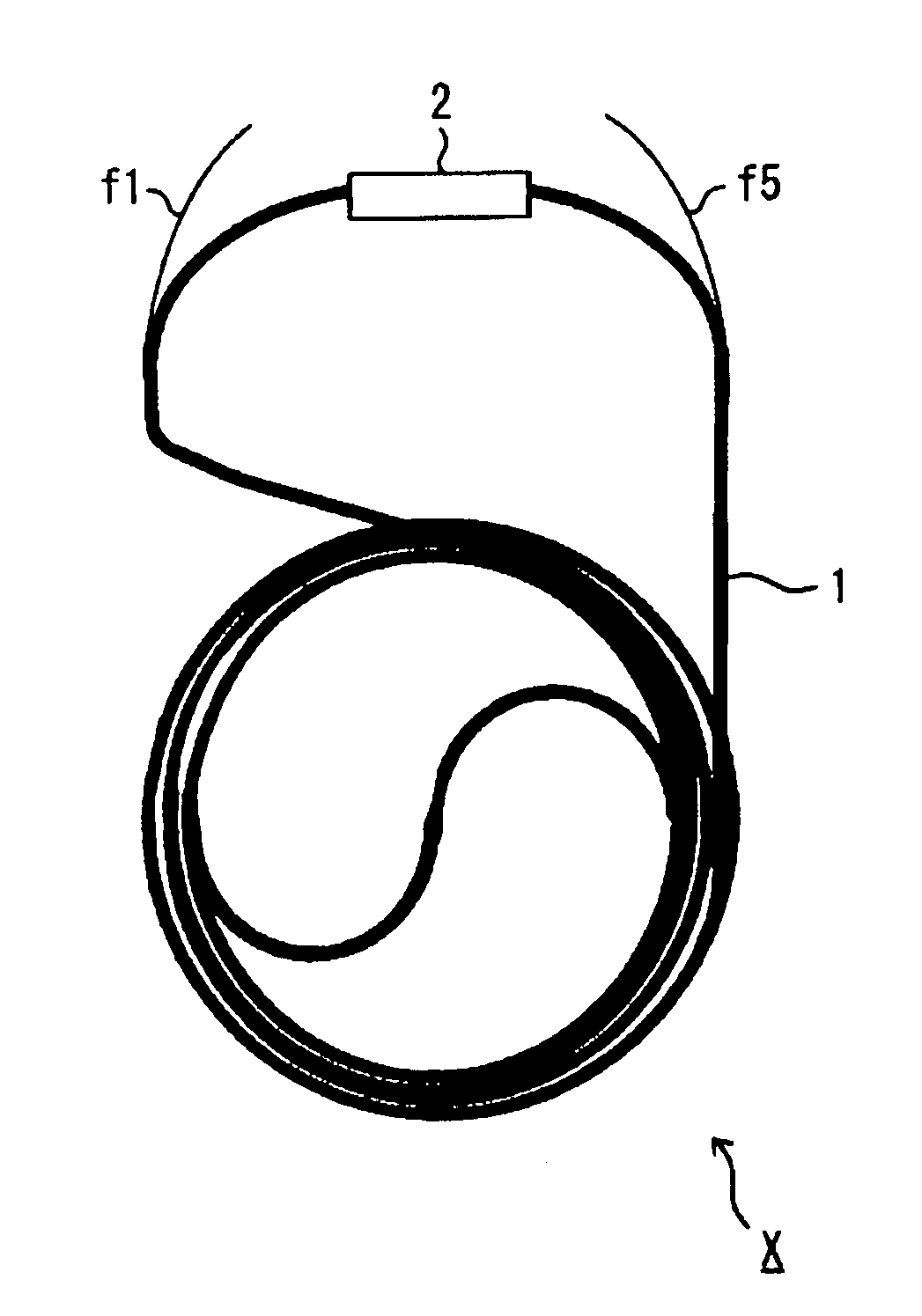Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Reliable environment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
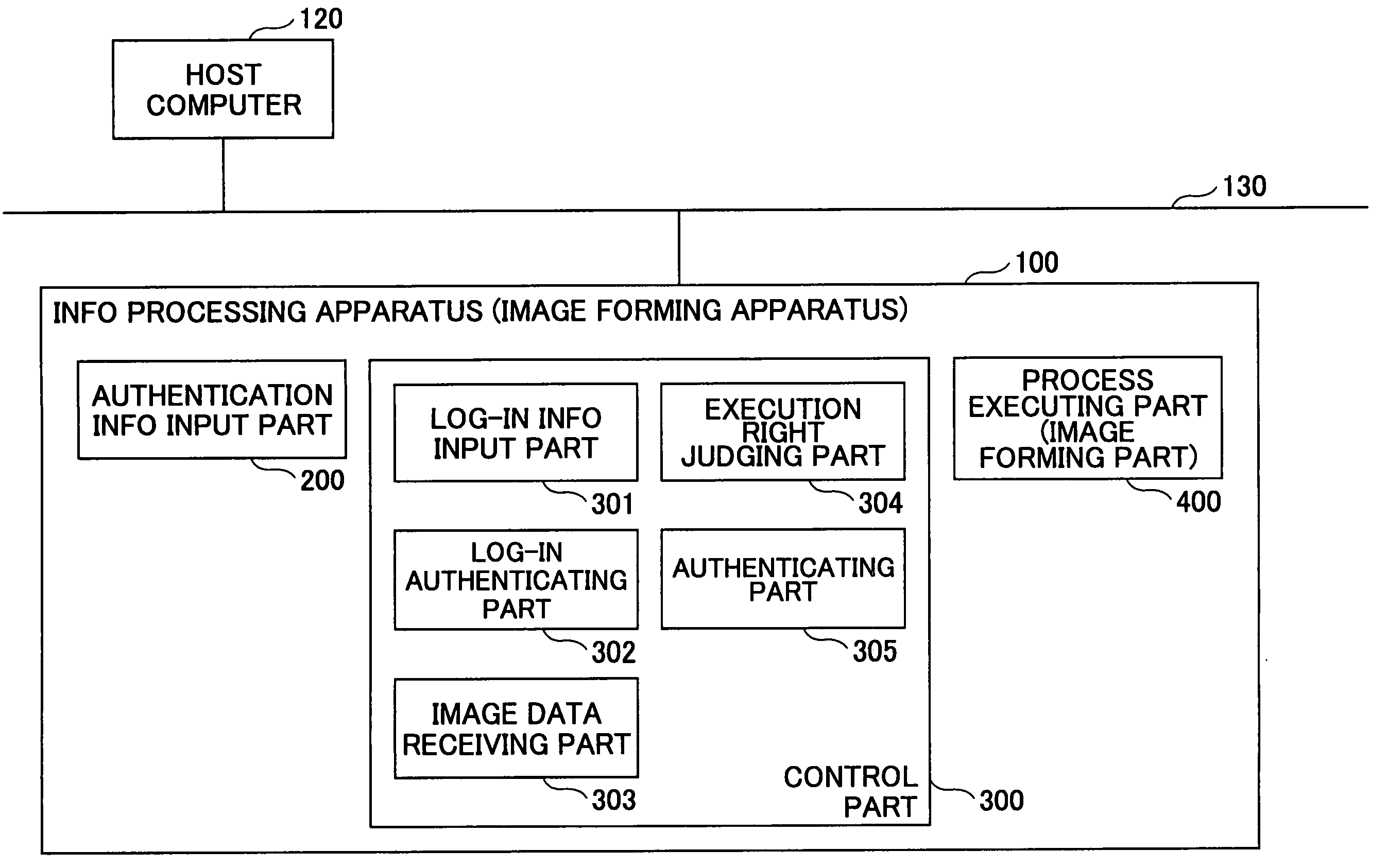
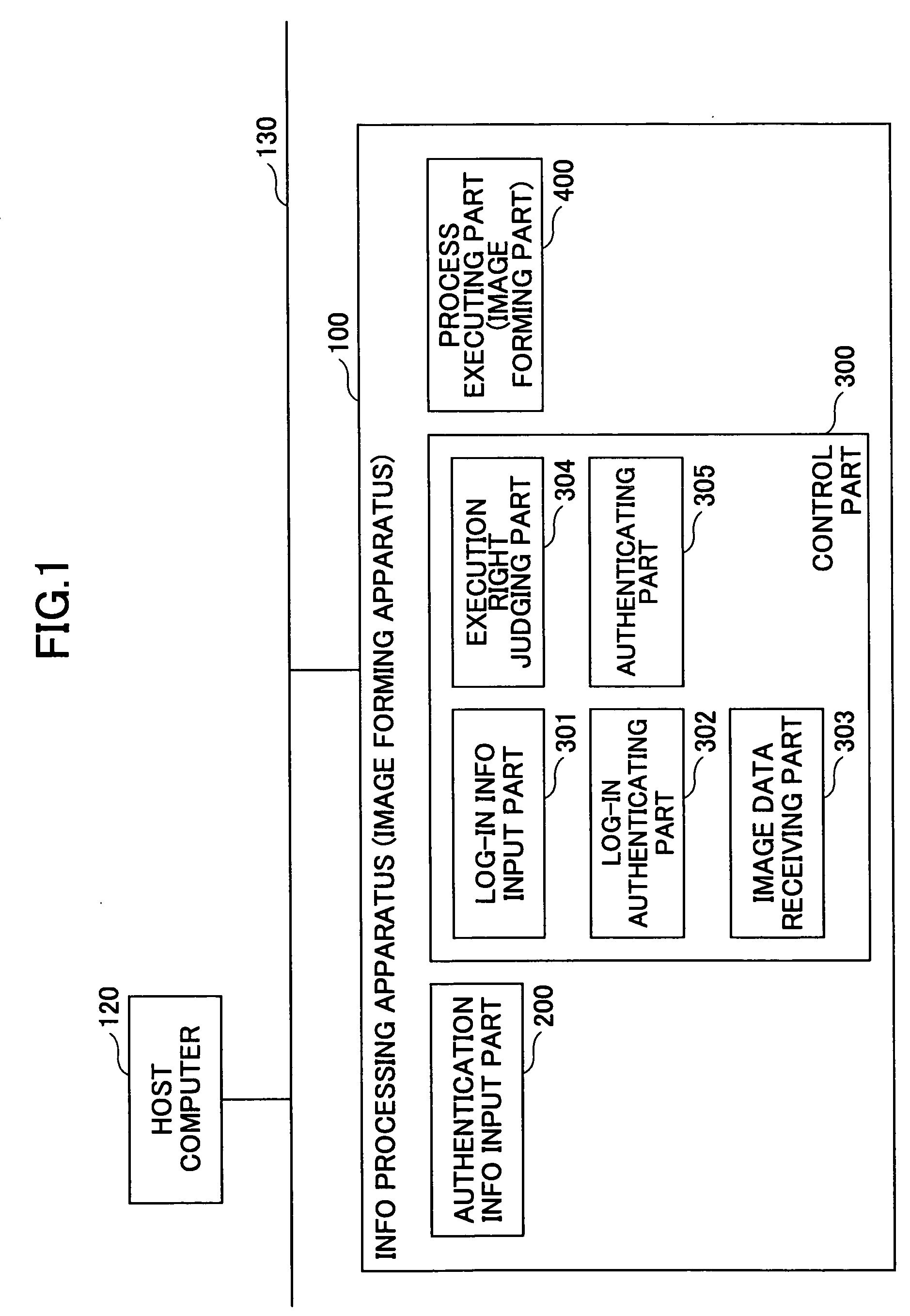
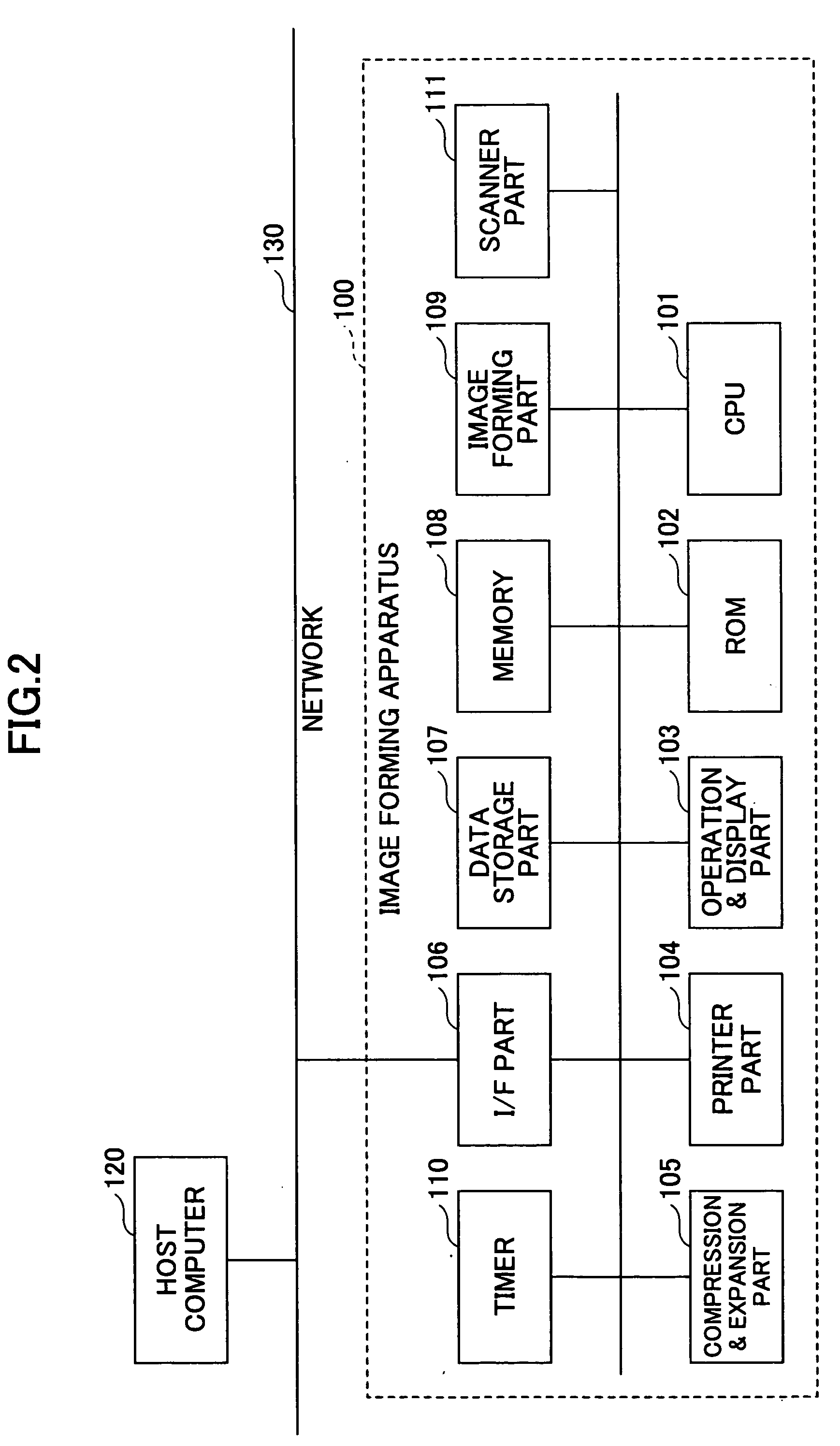
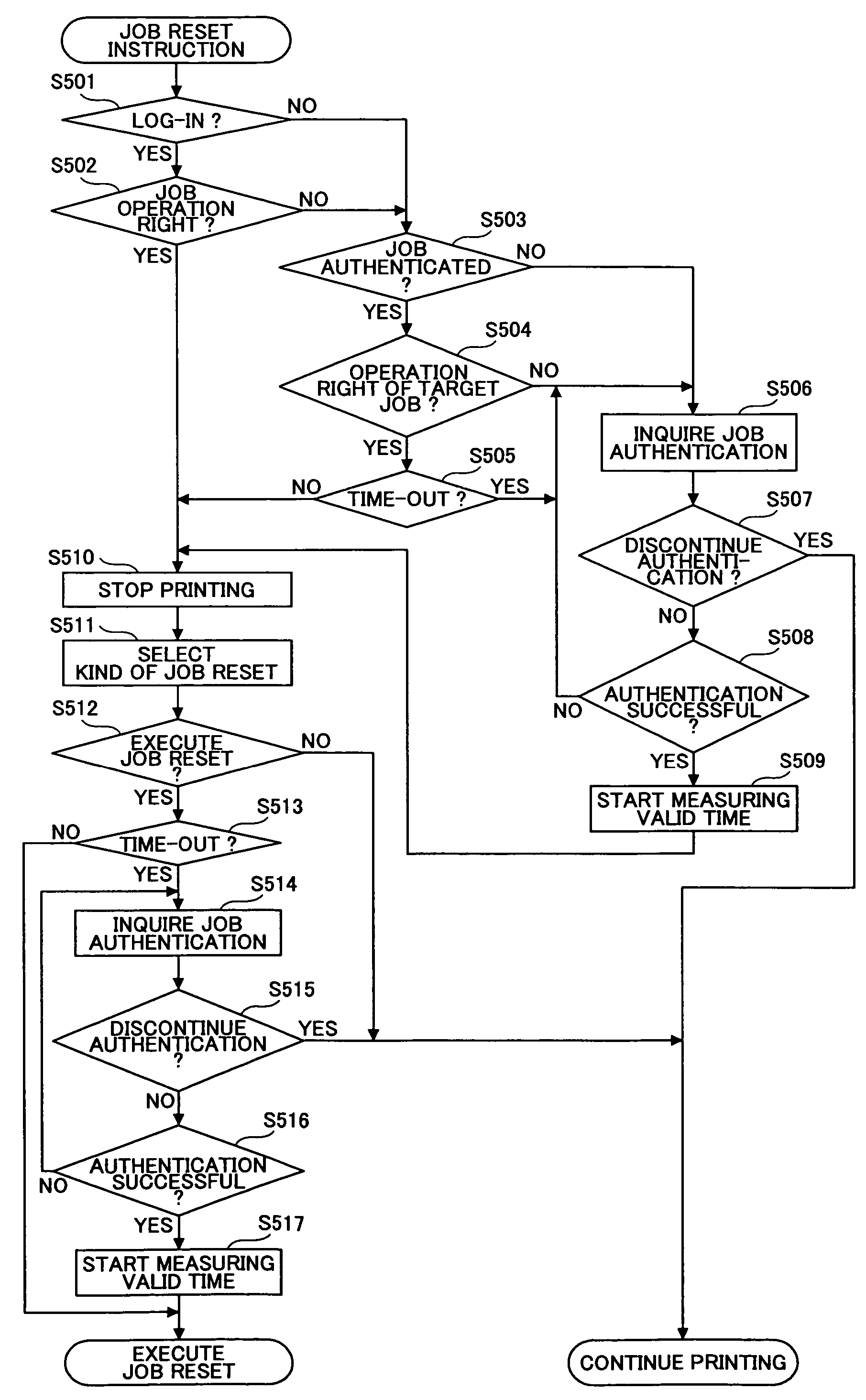
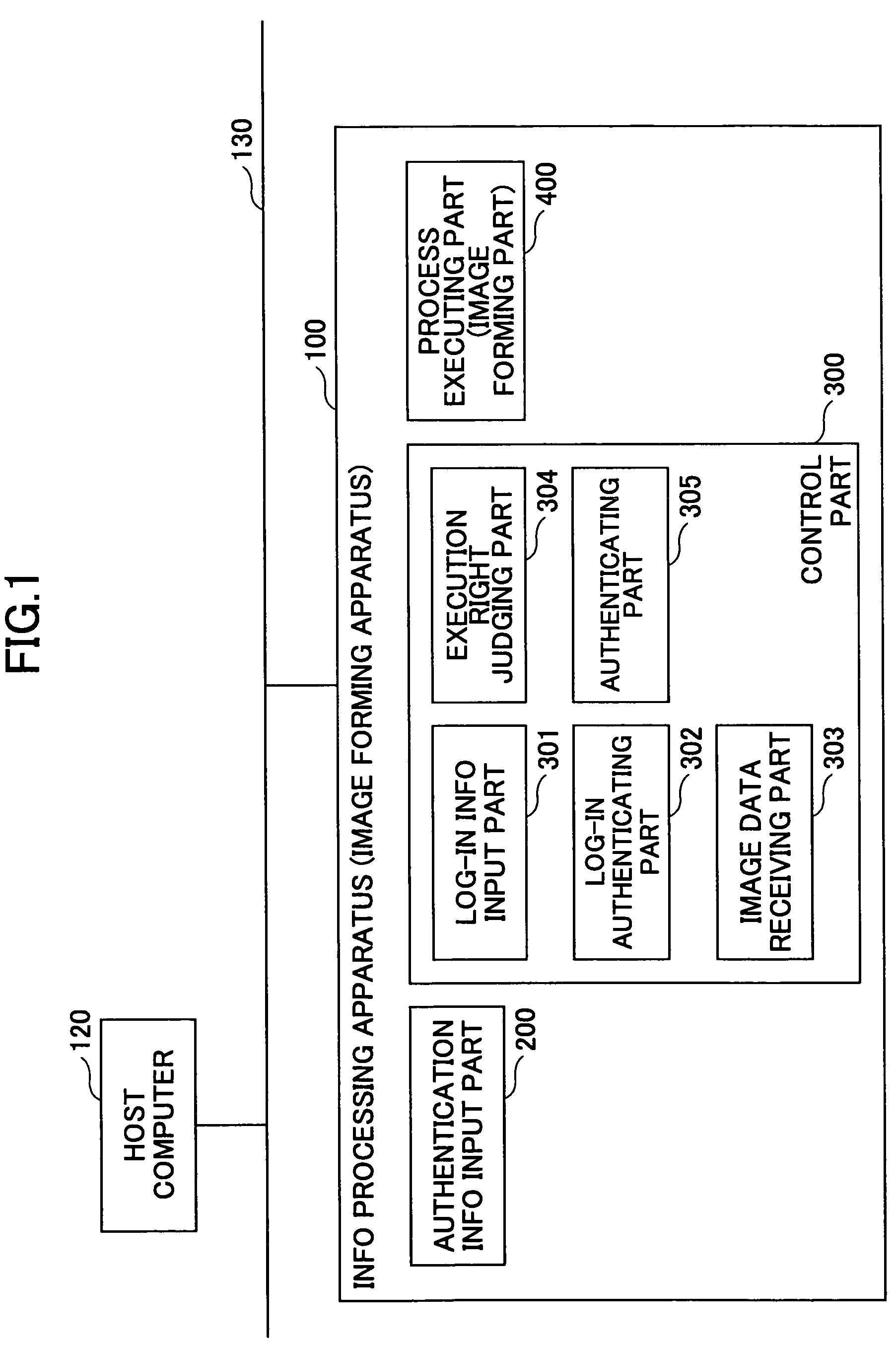
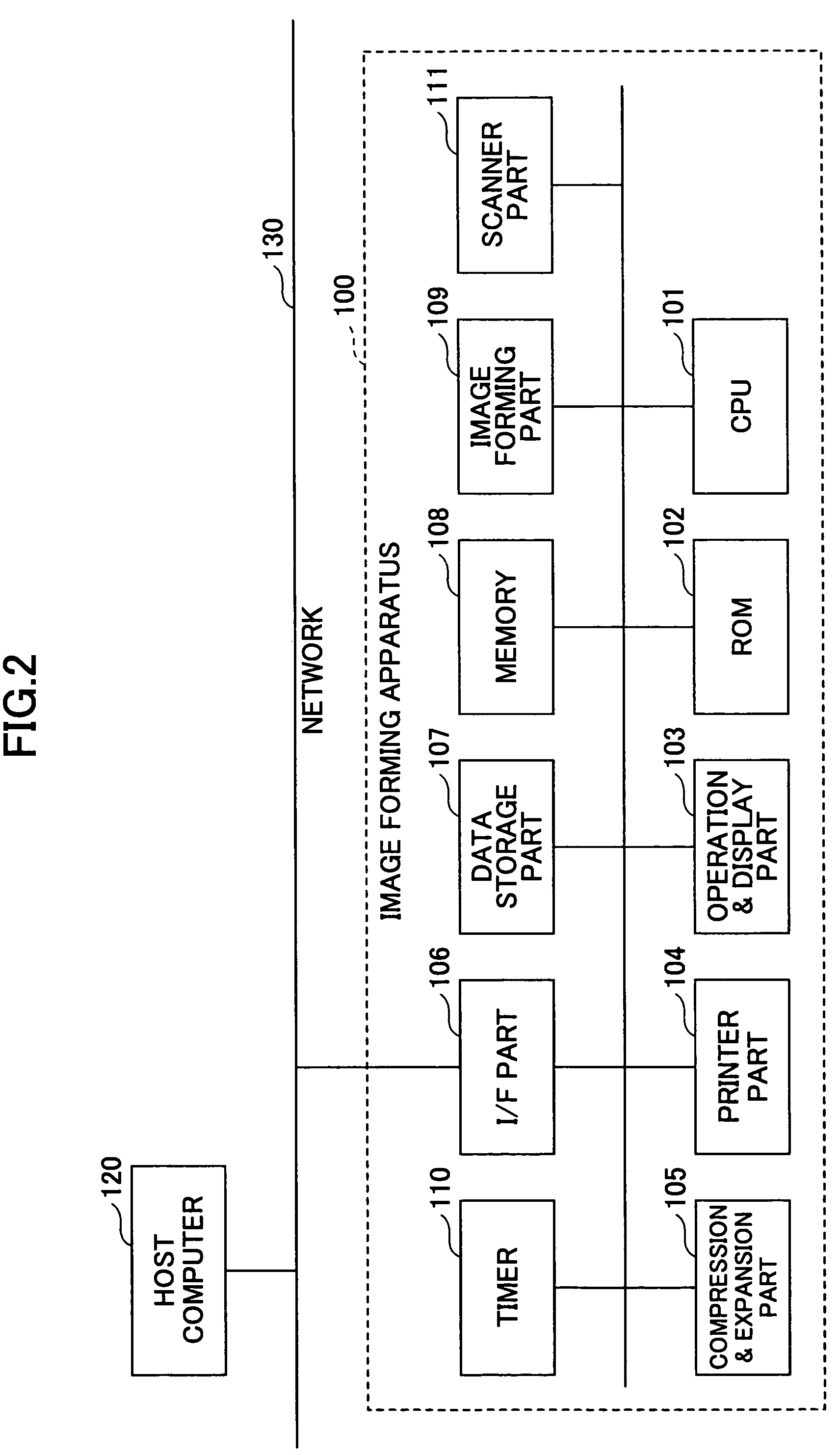
Image forming apparatus, information processing apparatus, information processing system, authentication method and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveUS20050183141A1Improve reliabilityReliable environmentReliability increasing modificationsMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsInformation handling systemInformation processing
An image forming apparatus includes an input part to input authentication information for authenticating a predetermined operation with respect to a registered printing job, an input part to input log-in authentication information for authenticating the predetermined operation from an operation part, an image forming part to form an image of the printing job, and a control part to request input of the authentication information for authenticating the predetermined operation with respect to a printing job that is being executed by the image forming part when the predetermined operation is made from the operation part in a logged in state, and authenticating the predetermined operation with respect to the printing job when authentication of the authentication information input by the input part is successful.
Owner:RICOH KK
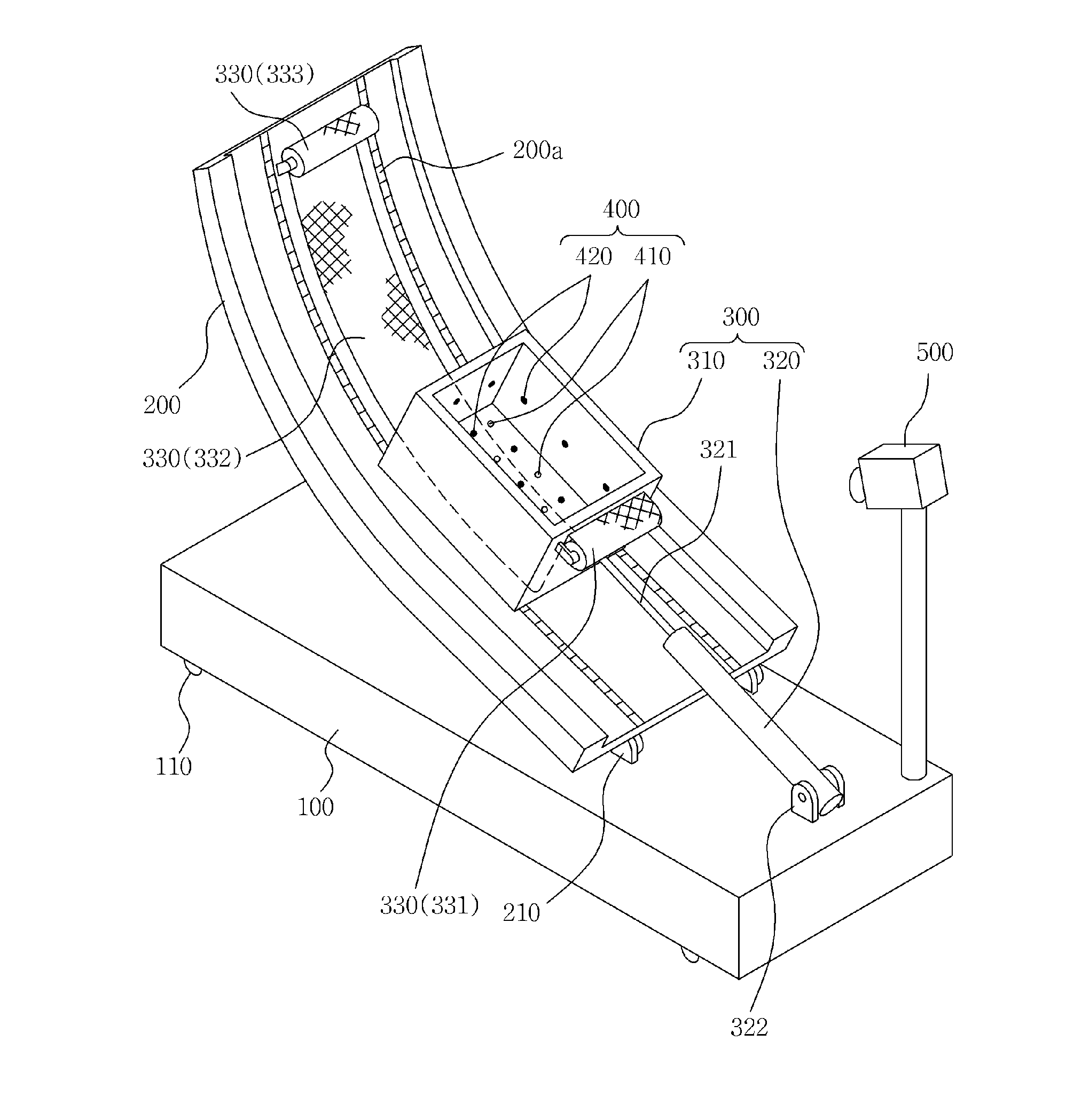
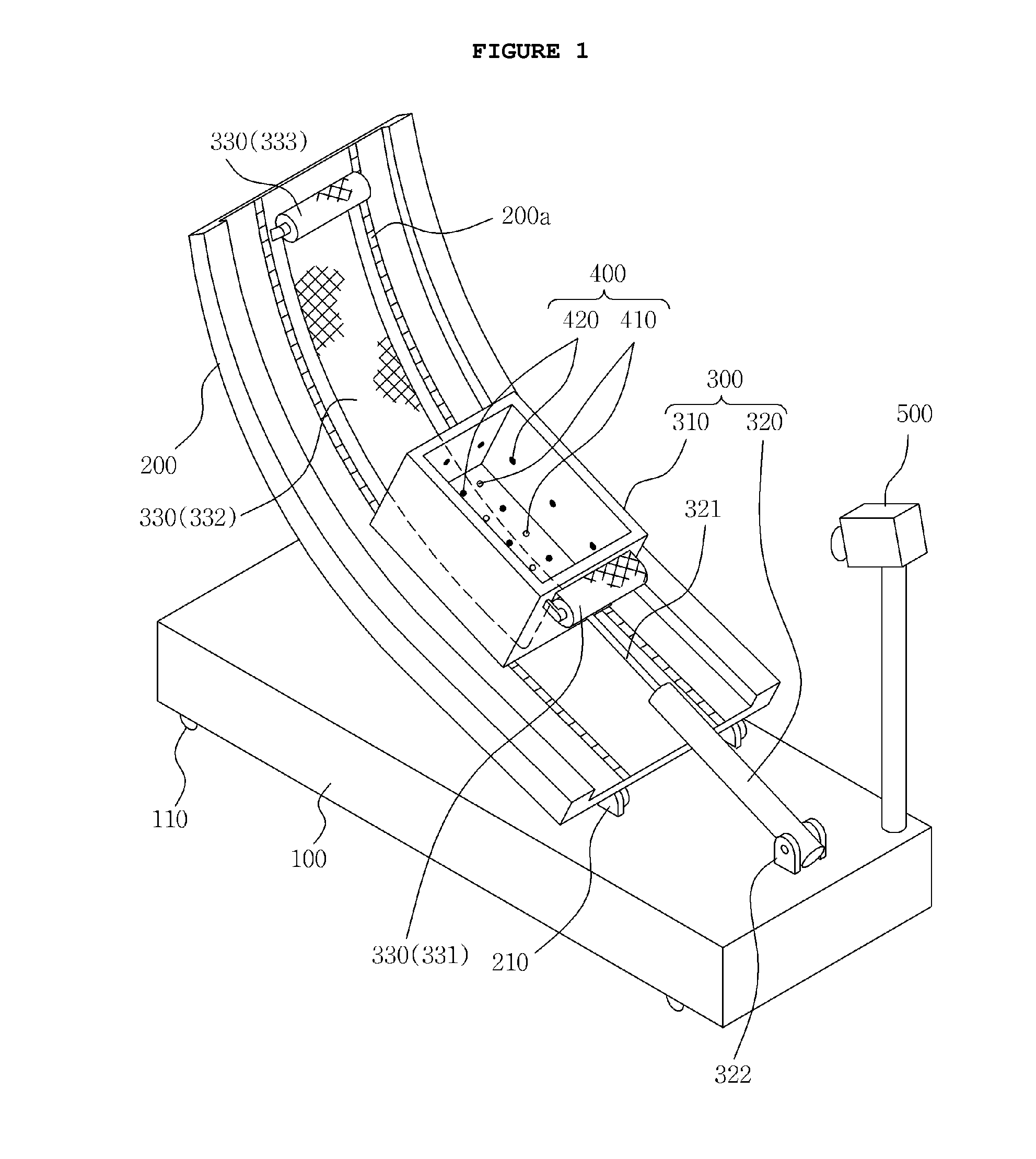
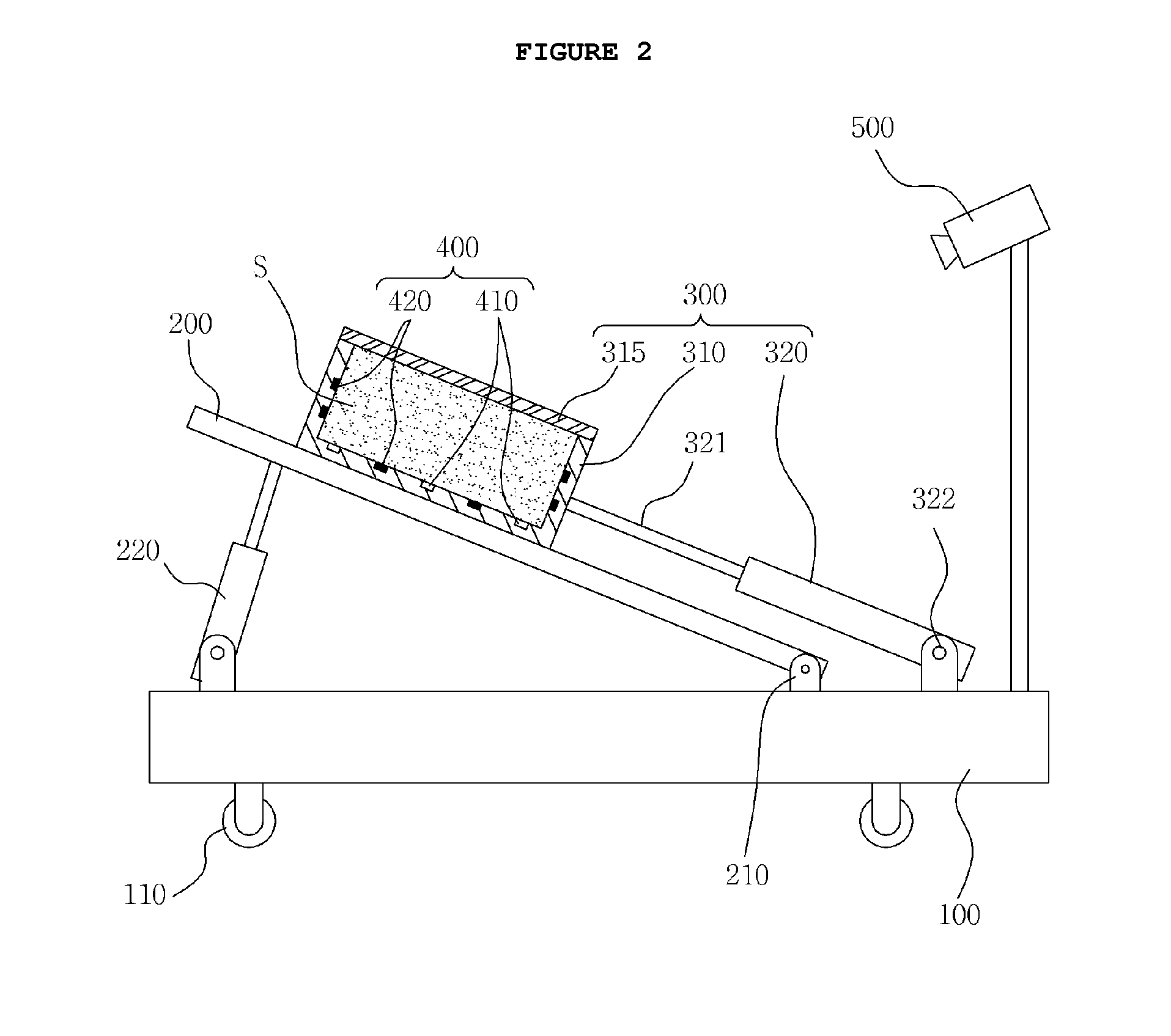
Test apparatus for early landslide detection fully-connected with pore water pressure, surface displacement and shear surface
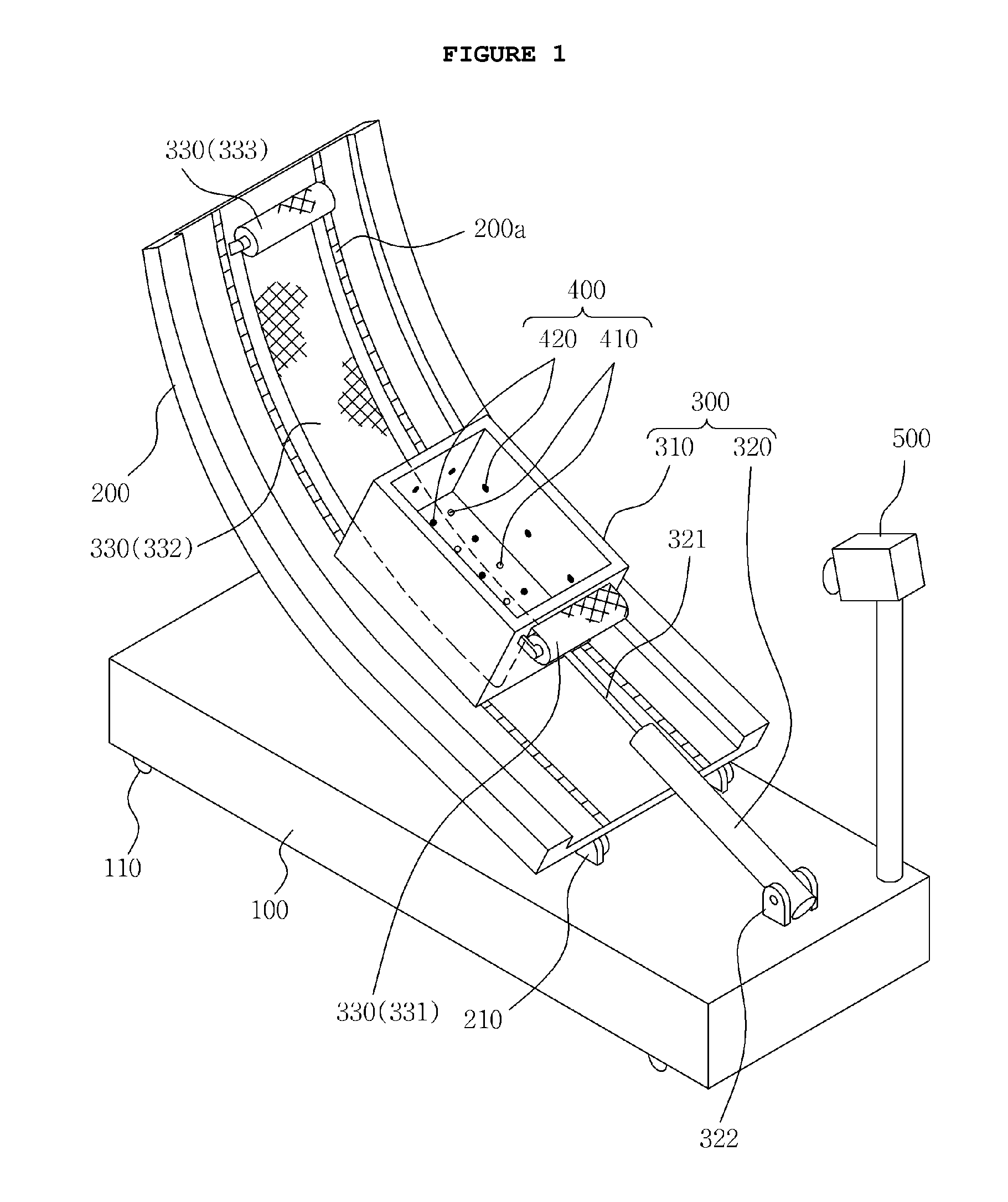
ActiveUS20160047724A1Reliable test environmentSmoothly pullForce measurementEarth material testingEngineeringFactor of safety
Disclosed herein is a test apparatus for early landslide detection fully-connected with pore water pressure, surface displacement and shear surface. The test apparatus calculates a factor of safety of a slope based on variation in pore water pressure, surface displacement and shear surface of a soil mass, and predicts a change in factor of safety, thus making early landslide detection possible. In the test apparatus, while a container of a slider is moved with a soil mass loaded into the container, shear surface and surface displacement environment is provided, and the shear strength and the shear stress of the soil mass can be calculated based on the pore water pressure and the weight of the soil mass. Thereby, the factor of safety of the soil mass can be calculated, and early landslide detection can be realized by using variation of the factor of safety of the slope.
Owner:KOREA INST OF GEOSCI & MINERAL RESOURCES
Horizontally polarized omni-directional antenna
InactiveUS20050116874A1Improve broadband impedance matchImprove reception/transmittanceAntenna arraysAntenna supports/mountingsDielectricCoaxial cable
An antenna apparatus comprising bent dipoles and fed by a quarter-wave balun transformer with a single coaxial cable feed is disclosed. In this embodiment, the antenna elements are patterned onto a dielectric circuit board which is then mounted horizontally into a molded shell. The antenna is tuned by trimming the bent dipoles patterned on the circuit board.
Owner:FRC COMPONENT PROD
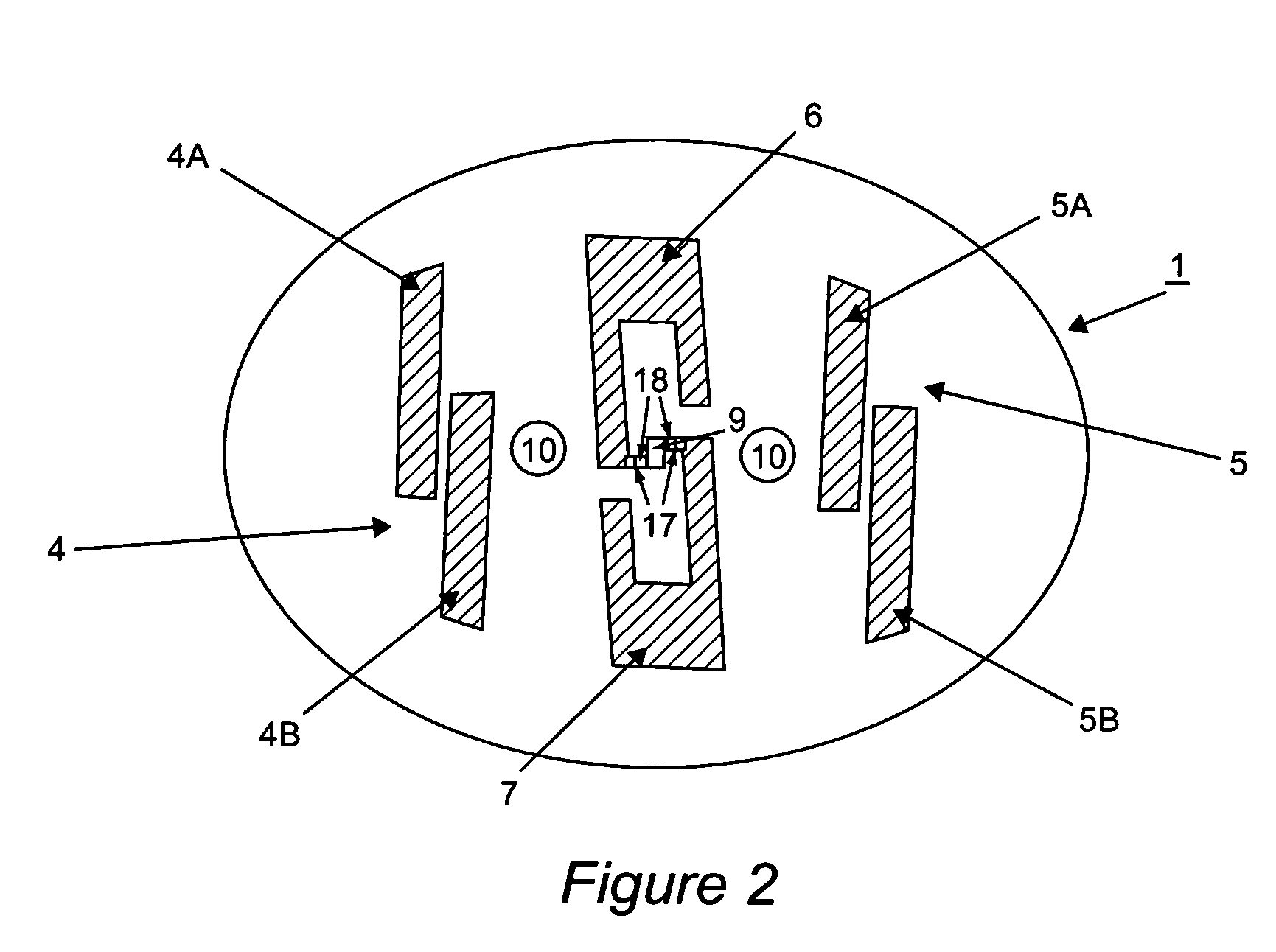
Method & arrangement for calculating a conformity between a representation of an environment and said environment
ActiveUS20110066313A1Reliable environmentImprove conformityInstruments for road network navigationAnalogue computers for trafficComputer scienceBuilding construction
The present invention concerns a method for determining a conformity between a representation of an environment and said environment, wherein said representation of the environment constitutes a representation in at least two dimensions, where a distance between two points in the representation has a known relation to the corresponding distance in said environment, characterised in that said determination involves the step of determining a first set of parameter values for a first position in said representation of the environment, comparing said first determined set of expected parameter values with a second set of parameter values, where said second set of parameter values has been determined for a second position, where said second position constitutes a position in said environment that essentially corresponds to said first position, and using said comparison to determine a measure of conformity between said environment and said representation of the environment. The invention also concerns an arrangement and the mining and / or construction machine.
Owner:EPIROC ROCK DRILLS AB
Image forming apparatus, information processing apparatus, information processing system, authentication method and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveUS7657753B2Improve reliabilityReliable environmentReliability increasing modificationsMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsInformation processingImage formation
An image forming apparatus includes an input part to input authentication information for authenticating a predetermined operation with respect to a registered printing job, an input part to input log-in authentication information for authenticating the predetermined operation from an operation part, an image forming part to form an image of the printing job, and a control part to request input of the authentication information for authenticating the predetermined operation with respect to a printing job that is being executed by the image forming part when the predetermined operation is made from the operation part in a logged in state, and authenticating the predetermined operation with respect to the printing job when authentication of the authentication information input by the input part is successful.
Owner:RICOH KK
Laminated diffractive optical element and resin composition therefor
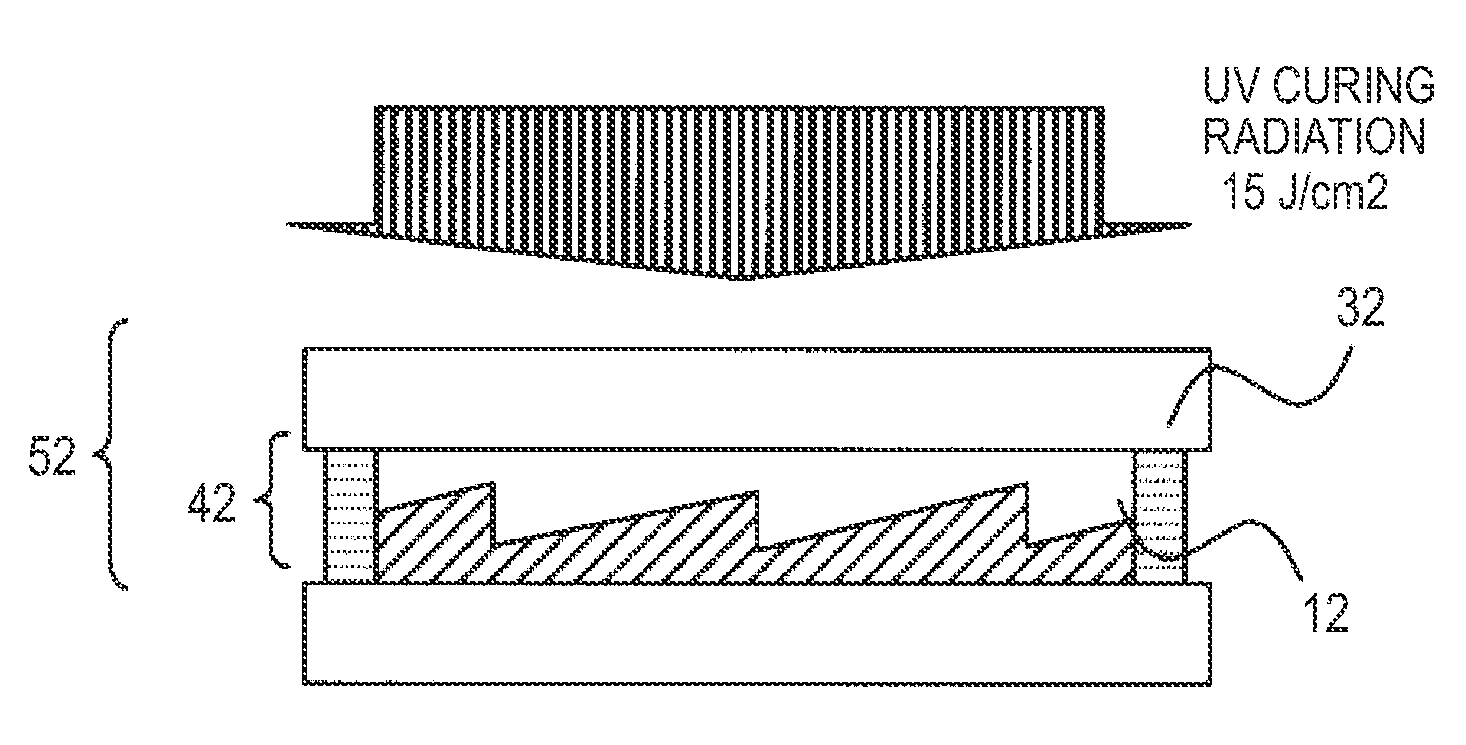
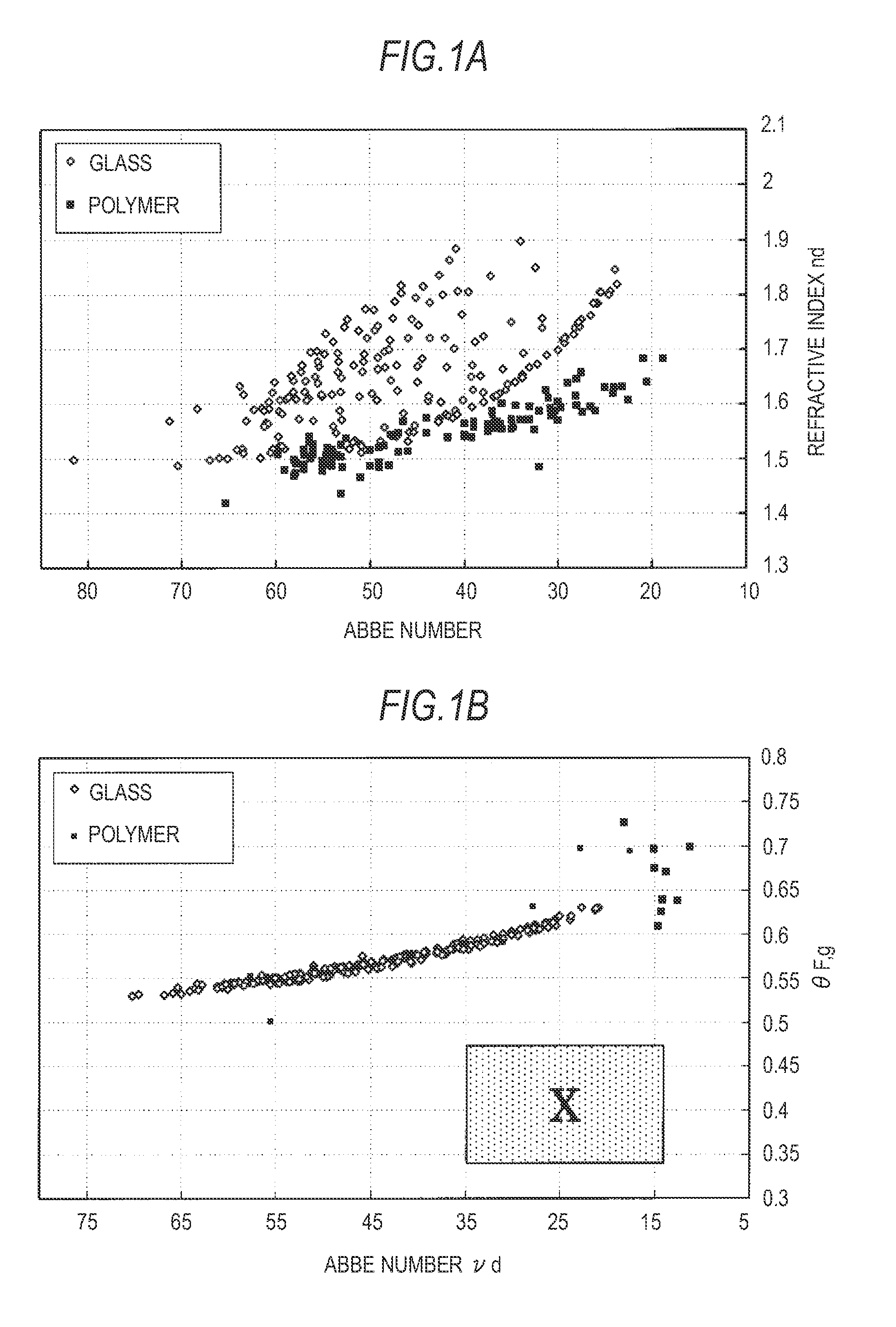
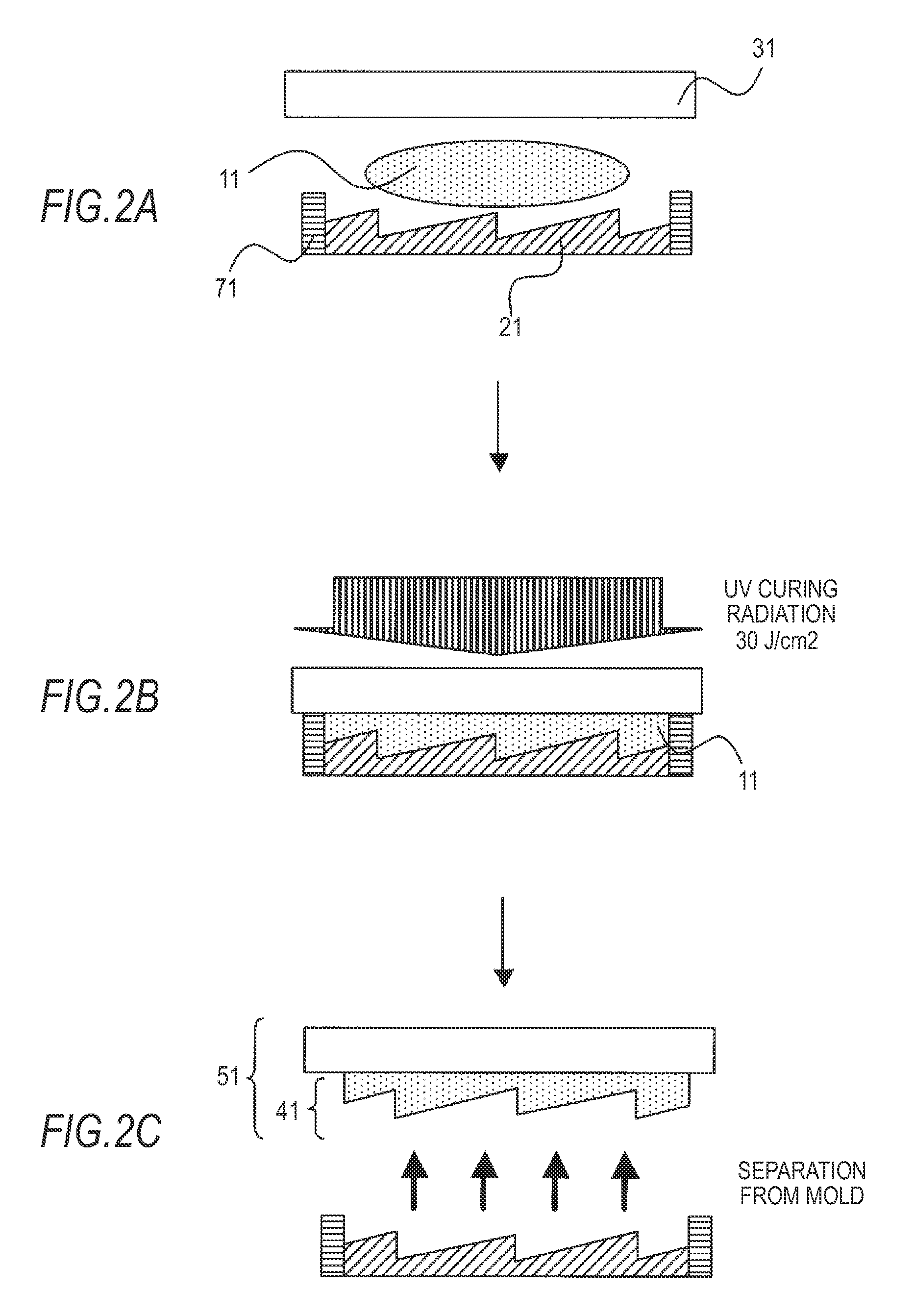
InactiveUS20090190224A1Eliminate the effects ofReliable environmentPhotomechanical apparatusOptical articlesTin dioxideAluminum doped zinc oxide
A resin composition includes a binder component having at least one of a monomer and an oligomer of one or more of a fluorine system and a silicone system having a polymerizable functional group in a molecule. The resin composition also includes fine metal oxide particles, and a polymerization initiator. The fine metal oxide particles include particles selected from the group of zinc oxide, indium oxide, tin oxide, antimony oxide, tin-doped indium oxide (ITO), antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO), zinc-doped indium oxide (IZO), aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO), and fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO).
Owner:CANON KK
Systems and methods for storage filing
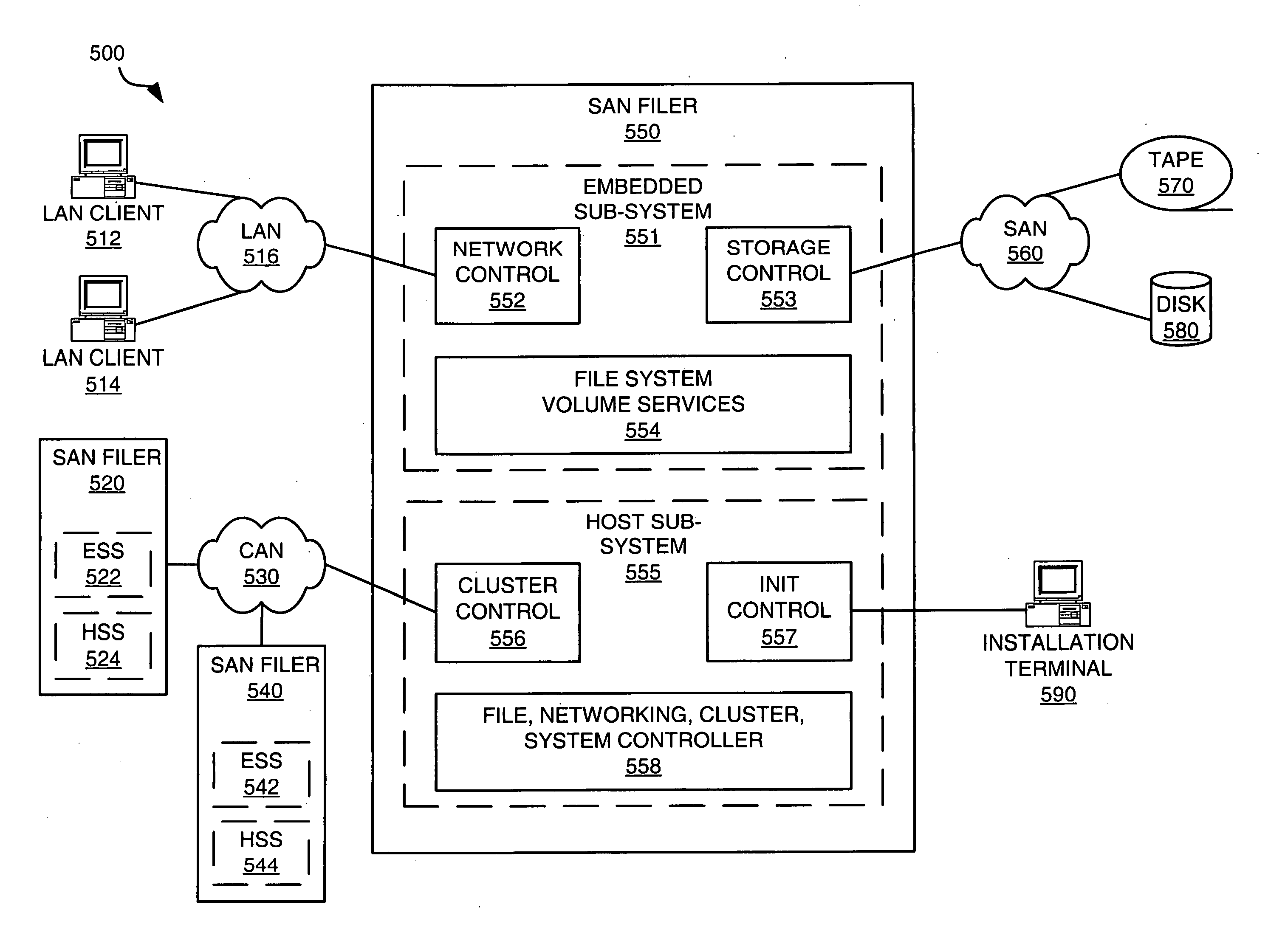
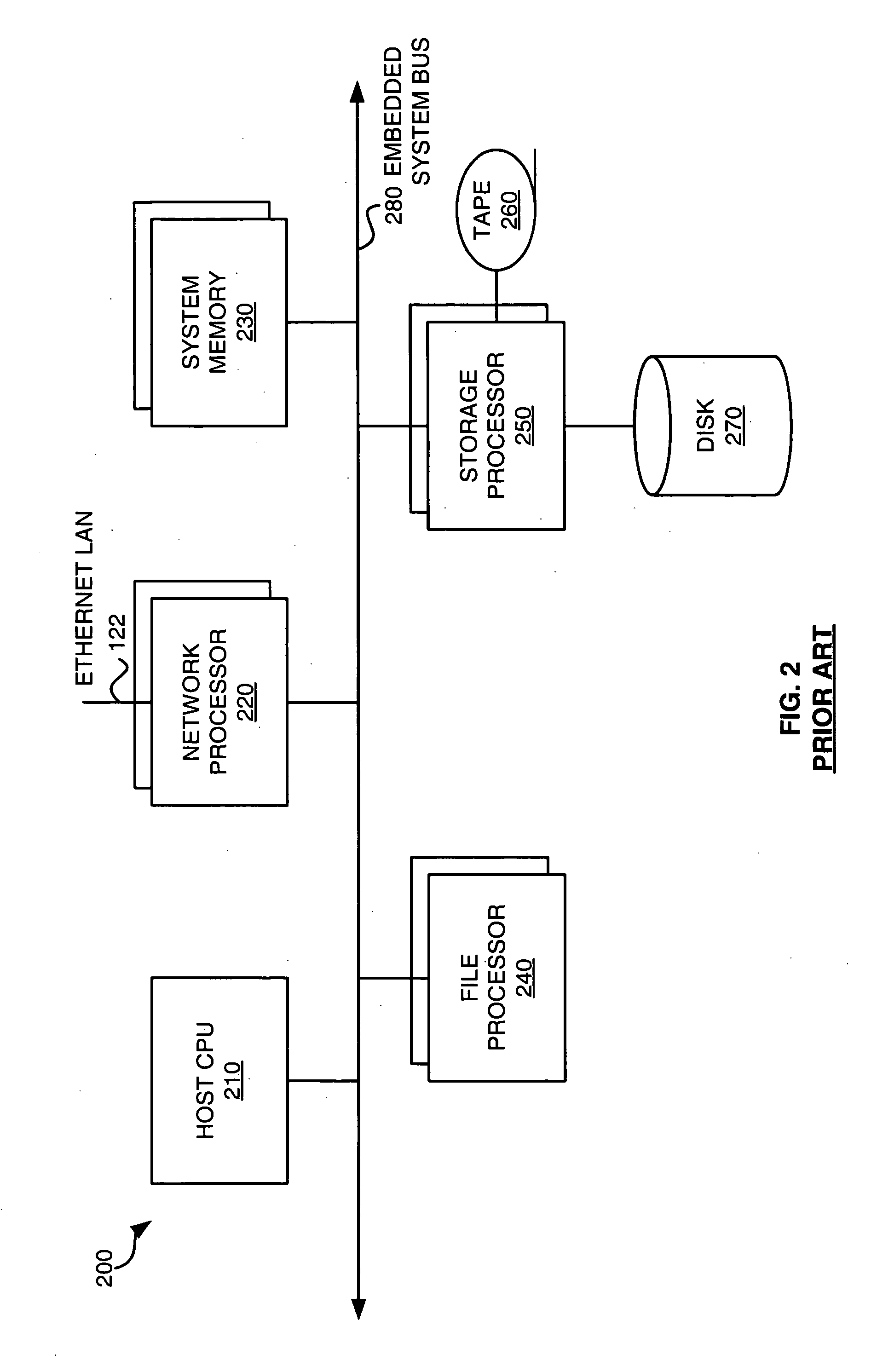
InactiveUS20050086427A1Efficient and scalable architectureGood flexibilityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionCoprocessorFile system
A storage filing system for a storage network includes a communication channel coprocessor, a file processor, and a storage processor. The communication channel coprocessor comprises a plurality of first symmetric processors. The communication channel coprocessor receives a request for data from a communication network. The communication channel coprocessor then processes the request to perform access control and determine a file system object for the data. The file processor comprises a plurality of second symmetric processors. The file processor determines a storage location for the data in the storage network using volume services based on the file system object. The storage processor reads the data from or writes the data to the storage location.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
Method, device and browser client for downloading files in mobile terminals
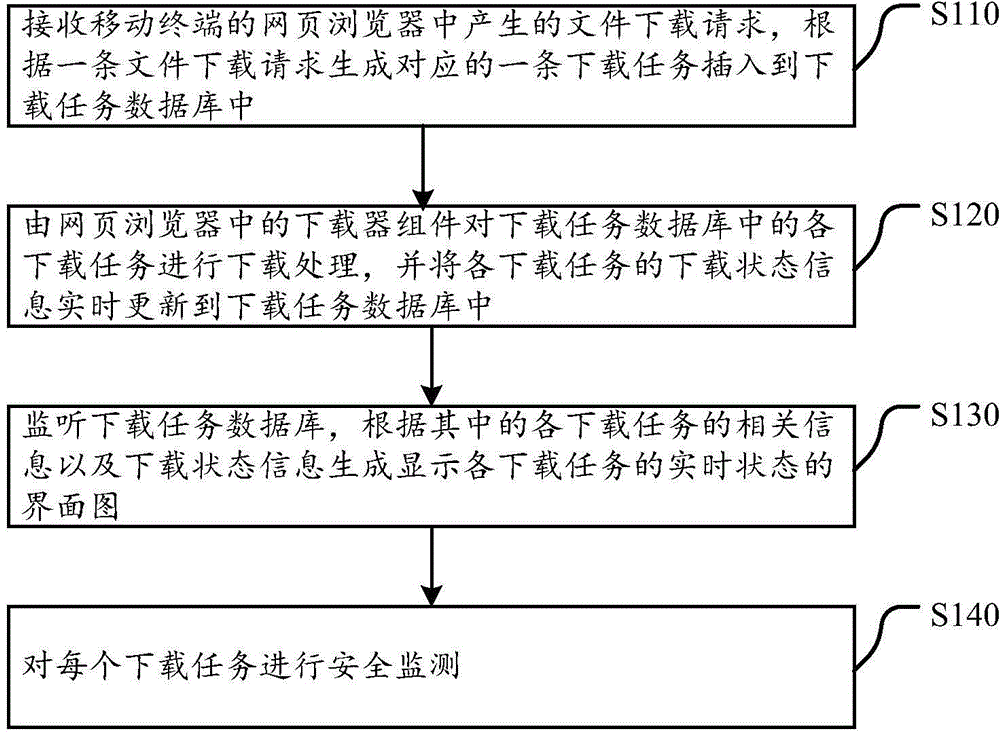
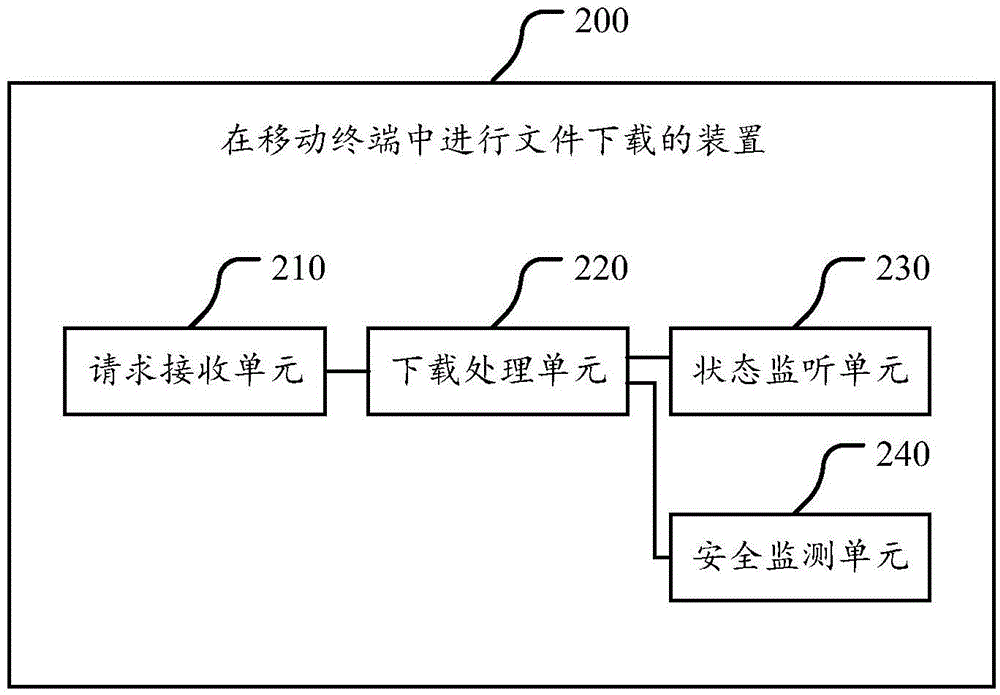
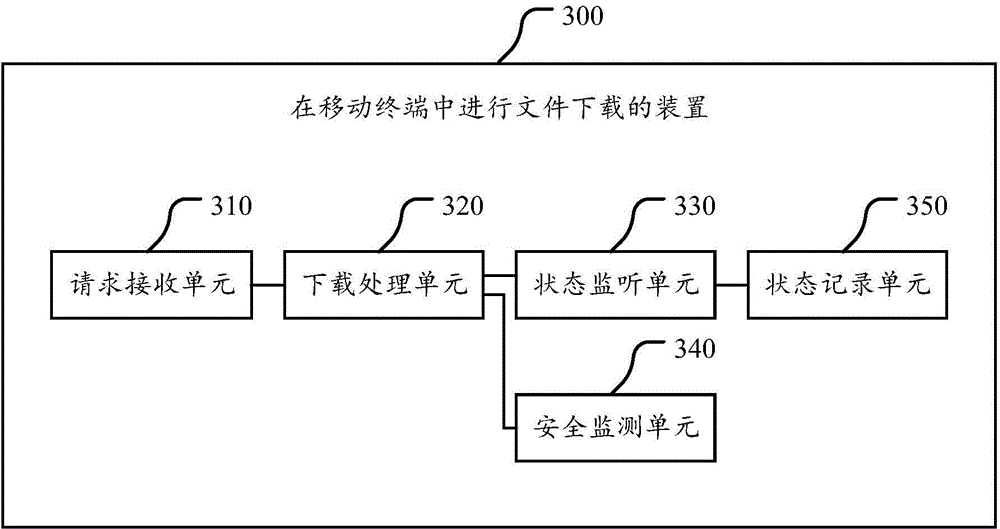
InactiveCN104462400AEnvironment safetyReliable environmentProgram initiation/switchingComputer security arrangementsWeb browserRelevant information
The invention discloses a method, a device and a browser client for downloading files in mobile terminals. The method includes receiving file downloading requests generated in web page browsers of the mobile terminals, generating a corresponding downloading task according to each file downloading request and inserting the downloading tasks into downloading task databases; carrying out downloading processing on the various downloading tasks in the downloading task databases by the aid of downloader assemblies in the web page browsers, and updating downloading state information of the various downloading tasks into the downloading task databases in real time; monitoring the downloading task databases and generating interface diagrams according to relevant information of the various downloading tasks and the downloading state information; monitoring the safety of each downloading task. The interface diagrams are used for displaying real-time states of the various downloading tasks. According to the technical scheme, the method, the device and the browser client have the advantages that safe, effective and reliable downloading environments and downloading experience can be provided for users by the aid of the method, the device and the browser client.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD +1
Optical fiber coil and production method therefor
InactiveUS20080101753A1Reduce economic costsReduce time costSagnac effect gyrometersCoupling light guidesSingle fiberEngineering
An optical fiber coil and a production method therefor make it unnecessary for spaces between single fibers to be widened and for stress to be applied to the single fibers, and in which time and economic costs are low. In the optical fiber coil, an optical fiber ribbon is formed by arranging in parallel plural of single fibers and by integrally covering the single fibers with a covering portion, and ends of the ribbon are connected so that an end of at least one single fiber is connected to an end of another single fiber.
Owner:TOMOEGAWA CO LTD +2
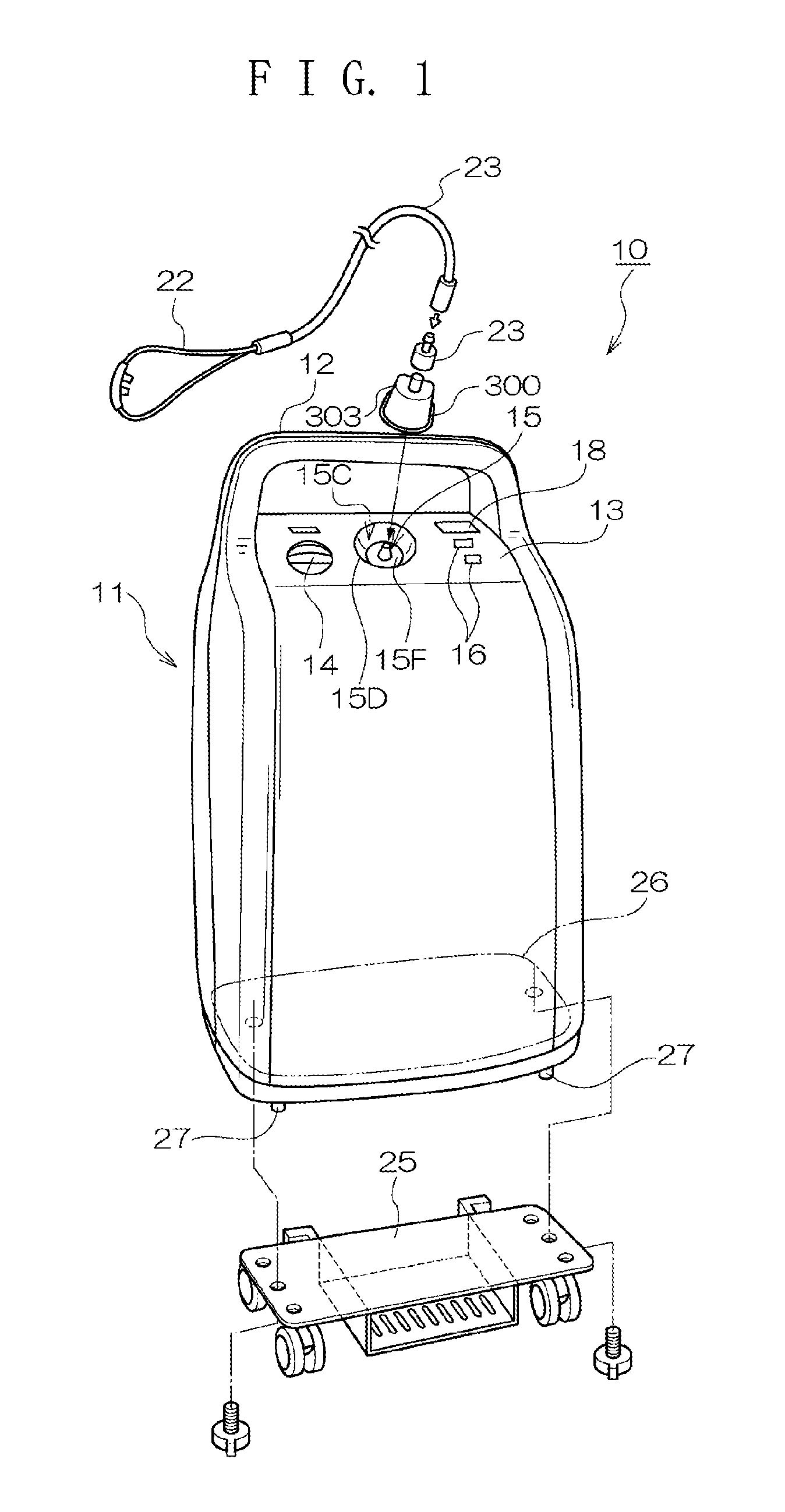
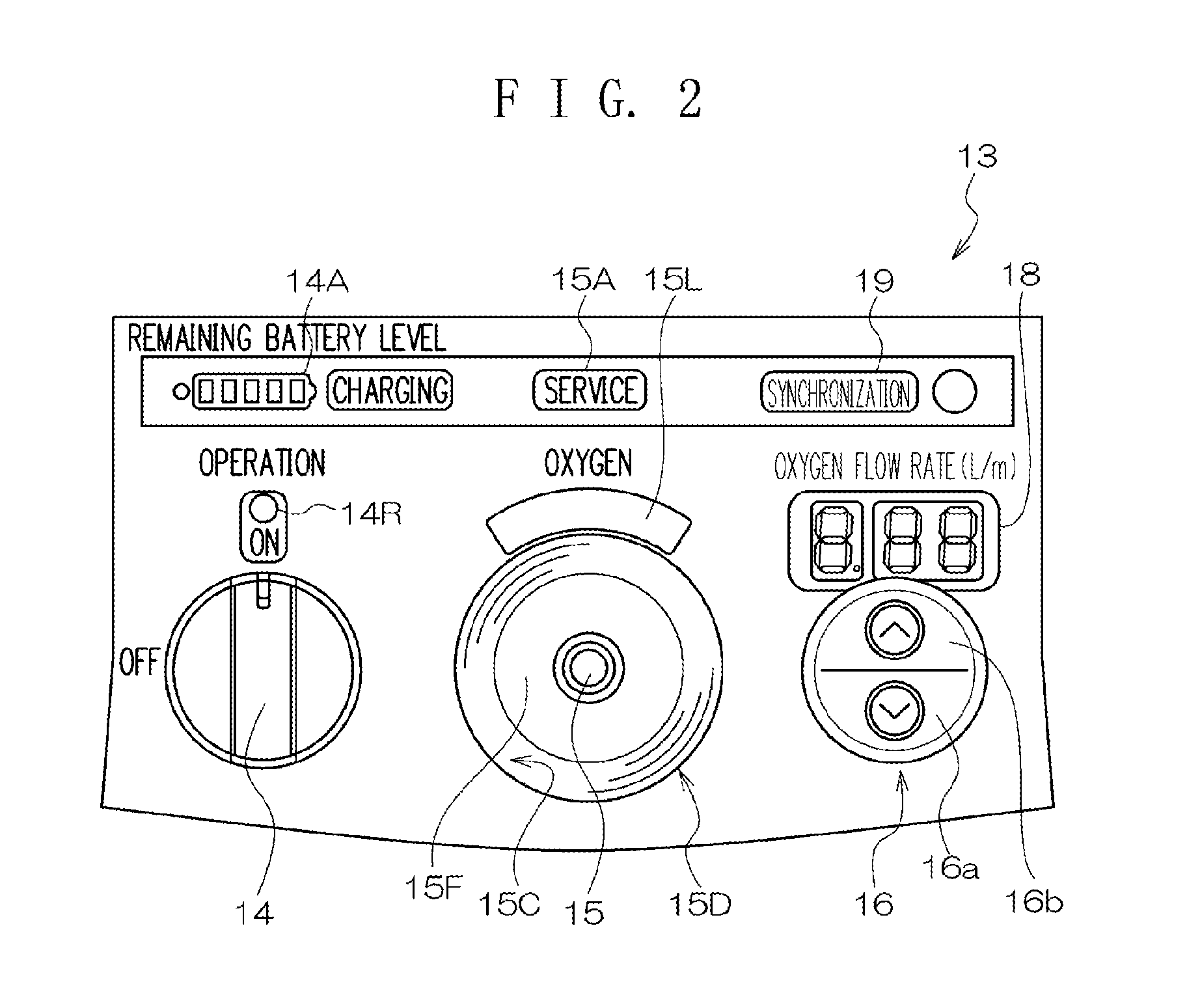
Overheating detection unit and oxygen concentrator
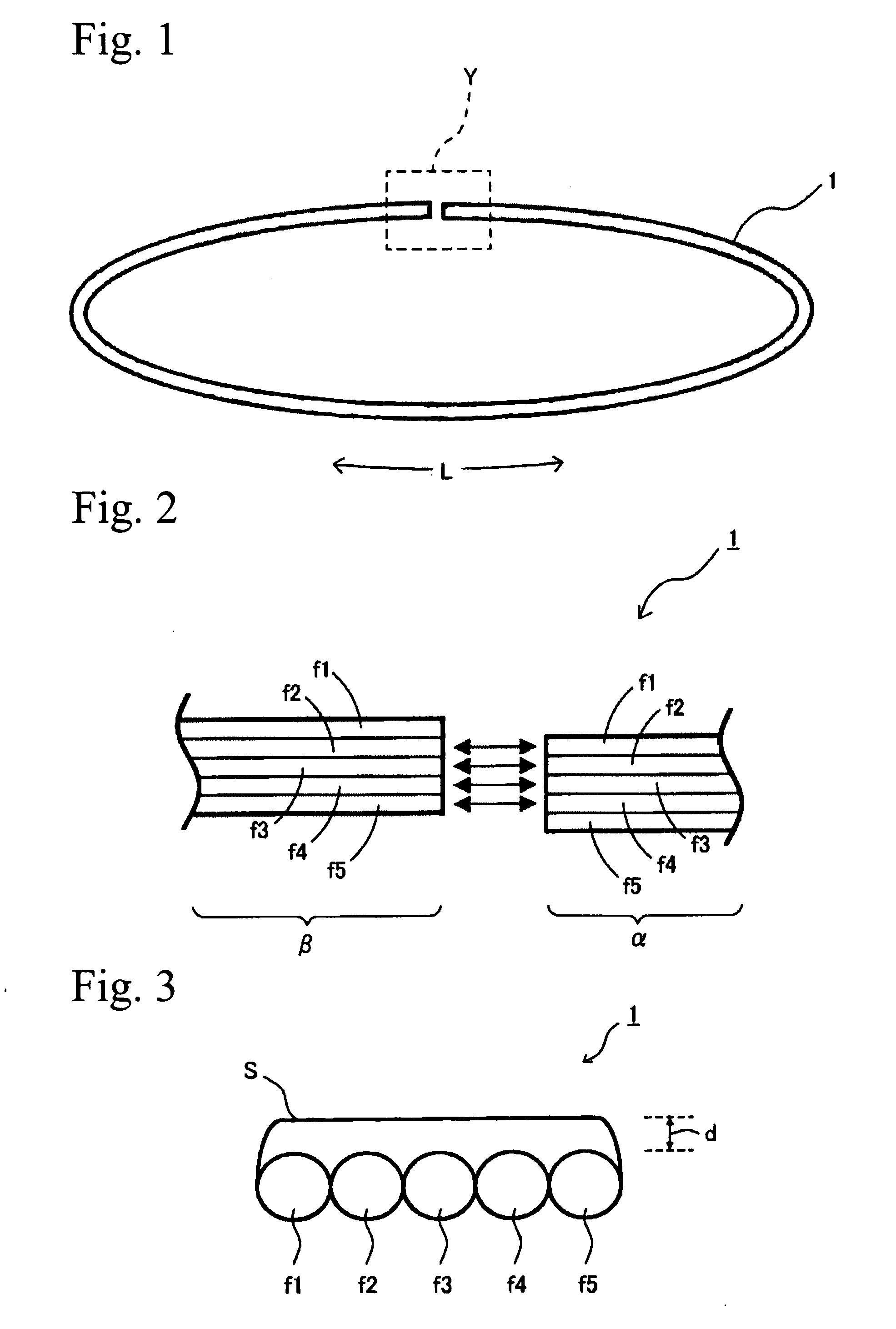
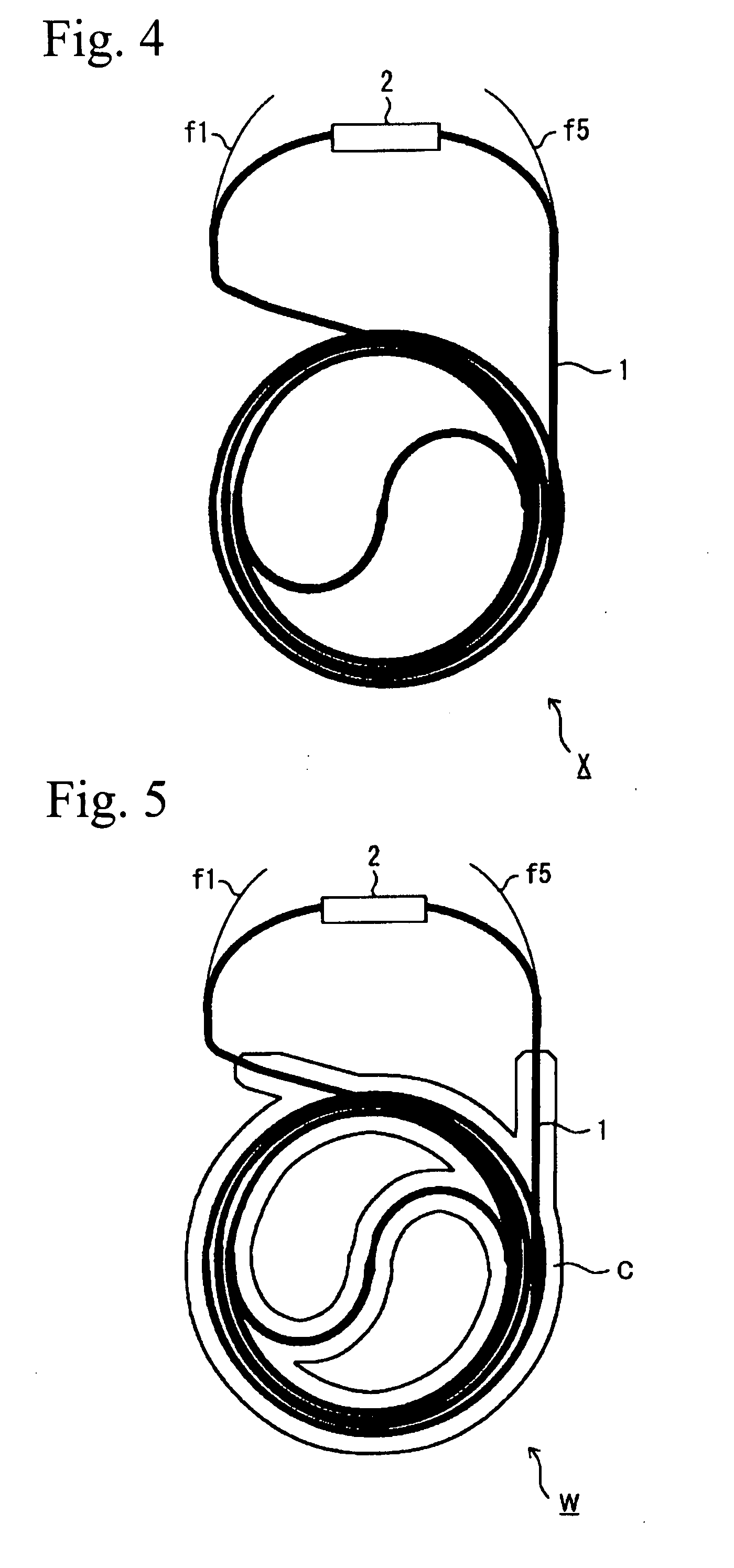
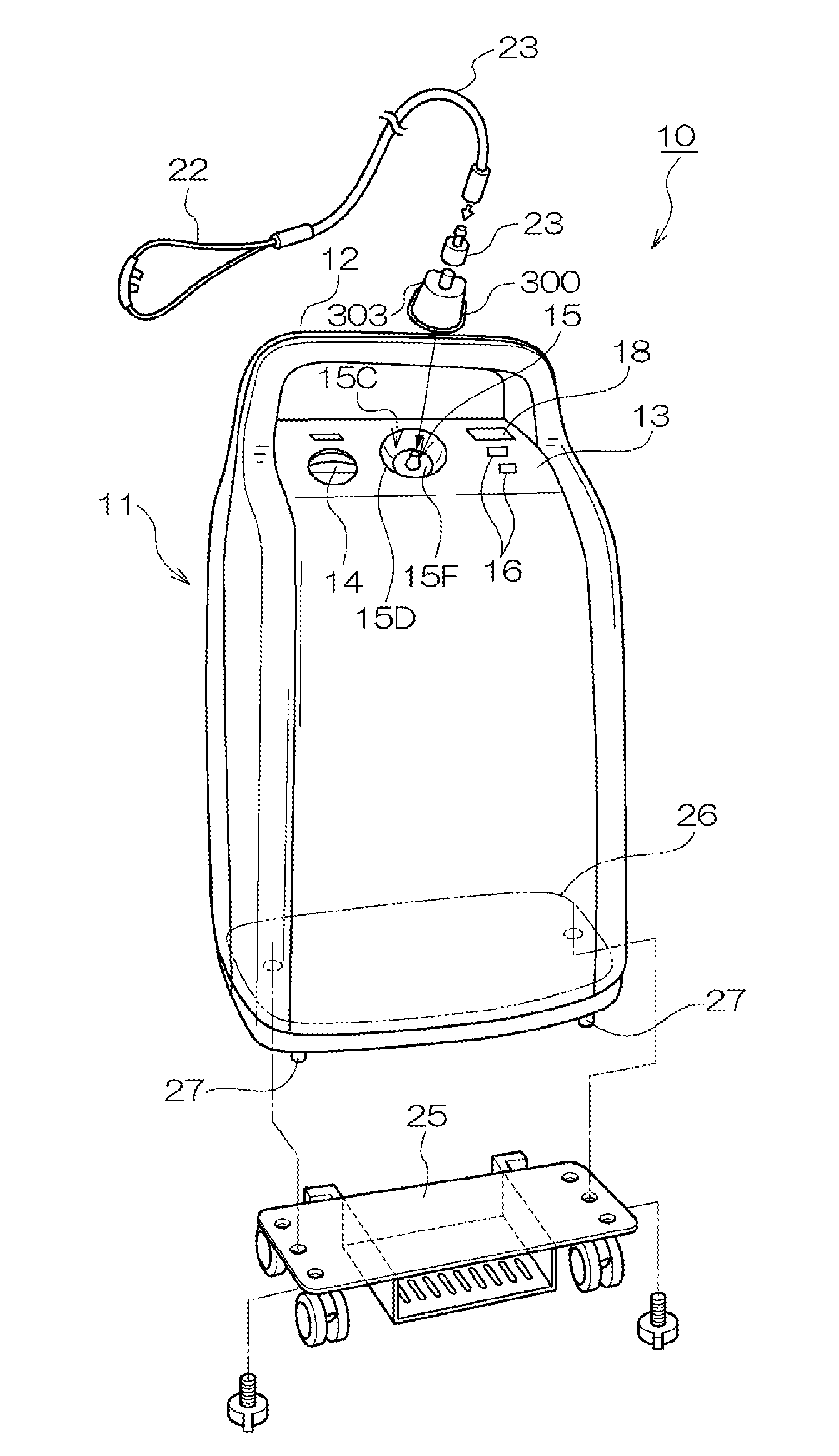
InactiveUS20130299005A1Reliable environmentEnsure safetyRespiratorsOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideEngineeringBlock structure
An overheating detection unit is attached between an oxygen concentrator and a cannula, making it possible to reliably detect a high-temperature environment to cut the supply of oxygen when a user inhales oxygen using the cannula and is exposed to a fire or an abnormal high-temperature environment. An overheating detection unit includes a main body including a connecting member connected to an oxygen outlet and an oxygen outlet portion connected to a tube and also includes a housing covering the main body. The main body includes a temperature sensor in the oxygen outlet portion to detect the temperature of the oxygen outlet portion and a blocking structure portion that blocks a passage between the connecting member and the oxygen outlet portion to cut the supply of oxygen when the temperature sensor detects a temperature equal to or higher than a predetermined temperature.
Owner:IKIKEN
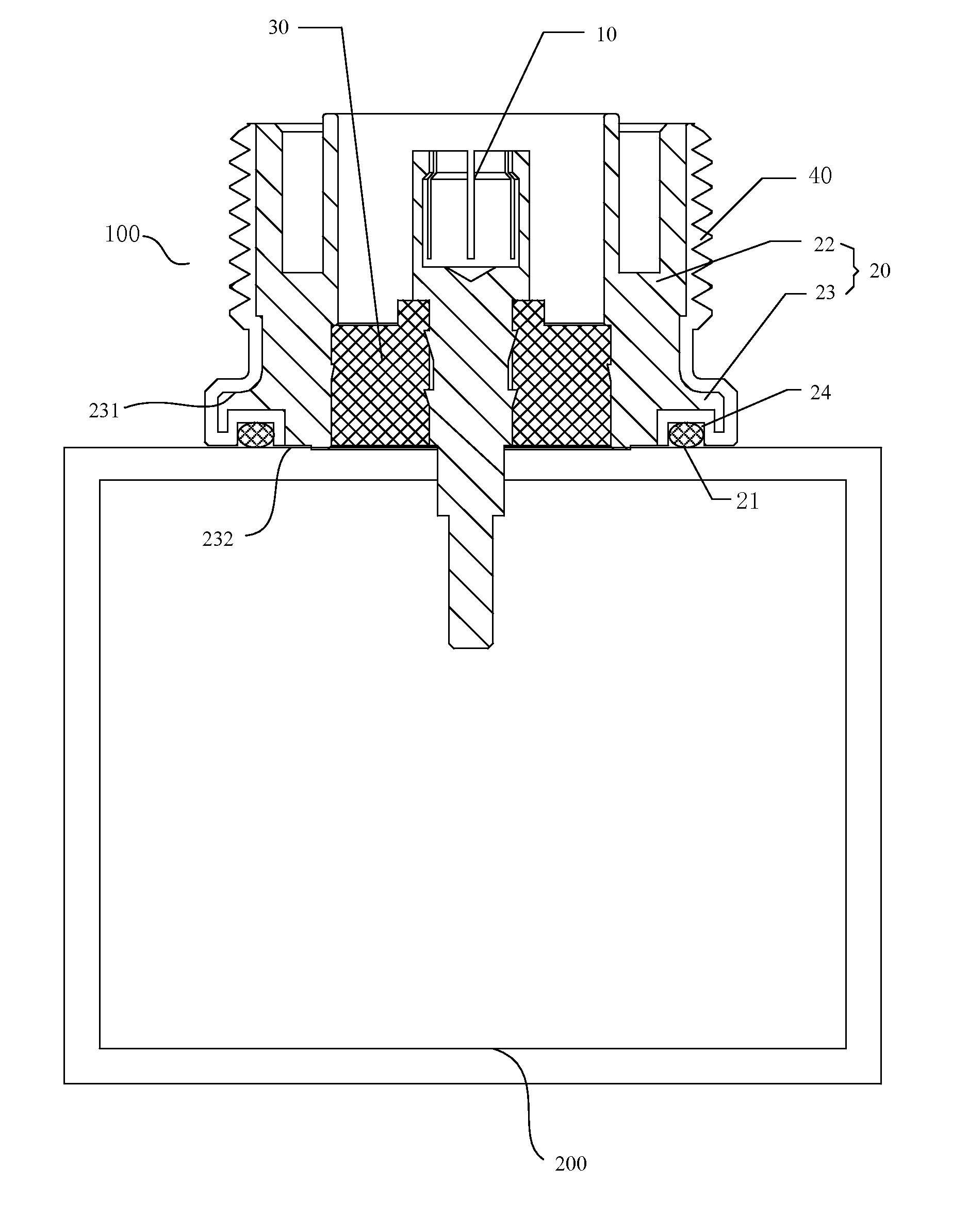
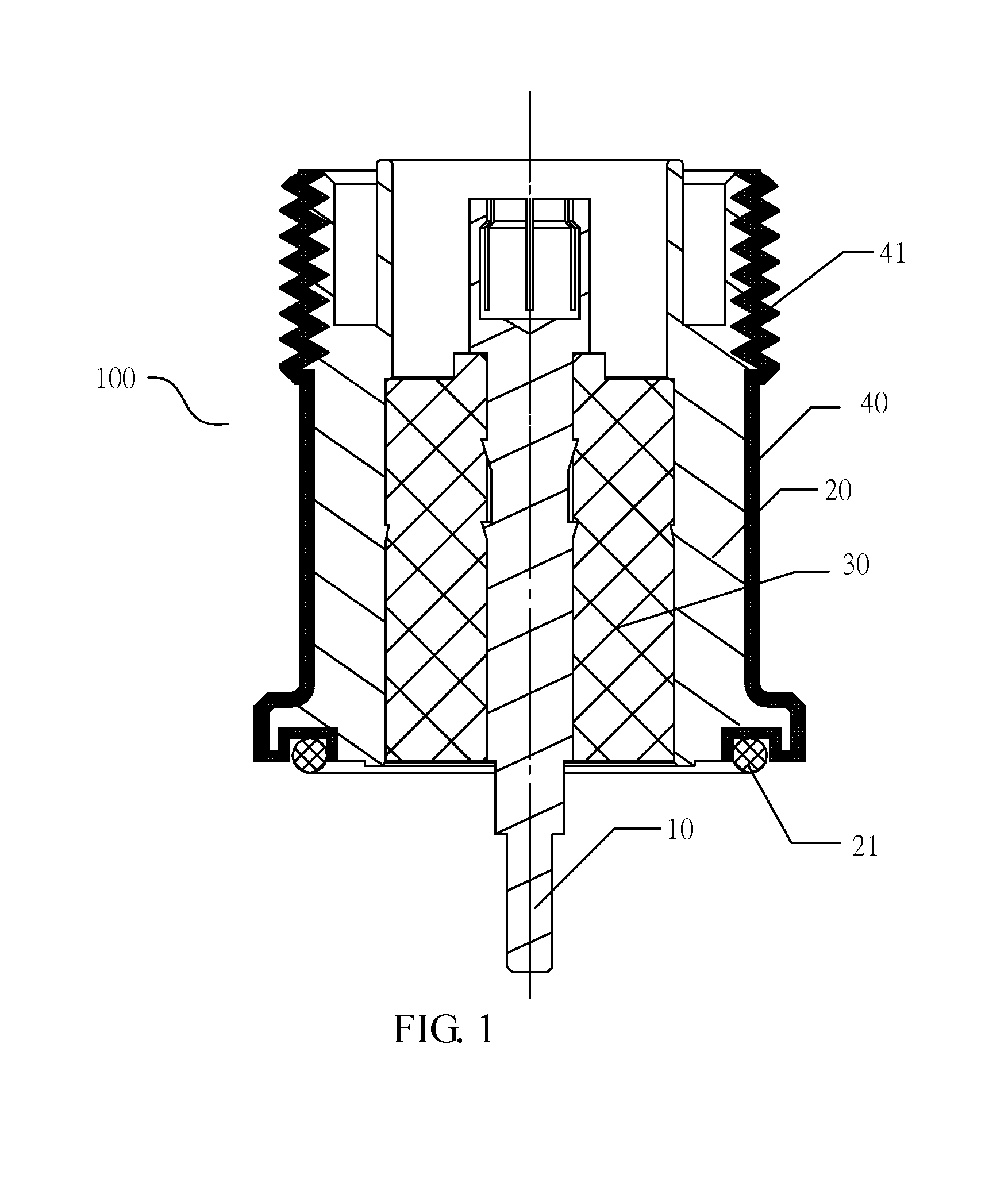
Cavity filter, connector and manufacturing processes thereof
ActiveUS20150061794A1Improve the environmentLess human interventionLine/current collector detailsCoupling contact membersElectrical conductorManufacturing technology
The present disclosure relates to a cavity filter, a connector and manufacturing processes thereof. The cavity filter comprises a cavity, a cover plate and a connector disposed on the cavity or the cover plate; an end of the connector is connected with internal devices inside the cavity filter and the other end of the connector is connected with external communication devices; and the connector comprises an inner conductor and a metal enclosure disposed coaxially and an insulation medium disposed between the metal enclosure and the inner conductor, and a non-metal layer is disposed on an outer peripheral surface of the metal enclosure. The connector of the present disclosure is formed with a non-metal layer on the outer peripheral surface of the metal enclosure thereof, which can improve the moisture-proof capability, the salt-mist-proof capability, the mould-proof capability and the reliability of the connector and the cavity filter.
Owner:ANHUI TATFOOK TECH CO LTD
Bonding structure of bonding wire
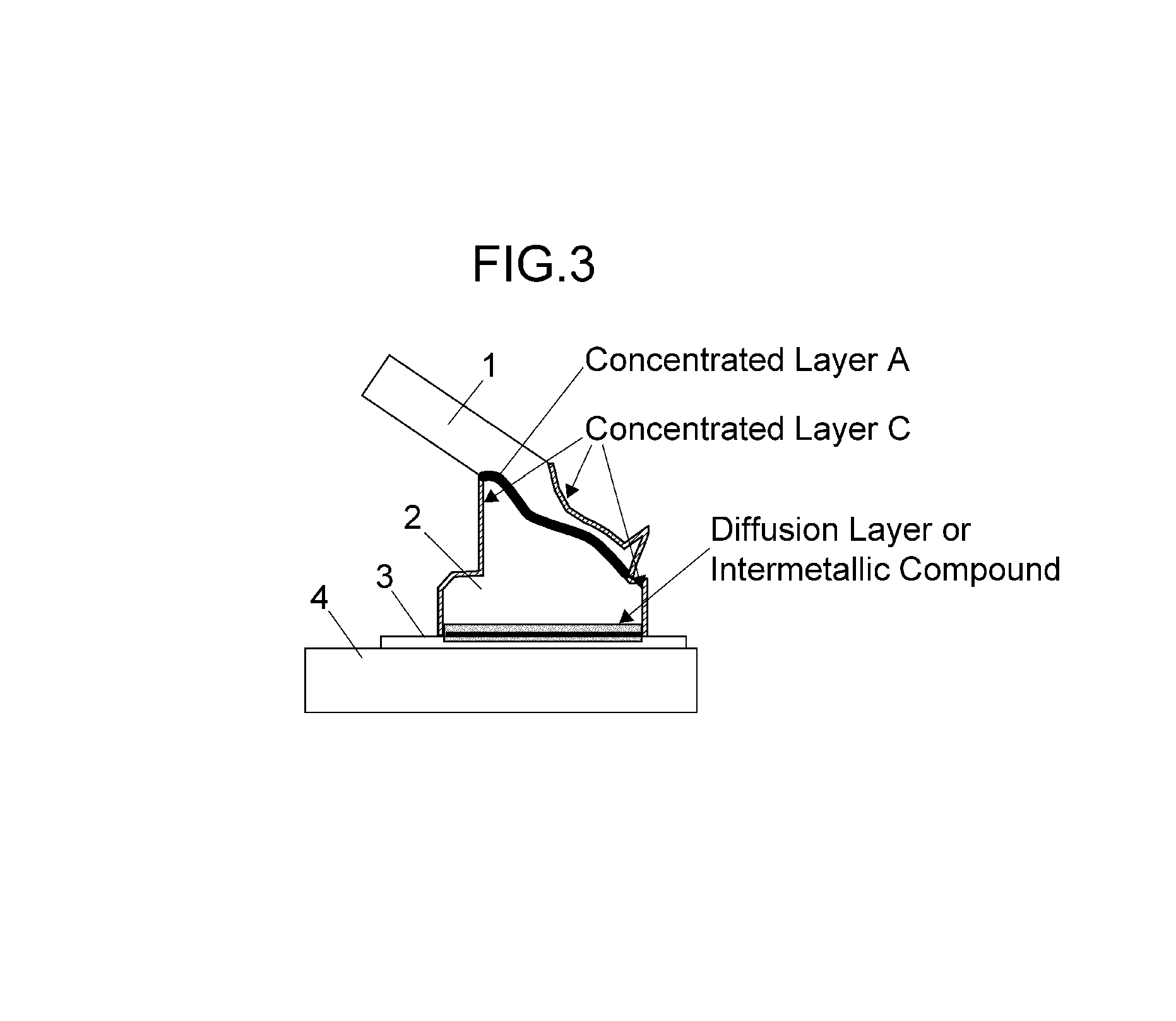
ActiveUS20110104510A1High bonding strengthImprove continuous operabilitySolid-state devicesWelding/cutting media/materialsEngineeringCopper
The invention is aimed at providing a bonding structure of a copper-based bonding wire, realizing low material cost, high productivity in a continuous bonding in reverse bonding for wedge bonding on bumps, as well as excellent reliability in high-temperature heating, thermal cycle test, reflow test, HAST test or the like. The bonding structure is for connecting the bonding wire onto a ball bump formed on an electrode of a semiconductor device, the bonding wire and the ball bump respectively containing copper as a major component thereof. The bonding structure comprises a concentrated layer A provided at an interface of a bonding part of the ball bump and the bonding wire, wherein the concentration of a metal R other than copper in the concentrated layer A is not less than ten times the average concentration of the metal R in the ball bump; and a concentrated layer B provided at an interface of a bonding part of the ball bump and the electrode, wherein the concentration of the metal R in the concentrated layer B is not less than ten times the average concentration of the metal R in the ball bump.
Owner:NIPPON MICROMETAL CO LTD
Horizontally polarized omni-directional antenna
InactiveUS7006051B2Improve reception/transmittanceMinimizing reception/transmittanceAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectricCoaxial cable
Owner:FRC COMPONENT PROD
Method and system of automatic control
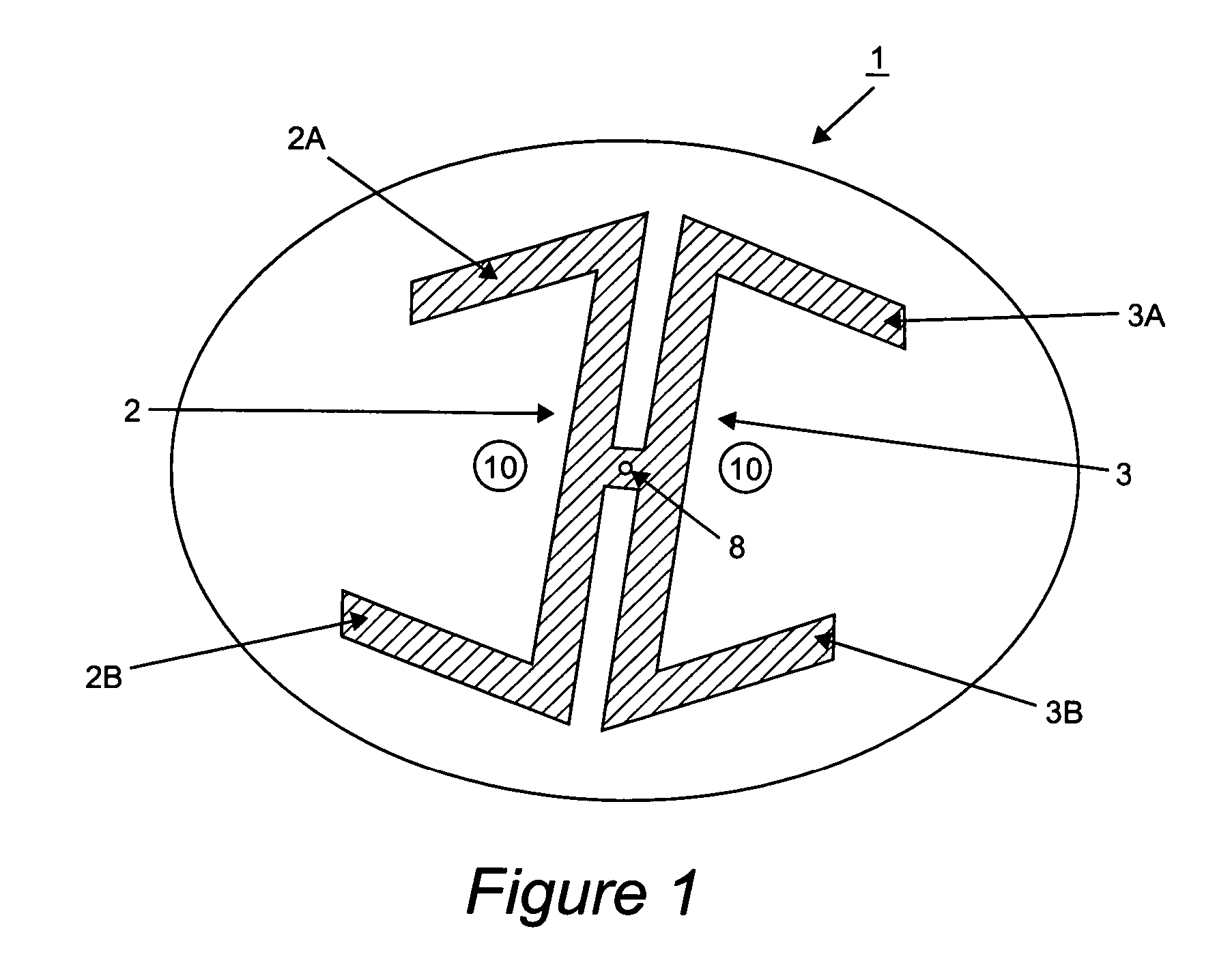
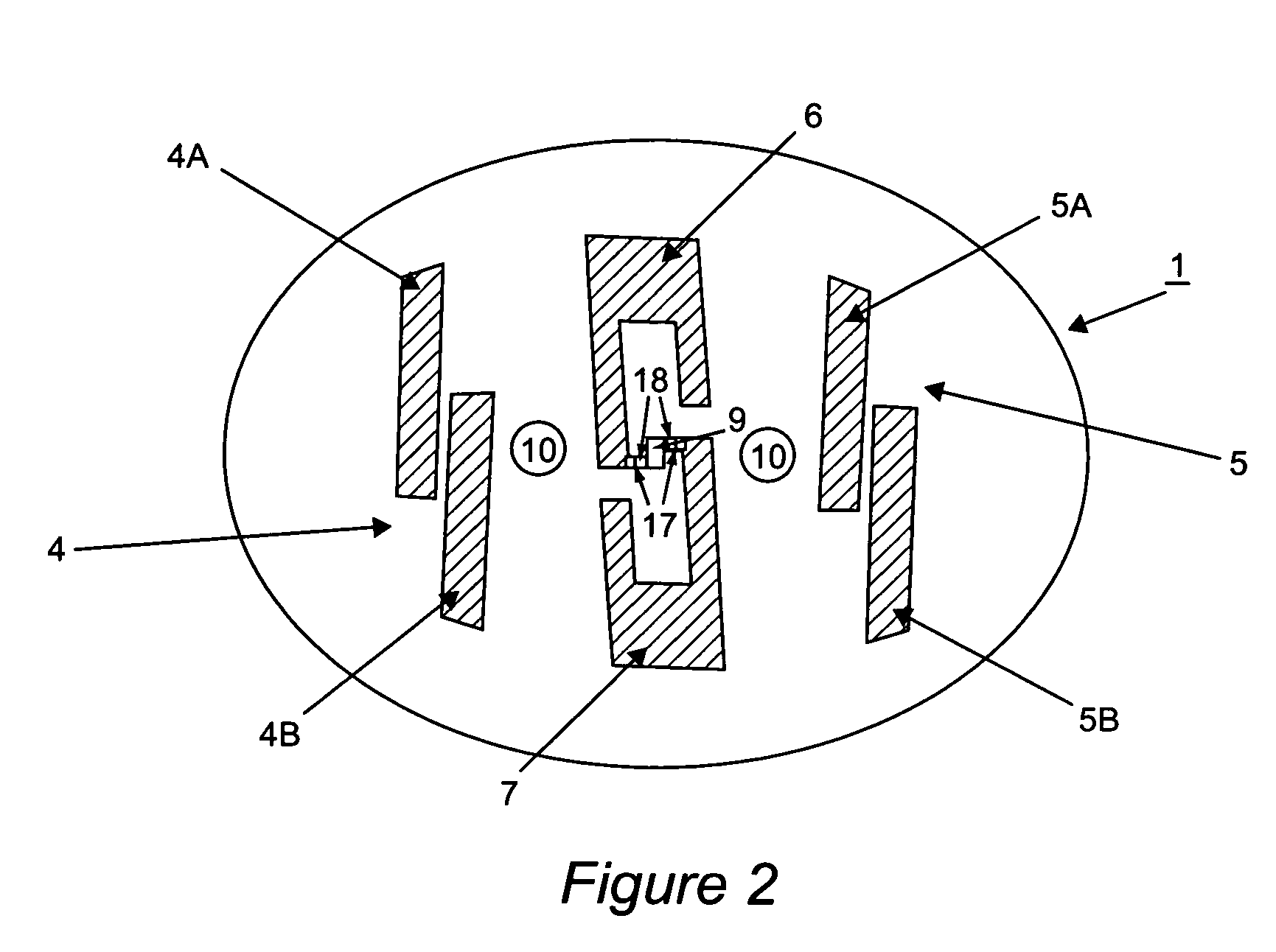
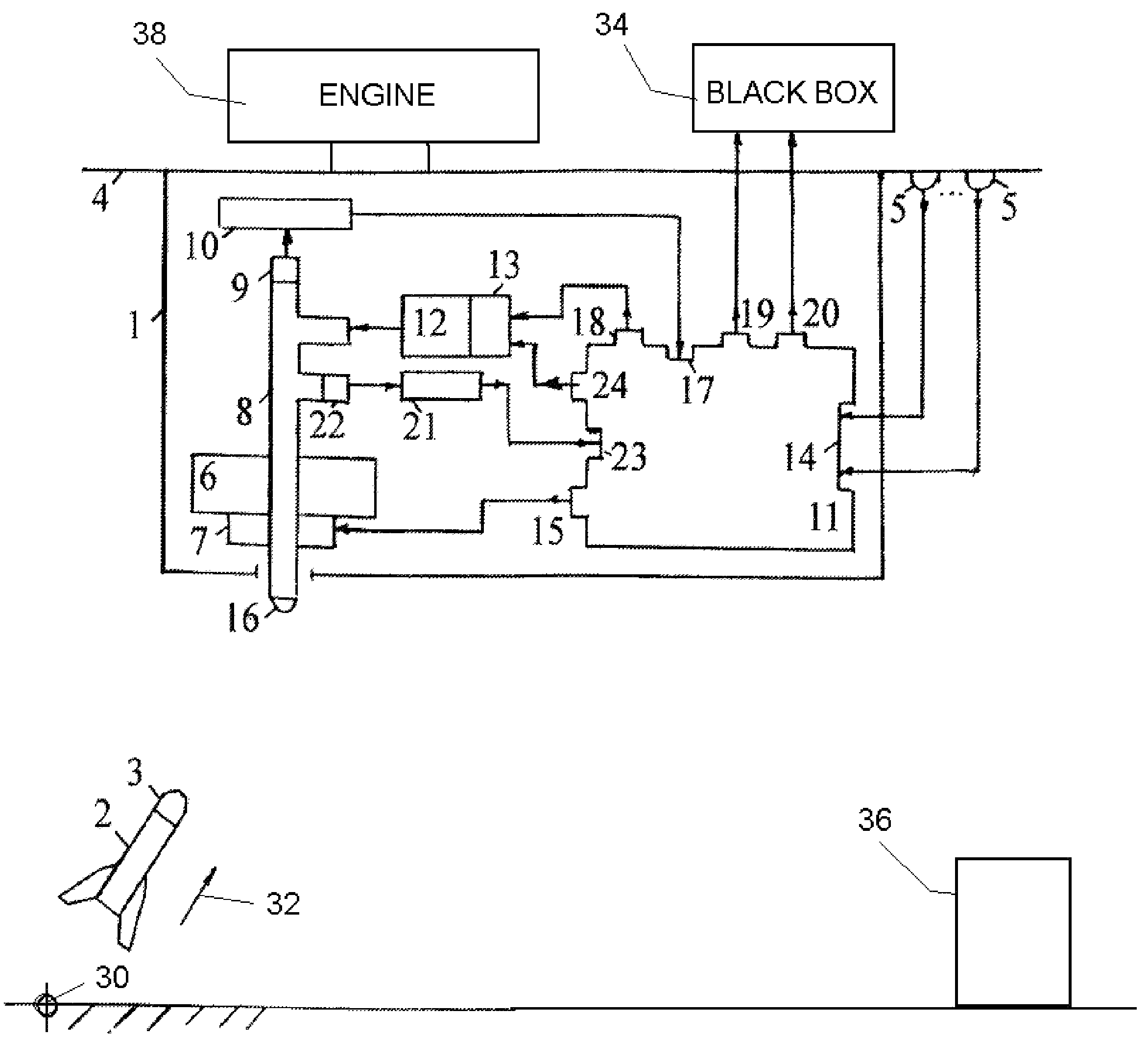
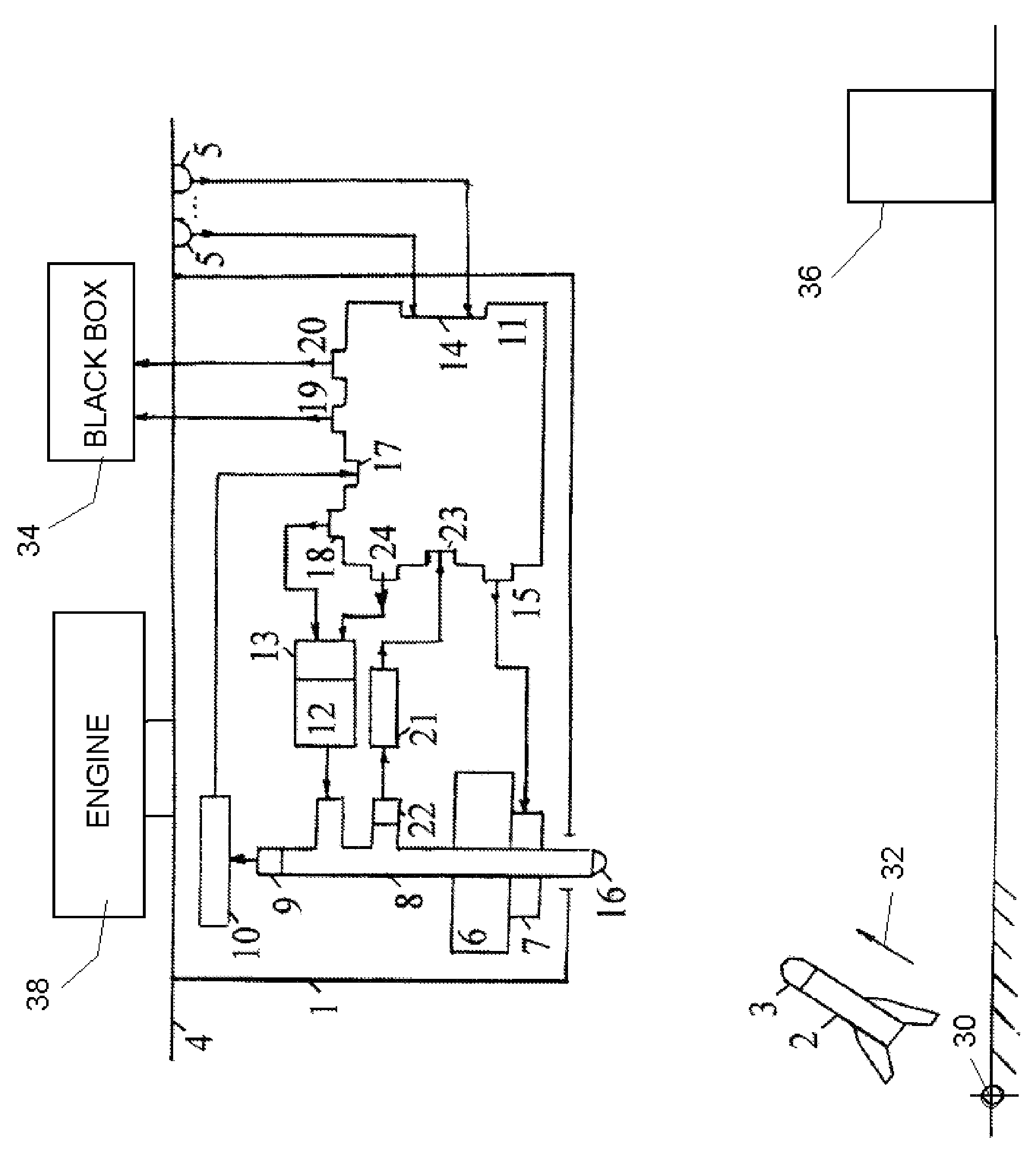
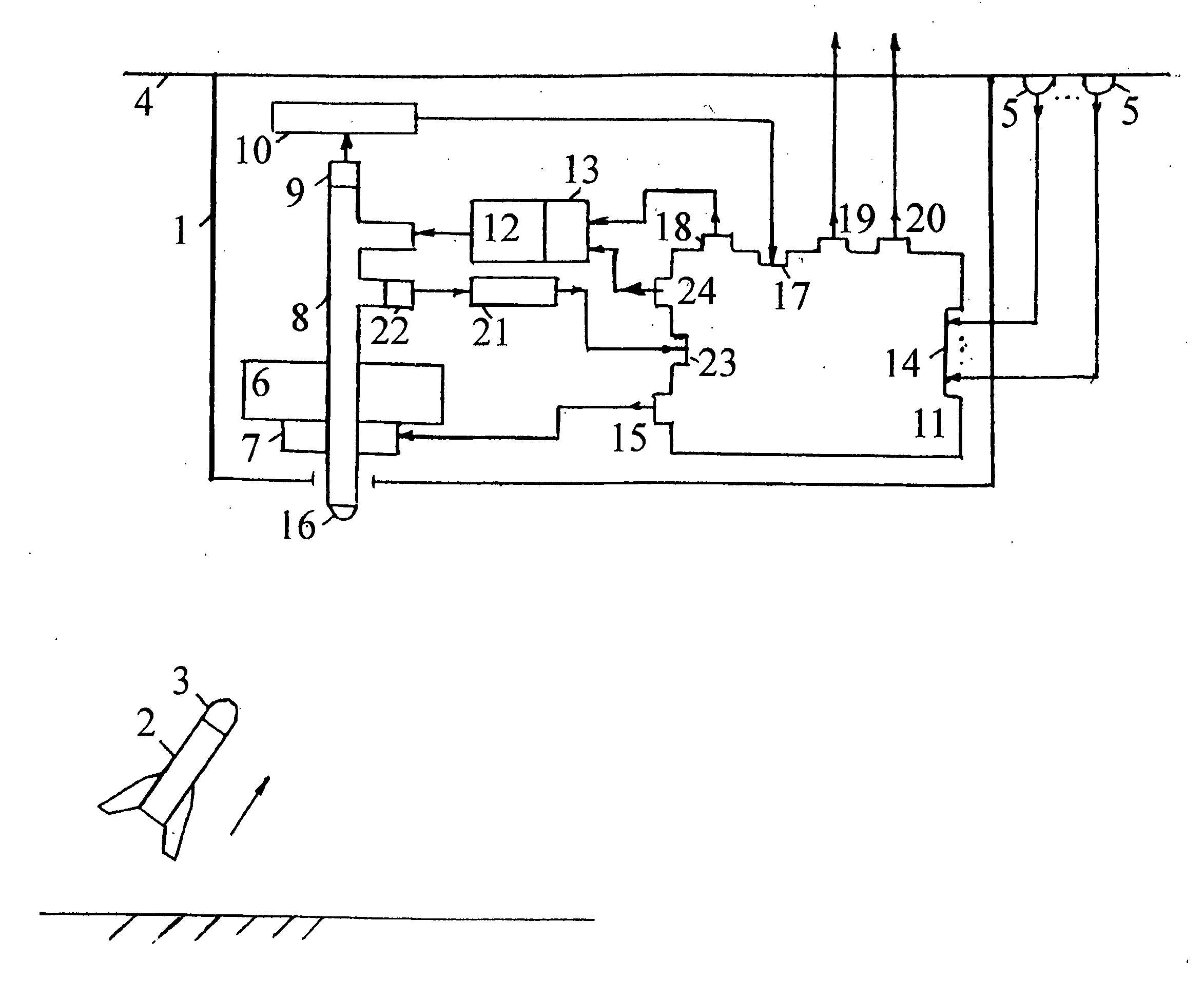
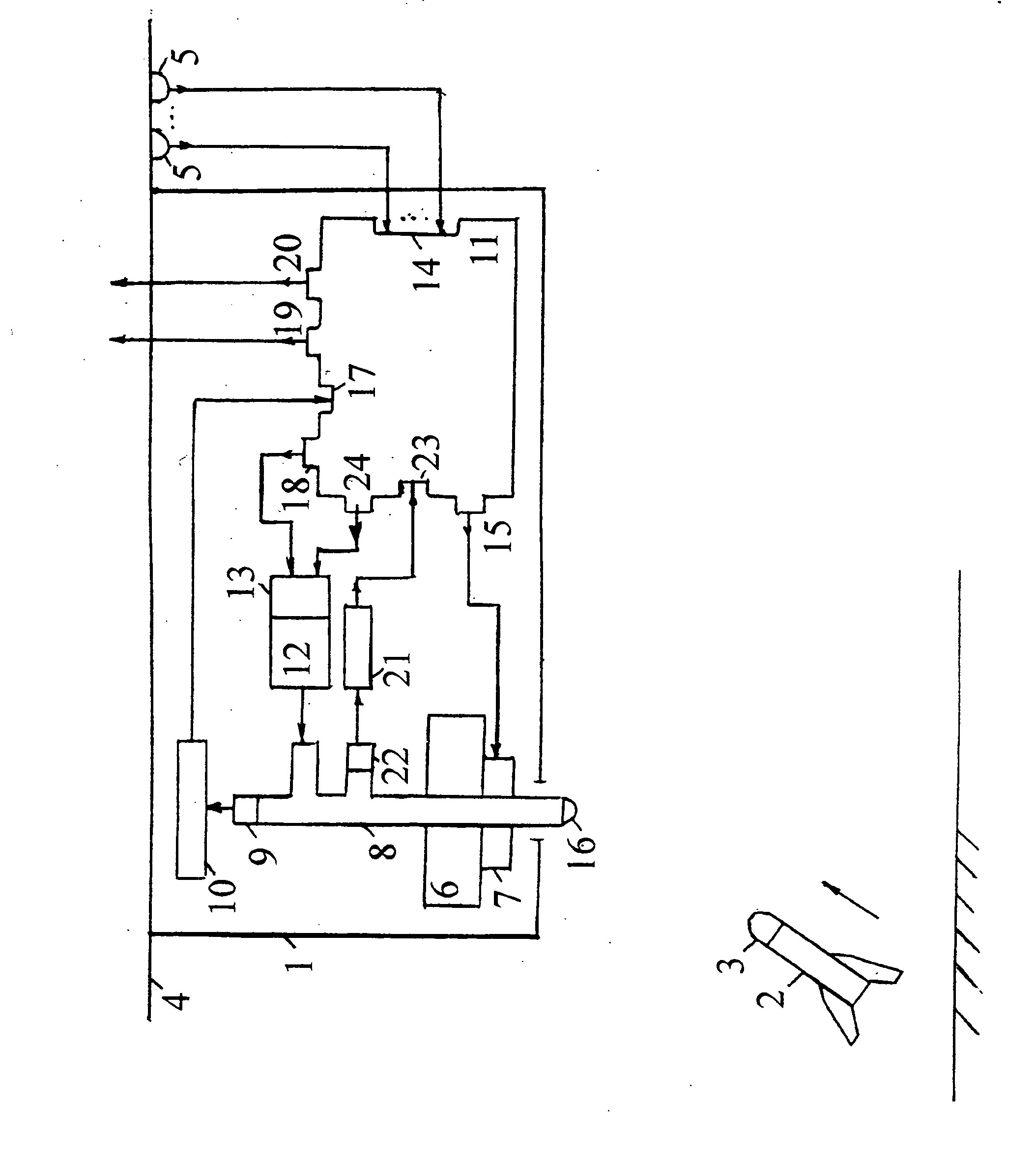
InactiveUS7521655B2Reduce probabilityReliable environmentDefence devicesWave based measurement systemsAutomatic controlPulsed laser radiation
A method and apparatus for protecting a civil aircraft from missiles with infrared seeker heads includes detecting a launch of a missile from a location of launch, the missile having an infrared seeker head with an infrared sensitivity range, a power and an operation frequency, continuously determining instantaneous coordinates of the missile in flight after the launch and generating pulsed laser radiation. A wavelength range of the pulsed laser radiation is within the sensitivity range of the infrared seeker head, a power of the pulsed laser radiation exceeds the power of radiation of the aircraft engine in the sensitivity range of the infrared seeker head and a pulse repetition frequency of the pulsed laser radiation is at about the operation frequency of the infrared seeker head. The method includes sending the pulsed laser radiation to the instantaneous coordinates of the missile in flight.
Owner:ZAKRYTOE AKTSIONERNOYE OBSCHESTVO STIVT
Control system of trailer lamp
ActiveCN102101457AReduce wiring complexityImprove reliabilityElectric light circuit arrangementOptical signallingMicrocontrollerControl system
The invention relates to a control system of a trailer lamp, which improves the reliability of a trailer system and brings great convenience to the maintenance of vehicles. The control system comprises a main control module and a slave control module which are connected through a power line and a communication line, wherein the main control module comprises a singlechip processing circuit which is respectively connected with a switch signal detection circuit, a power circuit and a communication circuit; the slave control module comprises a singlechip processing circuit which is respectively connected with a lamp driving circuit and the power circuit; the power circuit is connected with the communication circuit; and the lamp driving circuit is connected with the trailer lamp.
Owner:XIAN KING TRUCK ELECTRON
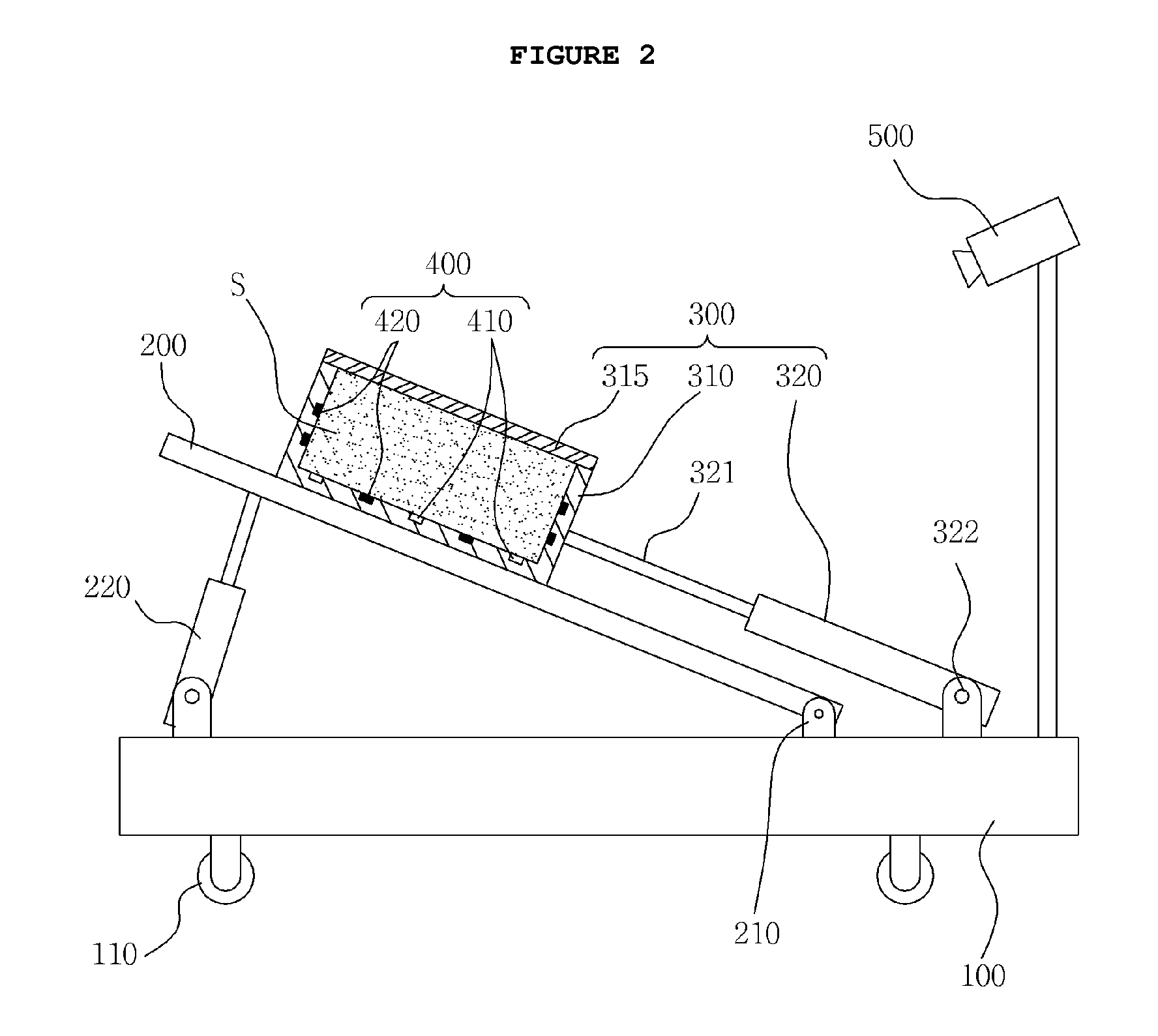
Test apparatus for early landslide detection fully-connected with pore water pressure, surface displacement and shear surface
ActiveUS9488561B2Reliable environmentPrevent leakageEarth material testingFluid pressure measurementShear stressPore water pressure
Disclosed herein is a test apparatus for early landslide detection fully-connected with pore water pressure, surface displacement and shear surface. The test apparatus calculates a factor of safety of a slope based on variation in pore water pressure, surface displacement and shear surface of a soil mass, and predicts a change in factor of safety, thus making early landslide detection possible. In the test apparatus, while a container of a slider is moved with a soil mass loaded into the container, shear surface and surface displacement environment is provided, and the shear strength and the shear stress of the soil mass can be calculated based on the pore water pressure and the weight of the soil mass. Thereby, the factor of safety of the soil mass can be calculated, and early landslide detection can be realized by using variation of the factor of safety of the slope.
Owner:KOREA INST OF GEOSCI & MINERAL RESOURCES
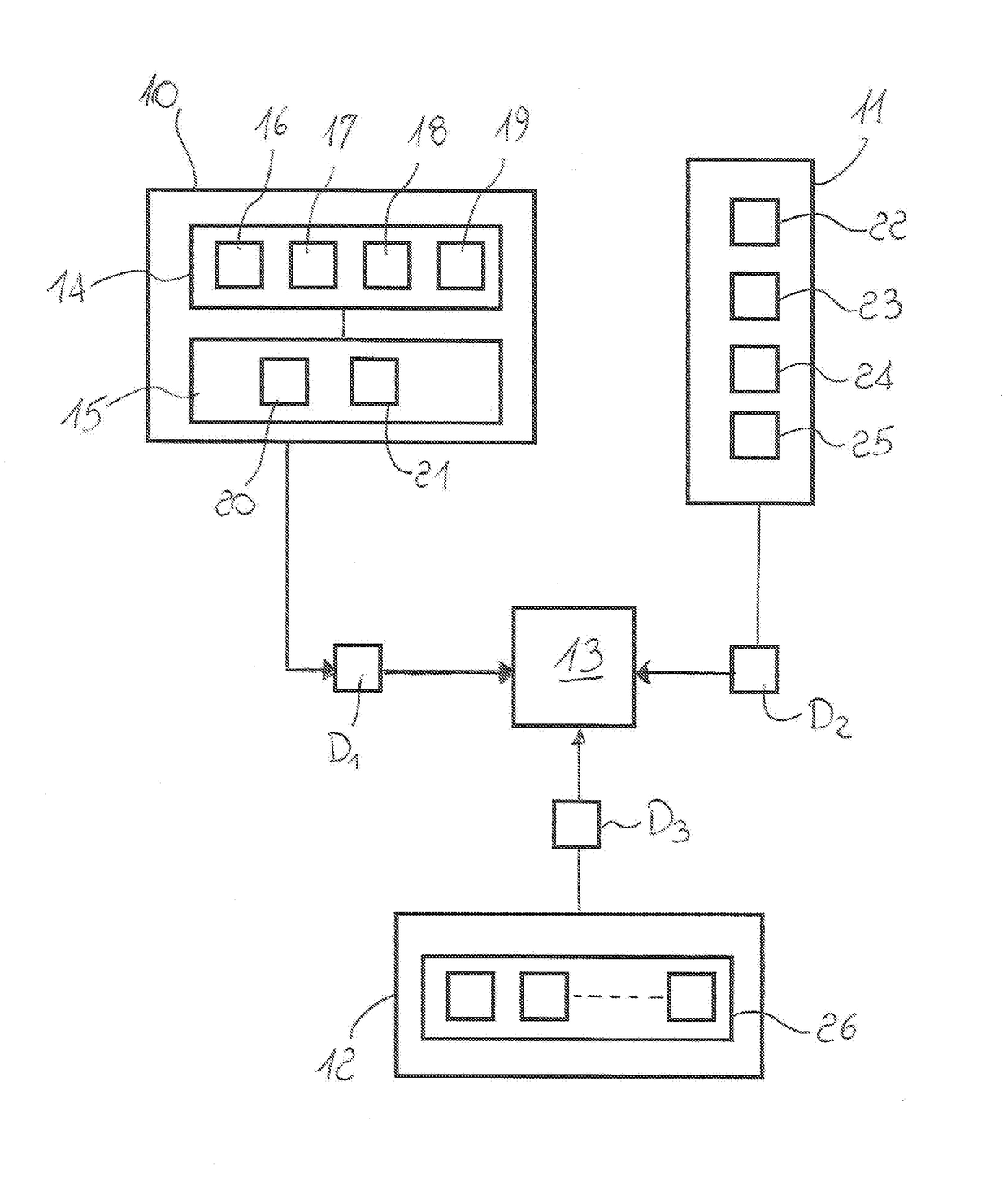
Station for the integrated monitoring of environment and traffic
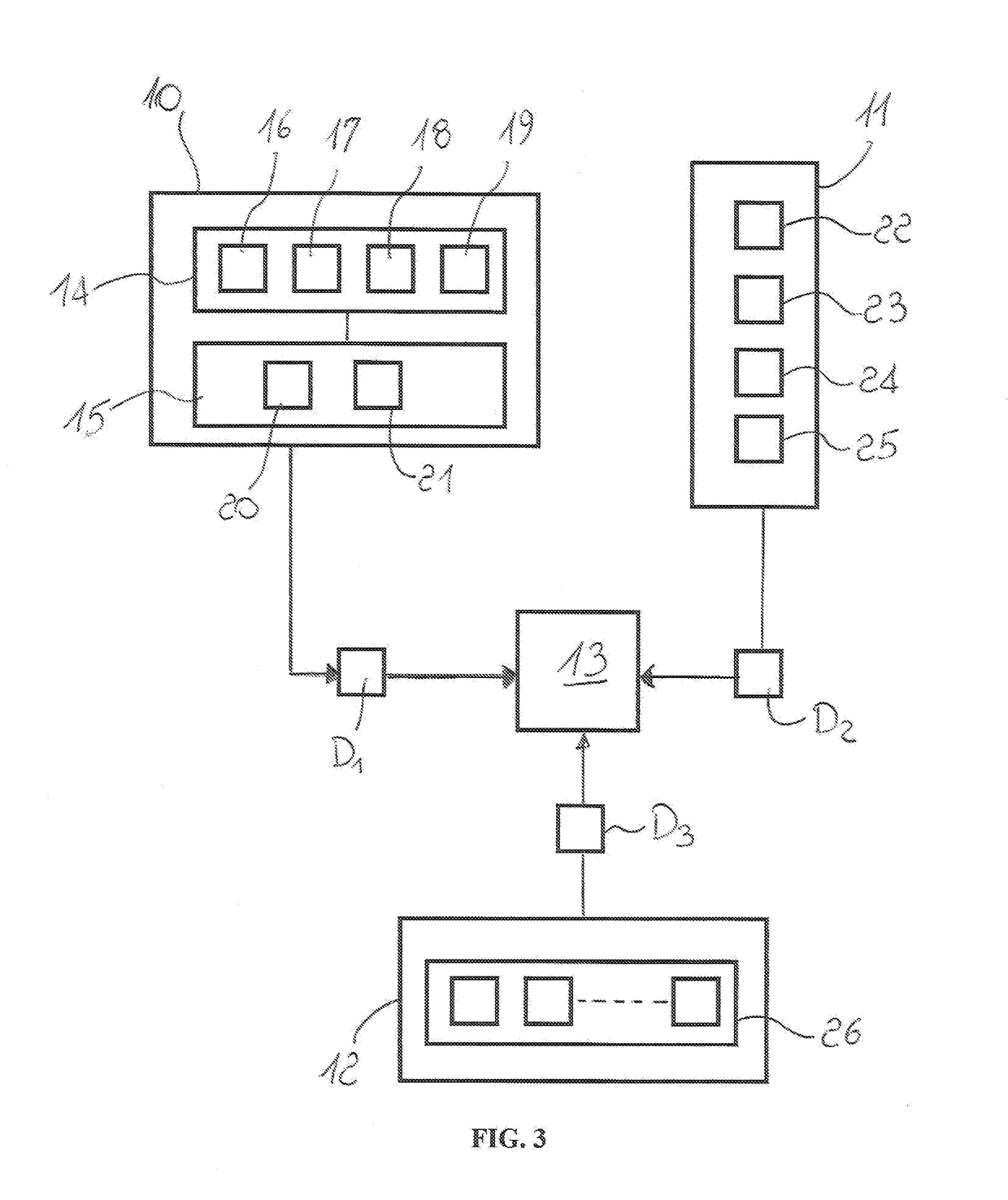
InactiveUS20170276658A1Easy positioningEasy to transportDetection of traffic movementMaterial analysisTraffic capacityIntegrated monitoring
A station for the integrated monitoring of environment and traffic comprises a local unit (2) adapted to be positioned at an area to be monitored and comprising first means (10) for collecting first data (D1) relative to the concentration of pollutants in the air, second means (11) for monitoring the traffic flow in the monitored area and for collecting corresponding second data (D2), a data processing unit (13) adapted to receive the first data (D1) and the second data (D2) for the correlation thereof and for generating information relative to the traffic and to the air quality in the monitored area in a predetermined time period, third means (12) for collecting third data (D3) relative to the weather condition in the monitored area adapted to be transmitted to the data processing unit (13).
Owner:AIRTRAFF DI MAURO ZILIO
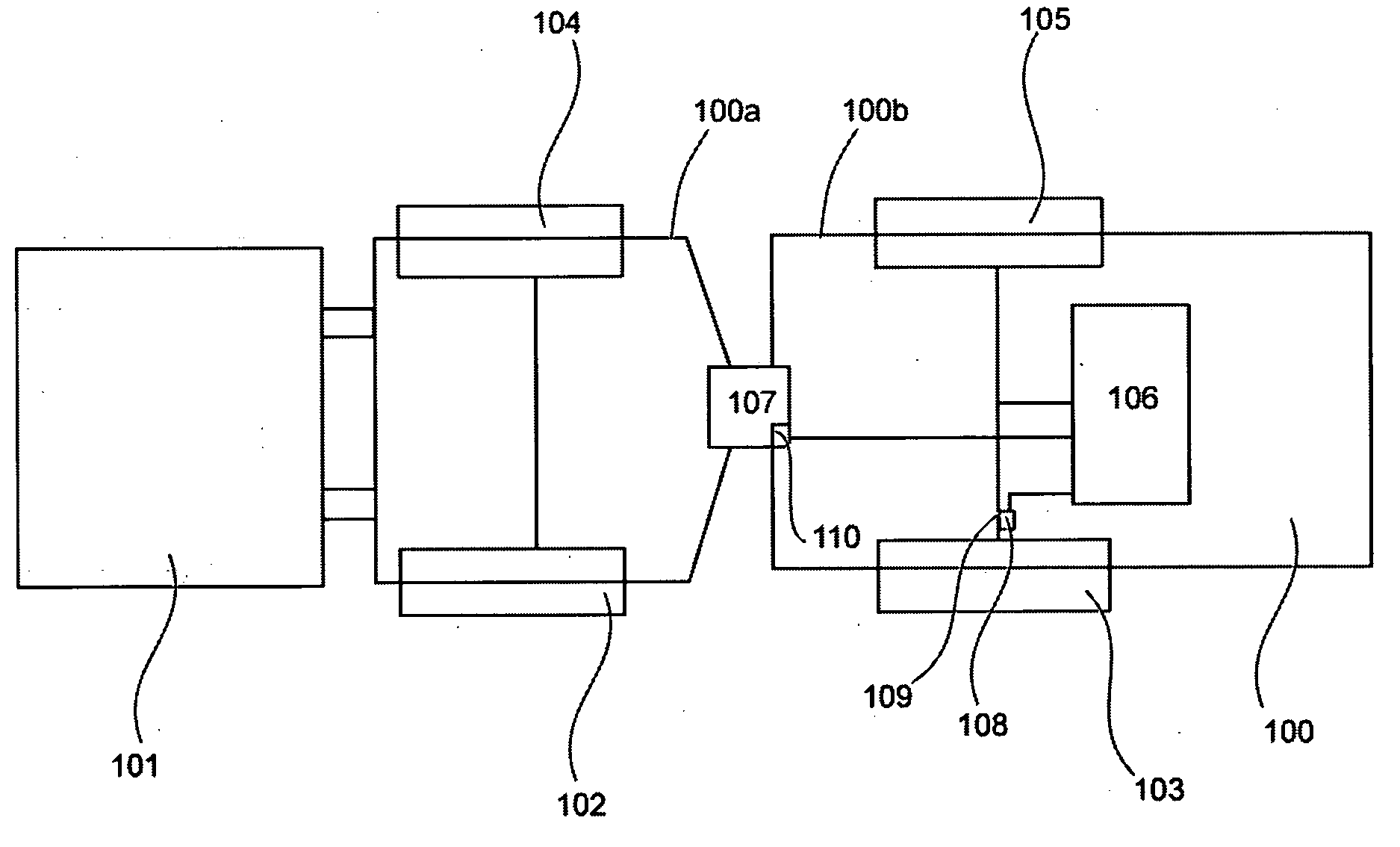
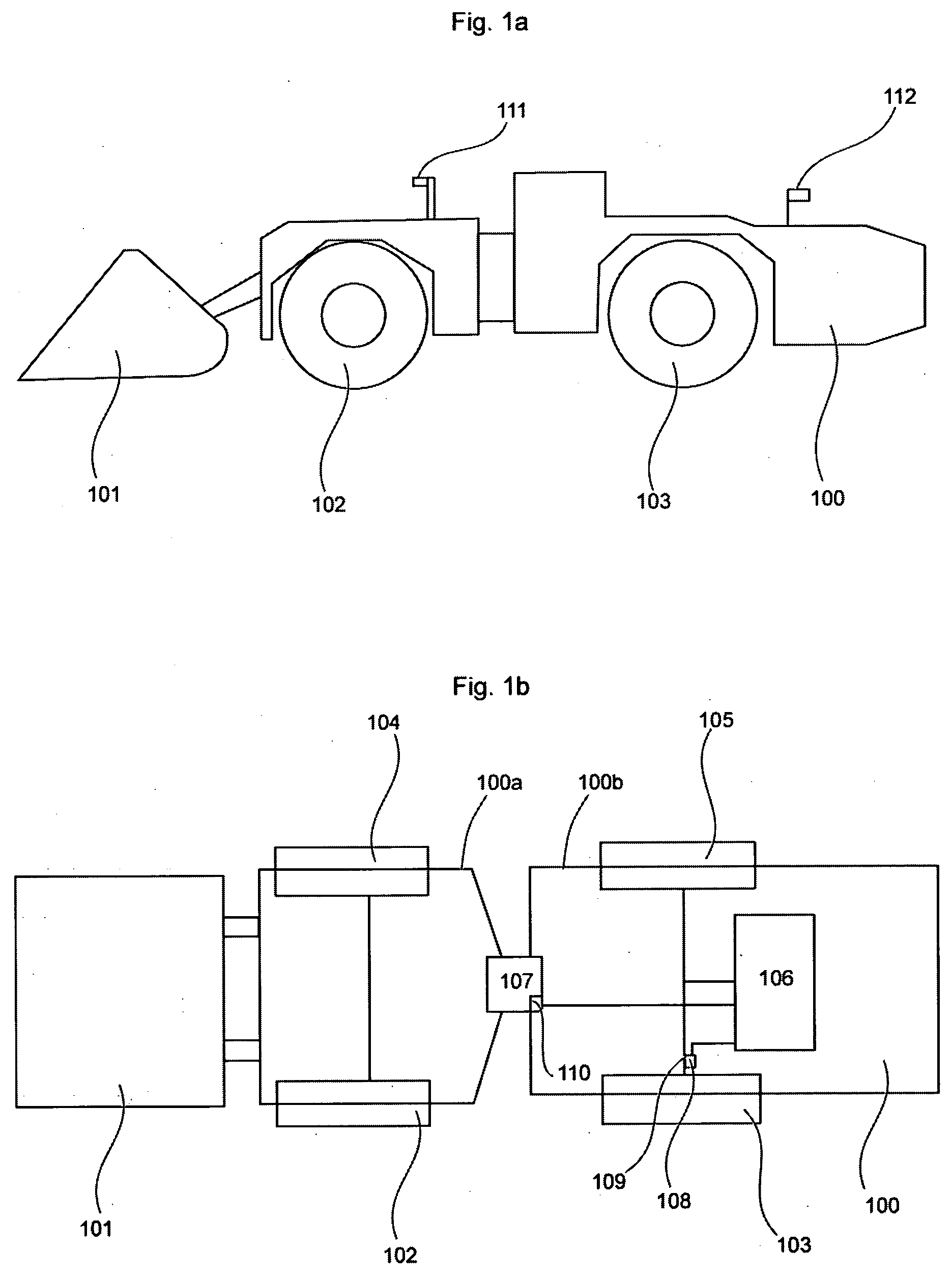
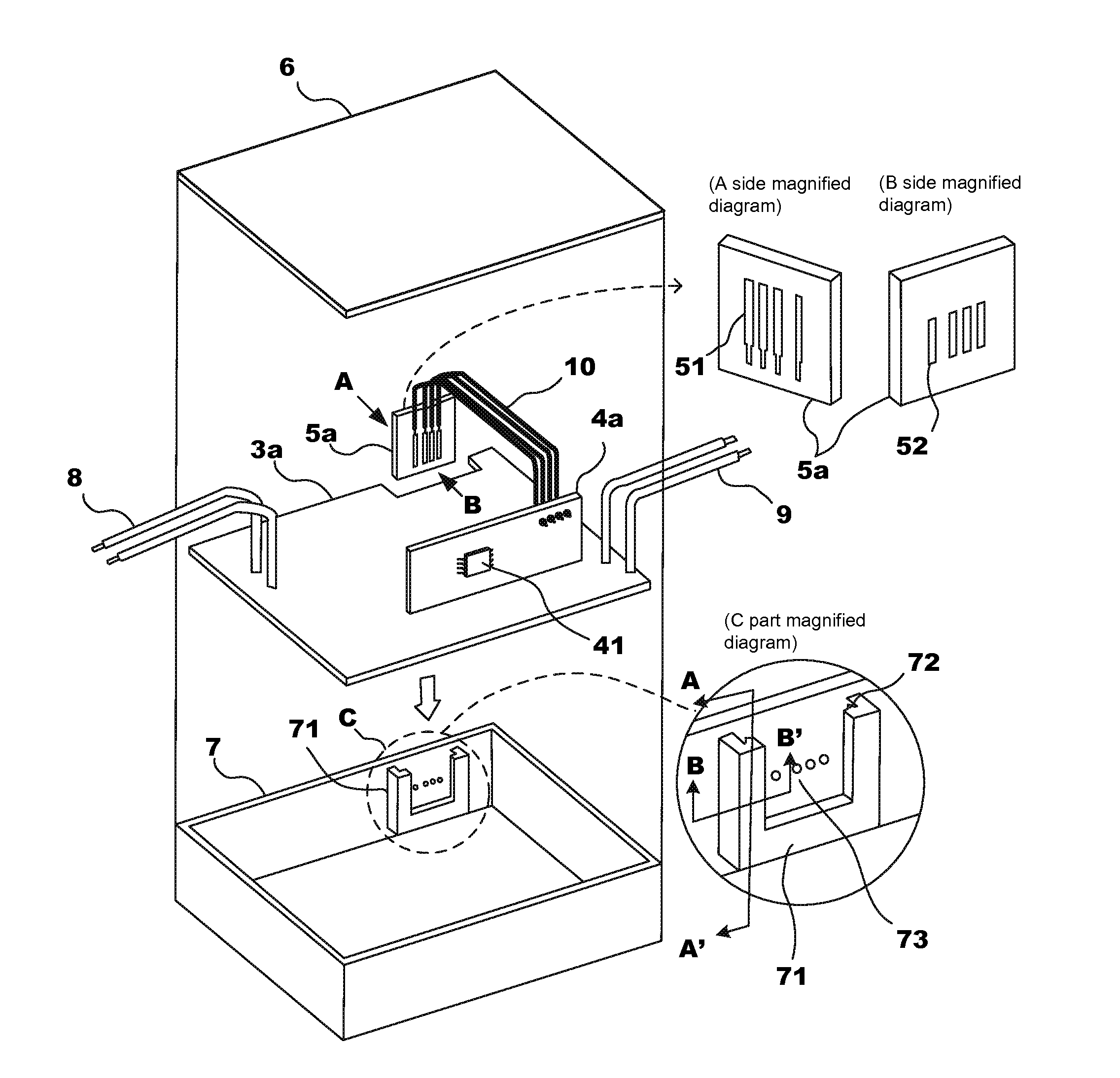
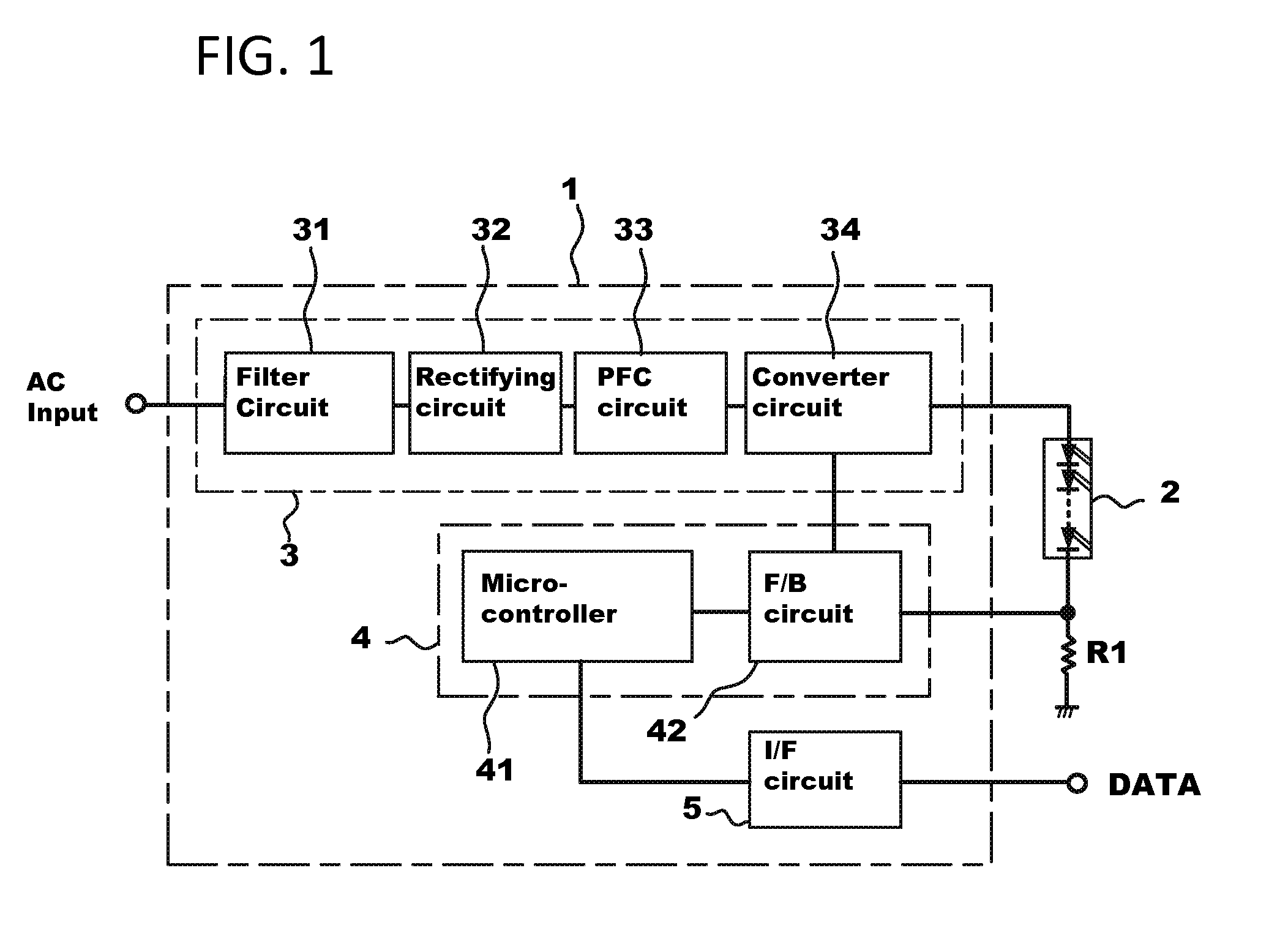
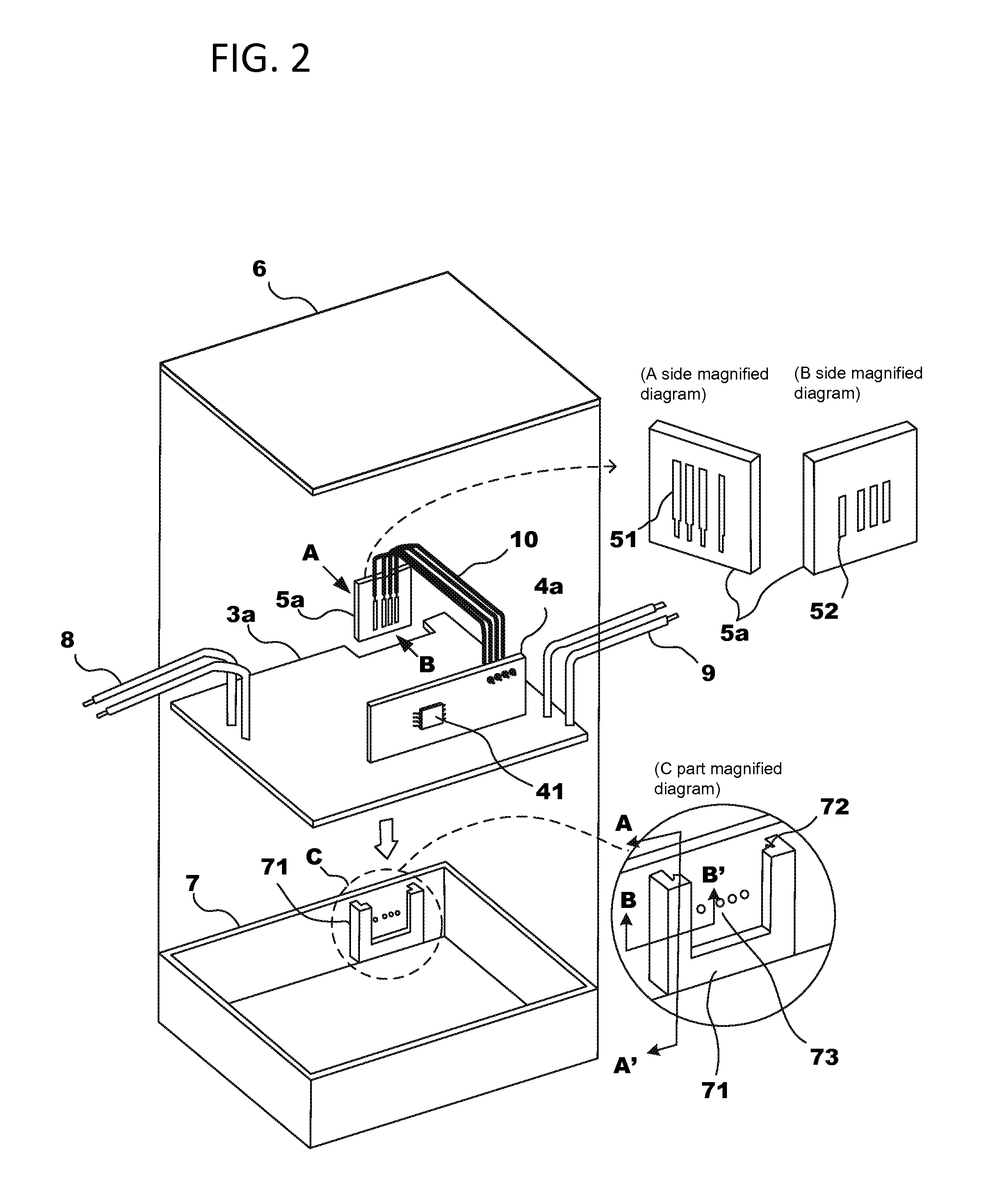
Power supply device
InactiveUS20130099699A1Ensure a high degree of airtightnessReliable environmentMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlOn boardControl circuit
A power supply device containing a first board, a second board, an enclosure into which the first board and the second board are installed, a power supply unit which supplies power to an external load, a control circuit unit for controlling output current and / or output voltage from the power supply unit to the external load, the control circuit unit being embedded on the first board, a memory which stores control information, the memory being utilized in the control circuit unit for controlling the output current and / or the output voltage from the power supply unit, and an interface unit which is capable of receiving the control information from an external device and transmitting the control information to the memory, the interface unit being embedded on the second board which is physically separated from the first board.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
Laminated diffractive optical element and resin composition therefor
InactiveUS8124324B2Eliminate the effects ofReliable environmentPhotomechanical apparatusOptical articlesTin dioxideAluminum doped zinc oxide
A resin composition includes a binder component having at least one of a monomer and an oligomer of one or more of a fluorine system and a silicone system having a polymerizable functional group in a molecule. The resin composition also includes fine metal oxide particles, and a polymerization initiator. The fine metal oxide particles include particles selected from the group of zinc oxide, indium oxide, tin oxide, antimony oxide, tin-doped indium oxide (ITO), antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO), zinc-doped indium oxide (IZO), aluminum-doped zinc oxide (AZO), and fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO).
Owner:CANON KK
High speed switch
ActiveUS20200075274A1Increased operation speedImprove reliabilityContact vibration/shock dampingHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesEngineeringInterrupter
A high speed switch comprises an interrupter unit connected to a main circuit and including a movable electrode and a driving electrode for opening or closing the main circuit; a driving unit including a repulsion coil for providing a driving force for moving the movable electrode of the interrupter unit, and a repulsion plate disposed opposite to the repulsion coil; a guide rod part connecting the movable electrode of the interrupter unit to the repulsion plate, having a latch groove formed therein, and reciprocating vertically according to movements of the repulsion plate; and a state-holding unit for regulating the movement of the guide rod part, wherein the state-holding unit comprises: a latch; a latch elastic member; and a latch coil.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
Stand pipe fixing device
InactiveCN102235154ASimple structureEasy to operateDrilling rodsDrilling casingsSlide plateOperation safety
The invention discloses a stand pipe fixing device provided with a sliding rail, wherein the sliding rail is provided with two corresponding sliding plates; one ends of the two sliding plate are respectively and correspondingly provided with a hydraulic cylinder; the other ends of the two sliding plates are respectively and correspondingly provided with a semi-annular barrel; the two sliding plates are connected into a whole by a locking mechanism; the hydraulic cylinder rods of the hydraulic cylinders and the sliding plates are connected into a whole by a flange plate; a plurality of reinforcing vertical boards are fixed around the semi-annular barrels; and the upper end and the lower end of each semi-annular barrel are respectively provided with an upper support plate and a lower support plate. According to the invention, a stable and reliable environment can be provided for supporting stand pipes so as to bring convenience for cutting abandoned pipe end sockets and installing drawing heads; meanwhile, system operation safety is improved.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Electro-Optical Distance Meter
ActiveUS20180011177A1Improve ranging accuracyImprove reception qualityElectromagnetic wave reradiationFiberArithmetic processing unit
An electro-optical distance meter comprises a light source for emitting a distance measuring light, a distance measuring optical system for leading a distance measuring light to a photodetector, an internal reference optical system for leading a part of the distance measuring light as an internal reference light to the photodetector, and an arithmetic processing unit for performing a distance measurement based on light receiving results of the distance measuring light and the internal reference light, wherein the internal reference optical system comprises a condenser lens, a scattering plate for scattering the internal reference light and for forming a secondary light source, and an optical fiber for leading the internal reference light to the photodetector and the internal reference optical system is constituted in such a manner that a light component of the internal reference light emitted from an arbitrary point within a whole surface of the secondary light source enters the optical fiber.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Ultra-oil-resistant and ultra-low-temperature-resistant photoelectric comprehensive cable for rail transit vehicle and production method for cable
ActiveCN104681135AFast processingReduce power consumptionFlexible cablesCable/conductor manufactureElectrical conductorInsulation layer
The invention discloses an ultra-oil-resistant and ultra-low-temperature-resistant photoelectric comprehensive cable for a rail transit vehicle. A power transmission part comprises a conductor and an insulation layer, and the conductor is coated with the insulation layer; a signal control part comprises a ceramic silicone rubber fire-resistant insulation wire core; a light communication transmission part comprises one or more of a layer-stranded full-dry light transmission unit, a full-dry light unit of a central tube, a layer-stranded filled light unit and a filled light unit of the central tube; the power transmission part, the signal control part and the light communication transmission part are twisted to form a cable core; the cable core is coated with a shielding layer; the shielding layer structure is formed by braiding shielding monofilaments with the braided density not smaller than 80%; the shielding monofilaments are not smaller than 0.11 mm in outer diameter; a metal composite belt with the thickness not smaller than 0.063 mm is used for unwrapping in the shielding layer structure, the metal surface of the metal composite belt is contacted with the shielding layer structure during unwrapping, or a semi-conductive belt with the single-layer lap rate not smaller than 20% is used for wrapping; the shielding layer structure is sleeved with a sheath layer.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN TECH IND WIRE&CABLE SYST CO LTD
Water-tree-retardant crosslinked polyethylene cable material and cable prepared from same
InactiveCN104910503AEffective protectionNot easily oxidizedInsulated cablesInsulated conductorsLinear low-density polyethyleneLow-density polyethylene
The invention belongs to the technical field of materials and wire cables, and relates to a water-tree-retardant crosslinked polyethylene cable material. The invention is characterized in that the cable material is prepared from linear low-density polyethylene, styrene, polyurethane thermoplastic elastomer, polyethyleneglycol, ethylene-ethyl acetate copolymer, polyethylene wax or paraffin, commercially available nucleator 4030 for wire cable plastics, di-tert-butyl peroxide, benzoperoxide, commercially available antioxidant 300 for plastics or commercially available antioxidant 1010 for plastics or commercially available antioxidant 168 for plastics, and carbon black, wherein the weight ratio of the linear low-density polyethylene to the styrene is 8-10. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the cable material and a water-tree-retardant cable using the cable material. The cable has the advantages of favorable waterproofing effect, simple structure, more stable electric / mechanical / environmental properties, higher reliability and the like, is easy to produce and does not generate water trees.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGLI GRP CO LTD
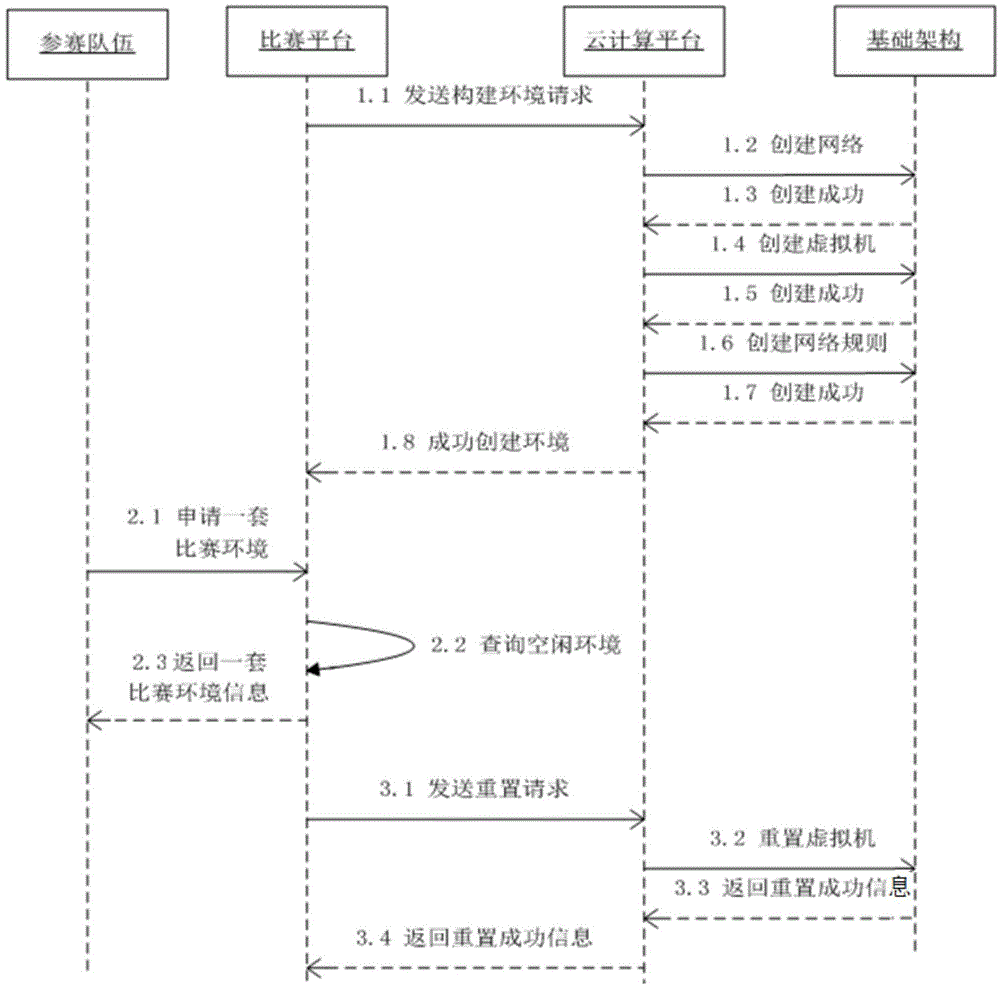
Method and system for batch construction and distribution of network security match environments
The invention discloses a method and system for batch construction and distribution of network security match environments. Included are a match platform, a cloud computing platform and a base frame. The match platform customizes an environment template according to match requirements. The cloud computing platform carries out batch construction of match environments by using virtualization technology according to the environment template, and a match environment resource pool is formed after the batch construction succeeds; a user logs in the match platform through a browser, transmits a message to the match platform and applies for a set of match environments, and the match platform distributes a set of unoccupied match environments; and when the match environments applied by the user fail in use, the equipment in the match environments are reset by using the virtualization technology through the match platform and the cloud computing platform to restore to the initialized state defined by the environment template. The invention has the following advantages of adapting to matches of all scales, quickly applying for match environments, providing a mechanism that ensures the fairness of the match, and ensuring the environments to be reliable and easy to maintain.
Owner:HUNAN HEETIAN INFORMATION TECH
Sealing device for part surface treatment
PendingCN108085472AAvoid spreadingAvoid wastingFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesThermal insulationSilicone rubber
The invention provides a sealing device for part surface treatment, and belongs to the field of part processing equipment; the sealing device for part surface treatment includes a furnace body arranged at the outermost; the inner wall of the furnace body is provided with a thermal insulation layer, the thermal insulating layer is made of a foam material, and a sealing door is arranged on one sideof the furnace body; a silicone rubber seal ring is arranged between the sealing door and the furnace body, is fixed at the periphery of the sealing door and has an arc shape outwardly raised; the silicone rubber seal ring is arranged in a manner of protruding the height of the sealing door. The sealing device has good sealing performance and high degree of automation.
Owner:TIANJIN KAIDA HEAVY HYDROPOWER EQUIP MFG
Cavity filter, connector and manufacturing processes thereof
ActiveUS9543629B2Improve “ ” and reliabilitySimple processLine/current collector detailsCoupling contact membersElectrical conductorMoisture
The present disclosure relates to a cavity filter, a connector and manufacturing processes thereof. The cavity filter comprises a cavity, a cover plate and a connector disposed on the cavity or the cover plate; an end of the connector is connected with internal devices inside the cavity filter and the other end of the connector is connected with external communication devices; and the connector comprises an inner conductor and a metal enclosure disposed coaxially and an insulation medium disposed between the metal enclosure and the inner conductor, and a non-metal layer is disposed on an outer peripheral surface of the metal enclosure. The connector of the present disclosure is formed with a non-metal layer on the outer peripheral surface of the metal enclosure thereof, which can improve the moisture-proof capability, the salt-mist-proof capability, the mold-proof capability and the reliability of the connector and the cavity filter.
Owner:ANHUI TATFOOK TECH CO LTD
Mooring chain steel and production process thereof, and mooring chain and production process thereof
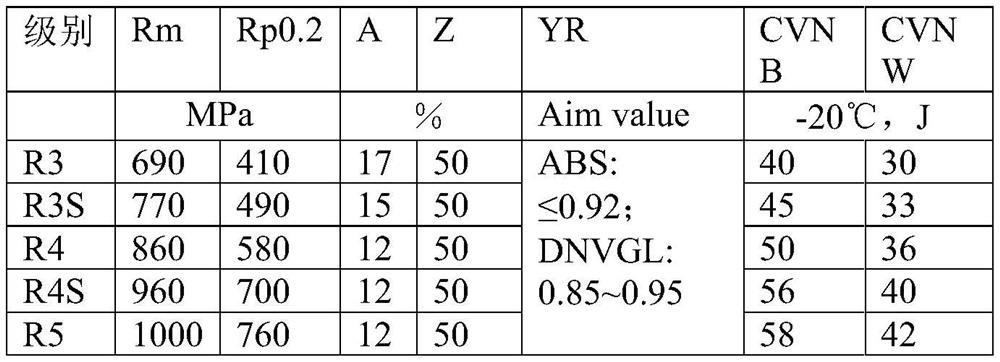
The mooring chain steel comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.18 to 0.32 percent of C, 1.95 to 2.60 percent of Mn, 0.15 to 0.50 percent of Si, 0.45 to 1.20 percent of Cr, 0.008 to 0.250 percent of Mo, 0.02 to 1.20 percent of Ni, less than or equal to 0.40 percent of Cu, less than or equal to 0.005 percent of S, 0.005 to 0.250 percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.35 percent of (V + Ti + Nb), less than or equal to 0.06 percent of (Sn + As + Sb), 0.0005 to 0.0040 percent of Ca, 0.010 to 0.025 percent of REM, 0.004 to 0.024 percent of N, less than or equal to 0.002 percent of O, less than or equal to 0.00015 percent of H and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. On the basis of improving the cost performance of R3, R4 and R4S grade mooring steel, by utilizing the river-bay effect of Mn influencing a continuous cooling curve of structural steel, namely similar to the influence rule of Mo, as the content of alloy Mn is increased to a certain amount, the continuous cooling curve of the steel begins to be bent, a component system for increasing cheap elements Mn and Al and reducing precious elements Mo and Ni is designed, and through trial production of the steel and a chain, the cost performance of the steel is improved. The effects of reducing the cost of the chain product and improving the obdurability of the chain product are achieved. The invention further relates to a mooring chain and a production process thereof.
Owner:SHANGHAI BAINITE CHAIN MATERIAL TECH CO LTD +1
Bonding structure of bonding wire
ActiveUS9331049B2Easy to operateHigh bonding strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringCopper
The invention is aimed at providing a bonding structure of a copper-based bonding wire, realizing low material cost, high productivity in a continuous bonding in reverse bonding for wedge bonding on bumps, as well as excellent reliability in high-temperature heating, thermal cycle test, reflow test, HAST test or the like. The bonding structure is for connecting the bonding wire onto a ball bump formed on an electrode of a semiconductor device, the bonding wire and the ball bump respectively containing copper as a major component thereof. The bonding structure comprises a concentrated layer A provided at an interface of a bonding part of the ball bump and the bonding wire, wherein the concentration of a metal R other than copper in the concentrated layer A is not less than ten times the average concentration of the metal R in the ball bump; and a concentrated layer B provided at an interface of a bonding part of the ball bump and the electrode, wherein the concentration of the metal R in the concentrated layer B is not less than ten times the average concentration of the metal R in the ball bump.
Owner:NIPPON MICROMETAL CO LTD
Method and system of automatic control
InactiveUS20070090228A1Reduce probabilityEnsure protection reliabilityDefence devicesWave based measurement systemsTransceiverAutomatic control
The invention relates to aircraft automatic control systems. Its use for providing flight safety of civil aircrafts allows to obtain the technical result in the form of reducing a probability of a missile hit on a civil aircraft and ensuring protection reliability in optical interference environment. This technical result is achieved in the method due to steps of: determining the fact of a missile launch; determining missile coordinates in every time moment; generating pulse periodic laser radiation, wherein a wavelength range of the laser radiation is within a sensitivity range of infrared seeker head, a power of the laser radiation exceeds the power of radiation of the aircraft engine in the sensitivity range of the infrared seeker head, and a pulse repetition frequency is close to typical operation frequency of the infrared seeker head; and sending the laser radiation to the point of presence of the missile in the given time moment. This result is ensured in the system by arranging at an aircraft and employing sensors of missile launch fact and coordinates, a transceiver having a turn drive and an optical channel which output is connected to a sensor of missile coordinates at a missile flight trajectory, an on-board calculator, and a laser radiation generator having an actuation device.
Owner:ZAKRYTOE AKTSIONERNOYE OBSCHESTVO STIVT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com