Patents
Literature
91 results about "Metal oxide silicon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
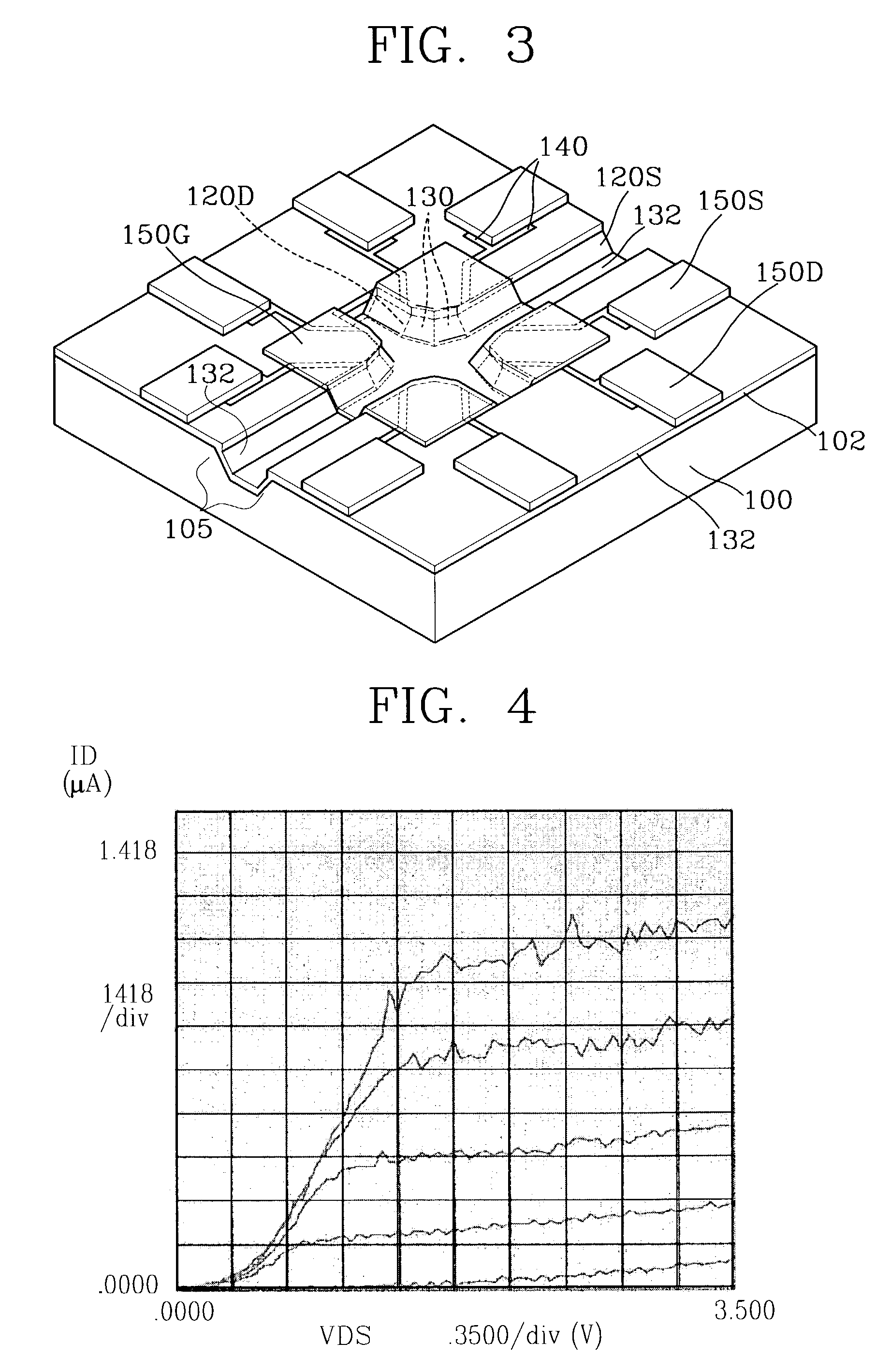
Method and apparatus improving gate oxide reliability by controlling accumulated charge
ActiveUS20070069291A1Improving nonlinear responses and harmonic and intermodulaton distortion effectsReduce non-linearitySolid-state devicesElectronic switchingMOSFETDielectric
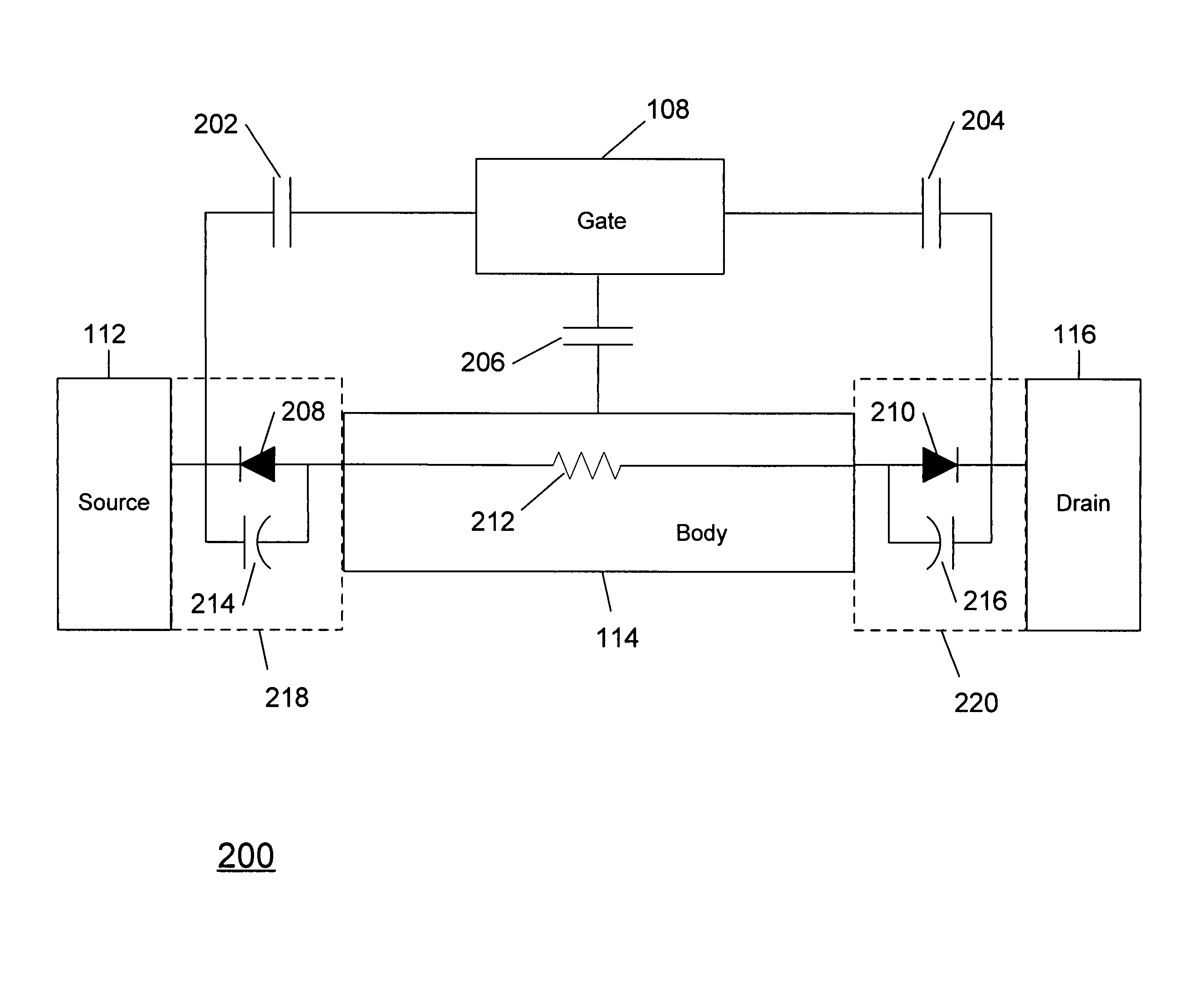
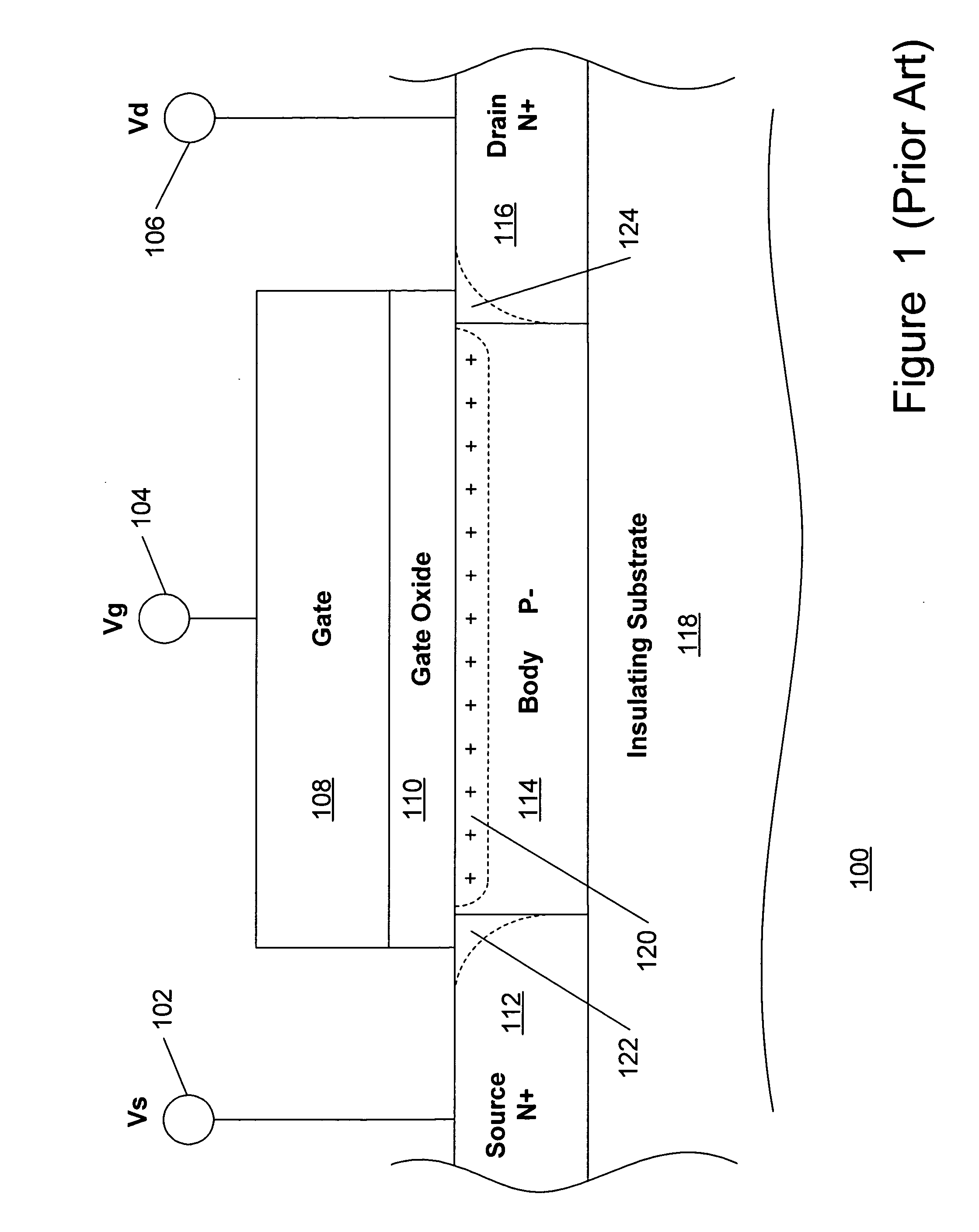
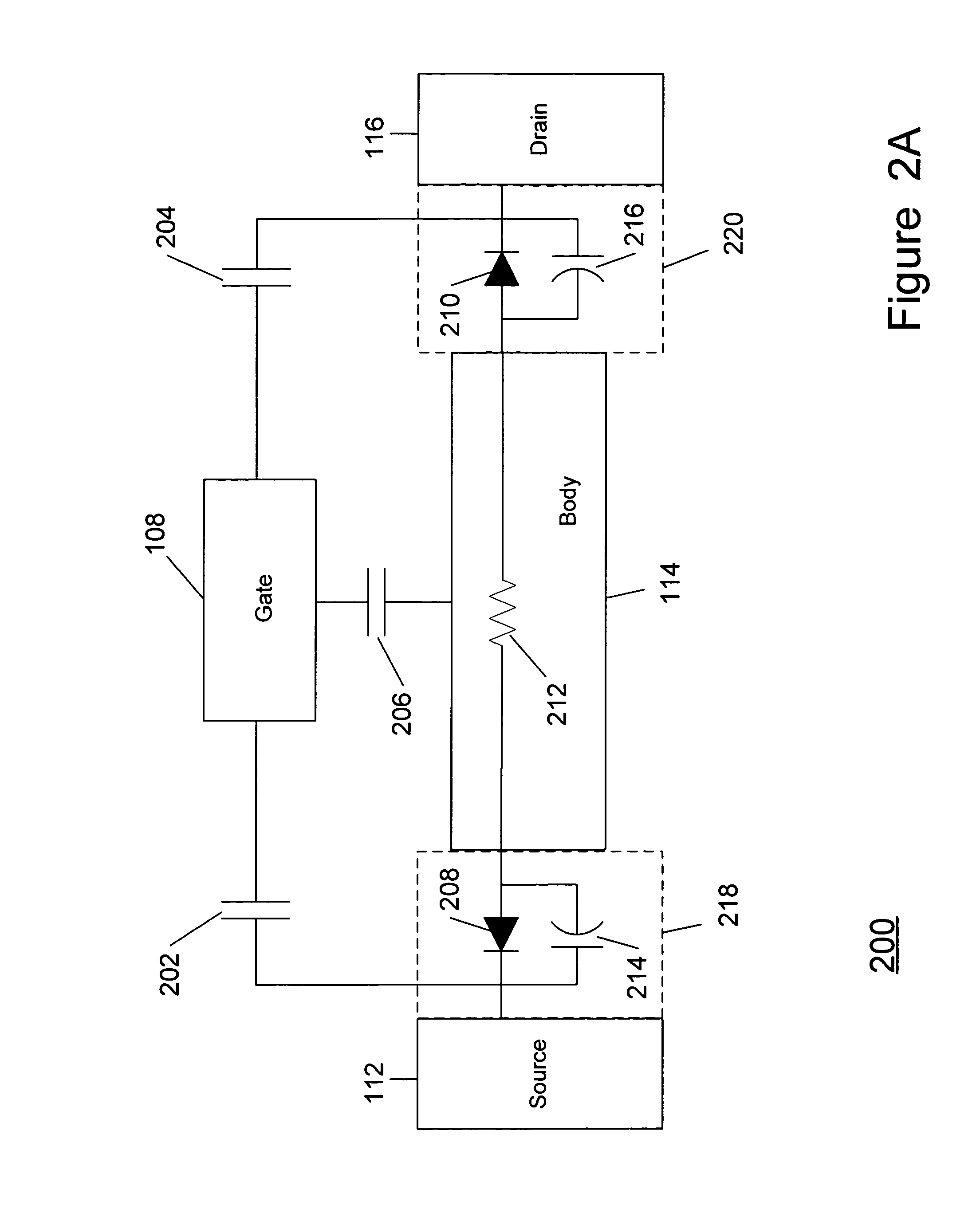
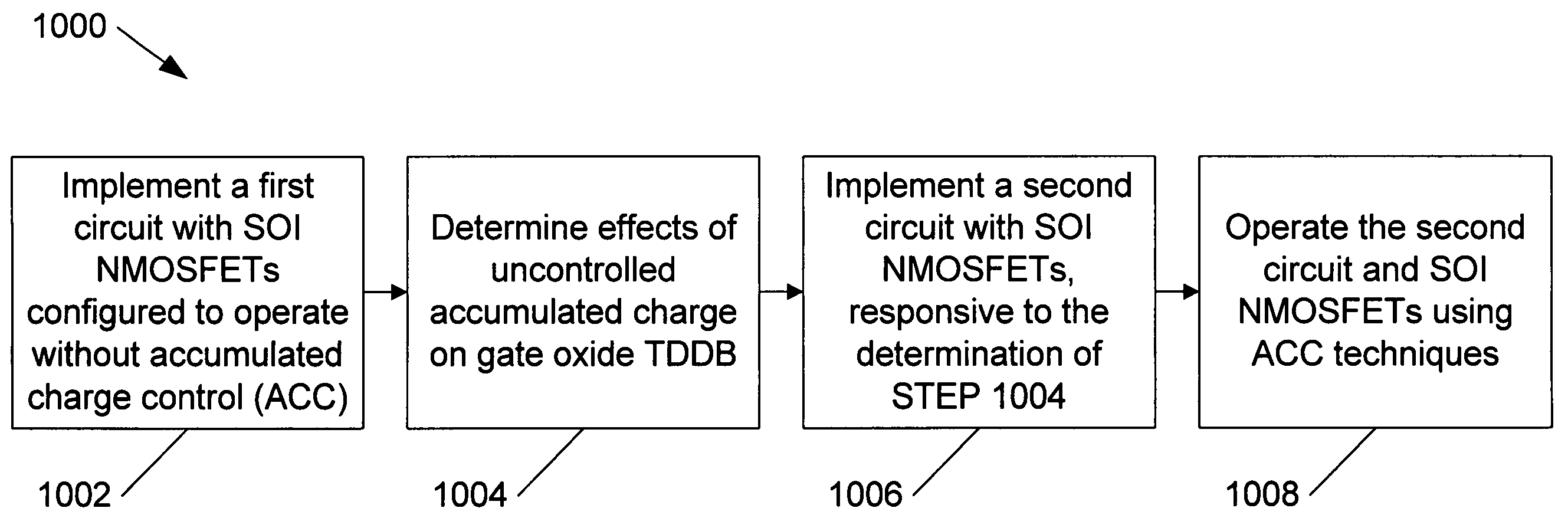
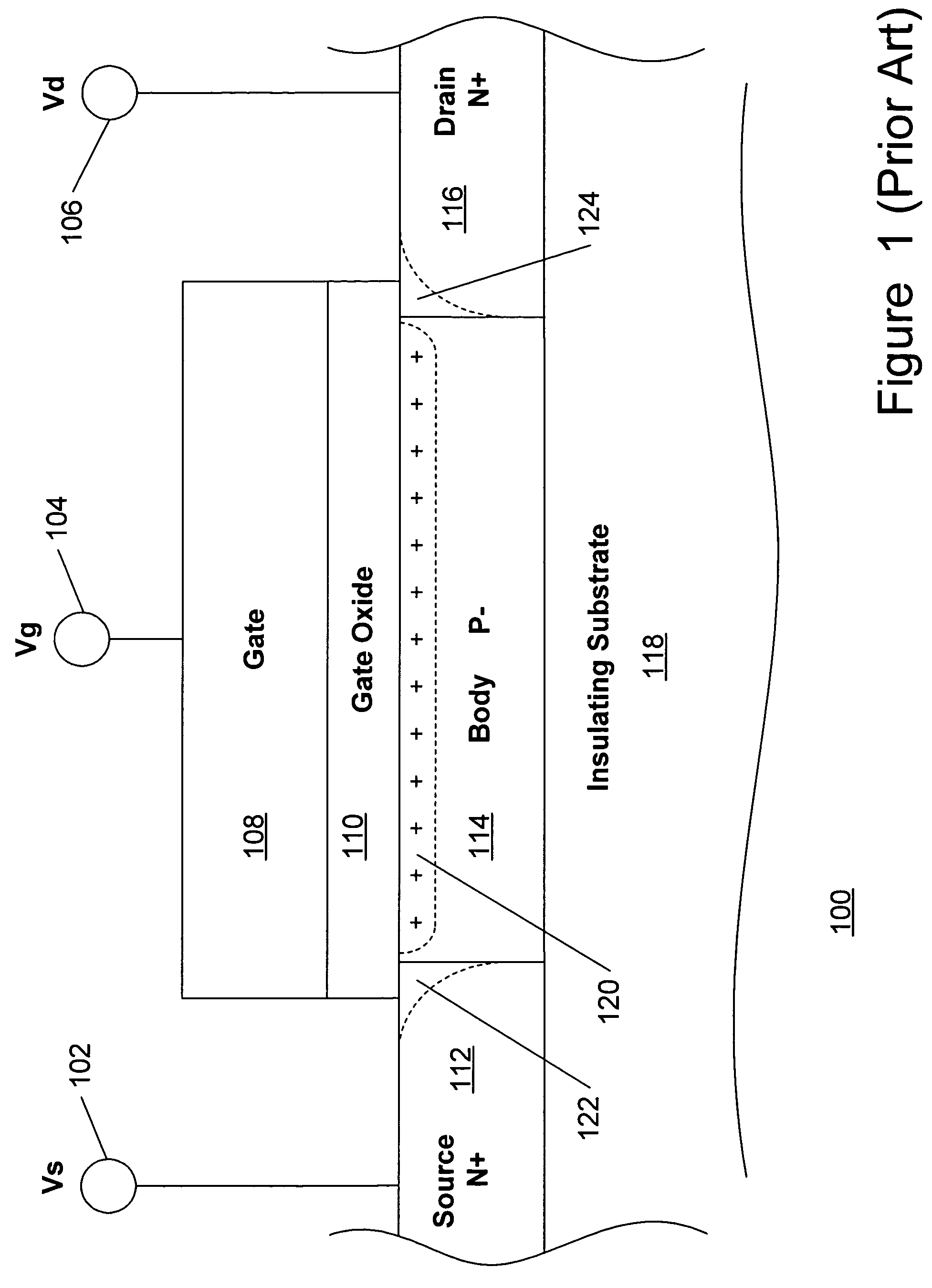
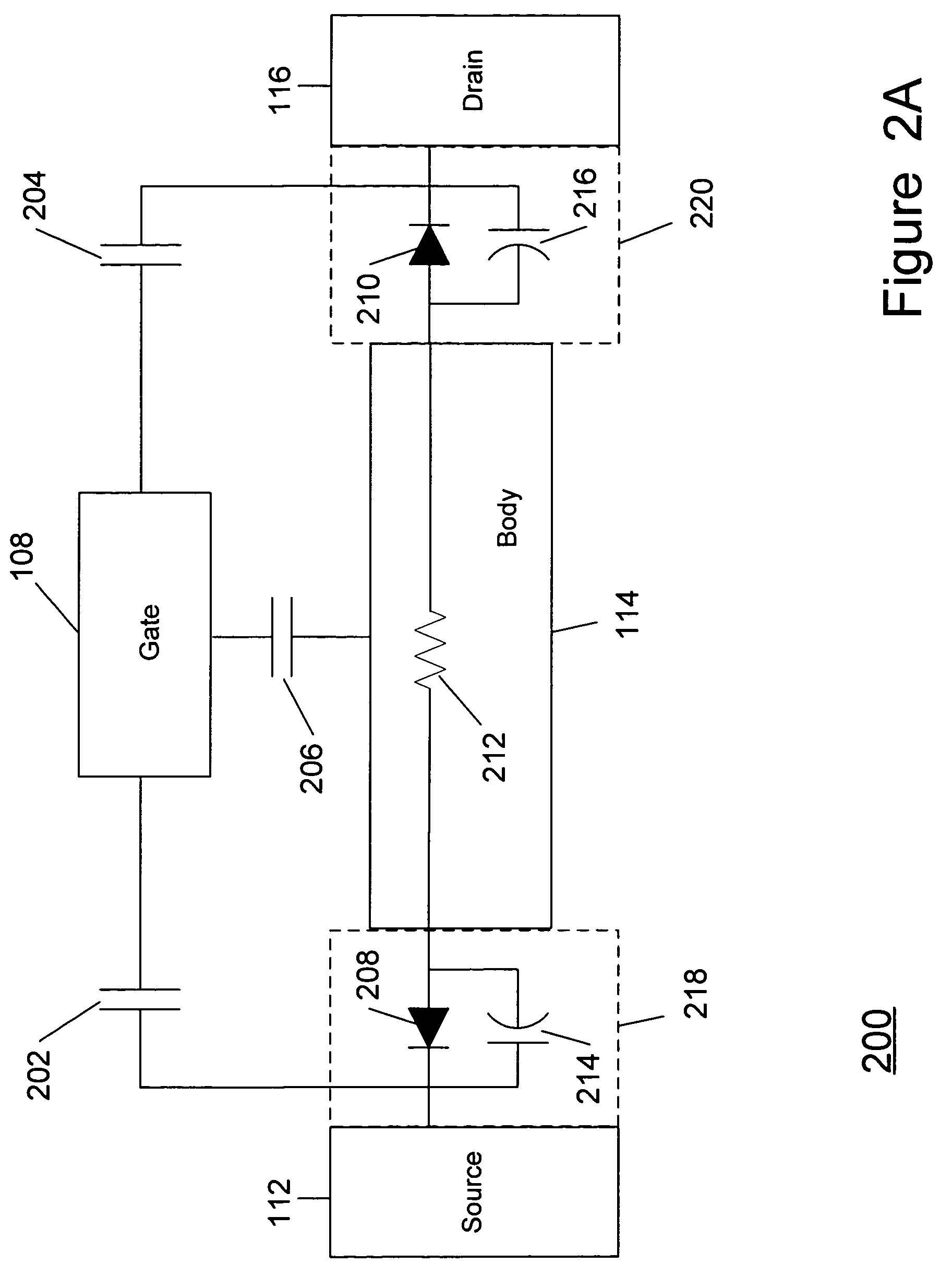
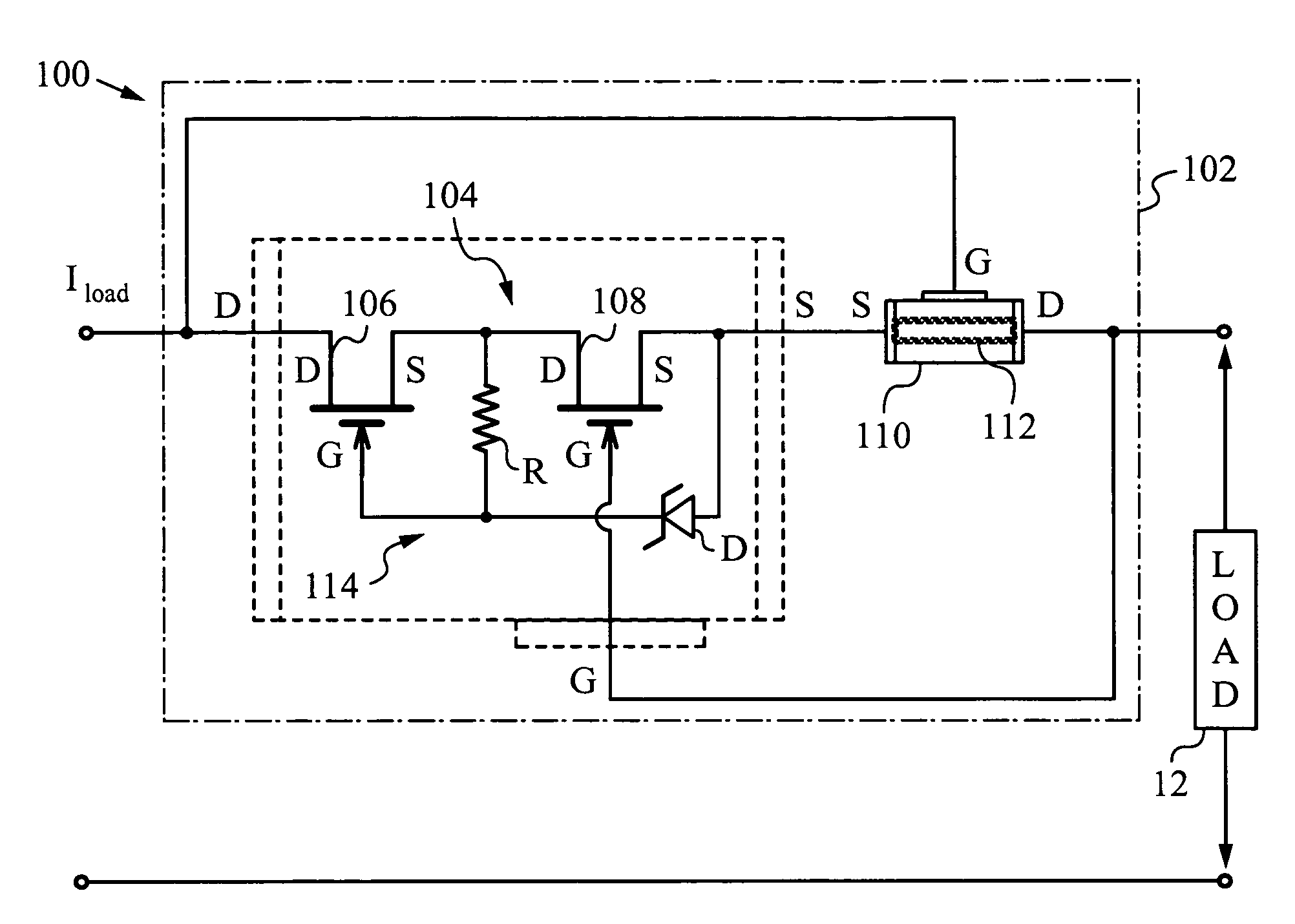
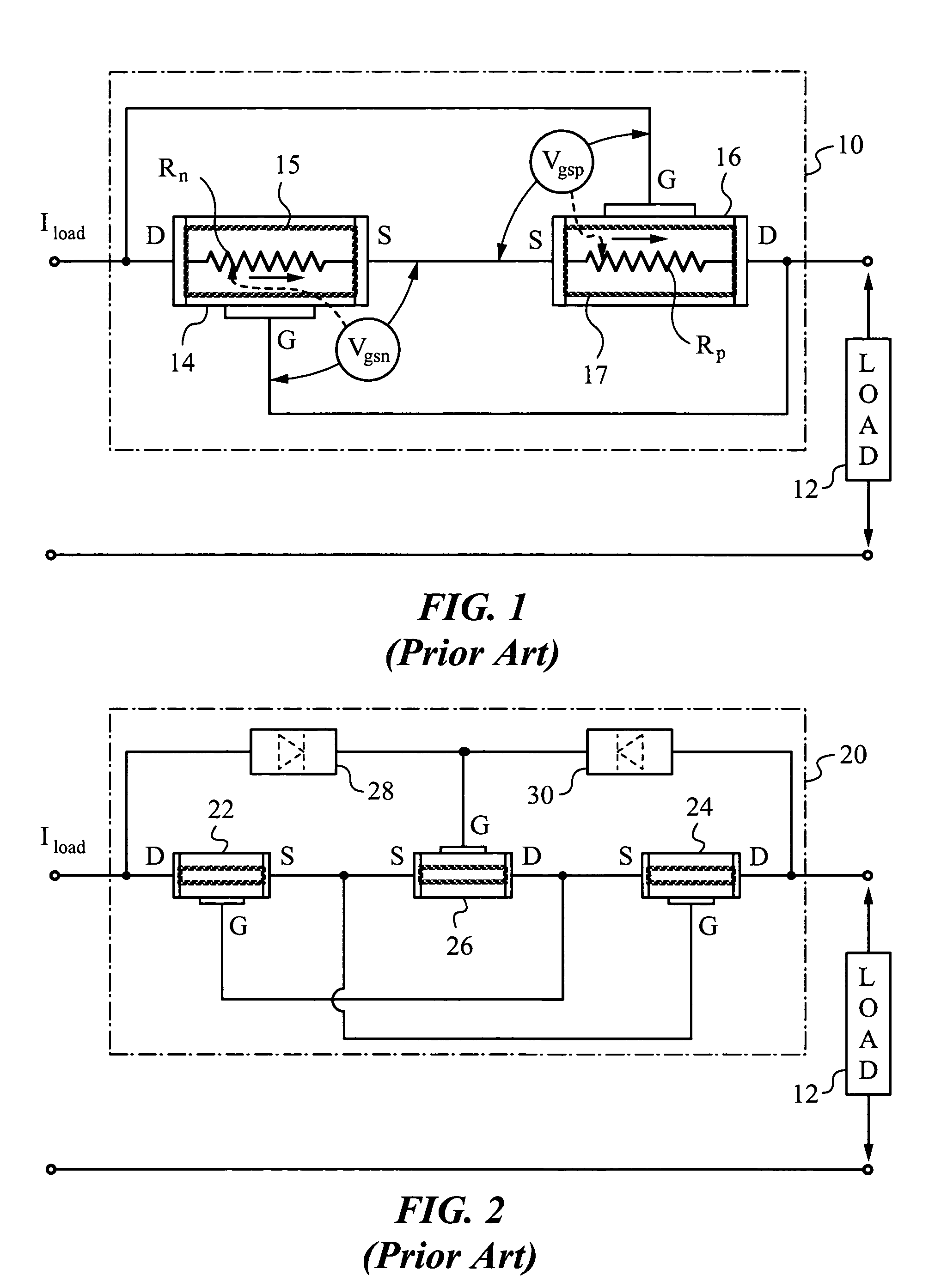
A method and apparatus are disclosed for use in improving the gate oxide reliability of semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) metal-oxide-silicon field effect transistor (MOSFET) devices using accumulated charge control (ACC) techniques. The method and apparatus are adapted to remove, reduce, or otherwise control accumulated charge in SOI MOSFETs, thereby yielding improvements in FET performance characteristics. In one embodiment, a circuit comprises a MOSFET, operating in an accumulated charge regime, and means for controlling the accumulated charge, operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. A first determination is made of the effects of an uncontrolled accumulated charge on time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. A second determination is made of the effects of a controlled accumulated charge on TDDB of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. The SOI MOSFET is adapted to have a selected average time-to-breakdown, responsive to the first and second determinations, and the circuit is operated using techniques for accumulated charge control operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. In one embodiment, the accumulated charge control techniques include using an accumulated charge sink operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET body.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Microbial pesticidal composition
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
Method and apparatus improving gate oxide reliability by controlling accumulated charge
ActiveUS7890891B2Improving nonlinear responses and harmonic and intermodulaton distortion effectsReduce non-linearitySolid-state devicesElectronic switchingMOSFETDielectric
A method and apparatus are disclosed for use in improving the gate oxide reliability of semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) metal-oxide-silicon field effect transistor (MOSFET) devices using accumulated charge control (ACC) techniques. The method and apparatus are adapted to remove, reduce, or otherwise control accumulated charge in SOI MOSFETs, thereby yielding improvements in FET performance characteristics. In one embodiment, a circuit comprises a MOSFET, operating in an accumulated charge regime, and means for controlling the accumulated charge, operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. A first determination is made of the effects of an uncontrolled accumulated charge on time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. A second determination is made of the effects of a controlled accumulated charge on TDDB of the gate oxide of the SOI MOSFET. The SOI MOSFET is adapted to have a selected average time-to-breakdown, responsive to the first and second determinations, and the circuit is operated using techniques for accumulated charge control operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET. In one embodiment, the accumulated charge control techniques include using an accumulated charge sink operatively coupled to the SOI MOSFET body.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
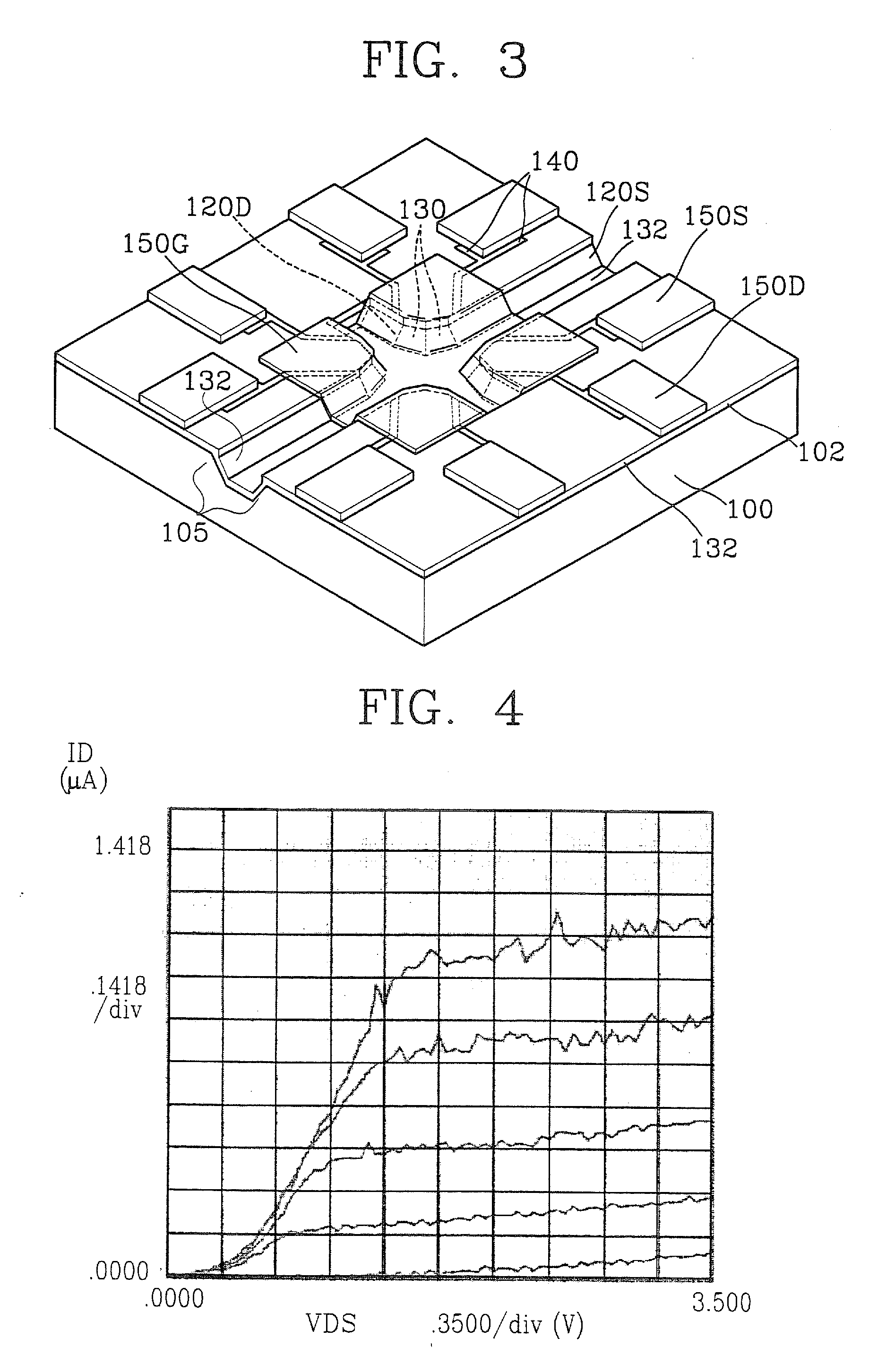
Molecular detection device and chip including MOSFET
InactiveUS7235389B2Short timeEasy to highly integrate-andMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMOSFETCoupling
A molecular detection chip including a metal oxide silicon-field effect transistor (MOSFET) on sidewalls of a micro-fluid channel and a molecular detection device including the molecular detection chip are provided. A molecular detection method, particularly, qualification methods for the immobilization of molecular probes and the binding of a target sample to the molecular probes, using the molecular detection device, and a nucleic acid mutation assay device and method are also provided. The formation of the MOSFET on the sidewalls of the micro-fluid channel makes easier to highly integrate a molecular detection chip. In addition, immobilization of probes directly on the surface of a gate electrode ensures the molecular detection chip to check for the immobilization of probes and coupling of a target molecule to the probes in situ.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of forming a contact structure
ActiveUS20090280641A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerOxygen
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Photomask blank, photomask and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20060088774A1Reduce the burden onImprove accuracyDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideChromium nitride
Owner:TOPPAN PHOTOMASK CO LTD +1
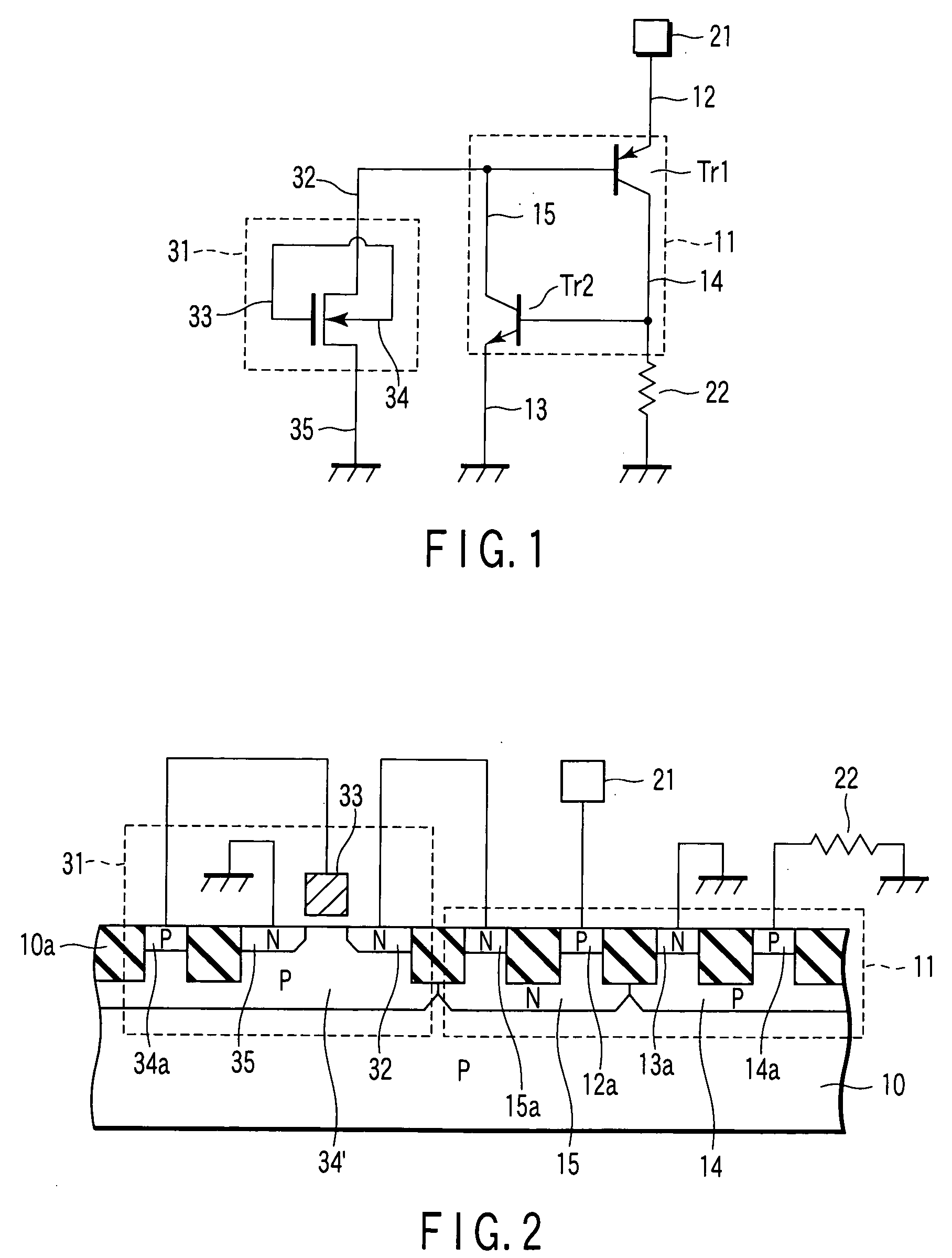
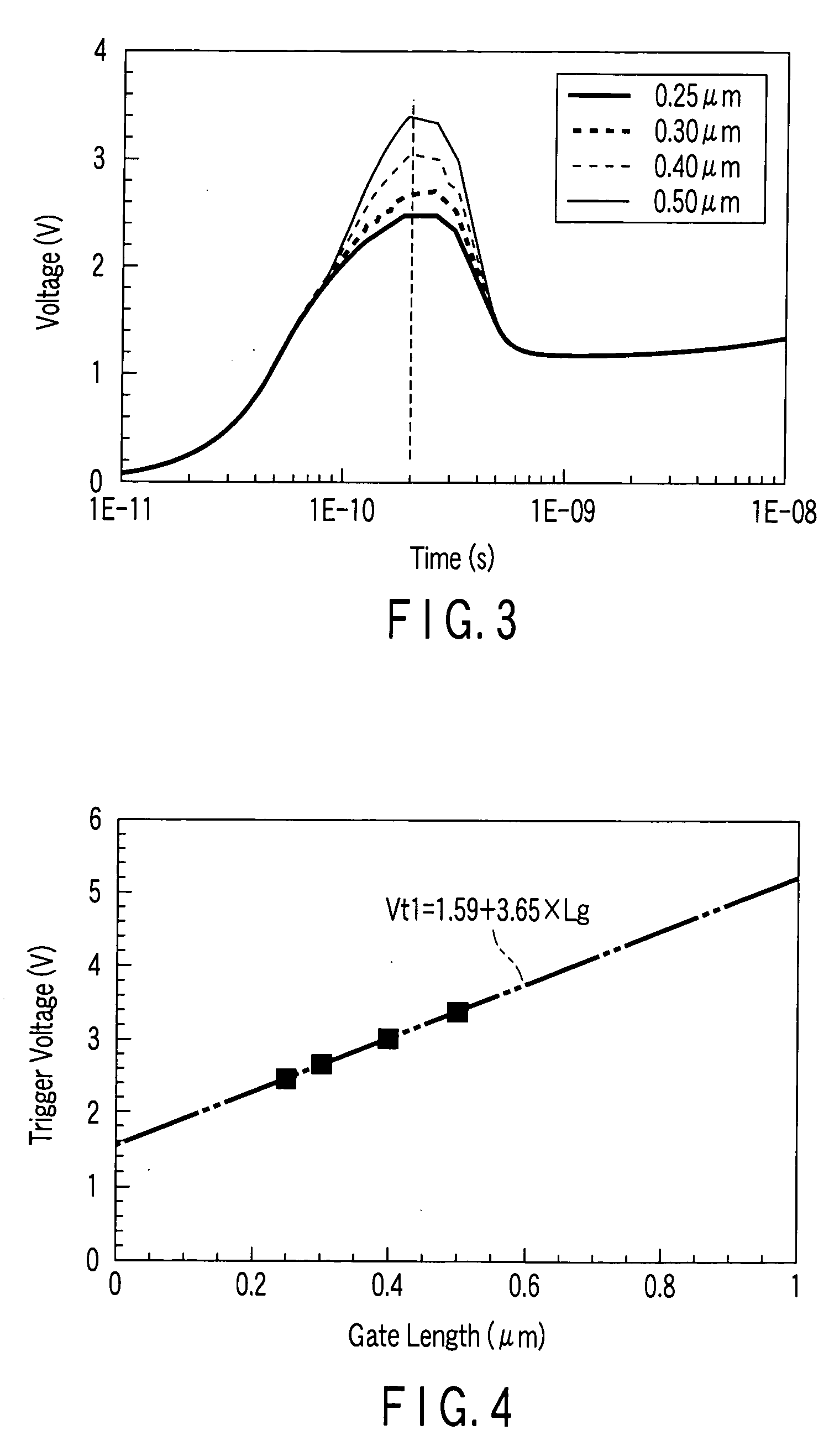
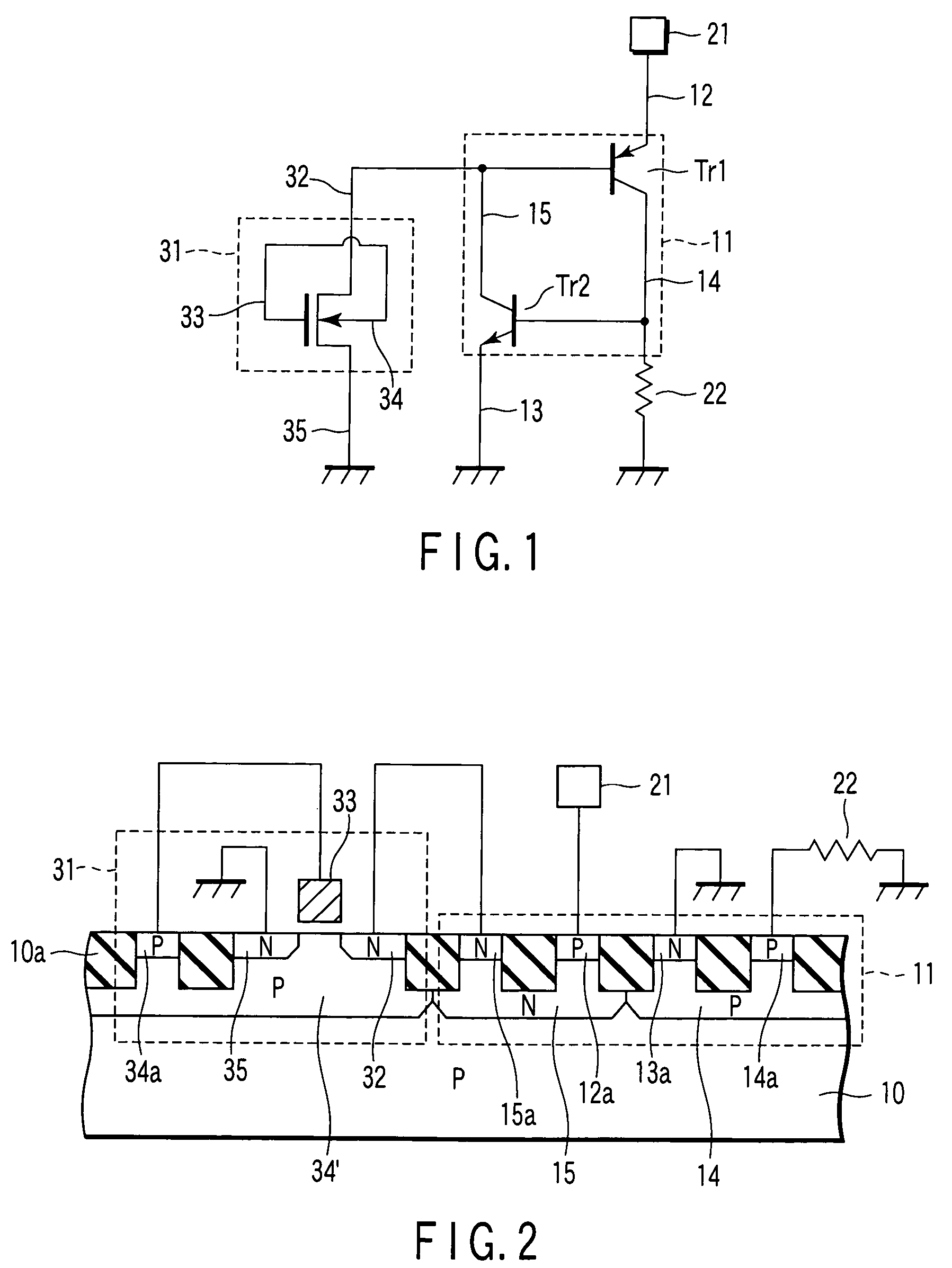
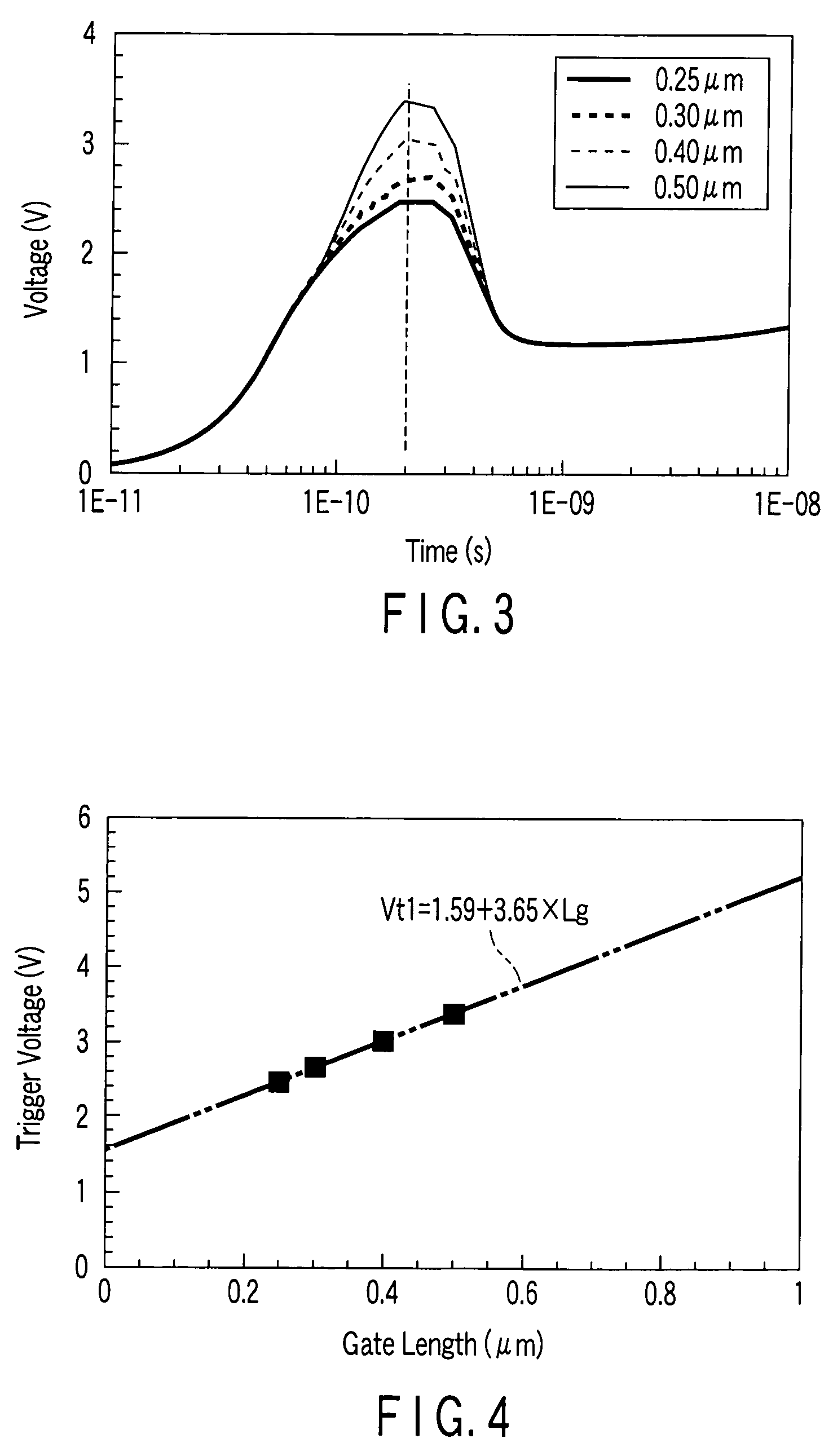
Semiconductor device including metal-oxide-silicon field-effect transistor as a trigger circuit
InactiveUS20060244071A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon-controlled rectifierDevice material
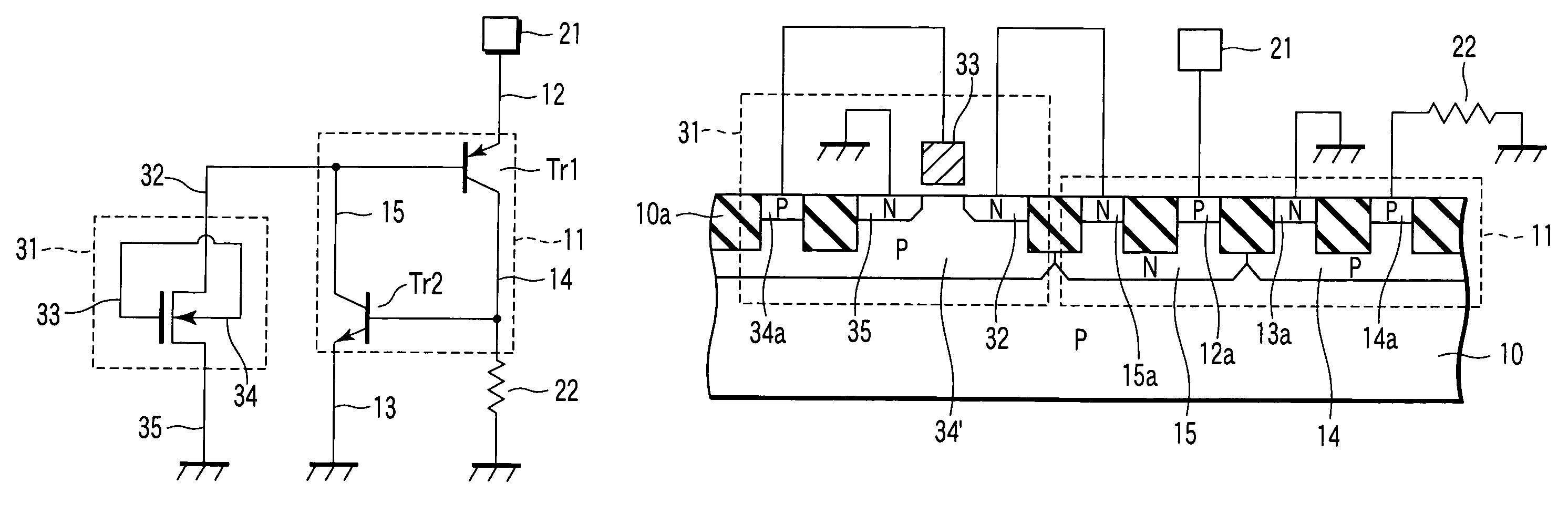
A semiconductor device includes a silicon-controlled rectifier to protect an internal circuit from electrostatic discharge damage and a first metal-oxide-silicon field-effect transistor to apply a trigger voltage to the silicon-controlled rectifier. The first metal-oxide-silicon field-effect transistor including a gate electrode and a substrate which are electrically connected to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
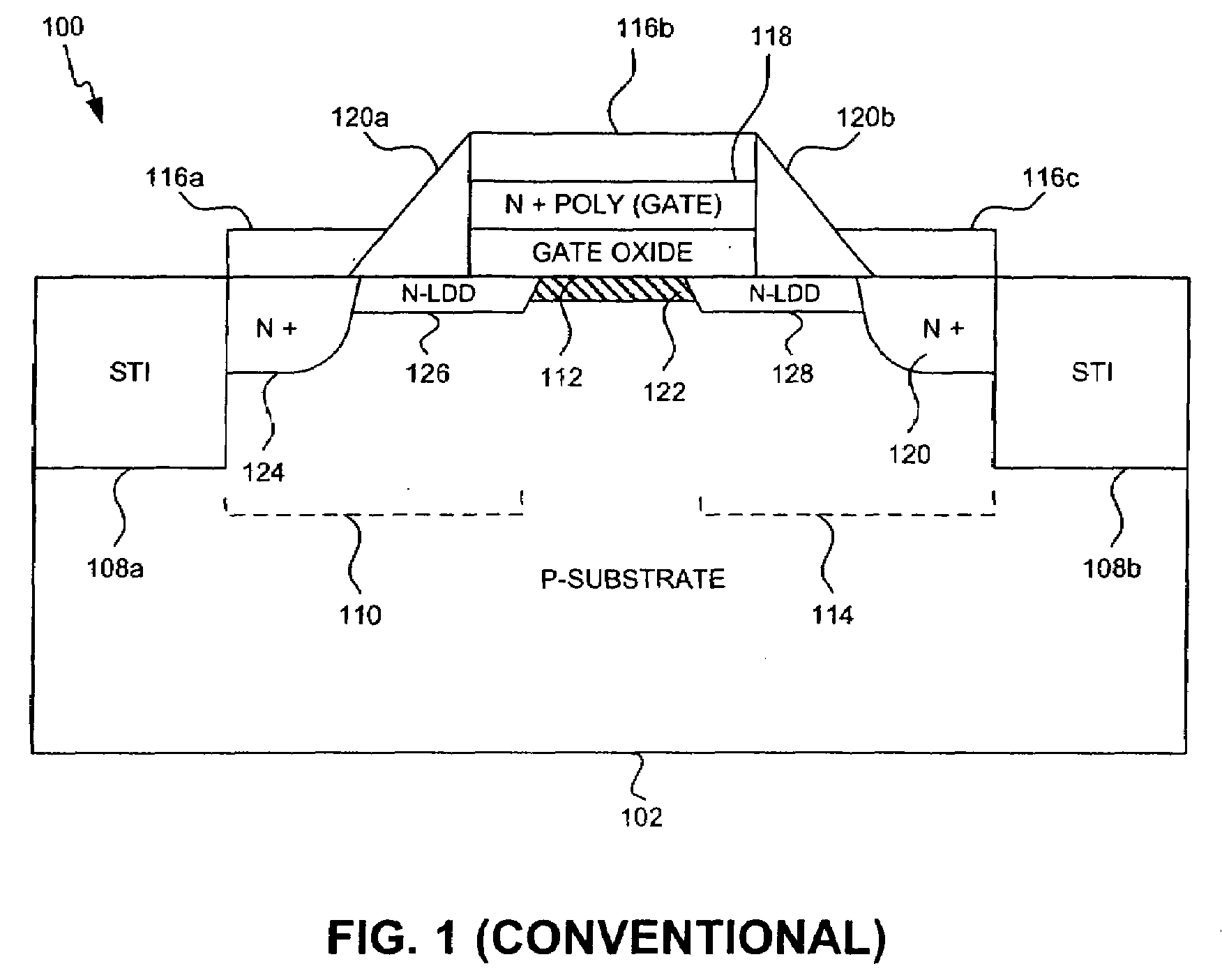
Semiconductor device with increased breakdown voltage
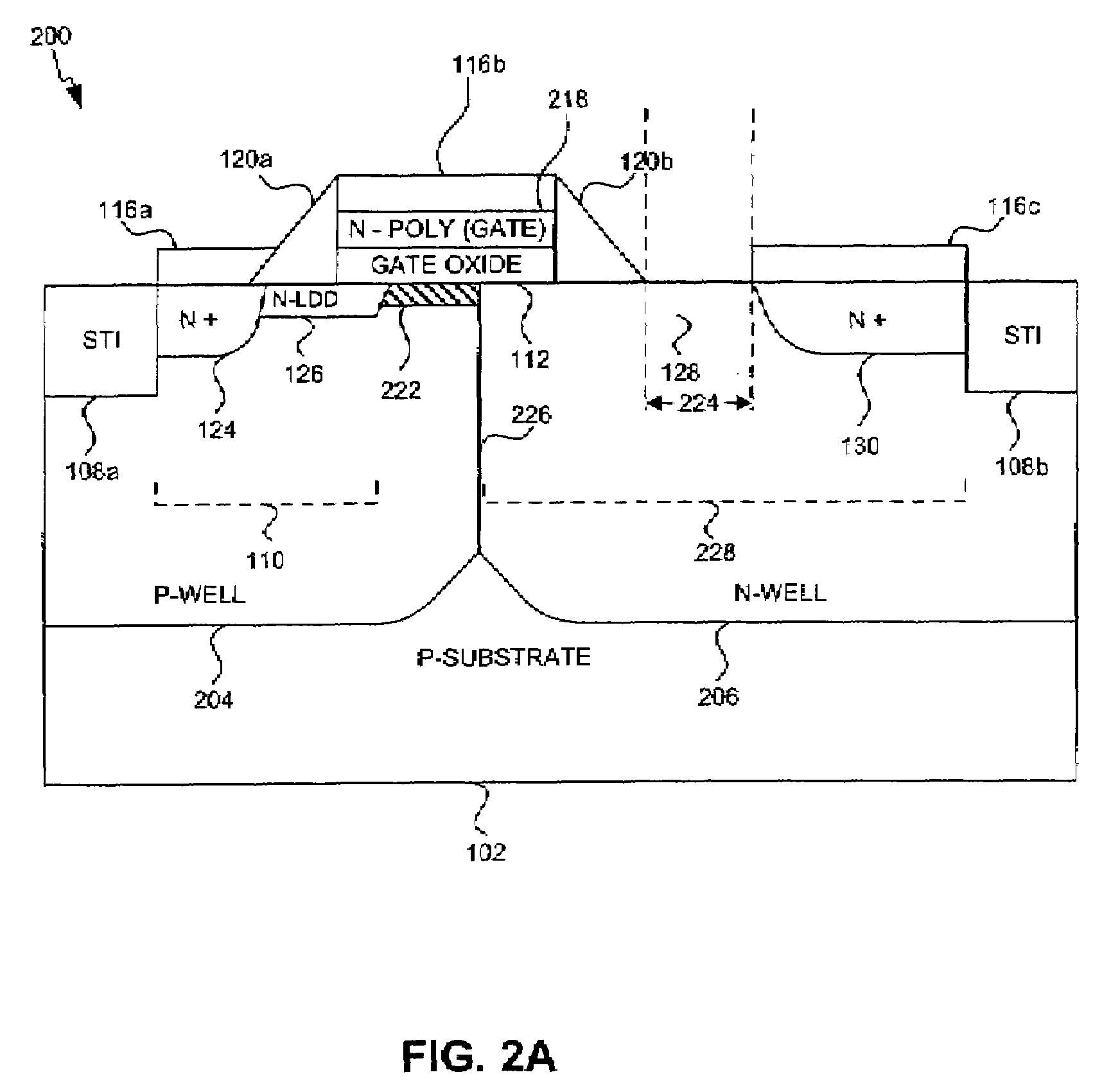
InactiveUS20080023760A1Additional maskingAdditional processing costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETCMOS
Optimization of the implantation structure of a metal oxide silicon field effect transistor (MOSFET) device fabricated using conventional complementary metal oxide silicon (CMOS) logic foundry technology to increase the breakdown voltage. The techniques used to optimize the implantation structure involve lightly implanting the gate region, displacing the drain region from the gate region, and implanting P-well and N-Well regions adjacent to one another without an isolation region in between.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Vertical metal oxide silicon field effect semiconductor diodes
InactiveUS6537921B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVoltage dropField effect
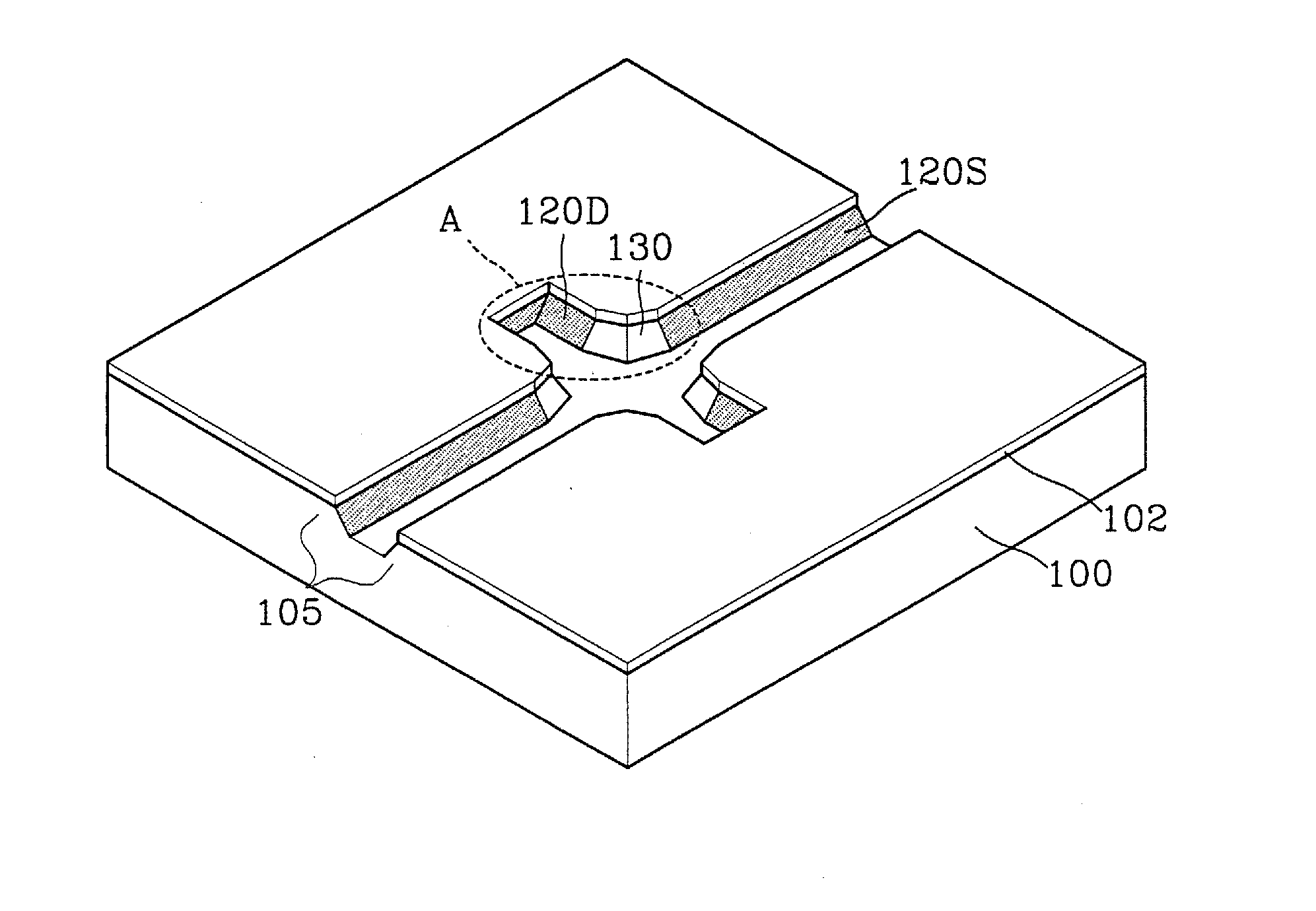
The present invention includes methods and apparatus as described in the claims. Briefly, semiconductor diodes having a low forward conduction voltage drop, a low reverse leakage current, a high voltage capability and avalanche energy capability, suitable for use in integrated circuits as well as for discrete devices are disclosed. The semiconductor diodes are diode configured vertical cylindrical metal oxide semiconductor field effect devices having one diode terminal as the common connection between the gates and drains of the vertical cylindrical metal oxide semiconductor field effect devices, and one diode terminal as the common connection with the sources of the vertical cylindrical metal oxide semiconductor field effect devices. The method of manufacturing the vertical cylindrical metal oxide semiconductor field effect devices is disclosed. Various device terminations can be employed to complete the diode devices. Various embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ARRAY OPTRONIX
Building block for a secure CMOS logic cell library
Owner:RAMBUS INC +1
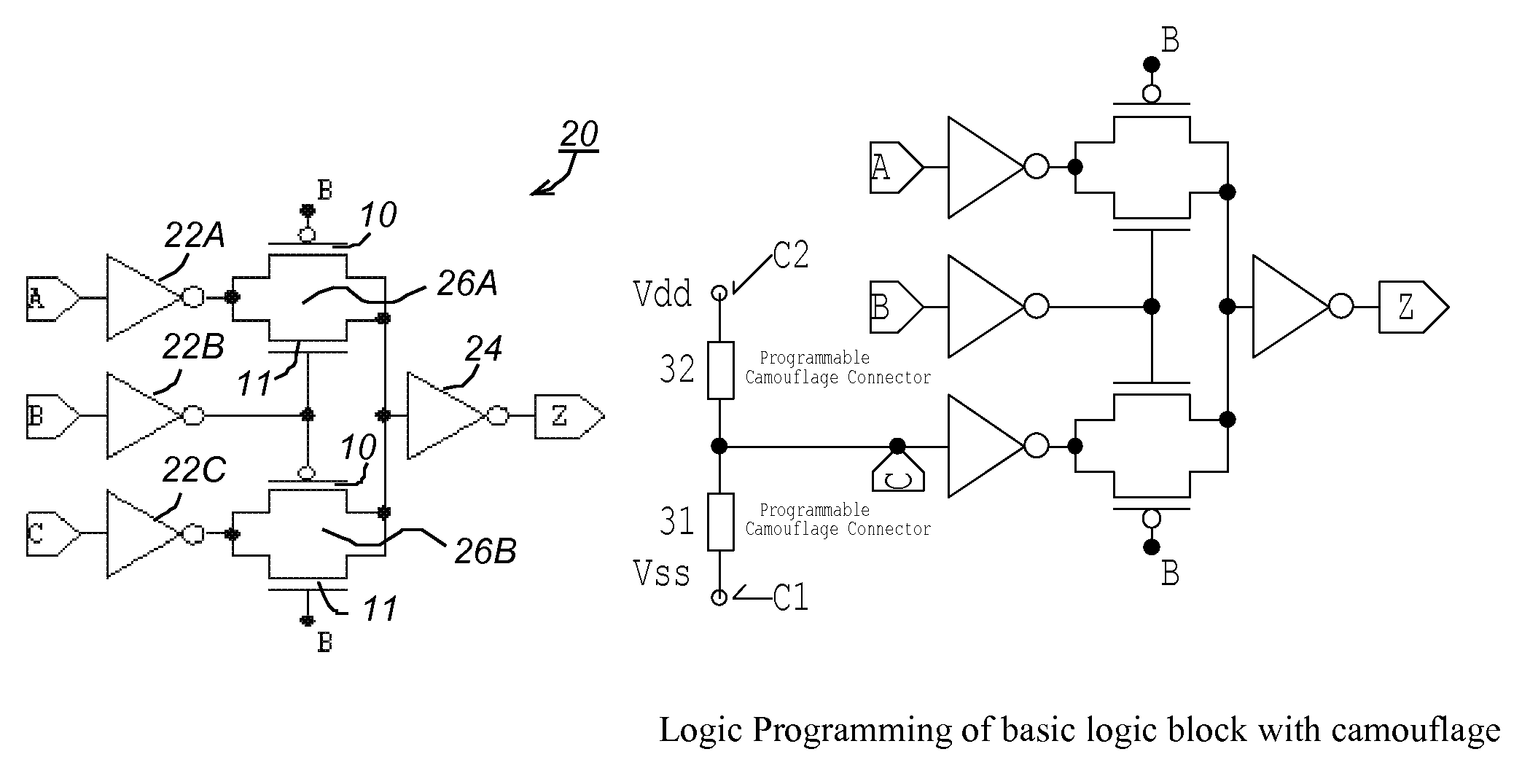
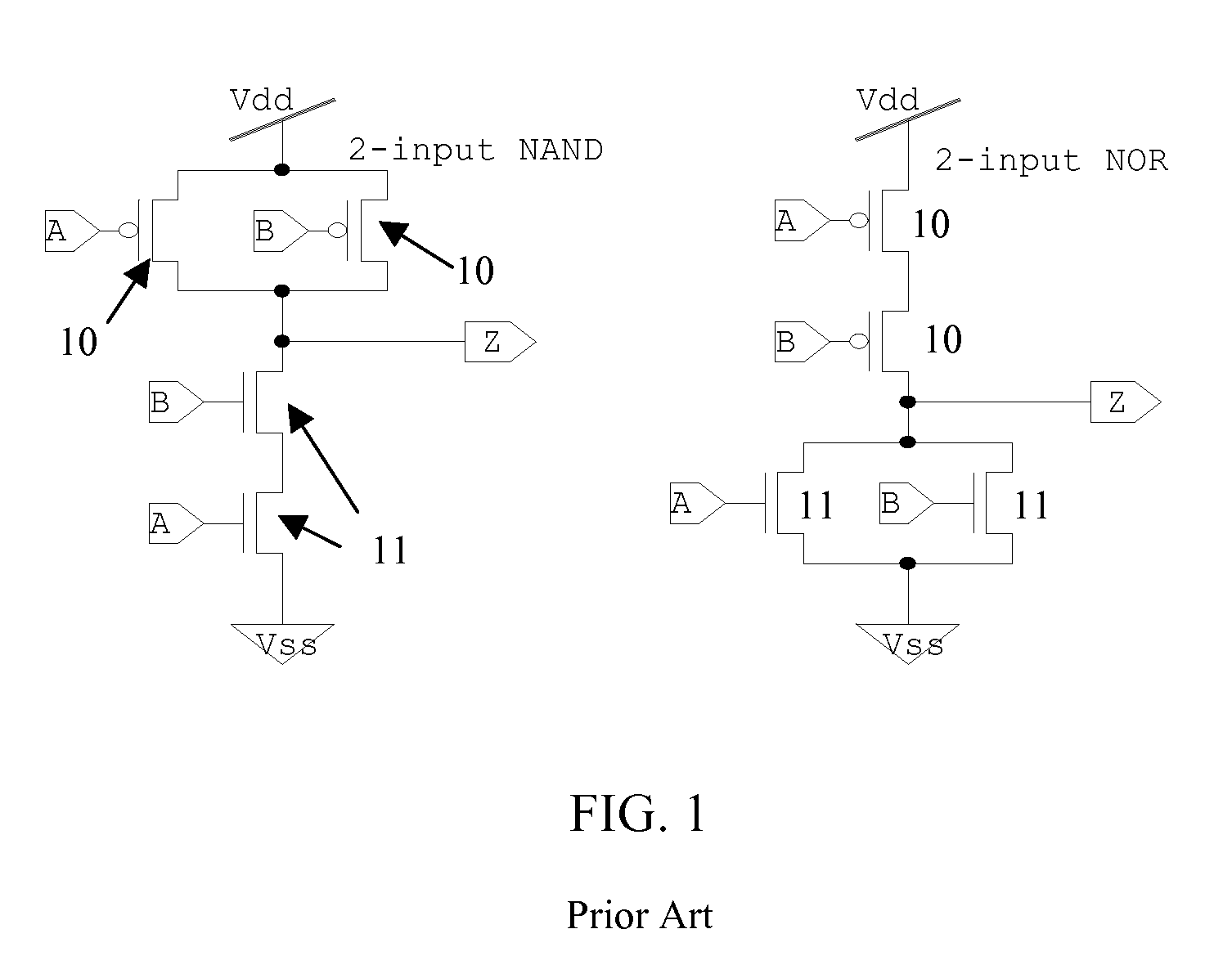
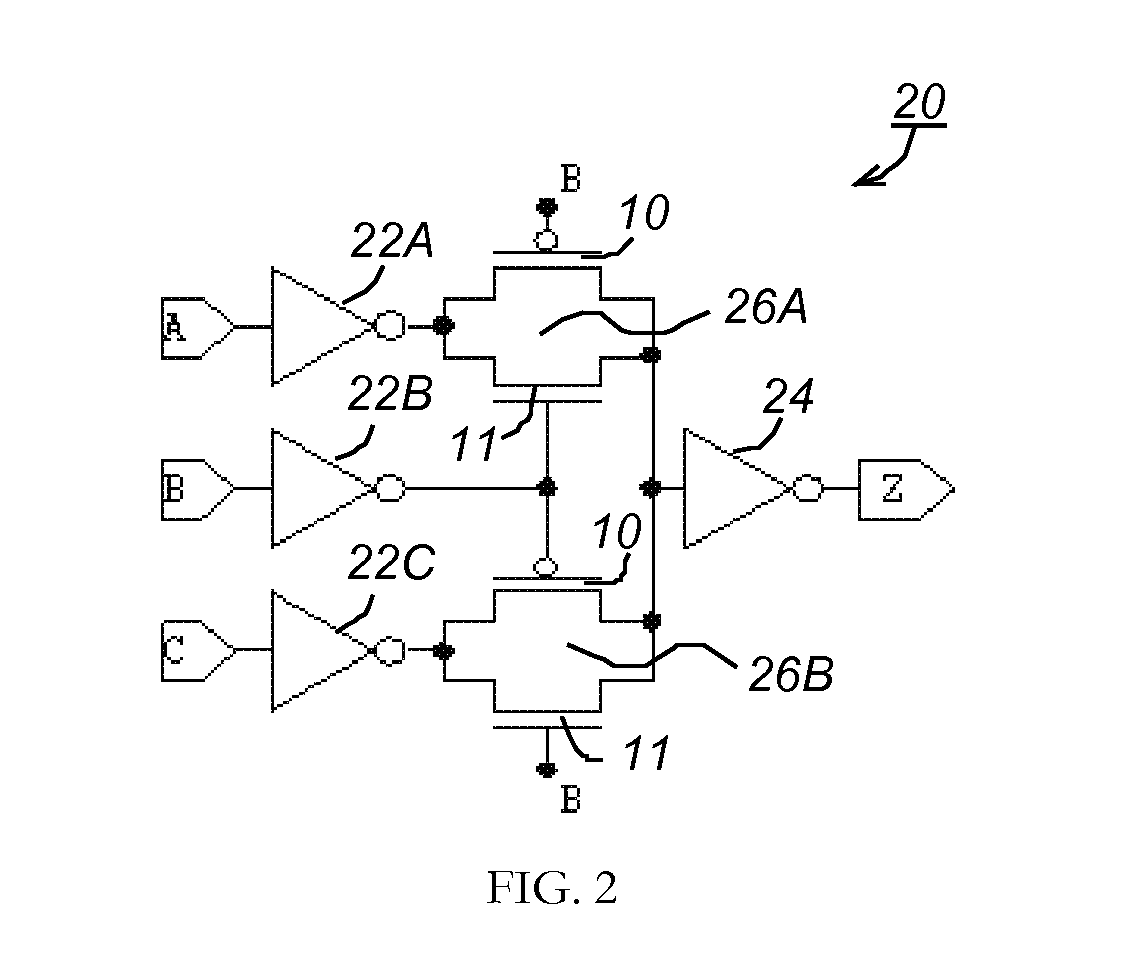
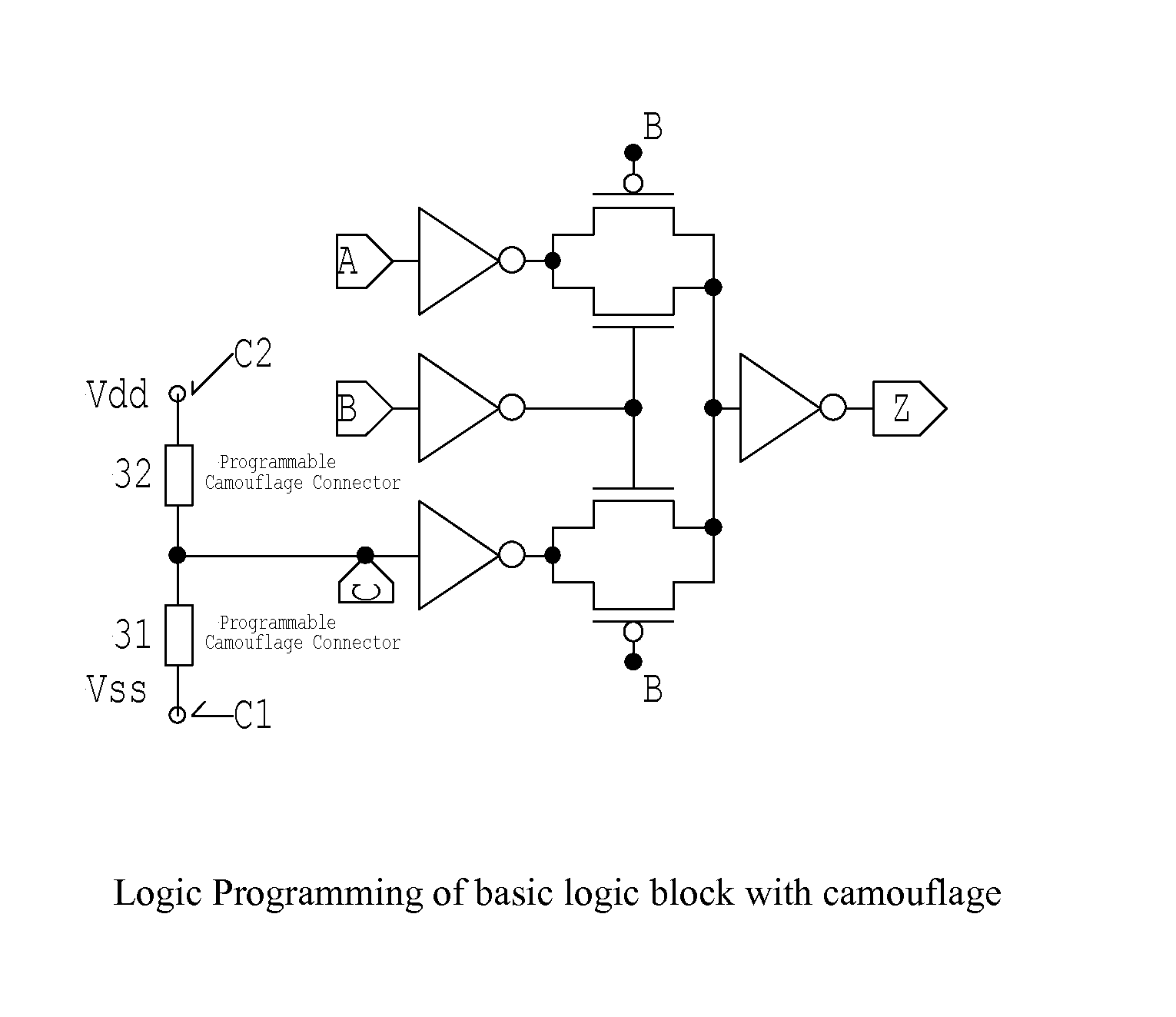
Building block for a secure CMOS logic cell library
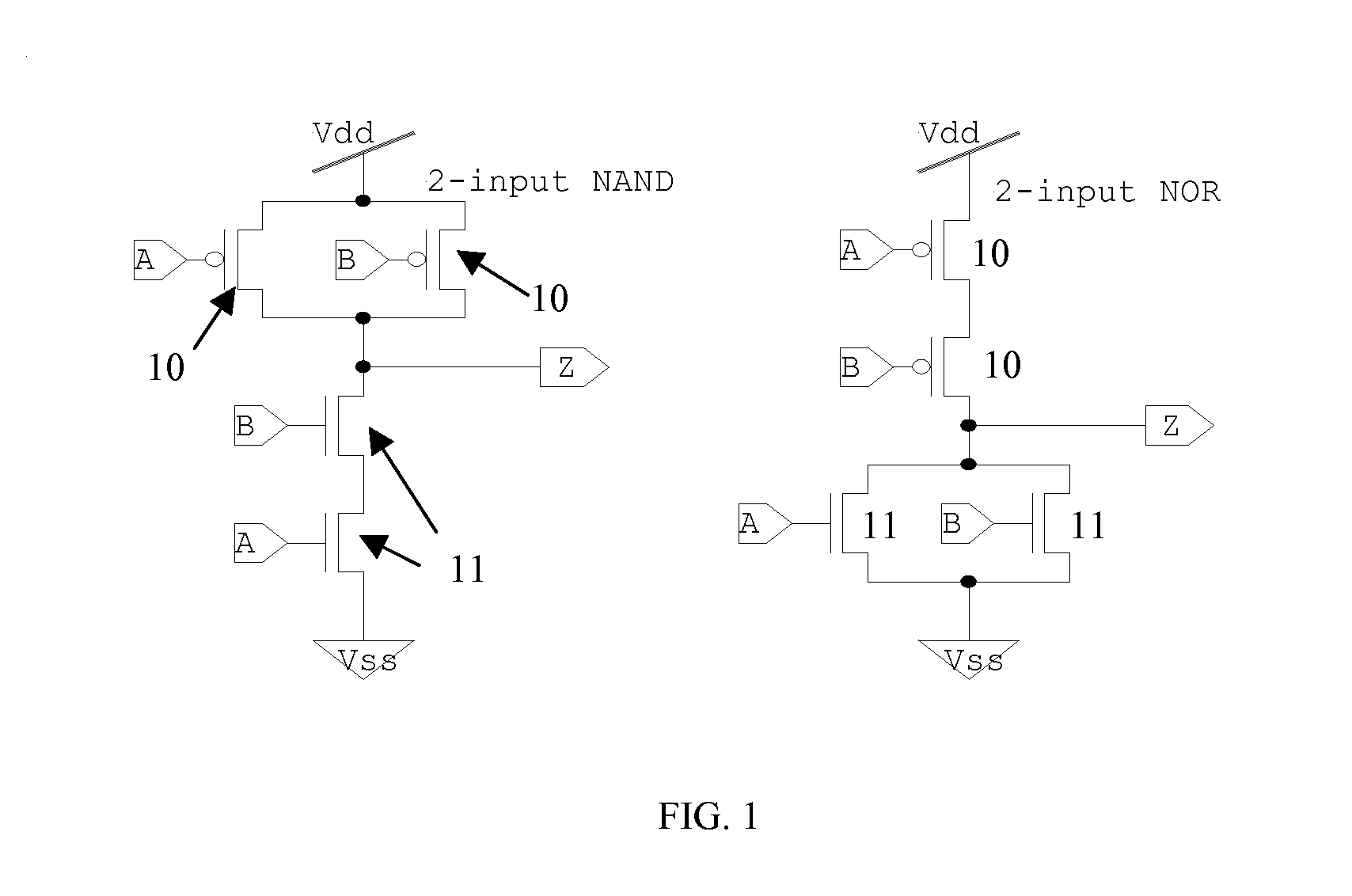
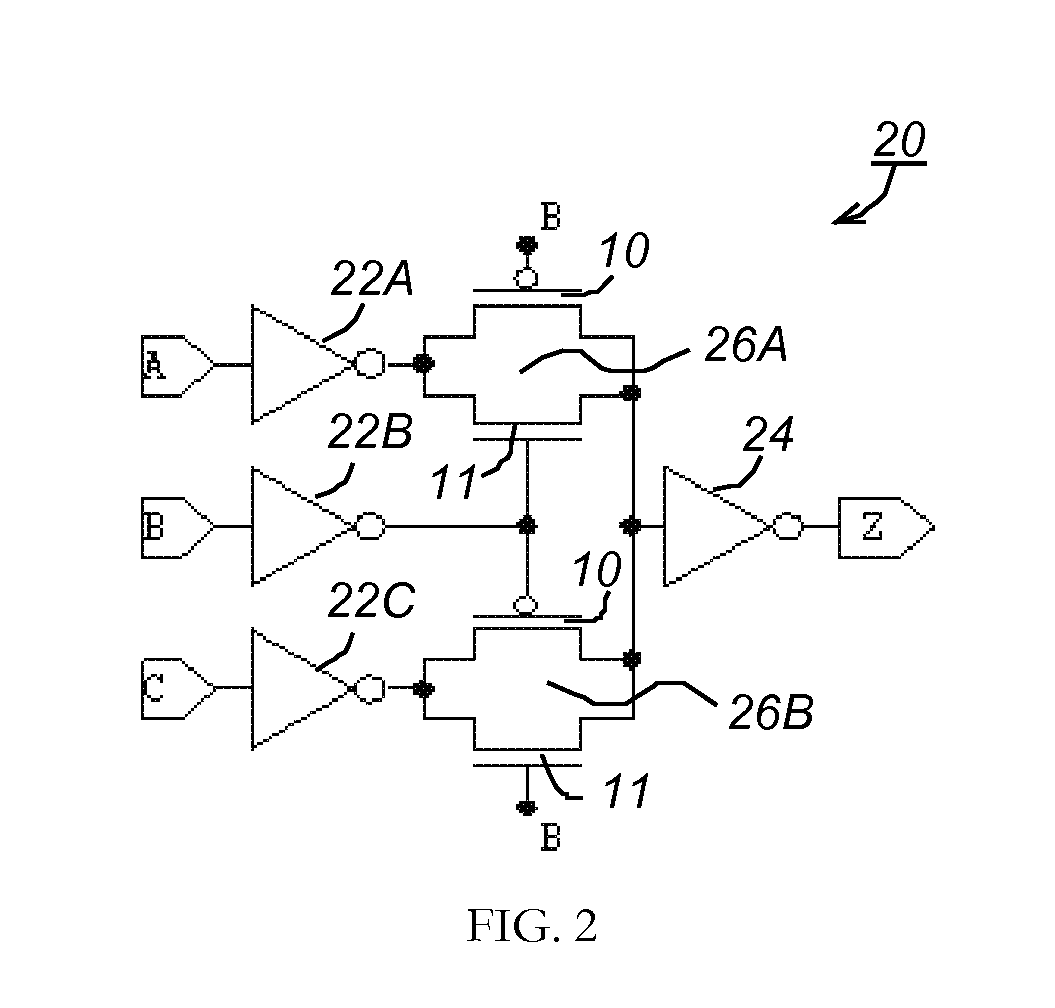
A logical building block and method of using the building block to design a logic cell library for CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Silicon) ASICs (Application Specific Integrated Circuits) is disclosed. Different logic gates, built with the same building block as described in this invention, will have the same schematics of transistor connection and also the same physical layout so that they appear to be physically identical under optical or electron microscopy. An ASIC designed from a library of such logic cells is strongly resistant to a reverse engineering attempt.
Owner:RAMBUS INC +1
Methods of making a molecular detection chip having a metal oxide silicon field effect transistor on sidewalls of a micro-fluid channel
InactiveUS20070218610A1Convenient and highly integratedShort timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyMOSFETCoupling
A molecular detection chip including a metal oxide silicon-field effect transistor (MOSFET) on sidewalls of a micro-fluid channel and a molecular detection device including the molecular detection chip are provided. A molecular detection method, particularly, qualification methods for the immobilization of molecular probes and the binding of a target sample to the molecular probes, using the molecular detection device, and a nucleic acid mutation assay device and method are also provided. The formation of the MOSFET on the sidewalls of the micro-fluid channel makes easier to highly integrate a molecular detection chip. In addition, immobilization of probes directly on the surface of a gate electrode ensures the molecular detection chip to check for the immobilization of probes and coupling of a target molecule to the probes in situ.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High yield, high density on-chip capacitor design
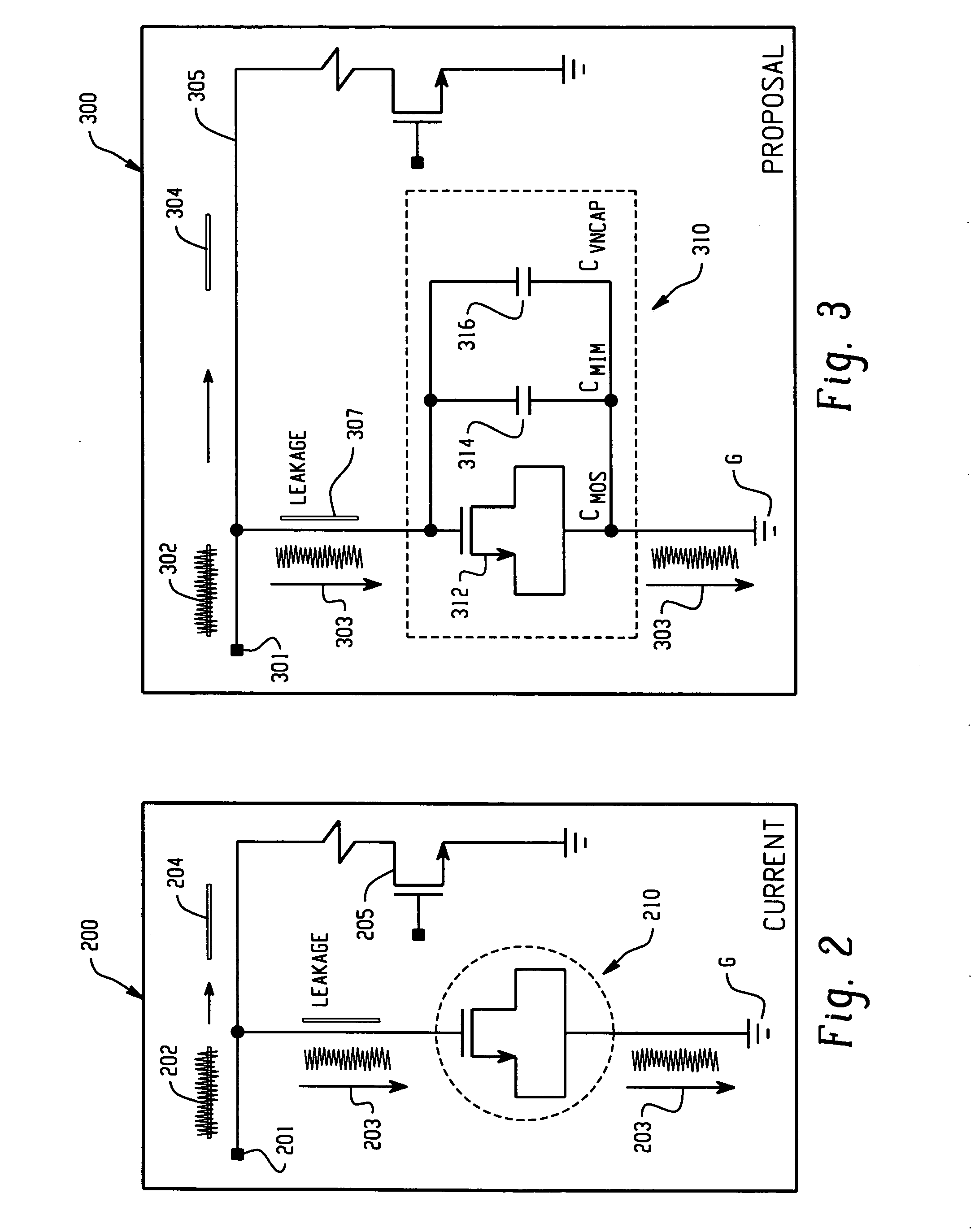
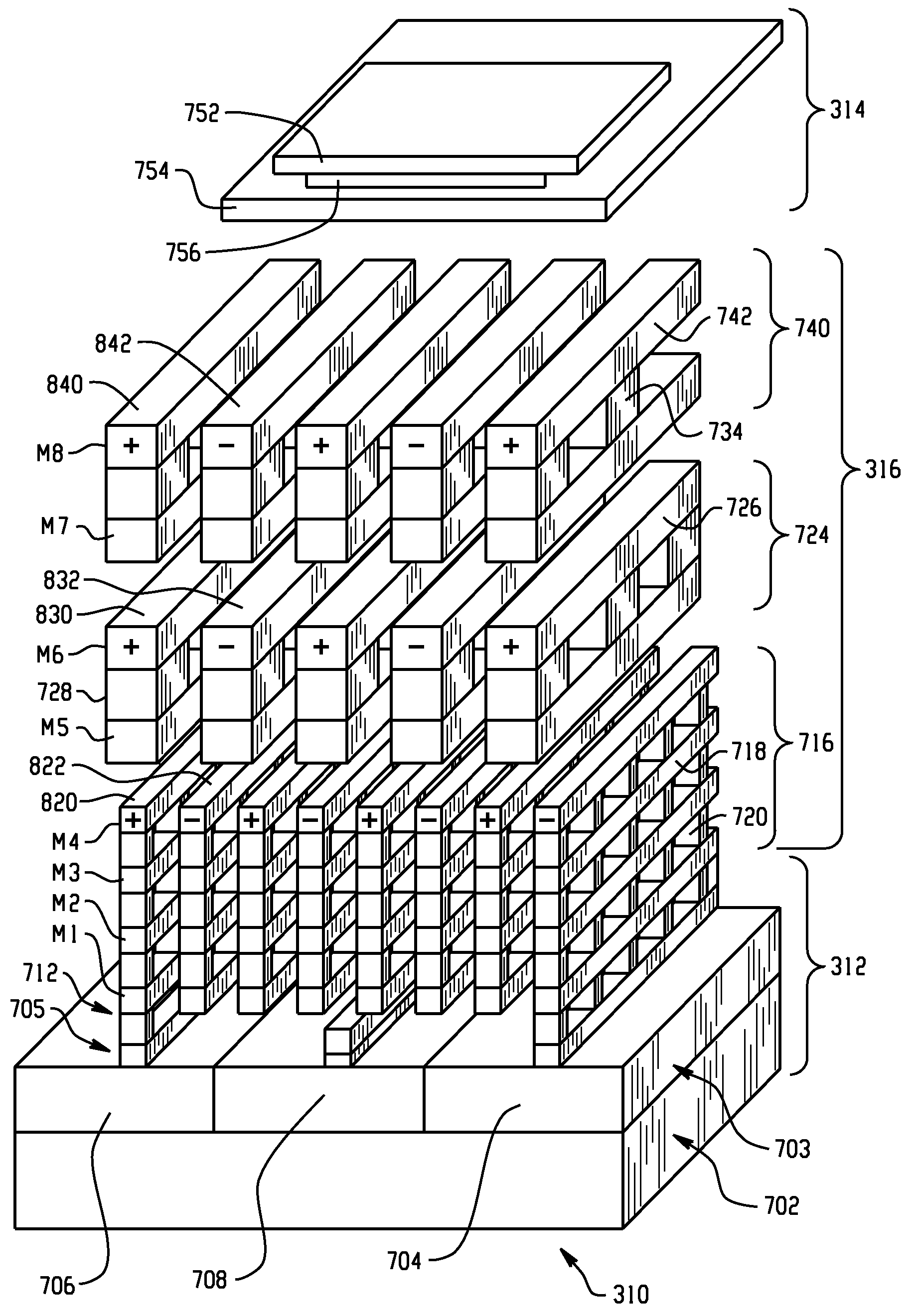
A capacitance circuit assembly mounted on a semiconductor chip, and method for forming the same, comprising a plurality of divergent capacitors in a parallel circuit connection between first and second ports, the plurality comprising at least one Metal Oxide Silicon Capacitor and at least one capacitor selected from the group comprising a Vertical Native Capacitor and a Metal-Insulator-Metal Capacitor. In one aspect, the assembly has vertical orientation, the Metal Oxide Silicon capacitor located at the bottom and defining the footprint, middle Vertical Native Capacitor comprising a plurality of horizontal metal layers comprising a plurality of parallel positive plates alternating with a plurality of parallel negative plates. In another aspect, a vertically asymmetric orientation provides a reduced total parasitic capacitance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High yield, high density on-chip capacitor design
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
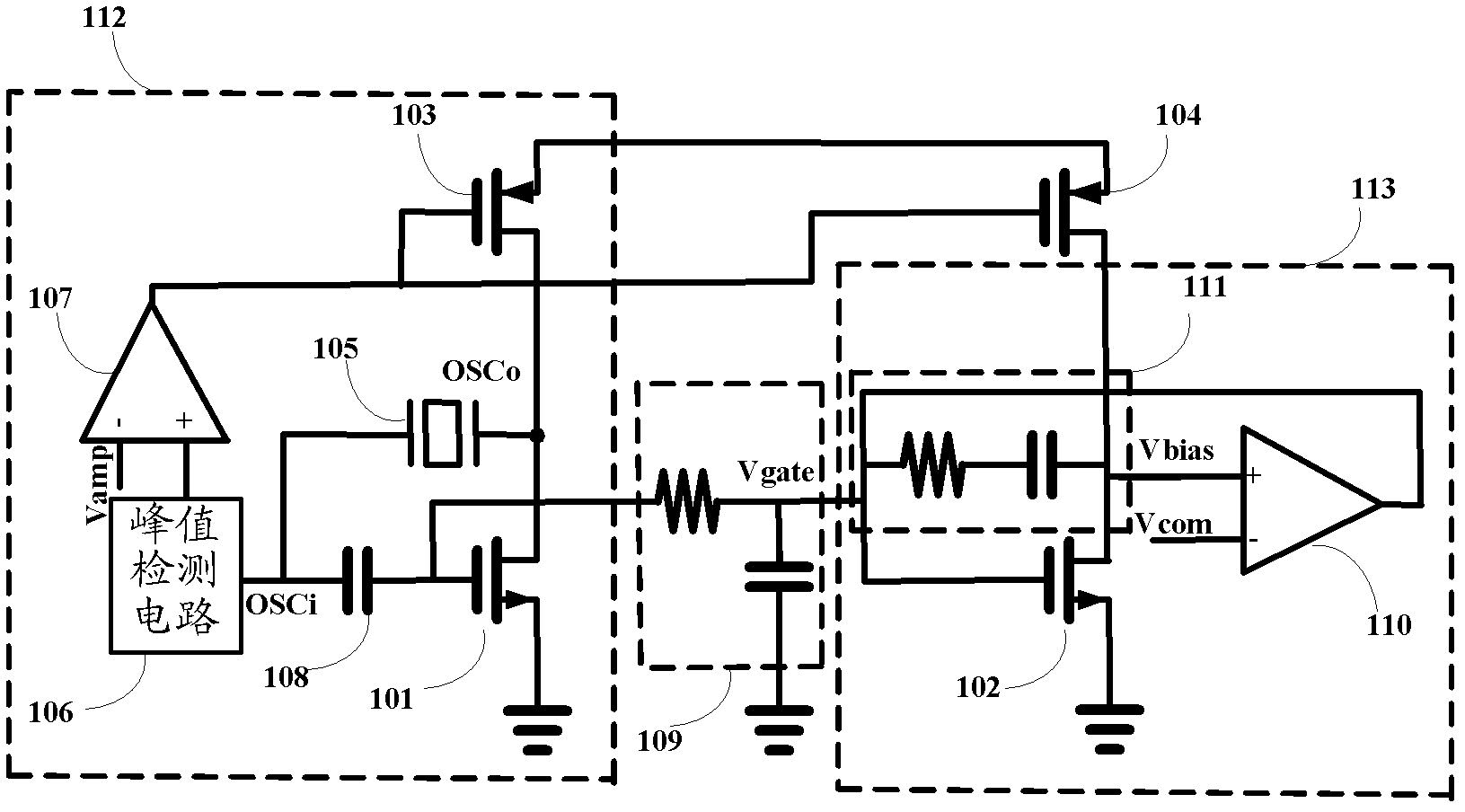
Novel crystal oscillator circuit
InactiveCN102624335AGuaranteed stabilityEasy to controlPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
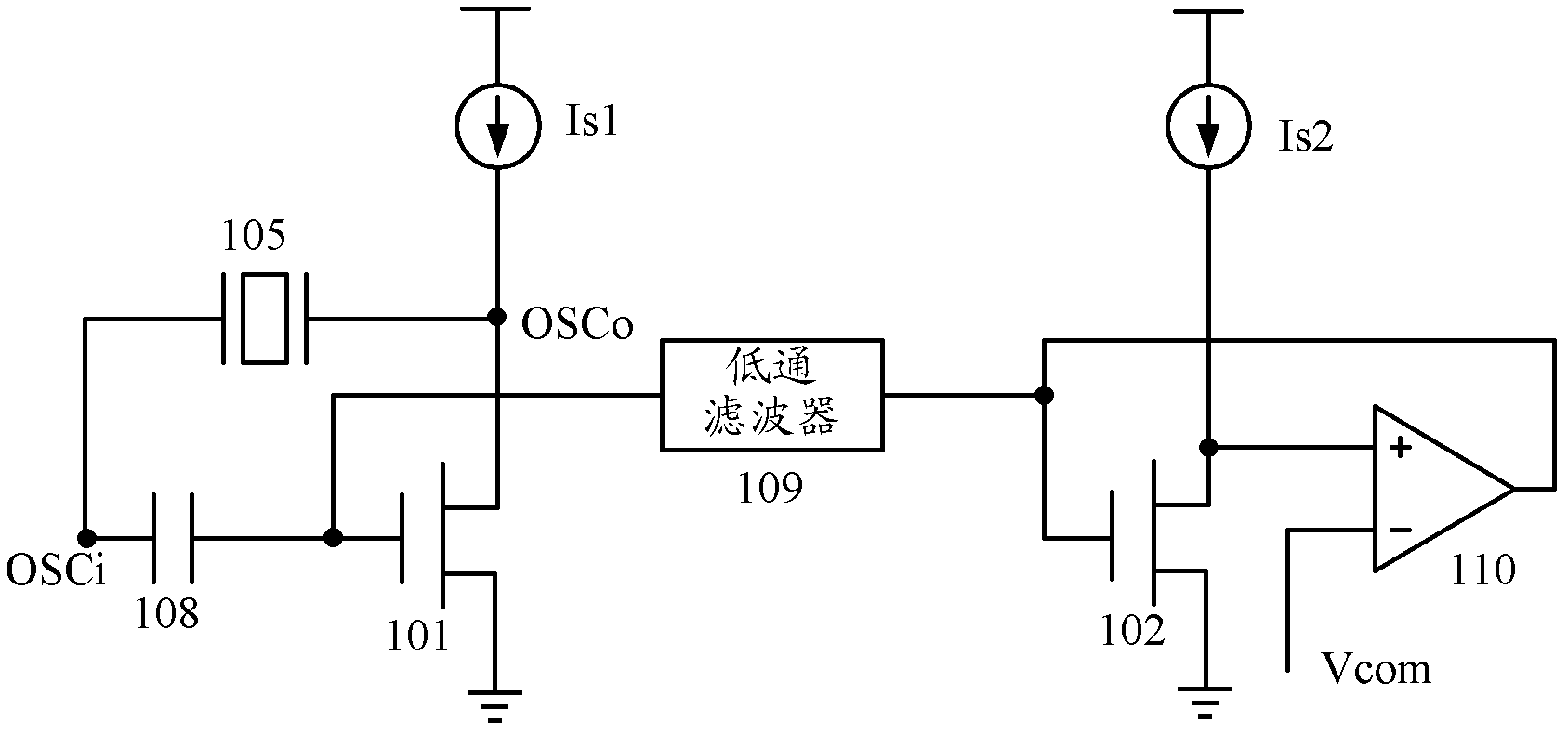
The invention relates to the field of circuit design, and discloses a novel crystal oscillator circuit. A principal oscillation metal-oxide-silicon (MOS) tube circuit is imaged, bias of a principle oscillation tube is indirectly controlled by controlling direct-current bias of an imaging tube, so that a direct-current level of a sinusoidal signal outputted by the crystal oscillator is biased to a preset value, control over the direct-current level of the output signal is realized, Miller compensation can be used for compensating the stability of a negative feedback control loop, and the stability of the system is guaranteed on the premise that not a very large chip area is occupied. An output signal of a peak detection circuit is compared with a second fixed level by a second operational amplifier so as to dynamically adjust a value of a bias current and to ensure that the output signal is maintained at preset amplitude.
Owner:HI TREND TECH SHANGHAI
Molecular detection methods using molecular detection chips including a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor
InactiveUS20080093229A1Convenient and highly integratedShort timeMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMOSFETCoupling
A molecular detection chip including a metal oxide silicon-field effect transistor (MOSFET) on sidewalls of a micro-fluid channel and a molecular detection device including the molecular detection chip are provided. A molecular detection method, particularly, qualification methods for the immobilization of molecular probes and the binding of a target sample to the molecular probes, using the molecular detection device, and a nucleic acid mutation assay device and method are also provided. The formation of the MOSFET on the sidewalls of the micro-fluid channel makes easier to highly integrate a molecular detection chip. In addition, immobilization of probes directly on the surface of a gate electrode ensures the molecular detection chip to check for the immobilization of probes and coupling of a target molecule to the probes in situ.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
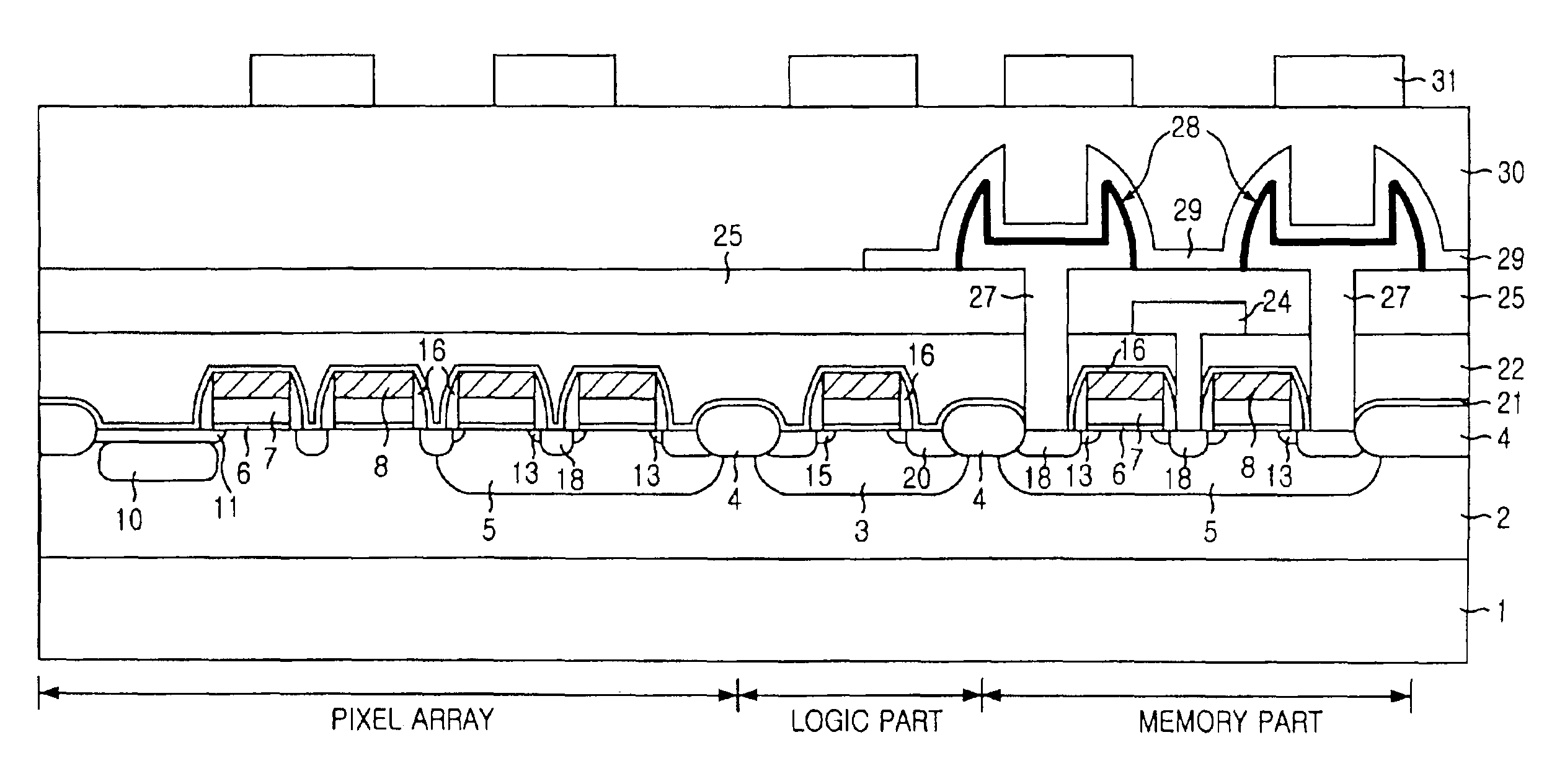
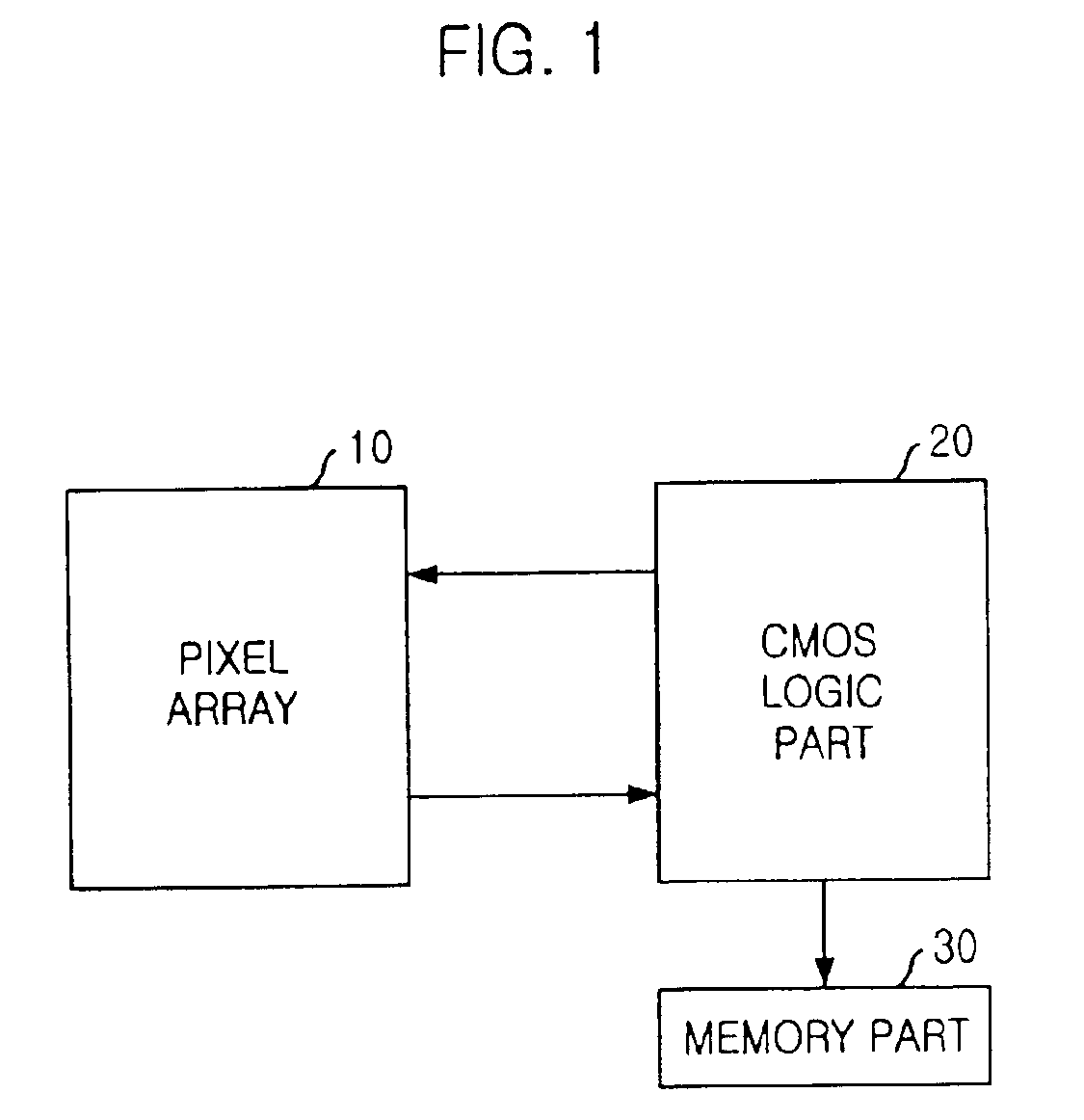
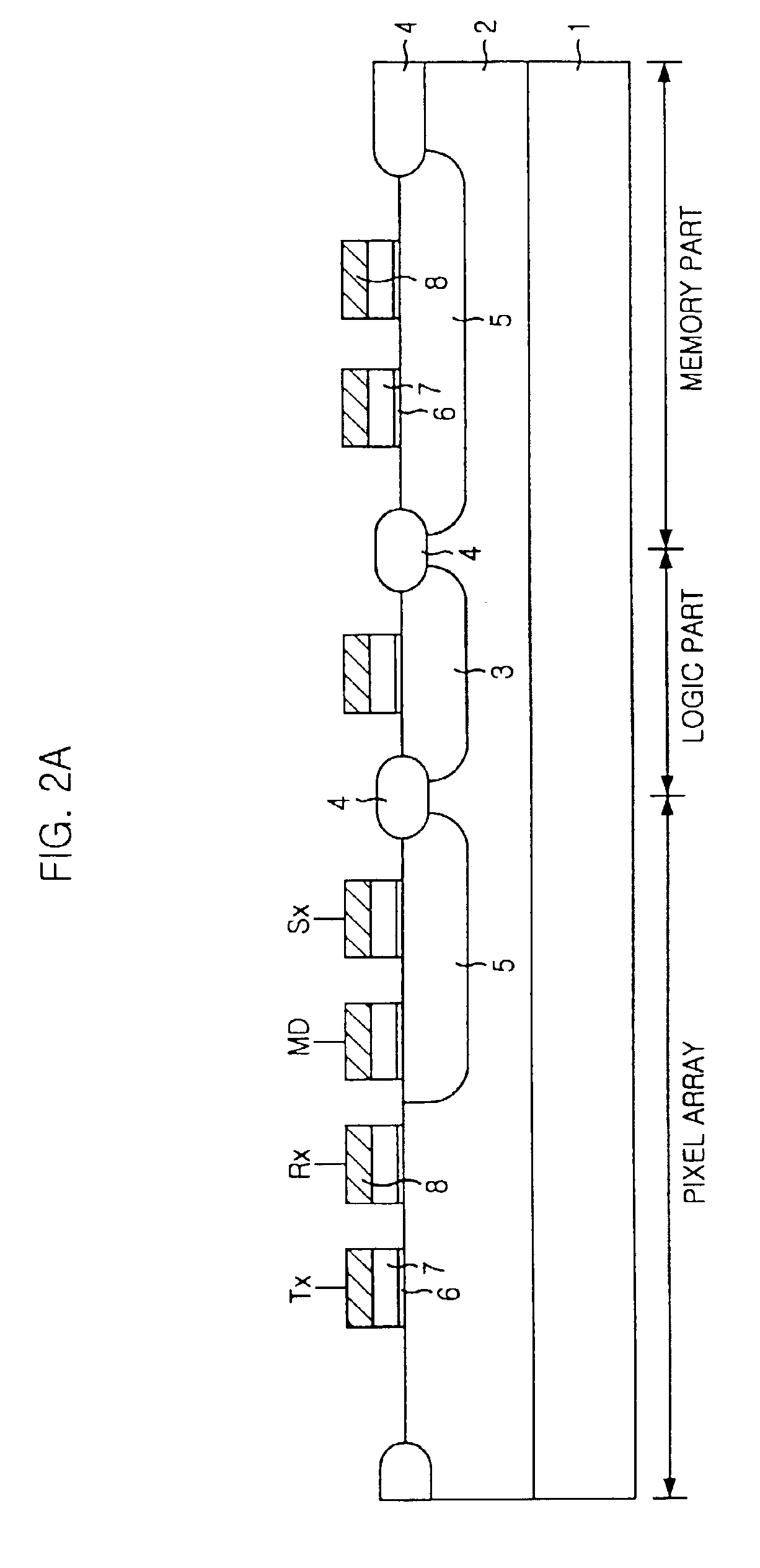
CMOS image sensor integrated together with memory device
The present invention relates to a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Silicon) image sensor; and, more particularly, to an image sensor integrated into one chip, together with a memory. The CMOS image sensor according to the present invention comprises: a pixel array formed on a chip, having a plurality of unit pixels; a logic circuit formed on the chip to process signals form the pixel array; and a memory formed on the chip to store outputs from the logic circuit, wherein the pixel array, the logic circuit and the memory are isolated from each other by insulating layers, whereby the pixel array, the logic circuit and the memory are integrated on the same chip.
Owner:PHOTONIC IMAGING SOLUTIONS INC
MOS varactor property detection method and MOS varactor manufacturing method using the same
InactiveUS20070093008A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceTest material
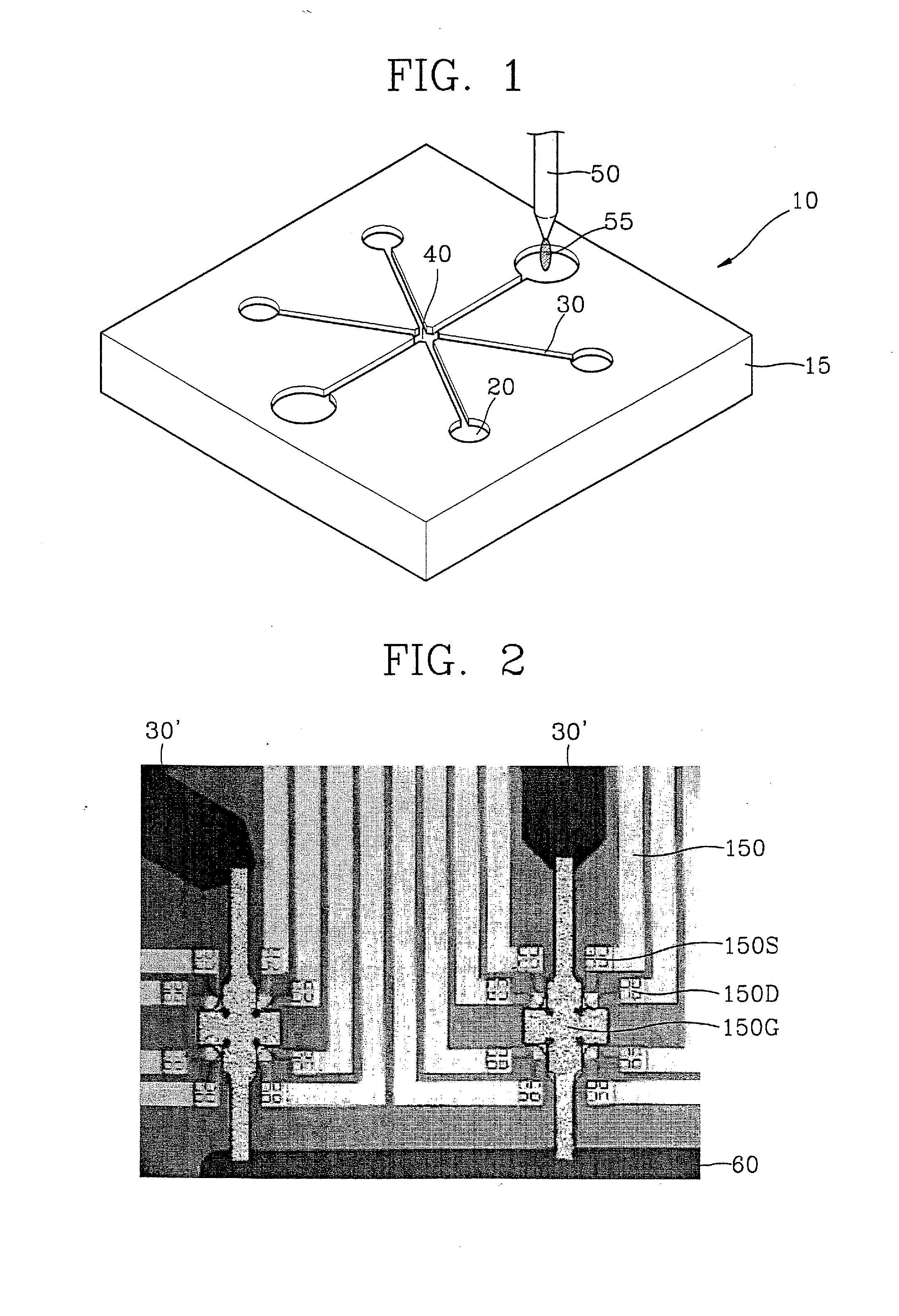
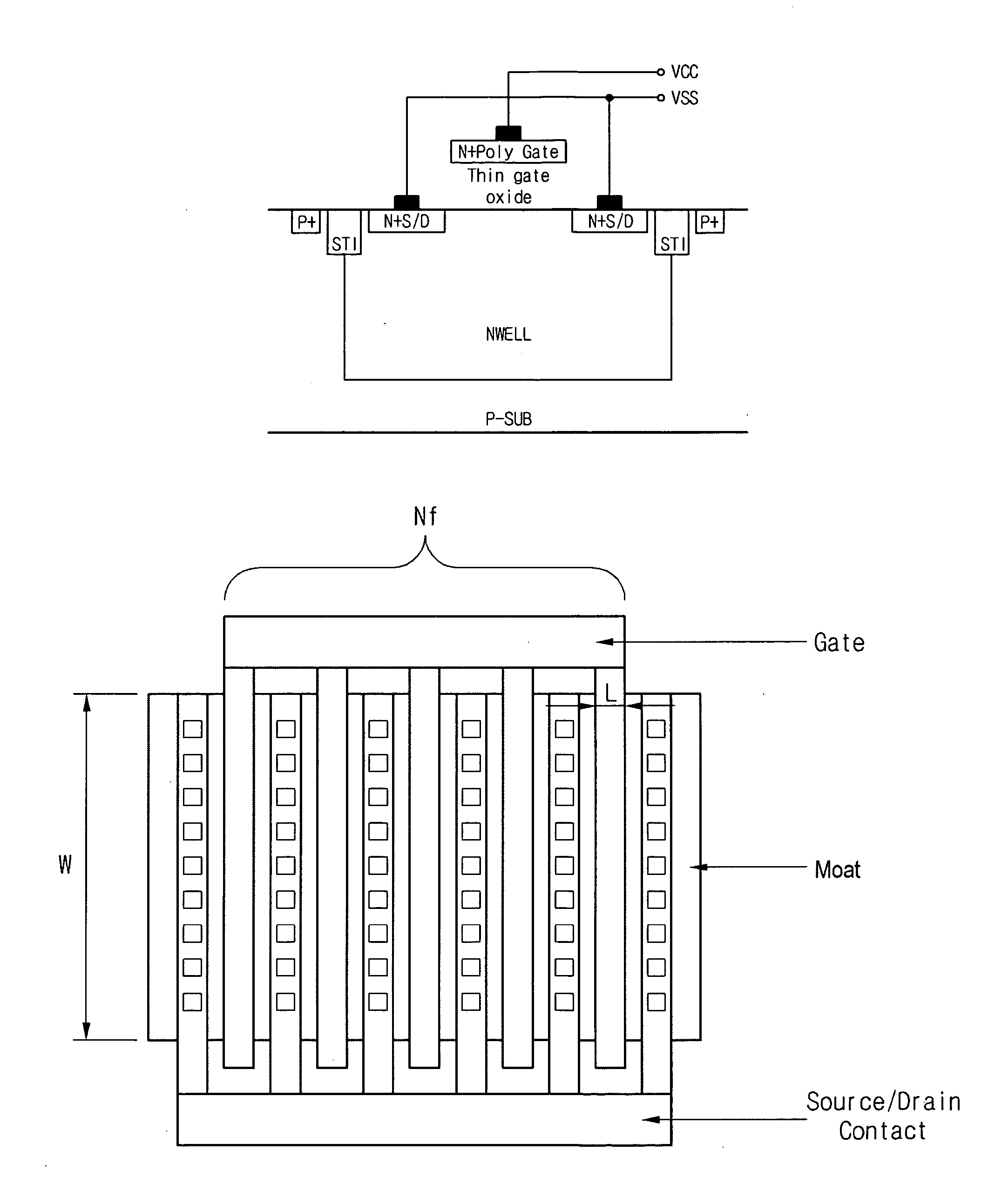
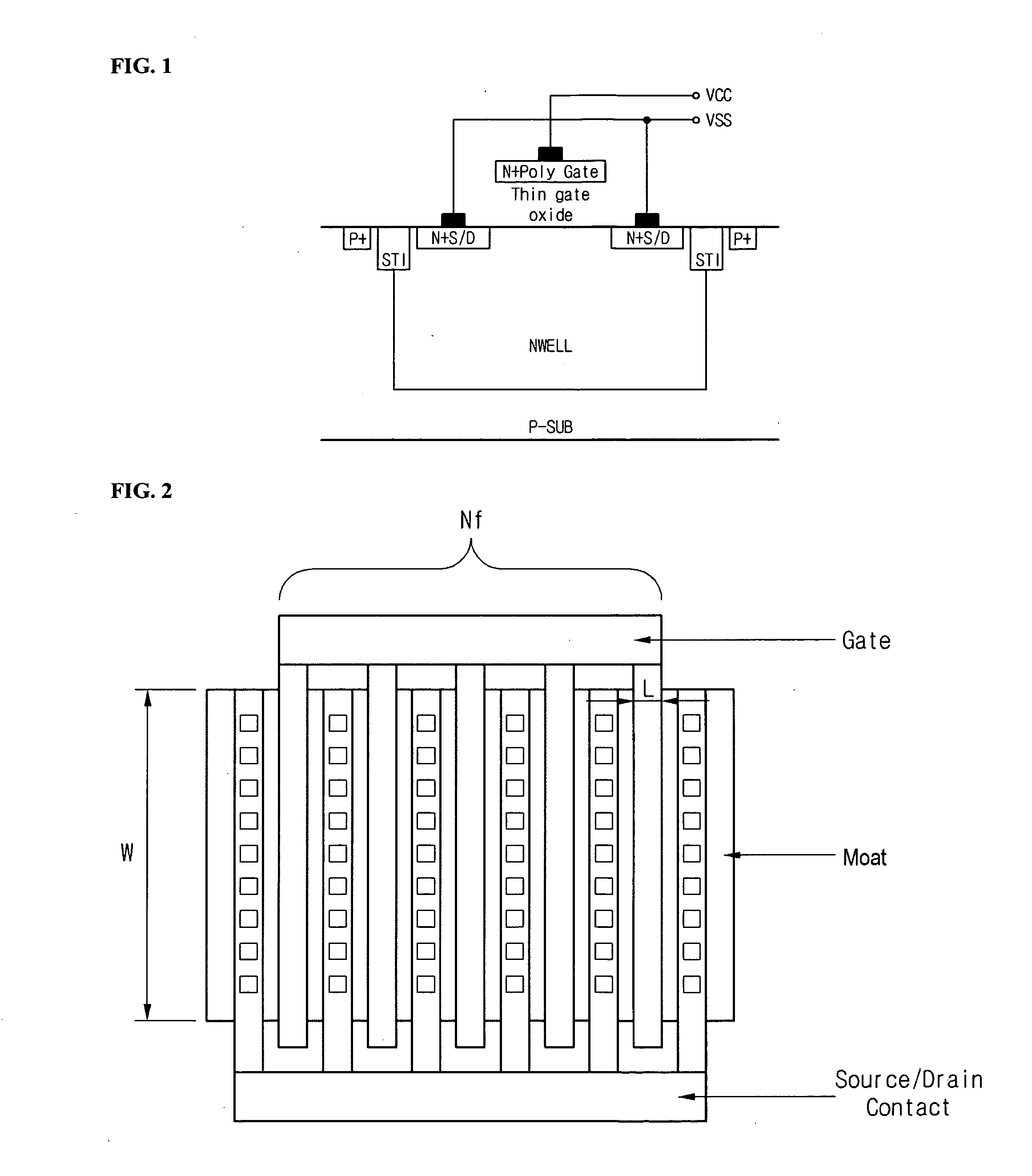
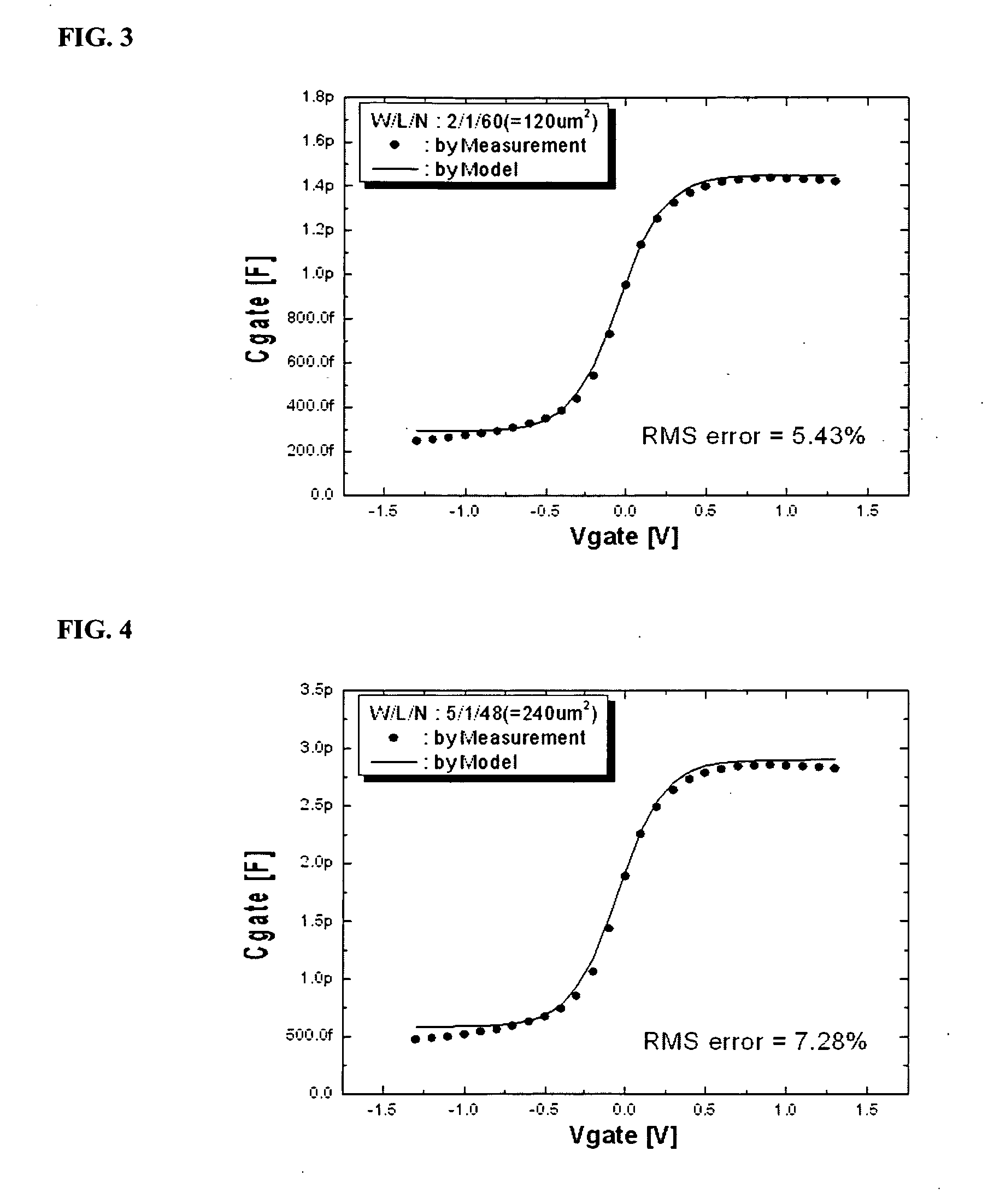
Disclosed is a method for detecting properties of a Metal Oxide Silicon (MOS) varactor, which includes: establishing a MOS varactor model equation in conjunction with an area of a gate; calculating values of the coefficients of the MOS varactor model equation through measurements for test materials; and extracting the properties of a capacitor of the MOS varactor using the calculated values of the coefficients. According to the method, the MOS varactor model equation can be expressed by Cgate=[Cigate×Area+Cpgate×Perimeter]×N, wherein, Cgate denotes gate capacitance for voltage applied to the gate, Cigate denotes intrinsic gate capacitance, Cpgate denotes perimeter gate capacitance, and N denotes the number of gate fingers. The MOS varactor model equation can be applicable to various sized capacitors, so that it is possible to estimate a gate capacitance for voltage applied to a gate, considering the differences due to the surface shapes of a device.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Metal oxide semiconductor device having mitigated threshold voltage roll-off and threshold voltage roll-off mitigation method thereof
ActiveUS20180190773A1Increase concentrationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChannel widthRoll-off
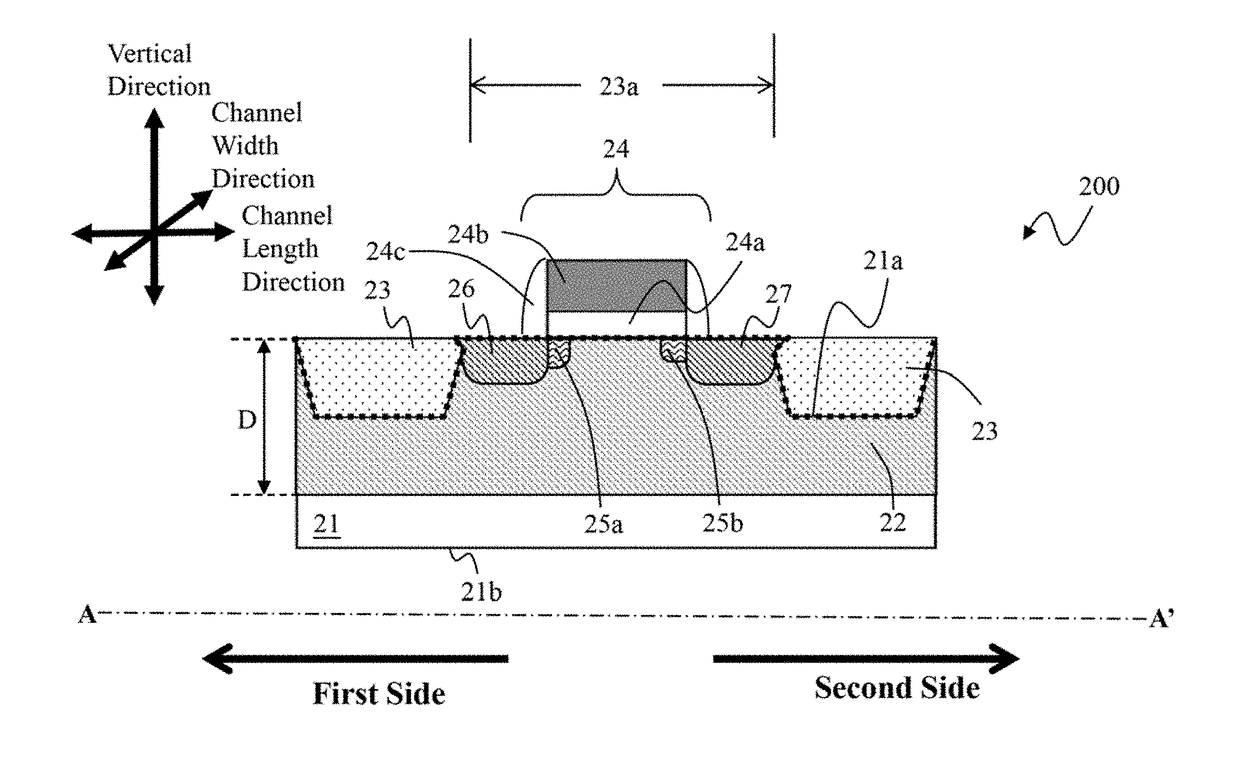
The present invention provides a MOS (Metal-Oxide-Silicon) device having mitigated threshold voltage roll-off and a threshold voltage roll-off mitigation method therefor. The MOS device includes: a substrate, a well region, an isolation region, a gate, two LDDs (Lightly-Doped-Drains), a source, a drain and a compensation doped region. The compensation doped region is substantially in contact with at least a part of a recessed portion along the channel length direction. Viewing from a cross-section view, at a boundary where the compensation doped region is in contact with the isolation region along the channel length direction, the compensation doped region has two doped region widths along the channel width direction, wherein, the two doped region widths of the compensation doped region are both not greater than 10% of the width of the operation region. Two doped region widths are defined as distances within an interior part and an exterior part of the operation region, respectively.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Apparatus and method for high-voltage transient blocking using low voltage elements
An apparatus and method for high-voltage transient blocking employing a transient blocking unit (TBU) that has at least one depletion mode n-channel device interconnected with at least one depletion mode p-channel device such that a transient alters a bias voltage Vp of the p-channel device and a bias voltage Vn of the n-channel device in concert. Specifically, the bias voltages are altered such that the p-channel device and n-channel device mutually switch off to block the transient. The depletion mode n-channel device employs a set of cascaded low-voltage depletion mode field effect transistors (FETs) such as metal-oxide-silicon field effect transistors (MOSFETs) connected source-to-drain to achieve the desired high-voltage operation of the TBU.
Owner:BOURNS INC
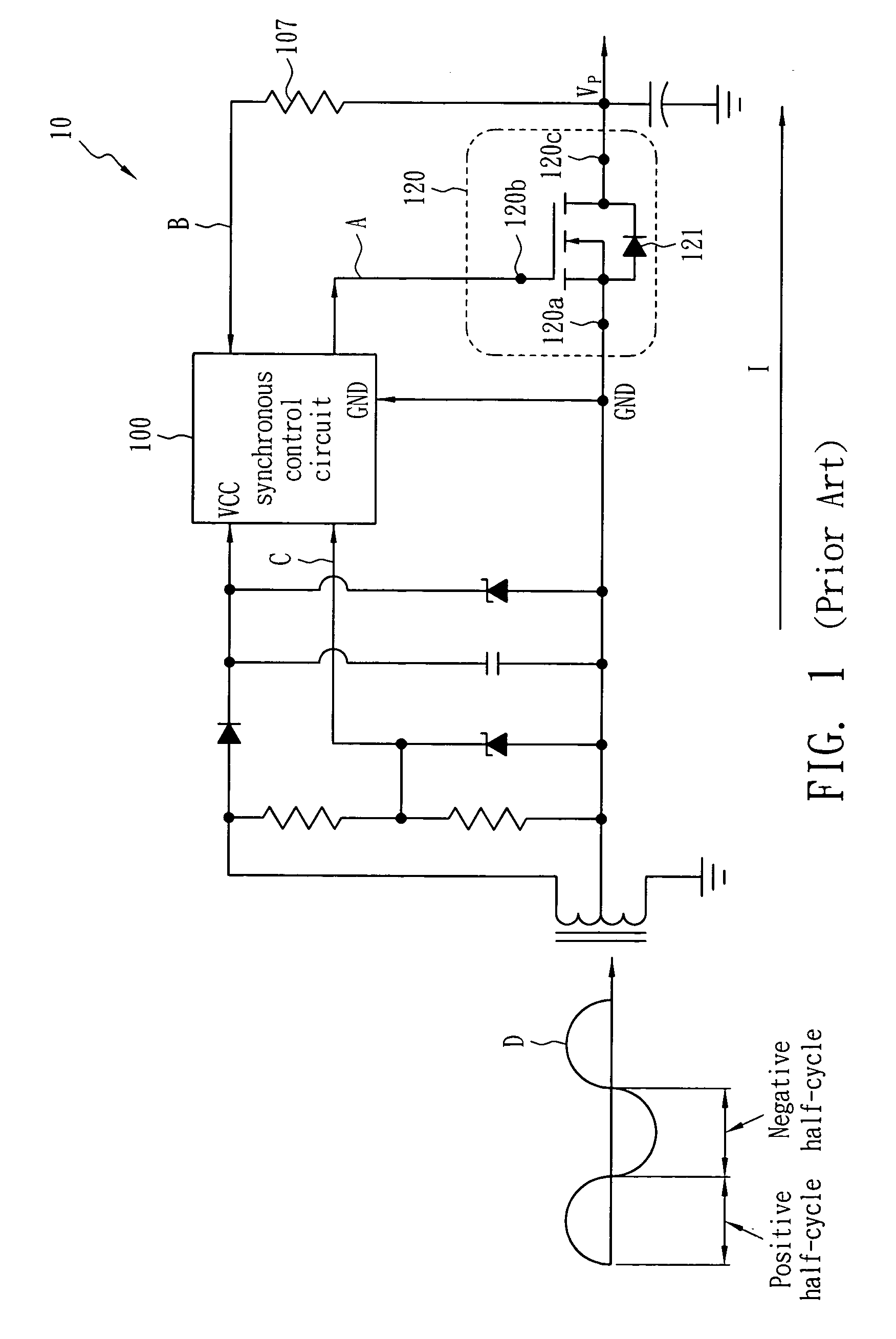
Anti-slide valve power supply control circuit of high speed train
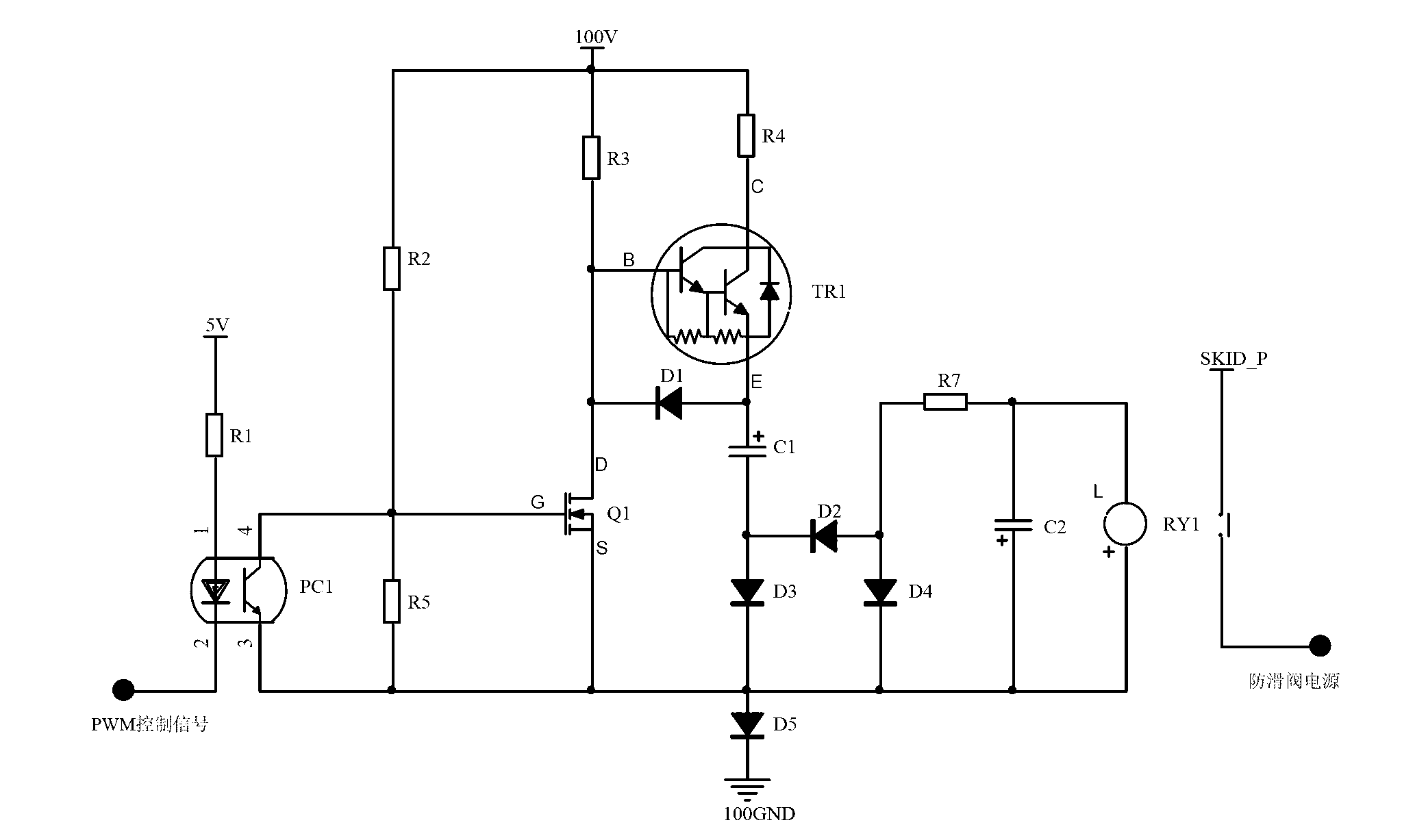
The invention relates to an anti-slide valve power supply control circuit of a high speed train. The anti-slide valve power supply control circuit mainly comprises an isolation optical coupler, an MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Silicon Field-Effect Transistor), a Darlington transistor, two charging and discharging capacitors, a power supply control relay and necessary resistors. The circuit smartly utilizes the matching of the MOSFET and the Darlington transistor to respectively complete charging and discharging of capacitors so that the relay keeps an electrification state when PWM (Pulse Wavelength Modulation) signals are input. The make-and-break of the MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Silicon Field-Effect Transistor) and the Darlington transistor is realized through the PWM signals so as to realize charging and discharging of the capacitors in each stage and maintain the control of a driving output relay. When the PWM control signals are in failure, the relay can be quickly cut off, and an anti-slide power supply is reliably cut off under the condition that the anti-slide valve or a driving circuit thereof or the anti-slide valve power supply control circuit is in failure, so that normal work of a braking system is ensured, and the safety and reliability of the braking system and the high speed train are improved.
Owner:NANJING CRRC PUZHEN HAITAI BRAKE EQUIP CO LTD
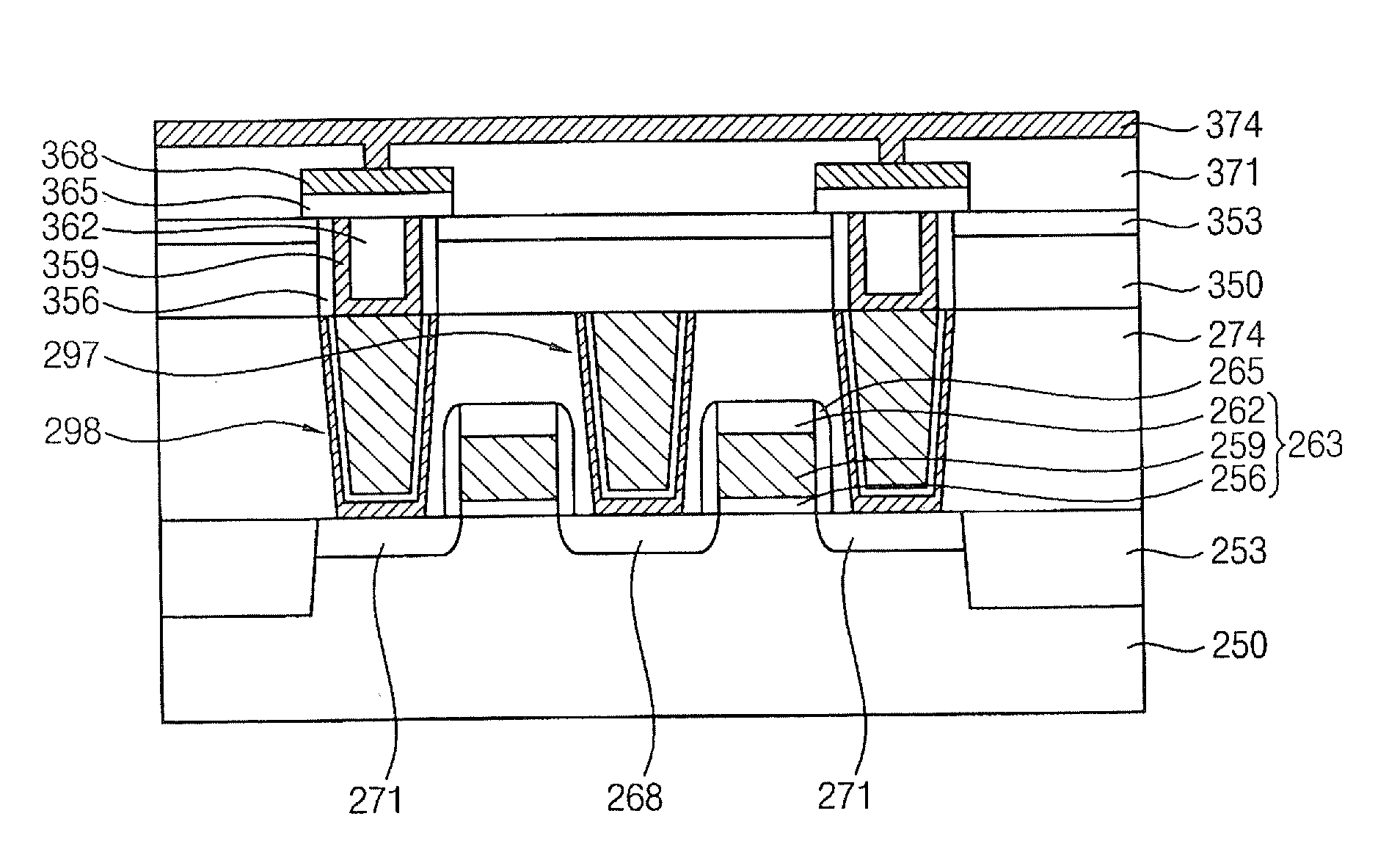
Circuit and method for suppressing gate induced drain leakage
ActiveUS7639066B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageEngineeringMetal oxide silicon
An electrical circuit comprising a first metal oxide silicon (MOS) n type field effect transistor (NFET) or p type field effect transistor (PFET) and a second MOS NFET or PFET of the same conductivity type as the first NFET or PFET, wherein the drain of the first NFET or PFET is directly connected to the source of the second NFET or PFET, and wherein the gate of the second NFET or PFET is at a voltage value which is equal to or lower than the drain voltage value of the second NFET or PFET in the case of an NFET and equal to or higher than the drain voltage value of the second NFET or PFET in the case of a PFET.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Method of fabricating complementary metal oxide silicon image sensor
ActiveUS20070148806A1High sensitivityHigh suppression characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenProtection layer
Provided is a method of fabricating a complementary metal oxide silicon image sensor. The method includes: applying a passivation oxide and a passivation nitride after forming a pad; selectively removing the passivation nitride in a pad region and a pixel region by a photolithography process, and performing a first cleaning process; performing a hydrogen anneal process; opening the pad by removing the passivation oxide in the pad region and performing a second cleaning process; applying a pad protective layer; performing a color filter array process, a planarization process, and a microlens process after the applying of the pad protective layer; and removing the pad protective layer in the pad region.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Gate driving circuit for power semiconductor element
ActiveUS8466734B2Avoid Equipment FailureSuppresses noise generationElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorMOSFETHigh resistance
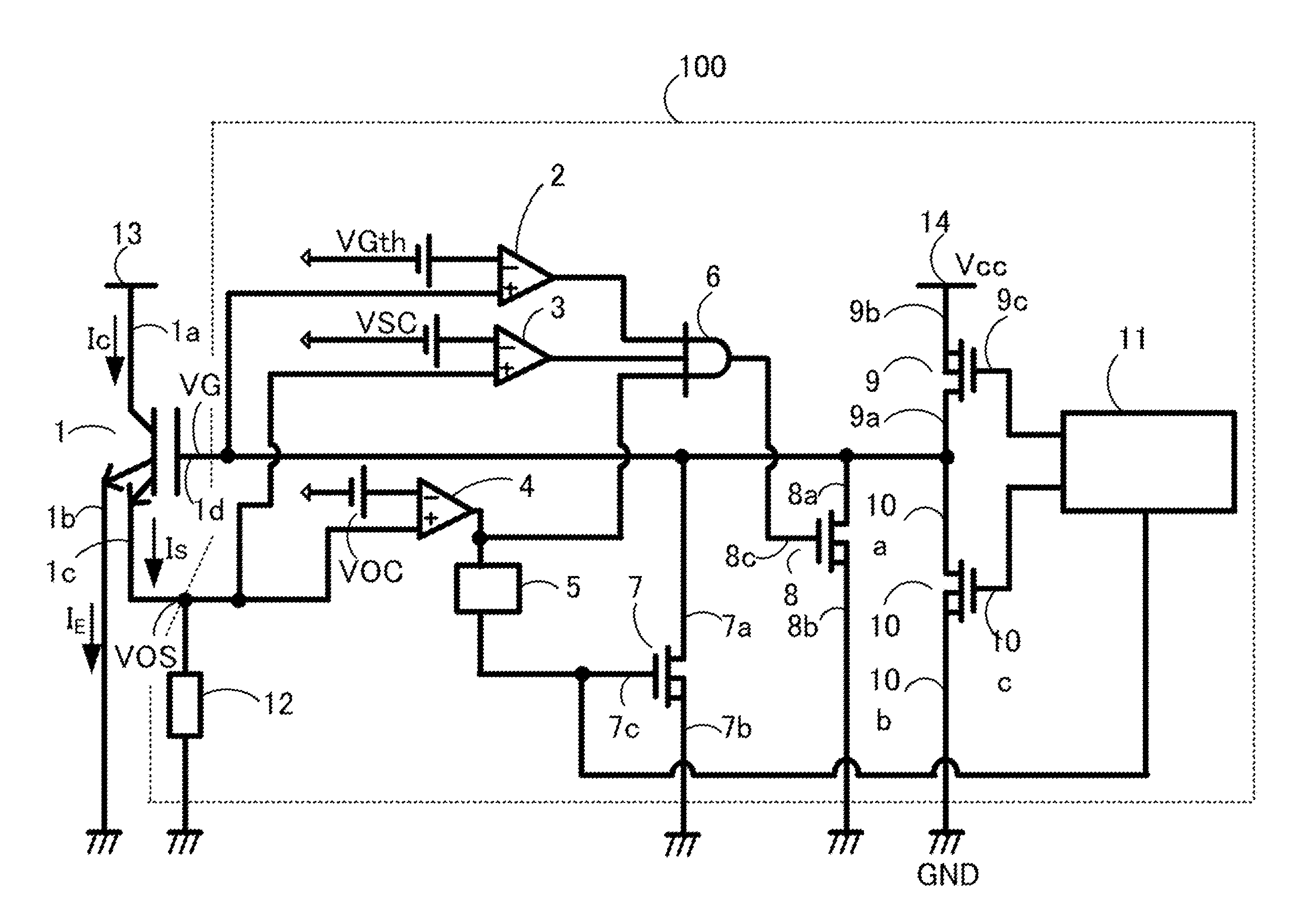
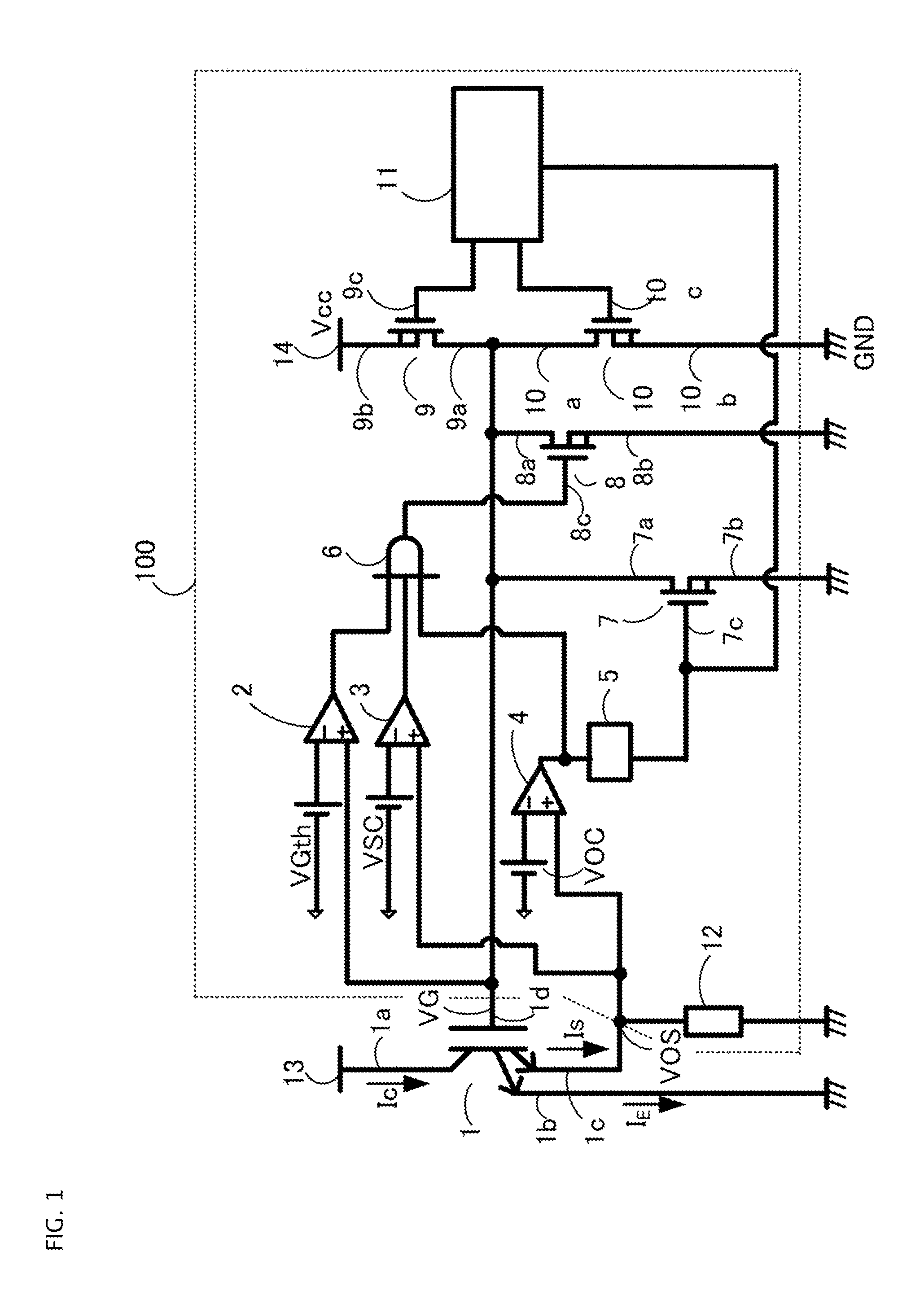
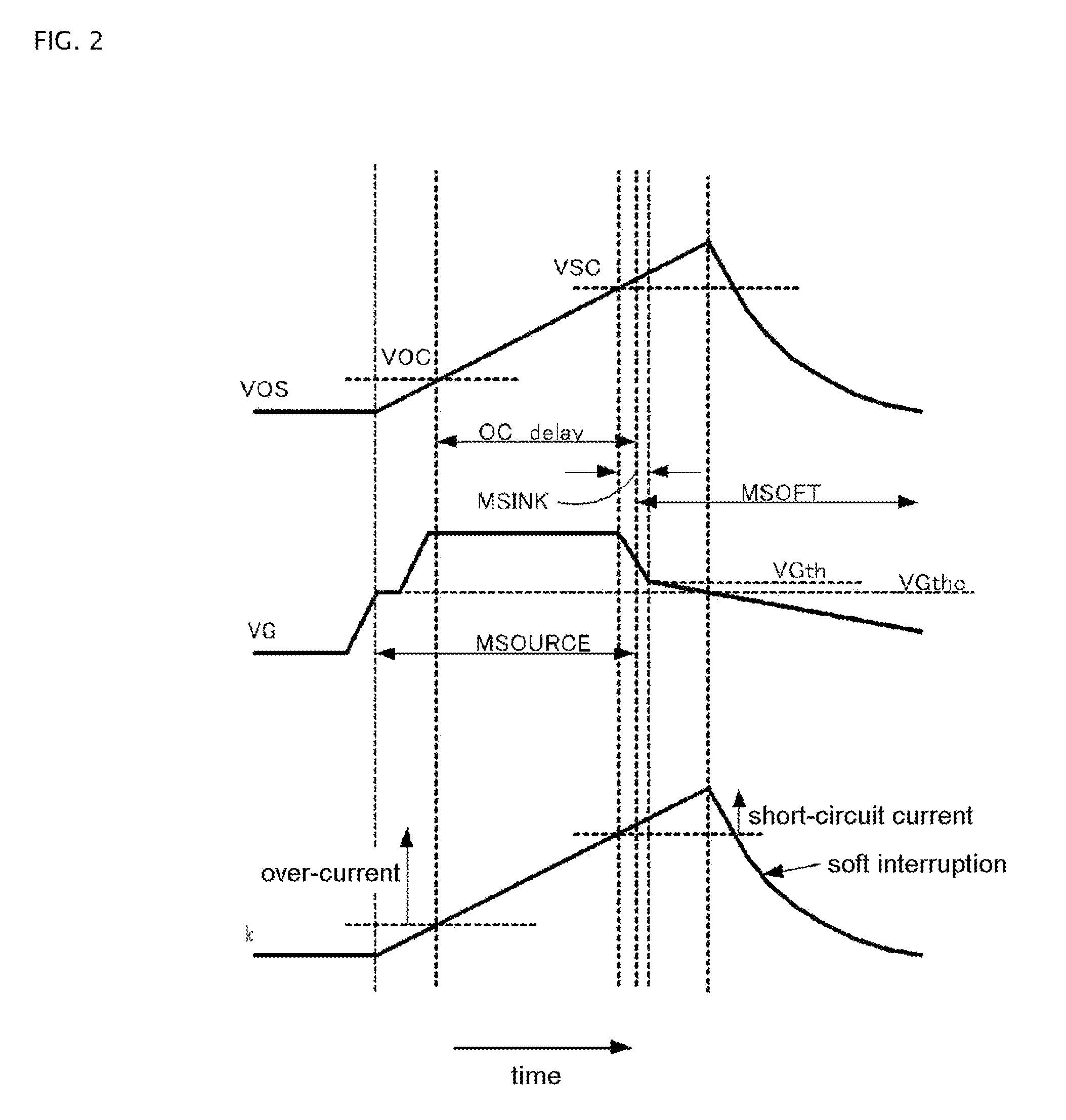
A gate driving circuit for driving a power semiconductor element can include a MSINK that is an n-channel metal-oxide silicon field-effect transistor (MOSFET) with a low resistance value for rapidly drawing out the charges accumulated on the gate of an insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT), and a MSOFT that is an n-channel MOSFET with a high resistance value for slowly drawing out the charges. By shifting the time for turning ON of these MOSFETs, soft interruption can be performed rapidly and surely when overcurrent or short circuit current flows in the IGBT. Therefore, device breakdown is minimized or avoided and noise generation is suppressed.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor device including metal-oxide-silicon field-effect transistor as a trigger circuit
InactiveUS7473973B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSilicon-controlled rectifierMetal oxide silicon
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
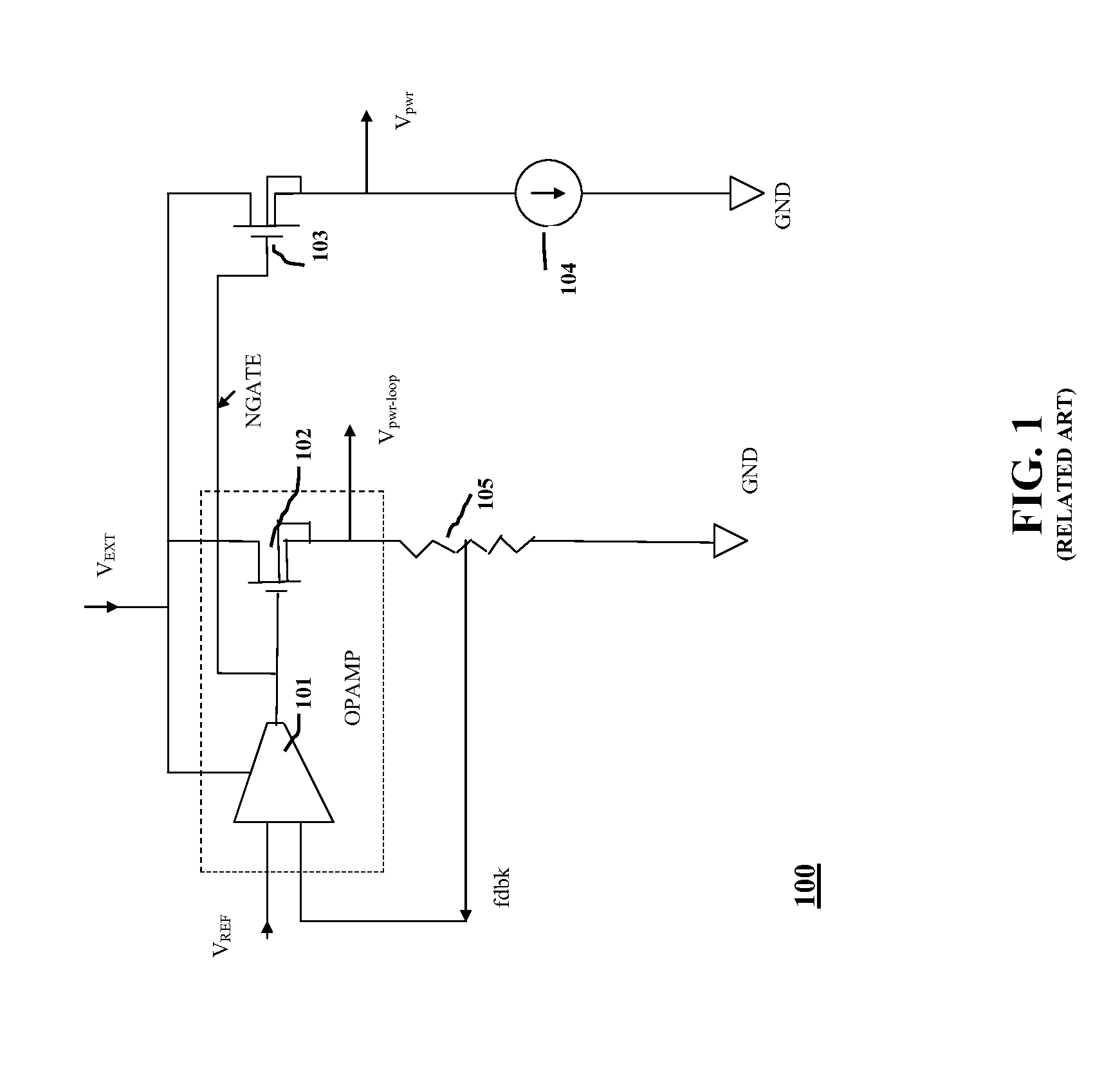
Trimming circuit and method for replica type voltage regulators
ActiveUS7880452B1Easy to tuneGreat output voltageElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
The present invention is directed to a trimming circuit and method for replica type voltage regulators. A voltage regulator circuit includes an operational amplifier (OPAMP) and a n-type metal oxide silicon (NMOS) device. An output of the OPAMP is coupled to a gate terminal of the NMOS device. The voltage regulator circuit includes a potential divider circuit comprising a plurality of discrete devices coupled in series. A source terminal of the NMOS device is coupled to the potential divider circuit to form an output feedback node. The body of the NMOS device is biased variably across a plurality of tap points formed between consecutive discrete devices in the potential divider circuit.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
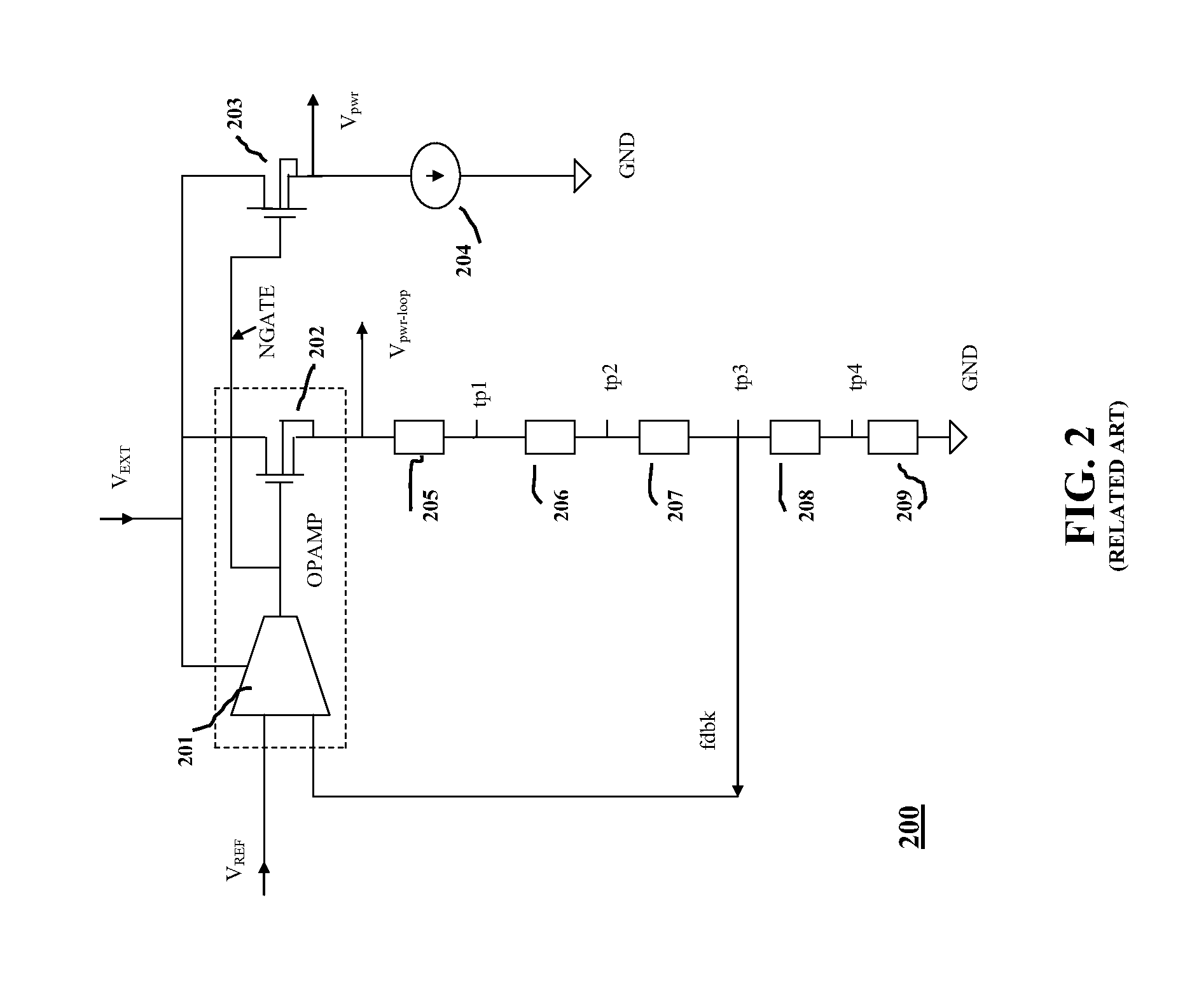
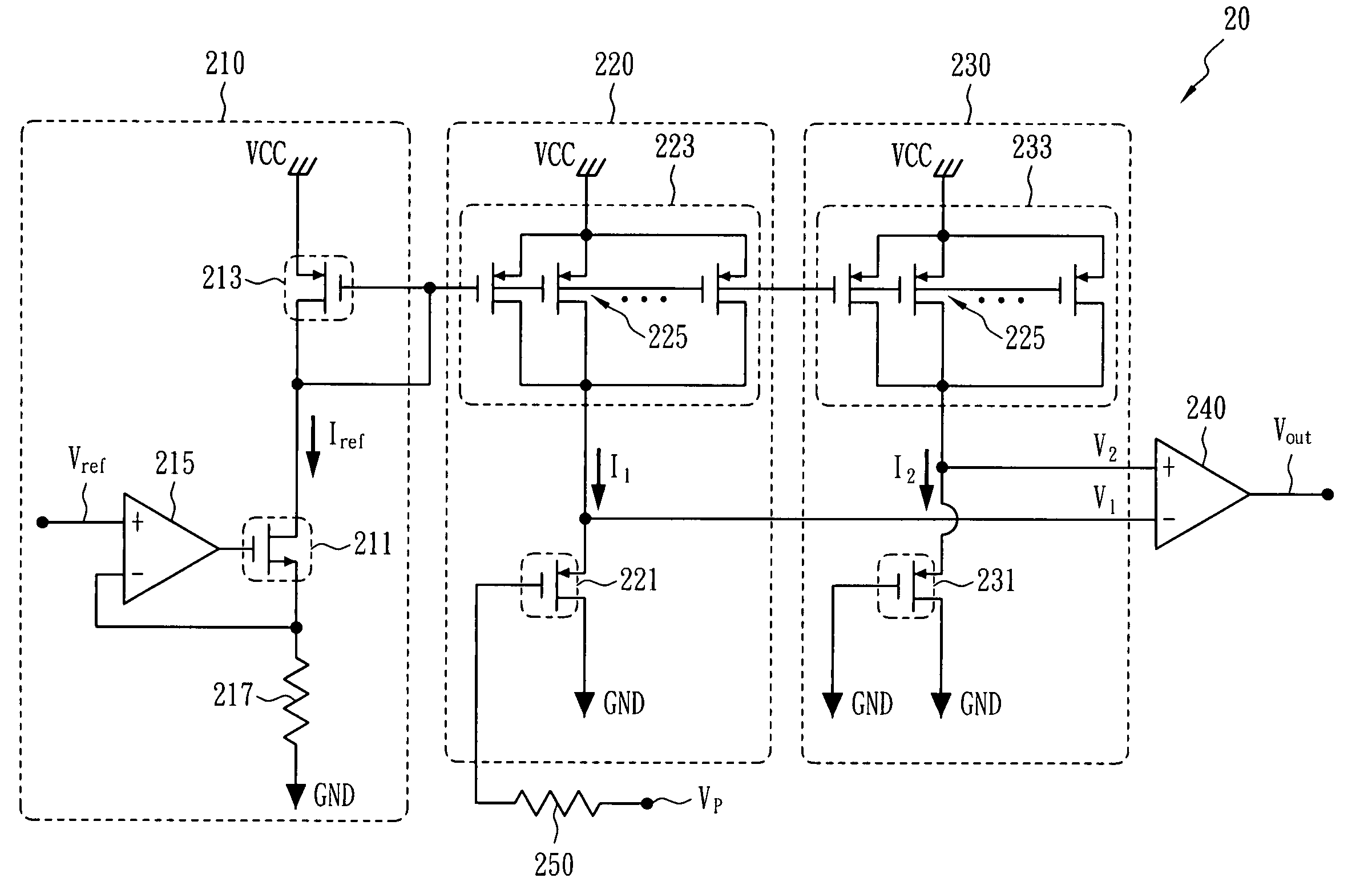
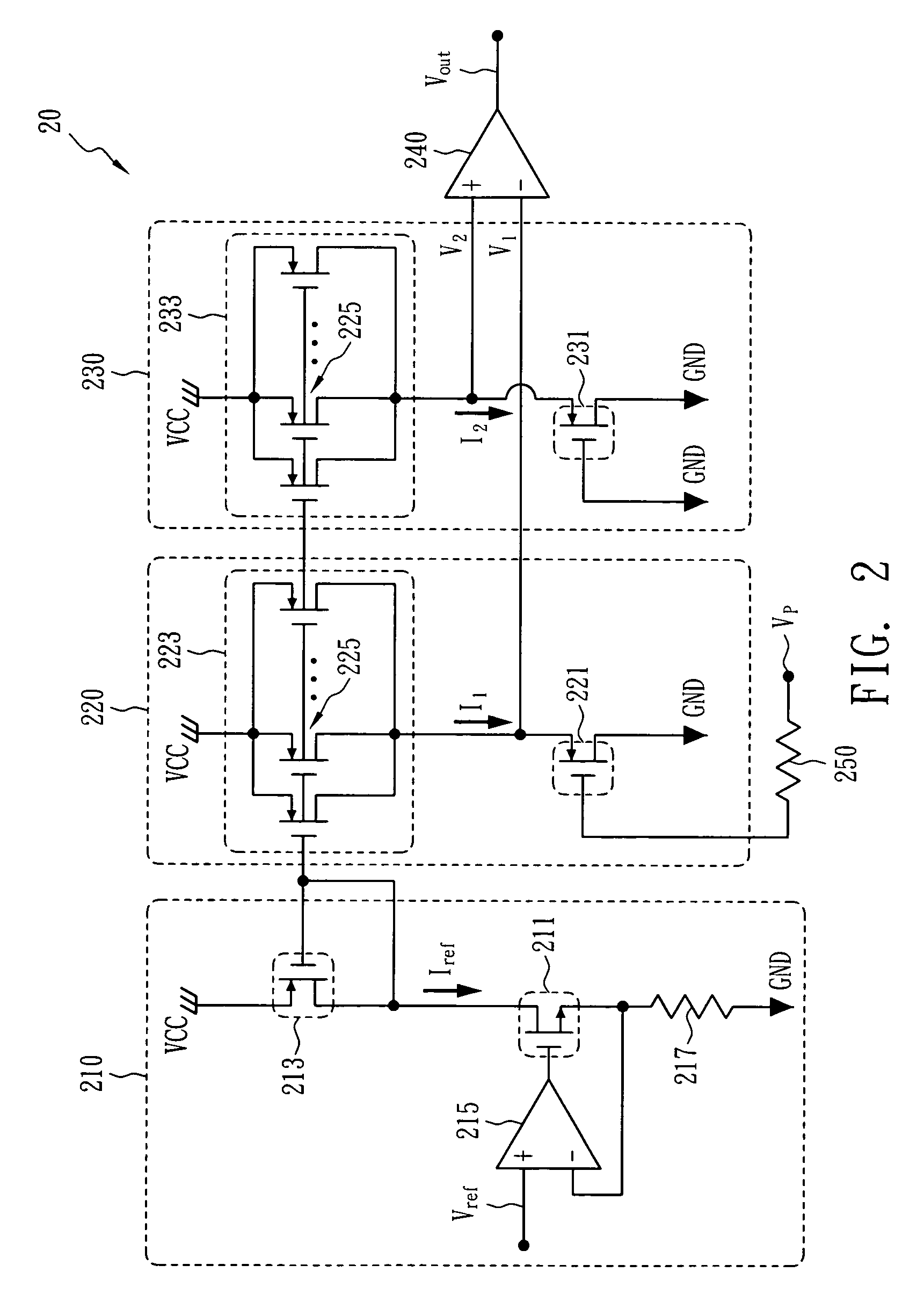
Negative voltage detection circuit for synchronous rectifier mosfet
InactiveUS20080309320A1Accurate detectionMeasurement using ac-dc conversionEfficient power electronics conversionMOSFETReference current
A negative voltage detection circuit for a synchronous rectifier metal oxide silicon field effect transistor (MOSFET). The circuit comprises a reference current source, a first circuit mirroring a first current based upon the reference current source and generating a first voltage based upon a detection voltage, a second circuit mirroring a second current based upon the reference current source and generating a second voltage, and a comparator having input ends to receive the first voltage and the second voltage, wherein a level of an output voltage of the comparator changes when the detection voltage is equivalent to a value predetermined according to a difference between the first current and the second current.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
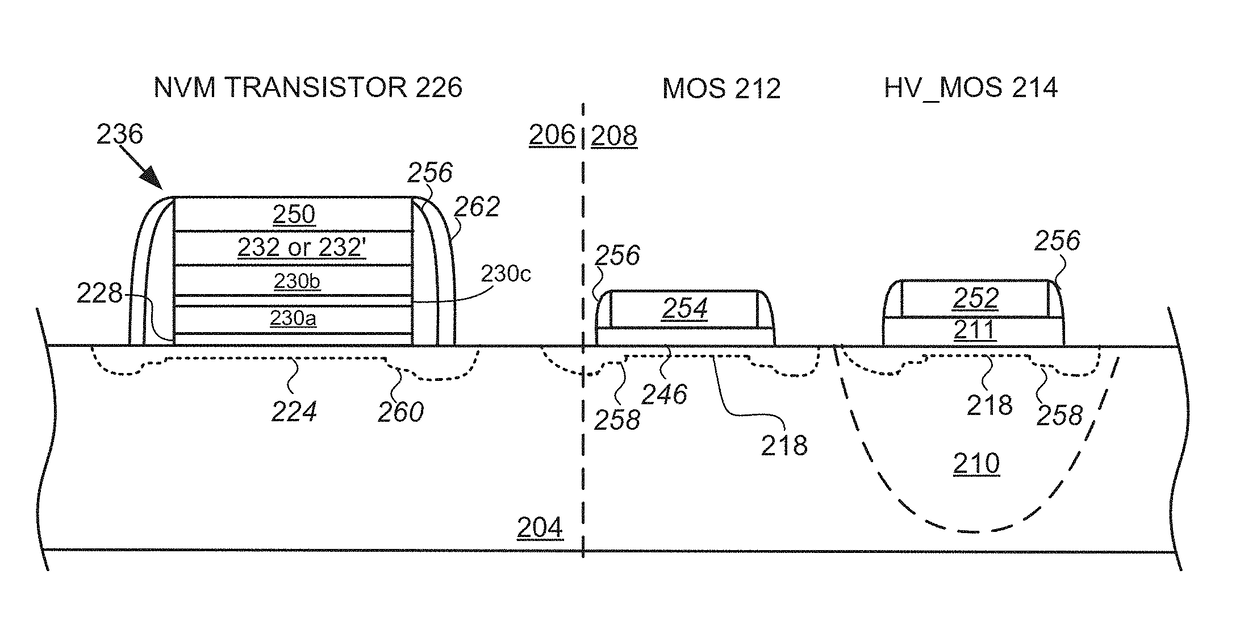
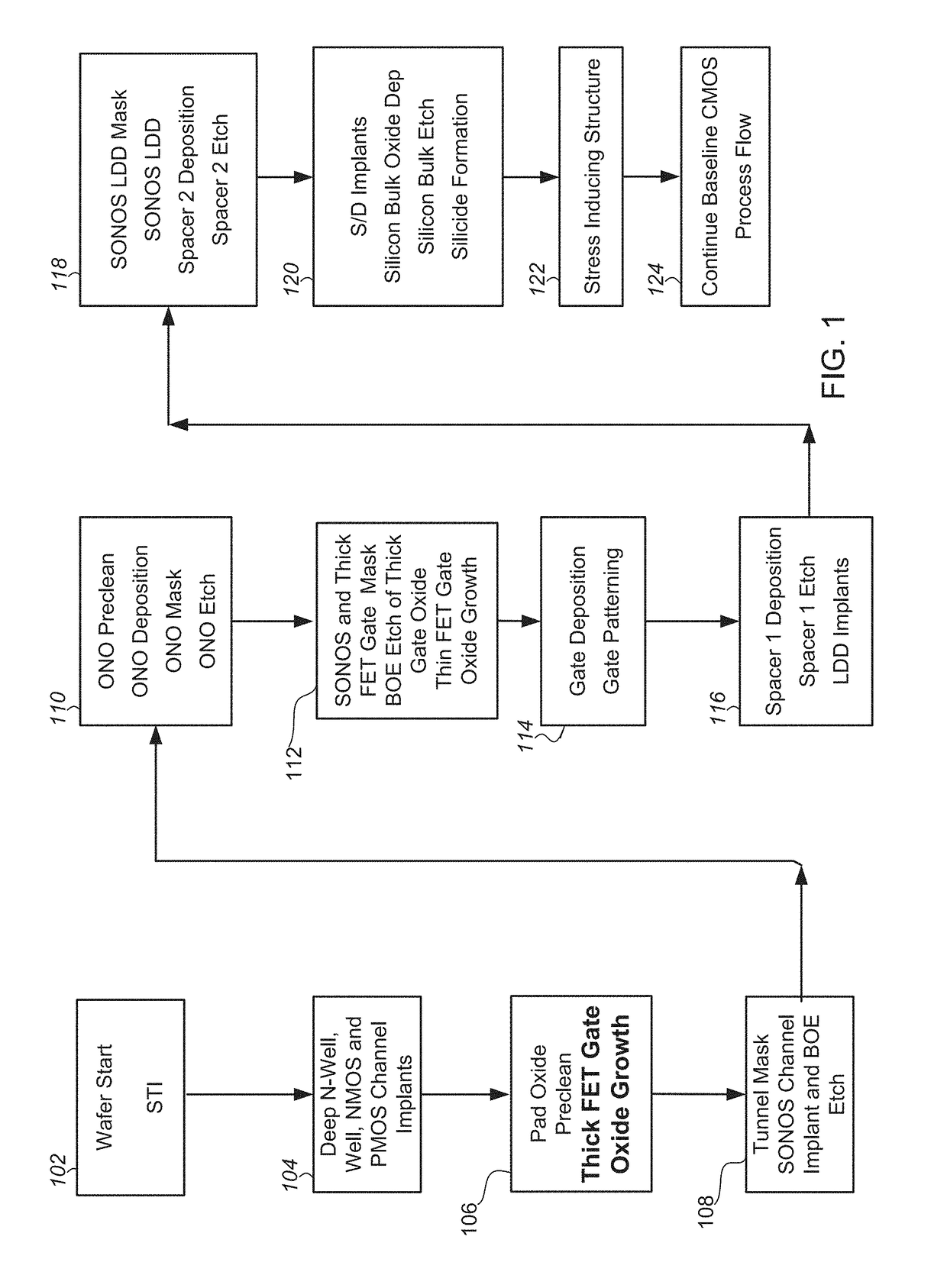
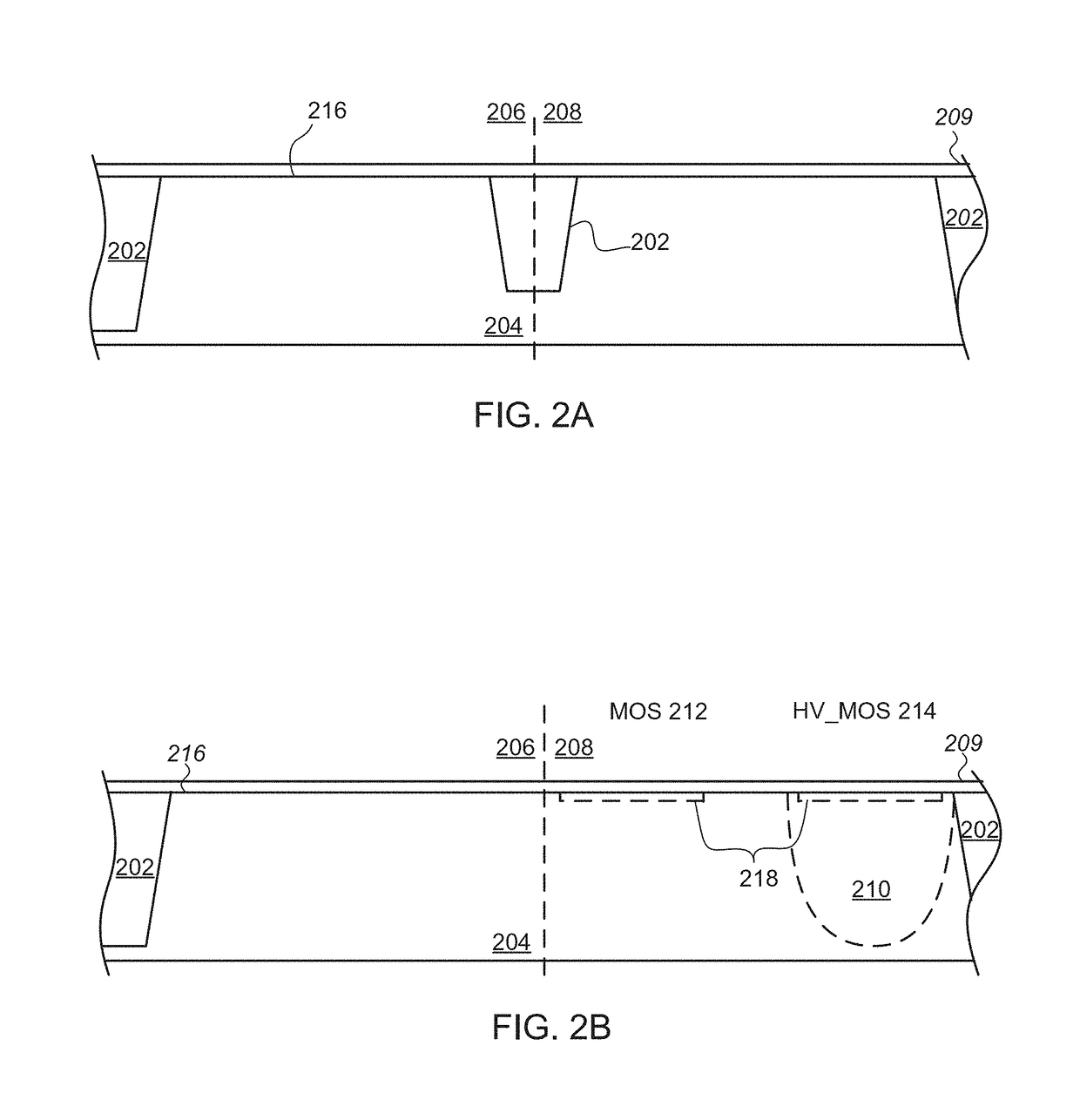
Method of integration of ONO stack formation into thick gate oxide CMOS flow
ActiveUS9824895B1Improvement in threshold voltage (VT) uniformityImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSSilicon oxide
A method of integrating a silicon-oxide-nitride-oxide-silicon (SONOS) transistor into a complementary metal-oxide-silicon (CMOS) baseline process. The method includes the steps of forming the gate oxide layer of at least one metal-oxide-silicon (MOS) transistor prior to forming a non-volatile (NV) gate stack of the SONOS transistor.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
Starter device for normally off JFETs
InactiveUS6975157B1Efficient supplyEasy to switchTransistorElectronic switchingMOSFETAudio power amplifier
A semiconductor switching device or amplifier combined in parallel with one or more active devices defined as starter devices. A starter device is used to reduce the terminal voltage of a switching device or amplifier to a dc level below about 0.4 volts which will then allow the switching device to easily change between the on or conducting state and the off or non-conducting state. Three different starter devices are utilized. The first being a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), the second a Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET), and the third consisting of three normally off JFETs connected serially. Generally, a single starter device is coupled across the terminals of a semiconductor switching device or amplifier, but it is possible and sometimes advantageous to couple two or more starter devices in parallel. In a first case, a symmetrical, normally off or enhancement mode JFET is used as the switch or amplifier. A starter device coupled between source and drain of the JFET will allow operation at dc voltage levels above 0.4 volts. In a second case, an asymmetrical, normally off JFET is used as the switch or amplifier. A starter device coupled between source and drain of the JFET will allow operation at dc voltage levels above 0.4 volts. In a third case, a normally off MESFET is used as the switch or amplifier. A starter device coupled between source and drain of the MESFET will allow operation at dc voltage levels above 0.4 volts.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
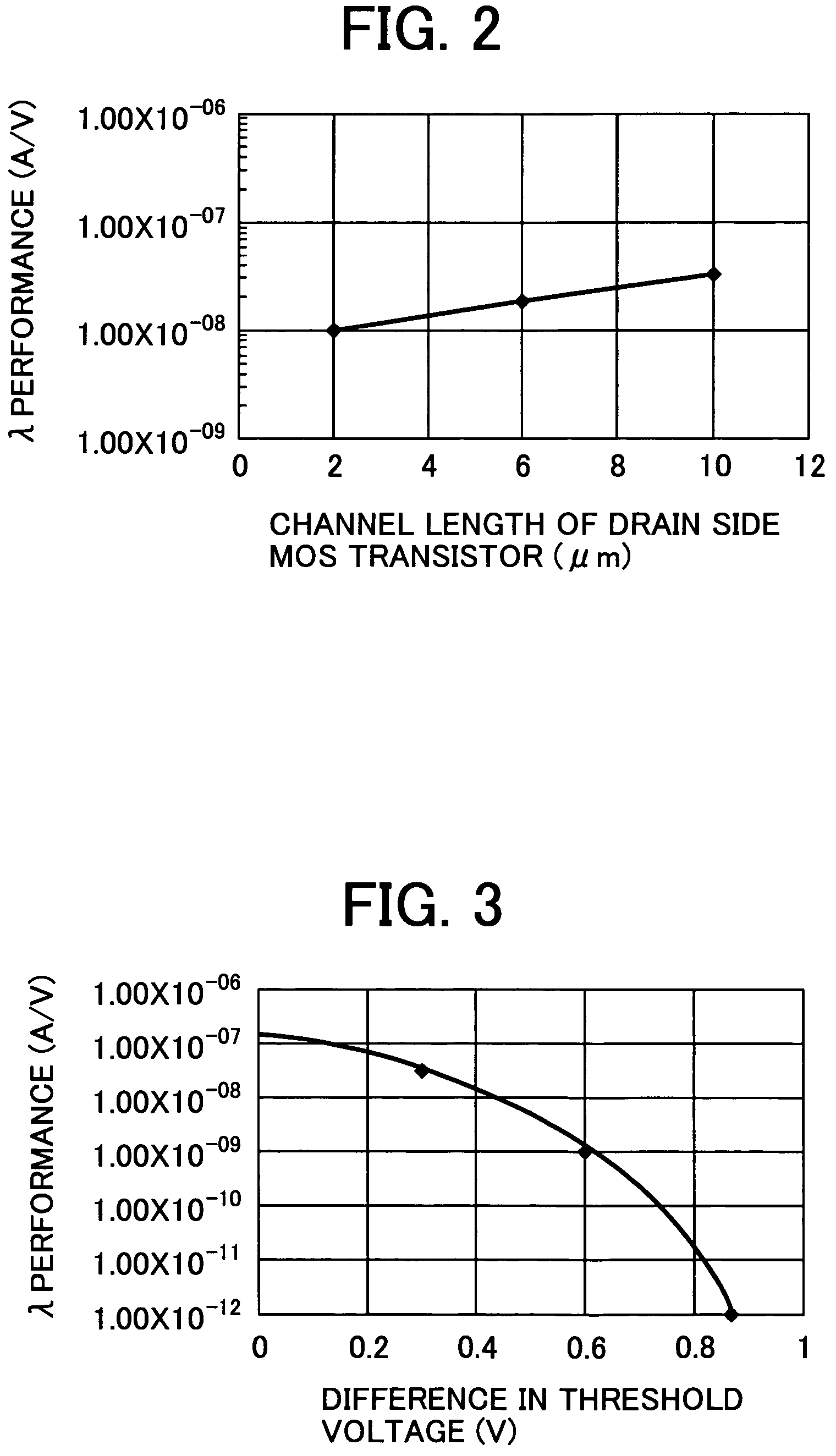
Metal oxide silicon transistor and semiconductor apparatus having high lambda and beta performances
A semiconductor apparatus includes a MOS transistor having a semiconductor substrate providing as a channel region between a source and a drain. A gate electrode is formed on the semiconductor substrate via a gate oxide film. A threshold voltage of the source side region of the MOS transistor is higher than that of the drain side region in a longitudinal direction of the channel region so that a saturation drain current can be constant and a λ performance can be improved while suppressing channel width and length.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com