Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Shorter read and write times" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
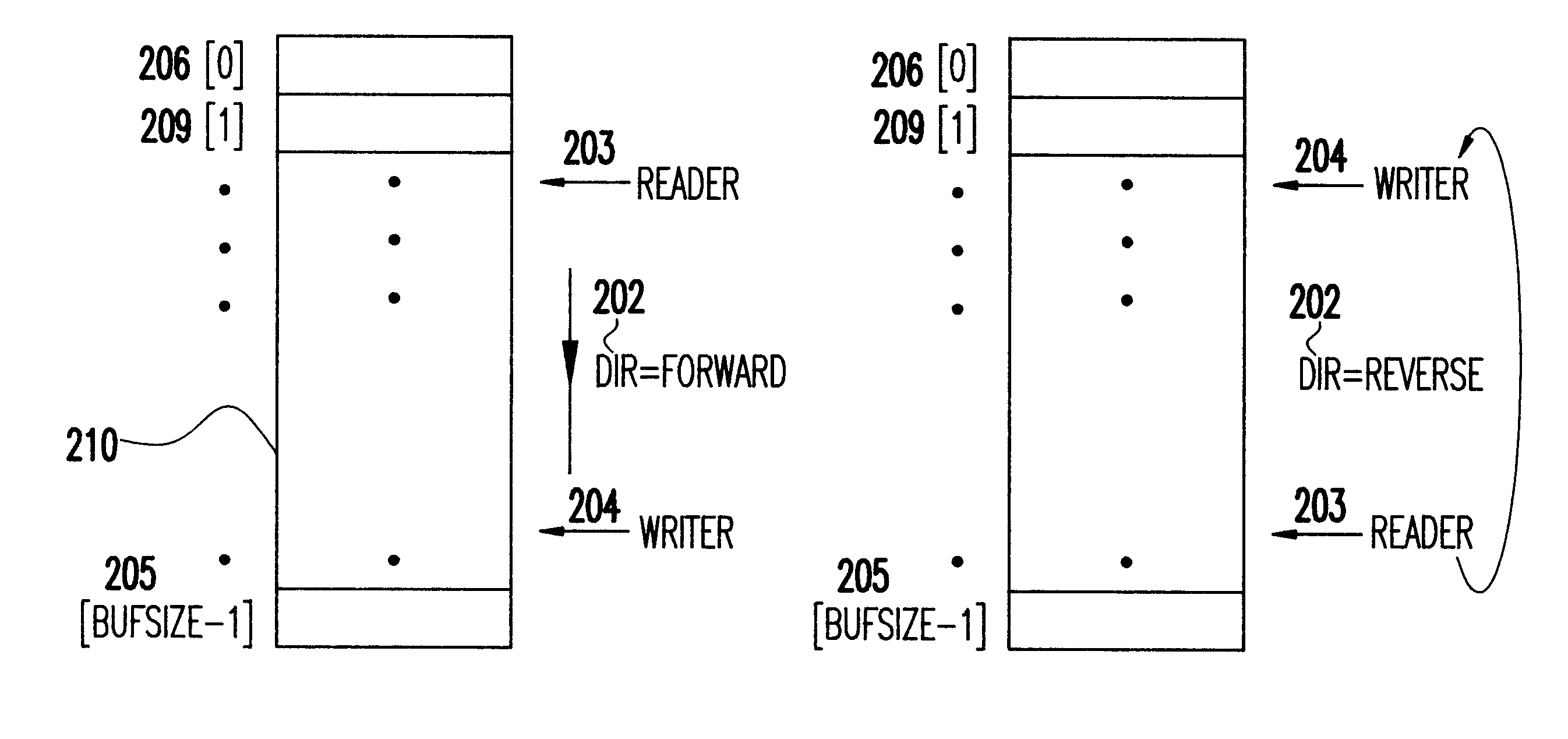
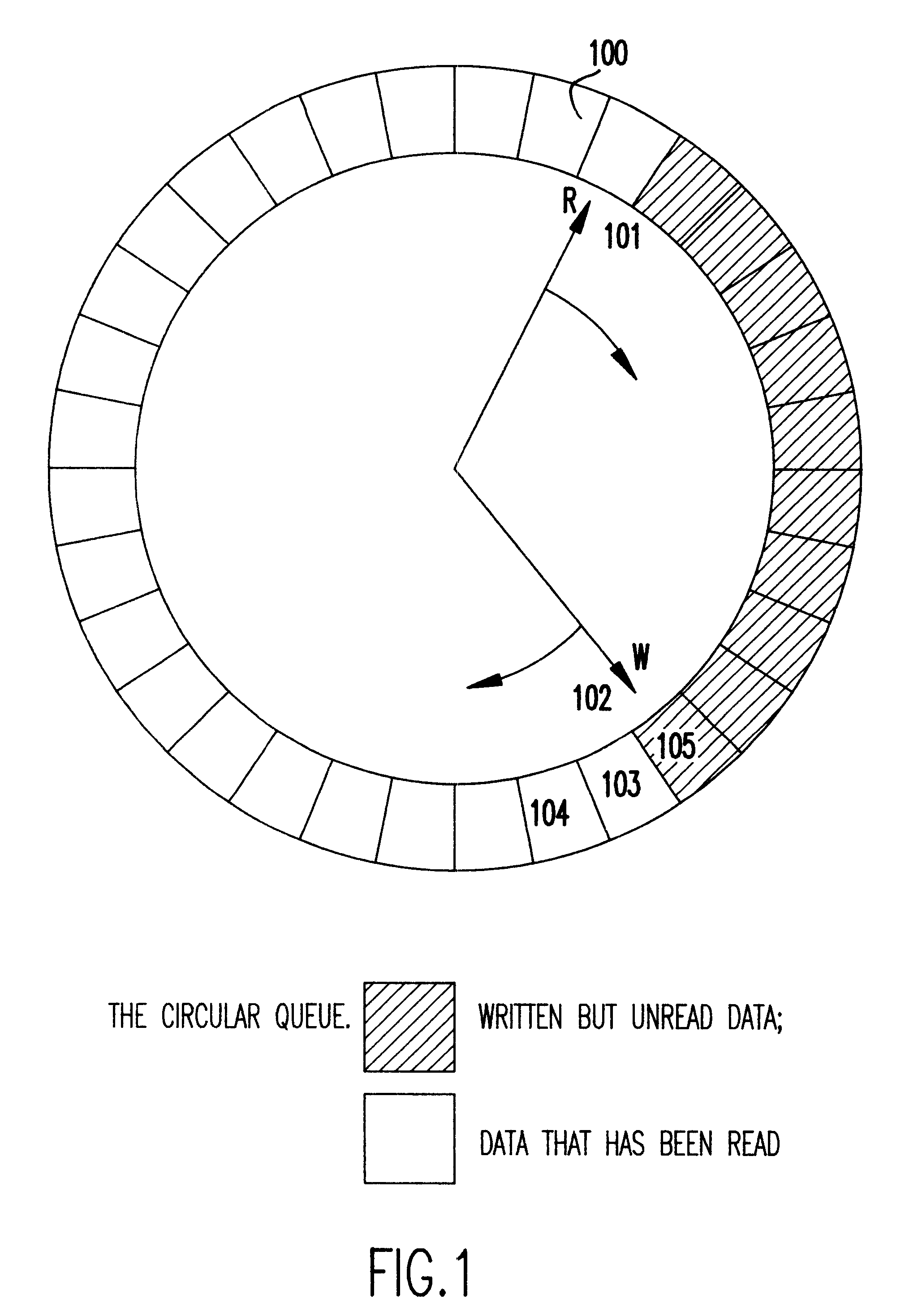
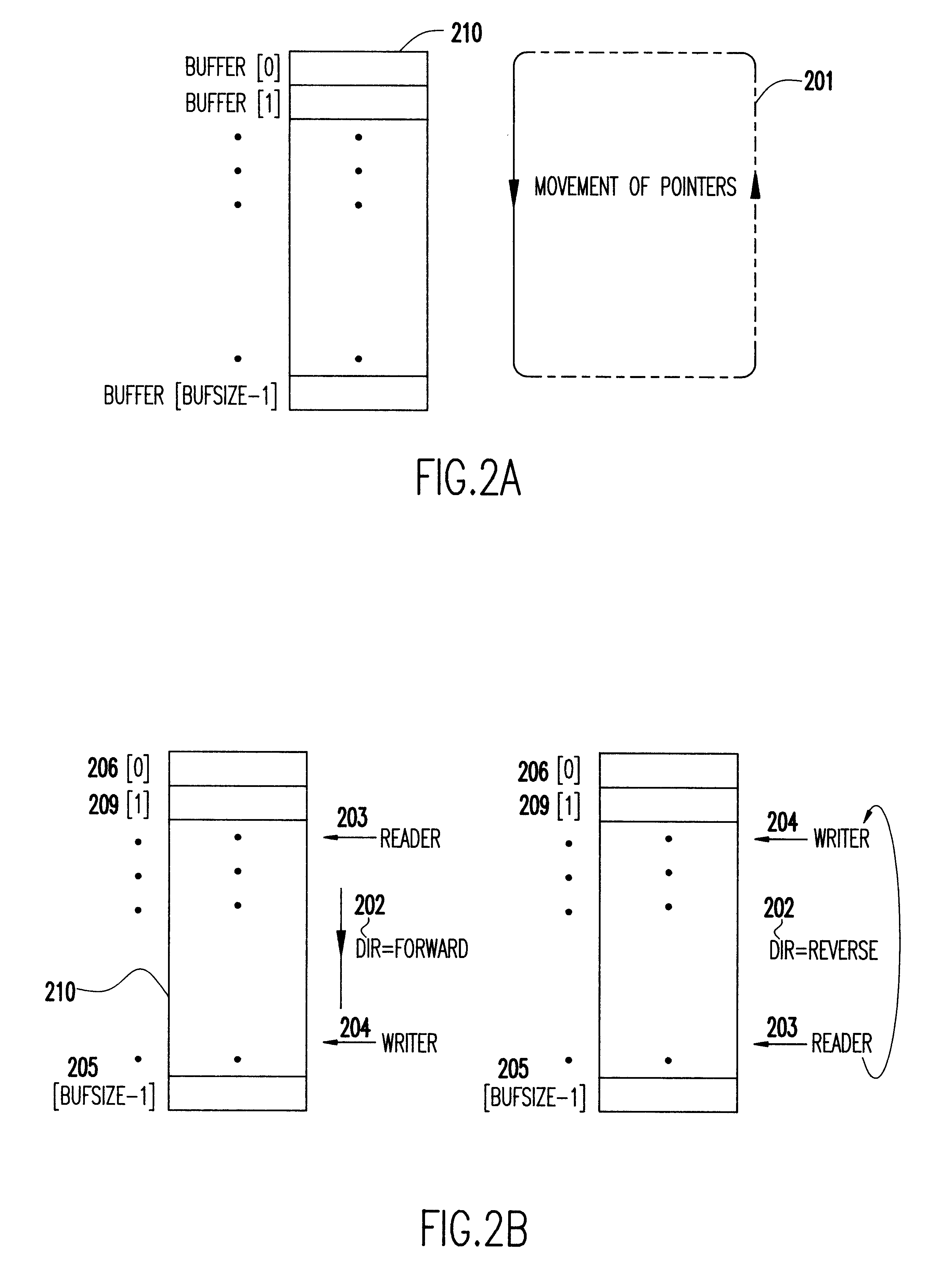
Two lock-free, constant-space, multiple-(impure)-reader, single-writer structures
InactiveUS6304924B1Shorter read and write timesReduce waiting timeSoftware engineeringData switching by path configurationDistributed computingCopying
Efficient support of synchronization in parallel processing is supported by methods for building two data structures that are optimal in that they permit simultaneous access to multiple readers and one writer without using any synchronization constructs such as locks and / or any special instructions. The structures rely on atomic read and / or write of some simple integral values to an underlying, actual or emulated, shared memory. No copying is required of any reader or writer. Each structure comprises a first-in-first-out (FIFO), constant-space, circular queue in which each reader and writer tracks shared bookkeeping data such as queue pointers. Readers are impure since they too write bookkeeping data. If a position of interest for access is beyond a boundary defining legitimate access, say trying to read an empty queue or write to a full queue, then access to the position is prevented until legitimization occurs. One of the structures can use the space in its queue to full capacity. The other structure can use its queue space only to part capacity. However, it has the advantage that it is simple. It keeps only queue pointers as bookkeeping data. Each constant-space queue can be generalized straightforwardly to a lock-optimal, variable-space queue.
Owner:IBM CORP
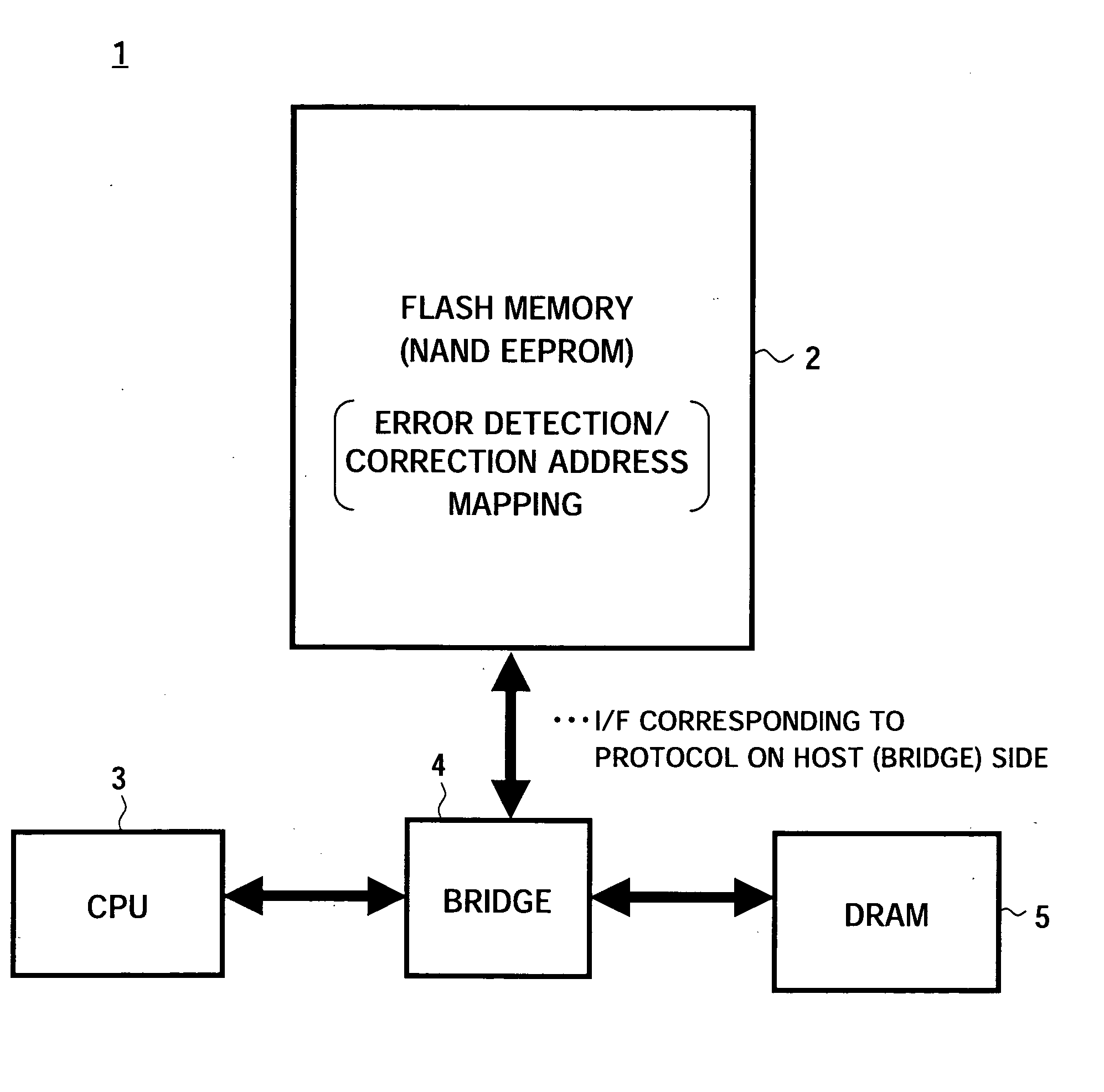
Semiconductor memory device and signal processing system
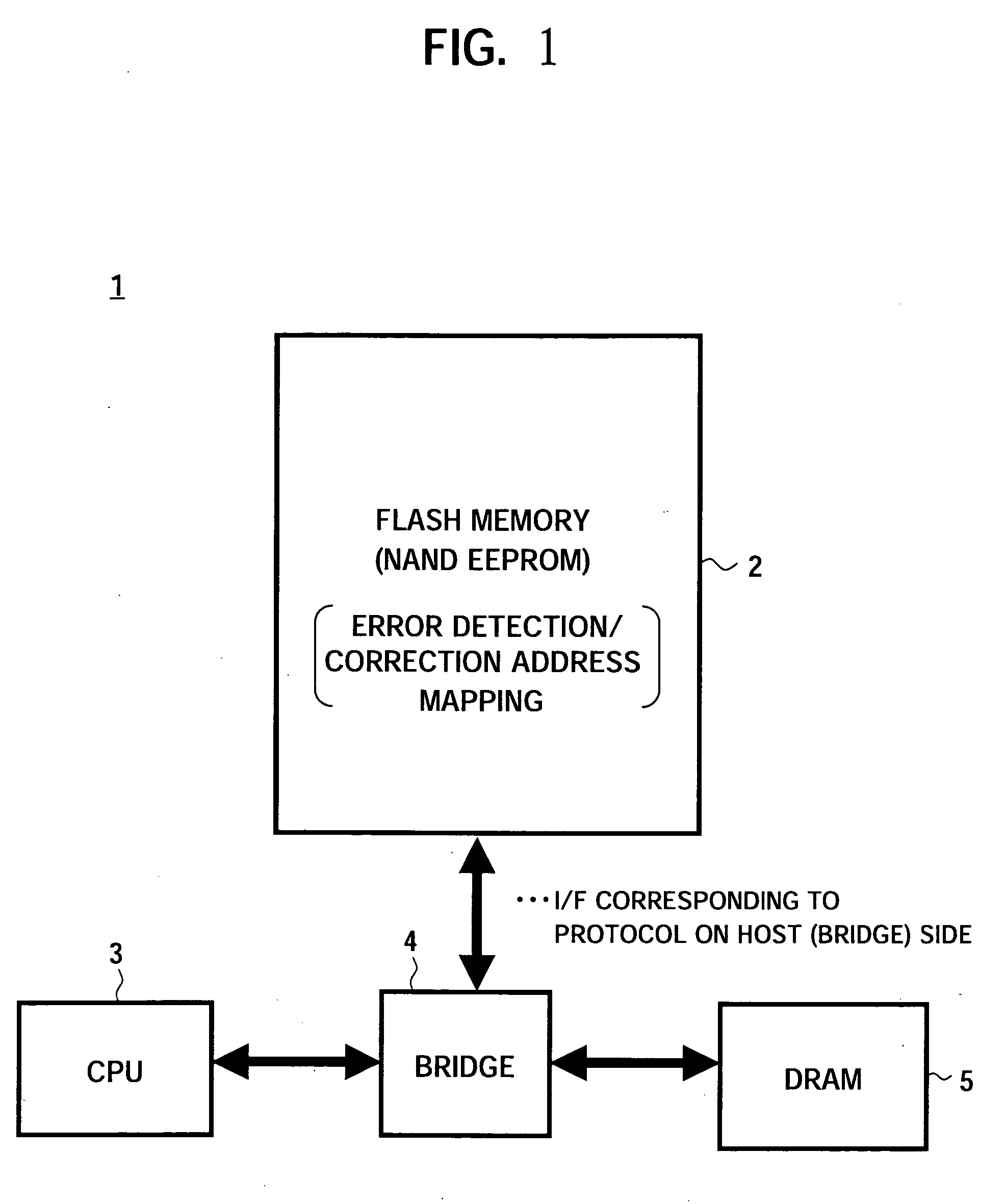
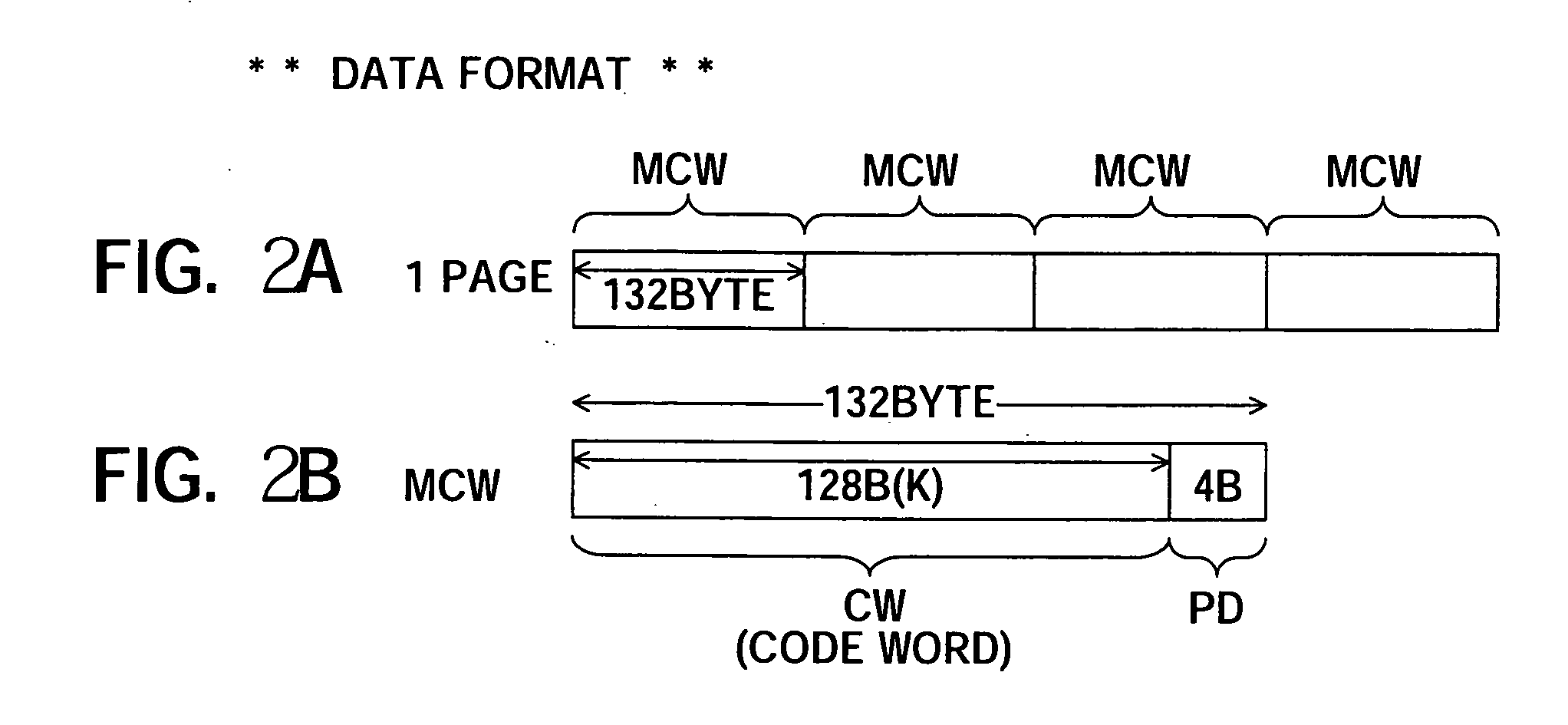
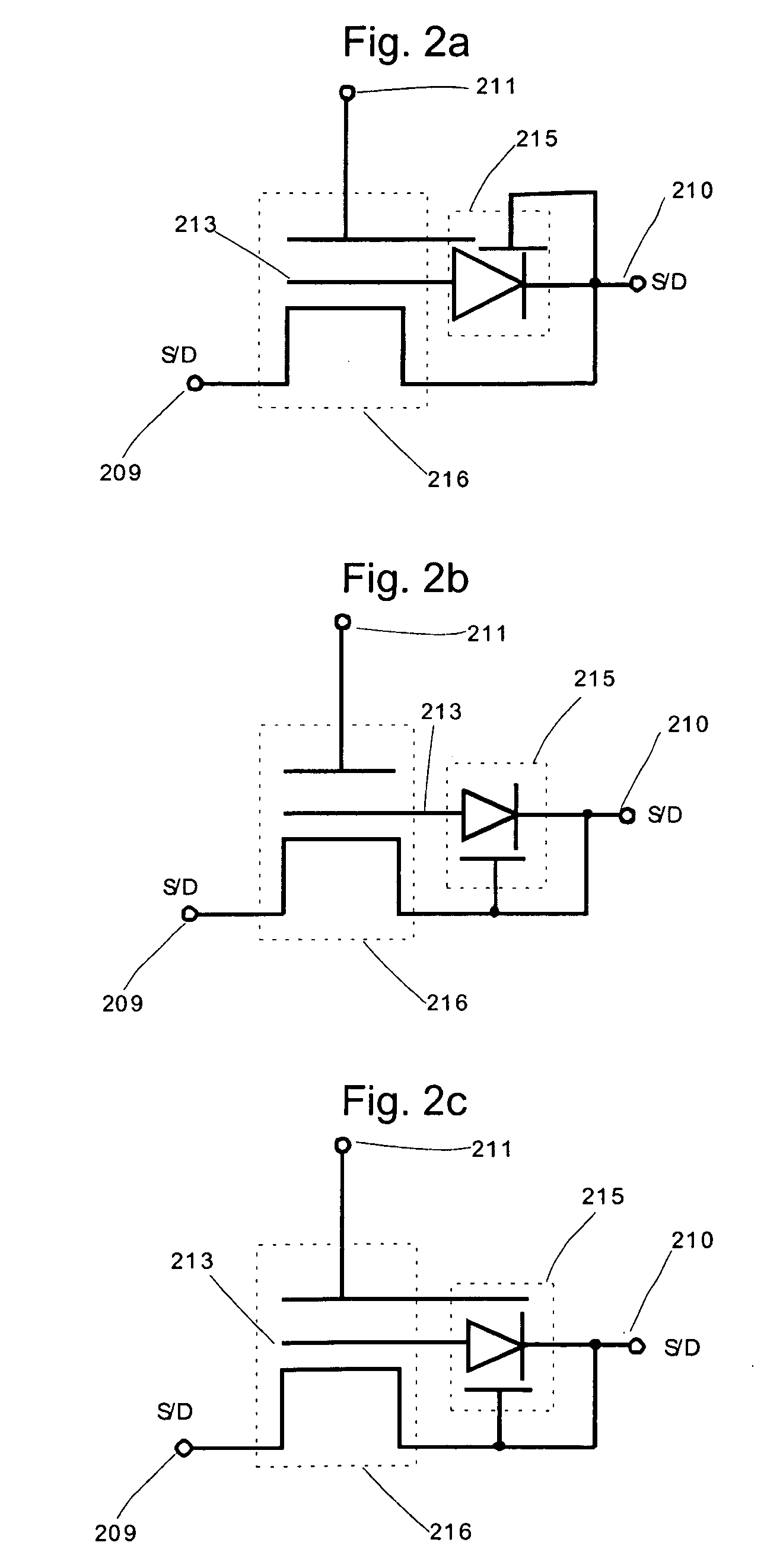
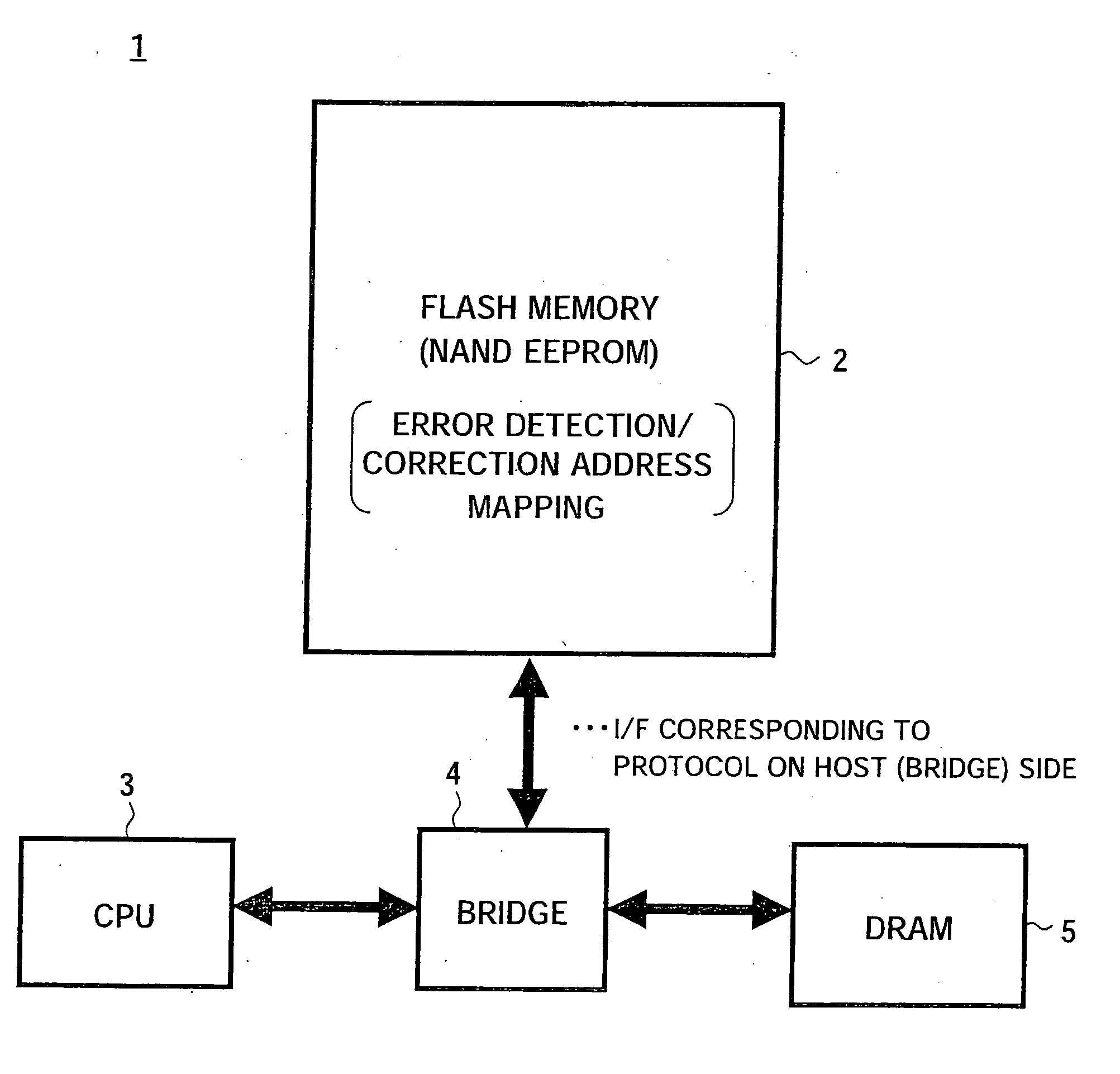
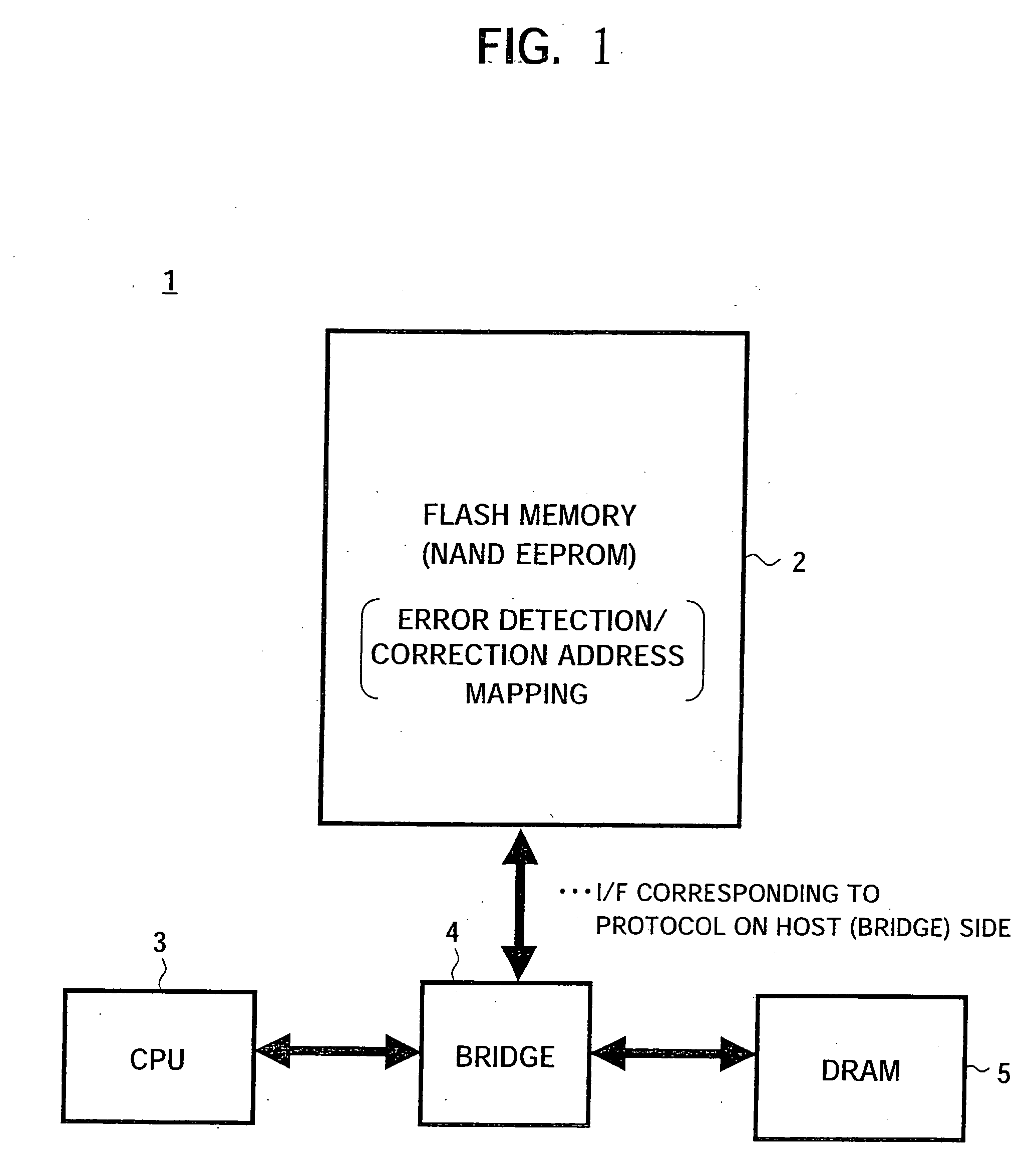
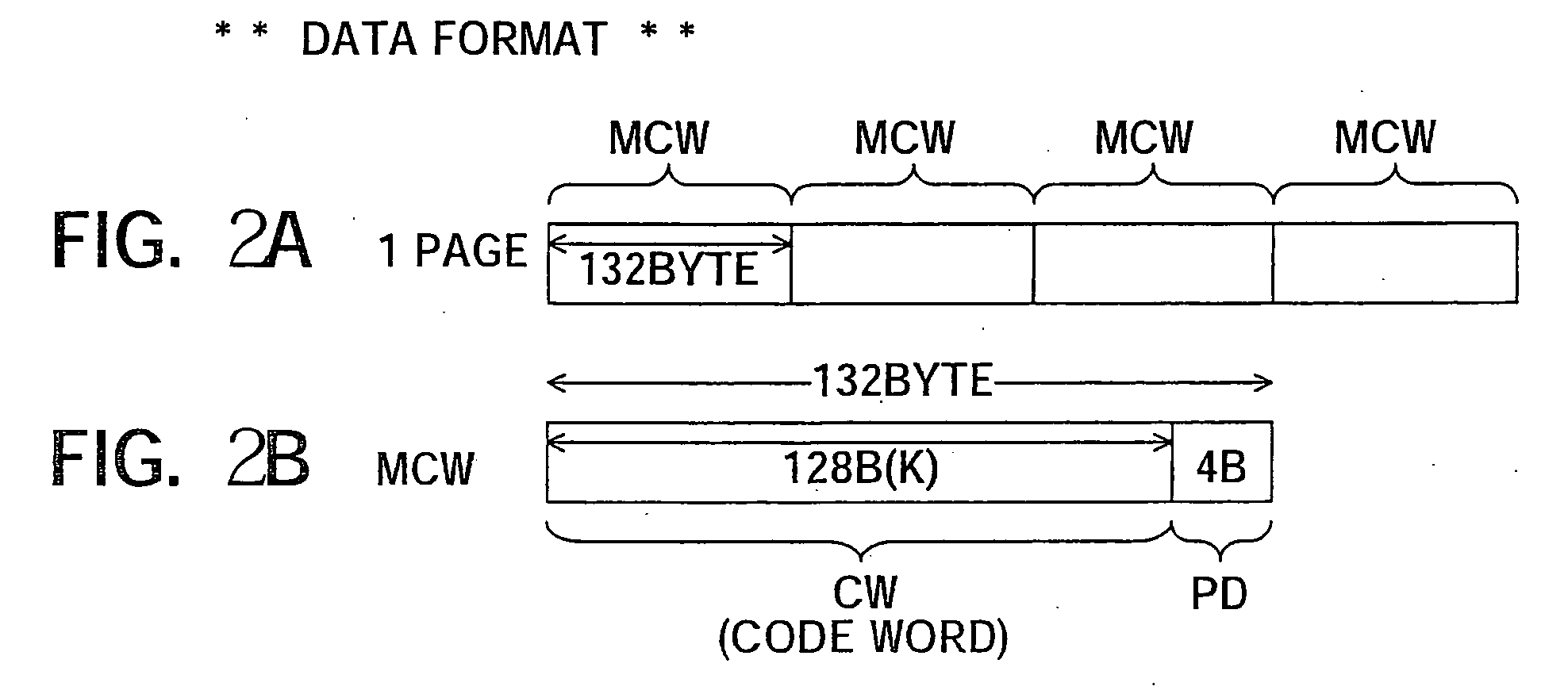
ActiveUS20050268208A1Improve error correction performanceShorten read timeRead-only memoriesCode conversionMemory bankSignal processing
A semiconductor memory device able to strengthen an error correction capability, able to shorten a write time and / or a read time, able to make a redundant memory unnecessary or smaller, and consequently able to achieve a reduction of size and a reduction of cost, provided with a data input portion for receiving 1 page's worth of data, dividing it to a plurality of code words, generating and adding check code (parity data), for each code word, successively forming main code words and transferring the same to a bank (A) or a bank (B), and a data output portion for receiving 1 page's worth of data including main code words transferred from the data latch circuit, correcting the error data when there is within a predetermined number of error data for each main code word, adding the error information for read each read code word except check code (parity data), and transferring the same to a host side, and a signal processing system using the same.
Owner:TESSERA ADVANCED TECH
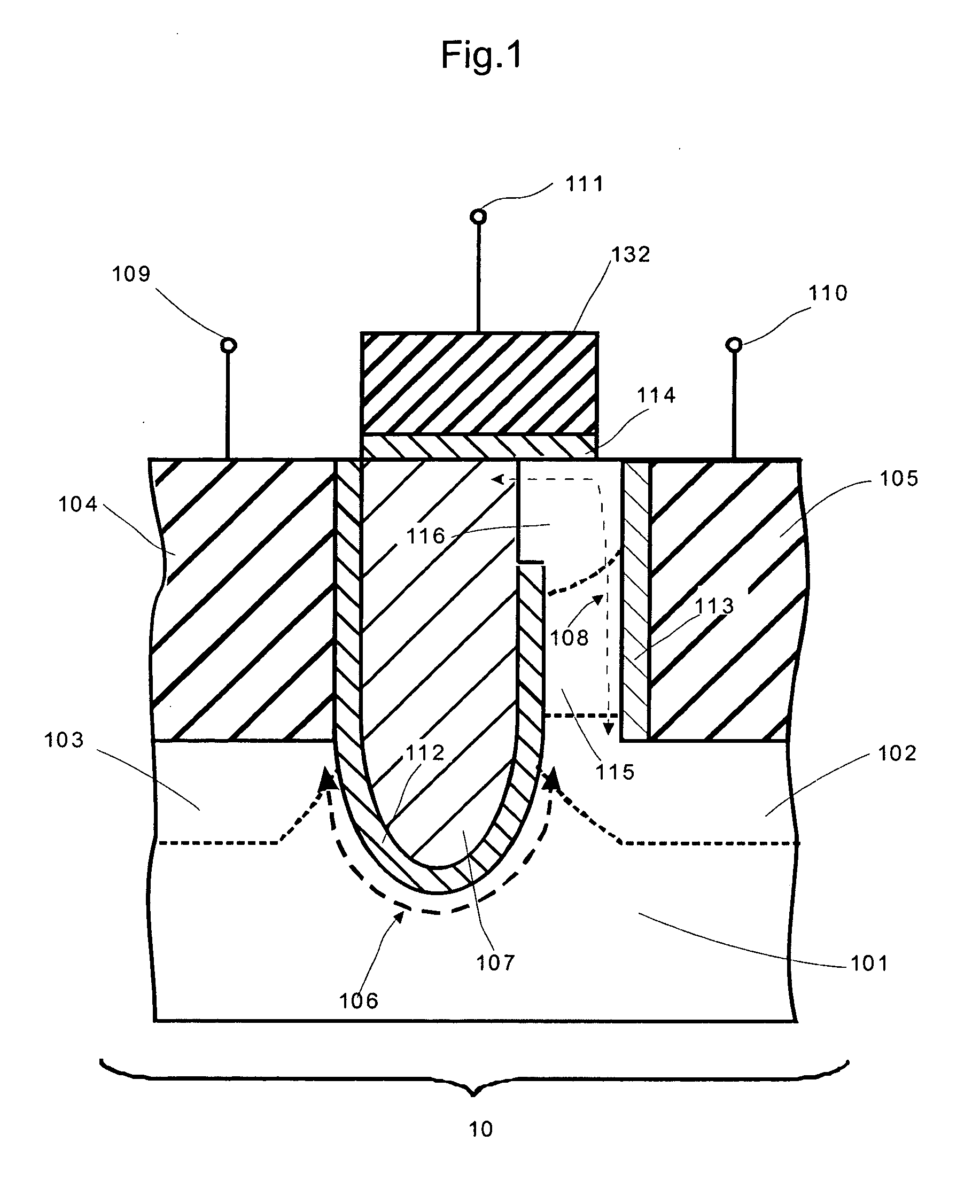
Transistor of semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
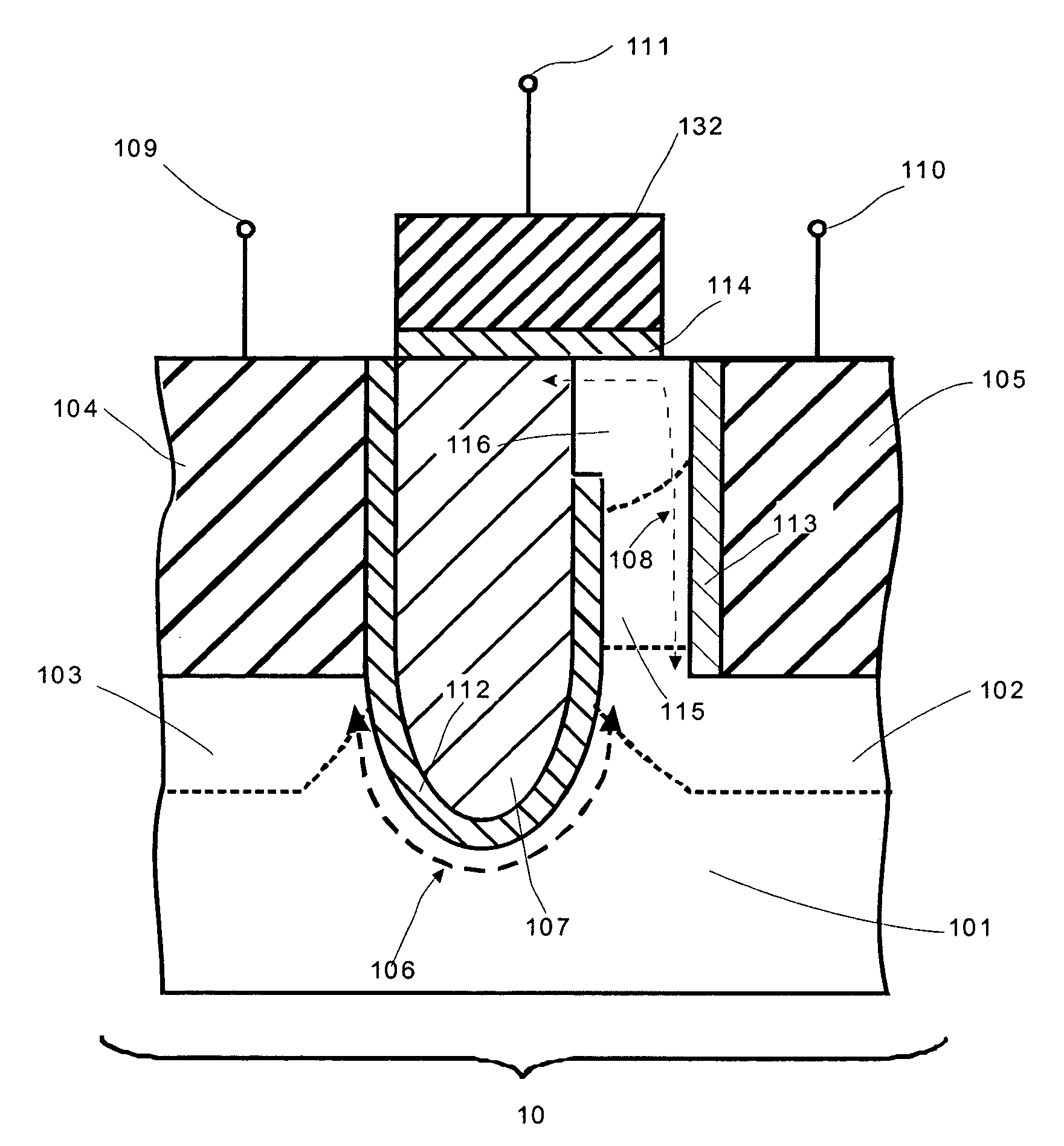
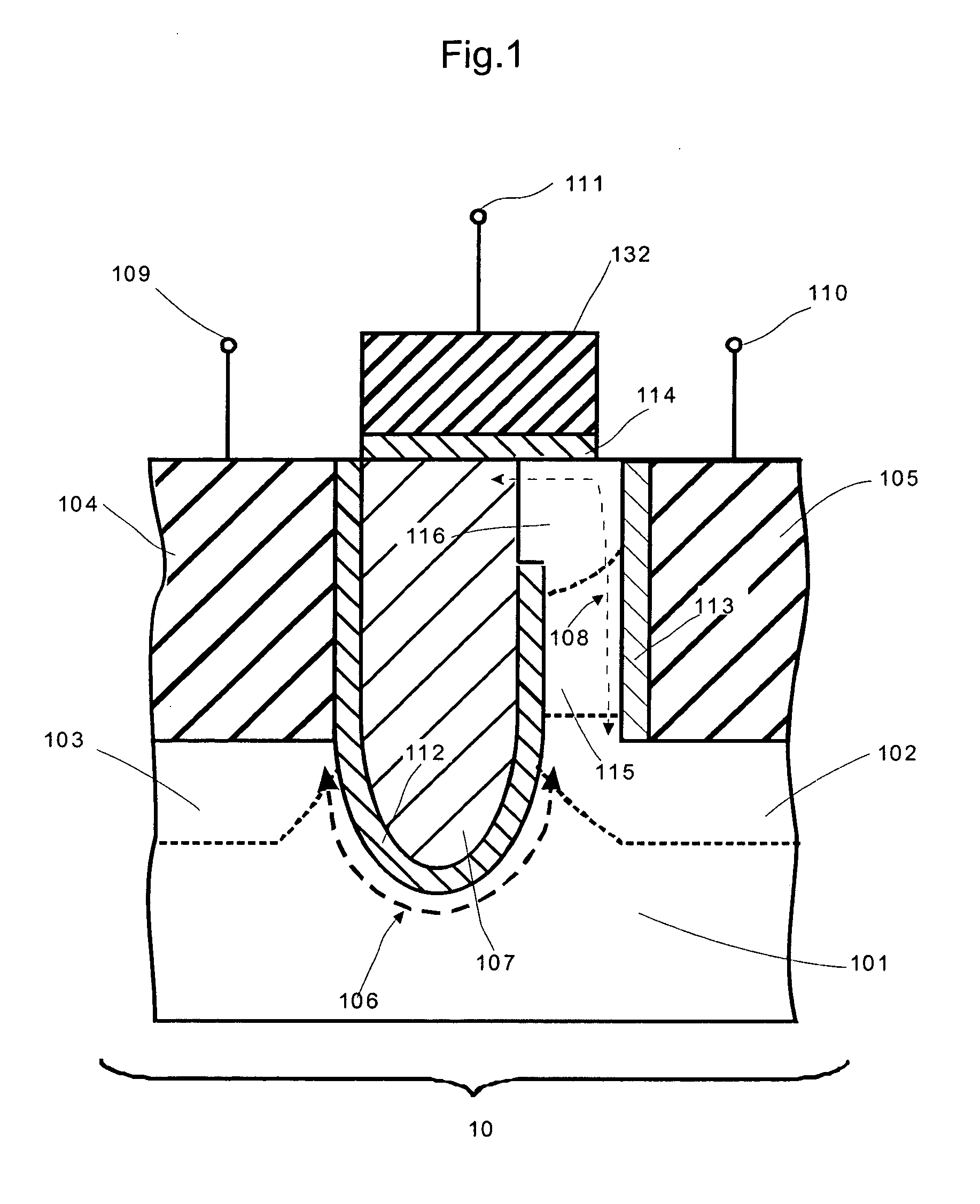
ActiveUS20110260242A1Lower work functionTotal current dropSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenNitrogen
Provided are a transistor of a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same. A gate induced drain leakage (GIDL) current is reduced by decreasing a work function at an upper portion of a gate electrode, and a threshold voltage of the transistor is maintained by maintaining a work function at a lower portion of the gate electrode at a high level, thereby reducing a leakage current of the transistor and reducing a read time and a write time of the semiconductor device. The transistor of the semiconductor device includes: a recess with a predetermined depth in a semiconductor substrate; a first gate electrode disposed within the recess; and a second gate electrode disposed on the first gate electrode into which ions of one or more of nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), arsenic (As), aluminum (Al), and hydrogen (H) are doped.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
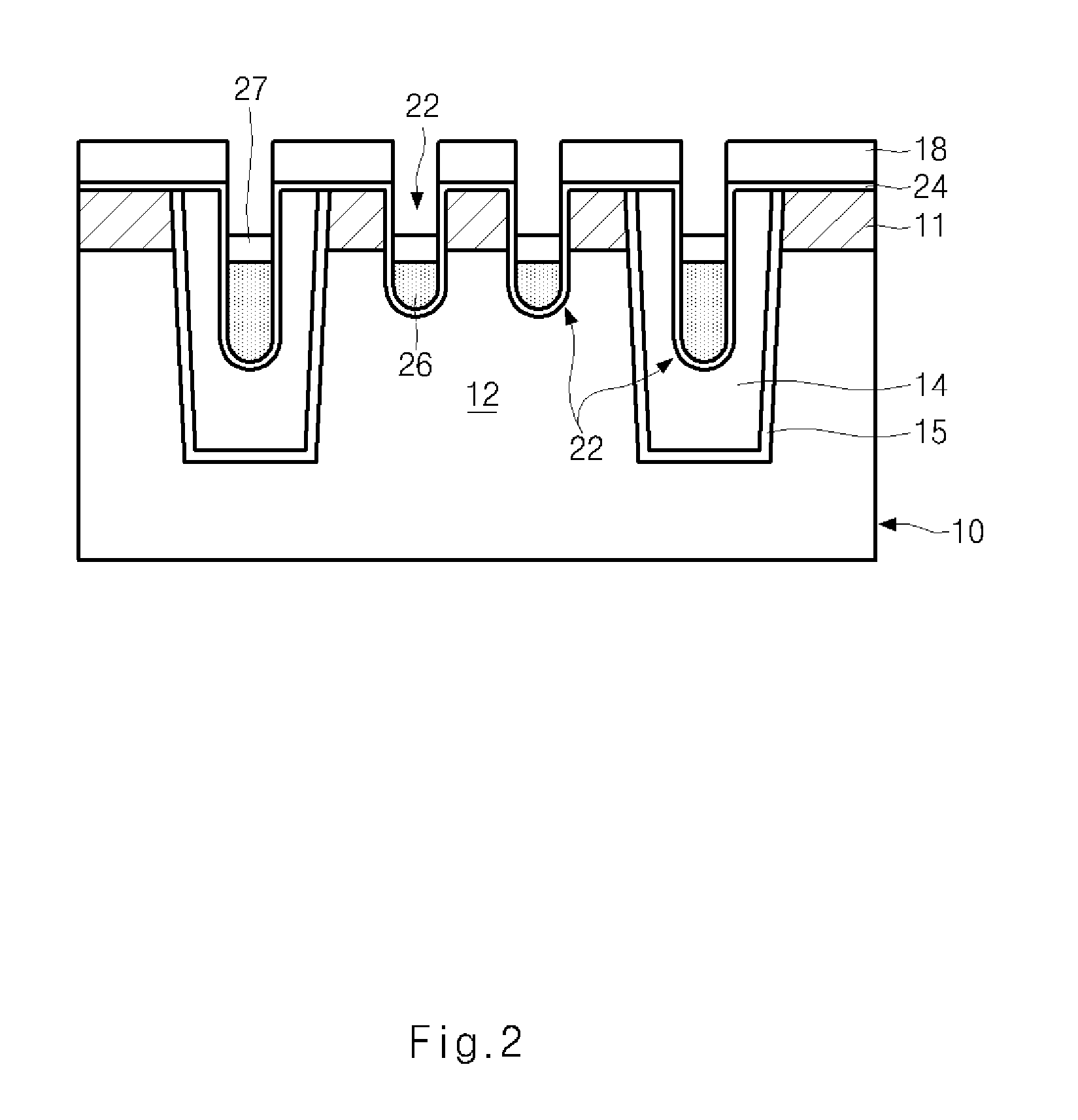
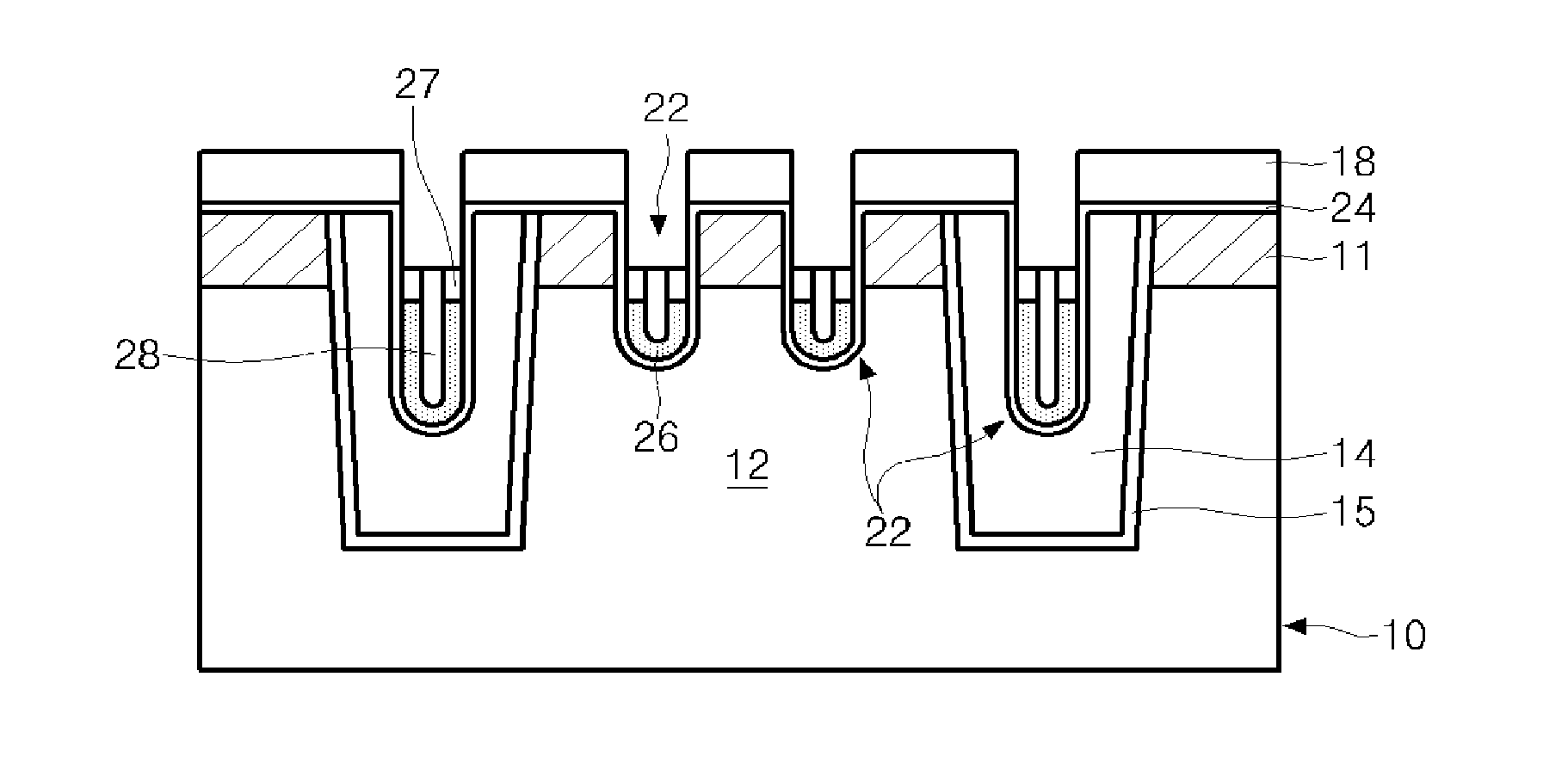
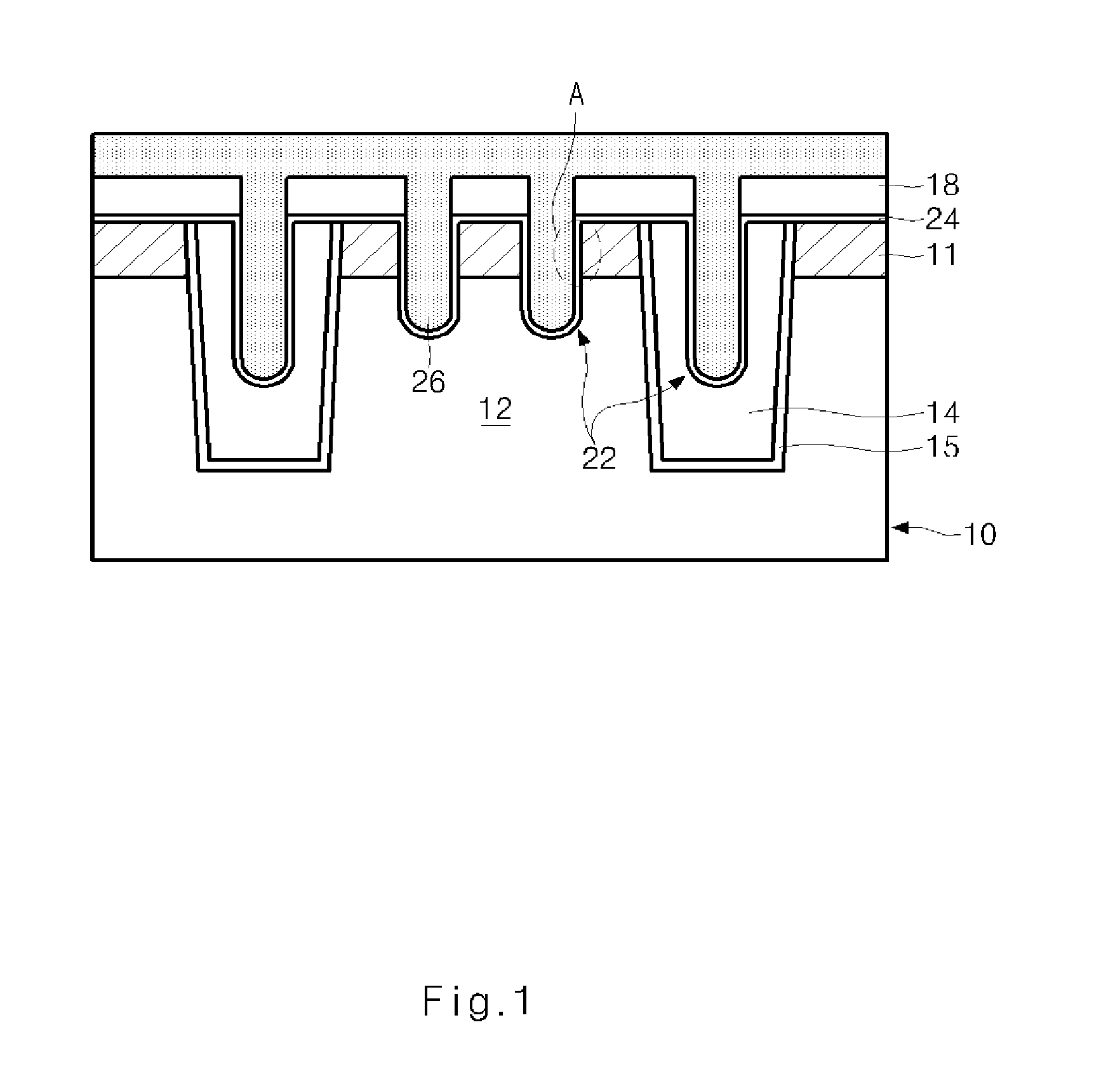
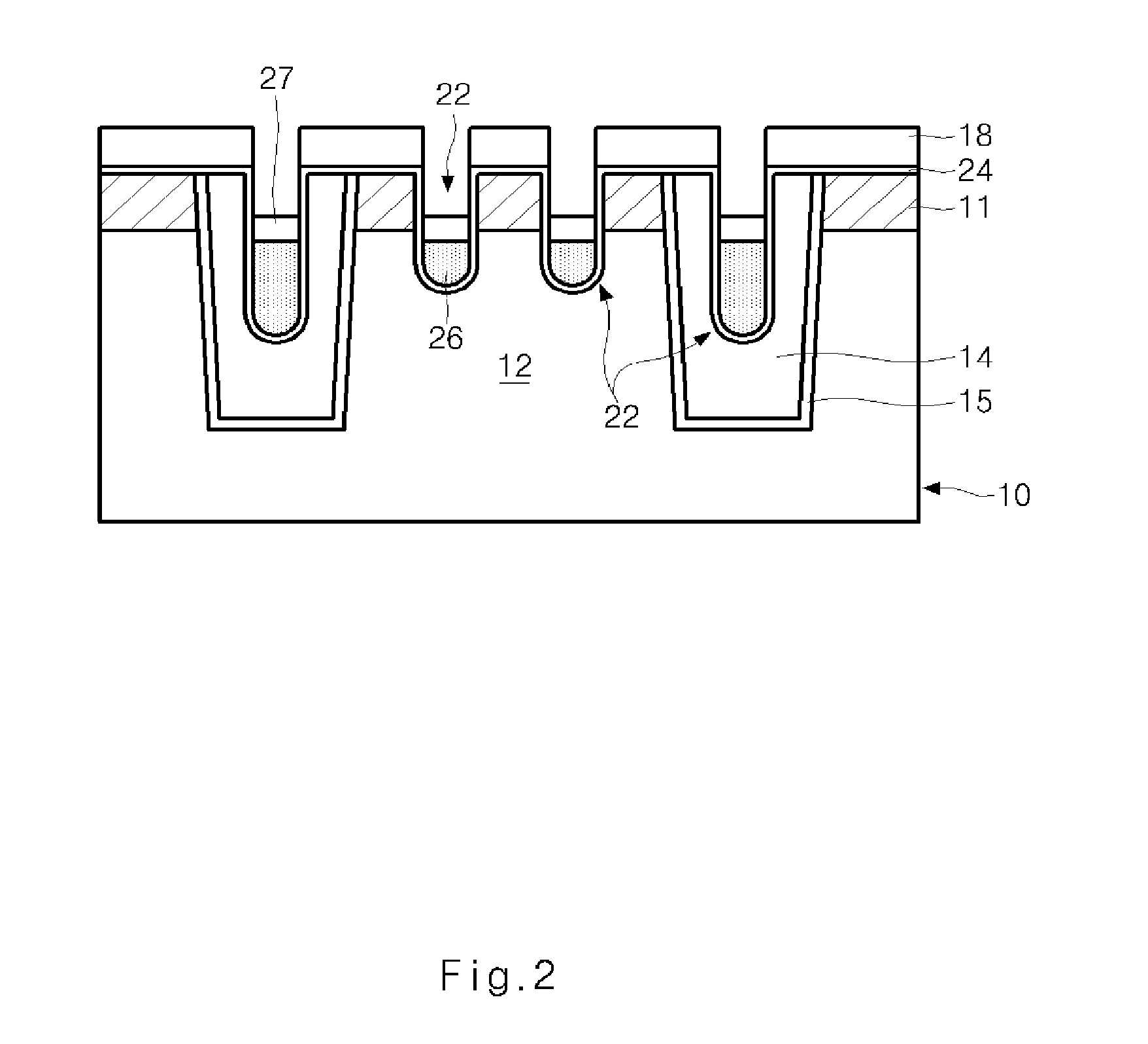
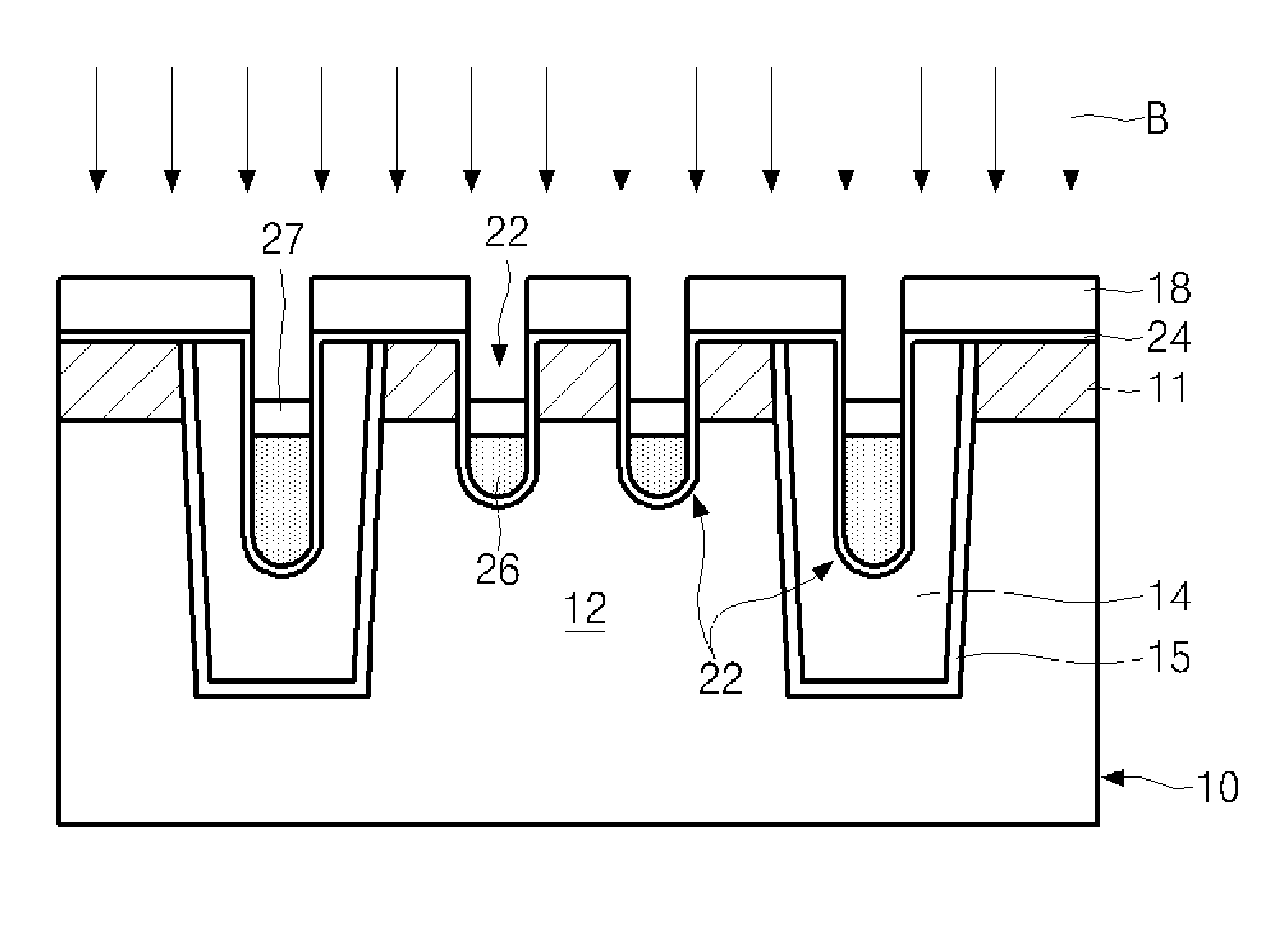
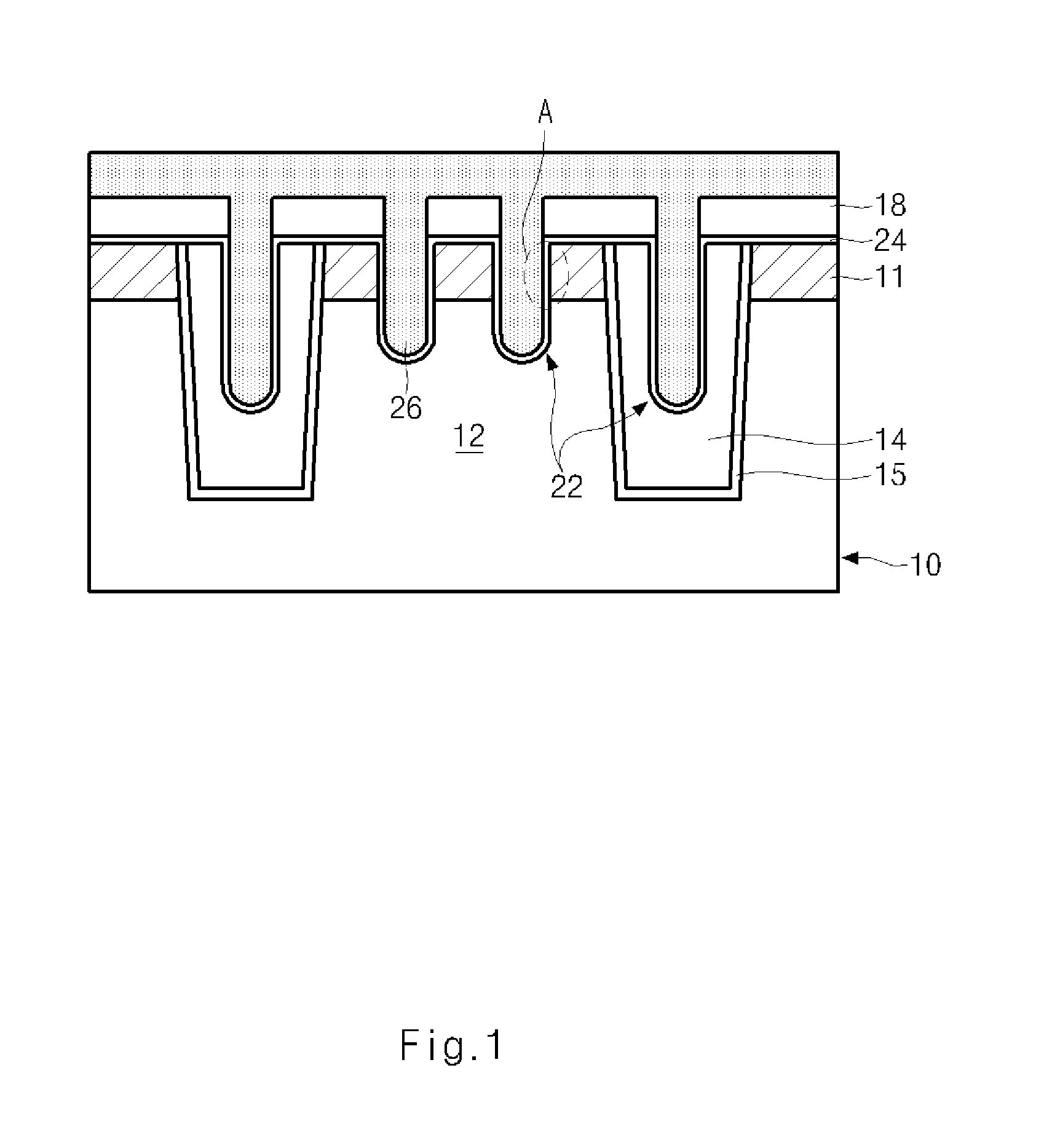
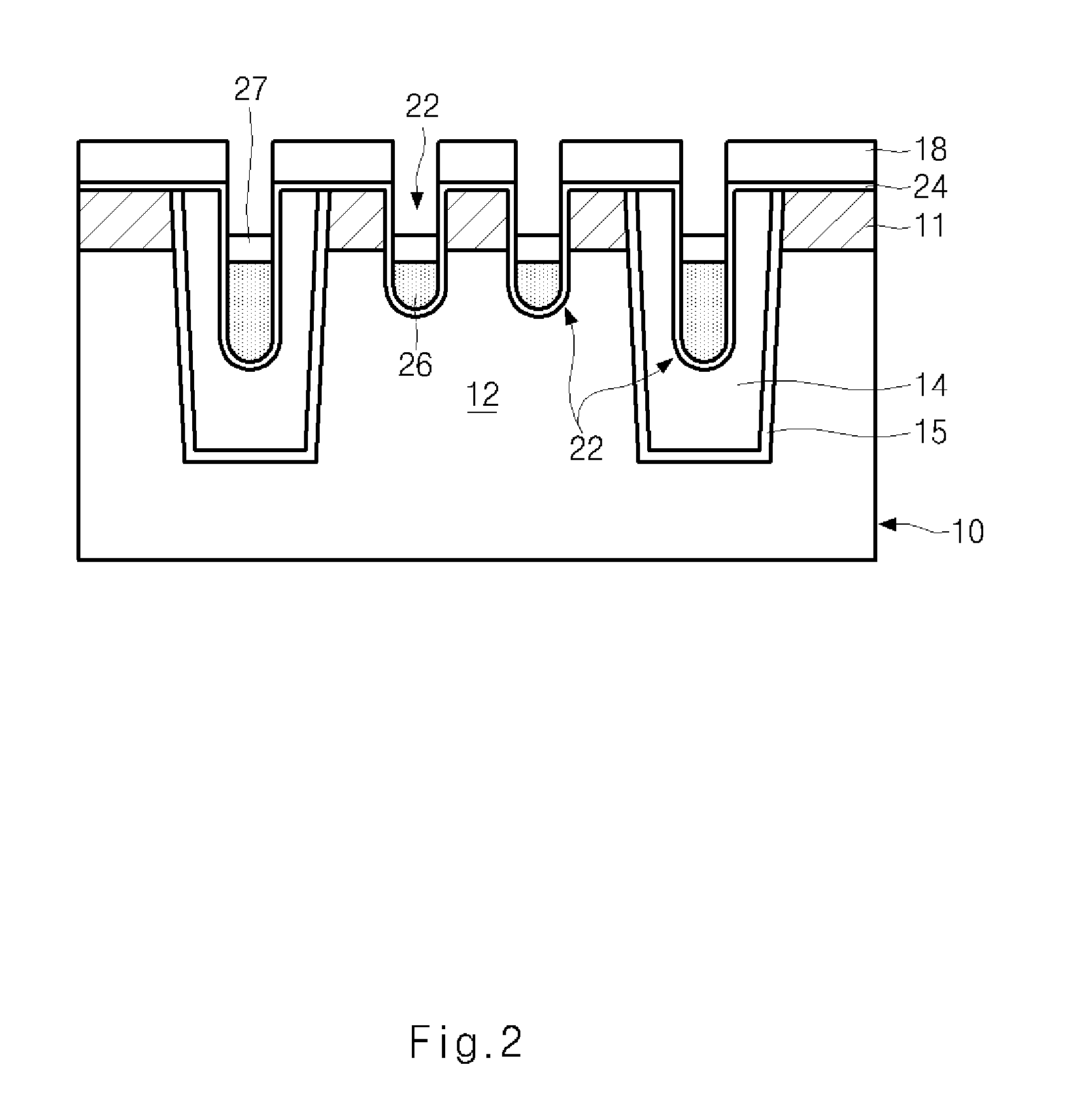
Semiconductor memory device and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20090185426A1Shorter read and write timesIncrease in sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesP–n diodeSemiconductor
The present invention discloses a semiconductor memory device comprising a source, a drain, a floating gate, a control gate, a recess channel and a gated p-n diode. The said p-n diode connects said floating gate and said drain. The said floating gate is for charge storage purpose, it can be electrically charged or discharged by current flowing through the gated p-n diode. An array of memory cells formed by the disclosed semiconductor memory device is proposed. Furthermore, an operating method and a method for producing the disclosed semiconductor memory device and array are described.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIENTAL SEMICONDUCTOR CO LTD
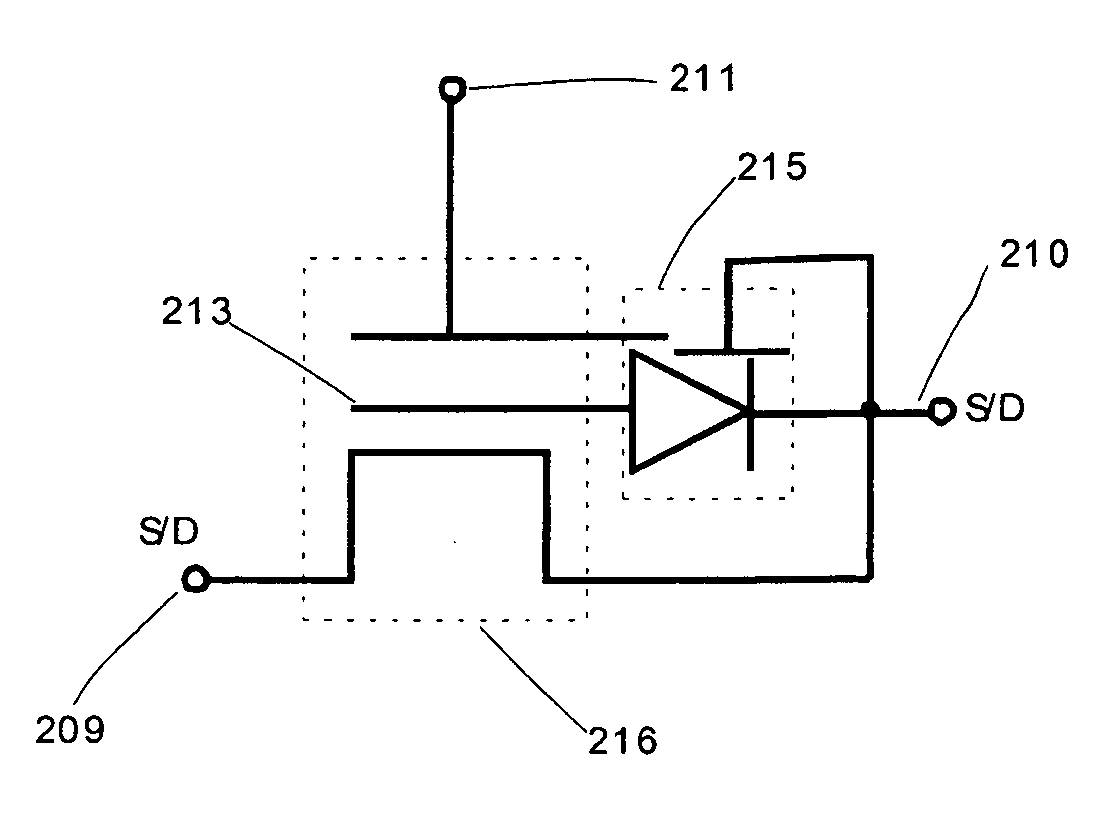
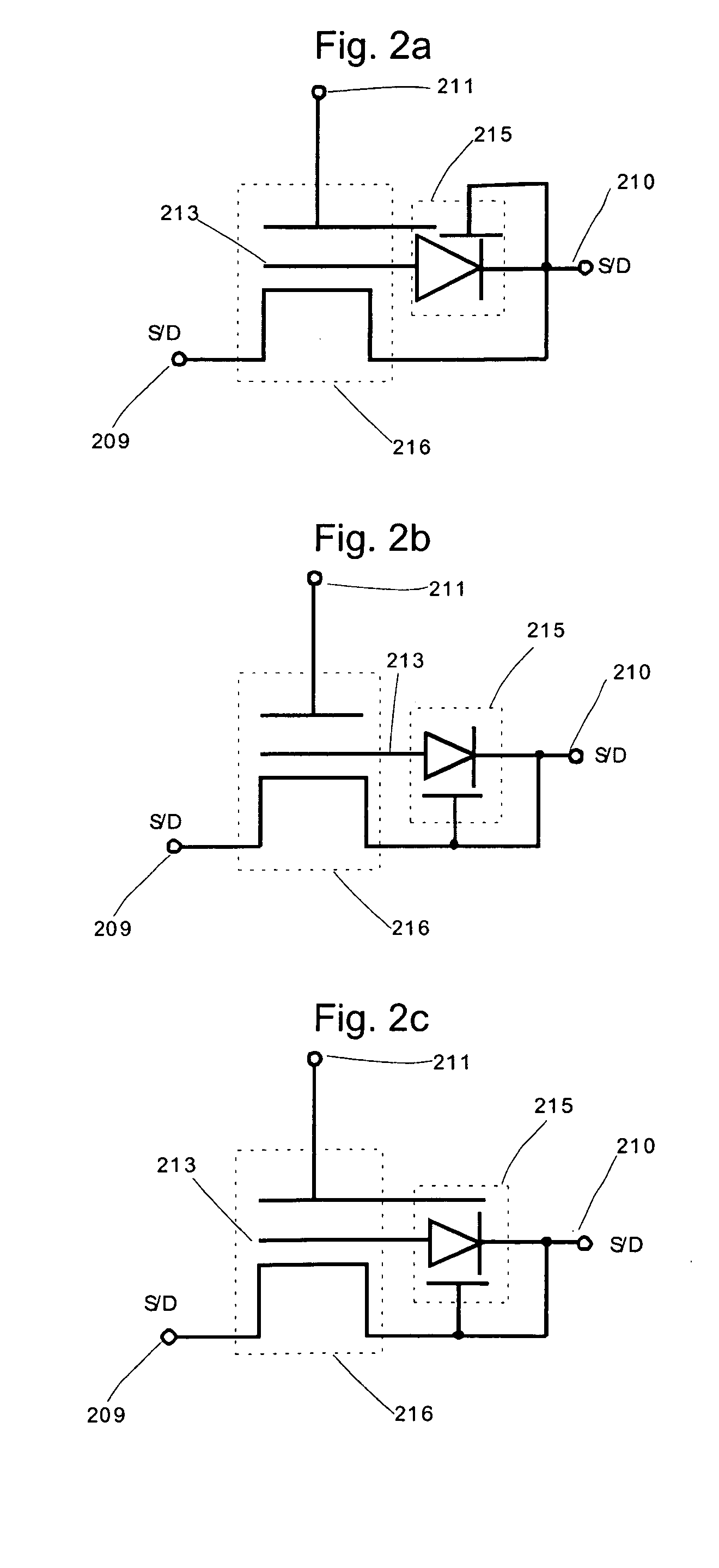
Semiconductor memory device and driving method thereof
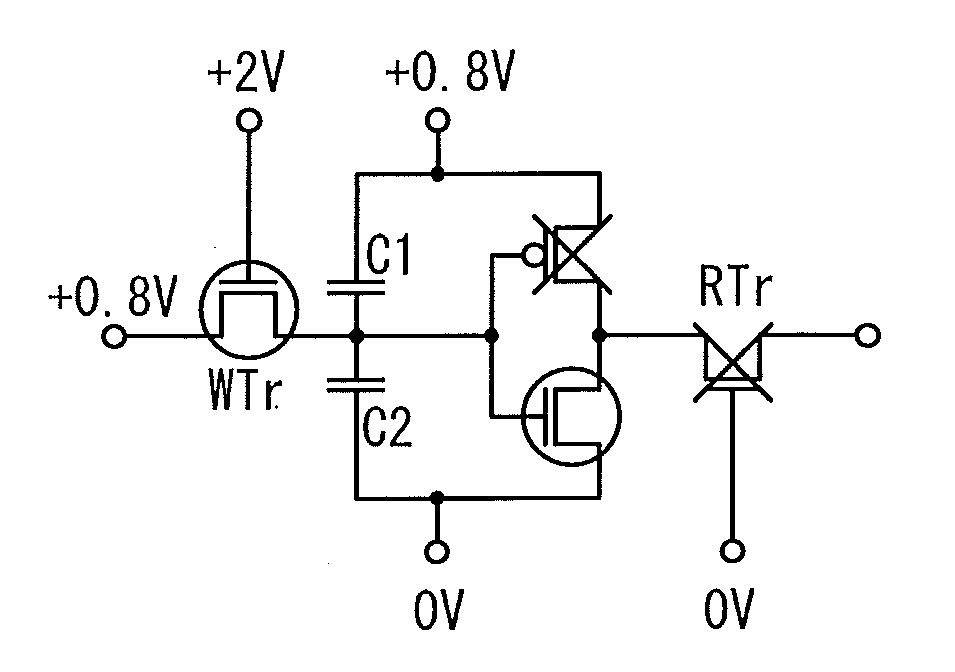
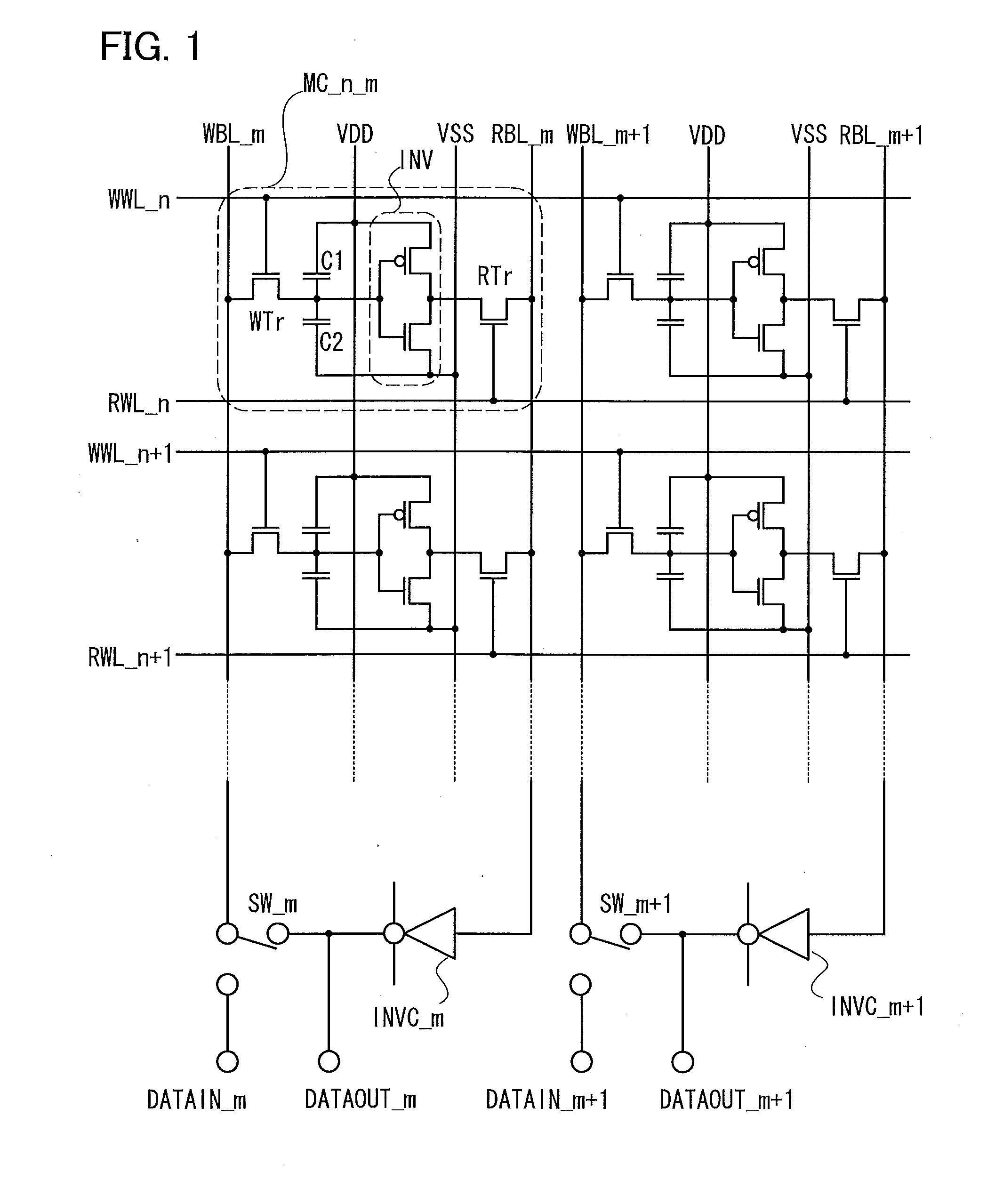
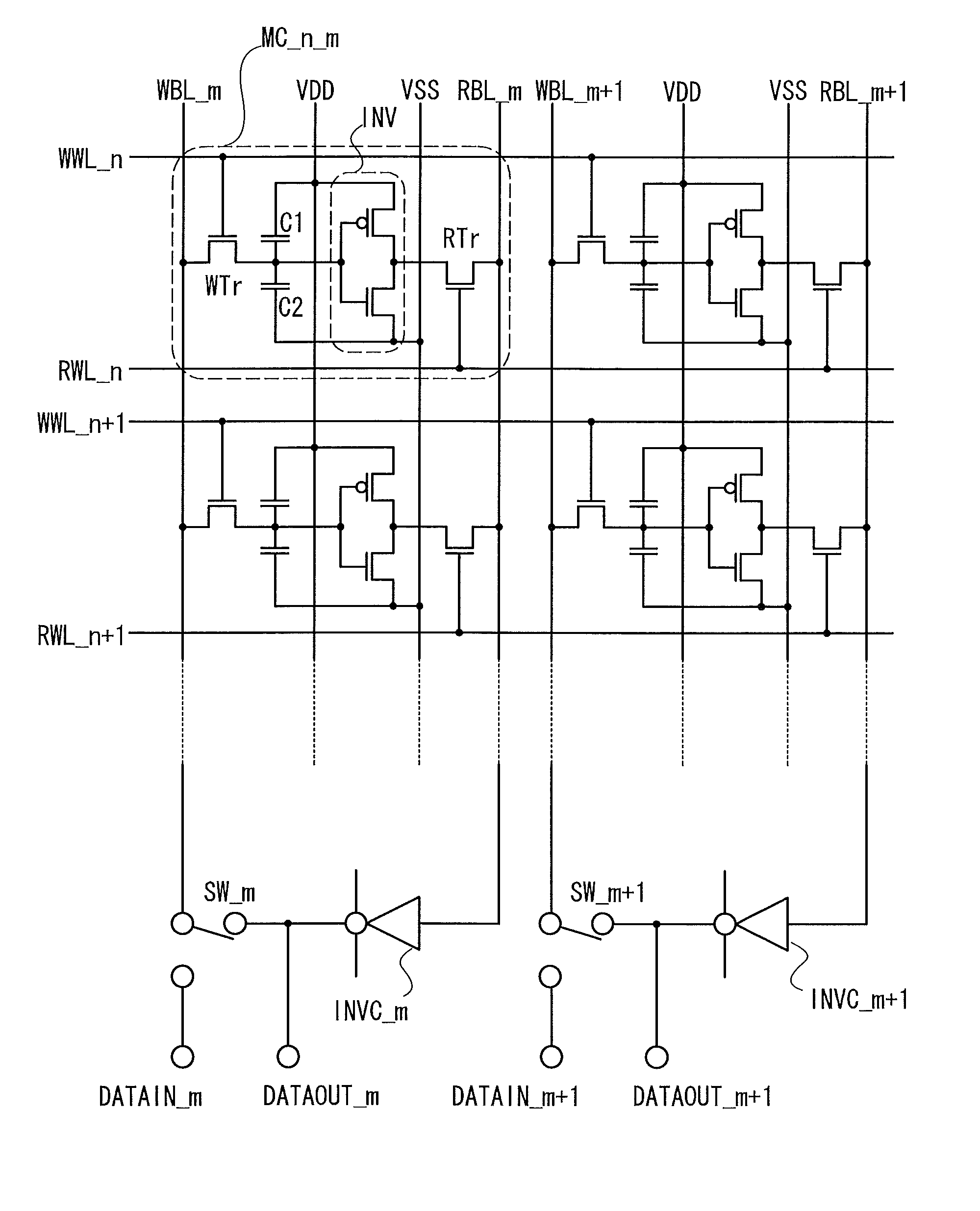
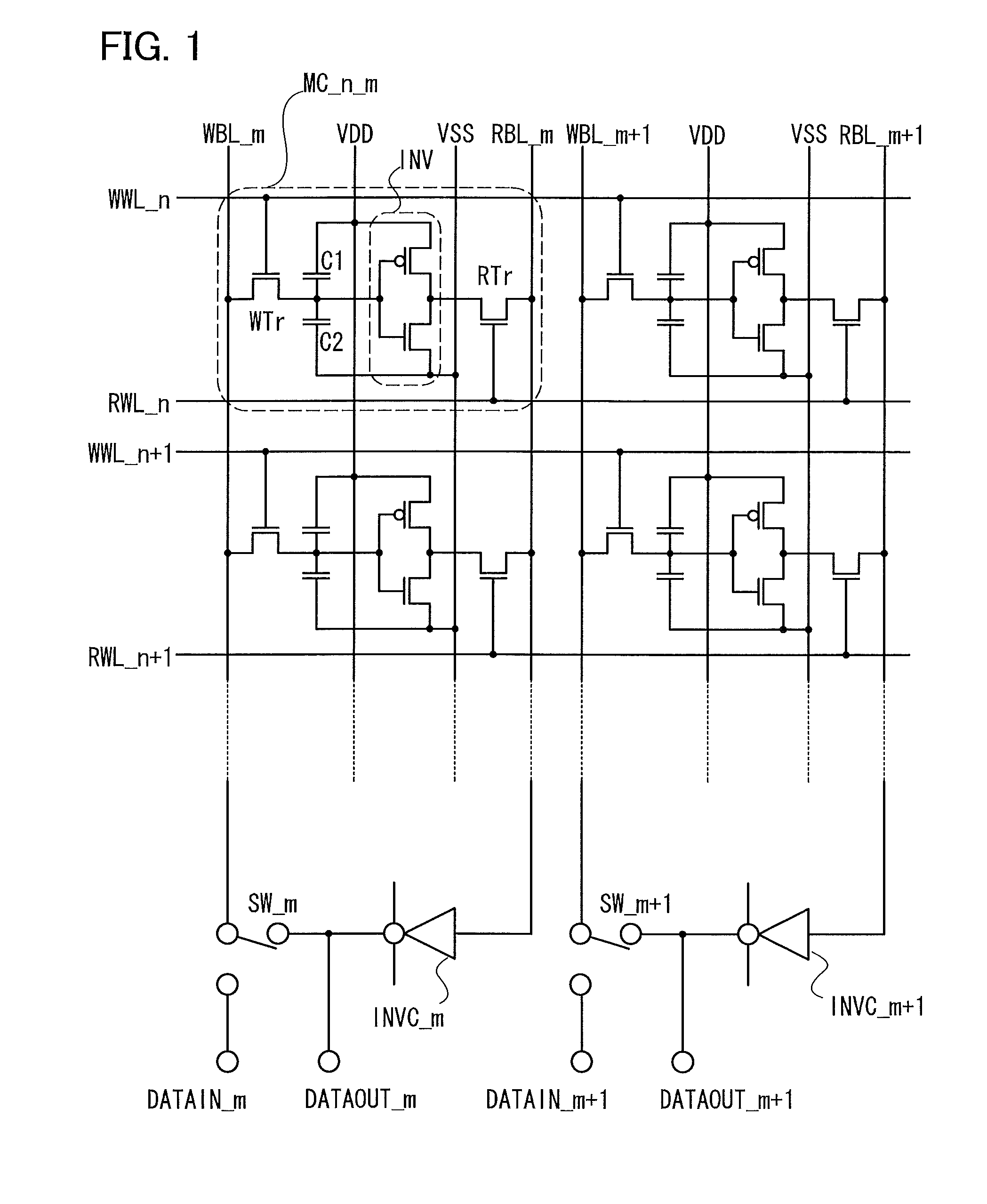
ActiveUS20120099360A1Less power consumptionReduce power consumptionDigital storagePower inverterPotential difference
In a memory cell, a transistor with extremely high off-resistance is used as a write transistor; a drain and a source of the write transistor are connected to a write bit line and an input of an inverter, respectively; and a drain and a source of a read transistor are connected to a read bit line and an output of the inverter, respectively. Capacitors may be intentionally disposed to the source of the write transistor. Alternatively, parasitic capacitance may be used. Since the data retention is performed using charge stored on these capacitors, a potential difference between power sources for the inverter can be 0. This eliminates leakage current between the positive and negative electrodes of the inverter, thereby reducing power consumption.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Cache system based on nonvolatile memory and software RAID
ActiveCN106528001AAvoid multiple visitsShorter read and write timesInput/output to record carriersRAIDGNU/Linux
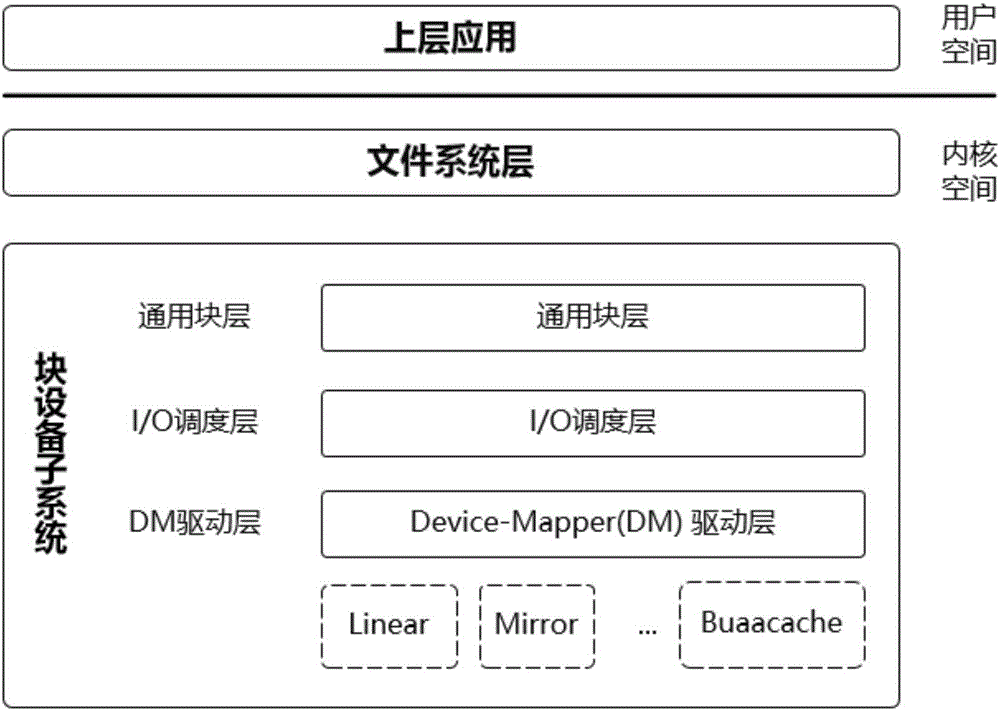
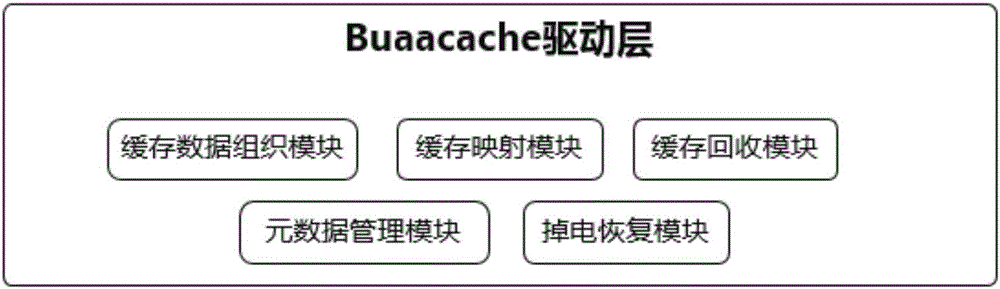
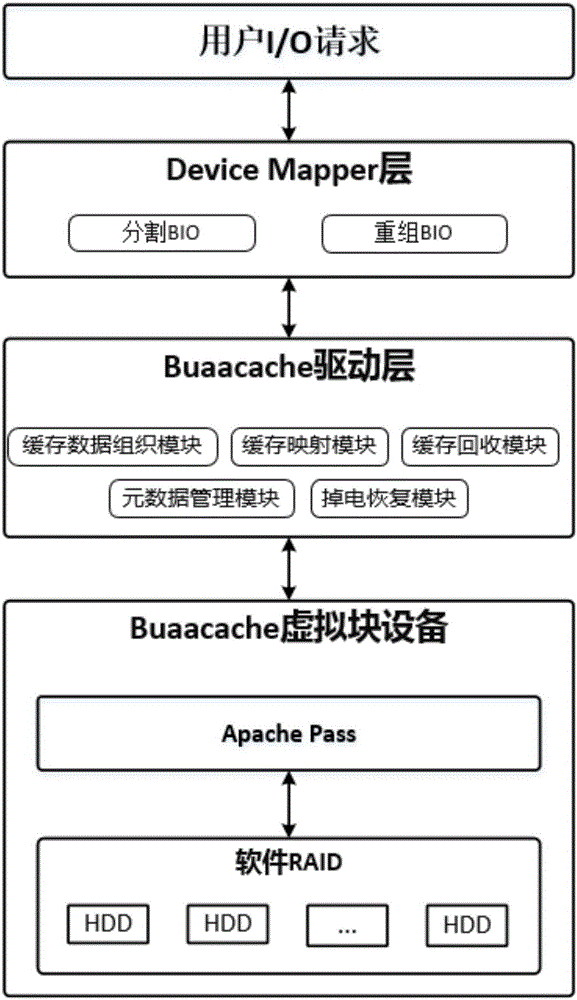
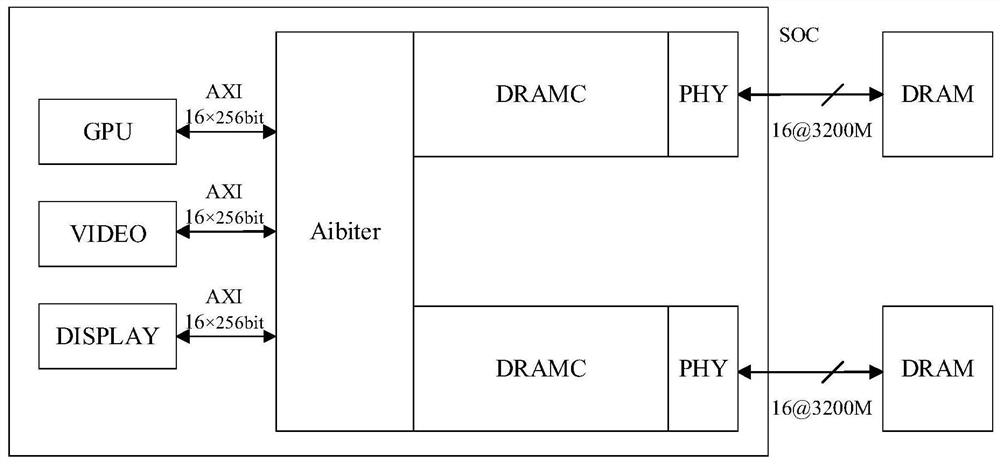
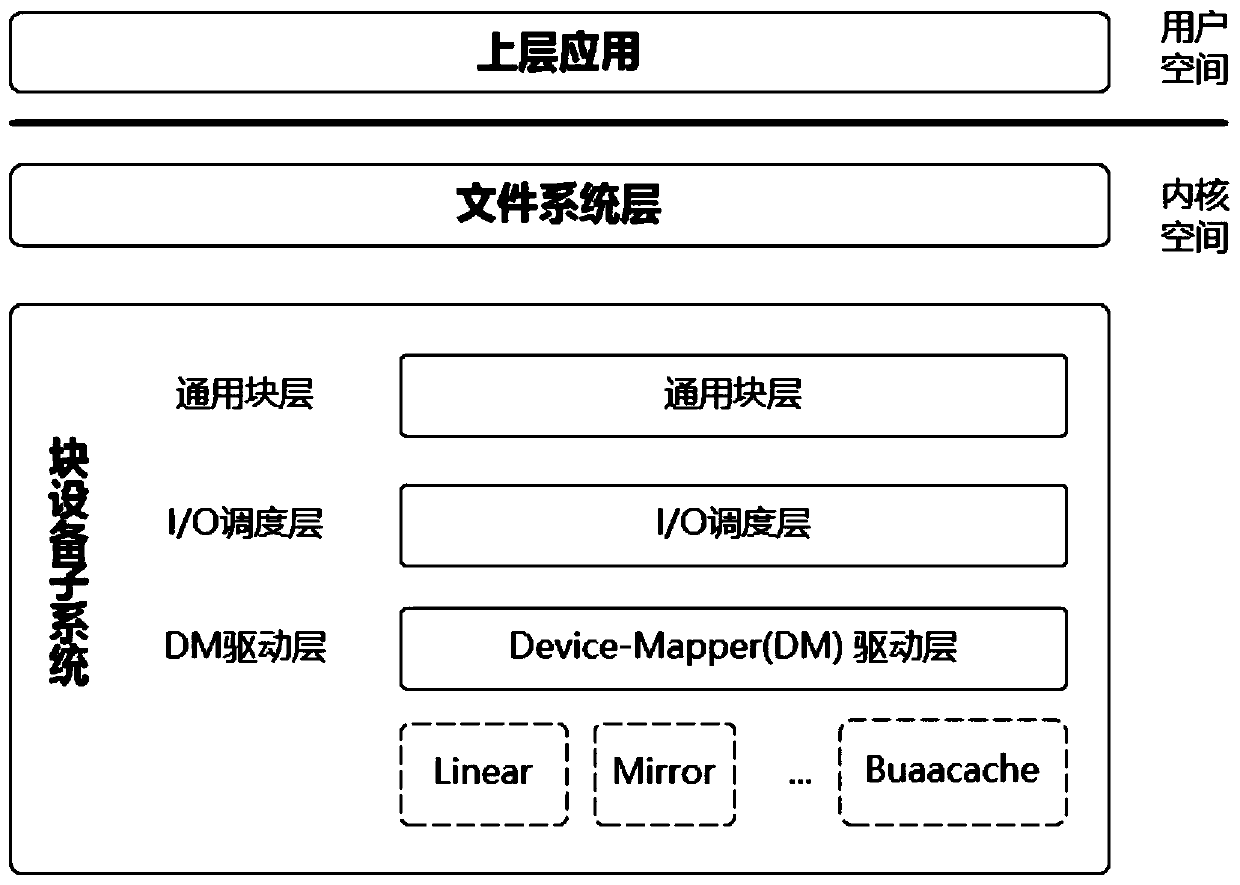
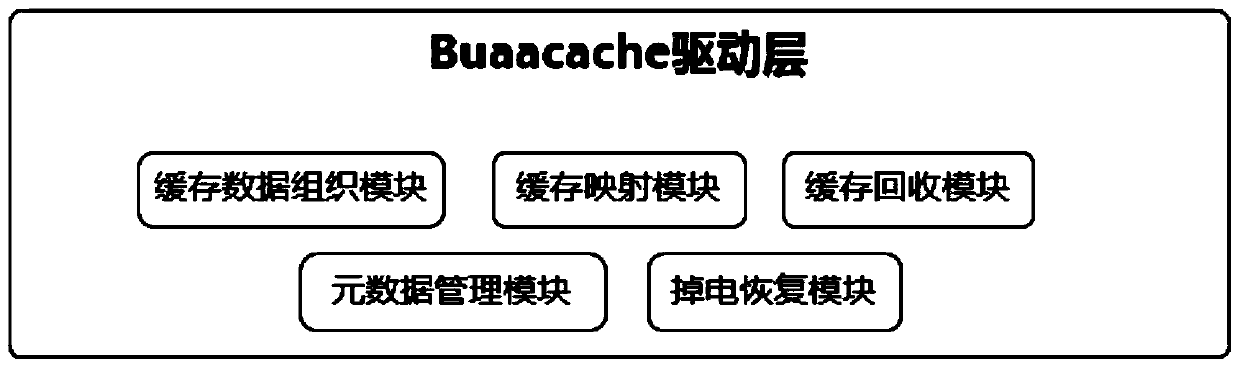
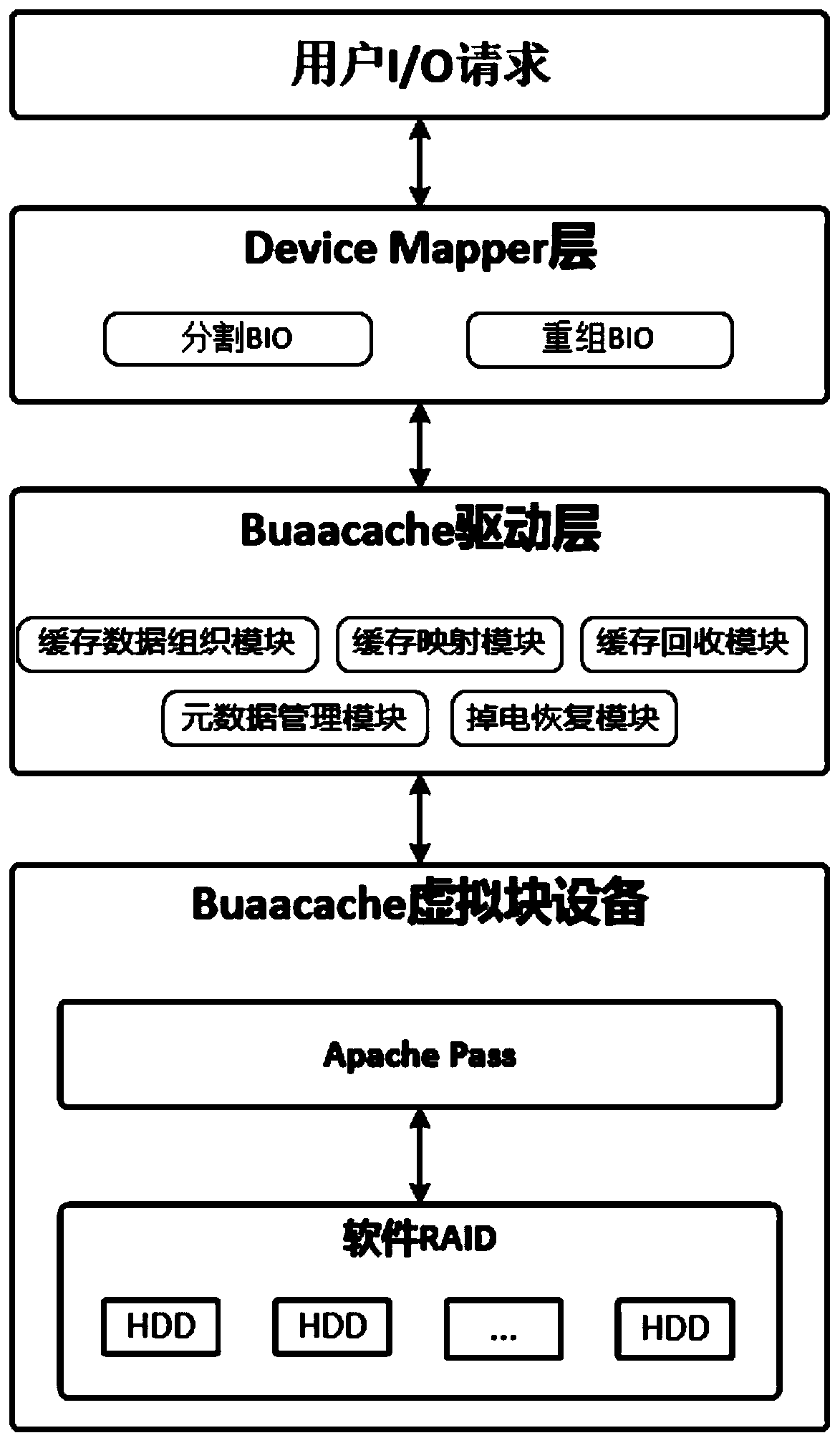
The invention provides a cache system based on a nonvolatile memory and a software RAID. The cache system is characterized in that the cache system is a novel storage system architecture by fusing a nonvolatile memory Apache Pass, a software RAID, and a Device Mapper driving module Buaacache. According to the invention, the software RAID is managed by means of the Device Mapper mechanism of the Linux, a high-speed device Apache Pass serves as the Cache of a low-speed RAID, and therefore a two-stage cache system is constructed. The Persistent Memory is characterized in that after the Persistent Memory is powered off, medium data is not lost, and the read-write performance is excellent. According to the invention, the Persistent Memory is selected as the cache of the software RAID, under the condition that the cost is far lower than that of a hardware RAID, the read-write performance of the software RAID approaches even exceeds the hardware RAID.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Mixed file system based on different storage media
ActiveCN103838853AImprove storage efficiencyImprove read and write speedSpecial data processing applicationsFile system typesGranularityFile system
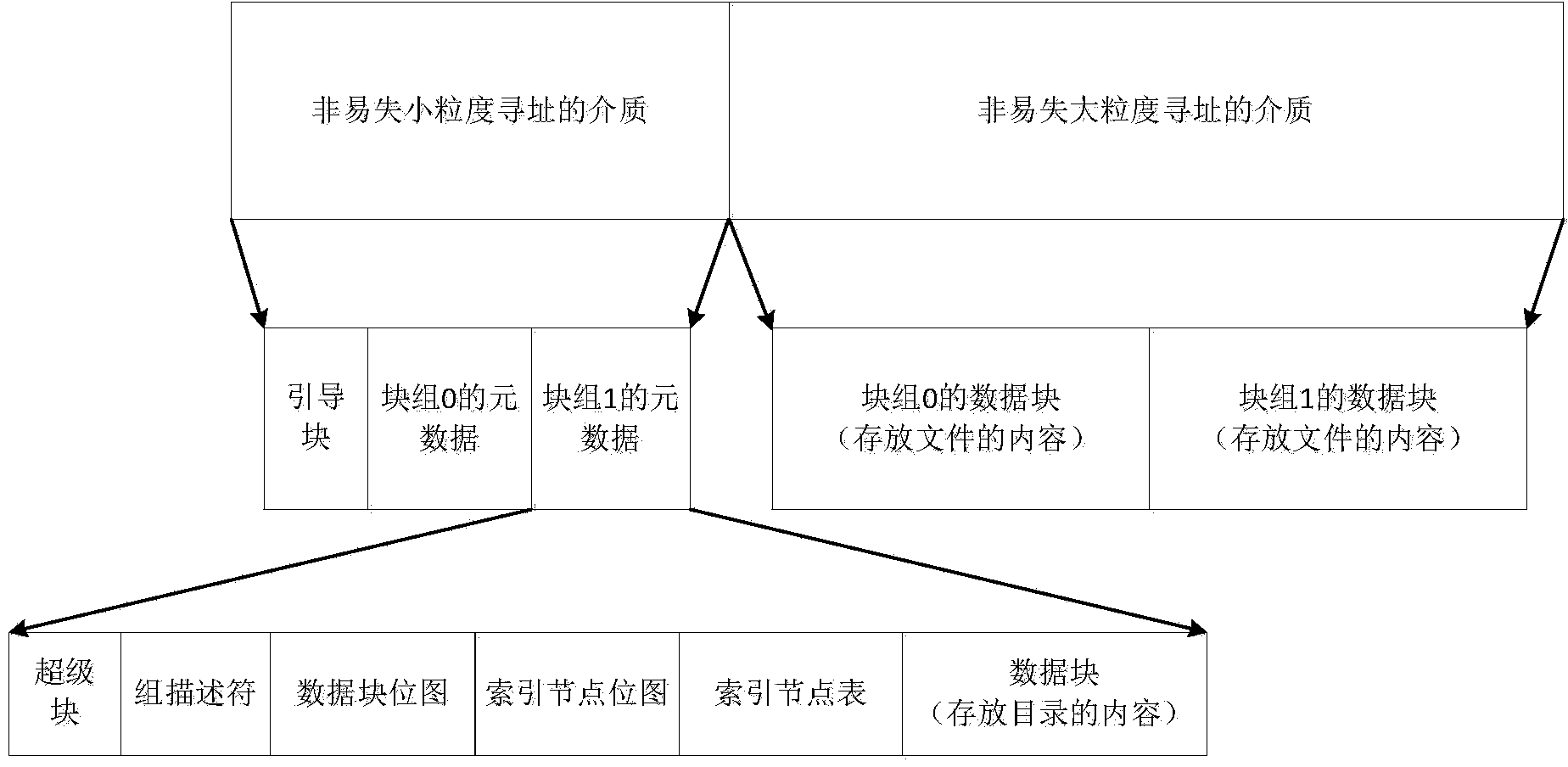
The invention discloses a mixed file system based on different storage media. The storage media comprise non-volatile small-granularity addressing media and non-volatile large-granularity addressing media, and the two kinds of media are addressed according to the unified sequence. The non-volatile small-granularity addressing media are used for storing metadata of the file system, and the non-volatile large-granularity addressing media are used for storing data of the file system. The file system calls different granularities of reading or writing for different address ranges under different situations. According to the mixed file system, large data volume reading and writing and small data volume reading and writing are allocated to the corresponding media according to different situations, the reading and writing speed is improved, and the storing efficiency of the file system is improved. The storage space is fully utilized, superfluous redundancy does not exist, additional I / O is reduced, and reading and writing performance is improved. The mixed file system has the high reliability, expandability and I / O speed.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Width detection method and width detection apparatus of record medium and record apparatus
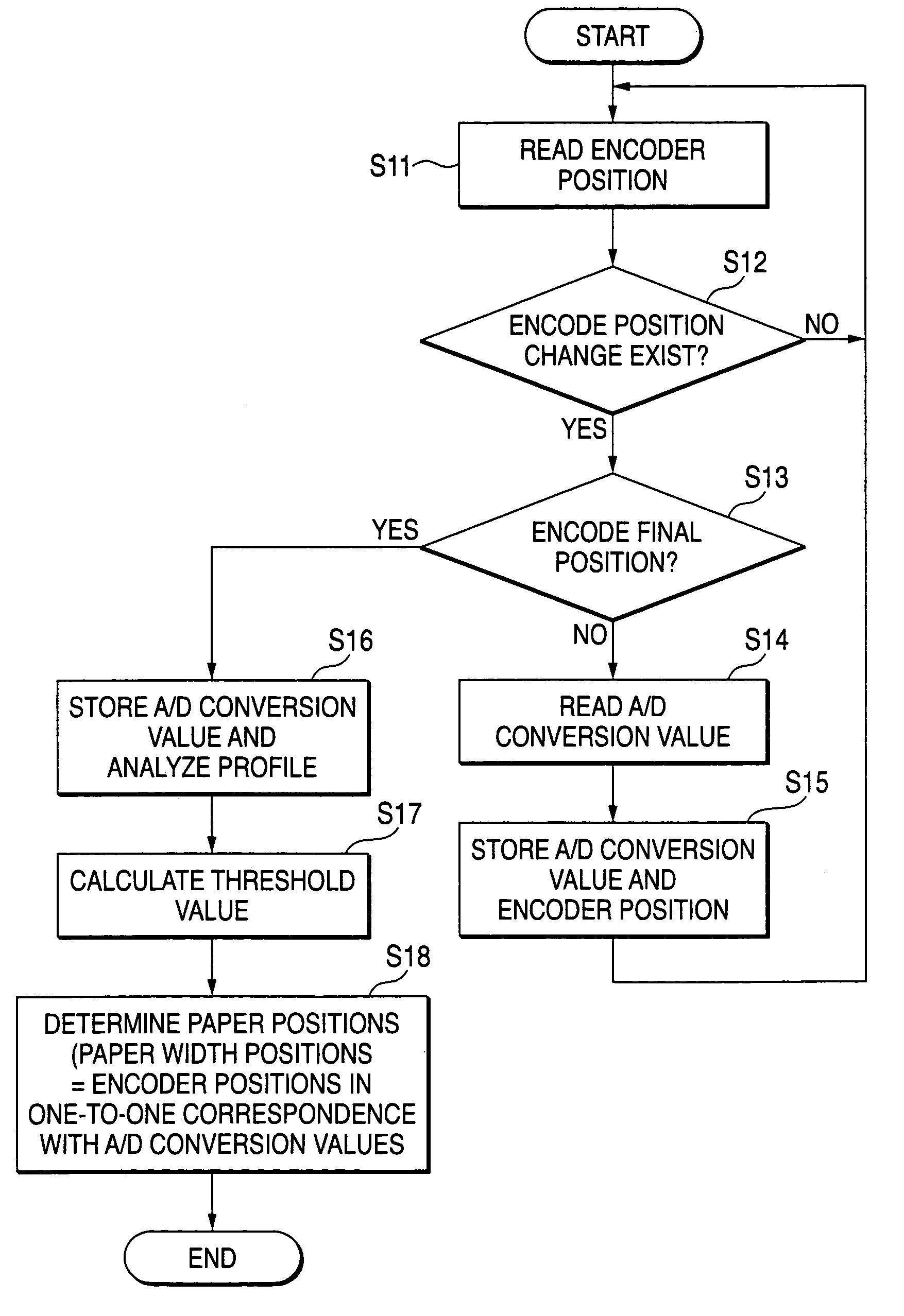
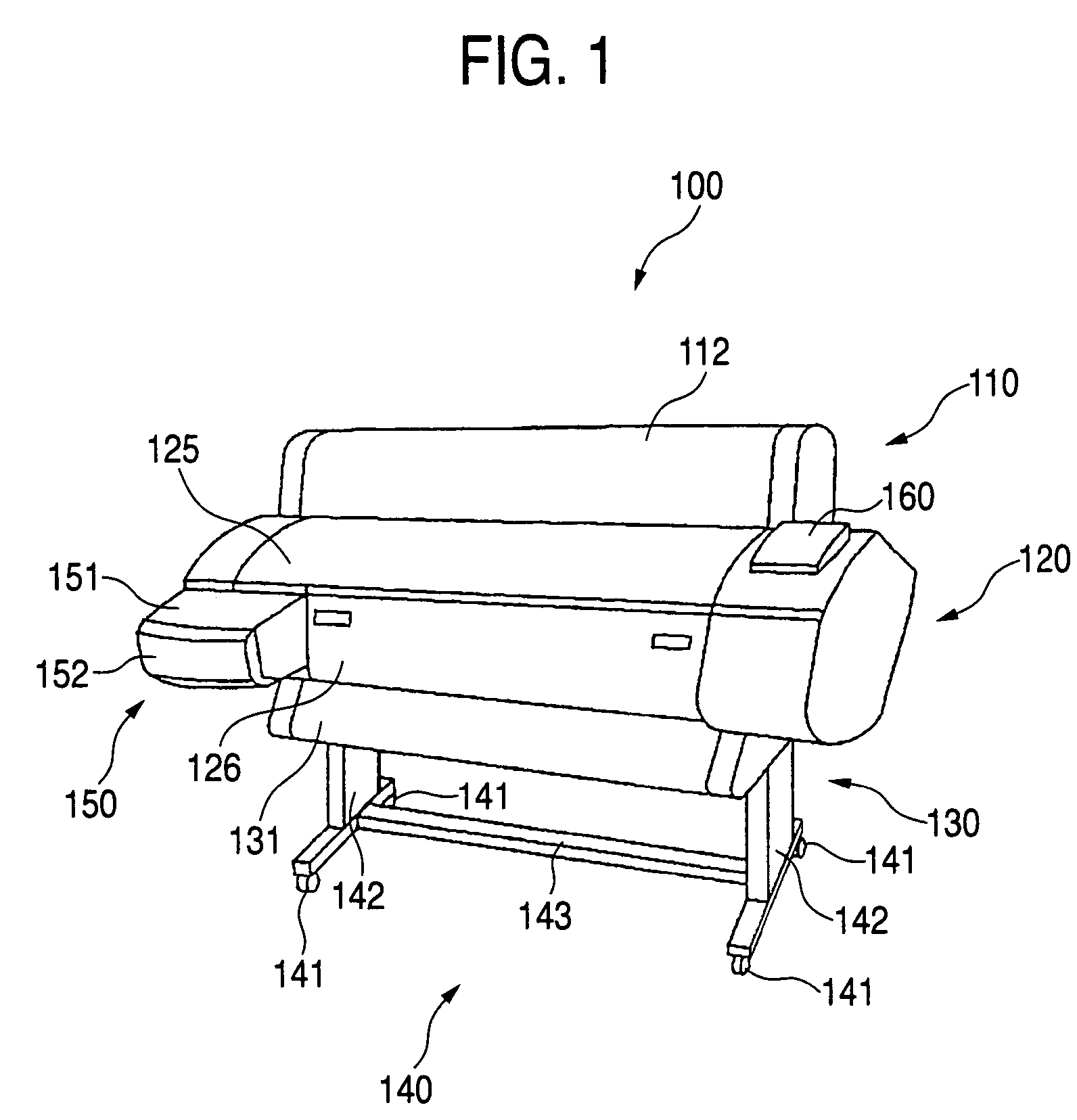
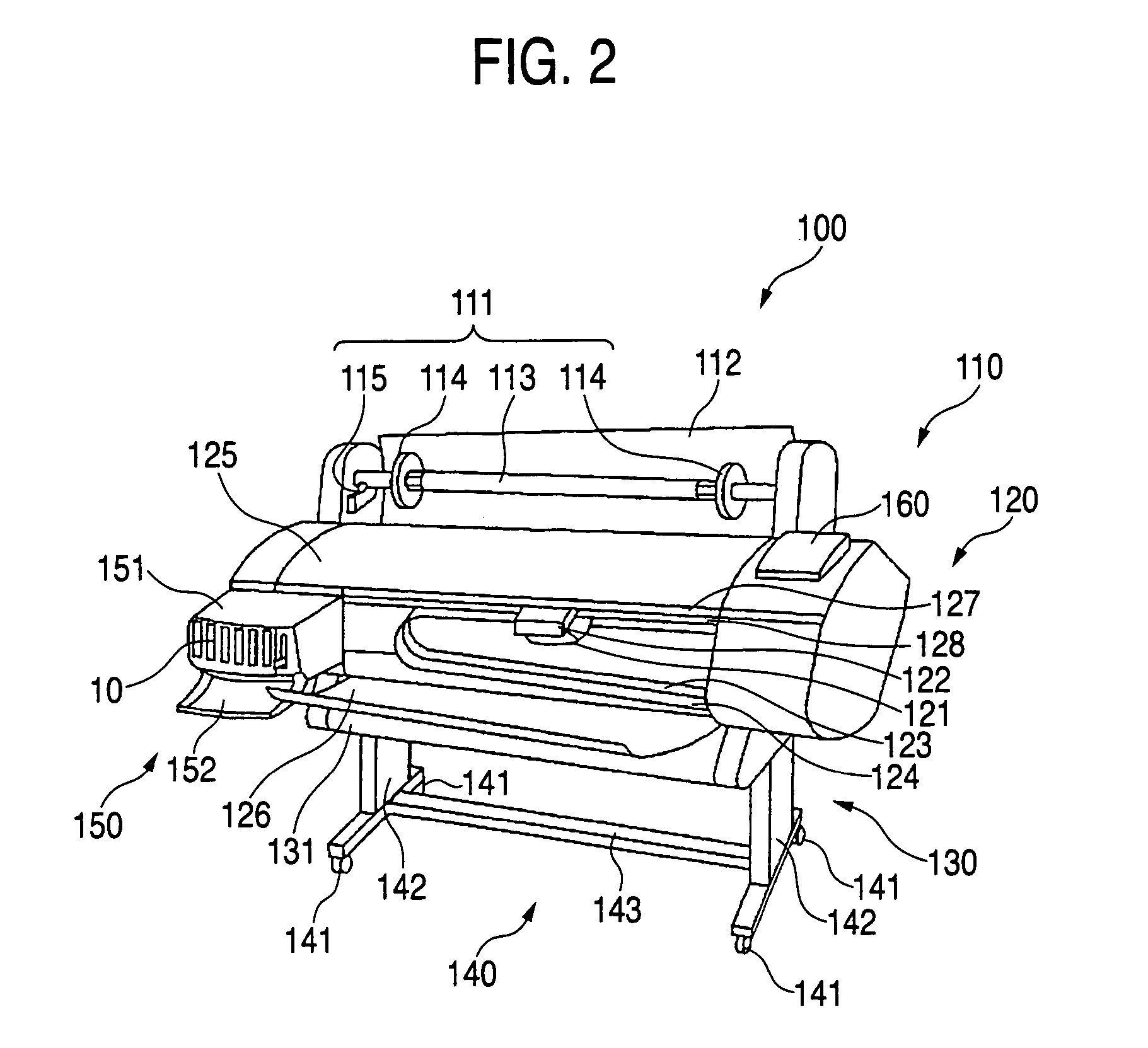
The values of the detection signals of a record medium and the placement face thereof detected as a recording head moves from one end of the record medium to an opposite end are stored. A predetermined threshold value is found based on a profile found from the stored values of the detection signals. Both ends of the record medium are determined according to the threshold value and the width of the record medium is found. Accordingly, the threshold value matching the used record medium can be set, so that an easy determination can be made as to whether or not change of the detection signal exceeding the threshold value occurs and change of the detection signal falling below the threshold value occurs, and the width of the record medium can be found accurately.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Semiconductor memory device and method of forming the same
ActiveUS8089801B2Shorter read and write timesIncrease in sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesP–n diodeSemiconductor
The present invention discloses a semiconductor memory device comprising a source, a drain, a floating gate, a control gate, a recess channel and a gated p-n diode. The said p-n diode connects said floating gate and said drain. The said floating gate is for charge storage purpose, it can be electrically charged or discharged by current flowing through the gated p-n diode. An array of memory cells formed by the disclosed semiconductor memory device is proposed. Furthermore, an operating method and a method for producing the disclosed semiconductor memory device and array are described.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIENTAL SEMICONDUCTOR CO LTD
Semiconductor memory system and signal processing system
ActiveUS20080115043A1Improve error correction performanceShorter read and write timesRead-only memoriesCode conversionMemory bankComputer science
A semiconductor memory device able to strengthen an error correction capability, able to shorten a write time and / or a read time, able to make a redundant memory unnecessary or smaller, and consequently able to achieve a reduction of size and a reduction of cost, provided with a data input portion for receiving 1 page's worth of data, dividing it to a plurality of code words, generating and adding check code (parity data) for each code word, successively forming main code words and transferring the same to a bank (A) or a bank (B), and a data output portion for receiving 1 page's worth of data including main code words transferred from the data latch circuit, correcting the error data when there is within a predetermined number of error data for each main code word, adding the error information for read each read code word except check code (parity data), and transferring the same to a host side, and a signal processing system using the same.
Owner:TESSERA ADVANCED TECH
Transistor of semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130316524A1Total current dropShorten read timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
Provided are a transistor of a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same. A gate induced drain leakage (GIDL) current is reduced by decreasing a work function at an upper portion of a gate electrode, and a threshold voltage of the transistor is maintained by maintaining a work function at a lower portion of the gate electrode at a high level, thereby reducing a leakage current of the transistor and reducing a read time and a write time of the semiconductor device. The transistor of the semiconductor device includes: a recess with a predetermined depth in a semiconductor substrate; a first gate electrode disposed within the recess; and a second gate electrode disposed on the first gate electrode into which ions of one or more of nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), arsenic (As), aluminum (Al), and hydrogen (H) are doped.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
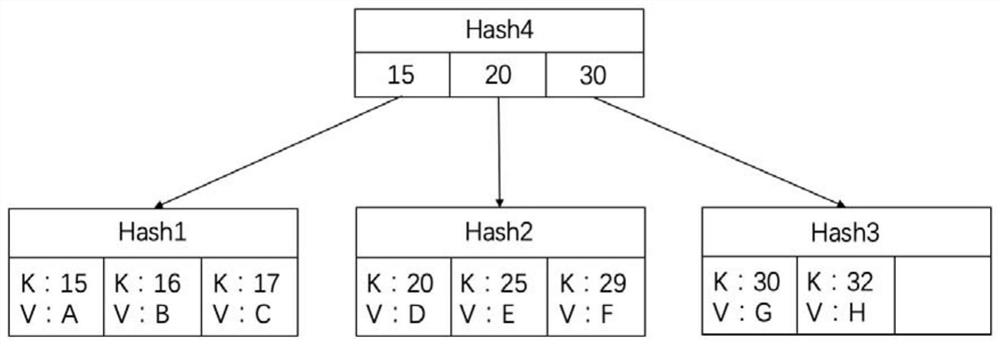
Multi-version data storage method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
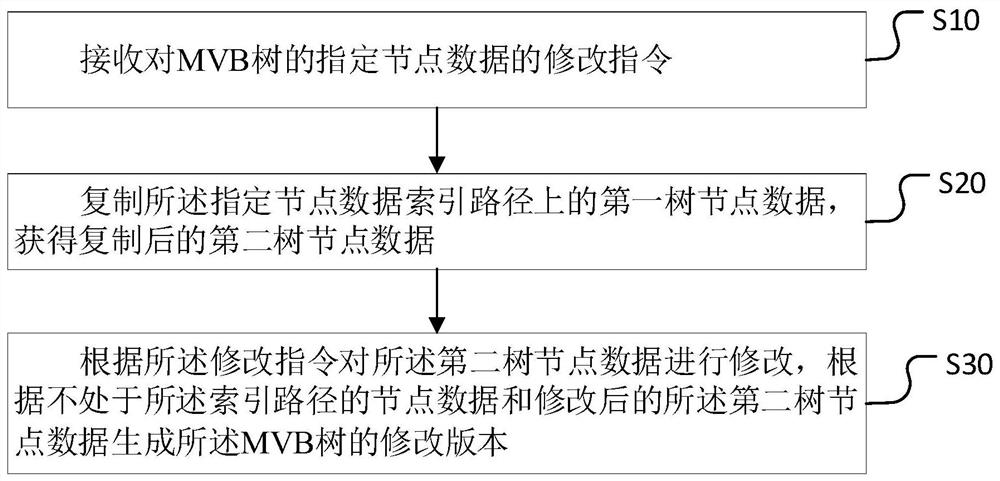
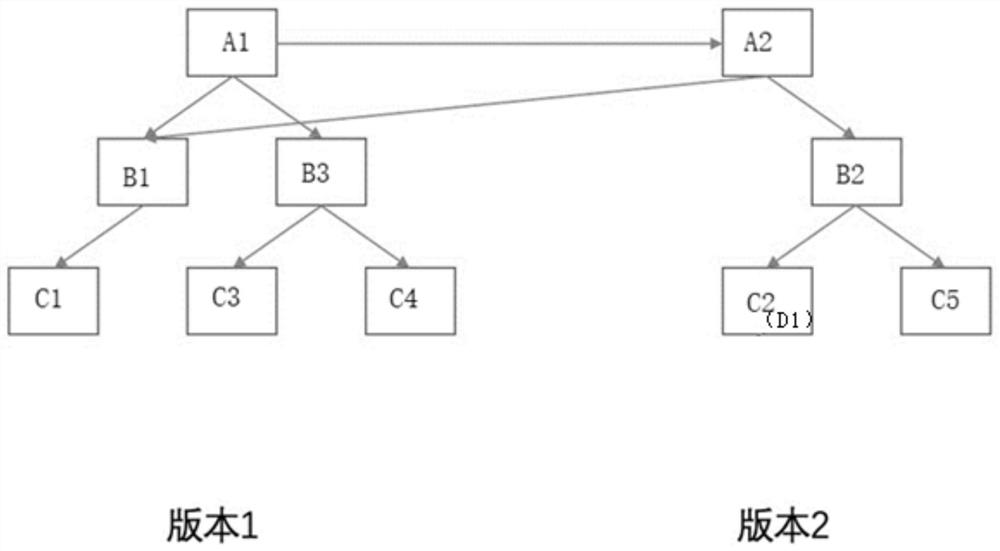
ActiveCN112579602AShort pathReduce the number of IOsDatabase updatingEnergy efficient computingPathPingSoftware engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of blockchains, and discloses a multi-version data storage method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of receiving a modification instruction for specified node data of an MVB tree; copying the first tree node data on the specified node data index path to obtain copied second tree node data; and modifyingthe second tree node data according to the modification instruction, and generating a modified version of the MVB tree according to the node data not in the index path and the modified second tree node data. According to the invention, the storage efficiency of the blockchain data can be improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU QULIAN TECH CO LTD
Phase change memory-based mapping management method and solid-state hard disk
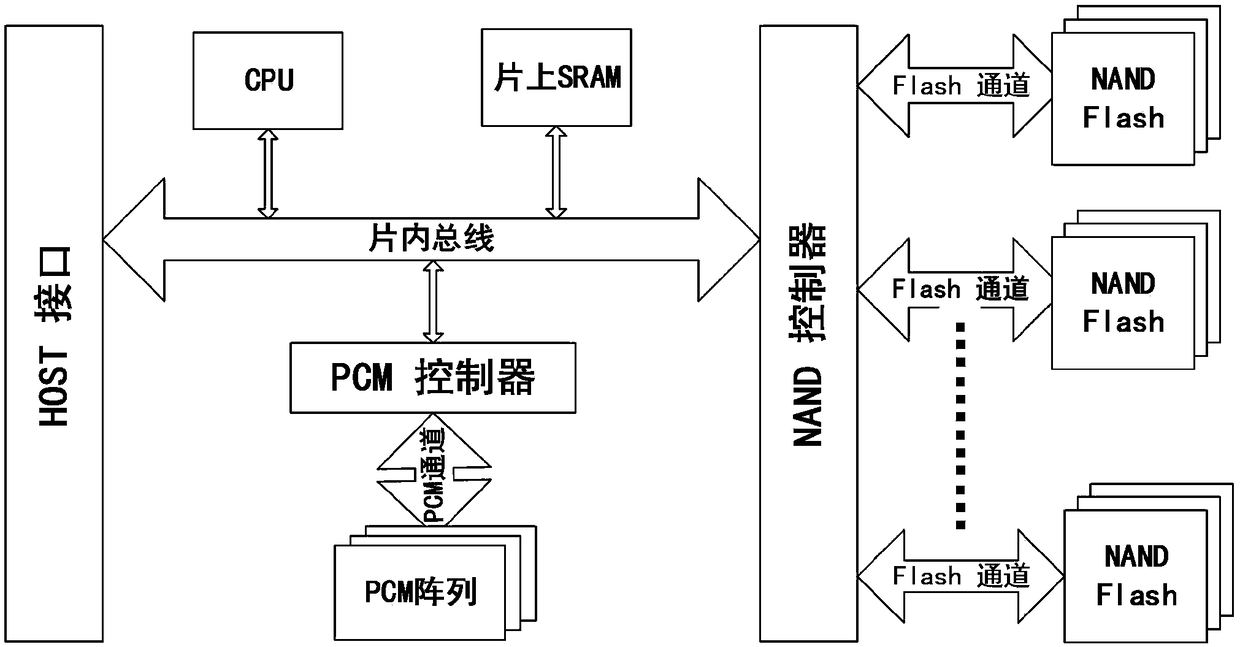
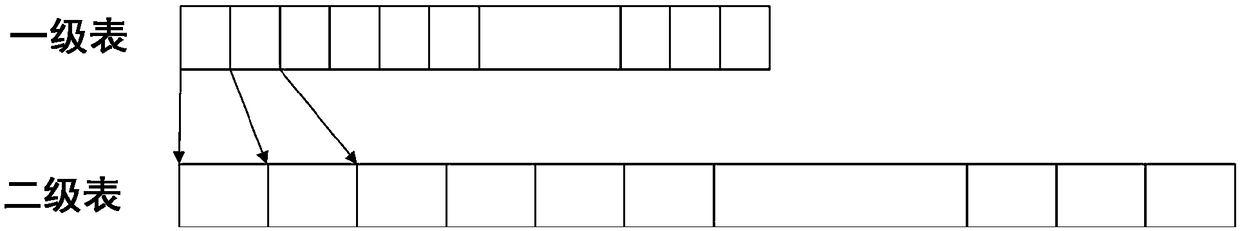
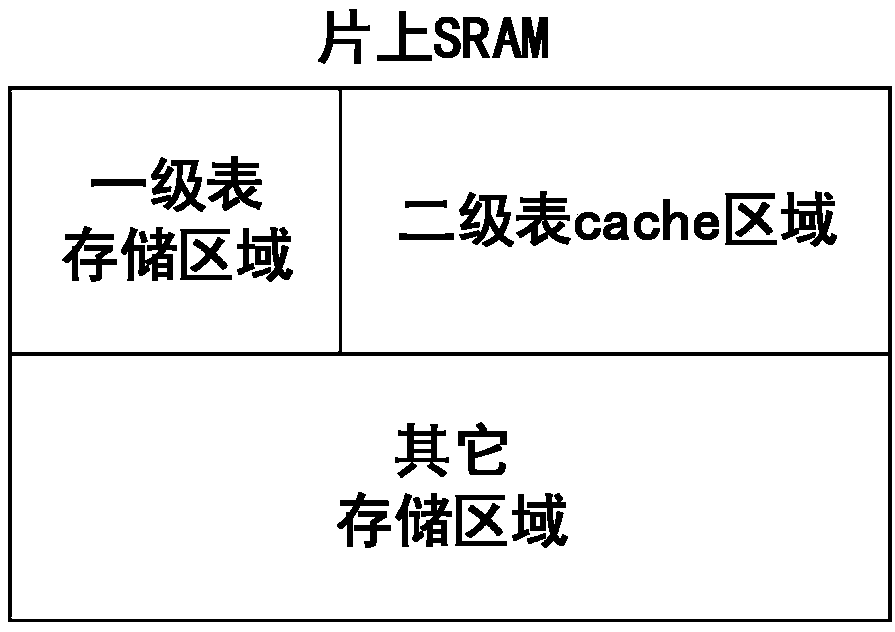
ActiveCN108647157AShorten the timeShorten completion timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCompletion timePhase-change memory
The invention discloses a phase change memory-based mapping management method and a solid-state hard disk, which is characterized in that two-level mapping table management is adopted and specificallycomprises a first level table and a second level table; the second level table is stored in the phase change memory PCM; the second level table records the relationship between the logical address and the physical address of all the user data pages; the second level table is divided into a plurality of second level table sub-units according to the granularity G; and the second level table sub-unit is used as a basic unit for cache of a hard disk controller to carry out data replacement; and by introducing the phase change memory for storing a mapping table, the read-write time of the phase change memory is much lower than that of NAND. According to the phase change memory-based mapping management method and the solid-state hard disk in the invention, the phase change memory is introducedin the NODRAM solid-state hard disk to replace the NAND for saving the complete mapping table; the time of the mapping table cache in the on-chip SRAM replacing the mapping table information is reduced, thereby achieving the effect of reducing the read-write instruction completion time and improving the read-write performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN YILIAN INFORMATION SYST CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS8599604B2Less power consumptionShorter read and write timesDigital storageWrite bitPower inverter
In a memory cell, a transistor with extremely high off-resistance is used as a write transistor; a drain and a source of the write transistor are connected to a write bit line and an input of an inverter, respectively; and a drain and a source of a read transistor are connected to a read bit line and an output of the inverter, respectively. Capacitors may be intentionally disposed to the source of the write transistor. Alternatively, parasitic capacitance may be used. Since the data retention is performed using charge stored on these capacitors, a potential difference between power sources for the inverter can be 0. This eliminates leakage current between the positive and negative electrodes of the inverter, thereby reducing power consumption.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Transistor of semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8530962B2Total current dropShorten read timeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenWork function
Provided are a transistor of a semiconductor device and a method for manufacturing the same. A gate induced drain leakage (GIDL) current is reduced by decreasing a work function at an upper portion of a gate electrode, and a threshold voltage of the transistor is maintained by maintaining a work function at a lower portion of the gate electrode at a high level, thereby reducing a leakage current of the transistor and reducing a read time and a write time of the semiconductor device. The transistor of the semiconductor device includes: a recess with a predetermined depth in a semiconductor substrate; a first gate electrode disposed within the recess; and a second gate electrode disposed on the first gate electrode into which ions of one or more of nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), arsenic (As), aluminum (Al), and hydrogen (H) are doped.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
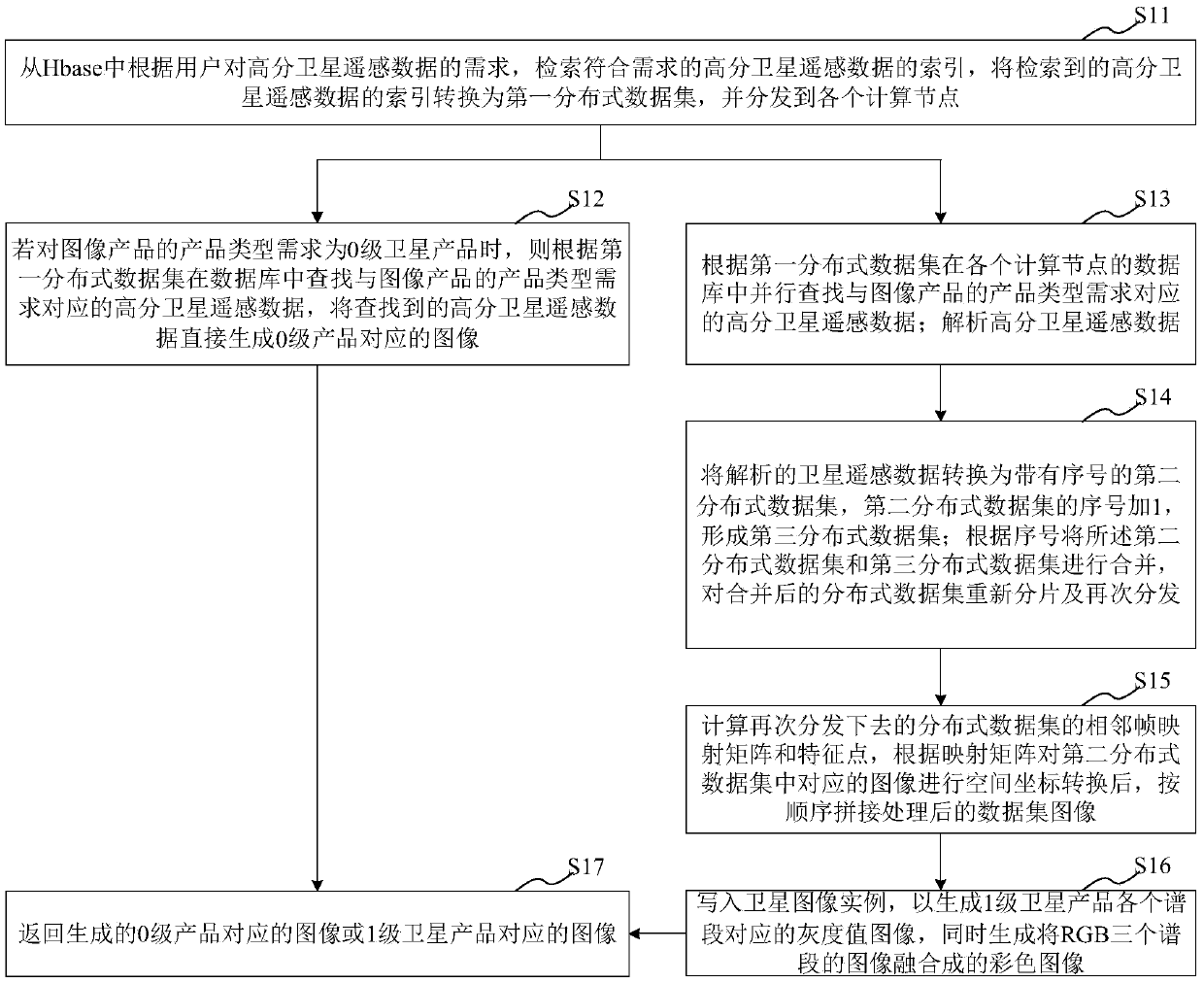
Distributed processing method/system for high-resolution satellite remote sensing data and medium
ActiveCN109657080AAccelerateReduce reading and writing timeGeometric image transformationStill image data indexingSensing dataSatellite remote sensing
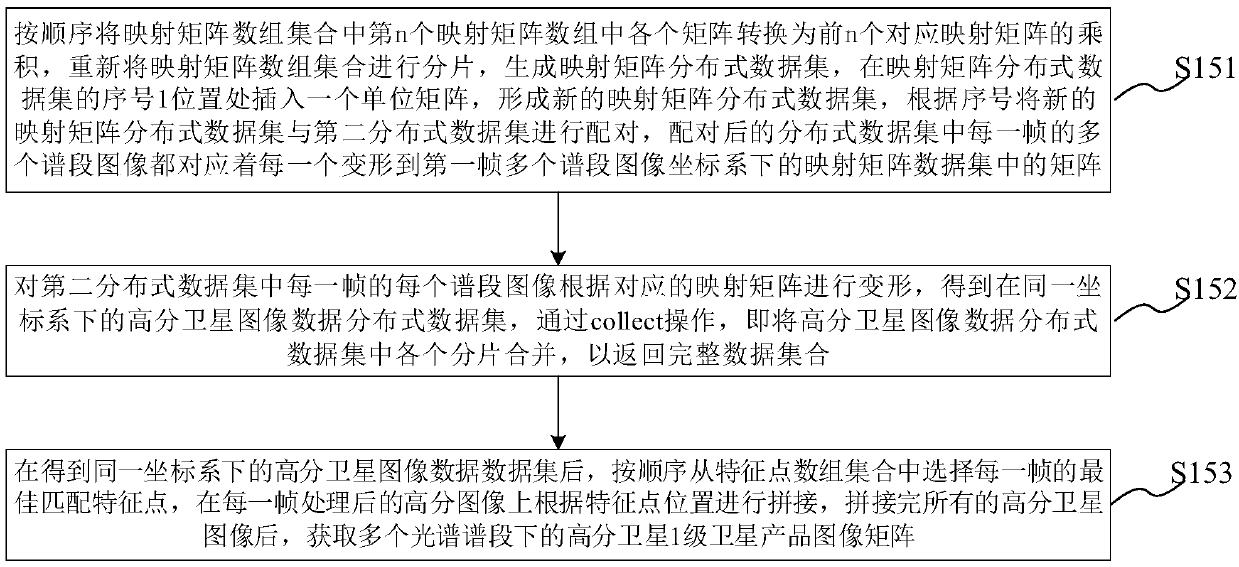
The invention provides a distributed processing method / system for high-resolution satellite remote sensing data and a medium, and the method comprises the steps: retrieving the index of the high-resolution satellite remote sensing data, converting the index into a corresponding first distributed data set, and distributing the first distributed data set to each computing node; If the satellite product is a 0-level satellite product, generating an image corresponding to the 0-level product; If the high-resolution satellite remote sensing data is a first-level satellite product, analyzing the high-resolution satellite remote sensing data, converting the high-resolution satellite remote sensing data into a second distributed data set with a serial number, and adding 1 to the serial number of the second distributed data set to form a third distributed data set; Combining the second distributed data set and the third distributed data set, and re-fragmenting and re-distributing the combined distributed data set; And performing an operation of calculating an image mapping matrix on the distributed data set to generate an image corresponding to the first-level satellite product. According to the method, the data processing speed and the product production speed are greatly increased, the hard disk data reading and writing time is shortened, and calculation processing can be rapidly completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
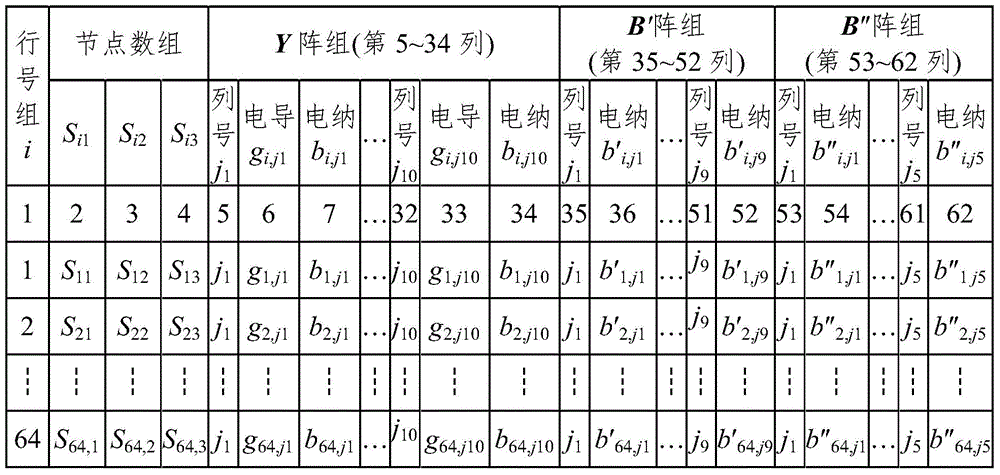
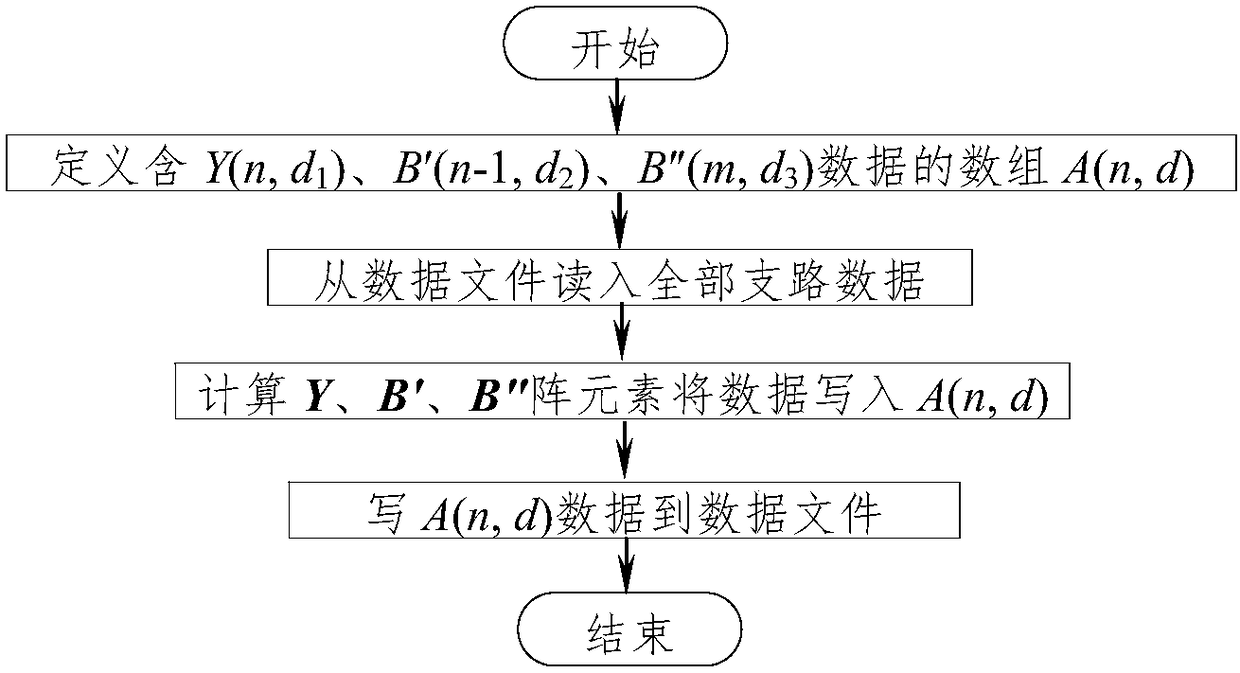
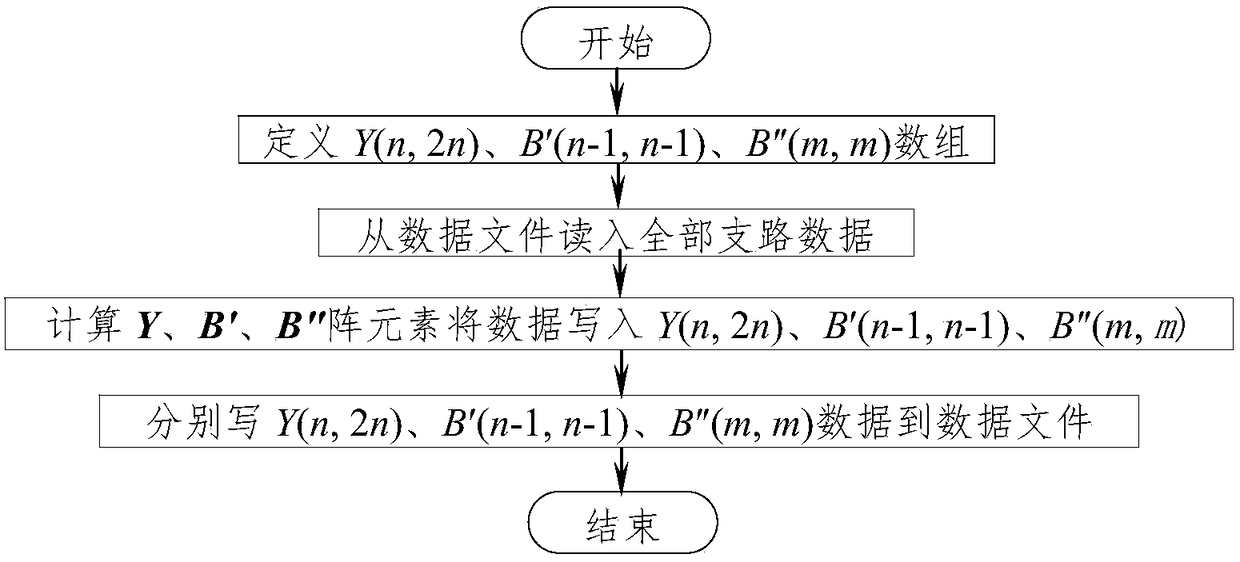
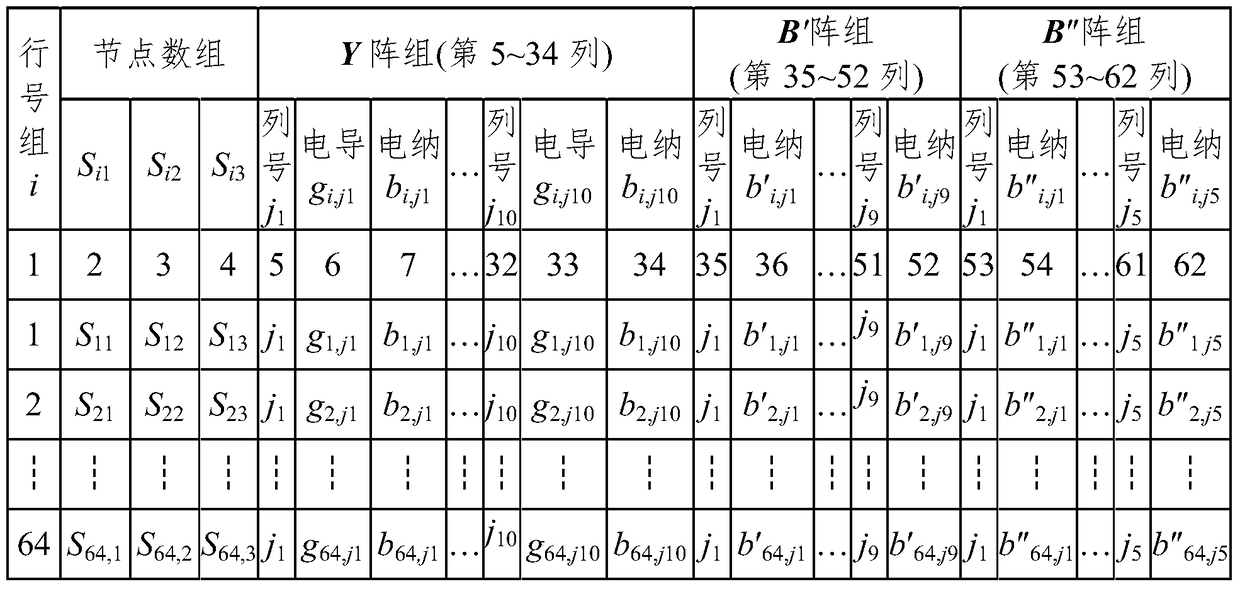
Rapid-reading-writing electric-power-system PQ-decomposition-method flow data storage method based on sparse technology
ActiveCN105786984AShorter read and write timesImprove read and write speedData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsNODALArray data structure
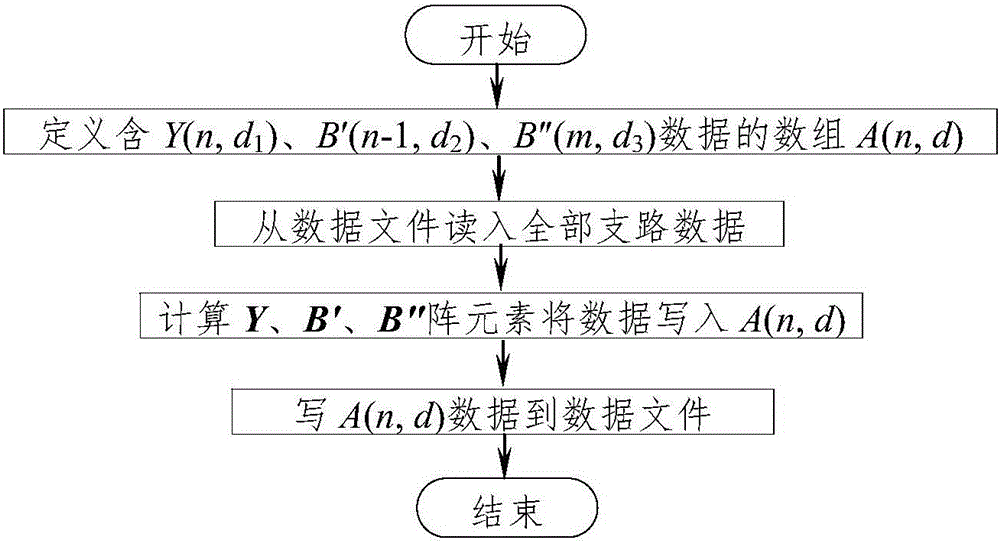
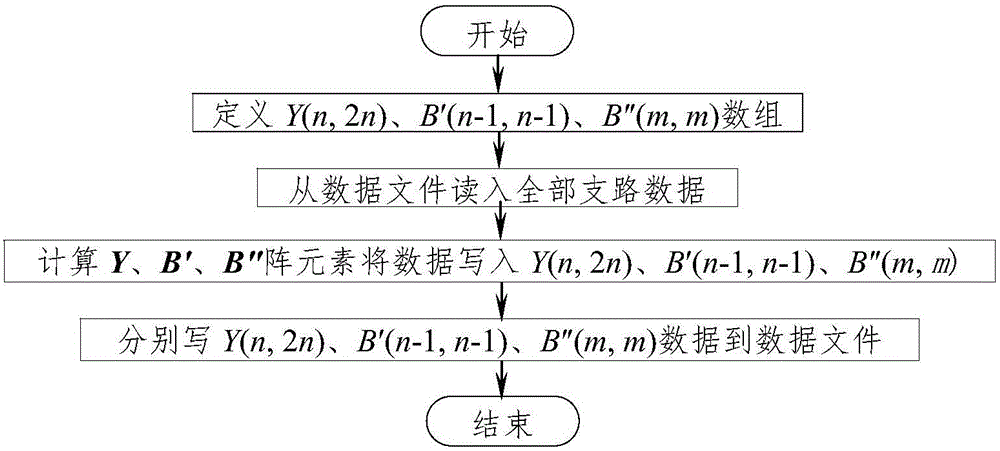
The invention discloses a rapid-reading-writing electric-power-system PQ-decomposition-method flow data storage method based on the sparse technology.The method includes the step that nonzero elements at the upper triangles and the lower triangles of arrays of Y(n, 2n), B'(n-1, n-1) and B''(m, m) in a traditional method are stored into an A(n, d) array formed by three virtual arrays of Y(n, d<1>), B'(n-1, d<2>) and B''(m, d<3>).The number of storage units is greatly decreased, the reading-writing speed of a data file and the calculating speed of I<pi> or I<qi> or P or Q during PQ-decomposition-method flow calculation are increased, the number of the storage units is also greatly decreased, and efficiency is greatly improved.Compared with the traditional method, the method has the advantages that as for an IEEE-118 node system, the largest number of the storage units is only 14.69% of that of the traditional method, the practical number of the storage units is only 6.66% of that of the traditional method, the data file writing time and the data file reading time are 14.32% and 7.29% of the data file writing time and the data file reading time of the traditional method respectively, and the larger the number of nodes is, the more obvious the advantages of the method are.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
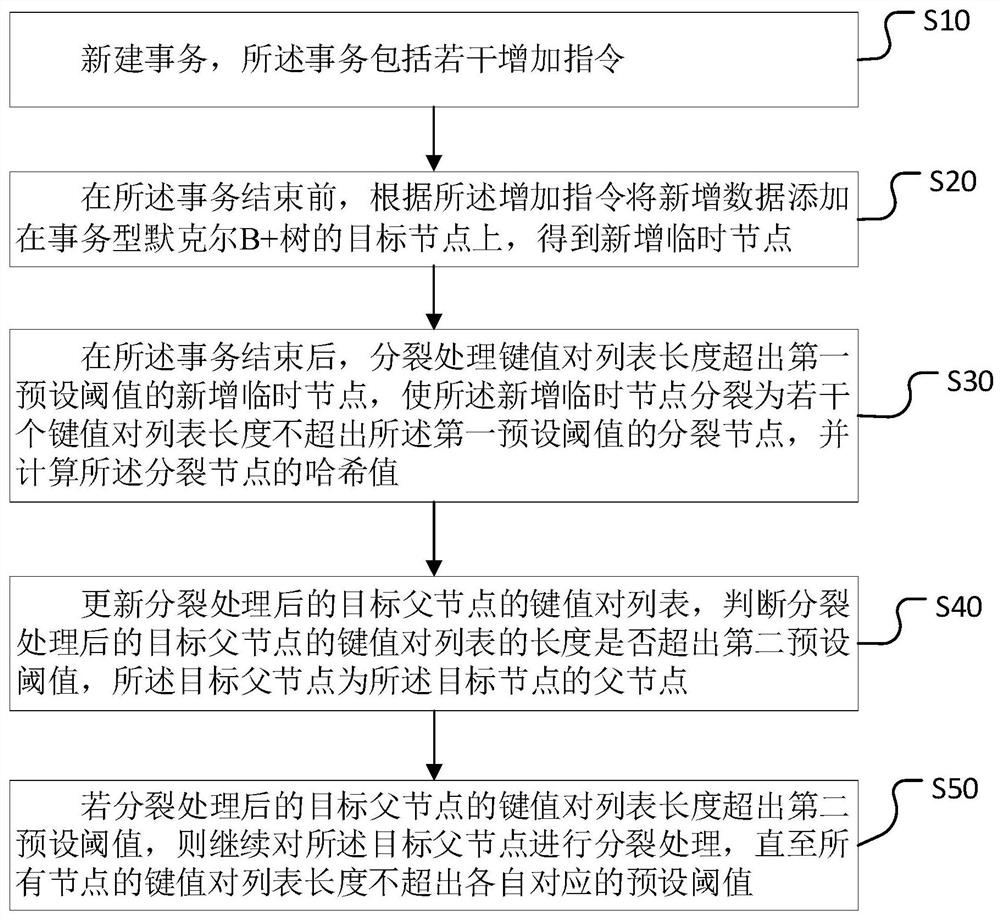
Data storage method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112559529AReduce processing timeSave computing resourcesDatabase distribution/replicationEnergy efficient computingPathPingData store
The invention relates to the field of block chains, and discloses a data storage method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium.The method comprises the steps of newly establishing a transaction, wherein the transaction comprises a plurality of adding instructions; before the transaction is finished, adding a newly-added temporary node according to the adding instruction; after the transaction is finished, splitting the newly added temporary node into a plurality of split nodes, and calculating hash values of the split nodes; updating the key value pair list of the target father node, and judging whether the length of the key value pair list of the target father node exceeds a second preset threshold value or not; and if yes, continuing to split the target father node until thekey value pair list lengths of all nodes do not exceed respective corresponding preset thresholds. Through asynchronous processing of transaction processing and node splitting and coupling of node splitting and hash calculation, the transaction processing efficiency can be improved, the IO frequency of paths and index values of a transaction type Merkel B + tree is reduced, and the disk read-write time is shortened.
Owner:HANGZHOU QULIAN TECH CO LTD
Mobile phone system file online modification method and device and storage medium
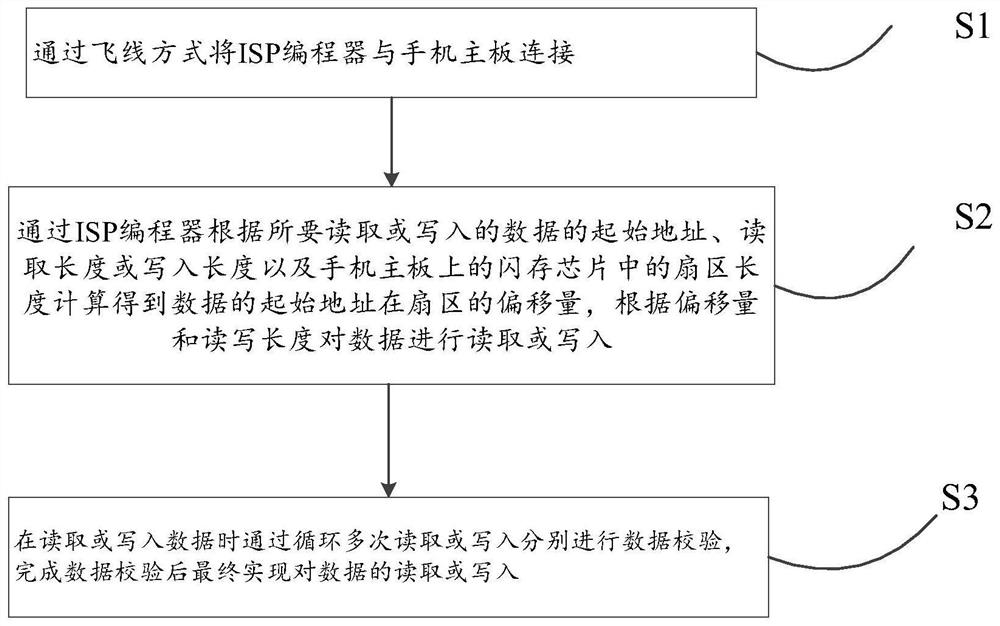
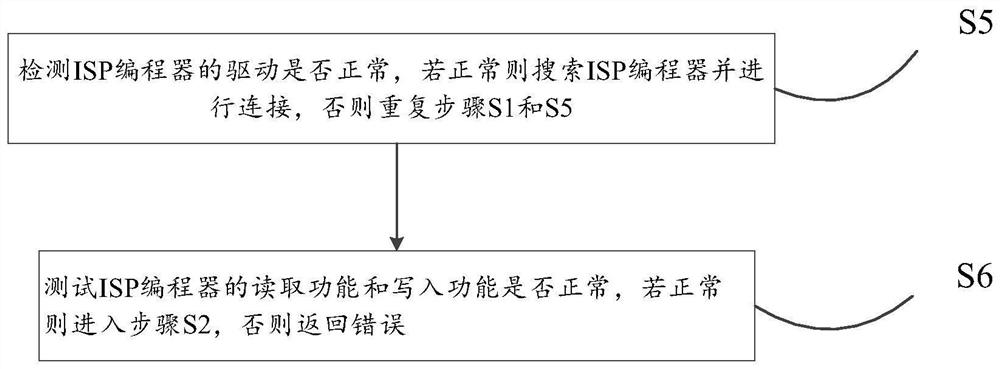
ActiveCN112083880AGuaranteed correctnessEnsure safetyInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSource Data VerificationEngineering
The invention discloses a mobile phone system file online modification method and device and a storage medium. The method comprises steps of connecting an ISP programmer with a mobile phone mainboardin a fly line mode; calculating the offset of the initial address of the data in a sector through an ISP programmer according to the initial address, the reading length or the writing length of the data to be read or written and the length of the sector in a flash memory chip on a mobile phone mainboard, and reading or writing the data according to the offset and the reading and writing length; and when the data is read or written, carrying out data verification respectively by circularly reading or writing for multiple times, and reading or writing the data finally after the data verificationis completed. Through the method, reading and writing of any position and any data size on the flash memory chip of the mobile phone can be realized. Moreover, the correctness and security of the data can be ensured after the data verification, and the data can be directly modified online, so that errors possibly caused by downloading and uploading mirror images are reduced, and the modificationtime can be shortened.
Owner:厦门市美亚柏科信息安全研究所有限公司
Apparatus, system, and method for redundant identification of a storage medium format
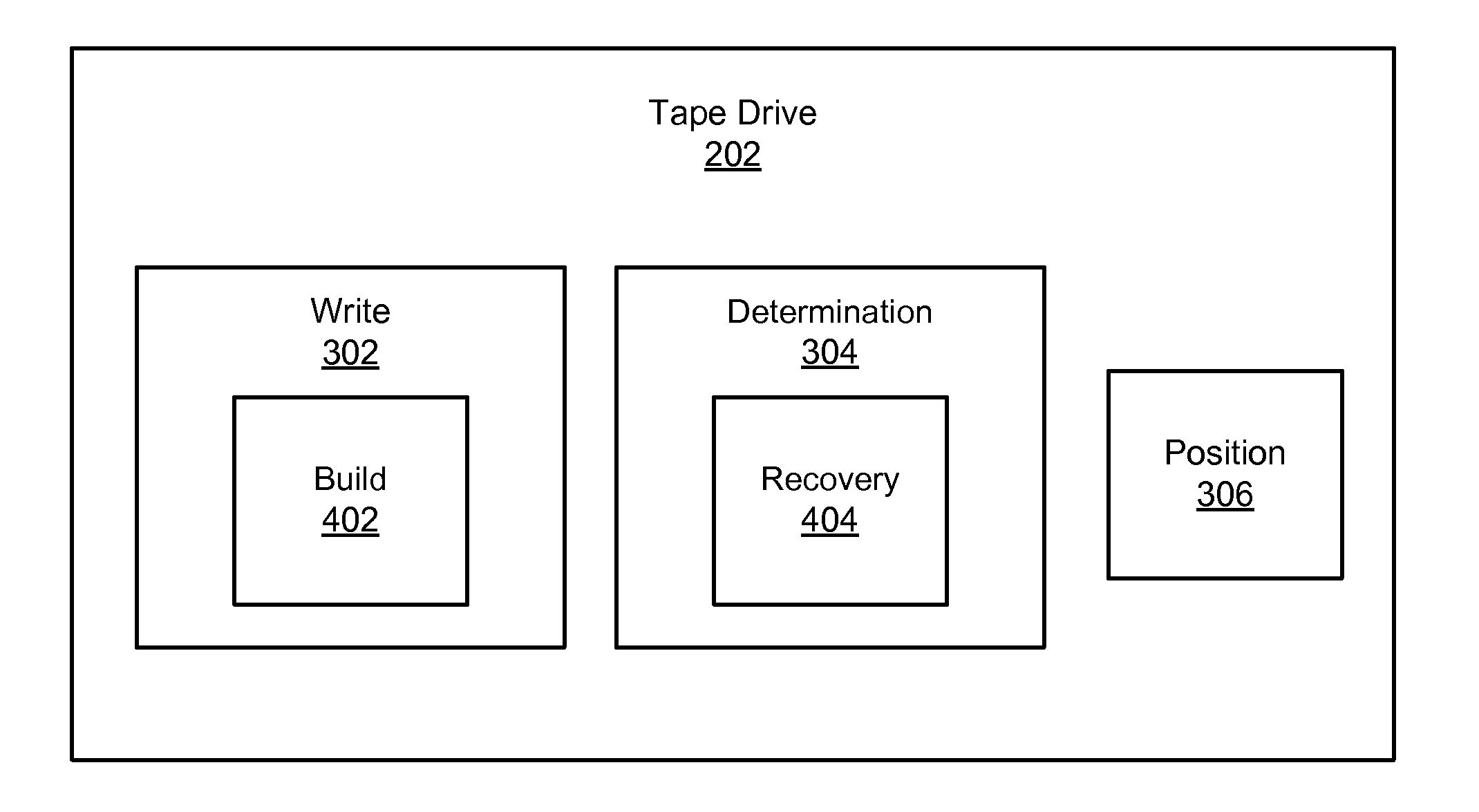
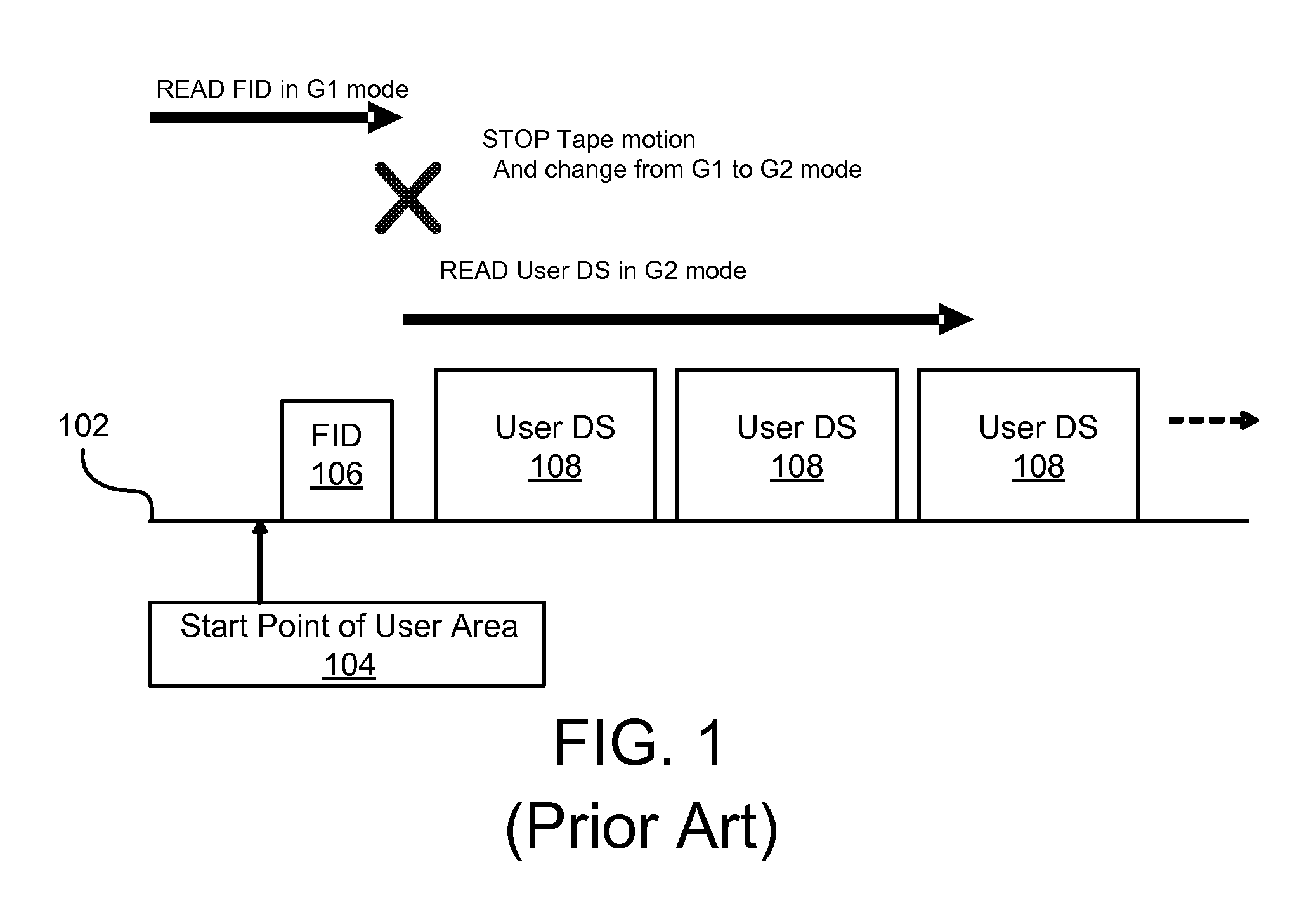
InactiveUS20080100946A1Shorten read timeShorten write timeFilamentary/web record carriersUsing non-detectable carrier informationData setComputer module
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for redundant identification of a storage medium format. The apparatus for redundant identification of a storage medium format is provided with a plurality of modules configured to functionally execute the necessary steps of writing a Format Identification Data Set (“FID”) to a plurality of predetermined locations on the storage medium, determining a format of the storage medium based on information in the FID, and setting a starting position on the storage medium for a subsequent operation, wherein the starting position is associated with the format of the storage medium. These modules in the described embodiments include a write module, a determination module, and a position module. In a further embodiment, the storage medium may include a data storage tape housed within a tape cartridge, wherein the tape cartridge further comprises a cartridge memory (“CM”) for storing a CM FID.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data read-write method and device and dynamic random access memory
ActiveCN111241007AIncrease power consumptionReduce power consumptionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationEngineeringComputer science
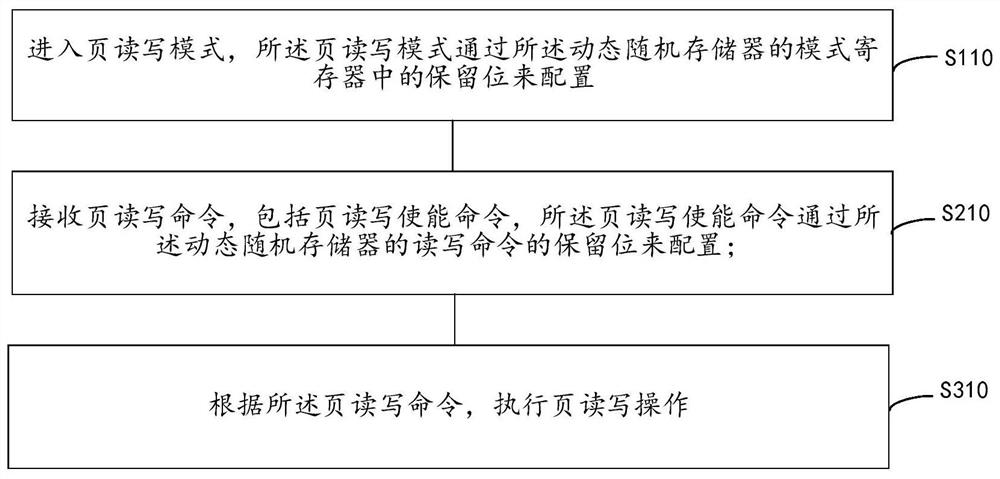
The invention provides a data read-write method, a read-write device and a dynamic random access memory. The method includes: entering a page read-write mode according to a mode selection command, wherein the page read-write mode command is configured through a mode register of the dynamic random access memory; receiving page read-write commands, wherein the page read-write commands comprise a page read-write enable command and a cross read command, the page read-write enable command is configured through a first reserved bit of a read-write command of the dynamic random access memory, the cross read command is configured through a second reserved bit of the read-write command of the dynamic random access memory, and the cross read command is used for controlling cross read-write data in aplurality of storage block groups; and executing cross page read-write operation according to the page read-write command.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
Method for quickly displaying monomer model in massive geographical information three-dimensional models
InactiveCN103412959AEffective displayQuick calculationSpecial data processing applications3D modellingPersonal computerMonomer
The invention relates to a method for quickly displaying a monomer model in massive geographical information three-dimensional models. The method comprises the following steps of (1) constructing the geographical information massive three-dimensional models; (2) constructing quick searching units; (3) constructing unique ID (identifications) of the quick searching units; (4) displaying the monomer model. The quick searching units in a region covered by a window display range can be quickly calculated; the searching and calculating speed can be increased by tens of thousands of times by finding out the required monomer three-dimensional model from the quick searching units; high-efficiency displaying of the massive geographical information three-dimensional models can be also realized even through a general commercial PC (personal computer) machine.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF SURVEYING & MAPPING +1
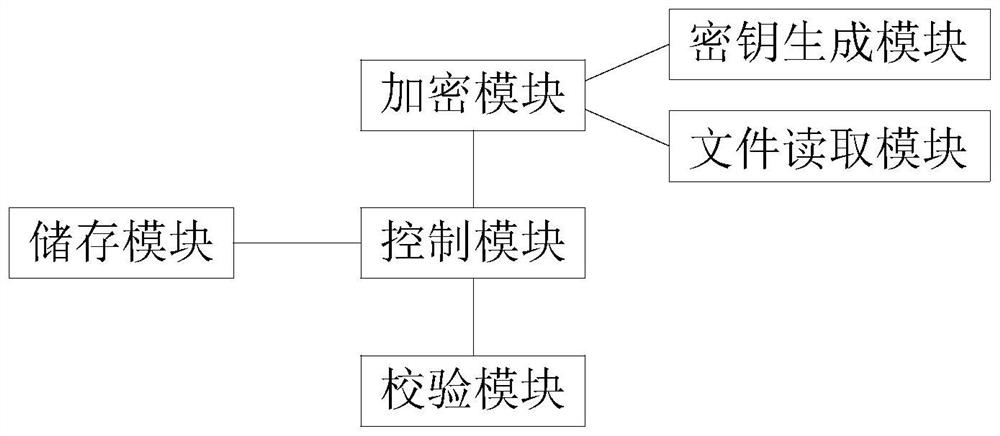
Audio and video encryption protection on-demand method and device and electronic equipment
PendingCN114143576AShorter read and write timesReduce not being read normallySelective content distributionHigh level techniquesFile transmissionEngineering
The invention discloses an audio and video encryption protection on-demand method, an audio and video encryption protection on-demand device and electronic equipment, and aims to solve the problems that in the prior art, the content of a playing end is easy to leak, the volume of an encrypted file is increased, and audio and video files need to be re-coded and re-decoded in encryption and decryption operation, so that the operation is time-consuming and labor-consuming. And the requirement on hardware is high. The video-on-demand method comprises the following steps: S1, encrypting and decrypting audio and video contents; s2, authorization of the cloud authorization center; and S3, client-side video-on-demand. According to the on-demand method and device and the electronic equipment, cache files are not generated in the on-demand process, file reading and writing time is shortened through file copying, destructive processing is carried out on each frame so that it can be guaranteed that audio and video file content is not read normally, the problem of content leakage of a playing end is prevented, the file transmission bandwidth requirement is low, and the file transmission efficiency is high. Time consumed for playing audio and video files to a player is short, playing and storage are both under authorization protection, content leakage is prevented, and the rerecording scene and time are further traced through rerecording watermarks.
Owner:广东爱视文化发展有限公司
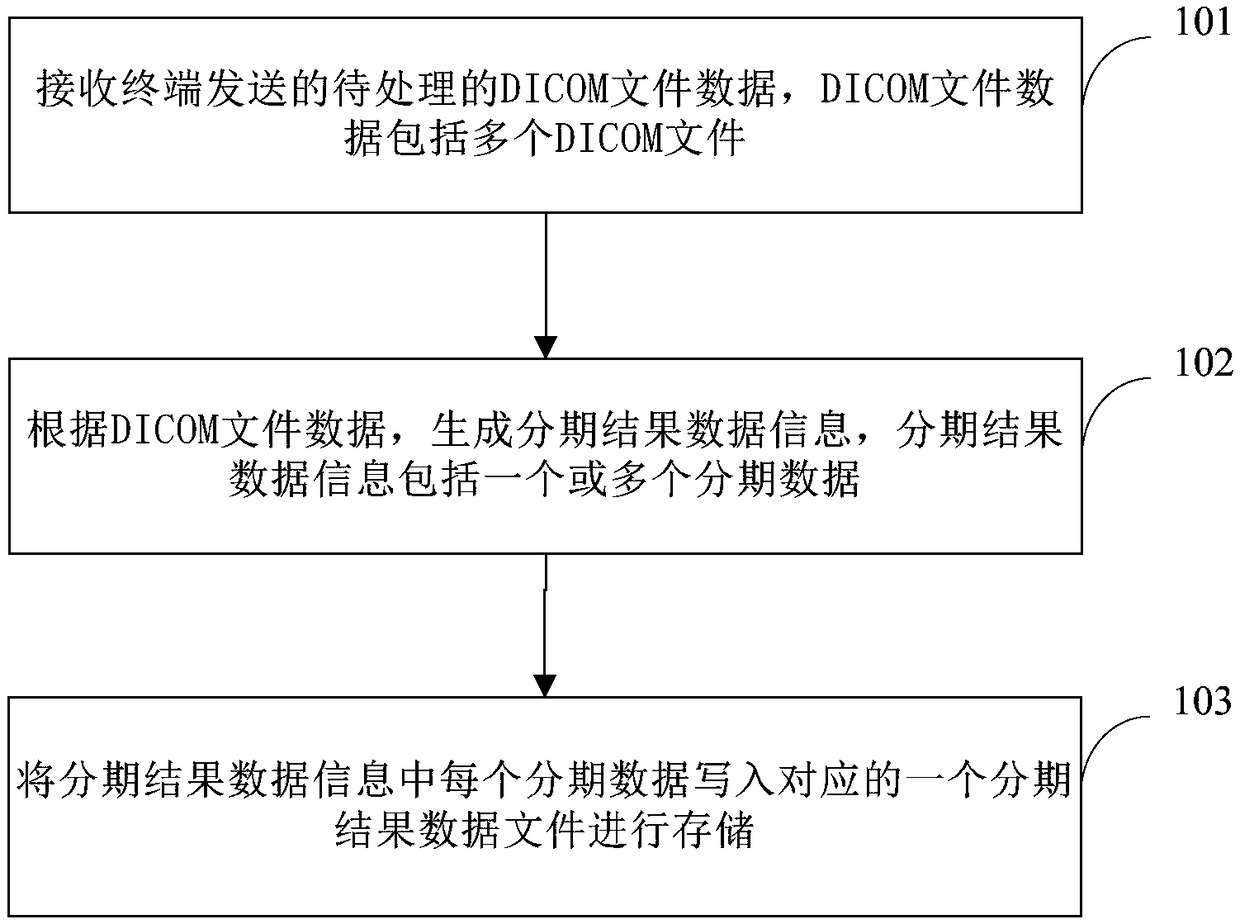
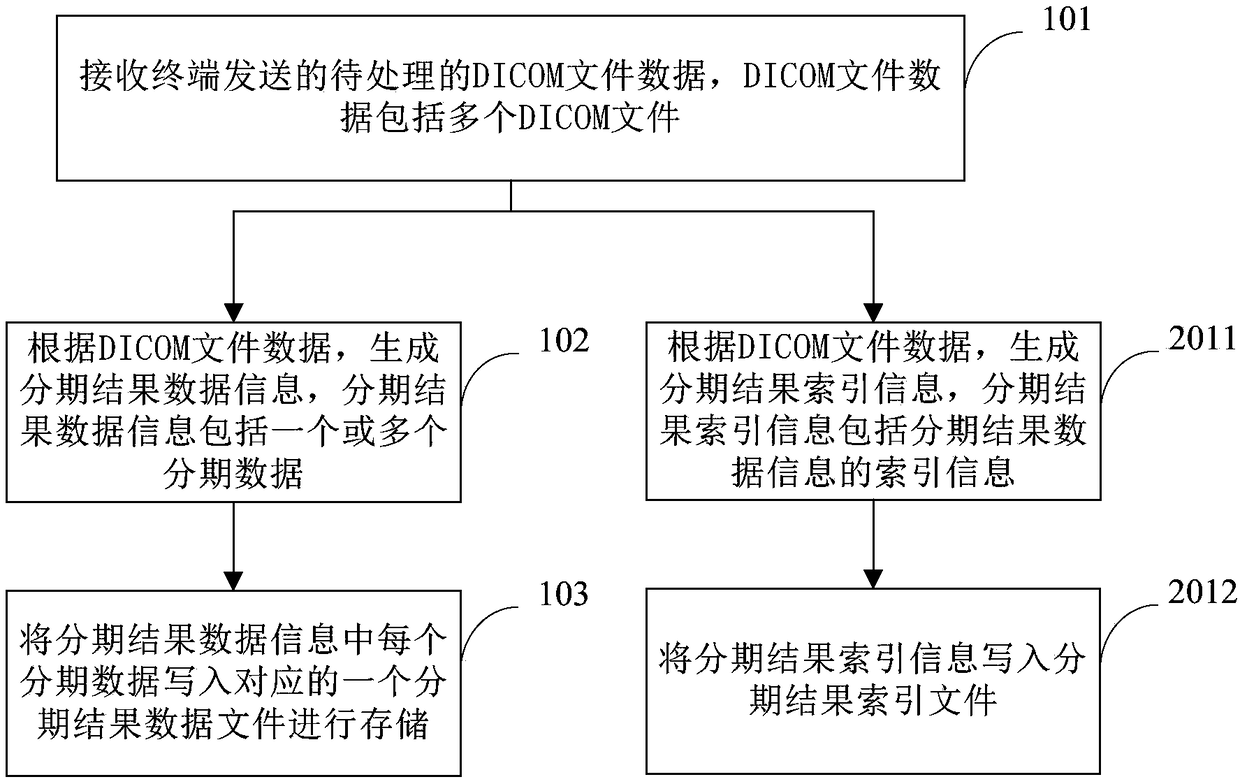
DICOM image processing method and server
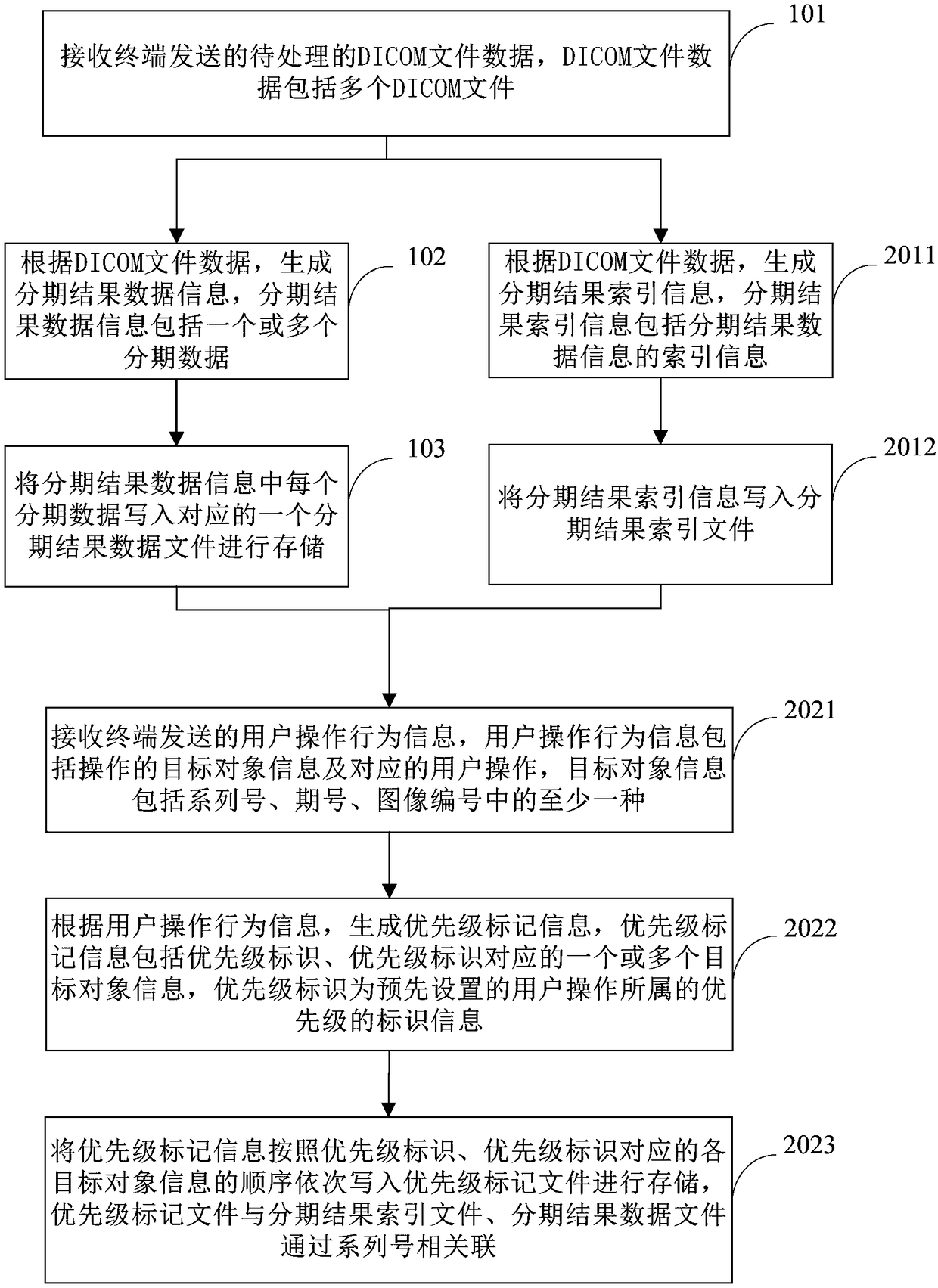
InactiveCN108877899AReduce transfer timeShorter read and write timesMedical imagesTransmissionDICOMImaging processing
The invention provides a DICOM image processing method and a server. The method comprises the steps of: receiving to-be-processed DICOM file data transmitted by a terminal, wherein the DICOM file datainclude multiple DICOM files; generating, according to the DICOM file data, staged result data information, wherein the staged result data information includes one or more than one piece of staged data; writing each piece of staged data in the staged result data information into one corresponding staged result data file for storage. Staged result data information is generated based on the plurality of DICOM files transmitted by the terminal, and each piece of staged data is rewritten into one corresponding staged result data file for storage, so that the plurality of DICOM files are rewritteninto large files for stage and network transmission time and disk reading-writing time are effectively reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MEDICAL EQUIP
A visual storage method for massive seismic data
ActiveCN112069135BReduce capacityShorter read and write timesFile/folder operationsSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionEngineering
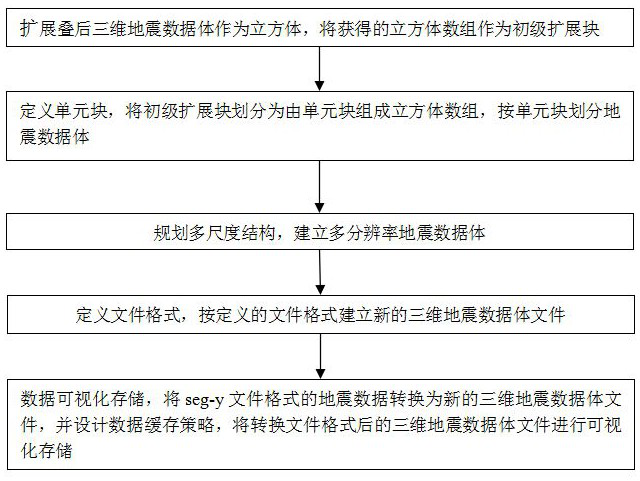
The invention discloses a method for visually storing massive seismic data, comprising: 1. expanding the post-stack three-dimensional seismic data body as a cube, and using the obtained cube array as a primary expansion block; 2. defining unit blocks, and dividing the primary expansion block into The cube array is composed of unit blocks, and the seismic data volume is divided according to the unit blocks; 3: plan the multi-scale structure, and establish the multi-resolution seismic data volume; 4: define the file format, and create a new 3D seismic data volume file according to the defined file format; 5 : Data visualization storage, convert the seismic data in seg‑y file format into a new 3D seismic data volume file, and design a data caching strategy to visually store the converted 3D seismic data volume file. The invention proposes a post-stack large-scale three-dimensional seismic data volume file format suitable for multi-directional and multi-scale reading and writing with block and hierarchical storage with balanced performance, which can store large-scale three-dimensional seismic data volumes and perform efficient reading and writing.
Owner:北京中恒利华石油技术研究所
Data reading and writing method, reading and writing device and dynamic random access memory
ActiveCN111240582BReduce power consumptionShorter read and write timesMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersComputer hardwareComputer architecture
The present invention provides a data reading and writing method, a reading and writing device and a DRAM. The reading and writing method includes: entering a page reading and writing mode, and the page reading and writing mode is configured through a reserved bit in a mode register of the DRAM . A page read / write command is received, including a page read / write enable command, and the page read / write enable command is configured through a reserved bit of the read / write command of the DRAM. Perform page read and write operations according to the page read and write commands. The reading and writing method of the present invention enables each reading and writing command to read and write a large amount of data, reduces the number of times of sending the reading and writing commands, improves the reading and writing speed, and reduces power consumption.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
A crash analysis method and system for binary programs
ActiveCN113268427BShorter read and write timesLow costSoftware testing/debuggingPoint spreadCrash analysis
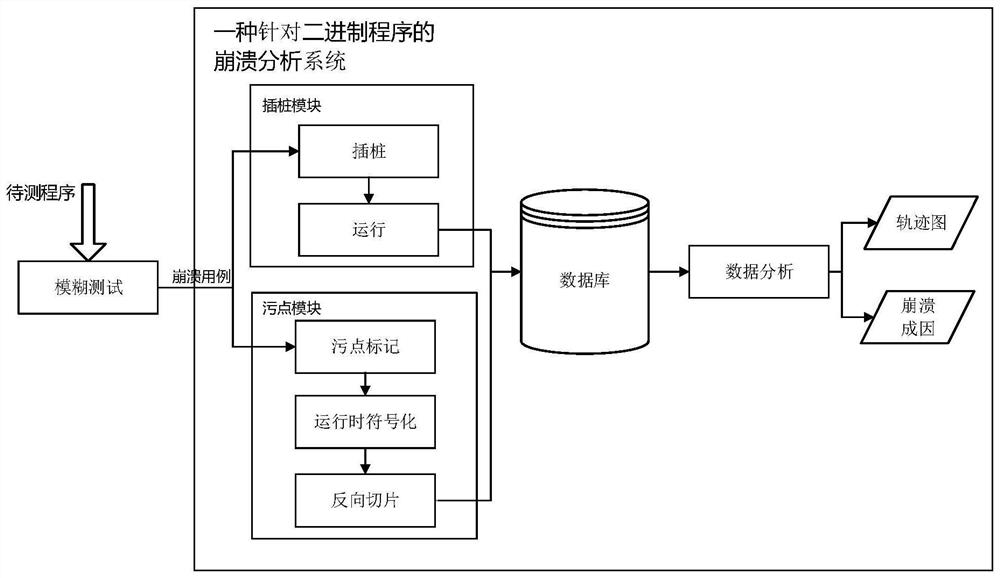
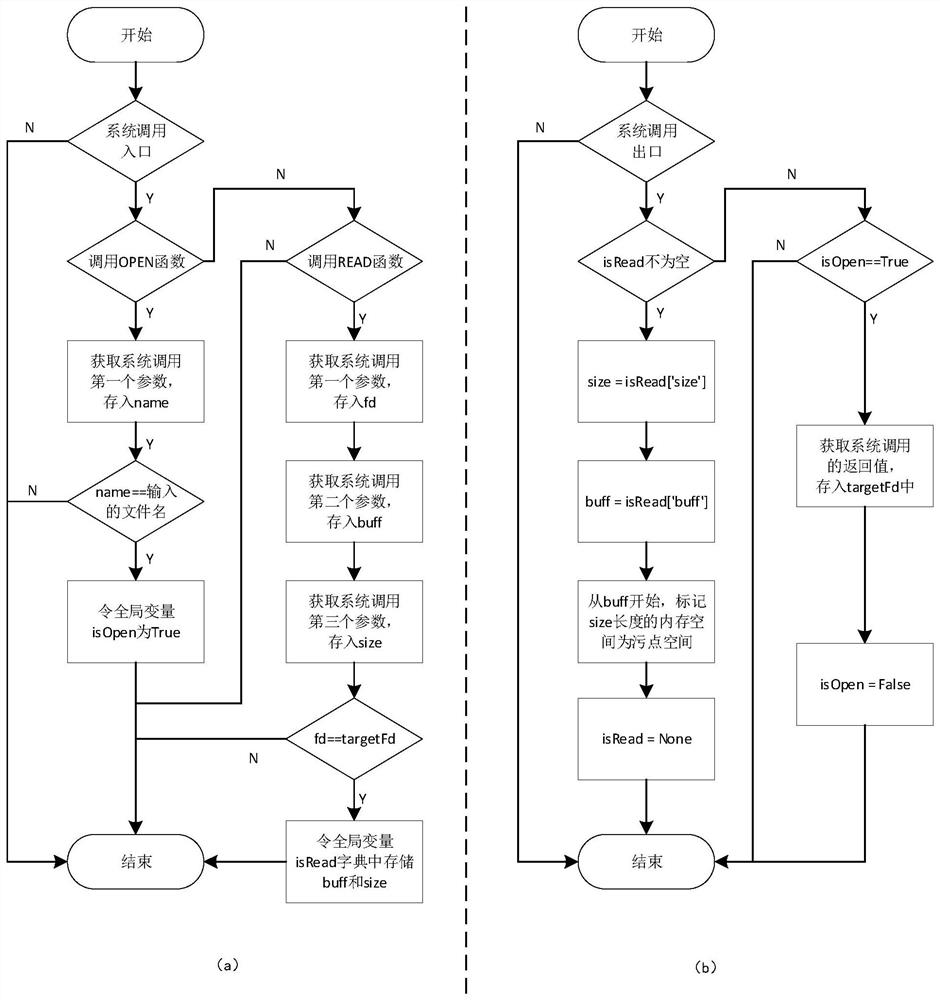
The present invention discloses a crash analysis method and system for binary programs, including steps: S1, information collection and processing, in this step, the instrumentation module performs code instrumentation on multiple key positions and basic blocks, and then runs the program , record information; the taint module takes the program input as taint, tracks the spread of taint during program execution, and at the same time, performs symbolic operation on each executed instruction, and finally performs reverse slice from the crash point according to the symbolic content , record information; S2, analyze based on the data processed in step S1, and obtain the program execution trajectory diagram, stain propagation trajectory diagram and crash causes, etc.; the present invention can analyze the program without source code, and collect the program running Crash information, crash backtracking, locating the crash point, determining the cause of the crash, etc., greatly reduces the cost of manual analysis, and can assist vulnerability analysts to quickly determine the mechanism of the program crash.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH CYBER SECURITY CO LTD
Data reading and writing method and device, dynamic random access memory
ActiveCN111241007BIncrease power consumptionReduce power consumptionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer architectureMode selection
The invention provides a data reading and writing method, a reading and writing device and a dynamic random access memory, which enters a page reading and writing mode according to a mode selection command, and the page reading and writing mode command is configured through the mode register of the dynamic random access memory; receiving page reading The write command includes a page read-write enable command and an interleave read command, the page read-write enable command is configured through the first reserved bit of the read-write command of the DRAM, and the interleave read command is configured through the The second reserved bit of the read and write command of the dynamic random access memory is configured, and the interleave read command is used to control the interleave read and write data in a plurality of memory block groups; according to the page read and write command, perform the interleave Page read and write operations.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
A cache system based on non-volatile memory and software raid
ActiveCN106528001BAvoid multiple visitsShorter read and write timesInput/output to record carriersDielectricRAID
The present invention proposes a cache system based on non-volatile memory and software RAID, which is characterized by a novel storage system architecture integrating non-volatile memory Apache Pass, software RAID and Device Mapper driver module Buaacache. The invention utilizes the Device Mapper mechanism of Linux to manage the software RAID, and uses the high-speed device Apache Pass as the Cache of the low-speed RAID, thereby constructing a two-level cache system. Persistent Memory has the characteristics of no loss of media data after power failure and excellent read and write performance. The present invention selects Persistent Memory as the high-speed cache of the software RAID, and realizes that the reading and writing performance of the software RAID is close to or even exceeds that of the hardware RAID under the condition that the cost is far lower than that of the hardware RAID.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A power system pq decomposition method power flow data storage method based on sparse technology that can be quickly read and written
ActiveCN105786984BShorter read and write timesImprove read and write speedData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsNODALArray data structure
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com