Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Increase loop bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
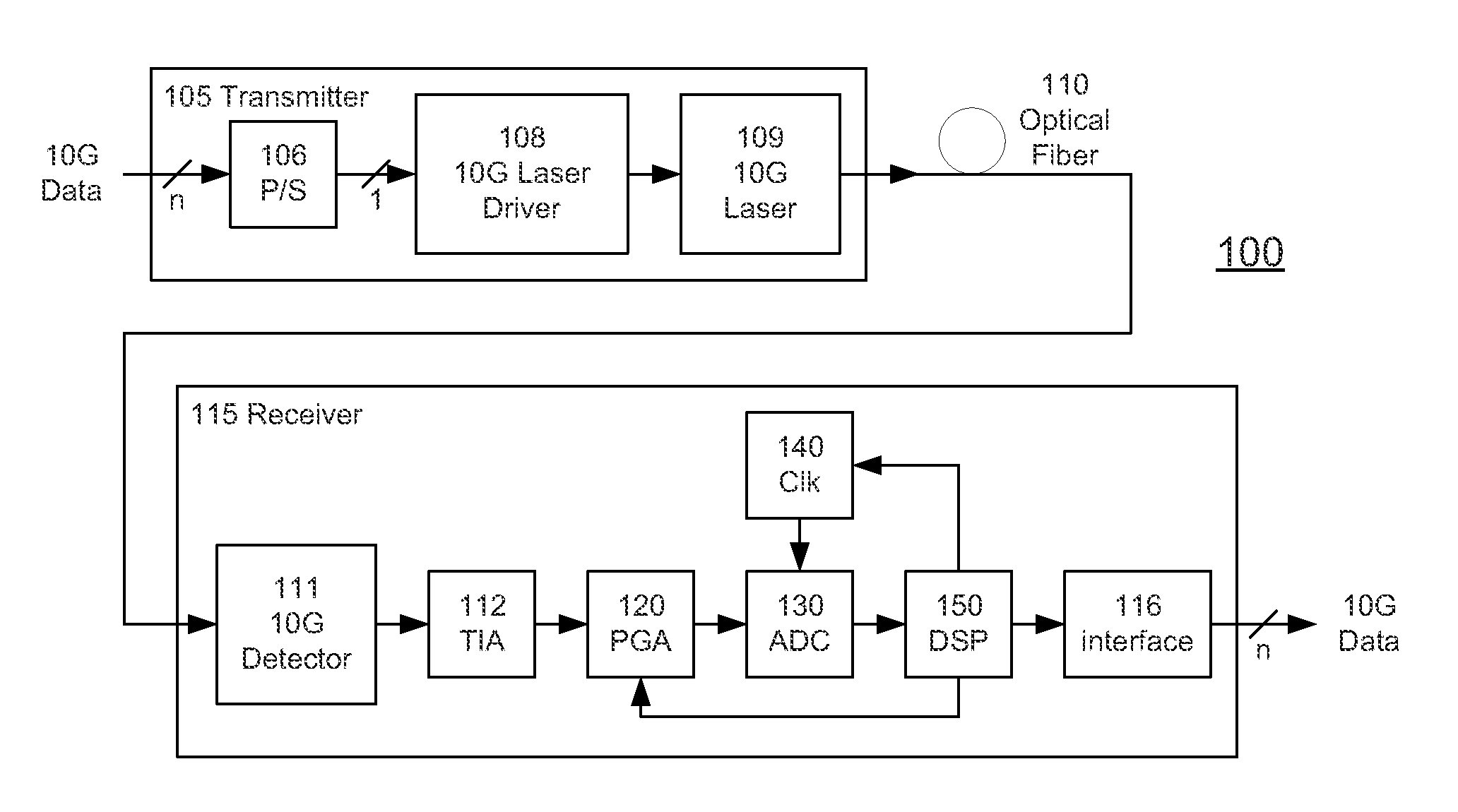
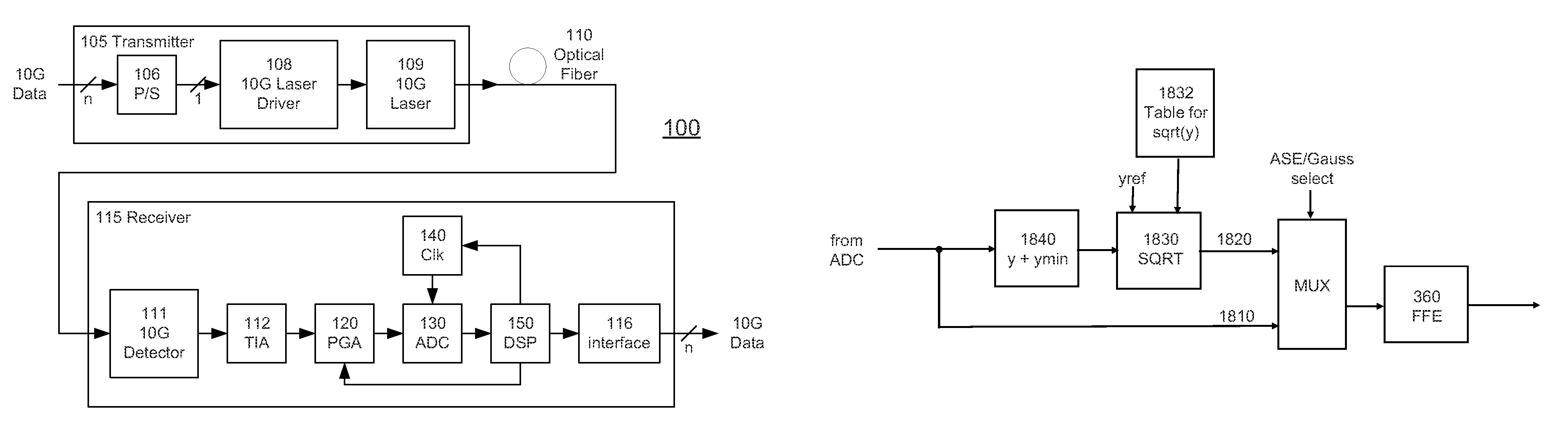
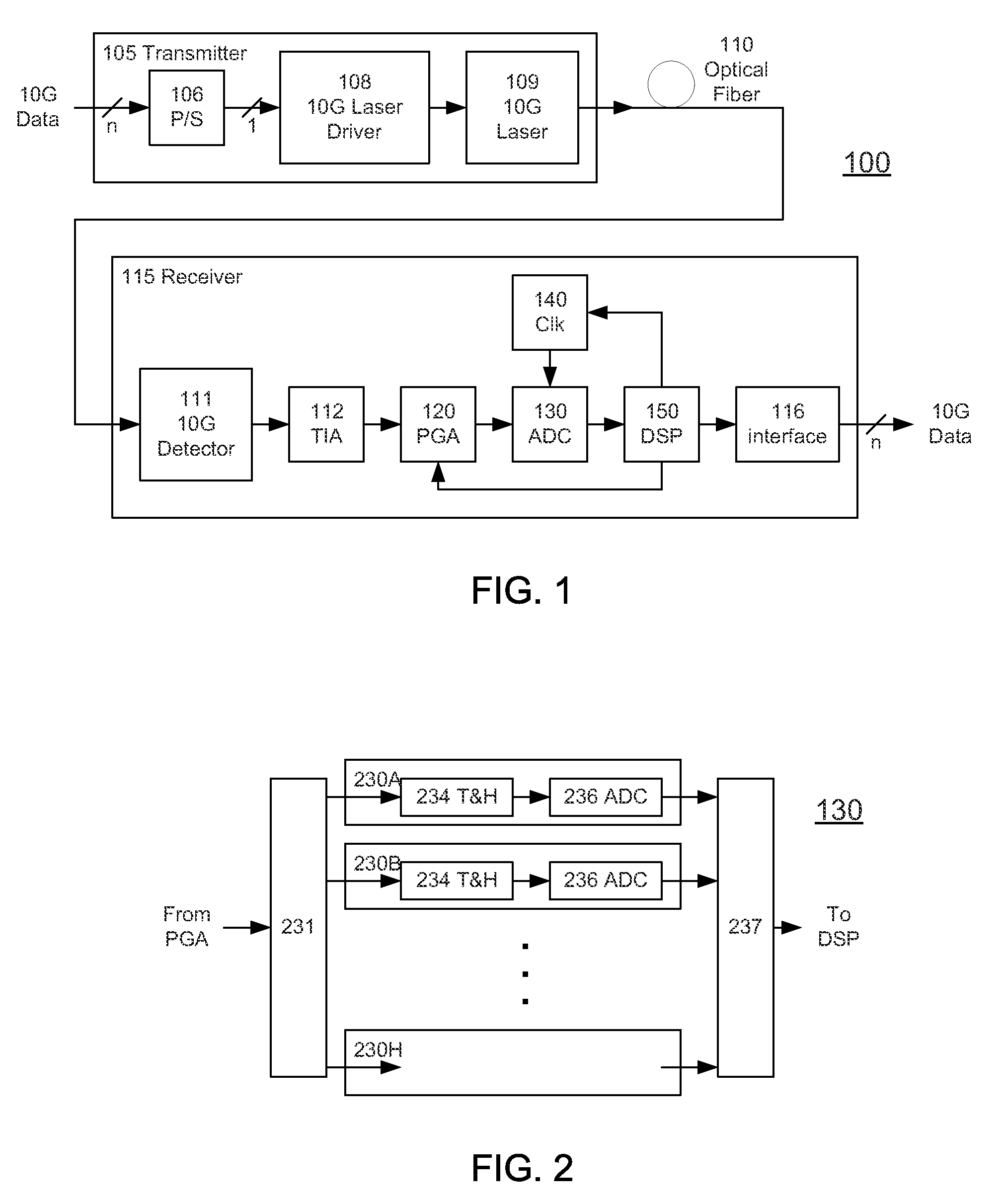
High-Speed Receiver Architecture
ActiveUS20080240325A1Overcome limitationsLower latencyAnalogue/digital conversionReceiver initialisationViterbi decoderTelecommunications link
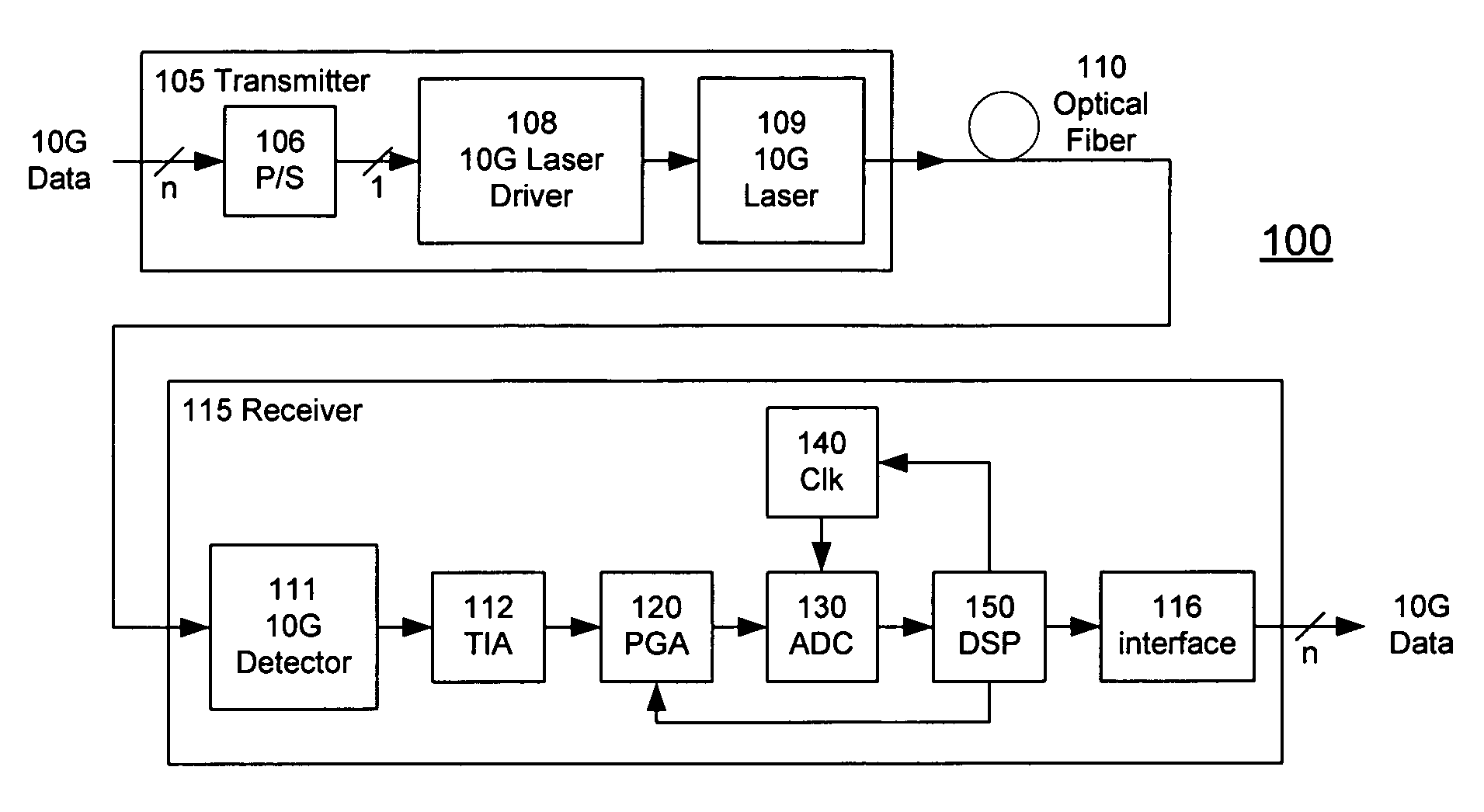
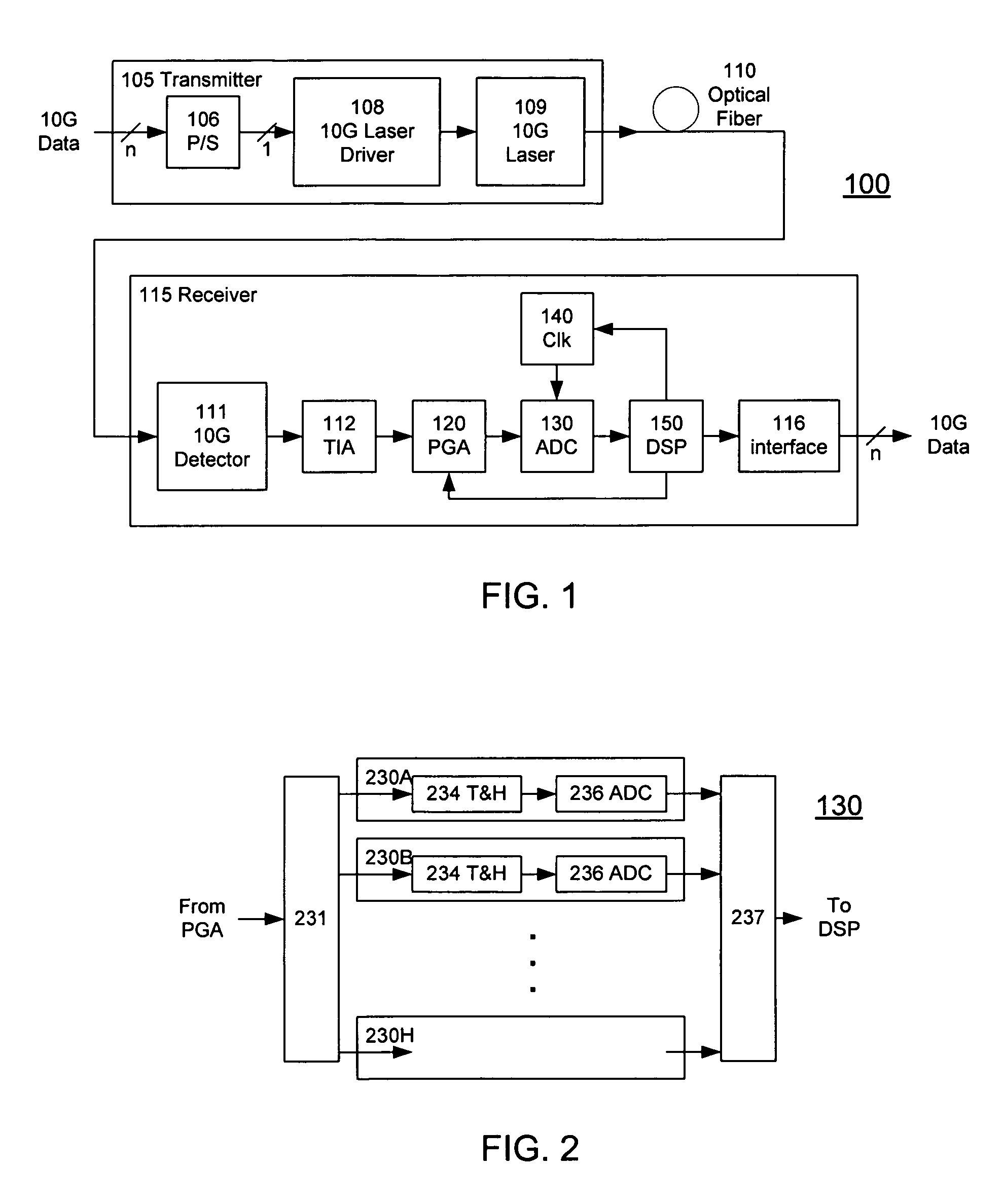
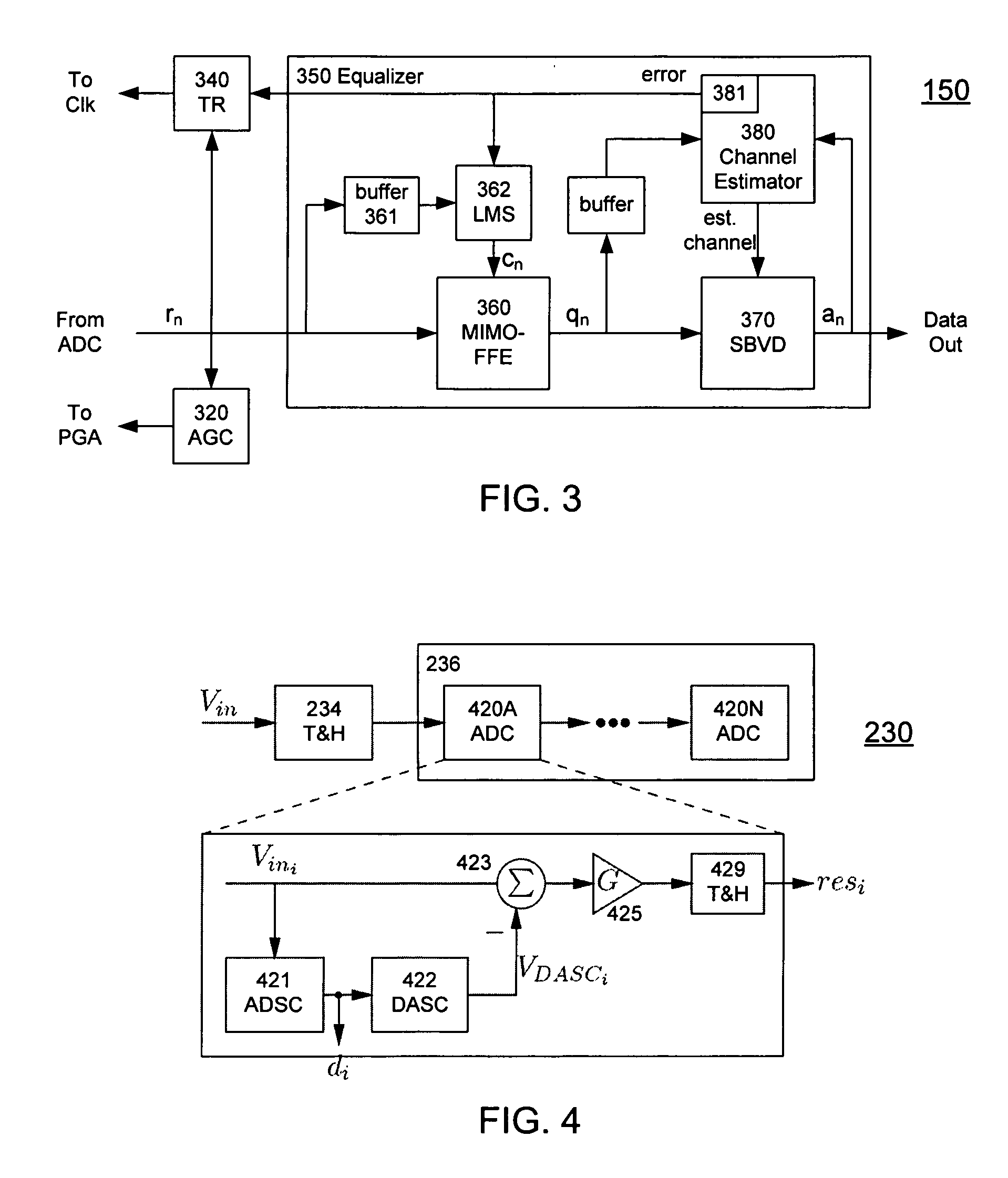
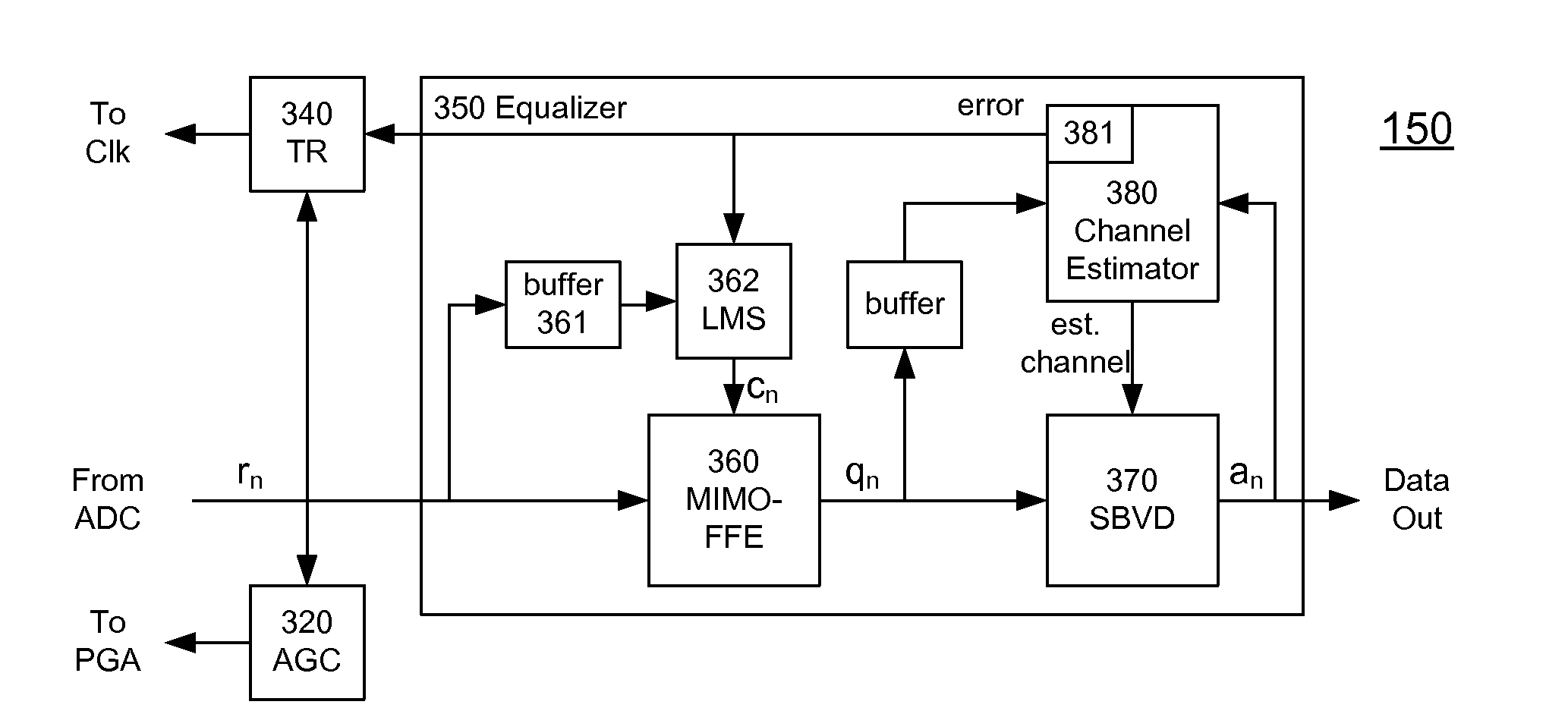
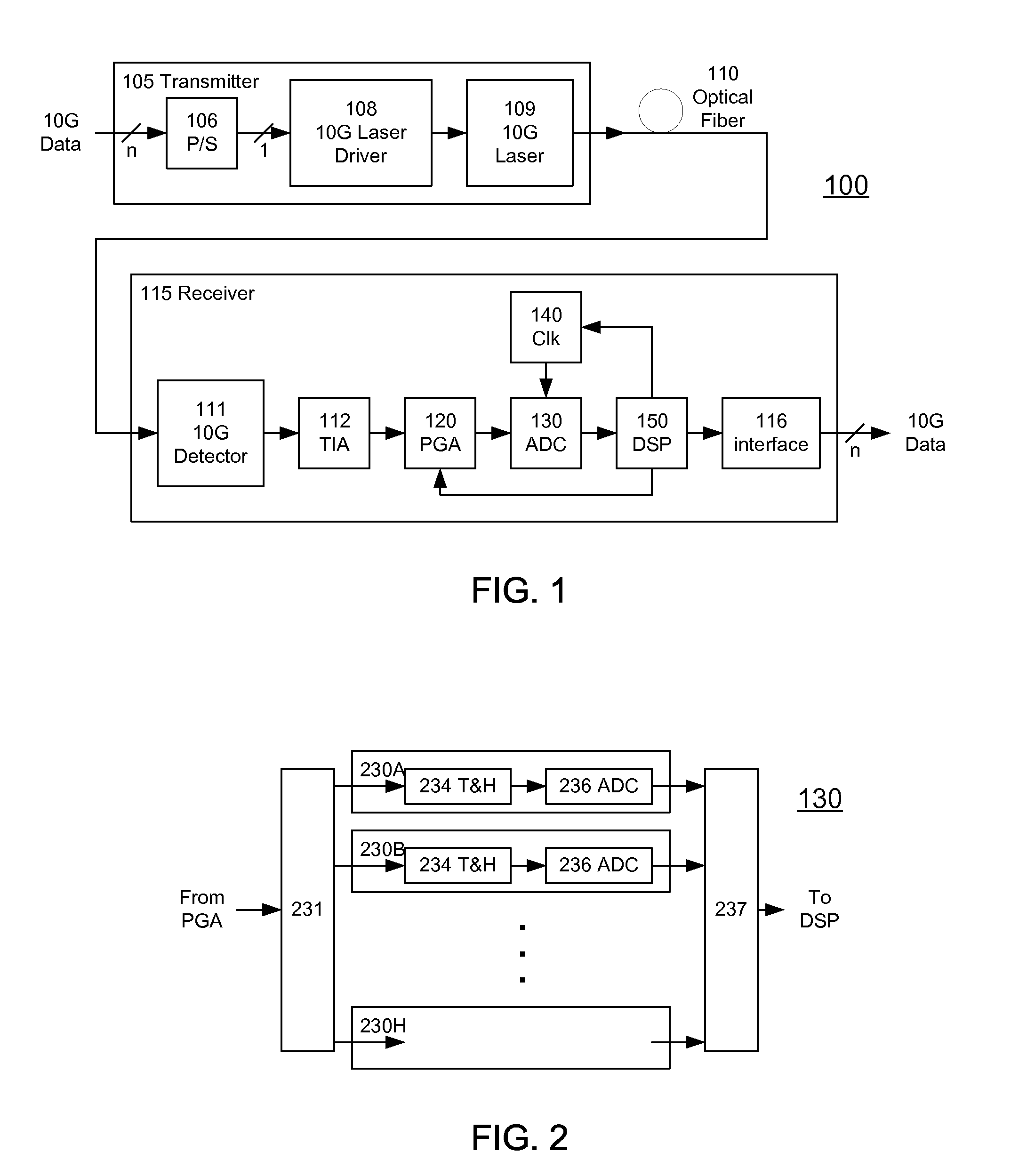
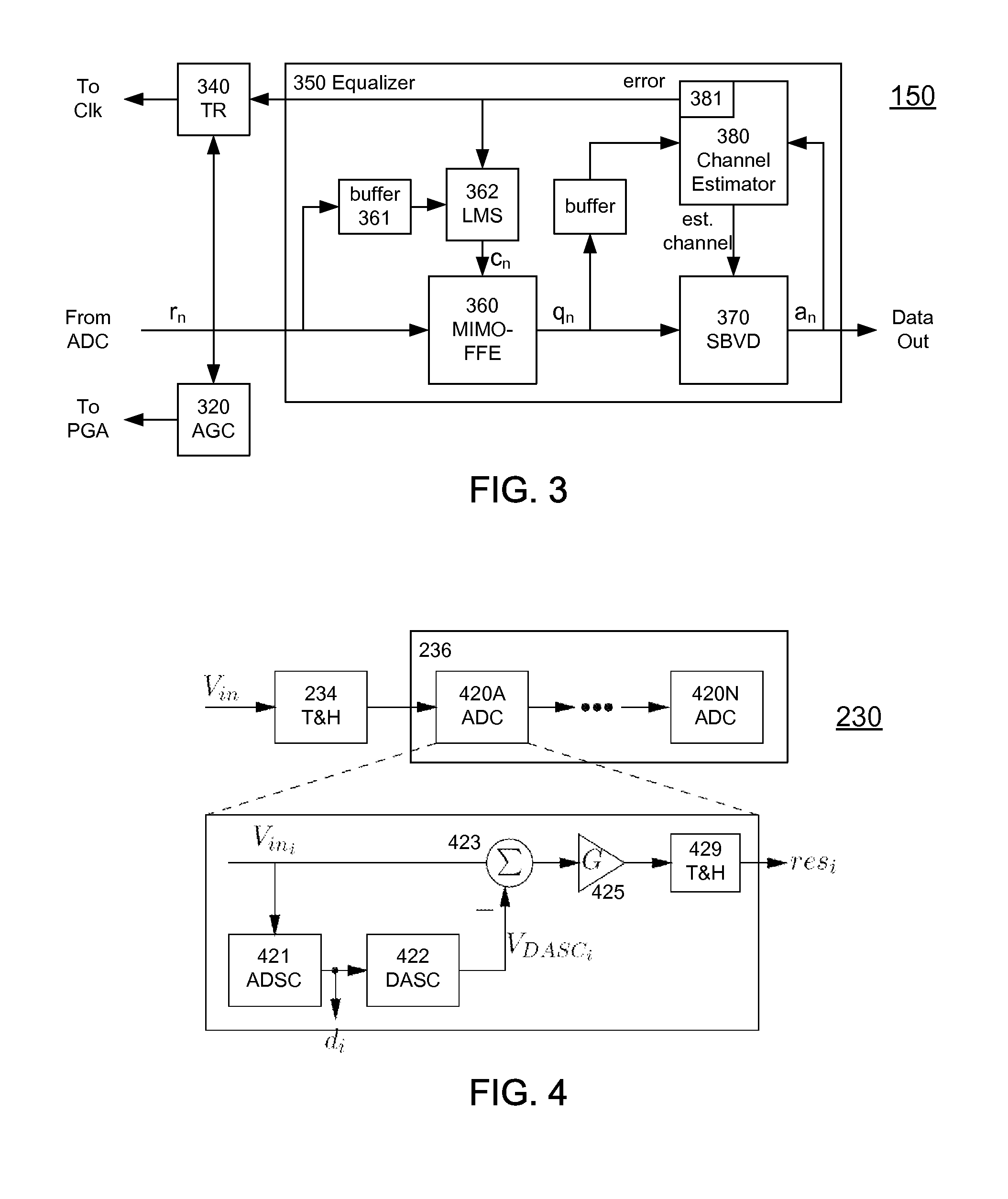
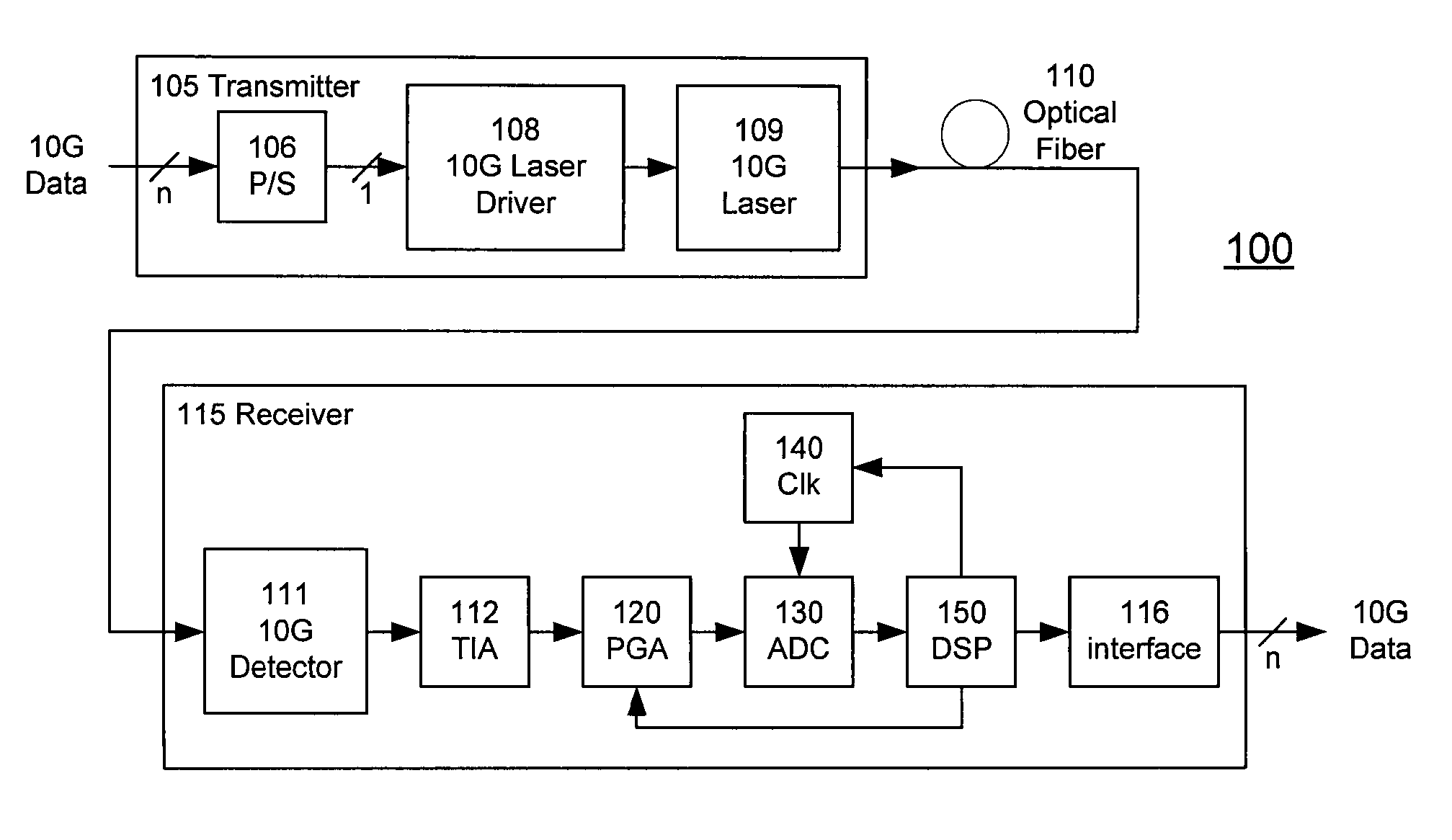
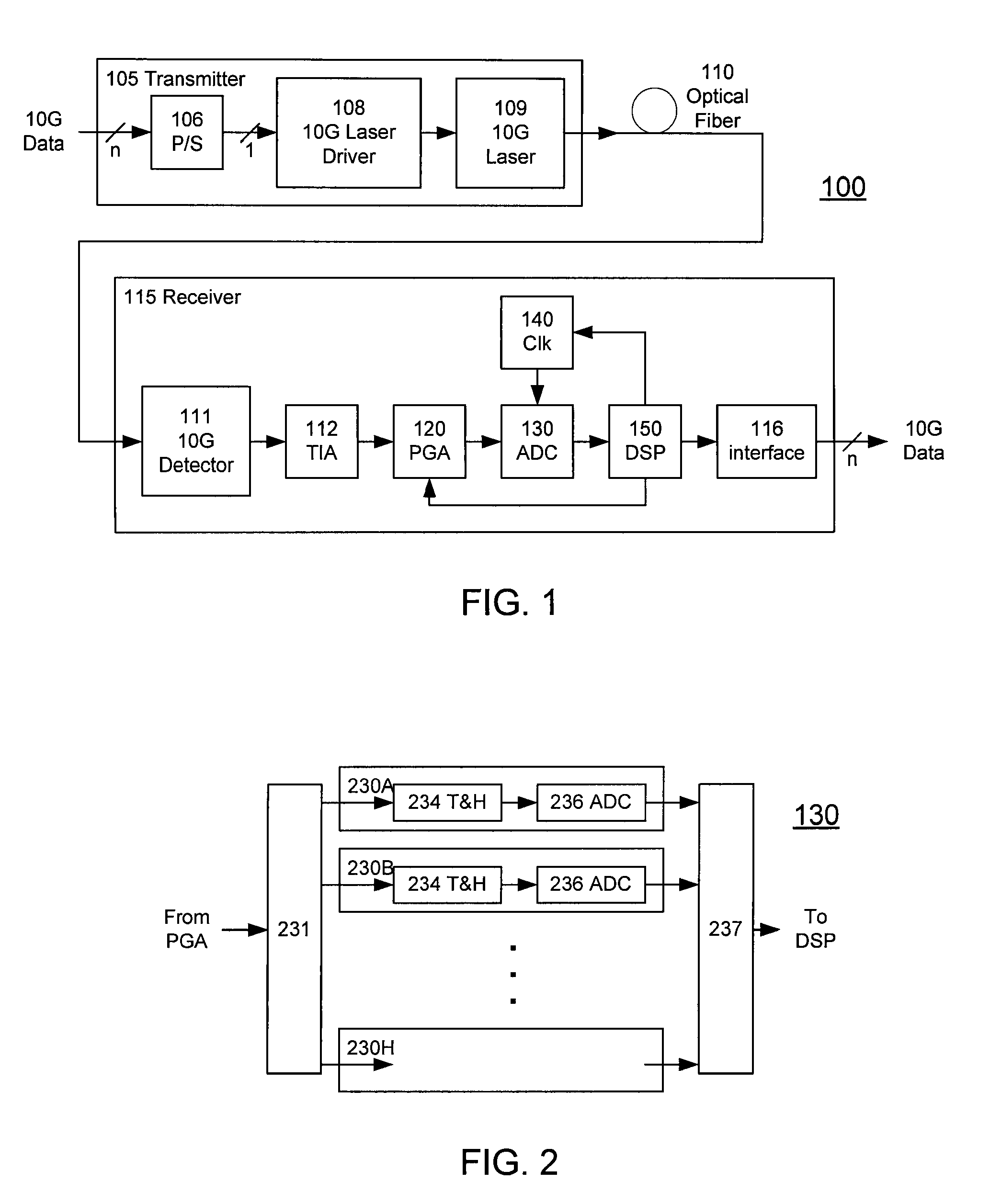
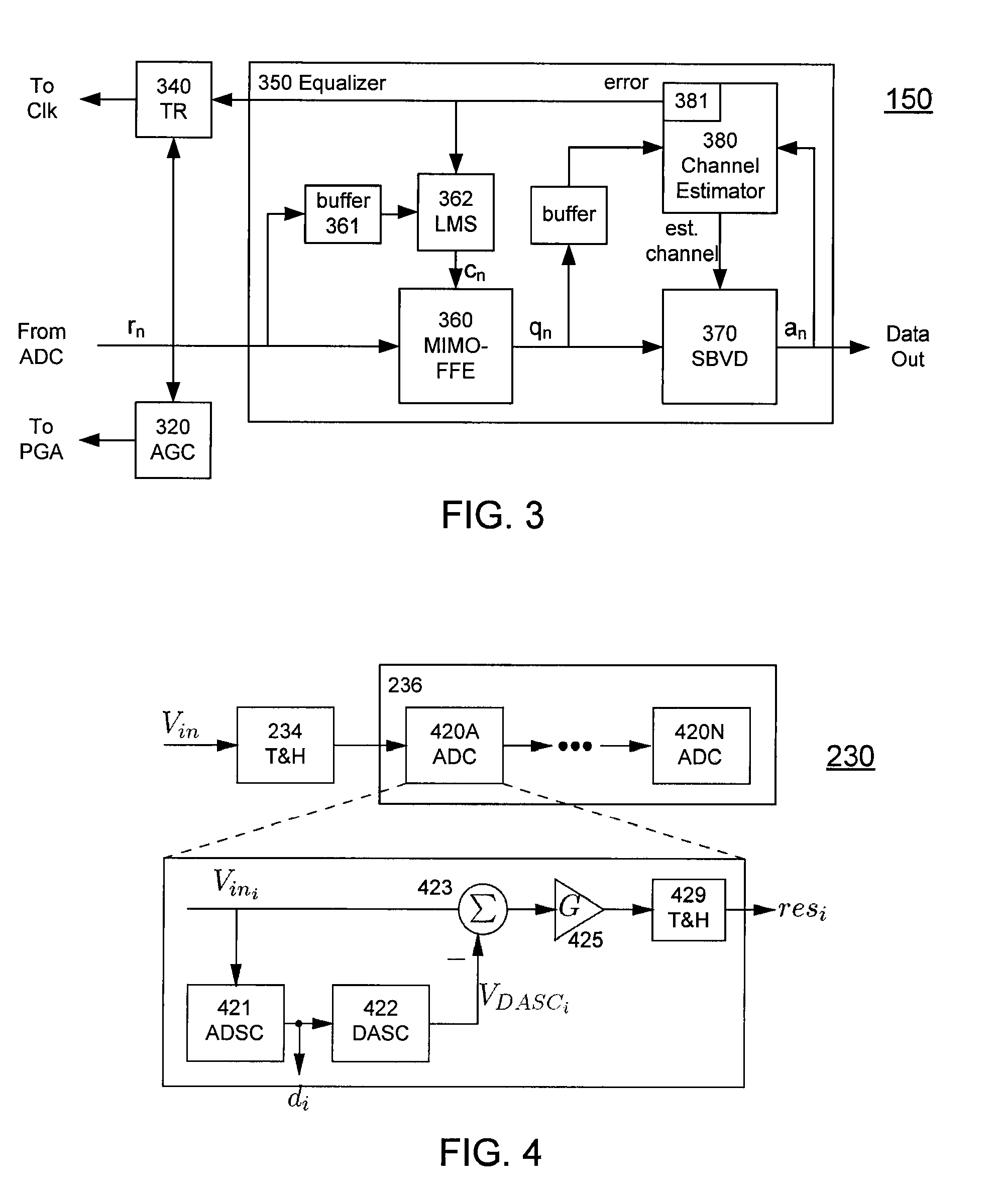
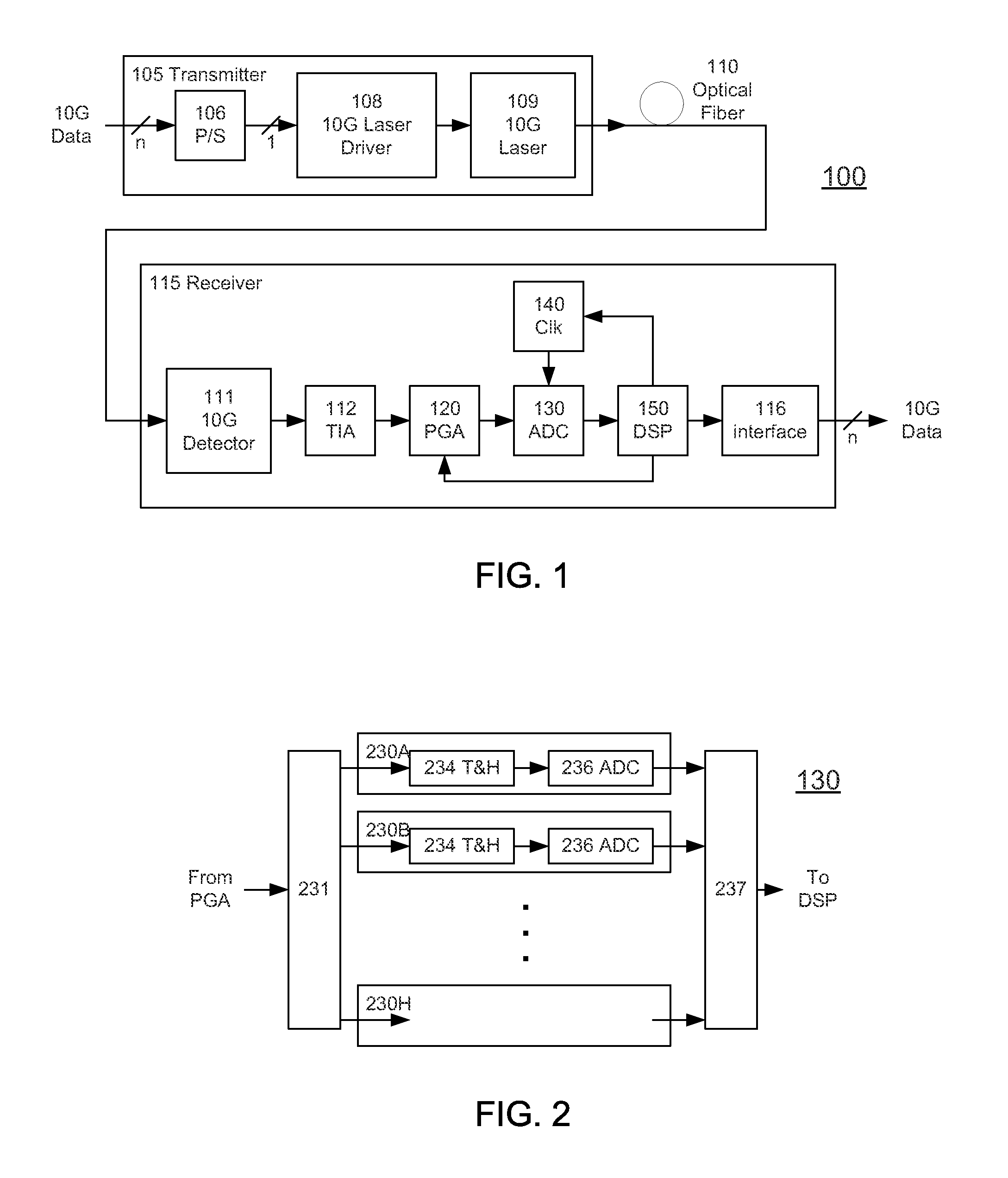
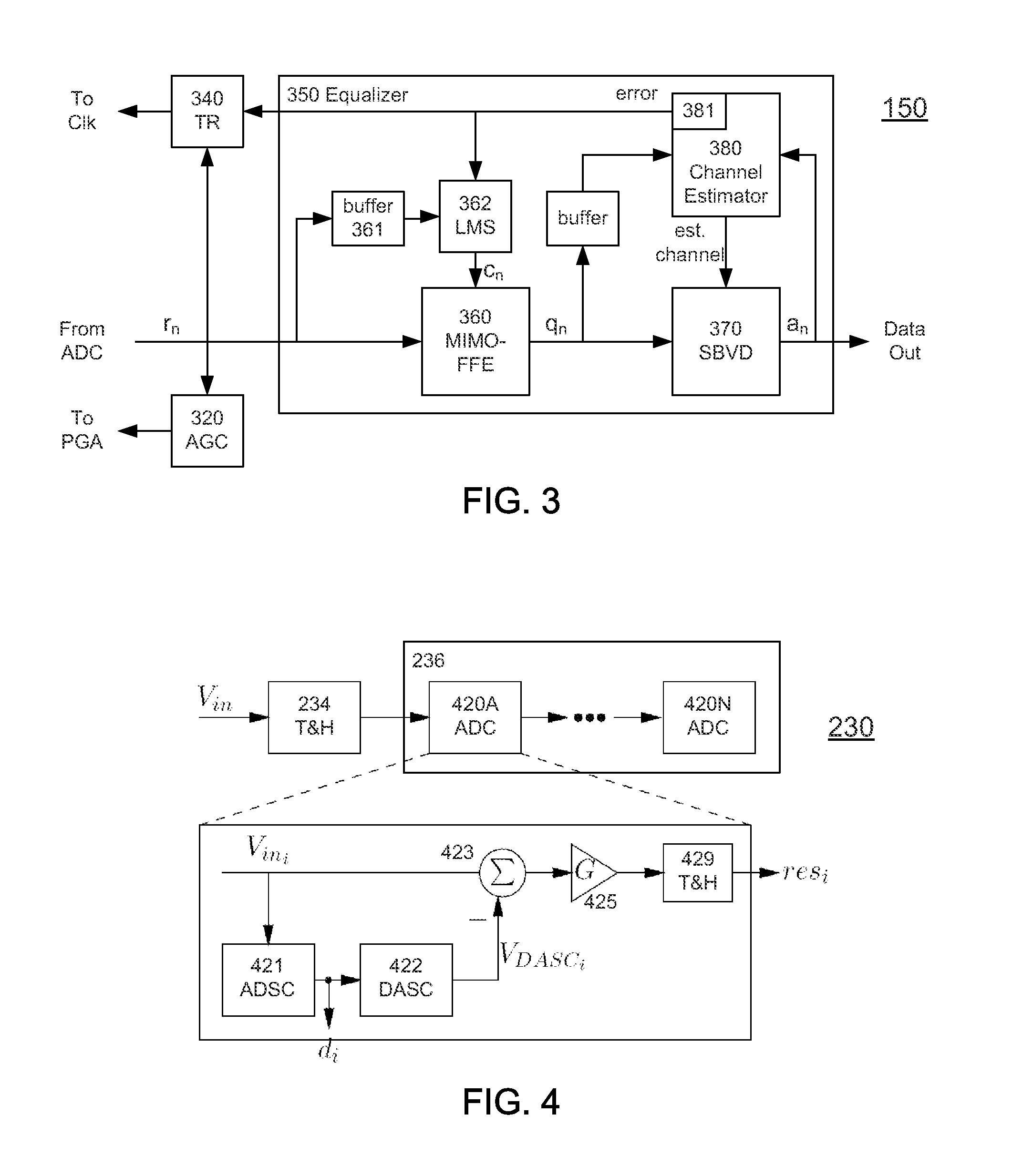
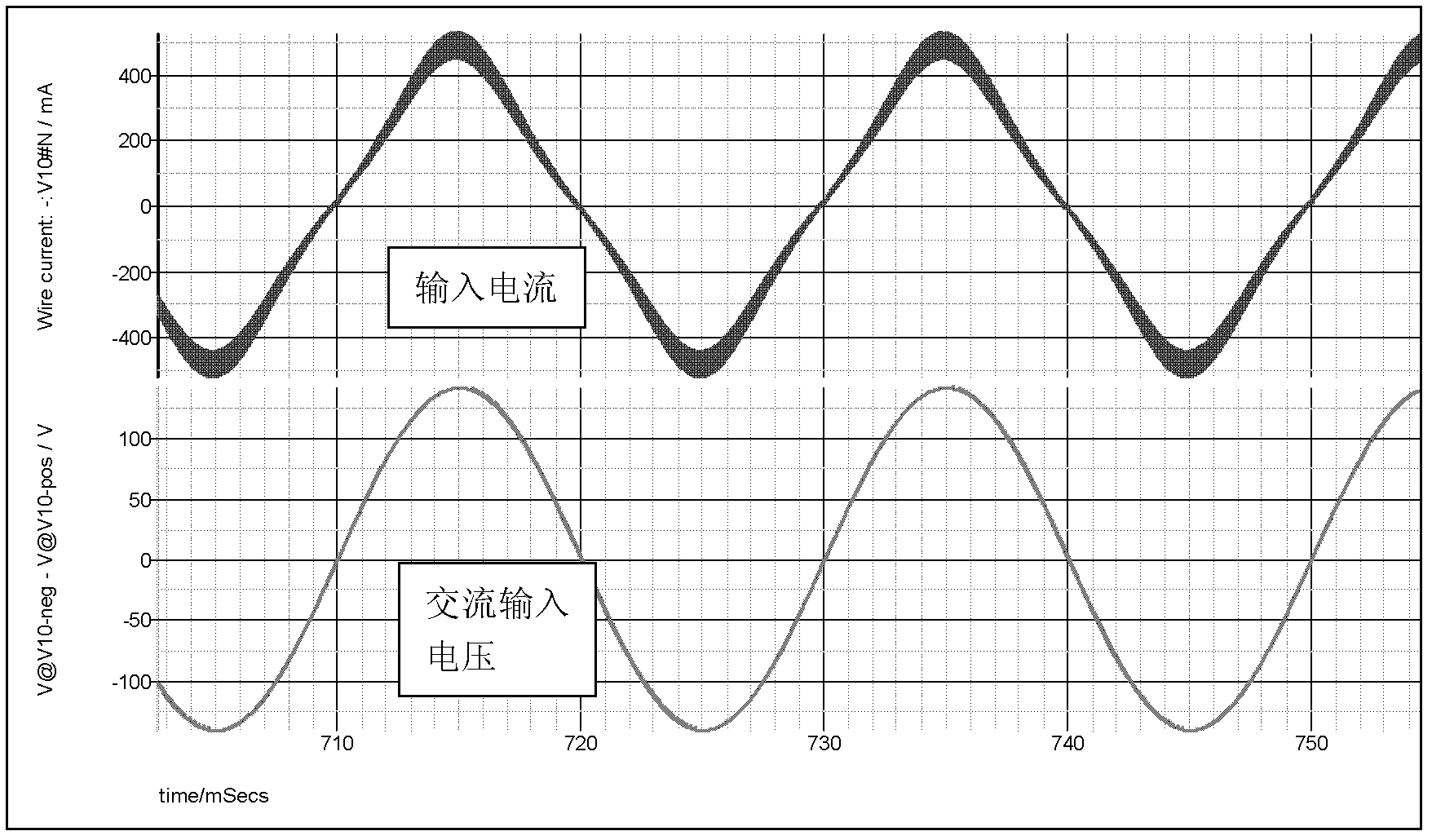
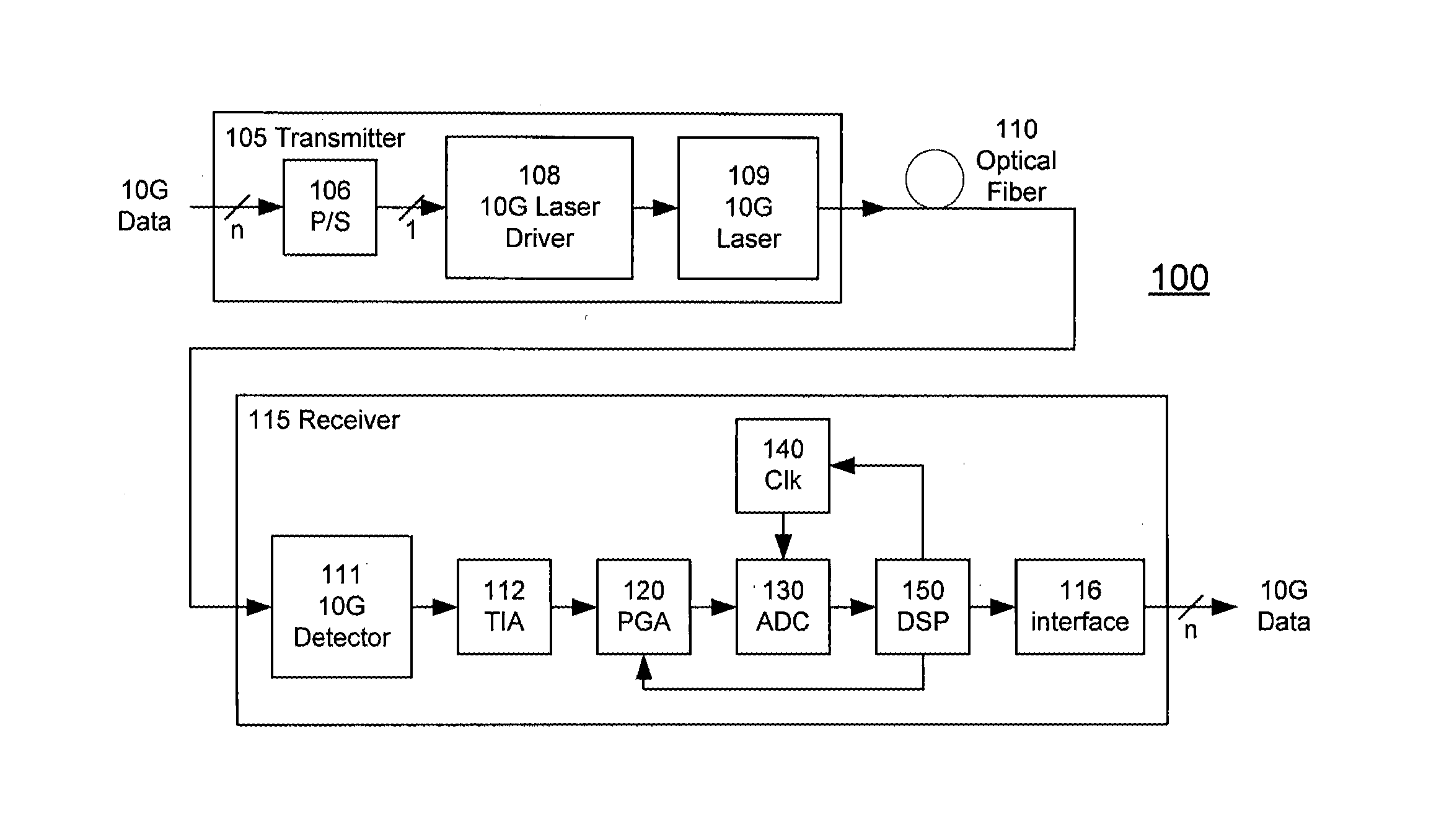
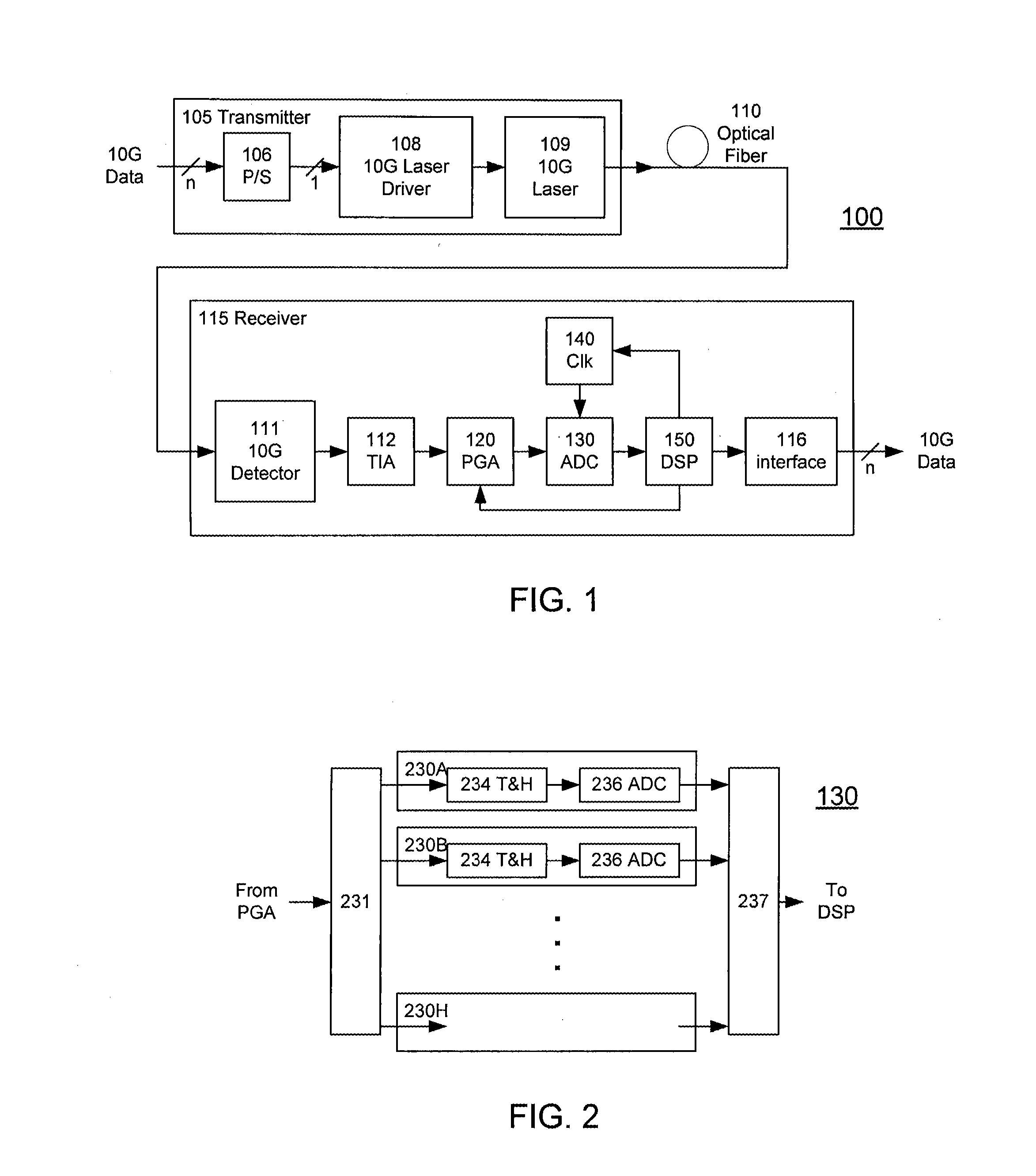
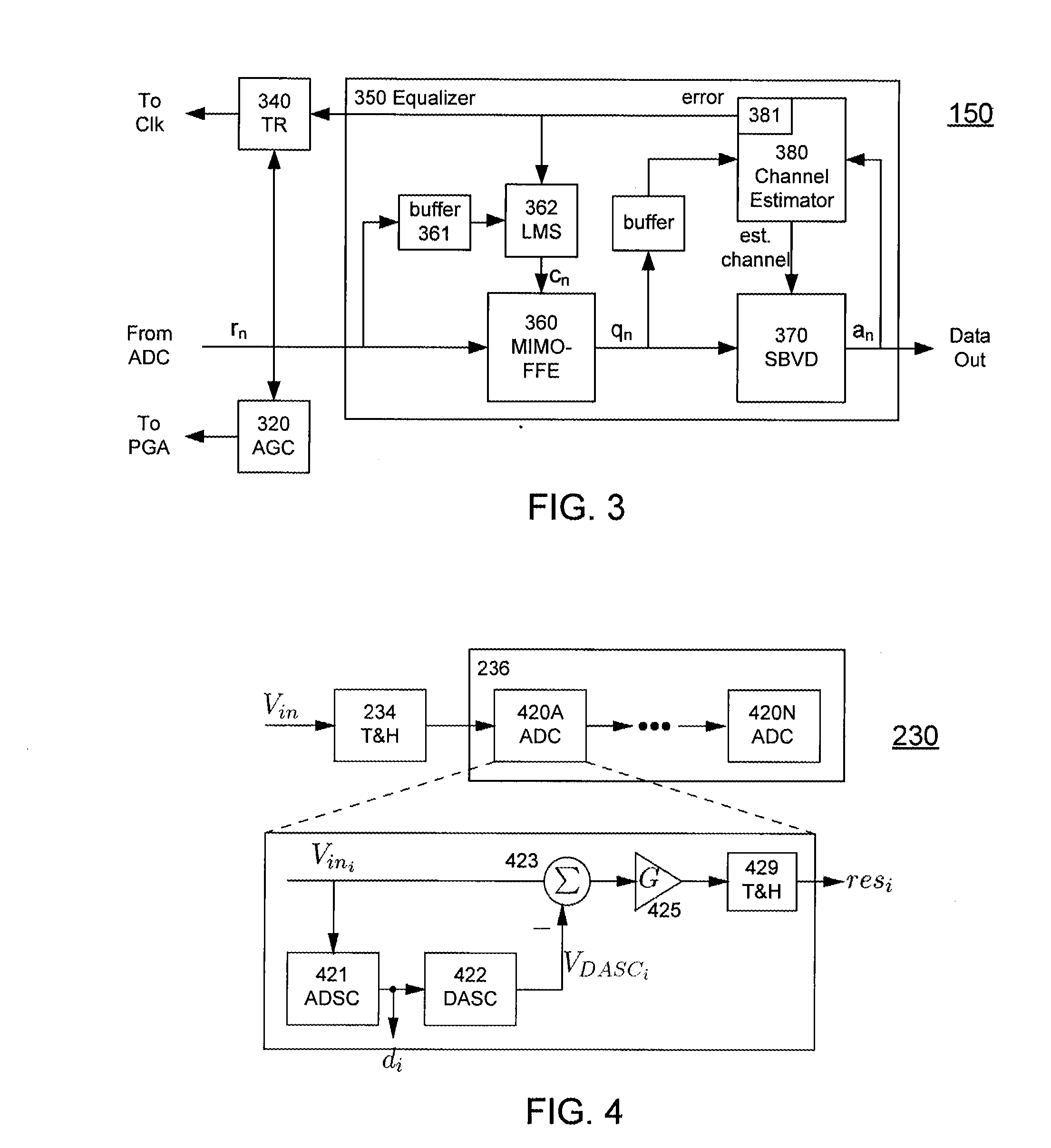
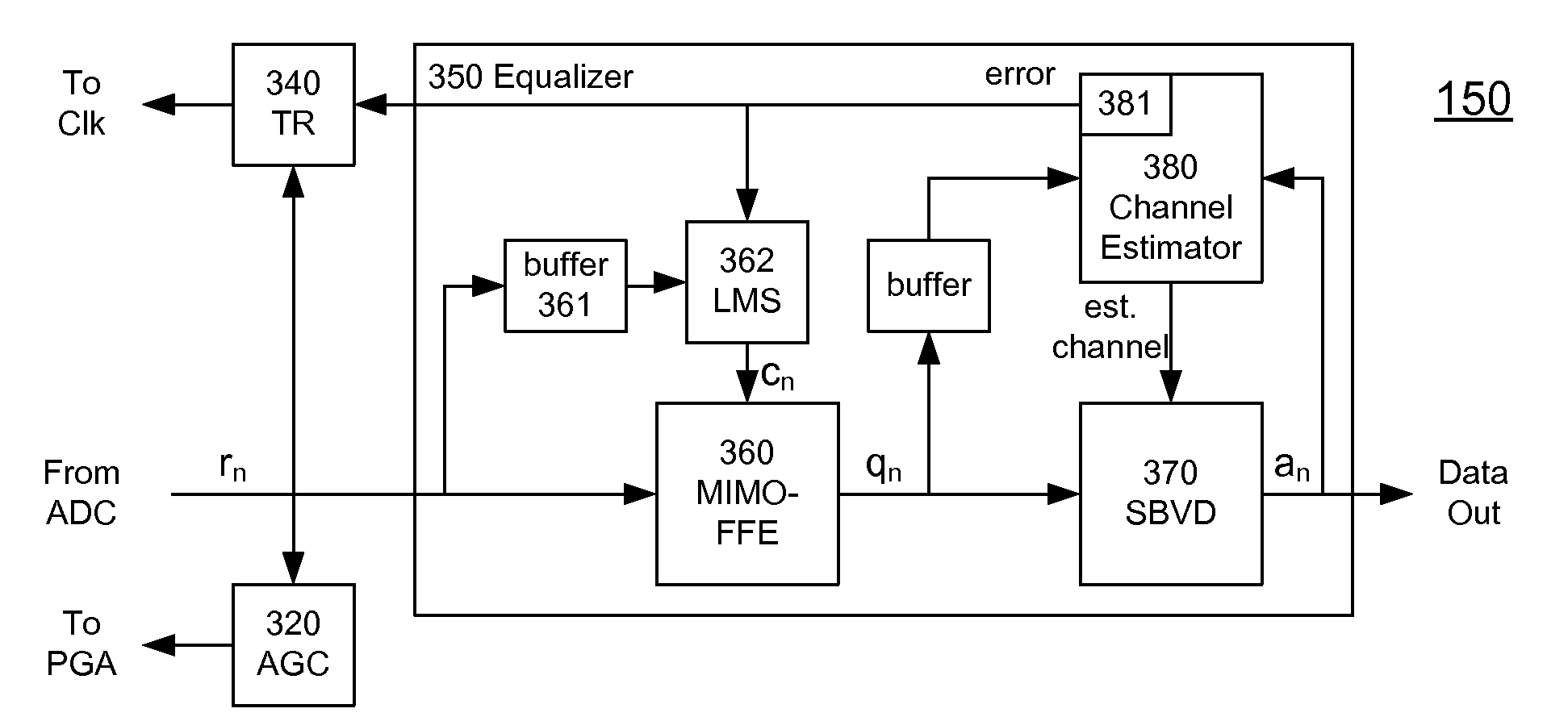
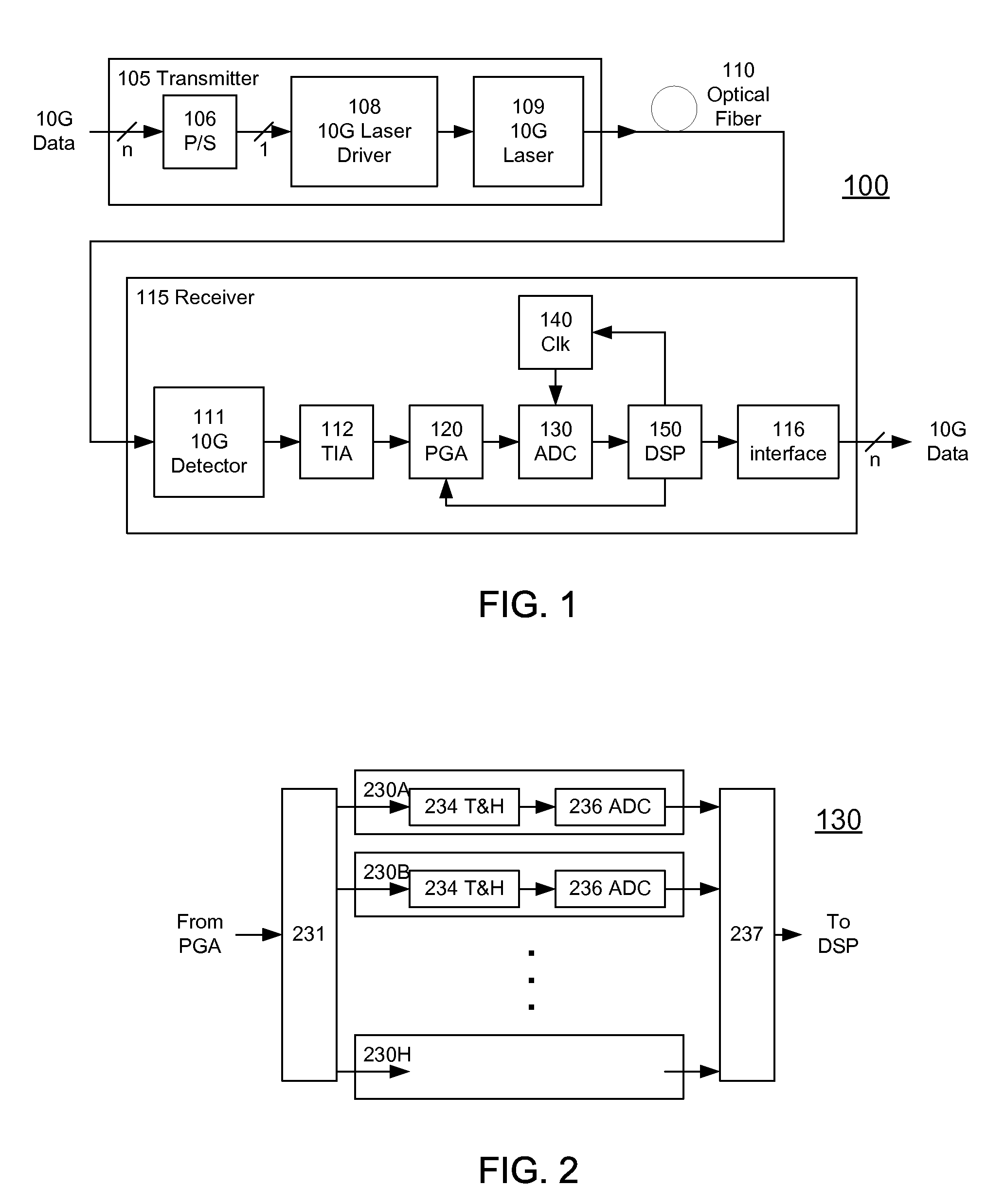
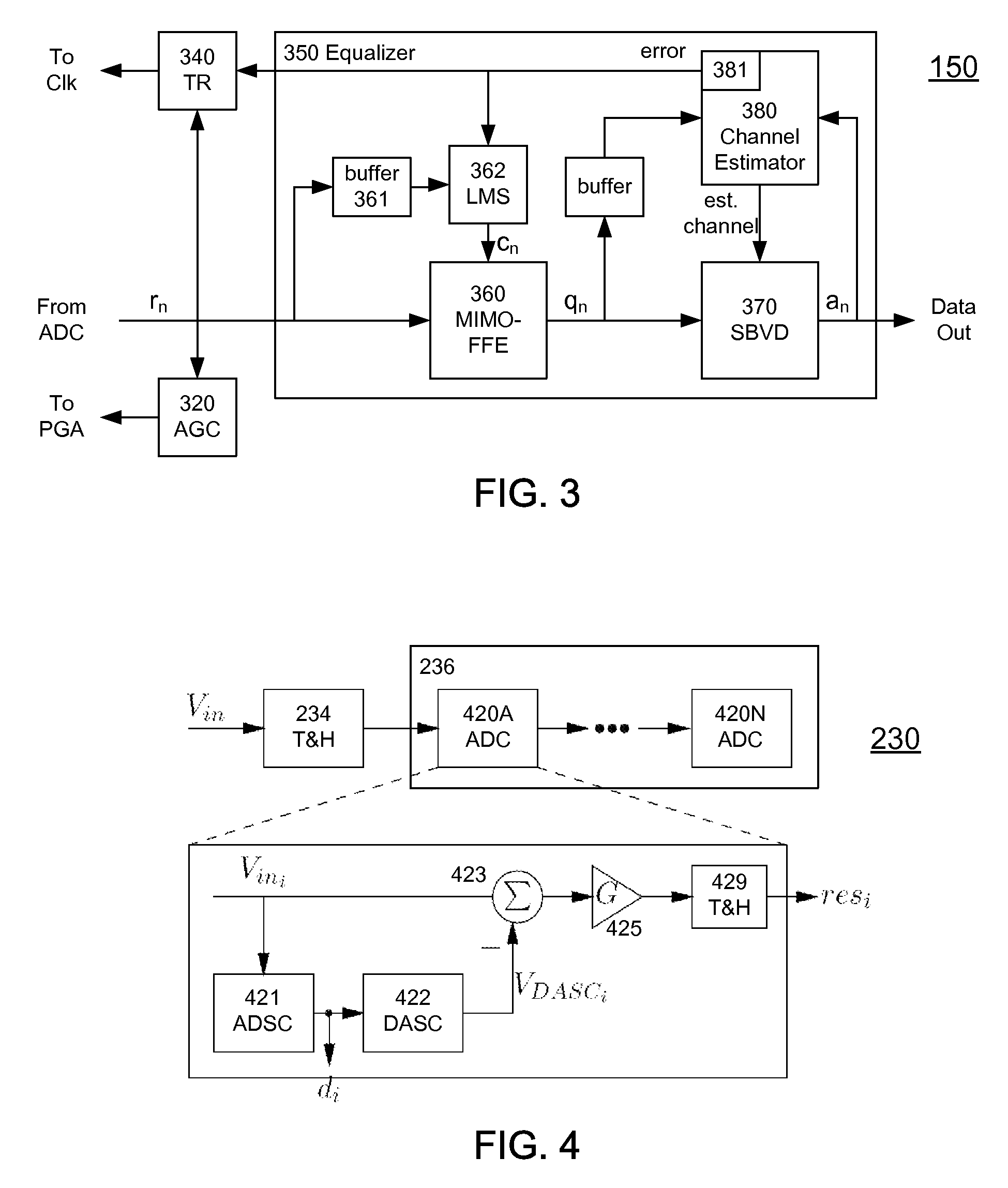
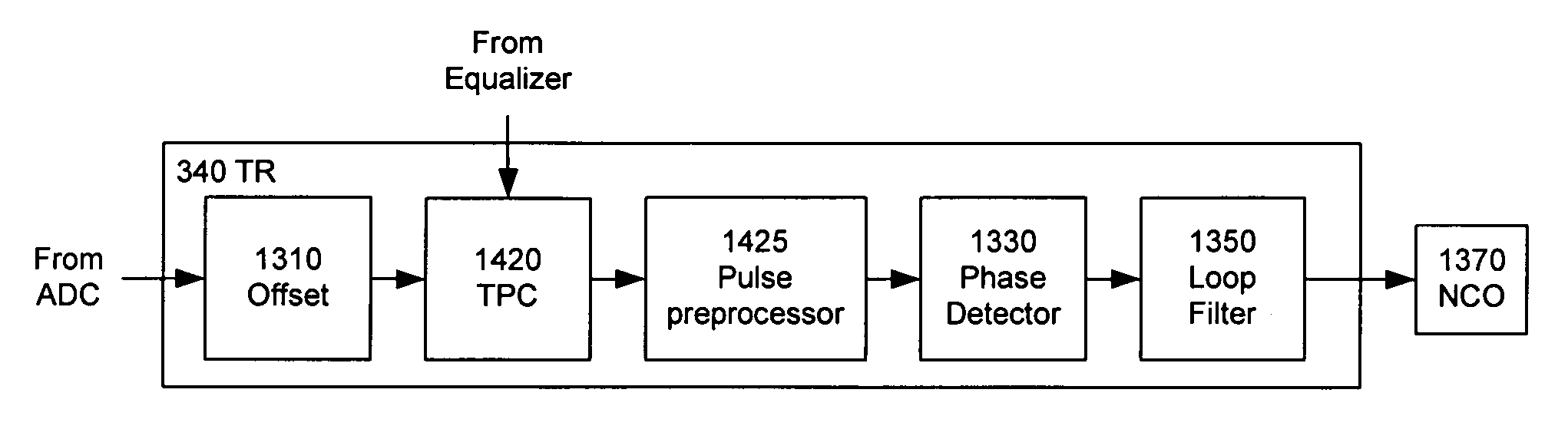
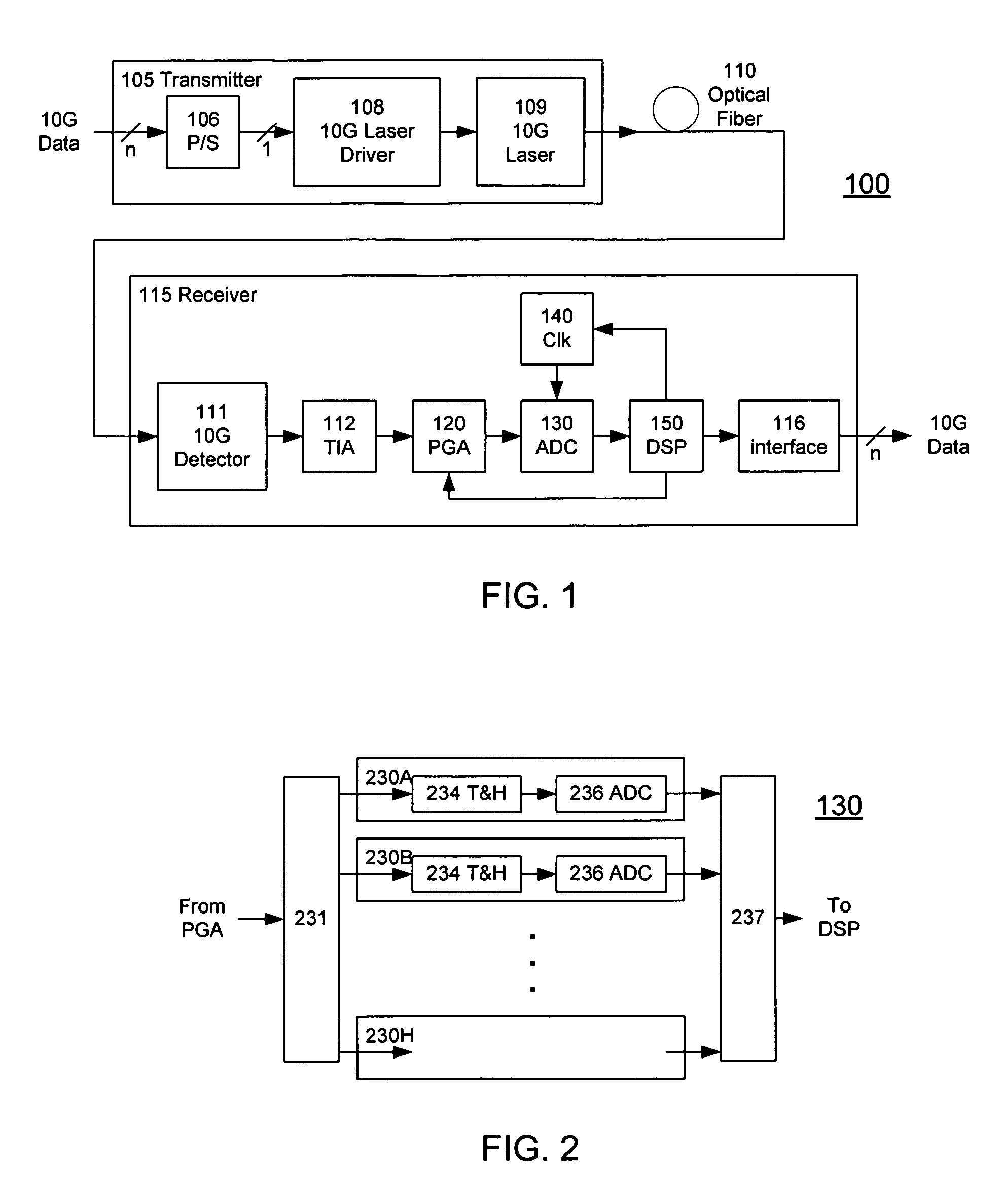
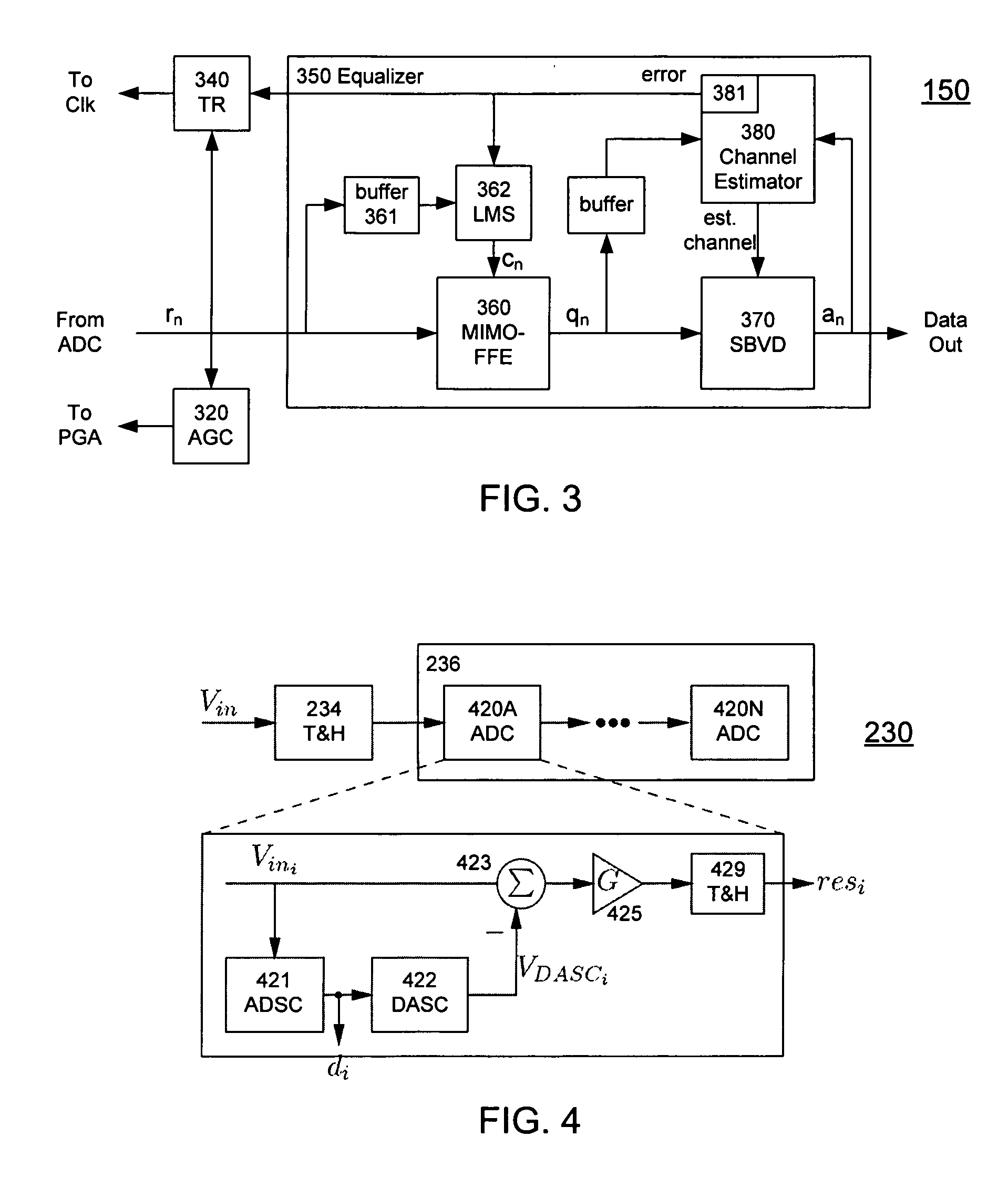
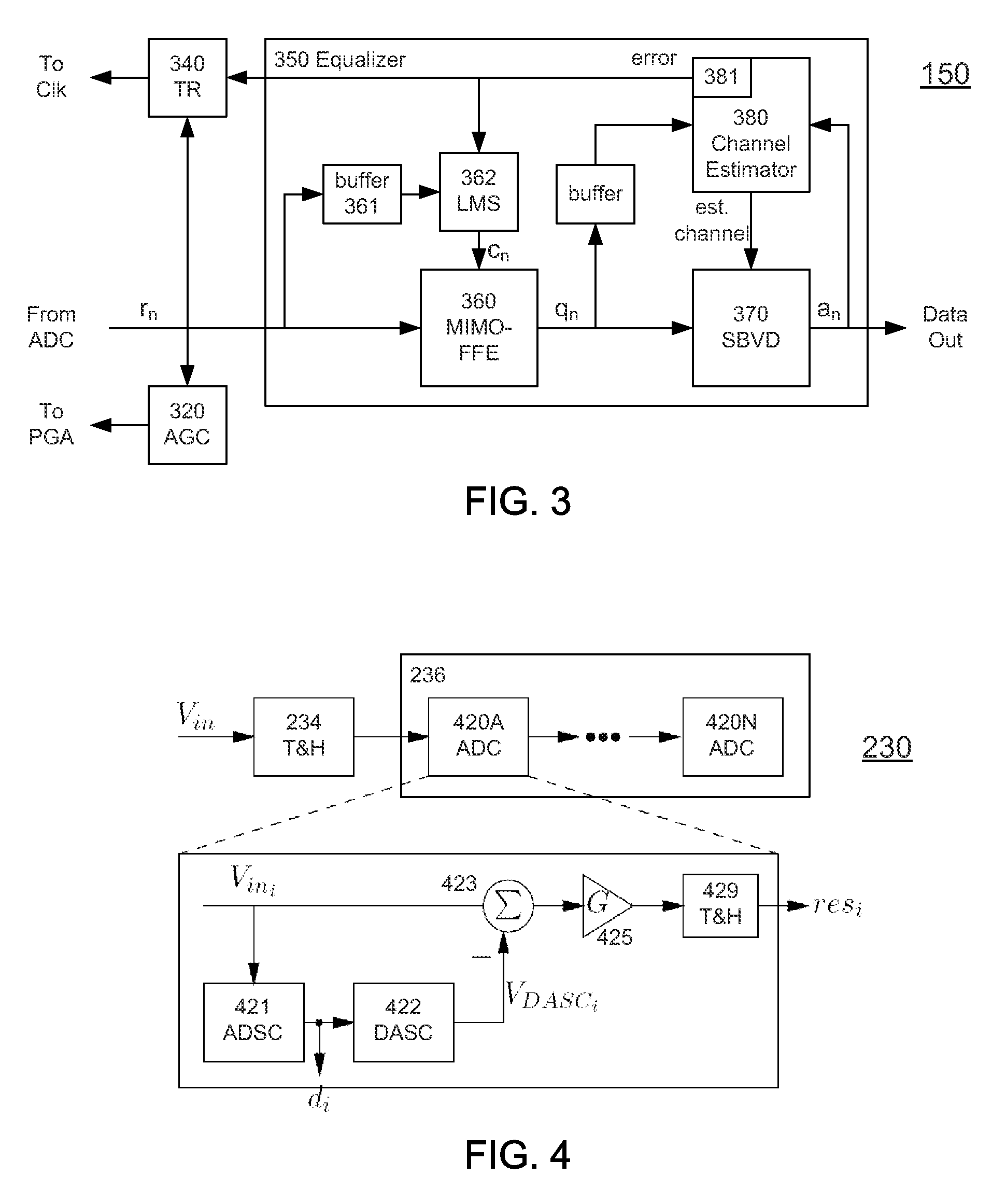
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Direct current offset cancellation for mobile station modems using direct conversion
InactiveUS6985711B2Easy accessRapid and accurate DC offset estimates and cancellation techniquesDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionRadio transmissionModem deviceOffset cancellation
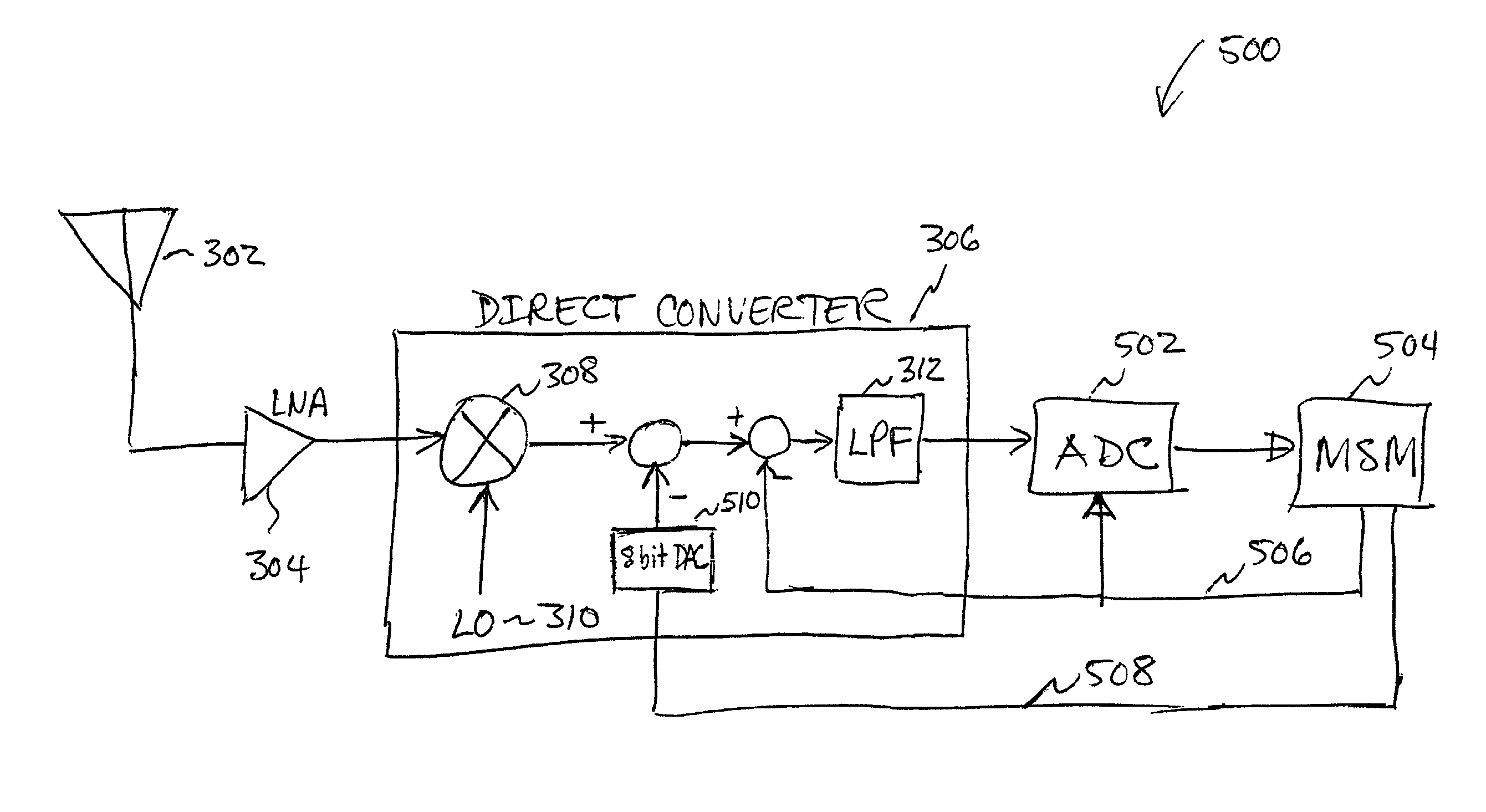
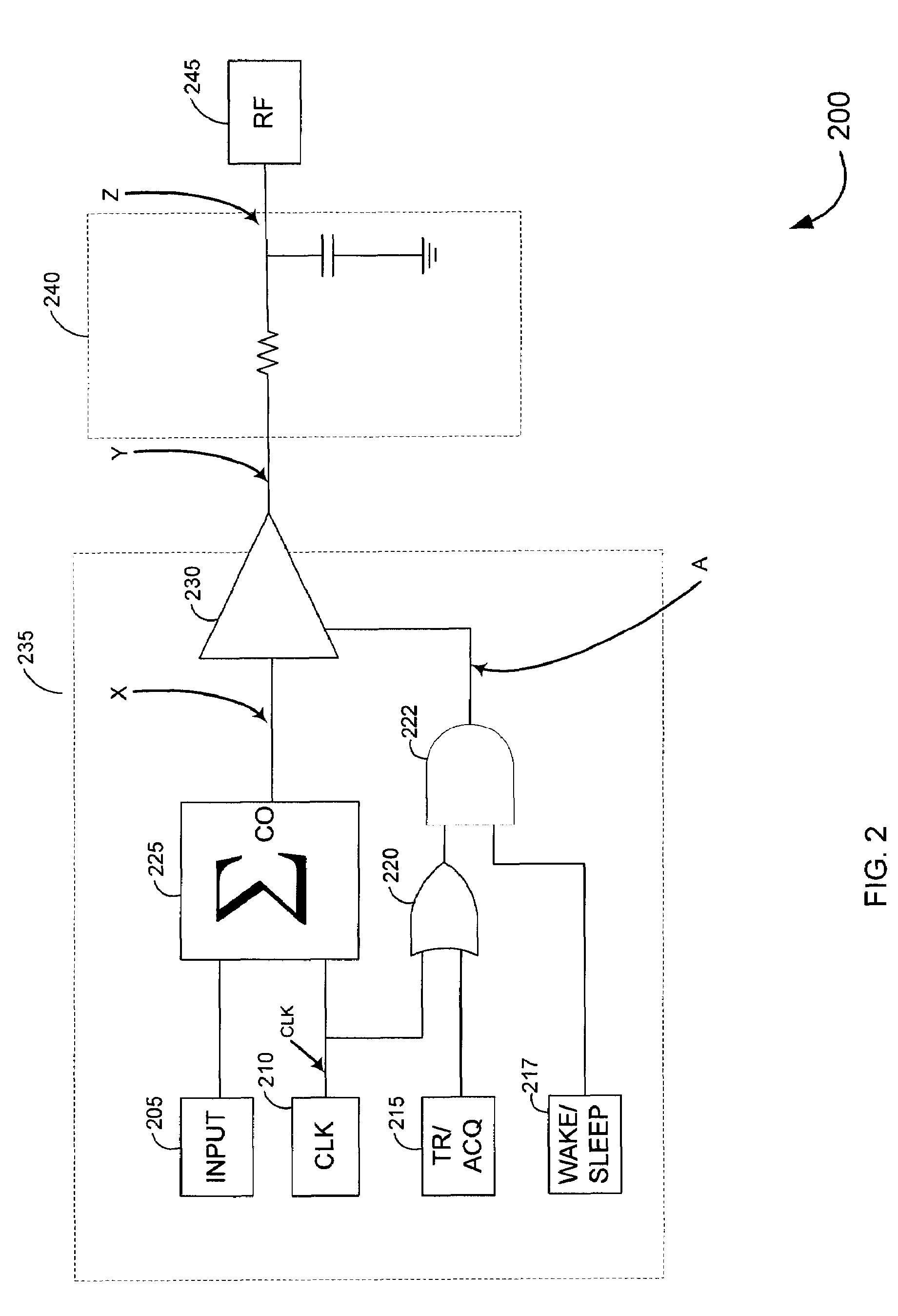
A system and method for canceling DC offset for Mobile Station Modems having direct conversion architectures. The present invention is a fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block that provides rapid and accurate DC offset estimates and cancellation techniques to support direct conversion architectures. The fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block combines four mechanisms to rapidly acquire and remove a DC offset estimate after power up, temperature changes, receiver frequency changes, and gain setting changes by increasing high pass loop bandwidth and adjusting DC offset levels at baseband. After removing the DC offset in large portions, the high pass loop bandwidth is decreased to fine tune the previous estimate and to remove any small variation in DC offset due to receiver self-mixing products.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Frequency-locked loop calibration of a phase-locked loop gain
InactiveUS7898343B1Reduce locking timeHigh frequency accuracyPulse automatic controlFrequency analysisNoise spectrumVariable-frequency oscillator
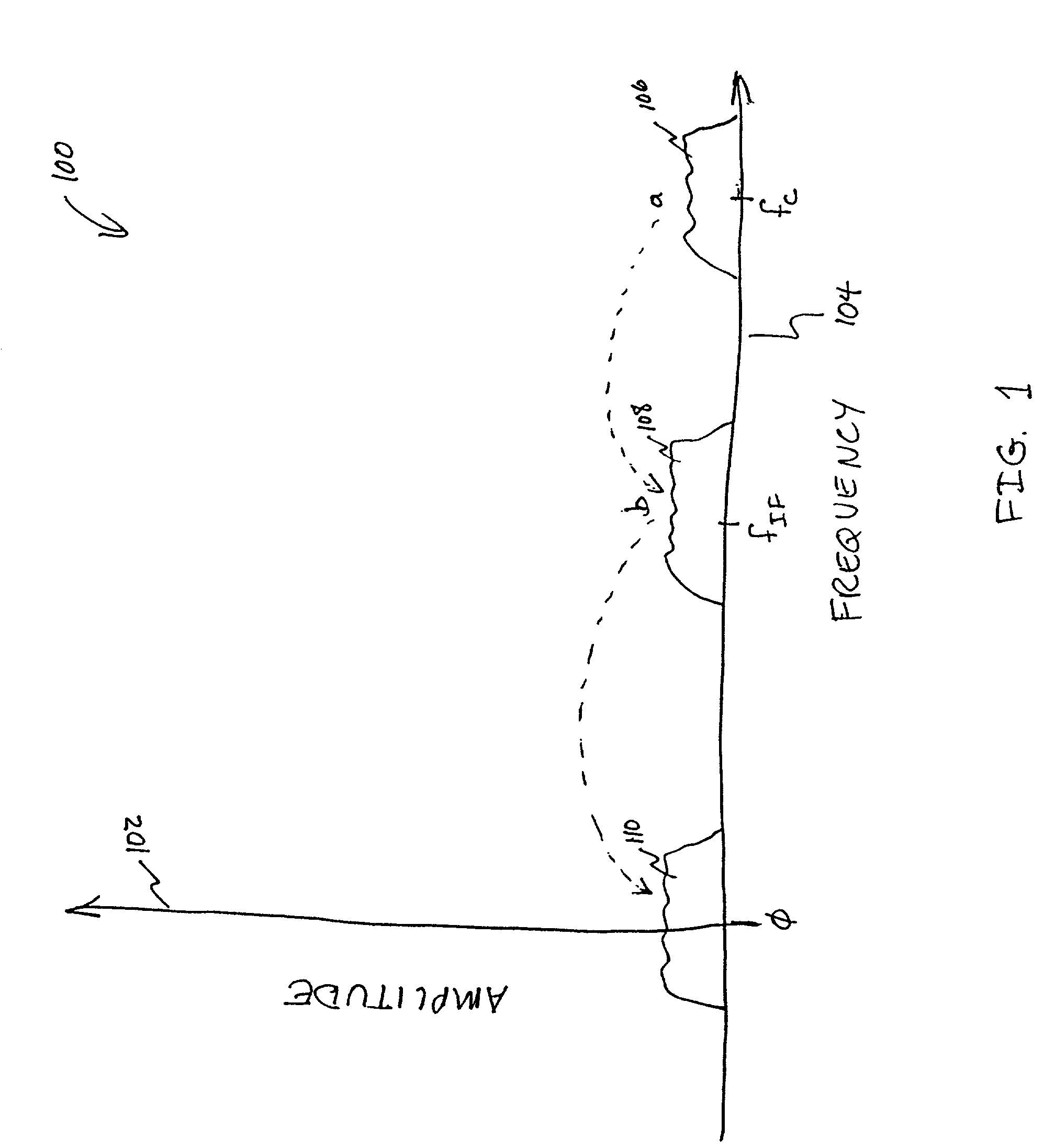
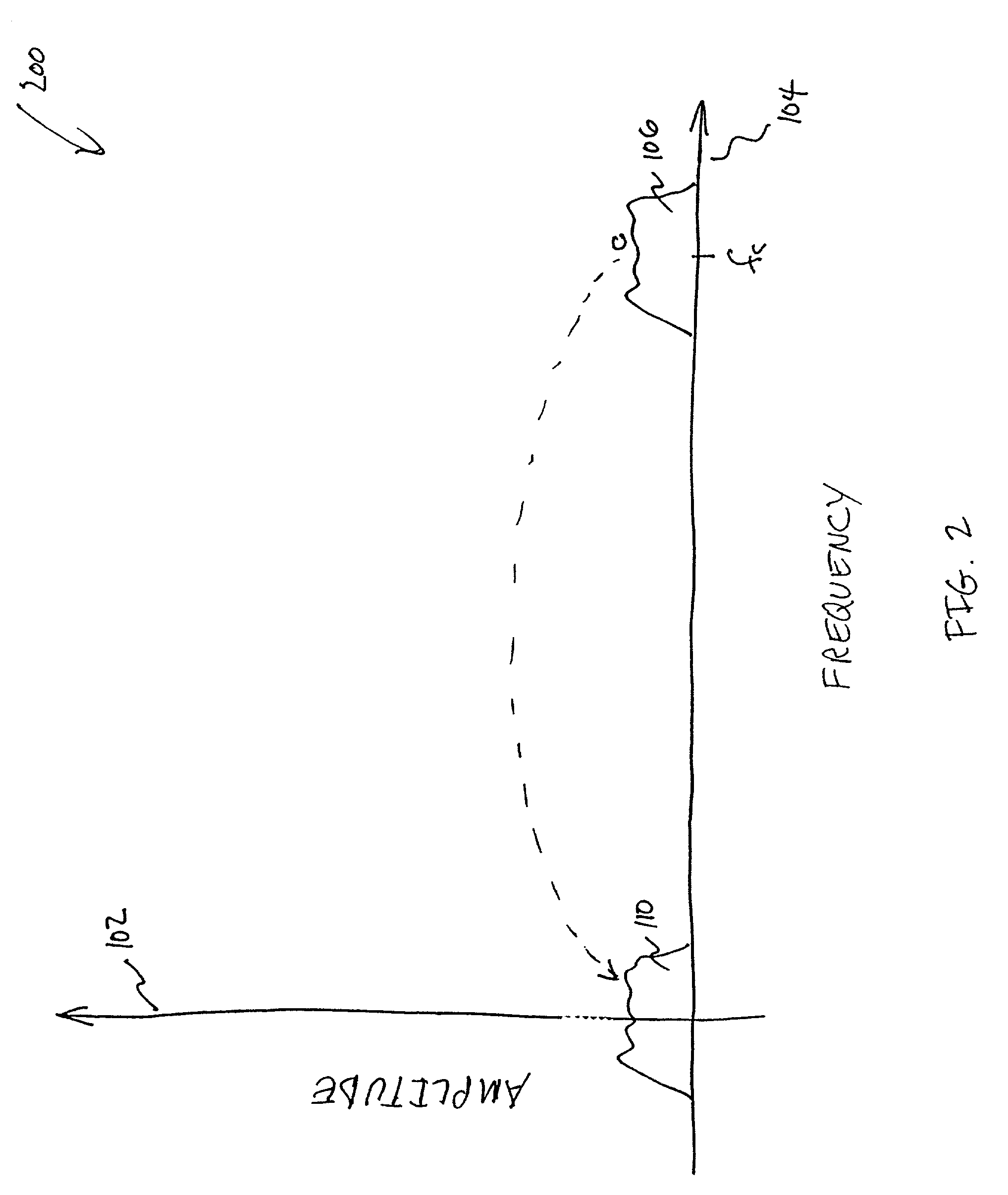
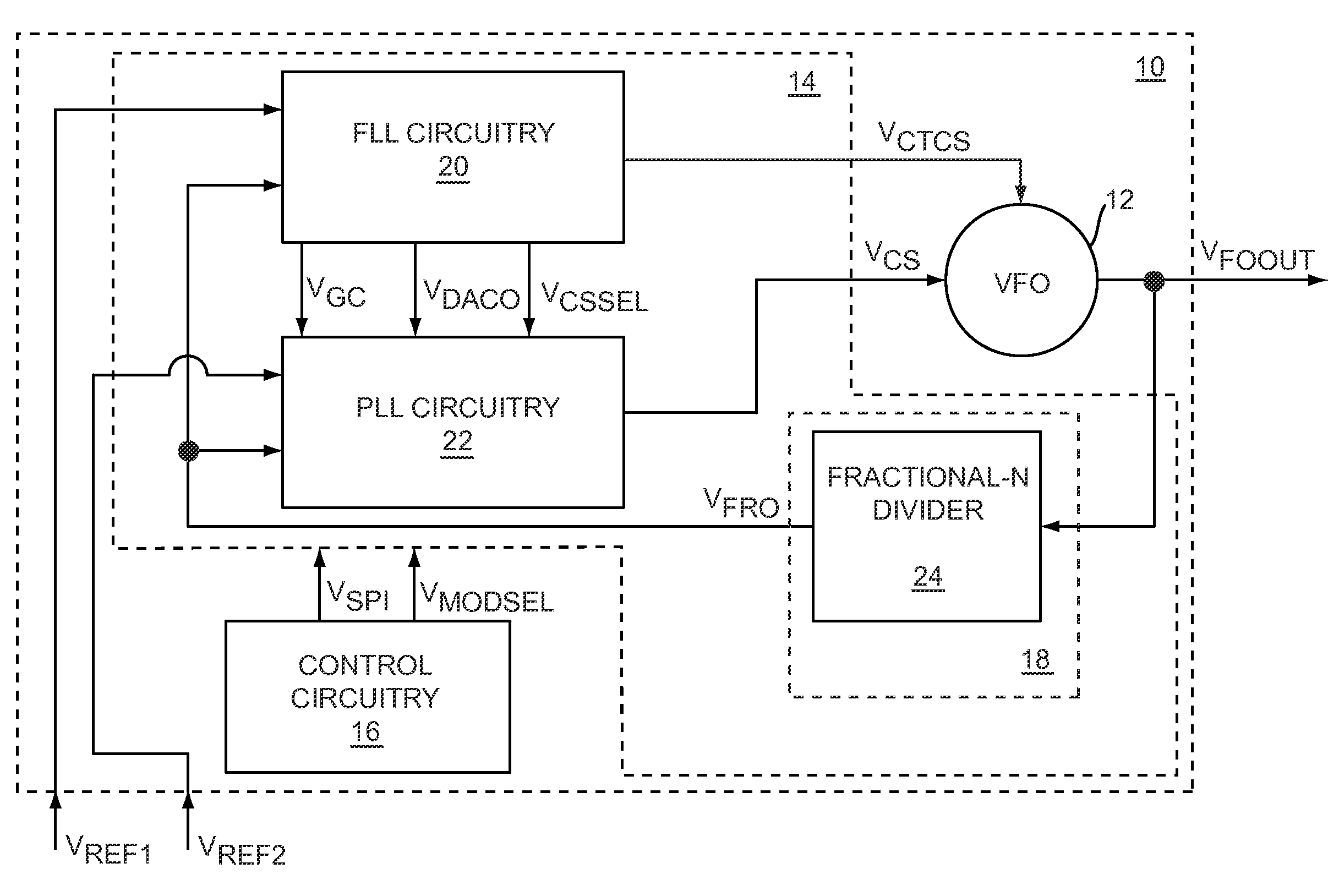
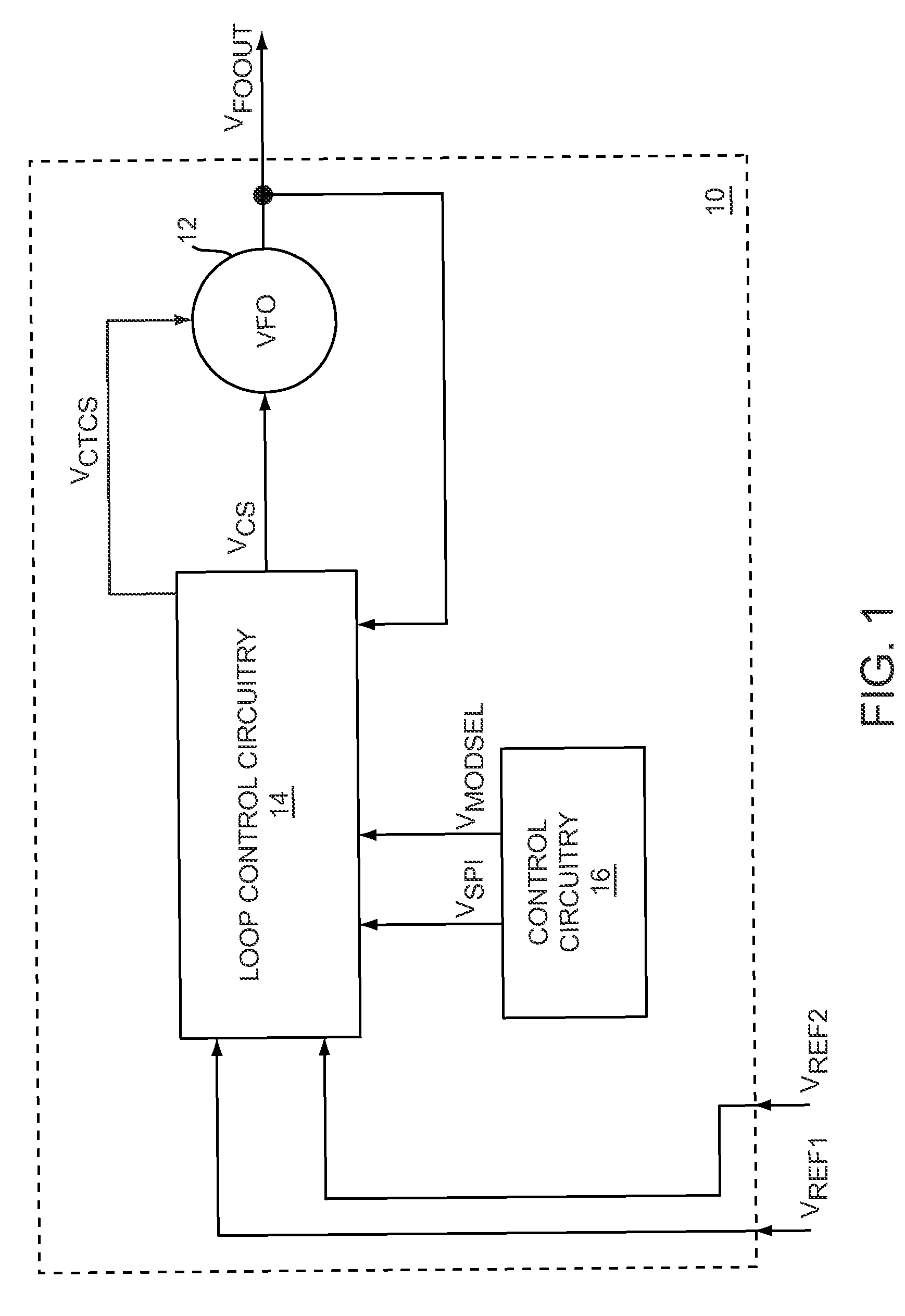
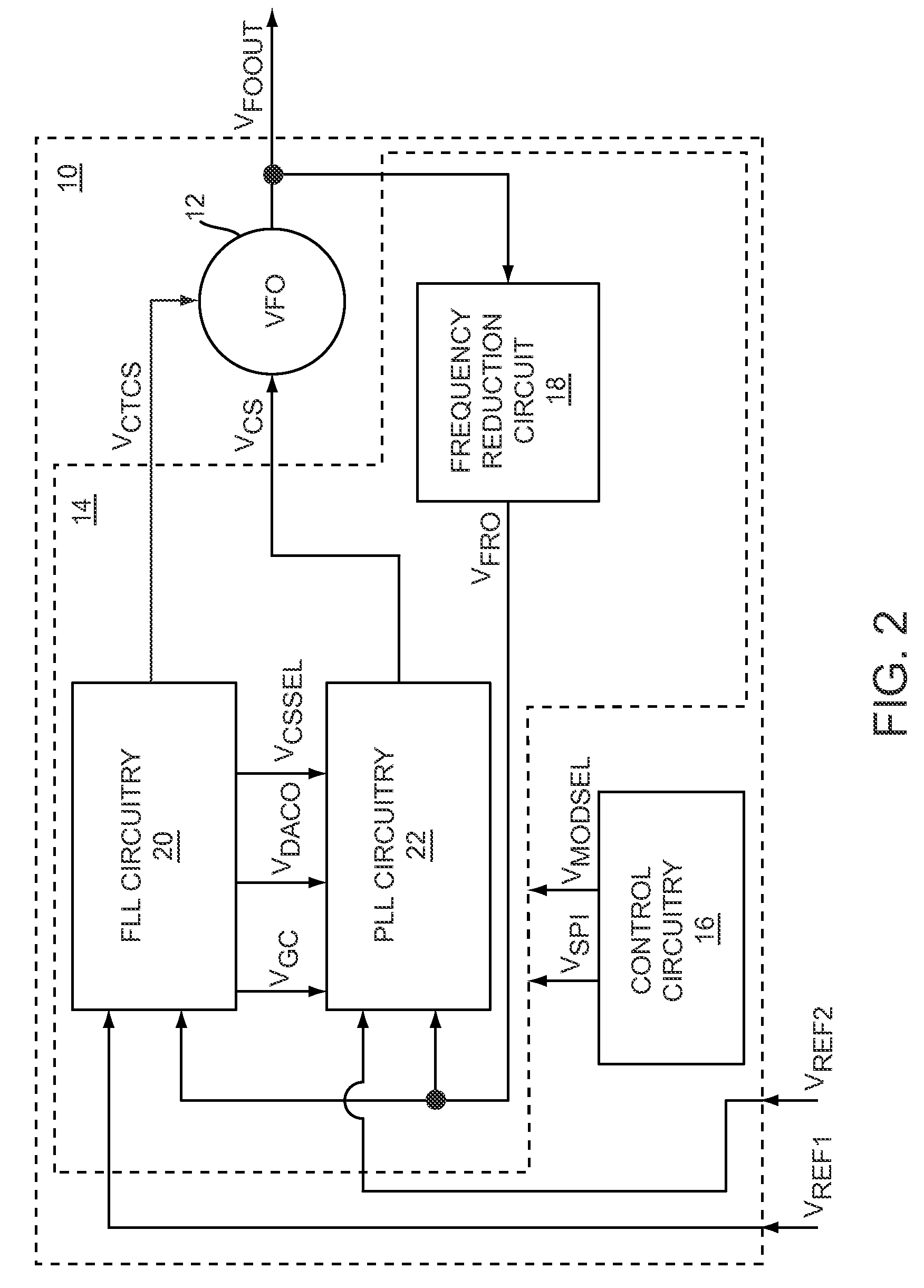
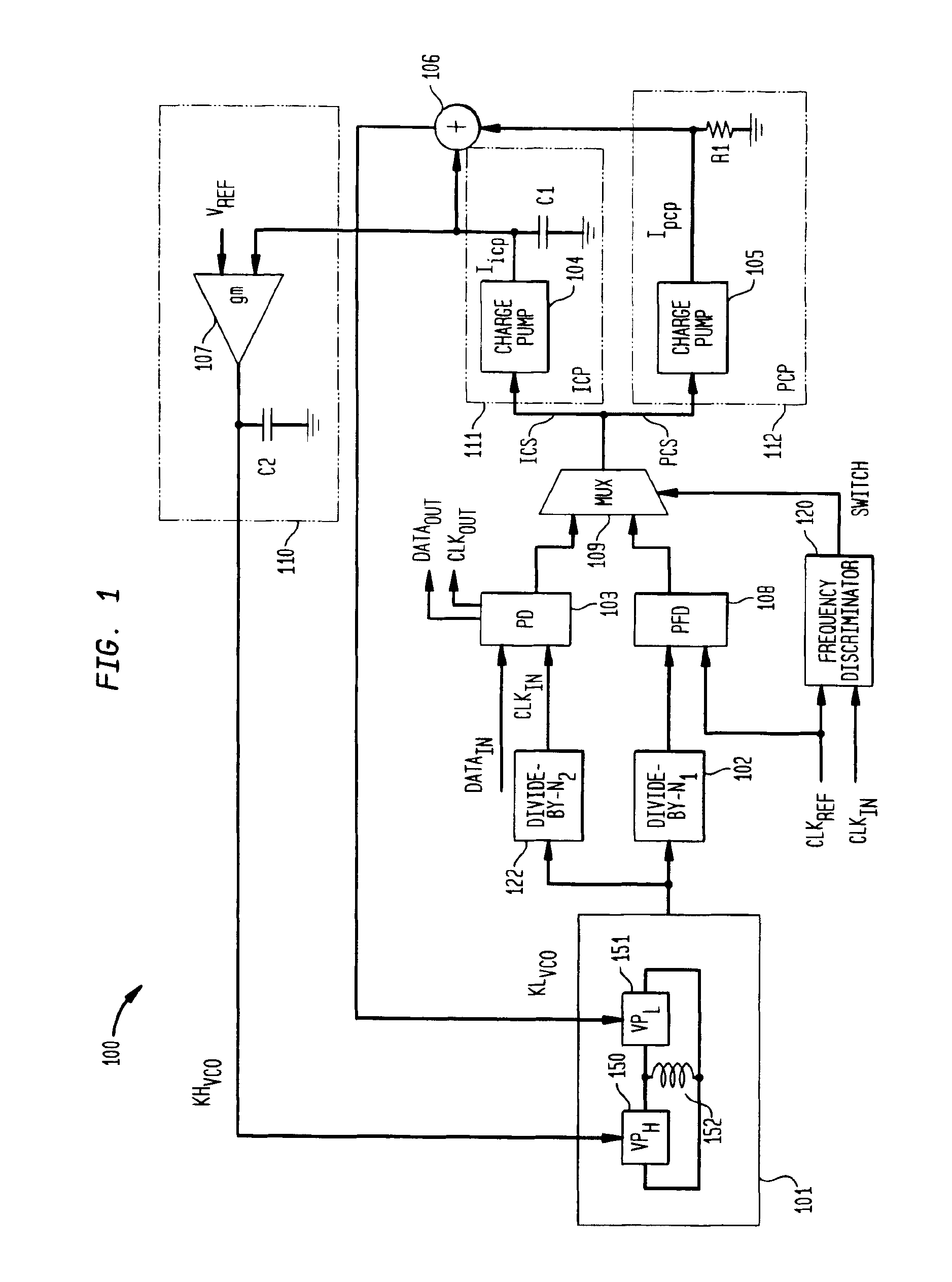
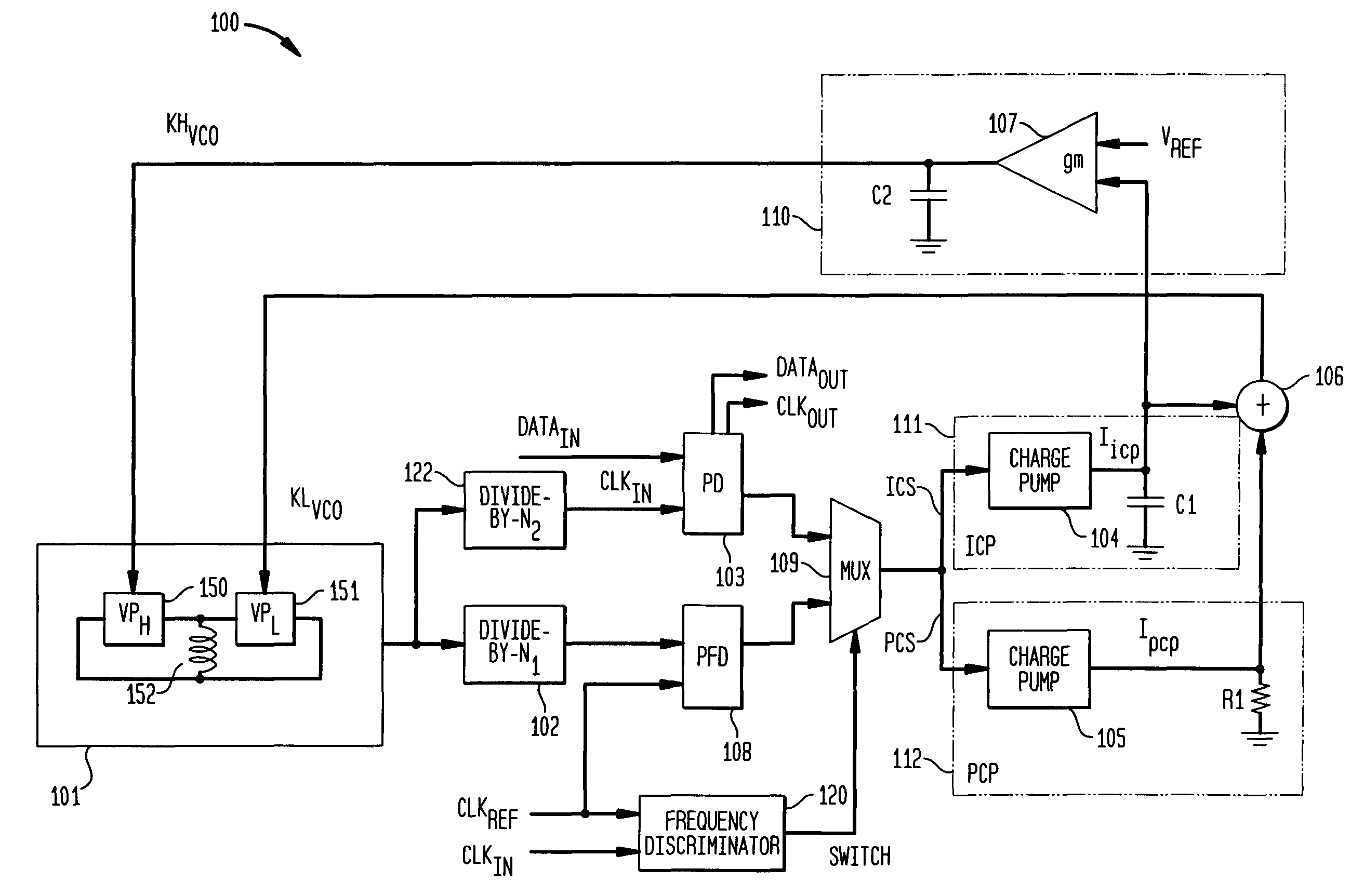
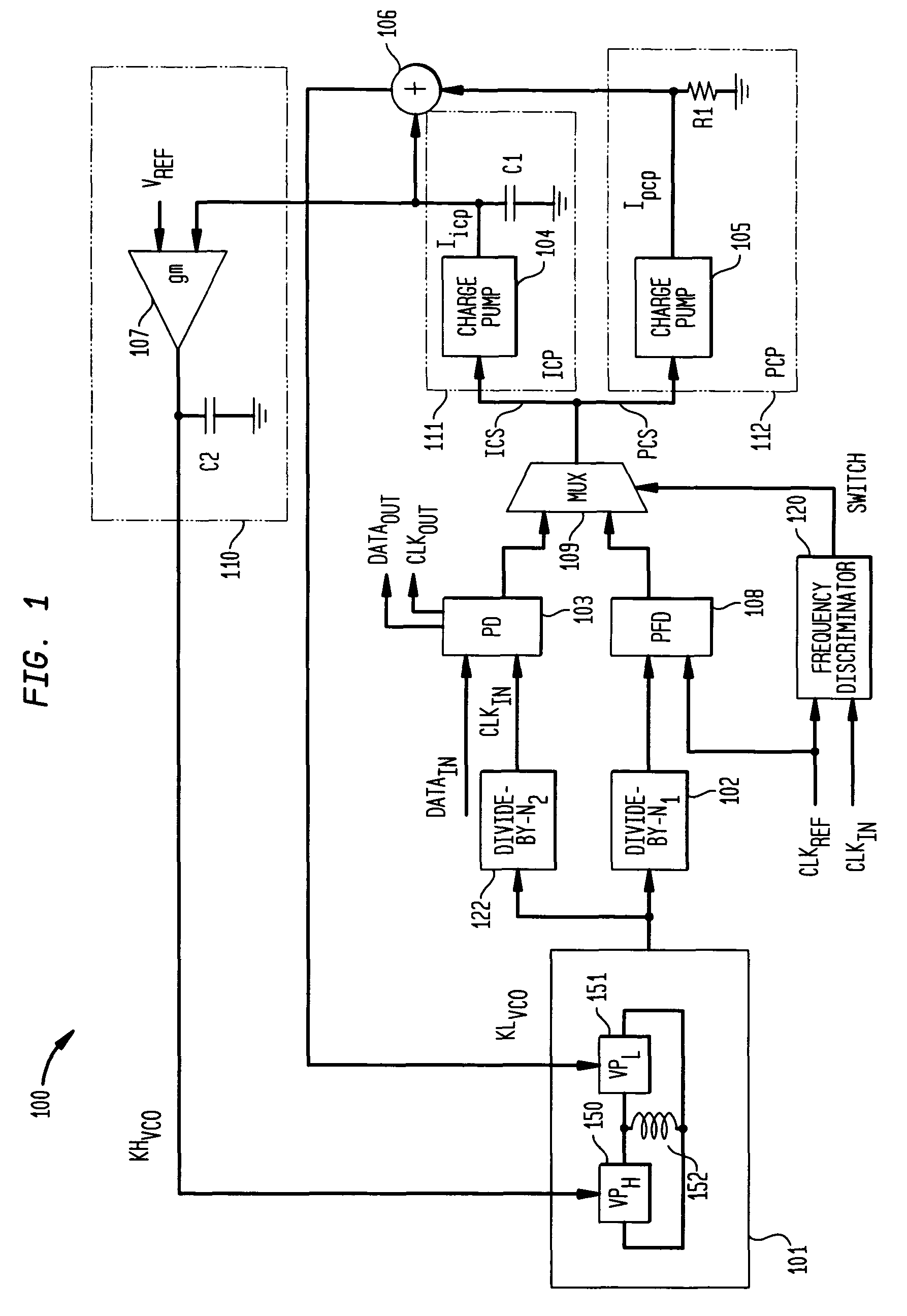
The present invention relates to a calibrated phase-locked loop (PLL), which has a calibration mode for measuring a tuning gain of a variable frequency oscillator (VFO) and a PLL mode for normal operation. Calibration information based on the tuning gain is used during the PLL mode to regulate a PLL loop gain. During the calibration mode, the calibrated PLL operates as a frequency-locked loop (FLL) for low frequency lock times, and during the PLL mode the calibrated PLL operates as a PLL for high frequency accuracy and low noise. By regulating the PLL loop gain, the desired noise spectrum and dynamic behavior of the PLL may be maintained in spite of variations in the operating characteristics or in the characteristics of the PLL components.
Owner:QORVO US INC
High-Speed Receiver Architecture
ActiveUS20090185613A1Overcome limitationsLower latencyAnalogue/digital conversionMultiple-port networksViterbi decoderTelecommunications link
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
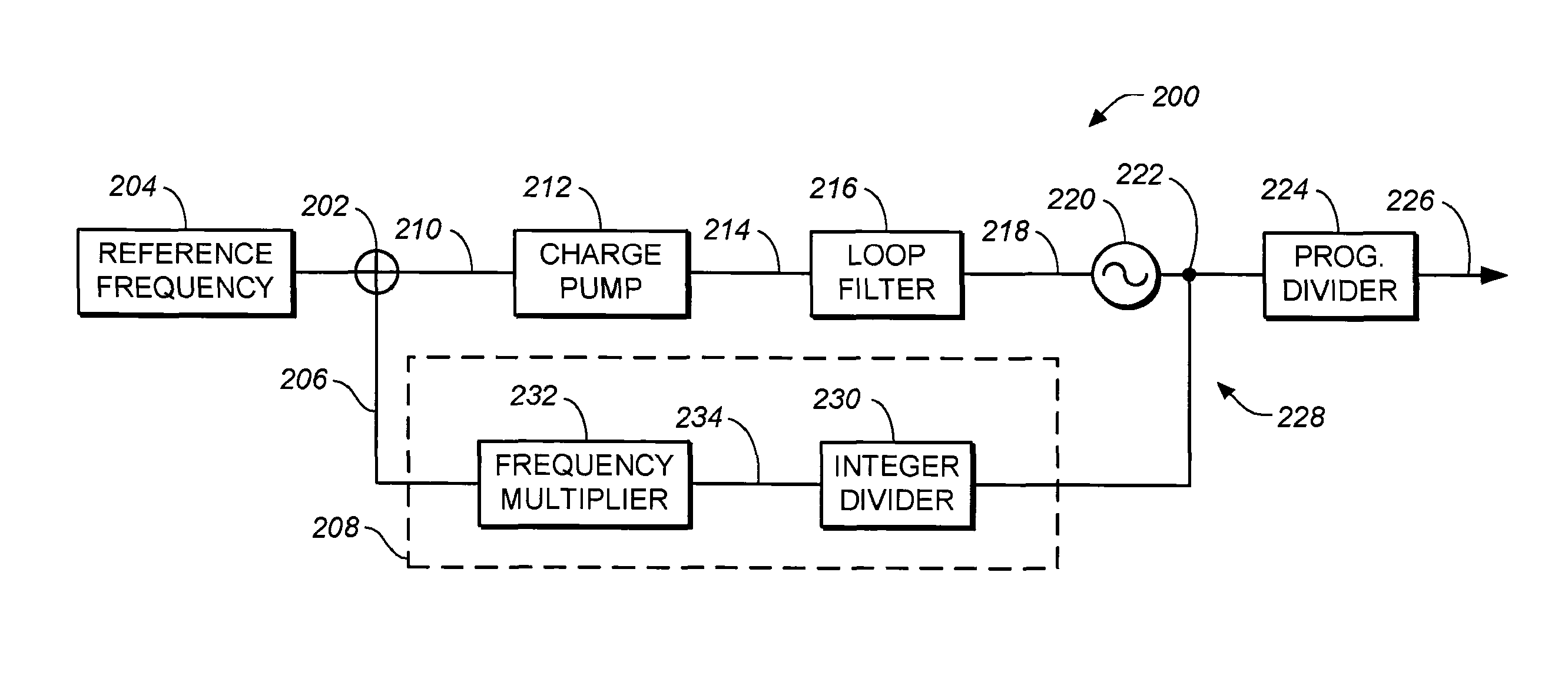
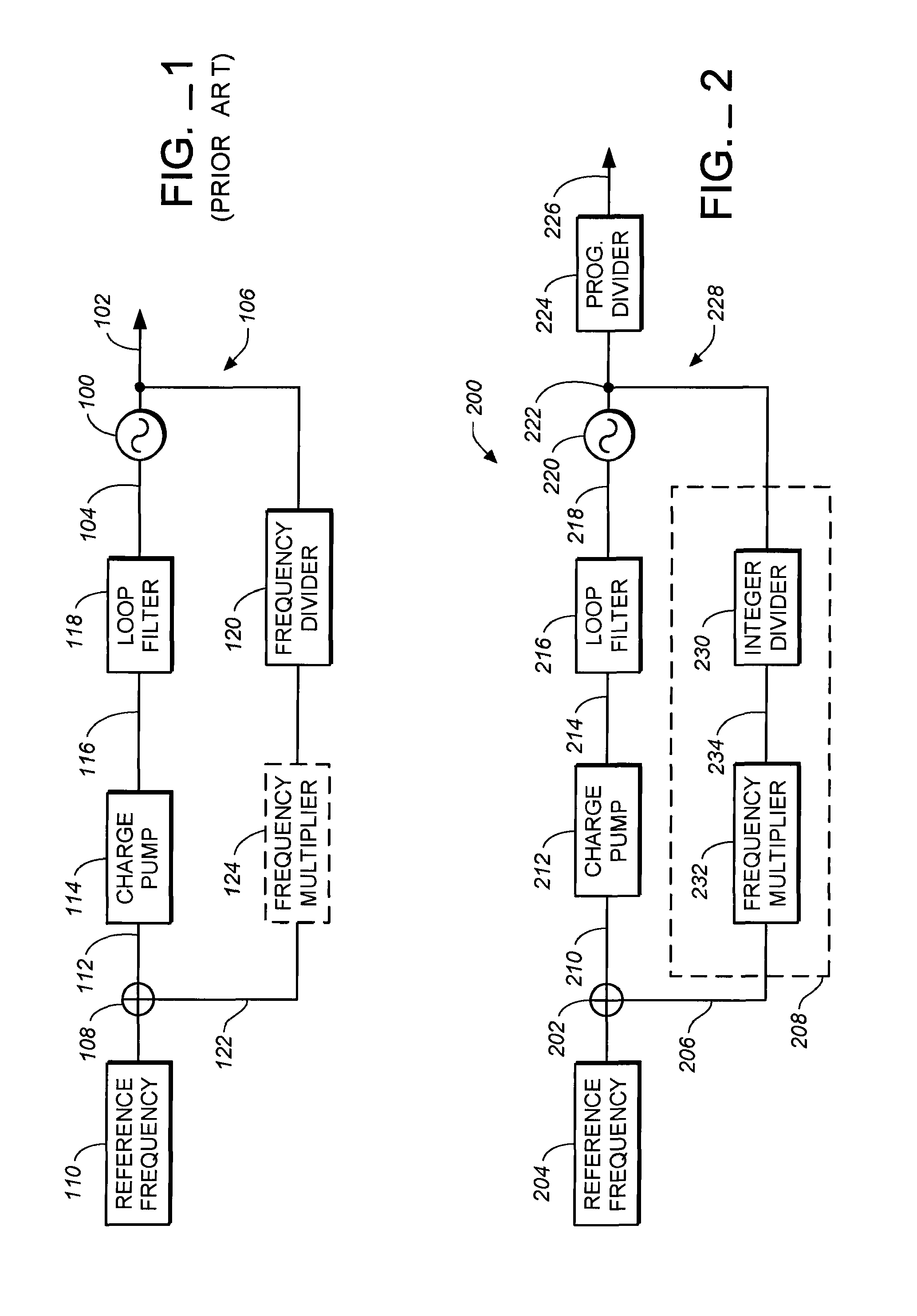
PLL-based frequency synthesizer
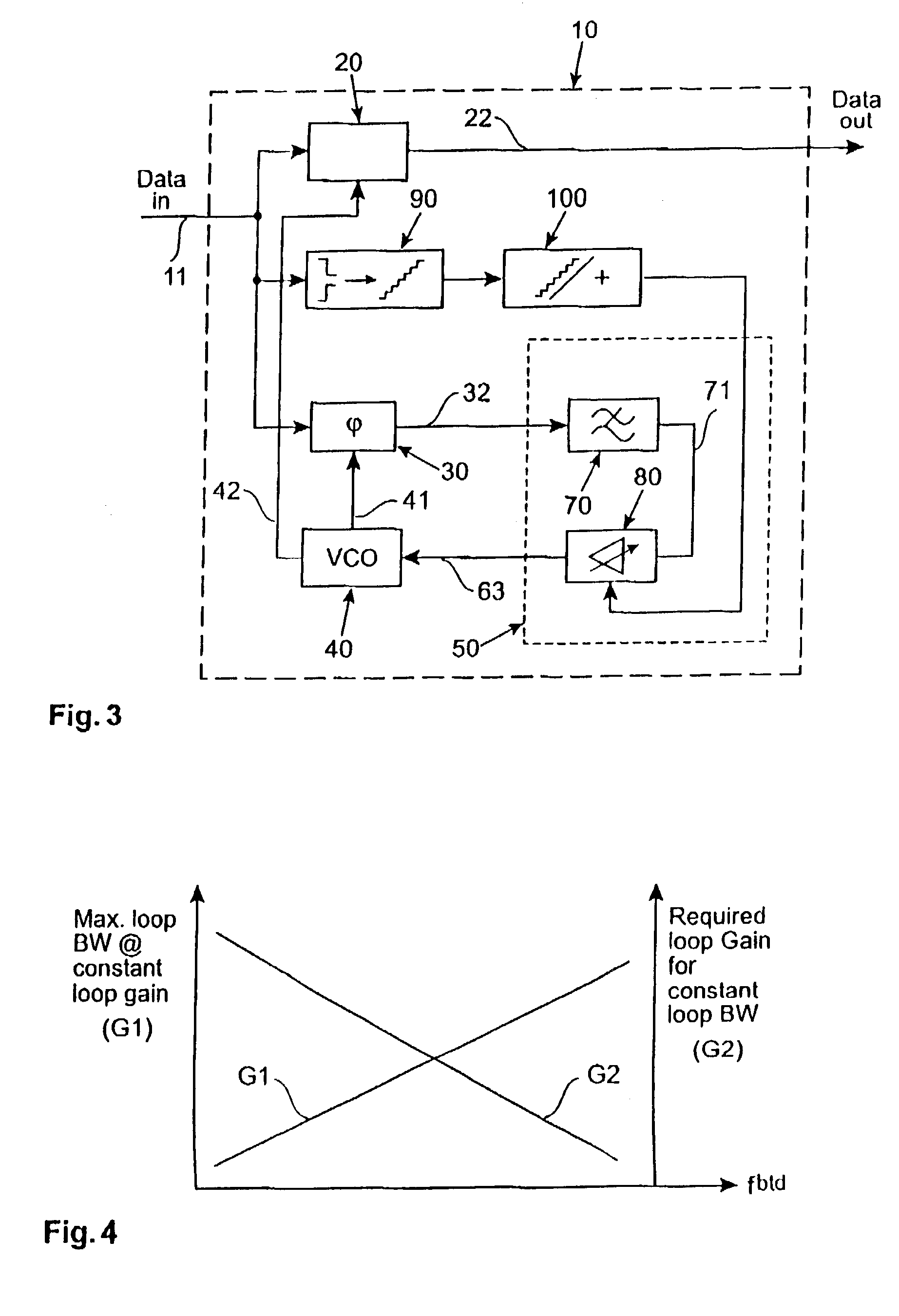
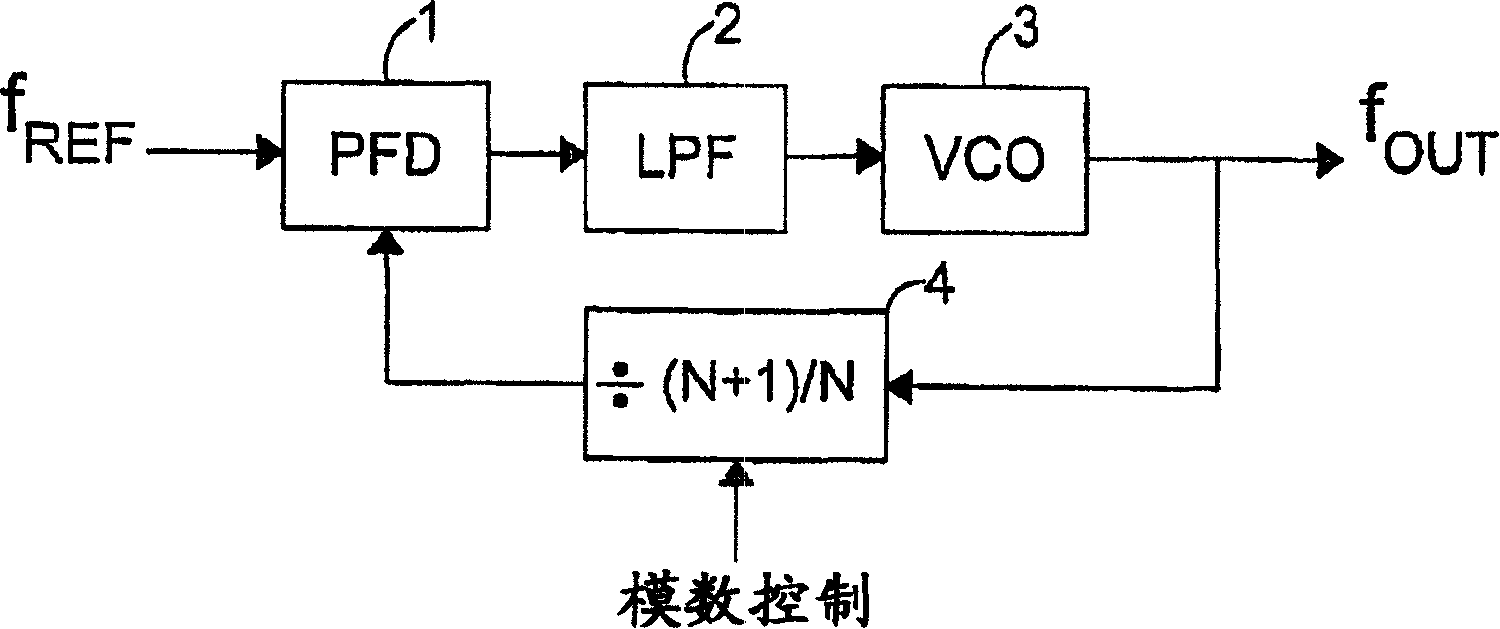
InactiveUS20060139109A1Fast convergenceIncrease loop bandwidthMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlLoop filterPhase difference
The frequency synthesizer includes a phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL includes an oscillator controlled to deliver an output signal at a predefined output frequency, a variable frequency divider to convert the output signal into a divided-frequency signal, a phase comparator to produce a signal measuring a phase difference between the divided-frequency signal and a reference signal at a reference frequency, and a loop filter to control the oscillator on the basis of the measurement signal. To increase the speed of convergence of the synthesizer if the set point is changed, the loop filter of the PLL is a fractional, i.e. non-integer, order low-pass filter.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Clock data recovery system
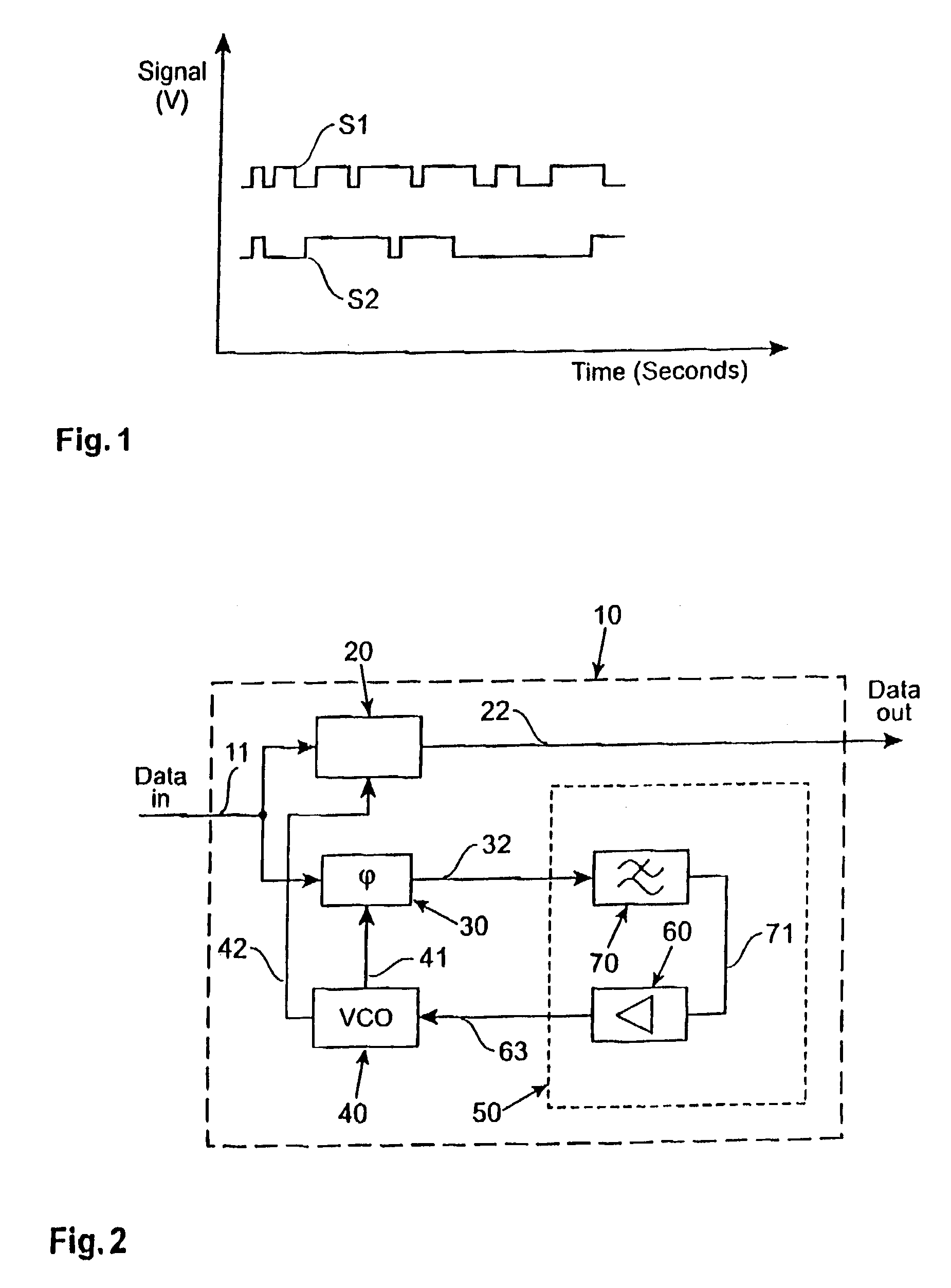
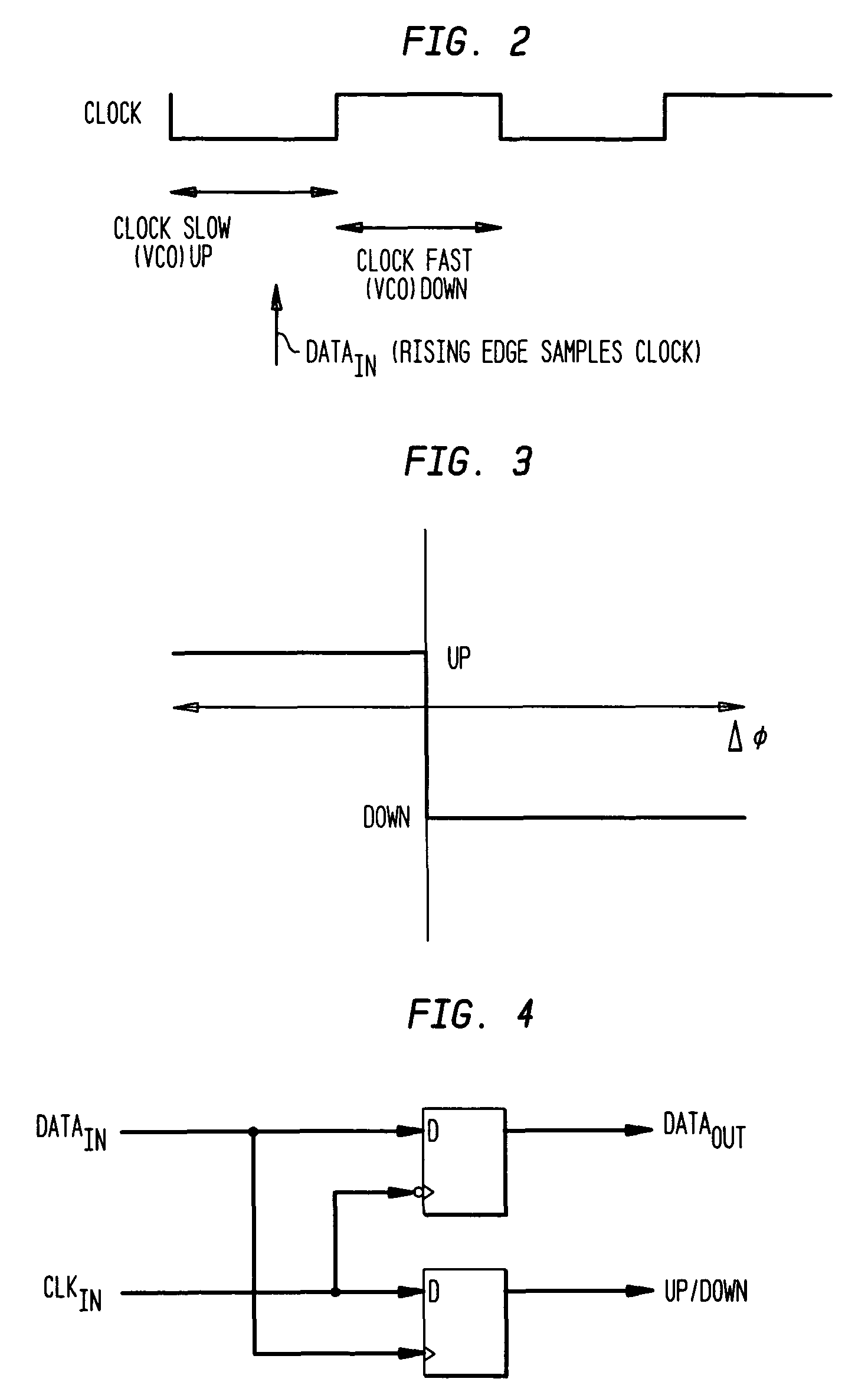
ActiveUS6981168B2Increase fashionIncrease loop bandwidthError preventionModulated-carrier systemsPhase detectorControl signal
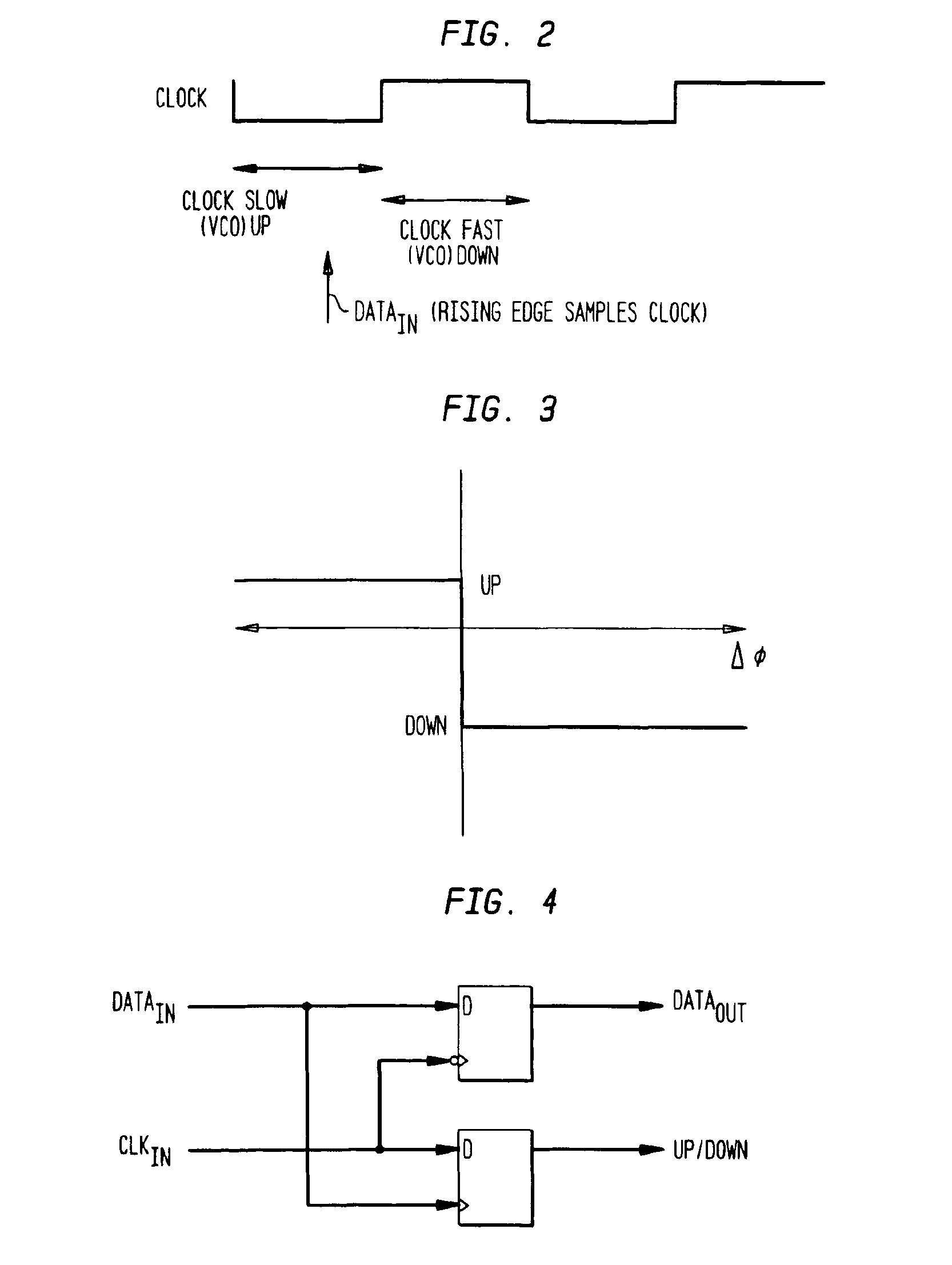
A clock data recovery system is provided for resampling a clock signal according to an incoming data signal stream. It comprises a clock generator for generating said clock signal wherein one of the frequency and phase of that clock signal is dependent upon a control signal. It is further provided a phase detector operable to detect the phase difference between said clock signal and said incoming data signal stream and is operable to generate a phase difference signal. A loop controller has a variable-gain and is operable to control said clock generator by generating said control signal. That control signal is dependent in said phase difference signal and that variable-gain. The variable-gain is dependent upon a transition rate of the incoming data signal stream. The loop controller can comprise a low-pass filter to generate from the phase difference signal a low-pass filered phase signal and to adjust the bandwidth of the clock data recovery system. The loop controller further can comprise a variable-gain element to amplify the filtered signal in accordance with a received bit transition rate provided by a bit transition detector and a density calculator.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
High-speed receiver architecture
ActiveUS7852913B2Lower latencyIncrease loop bandwidthAnalogue/digital conversionMultiple-port networksViterbi decoderFiber
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Adaptive loop bandwidth circuit for a PLL
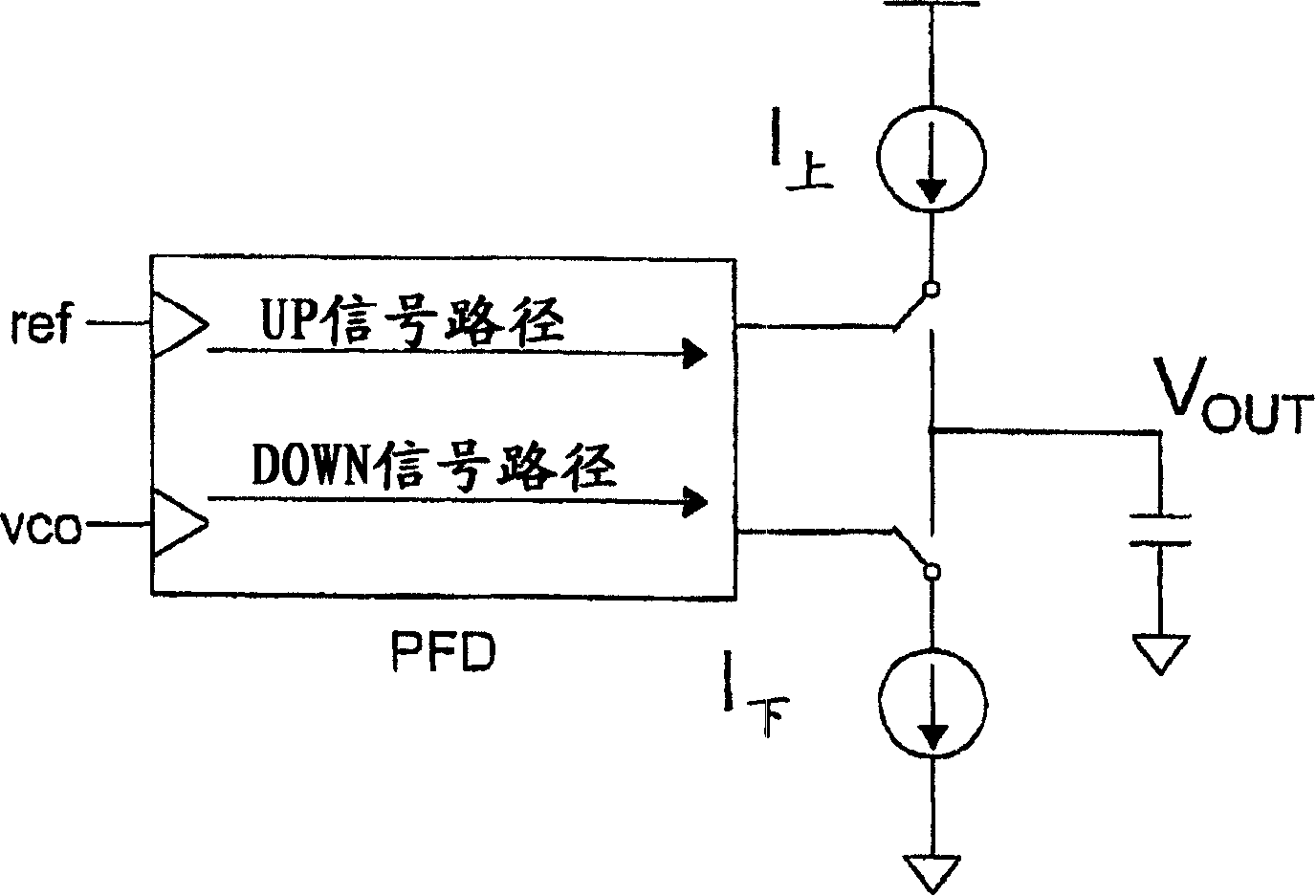
InactiveUS6909329B2High resolutionIncrease loop bandwidthPulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase anglePhase detectorPhase shifted
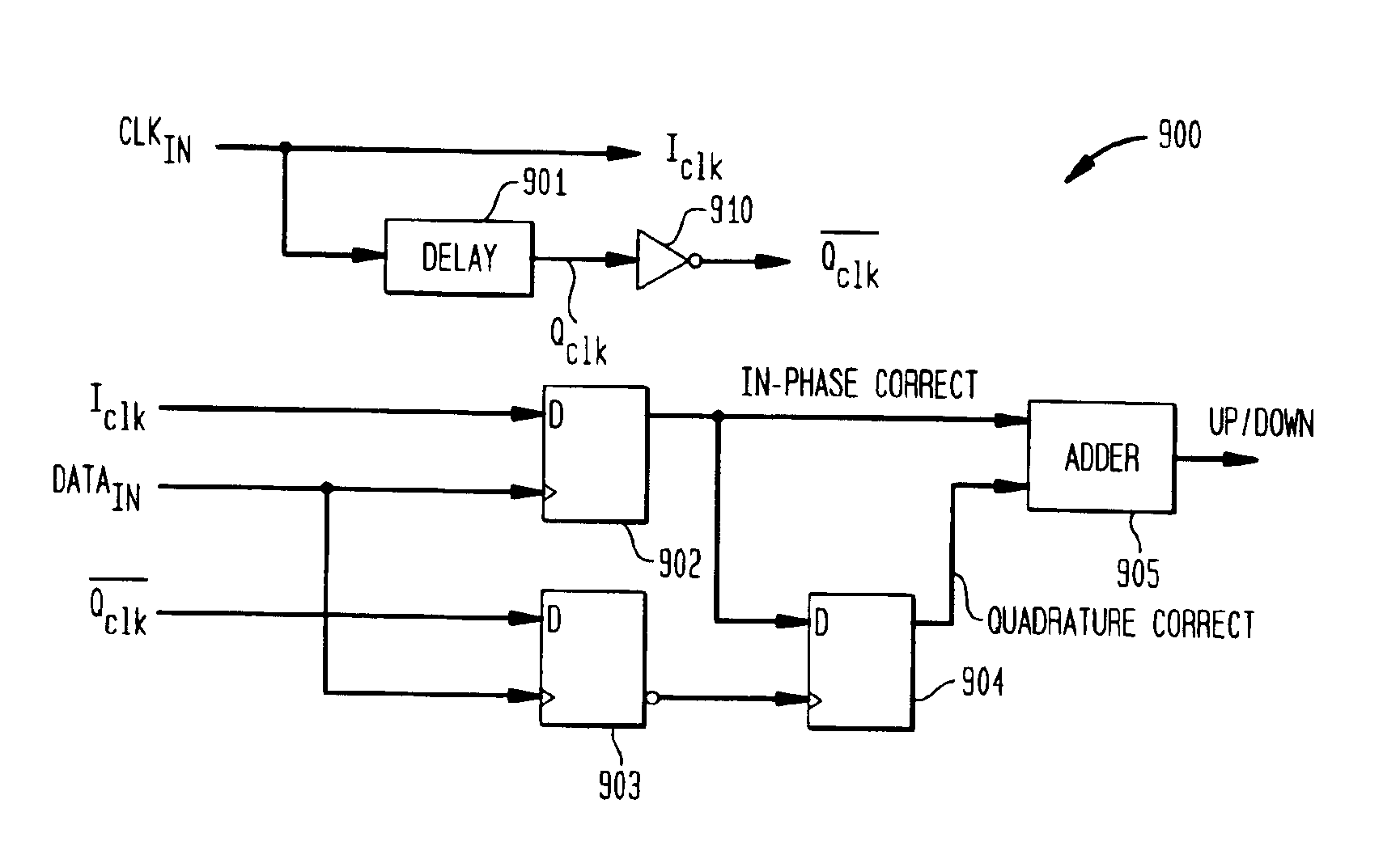
A phase-locked loop (PLL) employs a phase detector (PD) generating an up / down signal based on the phase error between a data signal and a clock signal input to the phase detector. The PD senses excess jitter and extends the loop bandwidth to accommodate such excess jitter. Phase error is derived by sampling of the clock signal and at least one phase-shifted version of the clock signal by the data signal, and a retimed data is generated by the PD by sampling of the data signal by the clock signal. The sampled clocks are employed to generate a modified control signal with greater resolution in detecting the phase error, which, in turn, increases the loop bandwidth.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Direct drive light-emitting diode (LED) driver
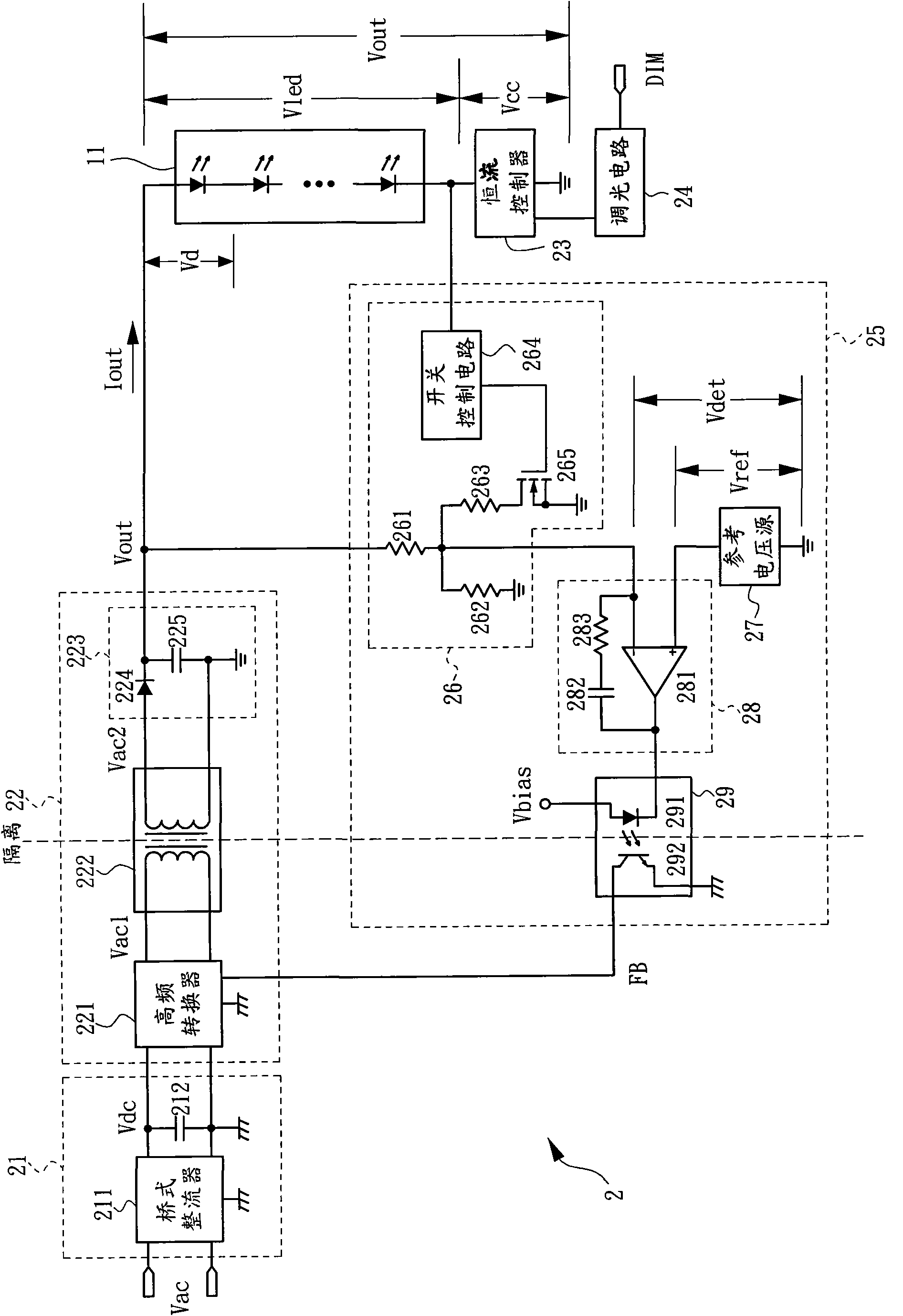
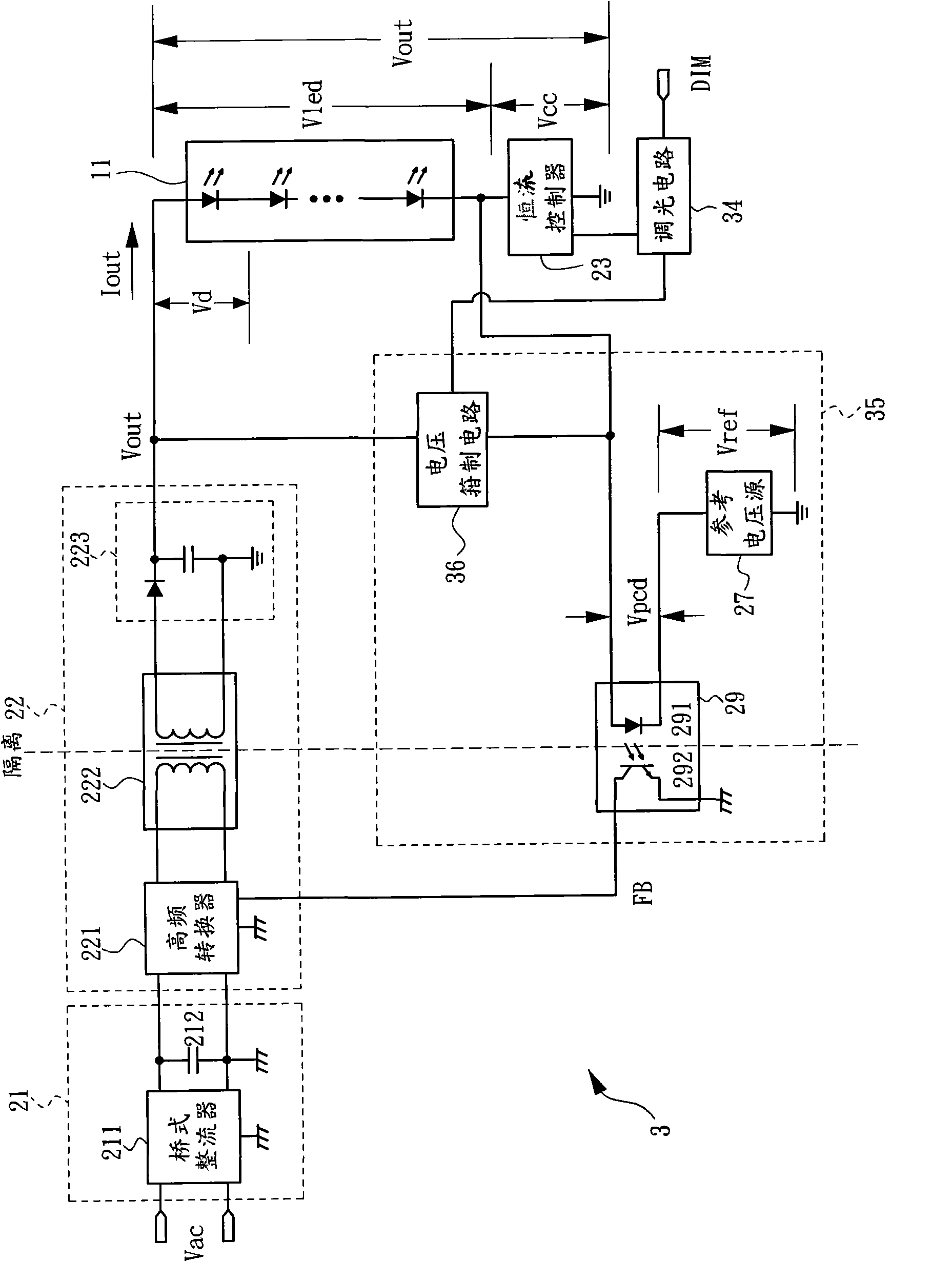
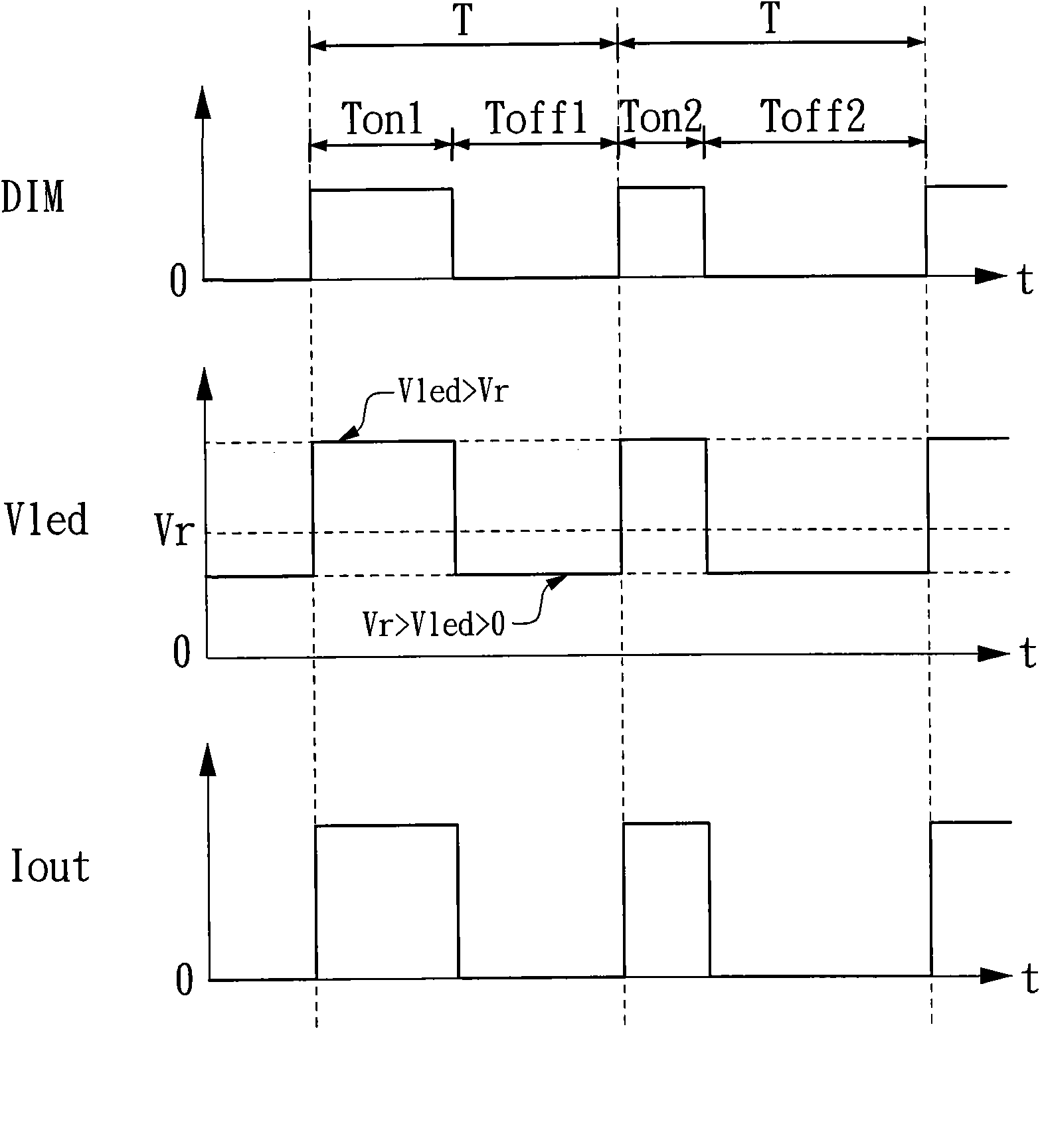
InactiveCN102387625AImprove stabilityImprove performanceElectric light circuit arrangementPower flowElectromagnetic interference
The invention belongs to the field of electronics and discloses a direct drive light-emitting diode (LED) driver. The driver adopts an isolation circuit to connect the output end of an LED lamp string and a constant current controller in coupling mode, output voltage of the driver changes automatically along with working voltage of the LED lamp string, and the driver can be applied to driving of the LED lamp string with various kinds of different working voltage. Accordingly, an error detection amplifying circuit in a feedback path is omitted, and stability and bandwidth of a return circuit are improved. Pulse width modulation (PWM) dimming can be conducted in a dimming range from 1% to 100% in uninterrupted mode. By means of the characteristics that when the working voltage of the LED lamp string is smaller than cut-in voltage of the LED lamp string, the current is zero, voltage difference of output voltage in an enabling period and a disabling period during PWM dimming is reduced, so that ripple voltage and electromagnetic disturbance are reduced.
Owner:TOP VICTORY INVESTMENTS
High-Speed Receiver Architecture
ActiveUS20110211842A1Overcome limitationsLower latencyOther decoding techniquesTransmission control/equalisingFiberViterbi decoder
A receiver (e.g., for a 10G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Arrangement, phase locked loop and method for noise shaping in a phase-locked loop
ActiveUS20060192620A1Reduce phase noiseIncrease loop bandwidthPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersPhase noiseFrequency spectrum
A noise shaping arrangement for a phase locked loop includes a first order sigma-delta modulator (500) arranged to provide a first-order quantized output and a feedback path output (508). A second order sigma-delta modulator (520) is arranged to receive the feedback path output (508) and provides a second order quantized output. A combination block (530) combines the first and second order quantized outputs to provide a combined third order quantized output (540), which provides noise shaping with a frequency notch spectrum. In this way a new quantization noise shape of third order is provided, such that quantization phase noise may be lowered, the PLL loop bandwidth may be increased, modulation phase error may be reduced and PLL locking speed increased.
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
Adaptive loop bandwidth circuit for a PLL
ActiveUS20050046490A1High resolutionIncrease loop bandwidthPulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase anglePhase detectorControl signal
A phase-locked loop (PLL) employs a phase detector (PD) generating an up / down signal based on the phase error between a data signal and a clock signal input to the phase detector. The PD senses excess jitter and extends the loop bandwidth to accommodate such excess jitter. Phase error is derived by sampling of the clock signal and at least one phase-shifted version of the clock signal by the data signal, and a retimed data is generated by the PD by sampling of the data signal by the clock signal. The sampled clocks are employed to generate a modified control signal with greater resolution in detecting the phase error, which, in turn, increases the loop bandwidth.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
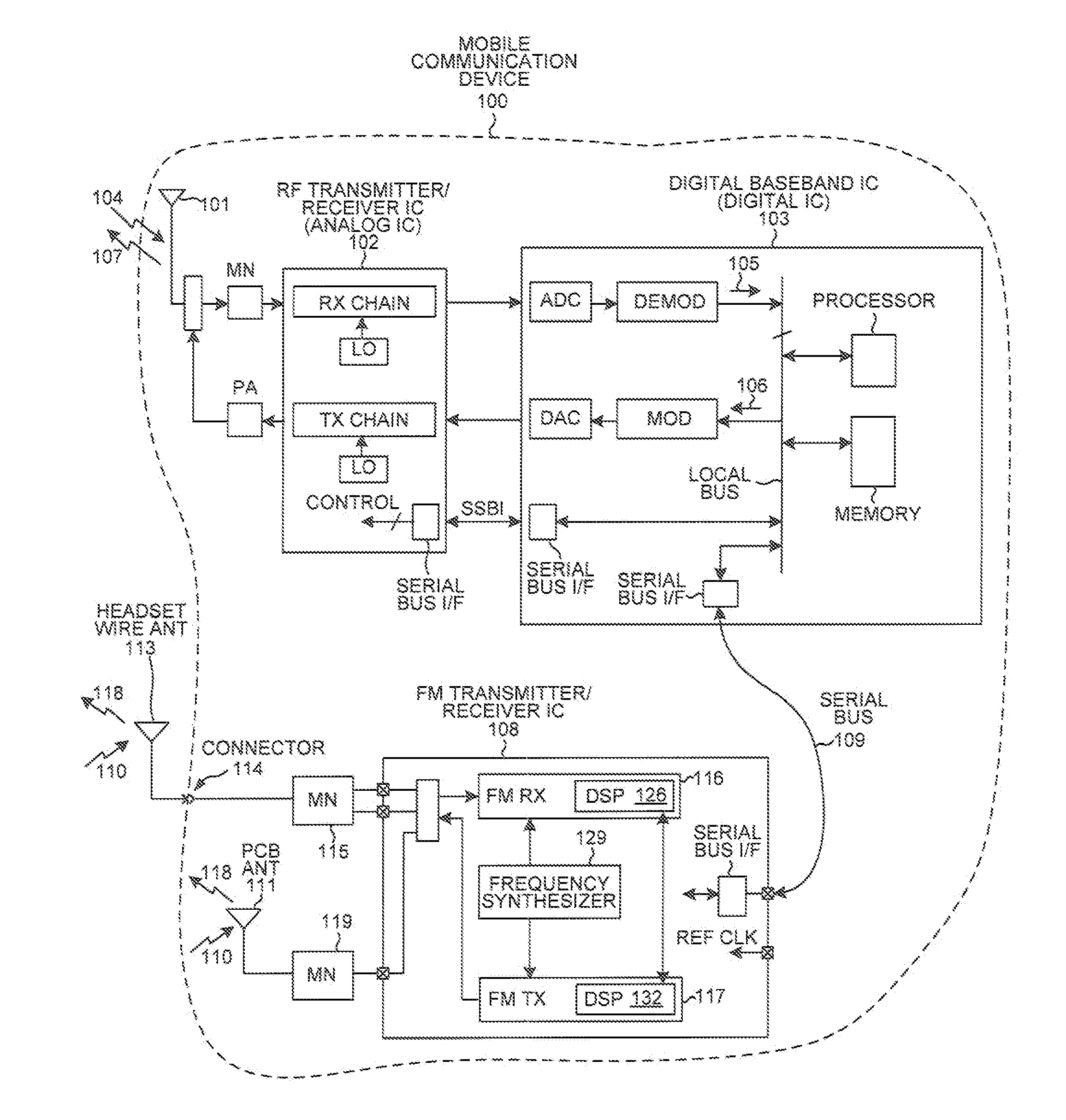
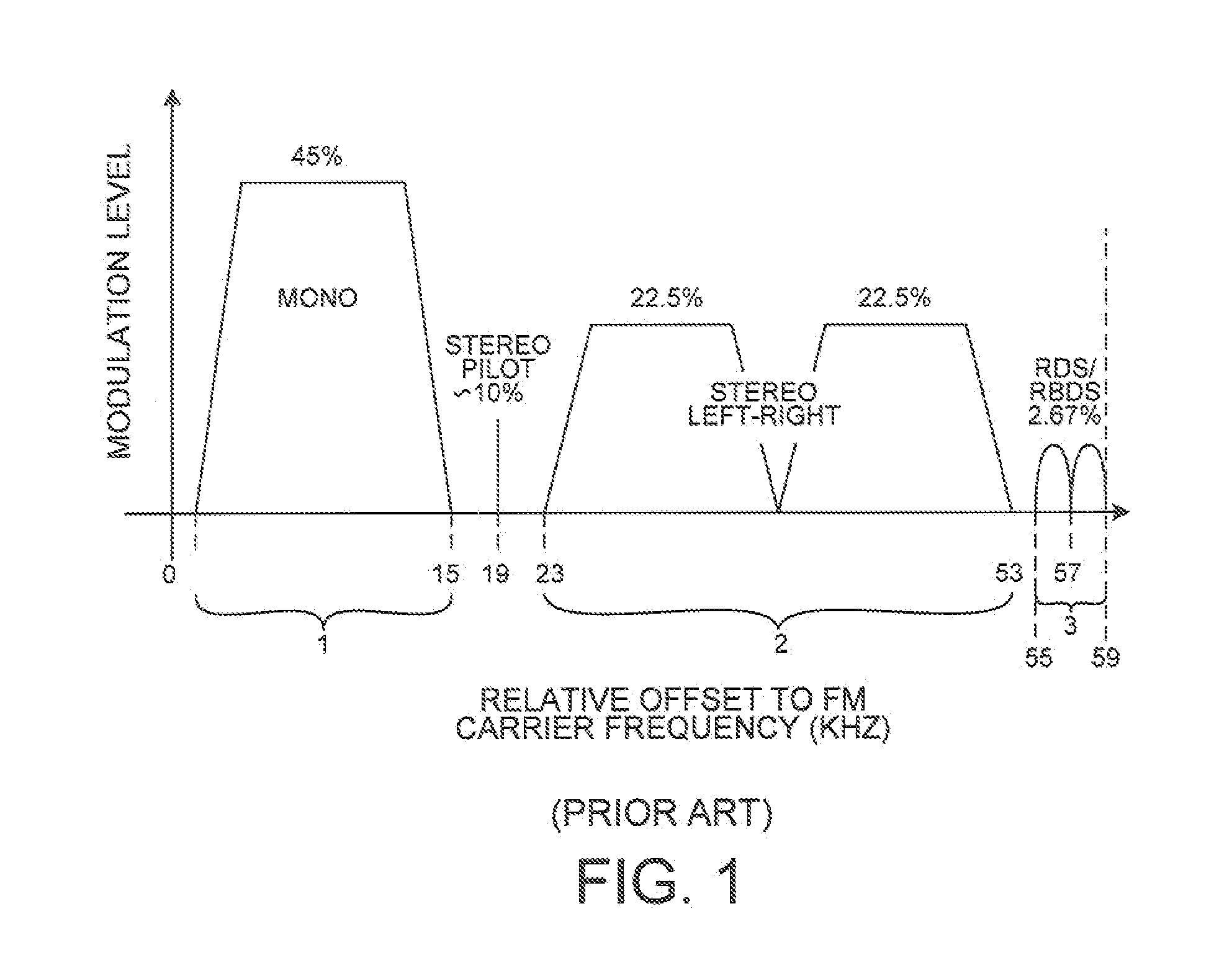
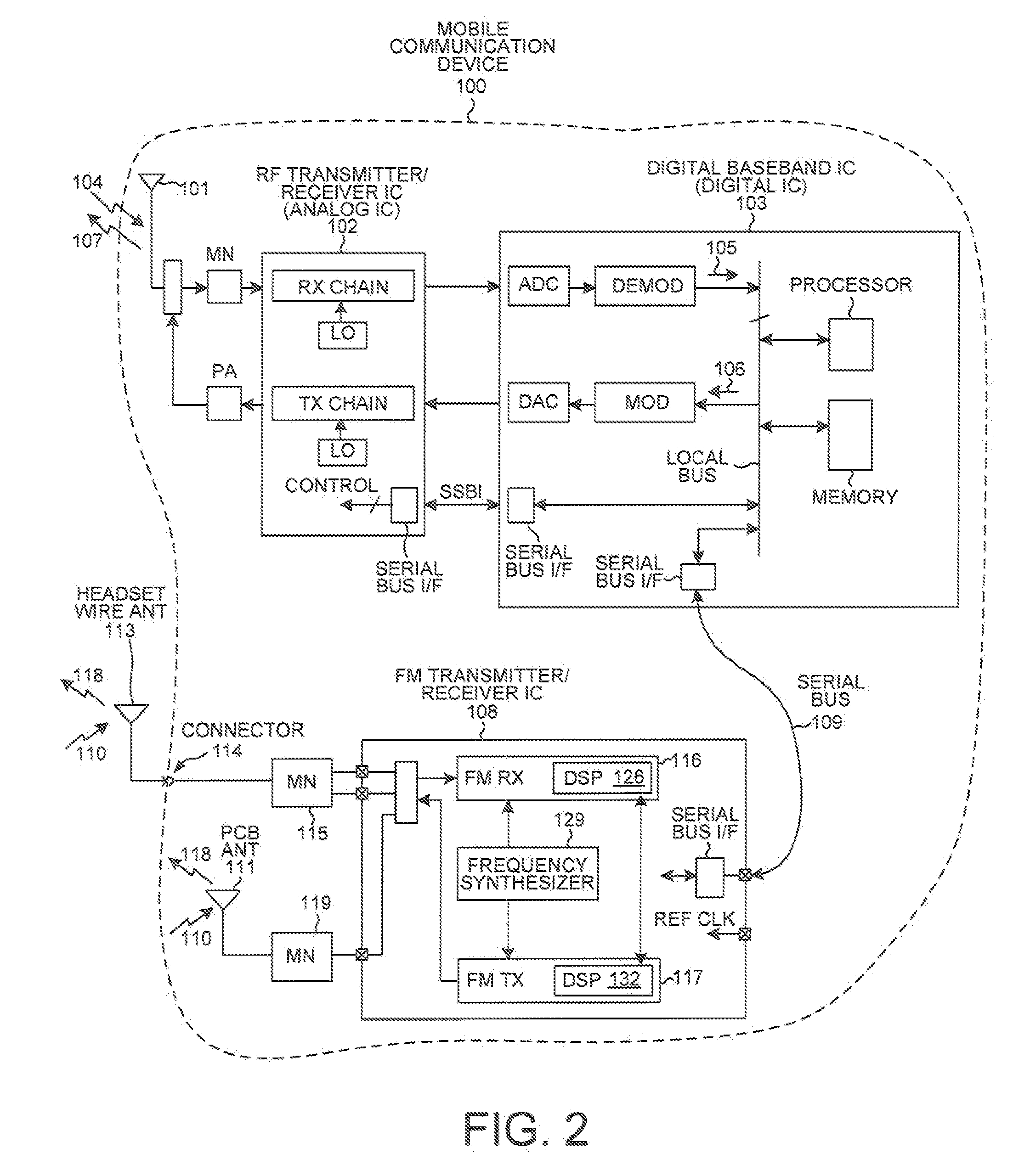
Jammer detection based adaptive pll bandwidth adjustment in FM receiver
ActiveUS20100273442A1Increase loop bandwidthReducing in-band residual FMPulse automatic controlSubstation equipmentSelf adaptiveEngineering
A frequency synthesizer within an FM receiver employs a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) to generate a Local Oscillator (LO) signal. The LO signal is supplied to a mixer. The FM receiver also includes jammer detection functionality. If no jammer is detected, then the loop bandwidth of the PLL is set to have a relatively high value, thereby favoring suppression of in-band residual FM. If a jammer is detected, then the loop bandwidth of the PLL is set to have a relatively low value, thereby favoring suppression of out-of-band SSB phase noise. By adaptively changing loop bandwidth depending on whether a jammer is detected, performance requirements on sub-circuits within the PLL can be relaxed while still satisfying in-band residual FM and out-of-band SSB phase noise requirements. By allowing the VCO of the PLL to generate more phase noise due to the adaptive changing of loop bandwidth, VCO power consumption can be reduced.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Digital signal receiver and method for receiving digital signal
InactiveUS6947497B1Promote recoveryQuick snapTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksAmplitude distortionSignal restoration
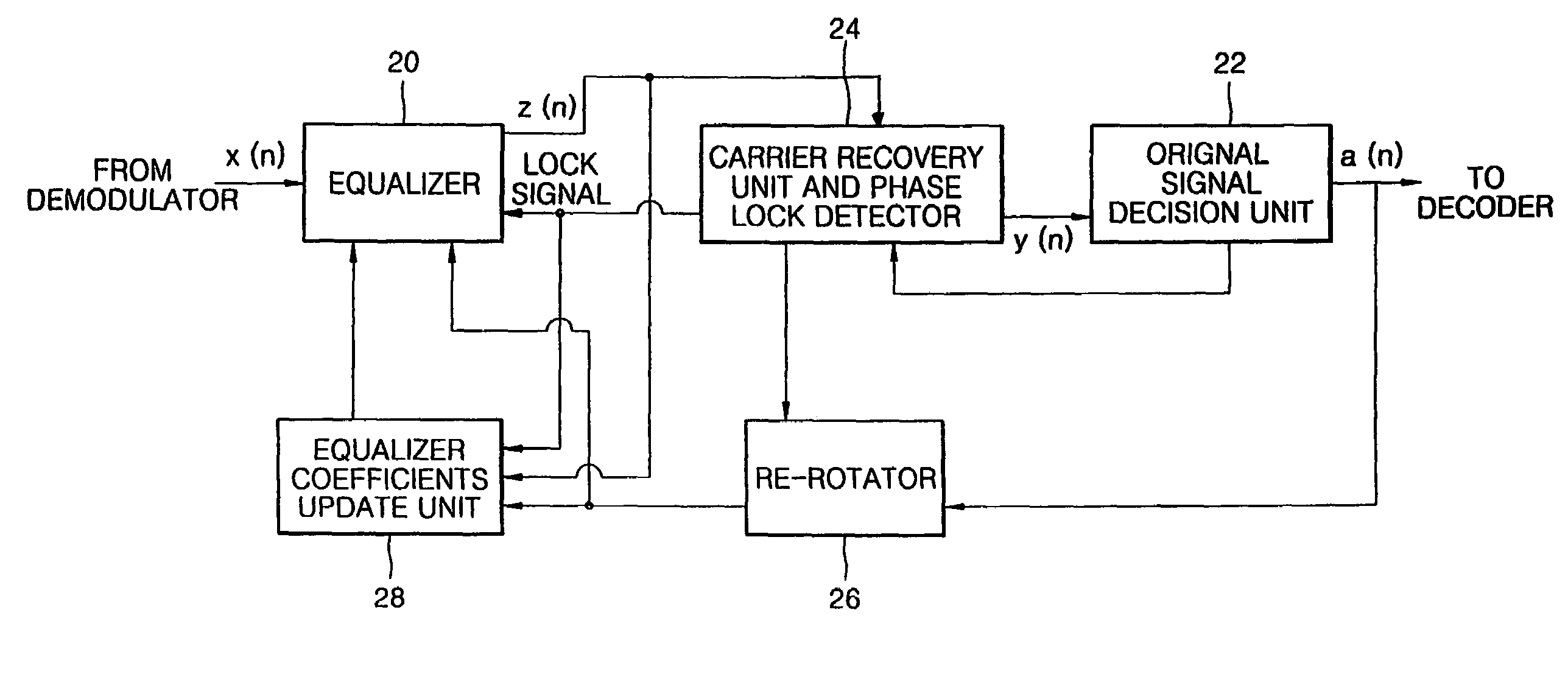
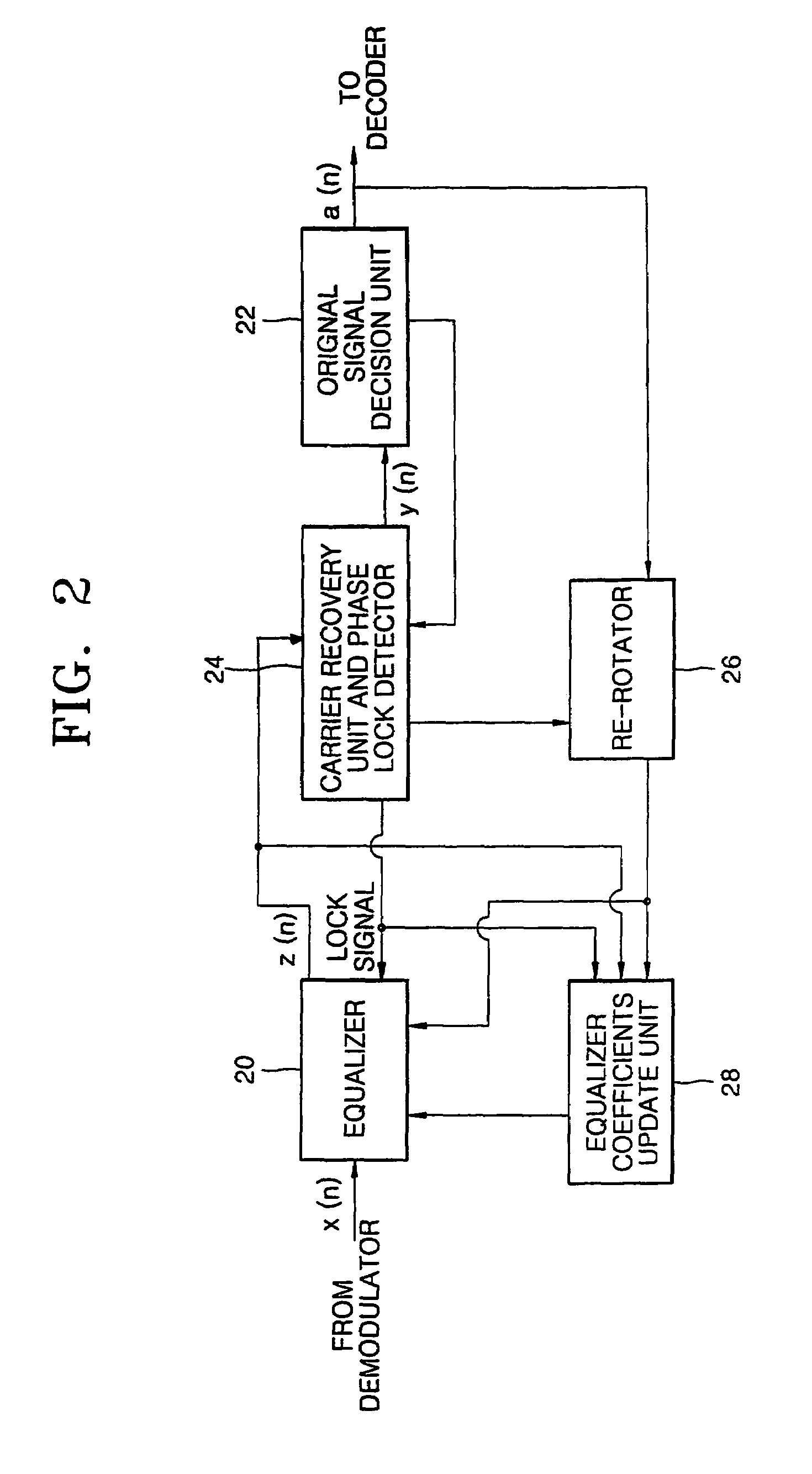
A digital signal receiver and a method for receiving a digital signal. The receiver includes an equalizing unit for compensating for an amplitude distortion of a received signal, an original signal decision unit for deciding an original signal from a signal which is compensated for the amplitude distortion, a carrier recovering and phase lock detecting unit for detecting a phase error between an input of the original signal decision unit and the decided original signal, and outputting a phase lock signal, a re-rotating unit for restoring the signal from the original signal decision unit to its original state and outputting a restored signal to the equalizer, and a coefficients updating unit for receiving the phase lock signal from the carrier recovering and phase lock detecting unit and the restored signal from the re-rotator unit, generating an error for updating the coefficients of the equalizer, and updating the coefficients of the equalizer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Frequency synthesizing circuit having a frequency multiplier for an output PLL reference signal
InactiveUS6933791B2Error accumulationIncrease loop bandwidthPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsDelay-locked loopFrequency multiplier
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Low output ripple wave parallel power-factor correction (PFC) transform control method and device
InactiveCN102427293AReduce DC output voltage/current rippleRaise the cutoff frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryPower factor correctorSingle phase
The invention discloses a low output ripple wave parallel power-factor correction (PFC) transform control method and device. The output end of a single-phase PFC convertor (TD) is connected in parallel with the output end of a DC (direct current) / DC convertor (DC-DC), and meanwhile energy is supplied to a load; the output positive end of the single-phase PFC convertor is mutually connected with the output positive end of the DC / DC convertor so as to form a 'Vo+' end, and meanwhile, the 'Vo+' end is connected with the positive end of the load; the output negative end of the single-phase PFC convertor is mutually connected with the output negative end of the DC / DC convertor so as to form a 'Vo-' end, and meanwhile, and the 'Vo-' end is connected with the negative end of the load; an input power supply of the DC / DC convertor is an auxiliary power supply; and an input source of the auxiliary power supply can generate the output of a rectifier circuit (REC), and the single-phase PFC convertor (TD) also can generate the output of the rectifier circuit (REC). The control method provided by the invention has the advantages of eliminating double line frequency output ripples of the traditional PFC convertor, meanwhile, improving the dynamic response of a system, and overcoming the problems that the traditional two-stage power-factor correction convertor is low in efficiency and high in cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
High-Speed Receiver Architecture
InactiveUS20110081152A1Lower latencyIncrease loop bandwidthAnalogue/digital conversionChannel estimationFiberViterbi decoder
A receiver (e.g., for a 10G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:CLARIPHY COMM
Self-adaptive slope compensation circuit
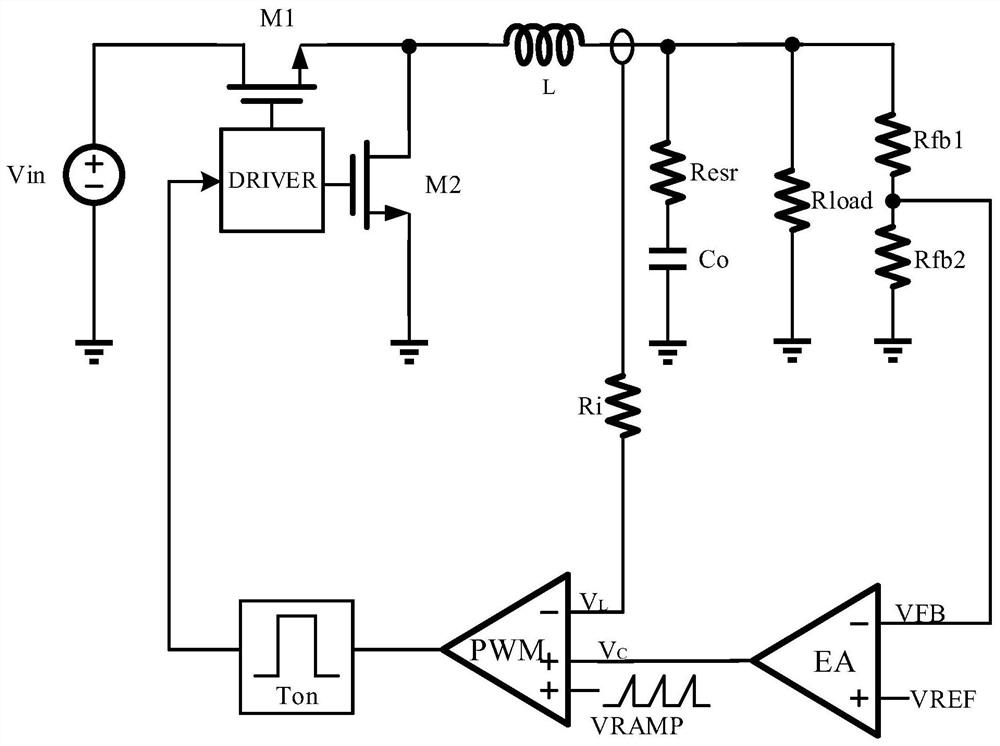
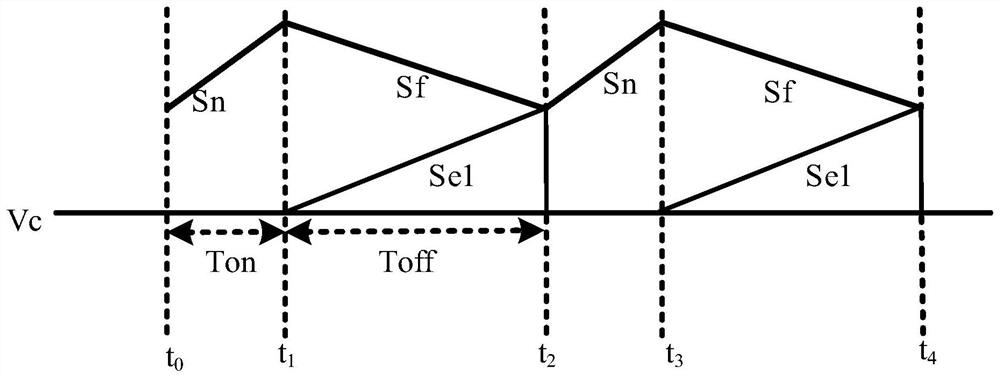
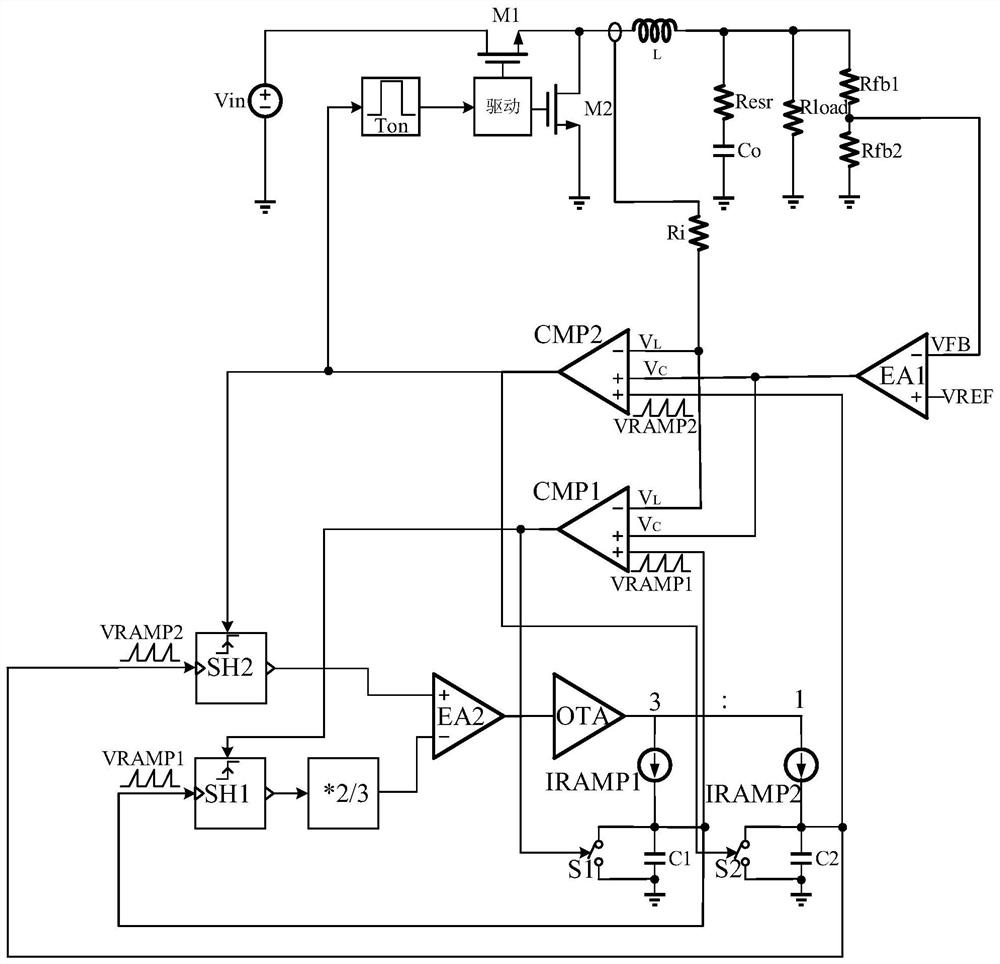
ActiveCN112803770ARealize adaptive adjustmentImprove signal-to-noise ratioDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationHemt circuitsMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a self-adaptive slope compensation circuit which is suitable for a converter in a current control mode, and realizes self-adaptive slope compensation by sampling and following an inductive current of the converter. A first slope voltage and a second slope voltage with fixed multiples are introduced, and the first slope voltage and the second slope voltage are sampled at two time points when an inductive current drops during an inductive current detection period. Then, the slope of the first slope voltage and the slope of the second slope voltage are regulated and controlled by measuring the size relation of the two sampling voltage values, and finally the relation between the slope of the first slope voltage and the slope of the second slope voltage and an inductive current declining slope can be fixed. In addition, a delay module is introduced into a control loop in the embodiment so that a control waveform can be achieved when there is no slope to be introduced, and introduction of an additional zero pole is avoided.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Jammer detection based adaptive PLL bandwidth adjustment in FM receiver
ActiveUS8437721B2Increase loop bandwidthReducing in-band residual FMPulse automatic controlSubstation equipmentLoop bandwidthLocal oscillator
A frequency synthesizer within an FM receiver employs a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) to generate a Local Oscillator (LO) signal. The LO signal is supplied to a mixer. The FM receiver also includes jammer detection functionality. If no jammer is detected, then the loop bandwidth of the PLL is set to have a relatively high value, thereby favoring suppression of in-band residual FM. If a jammer is detected, then the loop bandwidth of the PLL is set to have a relatively low value, thereby favoring suppression of out-of-band SSB phase noise. By adaptively changing loop bandwidth depending on whether a jammer is detected, performance requirements on sub-circuits within the PLL can be relaxed while still satisfying in-band residual FM and out-of-band SSB phase noise requirements. By allowing the VCO of the PLL to generate more phase noise due to the adaptive changing of loop bandwidth, VCO power consumption can be reduced.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
High-speed receiver architecture
ActiveUS8139630B2Lower latencyIncrease loop bandwidthAnalogue/digital conversionMultiple-port networksViterbi decoderFiber
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
High-speed receiver architecture
ActiveUS8483343B2Lower latencyIncrease loop bandwidthAnalogue/digital conversionReceiver initialisationViterbi decoderTelecommunications link
A receiver (e.g., for a 10 G fiber communications link) includes an interleaved ADC coupled to a multi-channel equalizer that can provide different equalization for different ADC channels within the interleaved ADC. That is, the multi-channel equalizer can compensate for channel-dependent impairments. In one approach, the multi-channel equalizer is a feedforward equalizer (FFE) coupled to a Viterbi decoder, for example a sliding block Viterbi decoder (SBVD); and the FFE and / or the channel estimator for the Viterbi decoder are adapted using the LMS algorithm.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
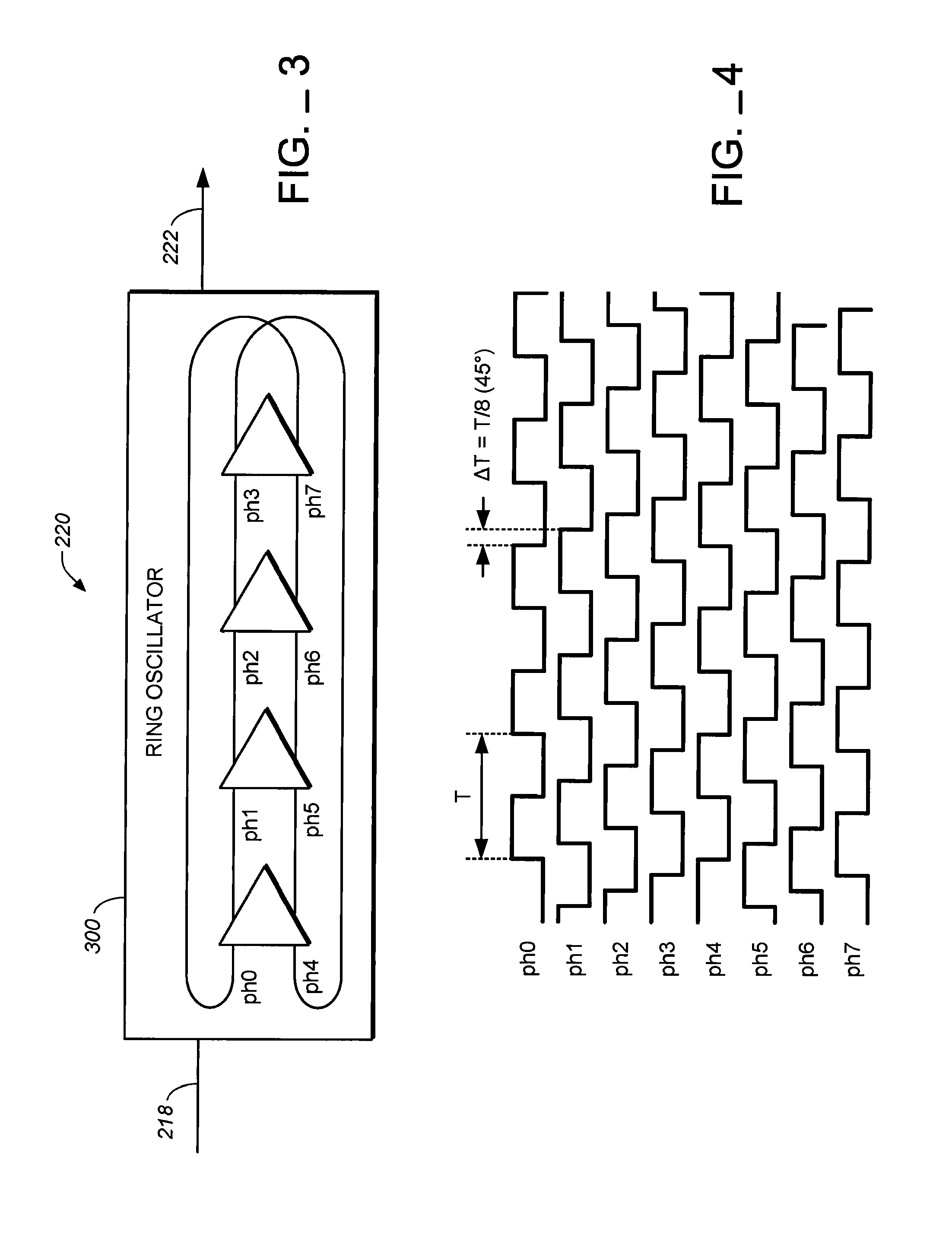
High bandwidth phase locked loop (PLL) with feedback loop including a frequency divider
ActiveUS7898306B1High frequency resolutionReduce noise and jitterPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersHigh bandwidthEngineering
A phase locked loop (PLL) is provided. In one implementation, the PLL includes a multiphase voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) operable to generate an output signal containing one or more phase signals, a programmable divider operable to divide a frequency of the output signal of the multiphase VCO to produce a divided frequency output signal, and a fractional divider to fractionally divide an input phase signal. The fractional divider can include an integer divider operable to receive the input phase signal and divide the input phase signal in accordance with an integer divisor to produce a divided signal as an input to the multiphase VCO, and a phase interpolator operable to select a phase signal from among the one or more phase signals output by the multiphase VCO, to produce an interpolated output signal having a desired frequency resolution.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Amplifier common-mode control method
ActiveUS9231542B1Reduce sensitivityImprove common-mode control loop bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthAudio power amplifierMode control
A fully differential amplifier performs common-mode voltage control while having reduced sensitivity to random offsets and mismatches and improved common-mode control loop bandwidth. The amplifier disclosed comprises an additional common-mode control sub-amplifier, which senses common-mode voltage of the fully differential main amplifier at nodes within the continuous-time signal path feedback network, compares the common-mode voltage sensed with a reference voltage, and regulates depending on the result of the comparison the output common-mode voltage via the existing continuous signal path feedback network. Furthermore the internal common-mode control can be implemented in such a manner as to provide a feed-forward transconductance function in addition to common-mode control if desired. Moreover it is possible to use feedback from other amplifier stages in an amplifier chain to implement common-mode feedback.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON UK
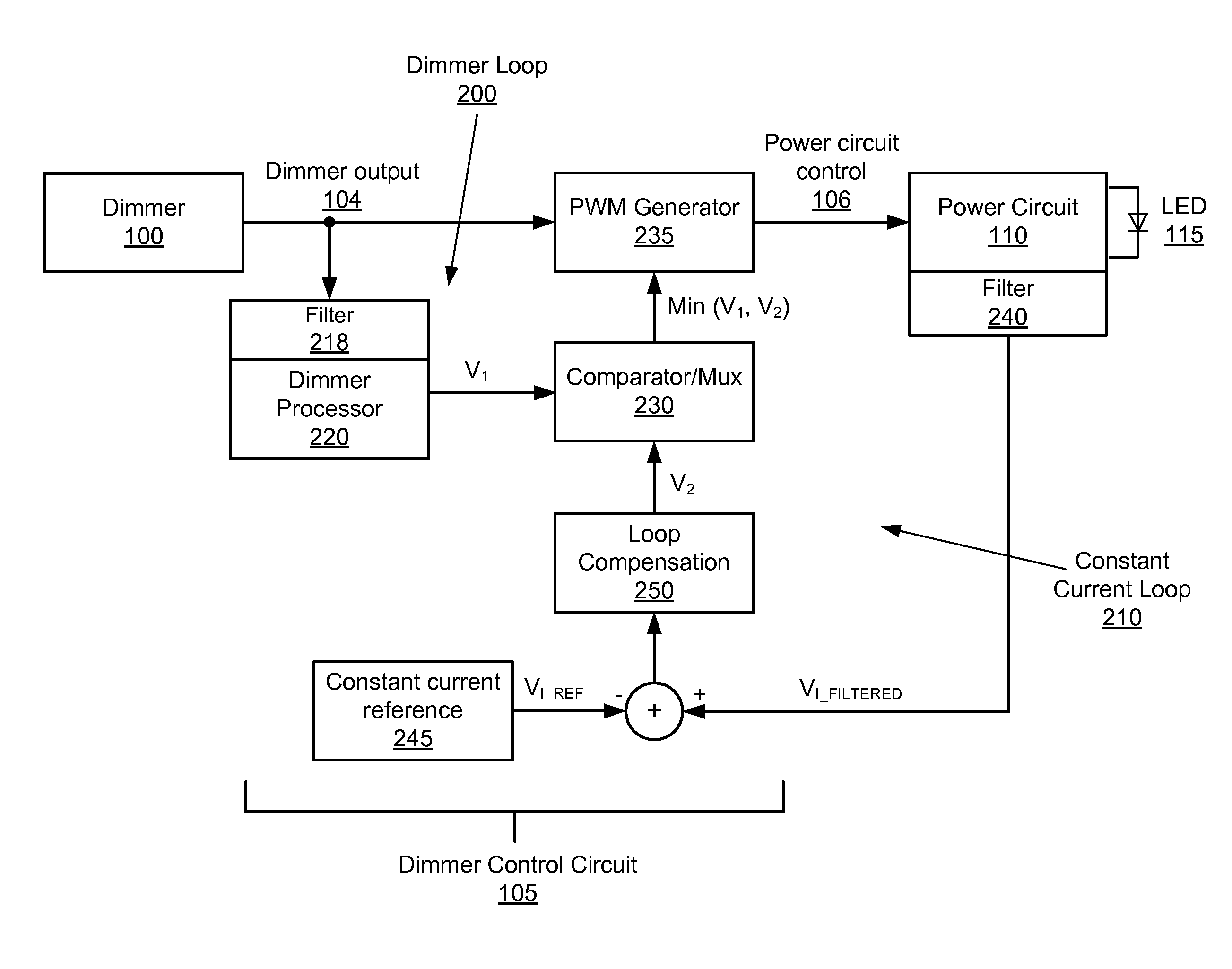
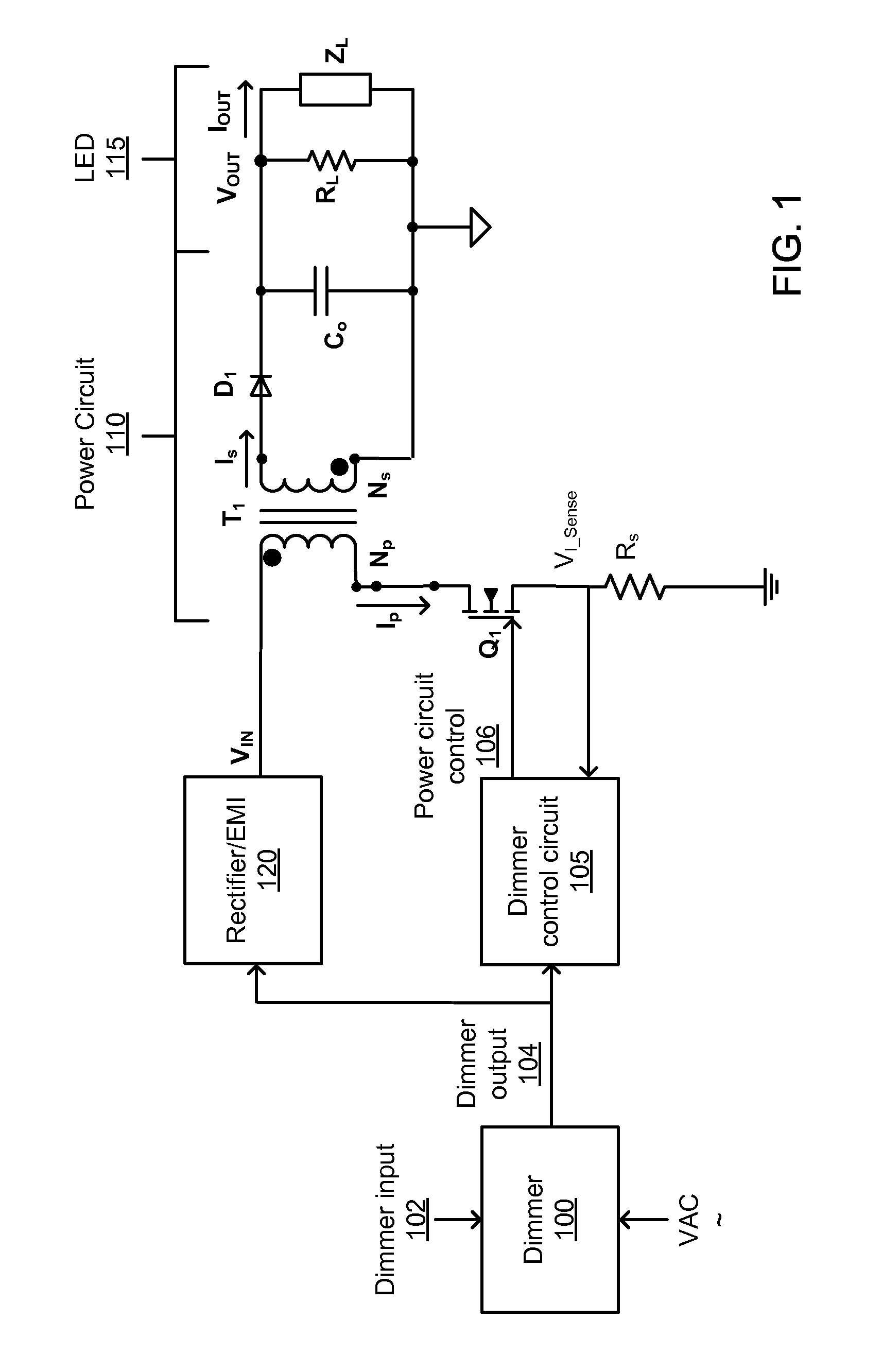
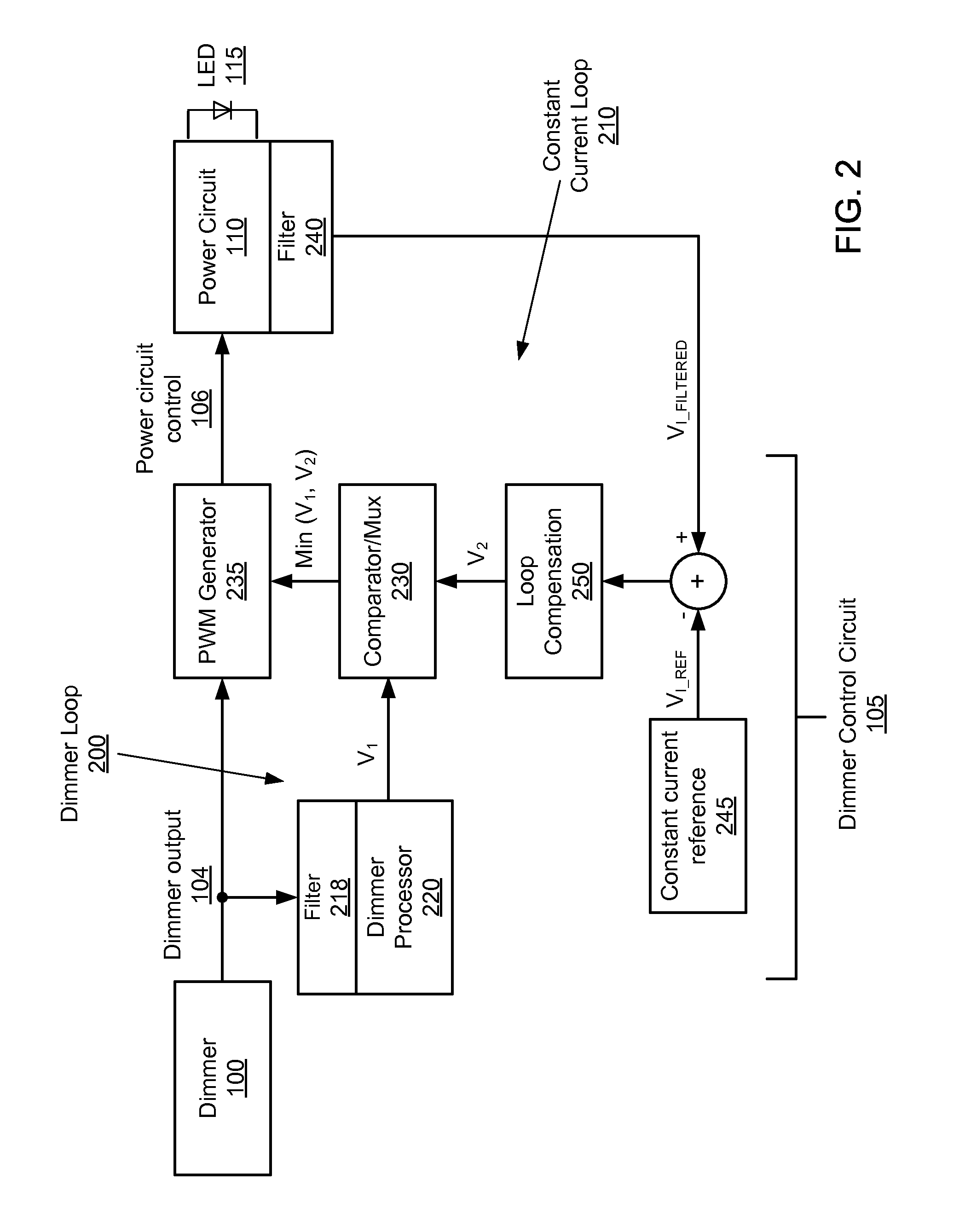
Filter bandwidth adjustment in a multi-loop dimmer control circuit
ActiveUS8723437B1Attenuation bandwidthShort response timeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDimmerEngineering
The embodiments disclosed herein describe the adjusting of filter bandwidths in a multi-loop LED dimmer control circuit based on received dimmer input signals. The bandwidth of a filter in an active loop (a loop driving an LED power circuit) is decreased to prevent signal noise and associated LED flickering. Likewise, the bandwidth of a filter in an inactive loop (a loop not driving the LED power circuit) is increased to a pre-determined maximum in order to improve response time and decrease potential overshoot or undershoot during dimmer adjustment.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
High-speed receiver architecture
ActiveUS8831074B2Lower latencyIncrease loop bandwidthModulated-carrier systemsOther decoding techniquesPattern recognitionTransceiver
A receiver (or transceiver) is selectable between a Gaussian mode and a non-Gaussian mode. In the non-Gaussian mode, a transformation block applies a non-linear transformation to signal samples to convert non-Gaussian noise in the signal samples to Gaussian or approximately Gaussian noise. In the Gaussian mode, the transformation block is bypassed. Samples are equalized using an equalizer configured to operate with a Gaussian or approximately Gaussian channel.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Single bit DAC with tristate driver
InactiveUS7321328B1Increase loop bandwidthElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsPulse sequencePeriodic Interval
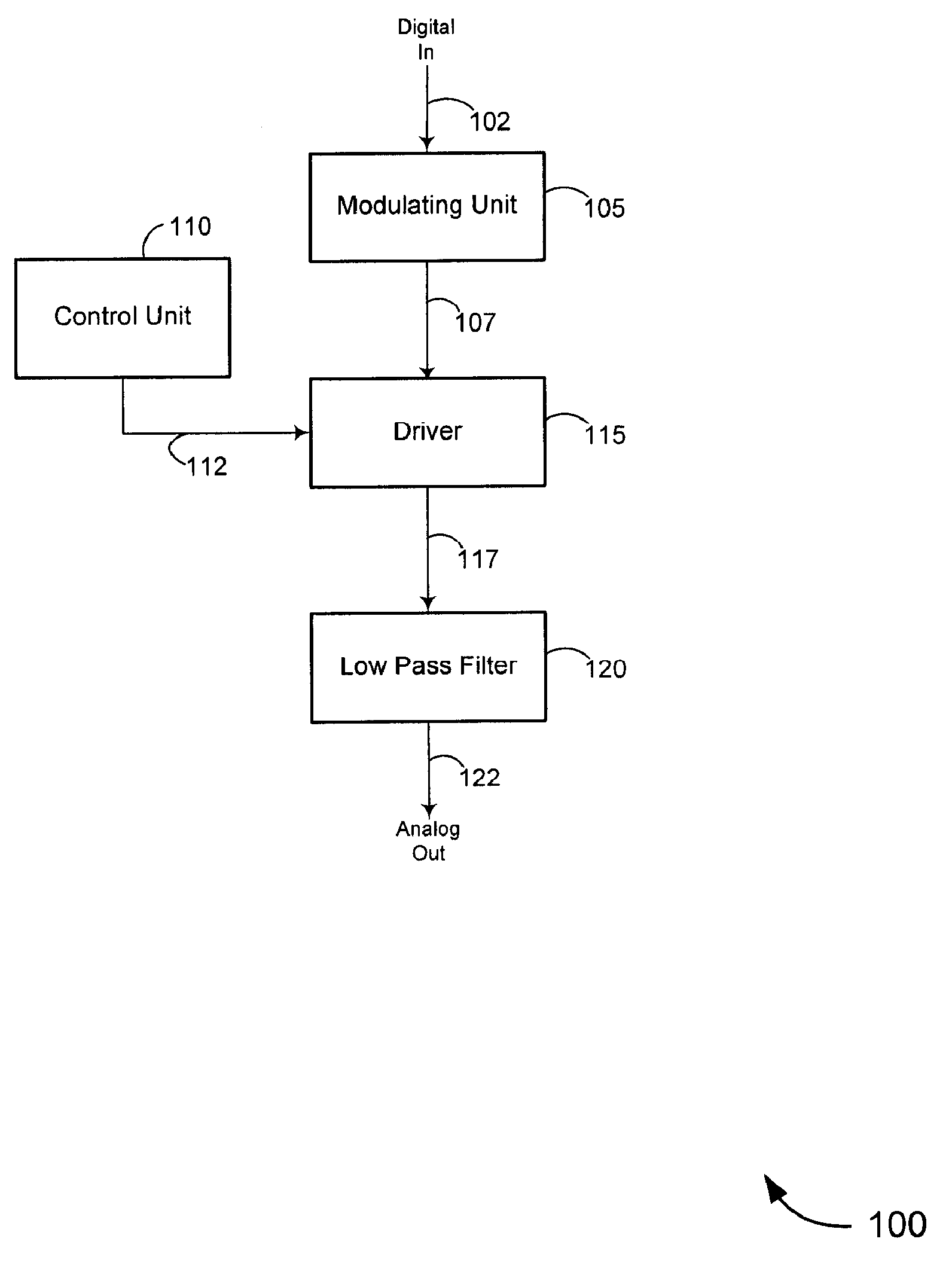
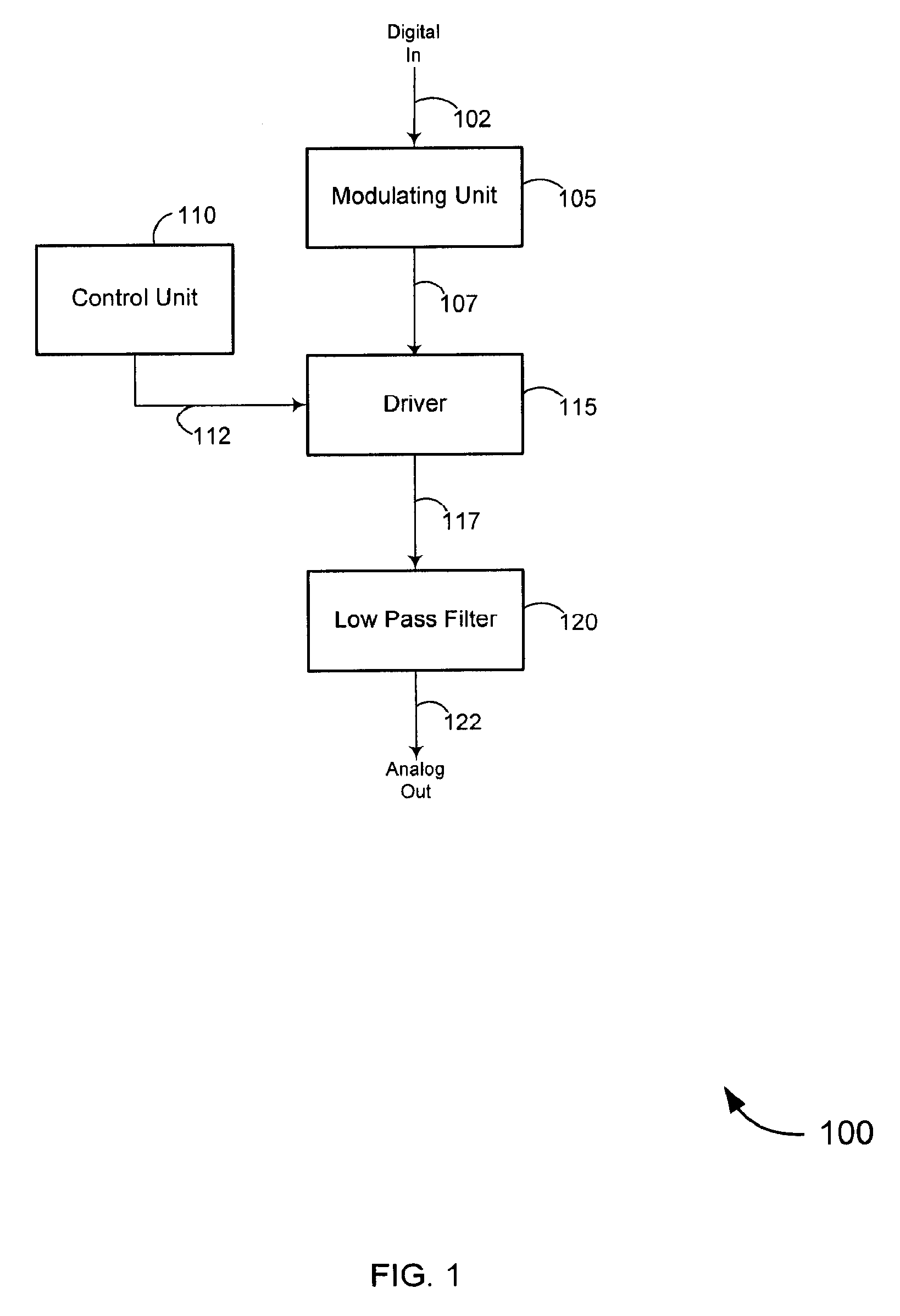
A method for producing an analog output from a digital input is described. A digital pulse train is received having an average value which is proportional to a digital conversion value. The digital pulse train is driven at a periodic interval to produce a modulated tristate-gate output. The modulated tristate-gate output is averaged to produce an analog output. Optionally, the pulse train is also driven at an additional periodic interval having a duty cycle of more, or less, than less than 50%. The pulse train may also be driven steadily.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Analogue and digital hybrid double-loop control stabilized current supply device
InactiveCN101958656ASuppress fluctuationsReduce complexityAc-dc conversion without reversalLow speedDigital feedback
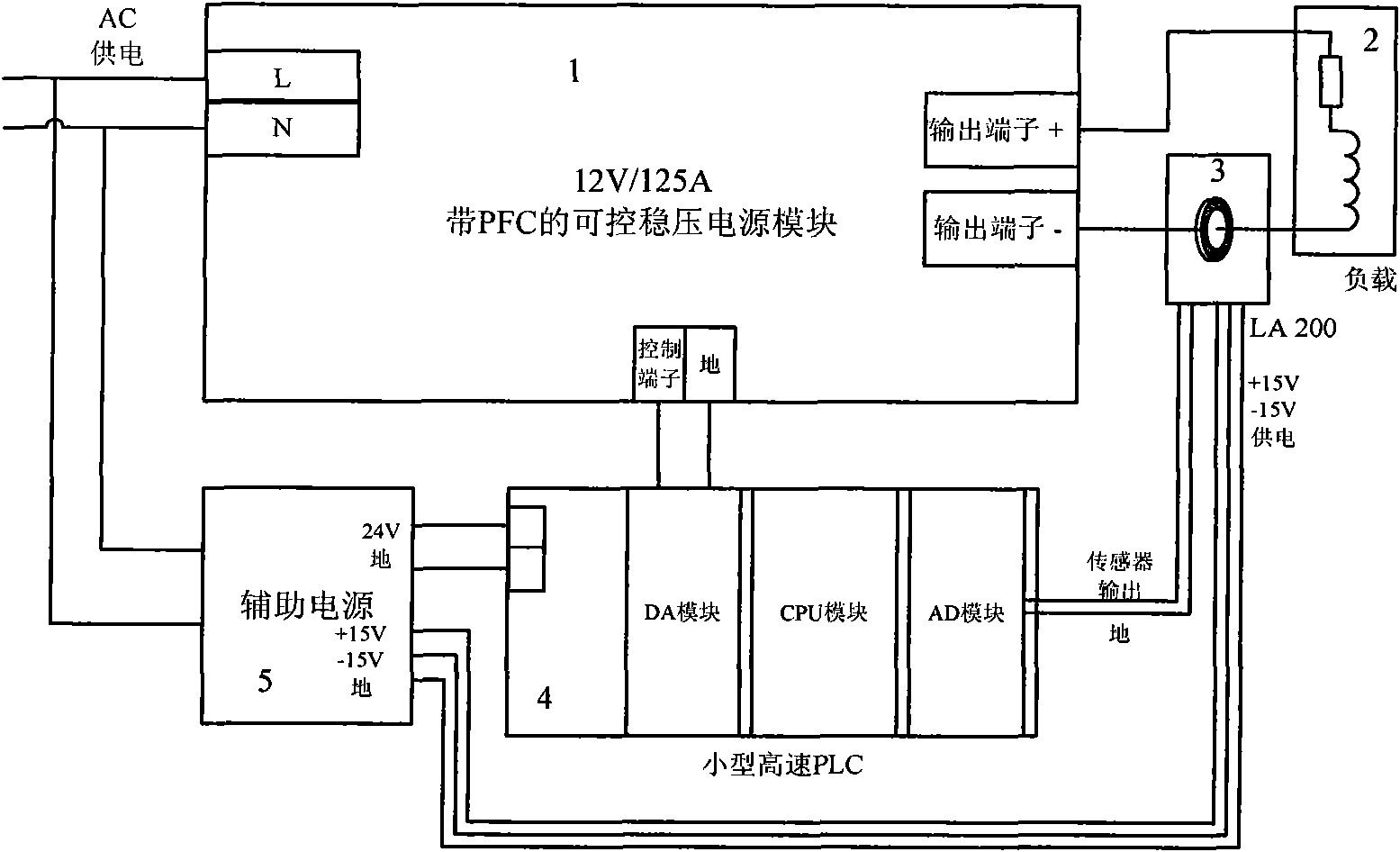
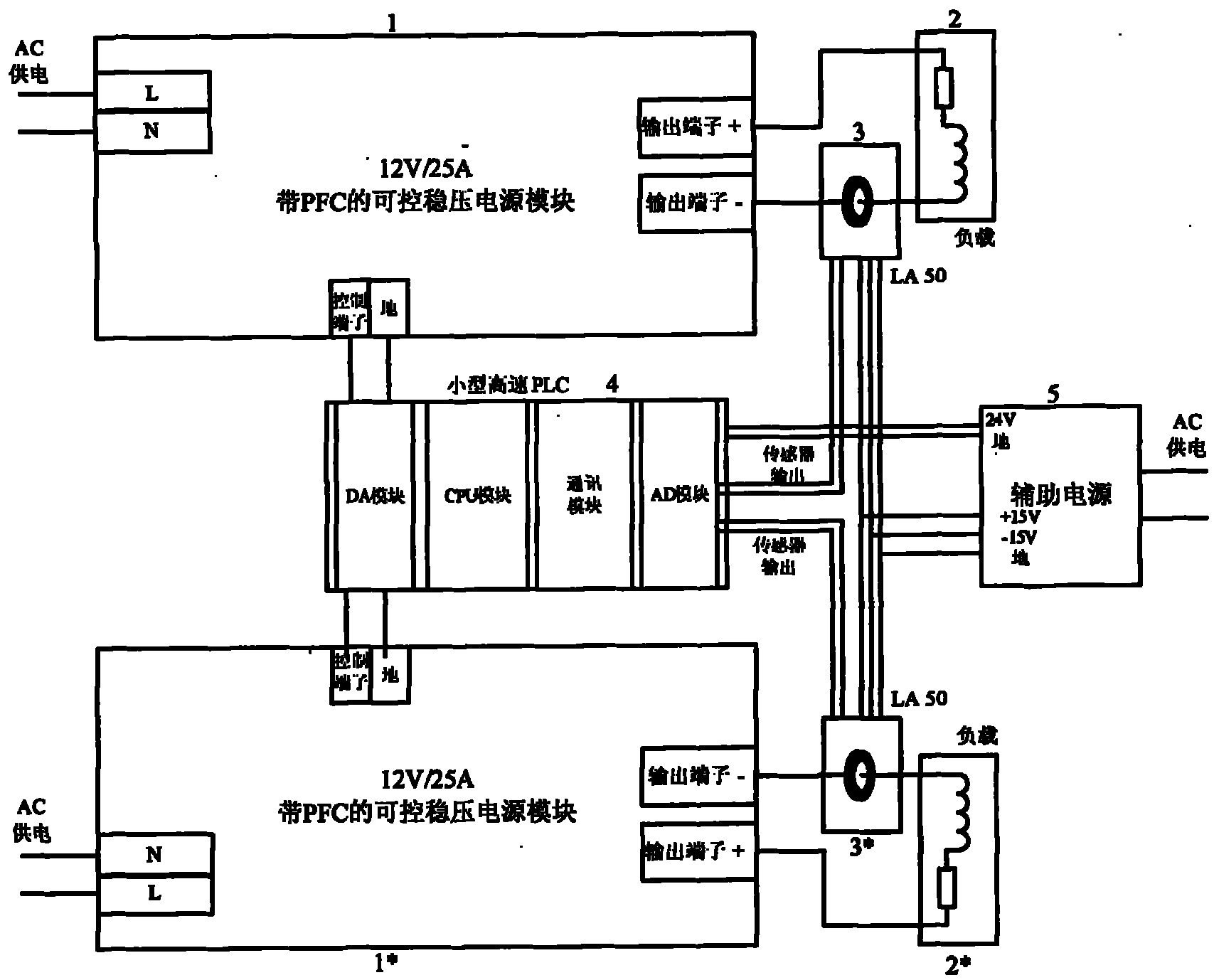
The invention discloses an analogue and digital hybrid double-loop control stabilized current supply device. The device comprises an adjustable alternating current to direct current (AC-DC) switch stabilized voltage supply, a load, a current sensor, a controller and an auxiliary power supply, wherein a cable at the output end of the AC-DC switch stabilized voltage supply (1) passes through the current sensor (3) and is connected with the load (2); the output end of the current sensor is connected with the input end of an analogue to digital (AD) converter of the controller (4); and the output end of a digital to analogue (DA) converter of the controller (4) is connected with the voltage control end of the adjustable AC-DC switch stabilized voltage supply. A high-speed analogue voltage loop serving as an inner loop is combined with a low-speed digital feedback current loop serving as an outer loop so as to fulfill the aims of achieving indexes of high dynamic performance and high static stability, reducing the technical complexity of a digital control card, lowering cost, making a power supply accordant with the compatibility standard of harmonic waves and electromagnetism, enhancing reliability and shortening the development time of the controller and an entire machine and achieve the advantage of giving consideration to both an analogue power supply and a digitized power supply.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for suppressing noise in a phase-locked loop circuit
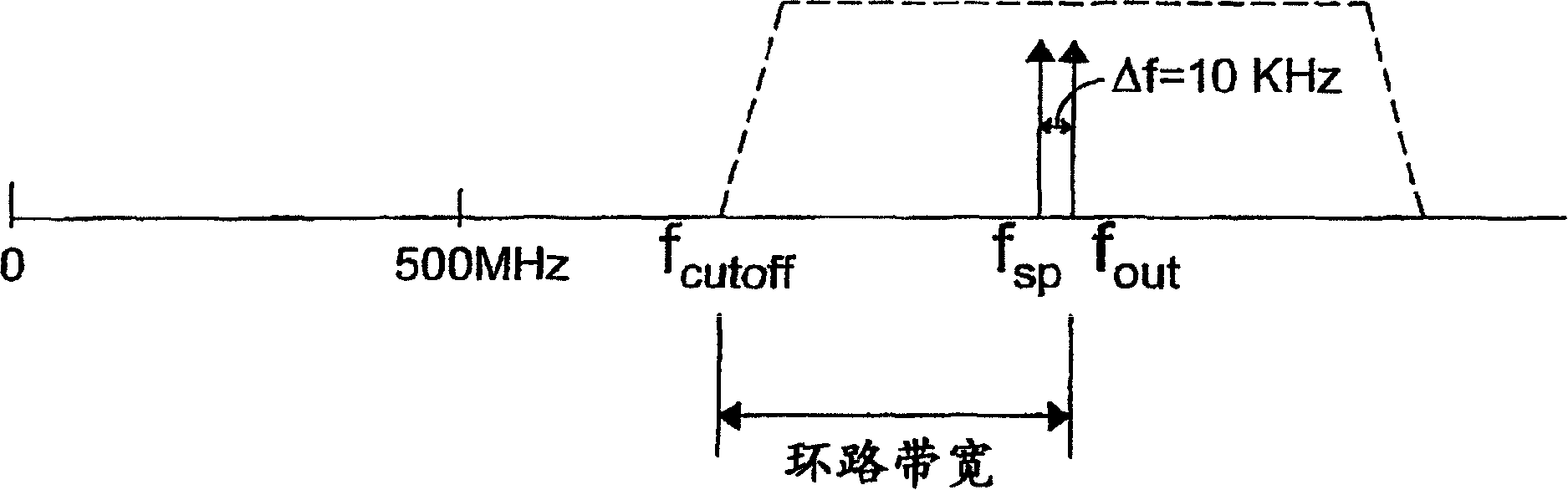
ActiveCN1708904AImprove signal-to-noise ratioIncrease loop bandwidthPulse automatic controlSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Phase locked loop circuit
Systems and methods for increasing the signal-to-noise ratio of a frequency generator suppress phase noise and noise generated by mismatches in internal generator circuits. This is accomplished using a modulation scheme that moves the spurious noise signal out of the generator's loop bandwidth. When shifted in this manner, the noise signal can be removed entirely or to any desired degree using, for example, filters located along the signal path of the generator. In one embodiment, the sigma-delta modulator controls the value of a swallow divider placed along the feedback path of the phase-locked loop in order to achieve the desired degree of noise rejection. In another embodiment, the reference signal input to the phase locked loop is modulated to achieve noise suppression. In another embodiment, the above forms of modulation are combined in order to achieve the desired frequency offset. With these modulation techniques, the signal-to-noise ratio of the frequency generator can be substantially improved while achieving faster lock times.
Owner:GCT SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Power factor correction device and power supply
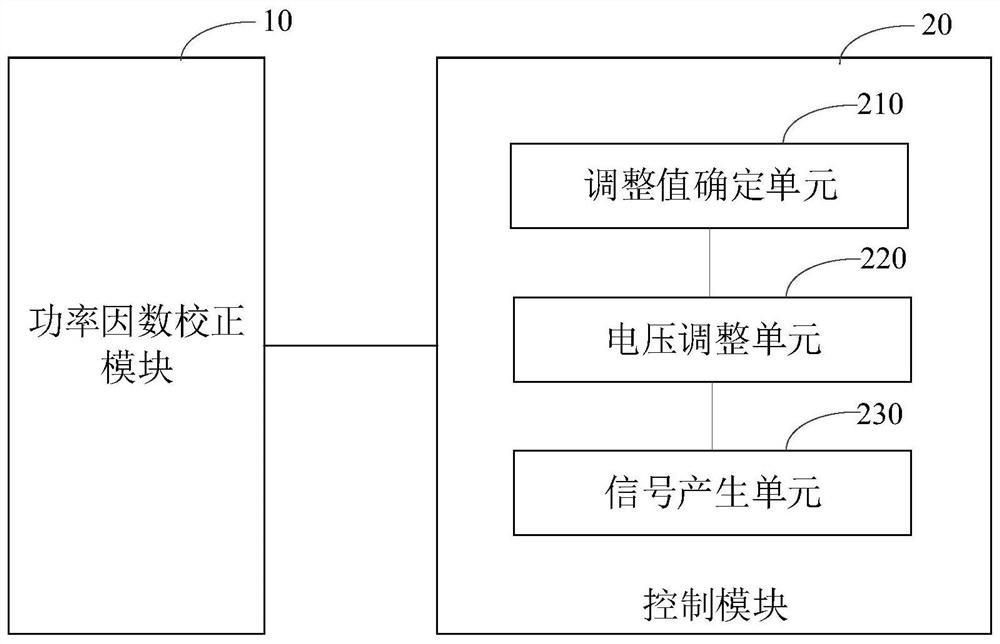
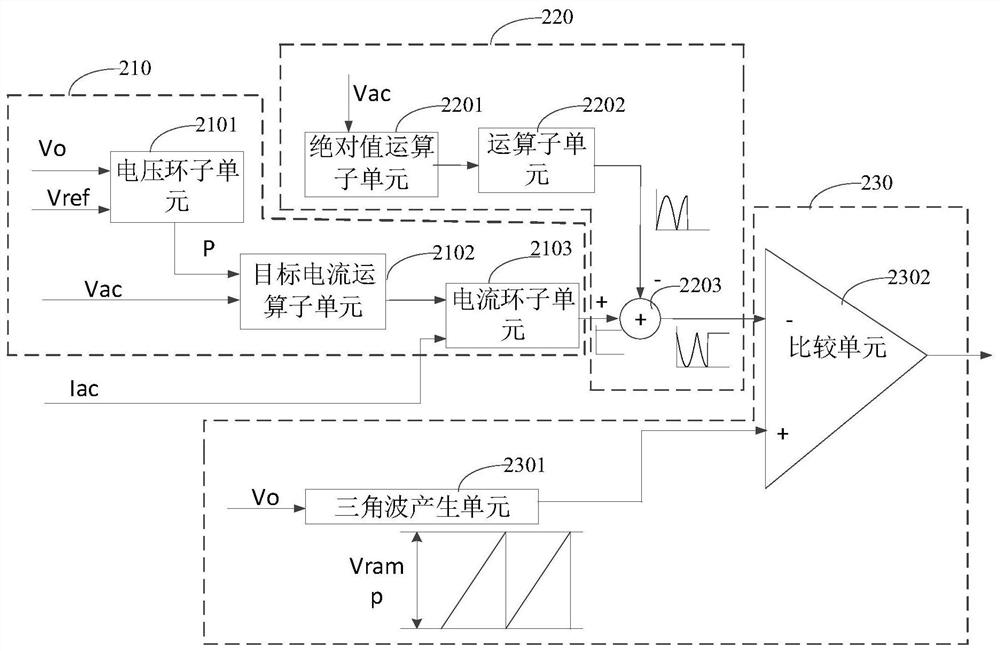
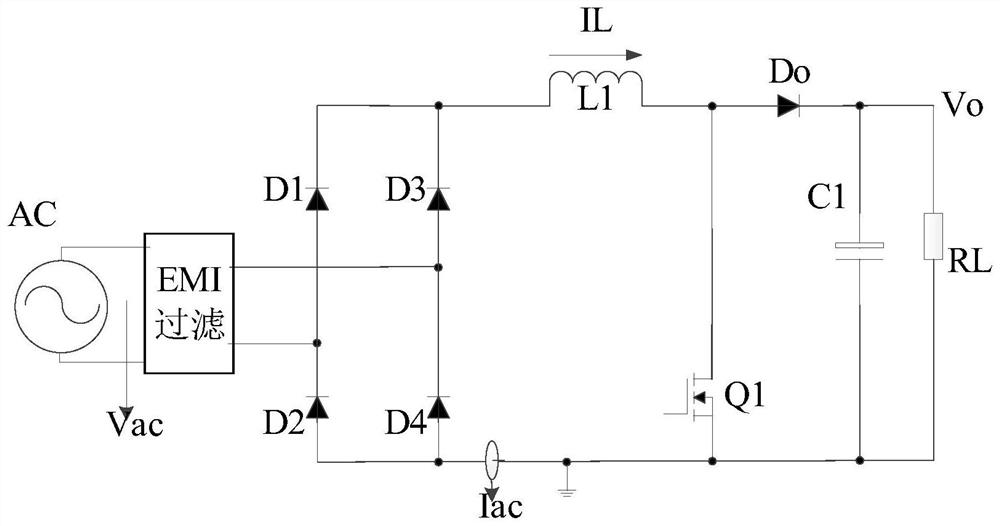
ActiveCN112803750AWork swing downIncrease loop bandwidthEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionControl signalComputational physics
The invention relates to a power factor correction device and a power supply. The power factor correction device comprises a power factor correction module and a control module, wherein the control module is used for outputting a control signal to control a conduction state of a transistor, and the control module comprises an adjustment value determining unit, a voltage adjusting unit and a signal generation unit; the adjustment value determining unit is used for determining a target current and determining an adjustment value according to the target current and the detection current of the inductor in the power factor correction module; the voltage adjusting unit is used for adjusting a feed-forward voltage signal obtained according to the alternating voltage of the input alternating current by using the adjusting value; and the signal generation unit is used for generating a control signal by using the adjusted voltage so as to control the conduction state of the transistor in the power factor correction module. According to the power factor correction device provided by the embodiment of the invention, the loop bandwidth of the PFC is improved, the current distortion is reduced, the THD (Total Harmonic Current Distortion) is reduced, the backward current of the totem-pole PFC is prevented, and the stability and the safety of the PFC are improved.
Owner:INVENTCHIP TECH CO LTD
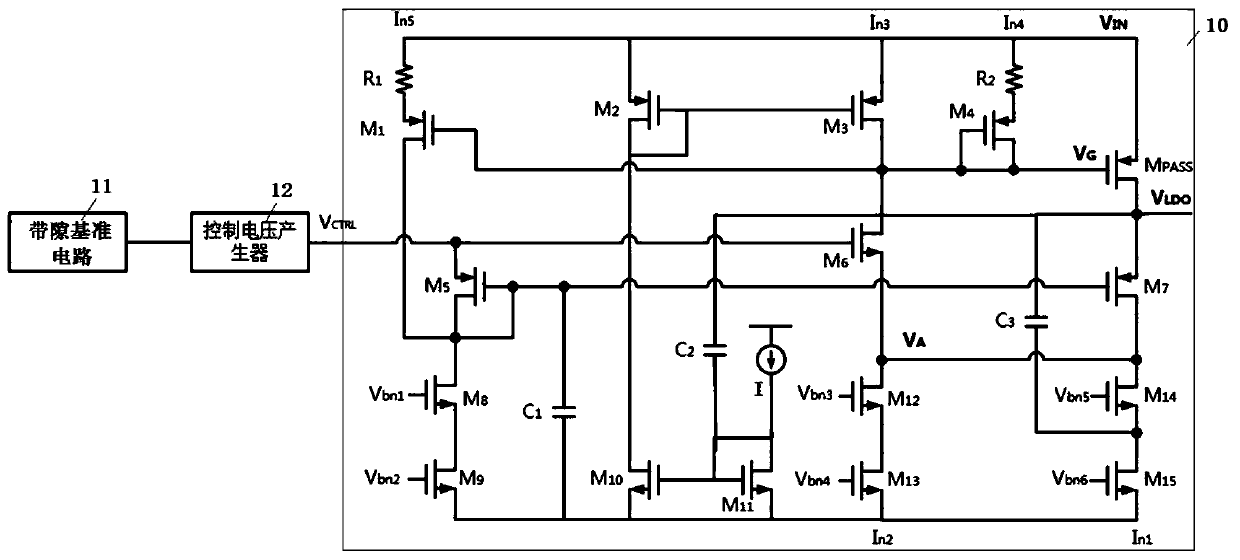
Fast transient response LDO and circuit thereof
ActiveCN110632970AReduce the overshoot valueReduce the impactElectric variable regulationCapacitanceFast path
The invention discloses a fast transient response LDO and a circuit thereof. The circuit comprises a fast path and a slow path, and the fast path is composed of a load transistor, a seventh transistorand a sixth transistor. The slow path is composed of a load transistor, a first transistor, a fifth transistor and a seventh transistor. The fast path is used for increasing the loop bandwidth, and the slow path is used for increasing the DC accuracy. A second capacitor and a third capacitor in the circuit can sense the load change, and correspondingly increase or decrease the current flowing through a fourteenth transistor and the third transistor by means of capacitive coupling. By accelerating the charge and discharge speed of a gate capacitor of the load transistor, the loop response speed is accelerated, and the overshoot value of the output voltage is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING SMARTCHIP MICROELECTRONICS TECH COMPANY +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com