Patents
Literature
33 results about "Hiv 1 integrase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
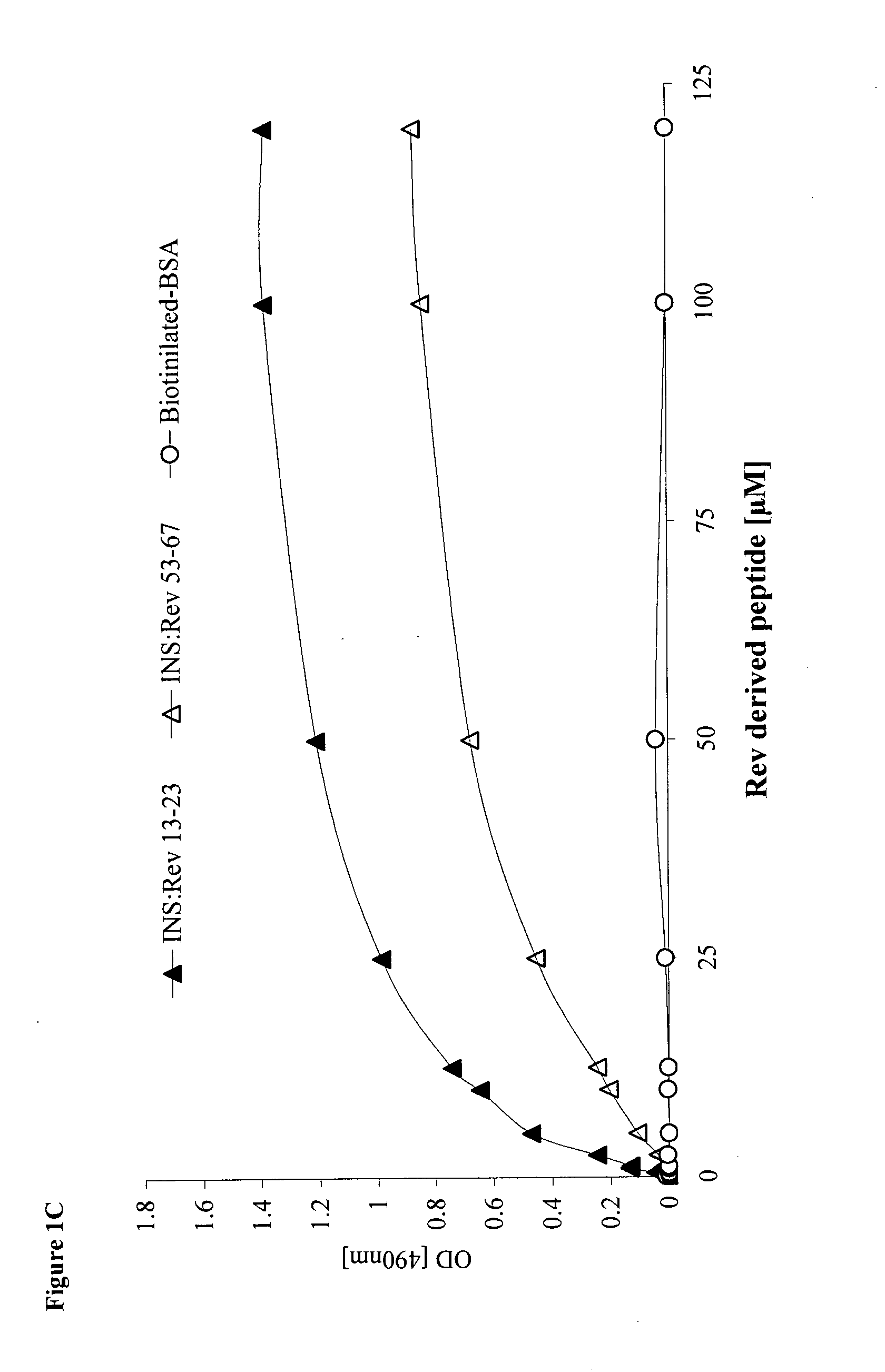
HIV-1 integrase inhibitor is useful for anti-HIV, with IC50 value of 0.33 µM,[1] which can target HIV-1 integrase and depress the activity in the treatment of HIV infection, AIDS, and other similar diseases characterized by integration of a retroviral genome into a host chromosome.
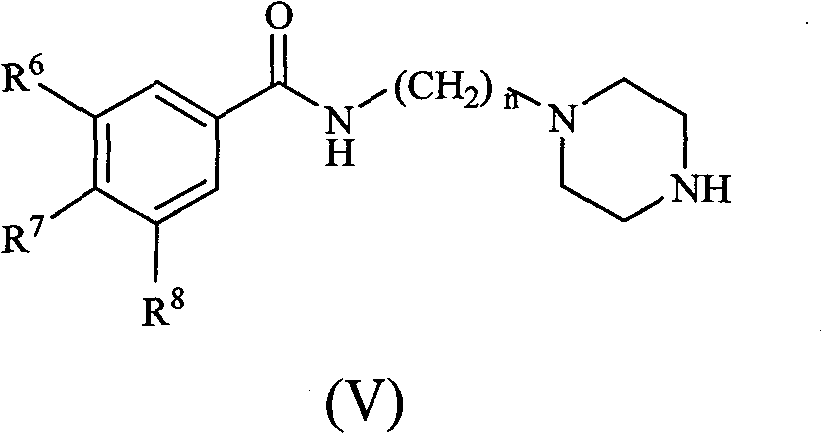
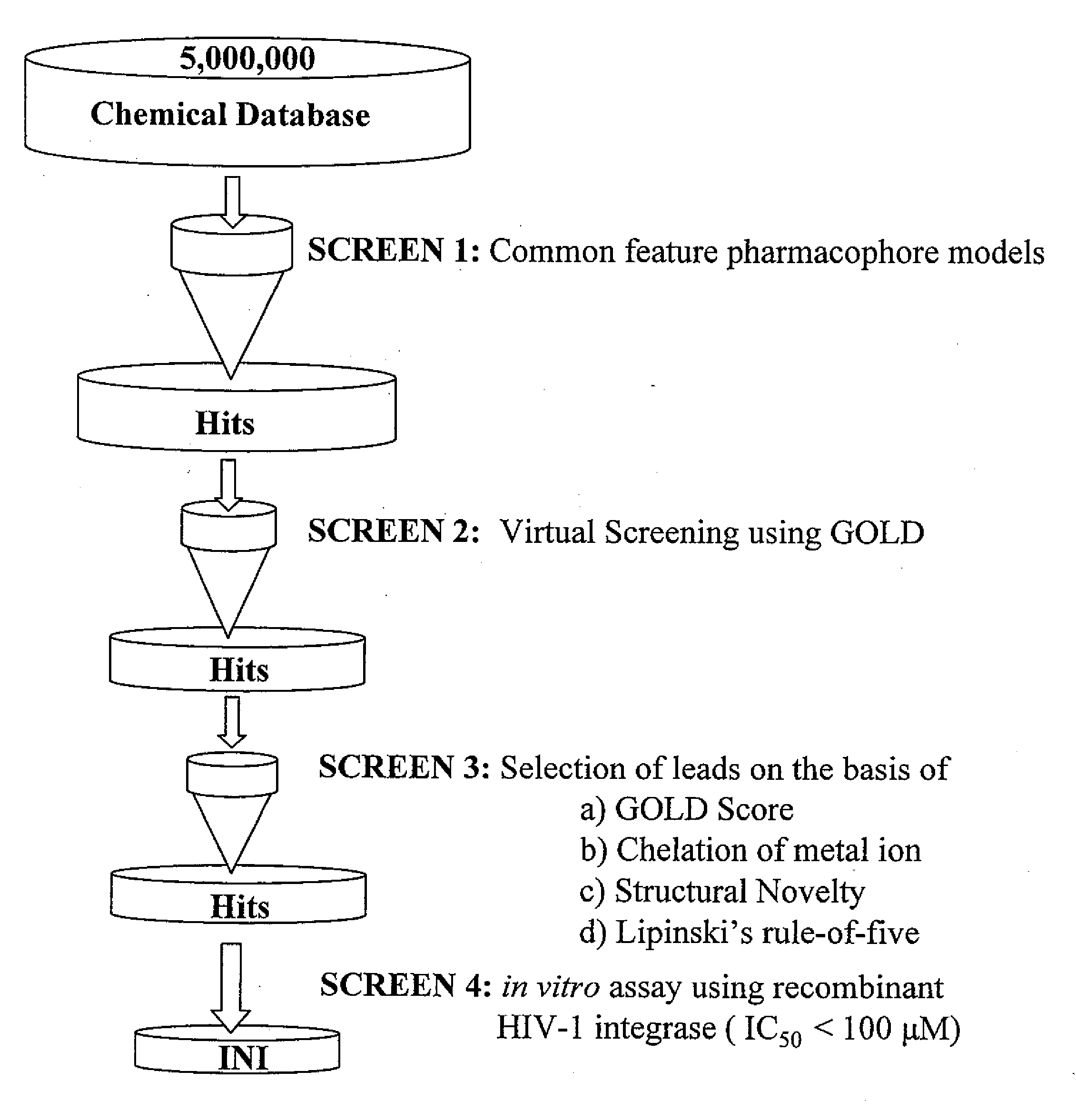
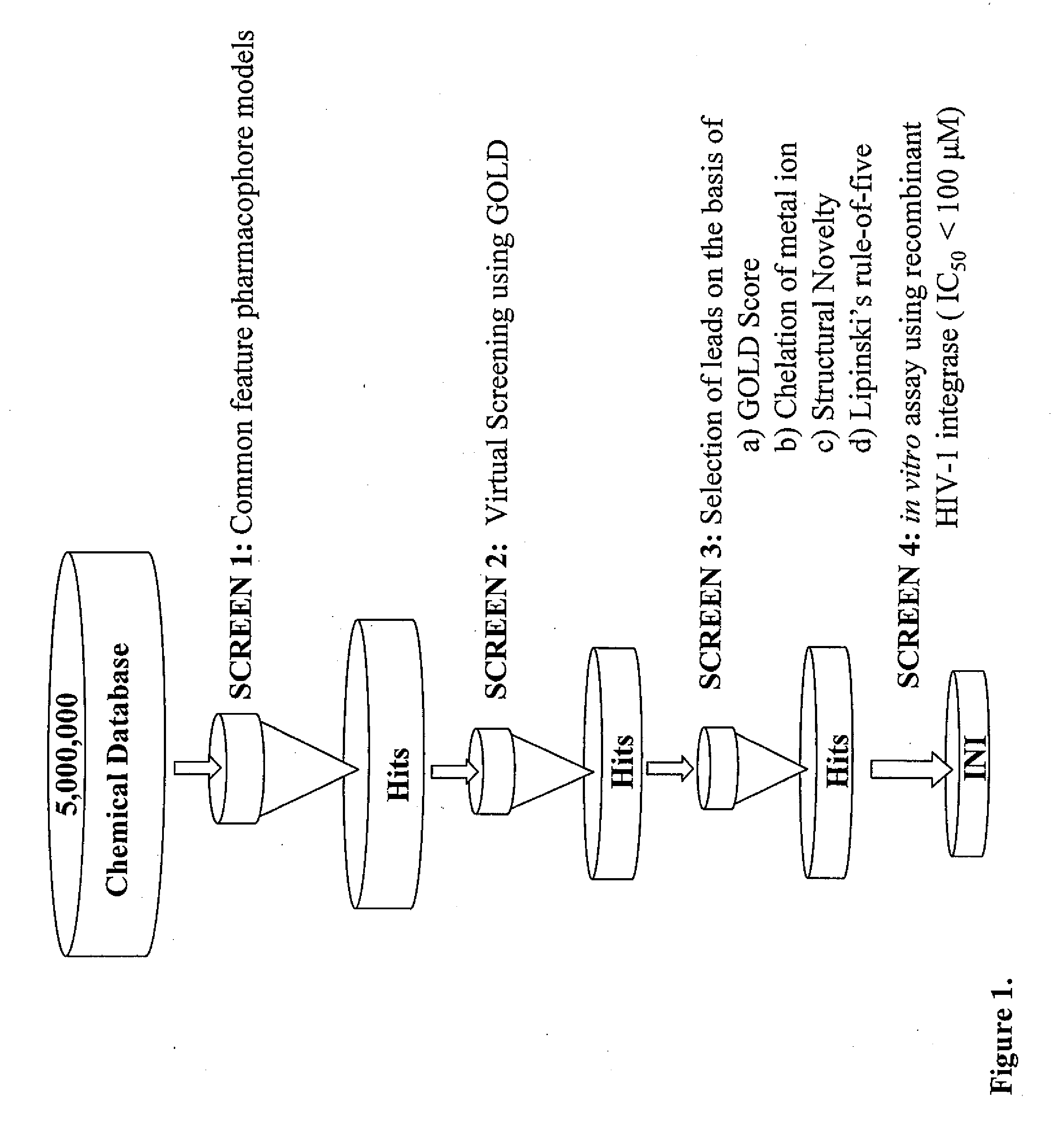
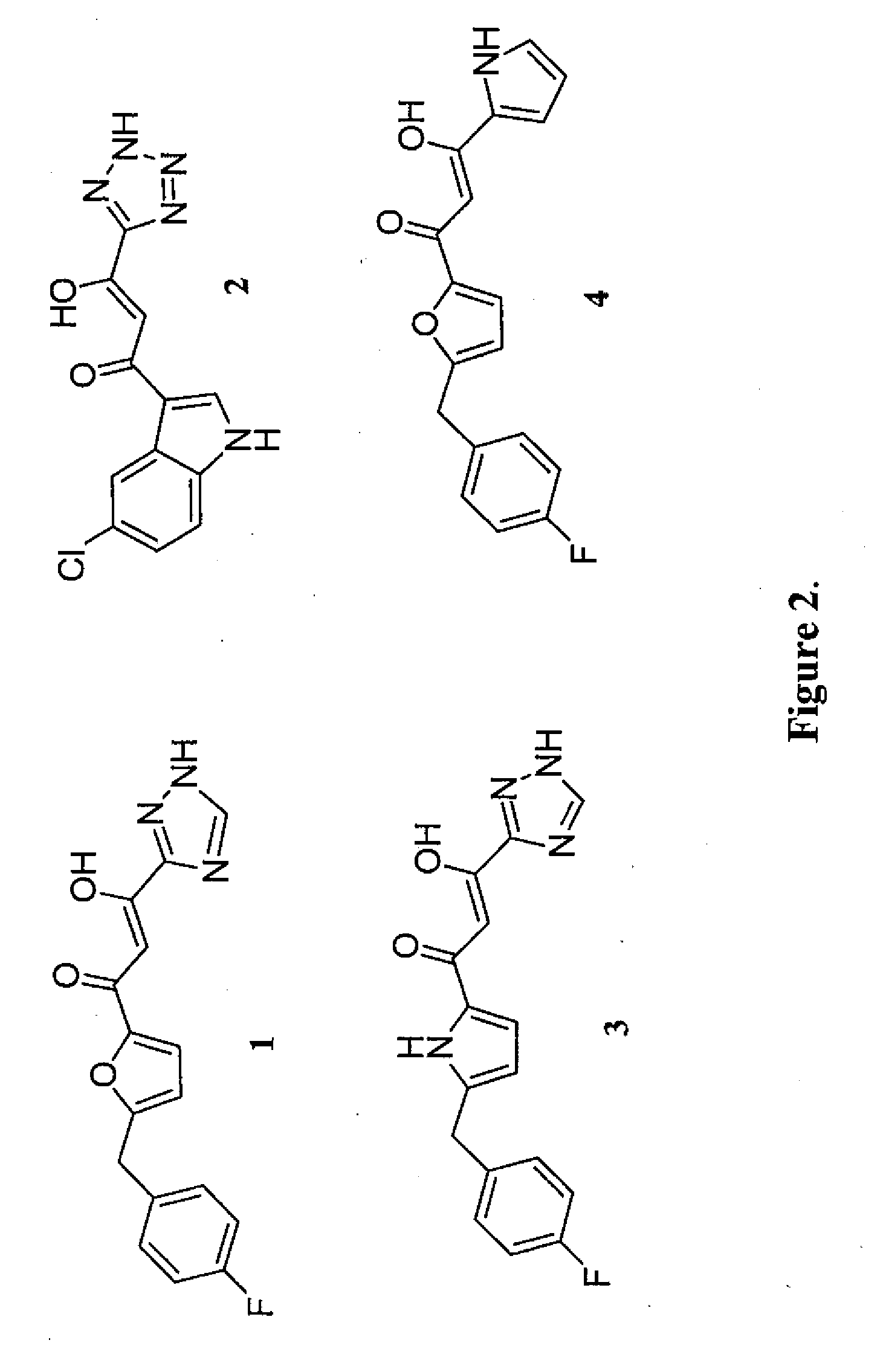
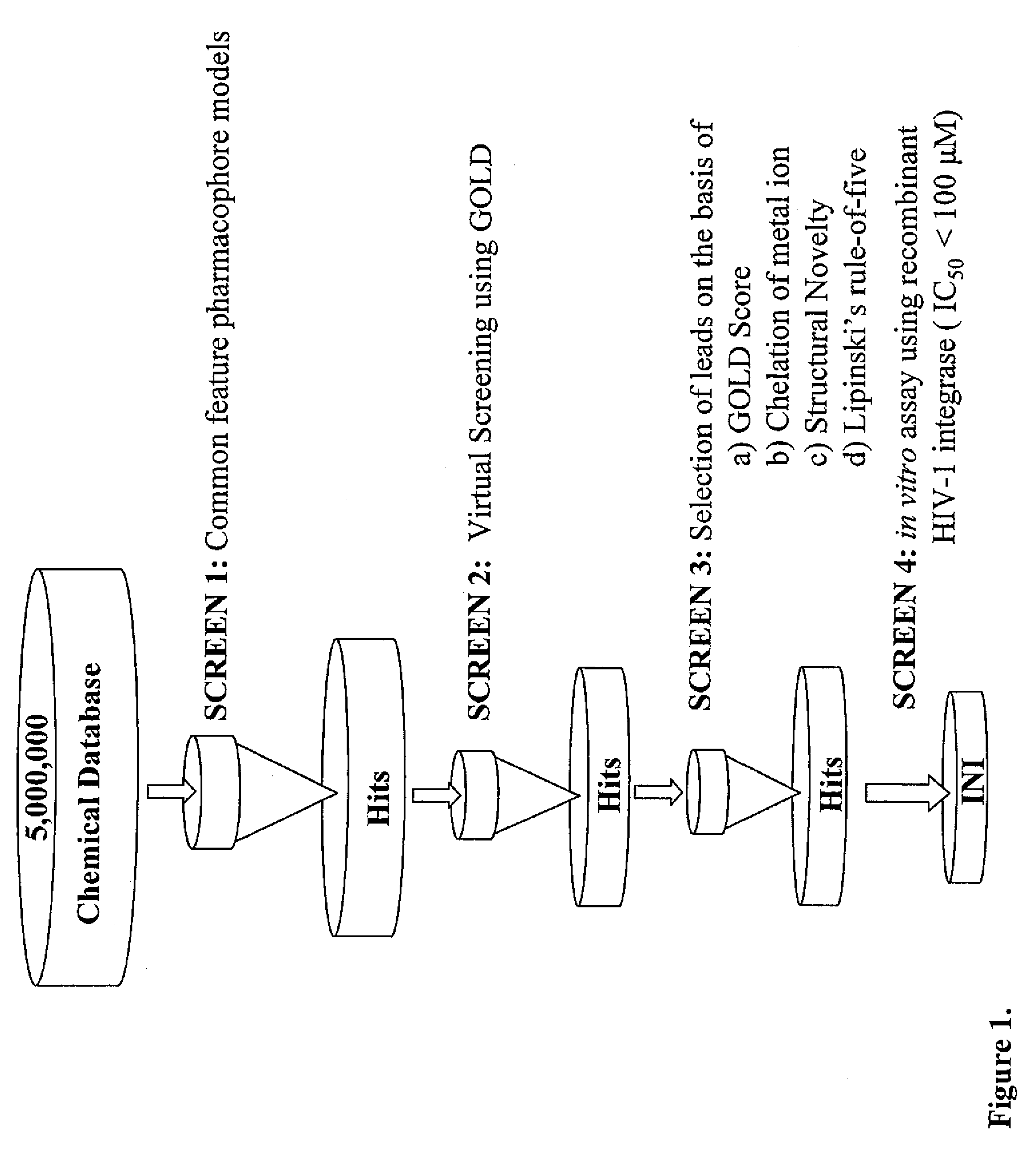
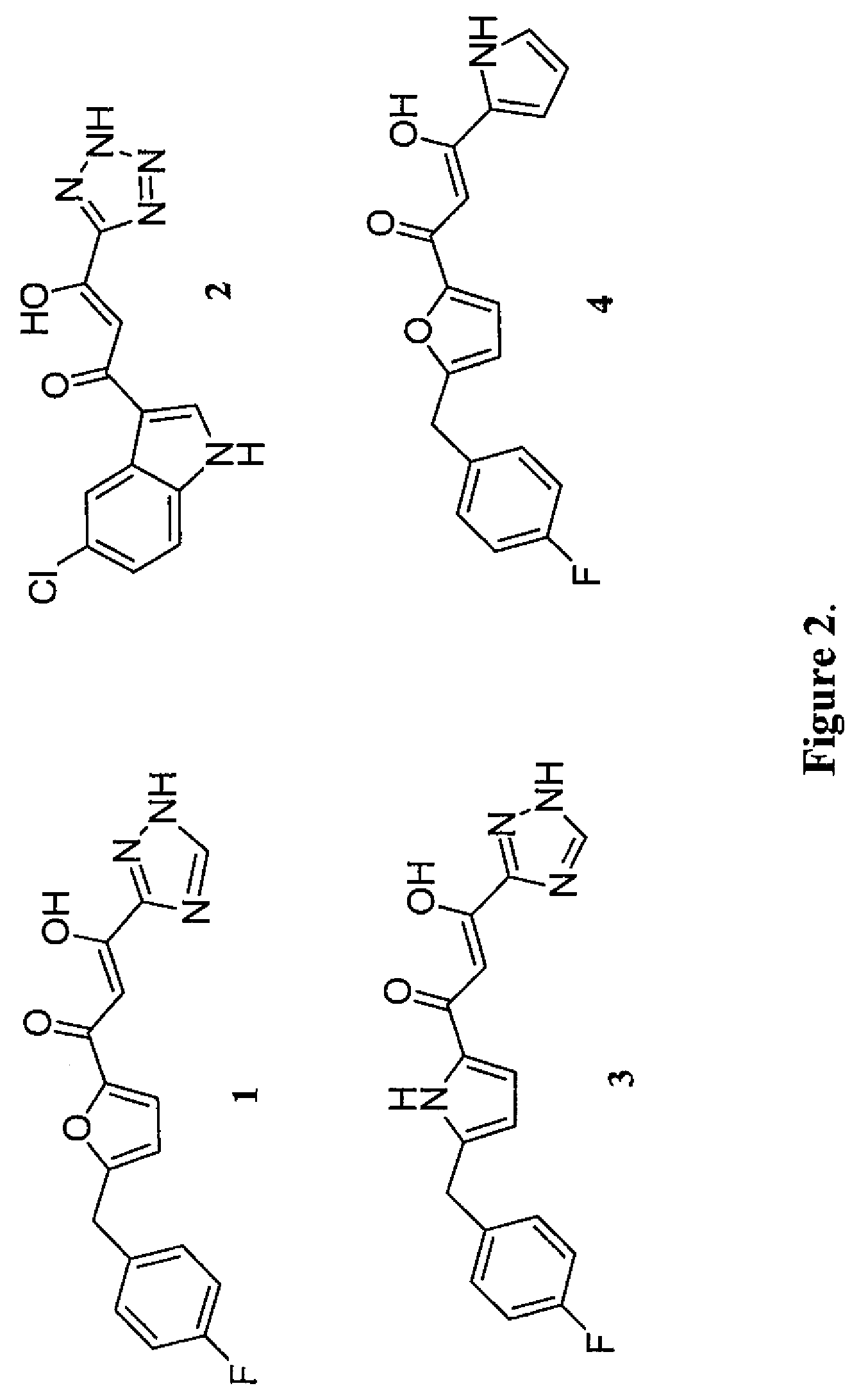
Compounds with hiv-1 integrase inhibitory activity and use thereof as Anti-hiv/aids therapeutics
Pharmacophore models to be used in drug design and discovery are provided. An in silico protocol and in vitro assays are presented. Compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts with HIV-1 integrase inhibitory and anti-HIV activity and use thereof in the treatment of HIV / AIDS and related infections either alone or in combination with all the known antiretroviral therapeutics are described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Combination therapy comprising the use of protein kinase C modulators and Histone Deacetylase inhibitors for treating HIV-1 latency
InactiveUS20100166806A1Adverse propertyPrevent HIV-1-induced cytotoxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryReverse transcriptaseHydroxamic acid
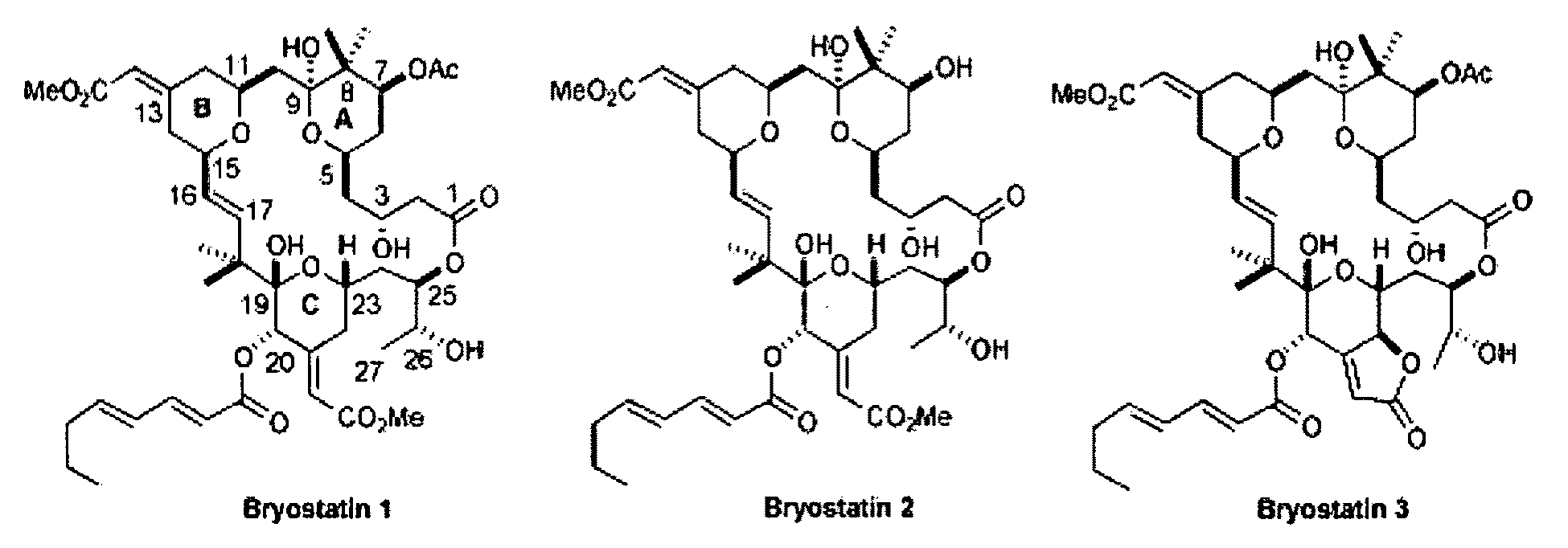
The invention relates to a combination of treatments, more particularly a combination treatment for HIV-1 infection. The present invention is directed to the use of bryostatin-1 and their natural and synthetic derivatives for AIDS therapy, in particular to the use of bryostatins in combination with other active drugs such as Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors and anti-retrovirals, for the treatment of HIV-1 latency. According to the present invention, we provide a combination therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 latency which employs bryostatin-1 (and analogues) and one of the following HDAC inhibitors; valproic acid, butyrate derivatives, hydroxamic acids and benzamides. While HDACi can be used in continuous dosing protocol, bryostatins can be used following a cyclical dosing protocol. Bryostatins can be formulated in pharmaceutical acceptable carriers including nanoparticles, phospholipids nanosomes and / or biodegradable polymer nanospheres. This combination therapy needs to be used in patients treated with antiretroviral therapy (HIV-1 protease inhibitors, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors, HIV-1 integrase inhibitors, CCR5 co-receptor inhibitors and fusion inhibitors).
Owner:APHIOS
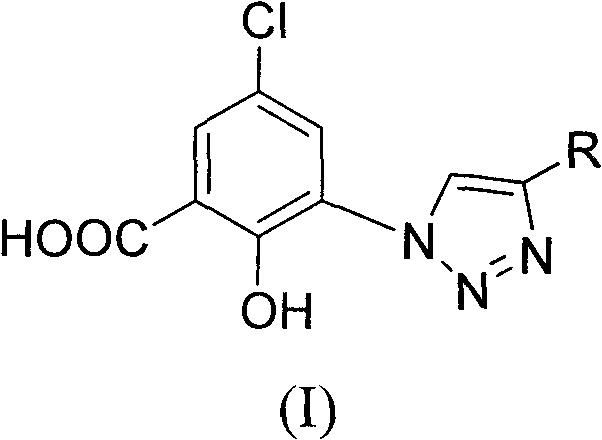
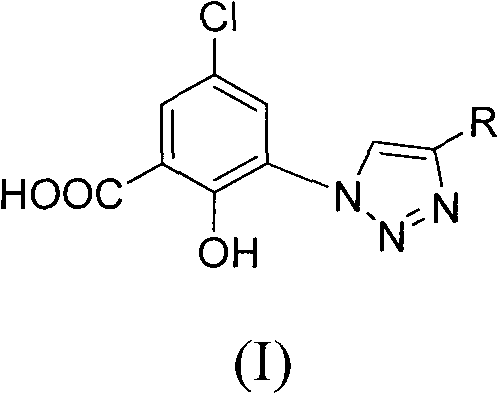
5-chlorol-2-hydroxyl-3-(4-substituted-1h-1,2,3-triazole) benzoic acid compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101812028AGood inhibitory effectReduce diseaseOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry5-chlorosalicylic acidBenzoic acid
The invention relates to a 5-chlorol-2-hydroxyl-3-(4-substituted-1H-1,2,3-triazole) benzoic acid compound expressed in the formula (I) as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The definition of R is shown as the specification. In the preparation method, 5-chlorolsalicylic acid used as a raw material is nitrified and reduced, is subjected to azidation and reacts with end alkyne to obtain the corresponding 5-chlorol-2-hydroxyl-3-(4-substituted-1H-1,2,3-triazole) benzoic acid compound. The compound has the inhibiting function on HIV-1 integrase, and the IC50 of part of the compound reaches 1.6 mircograms / mL, therefore, the compound is a stronger HIV-1 integrase inhibiting agent and is expected to be developed into a new HIV virus resistant medicament.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
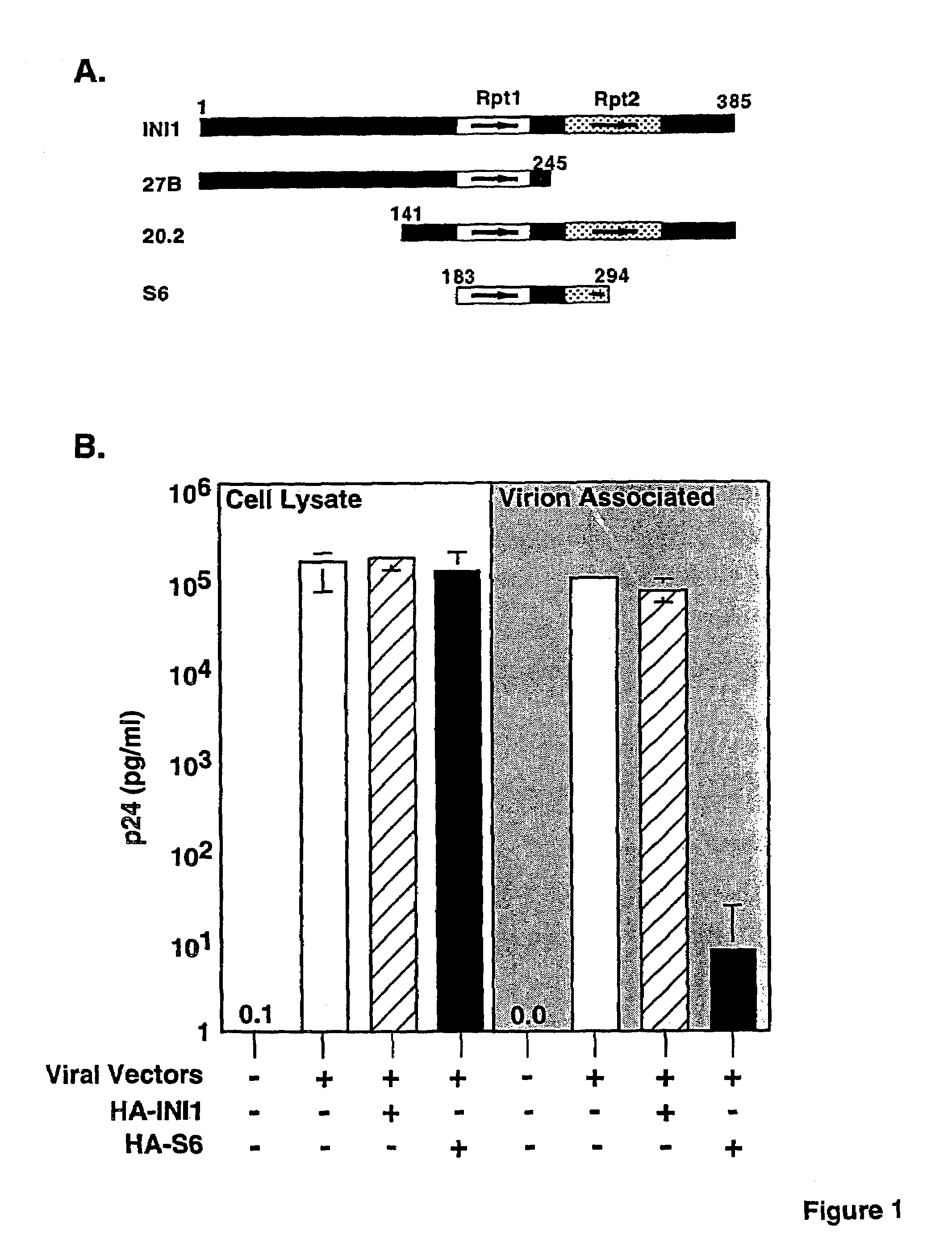
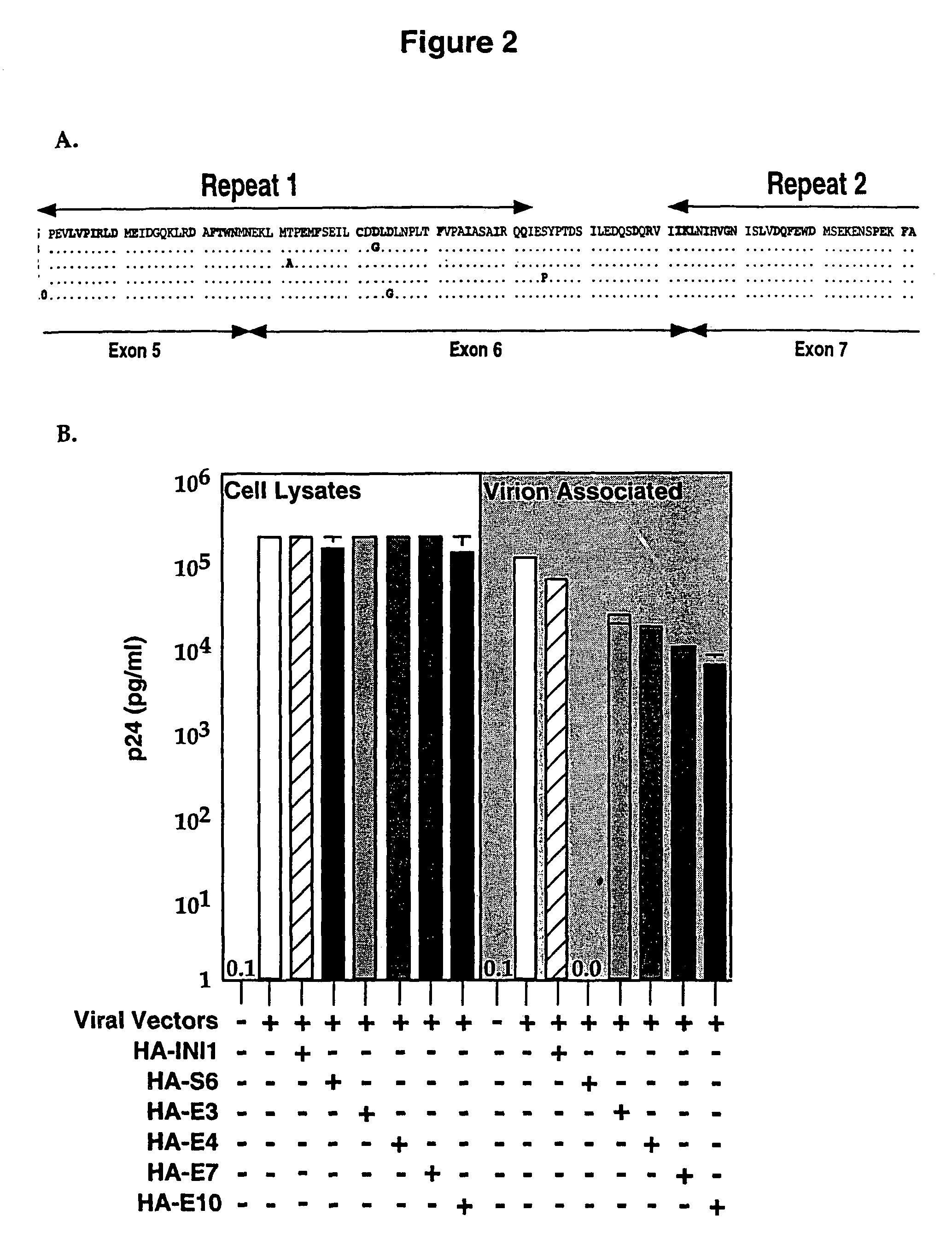
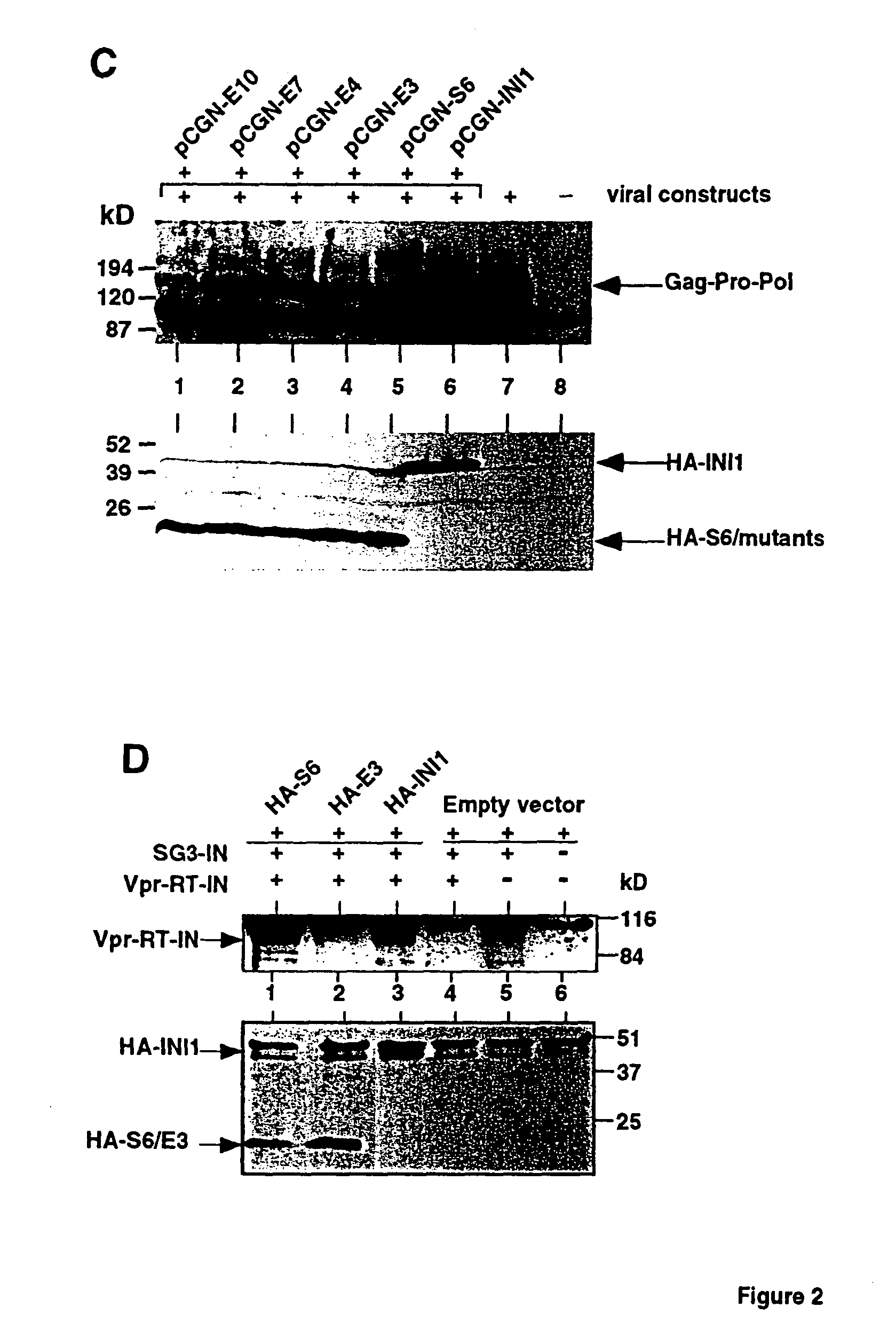
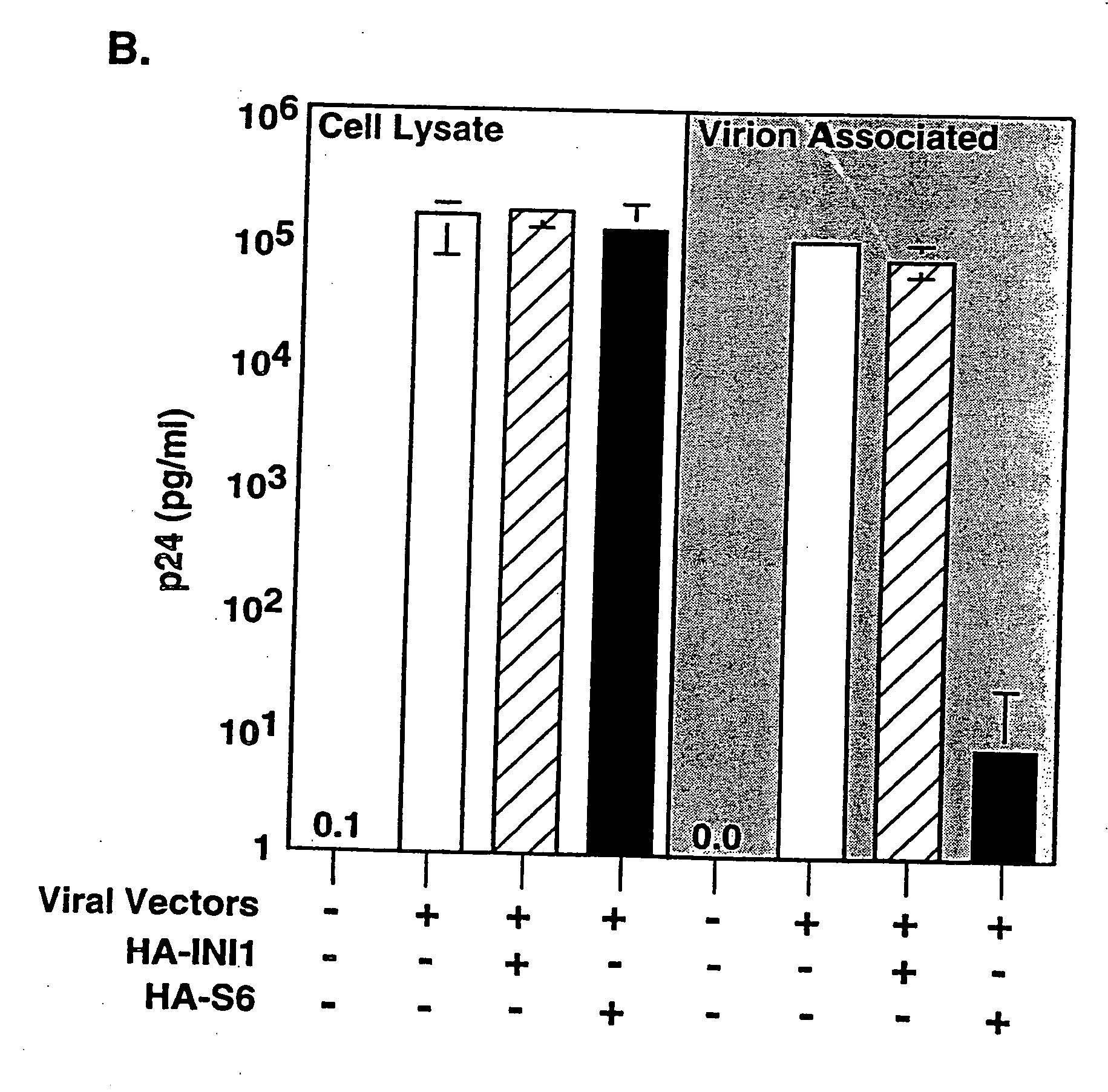
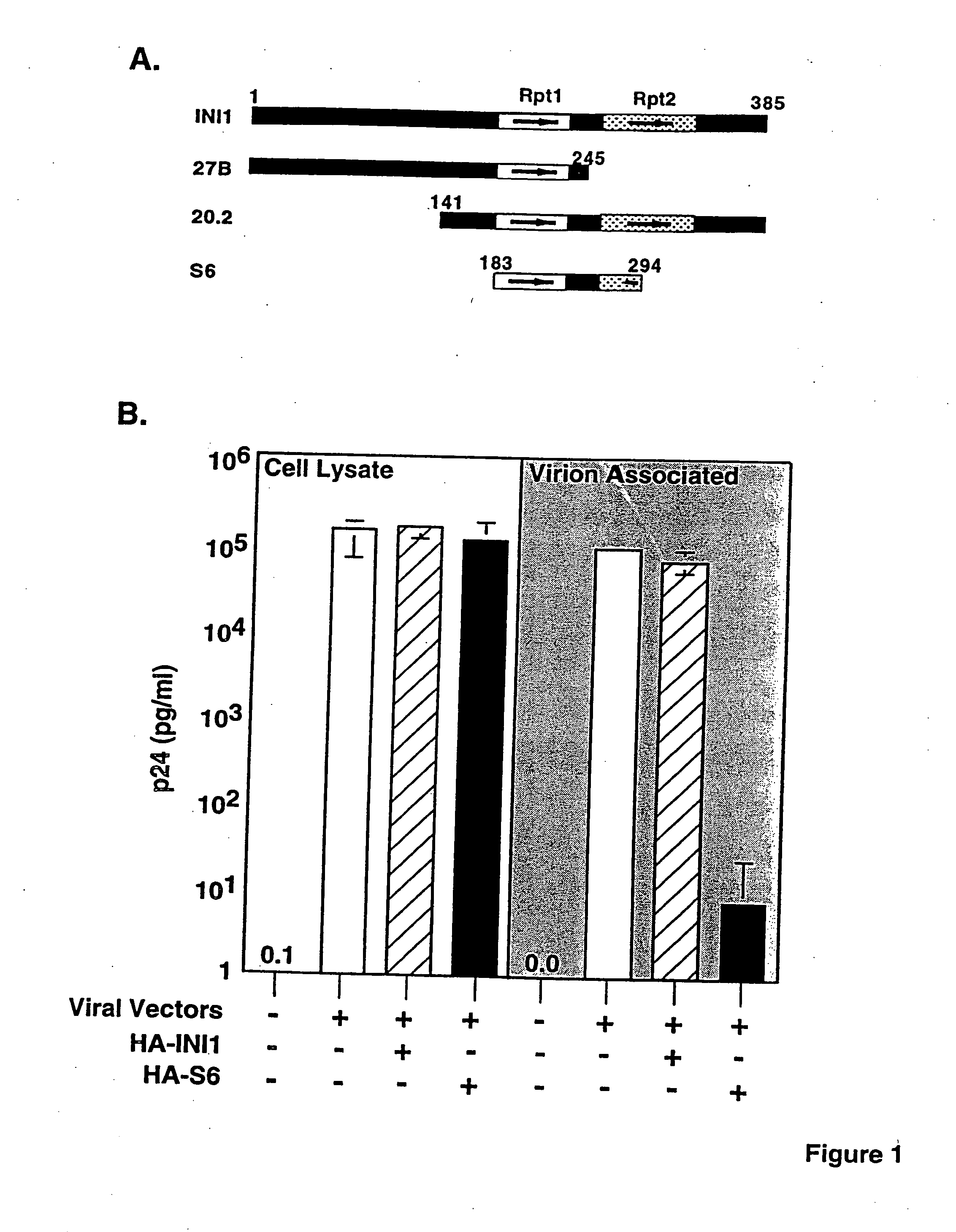
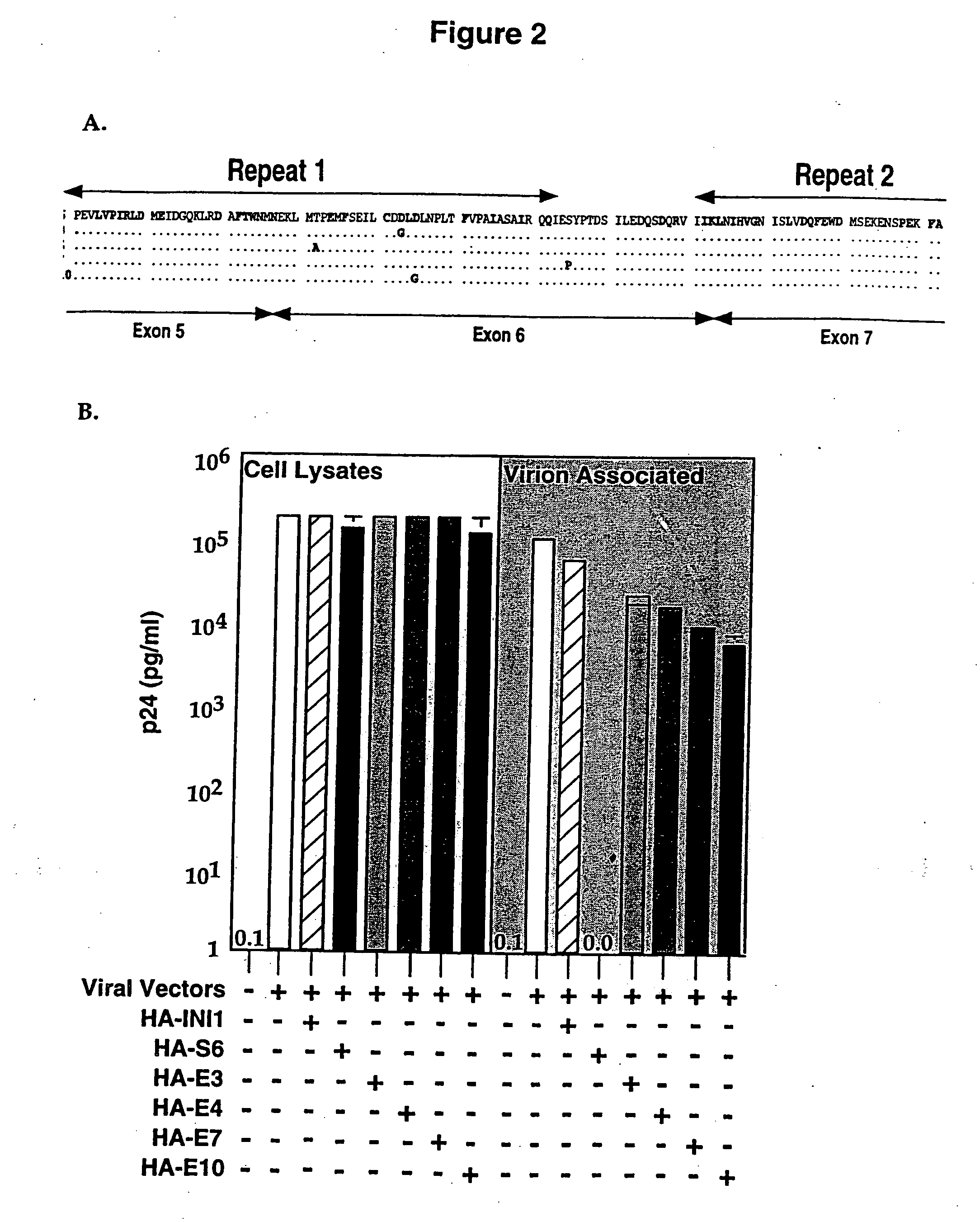
Inhibition of HIV-1 virion production by a transdominant mutant of integrase interactor 1(INI1)/hSNF5
Peptides comprising an Rpt1 domain of an INI1 / hSNF5 which inhibit HIV-1 production in a human cell, and vectors encoding those peptides are provided. Also provided are methods of inhibiting HIV-1 production in a cell, or spread of the HIV-1 to another cell, by treating the cells with the above peptides or vectors. Other methods of inhibiting HIV-1 production in a cell, or spread of the HIV-1 to another cell, by inhibiting production of INI1 / hSNF5 are provided. Additionally, methods of determining whether a test compound inhibits HIV-1 virion production in a mammalian cell, or spread of the HIV-1 to another cell, are provided. Those methods comprise determining whether the test compound inhibits the production of INI1 / hSNF5 or disrupts the interaction of HIV-1 integrase with INI1 / hSNF5.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Inhibition of HIV-1 virion production by a transdominant mutant of integrase interactor 1 (INI1)/hSNF5
Peptides comprising an Rpt1 domain of an INI1 / hSNF5 which inhibit HIV-1 production in a human cell, and vectors encoding those peptides are provided. Also provided are methods of inhibiting HIV-1 production in a cell, or spread of the HIV-1 to another cell, by treating the cells with the above peptides or vectors. Other methods of inhibiting HIV-1 production in a cell, or spread of the HIV-1 to another cell, by inhibiting production of INI1 / hSNF5 are provided. Additionally, methods of determining whether a test compound inhibits HIV-1 virion production in a mammalian cell, or spread of the HIV-1 to another cell, are provided. Those methods comprise determining whether the test compound inhibits the production of INI1 / hSNF5 or disrupts the interaction of HIV-1 integrase with INI1 / hSNF5.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
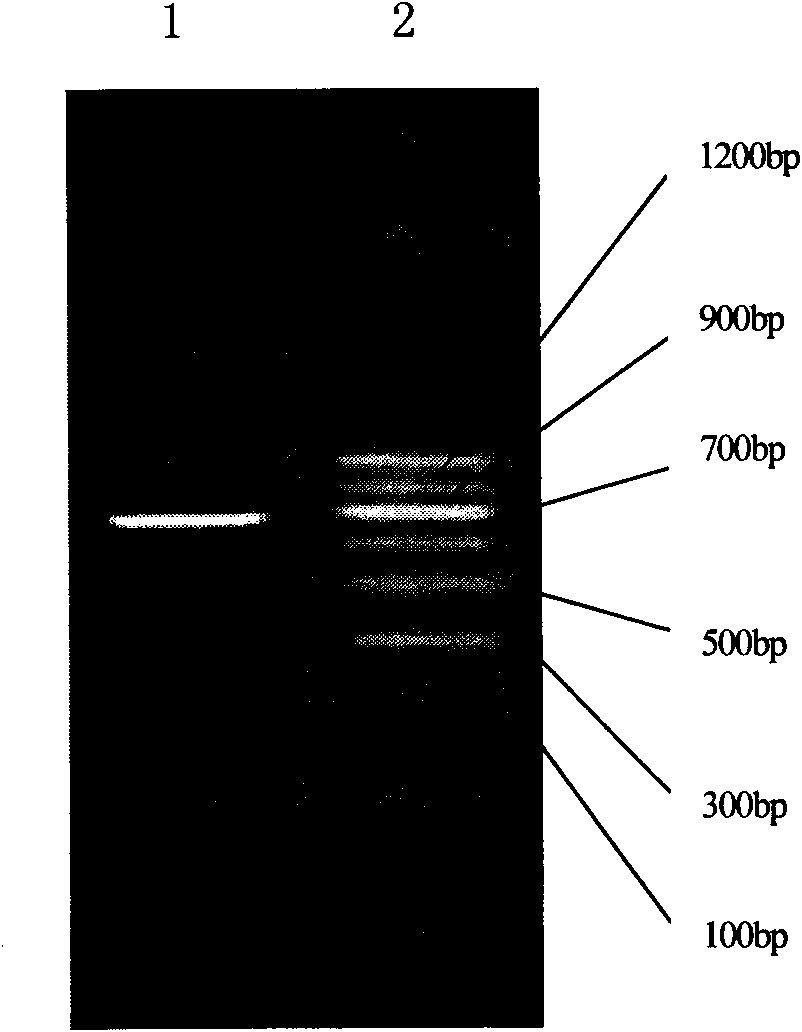
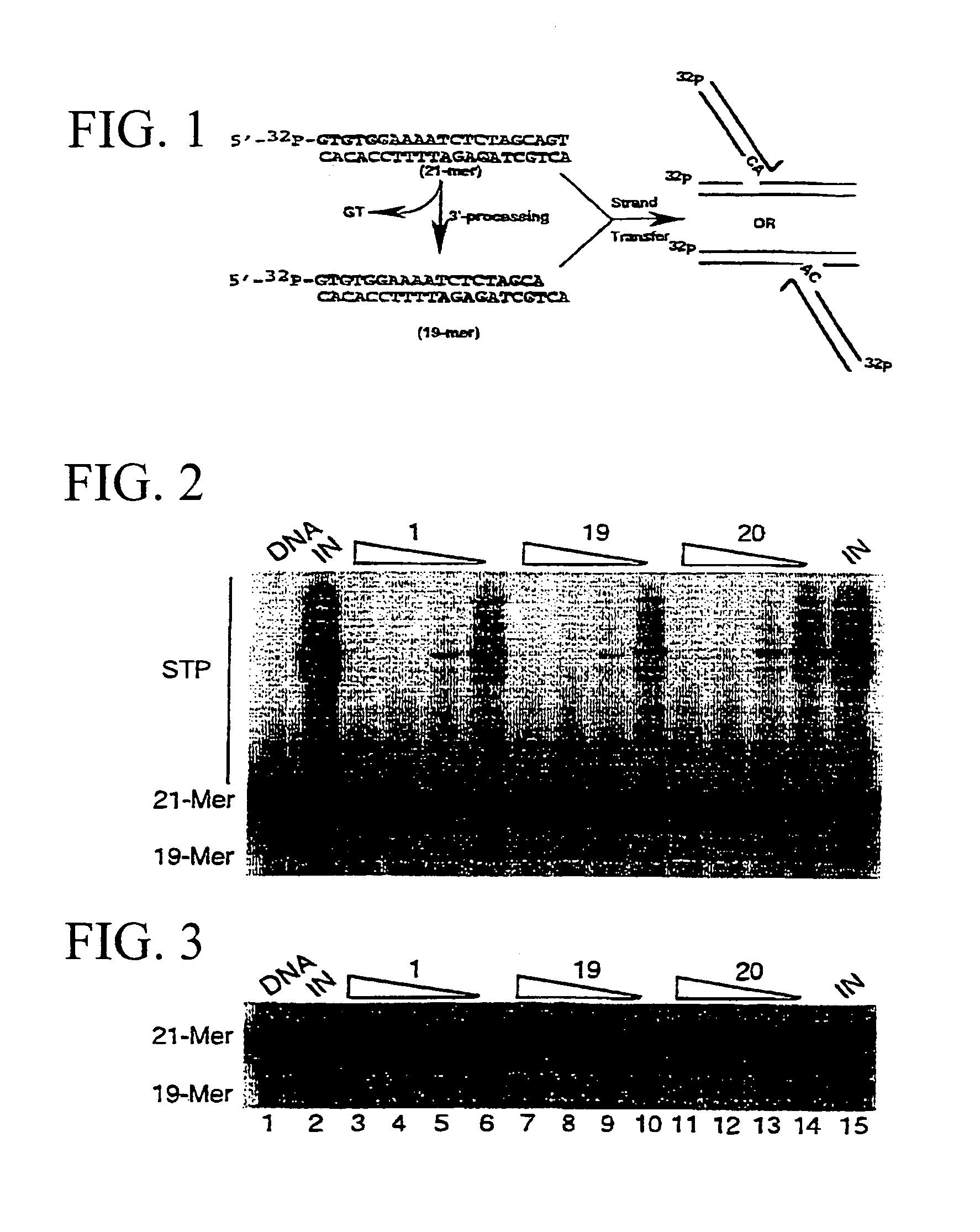
HIV-1 integrase expression bacterial strain and integrase inhibitor in-vitro screening model
ActiveCN101671646AEasy to operateLess distracting factorsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical synthesisInterference factor
The invention relates to an HIV-1 integrase expression bacterial strain and an integrase inhibitor in-vitro screening model. In the model, HIV-1 integrase soluble expression plasmid and expression plasmid with integrase LTR sequence are firstly established based on gene engineering technology, and established recombinant plasmid pET28a-IN is transferred into commercial colibacillus BL21 to obtainthe integrase expression bacterial strain; and then the integrase expression bacterial strain is cultured in large-scale, finally integrase is separated and purified, works on the substrate plasmid and is added into samples to measure the activity. The detection model overcomes the defects such as high cost, high background and more influence factors in the existing ELISA detection method; the detection model can carry out primary screening on various natural or chemically synthetic integrase inhibitors in-vitro largely and quickly; and the detection model is an HIV-1 integrase in-vitro screening model with the advantages of quick operation, flexibility, fewer interference factors and low cost.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Compounds with HIV-1 integrase inhibitory activity and use thereof as anti-HIV/AIDS therapeutics
Pharmacophore models to be used in drug design and discovery are provided. An in silico protocol and in vitro assays are presented. Compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts with HIV-1 integrase inhibitory and anti-HIV activity and use thereof in the treatment of HIV / AIDS and related infections either alone or in combination with all the known antiretroviral therapeutics are described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
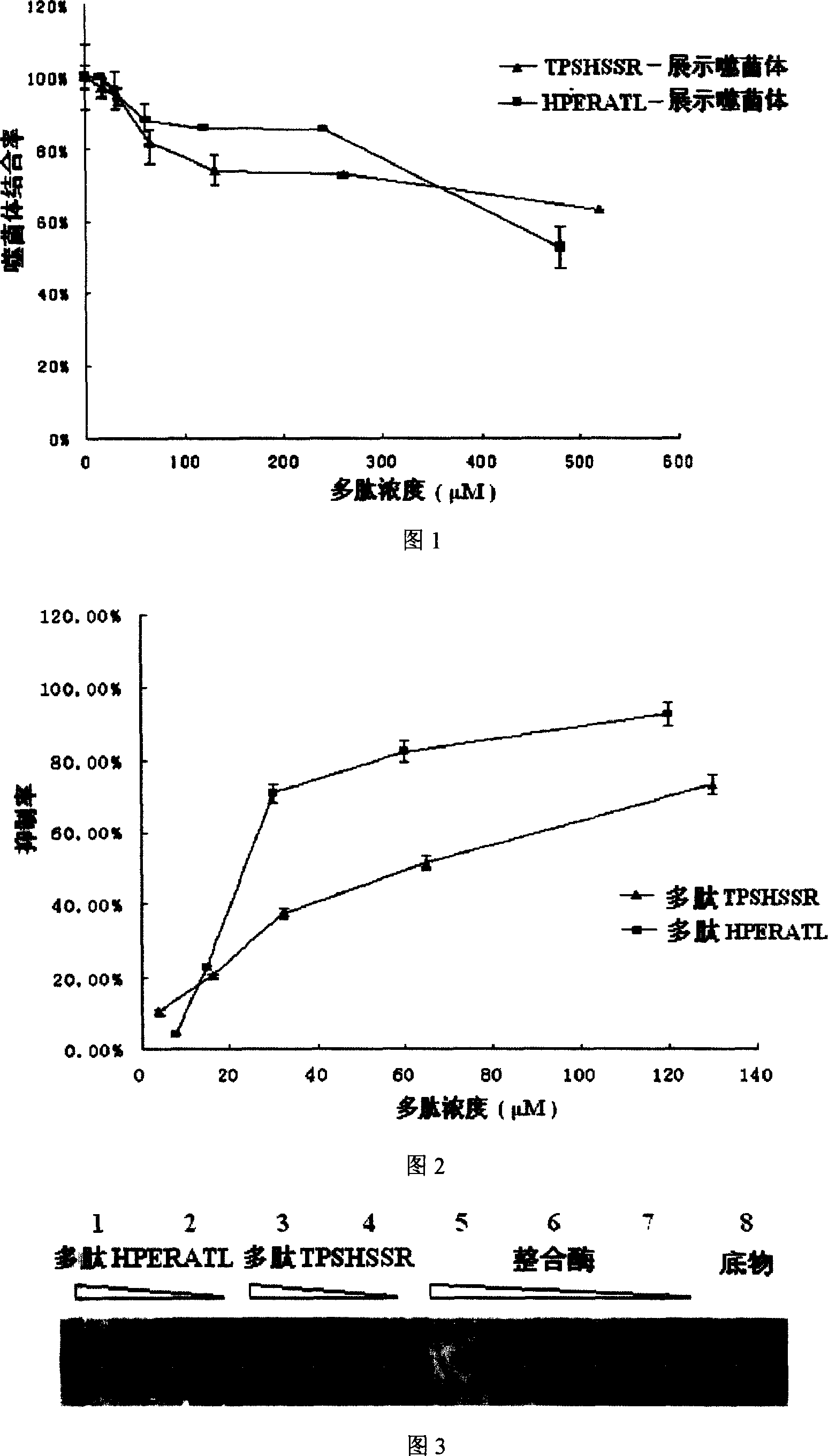
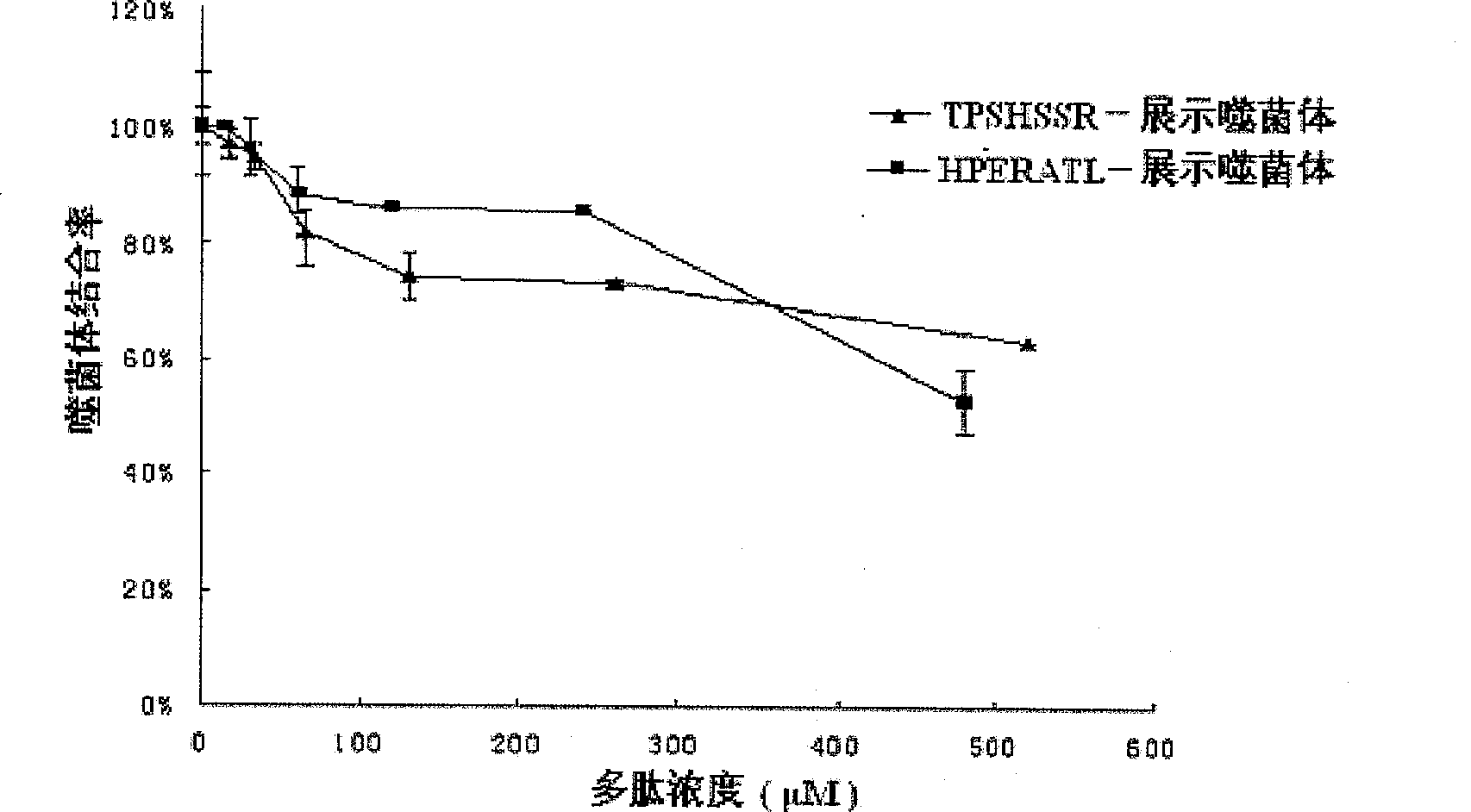
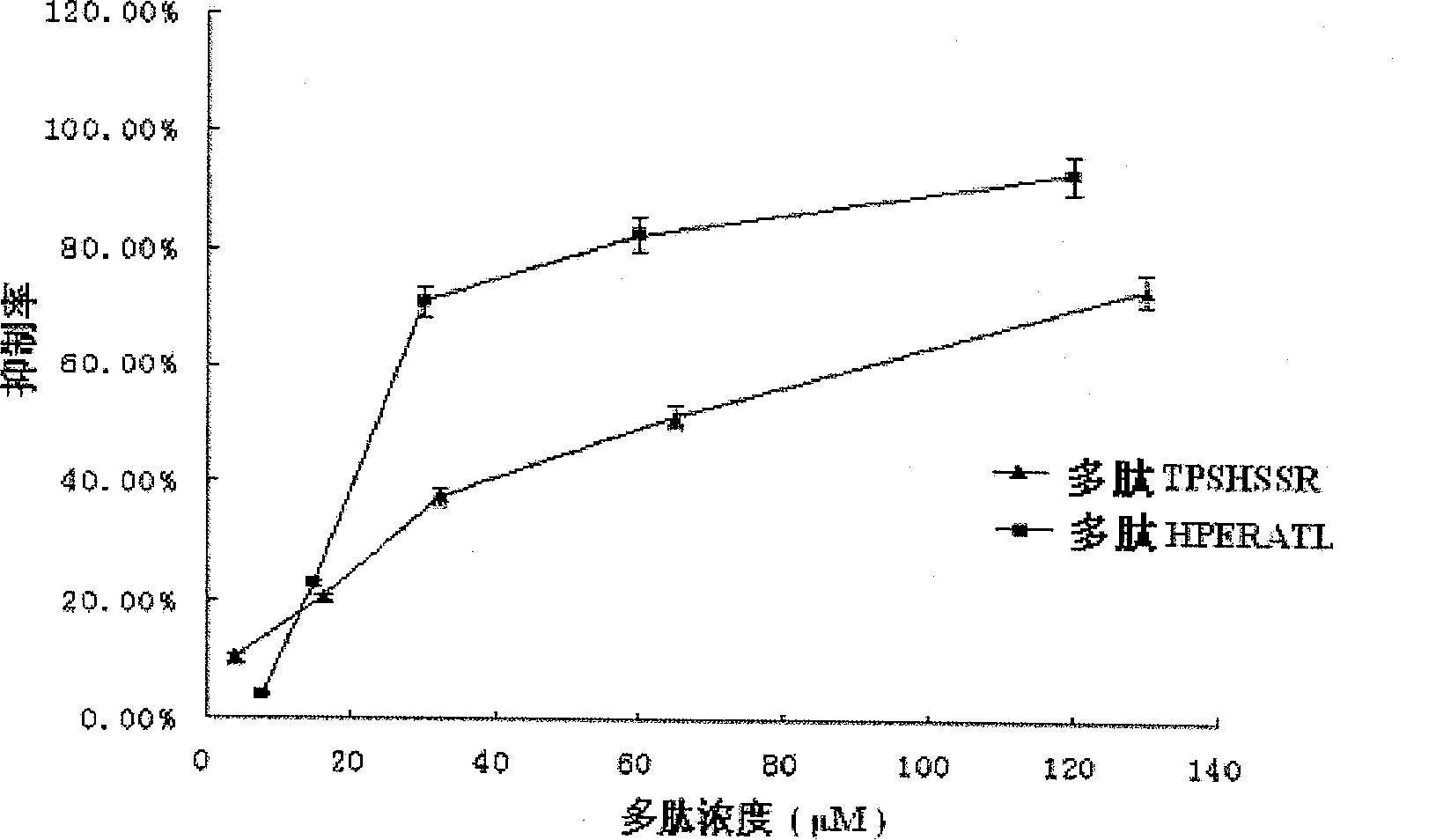
Integrase inhibiting peptide and its application in preparing AIDS-treating medicine
InactiveCN101020710AInhibitory activityInterrupt value-addedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsIntegrasesMechanism of action
The present invention provides one kind of integrase inhibiting peptide, which is selected from seven kinds of organic polypeptide compounds, a, b, c, d, e, f and g, with molecular weight of 974.3, 770.8, 822.9, 830.9, 849.0, 789.8 and 788.8 separately, is water soluble, and has amino acids connected through peptide bond and capacity of inhibiting the activity of HIV-1 integrase. The organic polypeptide compound of the present invention can inhibit the activity of HIV-1 integrase, and block the proliferation and life period of virus DNA in host cell, and may be applied in preparing medicine for treating AIDS. The present invention may be also used in the further research of integrase structure, action mechanism and AIDS-treating medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
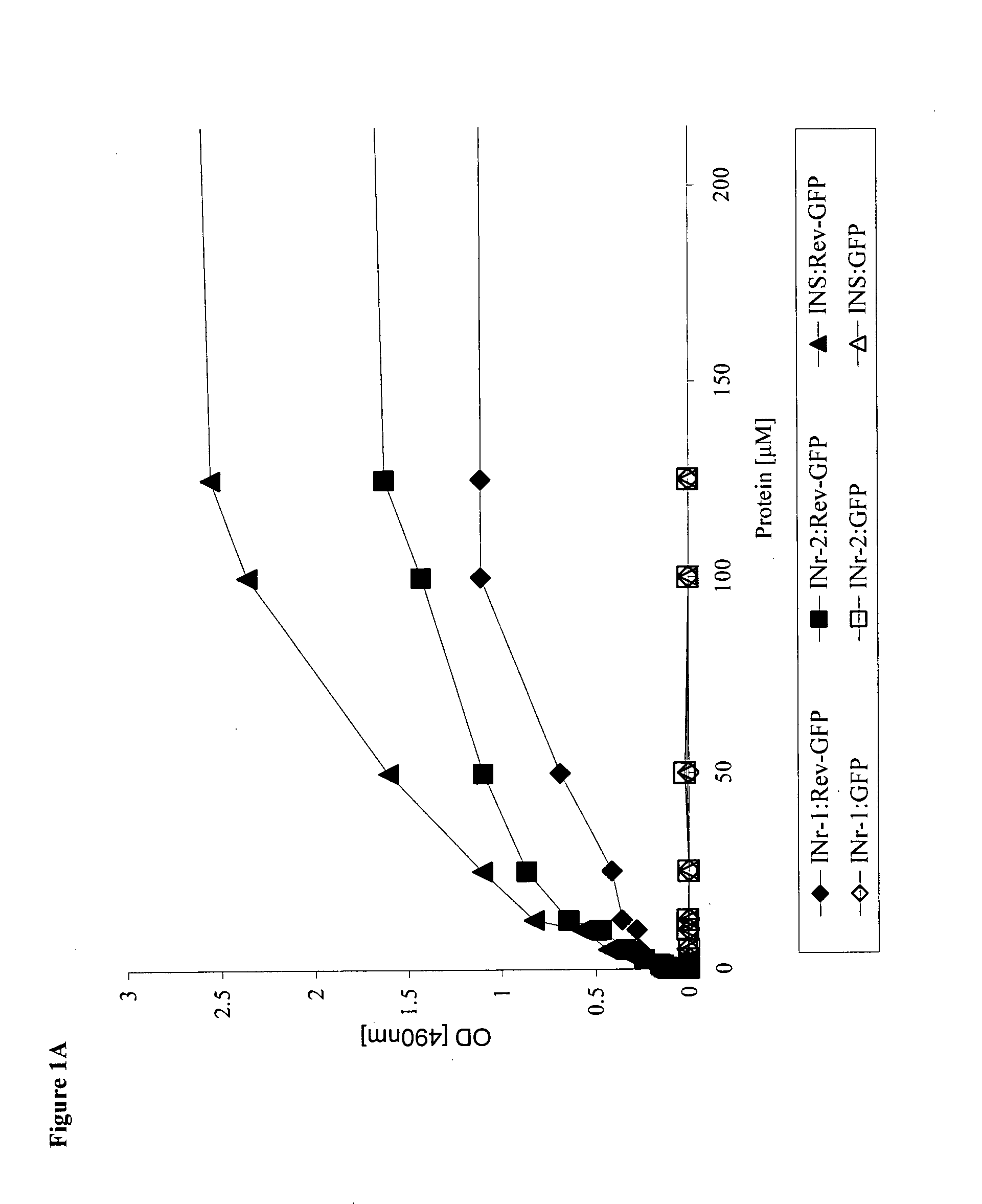
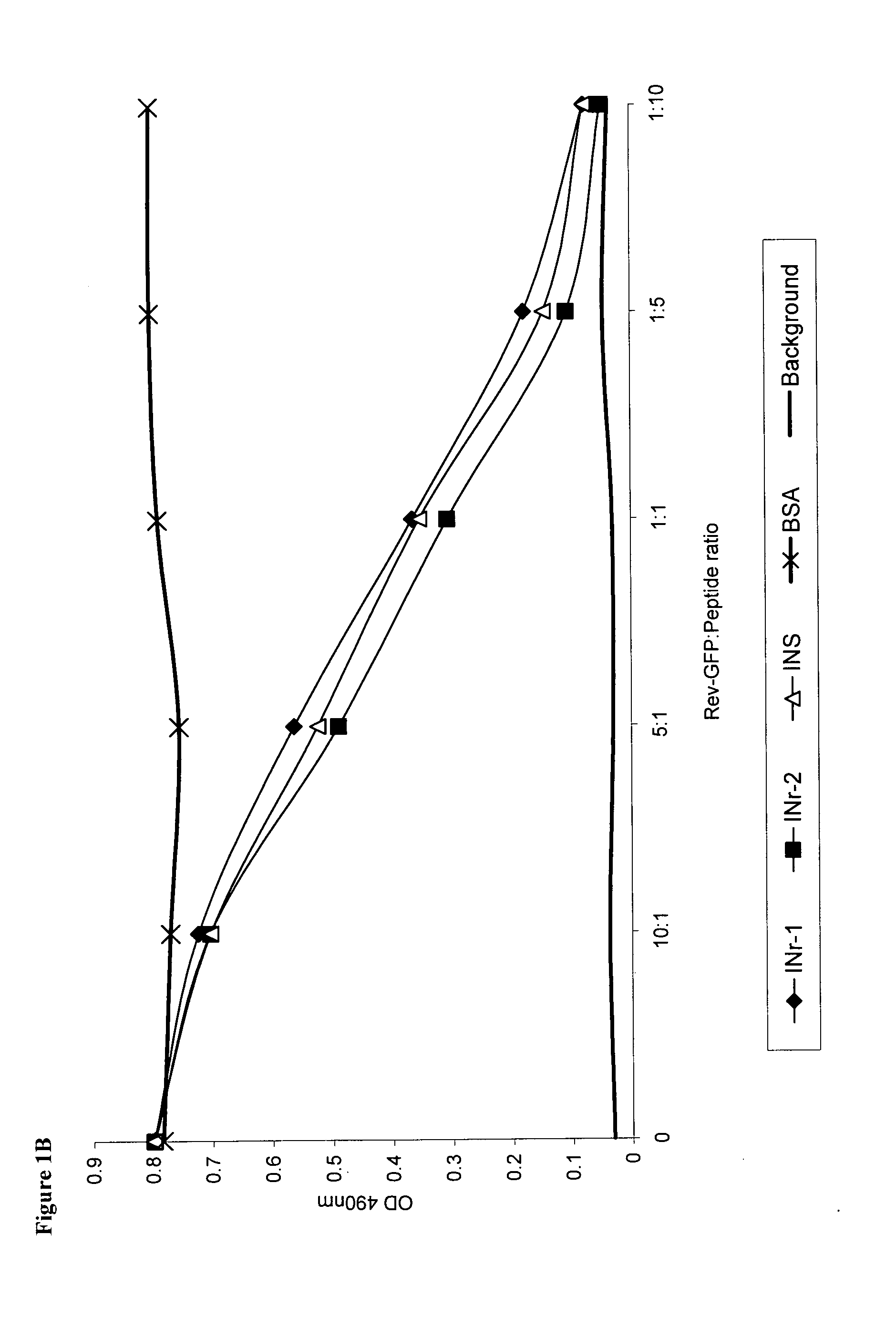
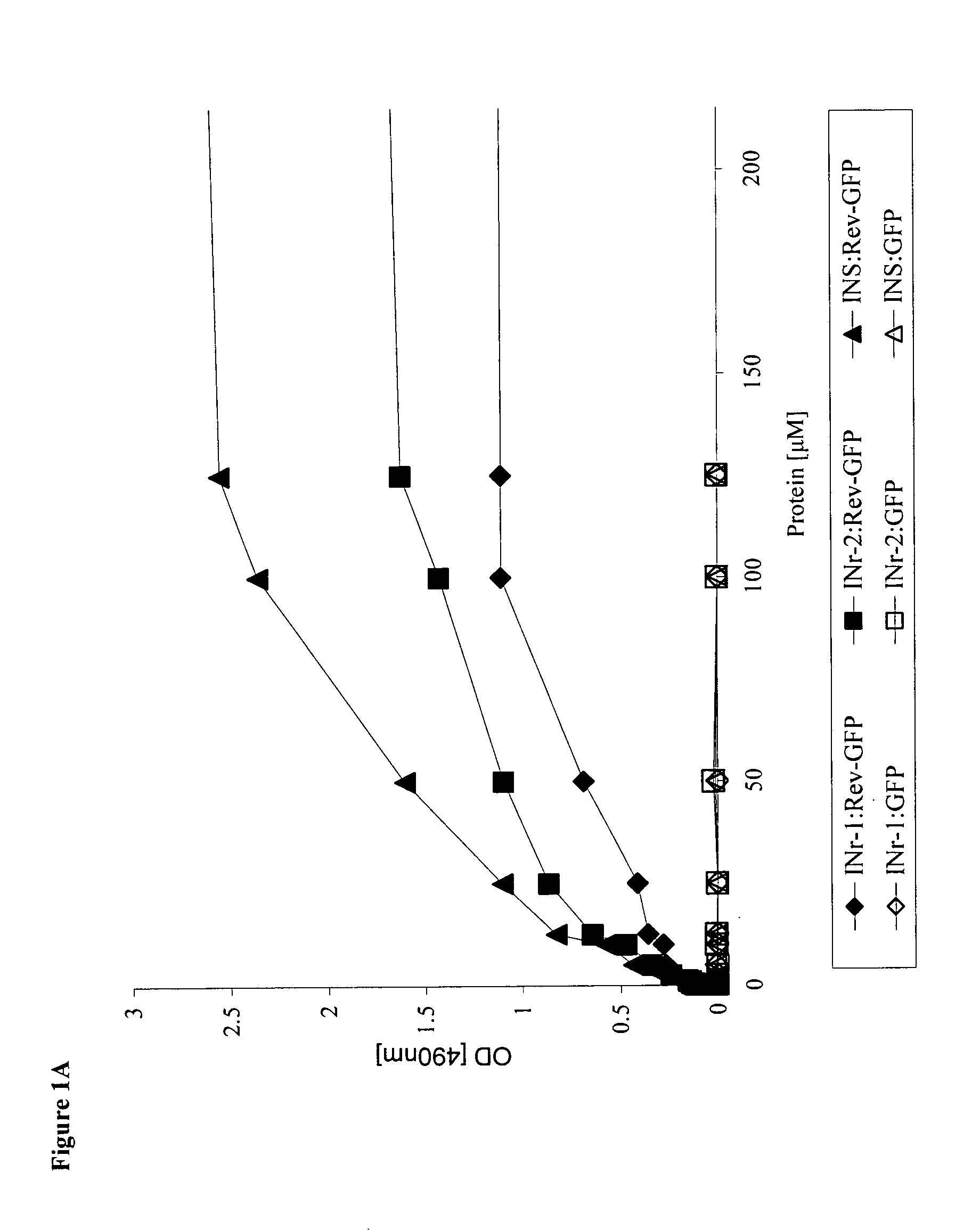
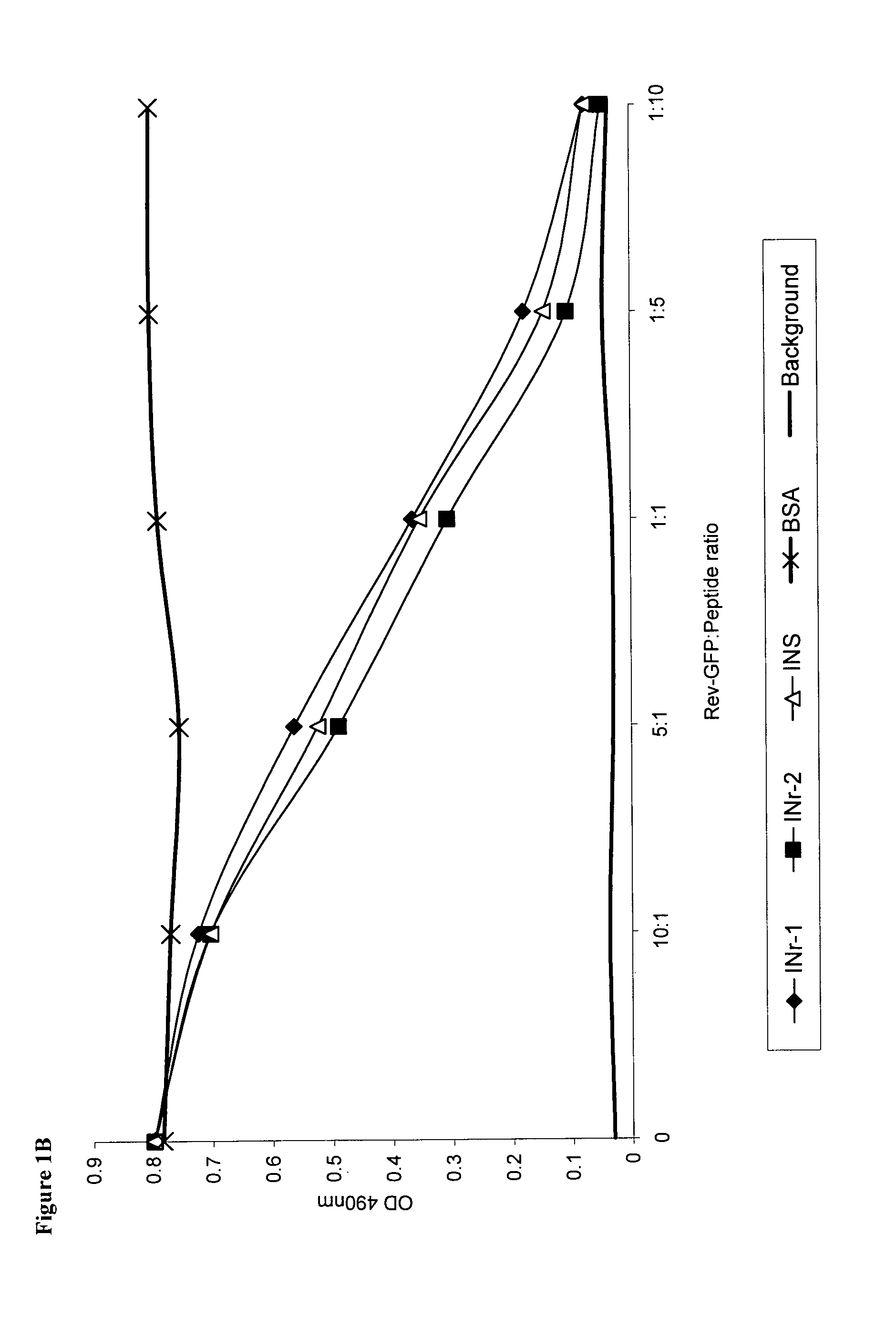
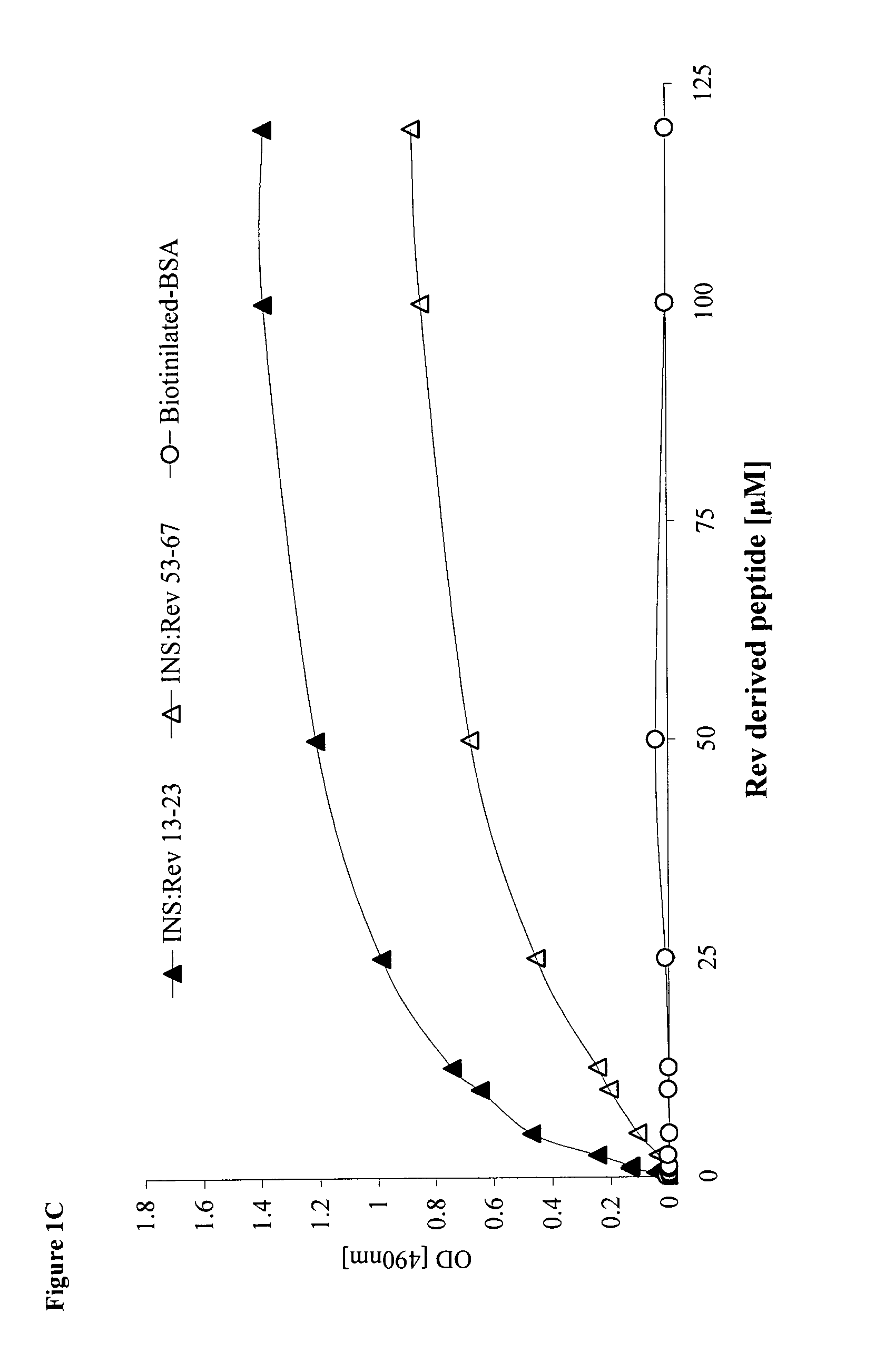
Hiv-1 integrase derived stimulatory peptides interfering with integrase -- rev protein binding
ActiveUS20110257082A1Useful in treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiocideInfected cellHiv 1 integrase
Isolated peptides comprising sequences derived from the protein integrase of HIV-1, as well as their analogs, mixtures, conjugates with permeability enhancing moieties, and pharmaceutical compositions are disclosed. The peptides and compositions are capable of selectively killing HIV-1 infected cells and are used in treatment of HIV infection and AIDS.
Owner:CODE PHARMA BV
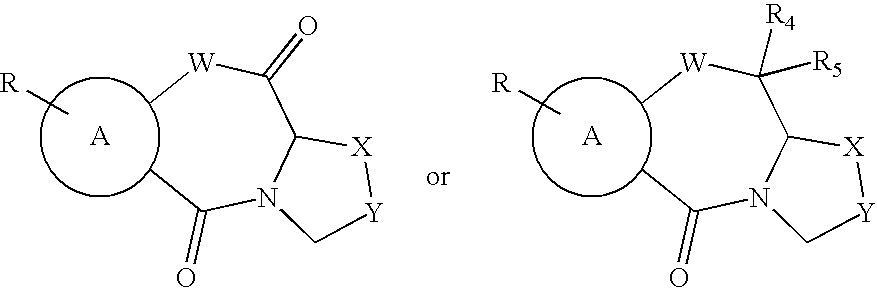
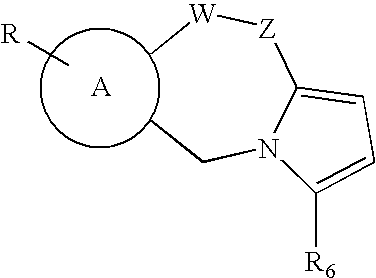
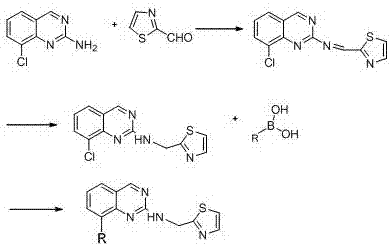
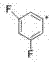
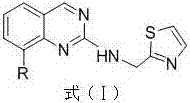
Thiazepine inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase
The present invention discloses non-catechol compounds, such as thiazolothiazepines, and analogs and derivatives thereof, which are anti-integrase inhibitors. The compounds, which are useful as treatments for HIV disease, include compounds (I), (II), (III), or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof wherein A is thiazole, benzene, naphthalene, pyridine, pyrimidine, pyrazine, or quinoline; R is one or more of H, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy, NO2, lower ester or carboxylic acid; X—Y is CH2—S, S—CH2, CH2—O, CH2—S(O). S(O)—CH2, CH2—CH2, CH2—CH2—CH2, or CH2—CH2—CH2—CH2; R4 is H or hydroxy; R5 is H, phenyl, or alkylamine; W is S or O; and R6 is H, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl or amine; and Z is S, O, CH2, CH2CH2, or C═O.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
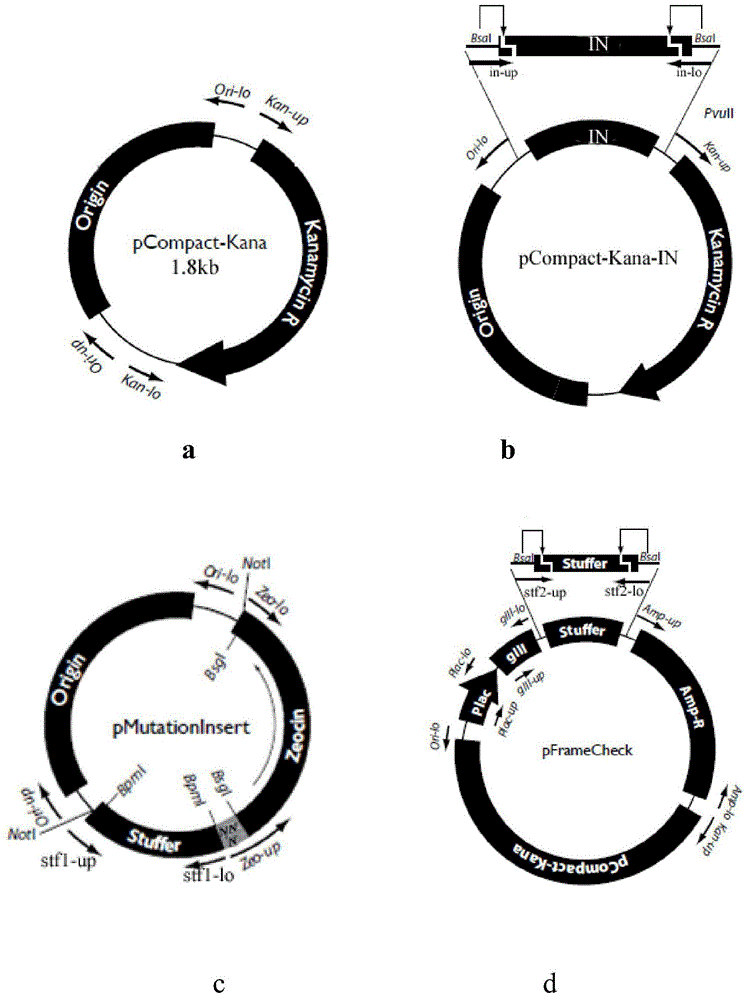
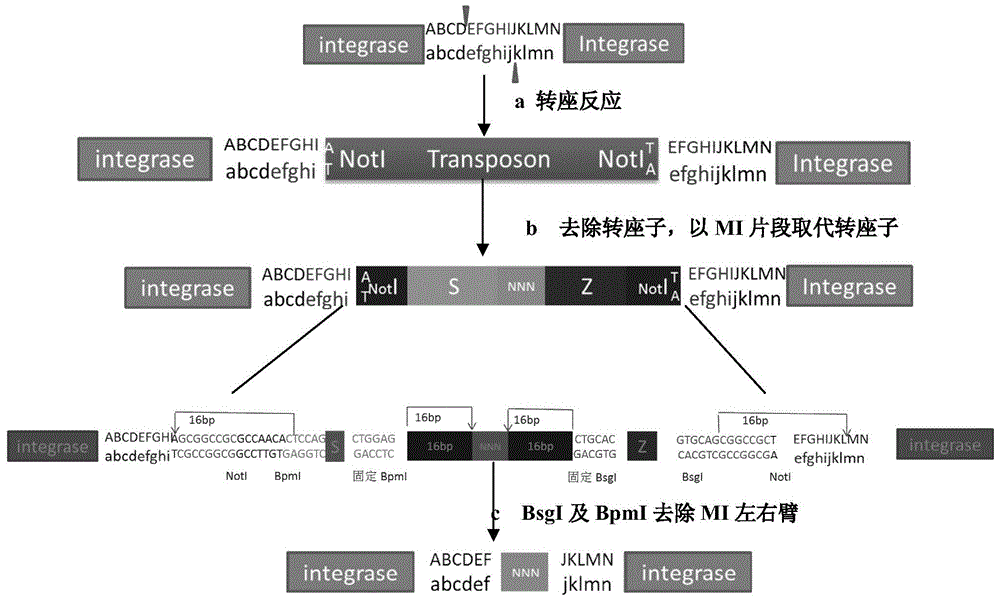
Construction method of HIV-1 integrase mutant library
InactiveCN104975353AHigh resolutionImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationProtein targetRestriction site
The present invention discloses a construction method of an HIV-1 integrase mutant library. The method comprises the following elements: (1) manufacturing gaps on random sites of a target gene by using transposition of transposon and restriction enzyme on both ends of the transposon, inserting mutation insertion boxes, using the restriction enzyme sites on the box to achieve replacement of three bases on the gene through digestion self-connection, and translating the target gene into protein to cause mutation o one or two consecutive amino acids on the target protein; and (2), using site-directed mutagenesis PCR to realize mutation of three bases, for the replacement of the original target gene and on the inserted mutation insertion boxes, from codons encoding cysteine into codons encoding other 19 amino acids, thereby increasing the diversity of the final mutant library.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
HIV-1 integrase derived stimulatory peptides interfering with integrase—Rev protein binding
ActiveUS9163067B2Useful in treatmentPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiocideInfected cellIntegrases
Isolated peptides comprising sequences derived from the protein integrase of HIV-1, as well as their analogs, mixtures, conjugates with permeability enhancing moieties, and pharmaceutical compositions are disclosed. The peptides and compositions are capable of selectively killing HIV-1 infected cells and are used in treatment of HIV infection and AIDS.
Owner:CODE PHARMA BV
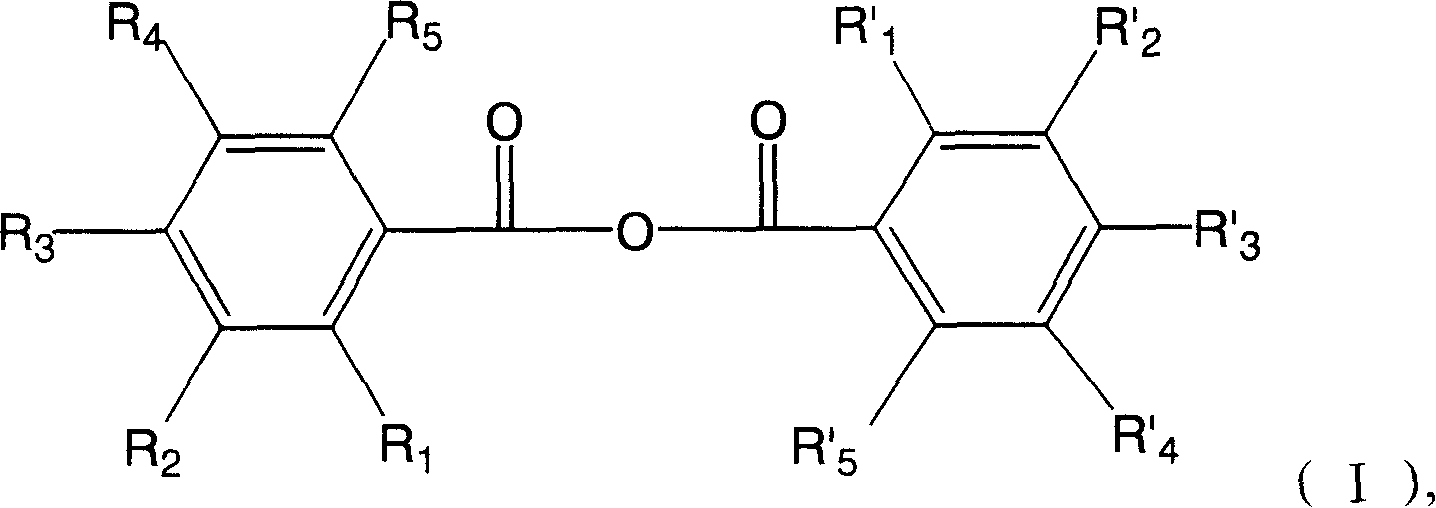
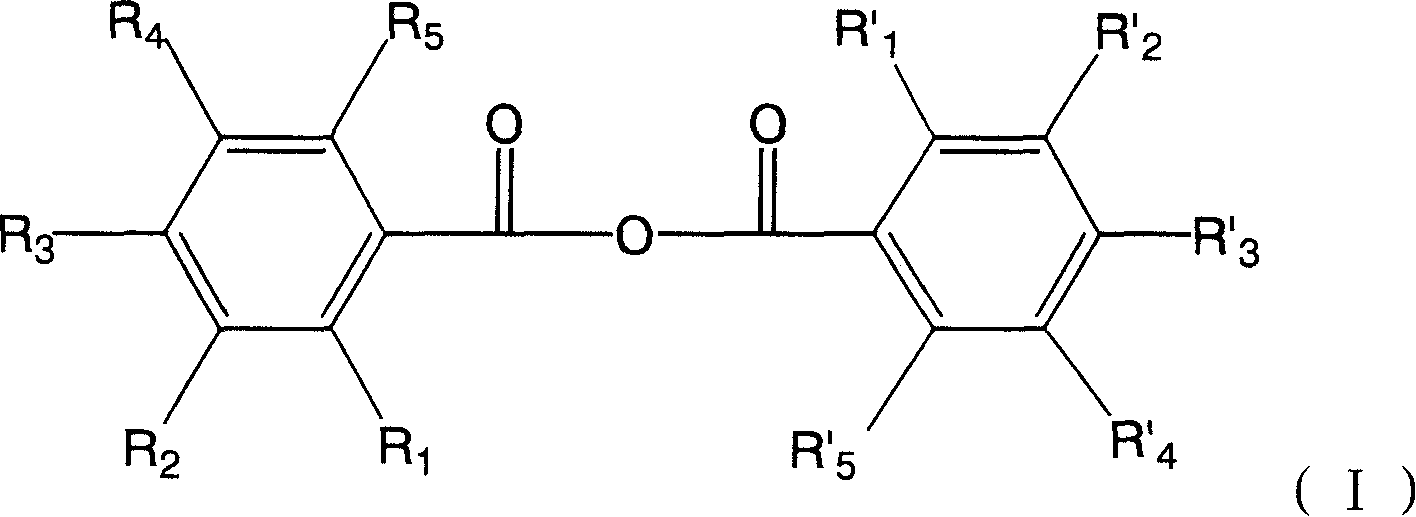
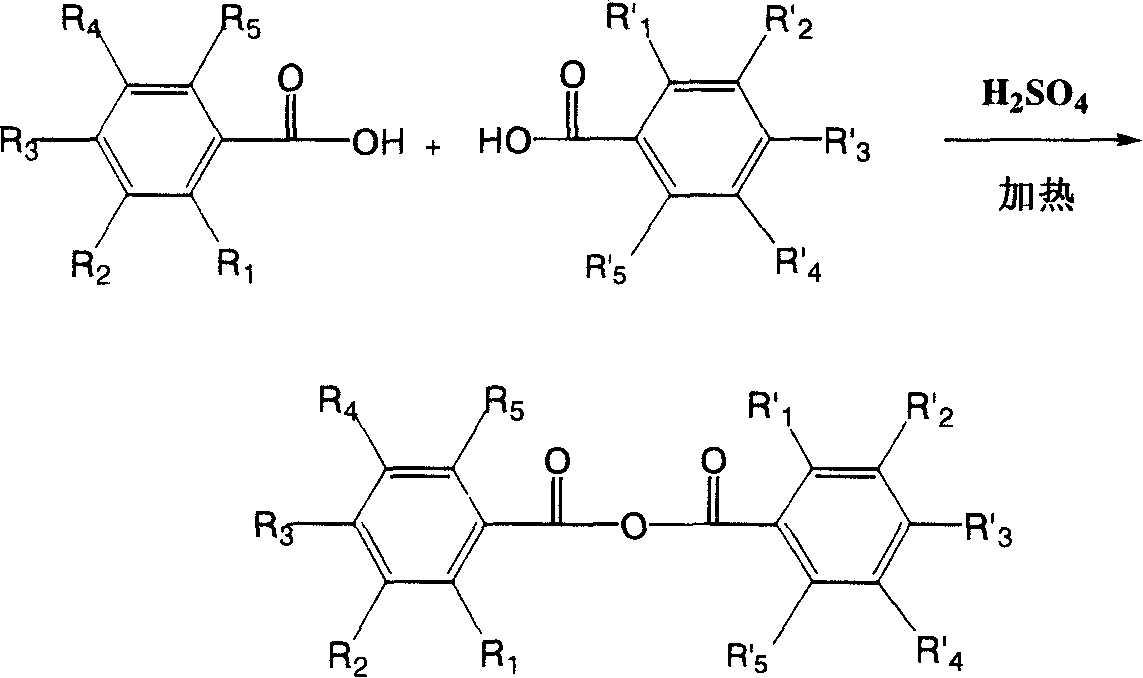
Hydroxyl benzoic anhydride dimer compound, preparation method and uses thereof
ActiveCN101200426APrevent relapseEfficient killingOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsHuman papillomavirusHerpes simplex virus DNA
The present invention discloses symmetric and asymmetric m-hydroxybenzoic acid dimer compounds with constitutional formula (I), and as well as a method of the preparation of and the function of such products. Basic framework m-hydroxybenzoic acid and as well as hydroxybenzoic acid replaced by the same or different hydroxyl groups are condensed into m-hydroxybenzoic acid dimer compound with a parent nucleus symmetric structure and with the replacement of the same or different number of hydroxyl groups, the pharmacological test proves that the product has the activities of anti-human papillomavirus, herpes virus and resist HIV-1 integrase inhibitors; the product is capable to resist the virus that can integrally enter the chromosome of human cell, inhibit the breeding of the virus that integrally enter into the chromosome, prevent the relapse of virus infection; in addition, the product has antitumor activity.
Owner:SHENGHUA GUANGZHOU PHARMA SCI & TECH
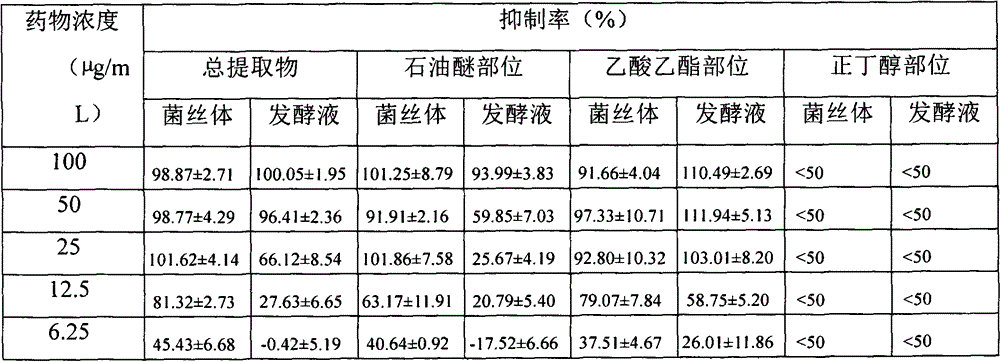
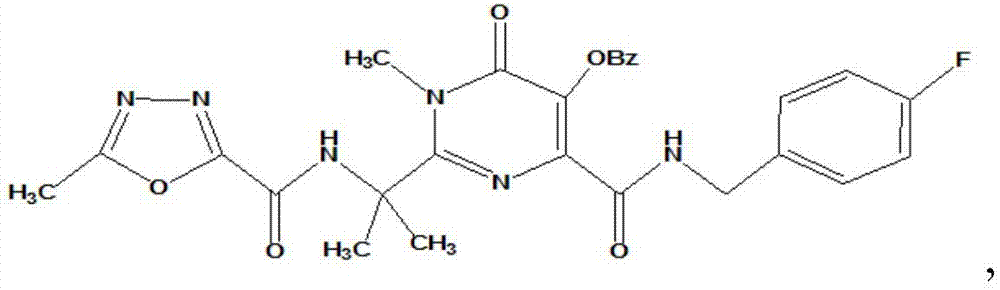
Drug for treating acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and preparation method thereof
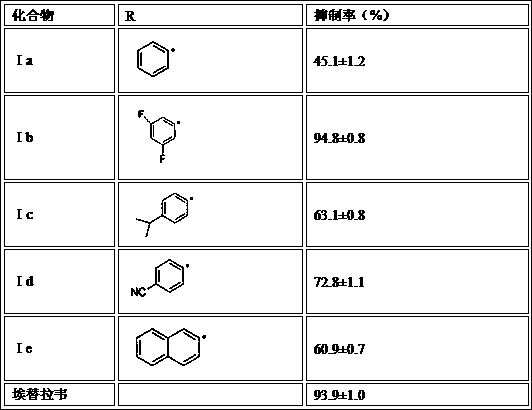
The invention discloses a drug for treating acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and a preparation method thereof. The chemical structure of the drug is a formula (I), when the concentration is 5 micrograms per milliliter, the inhibition rate of a compound HIV-integrase shown in the formula (I) is from 45% to 95%, and the inhibition rate of Ib is up to 94.8% and exceeds that of a listed drug Elvitegravir. The inhibition rate of Ia is relatively low and less than 50%. The compound shown in the formula (I) can be taken as a HIV-integrase inhibitor and used for treating the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Owner:梁山县疾病预防控制中心梁山县卫生检测检验中心
Inhibitors of hiv-1 integrase multimerization
ActiveUS20190381054A1Inhibition formationAvoid infectionHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusCompound (substance)
The disclosure generally relates to compounds of formulas (I) and (II)7 including compositions and methods for treating human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The disclosure provides novel inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds, and methods for using these compounds in the treatment of HIV infection.
Owner:INST FOR CANCER RES
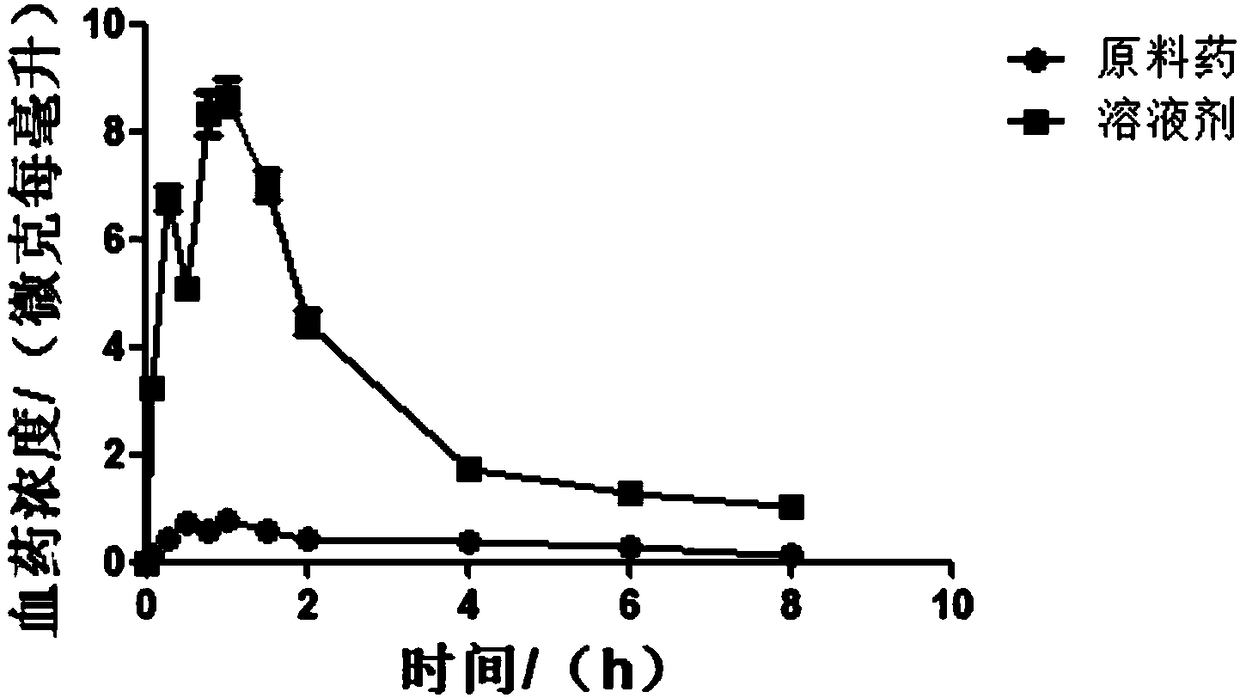
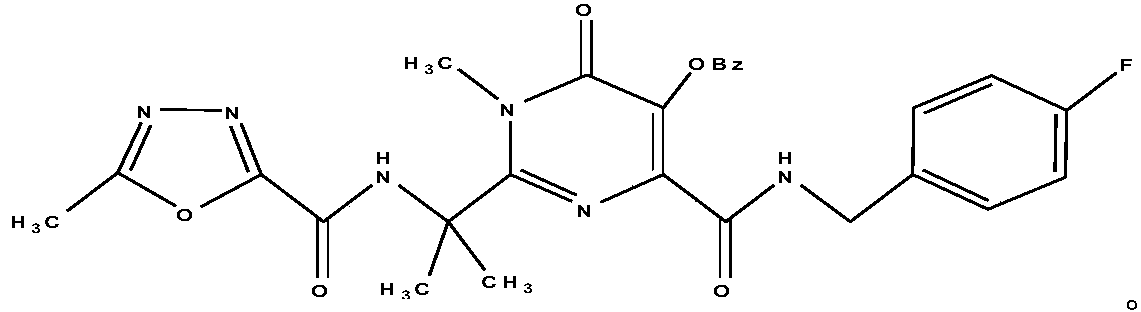
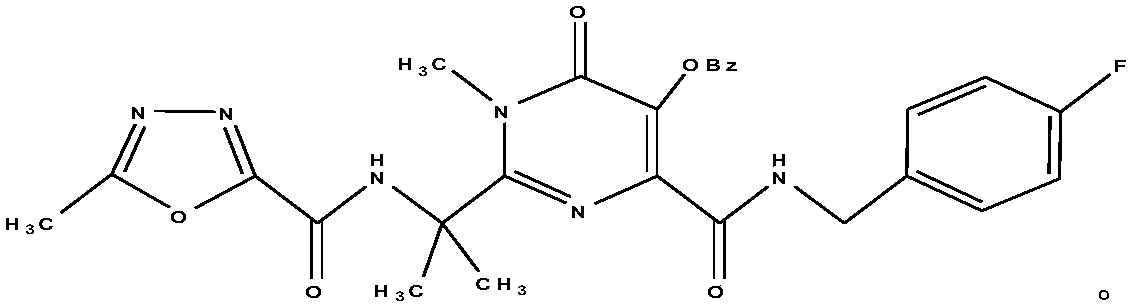
HIV-1 integrase inhibitor phospholipid complex, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN108434145AEasy to manufactureFast absorptionOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsIn vivo absorptionPhospholipid complex
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
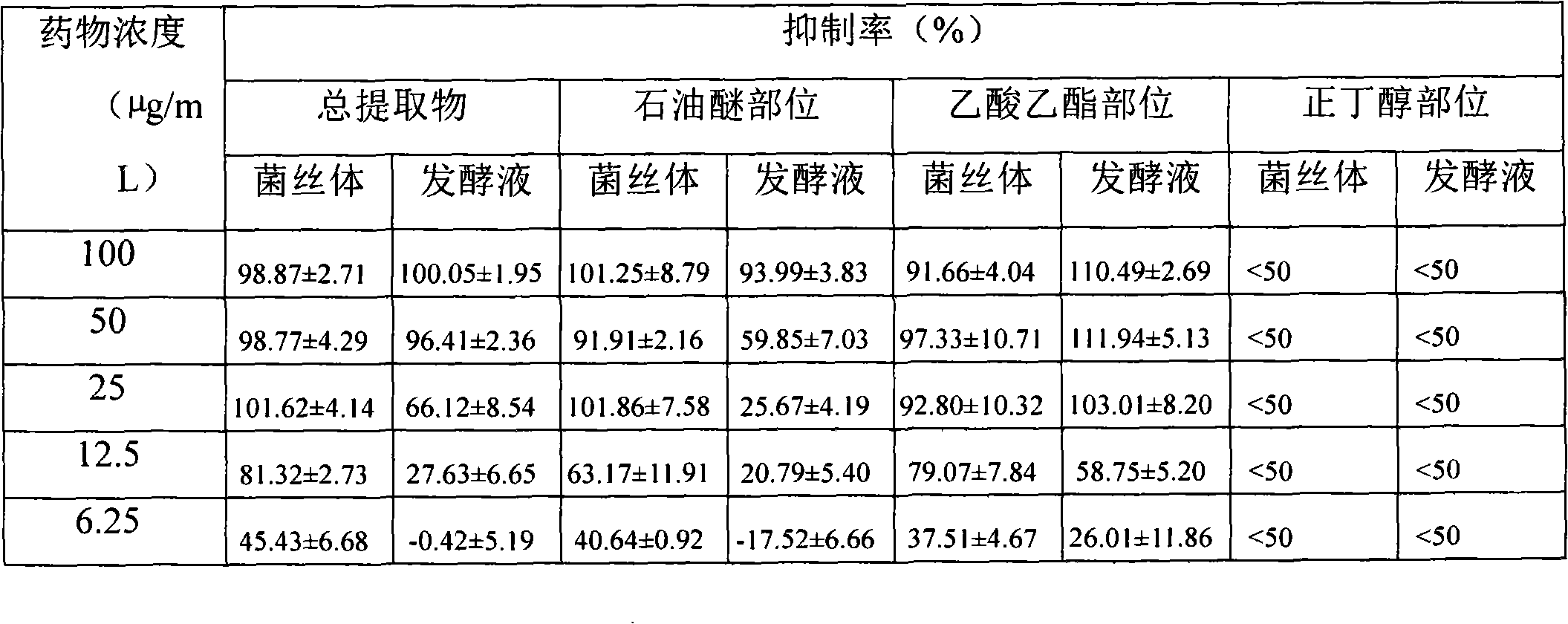
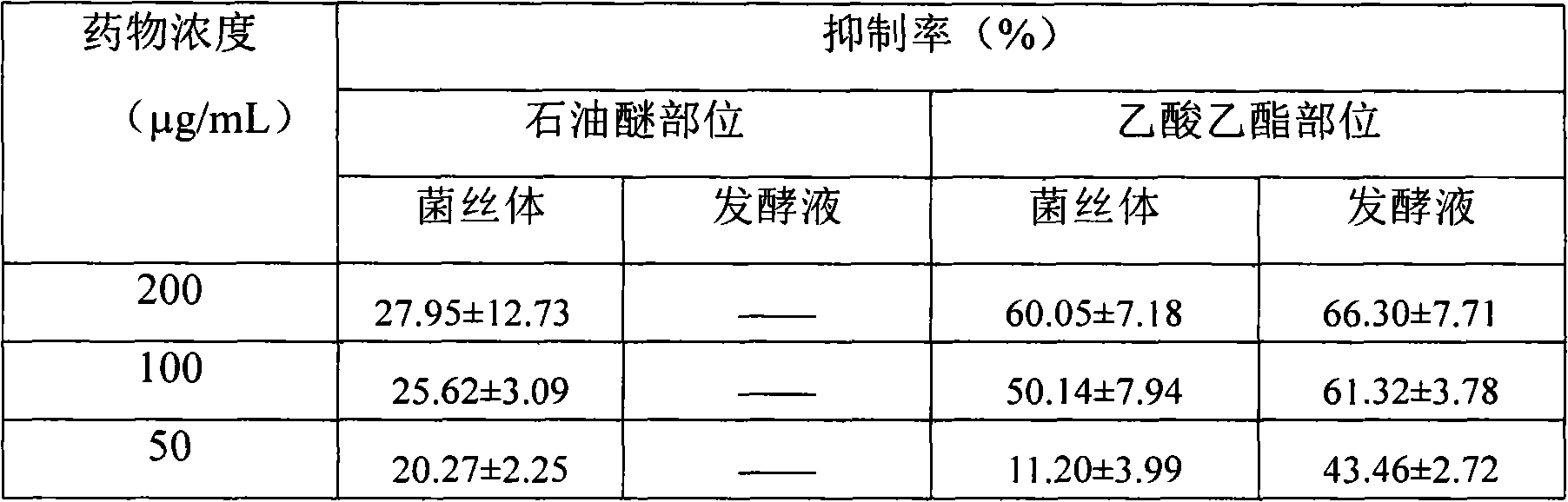
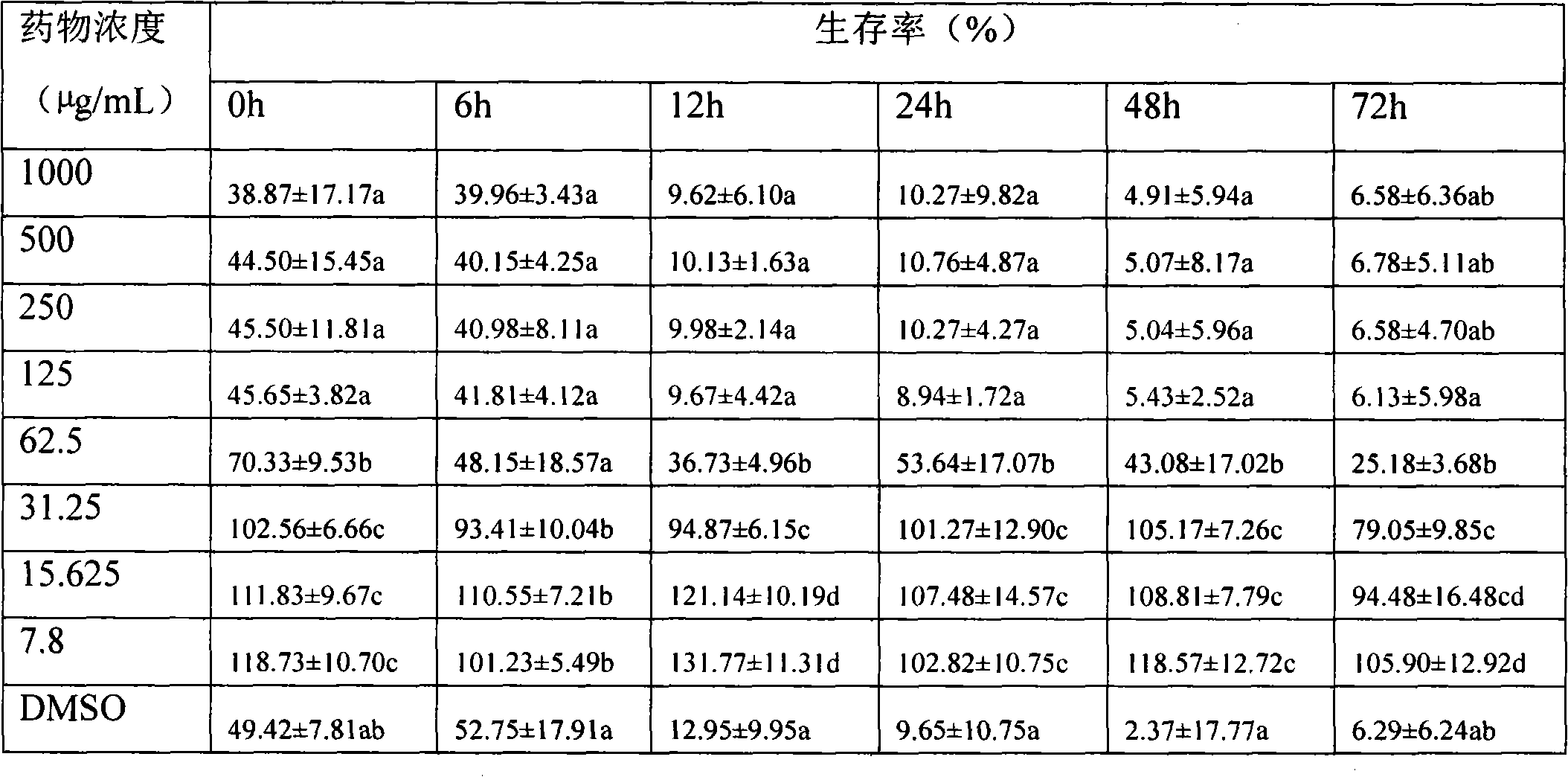
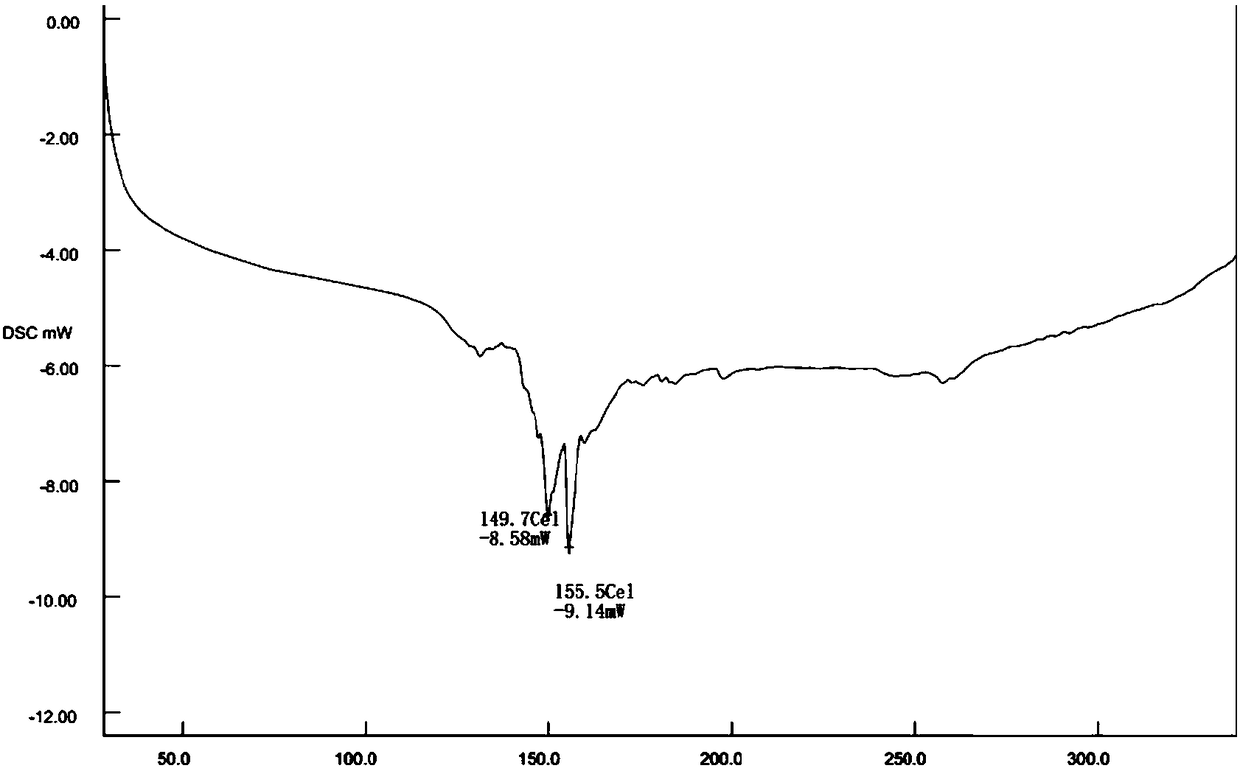
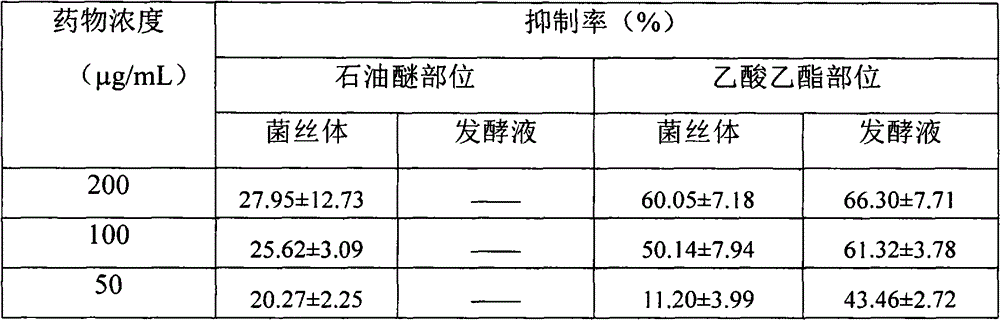
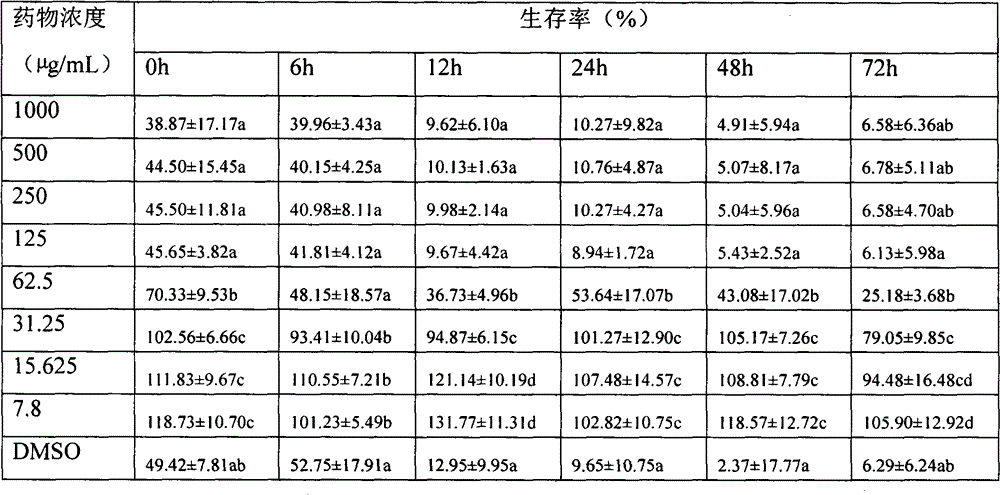
A preparation method of fungal extract for inhibiting human immunodeficiency virus
The invention provides a preparation method of a fungal extract for inhibiting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1). The dependent bacterial strain is hypoxylon fungi Q-s-4(hypoxylon sp.). The fungi Q-s-4 is fermented and cultured in liquid to prepare extract of fermentation products. The method can be applied to the mass industrial culture of fungi Q-s-4 and industrial production of extract of fermentation products by taking fermentation products as the raw materials. The extract prepared by the method has a prominent activity on inhibiting HIV-1 integrase, an antibacterial activity, and an important value on research and development of novel drugs for curing AIDS and bacterial infections.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
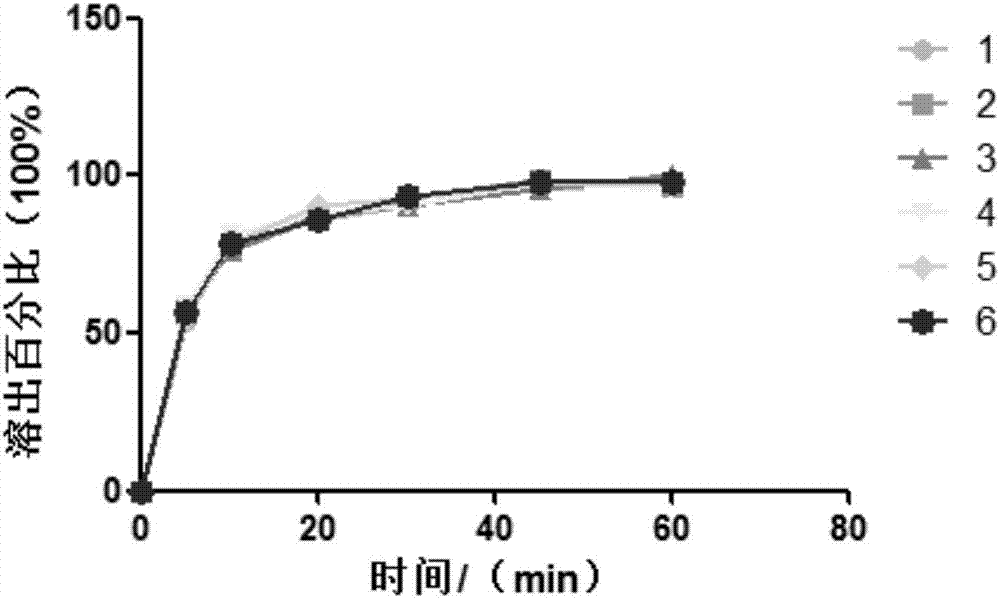
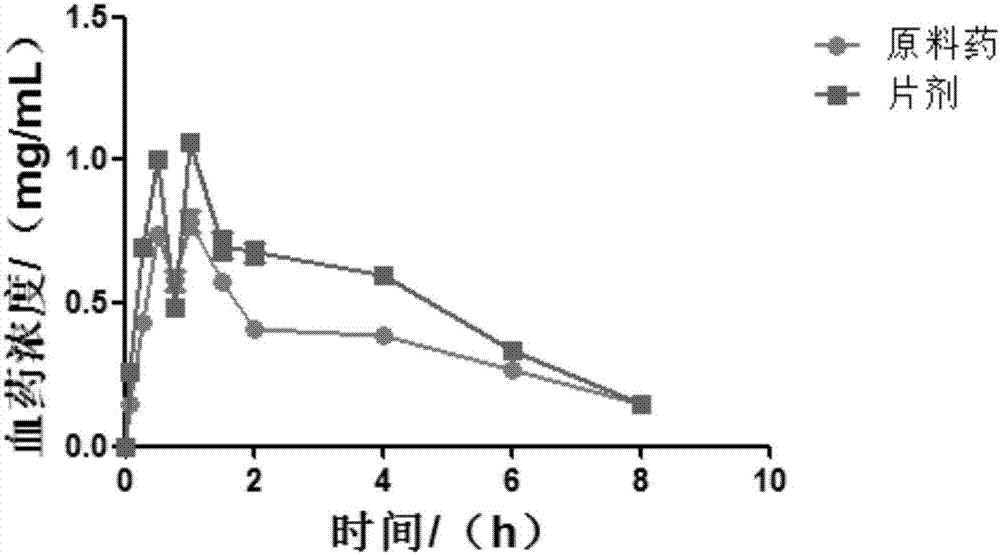
HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus-1) integrase inhibitor tablet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107028902AIncrease productionLow costOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsMedicineHuman immunodeficiency virus 1
The invention provides an HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus-1) integrase inhibitor tablet and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps: mixing an HIV-1 integrase inhibitor HIV-A5 with pharmaceutically acceptable auxiliary materials; pressing the materials to prepare the HIV-1 integrase inhibitor tablet. The method is simple in preparation process, mechanical in production, high in automation degree, large in output and low in cost, and the prepared HIV-1 integrase inhibitor tablet is high in dissolubility, short in disintegration time, stable in quality and convenient to carry, transport and store and is a solid preparation.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
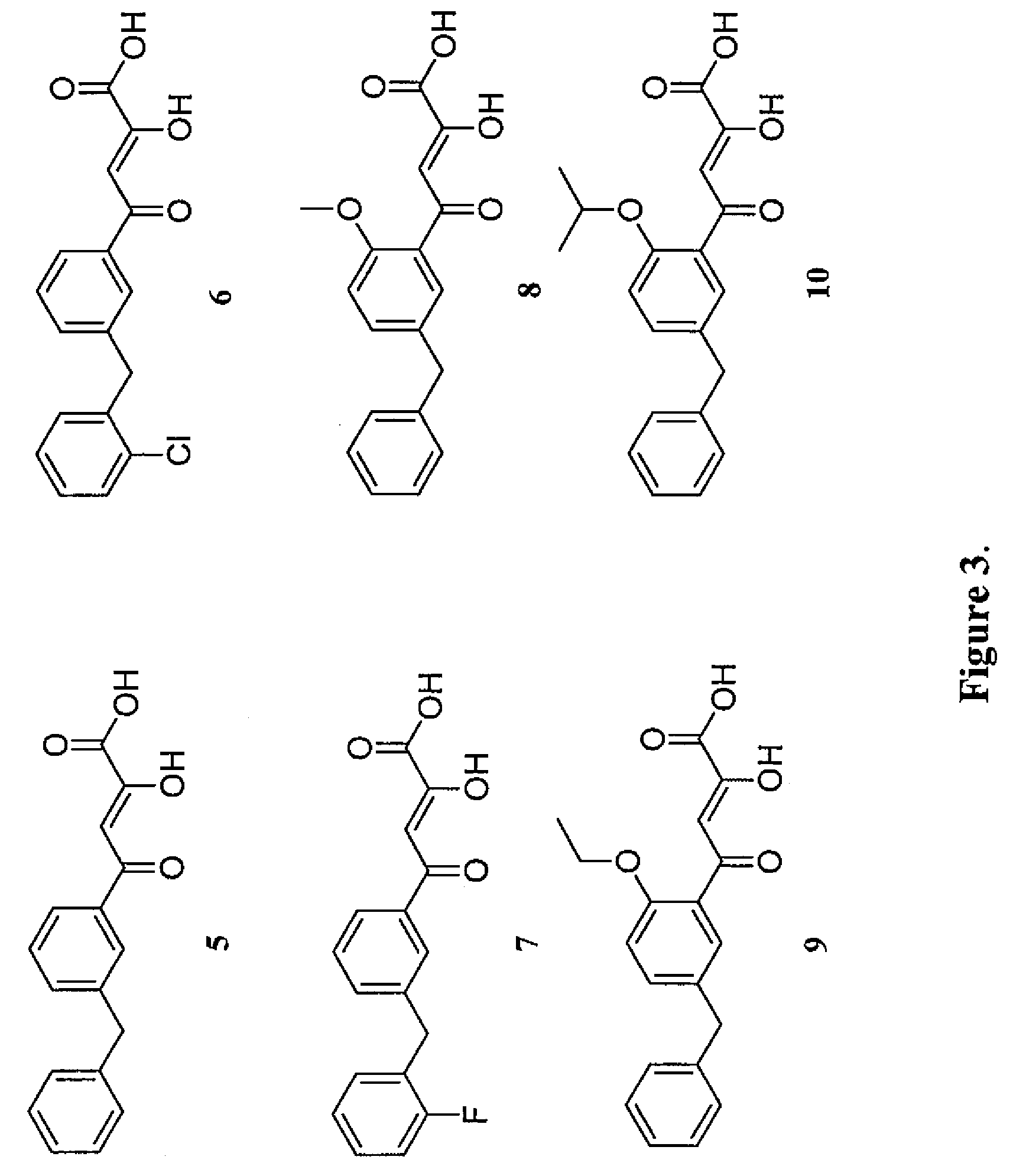
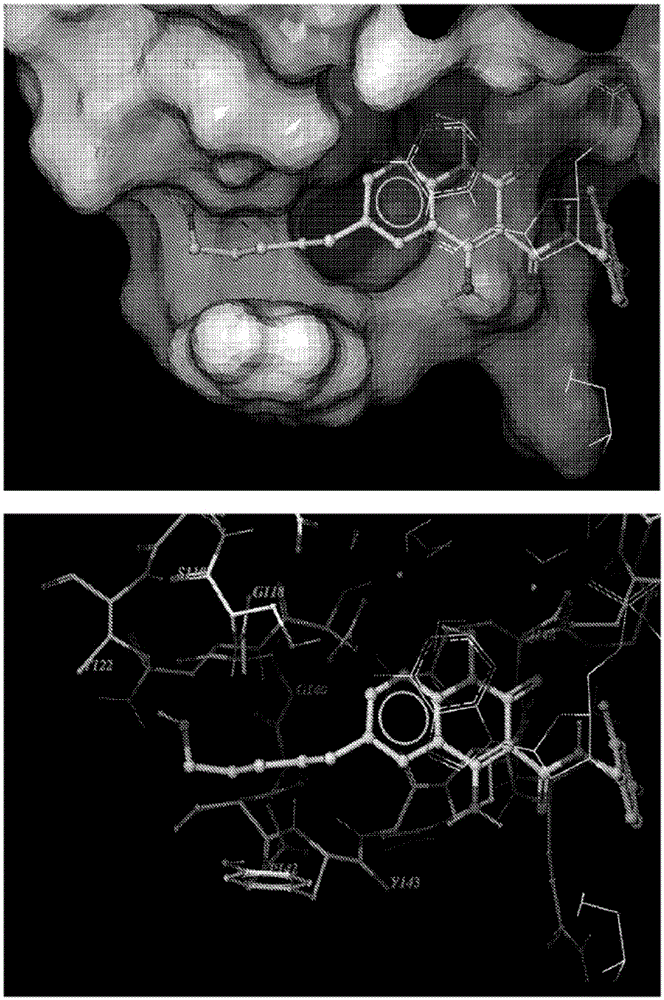
2,4-di-substituted amido-6-substituted-[1,3,5]triazine or miazines compound, preparation method, pharmaceutical combination and use of the same
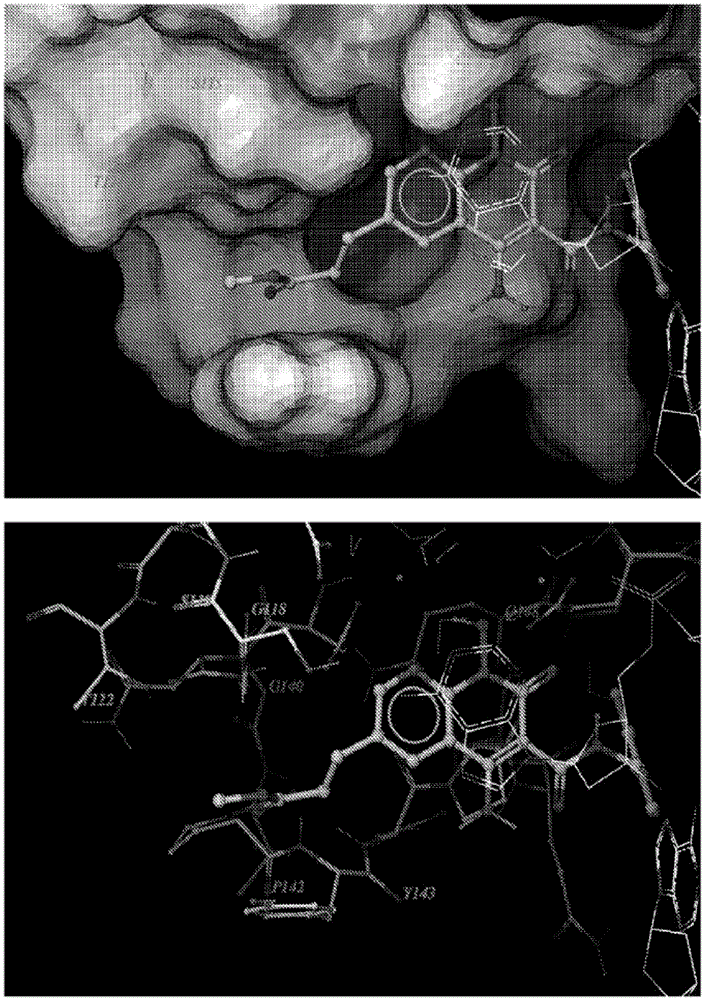
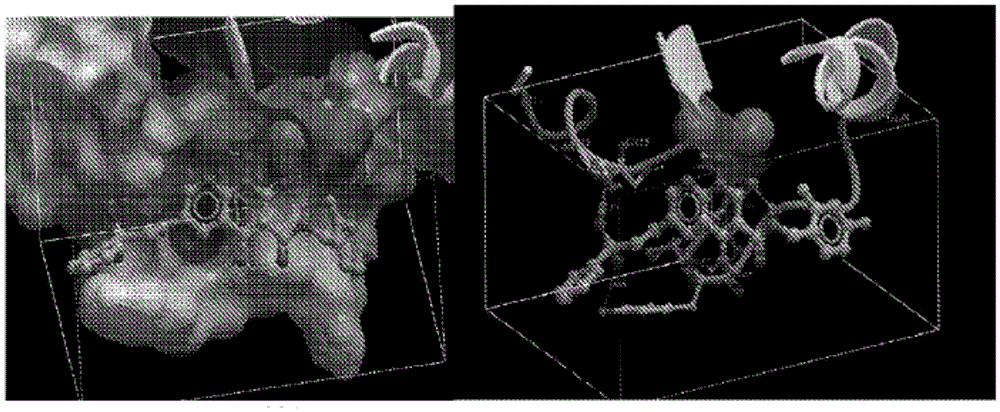
The invention relates to a novel 2, 4-disubstituted amino-6-substituted-(1, 3, 5) triazine or a 1, 3-pyrimidine derivative, the preparation method, a drug combination and the pharmacological usage; the structure general formula is shown as the formula (I), wherein, the definitions of R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, A, B, X, Y and Z are described in an instruction. The compounds and a HIV-1 integrase have high binding activity and can effectively inhibit the binding of the integrase with a substrate in a substrate competition test. Therefore, the compounds are stronger HIV-1 integrase inhibitors, which are expected to be developed into new anti-HIV drugs.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
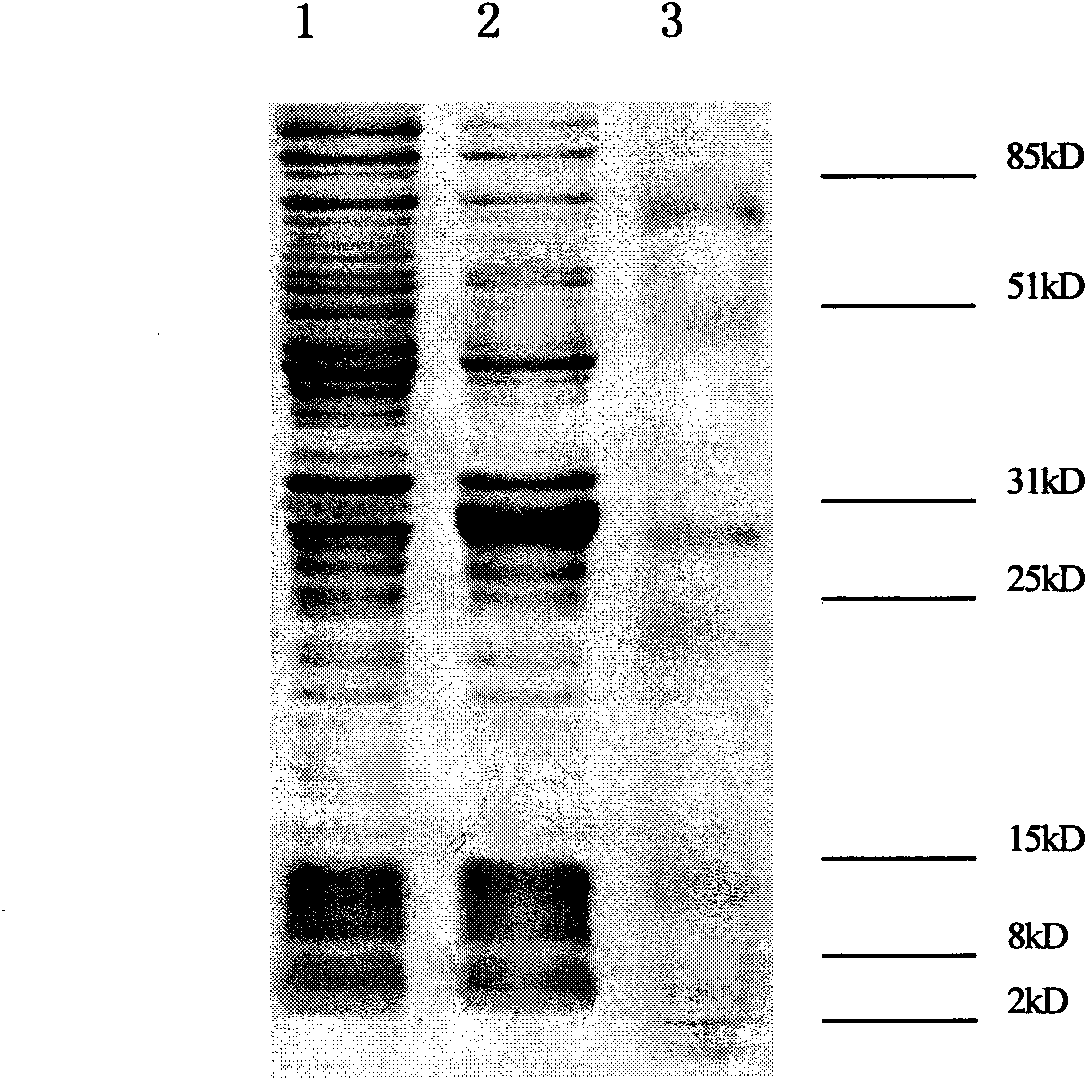
Method for preparing soluble HIV-1 integrase recombinant protein
InactiveCN103275945BGuaranteed normal growthImprove solubilityTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionSolubilityNormal growth
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
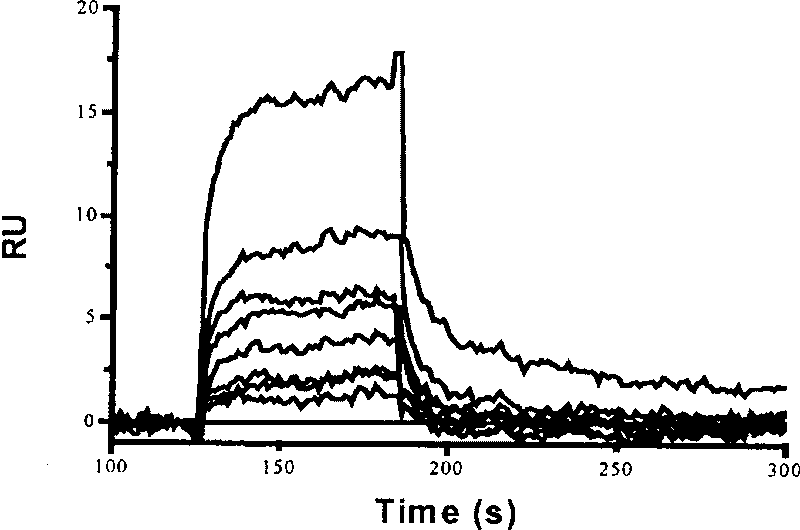
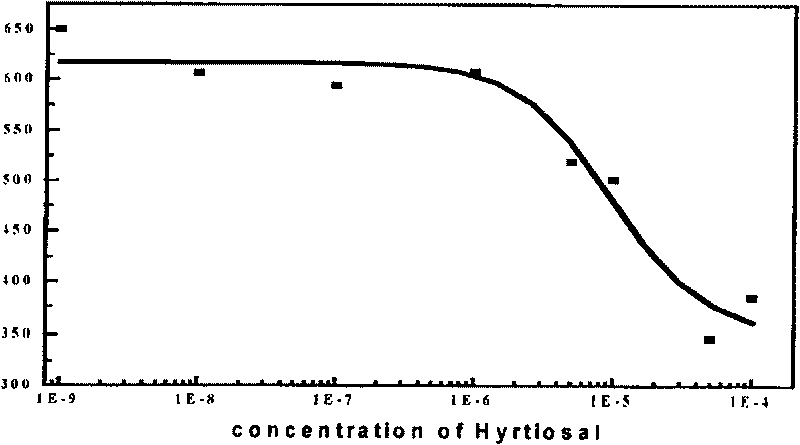
Medical use of compound hyrtiosal
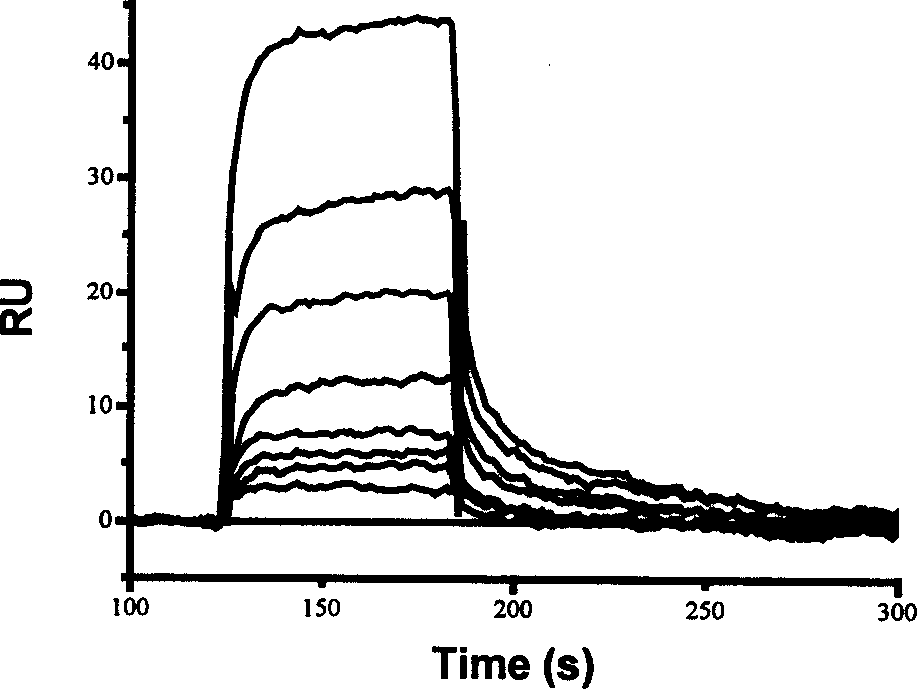
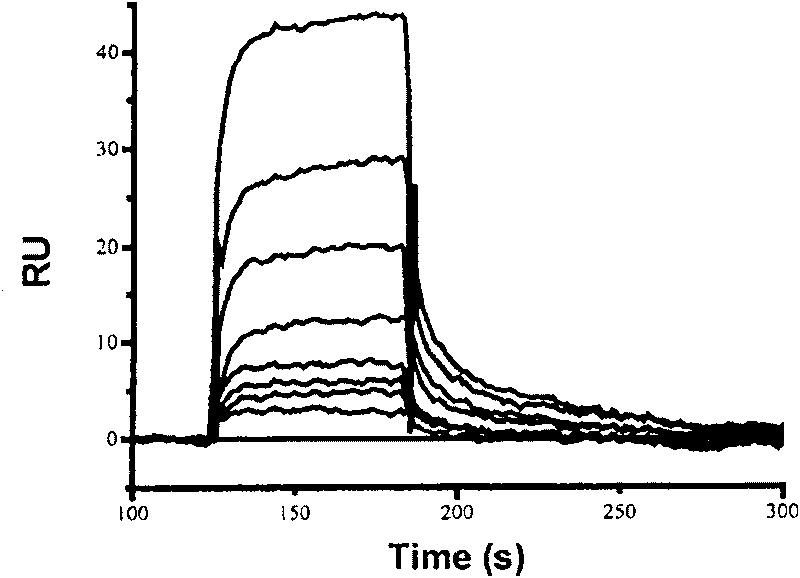
The present invention discloses one kind of compound, citioaldehyde. The compound, citioaldehyde has very high combination activity, KD=0.197 microM, with HIV-1 integrase, and effective inhibition ofthe combination of the integrase to the substrate, IC50=9.6 microM, in substrate competition test. Therefore, the compound will find its application in preventing and treating AIDS.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Integrase inhibiting peptide and its application in preparing AIDS-treating medicine
InactiveCN100543034CInhibitory activityIntegration inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesIntegrasesMechanism of action
The invention provides an integrase inhibitory peptide, which is one of seven polypeptide organic compounds selected from a, b, c, d, e, f, and g, soluble in water, and connected by peptide bonds between amino acids, capable of inhibiting HIV-1 integrase activity, the molecular weights are: 974.3, 770.8, 822.9, 830.9, 849.0, 789.8, 788.8. The polypeptide organic compound of the invention can inhibit the activity of HIV-1 integrase, interrupt the proliferation of virus DNA in host cells and its life cycle, and can be used in the preparation of drugs for treating AIDS. At the same time, it can also be used for further research on the structure, mechanism of action of integrase and AIDS treatment drugs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compounds for inhibiting drug-resistant strains of HIV-1 integrase
A method of inhibiting drug-resistant HIV-1 integrase in a subject comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof, having a structure of: wherein X is N, C(OH), or CH; Y is H or OH; each of Z1-Z5 is independently H or halogen; R4 is H, OH, NH2, NHR8, NR8R9 or R8; R5, R6, and R7 is each independently H, halogen, OR8, R8, NHR8, NR8R9, CO2R8, CONR8R9, SO2NR8R9, or R5 and R6 together with the carbon atoms to which R5 and R6 are attached form an optionally-substituted carbocycle or optionally-substituted heterocycle; and R8 and R9 is each independently H, optionally-substituted alkyl, optionally-substituted alkenyl, optionally-substituted alkynyl, optionally-substituted aryl, optionally-substituted cycloalkyl, optionally-substituted cycloalkylene, optionally-substituted heterocycle, optionally-substituted amide, optionally-substituted ester, or R8 and R9 together with the nitrogen to which R8 and R9 are attached form an optionally-substituted heterocycle.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
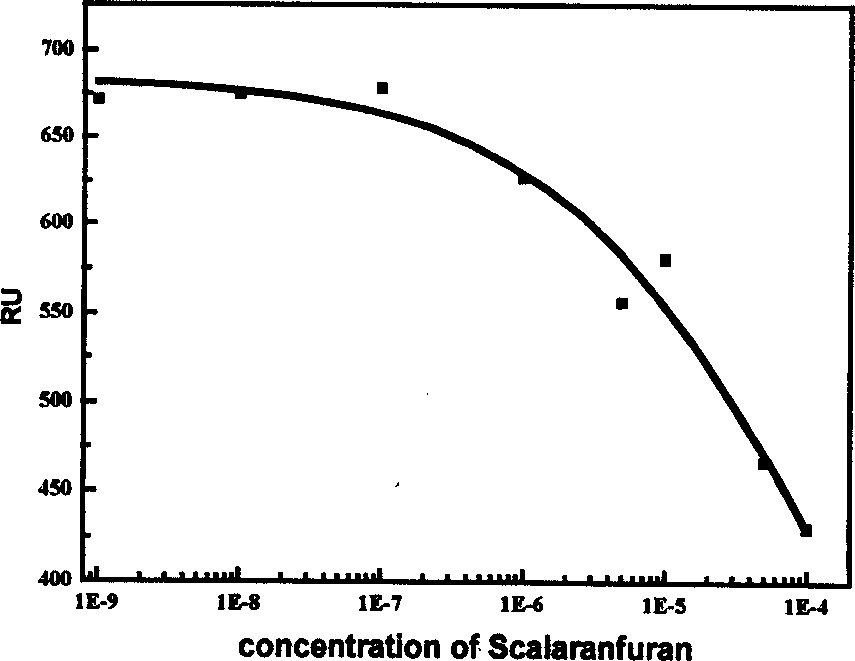
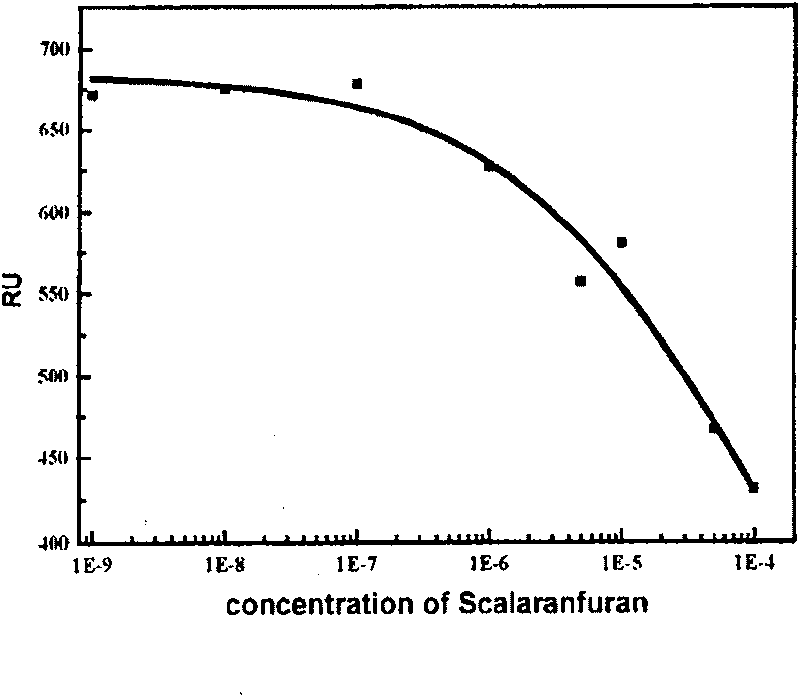
Use of compound scalarafuran
The present invention discloses one kind of compound, citiofuran. The compound, citiofuran has very high combination activity, KD=16.4 microM, with HIV-1 integrase, and effective inhibition of the combination of the integrase to the substrate, IC50=120 microM, in substrate competition test. Therefore, the compound exhibits very high medicine preparing value.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Use of compound scalarafuran
The present invention discloses one kind of compound, citiofuran. The compound, citiofuran has very high combination activity, KD=16.4 microM, with HIV-1 integrase, and effective inhibition of the combination of the integrase to the substrate, IC50=120 microM, in substrate competition test. Therefore, the compound exhibits very high medicine preparing value.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
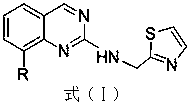
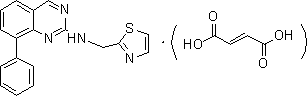
1‑n‑substituted benzyl‑6‑n'‑substituent‑2,3,6,9‑tetrahydro‑1h‑[1,4]oxazino[3,2‑g]quinolin‑9‑one ‑8‑Formic acid compound and its preparation method and application
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine compounds, and discloses a 1-N-substituted benzyl-6-N'-substituent-2,3,6,9-tetralin-1H-[1,4] benzoxazine [3,2-g] quinolone-9-ketone-8-formic acid compound and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the formula (I) of the 1-N-substituted benzyl-6-N'-substituent-2,3,6,9-tetralin-1H-[1,4] benzoxazine [3,2-g] quinolone-9-ketone-8-formic acid compound, R1 represents a benzyl or a substituted benzyl, and R2 represents hydrogen or an alkyl or a hydroxyalkyl or a substituted benzyl or a carboxyalkyl. The method comprises the steps that firstly, 2-amino-5-nitrophenol is used as a raw material, acetylation protection, affinity substitute ring closure and deprotection are performed, affinity substitute is introduced into substituted benzyl, nitro reduction is performed through stannous chloride, condensation is performed, Gould-Jacobs reaction ring closure is performed, affinity substitute is introduced into different substituent groups, and finally hydrolysis is performed to obtain the compound of the formula (I). The compound has the inhibiting effect on the HIV-1 integrase.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
HIV-1 integrase inhibitor solution agent, preparation process and applications thereof
InactiveCN108434146AGood dispersionFast absorptionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGlycerolSolvent
The invention provides an HIV-1 integrase inhibitor solution agent, a preparation process and applications thereof, wherein the HIV-1 integrase inhibitor HIV-A5 solution agent comprises: HIV-A5, wherein the mass concentration (g / ml) of the HIV-A5 in the solution agent is 0.3-5%; a solvent, wherein the solvent comprises at least one selected from 10-50% of ethanol, 5-15% of propylene glycol and 1-10% of glycerol and at least one selected from 1-10% of Tween 80 and 10-35% of Poloxamer 188; and optionally a coloring agent and a flavoring agent, wherein the mass concentrations (g / ml) of the coloring agent and the flavoring agent in the solution agent respectively are 0.01-0.09% and 0.01-0.1%. According to the present invention, the preparation process is simple; the drug is uniformly dispersedin the form of small molecules in the solvent, and is quickly absorbed by the body after the drug enters the body so as to quickly enter the tissue, the in vivo absorption capacity is improved, the bioavailability is high, the drug can be taken orally, and the medication is convenient.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
Preparation method of fungal extract for inhibiting human immunodeficiency virus
The invention provides a preparation method of a fungal extract for inhibiting human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1). The dependent bacterial strain is hypoxylon fungi Q-s-4(hypoxylon sp.). The fungi Q-s-4 is fermented and cultured in liquid to prepare extract of fermentation products. The method can be applied to the mass industrial culture of fungi Q-s-4 and industrial production of extract of fermentation products by taking fermentation products as the raw materials. The extract prepared by the method has a prominent activity on inhibiting HIV-1 integrase, an antibacterial activity, and an important value on research and development of novel drugs for curing AIDS and bacterial infections.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
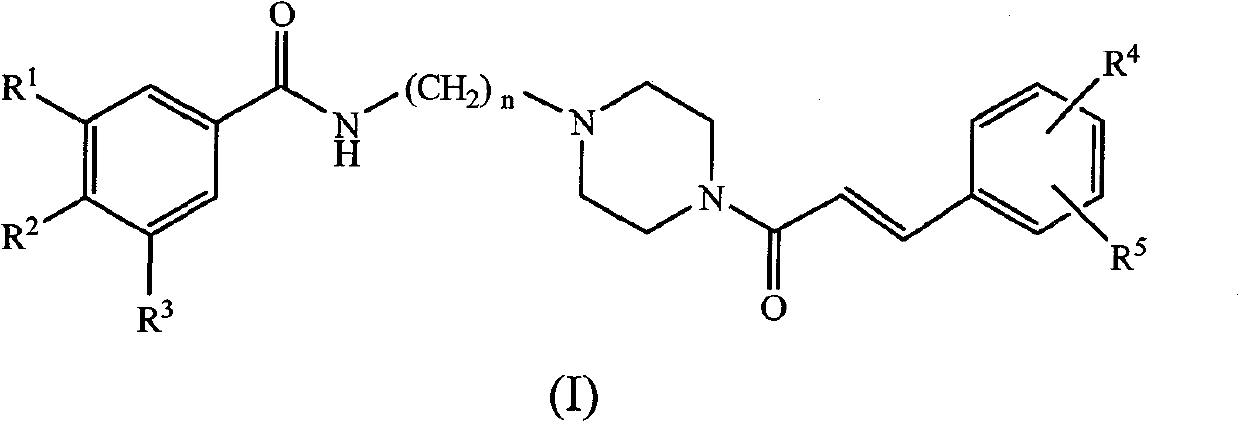
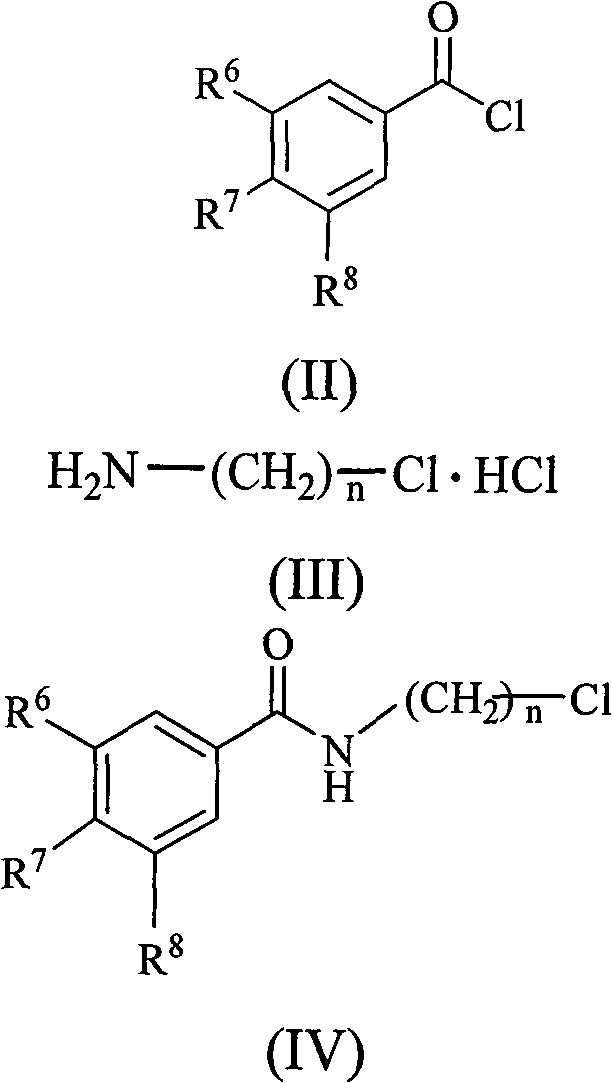
Substituted benzene propenyl piperazinyl alkyl polyhydric benzamide compound and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a (E)-N-3-(4-substituted benzene propenyl piperazine-1-base) alkyl benzamide compound shown in a formula (I) or a salt thereof, wherein R<1>, R<2> and R<3> express -H, -OH, -ONa, -OK or -ONH4, R<4> and R<5> express-H, halogen, C(1-3) linear or branched alkyl, -OH, -ONa, -OK, -ONH4, -NO2 or -CN, and n is an integer of 1-3. The invention also relates to a preparation methodof the compound, which comprises the following steps: synthesizing multi-alkoxy benzoyl chloride substituted alkylamine by using multi-substituted benzoyl chloride and hydrochloride of chlorinated alkyl amino as raw materials; carrying out reaction on the compound and piperazine to prepare N-piperazinyl alkyl multi-substituted benzamide; reacting with substituted benzene acryloyl chloride to prepare (E)-N-3-(4-substituted benzene propenyl piperazine-1-base) alkyl benzamide; acting with BBr3 or BF3 aether solution to be further hydrolyzed to generate the corresponding (E)-N-3-(4-substituted benzene propenyl piperazine-1-base) alkyl polyhydric benzamide compound, and then reacting with alkaline to generate the corresponding salt. The compound has inhibition function to HIV-1 integrase.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![2,4-di-substituted amido-6-substituted-[1,3,5]triazine or miazines compound, preparation method, pharmaceutical combination and use of the same 2,4-di-substituted amido-6-substituted-[1,3,5]triazine or miazines compound, preparation method, pharmaceutical combination and use of the same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/21a24be9-bee8-4643-b783-fcb93abe7cb3/a20061017002400691.PNG)
![2,4-di-substituted amido-6-substituted-[1,3,5]triazine or miazines compound, preparation method, pharmaceutical combination and use of the same 2,4-di-substituted amido-6-substituted-[1,3,5]triazine or miazines compound, preparation method, pharmaceutical combination and use of the same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/21a24be9-bee8-4643-b783-fcb93abe7cb3/a20061017002400692.PNG)
![2,4-di-substituted amido-6-substituted-[1,3,5]triazine or miazines compound, preparation method, pharmaceutical combination and use of the same 2,4-di-substituted amido-6-substituted-[1,3,5]triazine or miazines compound, preparation method, pharmaceutical combination and use of the same](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/21a24be9-bee8-4643-b783-fcb93abe7cb3/a20061017002400701.PNG)





![1‑n‑substituted benzyl‑6‑n'‑substituent‑2,3,6,9‑tetrahydro‑1h‑[1,4]oxazino[3,2‑g]quinolin‑9‑one ‑8‑Formic acid compound and its preparation method and application 1‑n‑substituted benzyl‑6‑n'‑substituent‑2,3,6,9‑tetrahydro‑1h‑[1,4]oxazino[3,2‑g]quinolin‑9‑one ‑8‑Formic acid compound and its preparation method and application](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9d90bcf2-2094-4aef-acad-3b8c590cfe4e/BDA0000688066280000021.png)
![1‑n‑substituted benzyl‑6‑n'‑substituent‑2,3,6,9‑tetrahydro‑1h‑[1,4]oxazino[3,2‑g]quinolin‑9‑one ‑8‑Formic acid compound and its preparation method and application 1‑n‑substituted benzyl‑6‑n'‑substituent‑2,3,6,9‑tetrahydro‑1h‑[1,4]oxazino[3,2‑g]quinolin‑9‑one ‑8‑Formic acid compound and its preparation method and application](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9d90bcf2-2094-4aef-acad-3b8c590cfe4e/BDA0000688066280000022.png)
![1‑n‑substituted benzyl‑6‑n'‑substituent‑2,3,6,9‑tetrahydro‑1h‑[1,4]oxazino[3,2‑g]quinolin‑9‑one ‑8‑Formic acid compound and its preparation method and application 1‑n‑substituted benzyl‑6‑n'‑substituent‑2,3,6,9‑tetrahydro‑1h‑[1,4]oxazino[3,2‑g]quinolin‑9‑one ‑8‑Formic acid compound and its preparation method and application](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/9d90bcf2-2094-4aef-acad-3b8c590cfe4e/BDA0000688066280000031.png)