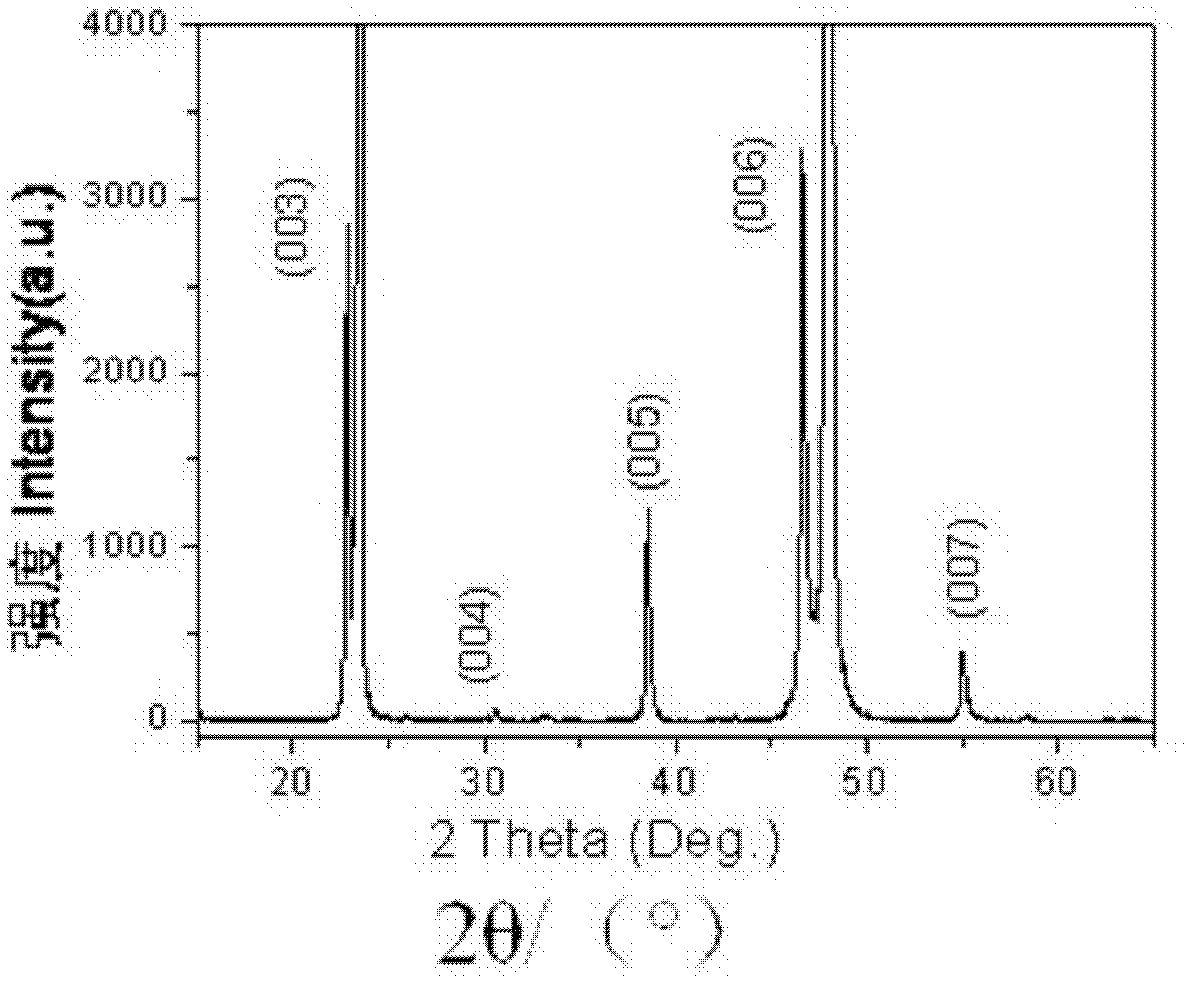
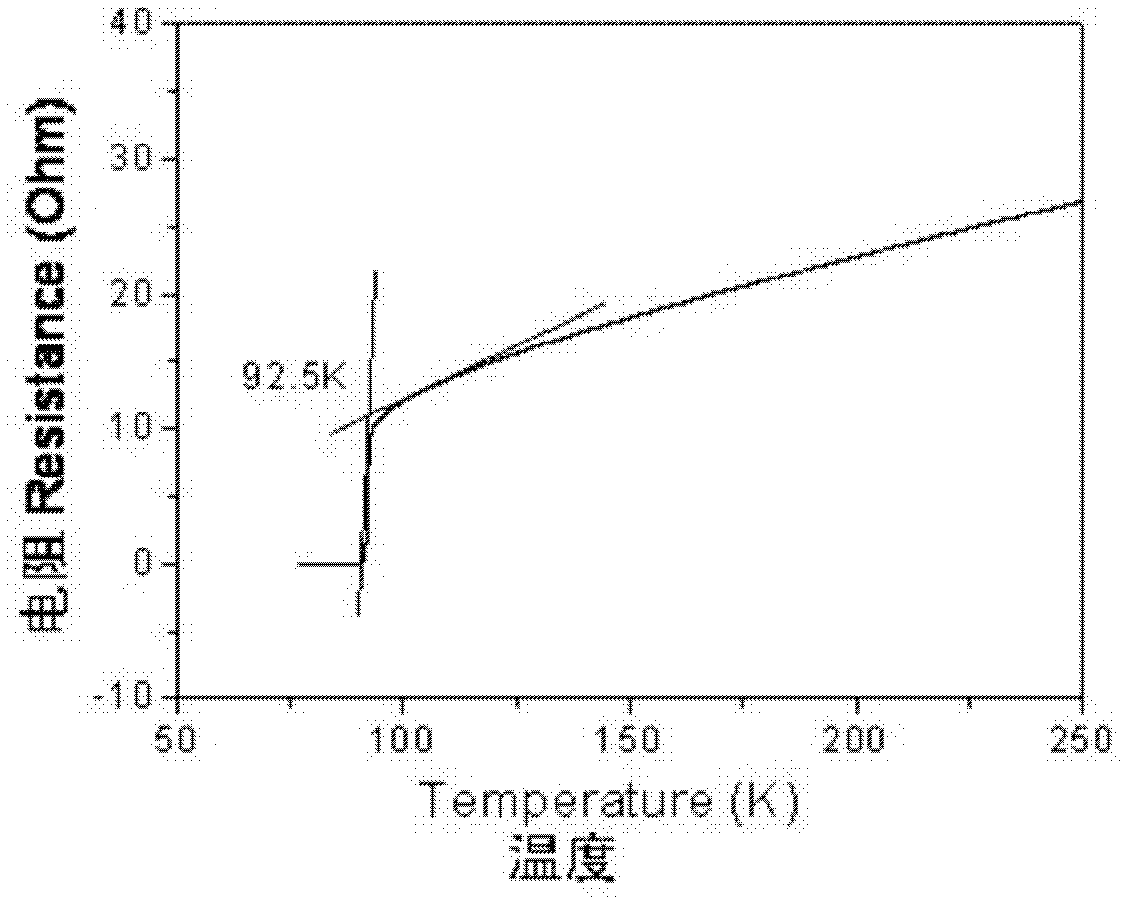
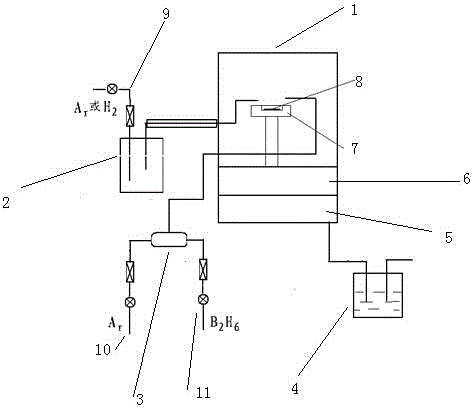
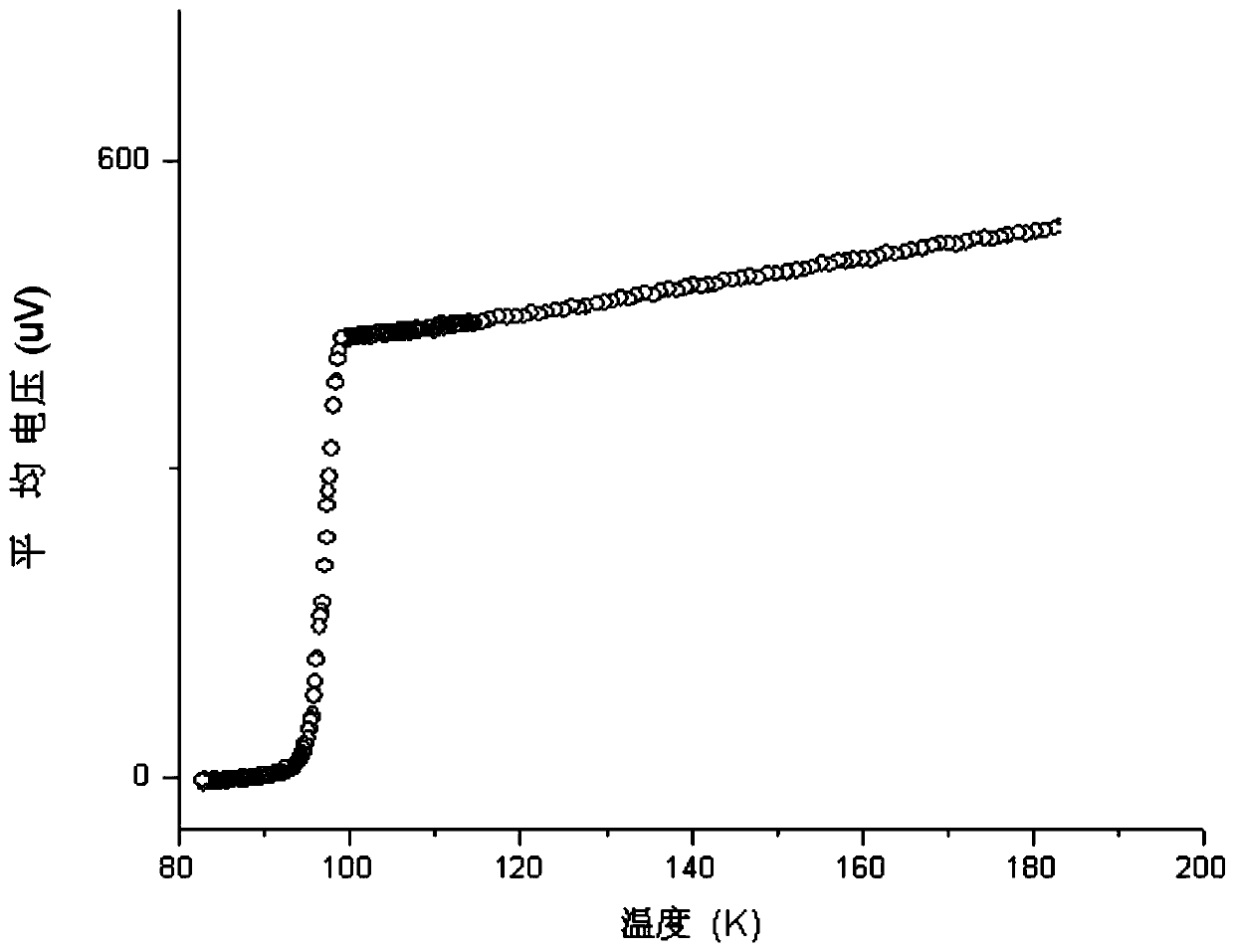
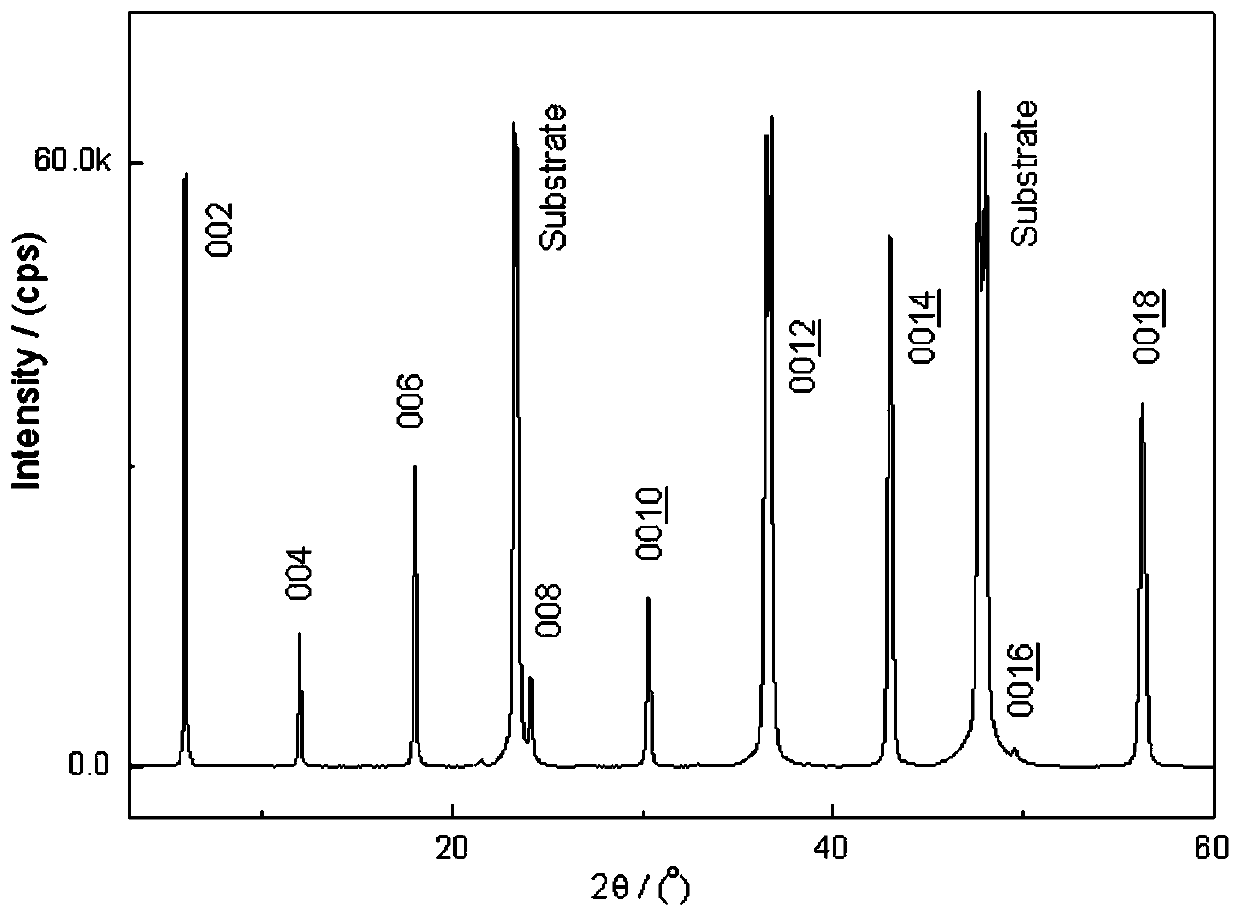
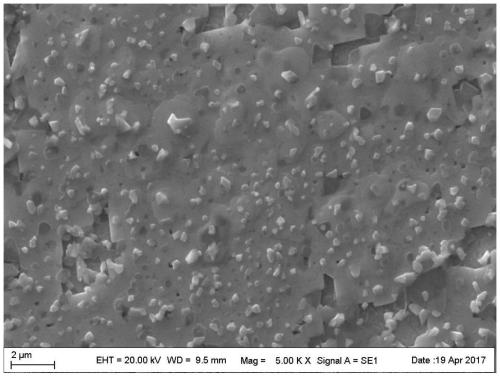
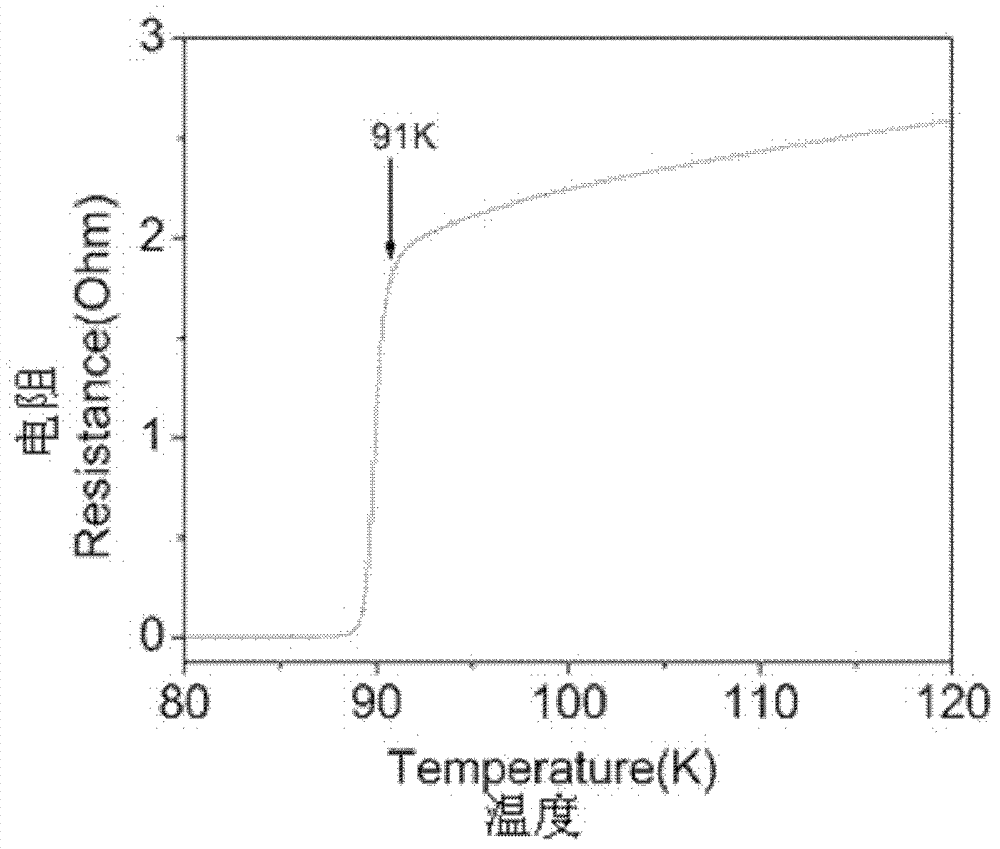
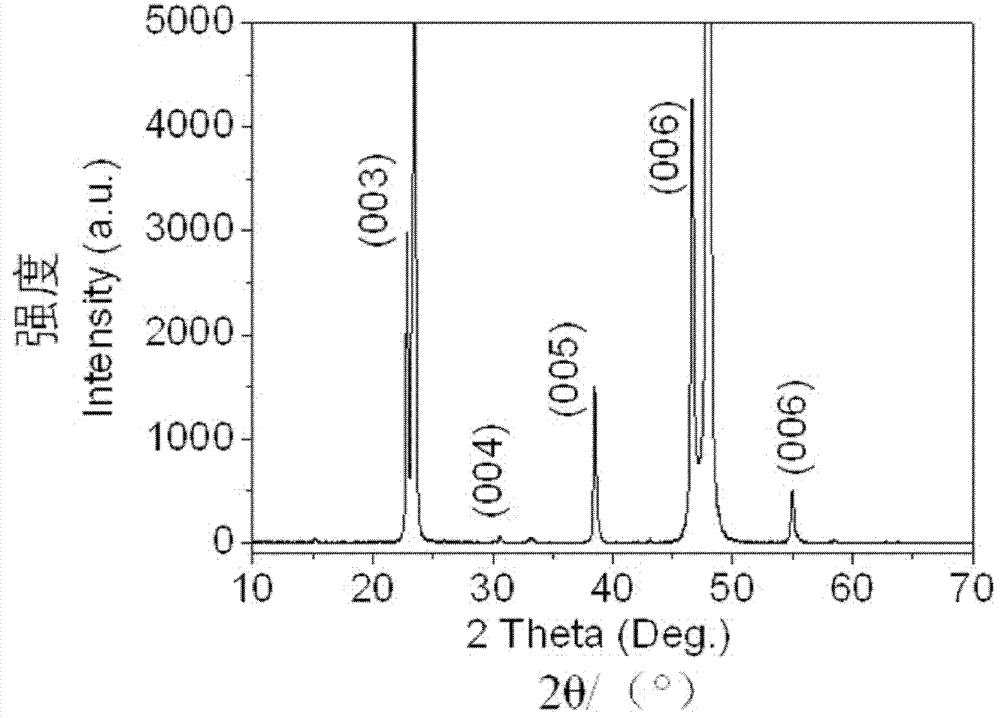
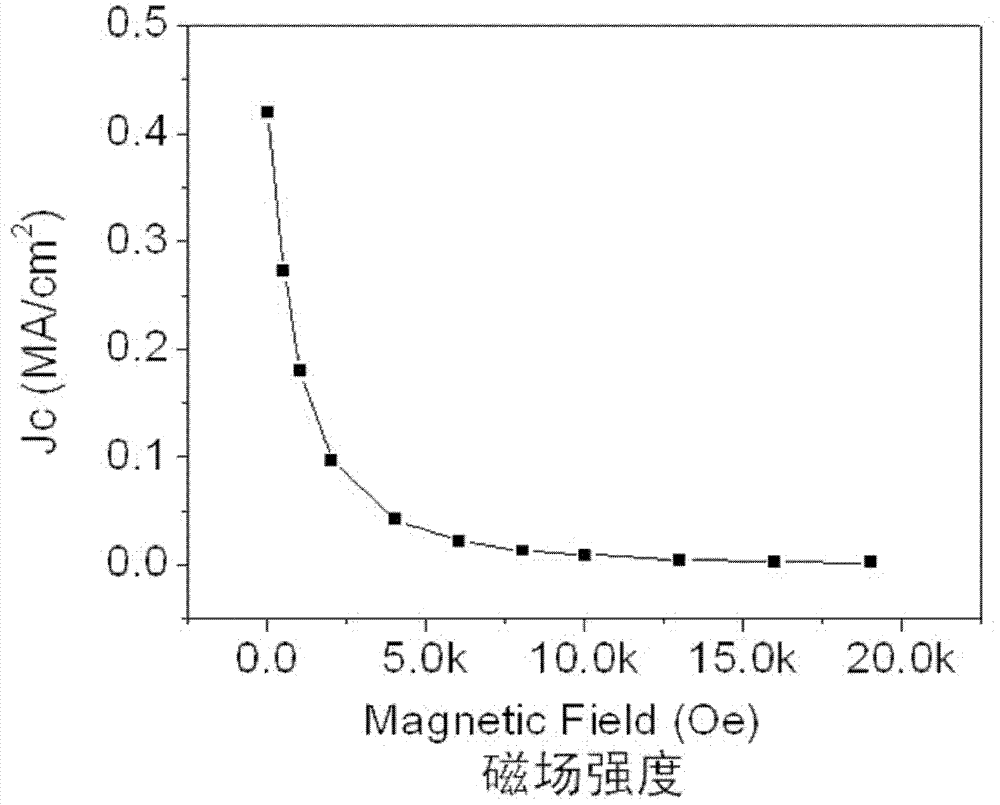
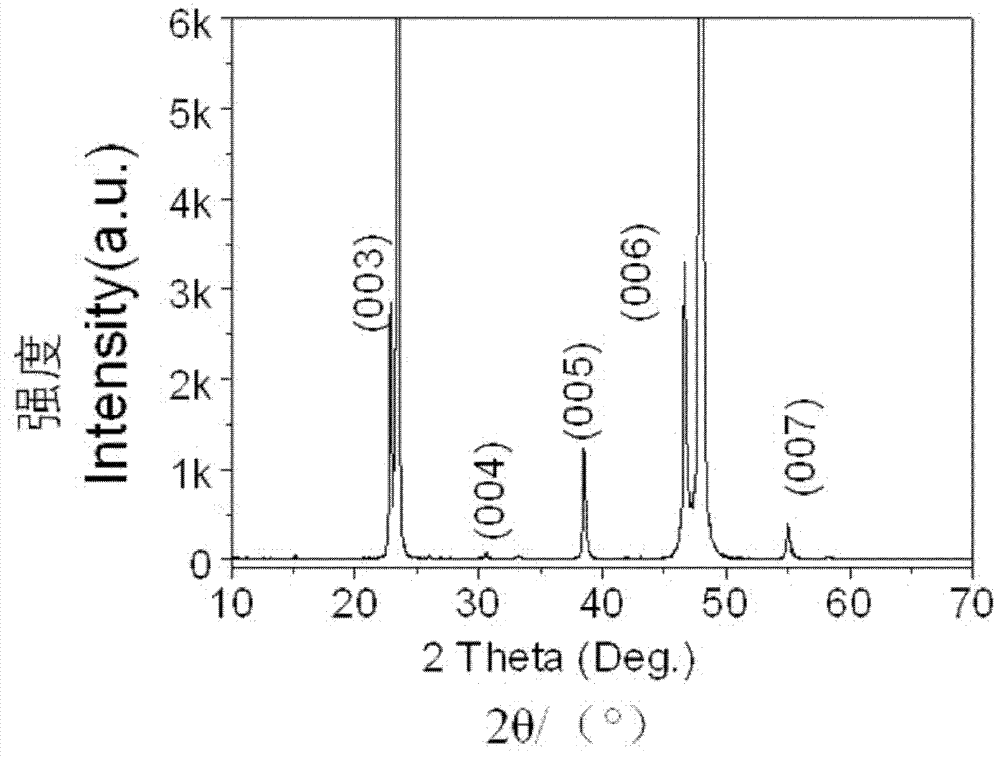
Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Good superconducting properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
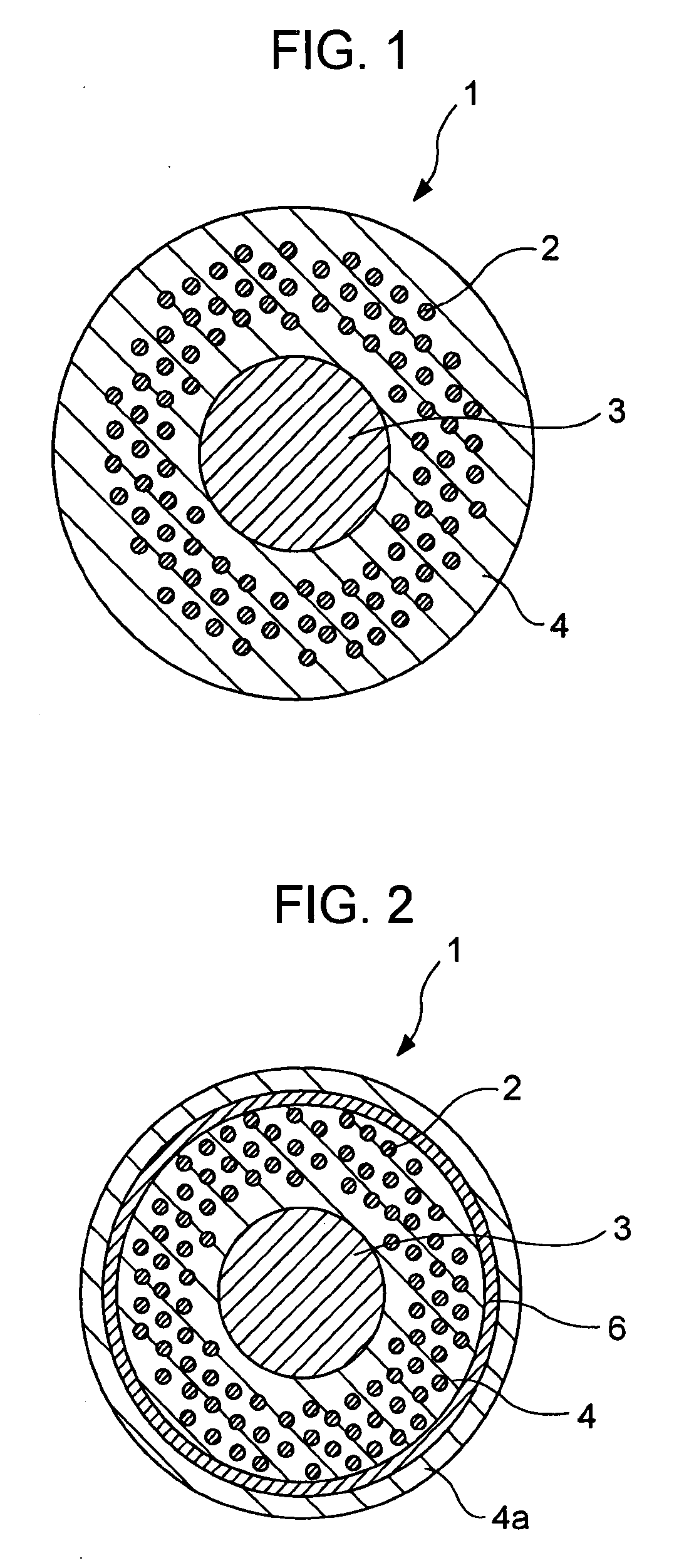
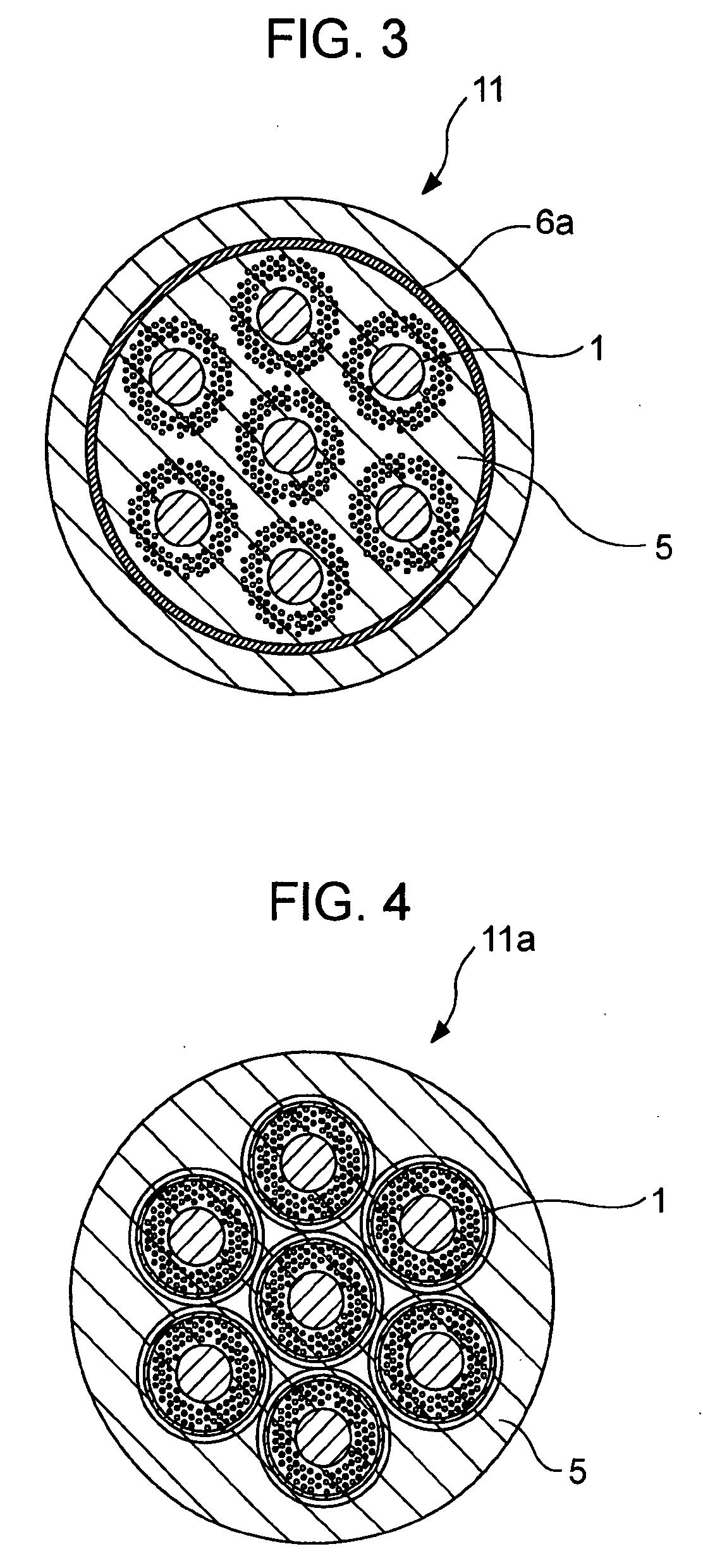
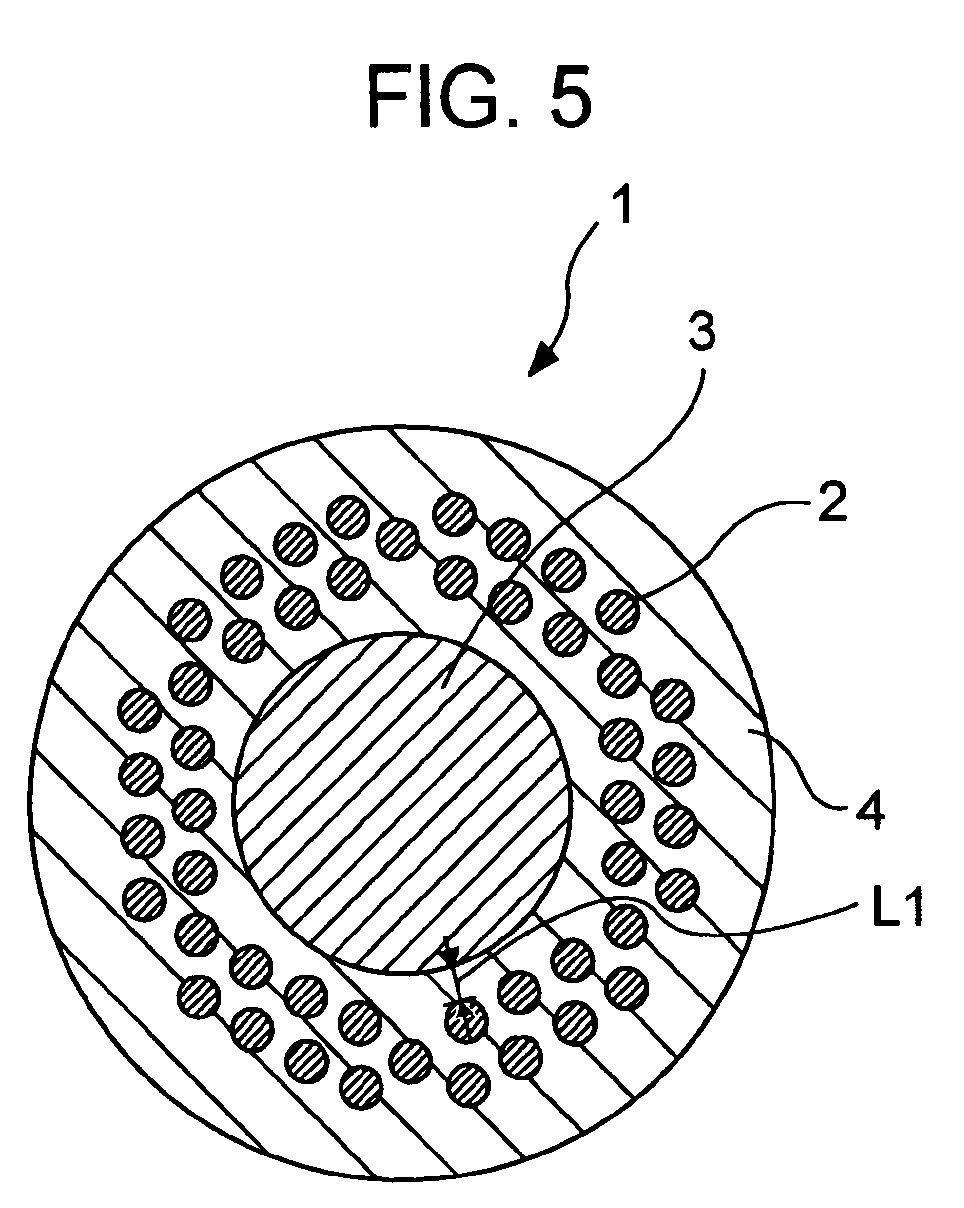
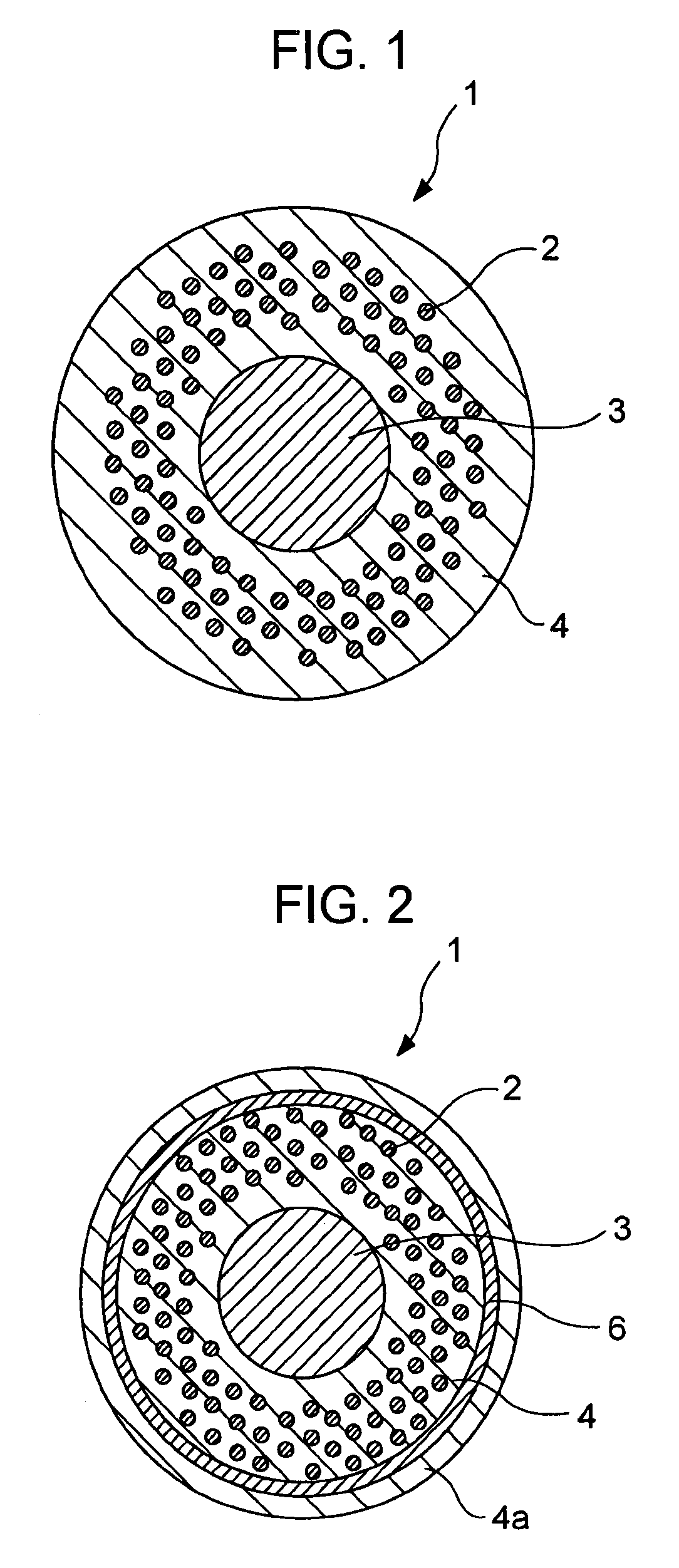
Precursor for manufacturing Nb3Sn superconducting wire and Nb3Sn superconducting wire
InactiveUS20070186998A1Increase the diameterSuperconducting property (or uniformity of electrical current) is excellentSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentAlloyCopper
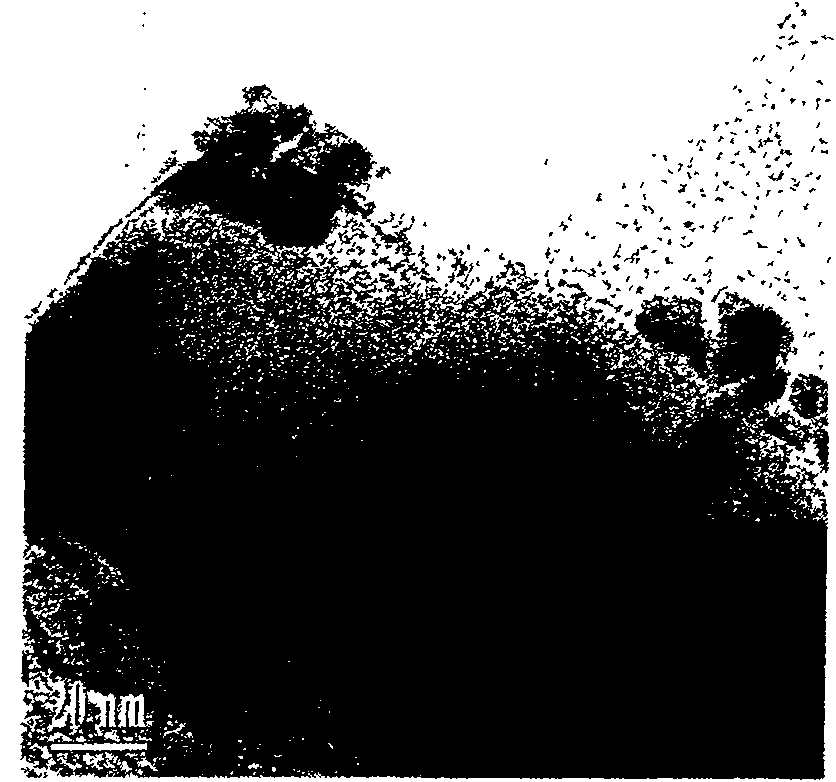
A precursor for manufacturing a Nb3Sn superconducting wire according to the present invention includes a mono-element wire including a Sn or Sn-based alloy core disposed at the, a Cu or Cu-based alloy matrix and a plurality of Nb or Nb-based alloy filaments surrounding the Sn or Sn-based alloy core, and a diffusion barrier layer and a stabilizing copper layer surrounding the Cu or Cu-based alloy matrix. In a final shape after a reduction process, the average diameter of the Nb or Nb-based alloy filaments is set to 5 μm to 30 μm, and the average distance between the Sn or Sn-based alloy core and the Nb or Nb-based alloy filaments nearest the Sn or Sn-based alloy core is set to 100 μm or less.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
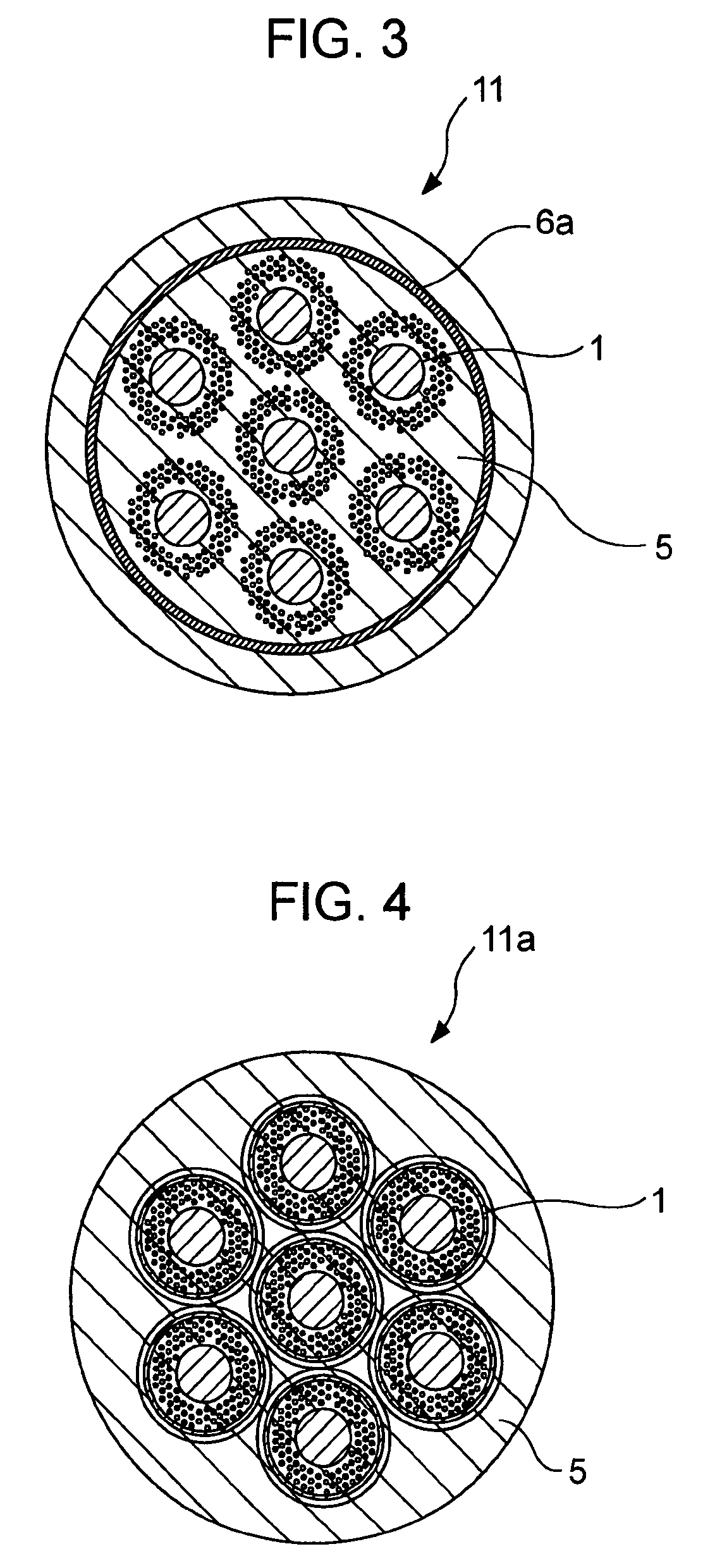
Nb-containing rod-shaped material for use in manufacture of superconducting wire and method for manufacture of Nb3Sn superconducting wire
InactiveCN101313373AEasy to processGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesHot workingRaw material
Disclosed is a Nb-containing rod-shaped material which can be used in the manufacture of a Nb3Sn superconducting wire and can impart good processability to Nb or a Nb-based alloy. Also disclosed is a method for manufacture of a superconducting wire having good superconducting properties by using the Nb-containing rod-shaped material. The Nb-containing rod-shaped material can be produced by the steps of: casting a raw material for the rod-shaped material in a mold having a circular or approximately circular cross-section to produce a molded article; and performing a hot working processing or a cold working processing of the molded article into a cylindrical or approximately cylindrical shape using a processing device having a circular or approximately circular cross-section.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Low-fluorine solution deposition and heat treatment process of YBCO (Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide) superconducting thin film
InactiveCN102443792AIncrease the critical current densityAvoid crackingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSolid/suspension decomposition chemical coatingFurnace temperatureMoisture
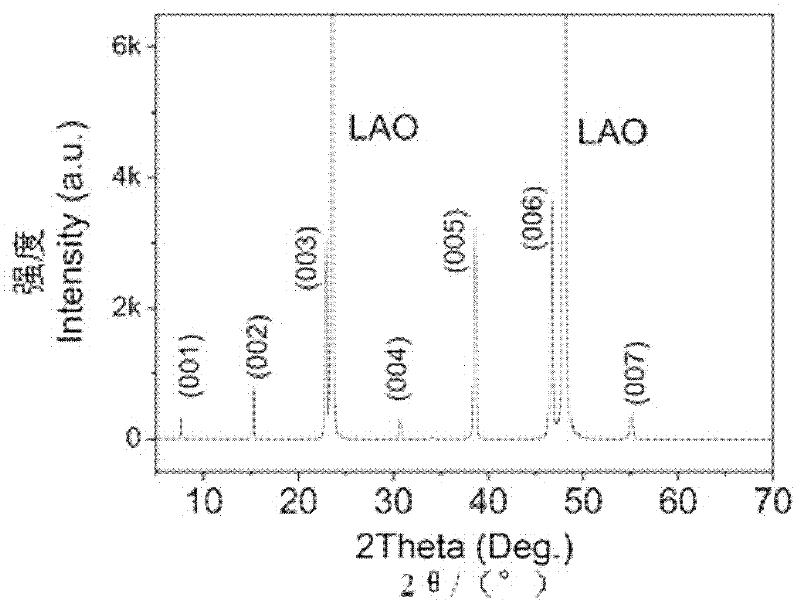
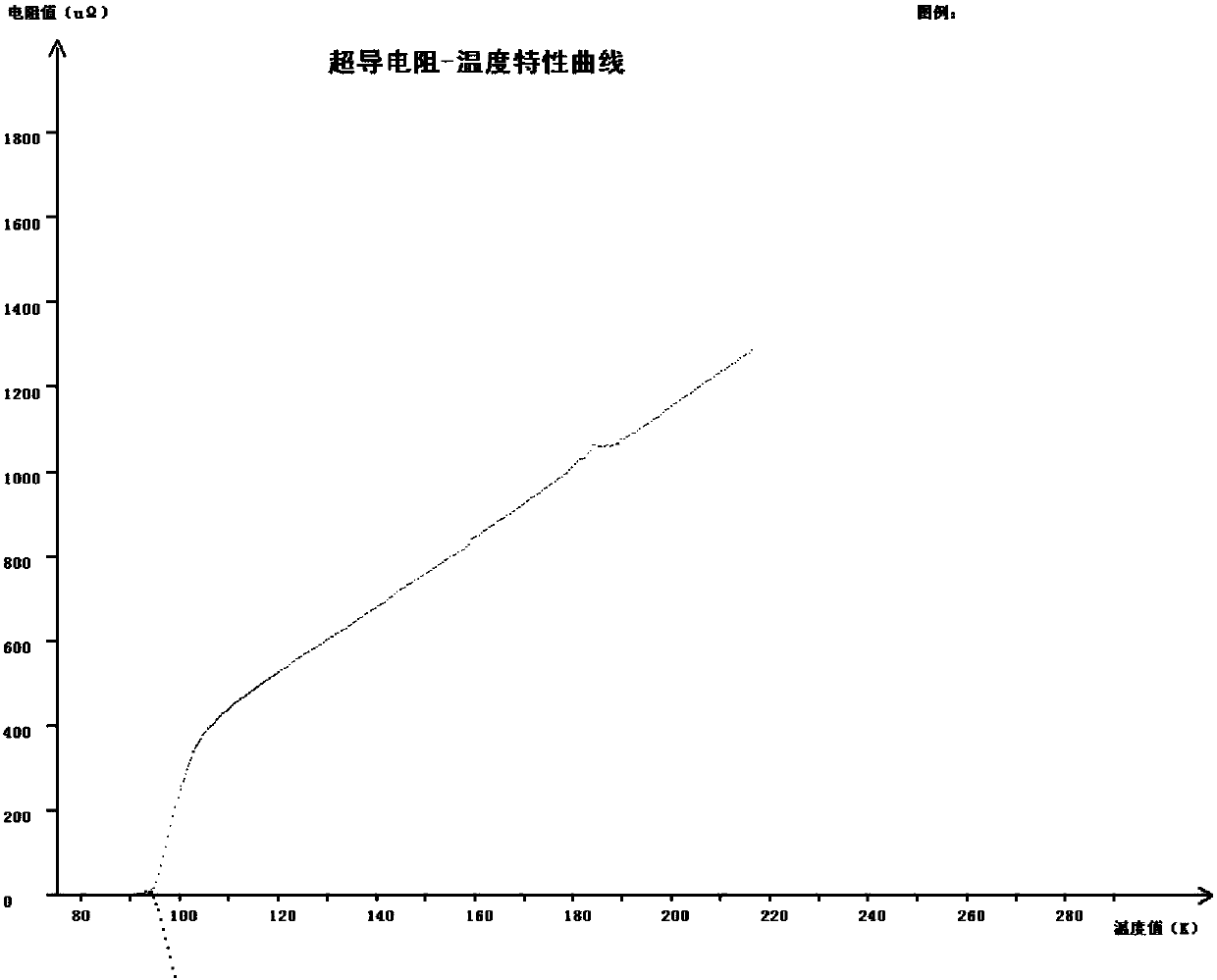
The invention provides a low-fluorine solution deposition and heat treatment process of a YBCO (Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide) superconducting thin film. The low-fluorine solution deposition and heat treatment process comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a low-fluorine YBCO solution; secondly, preparing and drying a gel thin film and pre-treating the dried film; and finally, carrying out final treatment on the dry film: using mixed gas of moisture oxygen gas and inert gas and keeping the mixed gas at the furnace temperature of 790-810DEG C for 1-2 hours; switching the atmosphereinto the mixed gas of dry oxygen gas and inert gas with the same oxygen partial pressure; continuously keeping the mixed gas at the furnace temperature of 790-810DEG C for 10-30 minutes; and finally,naturally cooling the mixed gas along with the furnace, switching the atmosphere into dry O2 after the temperature is reduced to 400-500 DEG C, preserving the heat for 2-4 hours, finally naturally cooling to room temperature along with the furnace and taking out a sample. The YBCO superconducting thin film which is finally obtained in the invention has a high c-axle texture and critical current density Jc as high as (1-5)*106A / cm<2> at the liquid nitrogen temperature.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method for synthesizing T1-2212 superconducting thin film by employing sol-gel method
InactiveCN103304232ASimple processReduce manufacturing costSuperconductor elements usageDiethylenetriamineSolvent
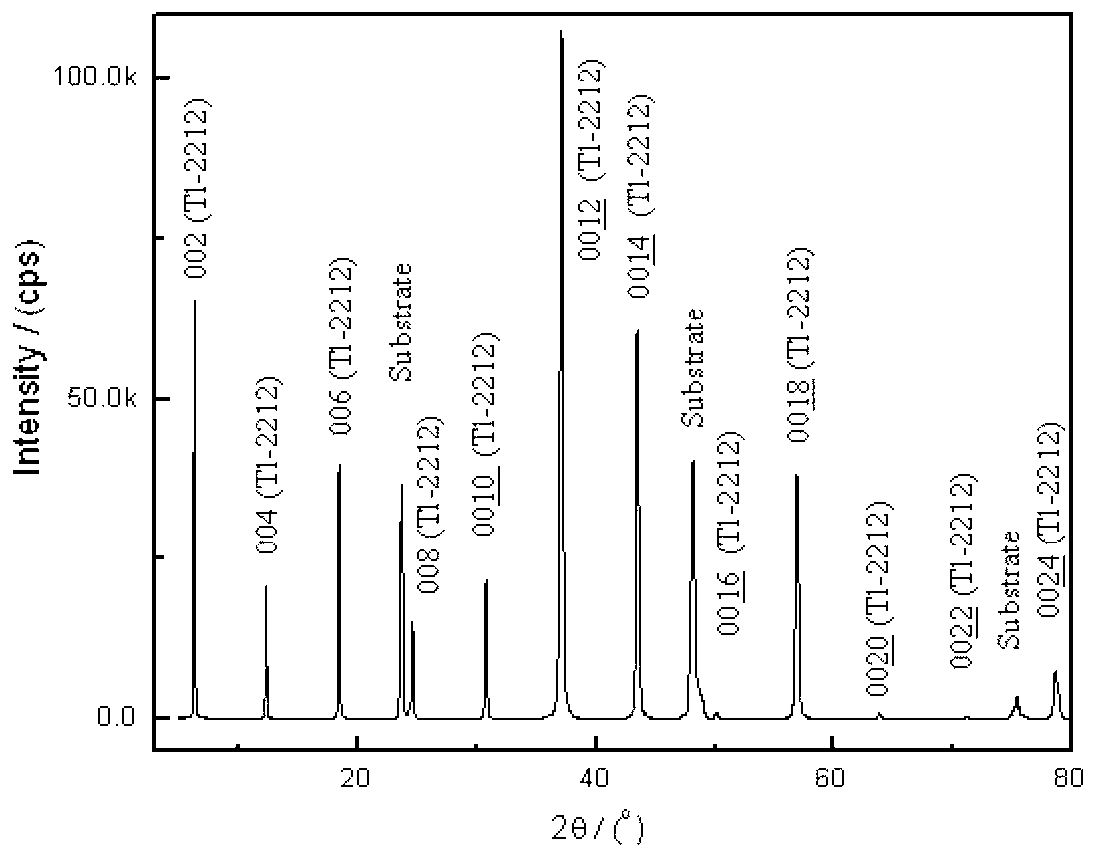
The invention discloses a preparation method for synthesizing a T1-2212 superconducting thin film by employing a sol-gel method. The method comprises the following steps: by taking thallium acetate, barium acetate, calcium acetate and copper acetate as initial raw materials, by taking lactic acid, alpha-methacrylic acid, diethylenetriamine, triethylene tetramine and methanol as complexing agents and solvents, and preparing the sol with proper viscosity. The sol has the characteristics of fewer materials, simple preparation process and easily and accurately controlled components; the T1-2212 superconducting thin film prepared by employing the sol has flat surface topography and good superconducting characteristics.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
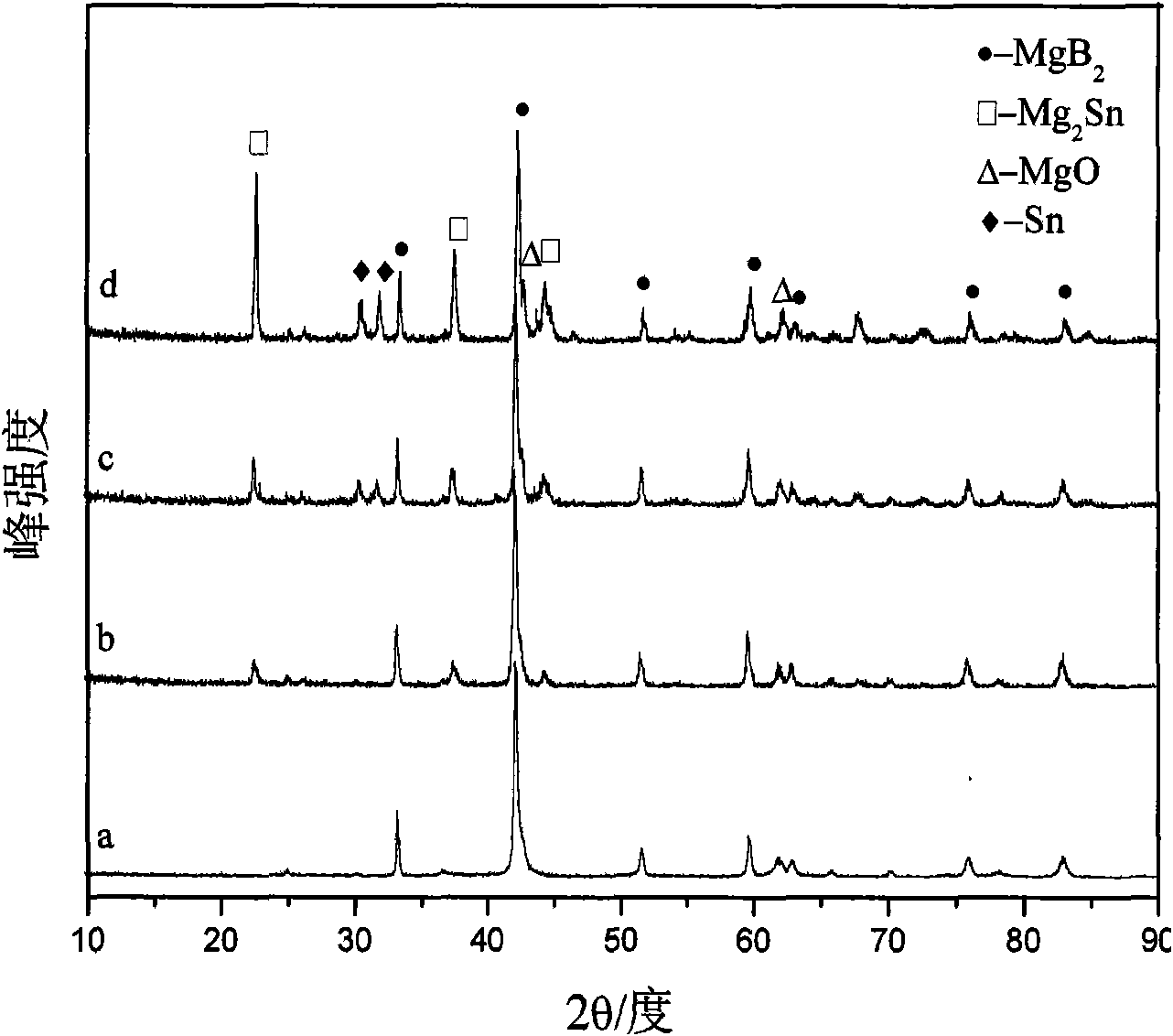
Low-temperature fast powder sintering method for superconductive MgB2 nano particle
InactiveCN101186306AUniform sizeEasy to prepareSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetal boridesFlux pinningRoom temperature
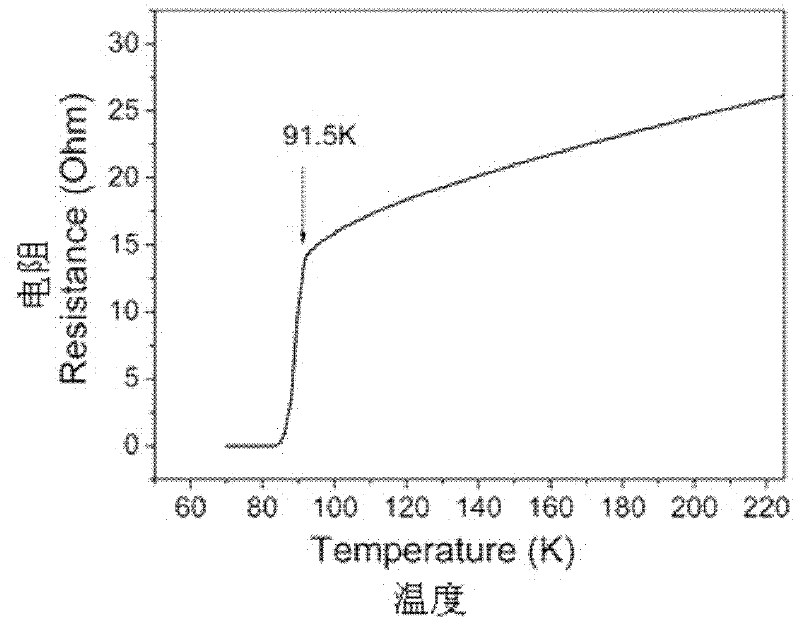
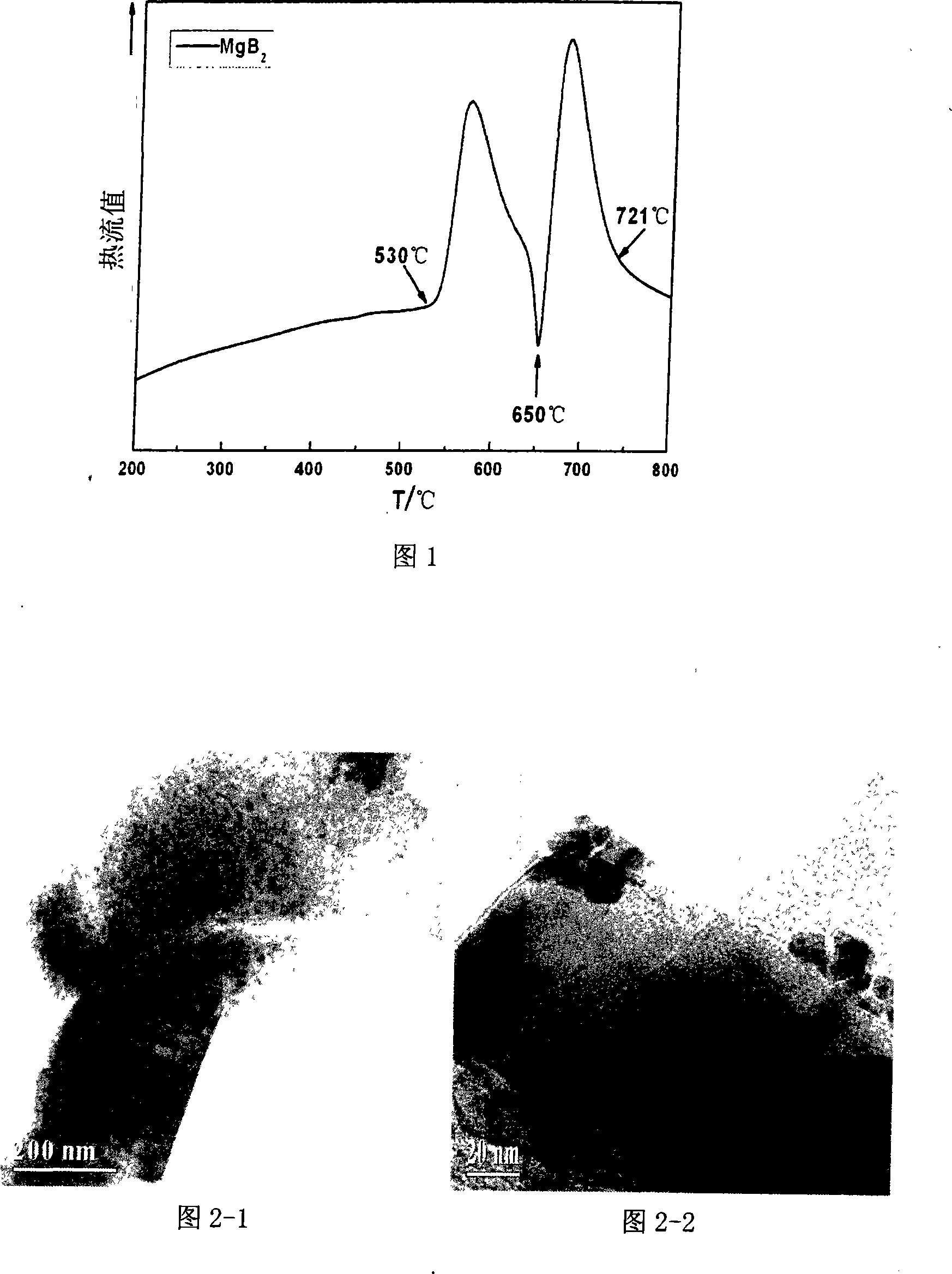
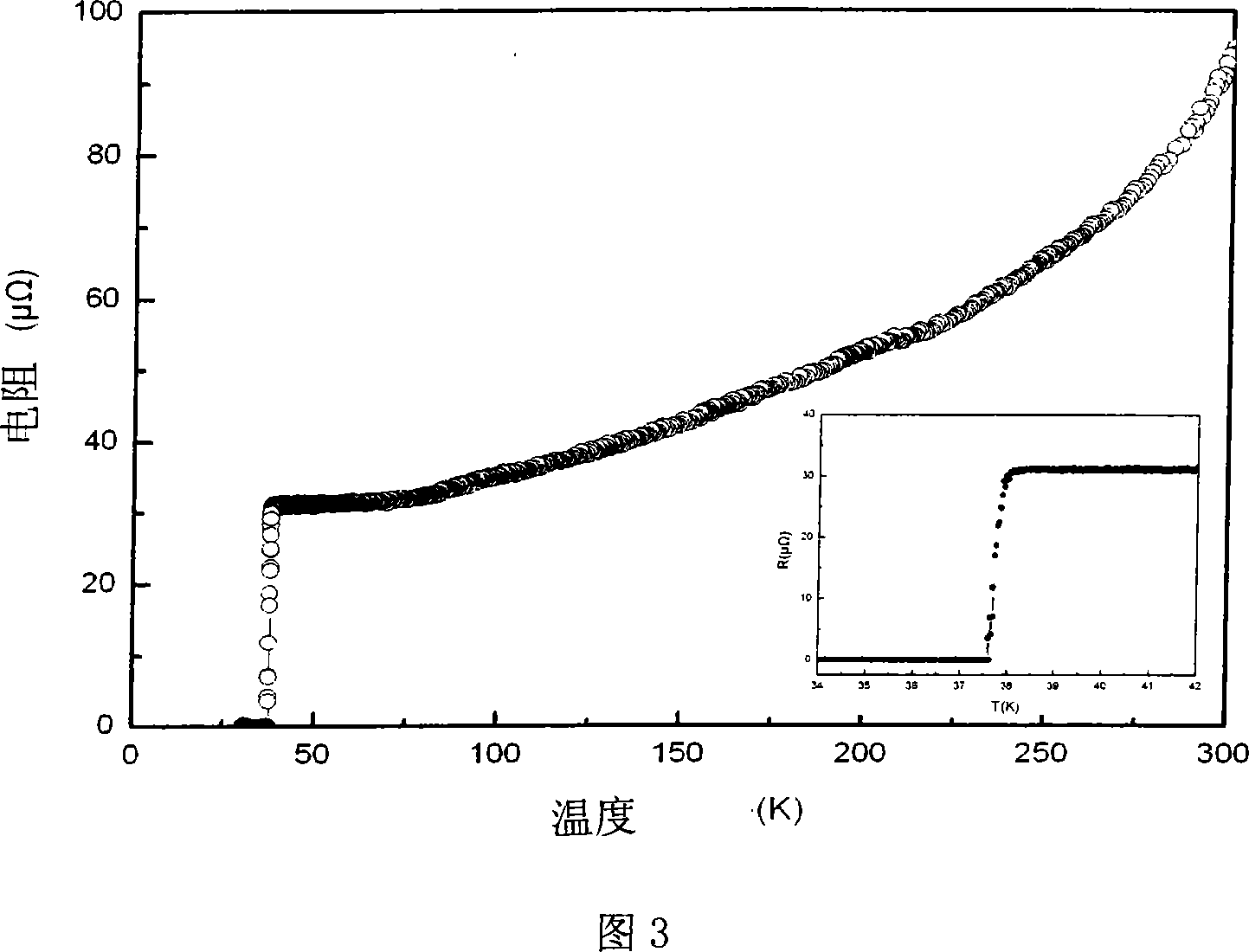
The invention discloses a low-temperature fast powder sintering method for a superconduct nano-particle MgB2, which comprises the steps: magnesium powder and amorphous boron are mixed according to atomic ratio: Mg:B is equal to 1-1.5:2, then the compound is grinded for 0.3 to 2 hours and is pressed into block under the pressure of 2-7MPa; the block is added into a heating device and is added with argon, and the temperature raises to 980K - 1010K at the speed of 20 - 40K / min, then the temperature lowers to room temperature at the speed of 40 - 50K / min, and the superconduct nano-particle MgB2 is made. The diameter of MgB2 of the invention is about 10 to 20nm; Tc value is up to 38.5K, when the MgB2 nano particles are used for measuring superconducting transition temperature, which can not only maintain superconducting transition temperature close to theoretical value, but also be taken as the center of flux pinning, thereby enhancing critical current density.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing MgB2 superconductive material
InactiveCN1569633ASimple manufacturing processGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetal boridesCrucibleFree cooling
The invention relates to a process for preparing MgB2 superconducting material which comprises the steps of, grinding B2O3 and Mg powder under the protection of oinert gas, loading the grinded raw material into ceramic crucible, sintering the crucible in vacuum pit furnace, naturally cooling down to room temperature in vacuum or under the inert gas protection status.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
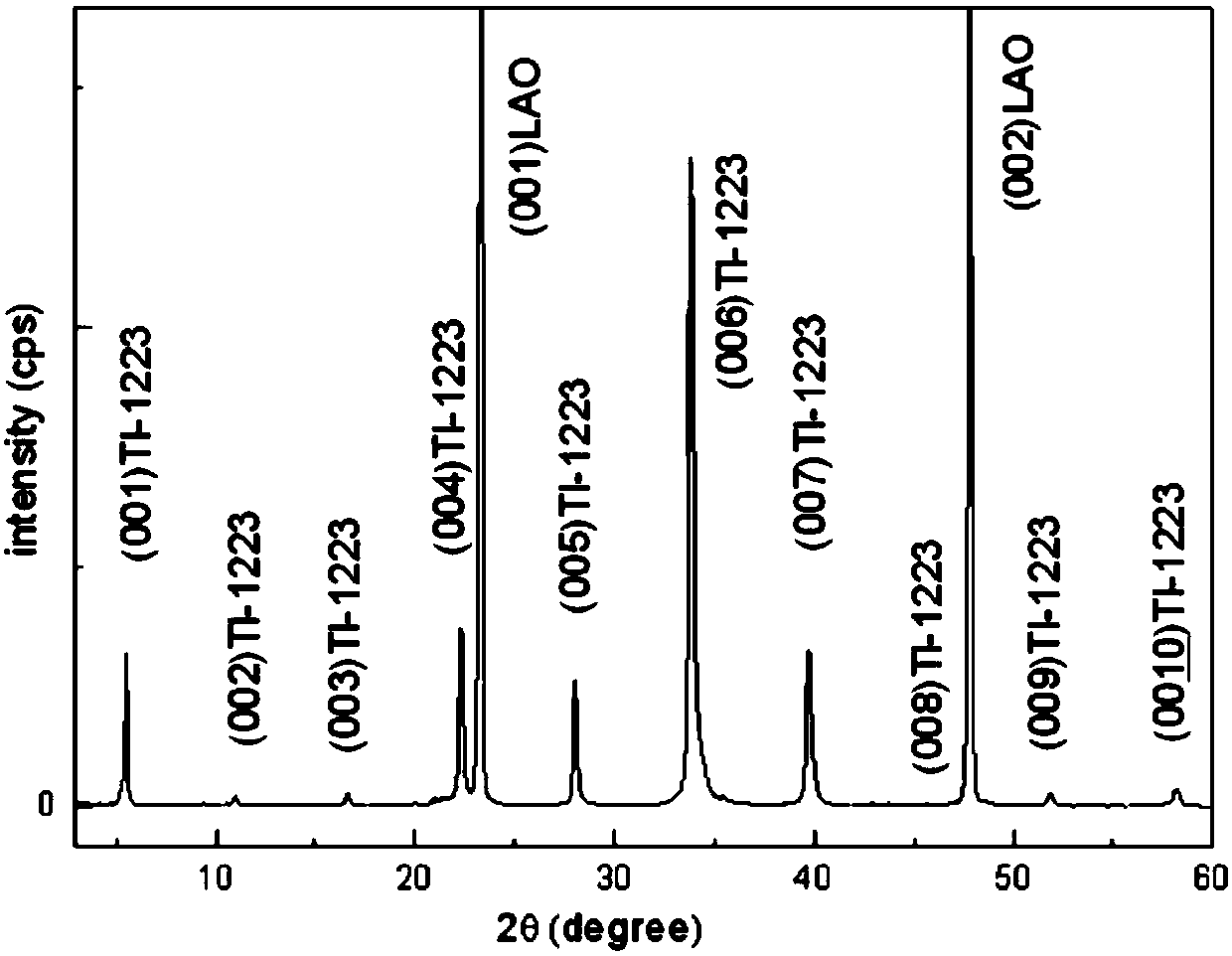
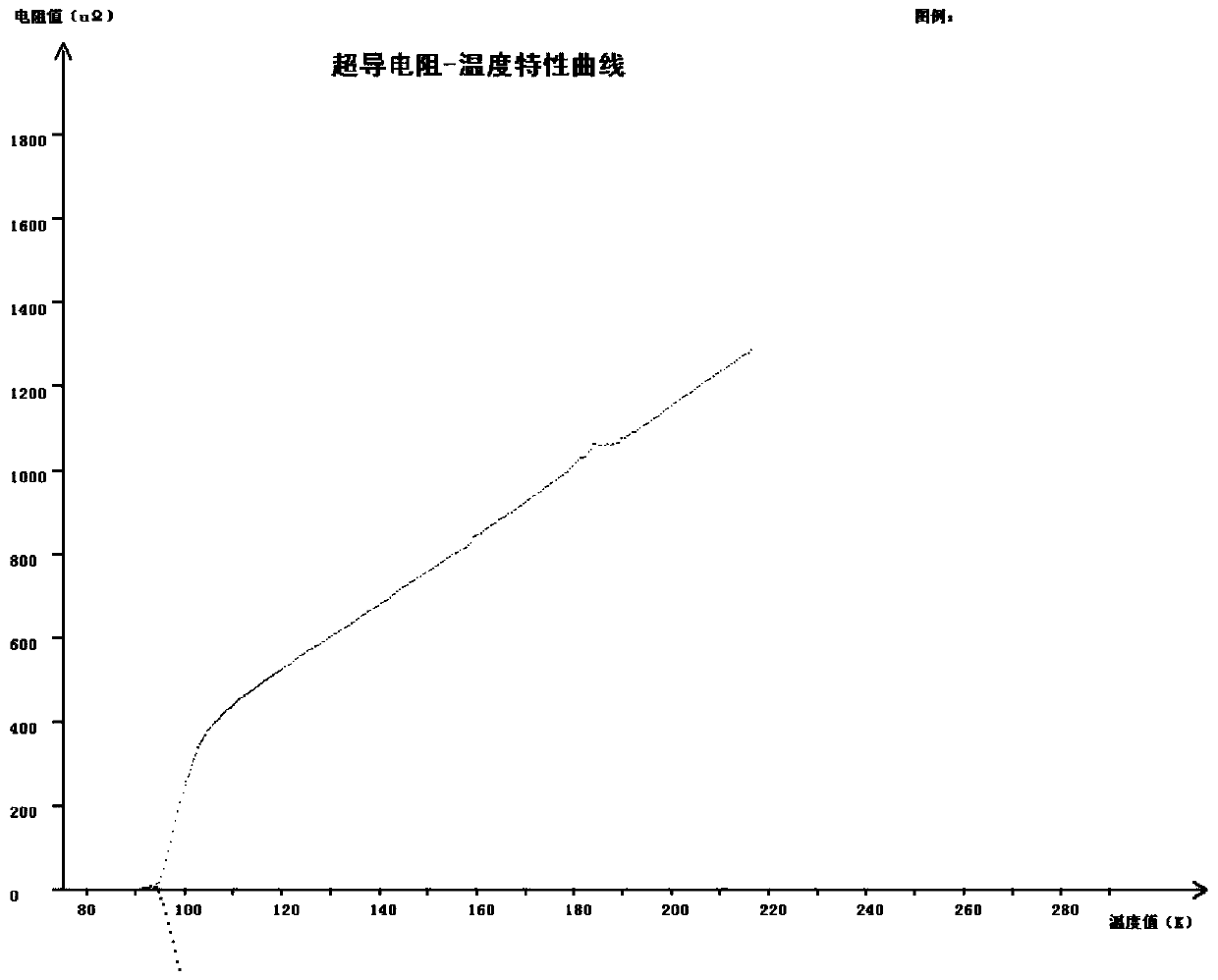
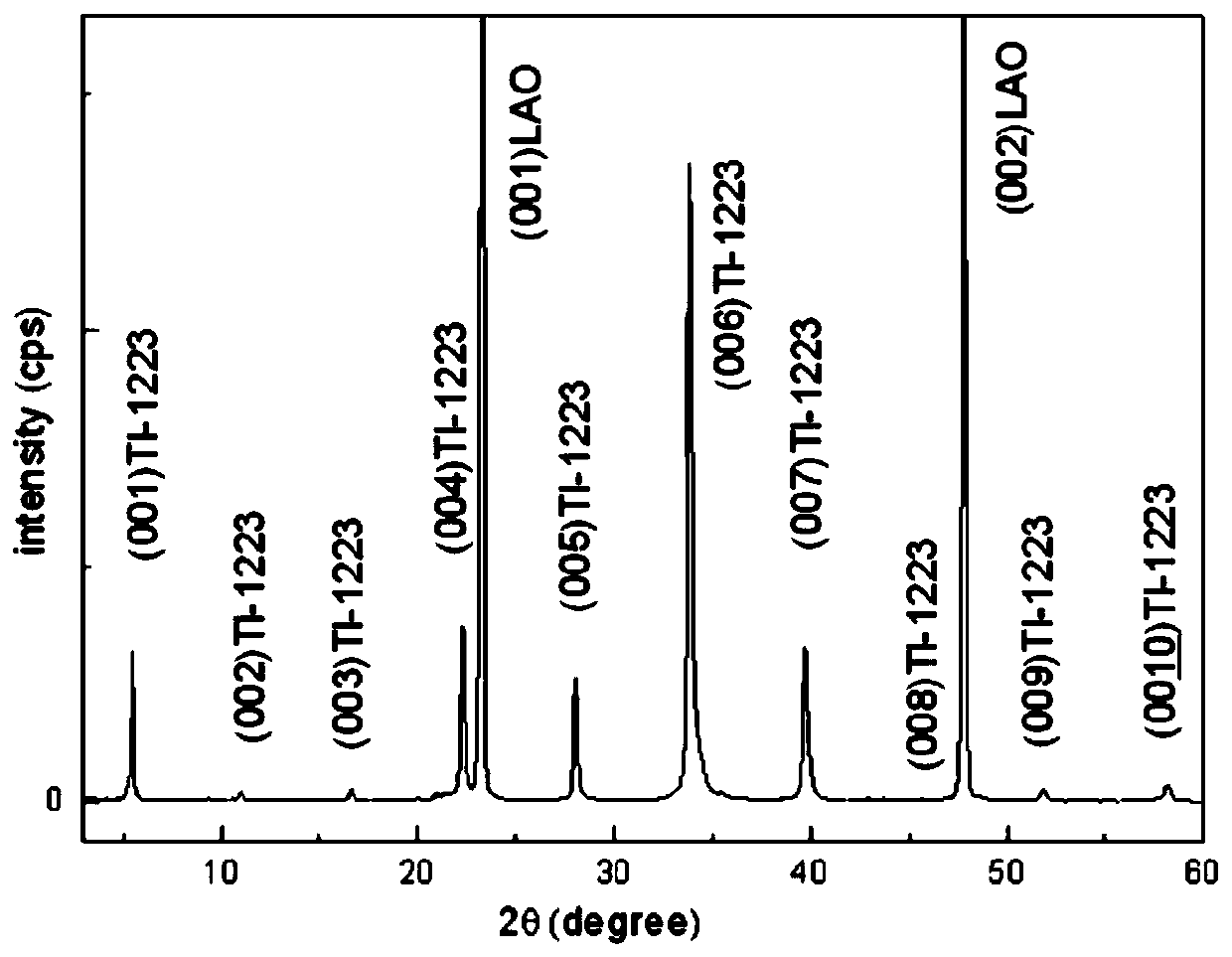
Method of preparing Tl-1223 superconductive thin film
ActiveCN107602112AFlat surfaceExcellent superconductivitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesThalliumOxygen
The invention discloses a method of preparing a Tl-1223 superconductive thin film. In the invention, a thallium-containing amorphous precursor film and a thallium-containing sintering accompanying target are sealed and coated with a silver foil or a gold foil, and then sintering is carried out in a sealed argon gas or a flowing oxygen environment. In the method, phase forming temperature zone of low-temperature phases, such as Tl-1212 and Tl-2212, can be crossed quickly and Tl-1223 superconductive phase temperature zone is directly reached, thus producing a pure-phase thin film. The method isshort in temperature increase / decrease time and constant temperature time and is low in production cost.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Metal Sn doped MgB2 superconductor and high-temperature rapid preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101591172AMaintain the superconducting transition temperature valueGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductivityAtomic ratio
The invention relates to a metal Sn doped MgB2 superconductor and a high-temperature rapid preparation method thereof. A structural formula of the superconductor is (Mg1.02B2)1-xSnx, wherein x=0.01-0.05. The method comprises the following steps: fully mixing Mg powder, B powder and Sn powder according to atomic ratio, pressing and preparing the mixture into a cylindrical flake under the pressure of 2 to 10 MPa, and then putting the cylindrical flake into a high temperature differential scanning calorimeter or a tubular sintering furnace for sintering; and continuously heating the cylindrical flake to 850 to 900 DEG C at heating rate of 5 to 20 DEG C per minute for sintering treatment, and cooling the cylindrical flake to room temperature at cooling rate of 30 to 40 DEG C per minute. The practical application field of MgB2 is in an around 3T magnetic field, so the method improves the superconductivity of the MgB2 superconductor in a short time by doping metal Sn and using a high-temperature sintering method. The preparation method is simple, has low cost of the raw materials and short preparation time, and is a quite potential research method; and simultaneously, the obtained superconductor has obvious superconductivity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Process for producing superconducting oxide material
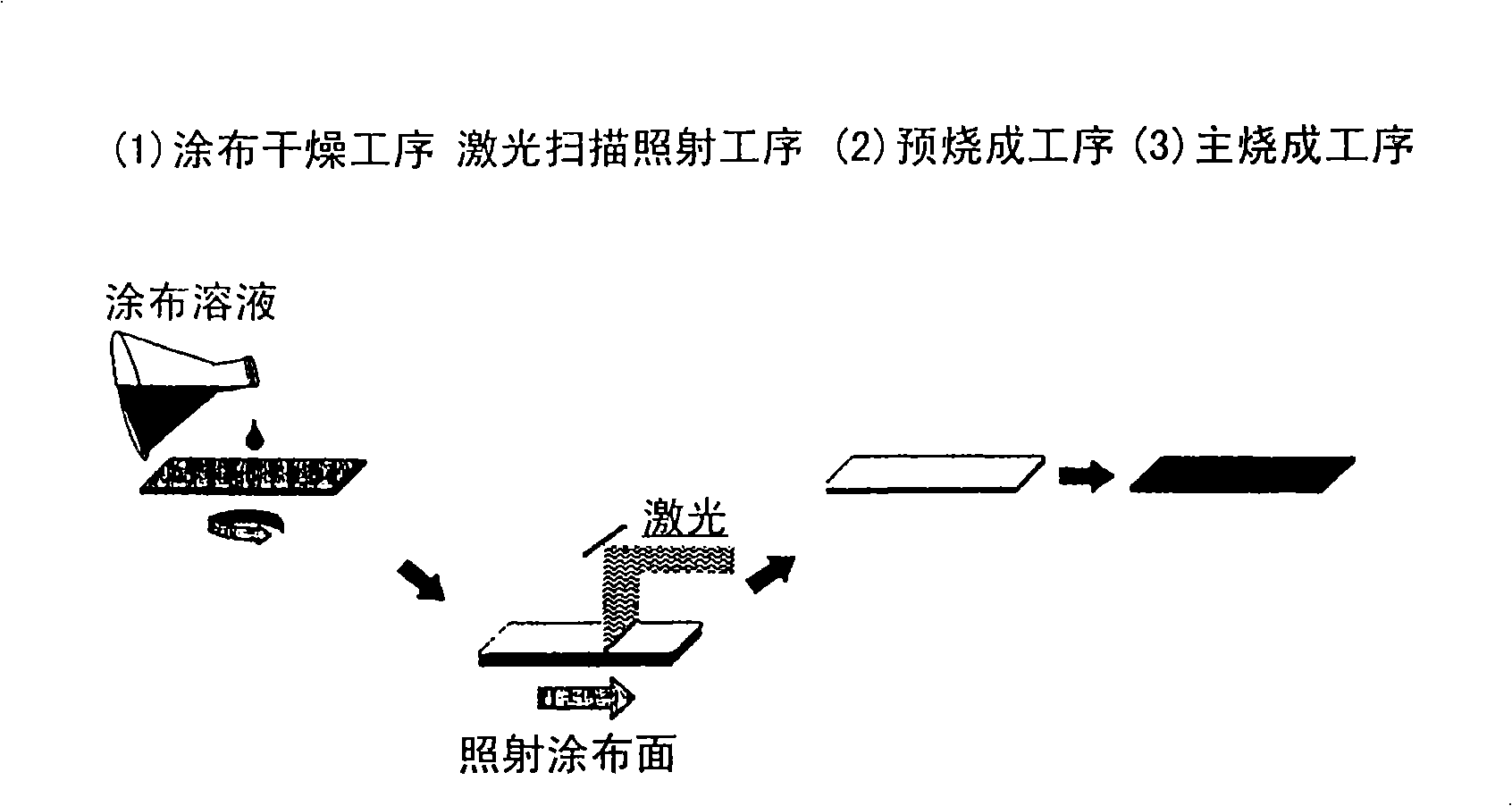
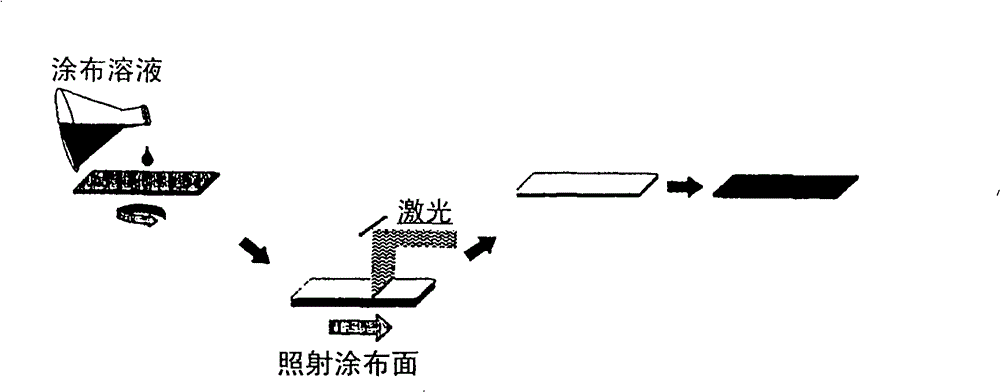
ActiveCN101542641AGood superconducting propertiesPrediction is simpleSuperconductors/hyperconductorsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingOrganic compoundLaser beams
The present invention provides a process for producing a superconducting material which can produce a large-area superconducting material having improved properties with high efficiency without ablation in the thermal decomposition of an organometal compound and the heat treatment of a superconducting substance. A process for producing a superconducting coating material, comprising conducting epitaxial growth through a step (1) of coating a solution of an organic compound of a metal, of which the oxide forms a superconducting substance, onto a support and drying the coating, a prebaking step (2) of thermally decomposingan organic component in the organometal compound, and a main baking step (3) of converting the thermal decomposition product to a superconducting substance. A laser beam isapplied in a period between step (1) and step (2) under such conditions that the intensity of the laser beam, the number of pulses, and the total energy amount of the laser beam satisfy a specific mathematical formula.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Re123 oxide superconductor and method for manufacturing same
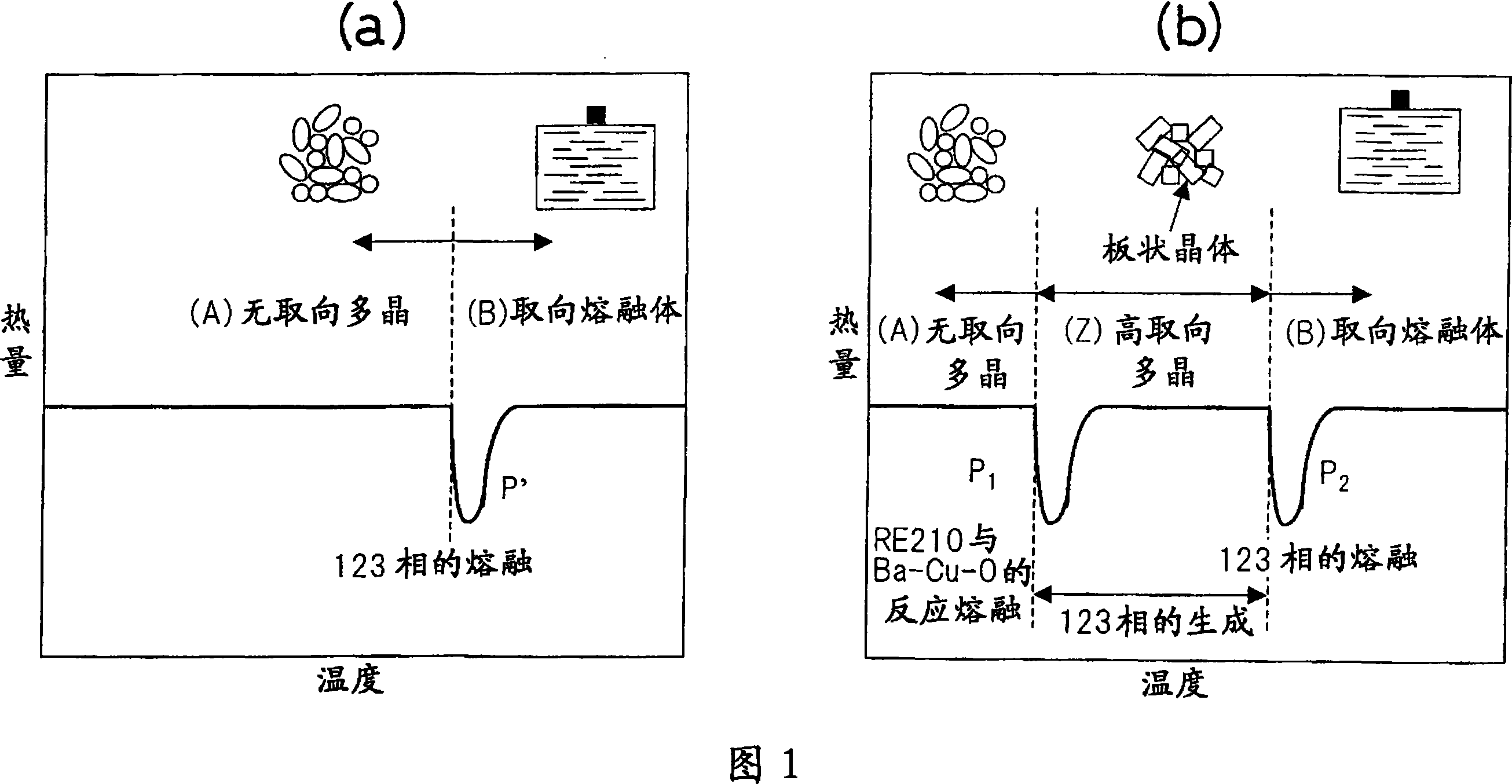
InactiveCN101147211AGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesLiquid nitrogenMaterials science
Disclosed is a long RE123 oxide superconductor stably having excellent superconducting characteristics at liquid nitrogen temperature, which can be used as a strand for a single-core or multicore wire material. Also disclosed is a method for mass-producing such a superconductor. Specifically disclosed is an RE123 oxide superconductor characterized by being composed of a conductive layer containing an REBa2Cu3O7-d oxide superconductor, which is made by using a mixed raw material including at least RE2BaO4 and a Bax-Cuy-Oz raw material, and a holding member for holding the conductive layer. In this connection, RE represents one or more elements selected from La, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and Y.
Owner:INT SUPERCONDUCTIVITY TECH CENT
Method of producing textured superconducting oxide bodies by the oxidation/annealing of thin metallic precursors and precursors and superconducting bodies produced by the method
InactiveUS20020146583A1Resistance to crackingGood superconducting propertiesWave amplification devicesSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentMetalCrystallite
An elongated superconducting body has a core of superconducting oxide grains, and a constraining nonsuperconducting boundary substantially superscribing the superconducting core. The core has thin dimension that is less than or equal to ten times the average length of the grains and the grains are oriented with their a-b crystallographic planes coplanar with a line extending in the longitudinally-extending direction of the core.
Owner:SANDHAGE KENNETH H +1
Method for preparing high-temperature superconducting gadolinium-barium-copper-oxygen thin film by utilizing chemical solution method
InactiveCN102603283BReduce manufacturing costSimple processMetallic material coating processesChemical solutionGadolinium oxide
Owner:江苏天诚智能集团有限公司 +1
A kind of method for preparing magnesium boride superconducting film
InactiveCN104513970BStable superconducting propertiesGood superconducting propertiesChemical vapor deposition coatingMetallurgyMagnesium diboride
The invention discloses a device and a preparation method for preparing a magnesium borate super-conducting film. The device comprises a deposition chamber, wherein a bubble meter is communicated with the deposition chamber through a pipeline; a gas mixing device is communicated with the deposition chamber through a pipeline; the deposition chamber is communicated with a waste gas treatment device. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a substrate; placing the substrate in a substrate container of a substrate heating device; closing the deposition chamber; vacuumizing; introducing 2 to 10 sccm of (Cp)2Mg and introducing Ar-diluted B2H6 gas to generate an MgB2 film; after a first layer of MgB2 film is generated, cutting off the (Cp)2Mg of the bubble meter and the Ar-diluted B2H6 gas supplied by the gas mixing device; vacuumizing the deposition chamber until the vacuum degree reaches 10 <-4> Pa, introducing 5 to 10 sccm of B2H6 gas; depositing an amorphous elemental boron layer at 450 DEG C to 600 DEG C; repeating the steps 3 to 5 to prepare a plurality of layers of MgB2 films. According to the device and the preparation method, the problems that the process is complicated, the preparation cost is high, the superconducting character of a finished product is degenerated because a sample is easily subjected to external pollution during a transferring process and the like in the prior art for preparing a multi-layer MgB2 superconducting film are solved.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
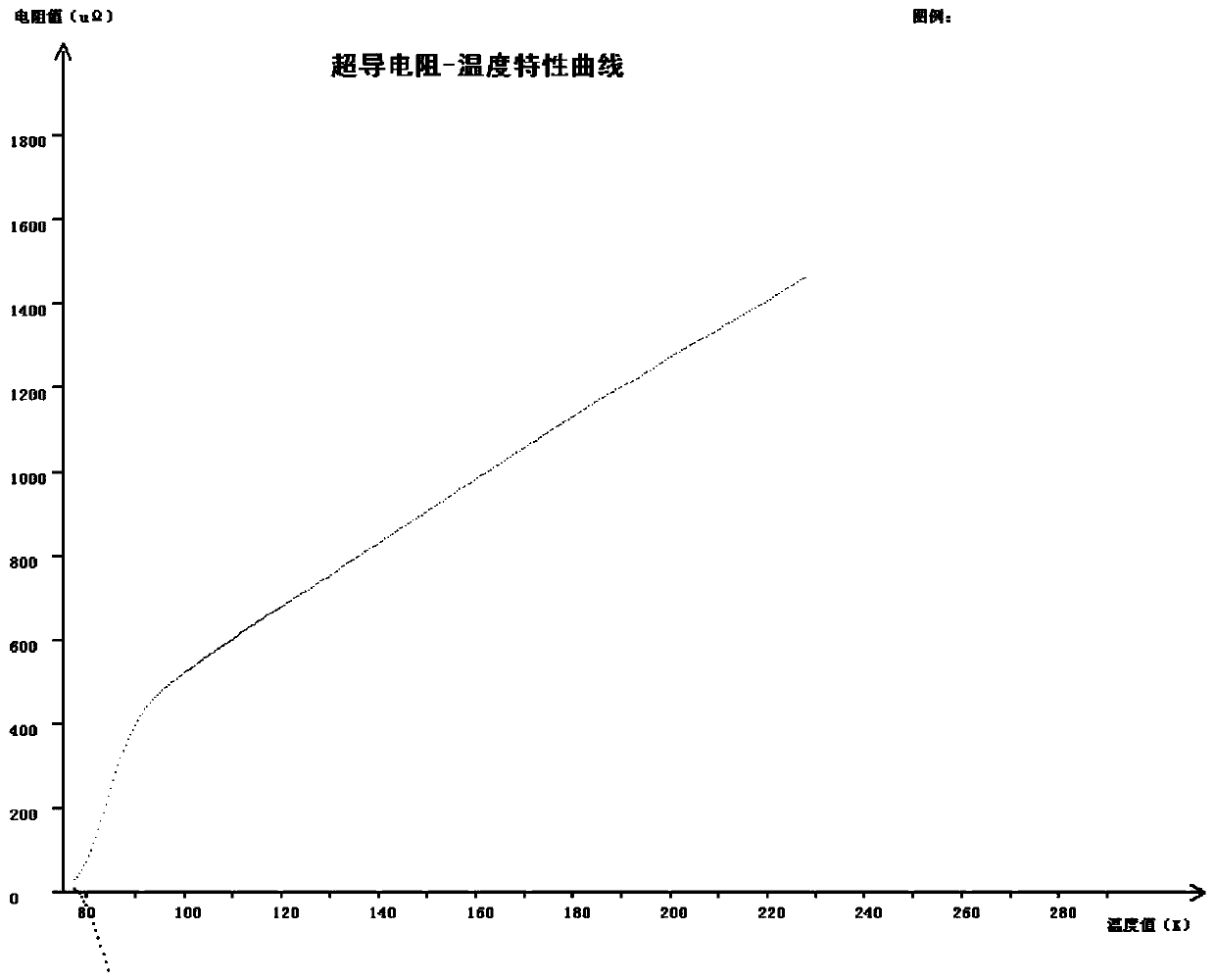
Rapid sintering preparation method of tl-2212 superconducting thin film
ActiveCN107437579BAvoid crackingFlat surfaceSuperconductor detailsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingThalliumThin membrane
The invention discloses a rapid sintering preparation method of Tl-2212 superconducting thin film. Silver foil or gold foil is used to seal and wrap the amorphous precursor film containing thallium and the burning target containing thallium, and the Sintering in the environment. The invention includes four processes including the preparation of a precursor film, the preparation of a thallium source accompanying firing target, the rapid temperature-raising sintering of the precursor film in an argon / oxygen environment, and the oxygen-supplementing heat treatment of a primary sample. Compared with the traditional sintering method, the sintering conditions for growing Tl‑2212 thin films using this technology are not affected by the deposition method of the precursor film, the powder particle size of the starting material of the thallium source accompanying firing target and its preparation method, avoiding the Due to the replacement of the manufacturer's raw materials and the pioneering film deposition method, it is necessary to re-explore the sintering process for a long time. At the same time, the method also greatly reduces the amount of the thallium source accompanying the burning target, shortens the heating and cooling time and constant temperature time, reduces the production cost, and improves the repeatability of the experiment.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
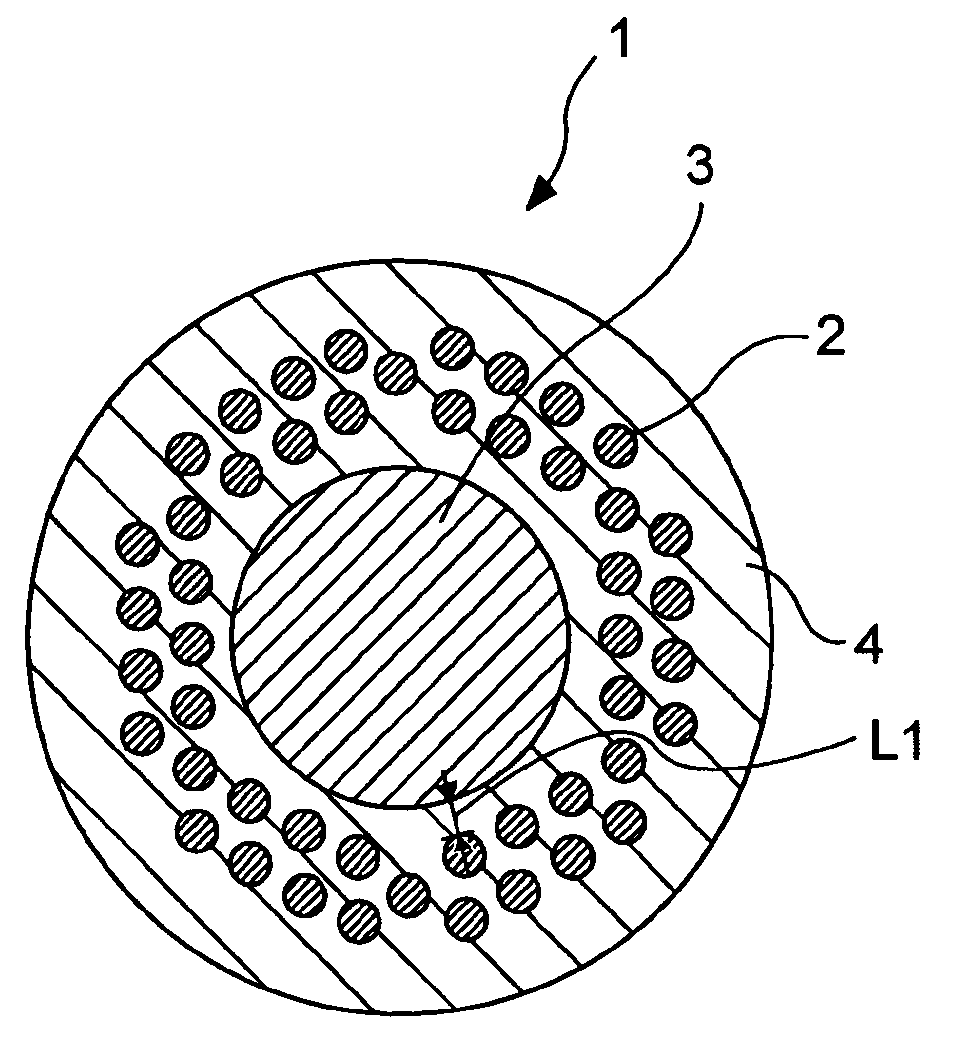
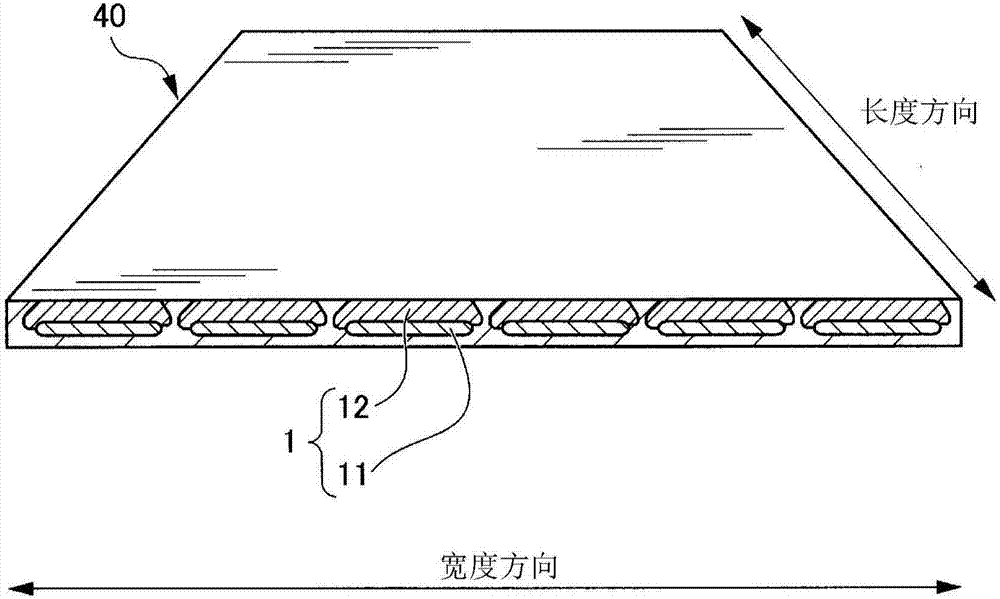
Process for applying polymer to individual conductors and HTS composite produced from the individual conductors
InactiveCN102549677AGood superconducting propertiesStable mechanical flexibilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesHigh-temperature superconductivityElectrical conductor
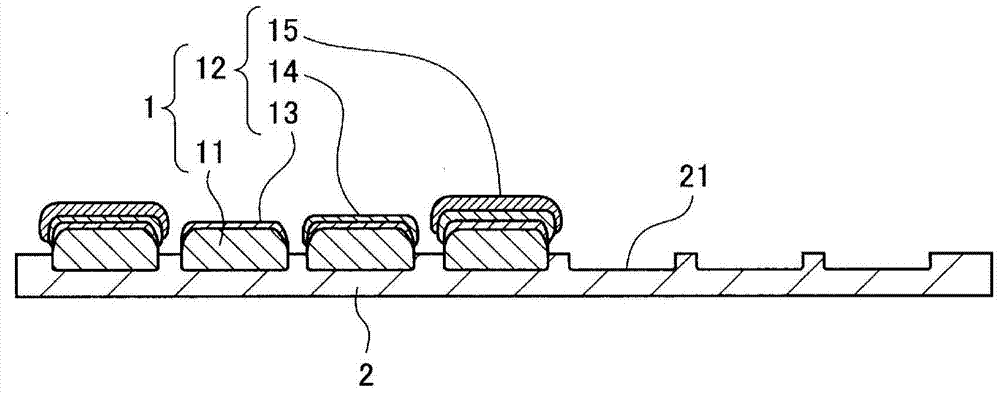
The present invention relates to a process for applying a polymer to at least one individual conductor (10) of a high-temperature superconductor (HTS) composite in the manner of a Roebel conductor. Furthermore, the invention specifies a high-temperature superconductor (HTS) composite produced using the process. The at least one individual conductor (10) comprises at least one substrate (11) and at least one superconducting layer. Particles (12) are applied to the individual conductor (2, 6). Then, a thermal treatment (3, 7, 8) is performed which results in partial or complete melting of the particles (12) and, after cooling, in a polymer layer (13) on the individual conductor (10).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Preparation method of high temperature superconductive film adopting modified low fluoride solution method
InactiveCN102531567BGood superconducting propertiesReduce manufacturing costSuperconductor detailsElectrical conductorOxygen
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high temperature superconductive film adopting a modified low fluoride solution method, which comprises the following steps: dissolving yttrium oxide, barium acetate and copper acetate as raw materials in a solvent using a complexing agent to obtain a low fluoride yttrium barium copper oxygen solution, preparing a gel film and drying, and performing pretreatment and end treatment of the film. The sol has easily adjustable composition, stable performance and good film forming property, the yttrium barium copper oxygen superconductive film can be easily prepared using the sol, and the heat treatment cycle is short and the process repeatability is high. In addition, the solution avoids the introduction of amine group, so as not only to avoid the loss of copper in the heat treatment, but also to avoid the problem that the film is easy to craze. The method of the invention is also used for preparing large-area or long-distance yttrium barium copper oxygen films and coated conductors, the obtained yttrium barium copper oxygen film has good surface smoothness and has good superconductivity.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Nb-containing rod-shaped material for use in manufacture of superconducting wire and method for manufacture of Nb3Sn superconducting wire
InactiveCN101313373BEasy to processGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesHot workingRaw material
Disclosed is a Nb-containing rod-shaped material which can be used in the manufacture of a Nb3Sn superconducting wire and can impart good processability to Nb or a Nb-based alloy. Also disclosed is a method for manufacture of a superconducting wire having good superconducting properties by using the Nb-containing rod-shaped material. The Nb-containing rod-shaped material can be produced by the steps of: casting a raw material for the rod-shaped material in a mold having a circular or approximately circular cross-section to produce a molded article; and performing a hot working processing or a cold working processing of the molded article into a cylindrical or approximately cylindrical shape using a processing device having a circular or approximately circular cross-section.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
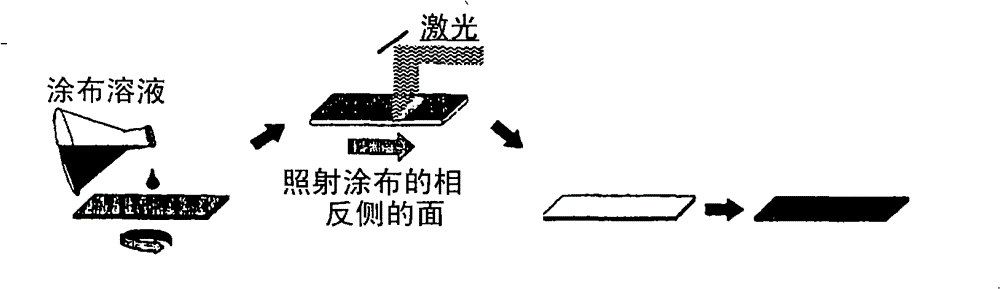
Process for producing superconducting oxide material
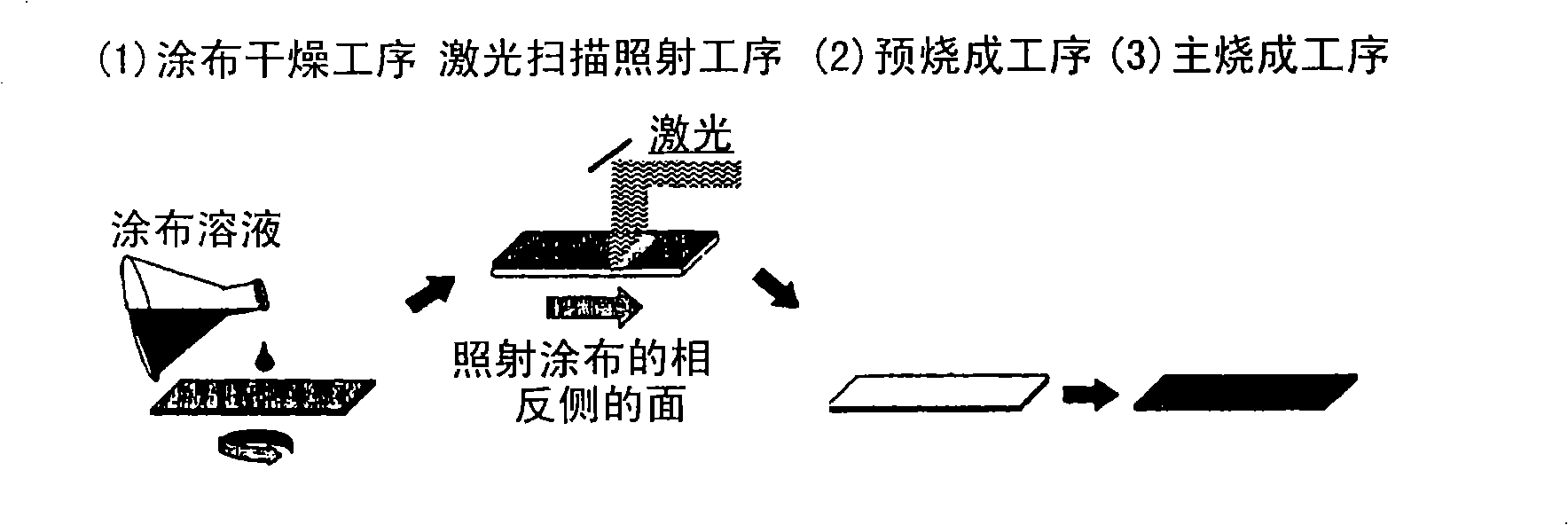
ActiveCN101542641BGood superconducting propertiesPrediction is simpleSuperconductors/hyperconductorsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingLaser lightOrganic compound
A method of producing a superconductive material involves the step (1) of applying a solution of an organic compound of metals, oxides of the metals forming a superconductive material, onto a support body to be subsequently dried, a provisional baking step (2) of causing organic components of the organic compound of the metals to undergo thermal decomposition, and a main baking process step (3) of causing transformation of the oxides of the metals into the superconductive material, thereby producing an epitaxially-grown superconductive coating material, wherein at the time of irradiation of a surface of the support body coated with the solution of the organic compound of the metals for forming the superconductive material, and / or of a surface of the support body, opposite to the surface coated with the solution of the organic compound of the metals, with the laser light, during a period between the steps (1) and (2).
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Precursor for manufacturing Nb3Sn superconducting wire and Nb3Sn superconducting wire
InactiveUS7718898B2Superconducting property (or uniformity of electrical current) is excellentPromote resultsSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentAlloyCopper
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Manufacturing method of superconducting conductor and superconducting conductor
ActiveCN105009228BGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsConductive materialInter layerElectrical conductor
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Metal Sn doped MgB2 superconductor and high-temperature rapid preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101591172BGood superconducting propertiesLow costMetal boridesStudy methodsStructural formula
The invention relates to a metal Sn doped MgB2 superconductor and a high-temperature rapid preparation method thereof. A structural formula of the superconductor is (Mg1.02B2)1-xSnx, wherein x=0.01-0.05. The method comprises the following steps: fully mixing Mg powder, B powder and Sn powder according to atomic ratio, pressing and preparing the mixture into a cylindrical flake under the pressure of 2 to 10 MPa, and then putting the cylindrical flake into a high temperature differential scanning calorimeter or a tubular sintering furnace for sintering; and continuously heating the cylindrical flake to 850 to 900 DEG C at heating rate of 5 to 20 DEG C per minute for sintering treatment, and cooling the cylindrical flake to room temperature at cooling rate of 30 to 40 DEG C per minute. The practical application field of MgB2 is in an around 3T magnetic field, so the method improves the superconductivity of the MgB2 superconductor in a short time by doping metal Sn and using a high-temperature sintering method. The preparation method is simple, has low cost of the raw materials and short preparation time, and is a quite potential research method; and simultaneously, the obtained superconductor has obvious superconductivity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing MgB2 superconductive material
InactiveCN1264749CSimple manufacturing processGood superconducting propertiesSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetal boridesCrucibleFree cooling
The invention relates to a process for preparing MgB2 superconducting material which comprises the steps of, grinding B2O3 and Mg powder under the protection of oinert gas, loading the grinded raw material into ceramic crucible, sintering the crucible in vacuum pit furnace, naturally cooling down to room temperature in vacuum or under the inert gas protection status.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation method of tl-1223 superconducting thin film
ActiveCN107602112BFlat surfaceExcellent superconductivitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesThalliumOxygen
The invention discloses a method of preparing a Tl-1223 superconductive thin film. In the invention, a thallium-containing amorphous precursor film and a thallium-containing sintering accompanying target are sealed and coated with a silver foil or a gold foil, and then sintering is carried out in a sealed argon gas or a flowing oxygen environment. In the method, phase forming temperature zone of low-temperature phases, such as Tl-1212 and Tl-2212, can be crossed quickly and Tl-1223 superconductive phase temperature zone is directly reached, thus producing a pure-phase thin film. The method isshort in temperature increase / decrease time and constant temperature time and is low in production cost.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
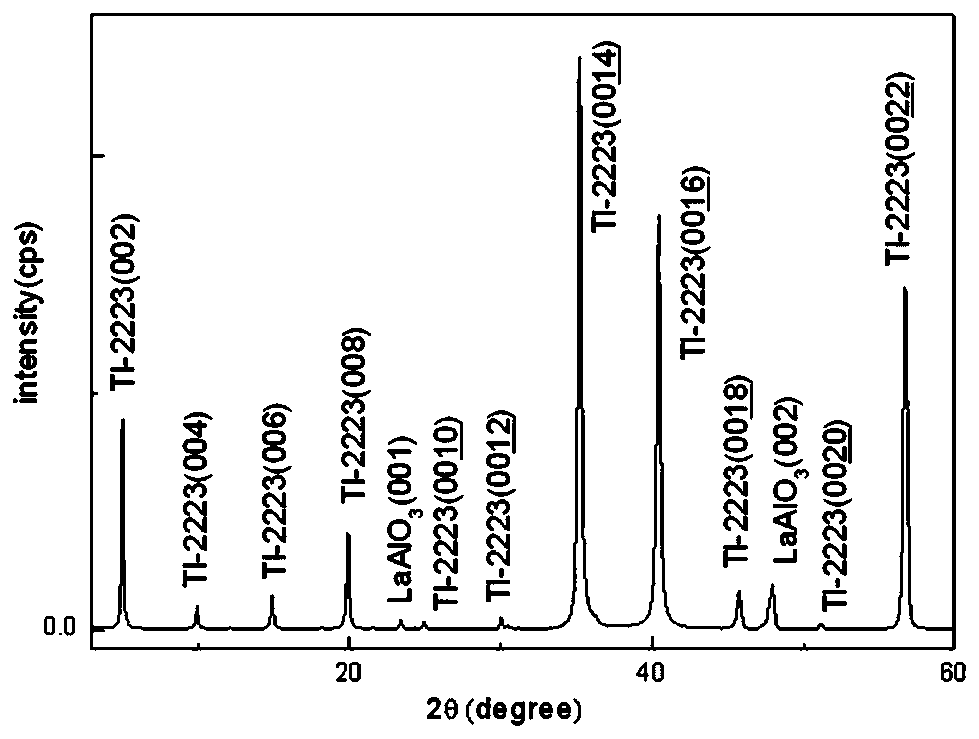
Preparation method of tl-2223 superconducting thin film
ActiveCN107482110BFlat surfaceAvoid crackingSuperconductor detailsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPhysical chemistryThallium
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Tl-2223 superconducting thin film. Silver foil or gold foil is used to seal and wrap an amorphous precursor film containing thallium and a burning target containing thallium, and place the film in a sealed argon or oxygen flow environment. Sintering; wherein, the metal ion molar ratio of Tl, Ba, Ca, Cu of the amorphous precursor film containing thallium is 2.4~4.5:2:2:3.2~3.8; Tl:Ba:Ca:Cu=0.8~1.2:2:1~2:2~3 Ba, Ca, Cu oxides and Tl 2 o 3 Made by sintering. The present invention can quickly cross the phase forming temperature zone of Tl-1212, Tl-2212, Tl-1223 and other low-temperature phases, and directly reach the superconducting phase temperature zone of Tl-2223, thereby preparing a pure-phase film, which has heating and cooling time and constant temperature time Advantages of short length and low production cost.
Owner:GUANGXI TEACHERS EDUCATION UNIV
Low-temperature fast powder sintering method for superconductive MgB2 nano particle
InactiveCN100558634CHigh densityUniform sizeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMetal boridesFlux pinningRoom temperature
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Process for applying polymer to individual conductors and HTS composite produced from the individual conductors
InactiveCN102549677BGood superconducting propertiesStable mechanical flexibilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Metal Sn doped MgB2 superconductor and low-temperature rapid preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101591171AThe critical transition temperature value does not decreaseGood superconducting propertiesRoom temperatureStructural formula
The invention relates to a metal Sn doped MgB2 superconductor and a low-temperature rapid preparation method thereof. A structural formula of the superconductor is (Mg1.02B2)1-xSnx, wherein x=0.01-0.05. The method comprises the following steps: fully mixing Mg powder, B powder and Sn powder according to atomic ratio, pressing and preparing the mixture into a cylindrical flake under the pressure of 2 to 10 MPa, and then putting the cylindrical flake into a high temperature differential scanning calorimeter or a tubular sintering furnace for sintering; and continuously heating the cylindrical flake to 550 to 600 DEG C at heating rate of 5 to 20 DEG C per minute for sintering treatment, and cooling the cylindrical flake to room temperature at cooling rate of 30 to 40 DEG C per minute. Analysis results show that the critical current density of the MgB2 superconductor is greatly improved compared with the MgB2 superconductor obtained under the same sintering condition. The preparation method is simple, the raw materials have low cost, the preparation temperature is low, the preparation time is short, the obtained superconductor has obvious superconductivity, and the method is a quite potential research method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for preparing nanostructure using photo-activation nano active water
InactiveCN101357748AFine and even textureUniform colorNanostructure manufactureUltravioletCurrent technology
The invention discloses a method for producing nanometer structure with nano-photocatalytic active water. Templates and nanometer materials to be processed are immerged in the nano-photocatalytic active water; under irradiation of ultraviolet, the nanometer materials are deposited on the templates to generate the nanometer structure. Nanometer atom in the active water can be deposited on the templates or a work piece to crank out a nanometer product, thus replacing methods of high temperature, microvacuum, electron beam, laser, and vapor phase, and the like, for producing the nanometer structure. The nanometer structure prepared by the method is compact, well distributed, and is provided with strong bonding force, and is characterized by distinct properties of mechanics, optics, heat exchange, electromagnetic, superconduct, electricity, physics, and chemistry, and the like, particularly, the nanometer structure can be applied to important fields of national defense, military affairs, medical treatment, epidemic situation, industry and agriculture, and has important significance, can be capable of being applied to key technology which can not be solved by current technology. The technical craft is simple and is suitable for industrialized production; the cost is low; the technique can become a technical revolution.
Owner:张金龙
Method for preparing gadolinium-barium-copper-oxygen (GdBCO) high-temperature superconducting thin film by using chemical solution method
InactiveCN102569636BReduce manufacturing costSimple processSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentChemical solutionGadolinium oxide
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Oxide superconductor and its manufacturing method
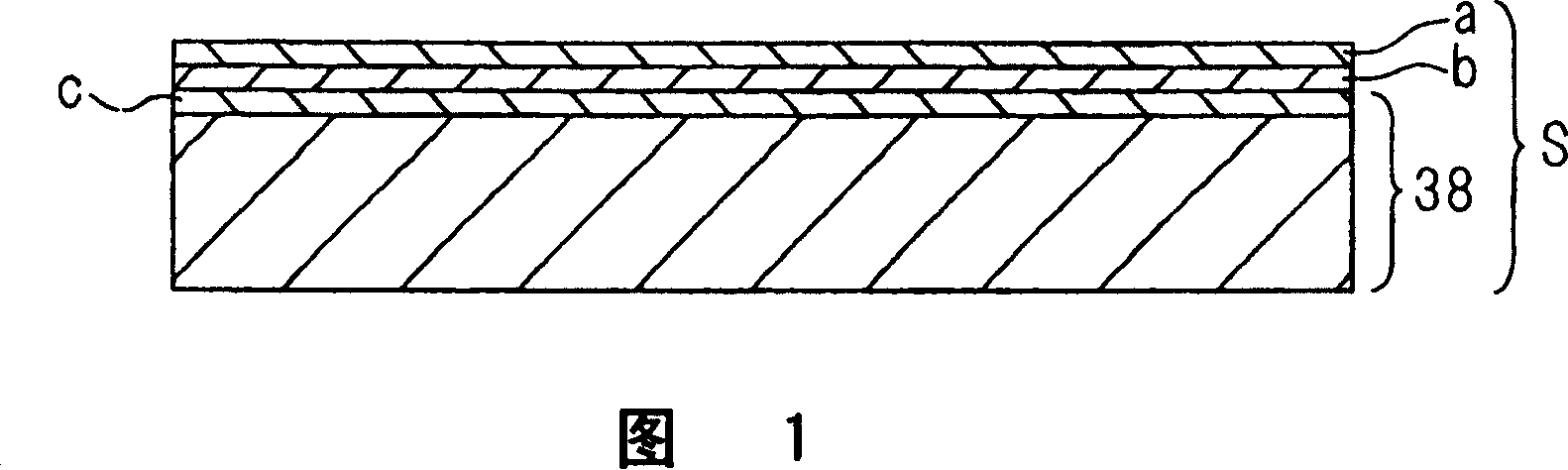
InactiveCN1302487CGood superconducting propertiesInhibited DiffusionSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSolid state diffusion coatingHigh concentrationElectrical conductor
The object of the present invention is to provide an oxide superconductor having superior strength and superconductor characteristics, and its production method. In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides an oxide superconductor layer (d) obtained by a method in which a raw material gas of an oxide superconductor is chemically reacted on a base material provided with an Ag layer (b) having a rolling texture formed on at least one side of a base material, a diffusion layer (c) in which Cu is diffused in Ag is formed on the surface of the above base material, and the above oxide superconductor layer is formed on the above diffusion layer; furthermore, an oxide superconductor comprising the sequential generation of a plurality of layers of oxide superconductor containing Cu by CVD on a base material provided with an Ag layer (25) having a rolling texture formed on at least one side of a base material, whereby the Cu content of the oxide superconductor layer (22a) immediately above the base material is made to have a higher concentration of Cu than the other oxide superconductor layers (22b,22c).
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com