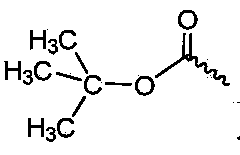
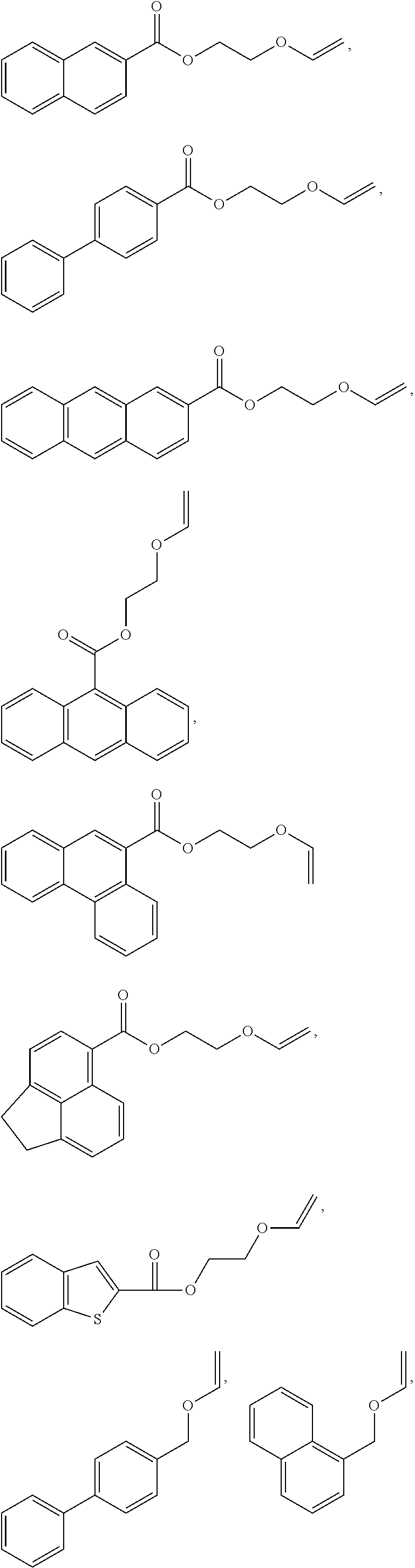
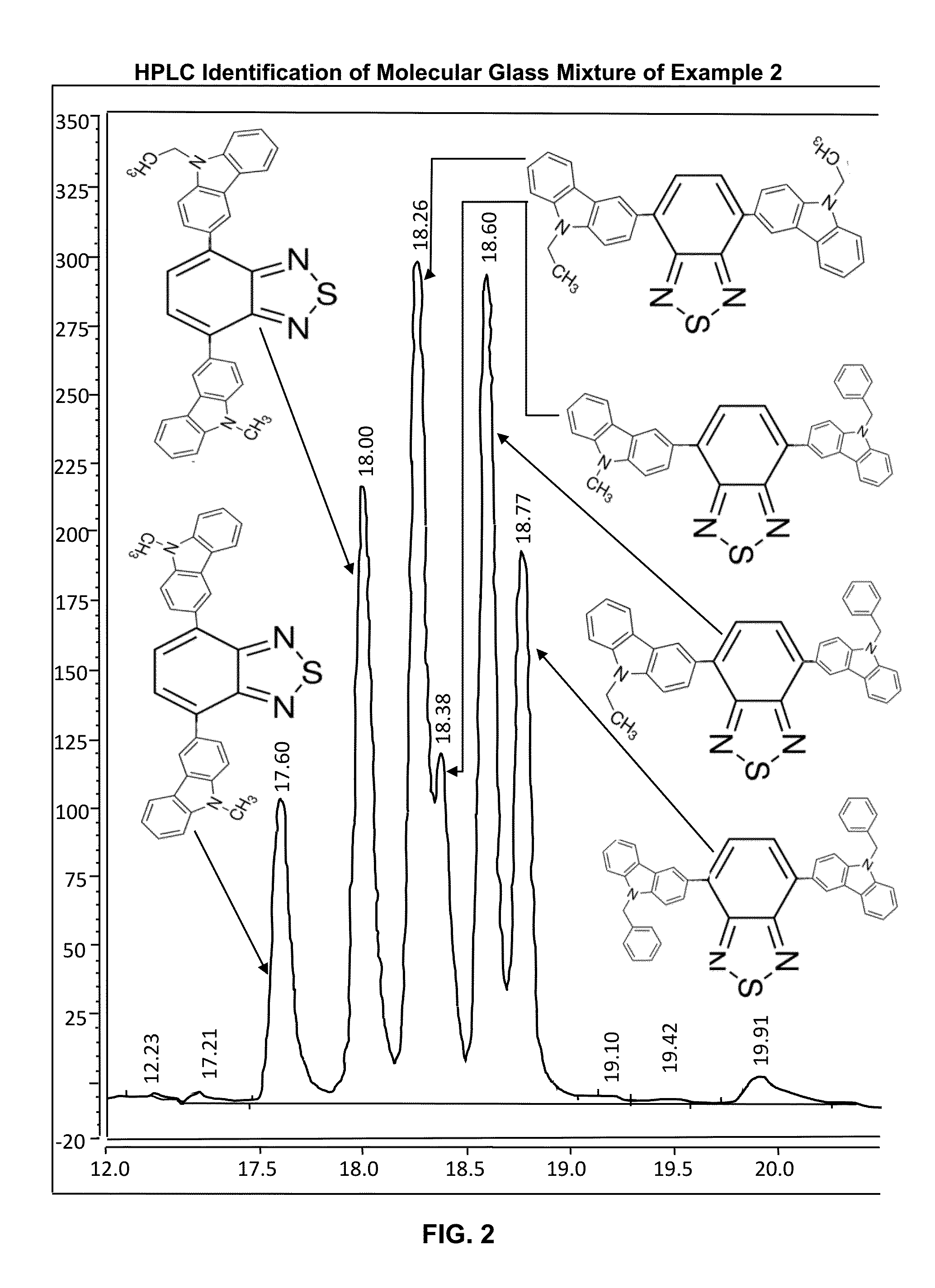
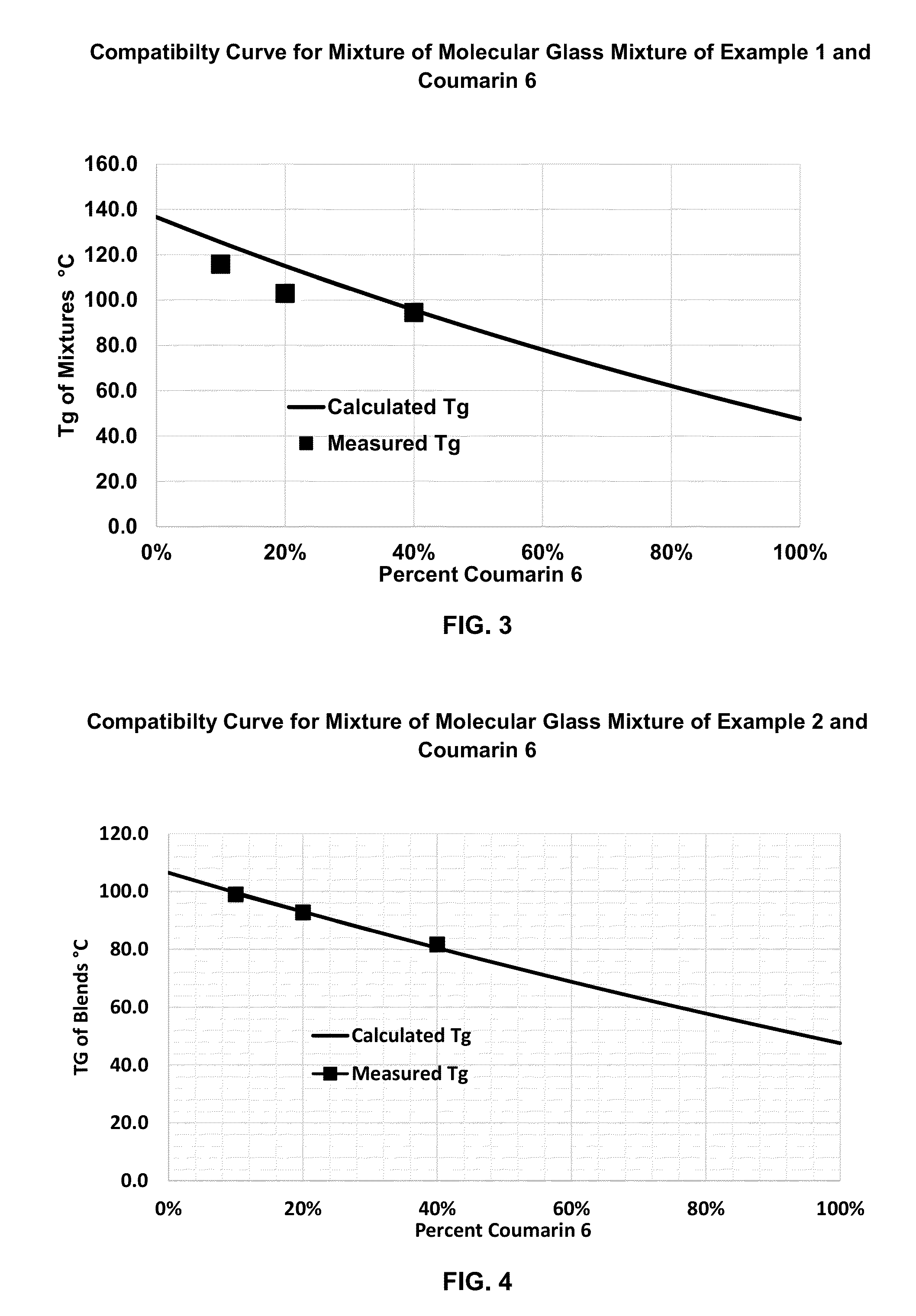
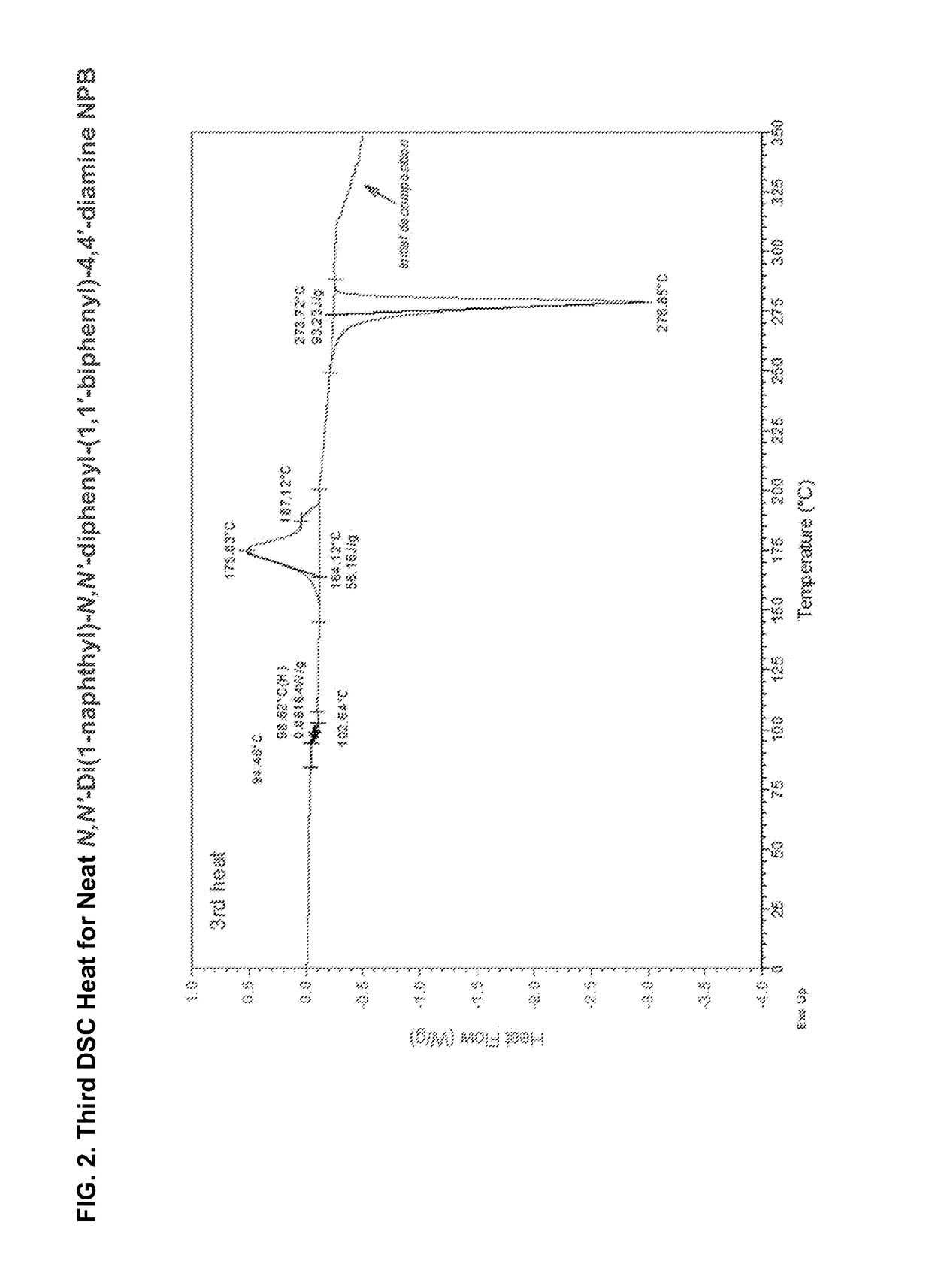
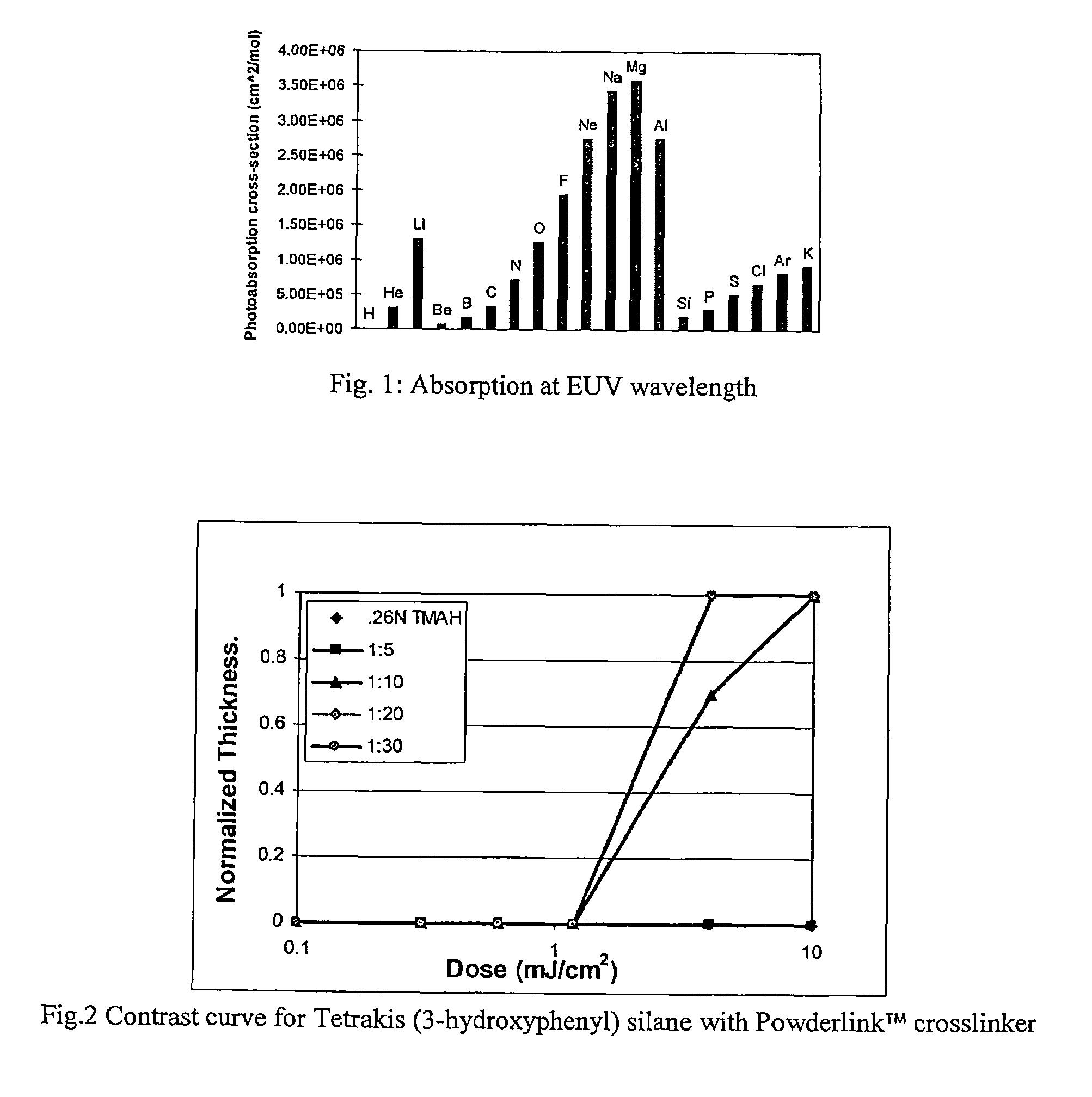
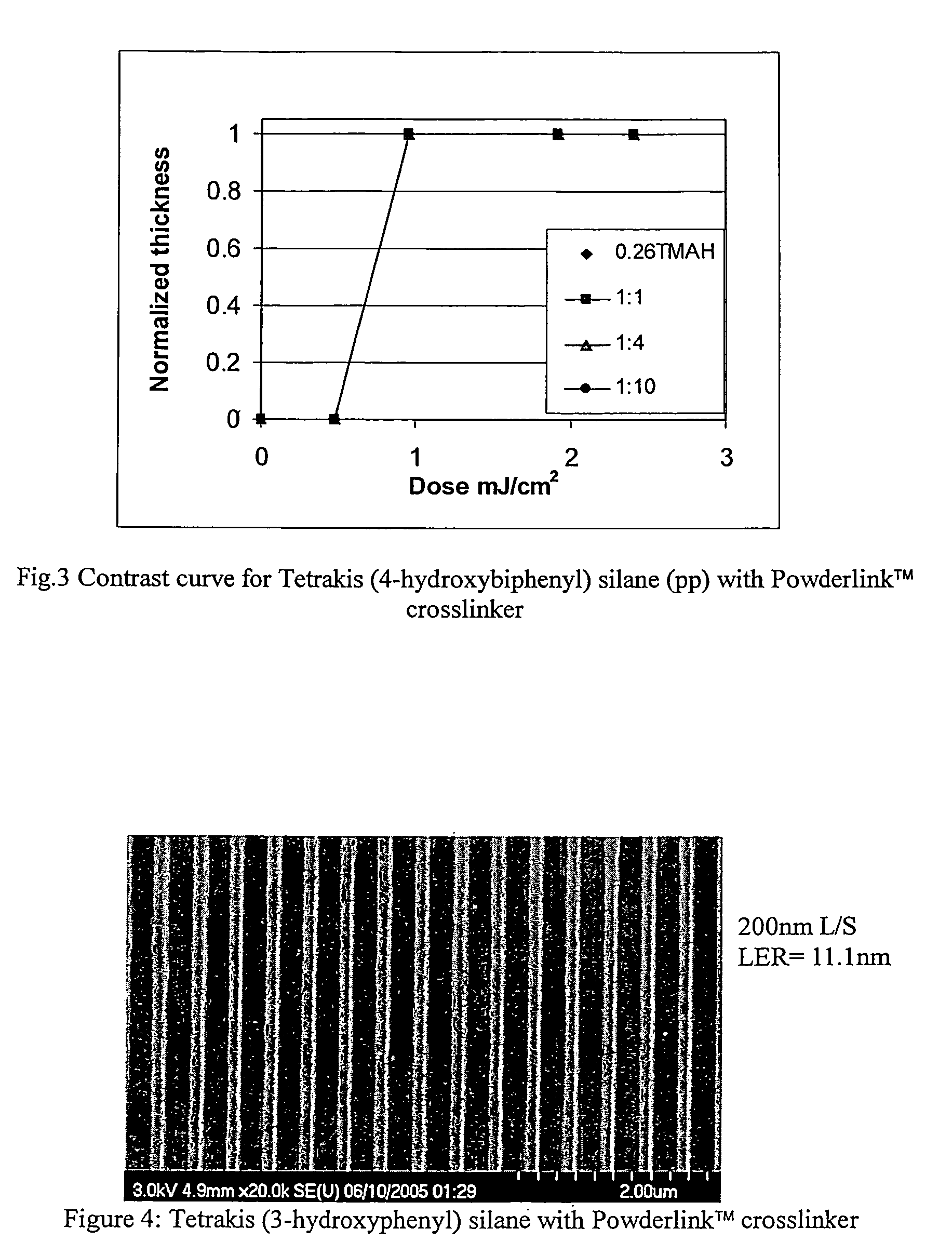
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Molecular glasses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Orthogonal Procesing of Organic Materials Used in Electronic and Electrical Devices
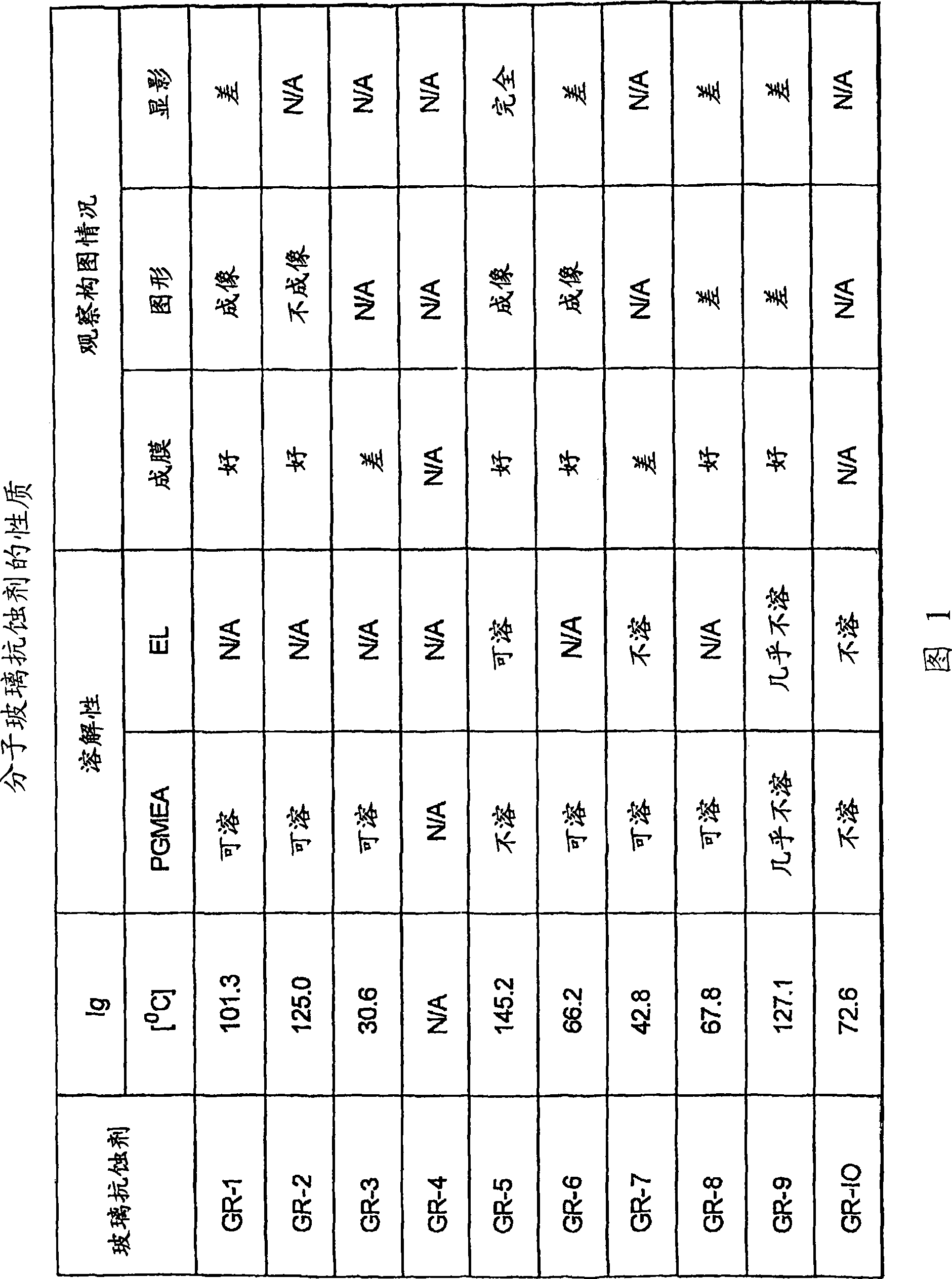
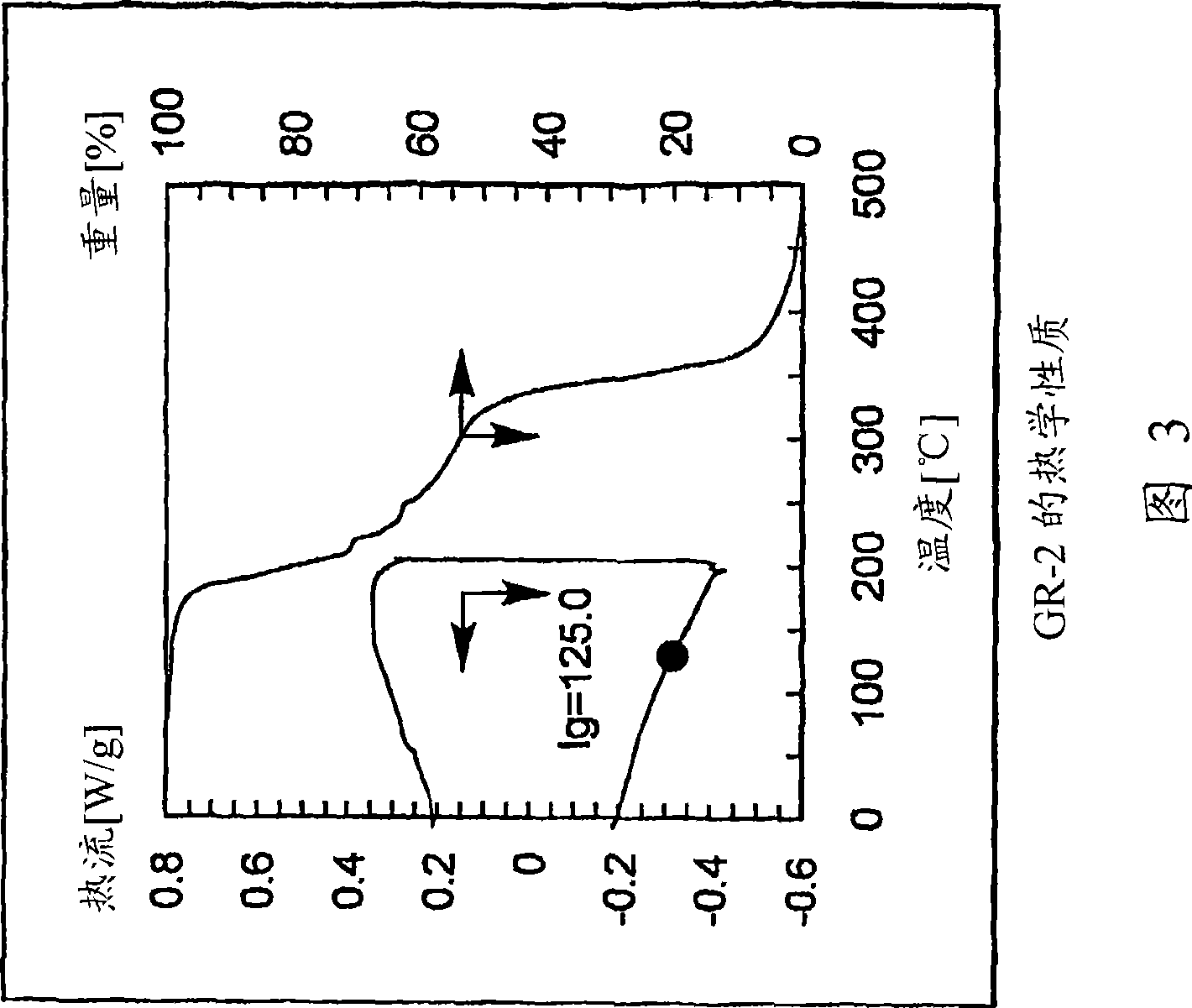
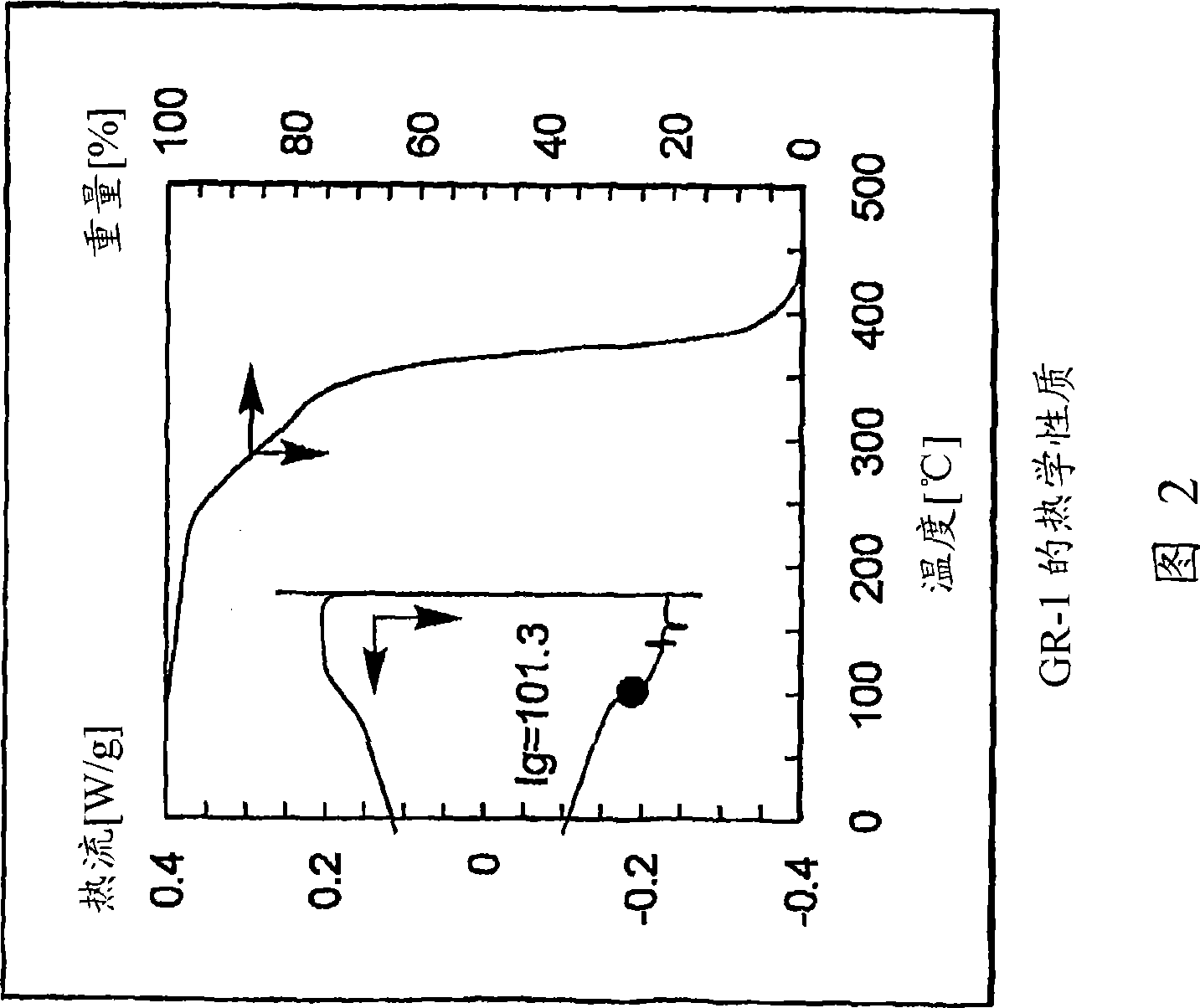
ActiveUS20110159252A1Avoid damageImprove throughputOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsOrganic structureMethacrylate
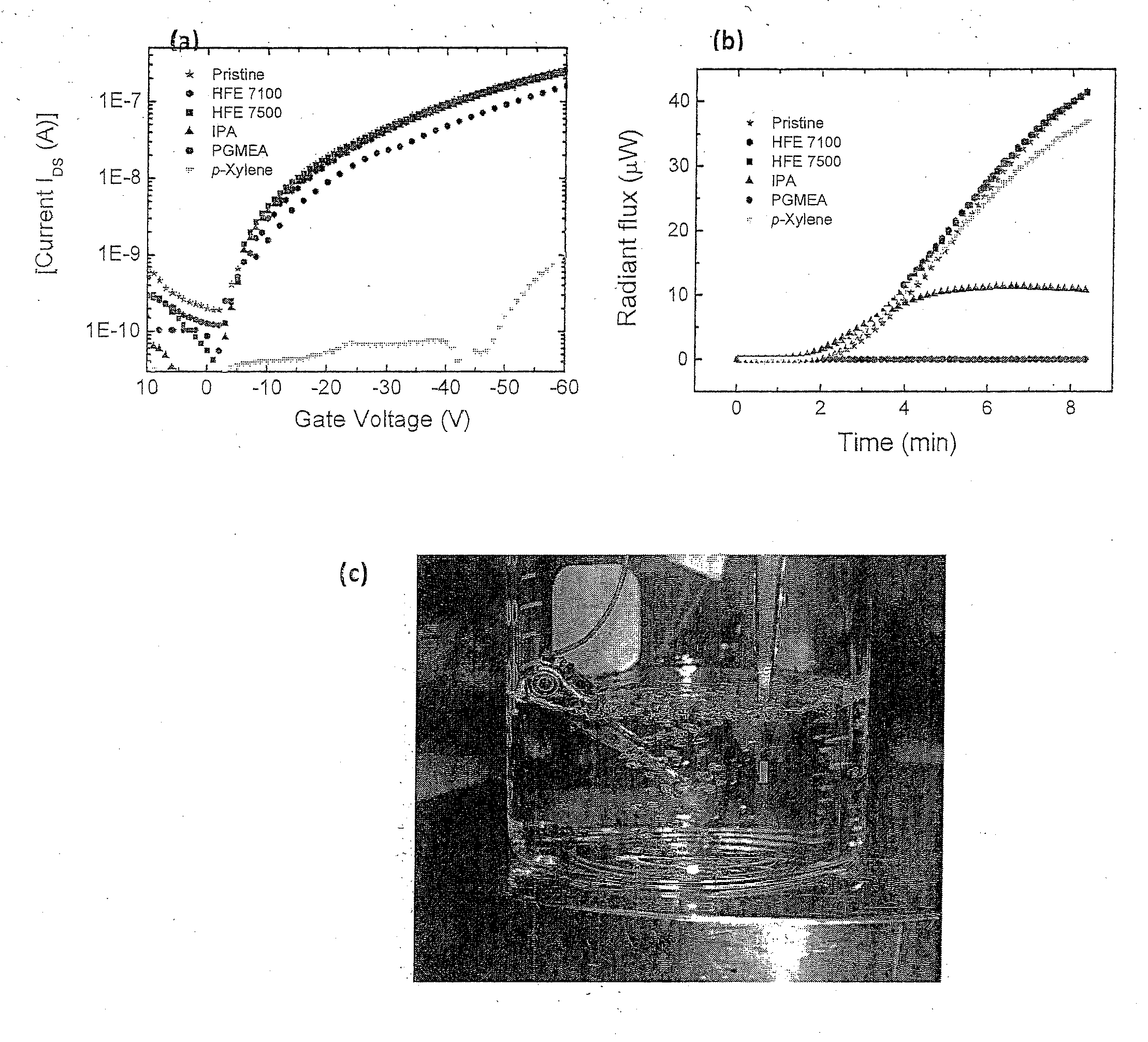
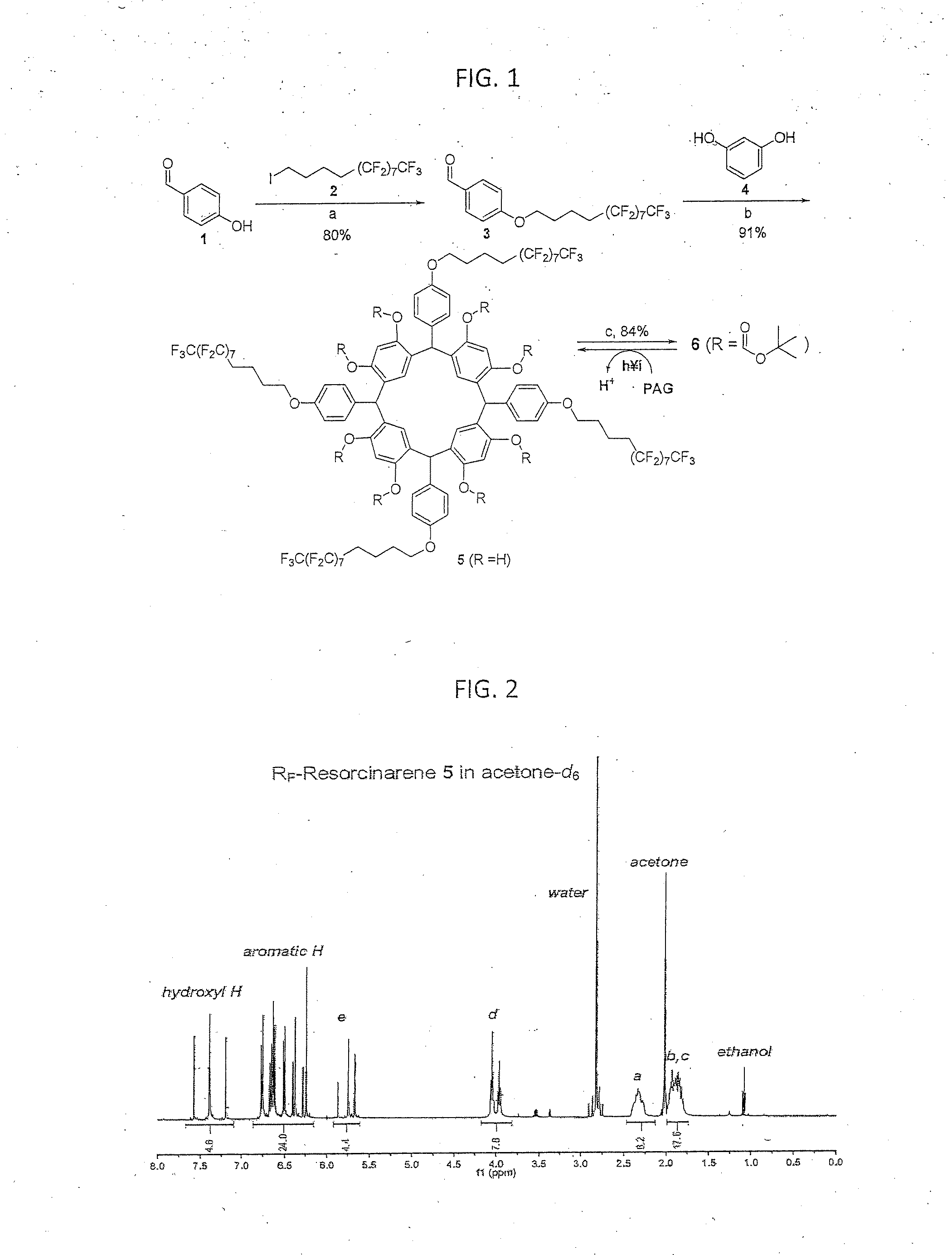
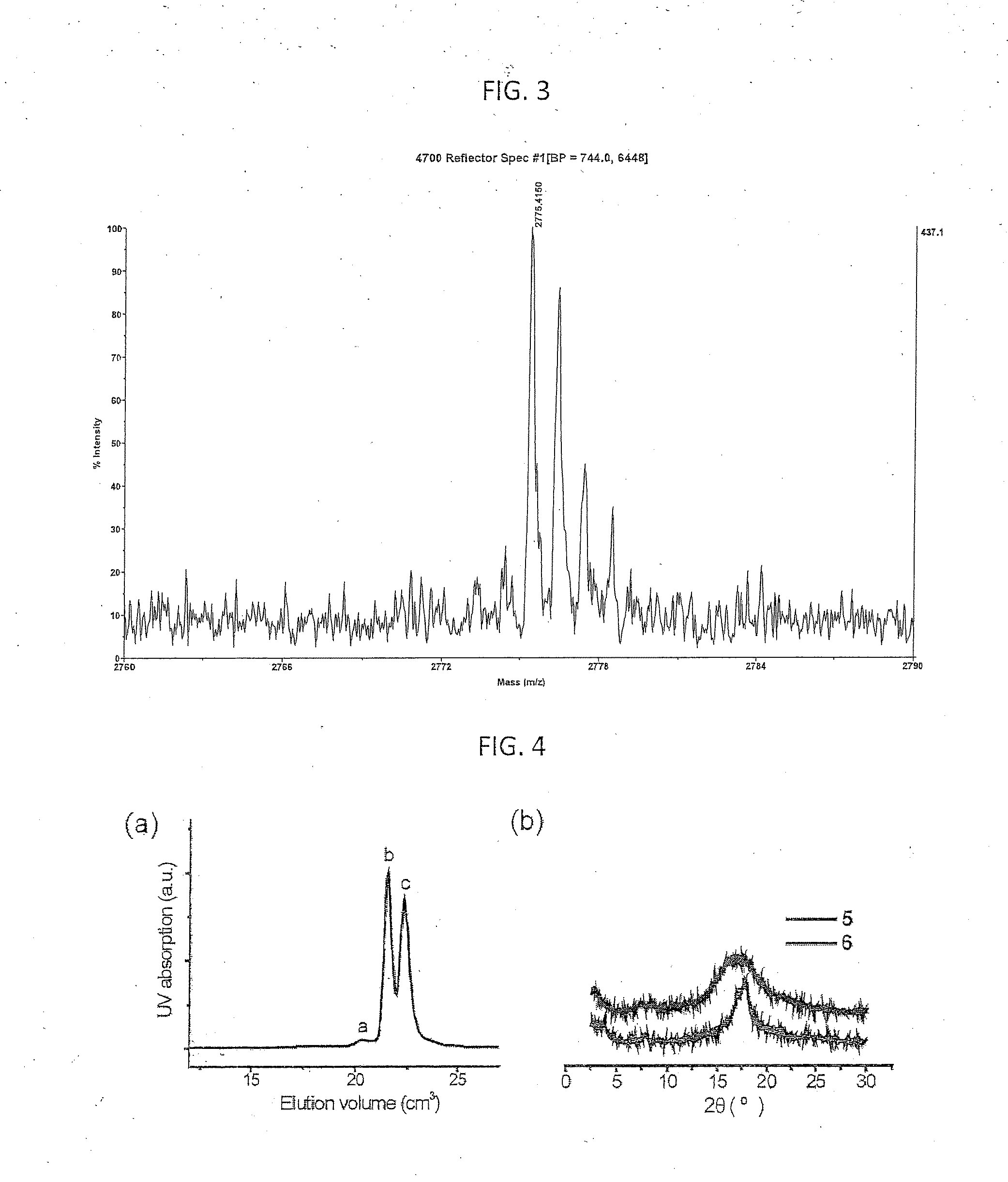
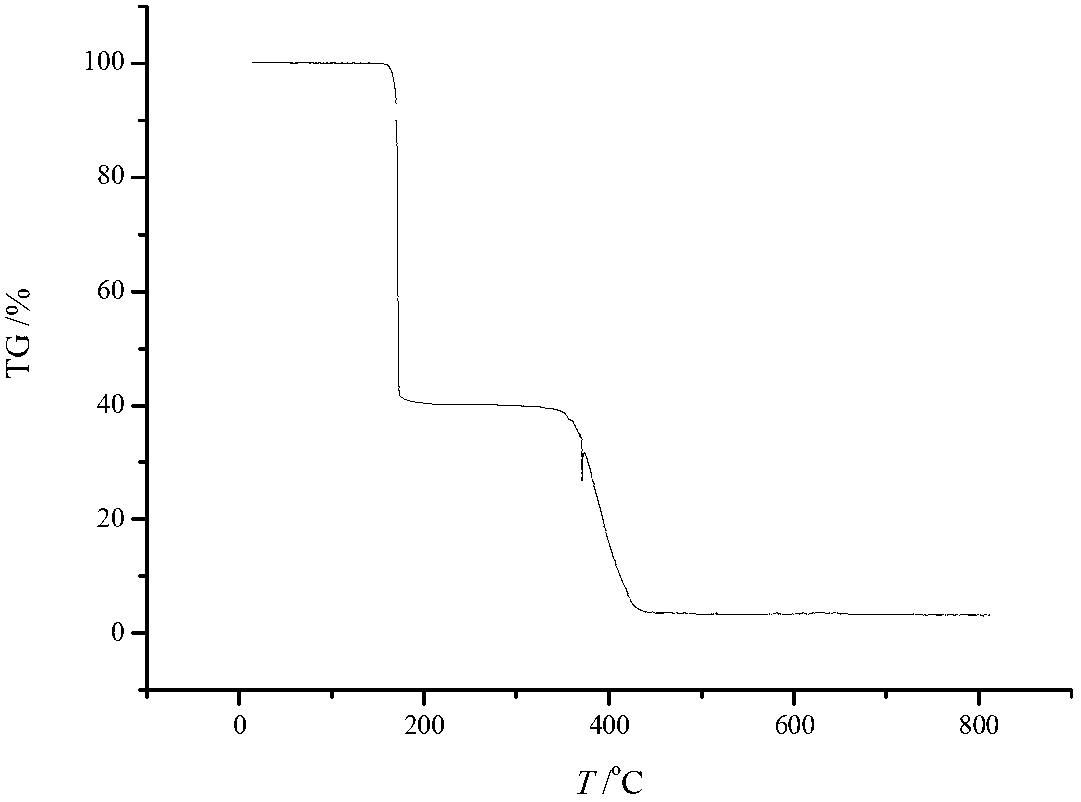
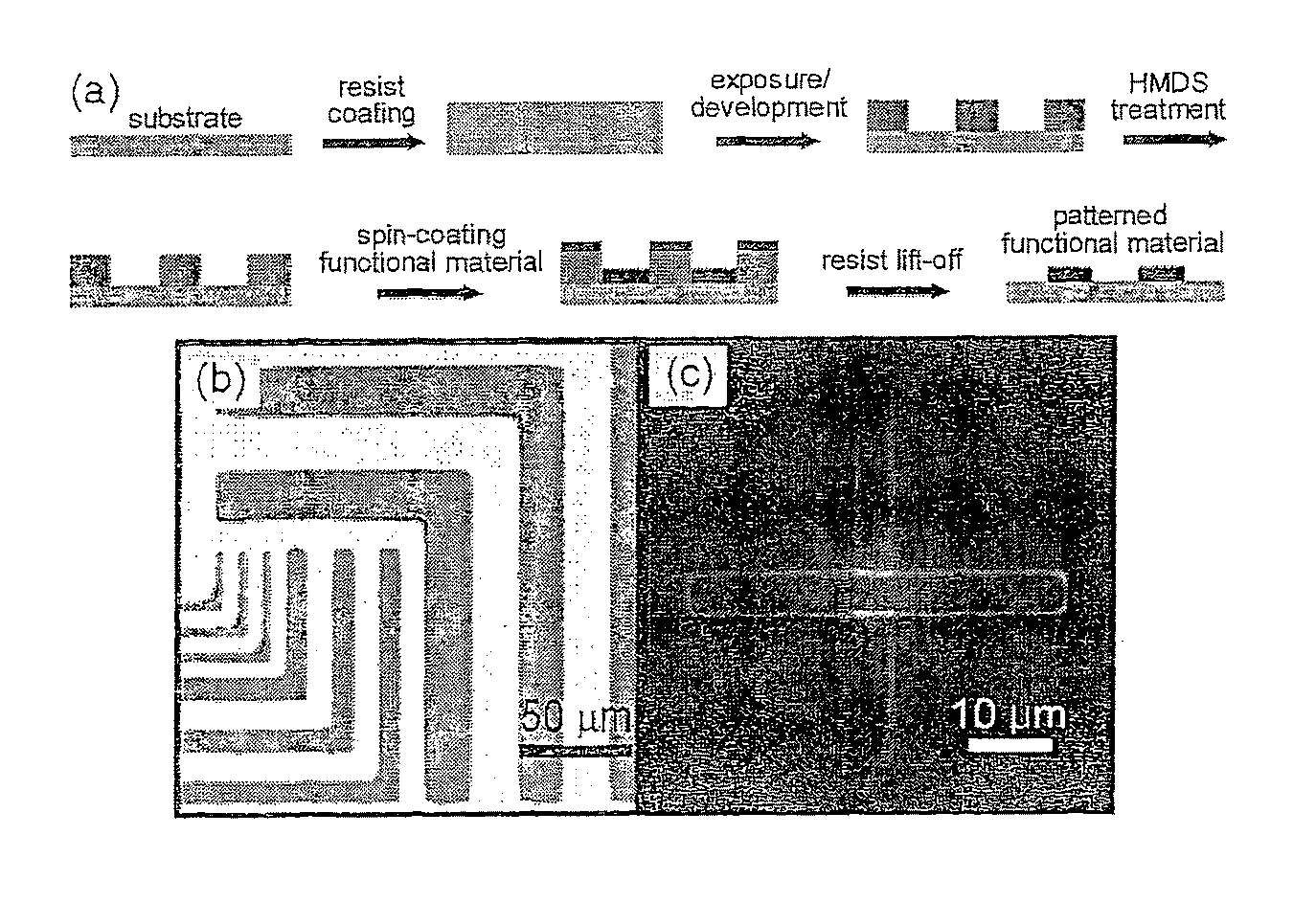
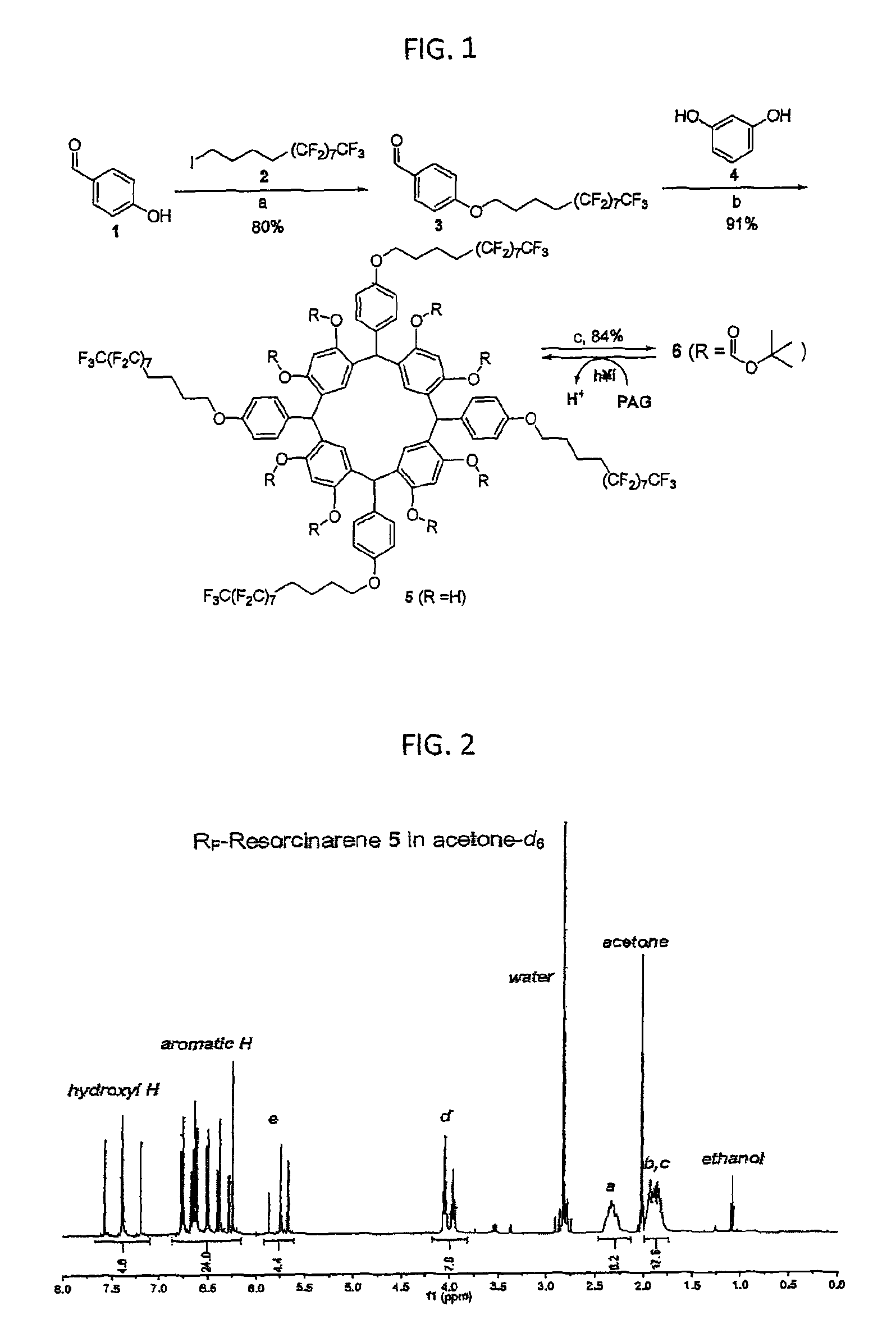
An orthogonal process for photolithographic patterning organic structures is disclosed. The disclosed process utilizes fluorinated solvents or supercritical CO2 as the solvent so that the performance of the organic conductors and semiconductors would not be adversely affected by other aggressive solvent. One disclosed method may also utilize a fluorinated photoresist together with the HFE solvent, but other fluorinated solvents can be used. In one embodiment, the fluorinated photoresist is a resorcinarene, but various fluorinated polymer photoresists and fluorinated molecular glass photoresists can be used as well. For example, a copolymer perfluorodecyl methacrylate (FDMA) and 2-nitrobenzyl methacrylate (NBMA) is a suitable orthogonal fluorinated photoresist for use with fluorinated solvents and supercritical carbon dioxide in a photolithography process. The combination of the fluorinated photoresist and the fluorinated solvent provides a robust, orthogonal process that is yet to be achieved by methods or devices known in the art.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
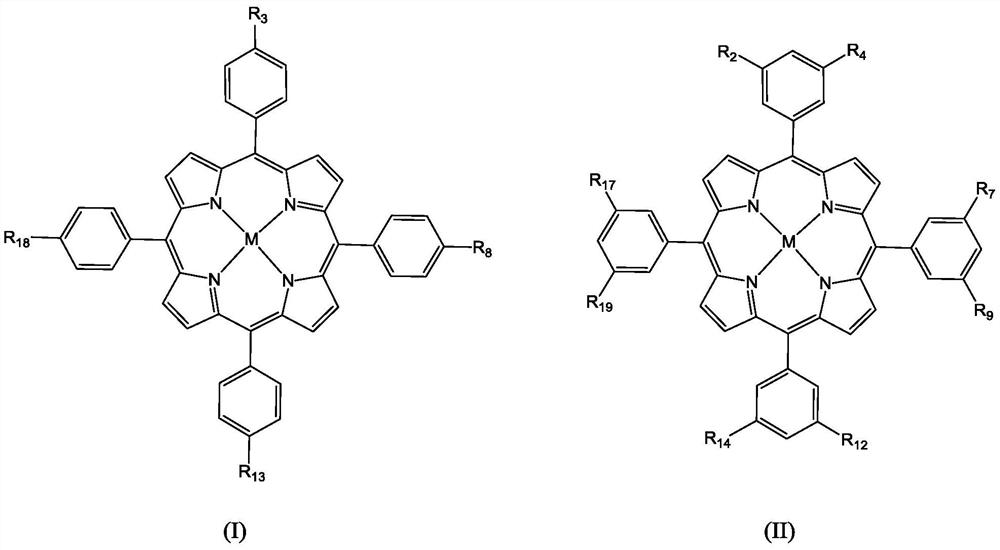
Molecular glass photoresist containing bisphenol A skeleton structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103304385AOrganic compound preparationPhotomechanical coating apparatusSolventNanoimprint lithography
The invention relates to a series of molecular glass photoresists (I and II) based on bisphenol A as a main body structure and a preparation method thereof. The molecular glass photoresists are compounded with a photo-acid generator, a crosslinking agent, a photoresist solvent and other additives to produce positive or negative photoresists; the positive or negative photoresists are placed on a silicon wafer through a spin coating method to prepare a photoresist coating layer with uniform thickness. The photoresist formula can be used in modern lithography technologies, such as 248nm lithography, 193nm lithography, extreme ultraviolet lithography, nanoimprinting lithography and electron beam lithography, and is especially suitable for an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) photo-lithographic process.
Owner:GUOKE TIANJI (BEIJING) NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Orthogonal processing of organic materials used in electronic and electrical devices
ActiveUS8846301B2Avoid damageImprove throughputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMethacrylateOrganic structure
An orthogonal process for photolithographic patterning organic structures is disclosed. The disclosed process utilizes fluorinated solvents or supercritical CO2 as the solvent so that the performance of the organic conductors and semiconductors would not be adversely affected by other aggressive solvent. One disclosed method may also utilize a fluorinated photoresist together with the HFE solvent, but other fluorinated solvents can be used. In one embodiment, the fluorinated photoresist is a resorcinarene, but various fluorinated polymer photoresists and fluorinated molecular glass photoresists can be used as well. For example, a copolymer perfluorodecyl methacrylate (FDMA) and 2-nitrobenzyl methacrylate (NBMA) is a suitable orthogonal fluorinated photoresist for use with fluorinated solvents and supercritical carbon dioxide in a photolithography process. The combination of the fluorinated photoresist and the fluorinated solvent provides a robust, orthogonal process that is yet to be achieved by methods or devices known in the art.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Starlike tetraphenylethylene derivative molecular glass, positive photoresist, positive photoresist coating and application thereof
ActiveCN104557552AGood rigid structureHigh glass transition temperatureOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSolubilityVitrification
The invention discloses starlike tetraphenylethylene derivative molecular glass, a positive photoresist, a positive photoresist coating and application thereof. The starlike tetraphenylethylene derivative molecular glass has the molecular structure shown in the description. The molecular glass is simple in synthesis process and suitable for industrial production; the tetraphenylethylene has a spatial solid geometrical skeleton adopting a rigid structure, can effectively inhibit molecular crystallization and is easy for film formation; the molecular glass has good solubility in various polar solvents, and has the characteristics of high glass transition temperature and high thermal stability, and can better meet requirements of a photoetching process; by adopting a spin coating method, a good film can be obtained, and the molecular glass can be used as the photoresist and can be prepared into the positive photoresist for photoetching through cooperation with other additives.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecular glass photoresists containing bisphenol a framework and method for preparing the same and use thereof
ActiveUS20150037735A1Increase photosensitivityHigh resolutionOrganic compound preparationPhotosensitive materialsCross-linkResist
The present invention provides a class of molecular glass photoresist (I and II) comprising bisphenol A as a main structure and their preparation. The molecular glass photoresist is formulated with a photoacid generator, a cross-linking agent, a photoresist solvent, and other additives into a positive or negative photoresist. A photoresist with a uniform thickness is formed on a silicon wafer by spin-coating. The photoresist formulation can be used in modern lithography, such as 248 nm photolithography, 193 nm photolithography, extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, nanoimprint lithography, electron beam lithography, and particularly in the EUV-lithography technique.
Owner:INST OF CHEM
Star-shaped adamantane derivative molecular glasses, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103804196AEasy to synthesizeAchieve separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAlkoxy groupPerylene derivatives
The invention discloses star-shaped adamantane derivative molecular glasses having the following structure shown in the description, wherein substituents R1-R12 are respectively hydrogen, hydroxy, alkoxy or acid sensitivity substituents; the substituents R1-R12 can be different or the same, but the substituents at a same benzene ring cannot both be hydrogen. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the star-shaped adamantane derivative molecular glasses. The method is simple in synthesis process, products of the steps of a reaction all can be separated from the system through a recrystallization or precipitation method. The molecular glasses can be used as photoresist main body materials made into thin films, and also can be used for photoetching.
Owner:国科天骥(北京)新材料技术有限责任公司
Semiconducting composition
ActiveUS20110260114A1Good film formingImprove mobilityConductive materialSolid-state devicesSemiconductorMolecular glasses
The present application discloses, in various embodiments, semiconducting layer compositions comprising a non-amorphous semiconductor material and a molecular glass. Electronic devices, such as thin-film transistors, are also disclosed. The semiconducting layer compositions exhibit good film-forming properties and high mobility.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for patterning nanoscale patterns of molecules on material surfaces
Probe-based methods for patterning a surface of a material are described. In particular, high resolution patterning of molecules on a surface of a material, such as nano-scale patterns with feature sizes of less than 30 nanometers, are described. In one aspect, a method for patterning a surface of a material includes providing a material having a polymer film. A heated, nano-scale dimensioned probe is then used to desorb molecules upon interacting with the film. The film includes a network of molecules (such as molecular glasses) which are cross-linked via intermolecular (noncovalent) bonds, such as hydrogen bonds.
Owner:IBM CORP
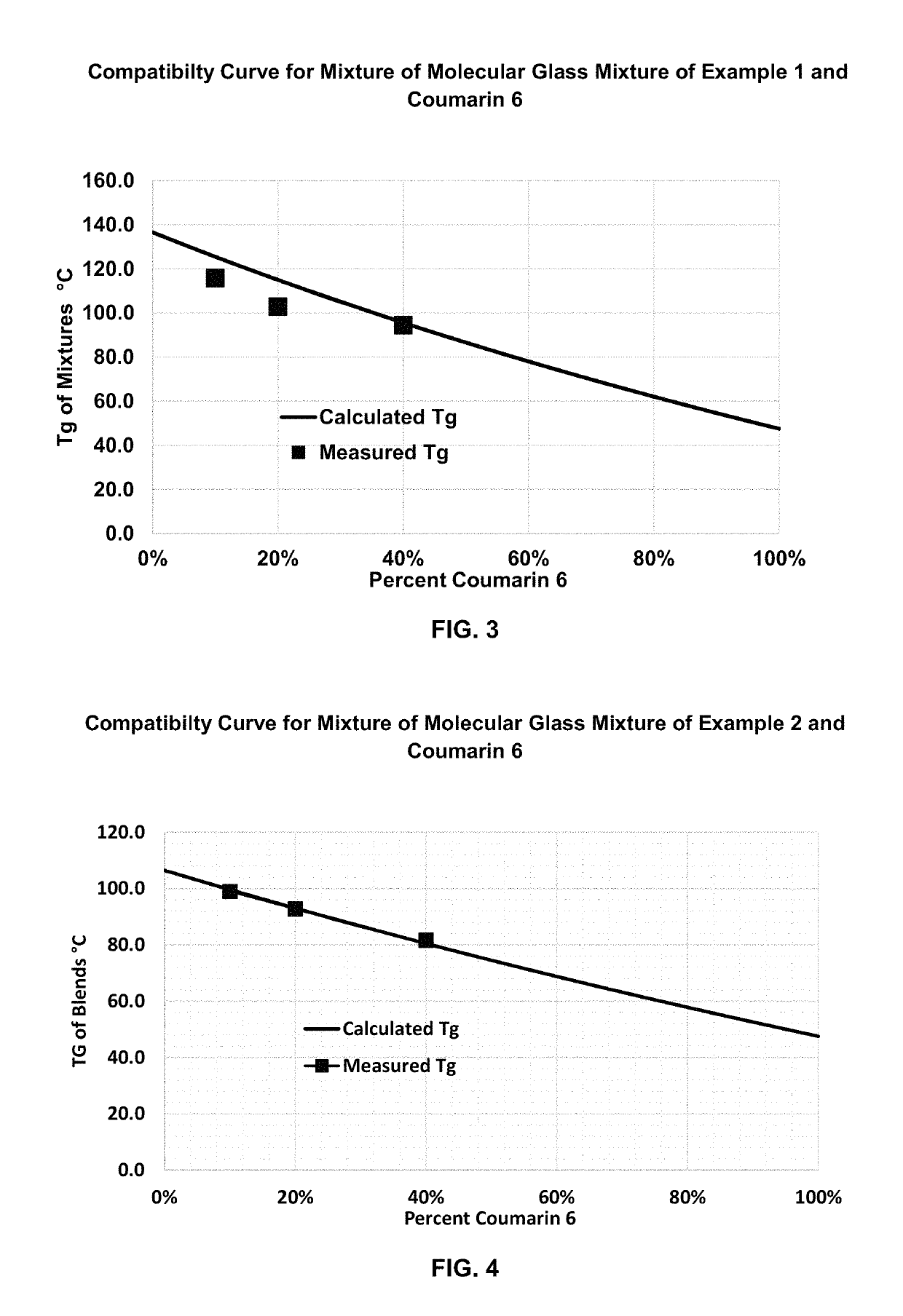
Crosslinkable, /Polymerizable and Combinations Thereof Charge-transporting Molecular Glass Mixtures, Luminescent Molecular Glass Mixtures, or Combinations Thereof for Organic Light Emitting Diodes and other Organic Electronics and Photonics Applications and Mothod of Making Same.
ActiveUS20150179714A1Modifies it propertyReduce the temperatureFinal product manufactureConductive materialChemical compoundPhotonics
The present invention provides crosslinkable, polymerizable and combinations thereof charge transporting molecular glass mixtures, luminescent molecular glass mixtures, or combinations thereof comprising at least two nonpolymeric compounds each independently corresponding to the structure (R1Y1)p[(Z1Y2)mR2Y3]nZ2Y4R3 wherein m is zero or one; n is zero up to an integer at which said compound starts to become a polymer; p is an integer of from one to eight; each R1 and R3 is independently a monovalent aliphatic or cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aromatic group or a multicyclic aromatic nucleus; R2, Z1, and Z2 each independently represent multivalent aliphatic or cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon groups having 1 to 20 carbon atoms or an aromatic group; and Y1, Y2, Y3, and Y4 each independently represent one or more linking groups. The present invention also provides methods for making the same.
Owner:MOLAIRE CONSULTING
Calixarene compound and photoresist composition comprising same
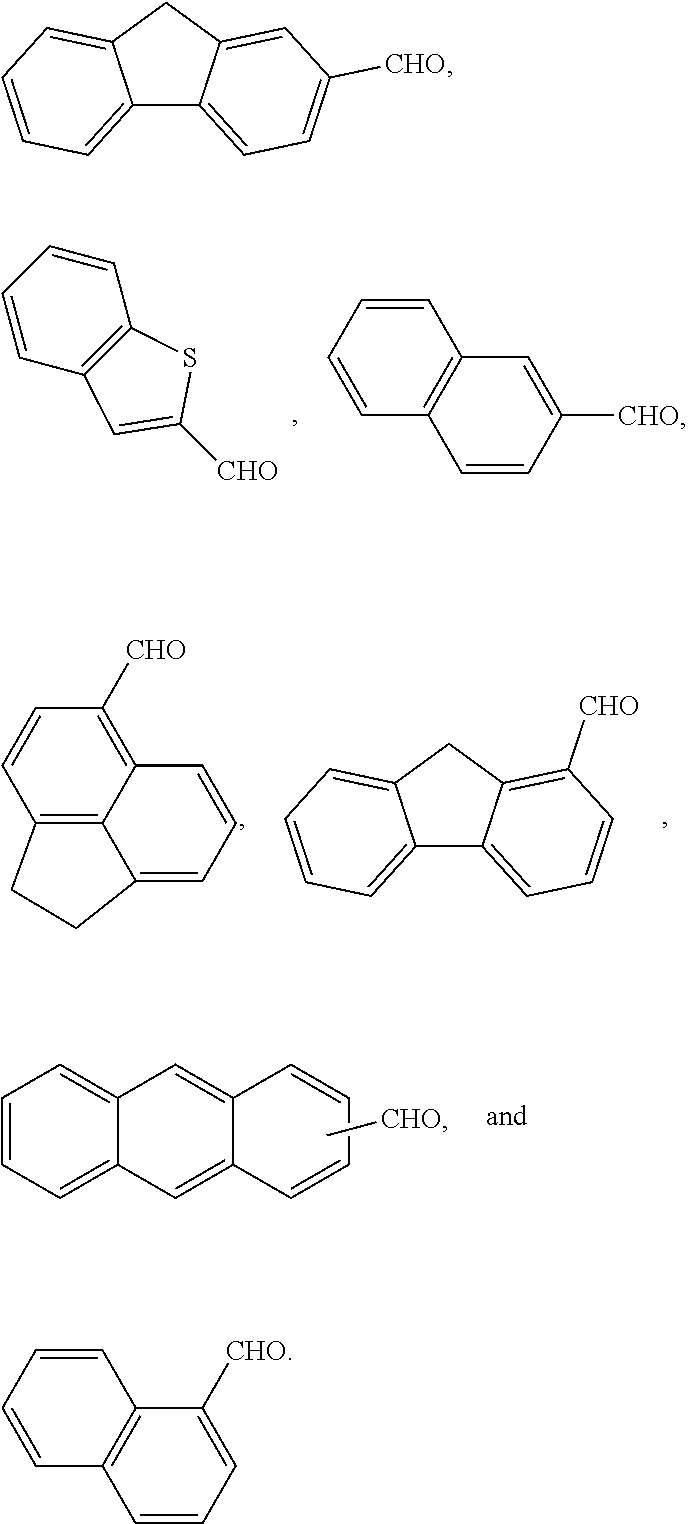
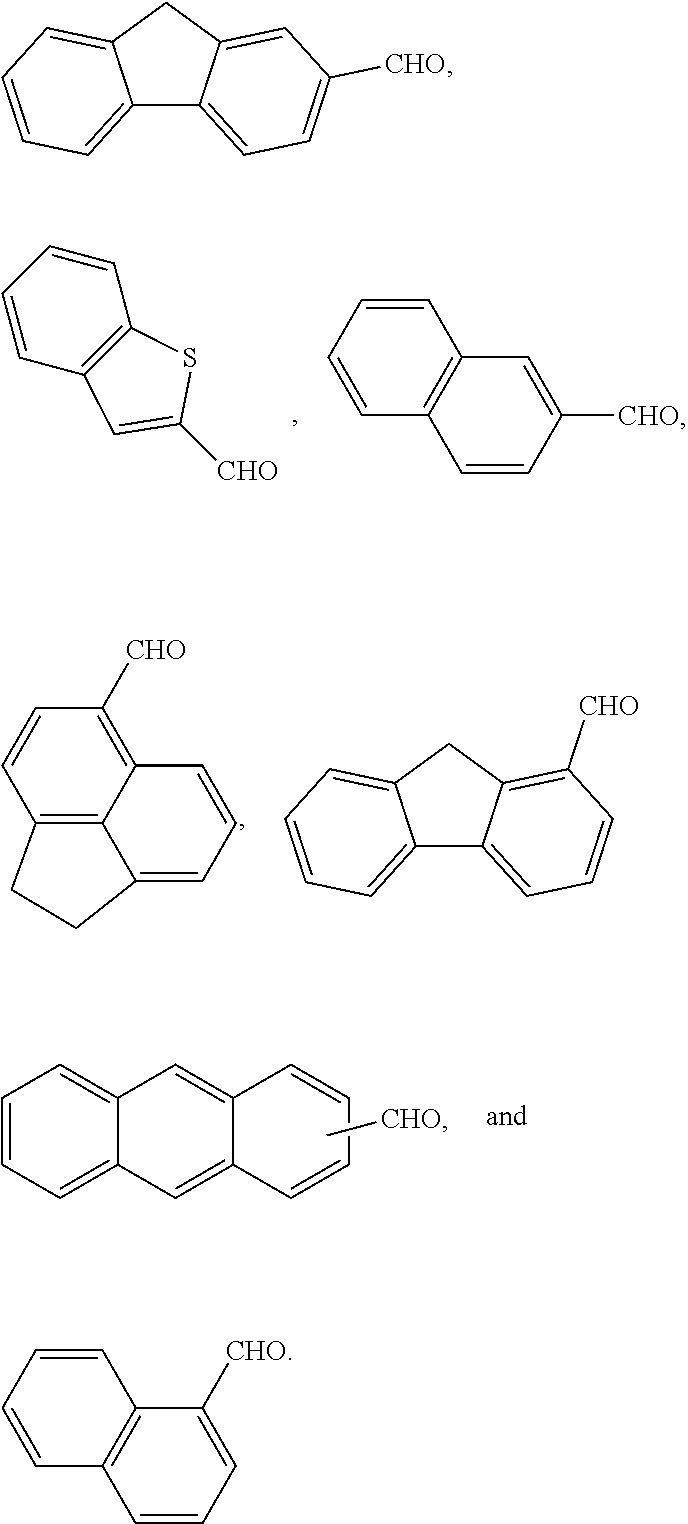
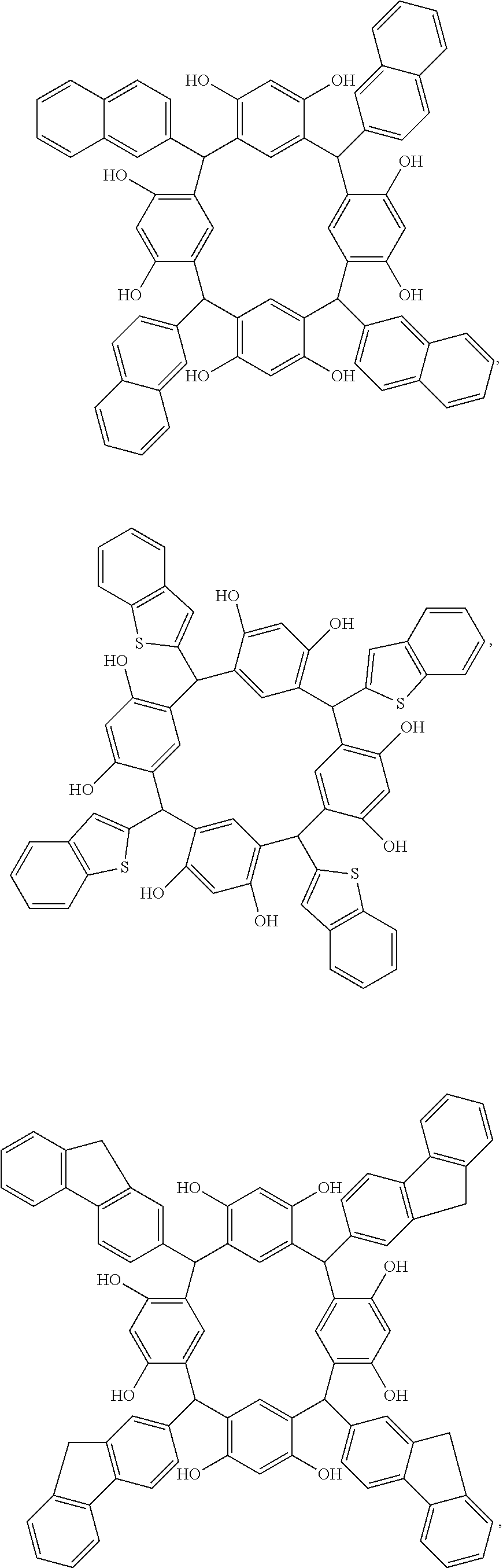
A molecular glass compound includes (A) a tetrameric reaction product of a specific aromatic compound having at least one hydroxy group, and a specific polycyclic or fused polycyclic aromatic aldehyde; and (B) an acid-removable protecting group as an adduct with the hydroxy group of the aromatic compound and / or a hydroxy group of the polycyclic or fused polycyclic aromatic aldehyde. A photoresist composition including the molecular glass compound, and a coated substrate including a layer of the photoresist composition are also disclosed.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
Non-crystallizable pi-conjugated molecular glass mixtures, charge transporting molecular glass mixtures, luminescent molecular glass mixtures, or combinations thereof for organic light emitting diodes and other organic electronics and photonics applications
ActiveUS10240084B2Enhance non-crystallizabilityHighly symmetric and rigid nucleiSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotonicsLight-emitting diode
The present invention provides charge transporting molecular glass mixtures, luminescent molecular glass mixtures, or combinations thereof comprising at least two nonpolymeric compounds each independently corresponding to the structure (R1Y1)p[(Z1Y2)mR2Y3]nZ2Y4R3 wherein m is zero or one; n is zero up to an integer at which said compound starts to become a polymer; p is an integer of from one to eight; each R1 and R3 is independently a monovalent aliphatic or cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aromatic group or a multicyclic aromatic nucleus; R2, Z1, and Z2 each independently represent multivalent aliphatic or cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon groups having 1 to 20 carbon atoms or an aromatic group; and Y1, Y2, Y3 and Y4 each independently represent a triple bond, a double bond, or a single bond link.
Owner:MOLAIRE CONSULTING
Calixarene and photoresist composition comprising same
ActiveUS20130078569A1Organic compound preparationElectric discharge tubesVinyl etherPhotoacid generator
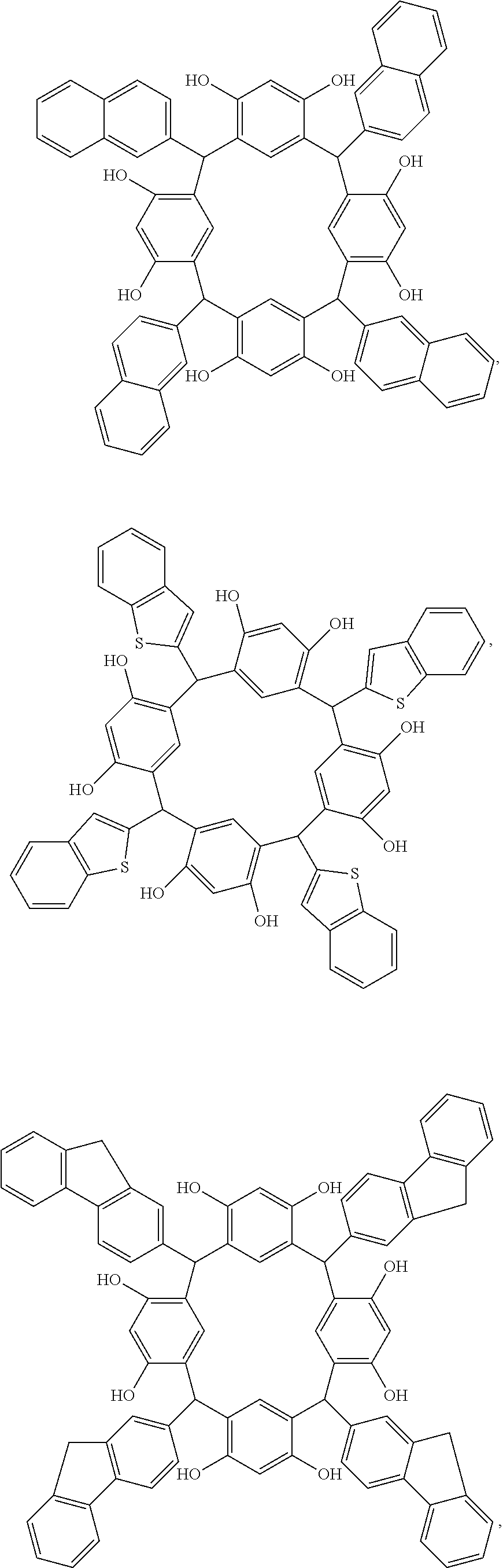
A molecular glass compound comprises a vinyl ether adduct of an aromatic vinyl ether of formula C(R1)2═C(R2)—O-(L)n-Ar1, and a calix[4]arene, wherein R1 and R2 are each independently a single bond, H, C1-20 alkyl, C1-20 haloalkyl, C6-20 aryl, C6-20 haloaryl, C7-20 aralkyl, or C7-20 haloaralkyl, L is a C1-20 linking group, n is 0 or 1, and Ar1 is a halo-containing monocyclic, or substituted or unsubstituted polycyclic or fused polycyclic C6-20 aromatic-containing moiety, wherein R1 and R2 are connected to Ar1 when either or both of R1 and R2 is a single bond and n is 0. A photoresist, comprising the molecular glass compound, a solvent, and a photoacid generator, a coated substrate, comprising (a) a substrate having one or more layers to be patterned on a surface thereof; and (b) a layer of a photoresist composition over the one or more layers to be patterned, and a method of forming the molecular glass compound, are also disclosed.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC +1
Adamantane Based Molecular Glass Photoresists for Sub-200 Nm Lithography
InactiveUS20080318156A1Preparation from carboxylic acid halidesSugar derivativesResistLithographic artist
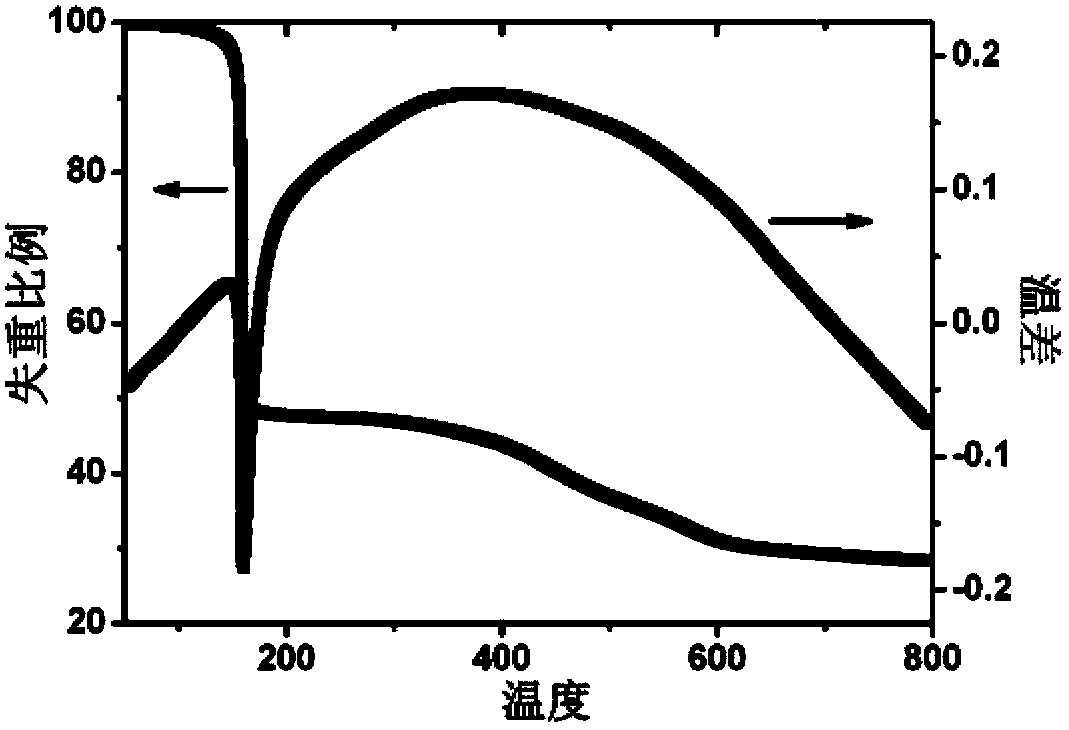
Disclosed are glass photoresists generated from adamantane derivatives containing acetal and / or ester moieties as novel high-performance photoresist materials. Some of the disclosed adamantane-based glass resists have a tripodal structure and other disclosed adamantane-based glass resists include one or more cholic groups. The disclosed adamantane derivatives can be synthesized from starting materials which are commercially available. By way of example only, one of many disclosed amorphous glass photoresists has the following structure:
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Calixarene compound and photoresist composition comprising same
A molecular glass compound includes (A) a tetrameric reaction product of a specific aromatic compound having at least one hydroxy group, and a specific polycyclic or fused polycyclic aromatic aldehyde; and (B) an acid-removable protecting group as an adduct with the hydroxy group of the aromatic compound and / or a hydroxy group of the polycyclic or fused polycyclic aromatic aldehyde. A photoresist composition including the molecular glass compound, and a coated substrate including a layer of the photoresist composition are also disclosed.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
Calixarene and photoresist composition comprising same
A molecular glass compound comprises a vinyl ether adduct of an aromatic vinyl ether of formula C(R1)2═C(R2)—O-(L)n-Ar1, and a calix[4]arene, wherein R1 and R2 are each independently a single bond, H, C1-20 alkyl, C1-20 haloalkyl, C6-20 aryl, C6-20 haloaryl, C7-20 aralkyl, or C7-20 haloaralkyl, L is a C1-20 linking group, n is 0 or 1, and Ar1 is a halo-containing monocyclic, or substituted or unsubstituted polycyclic or fused polycyclic C6-20 aromatic-containing moiety, wherein R1 and R2 are connected to Ar1 when either or both of R1 and R2 is a single bond and n is 0. A photoresist, comprising the molecular glass compound, a solvent, and a photoacid generator, a coated substrate, comprising (a) a substrate having one or more layers to be patterned on a surface thereof; and (b) a layer of a photoresist composition over the one or more layers to be patterned, and a method of forming the molecular glass compound, are also disclosed.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC +1
Dielectric layer for an electronic device
ActiveUS20100301344A1Plastic/resin/waxes insulatorsLiquid organic insulatorsDielectric layerMolecular glasses
A dielectric layer for an electronic device, such as a thin-film transistor, is provided. The dielectric layer comprises a molecular glass. The resulting dielectric layer is very thin, pure, and stable. Processes and compositions for fabricating such a dielectric layer are also disclosed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Biphenyl molecular glass and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102557930AReduce line width roughnessNo swellingOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCompound aBenzene
The invention relates to biphenyl molecular glass and a preparation method thereof, namely preparation of 2, 2' 1 2 (3, 5-di-tert-butyl-di-carbonate)-4, 4'-1 2 (di-tert-butyl-di-carbonate) biphenyl compound A and 2, 2', 4, 4'-4 (3, 5-di-tert-butyl-di-carbonate) biphenyl compound B. The diazotization reaction is conducted on 2, 2' 1 2 (3, 5-di-tert-butyl-di-carbonate)-4, 4'-benzidine under the condition of NaNO2 / H2SO4, then the 2, 2' 1 2 (3, 5-di-tert-butyl-di-carbonate)-4, 4'-benzidine is heated and hydrolyzed under the acidity condition, demethylation is conducted under the condition of BBr3 to obtain 2, 2' 1 2 (3, 5-dyhydroxy-phenyl)-4, 4'-diphenol, and finally the 2, 2' 1 2 (3, 5-dyhydroxy-phenyl)-4, 4'-diphenol reacts with (t-Boc)2O to obtain the compound A. The 2, 2' 1 2 (3, 5-di-tert-butyl-di-carbonate)-4, 4'-benzidine is diazotized and then mixed with potassium iodide to obtain 2, 2' 1 2 (3, 5-di-tert-butyl-di-carbonate)-4, 4'-biphenyl-diiodine. The 2, 2' 1 2 (3, 5-di-tert-butyl-di-carbonate)-4, 4'-biphenyl-diiodine conducts Suzuki reaction with 3, 5-dimethoxy benzene boric acid under catalyst of Pd(Ph3)4 / K2CO3 to obtain 2, 2', 4, 4'-4(3, 5-dimethoxy) biphenyl. 2, 2', 4, 4'-4(3, 5-dyhydroxy-biphenyl) is obtained by demethylation through the BBr3 under low temperature and reacts with the (t-Boc)2O to obtain the compound B.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Chemical amplification photoresist composition and application thereof in ultraviolet lithography
ActiveCN110032040AHigh sensitivityIncrease roughnessPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusFuranUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a chemical amplification photoresist compositions which are each prepared by taking a series of molecular glass compounds, which take tetraphenyl furan, tetraphenyl pyrrole, tetraphenyl thiophene, pentaphenylpyridine, tetraphenyl bisphenol A and calixarene bisphenol A, as cores as main body materials and taking a photoacid generator, a solvent and the like as auxiliary materials through combination. The photoresist composition is spin-coated on a substrate to prepare a photoresist film with uniform thickness, and the photoresist film is applied to ultraviolet light source exposure of 200-450nm, and is particularly suitable for far-field and near-field photoetching technologies, such as 365nm I line photoetching, 248nm deep ultraviolet photoetching, 436nm G line photoetching and the like, such as an ultraviolet exposure machine, 365nm laser direct writing near-field photoetching, 365nm laser interference photoetching and other ultraviolet photoetching technologies.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
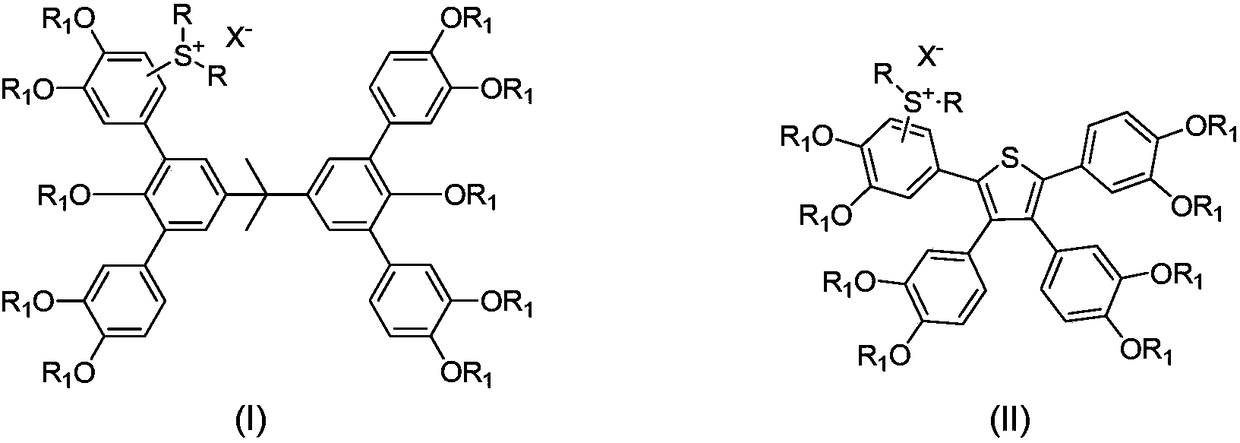
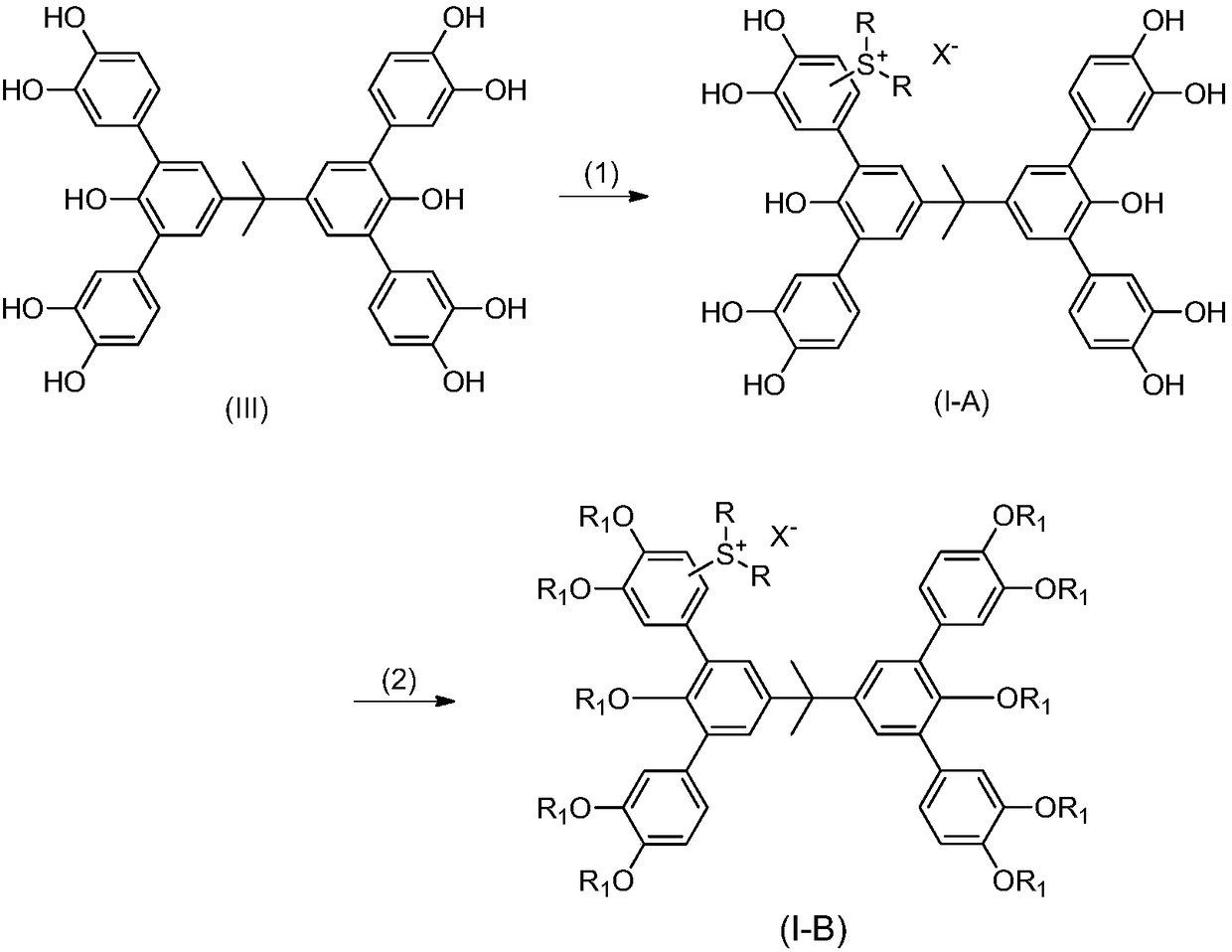
Sulfonium salt bonded phenol type molecular glass photoresist, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108147983AEvenly distributedHigh resolutionSulfonic acids salts preparationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCooking & bakingCross-link
The invention relates to a sulfonium salt bonded phenol type molecular glass photoresist, a preparation method and application thereof. The sulfonium salt bonded phenol type molecular glass photoresist is a stereoscopically asymmetrical amorphous small molecule compound, has relatively high melting point and glass-transition temperature (melting points being higher than 100 DEG C respectively), and can meet a photolithography requirement, so that the membrane structure is free of change during high-temperature baking. The compound can be individual or be compound with other photoresists, light-induced acid production agents and cross-linking agents into positive or negative photoresists, and a photoresist coating with uniform thickness can be obtained through a spin-coating method on a substrate. The formula of the photoresist can be used in modern photolithography such as 365 nm photolithography, 248 nm photolithography, 193 nm photolithography, extremely ultra-violet lithography andelectron beam lithography, and is particularly applicable to extreme ultra-violet lithography.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluoroalcohol containing molecular photoresist materials and processes of use
InactiveCN103261137AOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusResistCalixarene
Phenolic molecular glasses such as calixarenes include at least one fluoroalcohol containing unit. The fluoroalcohol containing molecular glasses can be used in photoresist compositions. Also disclosed are processes for generating a resist image on a substrate using the photoresist composition.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fused aromatic structures and methods for photolithographic applications
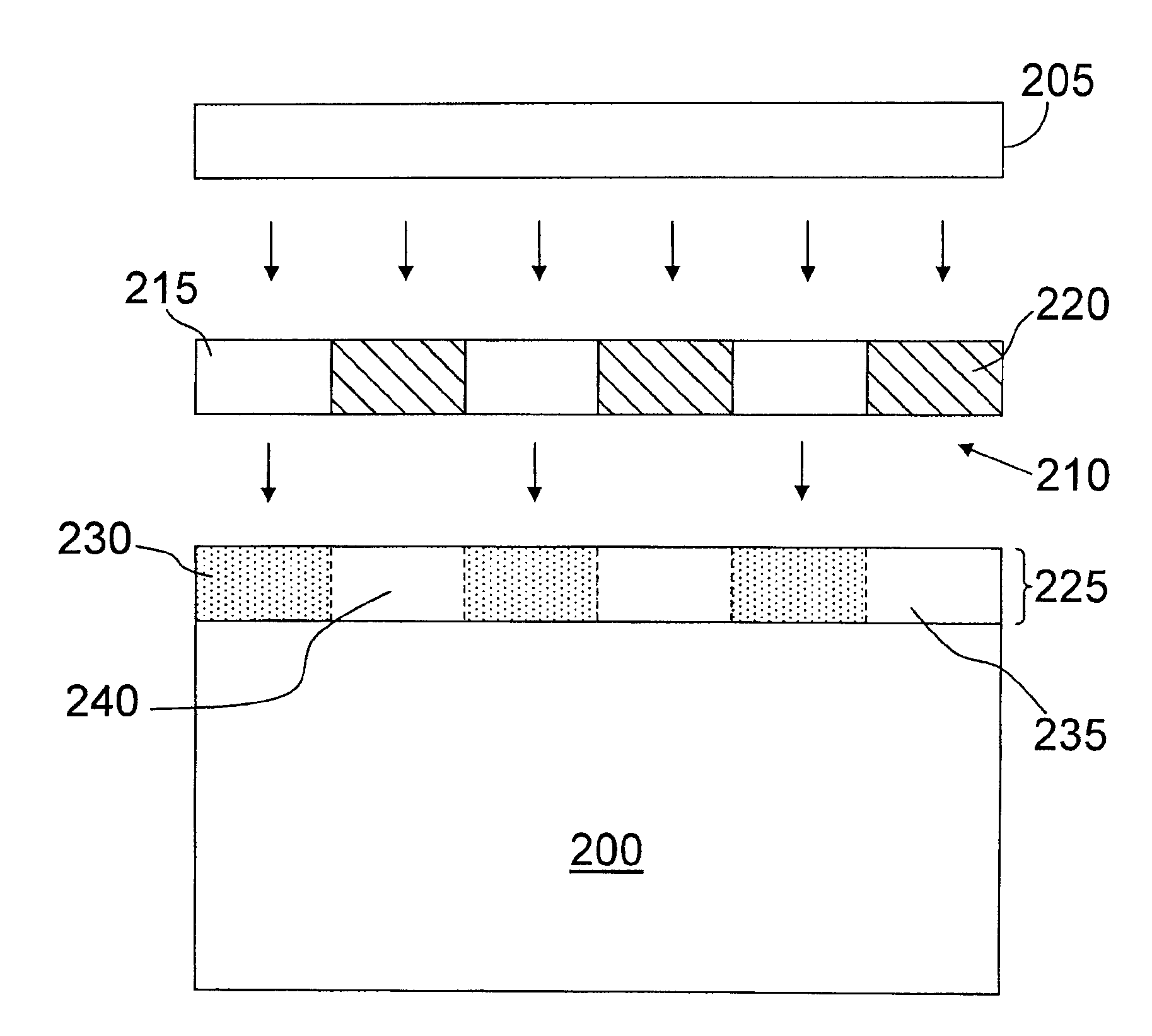
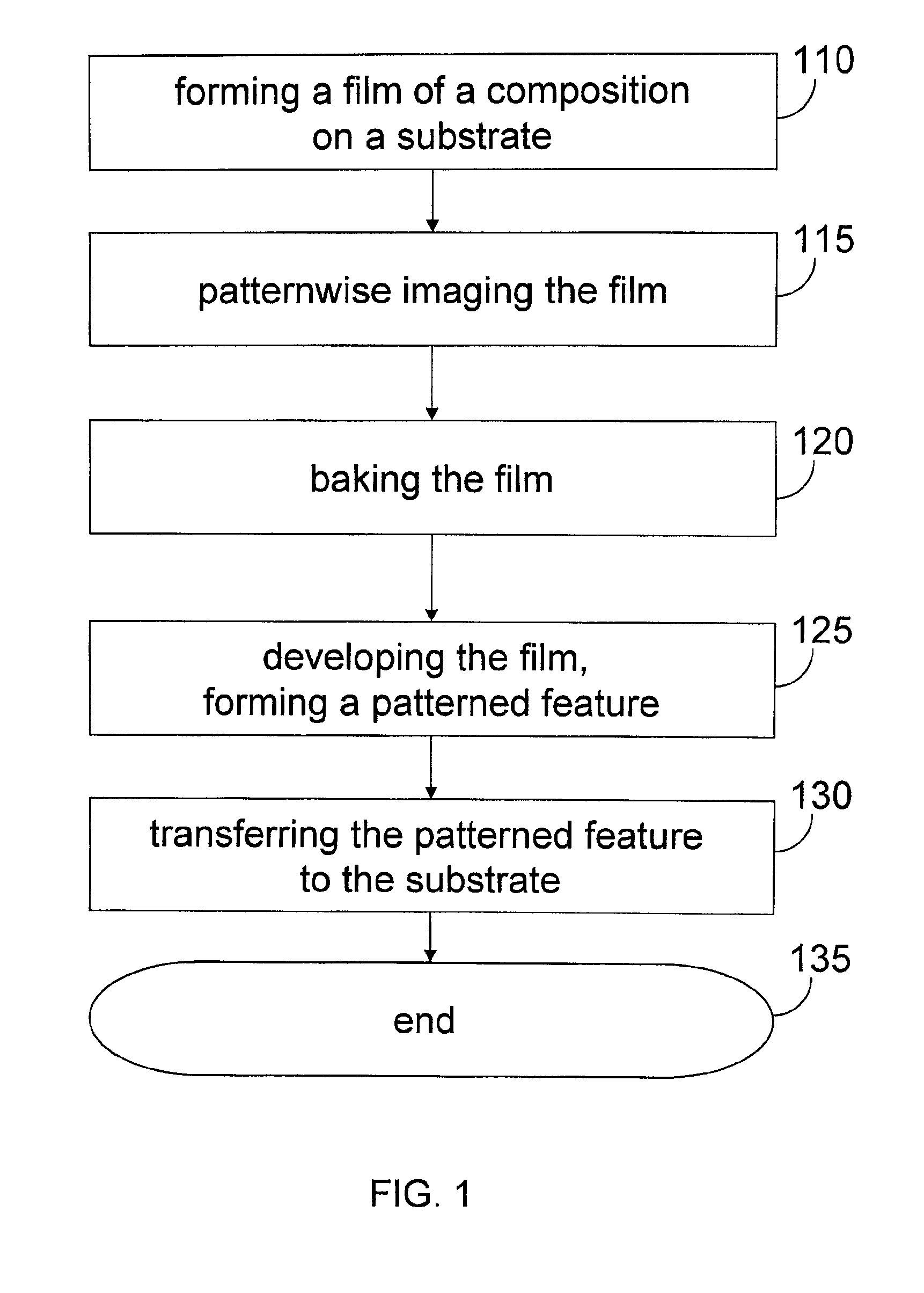
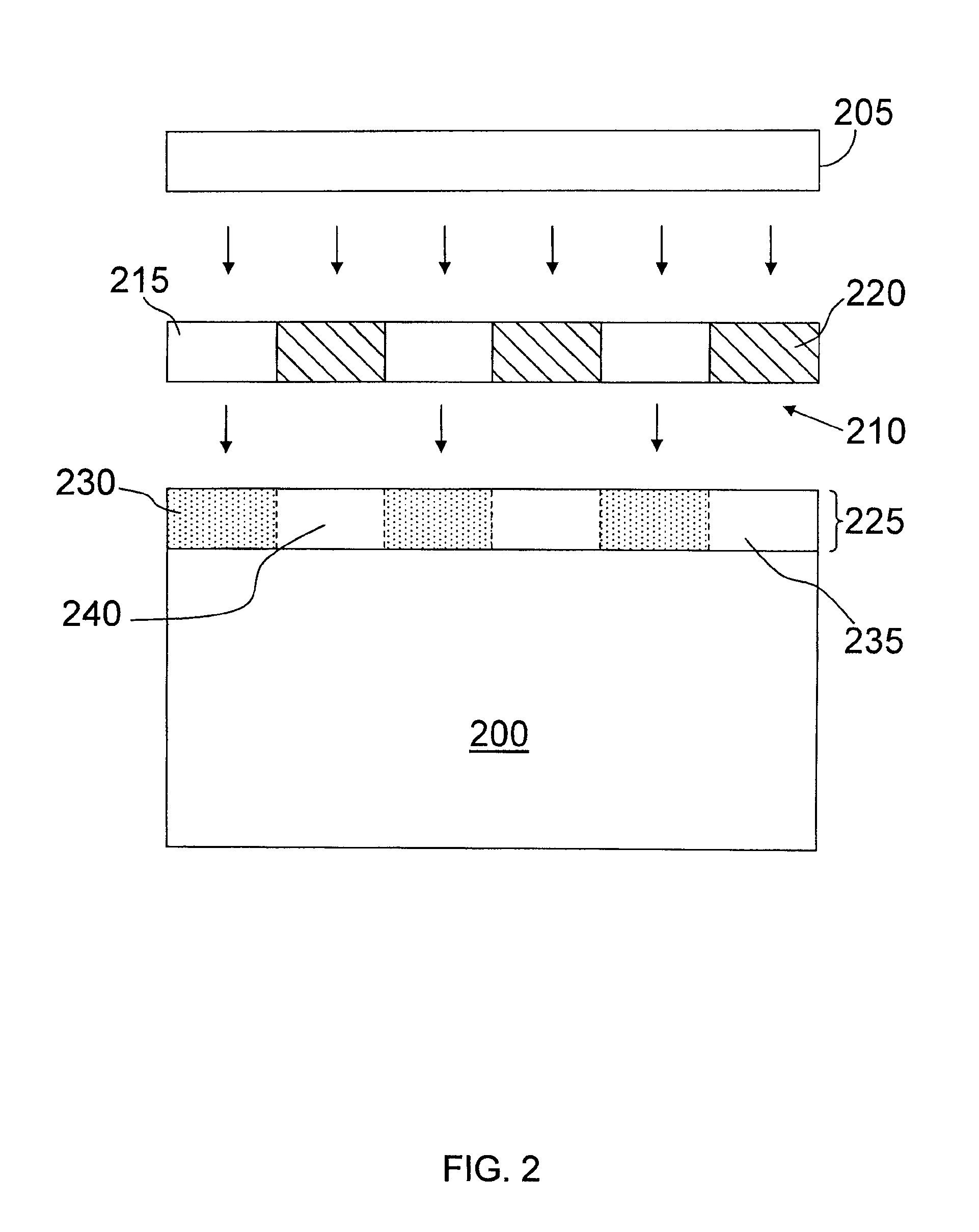
A resist composition and a method for forming a patterned feature on a substrate. The composition comprises a molecular glass having at least one fused polycyclic moiety and at least one base soluble functional group protected with an acid labile protecting group, and a photosensitive acid generator. The method includes providing a composition including a photosensitive acid generator and a molecular glass having at least one fused polycyclic moiety and at least one base soluble functional group protected with an acid labile protecting group, forming a film of the composition on the substrate, patternwise imaging the film, wherein at least one region of the film is exposed to radiation or a beam of particles, resulting in production of an acid catalyst in the exposed region, baking the film, developing the film, resulting in removal of base-soluble exposed regions, wherein a patterned feature from the film remains following the removal.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Non-crystallizable Pi-conjugated Molecular Glass Mixtures, Charge Transporting Molecular Glass Mixtures, Luminescent Molecular Glass Mixtures, or Combinations Thereof for Organic Light Emitting Diodes and other Organic Electronics and Photonics Applications
ActiveUS20150275076A1Good film formingReduce melt viscositySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingArylPhotonics
The present invention provides charge transporting molecular glass mixtures, luminescent molecular glass mixtures, or combinations thereof comprising at least two nonpolymeric compounds each independently corresponding to the structure (R1Y1)p[(Z1Y2)mR2Y3]nZ2Y4R3 wherein m is zero or one; n is zero up to an integer at which said compound starts to become a polymer; p is an integer of from one to eight; each R1 and R3 is independently a monovalent aliphatic or cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aromatic group or a multicyclic aromatic nucleus; R2, Z1, and Z2 each independently represent multivalent aliphatic or cycloaliphatic hydrocarbon groups having 1 to 20 carbon atoms or an aromatic group; and Y1, Y2, Y3 and Y4 each independently represent a triple bond, a double bond, or a single bond link.
Owner:MOLAIRE CONSULTING
Molecular Glasses With Functionalizable Groups
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN AS REPRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF NAT DEFENCE OF HER MAJESTYS CANADIAN GOVERNMENT
A star-shaped tetraphenylethylene derivative molecular glass, positive photoresist, positive photoresist coating and application thereof
ActiveCN104557552BGood rigid structureHigh glass transition temperatureOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSolubilitySolvent
The invention discloses starlike tetraphenylethylene derivative molecular glass, a positive photoresist, a positive photoresist coating and application thereof. The starlike tetraphenylethylene derivative molecular glass has the molecular structure shown in the description. The molecular glass is simple in synthesis process and suitable for industrial production; the tetraphenylethylene has a spatial solid geometrical skeleton adopting a rigid structure, can effectively inhibit molecular crystallization and is easy for film formation; the molecular glass has good solubility in various polar solvents, and has the characteristics of high glass transition temperature and high thermal stability, and can better meet requirements of a photoetching process; by adopting a spin coating method, a good film can be obtained, and the molecular glass can be used as the photoresist and can be prepared into the positive photoresist for photoetching through cooperation with other additives.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Noncrystallizable sensitized layers for OLED and oeds
InactiveUS20170162795A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emitting deviceMolecular glasses
Various embodiments of the present invention provide for a light emitting devices comprising a light emitting layer comprising an electroluminescent organic material dispersed in a matrix, wherein the electroluminescent organic material has a molecular weight less than about 2000 amu, the matrix comprises a nonelectroluminescent-nonpolymeric amorphous glass mixture, and each of the nonelectroluminescent-nonpolymeric organic molecular glass mixture and the electroluminescent organic material constitutes at least 20 percent by weight of the light emitting layer; and electrodes in electrical communication with the light emitting layer and configured to conduct an electric charge through the light emitting layer such that the light emitting layer emits light.
Owner:MOLAIRE CONSULTING
Molecular glass photoresists
InactiveUS7452658B2Transparency of shortPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusSilanesPhenyl group
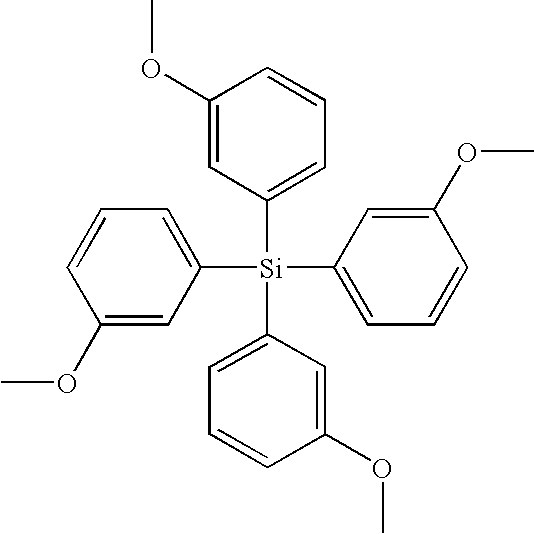
Several small molecule, molecular glasses are disclosed with new architectures designed for use as photoresists in semiconductor lithography. The disclosed photoresists are low molecular weight organic materials that demonstrate a glass transition temperature significantly above room temperature as well as a low tendency towards crystallization. The molecular glass photoresists have a tetrahedral silane molecular core with four phenyl groups or four biphenyl groups. Each phenyl group or each outer phenyl group of a biphenyl group has a methoxy or hydroxy group at the 3- or 4-position. For the biphenyl embodiments, the linkage may be meta-meta, meta-para, para-para or para-meta.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Adamantane based molecular glass photoresists for sub-200 nm lithography
InactiveCN101390015APreparation from carboxylic acid halidesSugar derivativesResistLithographic artist
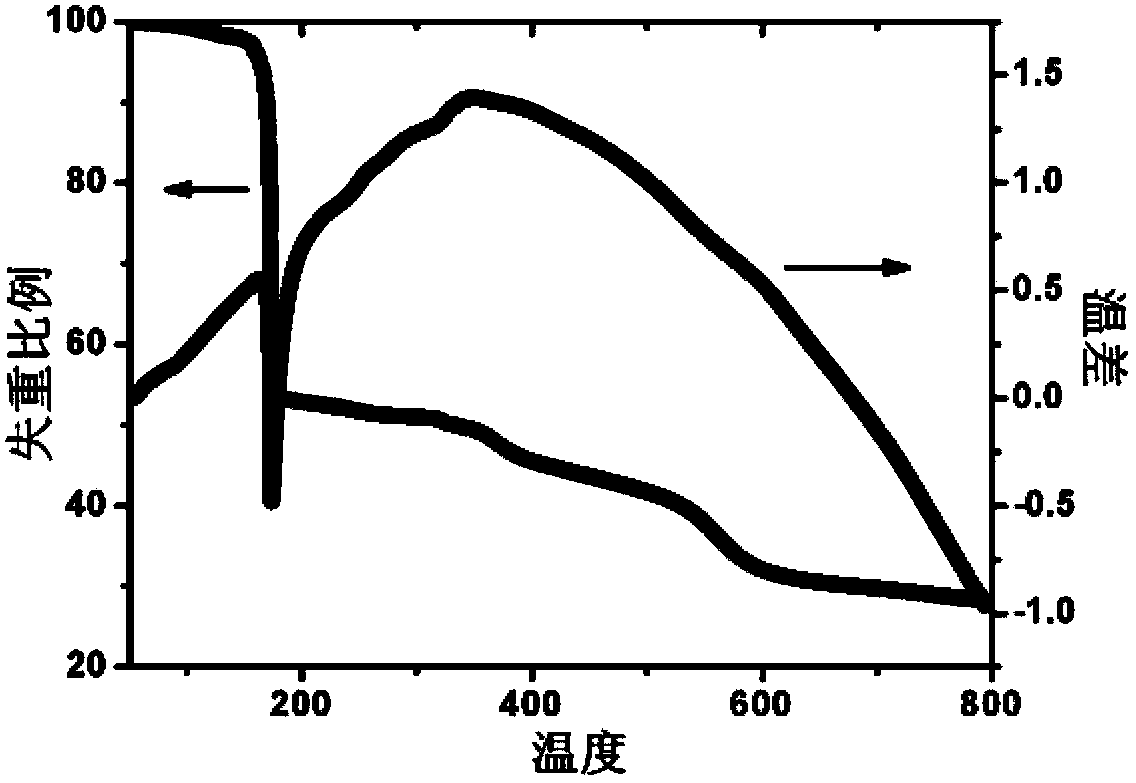
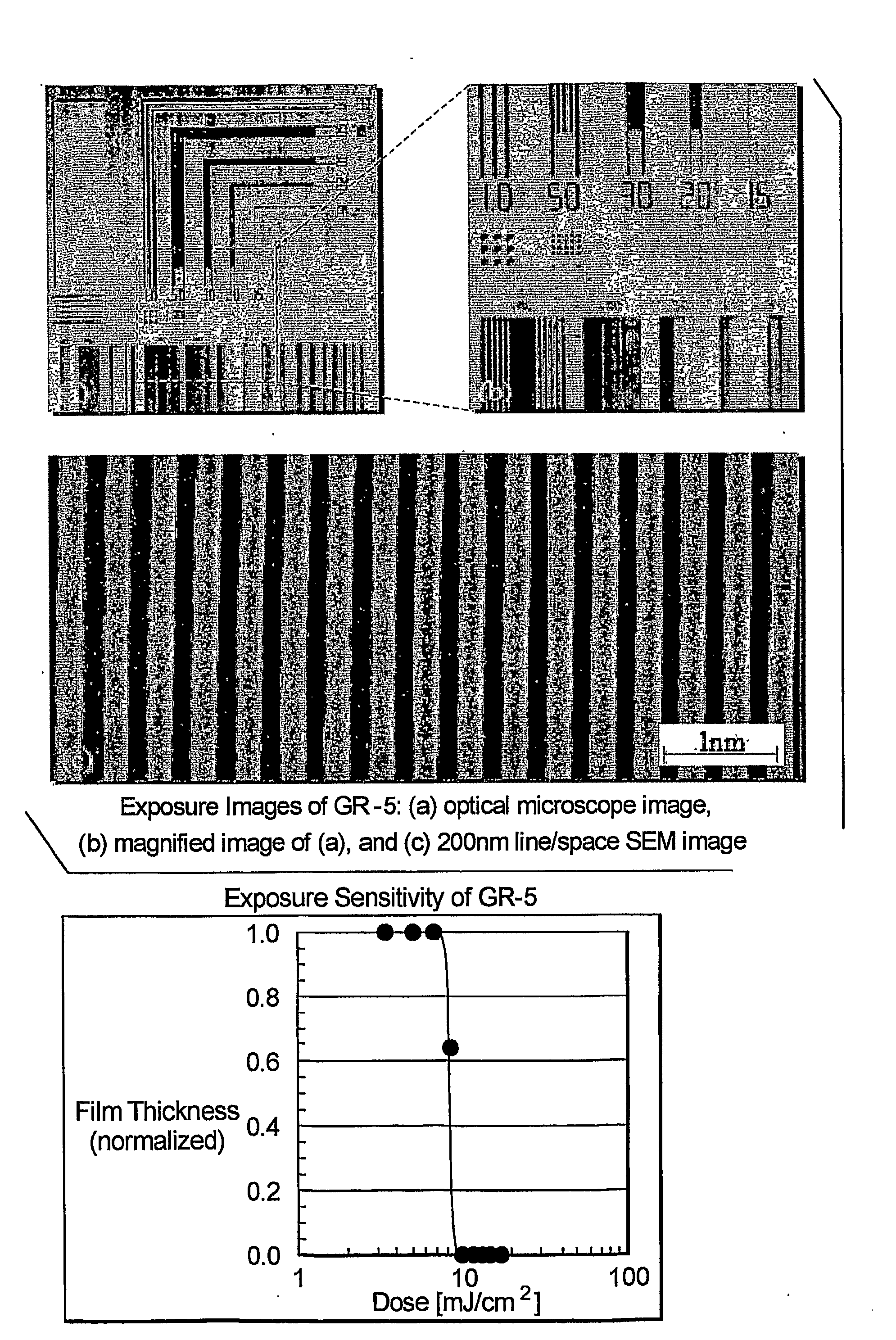
Disclosed are glass photoresists generated from adamantane derivatives containing acetal and / or ester moieties as novel high-performance photoresist materials. Some of the disclosed adamantane-based glass resists have a tripodal structure and other disclosed adamantane-based glass resists include one or more cholic groups. The disclosed adamantane derivatives can be synthesized from starting materials which are commercially available. By way of example only, one of many disclosed amorphous glass photoresists has the following structure: GR-5 Adamantane-l,3,5-triyltris(oxymethylene) tricholate.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
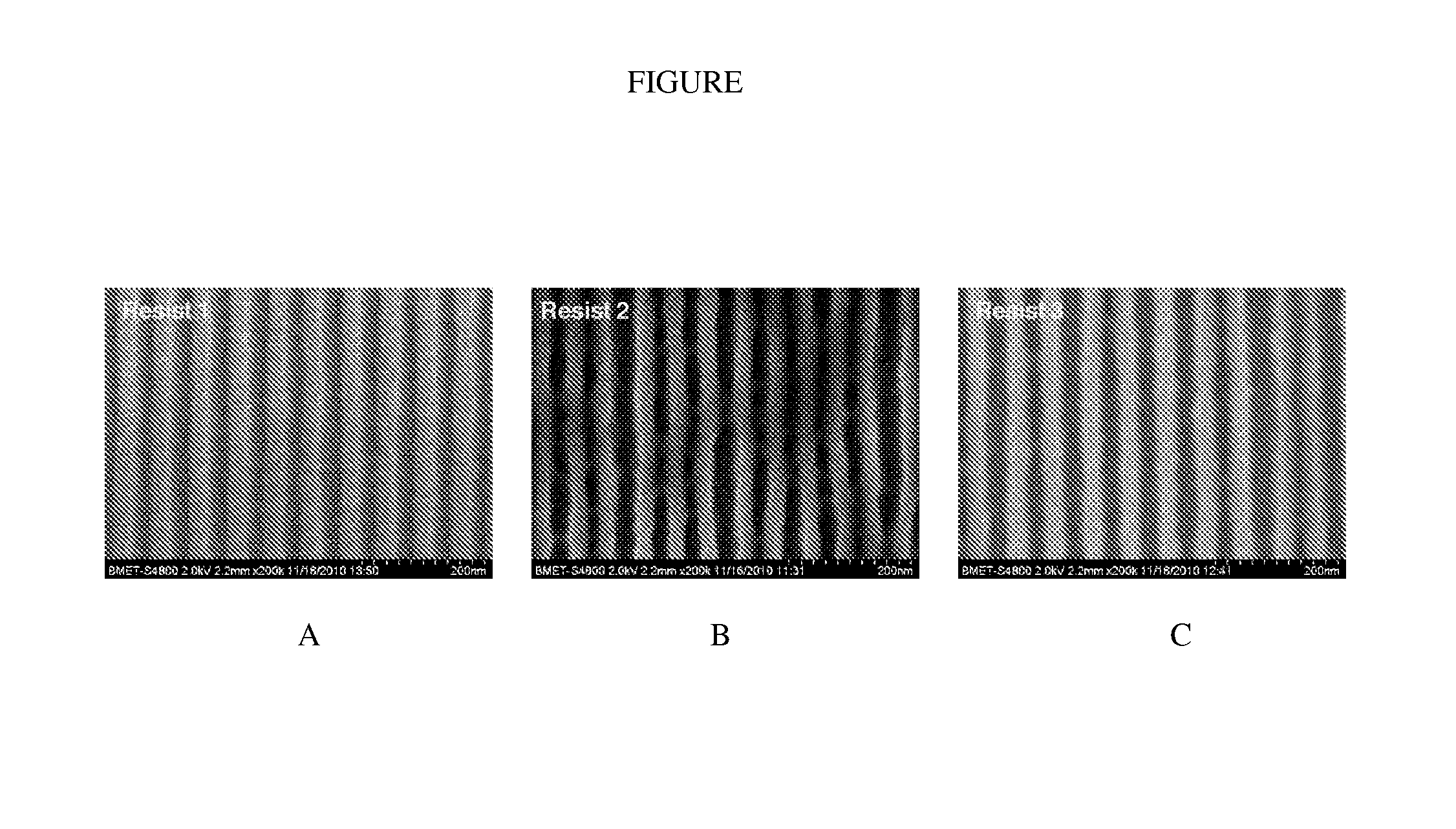
Negative tone molecular glass resists and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS9152043B2Reduce solubilityPhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive material processingSolubilityResist
The various embodiments of the present disclosure relate generally to resists and, more particularly, to negative tone molecular glass resists, and their associated methods of fabrication and use. In one embodiment of the present invention, a negative tone molecular glass-based resist comprises: a molecular glass, comprising, a molecular glass core, wherein the molecular glass core is not a polymer chain, and a functional group bound to the molecular glass core and configured to provide a decrease in solubility of the molecular glass; and an initiating component configured to produce a reactive species upon exposure to radiation, wherein the reactive species facilitates the decrease in solubility of the molecular glass.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
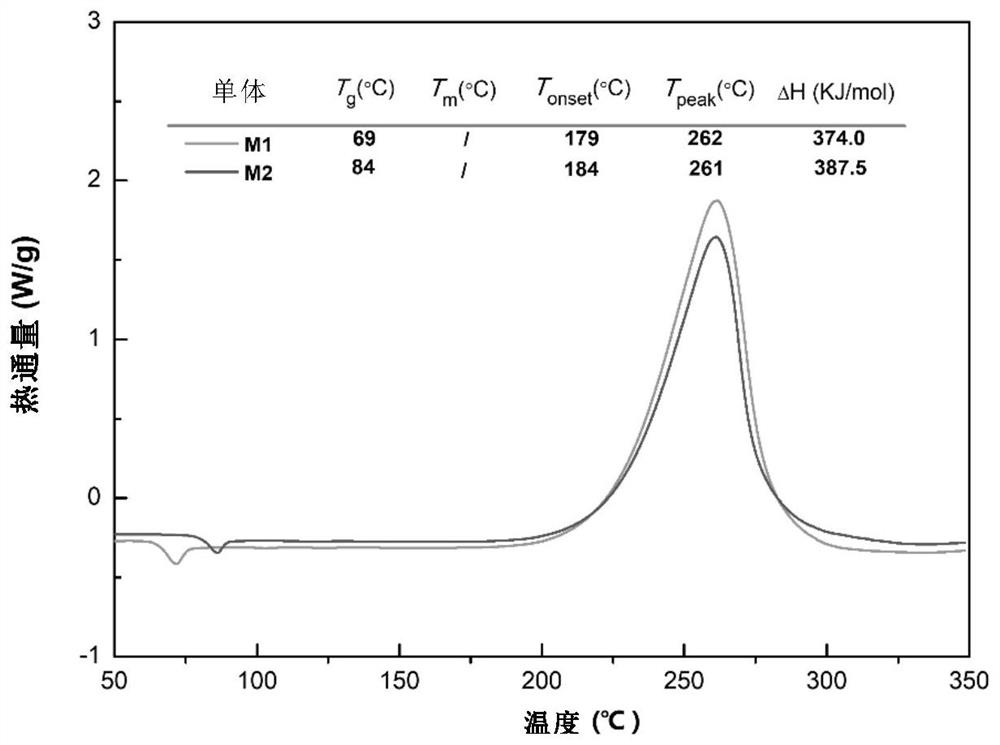
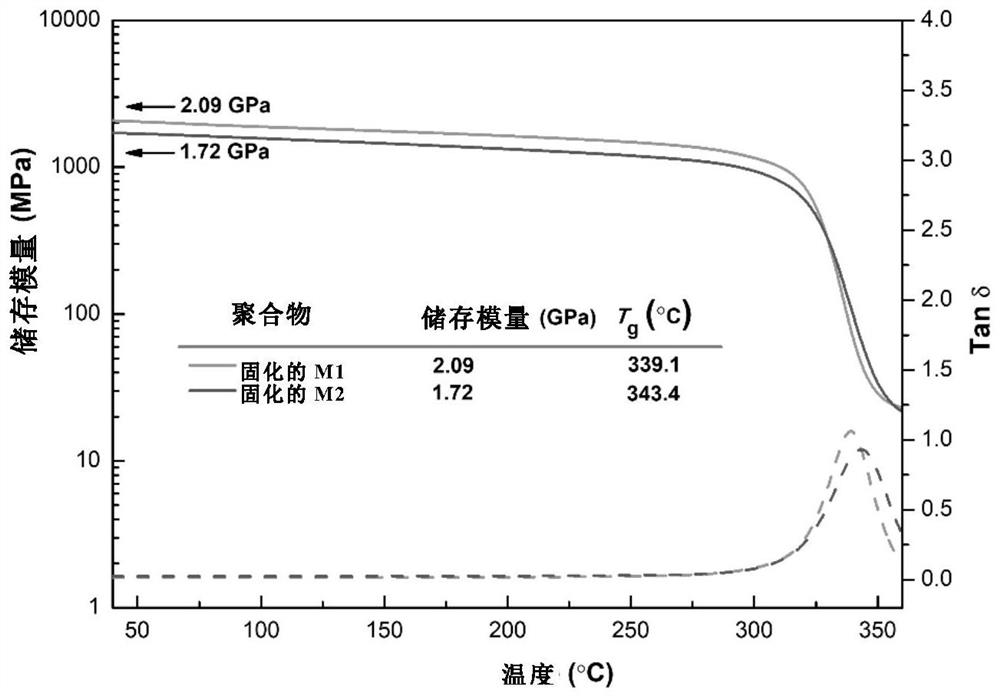
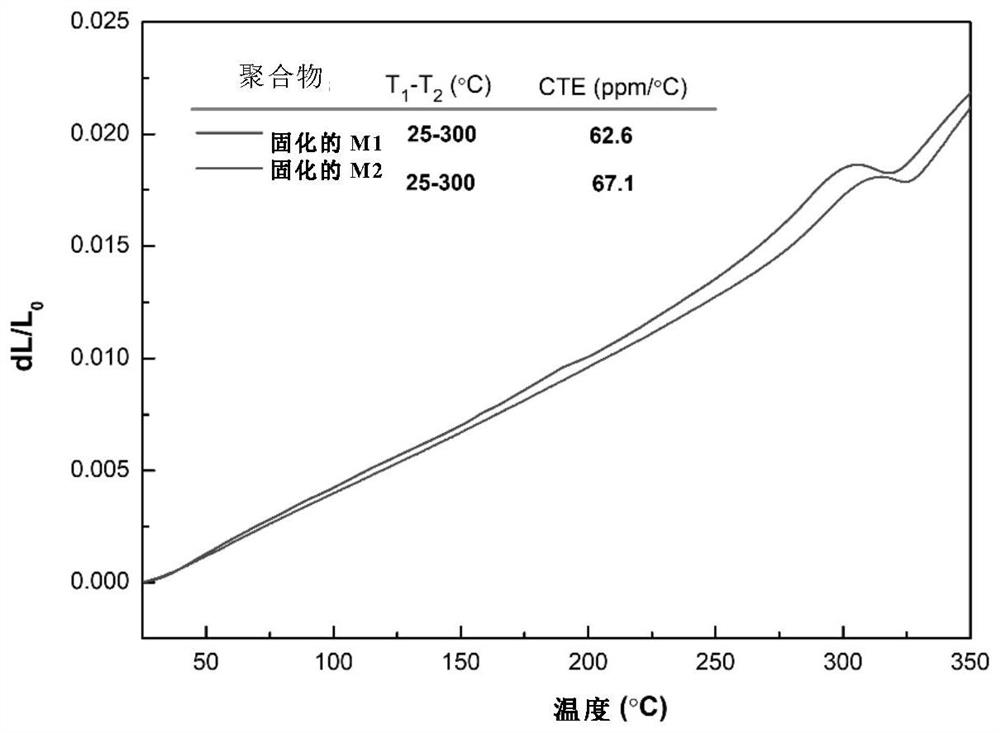
Synthesis method of molecular glass and application of molecular glass as high-frequency low-dielectric-constant material
The invention provides a synthesis method of molecular glass and application of the molecular glass as a high-frequency low-dielectric-constant material. Specifically, the invention provides a molecular glass monomer, the molecular glass monomer has a molecular structure as shown in a formula (I) in the specification; the molecular glass monomer has excellent processability and can form infusible and insoluble resin after high-temperature treatment; and the molecular glass only shows glass transition but has no melting point during heating and is similar to an amorphous state. The resin obtained by curing the molecular glass has high heat resistance and low water absorption, especially shows excellent dielectric constant and dielectric loss at high frequency, and can be widely applied to the fields of high-frequency communication, microelectronic industry, aerospace and the like as low-dielectric-constant matrix resin or a packaging material.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
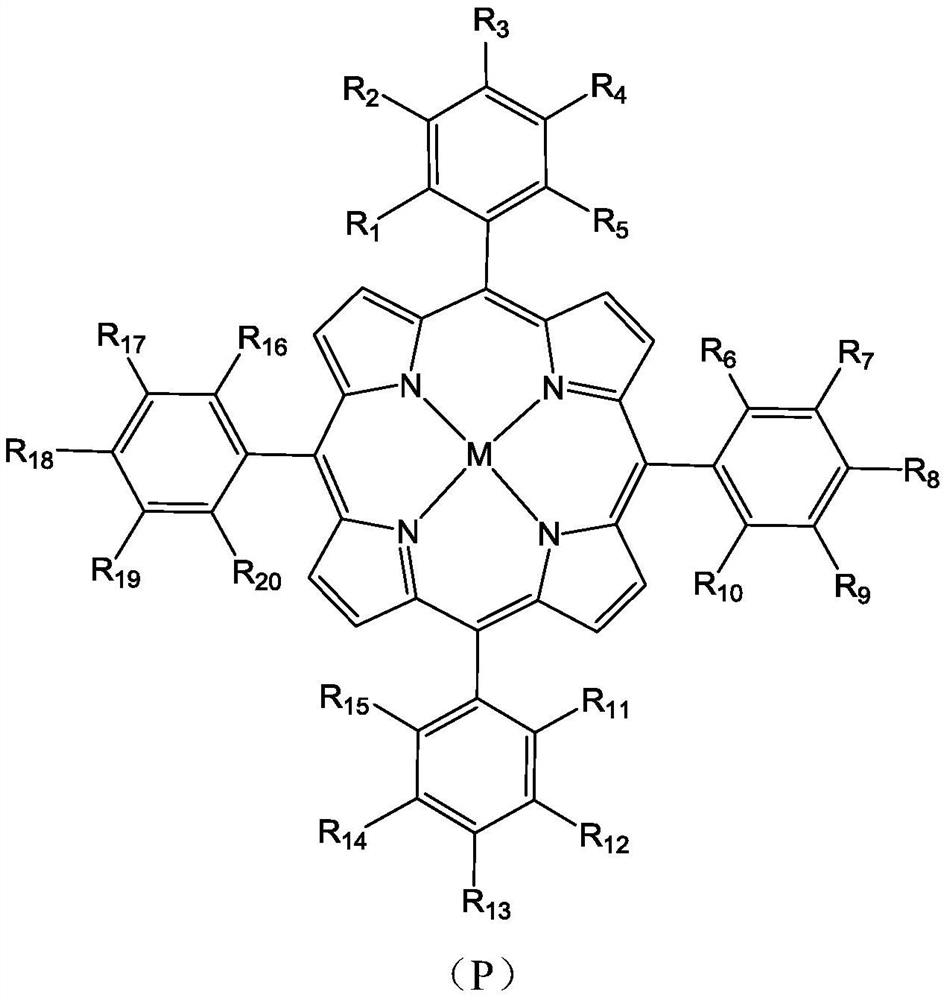
Molecular glass chemical amplification photoresist based on metalloporphyrin and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113004291AHigh melting pointHigh glass transition temperatureOrganic chemistryPhotomechanical apparatusPolymer scienceOrganic solvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoresists, and particularly relates to a molecular glass chemical amplification photoresist baed on metalloporphyrin as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A matrix component in the photoresist is a metalloporphyrin compound as shown in a formula (P) defined in the description. The matrix component is a stereosymmetric amorphous small molecule compound and can be dissolved in an organic solvent commonly used in the photoresist. The photoresist composition disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing a uniform thin film, and molecular glass serving as a matrix component is not separated out in a film preparation process. The thin film prepared from the photoresist composition disclosed by the invention has good resolution ratio, light sensitivity and adhesion, and is easy to store.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com