Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Small horsepower" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
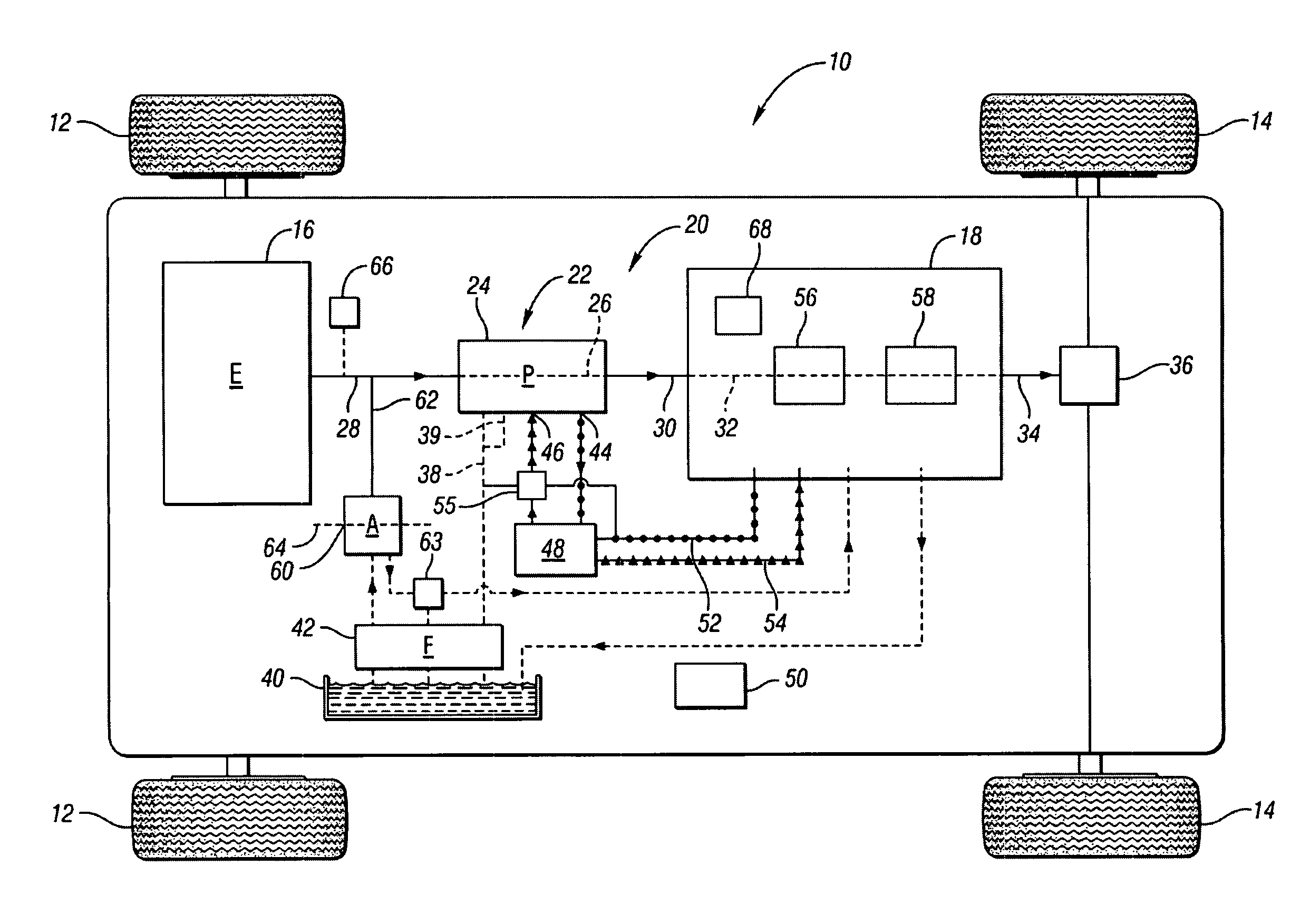
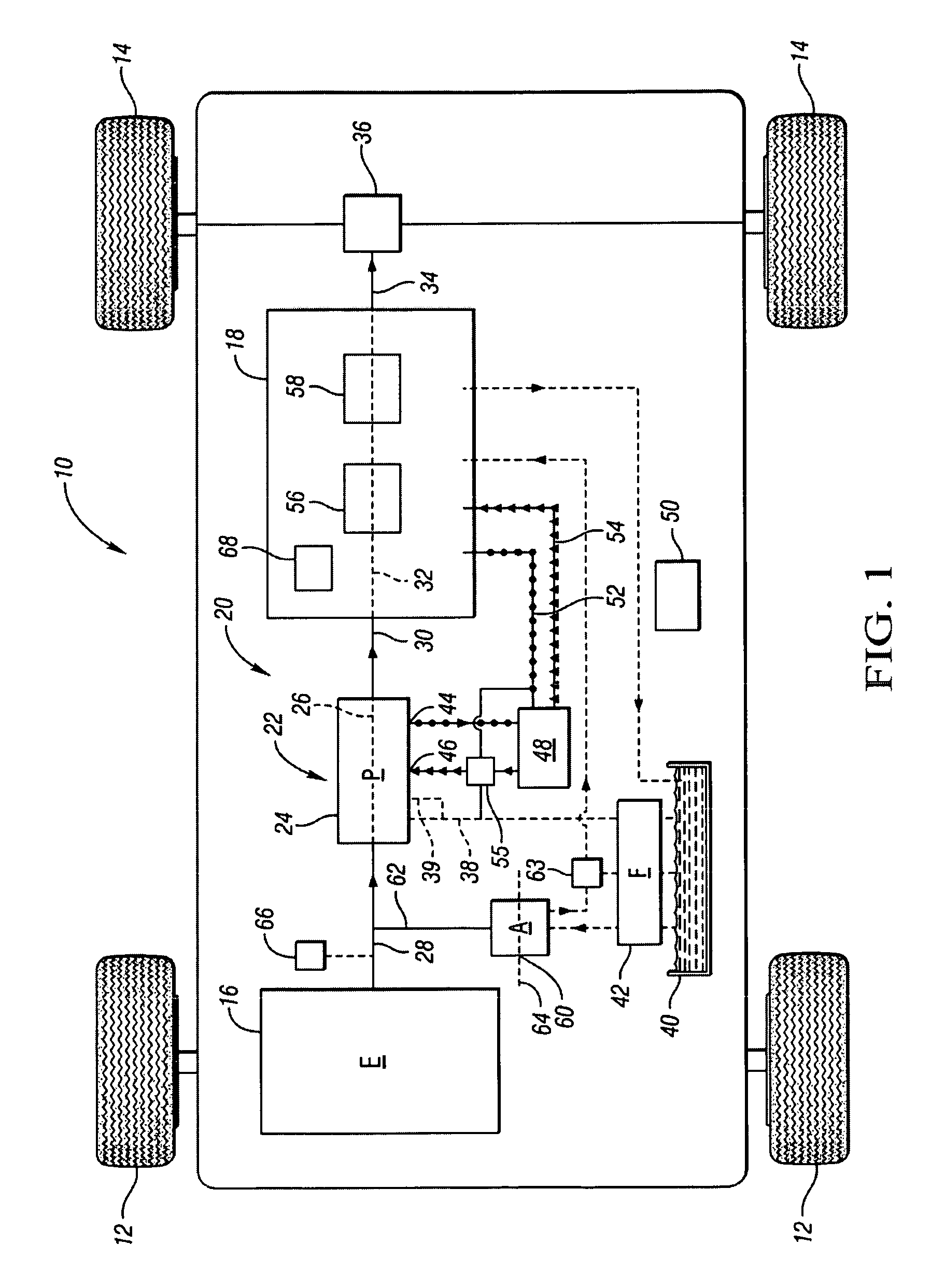
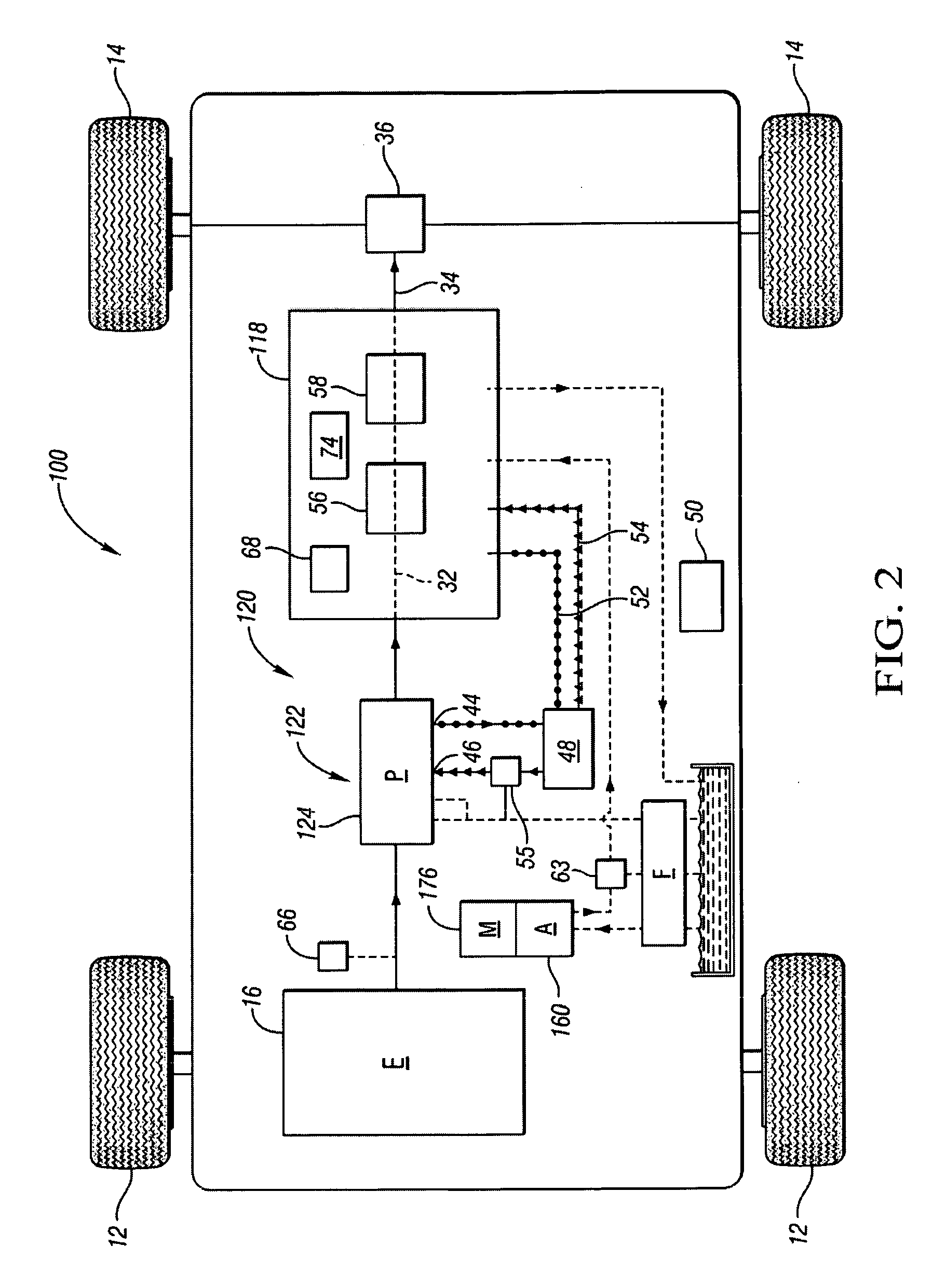
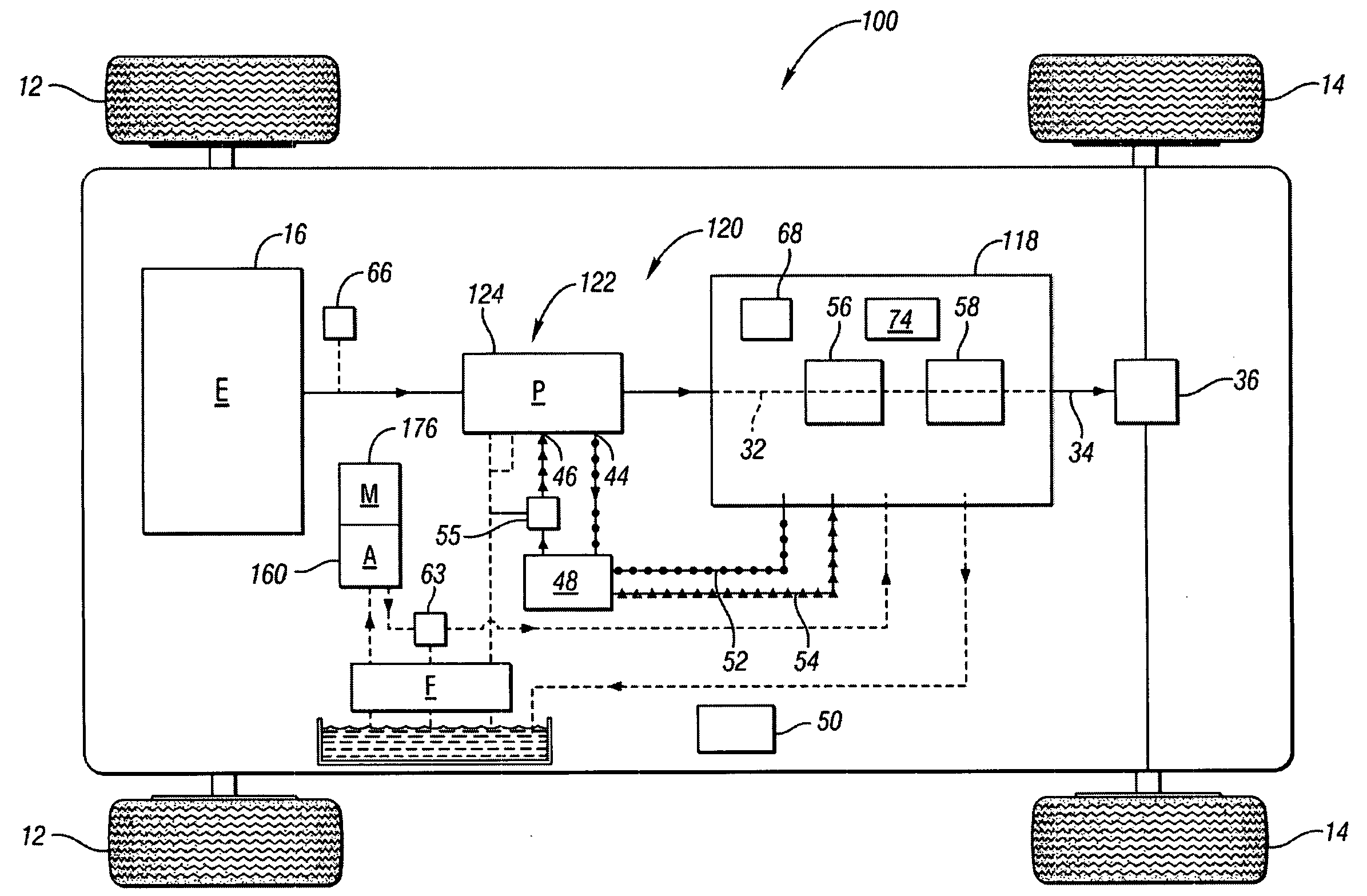
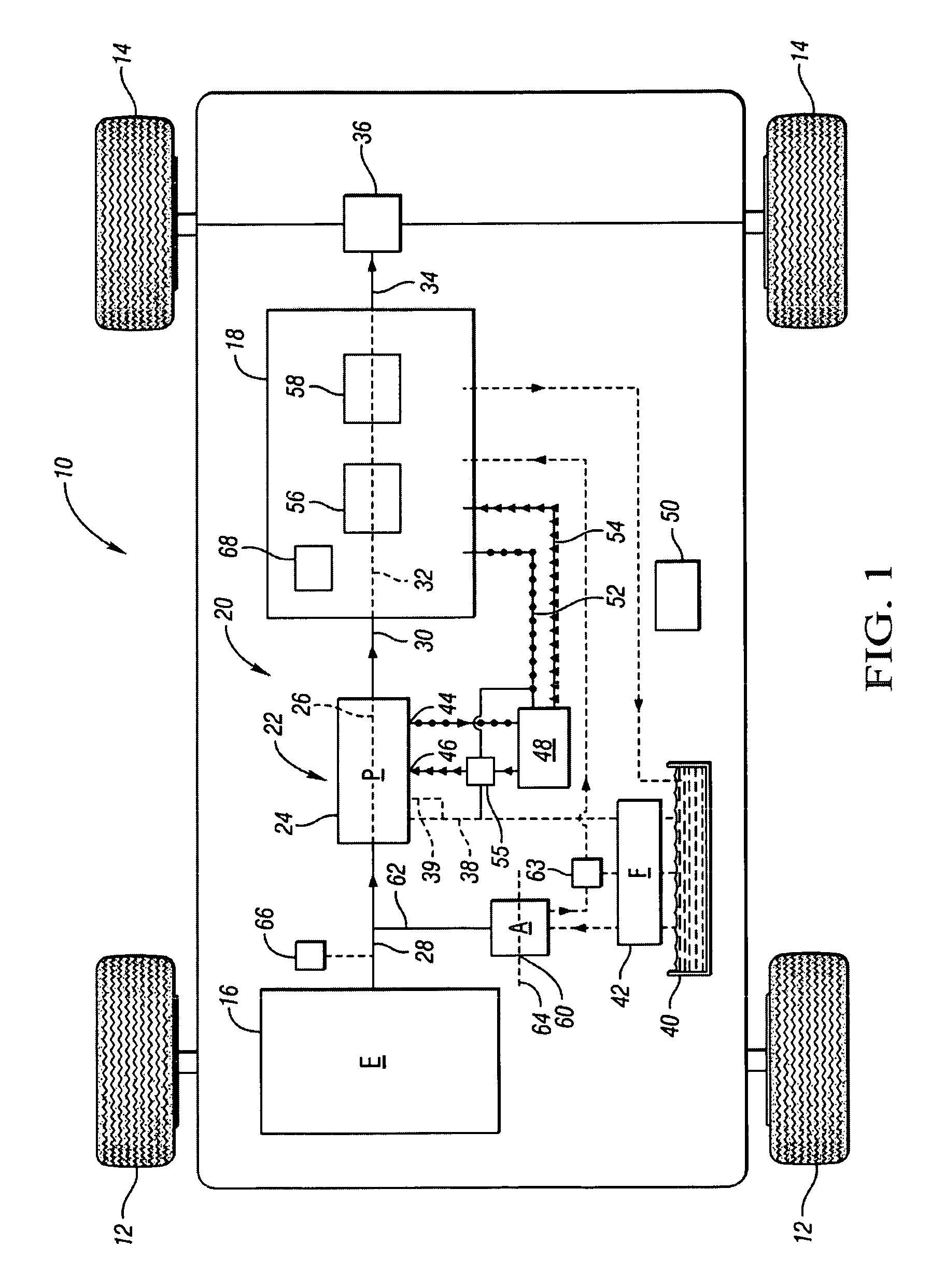
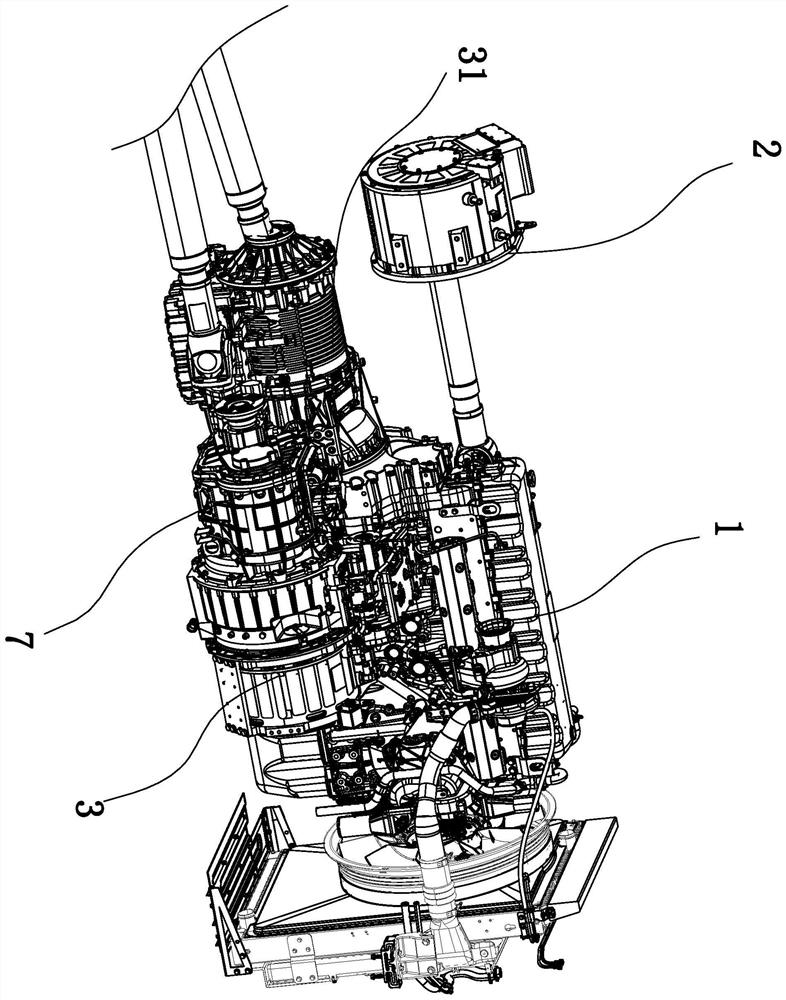
On-demand hydraulic pump for a transmission and method of operation
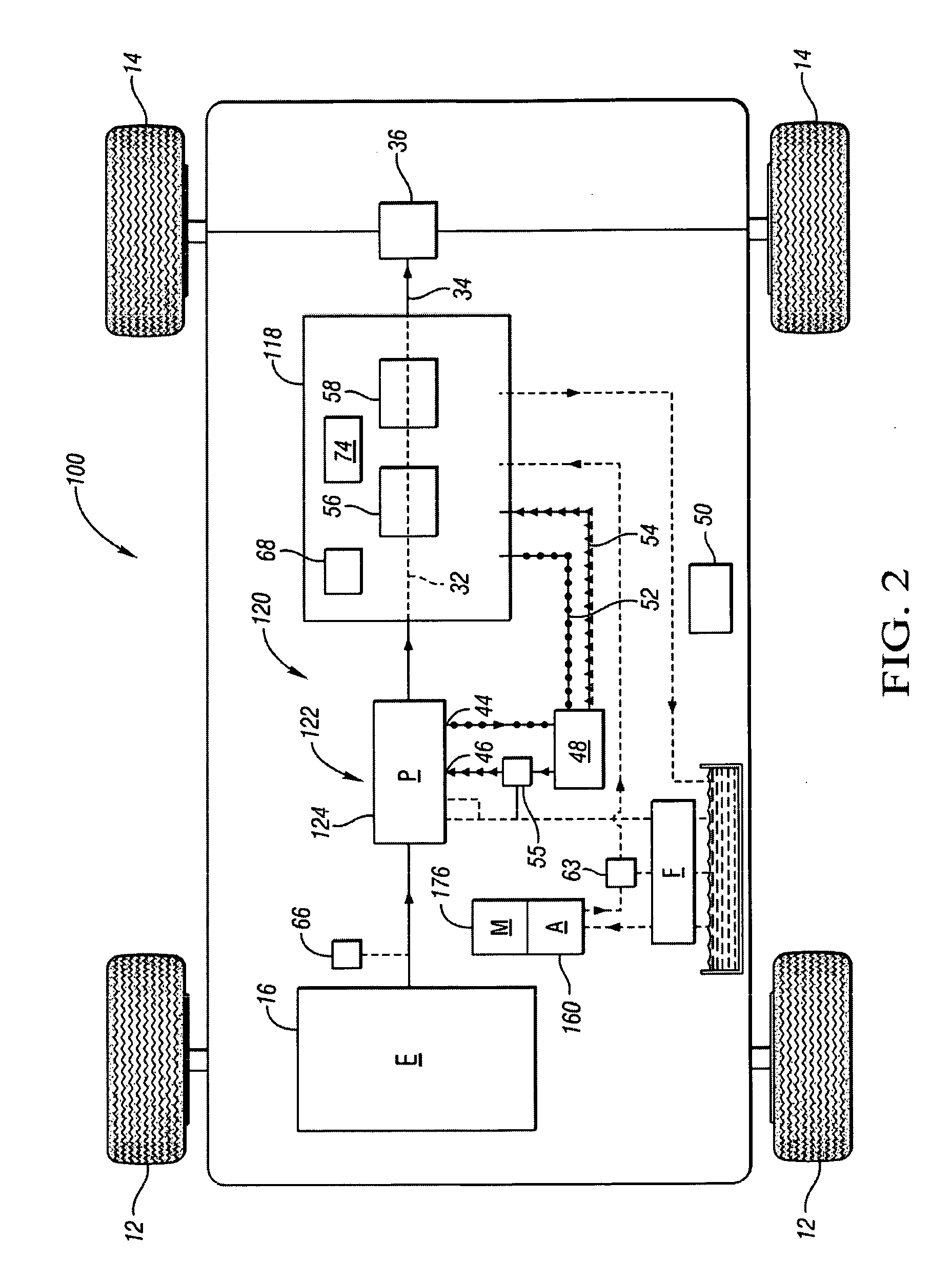
A fixed displacement binary pump is provided for a powertrain on a vehicle. A hydraulic system is operatively connected with first and second discharge ports of the pump and is operable to alternately permit fluid flow through both discharge ports (i.e., full displacement or volumetric output of the pump) or permit flow through only the first discharge port (i.e., partial displacement or volumetric output of the pump). The pump may be packaged in a front support of the transmission. An auxiliary pump may be provided that is operable to supplement the output of the binary pump or to be used when the binary pump is off. A method of operating the binary pump and auxiliary pump is provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
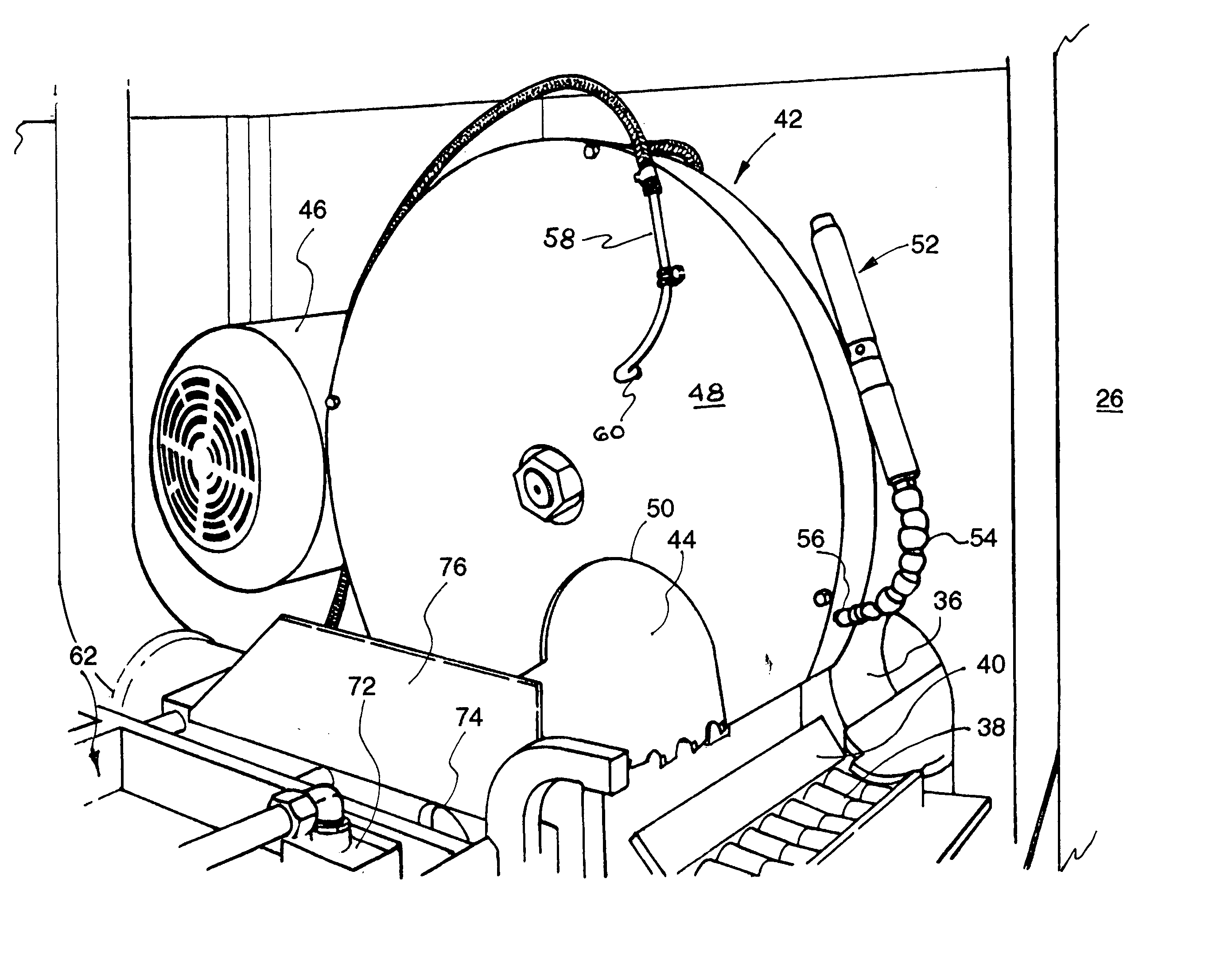
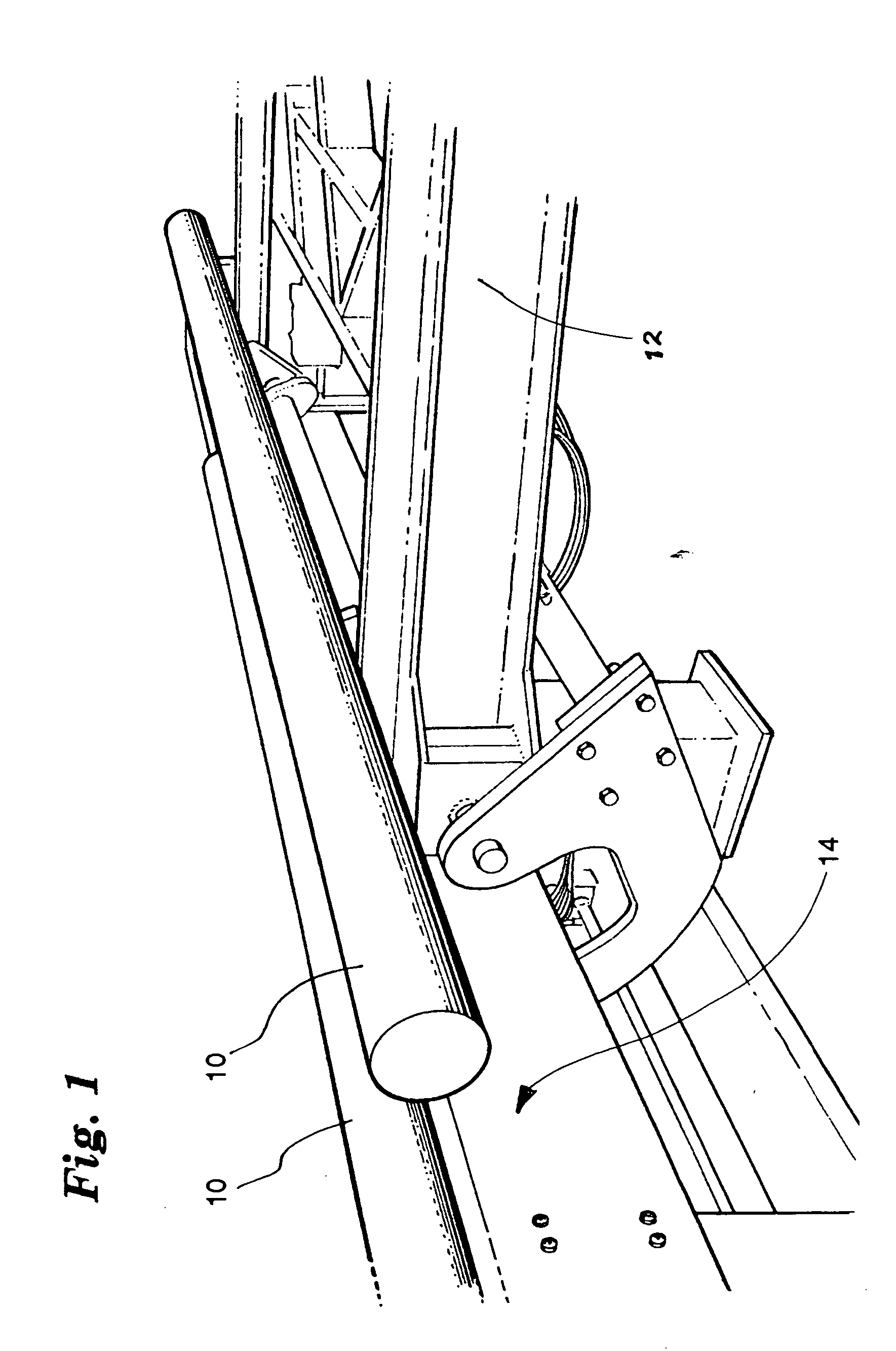
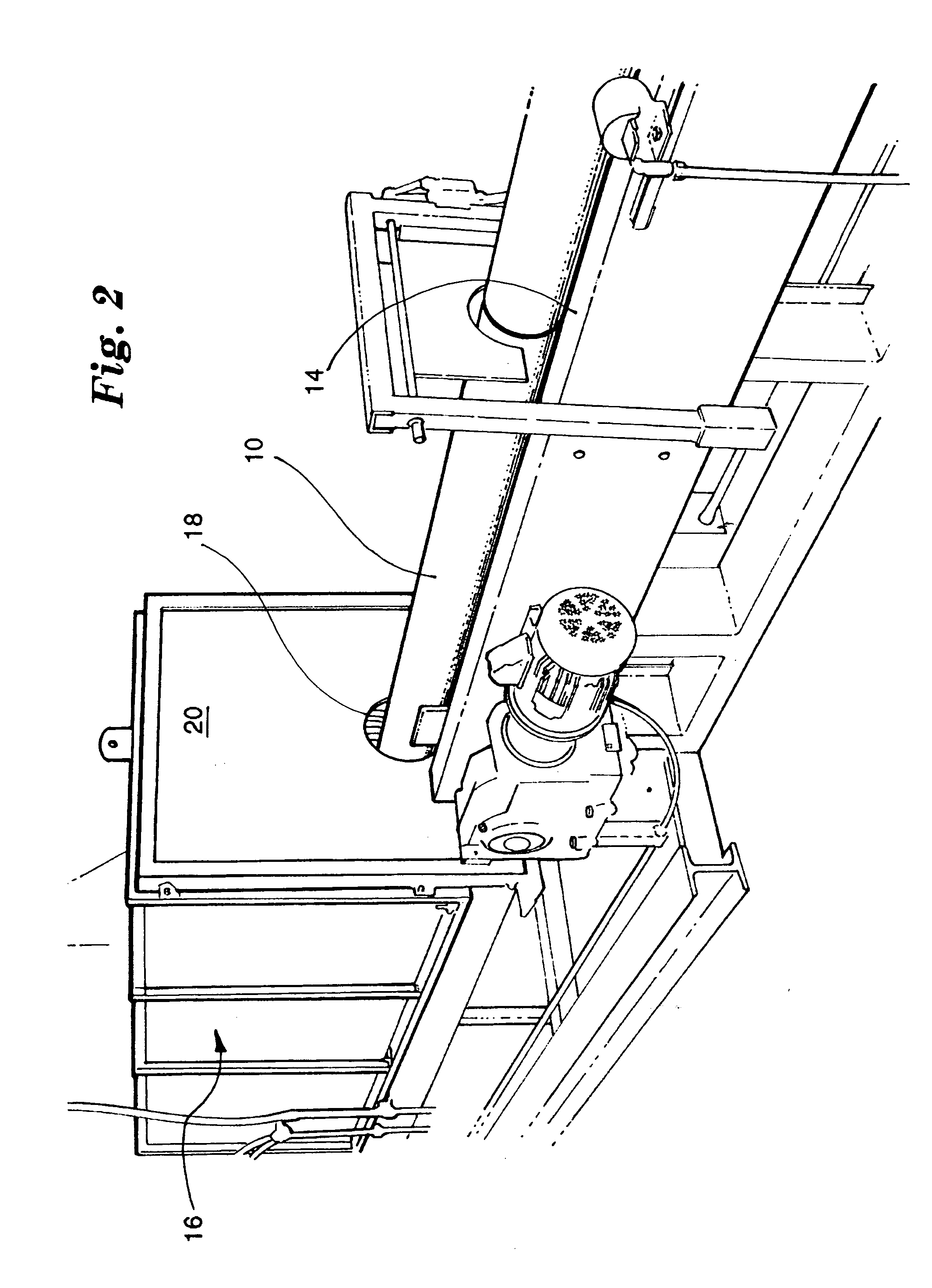
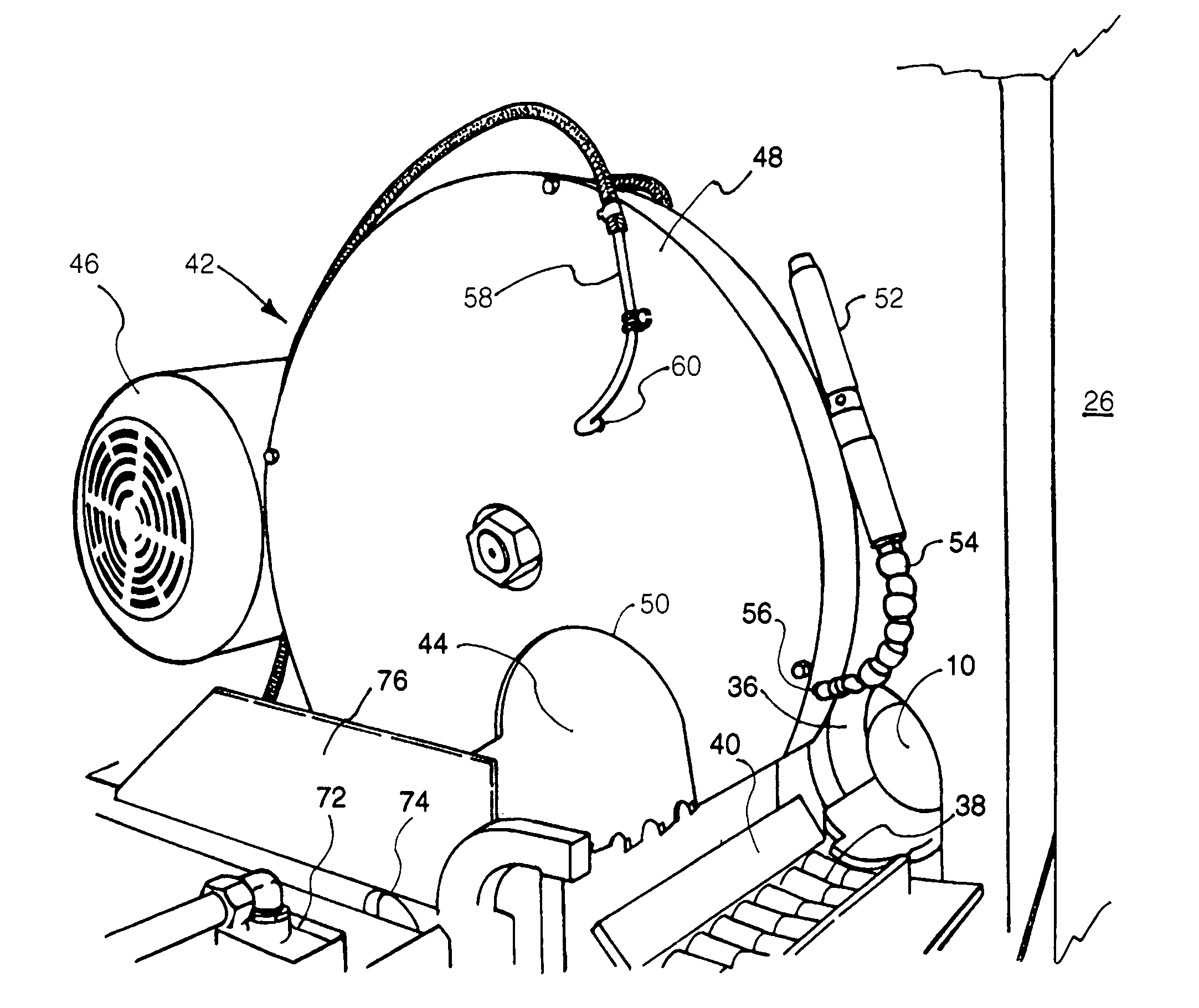
Hot cut aluminum billet saw
ActiveUS20050034502A1Reduce the temperatureLess scrapMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing accessoriesCross cutCircular saw
A process and apparatus for extruding aluminum into products, wherein aluminum logs are first heated to a predetermined temperature in a furnace, then are cut into billets of predetermined lengths, and then the billets, while still hot, are extruded into predetermined products in an extruder. In the process, the logs are cut into billets with a cross cut circular saw immediately after the logs are heated and before the logs are permitted to cool to a temperature below a suitable extruding temperature. The circular saw is cooled and lubricated during the cutting to as to restrain the saw from sticking in the heated aluminum and so as to maintain the temperature of the log at the cut within a predetermined range wherein the aluminum is relatively easy to cut and waste is minimized.
Owner:BELCO INDS
On-demand hydraulic pump for a transmission and method of operation
ActiveUS20090241535A1Less torqueImprove economyRotary clutchesGearing controlHydraulic pumpEngineering
A fixed displacement binary pump is provided for a powertrain on a vehicle. A hydraulic system is operatively connected with first and second discharge ports of the pump and is operable to alternately permit fluid flow through both discharge ports (i.e., full displacement or volumetric output of the pump) or permit flow through only the first discharge port (i.e., partial displacement or volumetric output of the pump). The pump may be packaged in a front support of the transmission. An auxiliary pump may be provided that is operable to supplement the output of the binary pump or to be used when the binary pump is off. A method of operating the binary pump and auxiliary pump is provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Bale processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100219275A1Less horsepowerLess fuel requirementMowersAnimal feeding devicesKnife bladesStructural engineering
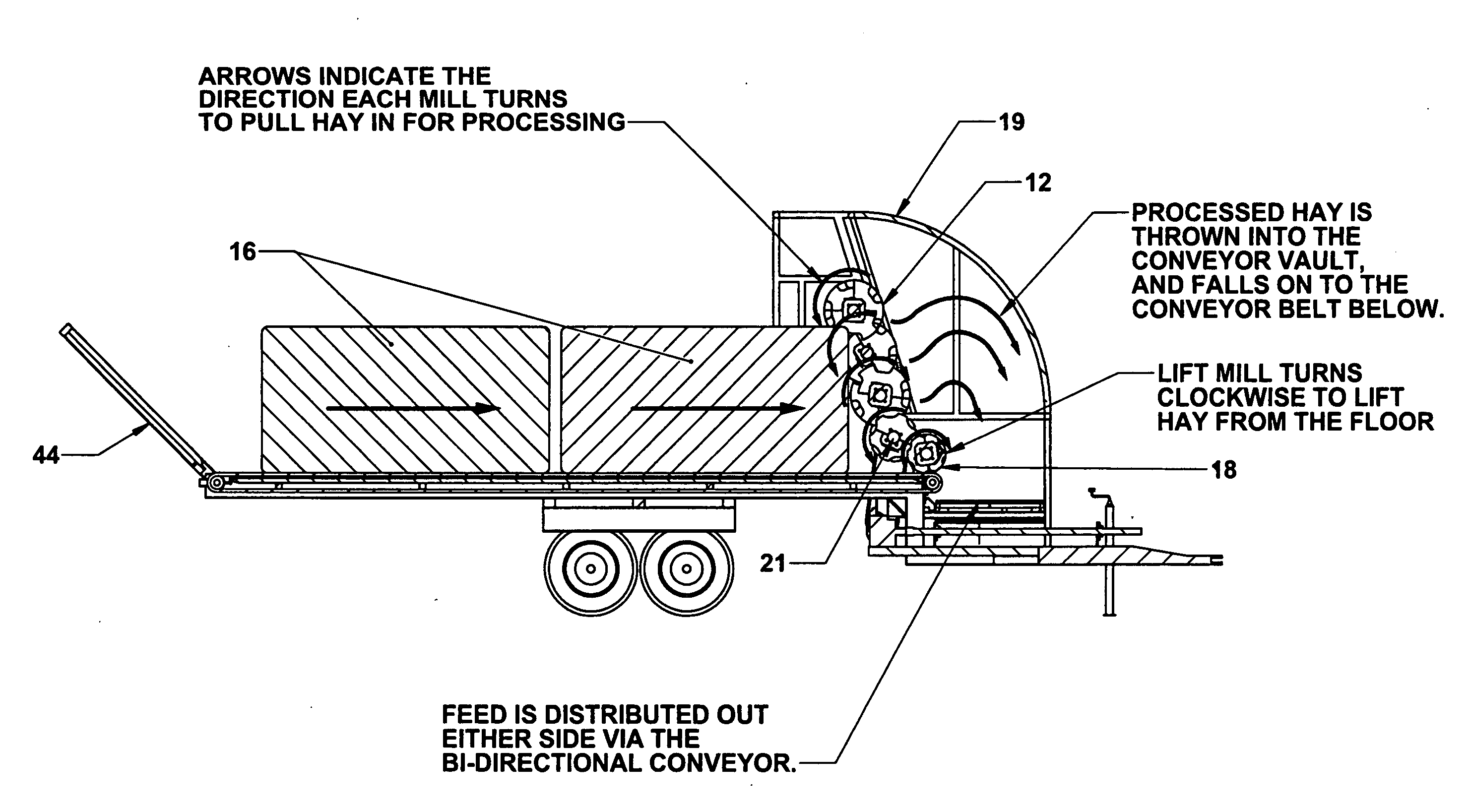
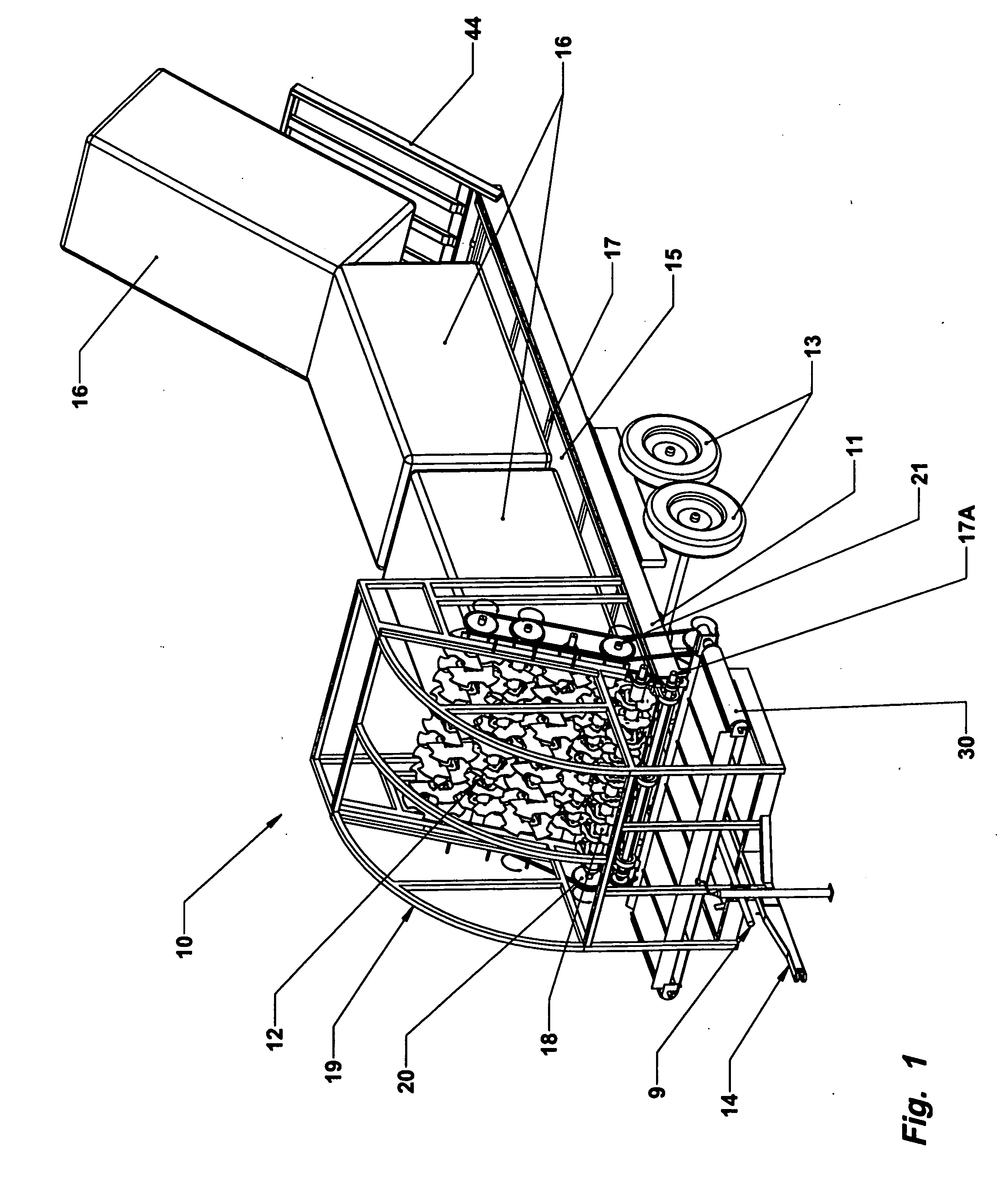
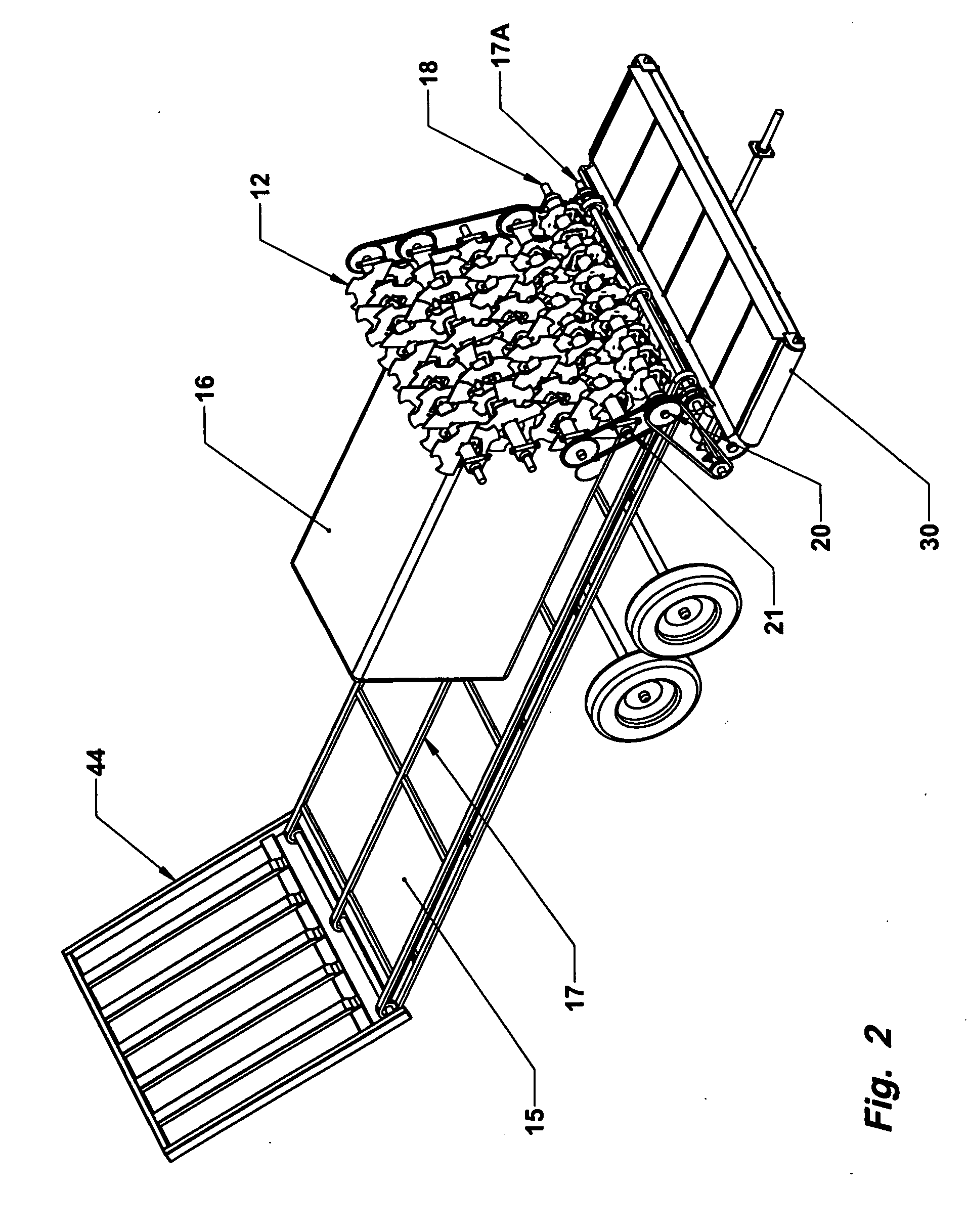
Bale processing apparatus is disclosed which includes an elongated bed for supporting bale of forage to be processed. Cutting blades are carried on transverse shafts at one end of the apparatus, and a conveyer advances the bale toward the cutting blades. The lowermost transverse shaft rotates opposite to the next adjacent transverse shaft. The cutting means further include an outwardly projecting blade to assist in cutting the forage material. In one embodiment, the cutting mill is tilted rearwardly.
Owner:WEISS LEONARD D
Aquatic sport assistance device
InactiveUS9198518B1Quickly in learning processFast processingLife-buoysDismountable chairsAquatic locomotionSurface water
An aquatic sport assistance device for use in surface water sports. An inflatable device using drop-stitch construction to provide a portable but rigid platform on which a user can sit to learn surface water sports. Two floats at a spaced relation to one another create an open space between the two floats. A deck disposed upon the two floats creates an open space between the seats and the surface of the water. This allows water skis or wake boards to rest below the deck on the surface of the water for a natural sitting position. Can be used with barefoot skiing. Device has three seat pads, allowing for use with water skis and wakeboards, and allowing for use as regular or goofy foot. Handles help a user to proper position for activity chosen. Fins give directional stability, allowing device to be towed directly behind boat or along boat wake.
Owner:MAYER DONALD J
Hydrocarbon production system and method of use
InactiveUS20080164034A1Extended service lifeEasy to produceConstructionsFluid removalFluid shearCoal
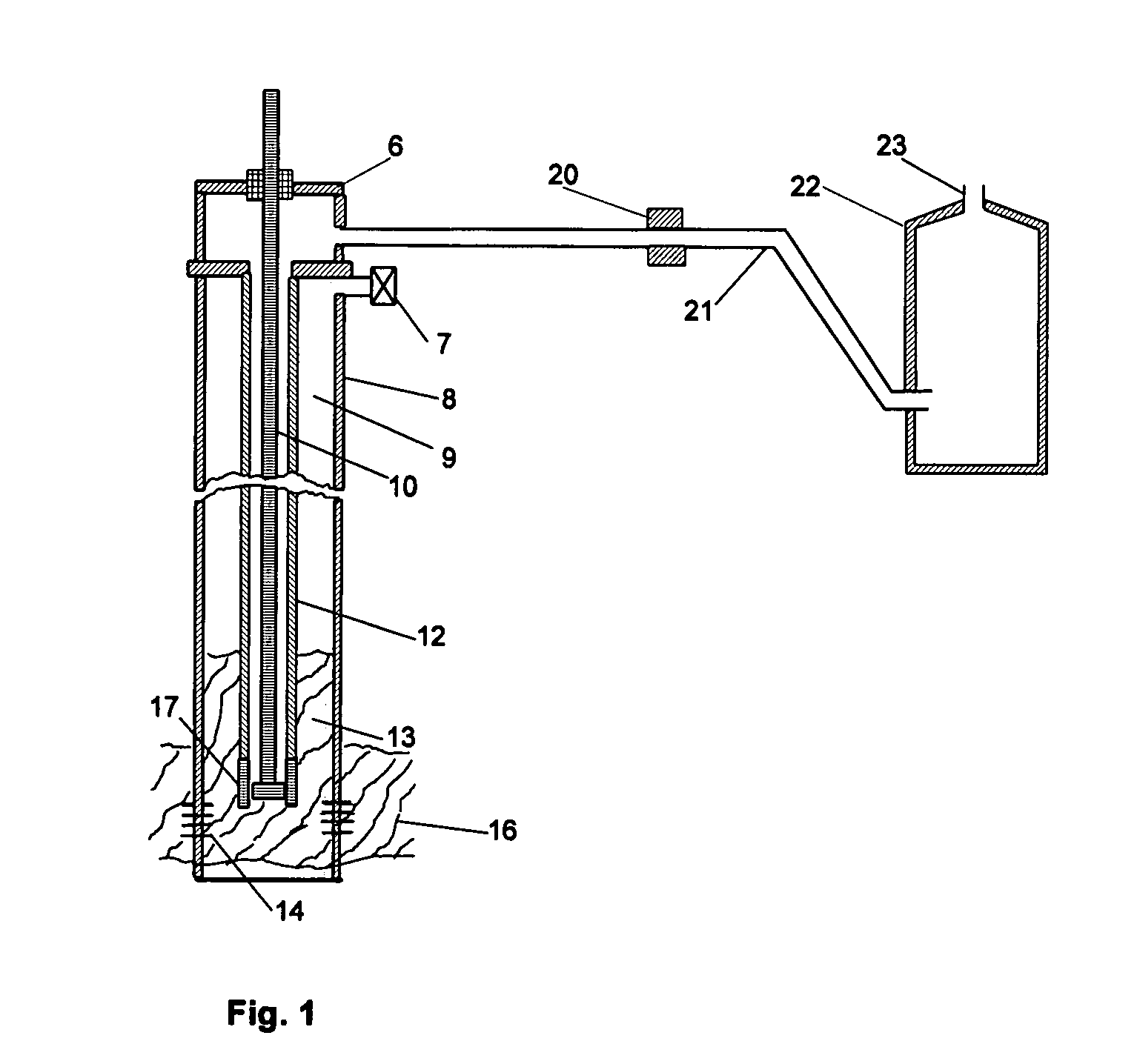
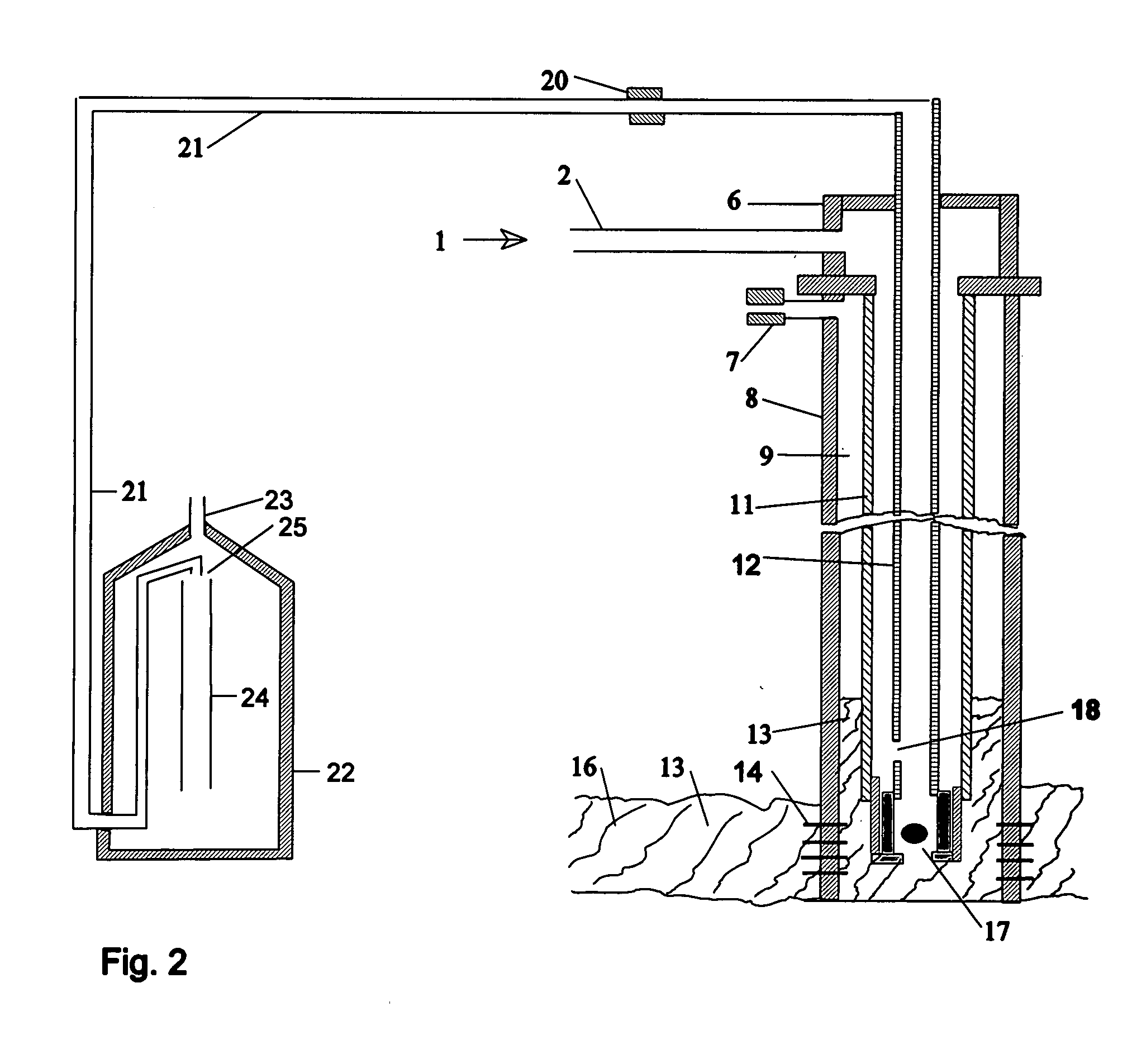
The method of the present invention employs a subsurface production pump to displace hydrocarbon fluid, including any and all accompanying ground water and / or earthen contaminants, from the subterranean hydrocarbon reservoir depth of an oil well to surface storage and handling facilities via the subsurface production tubing, wellhead and surface flow line. As the subsurface production pump operates, compressed gas, or a mixture of compressed gases of sufficient volume and force is fed into the lower end of the subsurface production tubing in proximity to, or at a point above the subsurface production pump to mix into the hydrocarbon production fluid column. The resultant and considerably reduced density of the subsurface hydrocarbon production fluid column provides a reduction of subsurface production pump loading with all types of subsurface production pumps, and an improvement of sucker rod fall time when sucker rod activated subsurface plunger pumps are employed. Due to the additional cubic volume of the injected compressed gas, the increased hydrocarbon production fluid and gas velocity within the subsurface production tubing and the surface flow line improves hydrocarbon fluid shear from the conduit walls and sucker rod surfaces, and prevents earthen contaminants such as sand, clay, shale, coal or other rock fragments, from precipitating, accumulating and blocking the flow of hydrocarbon production fluid within the subsurface production tubing and the surface flow line.
Owner:UTTLEY DENNIS FRLIN
Hot cut aluminum billet saw
ActiveUS7047784B2Reduce the temperatureReduce frictionMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing accessoriesCross cutCircular saw
A process and apparatus for extruding aluminum into products, wherein aluminum logs are first heated to a predetermined temperature in a furnace, then are cut into billets of predetermined lengths, and then the billets, while still hot, are extruded into predetermined products in an extruder. In the process, the logs are cut into billets with a cross cut circular saw immediately after the logs are heated and before the logs are permitted to cool to a temperature below a suitable extruding temperature. The circular saw is cooled and lubricated during the cutting to as to restrain the saw from sticking in the heated aluminum and so as to maintain the temperature of the log at the cut within a predetermined range wherein the aluminum is relatively easy to cut and waste is minimized.
Owner:BELCO INDS
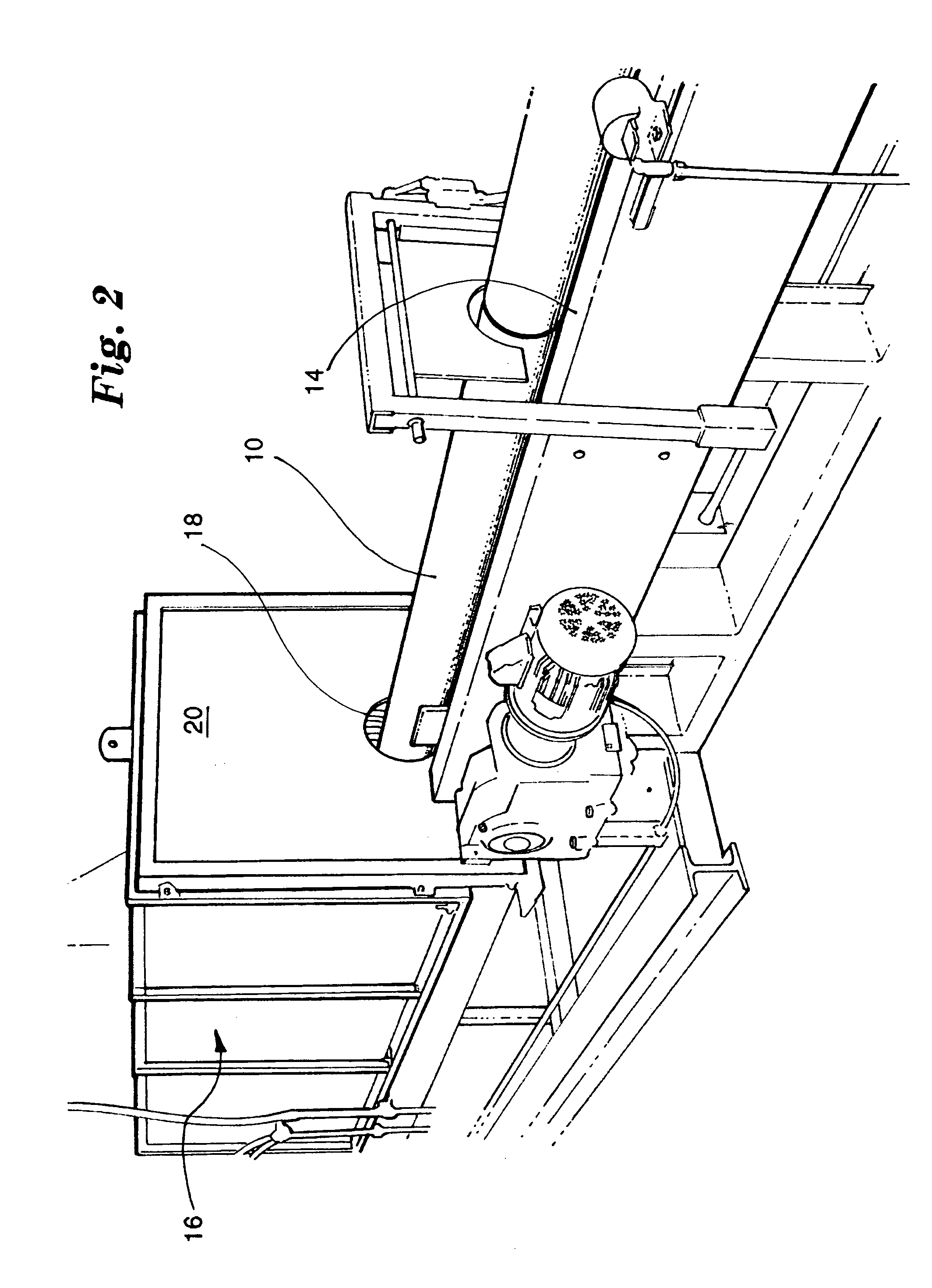
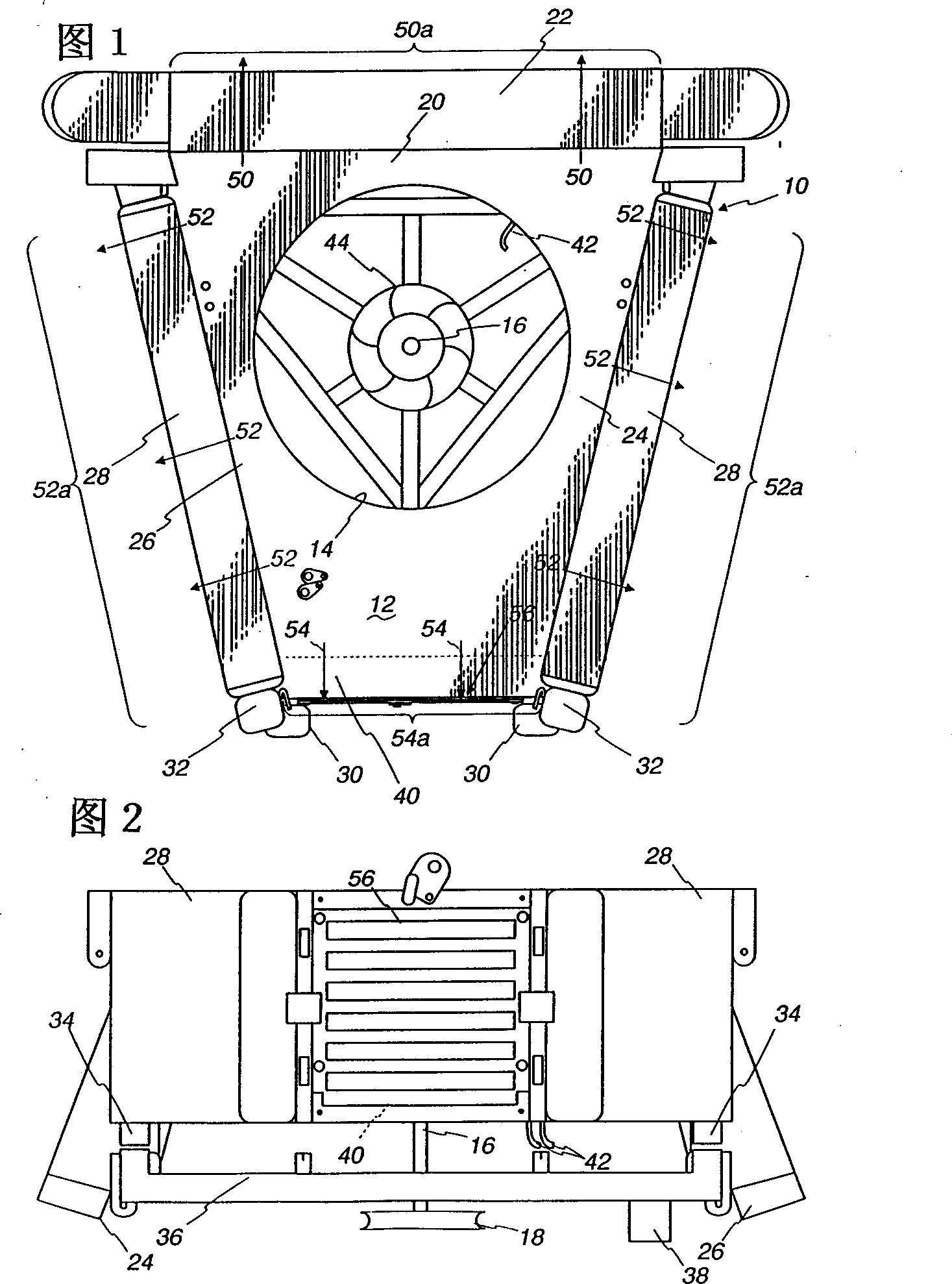
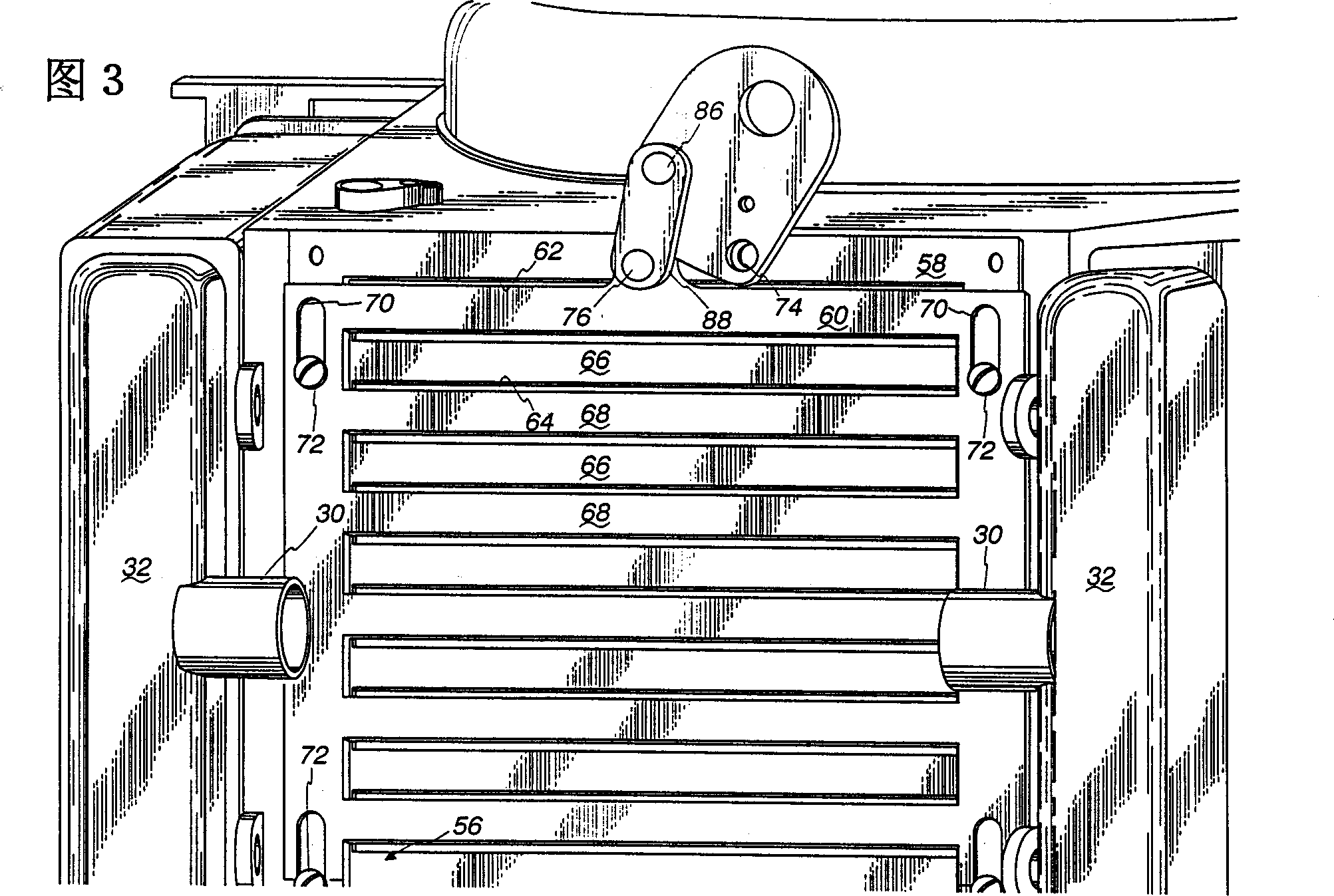
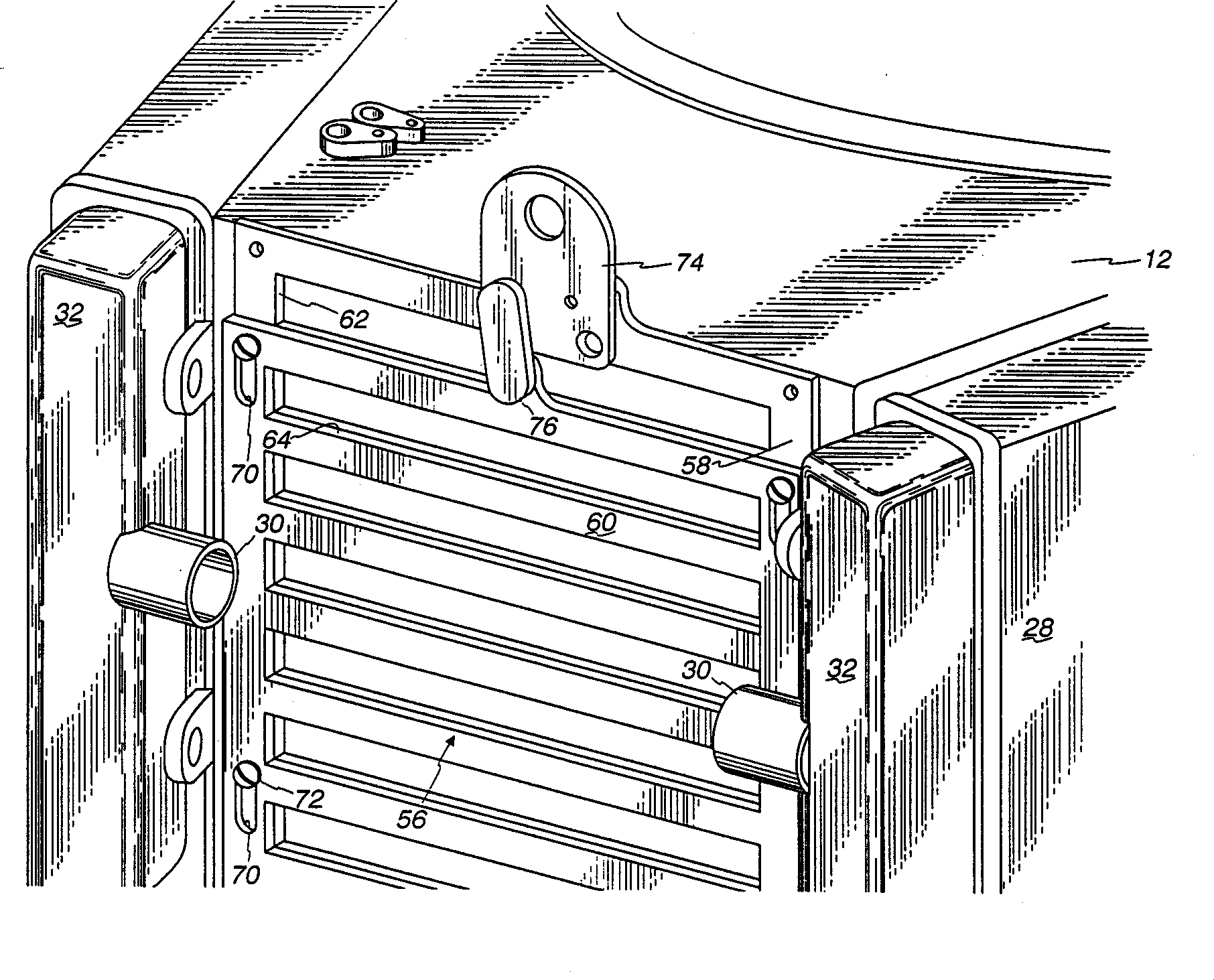
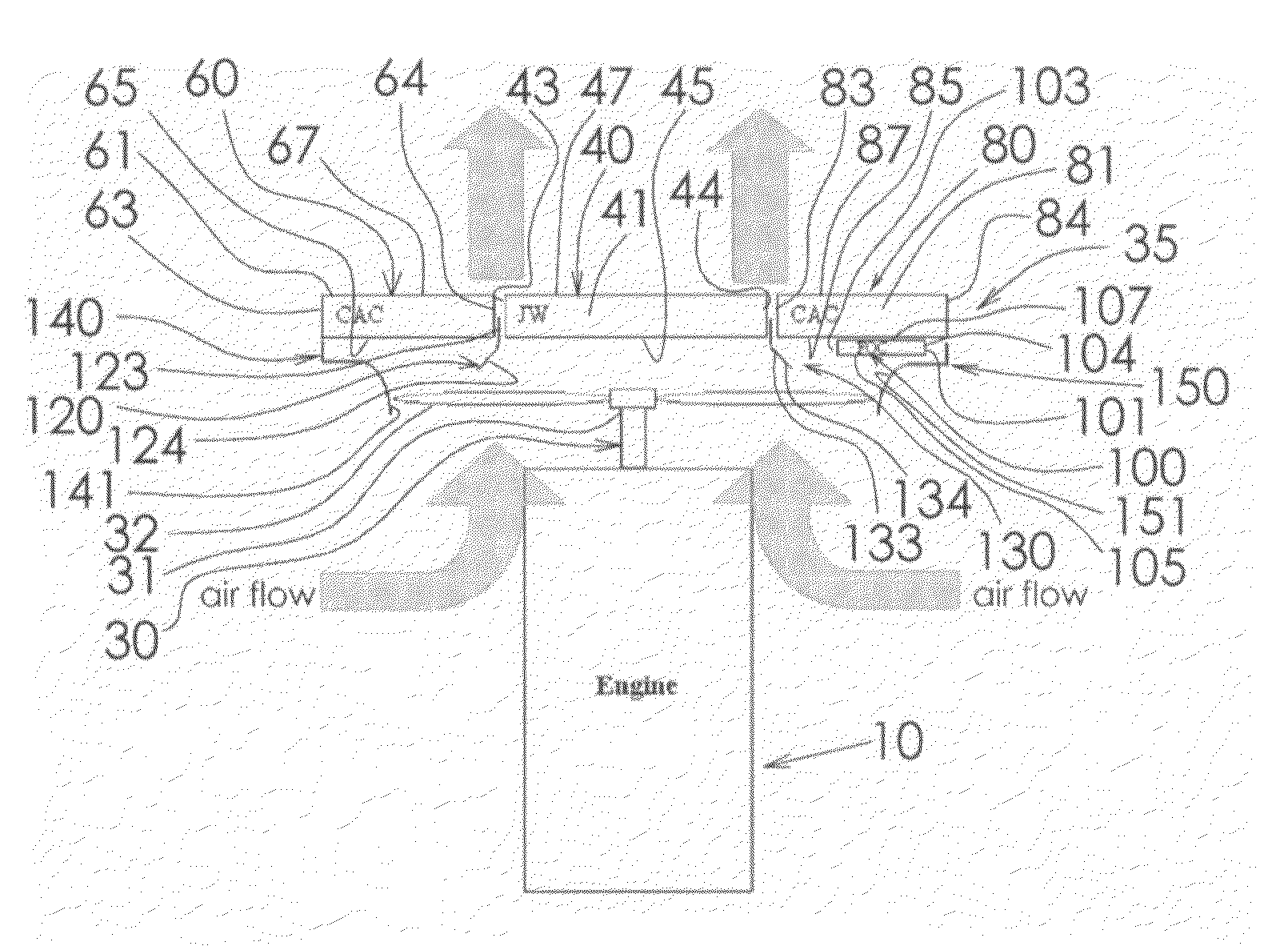
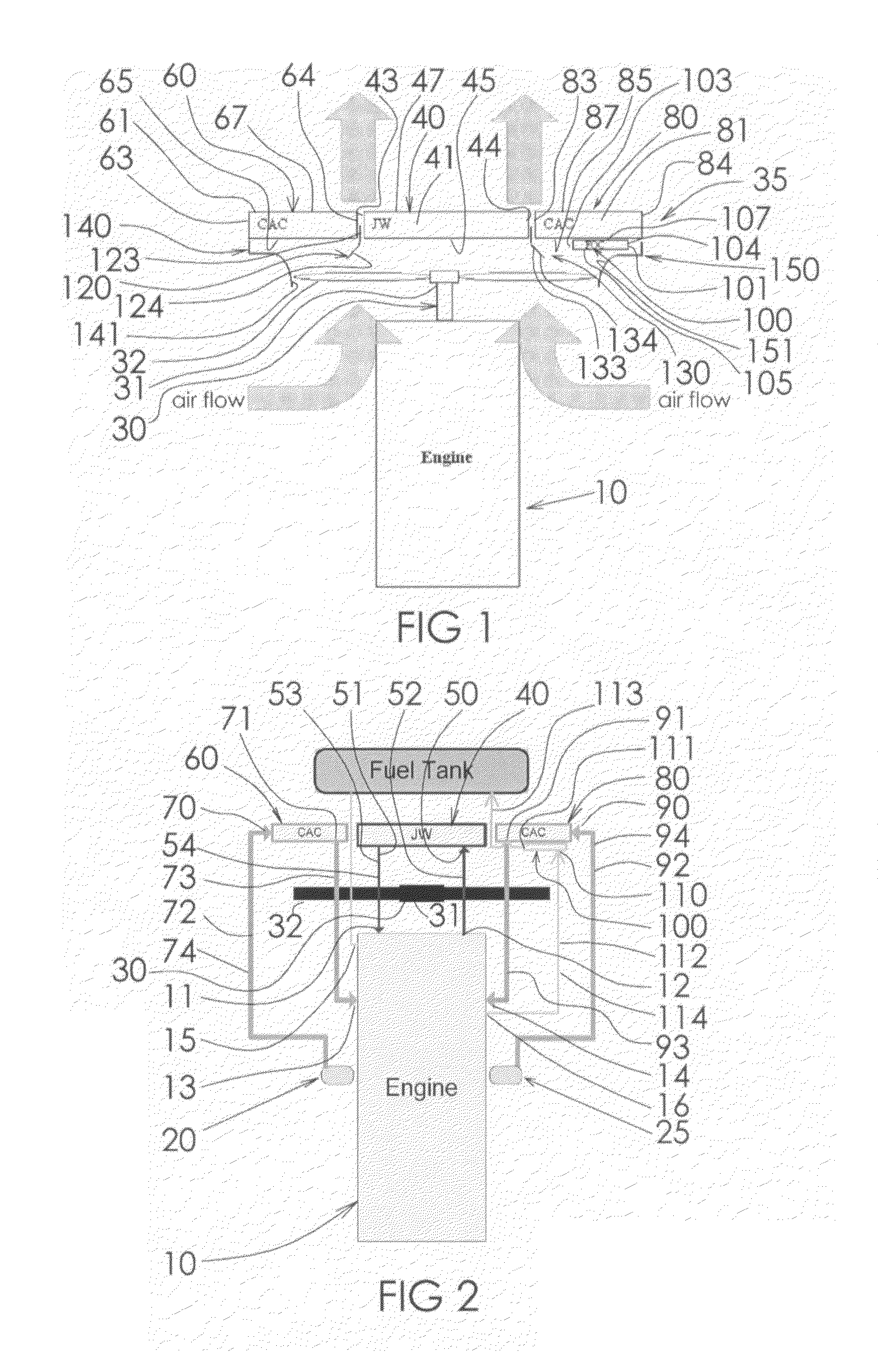
Cooling system of vehicles
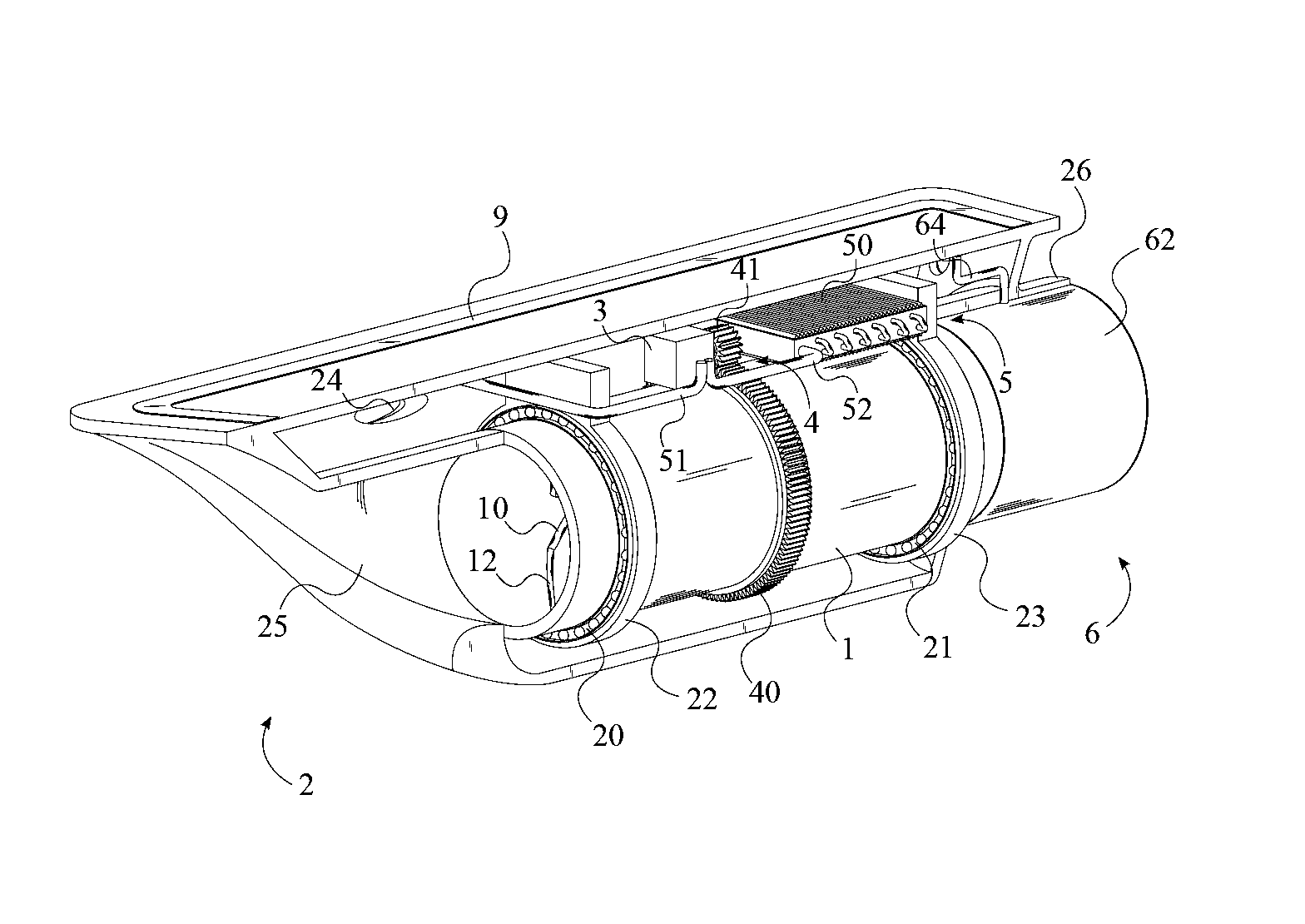
Fan horsepower requirements and the size of power train heat exchangers may be reduced in a vehicular cooling system that includes an inlet (14) for the receipt of ambient air and first and second heat exchangers (28), (40) in proximity to the inlet to receive ambient air therefrom and which are respectively adapted to receive first and second heat exchanger fluids by the ambient air. The first and second heat exchangers are in side by side, substantially non superimposed relation to define first and second air flow paths (52, 54) extending in fluid flow parallel to a respective one of the heat exchangers from the inlet to points (50), (52), (54) of discharge. A fan (44) flows air from the inlet through the flow paths and a shutter (56) is located in one of the flow paths (54) and is movable between first and second positions respectively restricting air flow and allowing relatively unrestricted air flow. An actuator (88) provided for moving the shutter (56) between the positions and a control (90, 98, 100) is provided for the actuator (88) which is responsive to power train and air conditioning system operating conditions.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
Heating and cooling system
ActiveUS7152421B2Avoid insufficient heatingSmall sizeAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesRecovery methodElectrical battery
Owner:PARKS IND LLC
Heating and cooling system
ActiveUS20050076666A1Avoid insufficient heatingSmall sizeAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesRecovery methodElectrical battery
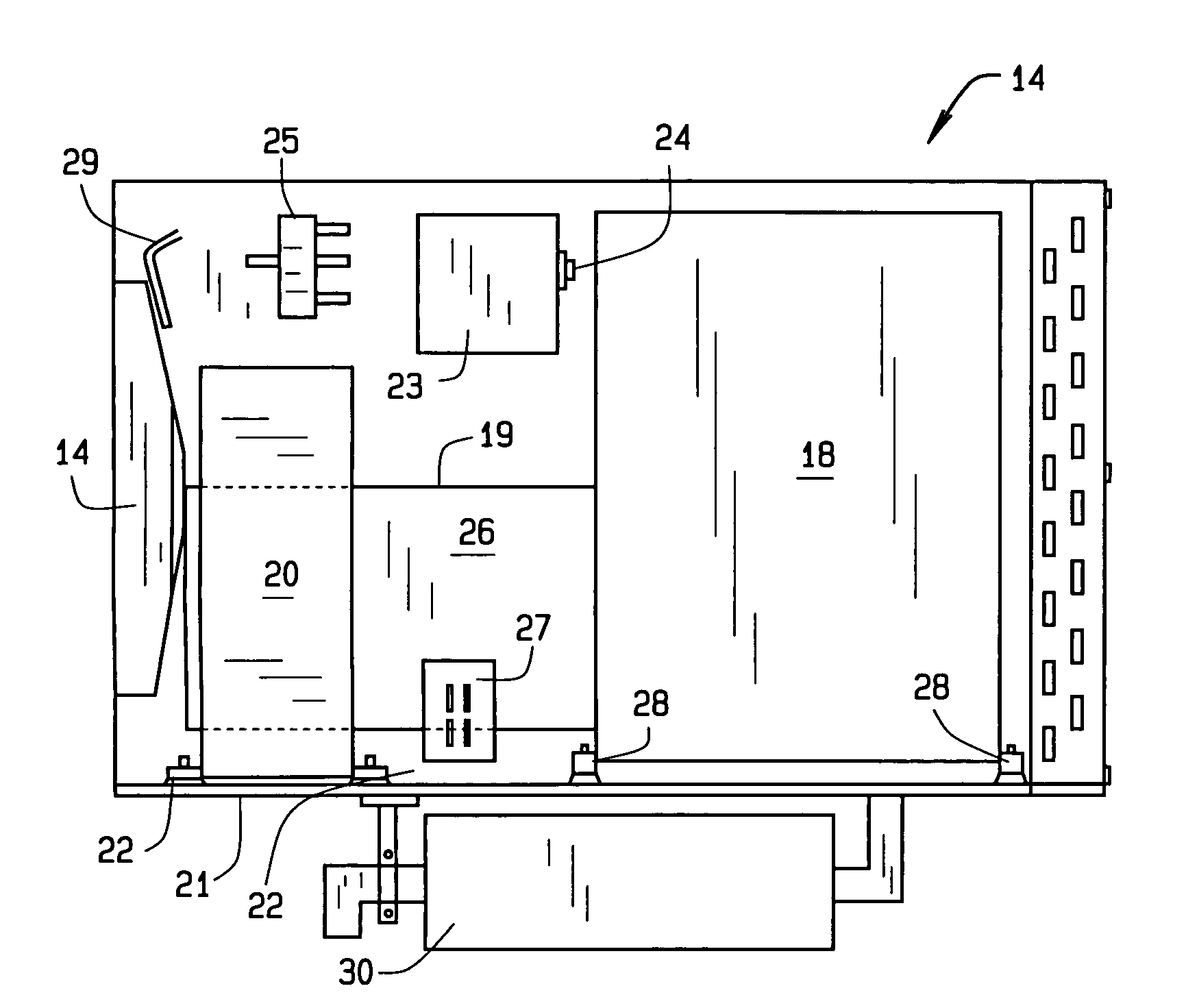
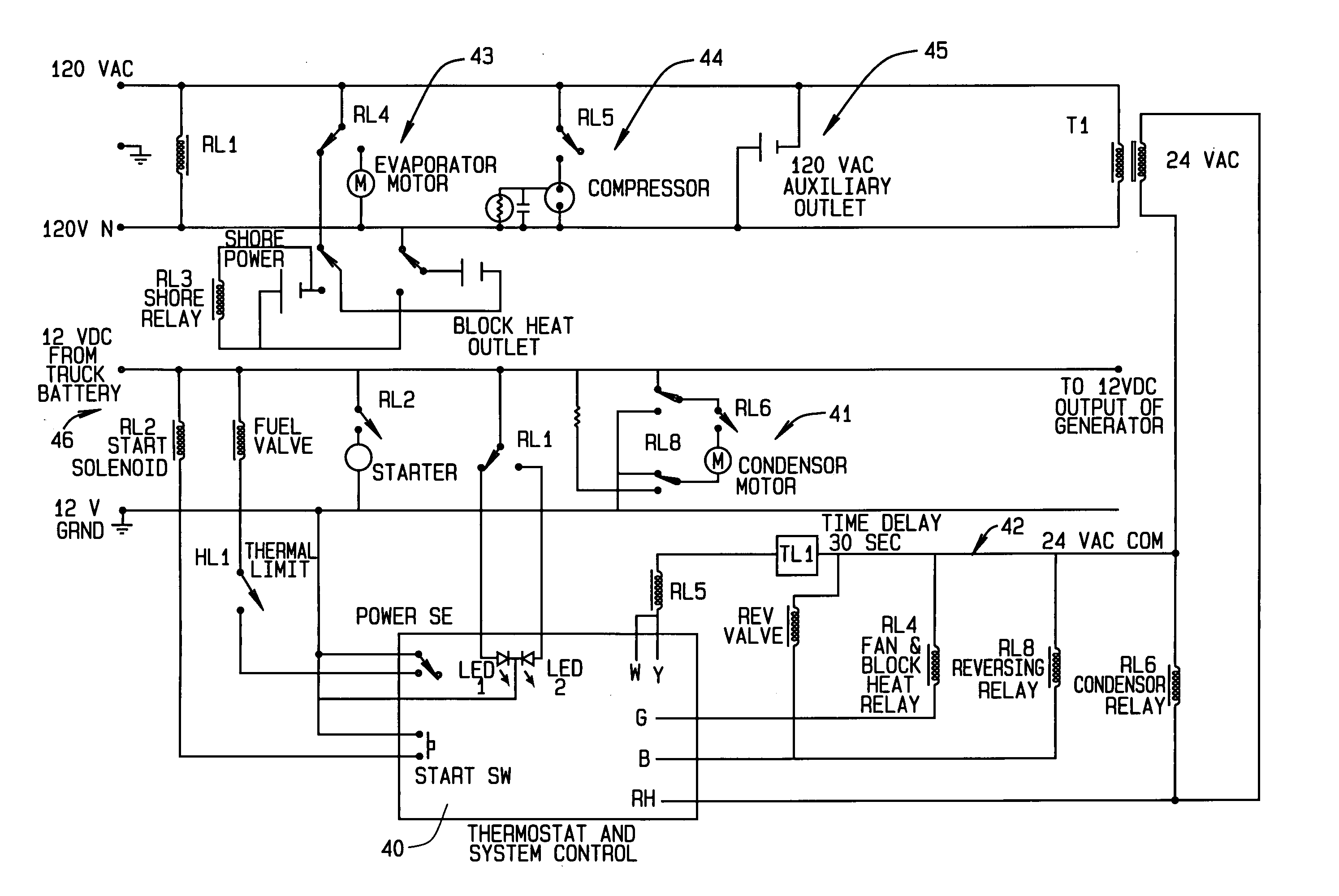
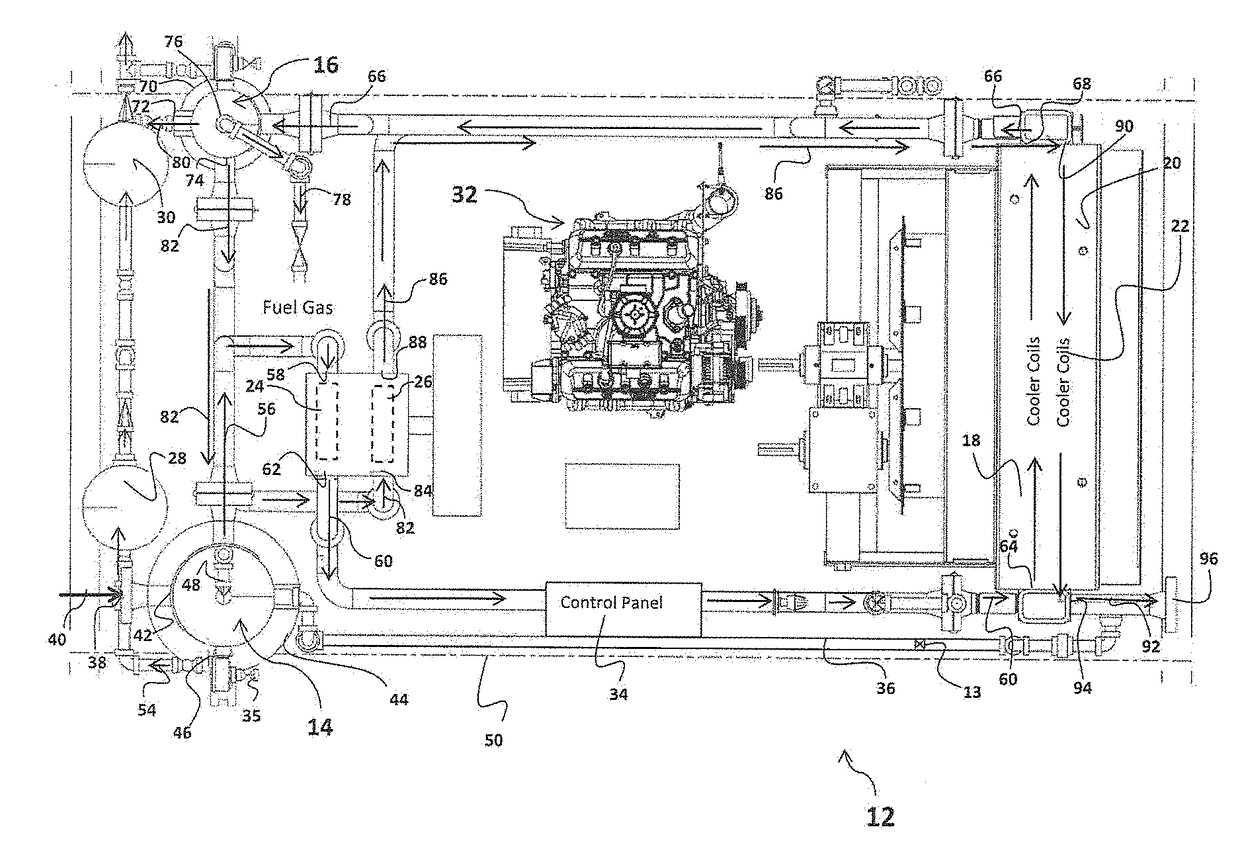
A heating and cooling system incorporates a heat pump that operates conventionally with air drawn from outside the system through its condenser coils that remove heat to the exterior for cooling. In the heating cycle, the condenser motor blower stops and reverses rotation. Outside air is drawn in by the condenser fan, is circulated across the diesel engine and generator, and is blown through the condenser coils outside of the unit. In the heating cycle, a circuit monitors the temperature of the compressor coil and controls the speed of the condenser motor. The heat recovery method of the system maintains power input to heat output ratios in excess of 2:1, even at low outside temperatures. The recovery method also allows the system to operate without defrost cycles. This system may provide auxiliary power, block heat, and battery charging, utilizing a small diesel engine and generator components, and can be installed within a truck, bus, boat, cabin, camper, and the like.
Owner:PARKS IND LLC
Method for digging water chestnuts by rotary cutting and digger employing same
The invention relates to a method for digging water chestnuts by rotary cutting and a digger employing the same. The method includes the steps: a water chestnut soil layer is divided into an upper soil seedling layer and a lower soil water chestnut layer, the upper soil seedling layer and the lower soil water chestnut layer are cut and divided by rotary cutting and forward movement of two upper and lower cutting wheels, with forward movement of a digging collector, and the upper soil seedling layer enters a digging blade and is discharged from an upper passage into a furrow behind the digging blade; the lower soil water chestnut layer enters a water chestnut collection passage of the digging blade, after screening, water chestnuts and soil are separated, and the broken soil falls into the furrow behind the digging blade through meshes; the water chestnuts obtained by screening enter a product collector. Therefore, automatic digging and collecting of water chestnuts is achieved.
Owner:吴润秀
Open core continuous helical fin marine drive system
ActiveUS9039348B1Decrease carbon base emissionLess horsepowerLiquid coolingPropulsion based emission reductionNacelleDrive motor
An open core continuous helical fin marine drive system for use with surface and subsurface marine vessels has a cylindrical fluid container nested within a nacelle enclosure having an intake port and an exhaust port tailpipe. The cylindrical fluid container is driven by a fluid container drive motor through a gear assembly including a pinion gear connected to the fluid container drive motor and an underwater ring gear connected to the cylindrical fluid container. A plurality of continuous helical fins connected along the inner wall of the cylindrical fluid container is positioned about a hollow center core and creates a horizontal centripetal fluid vortex thread along the hollow center core as the cylindrical fluid container rotates. An inflatable marine bladder is positioned aft of the cylindrical fluid container and can be engaged to an inflated configuration in order to compress the exiting water flow through the exhaust port tailpipe.
Owner:VORTEX SEADRIVE SYST
Split radiator maximizing entering temperature differential
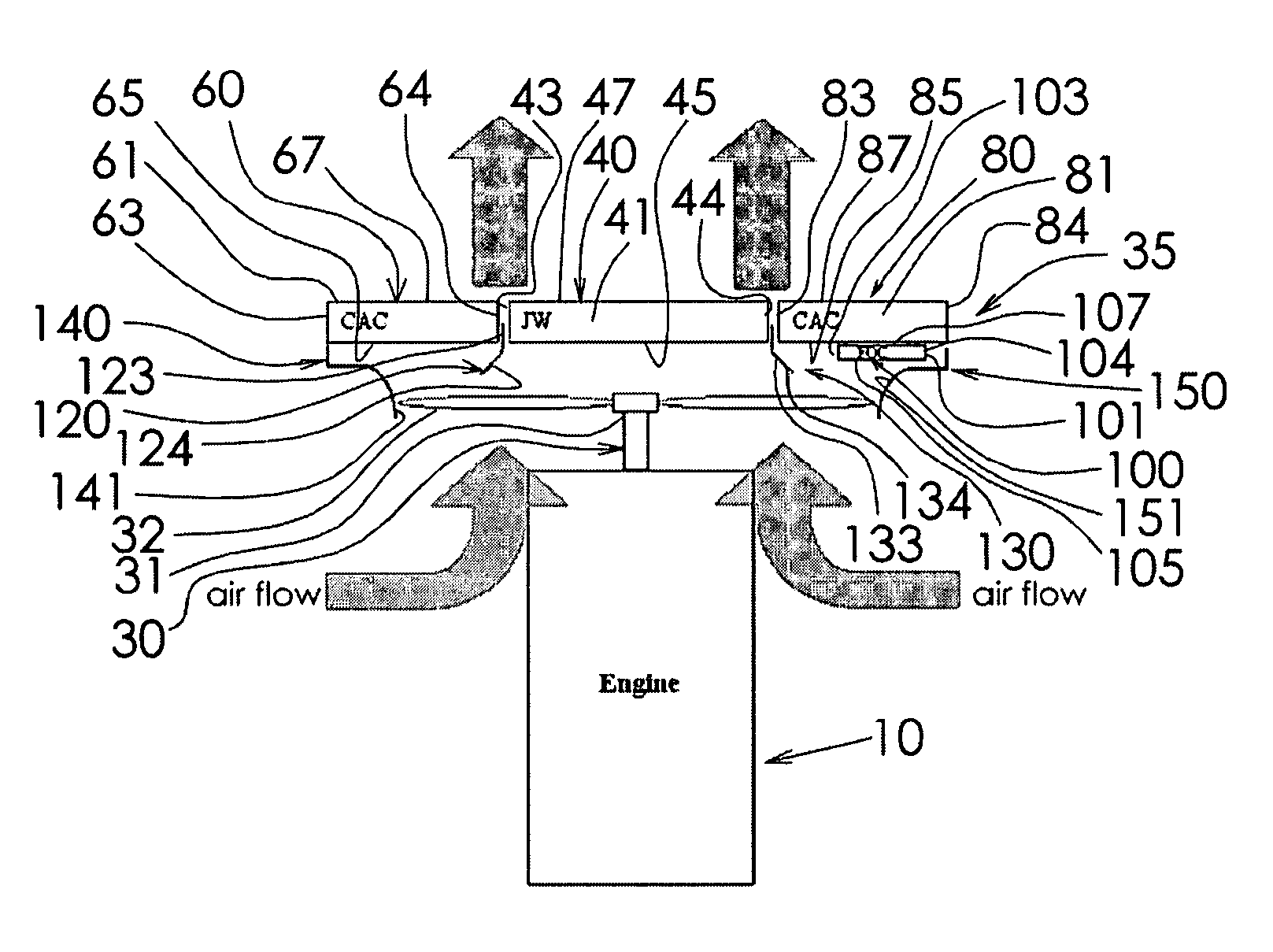
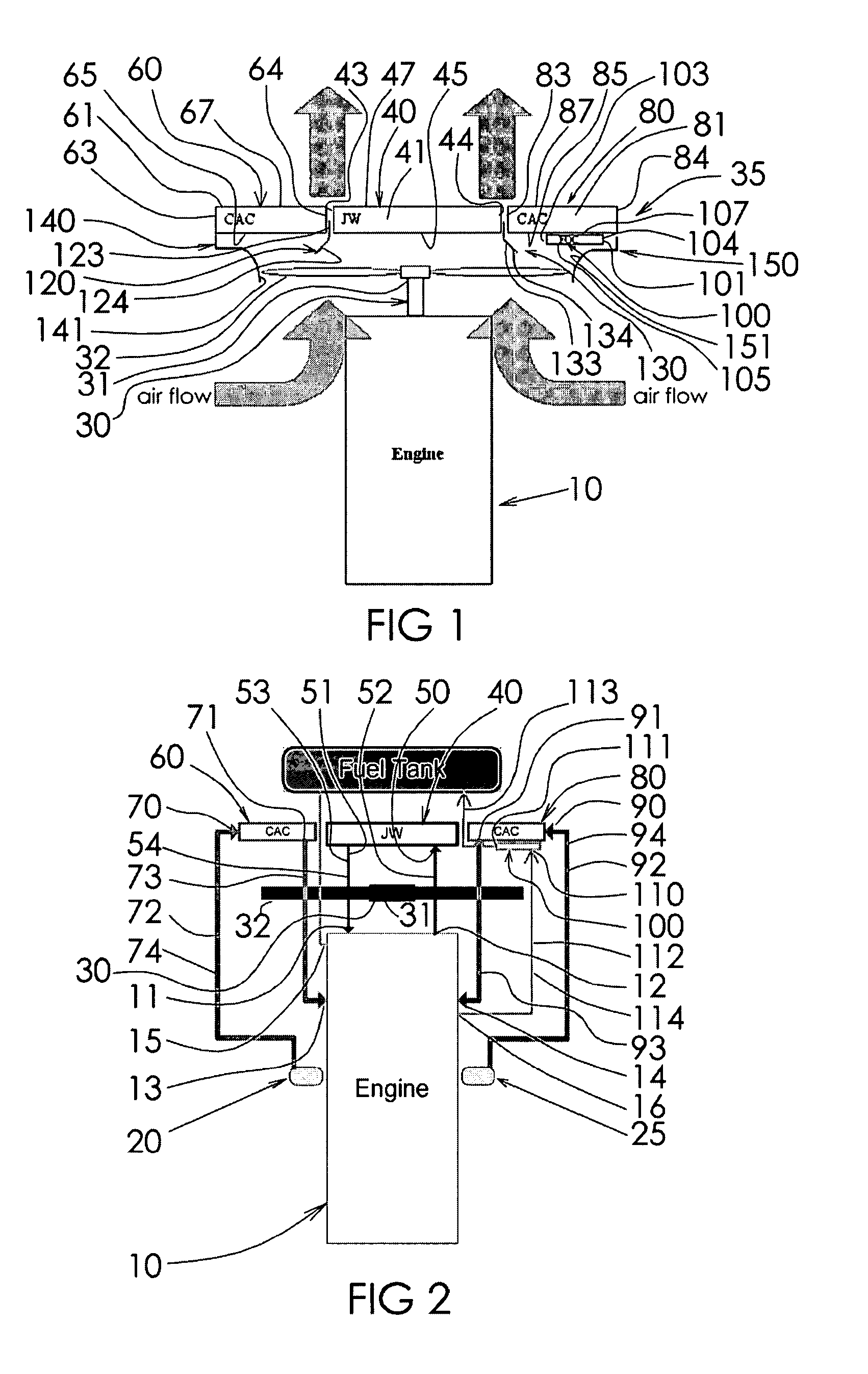
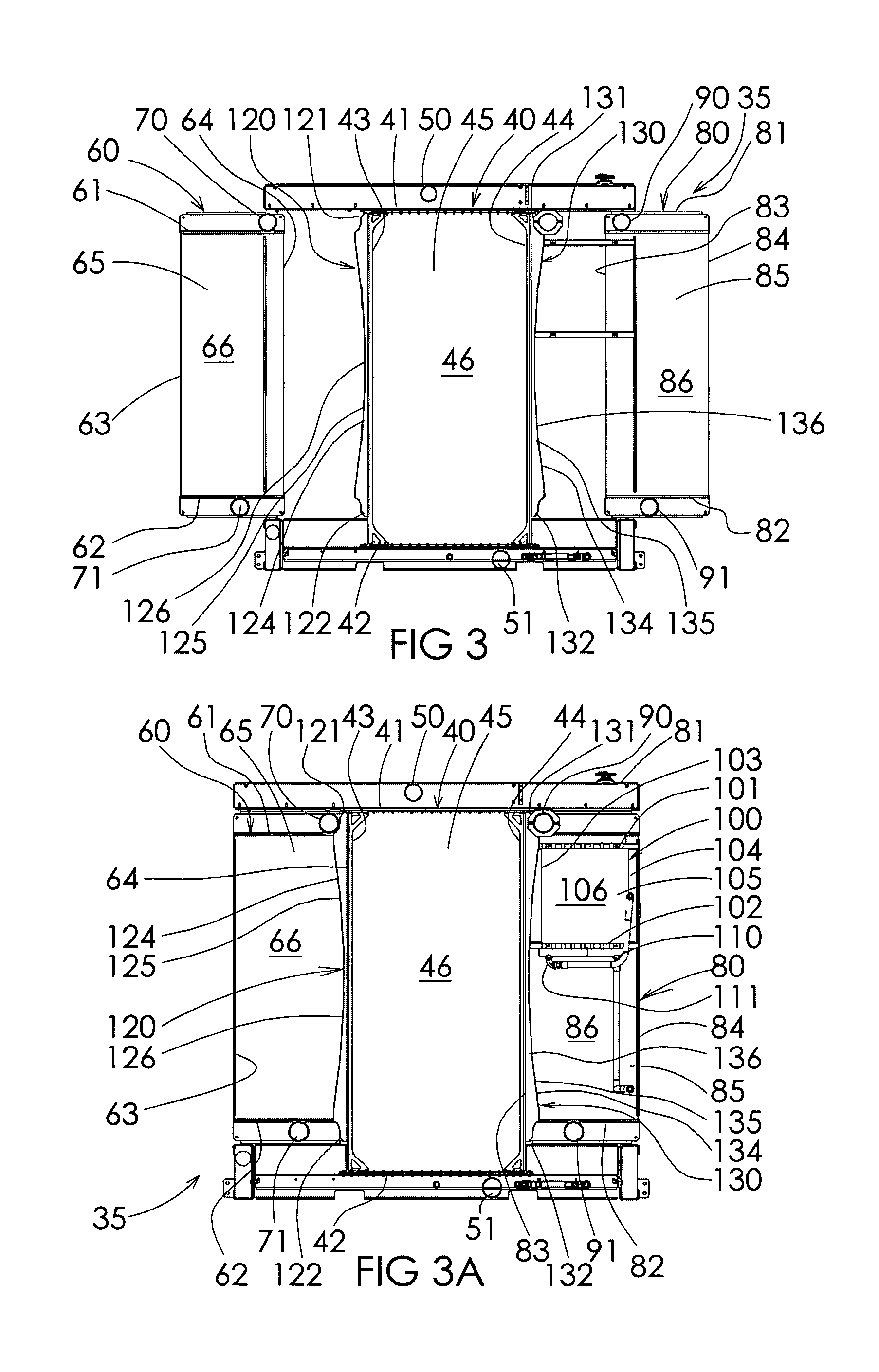
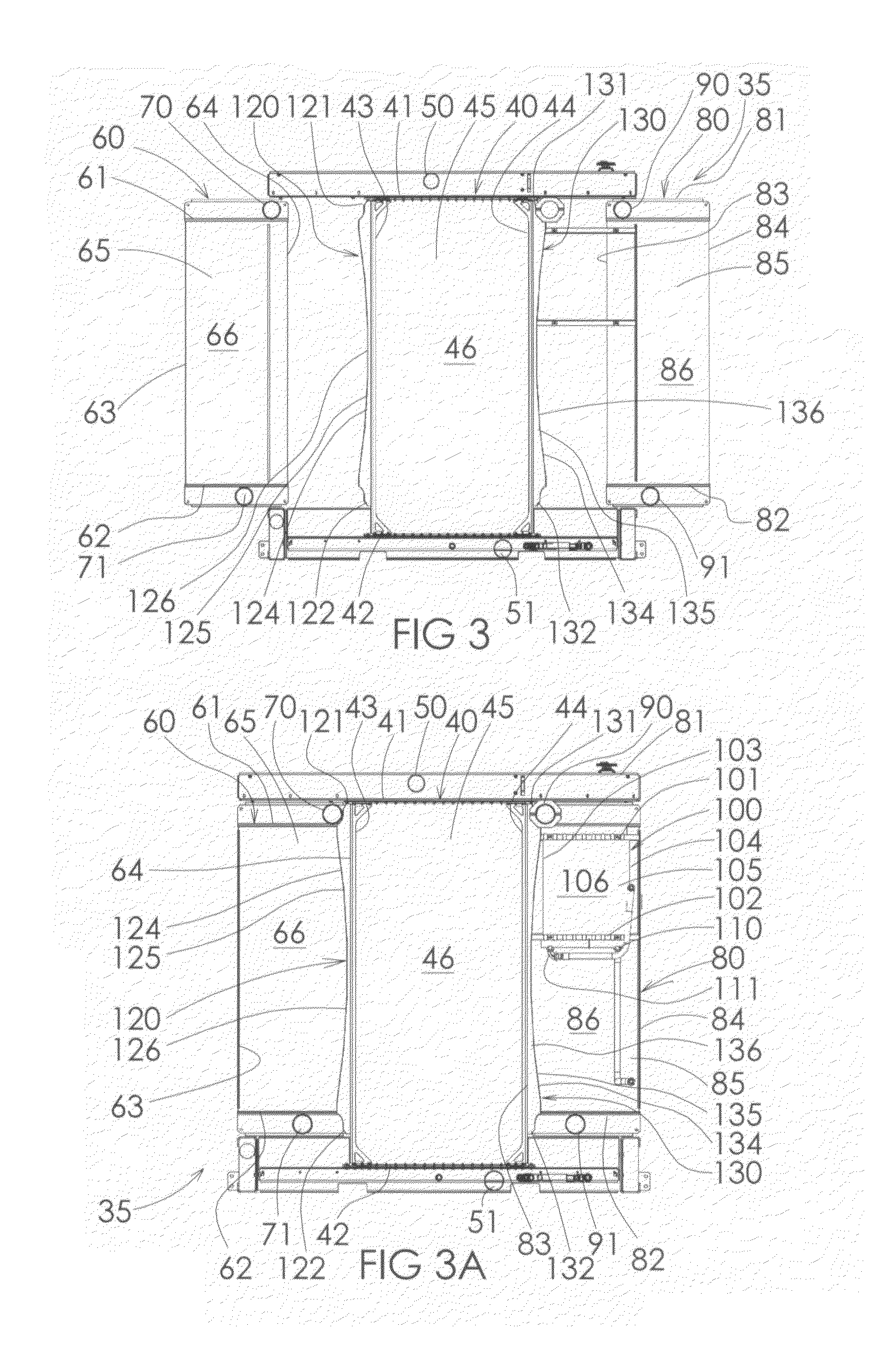
InactiveUS7703420B1Heat dissipationPrevent radial convective scrubbingLiquid coolingAir coolingTurbochargerEngineering
A heat exchanger is provided for dissipating heat from a dual turbocharged engine. The heat exchanger has a jacket water cooler, and first and second charge air coolers. The three coolers are arranged in parallel enabling each to operate with a maximum temperature differential, and have fronts that lie in parallel planes. Charge air from a first turbocharger is directly piped to the first charge air cooler, and charge air from the second turbocharger is directly piped to the second charge air cooler. A first baffle is between and upstream of the first charge air cooler and the jacket water cooler. A second baffle is between and upstream of the second charge air cooler and the jacket water cooler. The baffles can direct selected amounts of air to each of the three coolers and prevent radial convective scrubbing. A fuel oil cooler can also be provided.
Owner:IEA
Compression system
ActiveUS20180030931A1Small horsepowerLower requirementCasingsFuel supply apparatusEngineeringRevolutions per minute
The compression system comprises a main fluid inlet adapted to receive a production stream of natural gas; first and second stage scrubbers; first and second compression units; first and second heat exchange units; one or more liquid dump containers; and an engine. The engine operates within a range of 1600-2100 revolutions per minute and the compressed gas comprises a pressure within a range of 360-600 pounds per square inch. The system comprises a weight to thousand cubic feet of gas per day ratio of less than twenty.
Owner:PRECISION COMPRESSION LLC
Speed change device with coaxial connecting rod rolling disc
PendingCN107763181AIncrease torqueImprove enduranceGearing detailsFriction gearingsO-ringEngineering
The invention relates to a speed change device with a coaxial connecting rod rolling disc. The speed change device comprises a speed changer shell containing a body. The body comprises the coaxial connecting rod rolling disc, a force-input shaft, a centrifugal piece, a plurality of counterweight assemblies, a plurality of O rings and a plurality of sliding block assemblies. When the speed change device conducts actuation, the force-input shaft serves as a force applying point of the lever principle, the equal sliding block assemblies serve as weight points, and the arm of force is equal to thedistance between the force-input shaft and each equal sliding block assembly; the equal sliding block assemblies are arranged at the tail end of the connecting rod rolling disc, therefore, compared with the prior art, the arm of force is increased, the bearing force of the weight points is improved, the turning force of the speed change device is increased under the same motor force, and accordingly the motor force is saved; and in addition, U-shaped grooves for containing the equal sliding block assemblies are formed in the tail end of the connecting rod rolling disc, so that machining is easy during manufacturing, and the cost can be reduced.
Owner:陈鹏宇
Band saw structured hierarchical water chestnut picking shovel
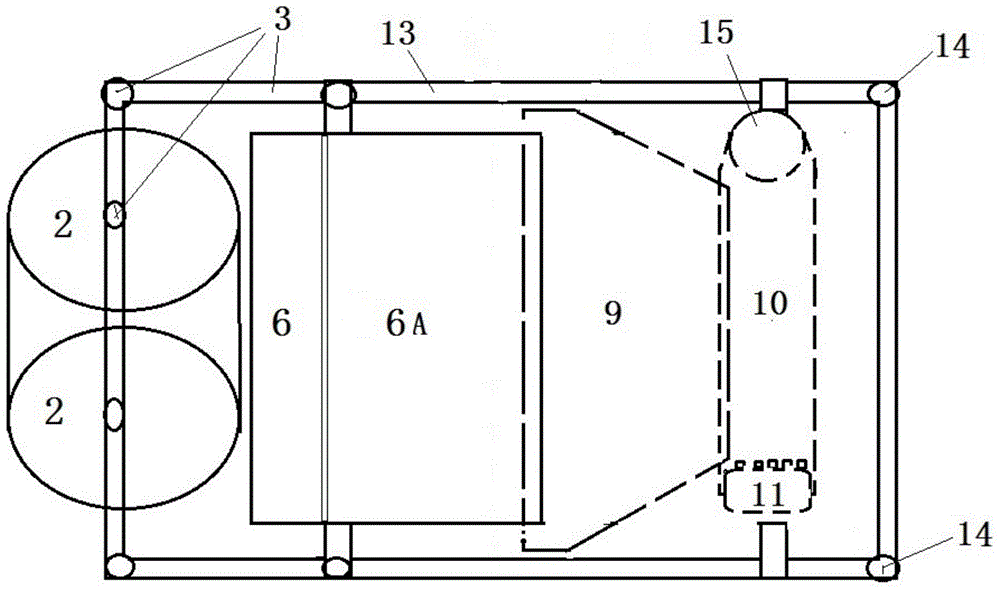
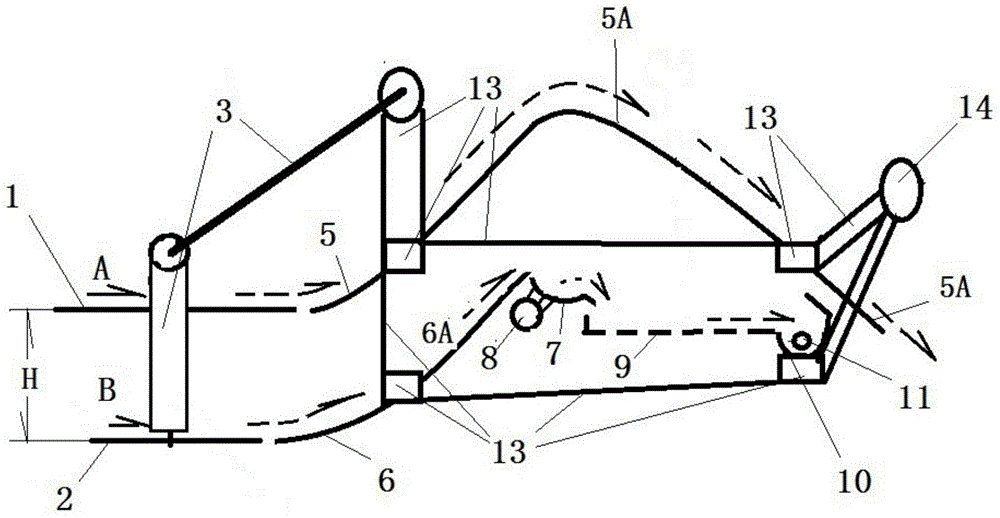
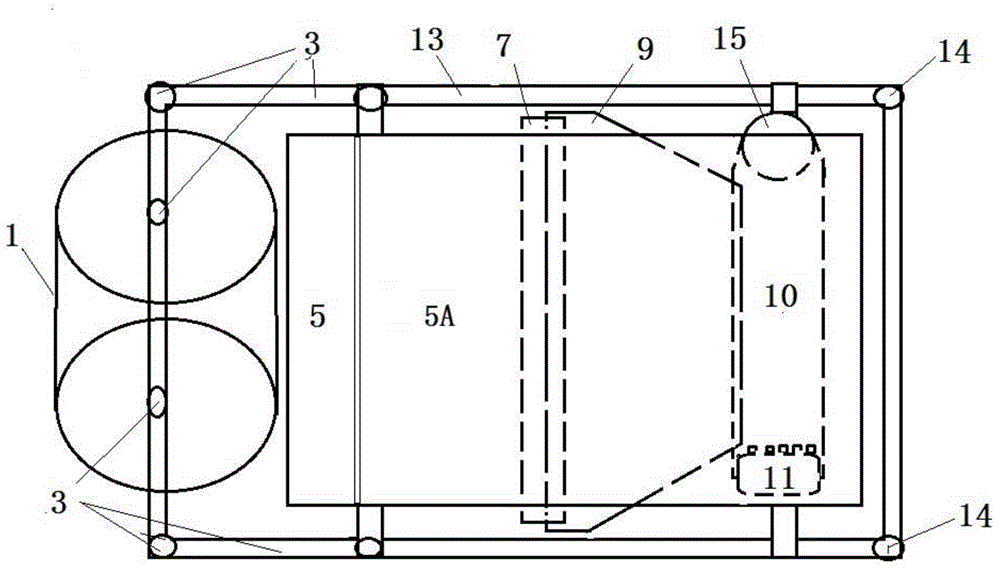
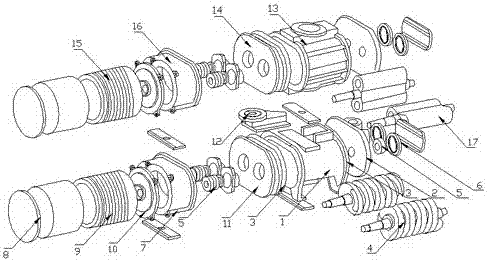
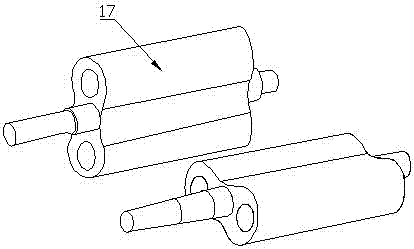
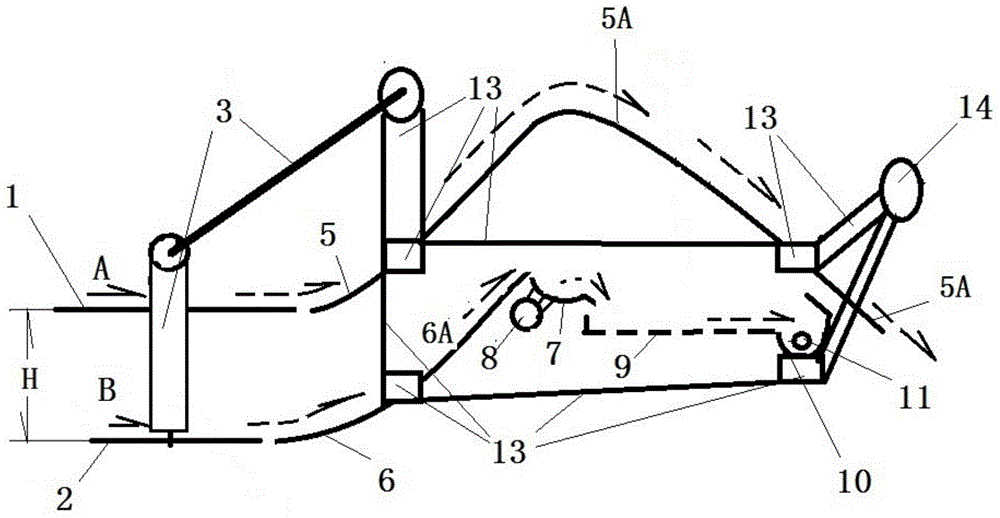
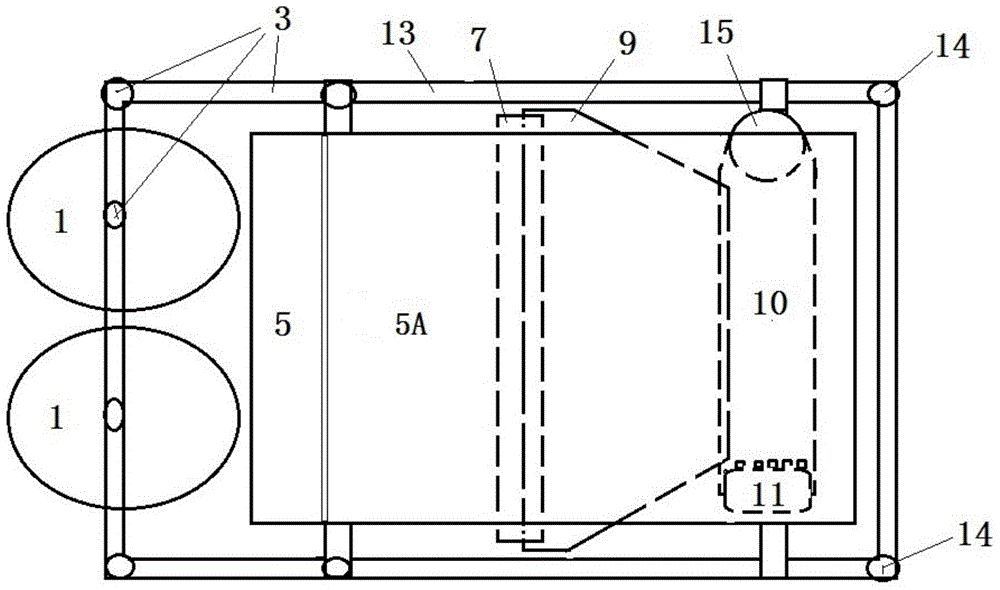
InactiveCN104145592ASolve the problem of limited power outputSmall horsepowerDiggersAgricultural engineeringSieve
The invention relates to a band saw structured hierarchical water chestnut picking shovel. The band saw structured hierarchical water chestnut picking shovel is characterized in that the picking shovel consists of an upper picking shovel and a lower picking shovel, the front end of the upper picking shovel is provided with a band saw structured upper picking cutting wheel (1), and an upper picking shovel passage (5) matched with the upper picking cutting wheel (1) is arranged behind the same and connected with a passage (5A); a band saw structured lower picking cutting wheel (2) is arranged at the front end of the lower picking shovel, and a lower picking shovel passage (6) matched with the lower picking cutting wheel (2), a passage (6A), a sieve hopper (7), a vibration sieve (9) and a collection tank (10) are sequentially arranged behind the lower picking cutting wheel (2). The band saw structured hierarchical water chestnut picking shovel has the advantages of simple structure, easiness in manufacturing, low cost, reliability in performance, effectiveness and the like.
Owner:廖煜明
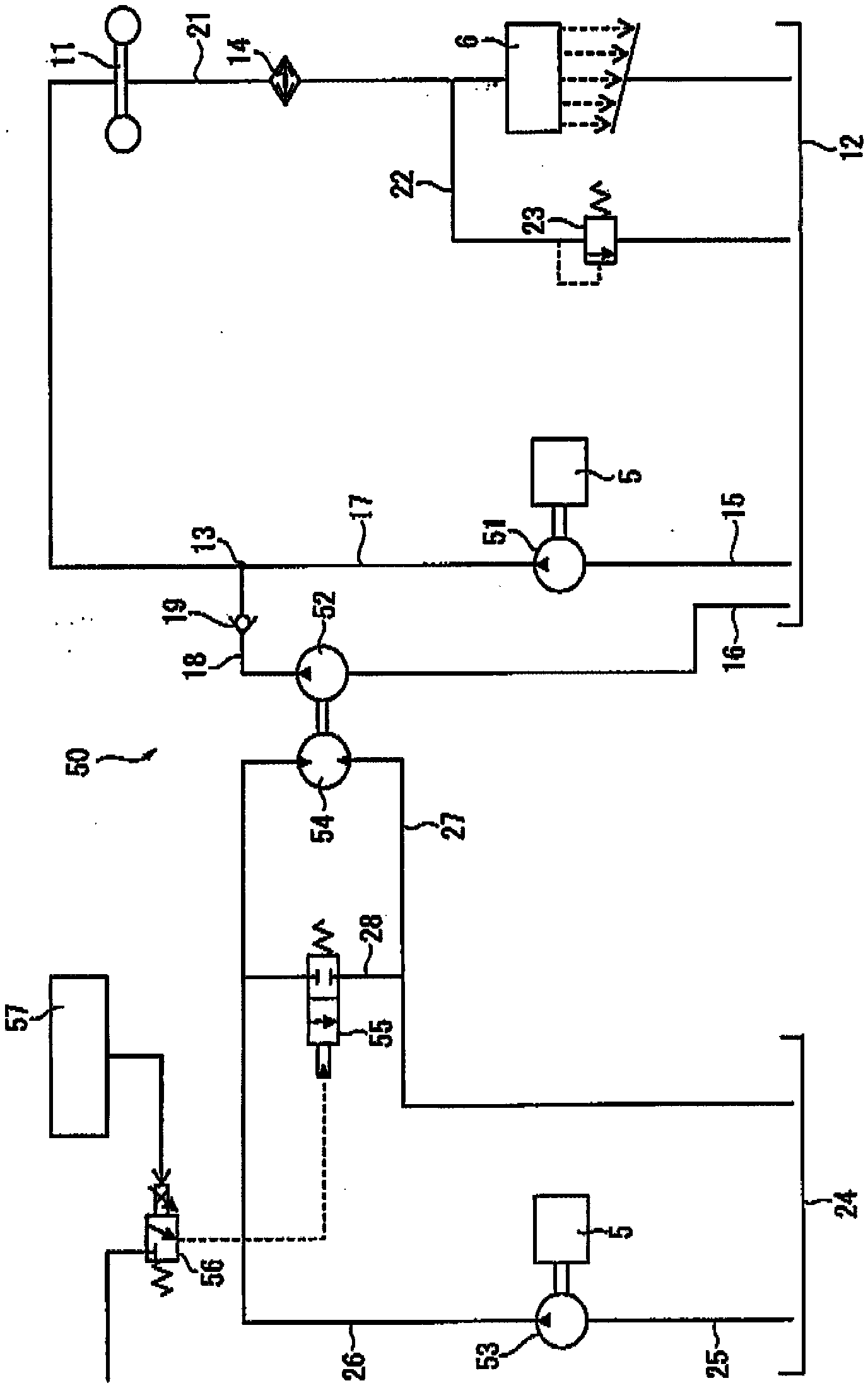
Dump truck
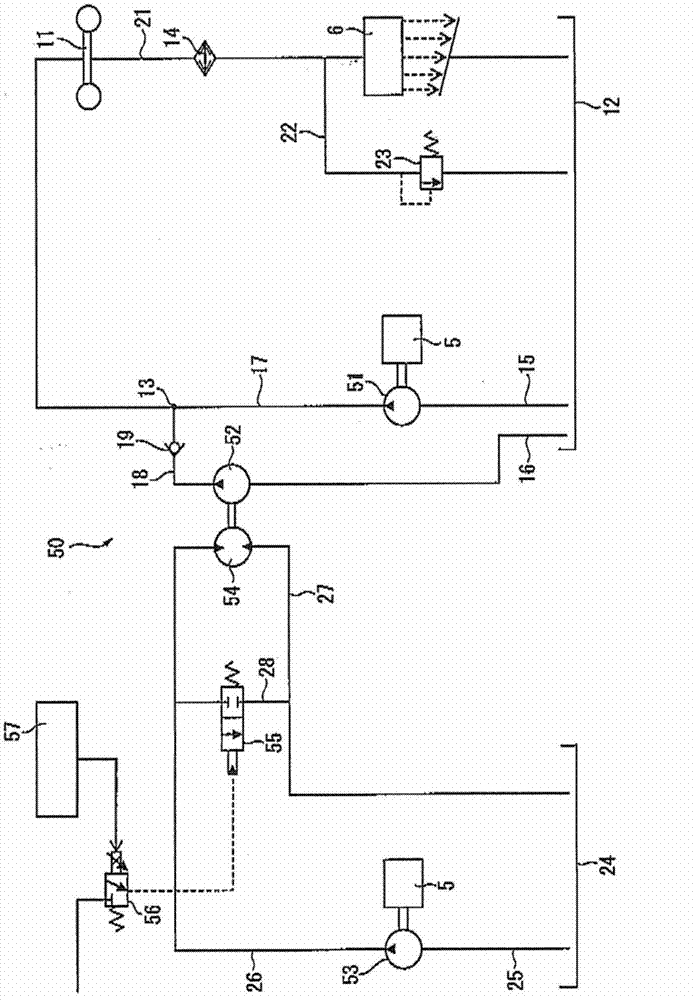
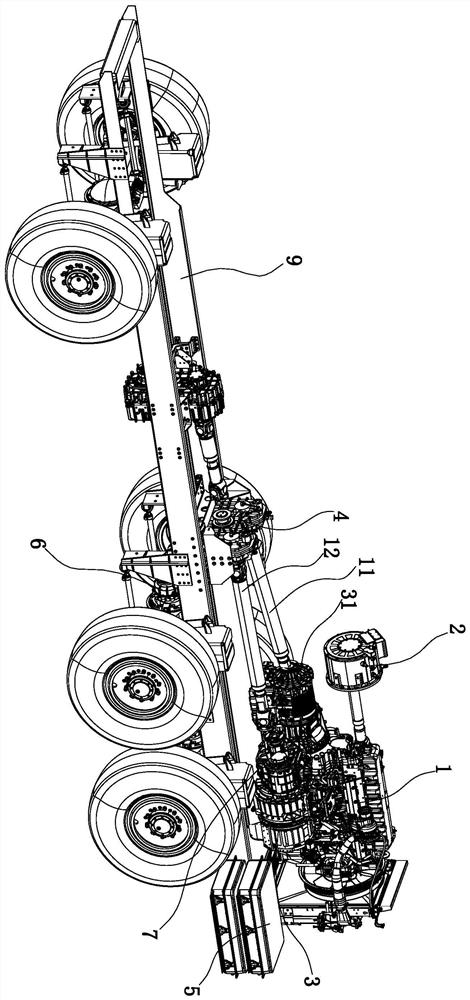
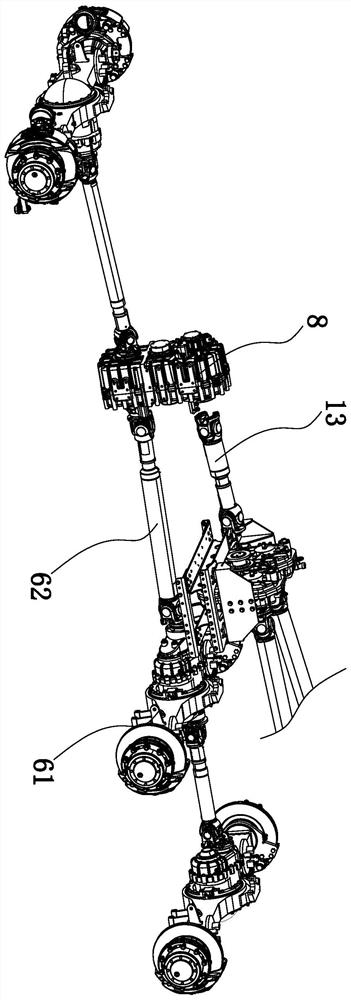
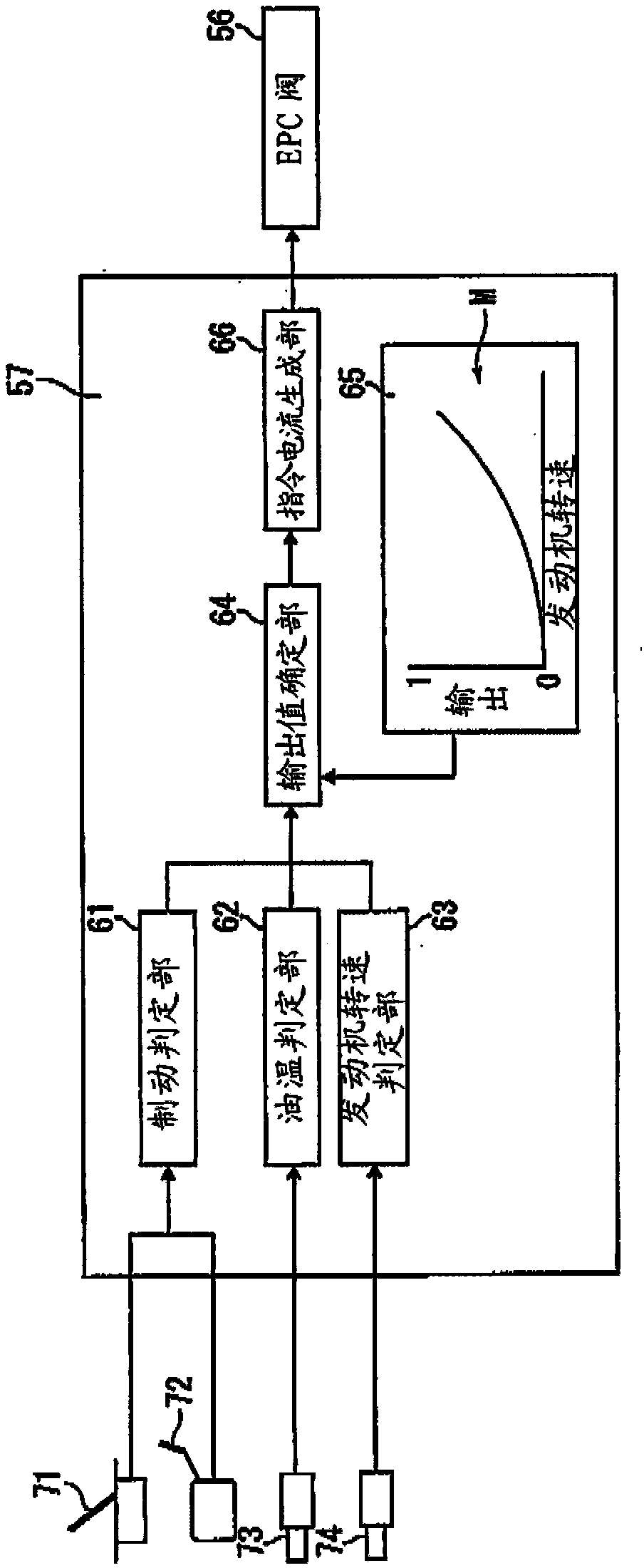
ActiveCN102959284APrevent leakageReduce internal pressureHydrostatic brakesGear lubrication/coolingHydraulic motorControl engineering
A dump truck includes: an oil-cooling center brake (11); a first hydraulic pump (51) supplying cooling oil to the center brake (11); a second hydraulic pump (52) supplying cooling oil to the center brake (11) in addition to the cooling oil from the first hydraulic pump (51); a hydraulic motor (54) driving the second hydraulic pump (52); a third hydraulic pump (53) supplying hydraulic oil to the hydraulic motor (54); an open / close valve (55) letting the hydraulic oil bypass the hydraulic motor (54); and a controller (57) controlling a bypass flow amount at the open / close valve (55). A capacity of the first hydraulic pump (51) corresponds to a flow amount of the cooling oil required to lubricate a transmission (6). A capacity of the second hydraulic pump (52) corresponds to a flow amount for compensating the cooling oil from the first hydraulic pump (51) when a brake is off. A capacity of the third hydraulic pump is smaller than the capacity of the second hydraulic pump (52).
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Boat lift brake apparatus
InactiveUS7090055B1Easy to operateSmall horsepowerSlipwaysWinding mechanismsEngineeringTorsion spring
A boat lift braking system includes a threaded shaft driven by the boat lift motor. A torsion tube disposed about the shaft carries an interiorly threaded nut that interengages the peripheral threads of the shaft. A rotor is mounted to the nut adjacent a brake pad that is supported by a ratchet component. A pawl mechanism cooperates with the ratchet component for limiting rotation of the ratchet component in a first direction and permitting rotation of the ratchet component about the shaft in a second direction. The torsion tube is connected through a reduction apparatus to the winder of the boat lift. When the lift is at rest, a torsion spring drives the torsion tube and rotor against the brake pad and the ratchet component interlocks with the pawl mechanism to hold the lift at a desired elevation. When the motor is driven to lower the lift, the shaft is driven within the torsion tube such that the rotor momentarily disengages the pad. Immediately thereafter, the torsion spring forces the rotor back against the pad and these counteracting forces continuously repeat to provide a controlled descent. When the motor is operated to raise the lift, the shaft is driven relative to the torsion tube such that the rotor and pad interlock. The ratchet component disengages the pawl and the torsion tube turns so that the lift can be elevated.
Owner:QUALITY BOAT ELEVATORS
Dry type spiral vacuum pump
InactiveCN107084135AFast exhaustSmall horsepowerRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsMachines/enginesWater vaporPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a dry-type screw vacuum pump. A pair of counter-rotating rotors are arranged inside the pump body. A high-pressure end plate is sleeved on a rotating shaft at one end of the rotor. A bearing is installed on the high-pressure end plate corresponding to the rotor, and a high-voltage bearing cover is installed on the outer side of the bearing. , the other end of the rotor is set with a low-pressure end plate, bearings are installed on the outside of the low-pressure end plate, the low-pressure end plate is connected to a gear box, the gear box is connected to a motor and an oil seal, the top of the motor is connected to a gear, and the gear is set at one end of the pump body. The top of the pump body is connected with a Lu-style booster pump, and the Lu-style booster pump is provided with a housing end plate assembly, a gear box assembly, a motor assembly and a Lu-style booster pump rotor. The beneficial effects achieved by the present invention are: effective solution When the existing dry screw vacuum pump pumps out a large amount of water vapor or other condensable gases, the exhaust speed decreases under the condition of maintaining low pressure, which wastes energy and damages the dry screw vacuum pump itself.
Owner:德耐尔节能科技(上海)股份有限公司
Potato harvester suitable for intercropping and interplanting
The invention discloses a potato harvester which is applicable to intercropping and interplanting; the potato harvester is characterized in that a rotation axis is arranged on the upper part of the front end of a frame; the left side and the right side of the frame are respectively hinged with a front swing rod and a rear rocking rod; a power transmission wheel and a clutch are arranged on the rotation axis; a power output wheel of a hand tractor transmits the power for the rotation axis; two ends of the rotation axis are respectively provided with a crank connecting rod mechanism; the connecting rods of the two crank connecting rod mechanism are respectively hinged at the top ends of the two rocking rods; the two sides of the front end of the screen sieve are hinged at the bottom ends of the two rocking rods and the rear end of the screen sieve is suspended at the rear end of the frame; digging shovel ends are respectively fixed at the bottom ends of the two front swing rods which are hinged with the rear rocking rods by cross connecting rods so as to lead the digging shovel and the screen sieve to swing together back and forth in parallel; the optimum frequency of the back and forth swing is 35 to 50 times / min and the back and forth swing amplitude is 8 to 10cm. The application has compact structure and small volume, can be applicable to the situations of the dry, wet, soft or hard soil and the like and is applicable to harvesting the potatoes with intercropping and interplanting.
Owner:郭庆才
Disc rotary cutting stratifying excavation water chestnut machine
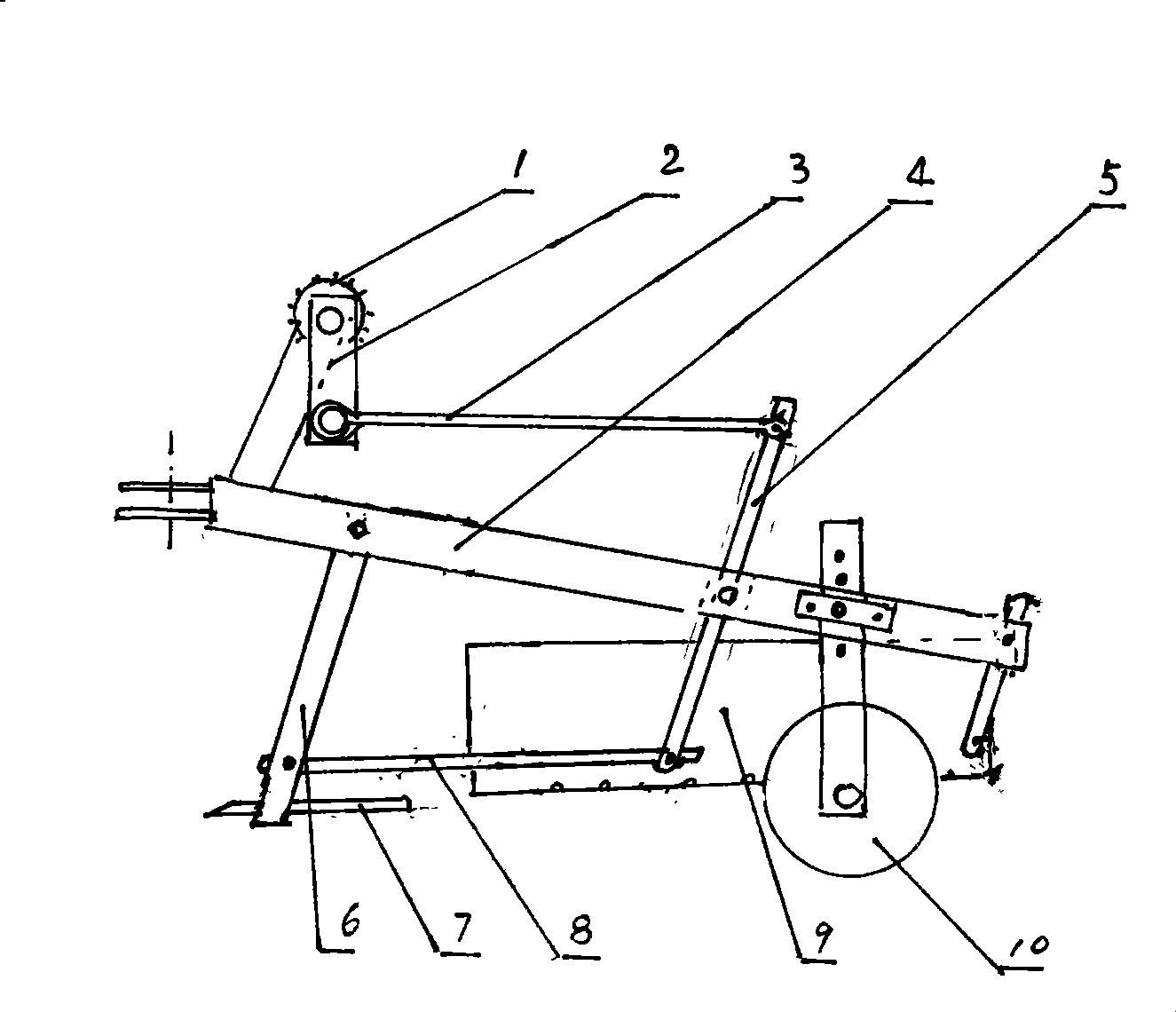
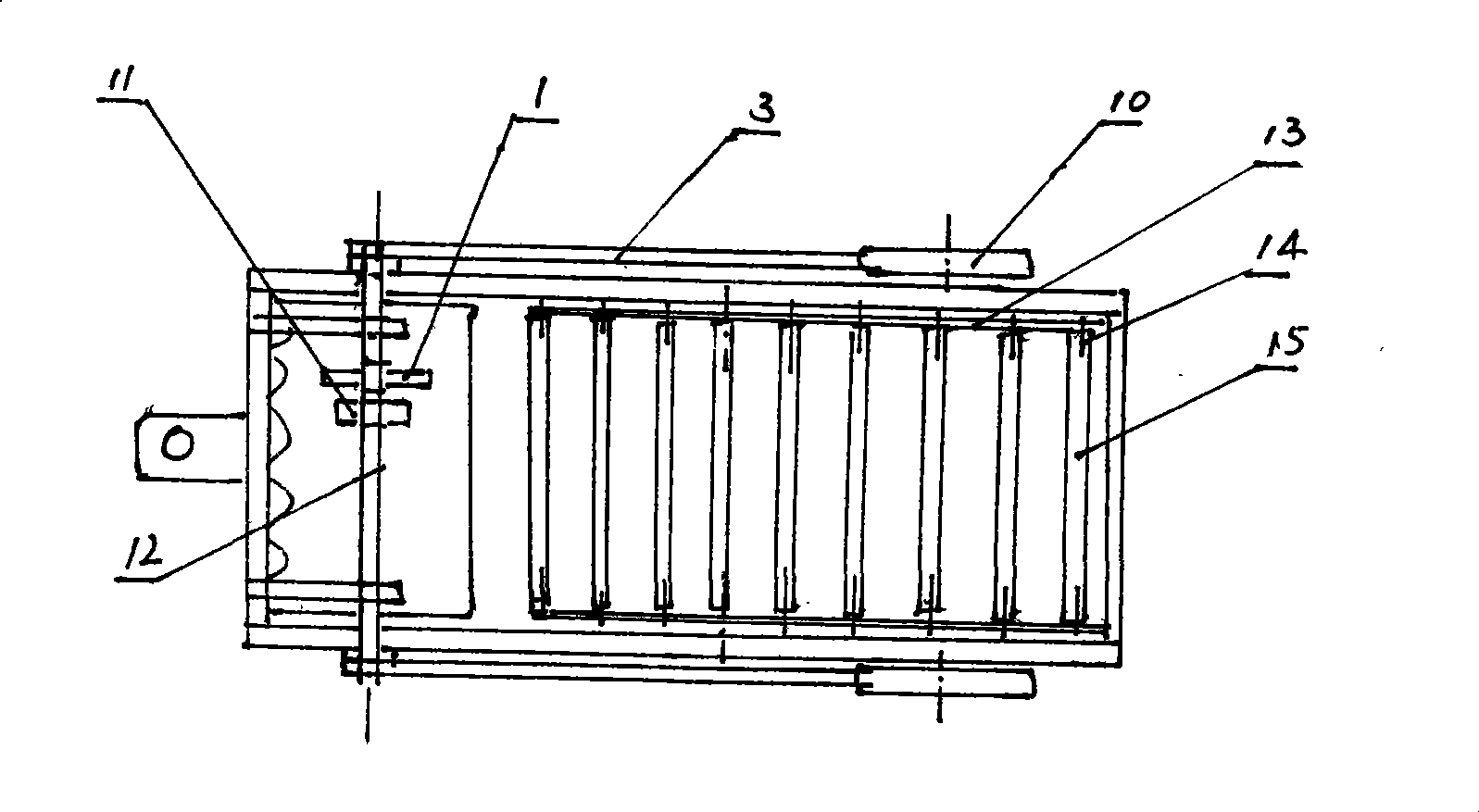
InactiveCN104145596ASolve the problem of limited power outputSmall horsepowerLiftersTopping machinesCircular discWater Chestnuts
The invention discloses a disc rotary cutting stratifying excavation water chestnut machine comprising an excavation shovel connected and combined with a power machine through a drive arm joint by the existing technology. The excavation shovel includes upper and lower shovel units, the front end of the upper shovel unit is provided with an upper excavation cutting wheel (1) composed of at least one disc saw, an upper excavation shovel channel (5) matched with the upper excavation cutting wheel (1) is arranged behind the upper excavation cutting wheel (1), and the upper excavation shovel channel (5) is connected to a channel (5A); the front end of the lower shovel unit is provided with a lower excavation cutting wheel (2) composed of at least one disc saw, a lower excavation shovel channel (6), a passage (6A), a meshed hopper (7), a vibration screen (9) and a collecting groove (10) which match with the lower excavation cutting wheel (2) are sequentially arranged behind the lower excavation cutting wheel (2). The machine has the advantages of simple structure, easiness for manufacture, low cost, reliable performance and fine effect.
Owner:廖煜明
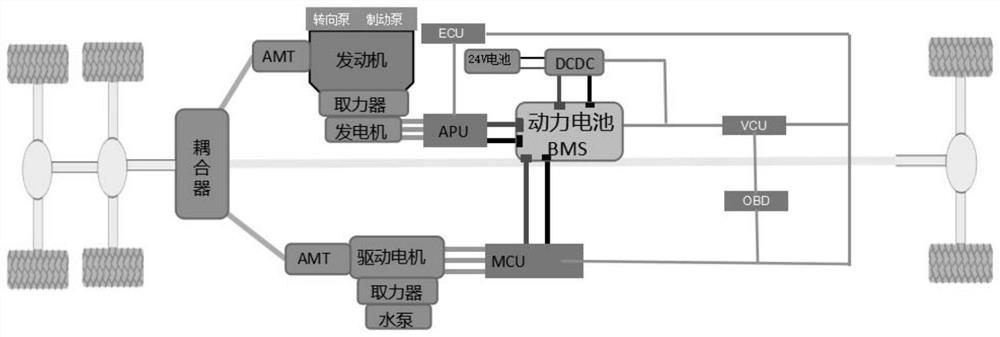
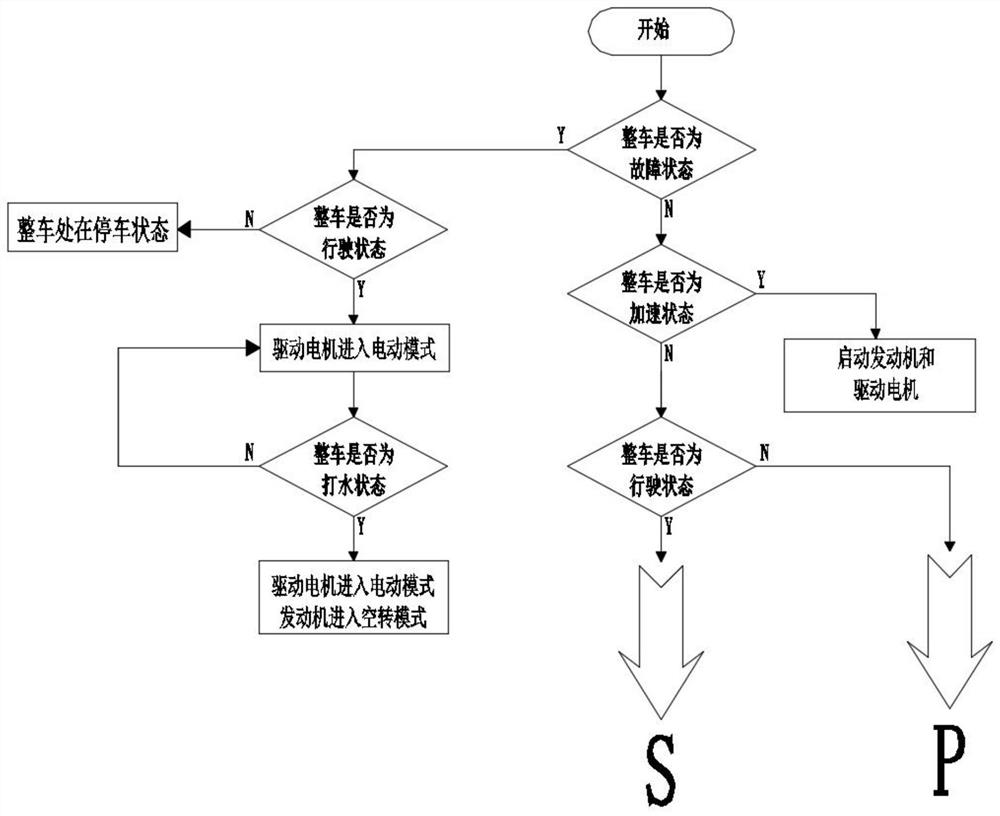
Parallel oil-electricity hybrid airport fire fighting truck chassis
PendingCN112124063ASolve the problem of poor startup acceleration performanceImprove acceleration performanceHybrid vehiclesElectrodynamic brake systemsPower couplingPower battery
The invention relates to the technical field of fire fighting, in particular to a parallel oil-electricity hybrid airport fire fighting truck chassis which comprises a chassis frame wheel frame and awater pump; the fire fighting truck chassis further comprises an engine, a driving motor, a power coupling box, an electric generator in transmission fit with the engine and a power battery; the output end of the engine is in transmission connection with a speed changing box, the output end of the speed changing box is in transmission connection with a first transmission shaft, the output end of the driving motor is in transmission connection with a second transmission shaft, the first transmission shaft and the second transmission shaft are both in transmission connection with the power coupling box, and the output end of the power coupling box is in transmission connection with a third transmission shaft; and the other end of the third transmission shaft is in transmission connection with a full-drive transfer case, and the electric generator and the driving motor are both electrically connected with the power battery. According to the parallel oil-electricity hybrid airport fire fighting truck chassis, the engine and the driving motor are connected in parallel for hybrid driving, so that the problem that the starting acceleration performance of the engine is poor is solved, theacceleration performance is improved, and the emission is reduced.
Owner:芜湖安行汽车科技有限公司
Split radiator maximizing entering temperature differential
InactiveUS7506618B1Heat dissipationPrevent radial convective scrubbingLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlTurbochargerEngineering
A heat exchanger is provided for dissipating heat from a dual turbocharged engine. The heat exchanger has a jacket water cooler, and first and second charge air coolers. The three coolers are arranged in parallel enabling each to operate with a maximum temperature differential, and have fronts that lie in parallel planes. Charge air from a first turbocharger is directly piped to the first charge air cooler, and charge air from the second turbocharger is directly piped to the second charge air cooler. A first baffle is between and upstream of the first charge air cooler and the jacket water cooler. A second baffle is between and upstream of the second charge air cooler and the jacket water cooler. The baffles can direct selected amounts of air to each of the three coolers and prevent radial convective scrubbing. A fuel oil cooler can also be provided.
Owner:IEA
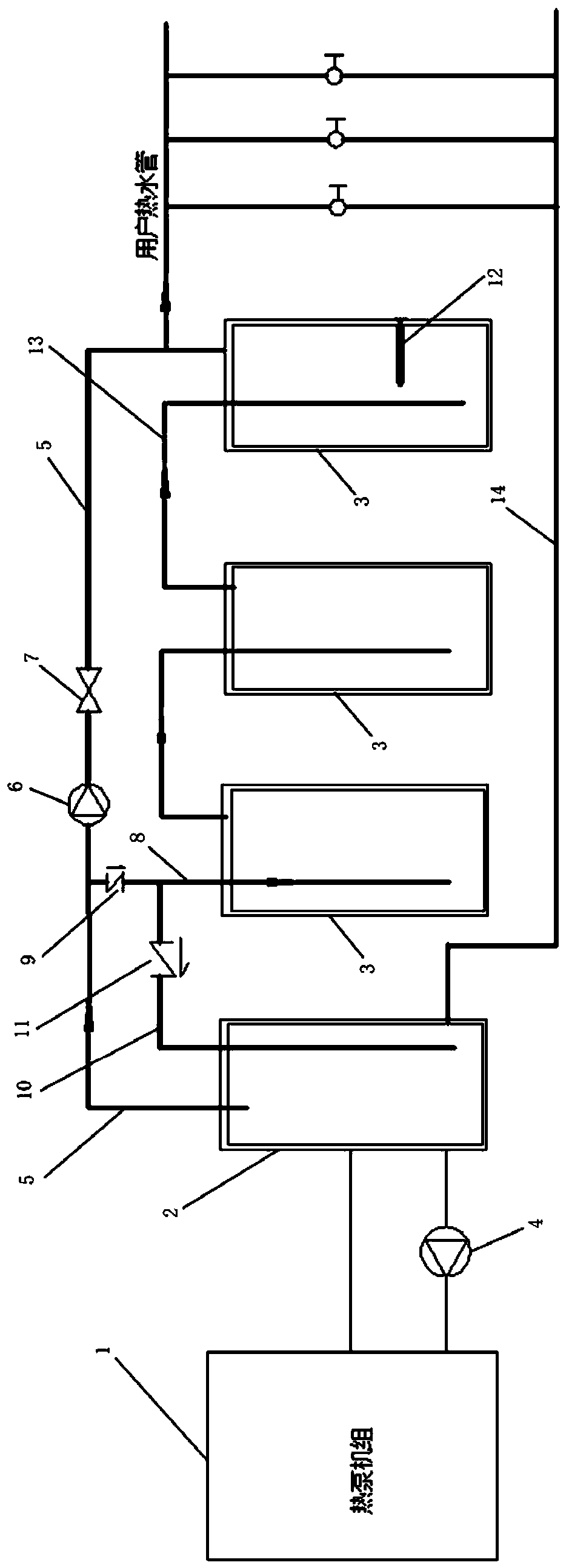
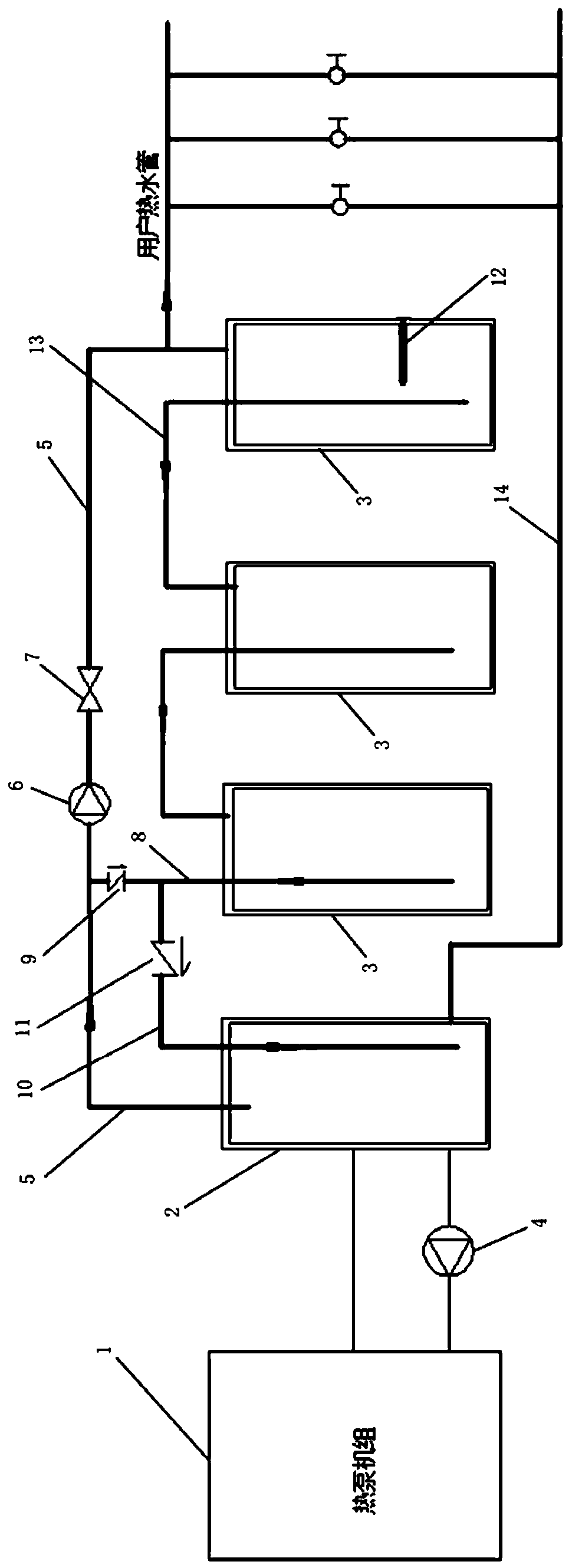
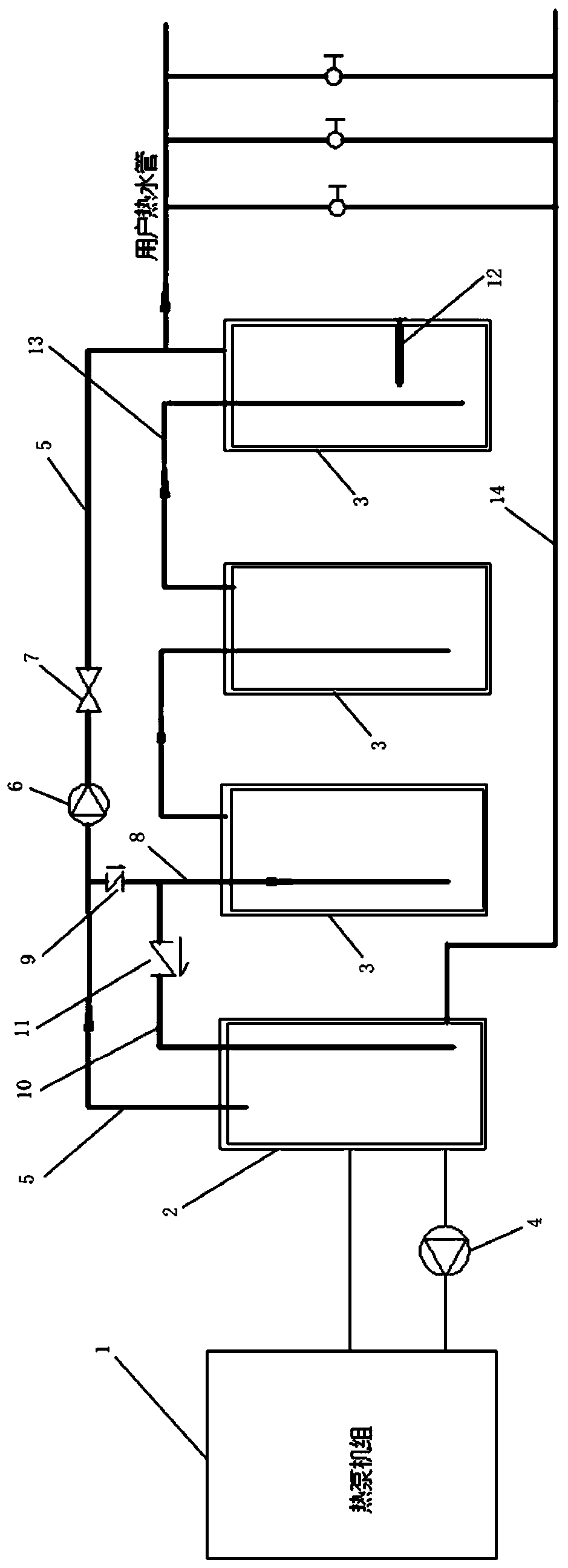
Novel pressure-bearing type hot water system
PendingCN111322659AIt is not easy to appear the phenomenon of hot and coldReduce initial investment costSpace heating and ventilation detailsWater heatersEnvironmental engineeringThermal water
The invention relates to a novel pressure-bearing type hot water system comprising a hot water device, a primary water tank and a secondary water tank; a hot water outlet of the hot water device is connected with the primary water tank, and a cold water inlet of the hot water device is connected with the primary water tank through a first circulating water pump; a hot water supply pipe is arrangedon the primary water tank, a second circulating pump is installed on the hot water supply pipe, the water outlet end of the circulating pump is connected with an electromagnetic valve, a first bypasspipe is arranged on the side, at the water inlet end of the second circulating pump, of the hot water supply pipe, and a first one-way valve is arranged on the first bypass pipe; a second bypass pipeconnected with the primary water tank is arranged on the side, at the water outlet end of the first one-way valve, of the first bypass pipe; a second one-way valve is arranged on the second bypass pipe; and the primary water tank is provided with a water replenishing port for replenishing water, and the secondary water tank is provided with a water outlet for connecting a hot water pipe of a user. The phenomenon that the temperature is suddenly cooled and suddenly heated when the user uses hot water is not easy to appear to the hot water system.
Owner:江苏光芒新能源股份有限公司
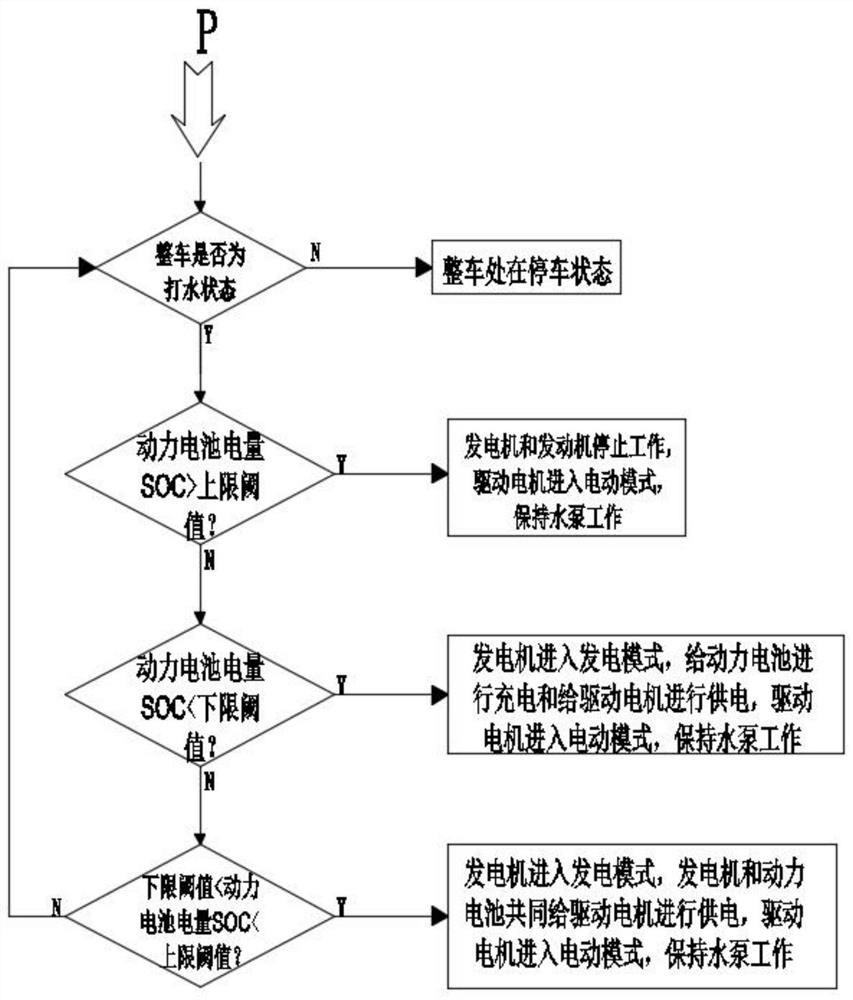
An electronic control system for the chassis of a parallel oil-electric hybrid airport fire truck
ActiveCN112109696BSolve the problem of poor startup acceleration performanceImprove acceleration performanceHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingPower batteryElectric machinery
The present invention relates to the technical field of fire trucks, in particular to an electric control system for the chassis of a parallel oil-electric hybrid airport fire truck, including steps: S1: start the engine and drive the motor to drive the chassis; S2: drive the engine to drive the chassis, and drive the motor The clutch is disconnected from the transmission system of the chassis, and the water pump is driven by the power take-off, and the driving motor is electrically connected to the power battery, and enters step S3; S3: If the SOC of the power battery is greater than the upper limit threshold, the engine drives the chassis, and the generator assists the power battery Supply power to the drive motor; if the power battery SOC is less than the lower threshold, the engine drives the chassis, and the generator charges the power battery and supplies power to the drive motor; if the lower threshold < power battery SOC < the upper threshold, the engine drives the chassis, and the power battery assists The generator supplies power to the drive motor, and the invention solves the problem of poor starting and accelerating performance of the engine, ensures no engine exhaust emission when the car is in the garage, and reduces the overall cost.
Owner:芜湖安行汽车科技有限公司
Dump truck
ActiveCN102959284BReduce consumptionReduced horsepower consumptionHydrostatic brakesGear lubrication/coolingHydraulic motorControl engineering
A dump truck includes: an oil-cooling center brake (11); a first hydraulic pump (51) supplying cooling oil to the center brake (11); a second hydraulic pump (52) supplying cooling oil to the center brake (11) in addition to the cooling oil from the first hydraulic pump (51); a hydraulic motor (54) driving the second hydraulic pump (52); a third hydraulic pump (53) supplying hydraulic oil to the hydraulic motor (54); an open / close valve (55) letting the hydraulic oil bypass the hydraulic motor (54); and a controller (57) controlling a bypass flow amount at the open / close valve (55). A capacity of the first hydraulic pump (51) corresponds to a flow amount of the cooling oil required to lubricate a transmission (6). A capacity of the second hydraulic pump (52) corresponds to a flow amount for compensating the cooling oil from the first hydraulic pump (51) when a brake is off. A capacity of the third hydraulic pump is smaller than the capacity of the second hydraulic pump (52).
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Method for purifying exhaust gas by micronizing washing liquid and matching disturbance flow
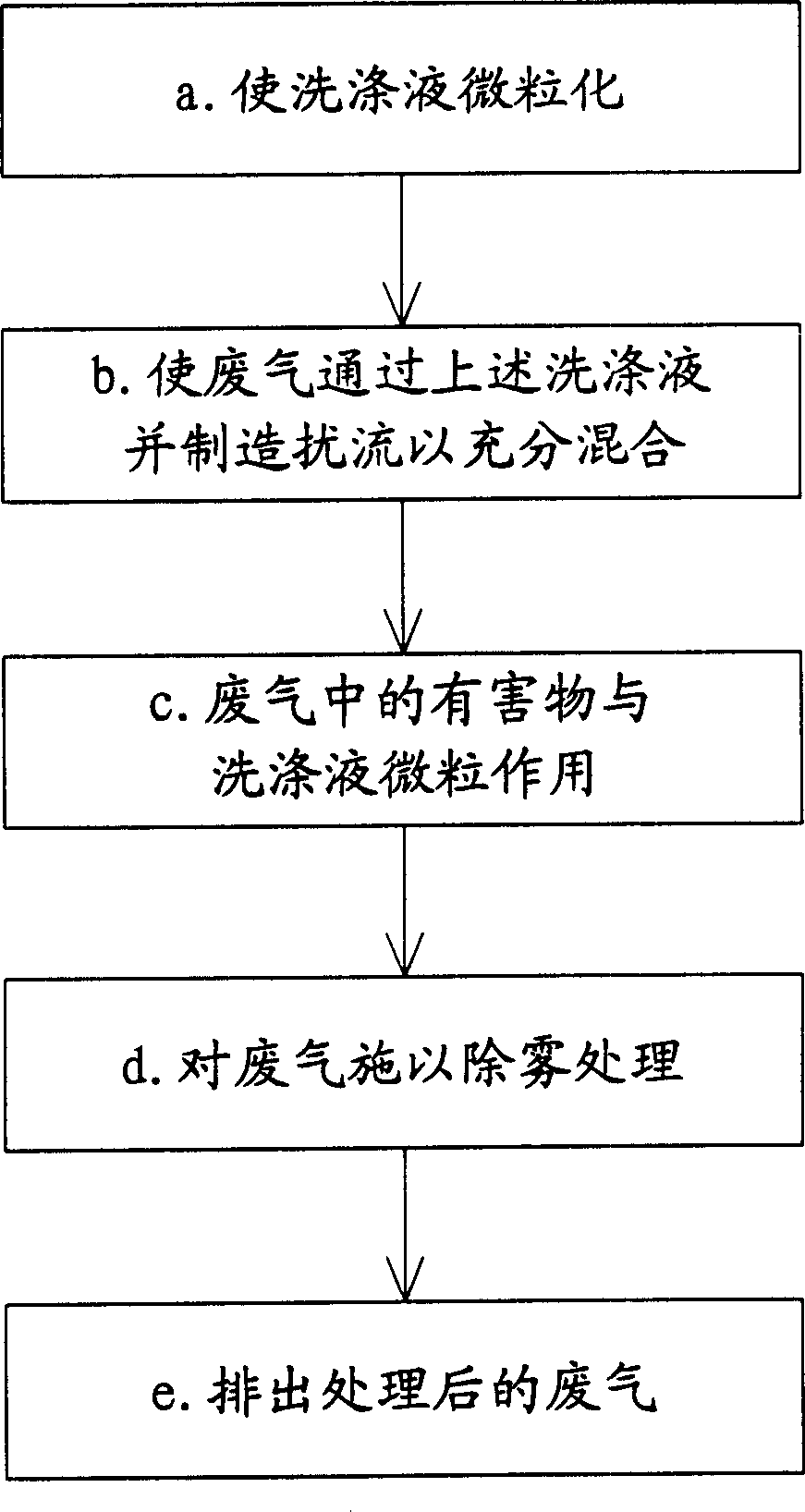
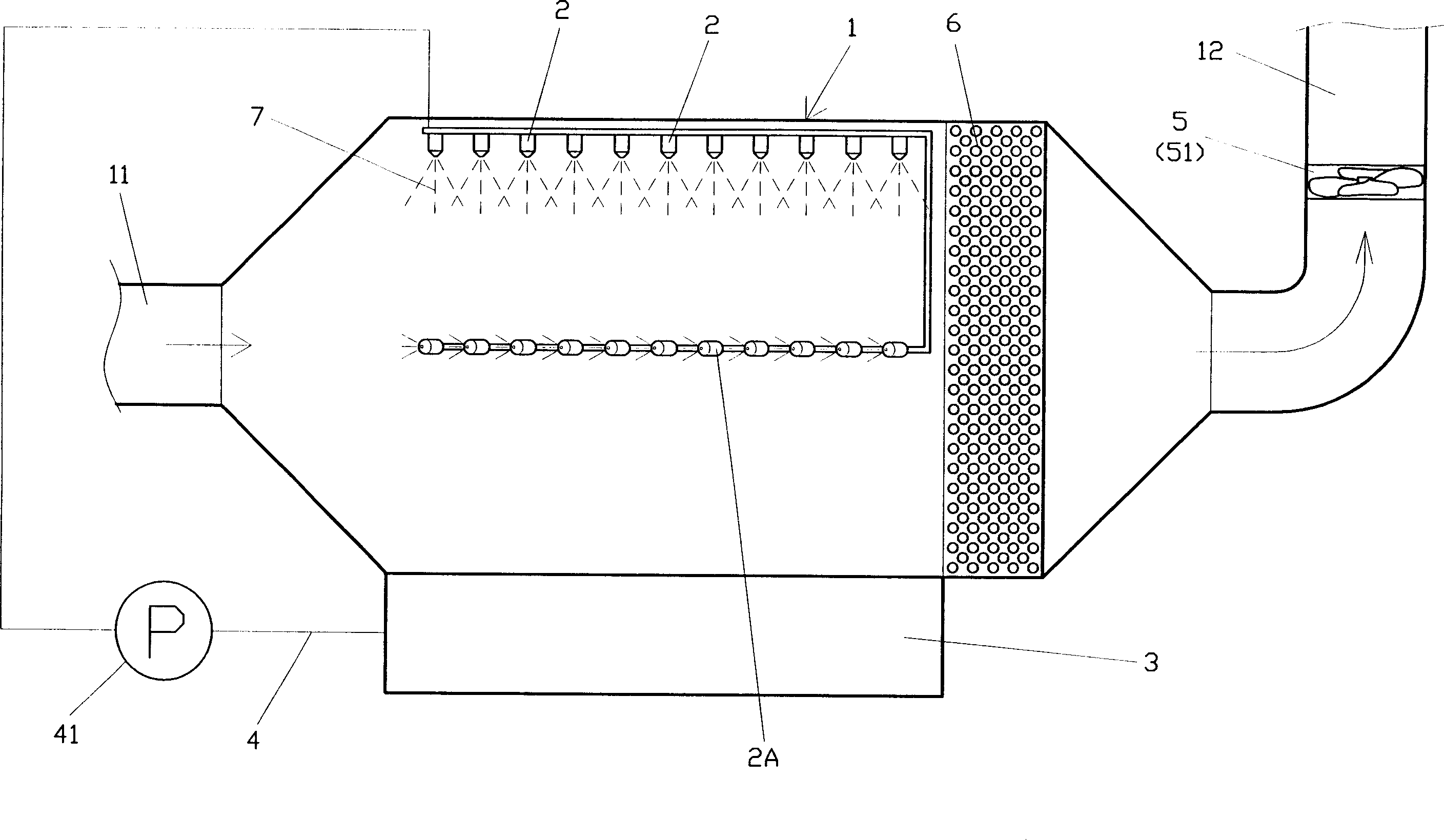
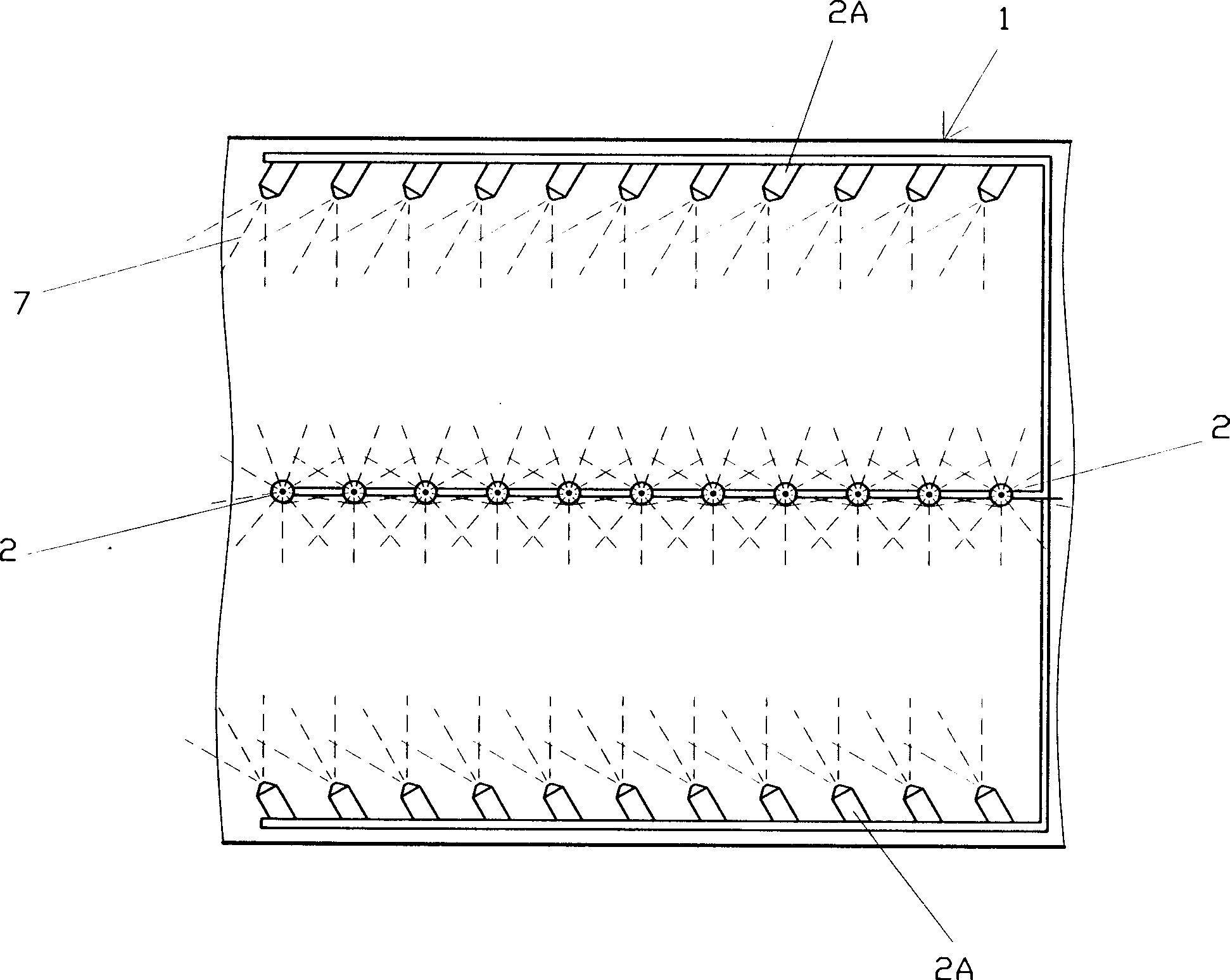
InactiveCN1899673AReduce usageSave operating costsDispersed particle separationEnvironmental engineeringExhaust gas
The process of purifying exhausted gas with micronized washing liquid and matched disturbance flow includes the following steps: 1. micronizing washing liquid; 2. passing waste gas through the micronized washing liquid and forming disturbance flow for well mixing; 3. reacting the harmful matters in the waste gas and the micronized washing liquid; demisting the waste gas; and 5. exhausting the purified waste gas. The waste gas purifying process has no need of filler and low power consumption.
Owner:林文豪 +1
Rotating continuous mixing machine
InactiveCN101099925BReasonable structureImprove mix qualityRotating receptacle mixersTransportation and packagingAgricultural engineeringContinuous mixing
The present invention discloses one kind of continuous rotary mixing machine, which includes one frame, rollers on the frame, one sandwiched cylinder possessing material inlet, material outlet and one jacket with steam inlet and steam outlet, spiral mixing blades fixed longitudinally on the inner wall of the cylinder, and one discharging unit set to the material outlet. The present invention has reasonable structure, high mixing quality and high mixing speed.
Owner:南通罗斯混合设备有限公司
Reciprocating Bounce Machine
The invention relates to a reciprocating bouncing exercise machine, comprising: pedals for users to stand on; a base located below the pedals; a driving device installed on the base, which includes: a motor, a speed reduction mechanism, an eccentric shaft and a transmission A connecting rod; and a buffer energy-saving mechanism, including: a plurality of guide posts, vertically fixed on the base and symmetrical to the center of the pedal; and a plurality of buffer accumulators, matched with a plurality of guide posts, each The buffer accumulator can move back and forth along the corresponding guide column, so that it can store part of the kinetic energy to provide a cushioning function when the pedal approaches the base downward, and can release the stored energy to provide a lift when the pedal leaves the base upward. Lifting auxiliary force. The reciprocating bouncing machine of the present invention has the effects of reducing the impact and wear on the structure, saving the energy consumption of the driving device, and prolonging the service life of the machine.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FEI EXERCISE & MASSAGER EQUIP
Orchard ditcher
InactiveCN104350841AComply with planting agronomic requirementsSmall horsepowerPlantingFurrow making/coveringAgricultural scienceAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a ditcher and relates to an orchard ditcher. The orchard ditcher is characterized by comprising a traction frame (1), wherein a guide rail (3) and a resistance plate guide pipe (20) are arranged on the traction frame (1), a sliding device (4) slides on the guide rail (3) and is fixedly connected with a plow standard (5), the plow standard (5) is fixedly connected with a plow body (6), one end of a thrusting oil cylinder (9) is articulated with a connecting rod (10), the other end of the thrusting oil cylinder (9) is articulated with the sliding device (4), one end of a push-down oil cylinder (21) is articulated with the traction frame (1), the other end of the push-down oil cylinder (21) is articulated with a resistance plate (2), and the resistance plate (2) is arranged inside the resistance plate guide pipe (20). The orchard ditcher can be used for reducing the requirement on the operating space while ensuring the operating efficiency, required power is low, the energy consumption is reduced and the orchard ditcher is suitable for orchard operations.
Owner:郭健
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com