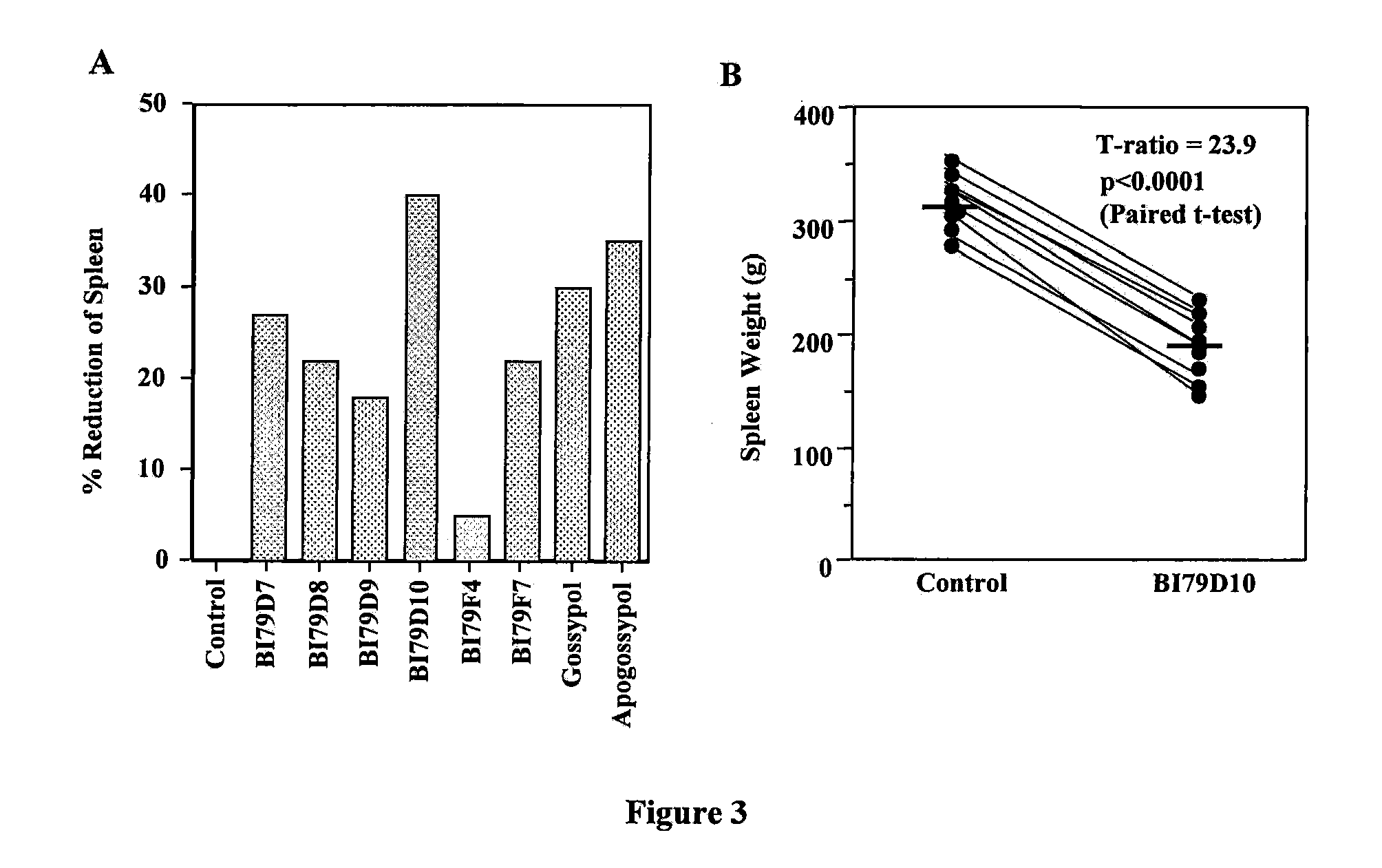
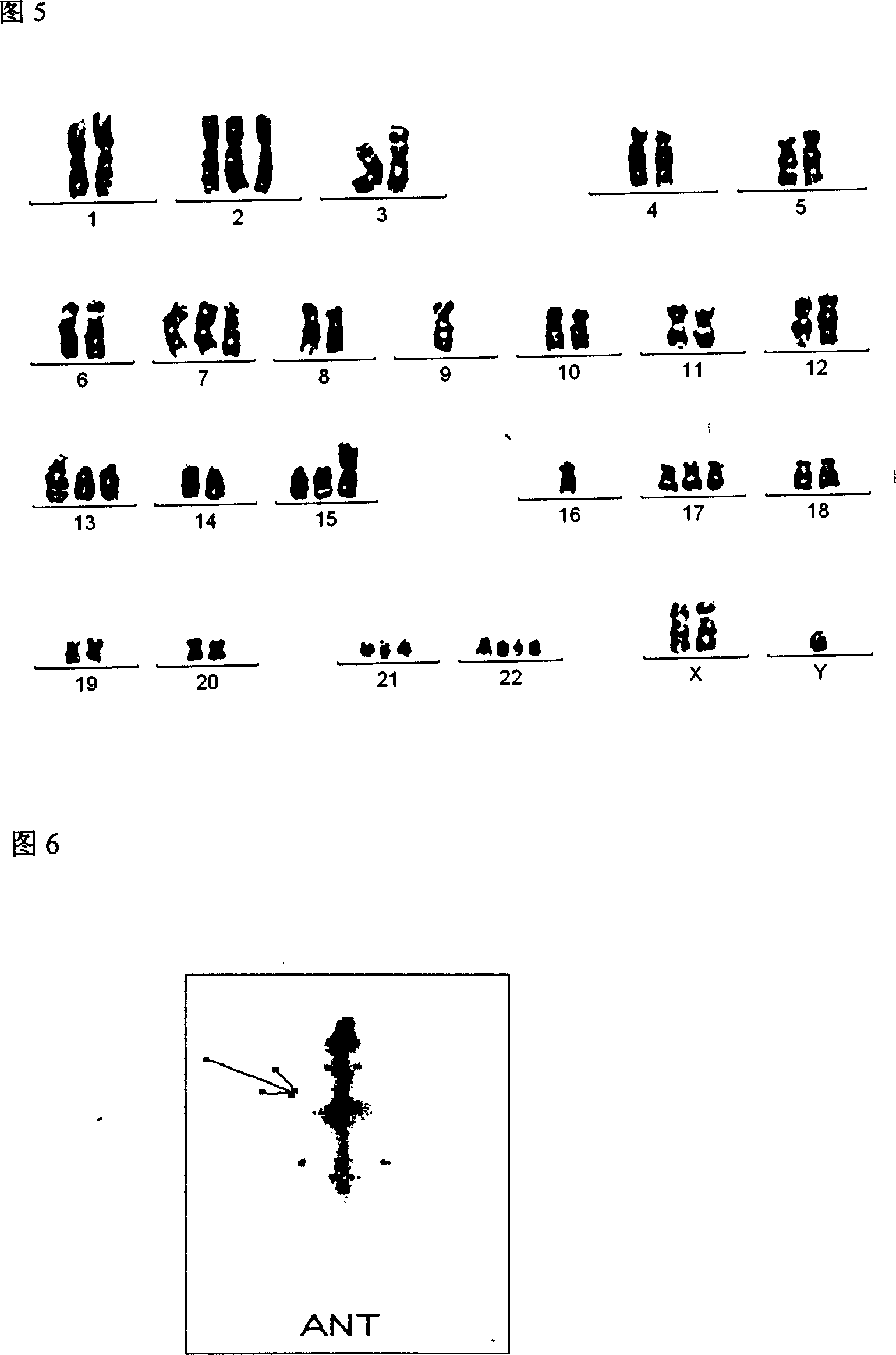
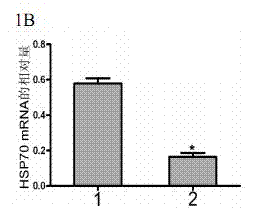
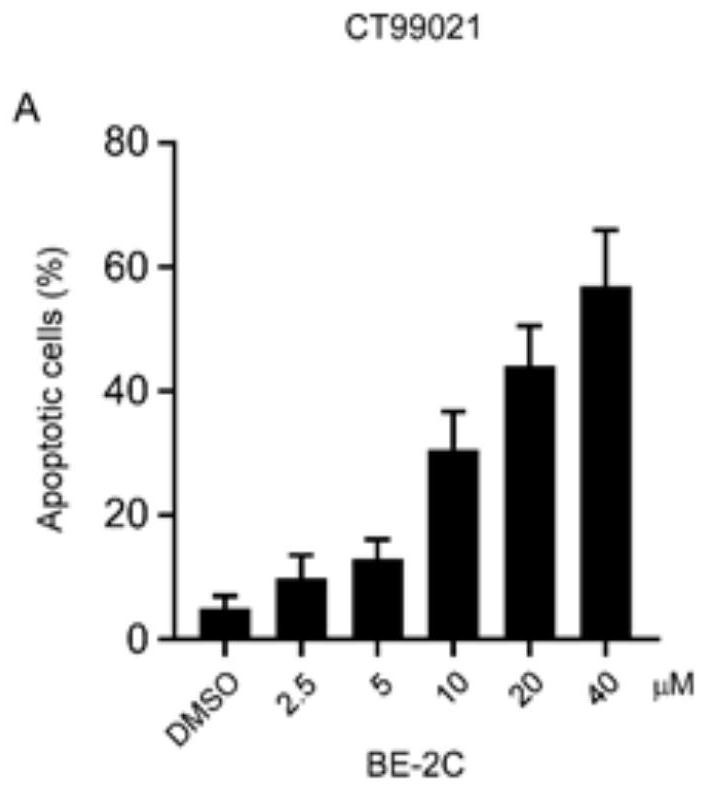
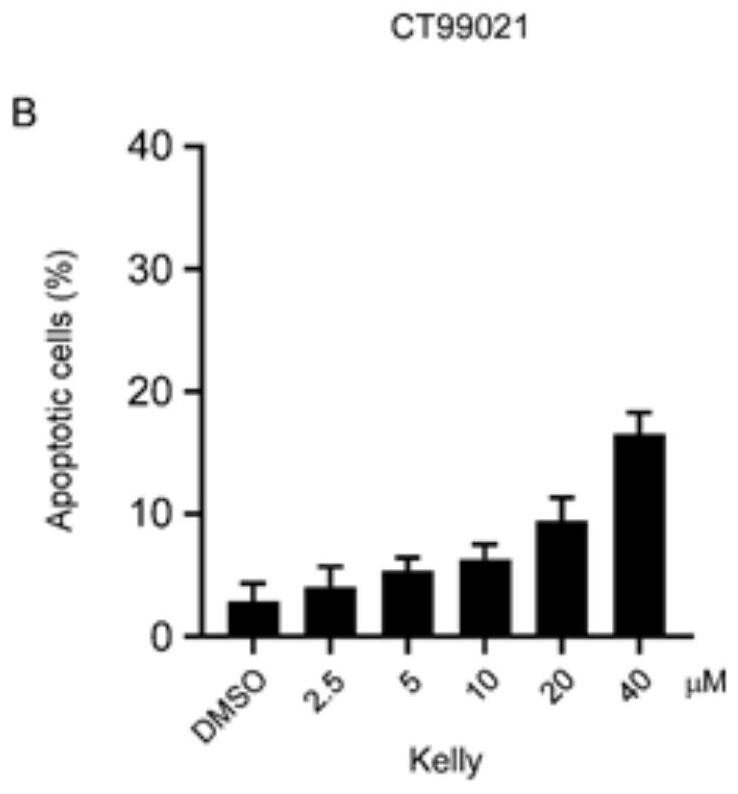
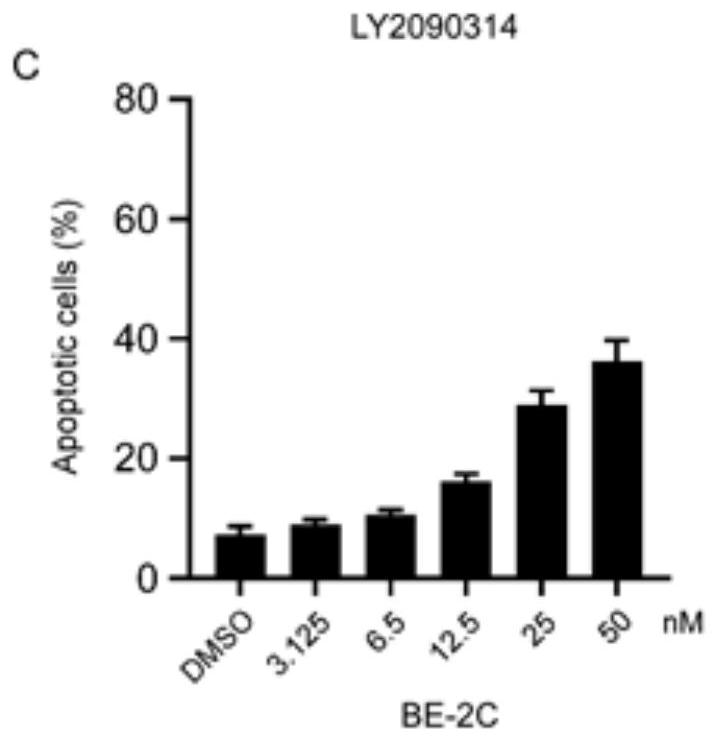
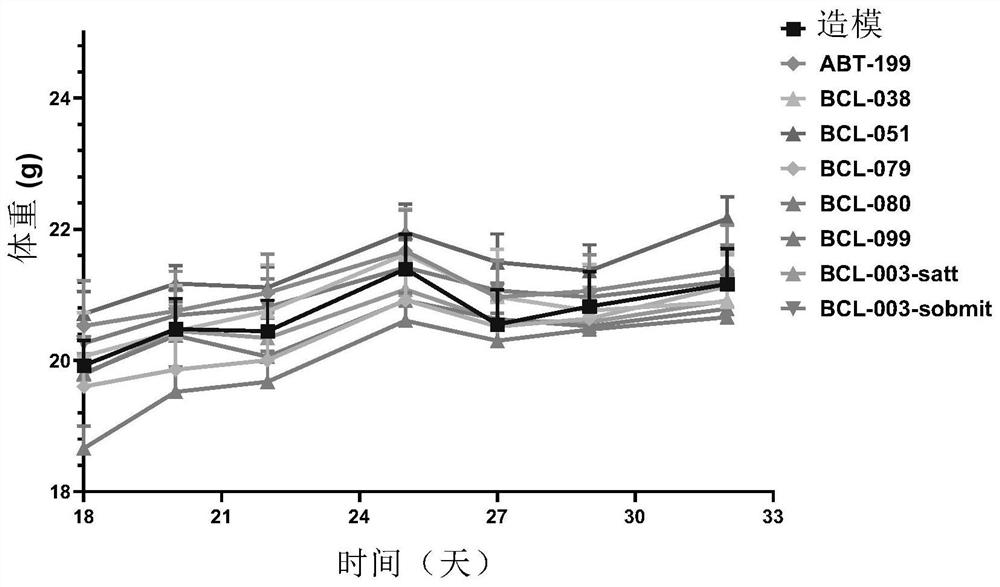
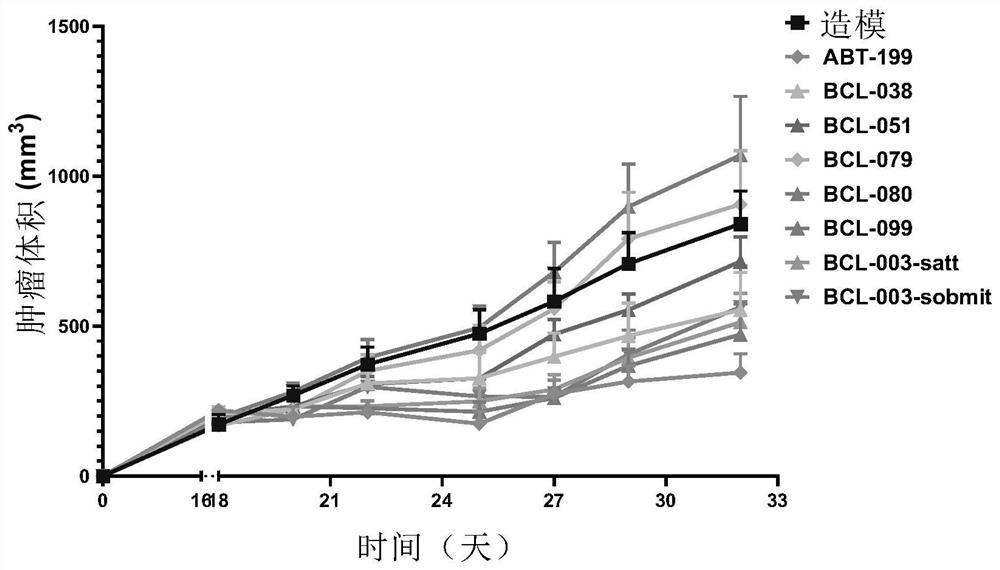
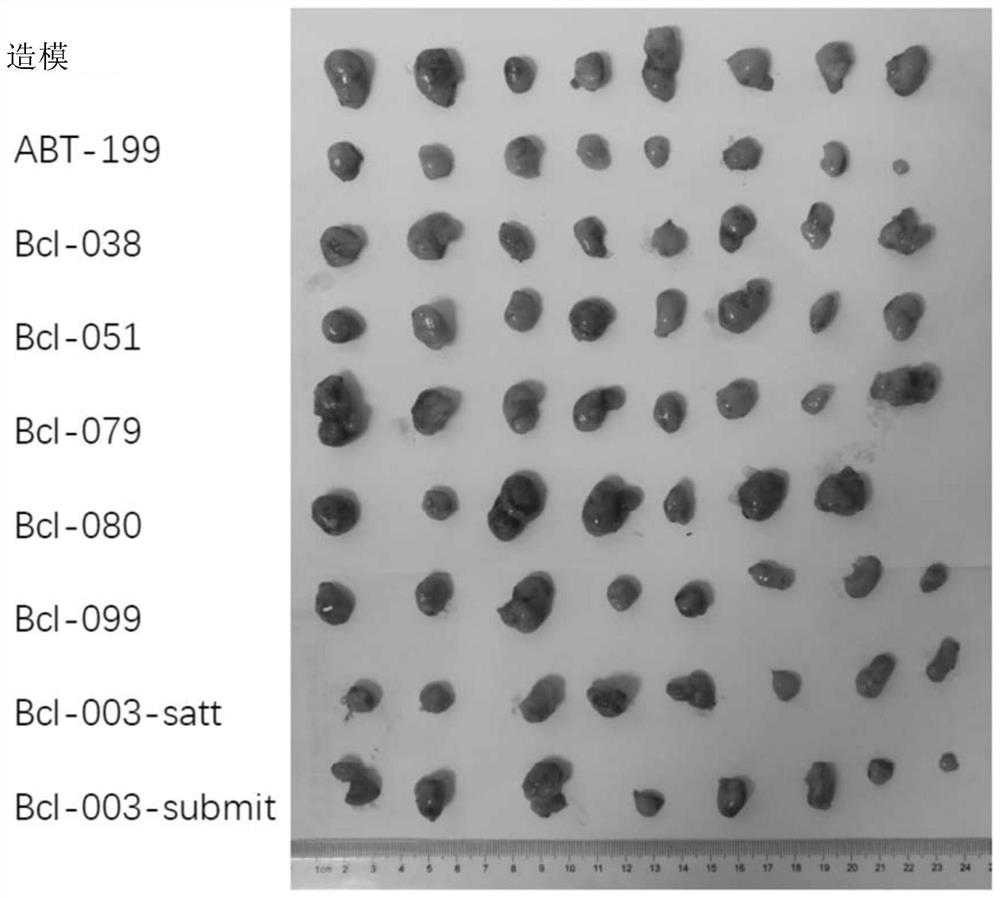
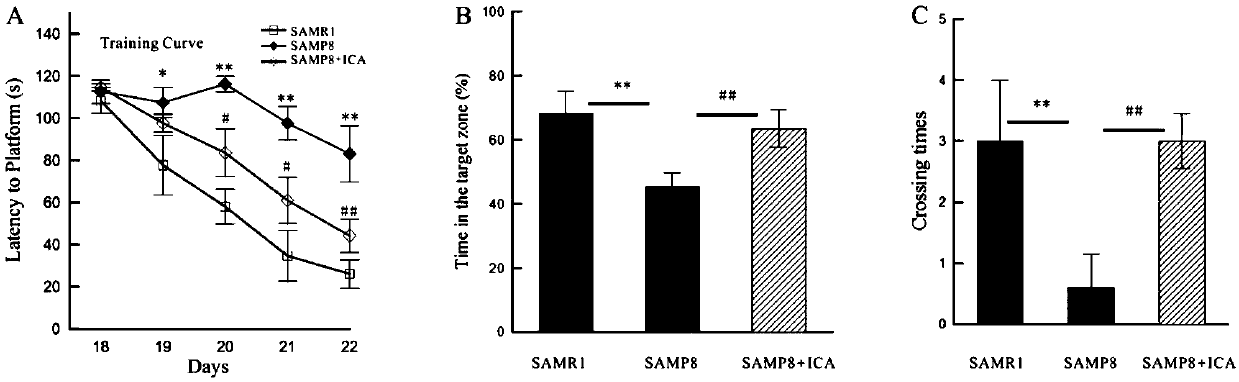
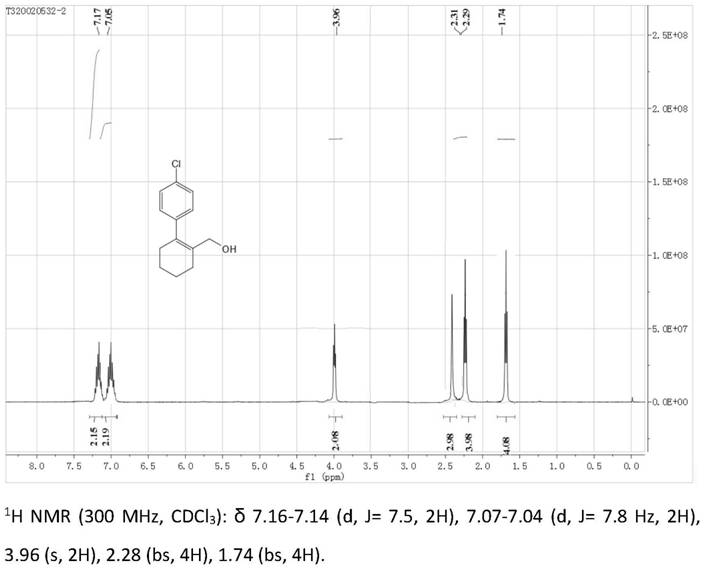
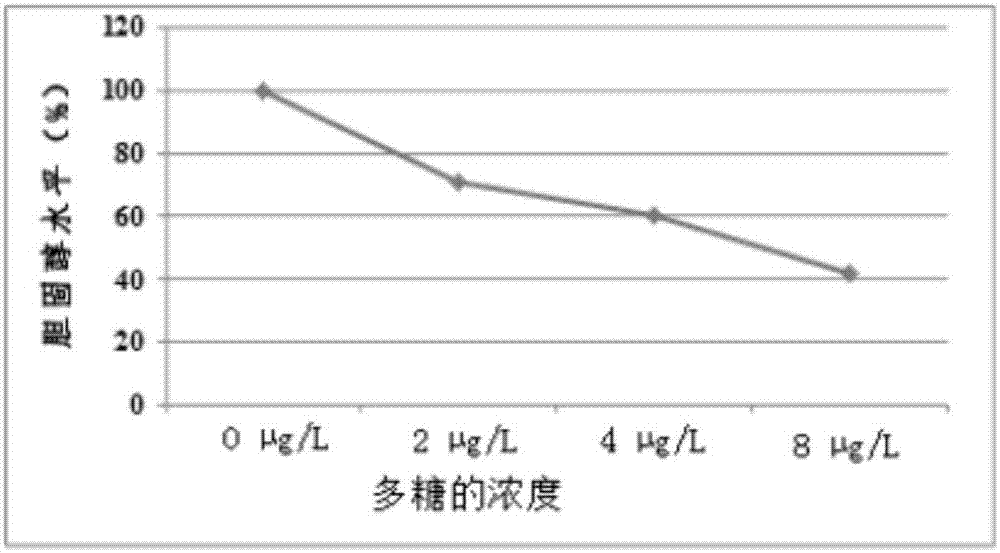
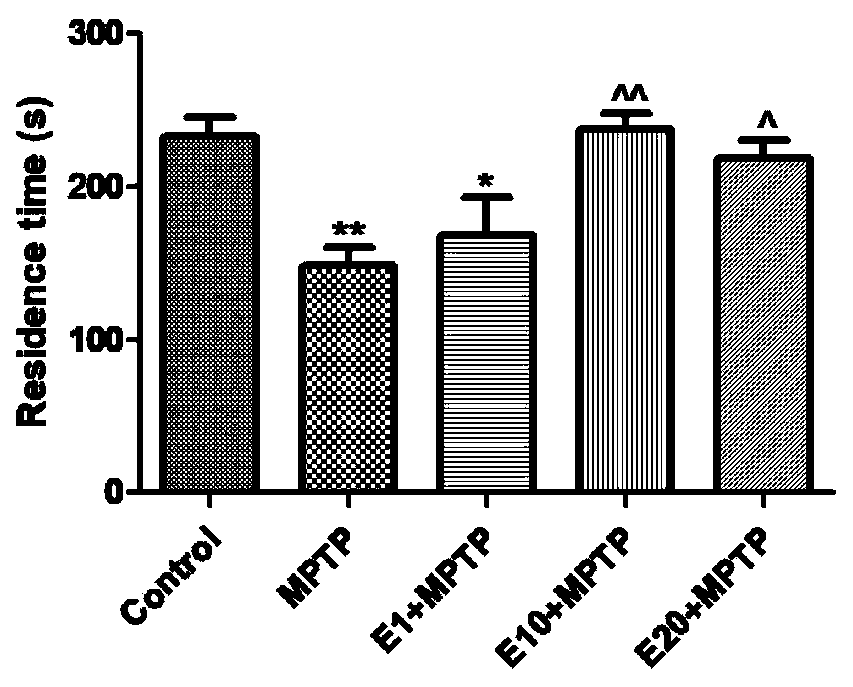
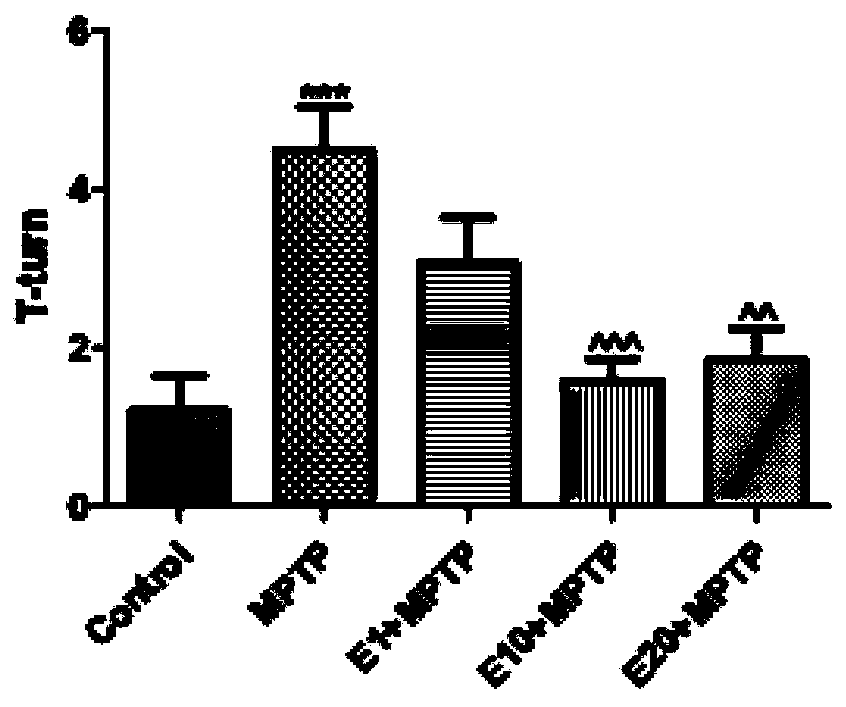
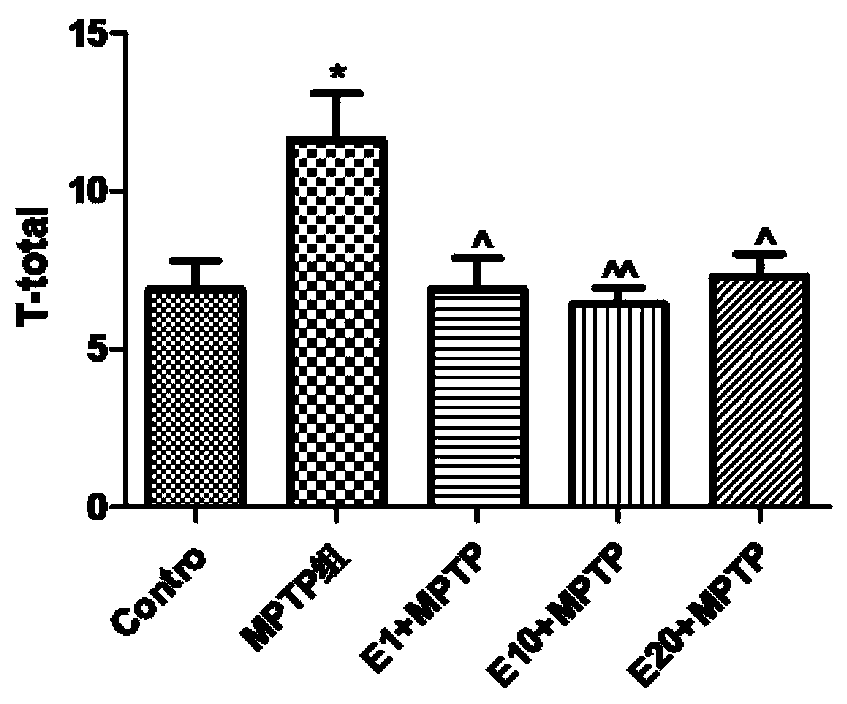
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Antiapoptotic protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical Definition of antiapoptotic. : inhibiting apoptosis Cancer results when cells grow faster and live longer than normal. Therefore increased activity of antiapoptotic proteins or decreased activity of proapoptotic proteins can contribute to the development of cancer.— Soren T. Eichhorst and Peter H. Krammer, The Lancet, 4 Aug. 2001.
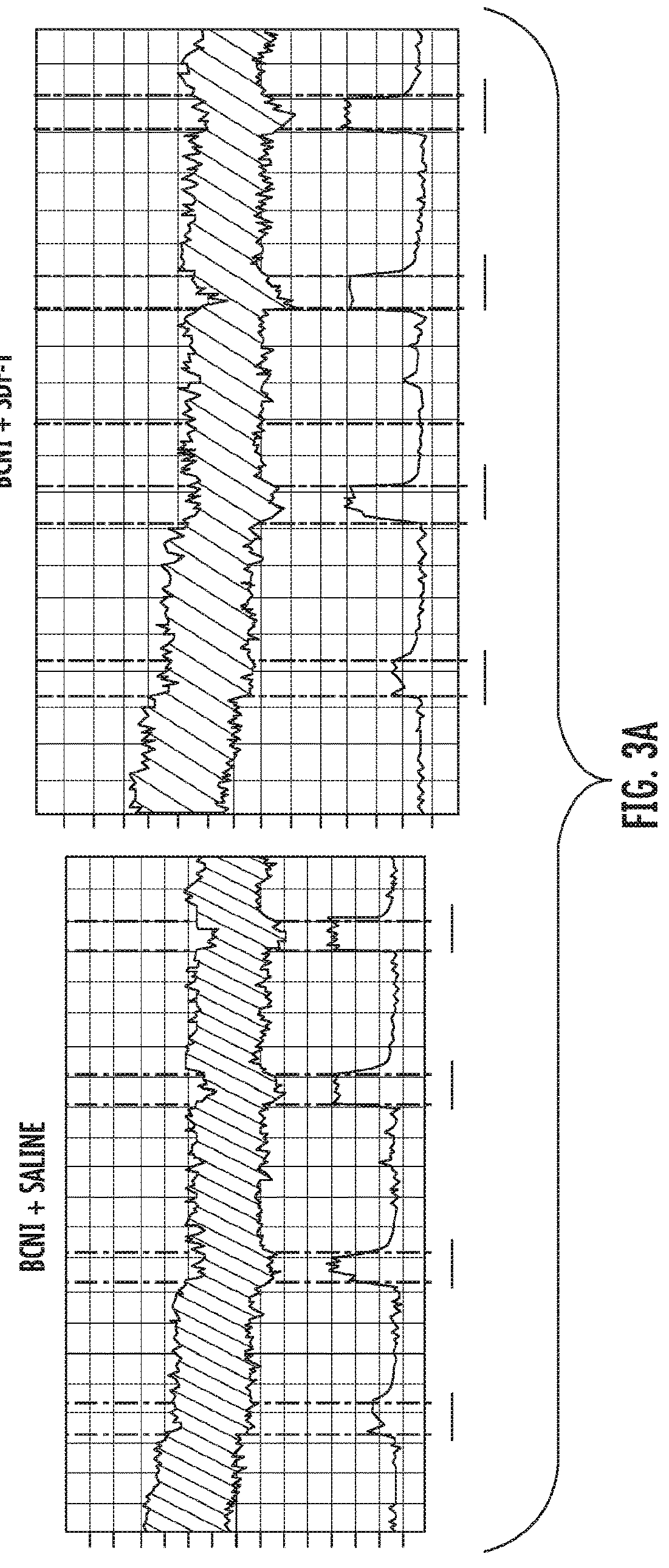
Neuroprotectin D1 protects against cellular apoptosis, stroke damage, alzheimer's disease and retinal diseases
InactiveUS20050075398A1Increase secretionReduce secretionBiocideSenses disorderRisk strokeRetinal pigment epithelial cell
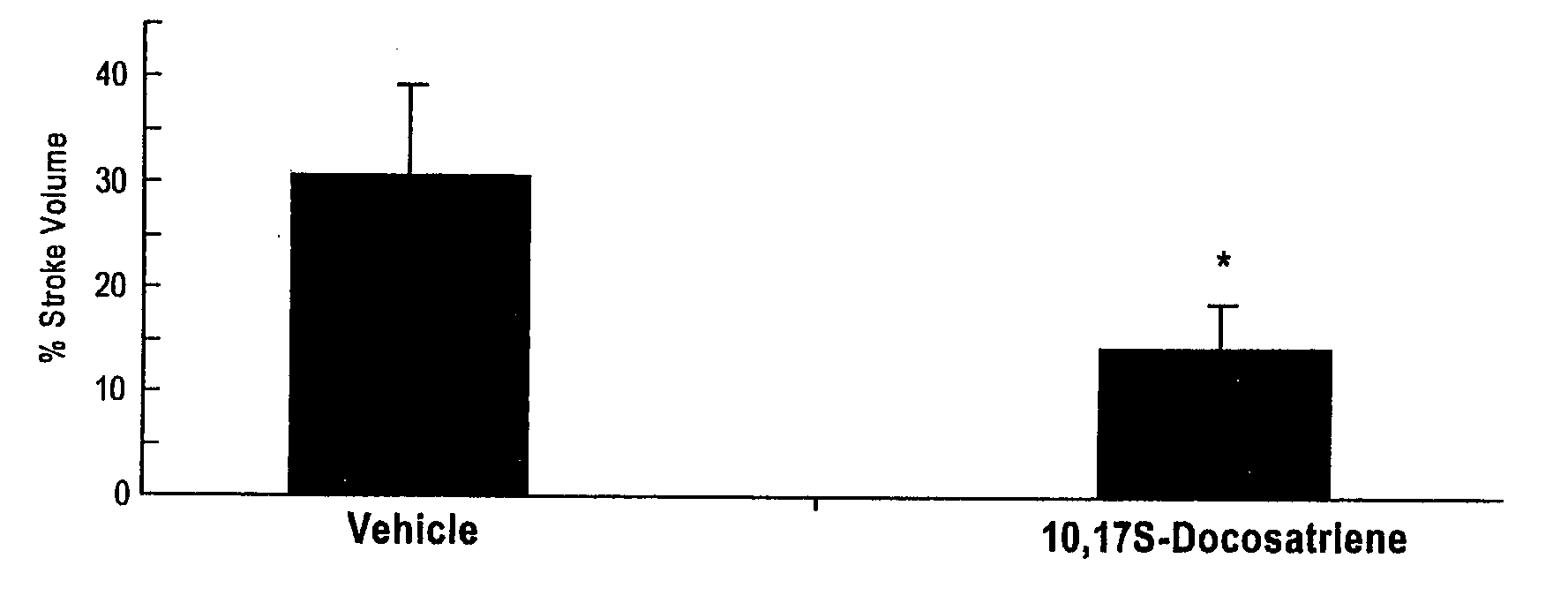
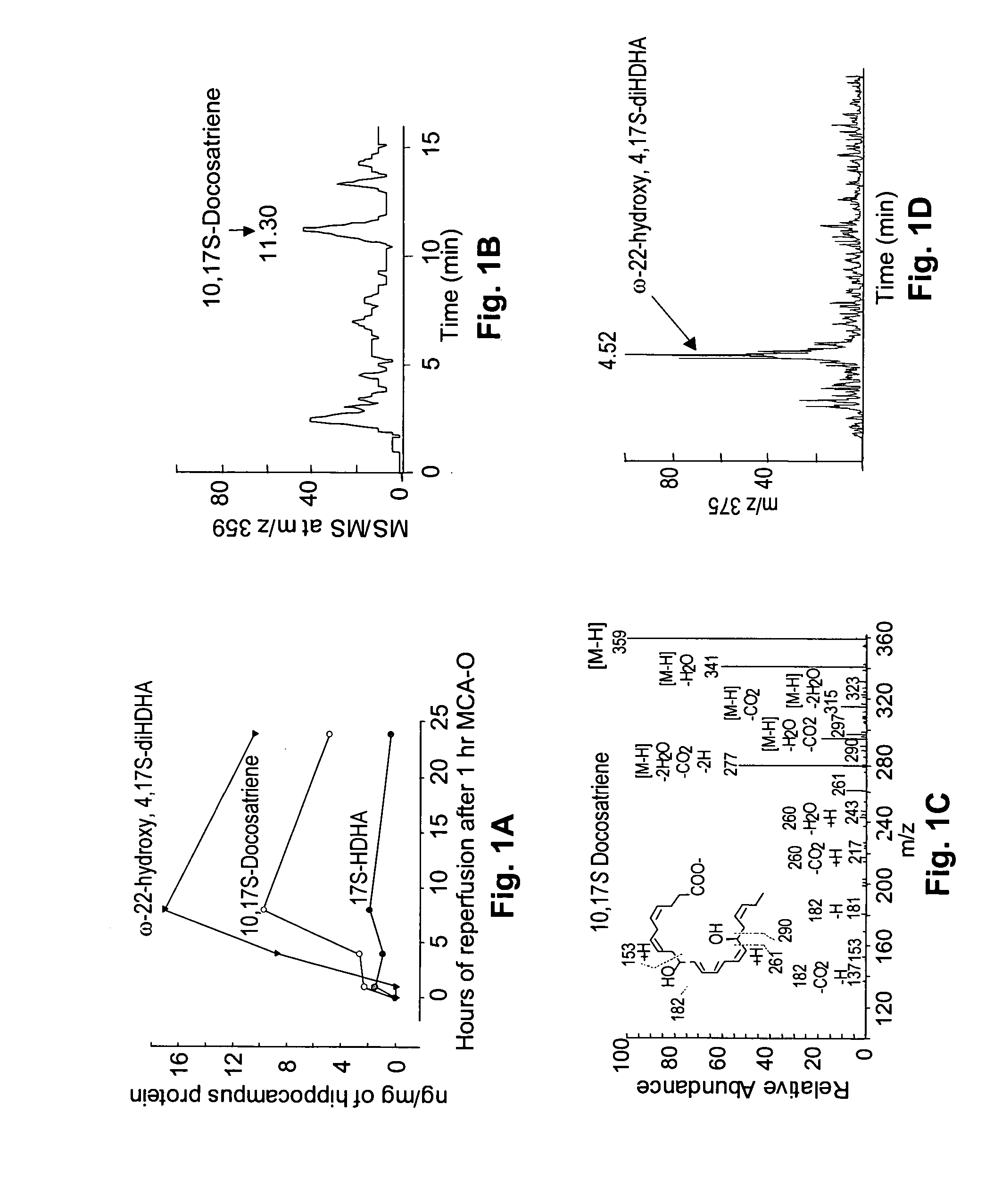
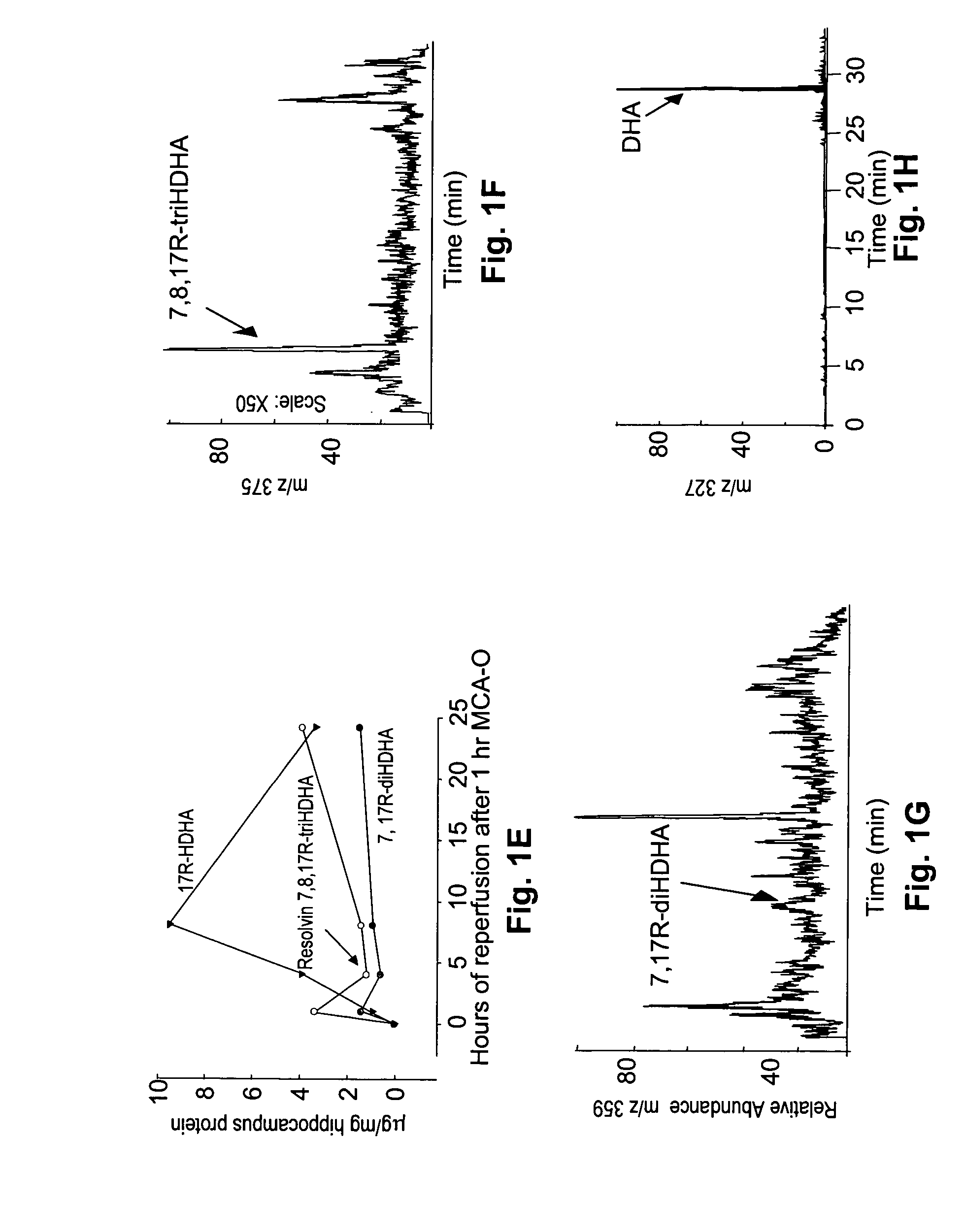
A unique DHA product, 10, 17S-docosatriene (“Neuroprotectin D1” or “NPD1”), was found to provide surprisingly effective neuroprotection when administered right after an experimental stroke. Moreover, both nerve cells and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells were found to synthesize 10,17S-docosatriene (NPD1) from DHA. NPD1 also potently counteracted H2O2 / TNFα oxidative stress-mediated cell apoptotic damage. Under the same oxidative-stress conditions, NPD1 up-regulated the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, and decreased expression of the pro-apoptotic proteins, Bad and Bax. Moreover, in RPE cells NPD1 inhibited oxidative stress-induced caspase-3 activation, IL-1β-stimulated human COX-2 promoter expression, and apoptosis due to N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E). Overall, NPD1 protected both nerve and retinal pigment epithelial cells from cellular apoptosis and damage due to oxidative stress. NPD1 concentration in the brain of Alzheimer's patients was found to be significantly decreased from that of controls. In cultured human brain cells, NPD1 synthesis was up-regulated by neuroprotective soluble β amyloid, and NPD1 was found to inhibit secretion of toxic β amyloid peptides.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
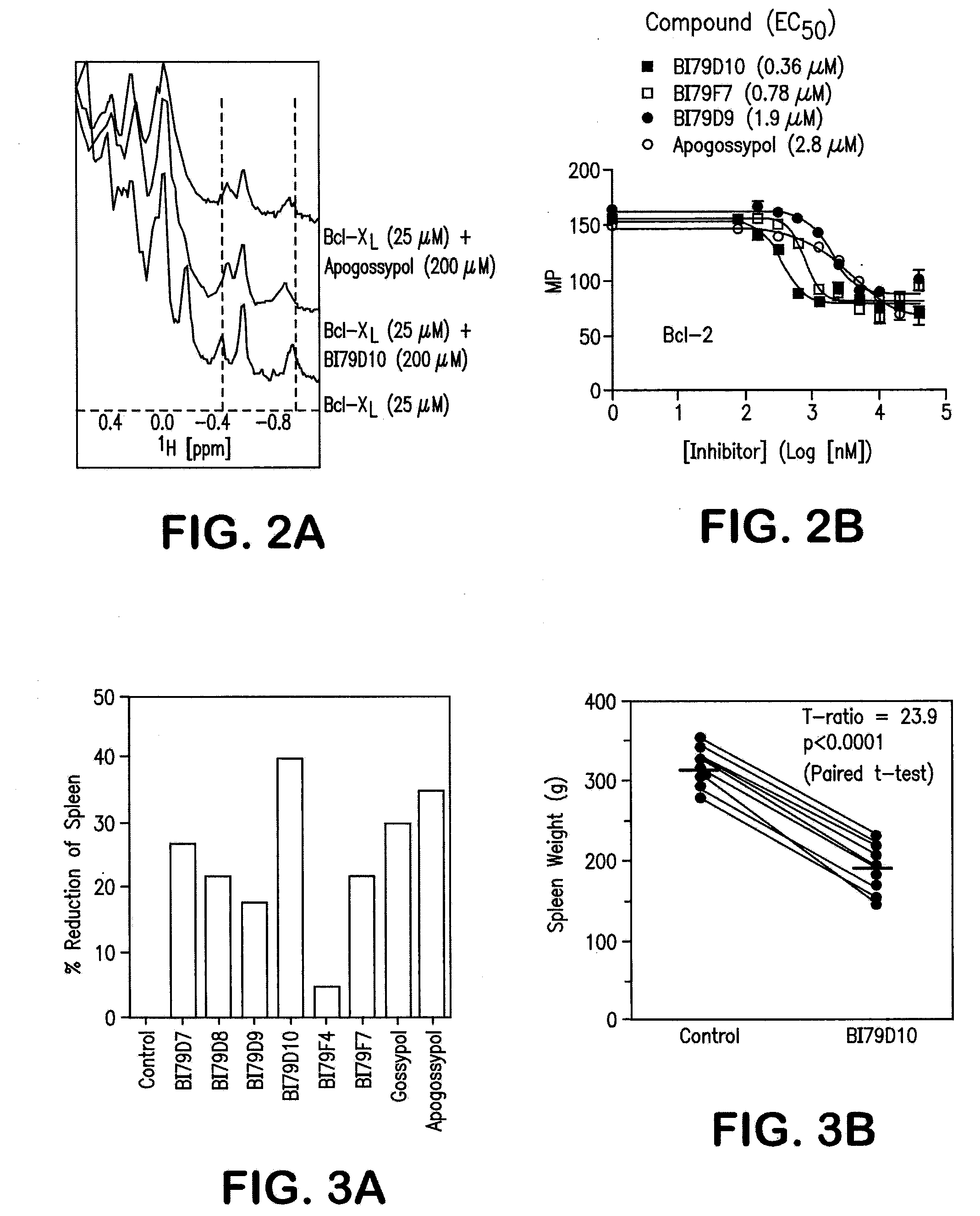
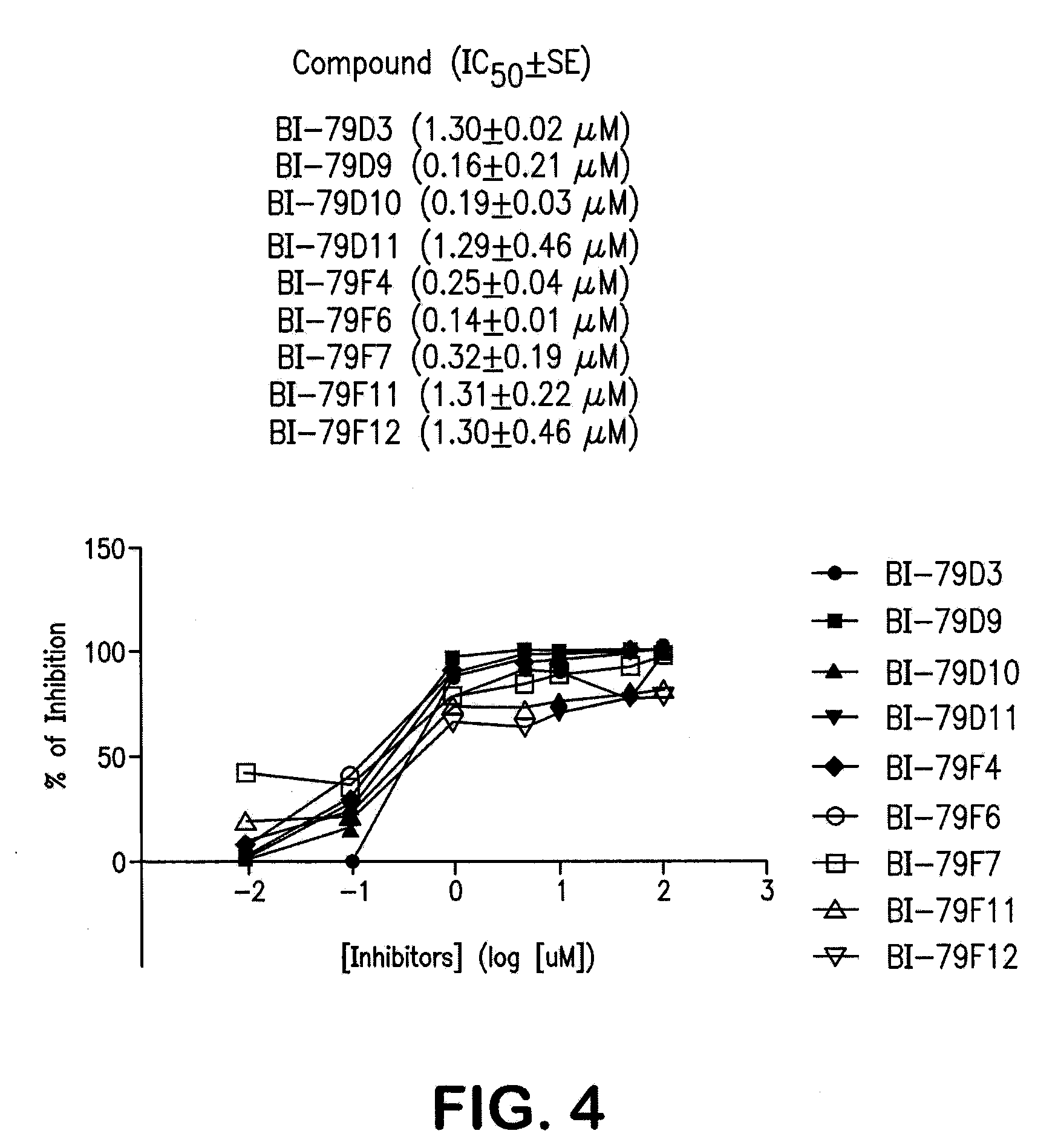
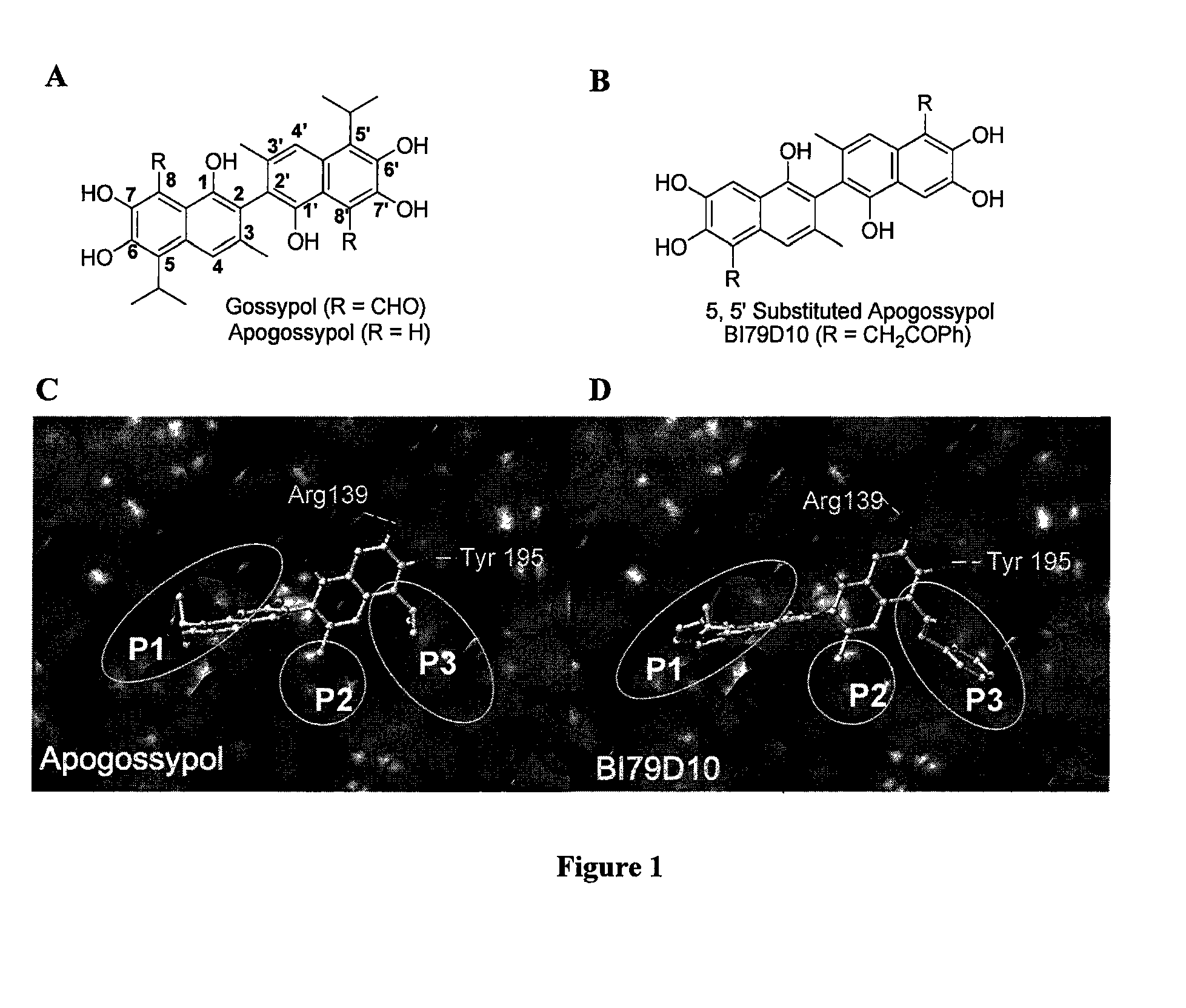
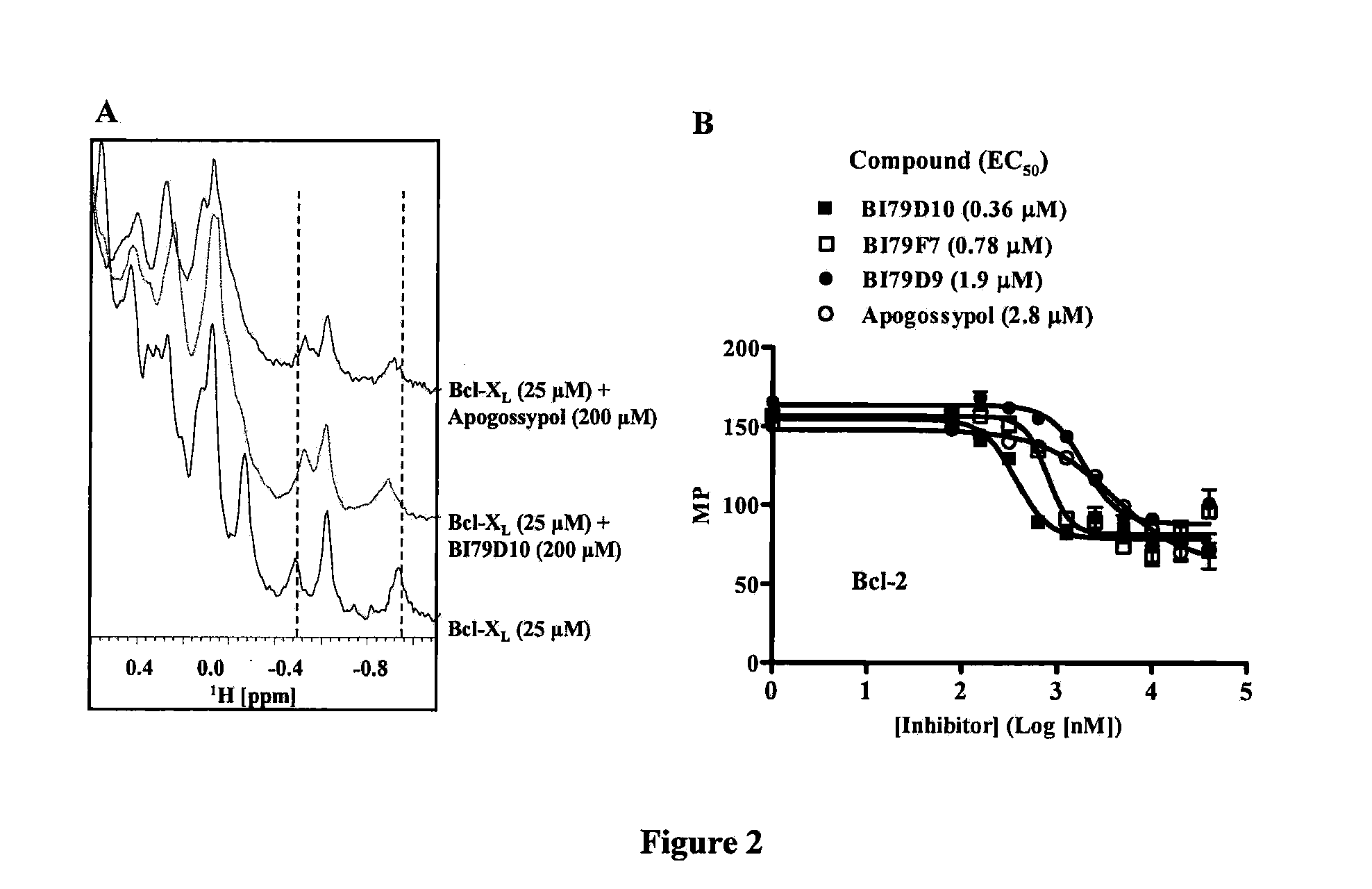
Naphthalene-based inhibitors of Anti-apoptotic proteins
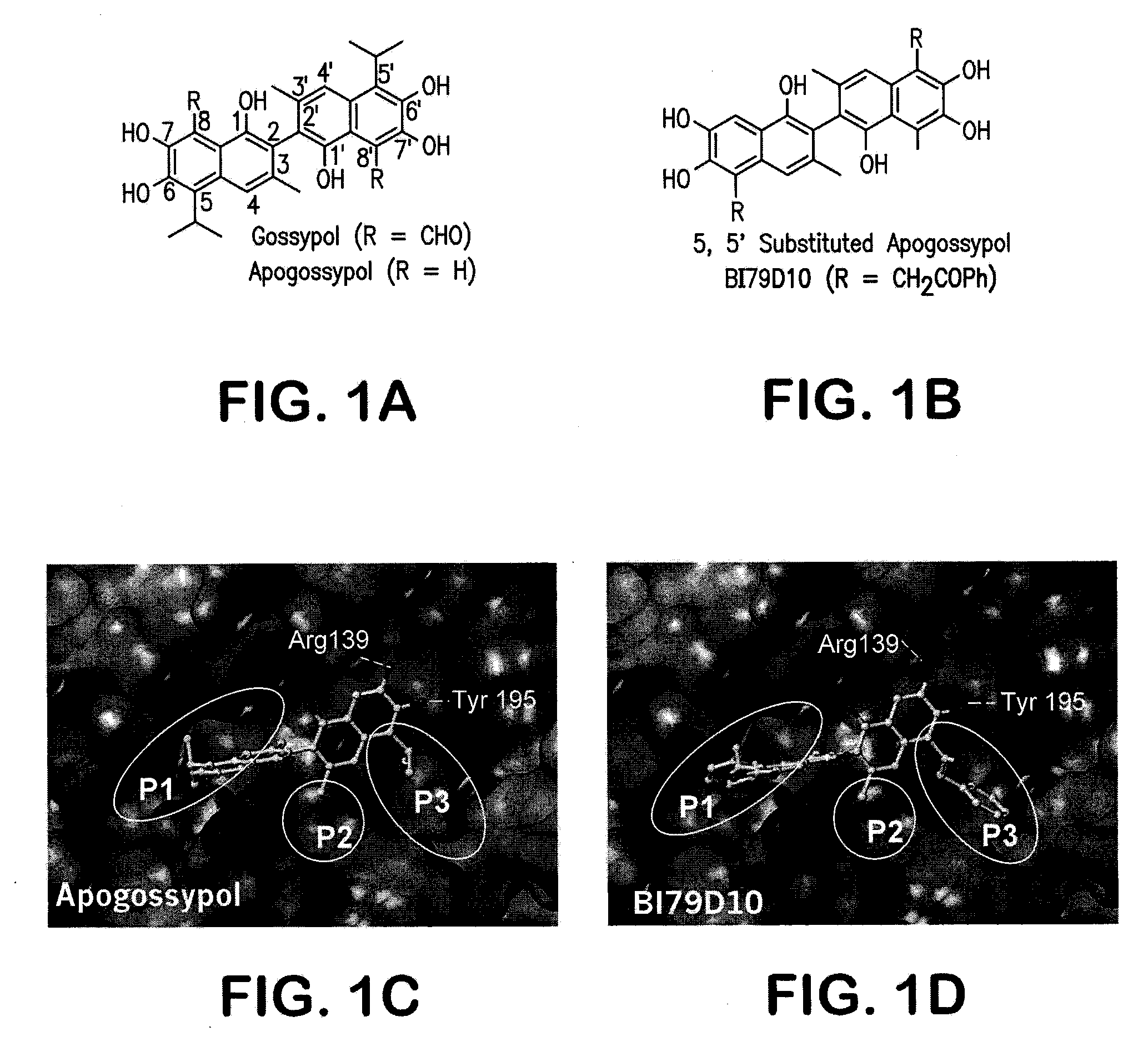
Methods of using apogossypol and its derivatives for treating inflammation is disclosed. Also, there is described a group of compounds having structure A, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, N-oxide, or solvate thereof are provided:wherein each R is independently selected from the group consisting of H, C(O)X, C(O)NHX, NH(CO)X, SO2NHX, and NHSO2X, wherein X is selected from the group consisting of an alkyl, a substituted alkyl, an aryl, a substituted aryl, an alkylaryl, and a heterocycle. Compounds of group A may be used for treating various diseases or disorders, such as cancer.
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Naphthalene-based inhibitors of anti-apoptotic proteins
Methods of using apogossypol and its derivatives for treating inflammation is disclosed. Also, there is described a group of compounds having structure A, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, N-oxide, or solvate thereof are provided:wherein each R is independently H, C(O)X, C(O)NHX, NH(CO)X, SO2NHX, or NHSO2X, wherein X is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, aryl, substituted aryl, alkylaryl, substituted alkylaryl, heterocycle, or substituted heterocycle. Compounds of group A may be used for treating various diseases or disorders, such as cancer.
Owner:BURNHAM INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Human lung adenocarcinoma self-transferring cell strain and its construction
A spontaneous transferring cell strain SPC-A-1BM is taken as human-lung adenocarcinoma SPC-A-1 cell strain. It has high spontaneous transferring rate and missed rate, lung transferring rate reaches to 80%, nodus lymphoideus transferring rate reaches to 85% and bone transferring rate reaches to 25%. It has excellent DNA cell stability and can be used to make research for human-lung adenocarcinoma transferring mechanism.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEST HOSPITAL
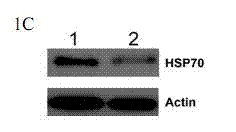
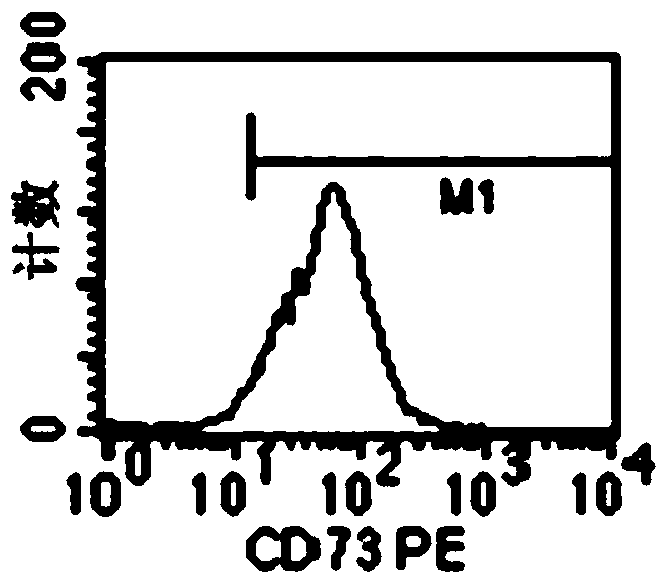
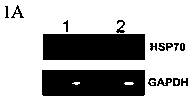
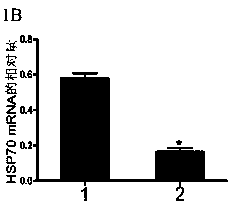
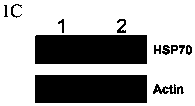
Method for regulating expression, quantity and activity of heat shock protein 70 and application thereof
ActiveCN102816792AIncreased sensitivityAdded treatment strategyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDeath ReceptorsTranscription Factor NF-kB
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a method for regulating expression, quantity and activity of a heat shock protein 70 and application thereof. The method provided by the invention can also regulate tumor tissue, activity of a transcription factor NF-kB, expression and activity of a death receptor DR4 and DR5, phosphorylation and activity of JNK and c-Jun, expression and activity of a p53 protein, expression and proapoptotic activity of proapoptotic molecules Bax, Bid, t-Bid, capsase 3, capsase 8 and capsase 9, and expression and activity of c-FLIP and Bcl-2, and promote apoptosis of tumor tissues and cells. The invention also relates to application of the above method to preparation of drugs cooperatively applied with cell apoptosis induced drug.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
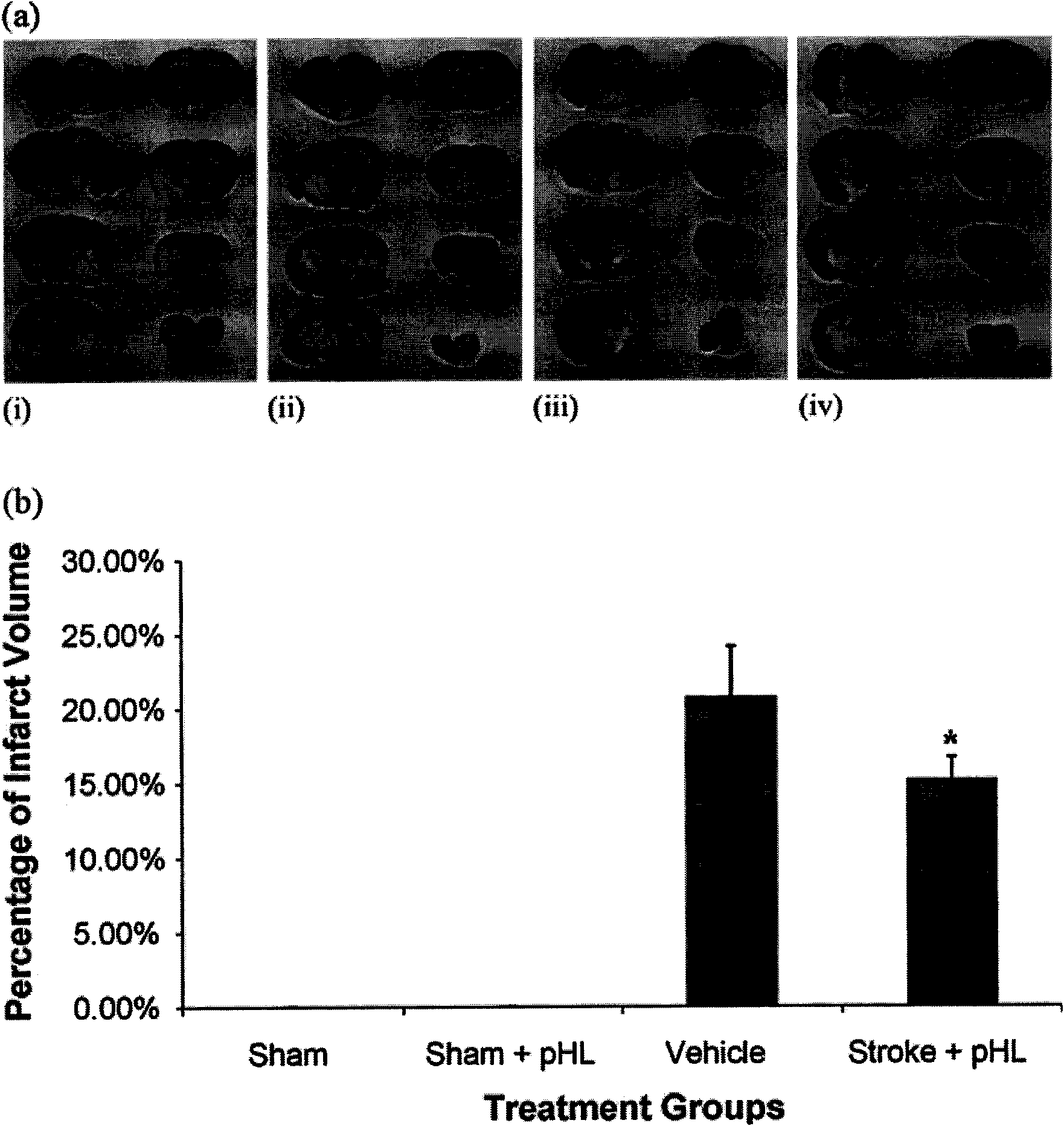
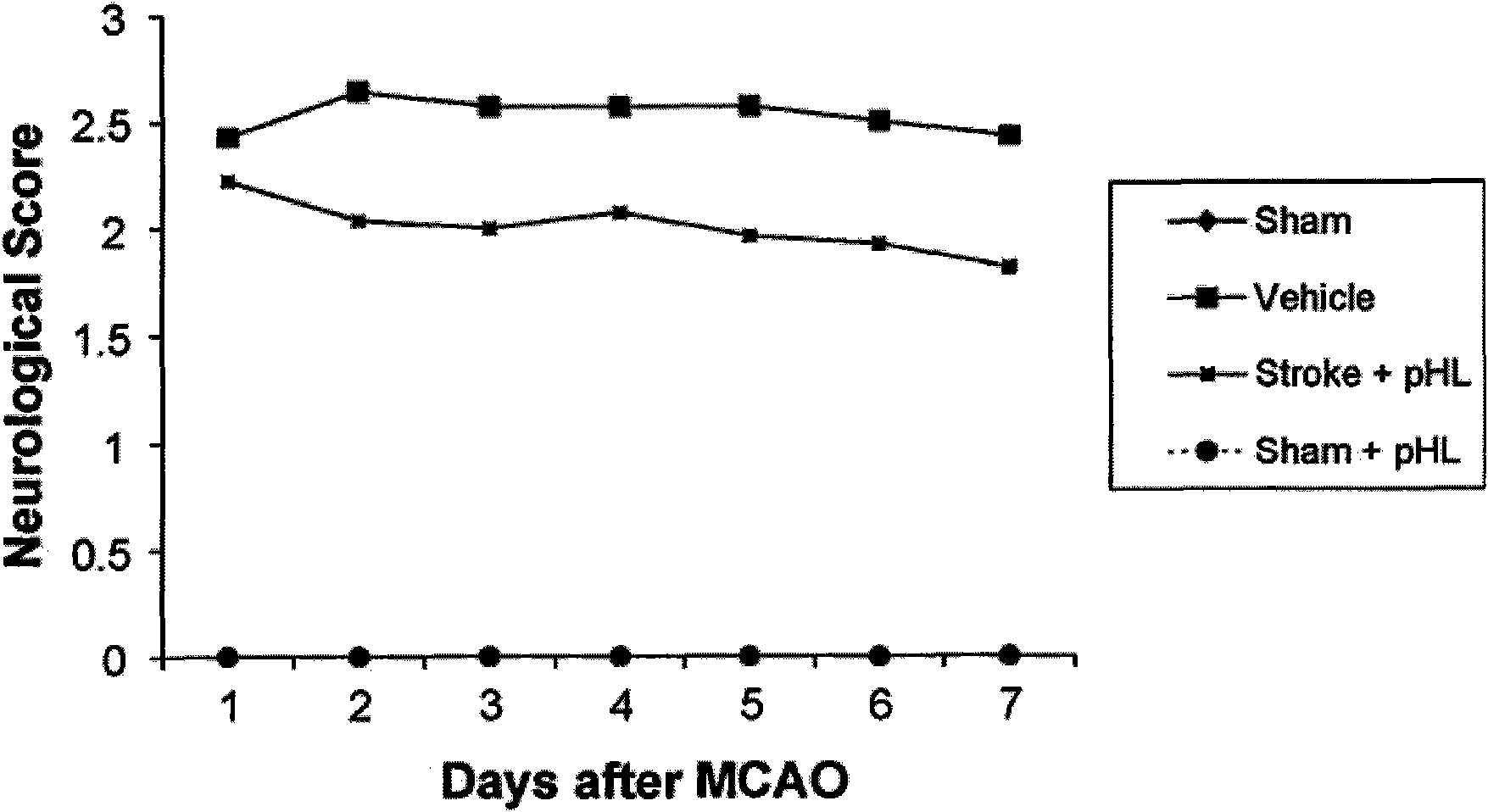
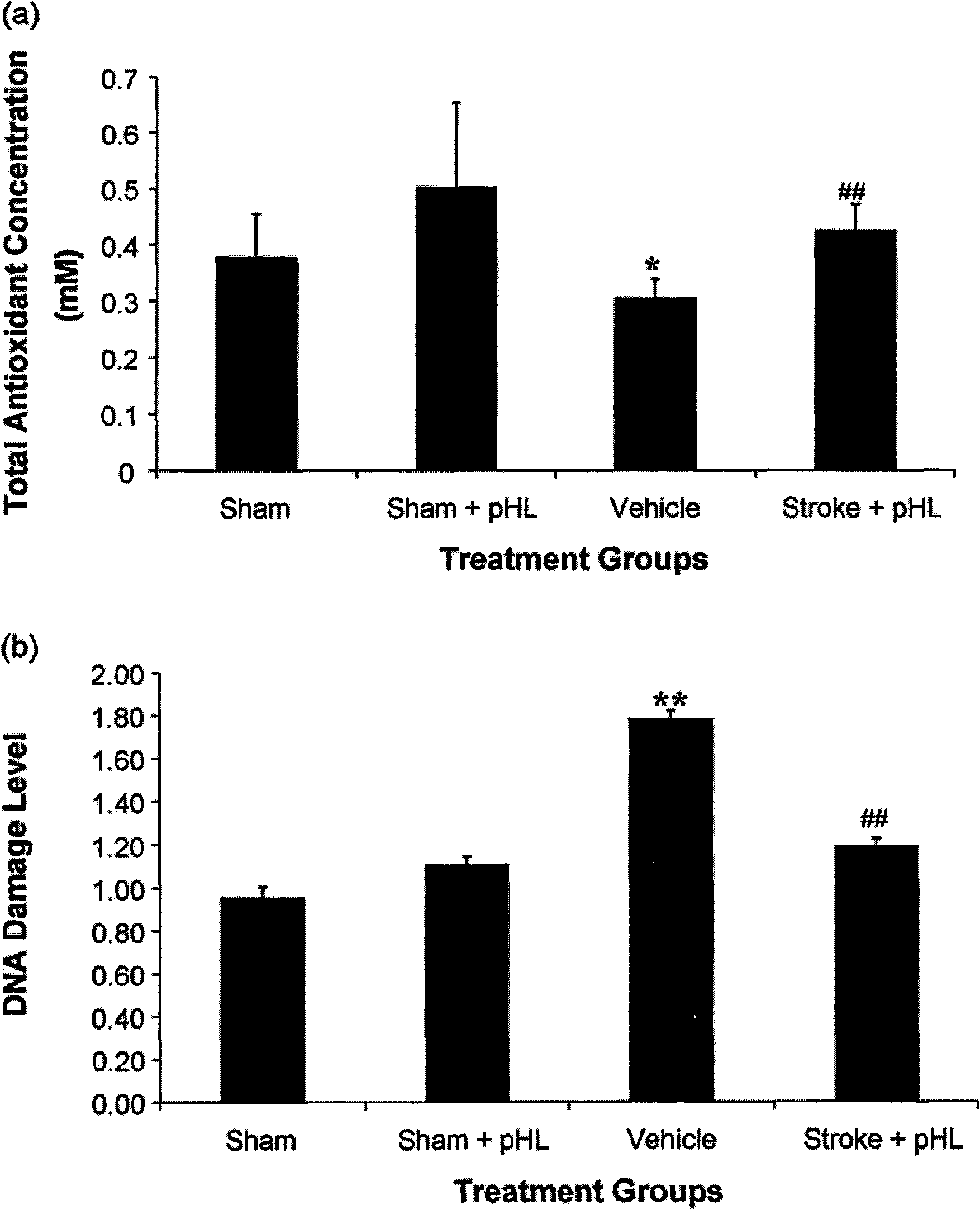
Application of purified motherwort extract in preparing nerve protection medicine for treating cerebral injury
InactiveCN101596232AReduced expression levelIncrease contentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntioxidantDNA oxidation
The invention belongs to the field of pharmacy and relates to a new application of a traditional Chinese medicine motherwort extract in pharmacy, in particular to the application of the purified motherwort extract in preparing nerve protection medicine for treating cerebral injury, especially the application of the purified motherwort extract in preparing brain protection medicine for treating artery obstruction in the brain. By an animal experiment of the purified motherwort extract, a result indicates that the brain stem volume is obviously reduced after the purified motherwort extract is applied, the obstacle grading of the nerve function is decreased by being compared with a contrast group, the total antioxidant concentration in plasma is increased, the DNA oxidation injury is reduced, the expression levels of apoptosis and apoptosis promoting protein are reduced, and the content of apoptosis resistance protein is also increased. The purified motherwort extract can be used for preparing the nerve protection medicine for treating the cerebral injury and can effectively treat cerebral apoplexy.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Small molecule composition and application thereof in preparation of medicine for treating neuroblastoma
ActiveCN114569616AIncreased apoptosisStrong synergyOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGlycogen synthase IPharmaceutical Substances
The invention discloses a small molecule composition and an application of the small molecule composition in preparation of a medicine for treating neuroblastoma, and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (Glygen synthase kinase 3beta, GSK-3beta) for promoting degradation of an MYC family member c-MYC has a function of promoting cancer progression in NB. The analysis on GSK-3beta substrate protein finds that the levels of N-MYC and Cyclin E1 protein and mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) are obviously reduced after the GSK-3beta is inhibited, and the level of anti-apoptotic protein MCL-1 is increased, so that the cell proliferation is obviously slowed down on the cell function. However, due to the fact that the detail of the MCL-1 protein level is enhanced, the cells are not subjected to obvious apoptosis under the treatment of a low-concentration GSK-3beta inhibitor. In subsequent experiments, the invention proves that the GSK-3beta inhibitor and the MCL-1 inhibitor cooperate to efficiently kill neuroblastoma for the first time.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of a human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell
ActiveCN105769910BImproved flow dynamicsProtect against pathological changesUnknown materialsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCardiac functioningAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The invention discloses application of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells in preparation of a preparation for treating a myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury generated after cardiopulmonary bypass.In the myocardial ischemia reperfusion process after the cardiopulmonary bypass, the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells can effectively prevent myocardial cells from being injured in myocardial ischemia reperfusion, obviously improve the cardiac functions, lower the levels of myocardial injury specific marker protein lactic dehydrogenase, creatine kinase isoenzyme and troponin I, lower the levels of a plasma inflammatory factor interleukin-8 and a tumor mecrosis factor-alpha, increase the content of the plasma inflammatory factor interleukin-10, obviously improve pathological changes of the myocardial tissue, reduce myocardial cell apoptosis, lower the expression level of cell apoptosis promoting protein, increase the expression quantity of anti-apoptoasis protein and can protect the functions of myocardial cell mitochondria.By preparing the human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells into an injection for treatment on the myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury generated after the cardiopulmonary bypass, the cardiac functions can be effectively protected, and postoperative complications of the cardiopulmonary bypass are relieved.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZUNYI MEDICAL COLLEGE
A method for regulating the expression, quantity and activity of heat shock protein 70 and its application
ActiveCN102816792BIncreased sensitivityAdded treatment strategyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPhosphorylationDeath Receptors
The invention belongs to the field of biological technology, and in particular relates to a method for regulating the expression, quantity and activity of heat shock protein 70 and its application. Utilizing the present invention can also regulate tumor tissue and intracellular transcription factor NF-κB and its activity, death receptor DR4 and DR5 expression and activity, JNK and c-Jun phosphorylation and activity, p53 protein expression and activity, pro-apoptosis Molecule Bax, Bid, t-Bid, capsase 3, capsase 8, capsase 9 expression and pro-apoptotic activity, anti-apoptotic protein c-FLIP and Bcl-2 expression and activity, promote tumor tissue and cell apoptosis. The present invention also relates to the application of the above-mentioned method in the preparation of medicines used in combination with apoptosis-inducing medicines.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
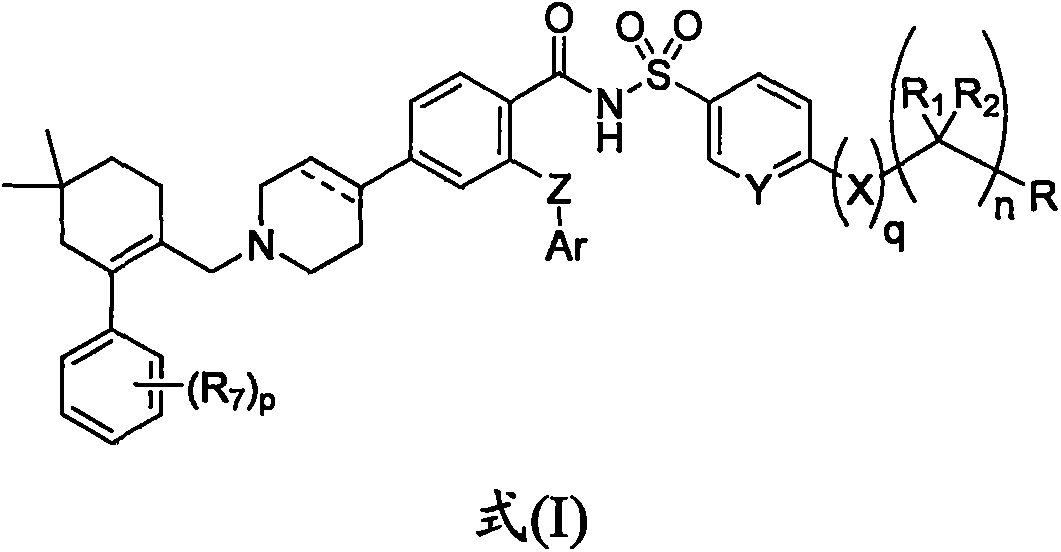
Anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 inhibitor and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides an anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 inhibitor and a preparation method and application thereof, and particularly provides a compound as shown in a formula (I), or an optical isomer, a tautomer or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The compound has excellent Bcl-2 inhibitory activity, so that the compound can be used for treating or preventing related mammalian diseases or symptoms caused by abnormal expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Application of icariin in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease
InactiveCN111544439AHigh expressionReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseWestern blot
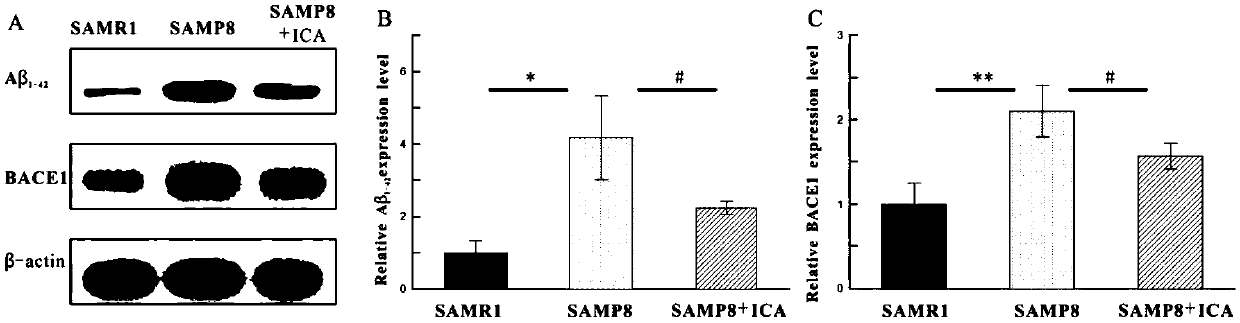
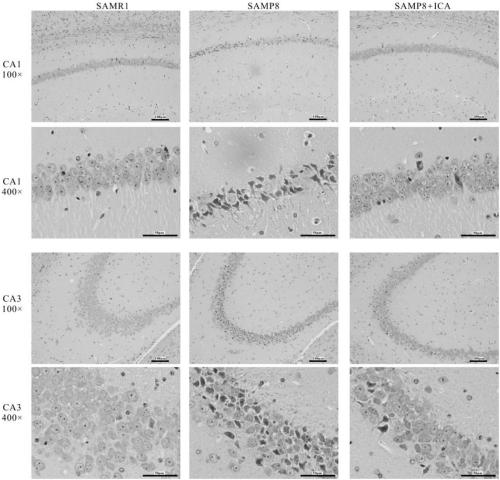
The invention relates to the application of icariin in the preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease. According to the invention, experiments such as a Morris water maze experiment, a Western blot experiment, an HE staining method and the like are carried out in an SAMP8 model mouse; it is proved that learning and memory disorder of SAMP8 mice can be reversed afterintragastric administration of ICA, icariin can down-regulate expression of BACE1 so as to reduce deposition of cytotoxic A beta 1-42. Besides, icariin can improve cognitive defects by increasing theexpression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, reducing the expression of pro-apoptotic protein Bax and remarkably increasing the ratio of Bcl-2 to Bax, so that neuronal apoptosis is inhibited, and neurons are protected. The invention provides further evidences for the clinical curative effect of icariin on Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:ZUNYI NO 1 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Novel BCL-2/BCL-XL inhibitor, pharmaceutical composition and application
The invention relates to a compound for inhibiting the activity of Bcl-2 / BCL-XL anti-apoptotic protein, a composition containing the compound and application of the compound serving as a synthetic drug, in particular to application of the compound serving as a drug for synthesizing a Bcl-2 / BCL-XL anti-apoptotic protein inhibitor and application of the compound to cancer.
Owner:长沙创新药物工业技术研究院有限公司
Bcl-2 selective inhibitor, and preparation method and usage thereof
InactiveCN109293656AEasy to understandOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseasePharmaceutical drug
Owner:CENTAURUS BIOPHARMA
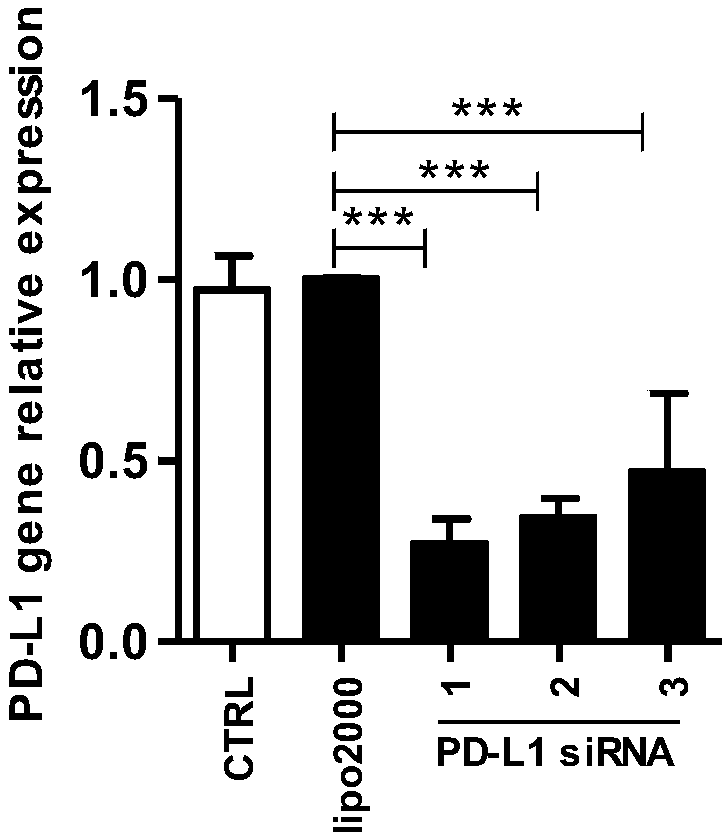
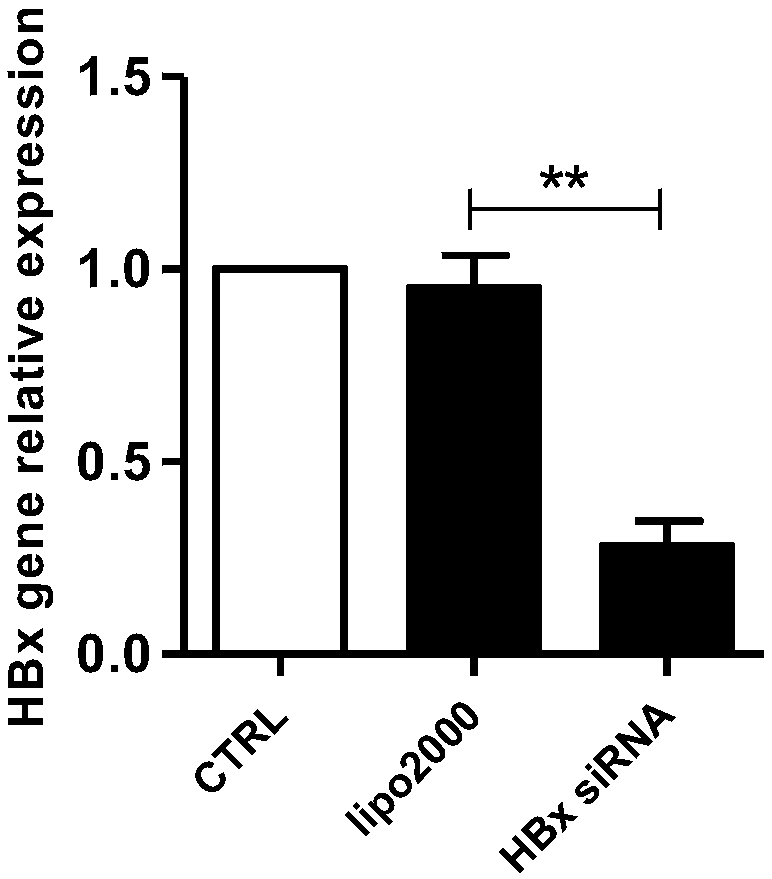
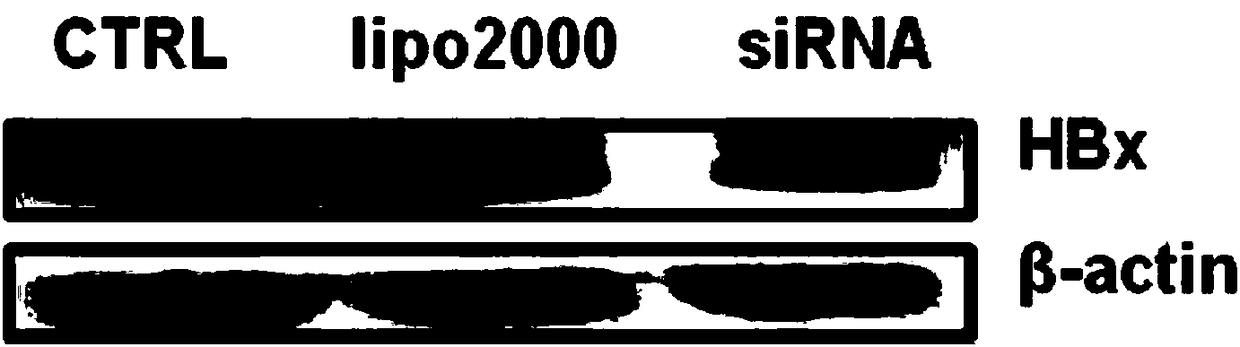
Application of bifunctional vector in inhibiting HBV (hepatitis B virus) infection
PendingCN108285907AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemWestern blotPD-L1
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and particularly relates to an application of a dual expression vector of silent RNA (ribonucleic acid) of PD-L1 and HBx target genes in inhibiting HBV (hepatitis B virus) infection. Compared with a monofunctional vector, pSIREN-shPD-L1-shHB constructed has a better inhibition effect on HepG2.2.15 cell proliferation and a better promotion effect on cell apoptosis; the detection of an intracellular anti-apoptosis protein expression situation via Western Blot finds that a bifunctional vector group can obviously reduce expression ofBcl-2 and Bcl-xl; and the detection of an intracellular anti-apoptosis protein gene expression situation via quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) finds that the bifunctional vector group canobviously reduce mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) expression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Preparation of compound of Au and anti-apoptotic protein antagonistic peptide and application of compound in synergistic induction of tumor cell apoptosis
ActiveCN114432340AReduce the effective doseGood curative effectPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsLymphocytic cellAPOPTOGENIC PROTEIN
The invention discloses preparation of a compound of Au and an anti-apoptotic protein antagonistic peptide and application of the compound in synergistic induction of tumor cell apoptosis, and relates to the field of anti-tumor drugs. Mixing a gold salt solution with the anti-apoptotic protein antagonistic peptide containing sulfydryl; under the conditions of certain temperature and pH, redox reaction is carried out, high-valence Au ions are reduced into Au atoms or monovalent Au ions, and Au acts on sulfydryl of polypeptide to form a compound AuP; the sulfydryl-containing anti-apoptotic protein antagonistic peptide is selected from polypeptides with an intracellular anti-apoptotic protein antagonistic function. The AuP compound has broad-spectrum anti-tumor activity, and compared with a common peptide-gold compound or gold compound, the AuP compound can inhibit the activity of thioredoxin reductase and antagonize the function of high-expression anti-apoptotic protein at the same time, the single-drug double-target synergistic effect is achieved, and the curative effect is remarkably improved. The compound can be used for treating various malignant tumors such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia, acute monocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
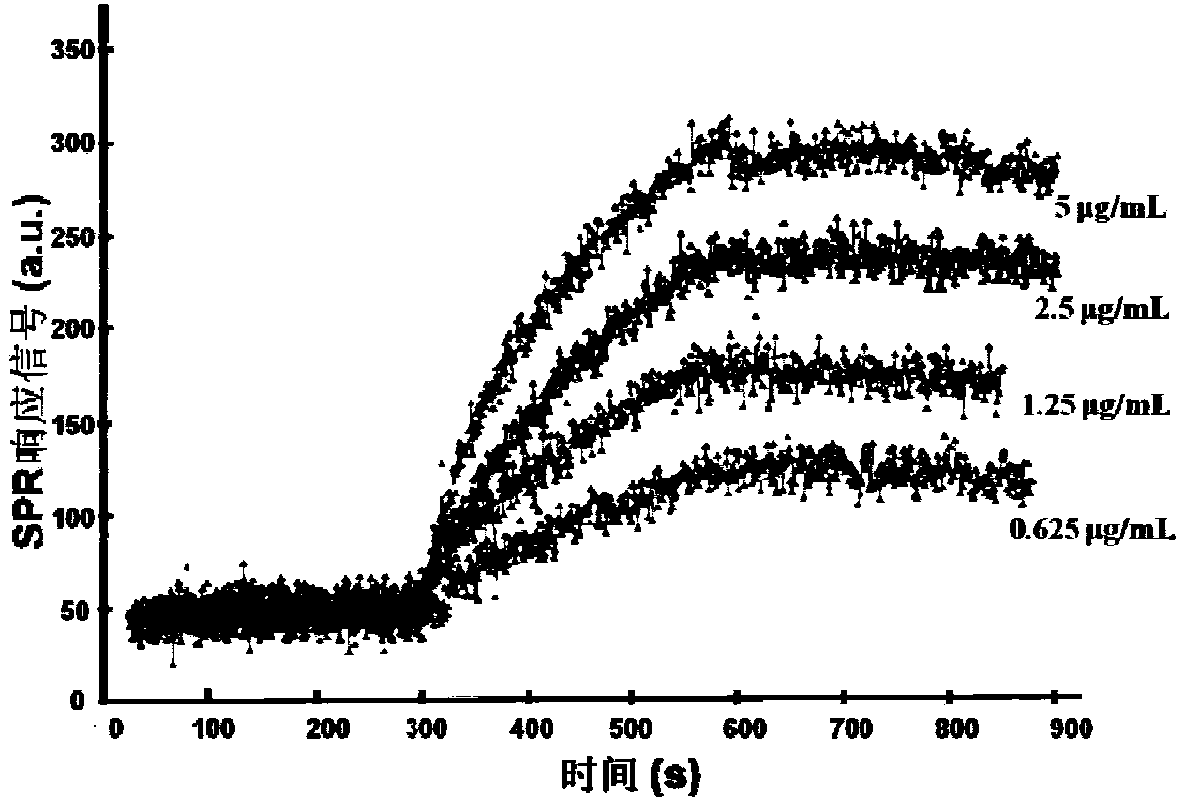
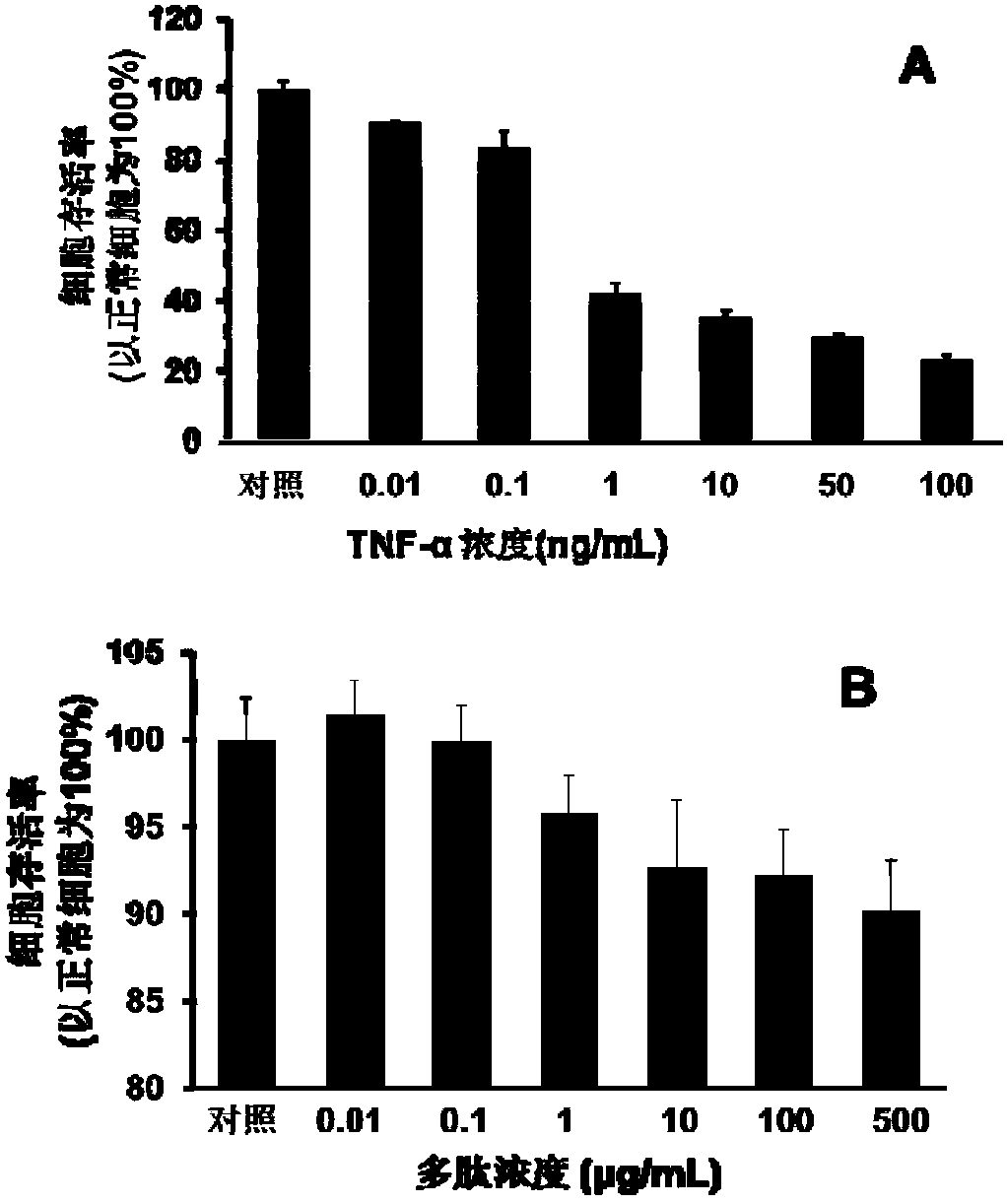
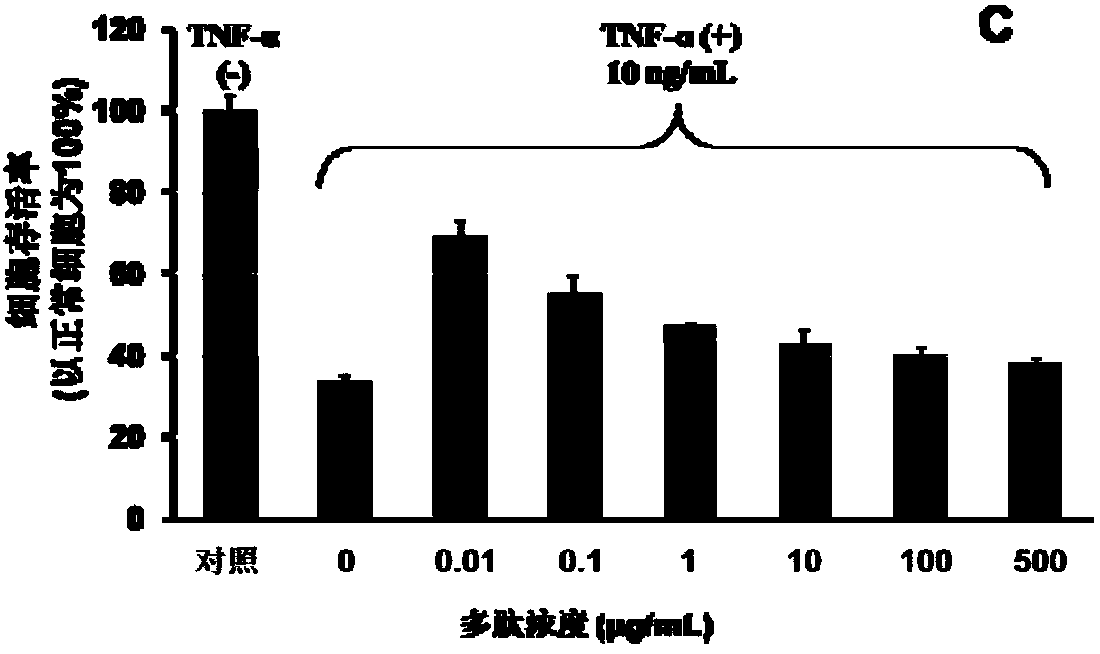
A kind of polypeptide combined with tumor necrosis factor and its application
ActiveCN104829697BInhibit apoptosisReduce the ratioPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseApoptosis pathways
The present invention relates to a polypeptide binding with tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha), and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the polypeptide and TNF-alpha have high affinity, and the polypeptide can be bound with the excess TNF-alpha to make the apoptosis promoting protein Bid in the apoptosis-related mitochondrion apoptosis pathway be down-regulated while make the anti-apoptosis protein Bcl-2 be up-regulated in the apoptosis-related mitochondrion apoptosis pathway so as to inhibit the apoptosis caused by TNF-alpha, such that the polypeptide can be used for preparation of TNF-alpha-related disease treating drugs. The present invention further provides a method for screening at the molecular and cellular level and researching the influence of the polypeptide antagonist on the TNF-alpha physiological effect, and applications thereof so as to provide the effective method for development of the low-cost anti-TNF-alpha drug.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
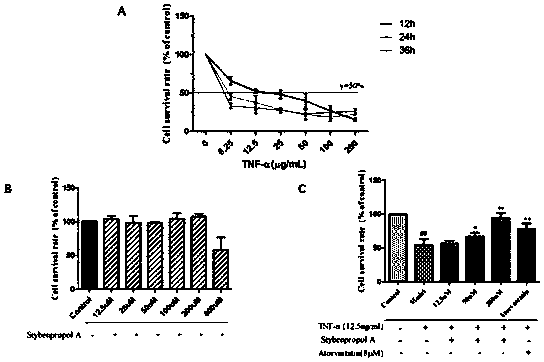
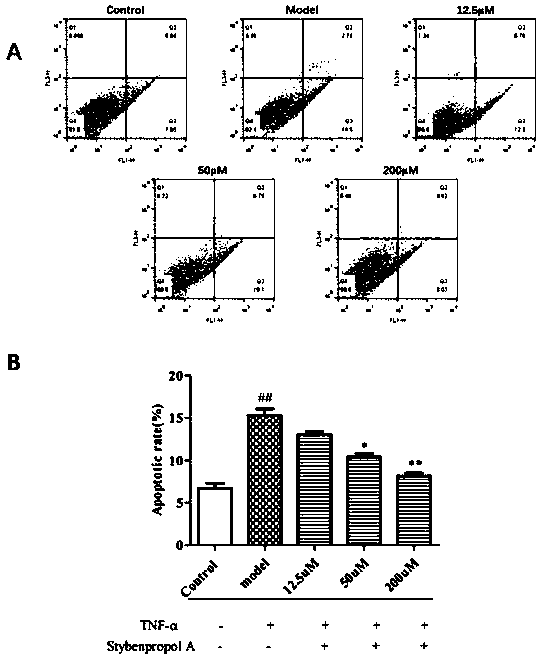
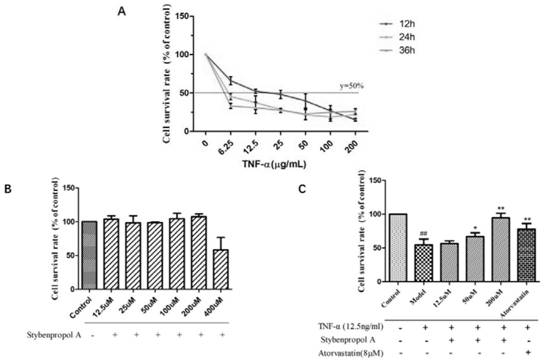
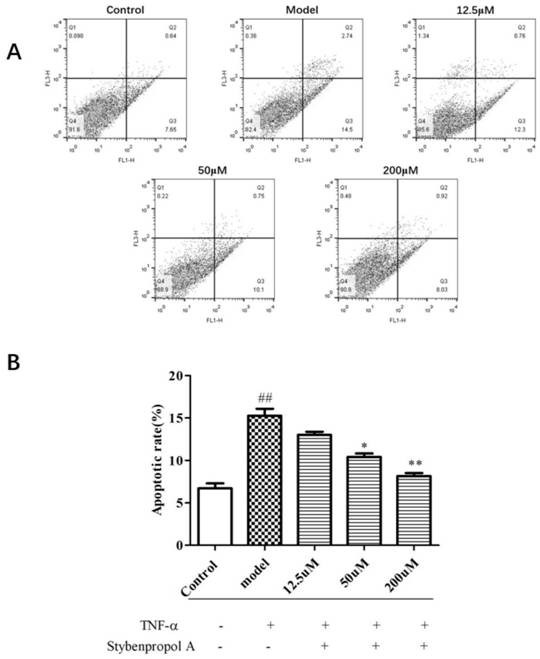
Compound stybenpropol a and its application in preventing and treating atherosclerosis
ActiveCN110668946AInhibit apoptosisInhibits inflammatory damageOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryInflammatory factorsNitric oxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and particularly discloses compound stybenpropol a and application thereof in improving atherosclerosis (AS). According to the invention, thenovel compound stybenprop a is extracted from benzoin, and research results show that in human umbilical vein endothelial cells HUVECs) injured by tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha), the stybenprop a can inhibit endothelial cell inflammatory damage by inhibiting TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappa b activation and nuclear translocation and enhancing expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 so as to increase the level of nitric oxide secretion and reduce the levels of vascular adhesion molecules and pro-inflammatory factors, the compound stybenpropol a can significantly inhibit TNF-alpha-induced inflammatory injury and apoptosis of the HUVECs, provides a new choice and approach for the development of anti-atherosclerosis drugs and has a good application prospect.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Polypeptide-human transferring factor concerned with anti-withering protein-16.94 and polynucleotide for encoding it
A polypeptide-human anti-wither protein associated transcription factor-16.94, the polynucleotide for coding, the process for preparing said polypeptide by DNA recombination, the application of said polypeptide in treating diseases such as tumor, immunopathy, etc, the antagonist of said polypeptide and its medical action, and the application of said polynucleotide are disclosed.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
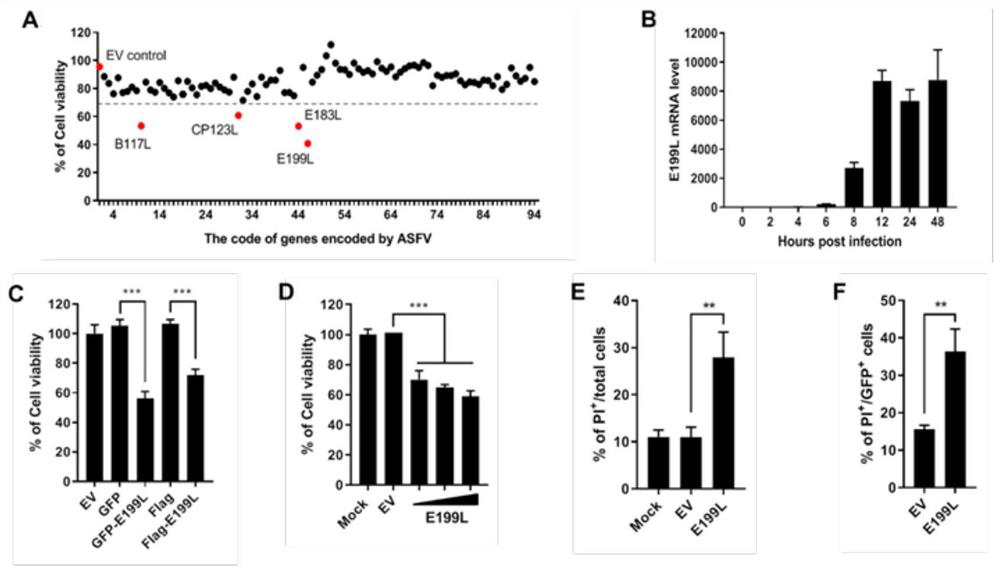
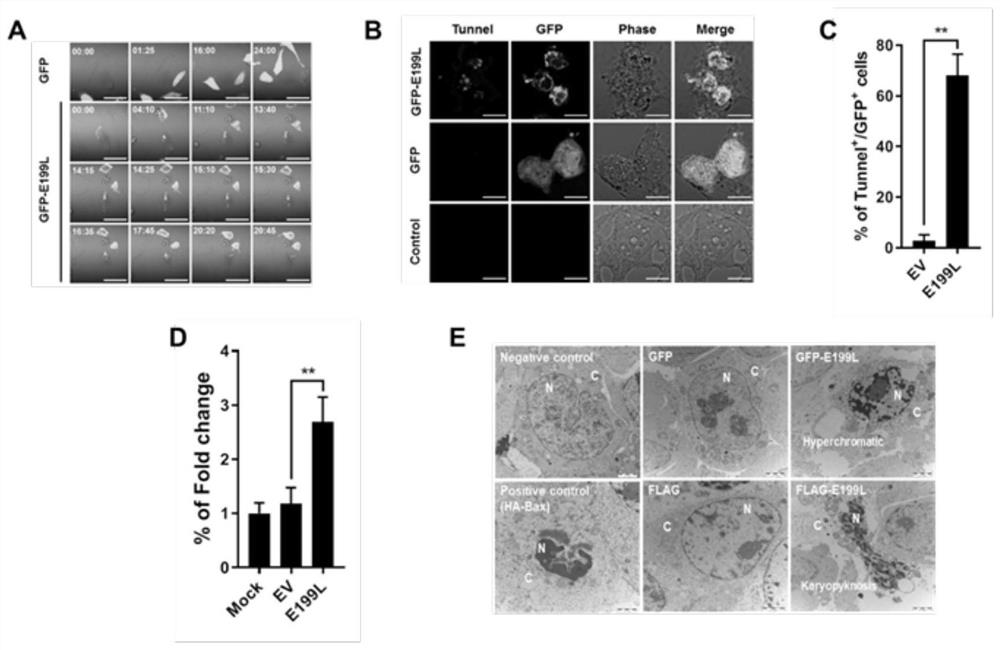
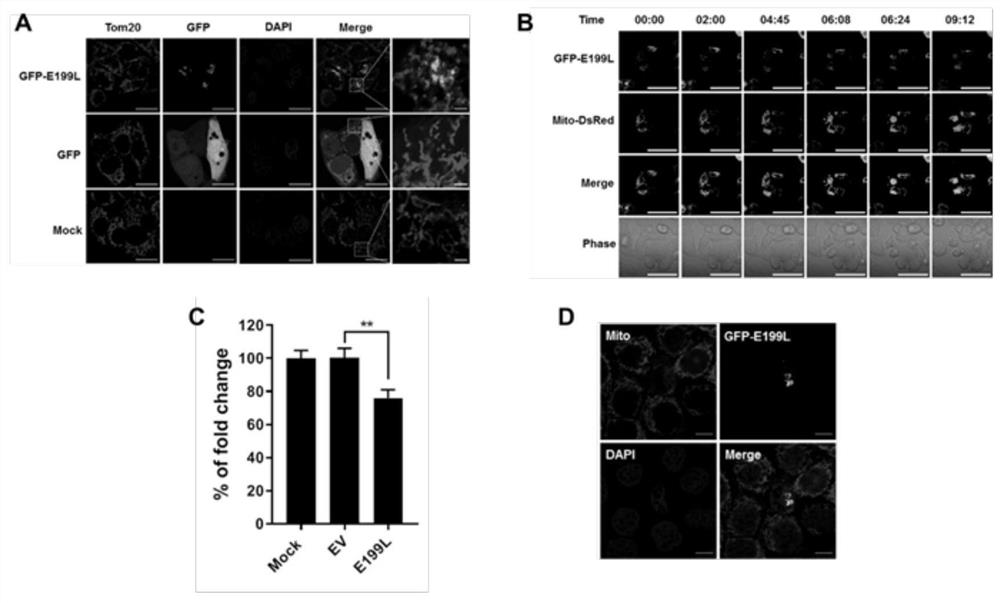
Application and method of E199L protein in promoting apoptosis
PendingCN114392345APromote apoptosisInduce apoptosisPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiinfectivesAntiapoptotic proteinApoptosis protein
The invention discloses application and a method of E199L protein in promoting cell apoptosis. The invention provides an application of E199L in promoting cell apoptosis, the E199L competitively destroys the interaction between anti-apoptosis proteins and BAK and / or BAX through the wide interaction between the E199L and the anti-apoptosis proteins such as BCL-XL, MCL-1, BCL-W and BCL-2A1, and finally induces cell apoptosis.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
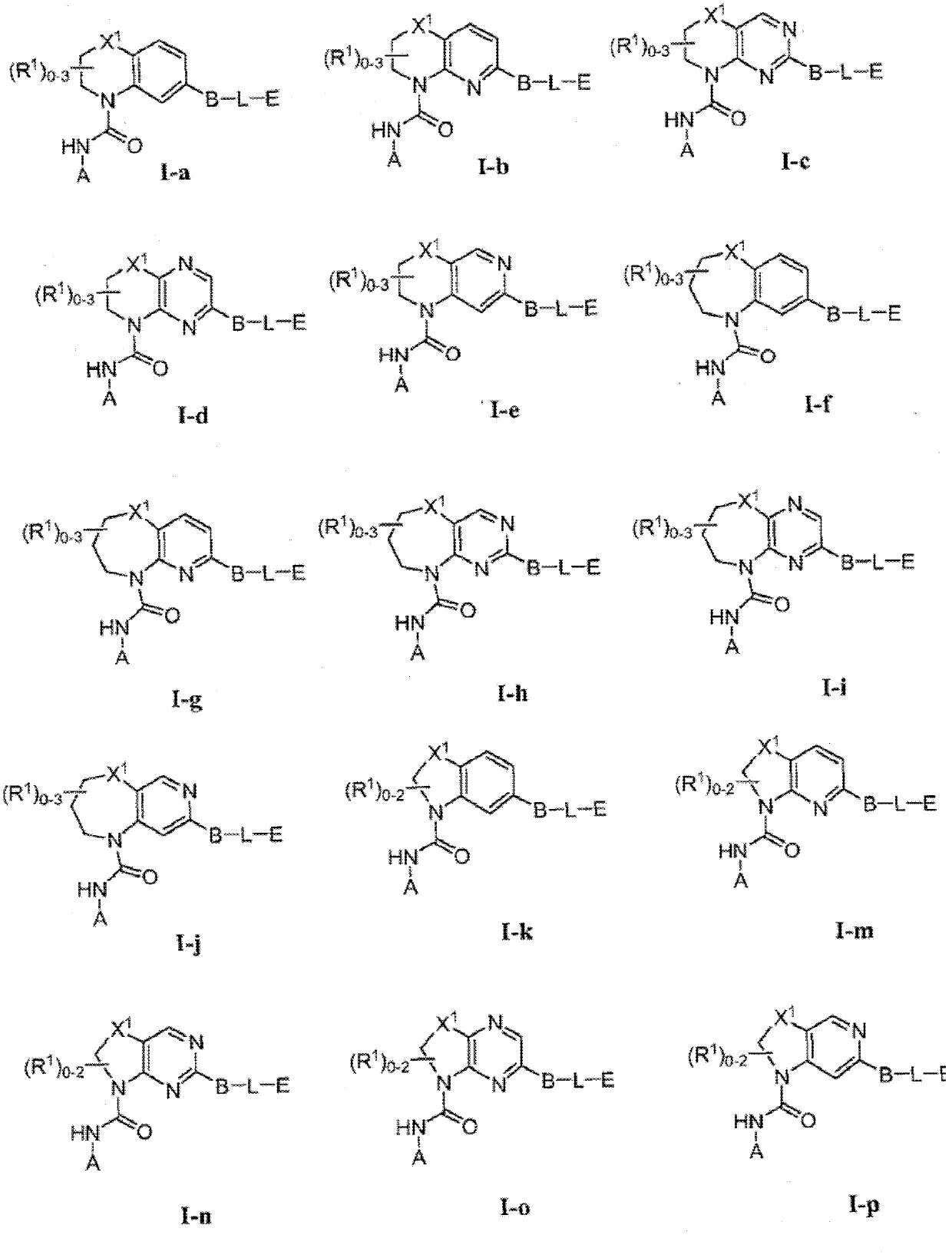
Heterocyclic compounds and methods of use
In one aspect, the present invention provides for a compound of Formula I in which the variable X1a, X1b, X1c, X1d, Q, A, R1, B, L, E, and the subscripts m and n have the meanings as described herein. In another aspect, the present invention provides for pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds of Formula I as well as methods for using compounds of Formula I for the treatment of diseases and conditions (e.g., cancer, thrombocythemia, etc) characterized by the expression or over-expression of Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic proteins, e.g., of anti-apoptotic Bcl-xL proteins.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +2
Methods for identifying agents that modulate apoptosis in cells that over-express a Bcl-2 family member protein
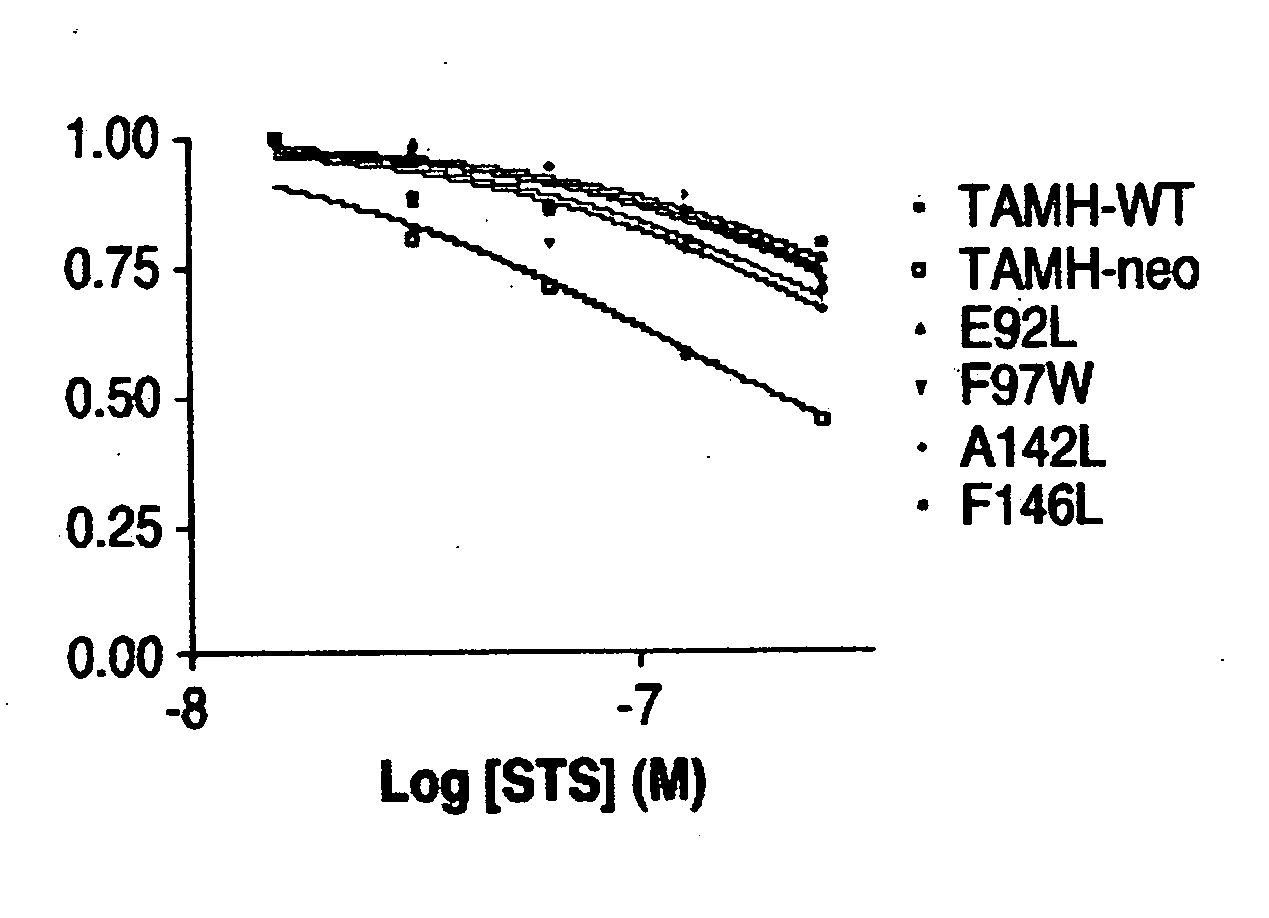
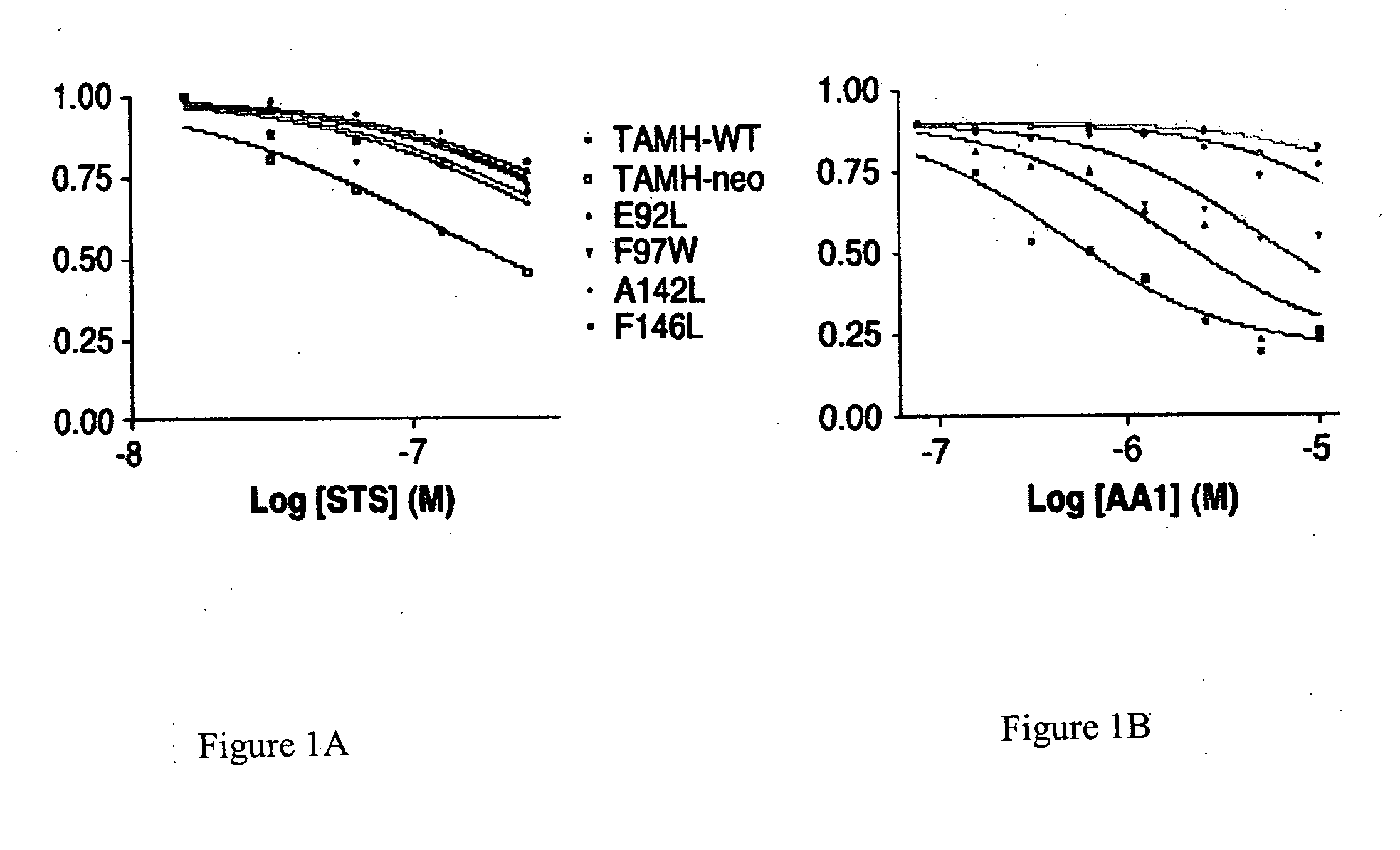
InactiveUS20060188948A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMutated proteinGlucose uptake
The present invention provides methods and combinations of methods for identifying agents that modulate the apoptotic state of a cell by binding to the hydrophobic groove of a Bcl-2 family member anti-apoptotic protein. In certain embodiments, the methods generally comprise the use of Bcl-2 family member proteins having one or more mutations in the hydrophobic groove that, relative to a corresponding protein lacking the mutation, affect, e.g., binding of desired agents or in vitro antimycin sensitivity without substantially altering tertiary protein structure. In these embodiments, the methods comprise the identification of agents that exhibit reduced binding affinities and / or other biological activities for the mutant proteins relative to the corresponding Bcl-2 family member lacking the mutation. In other embodiments, the methods generally comprise the detection of the ability of an agent to induce increased glucose uptake or lactate production in proportion to the level of expression of an anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member protein.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Medicine for resisting myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
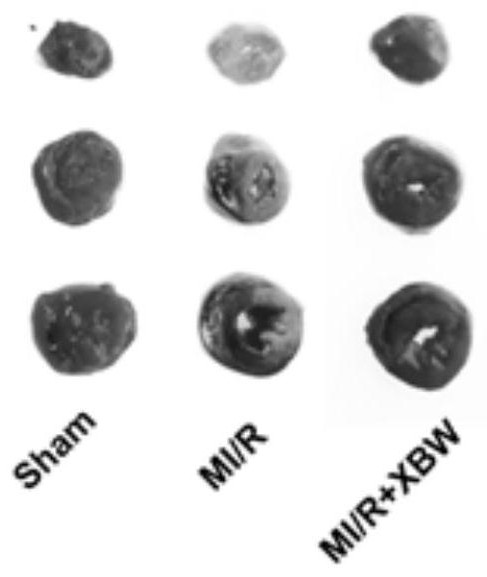
PendingCN111920871AImprove protectionInhibit apoptosisAmphibian material medical ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsPharmacologyCell injury
The invention provides a medicine for resisting myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. The medicine comprises Xinbao pills. The invention creatively discovers that the Xinbao pill can be used as a medicine for resisting myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury; the Xinbao pill can also be used for preparing a medicine for resisting myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury, has a very strong protection effect on hypoxic reoxygenation h9c2 myocardial cells in vitro, and can inhibit h9c2 cell injury caused by hypoxic reoxygenation; the area of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury rat heart infarction induced by coronary artery anterior left descending branch ligation and the content of CK-MB can be remarkably reduced in vivo, and myocardial cell apoptosis is inhibited; meanwhile, expression ofheart tissue apoptosis related protein can be inhibited, the proportion of anti-apoptosis protein is increased, and expression of cell autophagy related protein Beclin-1 and LC3II is inhibited. The invention provides a theoretical basis for researching a treatment strategy of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, and provides an embedding point for preparing a new medicine for resisting myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Owner:GUANGDONG XINBAO PHARMA TECH CO LTD
A kind of puma inhibitor and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN107304192BApoptosis blockInhibition of competitive bindingOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRadioprotective DrugsChemical compound
The present invention relates to the field of medical technology, specifically to a type of PUMA inhibitor and its preparation method and use. The PUMA inhibitor is a compound of the following formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Wherein, the definition of each substituent is as described in the specification. The compound of formula I or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the present invention can target PUMA protein, has good physical and chemical properties, good anti-apoptosis and radioprotective effects, and can selectively inhibit the interaction between PUMA protein and Bcl-2 class The competitive binding between anti-apoptotic proteins blocks cell apoptosis and effectively protects against bone marrow damage. The present invention provides novel ideas and strong evidence for the application of small molecule inhibitors of PUMA protein in radiation protection drugs, and is expected to become an efficient, low-toxic and stable clinical radiation protection drug.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
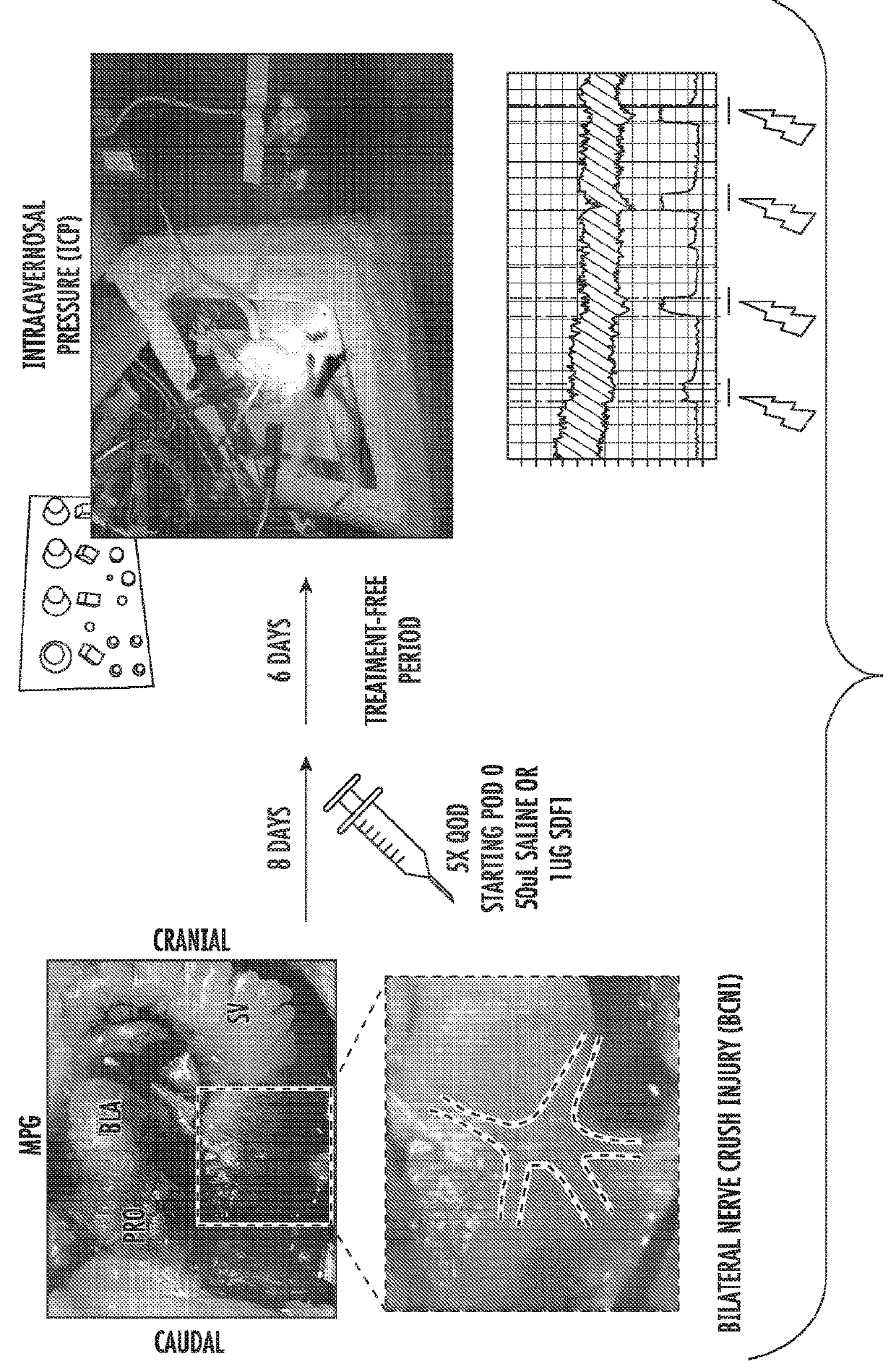
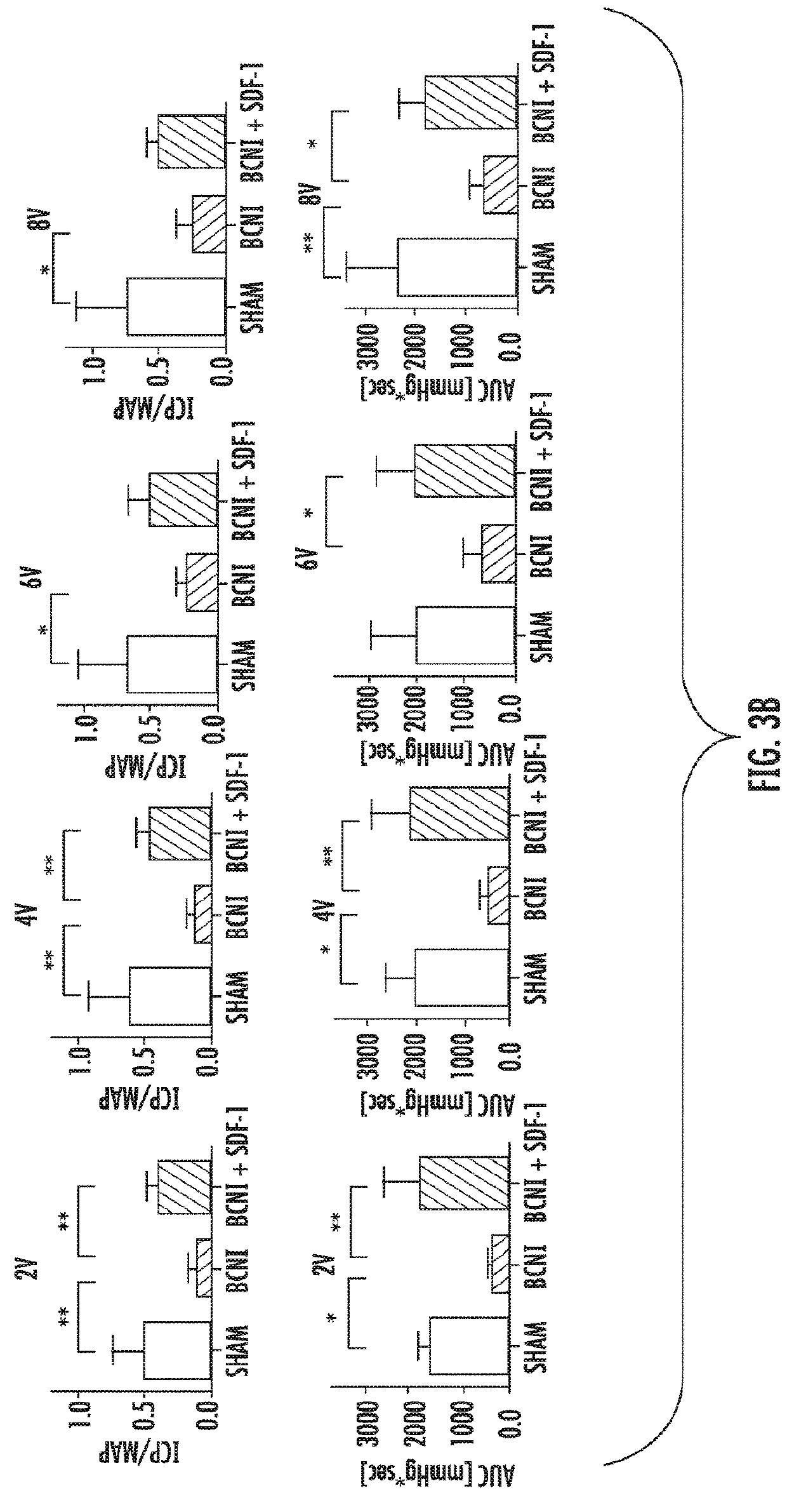
Stromal derived factor 1 and it's use in the prevention and treatment of erectile dysfunction
ActiveUS20200188483A1Promote growthImprove preservationChemokinesPeptide/protein ingredientsSexual impotencePelvic region
Stromal Derived Factor-1 (SDF-1) is a small, naturally occurring, potent chemokine with inherent angiogenic, neurogenic, anti-apoptotic protein, which is also a potent stem cell chemoattractant, cardiovascular disease, and other metabolic disturbances. The present invention provides methods for treating erectile dysfunction in a male subject comprising administering to the major pelvic ganglion supplying the cavernous nerves subject compositions comprising SDF-1. SDF-1 promotes stem cell activation, to the major pelvic ganglion supplying the cavernous nerves, helps cell preservation, and prevents adverse penile remodeling. It can be administered as a protein or by gene therapy including but not limited to plasmid DNA, viral transduction, or nanoparticle delivery directly to the penis or to the neurovascular bundle or other pelvic nerve structures during the time of surgery, or before injury, or to treat existing erectile dysfunction.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Corn stigma polysaccharide combined drug preparation
The invention relates to a corn stigma polysaccharide combined drug preparation and belongs to the technical field of drug application and aims to solve the problem of how to develop the hepatitis C virus resistant function of corn polysaccharide. The corn stigma polysaccharide combination drug preparation is prepared from components in parts by weight as follows: 1.3-1.8 parts of corn stigma polysaccharide, 0.3-0.7 parts of 2-deoxy-D-glucose, 5-15 parts of gelatin and 0-8 parts of a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The drug preparation can perform the functions of inducing IFN (interferon), down-regulating the content of cytomembrane cholesterol, influencing Jak-STAT antiviral signal channels and BAX-Bcl2 channels related with tumor apoptosis and promoting apoptosis of HCV infection cells by up-regulating apoptosis related protein and inhibiting anti-apoptosis protein.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY +1
Bcl-2 protein apoptosis inducer and application
PendingCN114478520APotent BCL2/BAK blocking activityPotent proliferation inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugAntiapoptotic protein
The invention discloses a Bcl-2 protein apoptosis inducer, and further discloses application of a compound and a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound in preparation of drugs for treating anti-apoptosis protein BCL-2 related diseases such as infectious diseases, immune diseases, inflammatory diseases and cell proliferation abnormality diseases. The compound provided by the invention has strong BCL2 / BAK blocking activity, has strong inhibitory activity on BCL-2 (G101V) and BCL-2 (D103Y), and has strong proliferation inhibitory activity on mutant cell strains. The compound can be applied to treatment of infectious diseases, immune diseases, inflammatory diseases or abnormal cell proliferation and the like which benefit from inhibition of the anti-apoptotic protein BCL-2 alone or in combination with other medicines.
Owner:HANGZHOU HERTZ PHARMA +1
Application of epimedin B in preparation of medicine for treating dopaminergic neuron damage
InactiveCN110613725AImprove motor coordinationIncrease voluntary activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBiopharmacologyNeuron
The invention belongs to the fields of cytobiology and pharmacology, and relates to an application of a natural medicine herba epimedii extract epimedin B, in particular to an application of epimedinB in preparation of a medicine for treating dopaminergic neuron damage. Expression of apoptotic protein is promoted by increase of dopaminergic neurons in brain substantia nigra due to dopaminergic neuron damage, and meanwhile, expression of tyrosine hydroxylase and anti-apoptotic protein is reduced. Epimedin B has remarkable anti-apoptotic activity, can be used for preparing medicines for preventing and / or treating neuronal apoptosis and related diseases thereof. The application has higher clinical application value and development prospects.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Compounds and methods of use
Owner:GENENTECH INC +2
Compound stybenpropol A and its application in preventing and treating atherosclerosis
ActiveCN110668946BInhibit apoptosisInhibits inflammatory damageOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryInflammatory factorsNitric oxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and specifically discloses a compound Stybenpropol A and its application in improving atherosclerosis (AS). The present invention extracts a novel compound Stybenpropol A from benzoin, and the research results show that in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), Stybenpropol A can inhibit TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation and nuclear translocation and enhanced expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, thereby inhibiting endothelial cell inflammatory injury, increasing nitric oxide secretion levels, reducing vascular adhesion molecules and pro-inflammatory factor levels, can significantly inhibit TNF- α-induced inflammatory injury and apoptosis of HUVECs provides a new option and approach for the development of anti-atherosclerotic drugs, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
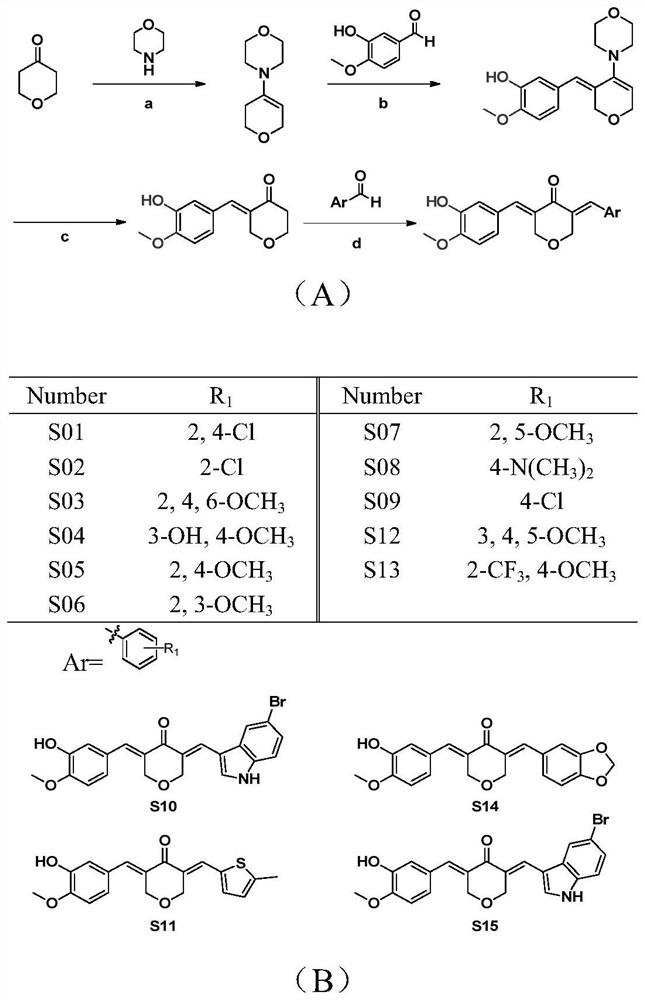
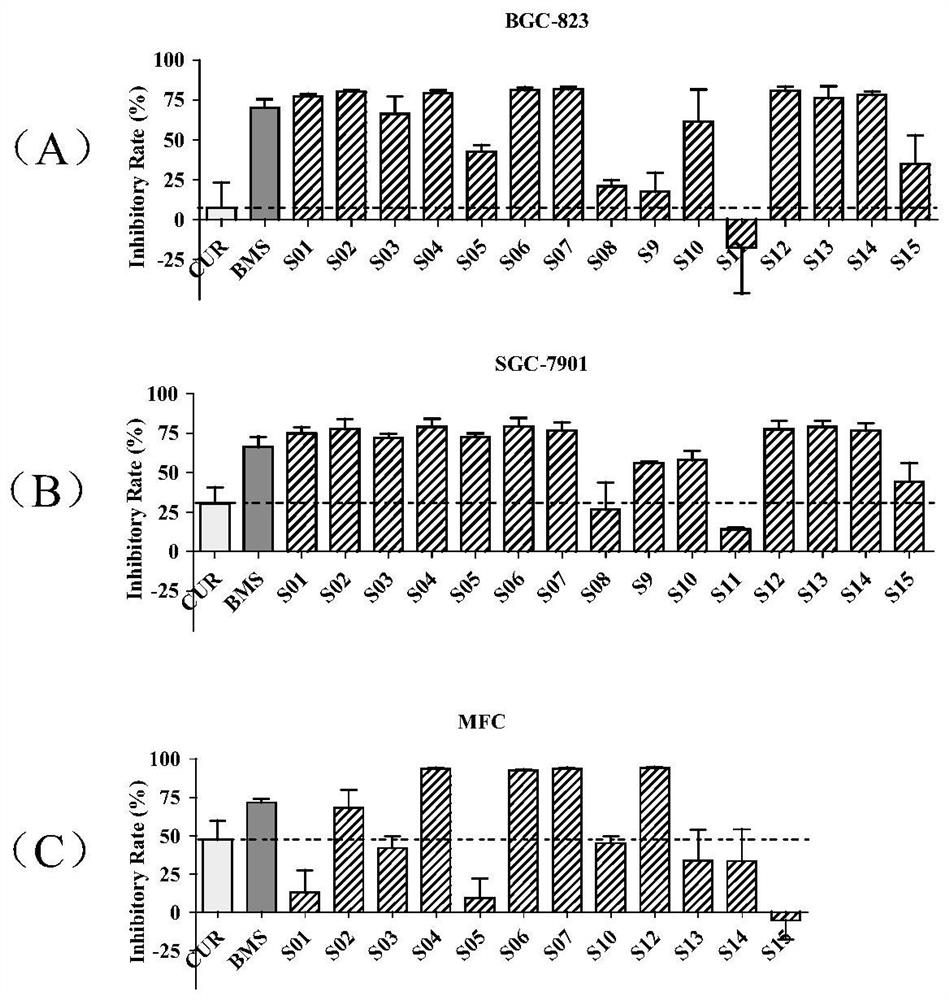
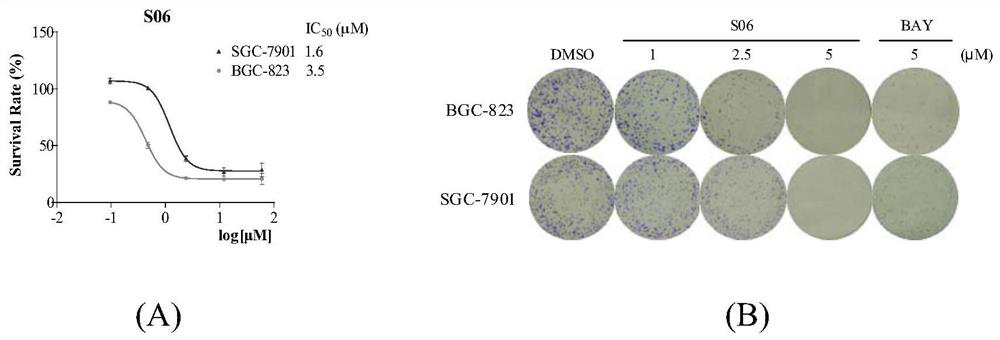
Asymmetric curcumin compounds and their application in the preparation of anti-gastric cancer drugs
ActiveCN107501219BGood curative effectIncreased sensitivityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsCancer drugsIrinotecan
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry and particularly relates to an application of asymmetric curcumine compounds to preparation of anti-gastric-cancer drugs. The compounds can effectively inhibit growth of gastric cancer cells BGC-823, SGC-7901 and MFC, inhibit formation of gastric cancer cell colonies, inhibit NF-kappaB signaling pathways in the gastric cancer cells, down-regulate expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, up-regulate expression of apoptin Bax and induce gastric cancer cell apoptosis, wherein the active compound S06 can effectively enhance anti-gastric-cancer activity of irinotecan and can serve as a potential anti-gastric-cancer drug.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com