Patents
Literature
51 results about "Process voltage temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
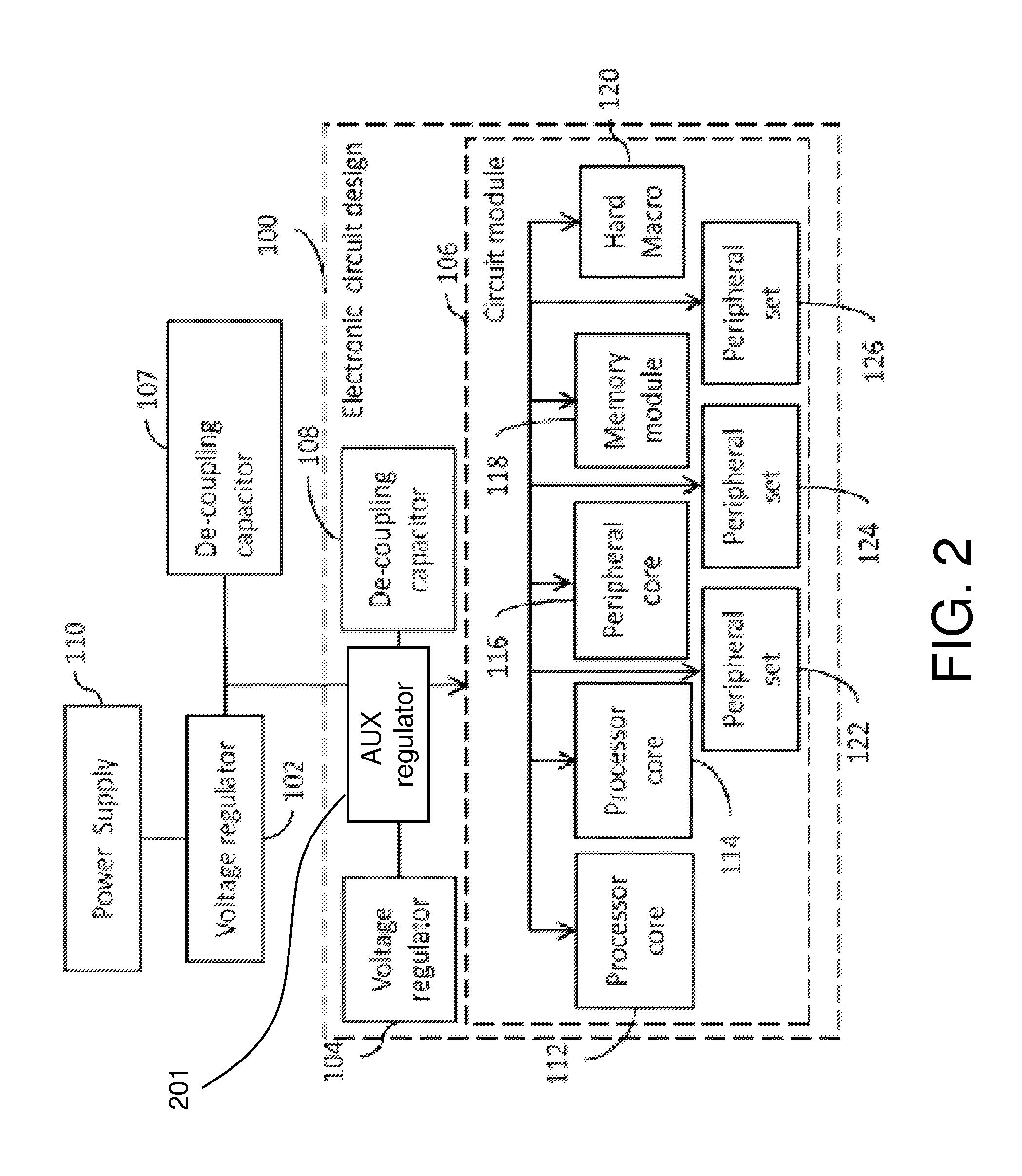
SRAM employing virtual rail scheme stable against various process-voltage-temperature variations
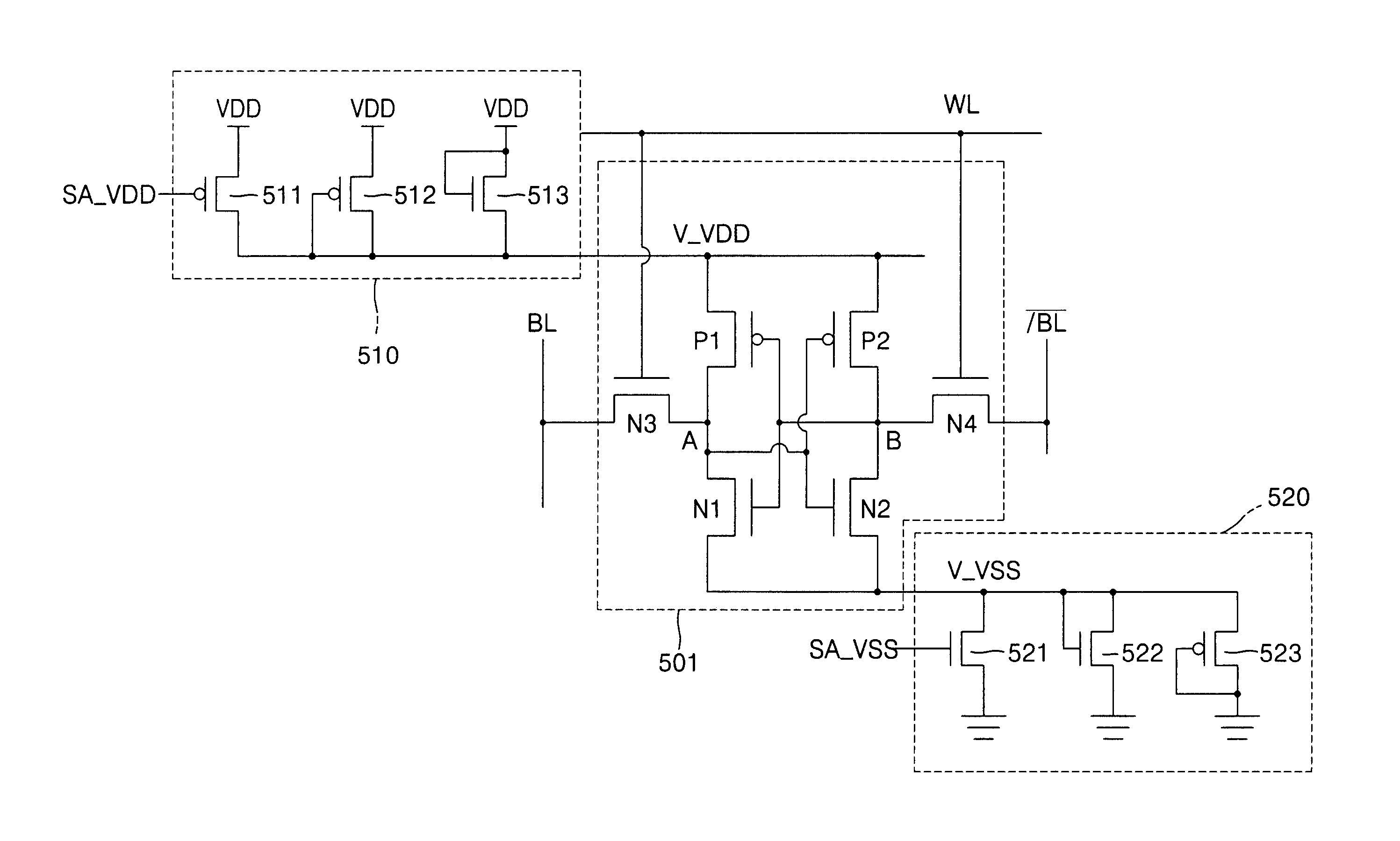
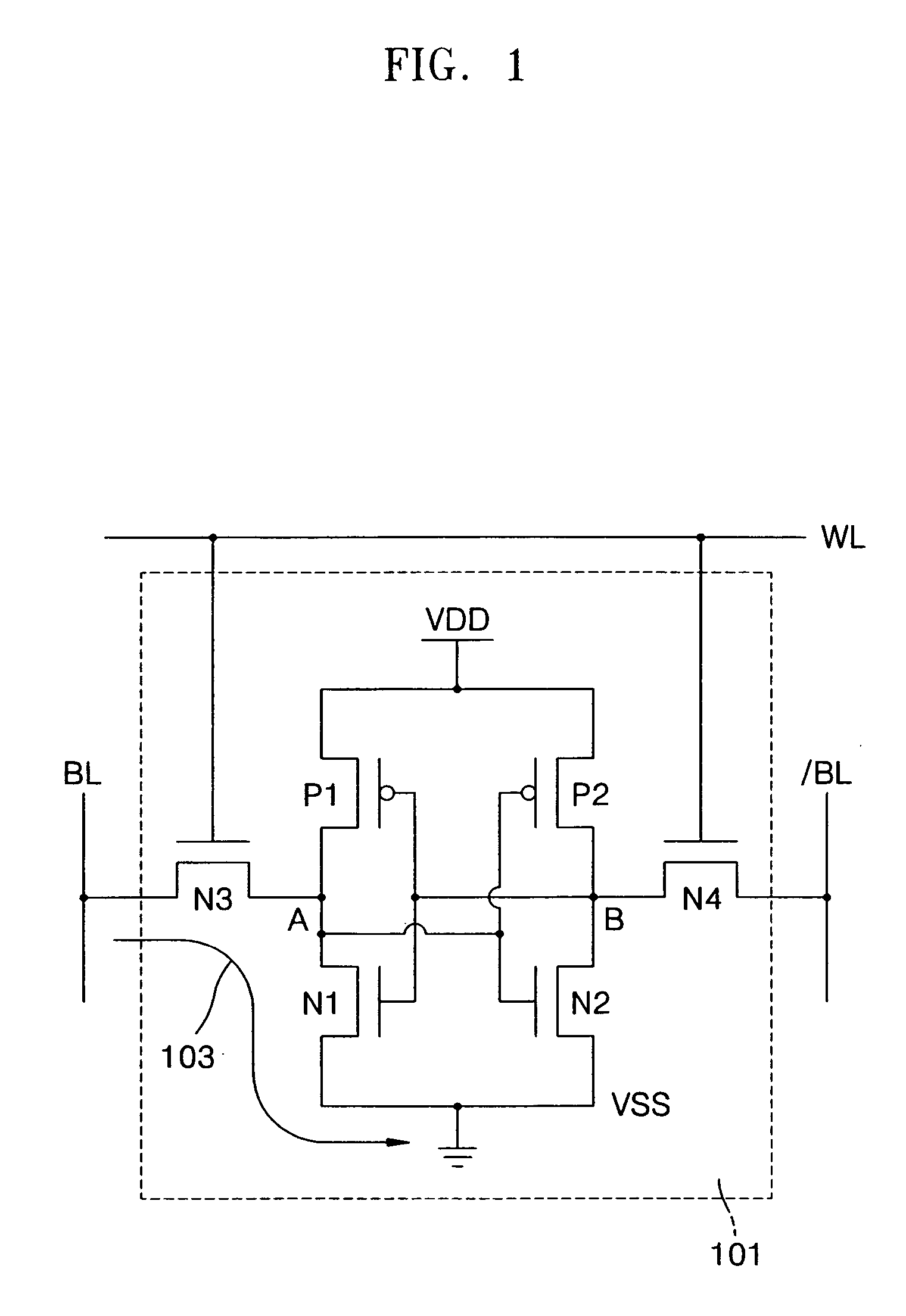
An SRAM employs a virtual rail configuration that is stable against process-voltage-temperature (PVT) variation. The SRAM provides a virtual power supply voltage to an SRAM cell that is obtained by lowering a power supply voltage by a threshold voltage of a transistor and a virtual ground voltage obtained by raising a ground voltage by a threshold voltage of a transistor. Due to the use of PMOS and NMOS transistors of diode types connected between the power supply voltage and the virtual power supply voltage and the use of NMOS and PMOS transistors of diode types connected between the ground voltage and the virtual ground voltage, a virtual power supply voltage level and a virtual ground voltage level that are stable even against various PVT variations are provided, so that low-leakage current characteristics are stable.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
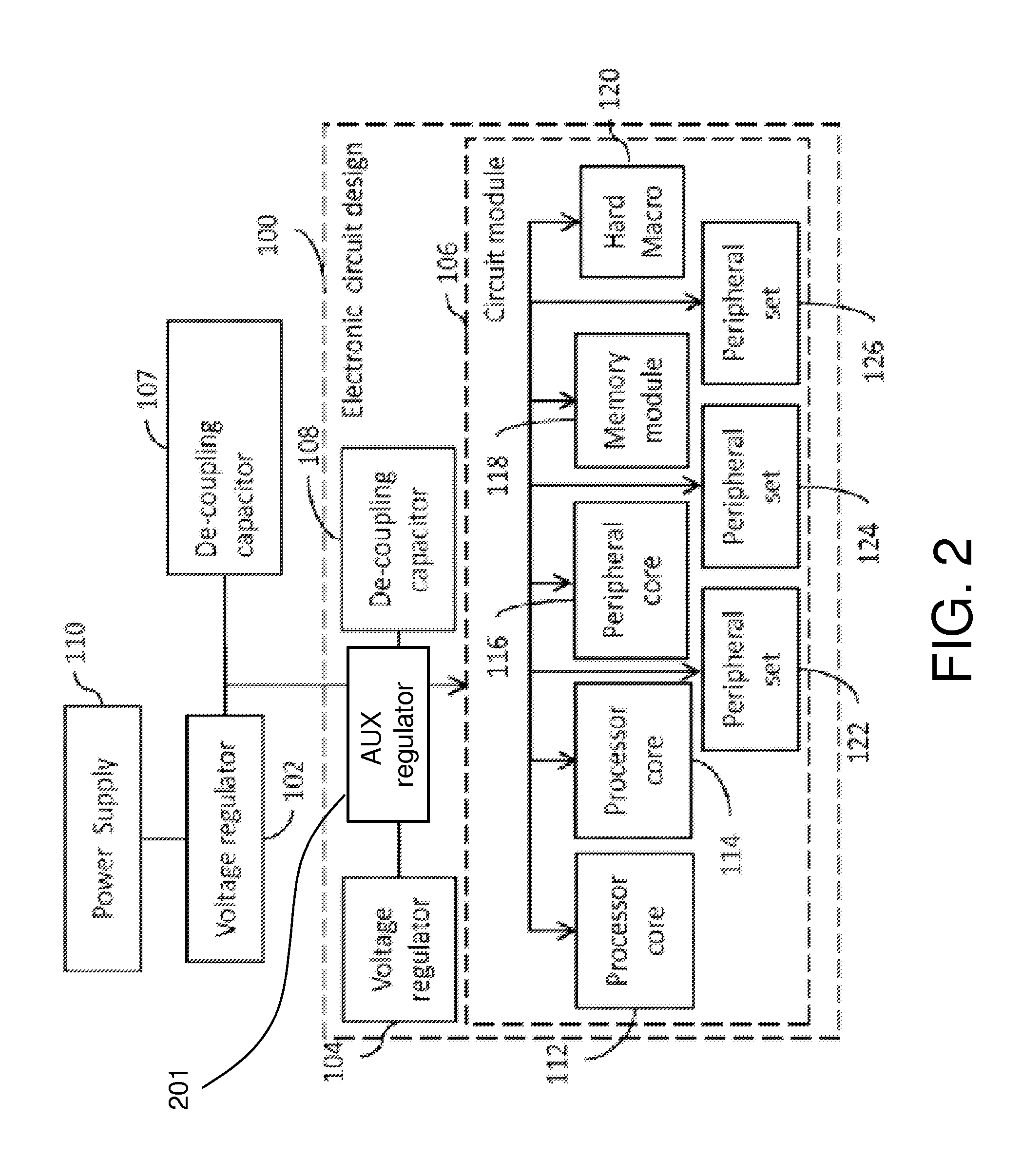
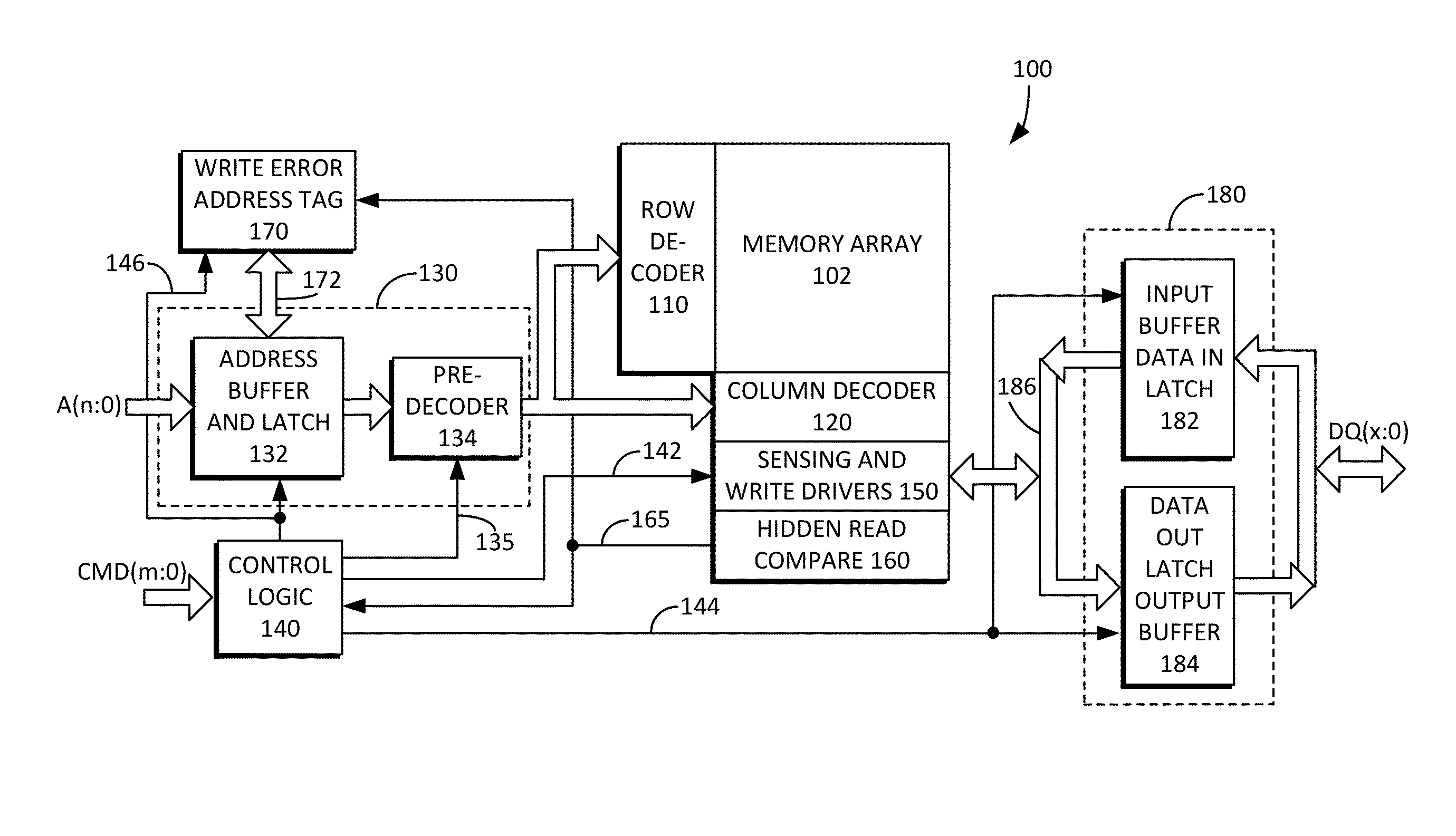
Method and system for providing a smart memory architecture
ActiveUS20130212431A1High rateHigh error rateDigital computer detailsComputer security arrangementsMemory addressSmart memory
A smart memory system preferably includes a memory including one or more memory chips, and a processor including one or more memory processor chips. The processor may include a common address / data / control memory bus that is configured to provide an asynchronous handshaking interface between the memory array and the memory processor. The processor can offload error data from the memory chip for analysis, and can store poor retention bit address information for memory refreshing in a non-volatile error retention memory. Program logic can also be included for memory address re-configuration. Power management logic can also be included, which may have a process-voltage-temperature compensation voltage generator for providing stable and constant read currents. An asynchronous handshaking interface is provided between the memory array and the memory processor. Write error tagging and write verification circuits can also be included.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
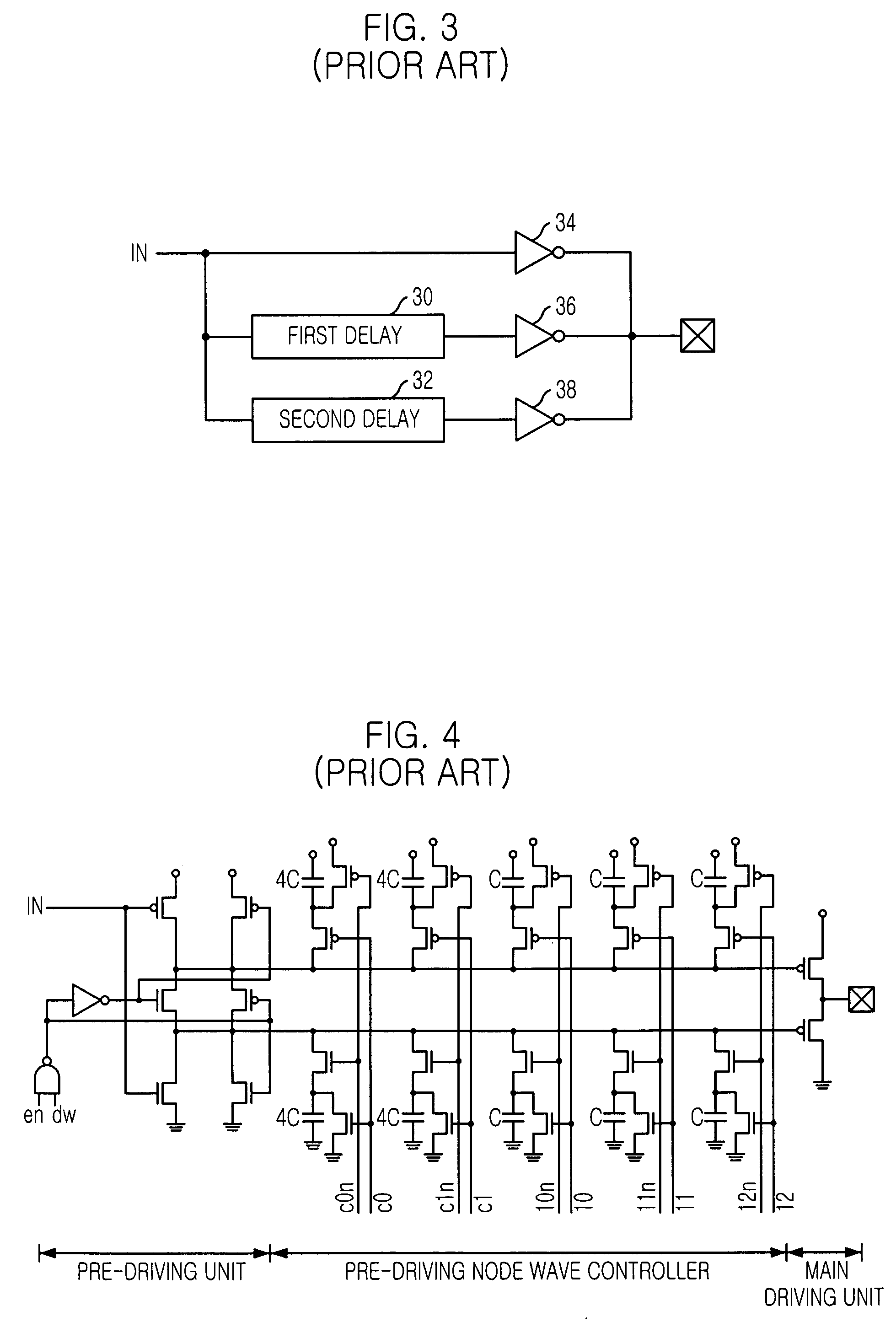
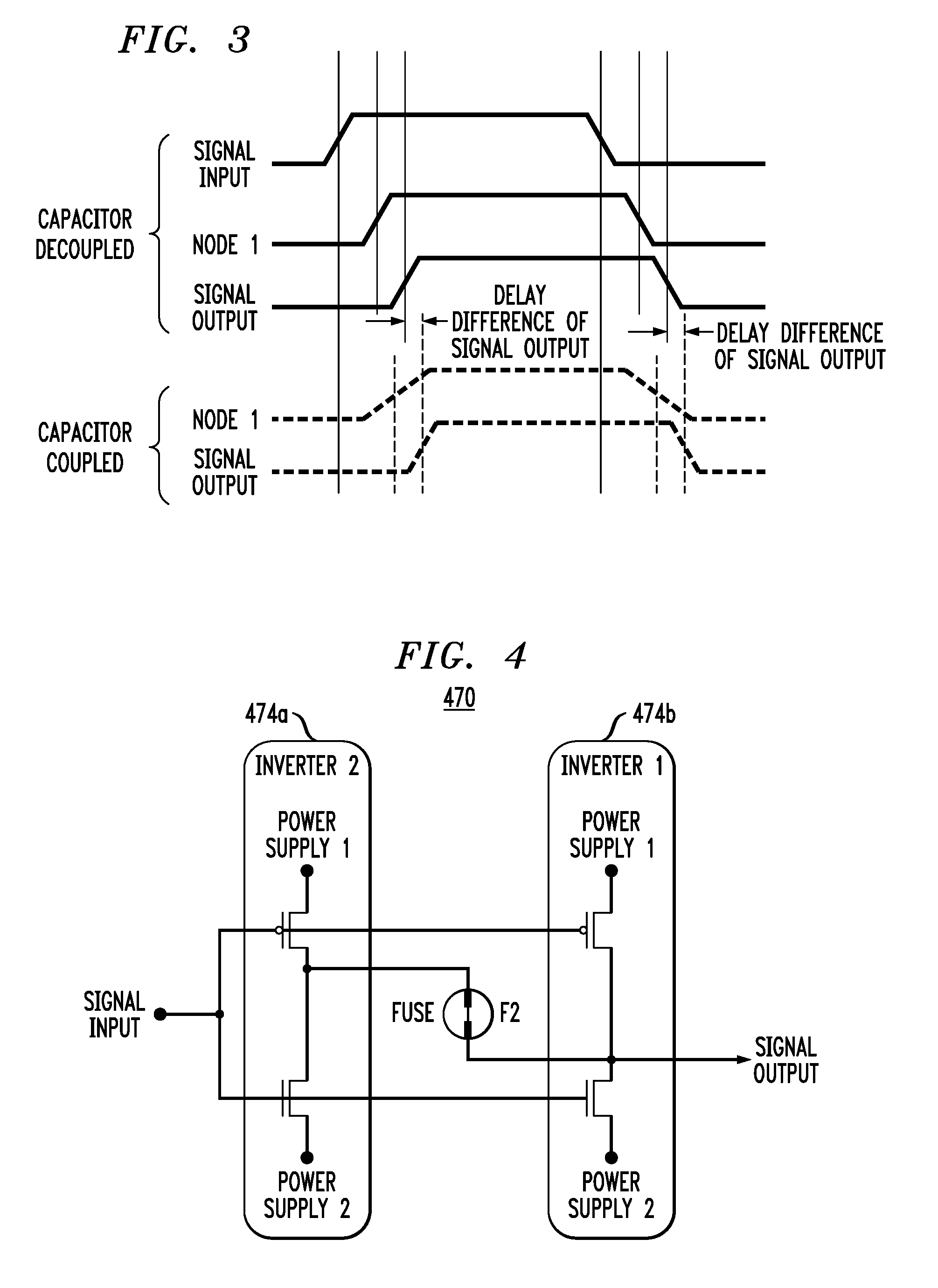
Slew rate controlled output driver for use in semiconductor device
An output driver for use in a semiconductor is capable of maintaining its slew rate constantly regardless of PVT(Process / Voltage / Temperature) variation. The output driver includes a pre-driving unit for pre-driving a data signal; a main driving unit for driving an output pad in response to the output signal of the pre-driving unit; and a slew rate modeling unit for generating a pre-driver bias signal to constantly maintain effective resistances of a pull-up path and a pull-down path of the pre-driving unit by modeling the pre-driving unit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
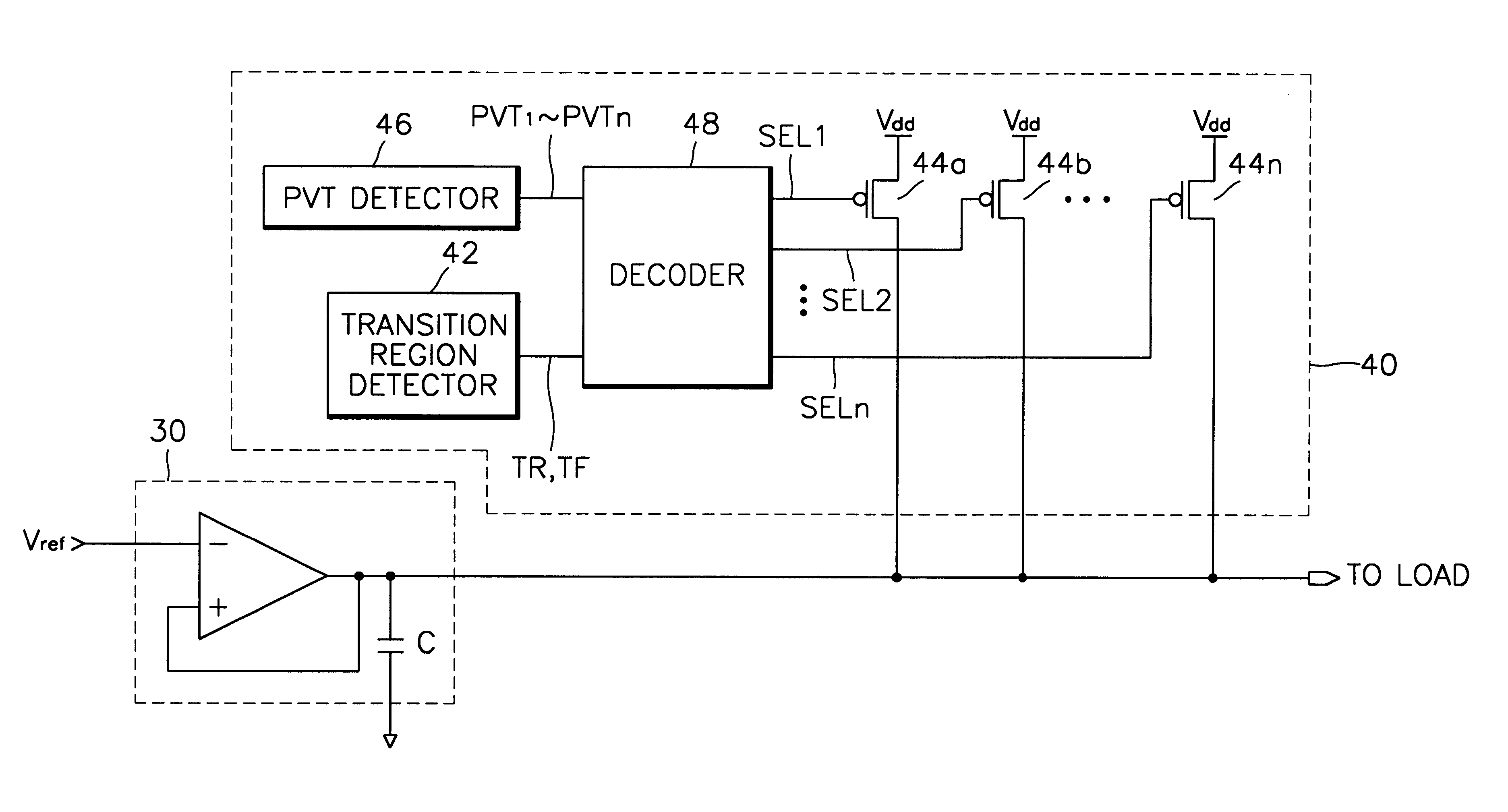
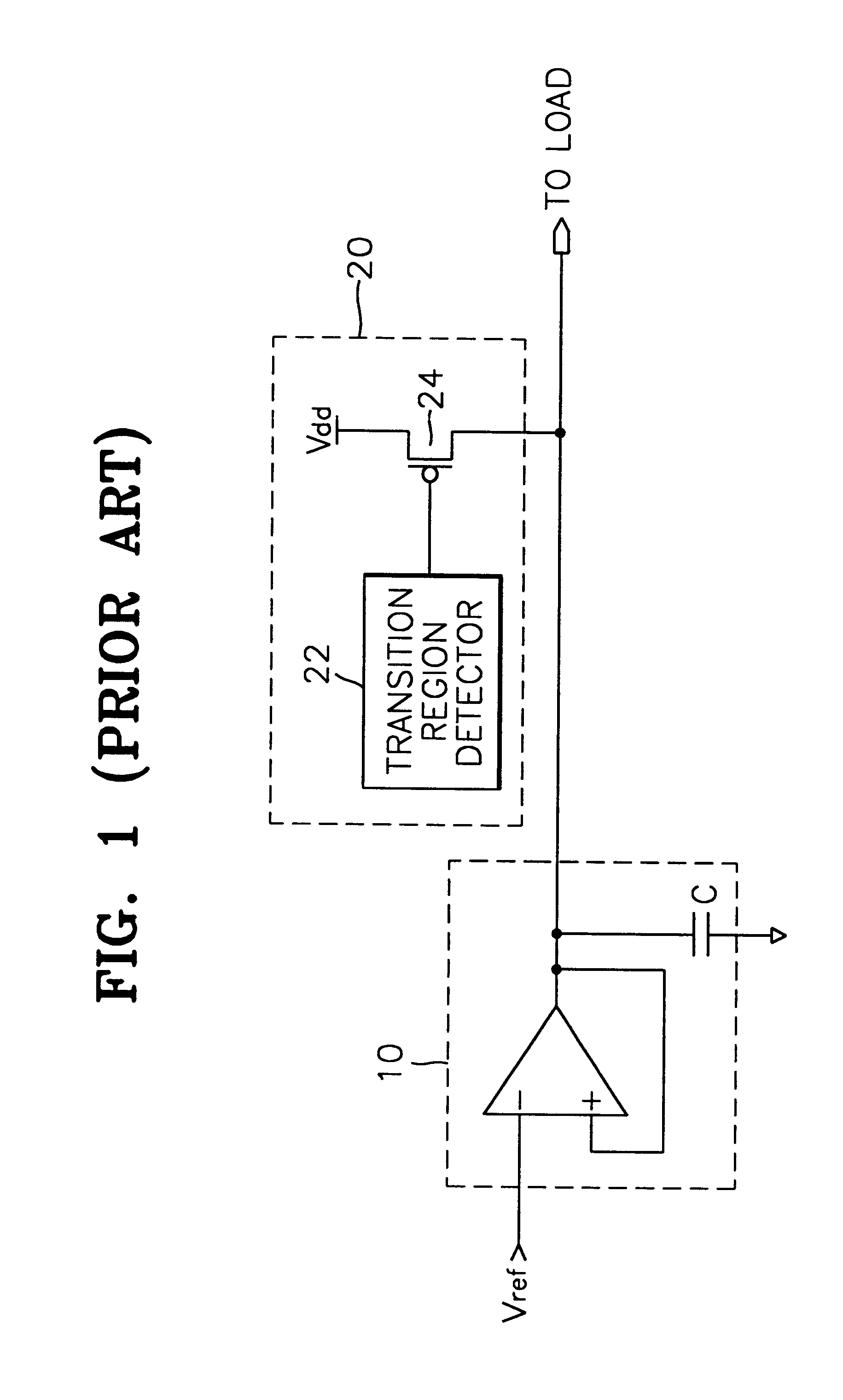
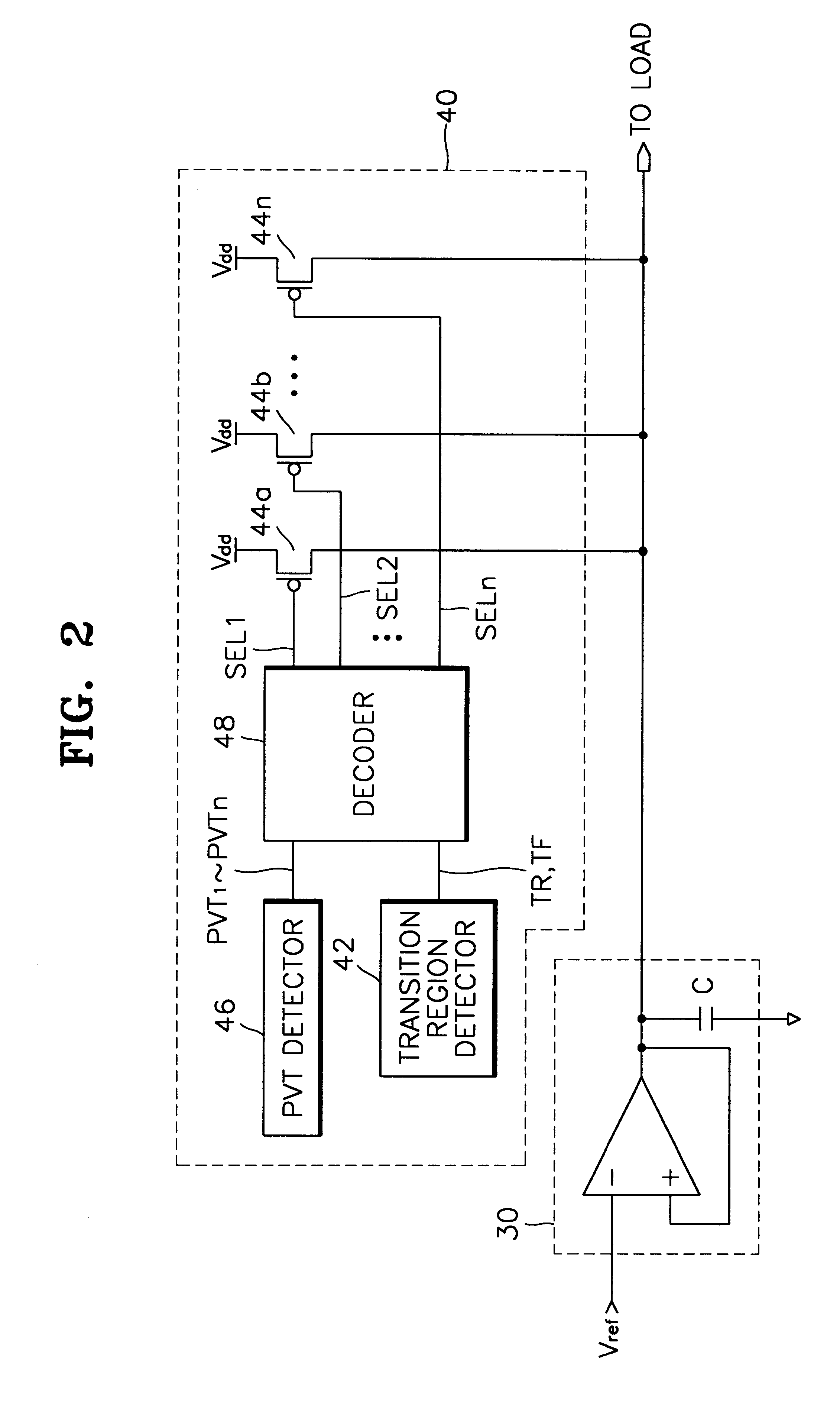
Charge compensator for voltage regulator
A charge compensator for a voltage regulator of a semiconductor device includes a process / voltage / temperature (PVT) detector for detecting characteristics of the semiconductor device varying dependent on a manufacturing process, a voltage in use and an operating temperature of the semiconductor device and for outputting state signals representing the detected characteristics; a plurality of pass transistors for providing charge to the load, connected between a power supply voltage and the output of the voltage regulator; and a decoder for selectively driving the plurality of pass transistors based on the state signals from the PVT detector. The charge compensator adjusts the amount of charge supplied to the voltage regulator in accordance with variations of the PVT characteristics, thereby suppressing voltage fluctuations in the output of the voltage regulator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
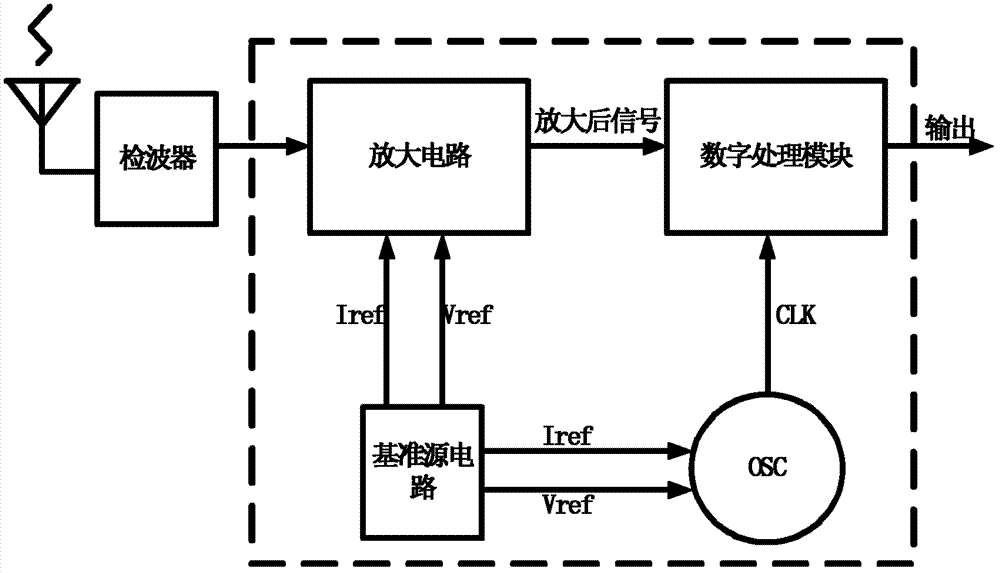
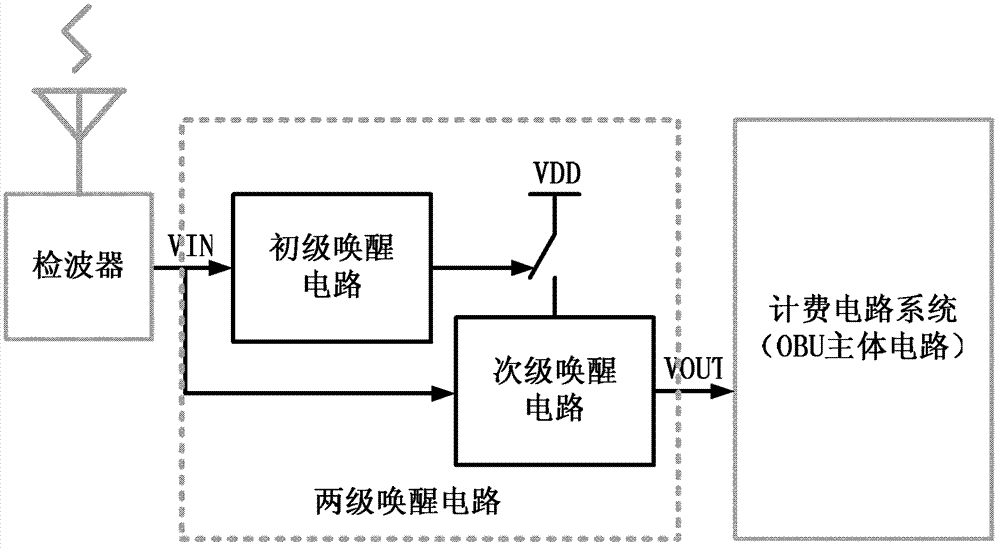
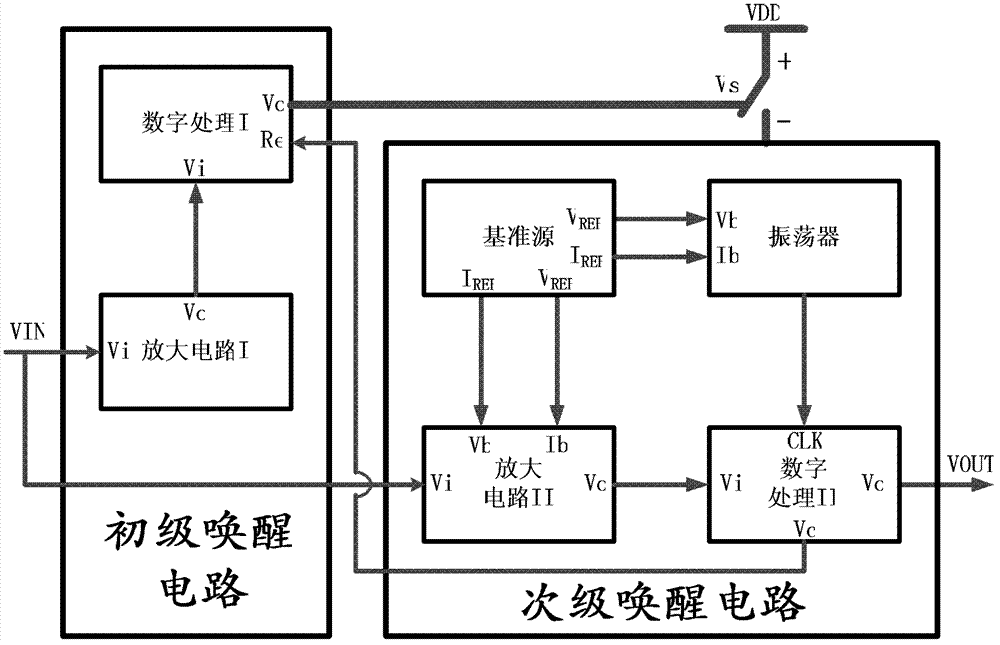
Two-stage wake-up circuit applicable to electronic toll collection system
ActiveCN103093508AEliminate distractionsSimple structureTicket-issuing apparatusIntegrated circuitProcess voltage temperature
The invention discloses a two-stage wake-up circuit applicable to an electronic toll collection (ETC) system, and relates to integrated circuit technique. The two-stage wake-up circuit applicable to the ETC system comprises a primary wake-up circuit and a secondary wake-up circuit. The primary wake-up circuit is low in power consumption and can work all the time under a standby state. The secondary wake-up circuit is moderate in sensitivity, good in stability, strong in process-voltage-temperature resisting ability, capable of accurately judging that whether an input signal is an ETC wake-up signal or not, but high in power consumption, the secondary wake-up circuit is in a dormant state under the standby state, and waking-up and dormancy of the secondary wake-up circuit are controlled by the primary wake-up circuit. According to the two-stage wake-up circuit, the primary wake-up circuit and the secondary wake-up circuit are combined to be used, so that the whole ETC two-stage wake-up circuit not only has the advantage of the primary wake-up circuit of being low in power consumption, but also has the advantages of the secondary wake-up circuit of being moderate in the sensitivity, good in the stability, low in mistake wake-up rate and the like. Meanwhile, a low-power-consumption wake signal amplifying circuit with no external polarization required is adopted in the primary wake-up circuit, and therefore power consumption of the primary wake-up circuit is lowered.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
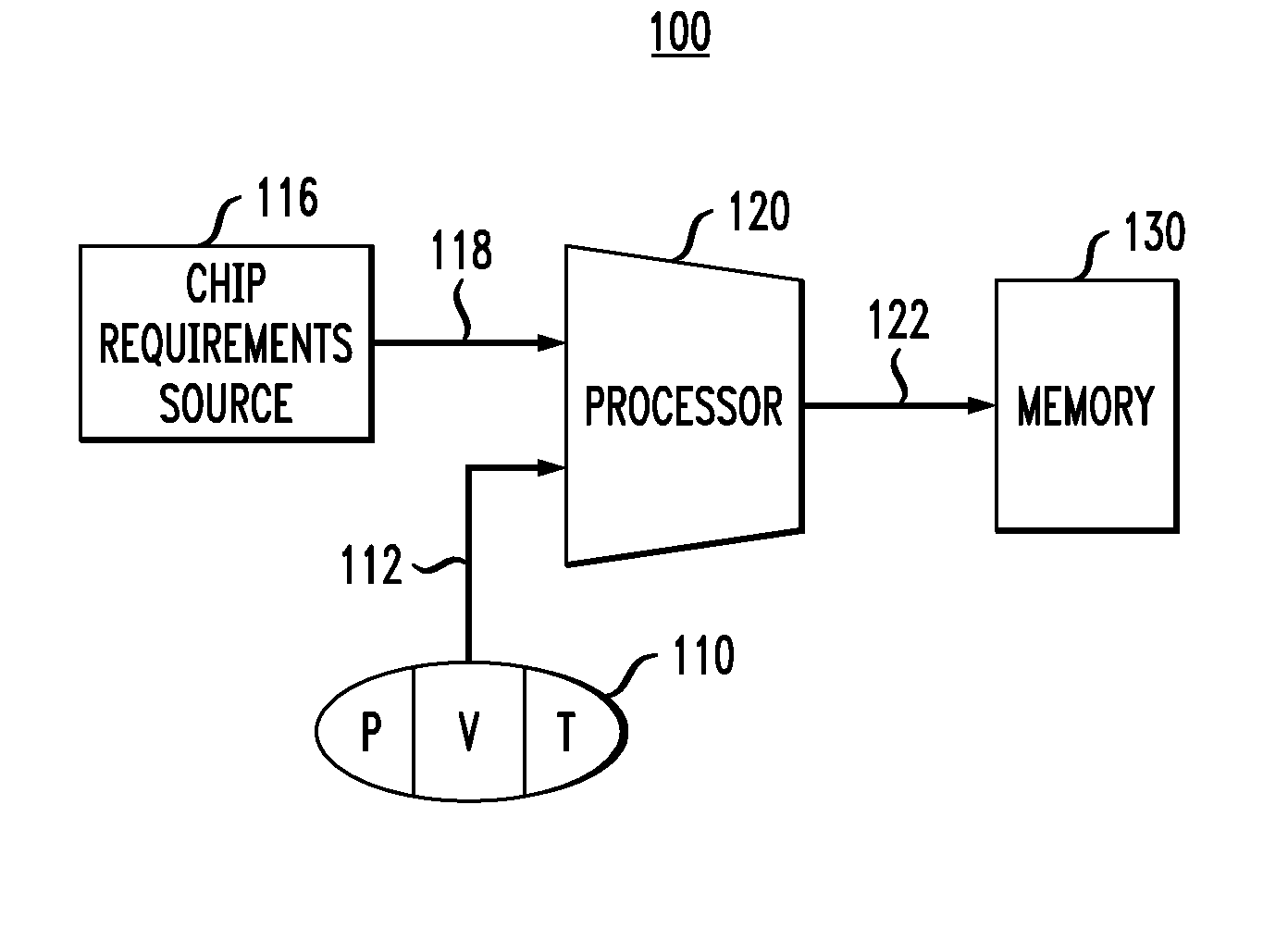
Integrated circuit having a memory with process-voltage-temperature control
ActiveUS20080117702A1Improve performanceProduce area savingDigital storageTemperature controlComputer science
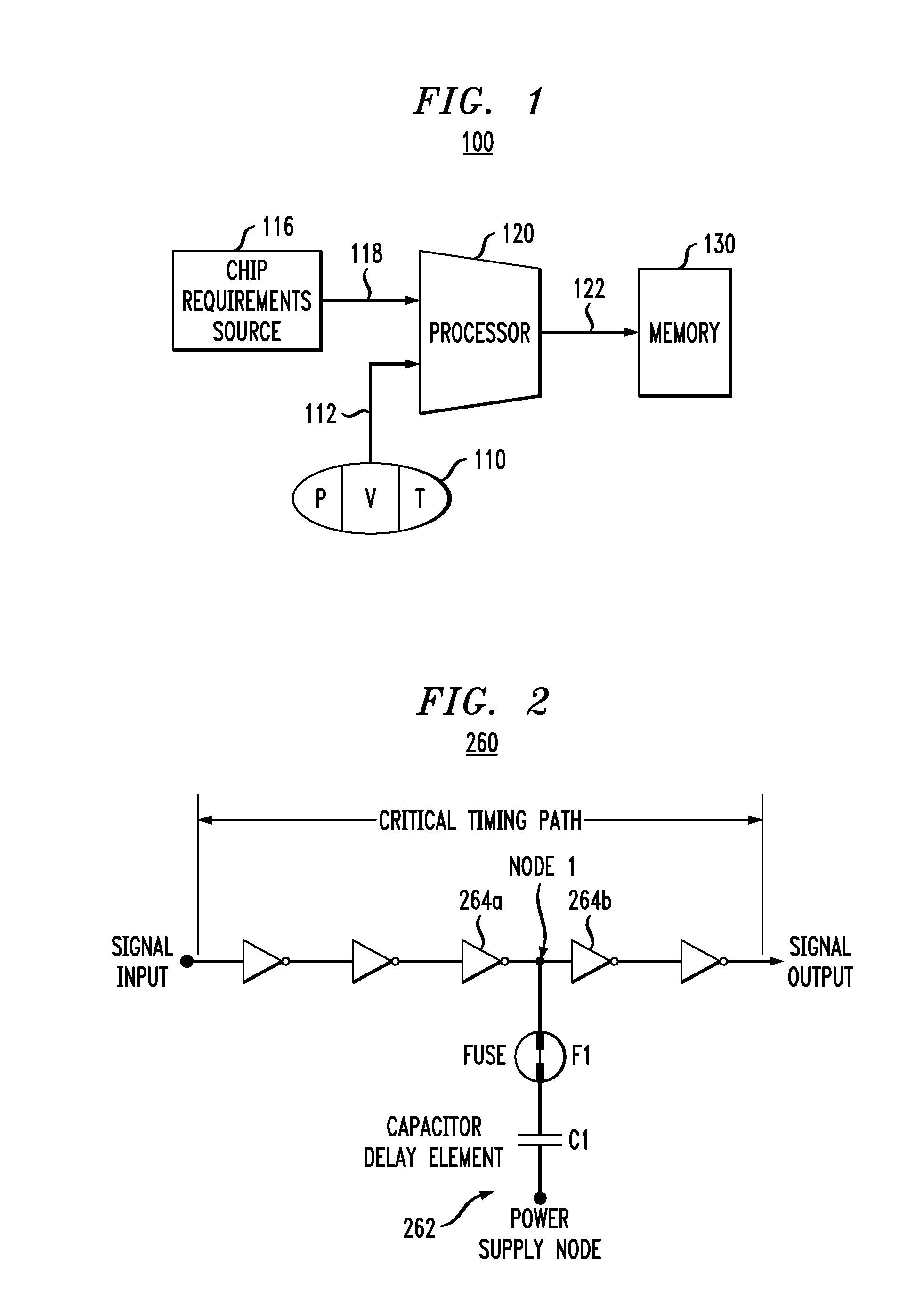
Certain embodiments of the inventions provide an integrated circuit (IC) having a processor operatively coupled to a PVT (process-voltage-temperature) source and an adjustable memory. The processor receives from the source an input characterizing the present PVT condition and generates a command for the memory based on that input. In response to the command, the memory adjusts its internal circuit structure, clock speed, and / or operating voltage(s) to optimize its performance for the present PVT condition. Advantageously, the ability to adjust the memory so that it can maintain its functionality and deliver an acceptable level of performance under unfavorable PVT conditions provides additional flexibility in choosing circuit design options, which can produce area savings and / or increase the yield of acceptable ICs during manufacture.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
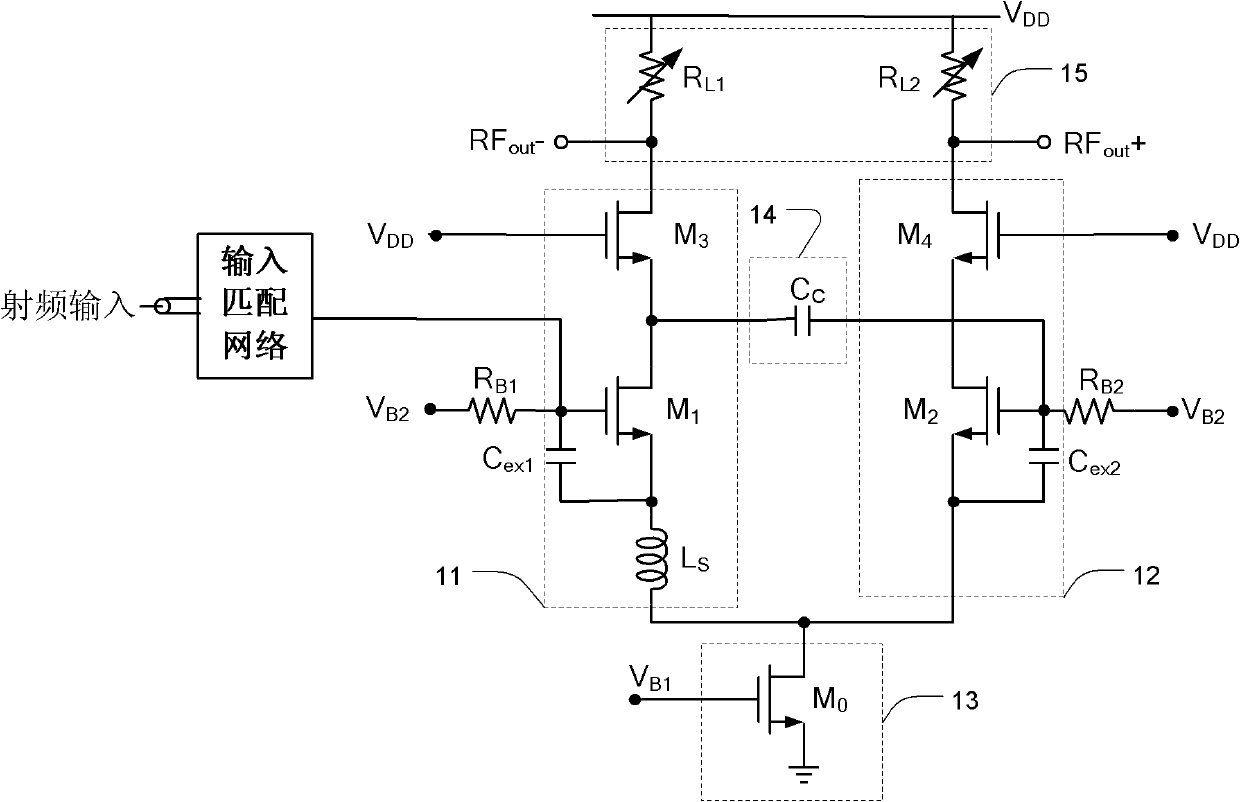
Low-noise amplifier adopting single-ended input and differential output
InactiveCN102163955AImprove differential symmetryAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersVIT signalsProcess voltage temperature
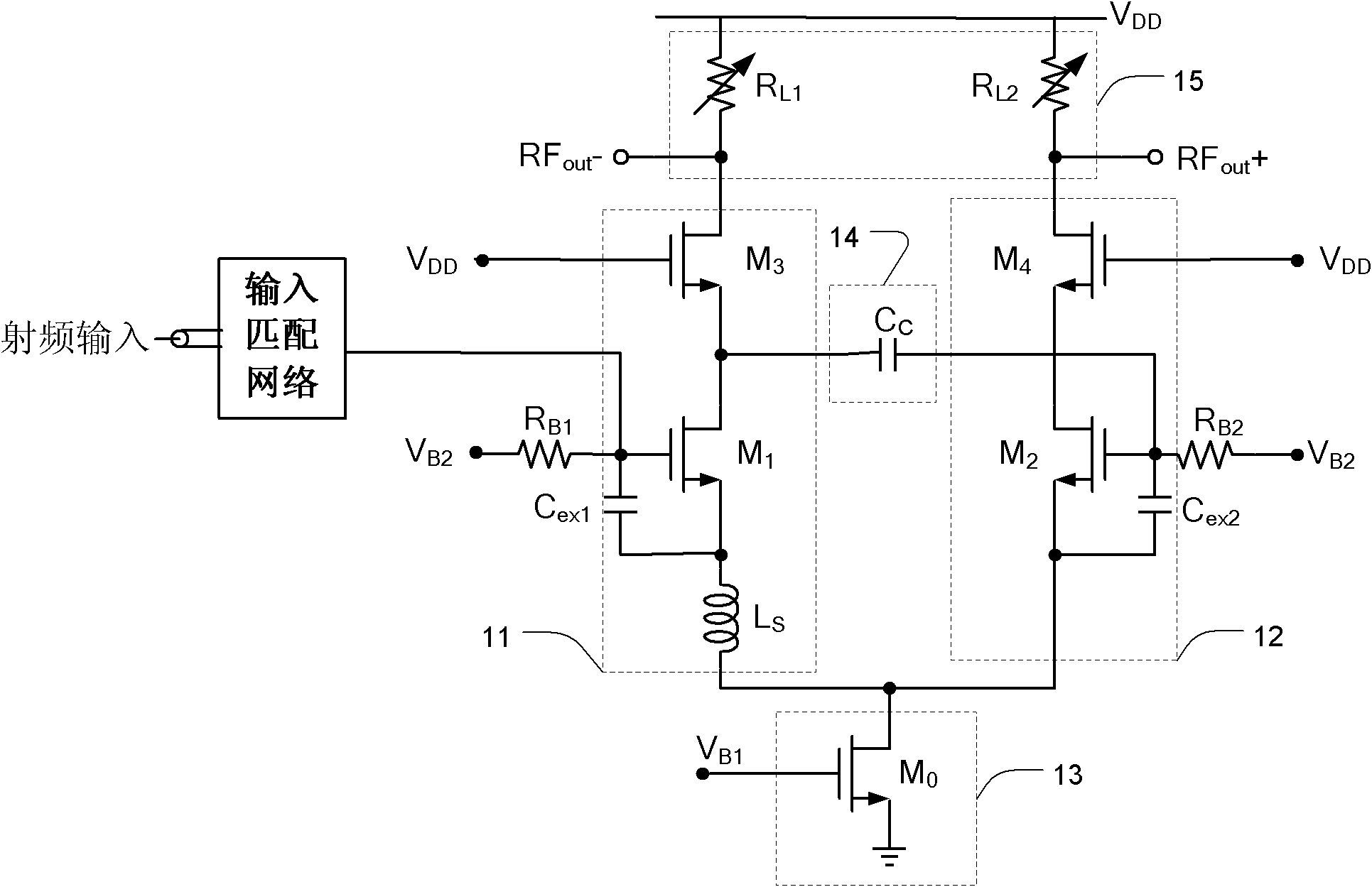
The invention provides a low-noise amplifier adopting single-ended input and differential output. The low-noise amplifier comprises a first circuit, a second circuit, a tail current source tube circuit, a compensation circuit and a biasing circuit. The first circuit comprises at least one first field effect transistor. The input end of the first circuit is connected to the output end of an input matching network, and the output end of the first circuit is connected to an output matching network. The second circuit comprises at least one second field effect transistor, and is connected with the first circuit to form a differential pair structure. The output of the second circuit is connected with the output matching network. The tail current source tube circuit is connected with a common connection point of the first and second circuits. The compensation circuit is bridged between the first and second circuits, and is used for compensating an output signal of the second circuit to match the output signals of the first and second circuits. The biasing circuit is connected with the first and second circuits, and is used for providing DC bias. The low-noise amplifier has the advantages that: 1) the output signals are symmetrically differential; and 2) the overall gain of the amplifier is relative constant at various process voltage temperatures.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINPUZHEN MICROELECTRONICS
Slope wave generation circuit as well as digital to analog conversion circuit and fingerprint recognition system thereof
ActiveCN104393856AEasy to implementAutomatically adjust the highest point voltage valuePulse generatorPrint image acquisitionAudio power amplifierControl signal
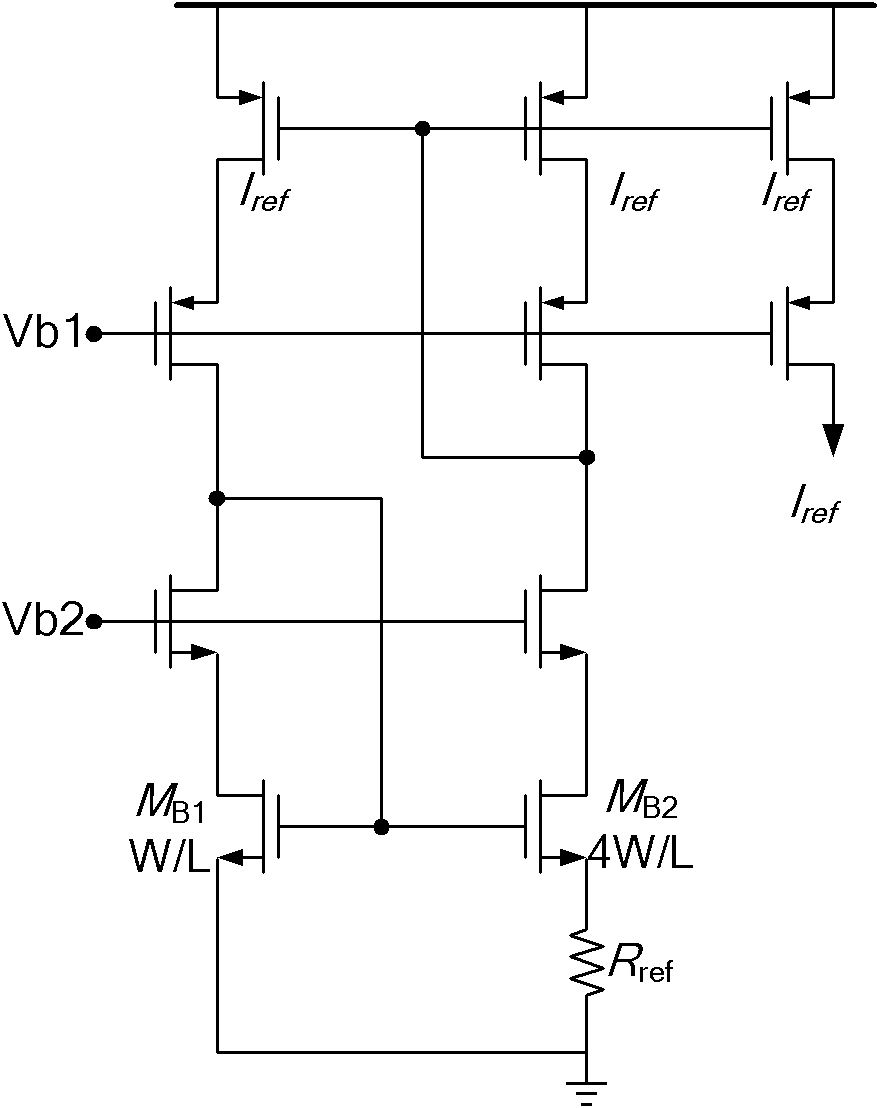
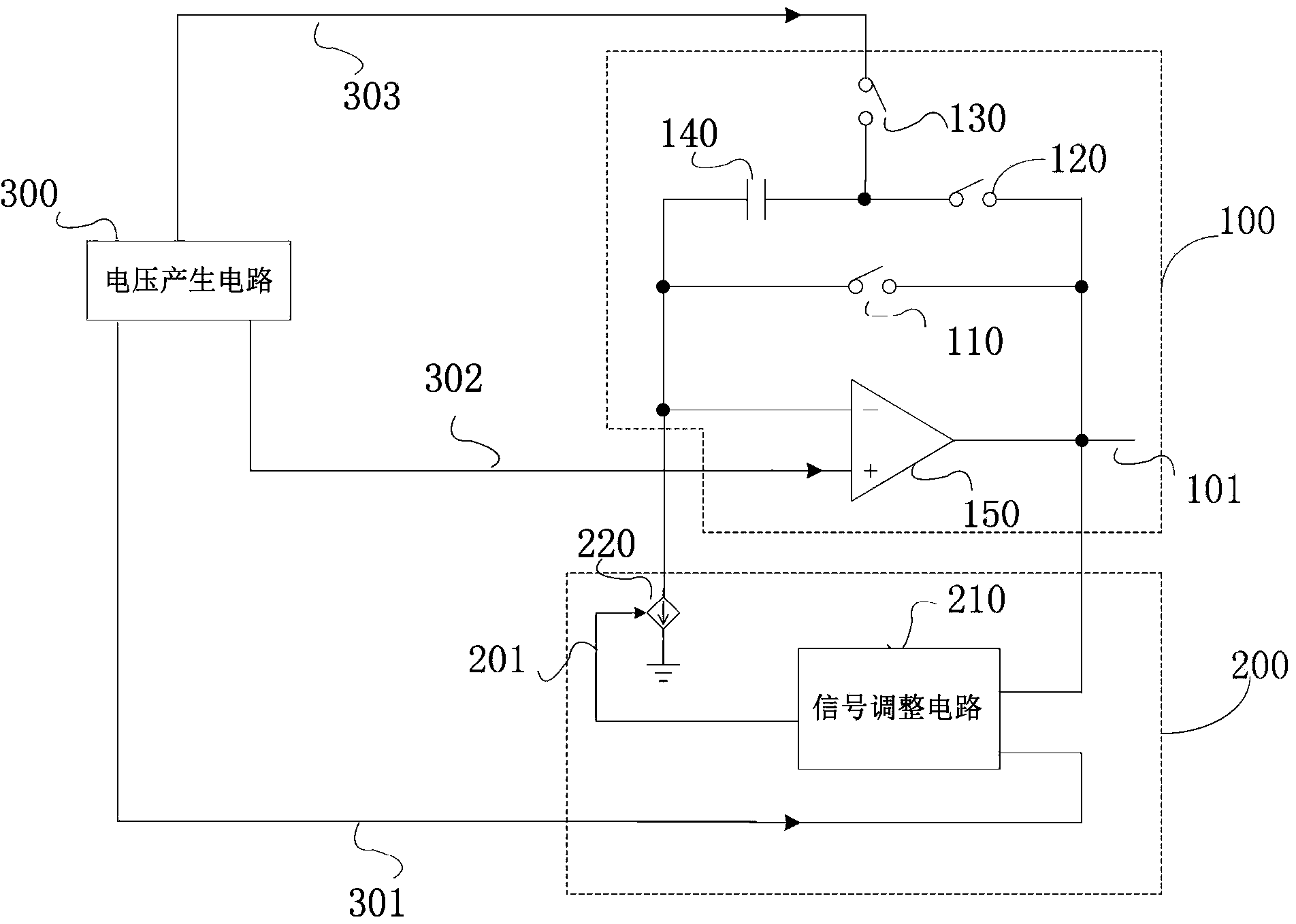
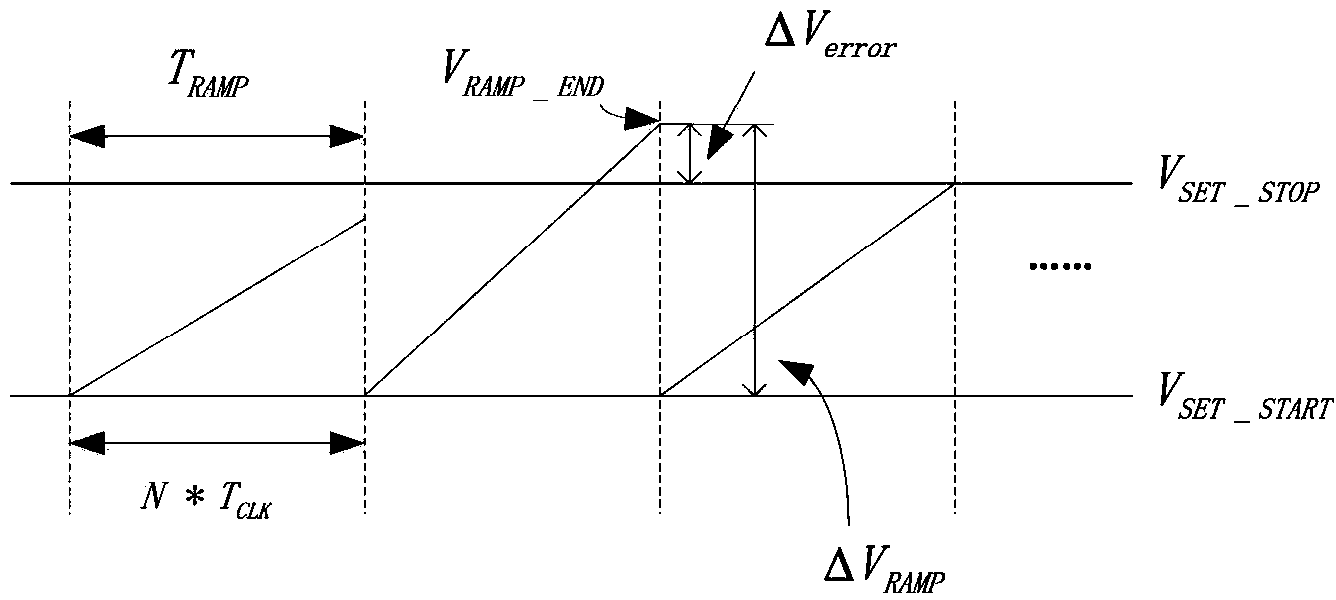
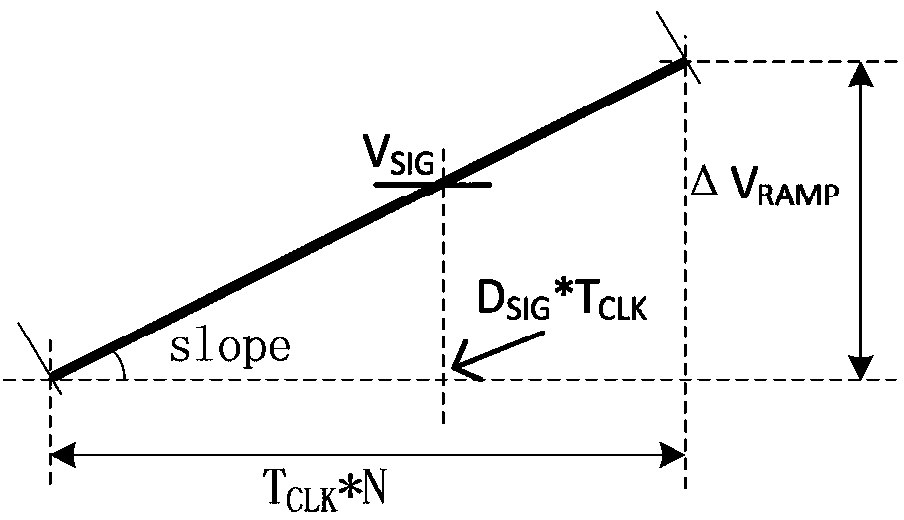
The invention discloses a slope wave generation circuit as well as a digital to analog conversion circuit and a fingerprint recognition system thereof, belonging to the field of fingerprint recognition technologies. The slope wave generation circuit comprises an integrating circuit, a signal adjustment circuit and a voltage generation circuit, wherein the integrating circuit is used for outputting a slope wave signal; the signal adjustment circuit comprises a feedback control loop and a transconductance amplifier which are connected in series, the feedback control loop monitors the slope wave signal output by the integrating circuit and outputs an adjustment control signal to the transconductance amplifier, and the transconductance amplifier corrects the slope wave signal output at the next period by the integrating circuit according to the adjustment signal; the voltage generation circuit is used for respectively outputting reference voltage signals to the integrating circuit and the signal adjustment circuit. By adopting the fingerprint recognition system of the invention, the problem of performance deterioration of the fingerprint system, which is caused by influence of PVT (Process Voltage Temperature) on the slope wave generation circuit and a clock generator, can be solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GOODIX TECH CO LTD
Method and system for providing smart memory architecture
A smart memory system preferably includes a memory including one or more memory chips, and a processor including one or more memory processor chips. The processor includes a common address / data / control memory bus that is configured to provide an asynchronous handshaking interface between the memory array and the memory processor. The processor can offload error data from the memory chip for analysis, and can store poor retention bit address information for memory refreshing in a non-bolatile error retention memory. Porgram logic can also be included for memory address re-configuration. Power management logic can also be included, which can have a process-voltage-temperature compensation voltage generator for providing stable and constant read currents. An asynchronous handshaking interface is provided between the memory array and the memory processor. Write error tagging and write verification circuits can also be included.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Compensation of voltage-to-current converter
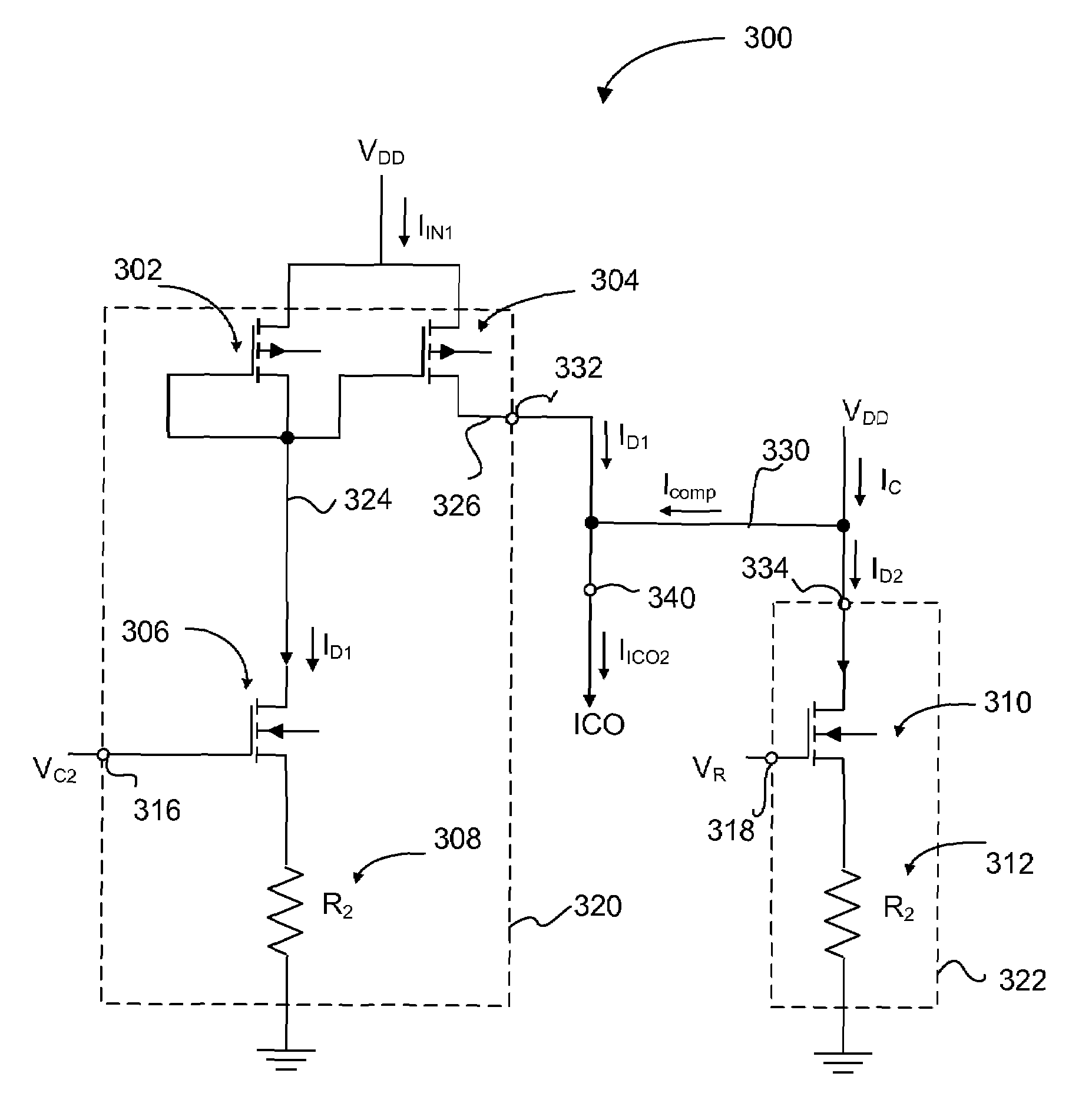
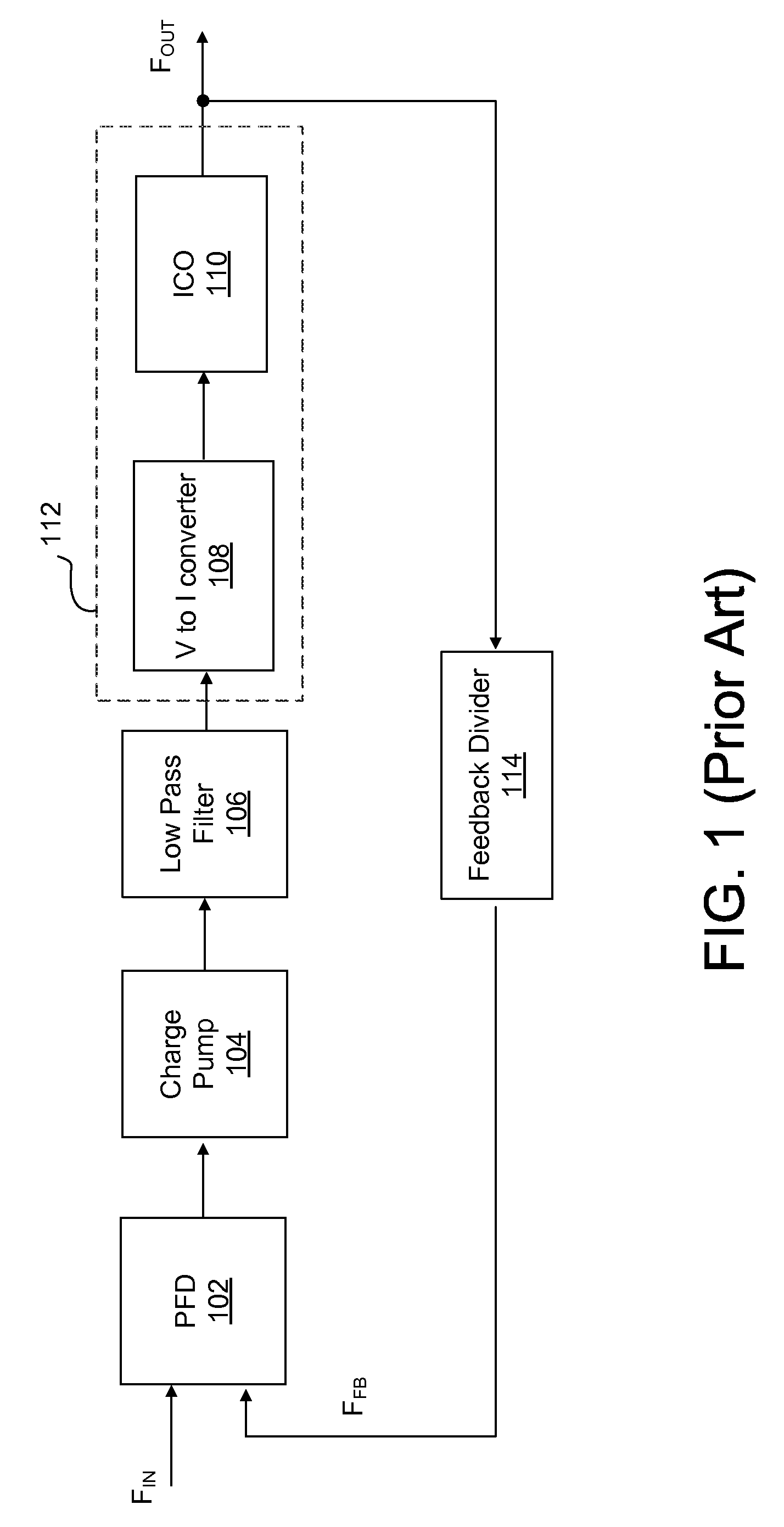
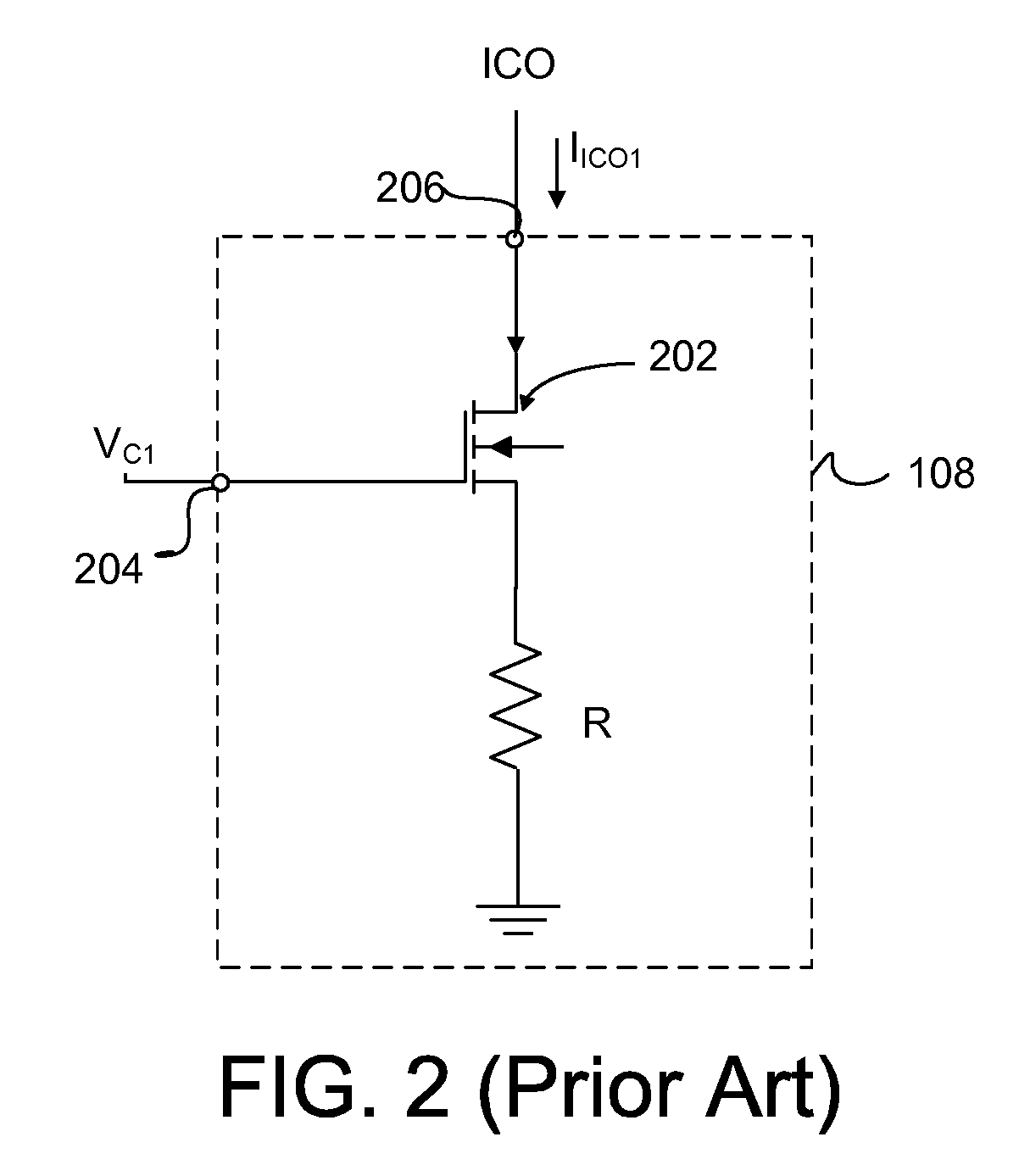
A voltage-to-current converter providing an output current with compensation for process-voltage-temperature (PVT) variations of a component in the voltage-to-current converter. The voltage-to-current converter includes a first voltage-to-current converter branch, a second voltage-to-current converter branch, and a compensation current path. The first voltage-to-current converter provides a first current to the output of the voltage-to-current converter based on a variable control voltage. The second voltage-to-current converter branch provides a second current based on a fixed voltage. The compensation current path provides a compensation current from the second voltage-to-current branch to the first voltage-to-current converter branch compensating variations in the first current caused by the PVT variations of the component in the first voltage-to-current converter branch.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
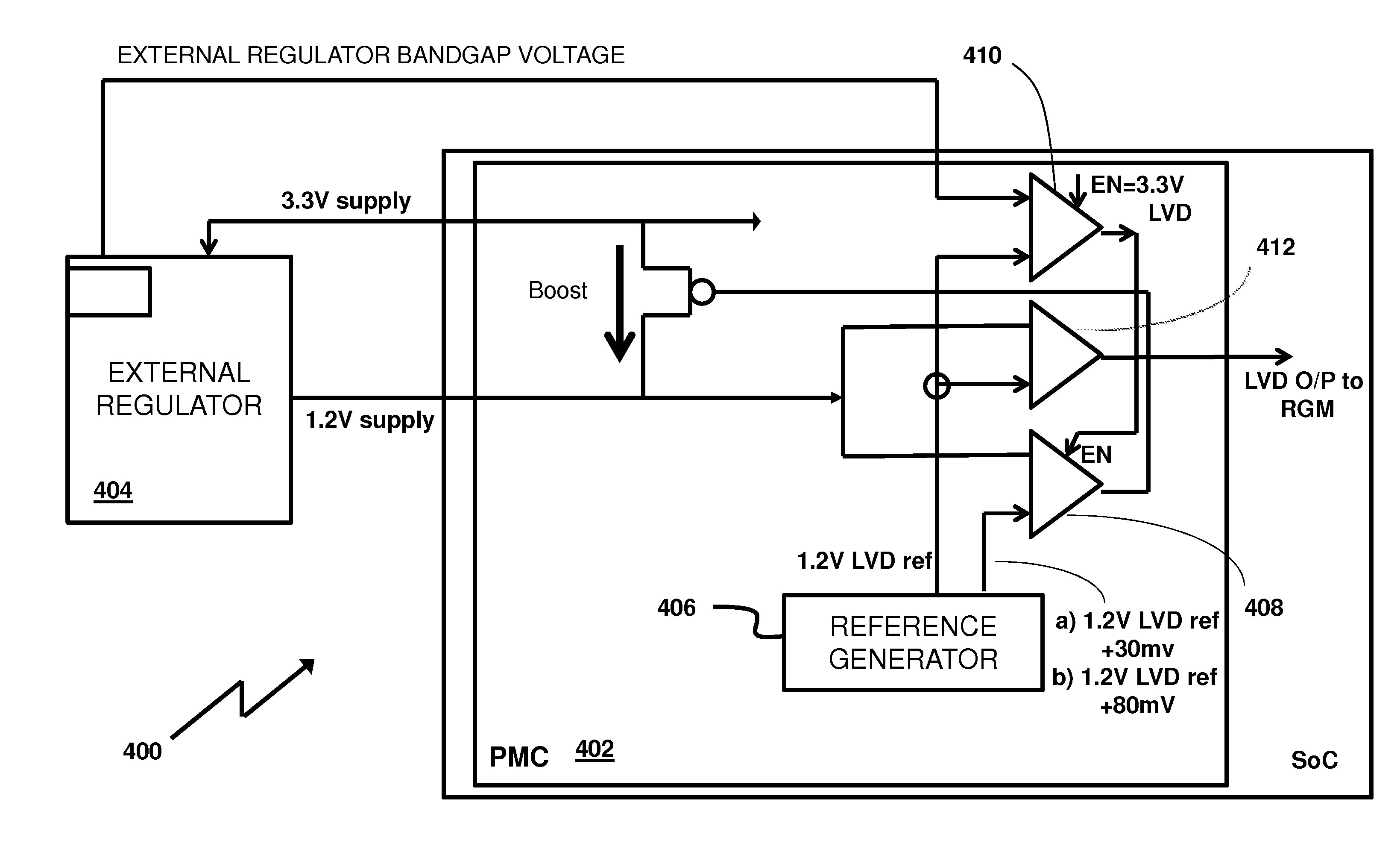
Voltage regulation subsystem
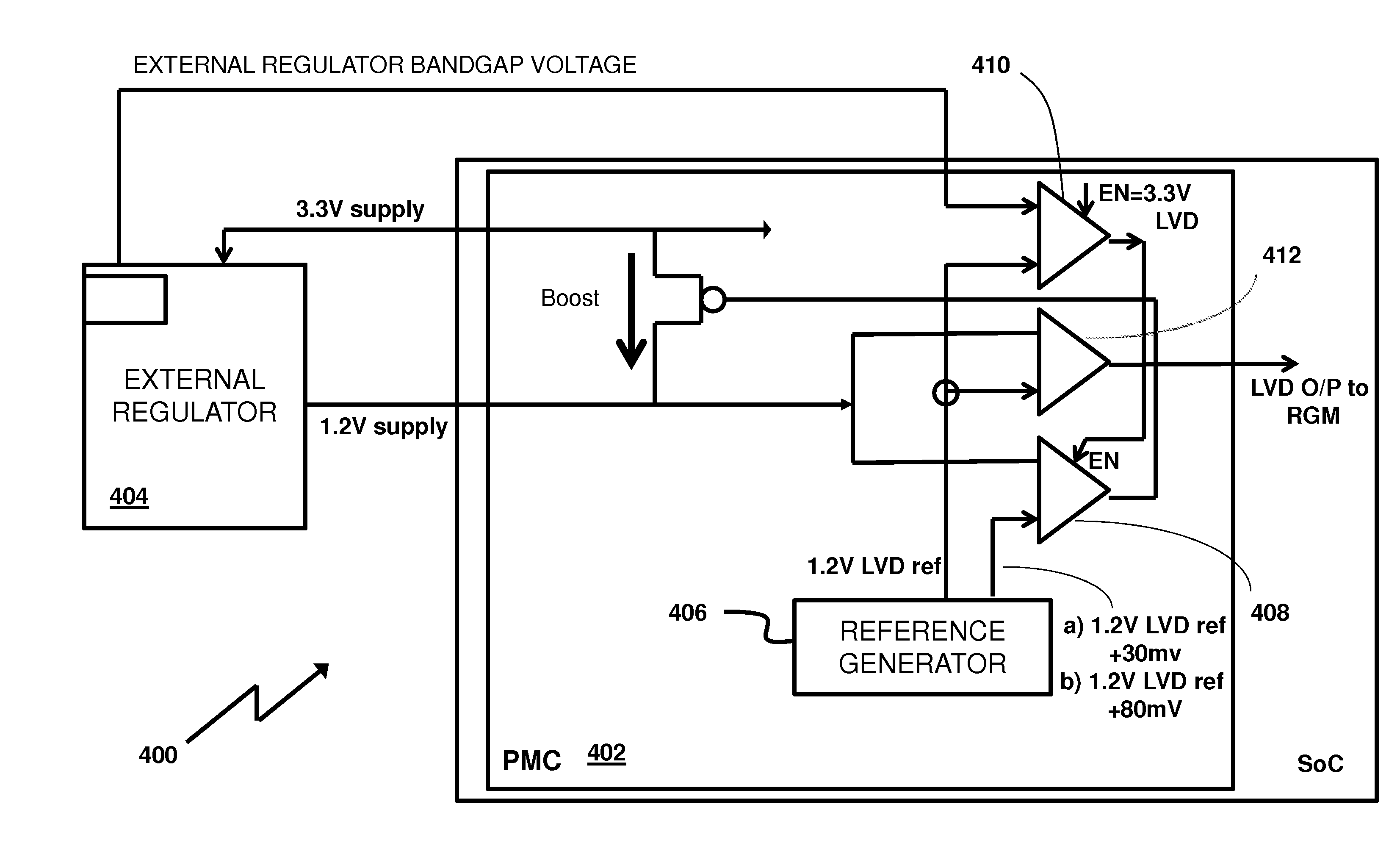
A voltage regulation subsystem for a microprocessor has both internal and external regulation modes. An internal auxiliary voltage regulator is selectively enabled to overdrive the voltage. The enablement of the auxiliary voltage regulator is contingent upon a comparison of bandgap references of the internal and external regulators used in the respective regulation modes, which boosts the supply voltage, enables circuitry supplied by the external regulator (with the assistance of auxiliary voltage regulators) to boot robustly in extreme Process-Voltage-Temperature (PVT) conditions.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and system for providing a smart memory architecture
ActiveUS9069719B2High rateHigh error rateInput/output to record carriersDigital computer detailsMemory addressSmart memory
A smart memory system preferably includes a memory including one or more memory chips, and a processor including one or more memory processor chips. The processor may include a common address / data / control memory bus that is configured to provide an asynchronous handshaking interface between the memory array and the memory processor. The processor can offload error data from the memory chip for analysis, and can store poor retention bit address information for memory refreshing in a non-volatile error retention memory. Program logic can also be included for memory address re-configuration. Power management logic can also be included, which may have a process-voltage-temperature compensation voltage generator for providing stable and constant read currents. An asynchronous handshaking interface is provided between the memory array and the memory processor. Write error tagging and write verification circuits can also be included.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
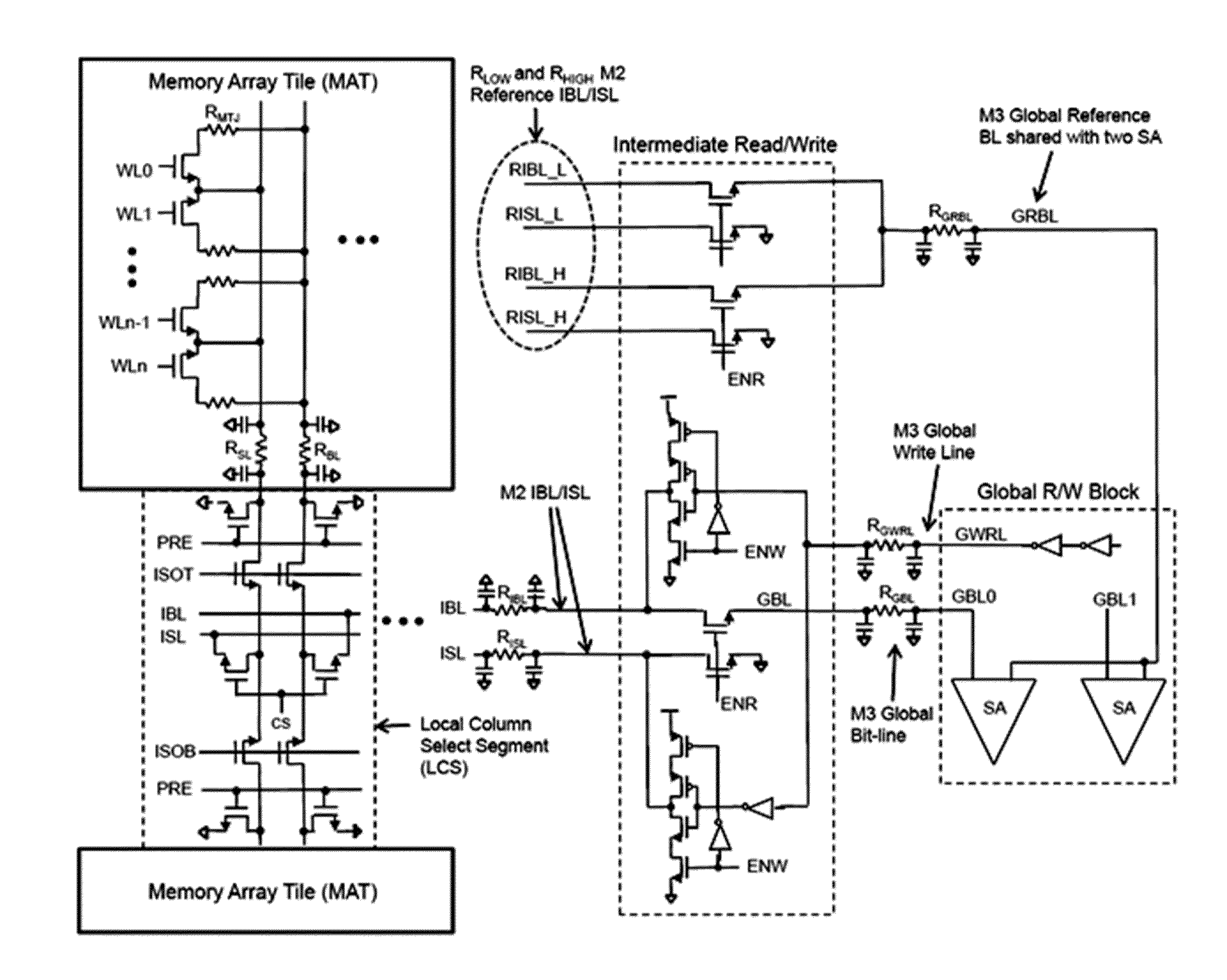
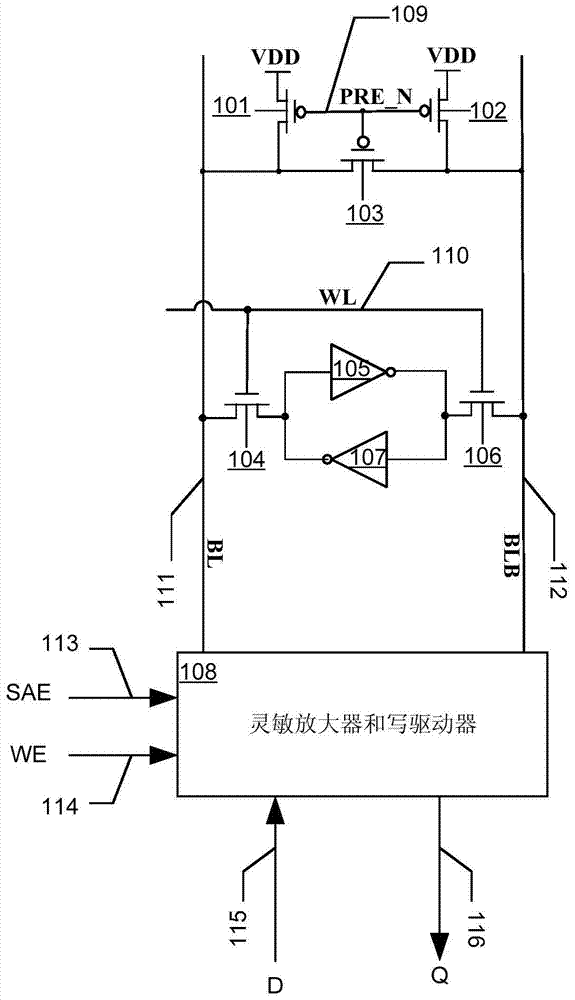
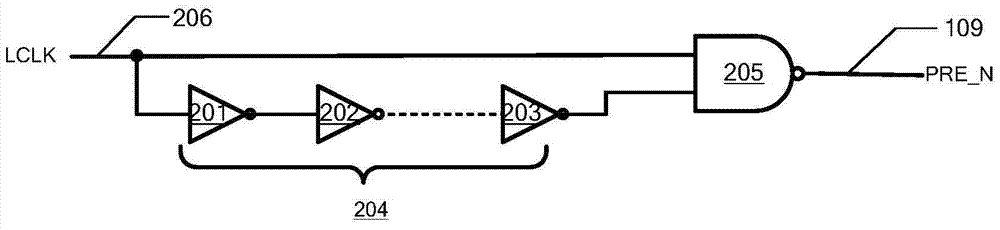
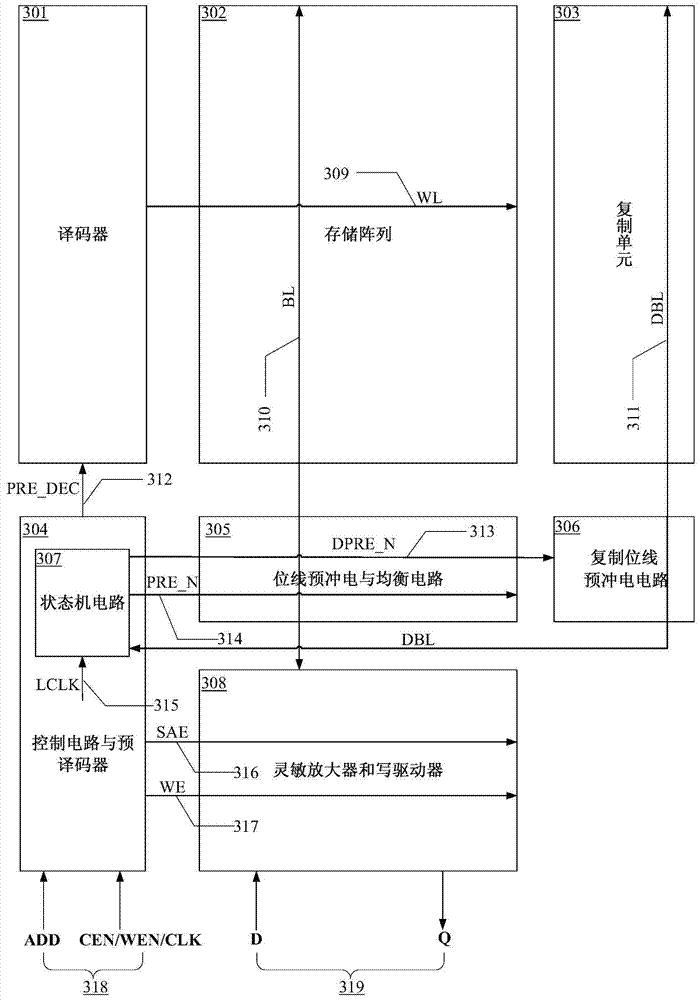
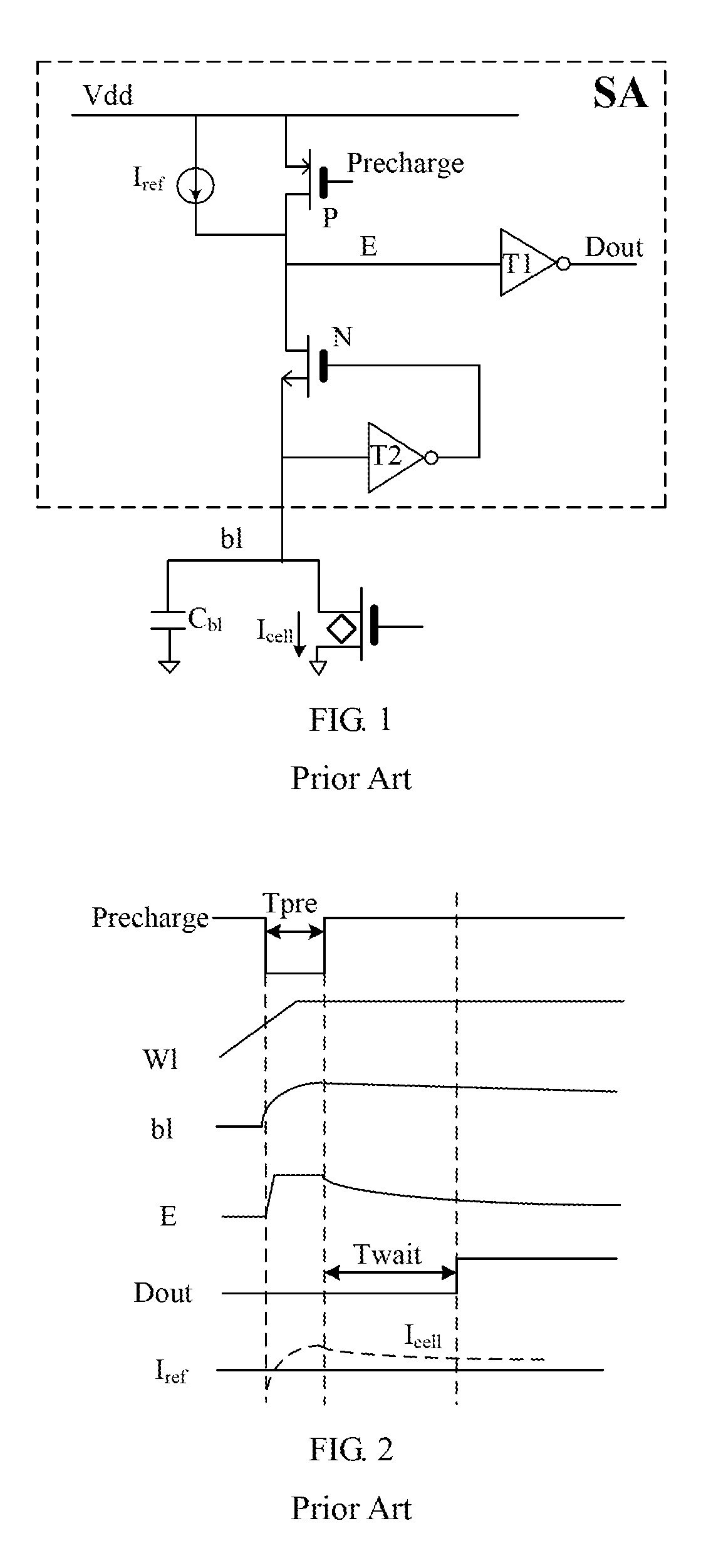
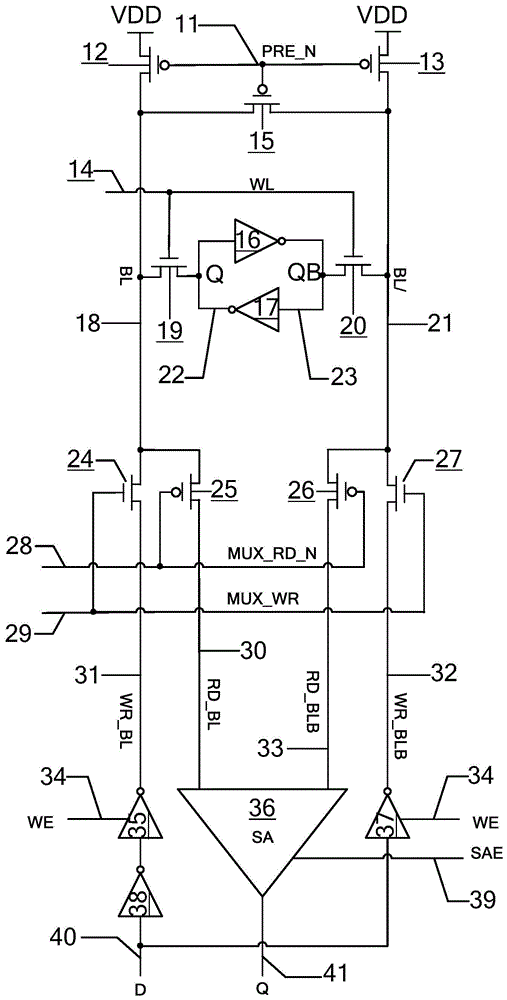
Static random access memory and bit line pre-charging self-timing circuit thereof
ActiveCN103943142AGood resistance to process voltage temperature deviationPrecise self-timerDigital storageStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
The invention provides a static random access memory and a bit line pre-charging self-timing circuit thereof. A duplication unit is used for simulating load on a normal bit line; a duplication bit line pre-charging circuit is used for simulating a pre-charging circuit of the normal bit line and pre-charging and resetting a duplication bit line; a state machine circuit is used for controlling conversion between beginning and ending states of duplication bit-line pre-charging operations and producing self-timing signals for normal bit-line pre-charging operations. The circuit simulates the pre-charging process of the normal bit line so as to provide accurate self-timing for bit-line pre-charging operations of the static random access memory at different process voltage temperatures. Compared with a traditional method for generating a bit-line pre-charging signal in a delay mode based on a phase inverter chain, the circuit has excellent capability of resisting deviation of process voltage temperature.
Owner:XI AN UNIIC SEMICON CO LTD
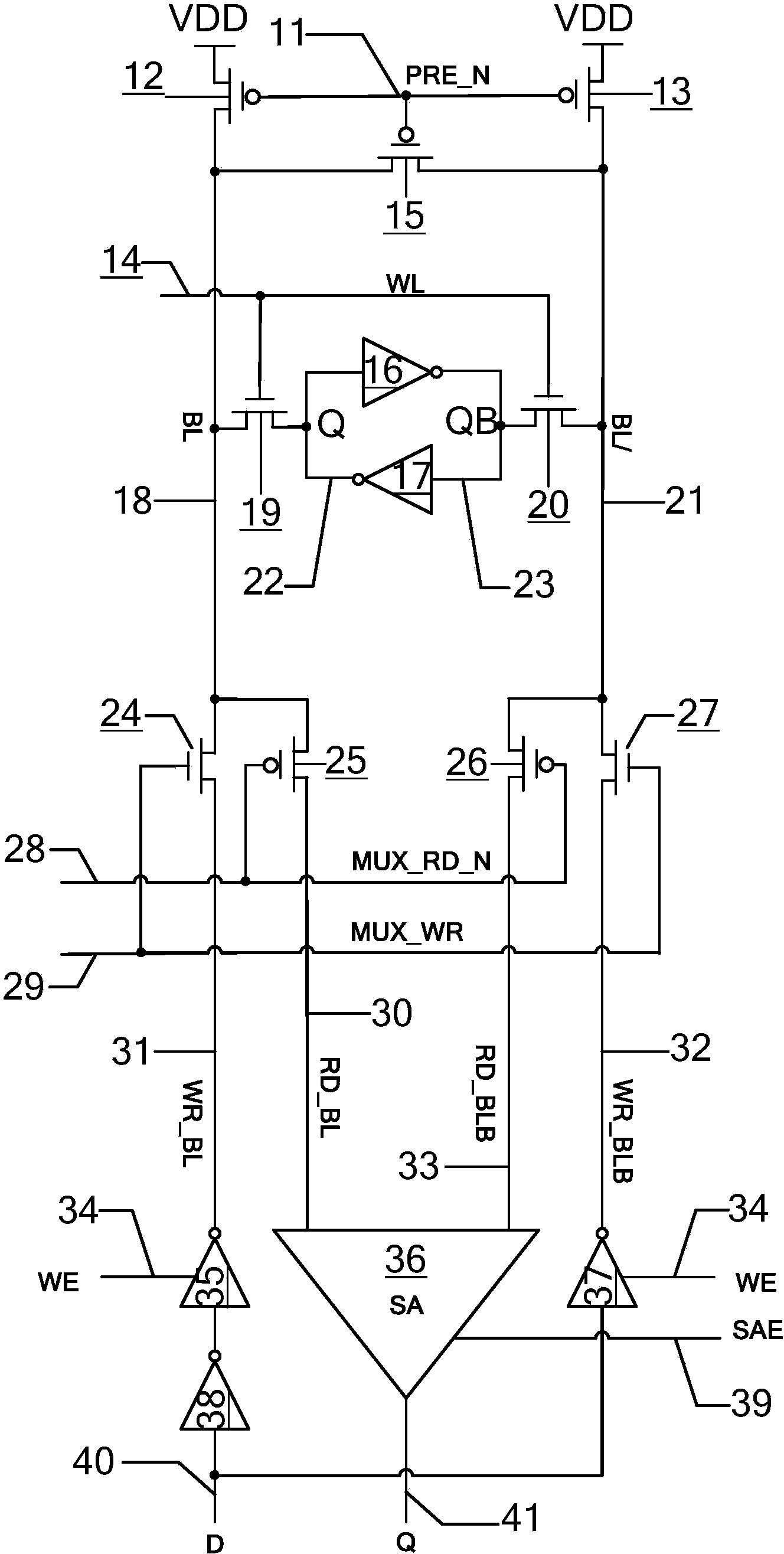
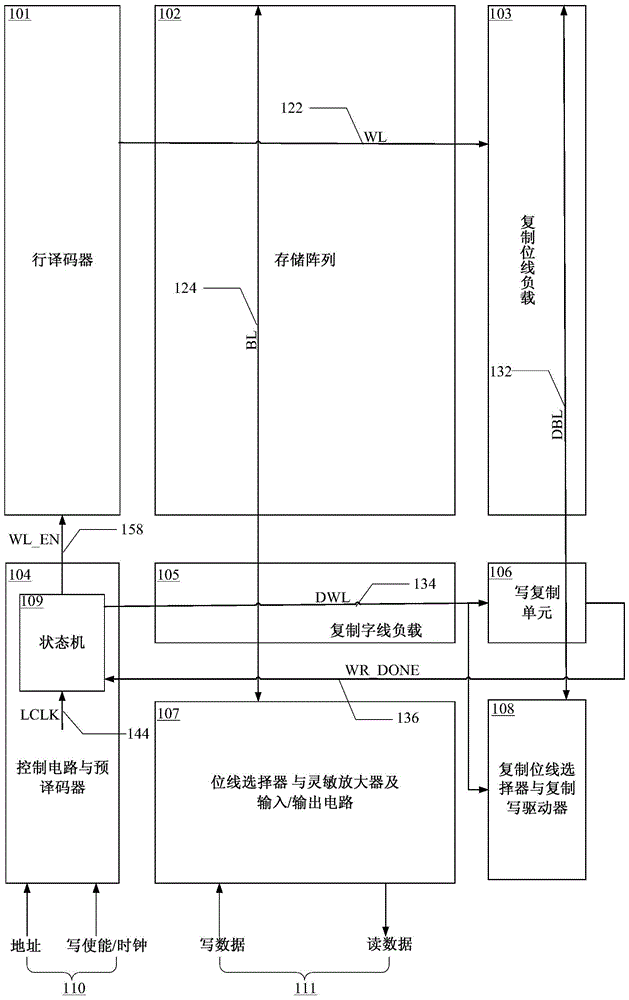
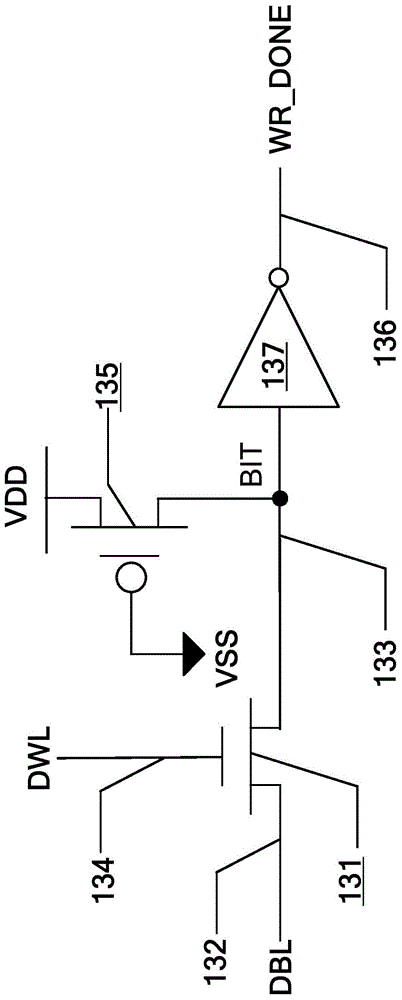
Copy-on-write circuit suitable for static random access memory
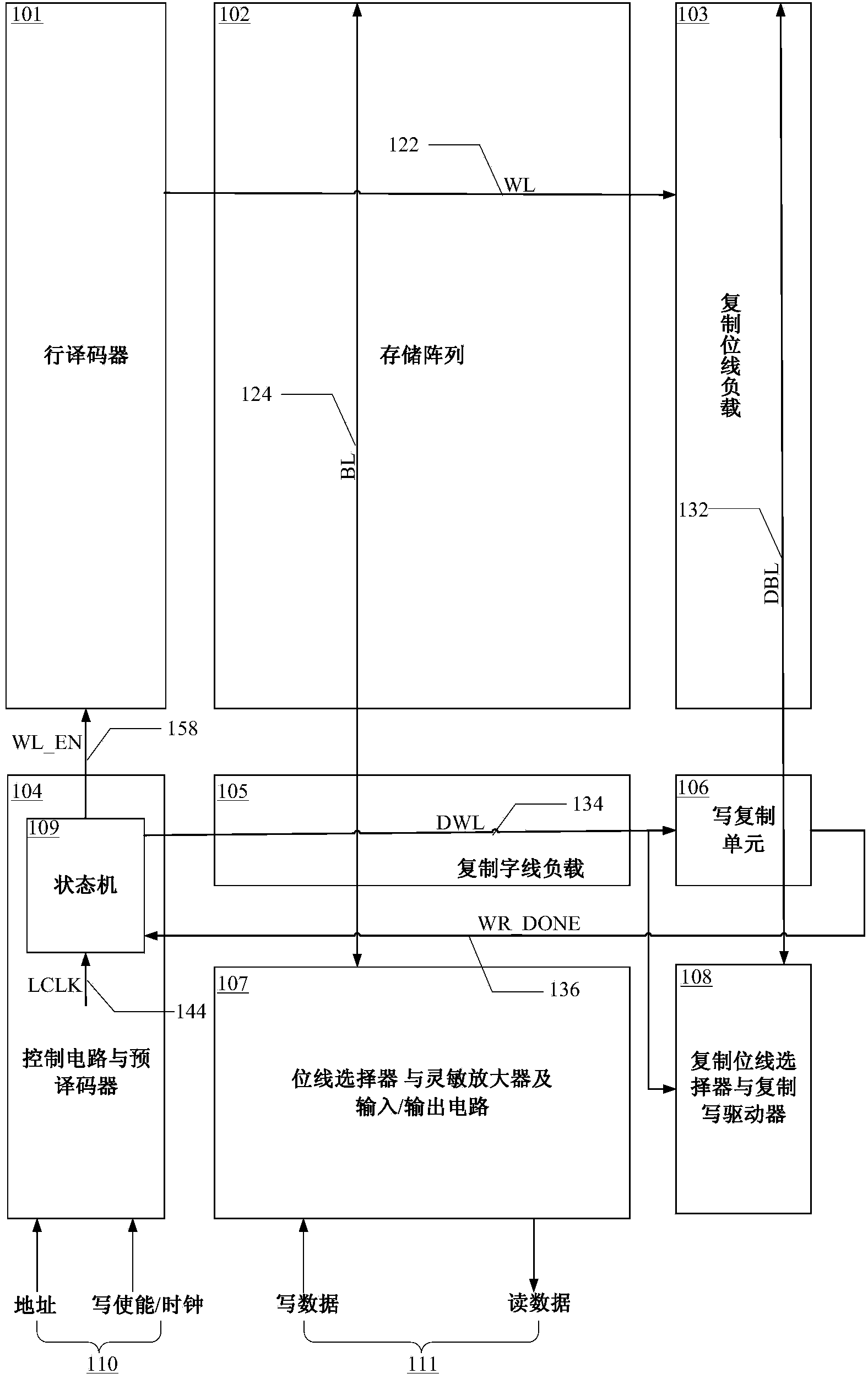
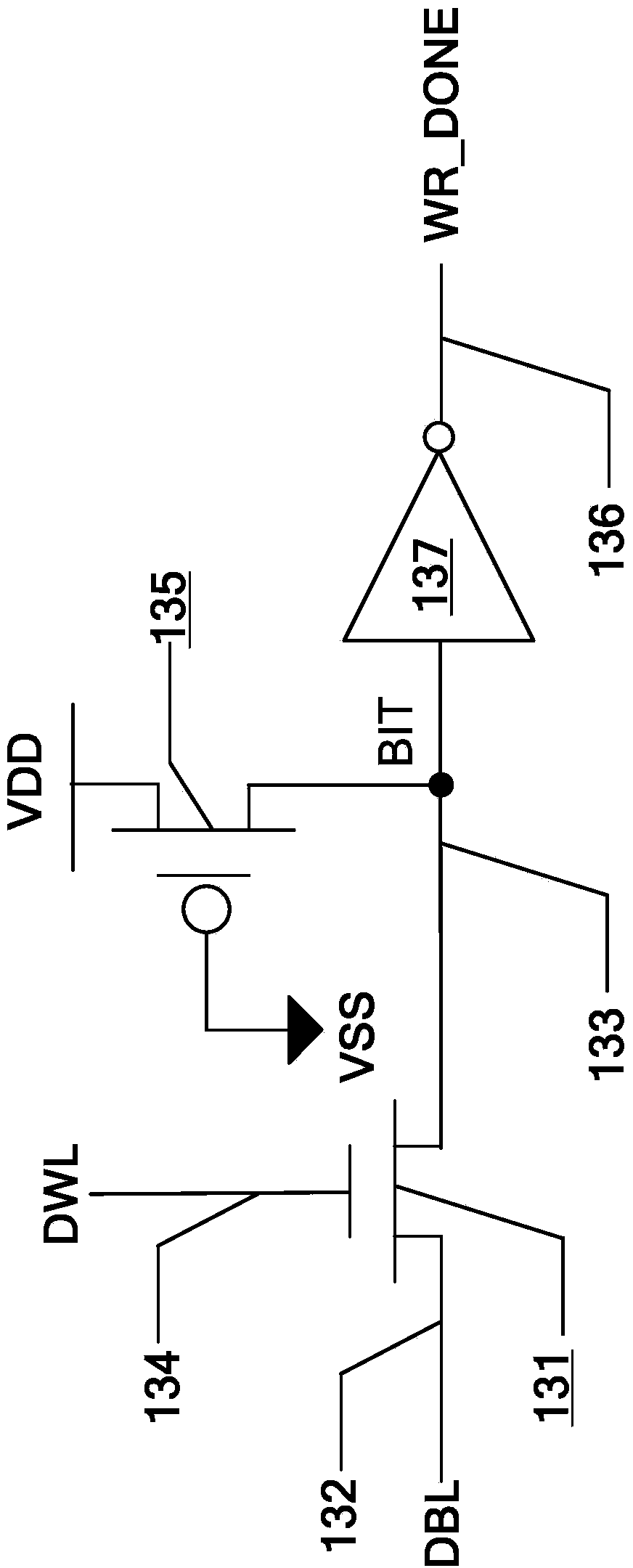
ActiveCN103871461APrecise self-timerWord line pulse width downDigital storageBit lineStatic random-access memory
The invention provides a copy-on-write circuit suitable for a static random access memory. The copy-on-write circuit consists of a copy word line load, a copy bit line load, a copy bit line selector, a copy-on-write selector, a copy-on-write unit, a state machine, a line decoder, a storage array, a control circuit, a pre-decoder, a bit line selector, a sense amplifier and an input / output circuit, wherein the copy word line load is used for simulating load on a word line during normal write operation; the copy bit line load is used for simulating load on a bit line during the normal write operation; the copy bit line selector and the copy-on-write driver are used for simulating the bit line selector and the write driver during normal write operation; the copy-on-write unit is used for simulating a storage unit which is rewritten during the normal write operation; the state machine is used for switching between a start state and an end state for the normal write operation. By simulating normal '0' write operation, the accurate self-timing is provided for write operation under different process voltage temperatures of the static random access memory. Compared with the prior art, the copy-on-write circuit has the advantages that the bit line pulse width is reduced by 20 percent during the write operation.
Owner:XI AN UNIIC SEMICON CO LTD
Charge transfer RC relaxation oscillator
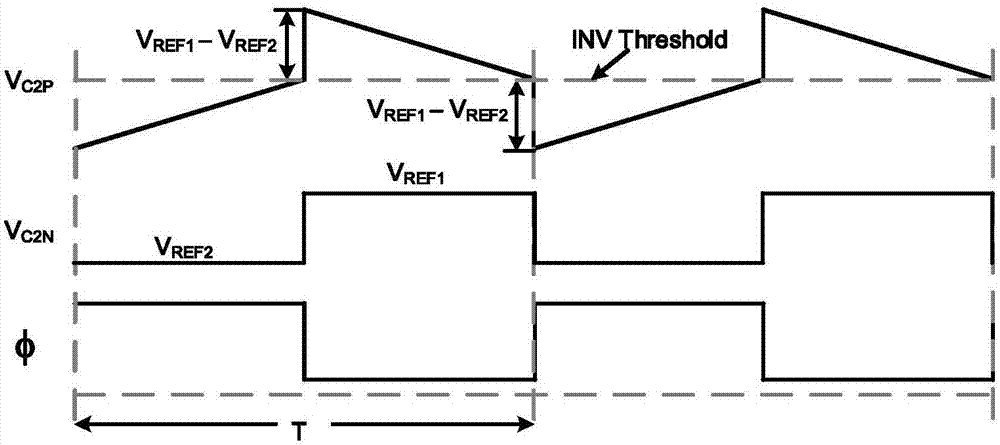
The invention relates to a charge transfer RC relaxation oscillator applied to low power consumption equipment. Compared with a relaxation oscillator circuit structure in the background technology, the charge transfer RC relaxation oscillator uses a pseudo inverter chain to replace a comparator so as to avoid the influence of imbalance and time-delay of the comparator on the clock frequency, following changes of technology, voltage and temperature. At the same time, the frequency of the oscillator is irrelevant to the charge and discharge current and the threshold of the pseudo inverter chain. In the charge transfer RC relaxation oscillator, traditional capacitor cathode grounding is changed as connection with two reference voltages alternately, the charge transfer RC relaxation oscillator utilizes the charge transfer mode to generate a triangular wave signal with a step voltage on the anode of the capacitor so as to be able to use a pseudo inverter to determine the magnitude of the level of the signal. The charge transfer RC relaxation oscillator provides a pseudo inverter chain structure which has no short circuit current, wherein the time delay does not change following power voltage, and the time delay of the inverter chain can be realized through adjustment of resistance value.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
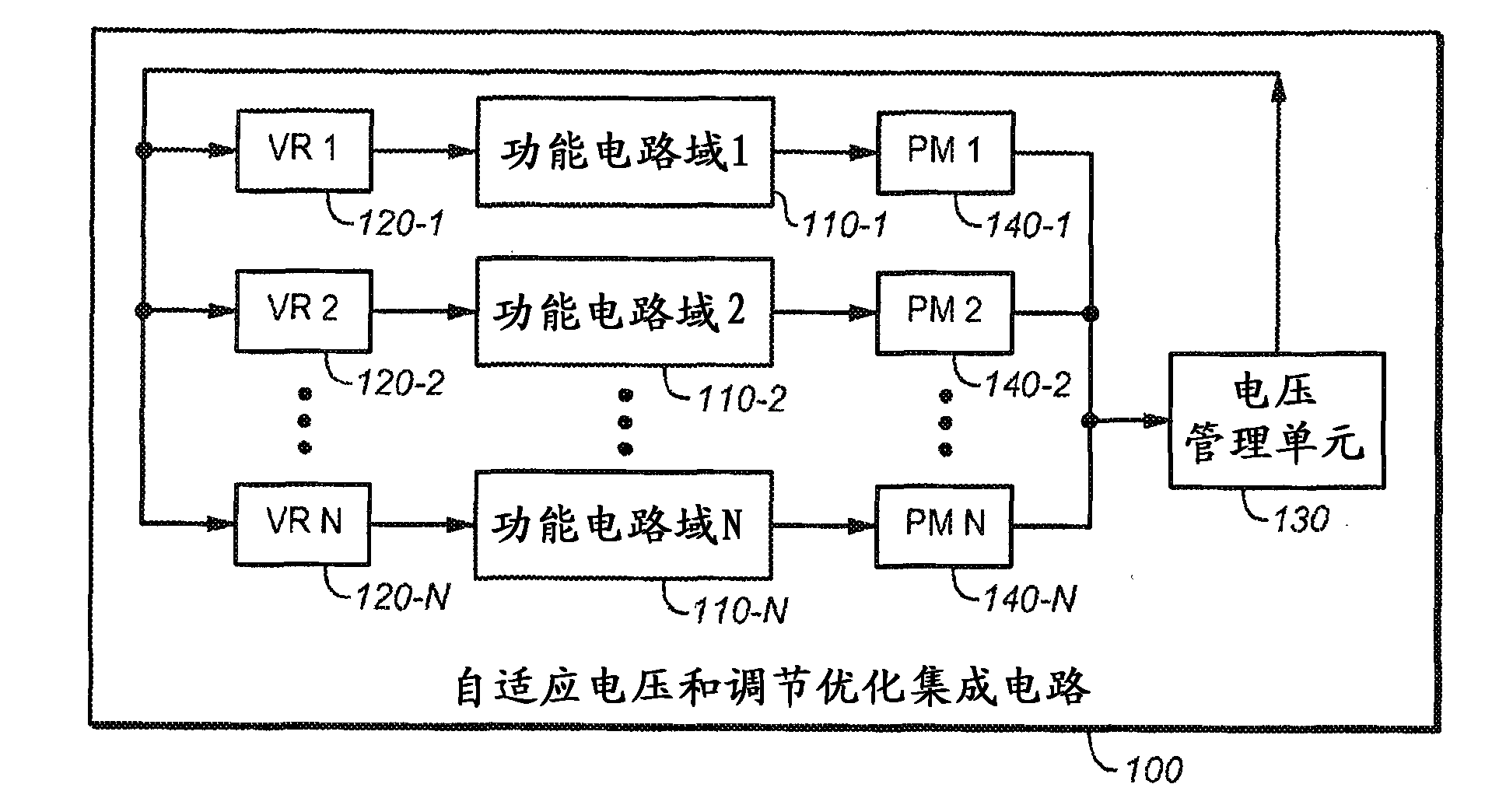
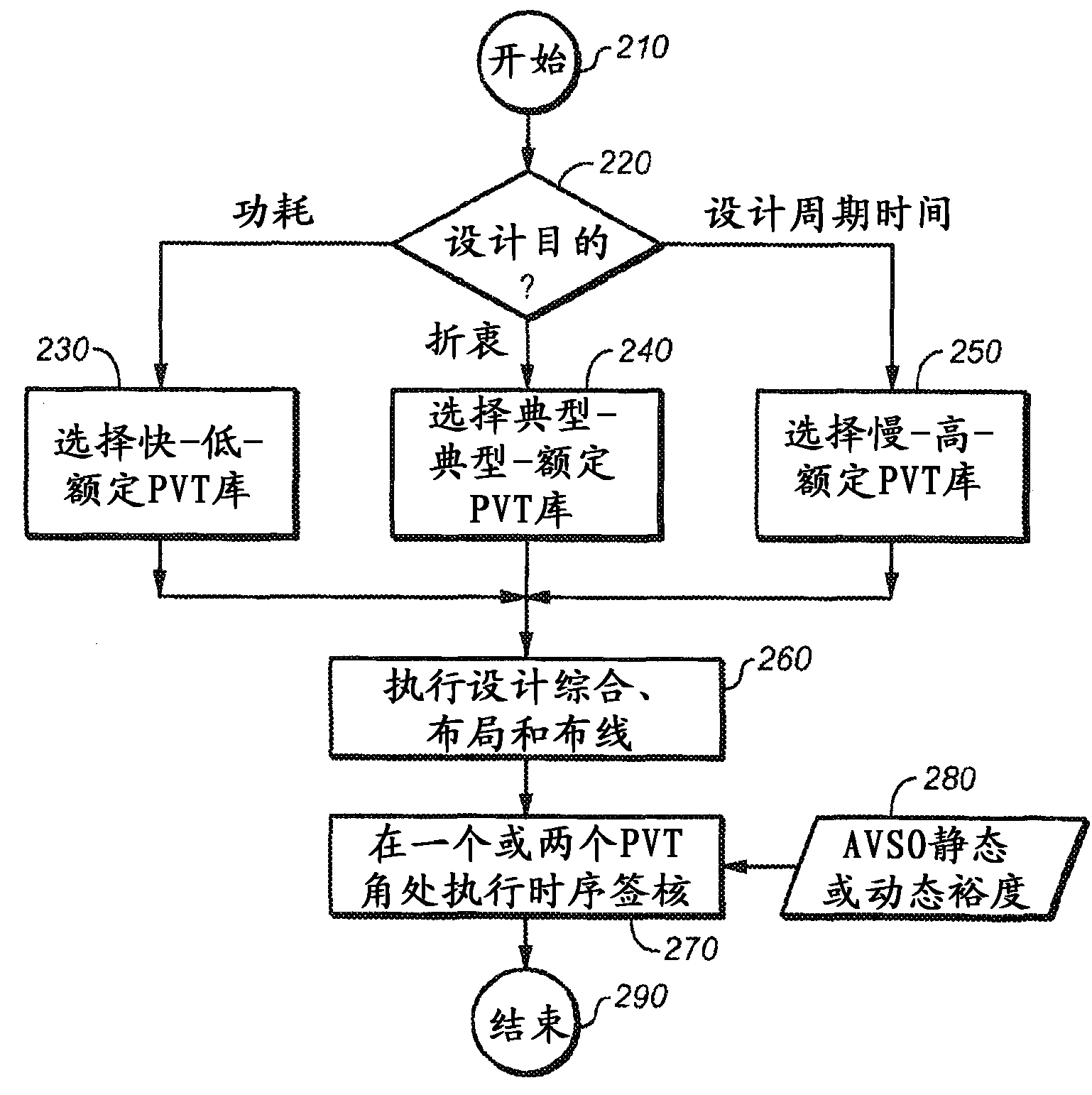
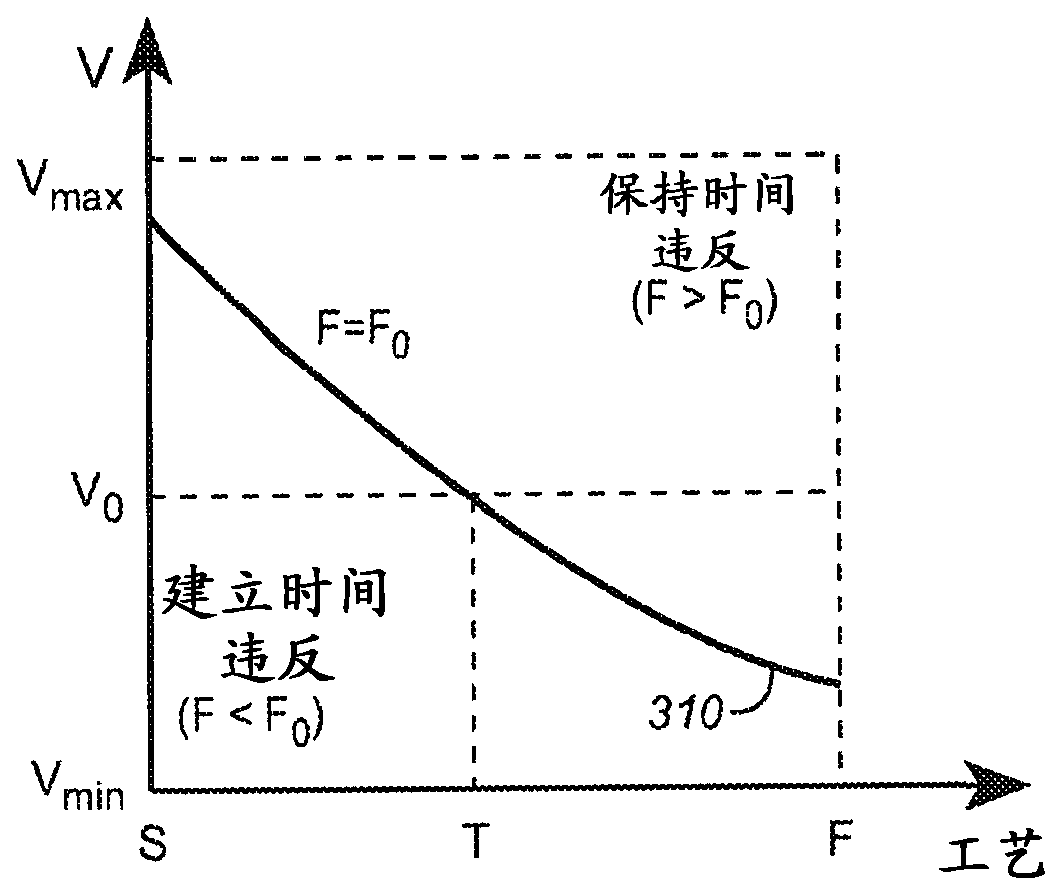
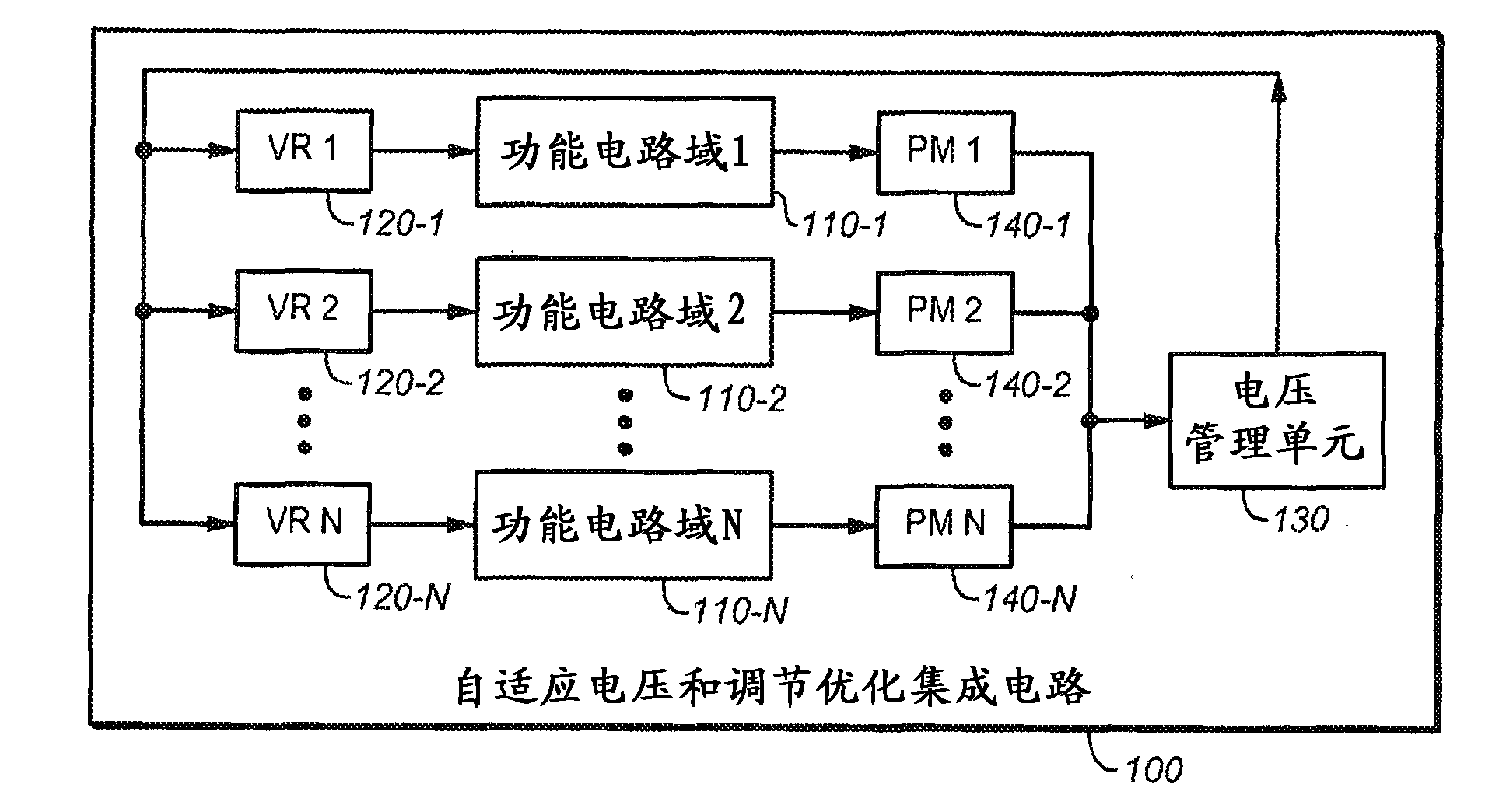
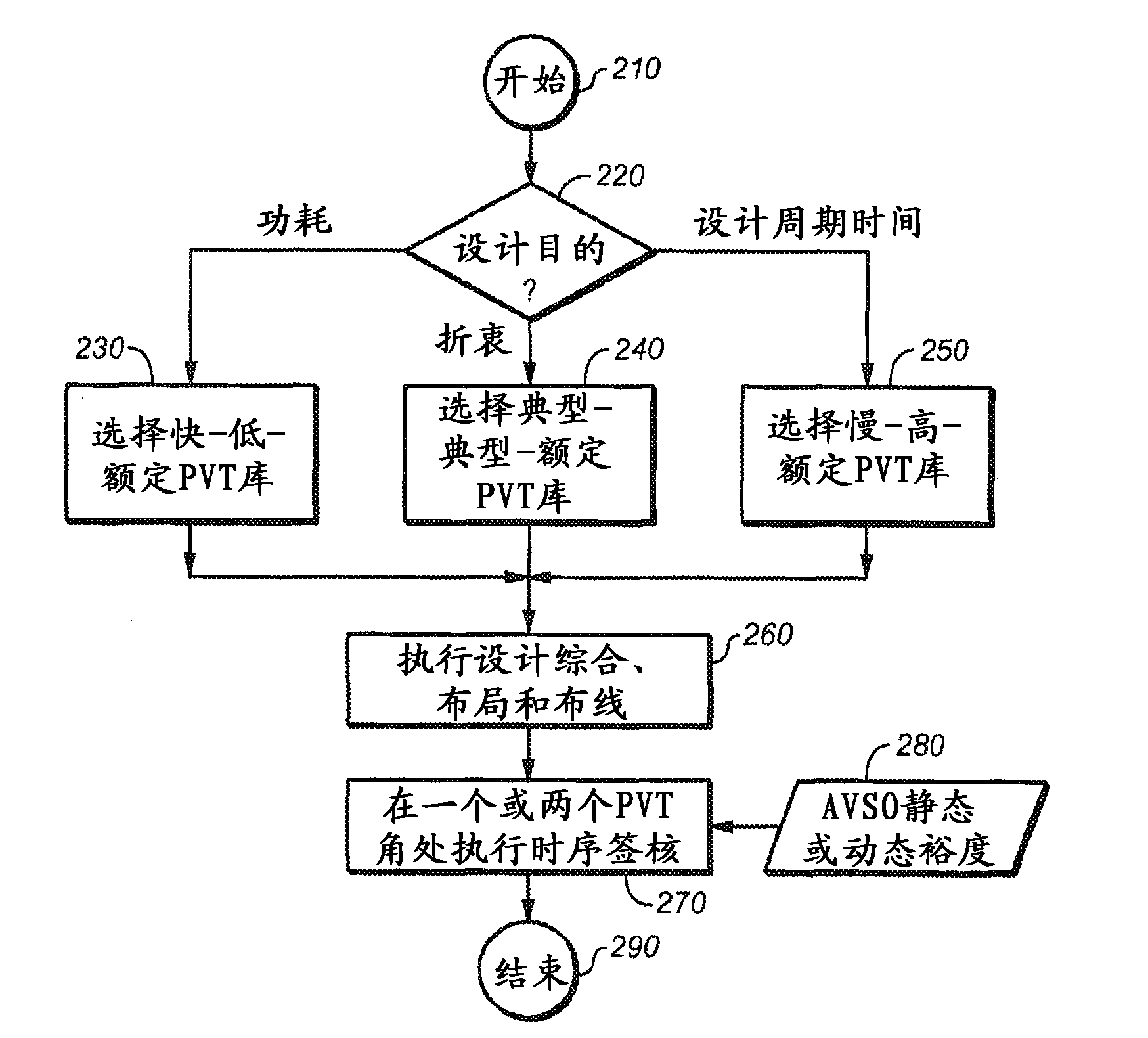
System and method for designing integrated circuits that employ adaptive voltage scaling optimization
ActiveCN102160054AEasy to understandEasy to useComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsProcess optimizationAdaptive voltage scaling
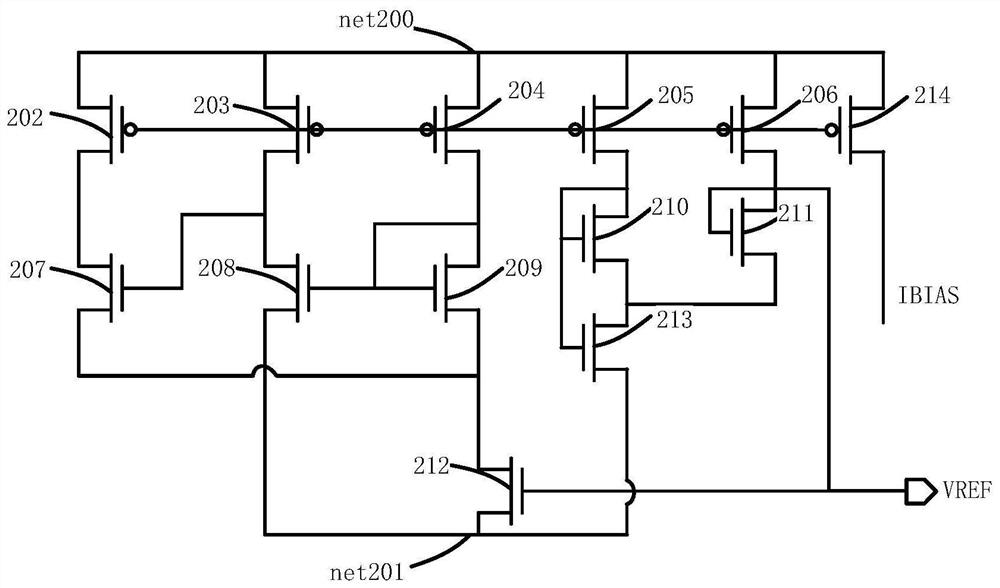
The represent invention relates to a design process optimization system and method for designing a circuit which may be an integrated circuit (IC) employing adaptive voltage and scaling optimization (AVSO). In one embodiment, the system includes: (1) a process-voltage-temperature (PVT) libraries database configured to contain PVT libraries of PVT characterizations of devices of cells from which the circuit is to be constructed, and (2) a PVT library selector coupled to the PVT libraries database and configured to receive a selection indicating a supplemental objective and respond to the selection by selecting one of the PVT libraries from the PVT libraries database, a timing signoff tool later employing at most two corners from the one of the PVT libraries to perform a timing signoff with respect to the circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Wideband CMOS gain stage
InactiveUS6927631B2Eliminate needDifferential amplifiersAmplifier protection circuit arrangementsCMOSEngineering
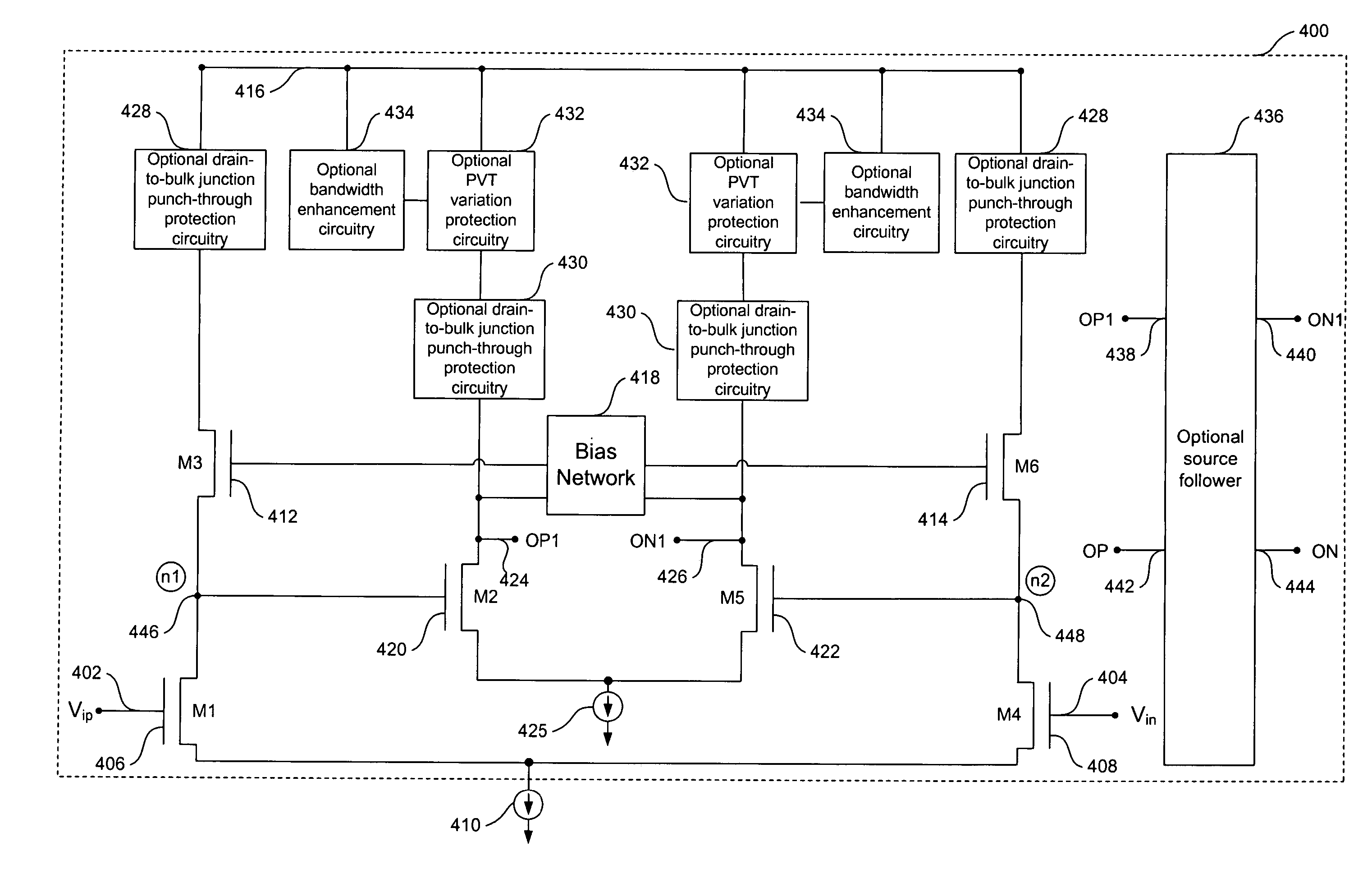
A CMOS gain stage includes biasing circuitry configured to insure saturation of a subsequent stage without a source follower circuit. The CMOS gain stage is optionally powered by a supply voltage that is greater than a permitted supply voltage for a processes technology that is used to fabricate the CMOS gain stage. In order to protect CMOS devices within the CMOS gain stage, optional drain-to-bulk junction punch-through protection circuitry is disclosed. A variety of optional features can be implemented alone and / or in various combinations of one another. Optional features include process-voltage-temperature (“PVT”) variation protection circuitry, which renders a gain relatively independent of process, voltage, and / or temperature variations. Optional features further include bandwidth enhancement circuitry.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
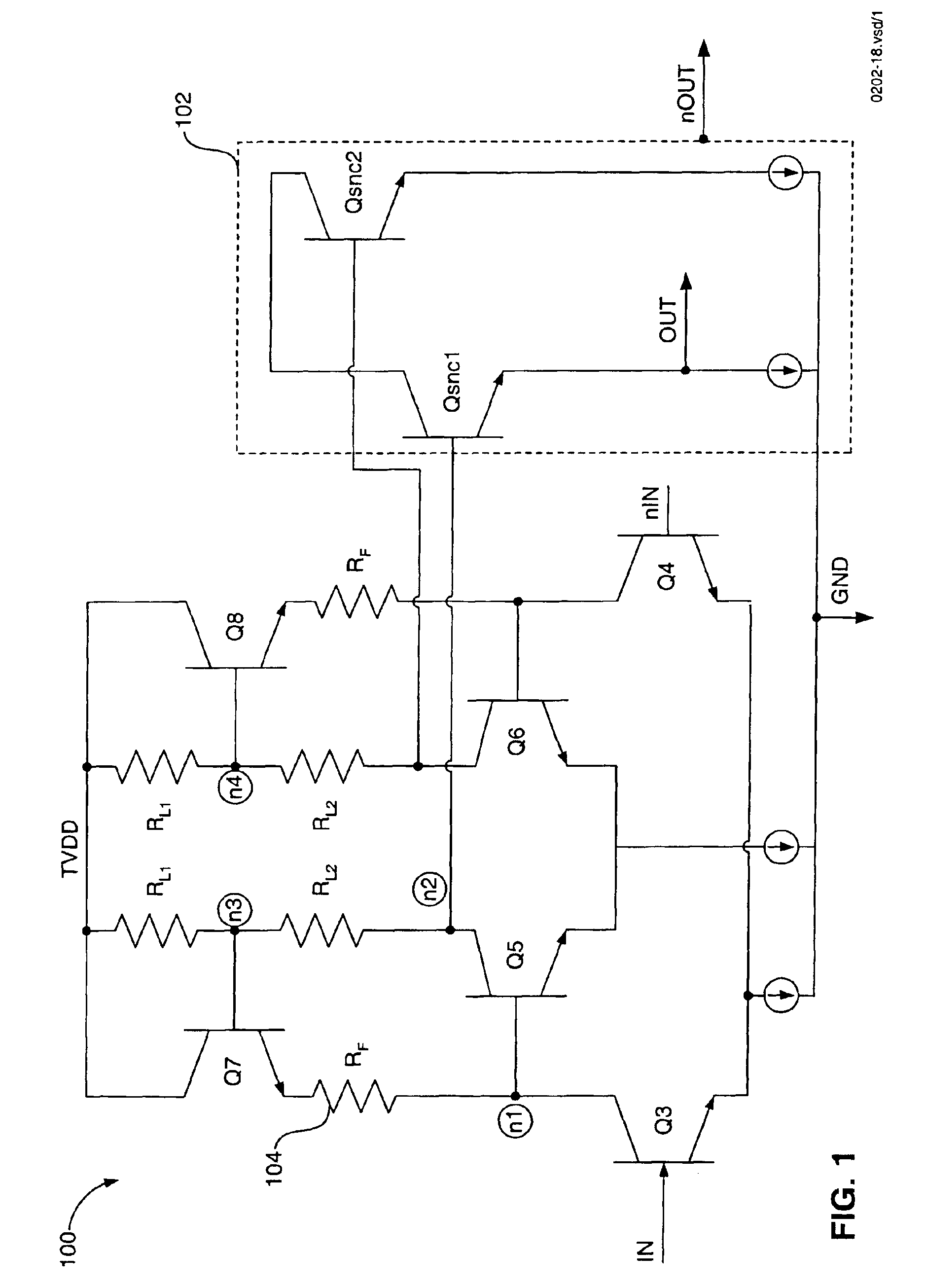
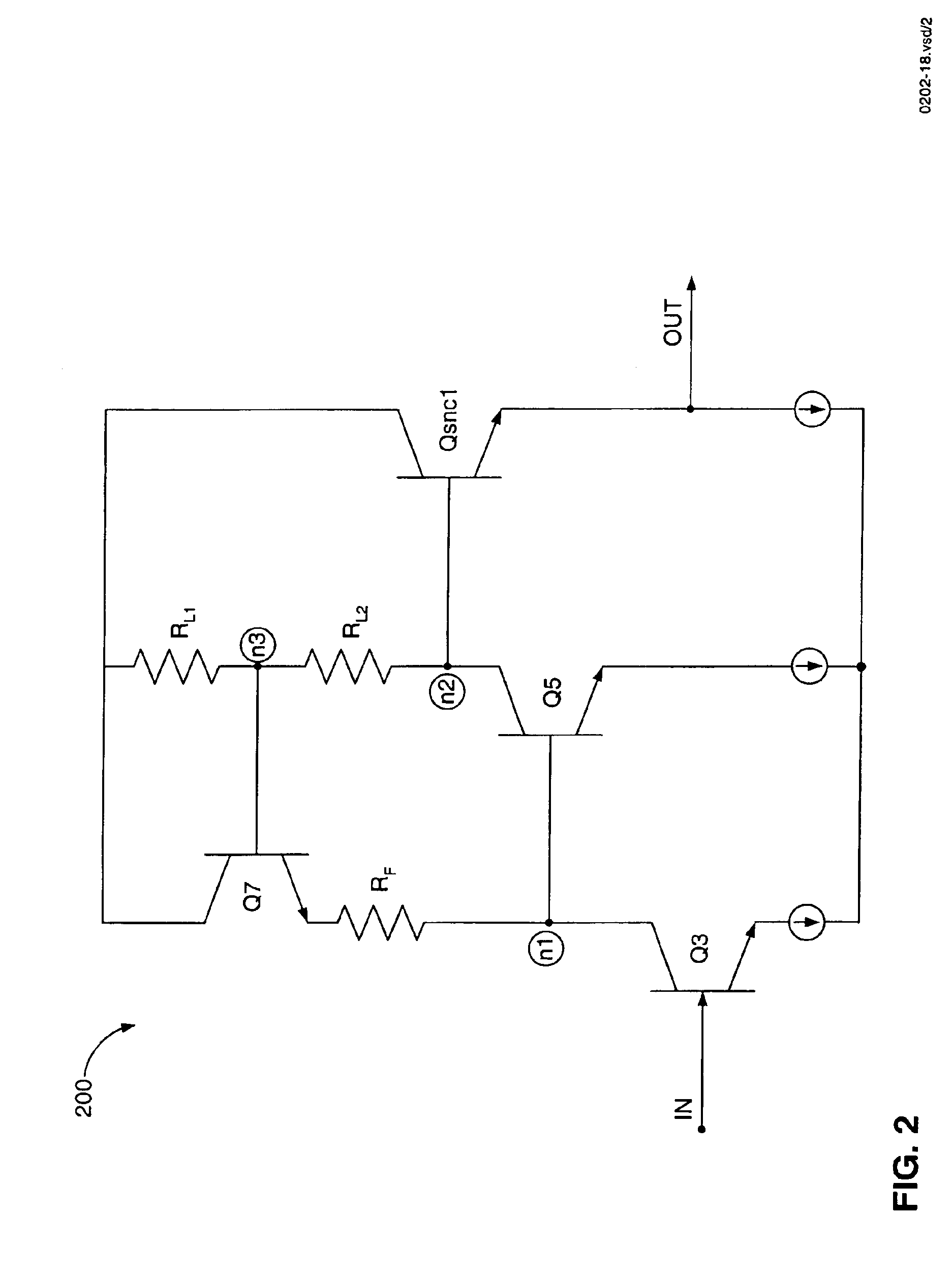
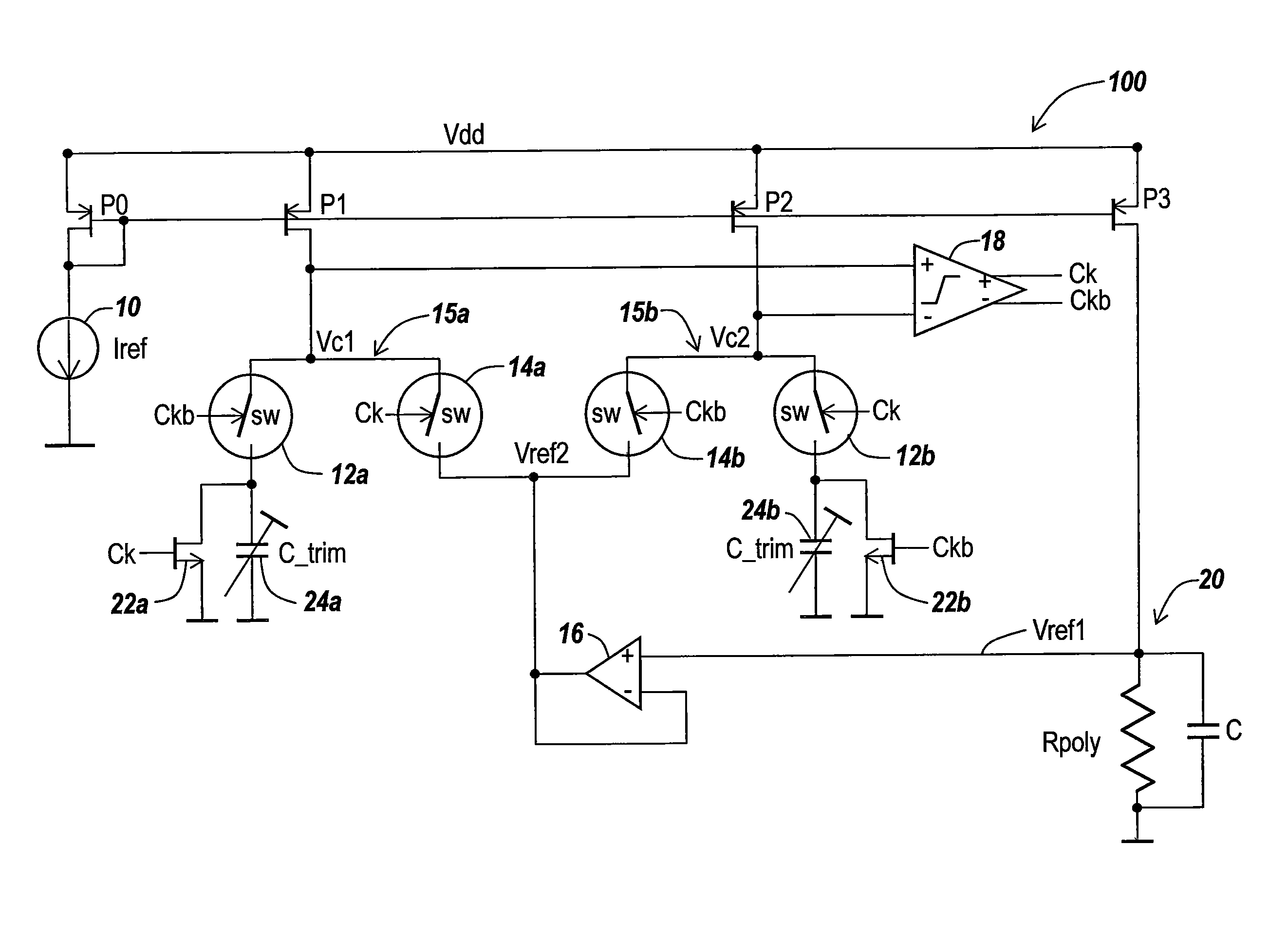
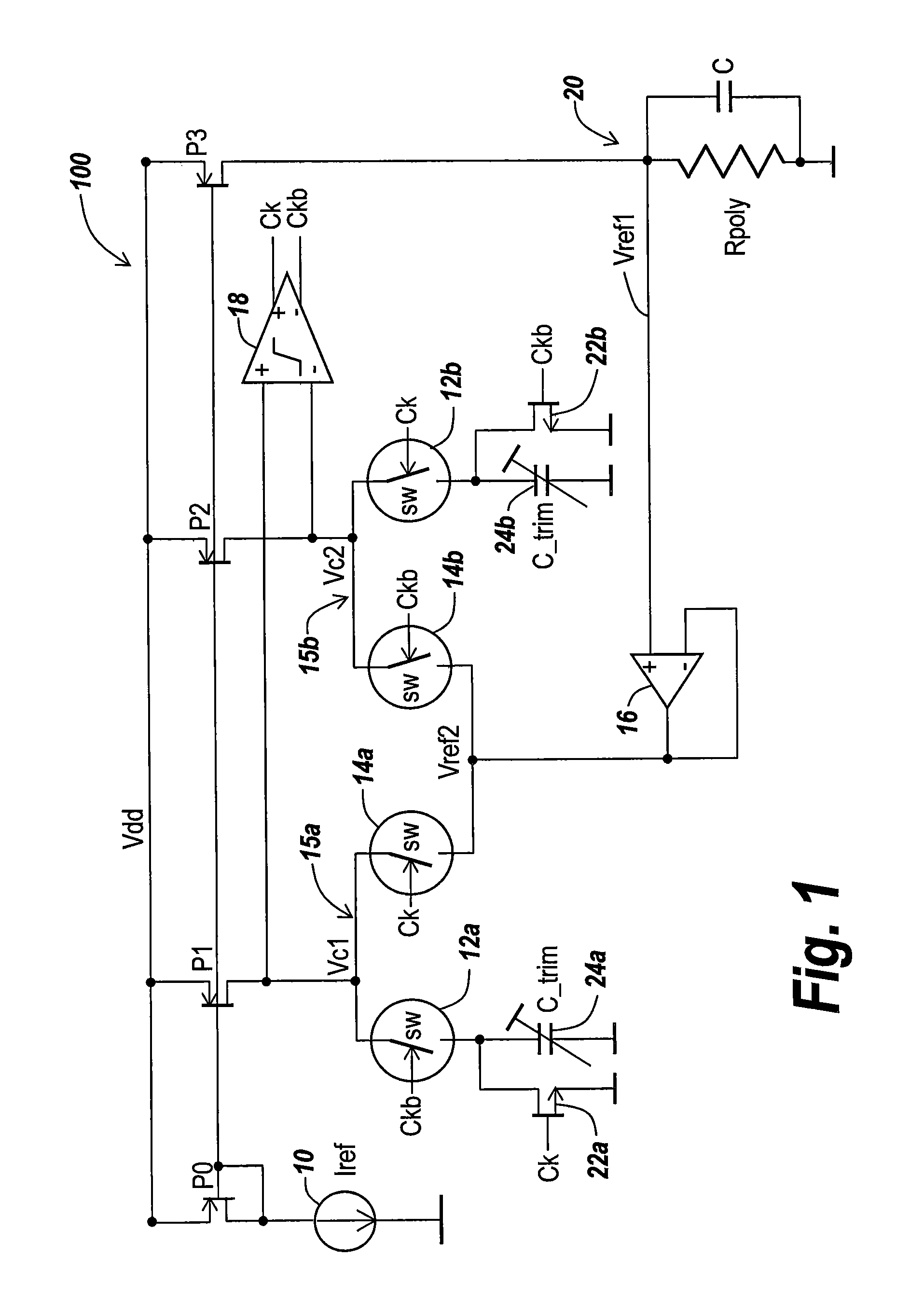
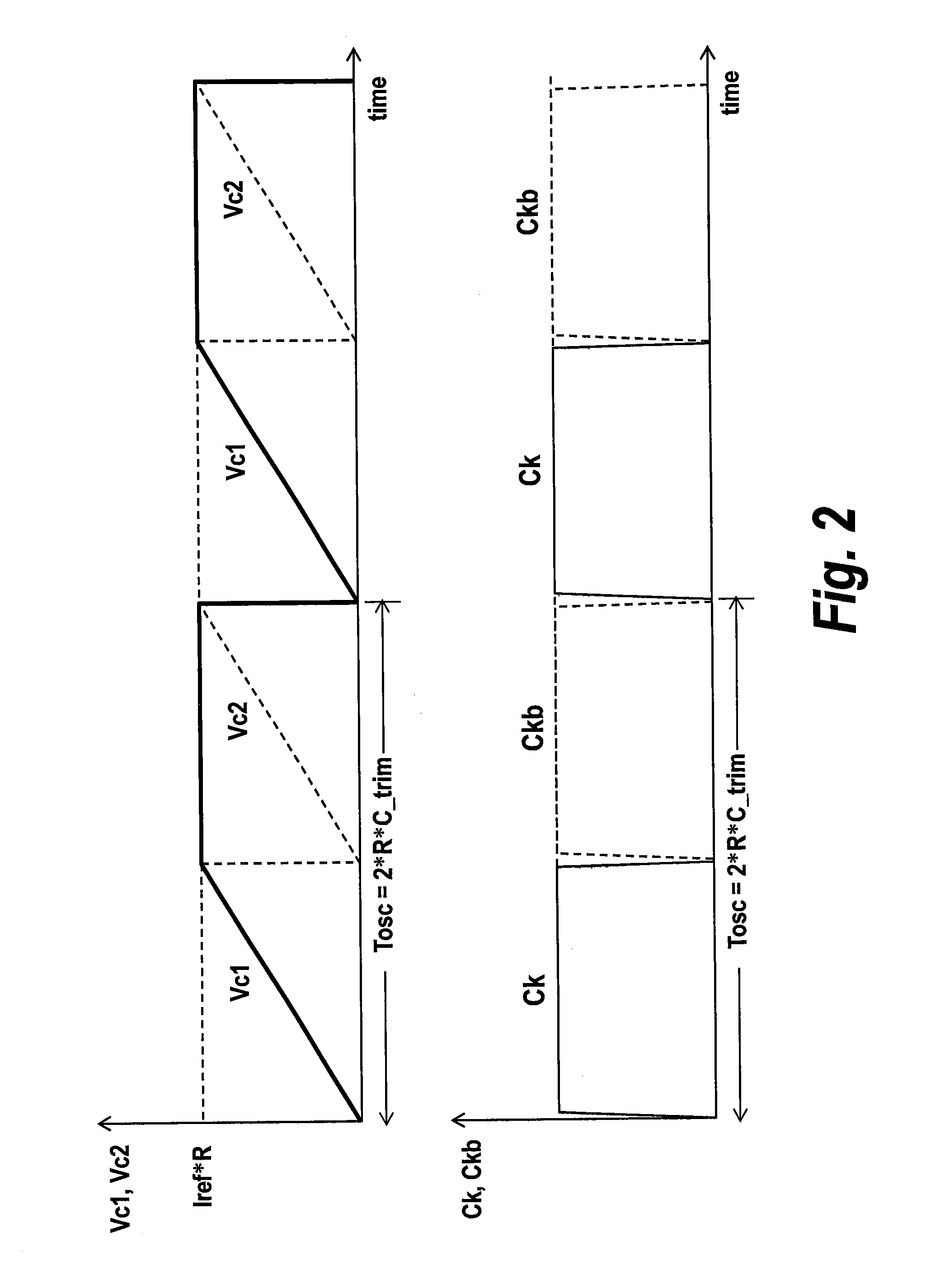
Integrated circuit devices having oscillator circuits therein that support fixed frequency generation over process-voltage-temperature (PVT) variations
ActiveUS9503059B1Improve fidelityMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlVoltage generatorSwitching signal
Oscillator circuits that support highly accurate fixed frequency generation over process, voltage and temperature (PVT) variations include a reference voltage generator, which is configured to generate a reference voltage across a resistor (e.g., high precision poly-resistor) therein. An auto-zeroing comparator is provided, which is configured to generate a differential clock signal (e.g., Ck, Ckb) at an output thereof. First and second switched capacitor circuits are further provided, which include matching first and second trim capacitors therein, respectively. The first and second switched capacitor circuits are configured to periodically drive respective first and second input terminals of the comparator at a first voltage level in an alternating back-and-forth sequence, in response to the reference voltage and a pair of switching signals derived from the differential clock signal.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Voltage regulation subsystem
Owner:NXP USA INC
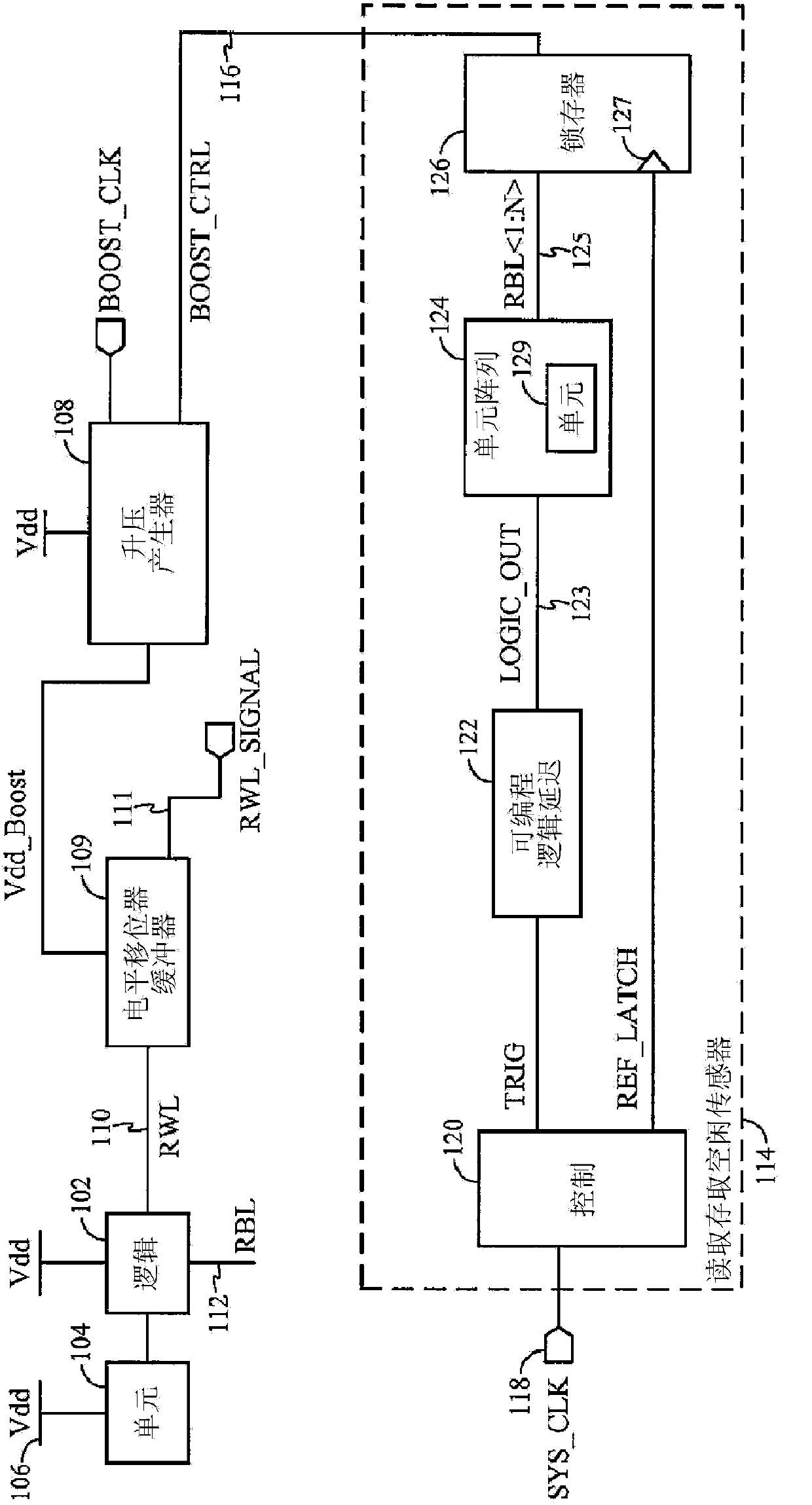
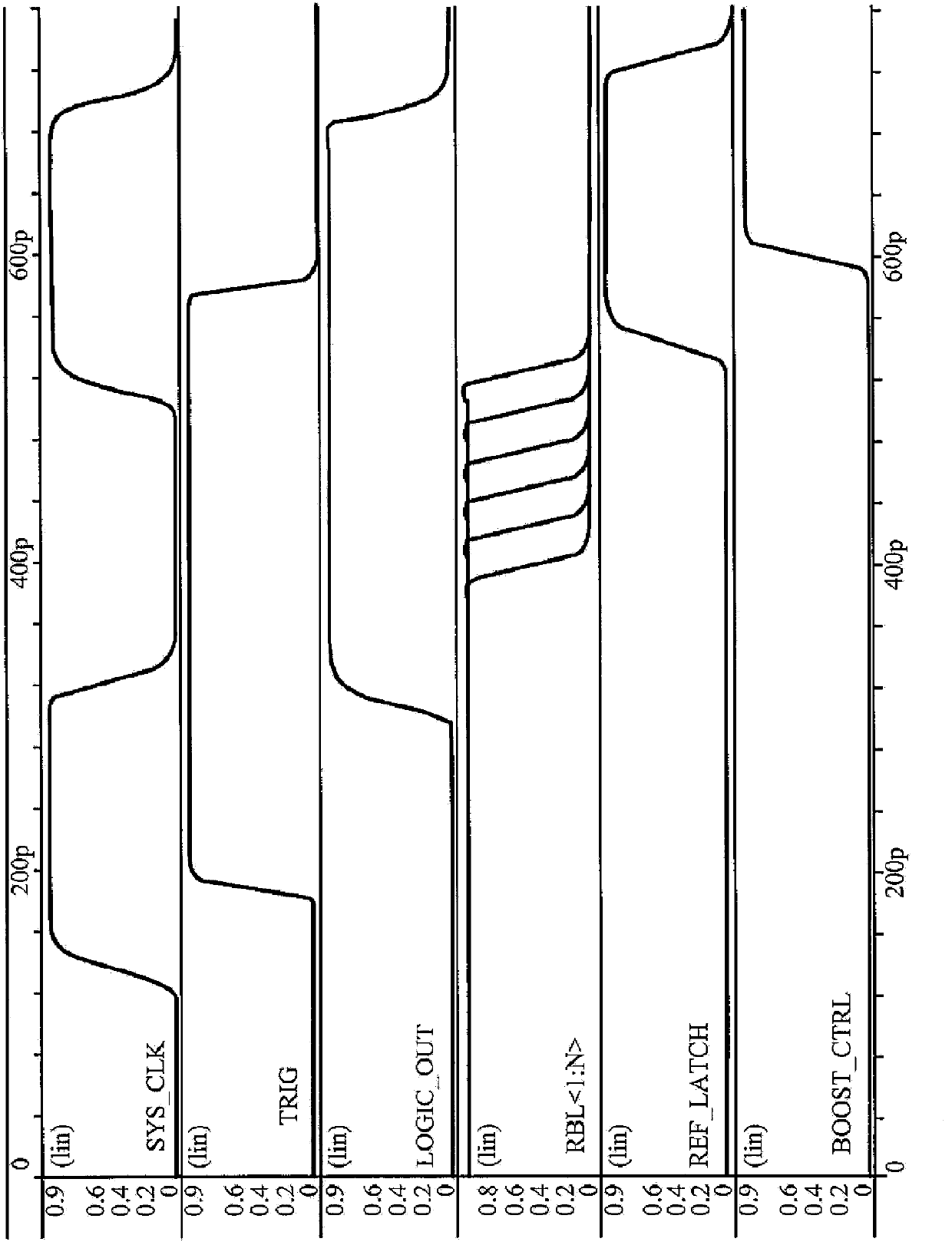
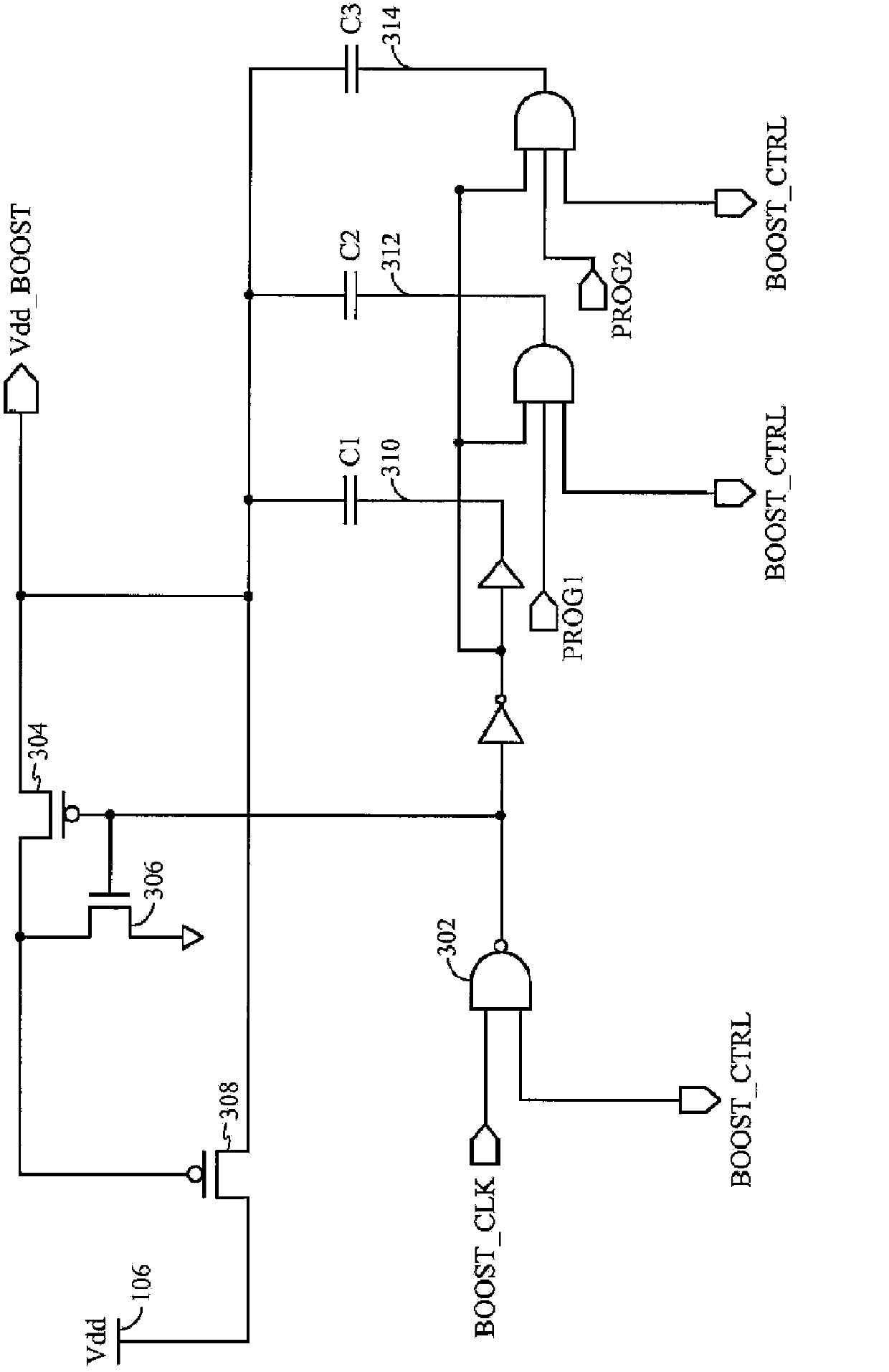
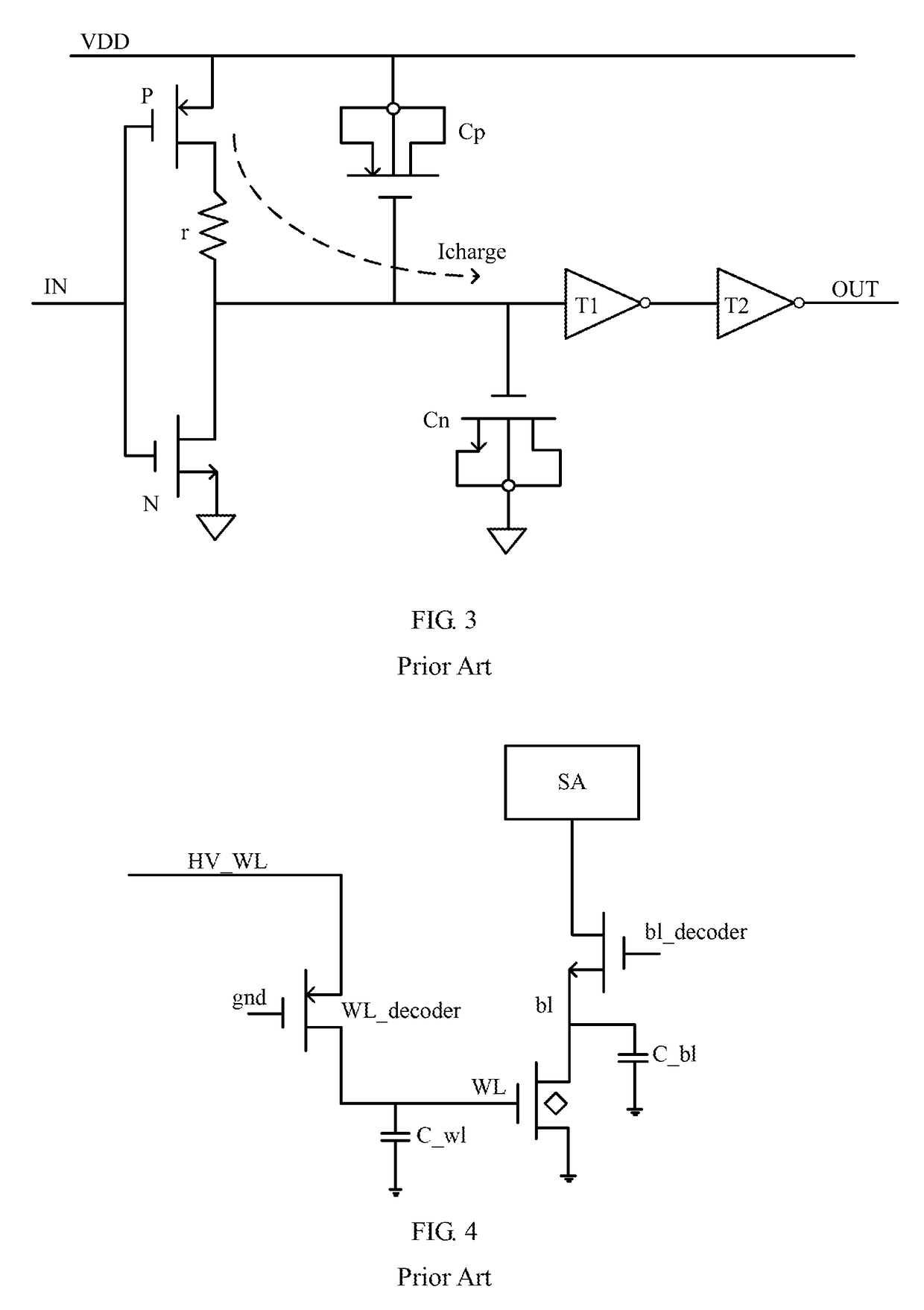
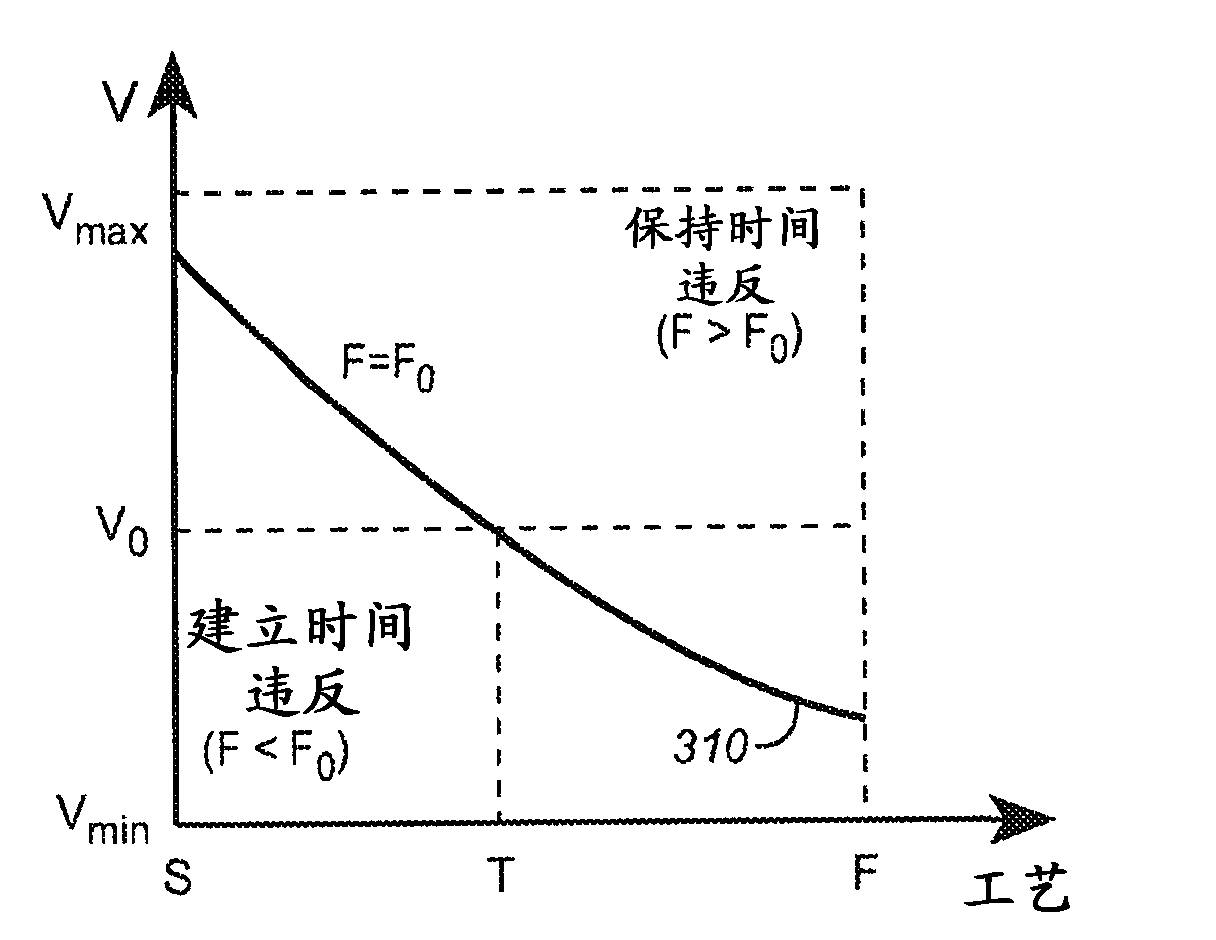
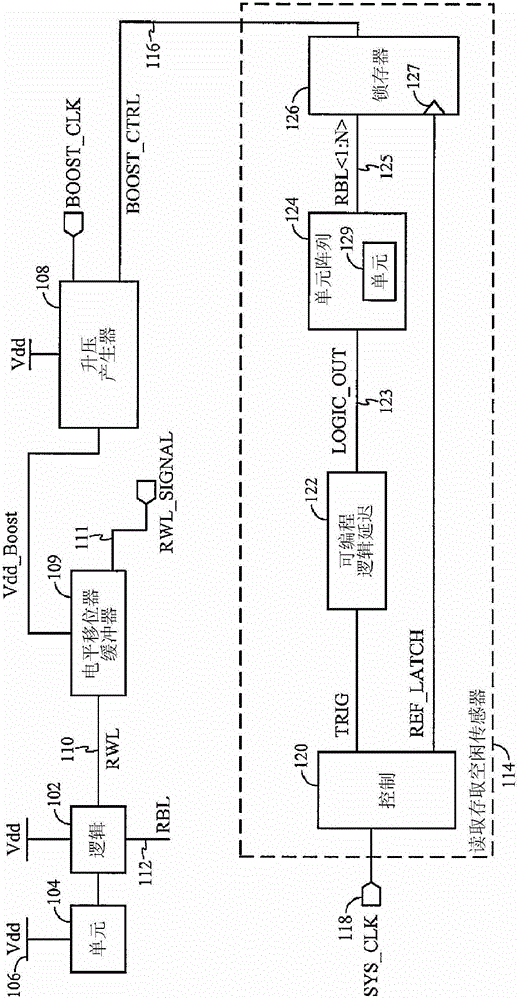
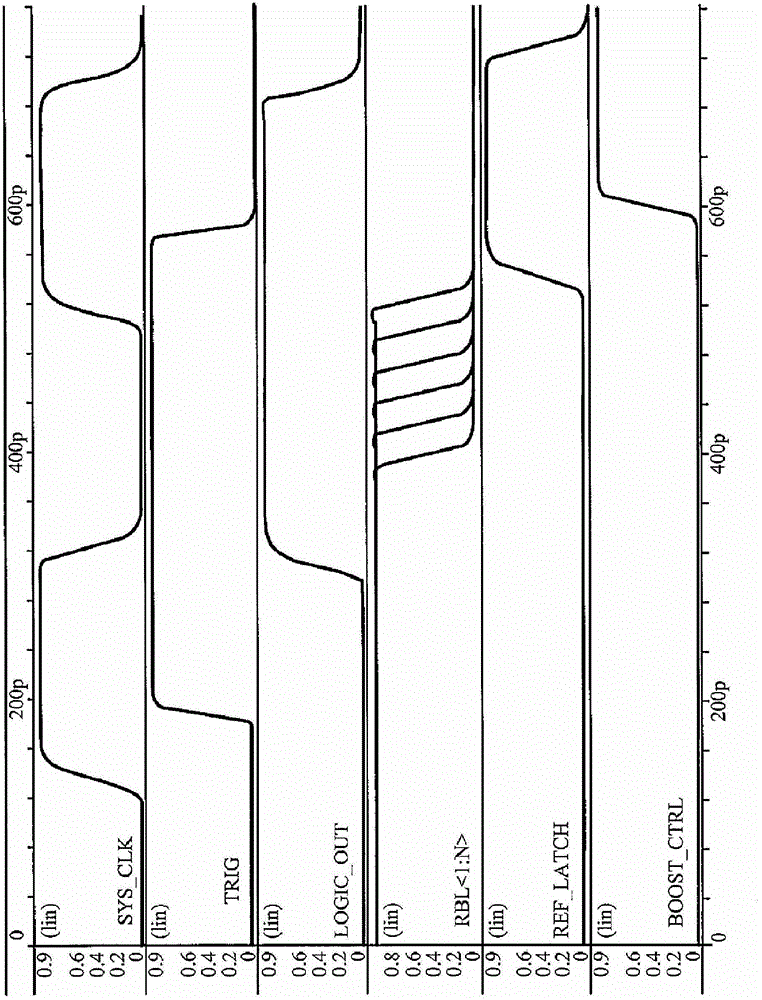
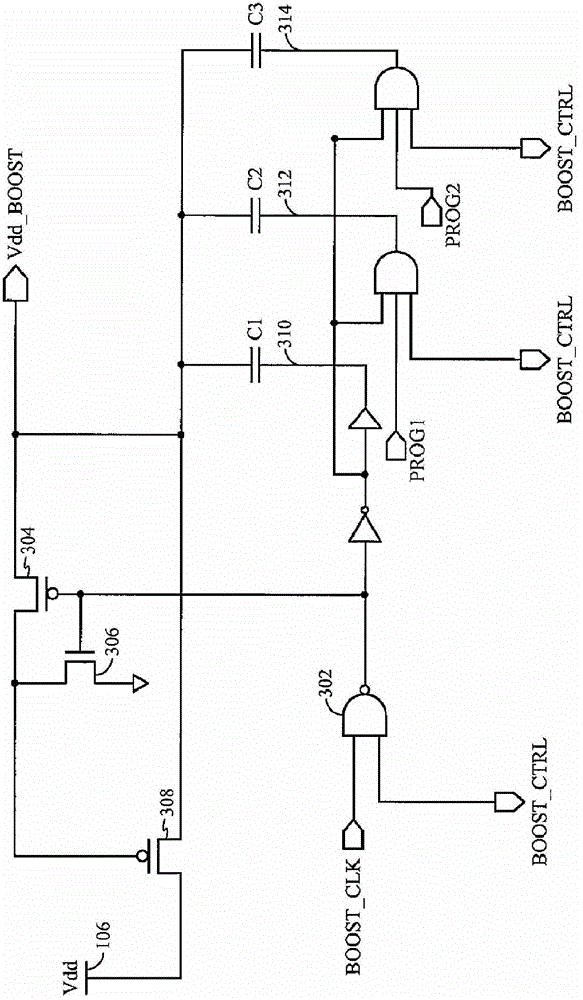
Adaptive read wordline voltage boosting apparatus and method for multi-port SRAM
Embodiments of the invention are directed to systems and methods for adaptively boosting the supply voltage to an SRAM (104) in response to process-voltage-temperature variations when needed. Embodiments include a critical path (114) that simulates a typical memory cell (104) and read-out circuit (102) in the SRAM. An indication of when to boost the supply voltage to the read-out circuits of the SRAM is provided by applying a trigger signal to a word-line input port (123) of the critical path and comparing the output (125) of the critical path with a reference-latch signal (127).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Wideband CMOS gain stage
A CMOS gain stage includes biasing circuitry configured to insure saturation of a subsequent stage without a source follower circuit. The CMOS gain stage is optionally powered by a supply voltage that is greater than a permitted supply voltage for a processes technology that is used to fabricate the CMOS gain stage. In order to protect CMOS devices within the CMOS gain stage, optional drain-to-bulk junction punch-through protection circuitry is disclosed. A variety of optional features can be implemented alone and / or in various combinations of one another. Optional features include process-voltage-temperature (“PVT”) variation protection circuitry, which renders a gain relatively independent of process, voltage, and / or temperature variations. Optional features further include bandwidth enhancement circuitry.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Circuits for control of time for read operation, using a current mirror circuit to mirror a reference current into the dummy device and generates time control signals based on the mirrored current
ActiveUS9595310B2Reduce energy consumptionRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierReference current
A circuit for control of time for read operation is disclosed which additionally incorporates a dummy device circuit and a dummy sensitive amplifier circuit, uses a current mirror circuit to mirror a reference current in a reference device circuit into the dummy device circuit to generate a mirrored current, and generates time control signals based on the mirrored current. Due to the same adaptation of the mirrored current to the size of a test device as the reference current, the time control signals are also adapted to the size of the test device. This addresses the problem of fixed time control signals arising from the use of a conventional RC relay circuit and enables the time control signals to change with the size of the test device as well as Process Voltage Temperature, thereby resulting in an effective reduction in average energy consumed in read operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
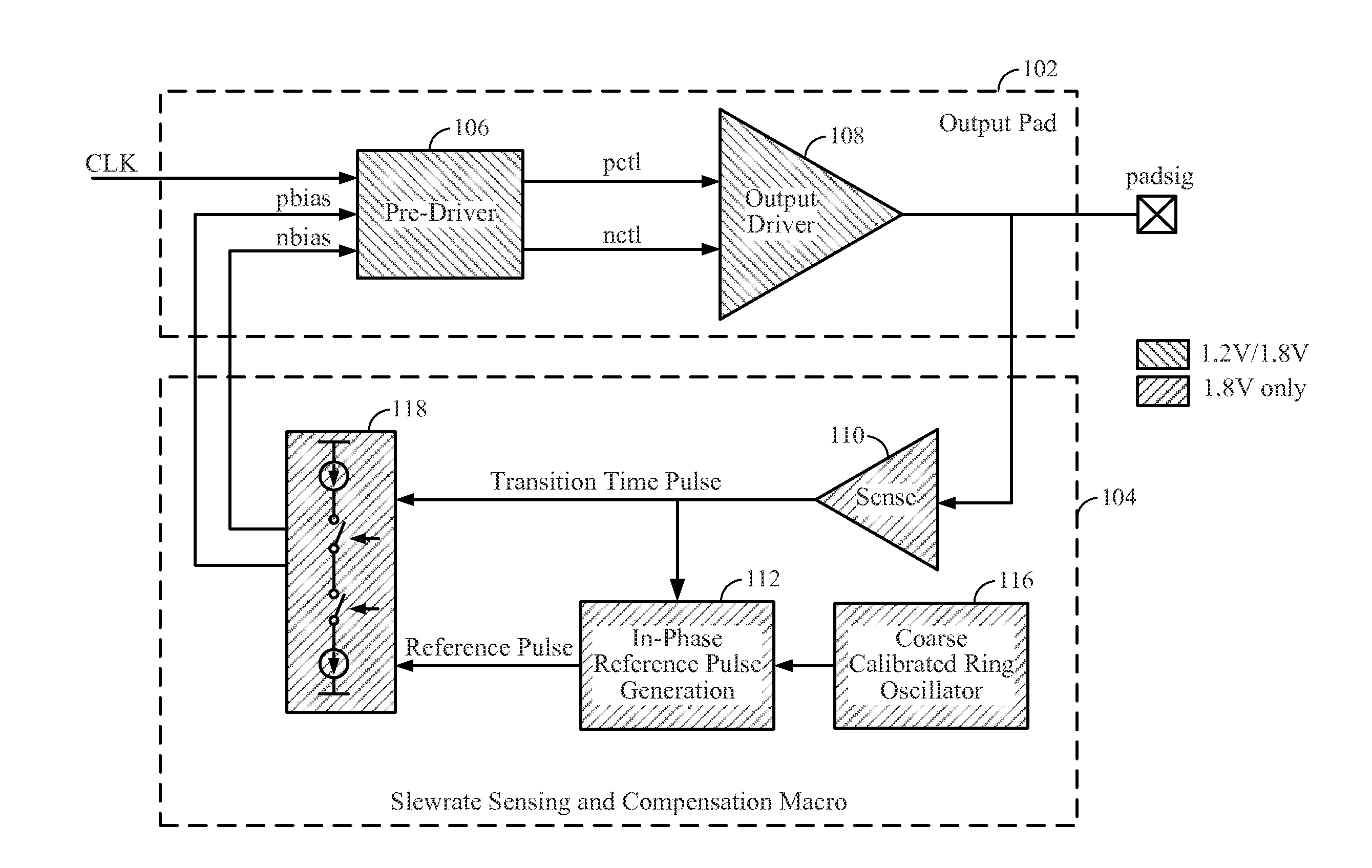
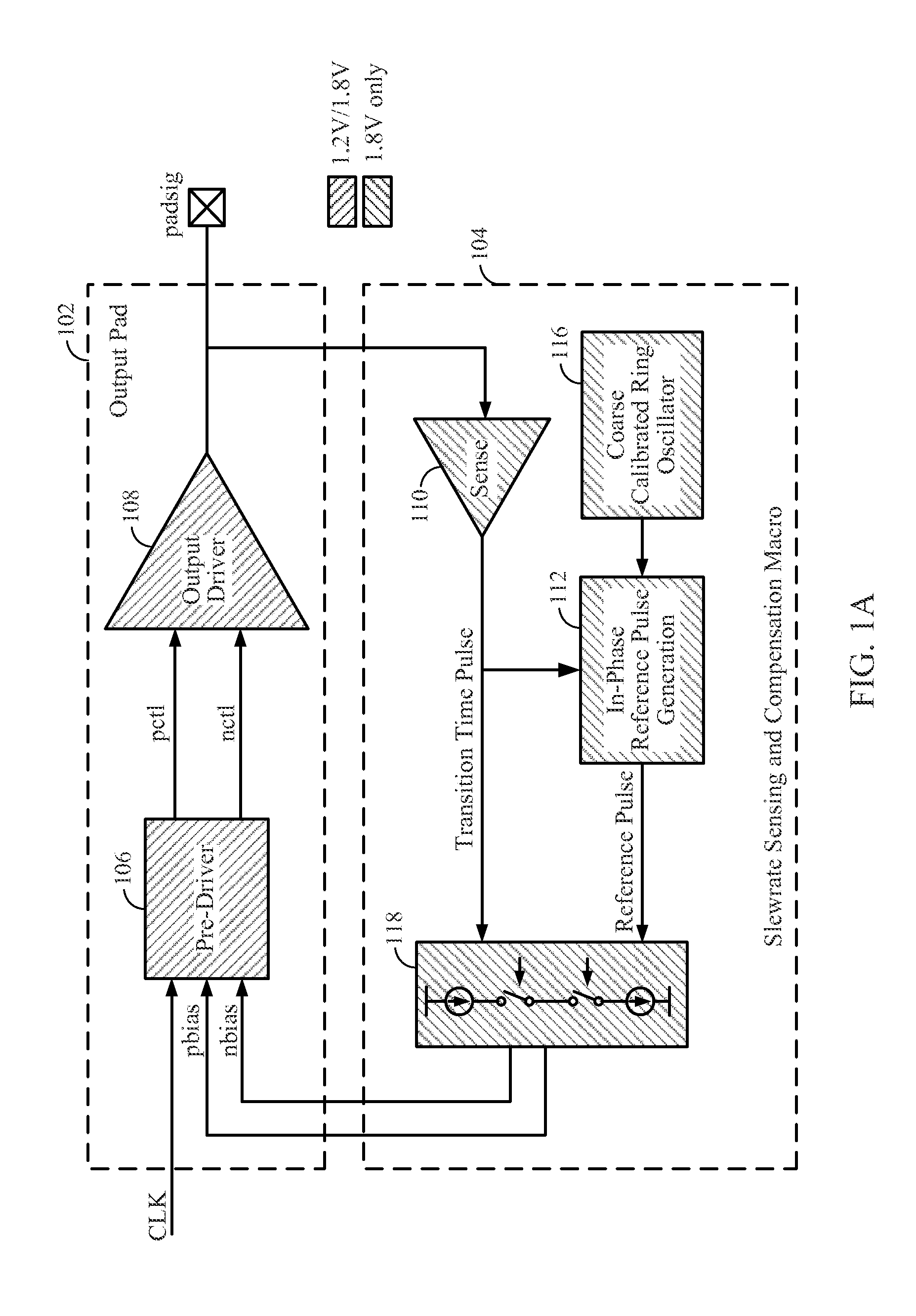
Transition time lock loop with reference on request
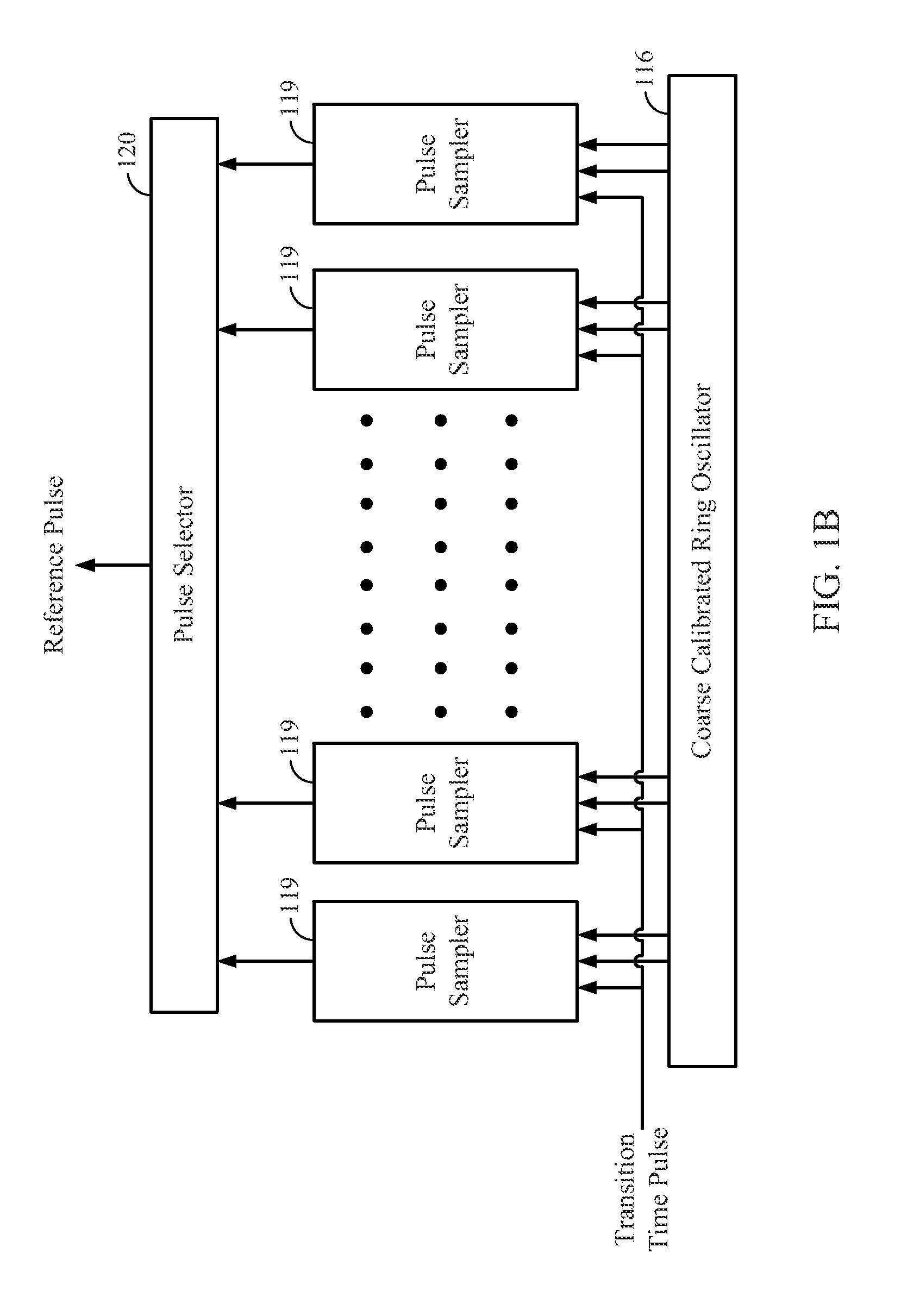
ActiveUS20130187692A1Full adjustmentPulse automatic controlVoltage/temperature variation compensationCapacitanceFeedback circuits
Output driver feedback circuitry limits output slew rates across a wide range of output loads. A transition time lock loop architecture of the feedback circuitry compares a transition time pulse with a reference pulse to adjusts transition time of an output signal for various process-voltage-temperature (PVT) process corners, output voltage domains and output capacitances. Reference pulse generation circuitry provides a reference pulse in phase with the transition time pulse for each rise and fall of the output signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Absolute time delay generating device
ActiveUS20100013536A1Maintain accuracyMaintain stabilityComputing operation arrangementsGenerating/distributing signalsTiming generatorTime delays
An absolute time delay generating device includes a PVT (process-voltage-temperature) detection device and a delay-timing generator. The PVT detection device includes at least a delay module and a signal phase / frequency control module. The delay module includes a control unit and a reference unit. The control unit differs from the reference unit in sensitivity of delay property to PVT. The delay module compares phase or frequency differences generated when origin signals pass through the control unit and reference unit respectively, and produce delay parameters of the delay module. The signal phase / frequency control module receives and compares the delay parameters to determine an ambient PVT condition for the absolute time delay generating device, so as to control and correct the delay-timing generator and thereby generate accurate absolute time delay. Under various PVT influences, the absolute time delay generating device is capable of generating accurate, absolute time signals.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Integrated circuit, memory device, and method of managing bit line voltage generating circuit
PendingCN112596596ARead-only memoriesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesBit lineMemory cell
The invention discloses an integrated circuit, a memory device, and a method of managing a bit line voltage generation circuit, in which the integrated circuit provides a stable clamping voltage to atleast one bit line connected to a memory cell of the memory device. The integrated circuit comprises an operational amplifier for receiving a first reference voltage, a feedback voltage and a compensation current and outputting an output voltage; and an output transistor providing an endpoint voltage as a feedback voltage and an output voltage, where the output voltage is a target voltage relatedto the clamping voltage. The operational amplifier is configured to be unbalanced, and the endpoint voltage of the operational amplifier is smaller than the first reference voltage. And the compensation current compensates the operational amplifier, so that the clamping voltage is substantially constant and independent of the PVT (process voltage temperature) effect.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
System for reducing leakage current of SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) by self-adapting process voltage and temperature
ActiveCN111739568AResistance to voltage fluctuationsReduce areaDigital storageThermometer applicationsStatic random-access memoryControl signal
The invention discloses a system for reducing leakage current of a static random access memory (SRAM) by self-adapting to process voltage and temperature, and belongs to the technical field of basic electrical elements. The system comprises a process voltage and temperature monitoring module, a voltage regulation module, a dummy load module, a switching tube module, a power tube module and a stateswitching control signal generation circuit module. After electrification, the whole system starts to work; the process voltage and temperature monitoring module outputs reference voltage values under the current process and temperature, and can resist certain power supply voltage fluctuation; in the switching process of entering sleep, the dummy load firstly works to stabilize the voltage regulation loop, pre-regulate the grid voltage of the power tube module, reduce the undershoot of the SRAM power supply voltage in the switching process, and then the dummy load is turned off; the SRAM canthoroughly enter a sleep mode after being regulated by the voltage regulation module and the power supply voltage is close to the output of the process voltage and temperature monitoring module. According to the invention, the SRAM power supply voltage can be adjusted to the optimal value in a self-adaptive manner under different process voltage and temperature conditions, so that the leakage current is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System and method for designing integrated circuits that employ adaptive voltage scaling optimization
ActiveCN102160054BEasy to understandEasy to useComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsProcess optimizationSelf adaptive
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Adaptive read word line voltage boosting device and method for multi-port SRAM
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems and methods for adaptively boosting supply voltage to static random access memory SRAM (104) when needed in response to process-voltage-temperature variations. Embodiments include simulating critical paths (114) of typical memory cells (104) and readout circuits (102) in the SRAM. Applying a trigger signal to the critical path's word line input port (123) and comparing the critical path's output (125) to a reference latch signal (127) provides a sense of when to go high to the SRAM An indication of the supply voltage of the circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
A write-copy circuit suitable for SRAM
ActiveCN103871461BPrecise self-timerWord line pulse width downDigital storageAudio power amplifierStatic random-access memory
Owner:XI AN UNIIC SEMICON CO LTD
Low-noise amplifier adopting single-ended input and differential output
InactiveCN102163955BImprove differential symmetryAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention provides a low-noise amplifier adopting single-ended input and differential output. The low-noise amplifier comprises a first circuit, a second circuit, a tail current source tube circuit, a compensation circuit and a biasing circuit. The first circuit comprises at least one first field effect transistor. The input end of the first circuit is connected to the output end of an input matching network, and the output end of the first circuit is connected to an output matching network. The second circuit comprises at least one second field effect transistor, and is connected with the first circuit to form a differential pair structure. The output of the second circuit is connected with the output matching network. The tail current source tube circuit is connected with a common connection point of the first and second circuits. The compensation circuit is bridged between the first and second circuits, and is used for compensating an output signal of the second circuit to match the output signals of the first and second circuits. The biasing circuit is connected with the first and second circuits, and is used for providing DC bias. The low-noise amplifier has the advantages that: 1) the output signals are symmetrically differential; and 2) the overall gain of the amplifier is relative constant at various process voltage temperatures.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINPUZHEN MICROELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com