Patents
Literature
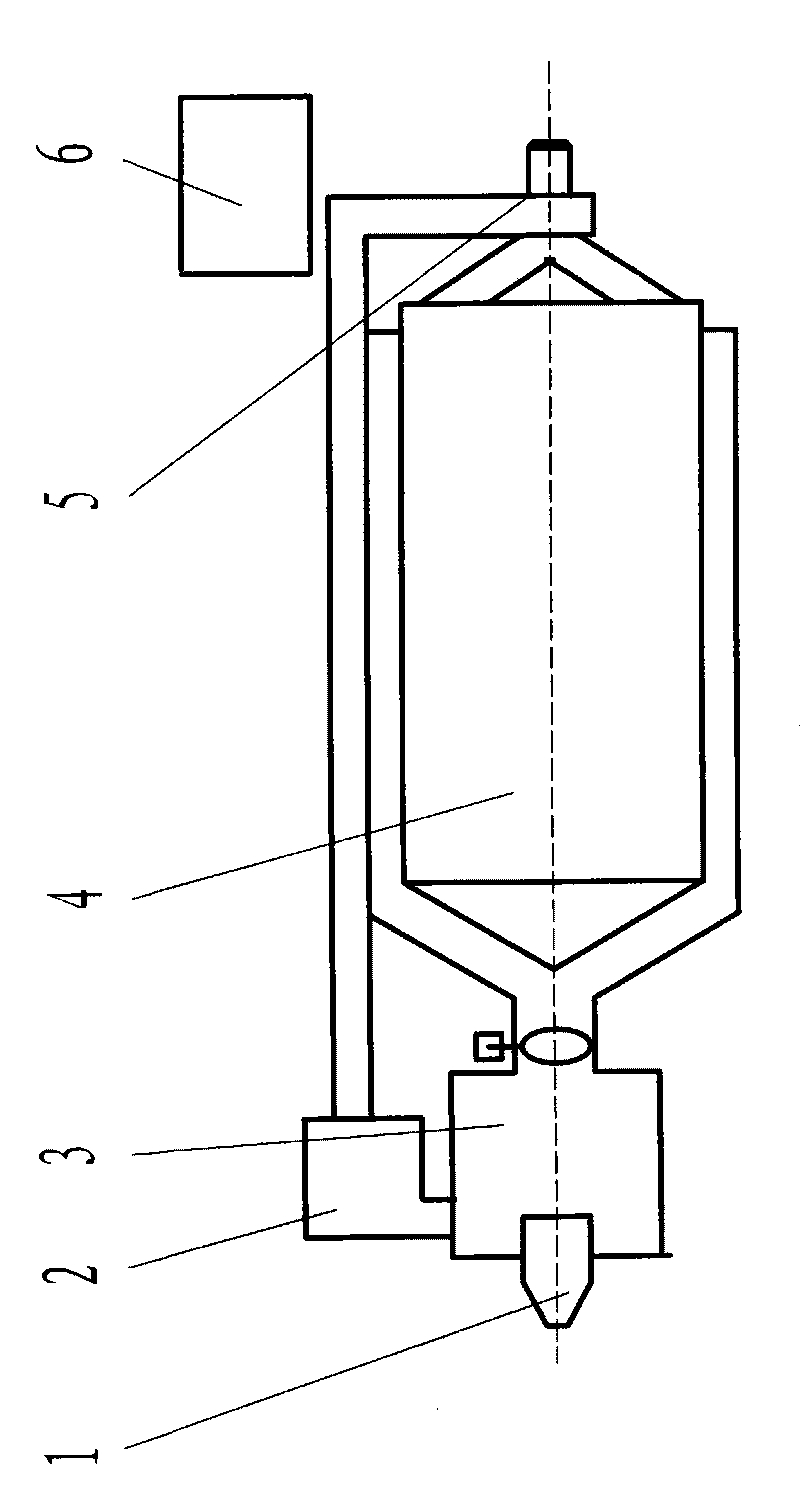
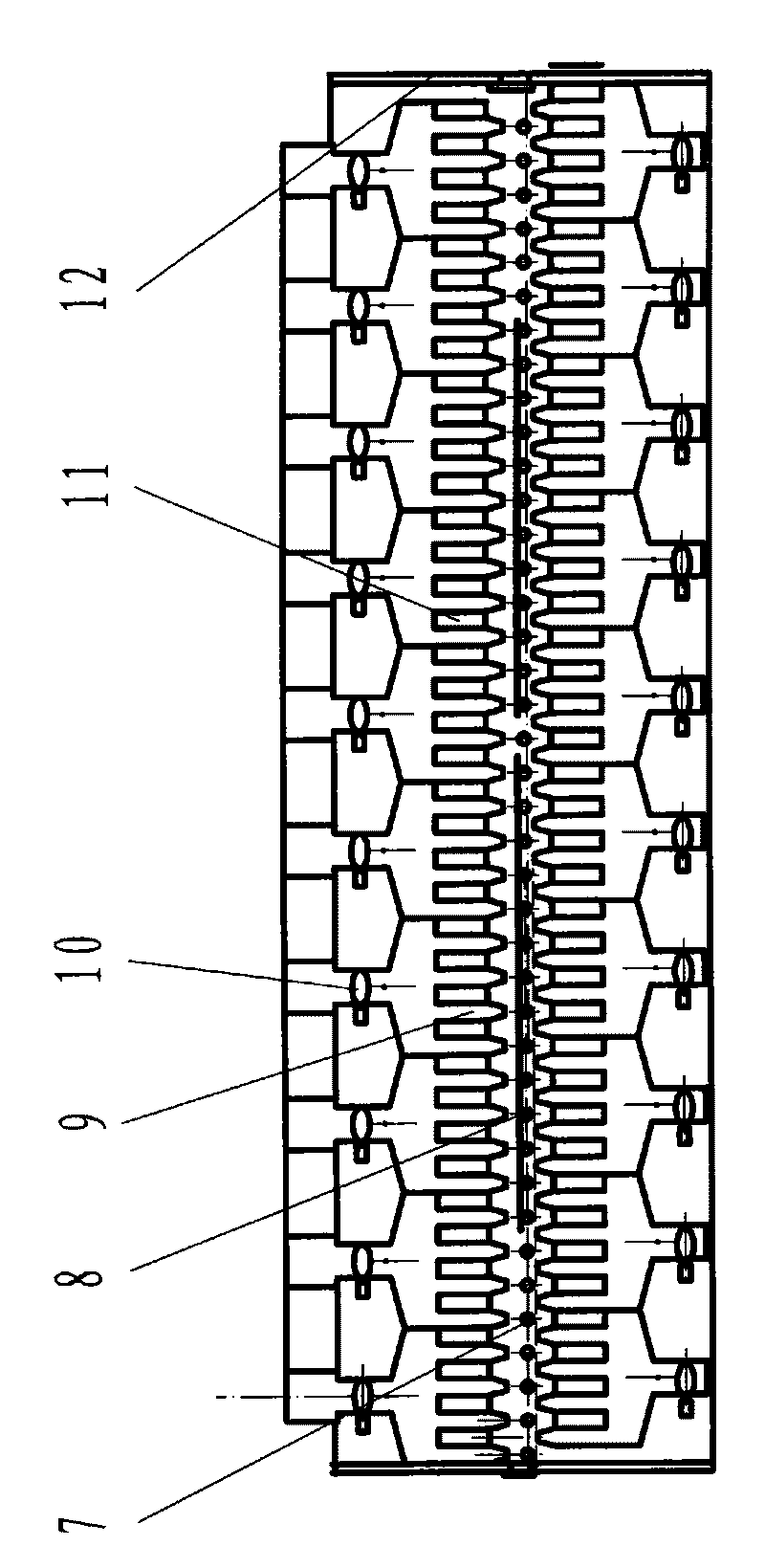
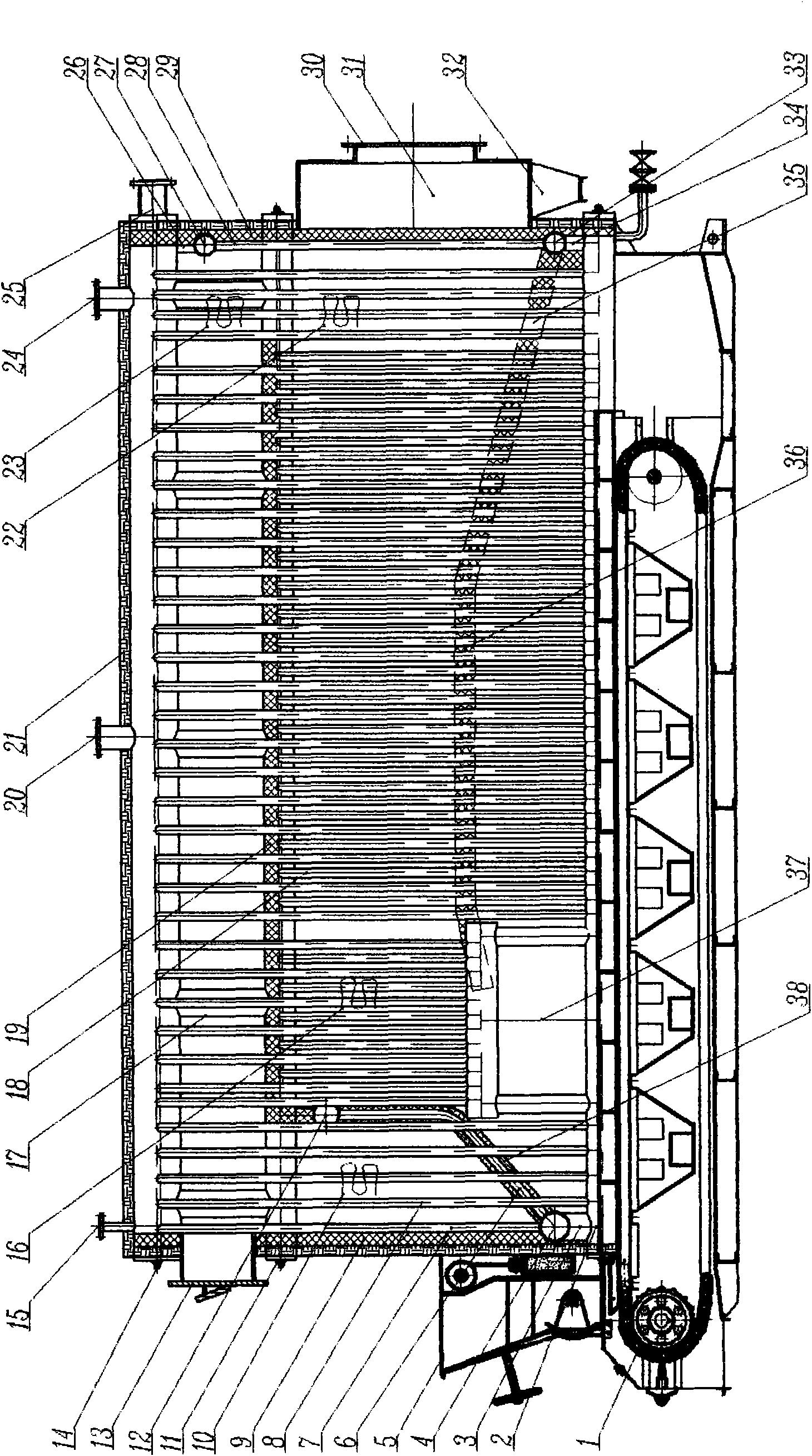
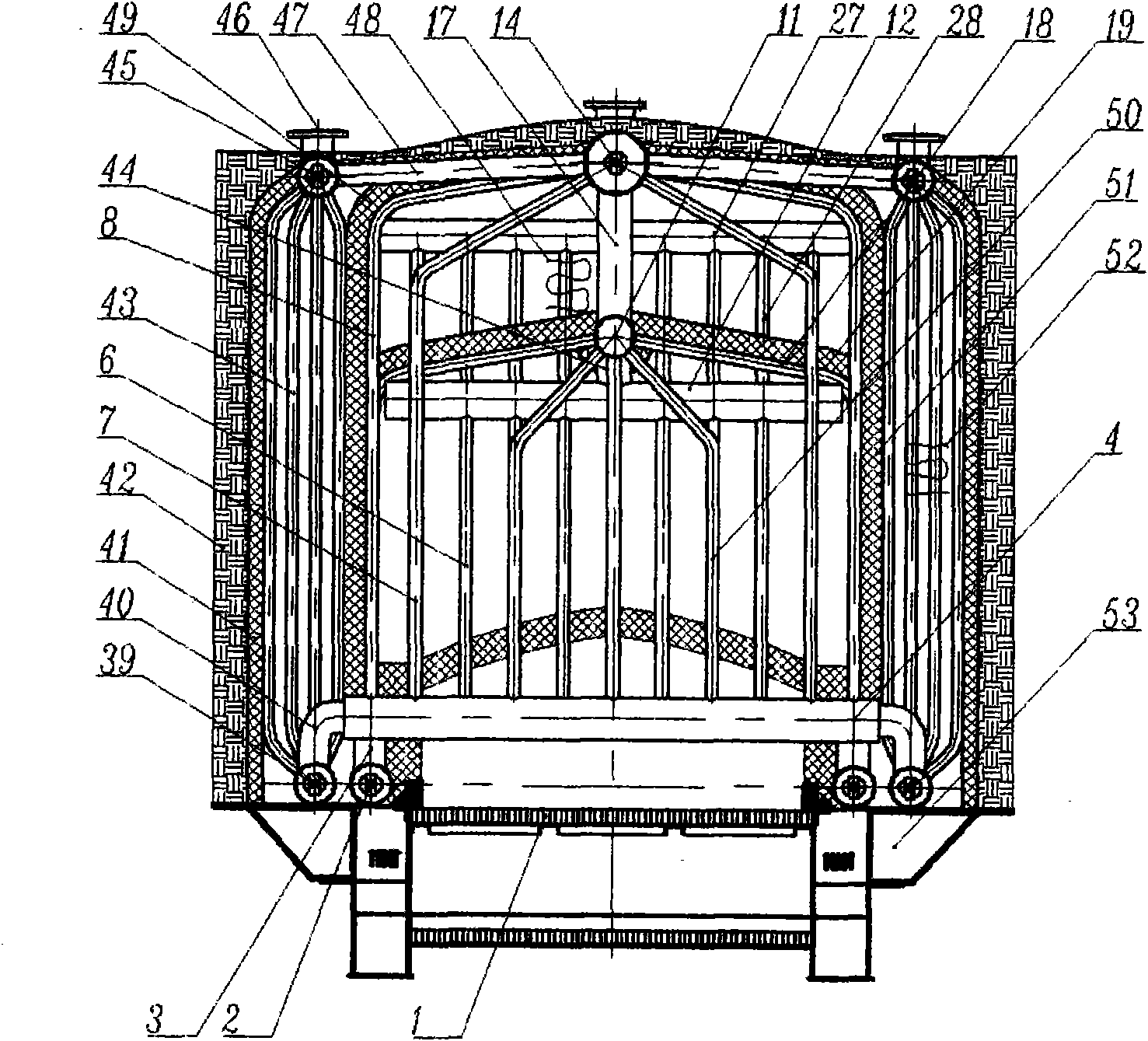
157 results about "Convective heating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
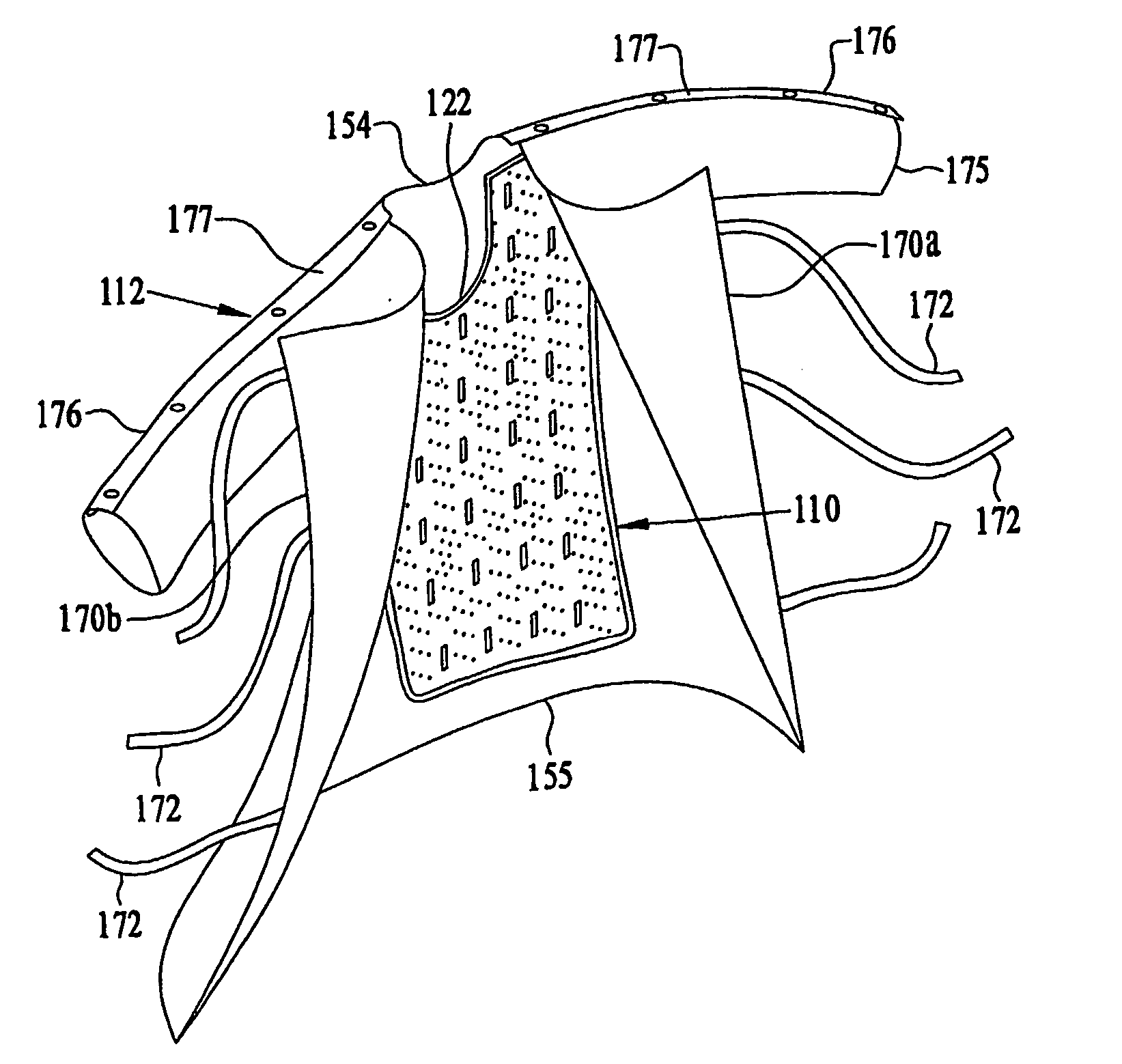
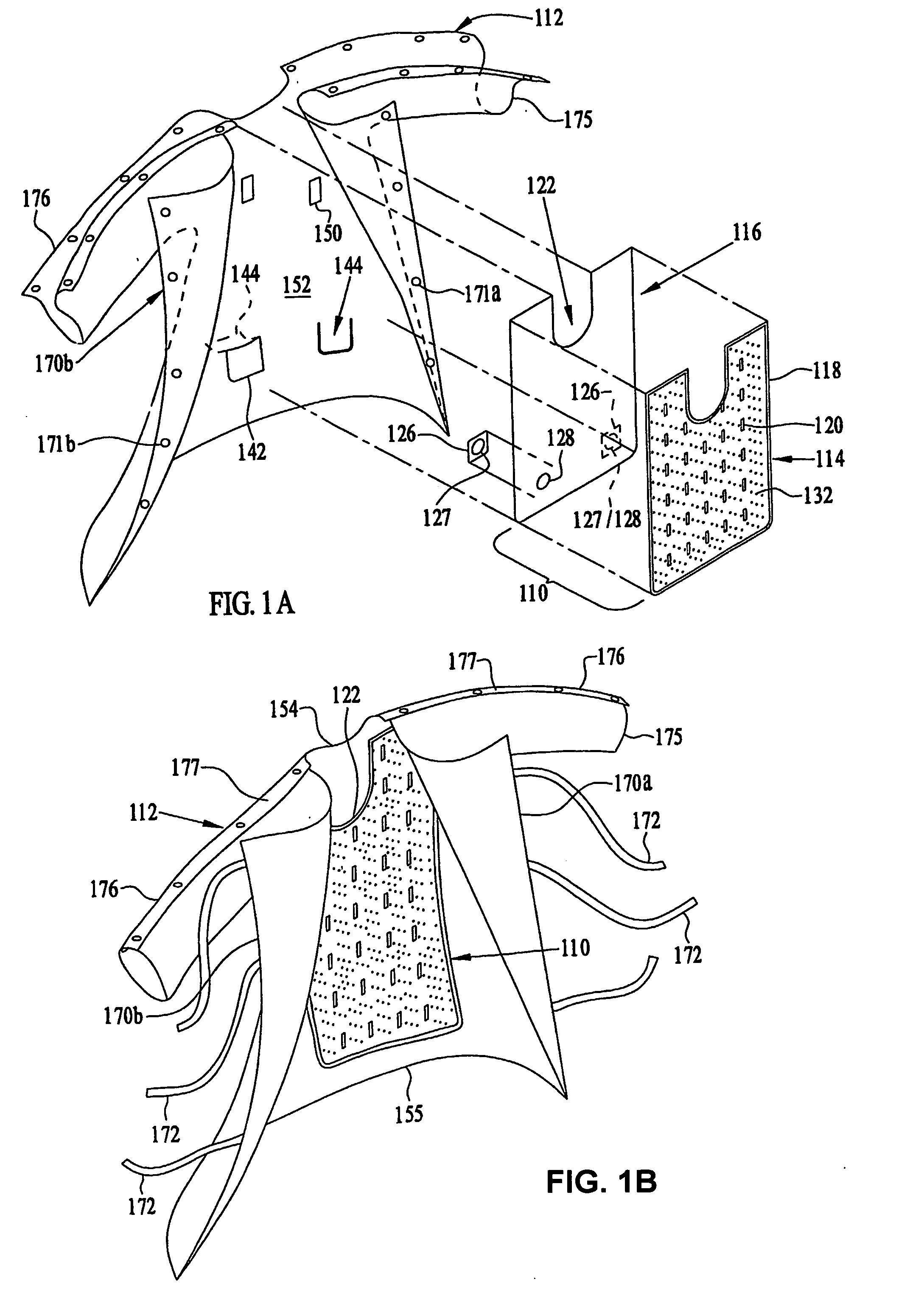
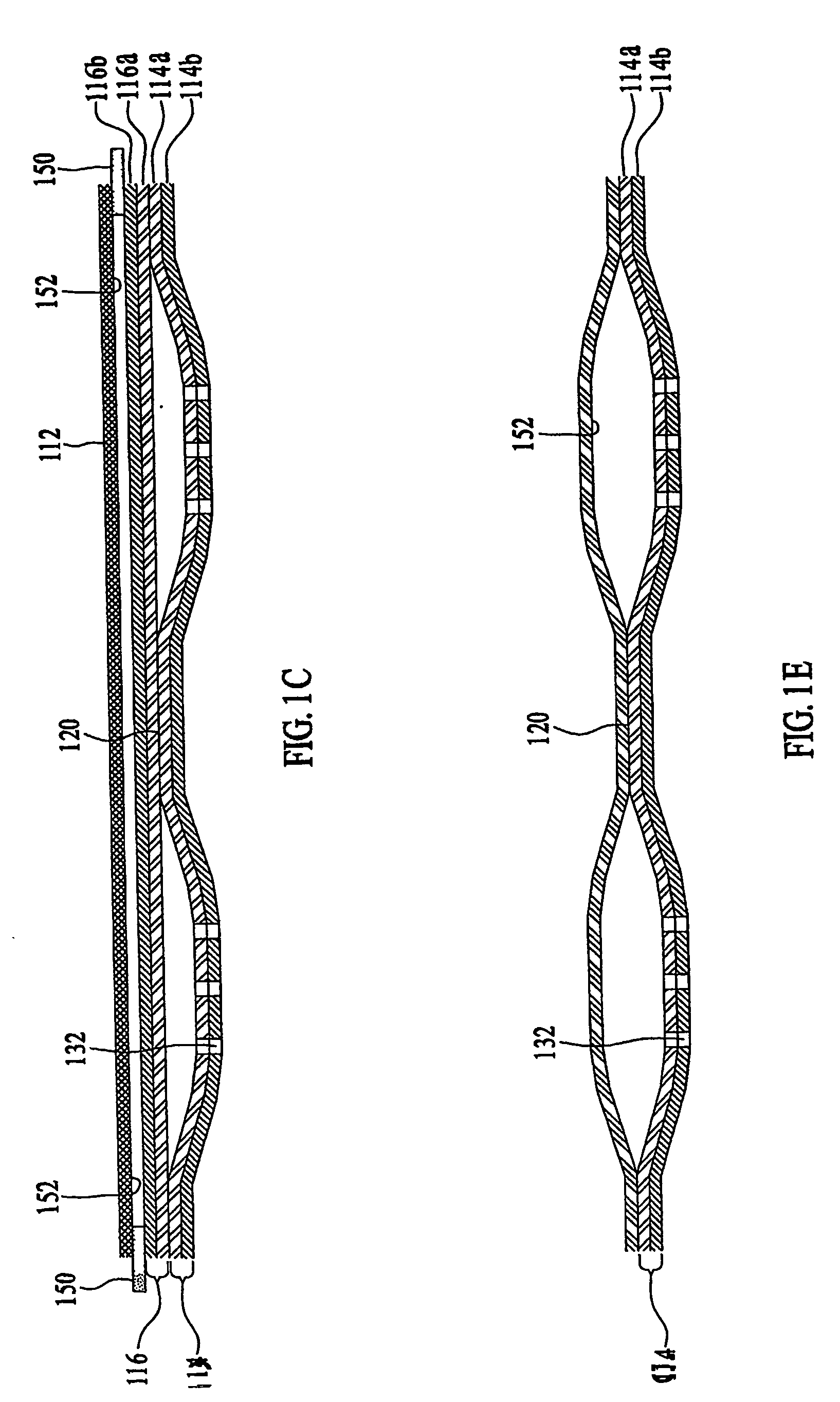
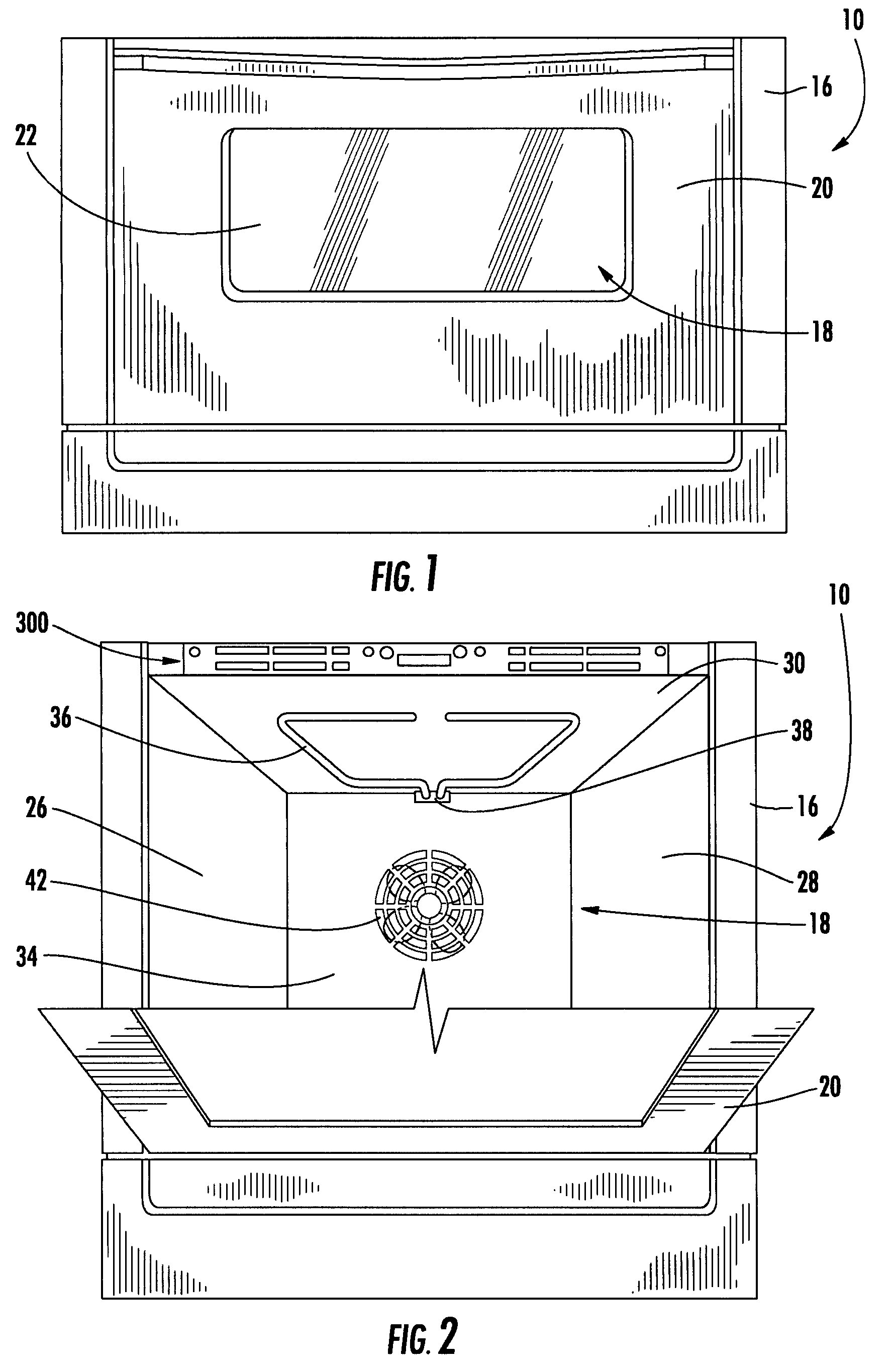
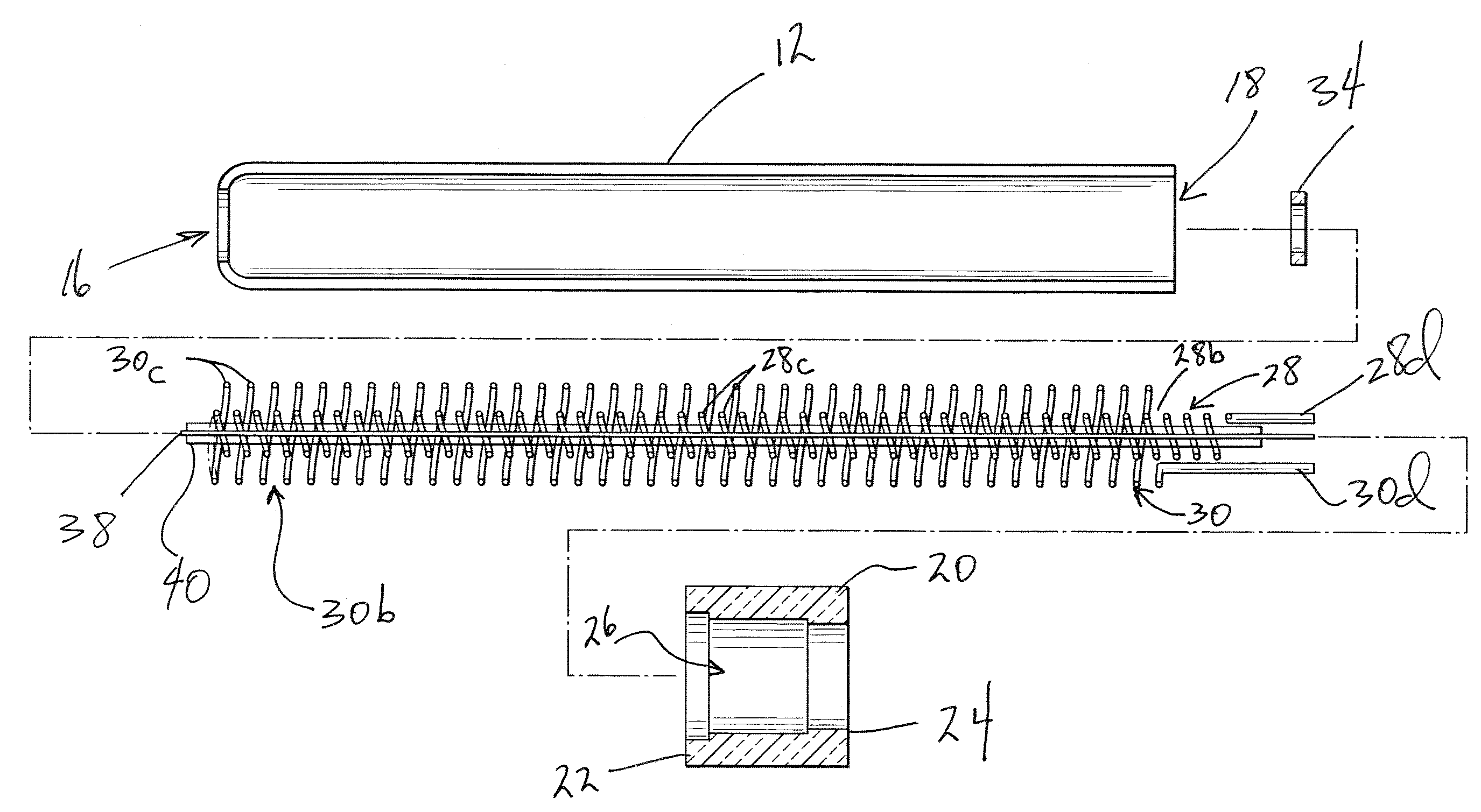
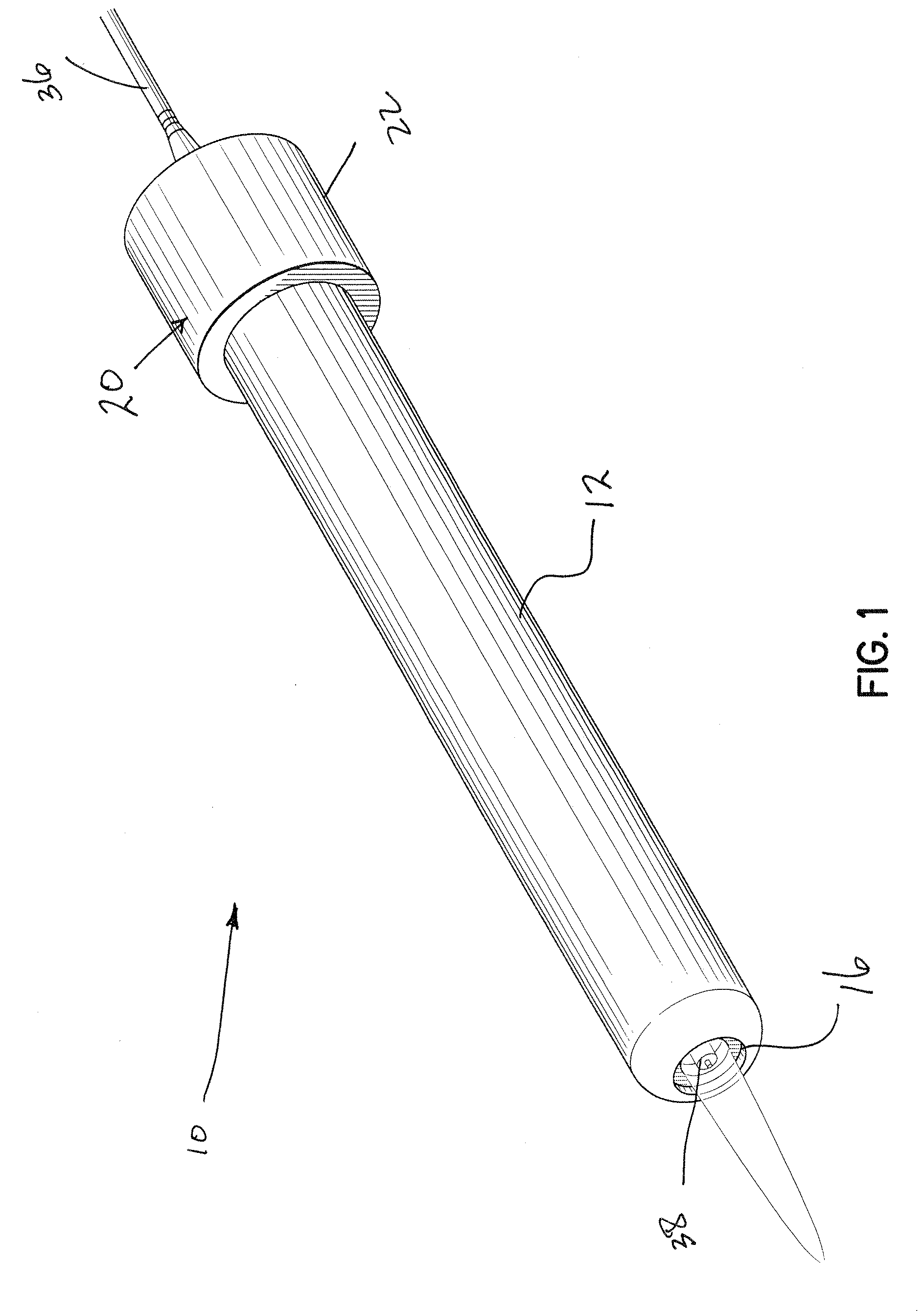
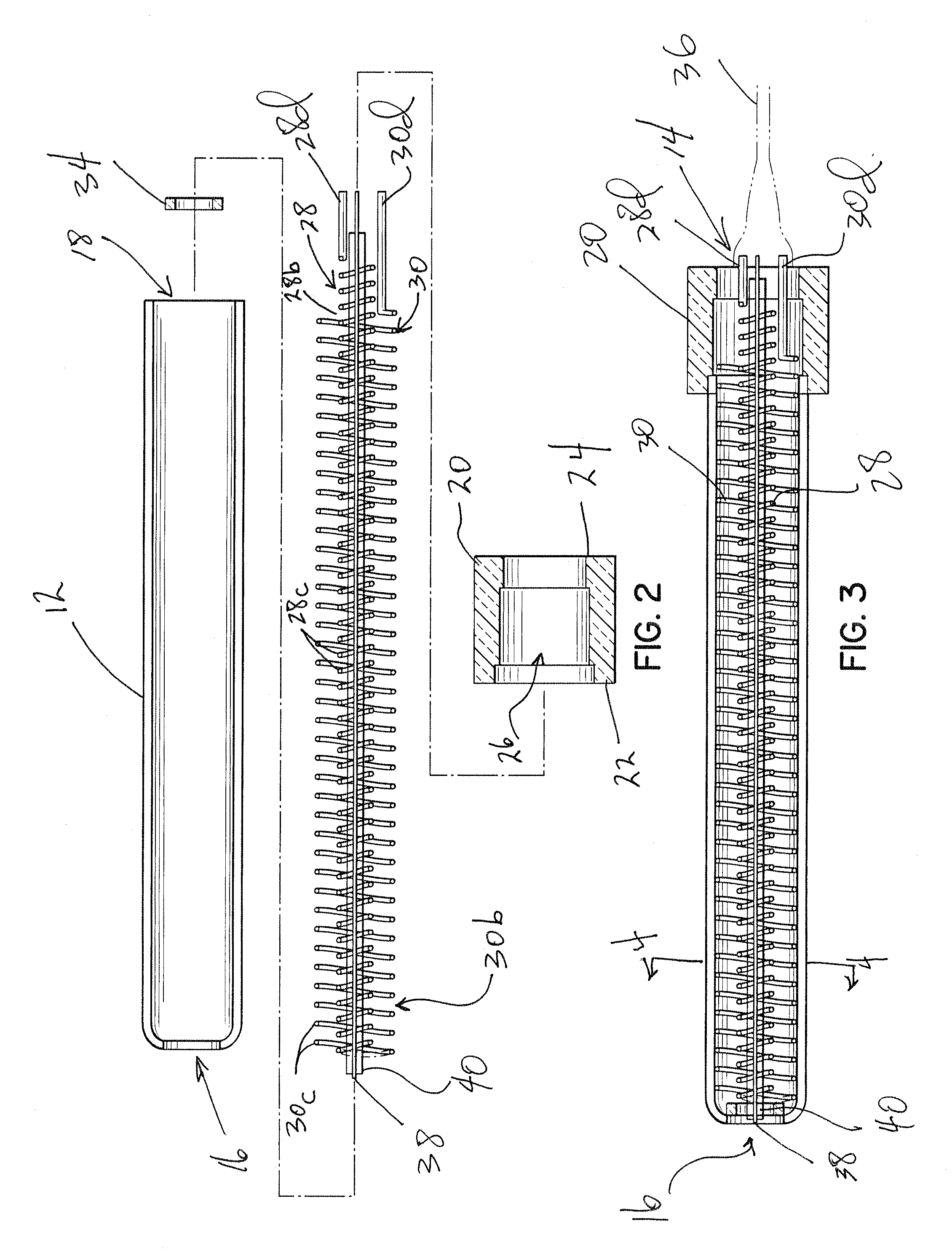
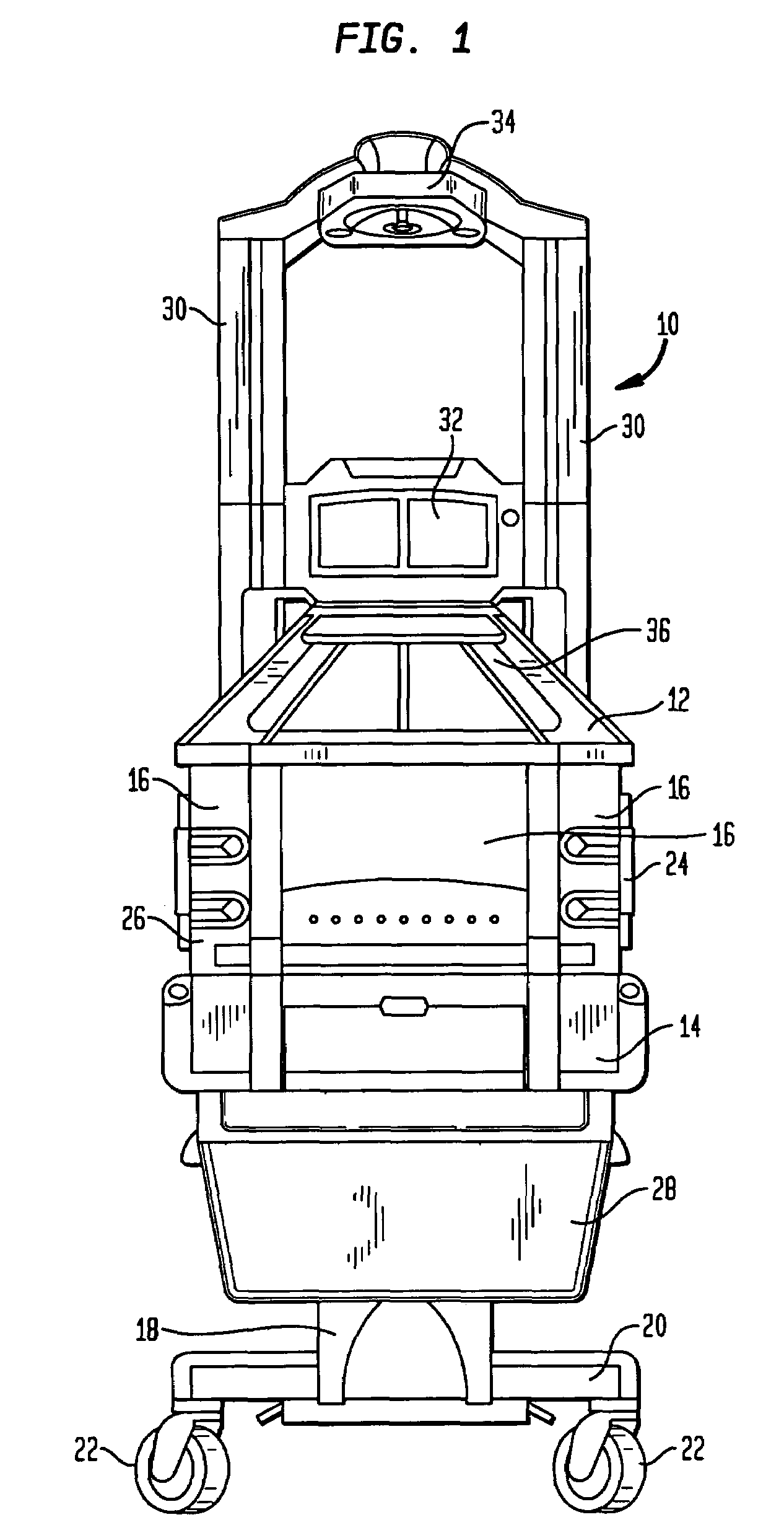
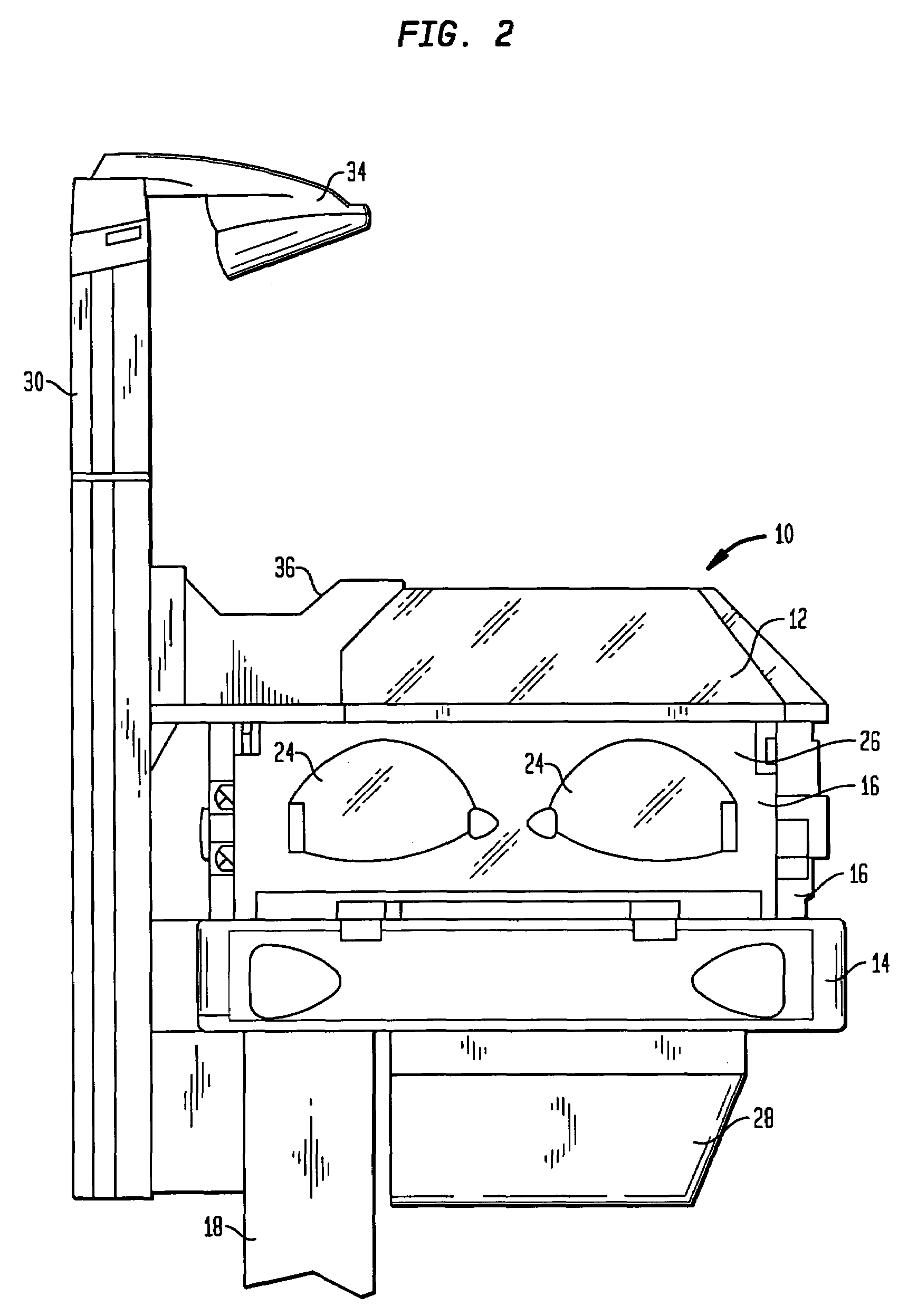
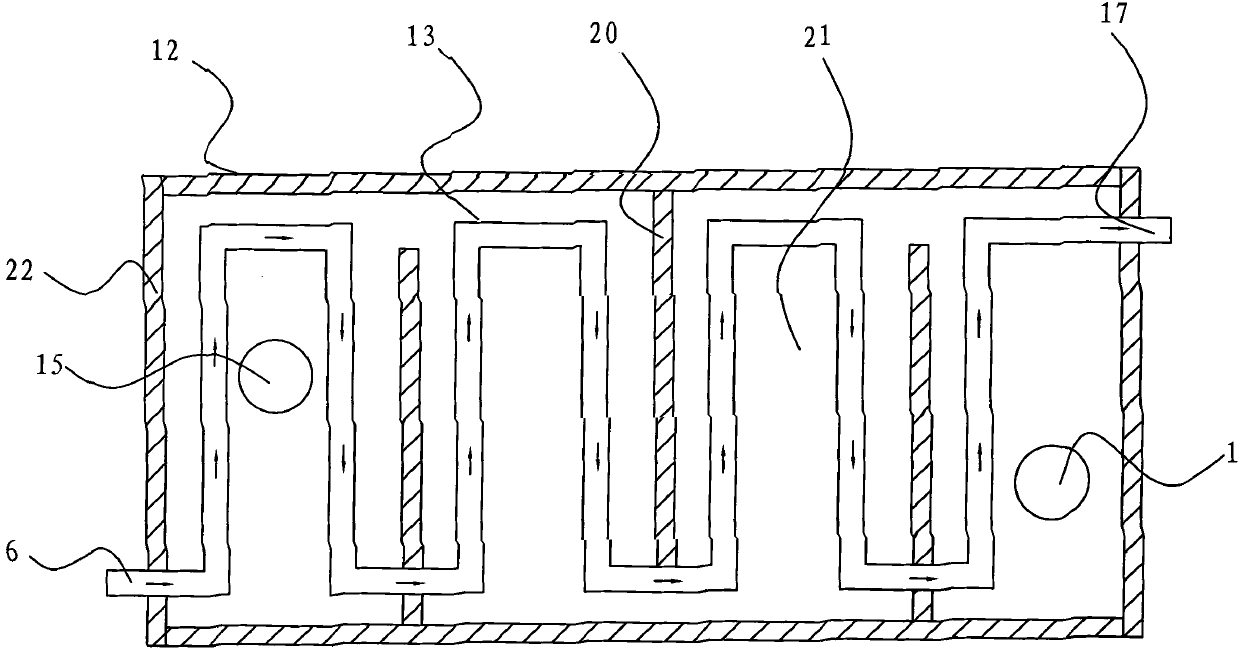
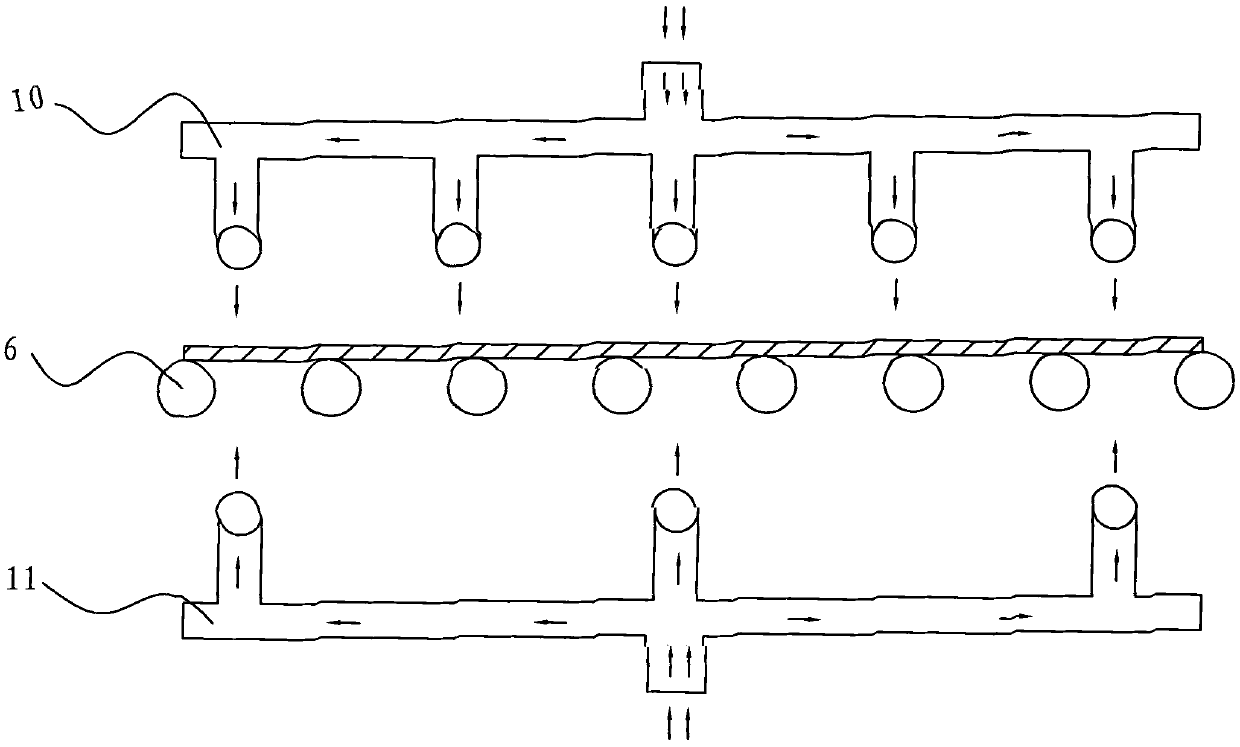
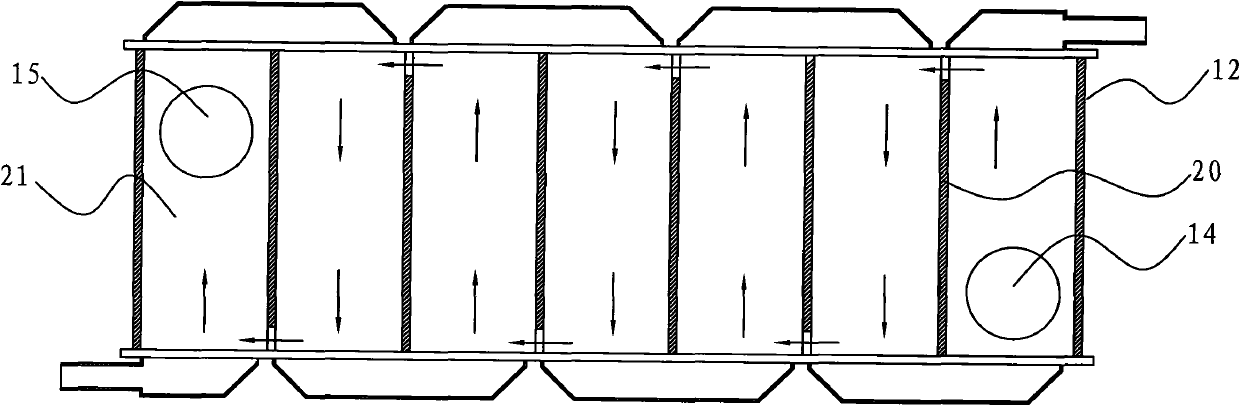
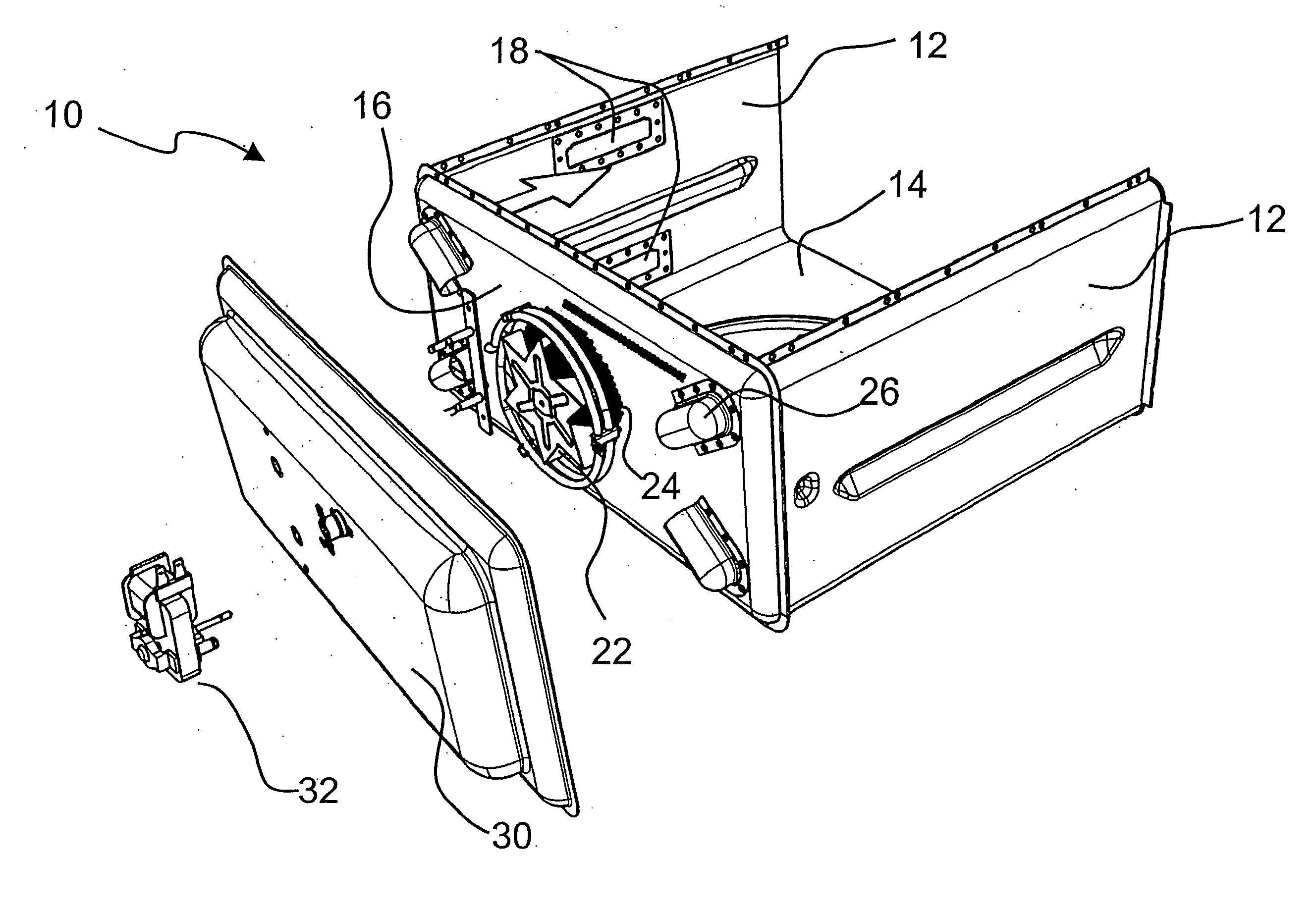
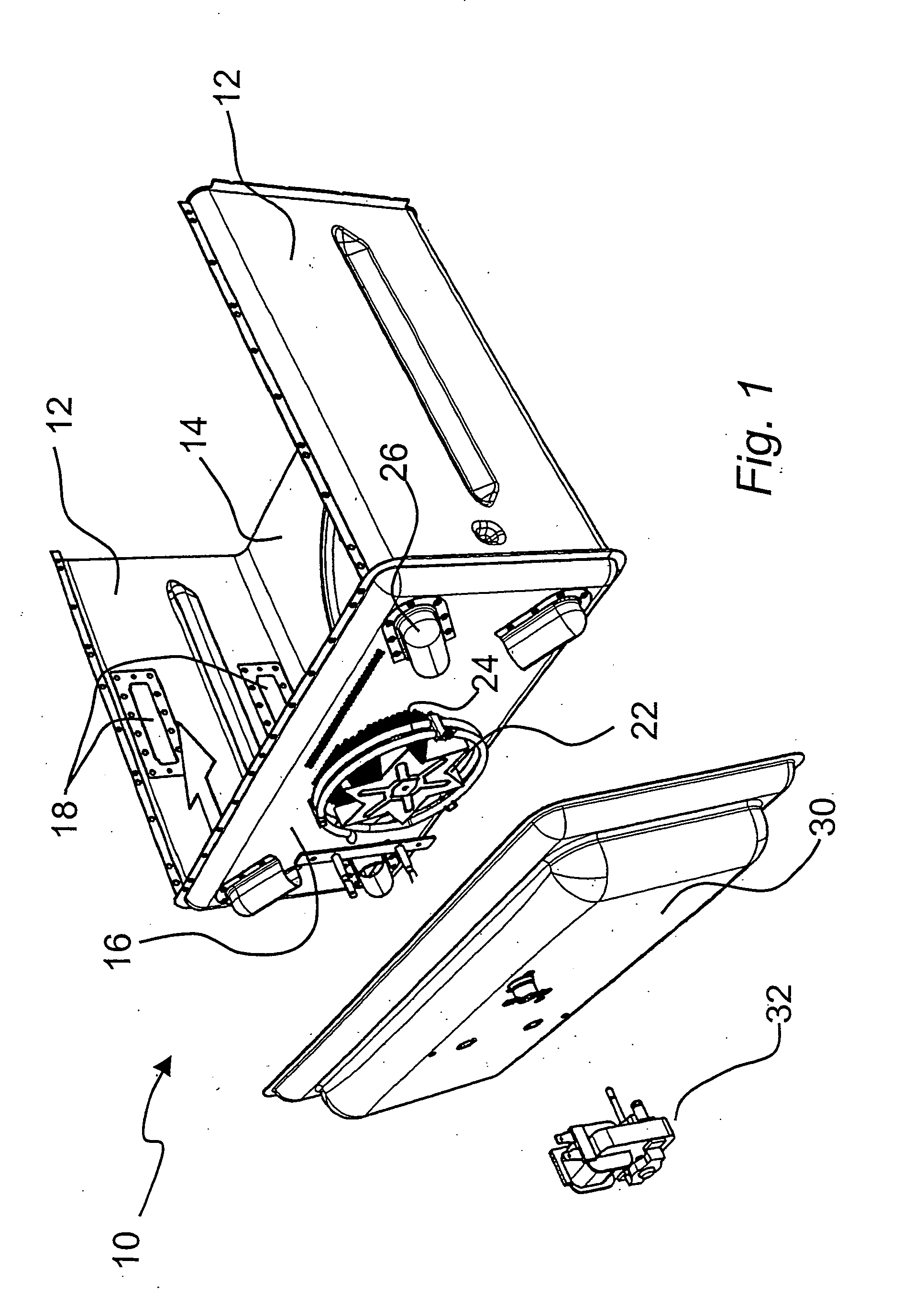
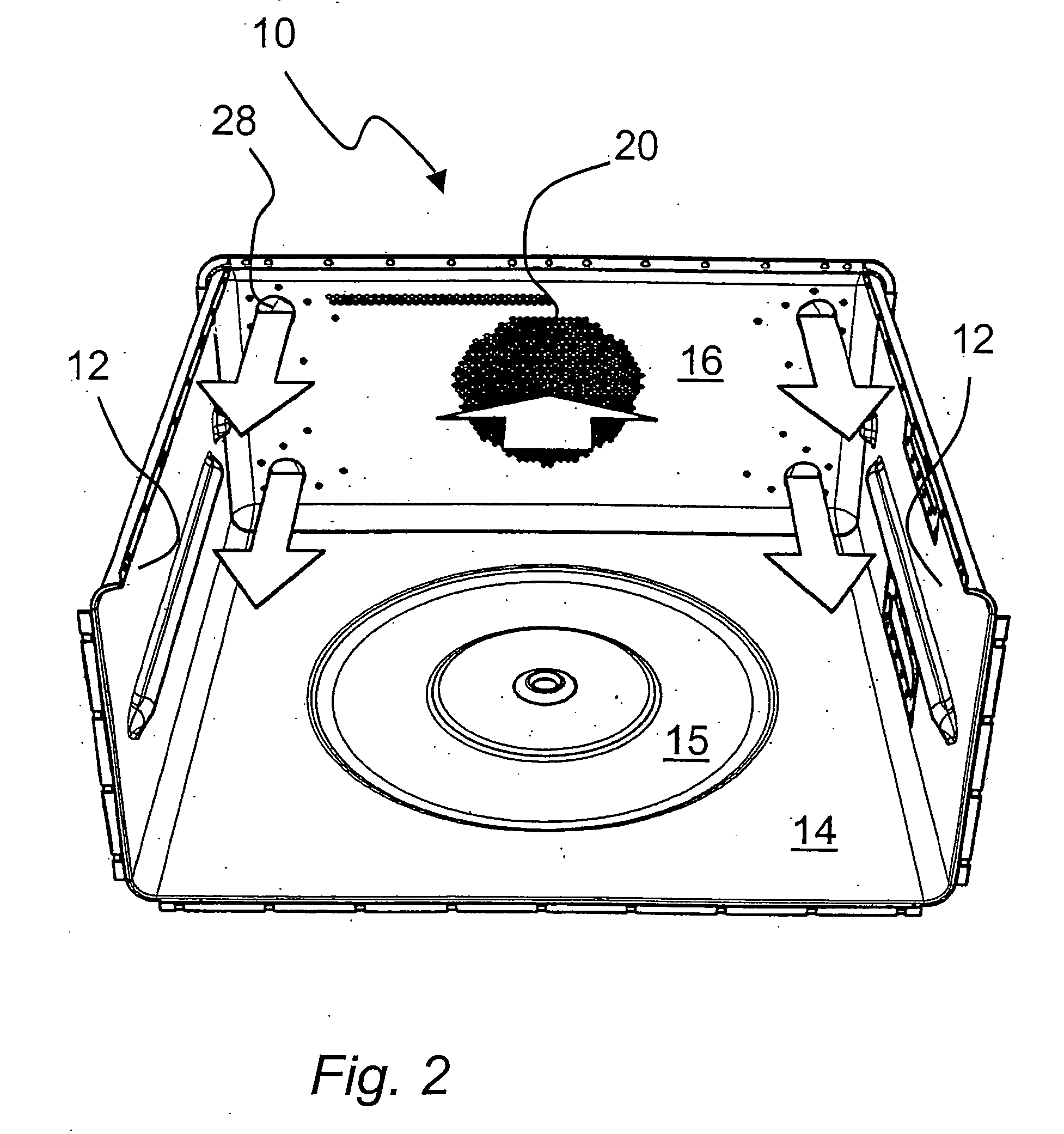
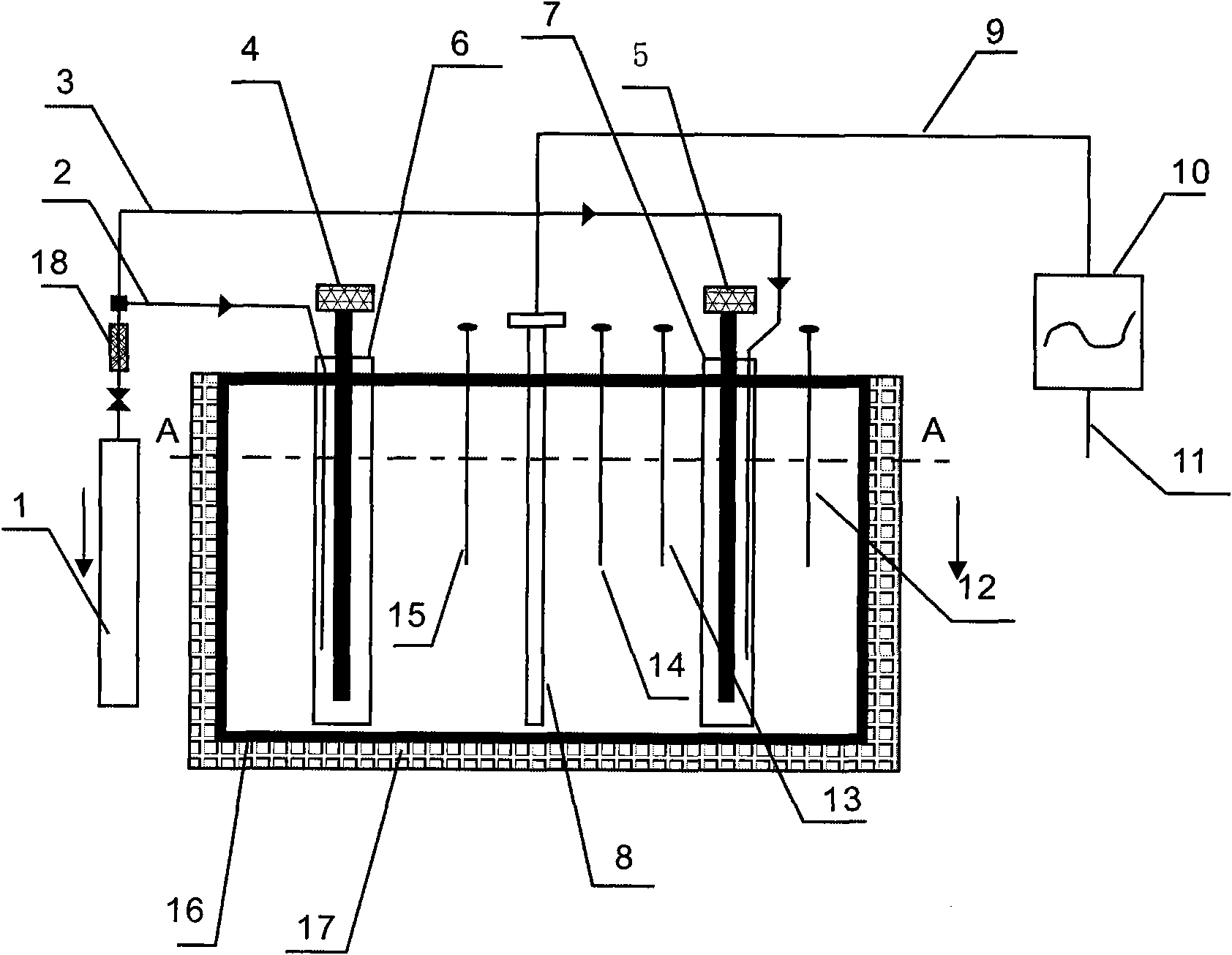
Patient comfort apparatus and system
InactiveUS20050143796A1Easily remove or adjustSimple to manufactureGarment special featuresCouplingsHospital gownThermal treatment
Apparatus and a system for thermally comforting a patient include pneumatic, convective providing thermal treatment for persons or animals, which is adapted for use in combination with a clinical garment such as a hospital gown, robe, bib, and other equivalents. The pneumatic convective device provides convective warming focused or directly primarily on the thorax or body core. The pneumatic convective device includes at least one inlet for being accessed through a clinical garment, a region in distribution with the inlet for distributing a stream of pressurized, thermally treated air, and a permeable member for emitting pressurized, thermally treated air from the distribution region.
Owner:GEN ELECTRIC CAPITAL +1
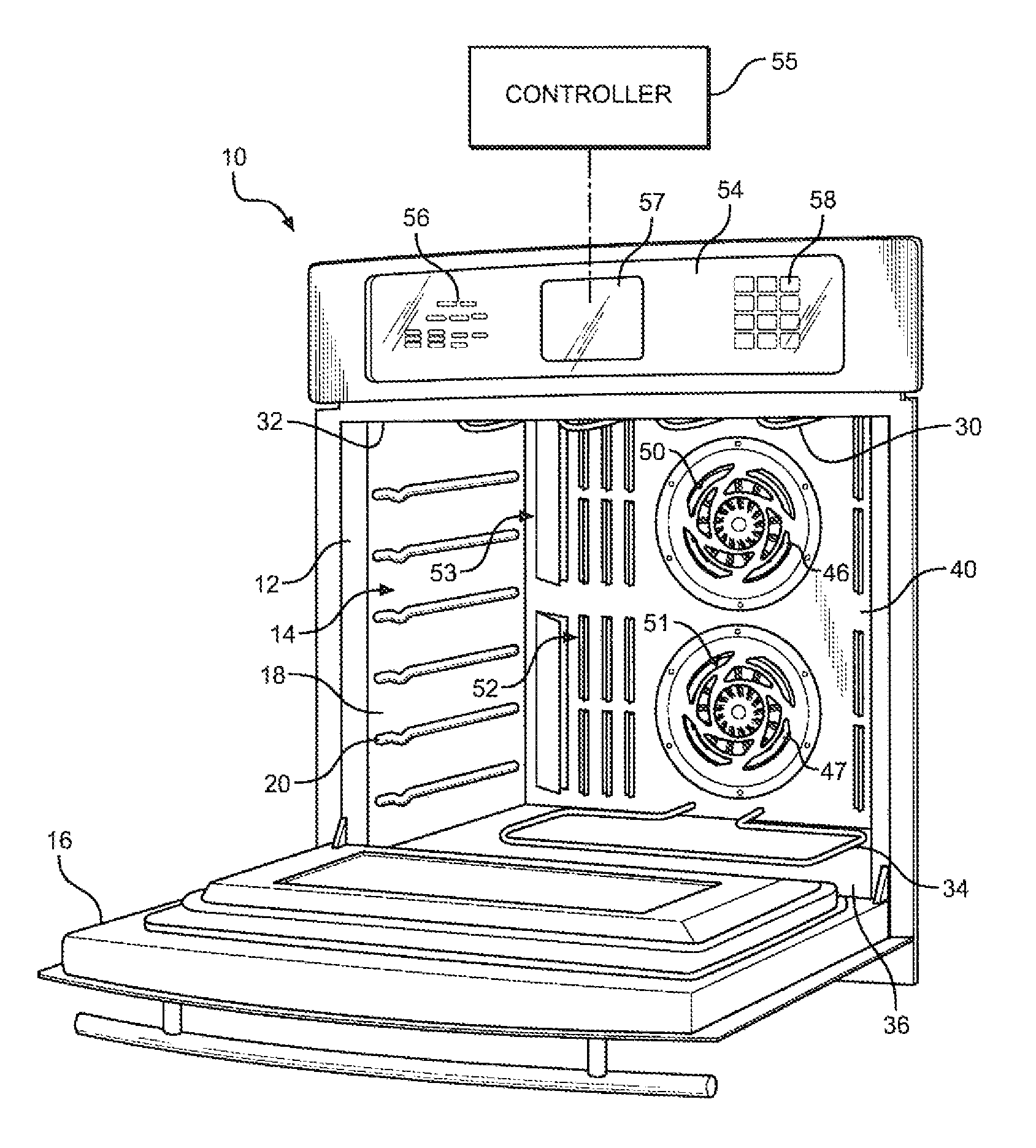
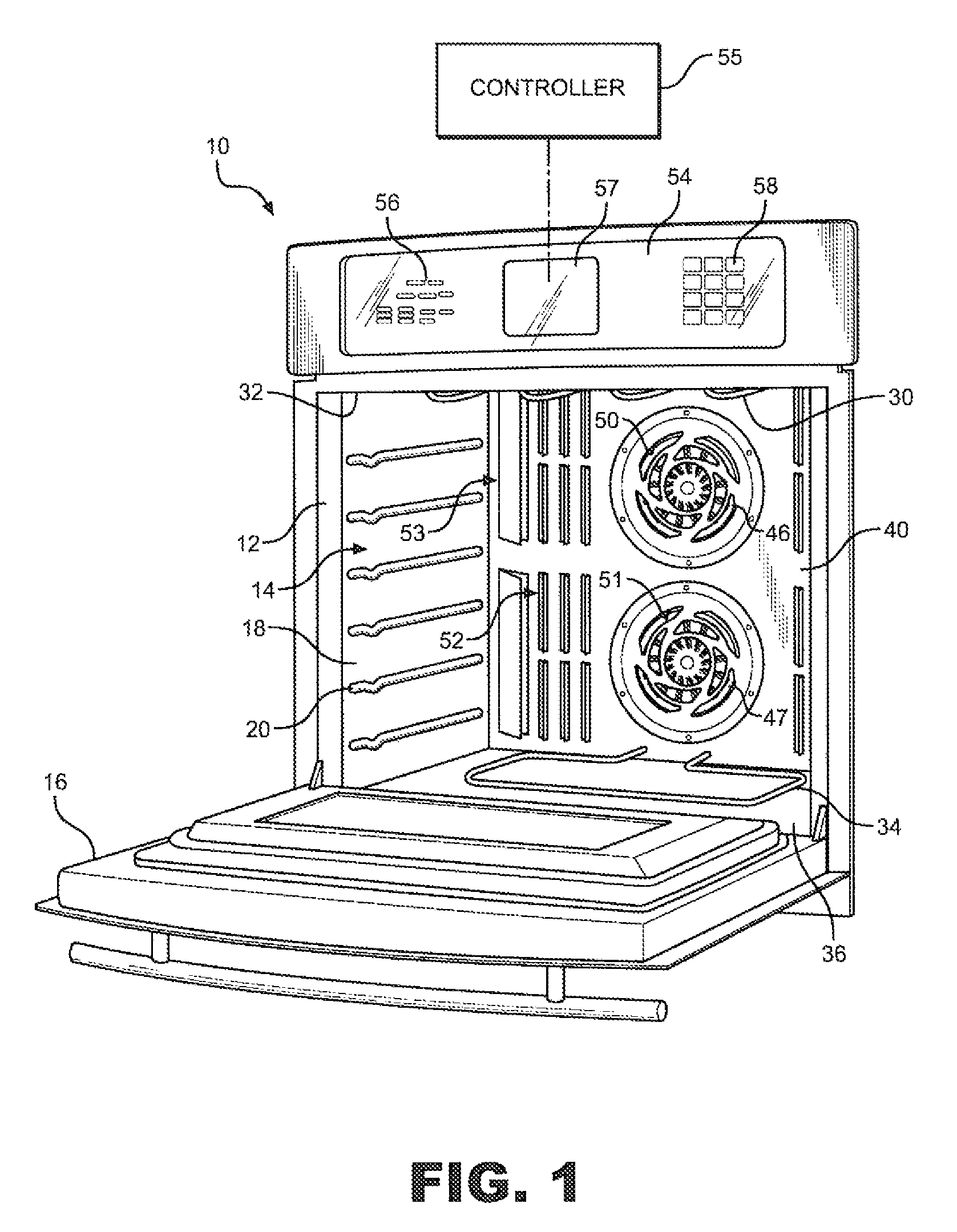
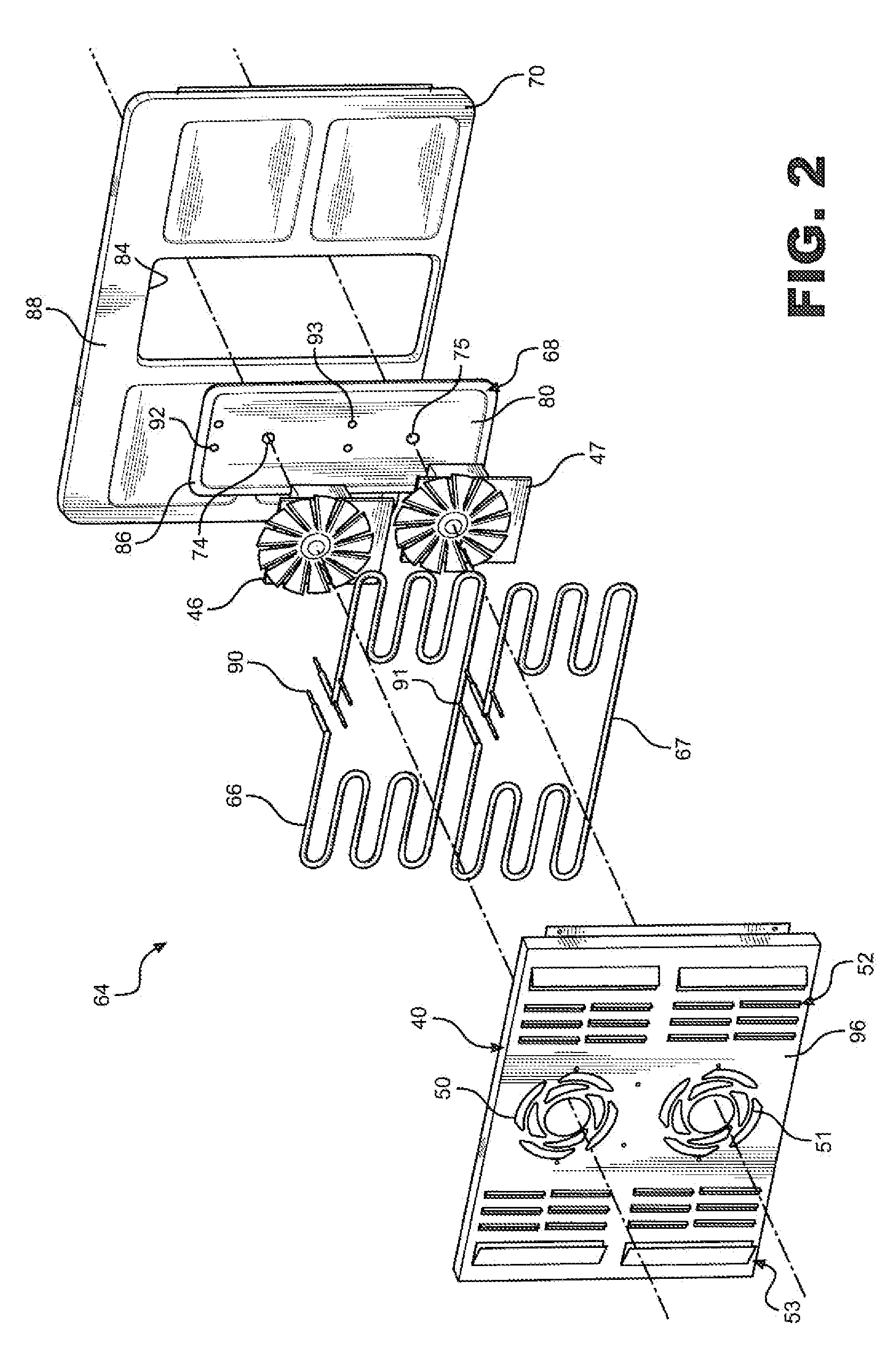
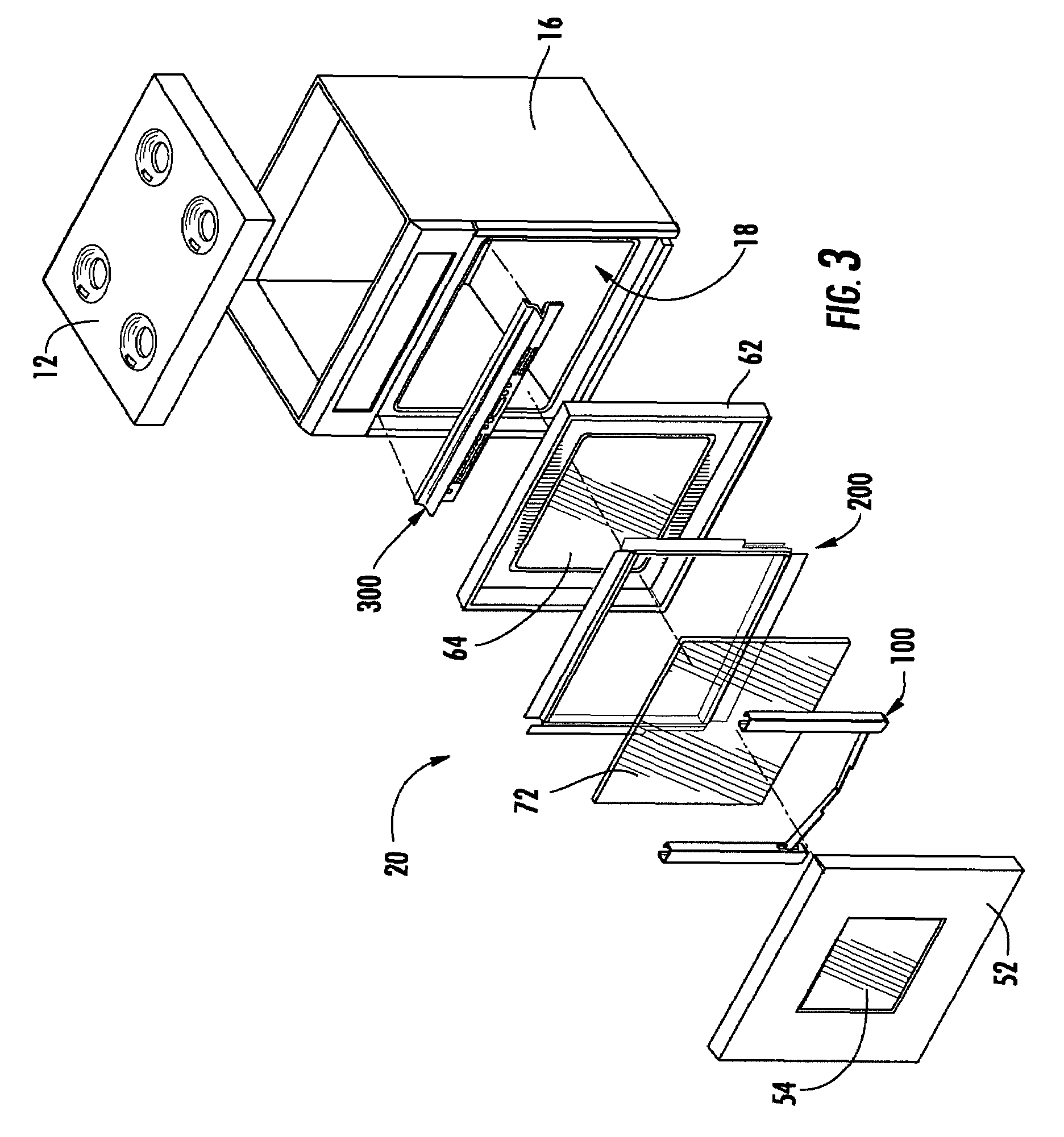
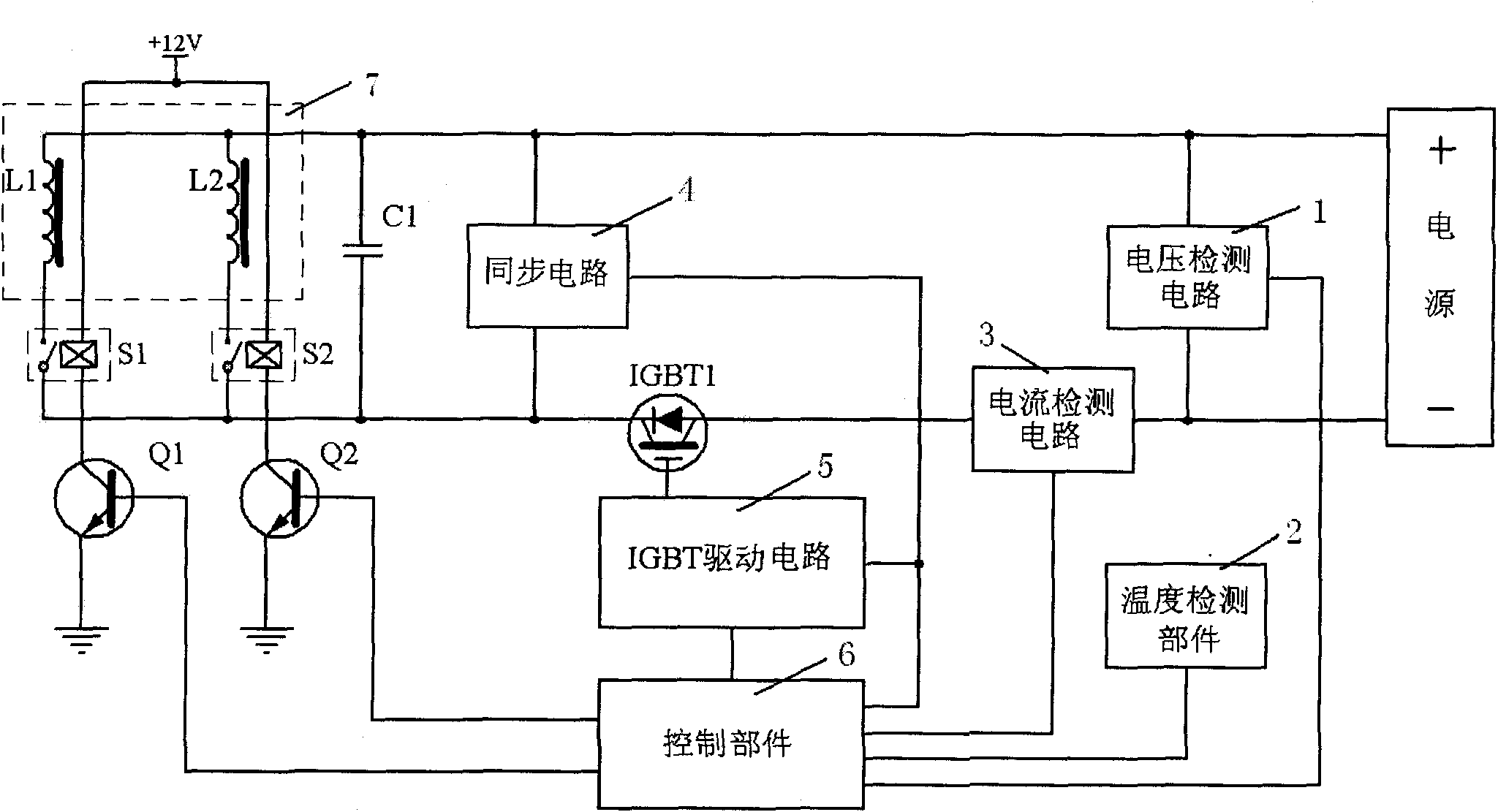
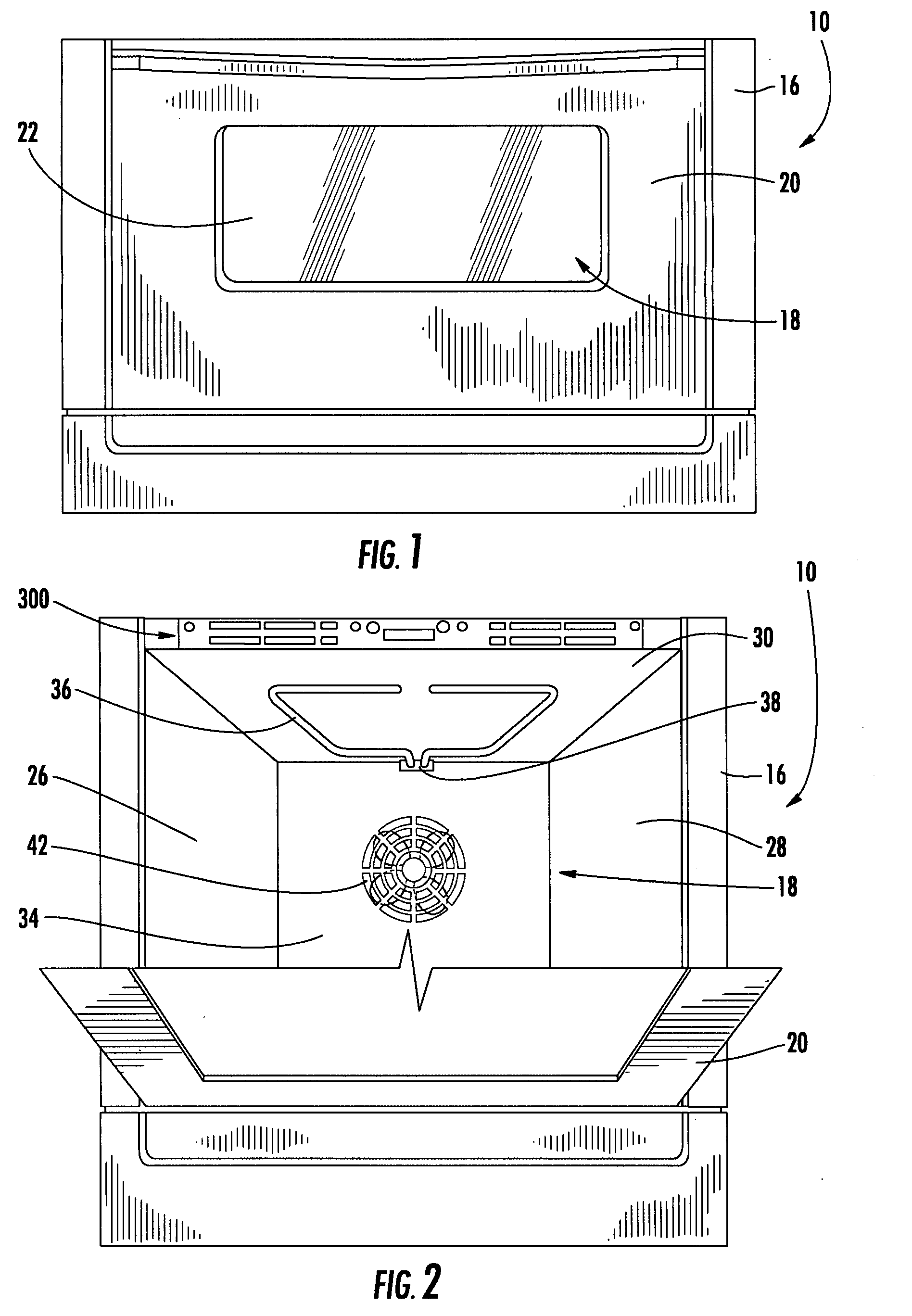
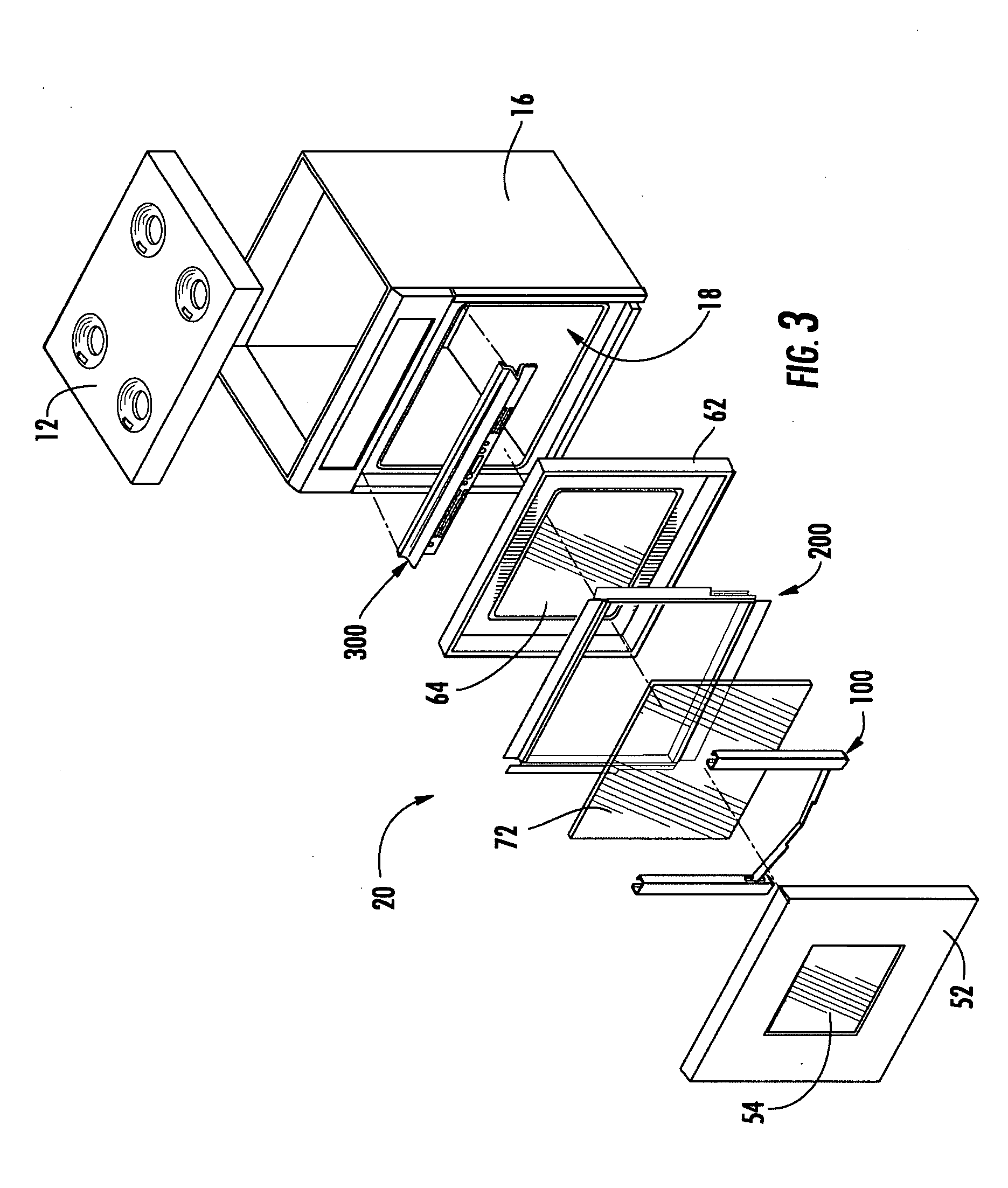
Priority controlled multi-fan convection oven
ActiveUS8304695B2Efficient and effective cookingDomestic stoves or rangesBaking ovenProcess engineeringConvective heating
A cooking appliance includes an oven provided with bake, broil and multiple convection heating elements, as well as plural, multi-speed fans, for cooking a wide range of food. The various heating elements are sequentially operated on a predetermined priority basis in order to, along with the fans, establish numerous effective cooking sequences, such as a bake mode, a convection bake mode with no preheat, a convection bake mode with rapid preheat, a convection bake mode with standard preheat, and a convection roast mode.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
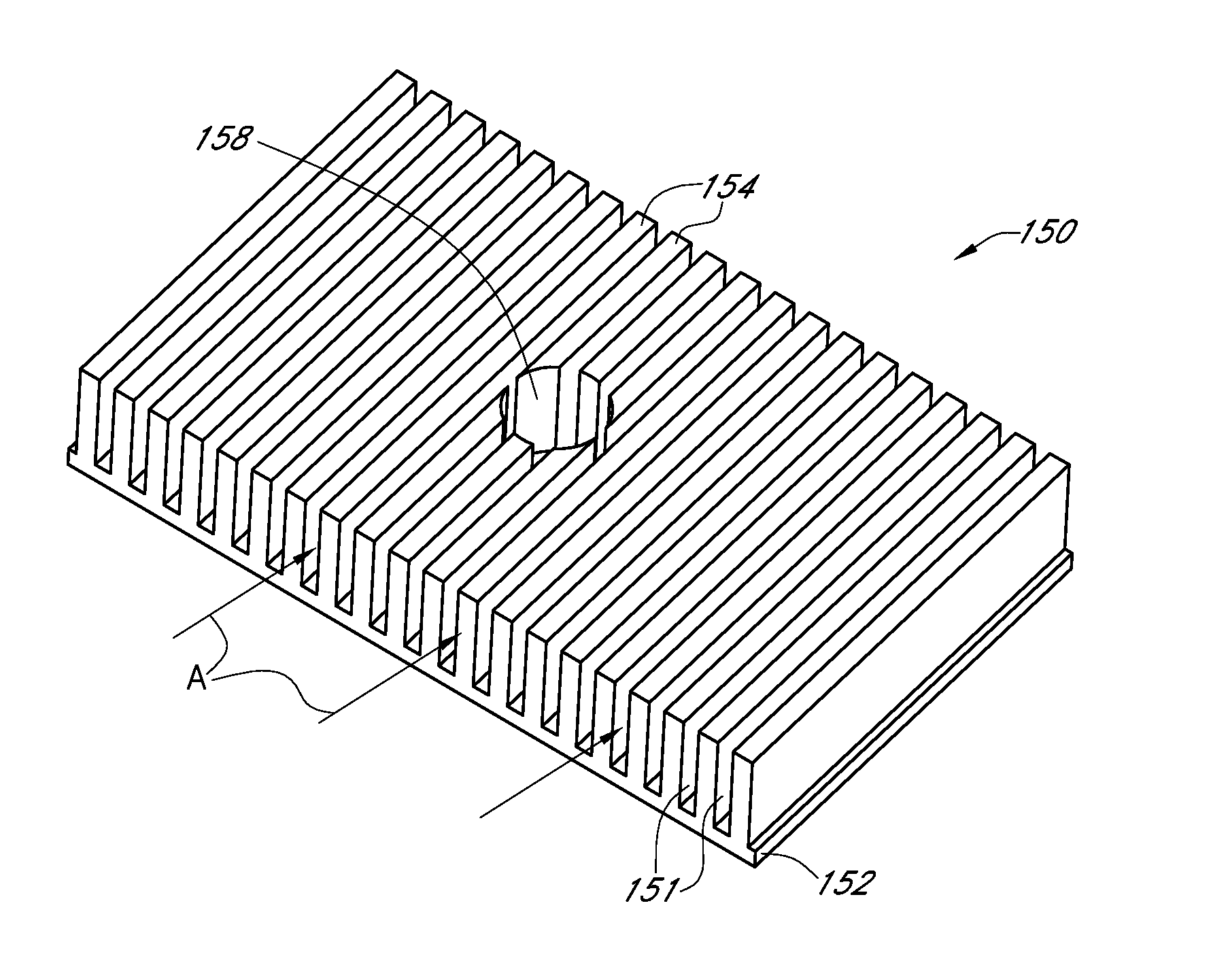
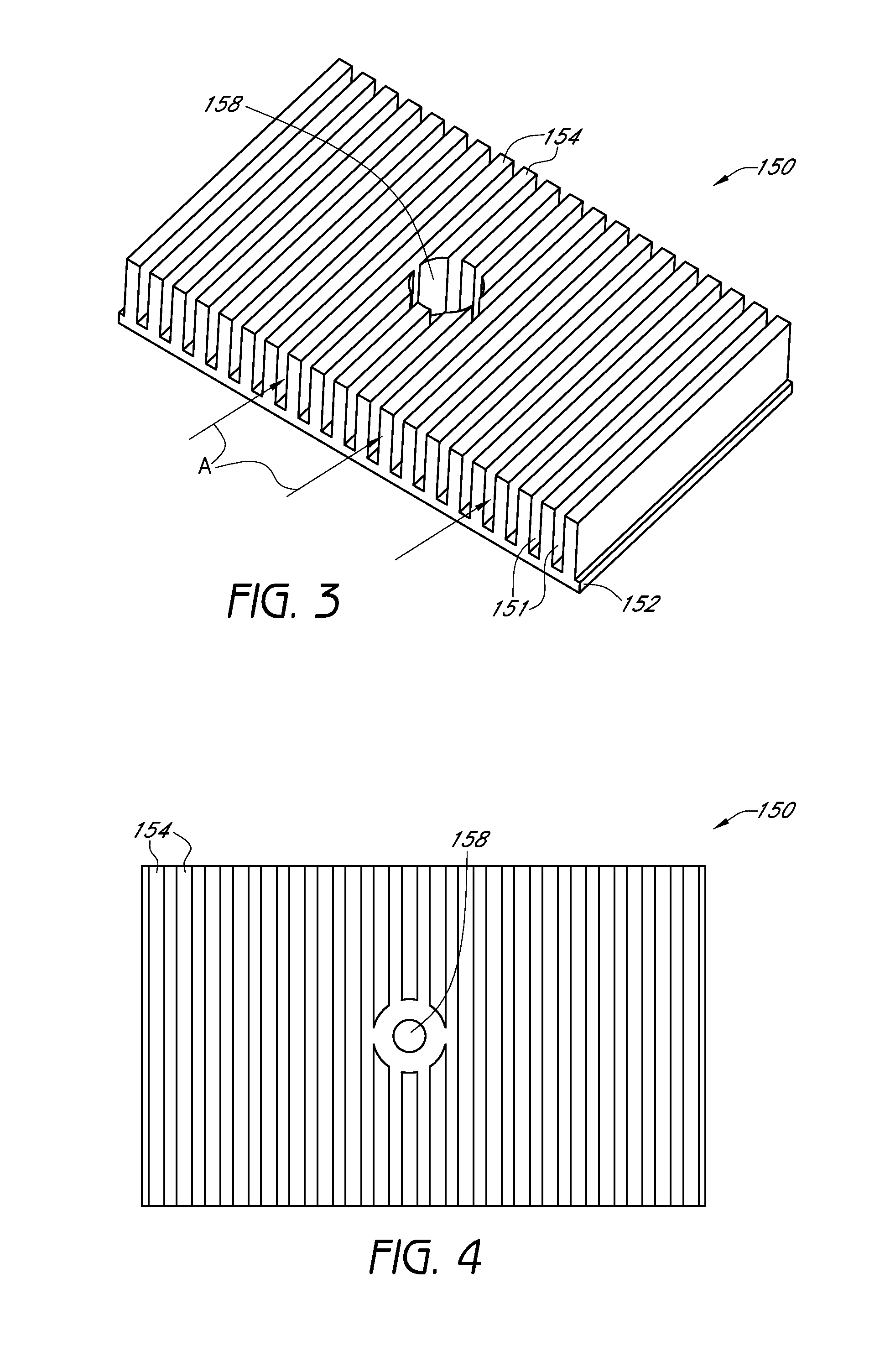
Convective heating device
InactiveUS20140131343A1Air heatersImmersion heating arrangementsConvective heatingElectrical current
A heating device comprises a heater having a first surface and a second surface, with the second surface being generally opposite of the first surface. The heater is configured to receive an electrical current and convert it to heat. The heating device additionally includes at least one heat transfer assembly positioned along the first and / or second surface of the heater. In one embodiment, the heat transfer assembly includes a plurality of fins that generally define a plurality of fin spaces through which fluids may pass. In some arrangements, the heating device comprises an outer housing that at least partially surrounds the heater and one or more of the heat transfer assemblies. Heat generated by the heater is transferred to the fins of the heat transfer assembly. In addition, fluids passing through the fin spaces are selectively heated when electrical current is provided to the heater.
Owner:GENTHERM INC
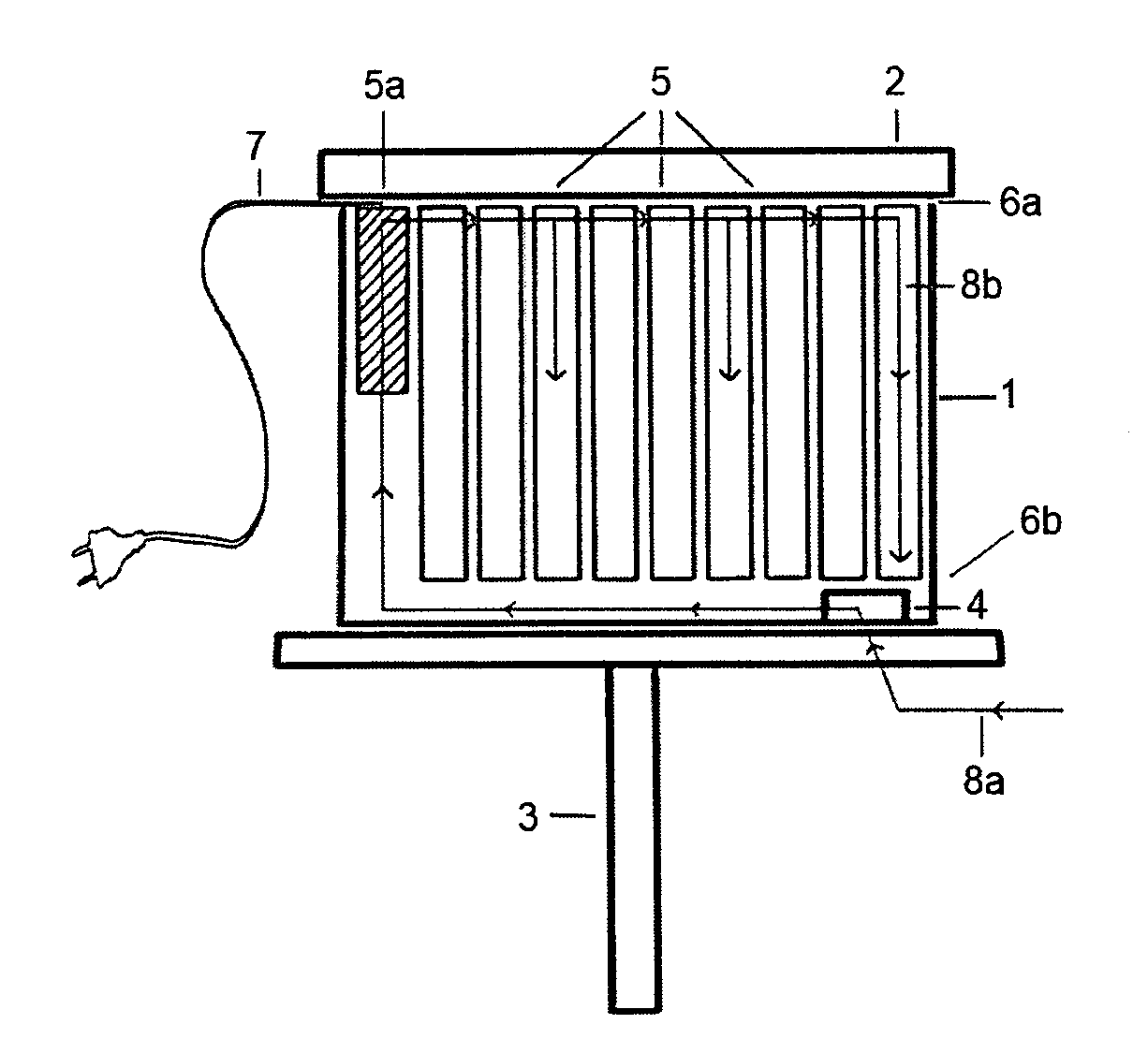
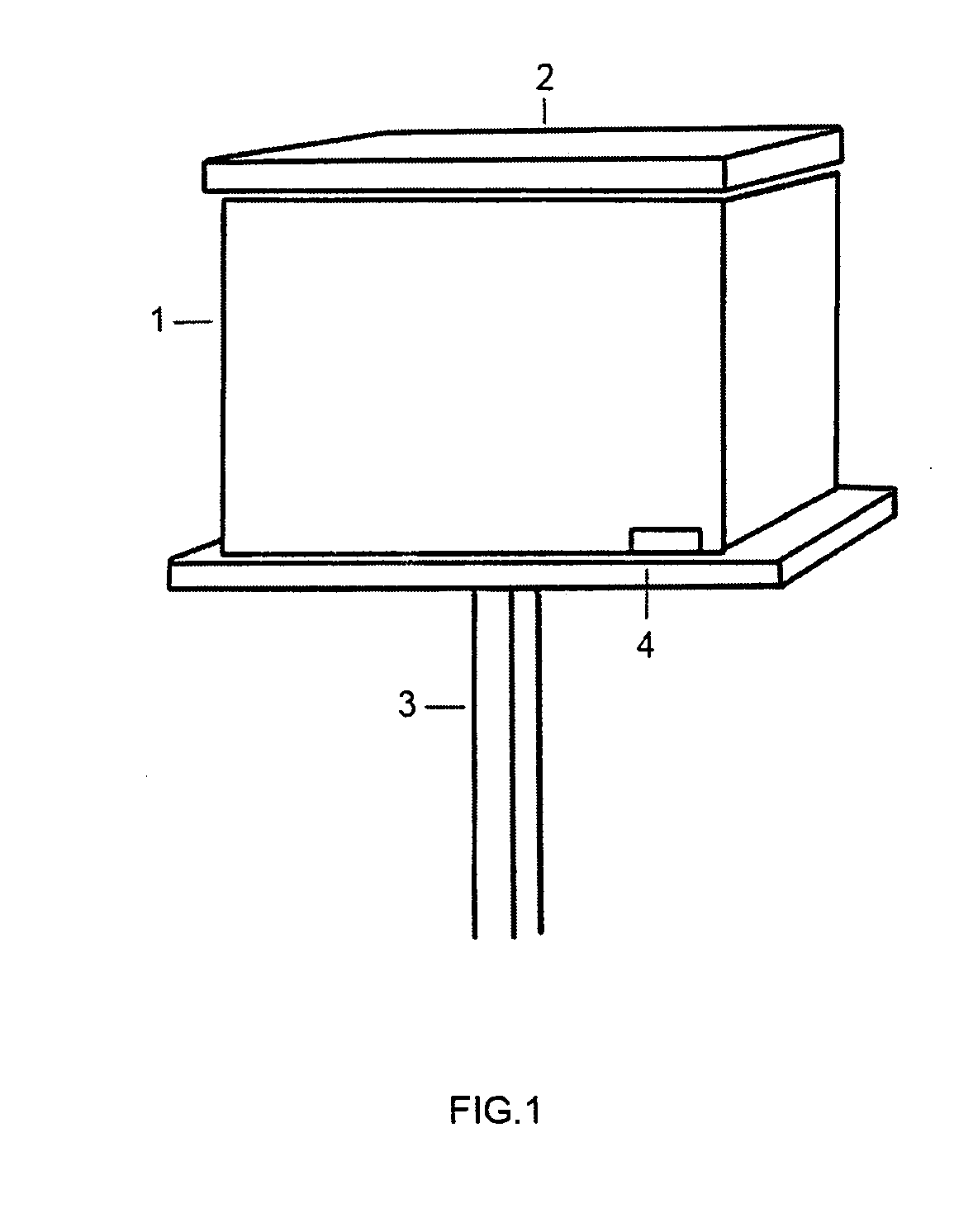
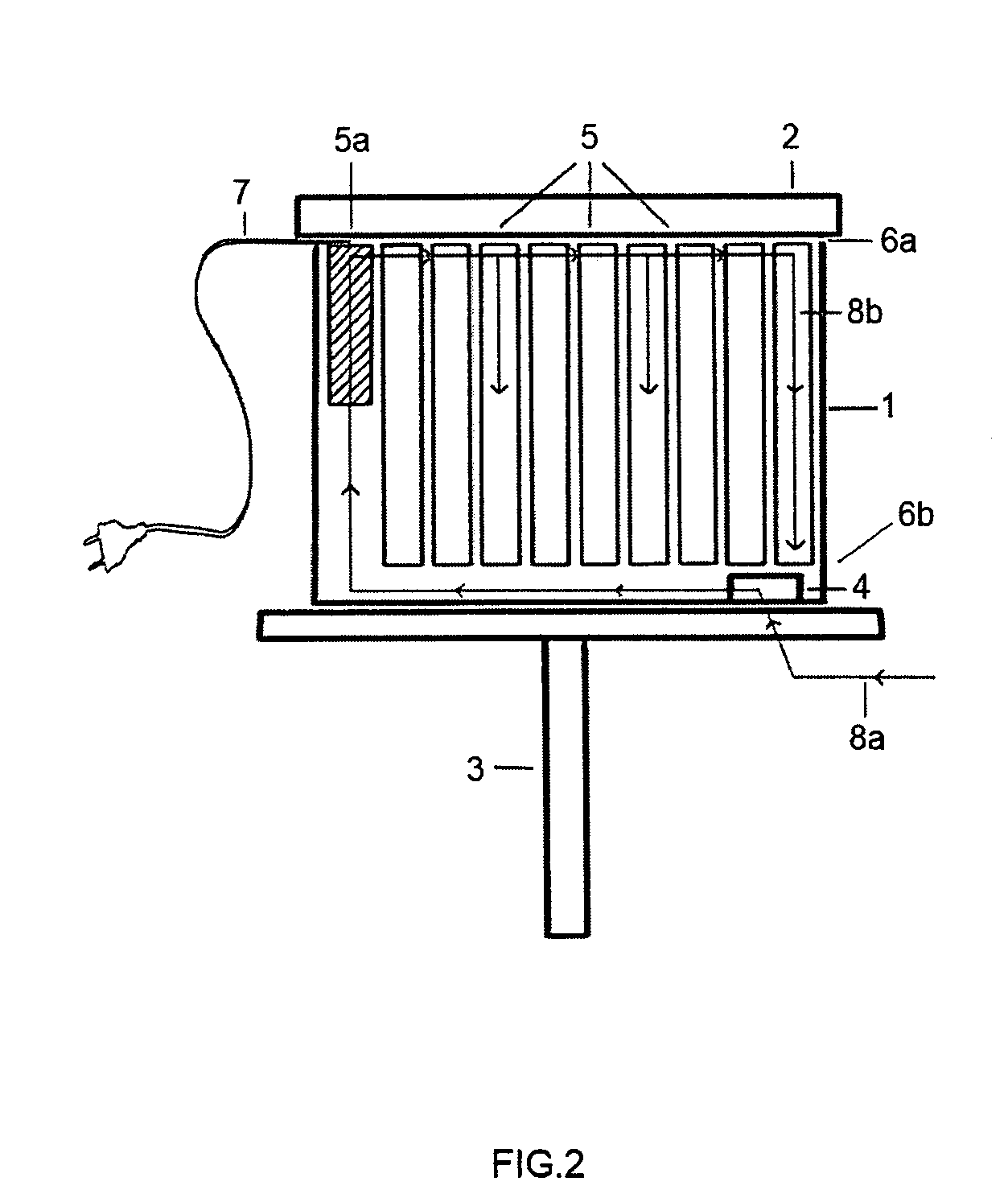
Device for hygienizing, warming, and dehumidifying a beehive
InactiveUS20080064298A1Increase productionReduce the amount of solutionBeehivesPower flowEngineering
A device 30 and associated process are described for hygienizing and warming beehives aiming at the improvement of the production of organic bee produce, said device comprising providing a bee box 1 containing frames 5 for honey production and bee housing, one frame 5a being left for inserting a ceramic block 11 provided with at least one row containing from 8 to 32 channels 11a and where the lower and upper ends of these channels 11a are opened towards the interior of the beehive, channels 11a being thermally insulated from the remaining of frame 5a with the aid of wings 15a, 15b and traversed by conducting filaments 14a, 14b connected to an energy source 20 through wire 7, whereby whenever electrical current traverses said filaments 14a, 14b the temperature inside said channels attains from 300-350° C. with the consequent heating of circulating air in the beehive by convection, the warmed air from the upper ends of said channels creating a negative pressure in the lower ends of same, whereby the outer colder air is sucked towards the interior of said channels, alternatively by using a fan or air pump, with the consequent extermination of the microorganisms present in the air as they cross warmed channels 11a.
Owner:JUNQUEIRA DE SOUZA MARCIO +2
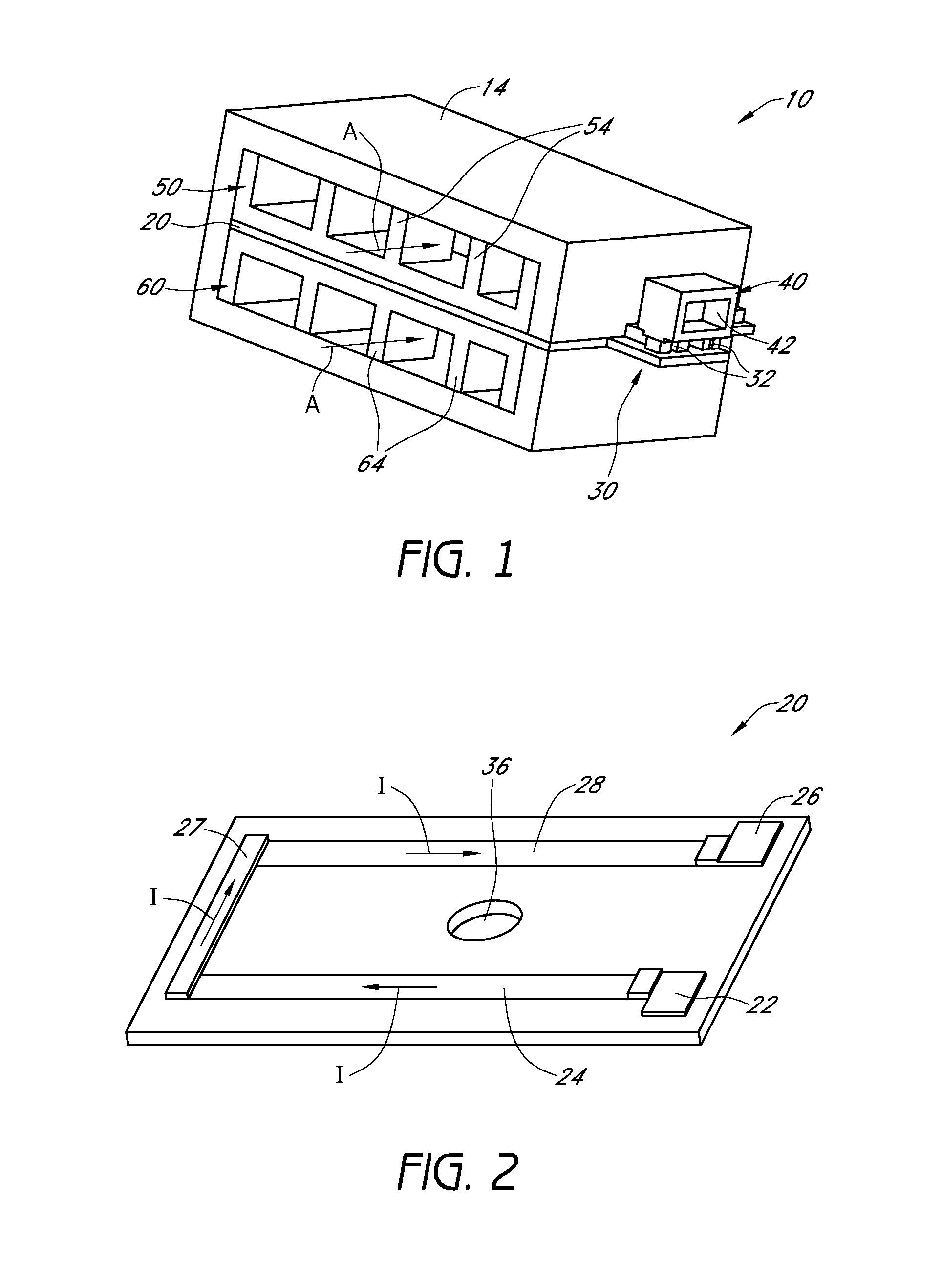
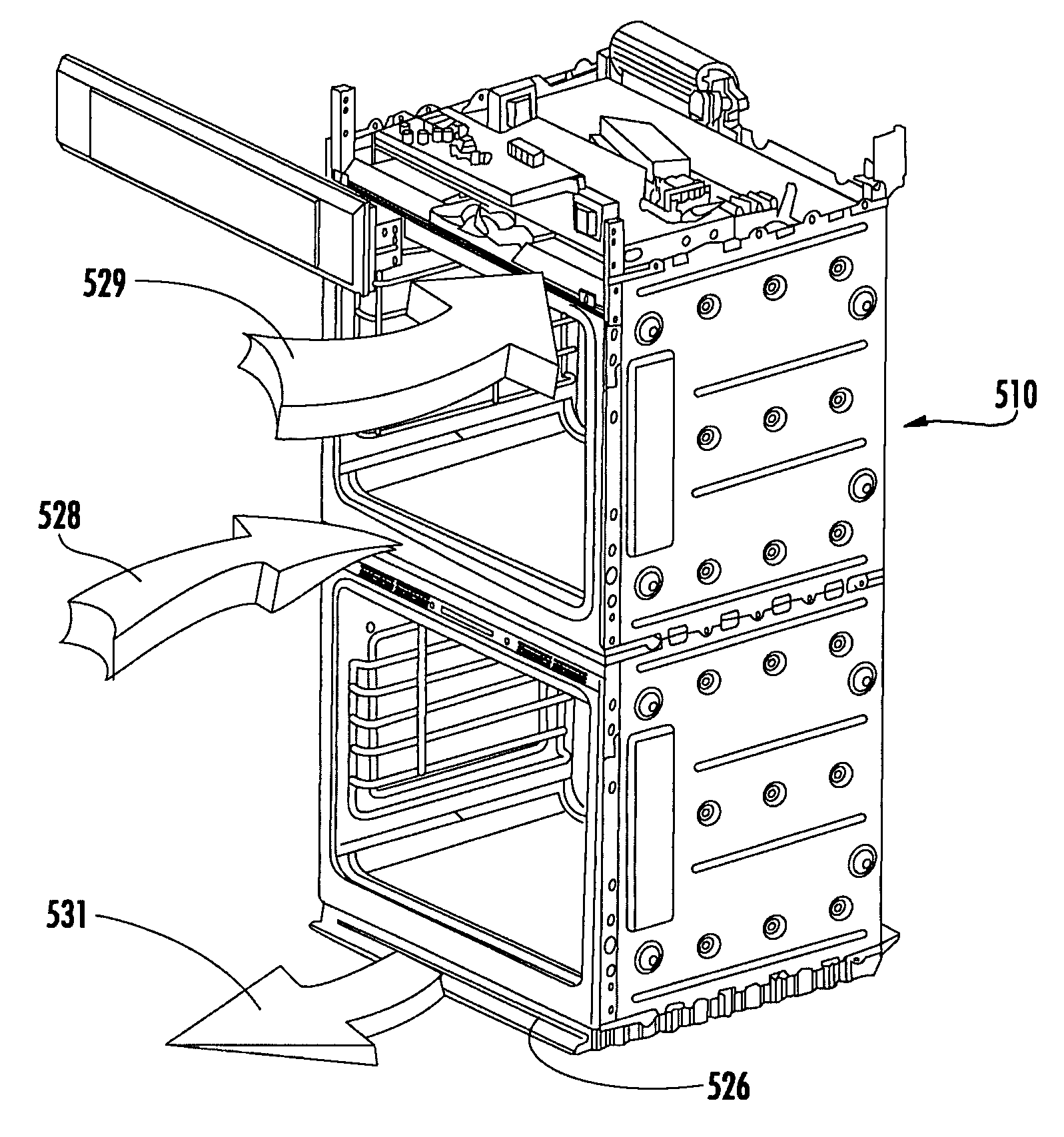
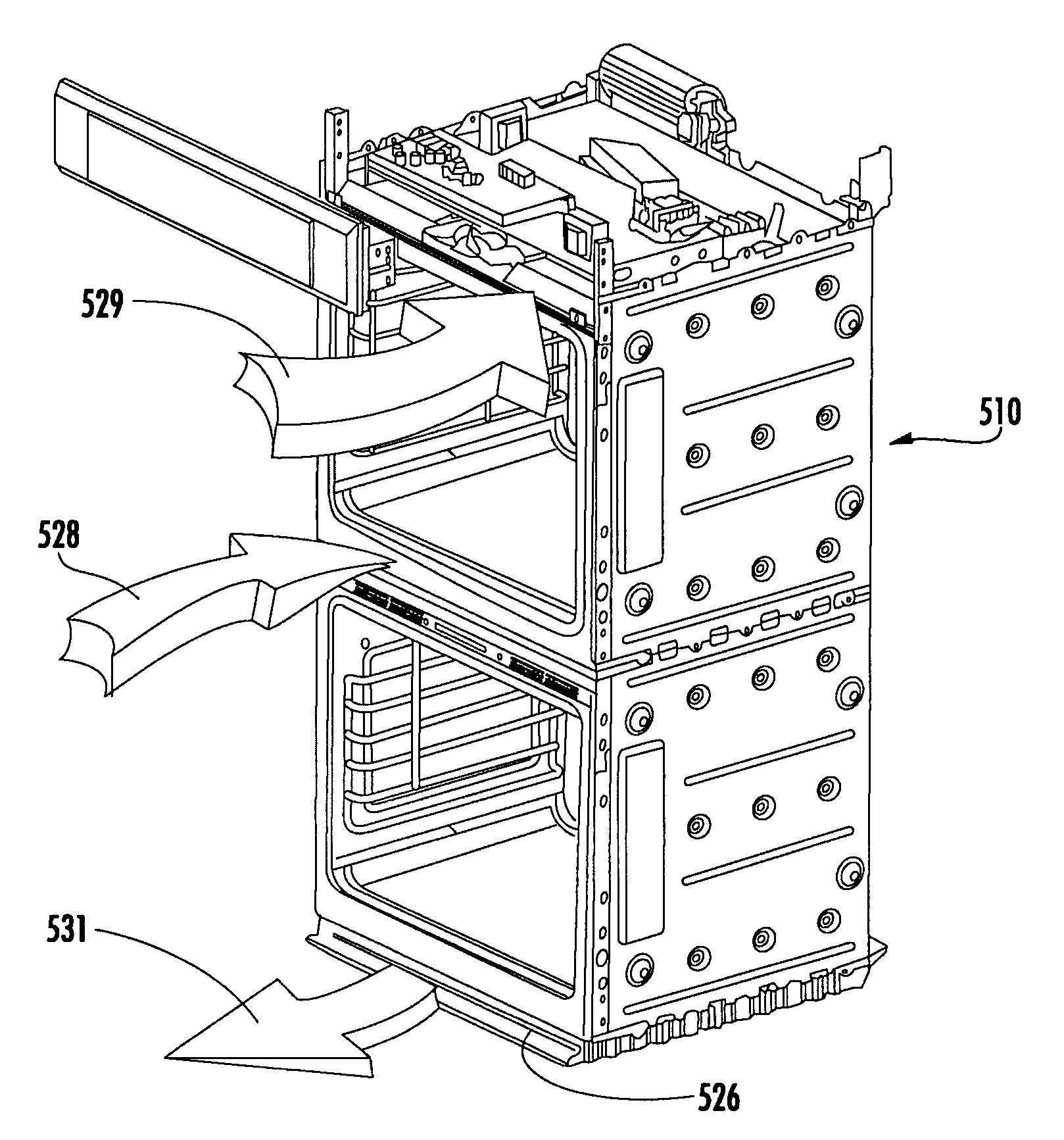
Cooking appliance having a latch plate shield for improved guidance of cooling air and exhaust air
Owner:BSH HOME APPLIANCES CORP
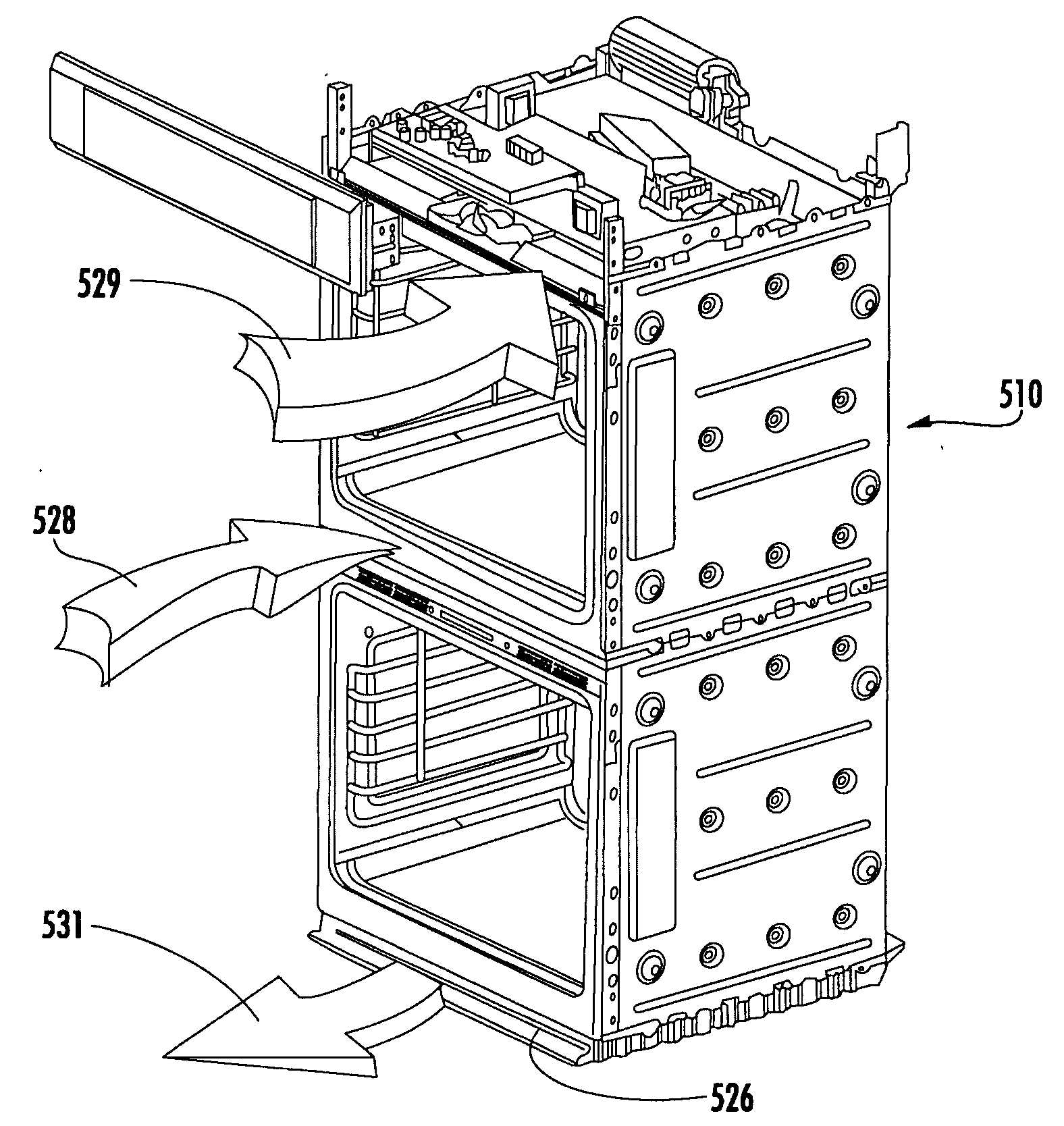
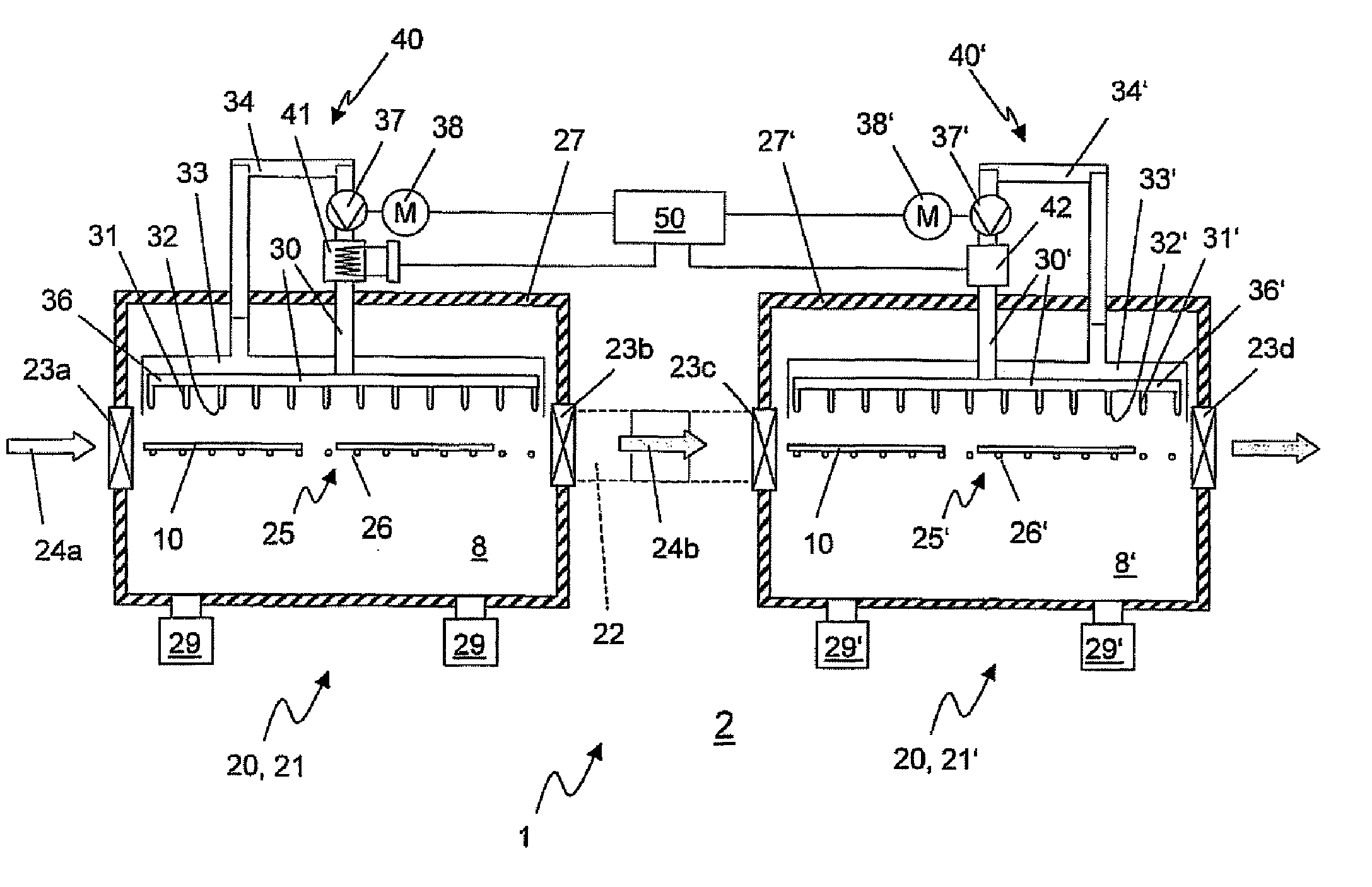
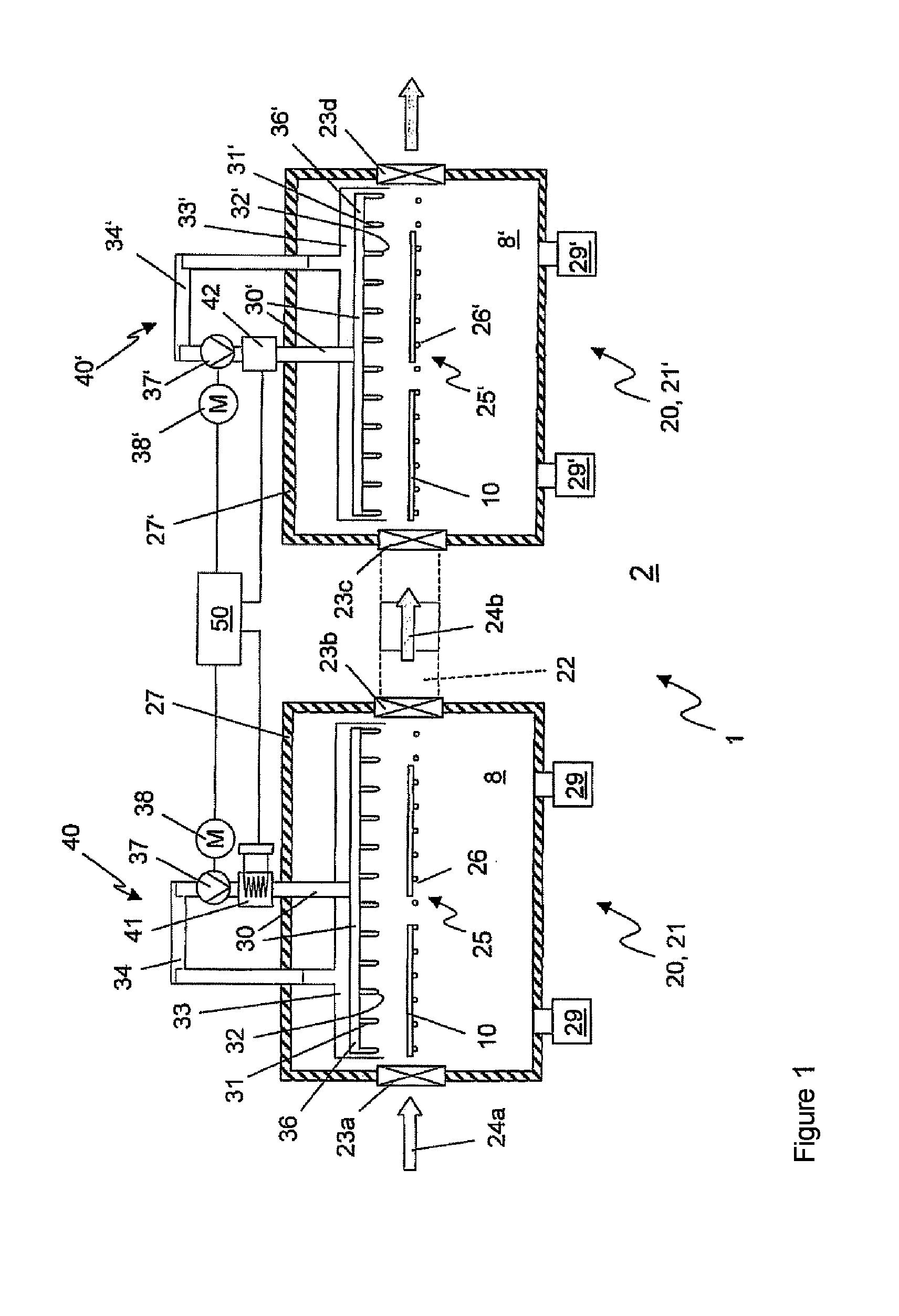
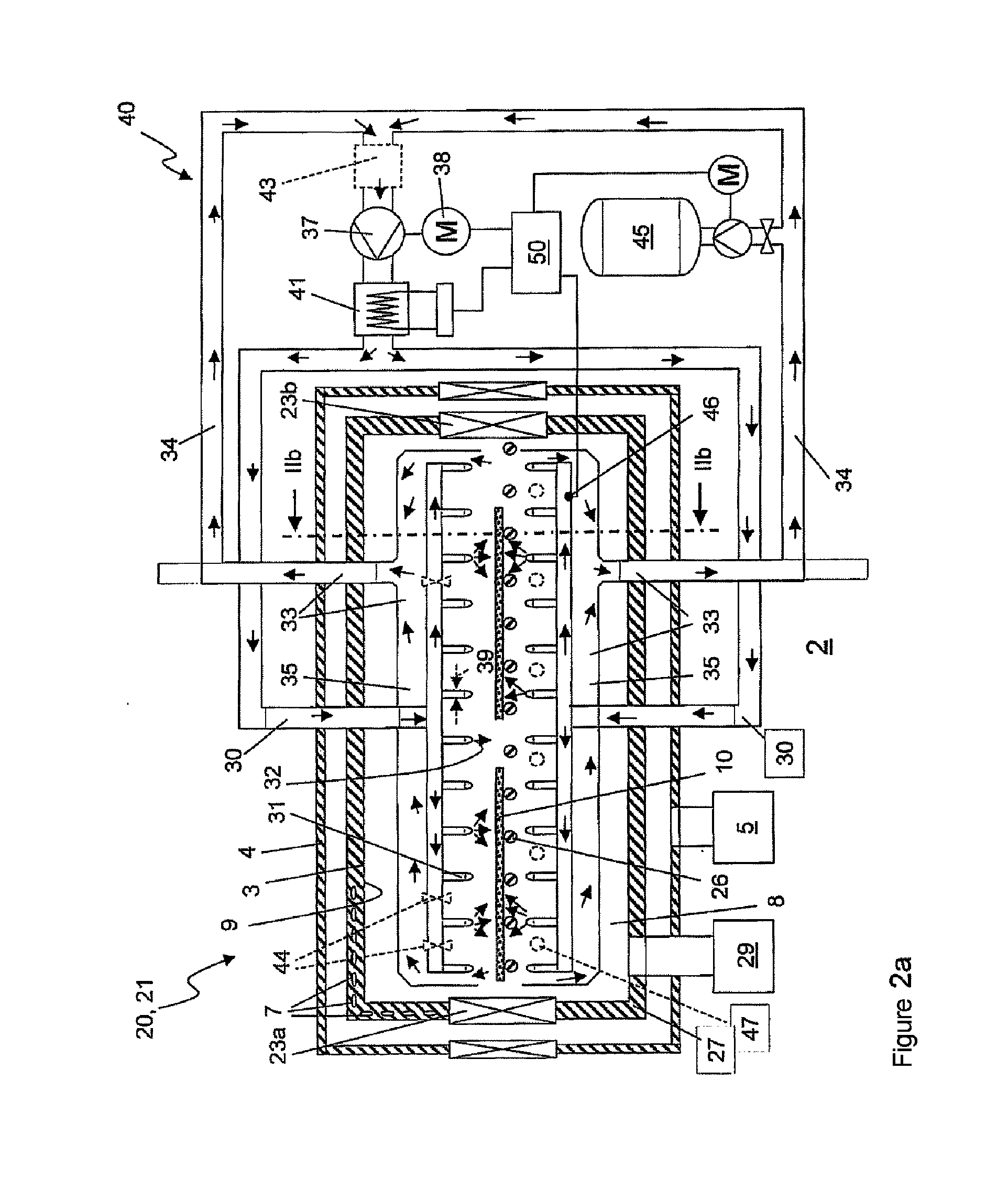
Double oven combination with an integrated cooling air and exhaust air flow arrangement
A double oven combination is configured to be “built-in” an area of a household—in other words, permanently secured relative to the household area and integrated with other elements of the household area to provide a consistent decorative appearance. The double oven combination comprises an upper oven and a lower oven each of which may be a convection or non-convection oven that cooks and heats food and other substances via radiant and convective heating, and a control panel. The double oven combination has an integrated cooling air and exhaust air flow arrangement for efficiently guiding exhaust air away from the upper oven and the lower oven while at the same time effectively flowing cooling air relative to the double oven combination to promote desired cooling of the double oven combination.
Owner:BSH HOME APPLIANCES CORP
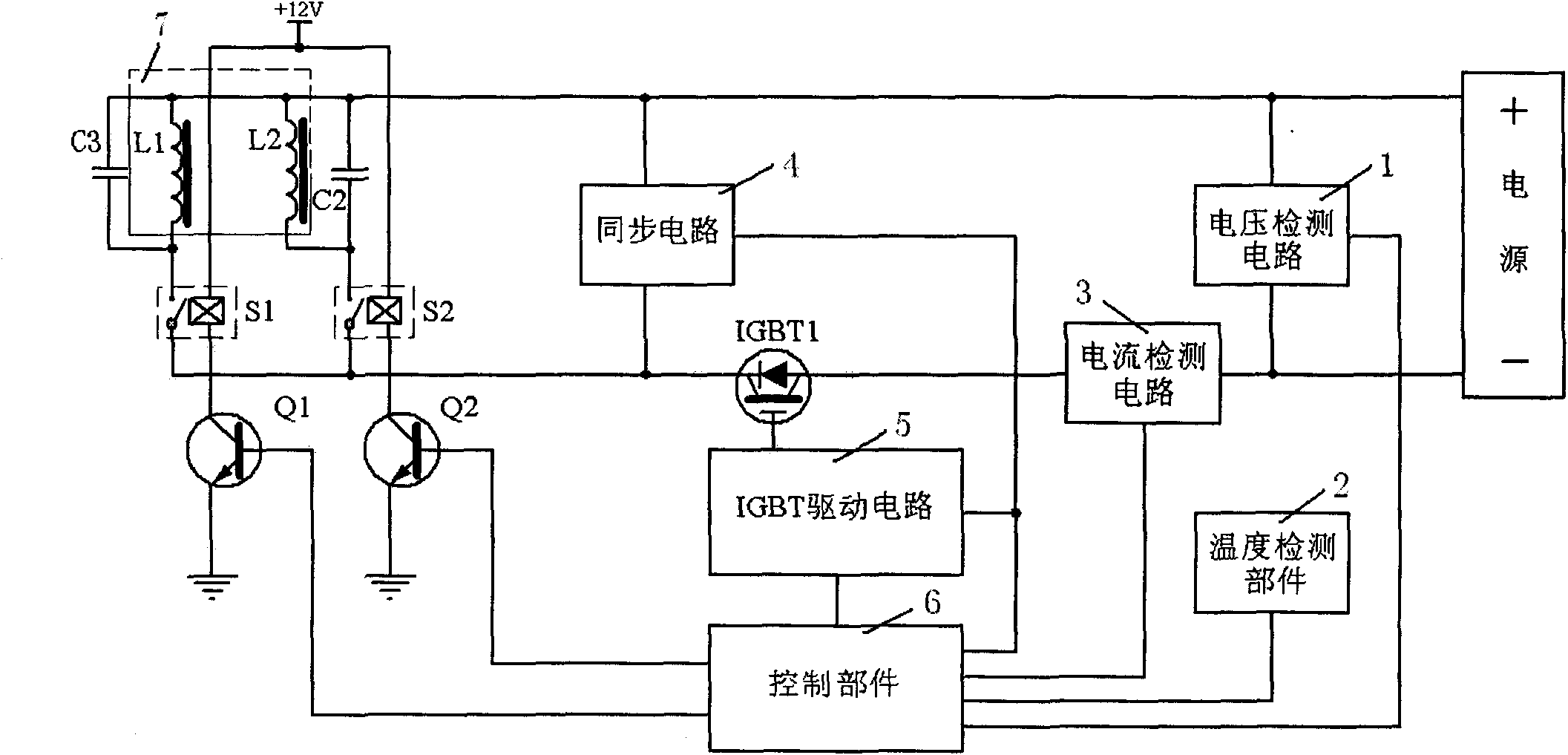
Convection heating control method of electromagnetic oven and heating control device
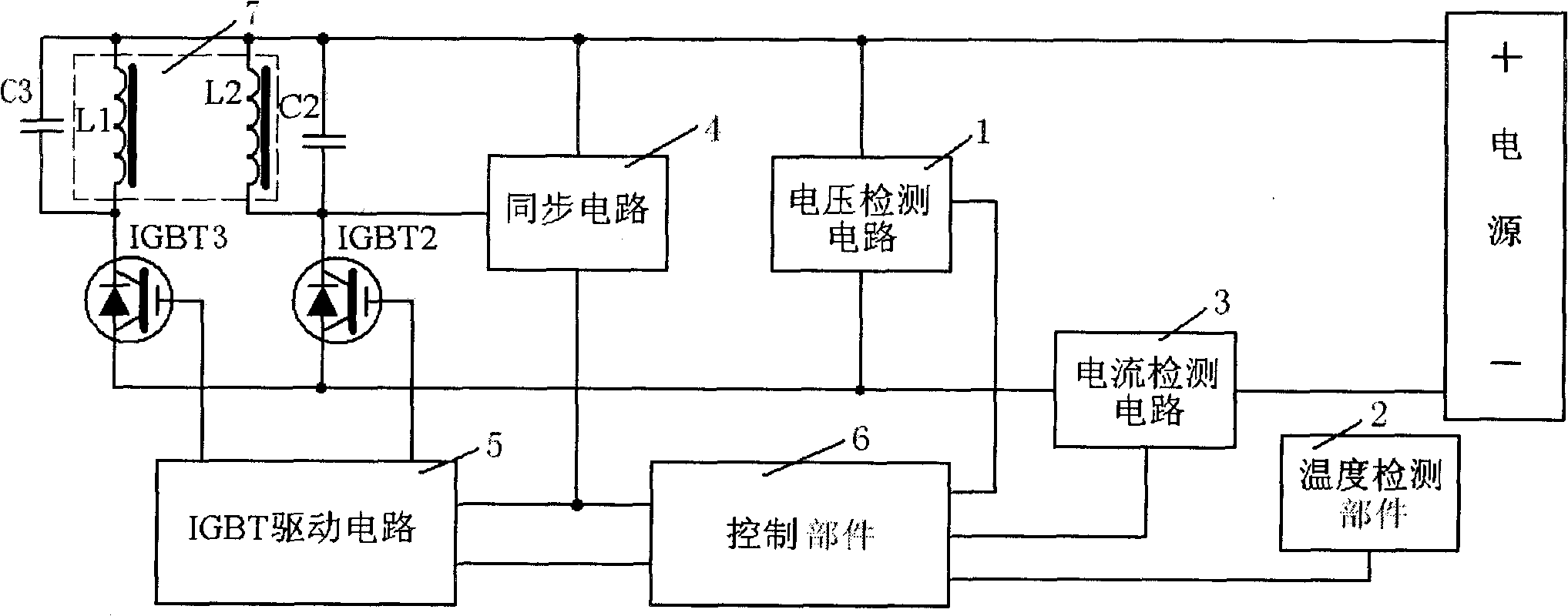
InactiveCN101808433AHeating evenlyPromote tumblingEfficient regulation technologiesInduction heating controlHeat controlEngineering
The invention discloses a convection heating control method of an electromagnetic oven, which is realized on the basis of a heating control device. The heating control device comprises a temperature detecting member, a heating member and a control member, wherein the heating member comprises at least two independent control electromagnetic coils, and the control member comprises a main controller, a timer and a presetting memory. The convection heating control method includes a heating-up stage A and a convection heating stage B. In addition, the invention aims to provide the heating control device for realizing the convection heating control method of the electromagnetic oven. Compared with the prior art, the invention controls the heating power proportioning of electromagnetic trays to drive a plurality of electromagnetic coils to alternatively and circularly heat a pot through distinguishing the volumes of heated foods and controls the heating coils in different positions to alternatively heat to enable the heated points of the pot to be changed along with the heating coils so that liquid in the pot is promoted to boil and convect, the foods are heated without blind angles and are uniformly heated, the nutriments of the foods can also be fully mixed, and the foods can be fully seasoned.
Owner:JOYOUNG CO LTD
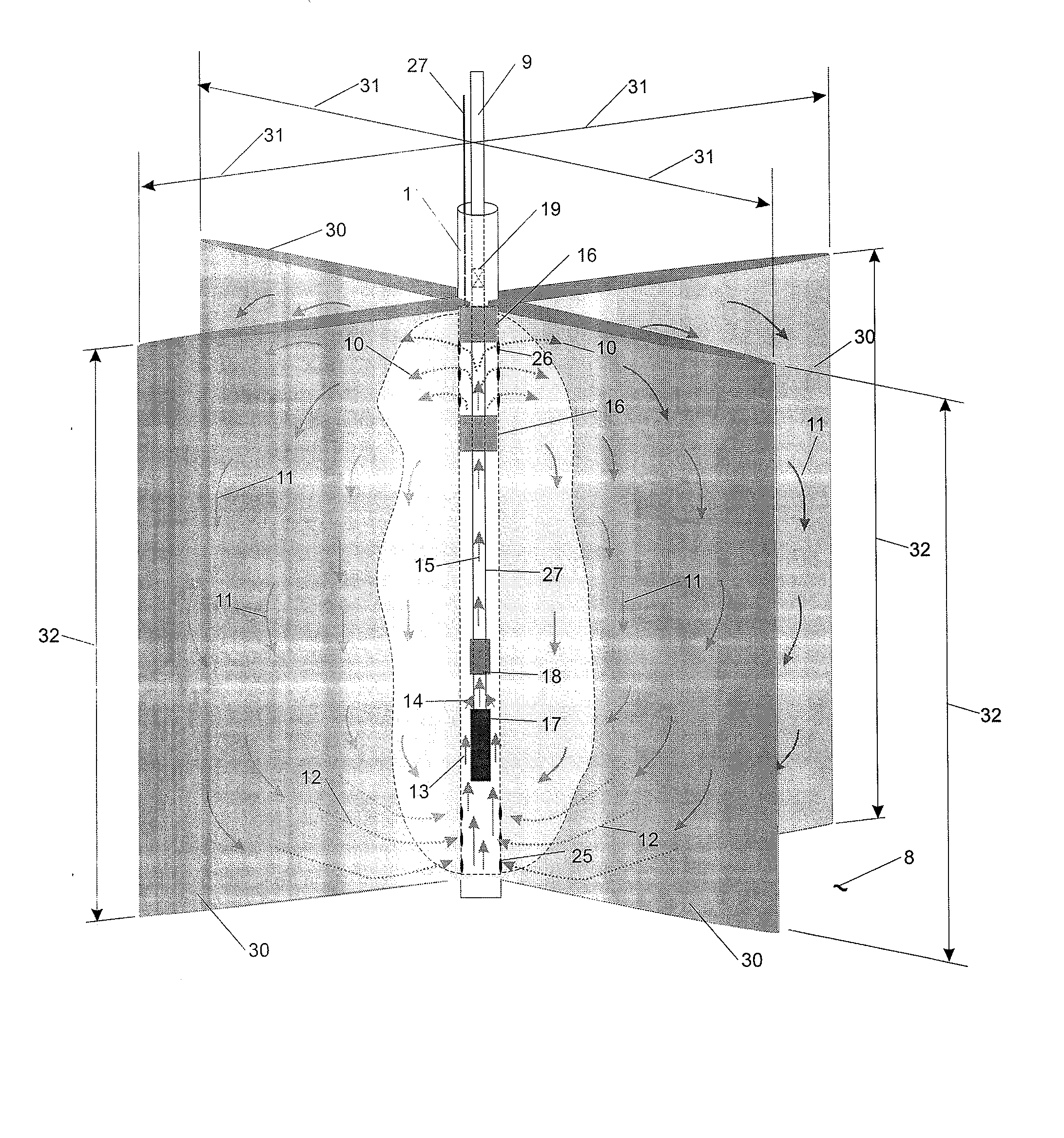
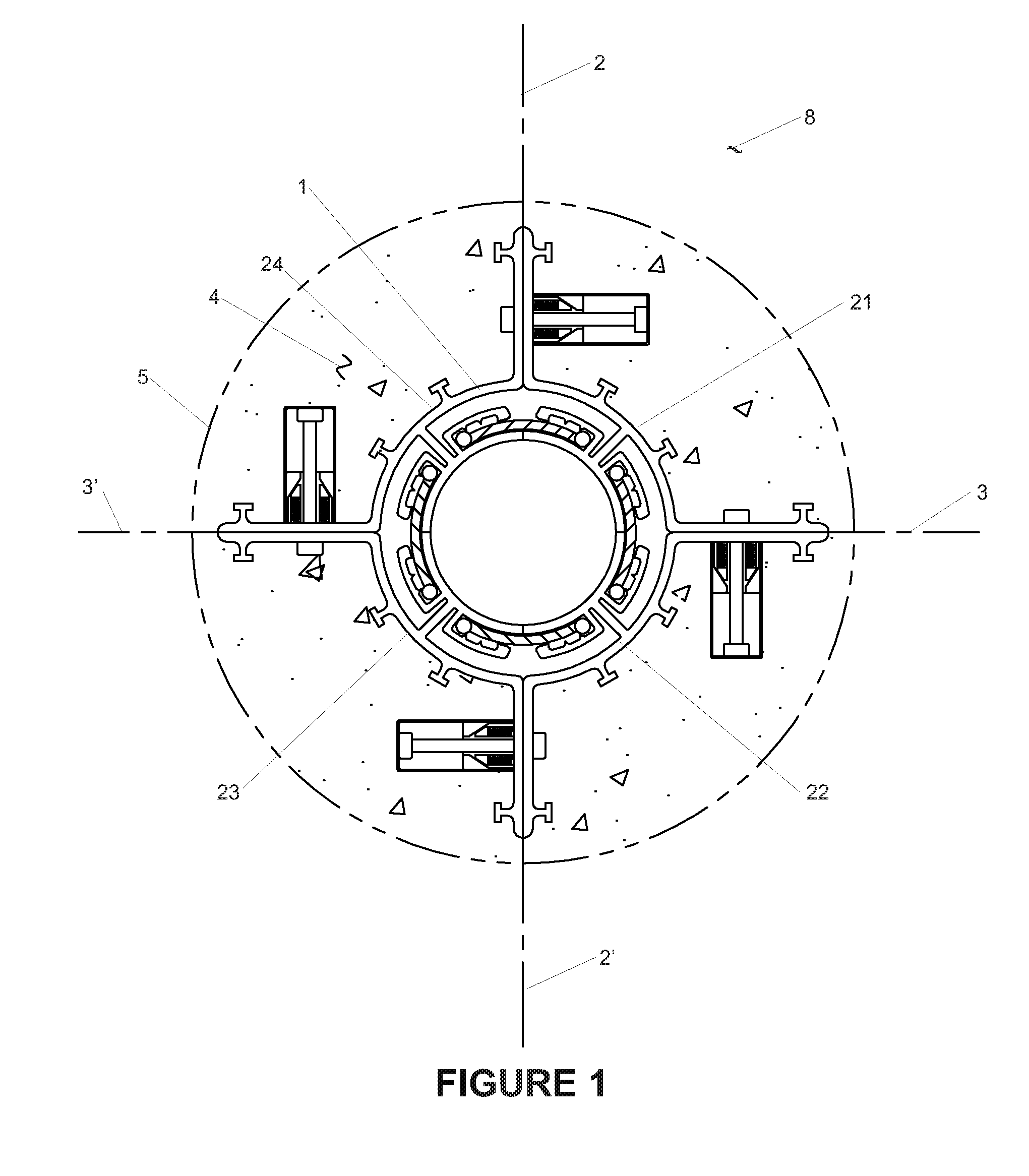
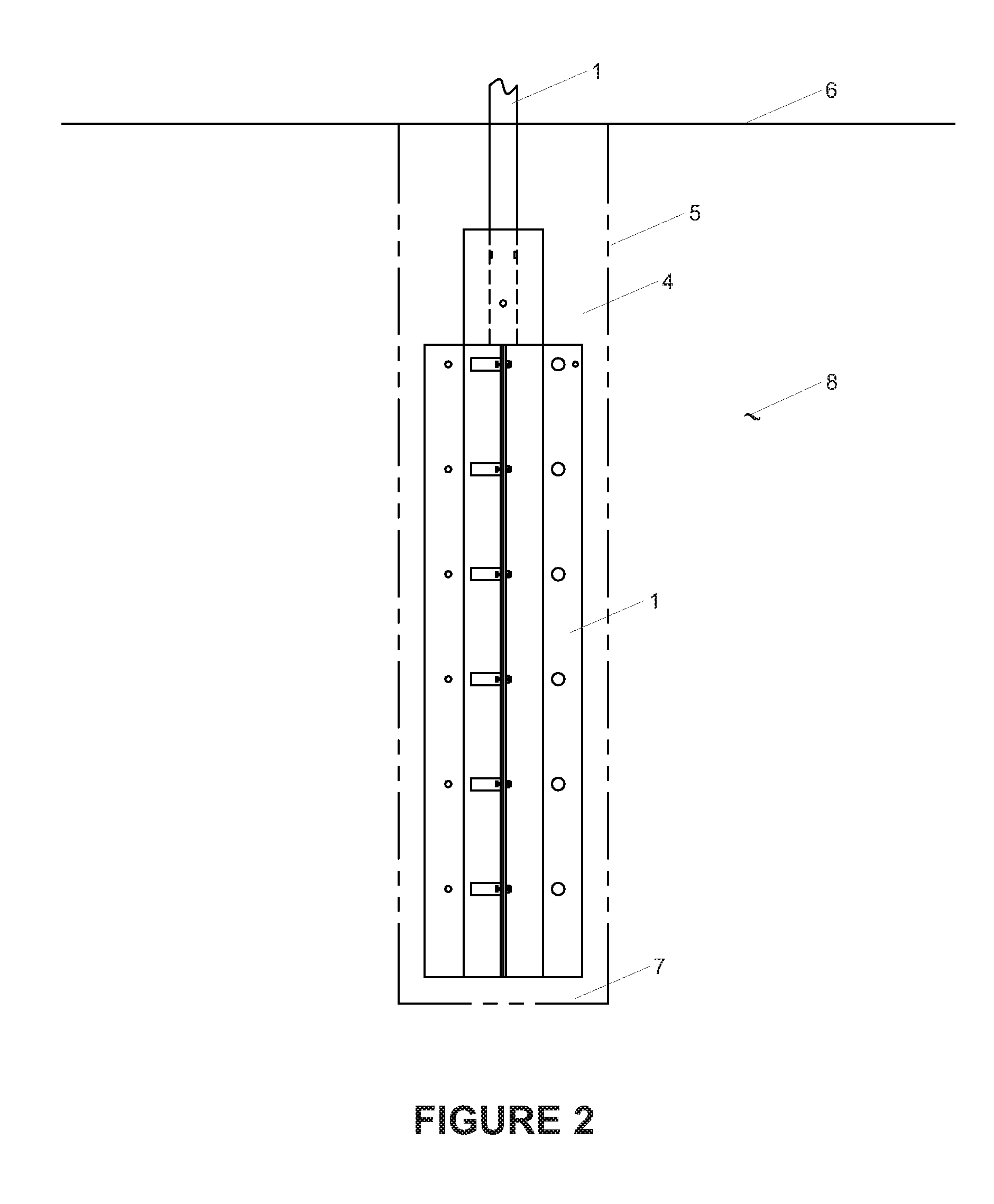
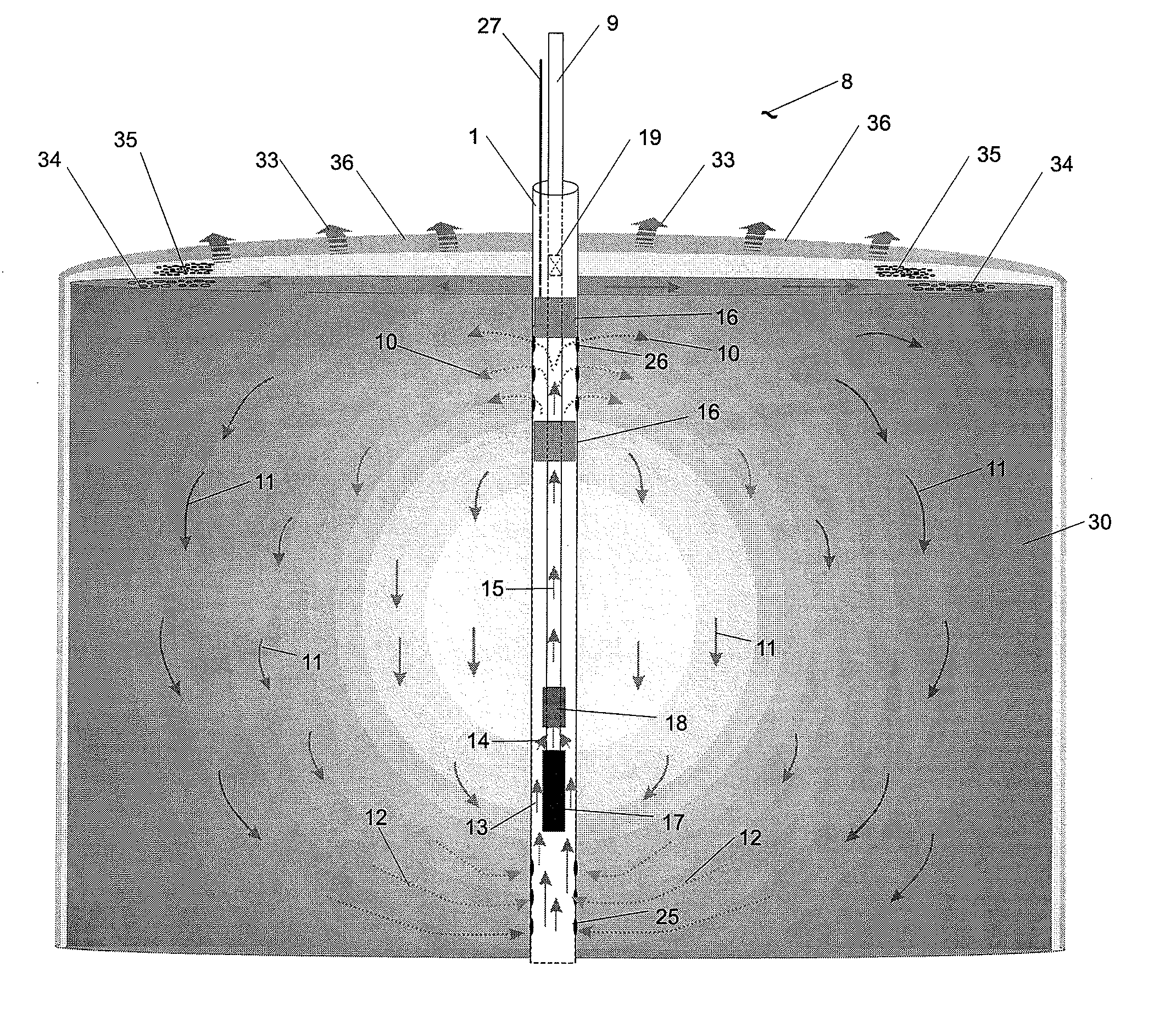
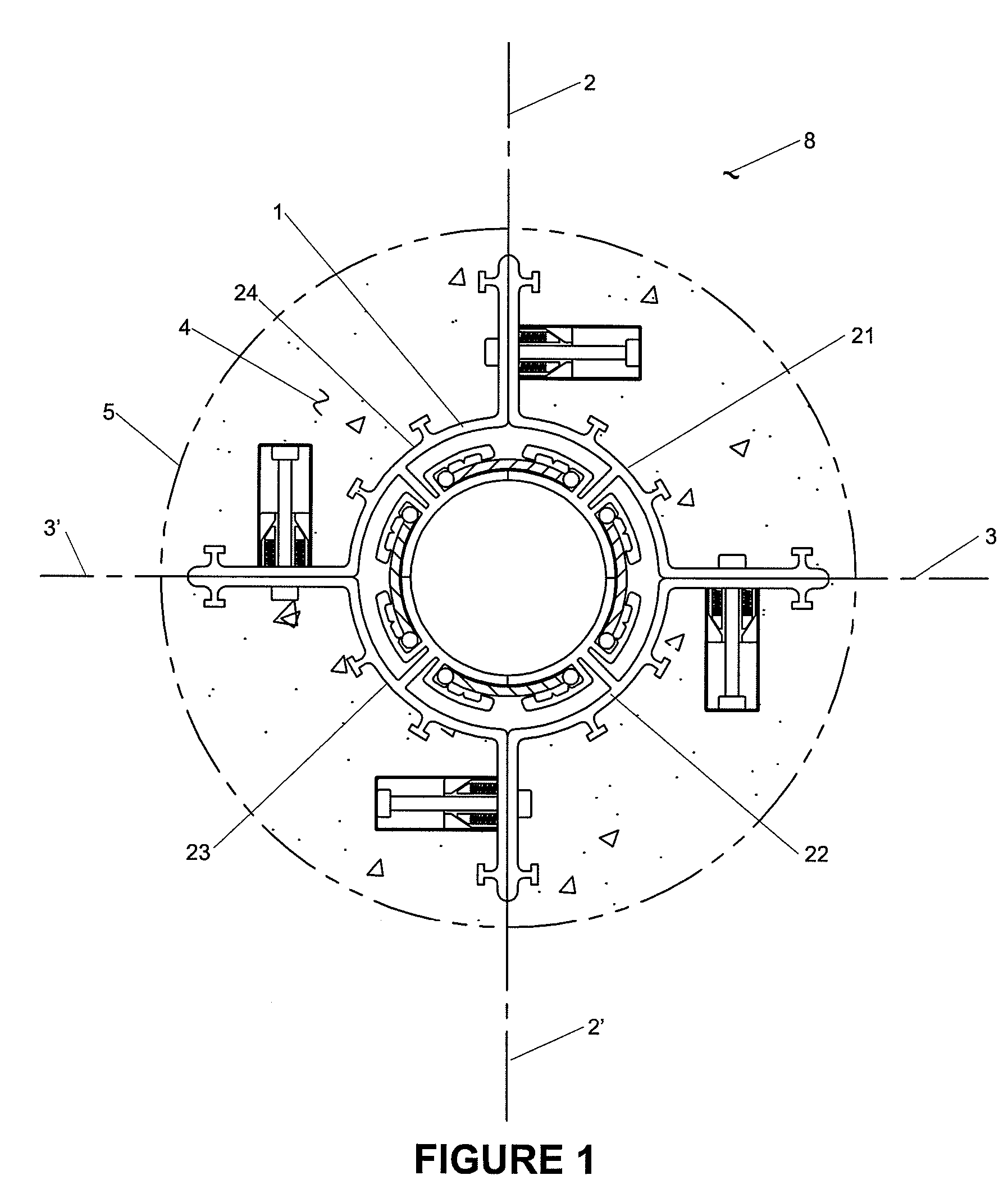
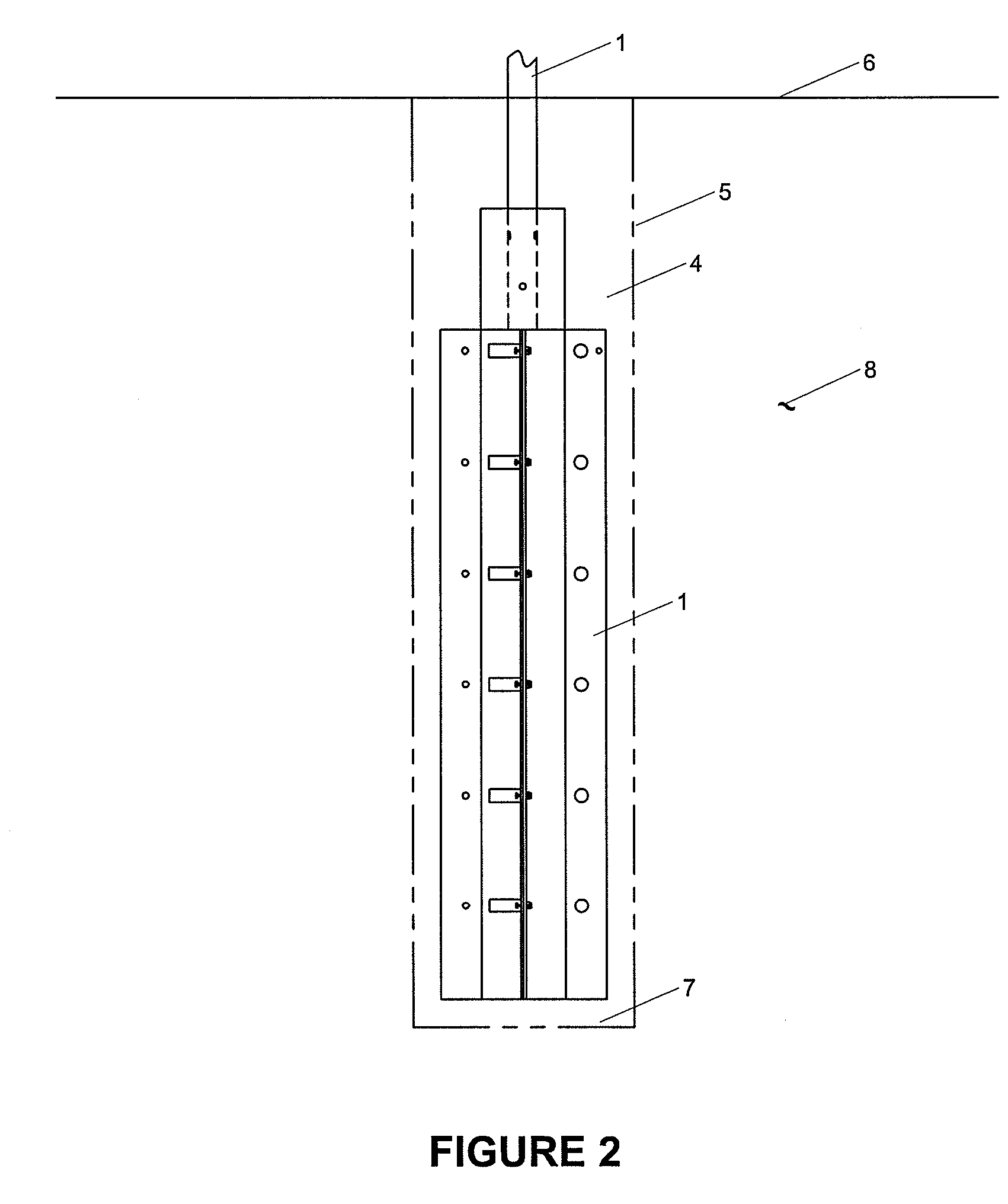
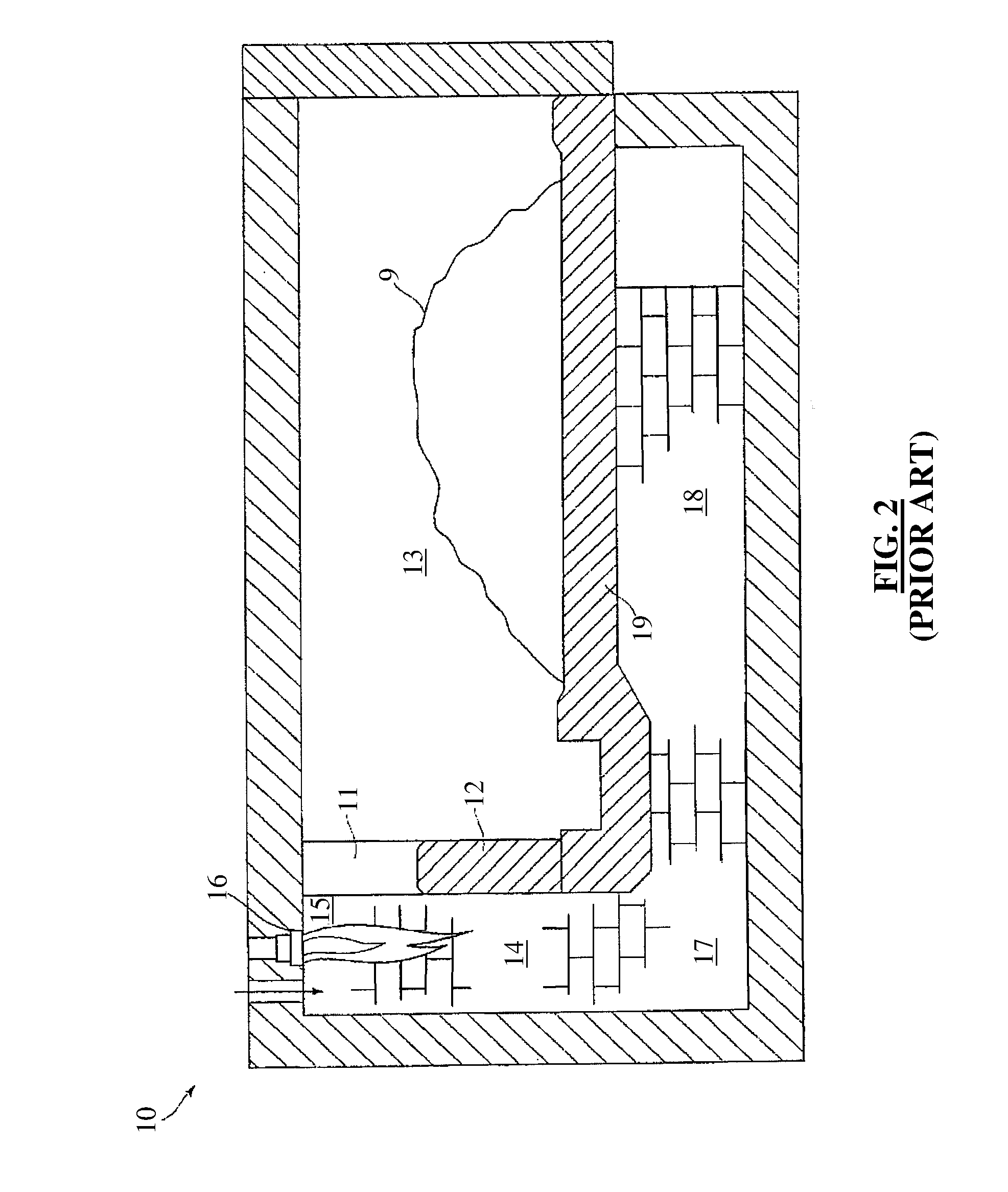
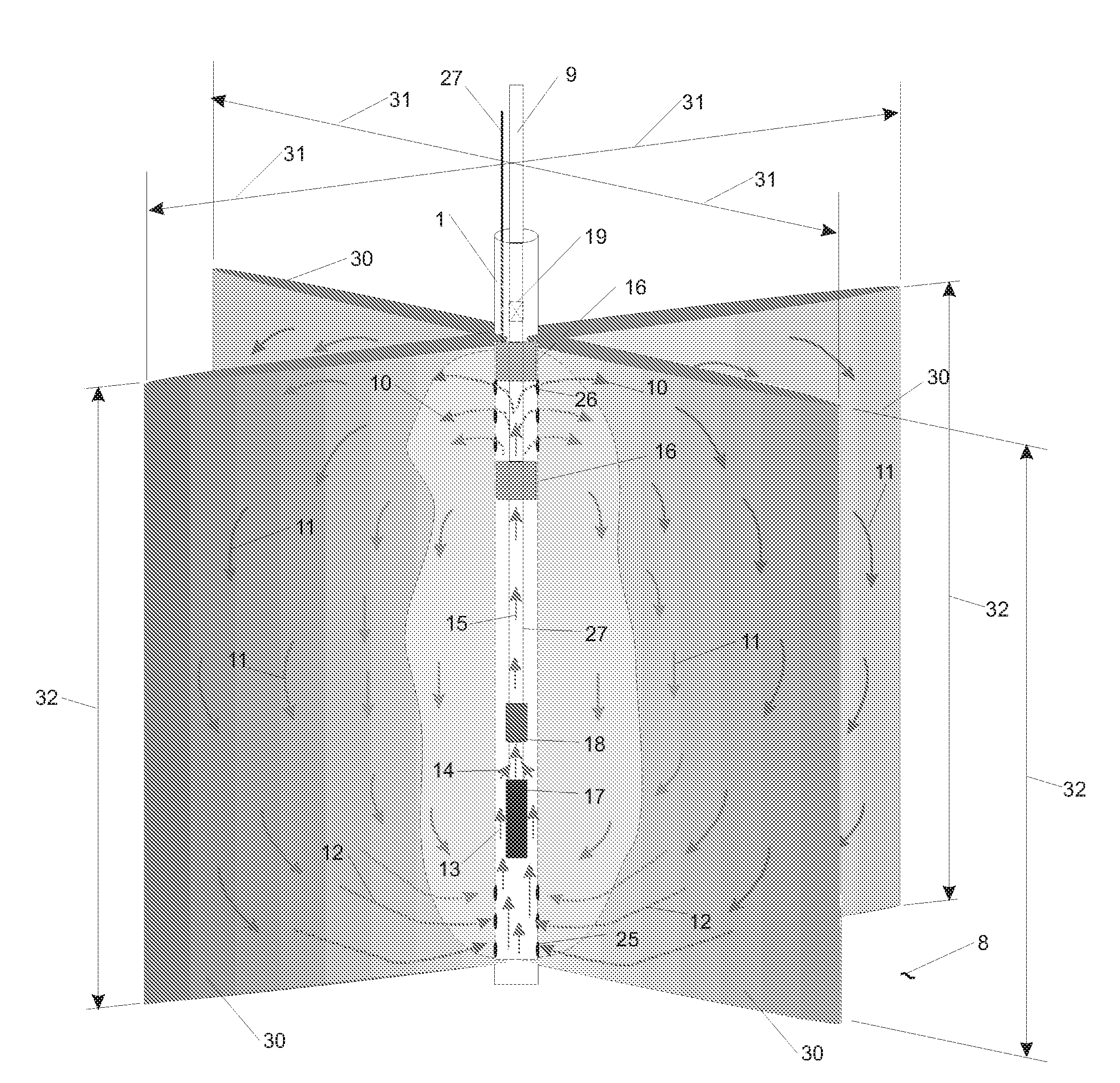
Enhanced hydrocarbon recovery by convective heating of oil sand formations
InactiveUS20070199710A1Well mixedMinimizing inflowInsulationFluid removalDiluentHydraulic fracturing
The present invention involves a method and apparatus for enhanced recovery of petroleum fluids from the subsurface by convective heating of the oil sand formation and the heavy oil and bitumen in situ by a downhole electric heater. Multiple propped vertical hydraulic fractures are constructed from the well bore into the oil sand formation and filled with a diluent. The heater and downhole pump force thermal convective flow of the heated diluent to flow upward and outward into the propped fractures and circulating back down and back towards the well bore heating the oil sands and in situ bitumen on the vertical faces of the propped fractures. The diluent now mixed with produced products from the oil sand re-enters the bottom of the well bore and passes over the heater element and is reheated to continue to flow in the convective cell. Thus the heating and diluting of the in place bitumen occurs predominantly circumferentially, i.e. orthogonal to the propped fracture, by diffusion from the propped vertical fracture faces progressing at a nearly uniform rate into the oil sand deposit. In situ hydrogenation and thermal cracking of the in place bitumen can provide a higher grade produced product. The heated low viscosity oil is produced through the well bore at the completion of the active heating phase of the process.
Owner:GEOSIERRA
Convective heating system for industrial applications
ActiveUS20070145038A1Deformation MinimizationMinimize gas flowAir heatersBathing devicesProcess engineeringSuperheated steam
A coil-in-coil electric heating assembly for industrial applications heats any gas through an annular space between the coils to very high temperatures. Gas is introduced into the annular space through one open end of a tubular enclosure and leaves through an opposite end after being significantly heated. Coils may be made from several heating element materials and may be wound in the same direction or opposite direction. The opposite winding direction often gives a higher temperature of the exit gas. Temperatures even as high as 1500° C. in the exit gas have been recorded. The heating system may be utilized to generate superheated steam for industrial applications even in a recirculating manner.
Owner:MHI HEALTH DEVICES
Enhanced Hydrocarbon Recovery By Convective Heating of Oil Sand Formations
The present invention involves a method and apparatus for enhanced recovery of petroleum fluids from the subsurface by convective heating of the oil sand formation and the heavy oil and bitumen in situ by a downhole electric heater. Multiple propped vertical hydraulic fractures are constructed from the well bore into the oil sand formation and filled with a diluent. The heater and downhole pump force thermal convective flow of the heated diluent to flow upward and outward into the propped fractures and circulating back down and back towards the well bore heating the oil sands and in situ bitumen on the vertical faces of the propped fractures. The diluent now mixed with produced products from the oil sand re-enters the bottom of the well bore and passes over the heater element and is reheated to continue to flow in the convective cell. Thus the heating and diluting of the in place bitumen occurs predominantly circumferentially, i.e. orthogonal to the propped fracture, by diffusion from the propped vertical fracture faces progressing at a nearly uniform rate into the oil sand deposit. In situ hydrogenation and thermal cracking of the in place bitumen can provide a higher grade produced product. The heated low viscosity oil is produced through the well bore at the completion of the active heating phase of the process.
Owner:GEOSIERRA
Enhanced hydrocarbon recovery by convective heating of oil sand formations
The present invention involves a method and apparatus for enhanced recovery of petroleum fluids from the subsurface by convective heating of the oil sand formation and the heavy oil and bitumen in situ by a downhole electric heater. Multiple propped vertical hydraulic fractures are constructed from the well bore into the oil sand formation and filled with a diluent. The heater and downhole pump force thermal convective flow of the heated diluent to flow upward and outward into the propped fractures and circulating back down and back towards the well bore heating the oil sands and in situ bitumen on the vertical faces of the propped fractures. The diluent now mixed with produced products from the oil sand re-enters the bottom of the well bore and passes over the heater element and is reheated to continue to flow in the convective cell. Thus the heating and diluting of the in place bitumen occurs predominantly circumferentially, i.e. orthogonal to the propped fracture, by diffusion from the propped vertical fracture faces progressing at a nearly uniform rate into the oil sand deposit. In situ hydrogenation and thermal cracking of the in place bitumen can provide a higher grade produced product. The heated low viscosity oil is produced through the well bore at the completion of the active heating phase of the process.
Owner:GEOSIERRA
Double oven combination with an integrated cooling air and exhaust air flow arrangement
ActiveUS20080185373A1Ensure efficient flowShow cabinetsDomestic stoves or rangesConvective heatingReflow oven
A double oven combination is configured to be “built-in” an area of a household—in other words, permanently secured relative to the household area and integrated with other elements of the household area to provide a consistent decorative appearance. The double oven combination comprises an upper oven and a lower oven each of which may be a convection or non-convection oven that cooks and heats food and other substances via radiant and convective heating, and a control panel. The double oven combination has an integrated cooling air and exhaust air flow arrangement for efficiently guiding exhaust air away from the upper oven and the lower oven while at the same time effectively flowing cooling air relative to the double oven combination to promote desired cooling of the double oven combination.
Owner:BSH HOME APPLIANCES CORP
Heating apparatus with removable container, such as for foodstuffs, and features for moderating heat flux to the removable container
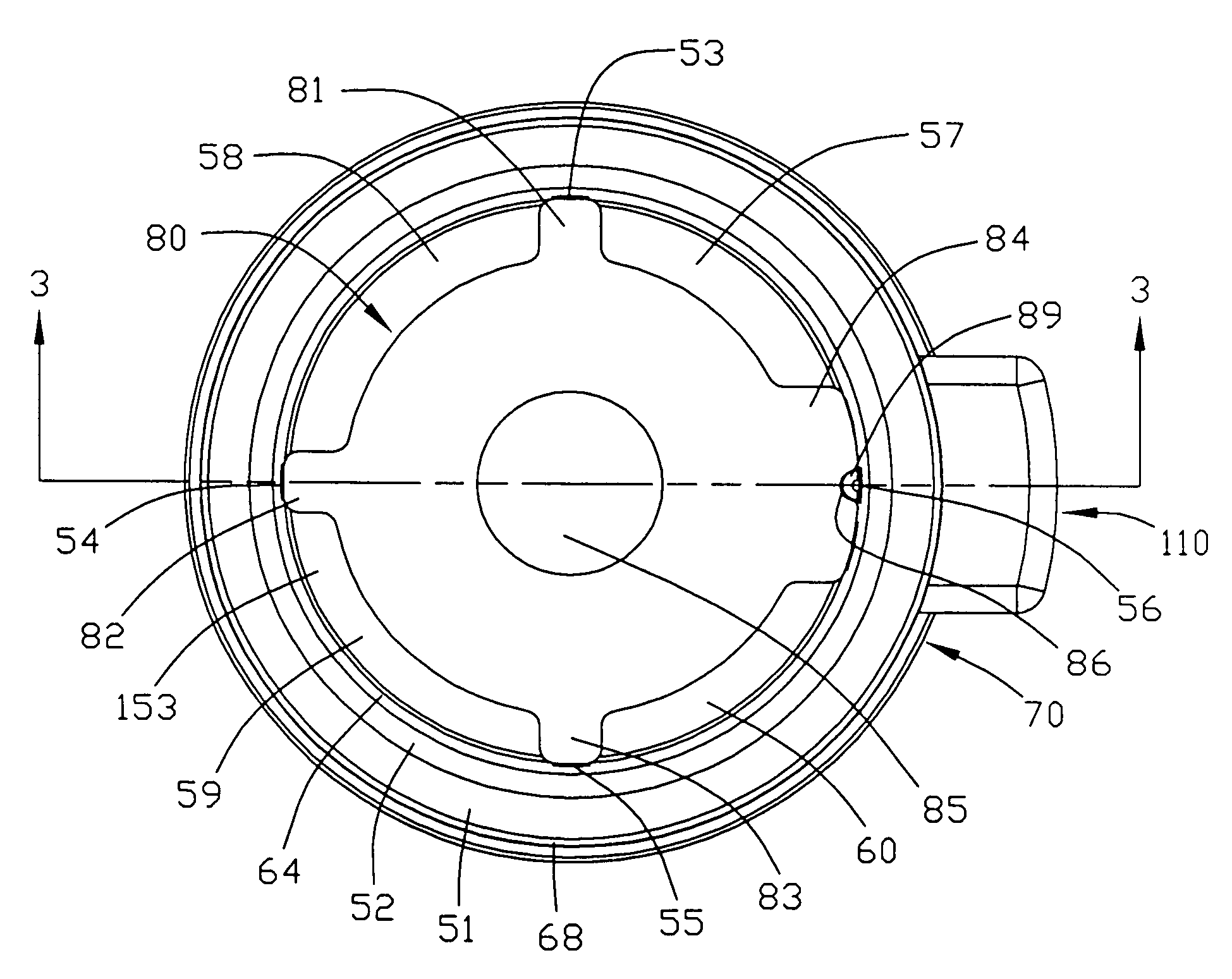
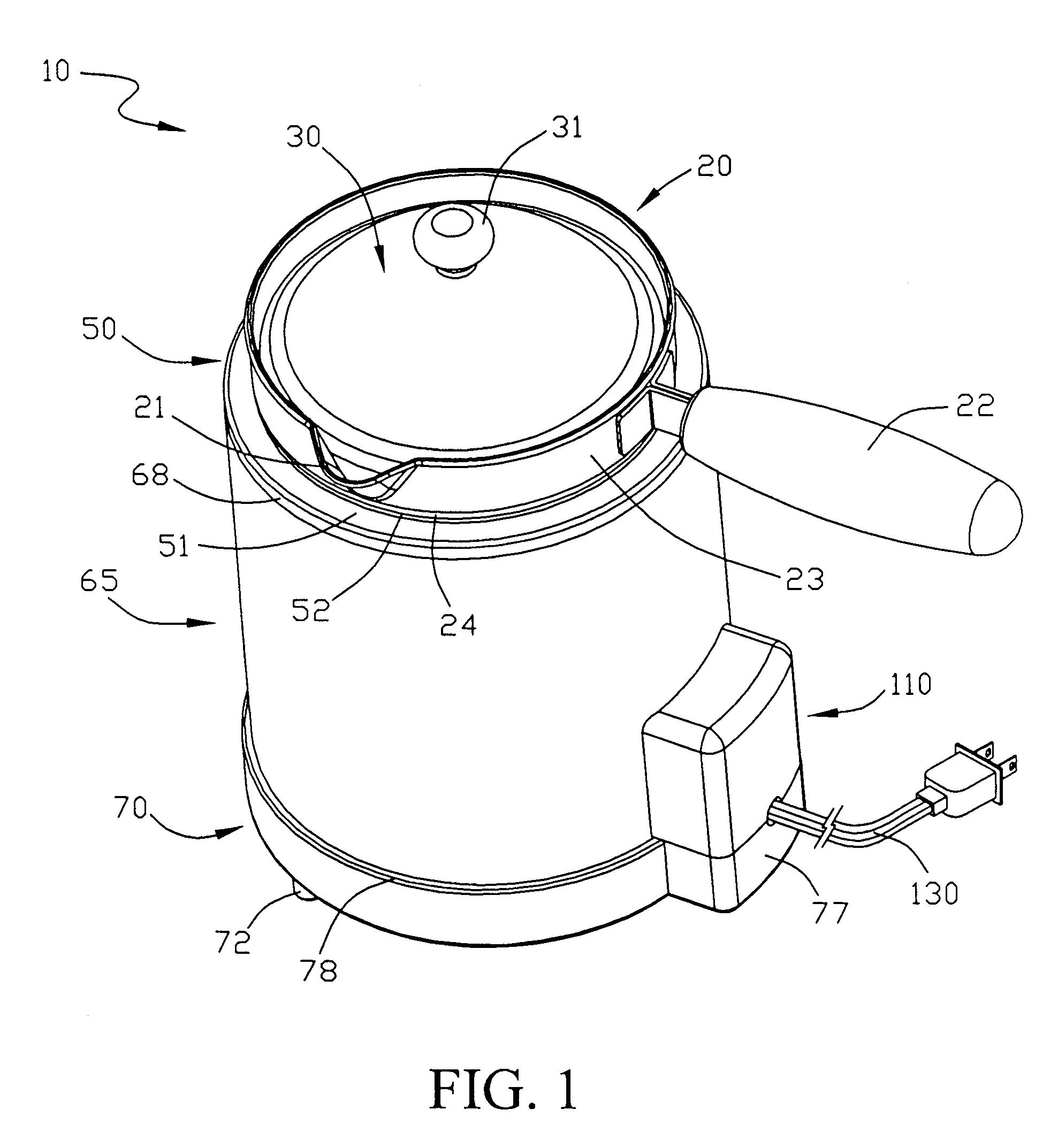
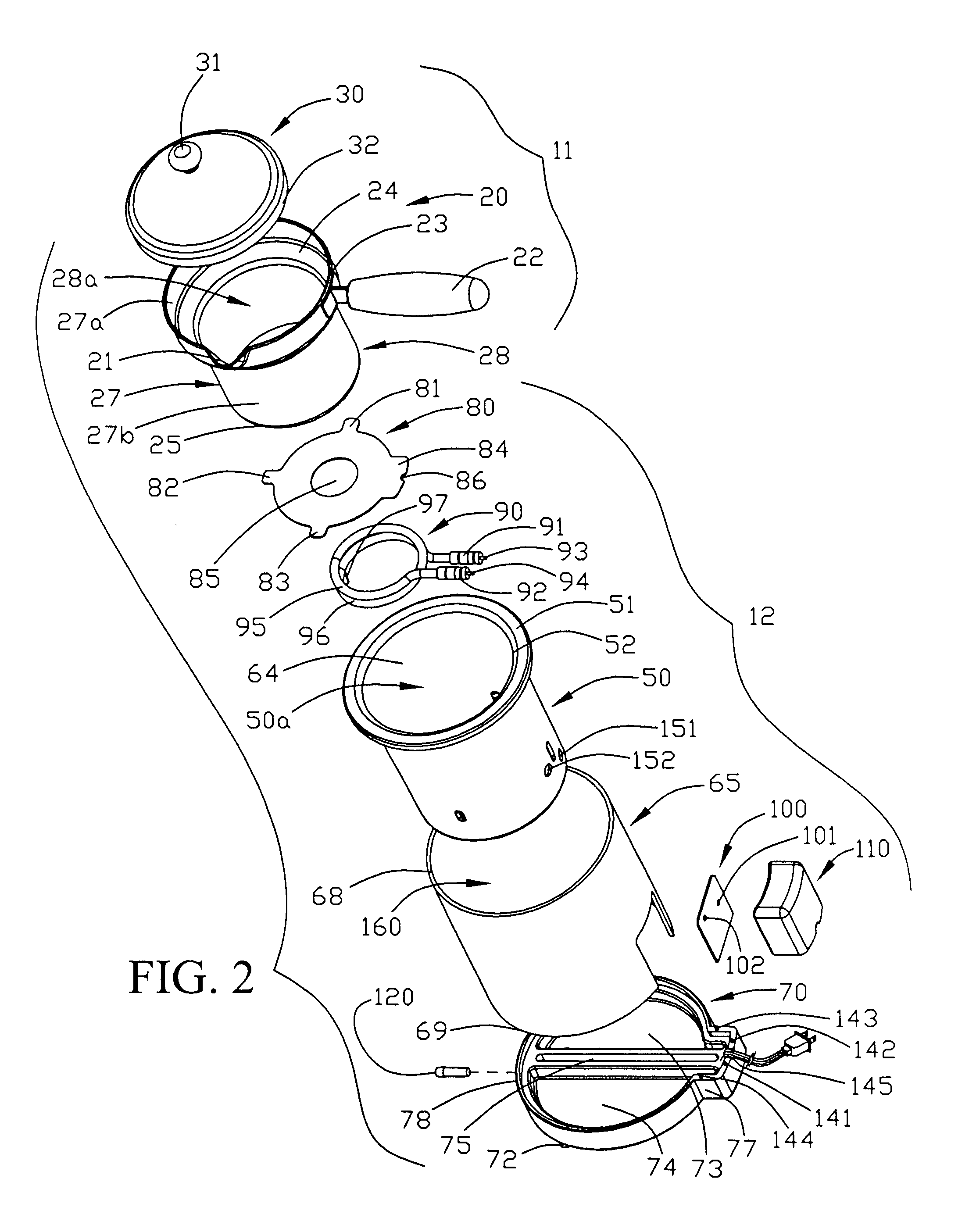
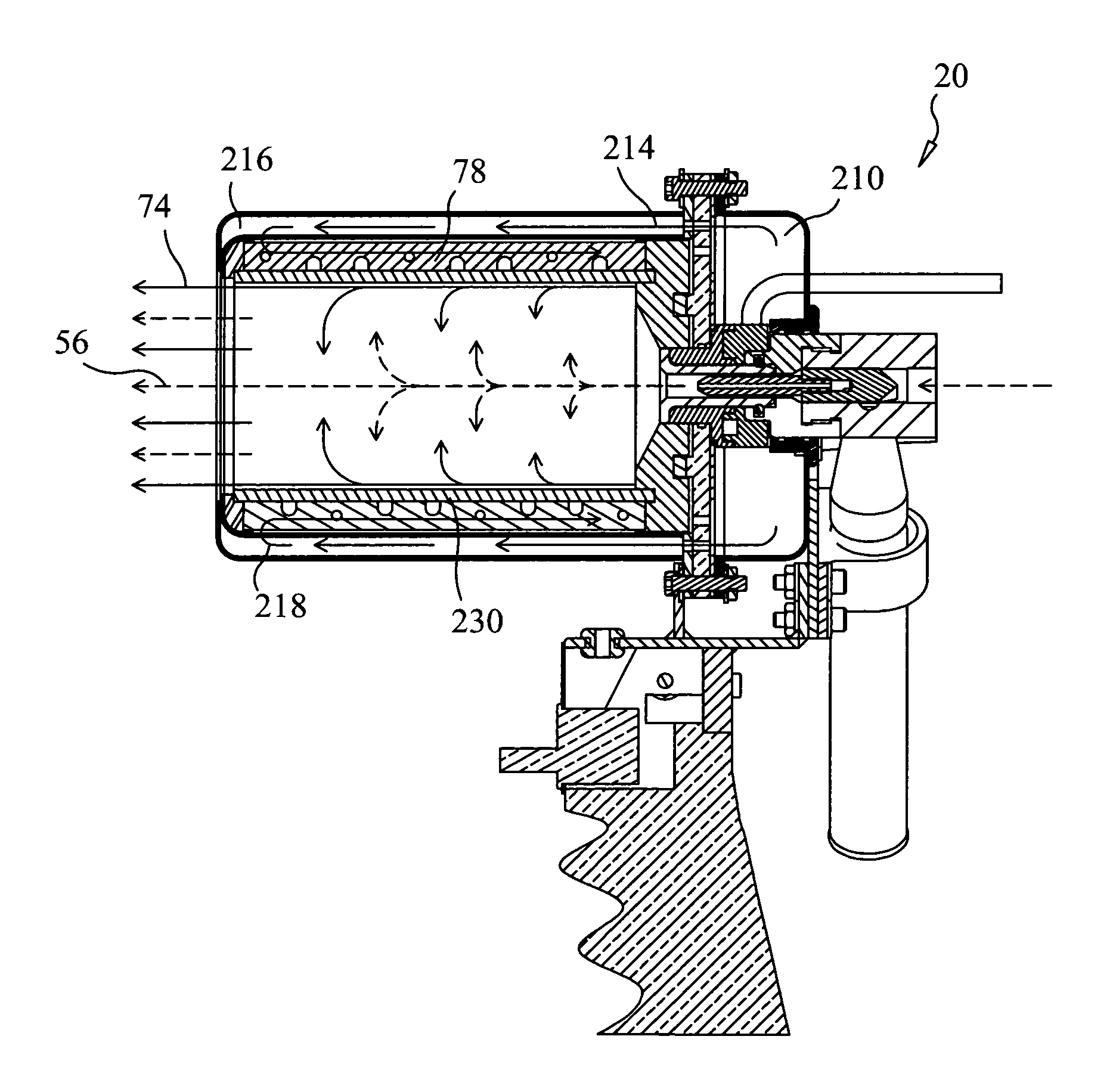
InactiveUS7167642B1Prone to feverEvenly heatedBoiling over preventionImmersion heating arrangementsHeat flowHeat flux
Apparatuses and methods for heating foodstuffs, or other contents sensitive to high heat flux, such as sauces and gravies, without sticking; so that watching and stirring of the foodstuff is not needed during heating. The novel apparatuses and methods provide such heating in a relatively quick time, such as one hour. A pitcher is shown which sets into a heating unit fitted with a heating element below a baffle that shields the bottom of the pitcher from radiant heat and has apertures which cause favorable convective heating which reduces the risk of sticking. The pitcher or pot is easily installed and removed from the heating unit and a close fit is formed in the installed position to retain heat between the pitcher and heating vessel. The methods include inducing a convective heat flow with the baffle and reduced direct radiant heat to reduce or prevent sticking.
Owner:WAGNER ALFRED R
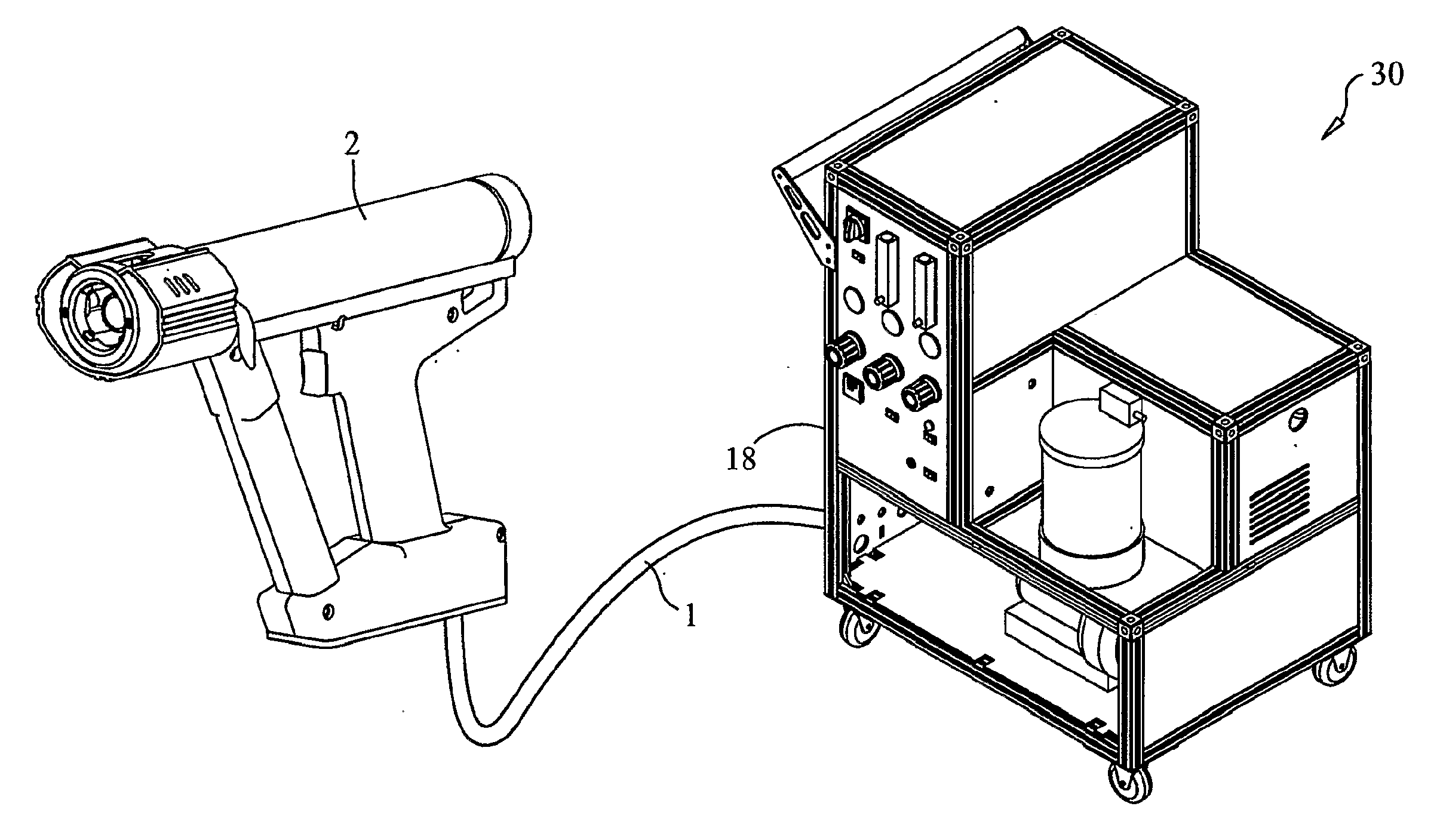
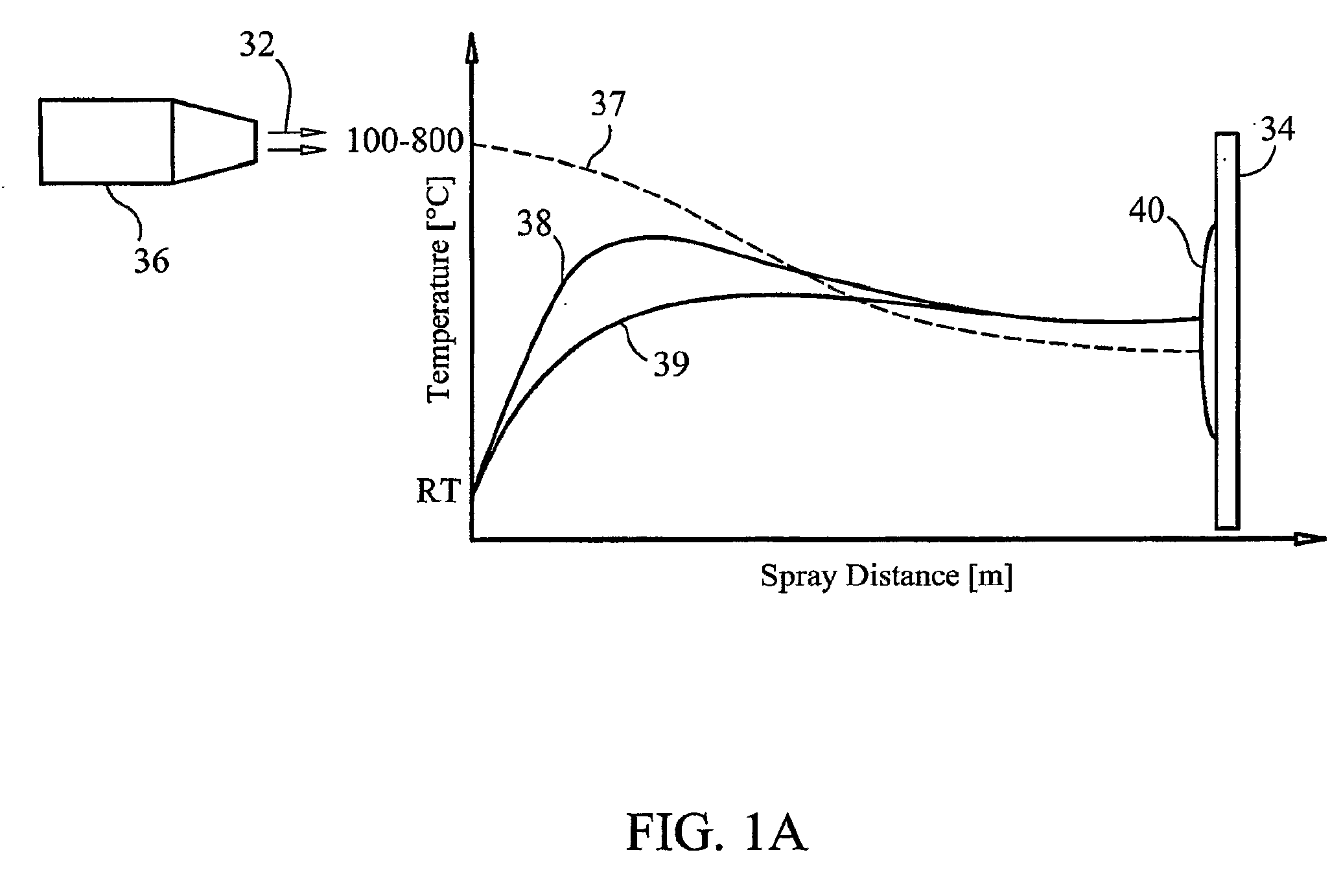
Thermal spray formation of polymer compositions
ActiveUS7959983B1Inexpensively appliedFacilitate thermal sprayingPretreated surfacesLiquid spraying apparatusEpoxyPolyester
A system and method for applying a material, such as a polymer composition, to a substrate, the method comprising mixing the material with a heated carrier gas stream, spraying the material through a nozzle, and radiant and convective heating of the material during transport. Preferred embodiments of the system and method can be used to spray polyetherimides, polyimides, polyamides, thermoset resins (e.g., and epoxies, polyesters and silicones), liquid crystal polymers, compositions comprising a blowing agent, compositions comprising a binder, compositions comprising a metallized material, compositions that produce an open cell foam, and compositions that produce a closed cell foam.
Owner:FARRAR LAWRENCE C +2
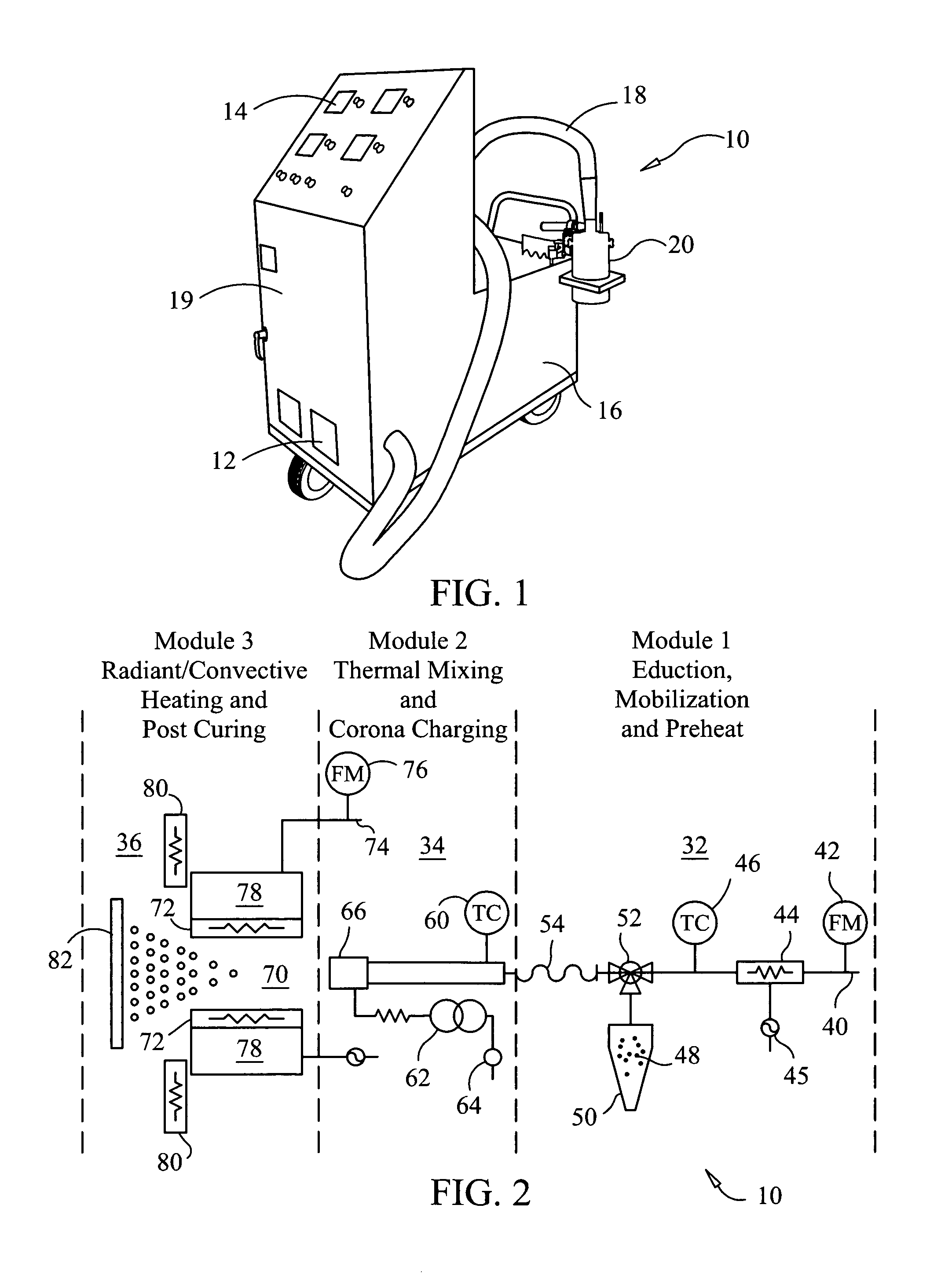
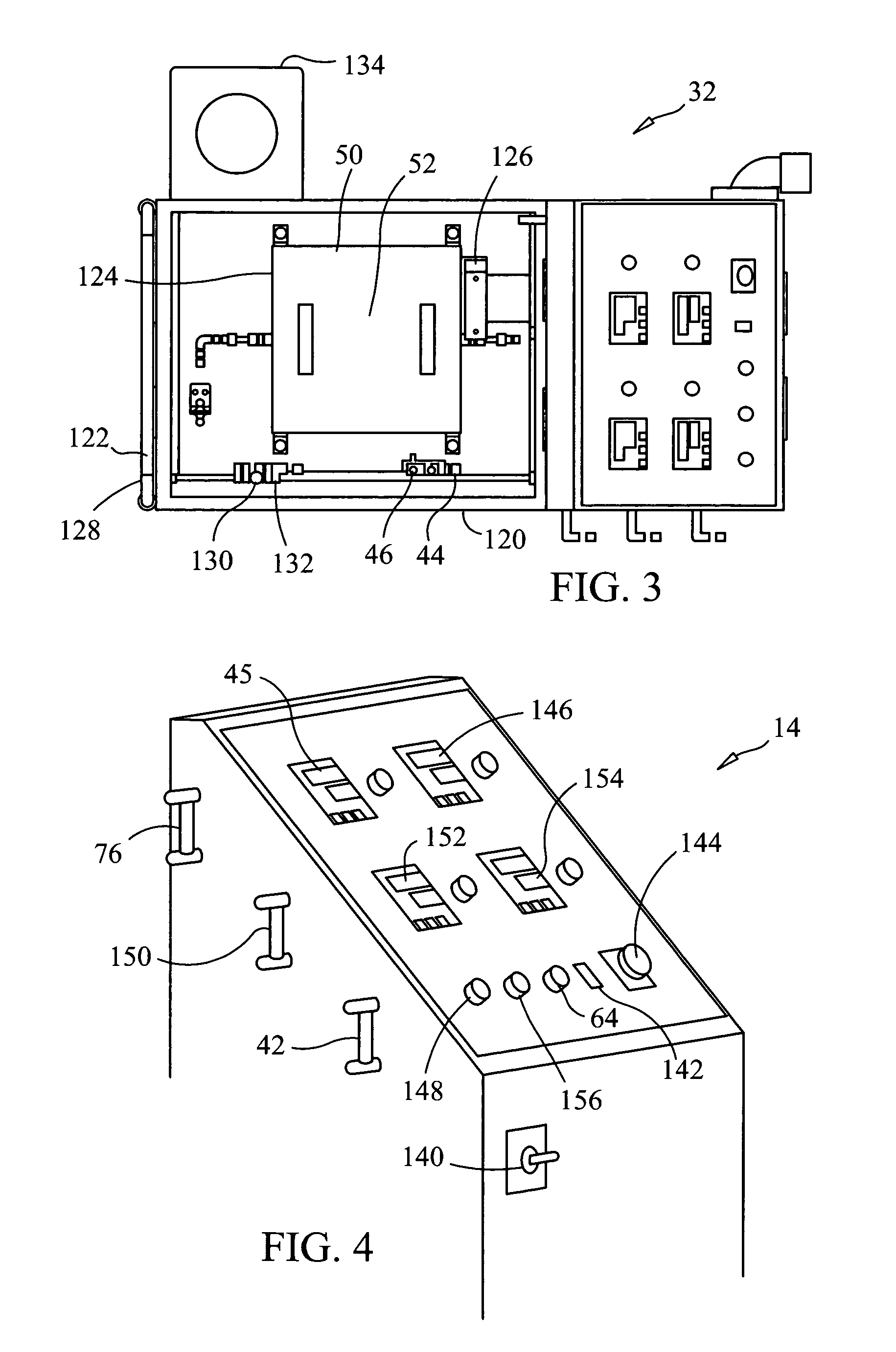
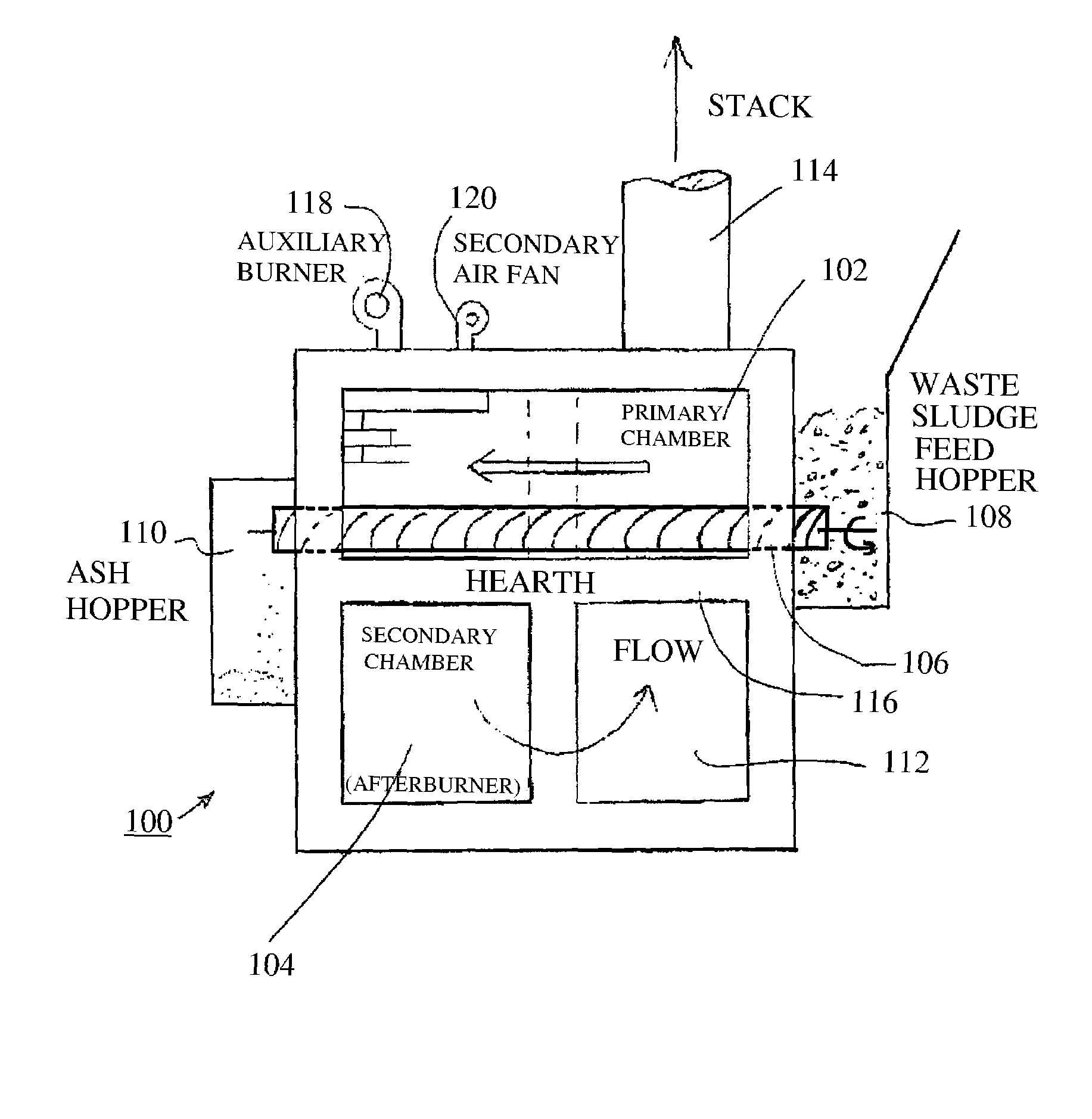
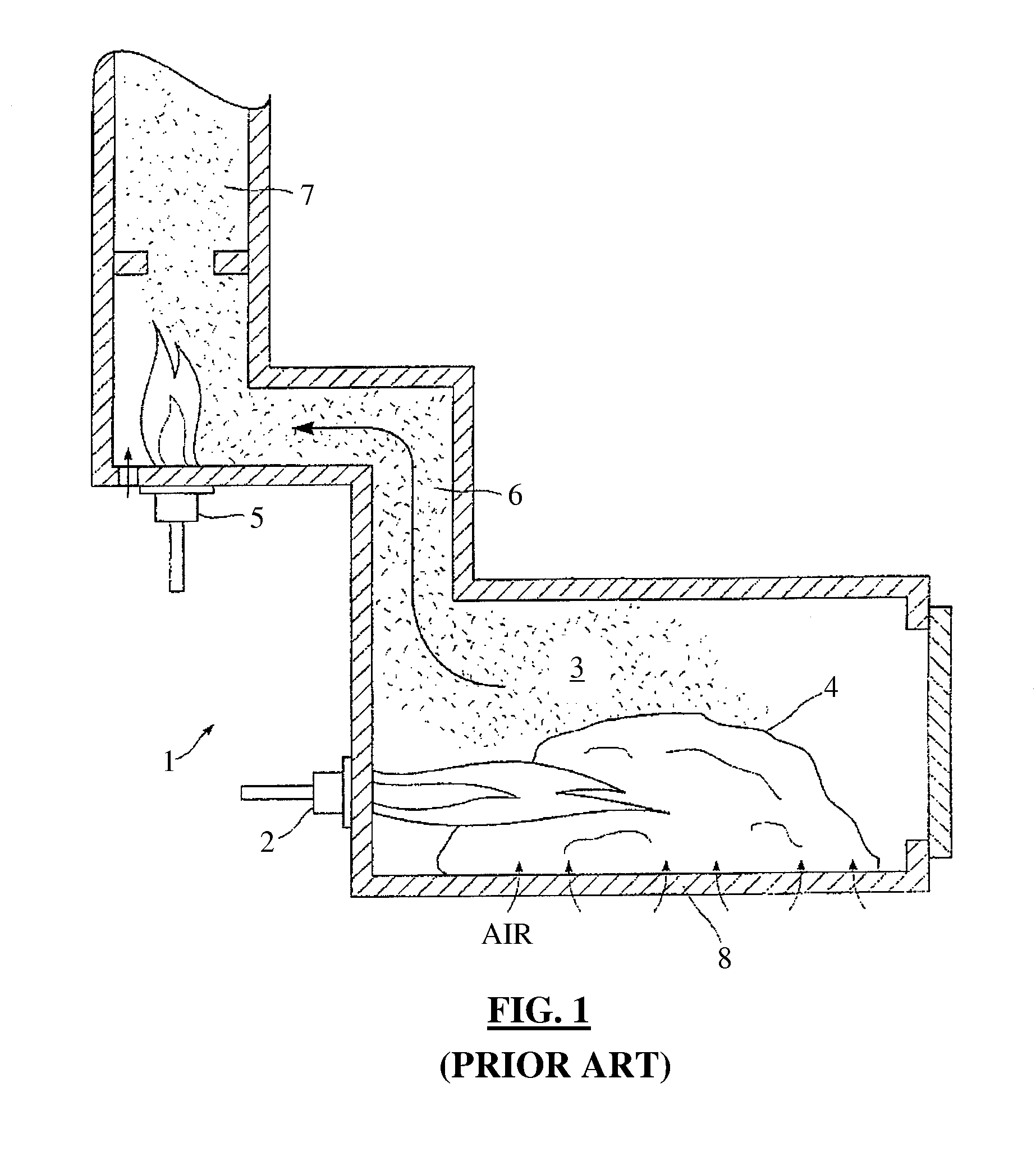
Gasifier and Incinerator for Biomass Sludge Destruction
A device for gasifying biomass sludge having particle size less than 1 cm, and 20% to 100% solids content has a primary chamber, a fume transfer vent, a mixing chamber which accepts fumes from the primary chamber, and an afterburner chamber in fluid communication with the mixing chamber. A secondary burner produces an initial heating flame within a vertical portion of the afterburner chamber. A heat transfer chamber is in fluid communication with the afterburner chamber. Heated gases from the afterburner chamber cause heating of the heat transfer chamber. The primary chamber has a heat conductive floor superimposed over the heat transfer chamber so that conductive and convective heating of the primary chamber occur. At least one primary auger is located crosswise in the primary chamber between a sludge feed hopper and an ash hopper. The heat transfer chamber underlies the primary auger near the end at the ash hopper.
Owner:ZEBREX ENVIRONMENTAL SYST
Enhanced hydrocarbon recovery by convective heating of oil sand formations
The present invention involves a method and apparatus for enhanced recovery of petroleum fluids from the subsurface by convective heating of the oil sand formation and the heavy oil and bitumen in situ by a downhole electric heater. Multiple propped vertical hydraulic fractures are constructed from the well bore into the oil sand formation and filled with a diluent. The heater and downhole pump force thermal convective flow of the heated diluent to flow upward and outward into the propped fractures and circulating back down and back towards the well bore heating the oil sands and in situ bitumen on the vertical faces of the propped fractures. The diluent now mixed with produced products from the oil sand re-enters the bottom of the well bore and passes over the heater element and is reheated to continue to flow in the convective cell. Thus the heating and diluting of the in place bitumen occurs predominantly circumferentially, i.e. orthogonal to the propped fracture, by diffusion from the propped vertical fracture faces progressing at a nearly uniform rate into the oil sand deposit. In situ hydrogenation and thermal cracking of the in place bitumen can provide a higher grade produced product. The heated low viscosity oil is produced through the well bore at the completion of the active heating phase of the process.
Owner:GEOSIERRA
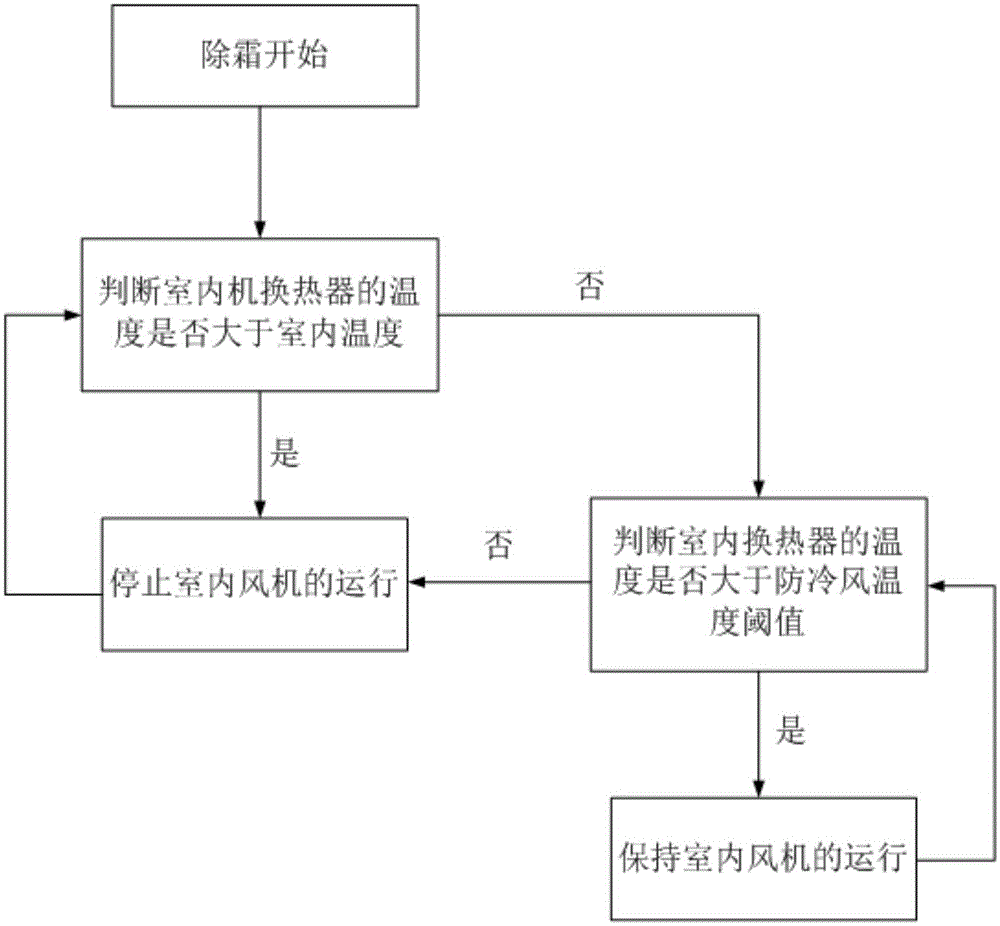
Air conditioner outdoor unit defrosting method
ActiveCN105135620AImprove energy efficiency ratioShorten defrosting timeSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusCold airBusiness efficiency
The invention relates to the technical field of an air conditioner defrosting and provides an air conditioner outdoor unit defrosting method. When the refrigeration mode is selected to perform defrosting, firstly an indoor fan stops operating to enable residual heat of an indoor heat exchanger to completely act on a refrigerant recycling back; when the temperature of the indoor heat exchanger is reduced to be lower than the indoor temperature, the indoor fan is started, indoor heater air is utilized to conduct convective heating on the indoor heat exchanger, and the indoor fan stops operating to prevent somatosensory cold air enabling human to obviously feel cold from being produced till the temperature of the indoor heat exchanger is reduced to reach a cold air preventing temperature threshold. In the whole defrosting process, the residual heat of the indoor heat exchanger is fully utilized, the indoor air heat is further properly utilized, accordingly the defrosting time is overall shortened, the defrosting efficiency is improved, and the overall energy efficiency ratio of an air conditioner is also improved.
Owner:GD MIDEA HEATING & VENTILATING EQUIP CO LTD +1
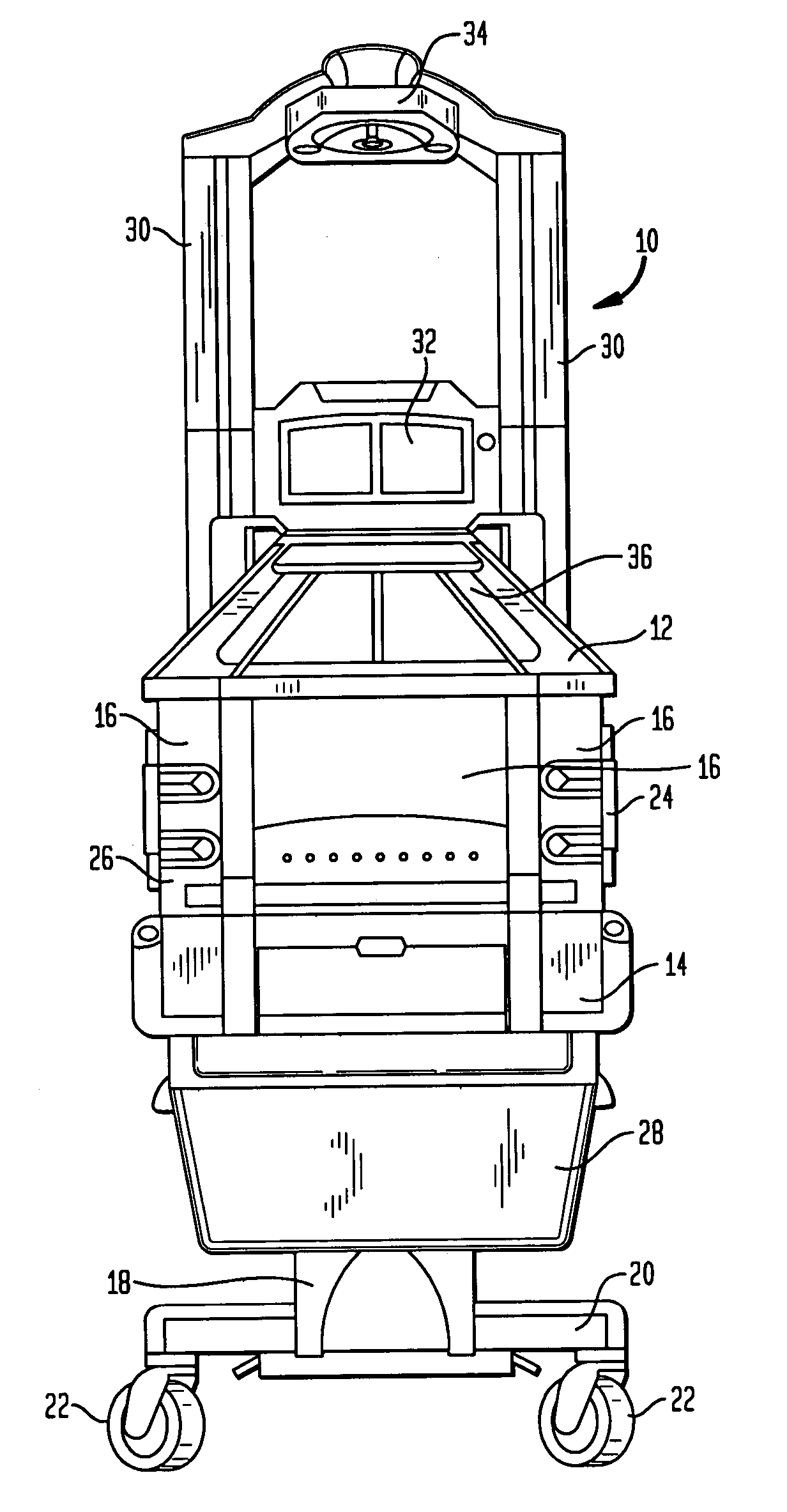
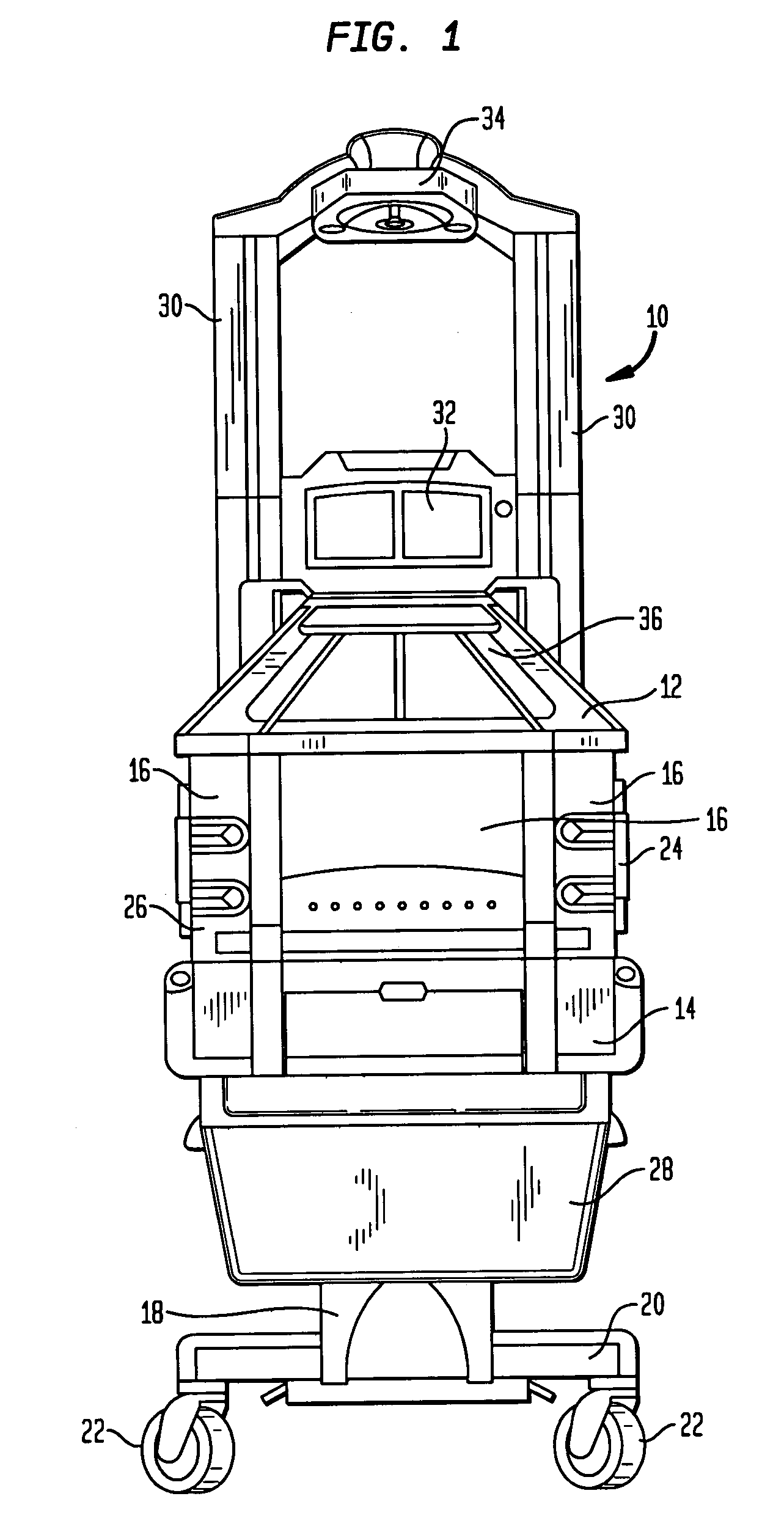
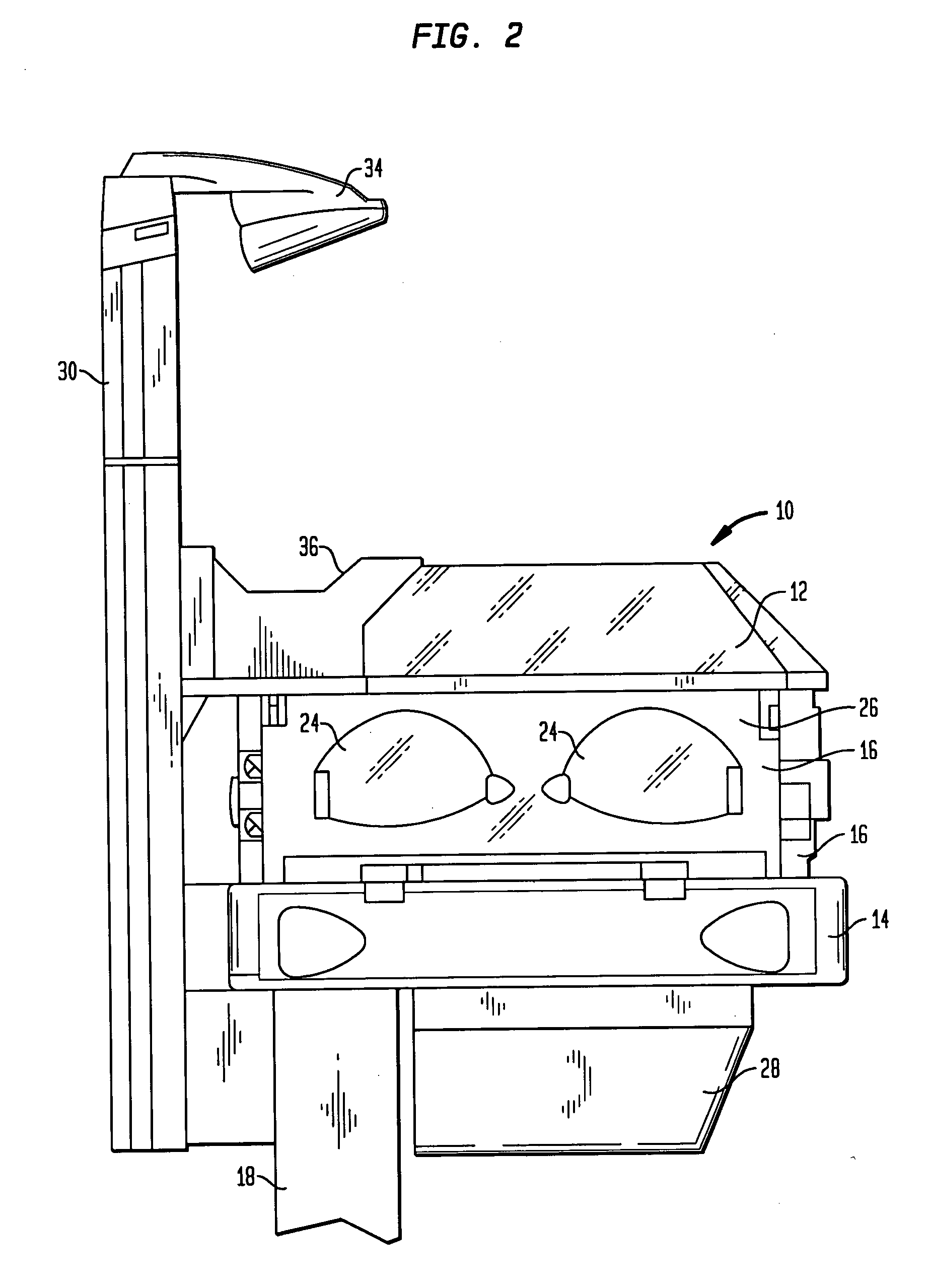
Infant care apparatus with fixed overhead heater
An infant care apparatus having a canopy movable with respect to an infant support for supporting an infant between a lower position enclosing the infant in an infant compartment and an upper position opening the infant compartment. The canopy has an opening and a door that can be closed to block the opening and opened to unblock the opening. A radiant heater is located in a fixed position above the infant support to direct infrared energy toward the infant support. When the canopy is in its lower position, a convective heating system warms the infant compartment. The door either closes as the canopy moves to its lower position or opens as the canopy moves to its upper position.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
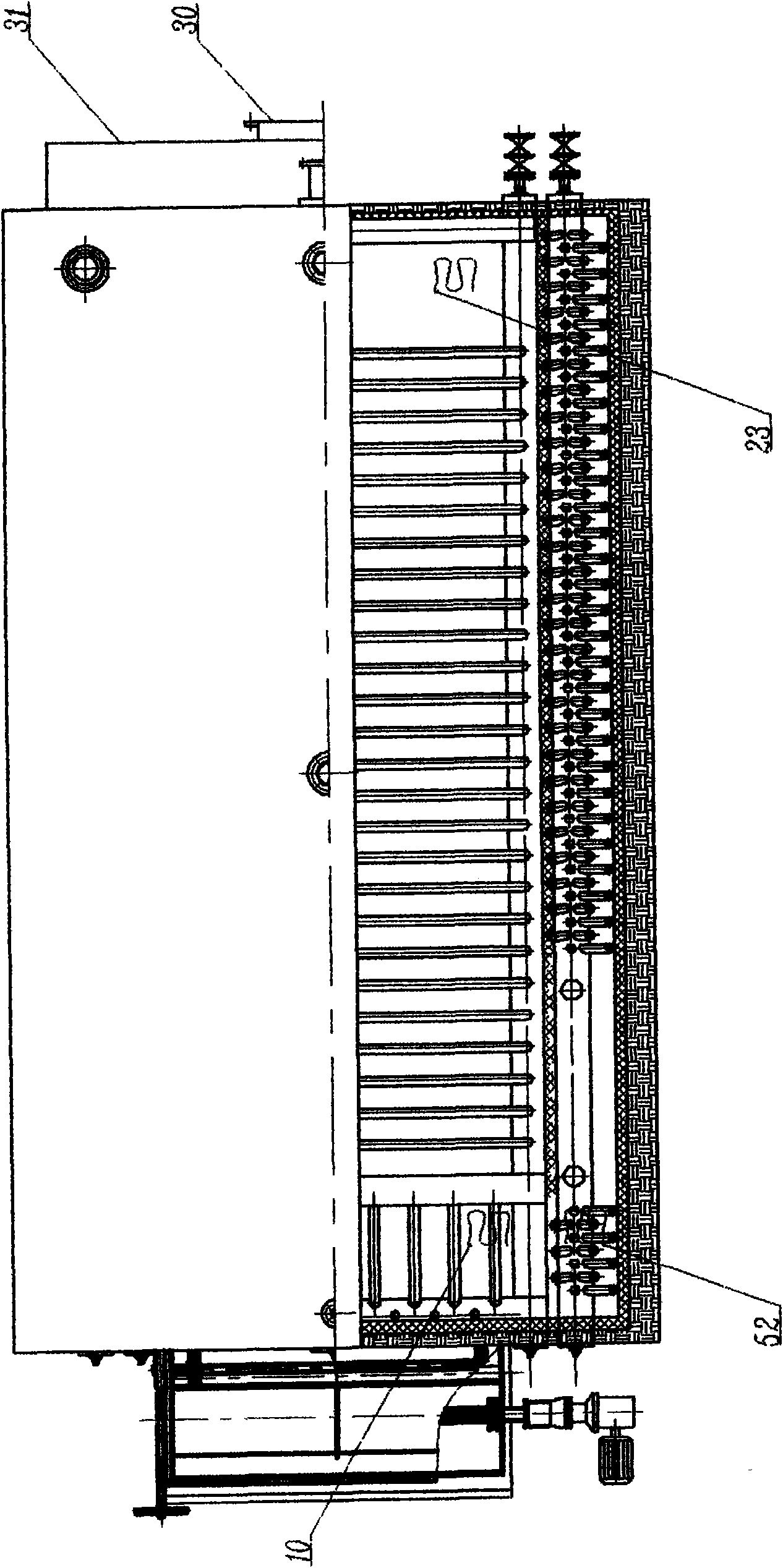
Energy-saving gas full-convection heating glass tempering furnace
InactiveCN101734844AImprove product qualityReduce manufacturing costGlass tempering apparatusGlass productionCombustion chamberMetallurgy
The invention relates to a novel energy-saving glass heat strengthening heating device, in particular to a glass tempering furnace adopting natural gas or industrial gas as energy and full-convection forced heating. The energy-saving gas full-convection heating glass tempering furnace mainly comprises a combustion chamber, a heat gas temperature pressure adjusting chamber, a high temperature forced convection heating chamber, a temperature and pressure measuring and process controlling system, a heat recycling system and the like. The energy-saving gas full-convection heating glass tempering furnace can improve the utilization efficiency of the energy maximally, saves the energy and reduces the production cost of tempered glass. The energy-saving gas full-convection heating glass tempering furnace is suitable for producing tempered glass for buildings or tempered glass for other purposes. The principle and structure of the energy-saving gas full-convection heating glass tempering furnace are suitable for glass tempering devices using liquid fuel such as diesel fuel as the energy.
Owner:王世忠
Full reverse convection unsealed water tube boiler
InactiveCN101957059AImprove production efficiencyReduce steel consumptionWater heatersWater channelEngineering
The invention discloses a full reverse convection unsealed water tube boiler. Upper and lower center headers, laterally symmetrical water wall headers, a water wall tube, upper and lower laterally symmetrical convection bank headers, a convection bank, front, rear, upper and lower transverse headers, communicating tubes and the like are respectively communicated to form a radiation convective heating surface and a natural circulation water channel; furnace walls are constructed on the outer side of the water wall and the outer sides of a ceiling and the convection bank to form a hearth and a three-return flue, so that the volume of the hearth can be increased with the same boiler volume to facilitate fully burning and settling dust in a soot furnace; the water channel and a soot channel are subjected to full reverse convection transverse washing to facilitate improving the heat exchange effect and reducing soot formation on the convective heating surface; and because of an unsealed structure, the natural circulation is safe, reliable and small in flow resistance, the overall structure process is advanced, the manufacturing is simple, and large, medium and small tubes can be adopted to replace drums of various boilers, so the steel consumption can be reduced by 30 percent, the manufacturing efficiency can be improved by 40 percent, the power consumption can be reduced by 20 percent, the initial discharge concentration of the soot can be reduced by 70 percent; therefore, the boiler has obvious advantages of energy saving, consumption reduction and emission reduction.
Owner:王森
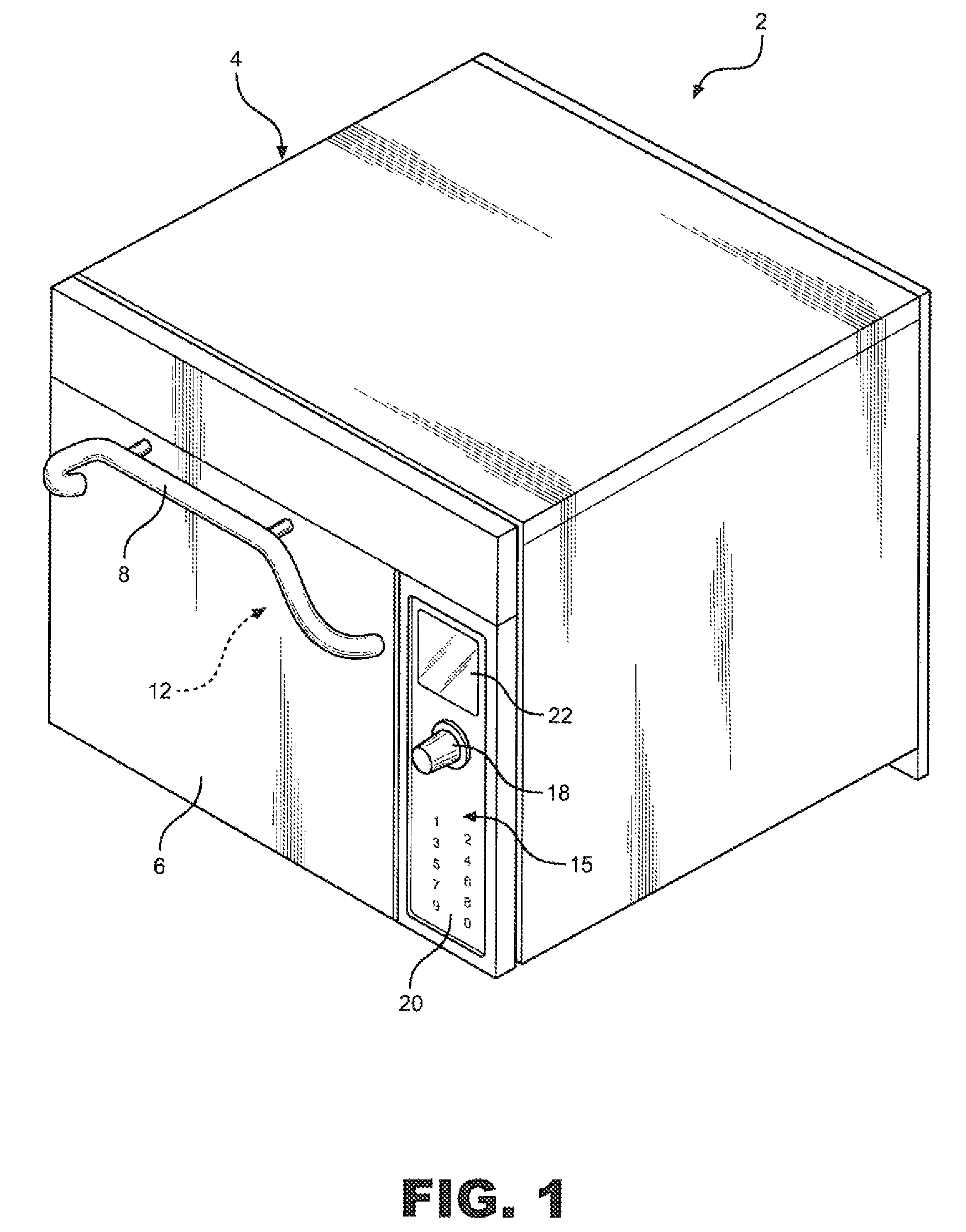
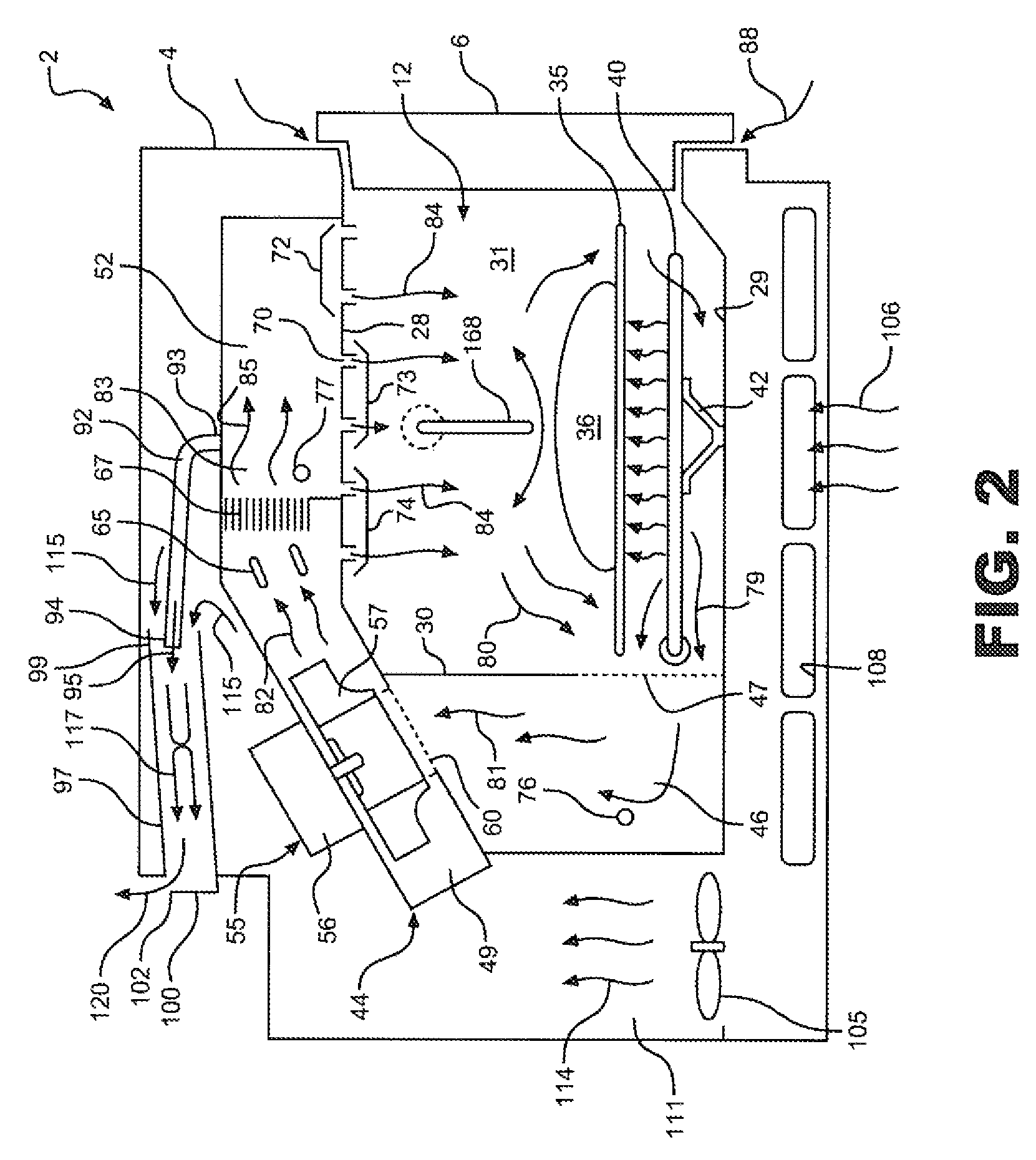
Device and treatment chamber for thermally treating substrates
InactiveUS20120171632A1Fast heatingFast coolingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHandling discharged materialTemperature controlProduct gas
A treatment chamber for thermal processing of an areal substrate including a transport arrangement for conveying and supporting the substrate during the thermal processing and a gas-guiding arrangement for convective heating or cooling of the substrate, where the gas-guiding arrangement has outlet openings, by means of which the temperature-controlled gas is guided onto the substrate, and where a removal arrangement is provided, by means of which the gases introduced into the treatment chamber via the gas-guiding arrangement can be removed in a targeted fashion, such that the treatment chamber can be embodied as a heat-treatment chamber or as a cooling chamber.
Owner:LEYBOLD OPTICS
Method and apparatus for treatment of biomass substrates
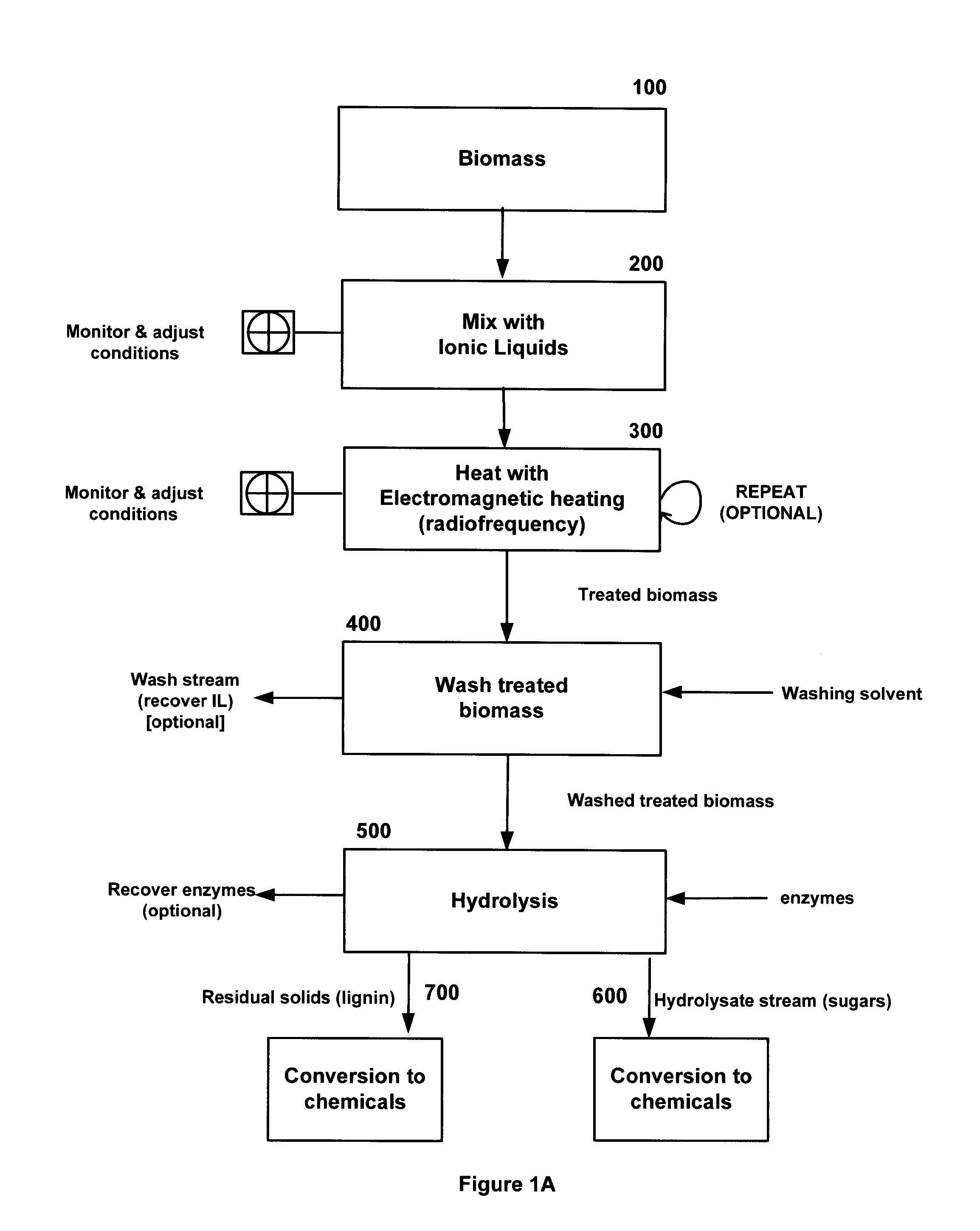
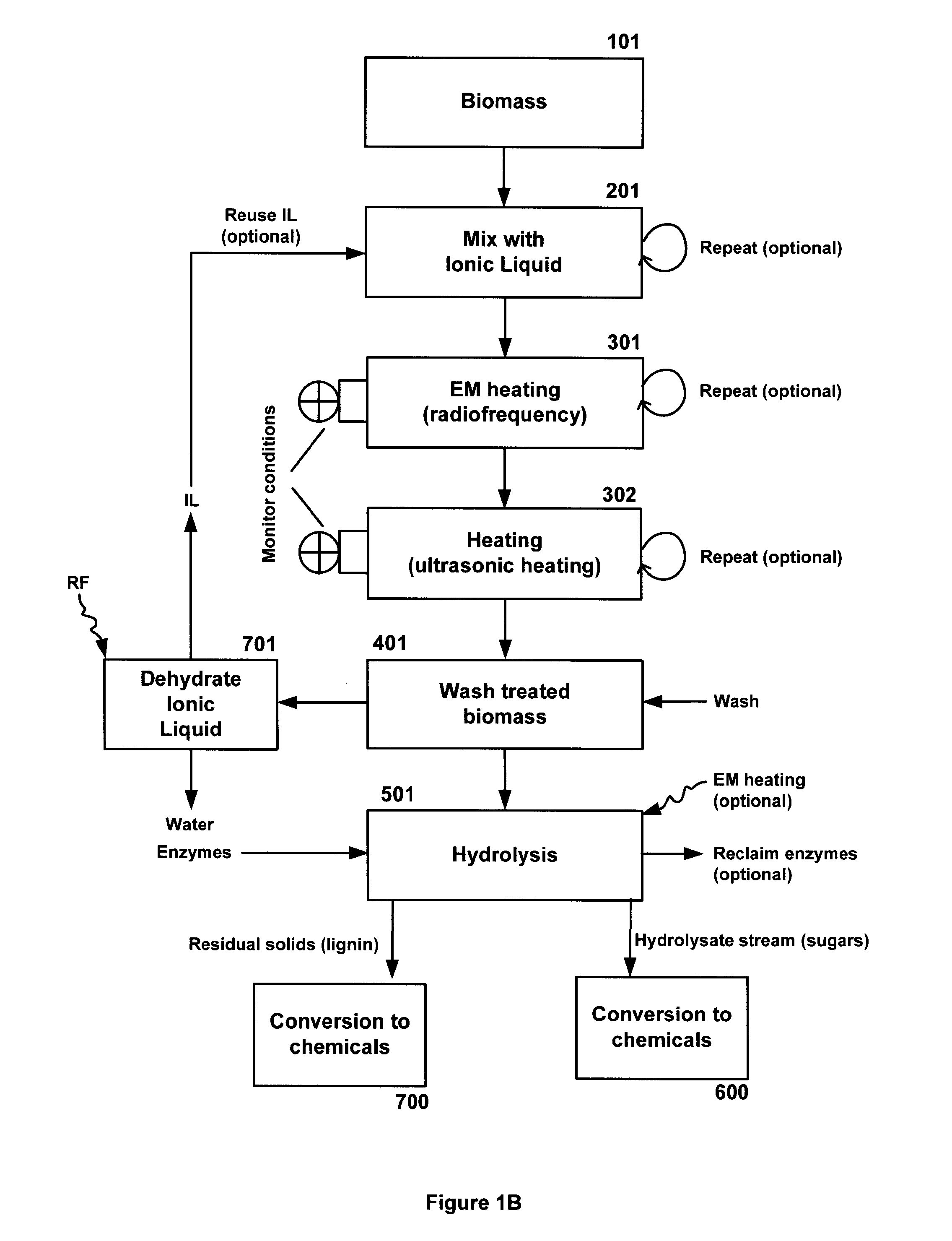
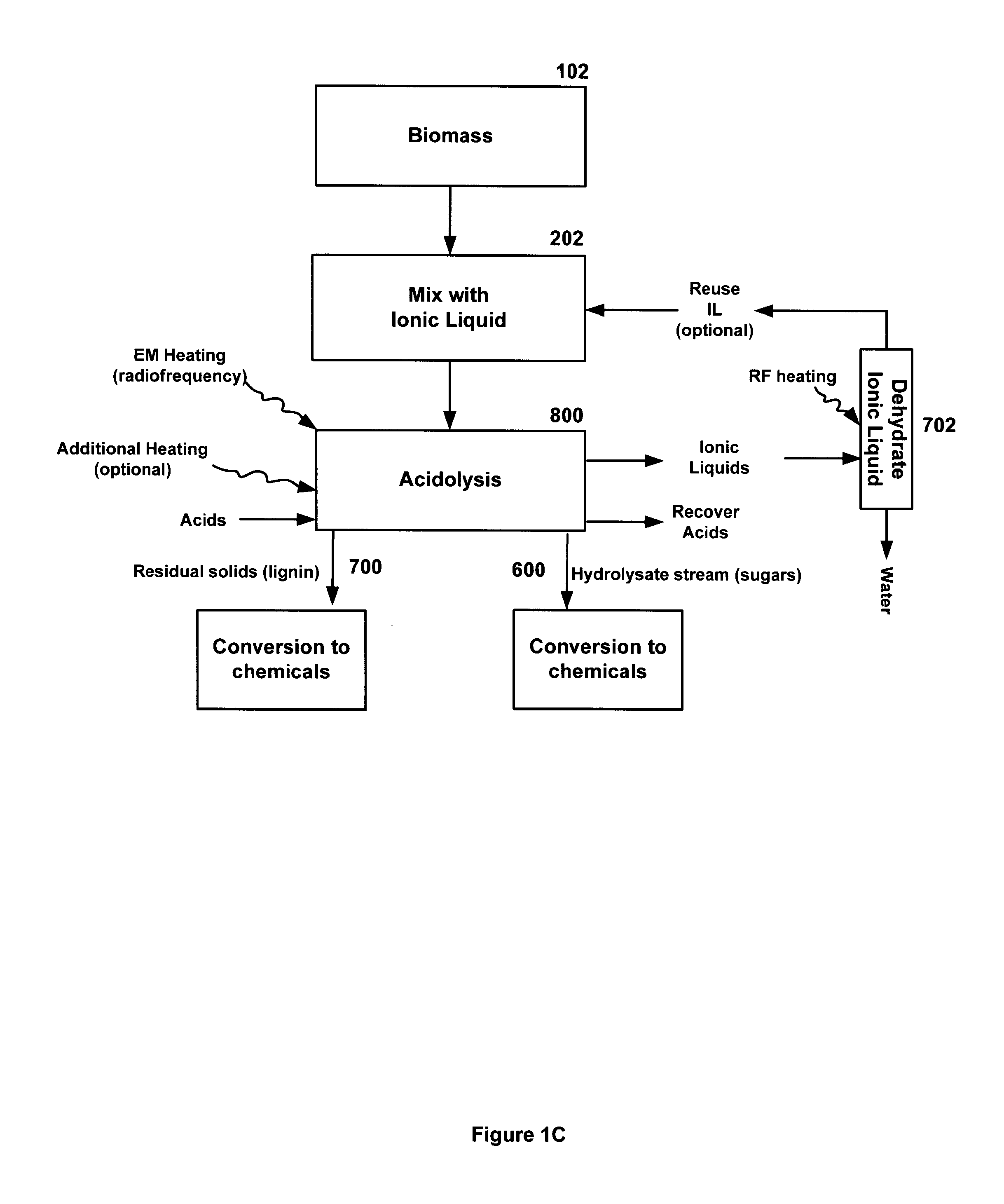
InactiveUS20140004563A1Effective uniform processingIncrease loadProcess control/regulationDrying solid materials with heatSugarRadio frequency
A system and method for the treatment of biomass comprising mixing a biomass with an ionic liquid (IL) to swell the biomass and electromagnetic (EM) heating, preferably radiofrequency (RF) heating, said biomass. Additionally, a method of acidolysis of biomass comprising mixing biomass in an ionic liquid (IL) to swell the biomass; adding an acid, to lower the pH of the biomass below pH 7; applying radio frequency (RF) heating to the biomass to heat to a target temperature range; applying ultrasonic heating, electromagnetic (EM) heating, convective heating, conductive heating, or combinations thereof, to the biomass to maintain the biomass at a target temperature range; washing the treated biomass; and recovering sugars and released lignin.
Owner:SUGANIT SYSTEMS INC
Infant care apparatus with fixed overhead heater
An infant care apparatus having a canopy movable with respect to an infant support for supporting an infant between a lower position enclosing the infant in an infant compartment and an upper position opening the infant compartment. The canopy has an opening and a door that can be closed to block the opening and opened to unblock the opening. A radiant heater is located in a fixed position above the infant support to direct infrared energy toward the infant support. When the canopy is in its lower position, a convective heating system warms the infant compartment. The door either closes as the canopy moves to its lower position or opens as the canopy moves to its upper position.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
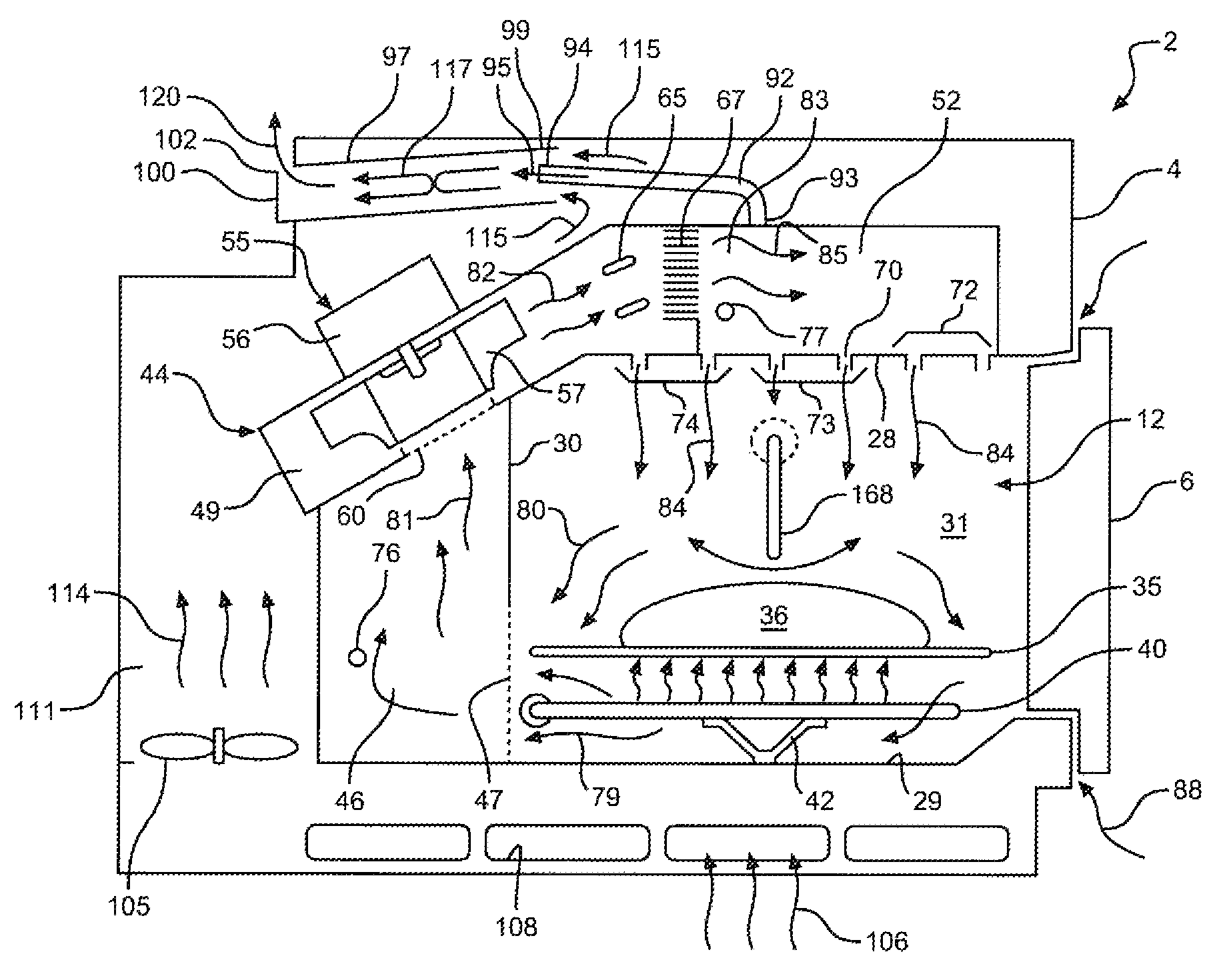
Temperature control for cooking appliance including combination heating system
ActiveUS8642928B2Self-cleaning stoves/rangesAir-treating devicesTemperature controlProcess engineering
Owner:ACP
Thermal spray formation of polymer coatings
InactiveUS20100009093A1Avoid contactLimited penetrationSpray nozzlesPretreated surfacesThermal sprayingPolymer science
A system (30) and method for fluidizing a polymer powder (11) to be sprayed, metering the material (12) and mixing it with a heated carrier-gas stream (13) to produce a spray (32), and using the spray (32) to transport the material (12) to a substrate (34) and radiant an convective heating of the material (12) during transport to achieve melting of the polymer powders (11).
Owner:SCOTT COGUILL L +4
Radiation heating furnace with external circulating device
InactiveCN101905948AShorten heating timeReduce energy consumptionGlass tempering apparatusExtracorporeal circulationAir compressor
The invention discloses a radiation heating furnace with an external circulating device. The furnace comprises a furnace body and the external circulating device on the outer side of the furnace body, wherein the furnace body consists of an elevating upper furnace body and a lower furnace body which is fixed on the ground; an upper heating unit and a lower heating unit are correspondingly arranged in the upper furnace body and the lower furnace body; a transmission roller way for conveying glass is arranged between the upper heating unit and the lower heating unit; and the external circulating device comprises an air compressor, an air storage tank, a heat exchanger, an induced draft fan, an air suction pipe, an upper gas ejector pipe and a lower gas ejector pipe and connecting lines thereof. The external circulating device of the invention is used, so that convective heating of glass is added based on radiation heating, the heating time of LOW-E glass and anti-radiation glass is shortened, and energy consumption is lowered to save energy; and heat is exchanged between cold and hot air to uniformly heat the upper and lower surfaces of the LOW-E glass and the anti-radiation glass, so that rejection rate is reduced, and product quality is improved and reaches the national standard of tempered glass.
Owner:杭州精工机械有限公司
Microwave oven with convection heating
ActiveUS20050051540A1High trafficPrevent escapeBaking ovenMicrowave heatingMicrowave ovenEngineering
A combined microwave and hot-air circulating cooking appliance is disclosed. The appliance has a plurality of air injection openings that are provided in a wall of the cooking cavity for injecting heated air into the same. Each of the injection openings is connected to a heating compartment an air conduit having such dimensions so as to prevent propagation of microwave energy through the conduit.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
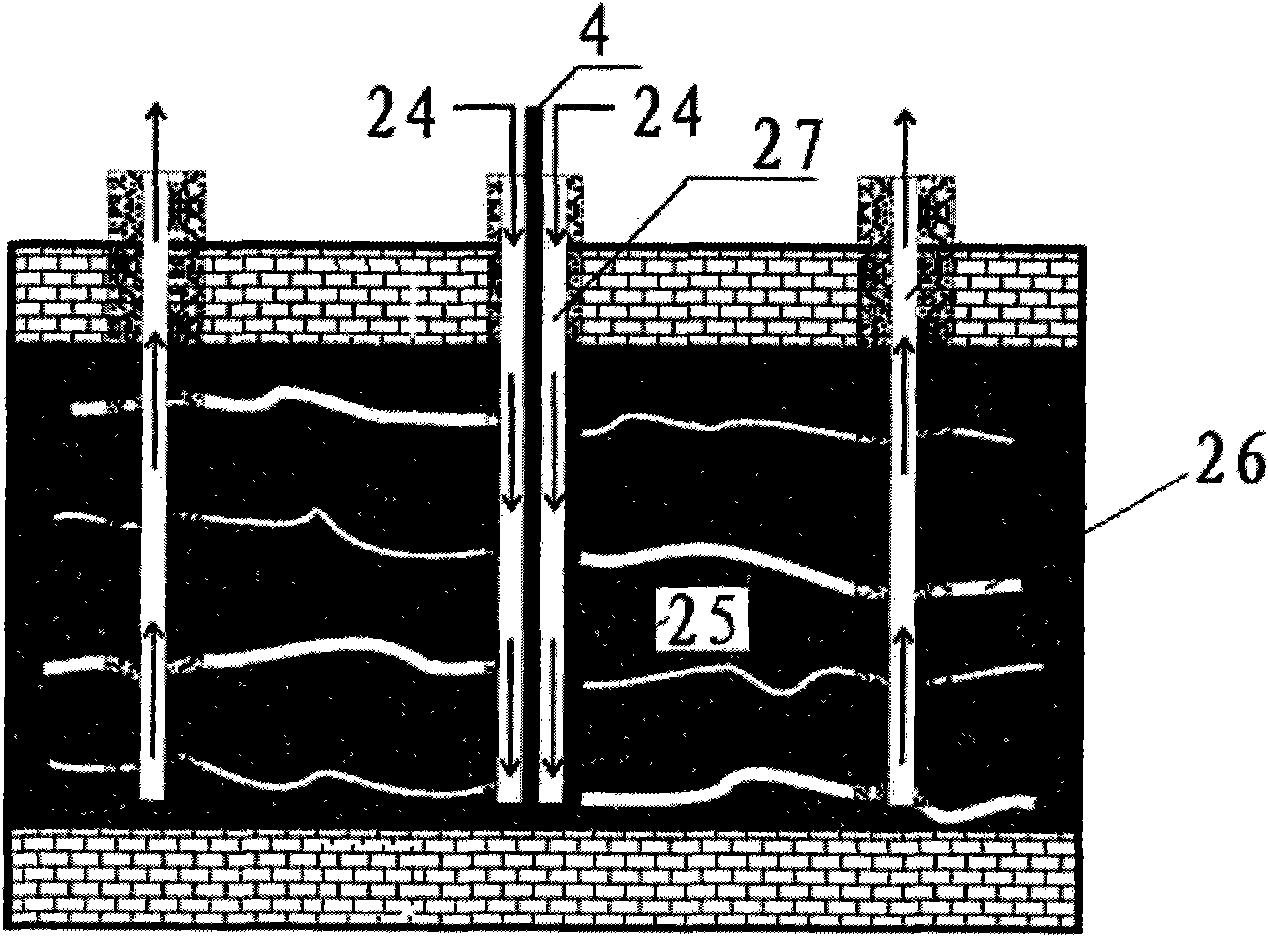
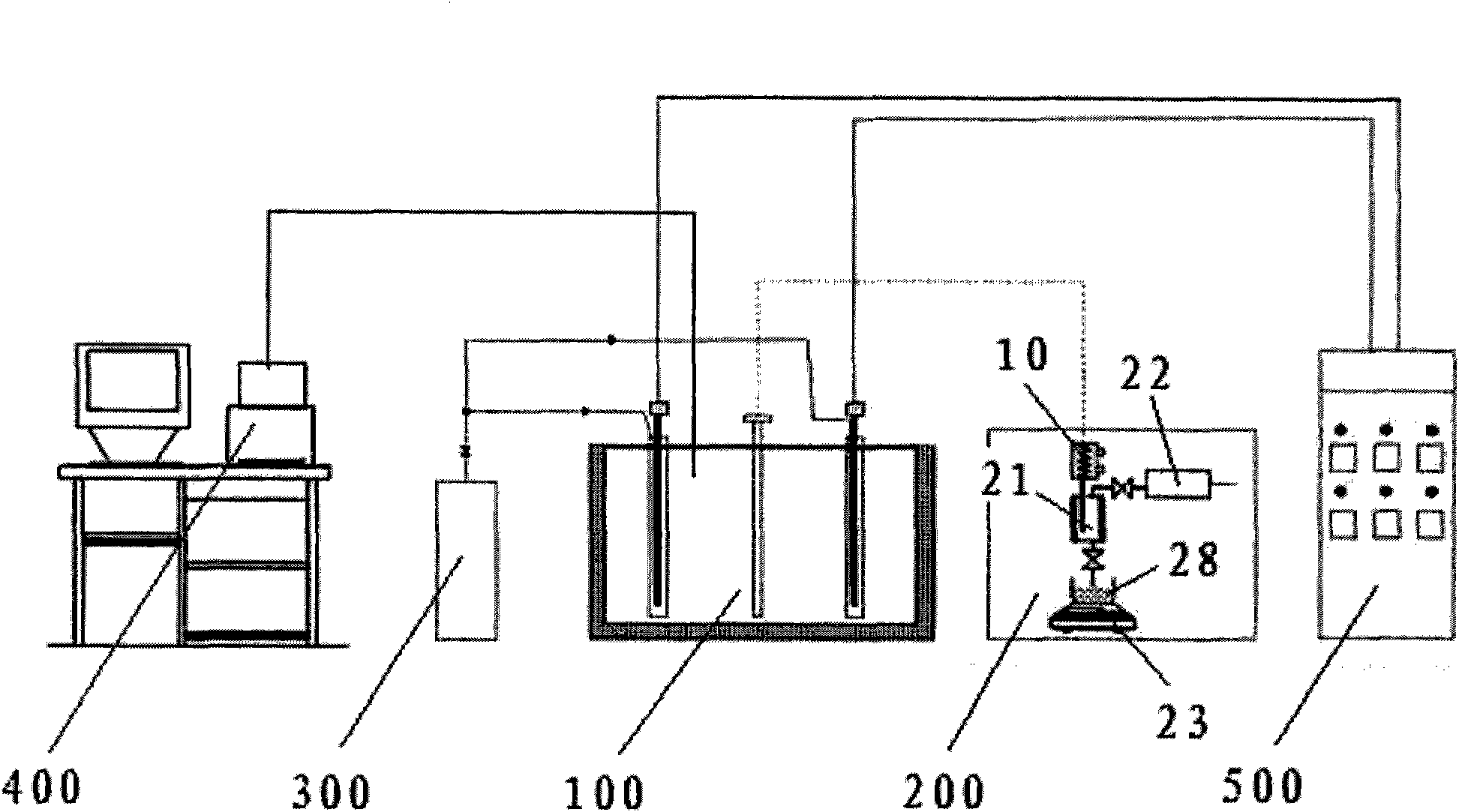
Oil shale in-place destructive distillation mining method and simulated experiment system thereof
ActiveCN102465691AImproves crack developmentImprove permeabilitySurveyFluid removalMeasurement deviceCarbon dioxide
The invention discloses an oil shale in-place destructive distillation mining method and a simulated experiment system thereof, belonging to the field of oil shale mining. According to the oil shale in-place destructive distillation mining method, fracture creation is carried out on a shale layer, thus fracture development and permeability of the shale layer are improved, the oil shale layer is directly subjected to conduction heating, gas is introduced into a heating region to form direct convection heating, thus heat transfer rate can be effectively increased, and recovery ratio of shale oil is increased. The simulated experiment system comprises a heating device, a gas injection device, a measurement device, a computer and a control device. According to the simulated experiment system, the heating device and the gas injecting device complete direct conduction of heat in a process of heating the oil shale and convection conduction of the gas, thus the experiment system can carry out heat conduction rule and shale oil mining condition under different temperatures and pressures when carbon dioxide is injected into oil shale in different regions for assisting electric heating, and provide parameters and development conceptions for a process of injecting gas for assisting electric heating in different regions.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Novel organic heat carrier furnace of biomass combustion membrane type wall
The invention relates to an organic heat transfer material heater of a novel biomass combustion film-typed wall, and pertains to incinerator equipment in the mechanical equipment field, in particular to a biomass combustion furnace taking waste wood, wood chips, straw and the like as fuels. The organic heat transfer material heater comprises a furnace body which is provided with burning equipment, a hearth, a reburning chamber and a tail smoke channel; the internal side of the furnace body is provided with a heat conducting oil pipe, the burning equipment is provided with a grate arranged under the furnace body and a feeding device correspondingly arranged at one end of the grate, the hearth is arranged at the other end of the grate, the top of the hearth is communicated with the top of the reburning chamber adjacently arranged, the reburning chamber is communicated with the tail smoke channel provided with a convective heating surface formed by the heat conducting oil pipe, and a smoke outlet is arranged above the top of the furnace body. The organic heat transfer material heater, effectively integrating an adiabatic combustion furnace and a conducting oil heat exchanger in one body, can not only reduce investment and occupied area, but also improve combustion efficiency, decrease maintenance cost of equipment operation, and prolong service life of the equipment.
Owner:常州联合锅炉容器有限公司
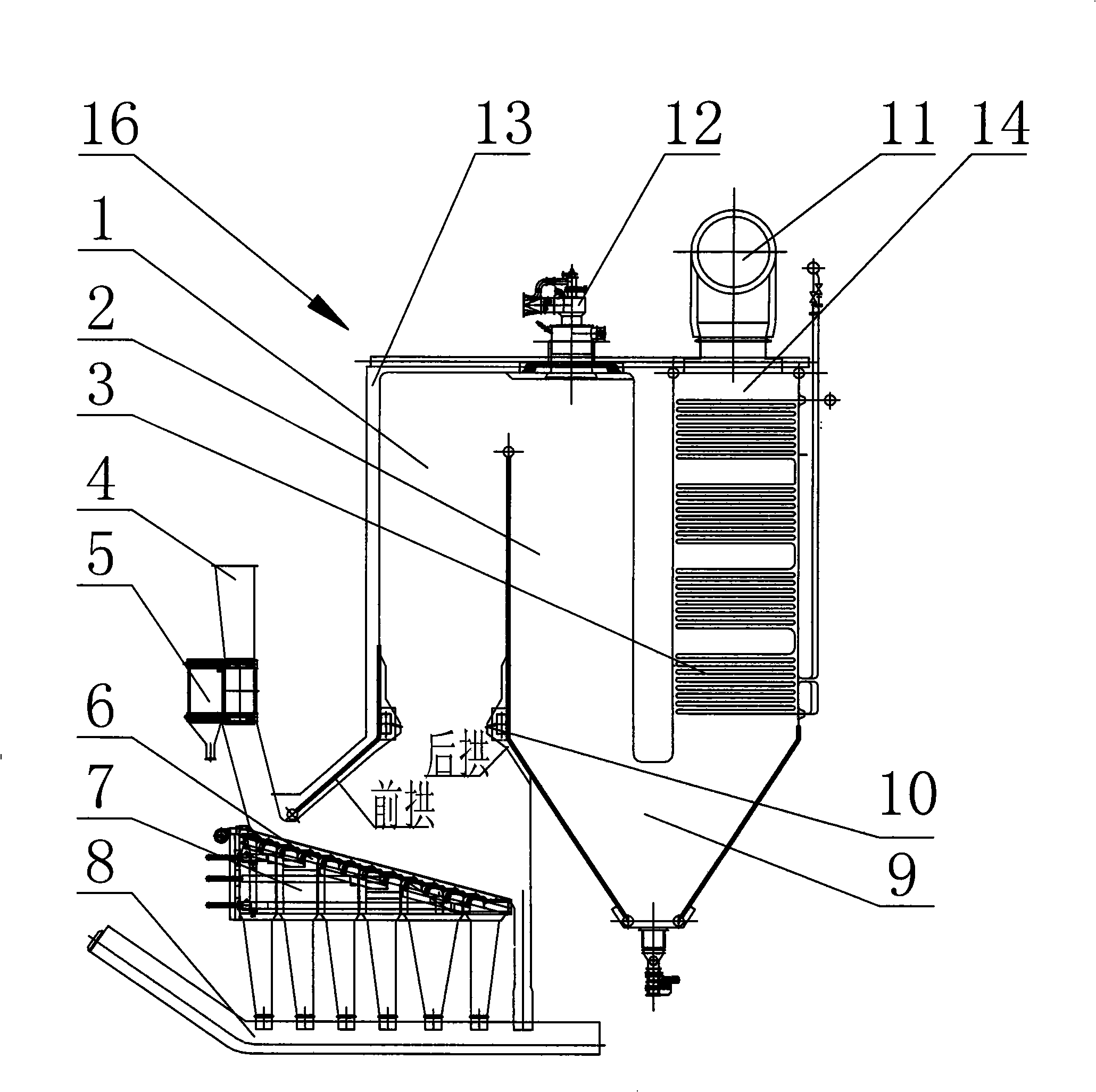
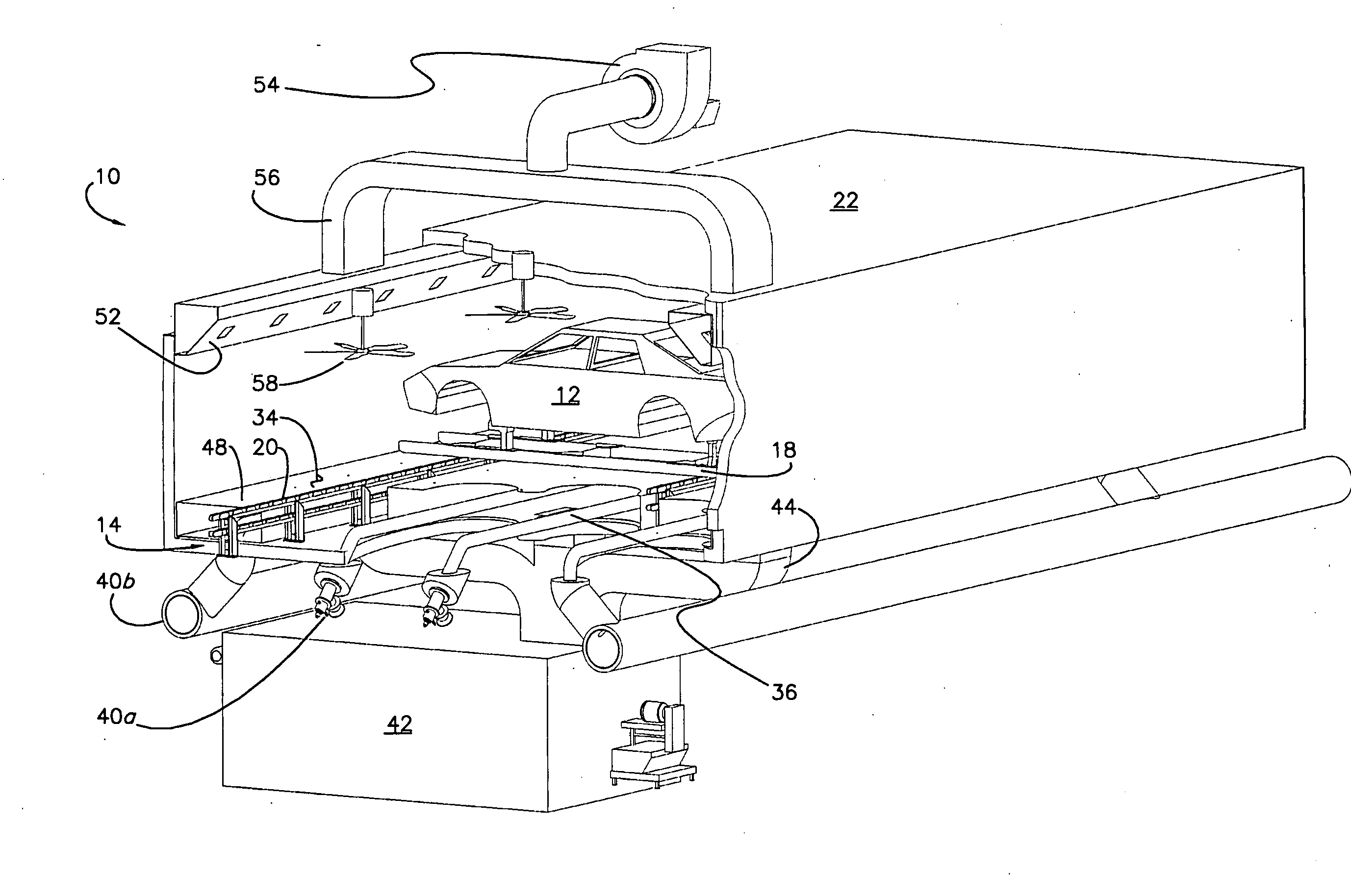
Transverse oven and method of baking workpieces
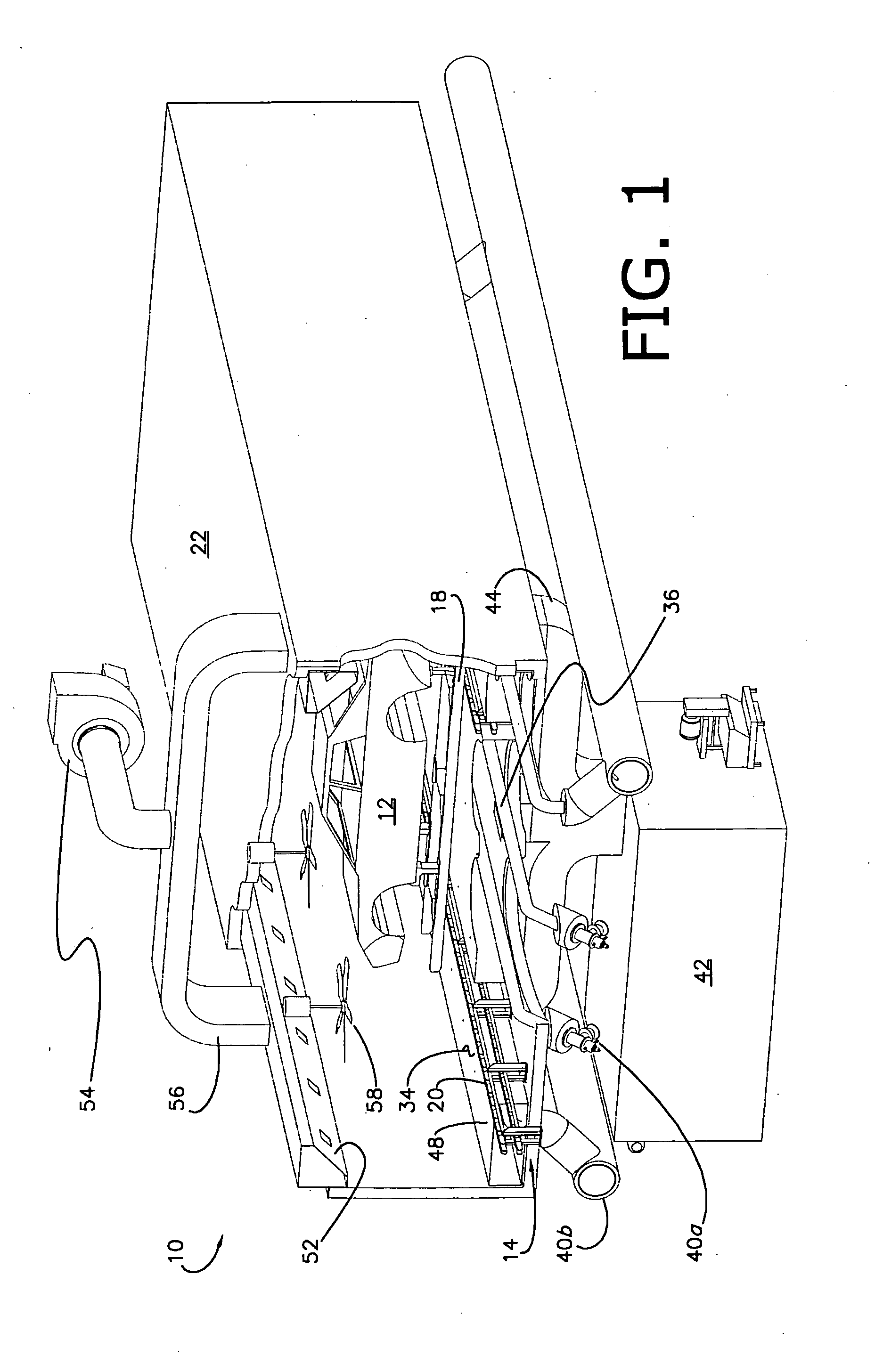
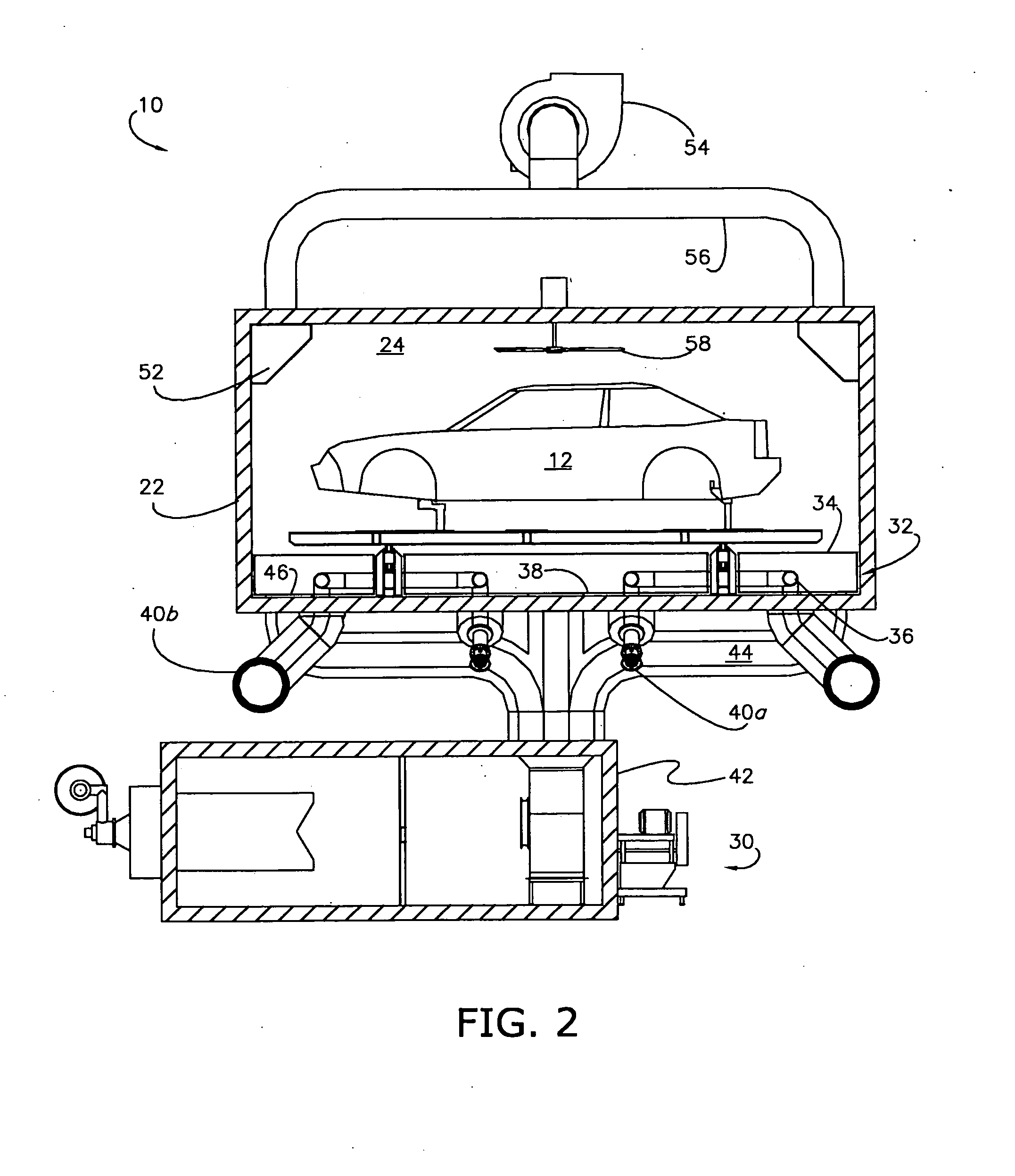
InactiveUS20100038353A1Increase widthFacilitates transverse bakingDrying solid materials with heatMuffle furnacesCooking & bakingCeiling fan
A manufacturing oven for and a method of baking a workpiece presenting a transverse orientation relative to the oven, includes dual radiant and convection heating sources operable to uniformly heat the workpiece by focusing convection heating air towards desirous parts of the workpiece, and preferably includes a chamber, a high emissivity false floor, at least one radiant heating element beneath the floor, at least one reflector beneath each element and configured to redirect radiant heat energy towards the floor, a fresh air heater for delivering fresh heated air into the chamber, an exhaust system for removing heated air and evaporated paint solvents from the chamber, and at least one ceiling fan operable to cause lighter heated air to flow from the ceiling of the chamber and towards the workpiece.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com