Patents
Literature
172 results about "Waveguide channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
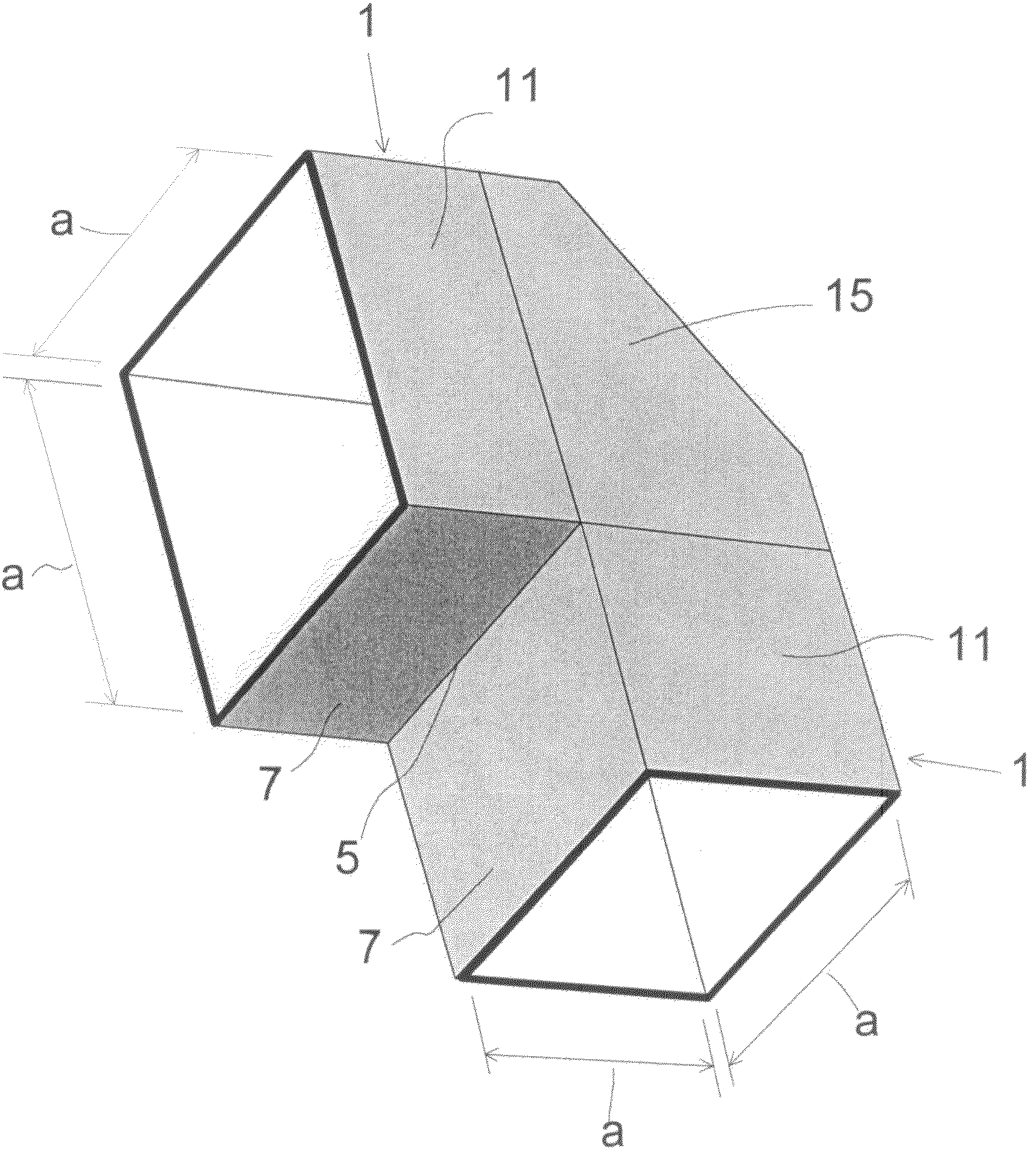
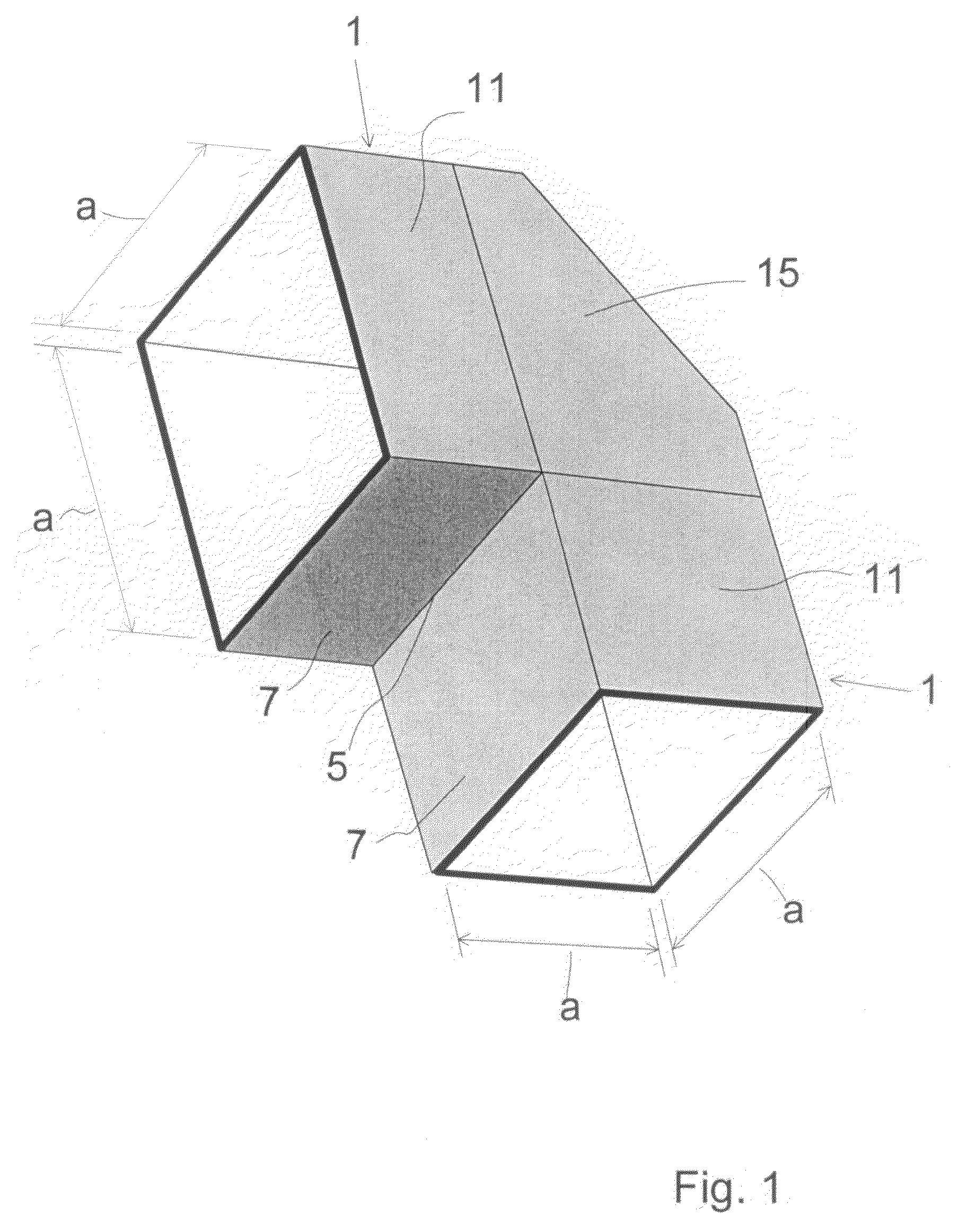
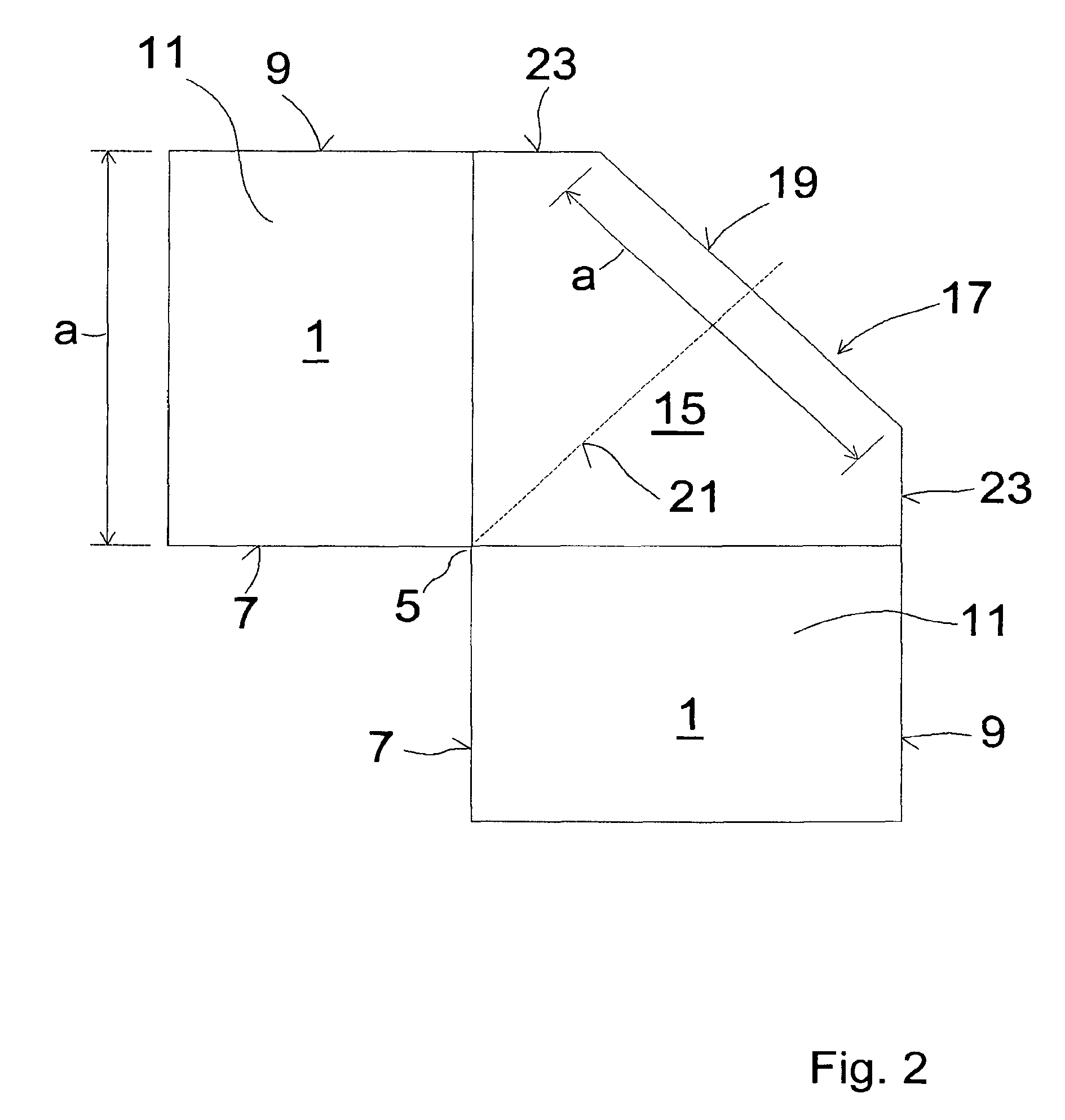
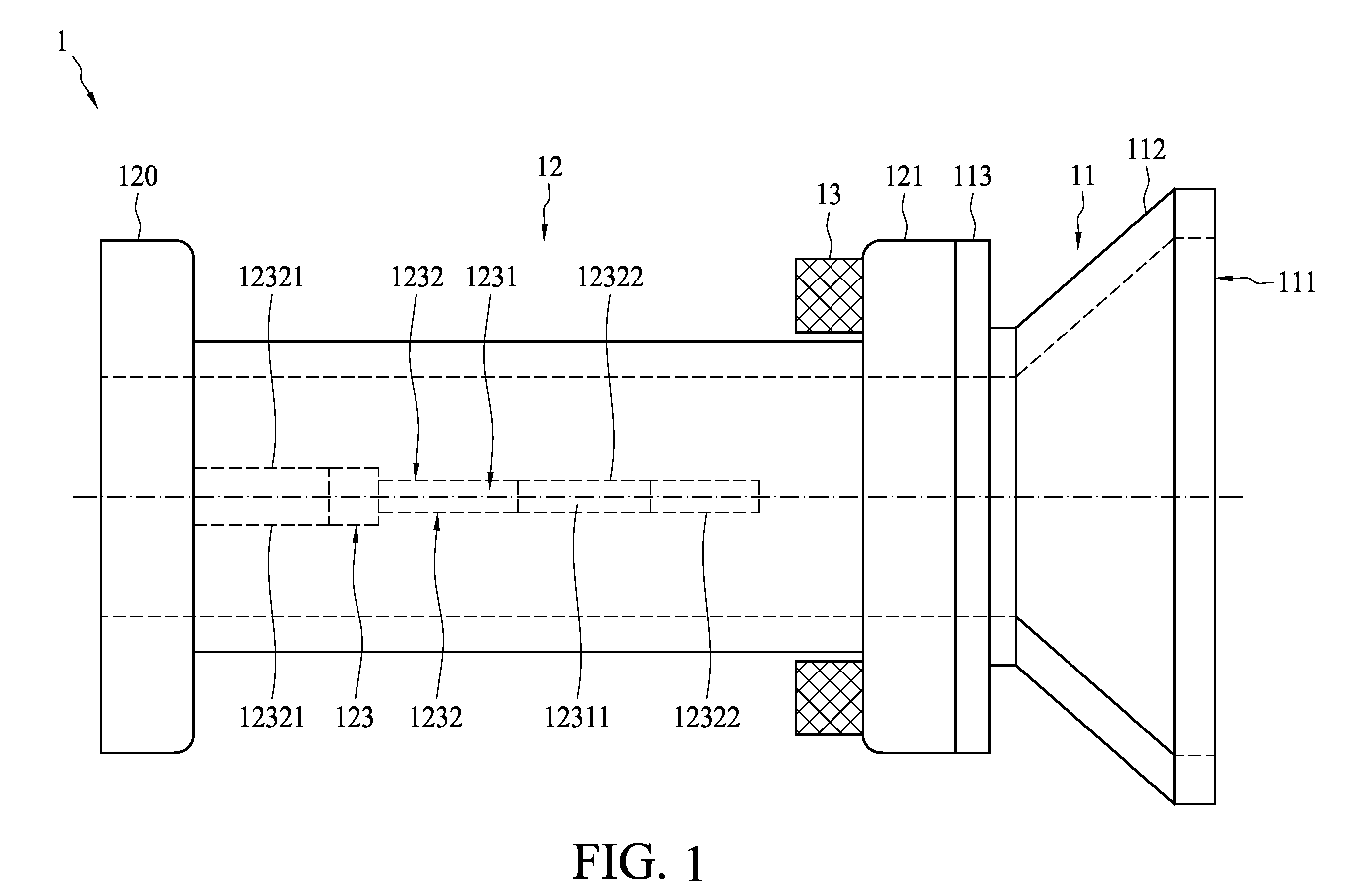
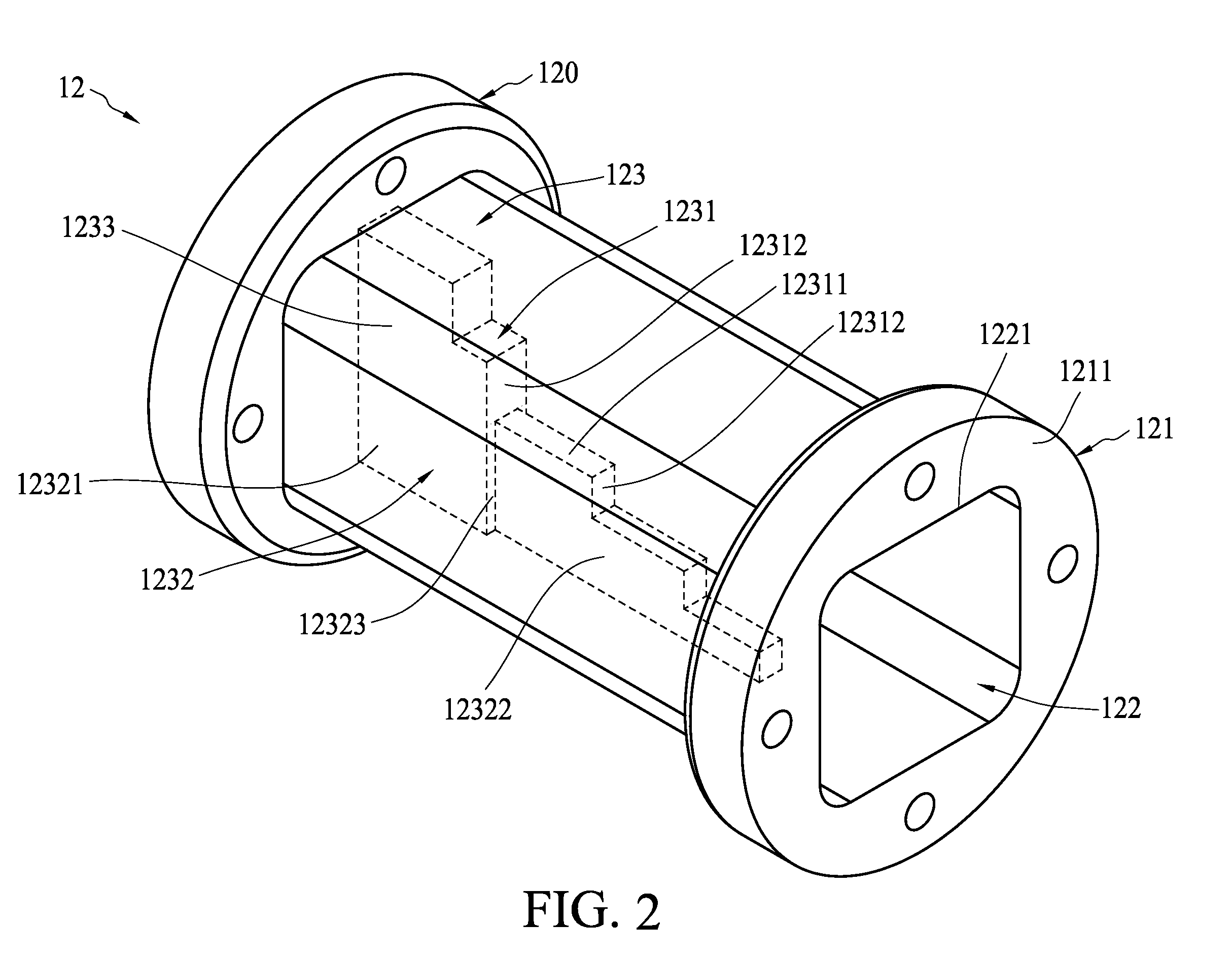
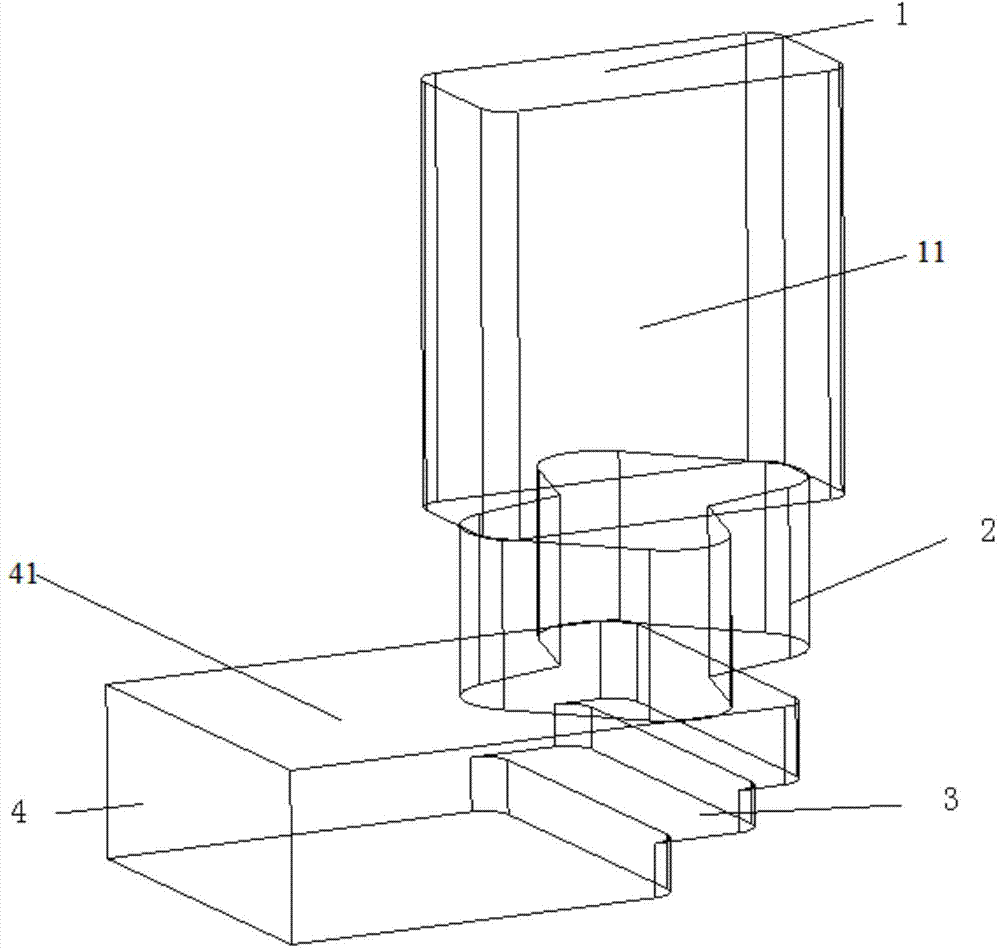
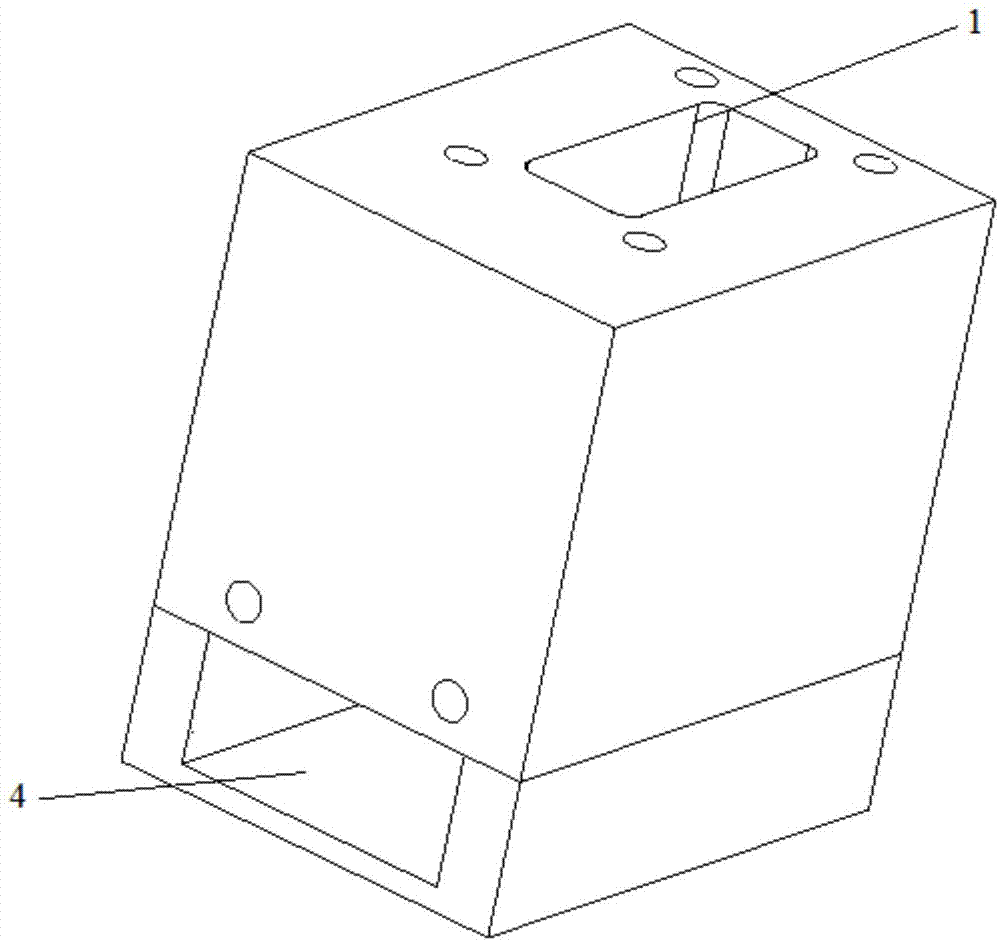
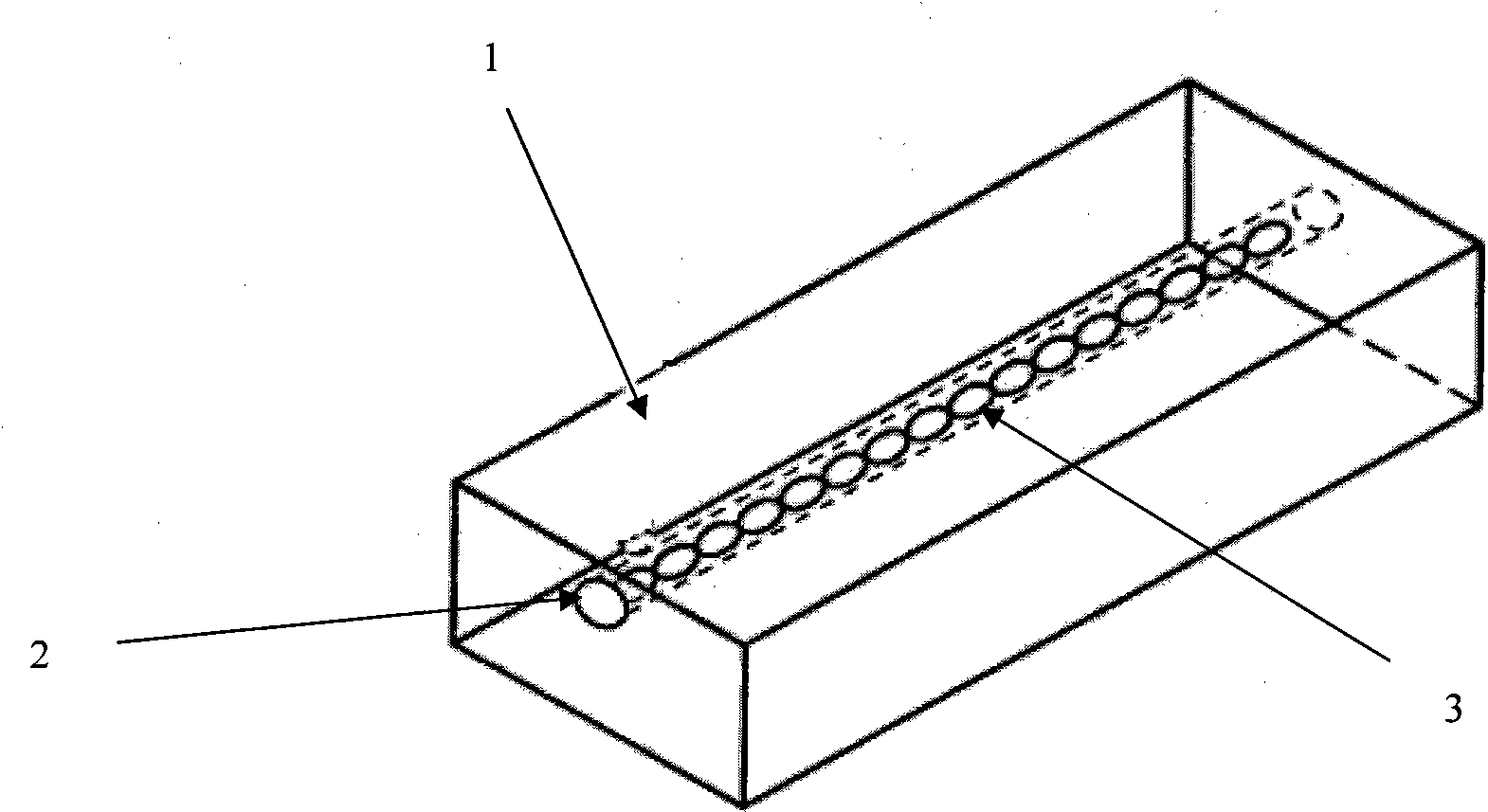
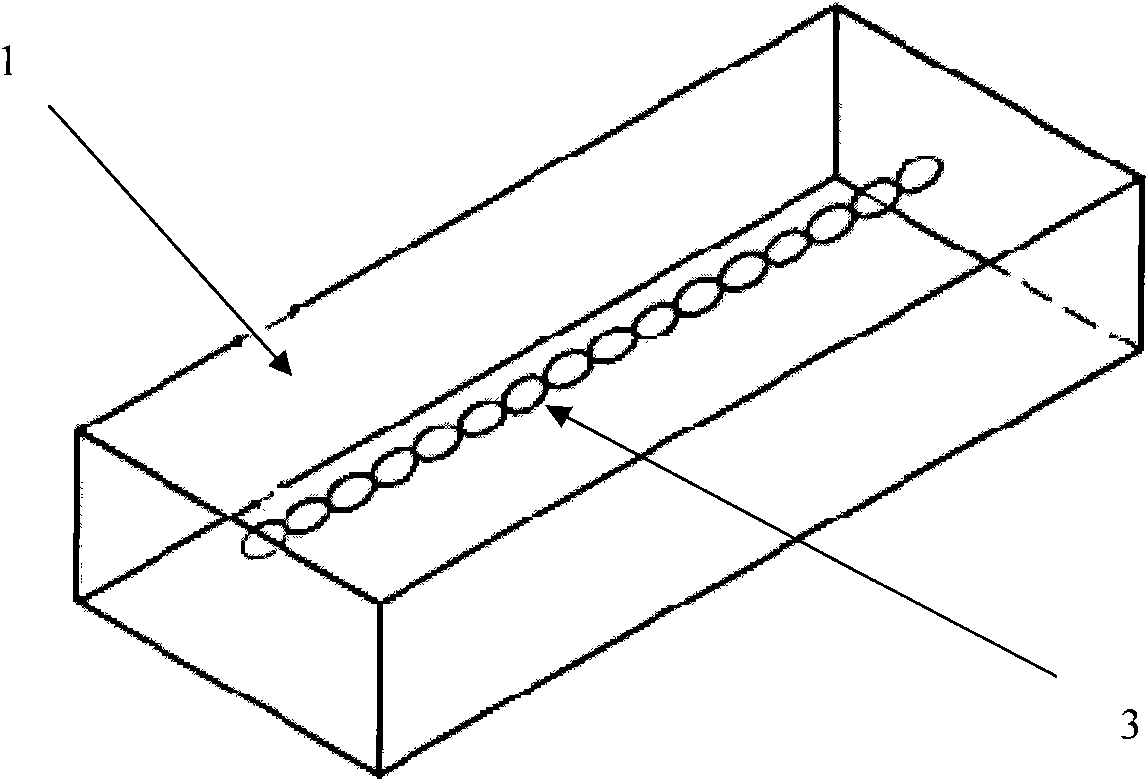
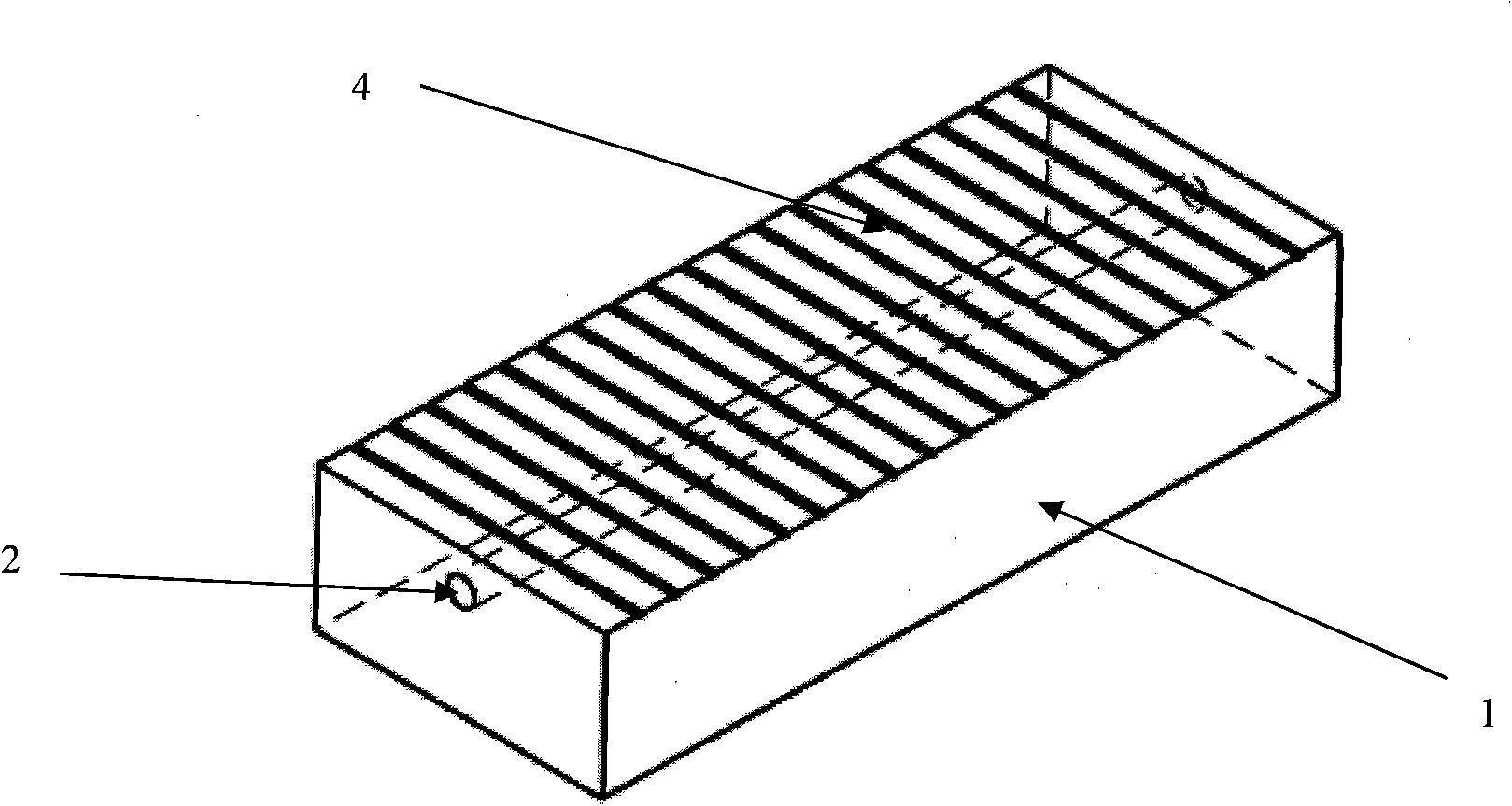
Waveguide bend having a square shape cross-section
InactiveUS7750763B2Improve electrical transmission performanceWaveguide type devicesSquare ShapeWaveguide channel
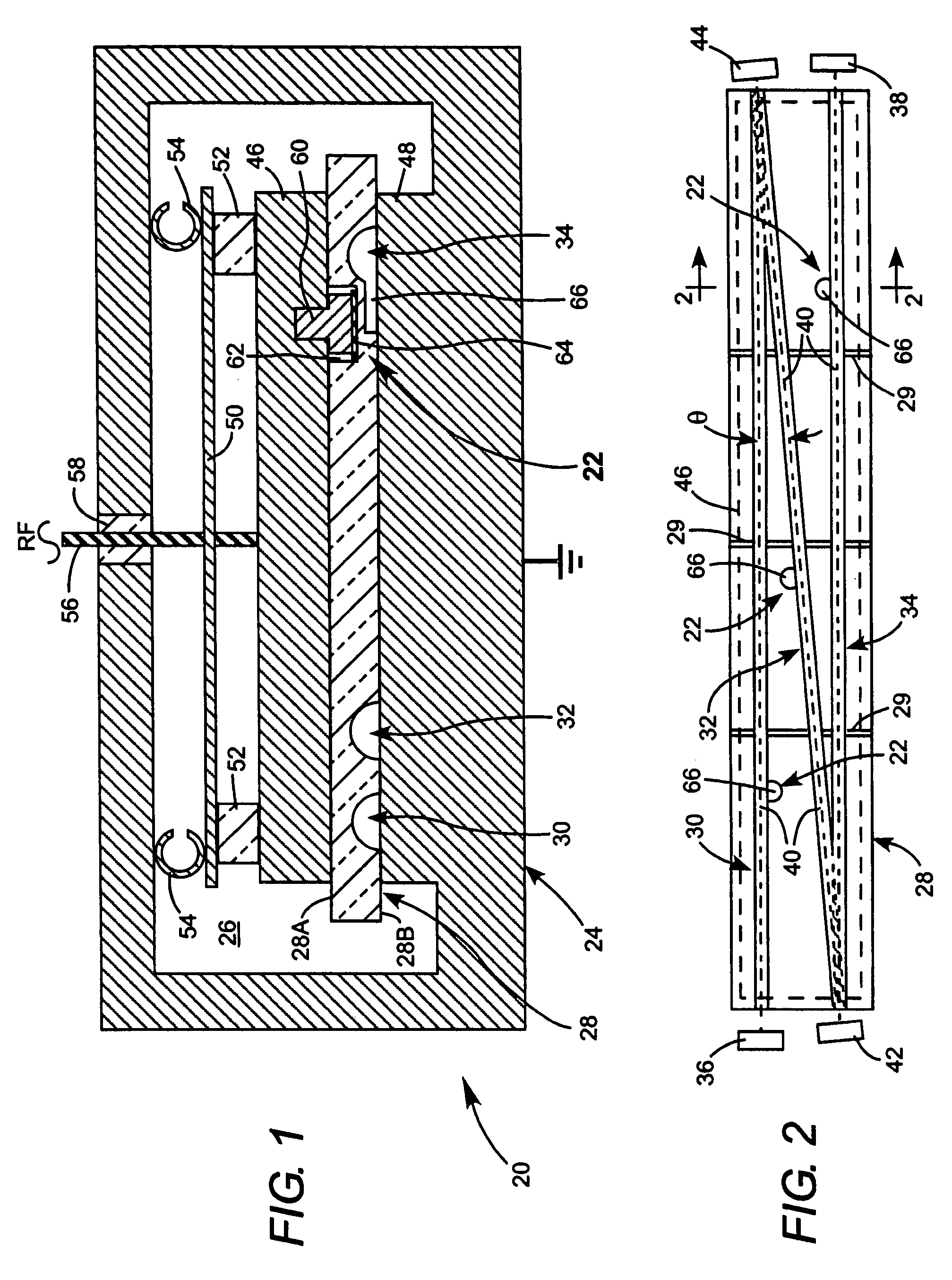
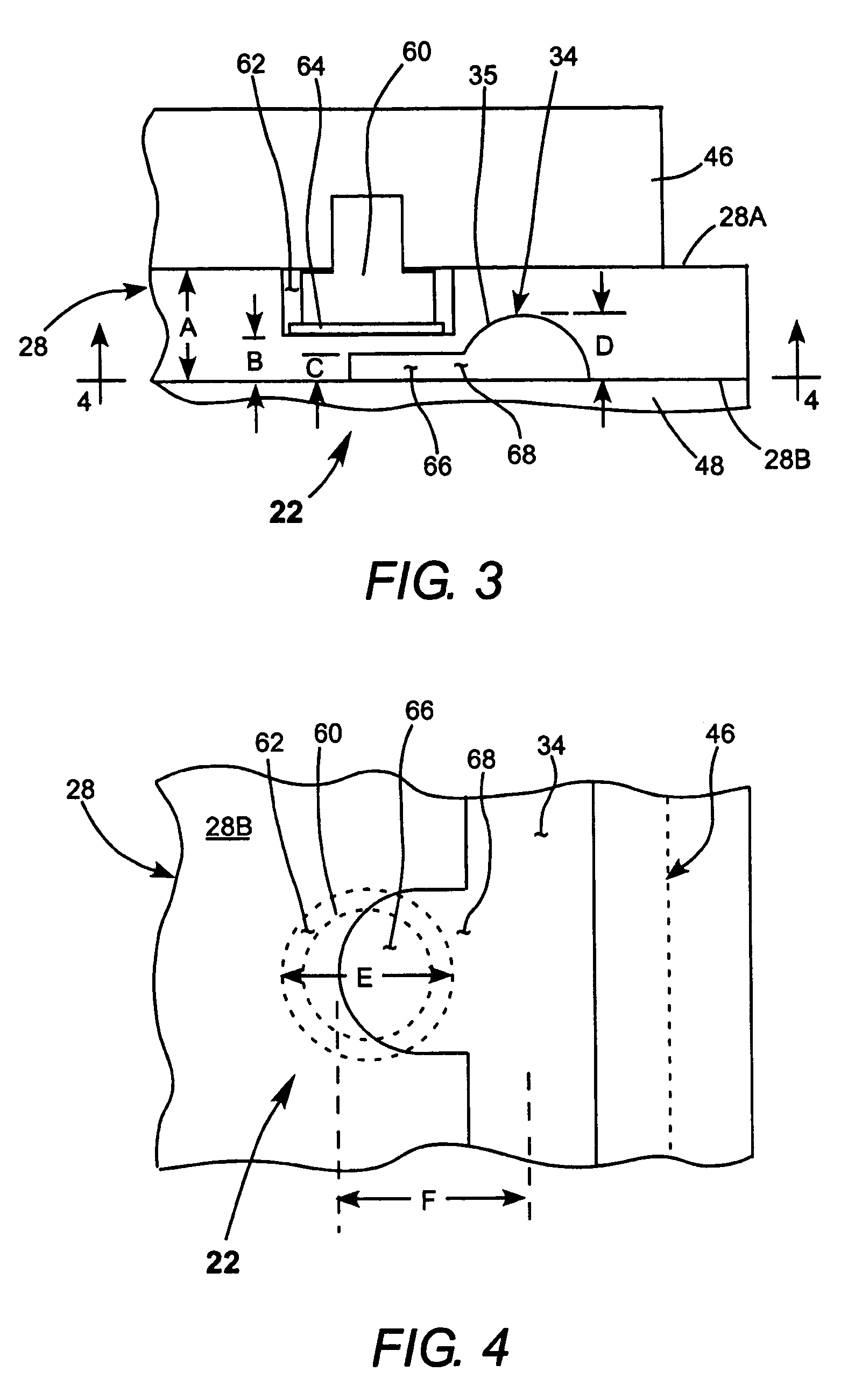
An improved 90° waveguide bend has the following features:the waveguide bend has two waveguide connectors located perpendicularly to each other,the waveguide connectors have a square internal cross section having an edge length (a),between the two waveguide connectors there is provided an angular portion producing the 90° change in direction,the angular portion has externally to the 90° change in direction a chamfer as a delimiting wall for the waveguide bend, the waveguide channel being outwardly delimited by the chamfer, andthe chamfer has in the plane of curvature a length corresponding to the edge length (a) of the waveguide connectors which are square in cross section, ±less than 0.5%.
Owner:KATHEIN WERKE KG
Optical off-chip interconnects in multichannel planar waveguide devices
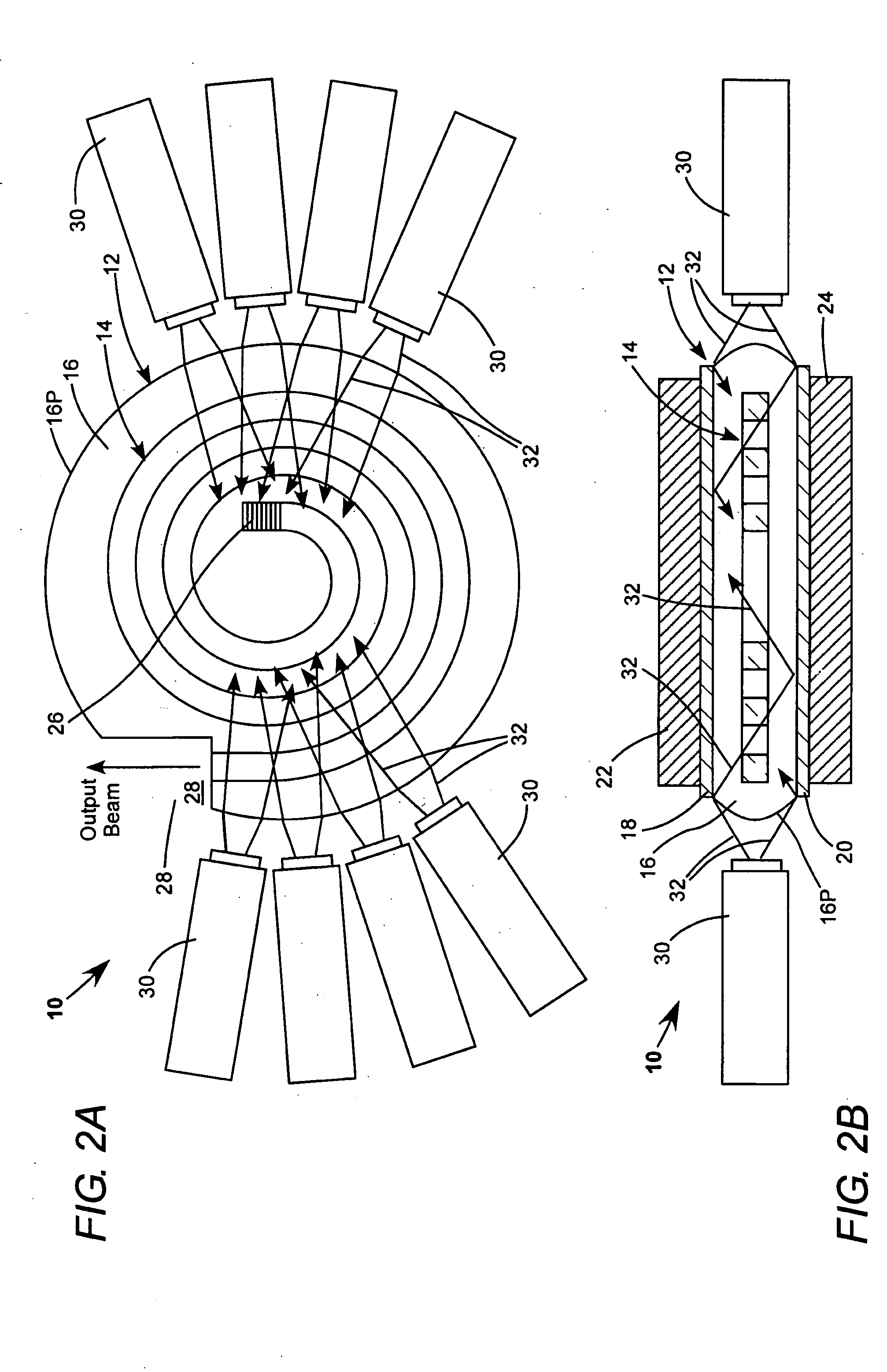
The multichannel waveguide device includes an array of waveguides located in a plane. Each waveguide channel has a redirecting element for redirecting a guided wave out of said plane, or vice versa. The redirecting elements are staggered in the direction of the waveguides so as to transform a one-dimensional array of in-plane waves into a two-dimensional array of out-of-plane waves, or vice versa.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Optical off-chip interconnects in multichannel planar waveguide devices
The multichannel waveguide device includes an array of waveguides located in a plane. Each waveguide channel has a redirecting element for redirecting a guided wave out of said plane, or vice versa. The redirecting elements are staggered in the direction of the waveguides so as to transform a one-dimensional array of in-plane waves into a two-dimensional array of out-of-plane waves, or vice versa.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
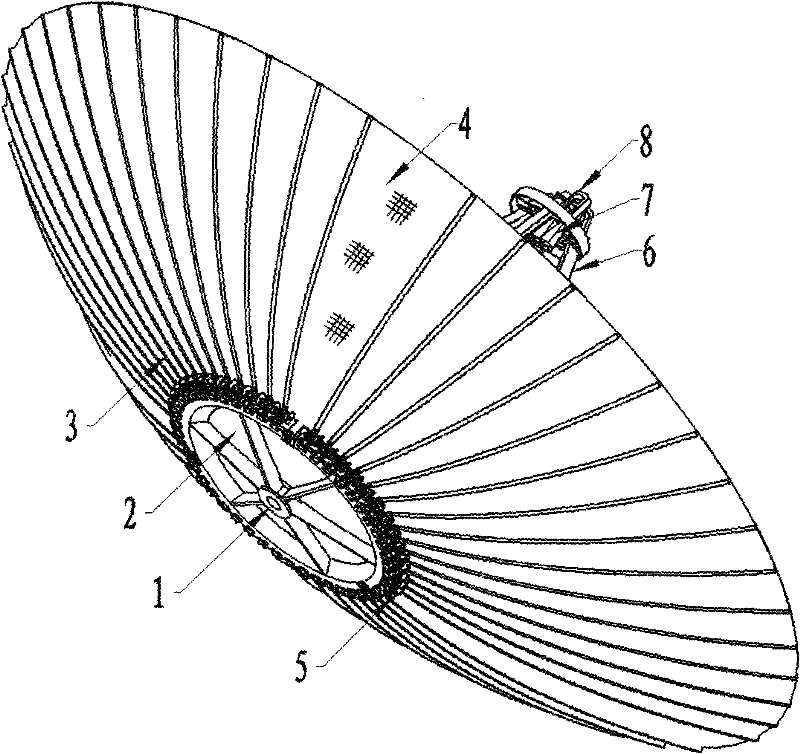
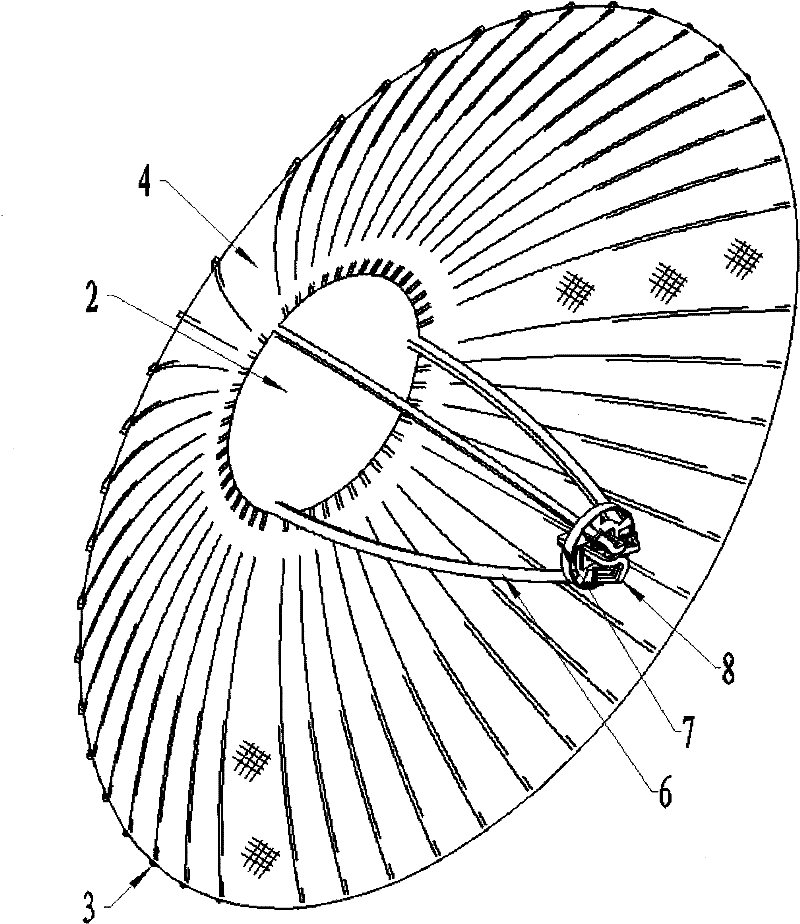
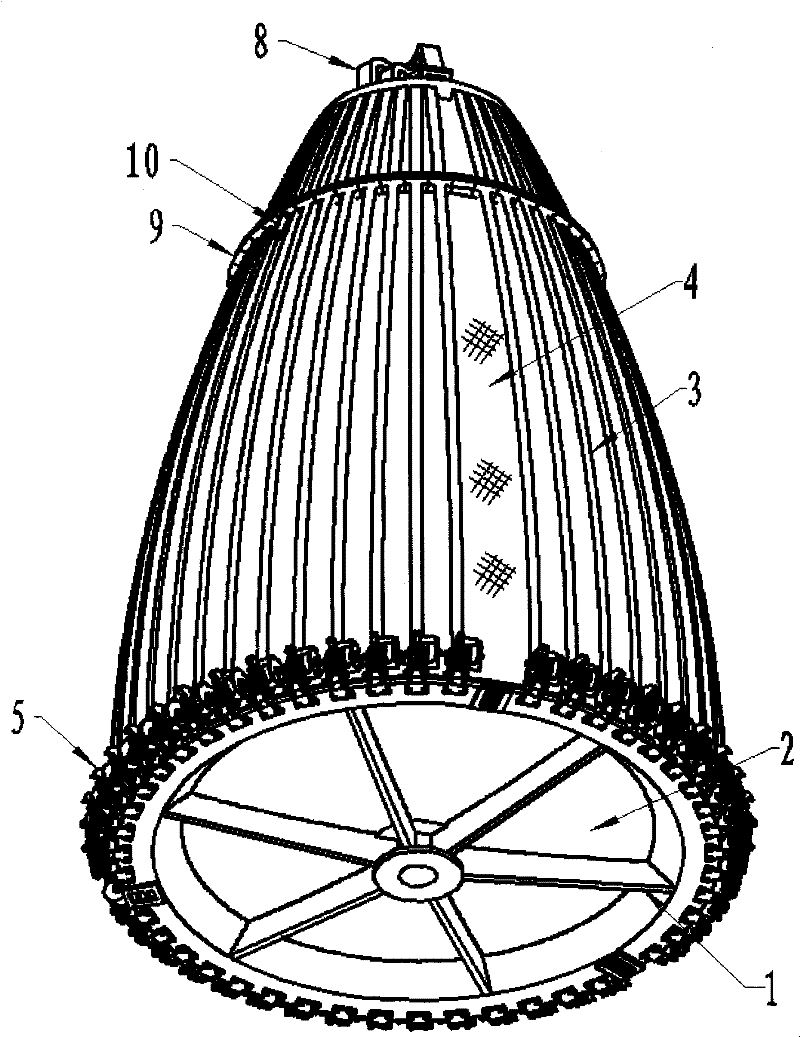
Umbrella type unfolded reticular antenna
InactiveCN102447156AReduce weightSmall size when foldedCollapsable antennas meansEngineeringLoudspeaker
The invention relates to an umbrella type unfolded reticular antenna which comprises a base; the base is fixed with a center solid reflecting surface; a plurality of waveguide type supporting rods are vertically connected with the center solid reflecting surface; a plurality of articulated mechanisms are fixed at the periphery of the edge of the base and are respectively connected with a radial rib so that the folded or unfolded radial ribs are uniformly distributed at the periphery of the center solid reflecting surface; reflecting screen meshes are fixed on the surfaces of the radial ribs and form a needed reflecting surface with the center solid reflecting surface; slotted type compressing blocks are fixed on the radial ribs, and annular compressing ropes are arranged in slots of the slotted type compressing blocks; the annular compressing ropes are tightened up to restrain the radial ribs in the foldable state to form an annular end-to-end closing structure; the annular compressing ropes are connected with a cutter which is used for cutting the annular compressing ropes; the articulated mechanisms are used for providing driving torque so as to unfold the radial ribs; the waveguide type supporting rods are internally provided with a plurality of feed waveguide channels; and a multiple-beam feed source loudspeaker array is arranged at the top of the supporting rods and is connected with the supporting rods through irregular waveguides.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
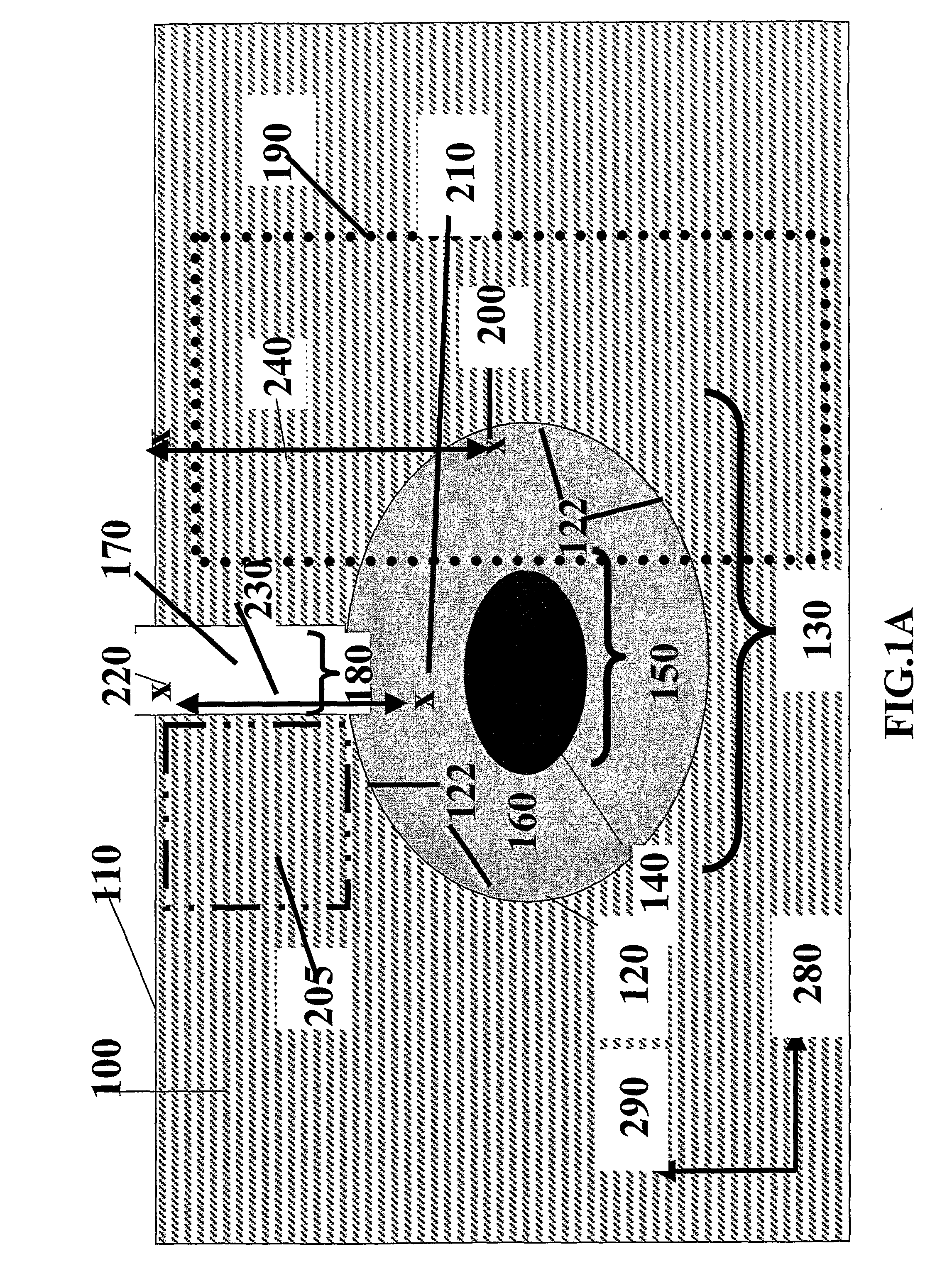
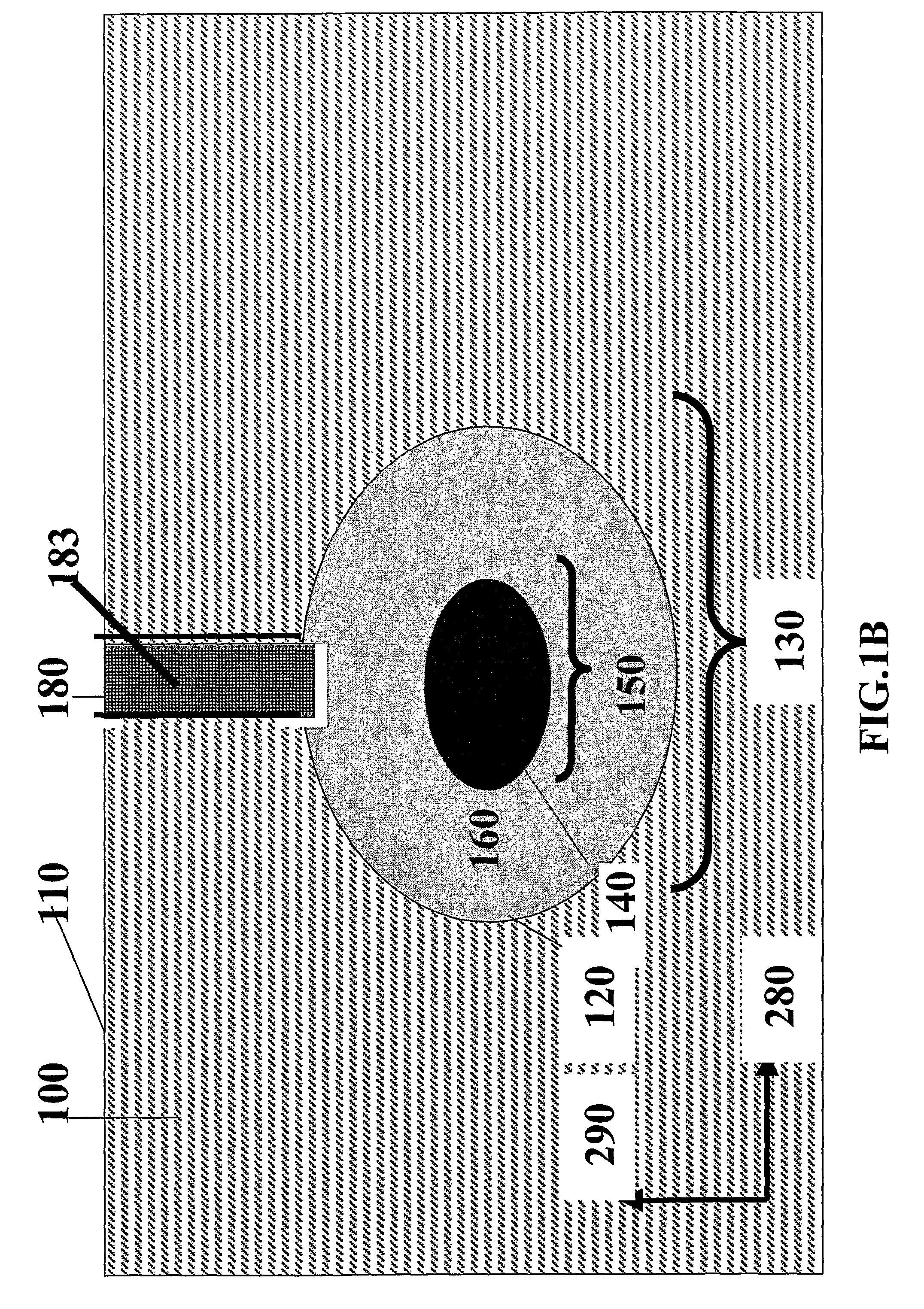
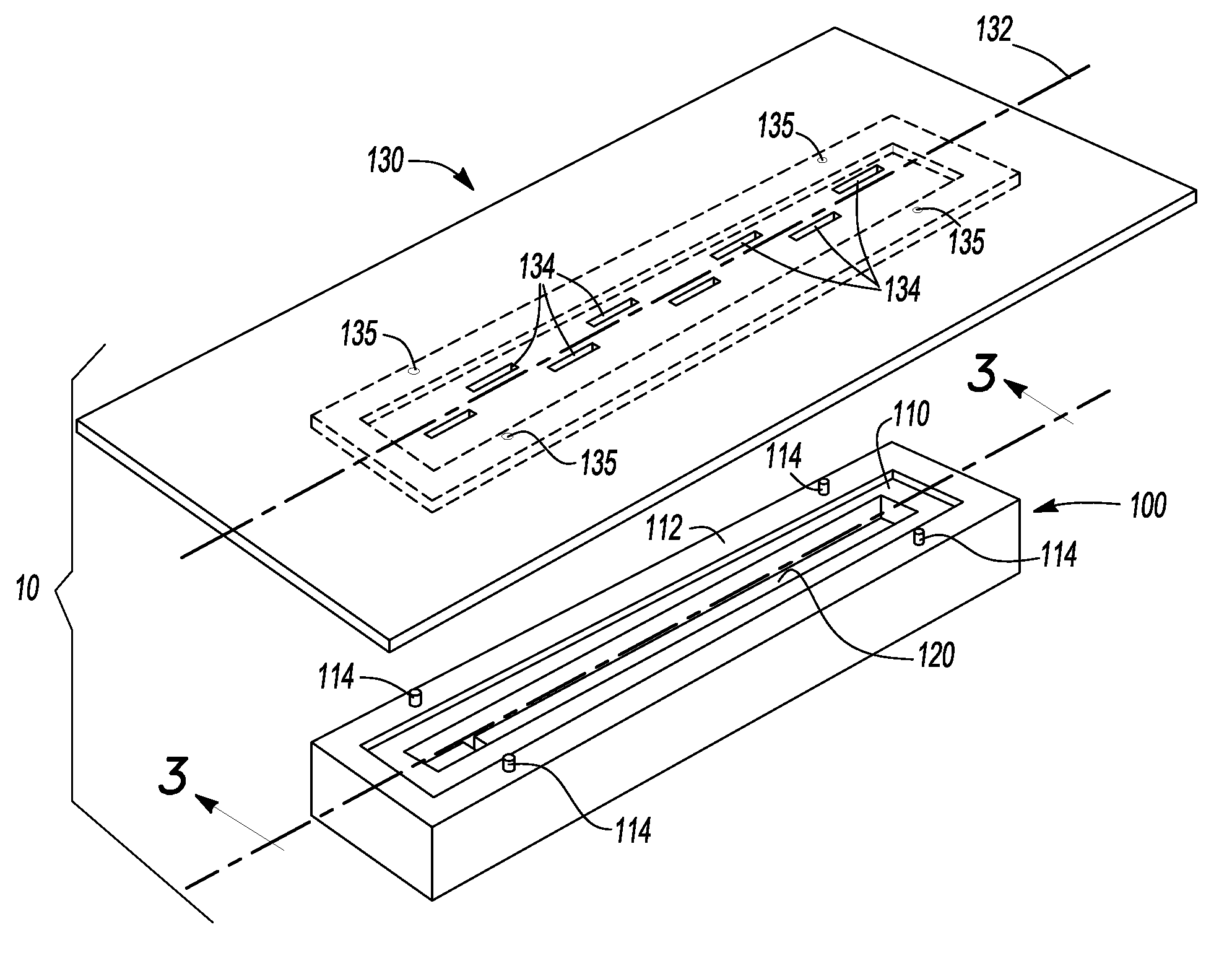
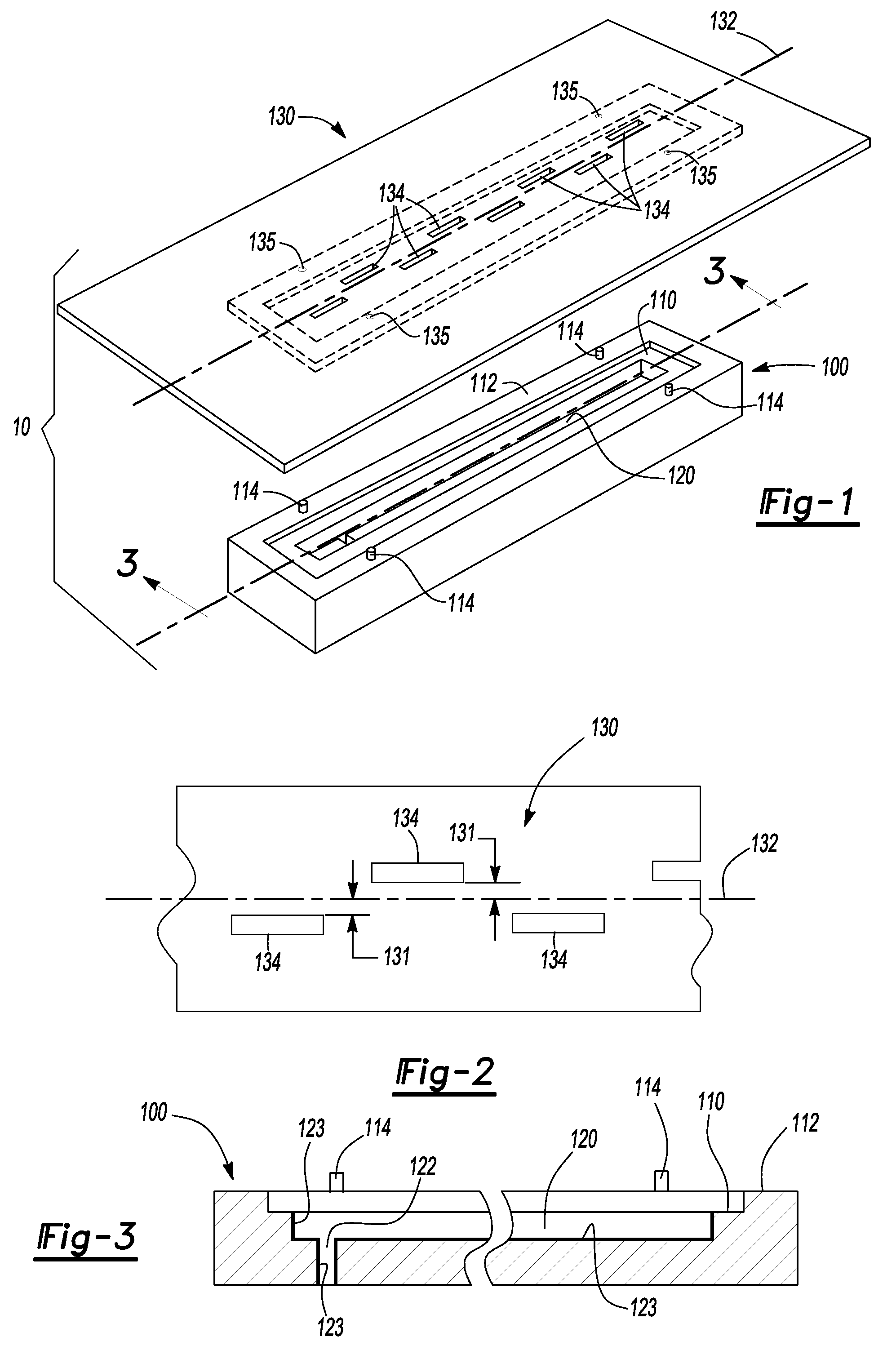
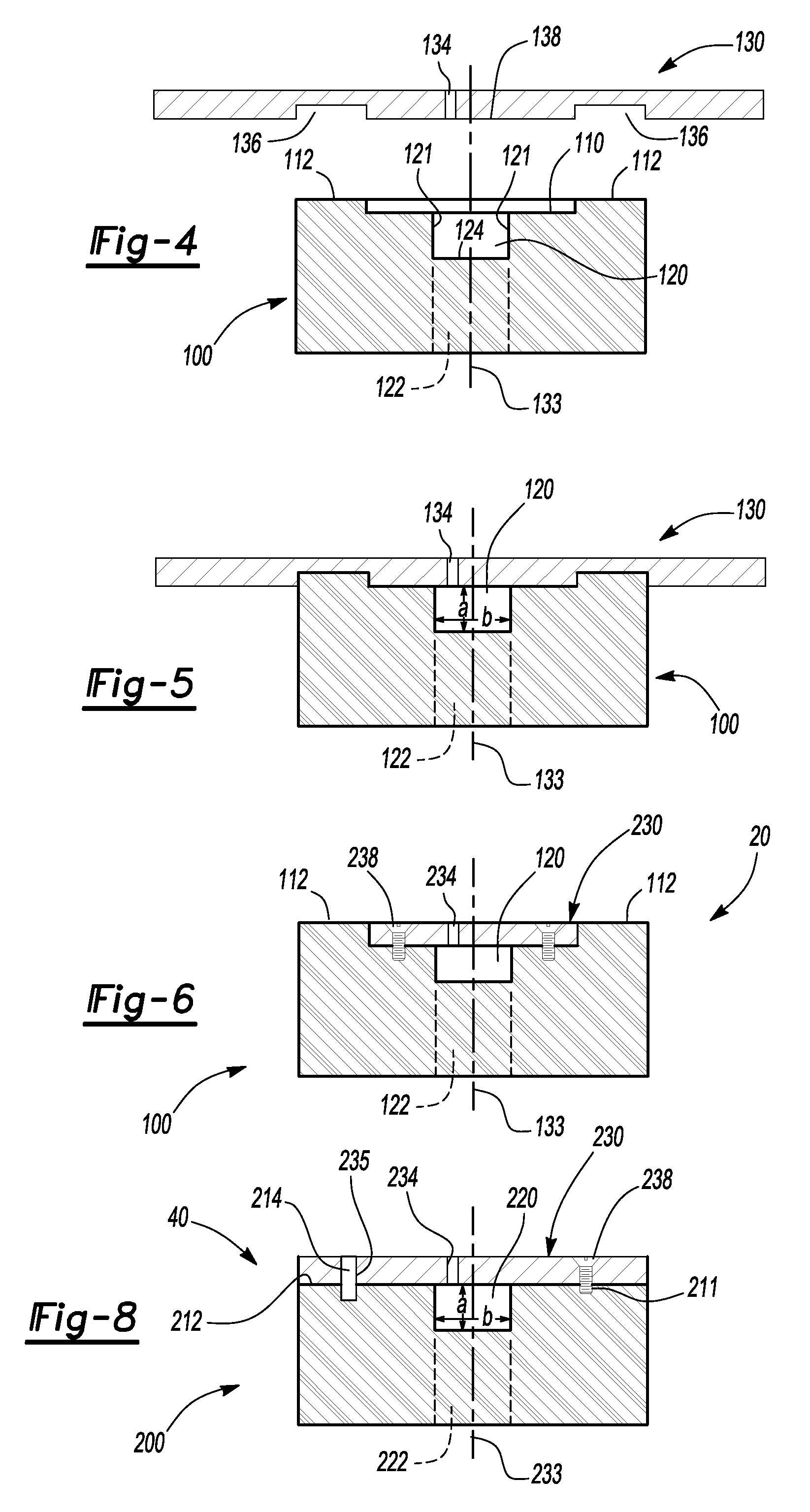
Embedded Channels, Embedded Waveguide And Methods Of Manufacturing And Using The Same
InactiveUS20080317423A1Satisfies needRibbon machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiomedical engineeringWaveguide channel
Waveguide(s) (130) including at least partially buried channels) (120) within substrate(s) (100) having at least one substantially planar surface (110) are disclosed. According to some embodiments at least part of the channel (120) is located beneath at least a portion of the substrate (100). According to some embodiments the waveguide channel (120) includes a substantially transparent core (140) and optional cladding (160) extending through the channel (120). Alternately, an inner surface of the channel (120) is highly reflective. Furthermore, structures for use as waveguides (130) and / or as microchannels for fluid flow are disclosed herein. Also disclosed are production methods for such waveguides and said structures (130) and said structures, and methods of using such waveguides (130).
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
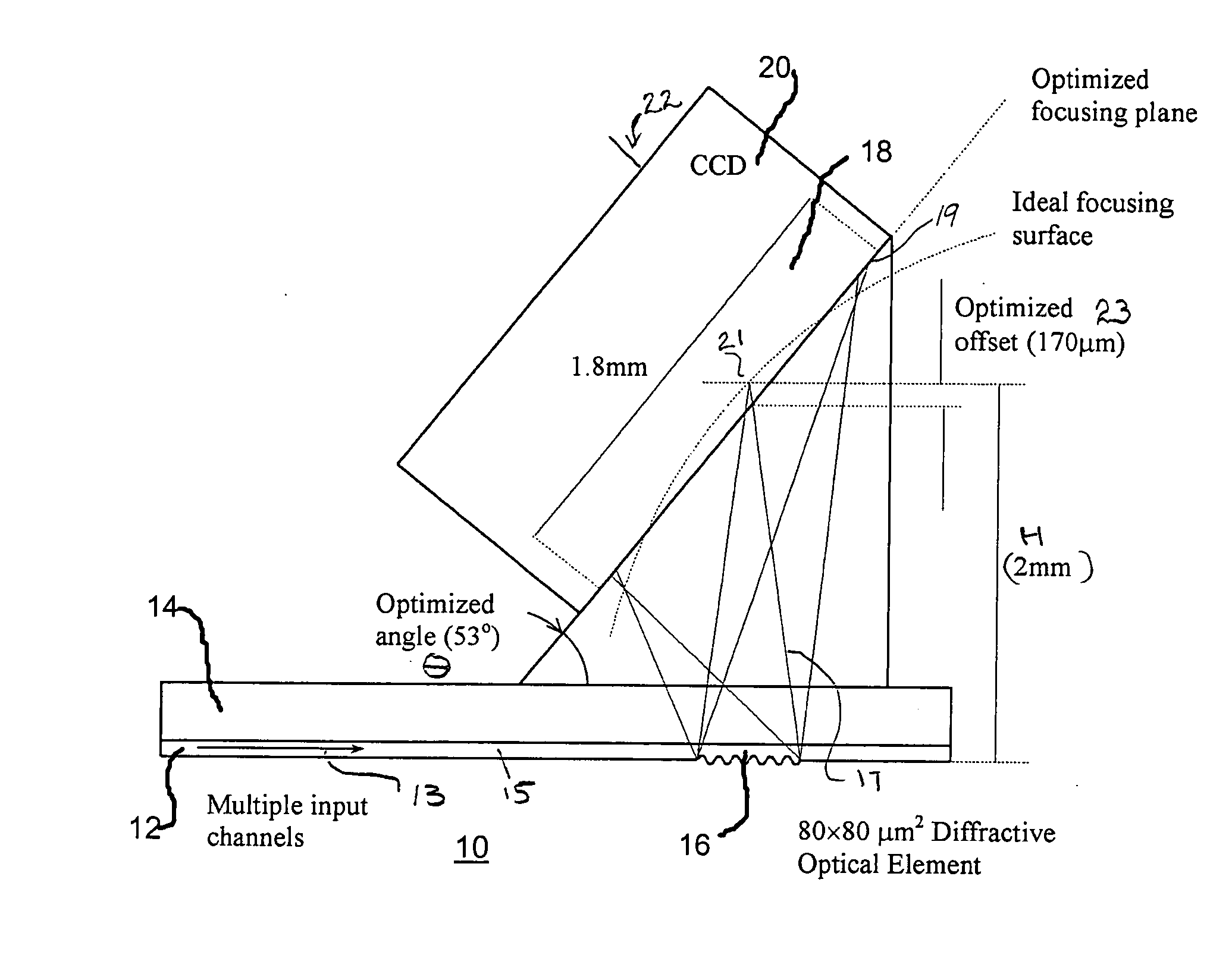
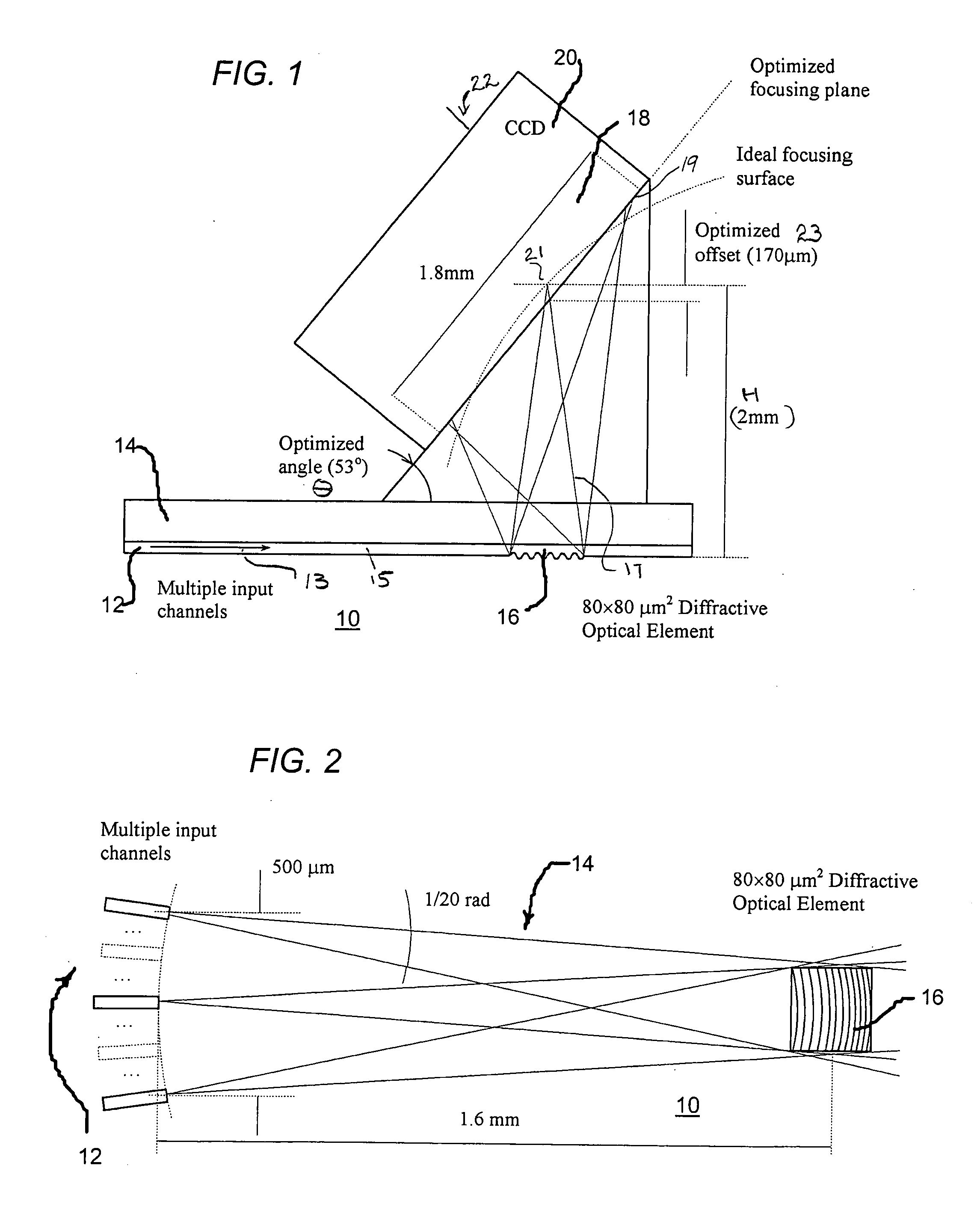
Diffractive imaging spectrometer
ActiveUS20050068526A1High resolutionWide spectral rangeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationImage resolutionVisible spectral range
A miniaturized diffractive imaging spectrometer (DIS) has a footprint less than 2×1 mm2, is about 2.5 mm tall (excluding an image detector, which in some embodiments may be a CCD matrix), and covers the entire visible spectral range from 400 nm to 700 nm with resolution of approximately from 2 nm to 4 nm across the field. The DIS is able to function with multiple input waveguide channels, and is flexible in its various possible configurations, as it can be designed to achieve better resolution or higher number of channels or wider spectral range or smaller size.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
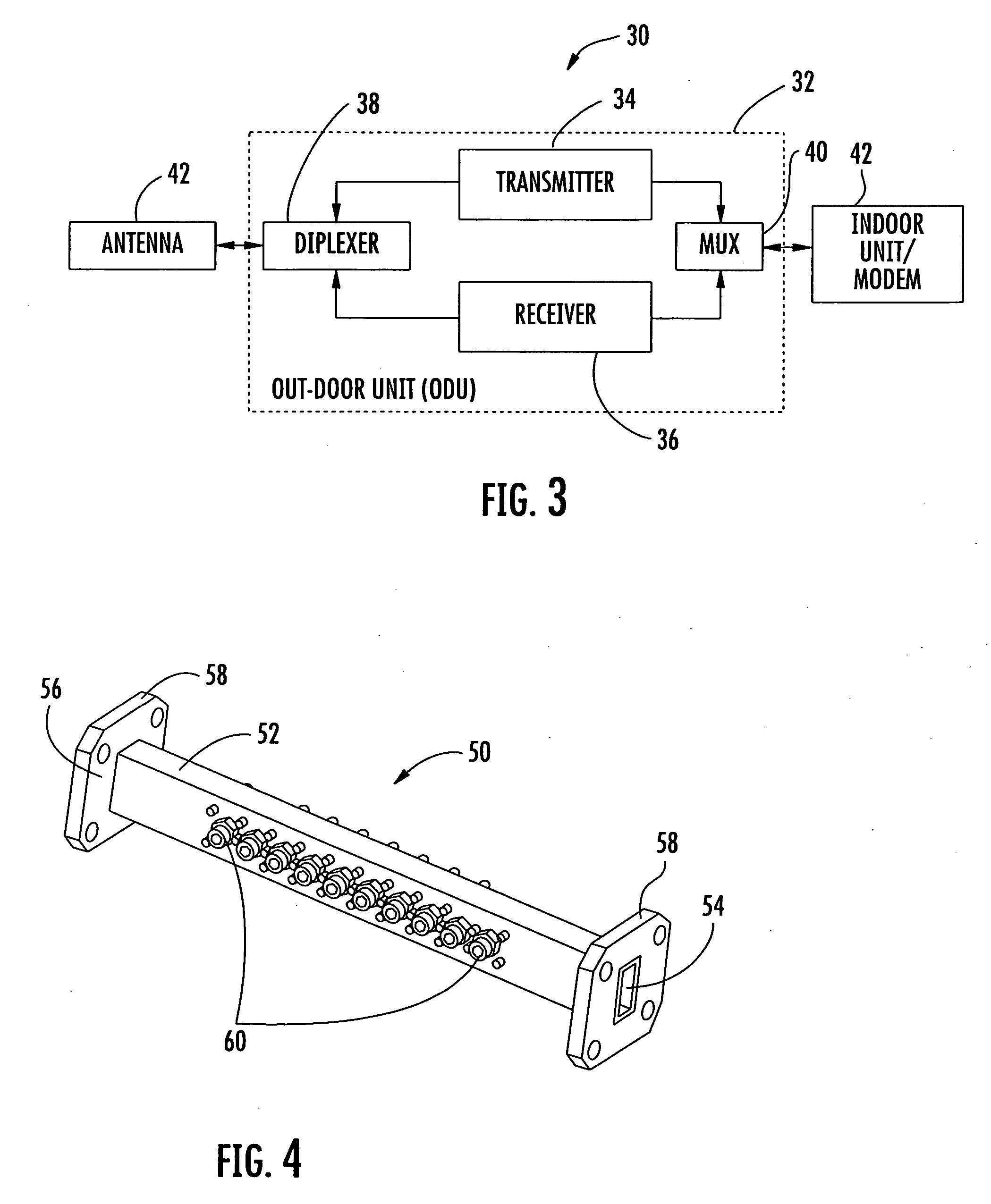
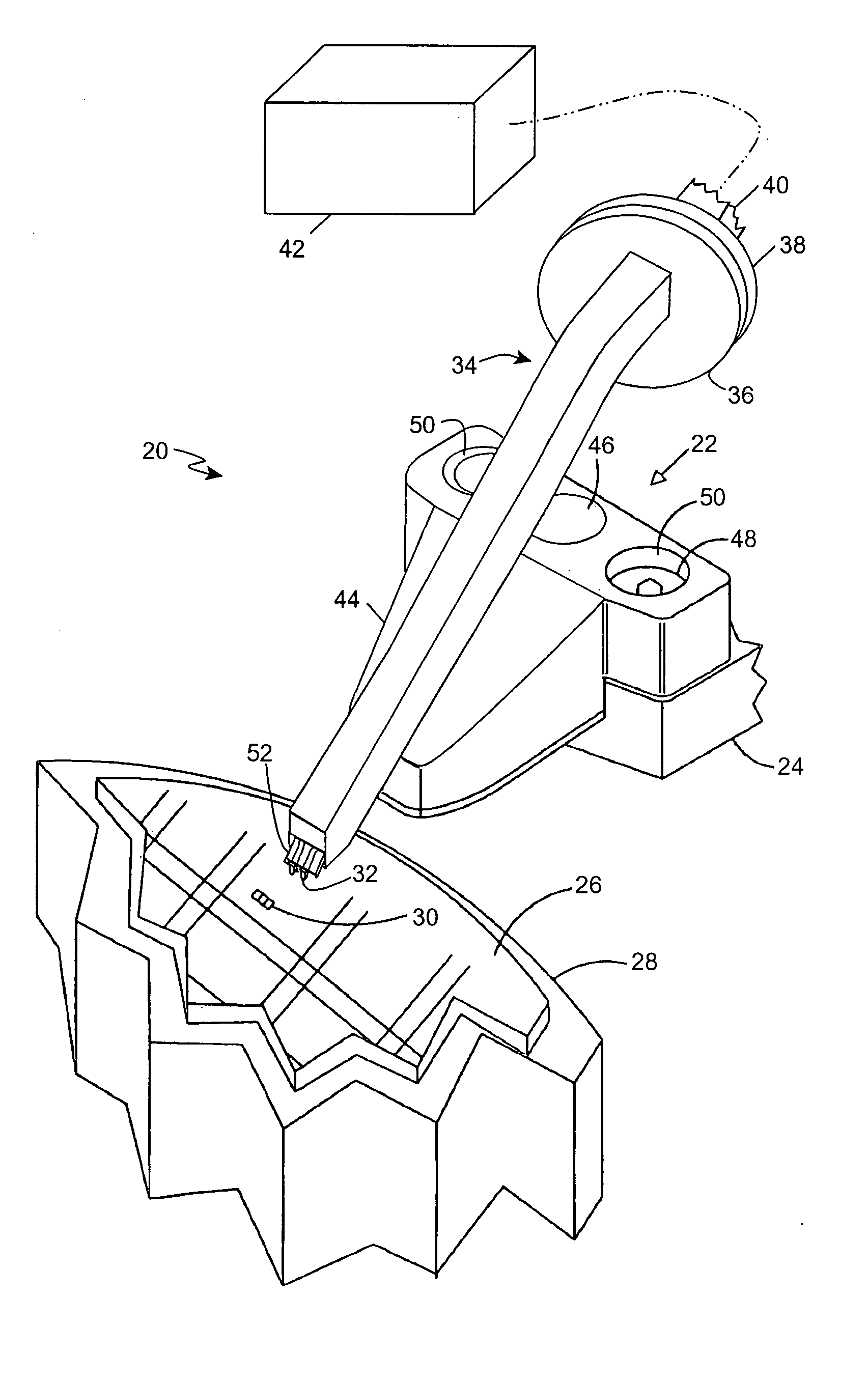
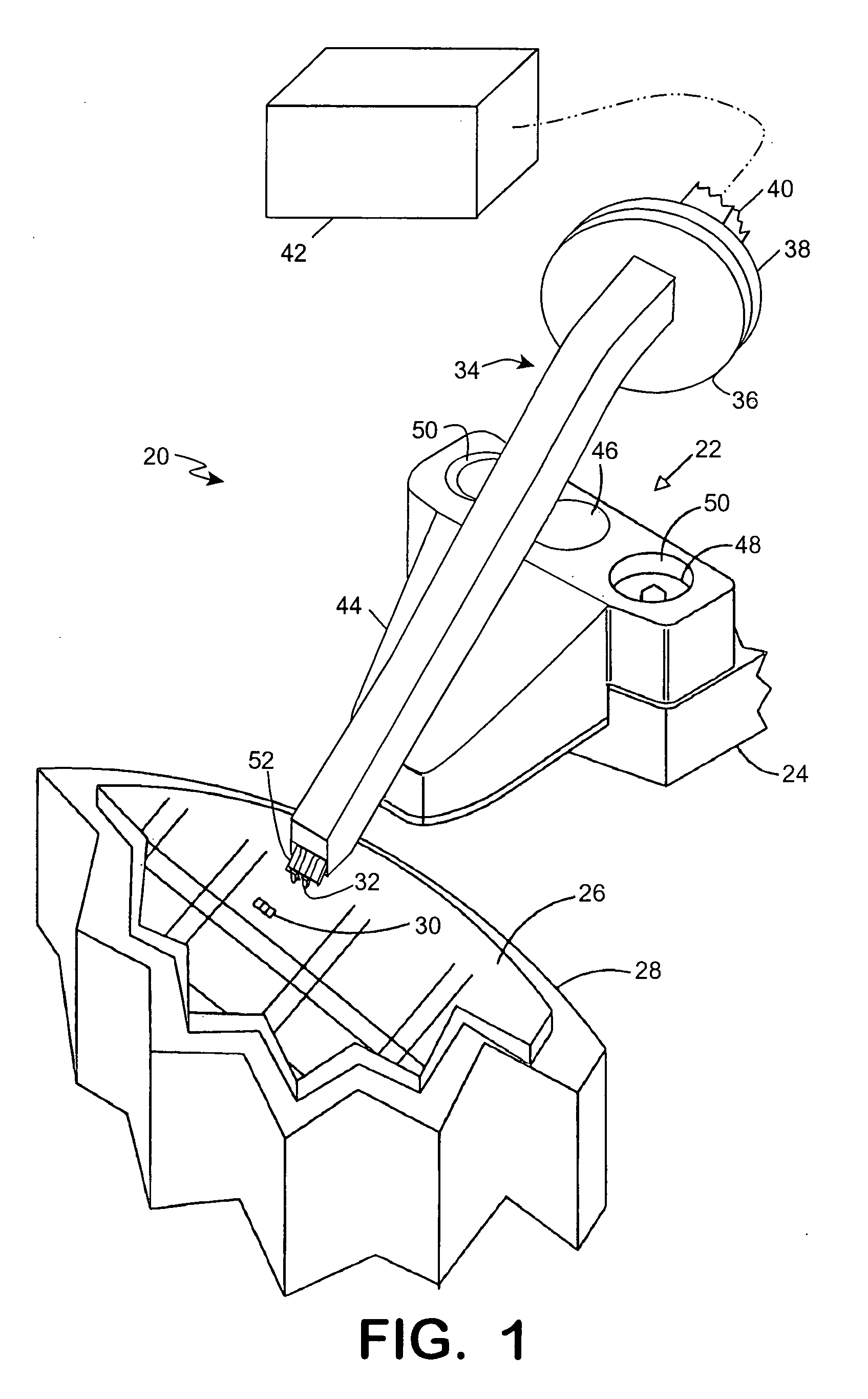
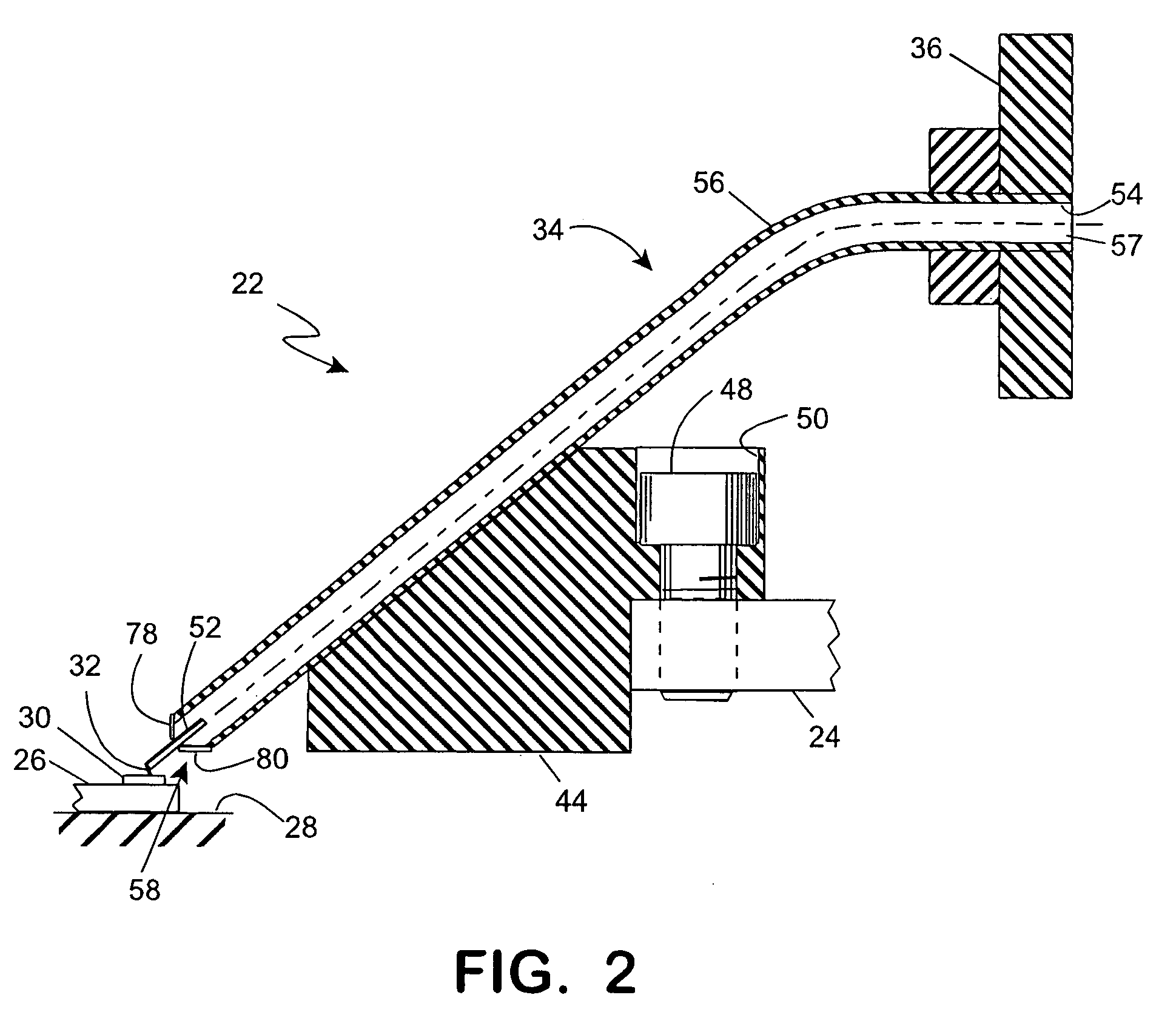
Waveguide antenna front end
ActiveUS20100102899A1Reduced dimensionSmall volumeAdditive manufacturing apparatusCoupling devicesHybrid couplerWaveguide channel
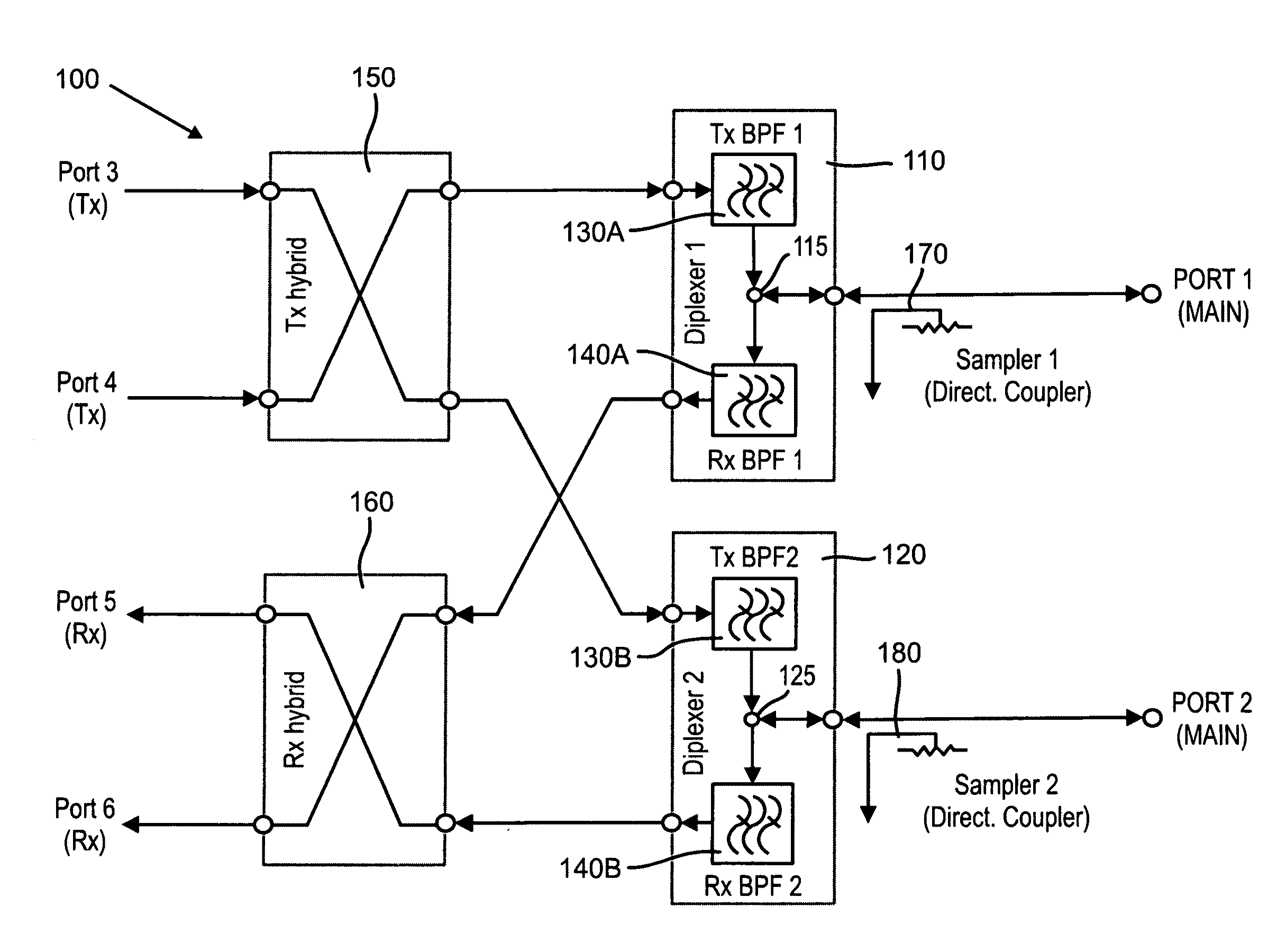
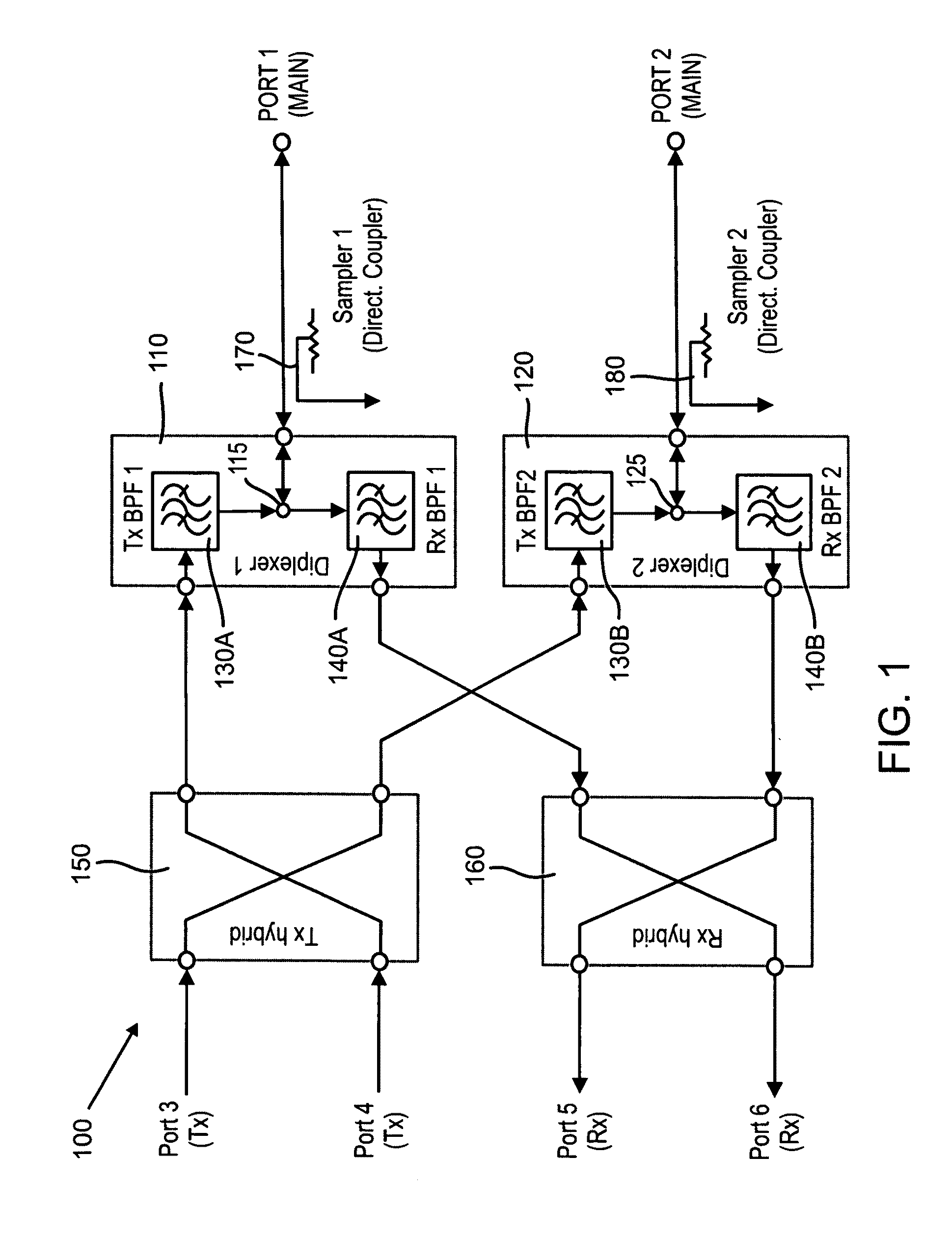
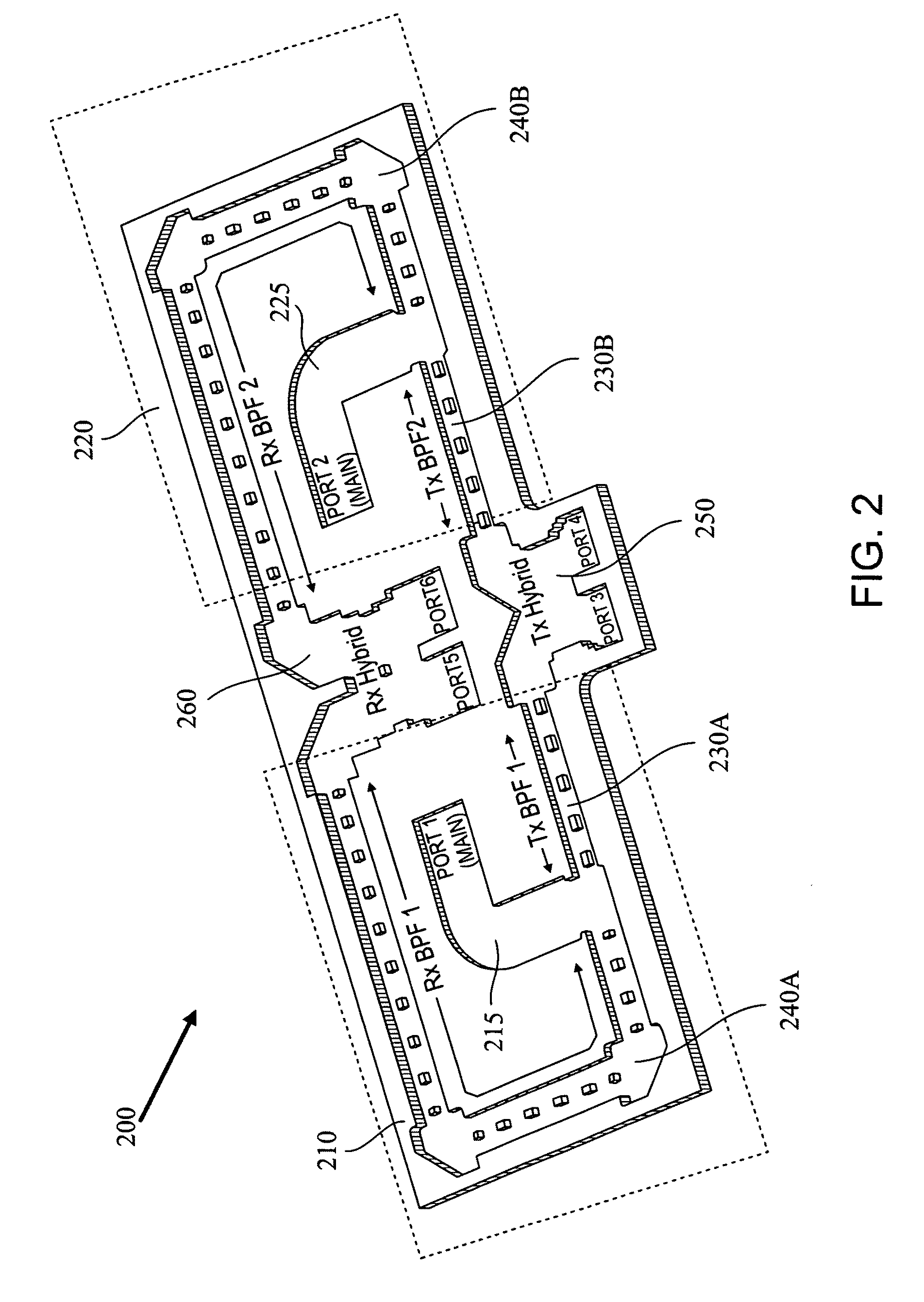
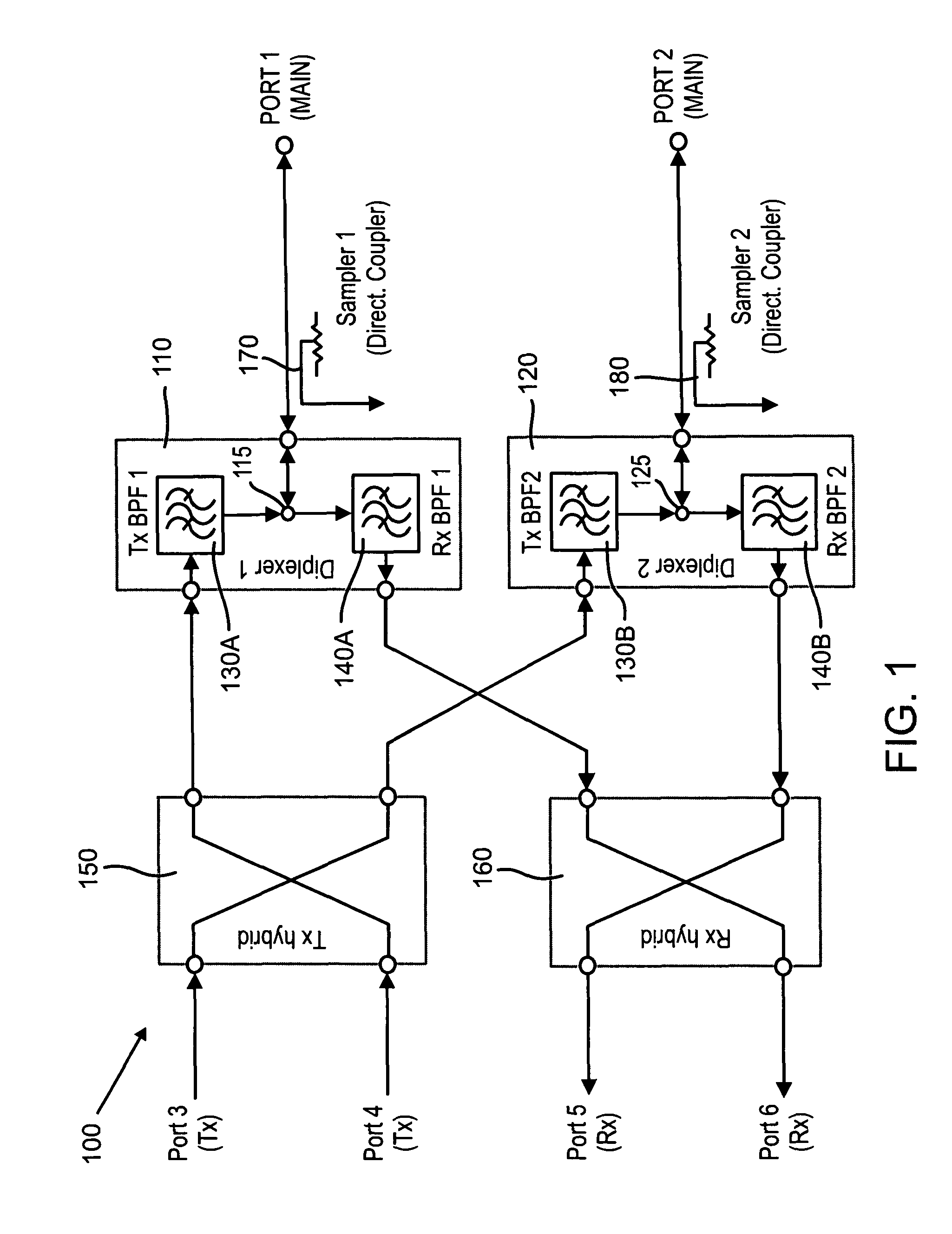
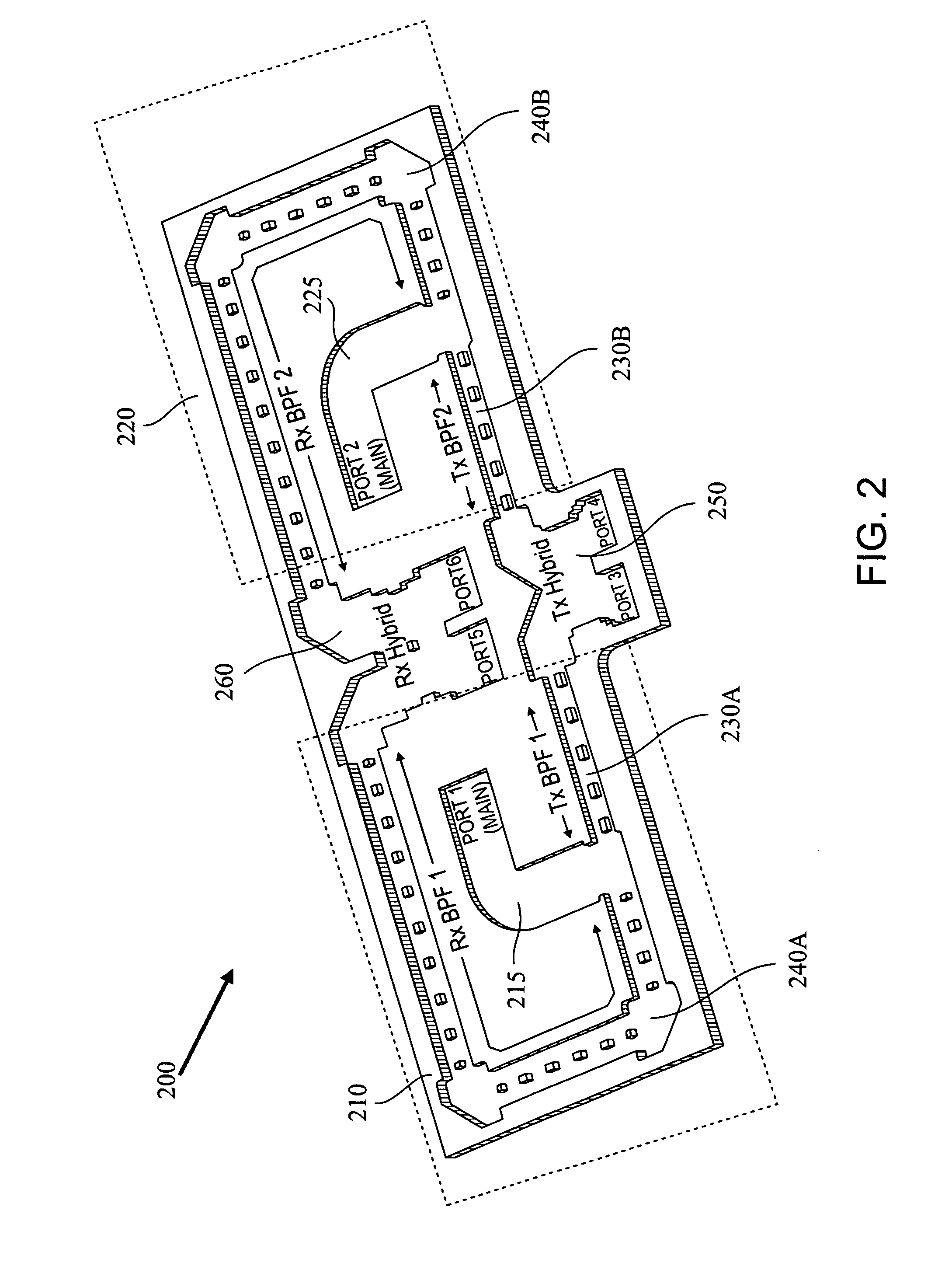
In some embodiments of the present invention, an antenna front end includes at least two diplexers. Each of the diplexers is defined with a channel within a single material block. Each channel is shaped to provide a diplexer which includes a coupler, a receive band filter and a transmit band filter, which are adjoined and matched to form a continuous waveguide channel. Some embodiments further include a transmit hybrid coupler and / or a receive hybrid coupler. The transmit hybrid coupler is formed as a channel within the material block and adjoined and matched to the two transmit band filters. The receive hybrid coupler is formed as a channel within the material block and adjoined and matched to the two receive band filters.
Owner:PANASONIC AVIONICS CORP
Integrated optic waveguide immunosensor
InactiveUS7537734B2High strengthOptical rangefindersMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorGratingTotal internal reflection
A composite waveguide for evanescent sensing in fluorescent binding assays comprising a substrate layer having one or more thin-film waveguide channels deposited thereon. Binding molecules having the property of binding with specificity to an analyte are immobilized on the surface of the thin-film channels. In preferred embodiments, the composite waveguide includes integral light input coupling means adapted to the thin-film channels. Light coupling means may include a grating etched into the substrate prior to deposition of the thin film, or a waveguide coupler affixed to the upper surface of the thin film. The waveguide coupler has an input waveguide of high refractive index which receives the laser light through one end, propagating it by total internal reflection. Propagated light is coupled evanescently into the thin film across a spacer layer of precise thickness with a lower index of refraction than that of the input waveguide or the thin-film waveguide.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
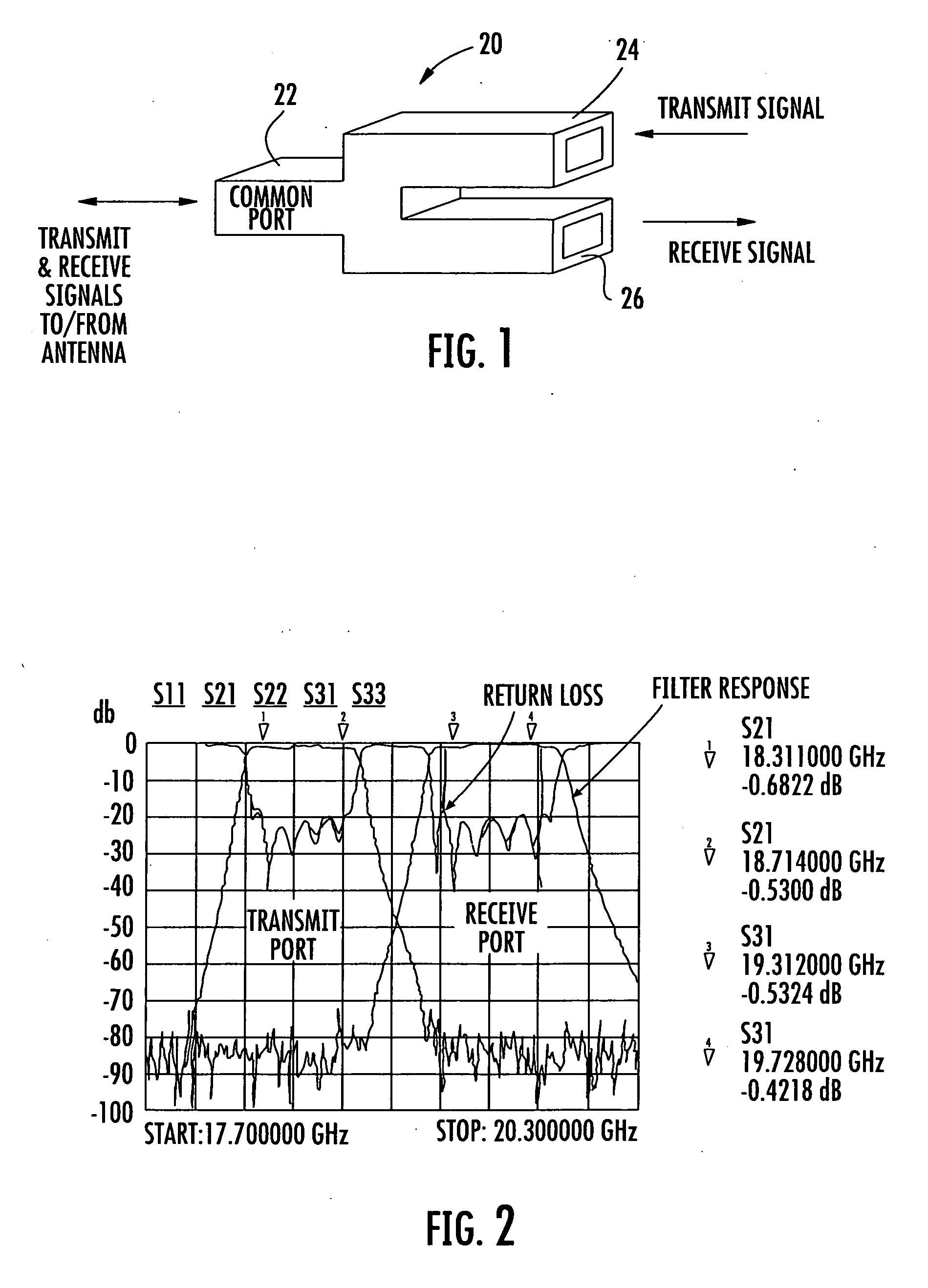
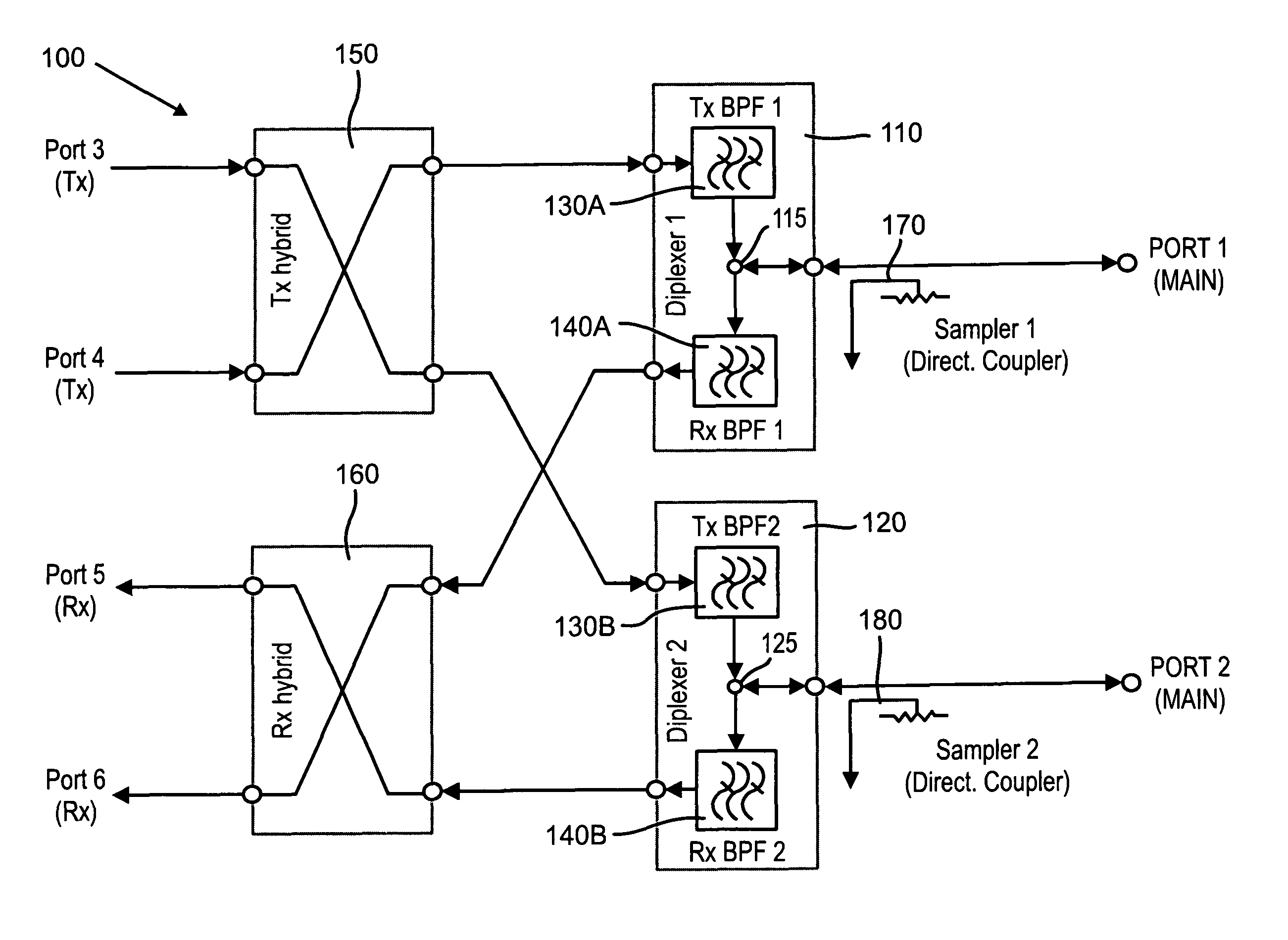
Waveguide diplexer
A diplexer includes a diplexer housing having transmit and receive waveguide channels formed therein. A cover is received on the diplexer housing over the transmit and receive waveguide channels. A septum is inserted between the diplexer housing and cover and configured to provide isolation between any transmitter and receiver signals and a desired frequency band of operation.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
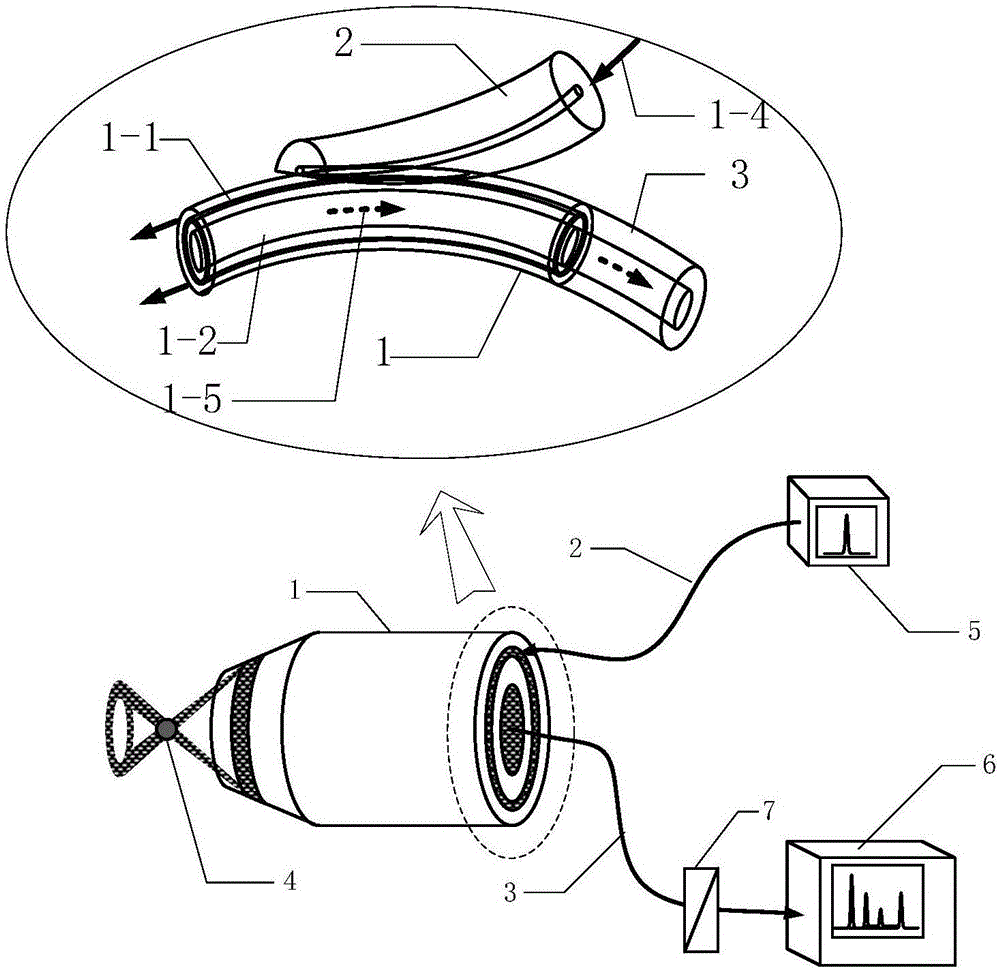
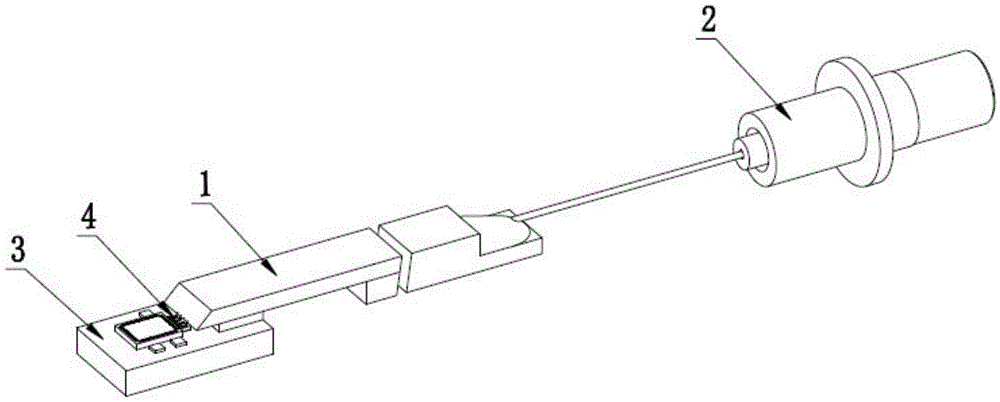
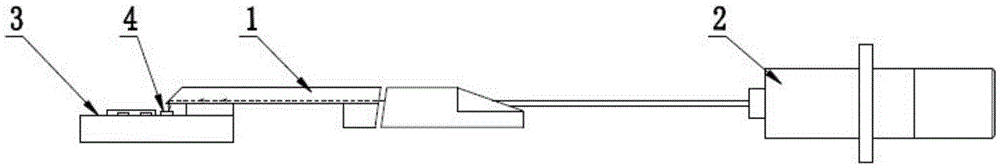
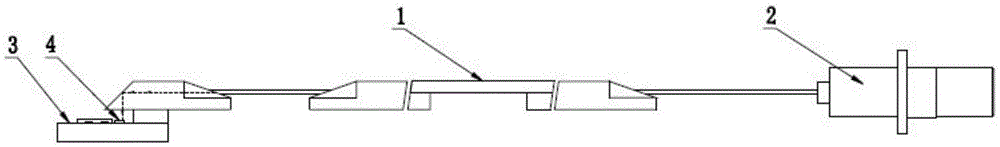
Optical tweezers type optical fiber Raman microprobe and manufacturing method
The invention provides an optical tweezers type optical fiber Raman microprobe and a manufacturing method. The probe has two optical channels which are coaxial, wherein an annular optical fiber core provides a Raman exciting light channel and a channel in the coaxial center is used for receiving Raman probe light; and by performing fine taper angle grinding on the fiber ends of coaxial dual waveguide channel optical fibers, a rotary symmetrical plane (or chambered surface) structure is formed. The structure can converge Raman exciting light transmitted by the annular core in a micron order, and on the one hand, the converged exciting light has an ability of capturing micron-order and nanoscale particles and on the other hand, the converged exciting light interacts with the particles, so that a back scattering Raman optical signal generated by the exciting light converged by the Raman scattering light can be collected and transmitted to a Raman spectrometer through an intermediate large-core fire cores. The microprobe provided by the invention can capture micro living matters of cell living bodies to effectively excite the Raman spectrum of the matters in cells and to obtain the Raman spectrum so as to achieve Raman measurement of micro liquids, single cells in living bodies and inner substances thereof.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Plastic waveguide slot array and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20100238085A1Antenna arrays manufactureLinear waveguide fed arraysInlet channelMetallic materials
The present invention discloses a waveguide antenna structure and a method of manufacture. The waveguide antenna structure can include a non-metallic substrate having a waveguide channel extending along a first direction and an inlet channel extending along a second direction. The inlet channel intersects with the waveguide channel and both channels are at least partially coated with a metallic material. The waveguide channel can have a generally U-shaped cross-section with an open side that is at partially enclosed by a slot plate that is attached to the non-metallic substrate.
Owner:UNIVERSTIY OF CALIFORNIA +1
Waveguide antenna front end
ActiveUS7821355B2Small volumeSmall shapeAdditive manufacturing apparatusCoupling devicesHybrid couplerWaveguide channel
In some embodiments of the present invention, an antenna front end includes at least two diplexers. Each of the diplexers is defined with a channel within a single material block. Each channel is shaped to provide a diplexer which includes a coupler, a receive band filter and a transmit band filter, which are adjoined and matched to form a continuous waveguide channel. Some embodiments further include a transmit hybrid coupler and / or a receive hybrid coupler. The transmit hybrid coupler is formed as a channel within the material block and adjoined and matched to the two transmit band filters. The receive hybrid coupler is formed as a channel within the material block and adjoined and matched to the two receive band filters.
Owner:PANASONIC AVIONICS CORP
CO2 waveguide laser with beryllium oxide waveguides
ActiveUS20050105581A1Active medium materialActive medium shape and constructionMicrometerWaveguide lasers
A pulsed, Q-switched, waveguide CO2 laser includes a plurality of waveguide channels formed in a block of a beryllium oxide ceramic material and is operated at a wavelength between about 9.2 and 9.7 micrometers. The laser has an output power up to 55% greater than that of a similarly configured laser, operated at the same wavelength and pulse conditions, but wherein the waveguide channels are formed in a block of an alumina ceramic material.
Owner:COHERENT INC
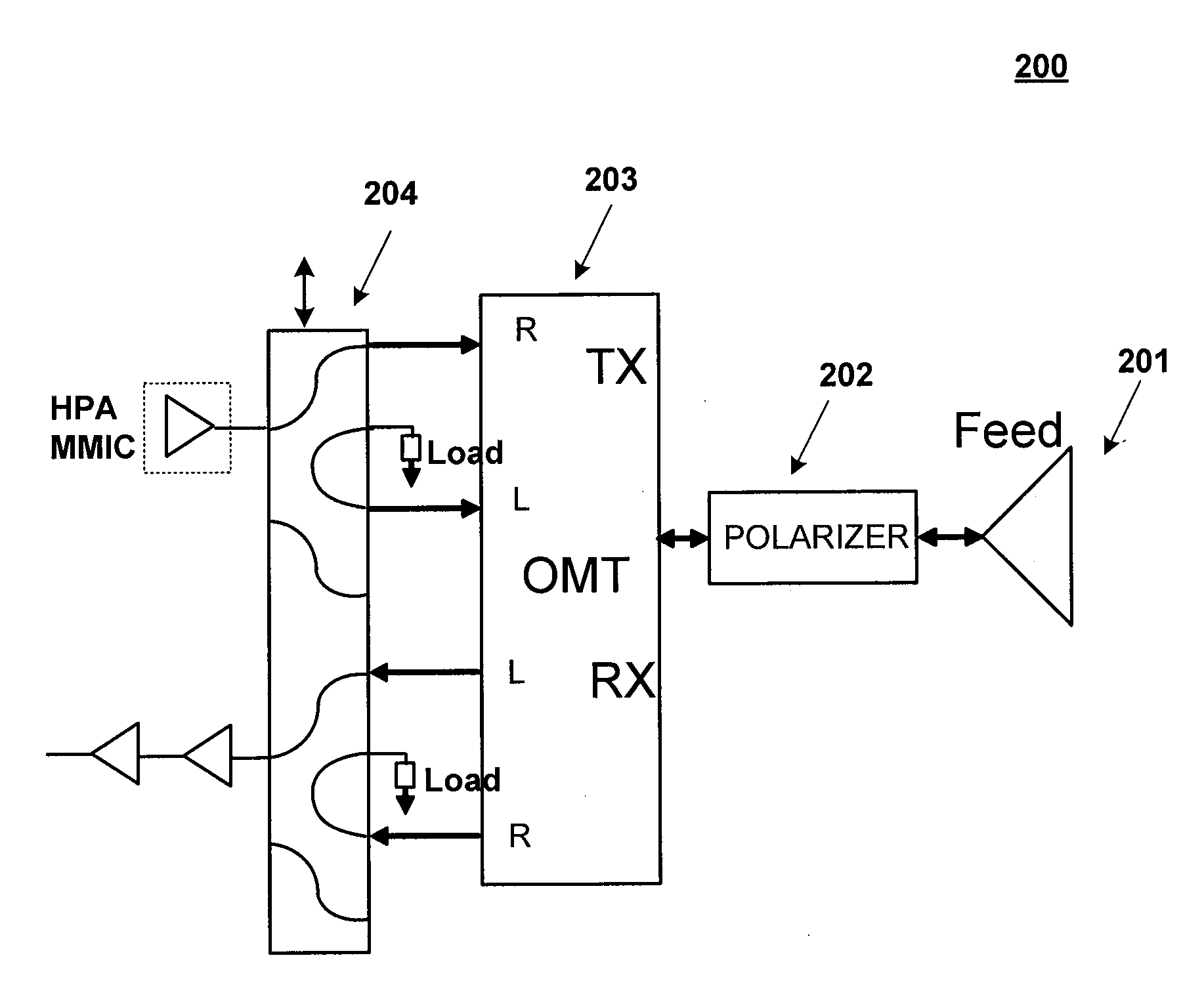
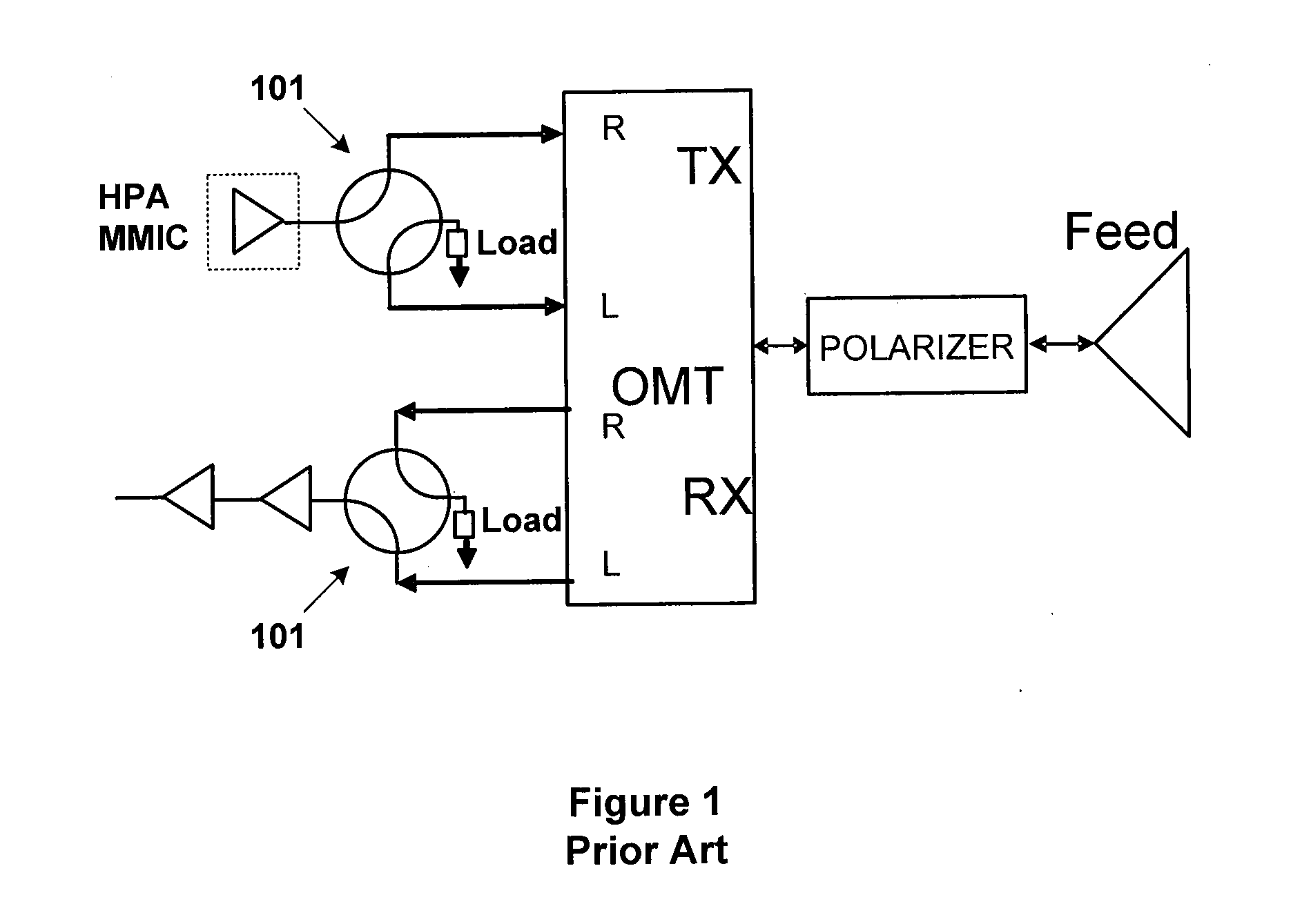
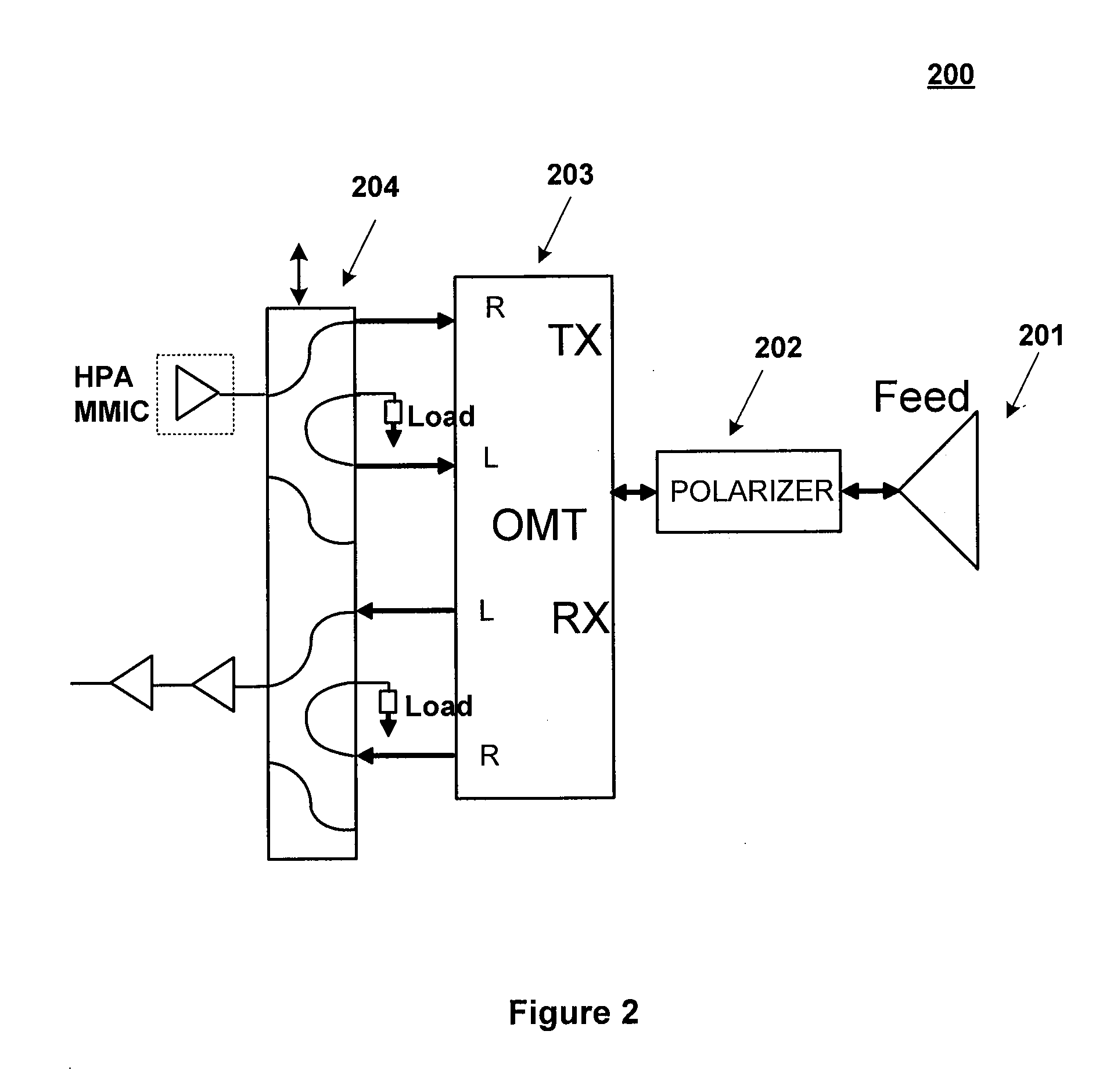
Polarizer and Waveguide Antenna Apparatus Using the Same
A polarizer includes a waveguide channel having a substantially square cross section and a septum disposed within the waveguide channel. The septum includes a stepped edge and two opposite stepped surfaces. The stepped surfaces are sectionally recessed toward each other along the direction pointing toward the interior of the waveguide channel, wherein the number of the steps of the stepped surface is greater than two, but smaller than the number of the steps of the stepped edge. In one embodiment, the square cross section may include a plurality of rounded corners and a plurality of edges extending correspondingly between the rounded corners, wherein the ratio of the radius of the rounded corner to the distance between two opposite edges is in a range of from 0.05 to 0.3.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS TECH INC
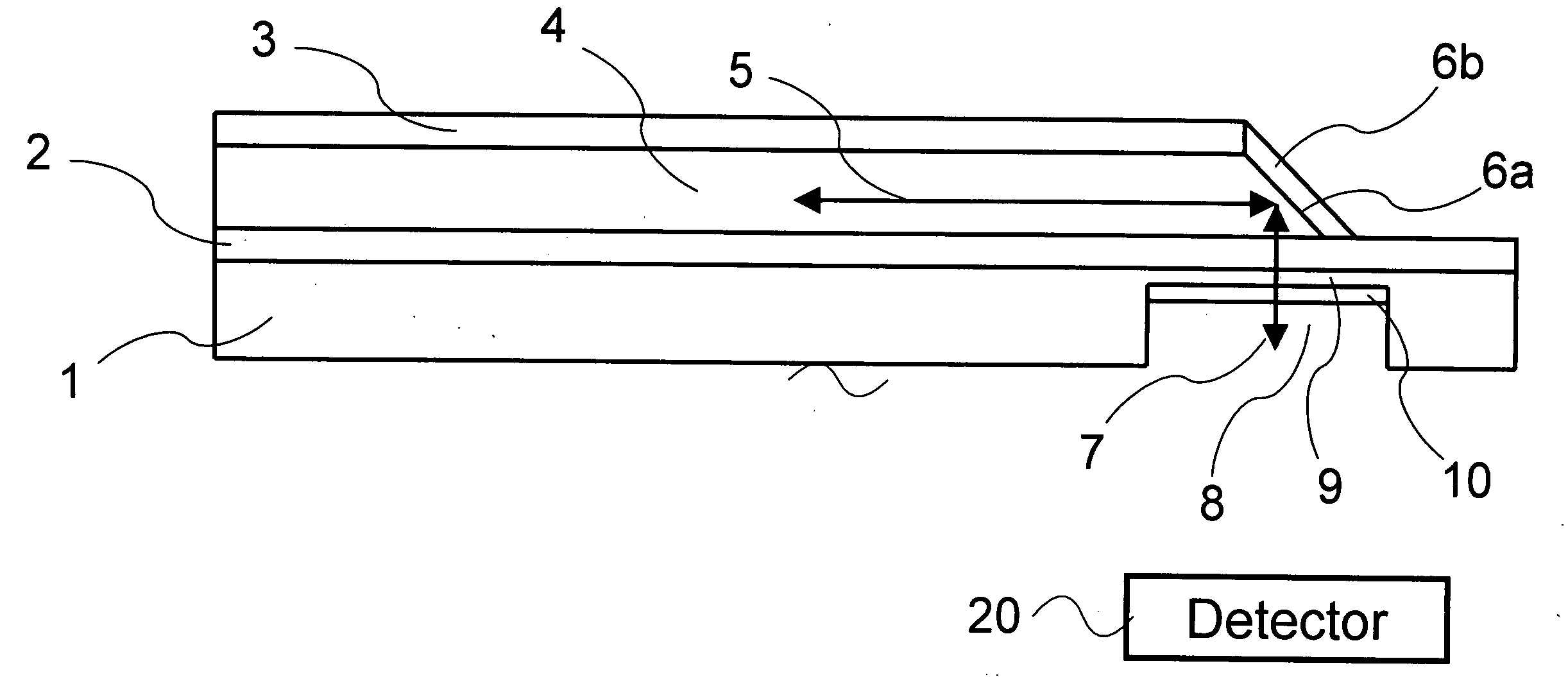
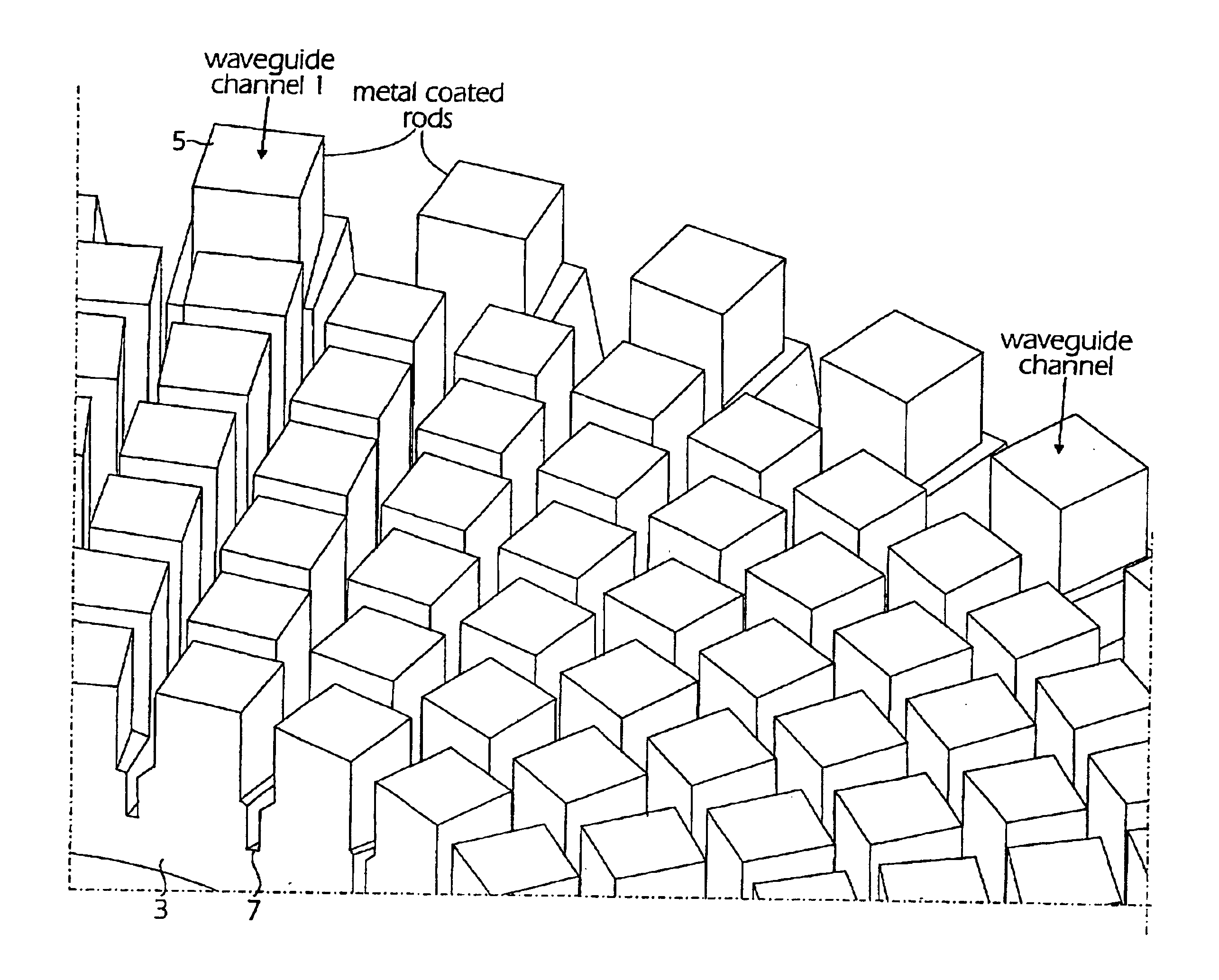
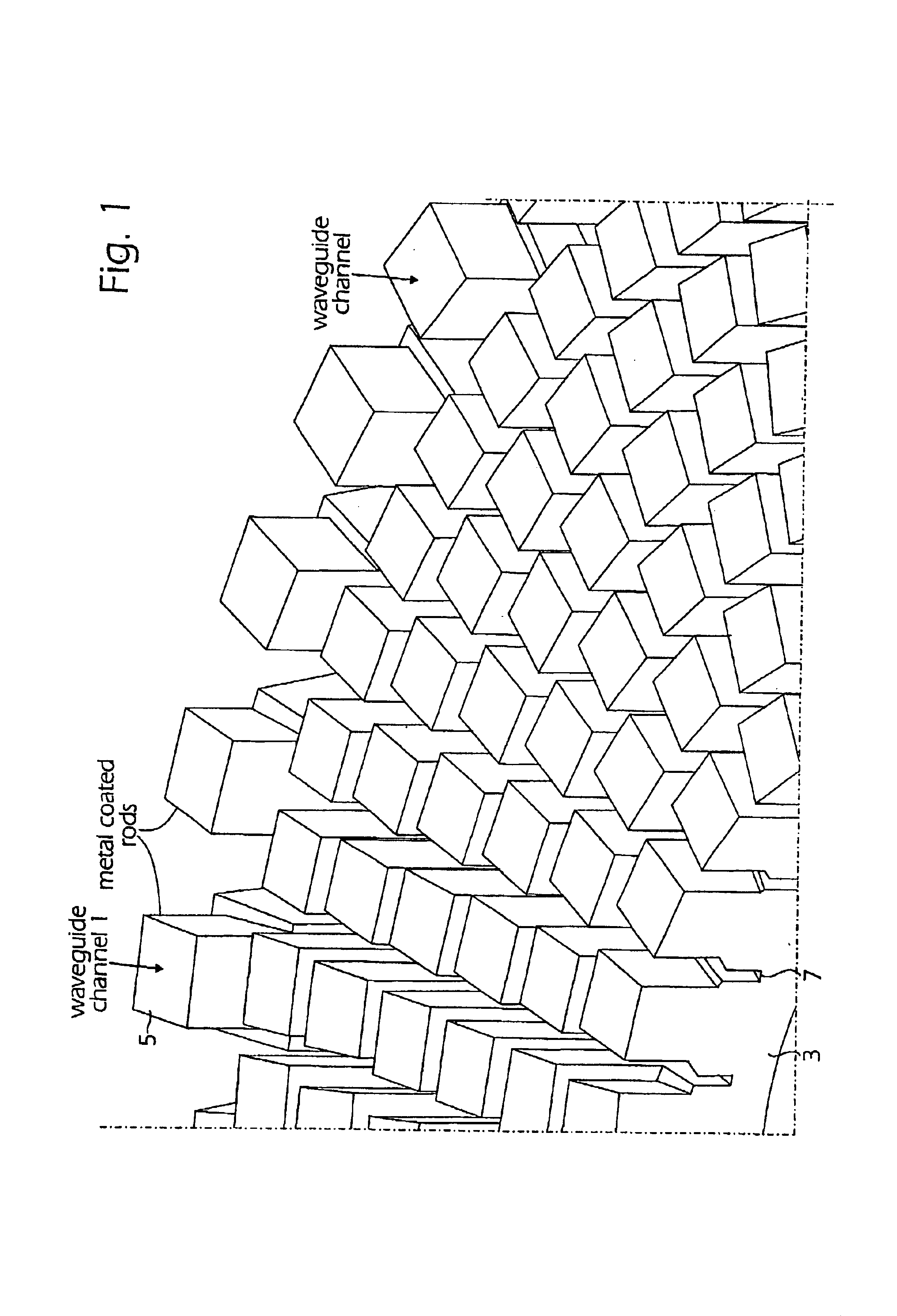
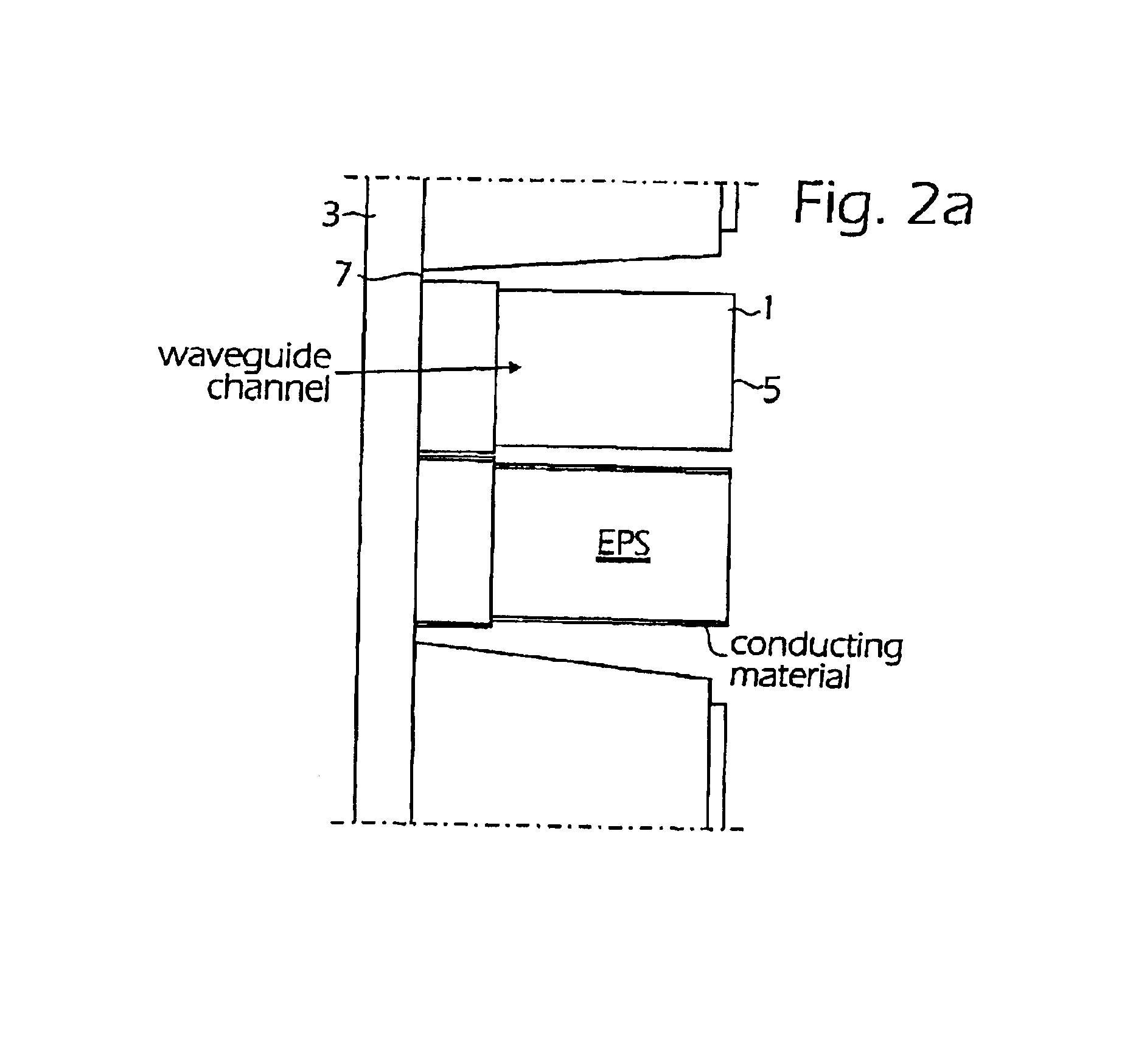
Method of fabricating waveguide channels
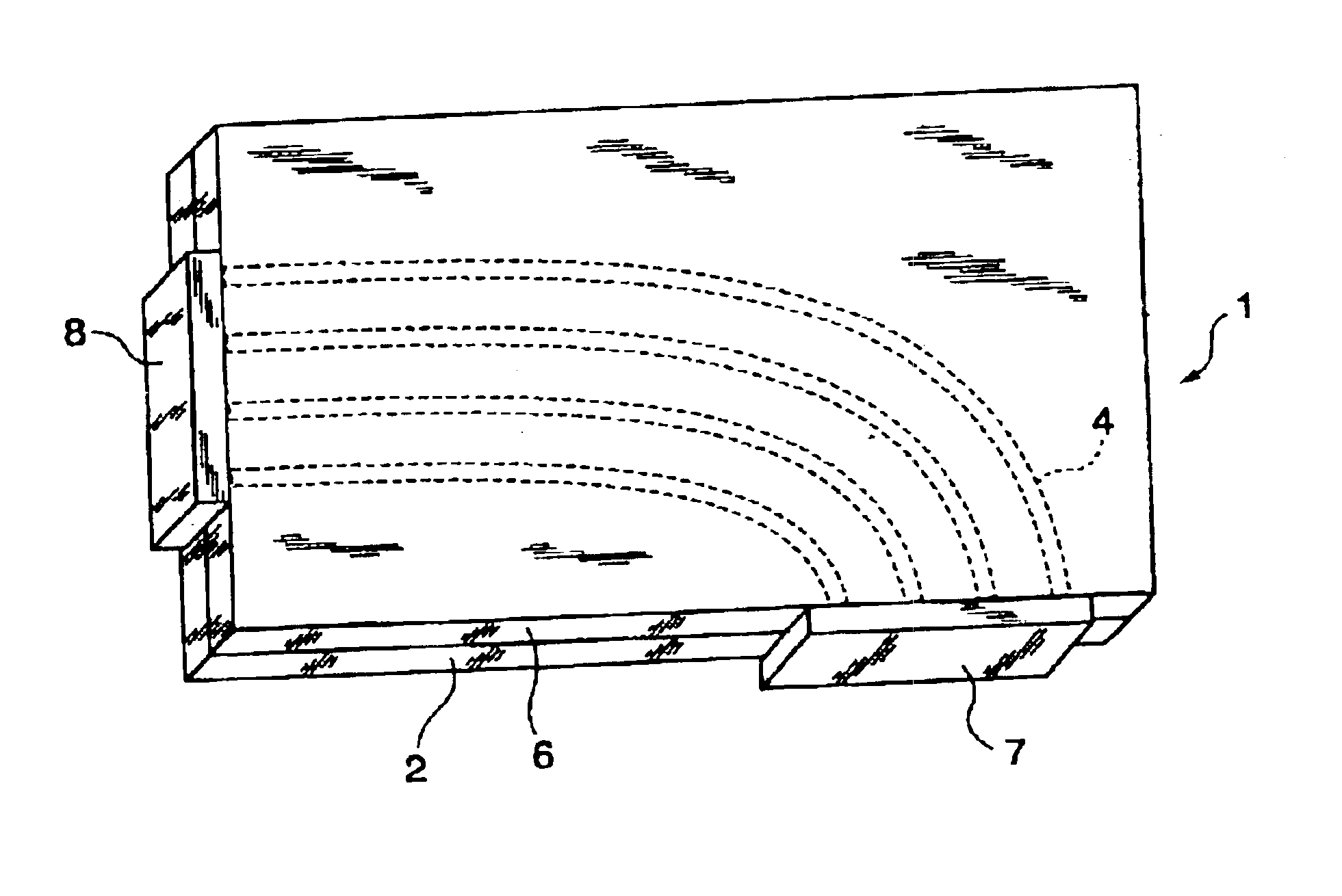
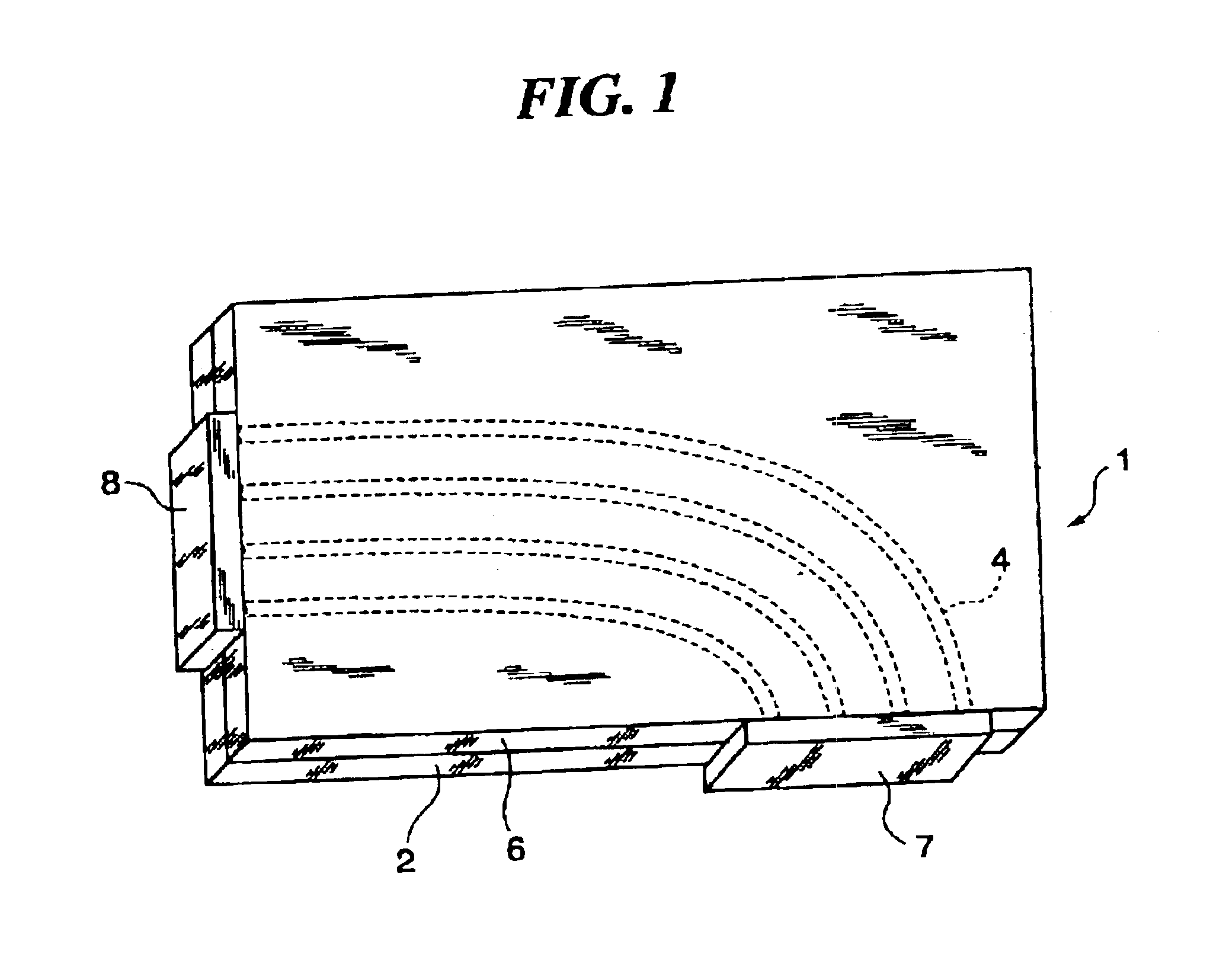
When manufacturing waveguides, for example densely located waveguide channels, for electromagnetic waves such as microwaves, the channels are produced from rod-shaped bodies (1) of a material permeable to the waves and non significantly attenuating the waves. The bodies (1) can for example project from a base plate (3) and their side surfaces are coated with electrically conducting material but not their free end surfaces (5). The interior of the bodies form the waveguide channels, which have their walls formed from the layer of electrically conducting material. By giving the rod-shaped bodies suitable shapes for example an antenna side or half of a waveguide antenna can be manufactured. The rod-shaped bodies can before applying the electrically conducting material be coated with one or several layers of non-attenuating and non-conducting lacquer filling pores and smoothing the surface of the bodies. Thereby, the layer of electrically conducting material obtains a smooth transition surface to the material of the bodies giving the channels good waveguide characteristics. If the material used in the bodies has a strong surface porosity, the channels formed from the rod-shaped bodies become strongly attenuating to the electromagnetic waves. A set of such bodies located at the sides of each other and having suitable dimensions of the bodies gives an element working strongly attenuating to the electromagnetic waves.
Owner:PETERSON STIG ANDERS
Polarizer and waveguide antenna apparatus using the same
A polarizer includes a waveguide channel having a substantially square cross section and a septum disposed within the waveguide channel. The septum includes a stepped edge and two opposite stepped surfaces. The stepped surfaces are sectionally recessed toward each other along the direction pointing toward the interior of the waveguide channel, wherein the number of the steps of the stepped surface is greater than two, but smaller than the number of the steps of the stepped edge. In one embodiment, the square cross section may include a plurality of rounded corners and a plurality of edges extending correspondingly between the rounded corners, wherein the ratio of the radius of the rounded corner to the distance between two opposite edges is in a range of from 0.05 to 0.3.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS TECH INC
Optical back plate interconnection system and communication equipment
ActiveCN101882955ARealize transmissionReduce lossCircuit optical detailsOrthogonal PCBs mountingHigh densityInterconnection
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Optical modulator
InactiveUS6600843B2Increase transfer speedIncrease distanceCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexElectron
An optical modulator has optical channels formed in a waveguide substrate in which two of the waveguide channel branches have reverse polarity relative to each other. In addition, the optical modulator has at least one of the following: 1) an electronic signal electrode and an electronic ground electrode are placed in proximity with opposite faces of the waveguide substrate, 2) a portion of said waveguide substrate is removed to afford a reduced electronic signal refractive index, and 3) the waveguide substrate has a fixing substrate attached to it with the refractive index of the fixing substrate lower than said refractive index of the waveguide substrate.
Owner:SRICO
Waveguide 90-degree turning structure with polarization turning function
InactiveCN104716406ASimple structureEnsure consistencyWaveguide type devicesPerpendicular polarizationWaveguide channel
The invention discloses a waveguide 90-degree turning structure with the polarization turning function. The waveguide 90-degree turning structure comprises a body. A horizontal polarization waveguide channel and a perpendicular polarization waveguide channel which are perpendicular to each other are arranged on the body. The waveguide 90-degree turning structure is characterized in that the horizontal polarization waveguide channel and the perpendicular polarization waveguide channel are connected through a butterfly-shaped cavity and a multistage stepped structure. The horizontal polarization waveguide channel and the perpendicular polarization waveguide channel are rectangular waveguide pipes, and a horizontal polarization waveguide channel opening and a perpendicular polarization waveguide channel opening are symmetric about the center line of the body. The structure is formed by machining and assembling two machined metal components. The waveguide 90-degree turning structure is simple and the polarization direction and the propagation direction can be turned by 90 degrees synchronously. Waveguide openings are symmetric about the center line, consistency is well guaranteed, large-scale production is facilitated, and the waveguide 90-degree turning structure is suitable for occasions with strict requirements for the position of the waveguide pipes.
Owner:PIVOTONE COMM TECH
Electromechanical polarization switch
In accordance with various aspects of the present invention, a method and system for electro-mechanical polarization switching in an antenna system is presented. The antenna system may comprise an integrated waveguide in a transceiver housing, where the waveguide has at least four channels. In an exemplary embodiment, a sliding switch is incorporated into the waveguide. The sliding switch is configured to switch the polarization of the antenna system by physically realigning the waveguide channels. The sliding switch may be electro-magnetically controlled. Furthermore, the polarization switching may be performed to assist in load balancing for a particular frequency and / or polarization combination.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Packaging structure of light receiving/ transmitting sub module and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105425351AExcellent performance indexQuality assuranceCoupling light guidesPigtailLight reflection
The invention relates to a packaging structure of a light receiving / transmitting sub module. The packaging structure comprises an arrayed waveguide grating chip, an optical fiber pigtail assembly and a photo-electric / electro-optic conversion circuit board, wherein one end face of the arrayed waveguide grating chip is ground to form a ground angle of more than 10 degrees, and the photo-electric / electro-optic conversion circuit board is horizontally placed below the arrayed waveguide grating chip; and the optical fiber channel of the optical fiber pigtail assembly is correspondingly connected with a waveguide channel on the other end face of the arrayed plane waveguide grating chip through an optical fiber. One end face of the arrayed waveguide grating chip is machined to form a certain reflective angle and then directly coupled with an arrayed photo-electric diode or a laser chip on the photo-electric / electro-optic conversion circuit board to manufacture the light receiving / transmitting sub module, and only one optical fiber pigtail assembly is needed, so that the overall structure is simple, the loss is low and the cost is low; the process flow is simplified in the method of coupling with spatial light reflection, the operation is convenient, and the packaging structure is suitable for batch production.
Owner:BROADEX TECH
Liquid core waveguide assembly and detecting system including the same
InactiveUS20110149286A1Overcomes drawbackCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLiquid coreFiber
A liquid core waveguide assembly includes: a waveguide-forming body formed with a waveguide channel and first and second fiber channels, transparent first and second partition walls, and a liquid inlet in fluid communication with the waveguide channel, the waveguide channel having a first end spaced apart from the first fiber channel by the first partition wall, and a second end spaced apart from the second fiber channel by the second partition wall; and at least one first optical fiber and at least one second optical fiber extending into the first and second fiber channels, respectively. A detecting system including the liquid core waveguide assembly is also disclosed.
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN OCEAN UNIVERSITY
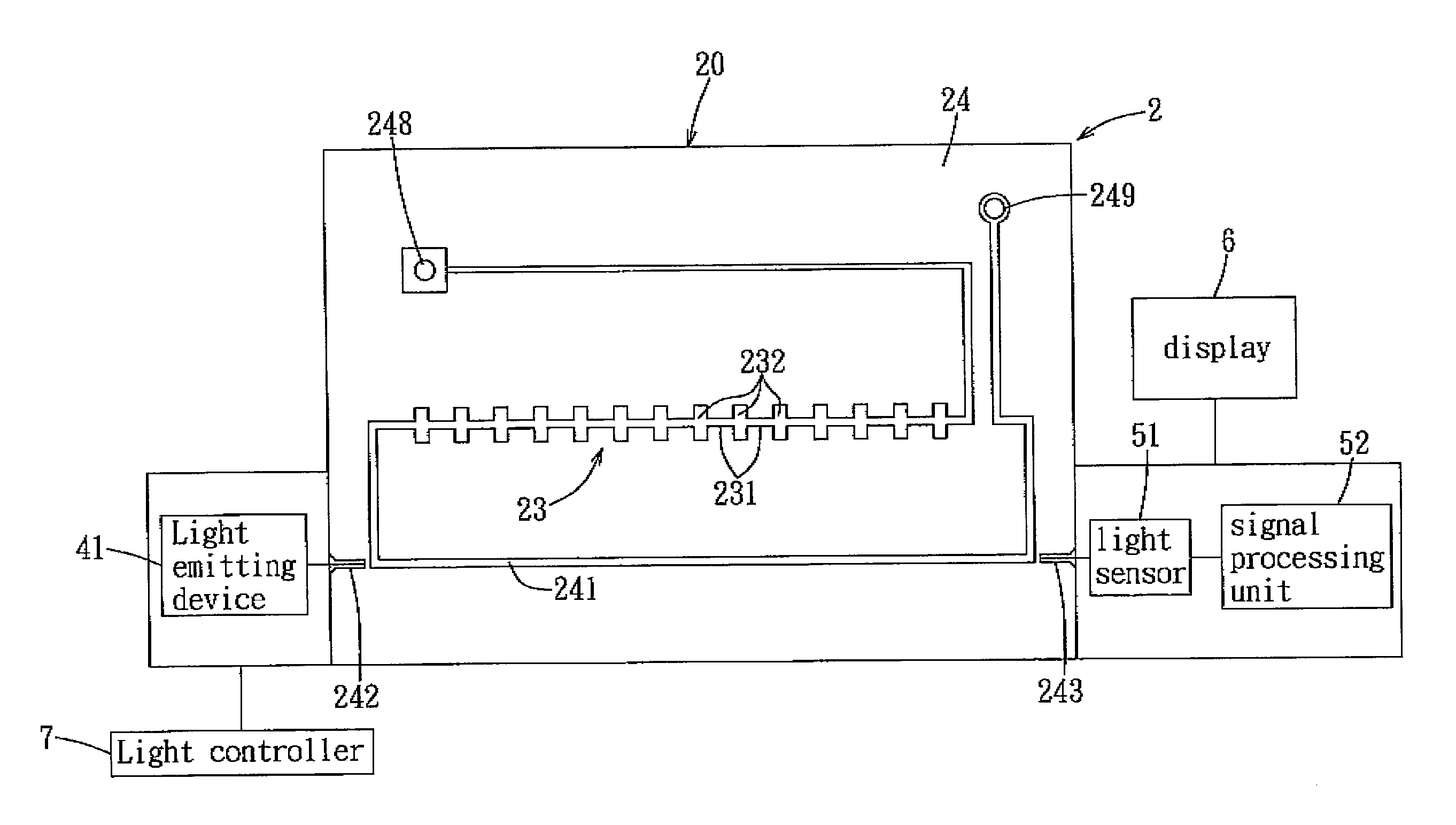
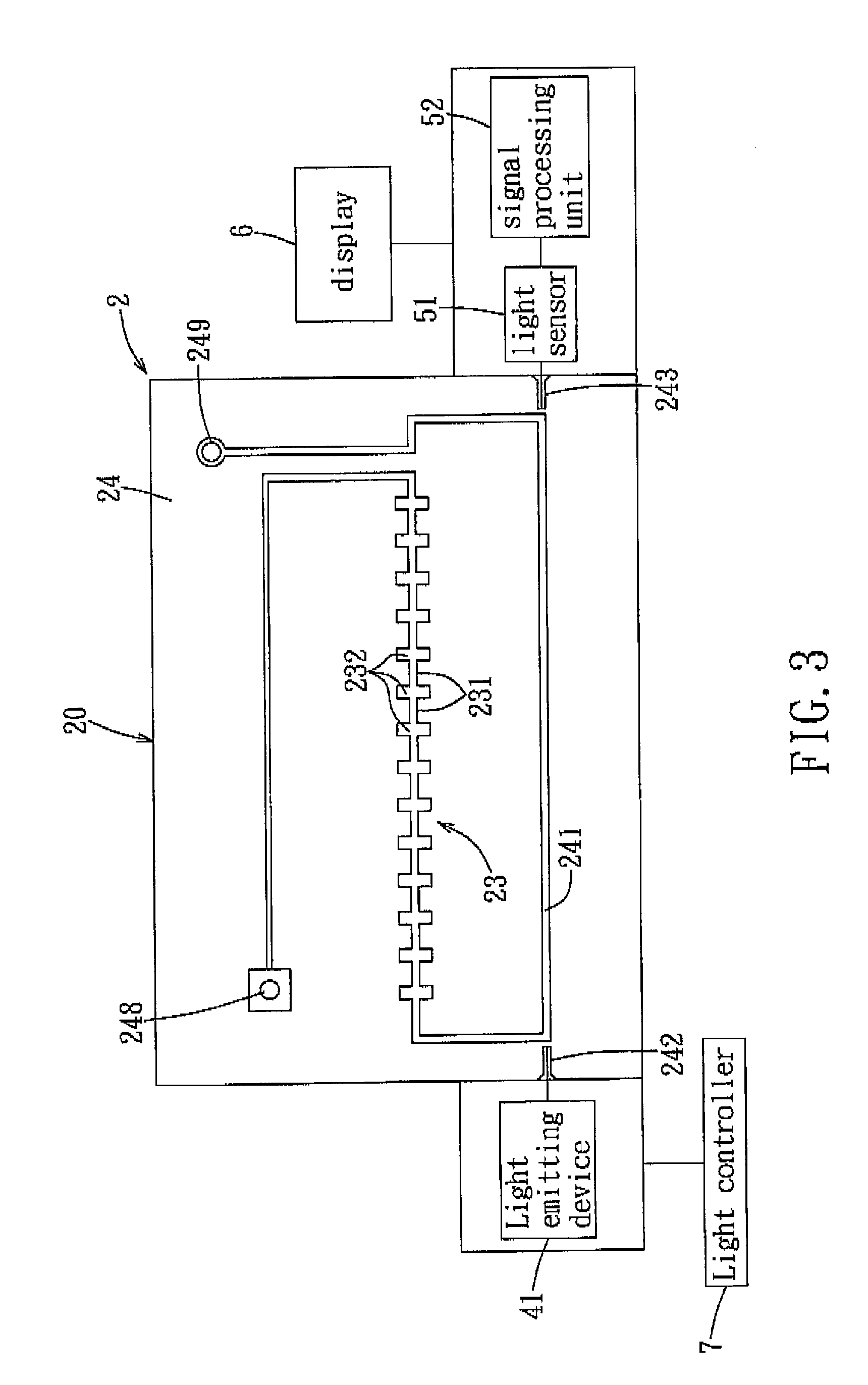
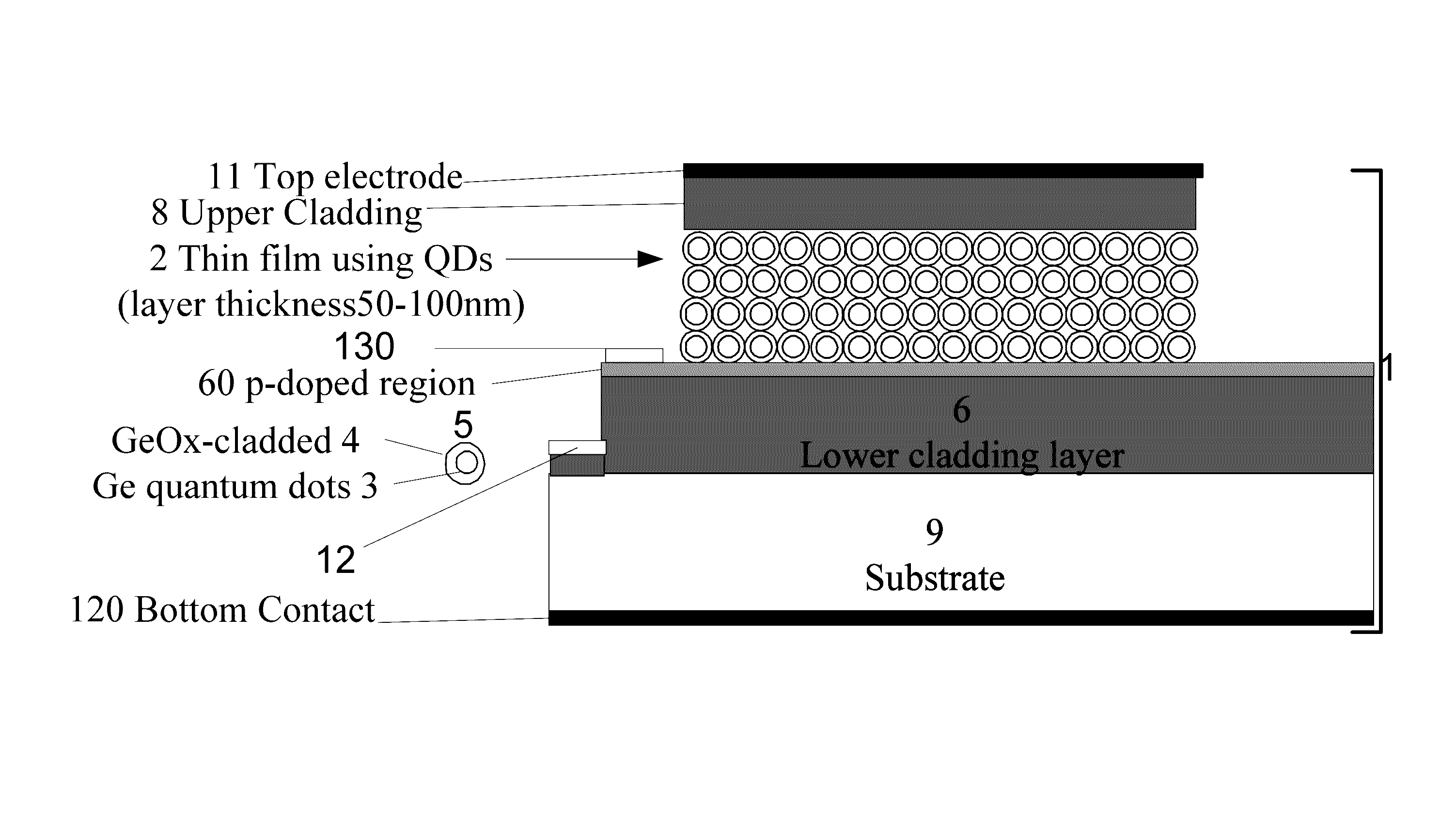
Article and method for implementing electronic devices on a substrate using quantum dot layers
Novel use of a cladded quantum dot array layer serving as a waveguide channel by sandwiching it between two cladding layers comprised of lower index of refraction materials is described to form Si nanophotonic devices and integrated circuits. The photonic device structure is compatible with Si nanoelectronics using conventional, quantum dot gate (QDG), and quantum dot channel (QDC) FET based logic, memories, and other integrated circuits.
Owner:JAIN FAQUIR CHAND +1
Monolithic wafer-scale waveguide-laser
InactiveUS20050169339A1Enhanced couplingActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionRare-earth elementCoupling
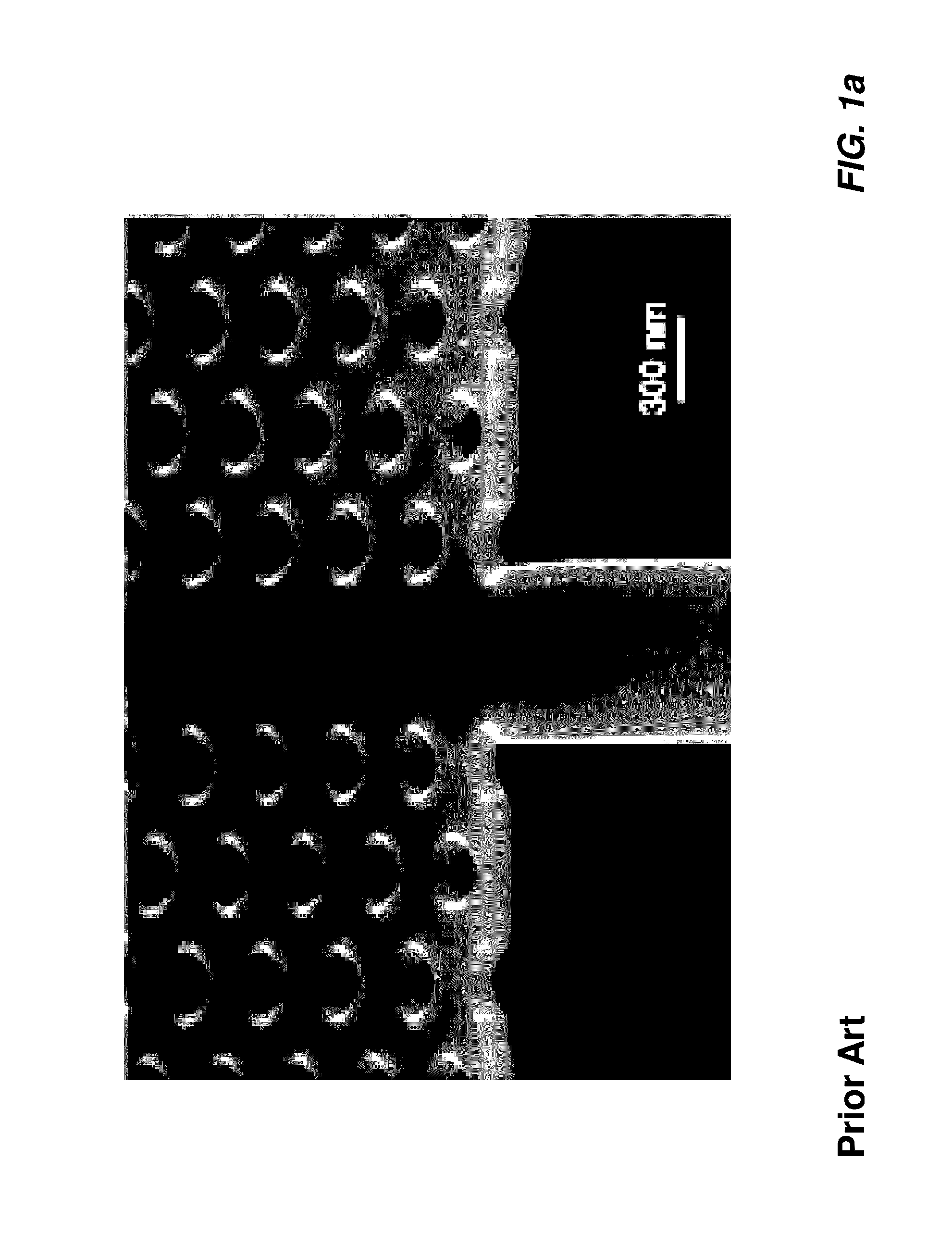
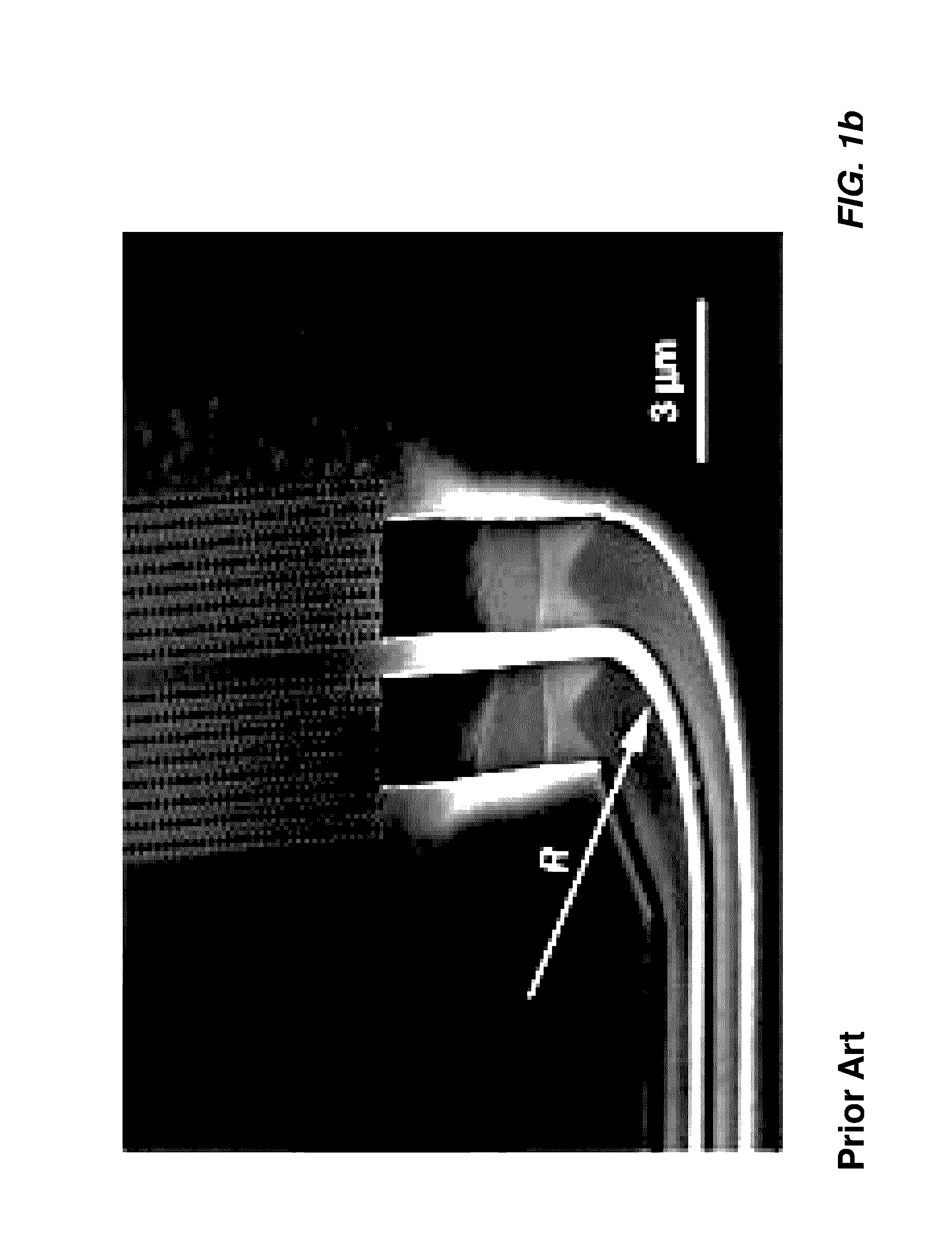
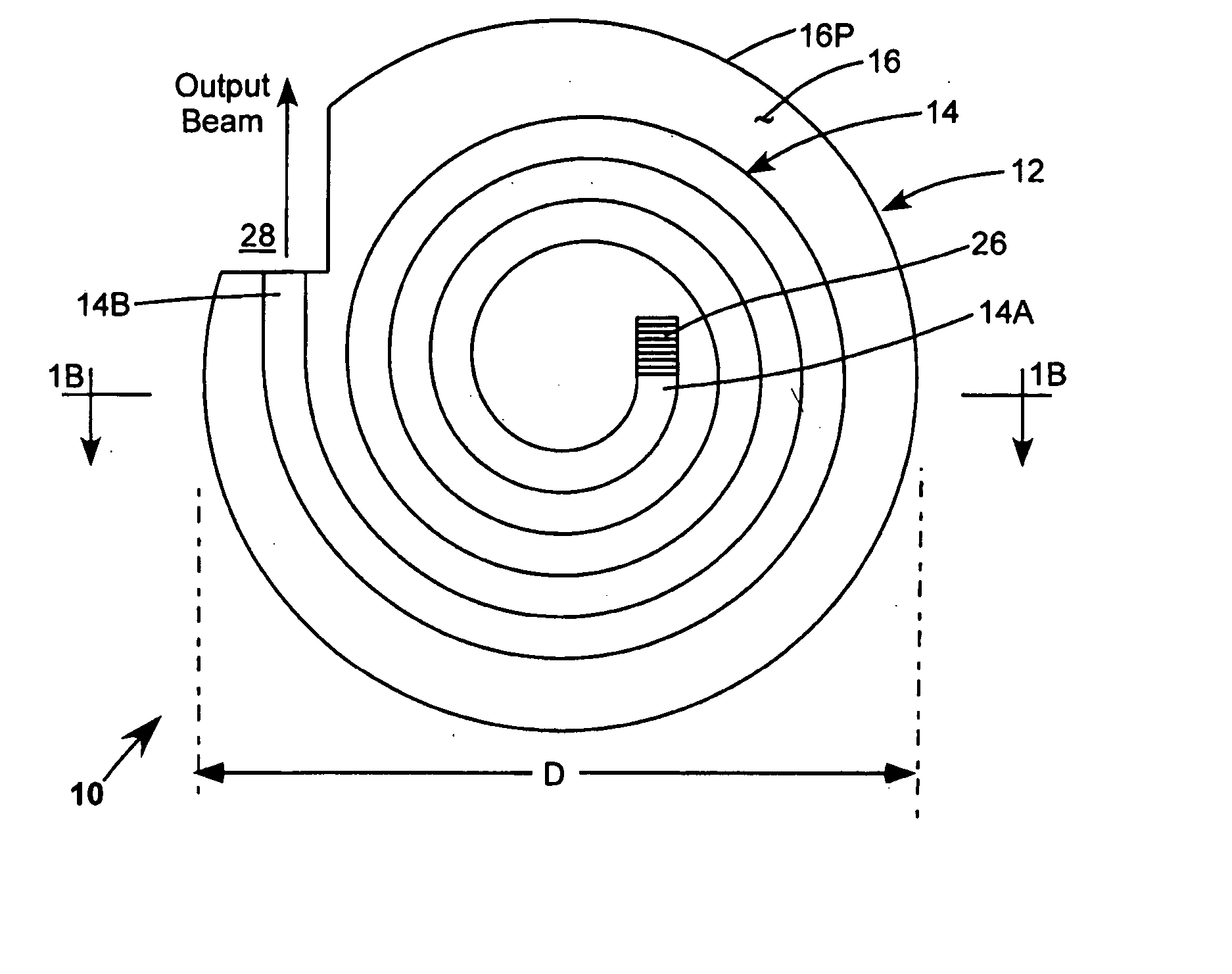
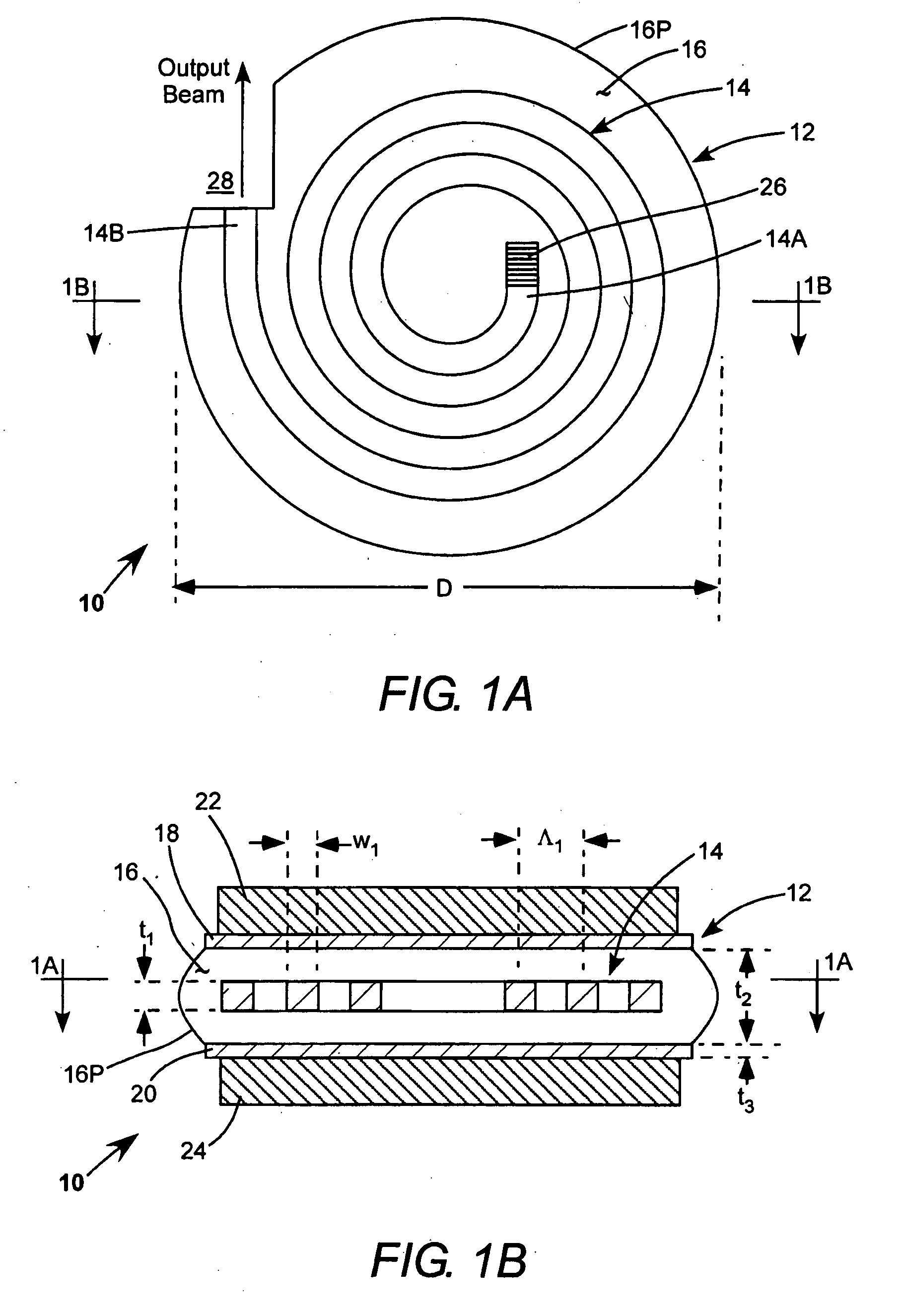
A waveguide laser is formed by starting with a glass disc doped with a rare earth element to define a lasant material. The disc is etched or machined to define an elongated waveguide channel having a spiral configuration. The open area between the walls of the waveguide channel is filled with a cladding material. An end reflector is formed on the radial inner end of the spiral waveguide. First cladding layers are formed on both sides of the spiral waveguide. A second cladding layer is deposited on at least one of the first cladding layers. A heat sink is connected to the second cladding layer. A plurality of optical pump sources are positioned about the side walls of the structure to excite the lasant material and generate a laser beam. In one preferred embodiment, the side walls of the structure are provided with a convex configuration to enhance pump coupling.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Surface enhanced fiber Raman probe
ActiveCN106596508ASimple structureCompact structureRaman scatteringFiberSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention provides a surface enhanced fiber Raman probe. A metal nano-layer used for surface enhancement is prepared at the fiber end of a coaxial double-waveguide channel fiber, then the fiber end is finely ground to form an arc frustum playing the role of reflecting and converging exciting light in an annular core, and the converged exciting light is just positioned on the metal nano-layer, so that the exciting light and a substance to be tested at the contact point of the end surface of the probe are sufficiently interacted. When the exciting light passes through the metal nano-layer, surface enhancement Raman signals are generated by assistance of stimulation of surface plasma waves and the interaction with detected substances, so that the detection sensitivity of the fiber Raman probe is greatly improved. The surface enhanced fiber Raman probe can be used for the accurate positioning contact type measurement of a surface enhanced Raman spectrum, and is particularly suitable for the acquisition and measurement of a positioning contact type surface enhanced Raman spectrum of living cell tissues.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Optical waveguide sensor and preparation methods thereof
InactiveCN101832792AImprove efficiencyReduce manufacturing costThermometers using physical/chemical changesCoupling light guidesLaser technologyRefractive index
The invention discloses an optical waveguide sensor and preparation methods thereof. The optical waveguide sensor comprises a structure as follows: an optical waveguide substrate medium consists of heat resisting optical materials and is provided with linear optical waveguides, and in which an optical grating structure is arranged in the linear optical waveguides. The invention further discloses many preparation methods of the structure. Another waveguide sensor comprises a structure as follows: the optical waveguide substrate medium consists of heat resisting optical materials and is provided with linear optical waveguides, and an optical grating structure is further arranged on the surface of the optical waveguide substrate. The invention further discloses many preparation methods of the structure. Because the optical waveguide apparatus has a simple module structure or a structure with few modules, the optical grating on the optical waveguide channel only has a harmonic module or few modules. When the environment temperature is changed, the refractive index of the optical waveguide material and the period of the optical waveguide grating can be changed, therefore, the change of temperature can be measured by measuring the change of wavelength of harmonic wave of the optical grating in the optical waveguide channel on the optical waveguide substrate. Due to the adoption of the laser technology and microelectronic production process, a plurality of optical waveguide grating sensing apparatuses can be further produced on a same substrate with low production cost and high efficiency.
Owner:无锡光芯科技有限公司
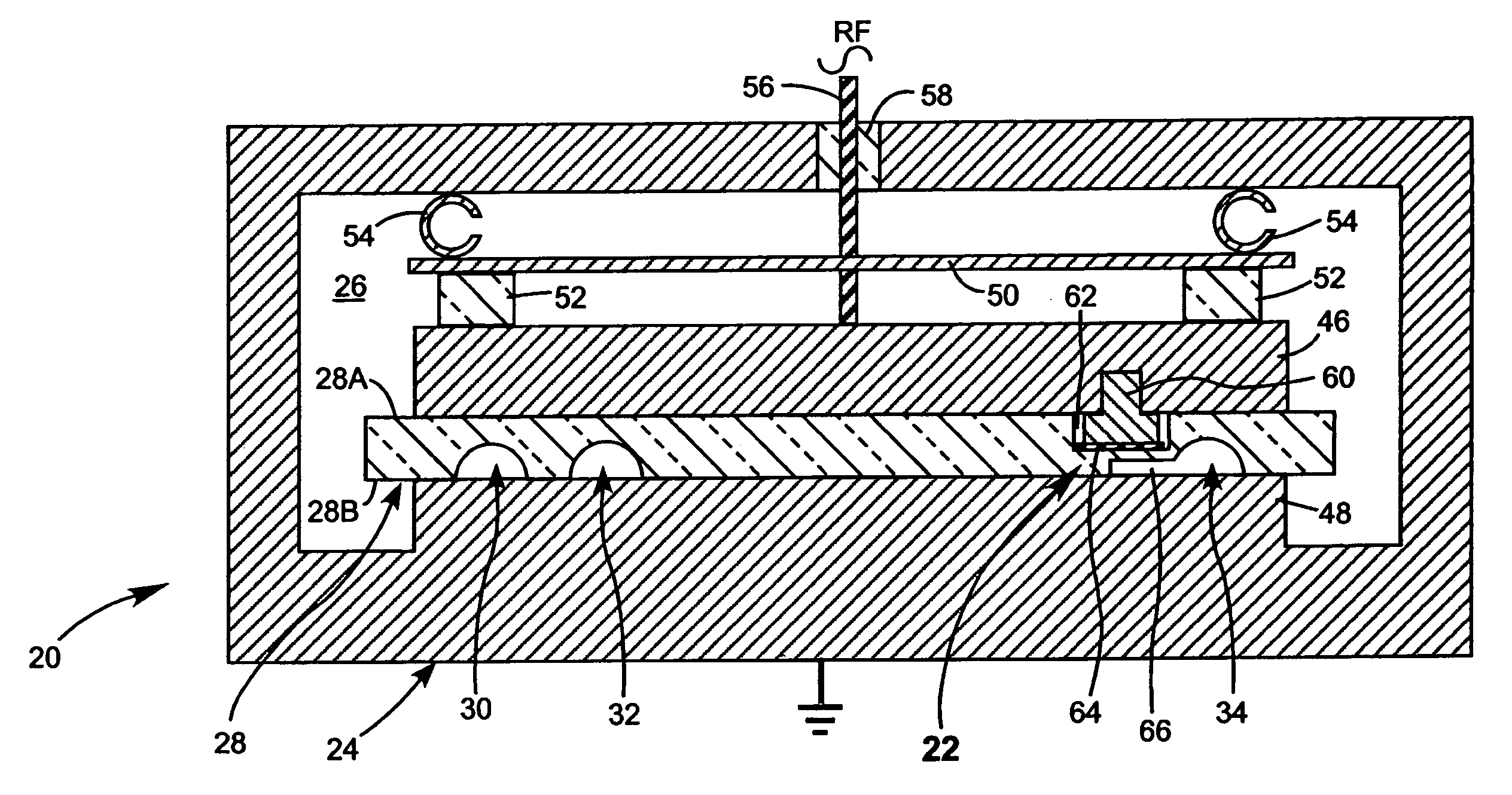
Discharge igniter for a waveguide CO2 laser
ActiveUS6999490B2Easy to igniteIgnited faster and more predictablyActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsLateral extensionGas laser
A waveguide gas laser includes an enclosure filled with a lasing gas. A ceramic block is provided with one or more waveguide channels. At least one of the waveguide channels includes an open region which is in fluid communication with a waveguide channel. Lasing gas in the enclosure fills the waveguide channels and the lateral extension. An electric field is applied across the lateral extension of the waveguide channel while simultaneously applying a smaller electric field across the waveguide channel. The electric field across the lateral extension ignites a discharge in the lateral extension that spreads into the lasing gas in the waveguide channel. The electric field across the waveguide channel is sufficient to sustain the discharge in the lasing in the waveguide channel.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Optical element and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6931167B2Simple methodLow costOptical articlesCoupling light guidesPolymer optical waveguideEngineering
A flexible optical element useful for optical wiring is provided, in which a light emitting portion is disposed to a core end face of a flexible polymeric optical waveguide channel sheet having a film substrate clad, a core and a clad layer covering the core. A method which enables of manufacturing the optical element in a simple and convenient manner at a low cost is also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Grating apodization technique for diffused optical waveguides
ActiveUS20070237457A1Simple technologyCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideGratingReflectance or Transmission Spectroscopy
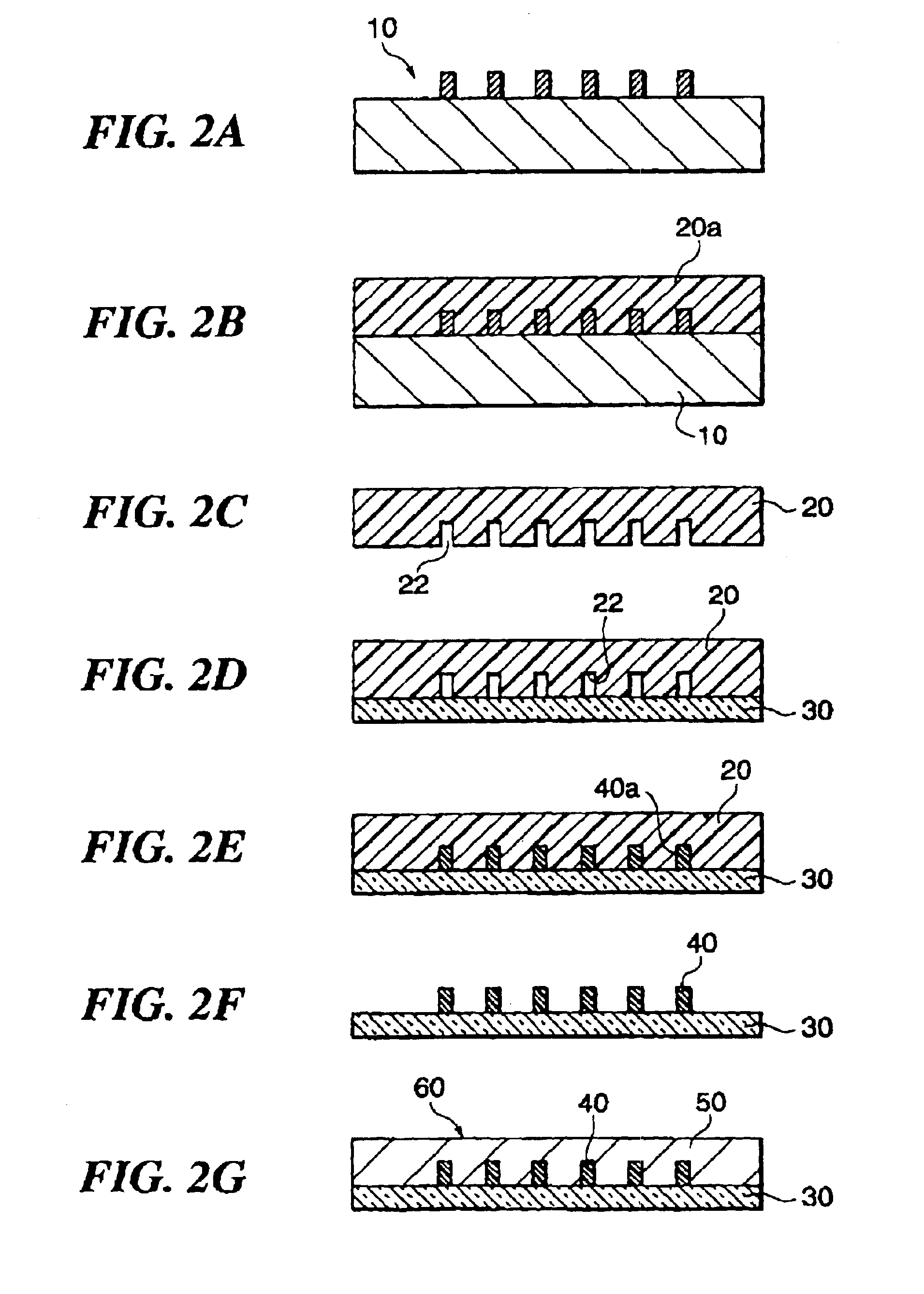
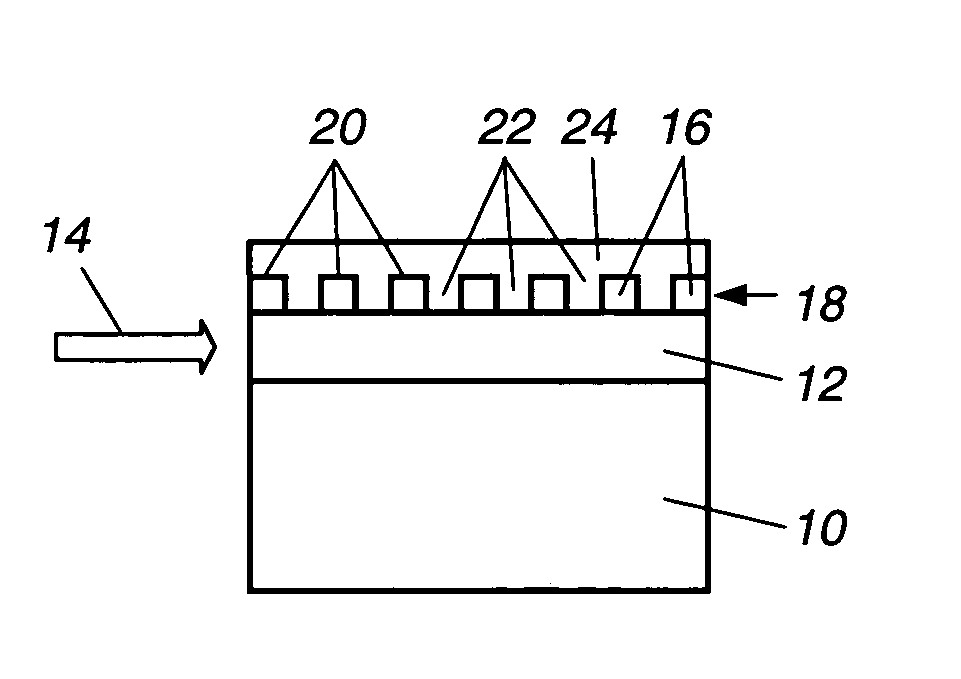
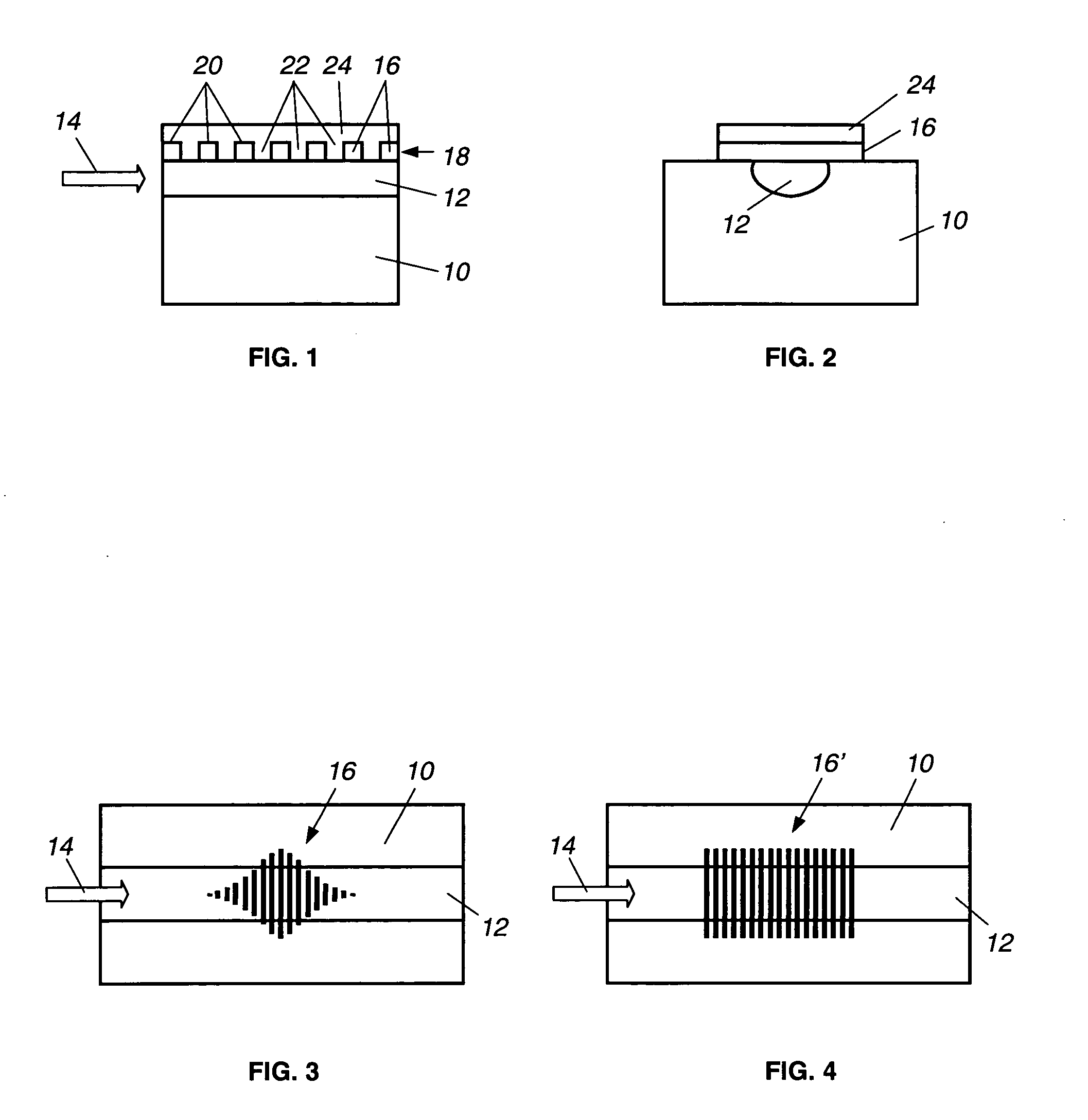
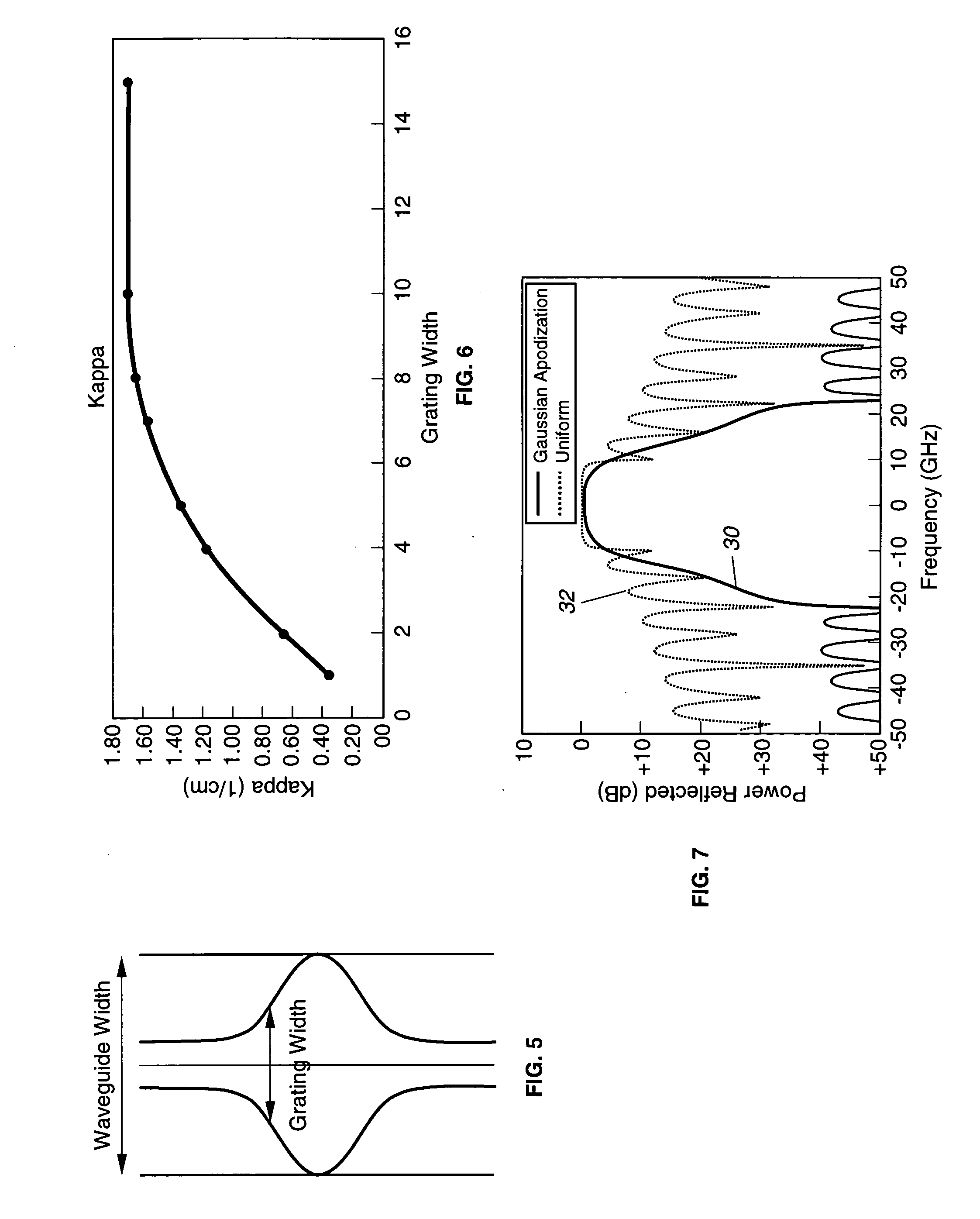
An optical channel waveguide having a reflection grating and a related method for its fabrication. The grating is apodized to provide a desired reflection or transmission spectral characteristic, by varying the grating width along the length of the grating in the direction of light propagation. The grating has multiple parallel elements extending across the waveguide channel width, and apodization is effected by appropriate selection of the width of each element relative to the width of the channel, without varying the grating duty cycle or other parameters.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com