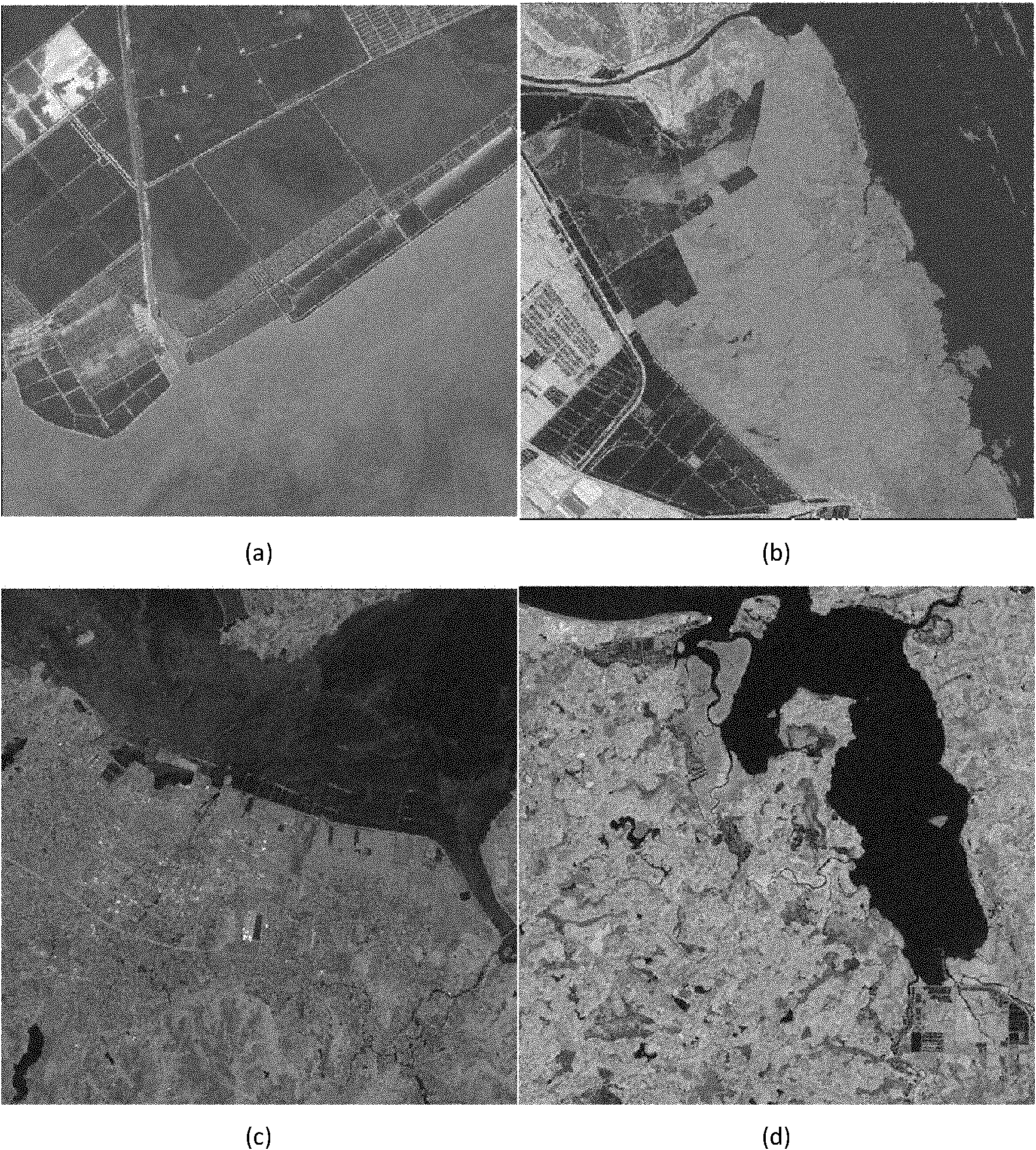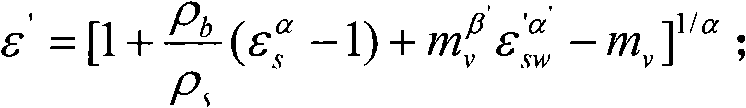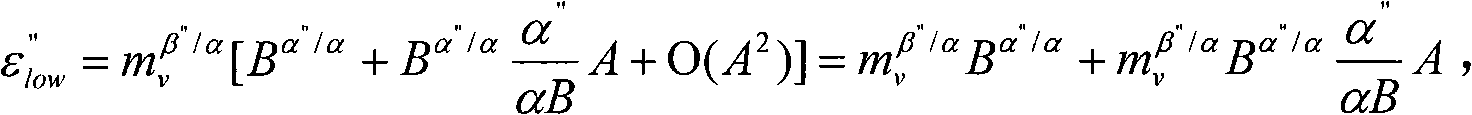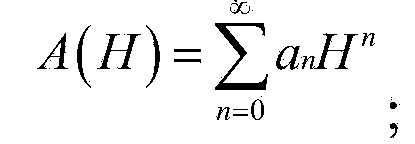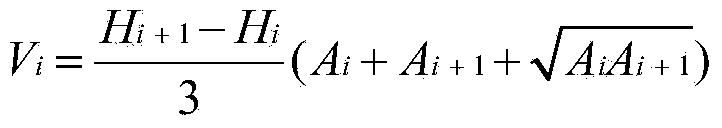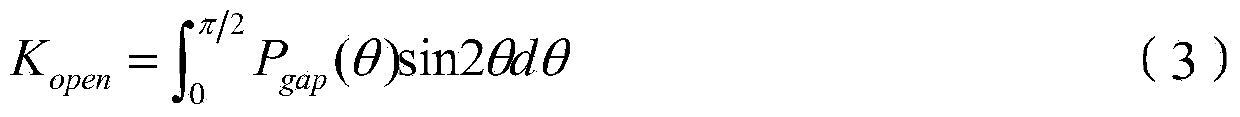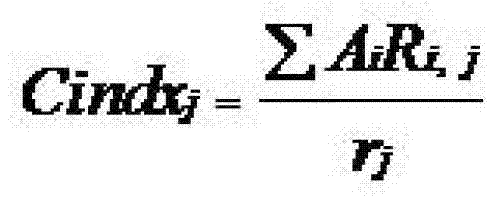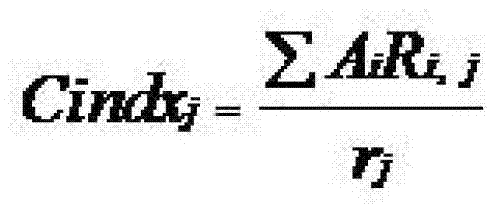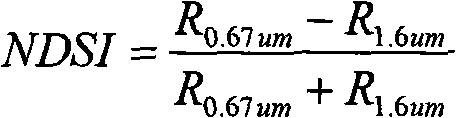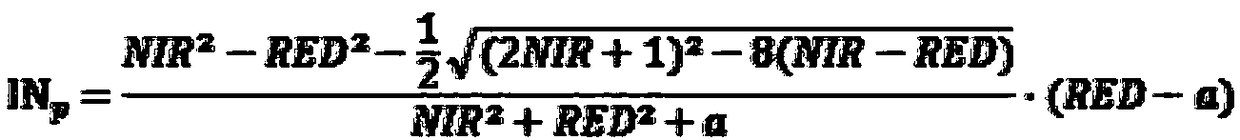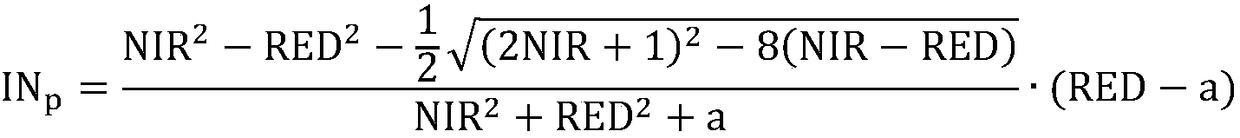Patents
Literature
32 results about "Water remote sensing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Water Remote Sensing studies the color of water through the observation of the spectrum of water leaving radiation. From the study of this spectrum, the concentration of optically active components of the upper layer of the water body can be concluded via specific algorithms. Water quality monitoring by remote sensing and close-range instruments has obtained considerable attention since the founding of EU Water Framework Directive.
Method for full automatic extraction of water remote sensing information in coastal zone
InactiveCN102054274AAchieve precise extractionMitigate the salt and pepper noise effectImage analysisComputer scienceCoastal zone
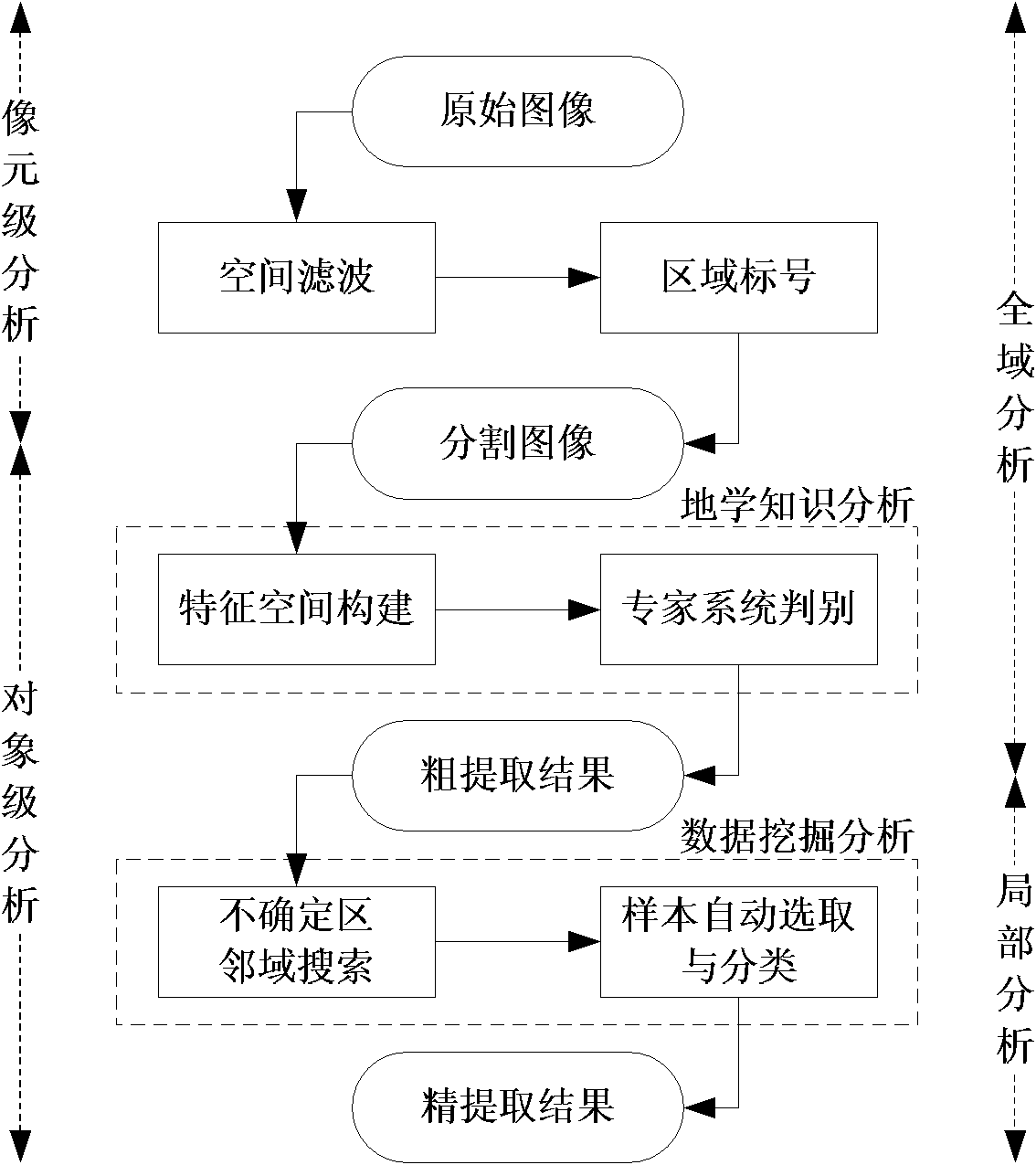
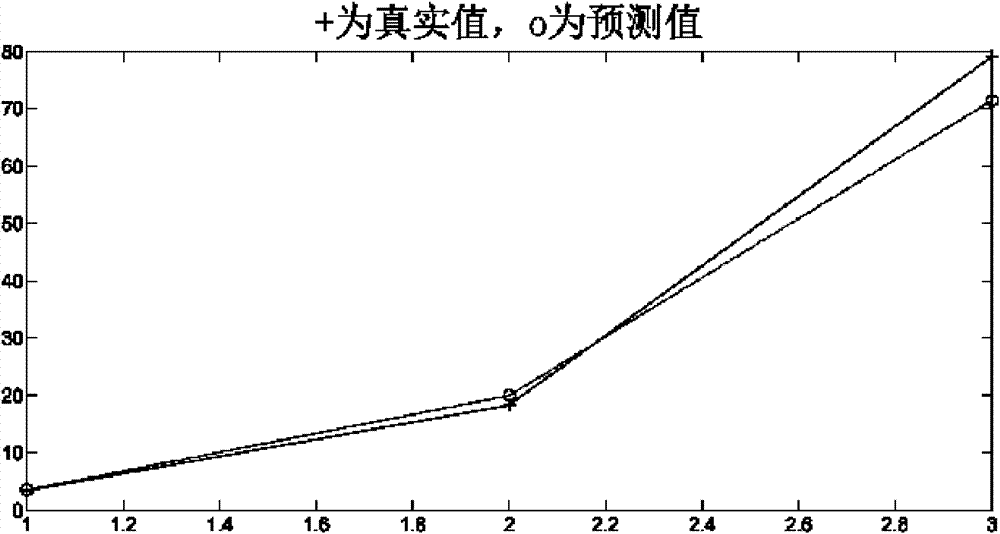
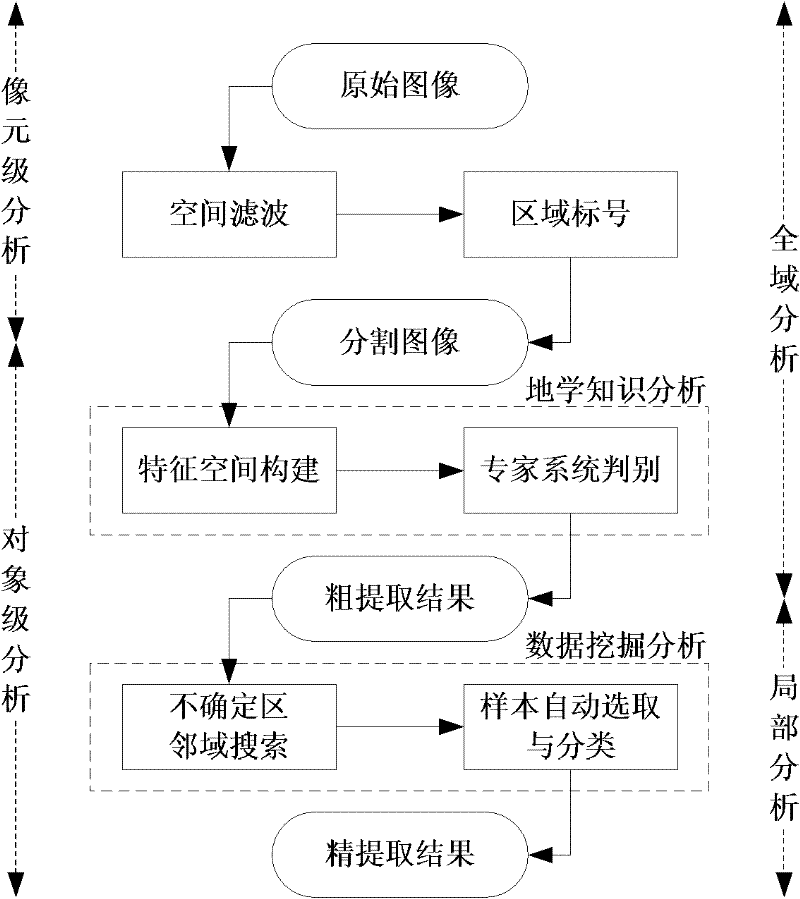
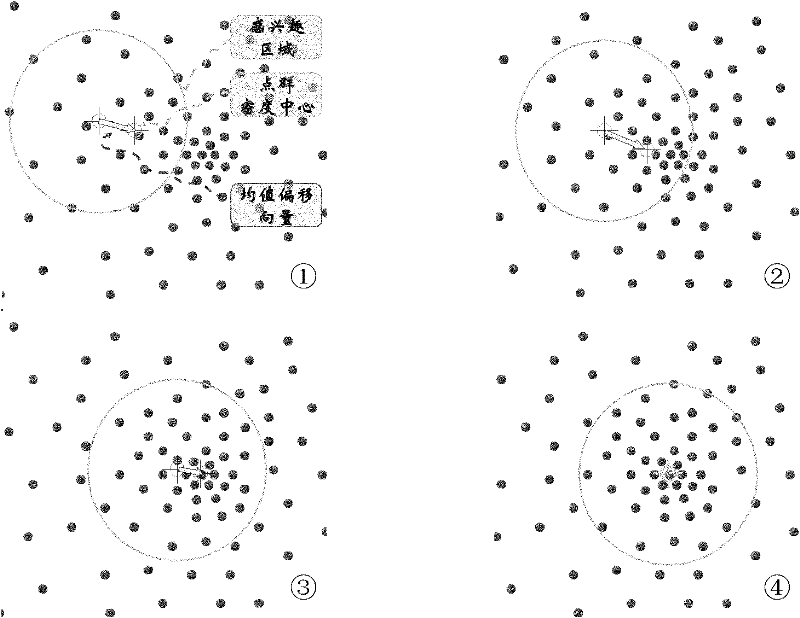
The invention discloses a method for full automatic extraction of water remote sensing information in a coastal zone and belongs to the field of methods for full automatic extraction of remote sensing information. The method comprises the steps of cutting a remote sensing image, roughly extracting water information and finely extracting water information, wherein scale conversion is performed twice in the process; the scale conversion performed at the first time is the scale conversion from bottom to up for converting an image element to an object; and the scale conversion performed at the second time is the scale conversion from up to bottom for converting the whole area to a local part. Compared with the prior art, the invention realizes a method combining geological knowledge with data mining in a scale conversion frame. The method is characterized by zero sample and zero parameter, and can be automatically operated completely. The method provided by the invention is suitable for various environments in a coastal zone of each sea area, has better stability, has higher precision of extraction results, has better extracting completeness and continuousness for detailed information than the traditional method, and can be directly applied to maintaining and updating the remote sensing thematic information of all-level national foundation geographic information databases.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Radar remote sensing-based detection method of soil alkalization
InactiveCN101614818AReduce dependencyCharacterize dielectric behaviorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlkali soilData information
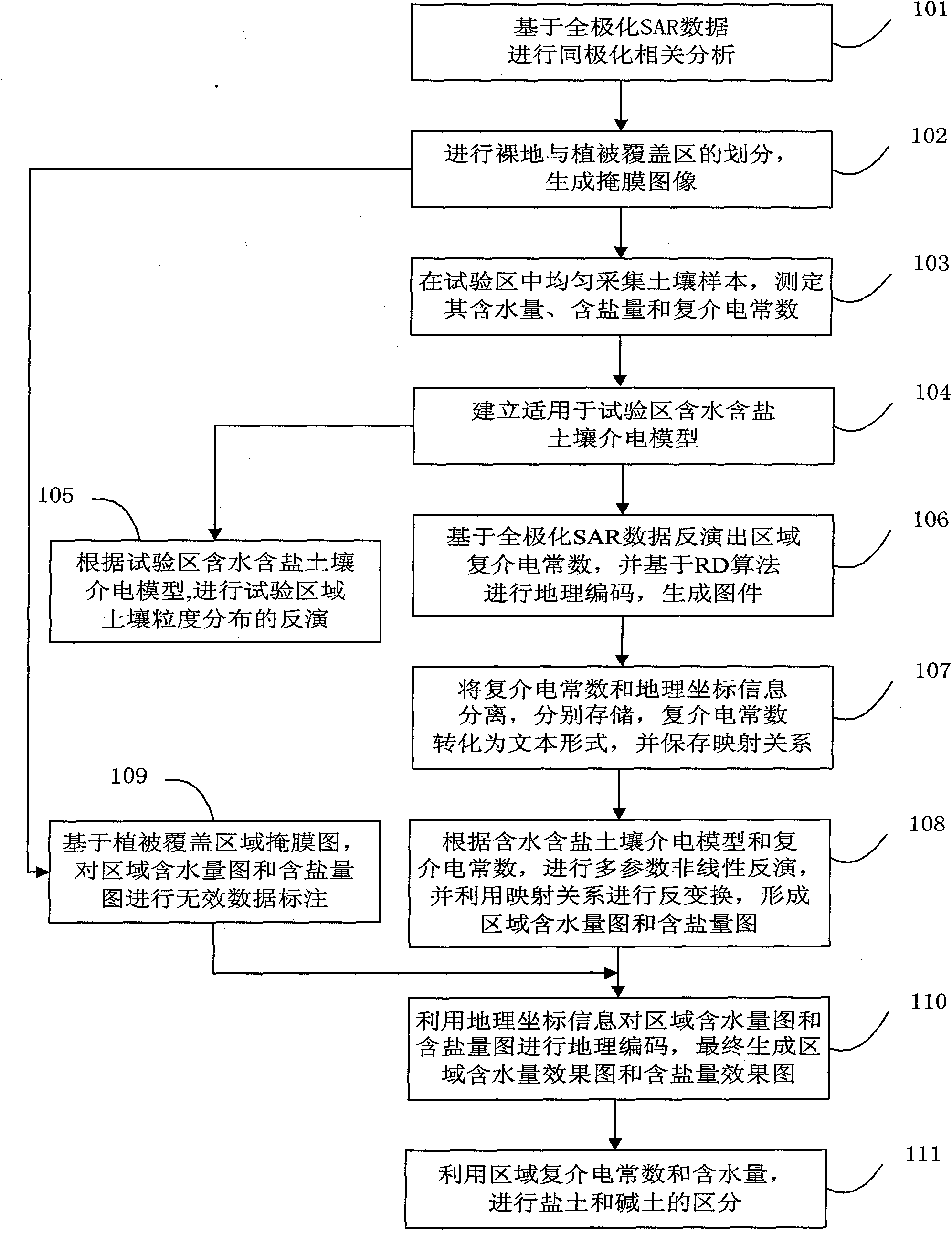
The invention discloses a radar remote sensing-based detection method of soil alkalization, comprising the following steps: computing the polarization parameter based on full polarimetric SAR data, dividing bare areas and vegetation-covered areas and generating images with masks; delimiting test areas and adopting measuring data to establish a dielectric model of moist salt soil; adopting the full polarimetric SAR data to invert a complex permittivity map and carrying out RD geocoding, data information separation and conversion; based on the dielectric model and the complex permittivity, adopting the genetic algorithm for inversion to obtain moisture contents and salt contents of areas, and integrating geographic coordinate information and a vegetation cover mask map to generate a moisture content map and a salt content map; adopting the complex permittivity and the moisture contents of areas to differentiate saline soil from alkali soil. By adopting the technical proposal of the invention, the moisture content and the salt content of the soil in saline areas can be obtained, the degree of dependence on ground assistant data is reduced and simultaneously the dielectric behavior of the moist salt soil can be better depicted.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
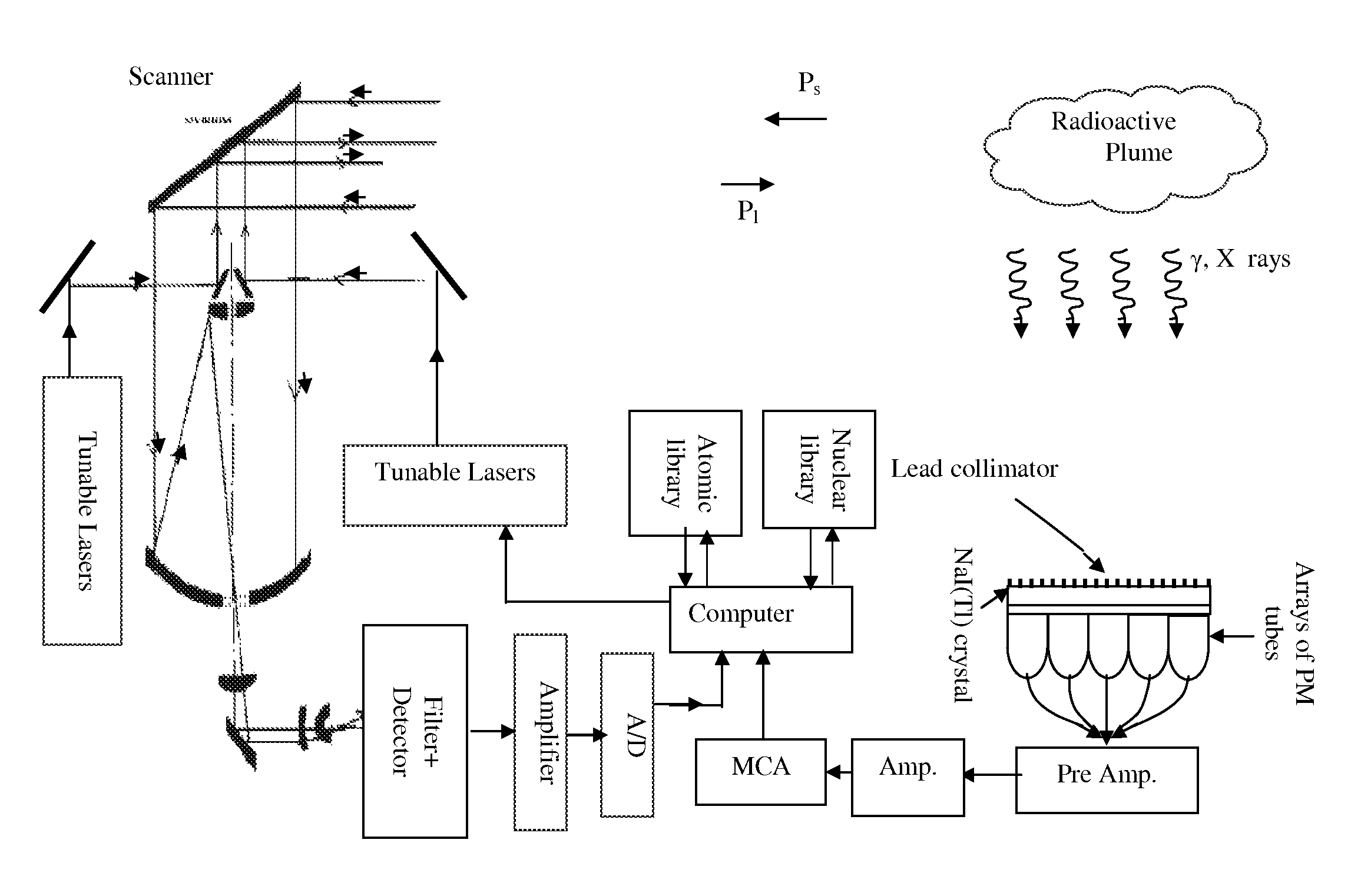
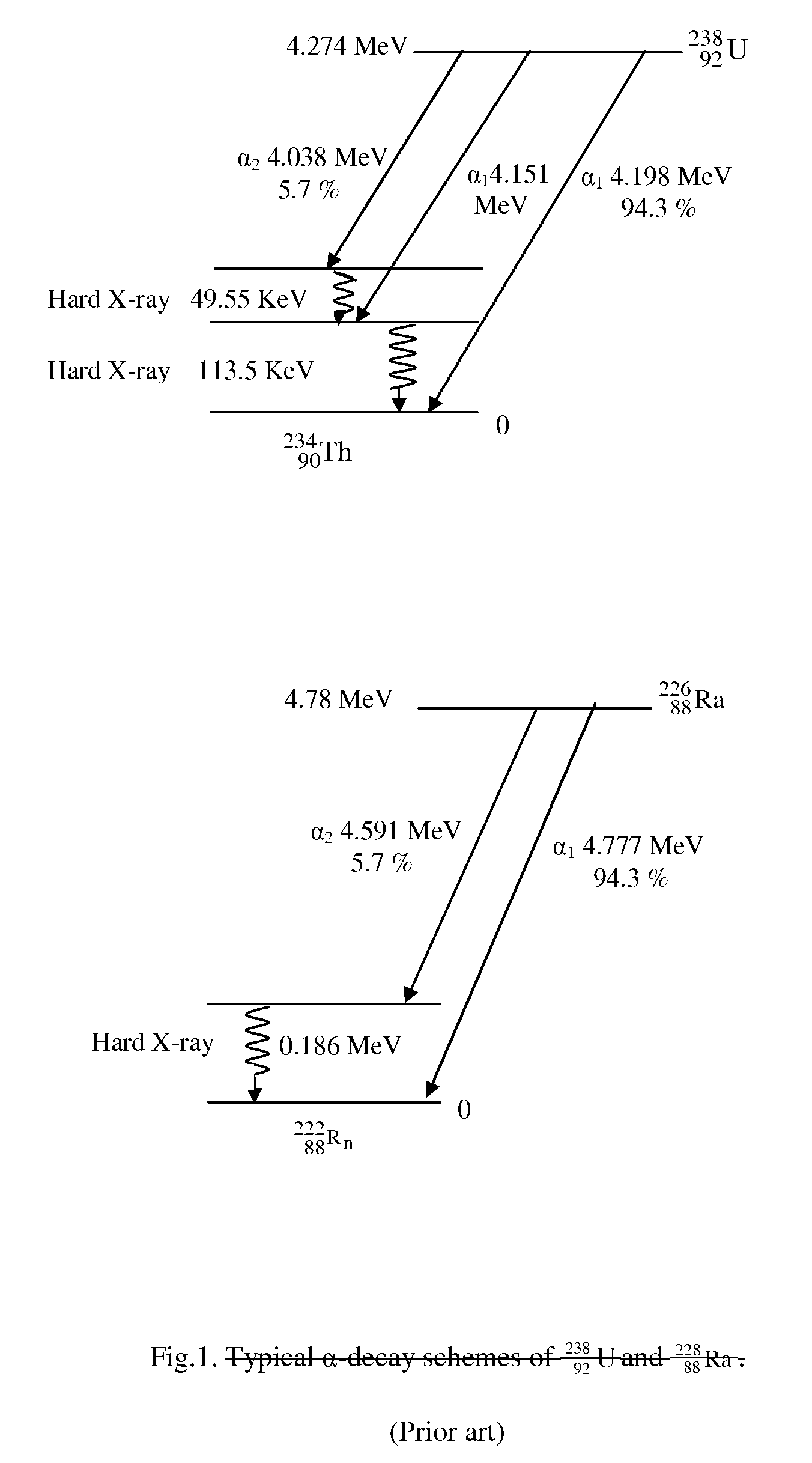
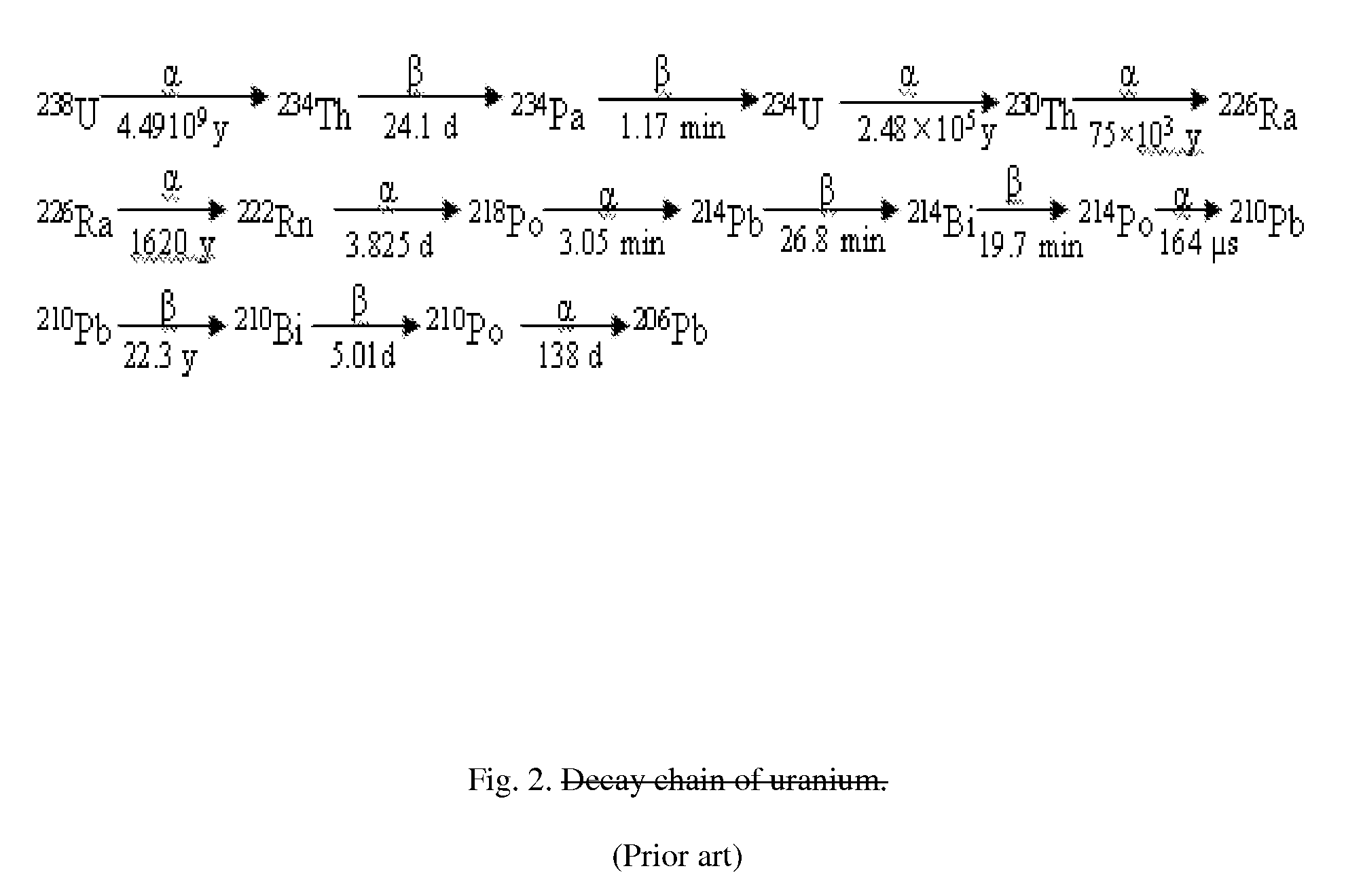
DIAL-Phoswich hybrid system for remote sensing of radioactive plumes in order to evaluate external dose rate
InactiveUS7566881B2Rapid responseHigh gainVolume/mass flow measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsDose rateNuclear power
An interactive combination of Phoswich detector array (PDA) and differential absorption lidar (DIAL) is proposed to trace the unknown radioactive plumes released into the atmosphere from a reactor stack, containment of the nuclear power plants, radioisotope separation laboratories, reprocessing plants or the uranium conversion facilities. The hybrid system represents a powerful technique for the prompt identification and quantification of the effluents with various radionuclide contents to determine the corresponding external dose rate accordingly.
Owner:SHAHI LAILA
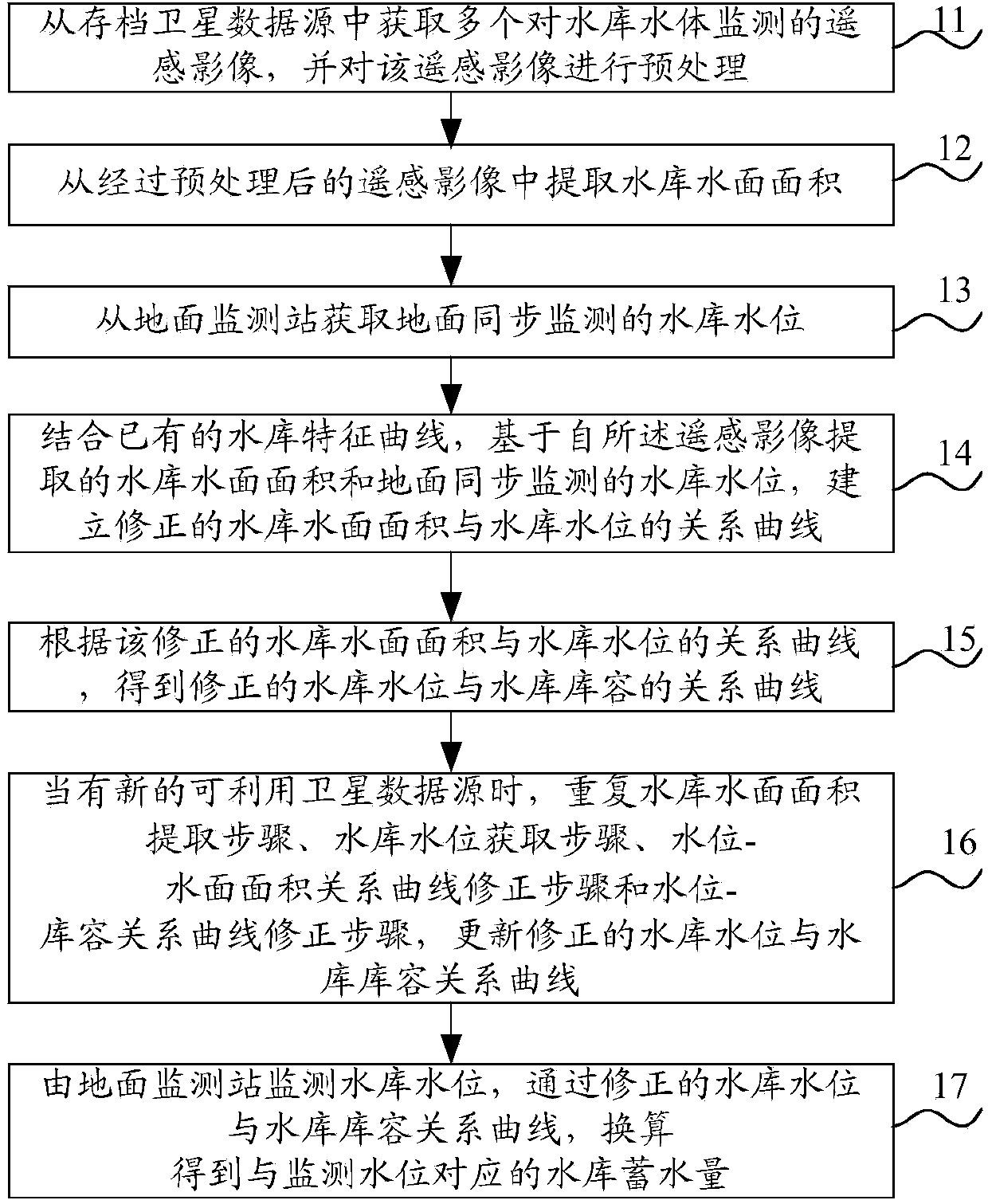
Reservoir water storage amount remote sensing and ground concurrent monitoring method
InactiveCN104613943AHigh precisionVolume measurement apparatus/methodsMeasuring open water depthSatellite dataData source
A reservoir water storage amount remote sensing and ground concurrent monitoring method is as follows: multi-period reservoir water monitoring remote sensing images can be acquired from archived satellite data sources, and the remote sensing images can be pretreated; reservoir water surface area can be extracted from the pretreated remote sensing images; ground synchronous monitoring reservoir water level can be acquired from a ground monitoring station; a correctional relation curve of the reservoir water level and the reservoir water surface area can be established; according to the correctional relation curve of the reservoir water level and the reservoir water surface area, a correctional relation curve of the reservoir water level and reservoir storage capacity can be acquired; when a new satellite data source is available, the above steps are repeated, the relation curve of the reservoir water level and the reservoir storage capacity can be updated and corrected; the reservoir water level can be monitored by the ground monitoring station, and the reservoir water storage capacity corresponding to the monitoring water level can be obtained by conversion according to the corrected relation curve of the reservoir water level and the reservoir storage capacity. The reservoir water storage amount remote sensing and ground concurrent monitoring method can effectively eliminate the influence of the characteristic curve changes of the reservoir after a long time running on reservoir water storage amount, and improves the accuracy of the reservoir water storage condition monitoring.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
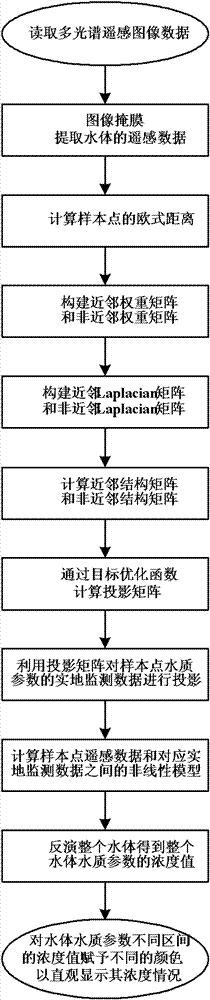
Manifold learning-based method for monitoring water quality by remote sensing
InactiveCN102128794ARealize water quality assessmentRealize monitoringComputing modelsScene recognitionHat matrixStudy methods
The invention discloses a manifold learning-based method for monitoring water quality by remote sensing, and particularly relates to a manifold learning-based method for monitoring water quality by multispectral remote sensing, which comprises the following steps of: training a sample point by a manifold learning method to obtain a projection matrix of water quality remote sensing data in low-dimensional embedded space; building a nonlinear model by using a support vector regression algorithm according to a feature matrix of the low-dimensional embedded space of the sample point and corresponding water quality parameter site monitoring data; and inverting an integral water body by utilizing the nonlinear model to obtain a concentration value of a water quality parameter of the integral water quality, and providing different colors for the water body according to different intervals in which the water body is positioned to display the concentration condition of the water quality parameter of the integral water body visually, so that the water quality evaluation and monitoring of the water body are realized. In the method, the essential law hidden in multispectral remote sensing image data is disclosed effectively, and the nonlinear problem of the water quality evaluation is solved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
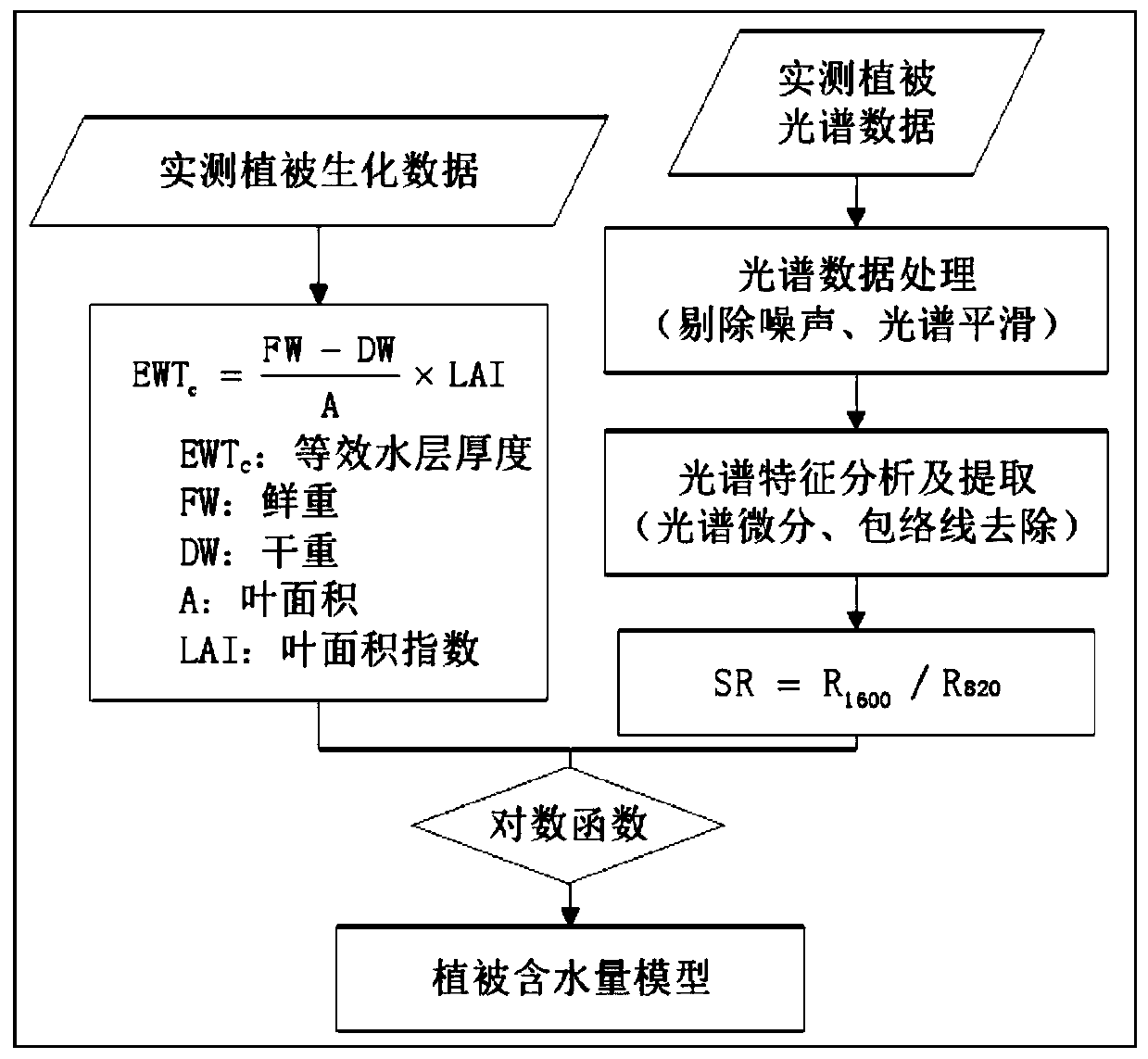
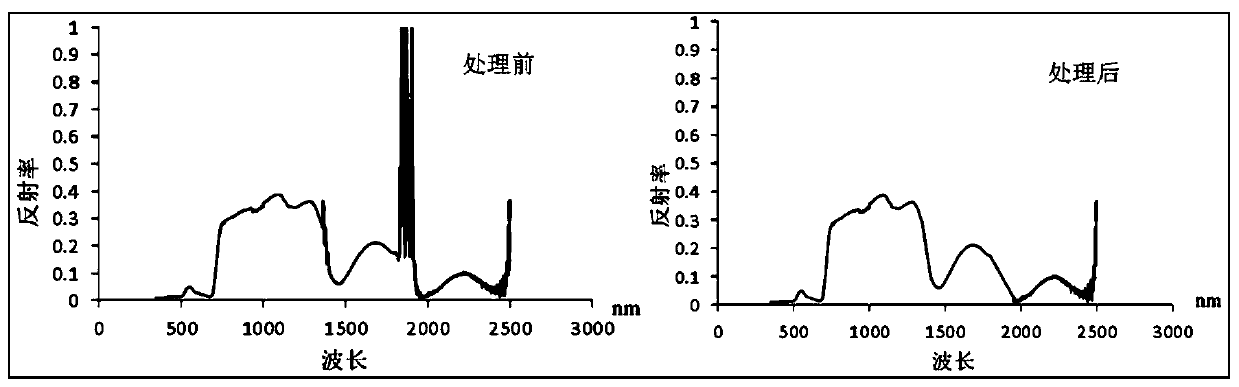
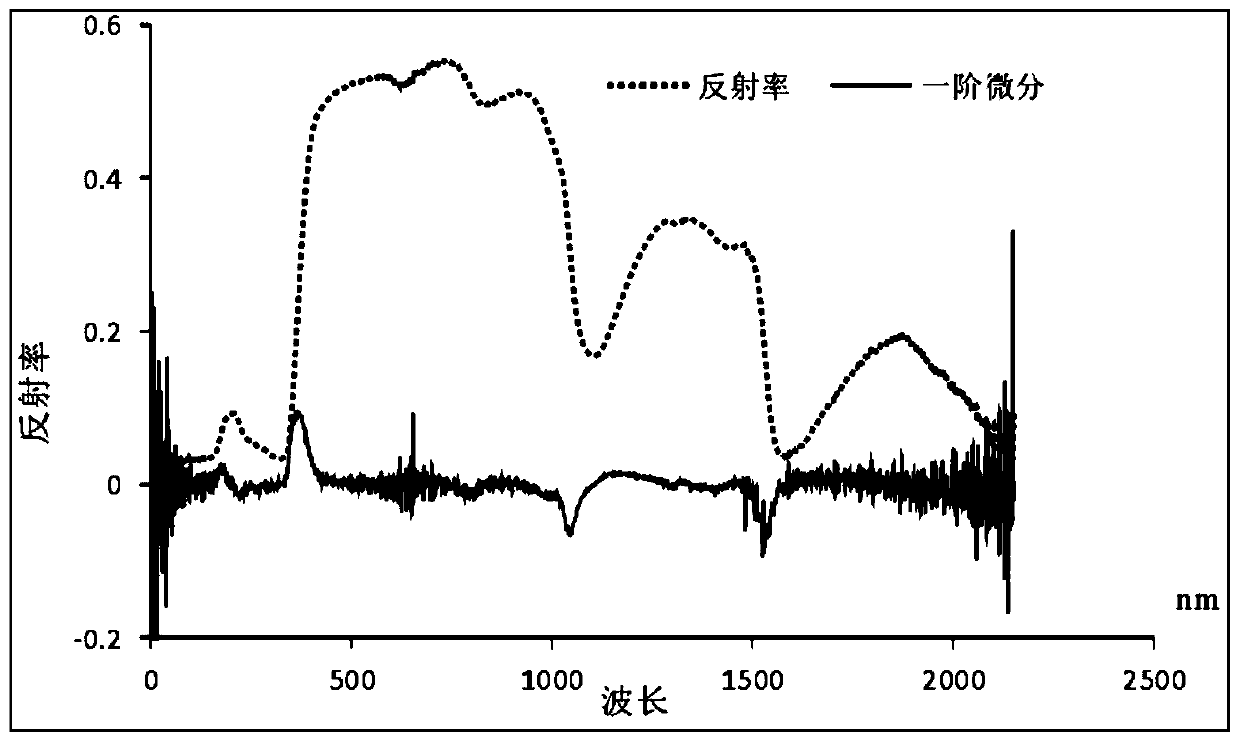
Land surface plant canopies ecological water content remote sensing retrieval method based on spectral analysis
InactiveCN110118742AAccurate portrayalMake up for the lack of accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansDry weightFeature extraction
The invention discloses a land surface plant canopies ecological water content remote sensing retrieval method based on spectral analysis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) actually measuring plant canopies spectrum data and biochemical data, wherein the biochemical data comprises fresh weight, dry weight and leaf area; (2) preprocessing the actually measured spectrum data and performing spectrum feature extraction; performing moisture noise removing, spectrum differential computation and envelope line removing; (3) computing and extracting the required plant index according to theactually measured reflecting spectrum feature; (4) preforming correlation analysis on the plant field actually measured spectrum data and the biochemical data, and establishing the model of the computed plant index and the plant water content; and (5) analyzing the remote-sensing image spectrum feature, and realizing the plant canopies ecological water remote-sensing quantitative retrieval by combining the plant water content model established through the actually measured data. By utilizing the method disclosed by the invention, the dynamic monitoring on the plant canopies ecological water content can be realized, and the monitoring accuracy is high.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
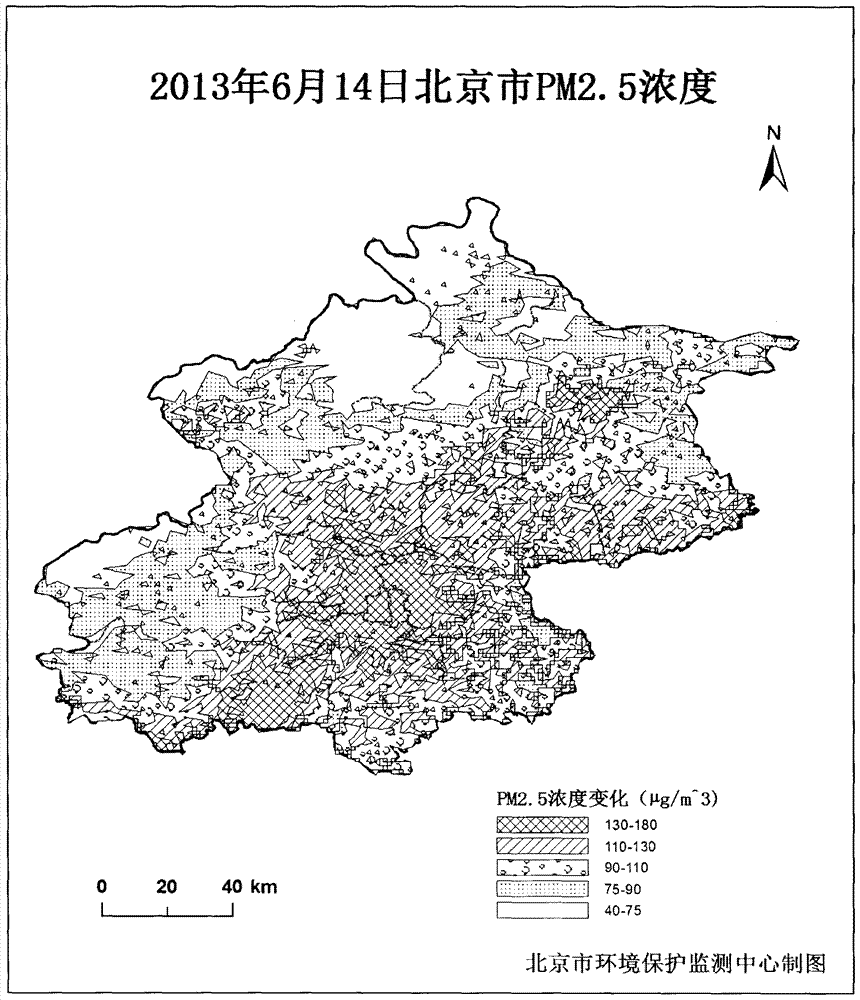
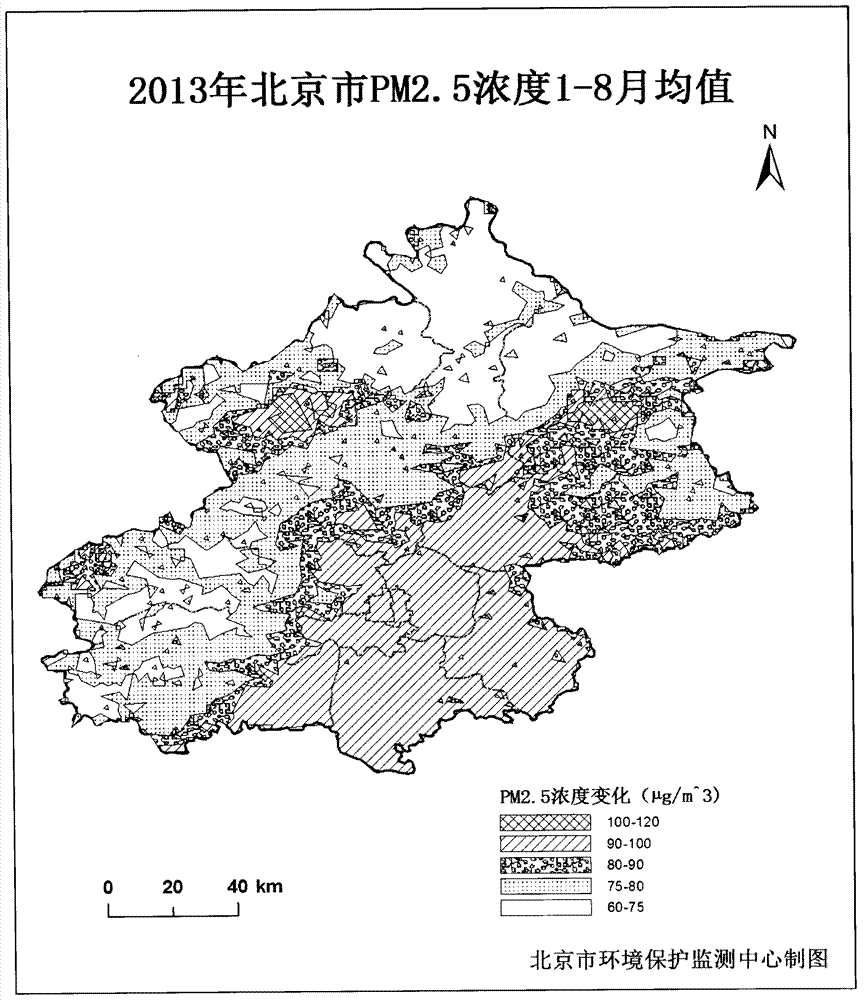
Method for monitoring mass concentration of near-surface fine particulate matter by satellite remote sensing
InactiveCN104280324AInversion data is accurateImprove accuracyParticle suspension analysisExtinctionFine particulate
The invention relates to a method for monitoring mass concentration of near-surface fine particulate matter by satellite remote sensing. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring radiation values of visible light and near-infrared light channels of a satellite sensor; calculating the appearance albedo of each piece of monochromatic light through the radiation value data of the monochromatic light; removing earth surface and atmosphere molecule contribution by virtue of the appearance albedo of each piece of monochromatic light, and calculating to obtain extinction contribution quantity of aerosol of each pixel; acquiring a PM2.5 mass concentration numerical value monitored on the surface, and performing linear fitting on the PM2.5 mass concentration numerical value with the extinction contribution quantity of aerosol measured by a corresponding satellite at a monitoring point, thereby obtaining a linear relation between the monitored PM2.5 mass concentration and the extinction contribution quantity of aerosol observed by the satellite; and finally, obtaining the satellite PM2.5 mass concentration of each pixel according to the linear relation. According to the method, the regional distribution and transmission change of the mass concentration of the near-surface particulate matter can be intuitively obtained, and a data support is provided for atmospheric pollution control.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENT
Regional terrestrial ecosystem respiratory monitoring method based on remote sensing
InactiveCN103513290AHigh precisionSolve the problem of lack of expressivenessOptical detectionGrowing seasonTime dynamics
The invention provides a regional terrestrial ecosystem respiratory monitoring method based on remote sensing. The monitoring method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining time series satellite remote sensing data within a region; S2, performing remote sensing retrieval to key parameters; S3, quantifying key physiological and ecological parameters of different vegetation forms based on land cover or land utilization data; S4, obtaining meteorological interpolation data of time series; S5, carrying out cloud removal to obtain vegetation growing season curve without noise impact; S6, determining the annual respiratory capacity of the regional terrestrial ecosystem. The method is based on the time series remote sensing data, considers spatial difference of the vegetation form, determines the ecosystem respiratory algorithm within the region, solves the problem that the regional terrestrial ecosystem respiratory monitoring only relies on meteorological data but is insufficient to express heterogeneous information of the land cover within large scale, improves the precision of regional scale ecosystem respiratory estimation, and accurately and quantitatively describes temporal dynamics of the respiration in different ecosystems.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
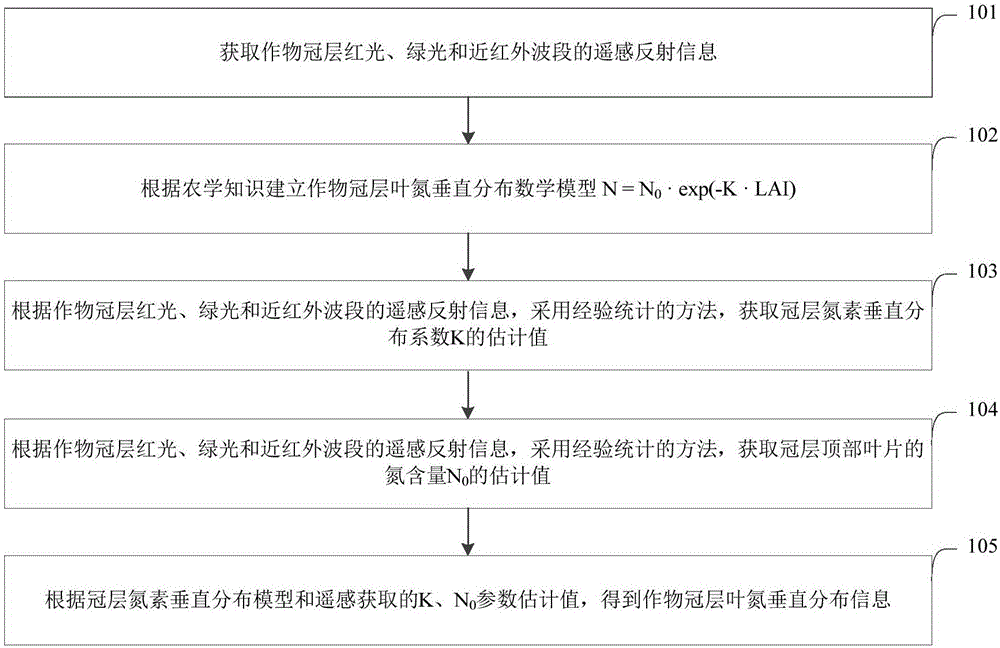
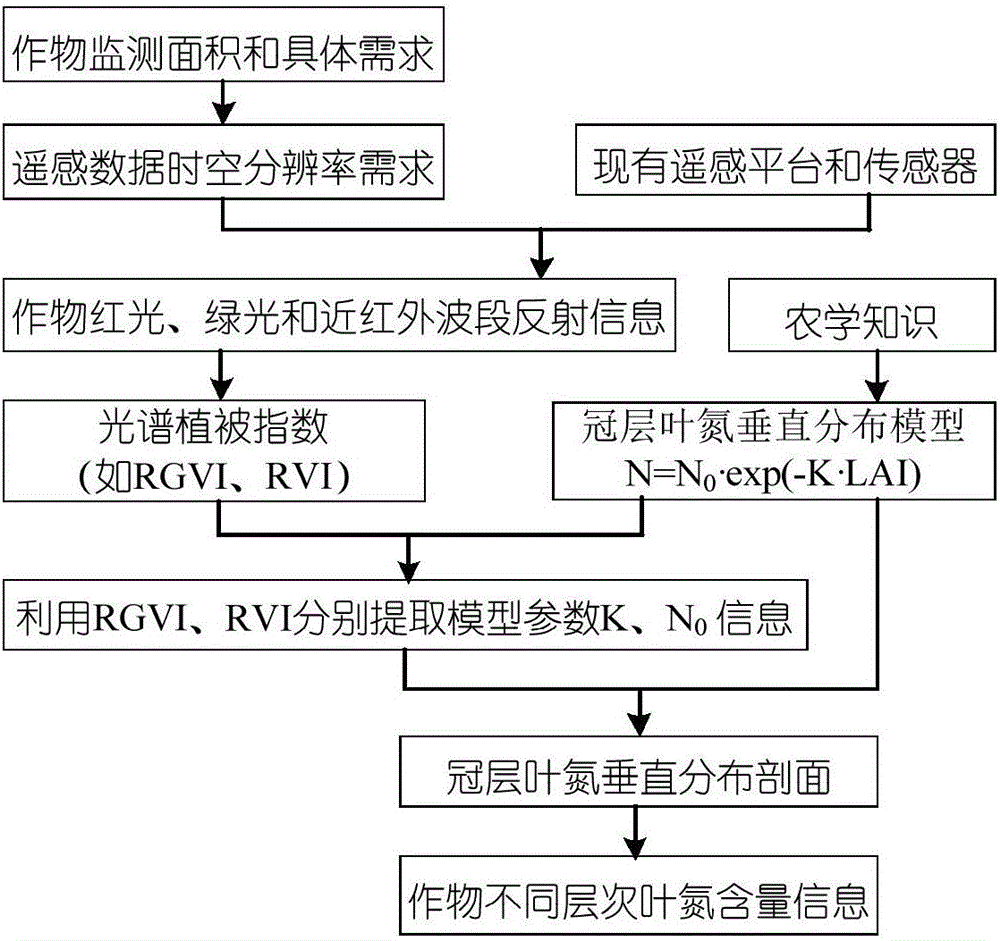
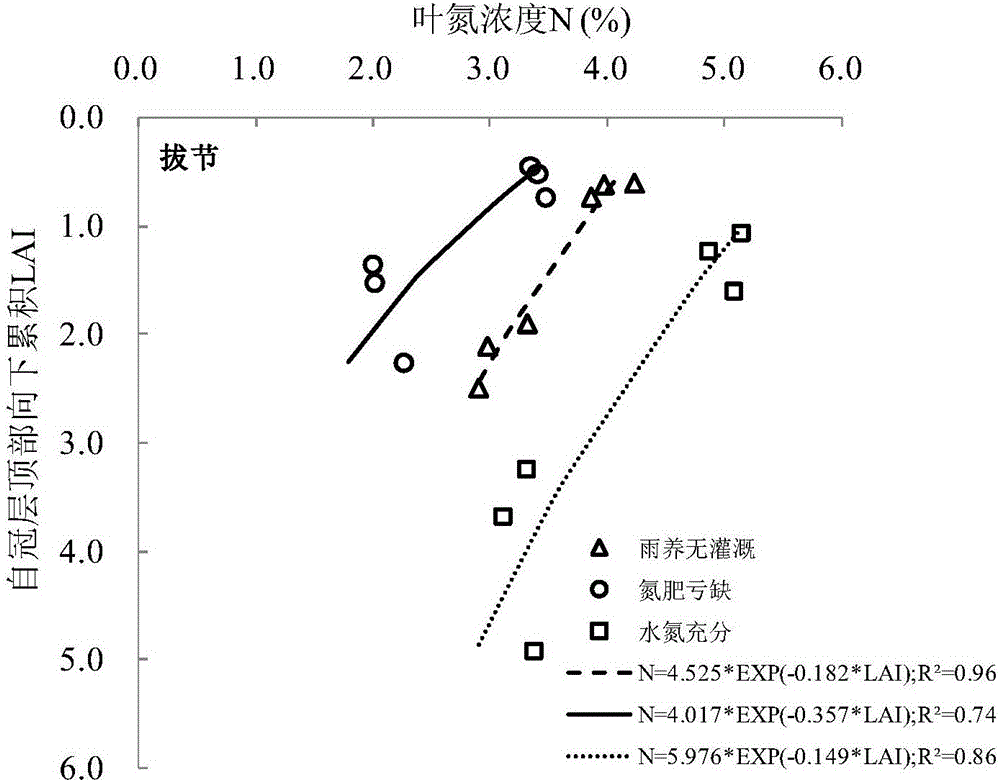
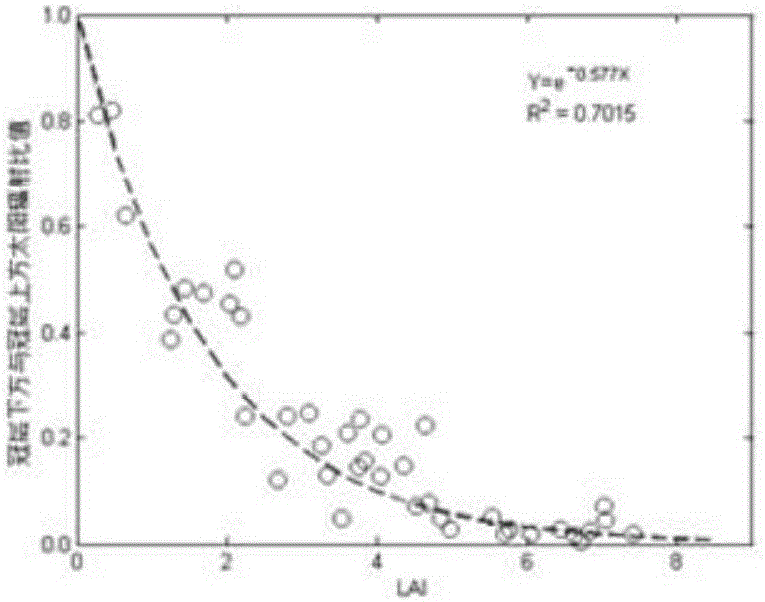
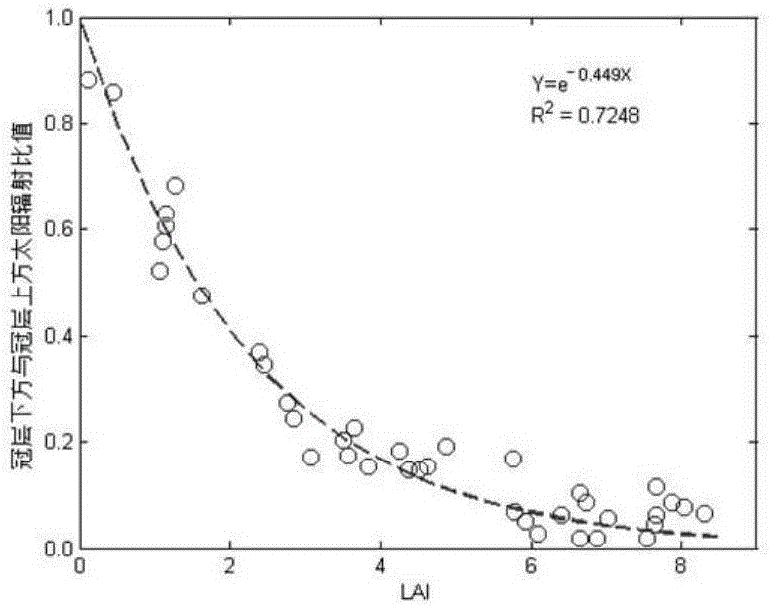
Canopy-leaf-nitrogen vertical distribution detection method and device based on remote sensing and agronomy knowledge
ActiveCN106525731ARealize high-precision remote sensing detectionMechanism strong and reliableColor/spectral properties measurementsNon destructiveMathematical model
The invention provides a canopy-leaf-nitrogen vertical distribution detection method and device based on remote sensing and agronomy knowledge. The method includes the steps that the remote sensing reflection information of red light, green light and near-infrared bands of a crop canopy is obtained; according to the agronomy knowledge, a crop-canopy-leaf-nitrogen vertical distribution mathematical model is established; according to the remote sensing reflection information of the red light, green light and near-infrared bands of the crop canopy, an empirical statistic method is adopted, and estimation values of the canopy-nitrogen vertical distribution model parameter K (namely, the vertical distribution coefficient) and N <0> (namely, the nitrogen content of canopy top leaves) are obtained; according to the canopy-nitrogen vertical distribution model and the estimation values of the parameter K and the N <0> obtained through remote sensing, crop-canopy-leaf-nitrogen vertical distribution information is obtained. According to the canopy-leaf-nitrogen vertical distribution detection method and device, the rapid non-destructive monitoring advantages of the remote sensing technology and the advantages of the mechanism performance and the universality of an agronomy knowledge model are fully used, and high-accuracy remote sensing detection of the different-level leaf-nitrogen concentration of crops is achieved; in other words, high-accuracy remote sensing detection of crop-leaf-nitrogen vertical distribution is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Under-forest illumination intensity estimation method based on remote sensing
ActiveCN107436193ALow costLarge scalePhotometry using electric radiation detectorsEstimation methodsGlobal solar radiation
The invention discloses an under-forest illumination intensity estimation method based on remote sensing, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, determining a to-be-detected region and illumination-related parameters, wherein the illumination-related parameters comprise the total time ht of the possible solar radiation in one day and the position parameters of the sun; 2, calculating the total solar radiation above a canopy, wherein the total solar radiation above the canopy in a to-be-detected region comprises the solar direct solar radiation in the direction of a local incidence angle, the scattered radiation and the reflected radiation of the ground surface, i.e., Gi=Bi+Di+Ri; 3, carrying out the inversion of a leaf area index through a remote sensing image, and calculating and obtaining the under-forest illumination intensity based on the Beer-Lambert law according to the total solar radiation above the canopy. The method provided by the invention is easy to implement, is low in cost, and is high in accuracy.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
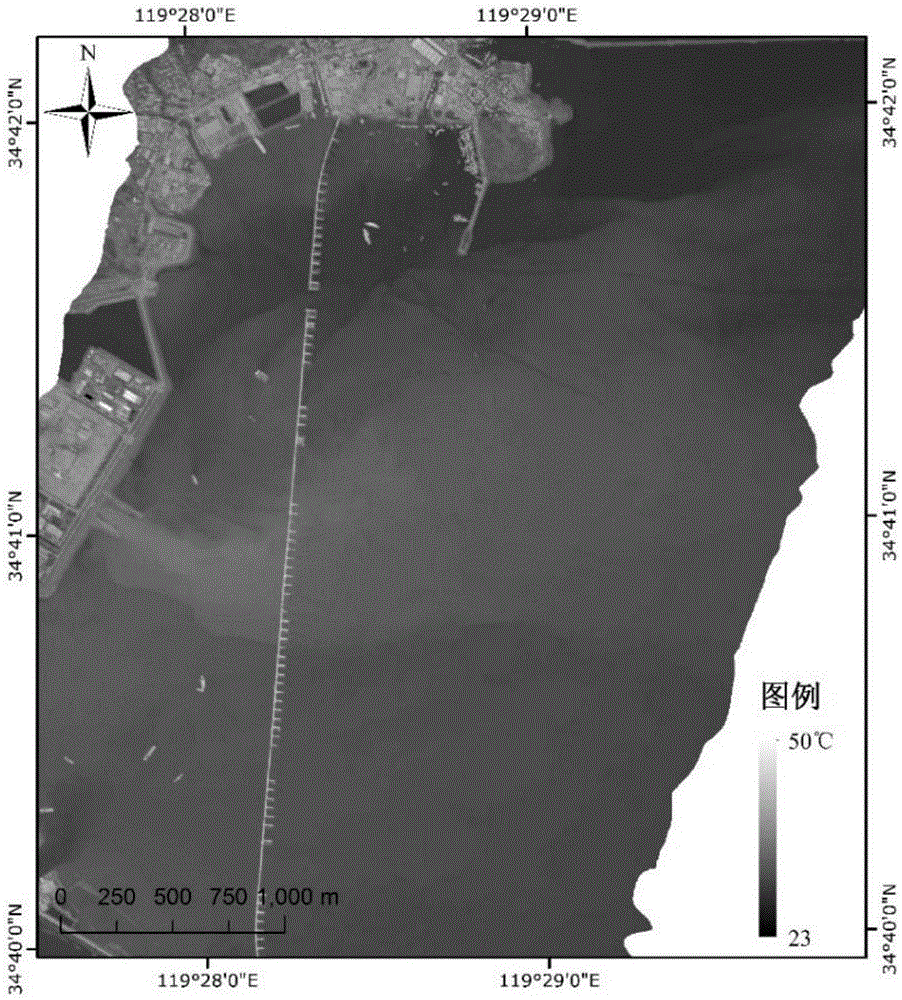
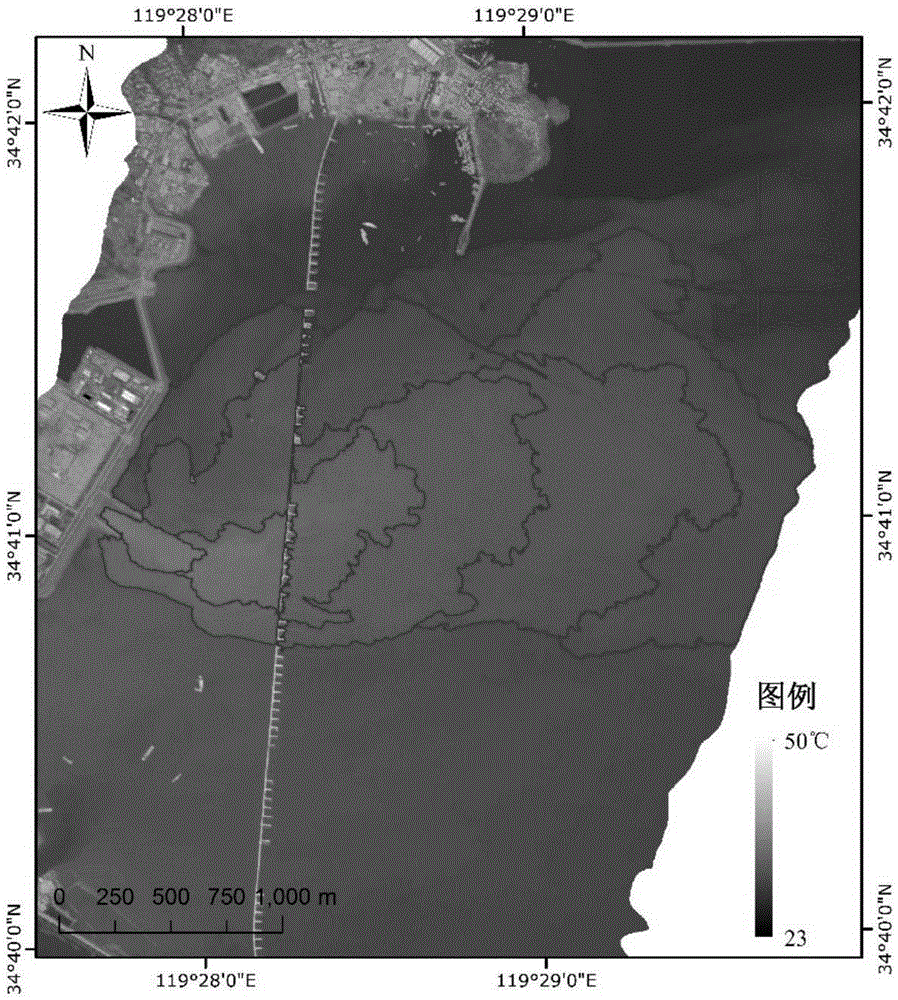
Extraction method for offshore industrial warm discharge water based on aerial remote sensing
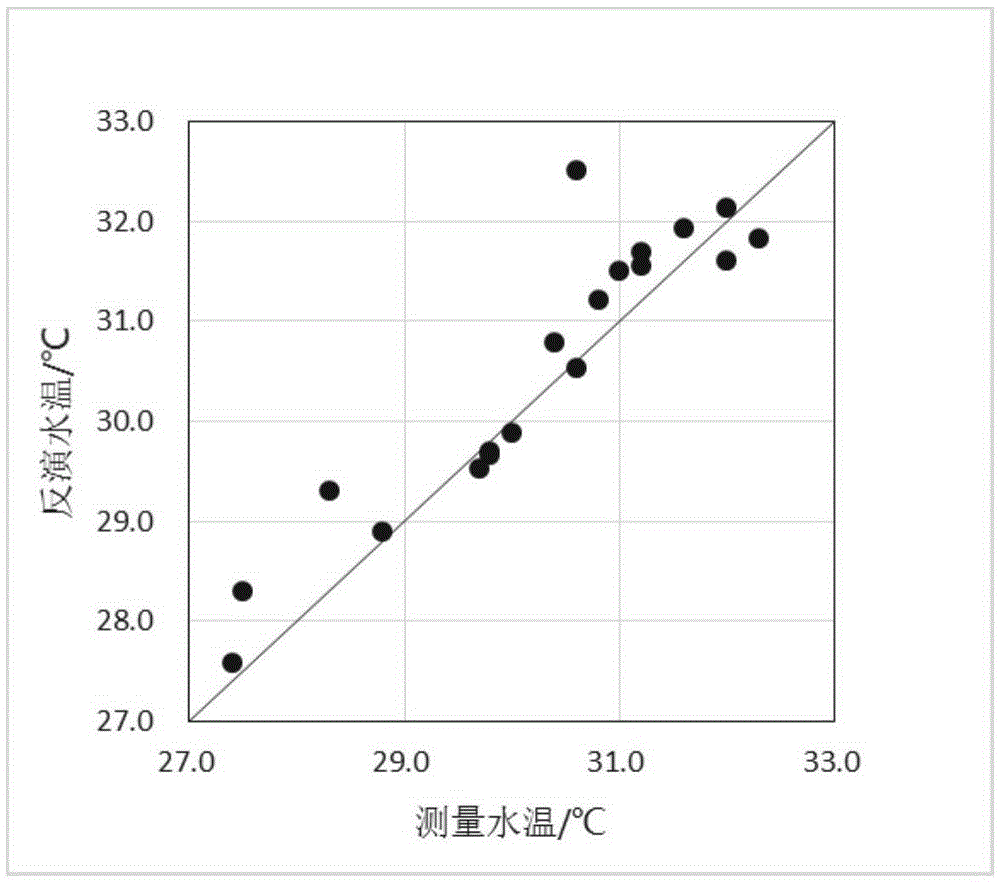
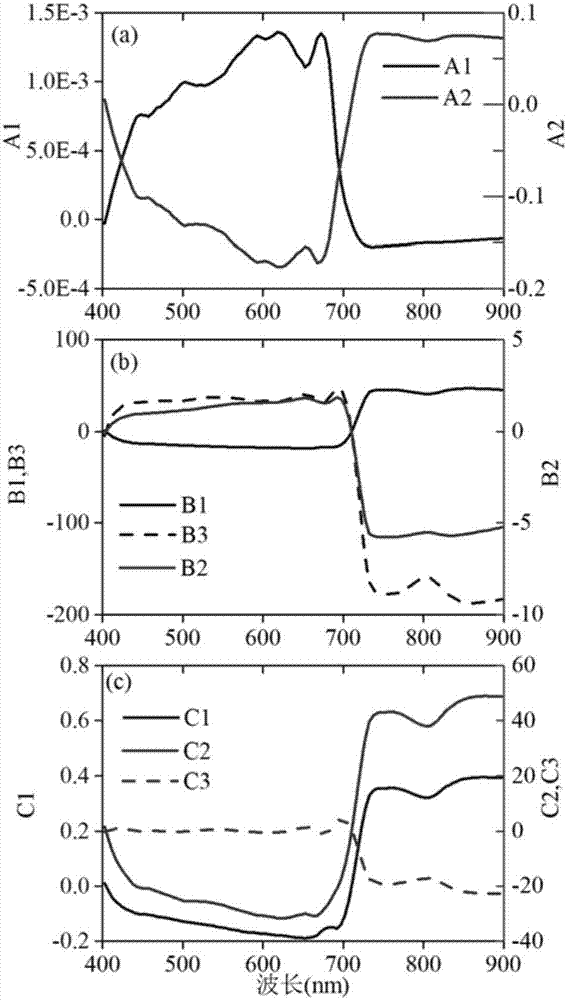
The invention discloses an extraction method for offshore industrial warm discharge water based on aerial remote sensing. The method comprises the following concrete steps: 1) calculating atmospheric parameters by utilizing MODTRAN5.3 software, inputting the atmospheric parameters to a simplified form of an atmospheric radiative transfer equation and subjecting aerial thermal infrared remote sensing data to sea-surface temperature inversion to transform a radiation brightness temperature of a pixel into a temperature; 2) comparing the sea-surface temperature obtained by inversion in the step 1) with a synchronously-measured ground temperature, calculating an error of temperature inversion results, and correcting the results by utilizing the synchronously-measured ground temperature if the error is greater than 0.5 K; 3) extracting a temperature-rising area by using an image segmentation technology; and 4) simulating a sea-surface natural temperature in the temperature-rising area based on a sea-surface temperature in a non-temperature-rising area, subtracting the simulated sea-surface natural temperature in the temperature-rising area with the sea-surface temperature in the same area so as to obtain the temperature-rising value of the temperature-rising area. The extraction method provided by the invention has the following advantages: inversion accuracy is high; and the needs of the offshore industrial warm discharge water for temporal resolution and spatial resolution are met.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
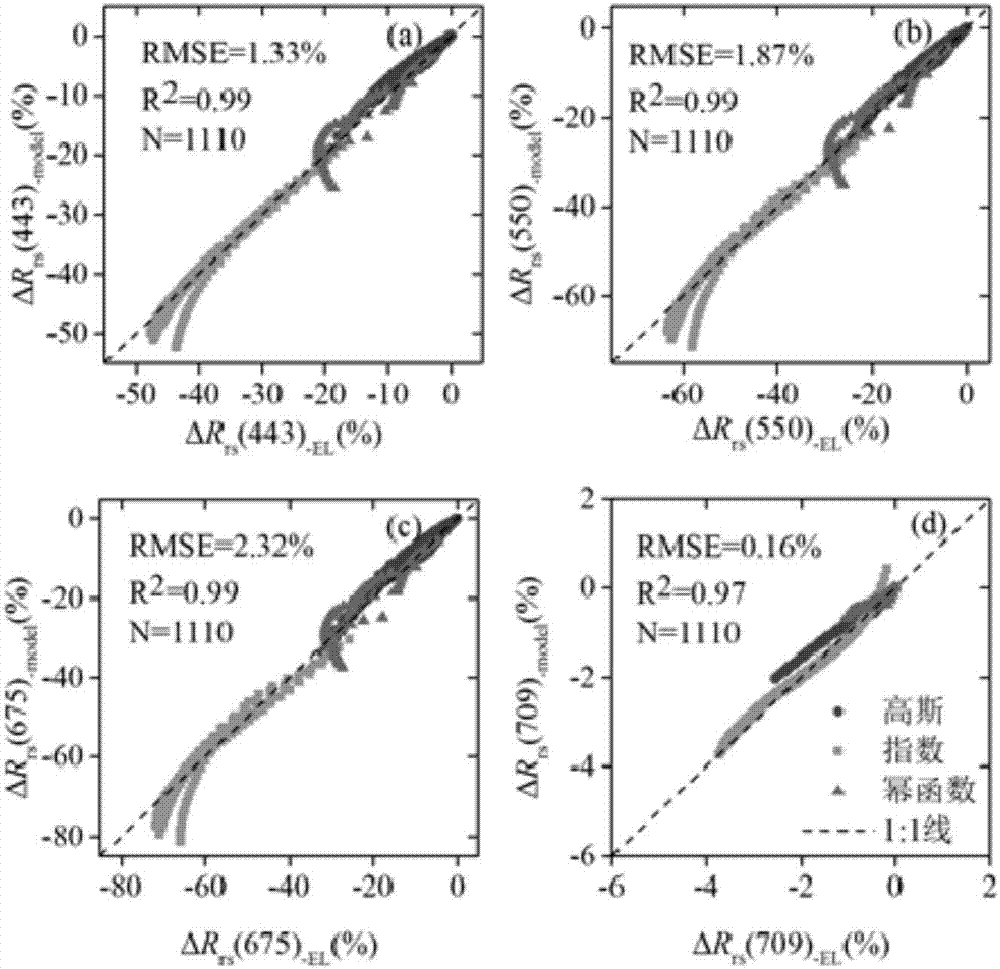
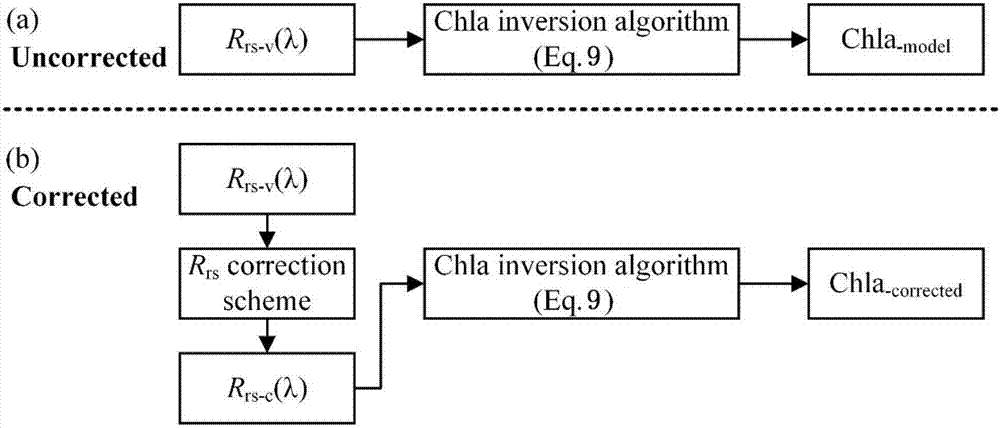
Correcting method for remote sensing reflectivity of vertical inhomogeneous alga water
ActiveCN107014779AHigh precisionAccurate acquisitionScattering properties measurementsComputer scienceCorrection method
The invention relates to a correcting method for a remote sensing reflectivity of vertical inhomogeneous alga water. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the remote sensing reflectivity under the vertical inhomogeneous condition of different alga vertical direction patterns and a corresponding relative error Delta Rrs of the remote sensing reflectivity under the vertical homogeneous condition; establishing a remote sensing reflectivity correcting algorithm for the vertical inhomogeneous alga water according to a relation between the Delta Rrs and the structure parameters of different alga vertical direction patterns; regarding the remote sensing reflectivity of vertical inhomogeneous alga water as the remote sensing reflectivity of vertical homogeneous water. The traditional lake water color remote sensing is established on the basis of the assumption of vertical homogeneous water, but under a practical condition, the change in the vertical direction of the alga in eutrophic lake is large. According to the method provided by the invention, the influence of the vertical inhomogeneous alga water on the application precision of the traditional lake water color remote sensing algorithm can be reduced and the water remote sensing reflectivity under the vertical homogeneous alga distribution condition and the normalized equivalent condition can be acquired.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
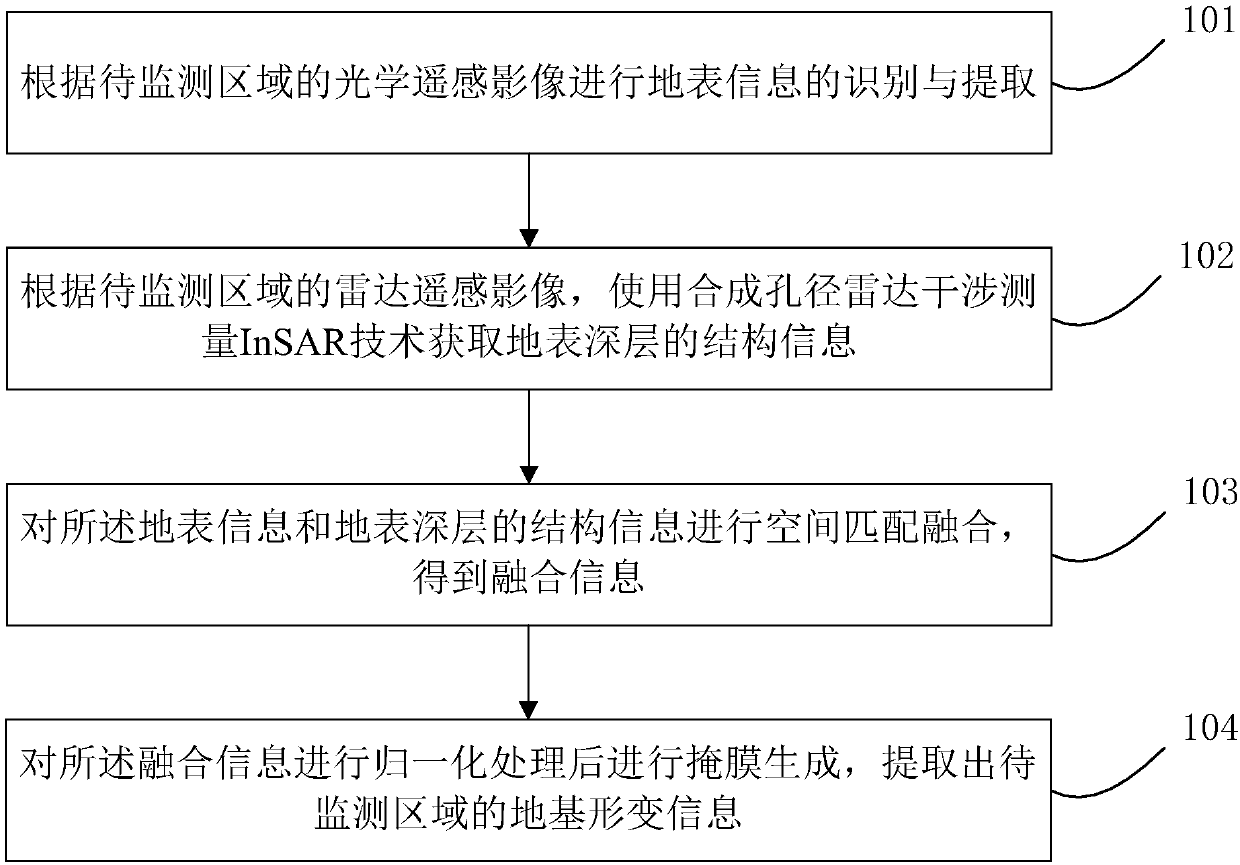
Safety monitoring method and system for traffic infrastructure
ActiveCN107944377AImprove traffic safetyRealize high-precision monitoringCharacter and pattern recognitionSynthetic aperture radarRadar
The invention discloses a safety monitoring method and system for traffic infrastructure. In the method, road extracting and monitoring technology combining high-resolution optical remote sensing technology and synthetic aperture radar interferometry technology is adopted; optical remote sensing images are used to carry out earth surface information identification and extraction, earth surface classification, road extraction and the like; based on the radar remote sensing images, InSAR technology is used to obtain deeper structural information, such as settlement, deformation and the like of transportation facilities. Through combination of optical remote sensing and radar remote sensing, recognition of road surface conditions and high-precision monitoring of earth surface deformation conditions of traffic facilities can be achieved in a coordinated manner, and effective support can be provided for improving road safety.
Owner:赤湾通信卫星应用技术(深圳)有限公司
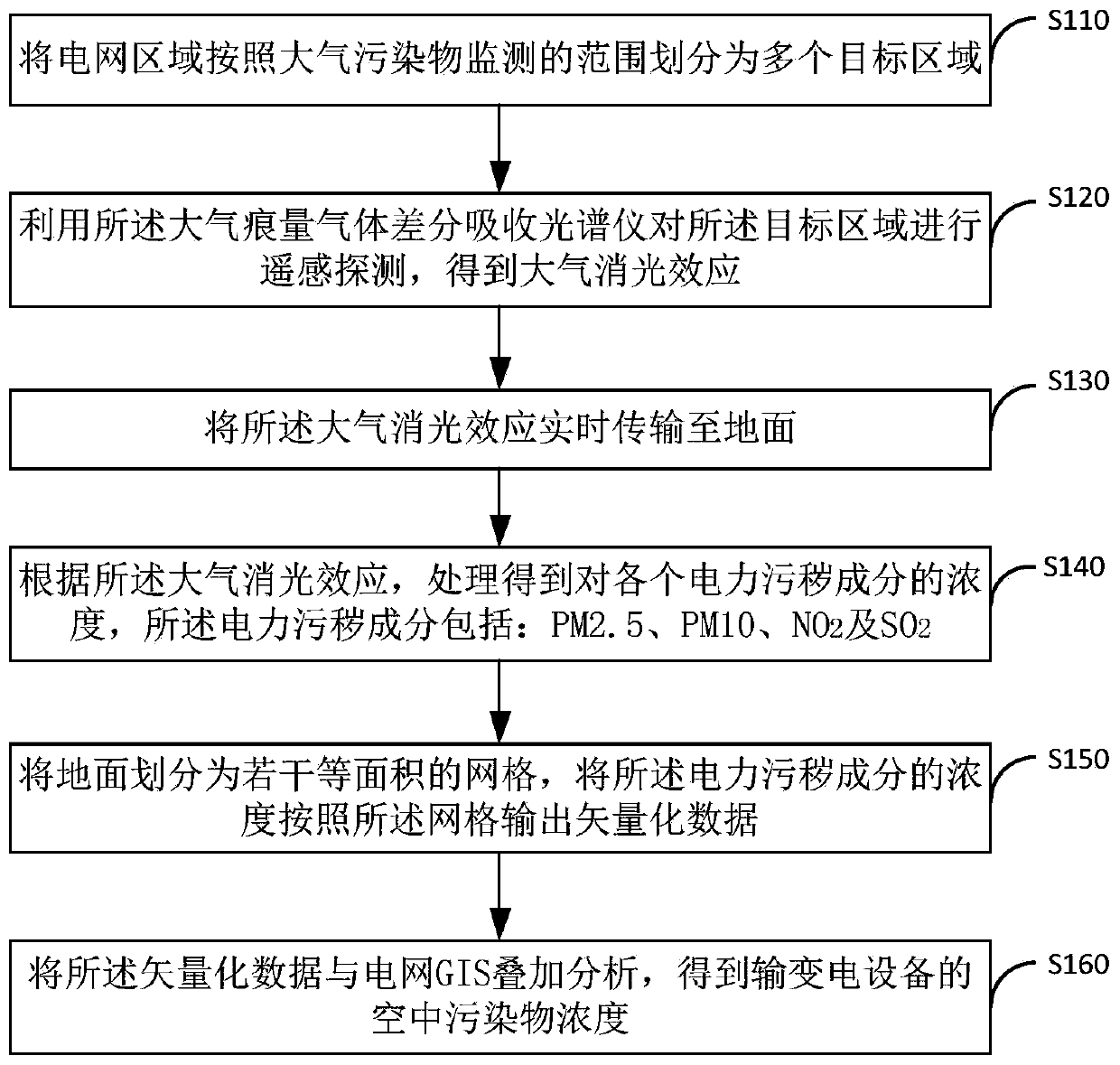
Method and system for monitoring concentration of power grid pollutant based on satellite remote sensing
ActiveCN110274916AThe acquisition process is objective and stableImprove efficiencyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationColor/spectral properties measurementsExtinctionData acquisition
The invention discloses a method and a system for monitoring the concentration of a power grid pollutant based on satellite remote sensing. An environmental satellite carries an atmospheric trace gas differential absorption spectrometer, and a power grid area is divided into a plurality of target areas according to the monitoring range of atmospheric pollutants; remote sensing detection on a target area is performed by using the atmospheric trace gas differential absorption spectrometer to obtain an atmospheric extinction effect; the atmospheric extinction effect is transmitted to the ground in real time; the concentration of each electric power pollution component is processed and obtained according to the atmospheric extinction effect; the ground is divided into a plurality of grids with equal areas, and the vectorized data are output according to the concentration of the power pollution components; and the superposition analysis on the vectorized data and the power grid GIS is performed to obtain the air pollutant concentration. According to the method, each target area can be remotely sensed and detected in a high frequency and large range, each power pollution component can be accurately analyzed through the atmospheric extinction effect data, the quasi-real-time monitoring of the spatial distribution of each pollutant of the power grid is achieved, the data acquisition process is objective and stable, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
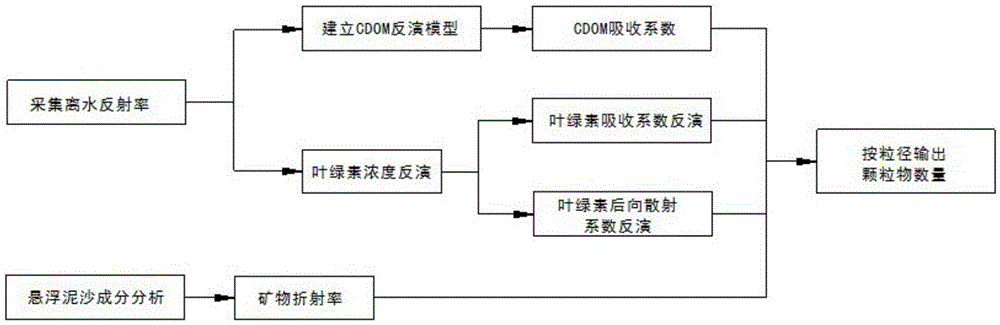
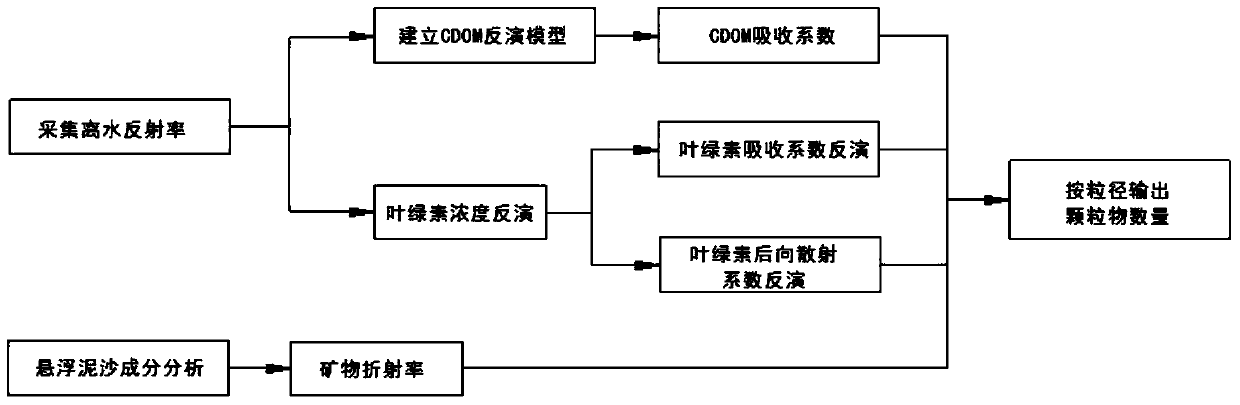
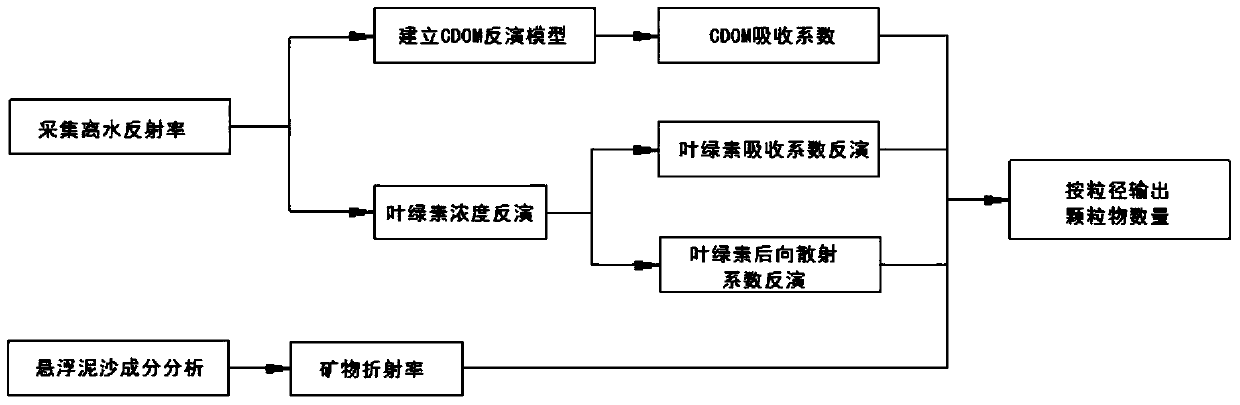
Method for monitoring particle size distribution of suspended sediment in water
ActiveCN105606498AIncrease profitEasy to implementParticle size analysisMineral particlesRefractive index
The invention provides a method for monitoring particle size distribution of suspended sediment in water. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring off-water remote-sensing reflectance of an inspection area and inverting a CDOM (Colored Dissolved Organic Matter) absorption coefficient of the inspection area according to the off-water remote-sensing reflectance; (2) inverting chlorophyll concentration of alga in the inspection area according to the off-water remote-sensing reflectance; (3) calculating a chlorophyll absorption coefficient and a chlorophyll backscattering coefficient according to the chlorophyll concentration; (4) analyzing mineral compositions in the suspended sediment, acquiring the particle diameter and complex refractive index of minerals, and calculating the backscattering coefficient and absorption coefficient of mineral grains via the relationship between the off-water remote-sensing reflectance and the backscattering coefficient and absorption coefficient of the mineral grains in Mie theoretical formula; and (5) constructing an ill conditioned equation according to the backscattering coefficient and absorption coefficient of the mineral grains and the off-water remote-sensing reflectance and acquiring information about the particle size distribution of the minerals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
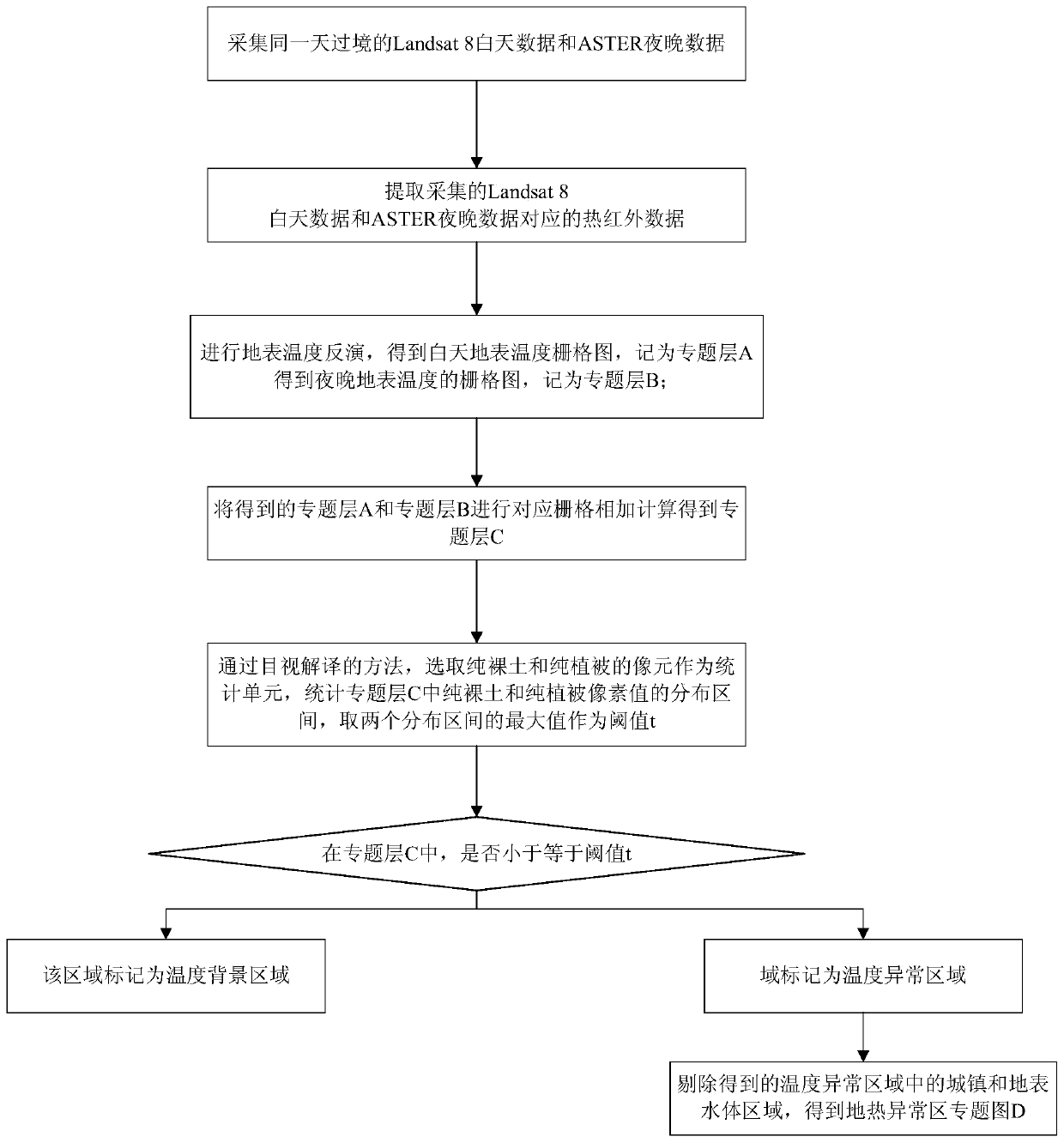
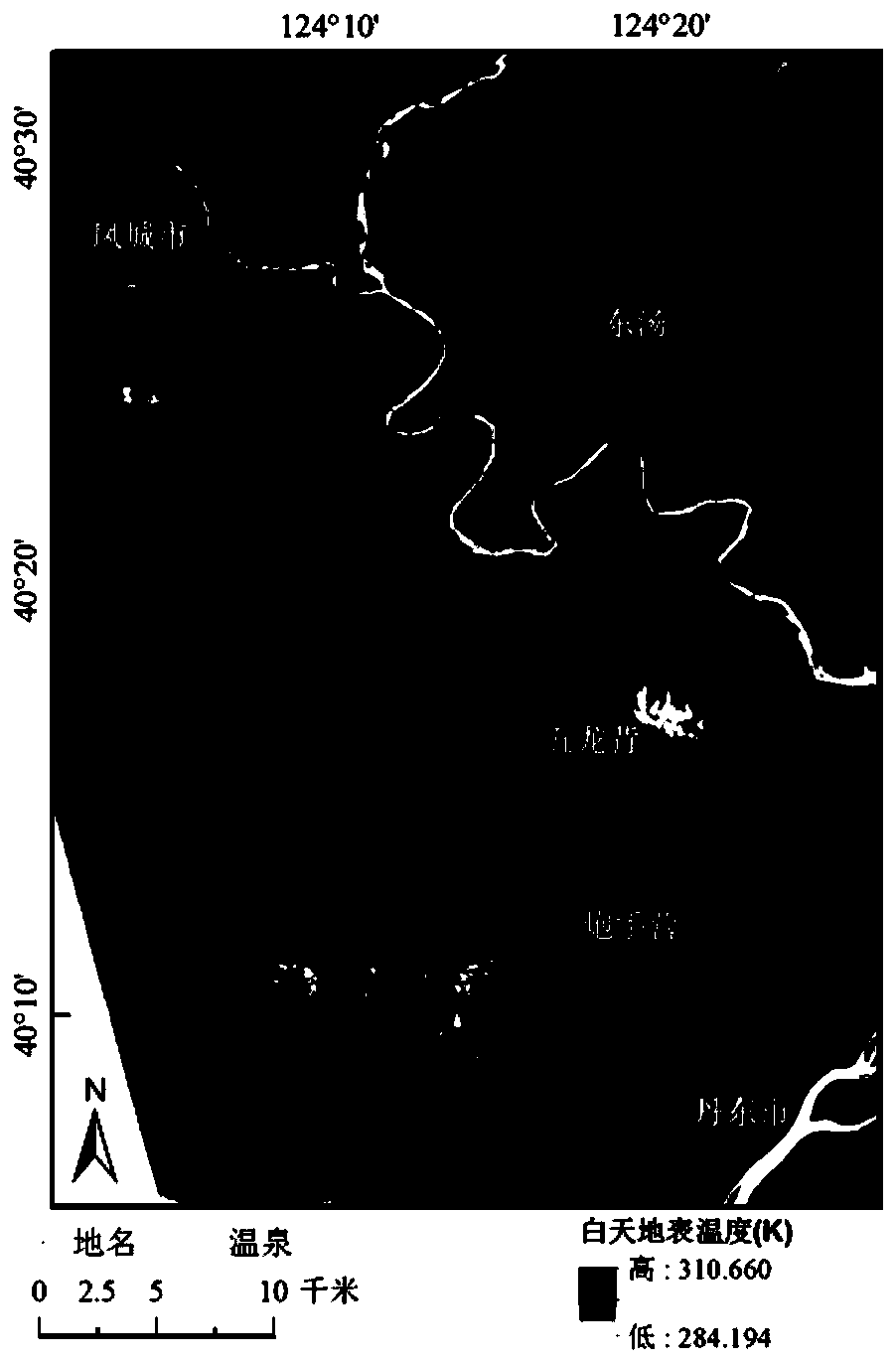
Method for delineating geothermal anomalies by using daytime and nighttime thermal infrared remote sensing
InactiveCN109901237AQuick searchImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryGeological measurementsUrban regionSurface water body
The invention provides a method for delineating geothermal anomalies by using daytime and nighttime thermal infrared remote sensing. The method includes the following steps that: Landsat 8 daytime data and ASTER nighttime data of the same day are acquired; the data are preprocessed; surface temperature inversion is performed, so that a daytime surface temperature grid map and a nighttime surface temperature grid map are obtained; corresponding grids are added, so that a thematic layer C can be obtained; a threshold t is calculated; in the thematic layer C, regions of which the temperature is lower than or equal to the threshold t are marked as temperature background regions, and regions of which the temperature is higher than the threshold t are marked as temperature anomaly regions; and urban regions and surface water body regions are removed from the temperature anomaly regions, so that a geothermal anomaly area thematic map D is obtained. According to the method of the invention, two kinds of thermal infrared remote sensing products with high spatial resolution are optimally selected so as to be used jointly, and therefore, it can be ensured that surface temperature products canhave high spatial resolution; daytime surface temperature and nighttime surface temperature are added, so that the relative cold and hot anomalies of natural objects at daytime and nighttime are eliminated, and surface high temperature anomalies under the influence of geothermy or human activities are highlighted; and the threshold is calculated according to bare soil and vegetations, so that surface temperature background values can be effectively suppressed, and surface temperature abnormal values are highlighted.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军研究院工程设计研究所严寒冻土设防工程设计站
Field remote sensing system for real-time quantification of total suspended solids (TSS) in surface waters from above-water spectral measurements
ActiveUS20190300412A1Easy to useImprove signal-to-noise ratioWater treatment parameter controlRaman/scattering spectroscopyCredit cardEngineering
A portable remote sensing system for real-time assessments of total suspended solids (TSS) in surface waters using above-water hyperspectral measurements. The system combines a miniature high signal-to-noise ratio spectrometer coupled to a credit card-size computer, lens, rechargeable battery, GPS, display panel, and dedicated software to derive TSS from above-water spectral measurements.
Owner:ARMSTRONG ROY
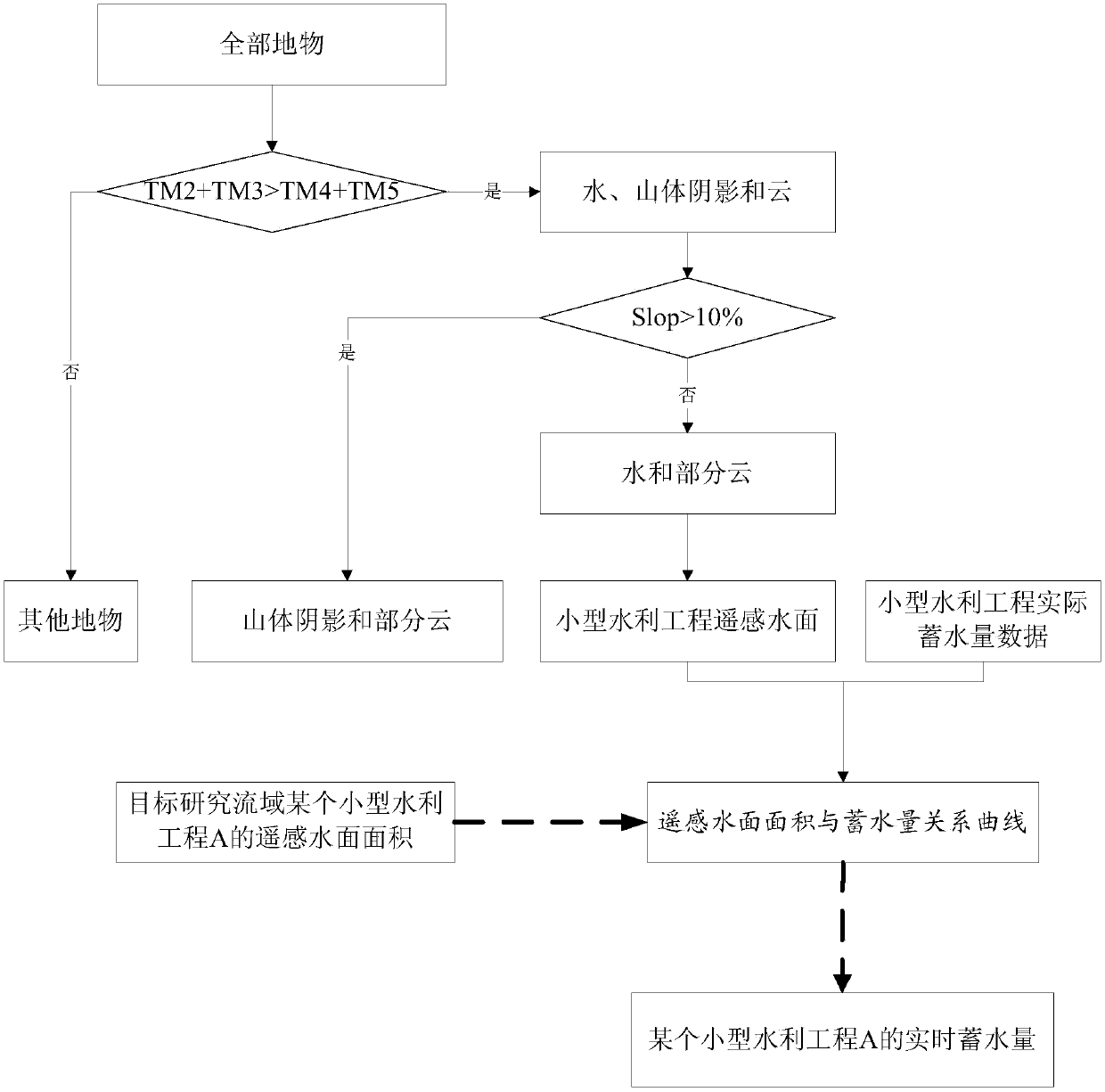
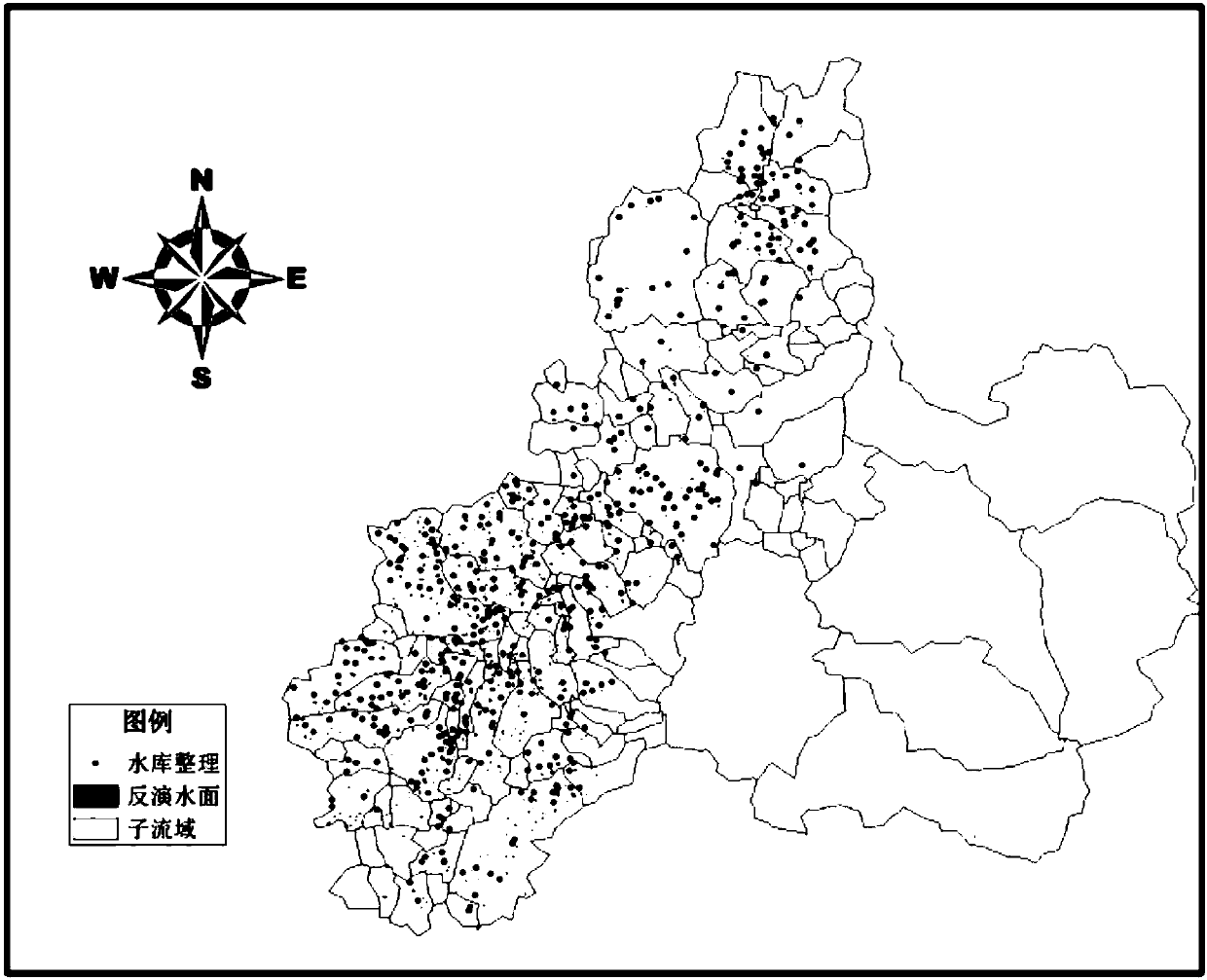
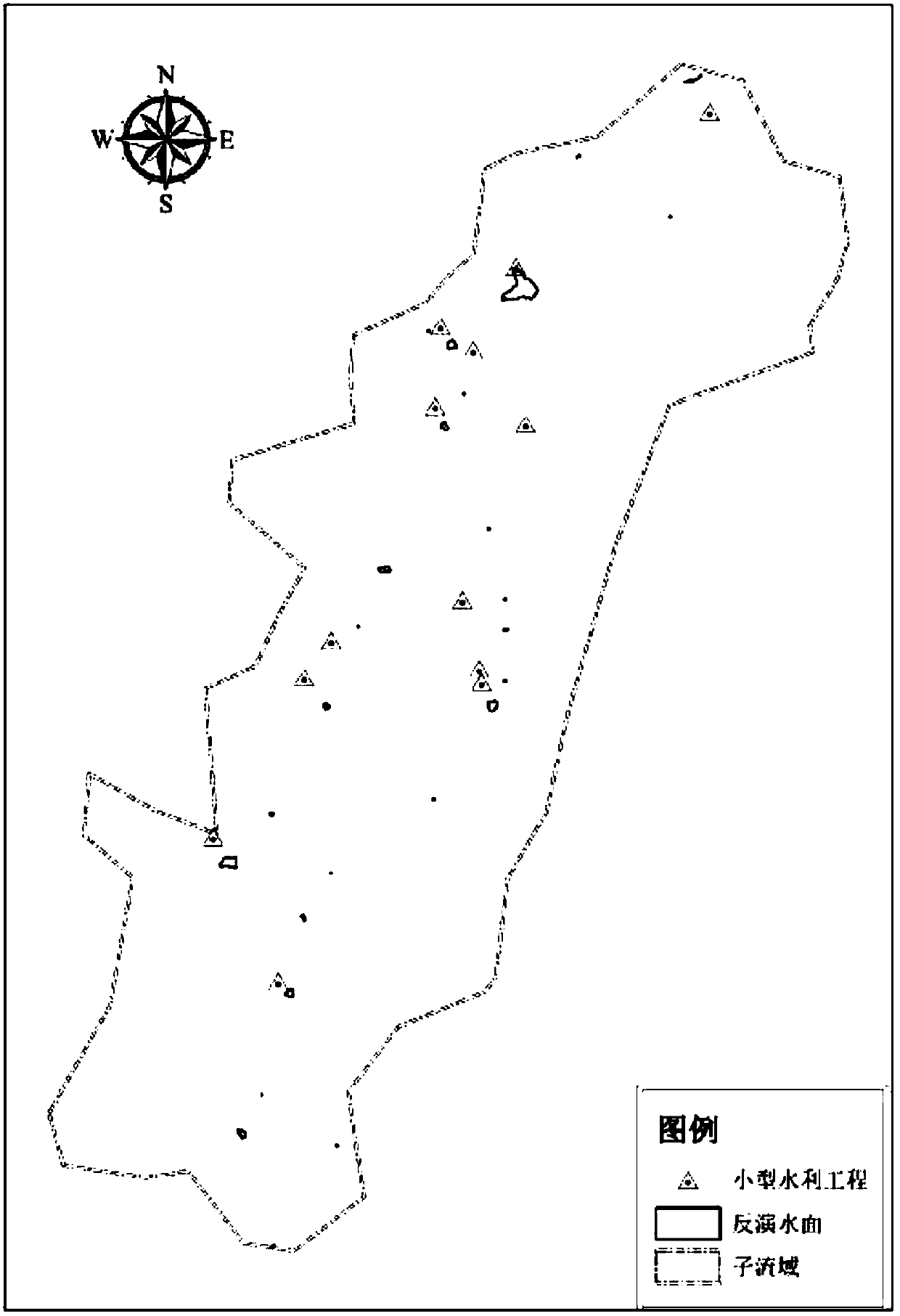
Small water conservancy project water surface area and water storage determination method based on remote sensing
InactiveCN107665338AHigh precisionImprove the accuracy of water surface distributionData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing dataWater storage
The invention discloses a small water conservancy project water surface area and water storage determination method based on remote sensing and relates to the remote sensing inversion / reservoir waterresource information / hydrologic monitoring field. The method comprises steps that remote sensing data including a target research basin and the distribution position and actual water storage data of all the small water conservancy projects in the target research basin are acquired; a water surface distribution map of the target research basin is extracted; remote sensing inversion maps of surfacesof the small water conservancy projects are acquired; quality check on remote sensing water surface area data of the small water conservancy projects in the water surface remote sensing inversion maps of water bodies stored by the small water conservancy projects is carried out; a remote sensing water surface area and water storage relationship curve of the target research basin is drafted through taking the remote sensing water surface areas of the small water conservancy projects as abscissas and actual water storage of the small water conservancy projects as ordinates in a coordinate system. The method is advantaged in that water surface extraction precision of the small water conservancy projects is improved, good universality is realized, and operation is simple and easy.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
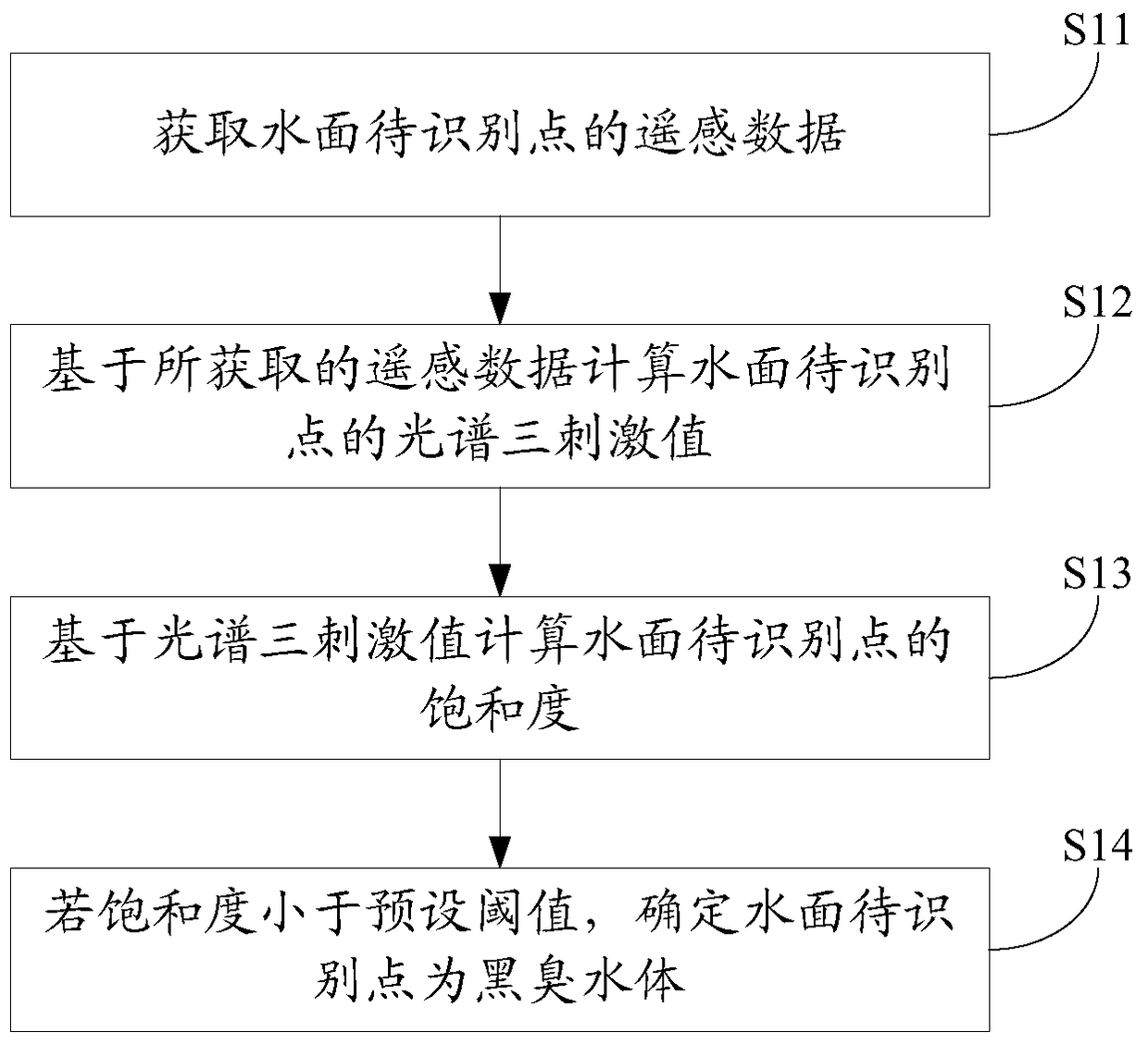
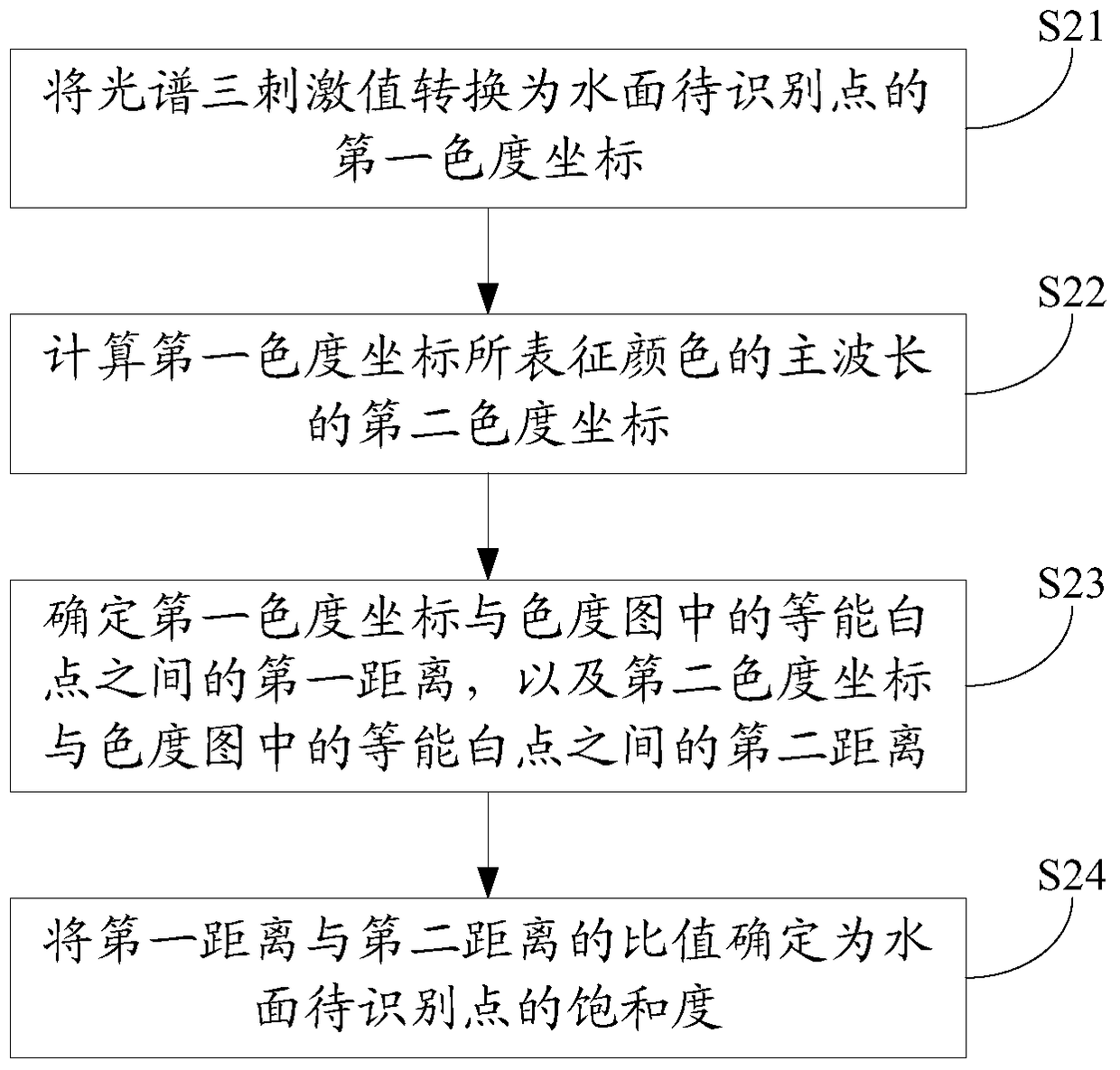
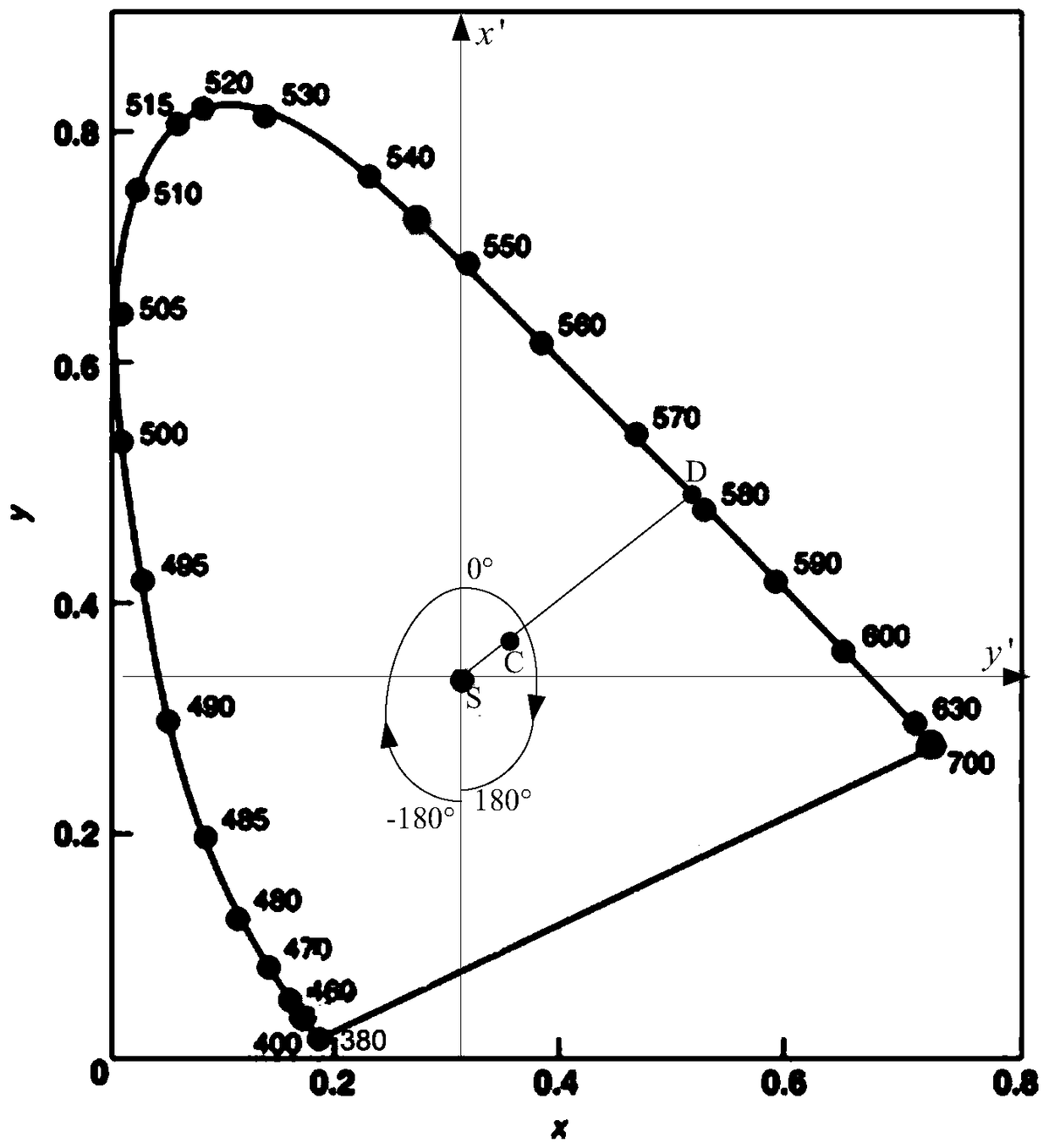
Remote sensing identification method and device for urban black and odorous water bodies
The embodiment of the present invention discloses a method and device for remote sensing identification of black and odorous water bodies in cities, which acquires remote sensing data of points to be identified on the water surface; calculates the spectral tri-stimulus value of the point to be identified on the water surface based on the obtained remote sensing data; calculates the tri-stimulus value based on the spectral tri-stimulus value The saturation of the point to be identified on the water surface; if the saturation is less than the preset threshold, it is determined that the point to be identified on the water surface is a black and odorous water body. It can be seen that the remote sensing identification method and device for black and odorous water bodies in cities provided by the embodiments of the present invention calculate the saturation based on remote sensing data, and identify whether the water body is black and odorous water bodies based on the saturation, which essentially reveals the difference between black and odorous water bodies in cities. The difference in water bodies realizes the identification of urban black and odorous water bodies, and fills the gap in remote sensing identification methods for urban black and odorous water bodies.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
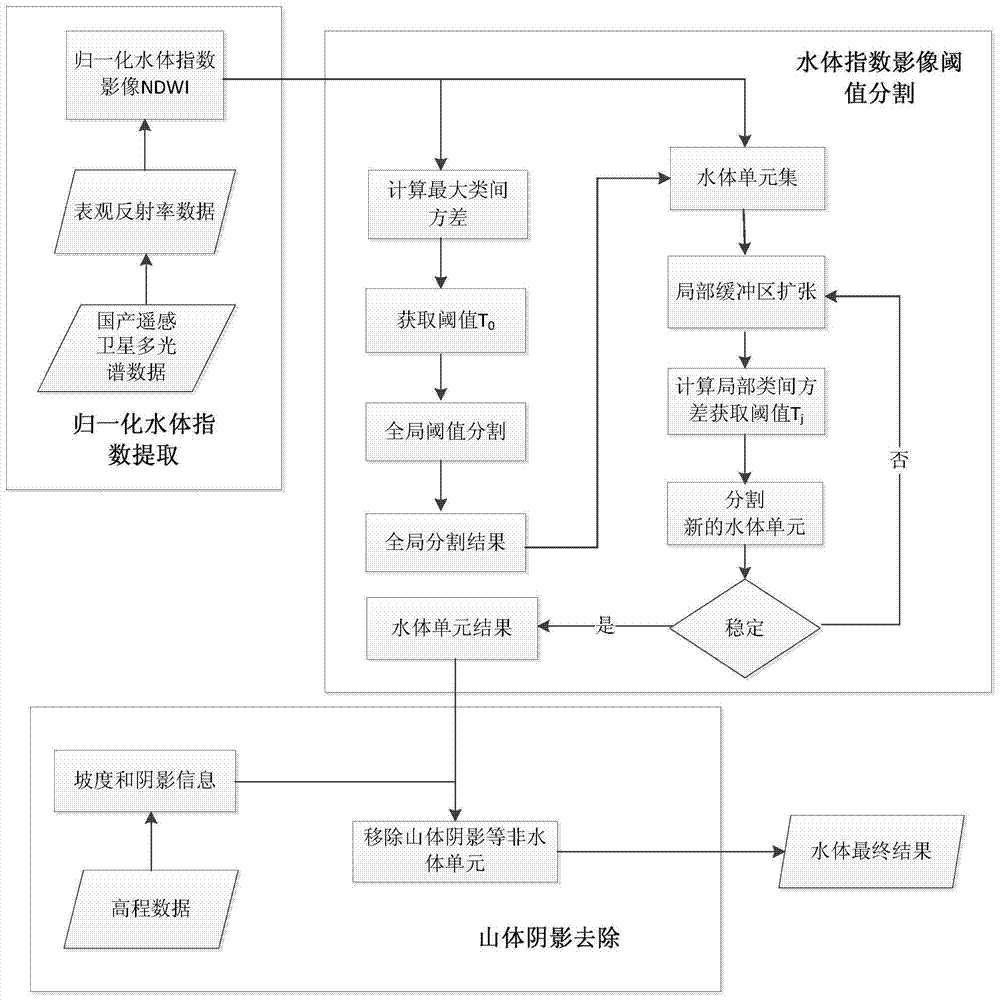
A method for automatic extraction of water body information from remote sensing satellite multispectral images
ActiveCN105046087BAccurate extractionIncreased maximum brightnessCharacter and pattern recognitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationData setMultispectral image
A method for automatic extraction of water body information from remote sensing satellite multispectral images is as follows: (1) extract the normalized water index from the apparent reflectance data of domestic remote sensing satellite multispectral images to form a normalized normalized water index image NDWI; (2) ) Perform global threshold segmentation based on the maximum inter-class variance algorithm on the normalized water index image to initially extract water body information; (3) perform local buffer expansion and threshold segmentation on the preliminary water body information to obtain a stable water body unit result set; ( 4) Obtain the slope and shadow information according to the elevation data and remove the shadow from the water body unit result set, and finally complete the water body information extraction. The invention adopts the method of computer automatic interpretation, utilizes the idea of from global segmentation to local iterative segmentation, and extracts the normalized water body index in a streamlined manner, with high extraction precision and easy engineering.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Meteorological drought monitoring and predicting method
PendingCN111950813ATo achieve the purpose of quantitative drought predictionImage enhancementImage analysisAtmospheric sciencesPrecipitationshed
The invention discloses a meteorological drought monitoring and prediction method, and belongs to the technical field of meteorological drought monitoring and prediction. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining precipitation remote sensing image data in a certain time period from an authority website; converting the remote sensing image data into precipitation; forming a monthly-scalecalculation time period by continuous 30 days, adding the precipitation of each day in the calculation time period to obtain the precipitation of the calculation time period, respectively calculatingthe precipitation of the calculation time period and the precipitation of the same period over the years, and calculating to obtain the monthly-scale precipitation mean percentage; and making a monthly-scale precipitation and mean percentage distribution diagram of the target area. According to the method, the weather conditions and the temperature ranges of all days in the future can be obtainedaccording to the weather forecast information issued by the meteorological department, the predicted precipitation mean square percentage of all days in the future is calculated, and therefore the purpose of conducting quantitative drought prediction on all days in the future is achieved.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Manifold learning-based method for monitoring water quality by remote sensing
InactiveCN102128794BBuild works wellEliminate dependenciesComputing modelsScene recognitionHat matrixStudy methods
The invention discloses a manifold learning-based method for monitoring water quality by remote sensing, and particularly relates to a manifold learning-based method for monitoring water quality by multispectral remote sensing, which comprises the following steps of: training a sample point by a manifold learning method to obtain a projection matrix of water quality remote sensing data in low-dimensional embedded space; building a nonlinear model by using a support vector regression algorithm according to a feature matrix of the low-dimensional embedded space of the sample point and corresponding water quality parameter site monitoring data; and inverting an integral water body by utilizing the nonlinear model to obtain a concentration value of a water quality parameter of the integral water quality, and providing different colors for the water body according to different intervals in which the water body is positioned to display the concentration condition of the water quality parameter of the integral water body visually, so that the water quality evaluation and monitoring of the water body are realized. In the method, the essential law hidden in multispectral remote sensing image data is disclosed effectively, and the nonlinear problem of the water quality evaluation is solved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for full automatic extraction of water remote sensing information in coastal zone
InactiveCN102054274BAchieve precise extractionMitigate the salt and pepper noise effectImage analysisComputer scienceWater remote sensing
Owner:NANJING UNIV
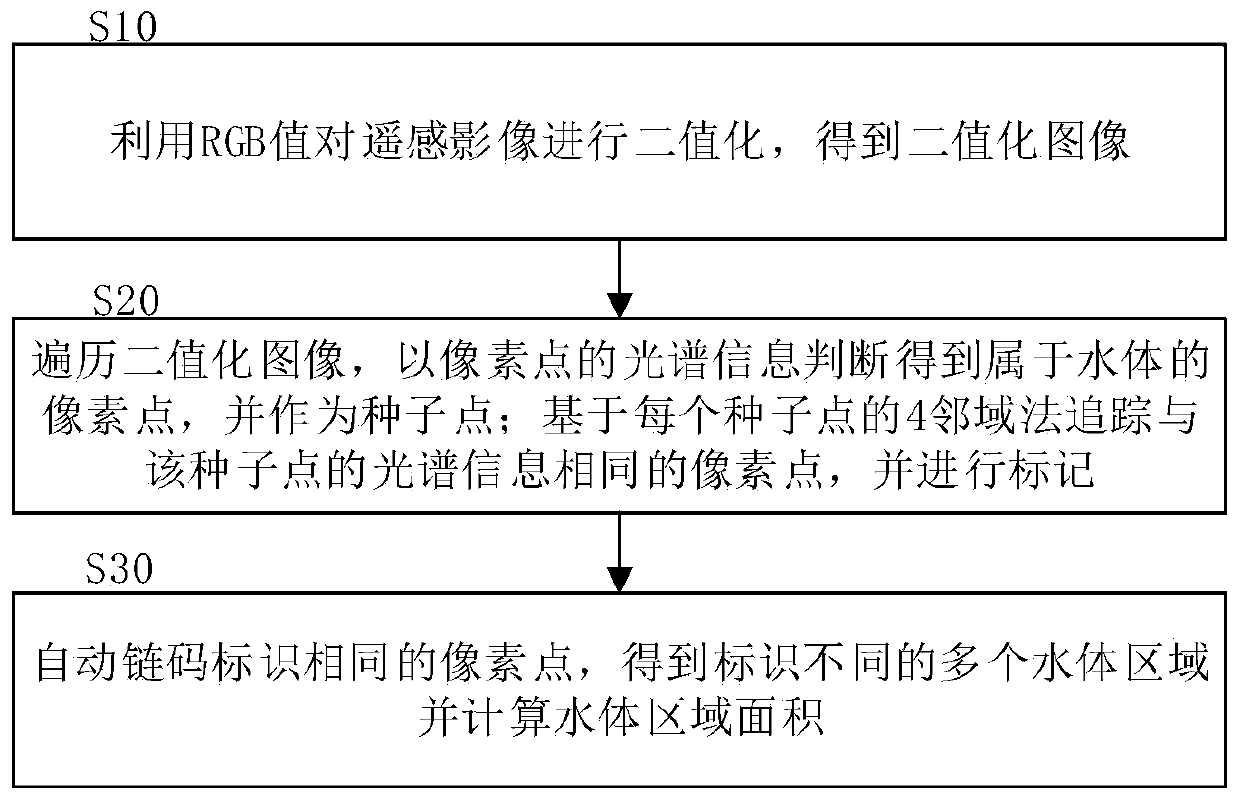
A Method for Recognition and Extraction of Water Body in Remote Sensing Image
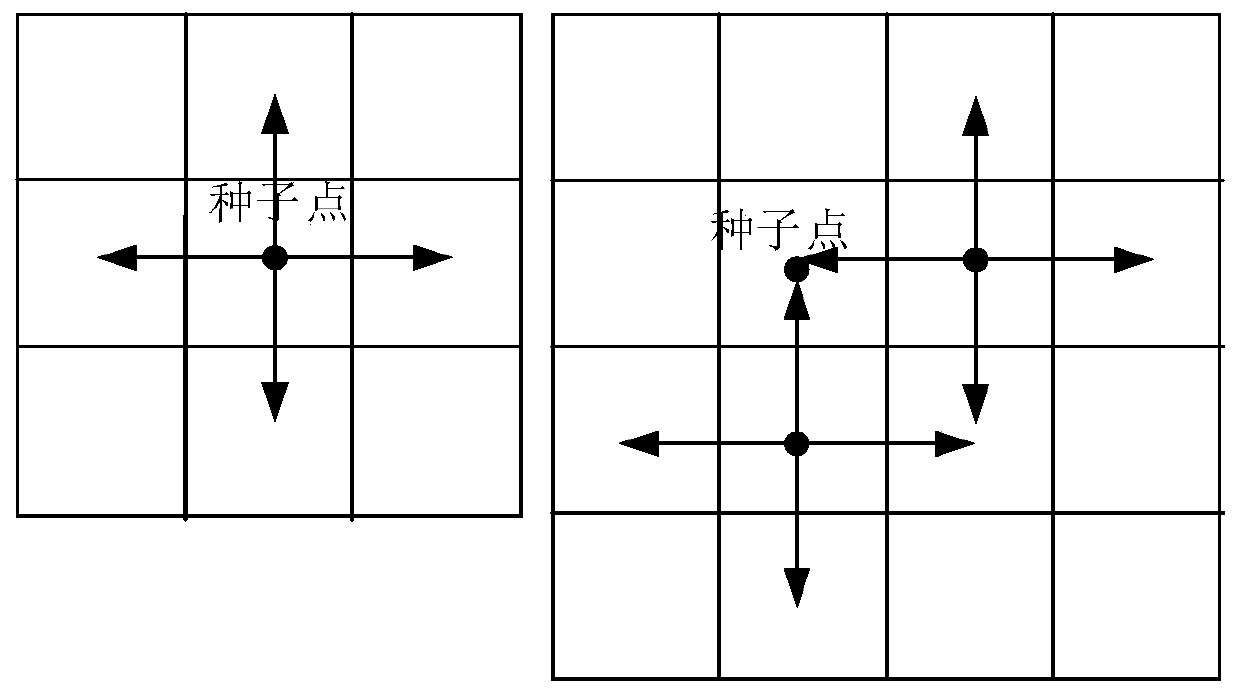
ActiveCN108564056BOvercome the limitations of remote sensing inversion extractionImprove extraction efficiencyScene recognitionComputer scienceChain code
The invention discloses a method for identifying and extracting water bodies from remote sensing images, comprising: using RGB values to binarize the remote sensing images to obtain binarized images; traversing the binarized images, using the spectral information of each pixel as a feature quantity Determine the pixel points belonging to the water body and use them as seed points; track the pixel points with the same spectral information as the seed point based on the 4-neighborhood method of each seed point, and perform Marking; the automatic chain code marks the same pixel, and obtains multiple water body areas with different marks, realizing the simultaneous identification and extraction of integrated multi-water body information in large-scale multi-water body areas. The invention realizes one-time intelligent individual identification and extraction of all water bodies above the scale in a large-scale multi-water body area, overcomes the limitation of single water body remote sensing inversion extraction, and has high extraction efficiency, simple operation and good precision.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
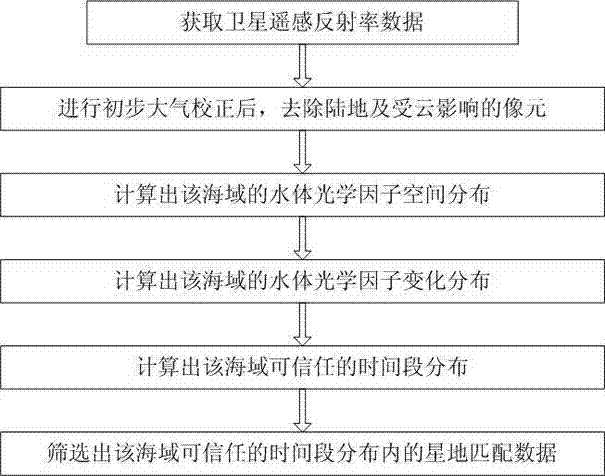
Method for selecting satellite-to-ground matched data through water-color remote sensing
InactiveCN103389073BGuaranteed reliabilityPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryFeature extraction algorithmOrbit
The invention discloses a method for selecting satellite-to-ground matched data through water-color remote sensing. The method comprises the following steps: aiming at a certain sea area, acquiring satellite remote sensing reflectance data of a static orbit satellite within a period of at least continuous three hours in the sea area; calculating the spatial distribution of optical water body factors in the sea area according to each satellite remote sensing reflectance datum; calculating the change distribution of the optical water body factors in the sea area by adopting a feature extraction algorithm to obtain credible time periods of different regions in the sea area, and further determining the satellite-to-ground matched data. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to implement and capable of effectively ensuring the reliability of the satellite-to-ground matched data.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Daytime and nighttime sea fog detecting method based on remote sensing of polarorbiting meteorological satellite
InactiveCN101452078BRealize real-time monitoringElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationOriginal dataMeteorological satellite
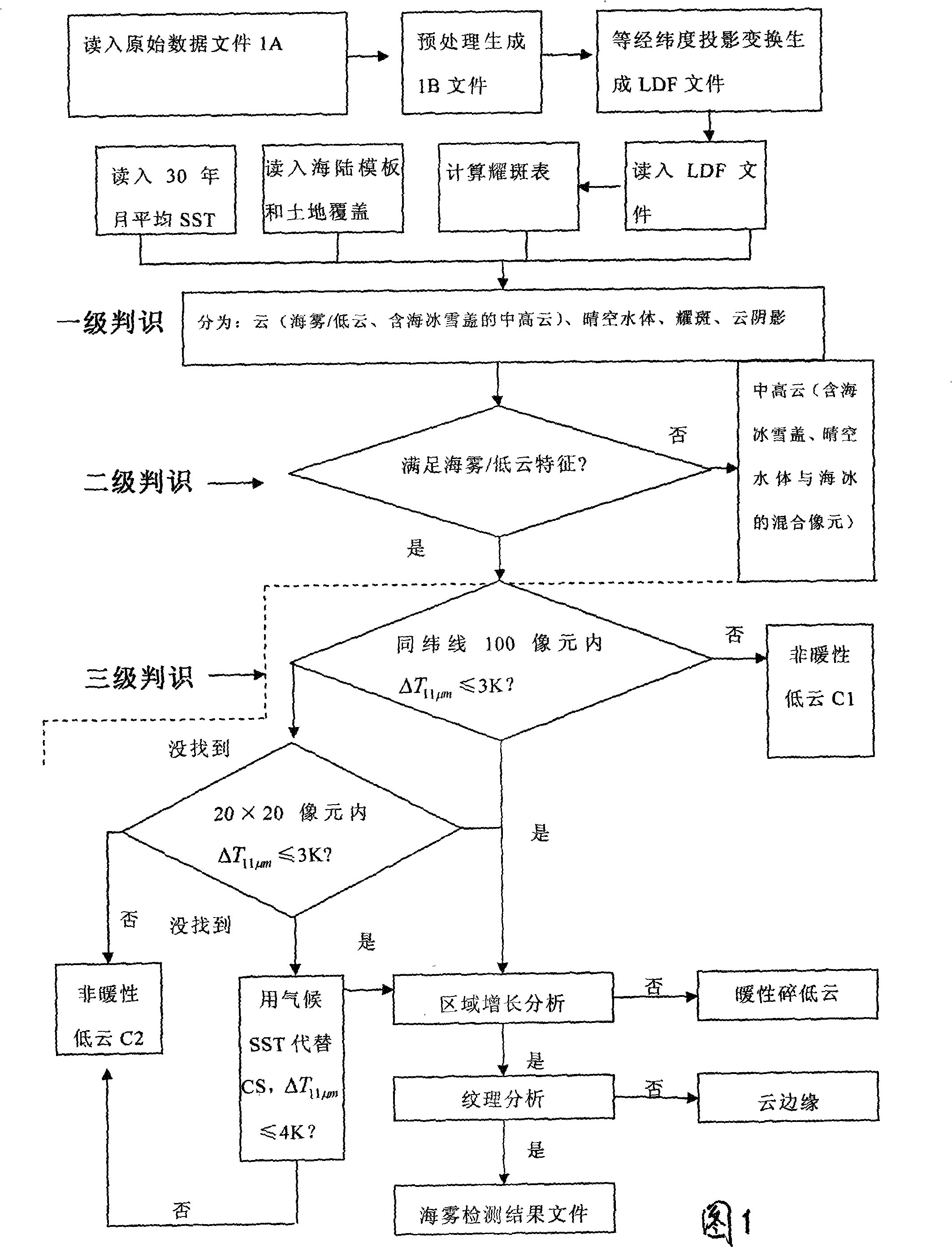
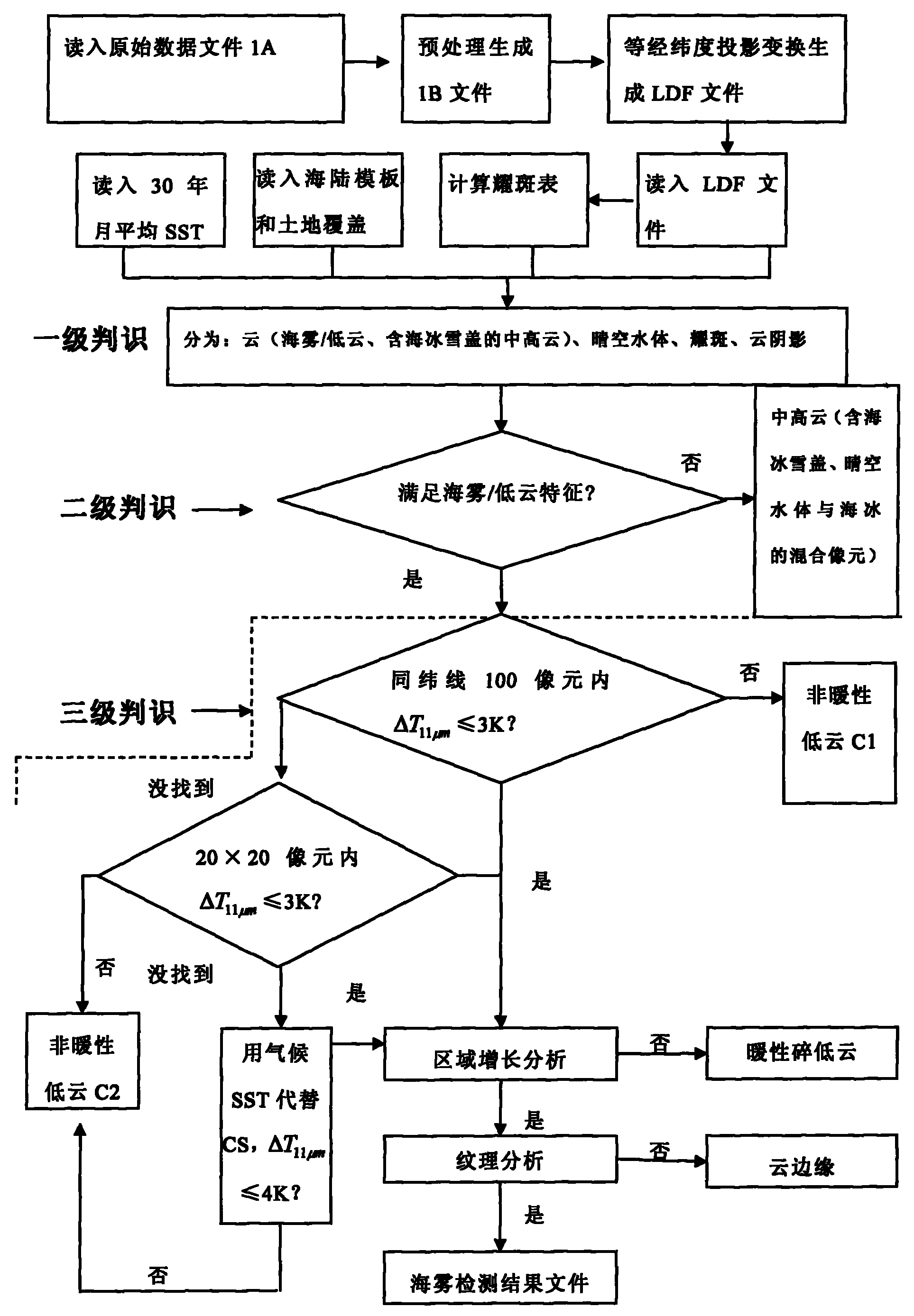
The present invention relates to a method for detecting sea fog at daytime and night with polar-orbiting meteorological satellite. The polar-orbiting satellite information is used. The original data file is read into. The medium-high cloud, the clear-air water, the solar flare water, the cloud shadow areas, the sea-ice-snow sheets, non-warm low clouds, warm broken low clouds and wind edges are respectively filtered with a three-stage determining method through comprehensively using the multi-channel optical spectrum information, NDVI index, NDSI index and average month SST in thirty years. The sea fog arrangement areas are obtained and the file comprising sea fog detecting result is generated. Namely the image display can be executed on a microcomputer with GRADS drawing software. The method according to the invention separates the sea fog from low cloud thereby realizing the real-time monitoring of sea fog. Effective meteorological information with real time monitoring is provided for the safe flying over sea surface, marine traffic transportation, seaport and coasting airport operation.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +1
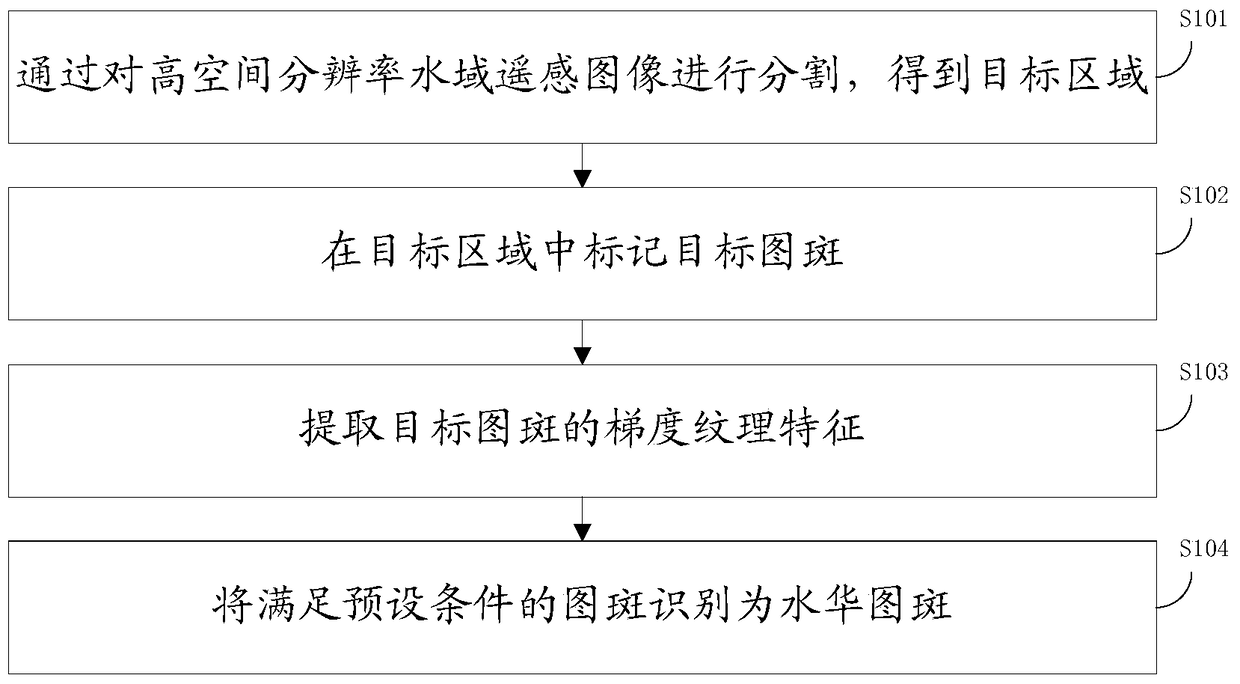
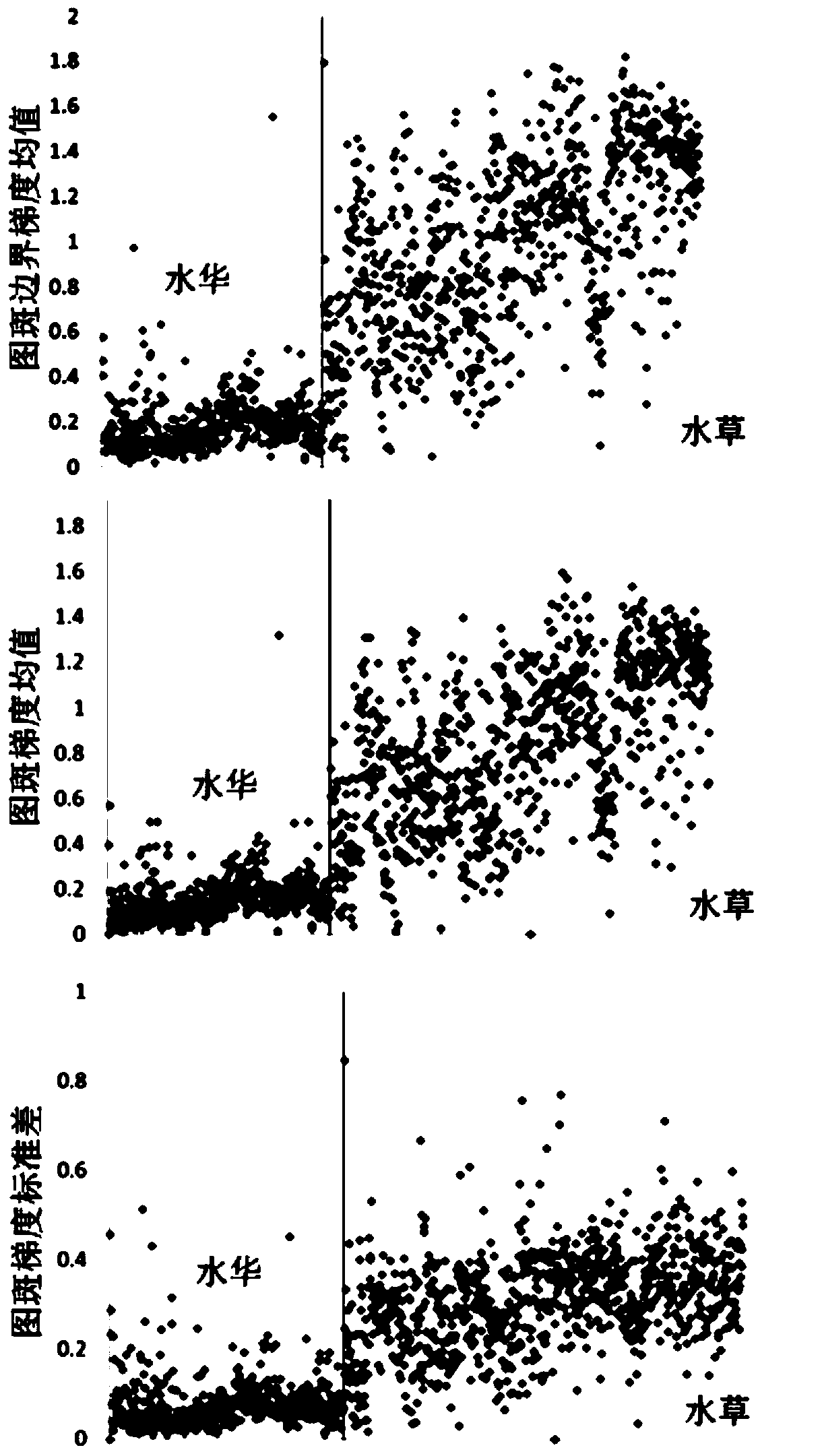
A method and device for water bloom recognition based on high spatial resolution images
ActiveCN105184252BImprove spatial resolutionIncrease reflectionCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer scienceWater remote sensing
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
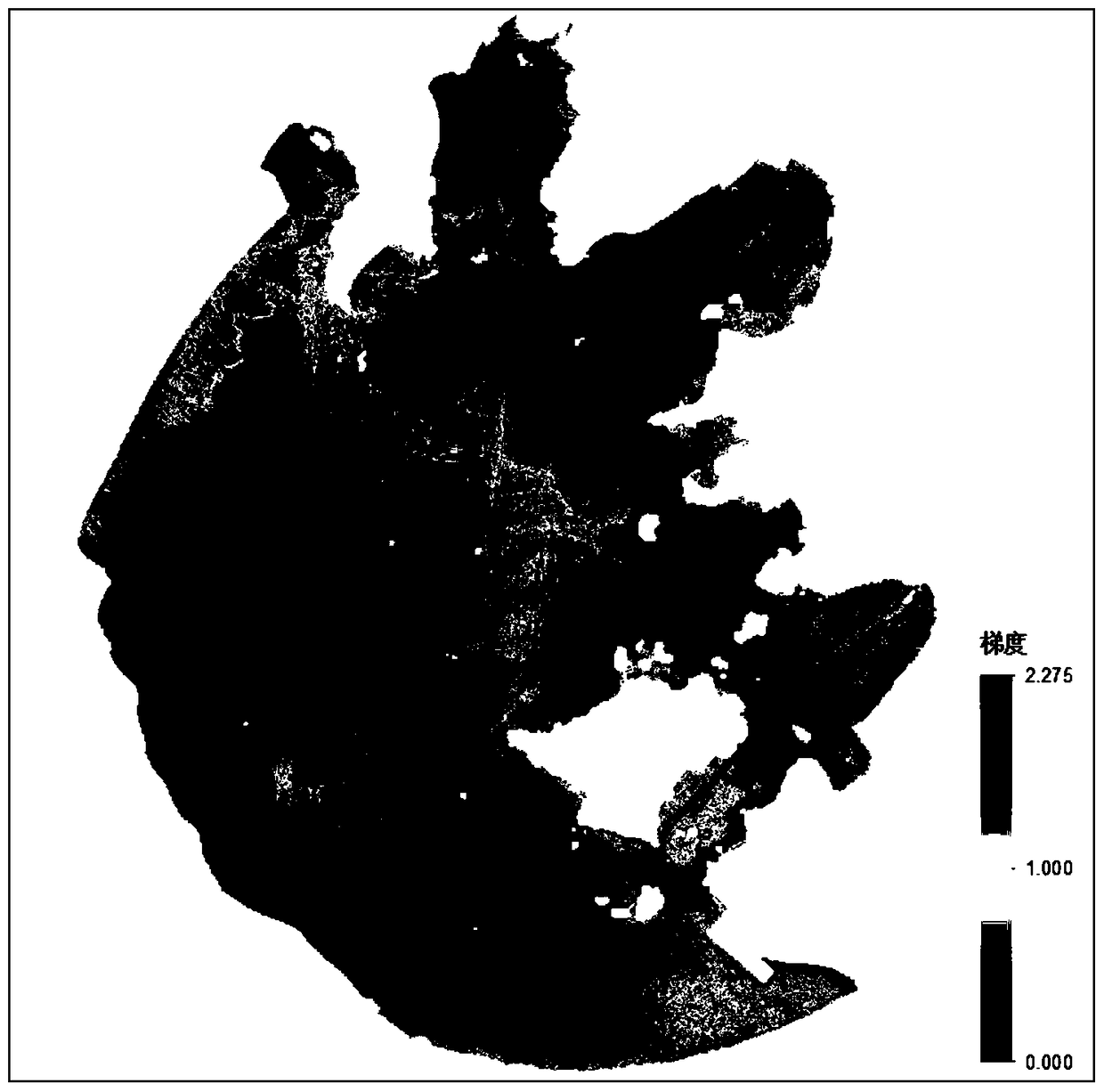
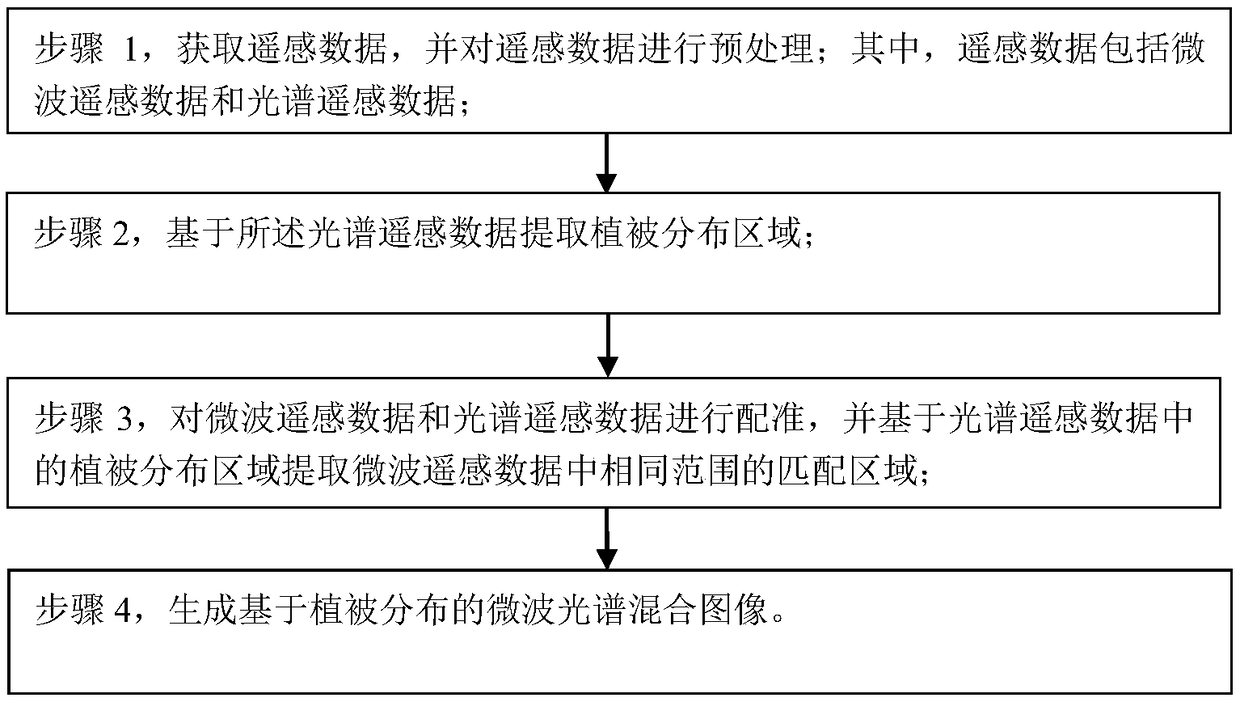
A Generation Method of Microwave Spectral Hybrid Image Based on Vegetation Distribution
ActiveCN107657631BOvercome the shortcomings of not being able to fully characterize itsImprove spatial resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisHybrid imageImage based
Owner:GEOVIS CO LTD
Three-dimensional remote sensing detection method of ocean water quality
ActiveCN104614348BAvoid blindnessOvercome limitationsAnalysis by material excitationNumerical controlSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
A method for monitoring particle size distribution of suspended sediment in water body
ActiveCN105606498BIncrease profitEasy to implementParticle size analysisMineral particlesRefractive index
The invention provides a method for monitoring particle size distribution of suspended sediment in water. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring off-water remote-sensing reflectance of an inspection area and inverting a CDOM (Colored Dissolved Organic Matter) absorption coefficient of the inspection area according to the off-water remote-sensing reflectance; (2) inverting chlorophyll concentration of alga in the inspection area according to the off-water remote-sensing reflectance; (3) calculating a chlorophyll absorption coefficient and a chlorophyll backscattering coefficient according to the chlorophyll concentration; (4) analyzing mineral compositions in the suspended sediment, acquiring the particle diameter and complex refractive index of minerals, and calculating the backscattering coefficient and absorption coefficient of mineral grains via the relationship between the off-water remote-sensing reflectance and the backscattering coefficient and absorption coefficient of the mineral grains in Mie theoretical formula; and (5) constructing an ill conditioned equation according to the backscattering coefficient and absorption coefficient of the mineral grains and the off-water remote-sensing reflectance and acquiring information about the particle size distribution of the minerals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com