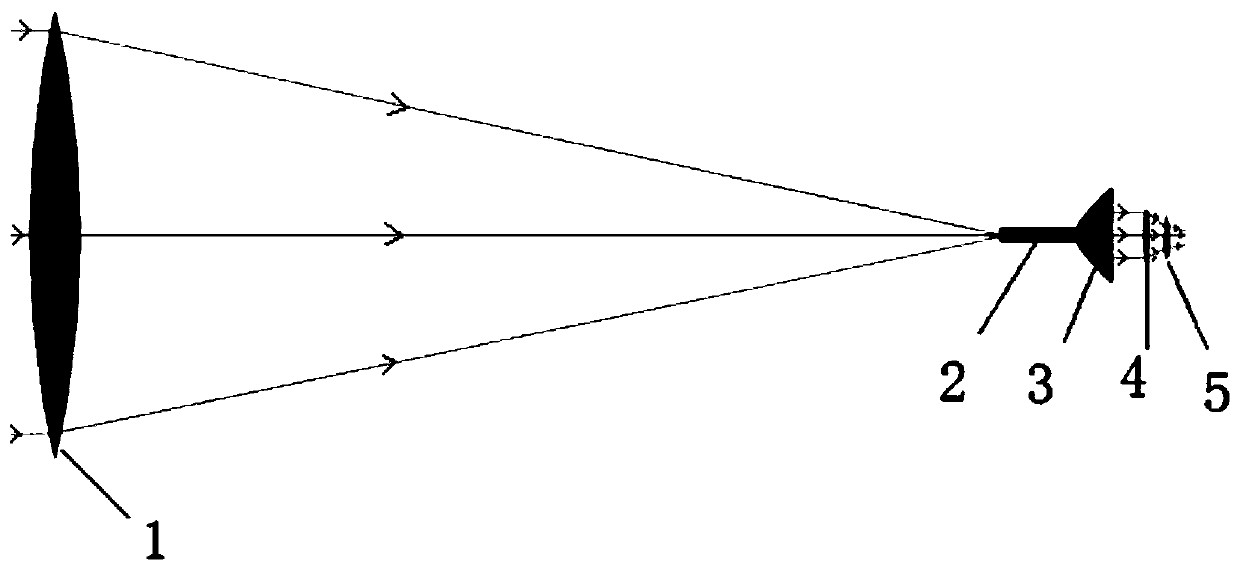
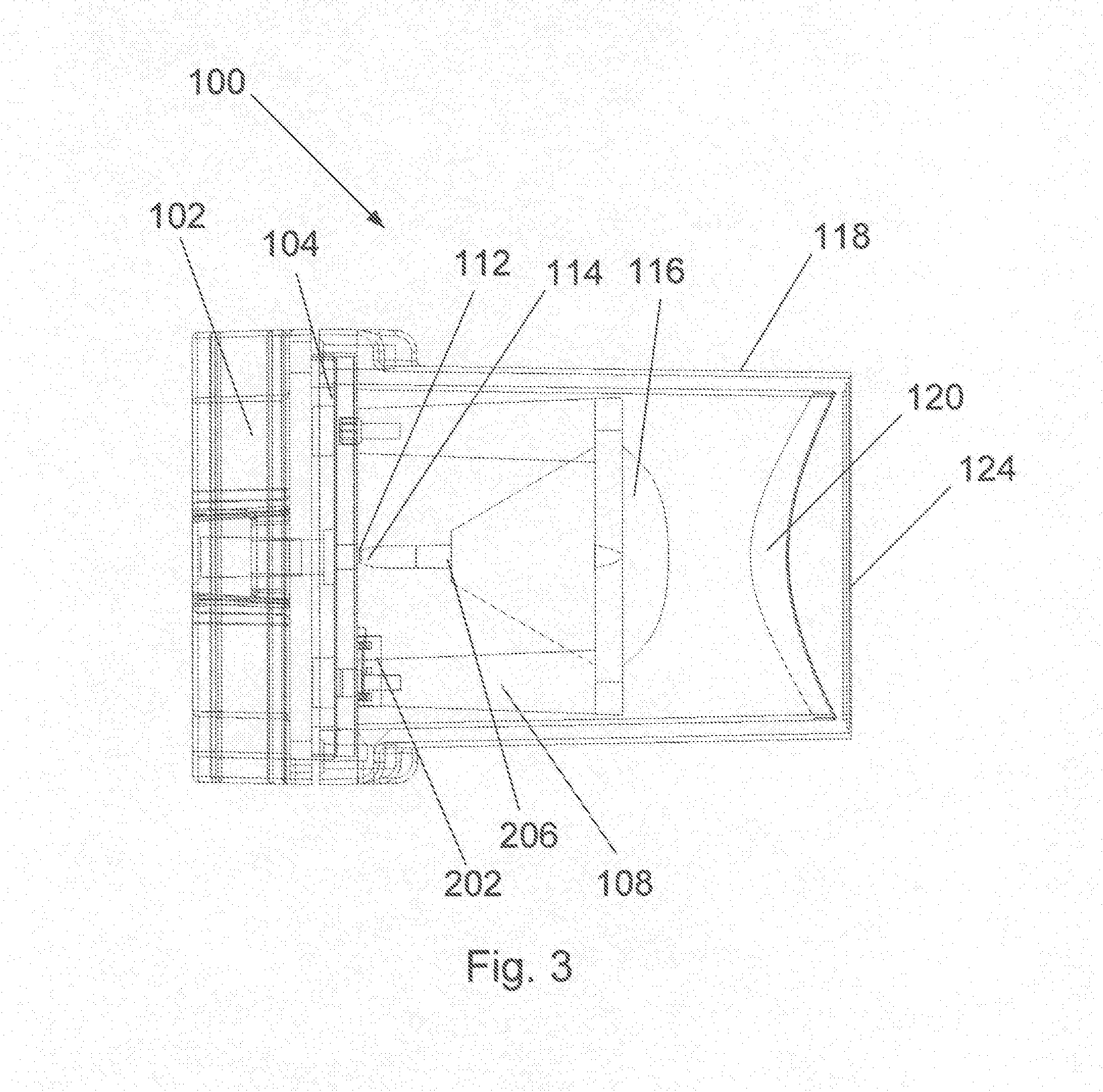Patents
Literature
30 results about "Nonimaging optics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
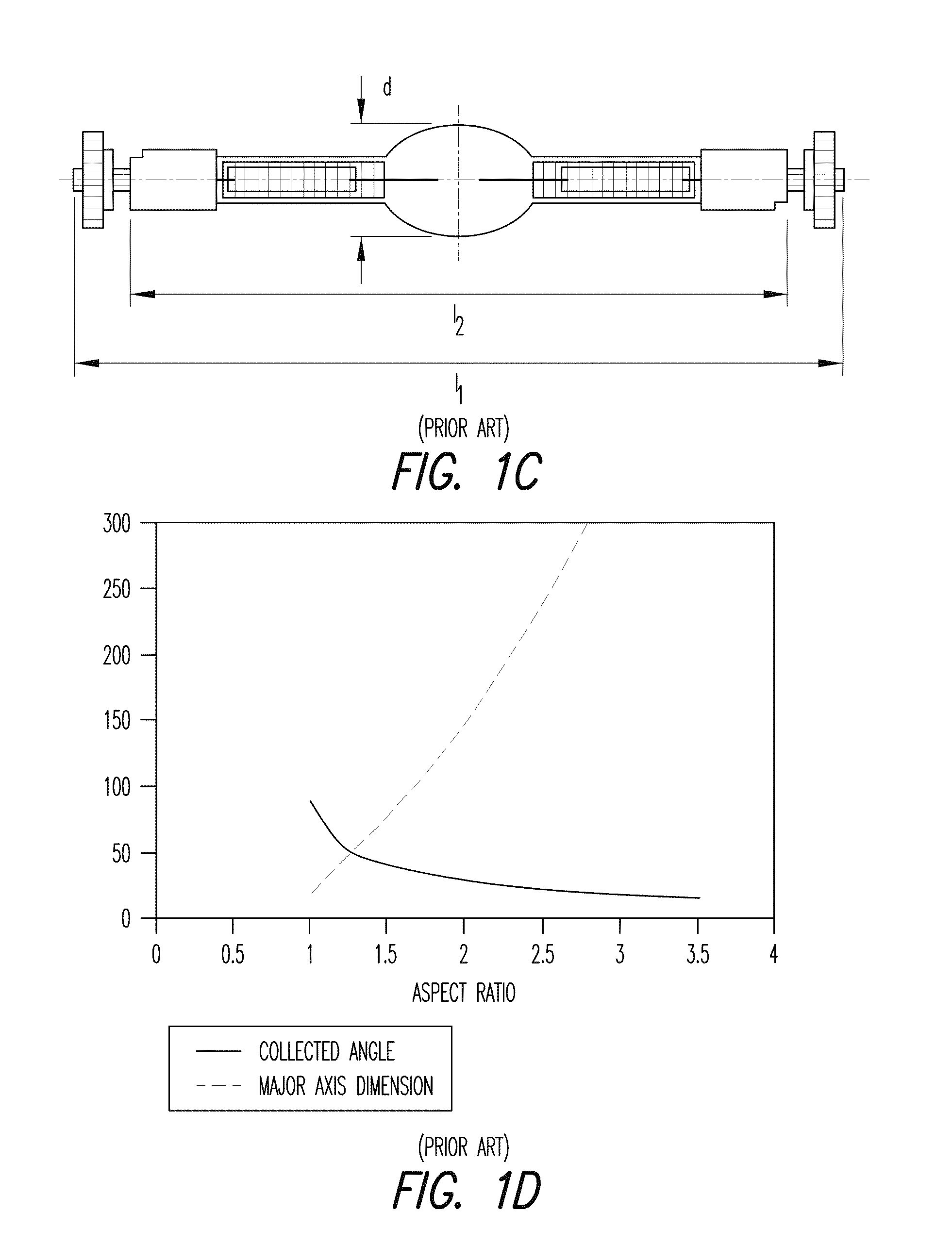
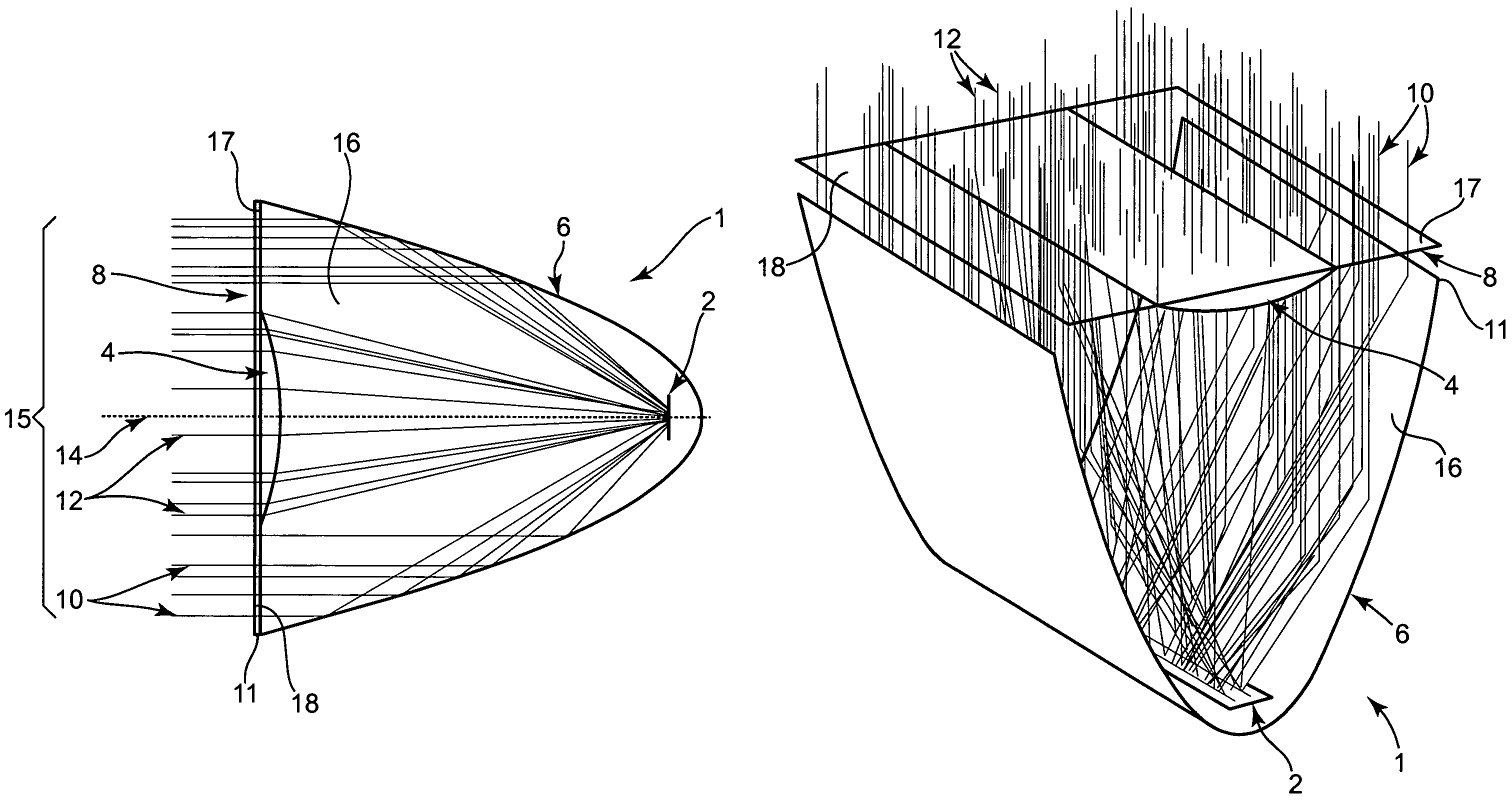
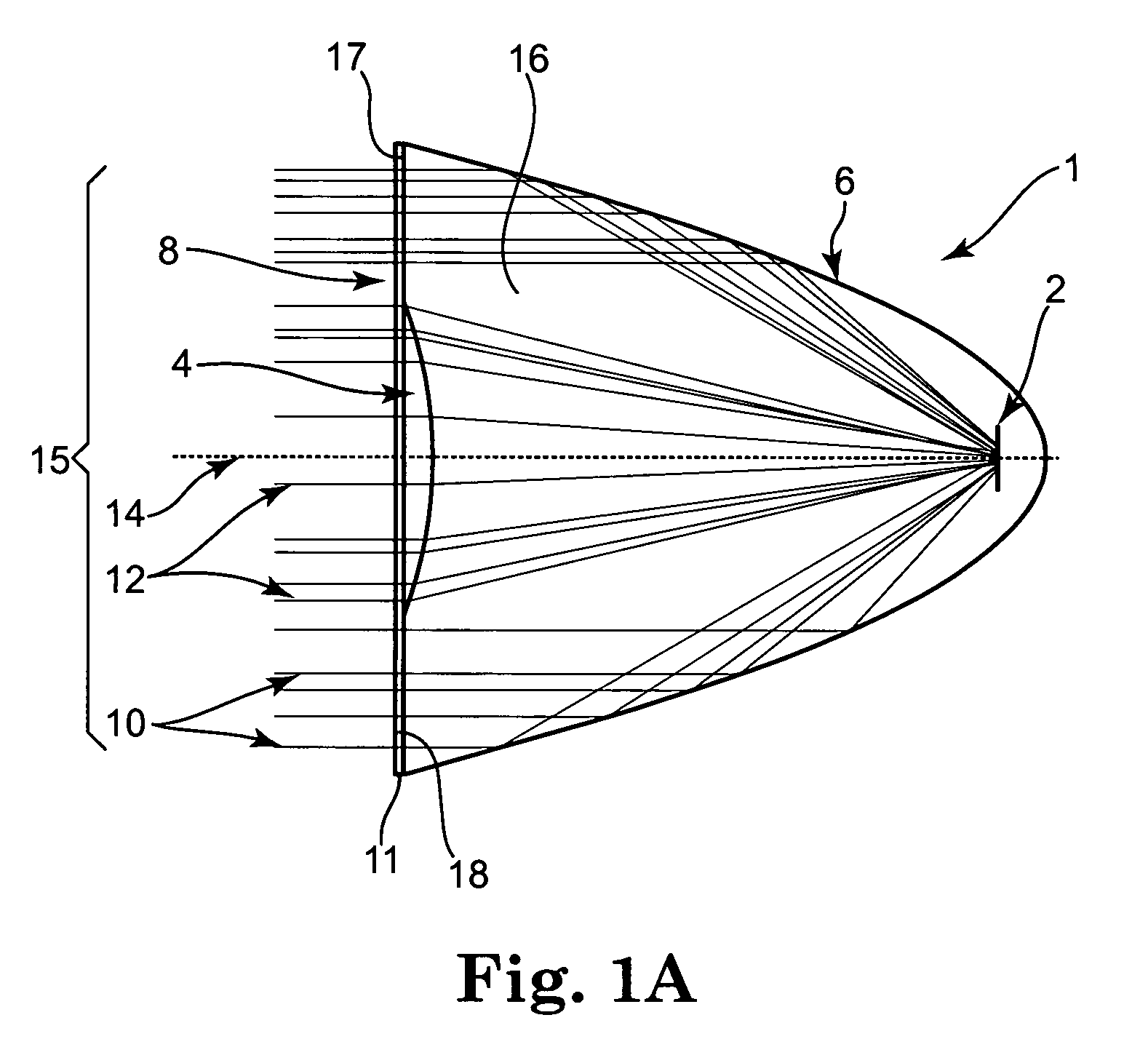
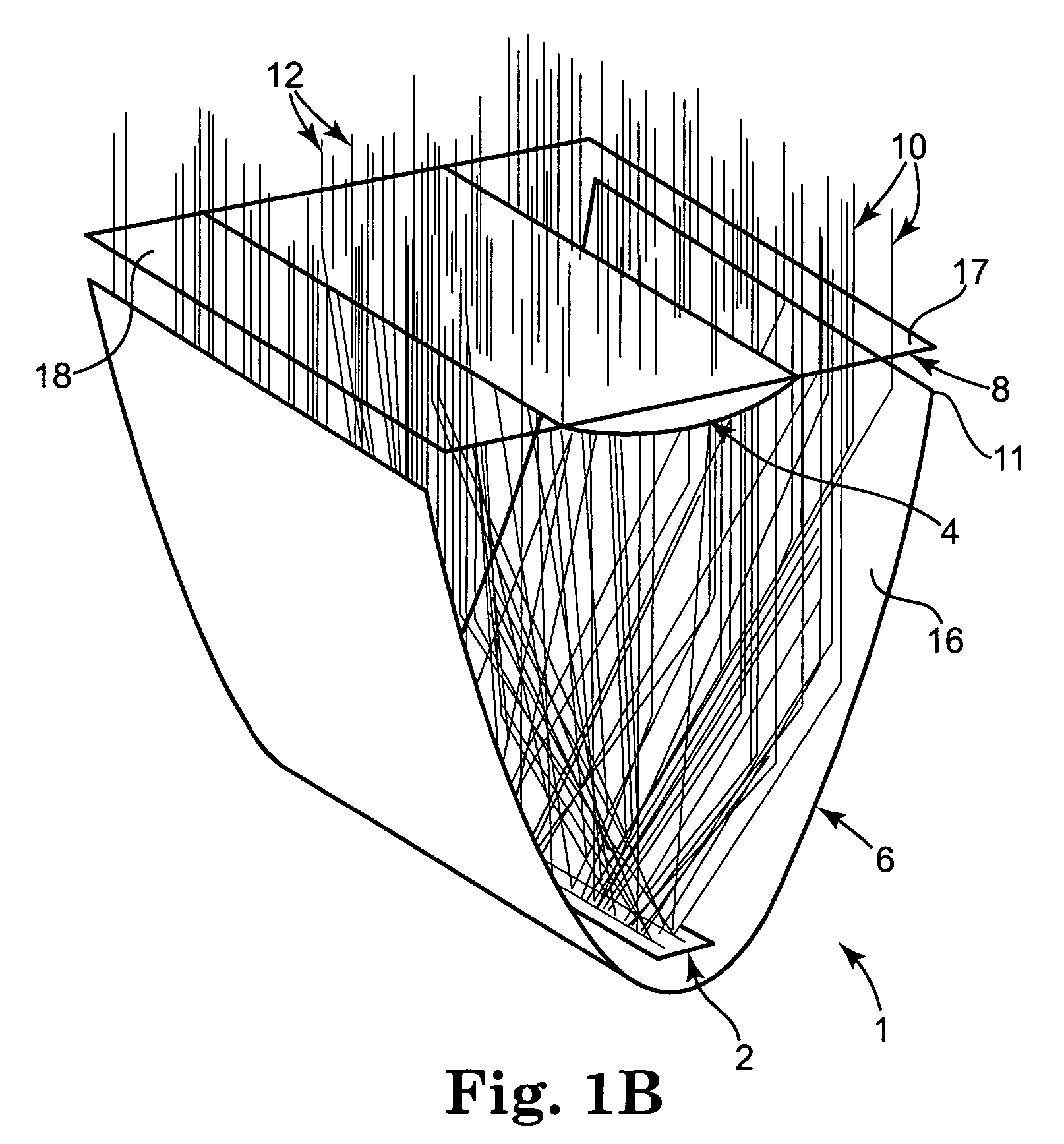
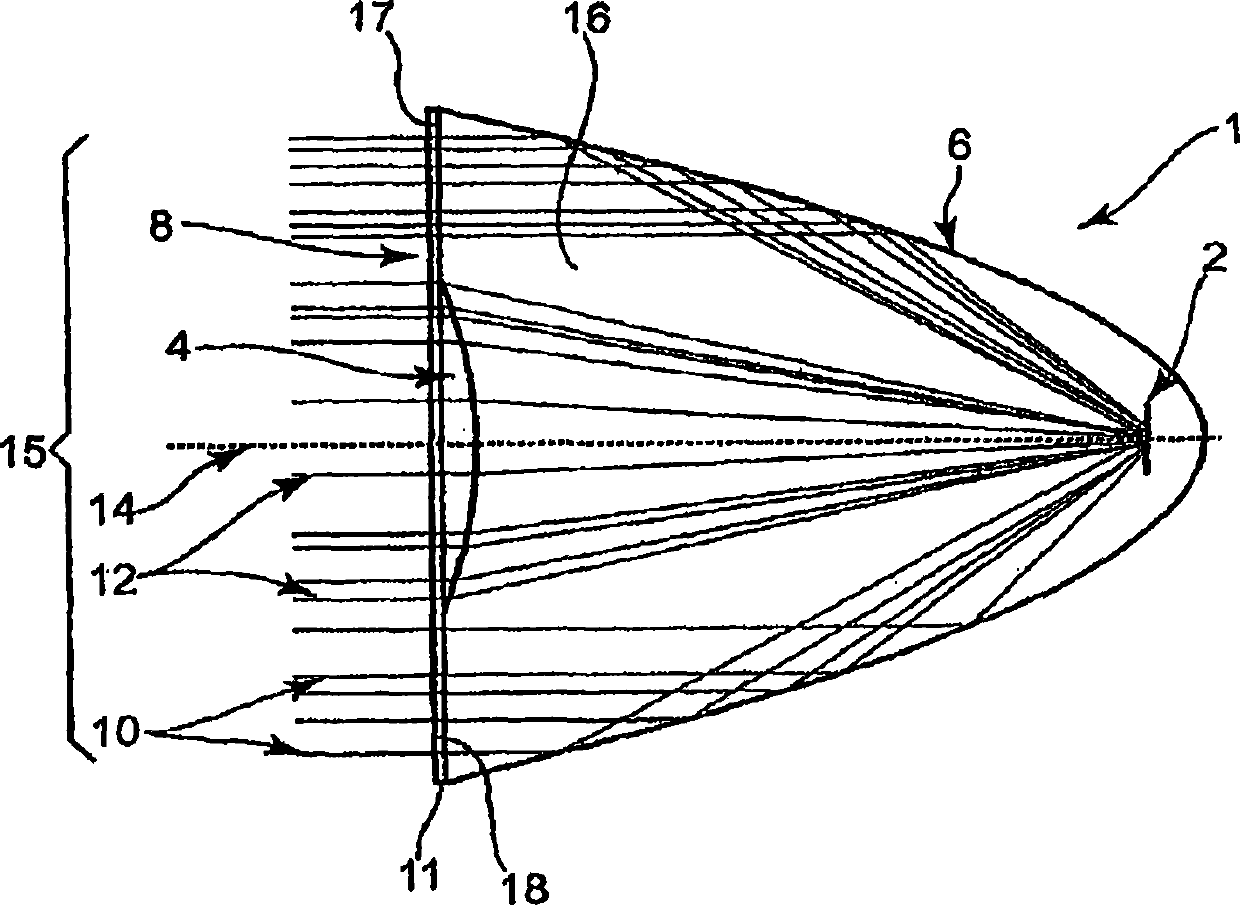
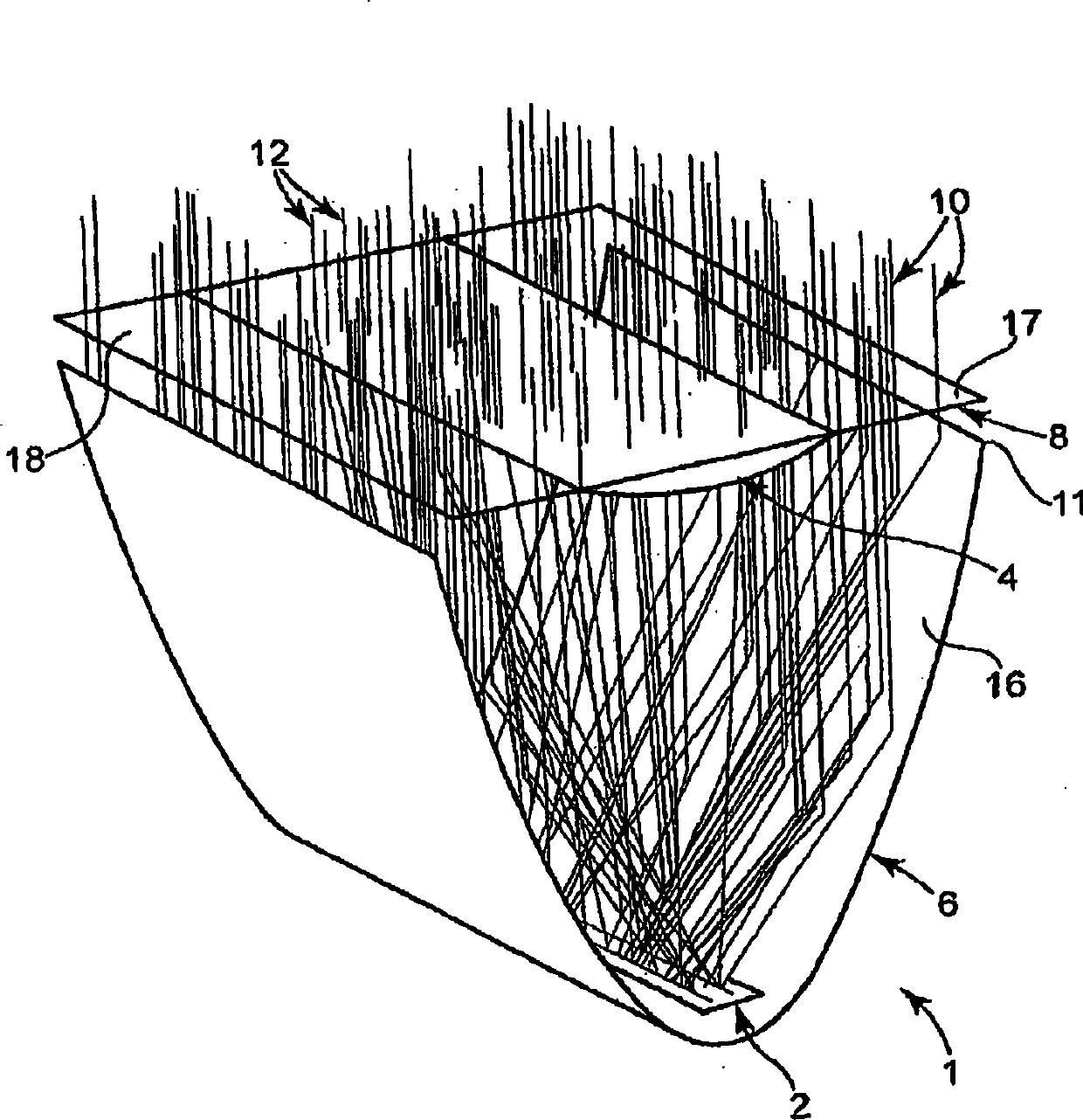
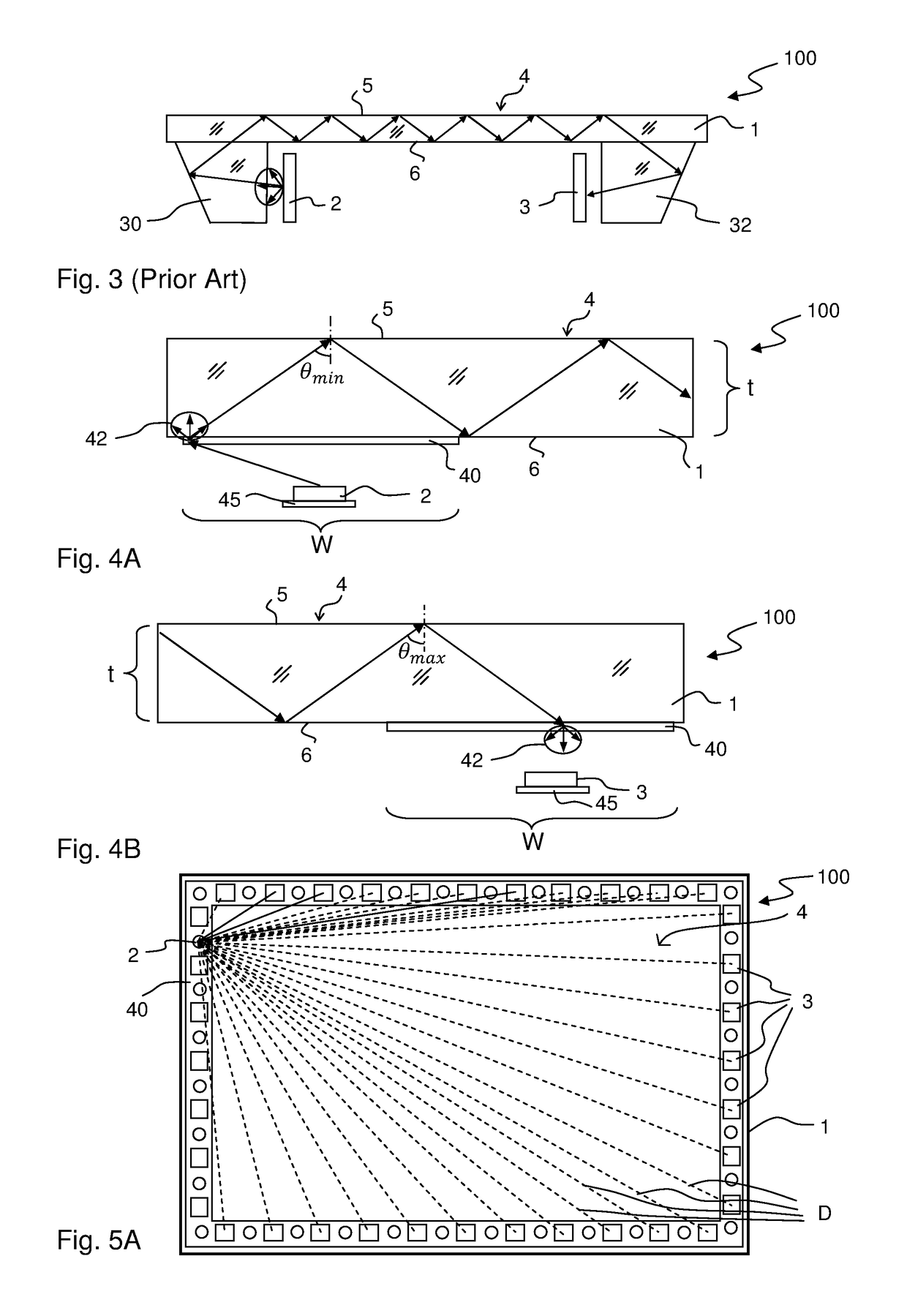
Nonimaging optics (also called anidolic optics) is the branch of optics concerned with the optimal transfer of light radiation between a source and a target. Unlike traditional imaging optics, the techniques involved do not attempt to form an image of the source; instead an optimized optical system for optimal radiative transfer from a source to a target is desired.
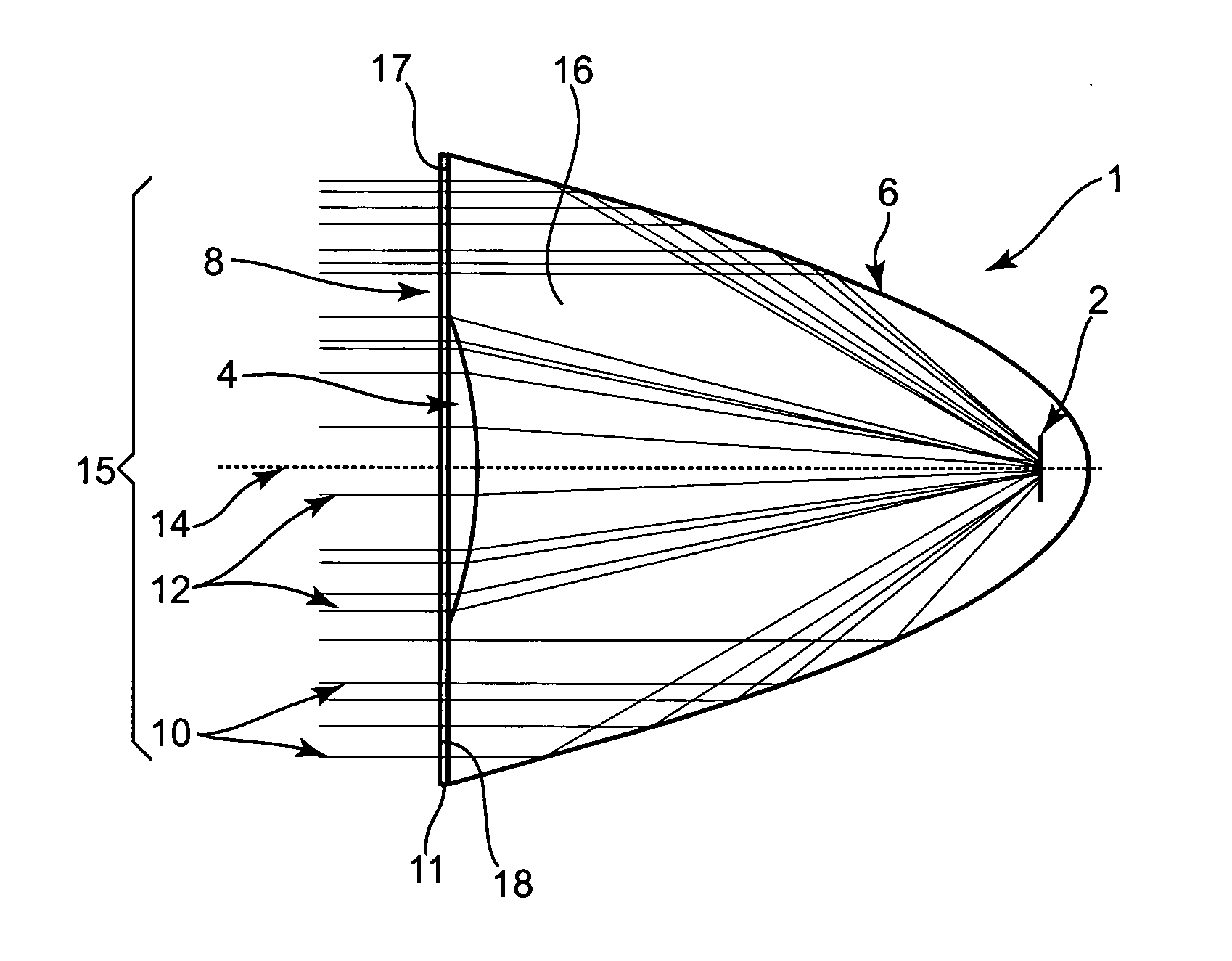
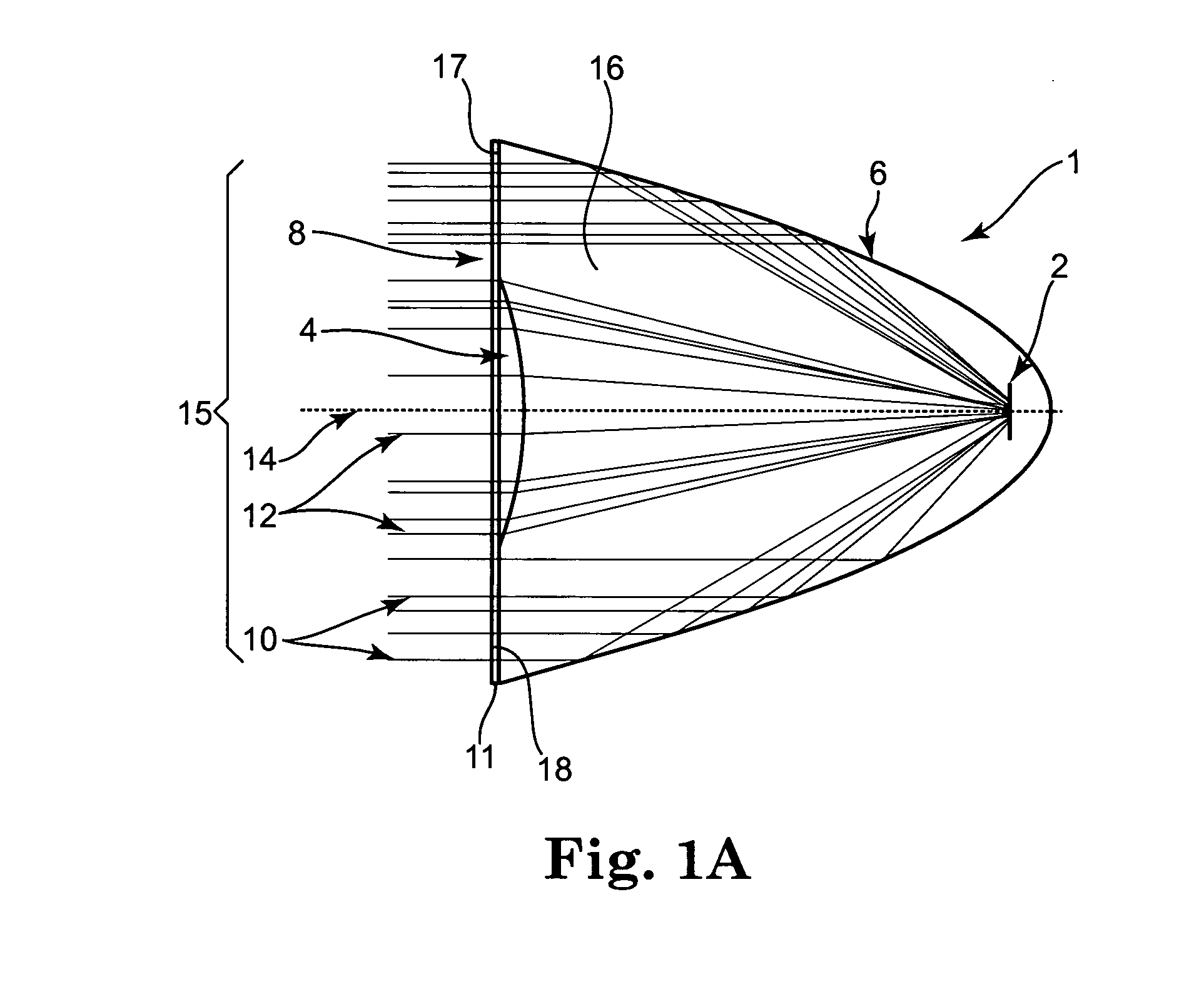
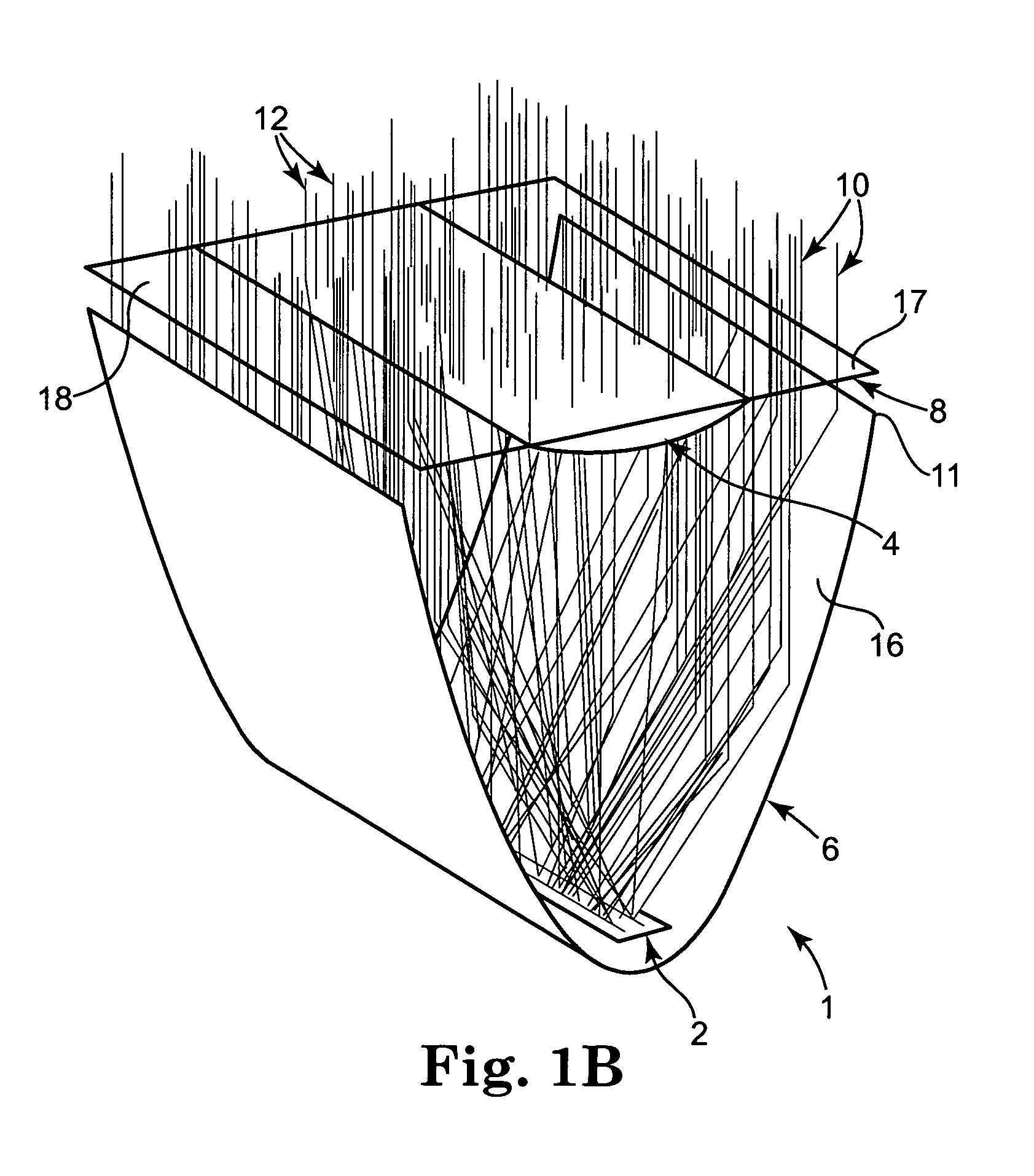
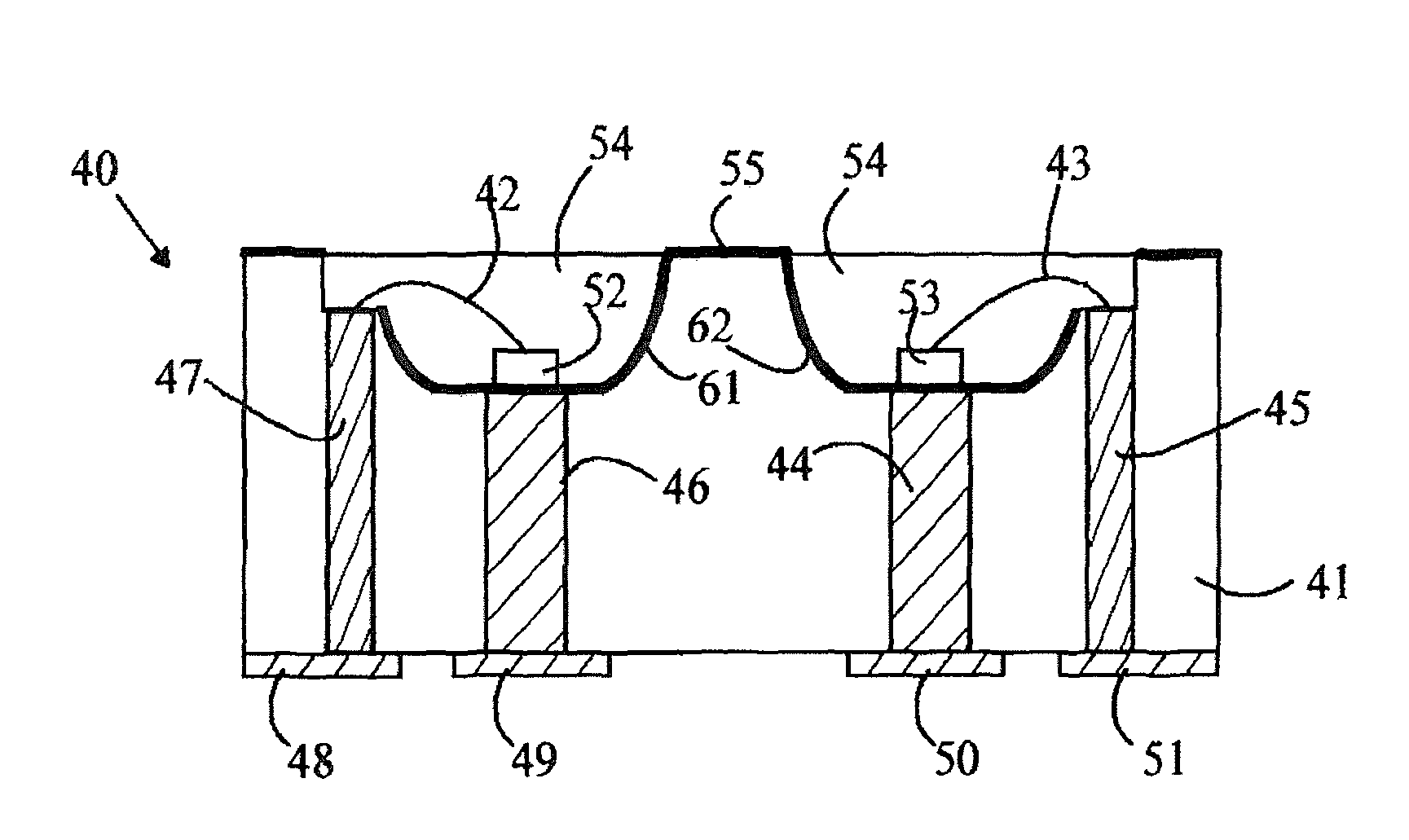
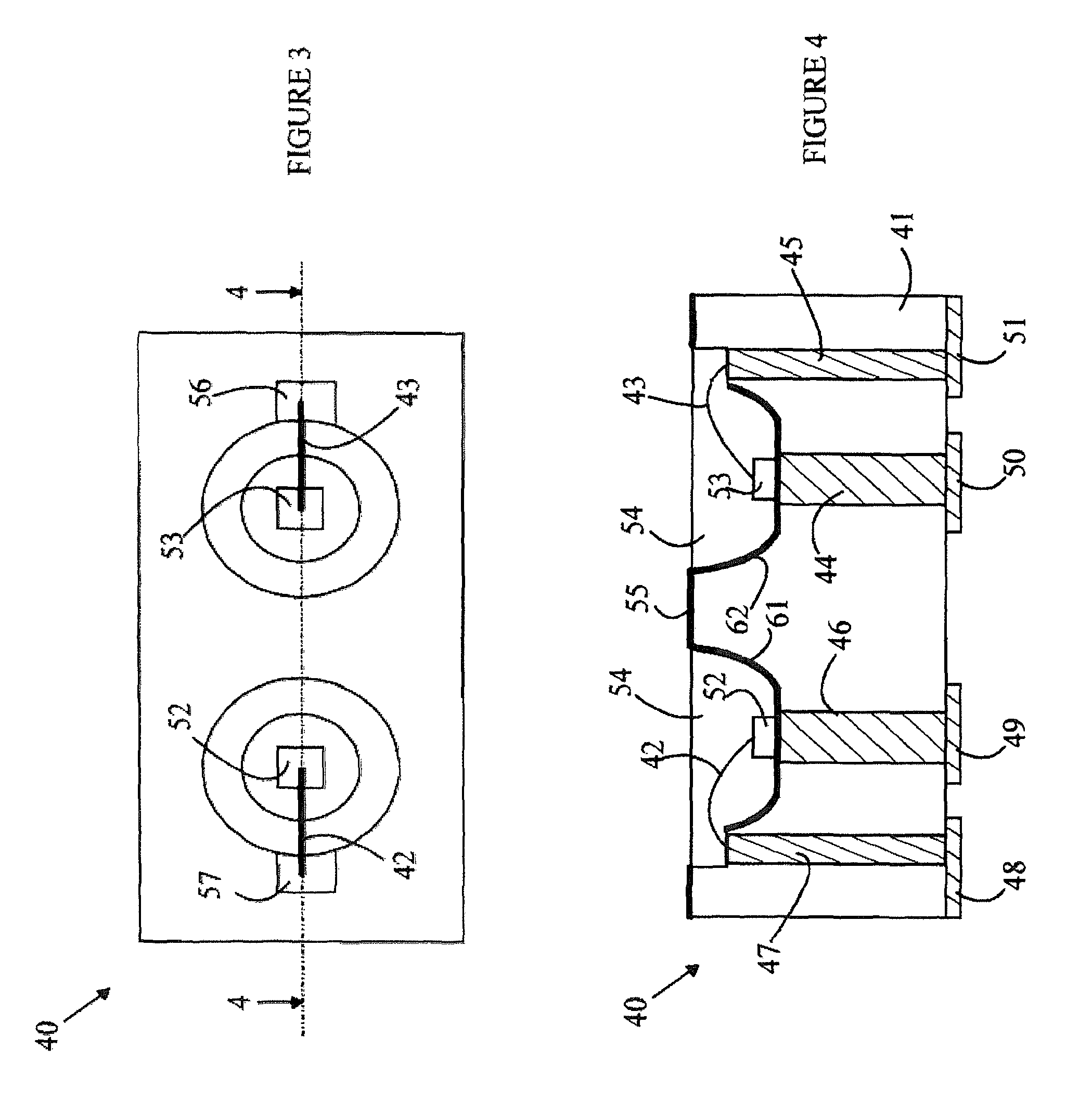
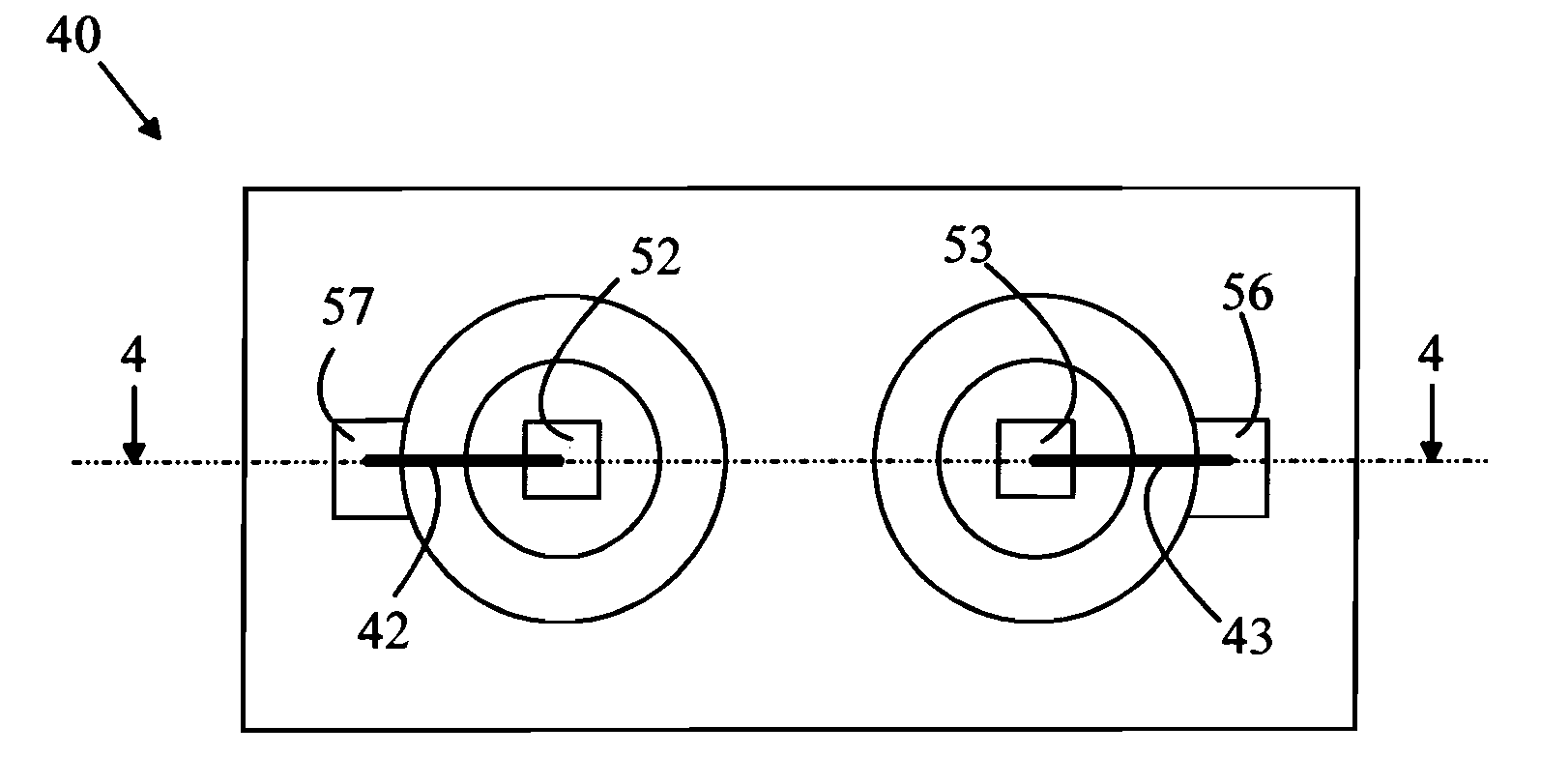
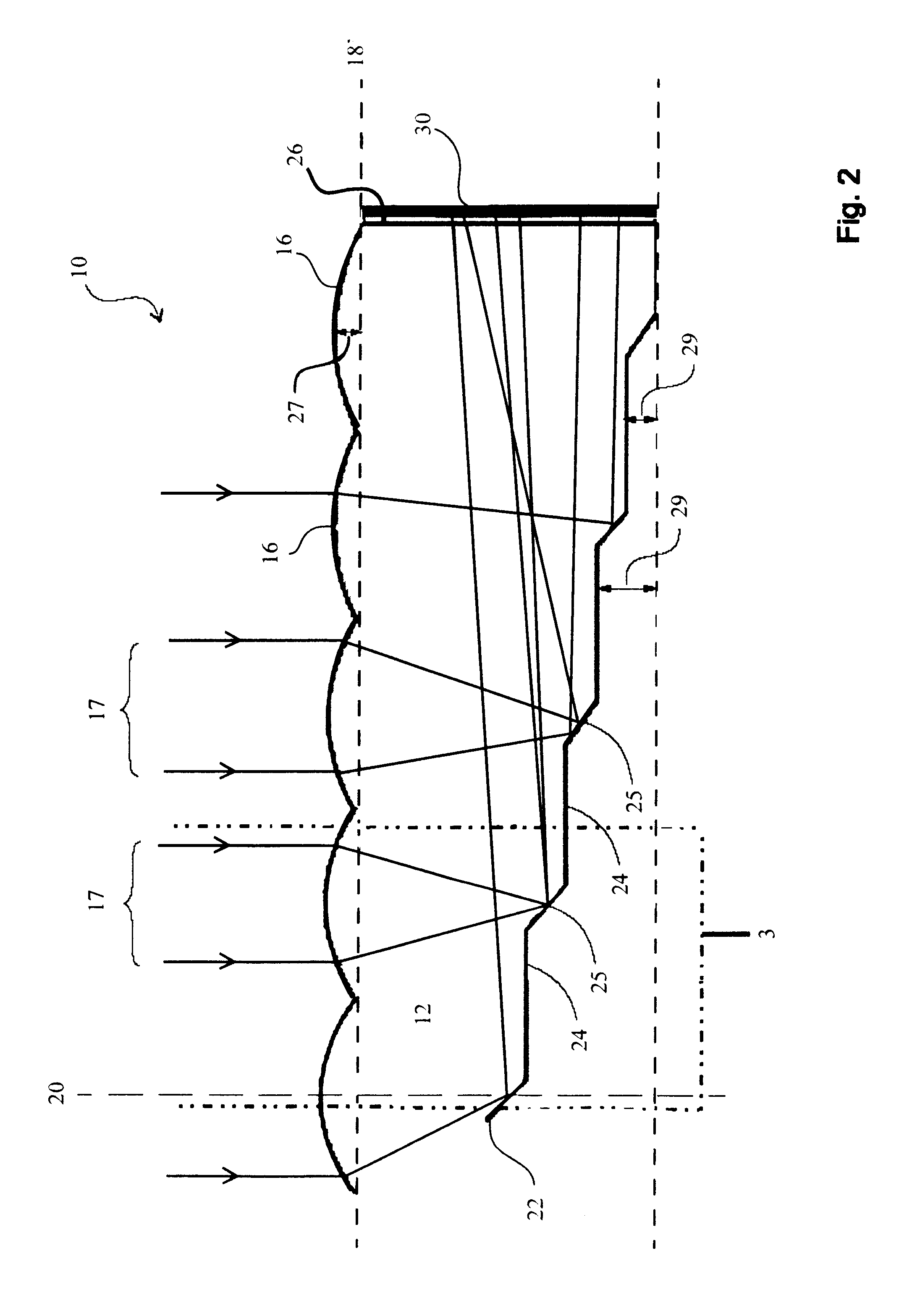
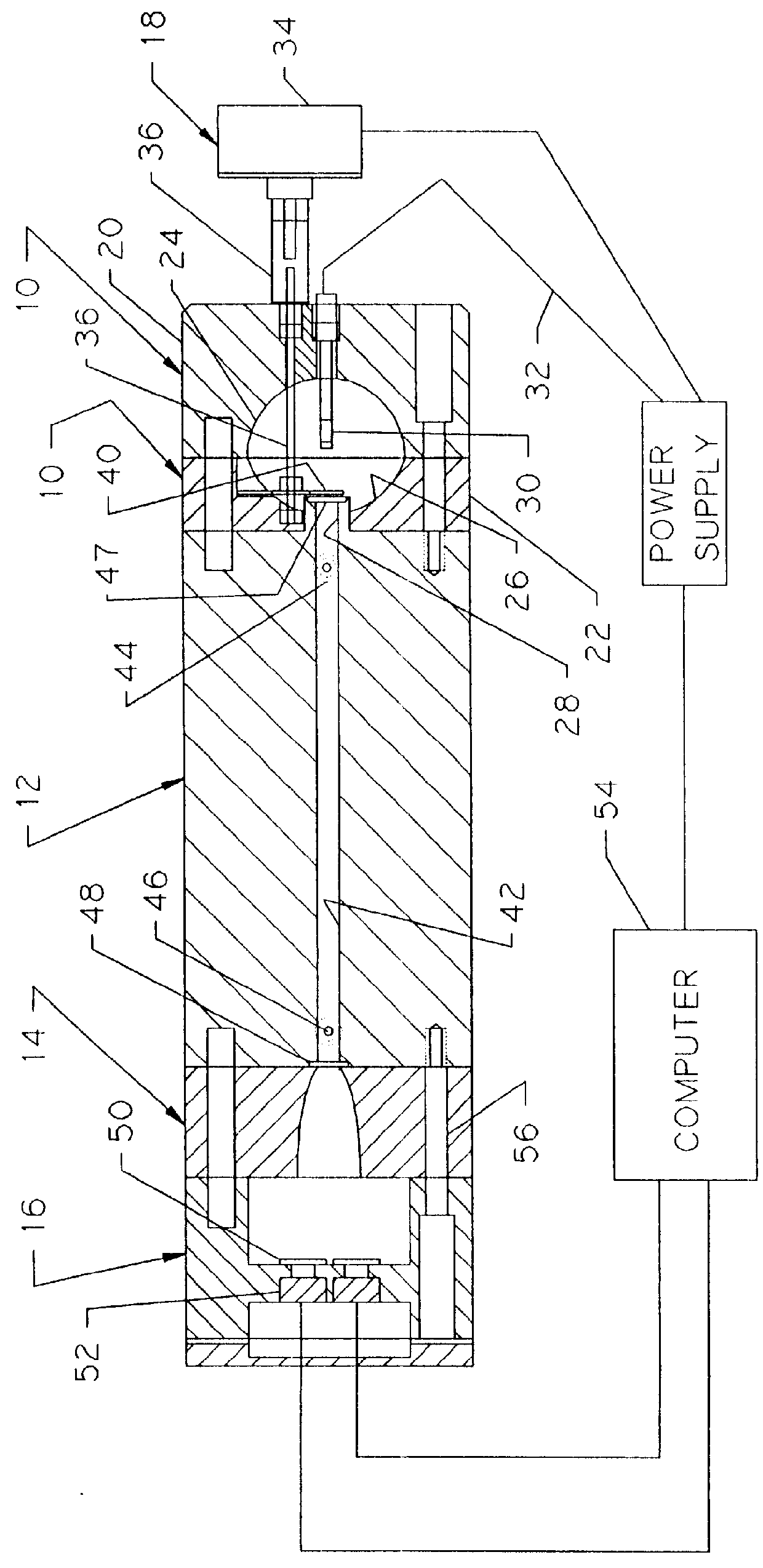
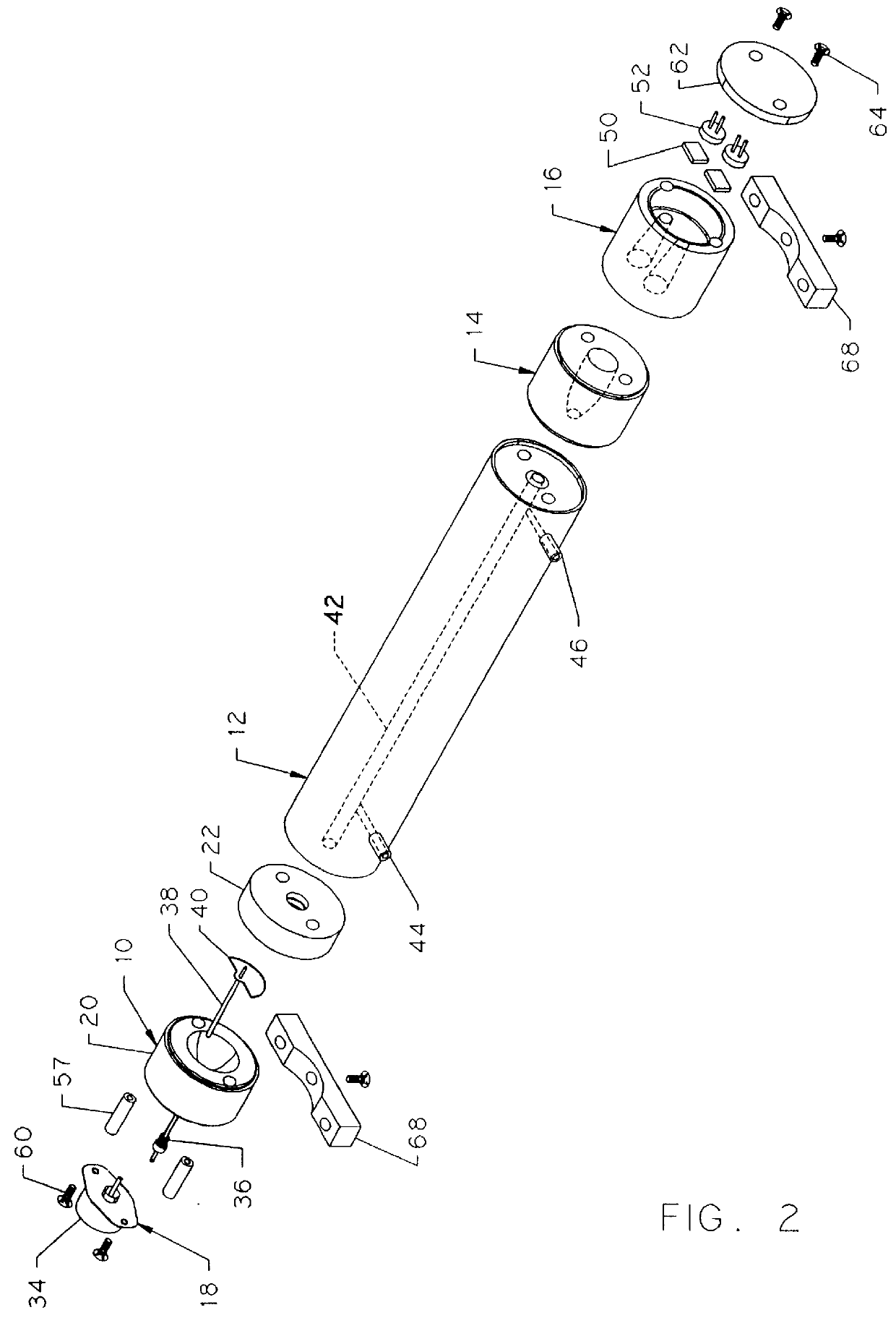
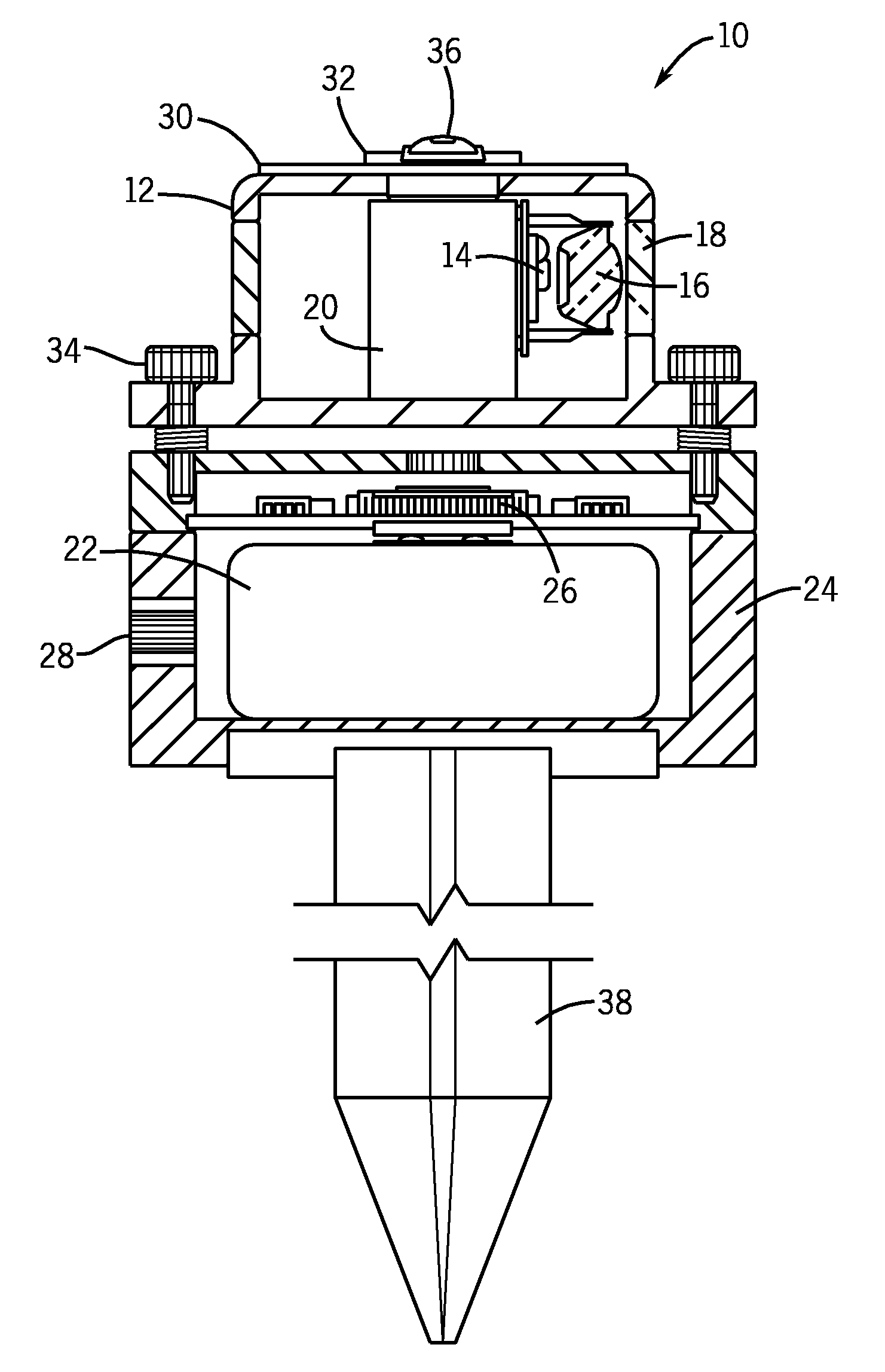
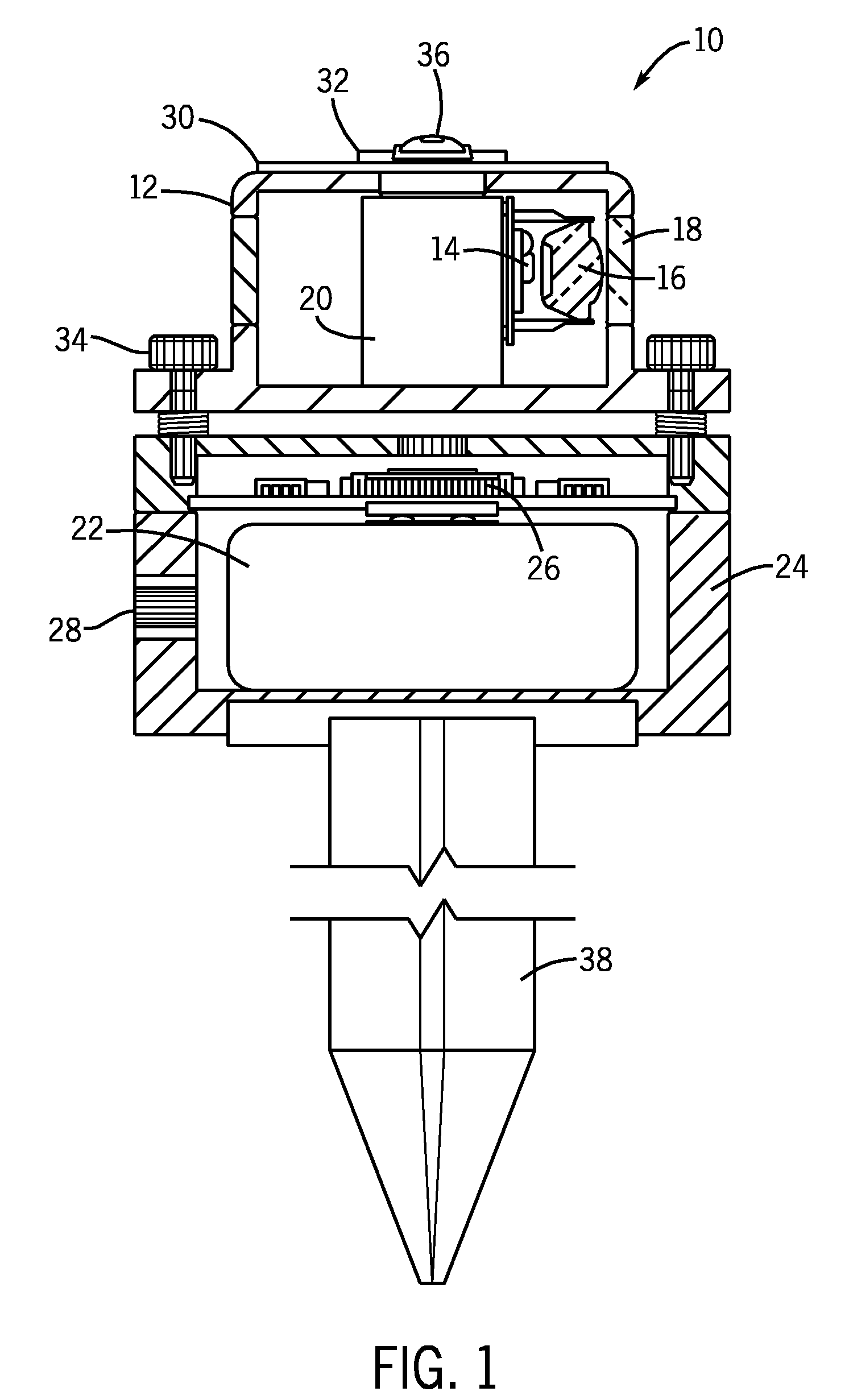
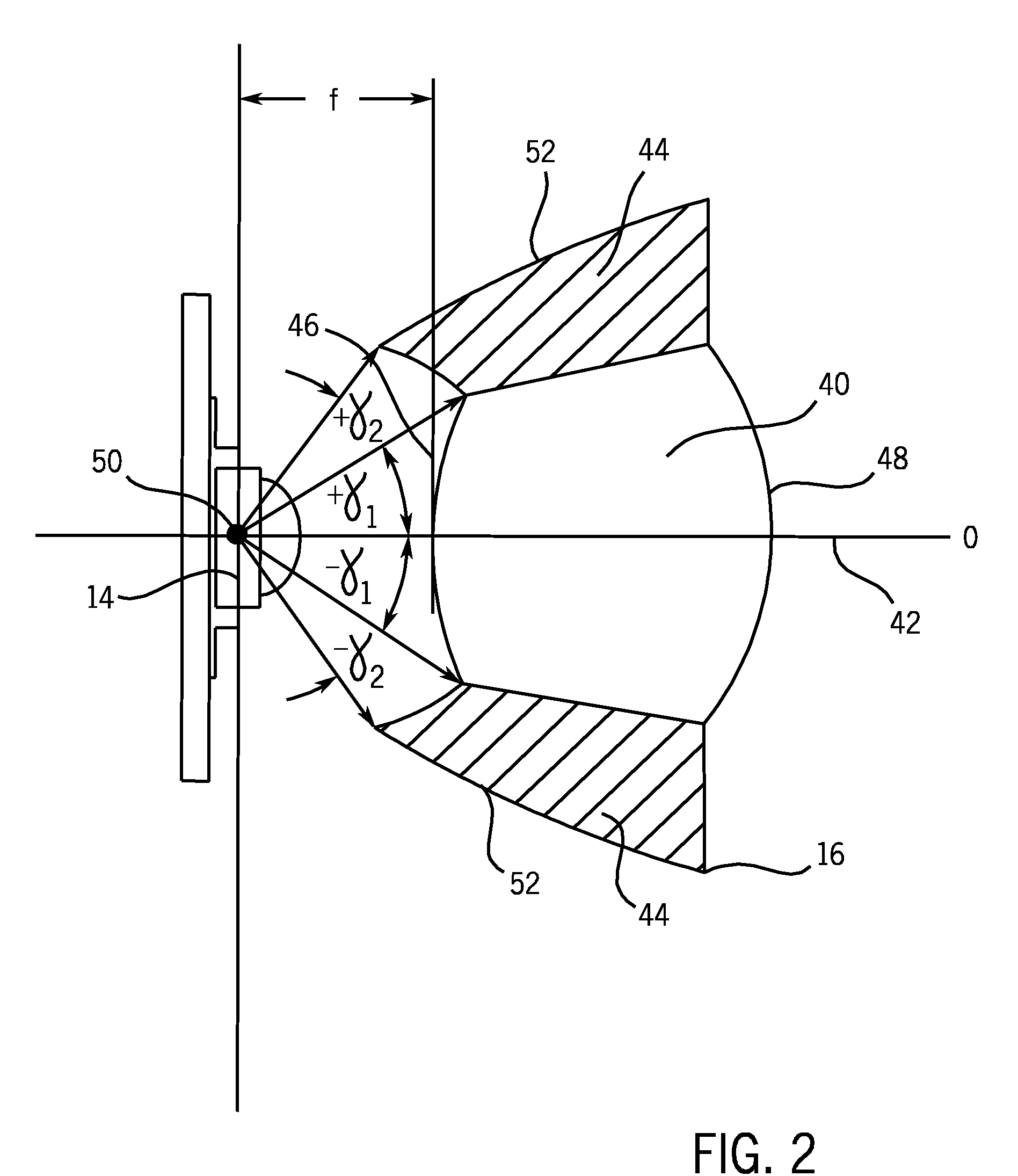
Hybrid primary optical component for optical concentrators
InactiveUS20070188876A1Avoiding conventional drawbacksSolar heating energyMirrorsConcentratorPhotovoltaic solar cell
A hybrid optical component that collects and concentrates incident light. The hybrid component includes both refractive and reflective elements. In preferred embodiments, refractive and reflective components focus rays on a common focal plane generally located at the bottom of the reflector where they are absorbed by a device such as a photovoltaic (solar) cell. Additionally, the optical component combines both imaging and non-imaging optical elements into a single device, for improved overall performance.
Owner:SUNCORE PHOTOVOLTAICS
Portable luminaire
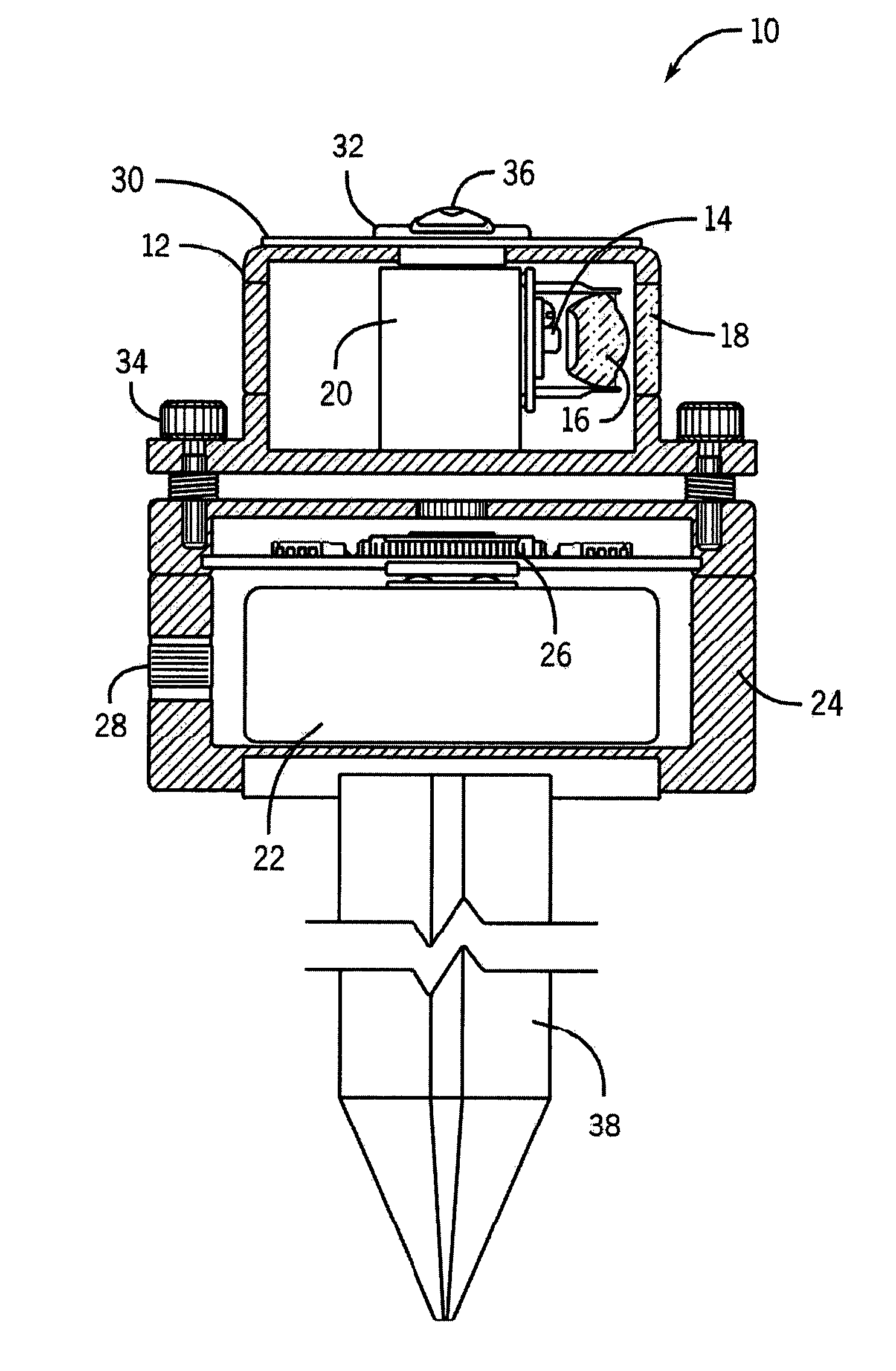
InactiveUS7503669B2Improve efficiencyEfficient compressionMechanical apparatusLighting support devicesNonimaging opticsTotal internal reflection
A portable luminaire includes an optical module, a power source and a housing. The optical module has at least one light emitting diode (LED) that emits light with a wide divergence, a non-imaging optical element and a transparent window. The non-imaging optical element (NIO) has a refractive member located around a LED optical axis and a total internal reflection member located around the refractive member. The refractive member and the total internal reflection member are integrated in a single transparent element having a mutual focal point. The NIO element collects a significant amount of light emitted by the LED with wide divergence located at the focal point to compress the collected light with high efficiency into a required pattern with a generally different angular distribution in a horizontal plane and a vertical plane, and to direct the compressed light outside of the luminaire.
Owner:FARLIGHT
Optical coupling in touch-sensing systems using diffusively transmitting element
InactiveUS20150205441A1Easy to assembleSuitable for mass productionDigital data processing detailsCoupling light guidesTotal internal reflectionFrustration
A touch-sensitive apparatus operates by light frustration and comprises a light transmissive panel with a front surface and a rear surface. Light emitters and light detectors optically face the rear surface along a perimeter of a touch-sensitive region on the panel. At least one non-imaging, diffusively transmitting optical element is arranged on the rear surface along the perimeter of the touch-sensitive region. The light emitters are arranged to emit a respective beam of light onto the non-imaging optical element so as to generate, by diffuse transmission, propagating light that propagates by total internal reflection inside the panel across the touch-sensitive region, and the light detectors are arranged to receive detection light generated, by diffuse transmission, as the propagating light impinges on the non-imaging optical element, so as to define a grid of propagation paths across the touch-sensitive region between pairs of light emitters and light detectors.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Light source system and an image projection system
InactiveUS20070165186A1Uniform strengthEnhanced couplingProjectorsColor television detailsIntegratorProjection system
A light source system comprises a light source disposed within a non-imaging optical element. The non-imaging optical element does not produce a direct image of the light source, and the output light field at the output surface of the non-imaging optical element has an intensity that is substantially uniform over the area of the output surface. A light source system of the invention is therefore smaller and lighter than a prior art system of the same output power, since there is no need to provide further components, such as an integrator, to homogenise the output light field.
Owner:SHARP KK
Optical transceiver with reduced height
ActiveUS7842957B2Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsTransceiver
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Optical Transceiver with Reduced Height
ActiveUS20080219673A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansTransceiverPhotovoltaic detectors
A transceiver having a light source die, a photodetector die and a substrate is disclosed. The substrate has a first well in which the light source die is mounted and a second well in which the photodetector die is mounted. The substrate has a reflective surface which blocks light leaving the light source from reaching the photodetector unless the light is reflected by an object external to the transceiver. The reflecting surface of the second well in the substrate is shaped to concentrate light received from outside the transceiver onto the photodetector, and in one aspect of the invention it comprises a non-imaging optical element. The light source is powered by applying a potential between first and second contacts on the light source die. A signal is generated between first and second contacts on the photodetector die in response to illumination of the photodetector die.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Beam projection systems and methods
InactiveUS20100165306A1Increase demandMinimizing its growthProjectorsCondensersCamera lensLight beam
Throughput efficiency of an optical system is enhanced by using a directional light source coupled to a non-imaging optical element matched to a size and acceptance angle of an imaging lens. In various embodiments, a beam projection system and accompanying method are described that include a lamp body formed from a dielectric material. A bulb, placed adjacent to the lamp body, has a fill that forms a plasma when RF power is coupled to the fill from the lamp body. An optical train is optically coupled to the bulb to transform light generated by the plasma. The optical train includes a non-imaging optical element, an aperture, and at least one imaging lens element.
Owner:LUXIM CORP
Hybrid primary optical component for optical concentrators
A hybrid optical component that collects and concentrates incident light. The hybrid component includes both refractive and reflective elements. In preferred embodiments, refractive and reflective components focus rays on a common focal plane generally located at the bottom of the reflector where they are absorbed by a device such as a photovoltaic (solar) cell. Additionally, the optical component combines both imaging and non-imaging optical elements into a single device, for improved overall performance.
Owner:SUNCORE PHOTOVOLTAICS
A hybrid primary optical component for optical concentrators
InactiveCN101375112AAvoid conventional disadvantagesSolar heating energyMirrorsConcentratorNonimaging optics
A hybrid optical component collects and concentrates incident light. The hybrid component includes both refractive and reflective elements. In preferred embodiments, refractive and reflective components focus rays on a common focal plane generally located at the bottom of the reflector where they are absorbed by a device such as a photovoltaic (solar) cell. Additionally, the optical component combines both imaging and non-imaging optical elements into a single device, for improved overall performance.
Owner:SOLIANT ENERGY INC
EUV condenser with non-imaging optics
InactiveUS7046338B2MirrorsSynthetic resin layered productsElectromagnetic radiationExtreme ultraviolet
An illumination system and condenser for use in photolithography in the extreme ultraviolet wavelength region has a first non-imaging optic element collecting electromagnetic radiation from a source and creates a desired radiance distribution. A second non-imaging optic element receives the electromagnetic radiation from the first non-imaging optic element and redirects and images the electromagnetic radiation. The electromagnetic radiation from the second non-imaging optic element is suitable for being received by other conventional optical surfaces to provide a desired radiance distribution with a desired angular distribution and desired shape. Facets are used to provide the desired illumination over the desired illumination field. Reflective facets may be placed on the second non-imaging optic, which can reduce the number of mirrors and increase efficiency. The condenser and illumination system are used in combination with a projection optic to project the image of a reticle or mask onto a photosensitive substrate, such as a semiconductor wafer. The condenser of the present invention provides an efficient condenser in a compact package and provides desirable illumination properties for imaging relatively small feature sizes of less than 0.13 microns.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Monolithic photovoltaic solar concentrator
InactiveUS20130104984A1Photovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic solar energyIn plane
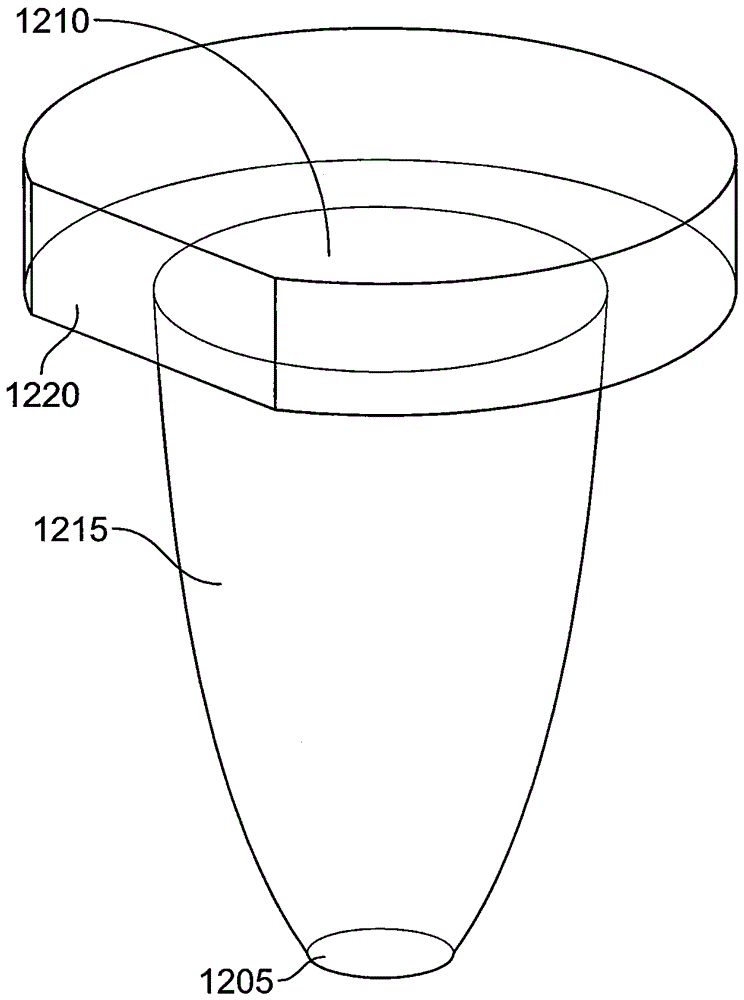
A photovoltaic solar collector and concentrator apparatus consists of a solid, one-piece, sun light transmitting, non-imaging optical element coupled to a photovoltaic cell. The photovoltaic solar collector and concentrator has an entry surface including focusing elements and an opposed surface including uncoated reflector elements. The focused sun light is directed by the reflector elements via total internal reflection directly towards the photovoltaic cell without any reflection from the entry surface. An additional redirecting element based on total internal reflection and integral with the collector and concentrator optical element is used to couple the sunlight from the reflector elements to a photovoltaic cell positioned in plane parallel to the entry surface.
Owner:MORGAN INNOVATION INC
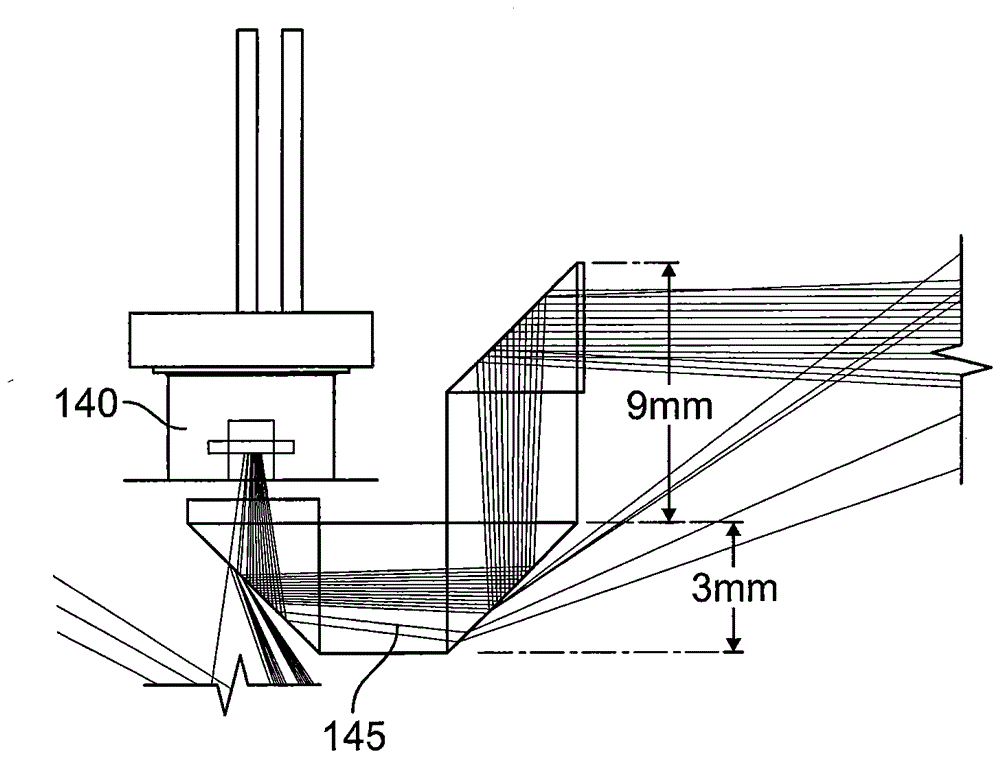
Scanning range finder
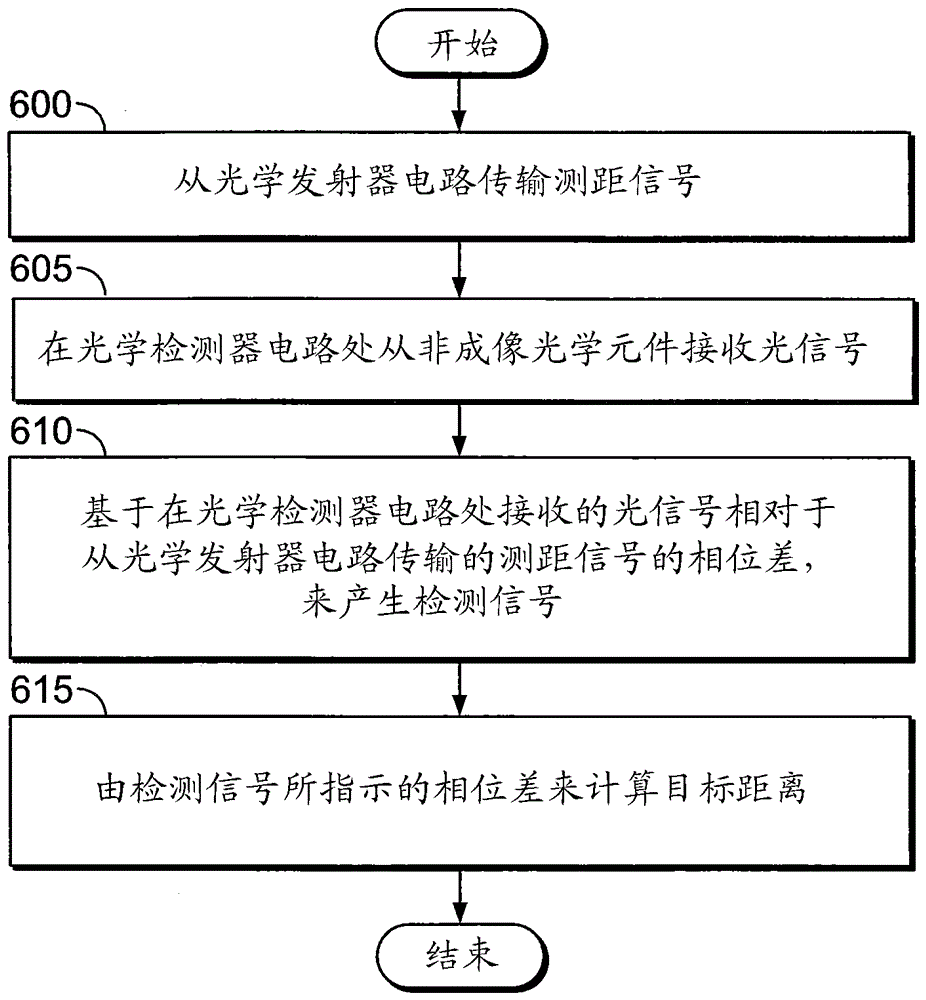
A scanning optical range finder in a mobile robot includes an optical emitter circuit, a non-imaging optical element, an optical detector circuit, and a ranging circuit. The non-imaging optical element is arranged to receive optical signals at an entrance aperture thereof responsive to operation of the optical emitter circuit, and to direct the optical signals to an output aperture thereof. The optical detector circuit is configured to receive the optical signals from the output aperture of the non-imaging optical element, and to generate detection signals based on respective phase differences of the optical signals relative to corresponding outputs of the optical emitter circuit. The ranging circuit is configured to calculate a range of a target from the phase differences indicated by the detection signals. Related devices and methods of operation are also discussed.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
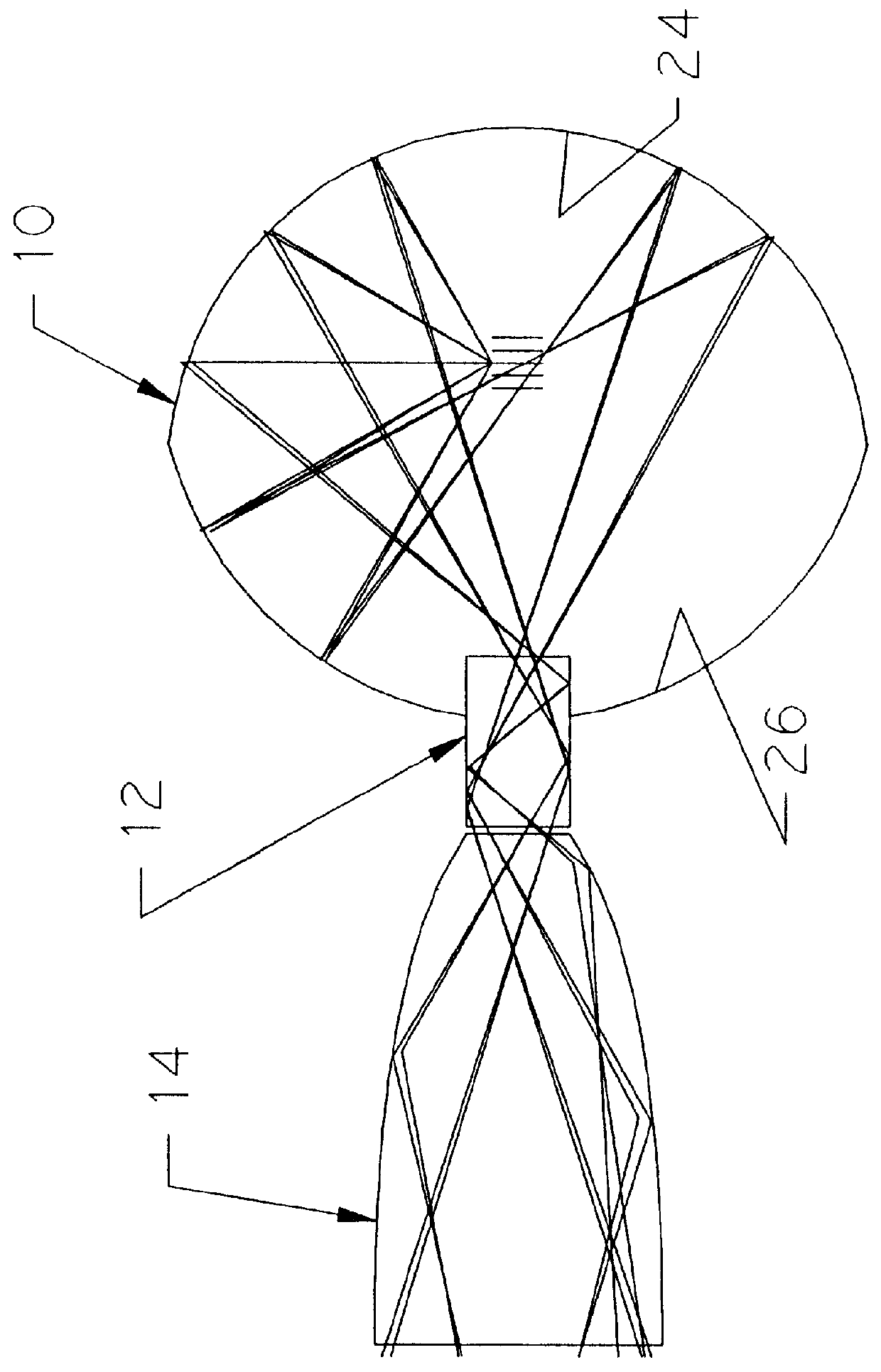
Spectral analyzer with new high efficiency collection optics and method of using same
InactiveUSRE36489E1Radiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotodetectorOptical axis
A spectral analyzer has a high efficiency optical collector having a first concave reflector portion and an opposed second concave reflector portion providing an exit passage therethrough, and a light emitting source of a predetermined wavelength range is positioned in the collector so that the light is collected and directed to the exit passage. A specimen holder is positioned adjacent the exit passage and has windows at its entrance and exit ends. An elongated reverse non-imaging optical member which has a peripheral wall reflecting light rays entering through the exit window of the holder reduces the angle of the rays relative to the optical axis of the optical member as they pass therethrough. The light passing through the exit end of the optical member enters a detector assembly including at least one photo detector sensitive to a predetermined wavelength of light, and at least one optical filter disposed between the optical member and the photodetector to pass light of the predetermined wavelength.
Owner:BACHARACH ACQUISITION CORP +1
Polarized light reuse imaging method and micro optical engine system based on optical wand
InactiveCN106707668AAchieve efficient segmentationAvoid wasted situationsProjectorsEyepieceBeam splitting
The invention discloses a polarized light reuse imaging method and a micro optical engine system based on an optical wand. Illuminating rays emitted by an LED illumination light source pass through the non-imaging optical element optical wand, a splitting lens and a polarized light conversion system to realize uniform light, beam splitting and shaping and polarized light conversion of the illuminating rays, and reaches an LCoS micro-display chip through collection and transfer of a follow-up relay system to form uniform illuminating spots; the illuminating spots illuminate an image on the LCoS micro-display chip to form a required image; and then, projection imaging is carried out on the image through a PBS polarizing prism, an imaging projection objective lens or an eye lens, wherein the optical wand serves as a generation source of a two-dimensional virtual light source array, the splitting lens carries out re-imaging on the two-dimensional virtual light source array formed at the front end of the optical wand, and the corresponding polarized light conversion system is added to a splitting surface of the illuminating rays to realize conversion of polarized light. The method can greatly improve light efficiency under the condition of basically not increasing size and cost of an original illumination system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CRYSTAL DISPLAY TECH
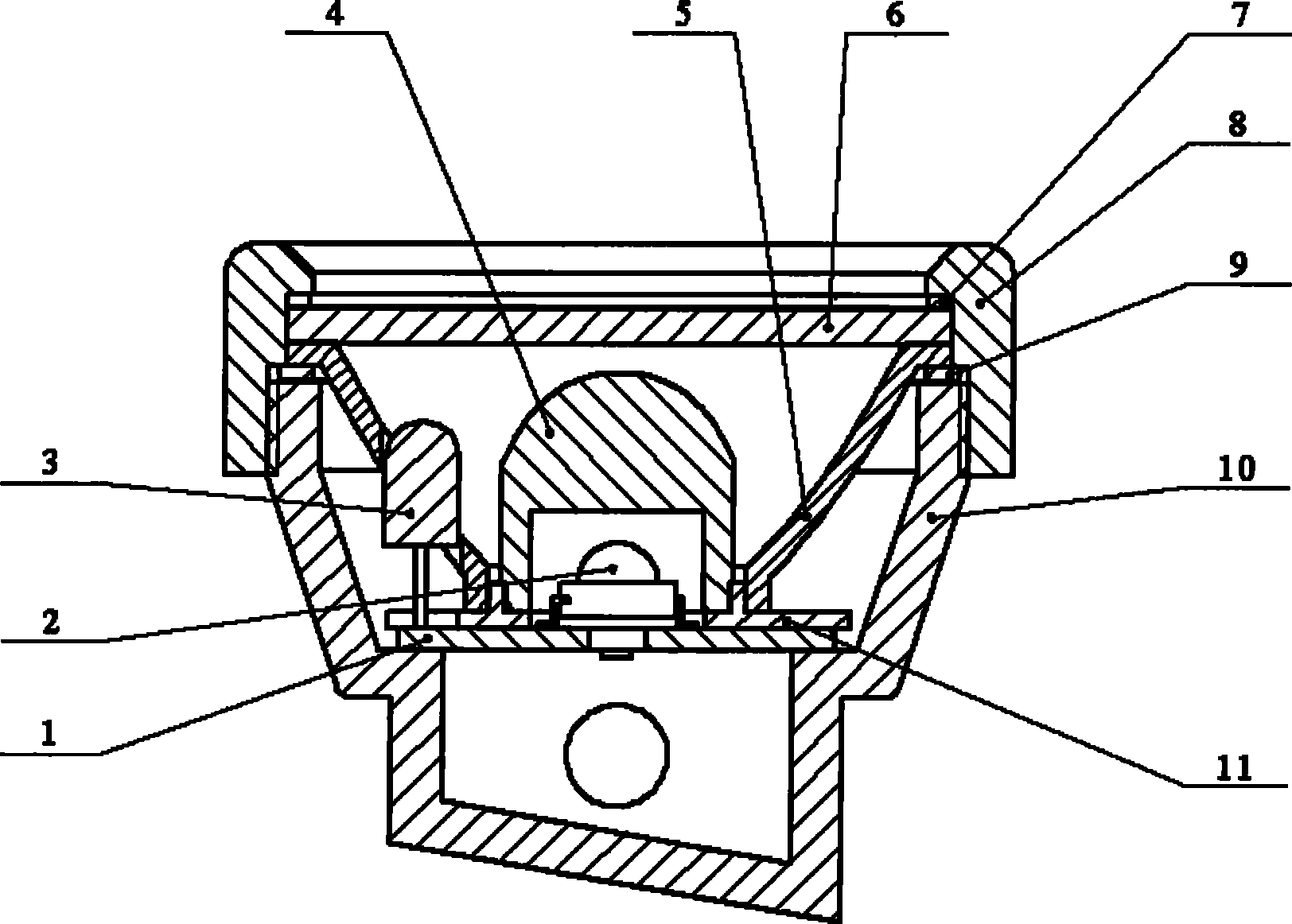
Light emitting diode emergency lighting module
InactiveUS8764238B2Good competitive advantageEasy to spreadPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesOn boardEngineering
LED “Chip-on-Board” (COB) metal core printed circuit board (PCB) technology operates in conjunction with high efficiency compact imaging and non-imaging optics to provide a compact emergency light offering high performance luminance levels (higher brightness) and enhanced life, at low cost. Thermal impedance between the LED junction and the heat sink is significantly reduced for COB technology by placing the LED die directly on a high thermal conductivity material substrate thereby increasing temperature dependant life and thermally dependant output power. Additionally, there is no encapsulant or domed optic over the LED thus making it possible to get a much more compact and efficient substantially Etendue preserving collection optic directly over the die.
Owner:INNOVATIONS & OPTICS
Method for shaping circular beams into ring beams
InactiveCN103309044AEliminate occlusionImprove light energy utilizationOptical elementsOptical antennaComputational physics
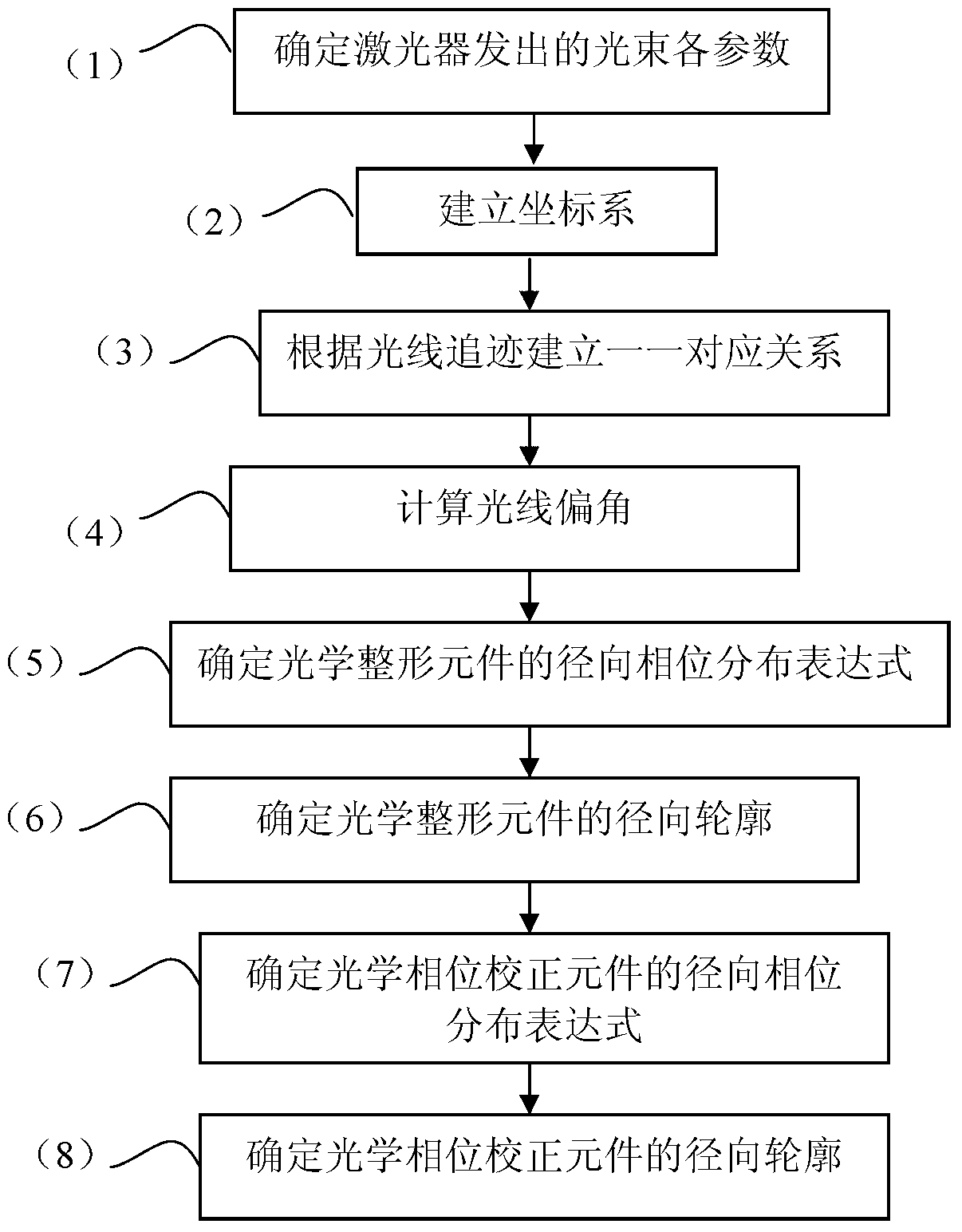
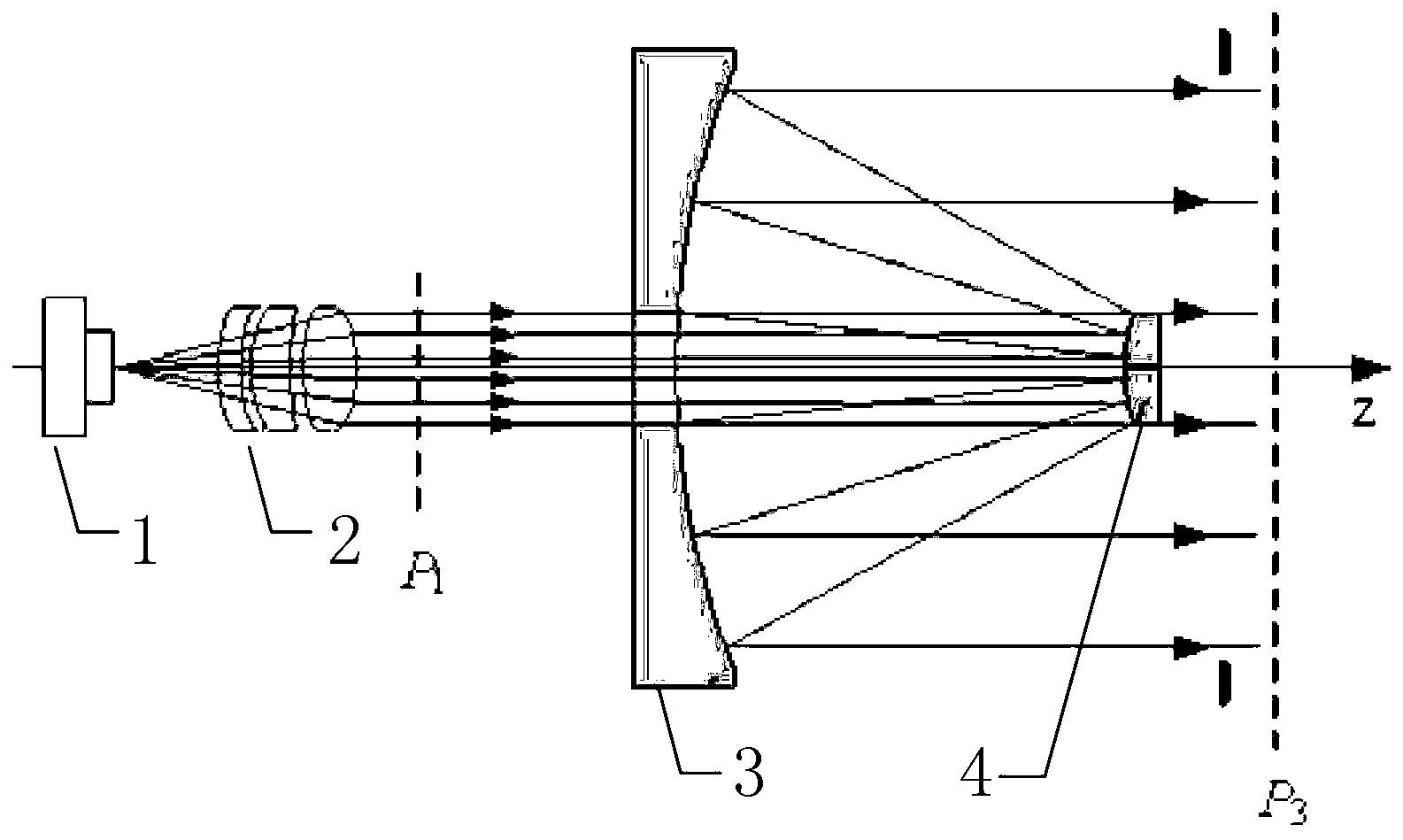
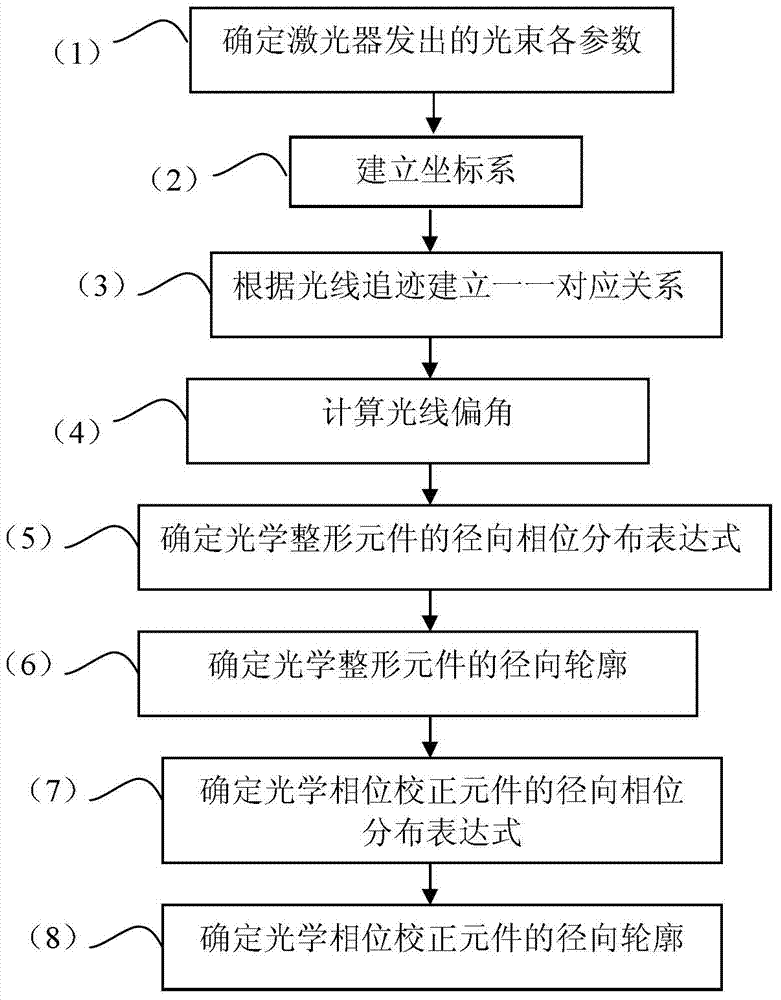
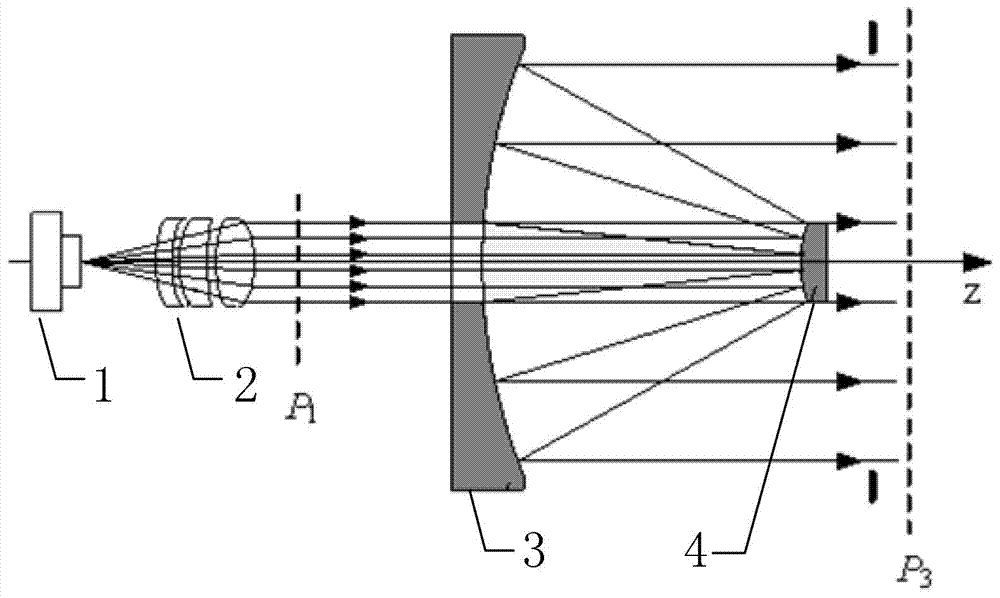
The invention discloses a method for shaping circular beams into ring beams, relates to the field of nonimaging optics, and aims solve the problem of energy loss caused by optical antennas. The method for shaping the circular beams into the ring beams includes steps of 1), determining each parameter of beams emitted by a laser; 2), establishing a coordinate system; 3), establishing one-to-one corresponding relation according to ray traces; 4), calculating deflections of the rays; 5), determining a radial phase distribution formula of an optical shaping component; 6), determining radial profiles of the optical shaping component; 7), determining a radial phase distribution formula of an optical phase correcting component; 8), determining radial profiles of the optical phase correcting component. The method for shaping the circular beams into the ring beams is applicable to the field of optics.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Portable luminaire
InactiveUS20080192467A1Improve efficiencyEfficient compressionPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesVertical planeTotal internal reflection
A portable luminaire includes an optical module, a power source and a housing. The optical module has at least one light emitting diode (LED) that emits light with a wide divergence, a non-imaging optical element and a transparent window. The non-imaging optical element (NIO) has a refractive member located around a LED optical axis and a total internal reflection member located around the refractive member. The refractive member and the total internal reflection member are integrated in a single transparent element having a mutual focal point. The NIO element collects a significant amount of light emitted by the LED with wide divergence located at the focal point to compress the collected light with high efficiency into a required pattern with a generally different angular distribution in a horizontal plane and a vertical plane, and to direct the compressed light outside of the luminaire.
Owner:FARLIGHT
High efficiency hybrid illumination system
ActiveUS9328898B1Improve collection efficiencyLow costLighting applicationsPlanar light sourcesLight beamCombined use
Principles of nonimaging optics, imaging optics, etendue matching, and the Constant Brightness Theorem are used to provide an ultra-efficient solid state lighting optical system for stage and theatrical profile spotlights. Used in combination, an array of high brightness light emitting diodes, a nonimaging optical transform element, and an image forming optical element enable the design of profile spotlights capable of high brightness, low electrical power consumption, sharp gobo imaging, adjustable beam intensity profiles, and use of current industry standard accessories and elements, such as gobos, blades and irises.
Owner:FLASCK RICHARD ARTHUR
Light source structure based on LED
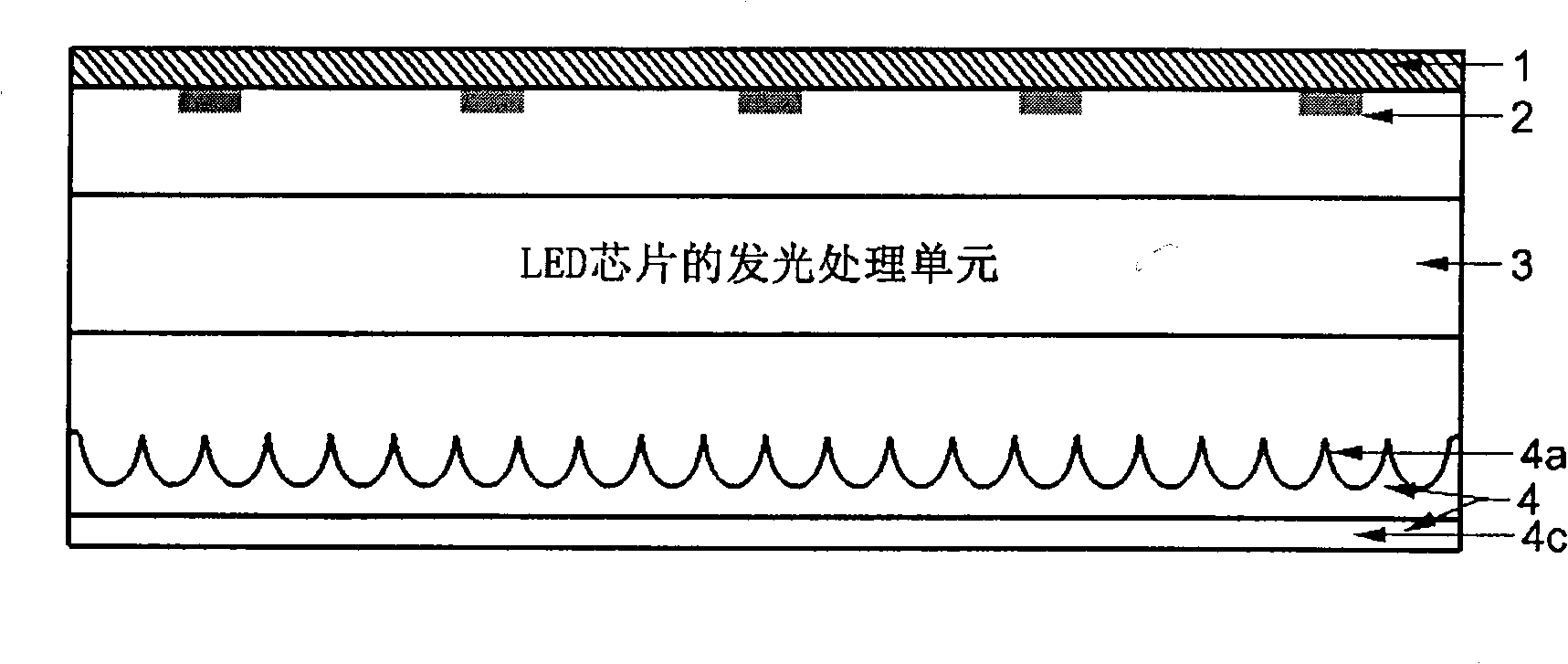
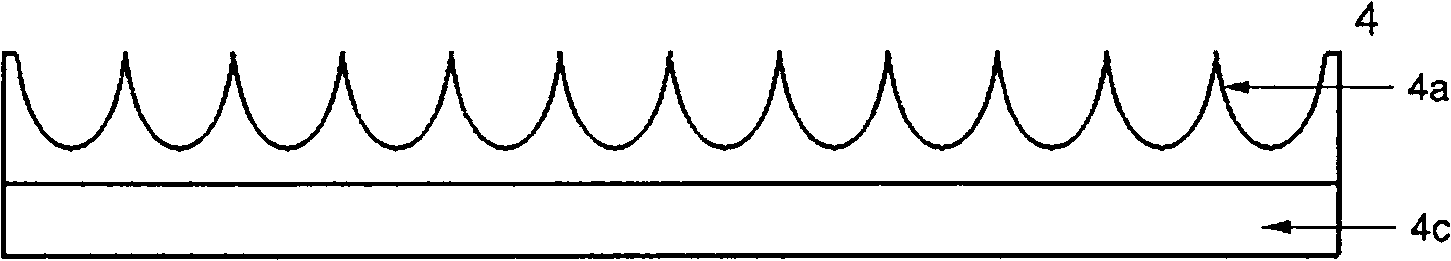
InactiveCN101493210ASolve UtilizationSolve brightnessPoint-like light sourceRefractorsLight-emitting diodeStructure based
The invention relates to a light source structure based on a light emitting diode (LED), which belongs to the technical field of LED application. The light source structure at least comprises a baseplate 1, an LED chip 2, a light-emitting processing unit 3 of the LED chip and an optical light scattering plate 4 designed by nonimaging optics, wherein, the LED chip 2 fixed on the baseplate 1 is the light-emitting source, the optical field distribution is processed by the light-emitting processing unit 3 of the LED chip including but not limited to on and then transmitted to the inner surface of the optical light scattering plate 4; at least one side of the optical light scattering plate 4 comprises a microstructure designed by nonimaging optics, the microstructure ensures the incident light to scatter, thus a light source structure with uniform luminance is formed. The light source structure provided by the invention has the advantages of comfort for human eyes, friendly environment and high utilization rate of the LED luminous energy; the structure can be made into flat shapes including but not limited to squareness, roundness, ellipse, sphericity, spheroidicity, and the like, and non-flat shapes including but not limited to spherical surface, ellipsoidal surface, cylindrical surface and the like, which can realize infinite extension.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
LED mine lamp using non-imaging optical system
InactiveCN101240886AReduce sizeControl illuminance distributionLighting applicationsLight source combinationsOptical axisLight energy
The present invention provides a LED miner's lamp using nonimaging optics, including a nonimaging optics, a casing part and a lighting circuit part, miner's lamp adopting aspherical composite lens and free surface reflector form the optical system, since the convexity of the composite lens and the reflecting surface of the reflector are free surfaces designed according to light distributing requirement, and optical line adjacent to the optical axis and optical line far from the optical axis are respectively controlled by the composite lens and free surface reflector, thus the size and the lighting distribution of the lighting area is more exact controlled, this improves utilization rate of the light energy and bas better visual effect.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Optical coupling in touch-sensing systems using diffusively transmitting element
InactiveUS9857916B2Easy to assembleSuitable for mass productionDigital data processing detailsCoupling light guidesTotal internal reflectionLight beam
A touch-sensitive apparatus operates by light frustration and comprises a light transmissive panel with a front surface and a rear surface. Light emitters and light detectors optically face the rear surface along a perimeter of a touch-sensitive region on the panel. At least one non-imaging, diffusively transmitting optical element is arranged on the rear surface along the perimeter of the touch-sensitive region. The light emitters are arranged to emit a respective beam of light onto the non-imaging optical element so as to generate, by diffuse transmission, propagating light that propagates by total internal reflection inside the panel across the touch-sensitive region, and the light detectors are arranged to receive detection light generated, by diffuse transmission, as the propagating light impinges on the non-imaging optical element, so as to define a grid of propagation paths across the touch-sensitive region between pairs of light emitters and light detectors.
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Laser optical fiber coupling device containing non-imaging optical element
InactiveCN102368107AOvercome the shortcomings of uneven light spots and light and dark stripesAvoid damageCoupling light guidesLight beamPlastic optical fiber
The invention provides a laser optical fiber coupling device containing a non-imaging optical element, belonging to the field of semiconductor illumination. The light source comprises a semiconductor laser tube, a non-imaging condensing lens and an optical fiber; the semiconductor laser tube emits light beams; the light beams are converged on the rear surface of the non-imaging condensing lens after passing through the non-imaging condensing lens; and then the light beams enter the optical fiber to form into a laser optical fiber source. According to the device provided by the invention, as the non-imaging condensing lens is adopted, the light emitted by the laser tube can be converged on the rear surface of the non-imaging condensing lens; meanwhile as the front surface aperture of the non-imaging condensing lens is large, the adjusting tolerance is large relative to the position of the laser tube. When the device is installed and positioned, the mechanical precision dependent on the metal holder can be ensured, and no fine adjustment is required. The adjusting process is simple, and the probability of damage of the laser tube and optical fiber due to caused by touching between the optical fiber and the laser tube during adjustment is reduced, so that the rate of finished product is increased, the adjusting time is reduced and the cost is reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large-aperture Fresnel lens-based long-distance wide-spectrum weak signal collection system
ActiveCN110470393AReduce weightReduce manufacturing costRadiation pyrometryCondensersCollection systemLight spot
The invention provides a large-aperture Fresnel lens-based long-distance wide-spectrum weak signal collection system. The system comprises a large-aperture Fresnel lens and a rear group system of thelarge-aperture Fresnel lens; the rear group system of the large-aperture Fresnel lens comprises a non-imaging optical element rear group and an imaging optical element rear group; the non-imaging optical element rear group comprises a light uniformizing rod and a total reflection collimator; and the imaging optical element rear group comprises a relay lens group; the large-aperture Fresnel lens, the light uniformizing rod, the total reflection collimator and the relay lens group are sequentially arranged along an optical path. According to the large-aperture Fresnel lens-based long-distance wide-spectrum weak signal collection system, the large-aperture Fresnel lens is adopted to replace a common lens array, and therefore, the weight and manufacturing cost of the lens are effectively reduced, the system is simple in structure and is easy to install and adjust; the rear group system of the large-aperture Fresnel lens adopts imaging optics and non-imaging optics, so that the defect thatthe large-aperture Fresnel lens is large in aberration is effectively eliminated, the diameter of a convergent light spot is reduced, and an energy collection rate is improved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
LED street lamp lens module
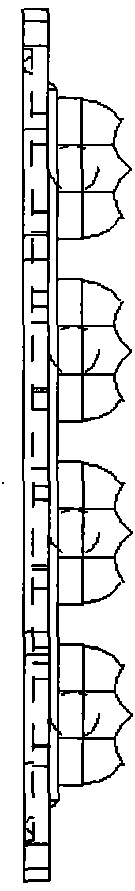
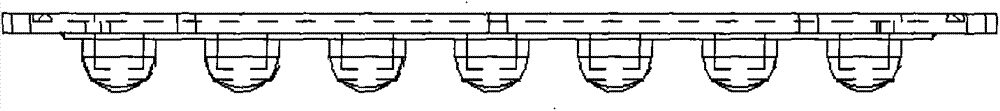
InactiveCN103499065AImprove utilization efficiencyEfficient use ofPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceLight spotPlastic materials
An LED street lamp lens module is composed of an upper composite curvature surface and a lower composite curvature surface which form a light distribution curved surface, and LED luminous particles are placed in a groove formed by the lower composite curvature surface. The light distribution curved surface is made of high luminousness anti-UV polymer plastic materials, the methods of nonimaging optics and free three-dimensional surface cutting are used, a multi-curved-surface lens module is designed according to the permutation and combination of a LED module and the first time distribution curve flux condition of lamp beads through professional optical software, when LED light passes through a lens optical curved surface, the light can be reflected and condensed, a lens is designed to be arranged right ahead and condenses light in a penetrating mode, an outer peripheral curved surface can further collect and reflect all side light, the two kinds of light are overlapped so that the perfect light and a beautiful light spot effect can be obtained, the light disorder between secondary optical fibers and lamp bead original light distribution conditions is avoided to the largest extent, and the utilization efficiency of light energy is improved.
Owner:山东光因照明科技有限公司
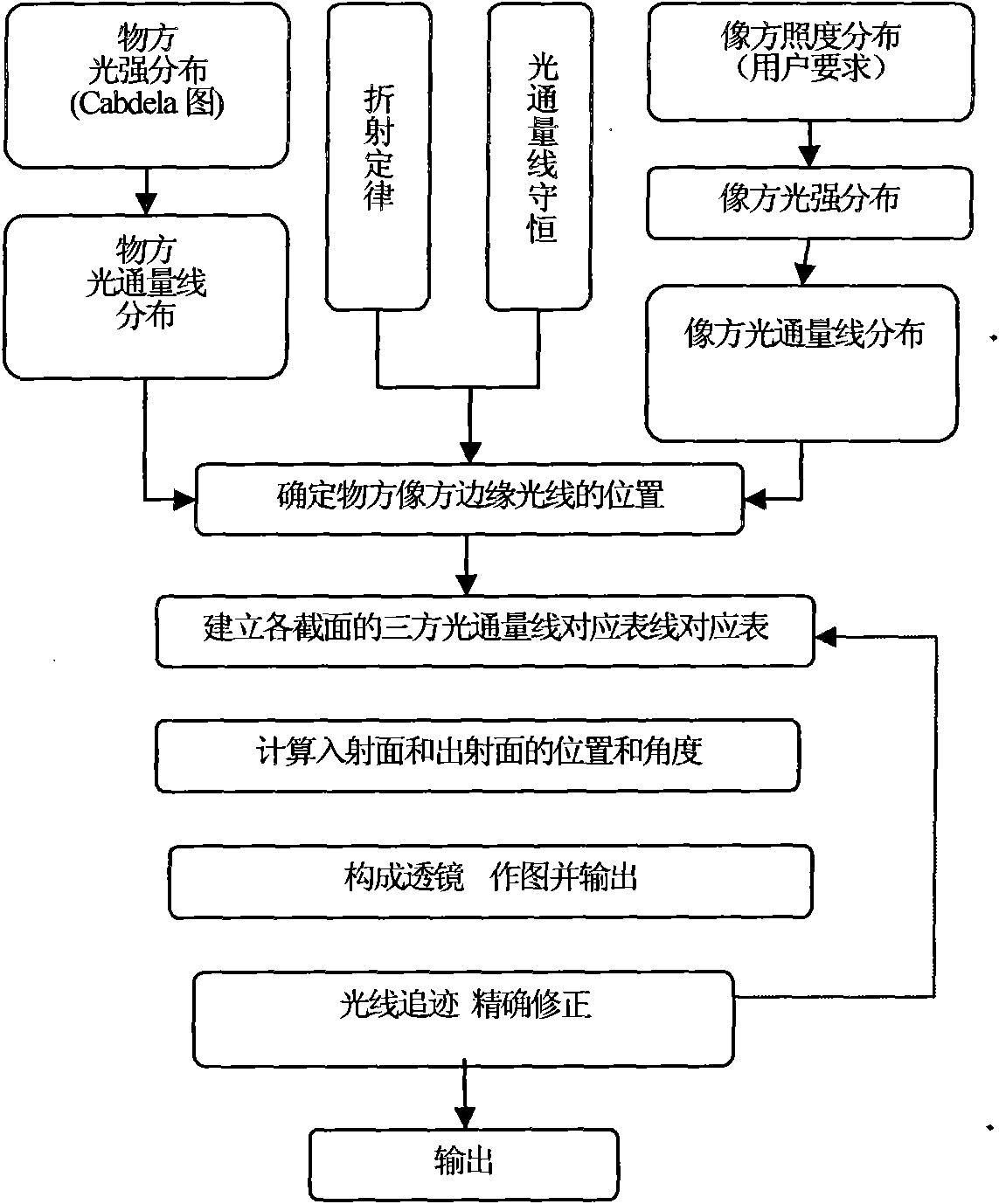
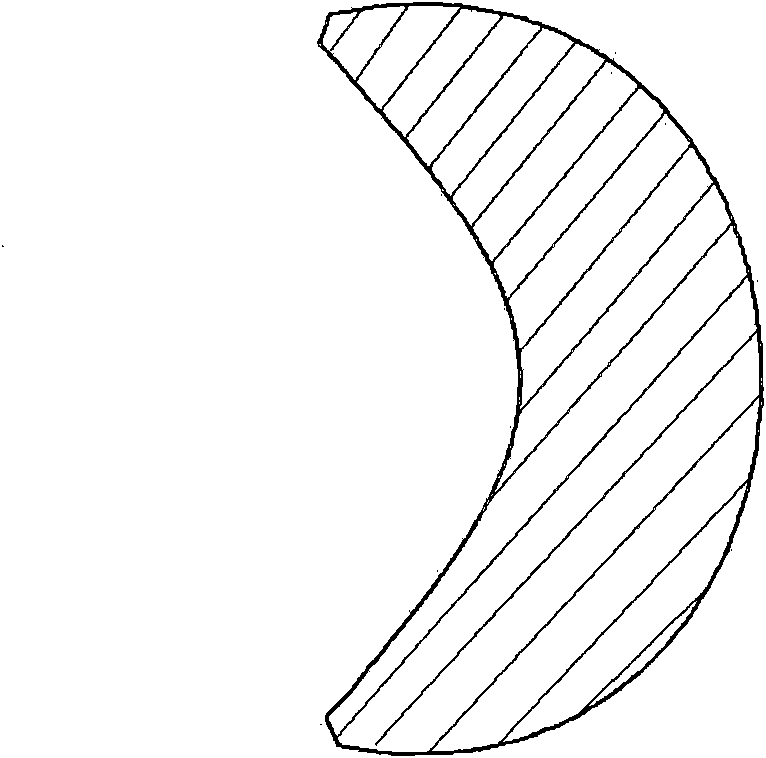
Design method of non-imaging optical element
The invention discloses a design method of a non-imaging optical element. In the method, an object space serves as a light source, and an image space serves as an irradiated plane. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing a concept of a luminous flux line, wherein the luminous flux line is a ray vector having determined energy; based on a light intensity distribution requirement of the object space, converting the light intensity distribution of the object space into the distribution of the luminous flux line according to a law that a product of light intensity and a solid angle is in proportion to the energy; based on an illumination distribution requirement of the image space, converting into the light intensity distribution of the image space, and then converting into the distribution of the luminous flux line according to the same law; following an energy conservation law, wherein the energy conservation law is a luminous flux line conservation law, the total number of the luminous flux lines of the object space and the image space is equal, and the luminous flux lines of the object space and the image space are in one-to-one correspondence; and gradually usinga refraction law or a reflection law for the respective luminous flux lines, and sequentially connecting obtained respective refraction small planes or reflection small planes to obtain the shape of the optical element. The method has a new optical design concept, and is simple, convenient, intuitive and quite high in applicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI SANSI ELECTRONICS ENG +3
Collection system of long-distance wide-spectrum weak signal based on large-aperture Fresnel lens
ActiveCN110470393BReduce weightReduce manufacturing costRadiation pyrometryCondensersFresnel lensCollection system
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
scanning distance meter
A scanning optical range finder in a mobile robot includes an optical transmitter circuit, a non-imaging optical element, an optical detector circuit, and a distance measurement circuit. The non-imaging optical element is arranged to receive an optical signal at the entrance aperture of the non-imaging optical element in response to operation of the optical transmitter circuit, and to direct the optical signal to an optical signal of the non-imaging optical element. output hole. The optical detector circuit is configured to receive the optical signal from an output aperture of the non-imaging optical element, and based on a respective phase difference of the optical signal relative to a corresponding output of the optical transmitter circuit, to generate a detection signal. The distance measuring circuit is configured to calculate the distance of the target from the phase difference indicated by the detection signal. Related apparatus and methods of operation are also discussed.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Photovoltaic concentrators based on non-imaging optics
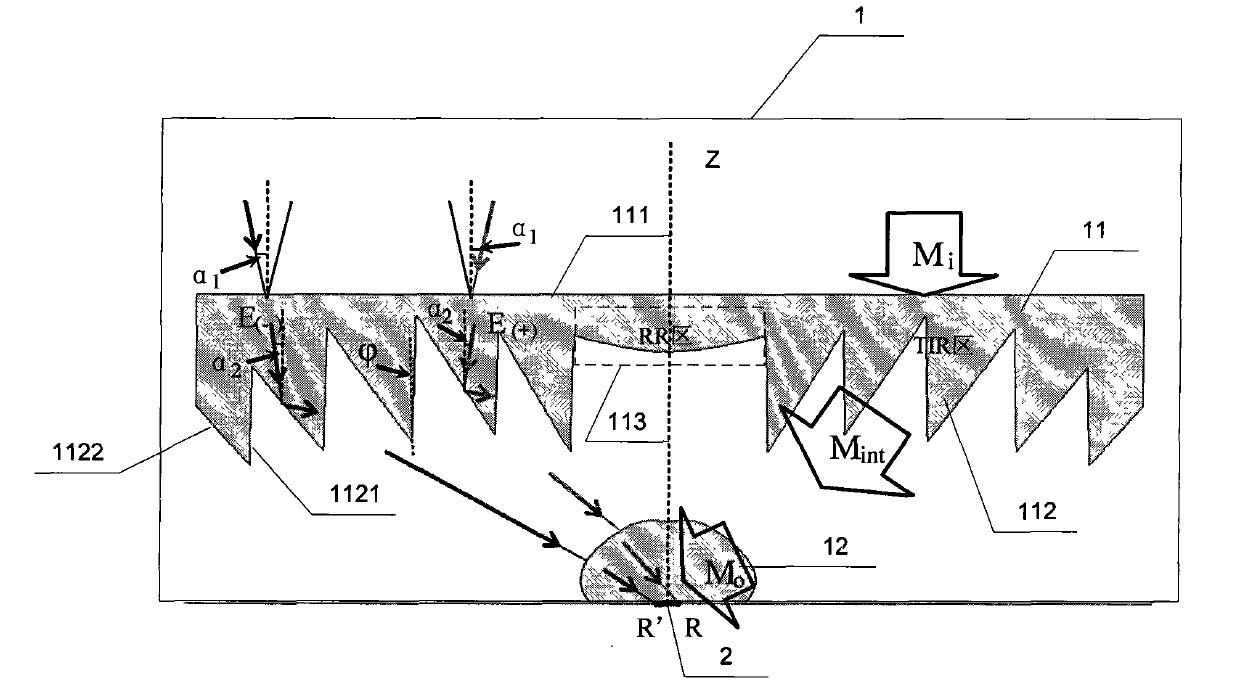
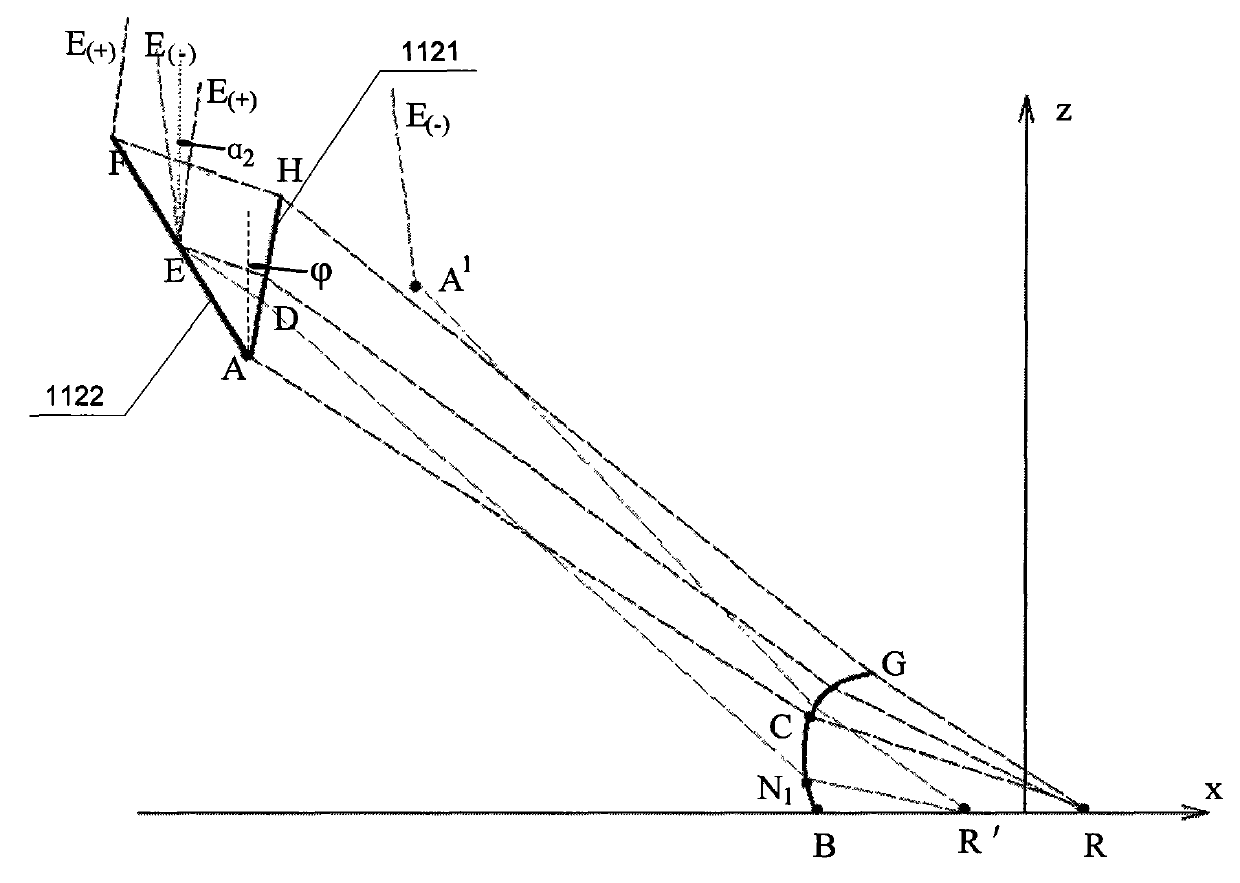
The invention relates to a photovoltaic optical collector based on nonimaging optics, belonging to a photovoltaic optical collector and solving the problems of high cost and low optical collection magnification in the optical collector with lower optical collection magnification in the prior art. The photovoltaic optical collector comprises an optical collector and a solar battery, wherein the optical collector comprises a main lens and a secondary lens, the upper surface of the main lens is a plane, the lower surface of the main lens is divided into two parts, one part is TIR region Fresnel teeth and the other part is an RR region, one side of the TIR region Fresnel teeth is provided with a refraction surface and the other side is provided with a total internal reflection surface, an included angle of the refraction surface and a z axis is Phi, and the refractive index of materials made into the main lens and the secondary lens are both n. The optical collector can reach about 1000 times of optical collection magnification, and has height to width aspect ratio of less than 0.5, optical collecting angle of more than 1 degree and optical efficiency of more than 80 percent. The invention is suitable for occasions and fields of photovoltaic optical collectors with higher optical collection magnification.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
LED mine lamp using non-imaging optical system
InactiveCN101240886BReduce sizeIncrease profitLighting applicationsLight source combinationsOptical axisLight energy
The present invention provides a LED miner's lamp using nonimaging optics, including a nonimaging optics, a casing part and a lighting circuit part, miner's lamp adopting aspherical composite lens and free surface reflector form the optical system, since the convexity of the composite lens and the reflecting surface of the reflector are free surfaces designed according to light distributing requirement, and optical line adjacent to the optical axis and optical line far from the optical axis are respectively controlled by the composite lens and free surface reflector, thus the size and the lighting distribution of the lighting area is more exact controlled, this improves utilization rate of the light energy and bas better visual effect.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method for shaping circular beams into ring beams
InactiveCN103309044BEliminate occlusionImprove light energy utilizationOptical elementsOptical antennaComputational physics
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com