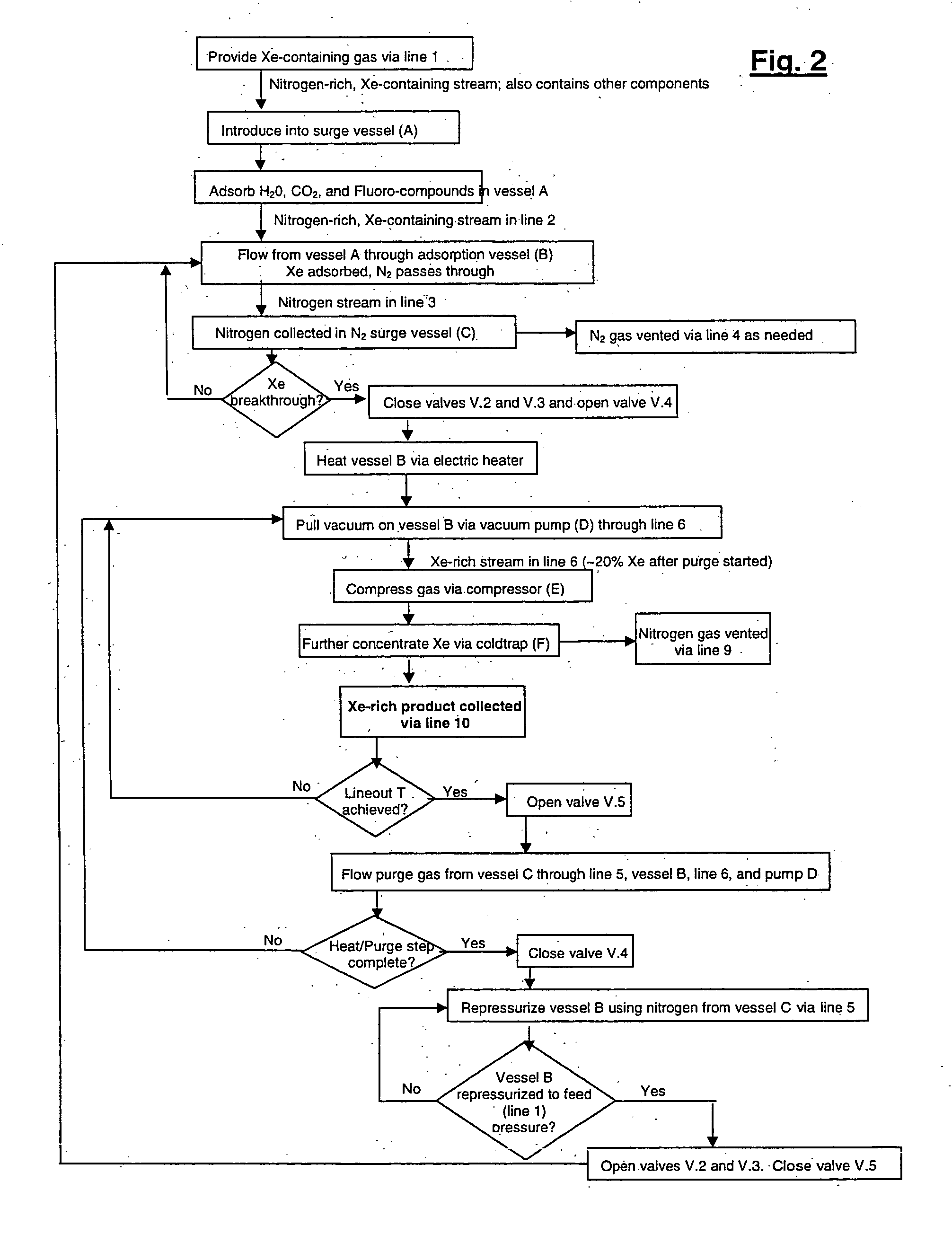
Xenon recovery system
A first aspect of a process of recovering xenon from feed gas includes: providing an adsorption vessel containing adsorbent having a Xe / N2 selectivity ratio <75; feeding into the adsorption vessel feed gas having an initial nitrogen concentration >50% and an initial xenon concentration ≧0.5%; evacuating the adsorption vessel; and purging the adsorption vessel at a purge-to-feed ratio ≧10. The final xenon concentration is ≧15× the initial xenon concentration. A second aspect of the process includes providing an adsorption vessel containing adsorbent having a Xe Henry's law Constant ≧50 mmole / g / atm; feeding into the adsorption vessel feed gas having an initial nitrogen concentration >50% and an initial xenon concentration ≧0.5%; heating and purging the adsorption vessel to recover xenon having a final concentration ≧15× its initial concentration. Apparatus for performing the process are also described.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Purification of air
ActiveUS8734571B2Large capacitySmall sizeNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentFeed temperatureChemistry
Reduction of water, CO2 and N2O in an air stream comprising: passing said air stream at a feed temperature through a first adsorbent, whose Henry's Law selectivity for CO2 / N2O is at least 12.5, and a second adsorbent, whose Henry's Law constant for CO2 is less than 1020 mmol / g / atom and whose Henry's Law selectivity for CO2 / N2O is at most 5; and passing a heated regenerating gas at a temperature which is between 20° C. and 80° C. to at least the second adsorbent, and passing a second regenerating gas at a temperature less than the temperature of the heated regenerating gas to the first and second adsorbents in a direction opposite to the feed direction; the second adsorbent occupying from 25% to 40% of the total volume of the adsorbents, and the temperature of the heated regenerating gas being 10° C. to 60° C. higher than the feed temperature.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Process and apparatus for hydrogen purification
ActiveUS20060254425A1Reduce the overall heightReduce concentrationOrganic chemistryNitrogen compoundsHydrogenSorbent
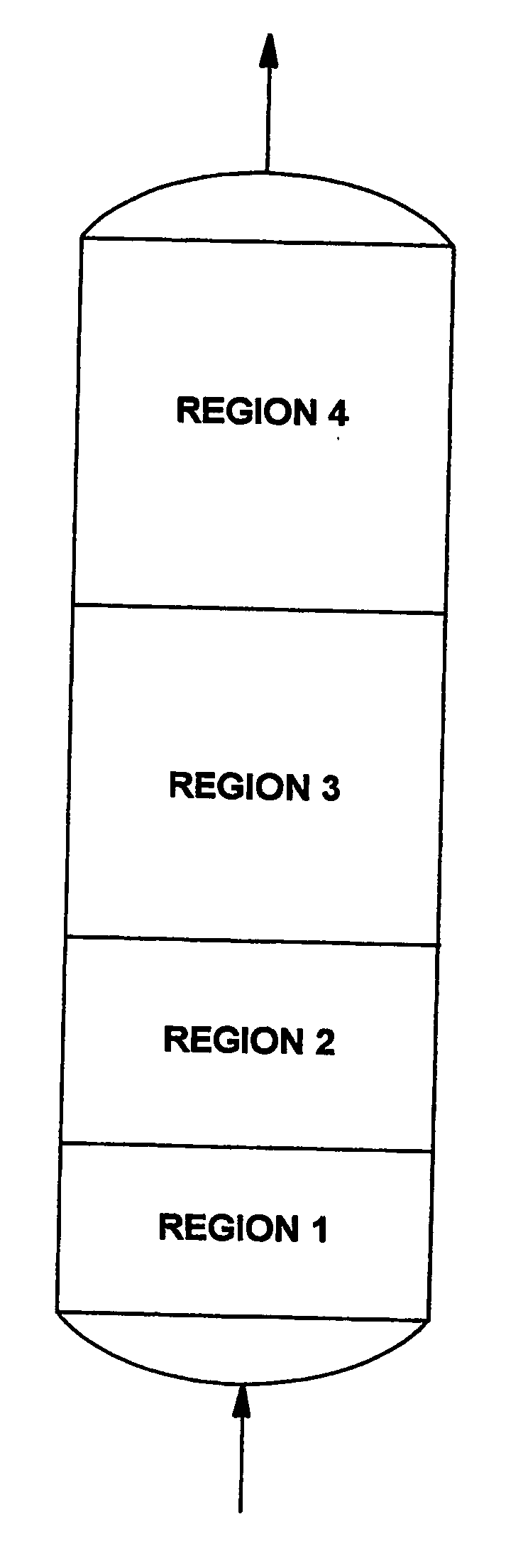
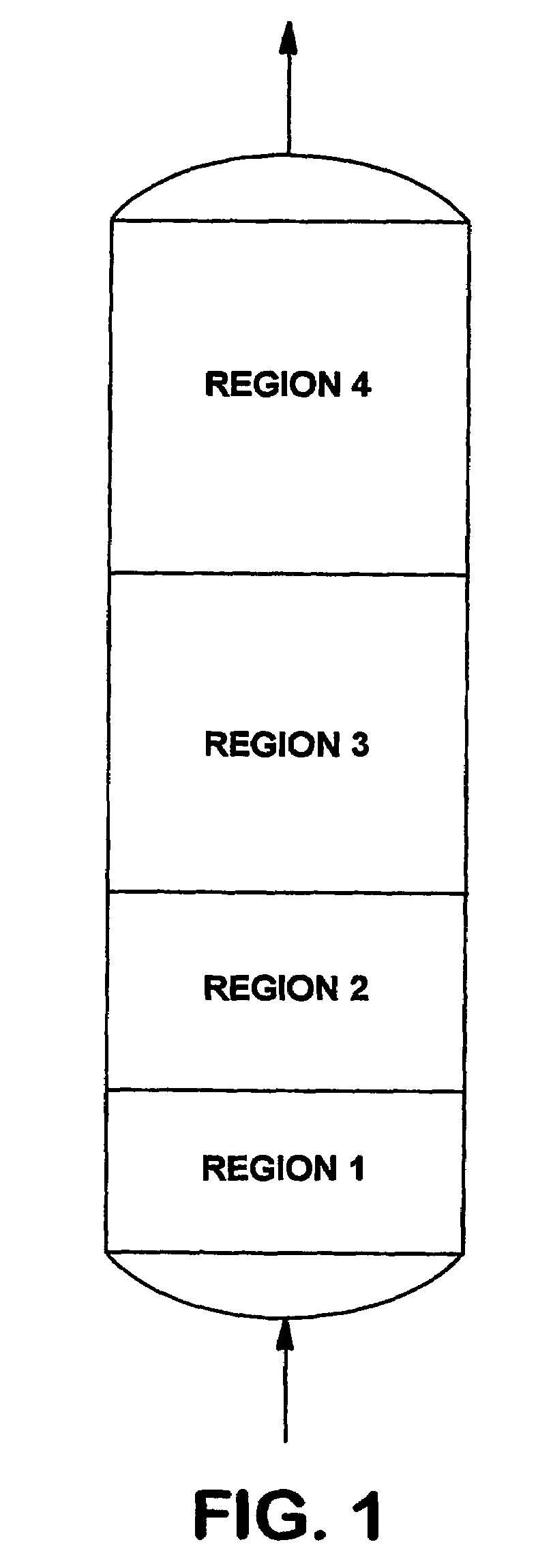
This invention discloses an optimum set of adsorbents for use in H2-PSA processes. Each adsorbent bed is divided into four regions; Region 1 contains adsorbent for removing water; Region 2 contains a mixture of strong and weak adsorbents to remove bulk impurities like CO2; Region 3 contains a high bulk density (>38 lbm / ft3) adsorbent to remove remaining CO2; and most of CH4 and CO present in H2 containing feed mixtures; and Region 4 contains adsorbent having high Henry's law constants for the final cleanup of N2 and residual impurities to produce hydrogen at the desired high purity.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Xenon recovery system
A first aspect of a process of recovering xenon from feed gas includes: providing an adsorption vessel containing adsorbent having a Xe / N2 selectivity ratio <75; feeding into the adsorption vessel feed gas having an initial nitrogen concentration >50% and an initial xenon concentration ≧0.5%; evacuating the adsorption vessel; and purging the adsorption vessel at a purge-to-feed ratio ≧10. The final xenon concentration is ≧15× the initial xenon concentration. A second aspect of the process includes providing an adsorption vessel containing adsorbent having a Xe Henry's law Constant ≧50 mmole / g / atm; feeding into the adsorption vessel feed gas having an initial nitrogen concentration >50% and an initial xenon concentration ≧0.5%; heating and purging the adsorption vessel to recover xenon having a final concentration ≧15× its initial concentration. Apparatus for performing the process are also described.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Process and adsorbent for hydrogen purification
This invention discloses an optimum set of adsorbents for use in H2-PSA processes. Each adsorbent bed is divided into four regions; Region 1 contains adsorbent for removing water; Region 2 contains a mixture of strong and weak adsorbents to remove bulk impurities like CO2; Region 3 contains a high bulk density (>38 lbm / ft3) adsorbent to remove remaining CO2; and most of CH4 and CO present in H2 containing feed mixtures; and Region 4 contains adsorbent having high Henry's law constants for the final cleanup of N2 and residual impurities to produce hydrogen at the desired high purity.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Carbon pyrolyzate adsorbent having utility for co2 capture and methods of making and using the same
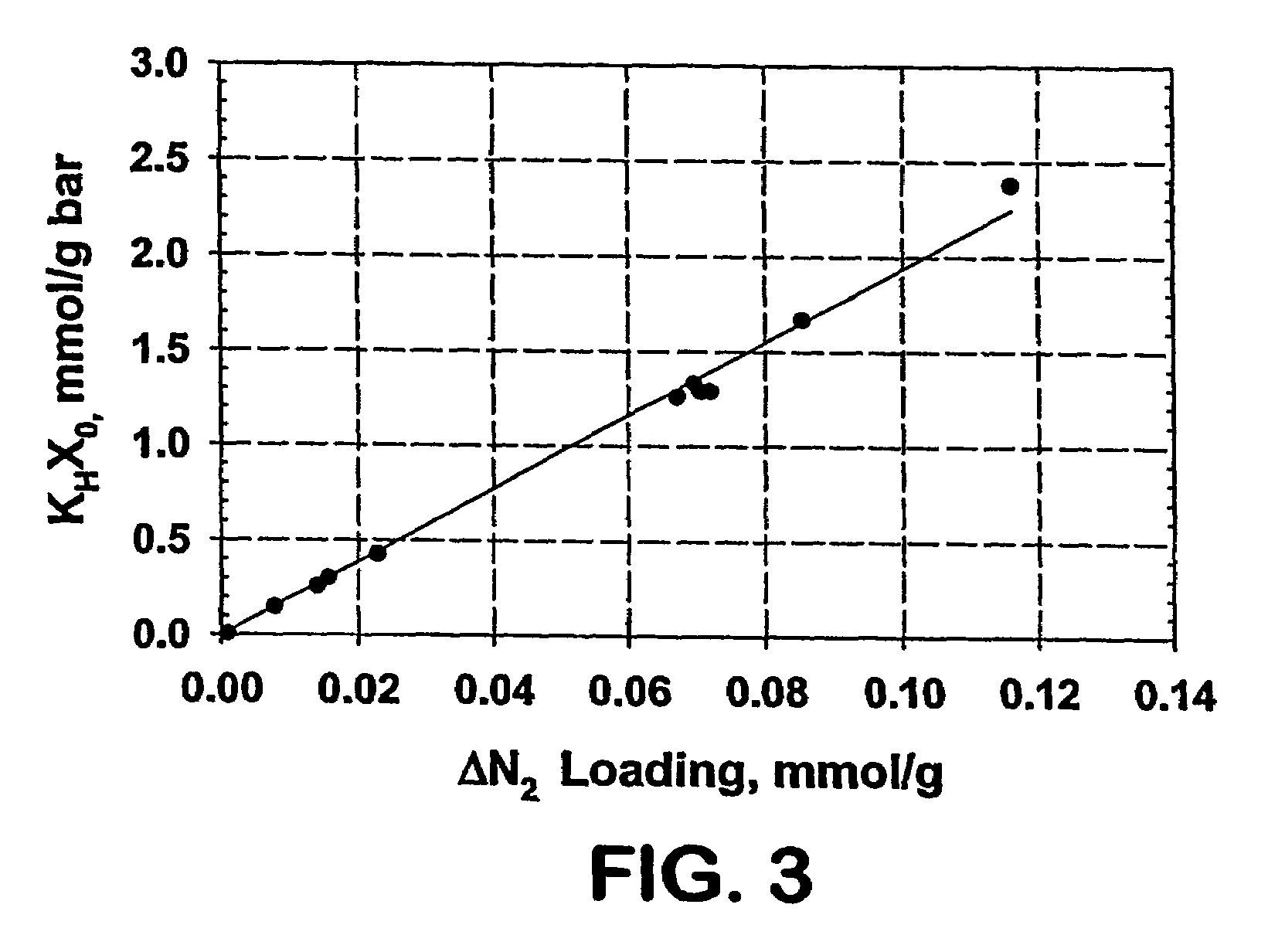
A particulate form carbon pyrolyzate adsorbent, having the following characteristics: (a) CO2 capacity greater than 105 cc / gram at one bar pressure and temperature of 273° Kelvin; (b) CO2 Working Capacity greater than 7.0 weight percent; (c) CO2 heats of adsorption and desorption each of which is in a range of from 10 to 50 kJ / mole; and (d) a CO2 / N2 Henry's Law Separation Factor greater than 5. The carbon pyrolyzate material can be formed from a polyvinylidene chloride-based polymer or copolymer, or other suitable resin material, to provide an adsorbent that is useful for carbon dioxide capture applications, e.g., in treatment of flue gases from coal-fired power generation plants.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
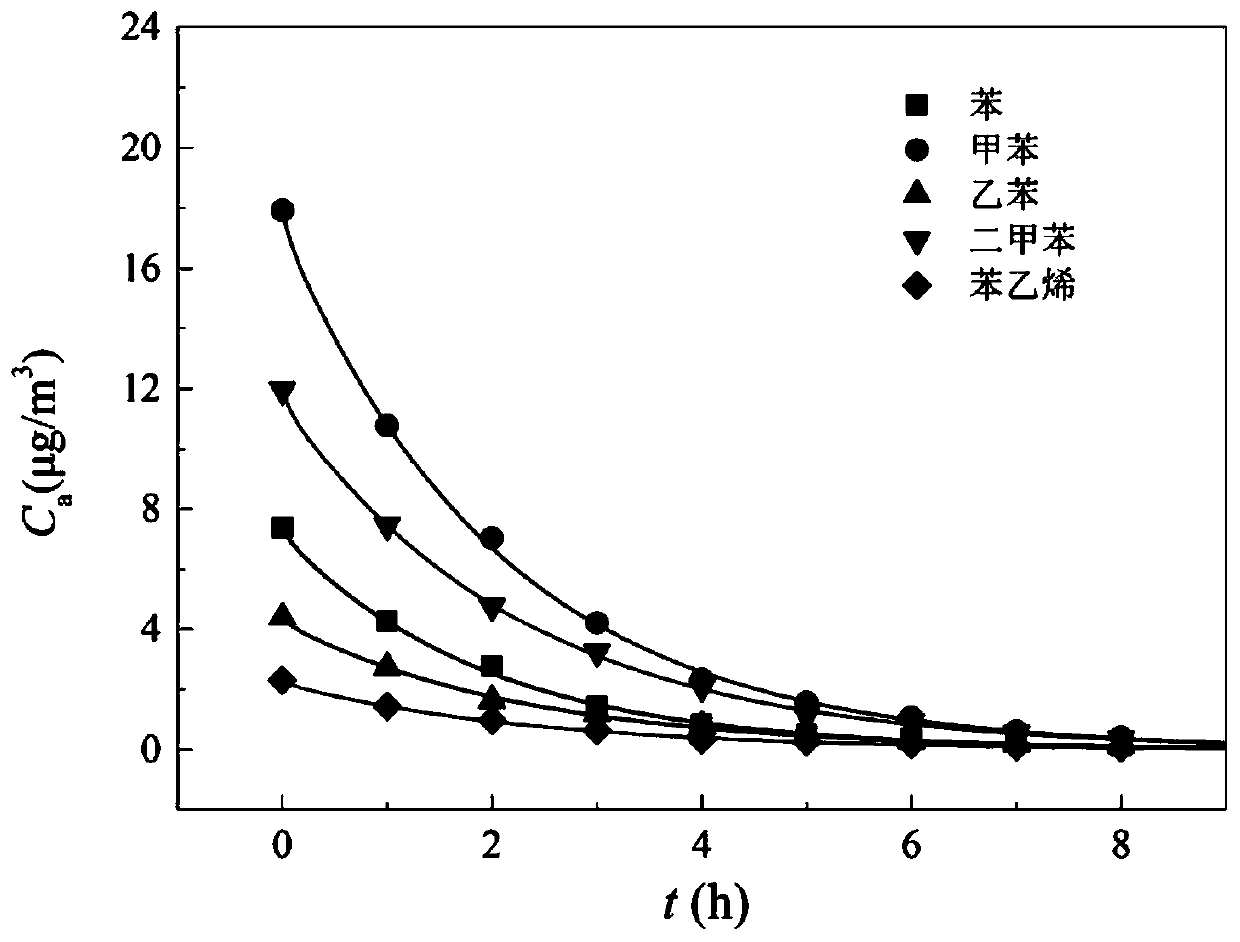
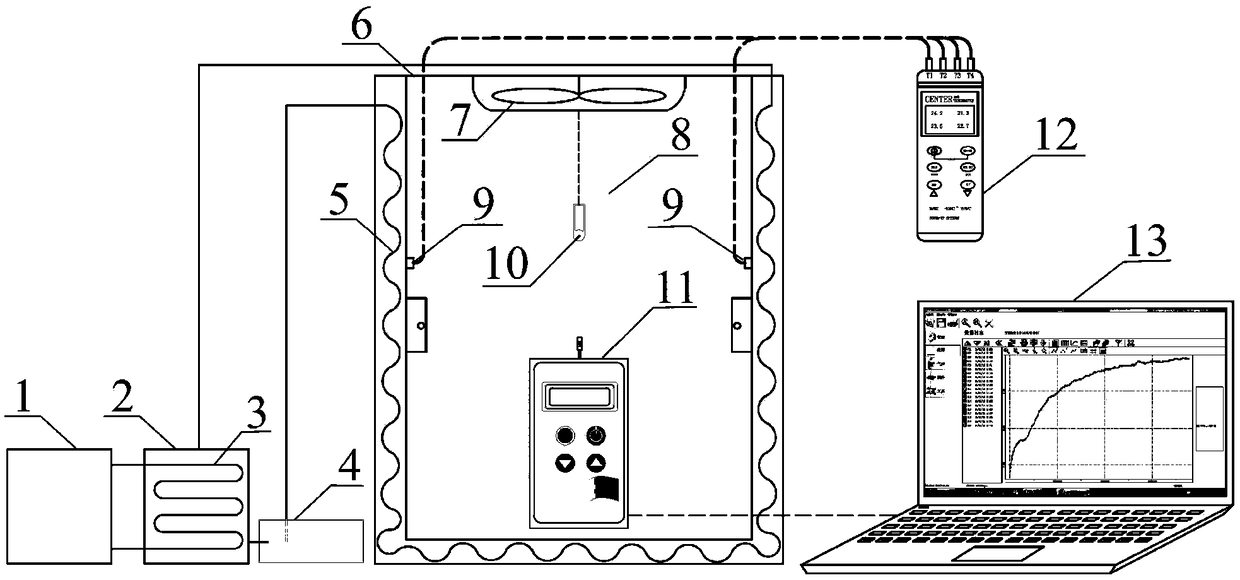
Method and device for measuring key parameters of VOC emission in in-vehicle non-metallic material
The invention provides a method for measuring key parameters of VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) emission in an in-vehicle non-metallic material, which is characterized by: deriving a balance emissionmodel of VOC in the non-metallic material at an environment cabin closed stage and a mass transfer diffusion model of the VOC in the non-metallic material at a direct current emission stage based ona mass transfer emission rule, a mass conservation law and a Henry's law, and measuring key parameters of an emission process of the in-vehicle non-metallic material in combination with actually measured data, wherein the key parameters comprise an initial emittable concentration C0, a distribution coefficient K, and a diffusion coefficient Dm. According to a device and the method for measuring the key parameters of the VOC emission in the in-vehicle non-metallic material, on the basis of a mass transfer diffusion rule and the mass conservation law of the VOC in the non-metallic material underdifferent conditions, the balance emission model of the VOC in the non-metallic material under the condition of closed environment cabin and the mass transfer diffusion model of the VOC in the non-metallic material under the condition of direct current emission are established, in combination with the actually measured data, the key parameters of the emission process of the in-vehicle non-metallic material are measured at the same time, wherein the key parameters comprise the initial emittable concentration C0, the diffusion coefficient Dm and the distribution coefficient K, thereby achieveing the goal of establishing a VOC prediction model of the in-vehicle non-metallic material.
Owner:BEIJING CATARC DATA TECH CENT
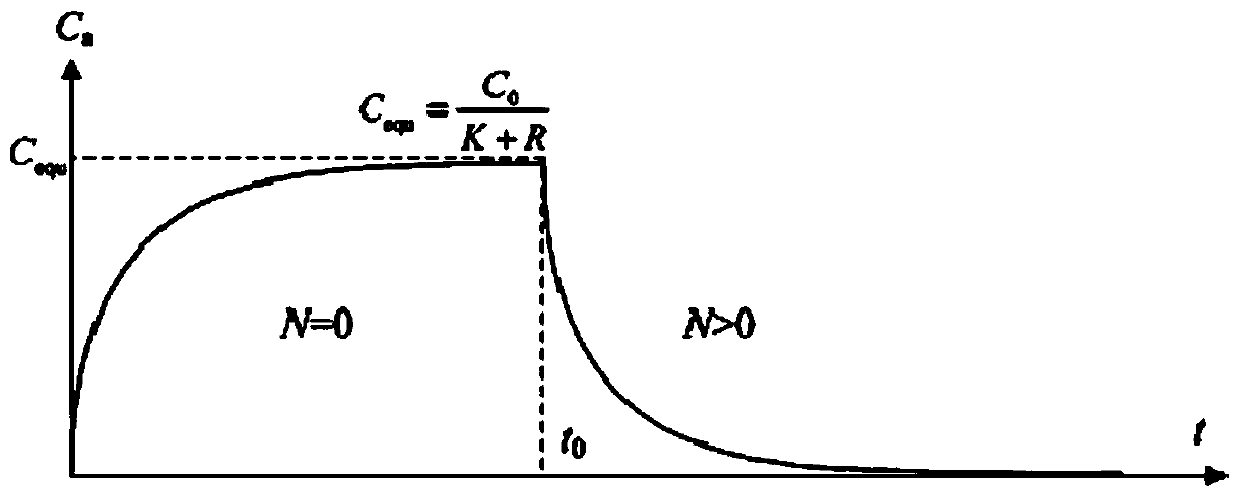
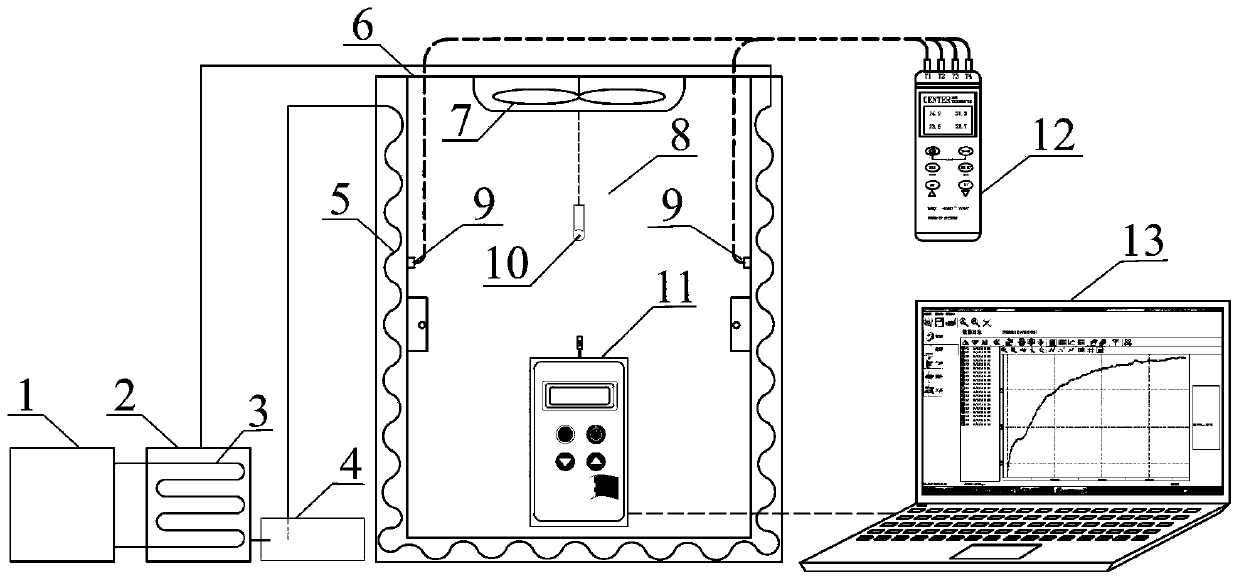
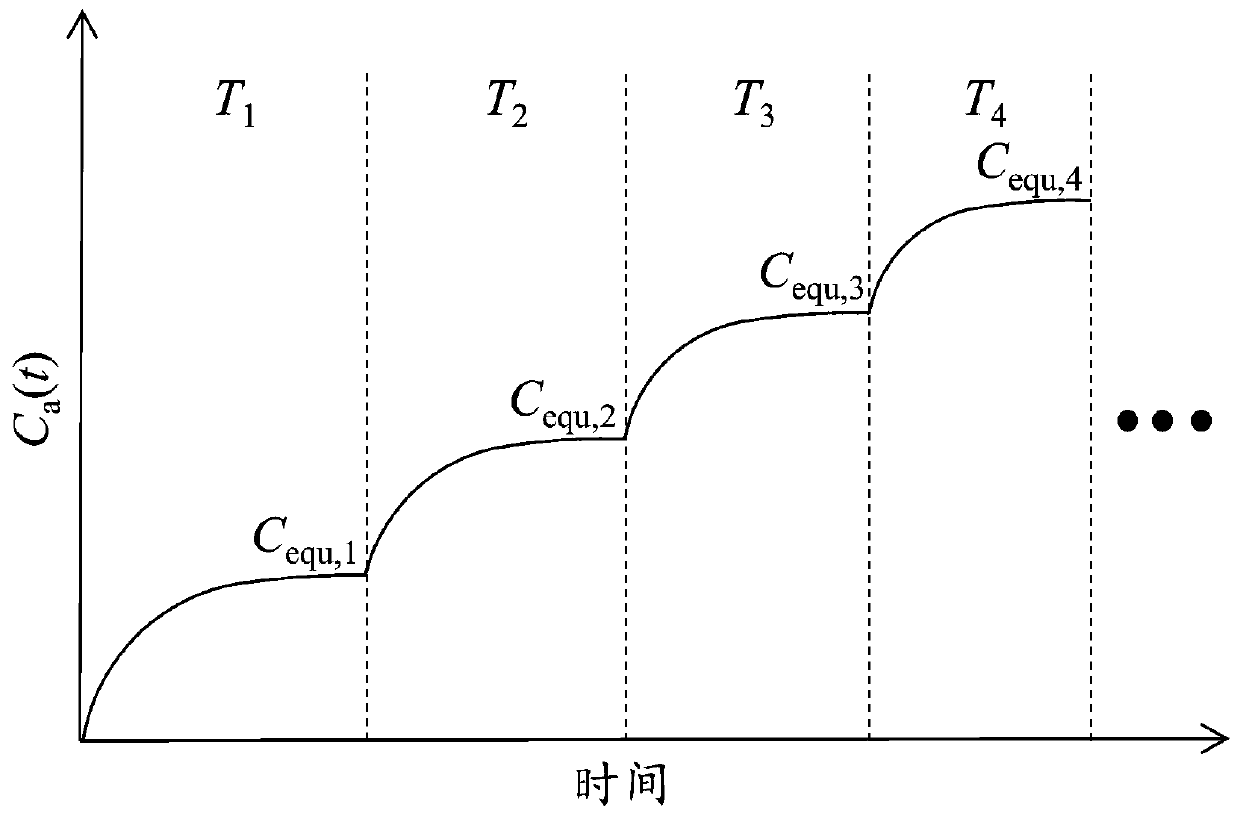
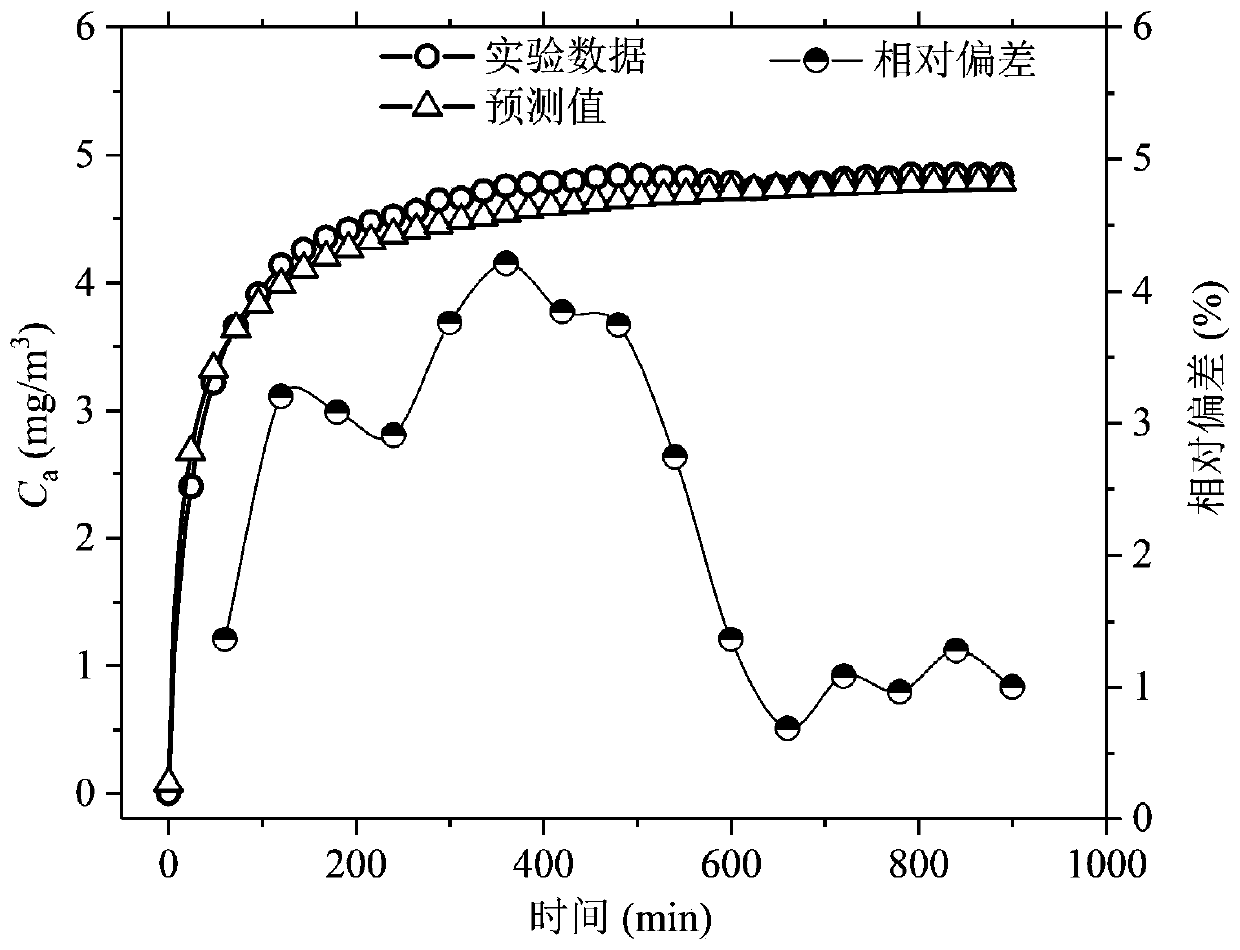
Step-temperature closed emission method for simultaneous determination of formaldehyde emission characteristic parameters of building materials at multiple temperatures
ActiveCN108918575AImprove measurement efficiencySave time and costMaterial thermal analysisSeparation coefficientEngineering
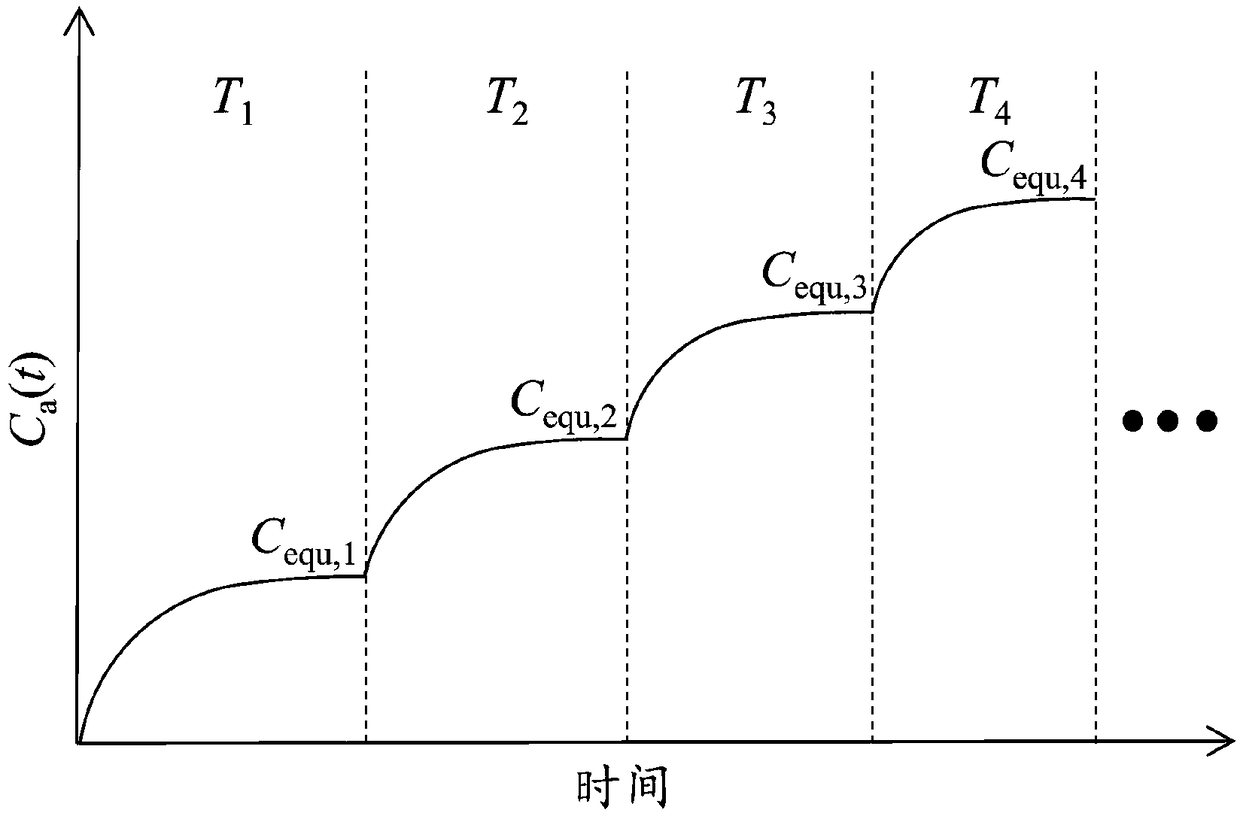
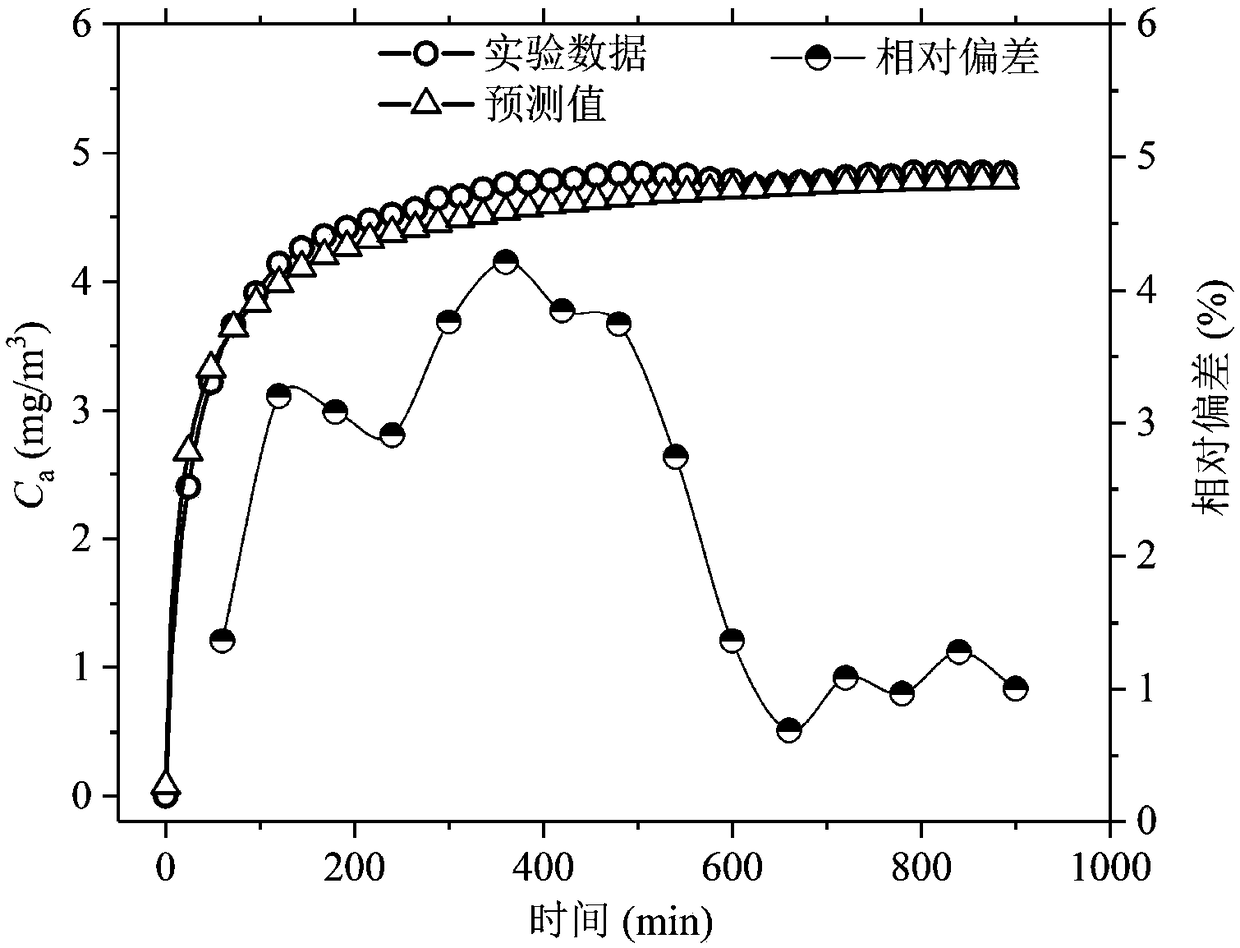
The invention relates to a step-temperature closed emission method for simultaneous determination of formaldehyde emission characteristic parameters of building materials at multiple temperatures. Based on a adsorption potential theory and a Henry's law, a functional relationship between a separation coefficient K and an initial dissipative concentration C0 is established, and an analytical formula of the equilibrium concentration Cequ of formaldehyde in the closed environment is derived. A sealed environment cabin is used to maintain a constant temperature and a humidity space, and the building material samples are subjected to formaldehyde emission test, and the formaldehyde hourly concentration and equilibrium concentration at the initial temperature are measured. The temperature is then raised and the corresponding new equilibrium concentration is measured. The above operations can be repeated in sequence to obtain a formaldehyde equilibrium concentration value at multiple temperatures. The nonlinear fitting is carried out on the formaldehyde hourly concentration at the initial temperature, the K at the temperature can be determined. When the Cequ of the building material at other temperatures is known, the K at the corresponding temperature can be quickly obtained by the ratio of the equilibrium concentrations, and the corresponding C0 can be calculated. The method greatlyimproves the measurement efficiency of formaldehyde emission characteristics.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Purification Of Air
ActiveUS20130319228A1Large capacitySmall sizeNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentFeed temperatureChemistry
Reduction of water, CO2 and N2O in an air stream comprising: passing said air stream at a feed temperature through a first adsorbent, whose Henry's Law selectivity for CO2 / N2O is at least 12.5, and a second adsorbent, whose Henry's Law constant for CO2 is less than 1020 mmol / g / atom and whose Henry's Law selectivity for CO2 / N2O is at most 5; and passing a heated regenerating gas at a temperature which is between 20° C. and 80° C. to at least the second adsorbent, and passing a second regenerating gas at a temperature less than the temperature of the heated regenerating gas to the first and second adsorbents in a direction opposite to the feed direction; the second adsorbent occupying from 25% to 40% of the total volume of the adsorbents, and the temperature of the heated regenerating gas being 10° C. to 60° C. higher than the feed temperature.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Draw solution for forward osmosis process
ActiveUS20160175777A1Prevent leakageReduce the amount of solutionOrganic chemistryGeneral water supply conservationStandard stateSemipermeable membrane
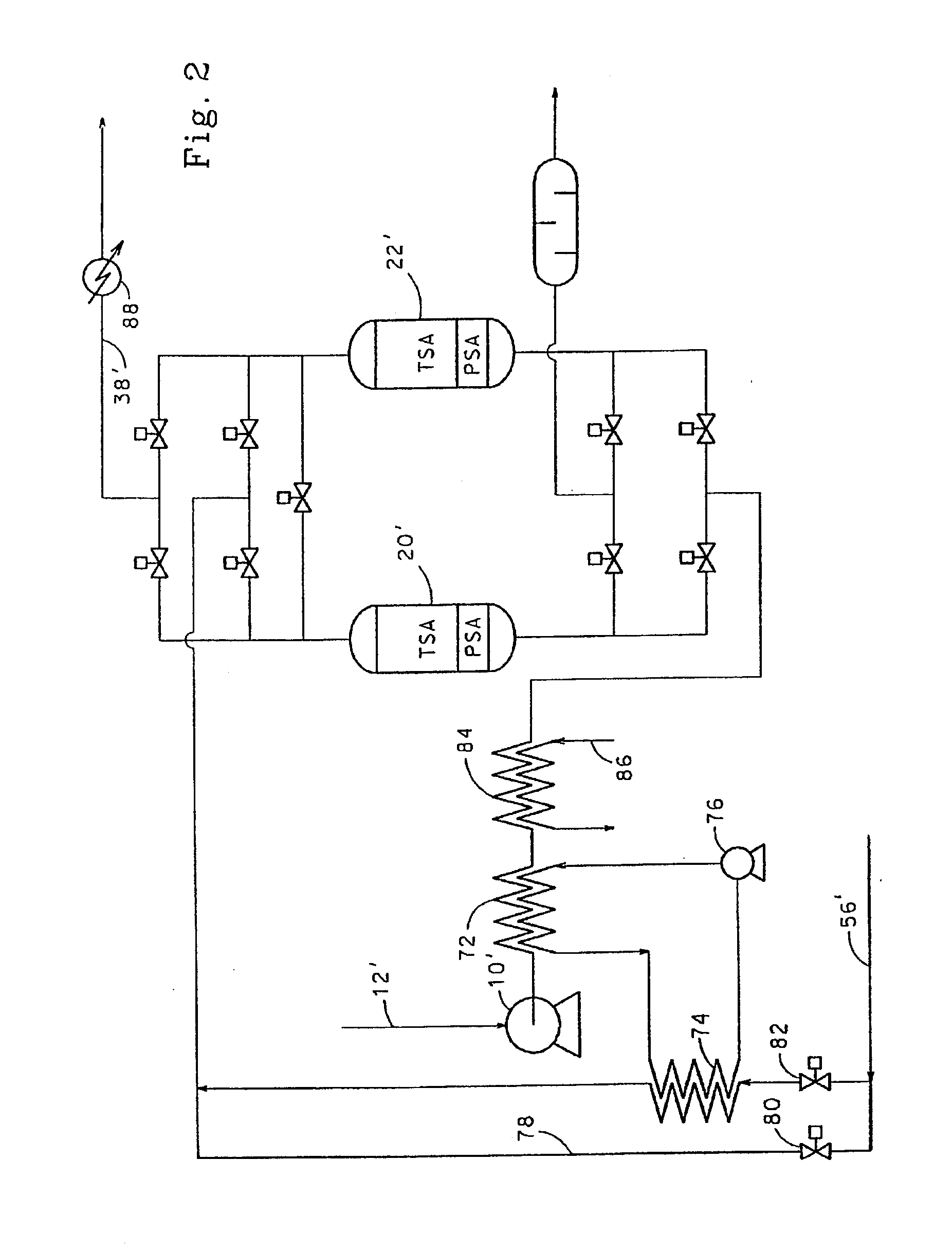
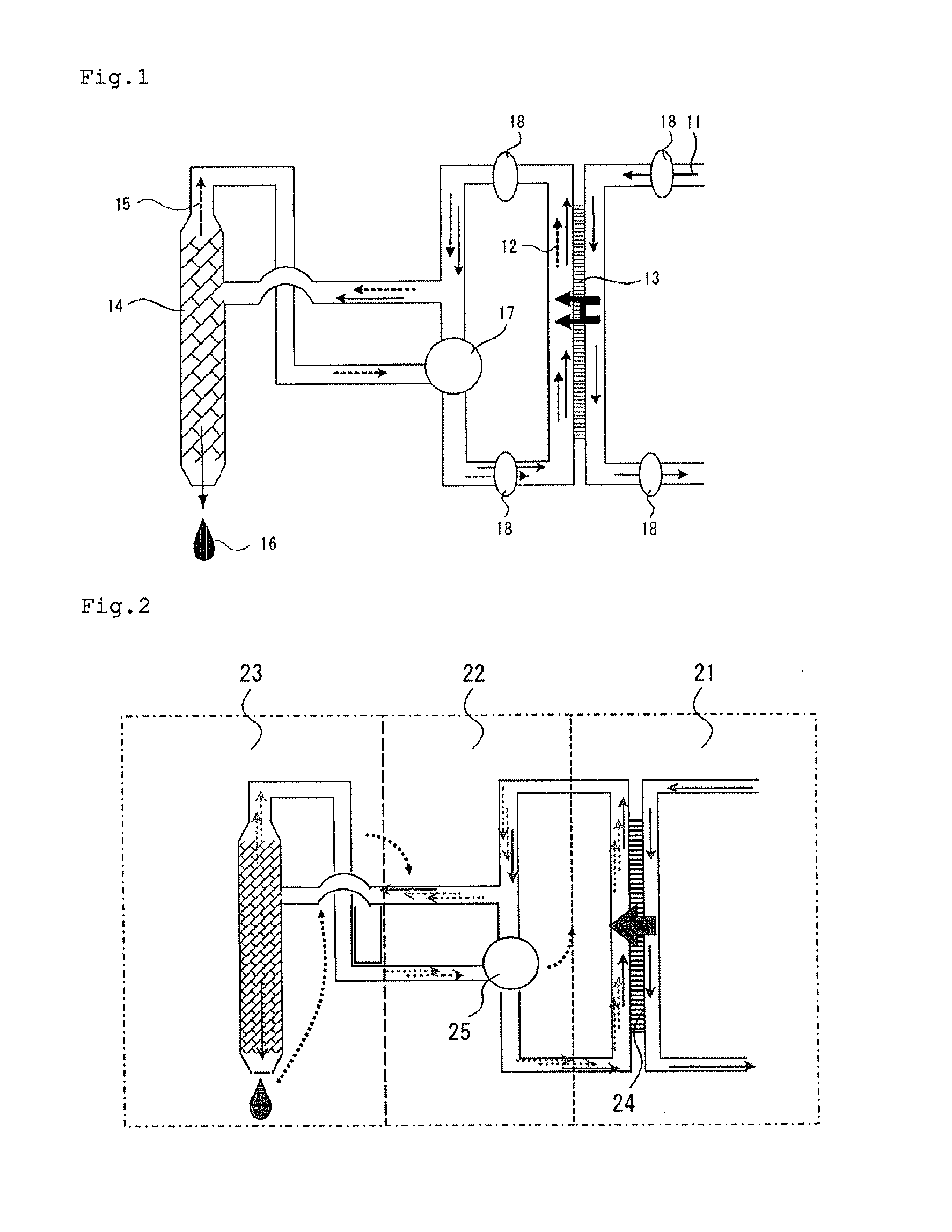
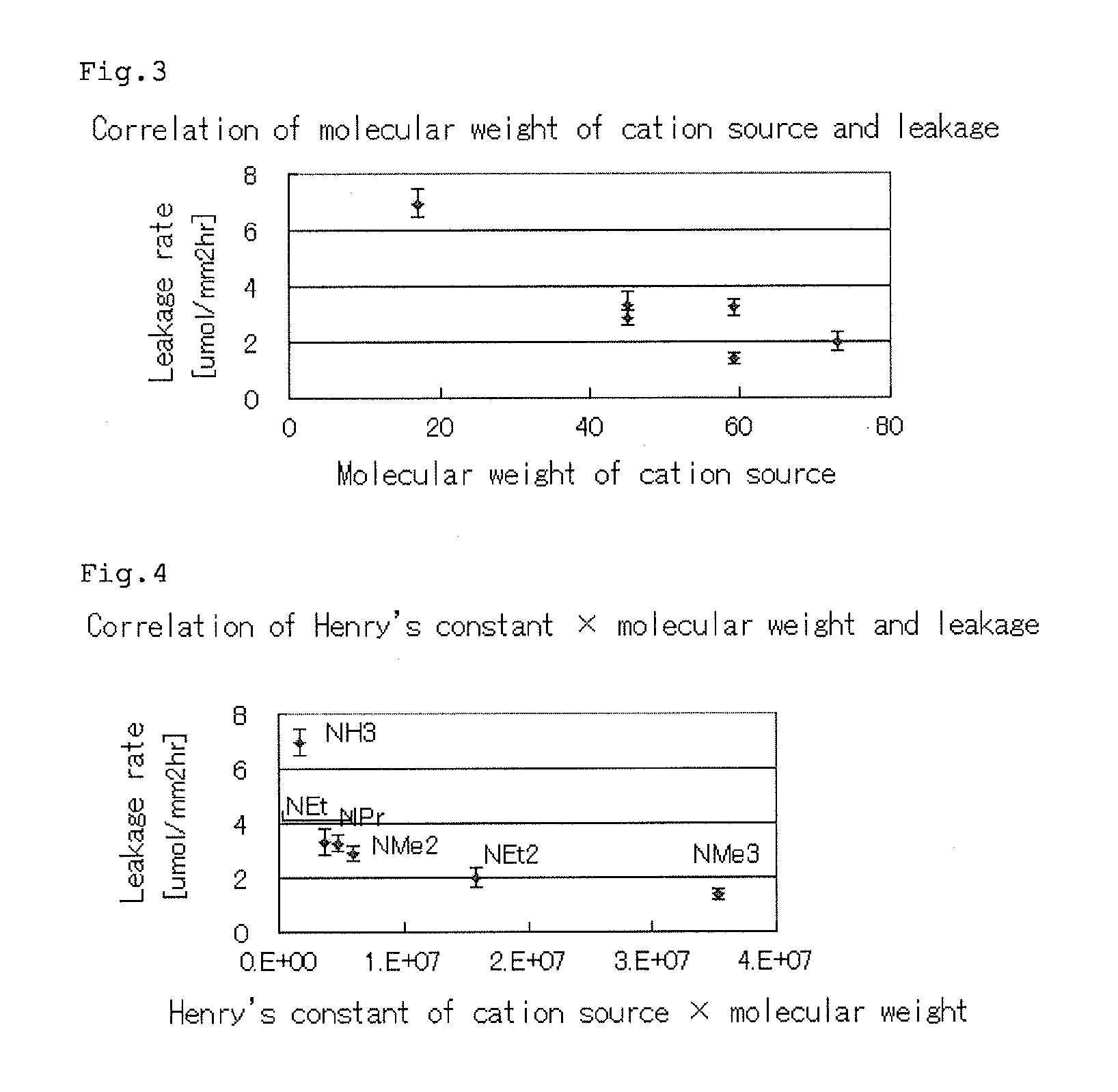
A forward osmosis apparatus is improved. A forward osmosis apparatus, comprising a diluting means for bringing a feed solution and a draw solution comprising a cation source and an anion source in an ionized state into contact through a semi-permeable membrane and diluting the draw solution with water separated from the feed solution by means of the semi-permeable membrane;a separating means for separating the draw solution that has been diluted by the diluting means into the cation source and anion source and into water; anda dissolving means, returning the cation source and the anion source that have been separated by the separating means to, and dissolving the cation source and anion source in, the draw solution that has been diluted;wherein the molecular weight of the cation source in an uncharged state is 31 or greater and the Henry's law constant of each of the anion source and cation source is 1.0×104 (Pa / mol·fraction) or greater in a standard state.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Process of absorbing detal gas from row material air flow
A process for removing nitrous oxide from a feed gas by contacting the gas stream with an adsorbent having a nitrous oxide Henry's law constant at 30 DEG C of 14 mmole / g / atm or higher and nitrous oxide / carbon dioxide Henry's law selectivity at 30 DEG C of less than 0.49, to form a purified gas stream and periodically regenerating the adsorbent at low temperature with a flow of regeneration gas at a temperature between 30 and 100 DEG C. The process is especially useful in air separation processes.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
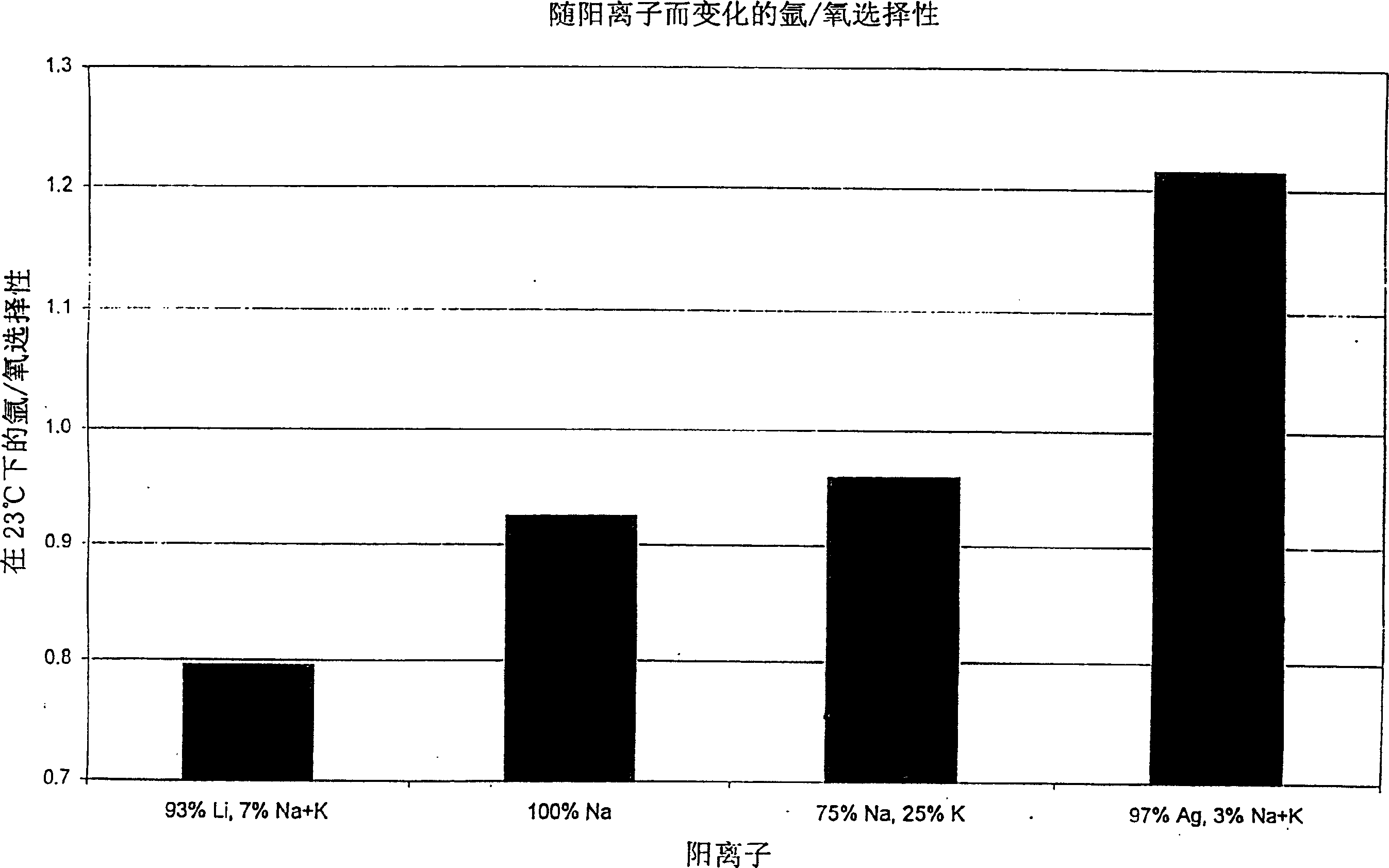
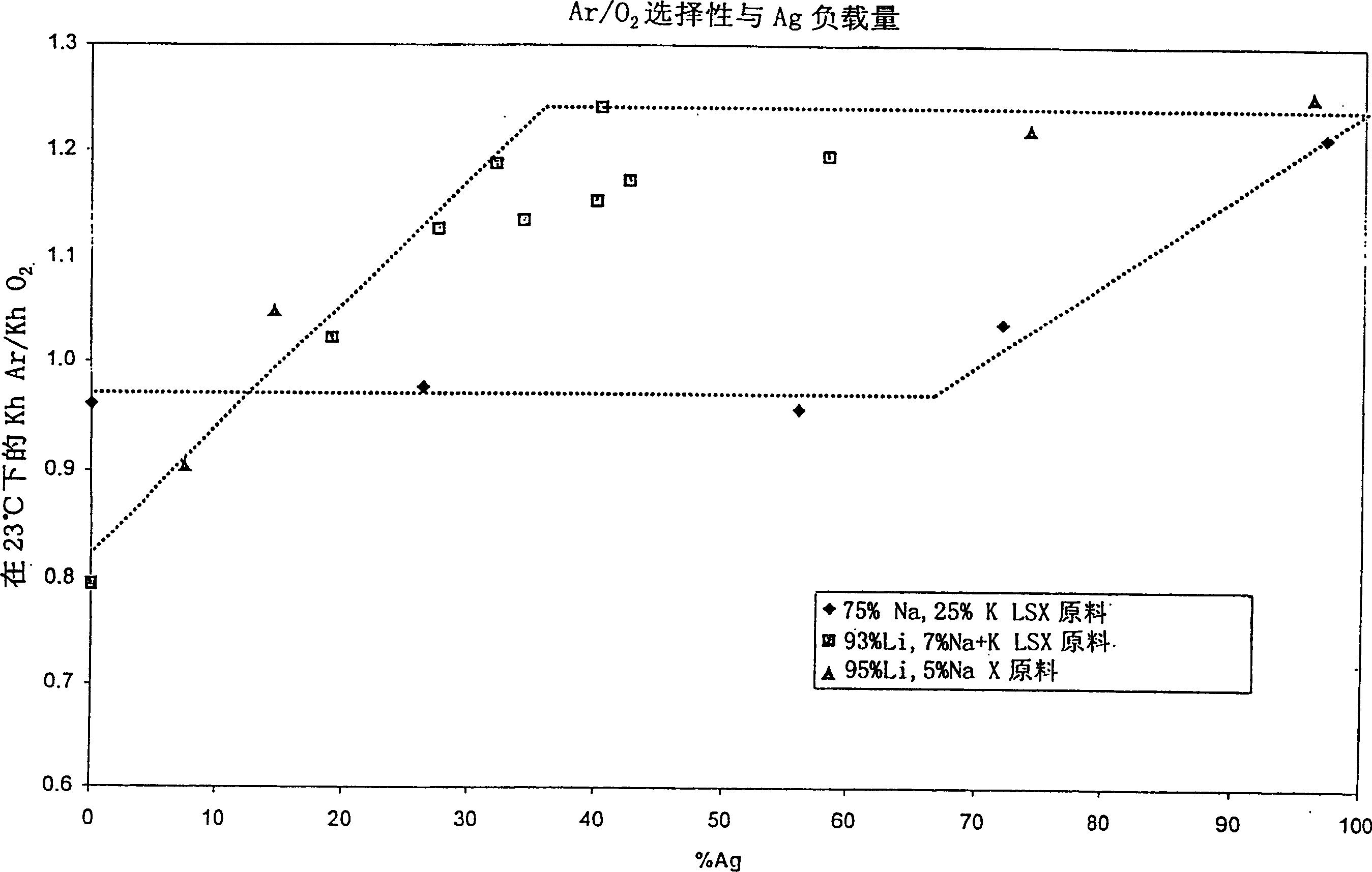
Argon/oxigen selective X-zeolite
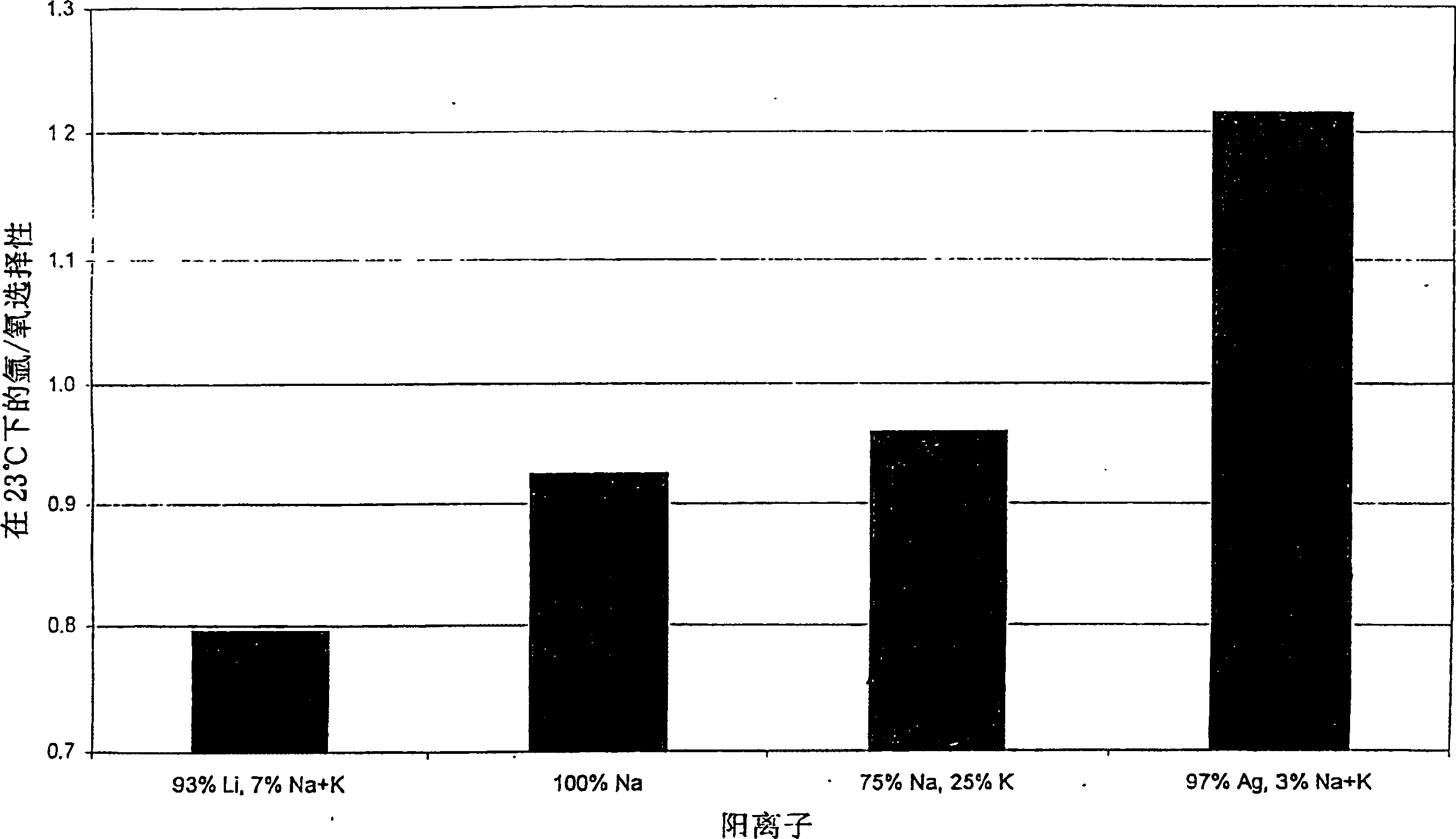
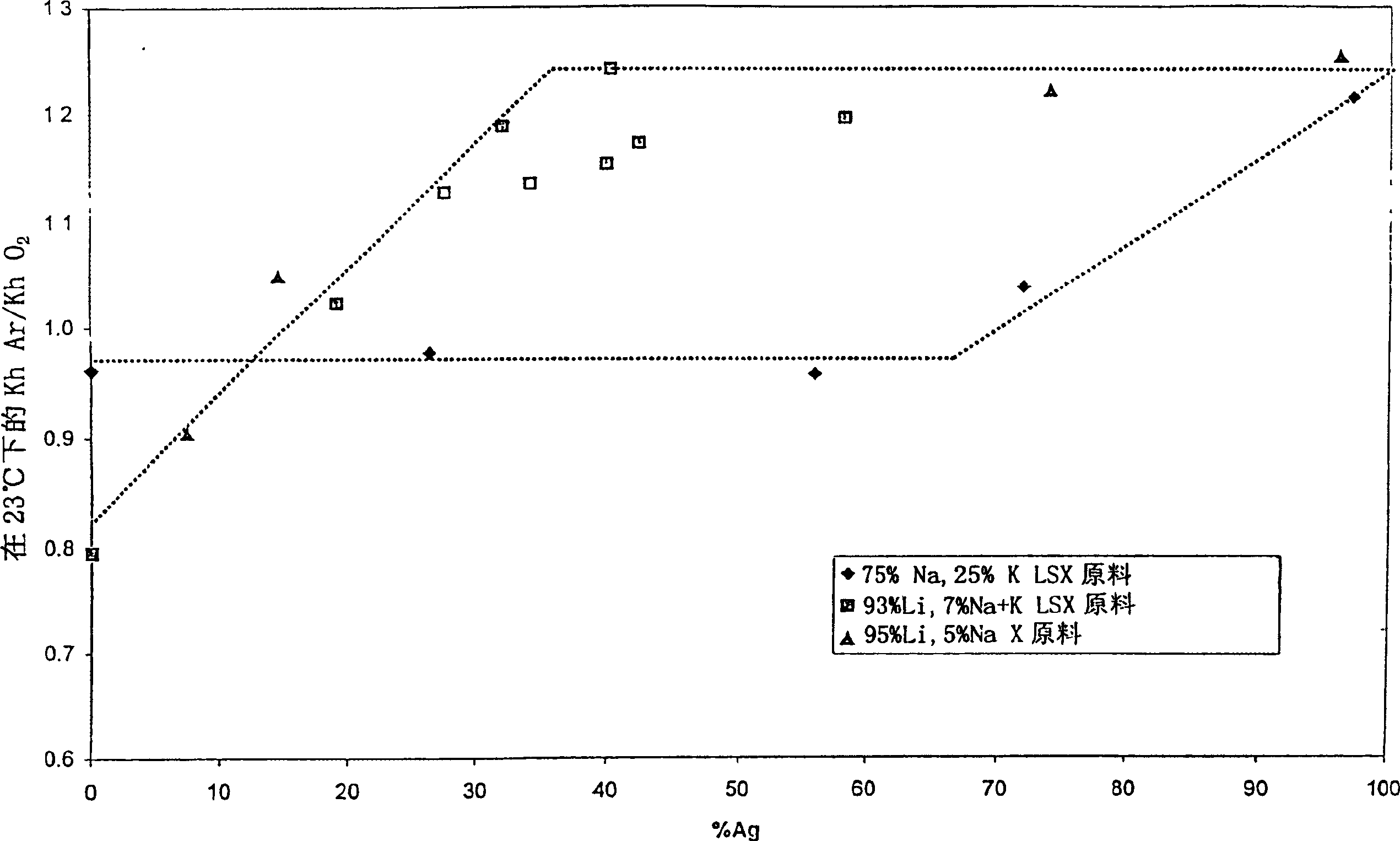
InactiveCN1385236AEnhanced Argon/Oxygen Selectivity RatioEfficient separationGas treatmentOther chemical processesOxygen levelChemistry
The invention discloses an AgX-type zeolite, the silver exchange capacity of which is 20-70%, the Henry's law selectivity ratio of argon / oxygen at 23°C is 1.05 or greater, and the zeolite has: a higher silver than The best combination of selectivity for argon compared to oxygen at lower exchange volume and cost. The material can be used in the oxygen VSA / PSA method to produce oxygen with a purity of more than 97%.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method and device for increasing carbon dioxide via agricultural water
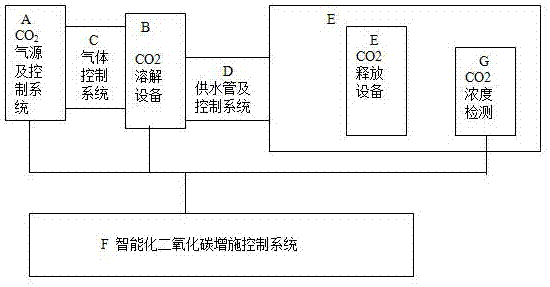
ActiveCN107306700AGas phase partial pressure dropEasy to controlAgriculture gas emission reductionGreenhouse cultivationDifferential pressureGas phase
The invention discloses a method and device for increasing carbon dioxide via agricultural water and belongs to the technical field of agricultural science. The method and device for increasing carbon dioxide employs a law (Henry's law) where carbon dioxide has changes in solubility under different gaseous differential pressures. Carbon dioxide is dissolved in agricultural water first; the carbon dioxide escapes from the solution in gaseous form and is released to the atmospheric environment; therefore, the concentration of carbon dioxide in a plant photosynthetic action region is increased, and synchronous integrated transporting and supplementing of water, gas and fertilizer can be achieved.
Owner:内蒙古环创富碳农业科技有限公司
Aqueous Ozone Monitor Utilizing Gas Stripping
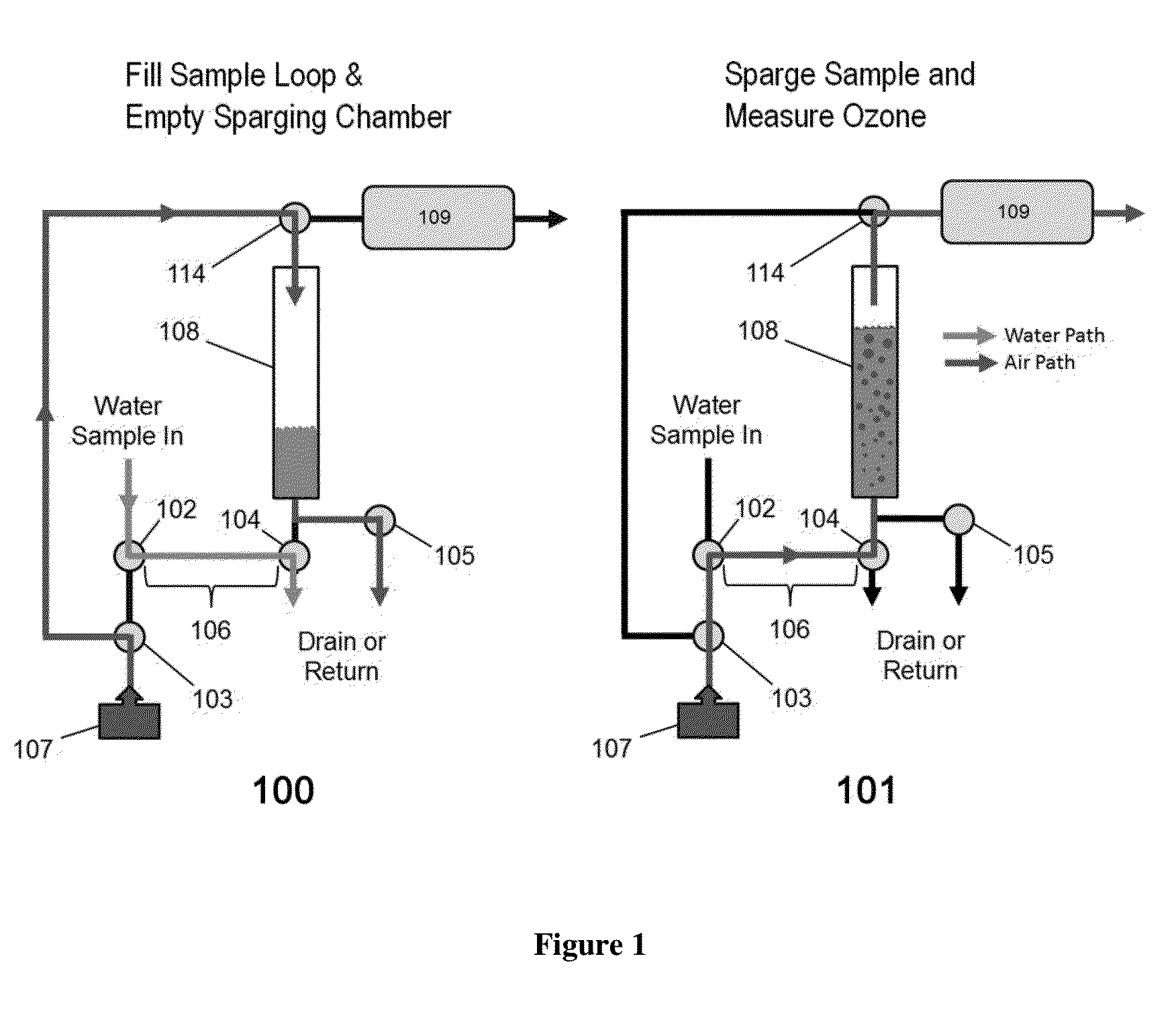
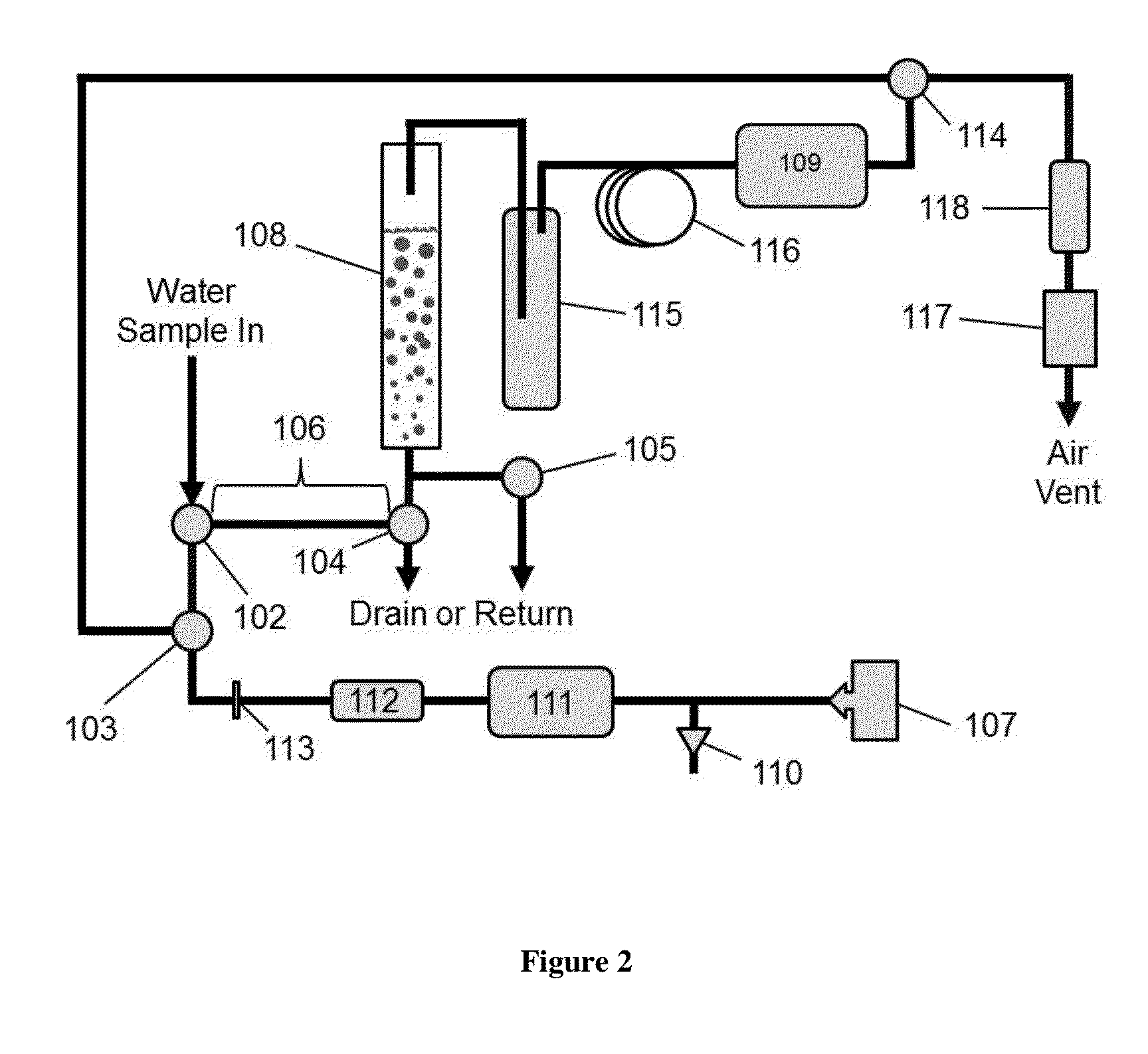
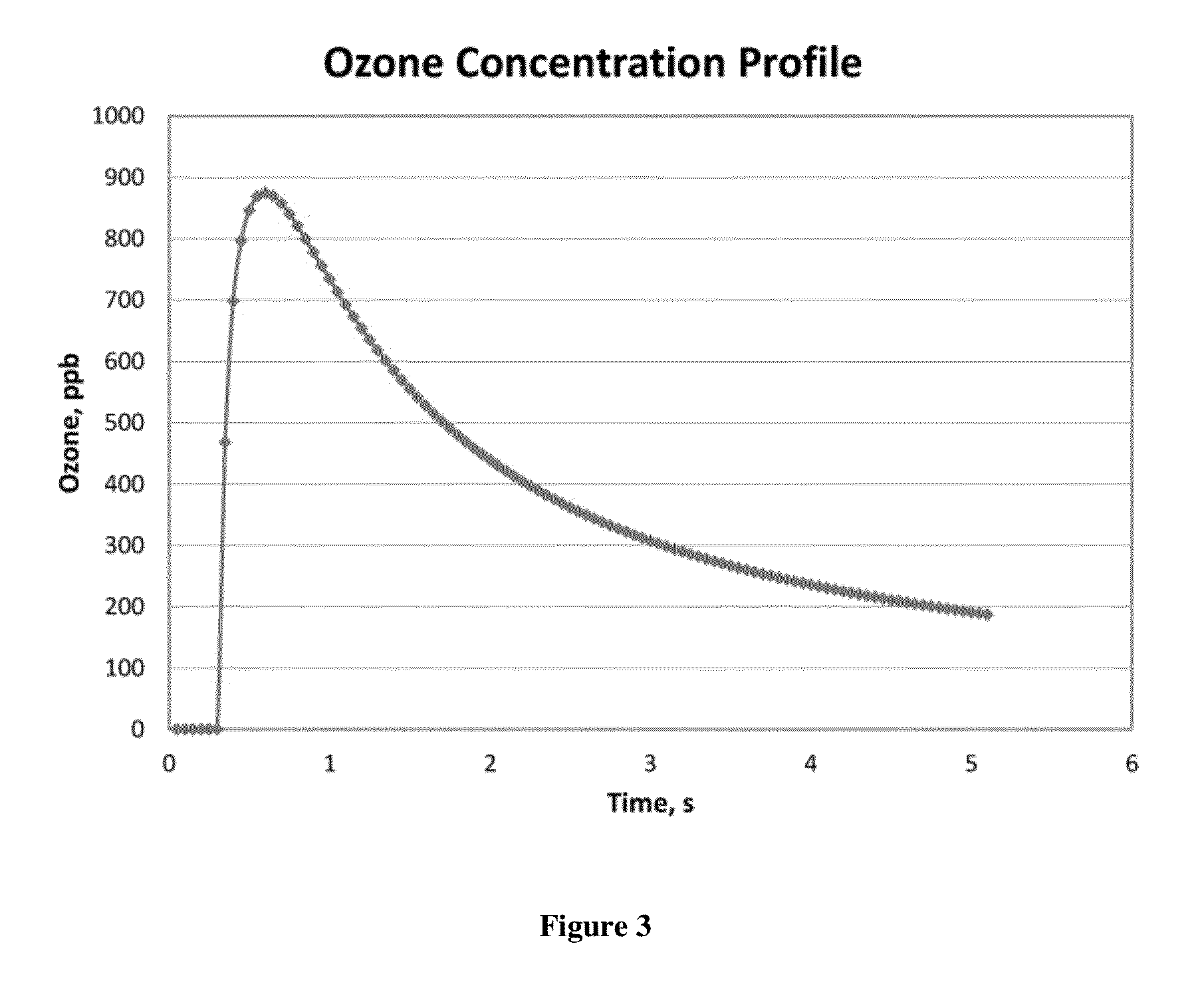
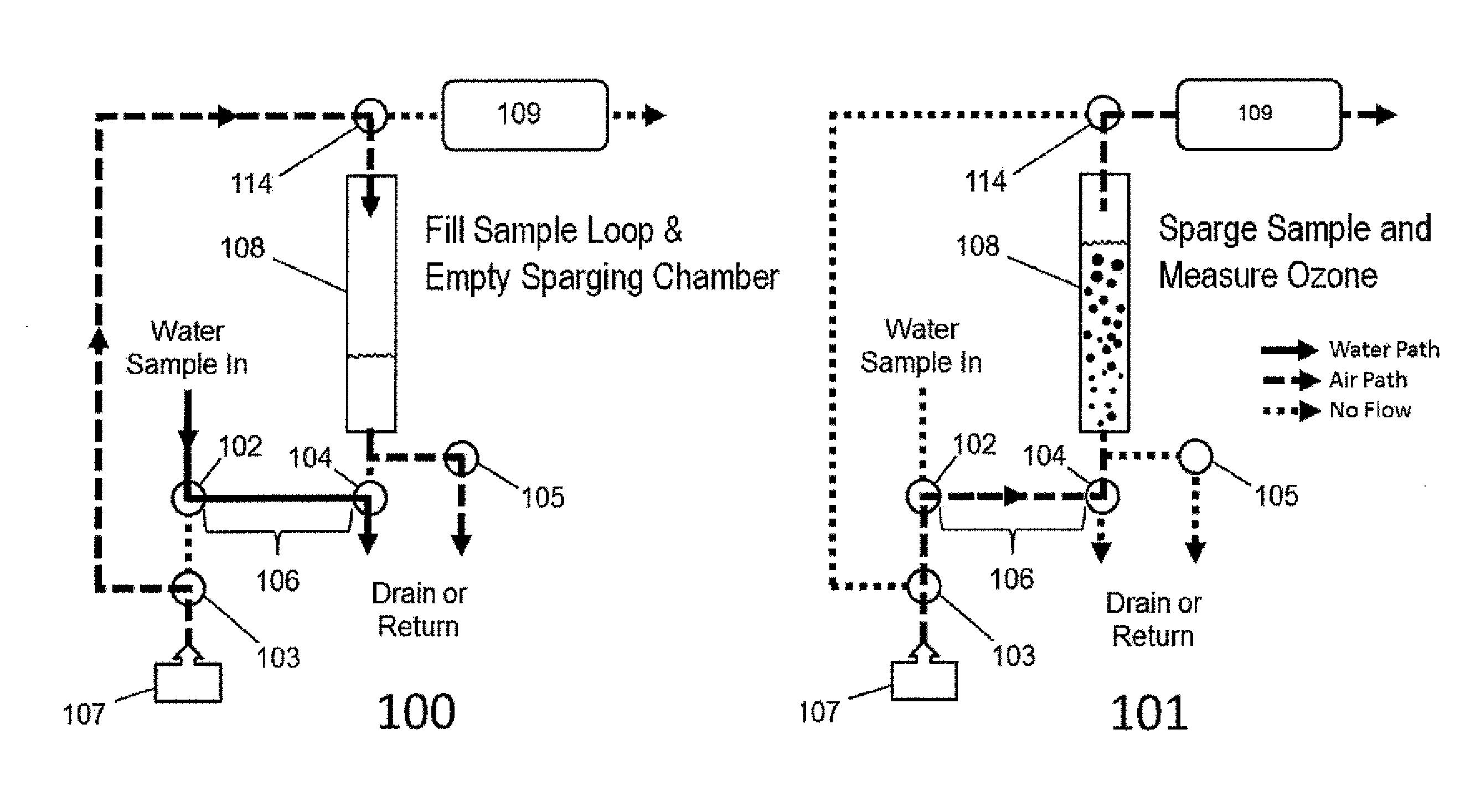
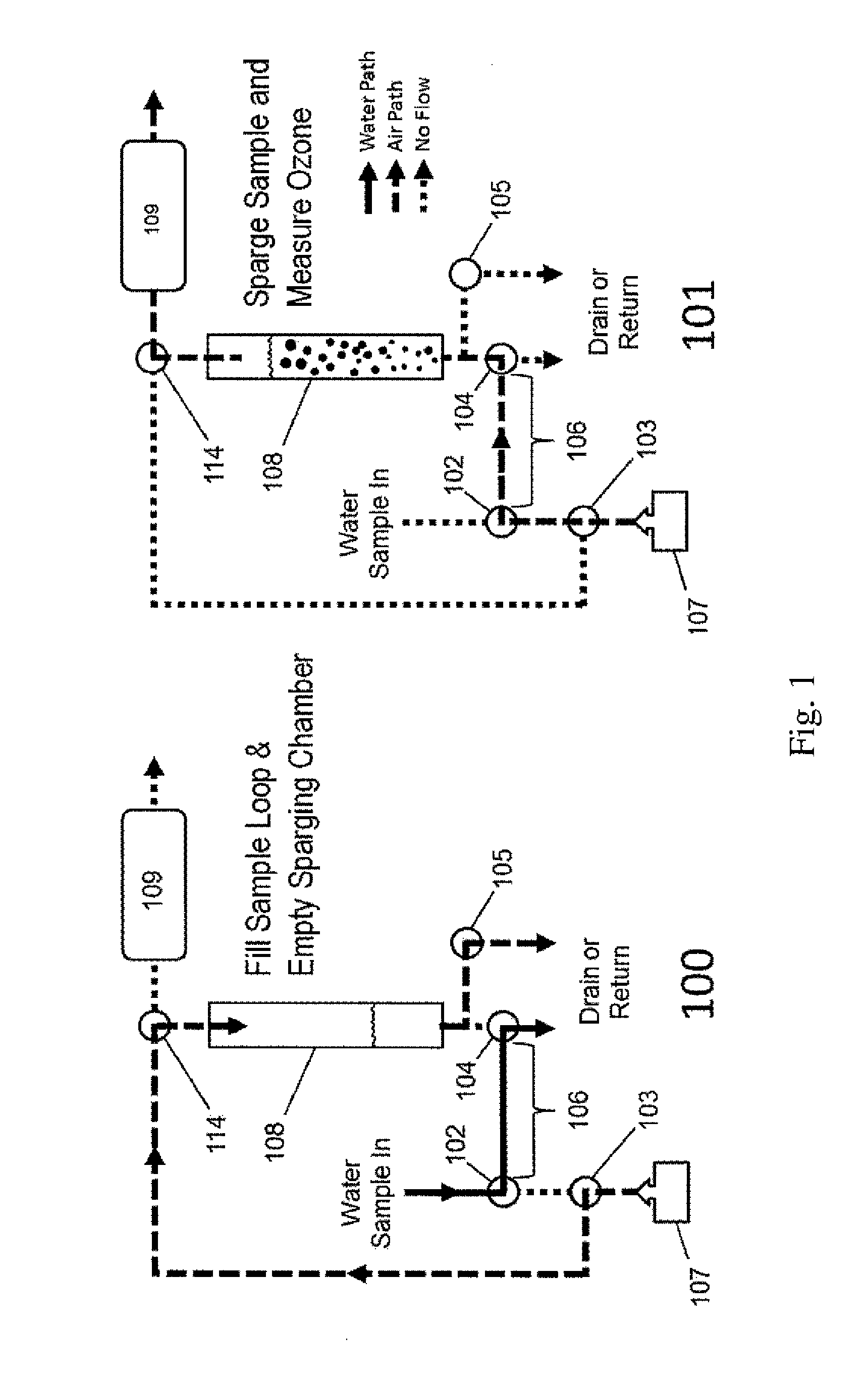
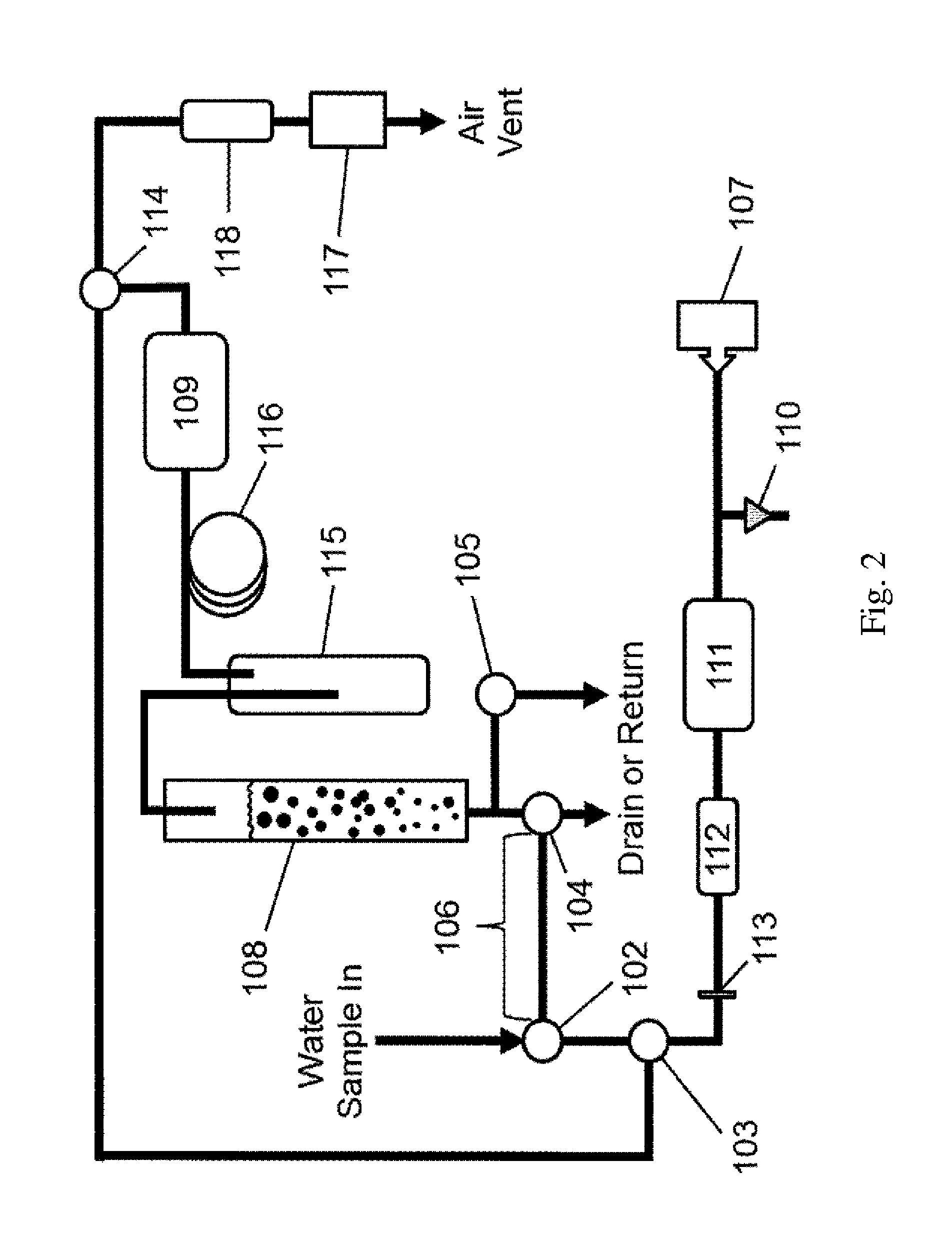
ActiveUS20150377772A1Measure is shortEliminating of methodWater treatment parameter controlSamplingTime profileGas phase
The present invention provides a means of measuring the concentration of ozone dissolved in water or another solvent. Small, discrete samples are sparged with air or another unreactive gas for a short period of time to measure a profile of ozone vs time in the sparge gas. The total amount of ozone in the original sample is obtained by integrating under the ozone vs time profile. A correction may be made for ozone remaining in the sample after a finite sparge time by integrating under the profile tail using a decay constant obtained from the measured ozone vs time profile. The method differs from previous methods based on sparging of the sample in that a Henry's Law equilibrium or constant ratio of ozone present in the gas and liquid phases is not assumed and the flow rates of sample and sparge gas are not continuous. Instead, discrete samples are analyzed by nearly complete sparging. The new method is applicable to dirty (impure) water because the ozone is measured in the absence of UV-absorbing and scattering impurities that may be present in the sample. The method applies to high purity water as well.
Owner:LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS
Single organic matter standard gas concentration detecting device and method
InactiveCN104614432ASimple structureImprove performanceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical oxygen demandFluid phase equilibrium
The invention discloses a single organic matter standard gas concentration detecting device and method which are used for solving the problem about organic gas concentration analysis in the standard gas production process. The single organic matter standard gas concentration detecting device comprises a gas-liquid phase balance device and a photoelectrocatalysis COD (chemical oxygen demand) measuring device, wherein in the gas-liquid phase balance device, to-be-detected gas enters a prepared standard solution through a valve, a gas pressure relief valve and a sand core filter plate to form small bubbles, and the concentration of organic matters in a liquid phase gradually get stable in the rising process of the bubbles in the liquid; in the photoelectrocatalysis COD measuring device, a TiO2 working electrode is irradiated by ultraviolet light, the organic matters in the liquid phase are oxidized through photoelectrocatalysis, coulomb electric charge is calculated through light current measurement, and a value of COD in the liquid is obtained. The concentration of the organic matters in the liquid is calculated according to an organic matter molecular formula, and the concentration of organic gas in gas is obtained in combination of the henry's law.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
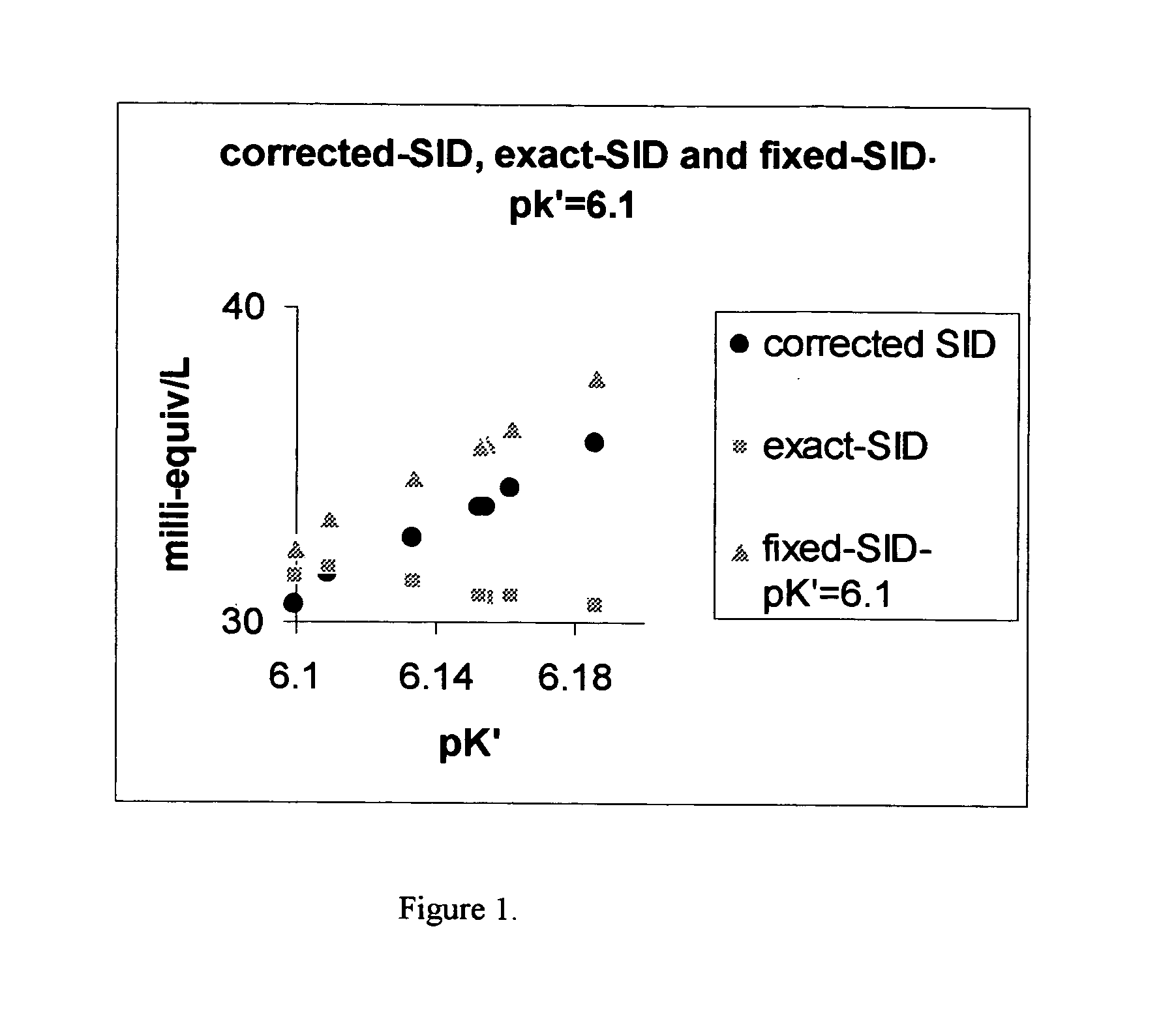
Accuracy improvement in strong ion difference for blood gas testing
InactiveUS20070208515A1Improve accuracyIncreasing health care costBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsAccuracy improvementStrong ion difference
An improved bicarbonate determination with variability of apparent dissociation constant in Henderson-Hasselbach equation or Henderson equation with Henry's law is described. The improved bicarbonate is utilized in the determination of improved Strong Ion Difference (SID) and Strong Ion Difference Excess (SIDE) as the change in SID from the reference value at pH=7.4, pCO2=5.33 Kpa (or 40 torr) for blood gas testing.
Owner:RANA AMAR PAL SINGH +2
Continuous type automatic measurement method and apparatus for radon in water
PendingCN108519492AHigh measurement accuracyCalculation method is simpleX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMaterial analysisContinuous measurementMeasurement device
The invention discloses continuous type automatic measurement method and apparatus for radon in water. In the invention, it is proved that radon gas exchanges between gas phase and liquid phase and satisfies Henry's Law, namely, dissolution equilibrium state; and the concentration of radon in water can be calculated by an equation of Cw = F*Cg; meanwhile, the invention provides experiment measurement steps of water temperature T relative to the equilibrium factor F. The measurement apparatus includes: a water filter unit, a gas-water exchanger unit, a water vapor condenser unit, and a radon detector unit. The measurement apparatus has simple operation, is high in intelligent degree, has digital measurement function, saves manpower and drying agent, can continuously measure the concentration of radon in water for a long period, is more complete, stable and accurate in measurement data of the radon in water, and can supply a more reliable digital measurement result for the radon in waterto observation of geologic structure and earthquake precursor.
Owner:BEGOOD TECH
Photo-switchable membrane and method
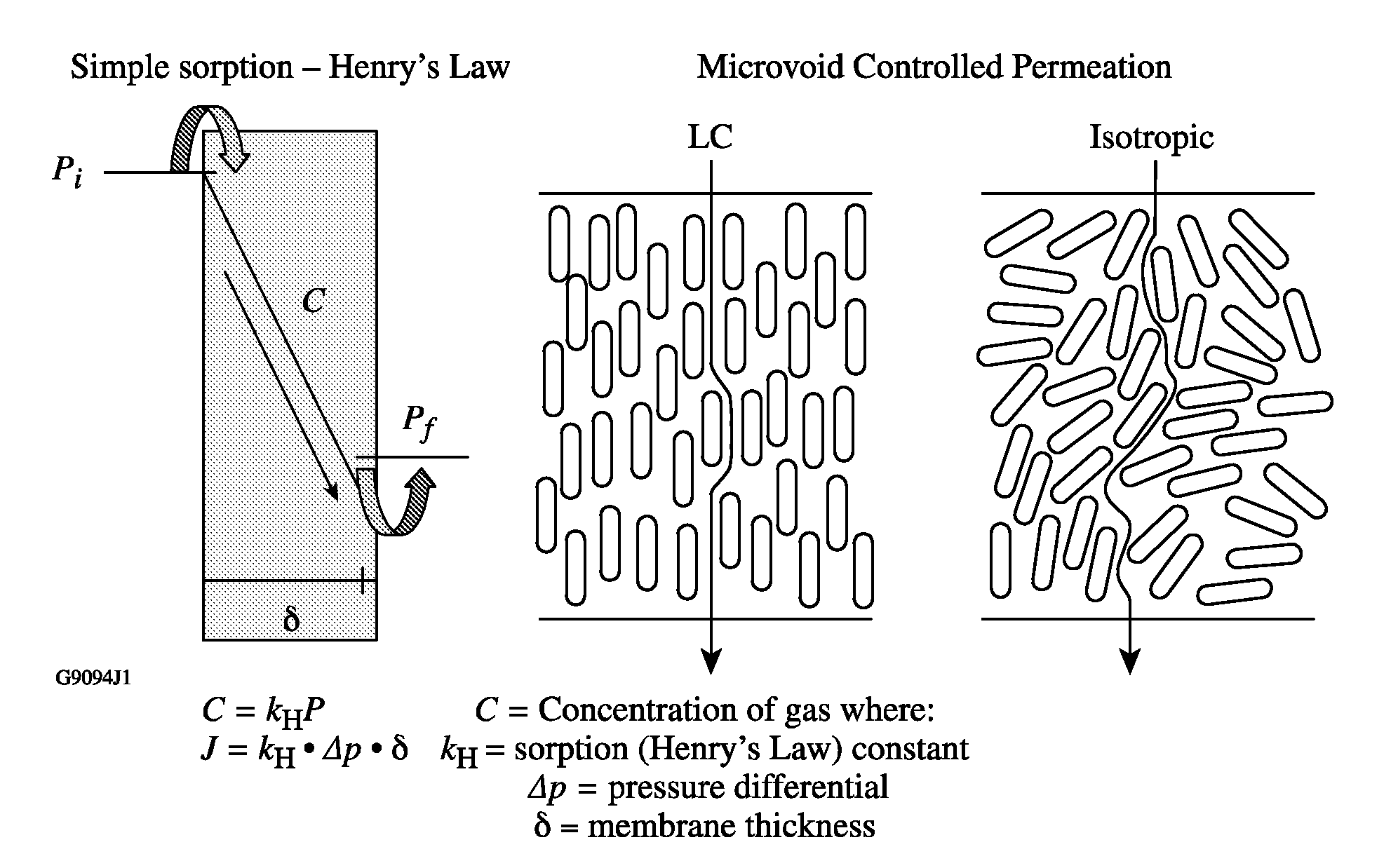
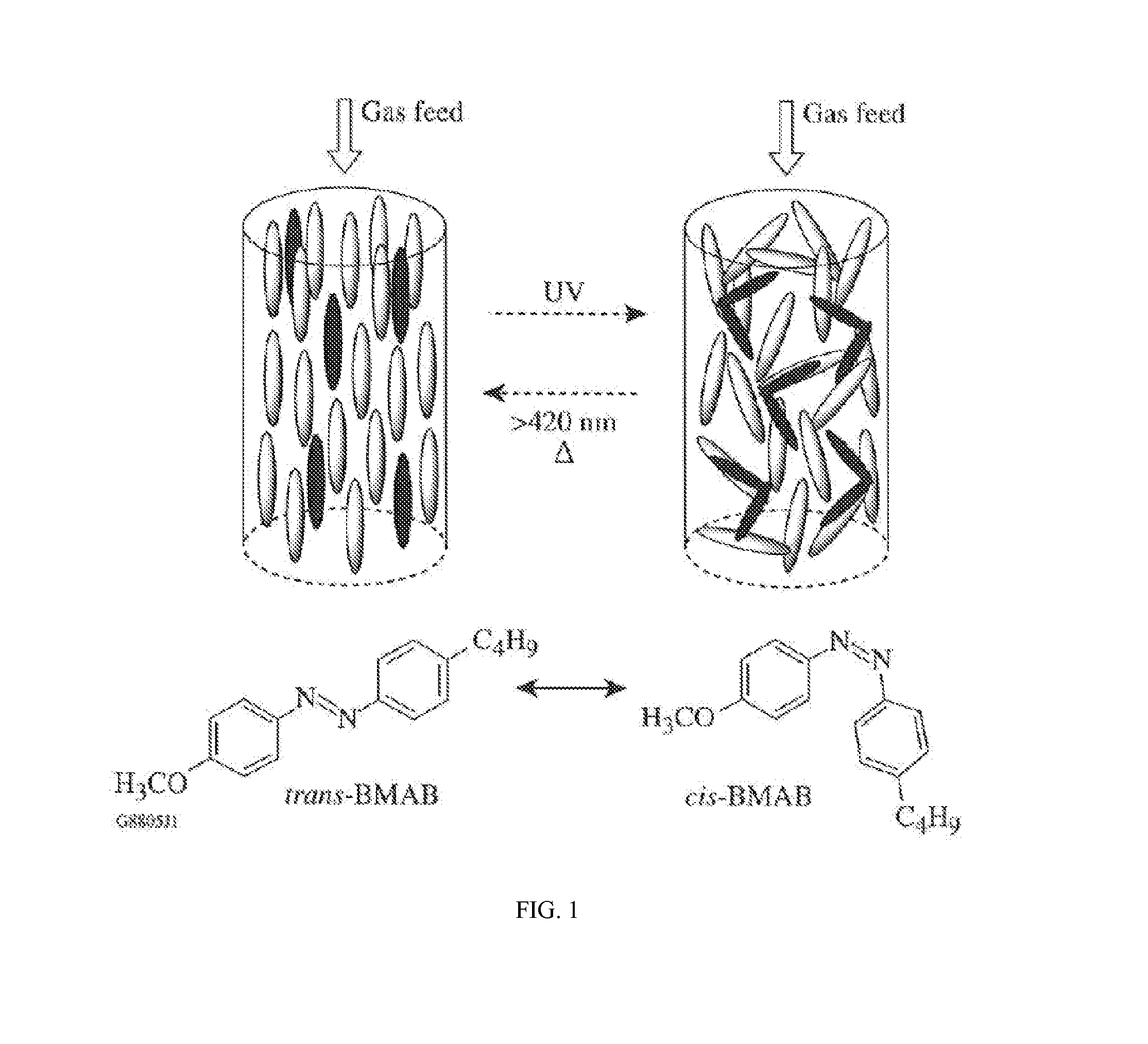
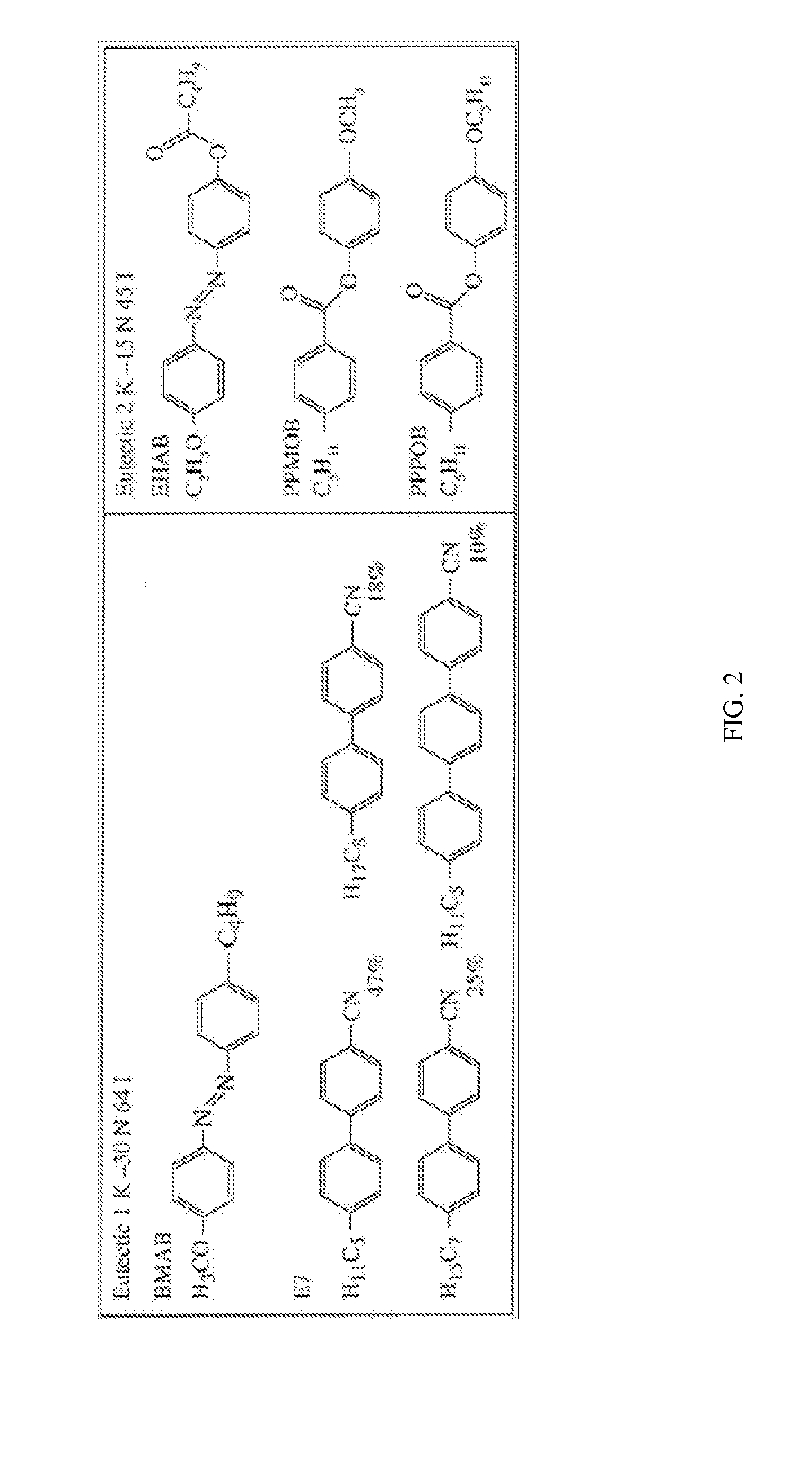
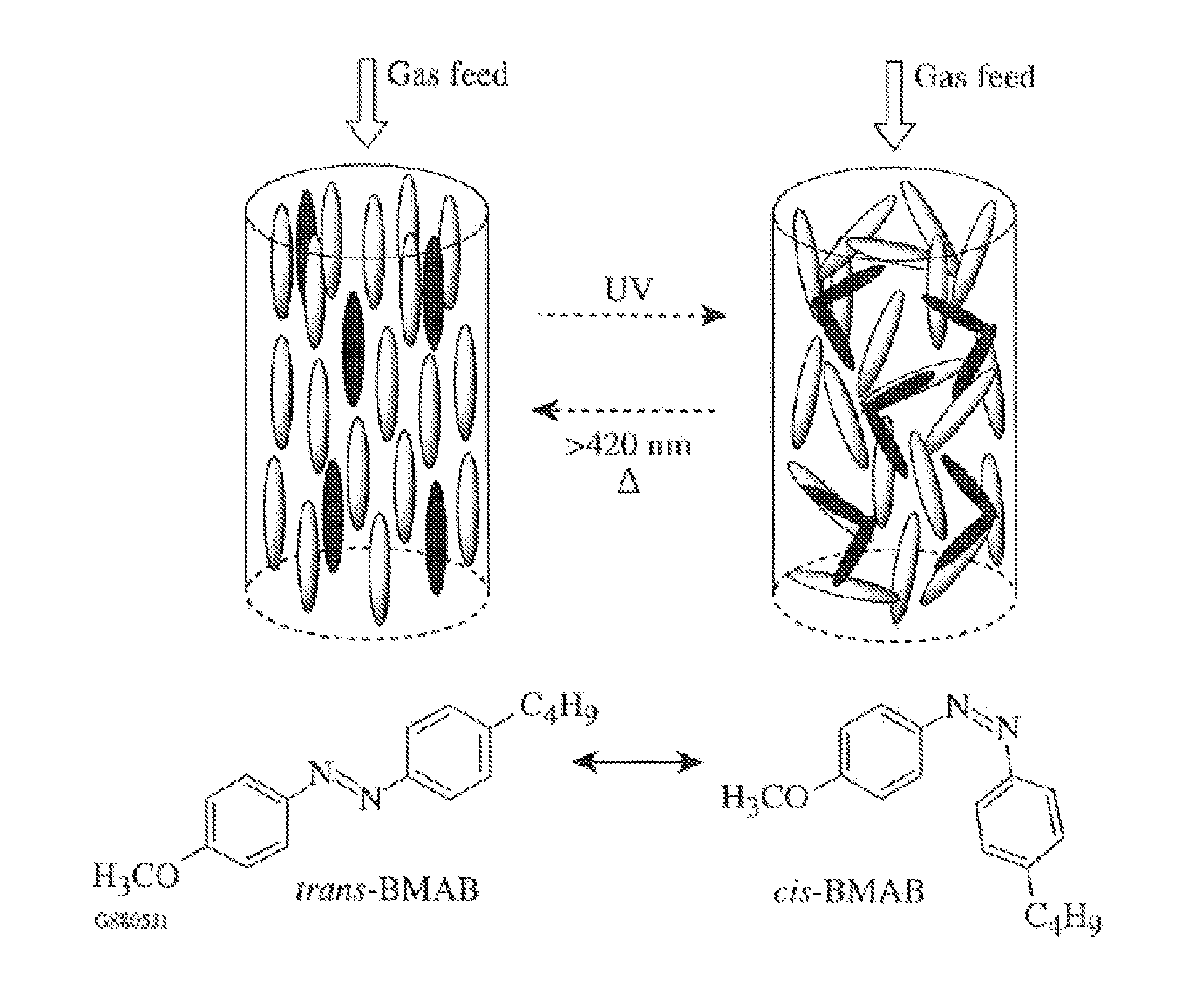
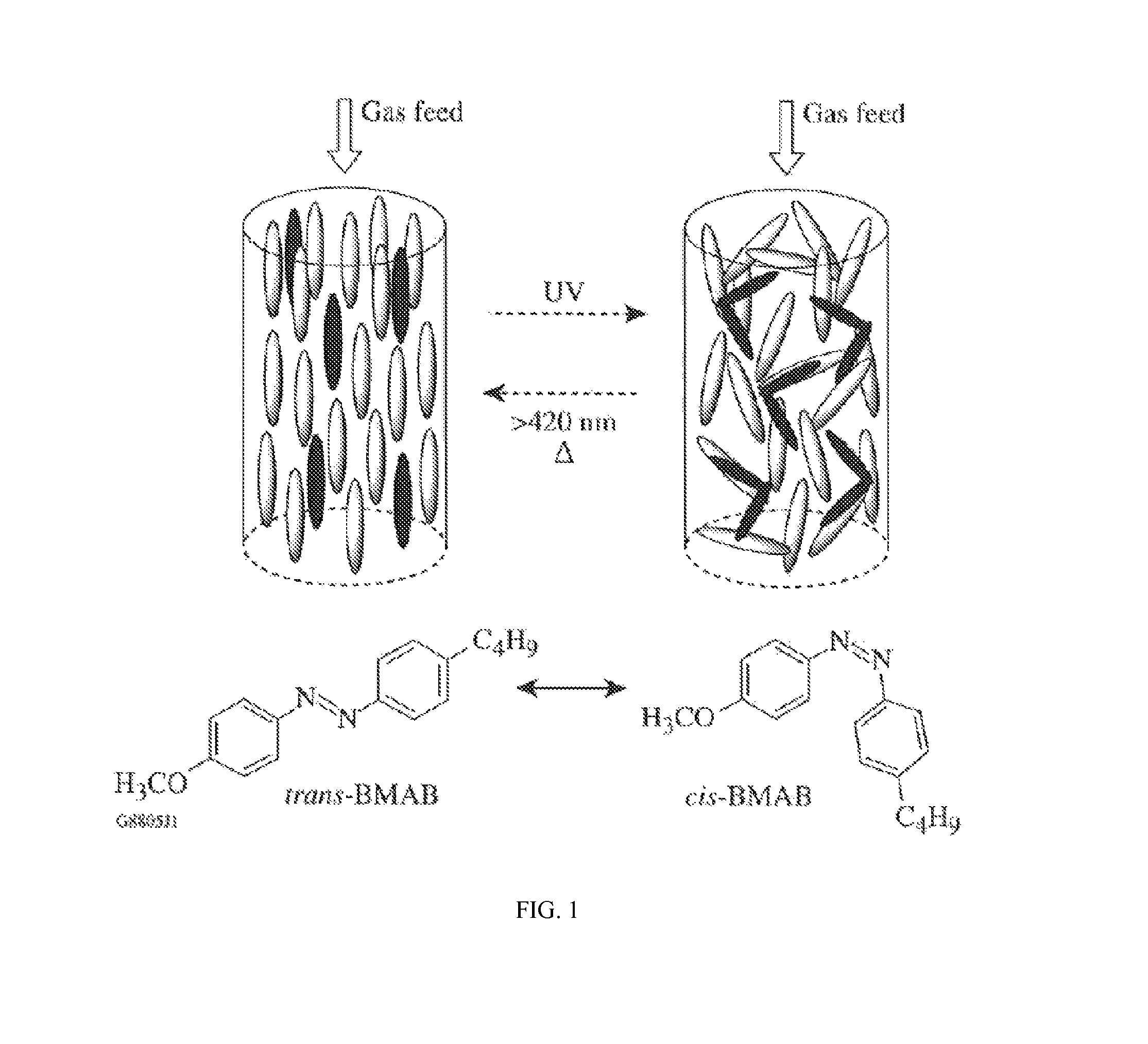
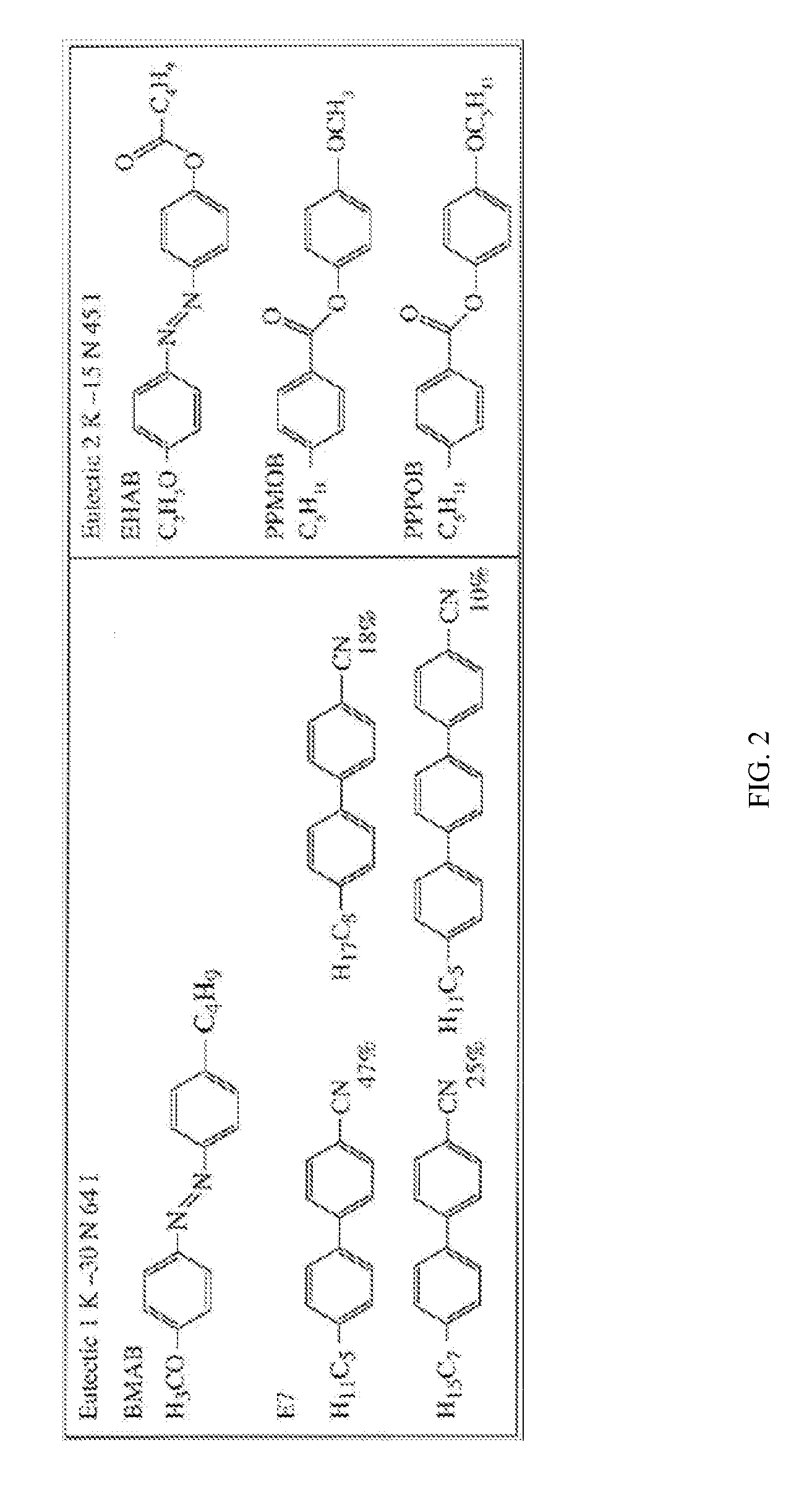
Switchable gas permeation membranes in which a photo-switchable low-molecular-weight liquid crystalline (LC) material acts as the active element, and a method of making such membranes. Different LC eutectic mixtures were doped with mesogenic azo dyes and infused into track-etched porous membranes with regular cylindrical pores. Photo-induced isothermal phase changes in the imbibed mesogenic material afforded large, reversible changes in the permeability of the photo-switchable membrane to nitrogen. For example, membranes imbibed with a photo-switchable cyanobiphenyl LC material demonstrated low permeability in the nematic state, while the photo-generated isotropic state demonstrated a 16×-greater sorption coefficient. Both states obey a high linear sorption behavior in accordance with Henry's Law. In contrast, membranes imbibed with a photo-switchable phenyl benzoate LC material showed the opposite permeability behavior to the biphenyl-imbibed membrane, along with nonlinear sorption behavior.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
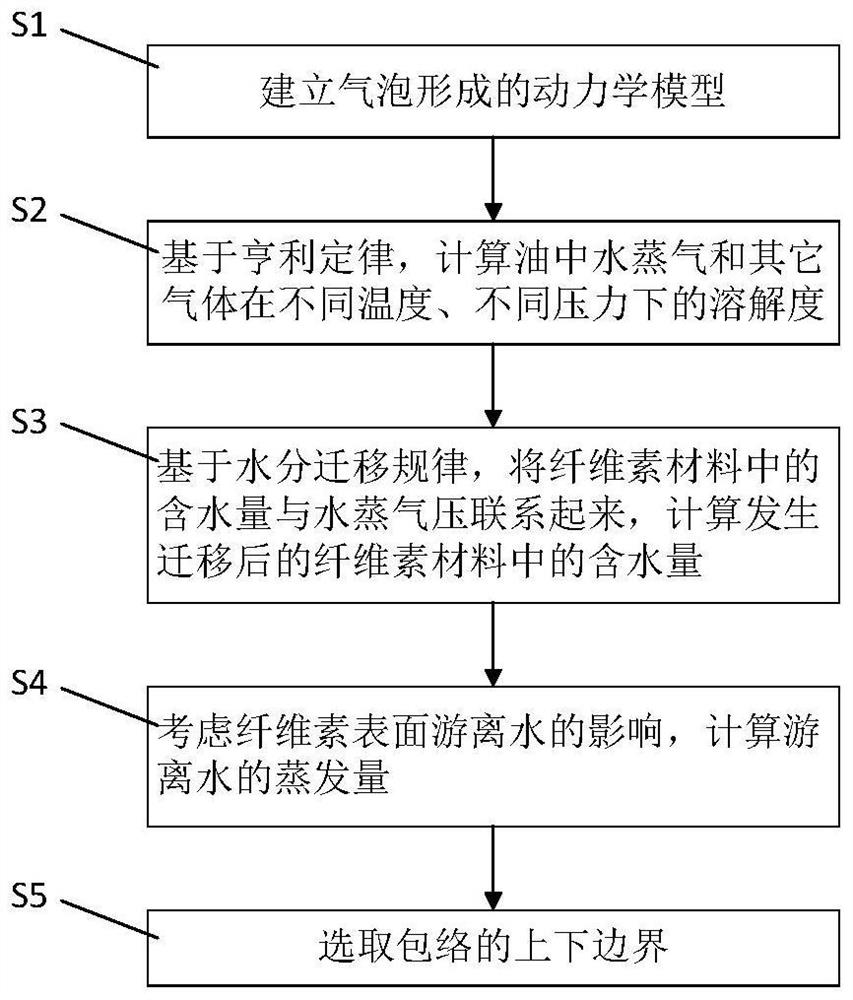
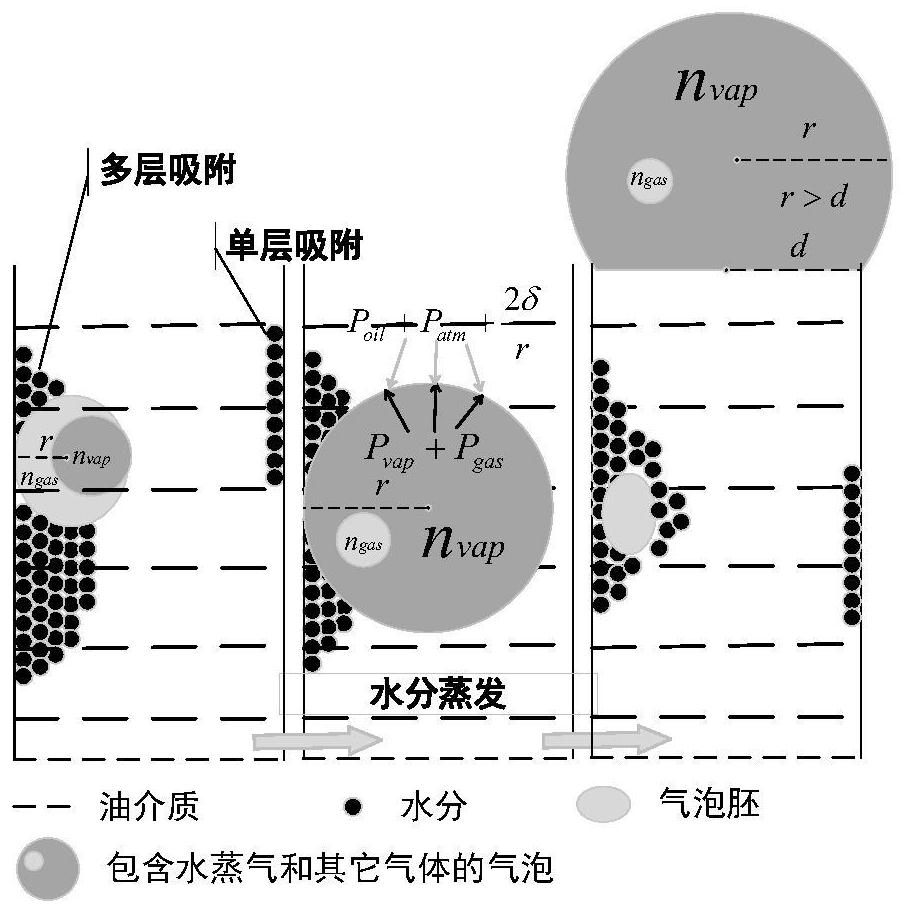
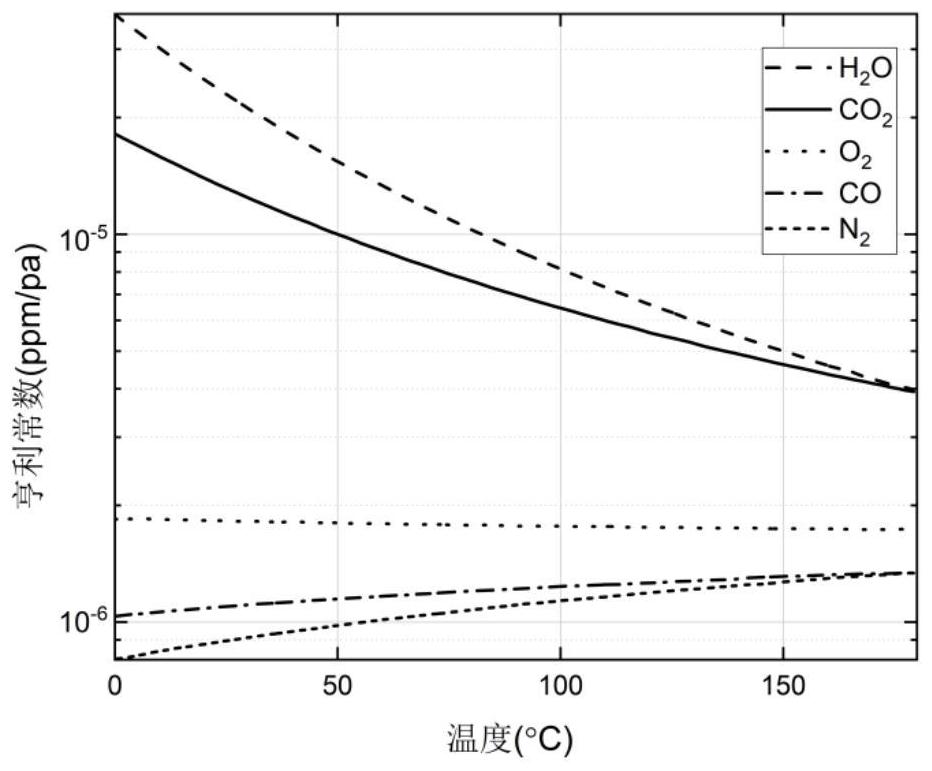
Method for detecting bubble effect in oil paper insulation based on initial temperature envelope
PendingCN114646850AImprove impactIncrease the impact of migrationTesting dielectric strengthThermometer applicationsCelluloseThermodynamics
The invention discloses a method for detecting a bubble effect in oil paper insulation based on initial temperature envelope. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a kinetic model formed by bubbles; on the basis of the Henry's law, the solubility of water vapor and gas except the water vapor in the oil at different temperatures and different pressures is calculated; on the basis of a water migration rule, the water content in the cellulose material is associated with the water vapor pressure, and the water content in the migrated cellulose material is calculated; the influence of free water on the cellulose surface is considered, and the evaporation capacity of free water is calculated; selecting upper and lower boundaries of the envelope; the method is based on a kinetic model formed by bubbles, influences of gas solubility in oil, a moisture migration rule, free water and the like on the envelope are considered, the envelope obtained through calculation can cover the bubble effect initial temperature obtained under different test conditions, the bubble generation risk in the transformer operation process is reduced, and the reliability of the transformer is improved. The method can be widely applied to an oil paper insulation system with the same dynamic description.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Aqueous ozone monitor utilizing gas stripping
ActiveUS9423340B2Measure is shortEliminating of methodWater treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesGas phaseTime profile
The present invention provides a means of measuring the concentration of ozone dissolved in water or another solvent. Small, discrete samples are sparged with air or another unreactive gas for a short period of time to measure a profile of ozone vs time in the sparge gas. The total amount of ozone in the original sample is obtained by integrating under the ozone vs time profile. A correction may be made for ozone remaining in the sample after a finite sparge time by integrating under the profile tail using a decay constant obtained from the measured ozone vs time profile. The method differs from previous methods based on sparging of the sample in that a Henry's Law equilibrium or constant ratio of ozone present in the gas and liquid phases is not assumed and the flow rates of sample and sparge gas are not continuous.
Owner:LUDLUM MEASUREMENTS
Production device, preparation method and use method of low-nitrogen carburant for clean steel refining
The invention discloses a production device, a preparation method and a use method of a low-nitrogen carburant for clean steel refining, belongs to the field of carbon and ferrous metallurgy, and relates to a method for reducing nitrogen content in steel and improving molten steel quality. The preparation method of the low-nitrogen carburant for clean steel refining is characterized in that according to the Henry's law (which is a theory related to solubility of gas in solid), nitrogen is removed from petroleum tar coke by a high temperature and then the petroleum tar coke is cooled to a natural temperature by a quenching method so that carburant nitrogen content is reduced and the excellent low-nitrogen carburant for clean steel refining is obtained. Compared with the common carburant, the low-nitrogen carburant for clean steel refining has very low nitrogen content and thus the low-nitrogen carburant can carry a small amount of nitrogen into steel so that steel nitrogen content is reduced. The low-nitrogen carburant for clean steel refining has fixed carbon content more than 97wt%, ash content less than 1.5wt%, volatile content less than 1.0wt%, sulfur content of 0.3wt% and nitrogen content less than 0.02wt%.
Owner:BEIJING SINOSLAG METALLURGICAL TECH
Argon/oxigen selective X-zeolite
An AgX-type zeolite having a silver exchange level of 20-70% and a Ar / O2 Henry's law selectivity ratio at 23° C. of 1.05 or greater has an optimum combination of selectivity for argon over oxygen at lower cost than higher silver exchange levels. This material can be used in oxygen VSA / PSA processes to produce oxygen at purities above 97%.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
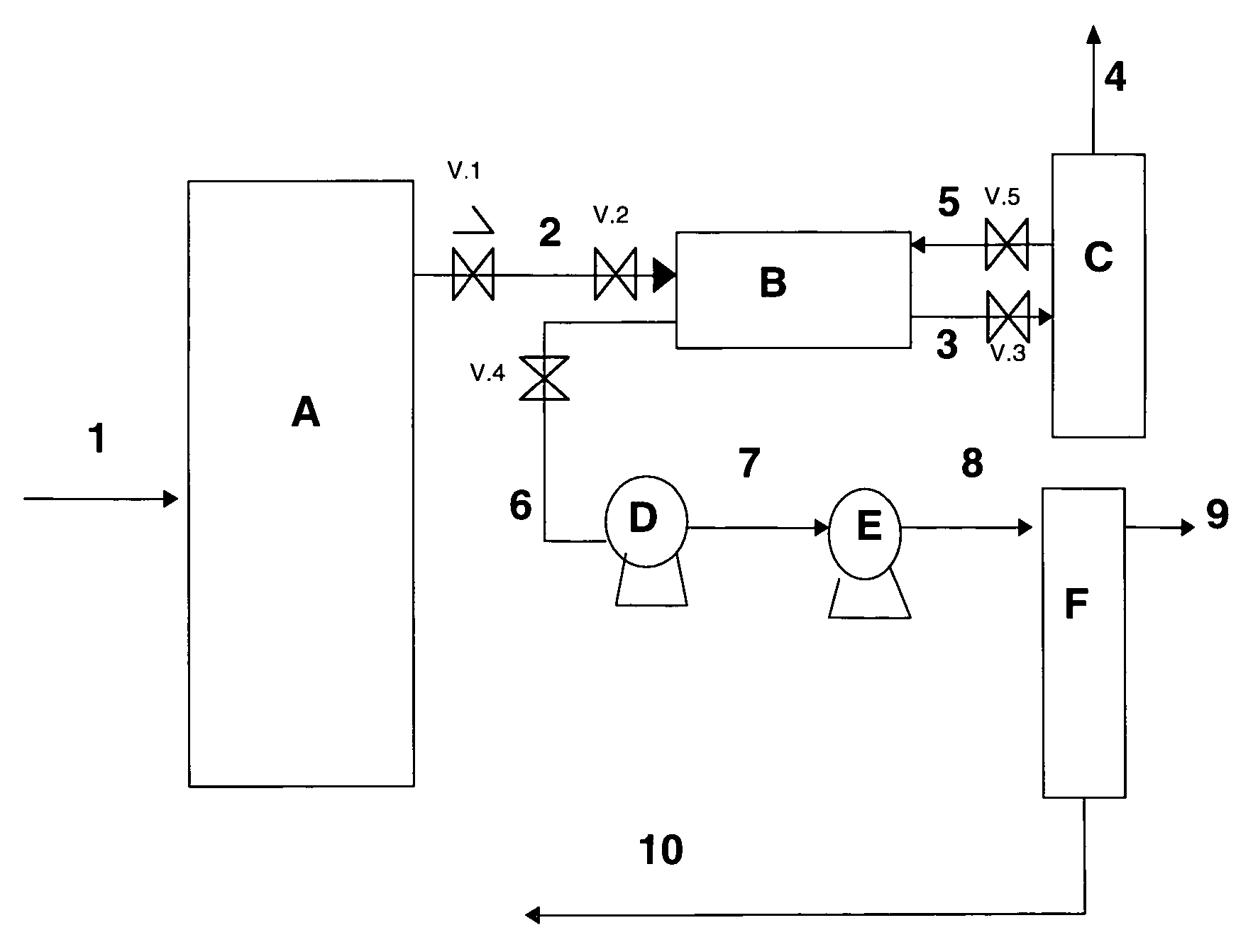
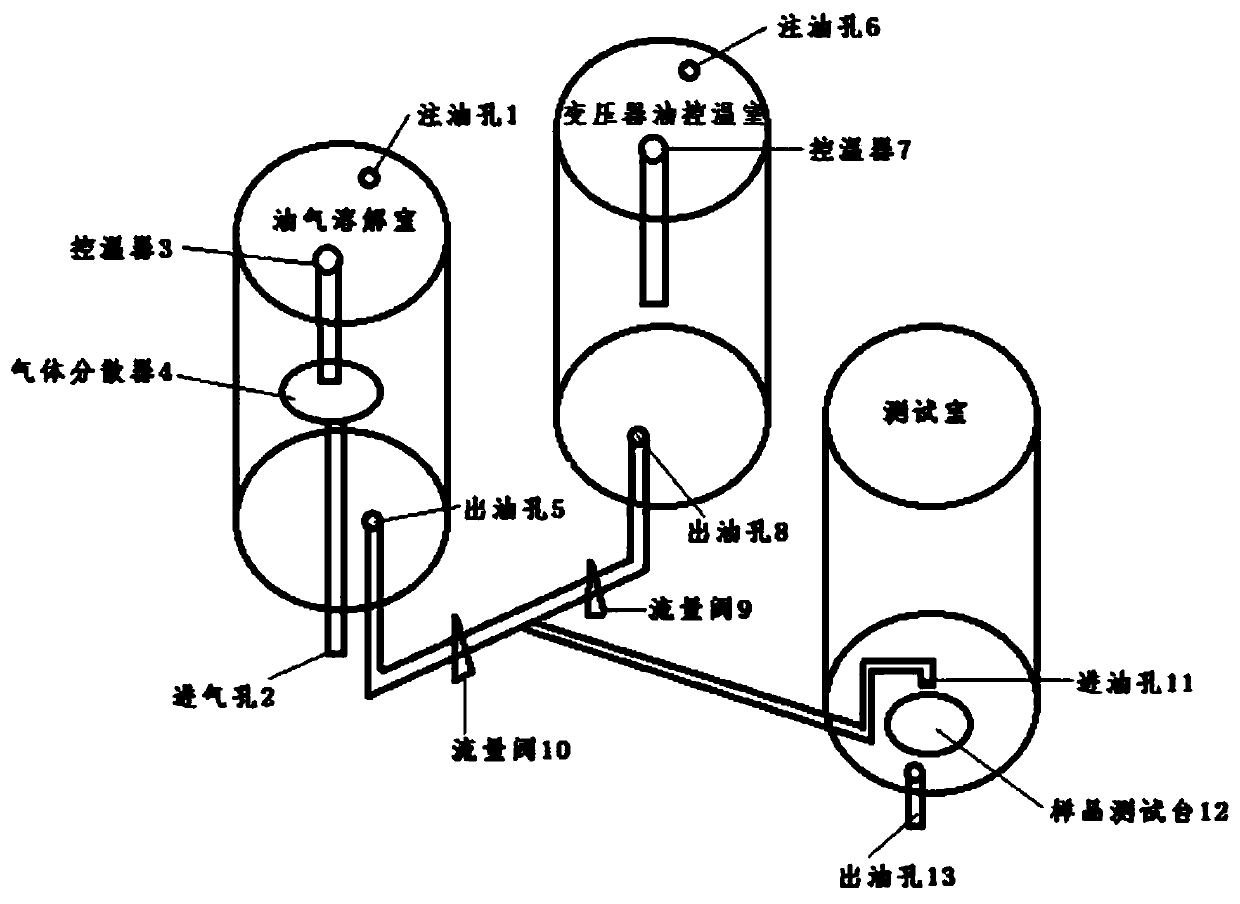
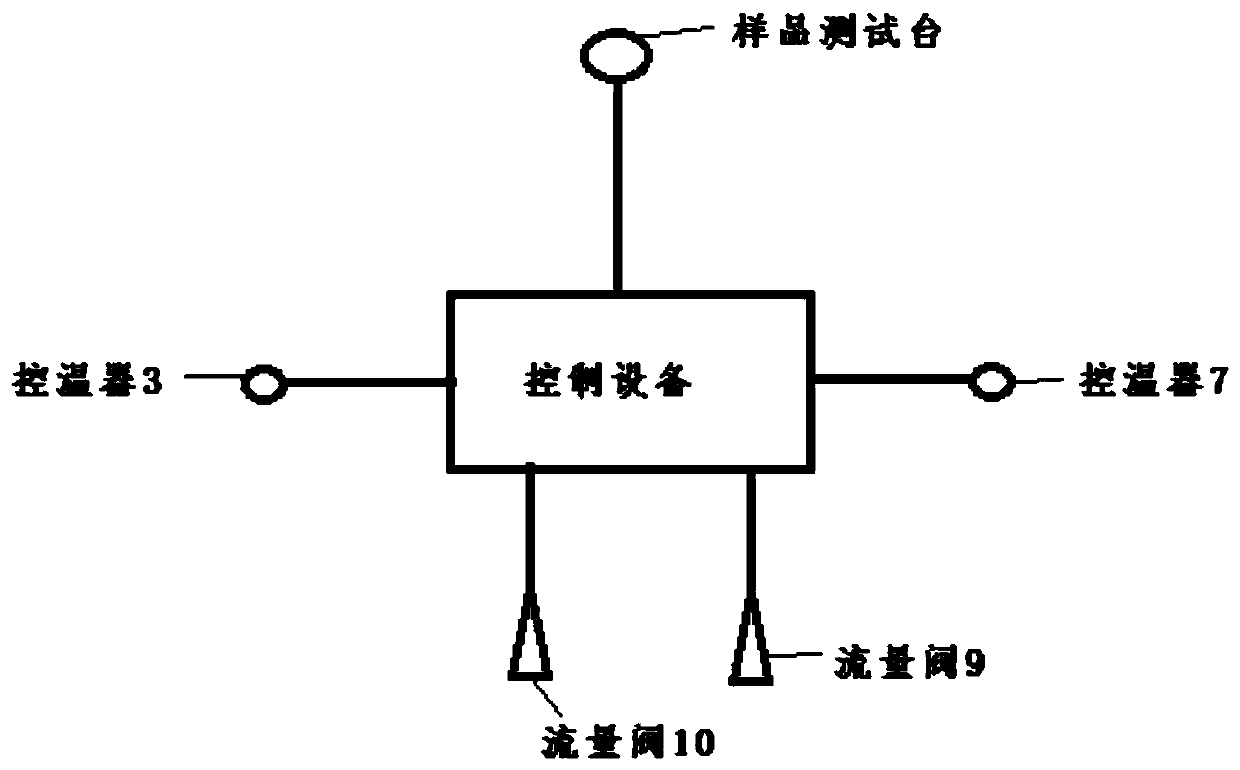
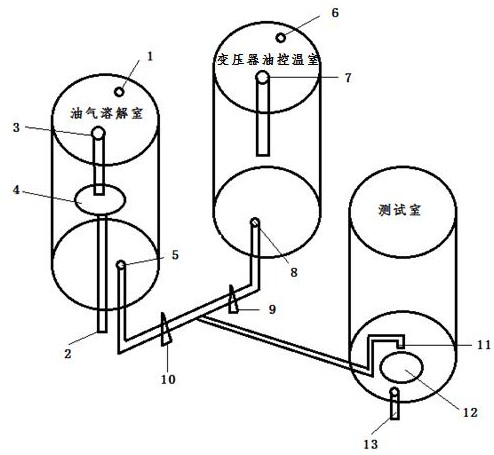
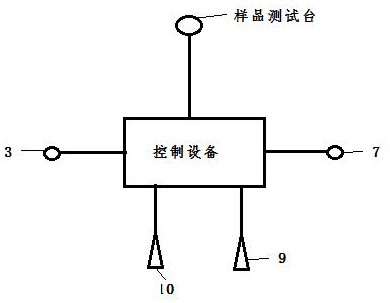
Preparation method of dissolved gas in transformer oil and preparation device
ActiveCN110152554AFast preparationTransportation and packagingMixing methodsTemperature controlTransformer oil
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dissolved gas in transformer oil and a preparation device. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing transformer oil a and transformer oil b which are identical, introducing a gas into the transformer oil a till a saturation state of the gas, adjusting the transformer oil a and the transformer oil b till an identical temperature, controlling a flow ratio of the transformer oil a and the transformer oil b according to a Wilhelm Ostwald coefficient led by the Henry's law, and finally preparing transformer oil of an appointeddissolved gas concentration. The preparation device comprises an oil-gas dissolving chamber, a transformer oil temperature control chamber, a testing chamber and control equipment, wherein the oil-gas dissolving chamber, the transformer oil temperature control chamber and the testing chamber are respectively connected with the control equipment. The preparation method of the dissolving gas in thetransformer oil, which is disclosed by the invention, is good in practicability, controllable in operation method, simple in step and good in repeatability. The preparation device disclosed by the invention has a wide application range, and can be used as a preparation device of dissolved gas oil of various types of oil.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
A step temperature rise airtight emission method for simultaneous determination of formaldehyde emission characteristic parameters of building materials at multiple temperatures
ActiveCN108918575BImprove measurement efficiencySave time and costMaterial thermal analysisThermodynamicsAnalytical chemistry
The invention relates to a step-temperature closed emission method for simultaneous determination of formaldehyde emission characteristic parameters of building materials at multiple temperatures. Based on a adsorption potential theory and a Henry's law, a functional relationship between a separation coefficient K and an initial dissipative concentration C0 is established, and an analytical formula of the equilibrium concentration Cequ of formaldehyde in the closed environment is derived. A sealed environment cabin is used to maintain a constant temperature and a humidity space, and the building material samples are subjected to formaldehyde emission test, and the formaldehyde hourly concentration and equilibrium concentration at the initial temperature are measured. The temperature is then raised and the corresponding new equilibrium concentration is measured. The above operations can be repeated in sequence to obtain a formaldehyde equilibrium concentration value at multiple temperatures. The nonlinear fitting is carried out on the formaldehyde hourly concentration at the initial temperature, the K at the temperature can be determined. When the Cequ of the building material at other temperatures is known, the K at the corresponding temperature can be quickly obtained by the ratio of the equilibrium concentrations, and the corresponding C0 can be calculated. The method greatlyimproves the measurement efficiency of formaldehyde emission characteristics.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A preparation method and preparation device of dissolved gas in transformer oil
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Forward osmosis device, and forward osmosis method
ActiveUS20160236951A1Prevent leakageReduce the amount of solutionWater treatment parameter controlMembranesStandard stateSemipermeable membrane
A forward osmosis apparatus is improved. A forward osmosis apparatus, comprising a diluting means for bringing a feed solution and a draw solution comprising a cation source and an anion source in an ionized state into contact through a semi-permeable membrane and diluting the draw solution with water separated from the feed solution by means of the semi-permeable membrane;a separating means for separating the draw solution that has been diluted by the diluting means into the cation source and anion source and into water; anda dissolving means, returning the cation source and the anion source that have been separated by the separating means to, and dissolving the cation source and anion source in, the draw solution that has been diluted;wherein the molecular weight of the cation source in an uncharged state is 31 or greater and the Henry's law constant of each of the anion source and cation source is 1.0×104 (Pa / mol·fraction) or greater in a standard state.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photo-switchable membrane and method
Switchable gas permeation membranes in which a photo-switchable low-molecular-weight liquid crystalline (LC) material acts as the active element, and a method of making such membranes. Different LC eutectic mixtures were doped with mesogenic azo dyes and infused into track-etched porous membranes with regular cylindrical pores. Photo-induced isothermal phase changes in the imbibed mesogenic material afforded large, reversible changes in the permeability of the photo-switchable membrane to nitrogen. For example, membranes imbibed with a photo-switchable cyanobiphenyl LC material demonstrated low permeability in the nematic state, while the photo-generated isotropic state demonstrated a 16×-greater sorption coefficient. Both states obey a high linear sorption behavior in accordance with Henry's Law. In contrast, membranes imbibed with a photo-switchable phenyl benzoate LC material showed the opposite permeability behavior to the biphenyl-imbibed membrane, along with nonlinear sorption behavior.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Energy-saving deoxidation system of industrial boiler
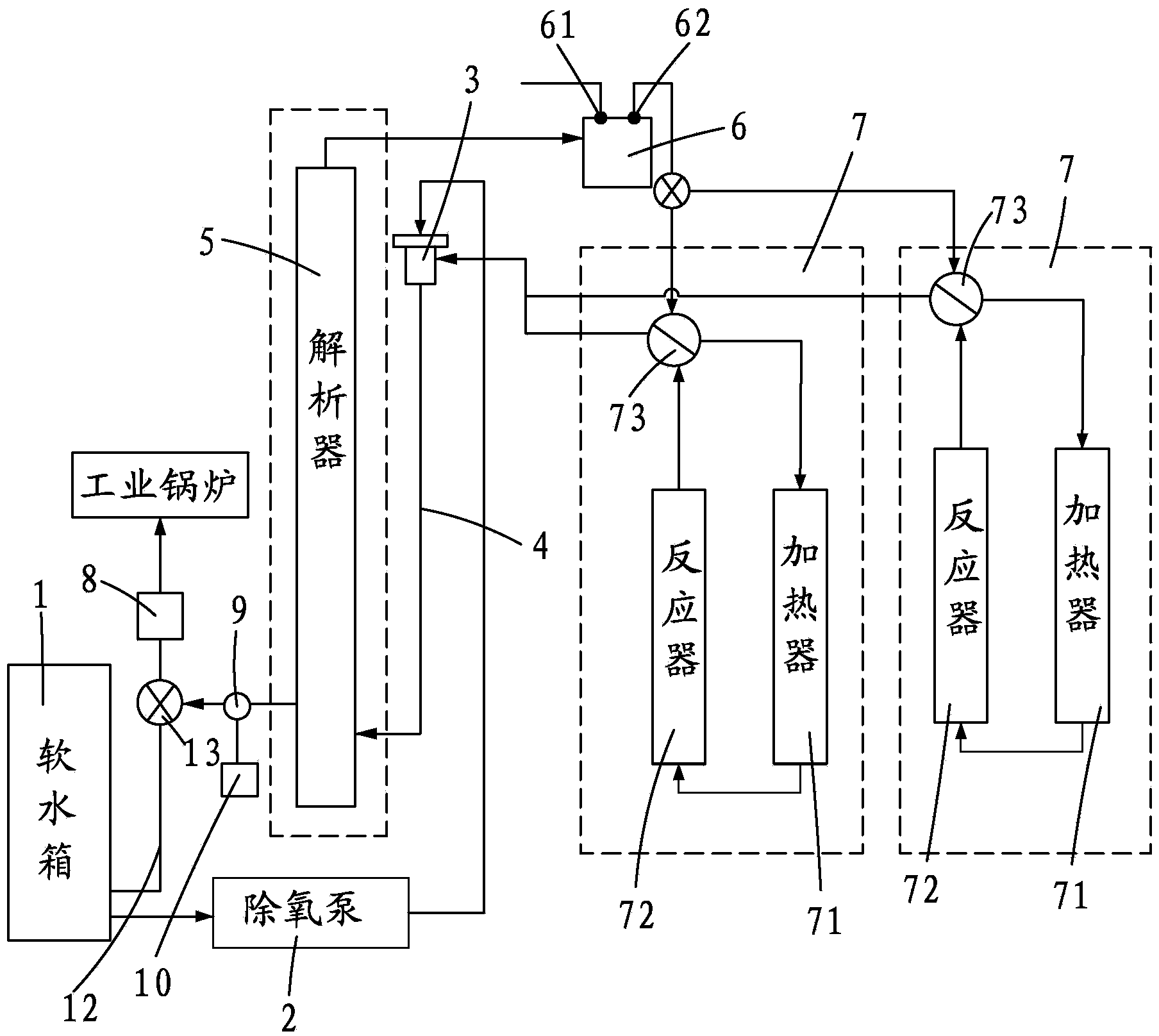
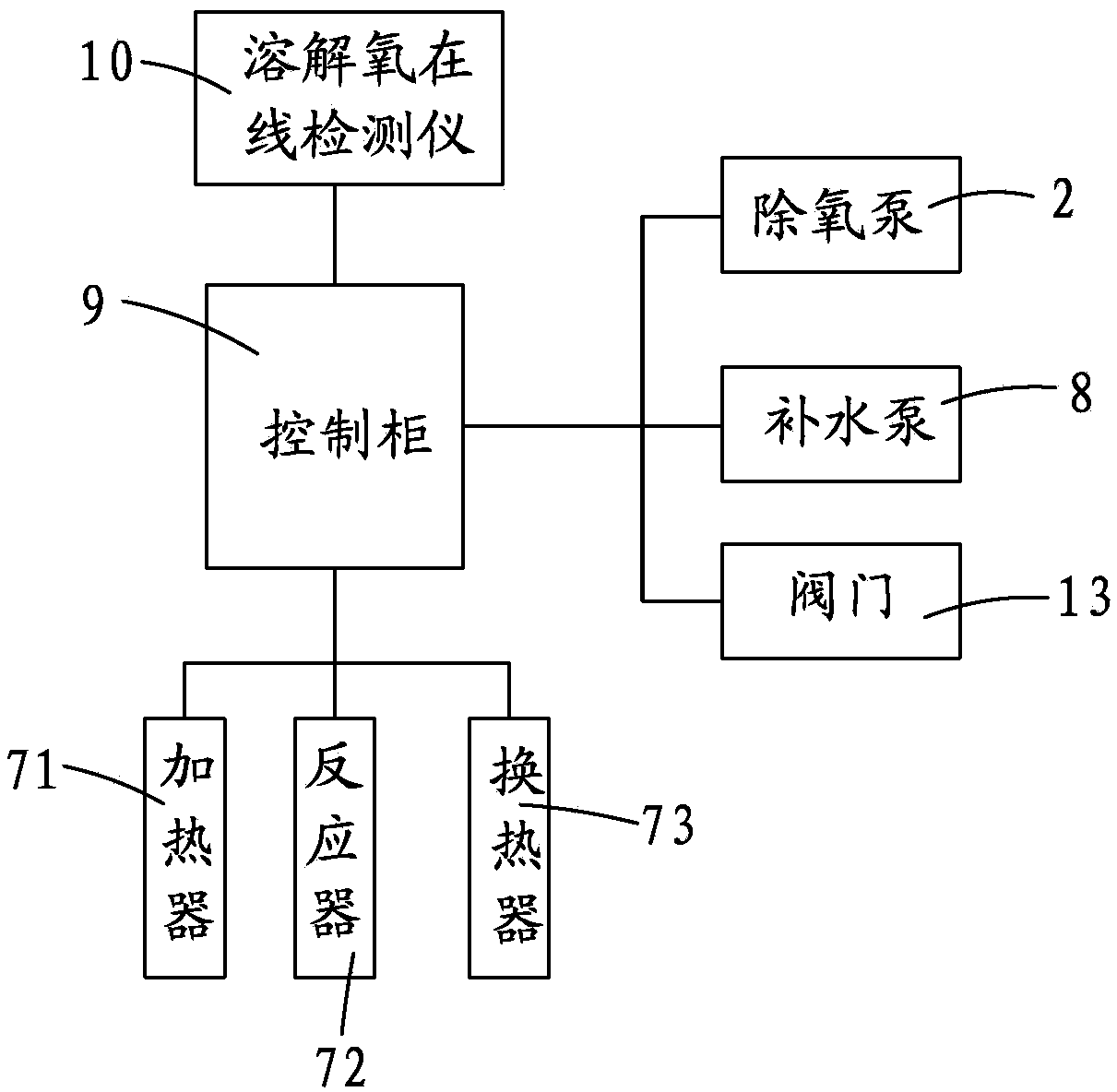
InactiveCN103818981ADoes not affect workEasy temperature controlWater/sewage treatment by degassingRecuperatorEngineering
The invention provides an energy-saving deoxidation system of an industrial boiler. The system comprises a soft water tank, a deoxidation pump, an ejector, a mixing pipe, an analyzer and at least two deoxidation combined bodies, wherein any one of the deoxidation combined bodies comprises a heater, a reactor and a heat exchanger which are sequentially connected end to end; and the water outlet of the soft water tank is connected with the deoxidation pump, the heat exchangers of the deoxidation pump and the deoxidation combined bodies are connected with the water inlet of the ejector, the water outlet of the ejector is connected with the water inlet of the analyzer through the mixing pipe, the water outlet of the analyzer is connected to the industrial boiler through a water supplementing pump, and a steam outlet is connected with a steam-water separator. The steam-water separator is provided with a water exhaust port and a gas exhaust port. The gas exhaust port is connected with the heat exchanger of the deoxidation combined body. The system provided by the invention based on henry's law is low in energy consumption and convenient to maintain.
Owner:江苏凯弘新能源管理有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com