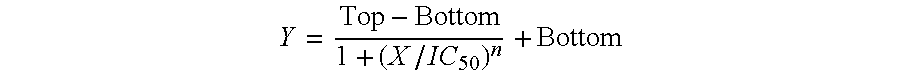Patents
Literature
43 results about "Histone Acetyltransferases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
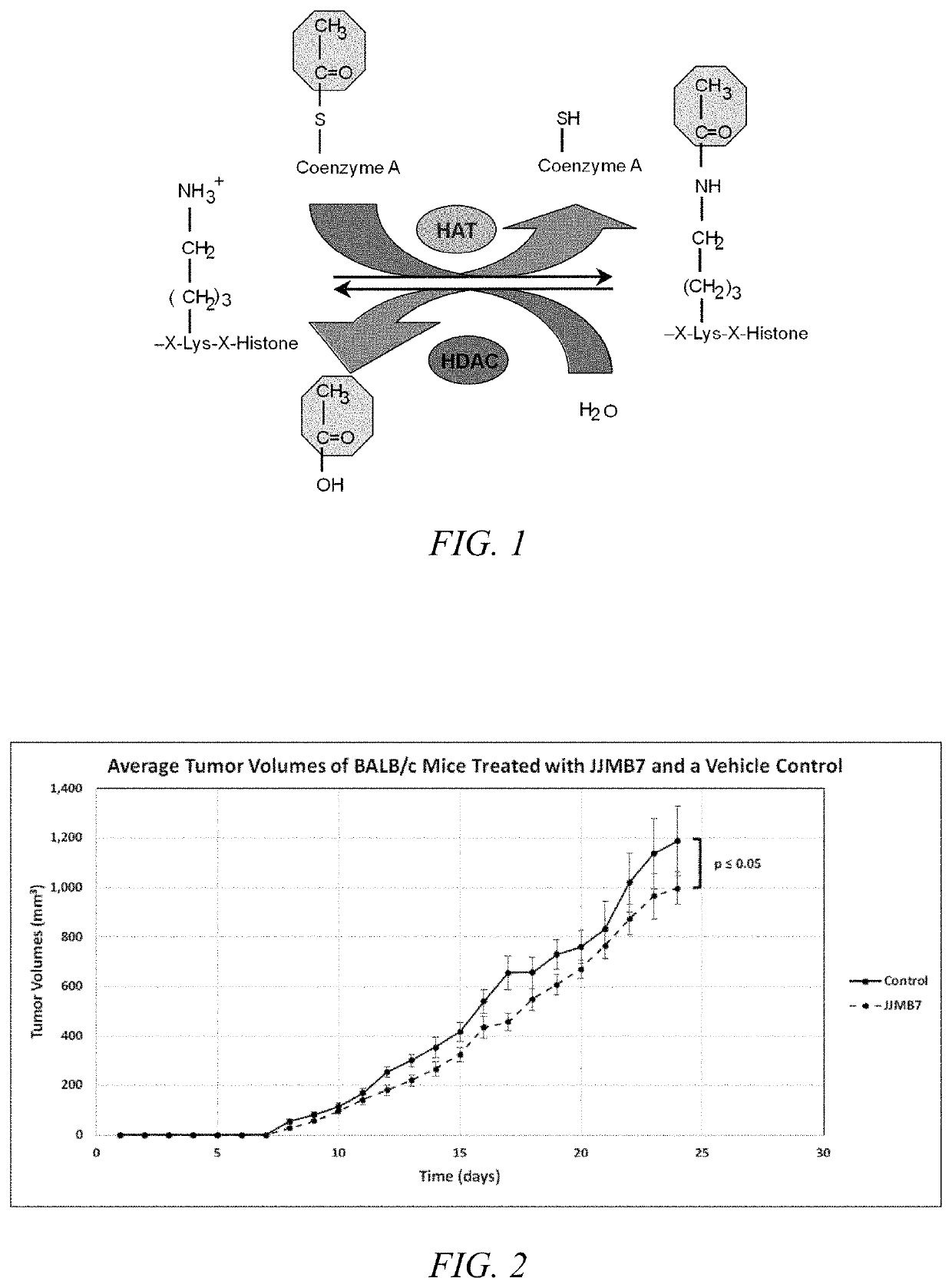
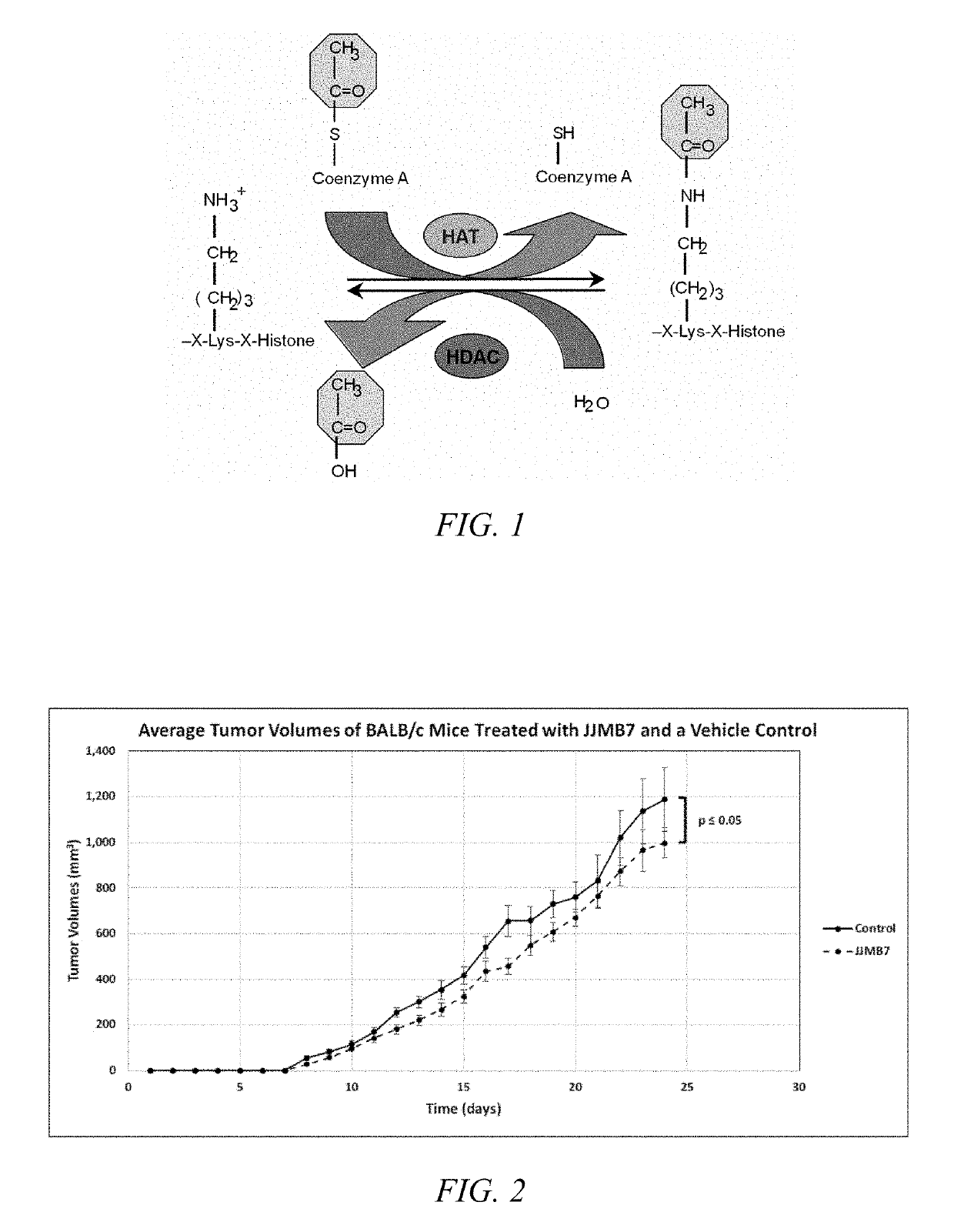
Enzymes that catalyze acyl group transfer from ACETYL-CoA to HISTONES forming CoA and acetyl-histones.
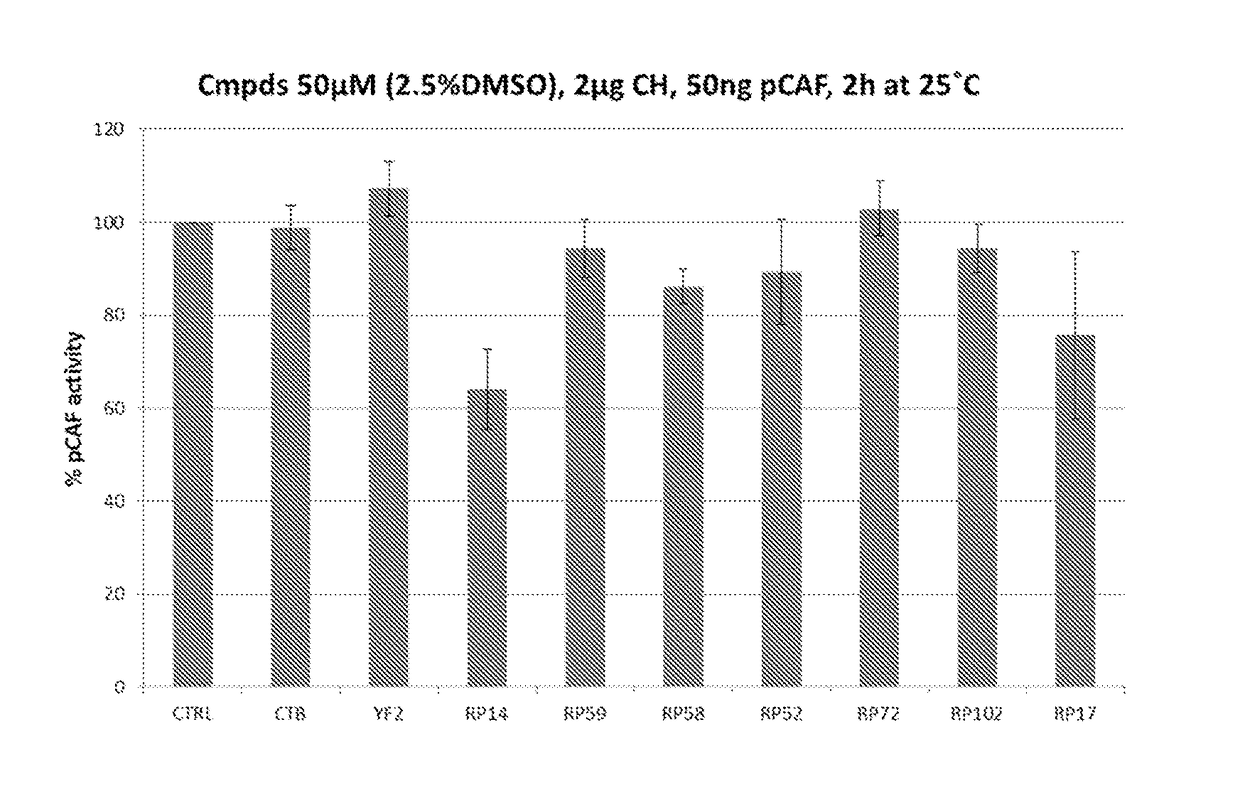
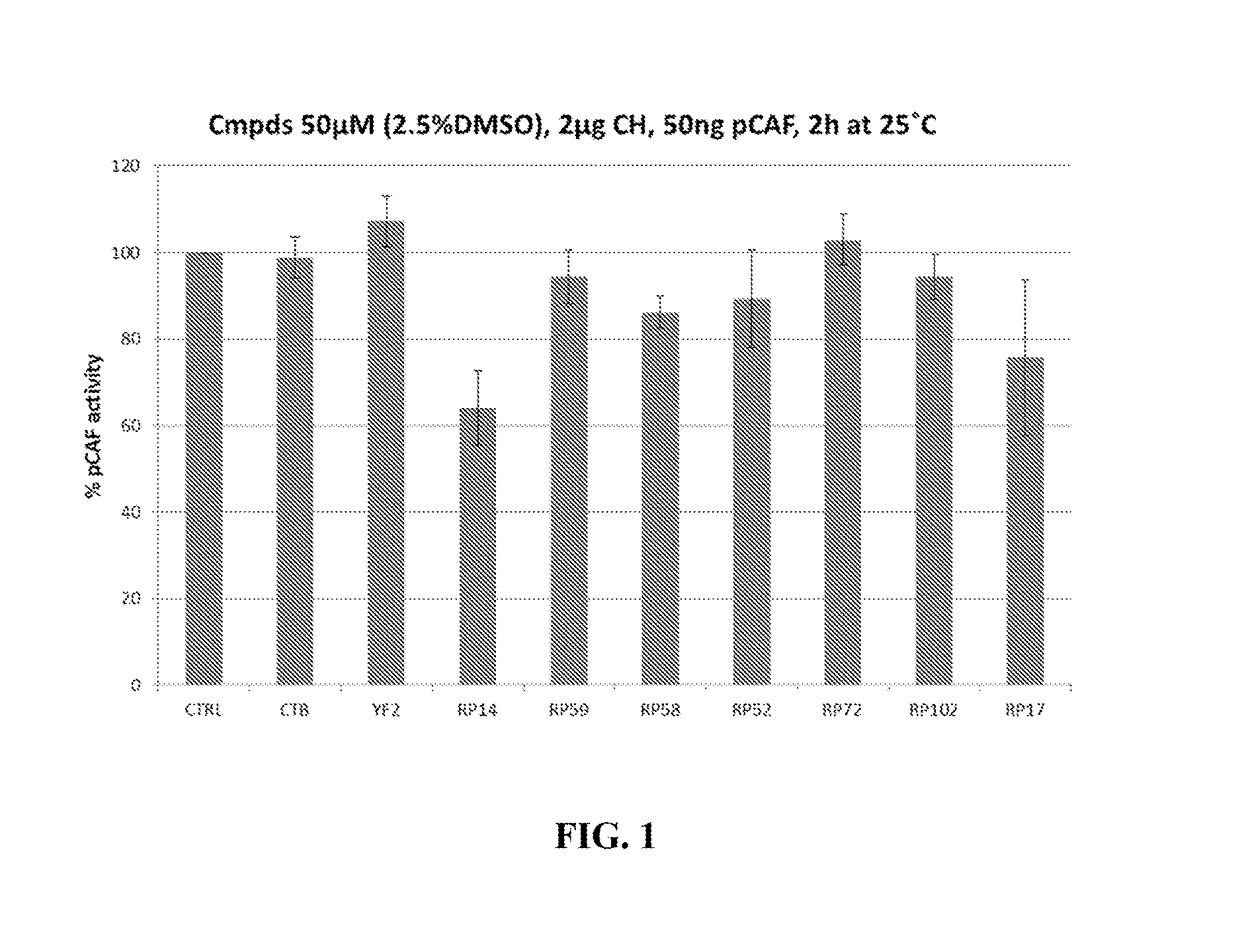
Hat acetylation promoters and uses of compositions thereof in promoting immunogenicity
InactiveUS20100166781A1Improving immunogenicityPromoting surfaceAntibacterial agentsBiocideMHC class IFactor ii
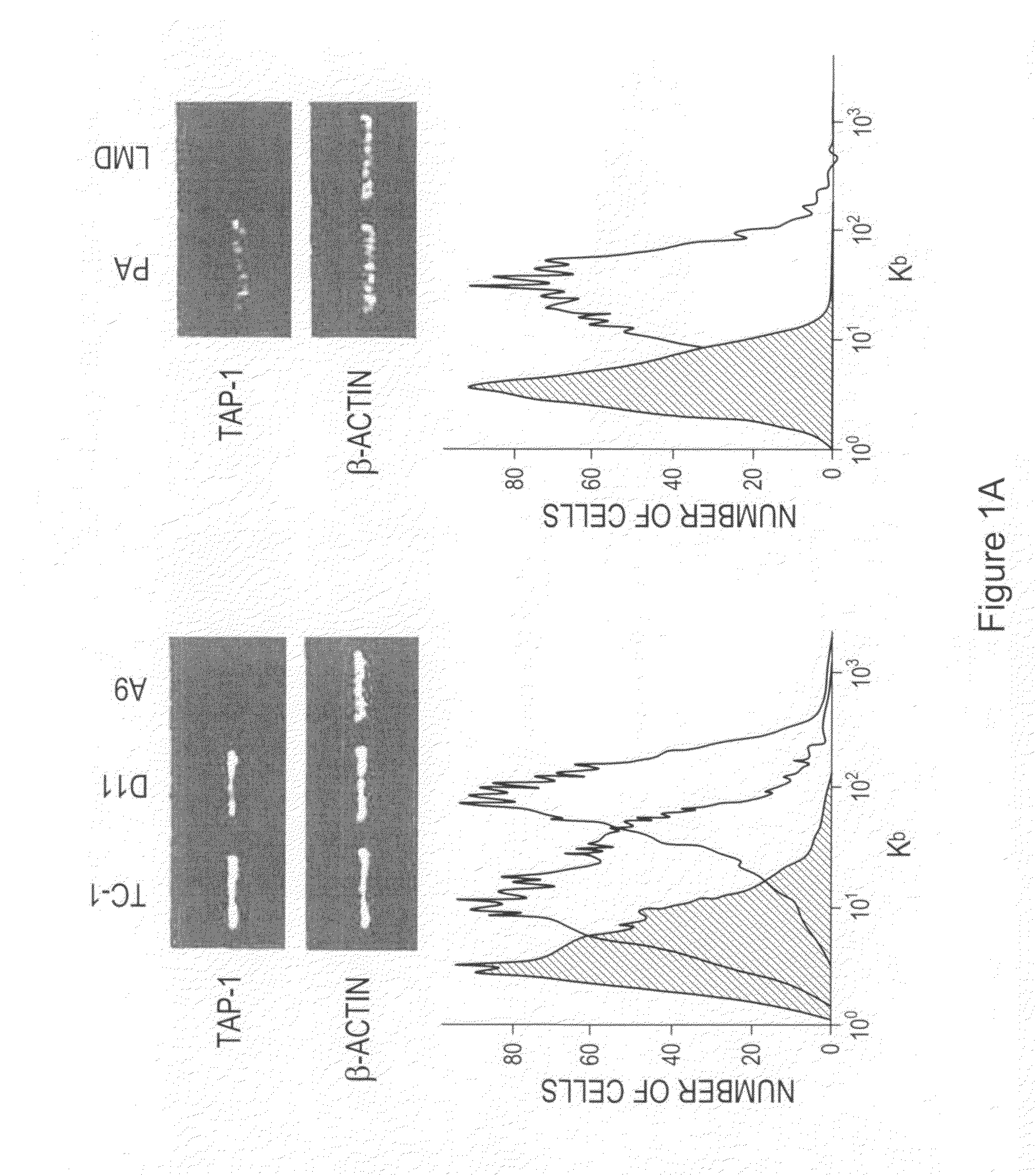
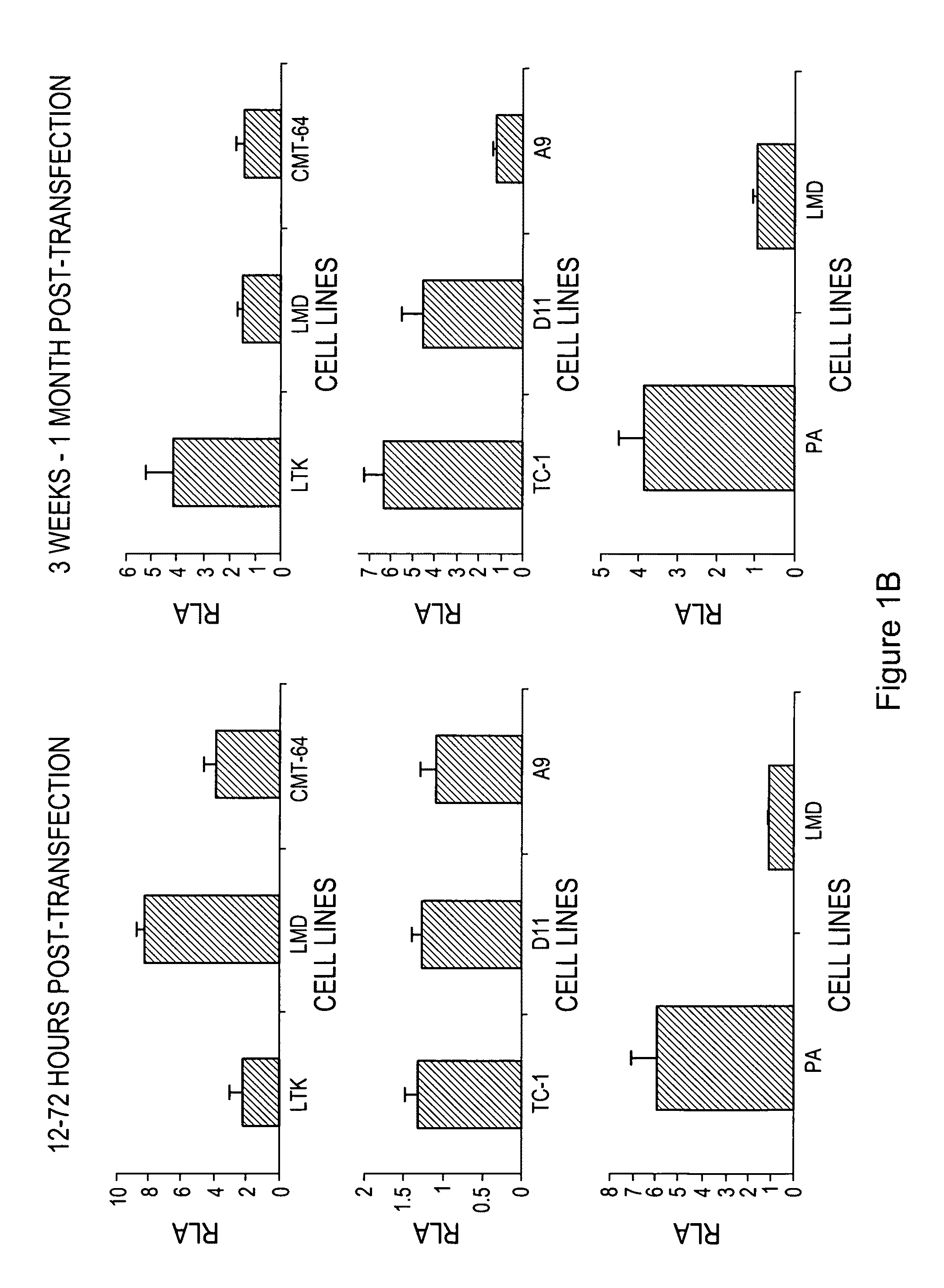
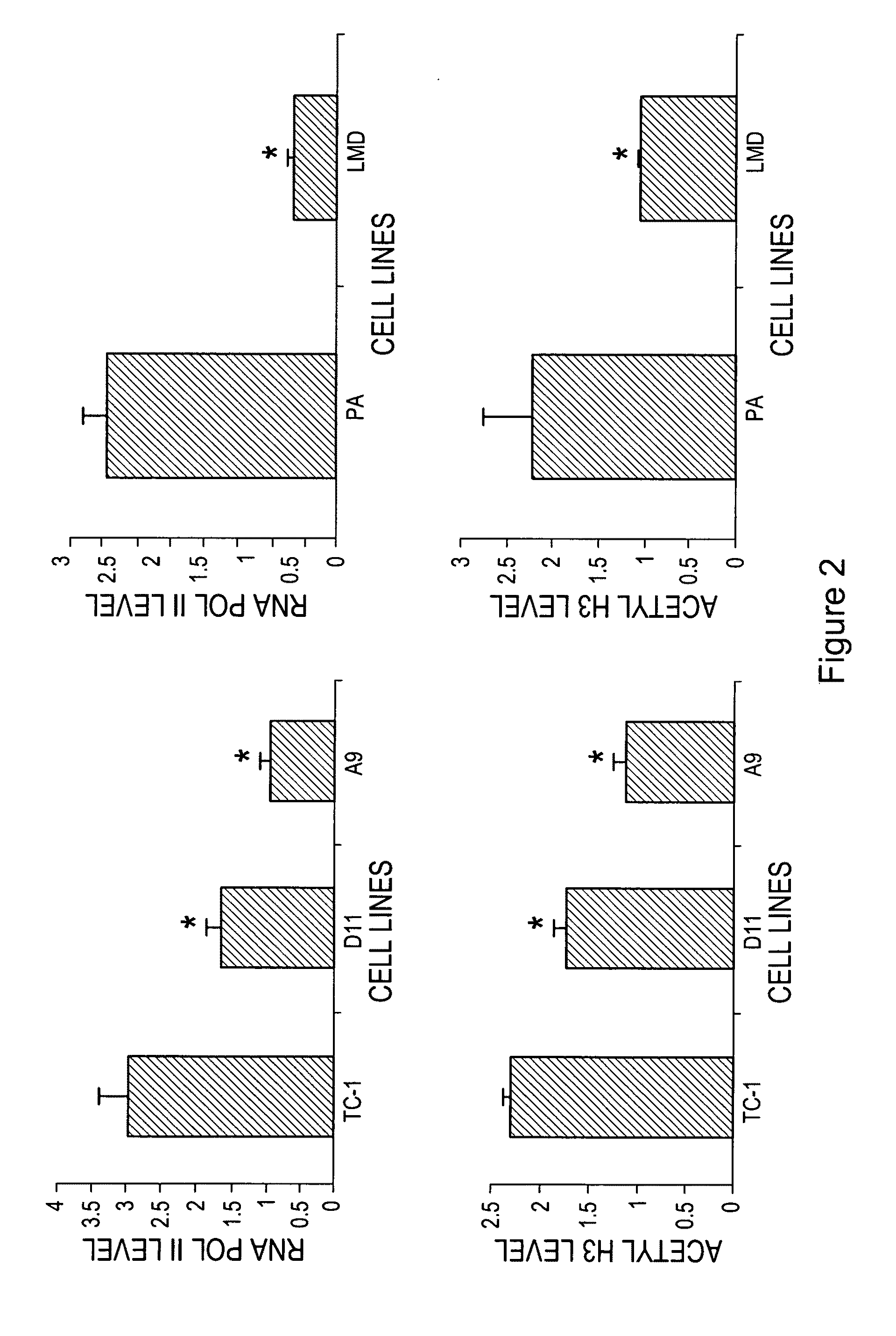
The invention provides processes and compositions for enhancing the immunogenicity of TAP-1 expression-deficient cells by increasing the presentation of MHC Class I surface molecules for detection by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte cells through increased TAP-1 expression, which comprises administering to the TAP-1 expression-deficient cells a TAP-1 expression increasing amount of a bio-acceptable substance that promotes transcription of TAP-1 gene in the cells to cause enhanced MHC Class I surface expression of the cells. The bio-acceptable substance may be a histone H3 deacetylase inhibitor, such as trichostatin A, a transcriptional co-activator having intrinsic histone acetyl transferase activity or a histone acetyl transferase comprising at least one member of the CBP / p300 protein family. The process and compositions increase the immunogenicity of the target cells to enhance their destruction by cytotoxic lymphocytes.
Owner:JEFFERIES WILFRED
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for accumulating acetylglucosamine and application thereof
ActiveCN105176903AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetylglucosamineGenetically engineered
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for accumulating acetylglucosamine and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis for accumulating the acetylglucosamine and the application thereof, recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS serves as an original strain, the glucosamine synthesizing route is enhanced by excessively expressing glucosamine histone acetyltransferase coding genes (CeGNA1) from caenorhabditis elegans, and the genetically engineered bacterium bacillus subtilis for accumulating the acetylglucosamine is obtained; the yield on the shake flask level reaches 7.31 g / L, and a foundation is laid for further producing the glucosamine by transforming the bacillus subtilis in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
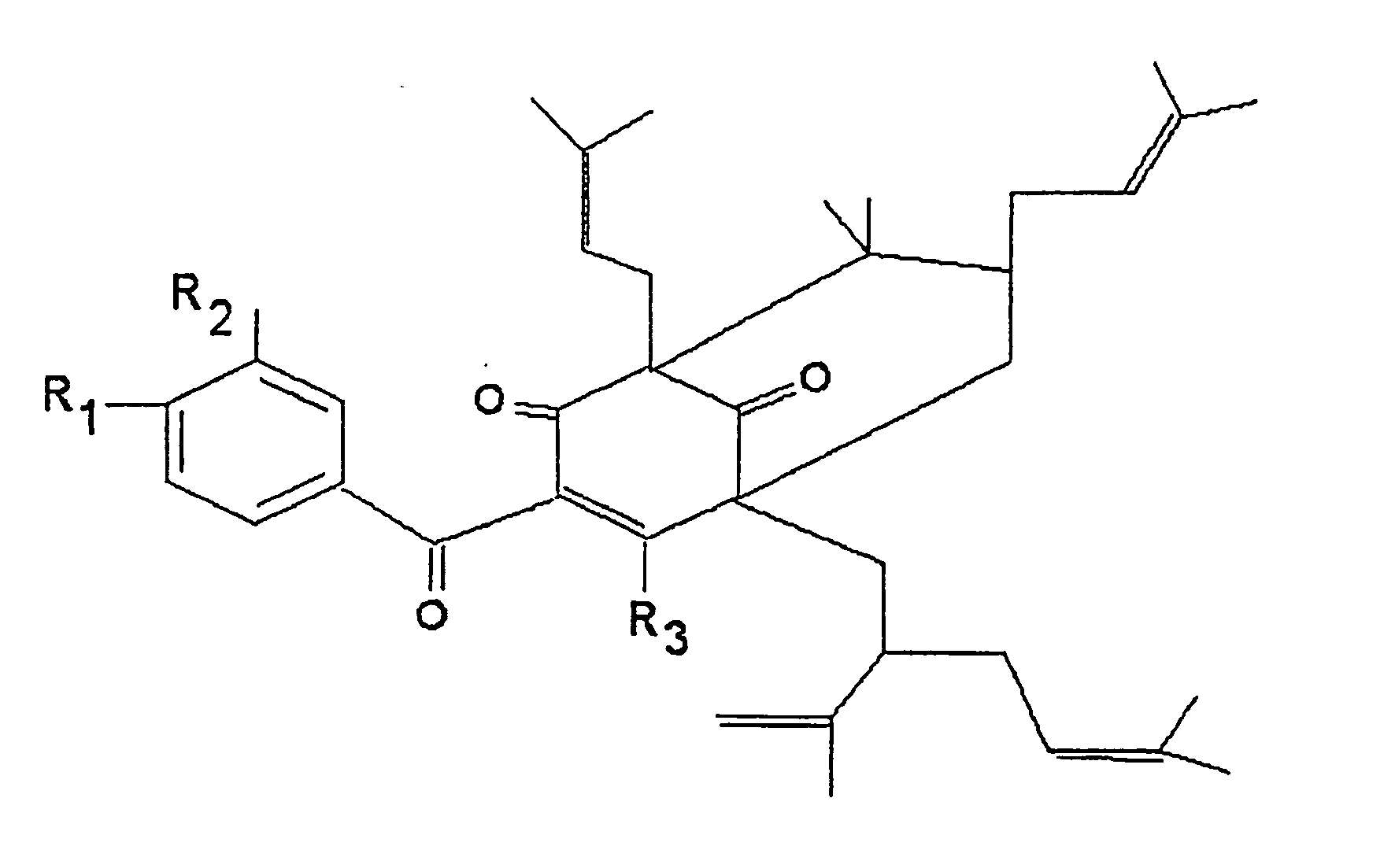
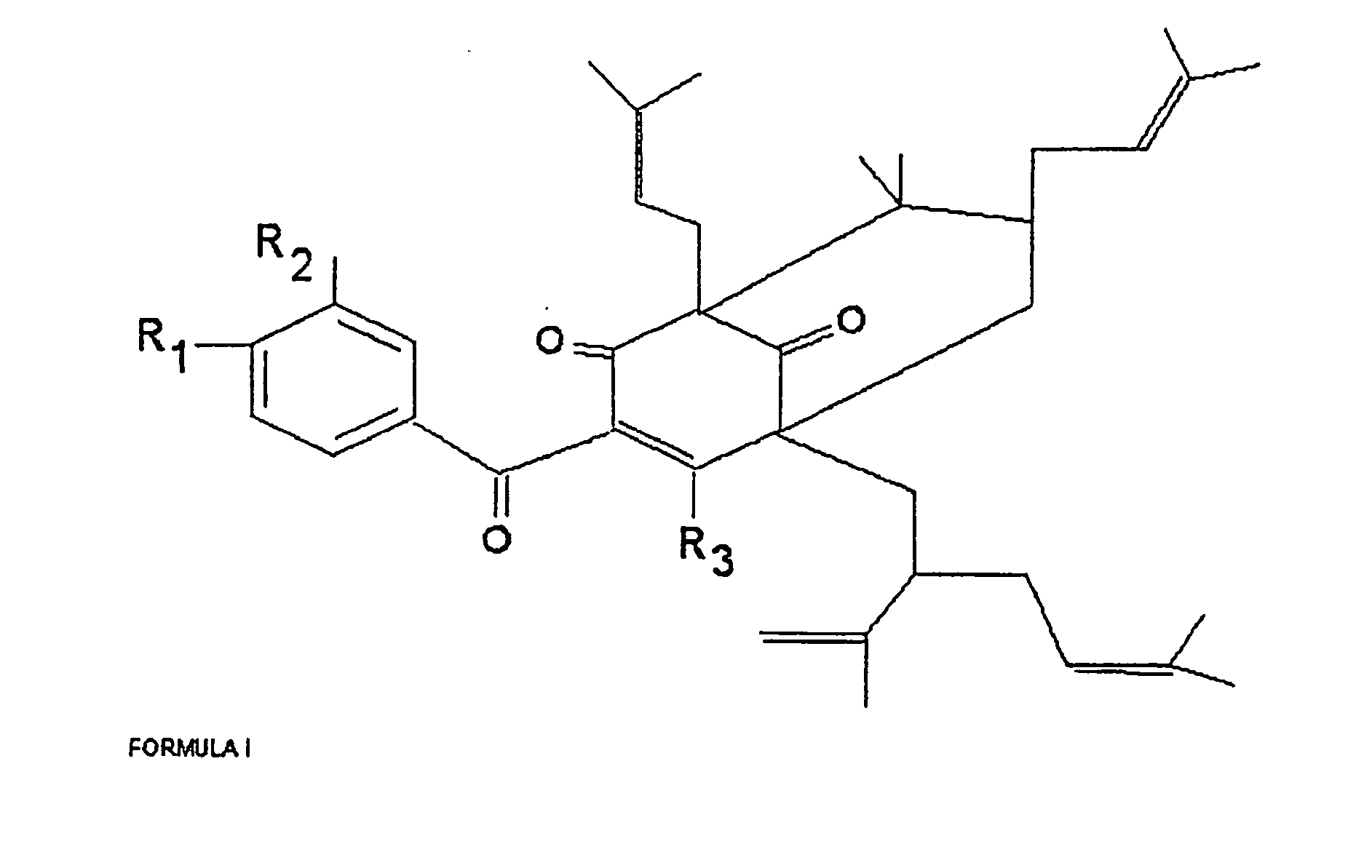
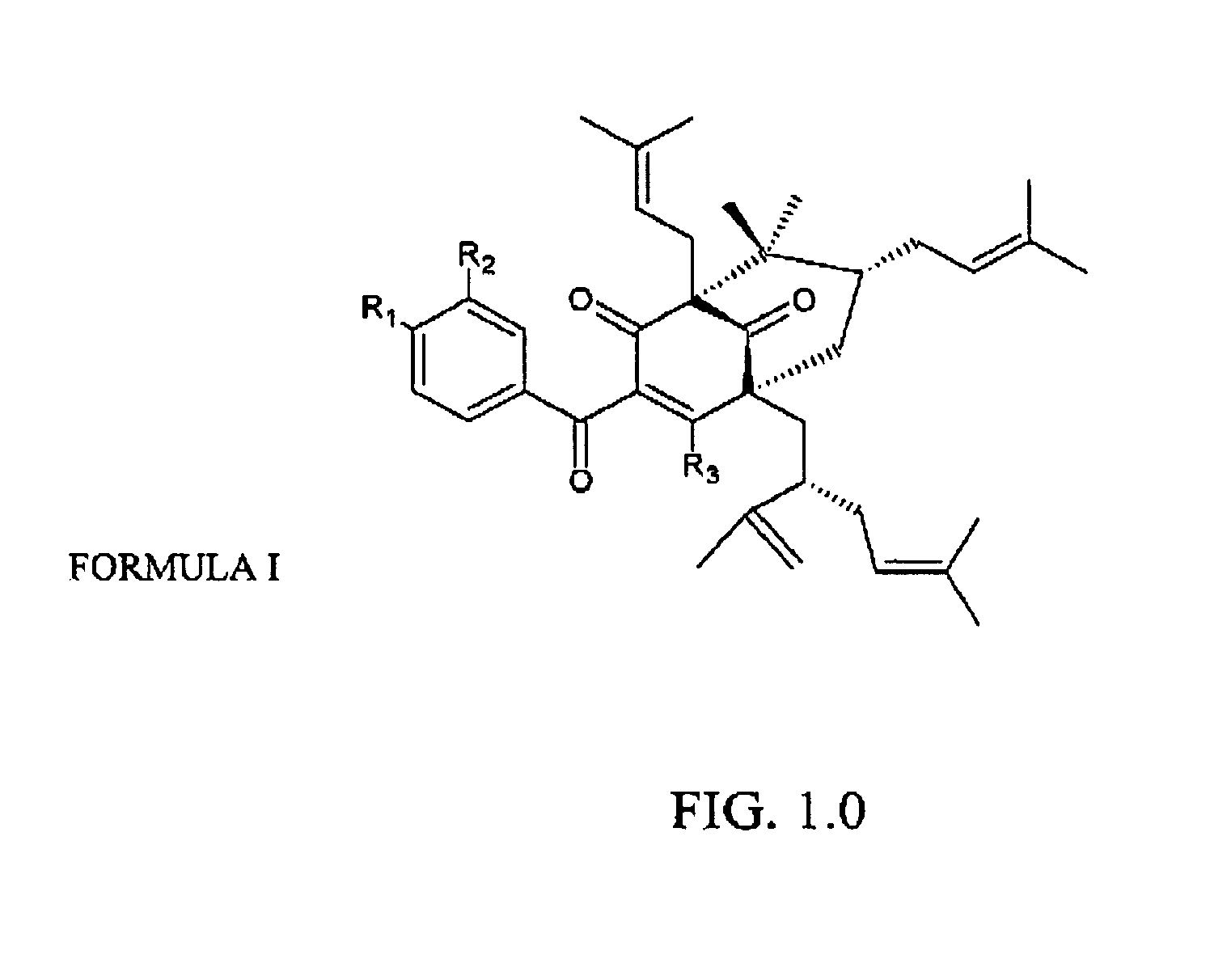
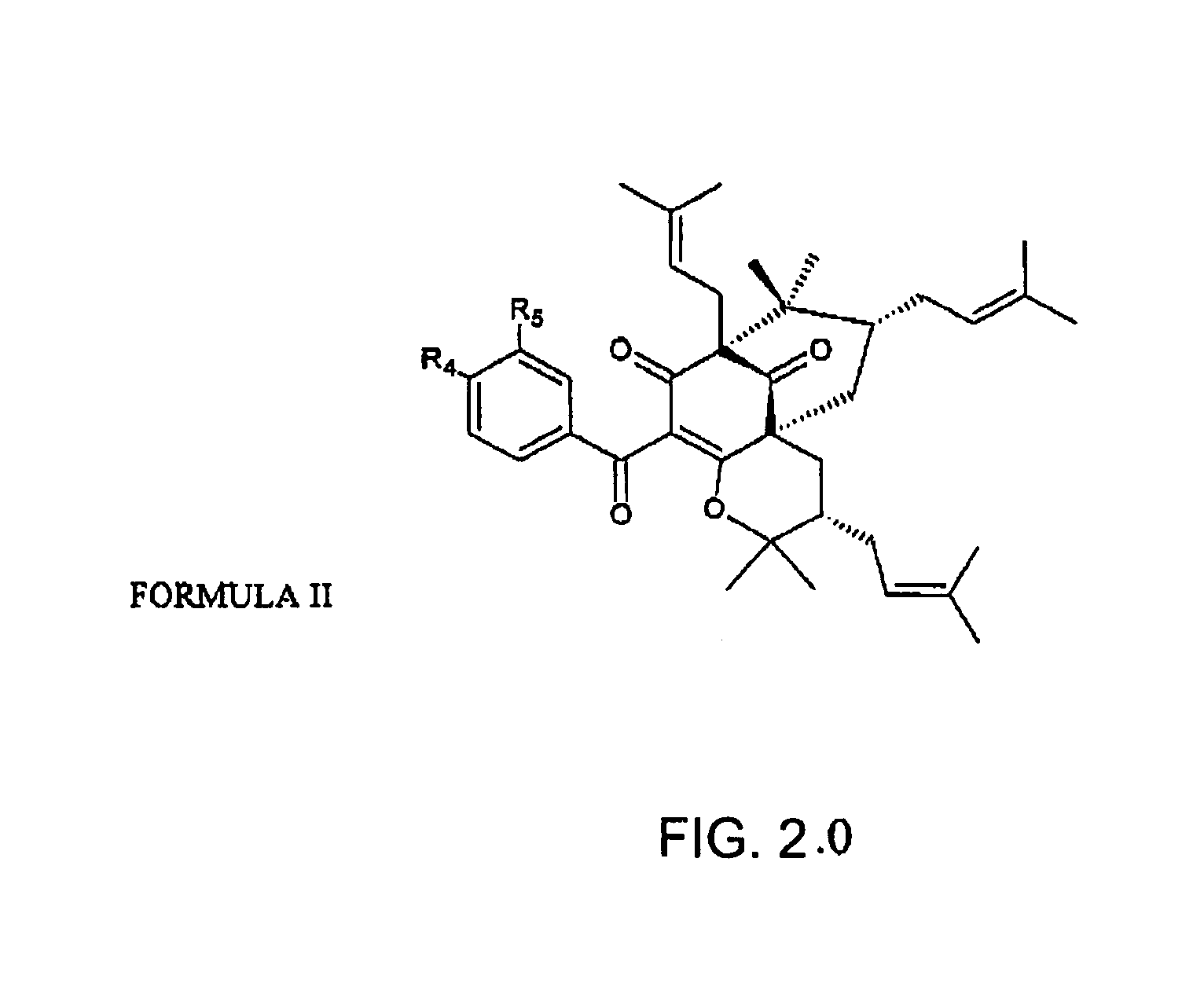
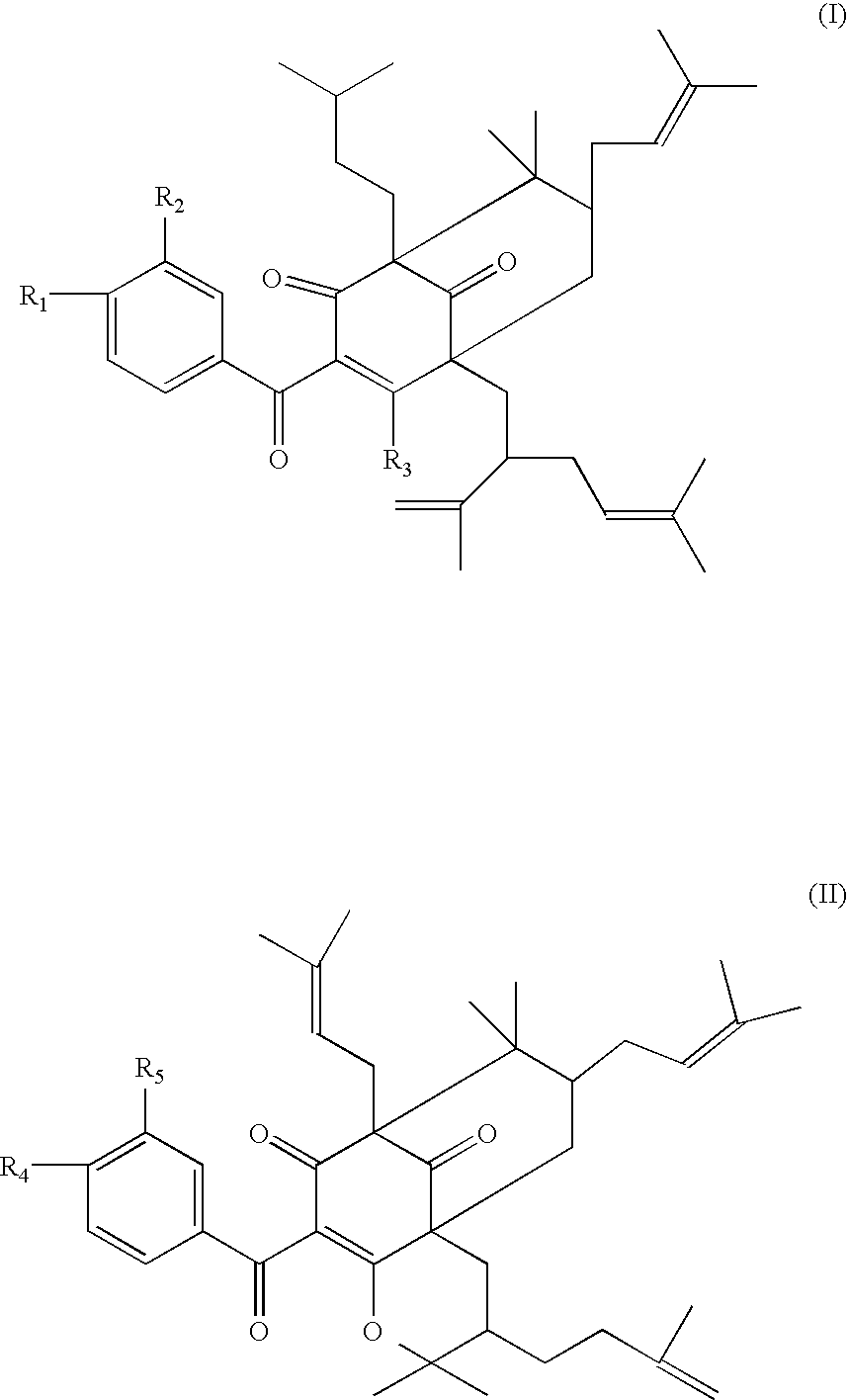
Polyisoprenylated Benzophenones and Their Isomers as Inhibitors of Histone Acetyltransferases and Uses thereof
In this patent we describe the purification of prenylated benzophenones from the fruit rinds of Garcinia species and its evaluation as an inhibitor for Histone acetyltransferases p300 and PCAF. We have found that prenylated benzophenones are potent HAT inhibitors of p300 (IC50-1 μM) and pCAF (IC50-15 μM). The inhibitors significantly repress the p300 HAT dependent transcriptional activation from in vitro assembled chromatin template but had no effect on transcription from DNA. These results suggest that the compounds could be specific to HATs. Thus these compounds should be useful as biological switching molecule for evaluating the role of p300 and PCAF in cellular functions and may be useful as new chemical entities for the development of anticancer drugs.
Owner:JAWAHARLAL NEHRU CENT FOR ADVANCED SCI RES
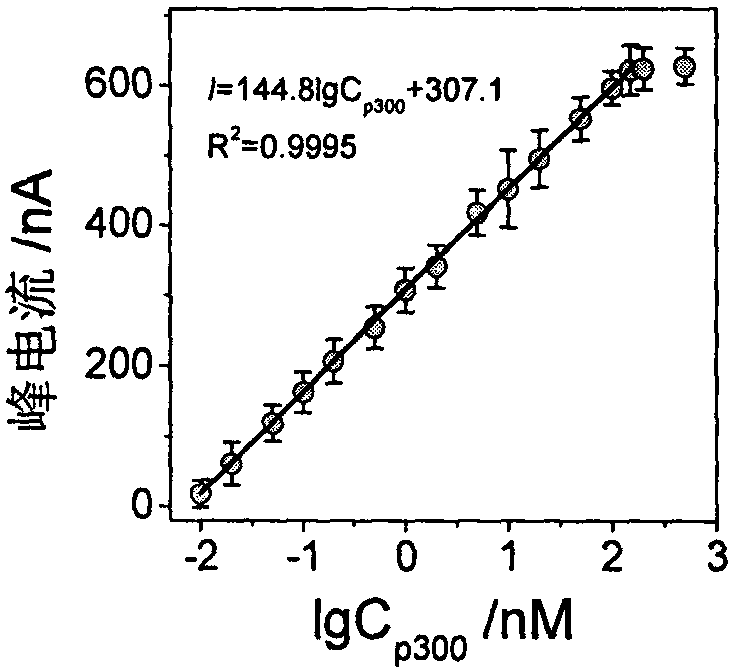
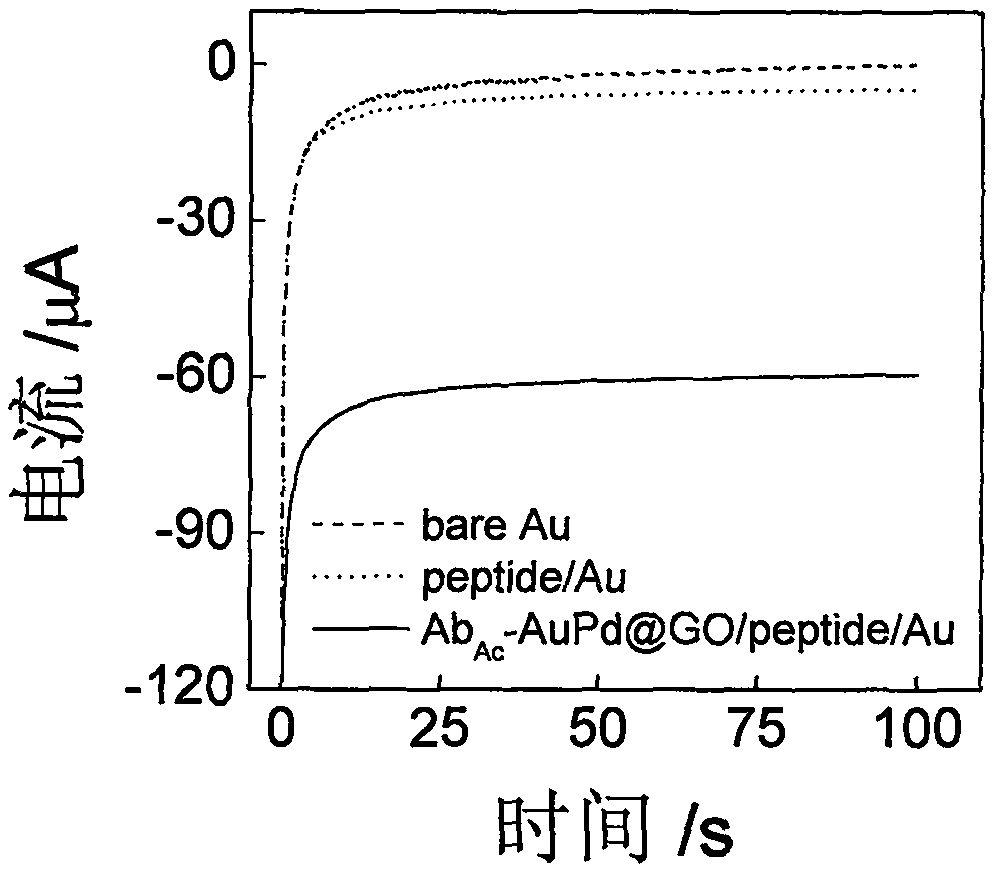
Construction method and application of electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor for detecting activity of histone acetyltransferase
ActiveCN108593751AHigh sensitivityAchieving High Sensitivity DetectionMaterial electrochemical variablesWater bathsUltrasonic dispersion
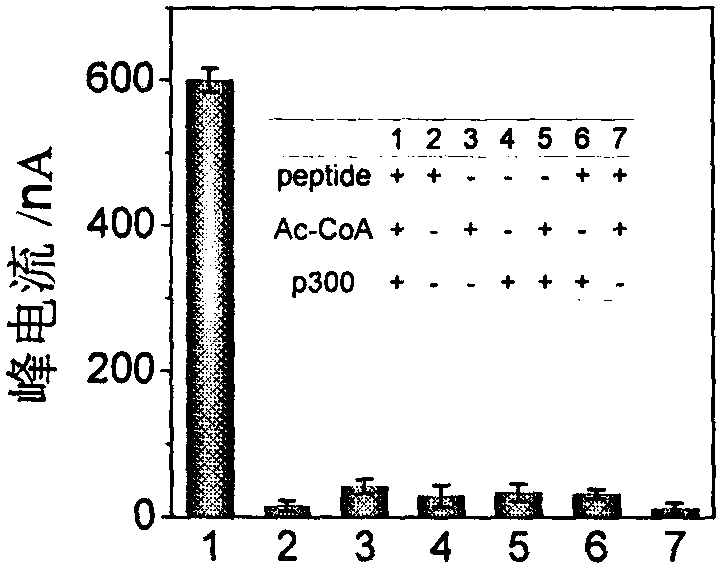
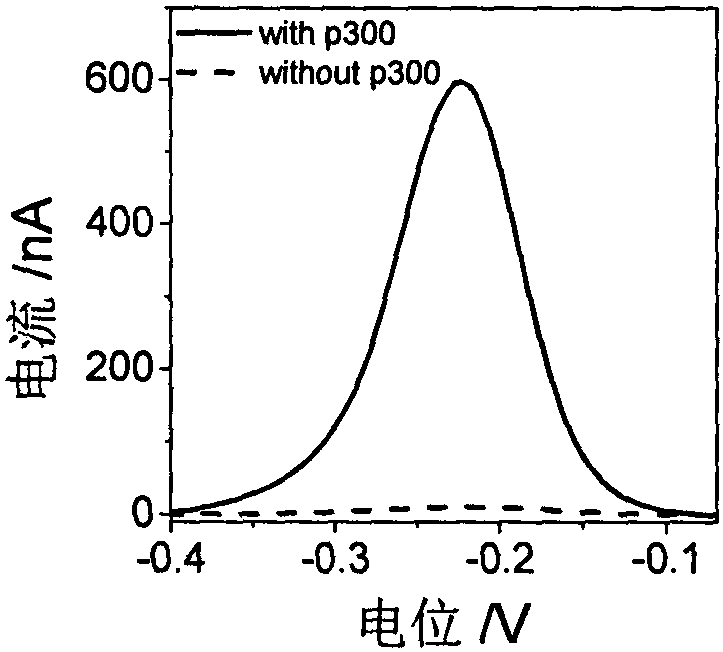
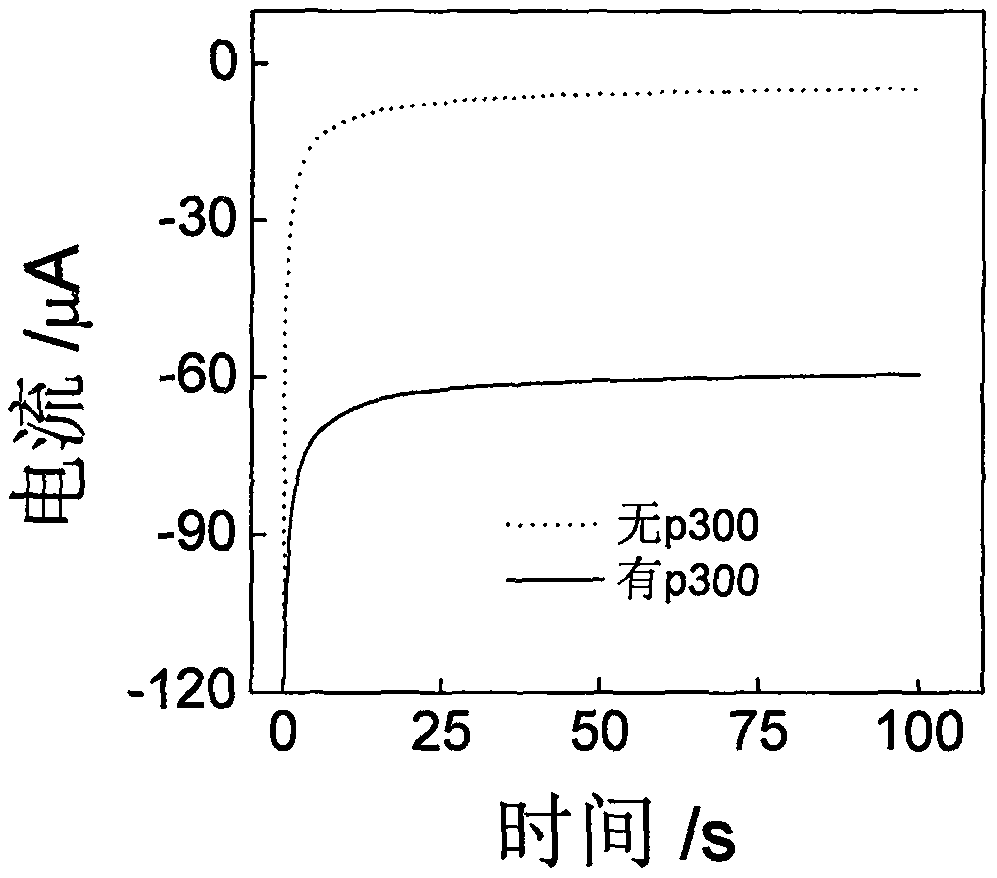
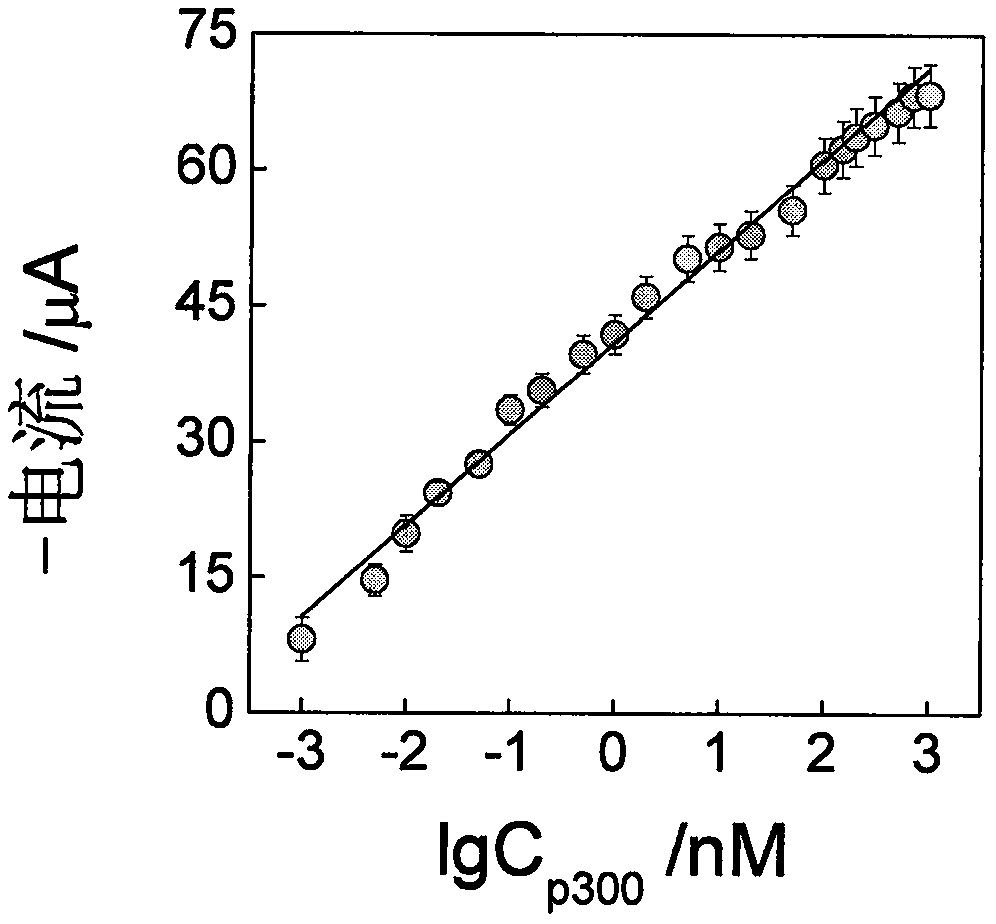
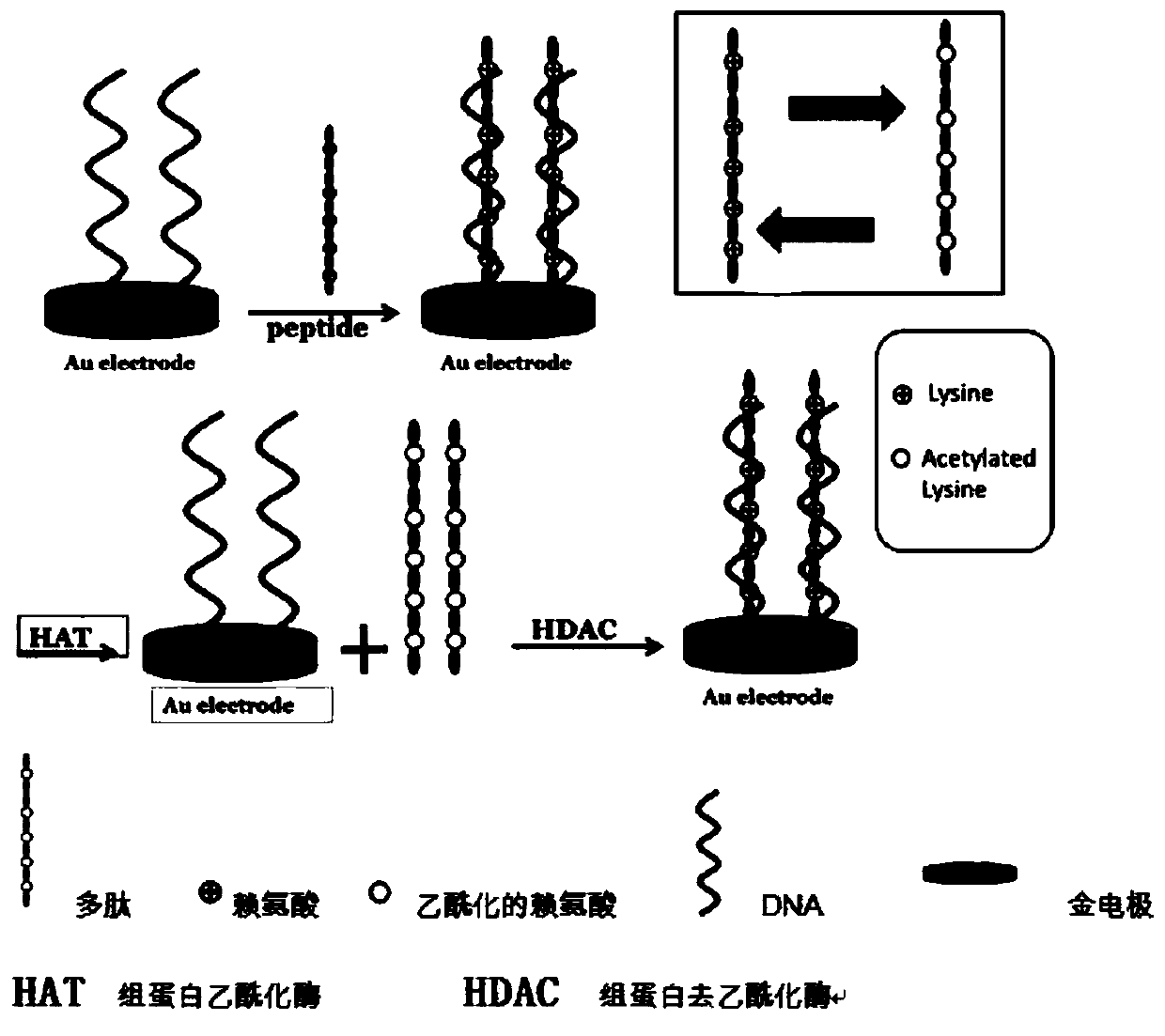
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of an electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor for detecting the activity of histone acetyltransferase. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing peptide / Au: respectively taking acetyltransferase p300, polypeptide and acetyl-CoA, fully mixing the taken substances in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.0), incubating the obtained solution in a constant-temperature water bath, taking and dropwise applying a catalytic reaction to the surface of a gold electrode, and incubating the gold electrode in a 4 DEG C refrigerator; (2) preparing MB&AuNPs@GO-Ab: mixing HAuCl4 and CTAB with water, adding ascorbic acid to the obtained reaction mixture, adding NaOH to obtain CTAB covered AuNPs, centrifuging and purifying the CTAB covered AuNPs, dispersing the purified CTAB covered AuNPs in an equal amount of water, adding GO to the obtained solution, performing ultrasonic dispersion, standing the dispersed solution for later use,adding an acetyl antibody, performing incubation, adding MB, and performing vibration and uniform mixing; and (3) producing the electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor: taking and dropwise applyingthe MB&AuNPs@GO-Ab to the surface of the peptide / Au, performing incubation at room temperature, and placing the produced sensor in the PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.0) to carry out electrochemical SWV test.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
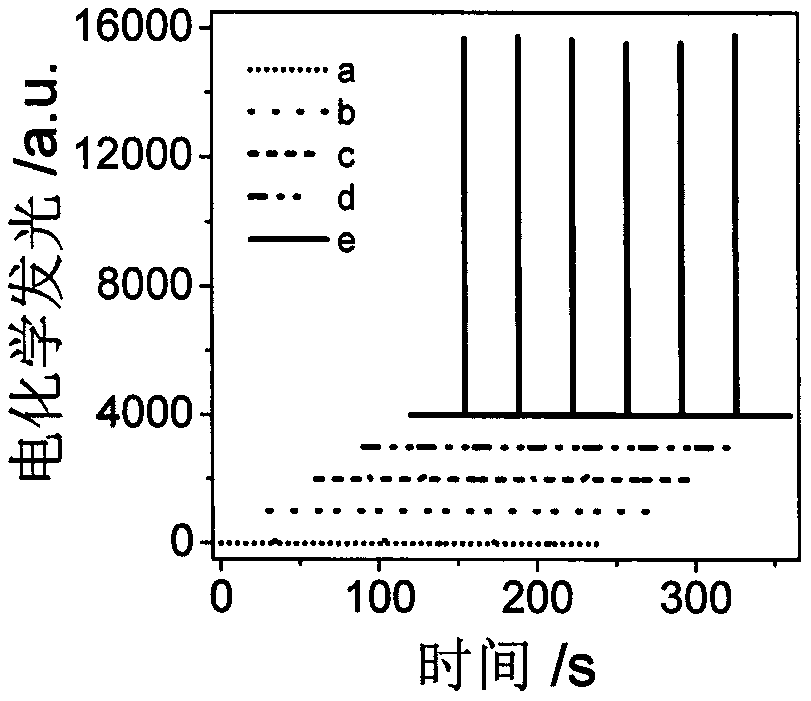
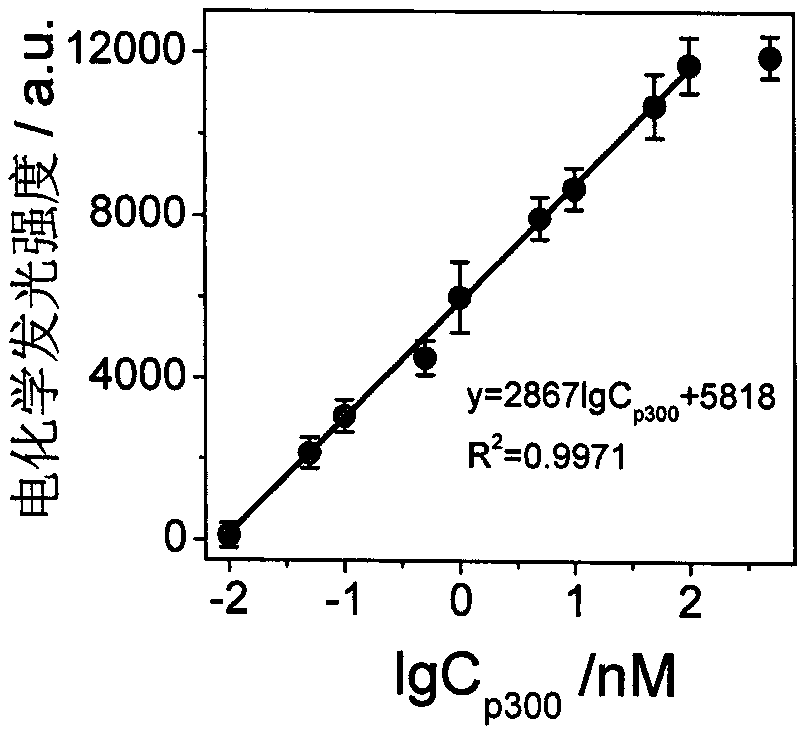
Manufactured histone acetyltransferase electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on DNA nano-prism and application of histone acetyltransferase electrochemiluminescence biosensor
ActiveCN109613093AStrong specificityThe result is accurateMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerElectrochemiluminescence
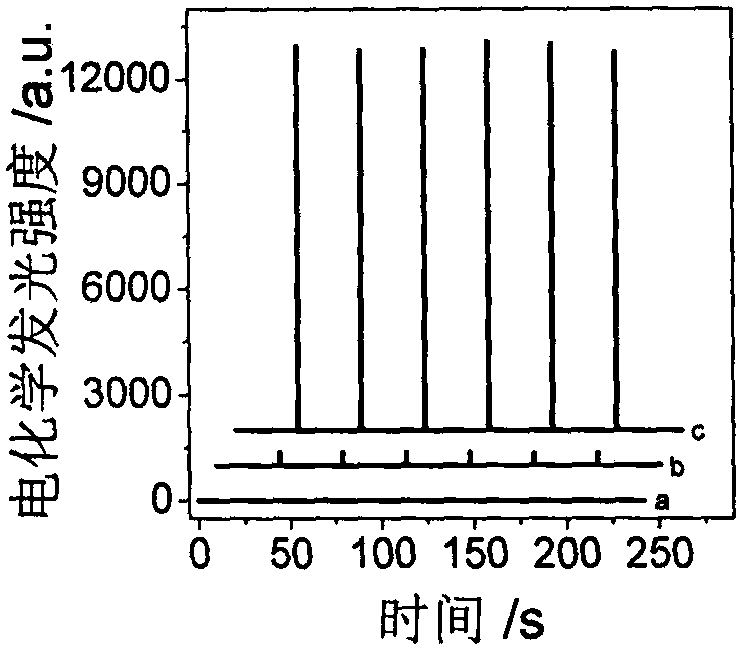
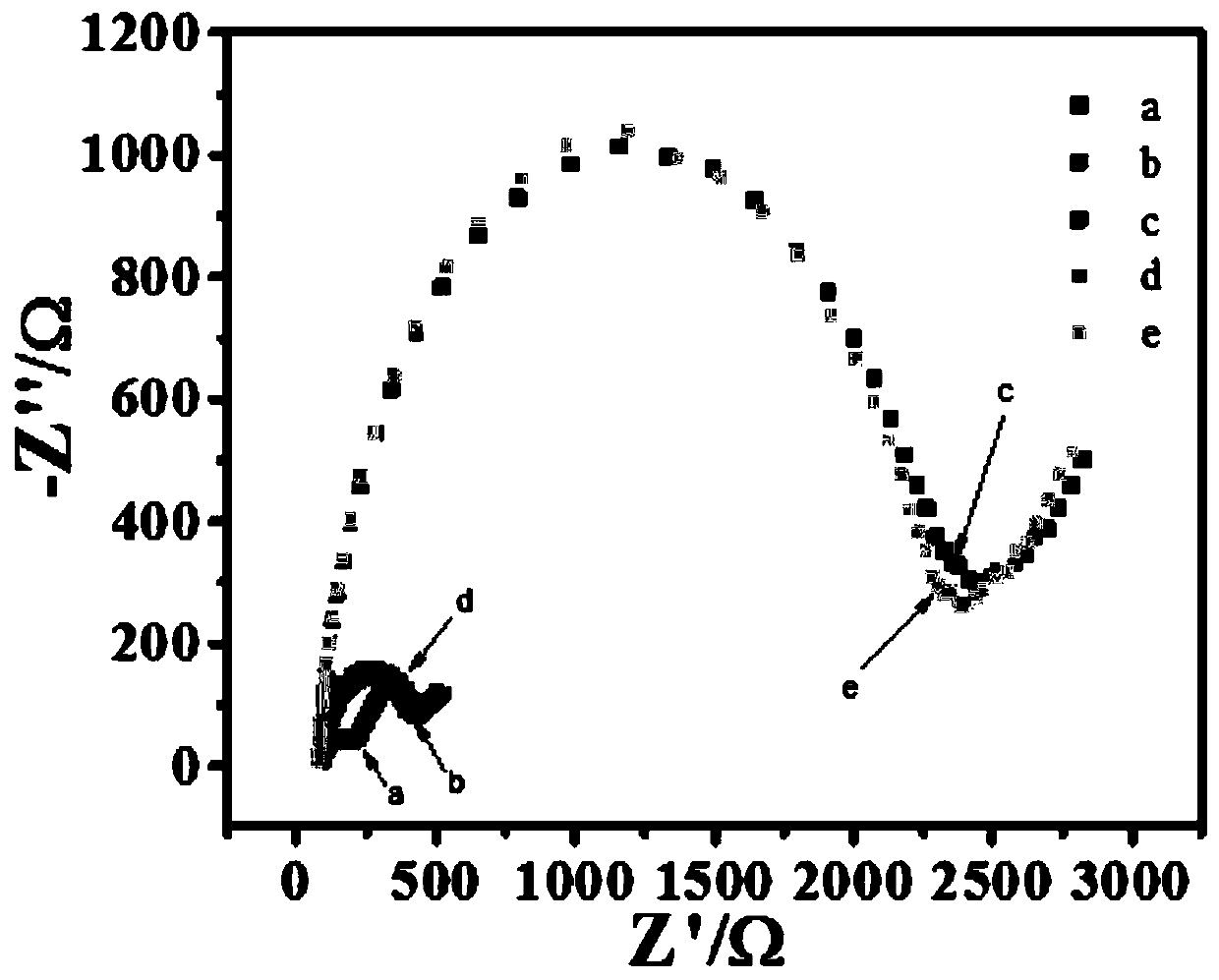
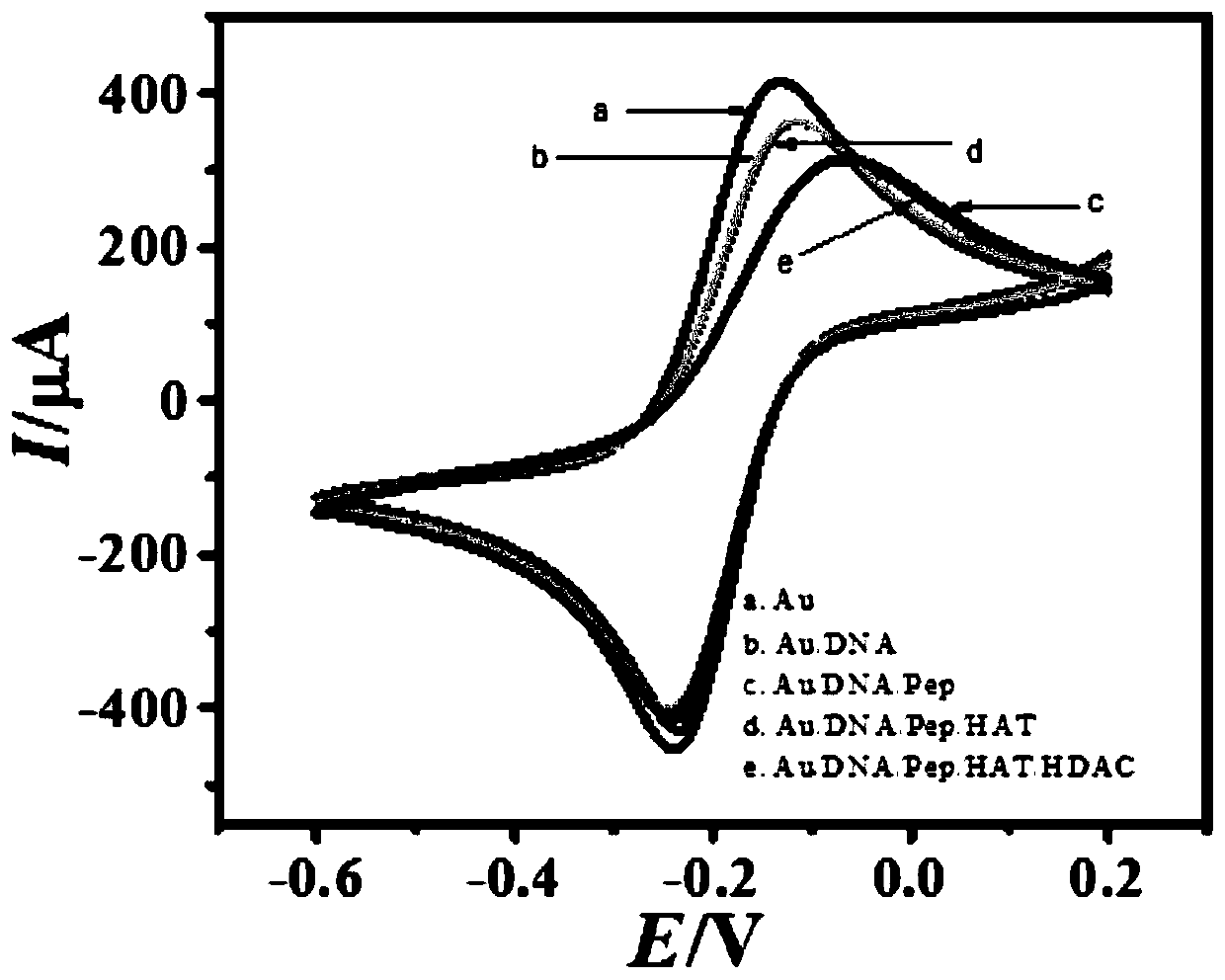
The invention discloses a manufactured histone acetyltransferase electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on a DNA nano-prism and application of the histone acetyltransferase electrochemiluminescencebiosensor. The histone acetyltransferase electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on the DNA nano-prism is manufactured through the specific steps that (1) HAT-aptamer reaction is carried out, specifically, firstly, acetylation reaction is carried out, HATp300 and polypeptide are separately selected, and acetylcoenzyme A is fully mixed in a phosphate buffer solution (PBS, 10mM, pH7.0); secondly, CoA aptamer is added to the reaction solution in the first step; and thirdly, cDNA is added to the solution in the second step; and (2) the electrochemiluminescence sensor is manufacture through a. Auelectrode, b. prism / Au electrode, c. cDNA / prism / Au electrode, d. H1-H2 / cDNA / prism / Au electrode and e. Ru / H1-H2 / cDNA / prism / Au electrode. In the acetylation reaction, the concentration of p300 and the small molecule inhibitor concentration thereof are changed, and the effect of a series of sensors on an electrochemiluminescence signal is investigated. The manufactured histone acetyltransferase electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on the DNA nano-prism and the application of the histone acetyltransferase electrochemiluminescence biosensor have the advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity, fast detection speed, accurate and reliable results and low cost.
Owner:山东博科诊断科技有限公司
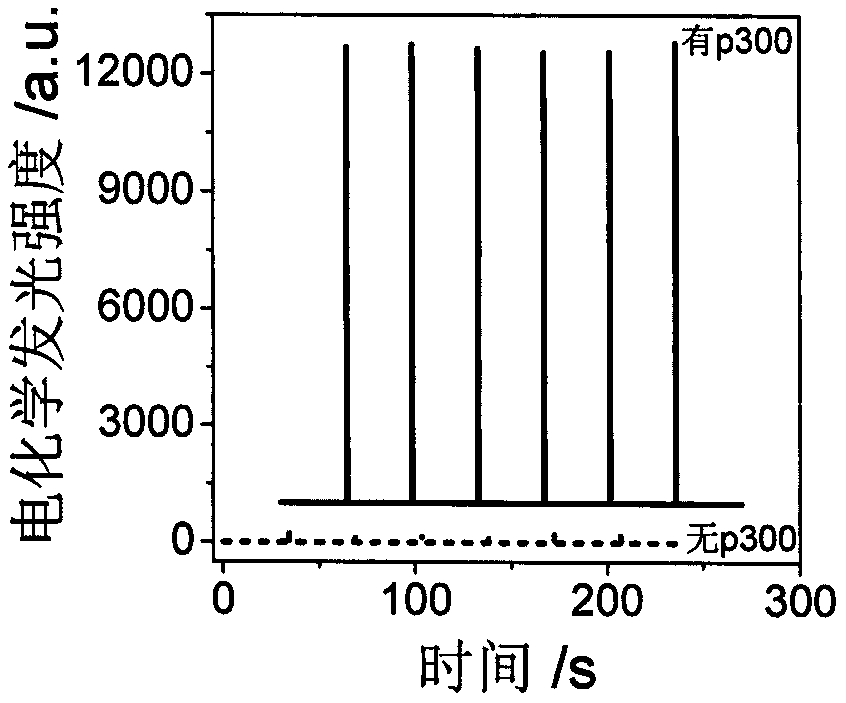
Electrochemical luminescence Faraday cage immunosensor for detecting histone acetyltransferase
ActiveCN108562738AHigh sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysisBinding siteBovine serum albumin
The invention discloses an electrochemical luminescence Faraday cage immunosensor for detecting histone acetyltransferase. The electrochemical luminescence Faraday cage immunosensor is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a capturing unit: synthesizing magnetic graphene oxide (GO); treating the magnetic graphene oxide with an EDC / NHS (1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride / N-Hydroxysuccinimide) solution and HCl in sequence; then combining with a capturing antibody Ab1; incubating at room temperature; finally adding BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin) to seal a non-specific binding site on the surface of the GO to obtain the capturing unit Ab1-nanoFe3O4@GO; (2) preparing a signal unit: connecting a recognition antibody Ab2 into a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) tetrahedron to synthesize tetrahedron-Ab2; then synthesizing nano-gold (AuNPs) and forming a compound GO@AuNPs by the nano-gold and graphene oxide; then combining the compound GO@AuNPs with tetrahedron-Ab2; then adding a Ru luminous body to prepare the signal unit; (3) preparing the Faraday cage immunosensor: dropping and coating an Ab1-nanoFe3O4@GO solution to the surface of an MGCE (Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode) to obtain Ab1-nanoFe3O4@GO / MGCE and recording as an electrode a; taking a p300 solution and dropping and coating on the Ab1-nanoFe3O4@GO / MGCE to obtain p300 / Ab1-nanoFe3O4@GO / MGCE, and recording as an electrode b; finally, taking a Ru-GO@AuNPs-tetrahedron-Ab2 solution and dropping and coating on the p300 / Ab1-nanoFe3O4@GO / MGCE to obtain a Ru-GO@AuNPs-tetrahedron-Ab2 / p300 / Ab1-nanoFe3O4@GO / MGCE, and recording as an electrode c, i.e., the electrochemical luminescence Faraday cage immunosensor.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
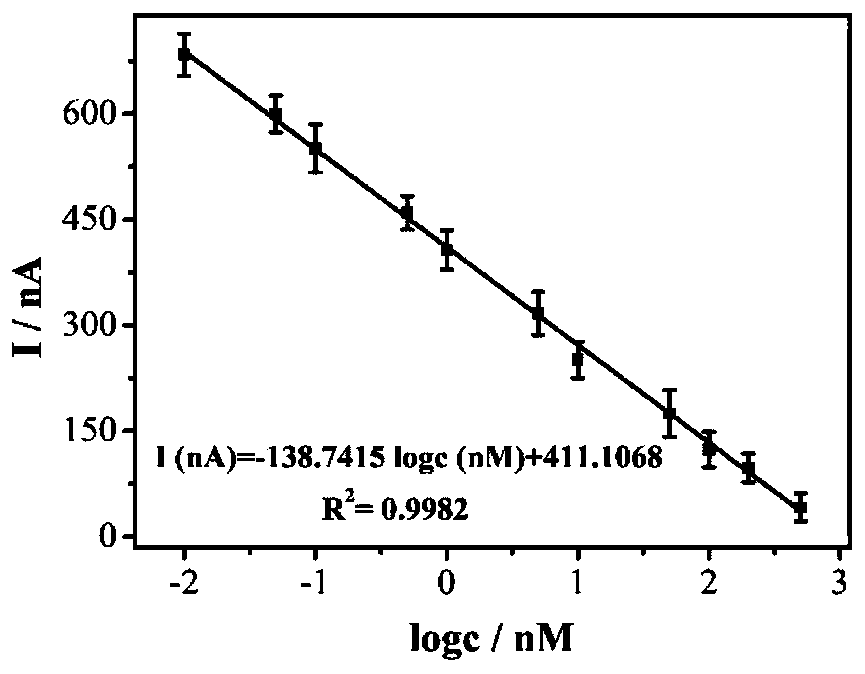
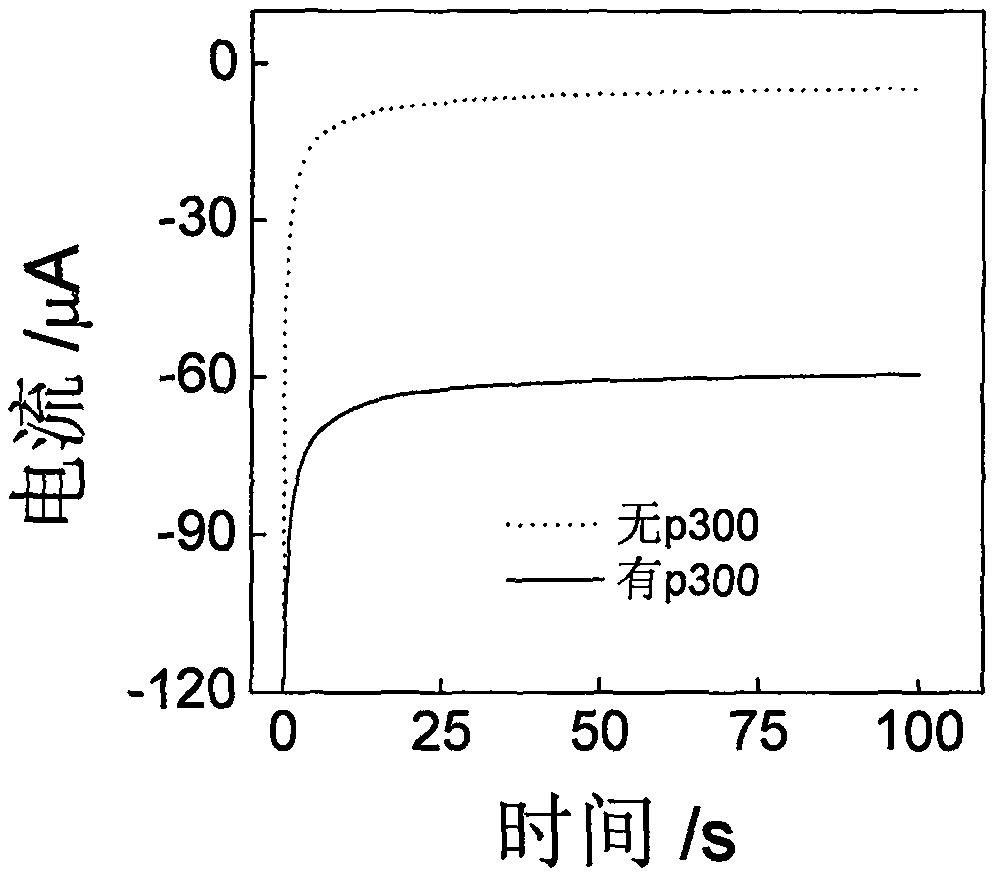
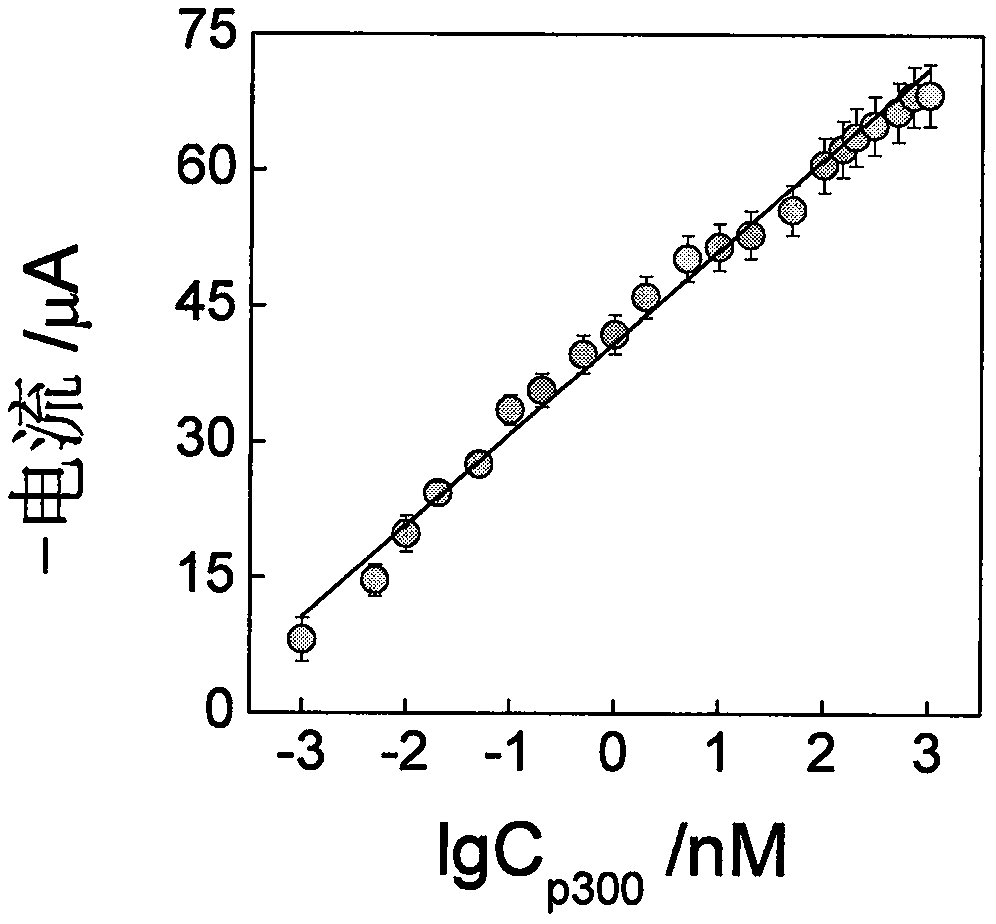
Histone acetyltransferase timing-current sensor based on gold-palladium nanoflower/graphene composite material and application thereof
ActiveCN110082403AHigh sensitivityRealize highly sensitive detectionMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneCurrent sensorElectrochemistry
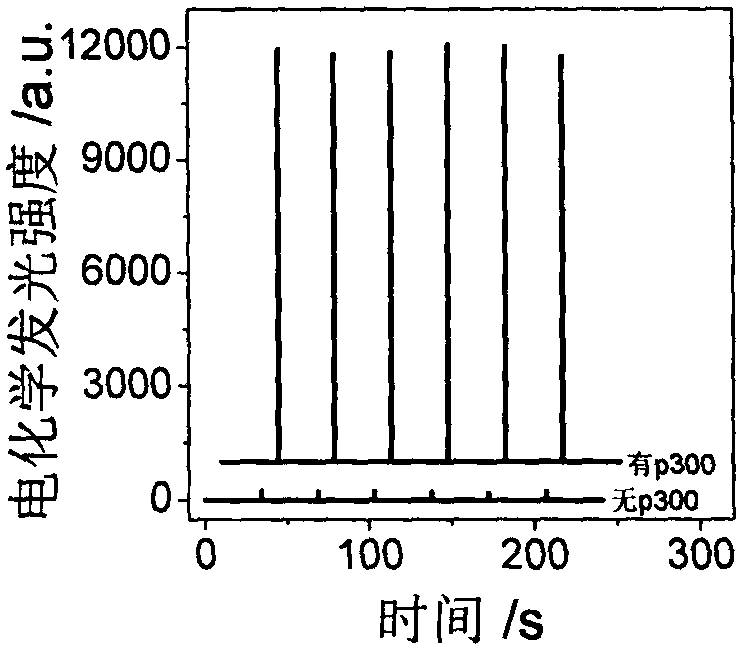
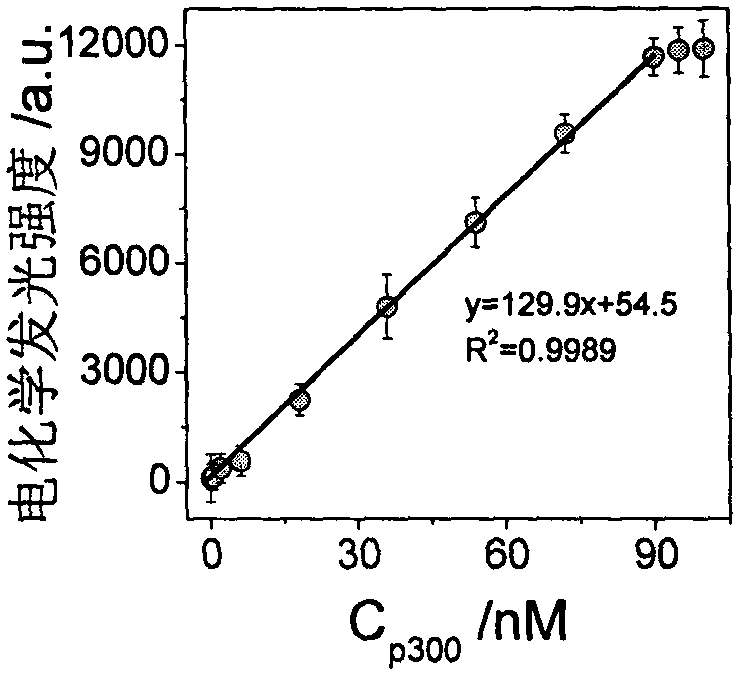
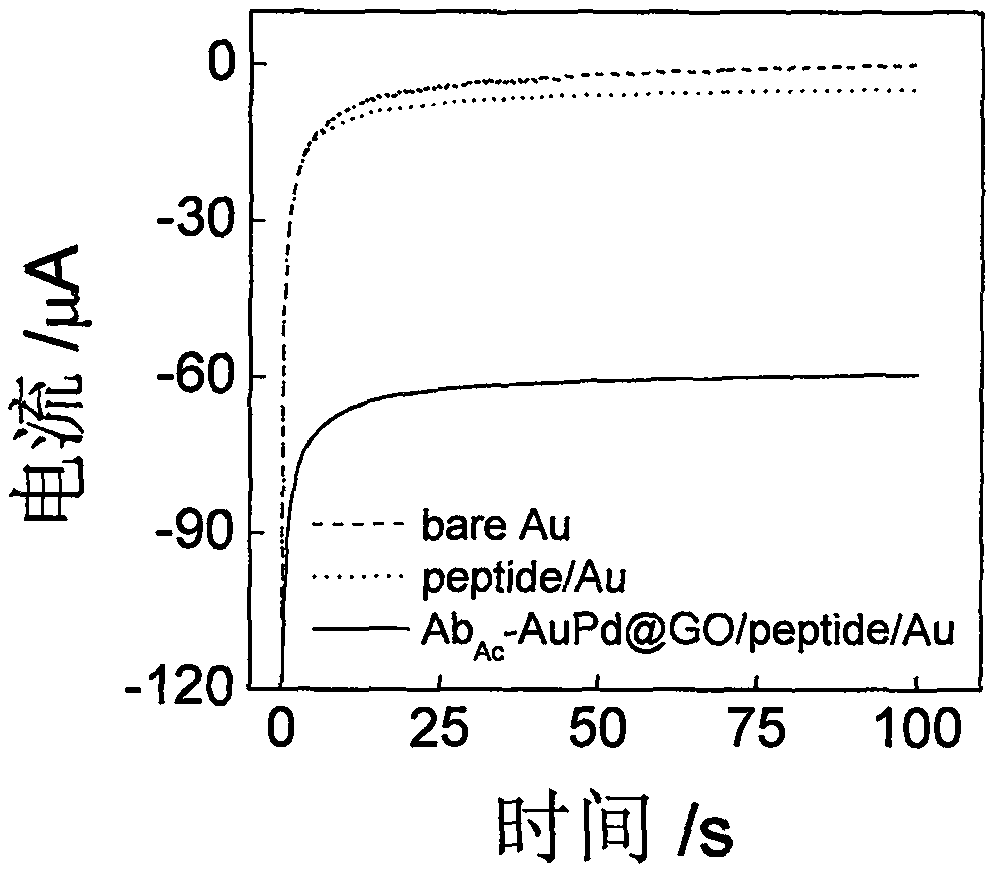
The invention discloses a histone acetyltransferase timing-current sensor based on gold-palladium nanoflower / graphene composite material and an application thereof. Firstly, substrate polypeptide is fixedly disposed on a surface of a gold electrode by using Au-S effect, and acetyl group on acetyl-CoA is transferred to the specific lysine residue of the substrate polypeptide by acetylation reaction. The generated acetylated polypeptide is used to specifically adsorb the acetyl antibody-gold palladium nanoflower / graphene composite material with stronger catalytic capability, and obvious electrochemical signals are generated in electrolyte solution containing hydrogen peroxide. During the acetylation reaction, p 300 concentration and small molecule inhibitor concentration thereof are changed,and the influence on the electrochemical signals of a series of prepared sensors is explored through specific binding effect of acetyl and acetyl antibodies. The histone acetyltransferase timing-current sensor has advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity, fast detection speed, reliable and accurate result, and low costs.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
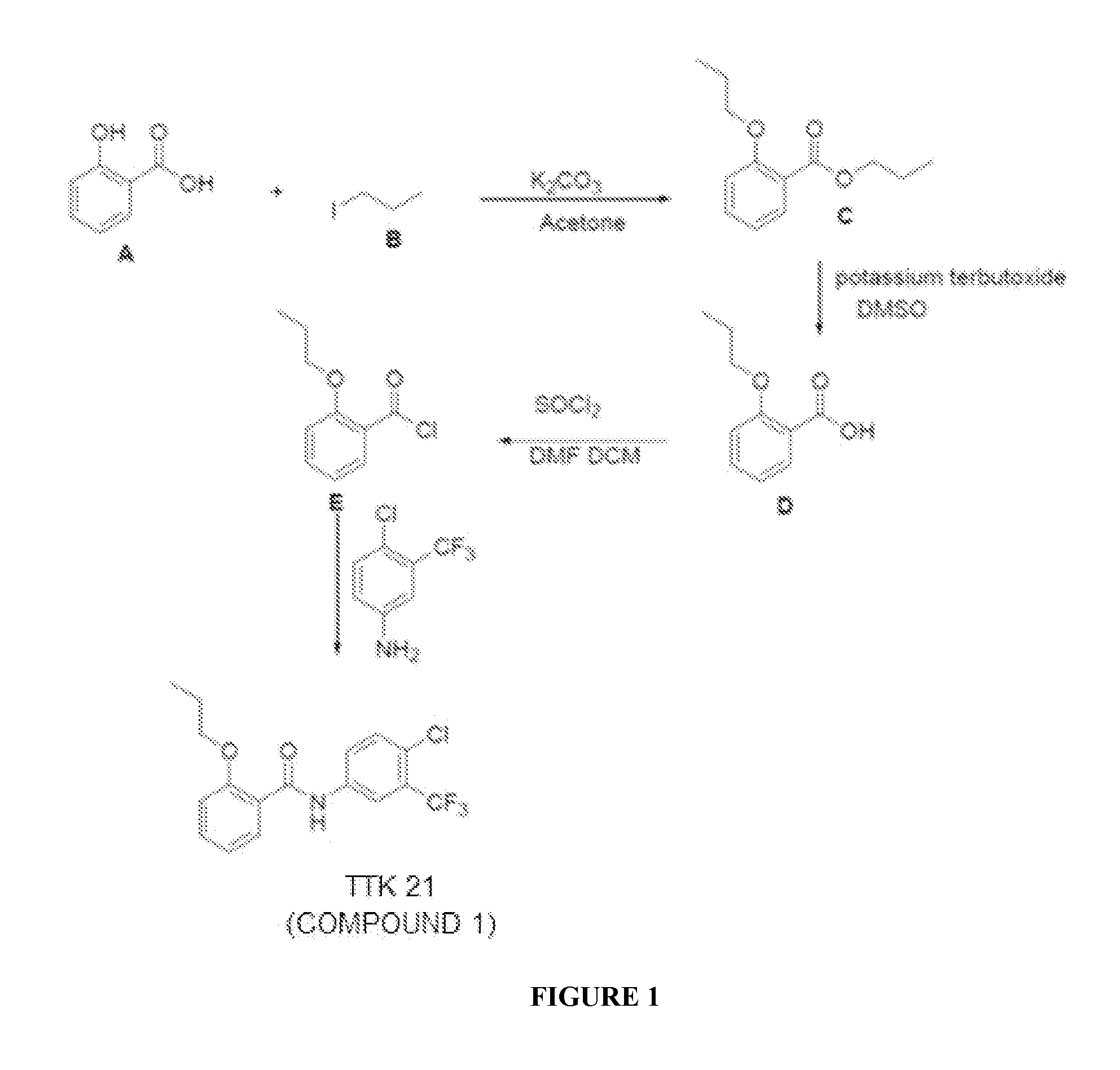
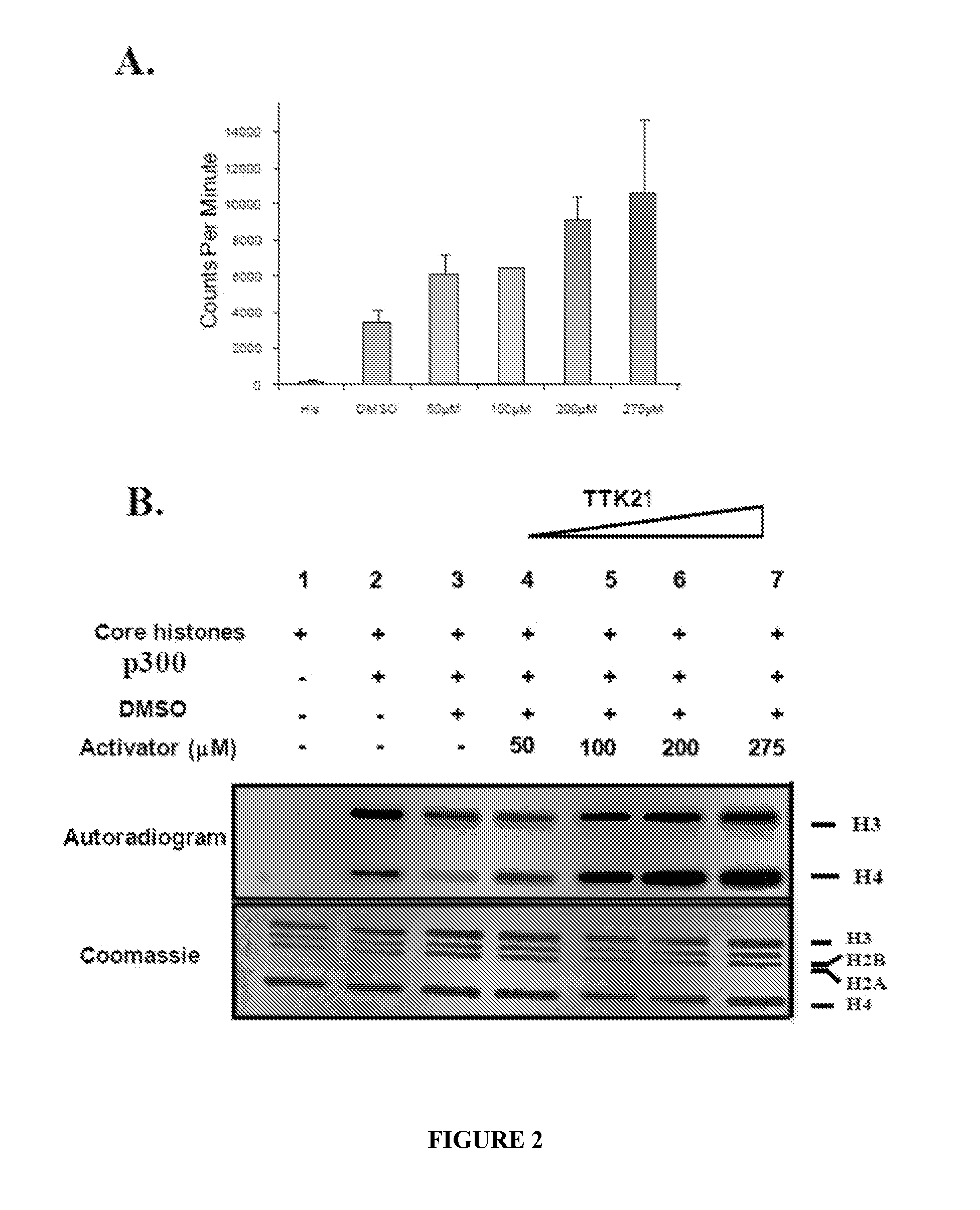
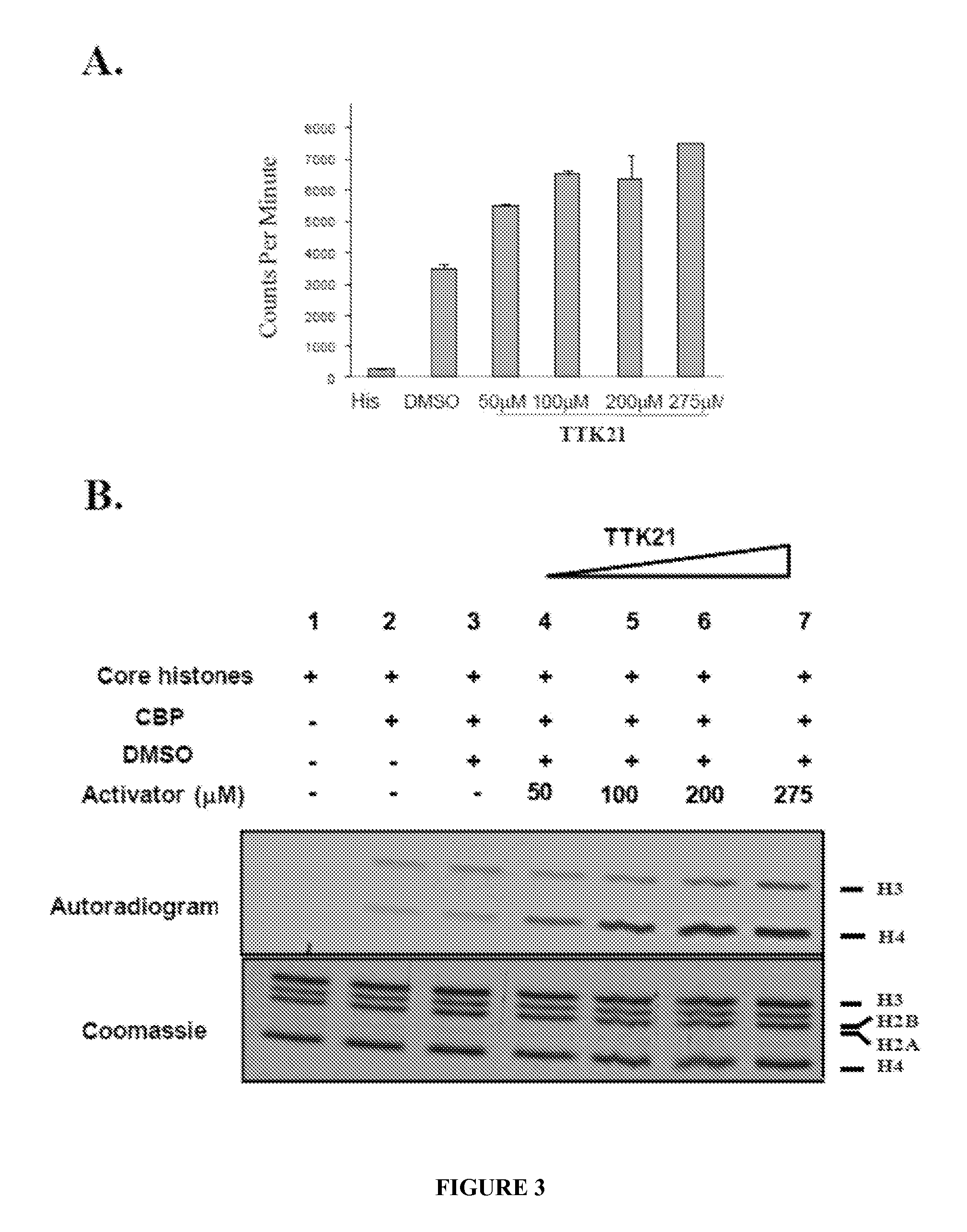
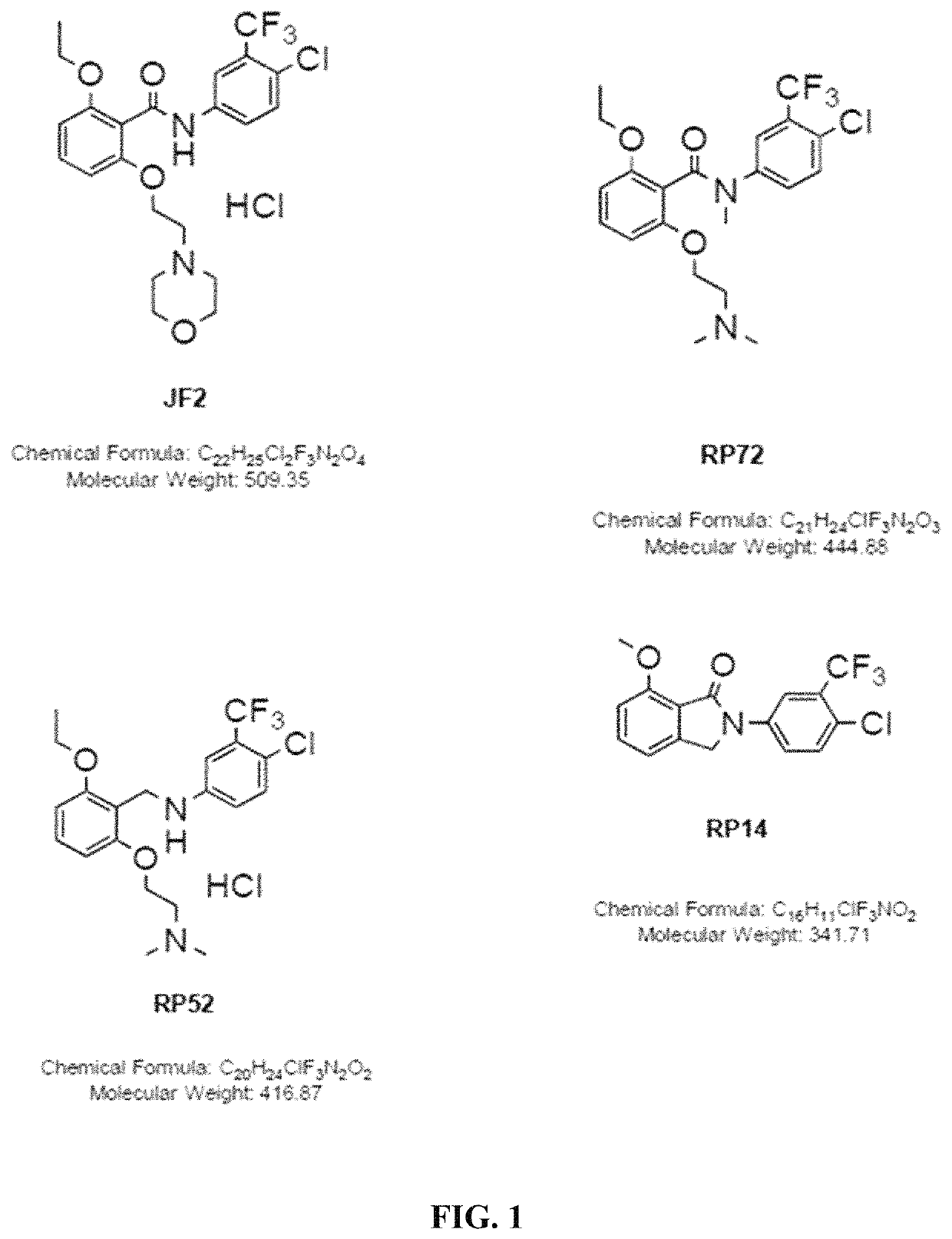
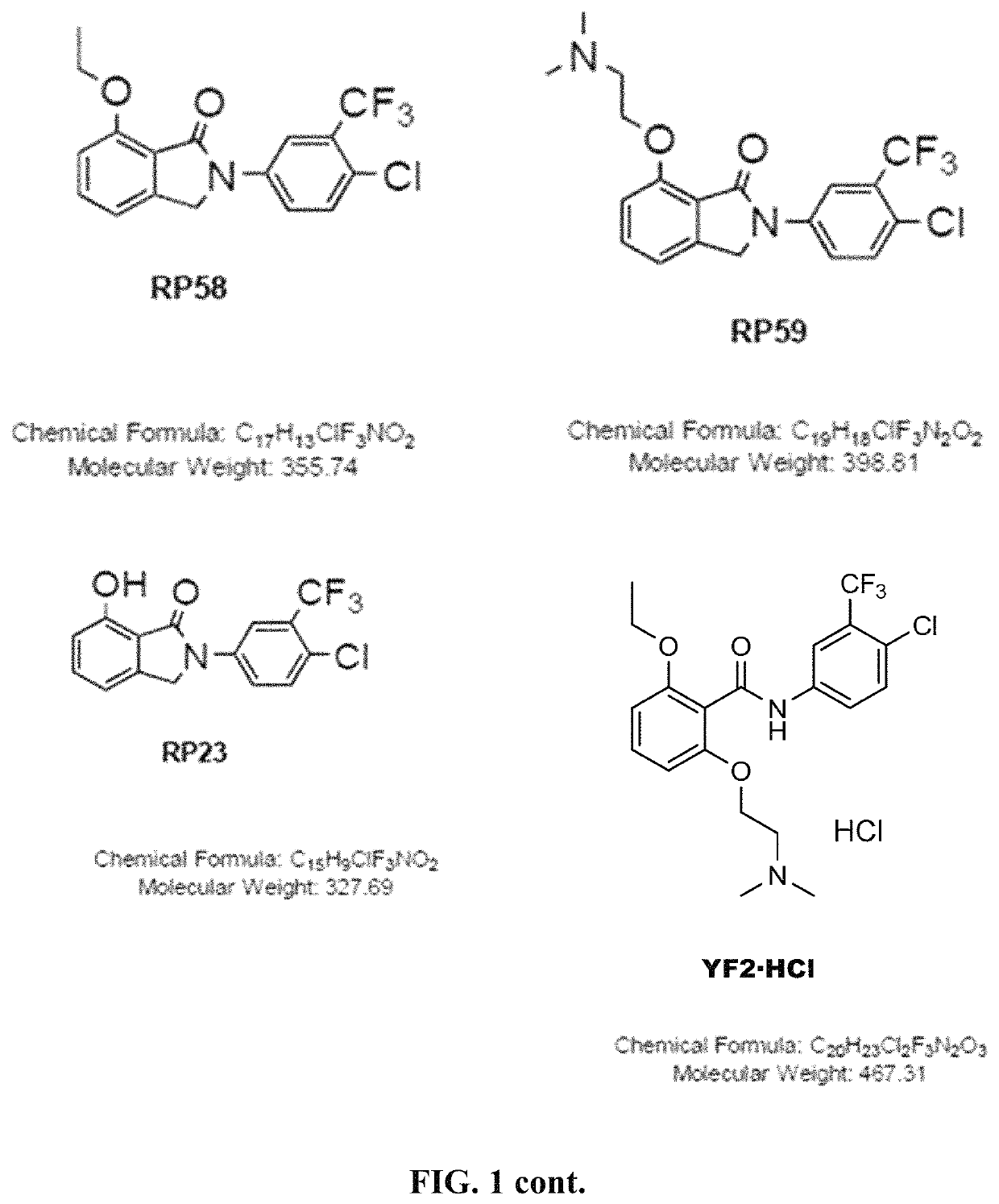
Nanosphere- histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activator composition, process and methods thereof
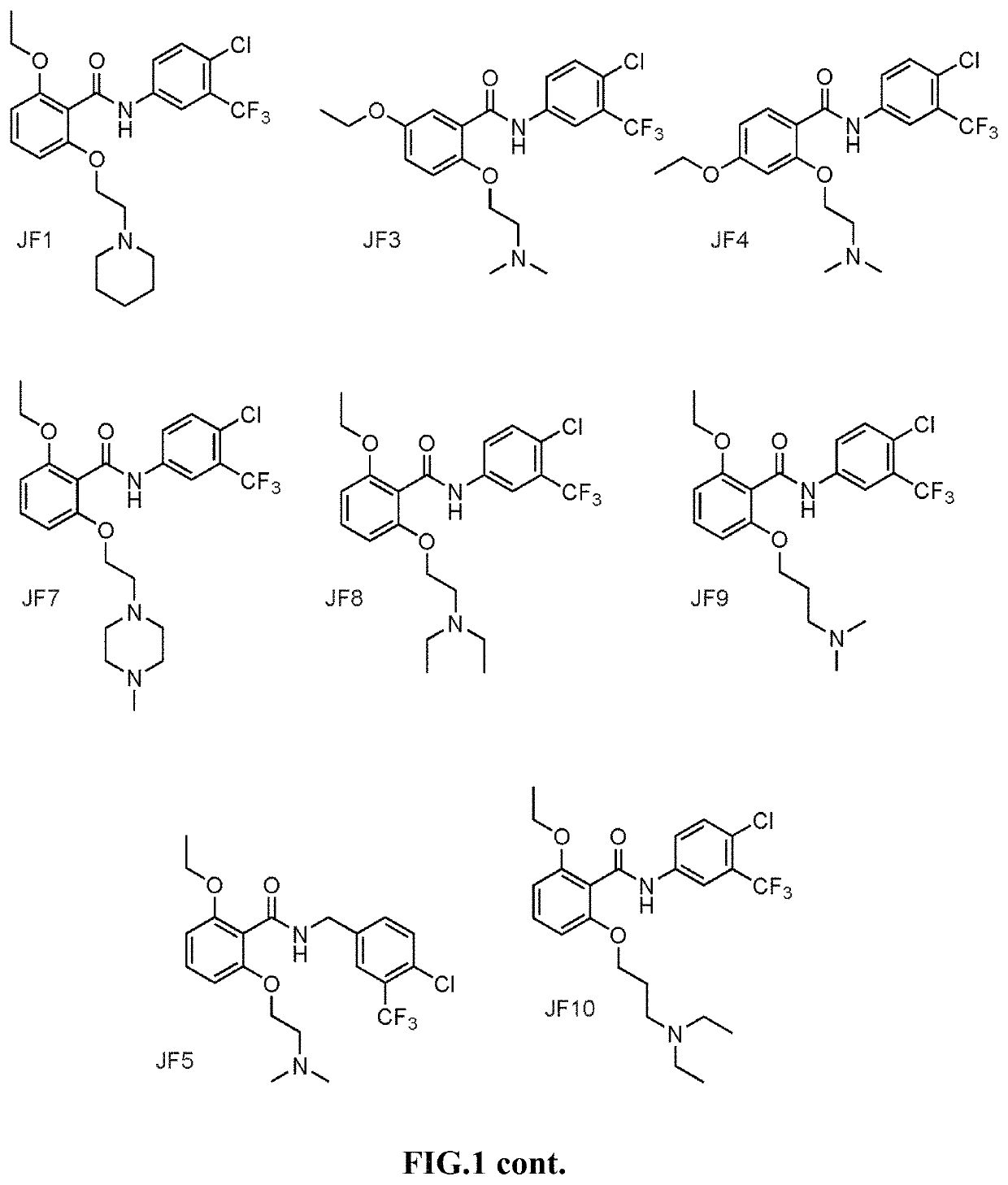
The present invention is in relation to a composition including nanosphere and histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activator. The nanosphere is carbon nanosphere (CSP) which is intrinsically fluorescent and the HAT activator is N-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-n-propoxy-benzamide. The N-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-n-propoxy-benzamide is covalently conjugated with the carbon nanosphere. The present invention further relates to a process for obtaining a composition including carbon nanosphere and Histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activator [N-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-2-n-propoxy-benzamide]. The composition is capable of crossing blood brain barrier and inducing histone acetylation in brain. Further, the composition is capable of increasing neurogenesis, as well as improving long-term memory formation. The composition manages pathological conditions to a subject in need thereof, such as aging-related, neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's in particular), neurological disorders, depression or other kinds of diseases in which increased HAT activity, neurogenesis and / or memory improvement would benefit.
Owner:JAWAHARLAL NEHRU CENT FOR ADVANCED SCI RES +1
Cancer Cell Apoptosis
InactiveUS20120190735A1Reduce proliferationLow toxicityBiocideNervous disorderB-cell apoptosisTumor necrosis factor alpha
There is described a therapeutic agent capable of directly or indirectly having an effect on the proteins N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA), Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), Tumour Necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a), Nuclear factor-kappa B (NFKB), Cyclin-dependent kinases, e.g. CDK2 / A and CDK5 / p25, Histone acetyltransferase (HAT) and Farnesyltransferase, simultaneously, sequentially or separately. There is especially described dexanabinol, or a derivative thereof, as the therapeutic agent.
Owner:E THERAPEUTICS LTD
A kind of recombinant Bacillus subtilis accumulating acetylglucosamine and its application
ActiveCN105176903BEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetylglucosamineGenetically engineered
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for accumulating acetylglucosamine and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis for accumulating the acetylglucosamine and the application thereof, recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS serves as an original strain, the glucosamine synthesizing route is enhanced by excessively expressing glucosamine histone acetyltransferase coding genes (CeGNA1) from caenorhabditis elegans, and the genetically engineered bacterium bacillus subtilis for accumulating the acetylglucosamine is obtained; the yield on the shake flask level reaches 7.31 g / L, and a foundation is laid for further producing the glucosamine by transforming the bacillus subtilis in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
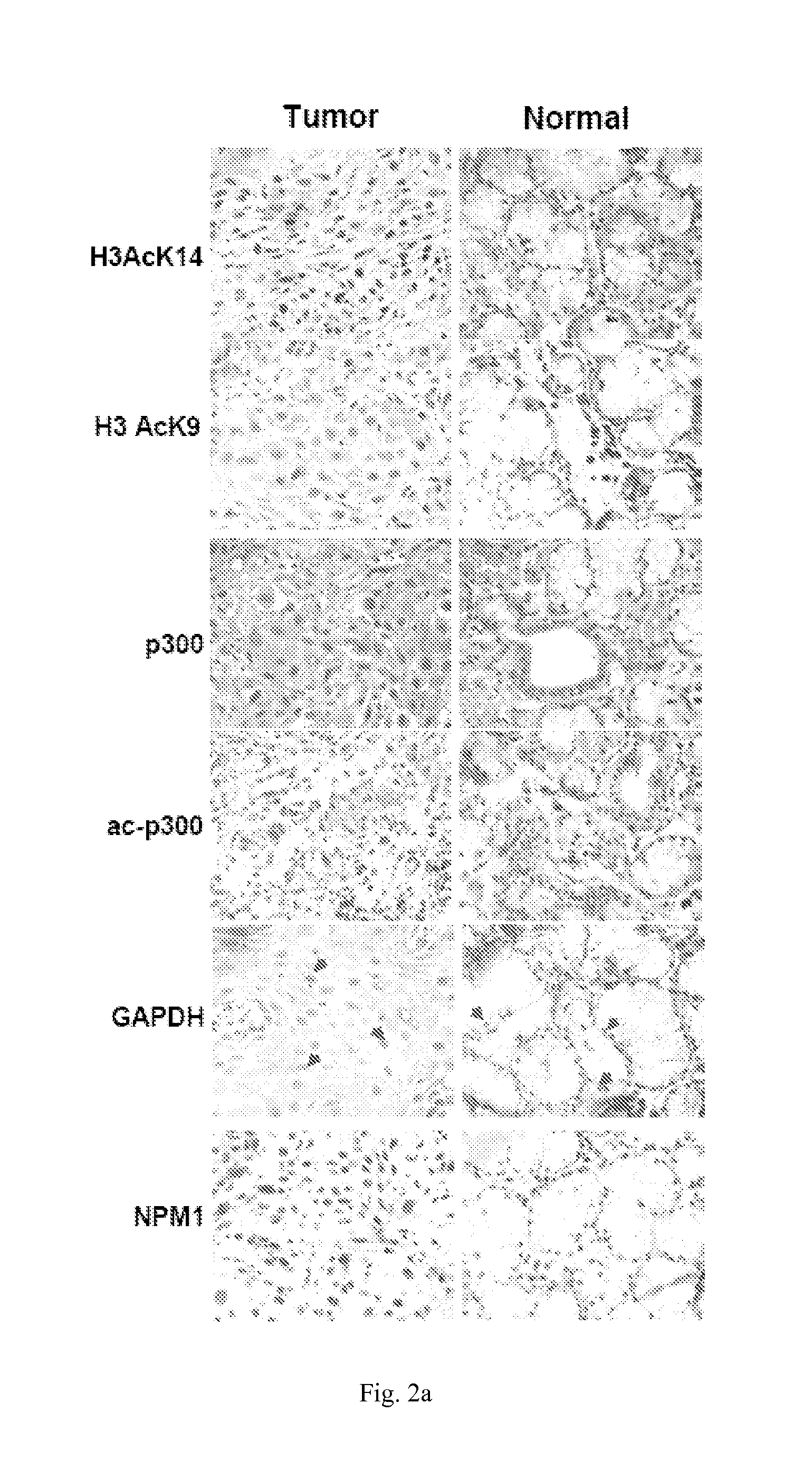
Inhibition of histone acetyltransferases by ctk7a and methods thereof
InactiveUS20120165384A1Inhibiting autoacetylation of p300BiocideOrganic active ingredientsAcetylationCancer research
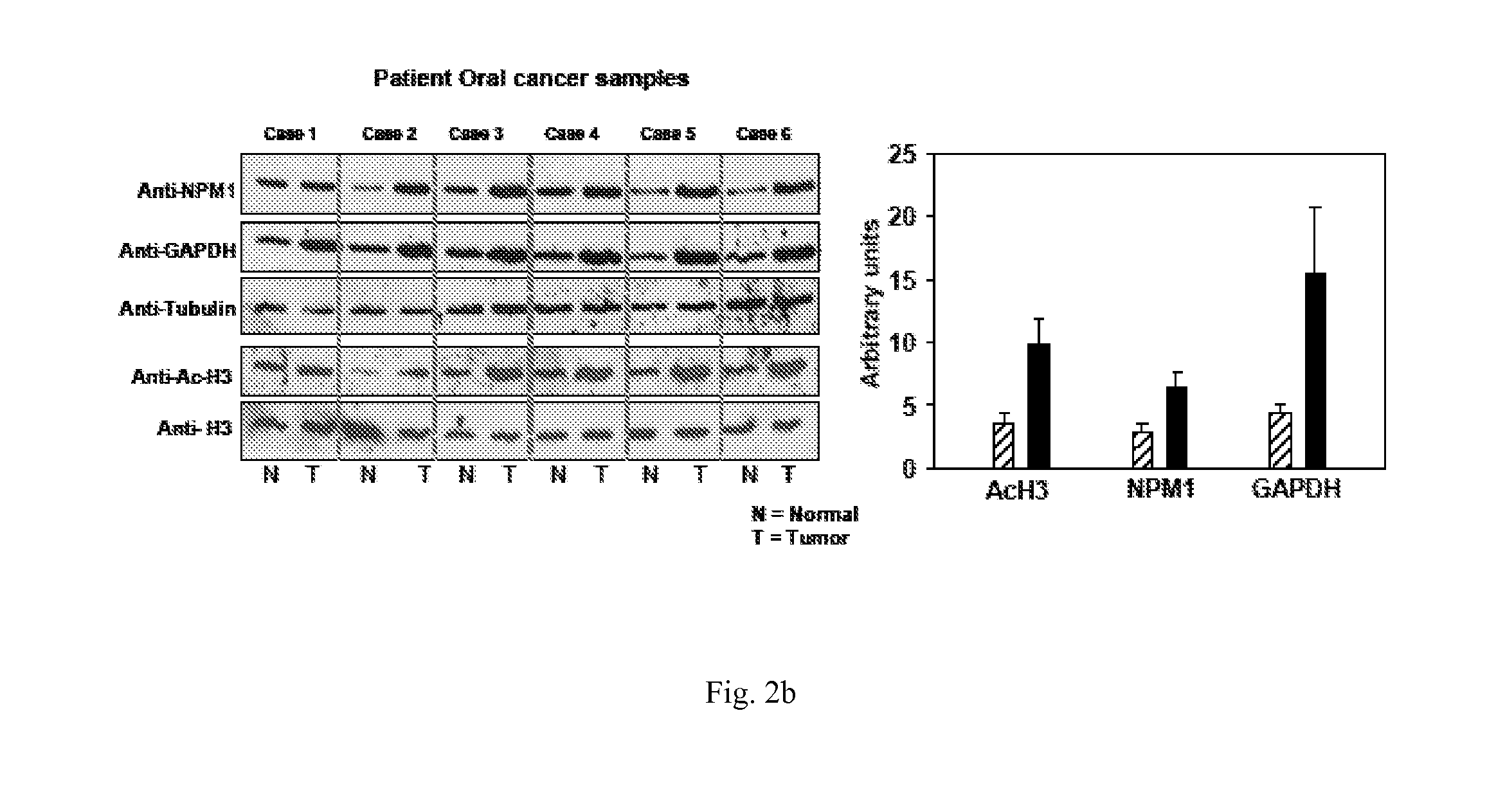
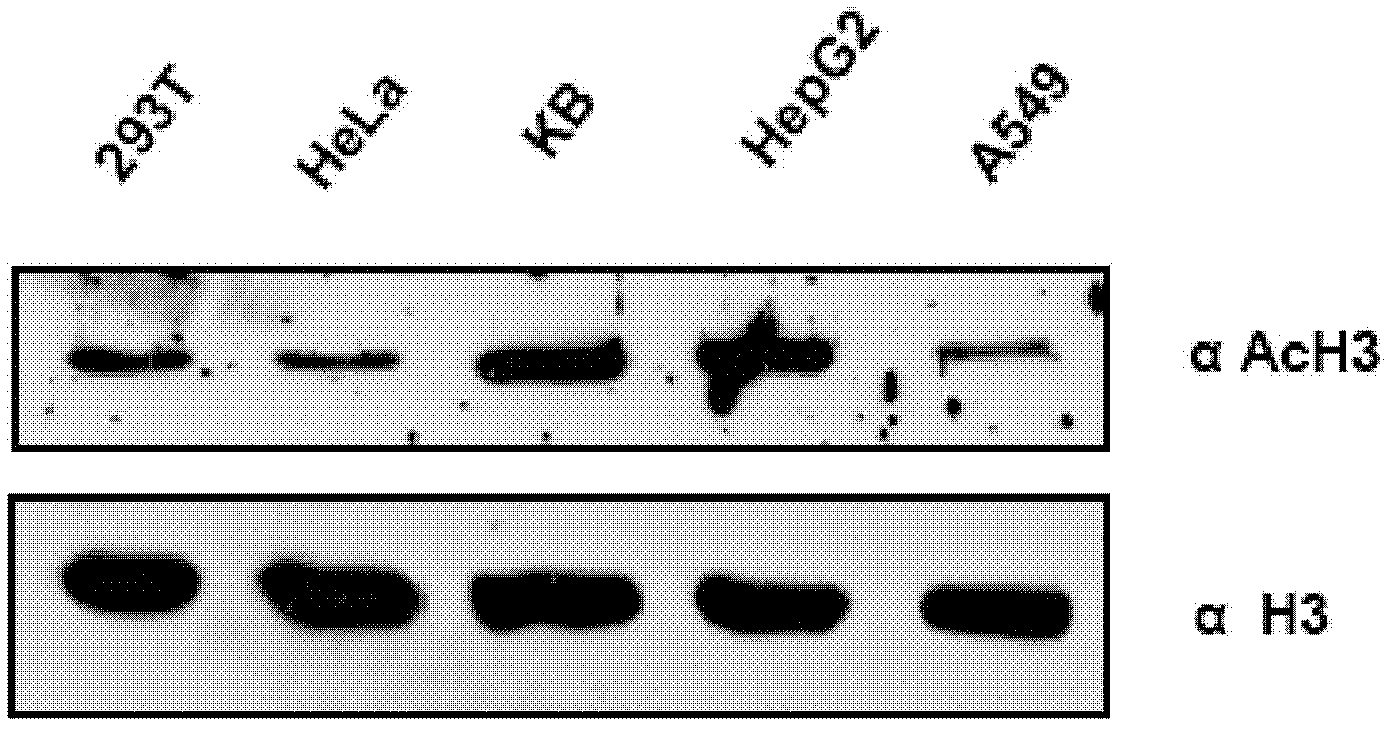
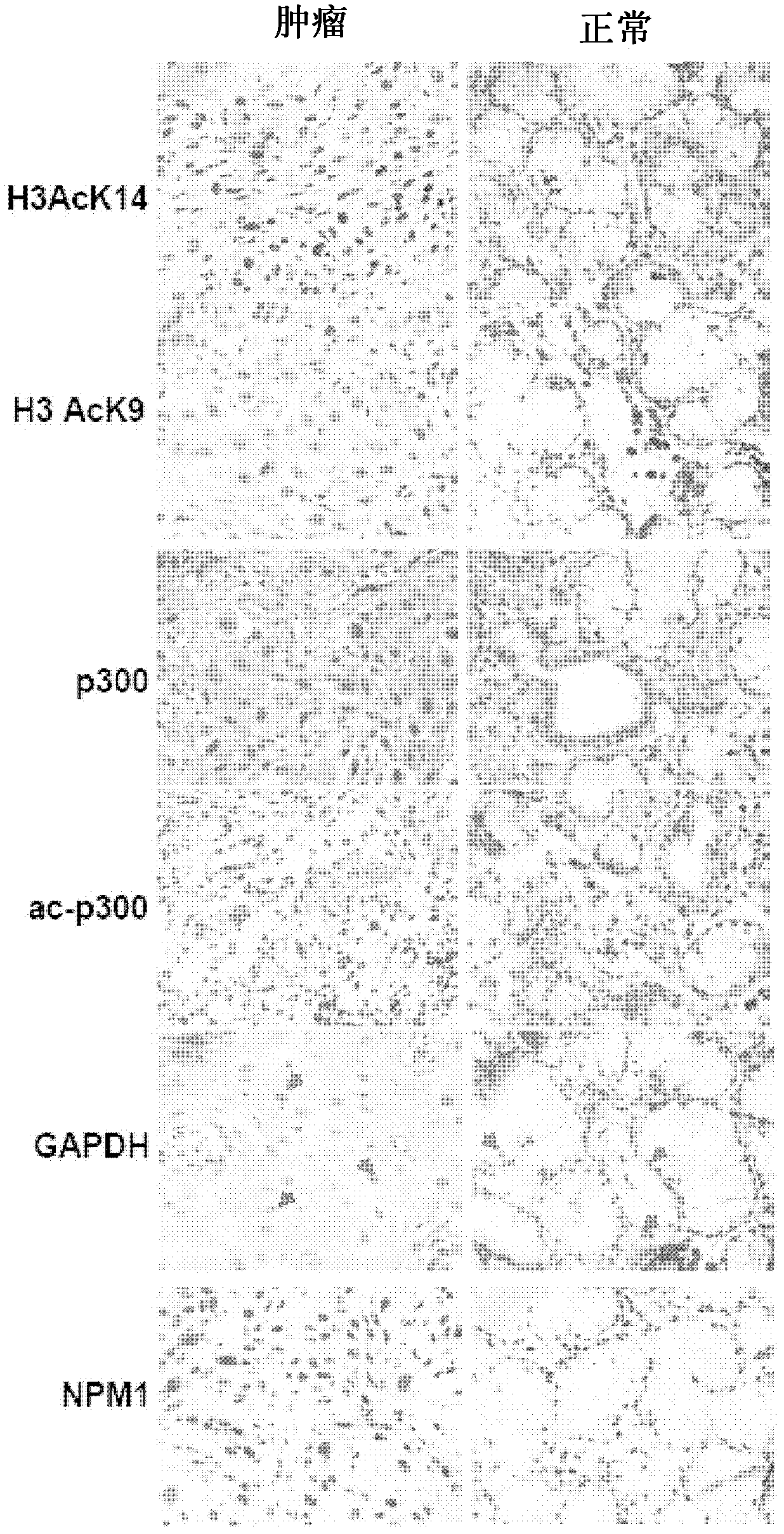
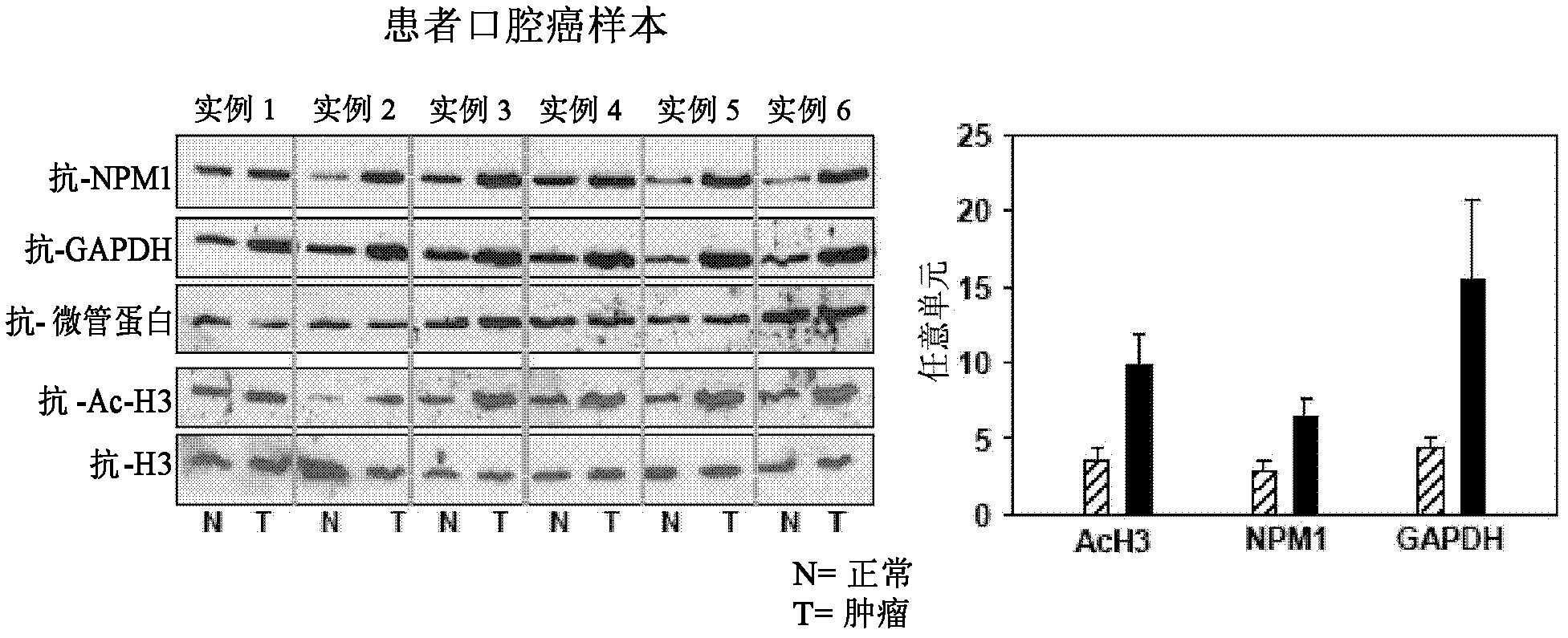
The present disclosure relates to a method for inhibiting histone acetyltransferases by derivative of curcumin, particularly CTK7A. The present disclosure also relates to identification of induction of autoacetylation of p300 and its inhibition by CTK7A. The disclosure also relates to induction of NPM1 and GAPDH overexpression and corresponding hyperacetylation of histone and methods thereof.
Owner:JAWAHARLAL NEHRU CENT FOR ADVANCED SCI RES
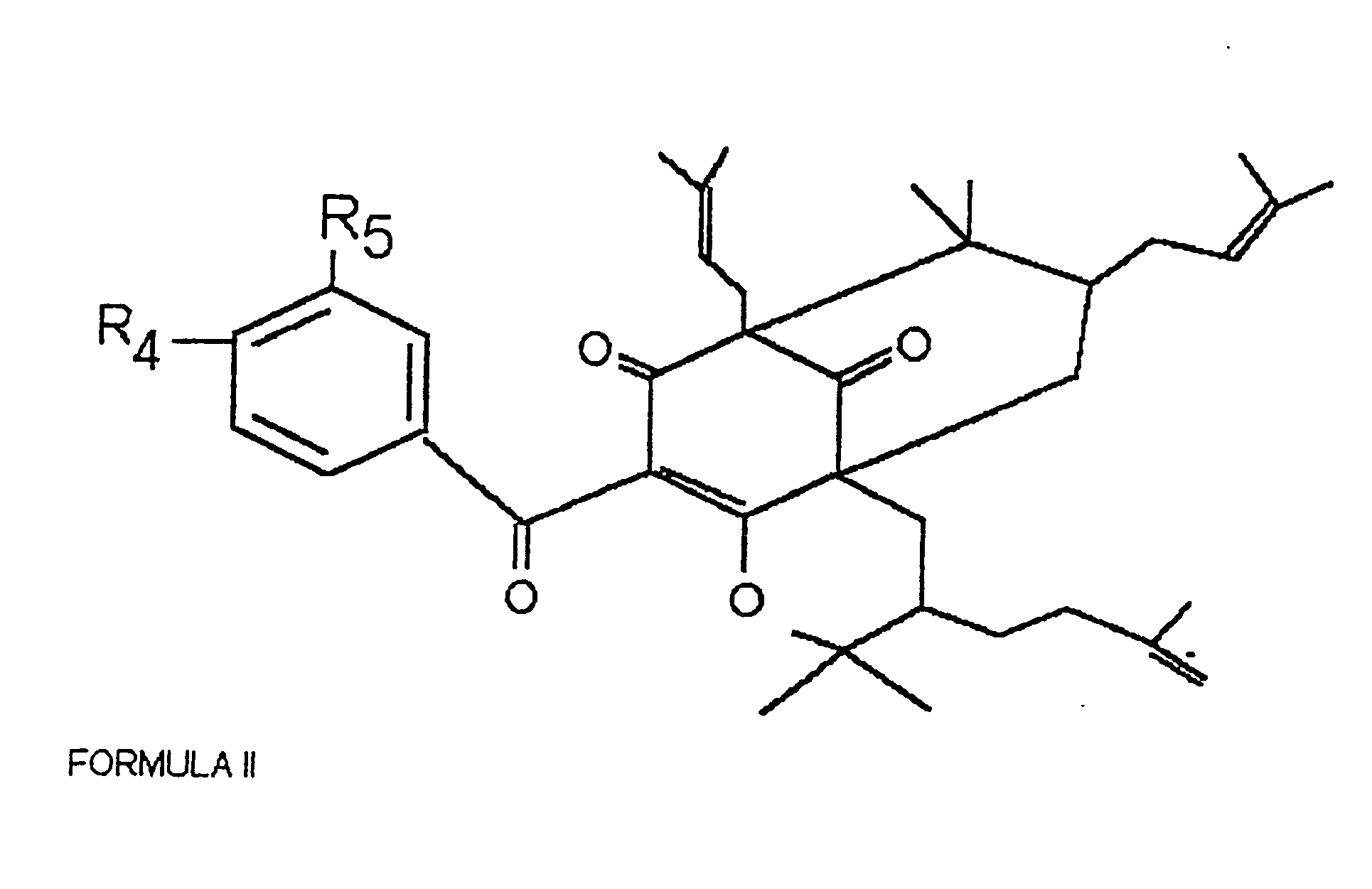
Polyisoprenylated benzophenones and their isomers as inhibitors of histone acetyltransferases and uses thereof
Owner:JAWAHARLAL NEHRU CENT FOR ADVANCED SCI RES
An impedance-type electrochemical biosensor based on electrostatic interaction, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107144603BEasy to prepareReduce energy consumptionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial impedanceElectricityElectrochemical biosensor
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
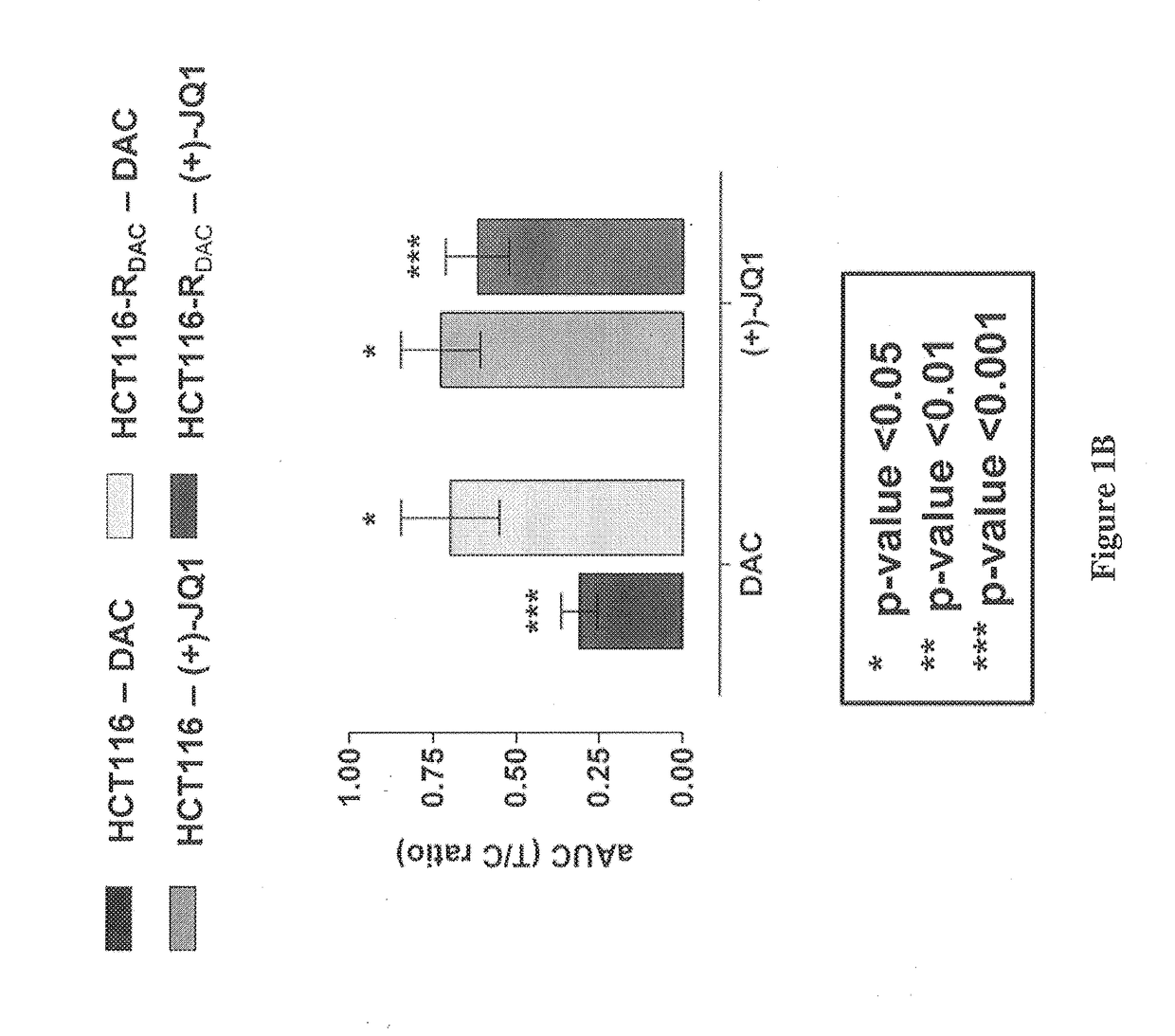
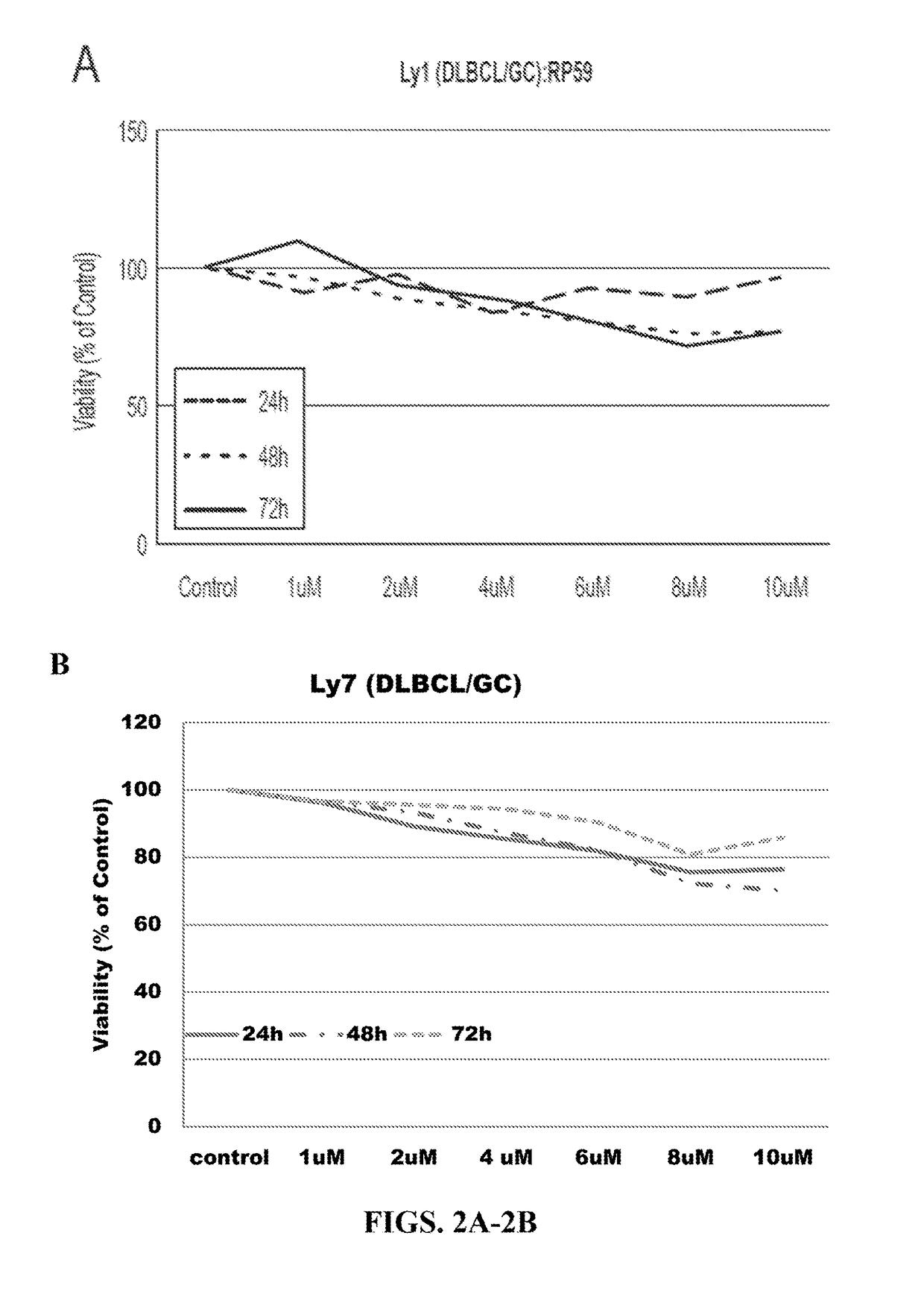
Method of predicting the tumor response to DNA methylation inhibitors and alternative therapeutic regimen for overcoming resistance
InactiveUS20180251847A1Reduce resistanceOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor responseCancer cell
Method for predicting sensitivity of a patient suffering from cancer to DNA methylation inhibitor therapy uses in vitro in cancer cells taken from the patient. Cells are compared with parent type cells for expression of bromodomain containing genes, of other listed genes, and / or of bromodomain containing proteins. Mutations involving the amino acid sequence of bromodomain containing genes and / or mutations involving non-synonymous change in amino acid sequence of other genes may be examined. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of inhibitors of DNA methyltransferase, histone acetyltransferase, histone methyltransferase, histone deacetylases, and / or histone demethylases are determined. Increase in (IC50) signifies cross-resistance. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of a selective BET bromodomain inhibitor is also determined, wherein decrease in the (IC50) signifies sensitivity. A combination therapy for cancers using bromodomain inhibitors in combination with DNA methylation inhibitors is also provided.
Owner:PALACKY UNIV
Histone acetyltransferase activators and uses thereof
InactiveUS20170182054A1Decreasing inclusion bodyImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAmyloid betaSynuclein
The invention provides compounds and compositions comprising compounds that modulate histone acyl transferase (HAT). The invention further provides methods for treating neurodegenerative disorders, conditions associated with accumulated amyloid-beta peptide deposits, Tau protein levels, and / or accumulations of alpha-synuclein as well as cancer by administering a compound that modulates HAT to a subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Inhibition of histone acetyltransferases by CTK7A and methods thereof
The present disclosure relates to a method for inhibiting histone acetyltransferases by derivative of curcumin, particularly CTK7A. The present disclosure also relates to identification of induction of autoacetylation of p300 and its inhibition by CTK7A. The disclosure also relates to induction of NPM1 and GAPDH overexpression and corresponding hyperacetylation of histone and methods thereof.
Owner:JAWAHARLAL NEHRU CENT FOR ADVANCED SCI RES
Electrochemical synthesis-based acetyl transferase electrochemical light-emitting sensor built by Ru-MOF and application of acetyl transferase electrochemical light-emitting sensor
ActiveCN110672590ARealize highly sensitive detectionHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAcetyltransferaseElectrochemiluminescence
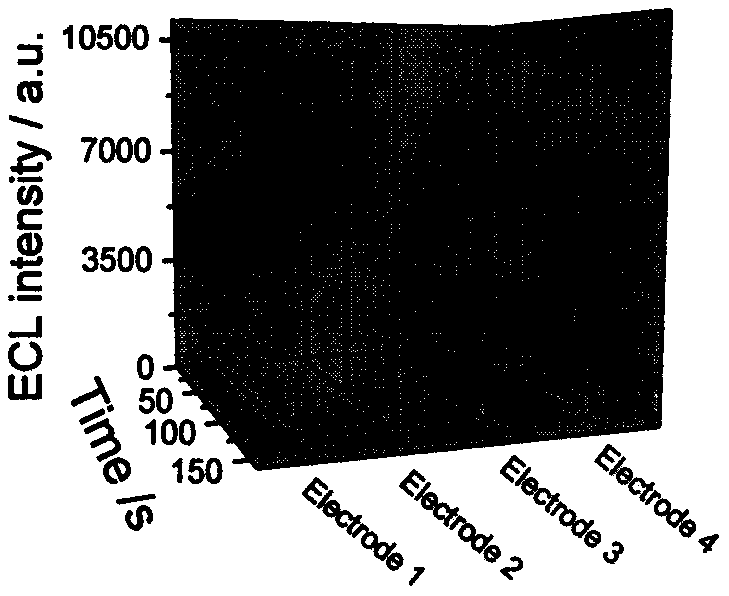
The invention discloses an electrochemical synthesis-based acetyl transferase electrochemical light-emitting sensor built by Ru-MOF and application of the acetyl transferase electrochemical light-emitting sensor. Ru(bpy) <3><2+>- functional MOF thin film is synthesized by an electrochemical auxiliary self-assembly method, the acetyl transferase electrochemical light-emitting sensor is simple synthesis step and relatively short in time and is friendly to environment. An ECL signal of the Ru-MOF can be quenched by Cu (II), an acetylation liquid is added, an acetyl product CoA and Cu (II) react to form a coper-sulfydryl coordination polymer, and the ECL signal is restored. On the basis, an electrochemical light-emitting biosensor is built and is applied to detection of histone acetyl transferase. The electrochemical light-emitting sensor provided by the invention has the advantages of performance stability and high sensitivity in application and can be widely applied to the field of clinic and medicine.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
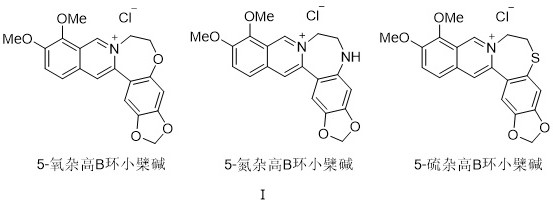
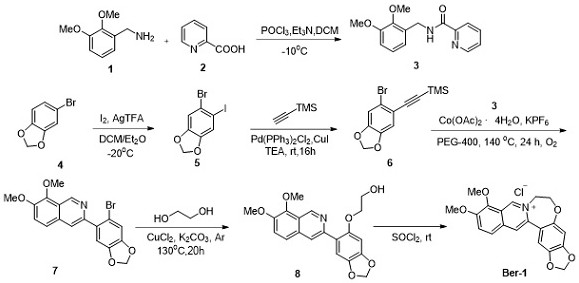
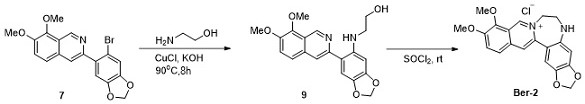
Heteroatom-containing novel high B-ring berberine analogues and C-H activation synthesis method thereof
PendingCN111808121ABreak the limitationsHigh synthesis efficiencyOrganic chemistryBerberineHeteroatom
The invention provides a heteroatom-containing novel high B-ring berberine analogue and a C-H activation synthesis method thereof. The novel high-B-ring berberine analogue with the potential p300 histone acetyltransferase inhibitory activity is prepared from 5-oxa-high B-ring berberine, 5-aza-high B-ring berberine and 5-thia-high B-ring berberine. According to the method, total synthesis is completed by virtue of desilicication and C-H activation / cyclization of cobalt-catalyzed N-picolinamide and arylacetylene silane. Compared with an existing report, the limitation of basic skeleton transformation of berberine is broken through, a novel structure type is provided, meanwhile, a more economical and efficient synthetic method of the berberine analogue is invented, and the berberine analoguehas a wide application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
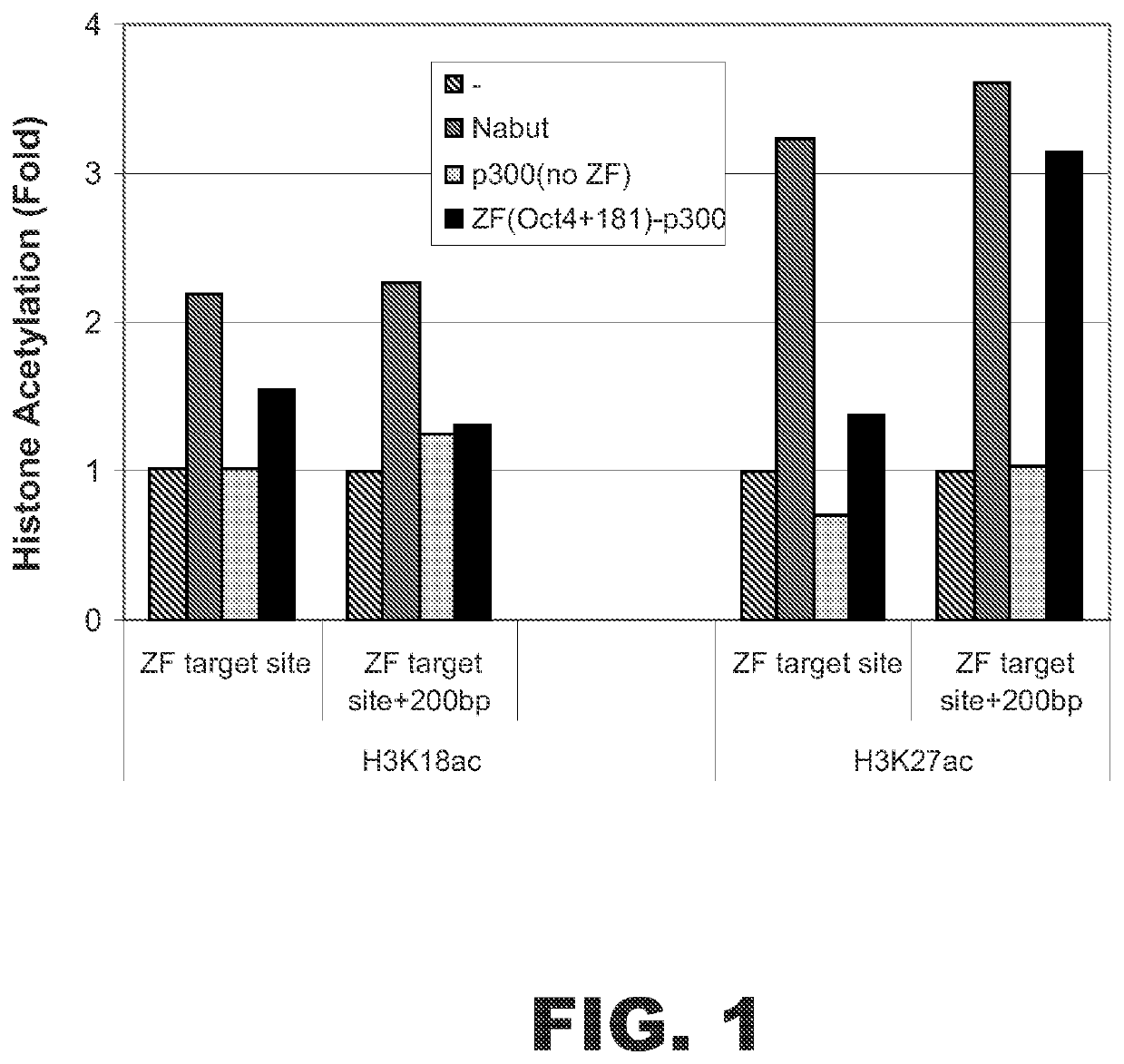
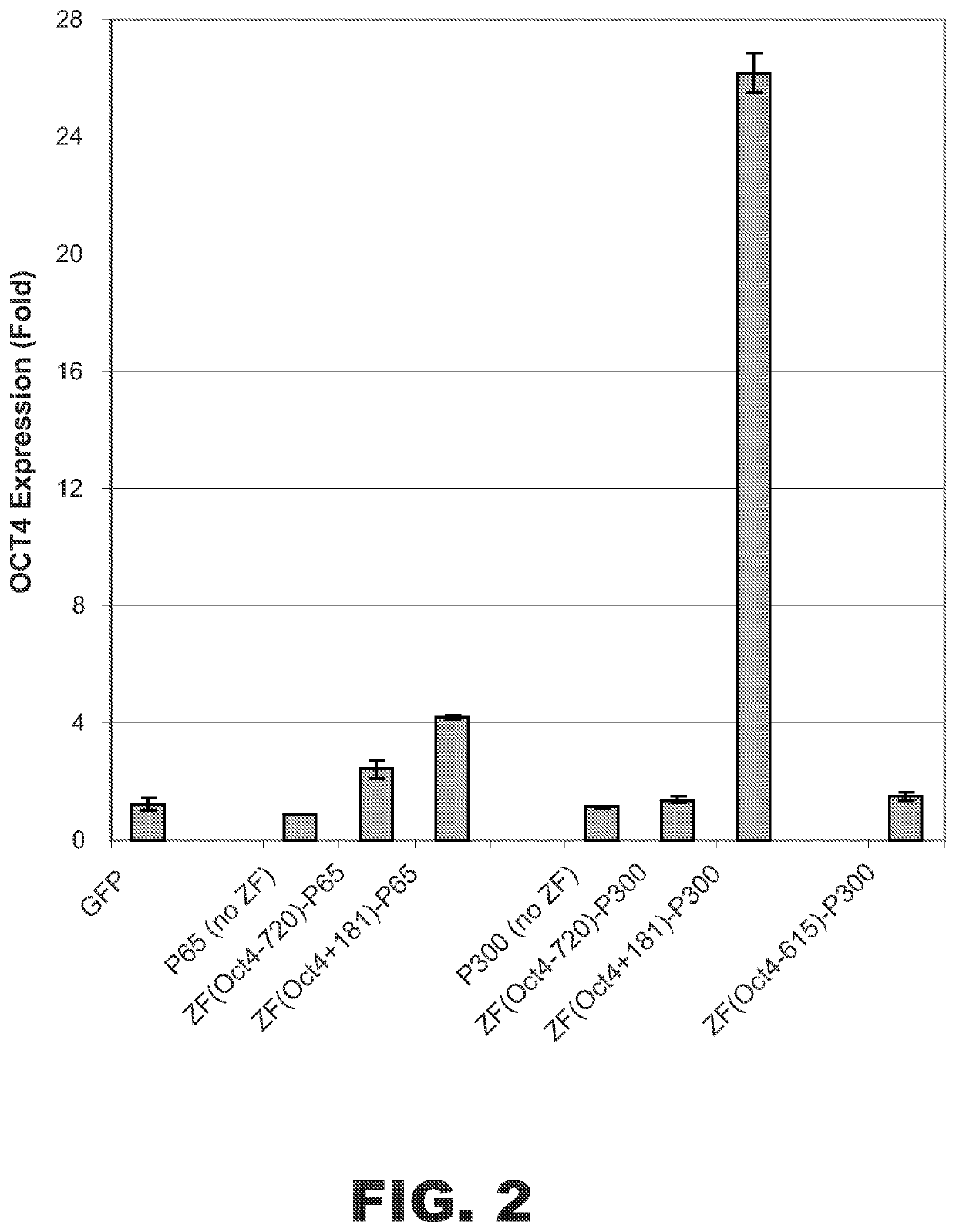
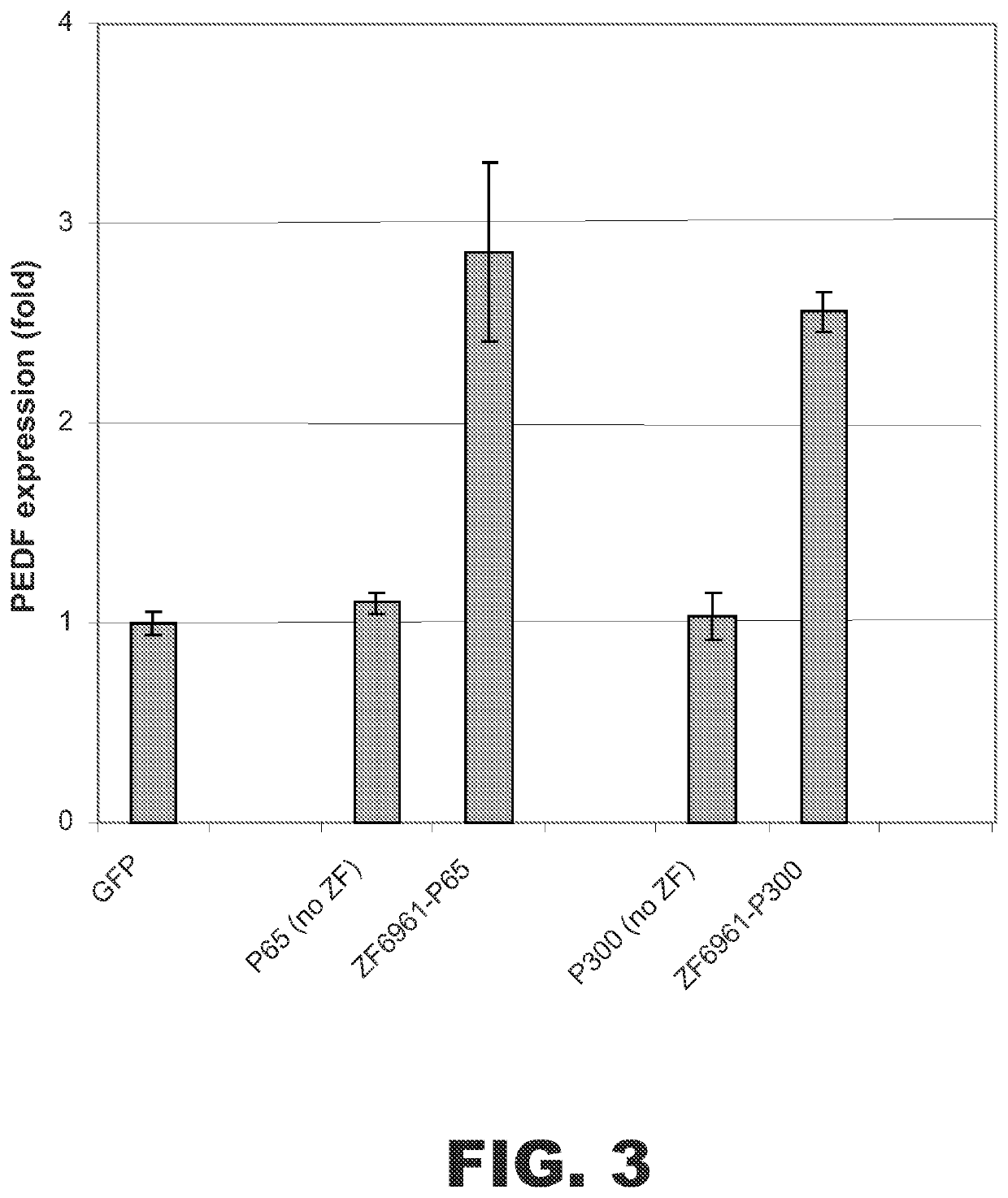
Targeted histone acetylation
ActiveUS10570378B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainDNA-binding domainA-DNA
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for acetylating histones at targeted chromosomal locations in a cell. In particular, the disclosure provides a fusion protein comprising a DNA binding domain and at least one histone acetyltransferase (HAT) domain, such that the DNA binding domain targets the fusion protein to a targeted chromosomal location and the HAT domain acetylates histones at the targeted location.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Use of histone acetyltransferase inhibitor amidoximes as anti-proliferative agents
Owner:TEXAS WOMAN'S UNIVERSITY
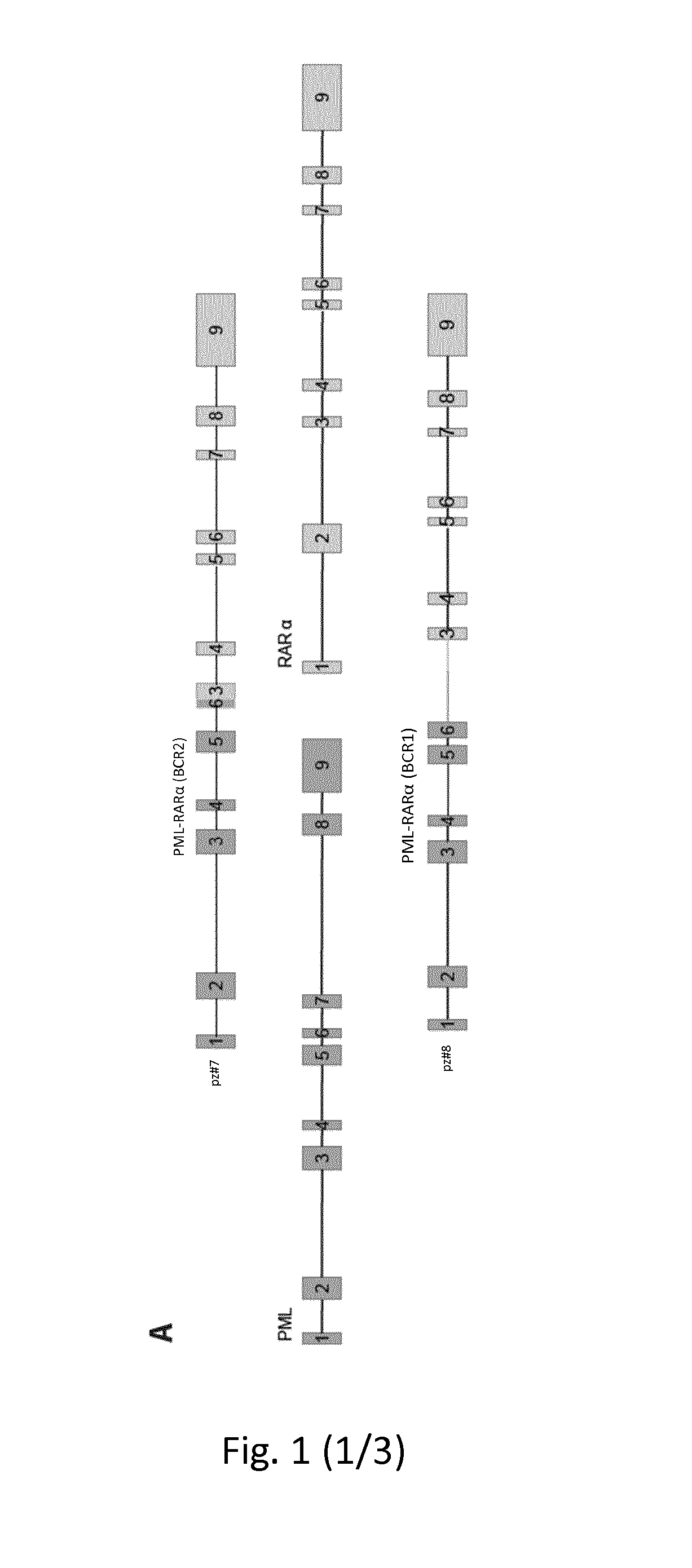
Method for the prognosis and/or treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia
InactiveUS20190284635A1Lower Level RequirementsReducing methylationOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEZH2Acetylation
The present invention relates to a method for the diagnosis of low overall survival acute promyelocytic leukemia and / or of predicting and / or monitoring the response and / or the efficacy of a therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia or to identify a subject to be treated with an inhibitor of HAT and / or an inhibitor of EZH2 by determining the acetylation or methylation status of specific relevant regions and relative kit and microarray. The invention also refers to histone acetyl transferase (HAT) inhibitor for use in the treatment of a solid or hematopoietic tumor.
Owner:EPI C SRL
Histone acetyltransferase activators and compositions and uses thereof
ActiveUS10653648B2Improve retentionNervous disorderMuscular disorderNeuro-degenerative diseaseCancer research
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Histone acetyltransferase modulators and uses thereof
ActiveUS9969677B2Decreasing inclusion bodyImprove the level ofNervous disorderOrganic chemistryAmyloid betaProtein level
The invention provides compounds and compositions comprising compounds that modulate histone acyl transferase (HAT). The invention further provides methods for treating neurodegenerative disorders, conditions associated with accumulated amyloid-beta peptide deposits, Tau protein levels, and / or accumulations of alpha-synuclein as well as cancer by administering a compound that modulates HAT to a subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Uses of histone acetyltransferase activators
InactiveUS20180050982A1Enhance memoryEasy to learnOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPharmaceutical medicineHistone protein
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Use of histone acetyltransferase inhibitor amidoximes as Anti-proliferative agents
ActiveUS20190167608A1Heavy metal active ingredientsAmine active ingredientsAnticarcinogenCancer cell
Owner:TEXAS WOMAN'S UNIVERSITY
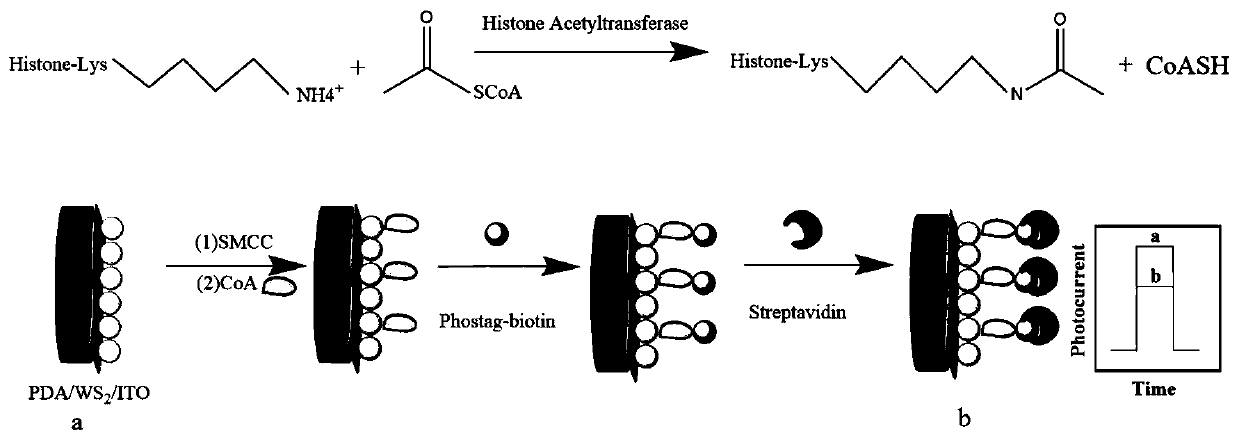
A photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting histone acetyltransferase activity and its preparation method
InactiveCN110161093BAchieve quenchingHigh detection sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesCoenzyme A biosynthesisStreptavidin
The invention discloses a photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting histone acetyltransferase activity and a preparation method thereof. The photoelectrochemical biosensor comprises an ITO electrode, stripped WS2, polydopamine, SMCC, coenzyme A, phos-tag-biotin, and streptavidin, wherein the stripped WS2, polydopamine, SMCC, coenzyme A, phos-tag-biotin, and streptavidin are sequentially modified on the surface of the electrode. According to the photoelectrochemical biosensor and the method in the invention, by utilizing good biocompatibility and conductivity of WS2 and specifically recognized avidin and biotin, quenching of a photoelectric signal is realized, and the detection sensitivity of the histone acetyltransferase is improved. The specificity of activity detection of the histoneacetyltransferase is improved by utilizing the specific binding and identification effects of maleimide in the SMCC to sulfydryl in the CoA. The detection method disclosed by the invention is simple,miniaturization of the instrument is realized, the method is easy to operate, and the detection of the activity of the histone acetyltransferase can be realized only by simply processing the surface of the ITO electrode.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A histone acetyltransferase chrono-current sensor based on gold-palladium nanoflowers/graphene composite and its application
ActiveCN110082403BHigh sensitivityRealize highly sensitive detectionMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneAntiendomysial antibodiesCurrent sensor
The invention discloses a time-current sensor of histone acetyltransferase based on gold-palladium nanoflower / graphene composite material and its application. First, a substrate polypeptide is fixed on the surface of a gold electrode by the action of Au-S, and the acetylated The acetyl group on the coenzyme A is transferred to the specific lysine residue of the substrate polypeptide, and the acetylated antibody-gold palladium nanoflower / graphene composite material with strong catalytic ability is specifically adsorbed by the generated acetylated polypeptide, A distinct electrochemical signal is produced in an electrolyte solution containing hydrogen peroxide. In the acetylation reaction, the concentration of p300 and its small molecule inhibitor were changed, and the effects on the electrochemical signals of a series of sensors were explored through the specific binding of acetyl and acetyl antibodies. The advantages are good specificity, high sensitivity, fast detection speed, accurate and reliable results, and low cost.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
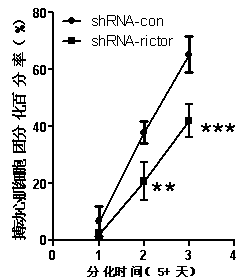
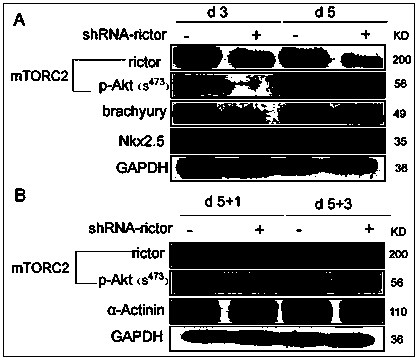
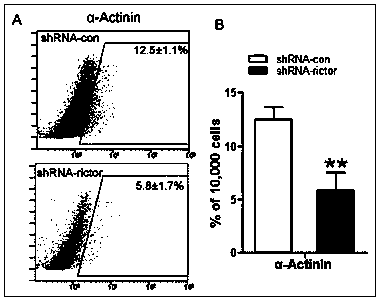
Pharmaceutical application of Rictor/mTORC2 in heart development and disease treatment
InactiveCN103439513AHigh activityPromote phosphorylationIndividual particle analysisBiological testingPhosphorylationDirected differentiation
The invention provides an application of rictor / mTORC2 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2) in in-vitro differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into myocardial cells, namely a research applicable to screening and evaluation of a myocardial cell differentiation promoter taking rictor / mTORC2 as a target. According to the application, the myocardial cells from in-vitro directional differentiation of the mouse embryonic stem cells are purified by a percoll reagent, and plasmids of a histone acetyltransferase transcriptional coactivator p300 coded with rictor are transfected, so that a rictor acetylation level in the myocardial cells is raised, phosphorylation of a rictor downstream effector Akt (ser473) is further promoted, the activity of mTORC2 is improved, and a cardiomyocyte hypertrophy model is constructed; and furthermore, the cardiomyocyte hypertrophy model is utilized, an effect of resveratrol on resisting myocardial hypertrophy is evaluated, and the discovery of a novel myocardial differentiation inducer is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
EP300/CREBBP inhibitor
The present invention provides a compound having excellent histone acetyl transferase inhibitory activity against EP300 and / or CREBBP, or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof. The compound is represented by the following formula (1) or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof:wherein ring Q1, ring Q2, R1, R2, R3 and R4 respectively have the same meanings as defined in the specification.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Method for detecting histone acetyltransferase based on nano-enzyme
ActiveCN112538518AEasy to operateLow detection limitMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAptamerPeroxidase
The invention discloses a method for detecting histone acetyltransferase based on nano-enzyme, and belongs to the field of nano-biological analysis and detection. According to the method, CuBi2O4 andK4[Fe(CN)6] undergo an in-situ reaction to generate CuBi2O4 / Bi4 [Fe(CN)6]3 with mimic peroxidase activity, and detection of HAT p300 is performed: when the target compound HAT p300 does not exist, a coenzyme A aptamer is hydrolyzed into dNMP by exonuclease I, and accordingly, generation of the nano-enzyme CuBi2O4 / Bi4 [Fe(CN)6]3 is inhibited; when the HAT p300 exists, the generated coenzyme A and the coenzyme A aptamer are catalyzed to undergo specific recognition, so that the coenzyme A aptamer cannot be hydrolyzed by the exonuclease I, and the CuBi2O4 / Bi4 [Fe(CN)6]3 with the mimic enzyme activity is smoothly generated, and typical chromogenic substrate 3,3',5,5'-tetramethyl benzidine is oxidized, and accordingly, a colorimetric signal is output. The method disclosed by the invention can sensitively detect the HAT p300 within a range of 0.3-200 nmol / L, the detection limit is as low as 0.09 nmol / L, and the method has a very excellent application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com