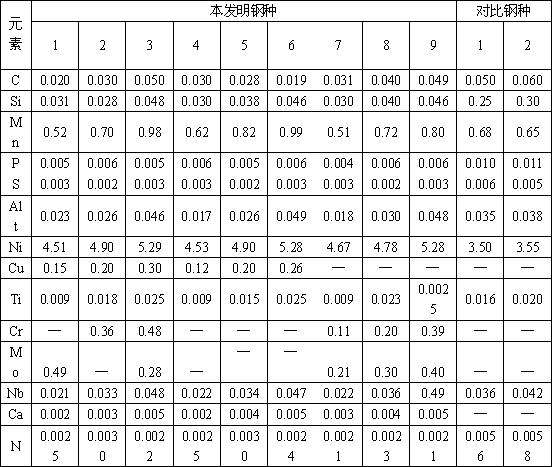
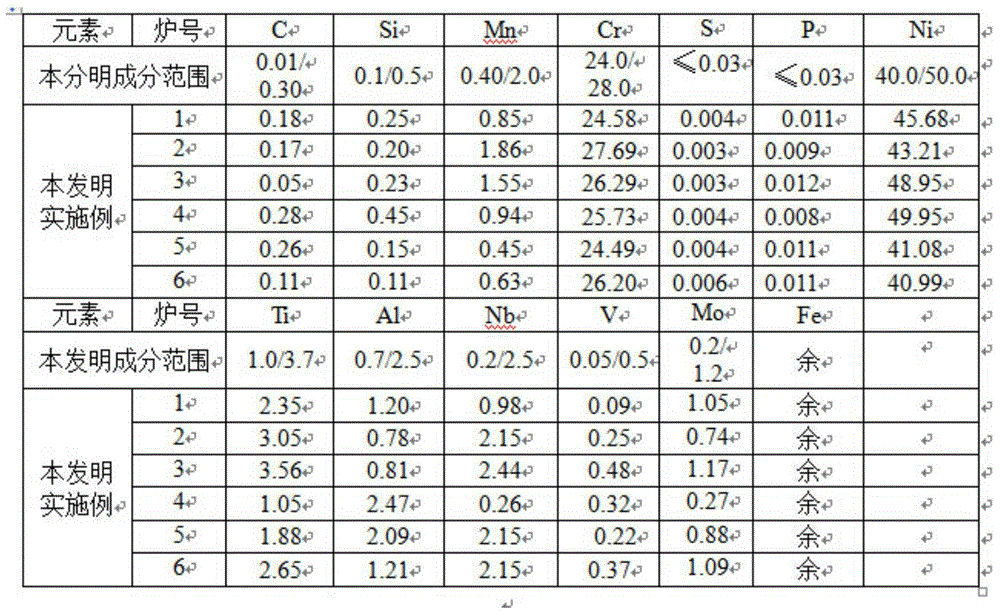
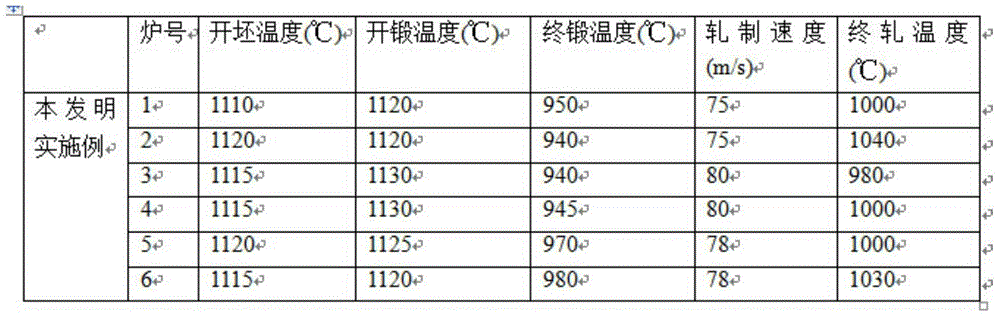
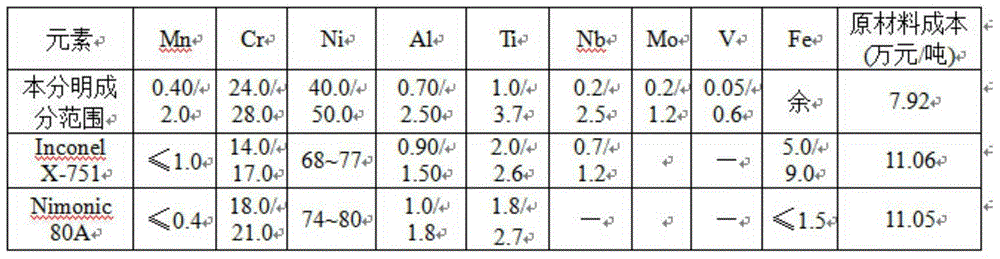
Patents
Literature
68results about How to "Reduce Ni content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
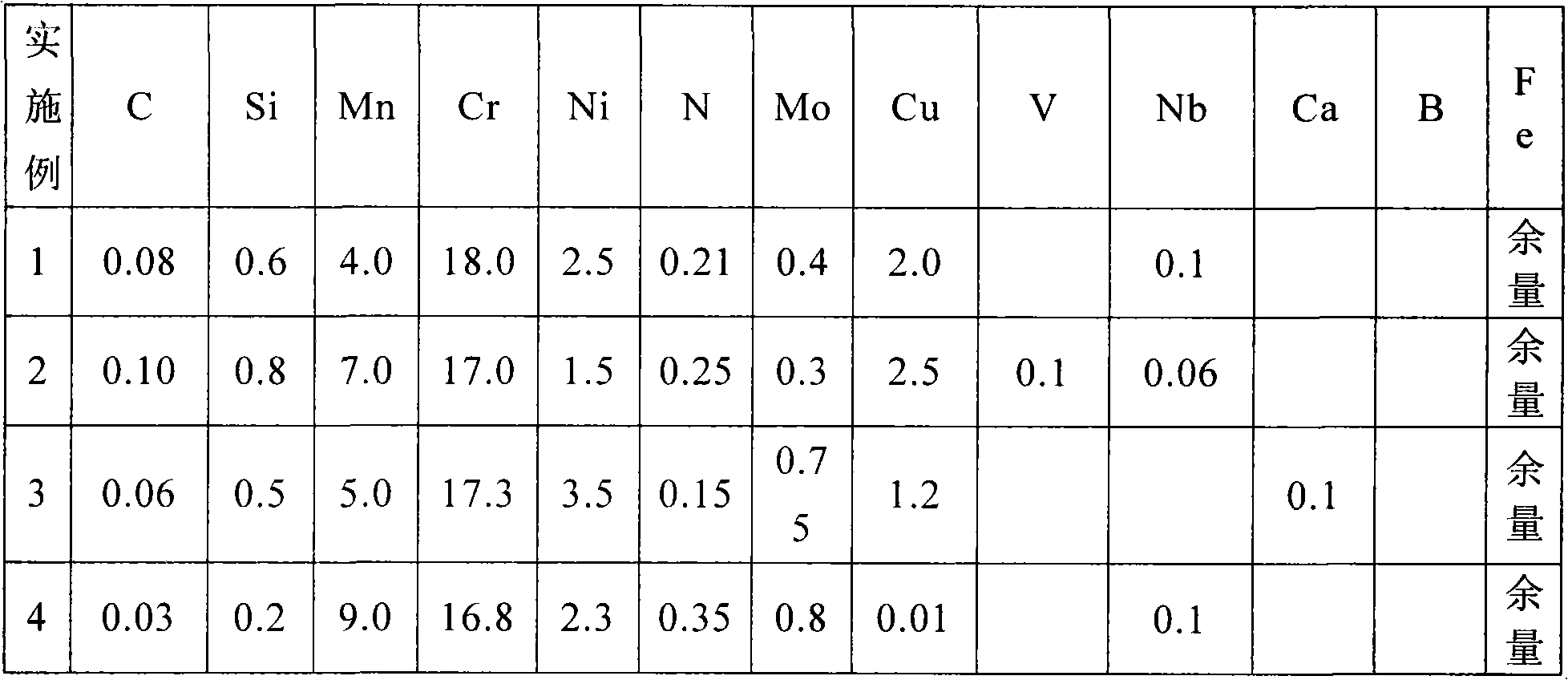
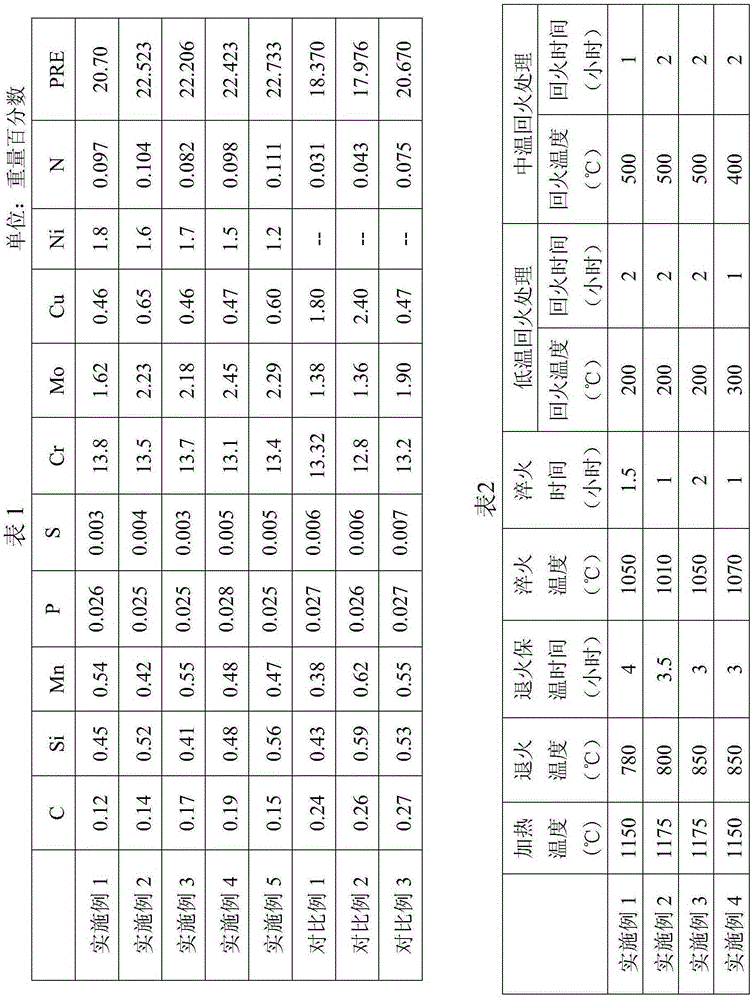
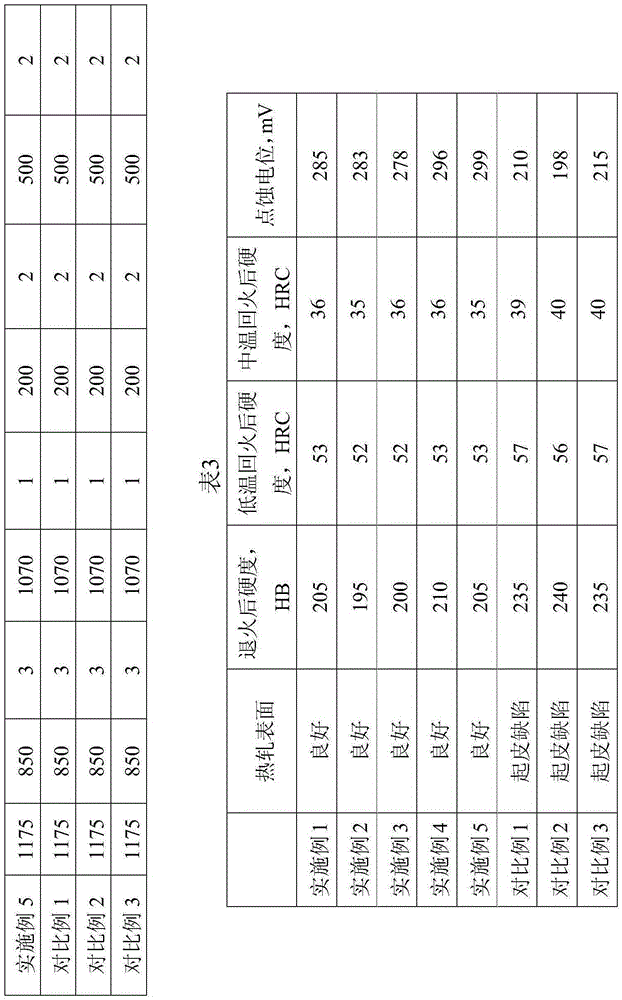
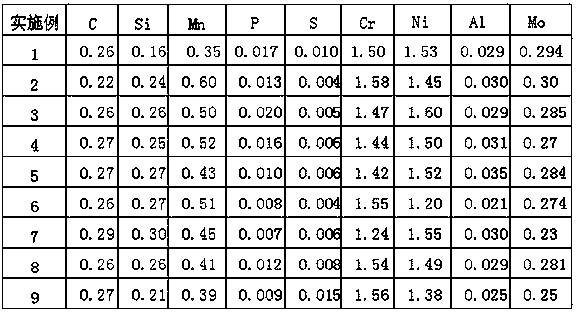
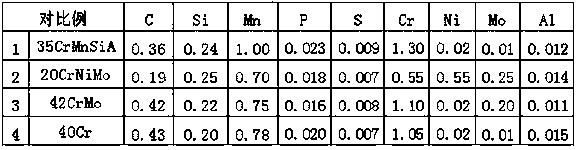
Molybdenum-containing nickel-saving austenitic stainless steel with excellent corrosion resistance and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102337481ALow costReduced corrosion resistancePitting resistance equivalent numberAustenitic stainless steel
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL
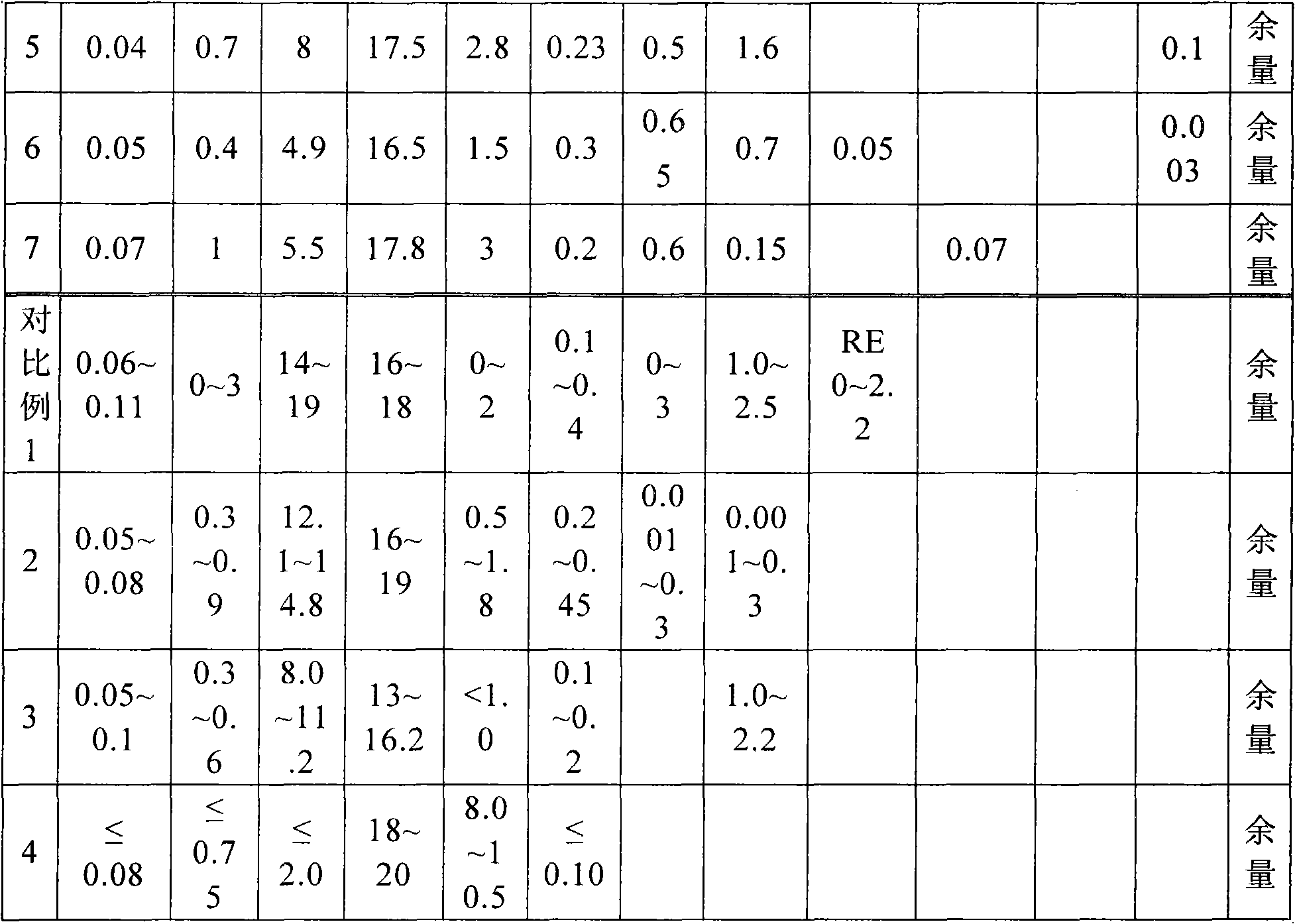
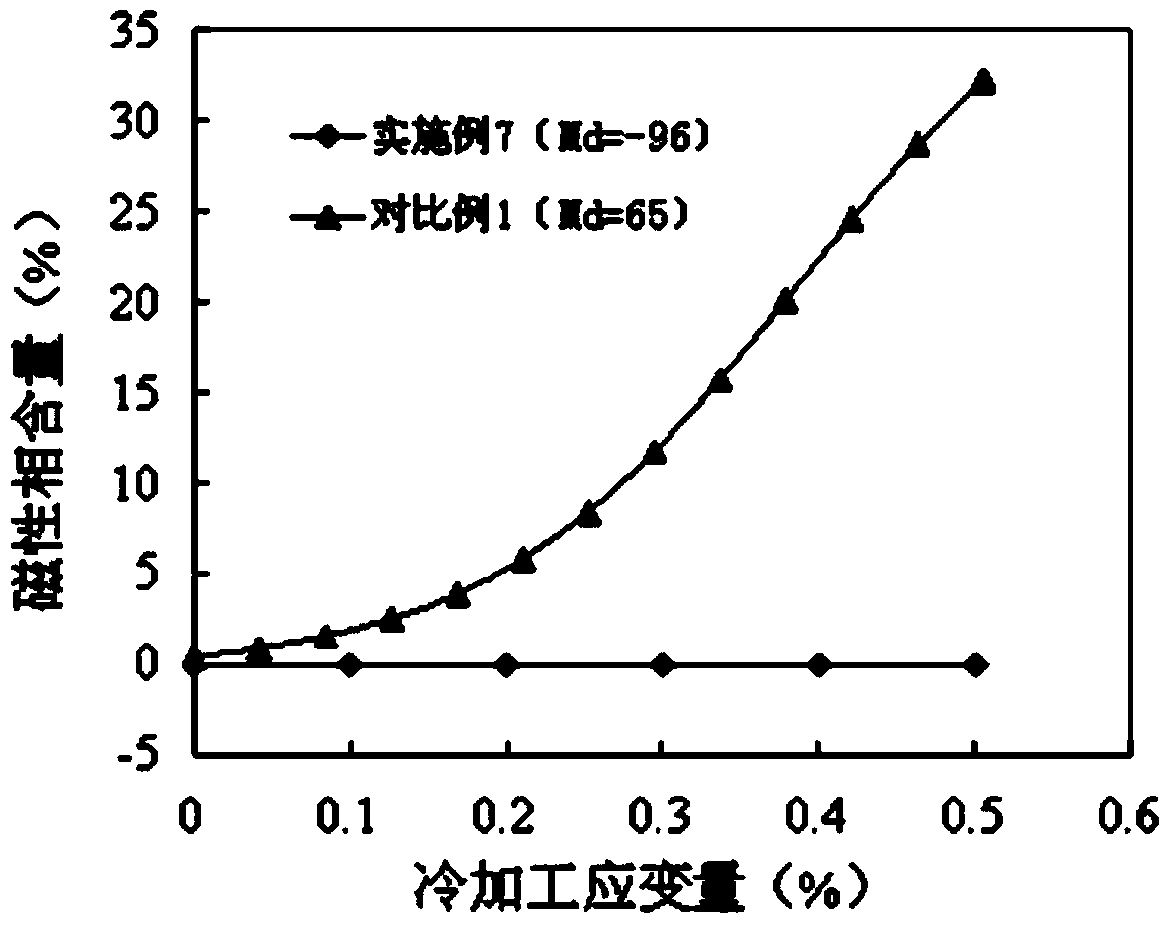
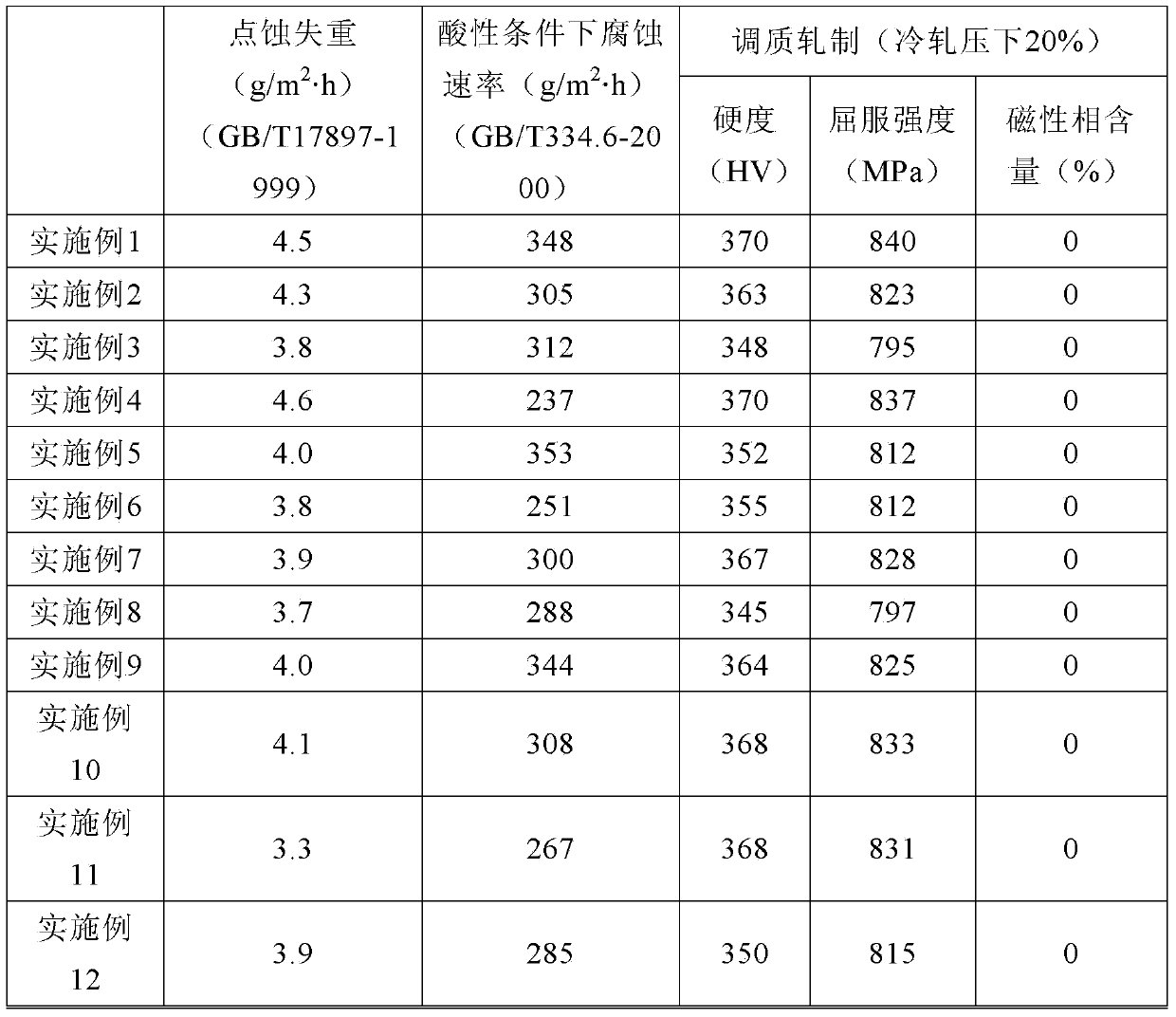
Non-magnetic hard austenitic stainless steel for precision electron and manufacturing method thereof
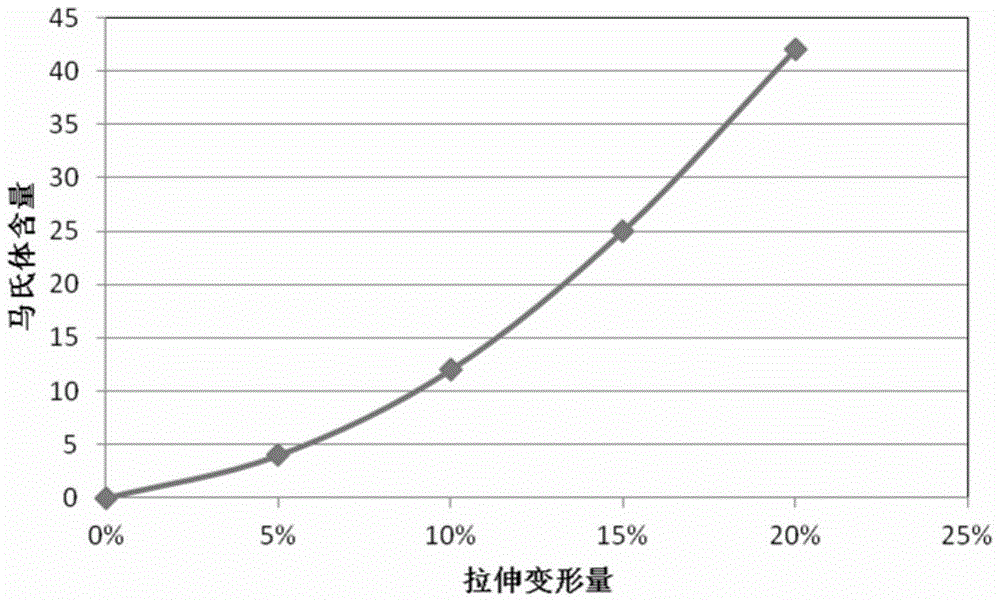
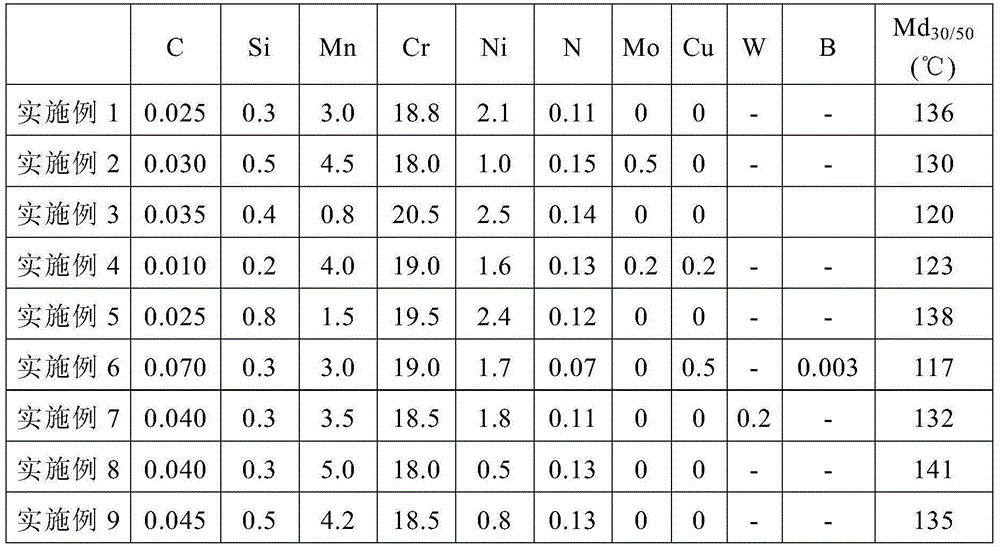
The invention relates to a non-magnetic hard austenitic stainless steel for precision electron and a manufacturing method thereof. The stainless steel comprises the following chemical components by weight percent: 0.06% to 0.10% of C, 0.51% to 0.8% of Si, 11.5% to 12.5% of Mn, 17.0% to 18.0% of Cr, 2.51% to 3.50% of Ni, 0.15% to 0.20% of N, 0.15% to 0.50% of Sn, 0.30% to 0.50% of Mo, 0.30% to 0.75% of Mo and W / 2, 2.0% to 2.5% of Cu and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein at least one of the components as follows is selected: less than or equal to 0.1% of V and less than or equal to 0.1% of Nb; and 30Sn%+5Mo%+2.5W%+Ni%+Cu%+0.5Si%-0.25Mn% is greater than or equal to 9.0. Based on the Cu-Mo-Sn-Si alloying, the adverse effect to the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in which the Ni is reduced and the Mn is added is eliminated, so that the stainless steel has the pitting corrosion resistance superior to 304 and can be prevented from being corroded by a reducing acid. Meanwhile, the temperature of Md30 / 50 is controlled to be lower than -75 DEG C and the austenitic stability is controlled to be superior to 304 and 305, so that the magnetic martensite phase transformation is avoided when the deformation of the stainless steel in cold machining is less than or equal to 50%. Thus, the non-magnetic performance of the hard austenitic stainless steel is also maintained.
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL
High-manganese ultralow temperature steel welding wire and welding process thereof
ActiveCN107186382AReduce Mn contentReduce Ni contentWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSteelmakingShielding gas
The invention discloses a high-manganese ultralow temperature steel welding wire. The high-manganese ultralow temperature steel welding wire comprises the chemical components, by mass, of 0.2%-0.4% of C, 18.0%-27.0% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.15% of Si, less than or equal to 0.005% of S, less than or equal to 0.02% of P, 1.0%-3.0% of Ni, 2.0%-4.5% of Cr, 0.2%-0.5% of Cu, 0.01%-0.06% of N and the balance Fe and residual elements commonly existing in steelmaking. A welding process of the high-manganese ultralow temperature steel welding wire adopts tungsten pole argon arc welding, the groove is in a V shape, the heat input amount is 4-21KJ, and protective gas adopts high-purity argon. The high-manganese ultralow temperature steel welding wire is made of an alloy with the high Mn content, the Ni content is decreased by a large margin, and accordingly the material cost is reduced significantly. According to the welding process, preheating before welding and heat treatment after welding are not needed, the process is simple and easy to implement. The strength, plasticity and toughness of the formed weld metal are well matched, and the formed weld metal has good toughness especially in the ultralow temperature environment of -196 DEG C.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Steel with high toughness and ultrahigh strength
The invention discloses steel with high toughness and ultrahigh strength, and belongs to the technical field of alloy steels. The steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.20 to 0.35 percent of C, 0.5 to 2.0 percent of Mn, 1.25 to 2.25 percent of Si, 2.0 to 5.0 percent of Cr, 0.5 to 2.5 percent of Ni, 0.3 to 0.8 percent of Mo, 0.01 to 0.10 percent of Nb, 0.05 to 0.3 percent of V, less than or equal to 0.005 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of P, and the balance of Fe. Compared with the conventional steel with ultrahigh strength, the steel has the advantages of ultrahigh strength, high fracture toughness, high hardening property and low cost.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Pressure container steel with high toughness at -140 DEG C and production method thereof
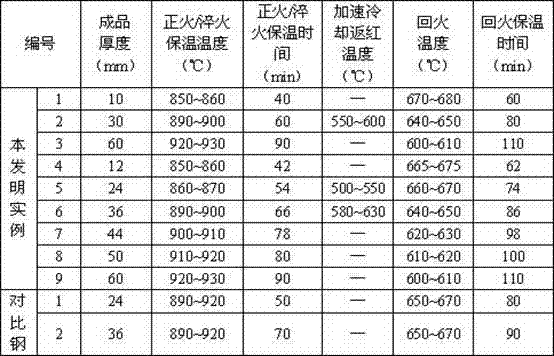
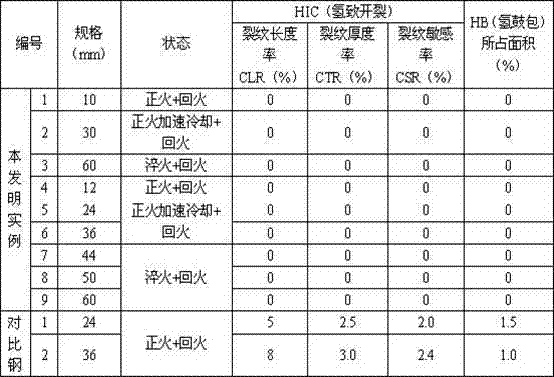
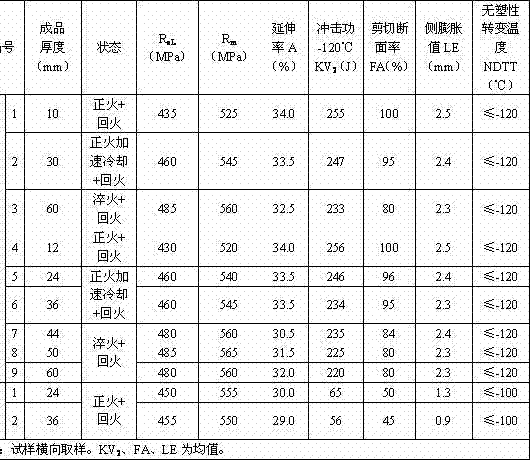
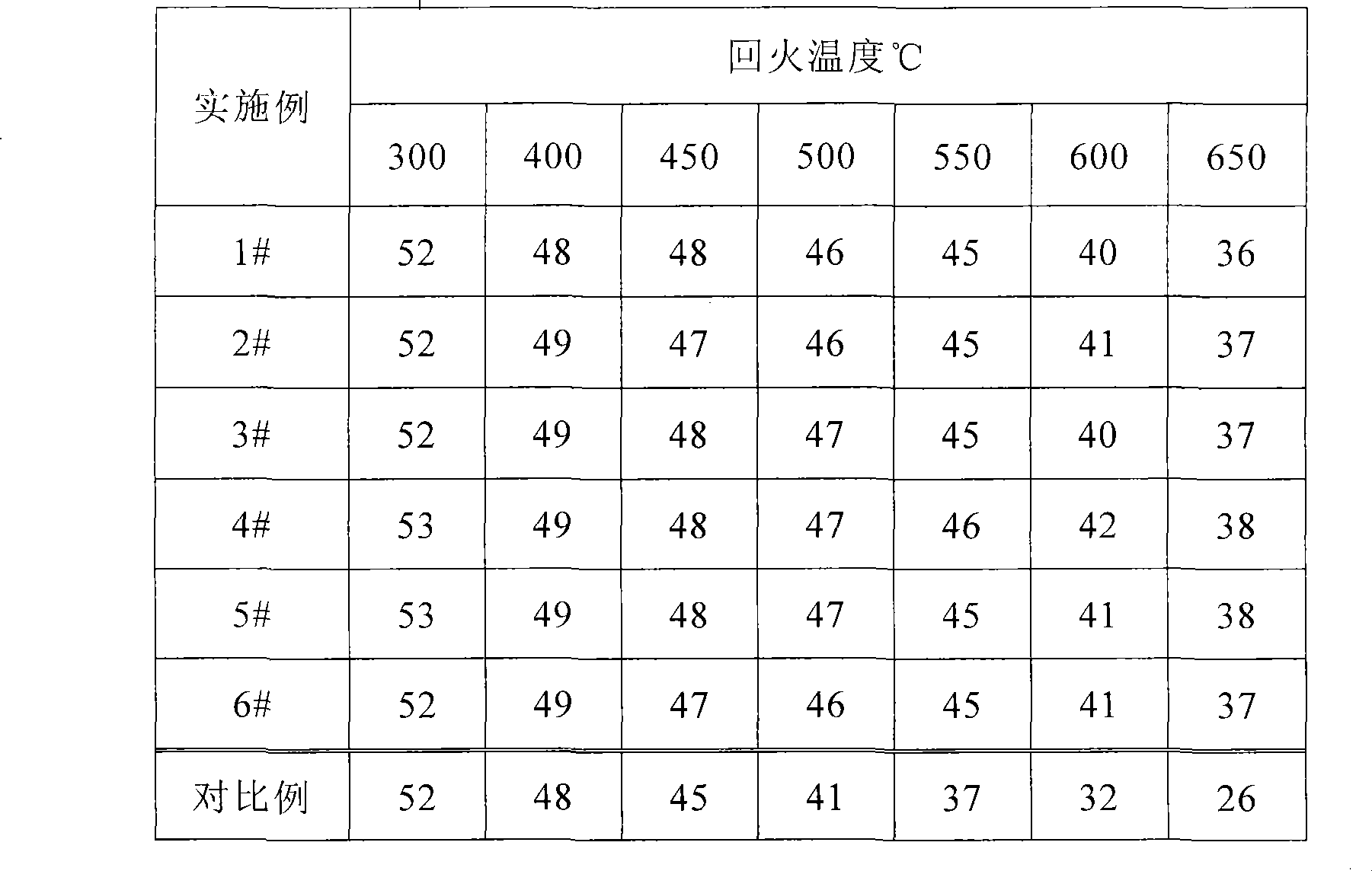
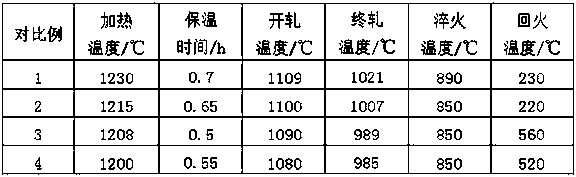
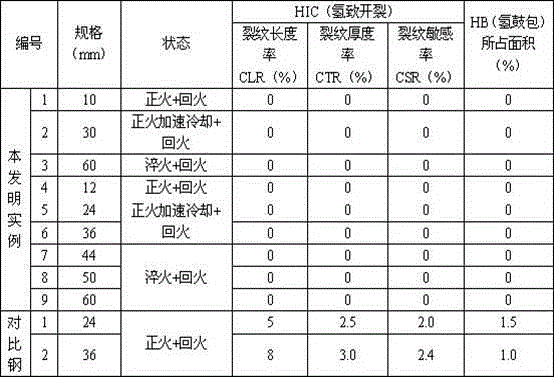
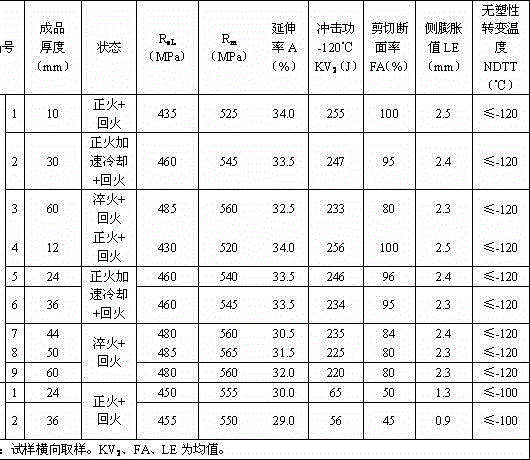
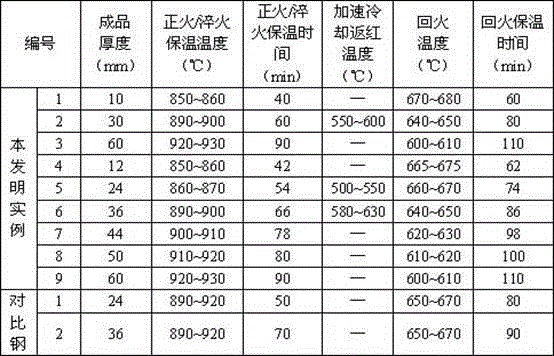
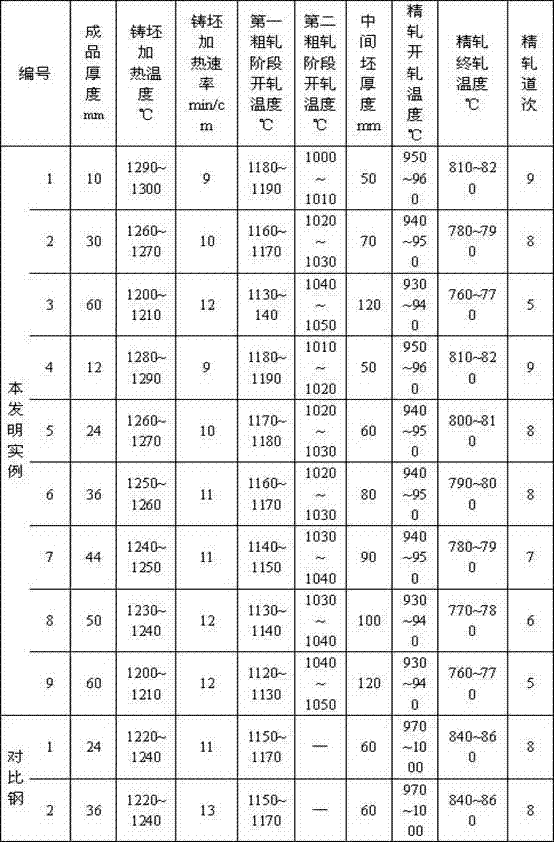
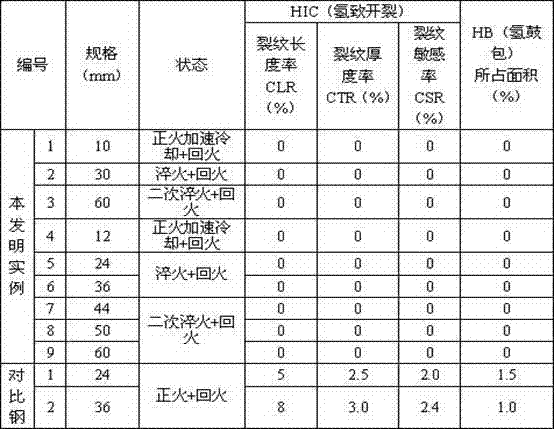
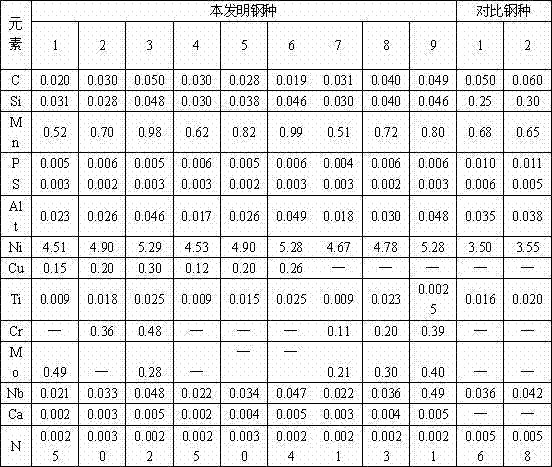
The invention relates to pressure container steel with high toughness at -140 DEG C. The pressure container steel comprises the following components by weight: less than or equal to 0.05 of C, less than or equal to 0.05 of Si, 0.50-1.00 of Mn, less than or equal to 0.006 of P, less than or equal to 0.003 of S, 0.015-0.050 of Alt, 4.50-5.30 of Ni, 0.02-0.05 of Nb, 0.008-0.025 of Ti, less than or equal to 0.004 of N and one or more of less than or equal to 0.50 of Cr, less than or equal to 0.50 of Mo, less than or equal to 0.30 of Cu and less than or equal to 0.005 of Ca. A process of the pressure container steel comprises the following steps: smelting and continuously casting to form a blank; heating a casting blank; rough rolling at a first stage; rough rolling at a second stage after cooling for the first time; finish rolling after cooling for the second time; and carrying out heat treatment according to the thickness of a steel plate for later use. When the pressure container steel is at -140 DEG C, KV2 is not less than 100J, a transverse crack thickness rate CTR is less than or equal to 3%, a transverse crack length rate CLR is less than or equal to 10%, a transverse crack sensitivity rate is less than or equal to 1.5%, the content of Ni is low, and the welding performance is excellent.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Nickel-saving type gas valve alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a nickel-saving type gas valve alloy and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of gas valve alloys. The nickel-saving type gas valve alloy comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.01-0.30% of C, 0.10-0.50% of Si, 0.40-2.0% of Mn, not more than 0.030% of P, not more than 0.030% of S, 24.0-28.0% of Cr, 40.0-50.0% of Ni, 0.7-2.5% of Al, 1.0-3.7% of Ti, 0.2-2.5% of Nb, 0.2-1.2% of Mo, 0.05-0.5% of V and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. A vacuum induction furnace is adopted for smelting, an electrode is poured, a gas is adopted for protecting an electroslag furnace for electroslag re-melting and cogging and forging are performed on a steel ingot to prepare a rolled compact. The cogging temperature of the steel ingot is 1120-1140 DEG C, the forging temperature of the steel ingot is 1120-1130 DEG C, the final forging temperature is 940-980 DEG C and the square rolled compact of 140mm*140mm is forged. The rolled compact passes through a rough rolling mill, an intermediate rolling mill, a finish rolling mill and a reducing and sizing mill and enters a high-speed wire rod rolling mill. The nickel-saving type gas valve alloy has the advantages of low cost, high tensile strength, high fatigue limit and good high-temperature oxidation resistance.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Pressure container steel having high toughness at -120DEG C, and its production method
A pressure container steel having a high toughness at -120DEG C comprises 0.06% or less of C, 0.05% or less of Si, 0.40-0.80% of Mn, 0.008% or less of P, 0.003% or less of S, 0.015-0.050% of Alt, 3.00-3.80% of Ni, 0.10-0.30% of Cu, 0.008-0.025% of Ti, and 0.004% or less of N, and also comprises one or above two of 0.50% or less of Cr, 0.50% or less of Mo, 0.040% or less of Nb, and 0.005% or less of Ca. A method for producing the pressure container steel comprises the following steps: carrying out smelting and continuous casting to form a casting blank; heating the casting blank; carrying out first-stage rough rolling; carrying out primary temperature control, and then carrying out second-stage rough rolling; carrying out secondary temperature control, and then carrying out fine rolling; and carrying out heat treatment according to the thickness of a steel plate for later use. The pressure container steel has a KV2 of 100J or more at -120DEG C, a transverse crack thickness rate (CTR) of 3% or less, a transverse crack length rate (CLR) of 10% or less, a transverse crack sensitivity rate (CSR) of 1.5% or less, a low Ni content and an excellent welding performance.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Economical long service life material for mechanical press forging die and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101440462AReduce Ni contentPlay a secondary strengthening effectMetal-working apparatusFurnace typesAlloy elementMechanical press
The invention provides an economic material with long service life used for a mechanical press forging die and a manufacture method thereof. The material comprises the following compositions by weight percentage: 0.42 to 0.46 percent of C, 0.20 to 0.40 percent of Si, 0.80 to 1.00 percent of Mn, 1.90 to 2.10 percent of Cr, 0.18 to 0.22 percent of V, 0.42 to 0.48 percent of Mo, 0.30 to 0.50 percent of Ni, less than or equal to 0.20 percent of Cu, 0.02 to 0.05 percent of Ti, 0.018 to 0.045 percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.012 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.013 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.0100 percent of N, and the balance being Fe. The method comprises the following steps: casting the compositions to a large steel ingot over 10 tons according to the proportion by electric furnace and external refine smelting; hot loading the steel ingot at a temperature more than or equal to 650 DEG C; heating a forge furnace at a heating speed of between 100 and 150 DEG C / hour to a temperature of between 1,220 and 1, 240 DEG to be insulated for over 5 hours; and forging the steel ingot into the dimension of a finished product by continuous upsetting and drawing out in one heat at a temperature of between 850 and 1,150 DEG C with ratio of forging reduction more than or equal to 5. Compared with the prior mechanical press forging die steel which is used most widely at home and abroad, the material has lower alloy element value, and improves the service life of the die almost by 1 time under the condition of using the same mechanical press forging die.
Owner:宝武特种冶金有限公司
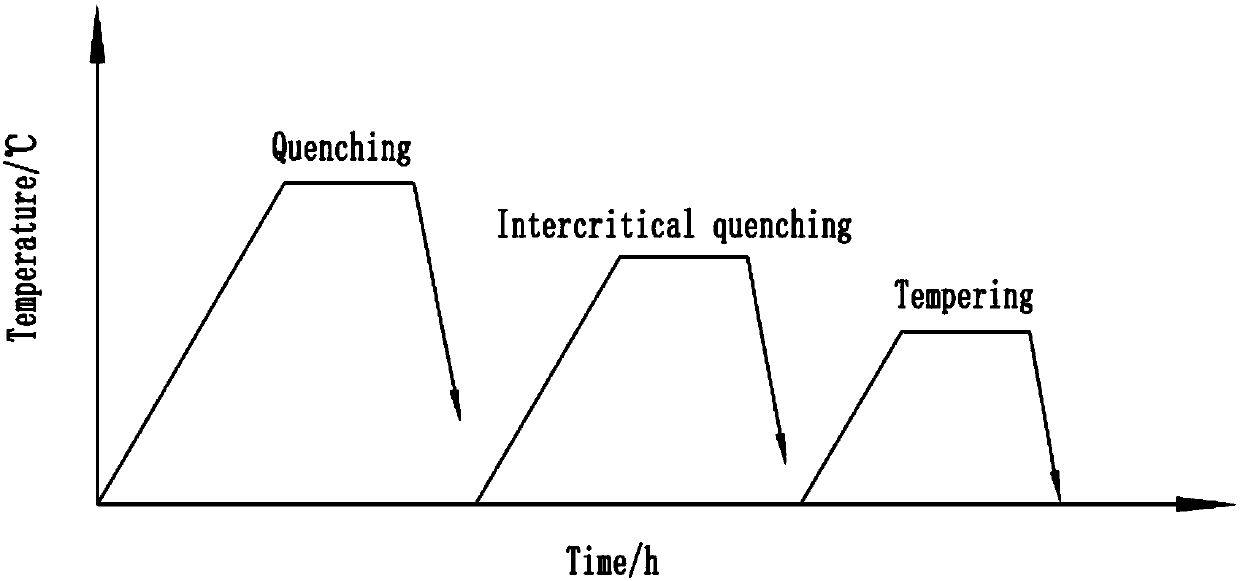
Nickel saving type 7Ni steel for ultralow temperature environment and heat treatment technology of nickel saving type 7Ni steel
ActiveCN107937824AWith horizontal low temperature performanceMeet the use requirementsToughnessQuenching
The invention discloses a nickel saving type 7Ni steel for an ultralow temperature environment and a heat treatment technology of the nickel saving type 7Ni steel, and belongs to the technical field of cryogenic steel. The nickel saving type 7Ni steel comprises the components of 7.00-7.60% of Ni, 0.02-0.06% of C, 0.03-0.80% of Si, 0.10-0.90% of Mn, 0.30-0.60% of Cr and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurities. The nickel saving type 7Ni steel is subjected to QLT heat treatment, specifically, a technology including a plurality of steps of high temperature quenching, two-phase region subcritical quenching and tempering is adopted. According to the nickel saving type 7Ni steel, excellent strength and plasticity combination and outstanding low-temperature toughness are achieved, the performance of the nickel saving type 7Ni steel reaches the level equal to 9Ni steel, the nickel saving type 7Ni steel can serve as structural steel in the ultralow temperature environment, the manufacturing cost is reduced, and very good economic applicability is achieved.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of forming laser cladding layer on surface of upright post of hydraulic bracket
ActiveCN102677044AHigh strengthEfficient claddingMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusOptoelectronicsAlloy
The invention provides a method of forming a laser cladding layer on the surface of an upright post of a hydraulic bracket. The method comprises the following steps of: step a). smelting a part of widths of (n-1)th laser cladding belt and laser cladding alloy powder used for forming the nth laser cladding belt through a laser beam to form the nth laser cladding belt, wherein n is an integer larger than or equal to 2; and step b). smelting a part of widths of the nth laser cladding belt and the laser cladding alloy powder used for forming (n+1)th laser cladding belt through the laser beam to form the (n+1)th laser cladding belt. The method provided by the invention can not only efficiently perform cladding, but also obtain a cladding surface with high strength.
Owner:SHANDONG ENERGY HEAVY EQUIP GRP DAZU REMANUFACTURING CO LTD
Economical duplex stainless steel with tensile strength larger than 1000 MPa and manufacturing method thereof
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL
Smelting and casting process for smelting high-nitrogen non-magnetic stainless steel by using argon oxygen furnace
The invention relates to a smelting and casting process for smelting high-nitrogen non-magnetic stainless steel by using an argon oxygen furnace. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, melting 510-530kg / t of returned stub bars, 300-320kg / t of high-carbon ferrochrome, 8-40kg / t of ferromolybdenum, 14-30kg / t of electrolytic nickel and 5-10kg / t of carburant by using an intermediate frequency furnace, sampling the steel when the temperature is greater than or equal to 1560 DEG C, and then, putting the steel into the argon oxygen furnace; then, supplementing alloy into the argon oxygenfurnace according to the sampling result, performing decarburization to be less than 0.01%, adding 10-25kg / t of special ferrosilicon for reduction, adding 200-240 kg / t of electrolytic manganese, adding 5-10kg / t of aluminum, raising the temperature, and adding 20-30kg / t of ferromanganese nitride alloy in two batches; discharging the steel into a steel ladle; and transferring the steel to a pouringstation to be molded by pouring by adopting a top pouring method, and adding 0.5-1kg / t of protecting slag into the mold. The process provided by the invention is environment-friendly and low in cost and increases the utilization ratio of molten steel by 8%; and by adding the protecting slag into the mold, the surface quality of an electrode blank is ensured, and mold release is facilitated.
Owner:HENAN ZHONGYUAN SPECIAL STEEL EQUIP MFG CO LTD
Process for producing stainless steel wires
InactiveCN105506510AGuaranteed performance indicatorsReduce Ni contentPerformance indexStainless steel wire
The invention discloses a process for producing a stainless steel wire. The furnace burden selected by the process is prepared from the following alloy elements in percentage by weight: 0.05-0.08 percent of C, at most 0.80 percent of Si, 0.45-0.65 percent of Mo, at most 2.0 percent of Mn, 0.40-0.50 percent of Ni, 1.30-1.60 percent of Al, at most 0.02 percent of S, 15.0-20.0 percent of Cr, 1.01-1.02 percent of Ti and the rest of Fe and inevitable impurities. Under the condition that the content of Ni is reduced, the process ensures the comprehensive performance index of the stainless steel wire and therefore is beneficial to reducing the cost.
Owner:浙江腾龙精线有限公司
High-strength anti-nodulation CNRE rare earth heat-resistant steel for furnace bottom roller and preparation method of high-strength anti-nodulation CNRE rare earth heat-resistant steel
InactiveCN112410664AImprove initial strengthReduce surface wearSolid solution strengtheningUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to the field of metallurgical machinery, in particular to high-strength anti-nodulation CNRE rare earth heat-resistant steel for a furnace bottom roller and a preparation methodof the high-strength anti-nodulation CNRE rare earth heat-resistant steel. The steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.2 to 0.5 percent of C, 1.5 to 2.5 percent ofSi, 6.0 to 13.0 percent of Mn, 16.0 to 26.0 percent of Cr, 1.0 to 6.0 percent of Ni, 0.3 to 2.0 percent of Mo, 0.05 to 0.50 percent of V, 0.05 to 0.50 percent of Nb, 0.2 to 0.6 percent of N, 0.005 to0.5 percent of RE and the balance of Fe. According to the high-strength anti-nodulation rare earth heat-resistant steel for the furnace bottom roller, strong solution strengthening and precipitationstrengthening effects are generated through C and N co-alloying and V and Nb micro-alloying, and the initial strength of the furnace bottom roller is improved; a high-temperature structure is stabilized by means of rare earth microalloying; the attenuation rate of high-temperature strength is reduced; surface abrasion of the furnace bottom roller is reduced; the anti-nodulation capacity is improved; moreover, an intermediate frequency furnace high-nitrogen alloying technology, a high-purity rare earth treatment technology and a centrifugal casting technology are adopted, so that a furnace bottom roller casting which is uniform in component, compact in structure and excellent in performance is obtained; and the technical problems of deformation, nodulation and the like of the furnace bottomroller can be effectively solved.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of NiTi shape memory alloy with porous surface
ActiveCN104404602AUnique interconnected porous structureUniform pore size distributionAnodisationSurgeryPorous layerShape-memory alloy
The invention provides a preparation method of NiTi shape memory alloy with a porous surface. The preparation method adopts a one-step anodic oxidation method, and specifically comprises the following steps: (1) surface pretreatment: grinding and polishing the NiTi shape memory alloy to make the NiTi shape memory alloy smooth; (2) anodic oxidation: using a two-electrode system, using the NiTi shape memory alloy after the surface pretreatment as an anode and graphite as a cathode in electrolyte, and applying certain voltage between the anode and the cathode so as to oxidize the anode. The NiTi shape memory alloy prepared by the preparation method has a titanium dioxide porous layer with the thickness of 5-7 microns on the surface, the porous layer has a unique communicated porous structure, and the pore size distribution is uniform; the Ni content of the porous layer is very low.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Heat-resistant regeneration die-cast aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a heat-resistant regeneration die-cast aluminum alloy and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of regeneration die-cast aluminum alloy preparation. The invention provides the heat-resistant regeneration die-cast aluminum alloy capable of reducing the preparation cost and the preparation method of the heat-resistant regeneration die-cast aluminum alloy. Chemical components of the heat-resistant regeneration die-cast aluminum alloy include 10.0%-12.0% of Si, 0.50%-0.75% of Ni, 0.95%-1.35% of Mg, 0.9%-1.4% of Fe, 0.20%-0.30% of Mn, 0.08%-0.12% of Cr, 0.015%-0.03% of B, smaller than or equal to 0.15% of an impurity element and the balance Al. The preparation method includes the steps that smelting is conducted; sampling is conducted to adjust the alloycomponents; refining is conducted after low-melting-point alloy addition; slag removal is conducted; and casting is conducted. According to the heat-resistant regeneration die-cast aluminum alloy andthe preparation method, Ni and Cu are replaced with the low-cost impurity element Fe, and the alloy cost is effectively reduced; and by means of the compound modification technology of the Mn, the Cr, the B and the like, the size of the iron-rich phase is refined, and the high-temperature strength of the alloy is ensured.
Owner:肇庆南都再生铝业有限公司 +2
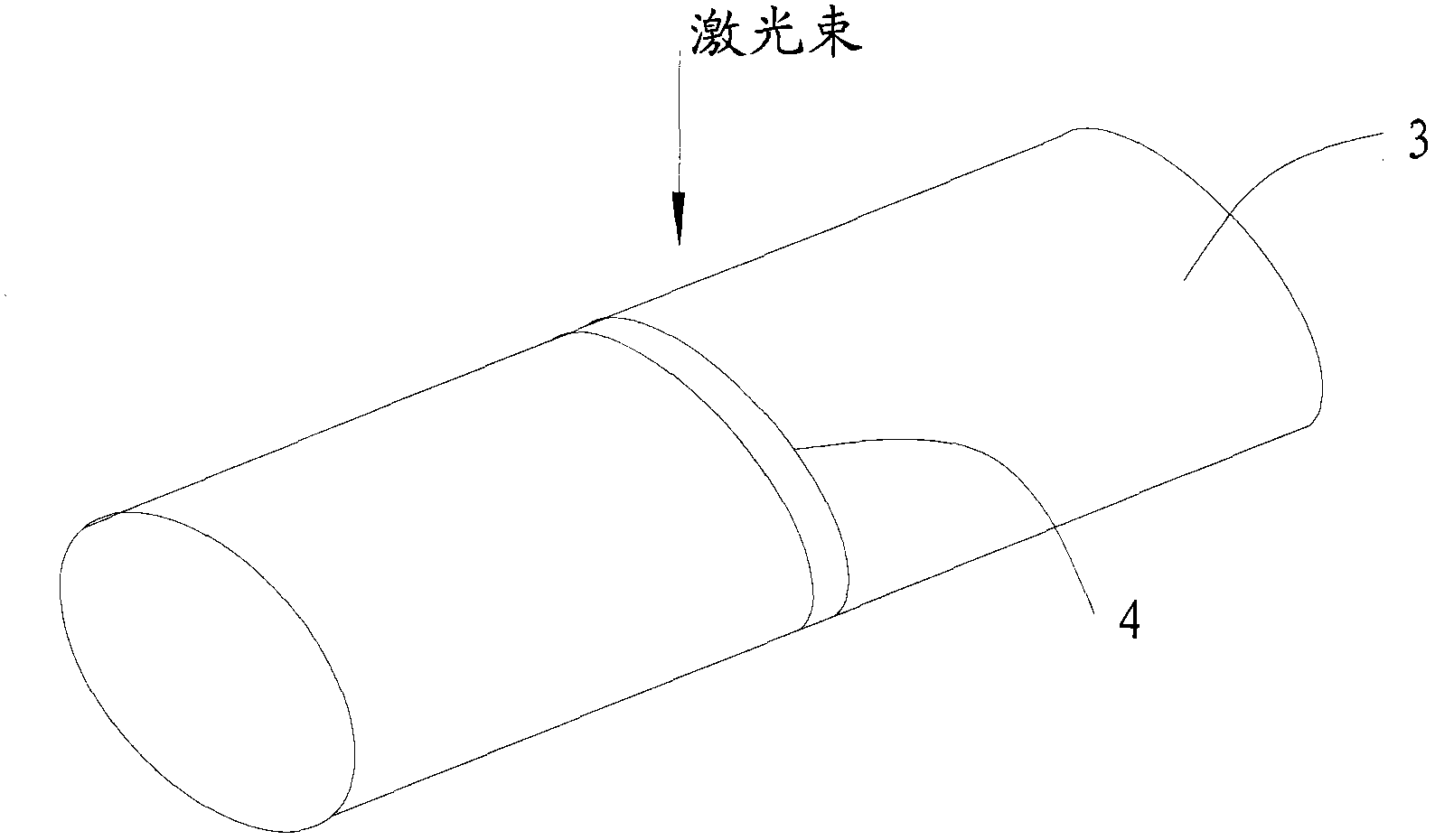
Laser cladding method
ActiveCN102677045AImprove absorption and utilizationImprove energy conversion efficiencyMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusSemiconductor materialsEnergy absorption
The invention provides a laser cladding method belonging to the field of laser machining. The laser cladding method is characterized in that a laser cladding layer is formed through melting alloy powder for laser cladding on the surface of an upright of a hydraulic support by utilizing a laser beam emitted by a semiconductor laser; the semiconductor laser takes a semiconductor material as a working substance and emits light by utilizing the transition of the semiconductor material between energy bands; and the upright of the hydraulic support is mainly made of 27SiMn alloy steel materials. The laser cladding method can be used for increasing the energy absorption efficiency of the laser beam and is high in electric energy utilization ratio so that the power consumption is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG ENERGY HEAVY EQUIP MFG GRP CO LTD +2
Nickel-saving type cobalt-free martensite aging ultrahigh strength steel
Alloy steel with no Co and less Ni is available to be thin-wall cylinders or springs or gears, containing (wt%): Ni 11.5-14.5, Cr 3.75-5.25, Mo 2.25-3.75, Ti 1.2-1.6, and elements following below not more than the value behind: C 0.03, Si 0.1, Mn0.1, Al 0.30, Co 0.50, S 0.01, P 0.01, O 30ppm, N 30ppm, balanced with Fe. It has high yield strength, high plasticity, toughness, and excellent machining performance.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Ultrahigh-strength welding structure steel plate and its manufacturing method
The invention discloses an ultrahigh-strength welding structure steel plate. The steel plate comprises 0.11-0.19% of C, 0.20-0.50% of Si, 0.90-1.40% of Mn, 0.005-0.030% of Ti, 0.30-1.00% of Cr, 0.1-0.5% of Cu, 0.15-0.35% of Ni, 0.15-0.60% of Mo, 0.010-0.050% of Als, 0.020% or less of P, 0.010% or less of S, 0.025-0.070% of V, 0.005% or less of Zr, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. Quenching and tempering treatments of the steel plate are carried out after rolling, the reheating temperature is 860-930DEG C, the temperature insulation is carried out for 1.0-2.5min / mm, and water quenching is carried out to obtain a quenching martensite structure; and a tempering treatment is carried out at 500-600DEG C, the heat insulation time is 1.0-3.0min / mm, and air cooling is carried out.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Martensitic stainless steel for building structure fastener and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105296877AGuaranteed hardnessIncrease C contentChemical compositionMartensitic stainless steel
The invention discloses martensitic stainless steel for a building structure fastener and a manufacturing method thereof. The martensitic stainless steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.10-0.20% of C, 0.05-0.15% of N, Si not more than 1%, Mn not more than 1%, P not more than 0.035%, S not more than 0.010%, 13.0-14.0% of Cr, 1.5-2.5% of Mo, 0.3-0.8% of Cu, 1.5-2.5% of Ni, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities; and the following conditions can be synchronously satisfied: the pitting equivalent weight PRE is more than 20%; and PRE=Cr+3.3 Mo+16 N. The prepared martensitic stainless steel has the pitting potential more than 270 mV, has the Rockwell hardness number of 52-54 HRC, has equivalent corrosion resistance to 304 stainless steel, and has high strength, high hardness and excellent hot working performance and cold forming performance.
Owner:BAOSTEEL STAINLESS STEEL
Corrosion-resistant copper alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a corrosion-resistant copper alloy and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of pretreating an electrolytic copper plate, an electrolytic nickel plate, an aluminum plate, a copper-iron intermediate alloy, a copper-manganese intermediate alloy and mixed rare earth, wherein the mixed rare earth is a mixture of La and Ce; weighing raw materials, wherein the raw materials comprise, by mass, 6-8% of Ni, 3-7% of Al, 1-1.6% of Fe, 0.4-1% of Mn, 0.032-0.045% of mixed rare earth and the balance Cu, and the percentage content of La is35-45%; sequentially putting the electrolytic copper plate, the electrolytic nickel plate, the copper-iron intermediate alloy, the copper-manganese intermediate alloy and the mixed rare earth wrappedby copper foil into a smelting furnace for primary smelting, and adding the aluminum plate into the smelting furnace for secondary smelting after smelting and deslagging; pouring the melt into a centrifugal casting machine for cooling and solidification to form a blank, and carrying out processing treatment to obtain a corrosion-resistant copper alloy ingot; and carrying out heating and preservingheat, and then putting the corrosion-resistant copper alloy ingot into an extrusion die for hot extrusion deformation processing to obtain the corrosion-resistant copper alloy.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Method for deeply removing impurities and enriching precious metals in complex lead bismuth alloy
InactiveCN110760688ARaise the gradeLow content of impurity elements, especially Ni contentProcess efficiency improvementLead bismuthCopper
The invention discloses a method for deeply removing impurities and enriching precious metals in a complex lead bismuth alloy. The method comprises the following steps of feeding, repeatedly removingimpurities, finally removing impurities and separating to obtain a precious metal alloy. The method aims at solving the technical problem that a complex lead bismuth alloy depth impurity removal process technology is innovatively adopted, copper, nickel and other impurities in the complex lead bismuth alloy are removed, the precious metals are extracted from the impurity-removed lead bismuth alloyby applying the core key technology of continuous vacuum distillation to enrich the precious metals, the obtained precious metal alloy and the precious metal grade are extremely high, the content ofvarious impurity elements, especially Ni, is low, oxidation blowing treatment is prone to be carried out in a Kaldo furnace process, and a qualified silver anode plate is obtained.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
High-strength, high-toughness and good-weldability steel for mine machinery and production method of steel
The invention discloses high-strength, high-toughness and good-weldability steel for mine machinery and a production method of the steel. The steel for mine machinery comprises, by mass, 0.22-0.29% ofC, 0.16-0.30% of Si, 0.35-0.60% of Mn, 1.24-1.58% of Cr, 1.20-1.60% of Ni, 0.23-0.30% of Mo, 0.021-0.035% of Al, 0-0.020% of P, 0-0.015% of S and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The production method comprises the treatment processes of smelting, continuous casting, heating, rolling and tempering. The chemical components are matched, Ni ensures high toughness, Cr, Ni, Mo and the like ensure high strength, the content of C is reduced to improve the weldability, the problem that similar steel cannot achieve high strength, high toughness and good weldability at the same time is solved,and the requirement of the mine machinery for the steel is met.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG IRON & STEEL
Pressure container steel having high toughness at -120 DEG C, and its production method
A pressure container steel having a high toughness at -120DEG C comprises 0.06% or less of C, 0.05% or less of Si, 0.40-0.80% of Mn, 0.008% or less of P, 0.003% or less of S, 0.015-0.050% of Alt, 3.00-3.80% of Ni, 0.10-0.30% of Cu, 0.008-0.025% of Ti, and 0.004% or less of N, and also comprises one or above two of 0.50% or less of Cr, 0.50% or less of Mo, 0.040% or less of Nb, and 0.005% or less of Ca. A method for producing the pressure container steel comprises the following steps: carrying out smelting and continuous casting to form a casting blank; heating the casting blank; carrying out first-stage rough rolling; carrying out primary temperature control, and then carrying out second-stage rough rolling; carrying out secondary temperature control, and then carrying out fine rolling; and carrying out heat treatment according to the thickness of a steel plate for later use. The pressure container steel has a KV2 of 100J or more at -120DEG C, a transverse crack thickness rate (CTR) of 3% or less, a transverse crack length rate (CLR) of 10% or less, a transverse crack sensitivity rate (CSR) of 1.5% or less, a low Ni content and an excellent welding performance.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Electric resistance alloy and its preparing process
Owner:丹阳市龙鑫合金有限公司
Pressure container steel with high toughness at -140 DEG C and production method thereof
The invention relates to pressure container steel with high toughness at -140 DEG C. The pressure container steel comprises the following components by weight: less than or equal to 0.05 of C, less than or equal to 0.05 of Si, 0.50-1.00 of Mn, less than or equal to 0.006 of P, less than or equal to 0.003 of S, 0.015-0.050 of Alt, 4.50-5.30 of Ni, 0.02-0.05 of Nb, 0.008-0.025 of Ti, less than or equal to 0.004 of N and one or more of less than or equal to 0.50 of Cr, less than or equal to 0.50 of Mo, less than or equal to 0.30 of Cu and less than or equal to 0.005 of Ca. A process of the pressure container steel comprises the following steps: smelting and continuously casting to form a blank; heating a casting blank; rough rolling at a first stage; rough rolling at a second stage after cooling for the first time; finish rolling after cooling for the second time; and carrying out heat treatment according to the thickness of a steel plate for later use. When the pressure container steel is at -140 DEG C, KV2 is not less than 100J, a transverse crack thickness rate CTR is less than or equal to 3%, a transverse crack length rate CLR is less than or equal to 10%, a transverse crack sensitivity rate is less than or equal to 1.5%, the content of Ni is low, and the welding performance is excellent.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Positive pole material and positive pole piece for lithium ion battery and lithium ion battery
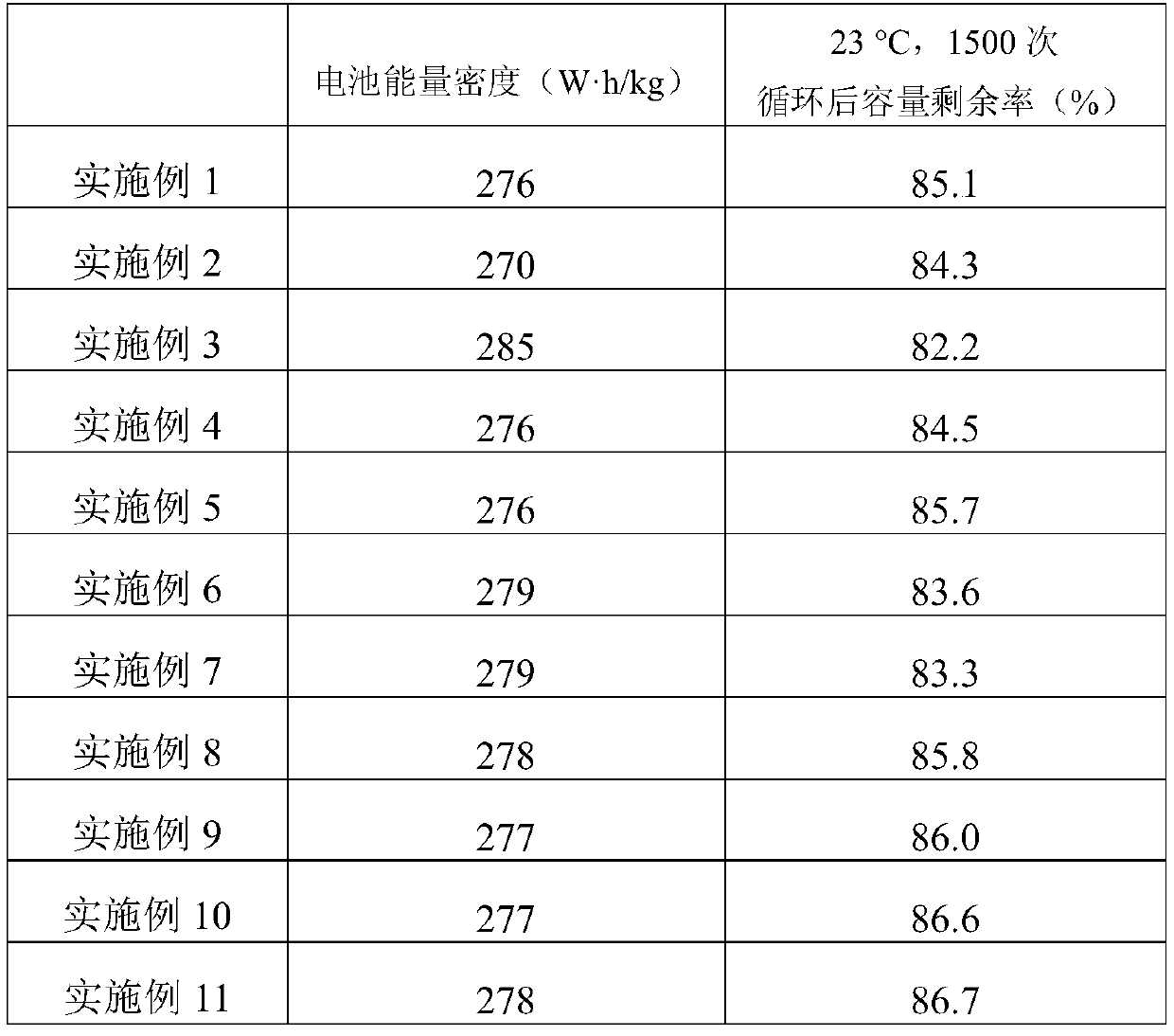
InactiveCN109888270AImprove stabilityIncrease energy densityCell electrodesSecondary cellsHigh energyPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a positive pole material and a positive pole piece for a lithium ion battery and a lithium ion battery. The positive pole material has the composition as shown in a formula (1): LiNixCoyAl1-x-yO2 (I); in the formula (I), and x and y simultaneously meet conditions that x is greater than or equal to 0.8 and smaller than or equal to 0.92, y is greater than or equal to 0.05 andsmaller than or equal to 0.2, and 1-x-y>0. The positive pole material, by adopting a nickel cobalt lithium aluminate material with the optimal composition, has excellent high-voltage cycling stability and a higher energy density.
Owner:昆山聚创新能源科技有限公司
Austenitic stainless steel having improved hydrogen embrittlement resistance, and high-pressure hydrogen gas container comprising same
InactiveCN110191972AReduce manufacturing costExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementVessel wallsSecondary cellsHigh pressure hydrogenHigh pressure
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Resource-saving high-temperature high-strength heat-resistant alloy steel material
PendingCN112030080AImprove high temperature oxidation resistanceRaise the ratioRare-earth elementAustenite
The invention discloses a resource-saving high-temperature high-strength heat-resistant alloy steel material. The alloy steel material consists of the following elements in percentage by mass: at least one of 0.25-0.6% of C, 0.5-2% of Si, less than or equal to 2.5% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.03% of P, less than or equal to 0.03% of S, 25-35% of Cr, 7-23% of Ni, 2-6% of W and 2-6% of Mo, 0.15-0.5% of N, 0.05-0.4% of rare earth element Re and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein the sum of the mass percents of all the elements is 100%. According to the alloy steel material, alow-cost austenite stabilization element N is used for replacing an expensive element Ni, the Ni content is saved by 50% or above compared with a traditional heat-resisting alloy with the ZG50Cr28Ni48W5 type brand, the production cost is reduced, and the high-temperature mechanical property and the high-temperature endurance property of the alloy steel material are superior to those of the heat-resisting alloy with the ZG50Cr28Ni48W5 type brand.
Owner:QINGDAO NPA IND
Preparation method of lithium ion battery cathode
InactiveCN111463404AImprove cycle performanceInhibit sheddingSecondary cellsPositive electrodesLithium-ion batteryBattery cell
The invention provides a preparation method of a cathode of a lithium ion battery, wherein the active substance layer of the cathode of the lithium ion battery comprises a first layer, a second layerand a third layer, and the active substances comprise LiNi0.35Mn0.4Co0.2Al0.05O2, LiNi0.2Mn0.5Co0.27Al0.03O2 and LiNi0.15Mn0.55Co0.28Al0.02O2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively preparing LiNi0.35Mn0.4Co0.2Al0.05O2, LiNi0.2Mn0.5Co0.27Al0.03O2 and LiNi0.15Mn0.55Co0.28Al0.02O2 into slurries; preparing the slurries of a first layer, a second layer and a third layer according to a mass ratio; and sequentially coating a current collector with the slurries, and drying to acquire the battery cathode. The battery prepared by the preparation method has excellent rate capability and cycle performance.
Owner:朱虎
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com