Patents
Literature
53 results about "Transmission dynamic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
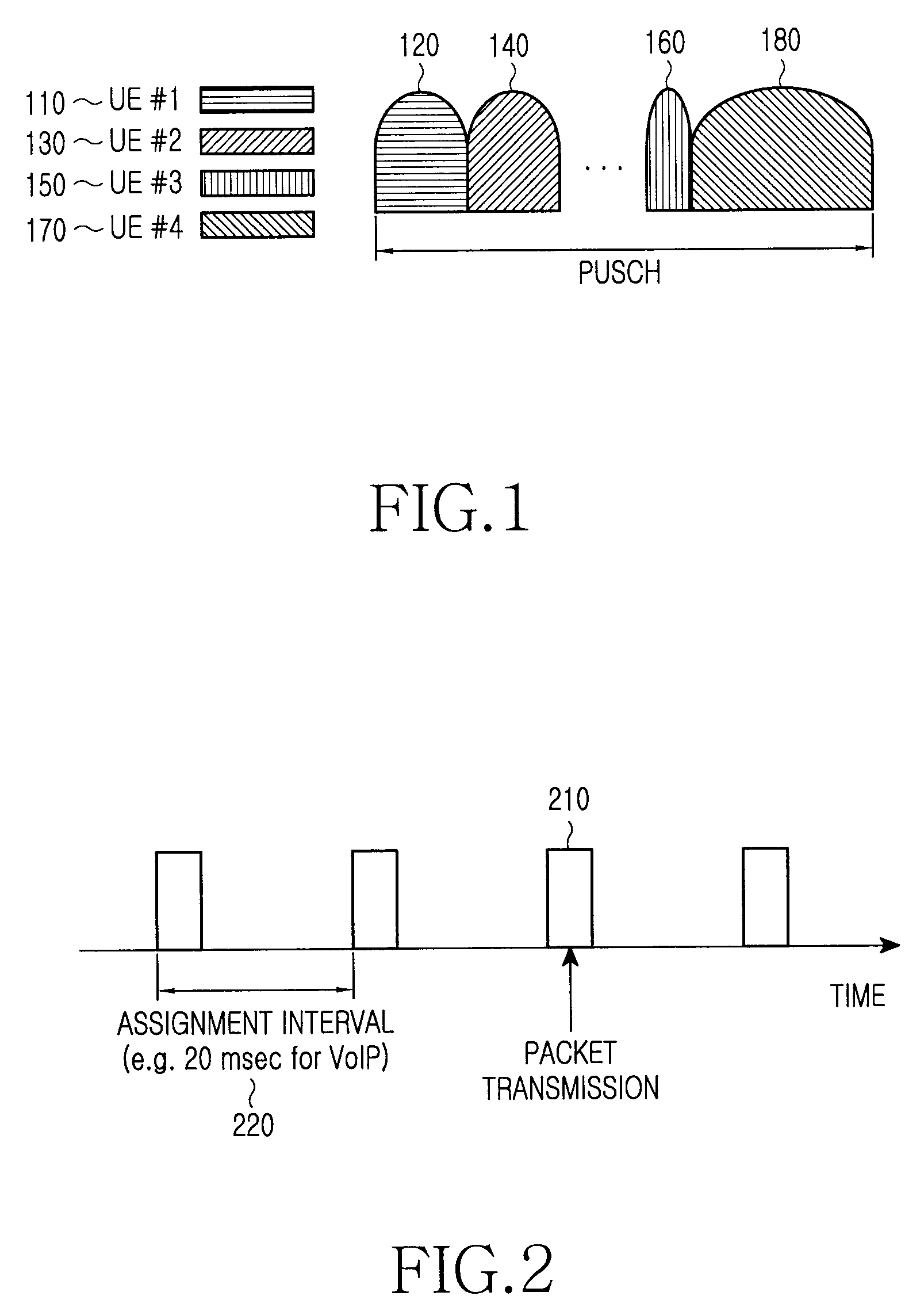
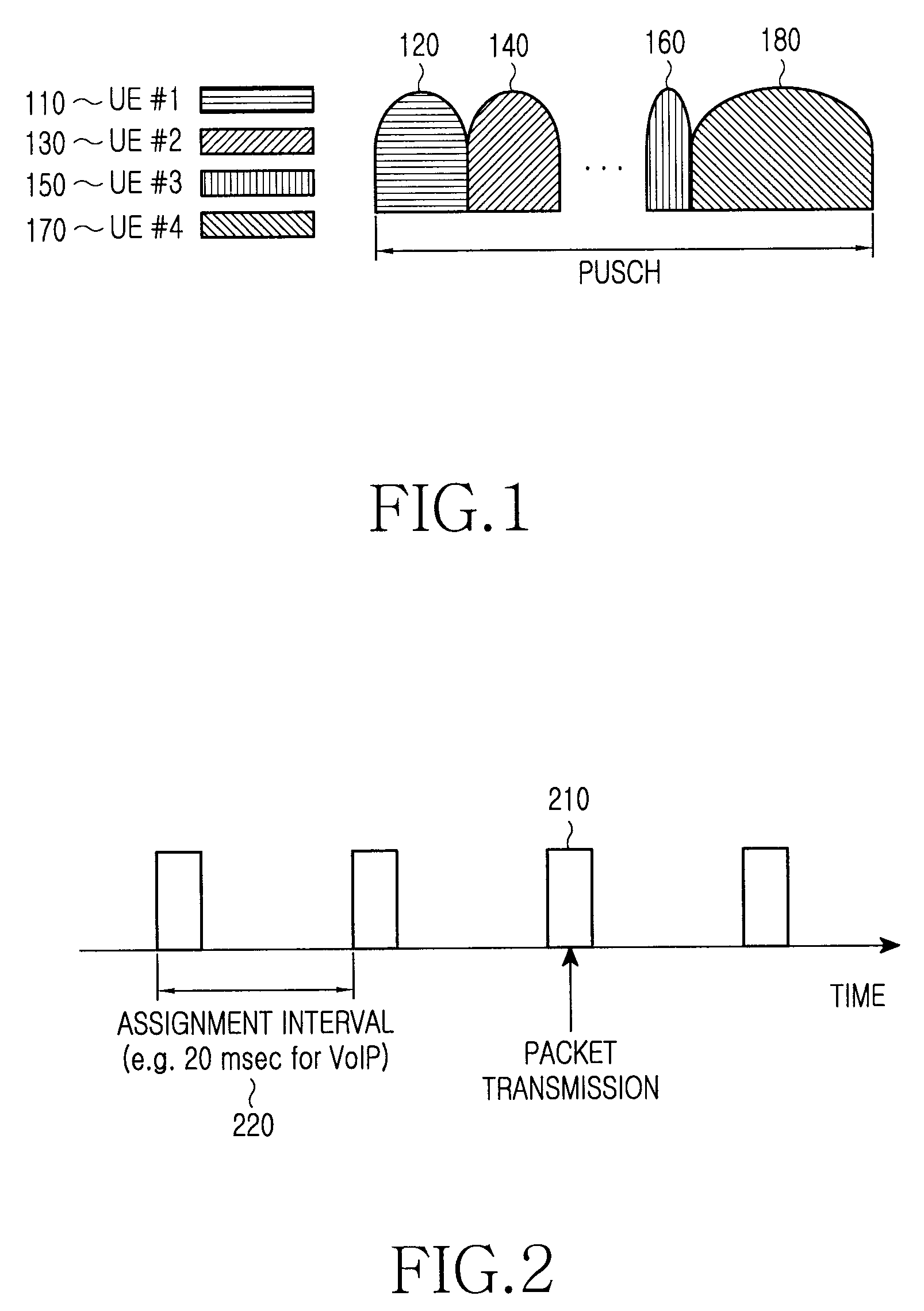
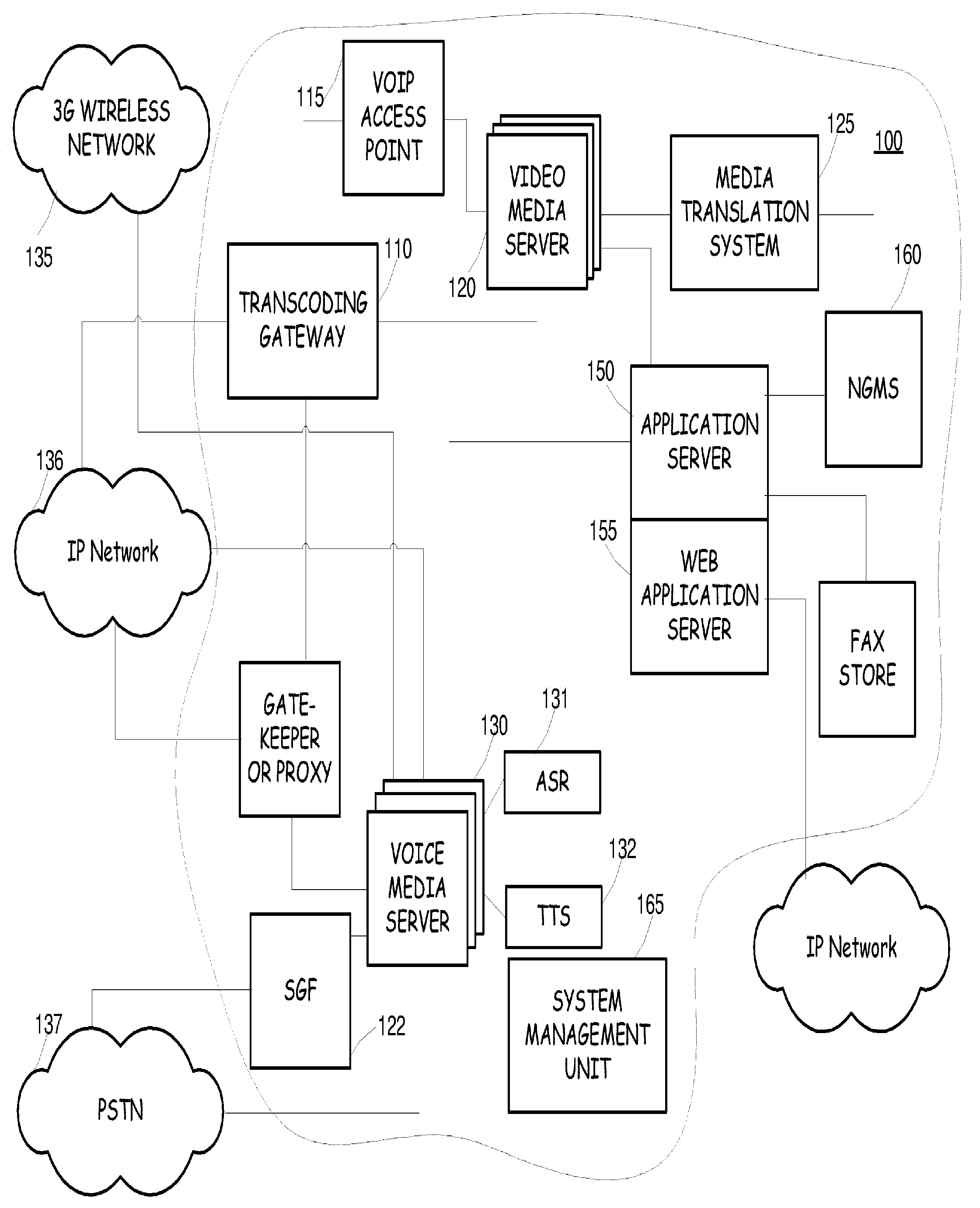
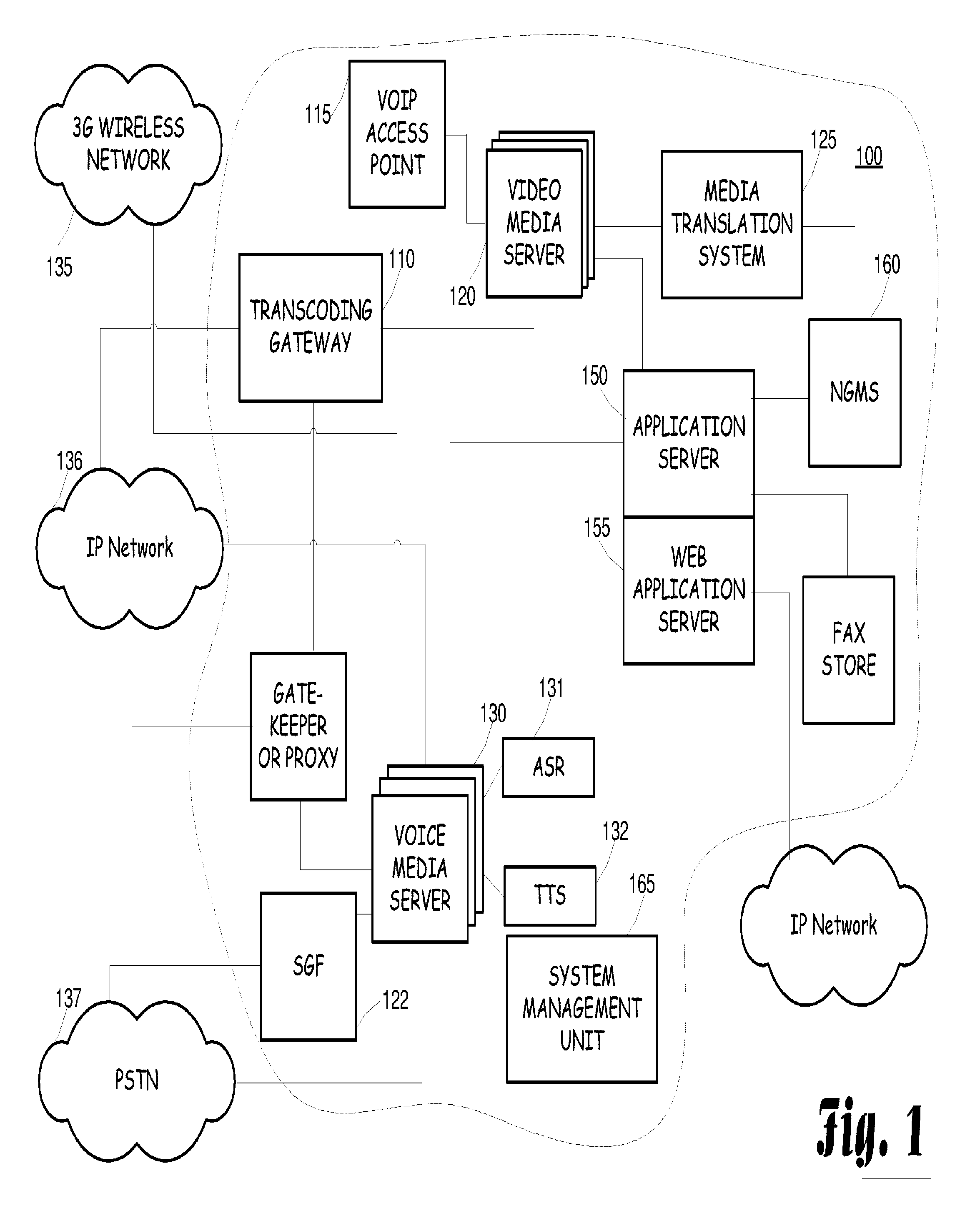
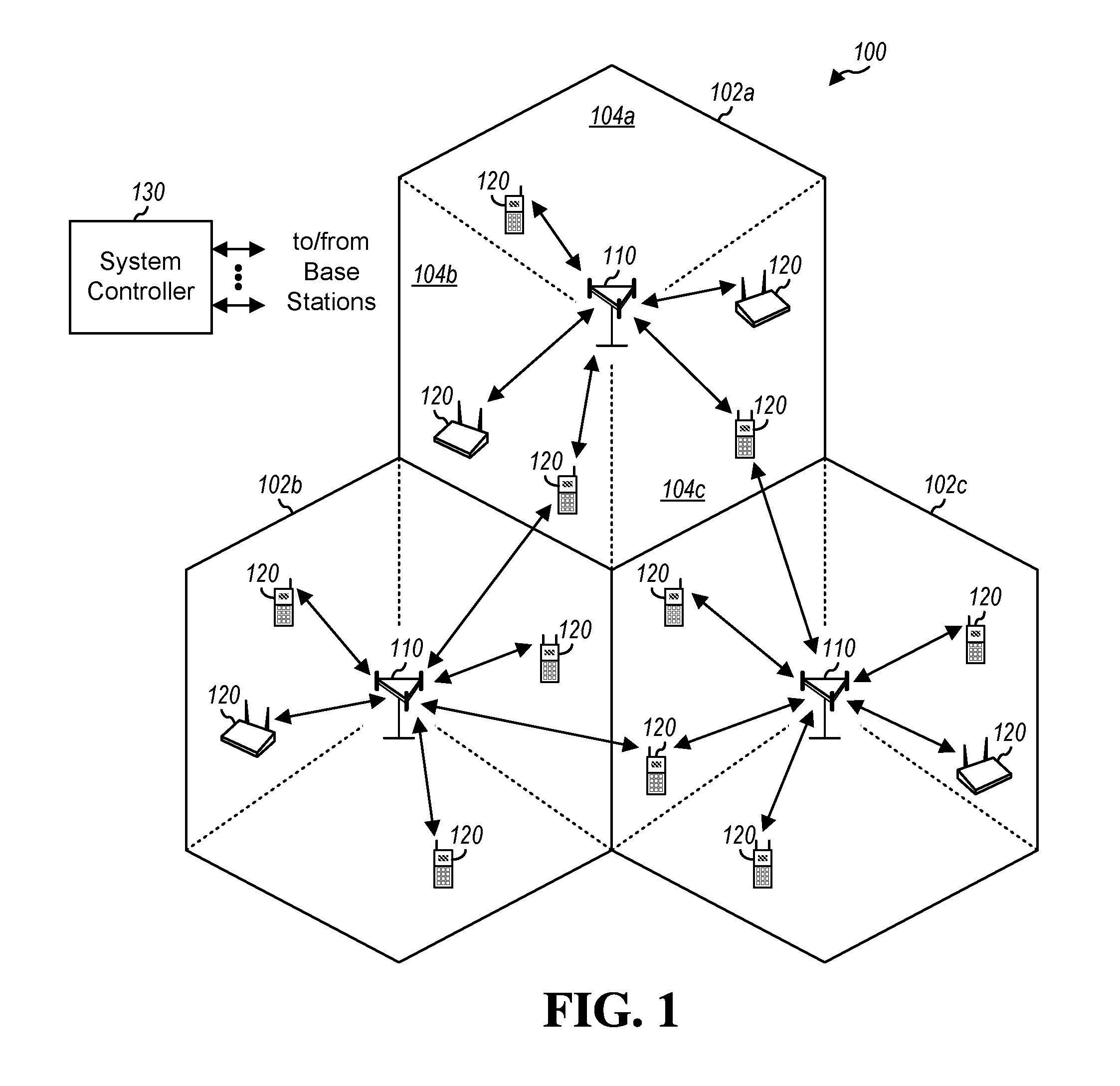
Joint use of multi-carrier and single-carrier multiplexing schemes for wireless communication
ActiveUS20100091919A1Restricts scheduler operationPromote disseminationTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationCarrier signalTransmission dynamic
A communication system that facilitates transmissions in accordance with a single-carrier (SC) multiplexing scheme, a multi carrier (MC) multiplexing scheme or a combination thereof is disclosed. Based on various factors such as attributes associated with a UE (user equipment) or availability of resources, a base station can signal to the UE an appropriate multiplexing scheme to be adopted for particular transmissions. The UE can be scheduled for transmission in a semi-static mode wherein the UE employs the transmission scheme for a particular time interval or it may change the mode dynamically for different transmissions. For transmissions from the UE comprising a plurality of data streams with dissimilar attributes, the base station implements a MIMO (multiple input multiple output) system for the UE. This facilitates a UE to dynamically switch between or simultaneously adopt the various multiplexing schemes for communications and thereby fully utilize advantages associated with the different schemes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
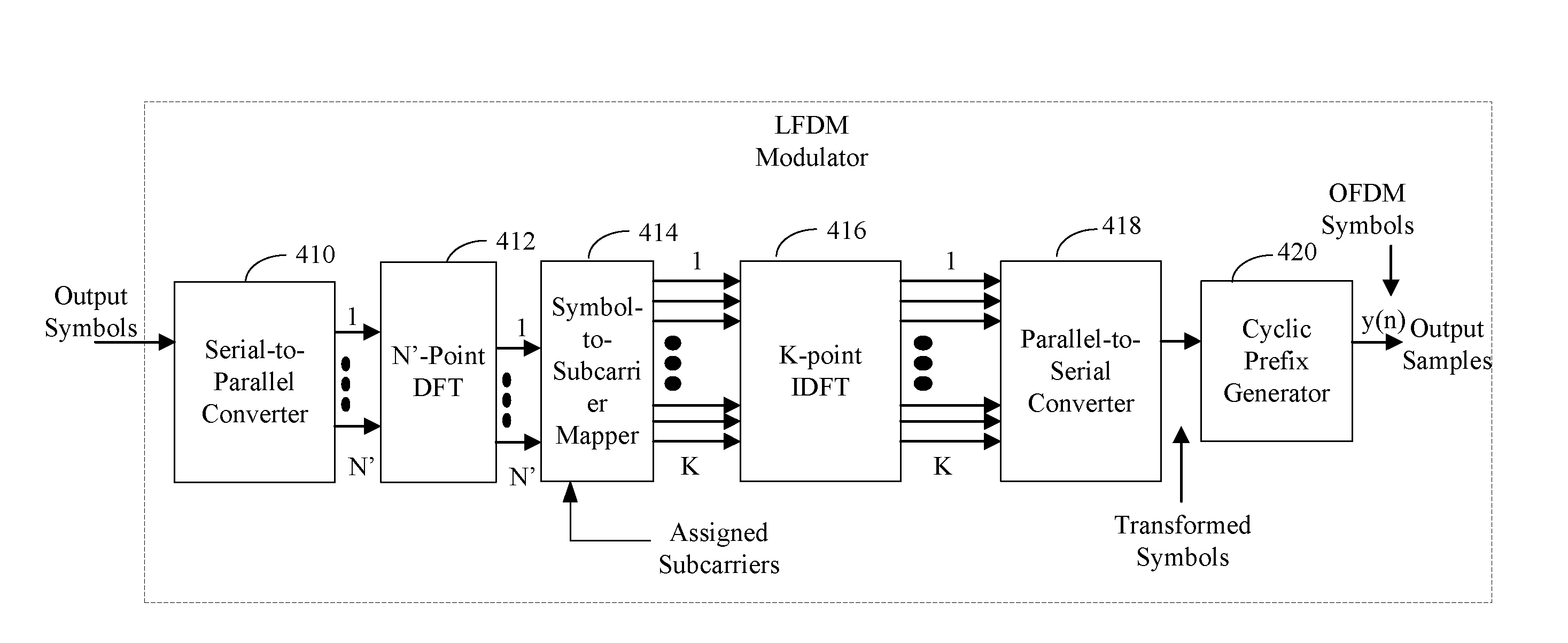
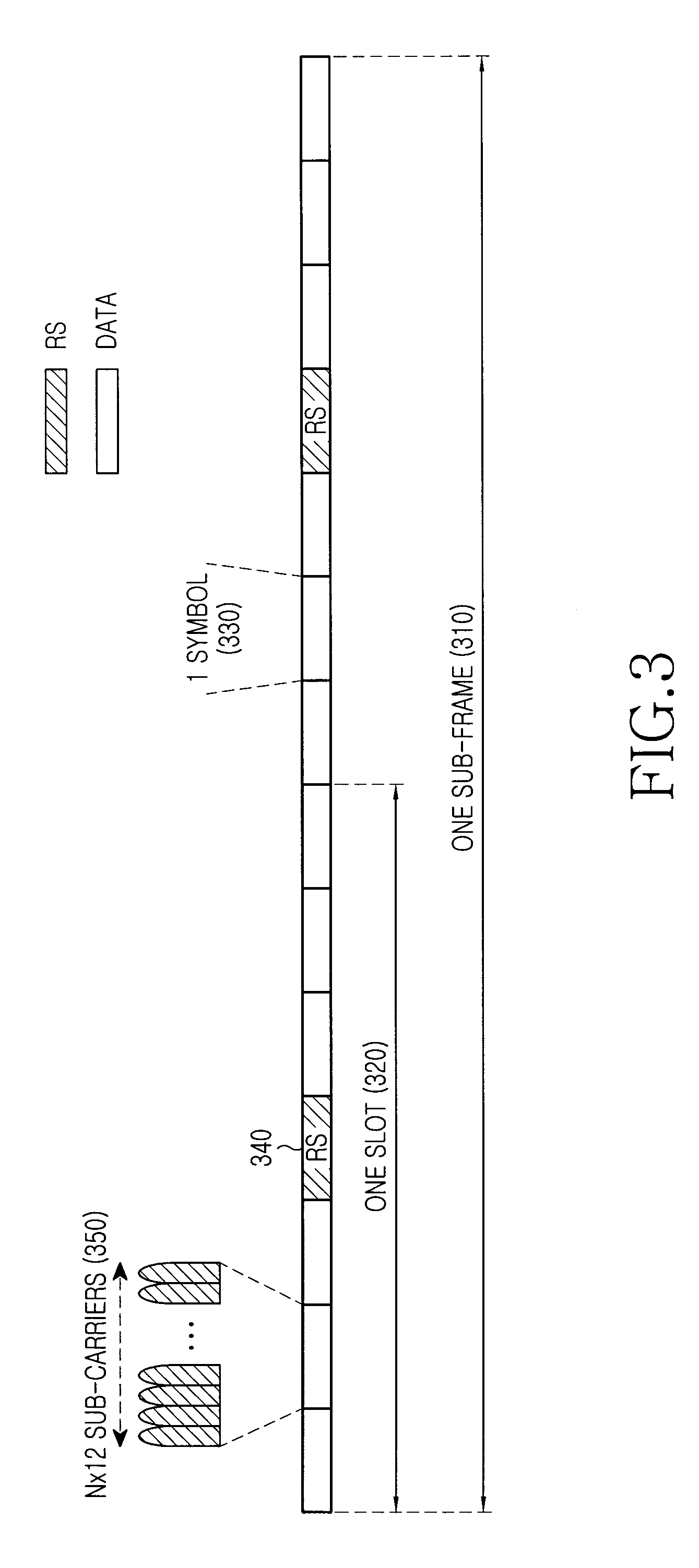
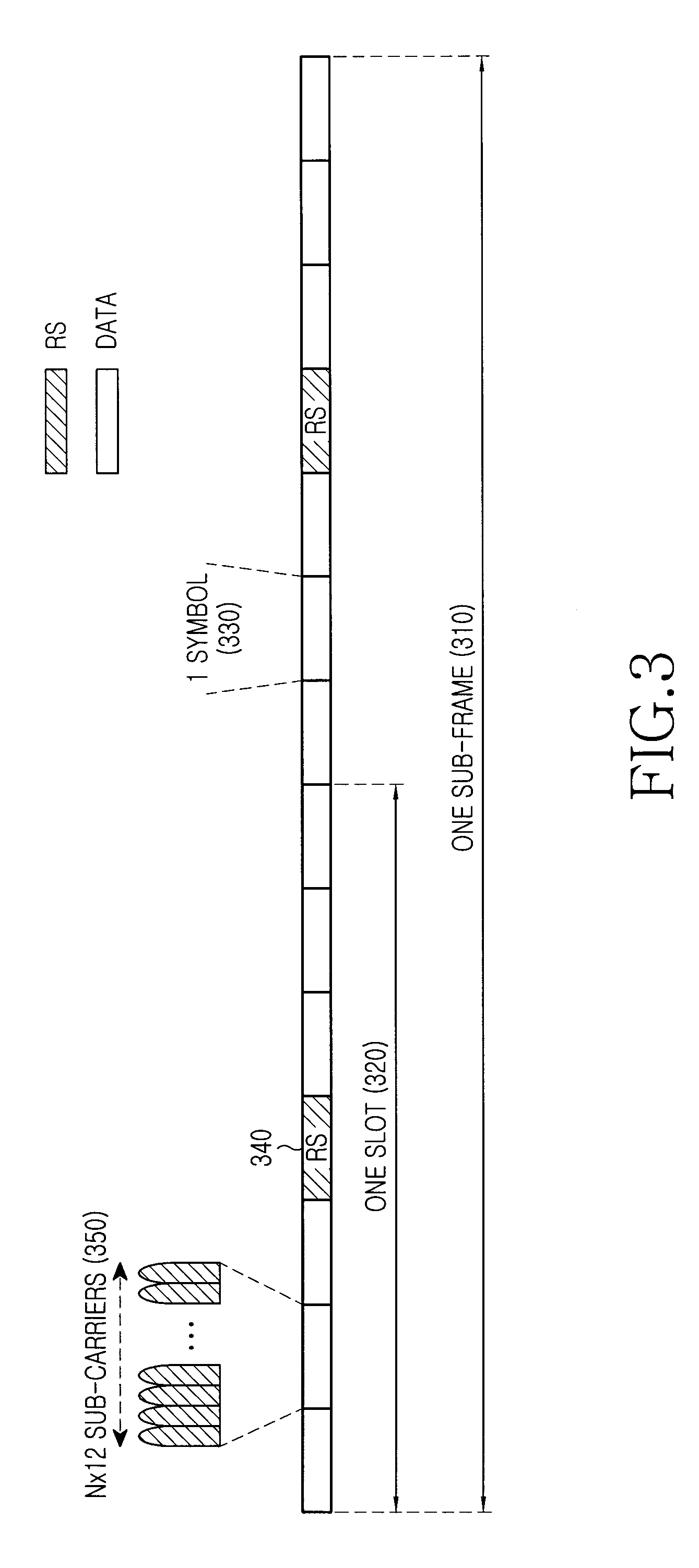
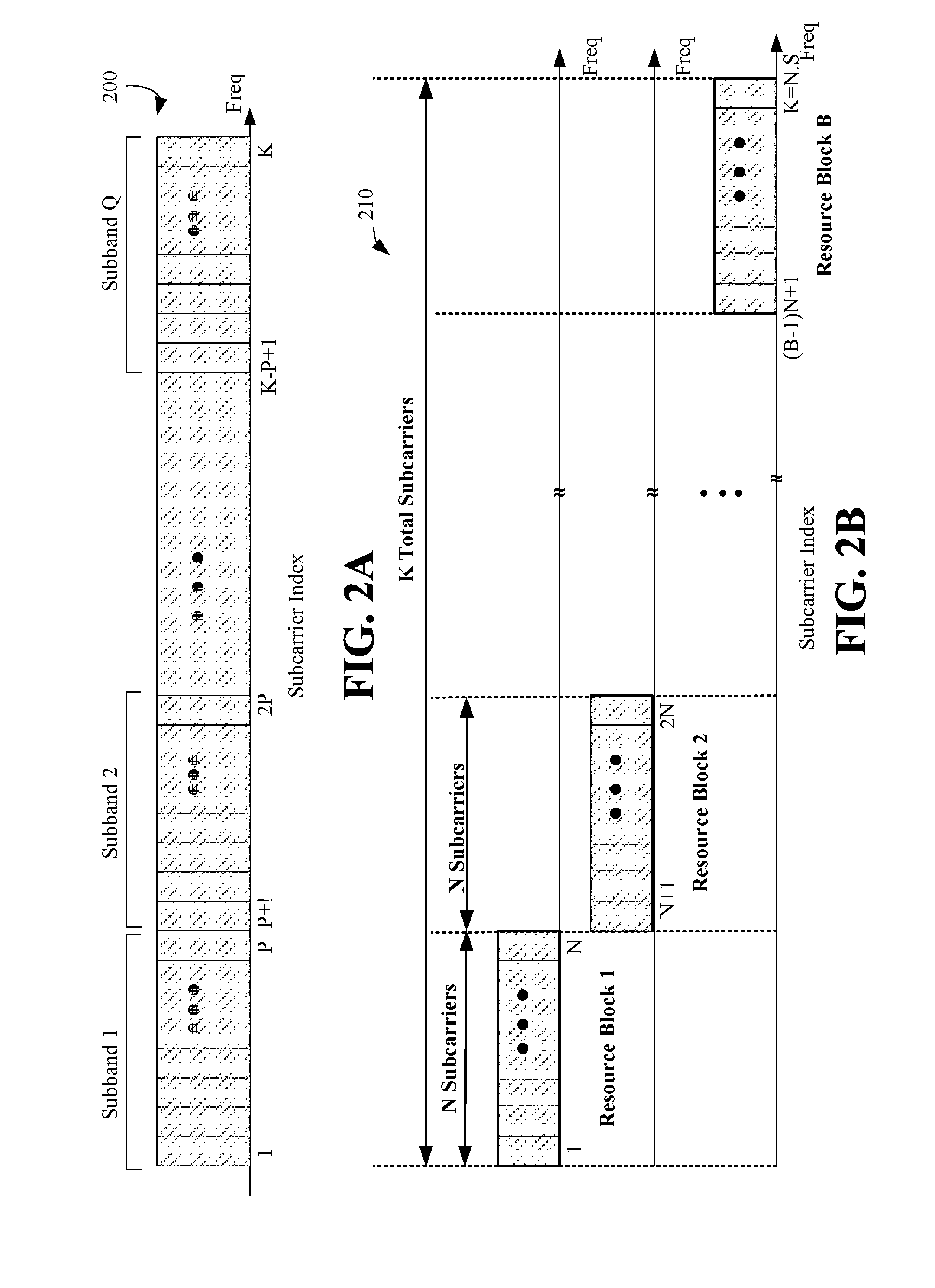
Partitioning of frequency resources for transmission of control signals and data signals in sc-fdma communication systems
ActiveUS20090010240A1Promote achievementMaximize Bandwidth UtilizationTransmission path divisionSignal allocationCommunications systemFrequency Unit
A method for the partitioning frequency resources used in the transmission of control signals and data signals by user equipments in a communication system. The control signals and data signals are for periodic transmission and dynamic transmission. Also provided is an apparatus and method for user equipments to determine the first frequency unit available for the transmission of dynamic control signals, such as acknowledgement signals associated respective reception of data signals configured through a scheduling assignment by a serving Node B. The utilization of the operating bandwidth is maximized by avoiding fragmentation and facilitates the achievement of reception reliability targets particularly for control signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
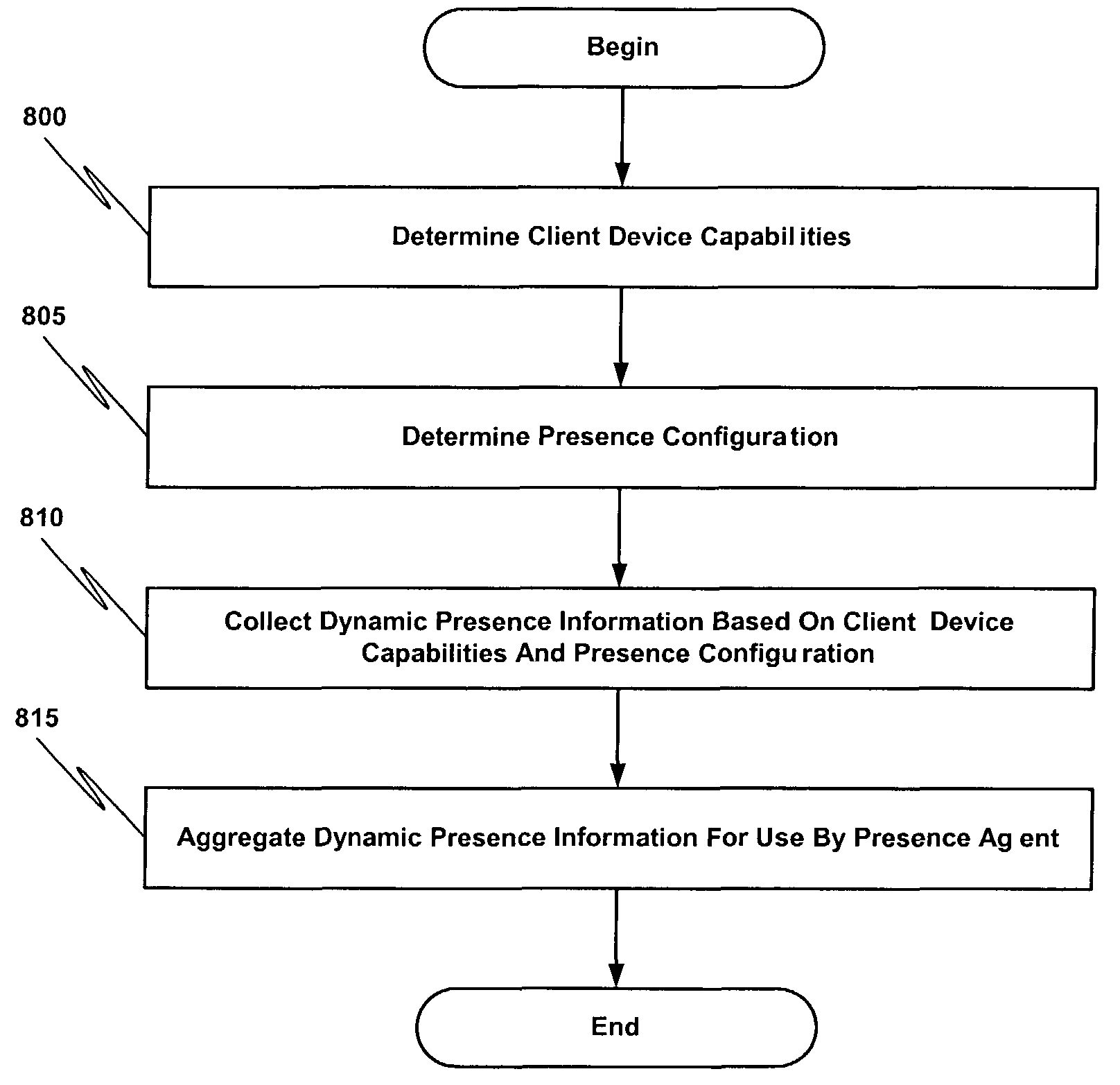
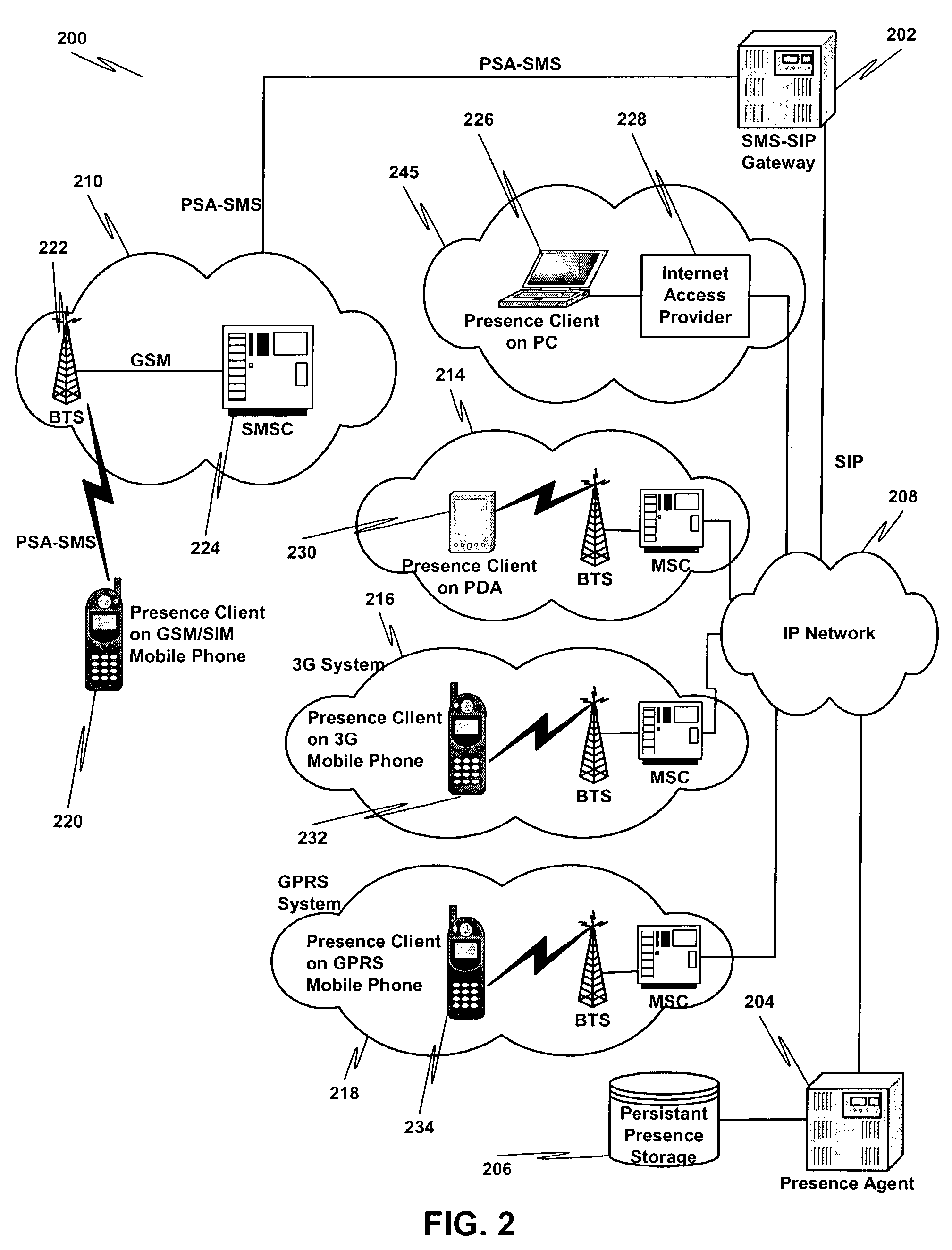
Detecting and transporting dynamic presence information over a wireless and wireline communications network
InactiveUS7844055B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsWired communicationTransport dynamics
A method for detecting and transporting dynamic presence information over a wireless and wireline communications network comprises determining client device capabilities relating to user presence information that may be obtained from the client device and determining a presence configuration of the client device. The presence configuration defines information to be provided to a presence agent. The presence configuration also defines one or more action to be performed upon notification of an event occurrence. The method also includes collecting dynamic presence information based at least in part on the client device capabilities and the presence configuration.
Owner:LINK US ALL
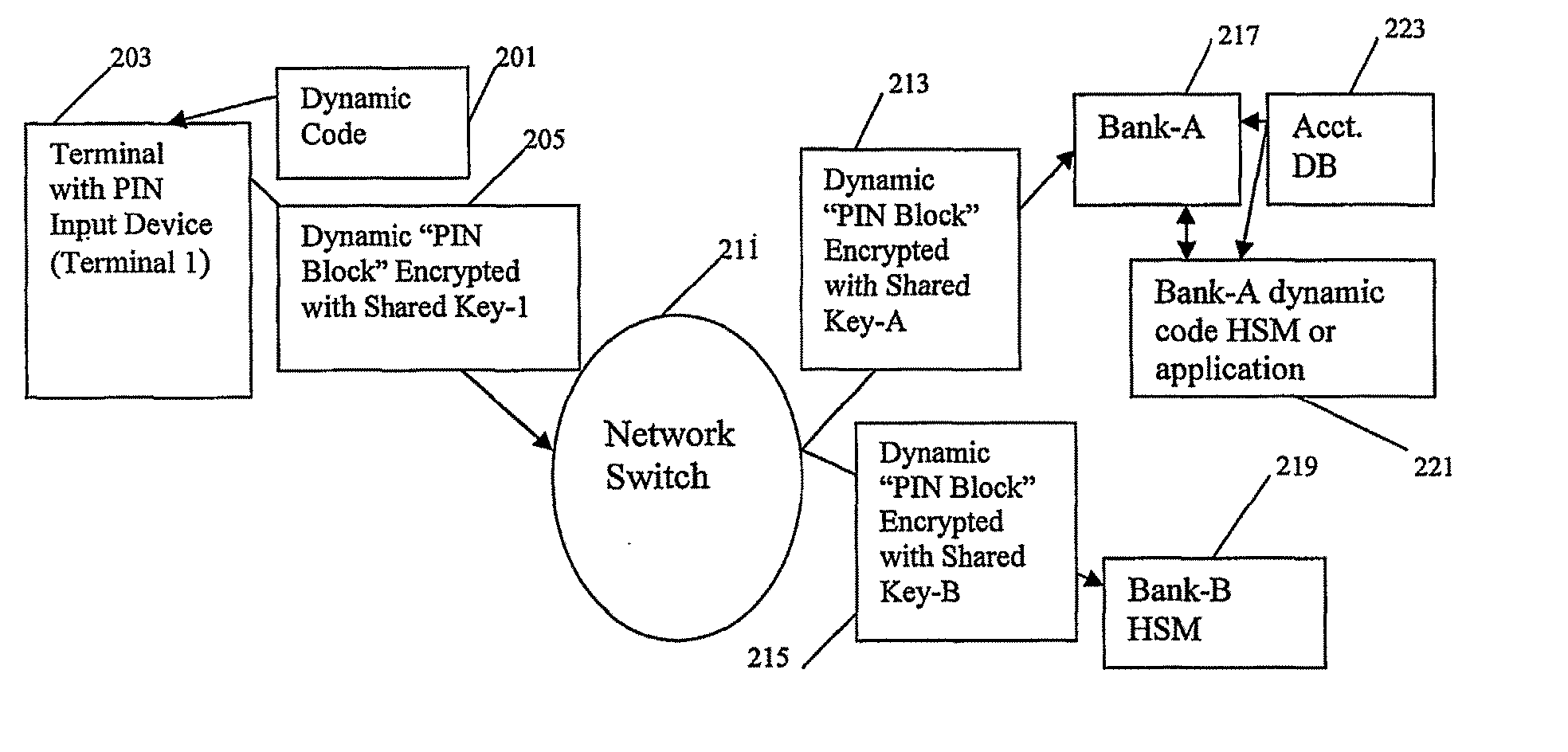
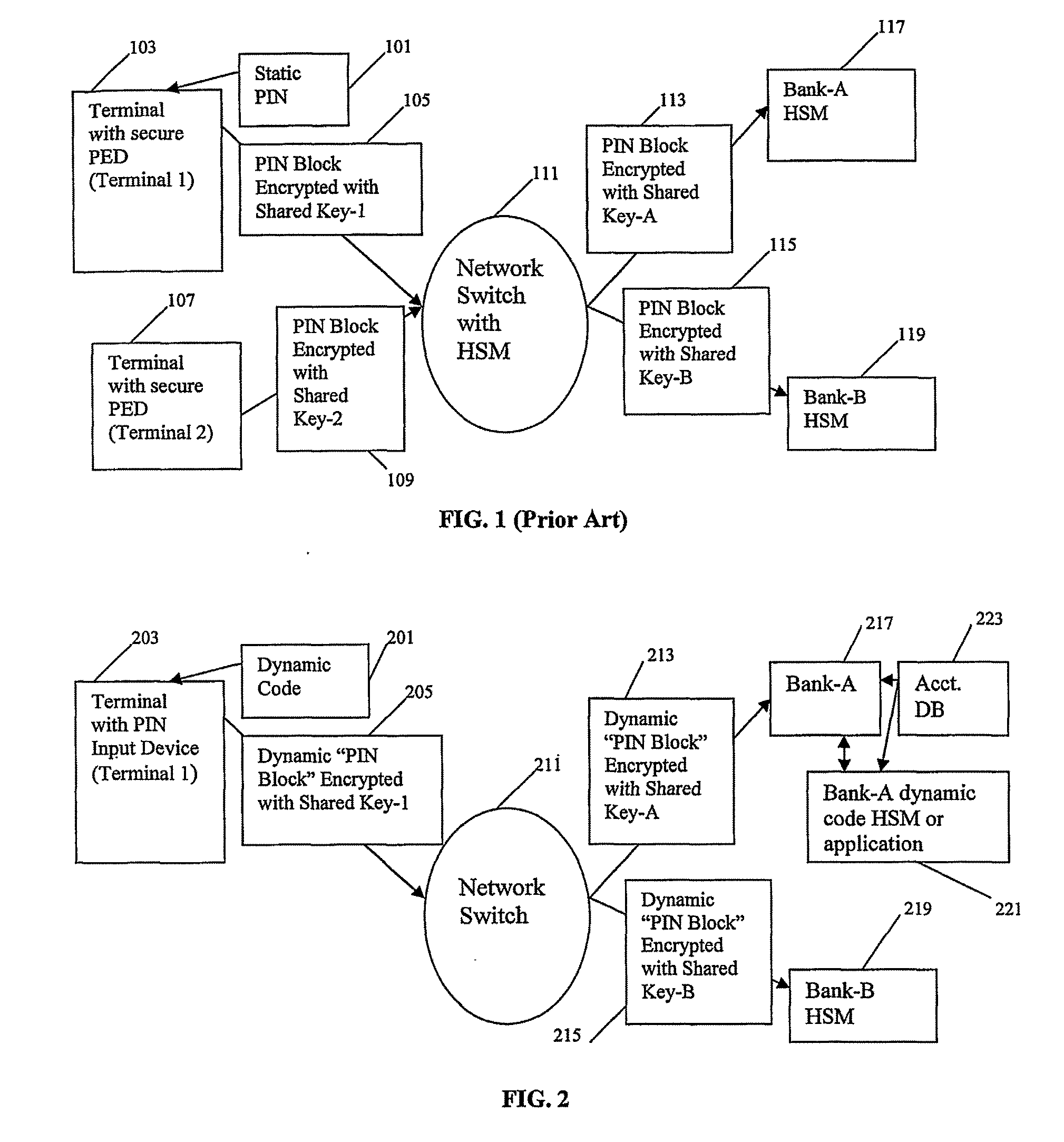
Method and system for performing a transaction using a dynamic authorization code
ActiveUS20070260544A1Reduce security costsEliminate requirementsComplete banking machinesFinanceFinancial transactionMessage passing
A method and apparatus for conducting a transaction involving transmission of a dynamic authentication code in place of a static PIN block using currently existing messaging standards or PIN acceptance devices. Minimal changes to existing processes an equipment are made while greatly improving security and fraud minimization.
Owner:MASTERCARD INT INC
Partitioning of frequency resources for transmission of control signals and data signals in SC-FDMA communication systems
ActiveUS8031688B2Maximize Bandwidth UtilizationAvoid fragmentationTransmission path divisionMultiplex communicationFrequency UnitCommunications system
A method for the partitioning frequency resources used in the transmission of control signals and data signals by user equipments in a communication system. The control signals and data signals are for periodic transmission and dynamic transmission. Also provided is an apparatus and method for user equipments to determine the first frequency unit available for the transmission of dynamic control signals, such as acknowledgement signals associated respective reception of data signals configured through a scheduling assignment by a serving Node B. The utilization of the operating bandwidth is maximized by avoiding fragmentation and facilitates the achievement of reception reliability targets particularly for control signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
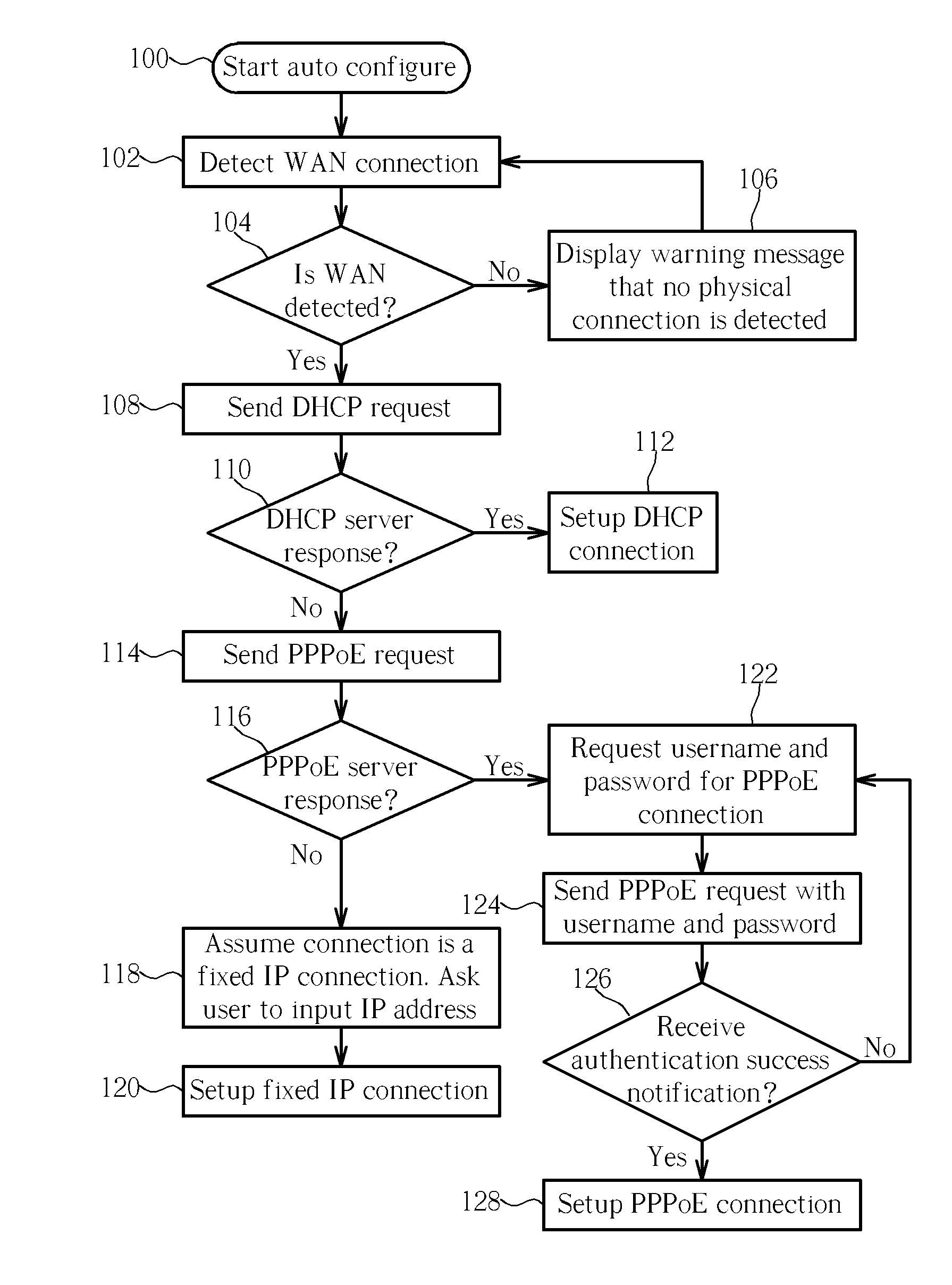
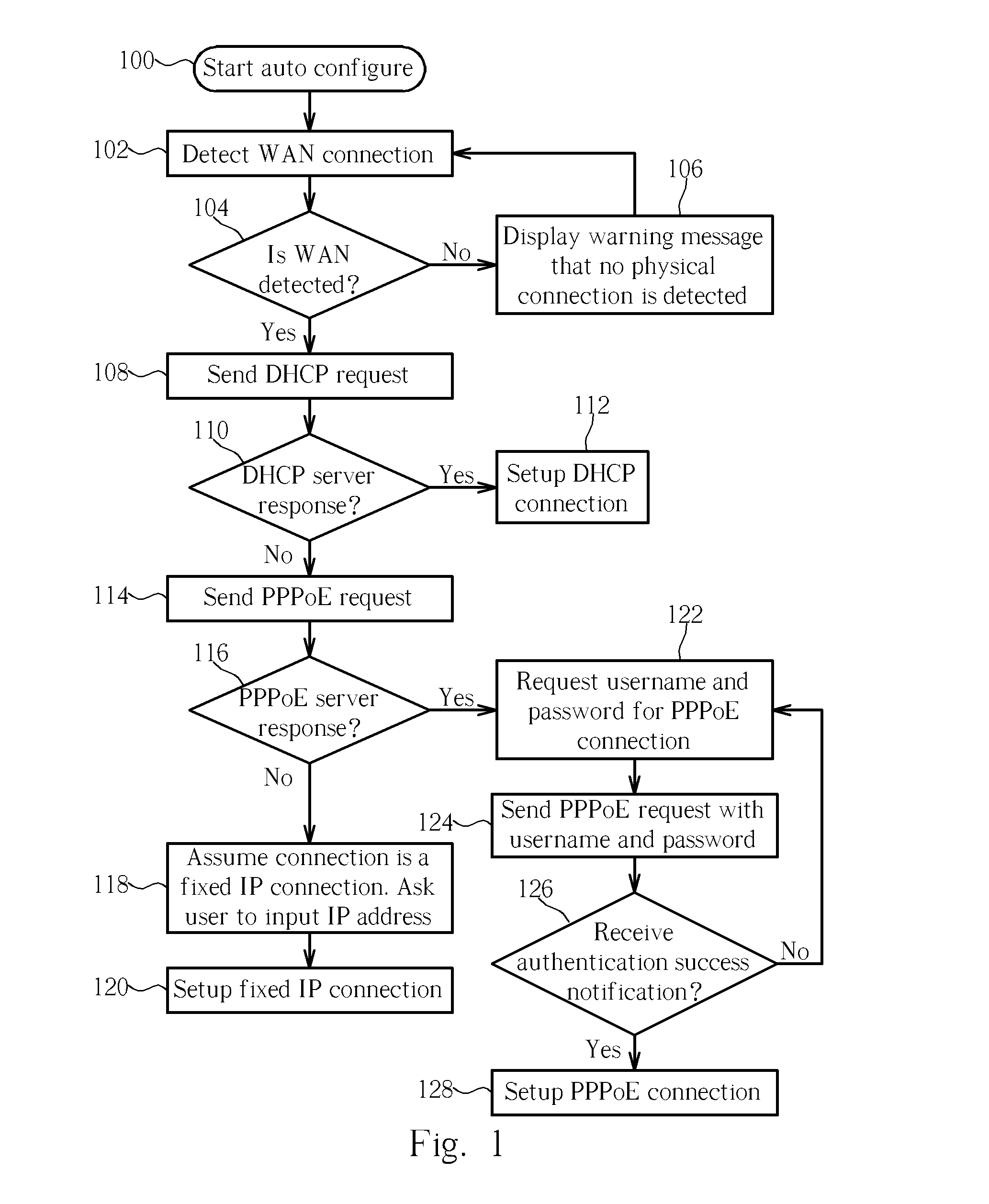
Method of setting up a wireless router
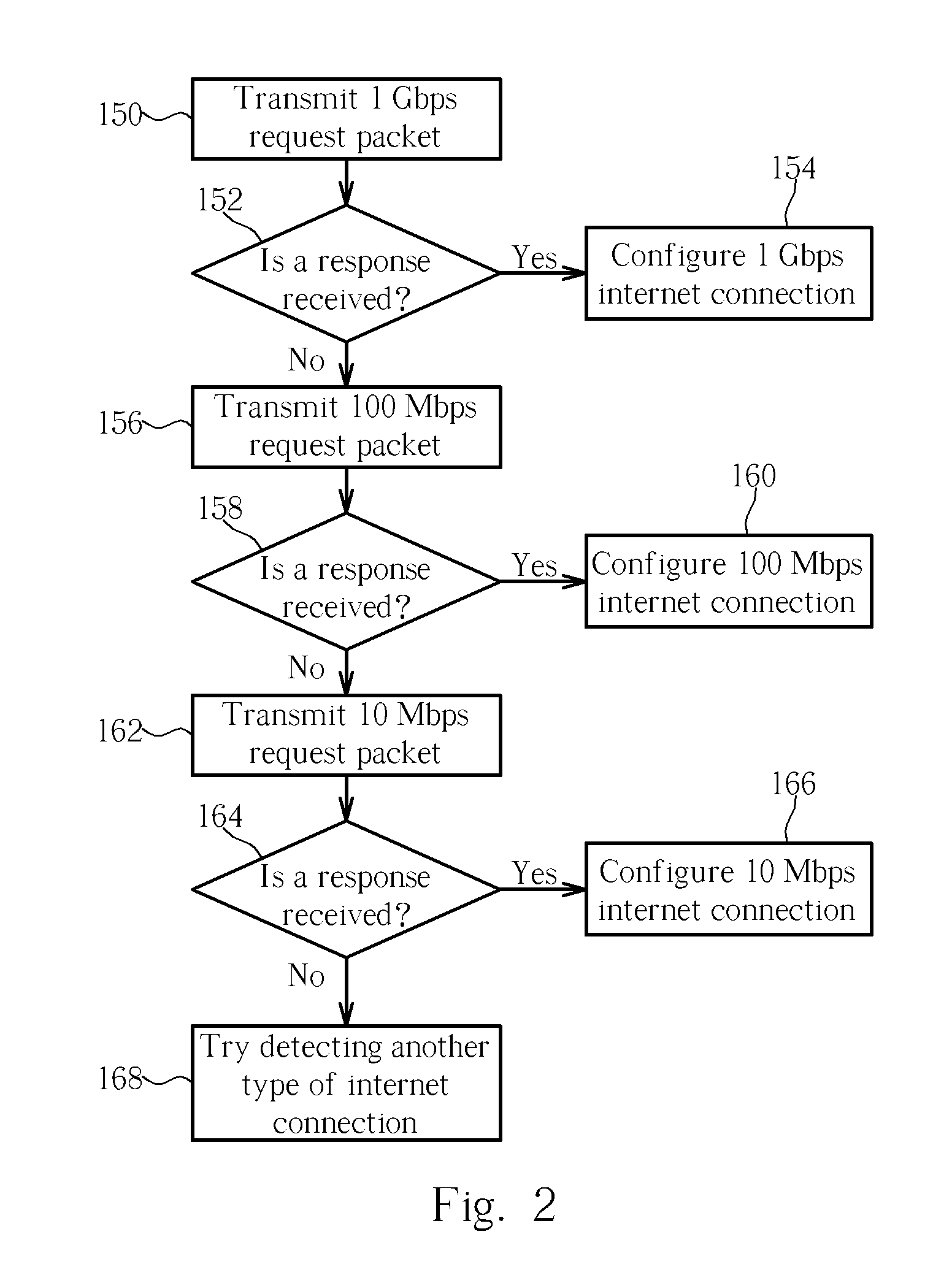
InactiveUS20070058538A1Quick Auto DetectError preventionTransmission systemsWireless routerPoint-to-Point Protocol
Owner:UNICATION
Physical analog test apparatus for canal pollutant transmission under temperature-hydraulic coupling action
InactiveCN101477106AAchieve recyclingSolve unmanageable puzzlesEarth material testingData acquisitionEngineering
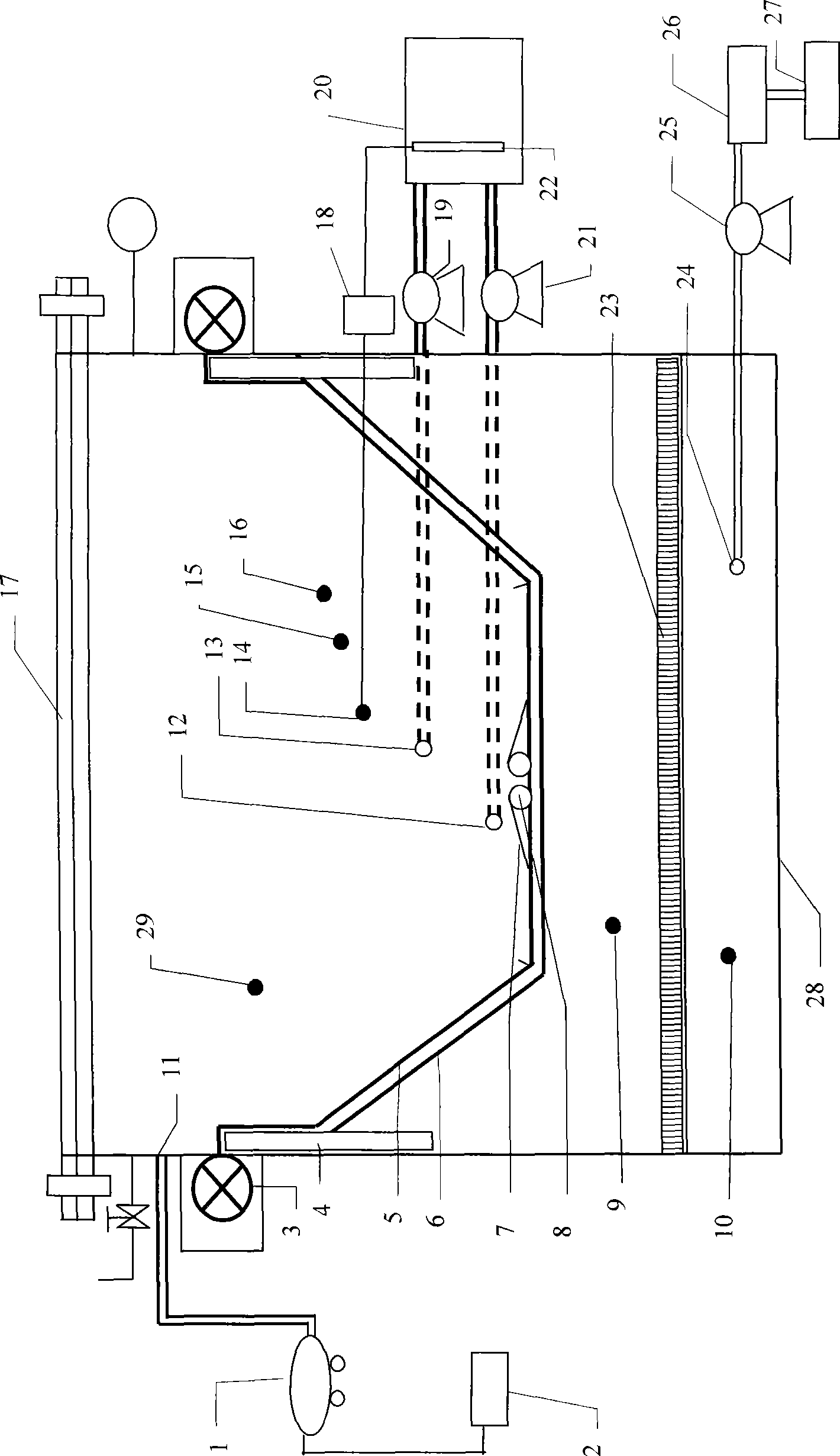
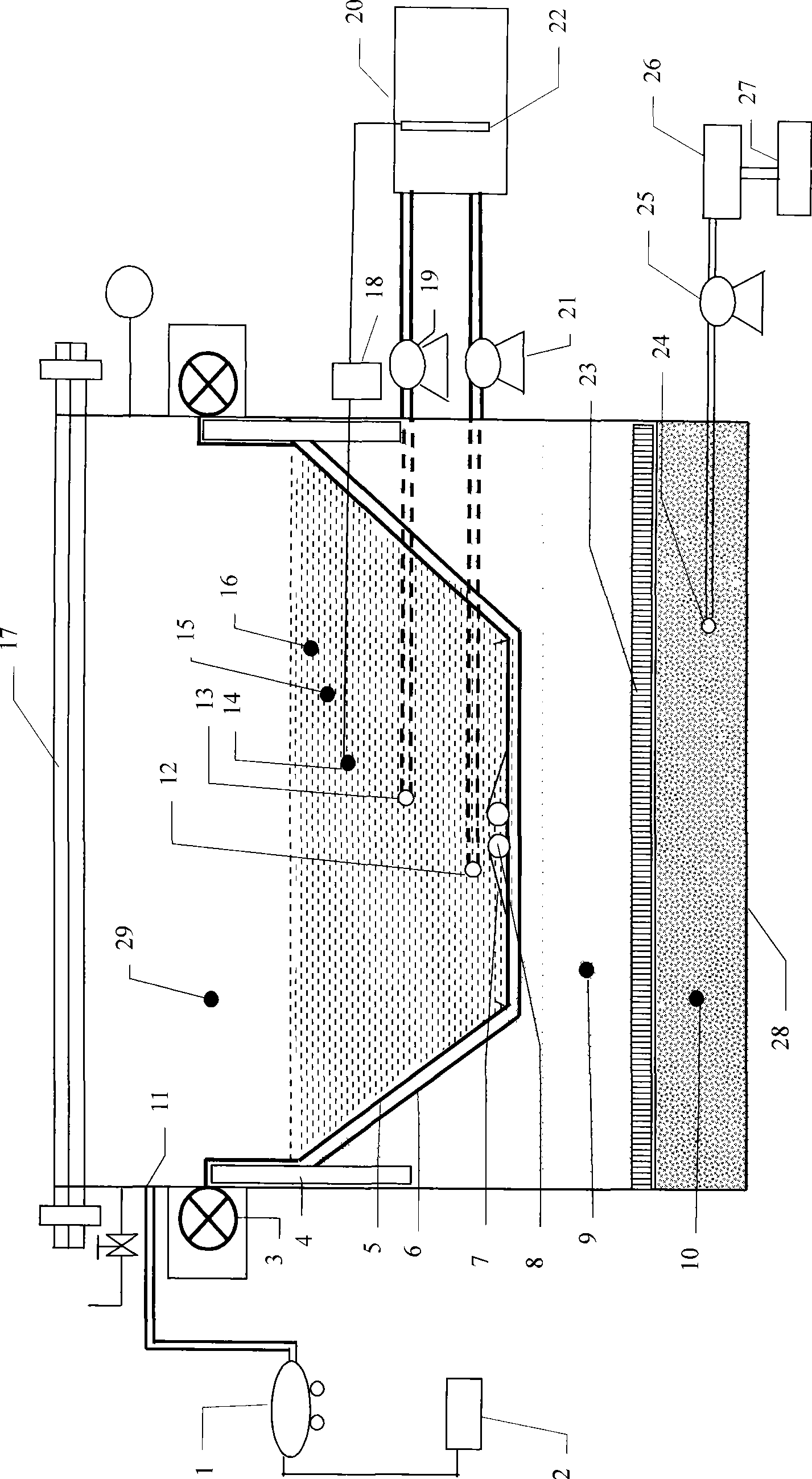
The invention discloses a physical simulation testing device used in graff contaminant transmission under the action of temperature-hydraulic coupling. The testing device comprises a simulation container, an air pressure control device, a temperature control device, a circulating water system and an online control and monitoring system. The testing system can realize physical simulation test of transmission dynamic characteristics of contaminants in rivers, aqueducts, sewage trenches and surrounding soil and ground water, and integrate monitoring, control and data acquisition; moreover, the testing system realizes real-time display and intelligent control of water level, temperature and pressure variations in the testing system, and carries out overall process acquisition, analysis and visualized input and output on testing data through a data acquisition program. The testing system has the characteristics of reasonable structure, convenient operation, high precision of testing data, quick automatic data acquisition, short testing cycle as well as ideal modularization, openness and expansibility, and the like. In addition, the testing system provides parameter basis to disclose the transmission mechanism of contaminants in soil and ground water under complicated environmental conditions and analyze migration and transformation rule, and also provides technical support for appraising pollution control and treatment technical proposals.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
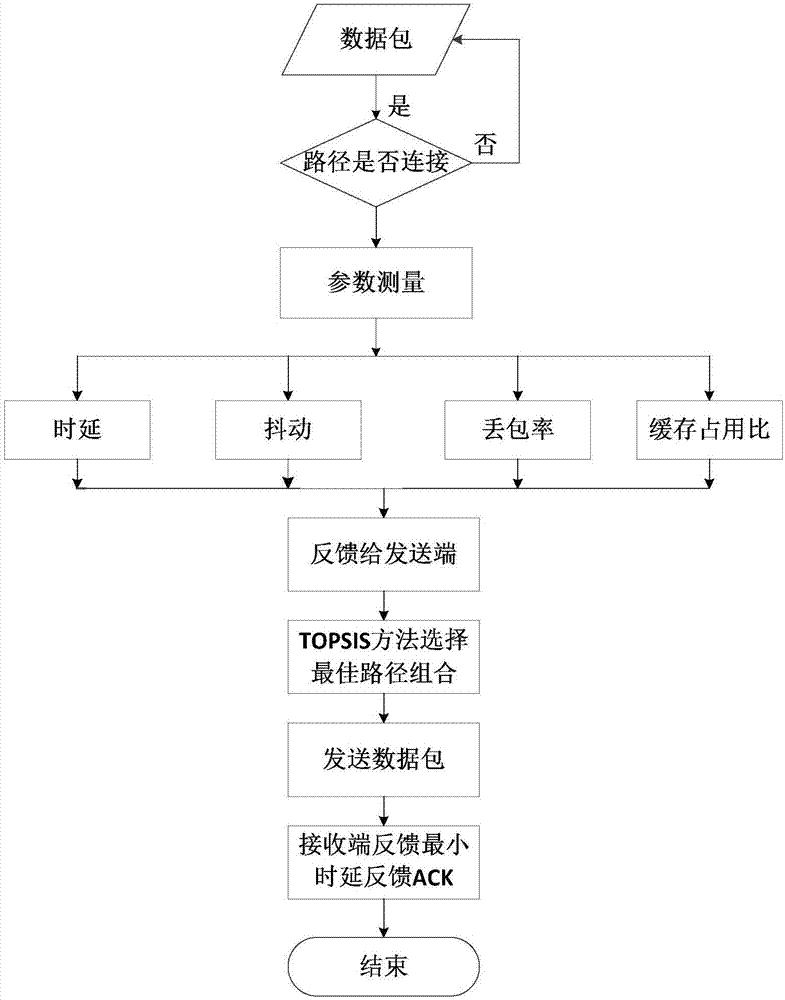
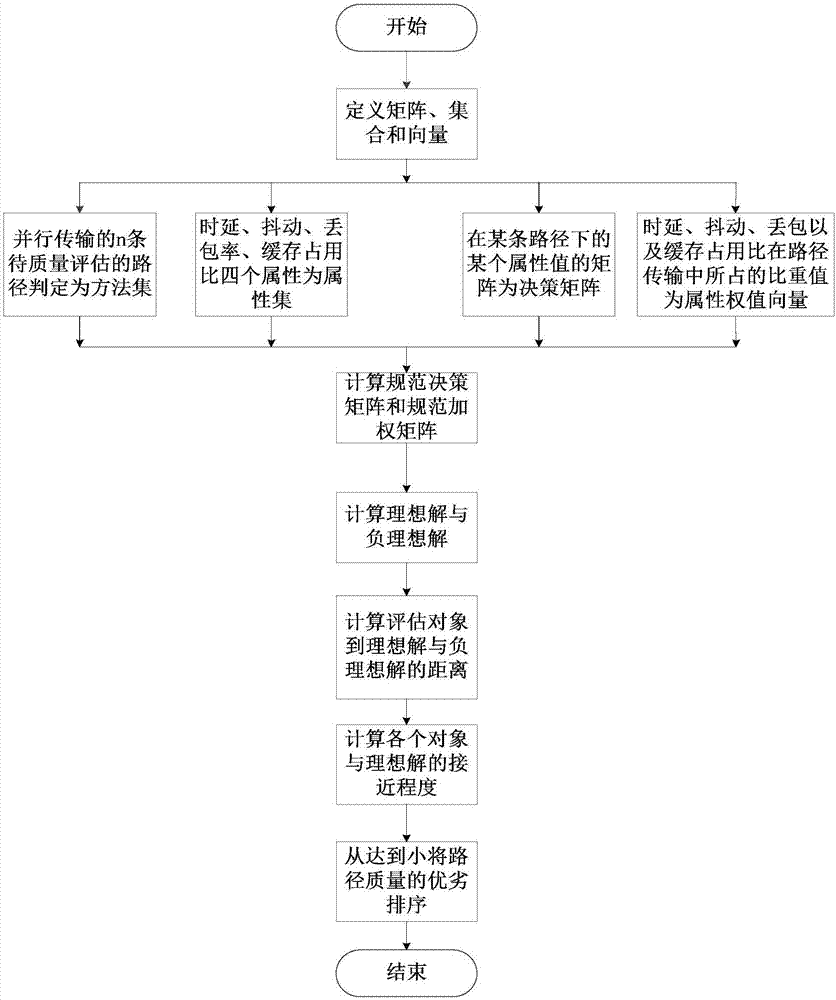
Multipath parallel transmission dynamic decision-making method based on path quality
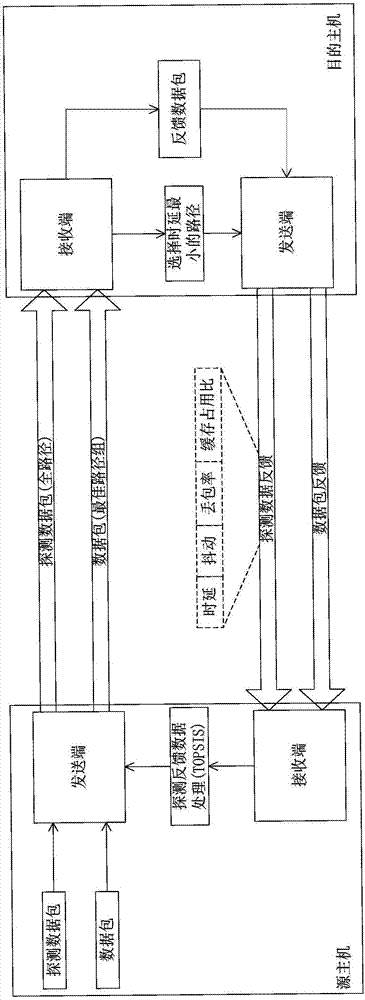
InactiveCN107426102AImprove throughputEfficient data transferError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksPacket lossData transmission
The invention discloses a multipath parallel transmission dynamic decision-making method based on path quality. In consideration of the influence on the whole network transmission performance by the path quality difference, the method comprises the following steps: firstly sending a detection data packet to measure four parameters for deciding the path quality in real time: delay, jittering, packet loss probability and cache occupation rate, feeding back the measured data to a sending end, and processing the measured data through a TOPSIS method in a sending end cache area, selecting out the most appropriate path combination for data transmission, and then sending the to-be-transmitted data packet, when the data packet arrives the receiving end, sending the selected path with the minimum delay to a feedback ACK to a receiving end. The design disclosed by the invention sufficiently gives full play to the advantage of the dynamic decision-making path, the network throughput out is improved, and the efficient data transmission is realized.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Beam pump dynamic load monitoring and methods
A pump monitoring system includes a monitoring device configured for attachment to a cable harness of a pump, a strain gauge configured to measure dynamic loading of at least one cable of the cable harness as the pump operates, a wireless transmitter configured to transmit the dynamic loading measurement, and an external device configured to receive the transmitted dynamic loading measurement.
Owner:PCS FERGUSON
Display method of information and terminal
ActiveCN106468998AStrong perceptionImprove experienceCircuit monitoring/indicationTexturing/coloringGraphicsComputer terminal
The invention discloses a display method of information and a terminal. The display method of the information comprises the steps of detecting whether the terminal is connected to external equipment currently or not; when the terminal is connected to the external equipment currently, conducting transmission of a transmission object between the terminal and the external equipment; when the transmission of the transmission object is conducted between the terminal and the external equipment, displaying a progress graph and a transmission dynamic picture on a screen of the terminal. The transmission dynamic picture comprises an object graph which moves from a starting point on the screen to an end point on the screen and disappears at the end point, and the object graph is used for indicating a transmission object. According to the display method of the information and the terminal, a user is enabled to have preferable experience of perception of connection conditions between the terminal and the external equipment.
Owner:HUAWEI MACHINERY
Beam pump dynamic load monitoring and methods
A pump monitoring system includes a monitoring device configured for attachment to a cable harness of a pump, a strain gauge configured to measure dynamic loading of at least one cable of the cable harness as the pump operates, a wireless transmitter configured to transmit the dynamic loading measurement, and an external device configured to receive the transmitted dynamic loading measurement.
Owner:PCS FERGUSON
Method of managing coexisting packet streams
ActiveUS20080232315A1Easy to manageCollisions of transmissionsConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemComputer science
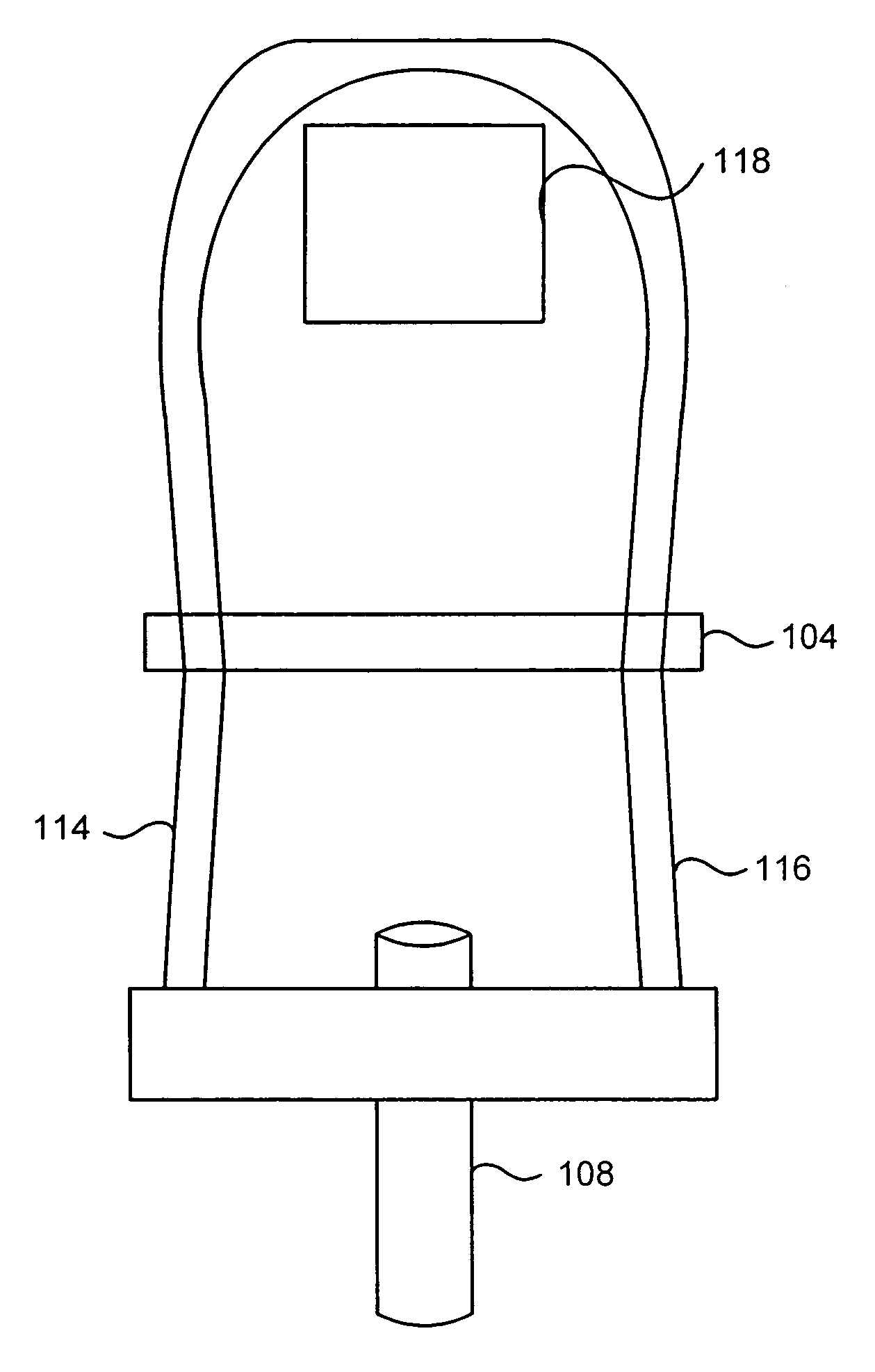
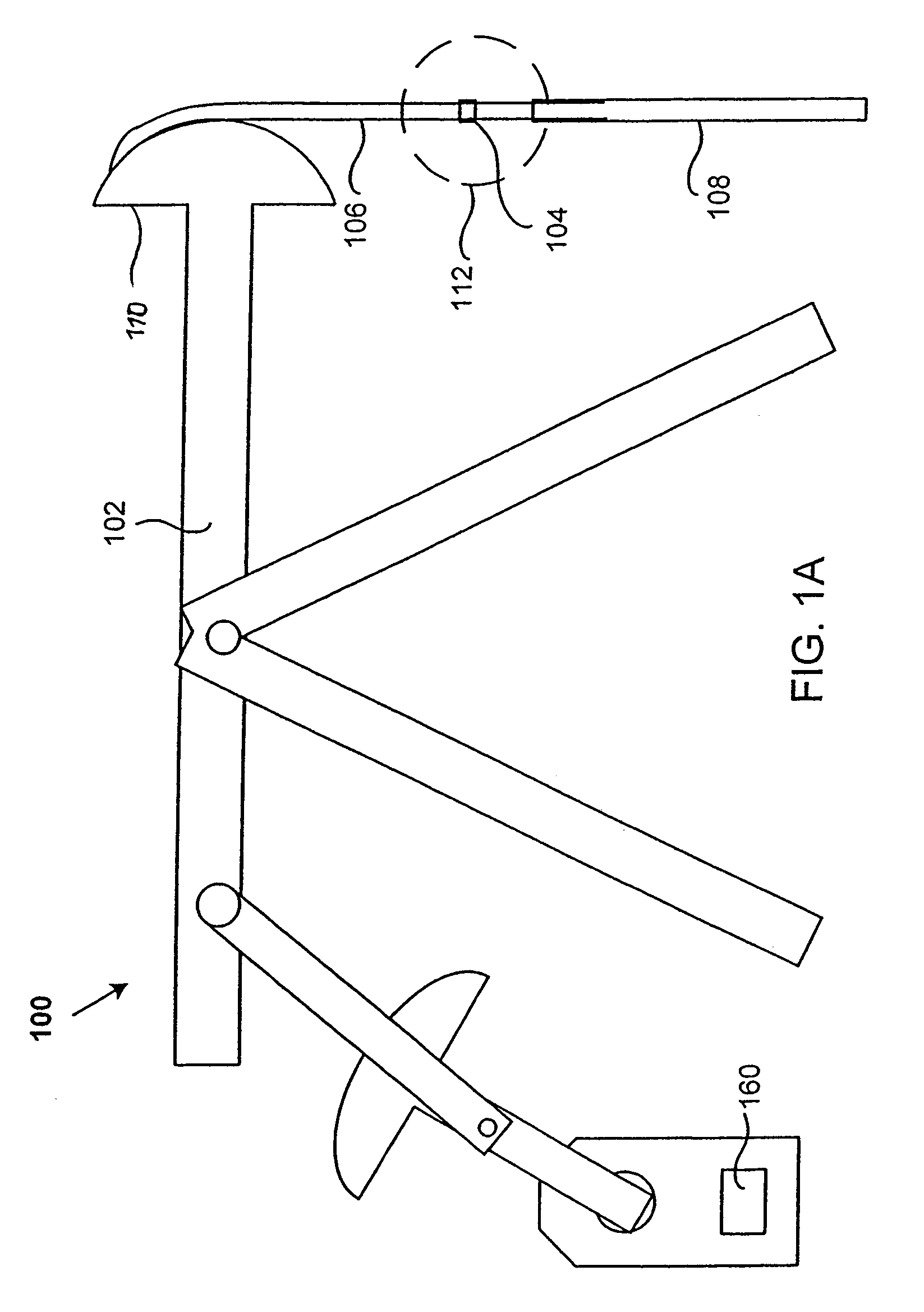
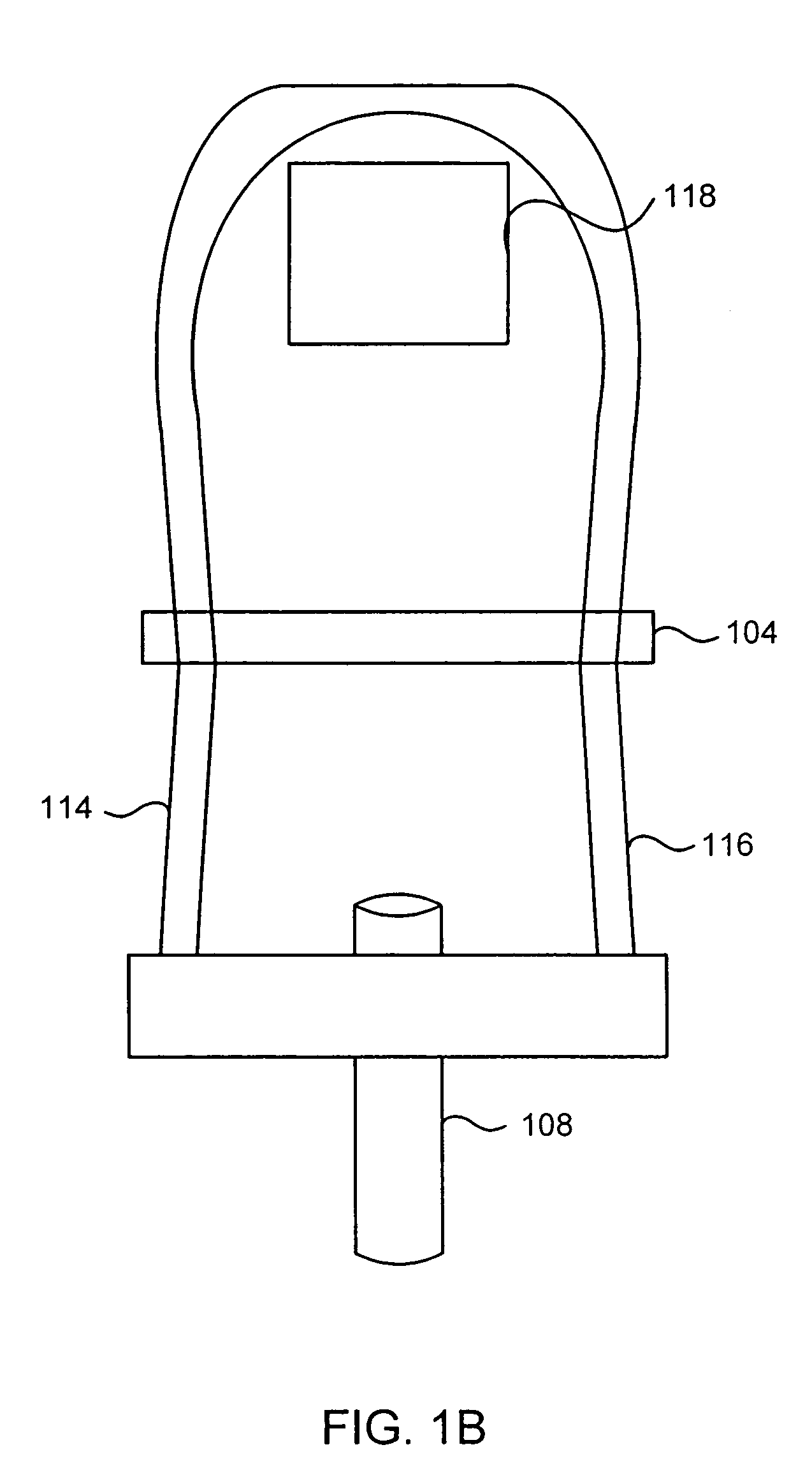
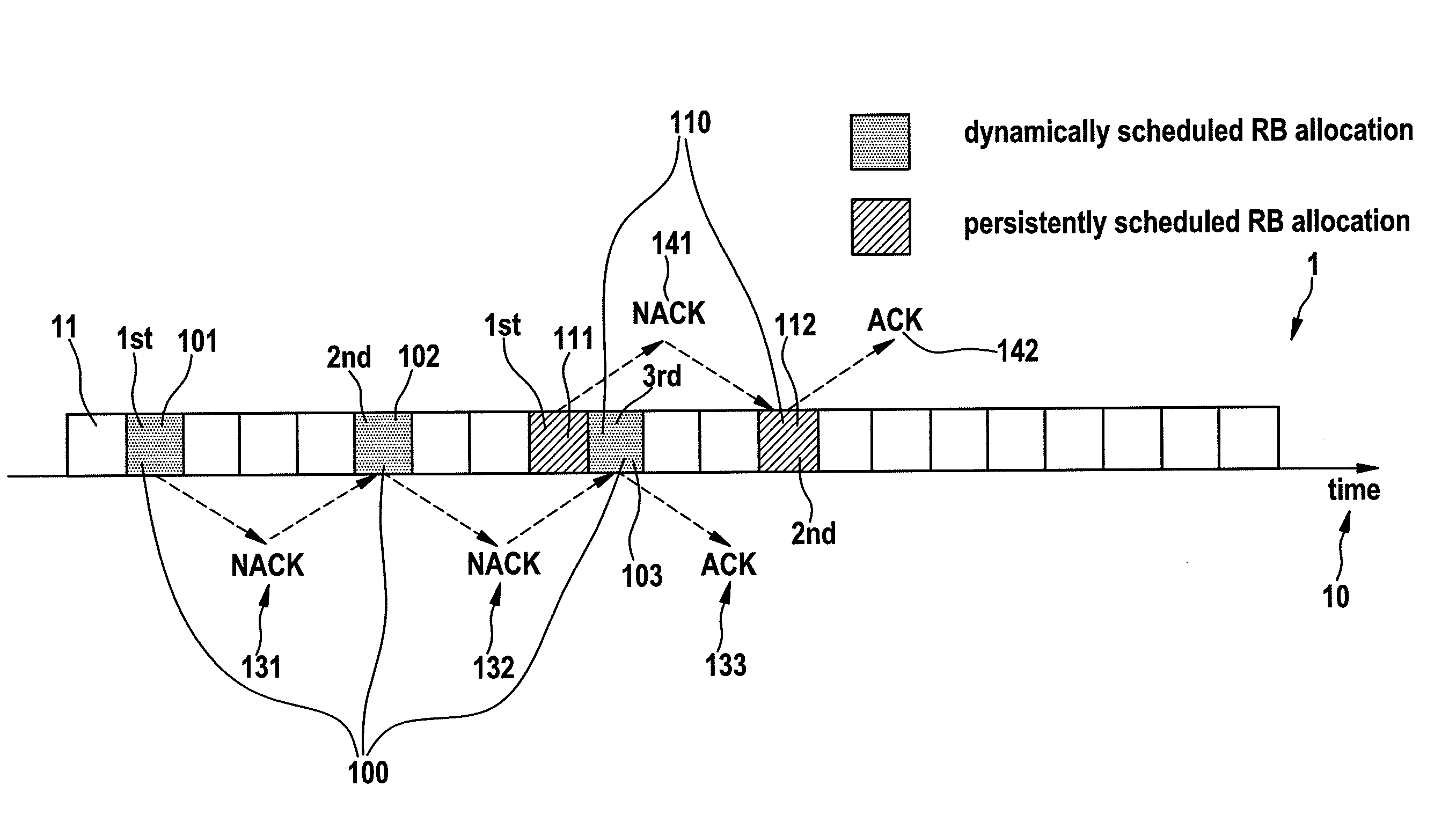
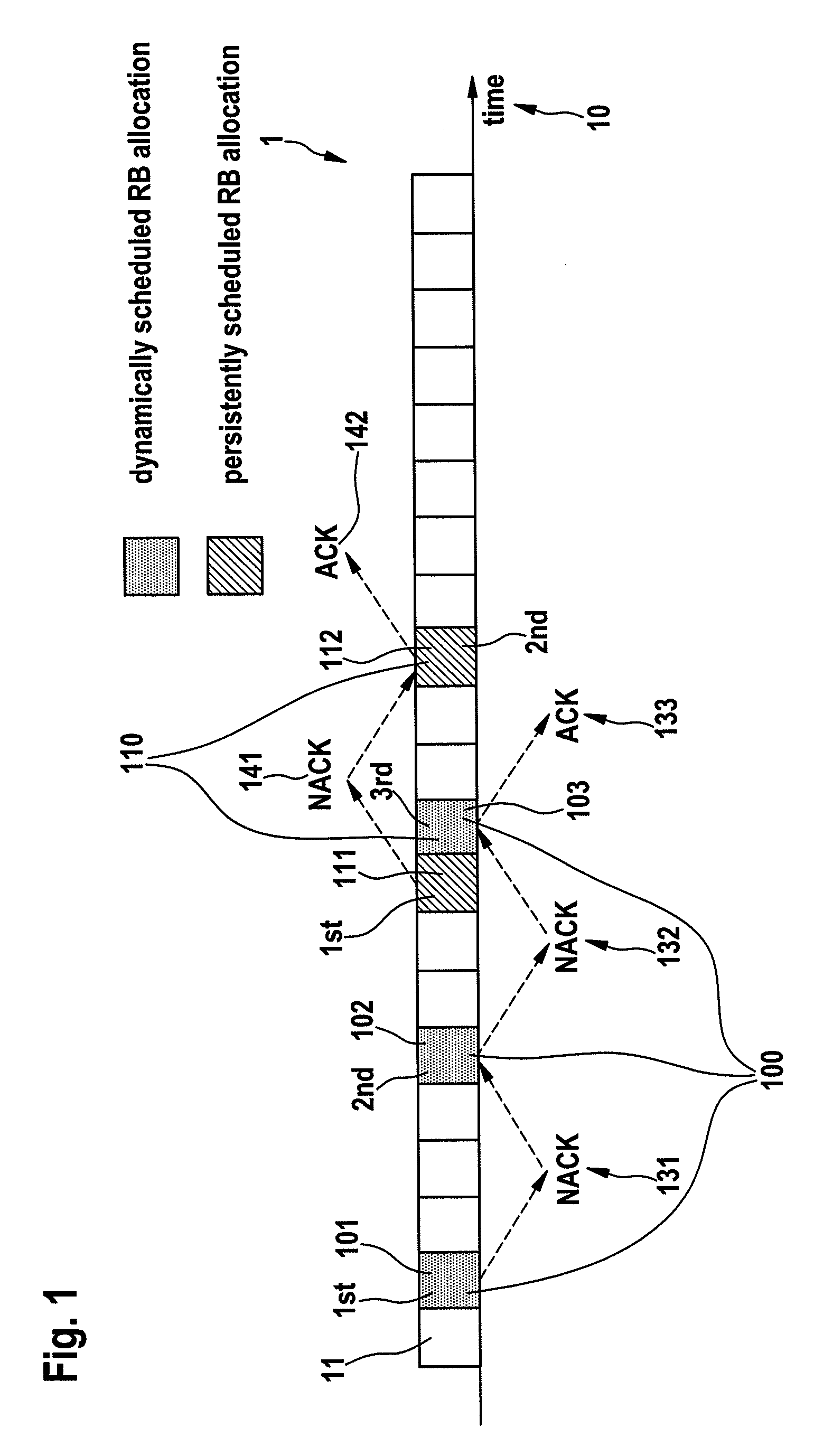
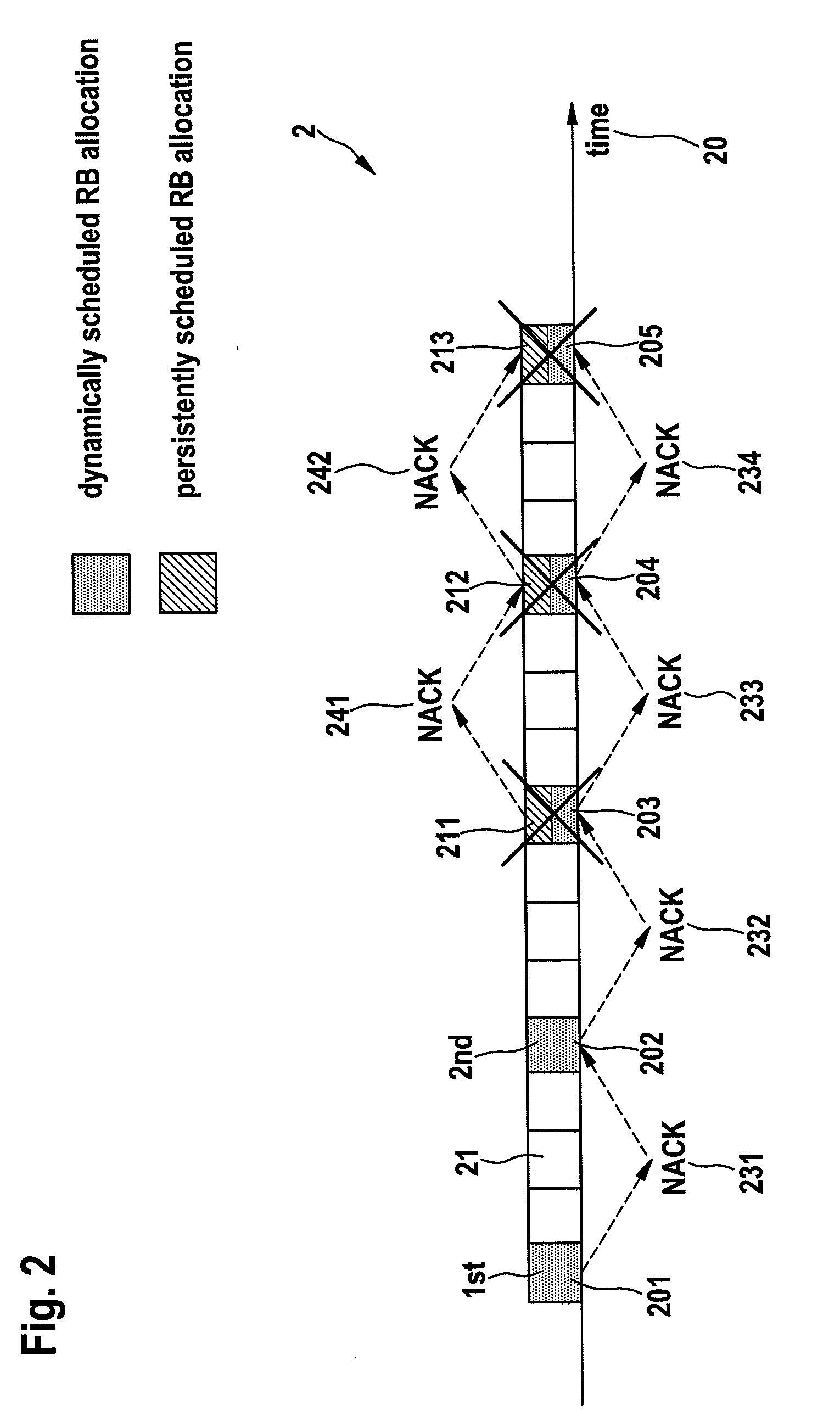
The invention concerns a method of managing coexisting packet streams (100, 110) in a wireless communication system, and a corresponding controller and a mobile terminal. A first packet stream (110) of the coexisting packet streams (100, 110) requires transmission resources of the wireless communication system at fixed time intervals, and a second packet stream (100) of the coexisting packet streams (100, 110) requires transmission resources of the wireless communication system at dynamically determined time intervals. A schedule defining allocations of transmission resources for the first packet stream (110) is set up. A request for an initial grant of transmission resources for a transmission of a data packet (101) of the second packet stream (100) is issued. In the process of allocating transmission resources to the second packet stream (100), the controller analyses the schedule of transmission resources allocated to the first packet stream (110) and thereby determines whether a retransmission (102, 103) of the data packet (101) associated with the second packet stream (100) is possible to collide with a transmission of a data packet (111, 112) associated with the first packet stream (110) according to the schedule. The controller transmits a parameter specifying a number N of retransmissions (102, 103) possible without such collision as part of the initial grant of transmission resources to the mobile terminal.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Partitioning of frequency resources for transmission of control signals and data signals in sc-fdma communication systems
ActiveUS20110317649A1Maximize Bandwidth UtilizationAvoid fragmentationTransmission path divisionSignal allocationCommunications systemFrequency Unit
A method for the partitioning frequency resources used in the transmission of control signals and data signals by user equipments in a communication system. The control signals and data signals are for periodic transmission and dynamic transmission. Also provided is an apparatus and method for user equipments to determine the first frequency unit available for the transmission of dynamic control signals, such as acknowledgement signals associated respective reception of data signals configured through a scheduling assignment by a serving Node B. The utilization of the operating bandwidth is maximized by avoiding fragmentation and facilitates the achievement of reception reliability targets particularly for control signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for embedded type transmission of dynamic data
InactiveCN101321123AAvoid gettingTake advantage ofData switching networksInformation transmissionApplication server
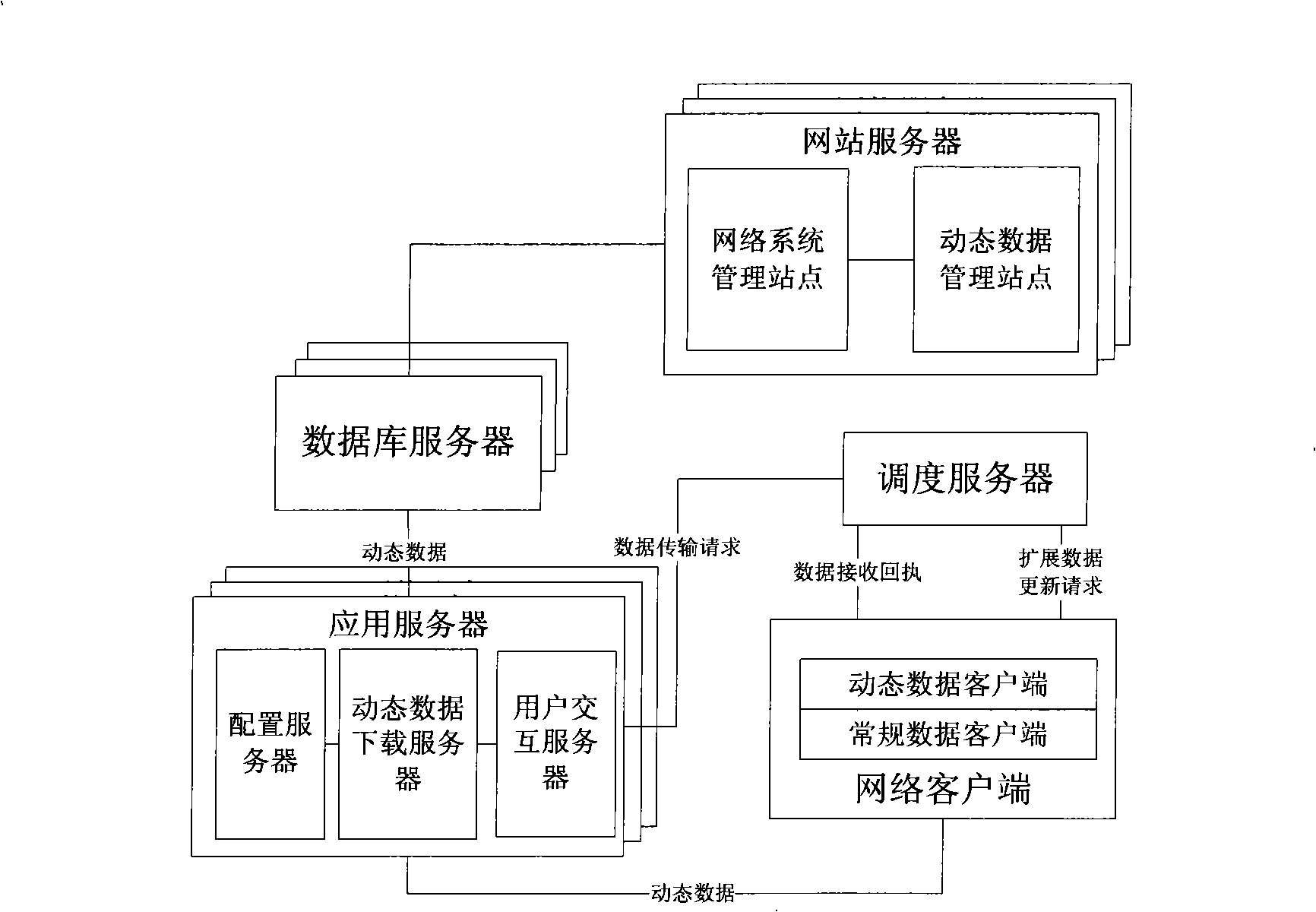
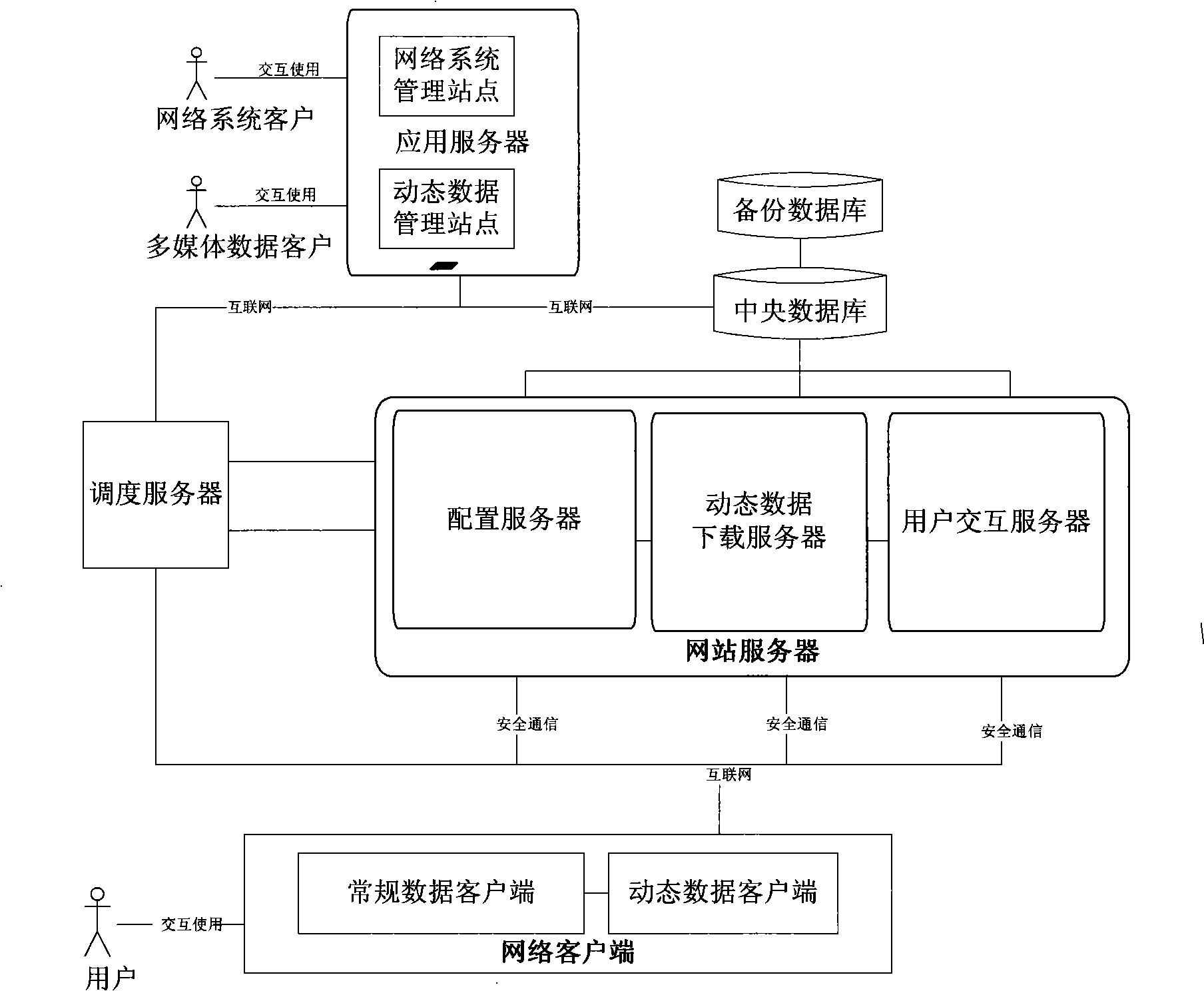
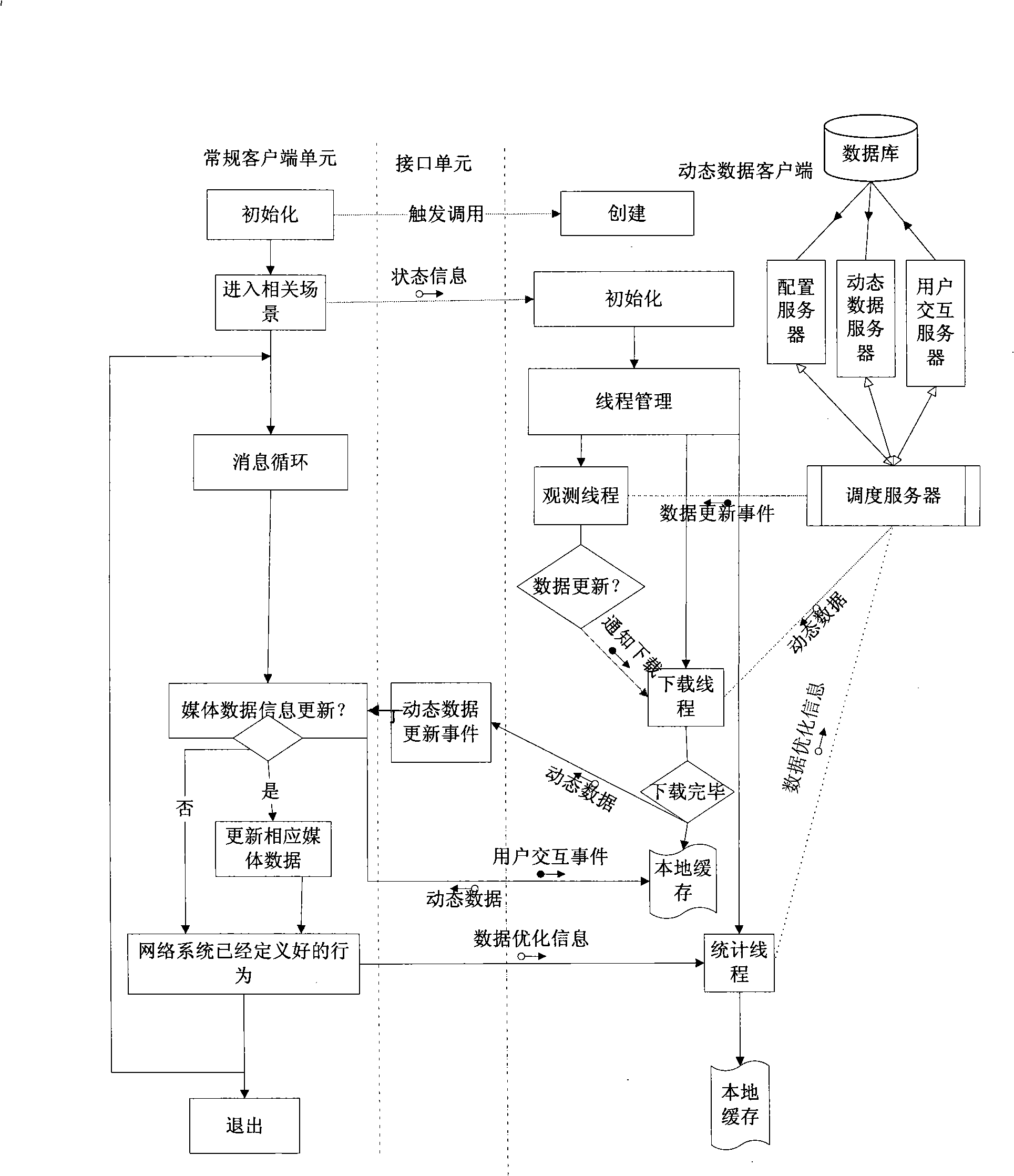
An embedded system of transmitting dynamic data in the technical field of the Internet transmission and the transmission method thereof, comprising a plurality of Web servers, a plurality of Application servers, network client, scheduling server and database server; wherein, the network client is connected with the scheduling server to send the extended data updating request, receive the dynamic data and returns to the data receiving receipt; the Web server is connected with the database server; the Application server is connected with the database server and the network client by the scheduling of the scheduling server to transmit the dynamic data. The invention correspondingly sends the information needed by the user terminal and receives the data receiving receipt sent by the user terminal according to the extended data updating request sent by the user terminal, and optimizes the content of the data sent by the user terminal and the transmission link according to the different data, thereby improving the information transmission efficiency.
Owner:爱德威软件开发(上海)有限公司
Transmission of system information
ActiveCN101682478AAssess restrictionTransmission link error control systemTelecommunicationsTransport system
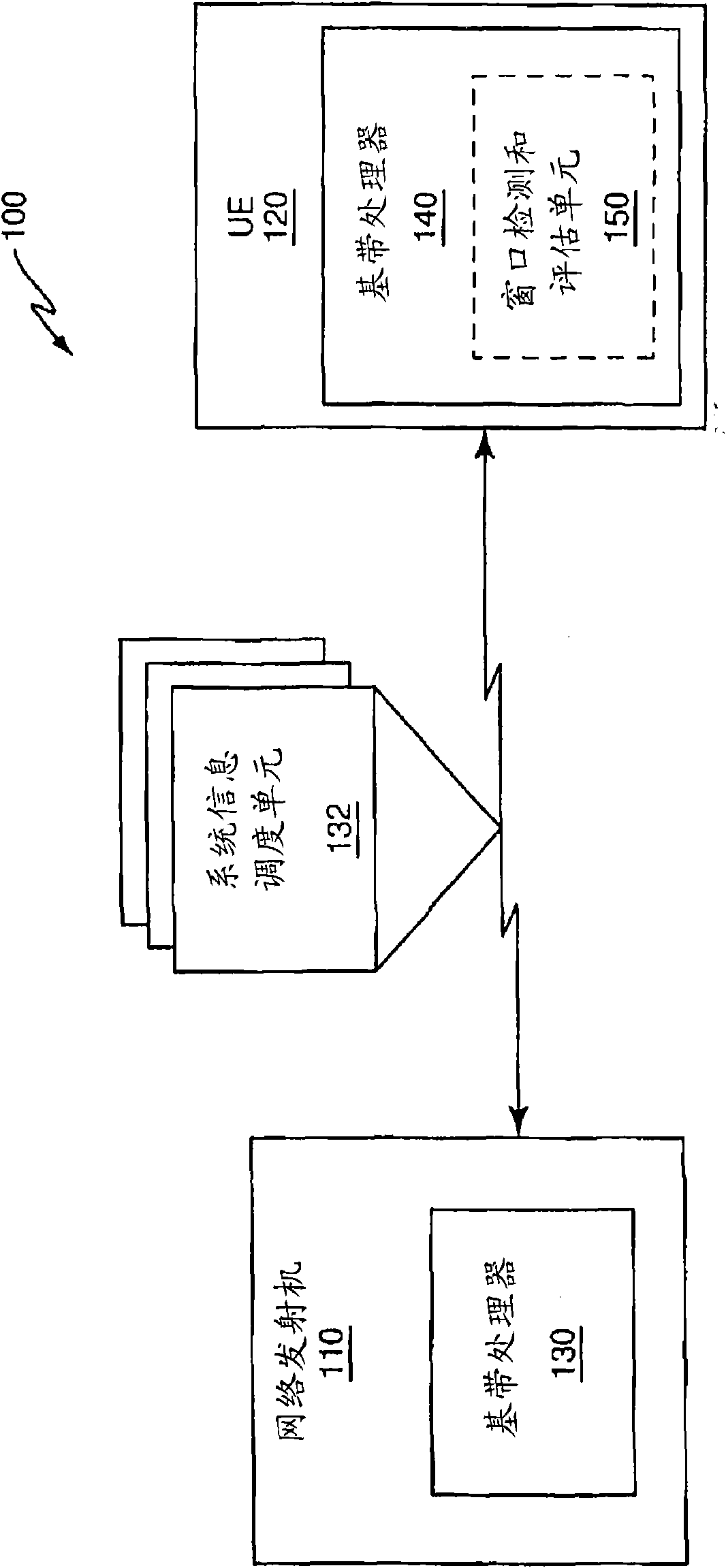
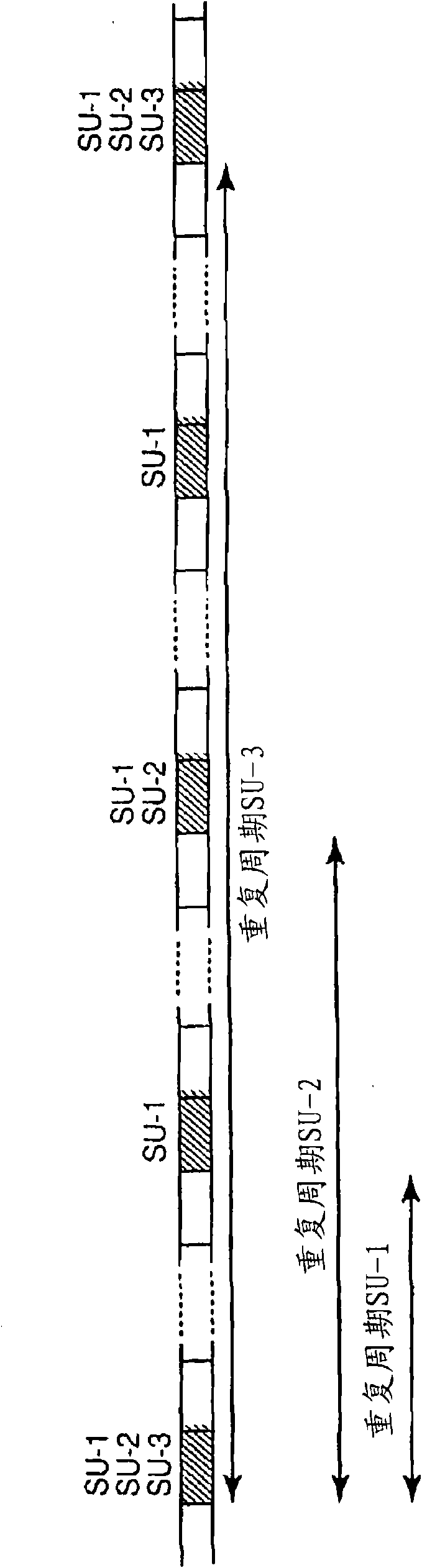
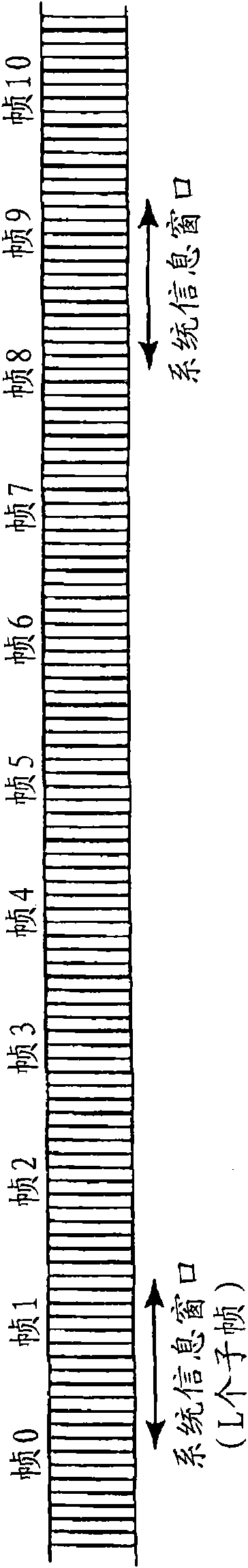
In one embodiment, a method of transmitting system information on a down link shared channel structured as successive subframes includes transmitting (400 - 416) system information in regularly occurring time windows, each time window spanning some number of successive subframes. The method further includes indicating (406 / 408) to receiving user equipment (120) which subframes within a given time window carry system information. The method and variations thereof are applied, for example, to the transmission of dynamic system information on the down link shared channel or other down link channel in a 3GPP E-UTRA wireless communication network (100).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
High-rate capacity power battery electrolyte
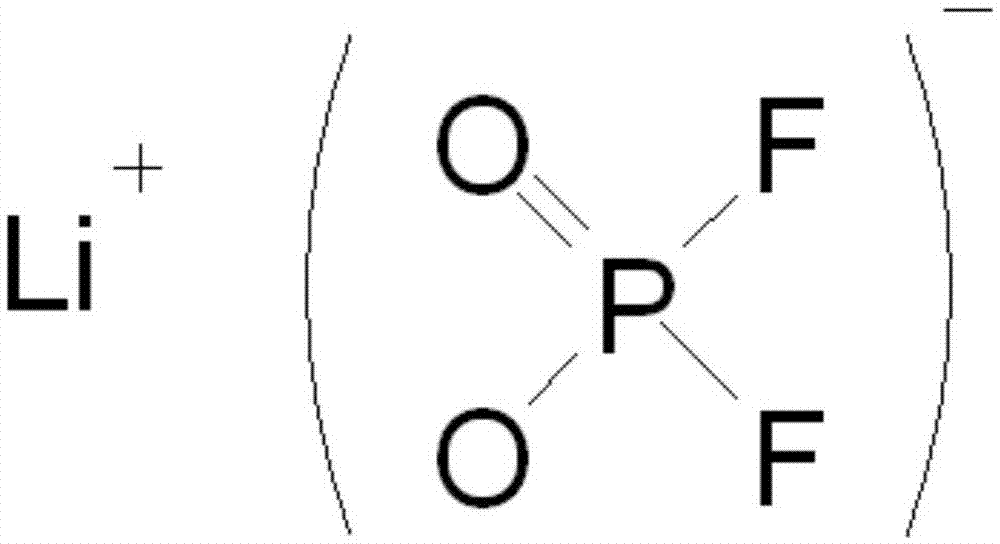
InactiveCN106920992AEnhanced Li+ transport kineticsImprove dynamic performanceSecondary cellsOrganic electrolytesPhosphorous acidPower battery
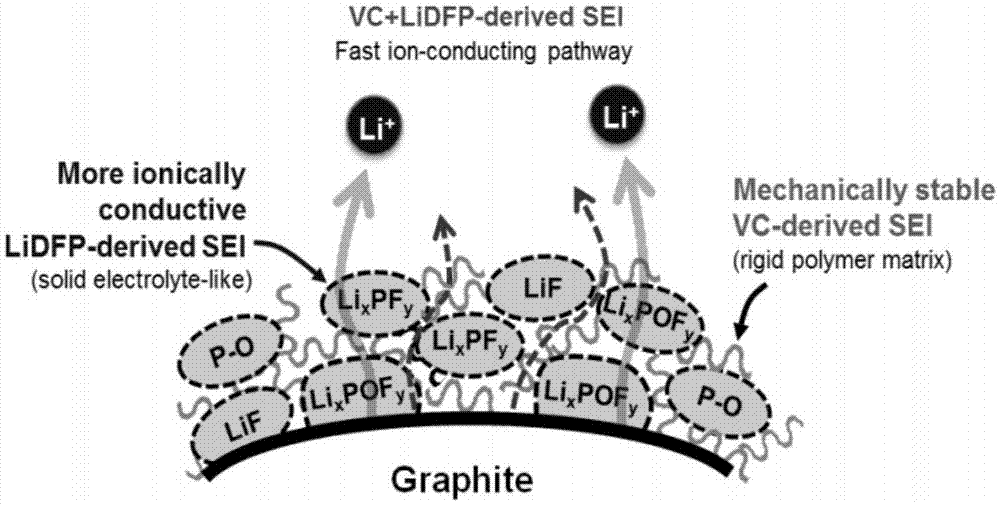
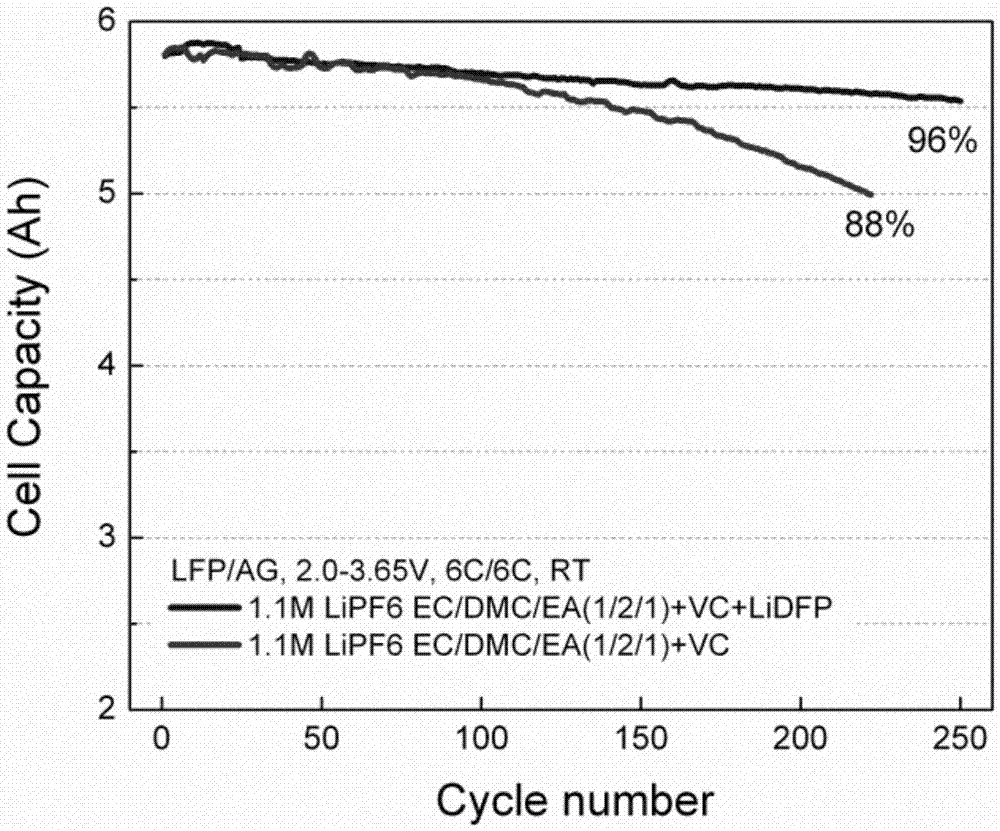
The invention provides a high-rate capacity power battery electrode. The high-rate capacity power battery electrode comprises a lithium salt, a non-aqueous organic solvent, a functional additive and a film formation additive, wherein the film formation additive is lithium salt bi-fluoride phosphorous acid. On the basis of an existing functional additive such as an electrolyte containing VC, a new lithium salt additive LiDFP is added, the chemical constituent of a solid electrolyte interface (SEI) film is optimized, Li<+> transmission dynamics of a negative electrode / electrolyte interface is improved, and high-rate cycle property of a power battery is improved.
Owner:OPTIMUM BATTERY CO LTD
Method applied in alternating current/direct current large power grid transient analysis of imitating direct current response
ActiveCN103094930AEasy to operateCalculation speedElectrical apparatusTransient stateTransient analysis
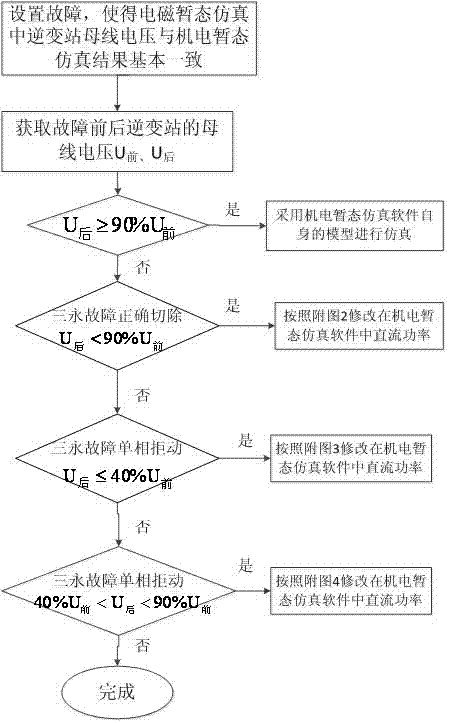
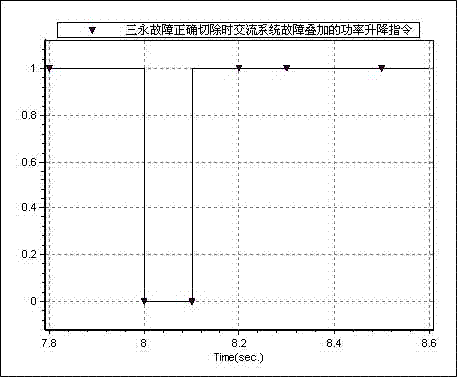
The invention discloses a method applied in alternating current / direct current large power grid transient analysis of imitating direct current response. Fault simulation is disposed in alternating current / direct current large power grid electromechanical transient simulation software. Faults are simulated in the power grid electromagnetic transient software, and contravariant station busbar voltage and the result of the electromechanical transient simulation software are in basic accordance. Power wave form of the direct current is simulated. The electromechanical transient simulation and differences of the direct current wave form simulated by the electromechanical transient simulation software are in comprehensive analysis under fault conditions. The faults are simulated in the electromechanical transient simulation software meanwhile a direct current power modification card is used for modifying a reference value of the direct current power. After the simulated comparison, power curve of the direct current is consistent with the trend of the electromagnetic transient simulation results. Multi-chapter direct currents are simulated. A system is in electromechanical transient stable simulation. The direct current transmission dynamic response is imitated to obtain systematical stable features of the alternating current / direct current. The method applied in the alternating current / direct current large power grid transient analysis of imitating the direct current response is easy to operate, quick in computation speed, high in accuracy degree and suitable for using in the alternating current / direct current interconnection big power grid electromechanical transient simulation analysis.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD
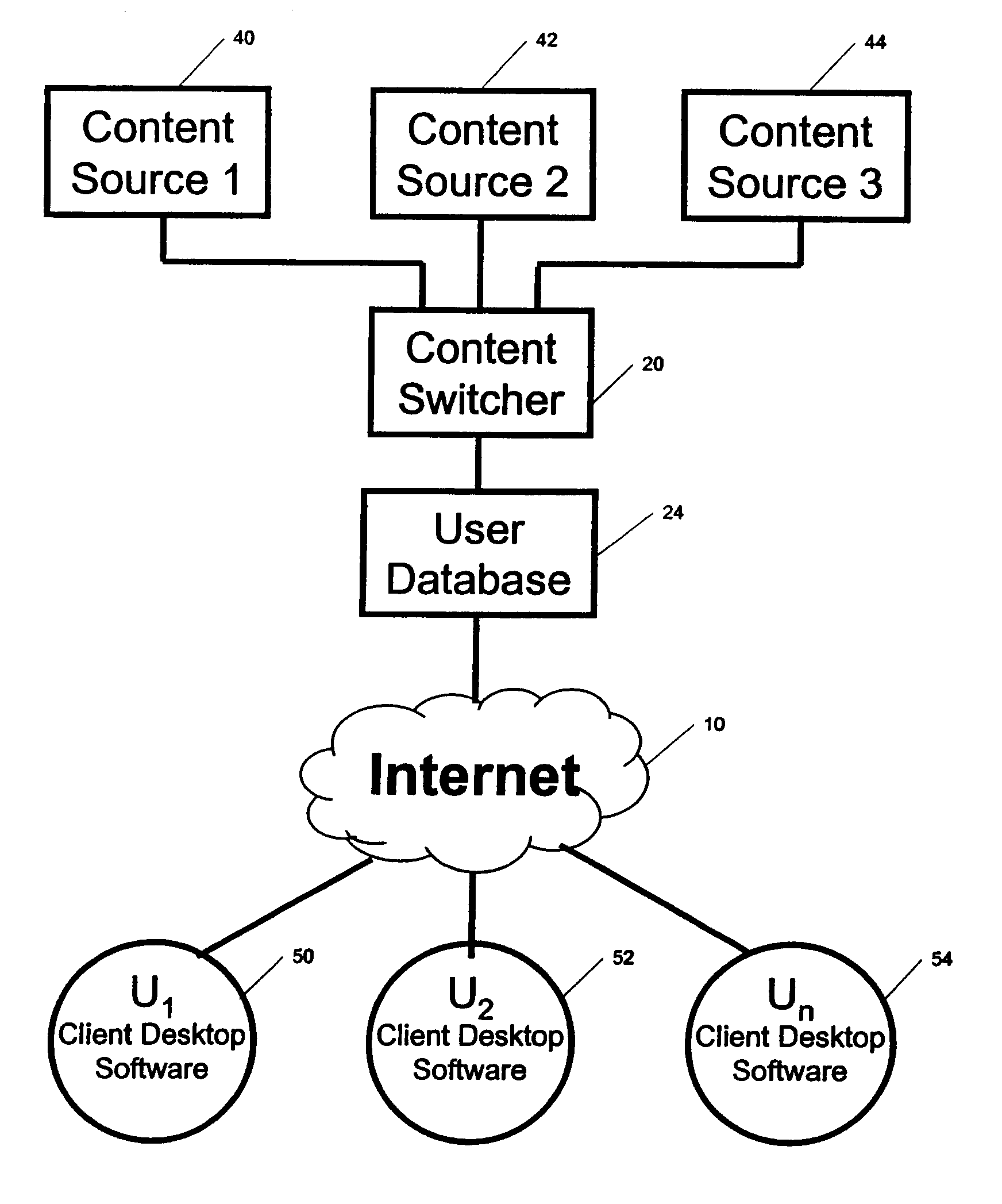
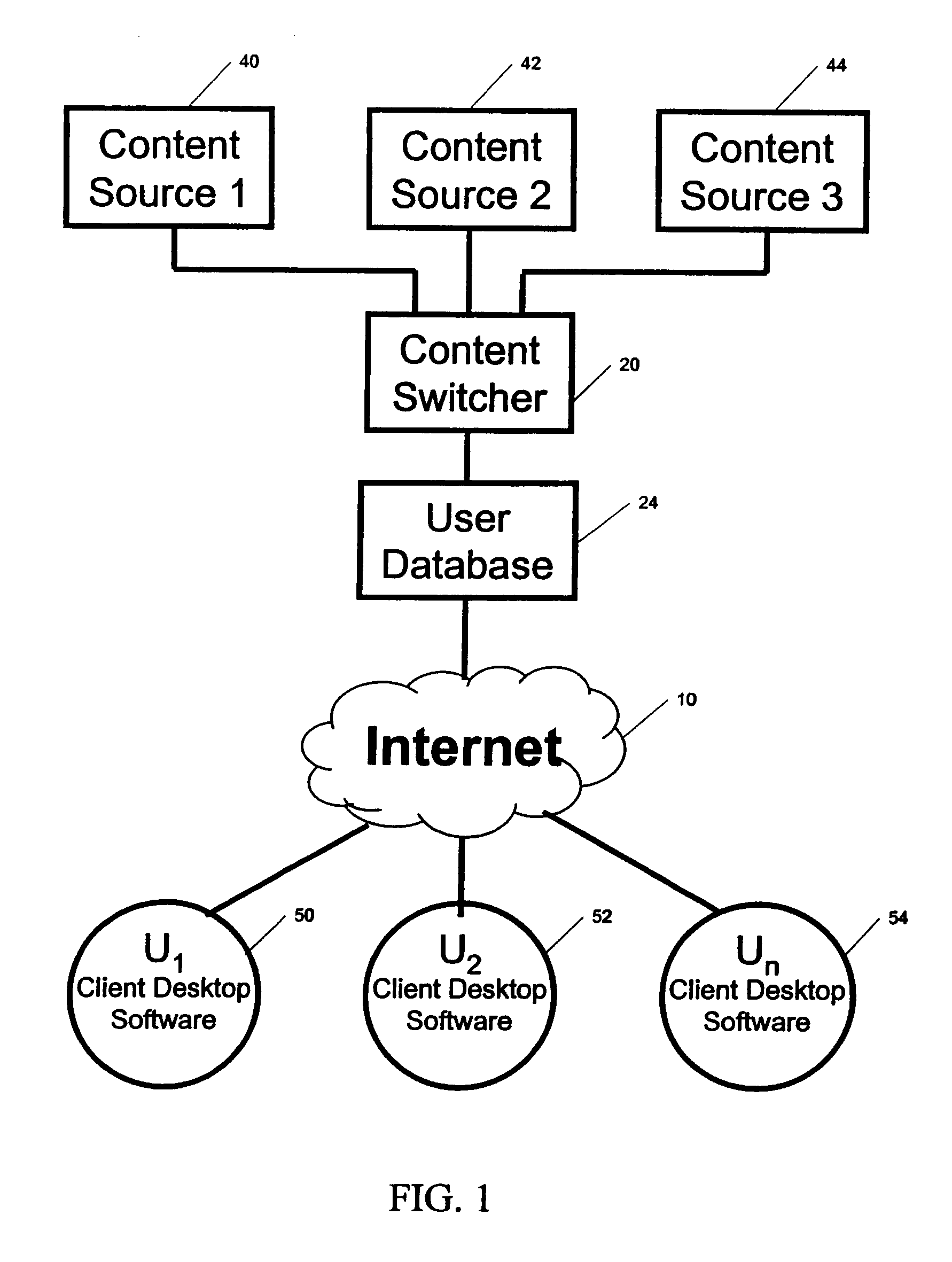
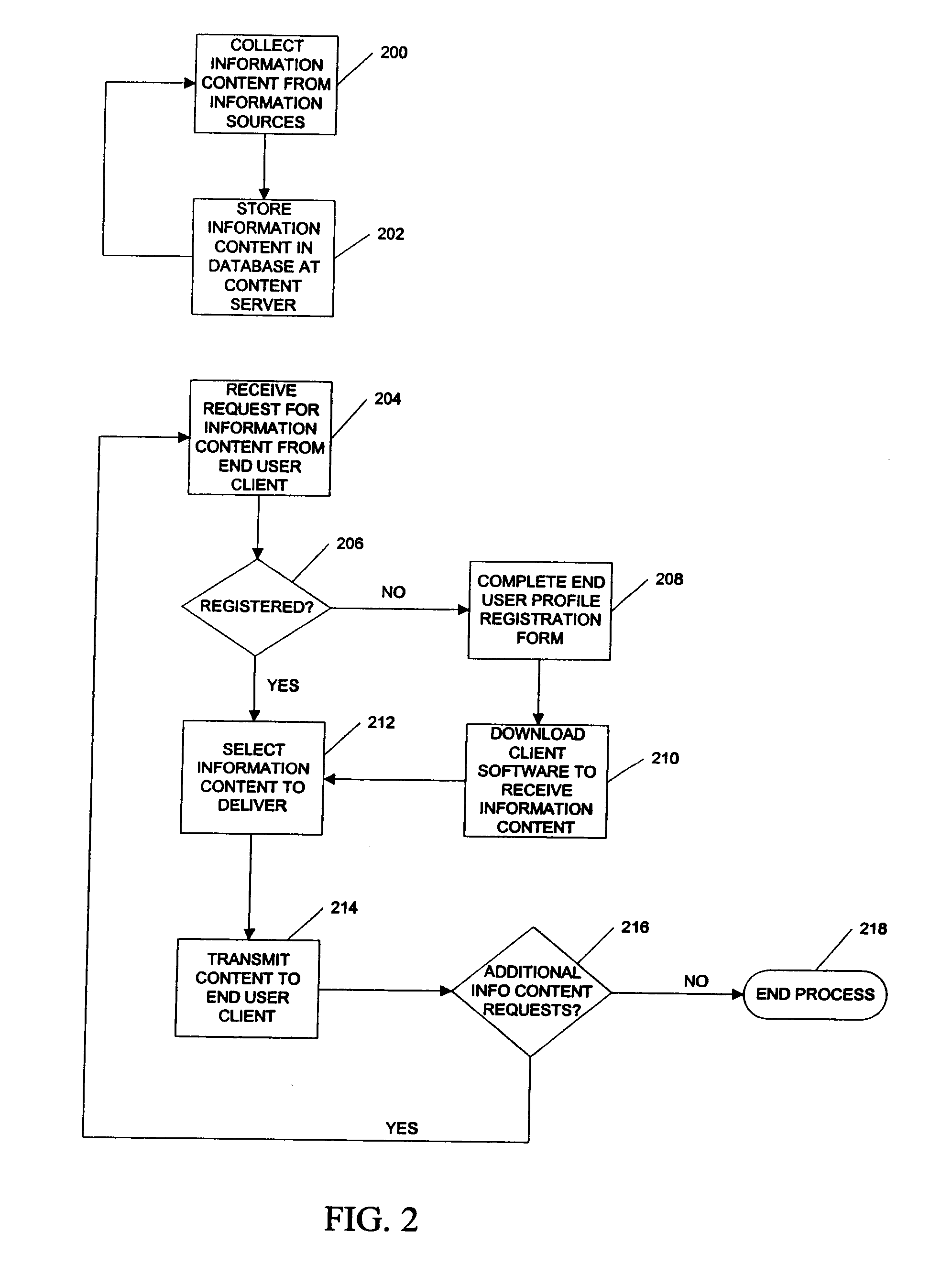
System and method for streaming of dynamic weather content to the desktop
InactiveUS20070288650A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData informationDirect-access storage device
A method, system and program product for streaming of dynamic information content over an interactive media such as the Internet. The dynamic content, such as dynamic weather data, is collected from a plurality of collection sources such as geographically distributed local weather reporting stations. The data information can be relatively static or dynamic, constantly changing data. The dynamic content is stored in databases maintained on a direct access storage device at the dynamic content server. The selection of dynamic content to be transmitted to the end user client is based on a demographic profile that is completed at the time of end user client registration and which precedes delivery of any selected content in response to end user client requests. An application resident on the dynamic content server streams selected content simultaneously to a plurality of end user client devices for each end user client request. An application resident on each end user client device generates a plurality of processing threads for a series of independent commands, each of which is transmitted to the dynamic content server at specified preset intervals and generates a server-selected response. In a weather content collection and delivery embodiment, local, real-time weather data can be received continuously from thousands of weather reporting stations, and transmitted simultaneously by the weather content server to millions of end user desktop clients, with each user receiving current weather data that is generated from a nearby weather collection station.
Owner:XAD
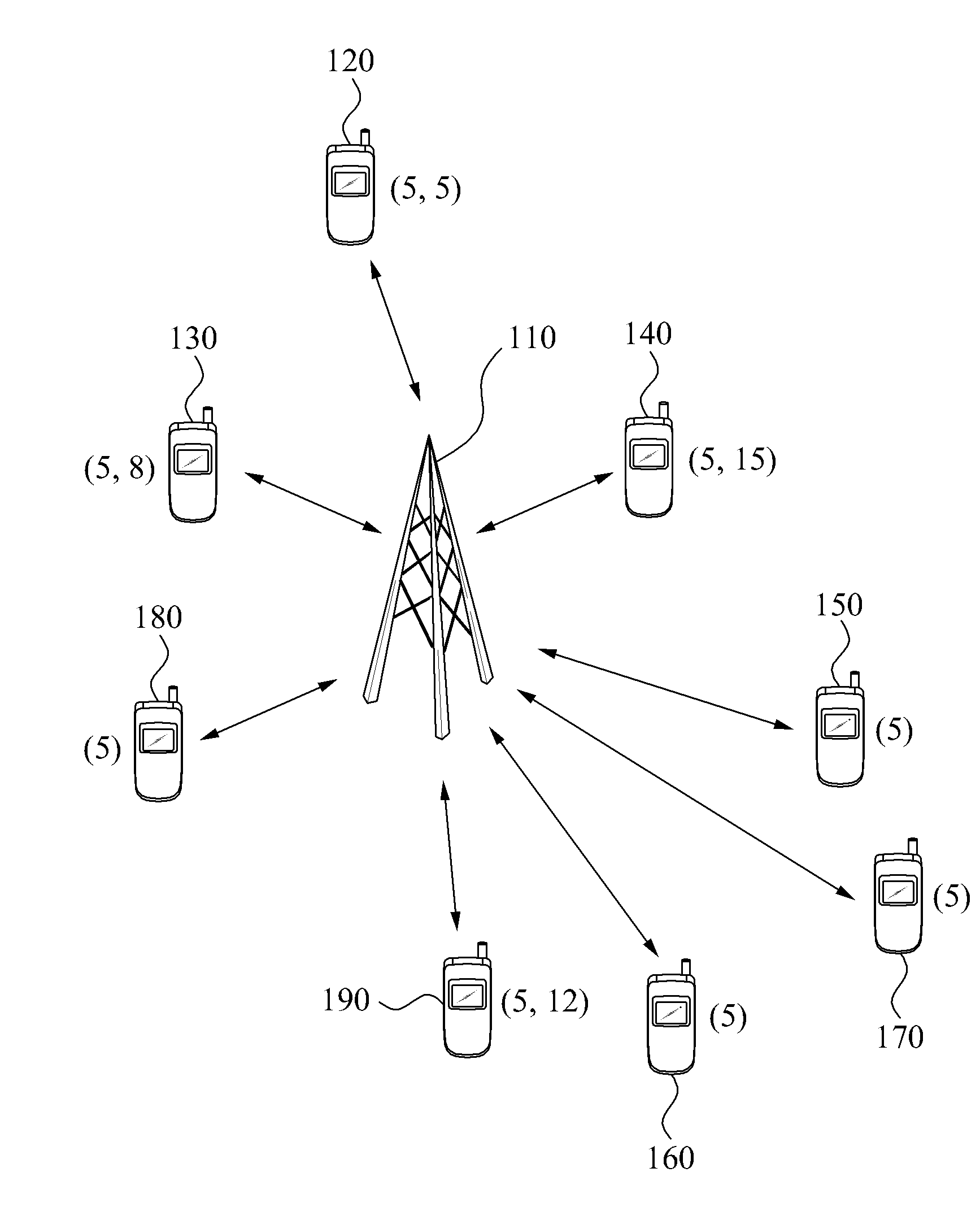
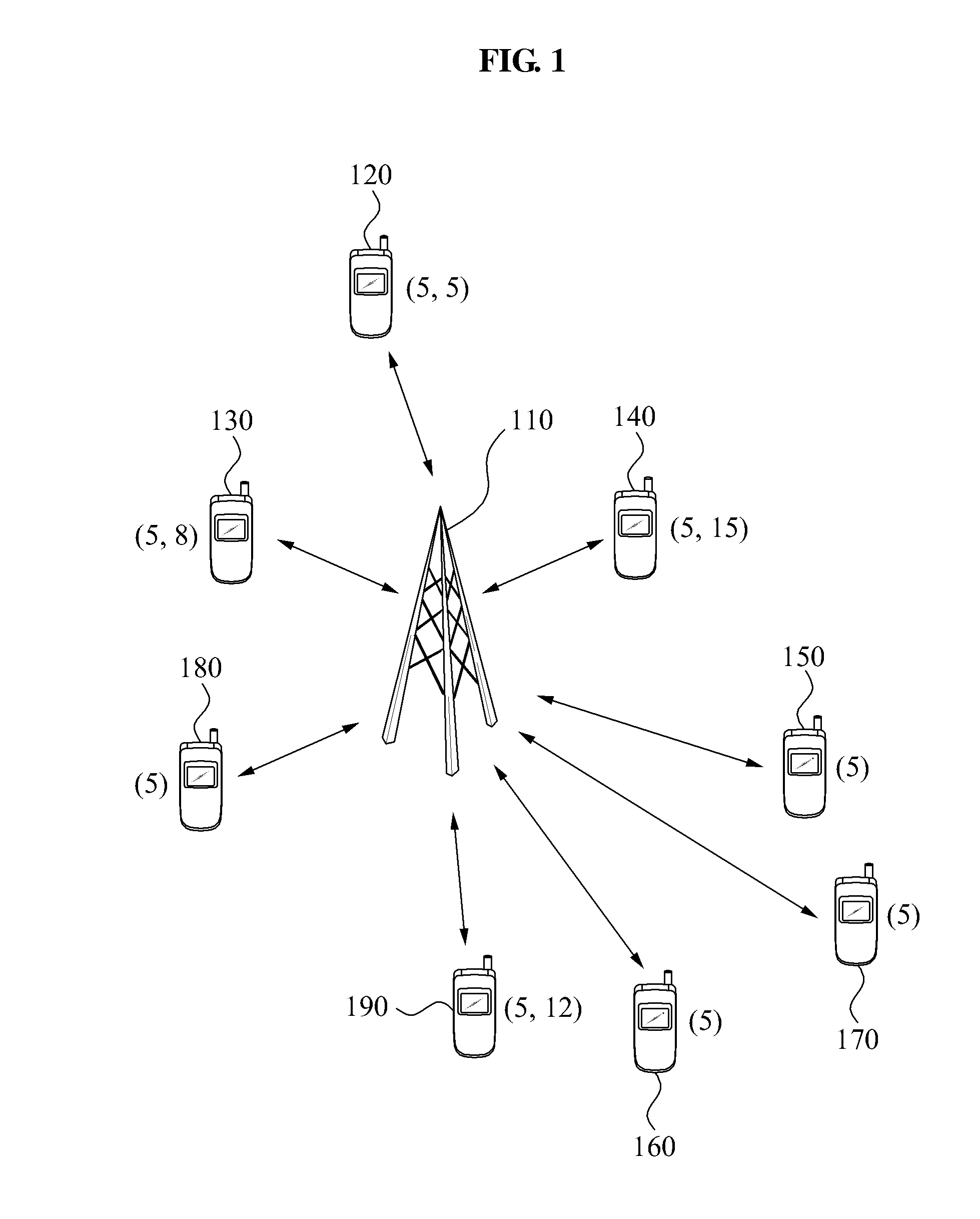
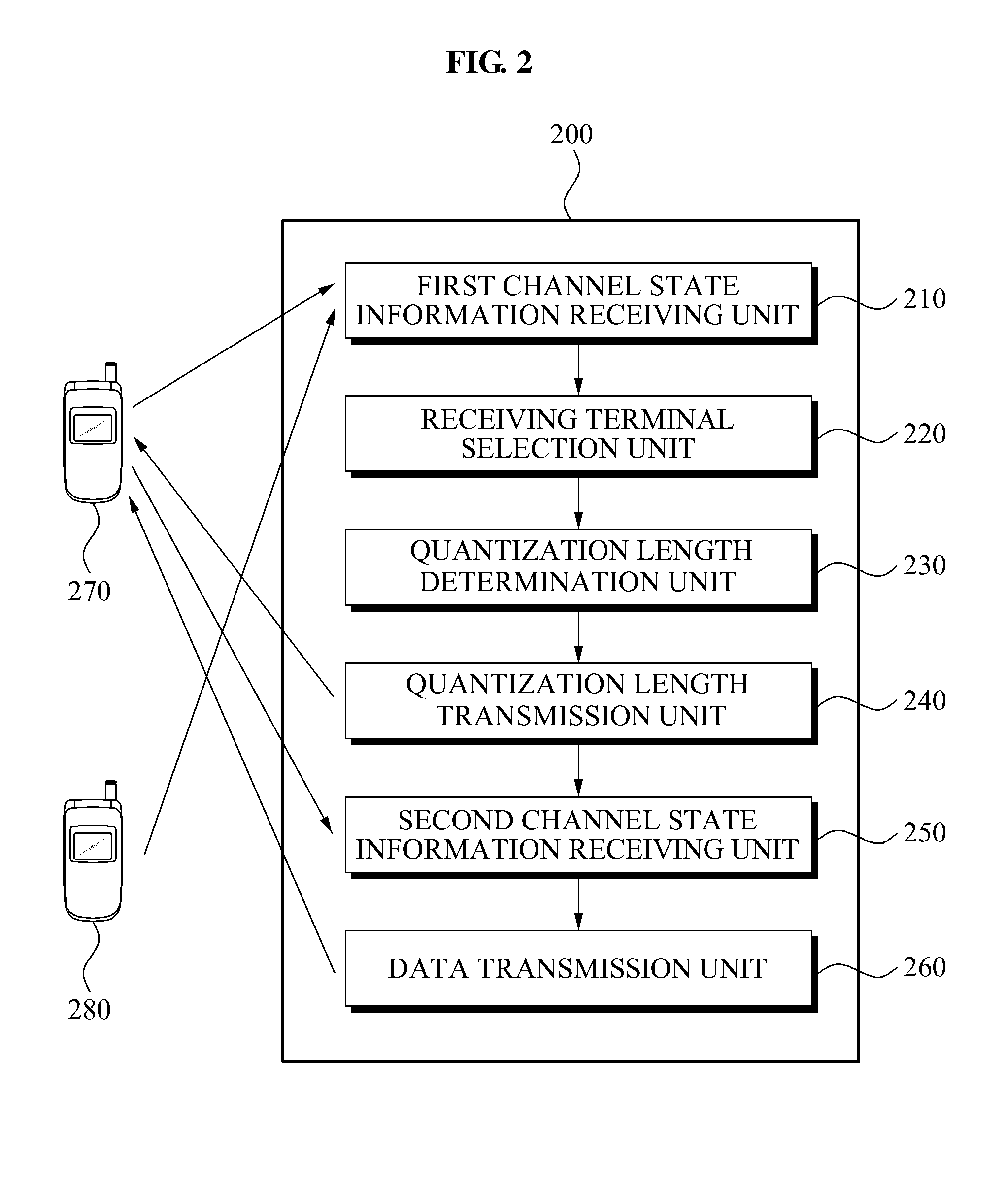
Apparatus and method for transmission of dynamic feedback channel information in a MIMO system
ActiveUS20100093361A1Radio transmissionWireless communicationChannel state informationData transmission
A base station apparatus and method of transmission of dynamic feedback channel information in a MIMO system. The base station apparatus includes a first channel state information receiving unit to receive a first channel state information; a receiving terminal selection unit to select at least one receiving terminal to receive data from among a plurality of terminals; a quantization length determination unit to independently determine a second quantization length of the selected receiving terminal; a quantization length transmission unit to transmit the second quantization length to the selected e receiving terminal; a second channel state information receiving unit to receive second channel state information from the selected receiving terminal; and a data transmission unit to transmit data to the selected receiving terminal using a plurality of transmission antennas of a base station based on the second channel state information.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
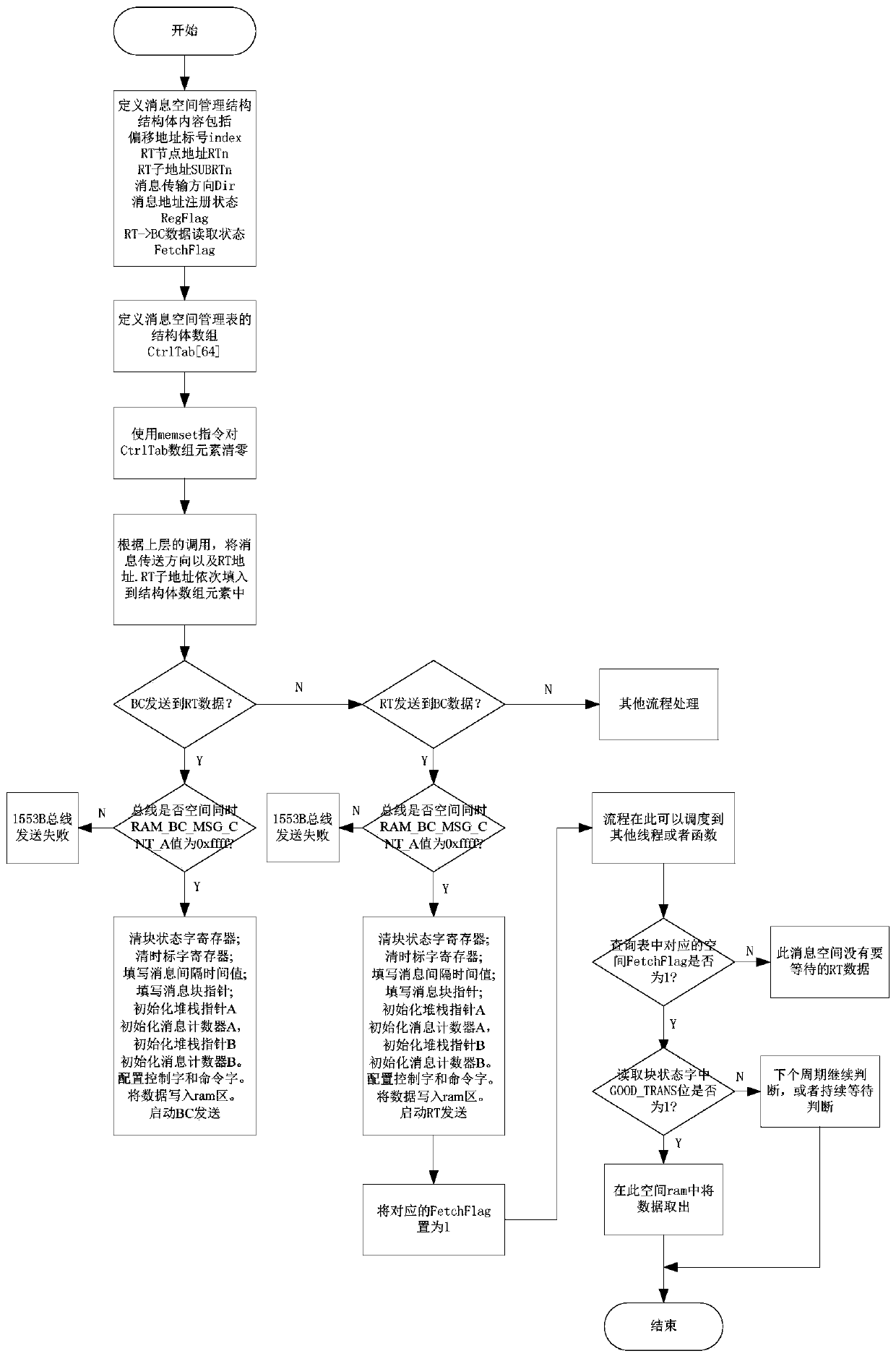
Message configuration processing method in 1553B bus BC mode based on management table
ActiveCN110750473AGuaranteed real-timeImprove reliabilityElectric digital data processingDynamic managementTerm memory
The invention belongs to the technical field of aerospace system data communication. and discloses a configuration processing method of a data message in a 1553B bus BC mode based on a management table. The method comprises the following steps: a structure is defined to describe the use state of a message space, in the initialization process, a bus memory area is registered in a message managementtable, data transmission from a BC to an RT is managed based on the message management table, data transmission from the RT to the BC is managed based on the message management table, and the messagemanagement table is cancelled in data transmission dynamic management. According to the invention, the defects of a data message configuration processing method in a BC mode of the existing 1553B busare overcome; a method based on a management table is provided, a structure is designed to describe the state of a 1553B message space, the message management table is adopted to manage receiving andsending of data between a BC and an RT, and the problem of efficient message management in the process of processing a large number of messages at high frequency through a 1553B bus is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG COMP TECH RES INST
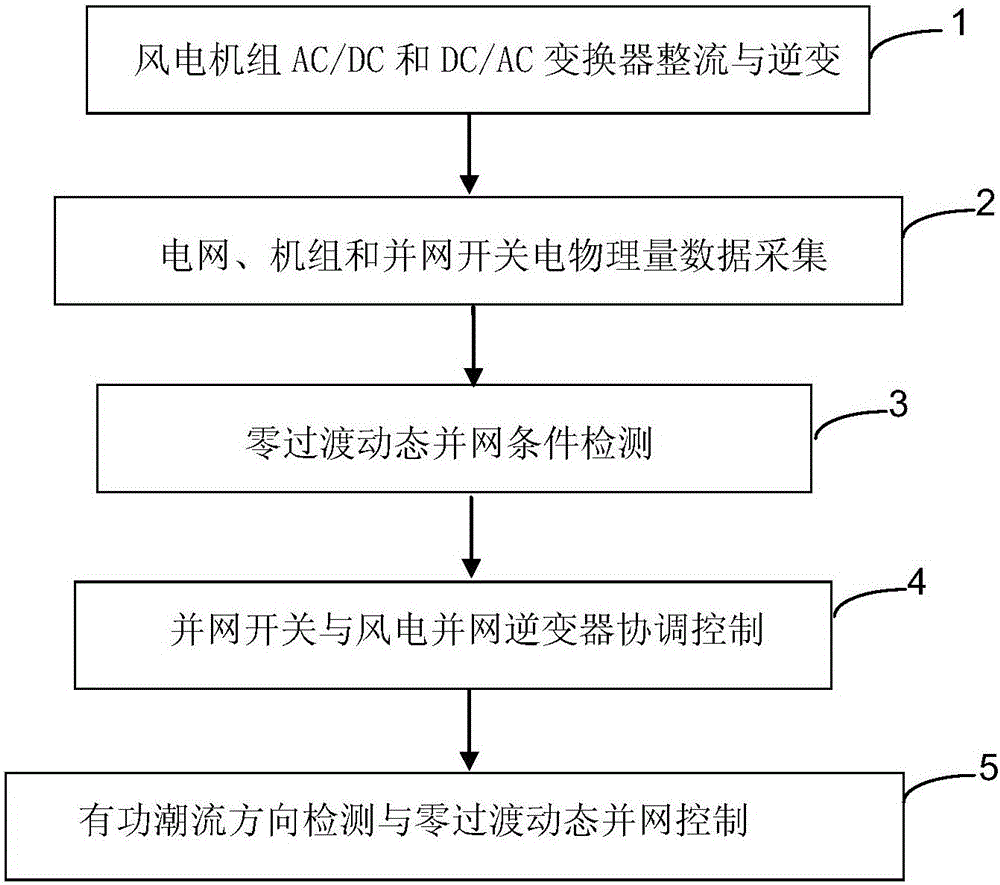
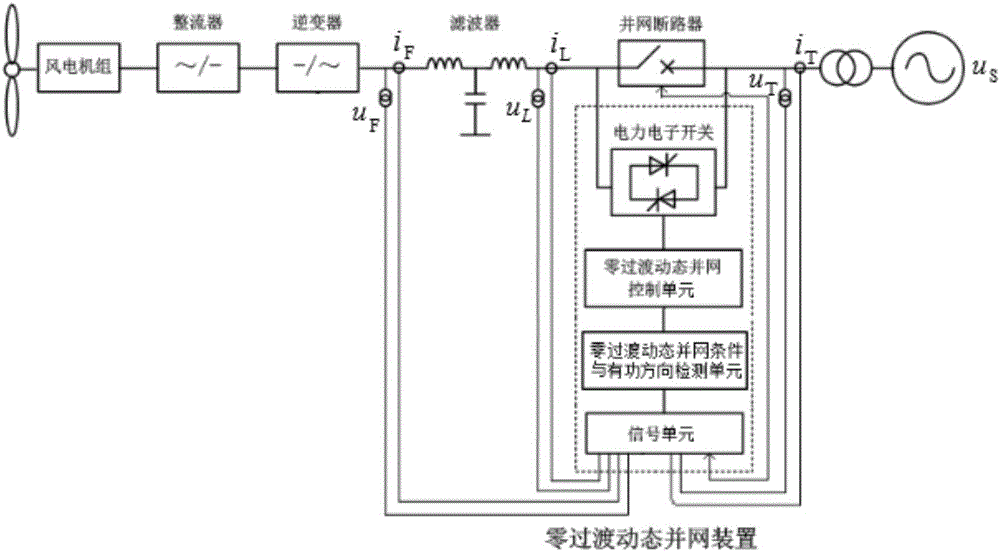
Method and device for wind generating set zero-transition dynamic grid connection
ActiveCN105958528AExtended service lifeReduce power lossSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationGrid-tie inverterNew energy
The invention discloses a method and a device for wind generating set zero-transition dynamic grid connection, and relates to the field of new energy resources. The method comprises the steps of carrying out wind generating set AC / DC converter and DC / AC converter rectification and inversion, acquiring electric physical quantity data of a power grid, a set and a grid-connected switch, detecting zero-transition dynamic grid connection conditions, carrying out grid-connected switch and wind generating set grid-connected inverter coordination control, and carrying out active power flow direction detection and zero-transmission dynamic grid connection control. The device disclosed by the invention is provided with a zero-transition dynamic grid connection signal unit, a zero-transition dynamic grid connection condition detection and active power flow direction detection unit, an electronic power switch unit and a zero-transition dynamic grid connection control unit. Compared with the prior art, the method and the device have the characteristics that a filter is energy-saving, the wind power generation efficiency is improved, the grid voltage quality is improved, and the service life of the grid-connected inverter is prolonged.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Water-transmission dynamic scaling experiment loop and method for non-metal pipe
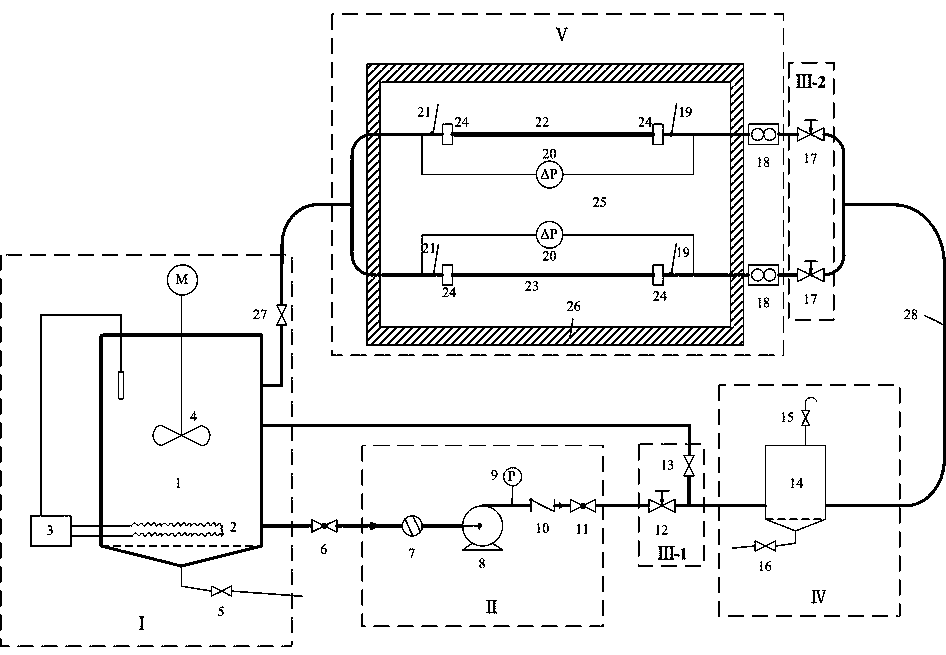
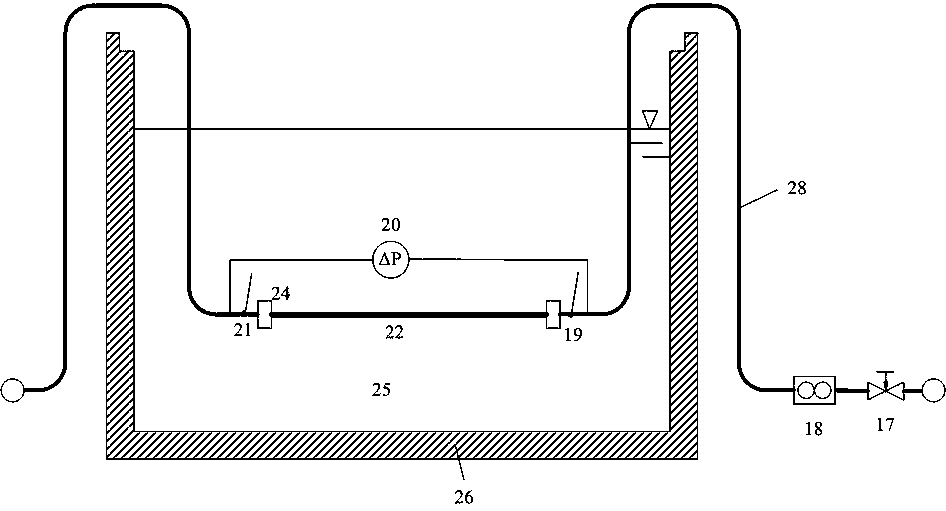
InactiveCN108732304AMinimizes the effects of foulingExperimental temperature is uniformMaterial analysisEngineeringAqueous solution
The invention discloses a water-transmission dynamic scaling experiment loop and method for a non-metal pipe. The loop and the method are used for carrying out a simulation experiment on the scaling characteristics of oil-field extraction and transportation pipelines. The loop comprises a liquid storage system I, a power system II, a flow adjusting system III, a pressure buffer system IV and a shunt-wound testing system V, wherein the liquid storage system is used for supplying a water solution with a uniform and stable temperature; the power system is used for supplying power to the experiment loop; the flow adjusting system is used for adjusting the flow of the water solution entering a test pipe section; the pressure buffering system is used for reducing the influence caused by the pressure fluctuation to the scaling of the test pipe section; and the shunt-wound testing system is used for measuring the variations of the scaling amounts of different tubular products along time. The invention further provides a method for carrying out an experiment test by virtue of the loop. According to the method, the variation of the scaling amounts along time under the conditions of differenttubular products, flows, ion concentrations, temperatures and the like can be measured, the basis is provided for the prevention and treatment on the site scaling of the oil field, and the method canbe used for developing and evaluating novel scale inhibitors.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Flexible DC transmission dynamic stability determining and controlling method
ActiveCN109659969ASimple methodGood for engineering practiceAc-dc conversionElectric power transfer ac networkEngineeringShort circuit ratio
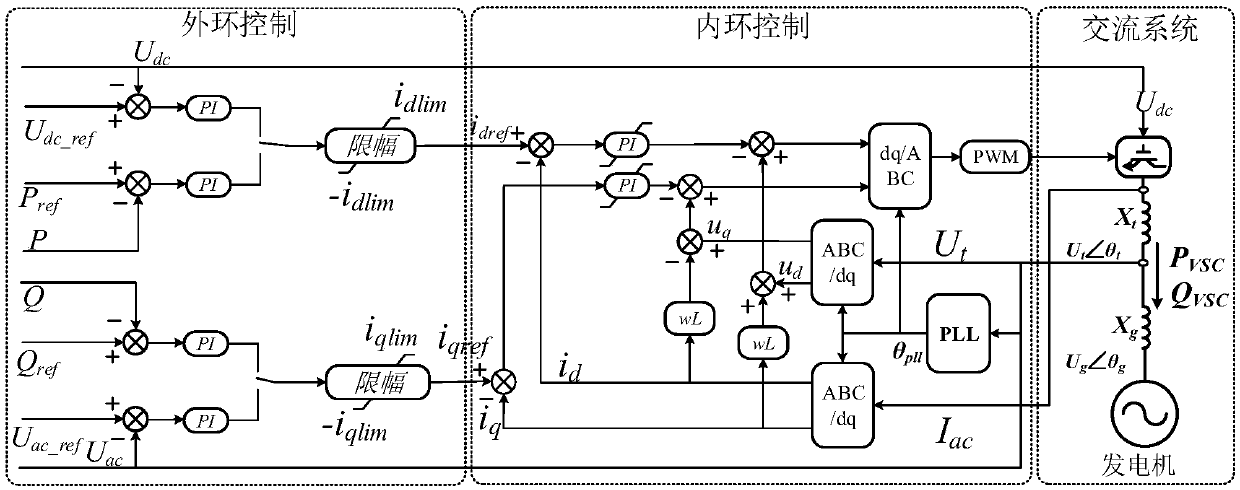
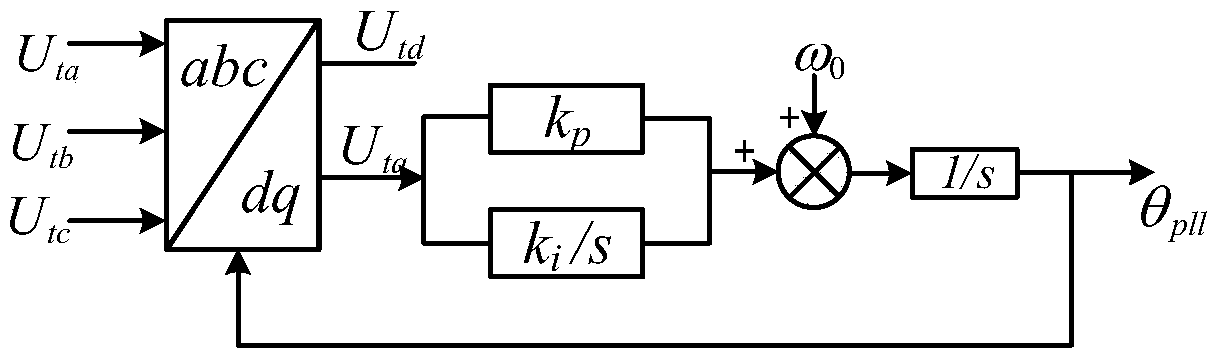
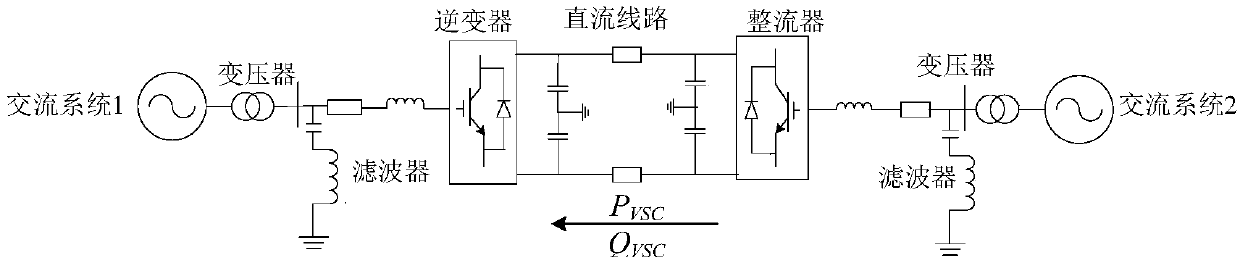
The invention discloses a flexible DC transmission dynamic stability determining and controlling method which comprises the steps of: unlocking a converter station of a flexible DC transmission system, and allowing the flexible DC transmission system to operate in a non-island control mode; extracting corresponding parameters of the flexible DC transmission system, wherein the parameters include an AC system voltage effective value Ut0, a flexible DC external reactive power Qvsc0, a gain kp of a phase locked loop PLL, and a proportional integral time constant ki of the phase locked loop PLL; calculating a short-circuit ratio SCR, the per-unit value of Ut0 and Qvsc0; calculating a key stable component; and checking the sign of the key stable component and determining the stability of the flexible DC transmission system. The method of the invention only needs to simply calculate the value of the key stable component, determines the stability of the system by the sign of the value, is simple and easy, and is beneficial to engineering practice.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
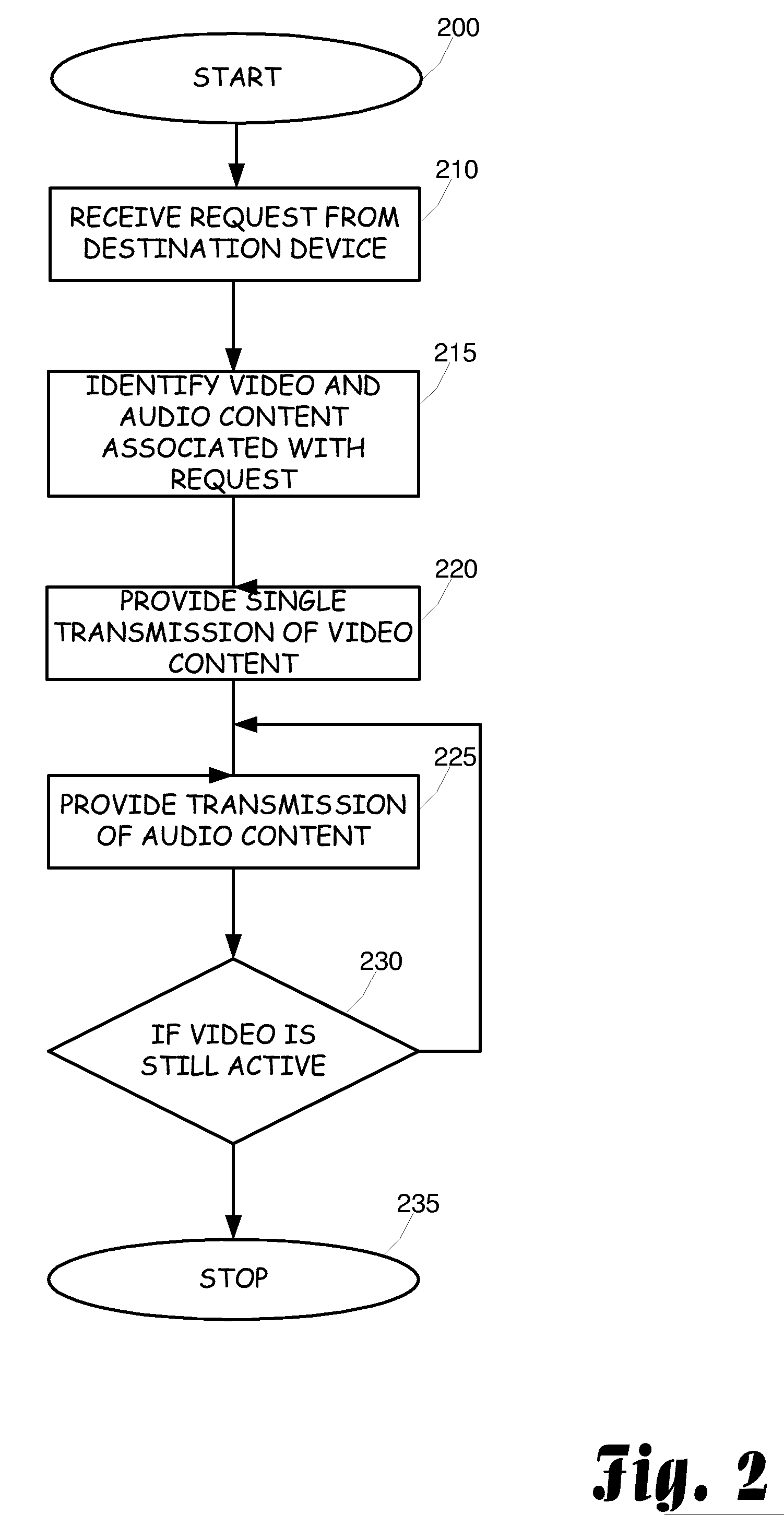
Bandwidth utilization for video mail
InactiveUS20070058614A1Reduce bandwidth requirementsEffective bandwidthInterconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationComputer graphics (images)Audio frequency
Video content is delivered in a bandwidth efficient manner to a destination device. The video content is analyzed and a compression operation is performed on the video content prior to delivery to the destination device. Any audio associated with the video content is maintained in synchronization with the video content. The compression of the video can be performed in a variety of manners including single transmission of static frames, combining substantially similar frames so that only a single frame representing the combination is transmitted, and only transmitting dynamically changing or active portions of the video content.
Owner:GLENAYRE ELECTRONICS INC
Joint use of multi-carrier and single-carrier multiplexing schemes for wireless communication
ActiveUS8705441B2Increase flexibilityWell formedTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationMultiplexingData stream
A communication system that facilitates transmissions in accordance with a single-carrier (SC) multiplexing scheme, a multi carrier (MC) multiplexing scheme or a combination thereof is disclosed. Based on various factors such as attributes associated with a UE (user equipment) or availability of resources, a base station can signal to the UE an appropriate multiplexing scheme to be adopted for particular transmissions. The UE can be scheduled for transmission in a semi-static mode wherein the UE employs the transmission scheme for a particular time interval or it may change the mode dynamically for different transmissions. For transmissions from the UE comprising a plurality of data streams with dissimilar attributes, the base station implements a MIMO (multiple input multiple output) system for the UE. This facilitates a UE to dynamically switch between or simultaneously adopt the various multiplexing schemes for communications and thereby fully utilize advantages associated with the different schemes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
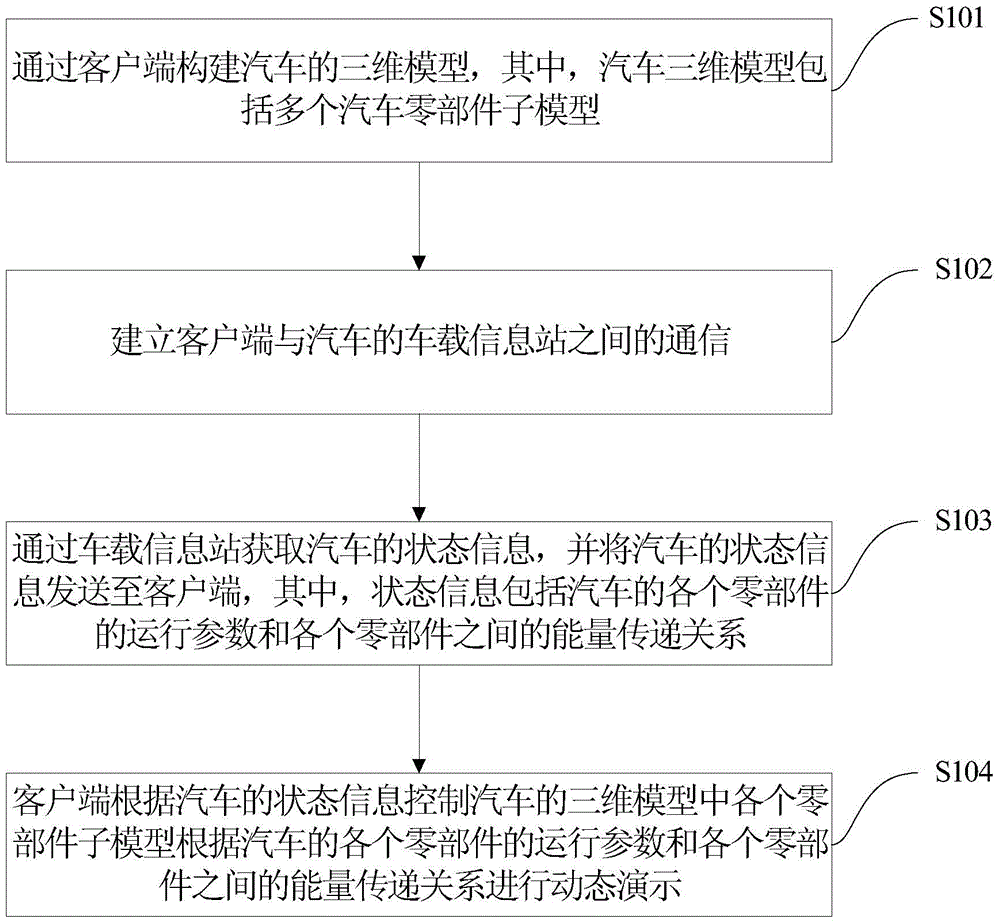
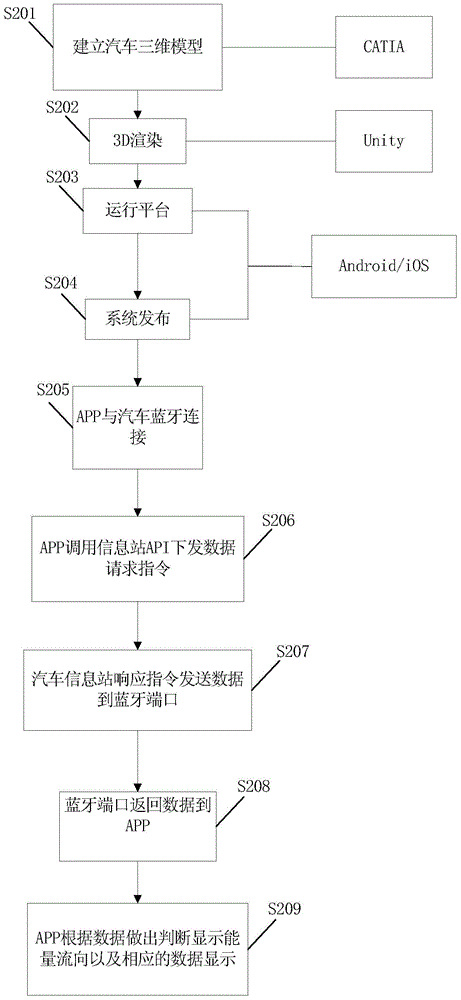
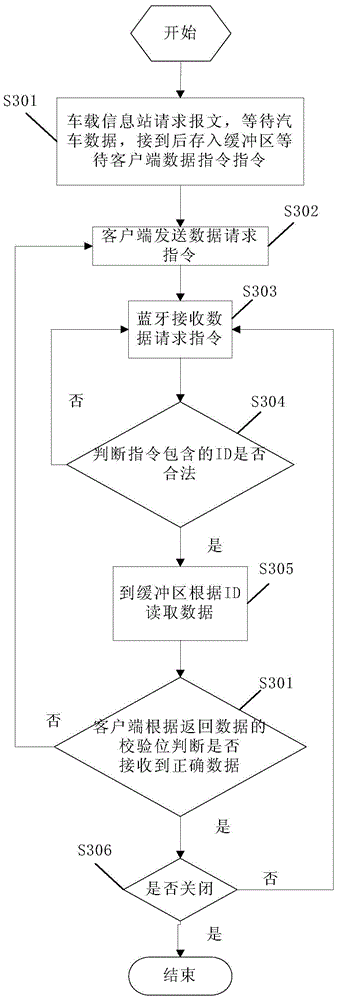
Model reappearing method and system of car energy flow direction
InactiveCN104636519AImprove interactive experienceDesigned to save fuelSpecial data processing applicationsClient-sideTransmission dynamic
The invention provides a model reappearing method of car energy flow direction. The method comprises the steps that a three-dimensional model of a car is established through a client side, and the car three-dimensional model comprises a plurality of car part submodels; communication between a client side and a car-mounted information station of the car is established; the state information of the car is obtained through the car-mounted information station and is sent to the client side, and the state information comprises operation parameters of various parts of the car and the energy transmission relation between the parts; and the client side controls the part submodels in the three-dimensional model of the car according to the state information of the car, and dynamic demonstration is carried out according to the operation parameters of the various parts of the car and the energy transmission relation between the parts. The energy transmission dynamic state during vehicle operation can be shown through the three-dimensional model, and accordingly guiding advice is provided for car designing such as how to save more oil. The invention further discloses a model reappearing system of the car energy flow direction.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
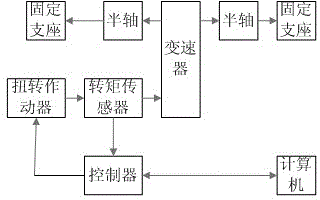
Test method for automotive transmission dynamo-static coupling torsional fatigue
The invention discloses a test method for automotive transmission dynamo-static coupling torsional fatigue. The method comprises steps of collecting transmission dynamic torque during car driving; installing the car transmission on a test system; calculating a frequency responding function of the system; calculating first excitation signals of a torsional actuator; exciting the torsional actuator by using the first excitation signals, collecting response signals of a torsional sensor, calculating responding error, calculating drive signal correction quantity corresponding to the error and recording a final drive signal when the error is no more than 5%; and regarding the final drive signal as input and conducting the torsional fatigue test of the car transmission. By the aid of the hydraulic servo torsional actuator and the remote parameter control, the dynamic torque of the car transmission during actual driving can be simulated accurately indoors under the condition of static torsion, and the test based on actual driving torsion has the advantages of being simple, efficient and accurate.
Owner:重庆理工清研凌创测控科技有限公司
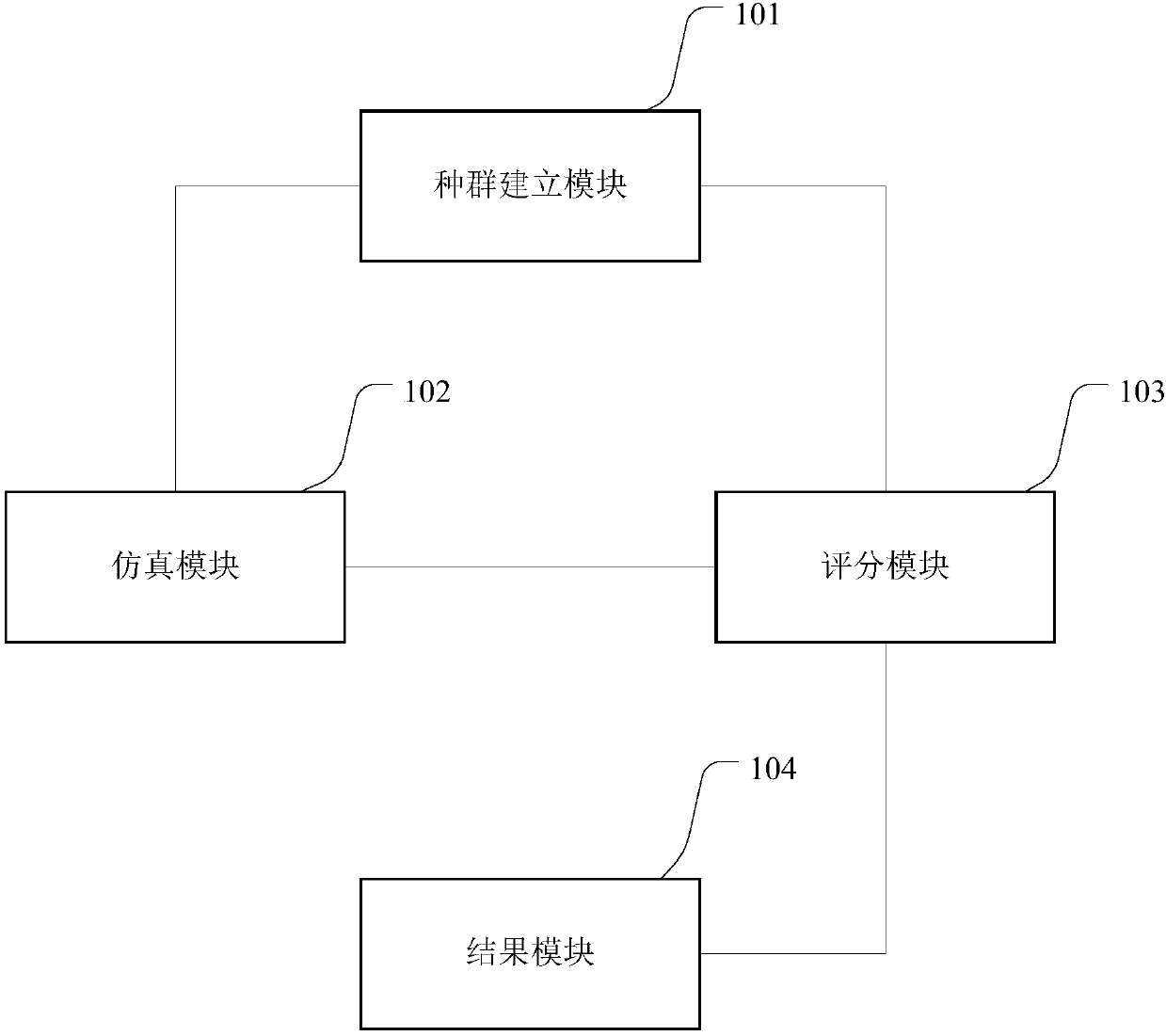
Charge-pump simulation method and simulation device
PendingCN107679282AReduce wasteStart fastDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationPerformance index
The application discloses a charge-pump simulation method and simulation device. The simulation method includes: a) establishing a population, wherein the population includes a plurality of individuals and is used to characterize a range of length and width numbers of a charge pump in a plurality of periods of charge transmission dynamics; b) executing circuit simulation of the charge pump to obtain simulation results of a plurality of simulation parameters; c) carrying out weighted scoring on the plurality of individuals according to the simulation results to obtain a score for each individual; and d) selecting an optimized individual according to the scores of the plurality of individuals. According to the charge-pump simulation method and device, an artificial-intelligence algorithm isutilized, a simulator is combined, and optimal design of multiple performance indexes of a charge-pump circuit is realized.
Owner:珠海博雅科技股份有限公司
System and method of transferring dynamic data in real time through wireless, server-less communication between a immobile computing device and a mobile computing device
InactiveUS20150326652A1Easily extend its functionalityOptimizationWireless commuication servicesTransmissionDynamic dataTransmission dynamic
A system and a method is configured for transferring dynamic data in real time through wireless, server-less communication between a immobile computing device and a mobile computing device.
Owner:DAVIS KERRY LEE
WeChat network evolutionary model construction method based on complex network
InactiveCN106204294AEasy to implementScale upData processing applicationsWebsite content managementNetworking protocolNetwork size
The invention discloses a WeChat network evolutionary model construction method based on a complex network. The method mainly comprises two stages, namely network initialization and network evolutionary generation. At the network initialization stage, the number of network initial nodes and the connection mode of the nodes are given; at the network evolutionary generation stage, a random connection mechanism and a preferential connection mechanism are adopted respectively. According to the method, a core evolutionary mechanism adopted in the WeChat network forming process is fused, and the generated evolutionary network can truthfully display topological characteristics of a real WeChat network and cannot be restricted by the network size. Thus, the evolutionary network can be used for analyzing various topological characteristics of the WeChat network and can also be used for studying the transmission dynamic mechanism of information in social networking. Based on this, a real network topological structure can be improved, a network protocol is optimized so that the transmission efficiency of the network topological structure can be improved, and meanwhile the method is beneficial for preventing and controlling propagation of Internet rumors so as to reduce damage caused thereby.
Owner:ENG UNIV OF THE CHINESE PEOPLES ARMED POLICE FORCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com