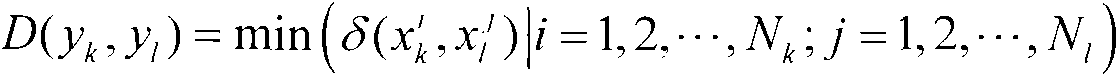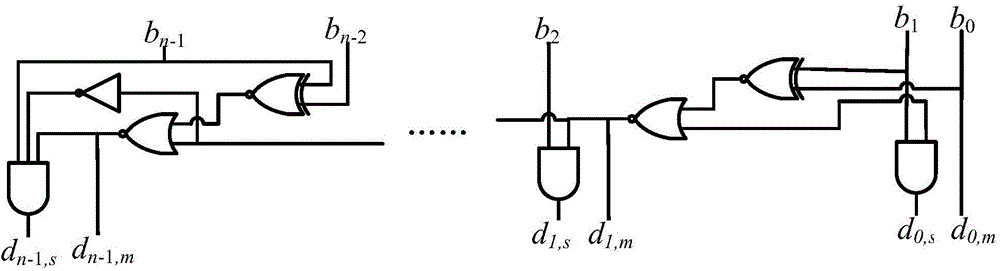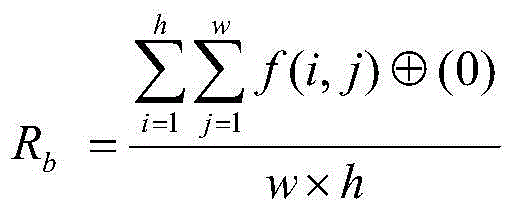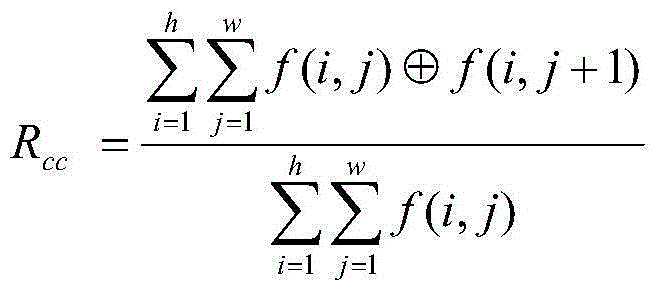Patents
Literature
179results about How to "Consider speed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
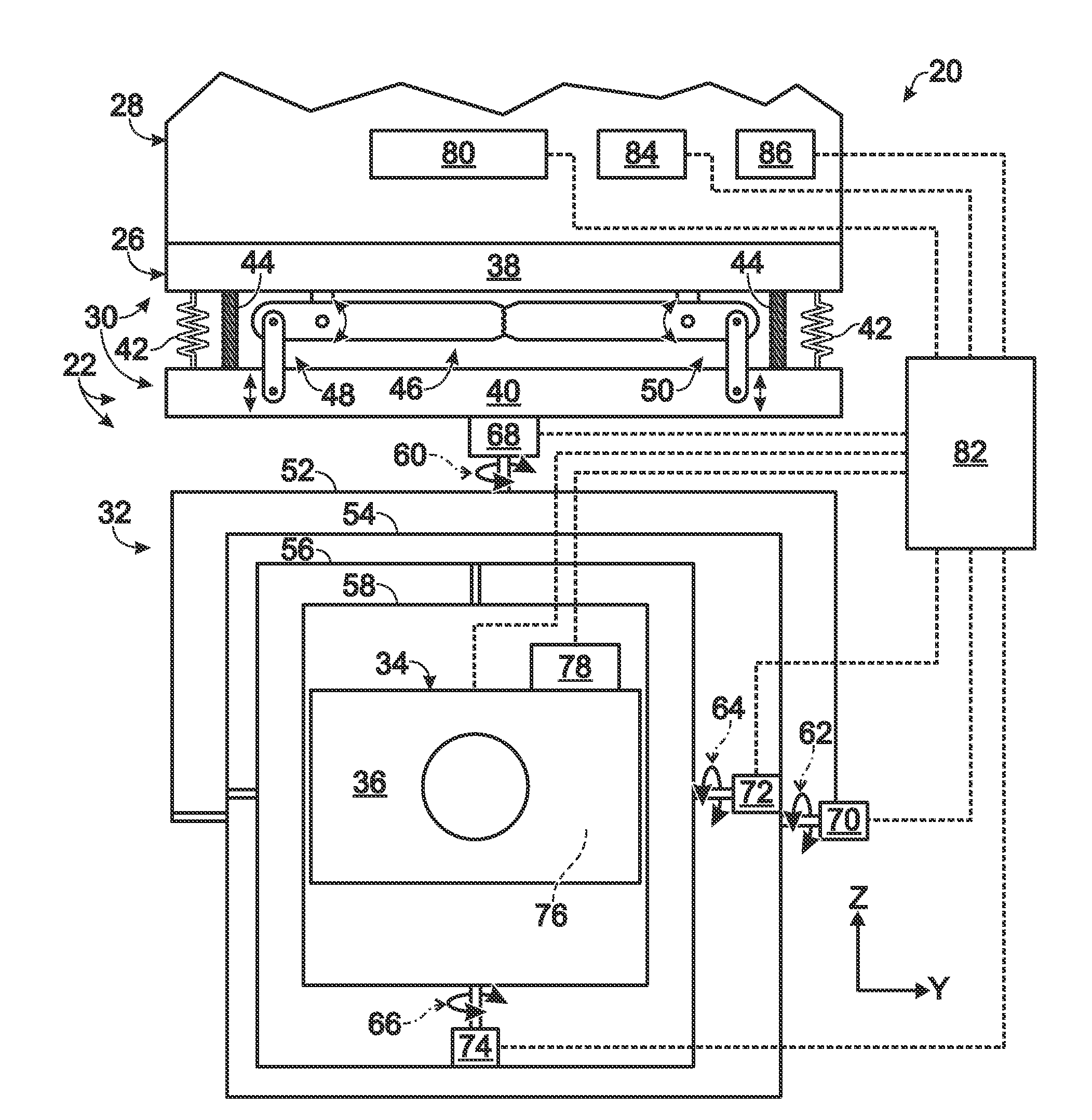
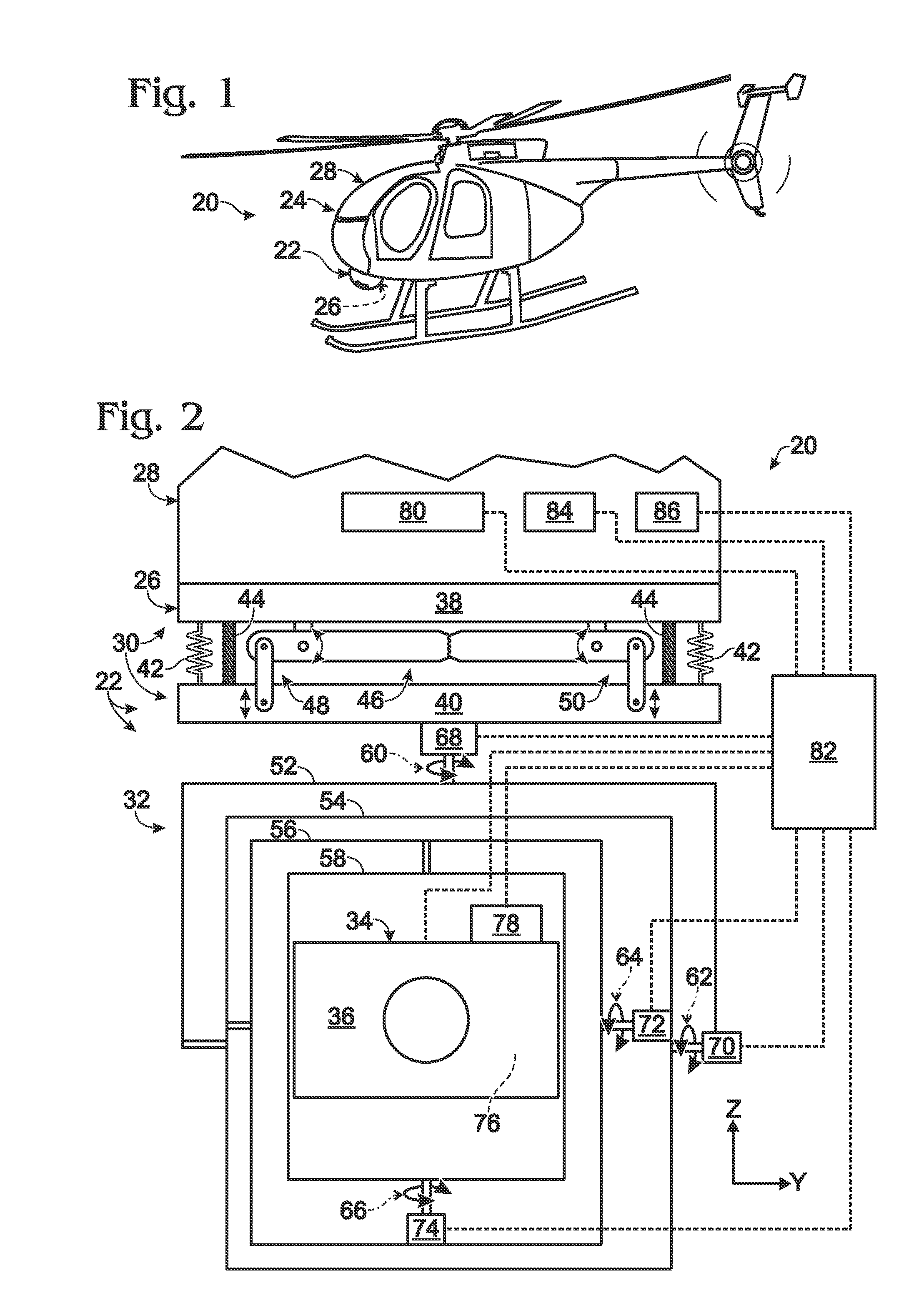
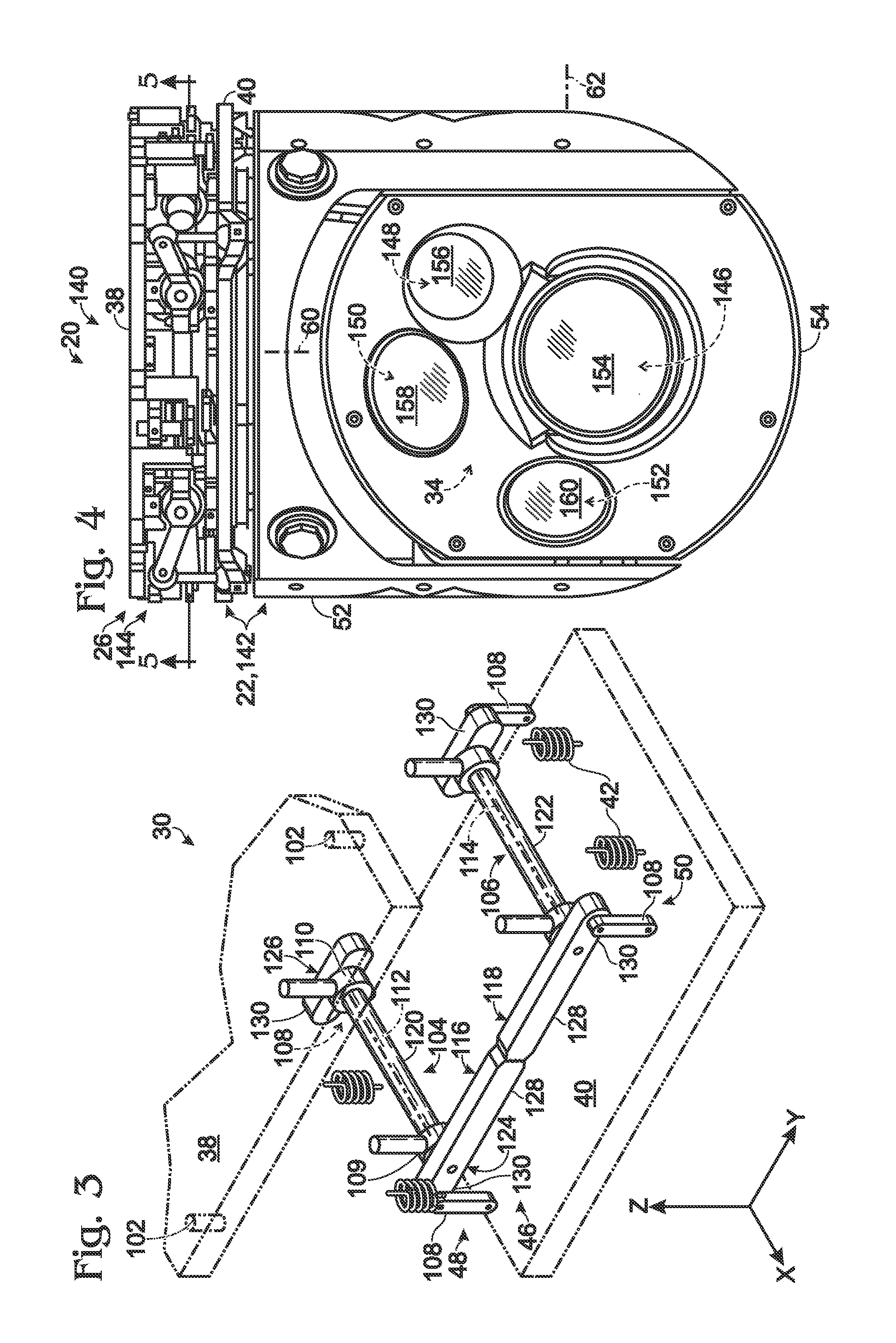
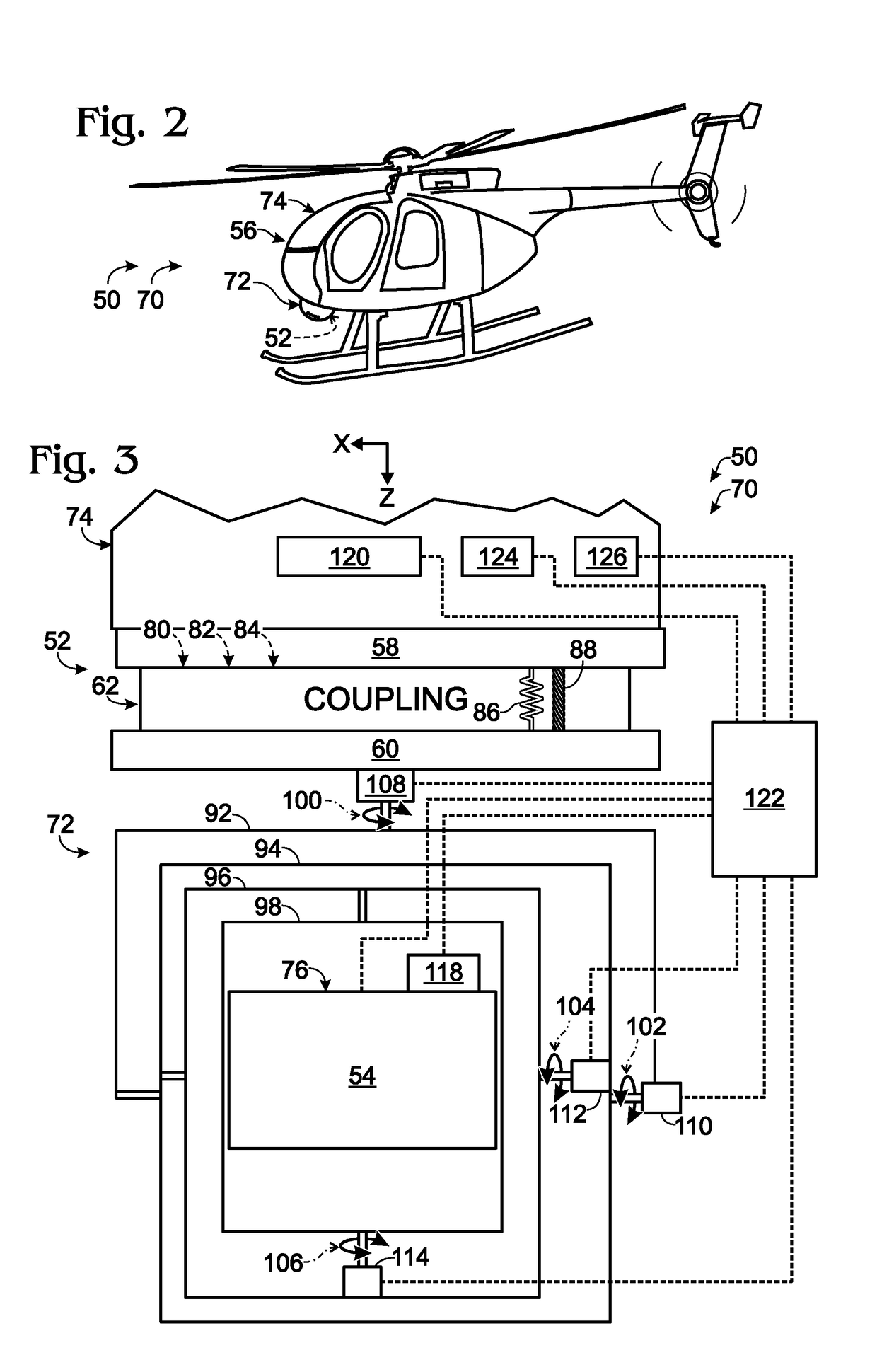
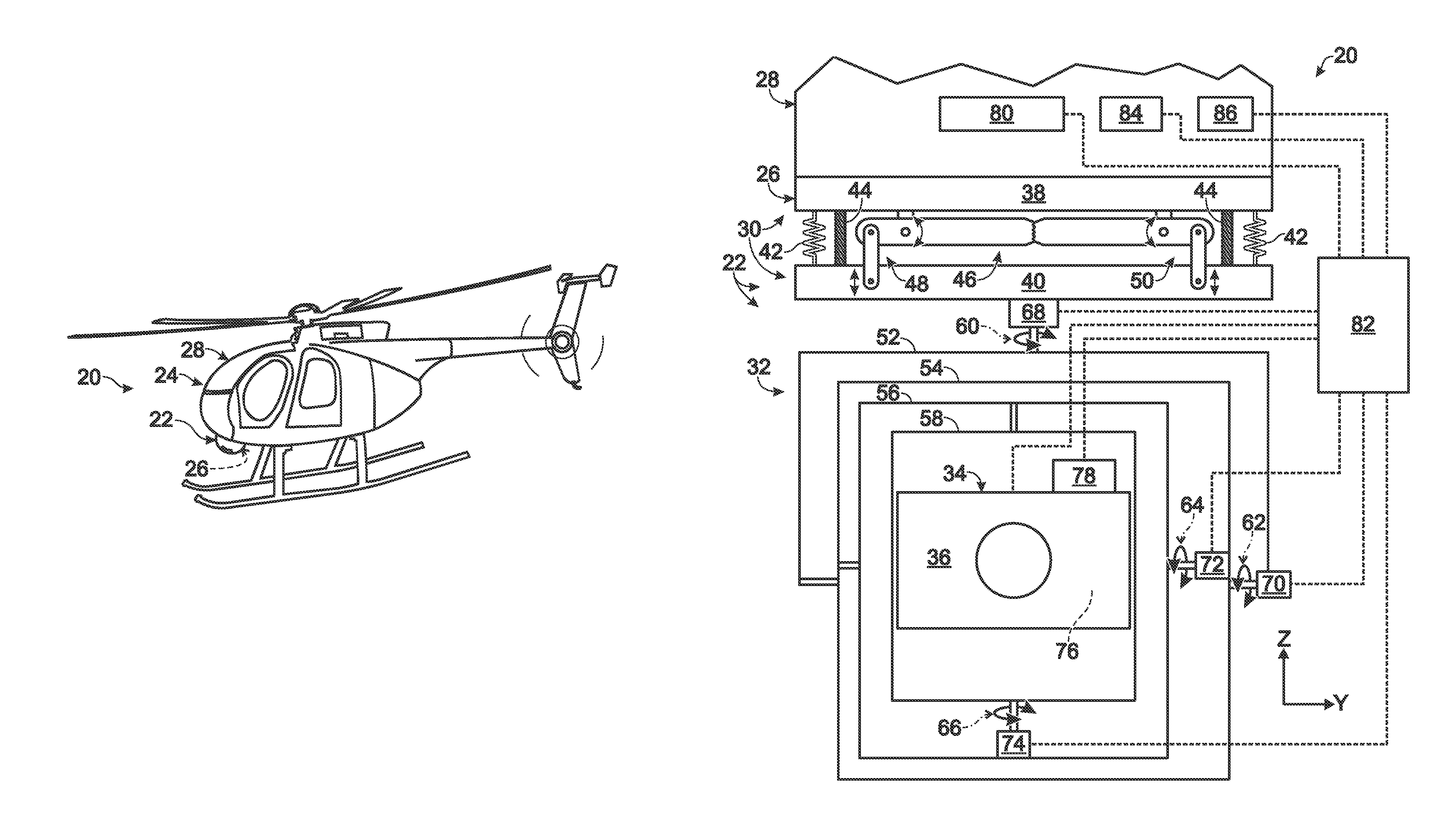
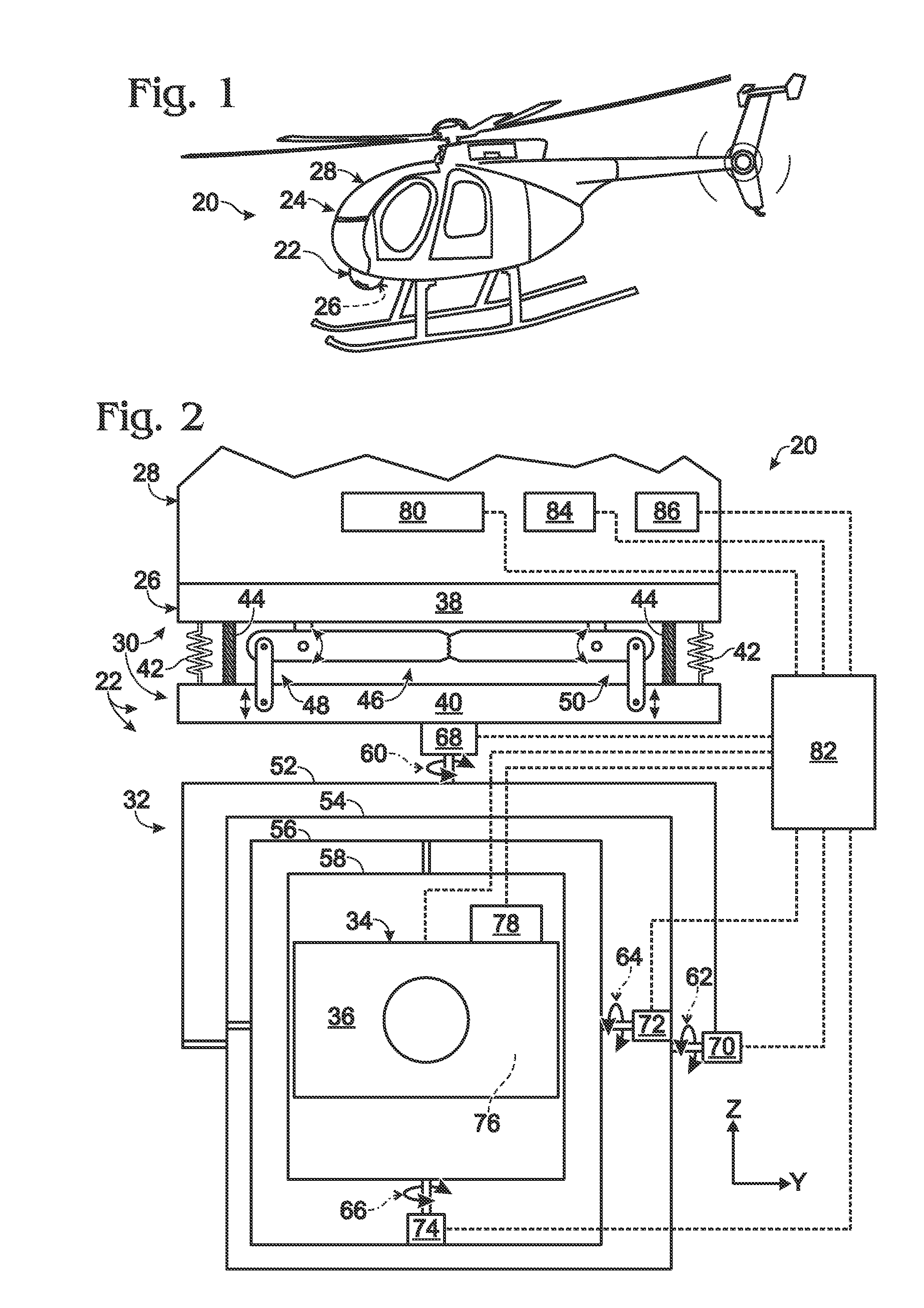
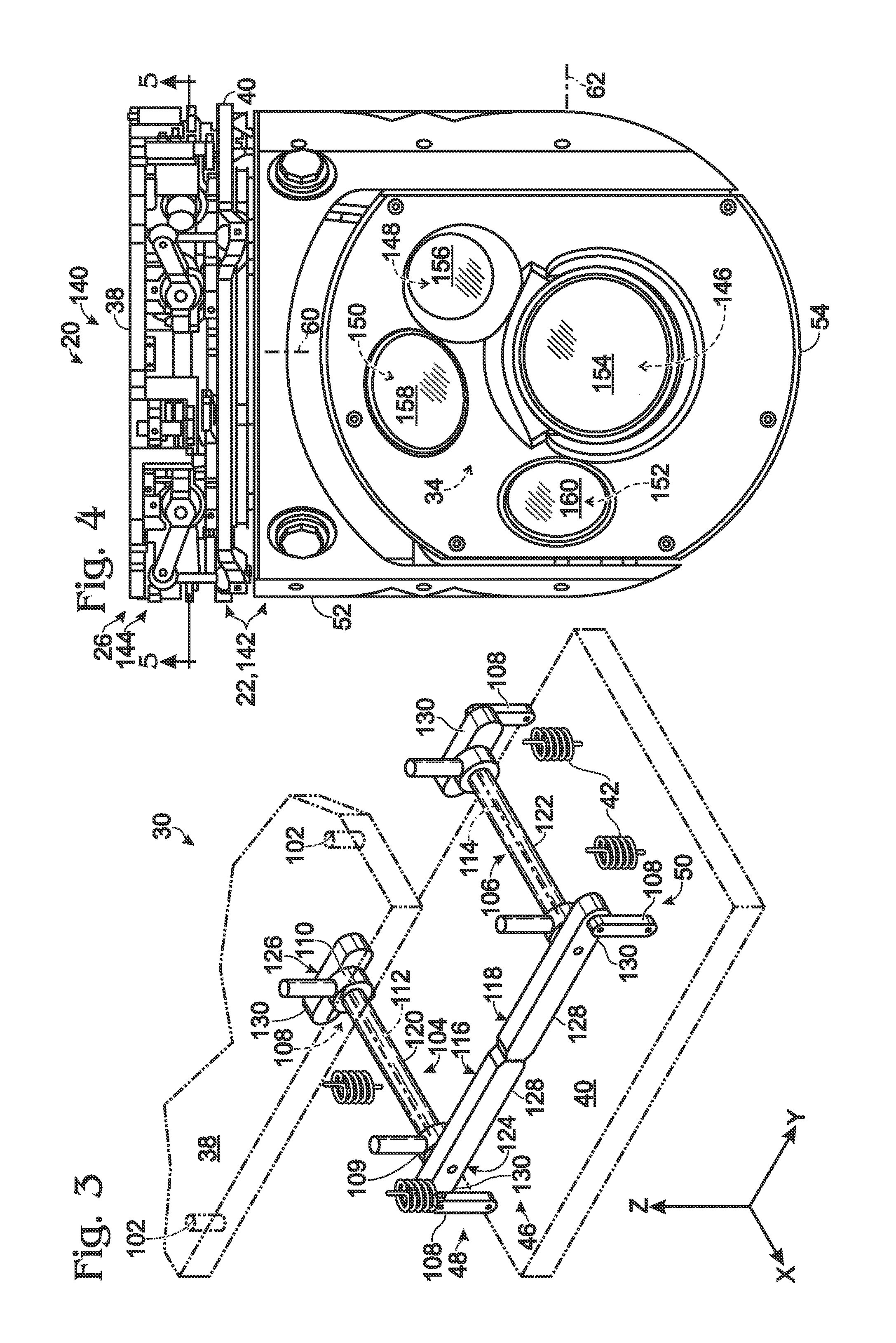
Gimbal system with linear mount
ActiveUS20120316685A1Pointing accuratelyImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsPortable framesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
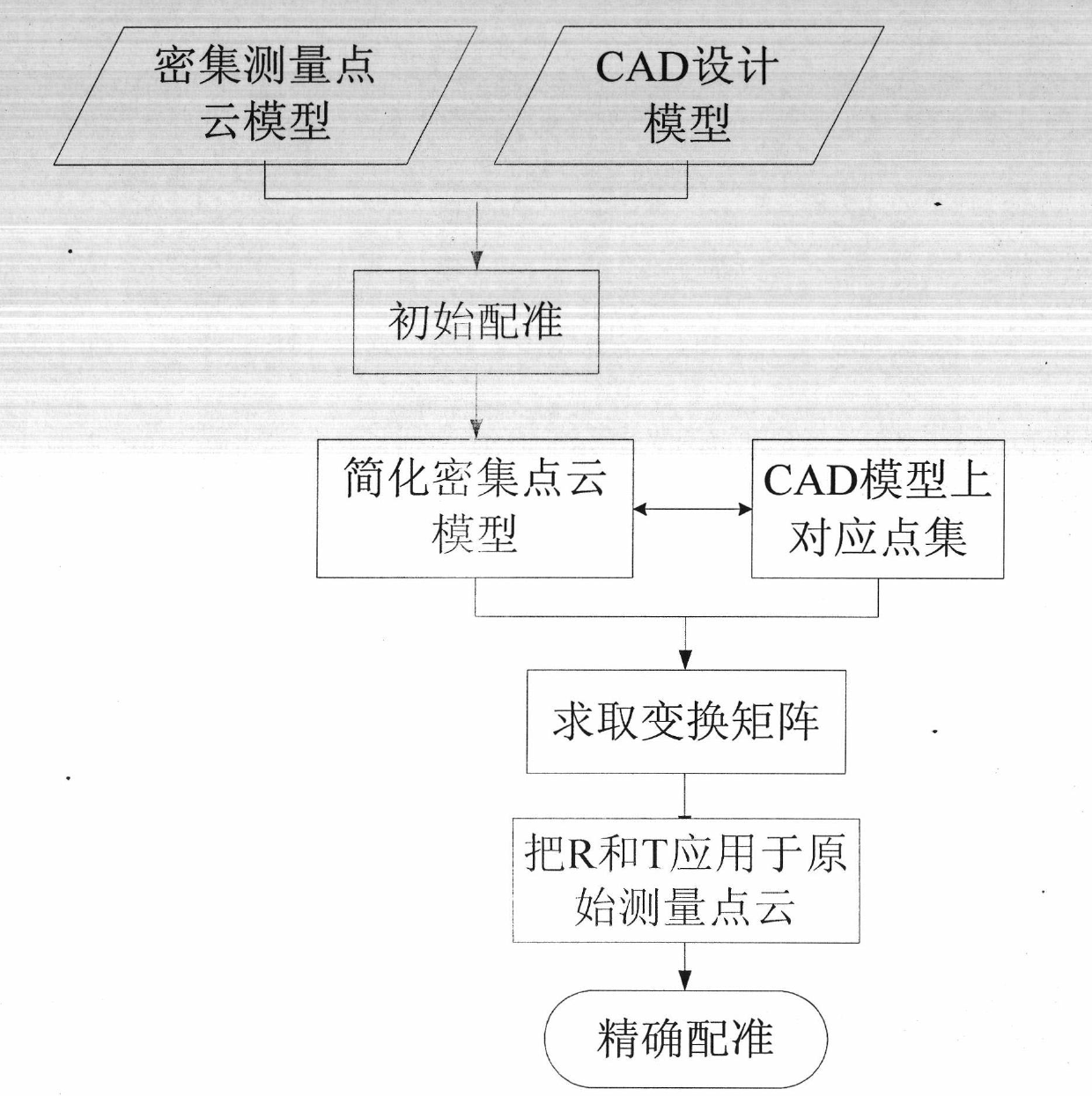
Rapid and accurate registration method of dense point cloud model
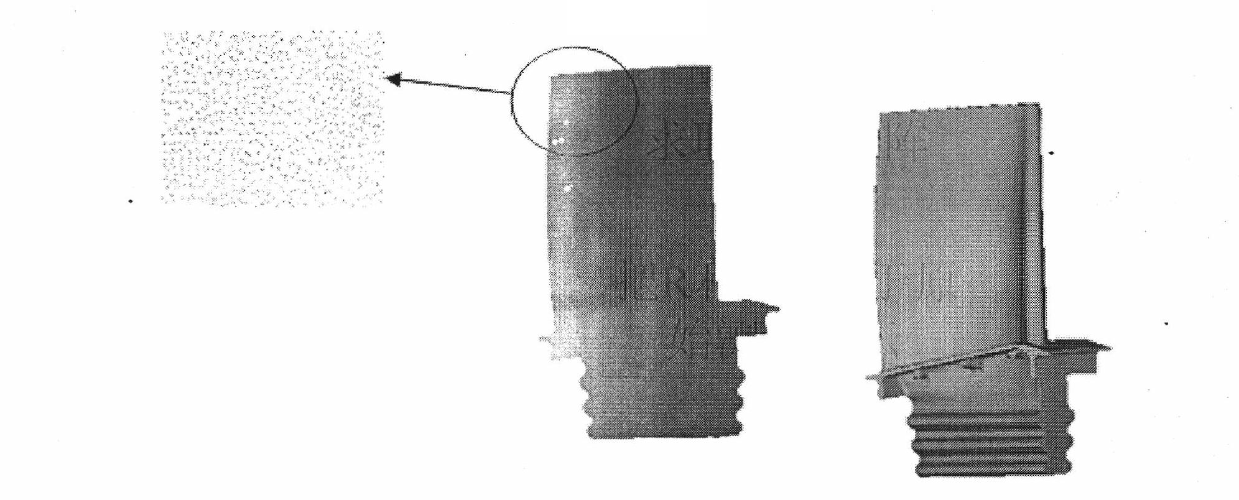
InactiveCN102169579AQuick registrationConsider speedImage analysisSingular value decompositionComputer Aided Design
The invention discloses a rapid and accurate registration method of a dense point cloud model, comprising the following steps of: realizing the initial registration of a turbine blade dense point cloud model and a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model through an alignment method; appropriately simplifying the obtained initially registered point cloud data; computing the rotation matrix and the translation matrix of each iteration in an SVD-ICP (Singular Value Decomposition-Iterative Closet Point) algorithm; and finally realizing the accurate registration of a control point set {P} and the CAD model by adopting the SVD-ICP algorithm. In the invention, under the premise of realizing the pre-registration of the point cloud model and the CAD model, the dense point cloud data are simplified; the simplified data are taken as a registered control point set; the total rotation matrix and the translation matrix are computed on the basis of the SVD-ICP algorithm; and the computed total transformation matrixes are applied to the original dense point cloud before the simplification so that the rapid registration of the dense point cloud and the CAD model is realized and the registration accuracy and the registration speed are considered simultaneously.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
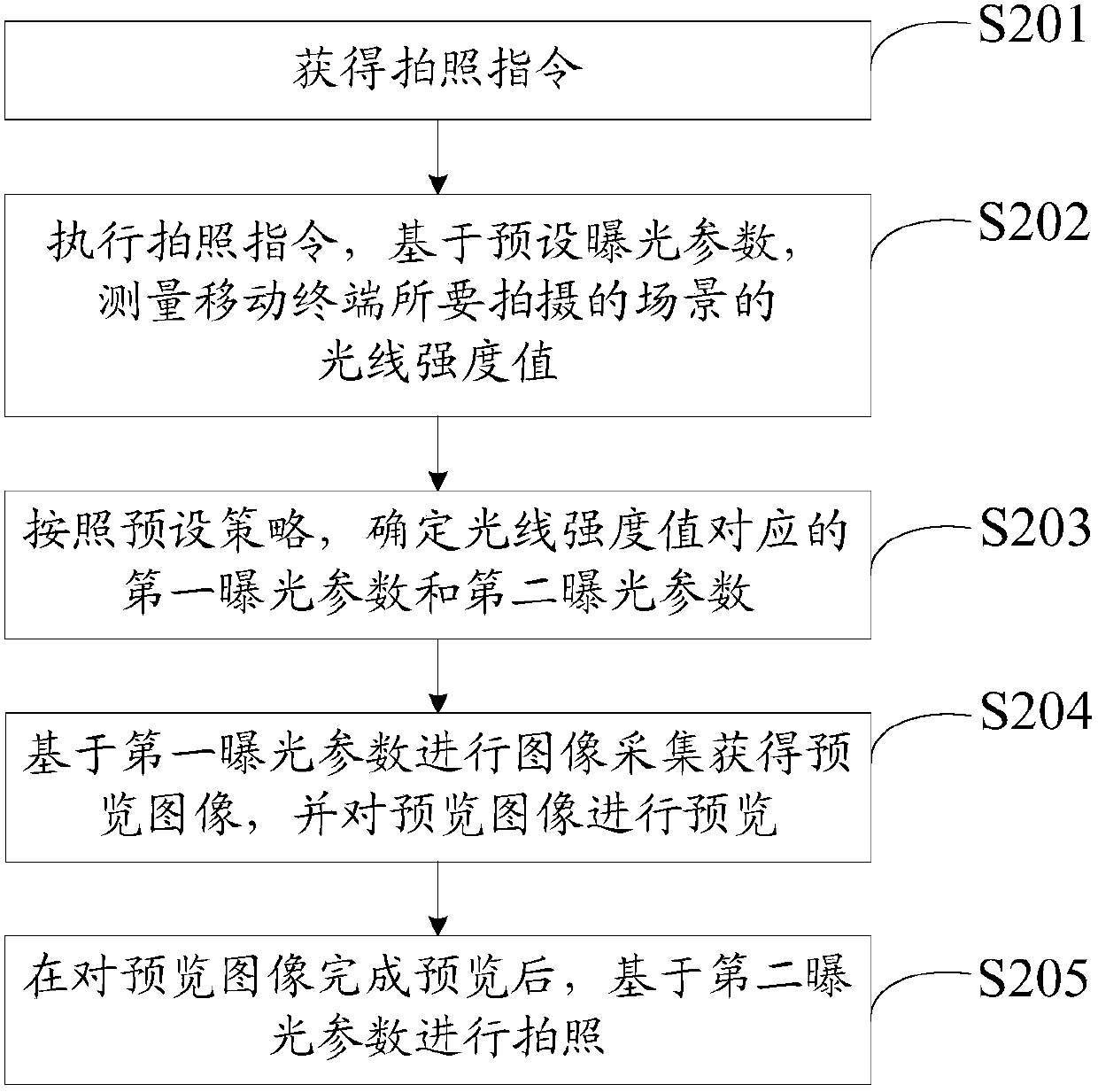
Photographing method and equipment and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN107613191AImprove accuracyGuaranteed image qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage acquisitionLight intensity
The embodiment of the invention discloses a photographing method which is applied to a mobile terminal. The method comprises the steps that a photographing instruction is acquired; the photographing instruction is performed, and the light intensity value of the scene to be photographed by the mobile terminal is measured based on the preset exposure parameter; a first exposure parameter and a second exposure parameter corresponding to the light intensity value are determined according to the preset strategy, wherein the second exposure parameter is different from the first exposure parameter; image acquisition is performed based on the first exposure parameter so as to acquire a preview image, and the preview image is previewed; and photographing is performed based on the second exposure parameter after previewing of the preview image is completed. The embodiment of the invention also discloses photographing equipment and a computer readable storage medium.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
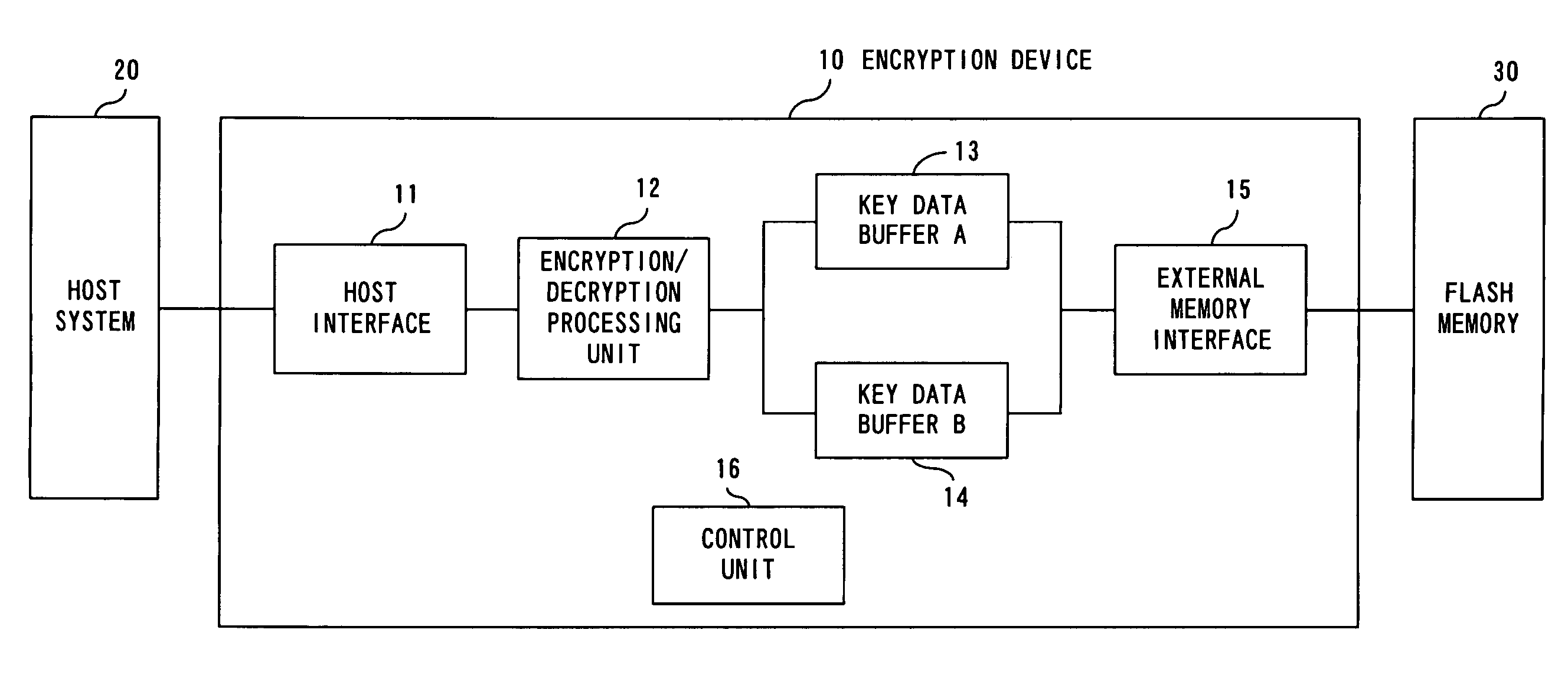
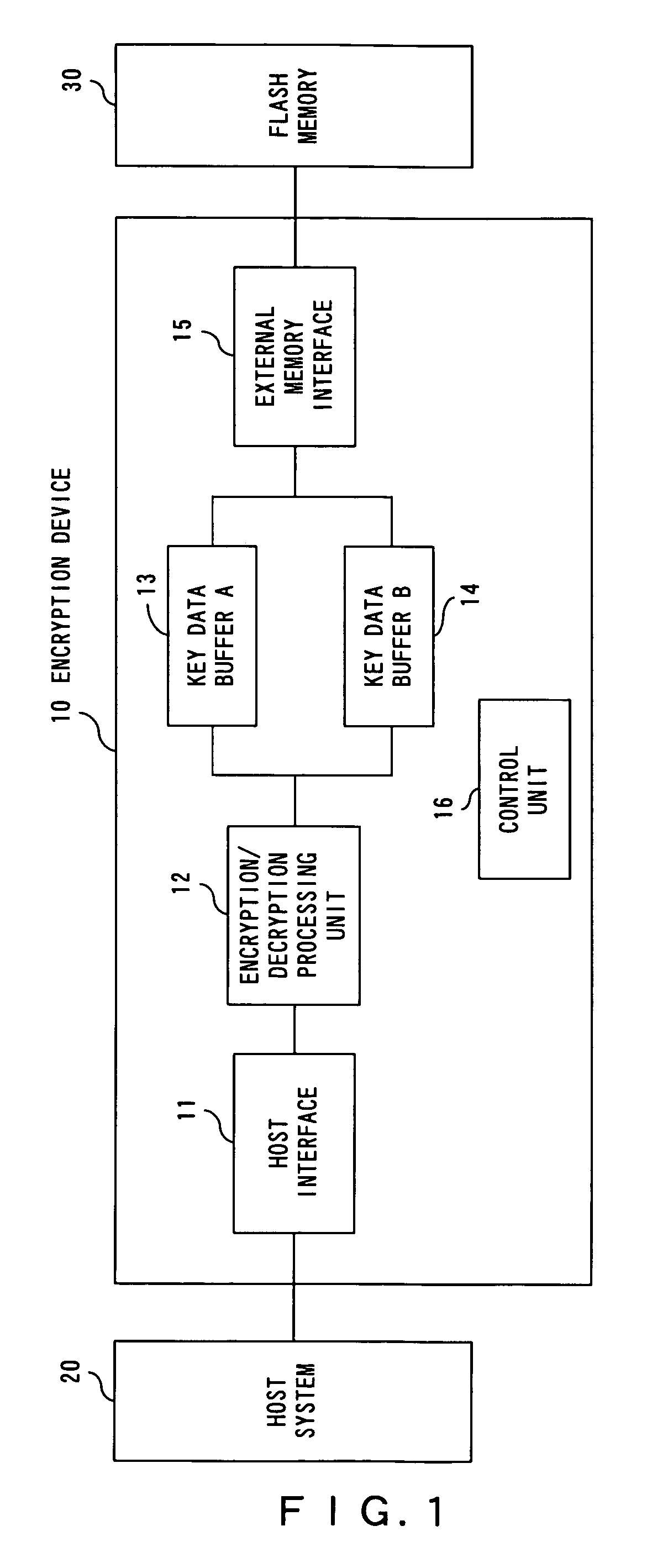
Encryption device
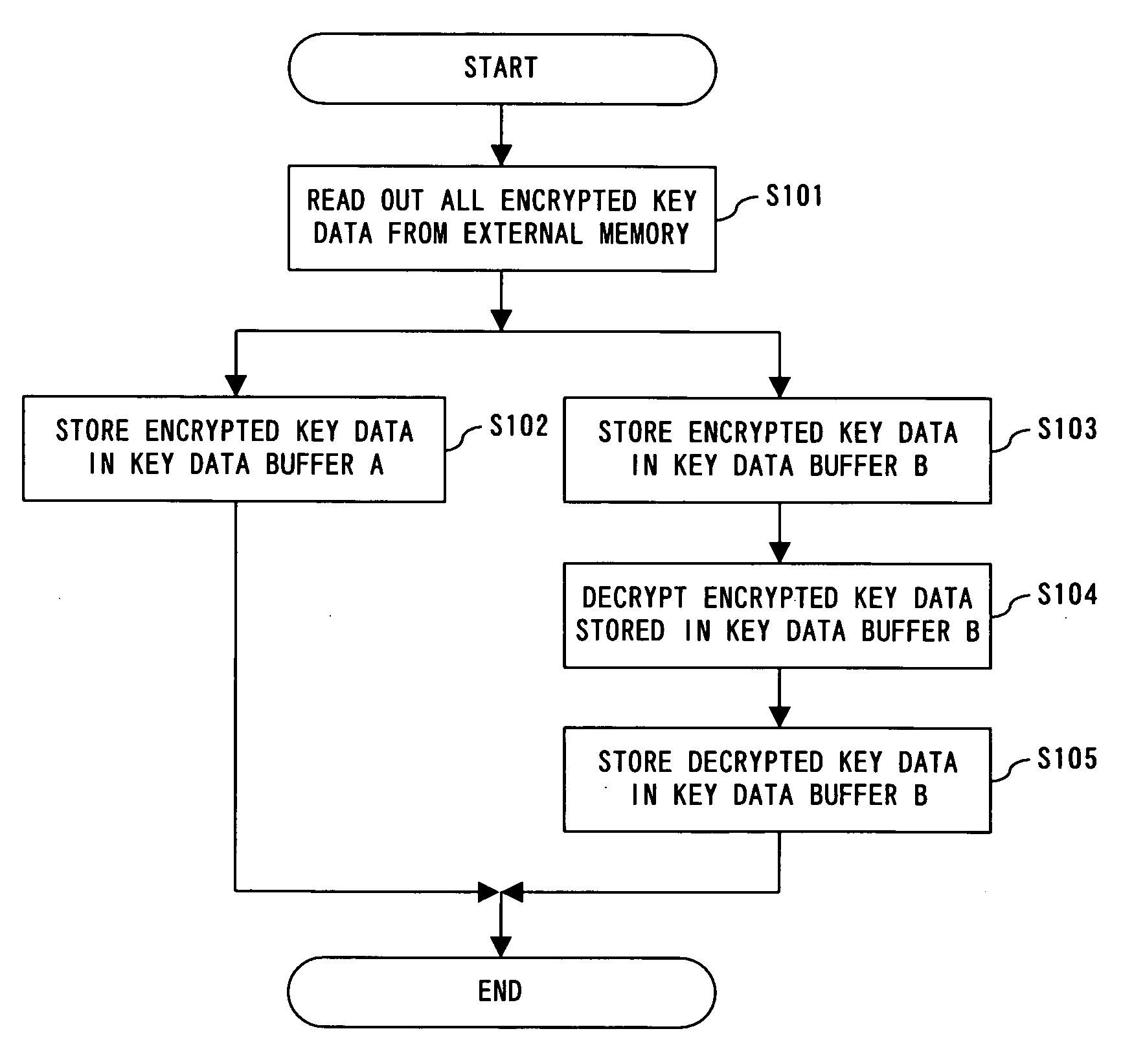
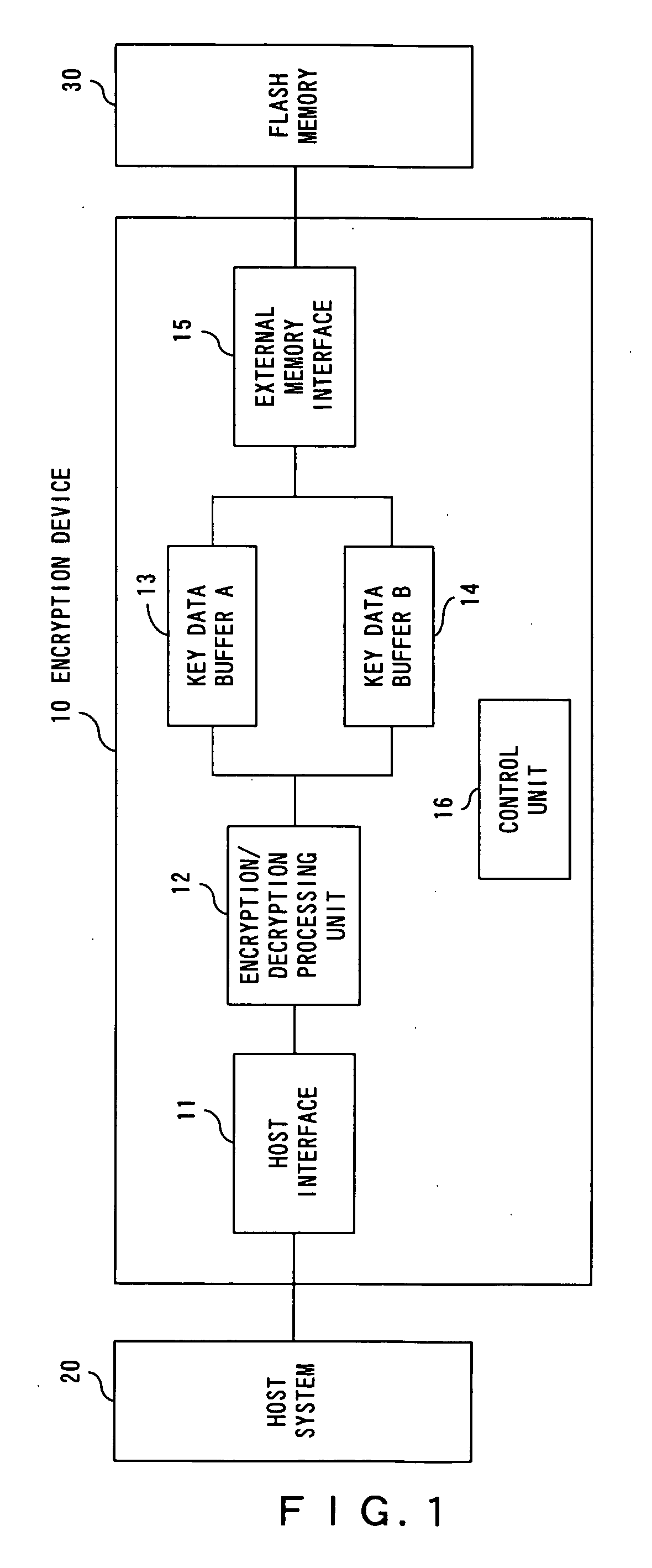
InactiveUS20070165864A1Processing speedReduce processing stepsKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionEncryption decryptionData storing
An encryption / decryption processing unit performs encryption / decryption processing of data transmitted from a host system, and encryption / decryption processing of key data used for encryption / decryption of the data. A key data buffer temporarily stores encrypted key data. A key data buffer temporarily stores unencrypted key data. An external memory interface controls flash memory attached outside, and reads / writes encrypted key data stored in the key data buffer.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
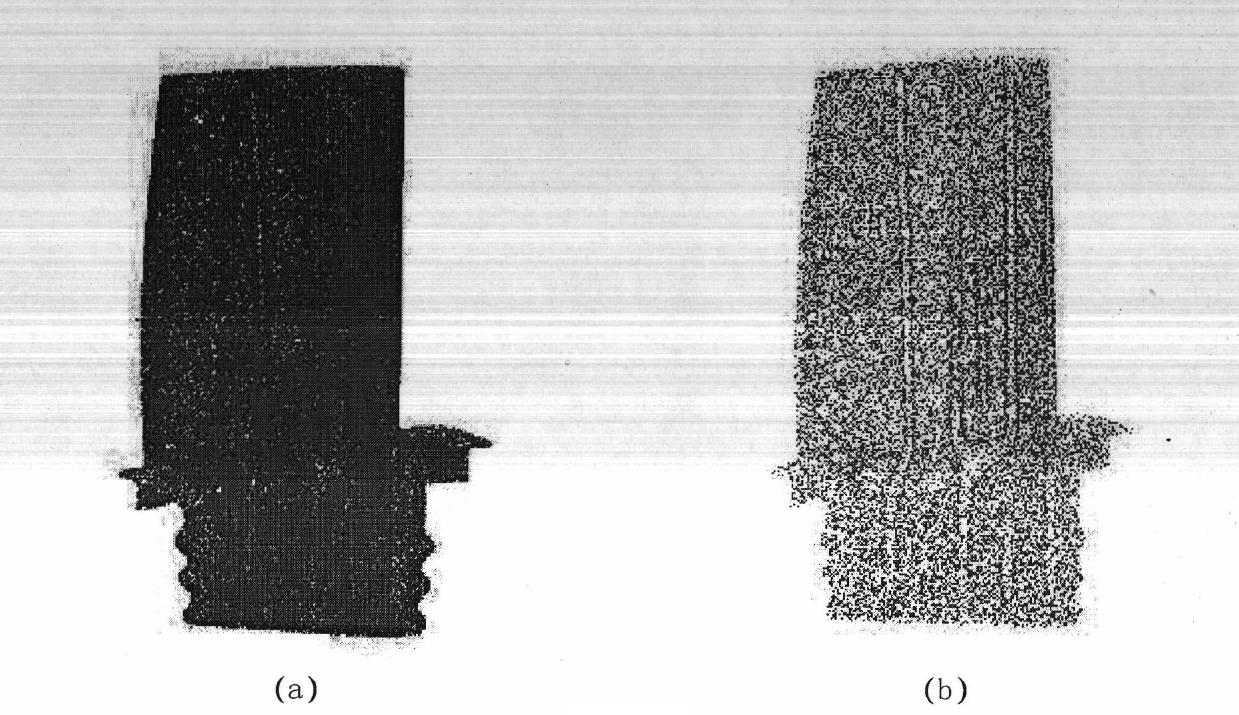
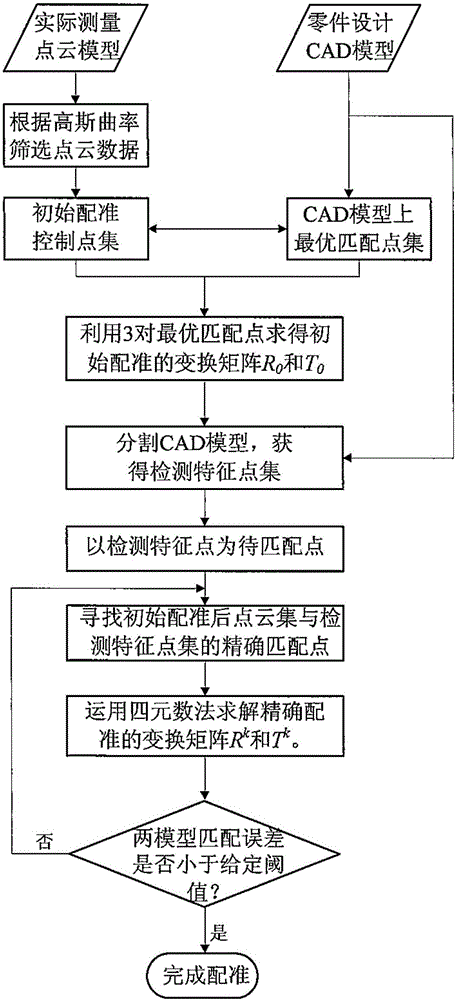
Point-cloud model and CAD model registering method based on detection features
ActiveCN106023156AImprove accuracySmall amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsPoint cloud
The invention discloses a point-cloud model and CAD model registering method based on detection features. The registering method comprises the following steps: selecting Gauss curvature abrupt change points from a point-cloud model to form an initial registering control point set, and solving a corresponding matching point set on a CAD model; according to constraint conditions, finding three matching point pairs from the two point sets; according to the matching point pairs, solving an initial translation matrix and an initial rotation matrix; segmenting the CAD model into standard graphs, and according to detection feature point arrangement rules of the standard graphs, acquiring points from the CAD model to form a detection feature point set; by use of the initial rotation matrix and the initial translation matrix, acting on all points of the point-cloud model so as to form a point-cloud point set after conversion; and for the point-cloud point set and the detection feature point set, searching for a rotation matrix and a translation matrix which accurately register with each other by use of an ICP algorithm. The registering method takes both a registering speed and registering precision into consideration, and improves robustness of accurate registering.
Owner:COMAC +1
Small current neutral grounding fault location method based on direction of transient state reactive power
ActiveCN103245879AGuaranteed Protection SensitivityGuaranteed protection reliabilityFault locationTransient stateEngineering
A small current neutral grounding fault location method based on the direction of transient state reactive power is characterized in that change of voltage or current serves as a failure starting condition, and after the starting, the zero sequence voltage is taken as the participating voltage if a detection point can be used for detecting the zero sequence voltage and if not, the following steps are performed: 1, confirming the fault phase as per characteristics of three transient state line voltages, and 2, confirming the transient state line voltage including the fault message as per the type of the fault phase, taking the transient state line voltage as the participating voltage, confirming the characteristic frequency range, and further building a digital filter to filter the participating voltage and the zero sequence current signal, so as to obtain the component within the characteristic frequency range; and then confirming the direction of the reactive power of all the detection points through utilizing the components of participating voltage and the zero sequence current within the characteristic frequency range, so as to further confirm the fault section. According to the invention, the transient voltage and current signals as well as zero sequence voltage and line voltage are utilized at the same time, the positioning reliability is higher, the adaptability is stronger, quick direction protection for ground fault of all the voltage classes is applicable at the same time, and the protection speed and reliability are taken into consideration.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +4
Electromyographic signal classification method based on multi-kernel support vector machine
InactiveCN101859377AReduce the numberImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodySignal classification
The invention relates to an electromyographic signal classification method based on a multi-kernel support vector machine. For a sample with complex distribution, based on the classification performance of a single-kernel support vector machine, the classification accuracy and the quantity of support vectors are easily influenced. The method combines a multi-kernel support vector machine method with a binary tree combination strategy and comprises the following specific steps of: collecting electromyographic signals of the lower limbs of a human body through an electromyographic signal acquisition instrument; denoising the electromyographic signals containing interference noise by using a wavelet coefficient inter-scale correlation denoising method; extracting the features of the denoised electromyographic signals to obtain the features of the electromyographic signals by using denoised wavelet coefficients; and classifying on the basis of the multi-kernel support vector machine. The method can well meet the multi-classification requirement of lower extremity prosthesis control, and takes into account both accuracy and instantaneity, and has broad application prospects in the multi-movement mode recognition of intelligent prosthesis control.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Circuit fault directional detecting and protecting method for power supply system
InactiveCN1614435AGuaranteed Protection SensitivityGuaranteed protection reliabilityEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionFault locationTransient stateElectric power system
A method for detecting line fault direction judges the fault direction by calculating instant idle power or specific frequency component idle power of transient state voltage current generated by the fault. The fault direction can be detected out quickly within 5 ms and tripping command is followed immediately to separate the fault line out for protection.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNYOUTH ELECTRIC TECH GRP CO LTD
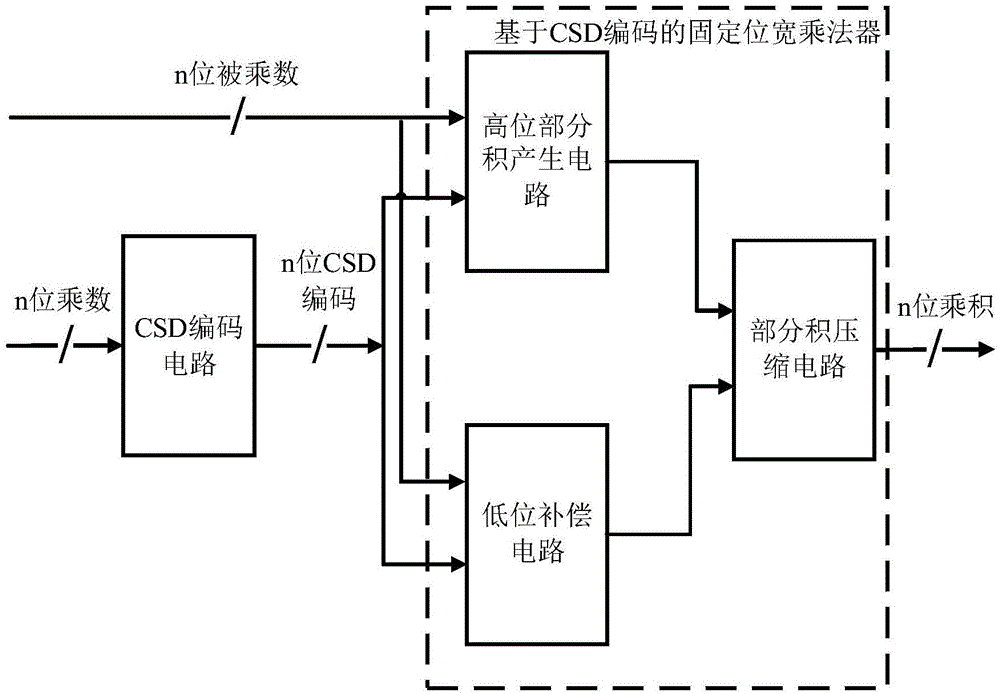
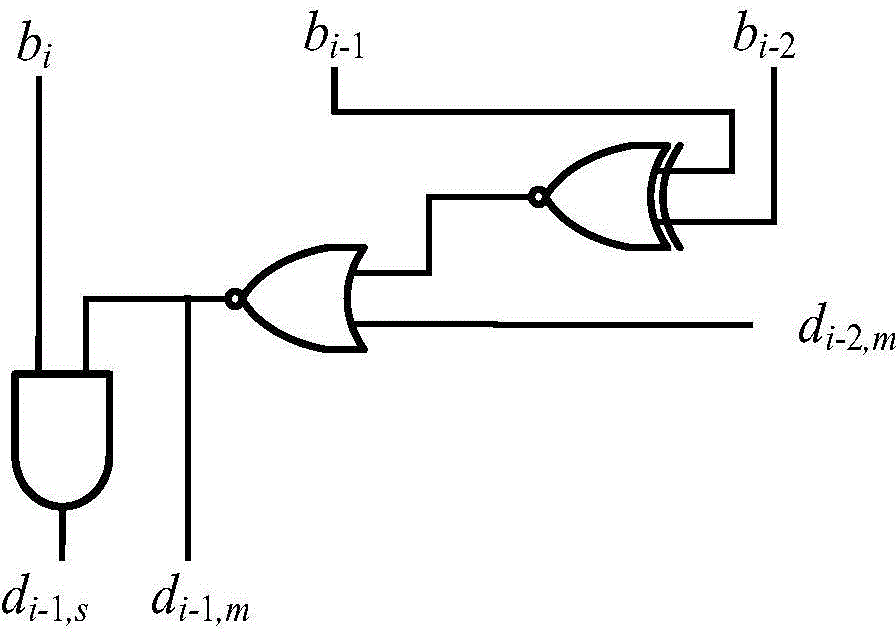
Fixed-bit-width multiplier with high accuracy and low energy consumption properties
InactiveCN105183424AHigh precisionReduce power consumptionDigital data processing detailsPartial productIntegrated circuit
The present invention relates to the technical field of integrated circuits, and in particular to a fixed-bit-width multiplier with high accuracy and low energy consumption properties. The fixed-bit-width multiplier with the high accuracy and low energy consumption properties comprises a CSD encode circuit, a high position partial product generation circuit, a low position compensation circuit and a partial product compression circuit, wherein an input port of the CSD encode circuit is connected to external input data, and an output port of the CSD encode circuit is connected to the high position partial product generation circuit and the low position compensation circuit; the high position partial product generation circuit is connected to the external input data, and an output port of the high position partial product generation circuit is connected to the partial product compression circuit; the low position compensation circuit is connected to the external input data, and an output port of the low position compensation circuit is connected to the partial product compression circuit; and an output port of the partial product compression circuit is connected to the external input data. The present invention has the beneficial effects that a fixed-bit-width multiplier with low energy consumption and a relatively high speed, and a practical fixed-bit-width multiplier design with high accuracy and low energy consumption are achieved. The fixed-bit-width multiplier of the present invention is particularly suitable for implementation of a high-accuracy multiplication with low energy consumption and a fixed bit width.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Pixel circuit and driving method thereof as well as display apparatus
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Non-volatile memory device and operation method thereof
ActiveCN103699344AImprove accuracyReduce data volumeInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData reorganizationVolatile memory
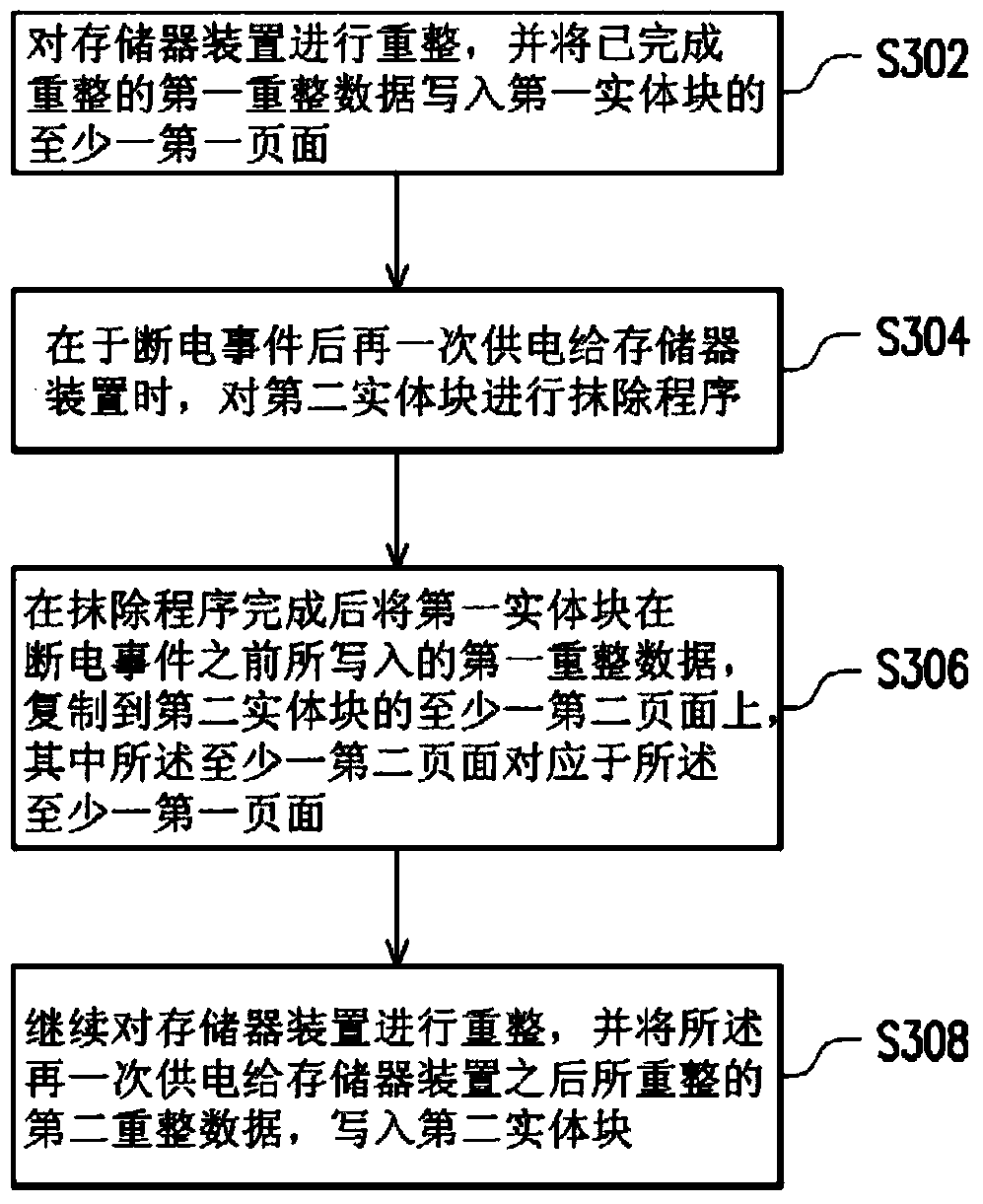
The present invention provides a non-volatile memory device and operation method thereof, wherein a non-volatile memory module of the non-volatile memory device includes a first physical block and a second physical block. The operation method includes the steps as follows. The non-volatile memory deviceshould be reformed and a first data reorganization completed restructuring should be wrote in at least one first page of the first physical block. When the non-volatile memory deviceis supplied power again after a power off event, the second physical block is conducted the erasing program. The first data reorganization wrote by the first physical block before the power off event is copied to at least one second page of the second physical block. The non-volatile memory device is continue to reform, and the second data reorganization reformed by the non-volatile memory device after the repeated power supply is wrote to the second physical block. The present invention can avoid the wrong data creating from reforming the non-volatile memory device after repeatedly supplying power to the non-volatile memory device.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Ground penetrating radar target detection method based on full convolution network
InactiveCN108830331AProcessing speedEasy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setData expansion
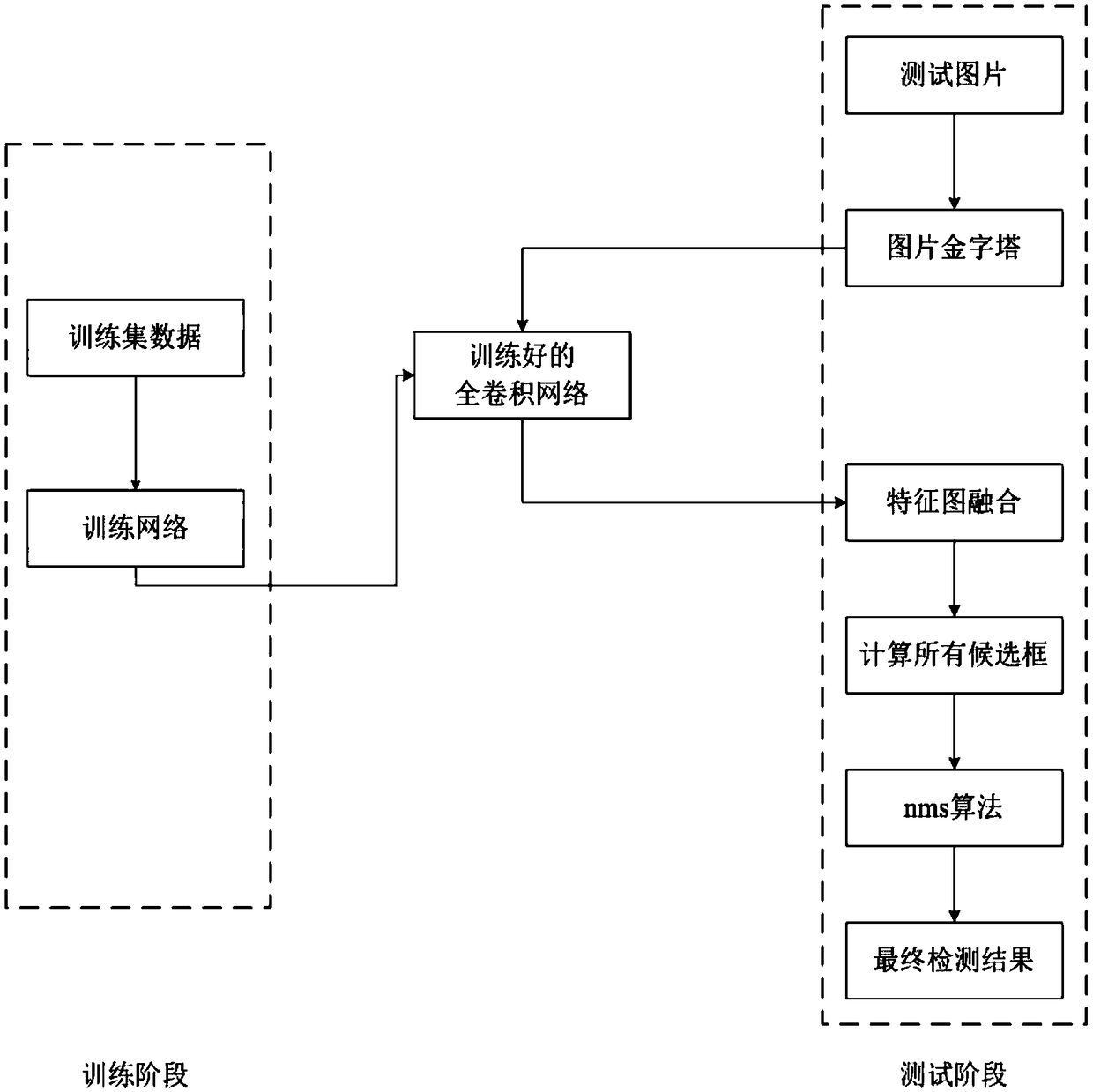
The invention discloses a ground penetrating radar target detection method based on a full convolution network, which comprises the steps of building a three-layer full convolution network to train aground penetrating radar data set, scaling an image to obtain different scales, then inputting into the network for convolution operation, outputting a heat characteristic map, performing mapping calculation on the heat map, and positioning the location of a target so as to complete the target detection. The network does not need to use a data set marked by a location box when being trained, can accept input pictures of any size, detects targets of different sizes and is high in speed. In the case of a small data volume of the ground penetrating radar, ground penetrating radar target detectionbased on the full convolution network is realized through data expansion. The algorithm has the advantages of high speed, high detection accuracy and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Intelligent mobile terminal scene character processing method
ActiveCN104408449AImprove accuracyAccurate removalCharacter recognitionState of artComputer terminal
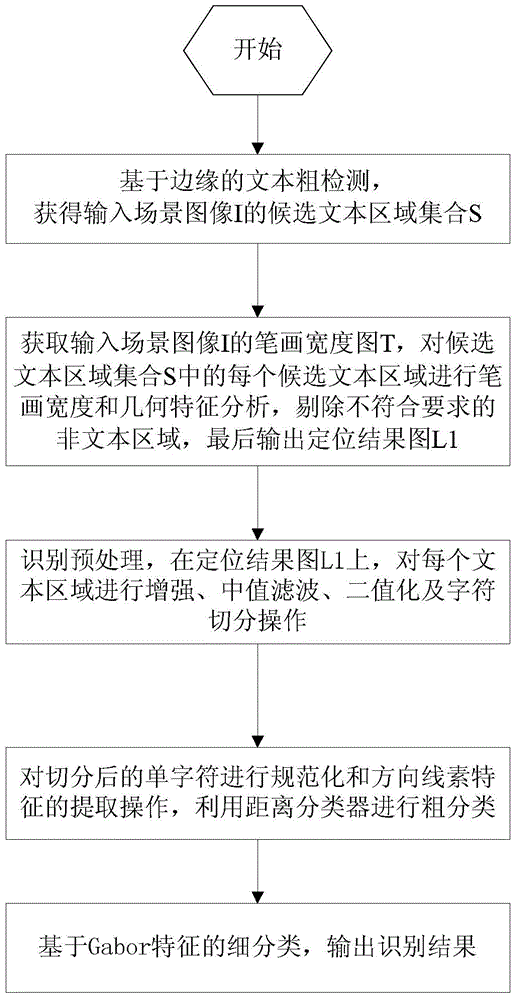
The invention relates to an intelligent mobile terminal scene character processing method. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, performing text coarse detection based on edges; step 2, obtaining a stroke width graph T of an input scene image I, analyzing the stroke widths and geometric characteristics of each candidate text area in a candidate text area set S, rejecting a non-text area not according with requirements, and finally outputting a positioning result graph L1; step 3, performing identification pretreatment; step 4, performing extraction operation of standard and directional element characteristics on segmented single characters; and step 5, performing fine classification based on Gabor characteristics. Compared to the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the following advantages: the accuracy is greatly improved, the recall rate is quite high, the time performance is substantially improved, and the accuracy of character identification is greatly enhanced.
Owner:XIDIAN NINGBO INFORMATION TECH INST
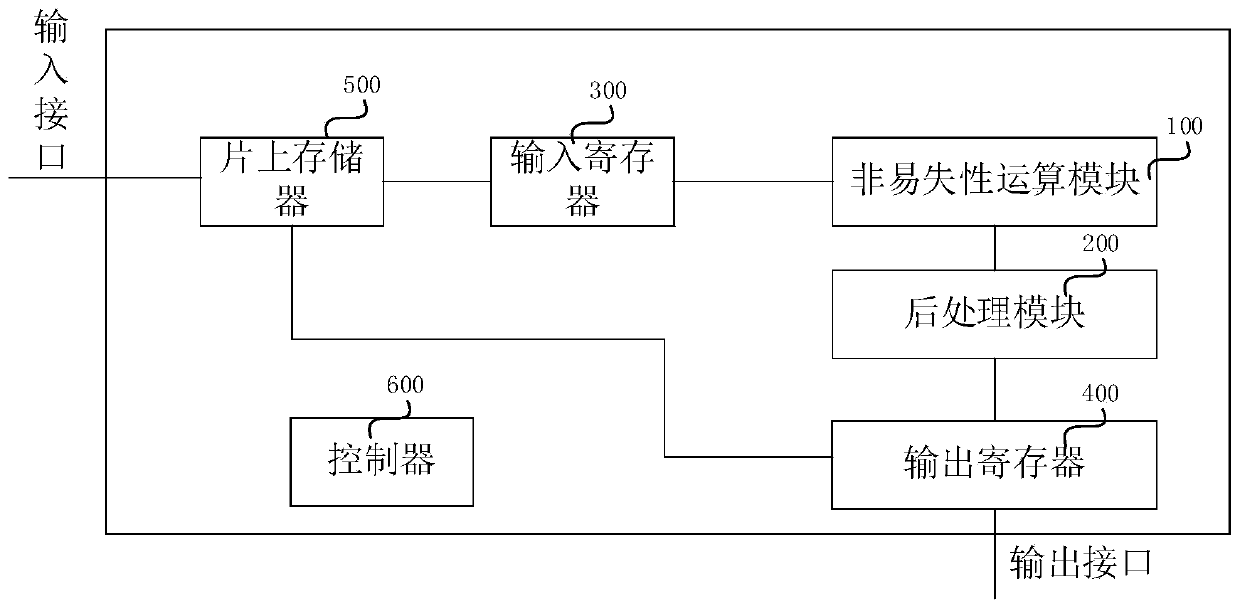
Chip for realizing binary neural network based on nonvolatile in-memory calculation and method
The invention provides a chip for realizing a binary neural network based on nonvolatile in-memory calculation and a method, and the chip comprises a nonvolatile operation module which is used for carrying out the matrix multiply-add operation on a first binary data packet received by the nonvolatile operation module and a second binary data packet pre-stored in the nonvolatile operation module, wherein the weight of the binary neural network is generally fixed during the reasoning process, and the input characteristics corresponding to each layer of neural network are generally changed alongwith the application. The weight of the binary neural network is used as the second binary data packet to be pre-stored in the nonvolatile operation module, and the input characteristics of the binaryneural network are loaded to the nonvolatile operation module, so that the matrix multiplication and addition operation can be realized in the nonvolatile operation module, and the problems of powerconsumption and time delay caused by data migration can be solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
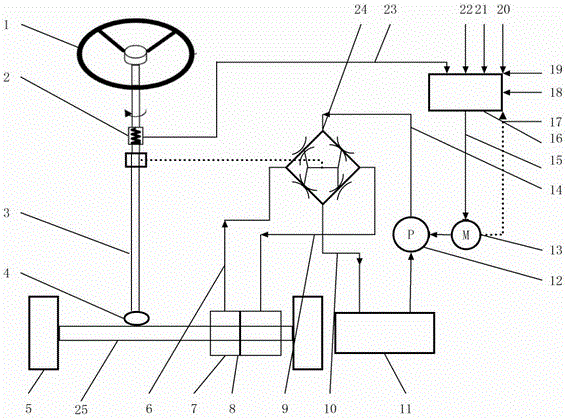
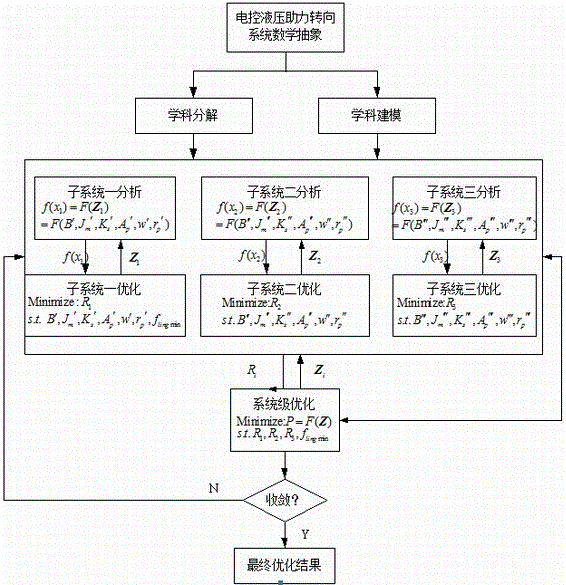
Electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system and multi-objective optimization method thereof
ActiveCN106004999AReduce energy consumptionReduce optimization operation timeFluid steeringMotor speedMachine parts
The invention relates to an electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system and a multi-objective optimization method thereof. The electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system comprises a steering machine part, a hydraulic power steering part, a signal sensor part and an electronic control unit ECU. A driver gives a steering instruction through the steering machine part, multiple signal sensors transmit a speed signal, a steering wheel angle signal, a motor speed signal and the like to the electronic control unit ECU, the electronic control unit ECU issues an instruction to the hydraulic power steering part, to drive hydraulic oil to conduct ideal power steering; meanwhile, the electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system is subjected to multi-objective optimization, the mechanical parameters of the electronically controlled hydraulic power steering system, and the parameters of a hydraulic system part are subjected to optimization design through a collaborative optimization method by taking the steering road sense, sensitivity and energy consumption as the objectives, so that the comprehensive performances of the steering road sense, sensitivity and energy consumption of the steering system are better.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
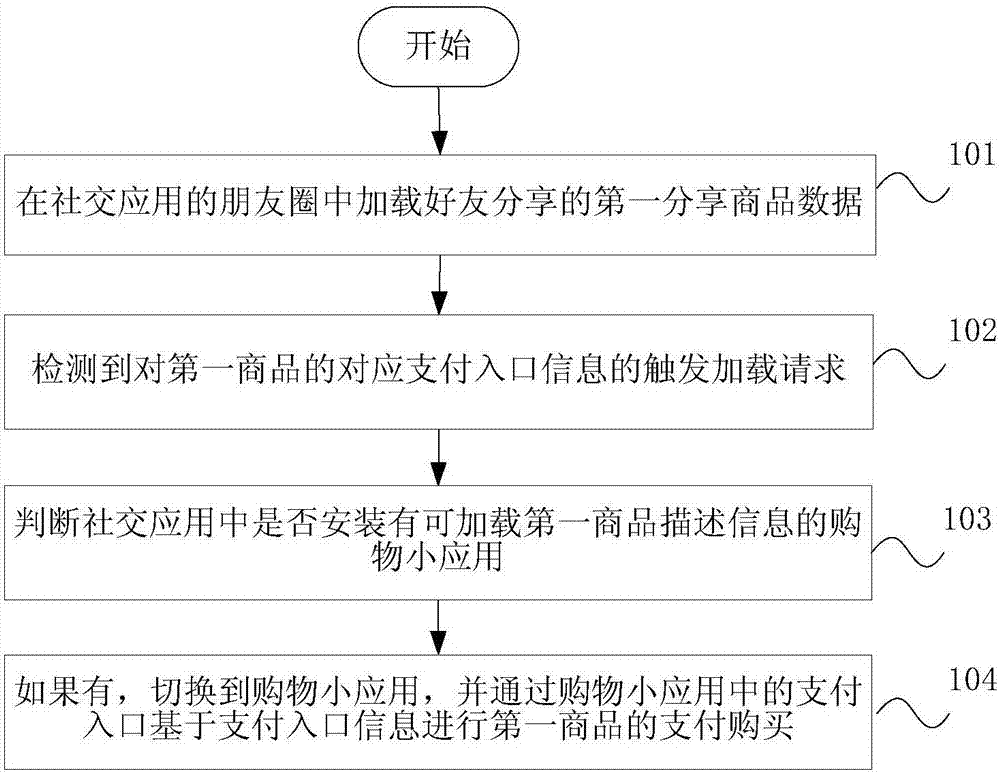
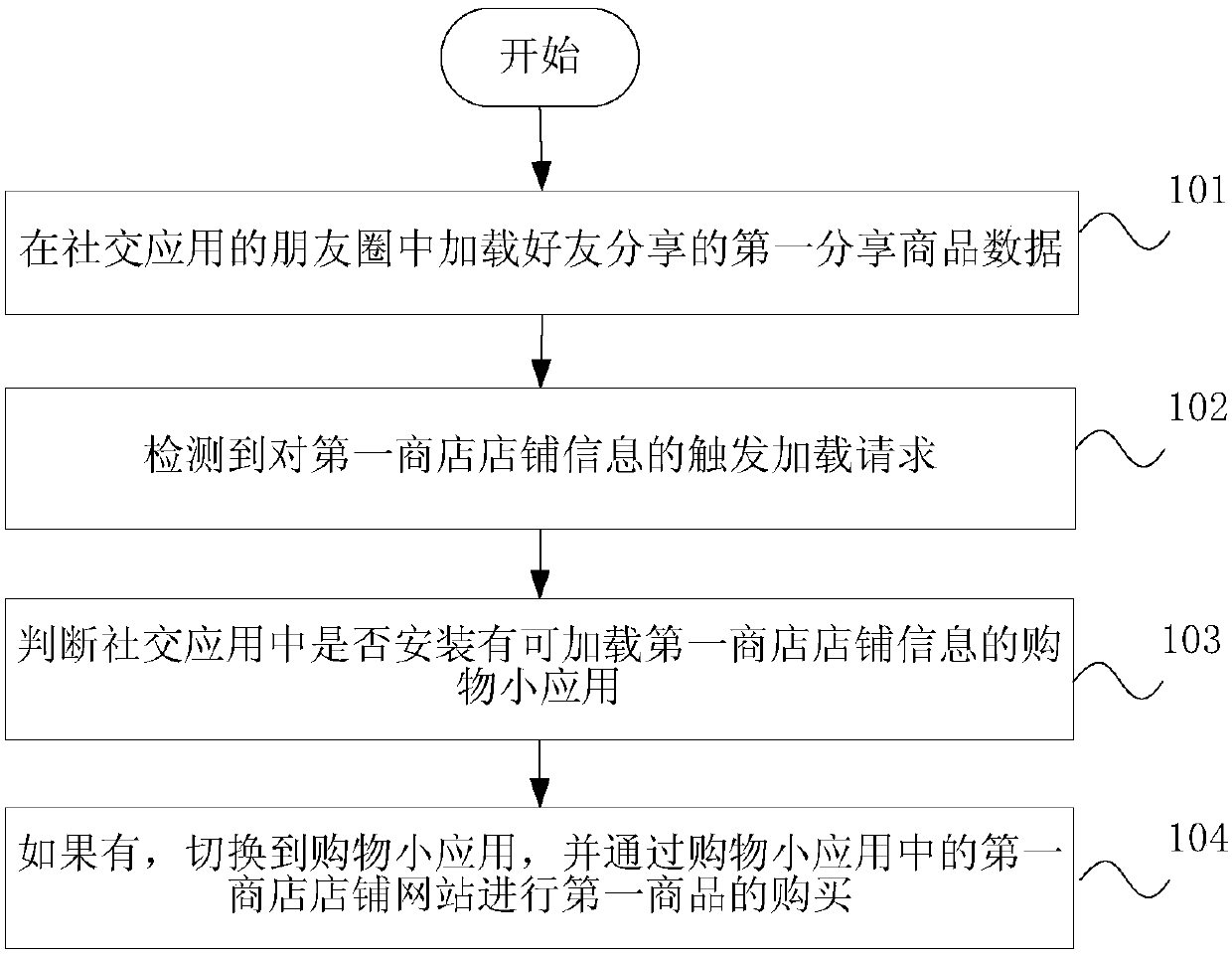
Method and device of processing commodity information in moments, and terminal
InactiveCN107544825AReduce occupancyReduce functionProgram loading/initiatingBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentE-commerce
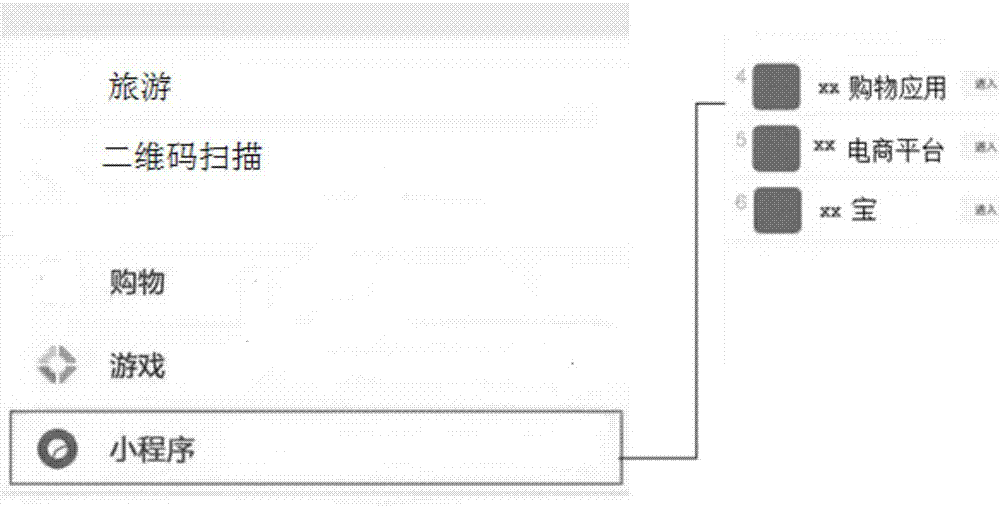
Embodiments of the invention disclose a method and a device of processing commodity information in moments, and a terminal. The method comprises the steps of loading data of a first shared commodity shared by a friend in moments of a social app, detecting a trigger loading request for corresponding payment entry information of the first commodity, switching to a shopping gadget, and paying to purchase the first commodity through a payment entry of the shopping gadget according to the payment entry information. According to the method, device and terminal, the shopping gadget can be started inthe social app, can be used for sharing the commodity in the social app and has functions of showing, commenting, purchasing and paying the shared commodity, further, the shopping gadget has almost the same function and mode as an original APP, and an e-commerce app installed locally is not invoked, so that less memory of a cellphone is used while fluent use experience is delivered, shopping is more convenient and the commodity is promoted more easily, and the user experience is improved.
Owner:BEIJING ANYUNSHIJI TECH CO LTD
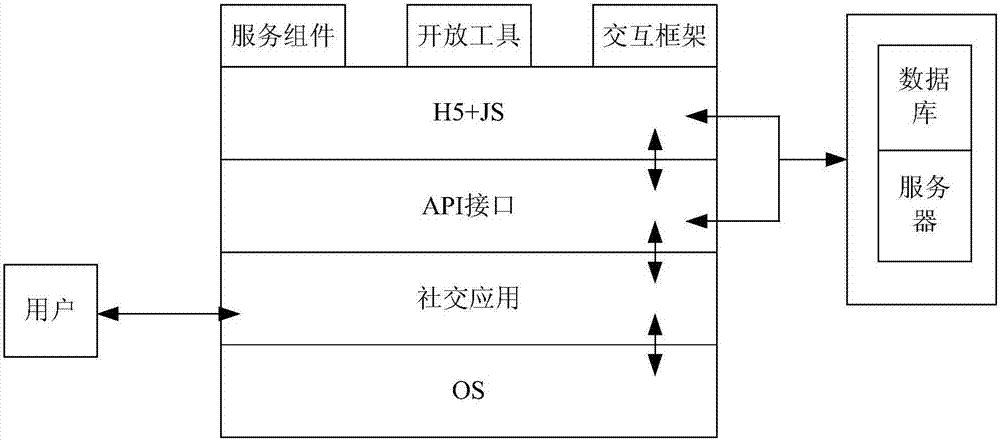
Wechat friend circle goods information processing method, device and mobile terminal
InactiveCN107563849AImplement functions and servicesBalance speed and experienceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMarine navigationMobile phone
The embodiment of the invention discloses a wechat friend circle goods information processing method, a device and a mobile terminal; the method comprises the following steps: loading first shared goods data shared by a friend in the friend circle of a social application, detecting a triggering loading request on the first shop information, switching to a shopping small application, and purchasingthe first goods in the first shop website of the shopping small application. The method, device and terminal can startup the shopping small application in the social application, can publish goods ads in the social application, can realize goods display, commenting, buying and payment functions, can provide map, navigation and merchant promotion functions in the social applications, and can provide functions and modes almost same with the original APP without invoking an e-business APP locally installed on the mobile phone, thus reducing mobile phone memory resource occupations, brining conveniences for user shopping and promotions, and improving user feelings.
Owner:BEIJING ANYUNSHIJI TECH CO LTD
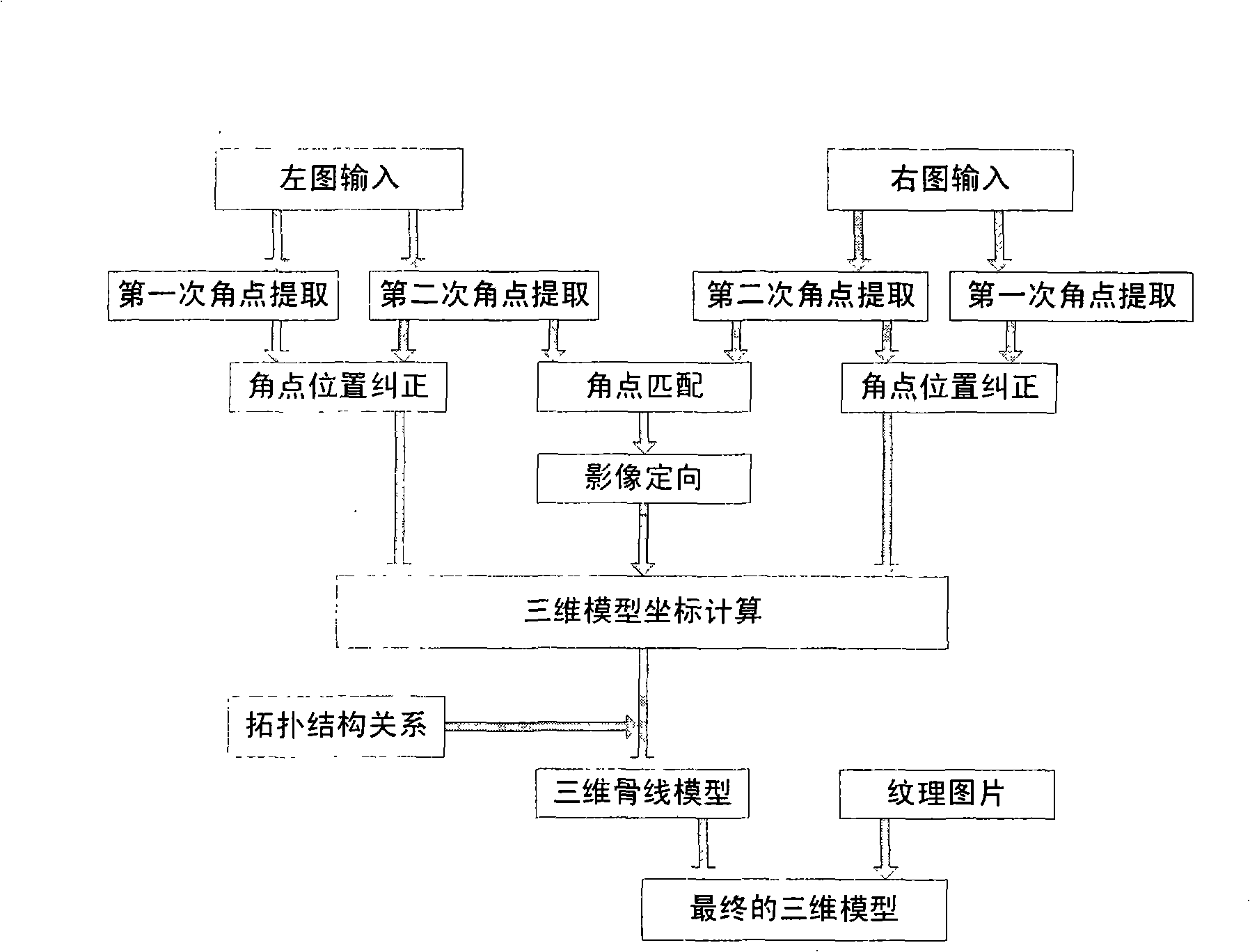
Three-dimensional architecture rapid modelling approach based on stereopair
The invention relates to a modeling method of a three-dimensional building based on stereo image pairs, which is characterized in that: corner points of the building are sequentially extracted from a left aviation image and a right aviation image according to the clockwise or counterclockwise direction; then the positions of the extracted corner points of the building are corrected according to the similar point-position pairs; the images are then carried out the automatic orientation, the calculation of a three-dimensional coordinate is carried out according to the result of the automatic orientation, and the calculation result finally utilizes an OPENGL tool to realize the three-dimensional display and multi-angle observation on a screen. The modeling method has two obvious advantages that: firstly, the algorithm is simple and effective, which is one of the effective ways for realizing the modeling of the three-dimensional building. Secondly, the modeling method can take account of both speed and fidelity. The extracted corner points are corrected, thus effectively reducing the position error of the corner points and taking account of both speed and fidelity.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
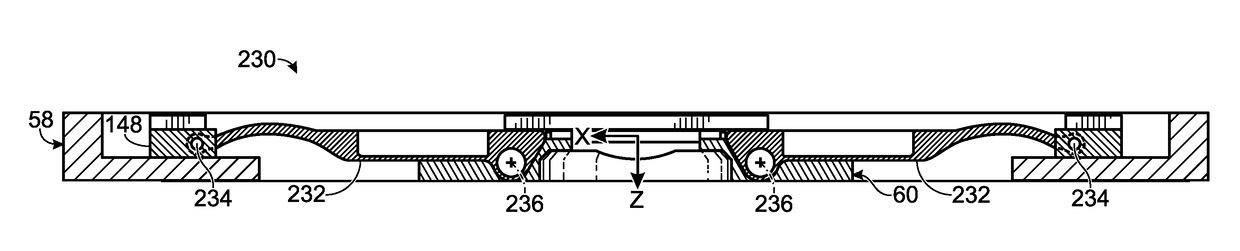
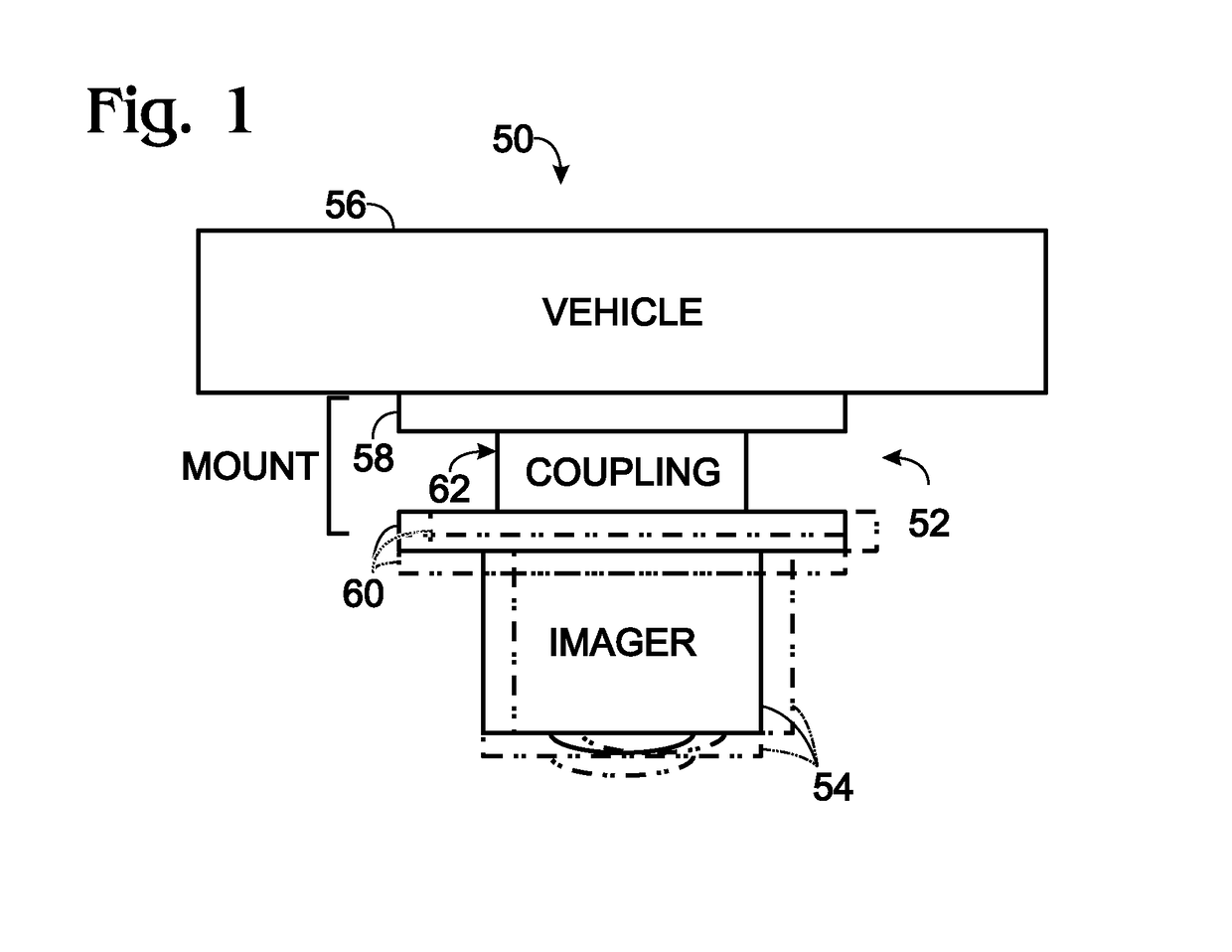
Anti-rotation mount
ActiveUS20180007248A1Pointing accuratelyImprove accuracyAircraft componentsTelevision system detailsImage detectorEngineering
Imaging system comprising an anti-rotation mount and an image detector. The mount may comprise a first frame member having a fixed relation to a set of mutually transverse X, Y, and Z axes, and a second frame member. The second frame member may be connected to the first frame member via a coupling assembly, such that the frame members are not permitted to rotate relative to one another. The mount also may comprise X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis coupling structures each formed at least partially by the coupling assembly and each permitting axial motion of the frame members relative to one another only substantially parallel to the X axis, Y axis, and Z axis, respectively. The image detector may be connected to the mount via the second frame member.
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
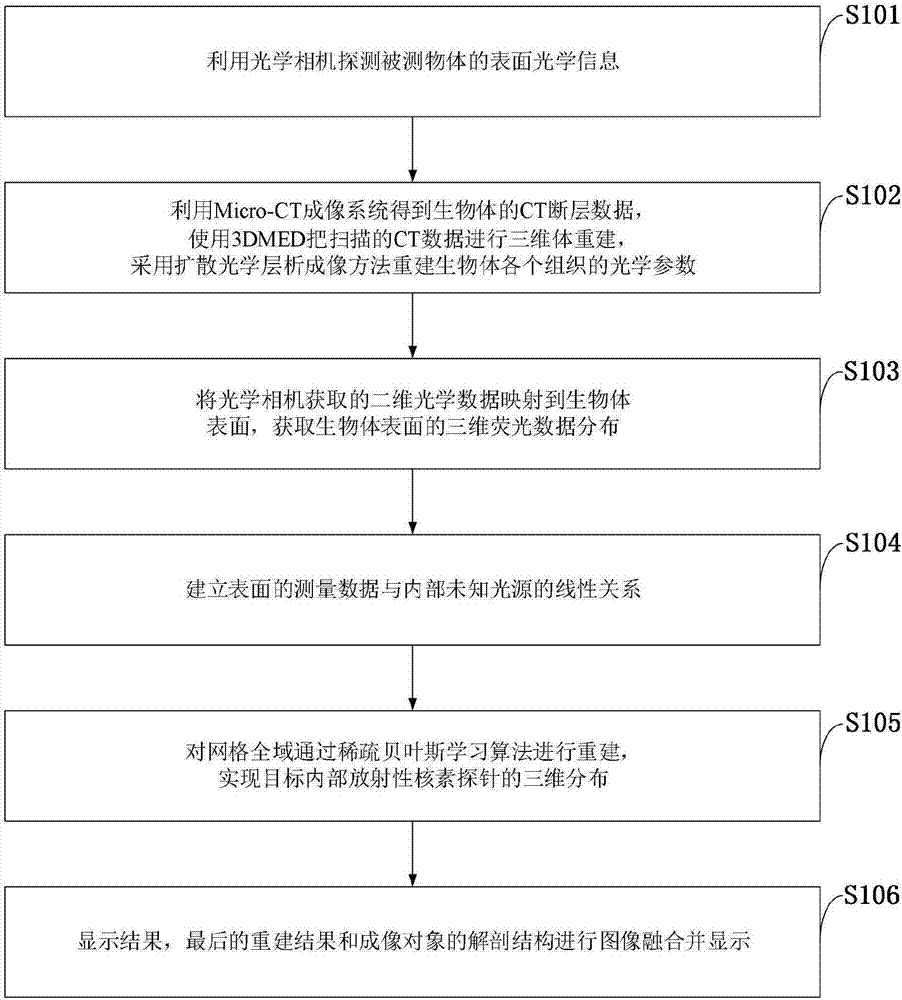
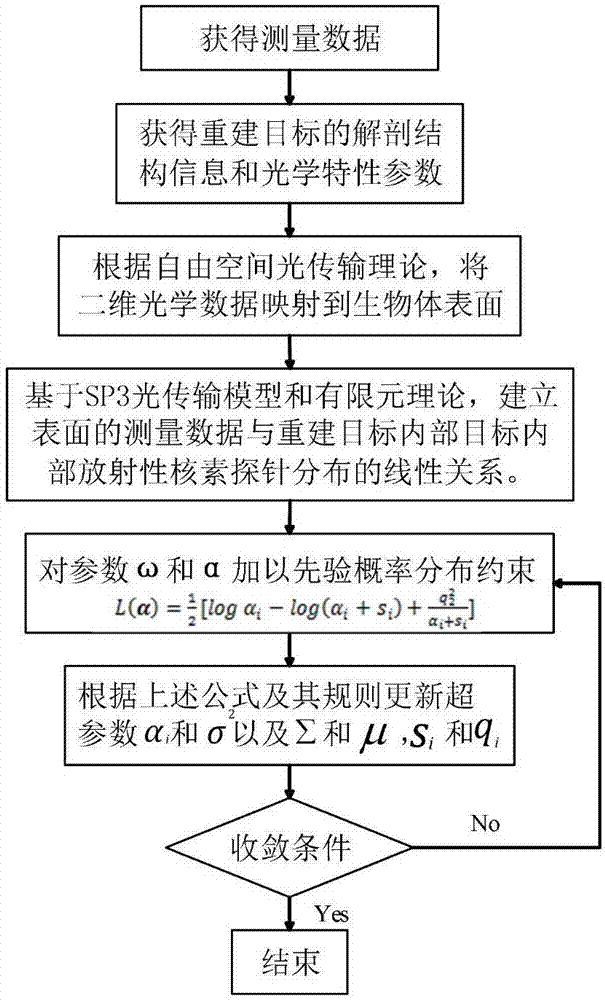
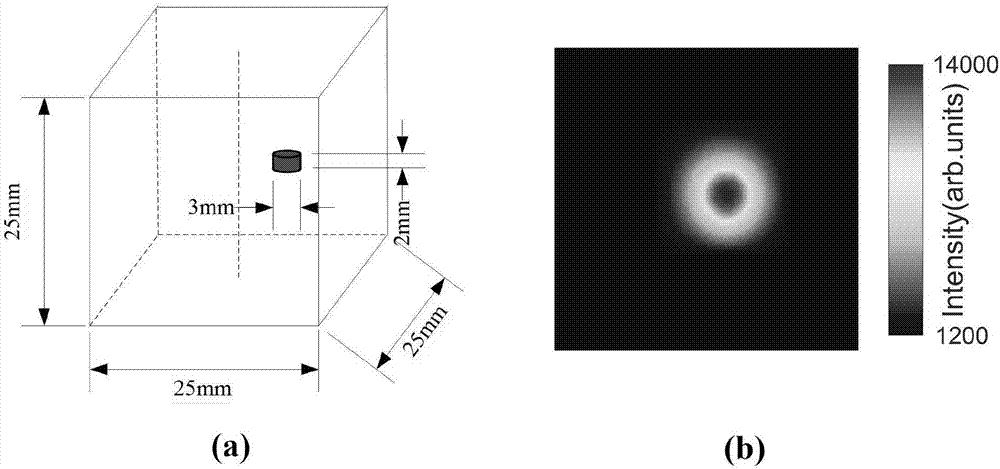
Single-view Cerenkov luminescence tomography reconstruction method
ActiveCN107392977AAvoid errorsReduce acquisition timeImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAnatomical structuresOptical tomography
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical molecular imaging, and discloses a single-view Cerenkov luminescence tomography reconstruction method. The method comprises: detecting surface optical information of a detected object by using an optical camera; acquiring organism organization structure information and optical property parameters; mapping two-dimensional optical data acquired by the optical camera to an organism surface to obtain three-dimensional fluorescent data distribution of the organism surface; establishing a linear relation between measured data of the surface and an internal unknown light source by using anatomical structure information of a reconstructed object and the optical property parameters as prior information; reconstructing a grid all domain via a sparse Bayesian learning algorithm to realize three-dimensional distribution of radionuclide probes inside a target; and performing image fusion and display on the reconstruction result and the anatomical structure of the imaged object. The method effectively improves the Cerenkov tomography reconstruction result, and has important application value in the fields of optical tomography three-dimensional reconstruction algorithms and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
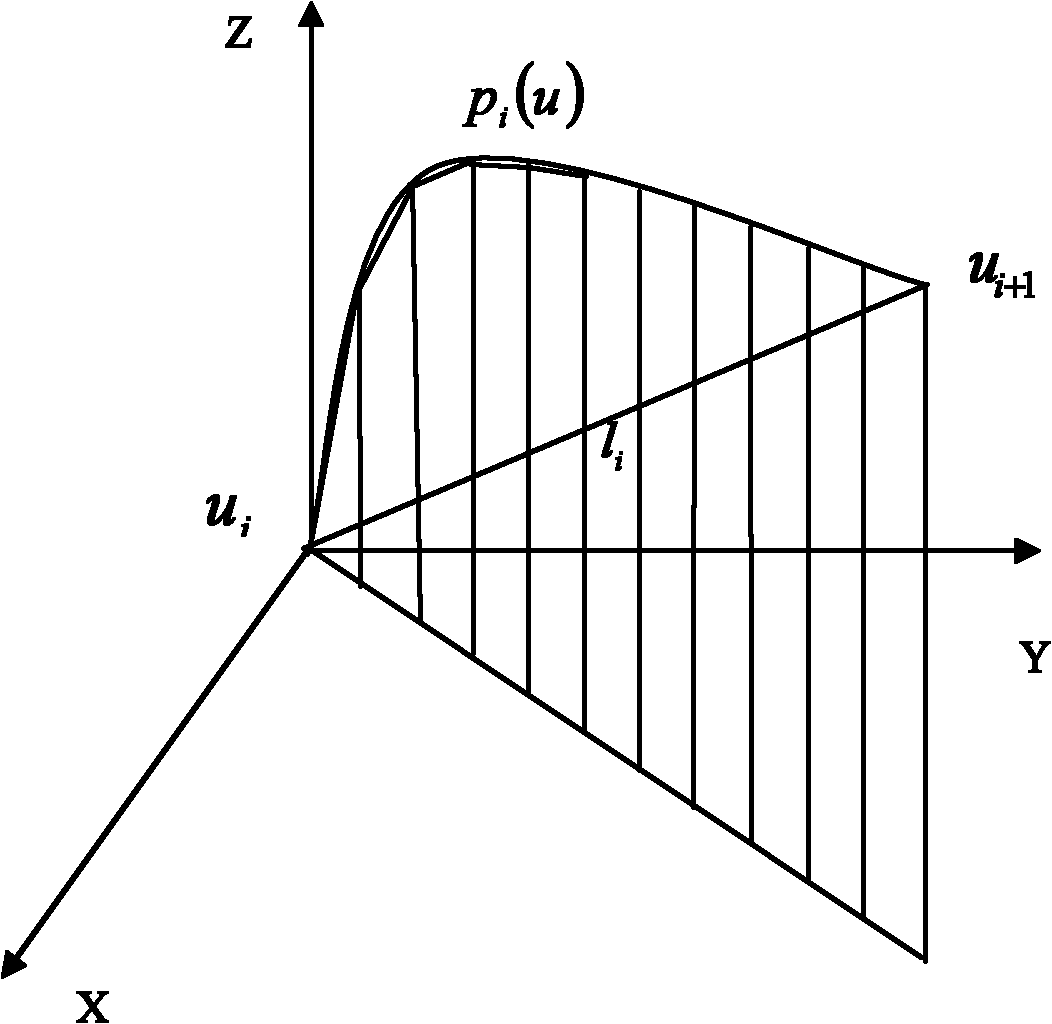
Motion control system based on non-uniform rational B-spline (NURBS) curve interpolation
The invention discloses a motion control system based on non-uniform rational B-spline (NURBS) curve interpolation. The system comprises an upper computer, a lower computer, a motor driver a motor and a mechanical structure which are connected sequentially; the upper computer calculates an interpolation point through an interpolation module, and transmits the calculated coordinate value list to the lower computer; the lower computer converts a coordinate value into the corresponding pulse number, sends a pulse to the motor driver, controls the motor to rotate and drives the mechanical structure to act; the interpolation module is an NURBS curve interpolation module, and solves the length of the whole curve by a large-density dicretization method; the interpolation period T and interpolation speed V are set, and the interpolation base step delta s and arch height error delta delta are solved and the relationship between the arch height error delta s and the required error delta 1 is compared. The invention provides the motion control system based on a NURBS curve interpolation method, in which the step speed and accuracy are considered together, the calculated amount is small and the NURBS interpolation is easy to implement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
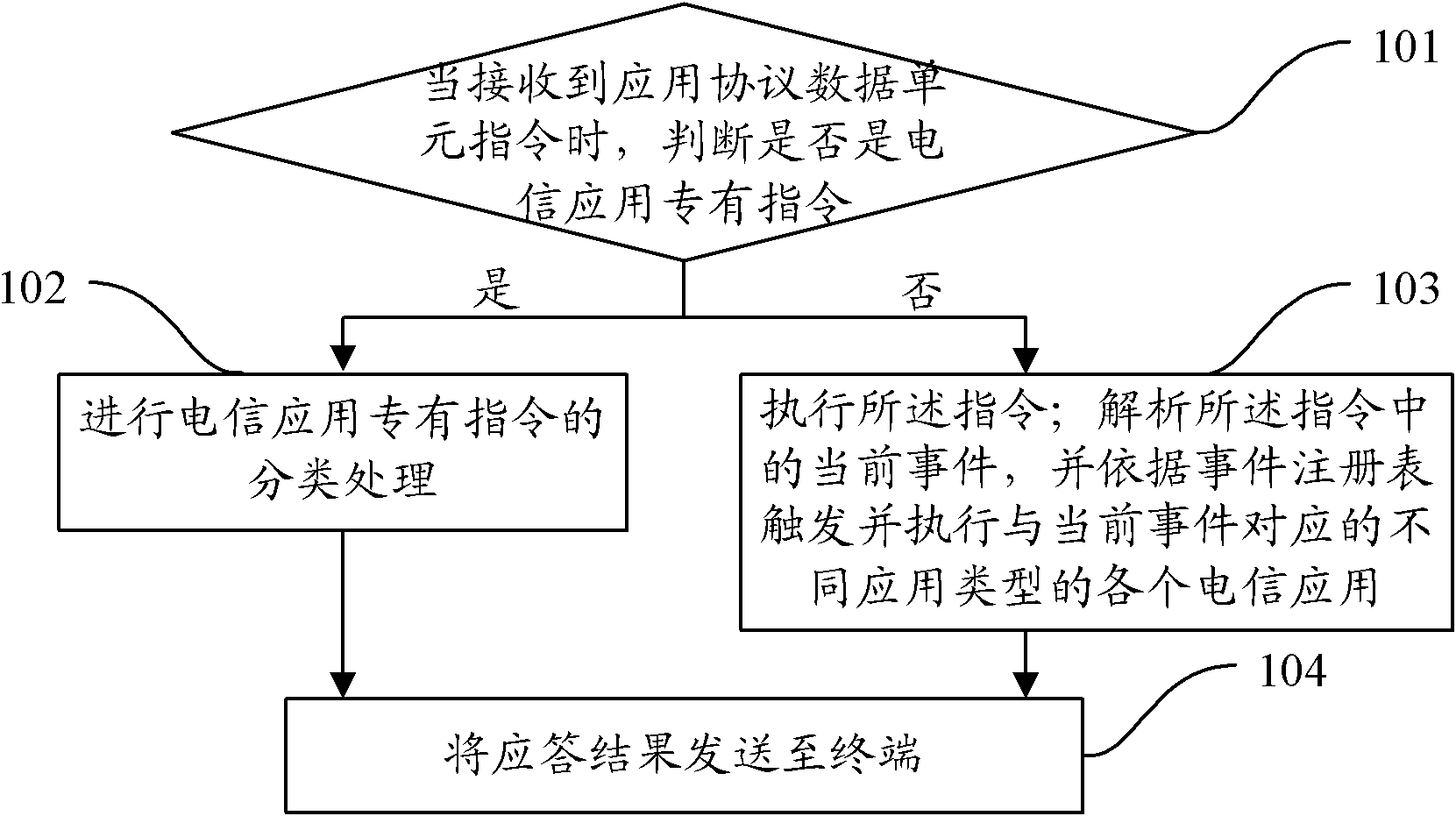
Smart card and method for integrating multiple telecom applications on same
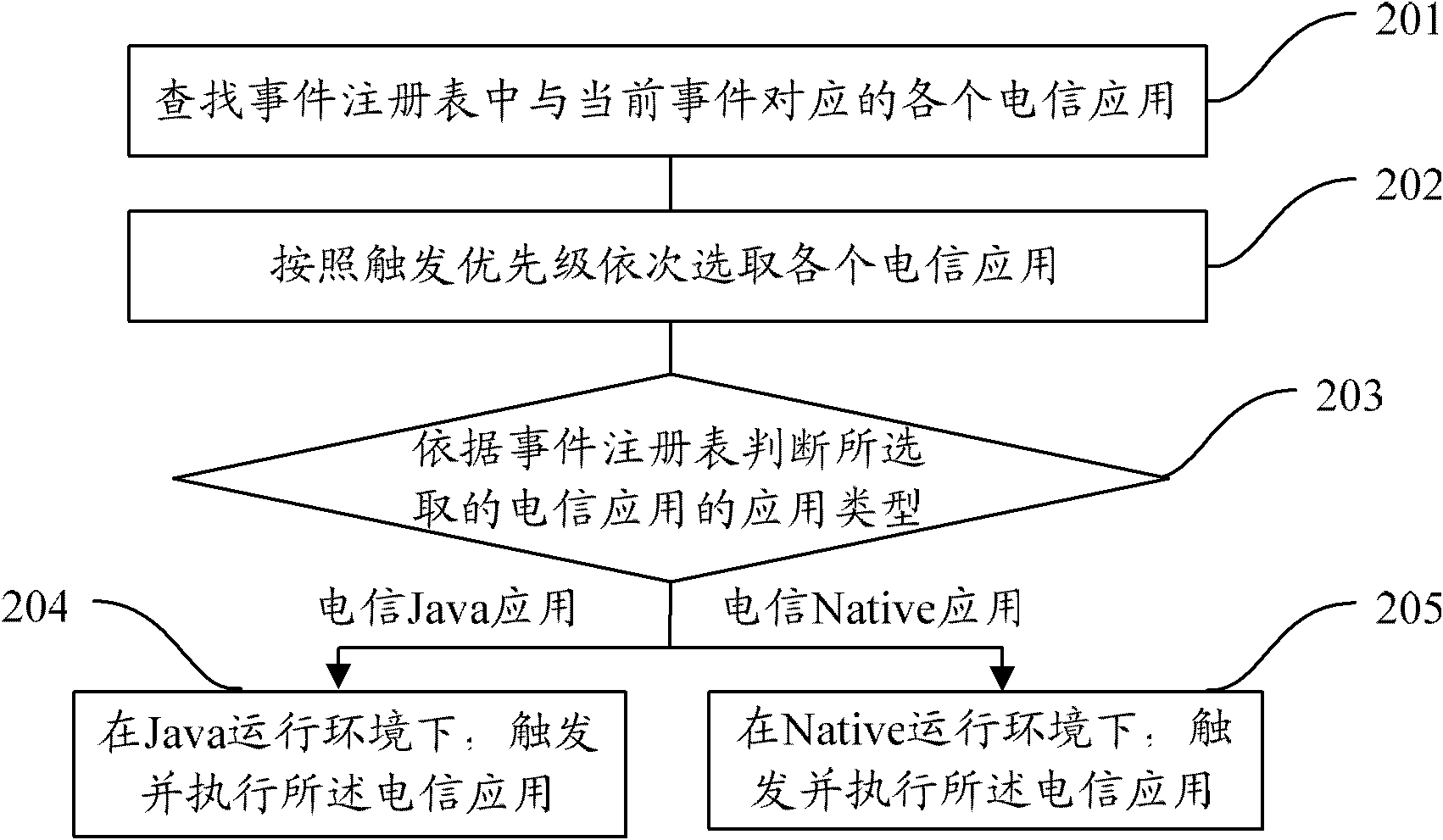
InactiveCN102054173AConsider speedConsider execution efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesSmart cardJava Card
The invention provides a smart card and a method for integrating multiple telecom applications on the same. The method comprises the following steps: when receiving application protocol data unit (APDU) instructions, judging whether the APDU instructions are the instructions special for telecom applications; if so, classifying the instructions special for telecom applications; if not, executing the instructions; and analyzing the current events in the instructions and triggering and executing various types of telecom applications corresponding to the current events according to an event registry. By adopting the smart card and the method, the advantages of both the Native card and the Java card can be considered, thus ensuring the executing speed of the smart card and simultaneously realizing addition and deletion of applications.
Owner:BEIJING WATCH DATA SYST
Power grid component cascading failure simulation method
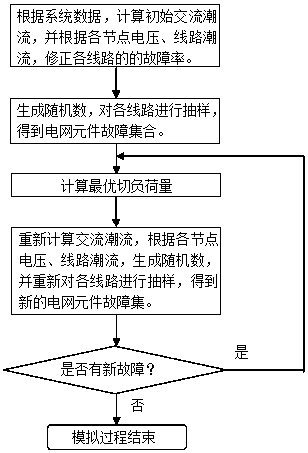
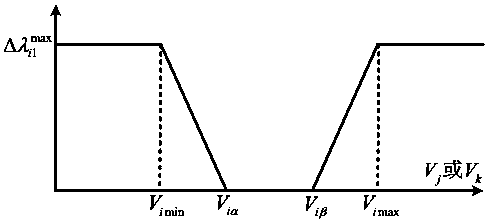
InactiveCN107069705ASimulation close to realityTaking into account the accuracyAc network circuit arrangementsCascading failureFailure rate
The invention discloses a power grid component cascading failure simulation method. According to the invention, voltage and line active power flow, which have great influences for the failure rate of a component, are selected to act as variables to correct the failure rate of the component so as to enable the simulation to be closer to the reality; traditional methods such as proportional load shedding, nearby load shedding and load shedding performed according to the importance degree of loads are abandoned when load shedding is performed, an optimal load shedding method is adopted, and all factors, which can be used for adjustment, in the system are comprehensively utilized, so that a problem of load shedding is well solved theoretically so as to acquire an operation scheme capable of enabling the overall benefit of the system to be the highest; and the power grid component cascading failure simulation method not only considers an alternating-current mode, but also considers a direct-current mode in power flow calculation, so that both the calculation accuracy and the calculation speed are well considered.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGXI POWER GRID CO LTD
Encryption device
InactiveUS7689836B2Processing speedReduce processing stepsKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationData storingExternal memory interface
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Gimbal system with linear mount
ActiveUS8844896B2Pointing accuratelyImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsPortable framesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
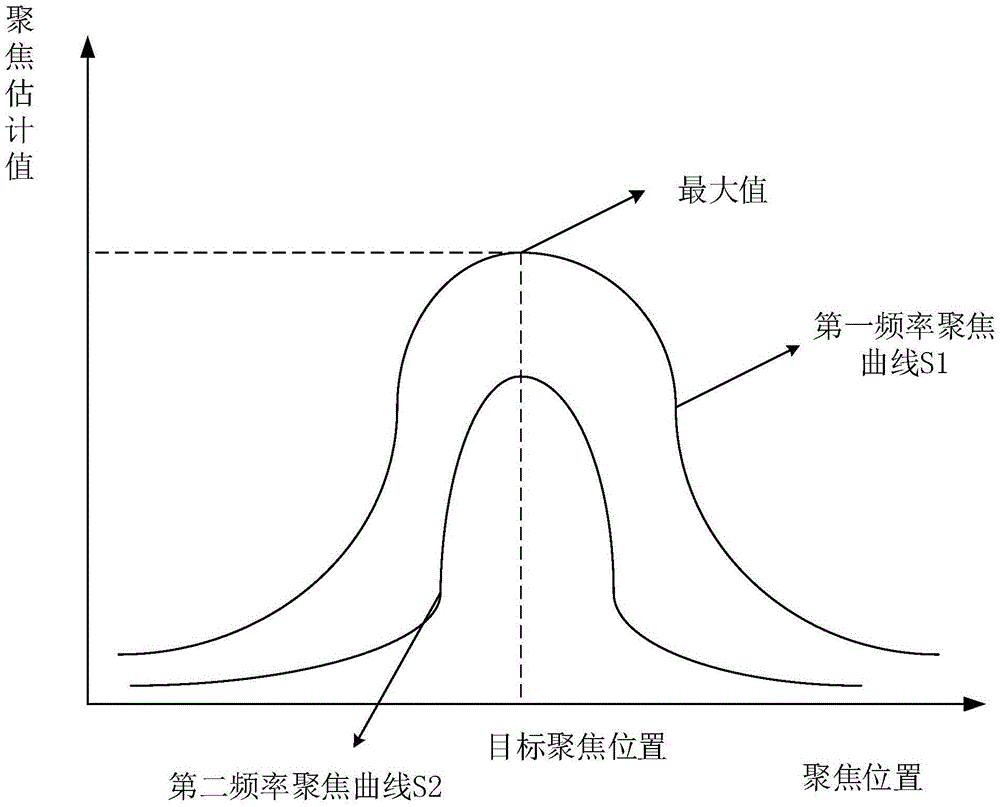
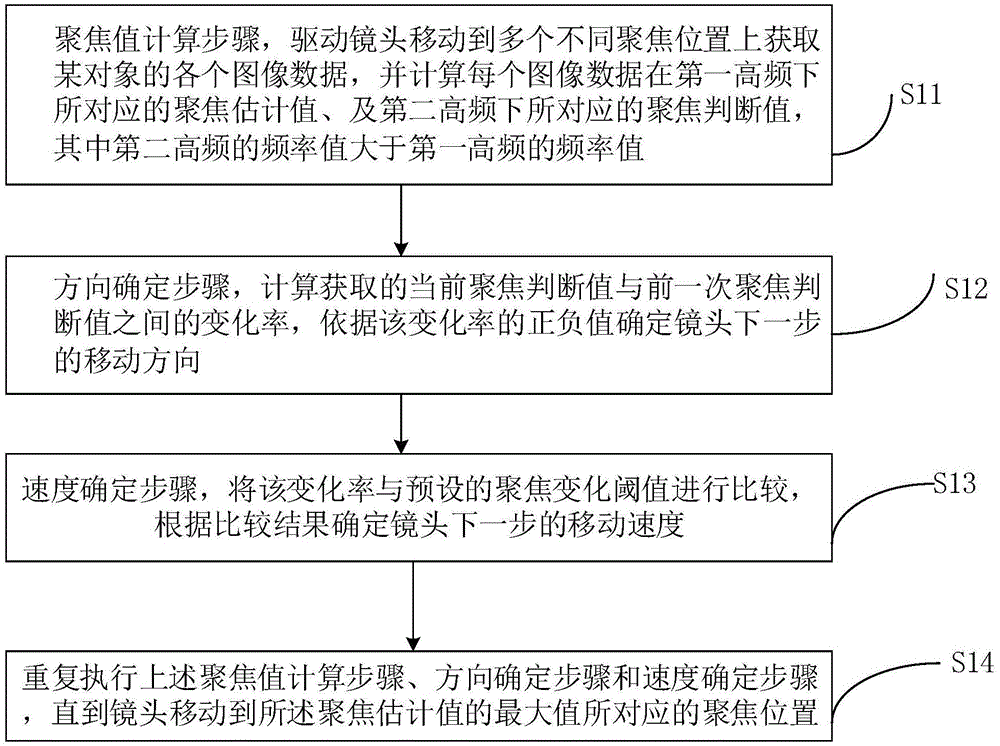
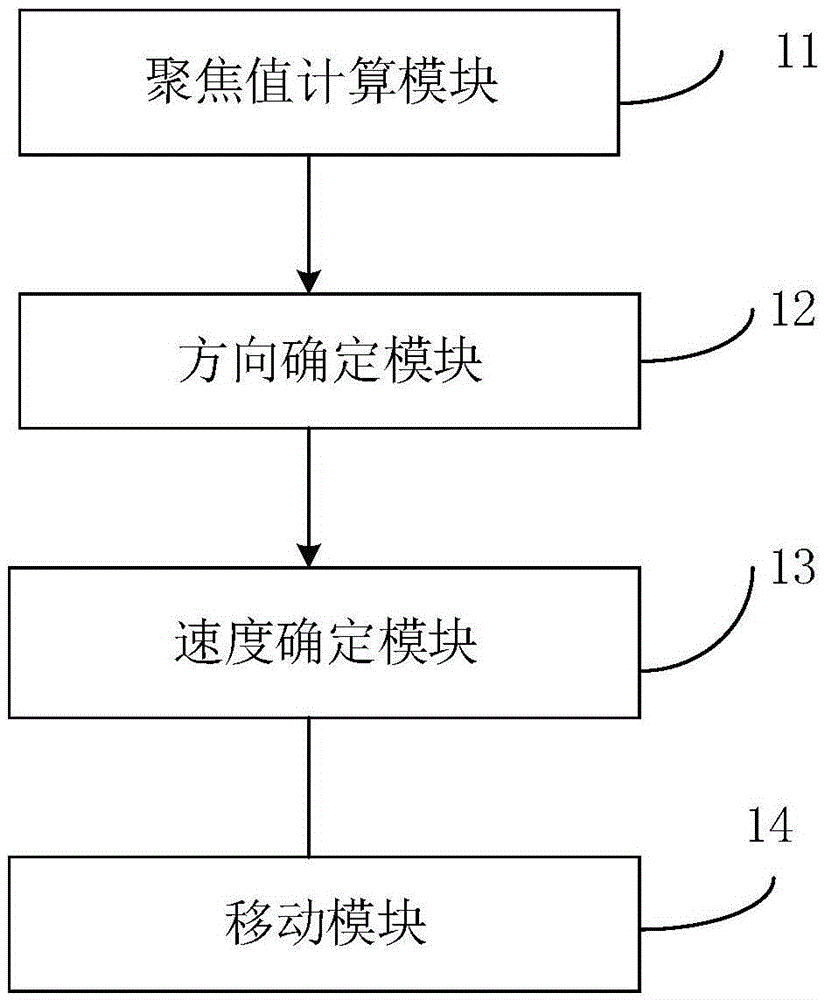
Quick and automatic focusing method and device for camera
ActiveCN105430279AImprove reliabilityImprove practicalityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer scienceImaging data
The invention relates to the technical field of focusing, and in particular relates to a quick and automatic focusing method and a quick and automatic focusing device for a camera. The quick and automatic focusing method comprises the steps of a focusing value computation step including moving a lens to a plurality of different focusing positions to obtain image data of an object, and computing an estimated focusing value corresponding to each image data under a first high frequency and a focusing judgment value corresponding to each image data under a second high frequency; a direction determination step including computing a change rate between the current focusing judgment value and the previous focusing judgment value, and determining the moving direction of the lens according to the sign of the change rate; a speed determination step including comparing the change rate with a preset focusing change threshold value, and determining the moving speed of the lens according to the comparison result; and repeatedly executing the above steps until the lens moves to the focusing position corresponding to the maximal estimated focusing value. According to the quick and automatic focusing method and device for the camera, the different moving speed is used at different position, the focusing time is effectively reduced, both the focusing speed and accuracy are improved, and very high reliability and practicability are provided.
Owner:成都全景智能科技有限公司
Robot indoor positioning system and method
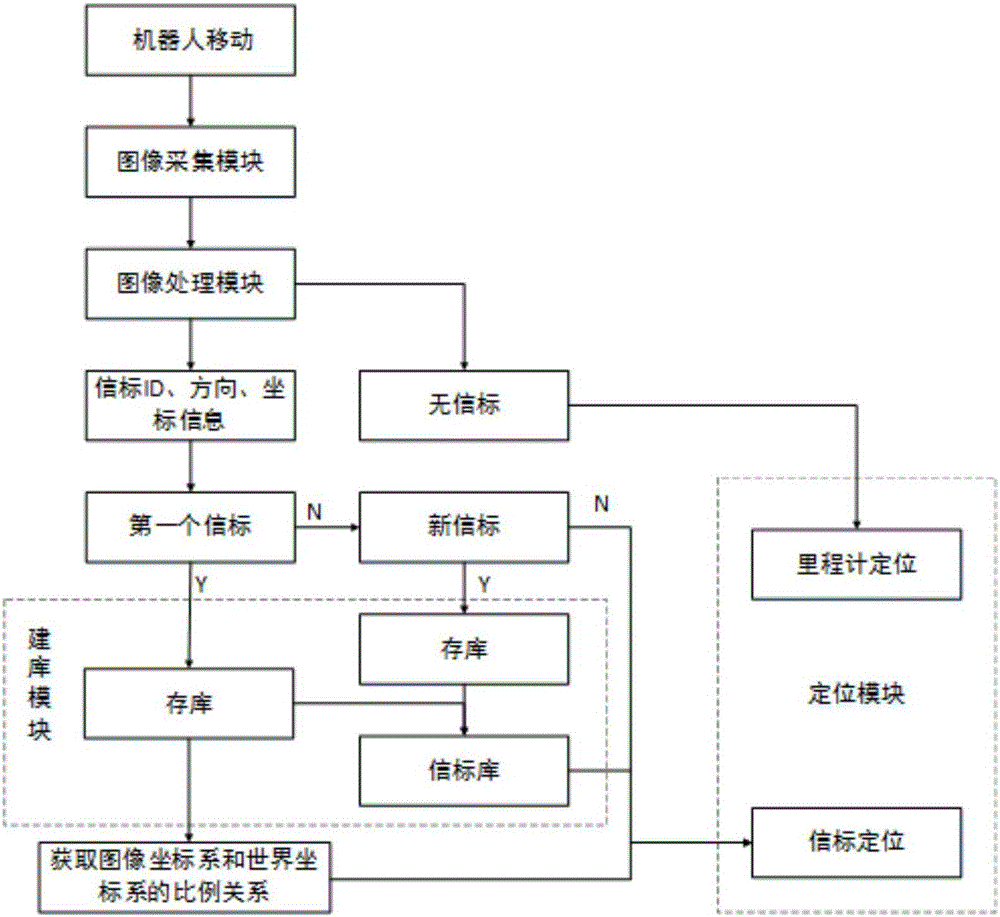
InactiveCN106370160AEasy to handleHigh speedPicture interpretationImaging processingPositioning system
The invention discloses a robot indoor positioning system including a robot, a ceiling and a plurality of beacons. The robot has an image acquisition module at the top of the robot, and an image processing module, a building block module and a positioning module are arranged inside the robot. The system of the invention can realize the real-time positioning in the room, and the accumulative error of the odometer is corrected based on the beacon positioning, and the processing speed is fast and the anti-interference ability is strong. The invention also discloses a robot indoor positioning method.
Owner:杭州国辰牵星科技有限公司
Hierarchical song rhythm search method
InactiveCN101364238AConsider speedElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionHum
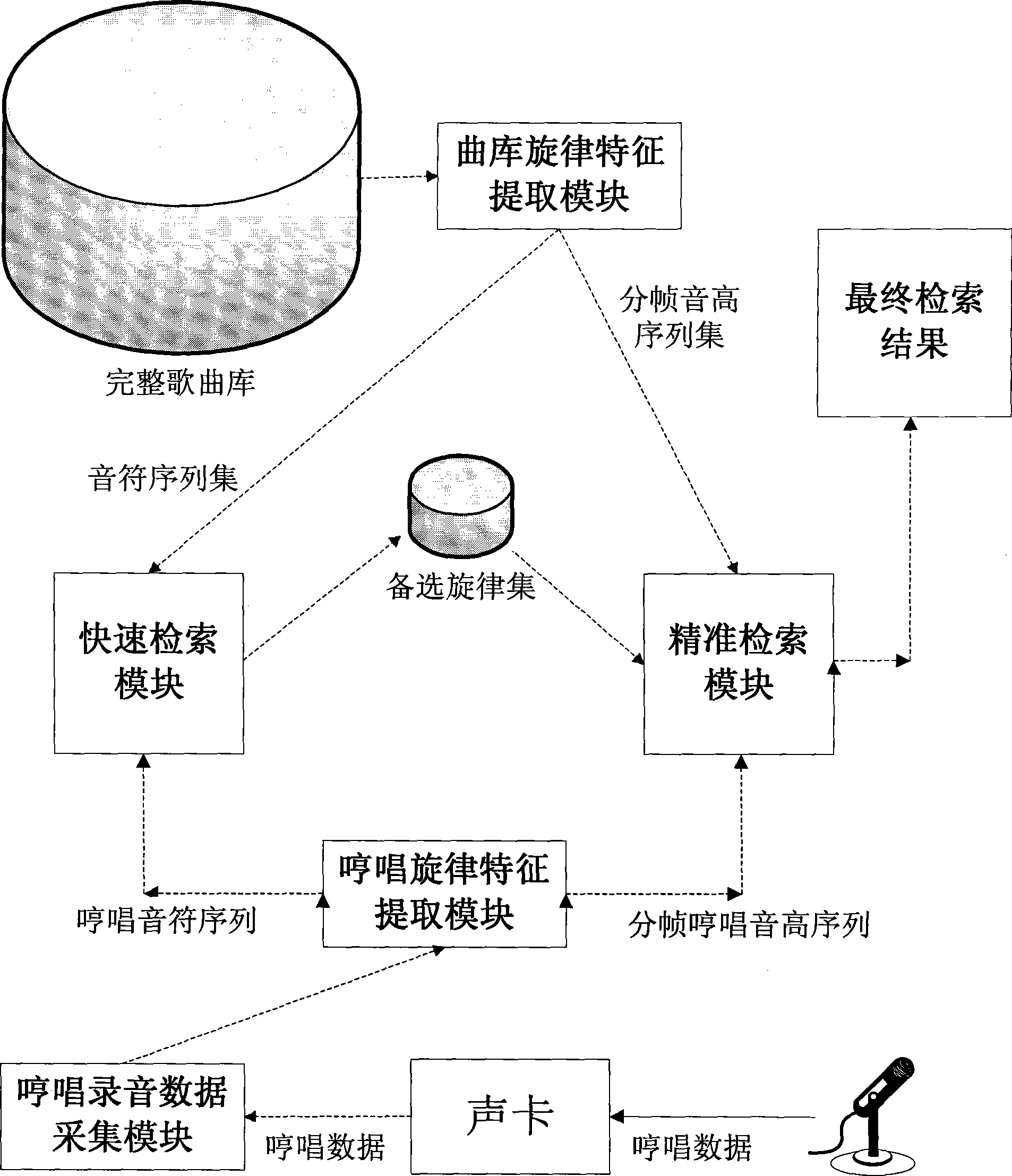
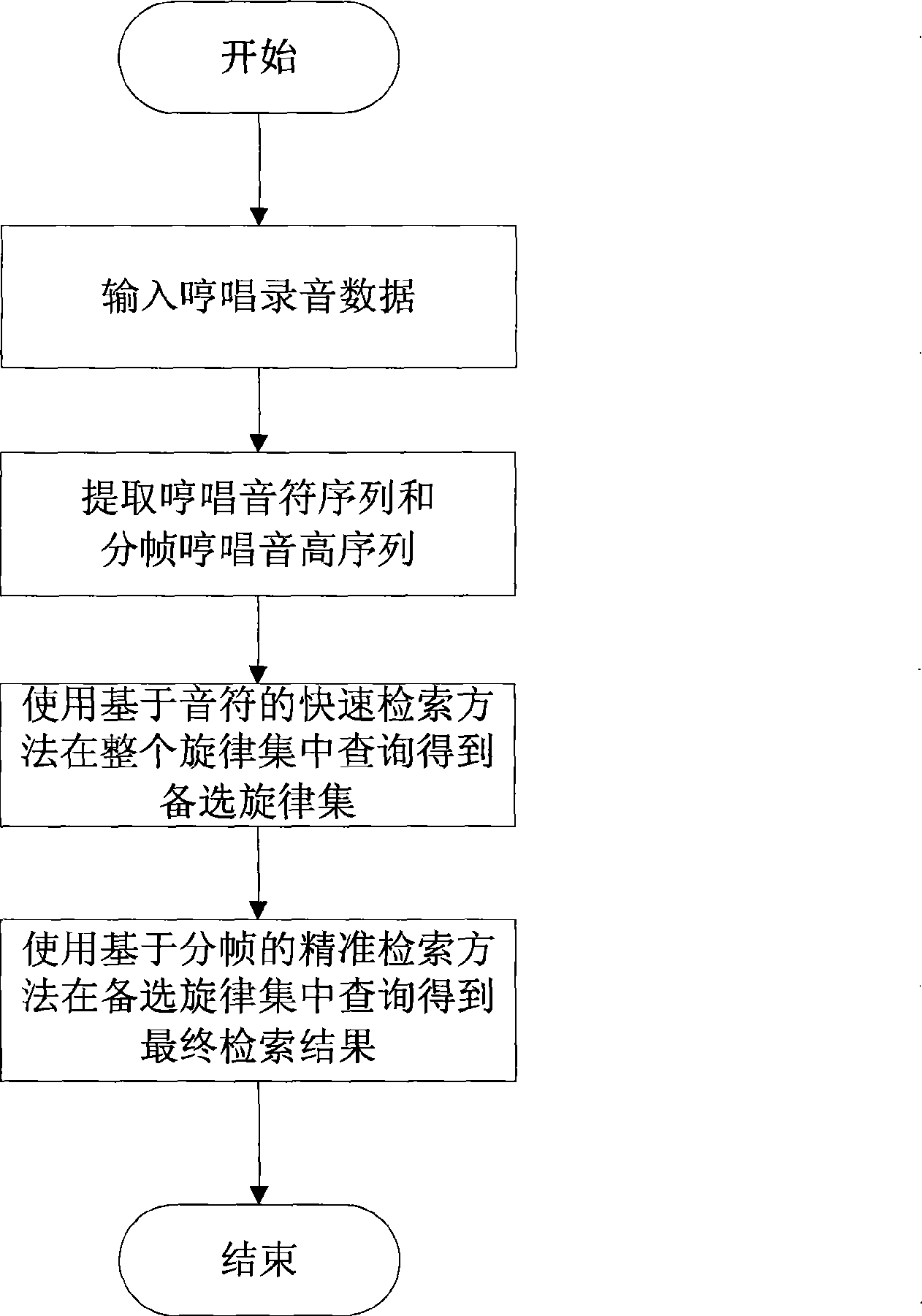
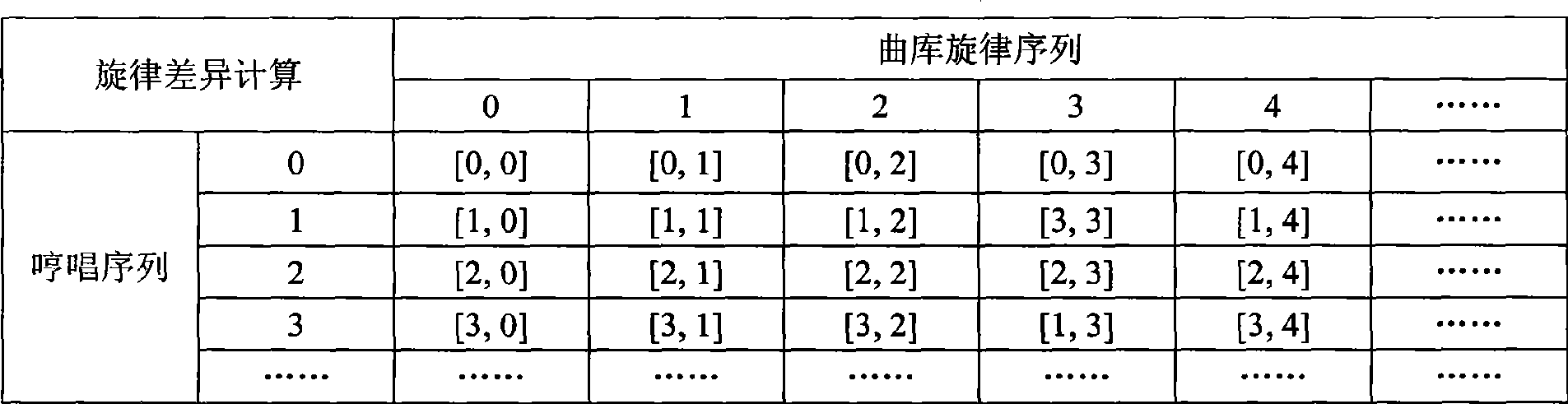
The invention provides a layer-progressive method for searching song melodies, which belongs to the melody search technical field, and is characterized in that a humming recording data acquisition module is arranged on a PC so as to save hums input from a speaker sound card as humming recording data; a humming melody feature extraction module extracts a humming note sequence and a framing humming pitch sequence which include melody features from the humming recording data; a song library melody feature extraction module extracts a note sequence and a framing pitch sequence from the midi file including song melodies; a quick search module performs a quick search in the whole song library for a relatively-small alternative melody set by a note-based search method; and an accurate search module performs a search in the alternative melody set for the ultimate result by a framing-based search method. The melody search method has the characteristics of high accuracy and high speed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
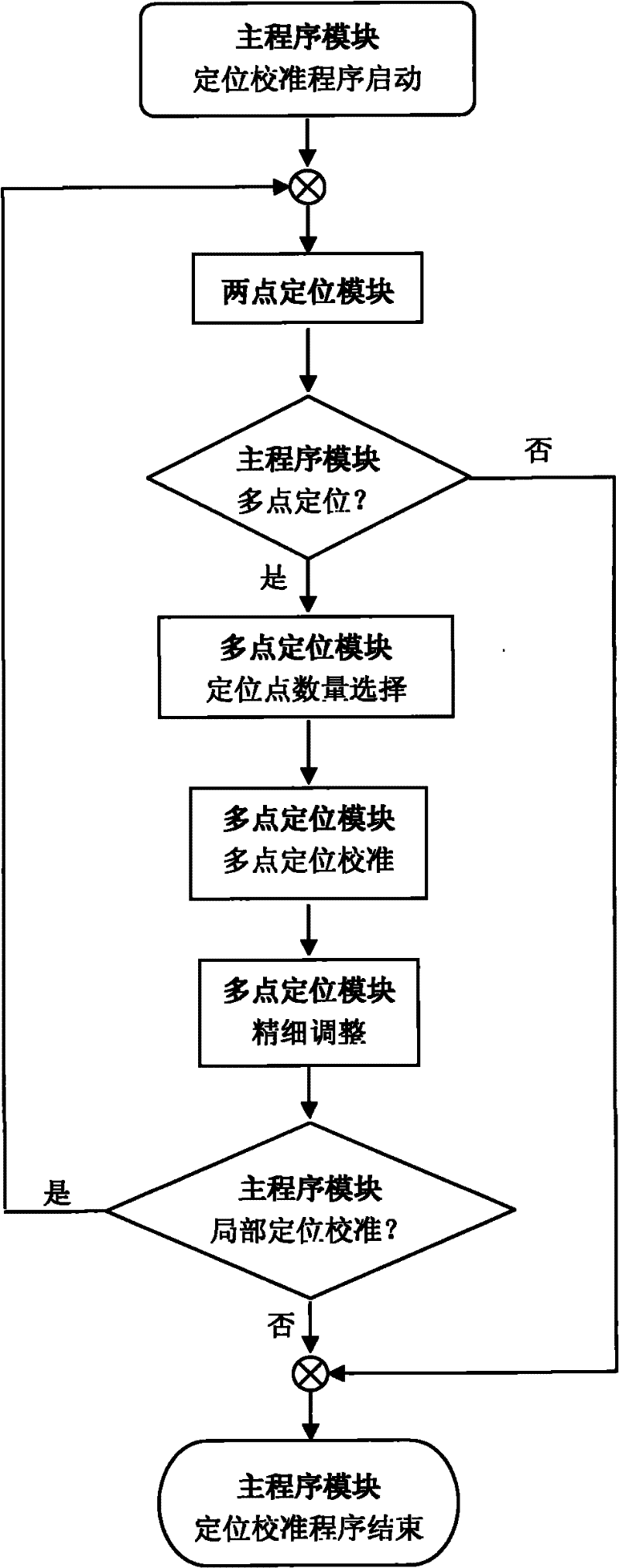
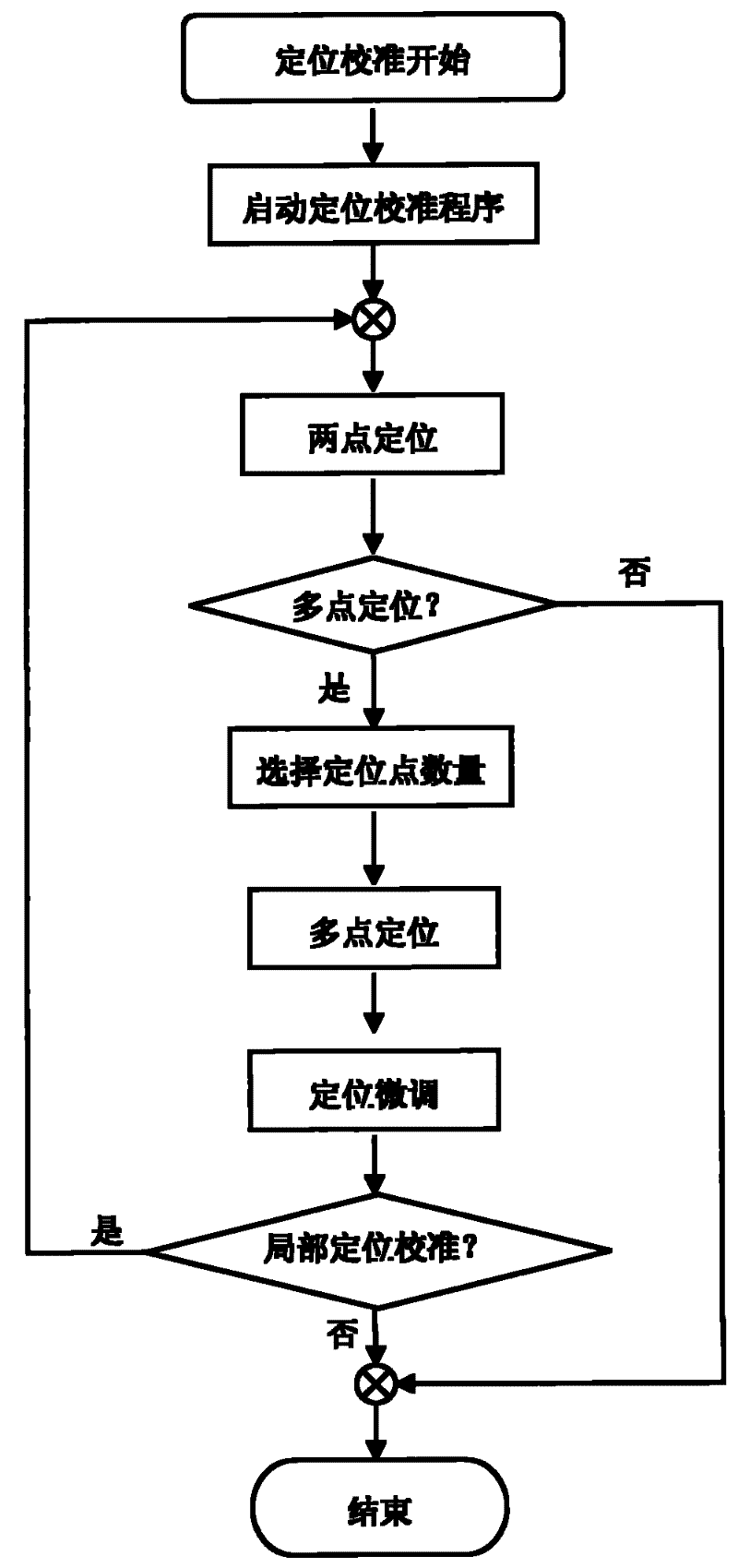
Intelligent positioning and calibration method
InactiveCN102193661AConsider speedEfficient intelligent positioning and calibration effectInput/output processes for data processingWhiteboardEnvironmental geology
Owner:BEIJING MOLY TECH
Slew-rate-limited driver
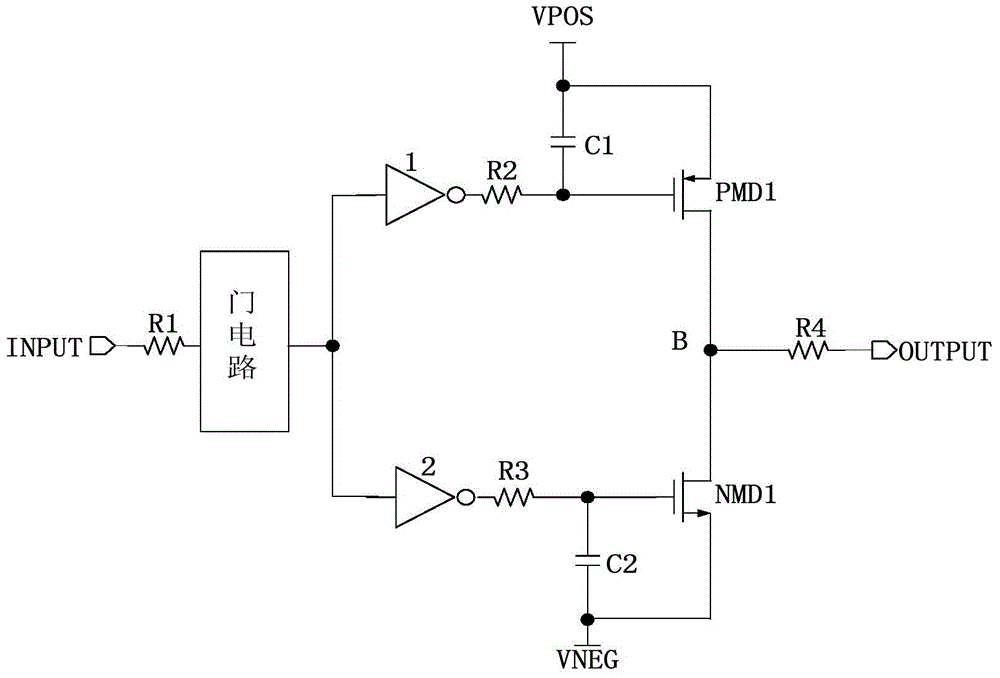
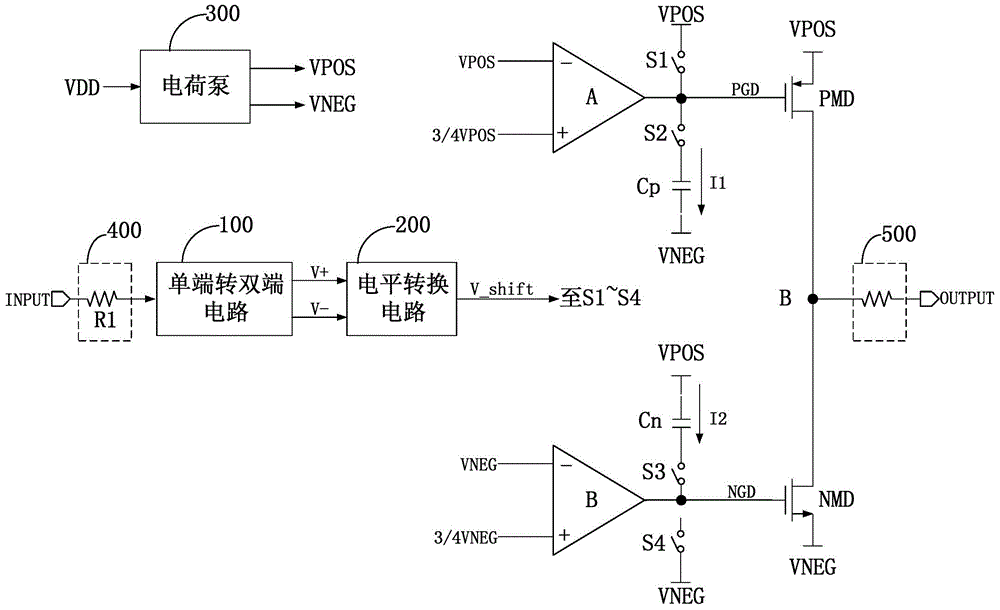
ActiveCN104467796AAvoid influenceReduce feedthrough problemsReliability increasing modificationsCapacitanceEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of micro-electronics, and particularly relates to a slew-rate-limited driver. Drive control is carried out on grid electrodes of a drive tube through two comparators, charging and discharging of a capacitor are carried out through a pull-up switch, a pull-down switch and a current source in a cooperative mode, the effect of controlling the output voltage slew rate is realized, and EMI and power source feed through problems can be effectively reduced. Meanwhile, the slew-rate-limited driver does not need a large resistor, and influence of the temperature excursion effect of the resistor on the output voltage slew rate is avoided. In addition, the slew-rate-limited driver is simple in circuit structure and easy to realize, output voltage in a wide temperature change range can still keep a stable slew rate, and the requirements for the speed and slew rate are also taken into account.
Owner:SHENZHEN STATE MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com