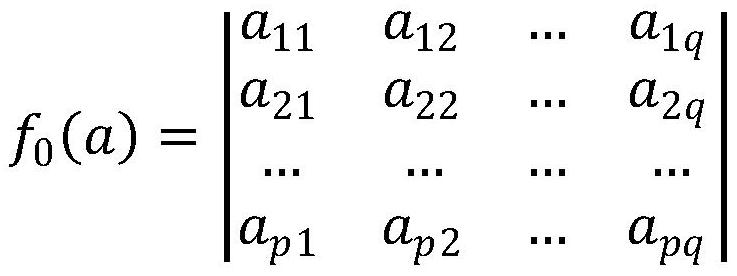
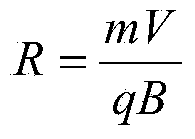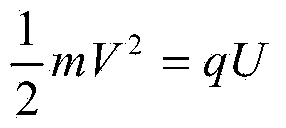Patents
Literature
55results about How to "Discrimination speed is fast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrical power distribution network single-phase earth fault type and phase distinguishing method
ActiveCN101452041ALess analogSimple calculationFault locationEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectric cablesElectric power
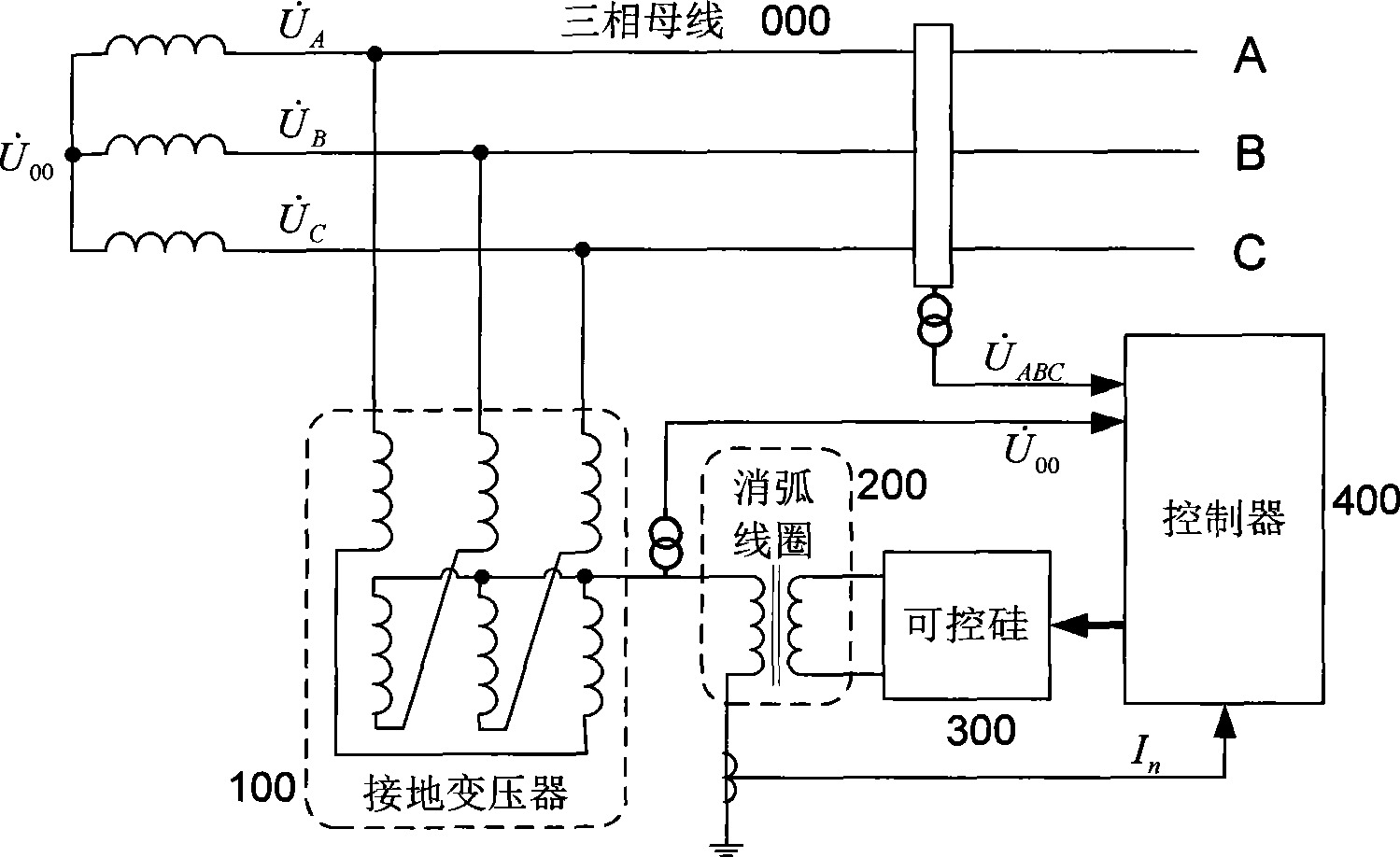
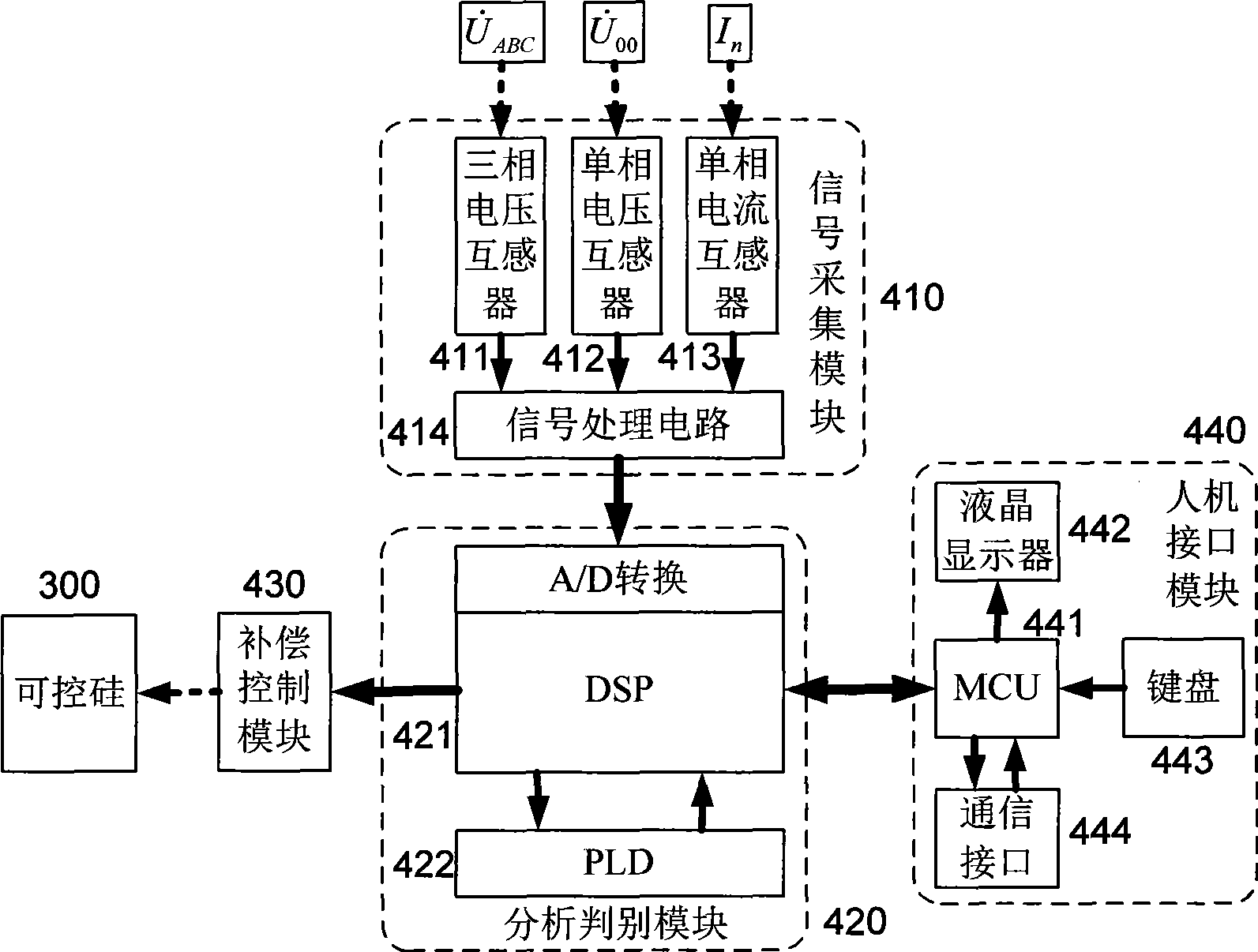
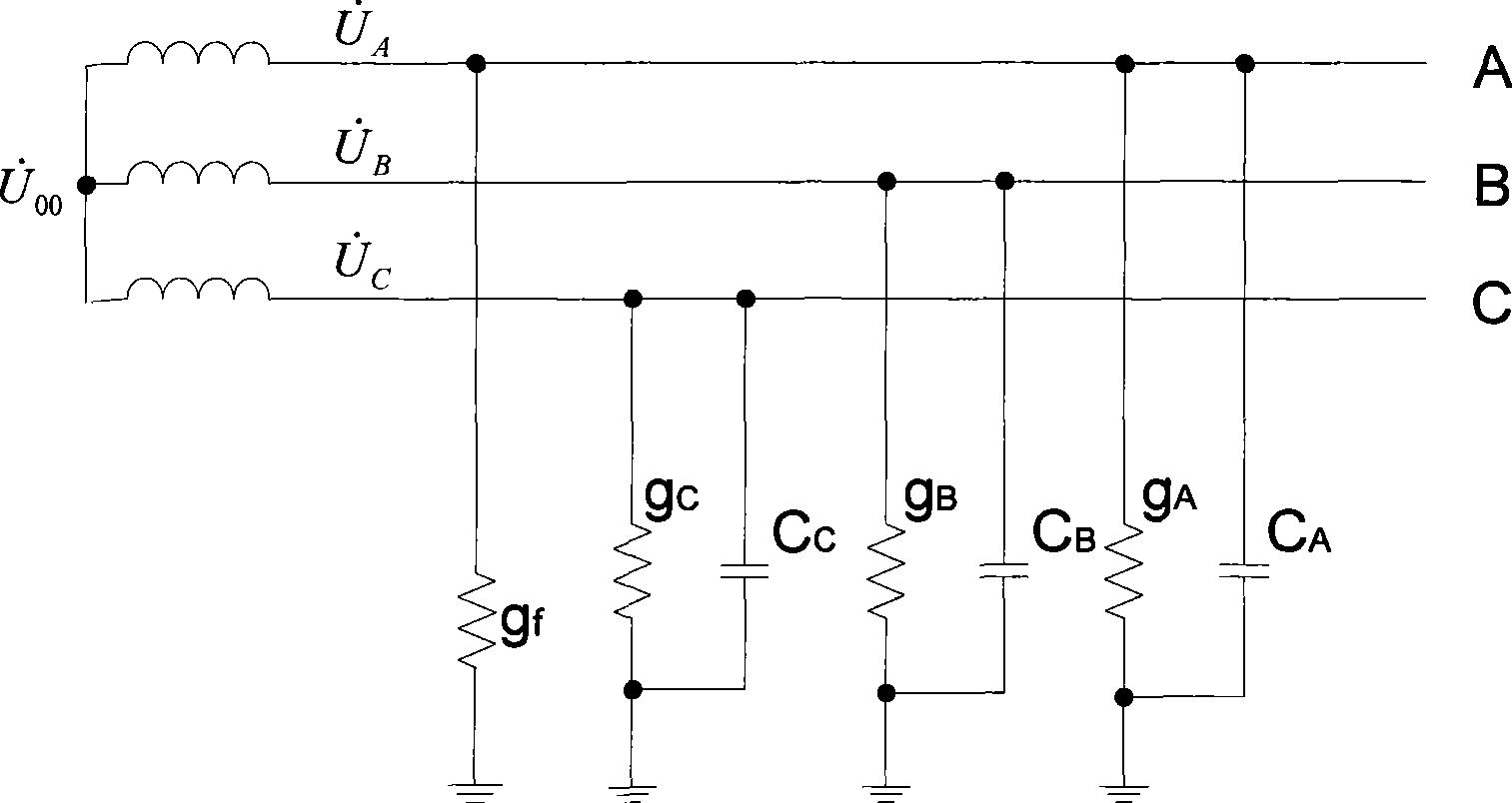
The invention discloses a distributing net single phase earth fault type and a distinguishing method of phase identification, relating to a distributing net single phase earth fault distinguishing method in the field of AC distributing net testing and relaying protection technology. According to the invention, through collecting three-phase voltage of the distributing net system and neutral point voltage of the distributing net system, phase angle of each eigenvector is computed through a special relation, the type of the fault and the phase identification can be fast distinguished through the phase angle distinguishing logic. The inventive working system is that a three-phase bus (000), a grounding transformer (100), a linear side of an arc suppression coil (200) are connected in turn with the earth; a controller (400), a thyristor (300) and a secondary side of an arc suppression coil (200) are connected in turn. The invention is simple in criterion, small in collection quantity, fast in distinguishing speed, high in accuracy, reliable in security, which is suitable for 3-66 KV distributing net based on an aerial line or a power cable.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
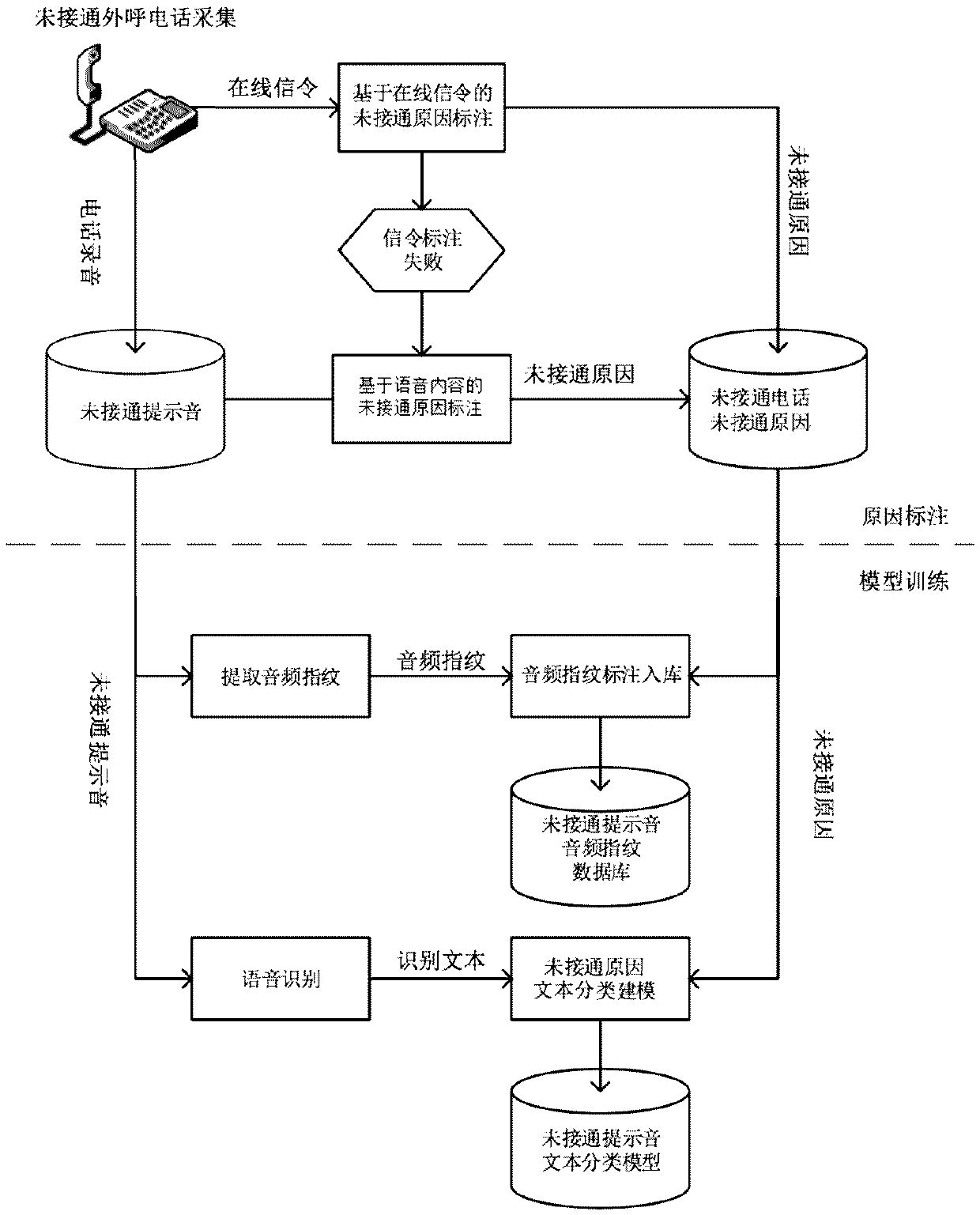
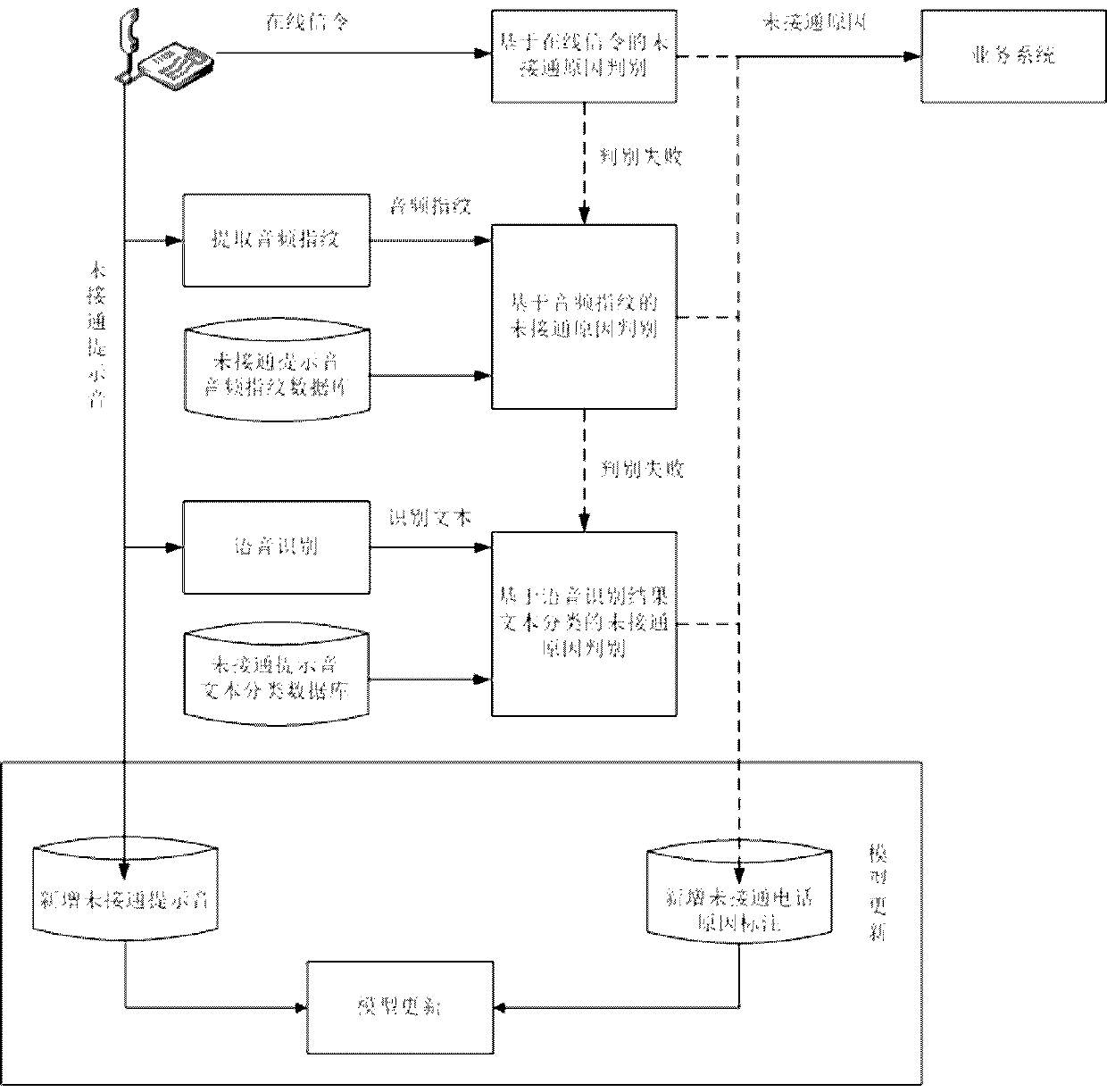
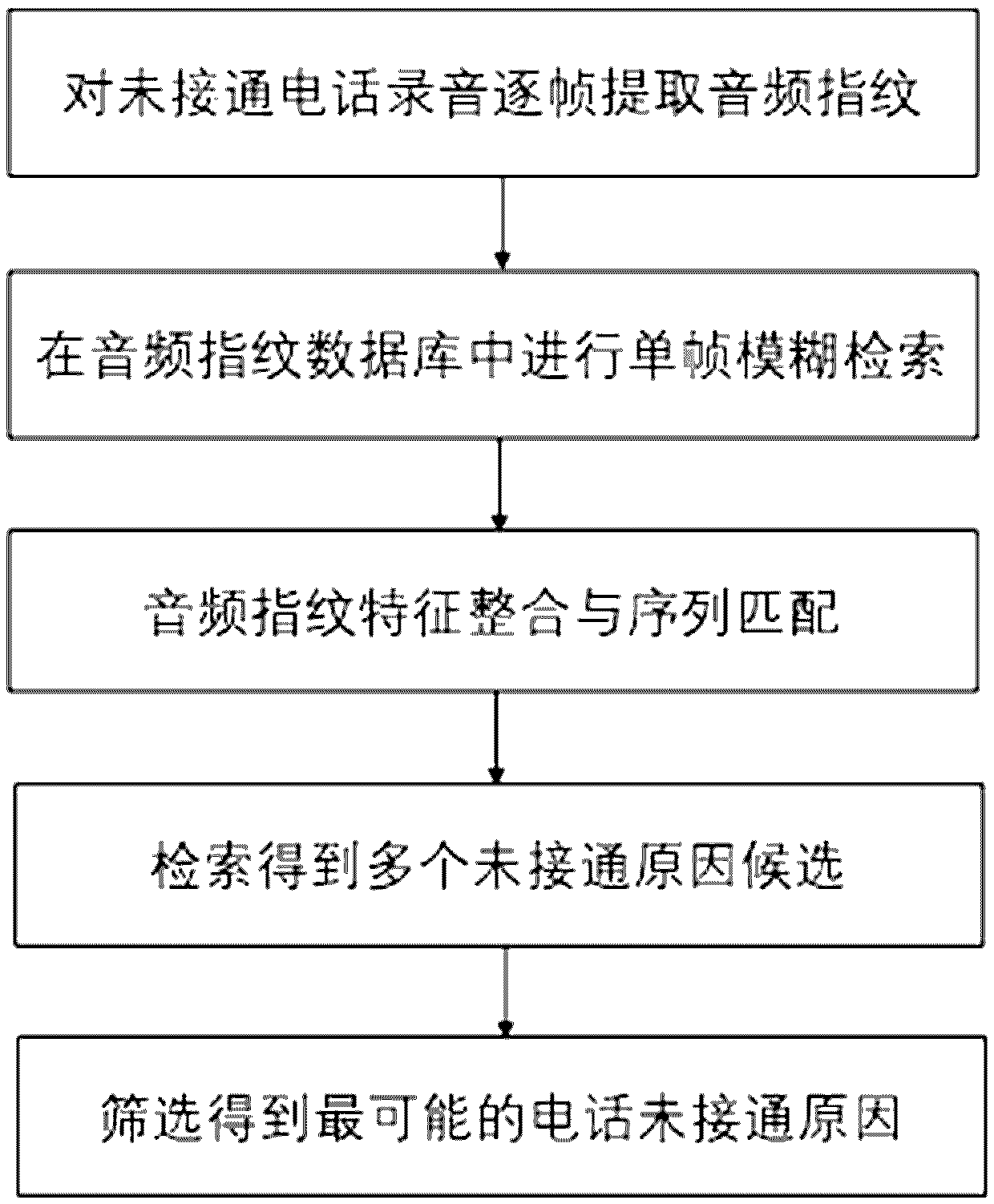
Phone-call recording access failure reason recognizing method
ActiveCN109658939ARealize automatic discriminationReduce missed detectionAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersText categorizationSignal classification
The invention belongs to the field of voice recognition, and particularly relates to a phone-call recording access failure reason recognizing method. The method comprises the following steps: markingaccess failure reasons by signals; if reasons cannot be obtained by signal classification, extracting an audio fingerprint characteristic sequence from to-be-recognized phone-call recording, and searching from an audio fingerprint database by the sequence; if matched fingerprints can be found out, marking the access failure reason for to-be-recognized phone-call according to access failure reasonlabels in fingerprint key values; and if the matched fingerprints cannot be found out, recognizing audio contents into text contents by automatic voice recognition, classifying in an access failure document classifying model by a text classifying method on the basis of the contents, and marking the to-be-recognized phone-call recording by access failure reason classifying results obtained by classification. The method can recognize recording files in an offline manner, streaming phone-call voice can also be recognized, the universality is high, and the phone-call recording access failure reason recognizing method is suitable for different application scenarios of the call center.
Owner:北京灵伴即时智能科技有限公司
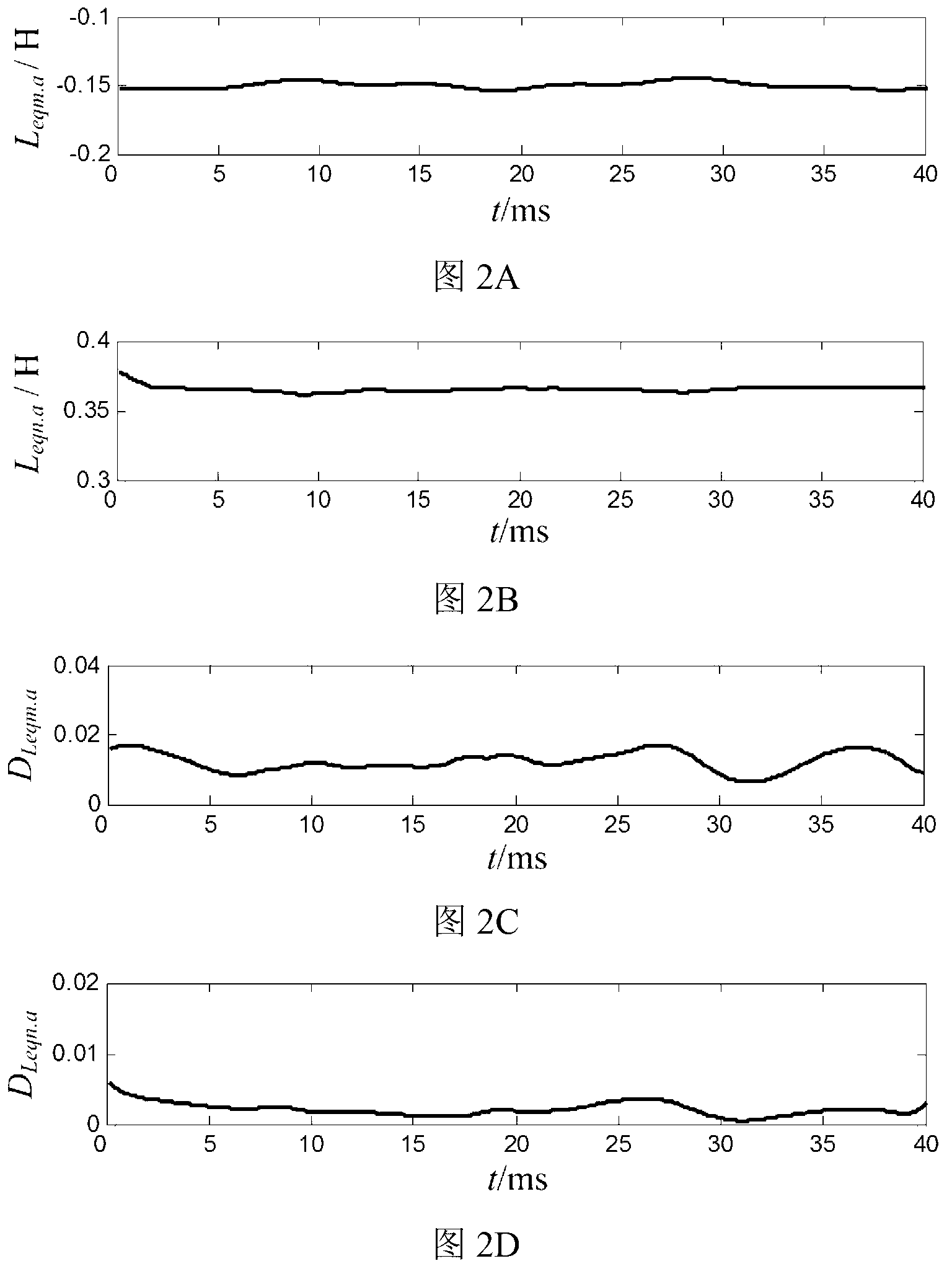
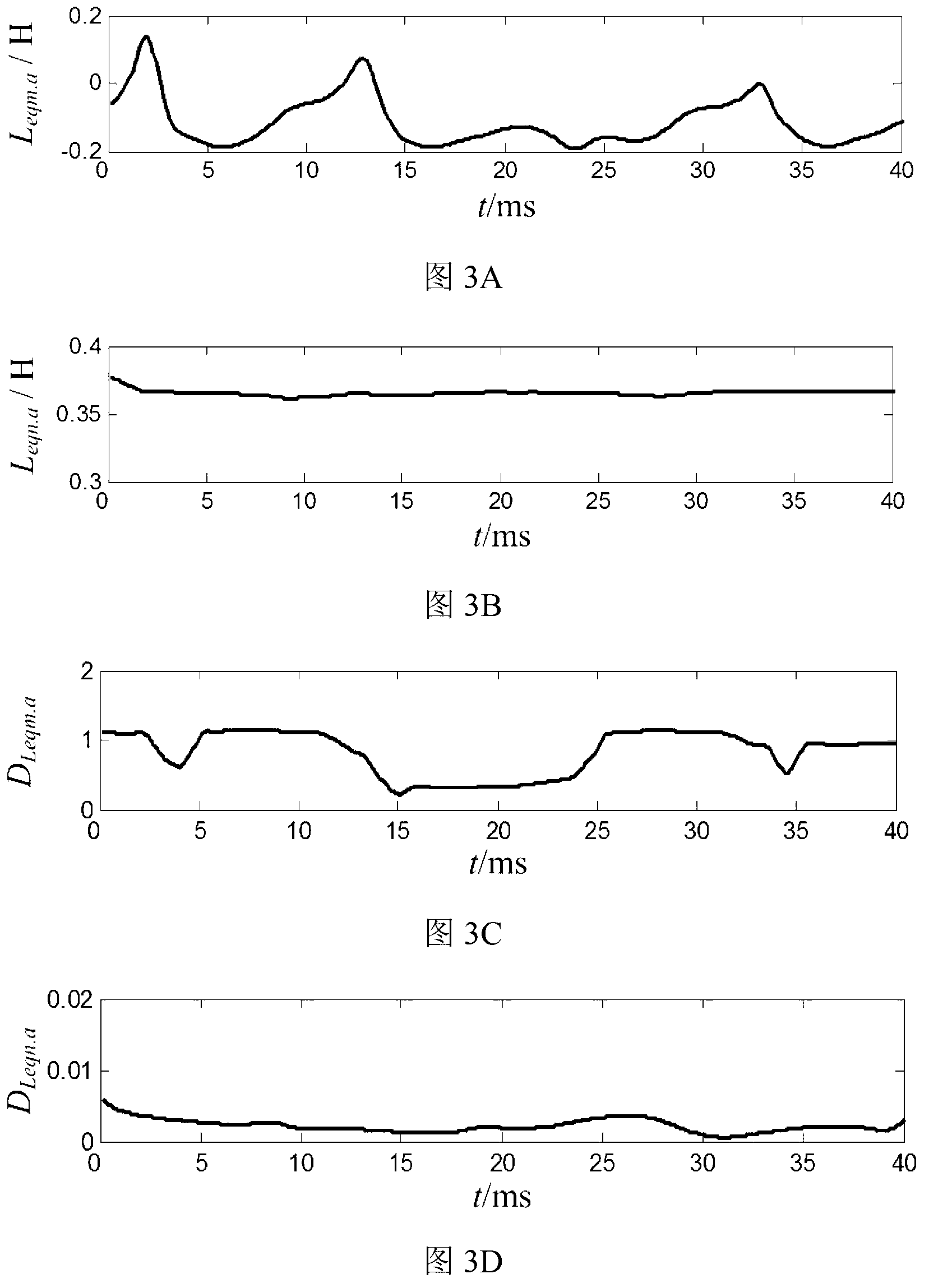
Novel current transformer saturation identification method
InactiveCN103323698ACriterion is easy to setDiscrimination speed is fastElectrical testingElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
Disclosed is a novel current transformer saturation identification method. The novel current transformer saturation identification method includes the steps that 1, three-phase voltage and electric current instantaneous value data at protective installation positions of current transformers are collected, and sampling results are recorded as ua(k), ub(k), uc(k), ia(k), ib(k) and ic(k); 2, the three-phase voltage and electric current fault component are calculated, namely, delta ua(k), delta ub(k), delta uc(k), delta ia(k), delta ib(k) and delta ic(k); 3, equivalent inductance and resistance parameters are calculated, namely, L(eq.j) and R(eq.j) (j=a, b ,c); 4, dispersion of the resistance parameters is calculated (j=a, b ,c); 5, whether all phases of mutual inductors are saturated is judged and recognized, if D(L(eq.a)) > epsilon, then the a-phase mutual inductor is judged to be saturated, if D(L(eq.b)) > epsilon, then the b-phase mutual inductor is judged to be saturated, and if D(L(eq.c)) > epsilon, then the c-phase mutual inductor is judged to be saturated. The novel current transformer saturation identification method is simple and reliable, and is not affected by system operation modes and fault initial phase angles because only short data windows are used.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Transformer substation acoustic signal feature extraction method based on MFCC
PendingCN110490071AAchieve preservationRealize analysisData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionFilter bankNeural network nn
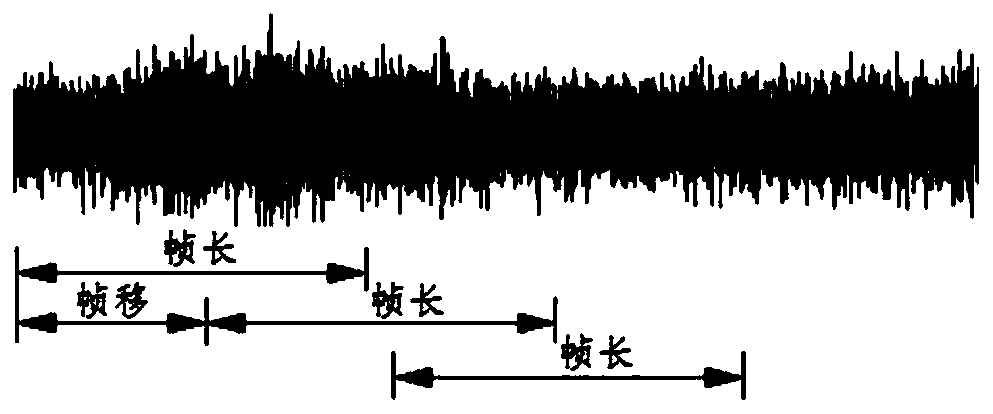
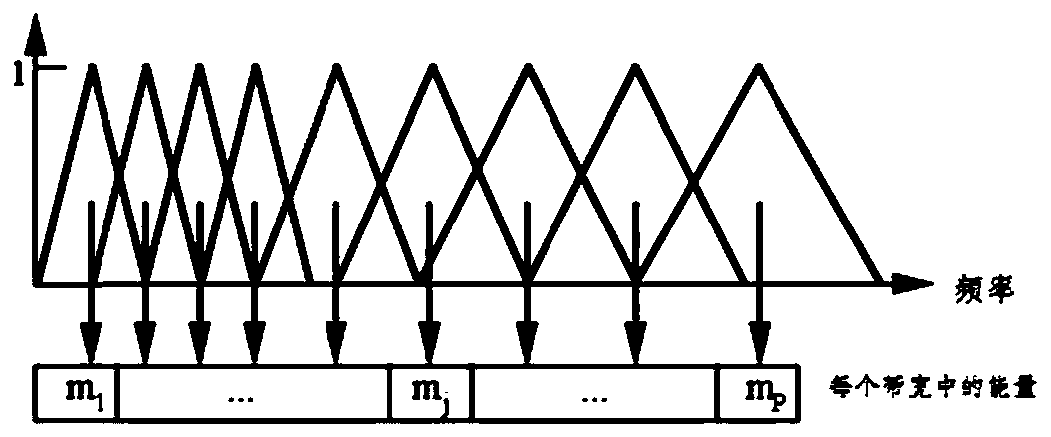
The invention discloses a transformer substation acoustic signal feature extraction method based on MFCC, and belongs to the field of monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: performing acoustic signal preprocessing, fast Fourier transform, Mel filter bank and logarithm DCT operation on a transformer acoustic signal in sequence, and extracting the characteristic quantity of the transformer acoustic signal; wherein the preprocessing comprises two steps of framing and windowing; converting the time domain signal into a frequency domain through fast Fourier transform, and calculatingan amplitude spectrum and spectral line energy of each frame; enabling the Mel filter bank to calculate energy for each frame of spectral line energy spectrum through the filter bank; carrying out logarithm DCT operation to obtain logarithms of the energy values, calculating an energy matrix and identifying the fault type in a fuzzy clustering or neural network mode. Distinguishing is carried outthrough timbre, extracted feature vectors have obvious difference, the operation speed is high, and the operation cost of a computer can be reduced; and the feature vectors are classified and markedby using a support vector machine algorithm, so that discrimination speed is high, accuracy is high and instruction is simple. The method can be widely applied to the field of operation monitoring andfault judgment of unattended substations.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Vivo face identification device for face recognition system
ActiveCN103020600AImprove securityImprove convenienceCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsLight beam
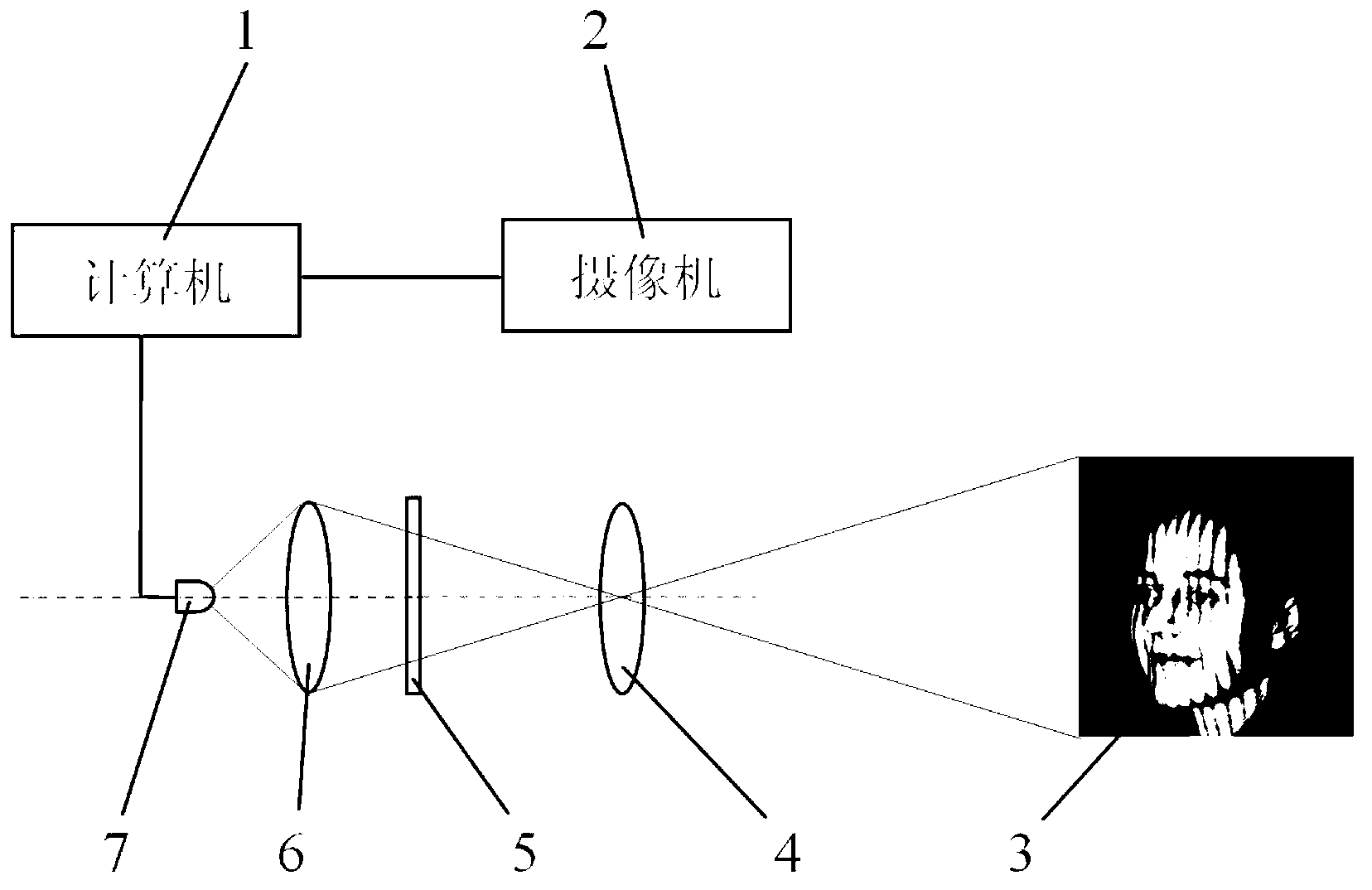
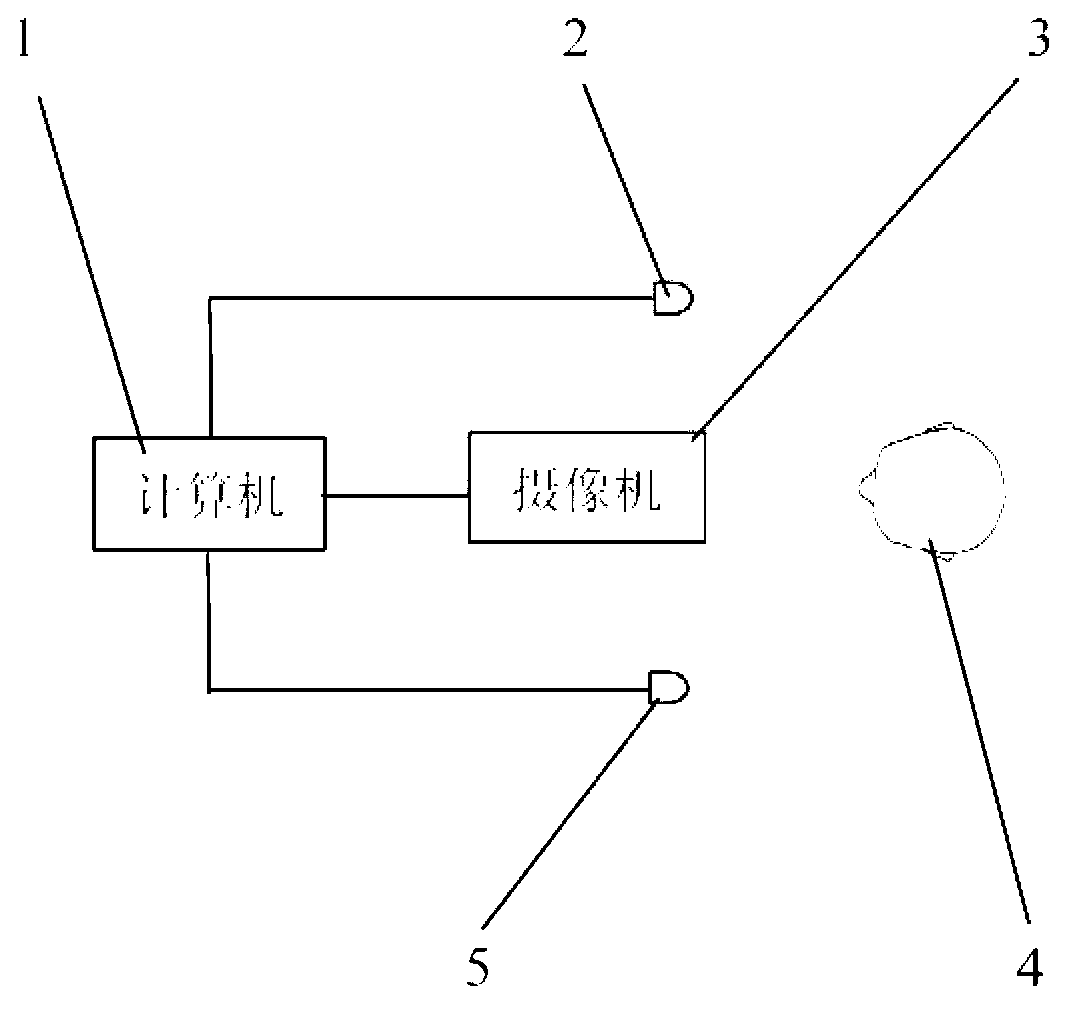
The invention relates to a vivo face identification device for a face recognition system and belongs to the face recognition technical field. The vivo face identification device for the face recognition system comprises a light source, a collecting lens, a lantern slide, a projection lens, a video camera and a computer, wherein the computer is respectively connected with the video camera and the light source, a light beam emitted from the light source irradiates on the lantern slide after passing through the collecting lens, and the projection lens projects an image of the lantern slide on an identified object. Compared with the prior art, the vivo face identification device for the face recognition system has the advantages of utilizing parallel lines which are projected out to identify the vivo faces, static graphic photos and dynamic screen images and being high in identification accuracy; not needing identified people to perform facial expression changes to cooperate with the identification, overcoming the defects that the prior art can only identify the static photos but can not identify the screen dynamic images and greatly improving the security and convenience of the face recognition system; being easy in structure, being reliable in work, being rapid in identification speed and being easy to implement.
Owner:UNISPLENDOUR CO LTD
Bearing roller image detection system, method and image detection device
InactiveCN104966300ASimplify the amount of informationSalient eigenvaluesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage detection
The invention discloses a bearing roller image detection method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, corresponding image parameters are debugged for different shooting environments; secondly, according to the related image parameters acquired in the first step, feature points of a standard piece are extracted, and standards for image recognition are determined; and finally, feature points of a tested piece are extracted and compared with the feature points of the standard piece for making a judgment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
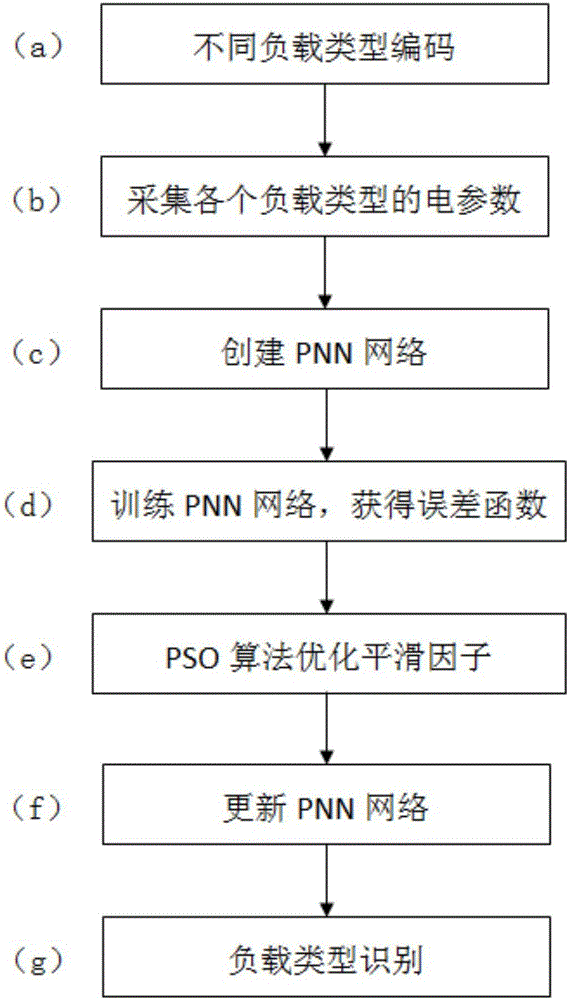
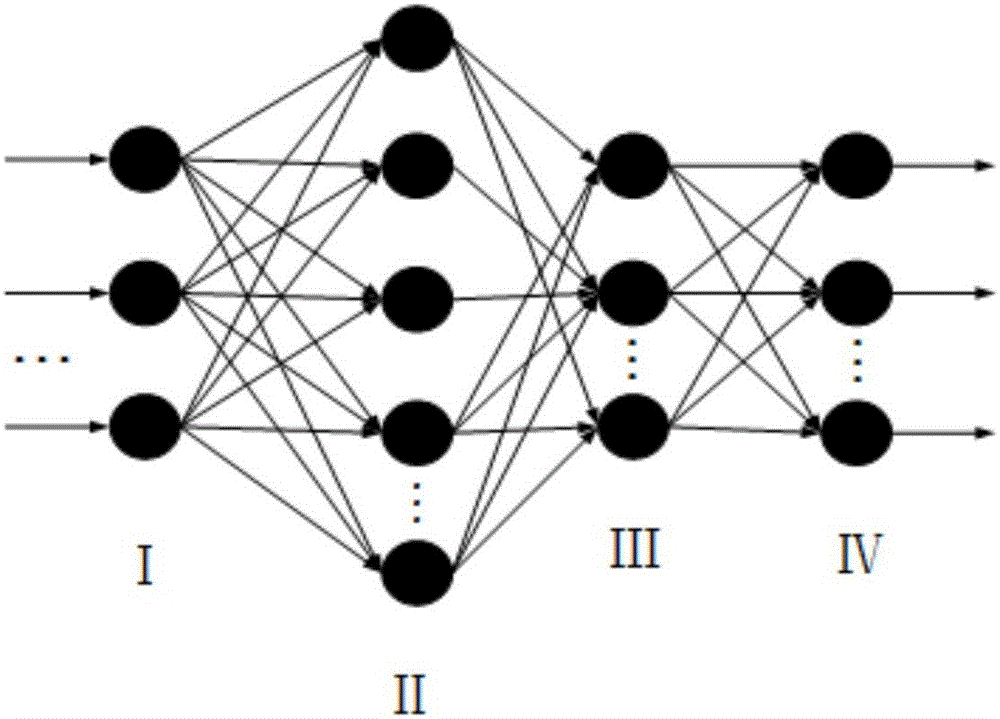
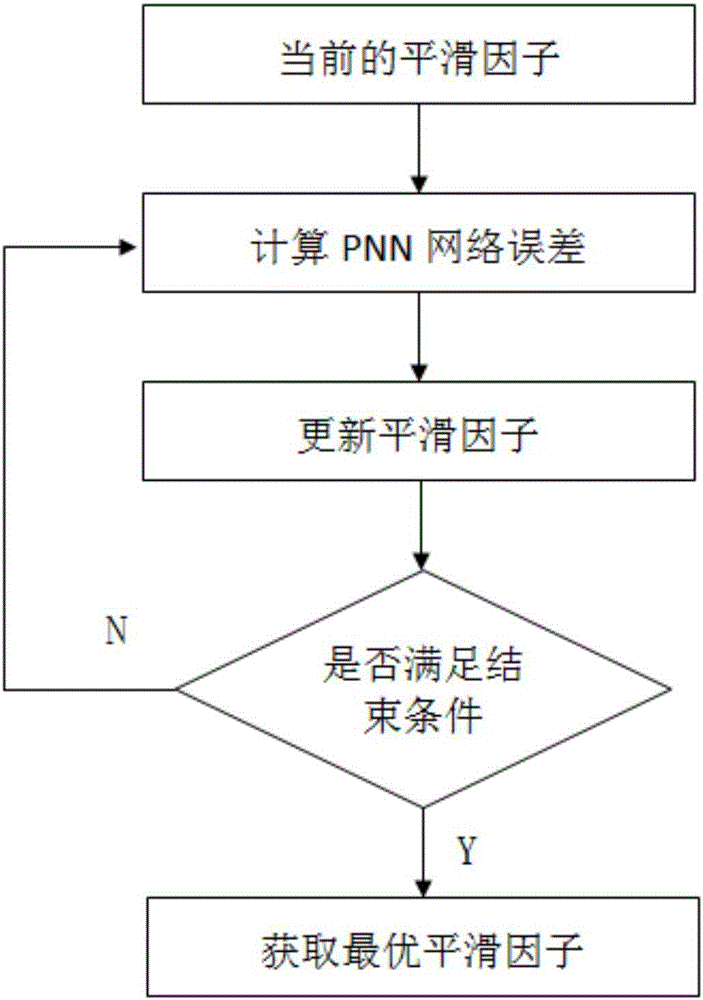
Load identification method based on improved probabilistic neural network
ActiveCN106327357ASolve the problem of electricity regulationDiscrimination speed is fastData processing applicationsArtificial lifeElectricityNetwork on
The invention discloses a load identification method based on an improved probabilistic neural network. The load identification method comprises steps of adopting a binary system to perform coding on a load type in an electricity usage network, establishing a coding library of load types, collecting an electric parameter of each load type, establishing a non-linear mapping relation between the electric parameter and the code of each load type, creating a probabilistic neural network, training the probabilistic neural network to obtain an error function, using the error function as a fitness function of a particle swarm algorithm, adopting the particle swarm algorithm to perform optimization on a smooth factor of the probabilistic neural network to obtain an optimal smooth factor, updating the probabilistic neural network according to the obtained optimal smooth factor to obtain an improved probabilistic neural network and performing recognition on the load type in the electricity usage network on the basis of the probabilistic neural network. The load identification method based on the improved probabilistic neural network can simultaneously identify multiple loads, improves speed of identifying a pernicious load under a multi-load mode, and can better realize recognition of restricted electric appliances and electricity usage control under a condition of multiple electric appliances.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method and system for distinguishing language of document image
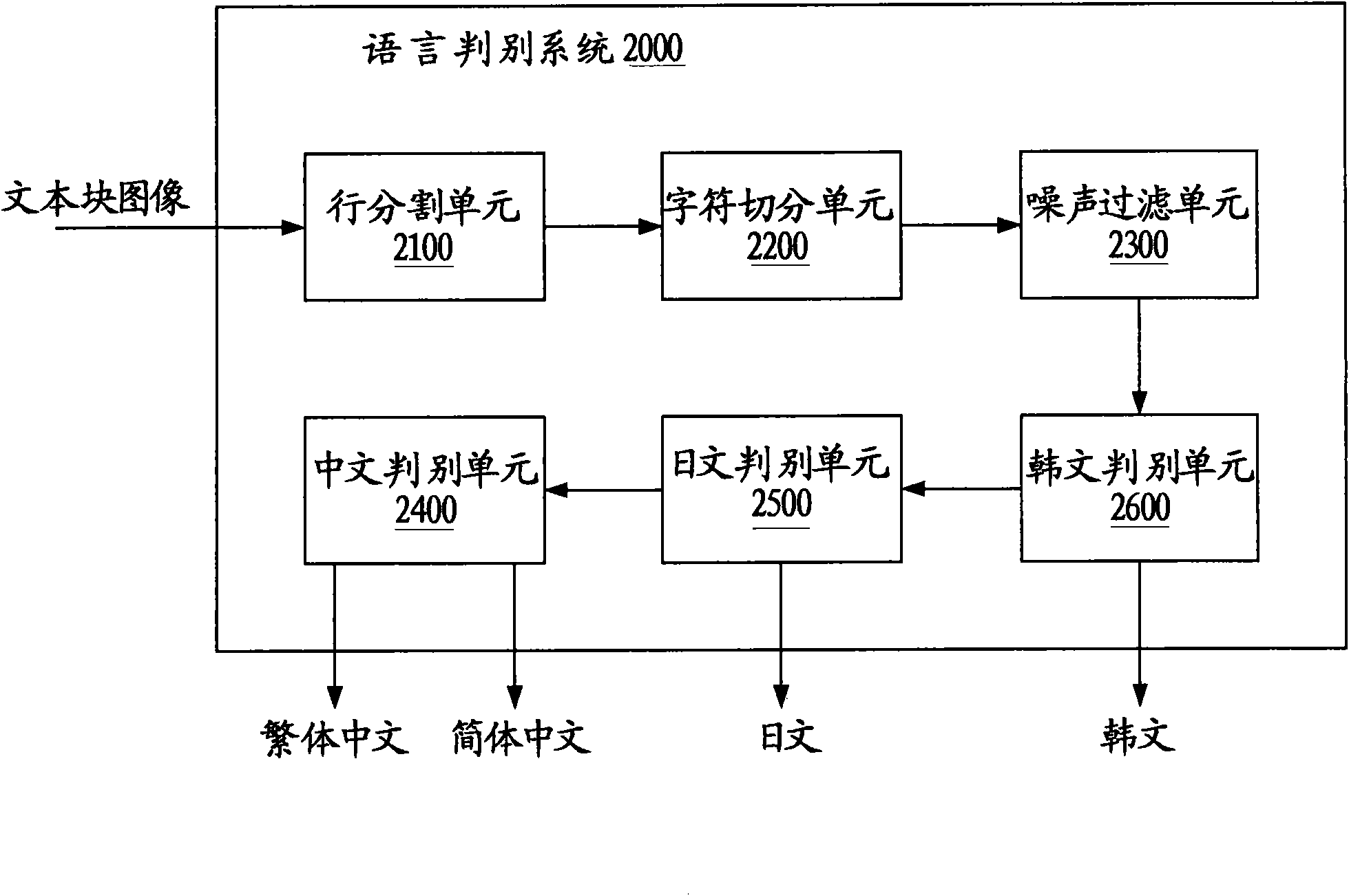
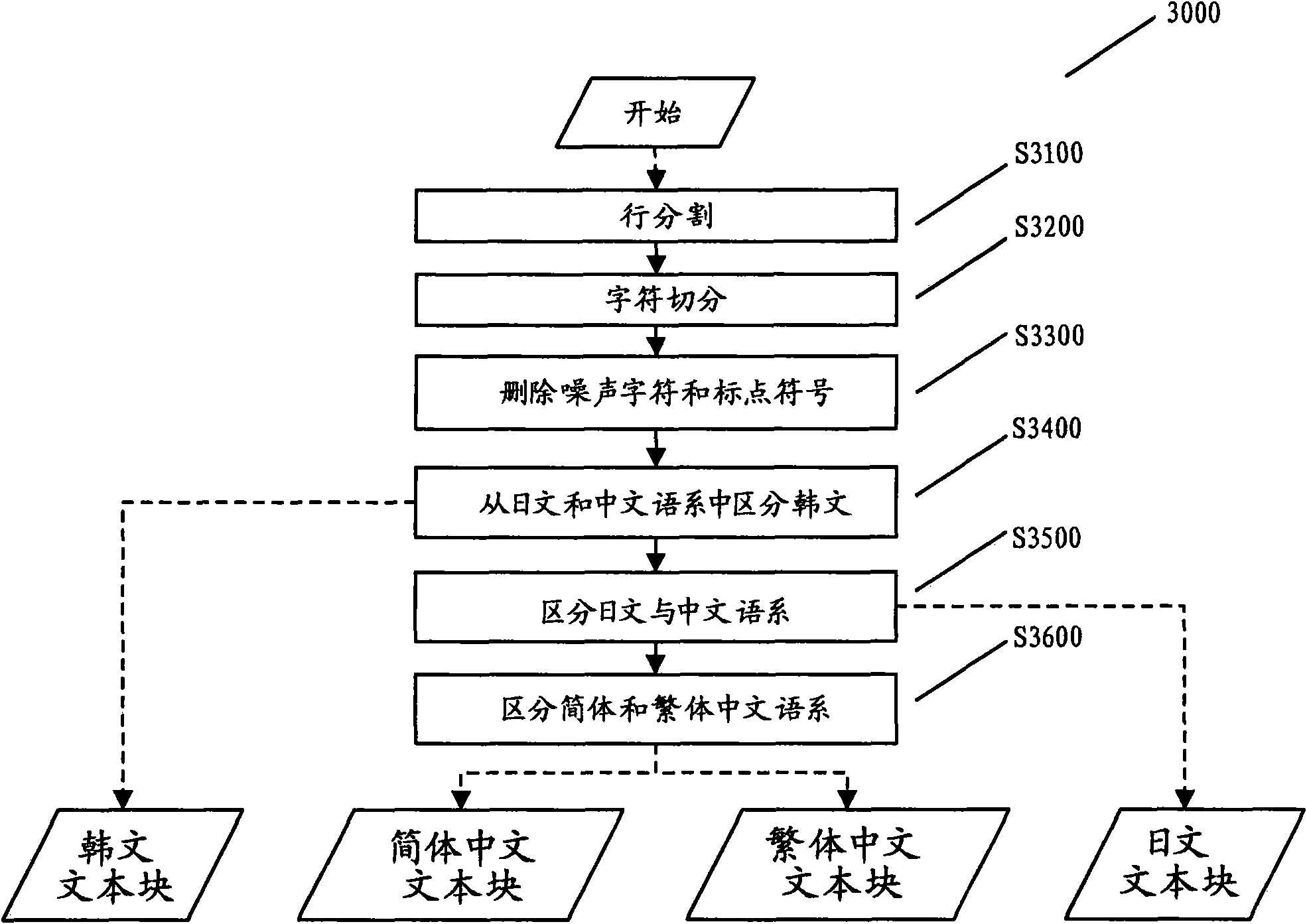
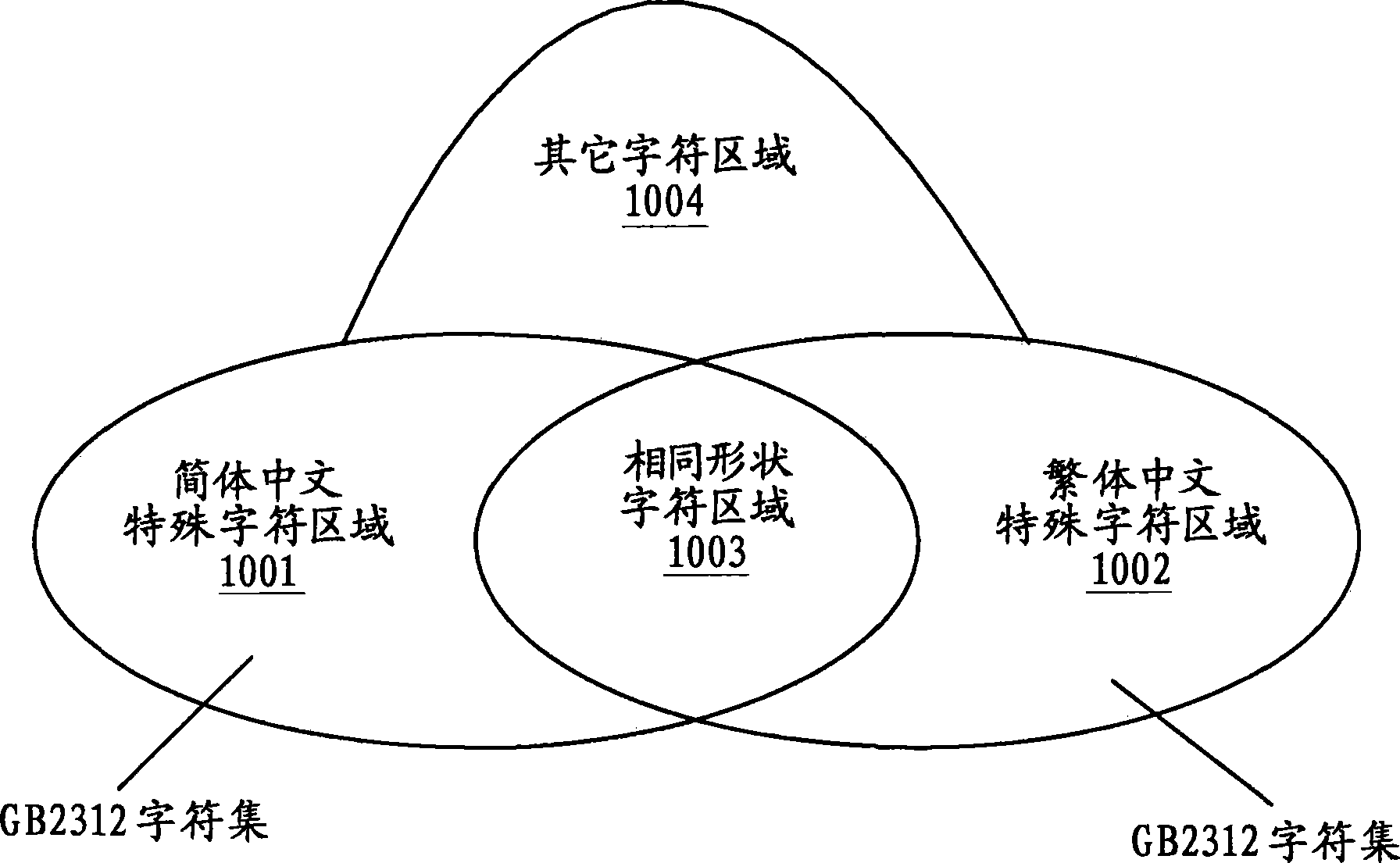
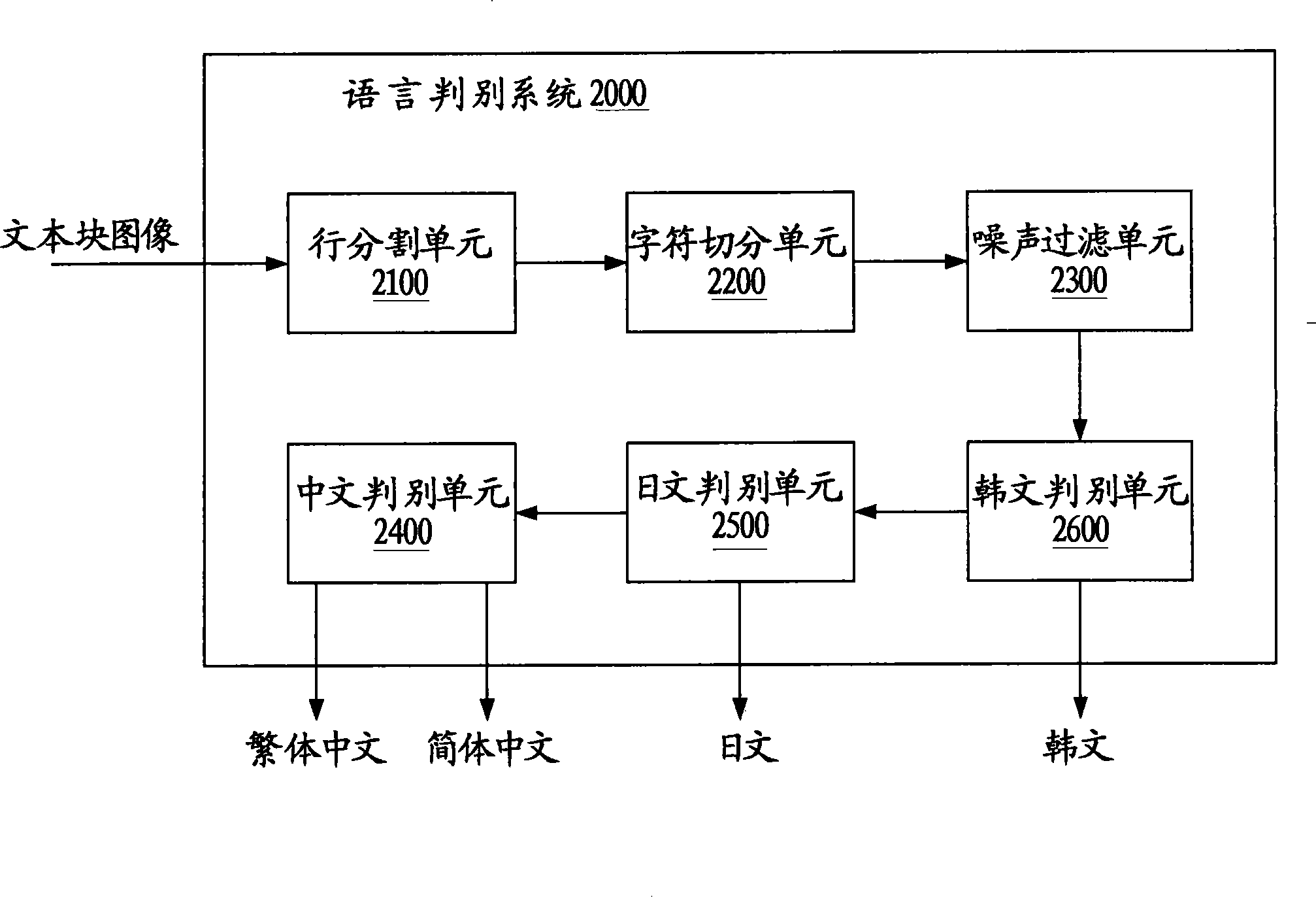
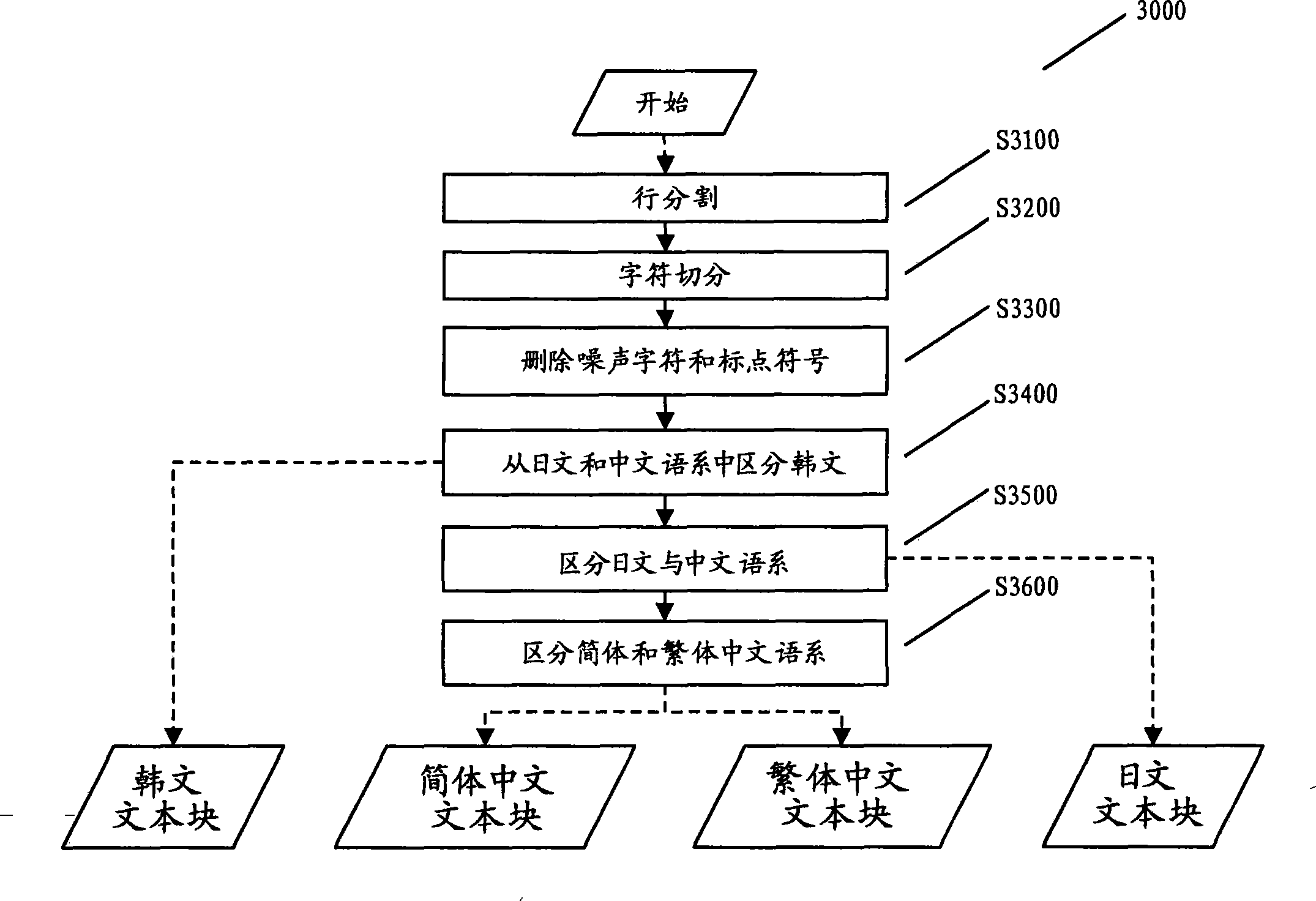
InactiveCN101593278ADiscrimination speed is fastHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a method and a system for distinguishing the language of a document image, comprising the following steps: detecting the round white pixel connection domain in the document block of the document file, and determining whether the document block is a Korean on the basis of the detecting the round white pixel connection domain.
Owner:CANON KK
Power grid abnormal state distinguishing method based on ring theory
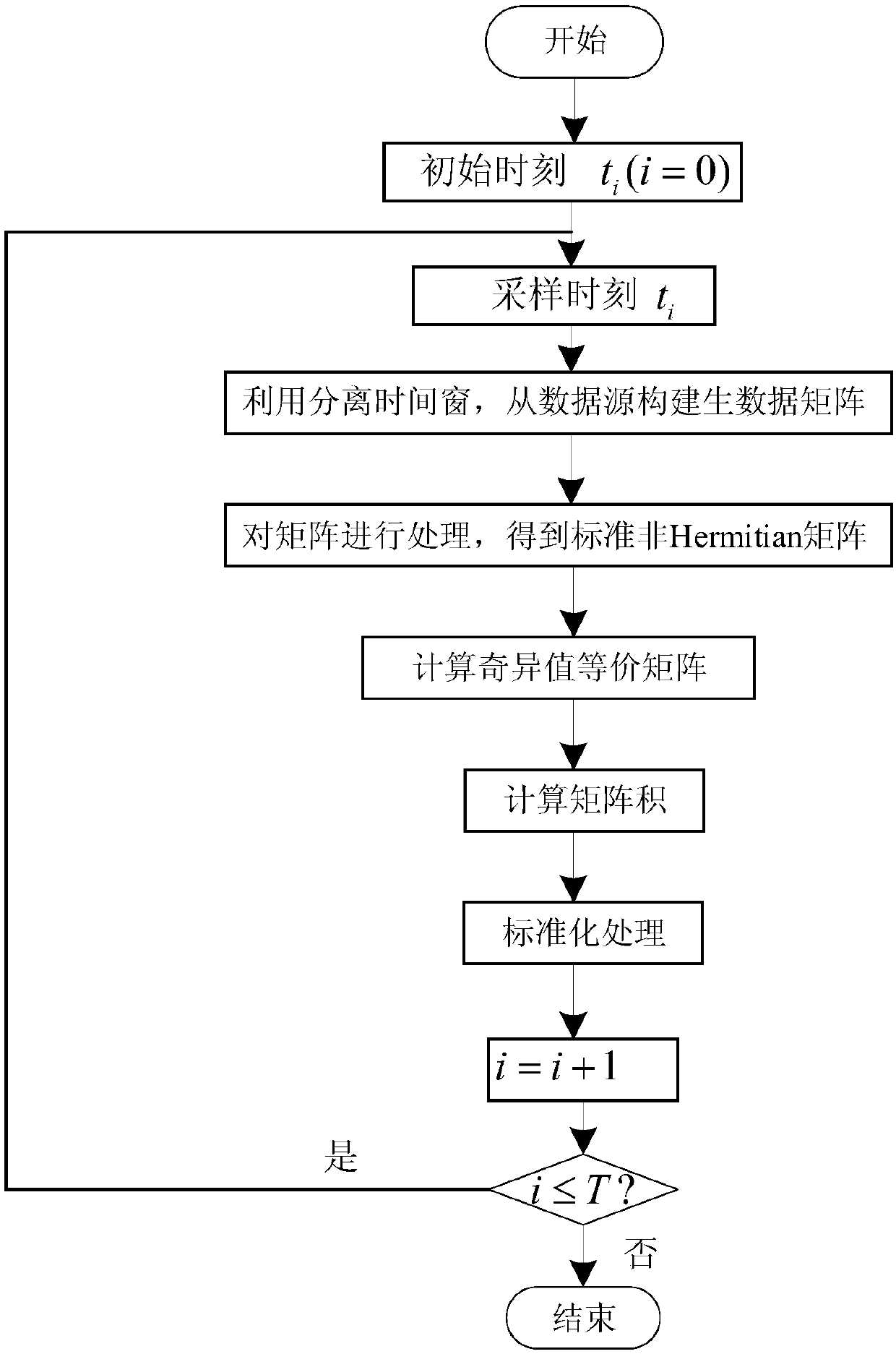
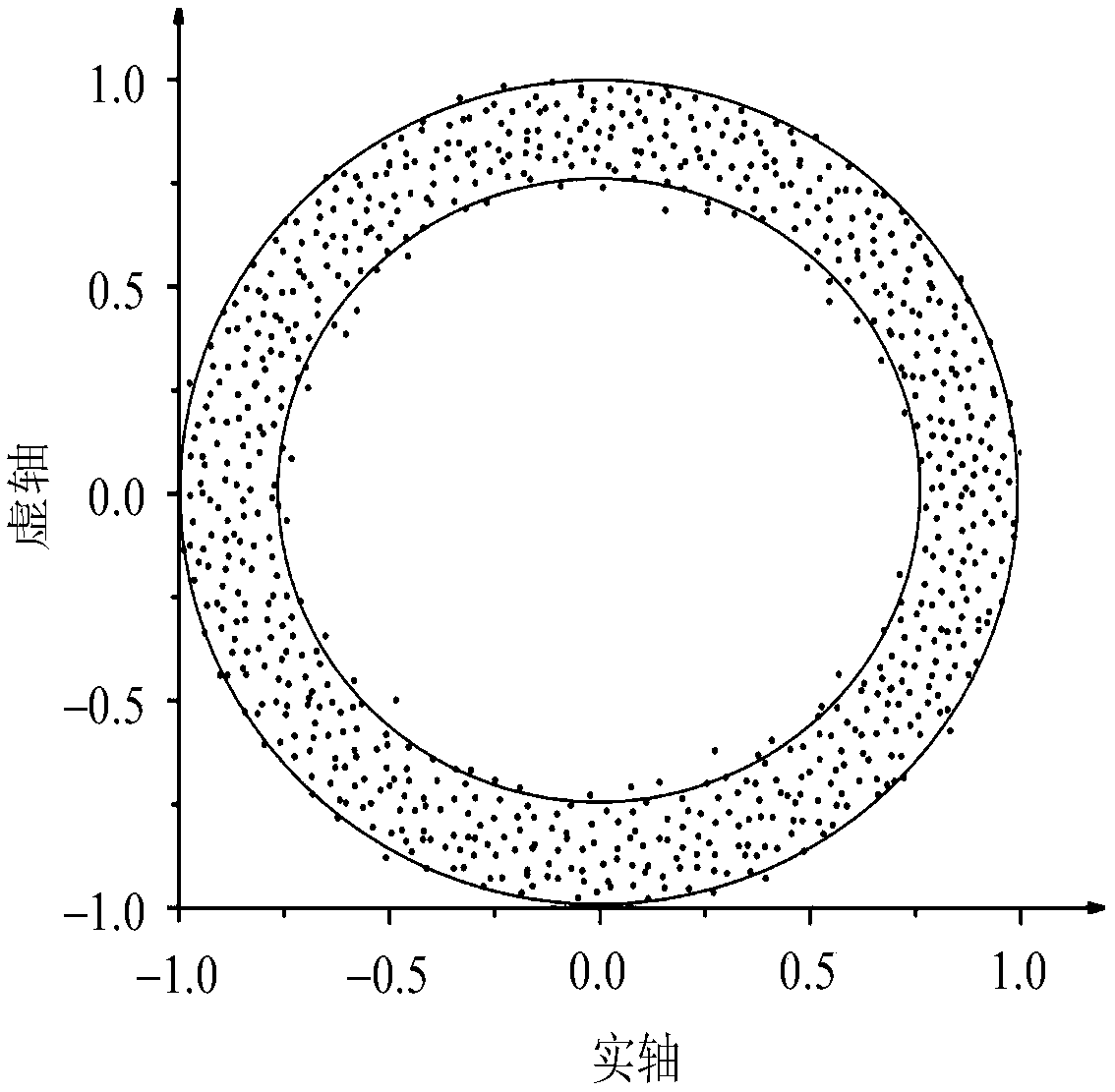
InactiveCN109061387ADiscrimination speed is fastEasy to visualize severityFault locationWide areaSliding time window
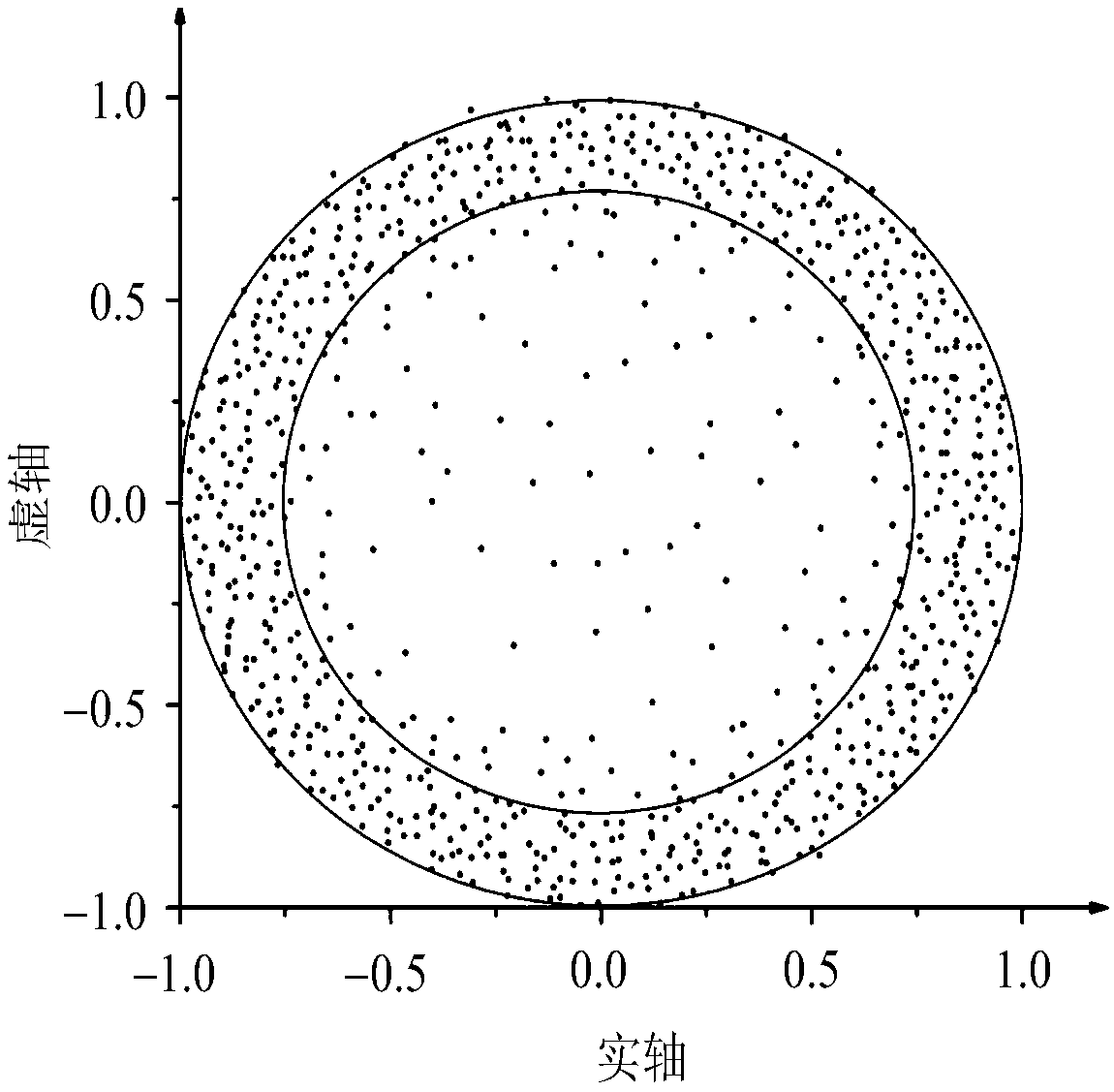
The invention relates to a power grid abnormal state distinguishing method based on ring theory. The method comprises the following steps of: forming an original data matrix by utilizing WAMS (Wide Area Measurement System) data with processing of sliding time window and matrix standardization processing to obtain a high-dimensional random matrix for a ring theory; carrying out spectrum analysis research on the processed random matrix, and analyzing the processed random matrix from the ring theory; data is distributed between an outer ring and an inner ring when a system is in normal operation,and a large number of abnormal data points within the inner ring start to appear when the system starts to have an abnormal situation, therefore constructing a criterion of abnormal states by comparing a length of a minimum characteristic value with an inner ring radius; and judging the severity of the abnormal states according to the proportion of inner ring data points in a ring graph. According to the power grid abnormal state distinguishing method based on ring theory, power grid state is analyzed from a data driving perspective by using the WAMS data, an evaluation index of power grid abnormal state is constructed through the ring theory, so that the power grid abnormal state and the severity thereof can be quickly identified, and power big data is fully utilized.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF EAST INNER MONGOLIA ELECTRIC POWER +4
Human identification device used for face recognition system
InactiveCN103077382AImprove securityImprove convenienceCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Identification device
The invention relates to a human identification device used for a face recognition system, belonging to the technical field of face recognition. The human identification device comprises a left light source, a right light source, a camera and a computer; the left light source and the right light source are respectively arranged at the right front side and the left front side of a to-be-recognized person and used for lighting the face of the to-be-recognized person; and the computer is respectively connected with the left light source, the right light source and the camera. The human identification device provided by the invention identifies the to-be-recognized person and a paper photo and a display screen through utilizing the positive and negative faces formed by a manner that the head of the to-be-recognized person shields the side lighting, the identification accurate rate is high. Compared with the prior art, the identification device does not need the to-be-recognized person to do expression changes to match the recognition, and moreover, the device solves the defects that in the prior art, only the dynamic photos can be identified and the dynamic screen images cannot be identified, thus, the security and convenience of the face recognition system are greatly improved; and meanwhile, by adopting the technical scheme provided by the invention, the system is simple and reliable in structure, fast in identification speed and easy in implementation.
Owner:UNISPLENDOUR CO LTD
Distance measurement method based on millimeter-wave radar, and relevant device
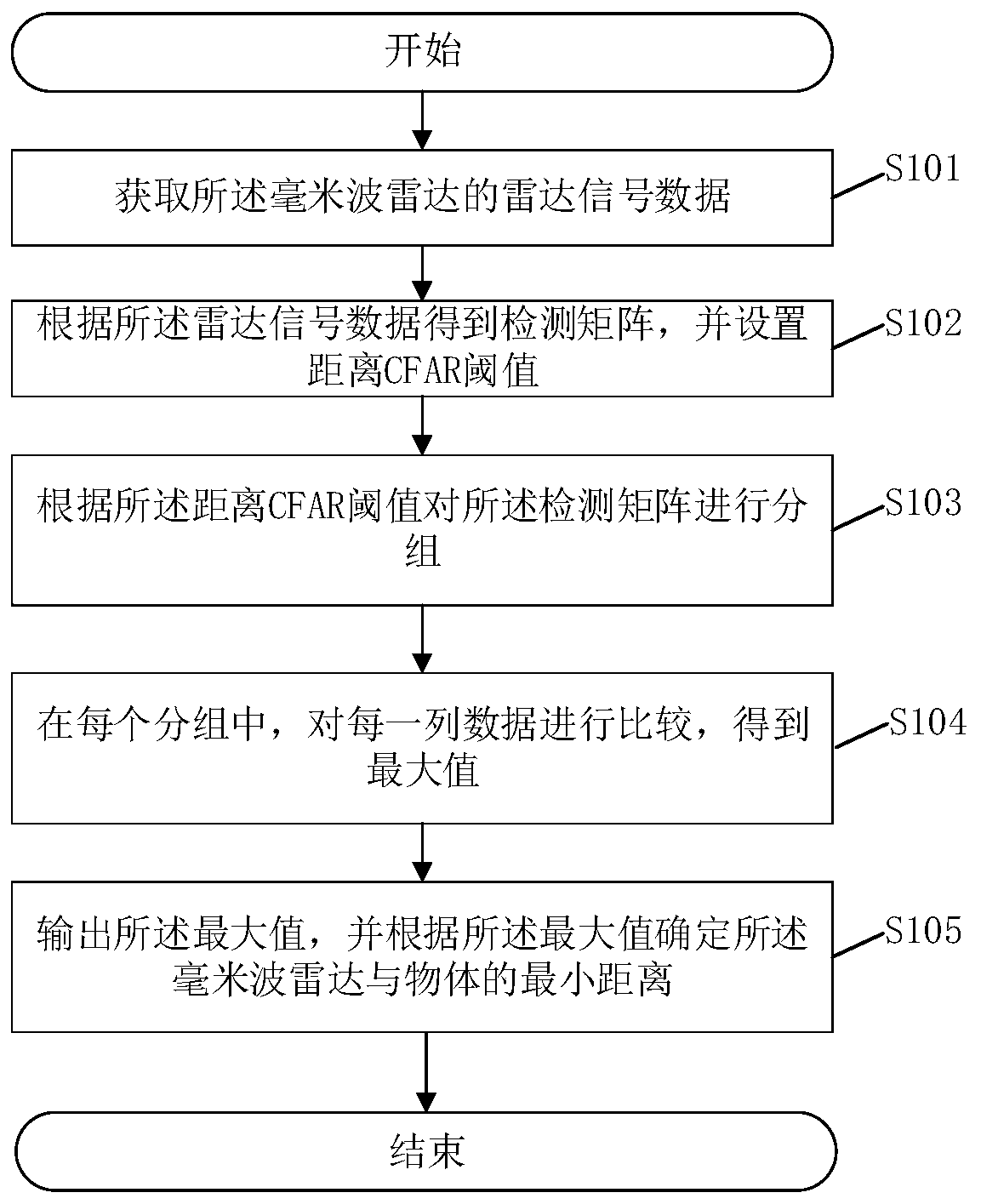
ActiveCN109991595ADiscrimination speed is fastImprove work performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionShortest distanceWork Performances
The invention provides a distance measurement method based on a millimeter-wave radar. The method comprises the following steps that: obtaining the radar signal data of the millimeter-wave radar; according to the radar signal data, obtaining a detection matrix, and setting a distance CFAR (Constant False-Alarm Rat) threshold value, wherein the line of the detection matrix represents distance, andthe row of the detection matrix represents speed; according to the CFAR threshold value, grouping the detection matrix; in each group, comparing data in each row to obtain a maximum value; and outputting the maximum value, and determining a minimum distance between the millimeter-wave radar and an object according to the maximum value. By use of the method, the distance data is distinguished in advance, a situation that the radar can not detect the object when the radar and the object are simultaneously static can be eliminated. Meanwhile, the distinguishing speed for the shortest distance between the radar and the object is greatly improved, and the working performance of the millimeter-wave radar is improved. The invention also provides a distance measurement system based on the millimeter-wave radar, a computer readable storage medium and the millimeter-wave radar, and also has the above beneficial effects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
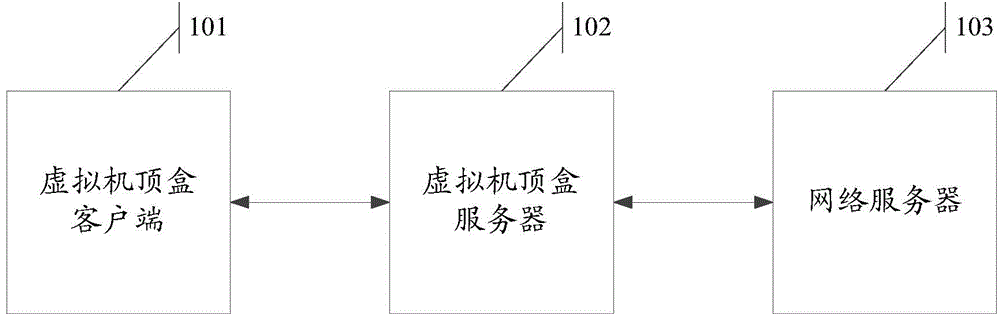
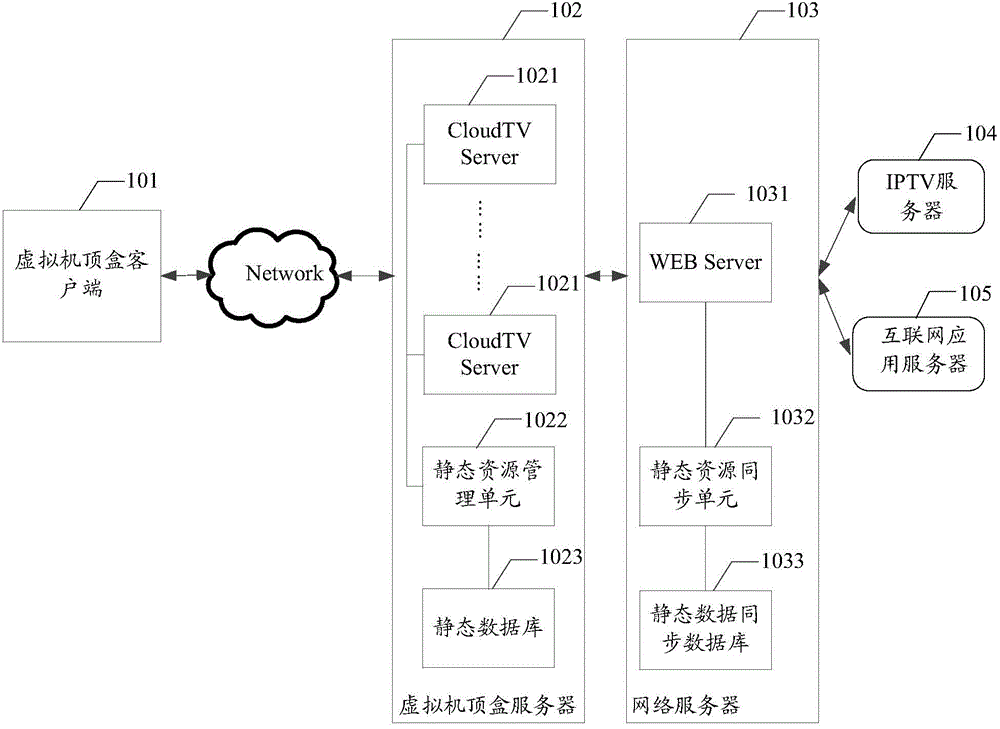
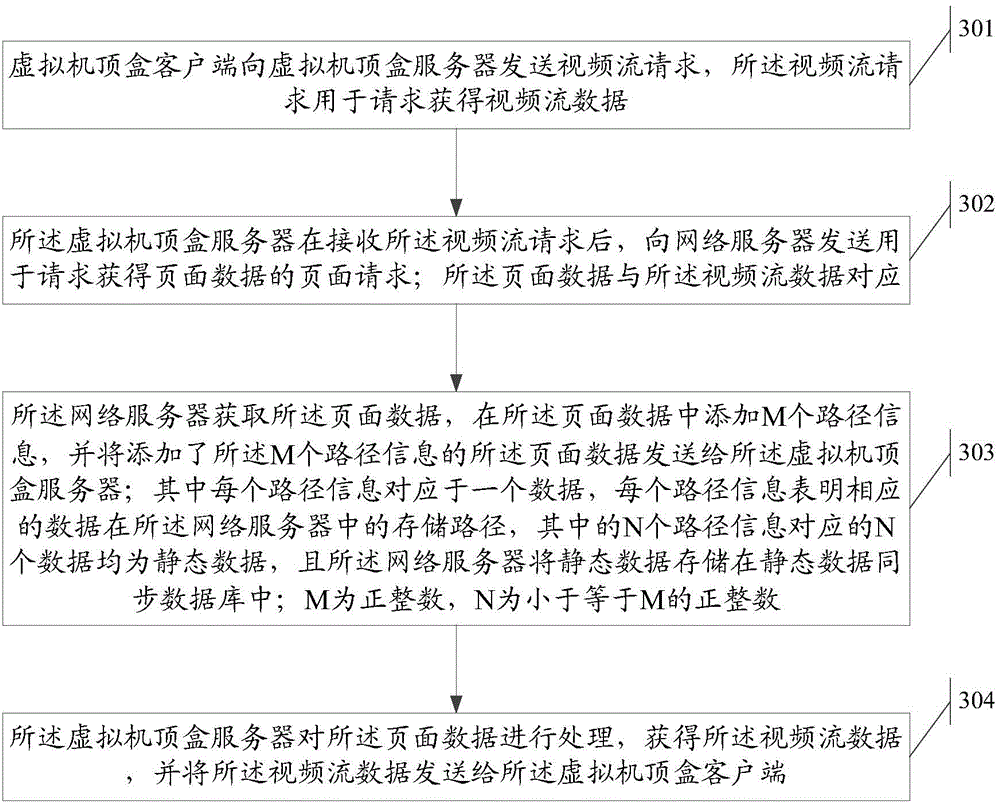
Video stream data acquisition method, page data transmission method, system and network server
ActiveCN105812839ADiscrimination speed is fastQuick responseSelective content distributionData synchronizationStream data
The invention discloses a video stream data acquisition method used for solving a technical problem that delay of a server increases due to response speed decline in a high concurrency scenario. The method comprises the following steps: a virtual set top box client end sends a video stream request to a virtual set top box server, the virtual set top box server sends a page request used for requesting page data to a network server, the network server obtains the page data, the page data is sent to the virtual set top box server after M pieces of path information is added to the page data, all of N pieces of data that N pieces out of the M pieces of information corresponds to is static state data which is stored in a static state data synchronization database via the network server, the page data is processed via the virtual set top box server and therefore video stream data is obtained, and the video stream data is sent to the virtual set top box client end. The invention also discloses a corresponding system, a page data transmission method and the network server.
Owner:HUAWEI CLOUD COMPUTING TECH CO LTD
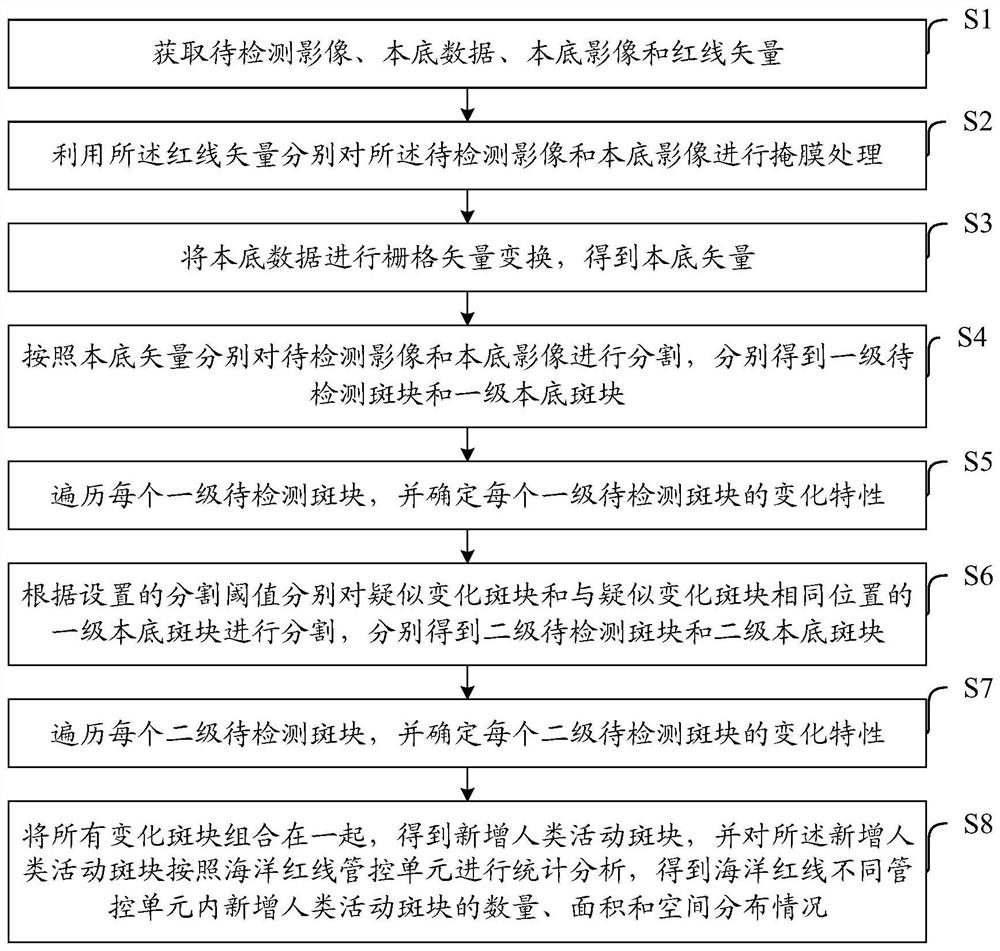
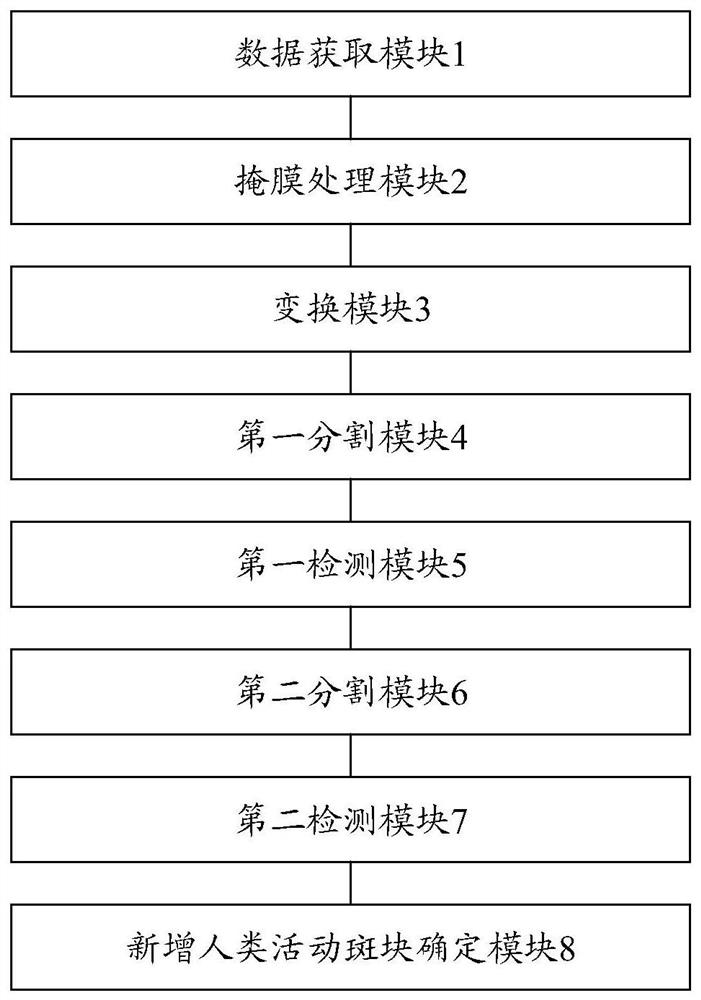
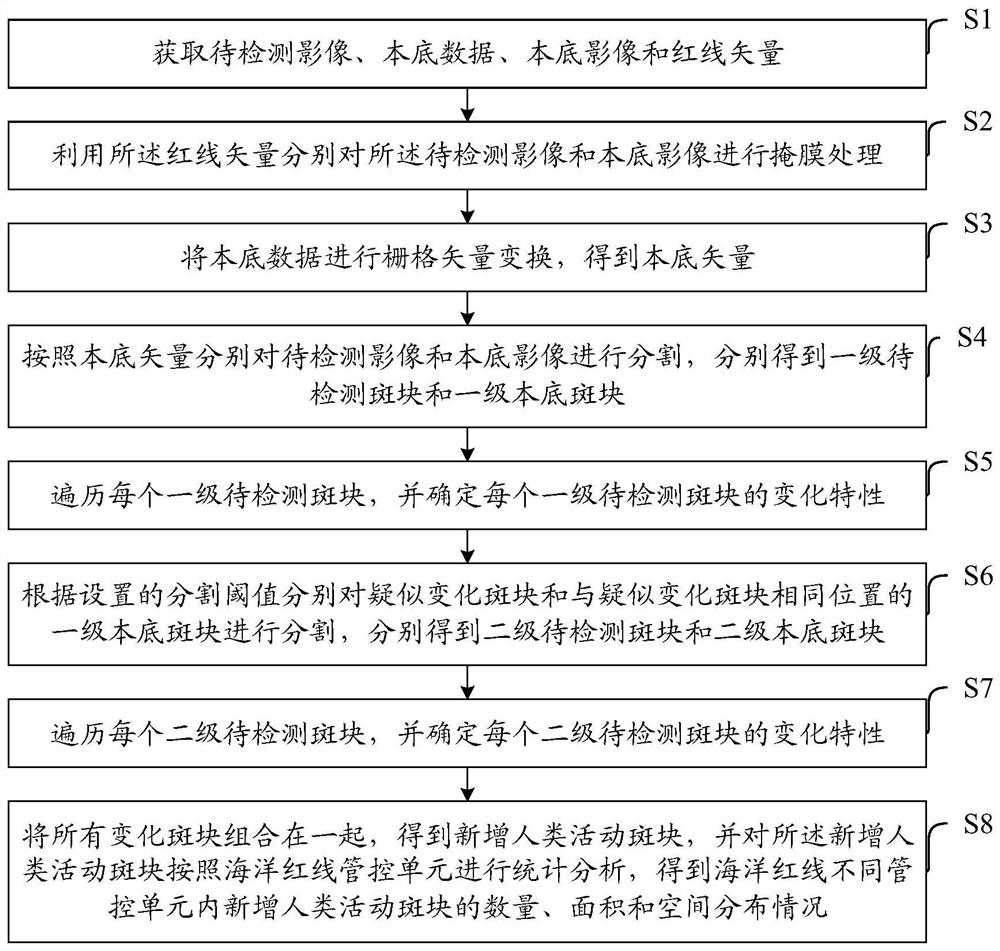
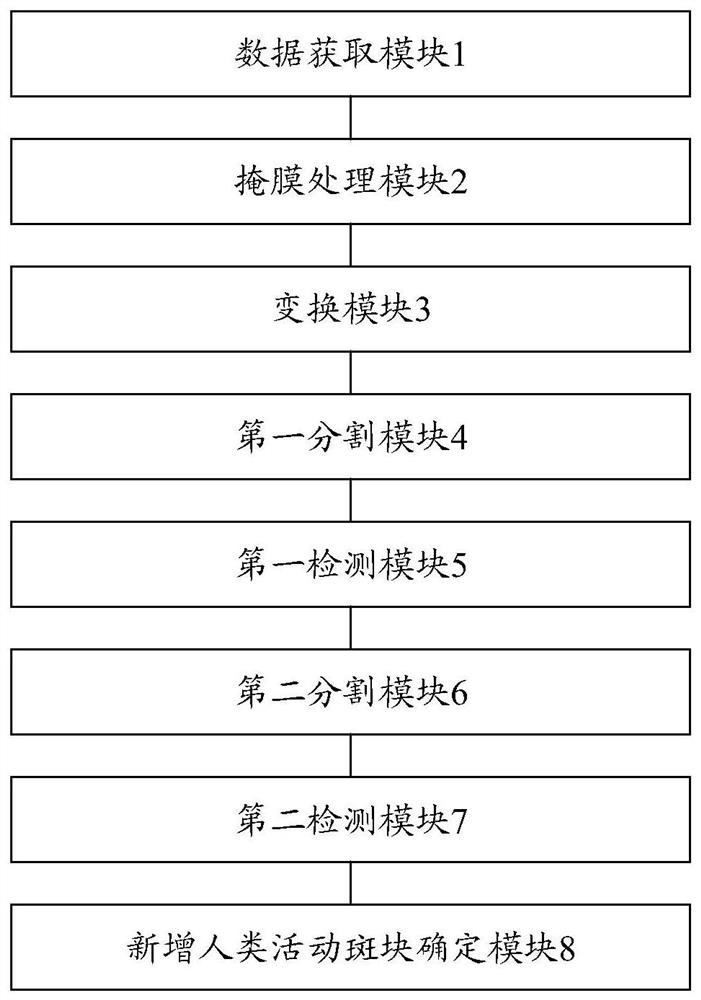
Method and device for automatically and quickly extracting newly-added human activity plaques on marine red line
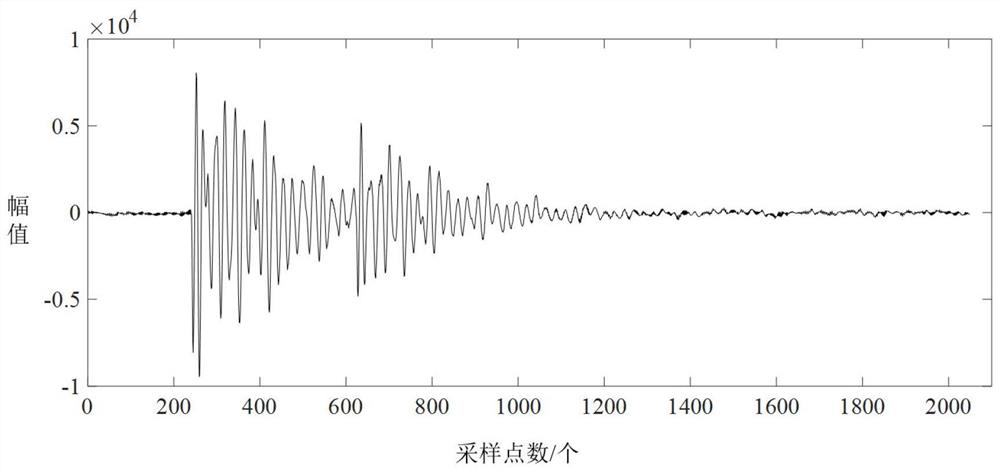
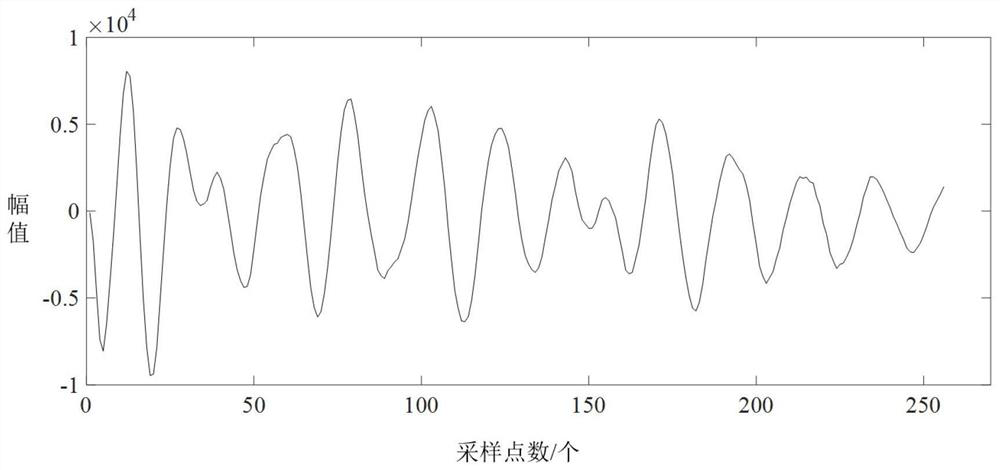
ActiveCN111680704AReduce "pseudo-change" recognition rateDetection speedCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionBackground image
The invention discloses a method and a device for automatically and quickly extracting newly-added human activity plaques on a marine red line, and belongs to the field of environmental monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: segmenting a background image and a to-be-detected image by utilizing a background vector, and judging segmented plaques one by one by utilizing a brightness statistical value and a spectral characteristic function to obtain changed plaques and suspected changed plaques; carrying out secondary segmentation on the suspected changed plaques and plaques corresponding to the background image according to the characteristics of spectrum, geometry, texture and the like, and judging the segmented plaques one by one by utilizing a brightness statistical value and a spectrum characteristic function to obtain changed plaques; merging all the changed plaques to obtain newly added human activity plaques; and counting the newly added human activity plaques to obtain the number and area of the newly added human activity plaques in the ocean red line. The method can automatically and quickly extract the position, number, distribution area and other informationof the newly added human activity plaques in the marine red line, and provides quick and accurate technical support for marine red line human activity supervision.
Owner:MINISTRY OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT CENT FOR SATELLITE APPL ON ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT
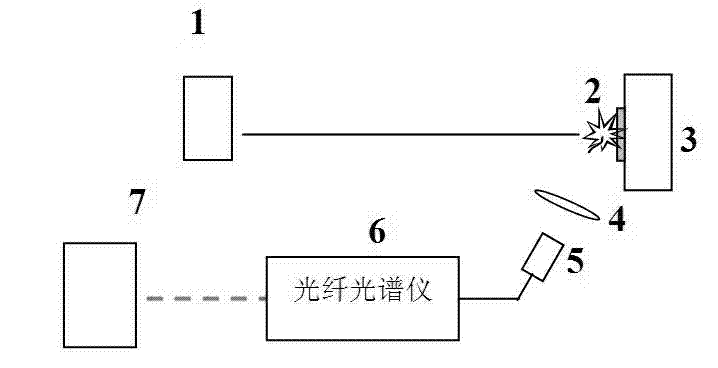
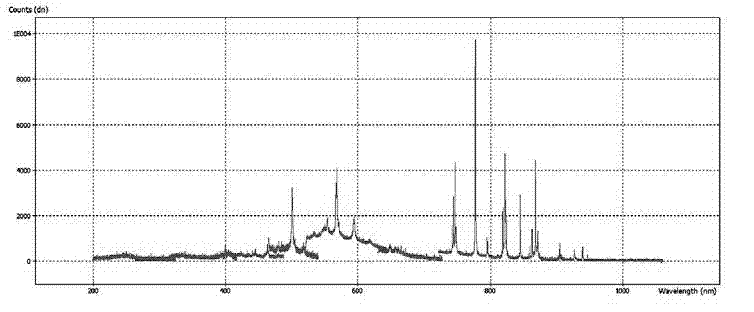
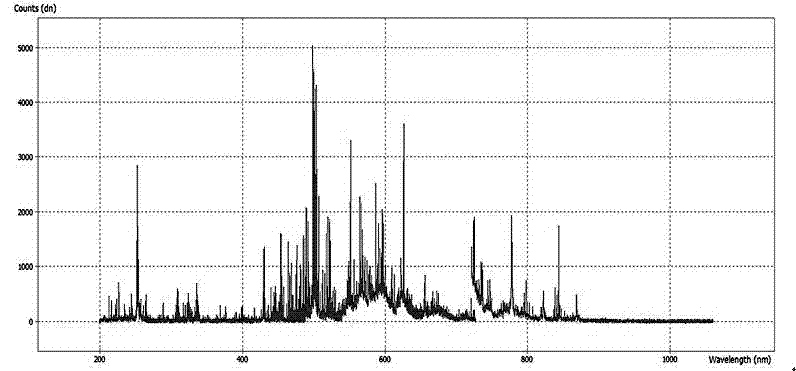
Discrimination method for laser damage on the surface of a film or an optical element and determination device thereof
InactiveCN102226764AImprove discrimination accuracyEliminate false positivesAnalysis by material excitationTest efficiencyFiber
The invention relates to a discrimination method and determination device for laser damage on the surface of a film or an optical element and a determination device therof. The prior art has the disadvantages of strong subjectivity, great working intensity and low testing efficiency. The invention provides a discrimination method for laser damage on the surface of a film or an optical element. According to the method, an operating laser beam carries out monopulse laser irradiation on a sample; if the surface of the sample has no damage, the surface does not produce plasma flash; if the surface is damaged, strong plasma flash is generated the moment the damage appears, and if a photoluminescence peak of an element not being N, O, H or C appears according to analysis of a flash spectrum, appearance of damage can be determined. The invention also discloses a determination device realizing the above-mentioned method. The device comprises a laser generator and a test board and is characterized by further comprising a convergent lens and a fibre-optical probe on the imaging surface of the convergent lens, wherein the fibre-optical probe, a fiber spectrometer and a computer are connected sequentially. According to the invention, high precision in the discrimination is obtained; the discrimination speed is fast; a wide variety of films can be discriminated; the construction of the determination device is simple.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
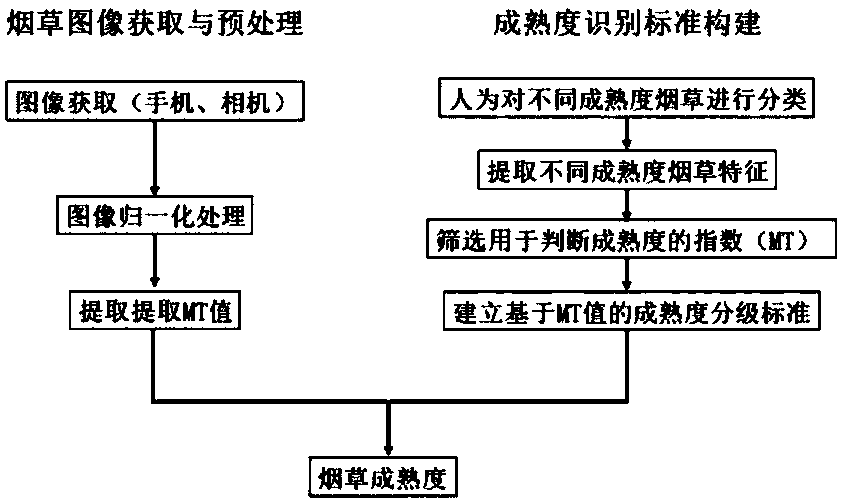
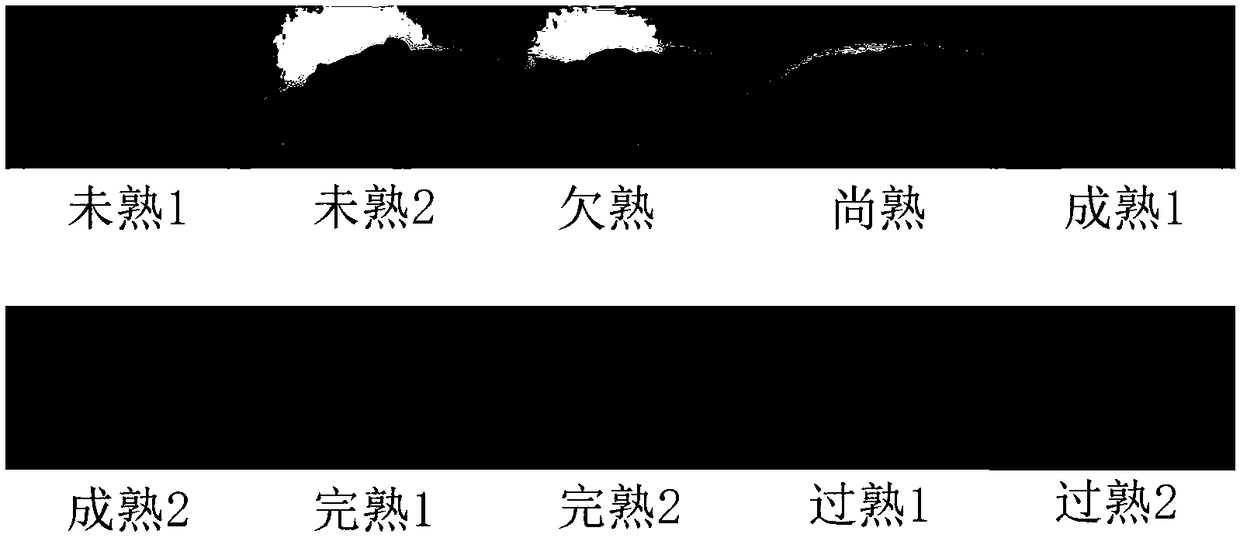
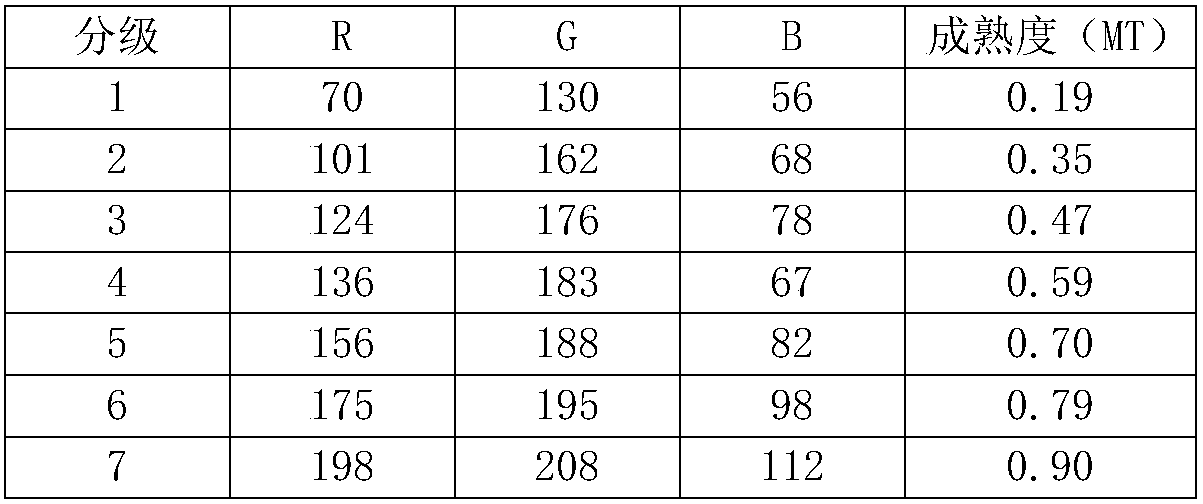
Distinguishing method of maturity degrees of tobaccos based on image analysis
PendingCN108198176ADiscrimination speed is fastImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisImage analysisComputer vision
The invention discloses a distinguishing method of maturity degrees of tobaccos based on image analysis. The distinguishing method comprises the following detailed steps: (1) classifying tobaccos of different maturity degrees through professional staffs; (2) acquiring different maturity degree images of the tobaccos; (3) acquiring tobacco images and performing normalization on the images; (4) performing normalization on the acquired tobacco images by utilizing an image analysis method; (5) extracting values of three components R, G and B of the images; (6) building maturity degree estimation parameters, screening characteristic parameters of existing known colors and a series of self-built characteristic parameters, and screening the all characteristic parameters by utilizing a person relevant analysis method; (7) acquiring an M value from the images, and judging a maturity degree value through contrasting maturity degree grading table; and (8), realizing image reading and maturity degree output through a phone app and computer software.
Owner:BIJIE COMPANY OF GUIZHOU TOBACCO
High-efficiency artificial intelligence anti-counterfeiting image recognition system and method
InactiveCN111709258AAdd non-image anti-counterfeiting feature pointsAdd preprocessorCharacter and pattern recognitionCommerceEngineeringImaging Feature
The invention relates to a system and a method for recognizing image information or feature points of an anti-counterfeiting marker based on an artificial intelligence technology. In the background technology, the artificial intelligence technology is rarely applied to anti-counterfeiting recognition. An existing artificial intelligence recognition method needs to be carried out, and modificationand optimization are carried out aiming at anti-counterfeiting image recognition characteristics. The invention provides an artificial intelligence anti-counterfeiting image recognition system and method. The method comprises the steps that personalized image feature type anti-counterfeiting marks are pasted on a product or a product package; an identity code and a traceability code with uniqueness are arranged on the personalized image feature type anti-counterfeiting mark; lines and patterns with special functions are arranged on the personalized image feature type anti-counterfeiting mark (2), and comprise a guide photographing pattern for assisting photographing and a correction guide pattern for correcting deformation. And a preprocessing program and an anti-counterfeit label fixing pattern are added, so that the artificial intelligence discrimination efficiency is improved.
Owner:西安立东行智能技术有限公司
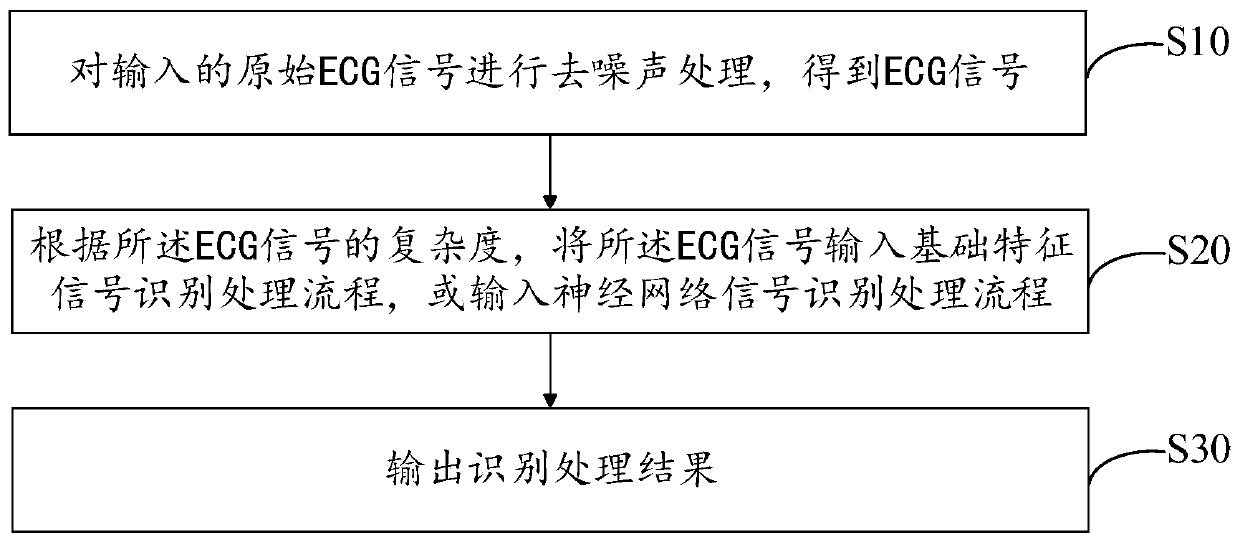
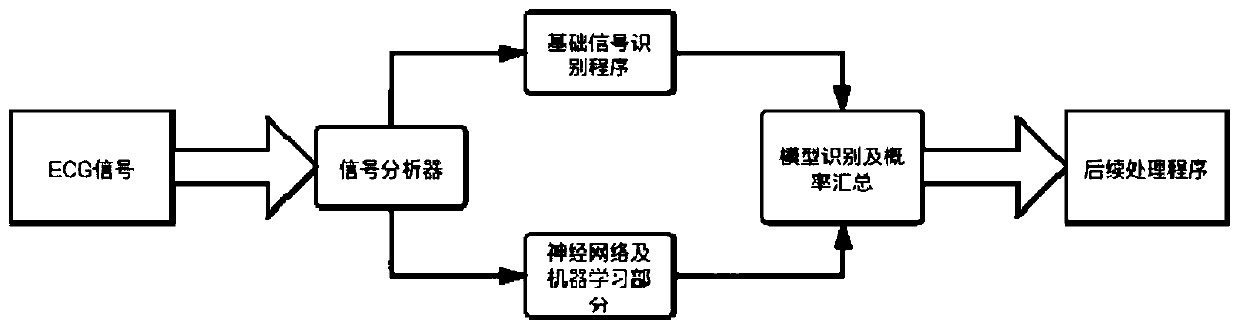
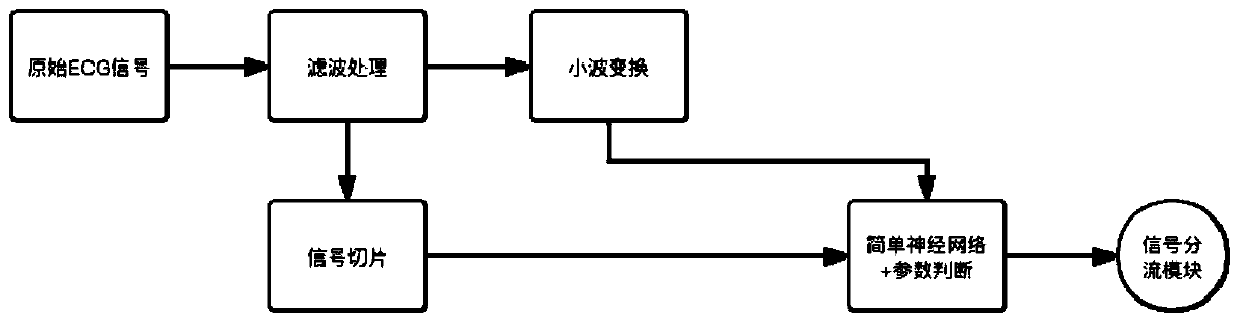
Quick recognizing and processing method and system for ECG signal
ActiveCN111528833AReal-time recognitionSimple processDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalComputer science
The invention discloses a quick recognizing and processing method and system for an ECG signal. The method comprises the following steps: denoising an input original ECG signal to obtain an ECG signal; inputting the ECG signal in a basic characteristic signal recognizing and processing flow or a neural network signal recognizing and processing flow according to the complexity of the ECG signal; and outputting a recognizing and processing result. The provided quick recognizing and processing method and system for the ECG signal improves the signal recognition efficiency and accuracy of analysisresults, and can be applied to various embedded platforms.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Intelligent alarming method for grid
ActiveCN101651345AReduce the number of classification combinationsReduce dimensionalityAlarmsSystems intergating technologiesAlgorithmObserver based
The invention discloses an intelligent alarming method for a grid. On the basis of a PMU point arrangement optimization, a grid observer based on a bus-bar node voltage is constructed to enable a failure and a node voltage to correspond to each other, and a decision tree and an algorithm supporting the cooperation of a vector machine are used for giving an alarm for a grid failure. The method utilizes the decision tree to reduce the classifying combination number and constructs a classifying performance value to represent the divisibility of each type; furthermore, the PMU point arrangement optimization is introduced to reduce the dimension number of the observer and greatly improve the judging speed and meet the real-time requirements of the failure alarm.
Owner:广东立胜综合能源服务有限公司 +1
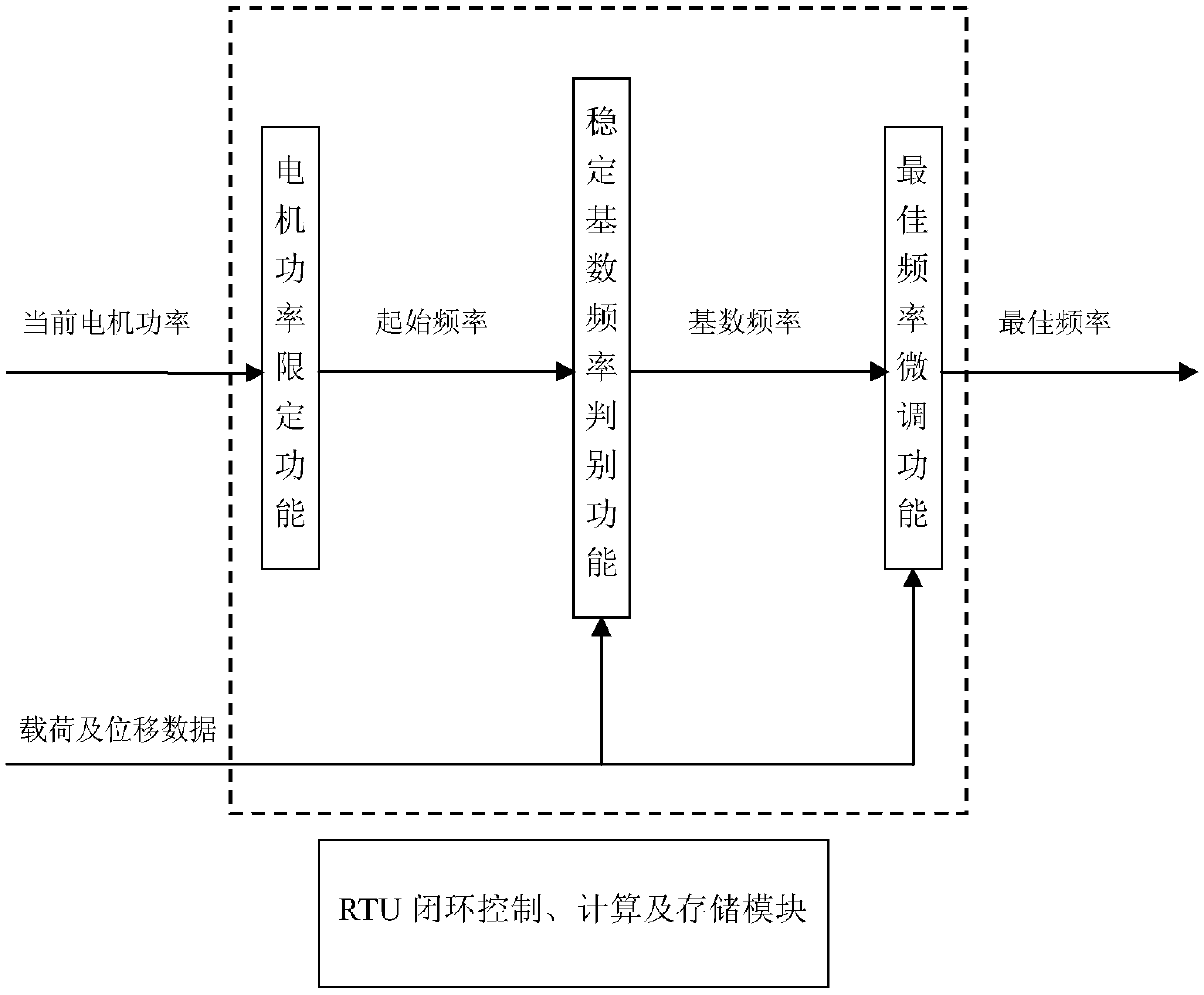
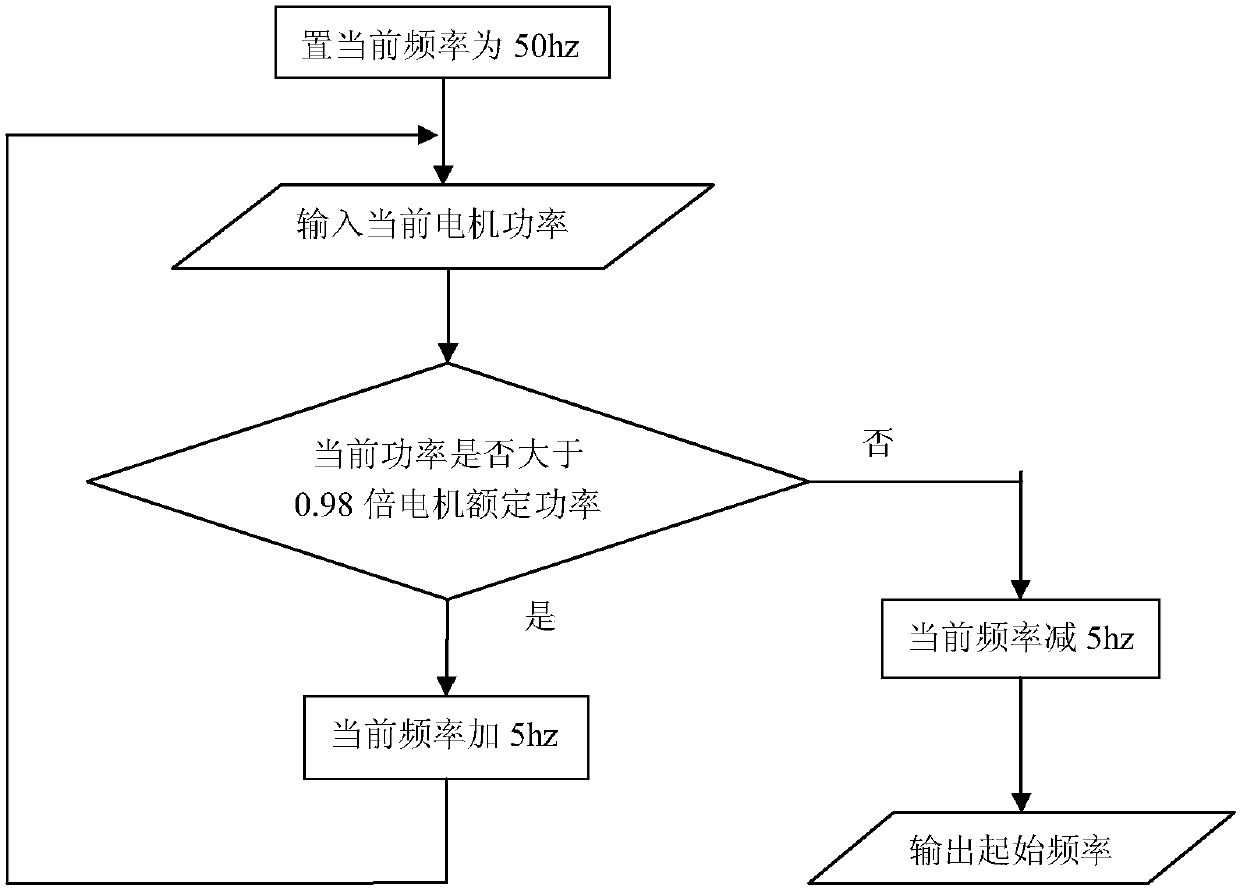
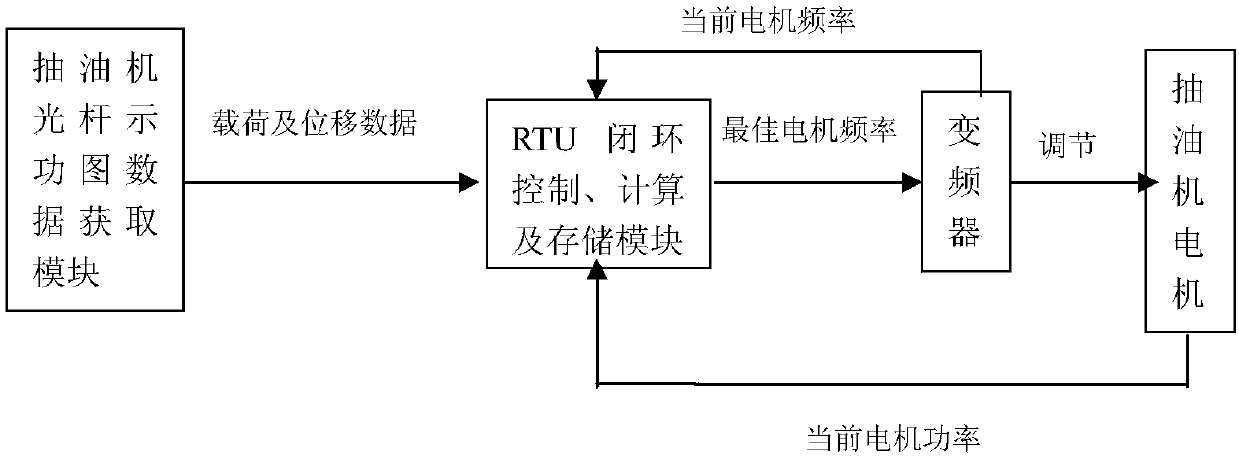
Optimal pumping frequency adjustment method for pumping unit
InactiveCN108415251AImprove accuracyReduce the amount of calculationAdaptive controlFrequency changerPunching
The invention provides an optimal pumping frequency adjustment method for a pumping unit. According to the method, a new pumping unit pumping frequency adjustment algorithm based on time series globalsearch is inserted in the existing digital pumping unit RTU measurement and control unit. The method comprises the specific steps that a motor power limiting technology is used to screen and determine the allowable frequency conversion range of a frequency converter; the maximum frequency of the pumping unit is set to the starting frequency, and the operation frequency is gradually reduced; for the collected polished rod load and displacement data of the pumping unit, the actual pump efficiency is calculated, and the product of the pump efficiency and frequency is used as the equivalent liquid production amount instead of the actual liquid production amount for data storage; the time series data of the equivalent liquid production amount are globally searched, and the optimal reasonable pumping frequency is quickly found; the motor frequency at the moment is taken as the optimal base frequency; and finally, the optimal base frequency of the pumping unit is finely adjusted to ensure that the optimal punching frequency can be accurate for a long time. The method is self-adaptive and can achieve the optimal pump efficiency under the premise that the pumping unit reaches the maximum liquid production amount.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Differential protection locking method for tail current of series transformer
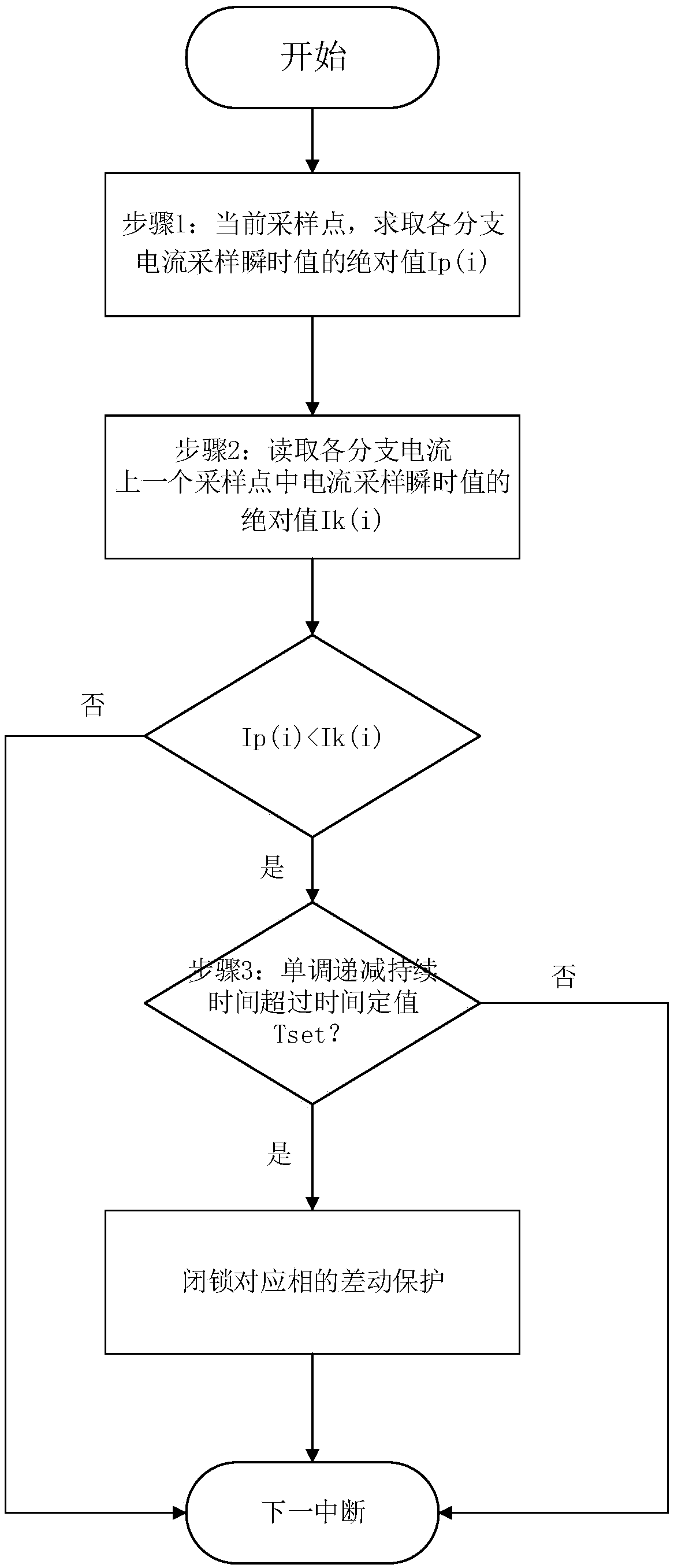
ActiveCN108695823APrevent misoperationShort calculation timeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase currentsPower grid
The invention provides a differential protection locking method for the tail current of a series transformer. The tail current is determined by utilizing the trend of a current sampling value in the phase current, differential protection is locked according to the phase, the tail current can be determined more accurately, protection is not refused during a fault, protection is not carried out formistake when the tail current occurs in the CT, accidents are prevented from expanding, and safe and stable operation of the power grid can be guaranteed more effectively.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +2
Device and method for identifying laser damages to optical film
ActiveCN103954680AImprove discrimination accuracyHigh precisionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaser lightOptical thin film
The invention discloses a method and a device for identifying laser damages to an optical film. The types of elements contained in damaged materials can be determined by acquiring mass-to-charge ratio distribution and performing mass spectrometric analysis and element judgment through computer software, so that damages to the film can be judged accurately and rapidly on line. The device adopting the method consists of a test sample stage, a mass-to-charge ratio acquisition system and a computer operation system. By adopting the method and the device, the damage state of the film or an optical element under strong laser light can be judged rapidly and accurately on line in real time. By applying the method to laser damage threshold test, integration, automation and intelligence of a test system can be realized.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Modern Chinese literary work author identification system and method
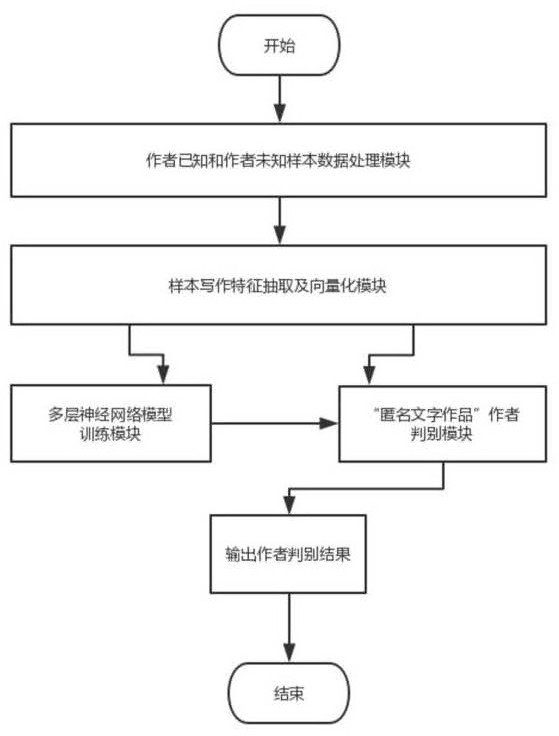
PendingCN111930947AFew training samplesHigh discrimination accuracyNatural language translationCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorFeature extraction
The invention discloses a modern Chinese literary work author identification system and method. The system comprises an author known and author unknown sample data processing module, a sample writingfeature extraction and vectorization module, a multi-layer neural network model training module and an anonymous literary work author discrimination module. The sample data processing module is used for making training sample data and discrimination sample data required by the author identification system; the writing feature extraction and vectorization module is used for extracting language features reflecting writing habits of an author so as to make a training sample vector and a discrimination sample vector; and the multi-layer neural network model training module is used for training a multi-layer neural network model by utilizing the training sample vector data and establishing a discrimination model. The discrimination module is used for discriminating an 'anonymous literary work'author by utilizing the discrimination model according to the writing habit language feature vector. According to the system and method, the identification precision of the'anonymous literary works' author within a specified range is very high and even can be close to 100%.
Owner:施建军
Method for preventing misoperation of zero-sequence direction components without influence of weak feedback
ActiveCN104795805ARealize identificationSmall amount of calculationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase currentsTime domain
The invention discloses a method for preventing misoperation of zero-sequence direction components without influence of weak feedback. The method includes (1), acquiring phase currents and phase voltages of line protection mounting positions; (2), extracting sudden change quantities of the phase currents and the phase voltages; (3), judging whether algorithms for preventing misoperation need to be started or not according to starting criteria for the algorithms for preventing misoperation, and carrying out a step (4) if the algorithms need to be started; (4), computing current error coefficients and voltage error coefficients of two ends of each line, judging whether the lines are perfect lines or not according to comprehensive error coefficient criteria, locking the zero-sequence direction components of the lines if the lines are the perfect lines. The zero-sequence direction components of the lines are not locked if the lines are not the perfect lines. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the perfect lines and the fault lines can be identified only by the aid of single-end electric quantity information of single-circuit lines; the error coefficients can be computed in time domains, and accordingly the method is low in computational complexity and high in judgment speed and sensitivity; the method is applicable to non-weak-feedback systems and weak feedback systems, and correct actions of the zero-sequence direction components always can be guaranteed.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +5
Synchronous phase modifier rotor winding weak turn-to-turn short circuit fault diagnosis method
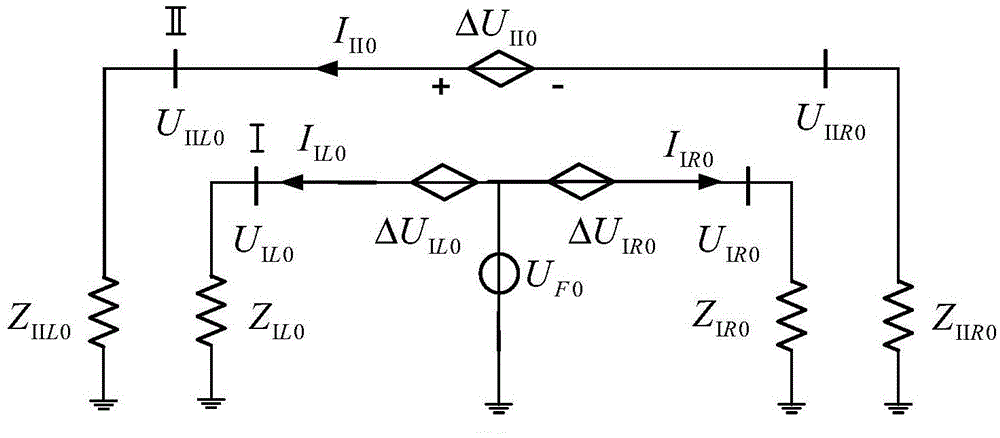
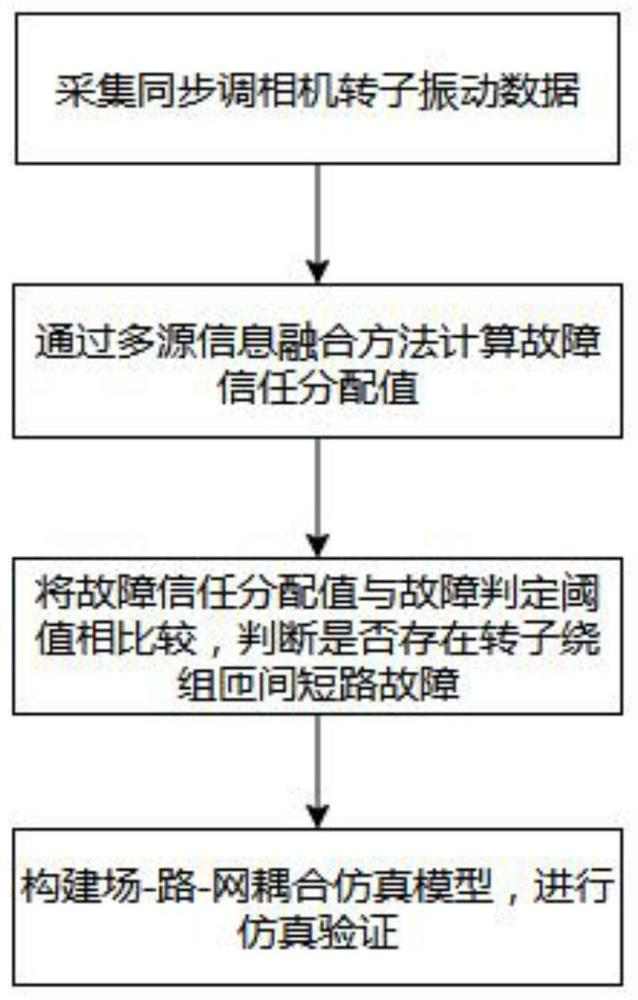
InactiveCN113156309AHigh sensitivityHigh resistance to electromagnetic field interferenceShort-circuit testingDynamo-electric machine testingControl engineeringAir gap flux density
The invention provides a synchronous phase modifier rotor winding weak turn-to-turn short circuit fault diagnosis method, which comprises the following steps: acquiring air gap flux density, rotor amplitude and stator amplitude of a synchronous phase modifier in real time, and selecting the air gap flux density, the rotor amplitude and the stator amplitude of the synchronous phase modifier before and after a fault as evidence bodies; calculating basic trust distribution functions of the three evidence bodies before and after the fault, fusing the three trust distribution functions by adopting an evidence fusion rule, calculating a fault trust distribution value, comparing the fault trust distribution value with a fault judgment threshold value, if the fault trust distribution value is greater than the fault judgment threshold value, judging that the fault exists, and otherwise, judging that the fault exists; and constructing a field-circuit-network coupling simulation model of high-voltage direct-current power transmission containing the synchronous phase modifier, and performing simulation verification. According to the synchronous phase modifier rotor winding weak turn-to-turn short circuit fault diagnosis method, the problem that the existing weak turn-to-turn short circuit fault diagnosis technology of the synchronous phase modifier is insufficient can be solved, and the detection precision of the turn-to-turn short circuit fault of the rotor winding of the synchronous phase modifier is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
A rapid identification device for mine water inrush source
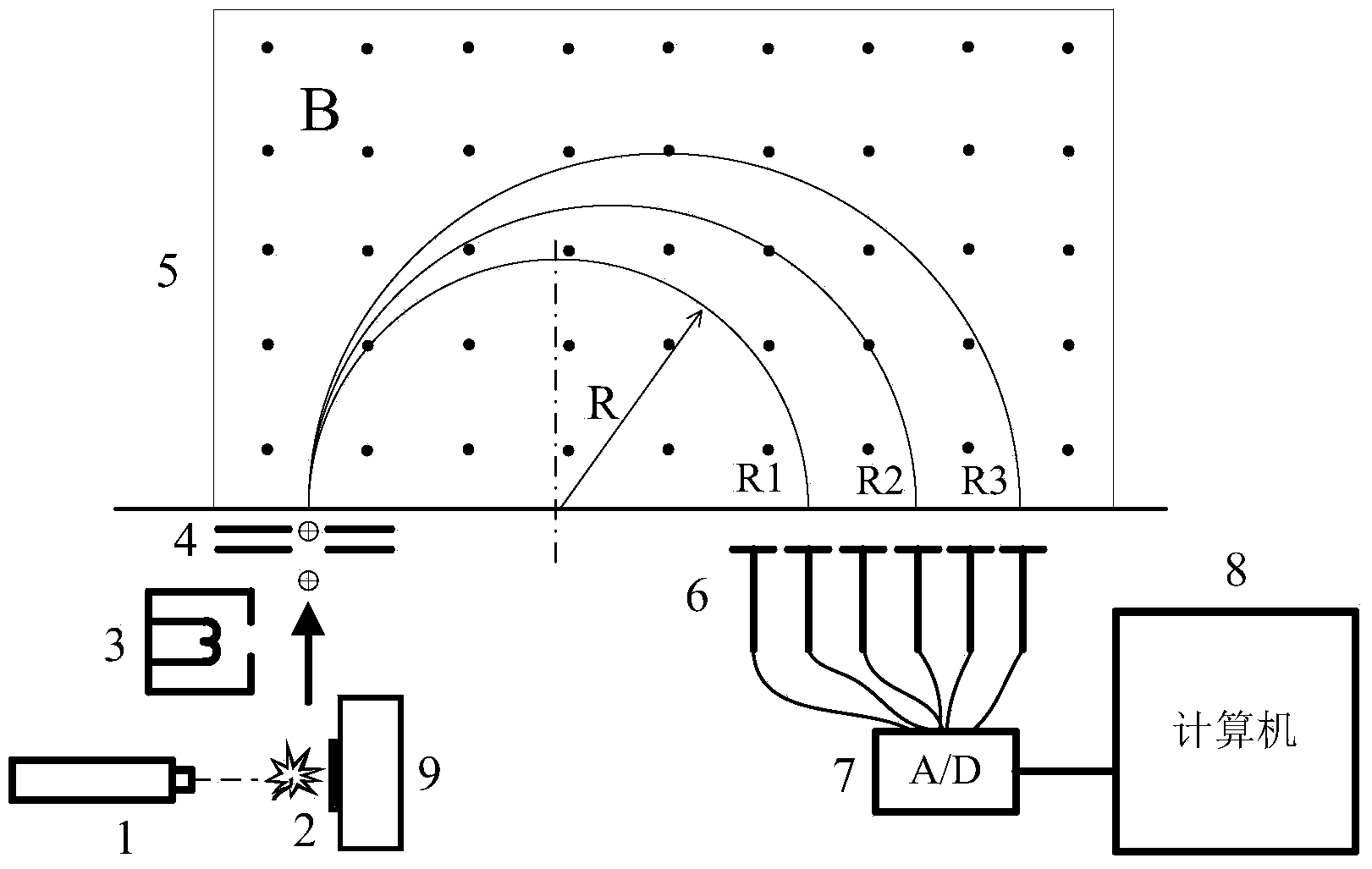
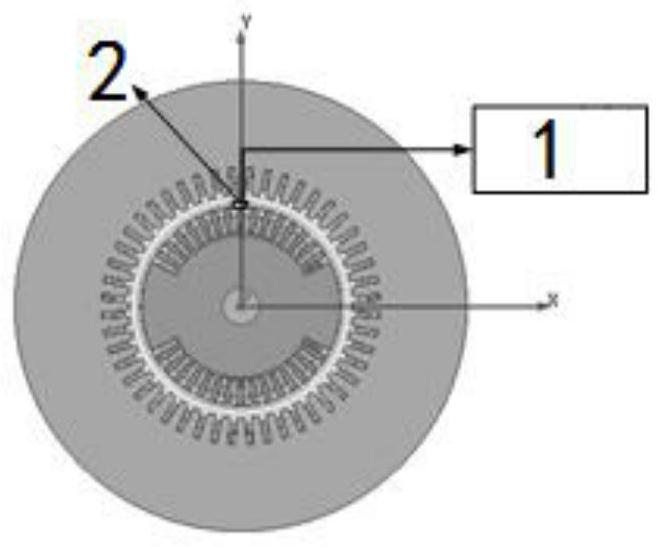
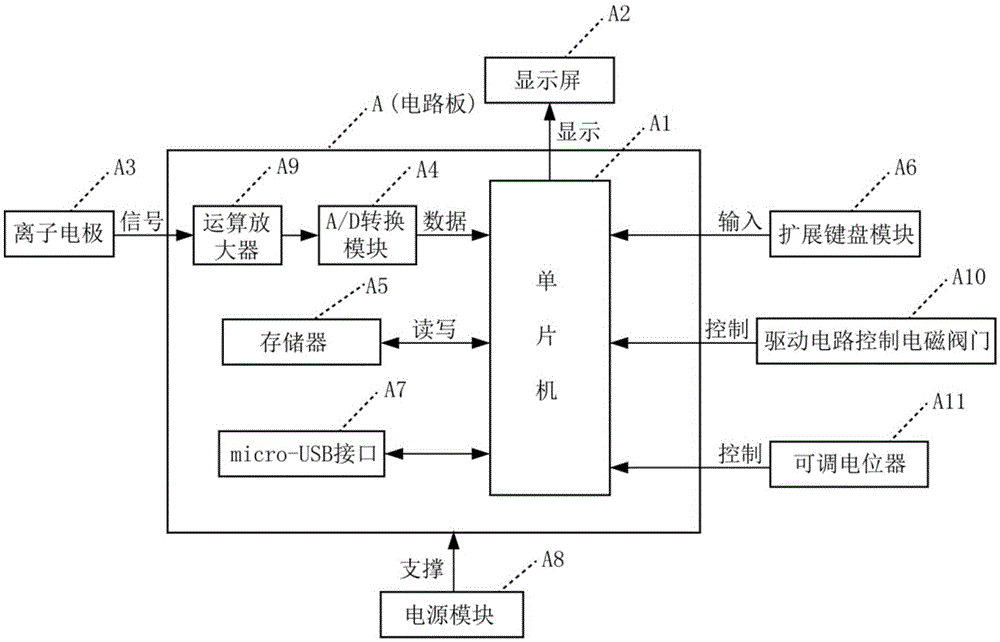
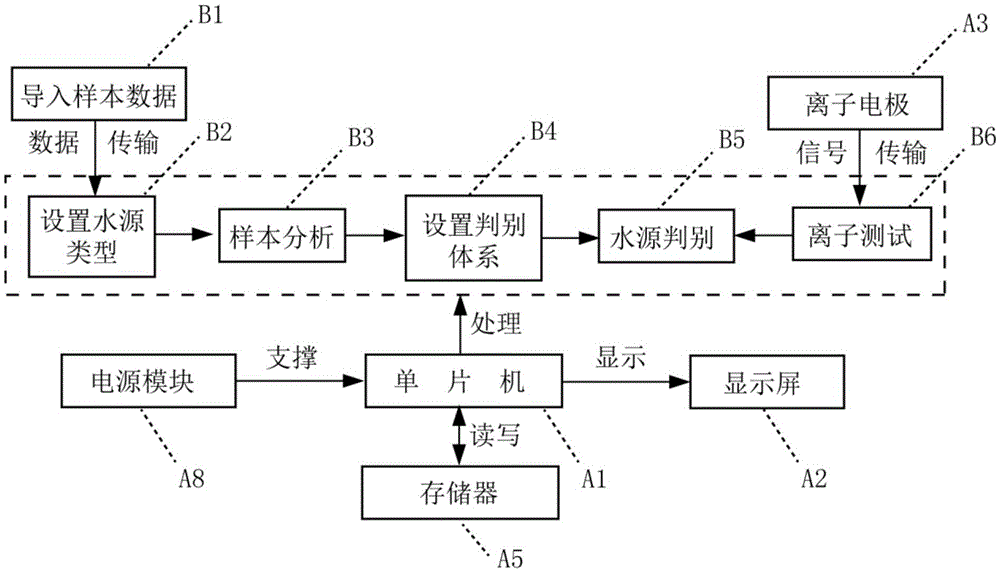
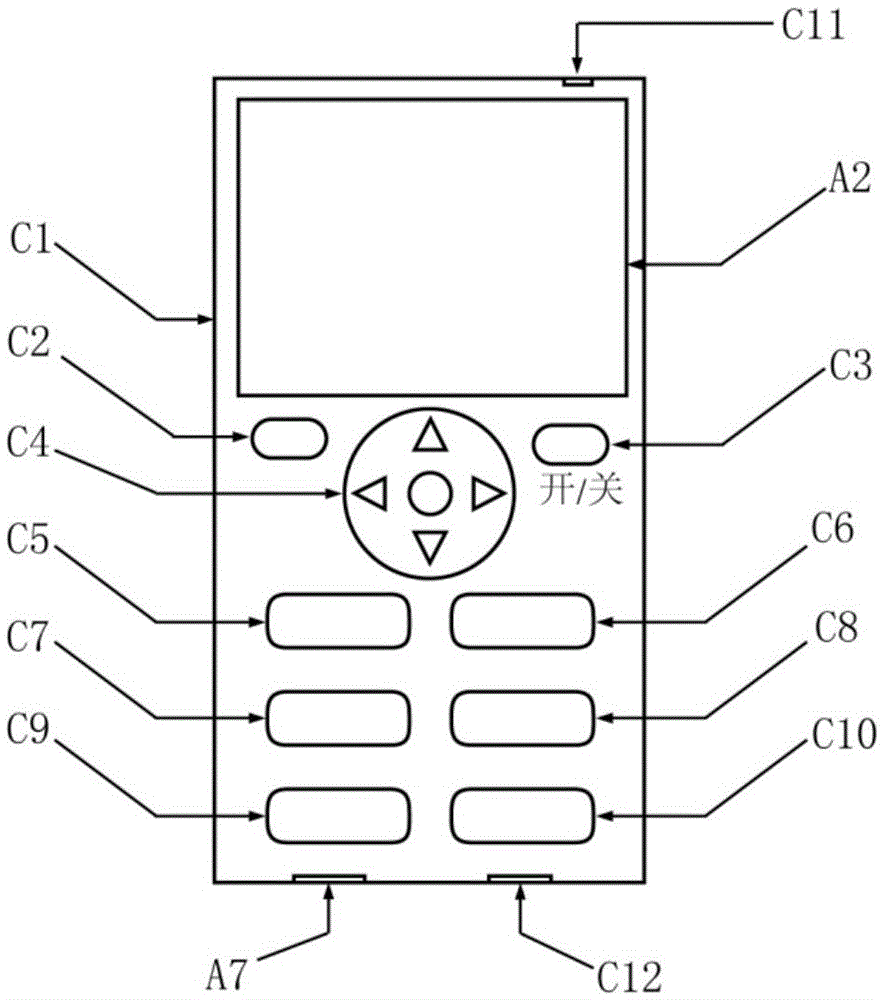
ActiveCN104297308BReduce security threatsDiscrimination speed is fastMaterial electrochemical variablesMicrocontrollerProcess systems
The invention discloses a device for rapidly distinguishing a water inrush source of a mine. The device comprises a shell panel which is provided with a power input interface, a switching on / off button, a mode conversion switch, a function button, a display screen, a micro-USB interface and an ion electrode connecting line interface; a circuit board arranged in a shell takes a singlechip as a core and is connected with the display screen, an A / D conversion module, a memory, the function button, the micro-USB interface and a power module. A method for building a water inrush source distinguishing process system comprises the steps of automatically building a characteristic ion-based distinguishing process system for the water inrush source of the mine by analyzing a known water source category sample in the memory; detecting the water sample by an ion electrode; calculating to obtain actual ion concentration by use of the singlechip according to a Nernst equation; and rapidly distinguishing according to the water inrush source distinguishing process system. According to the device, the characteristic ion detection and the water inrush source distinguishing are integrated, the sample is automatically analyzed, and the distinguishing system is built; the device is high in distinguishing speed, high in accuracy rate and convenient to carry.
Owner:HUAINAN MINING IND GRP +1
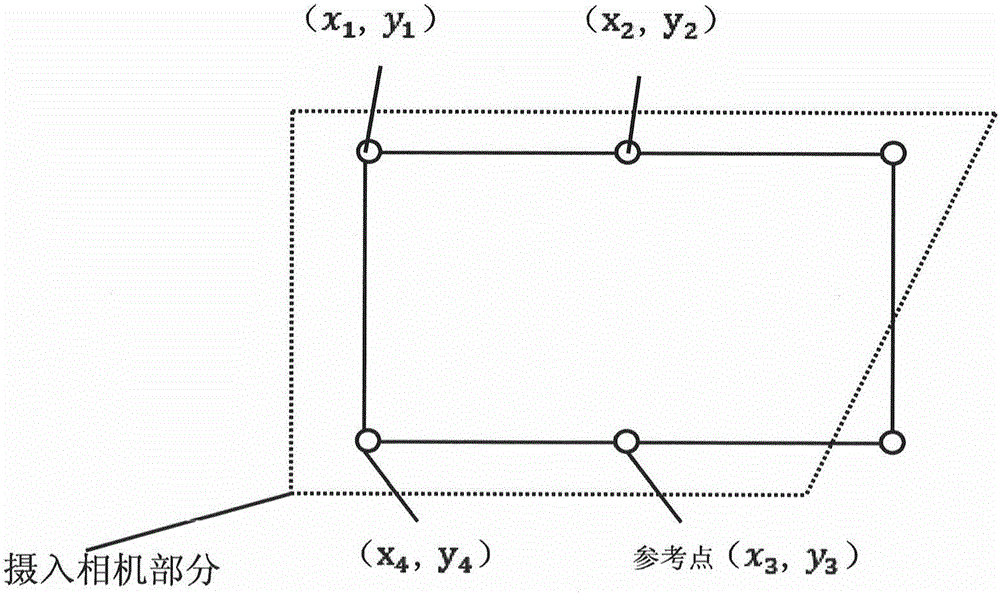
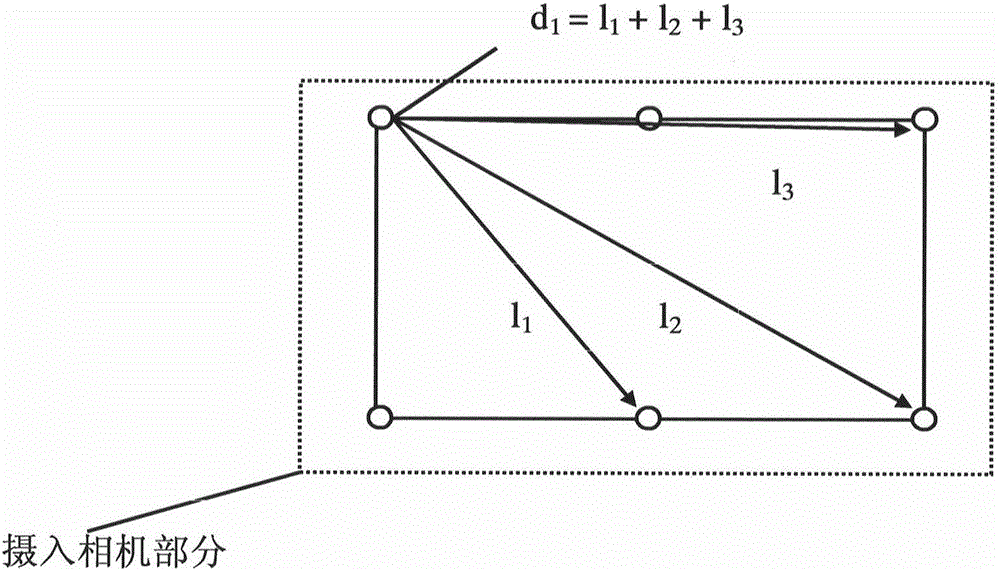
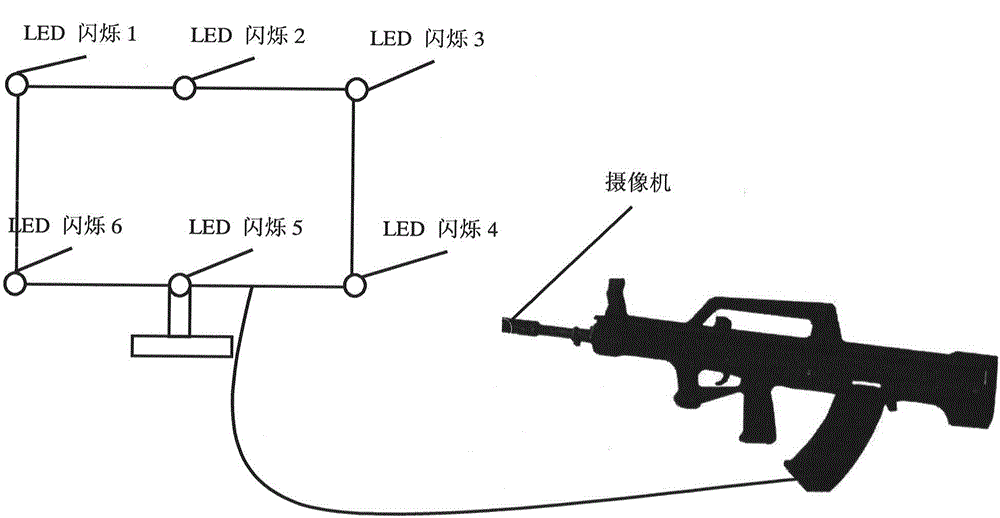
Method for distinguishing optical axis of camera in real time
InactiveCN105066964AReal-time determination of relative poseDiscrimination speed is fastPicture interpretationMachine visionOptical axis
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing the optical axis of a camera in real time, relates to a method for distinguishing relative poses of objects in machine vision in real time, and belongs to the field of machine vision. The method comprises steps as follows: Step one, LED flickers are mounted on a game display screen, a high-speed camera for acquiring images of the LED flickers mounted on the screen in real time is arranged in a virtual gun, and backlight removal treatment is performed on the acquired images of the LED flickers mounted on the screen; Step two, the mapping relation between acquired LED flicker positions and actual positions of the LED flickers on the game display screen is established according to parity of point numbers of the LED flickers, acquired by the virtual gun in real time, on the game screen and the LED flickers, and the relative poses of the objects in machine vision are distinguished in real time. According to the method, the position of the optical axis of the camera in machine vision is distinguished through LEDs arranged on the game display screen and calculation of the virtual gun mapping position relation, and the method is high in distinguishing speed and high in result precision and is slightly interfered by the outside.
Owner:RES INST OF BIT & ZHONGSHAN
A multi-station acoustic response signal analysis method for eggshell crack detection
ActiveCN110187006BImprove accuracyAvoid the effects of signal variabilityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalSignal waveAnimal science
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
The ocean red line adds an automatic and rapid extraction method and device for human activity plaques
ActiveCN111680704BReduce "pseudo-change" recognition rateDetection speedCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial imageBiology
The invention discloses an automatic and rapid extraction method and device for newly added human activity plaques on the ocean red line, belonging to the field of environmental monitoring. In this method, the background vector is used to segment the background image and the image to be detected, and the segmented plaques are discriminated one by one by using the luminance statistical value and the spectral feature function to obtain the changed plaque and the suspected changed plaque; the suspected changed plaque and the local The patches corresponding to the bottom image are segmented twice according to the characteristics of spectrum, geometry, and texture, and the segmented patches are identified one by one by using the luminance statistical value and the spectral feature function to obtain the changed patches; all the changed patches are combined to obtain a new Increase the number of human activity patches; make statistics on the newly added human activity patches, and obtain the number and area of the newly added human activity patches within the ocean red line. The invention can automatically and quickly extract information such as the position, quantity and distribution area of newly added human activity patches in the ocean red line, and provide fast and accurate technical support for the supervision of human activities on the ocean red line.
Owner:MINISTRY OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT CENT FOR SATELLITE APPL ON ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT
Method and system for distinguishing language of document image
InactiveCN101593278BDiscrimination speed is fastHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a method and a system for distinguishing the language of a document image, comprising the following steps: detecting the round white pixel connection domain in the document block of the document file, and determining whether the document block is a Korean on the basis of the detecting the round white pixel connection domain.
Owner:CANON KK
A method for discriminating the mixture of bosa devices
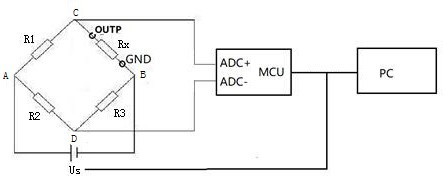
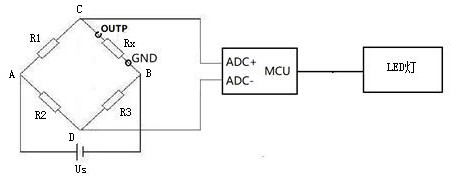
ActiveCN111426902BReduce the risk of mixingDiscrimination speed is fastElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingConvertersControl theory
The invention discloses a method for discriminating mixed materials of a BOSA device, which comprises: Step 1: first replace the variable resistor of the Huygens DC bridge with a fixed resistor, and then set a micro-processor containing a differential signal digital-to-analog converter MCU, and connect the ADC sampling end of the differential signal digital-to-analog converter to the intersection of the two arms of the Huygens DC bridge; Step 2: Insert the OUTP pin and GND pin of the BOSA device into the two ends of the measured resistance terminal, and sampled to obtain the sampled value; Step 3: The microprocessor MCU compares the sampled value with the preset threshold, and judges the type of BOSA device according to the comparison result. The invention can quickly distinguish the GPON OLT BOSA device and the EPON OLT BOSA device at low cost, and greatly reduces the risk caused by material mixing.
Owner:成都蓉博通信技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com