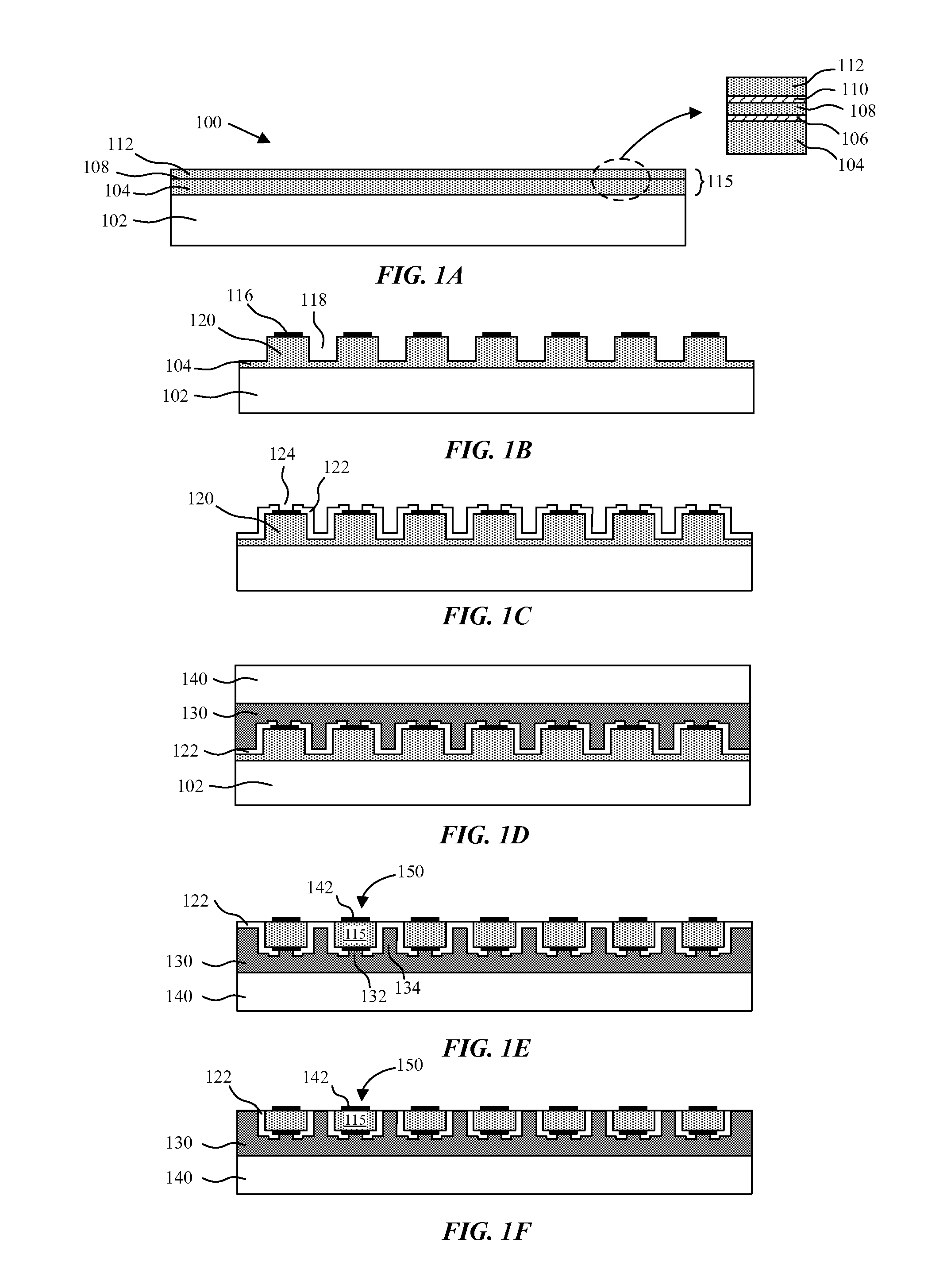
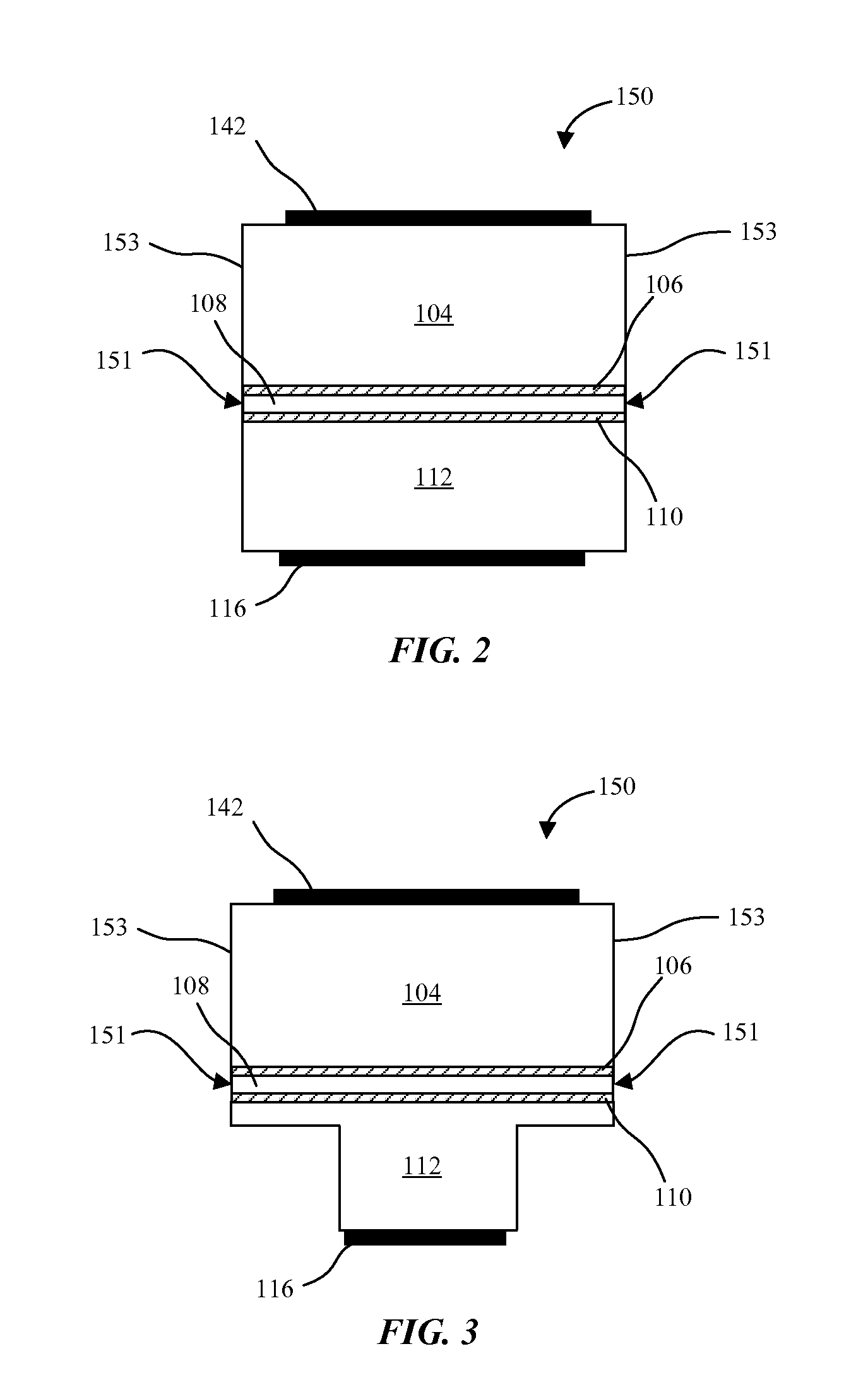
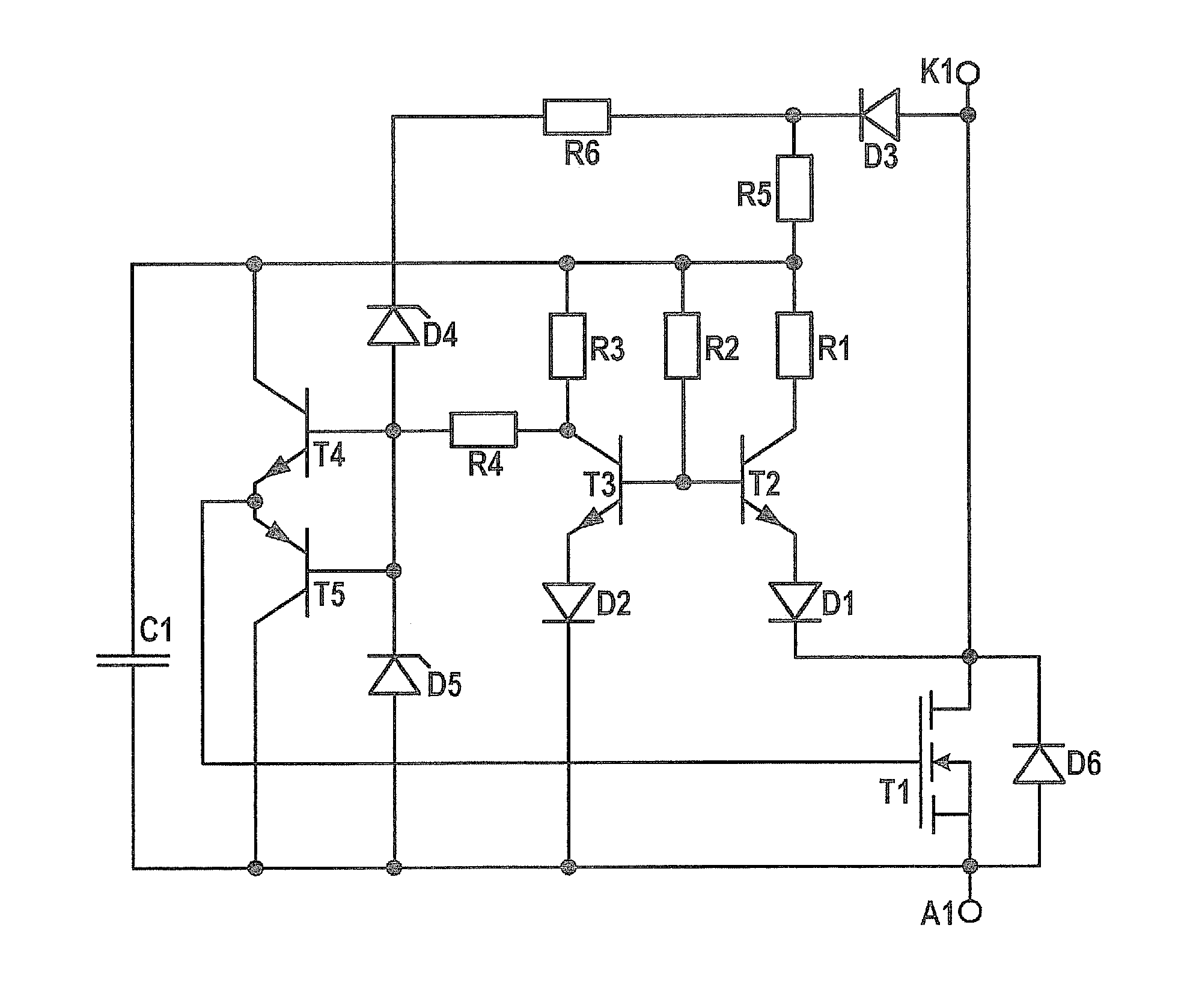
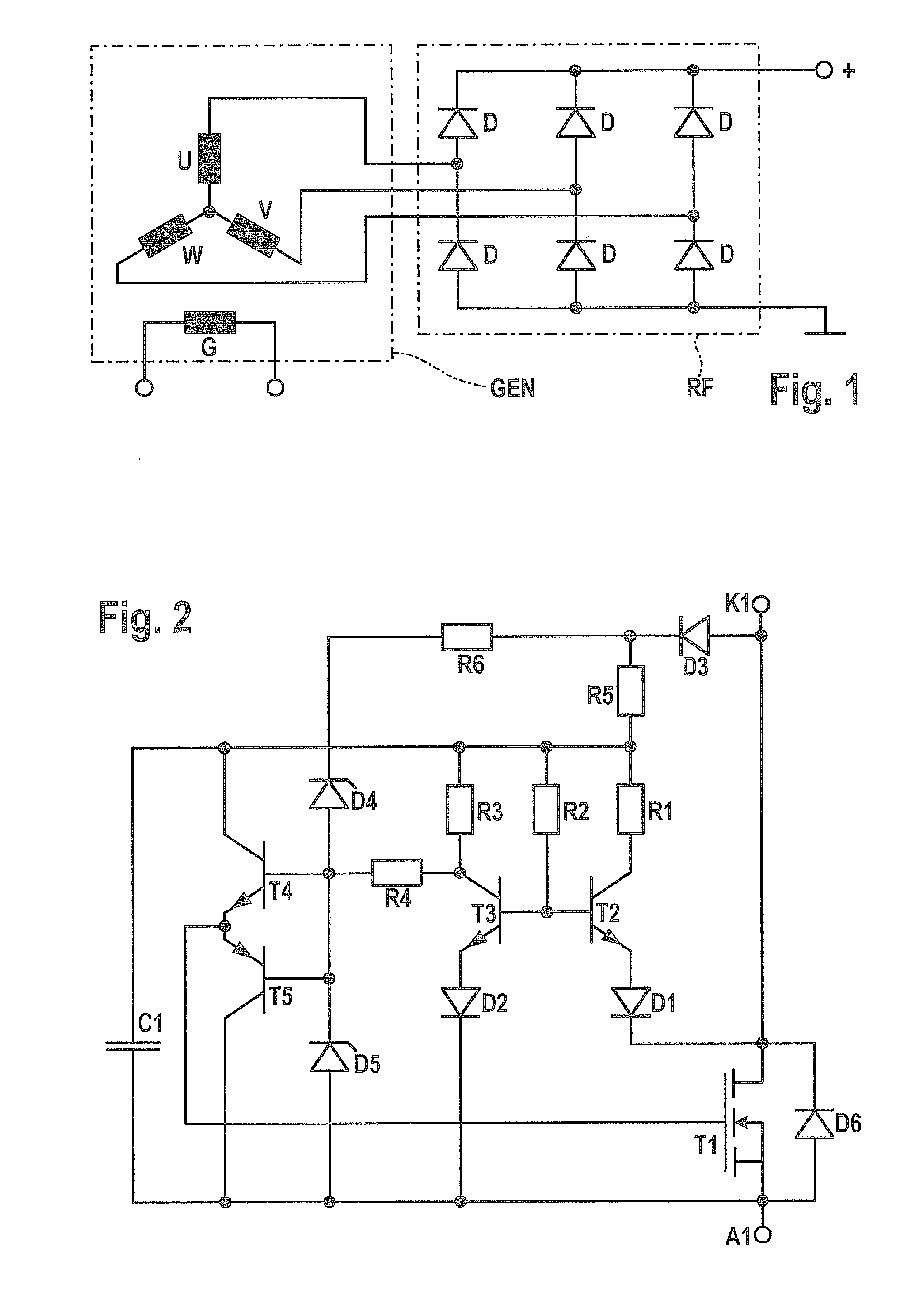
Patents
Literature
67 results about "P–n diode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
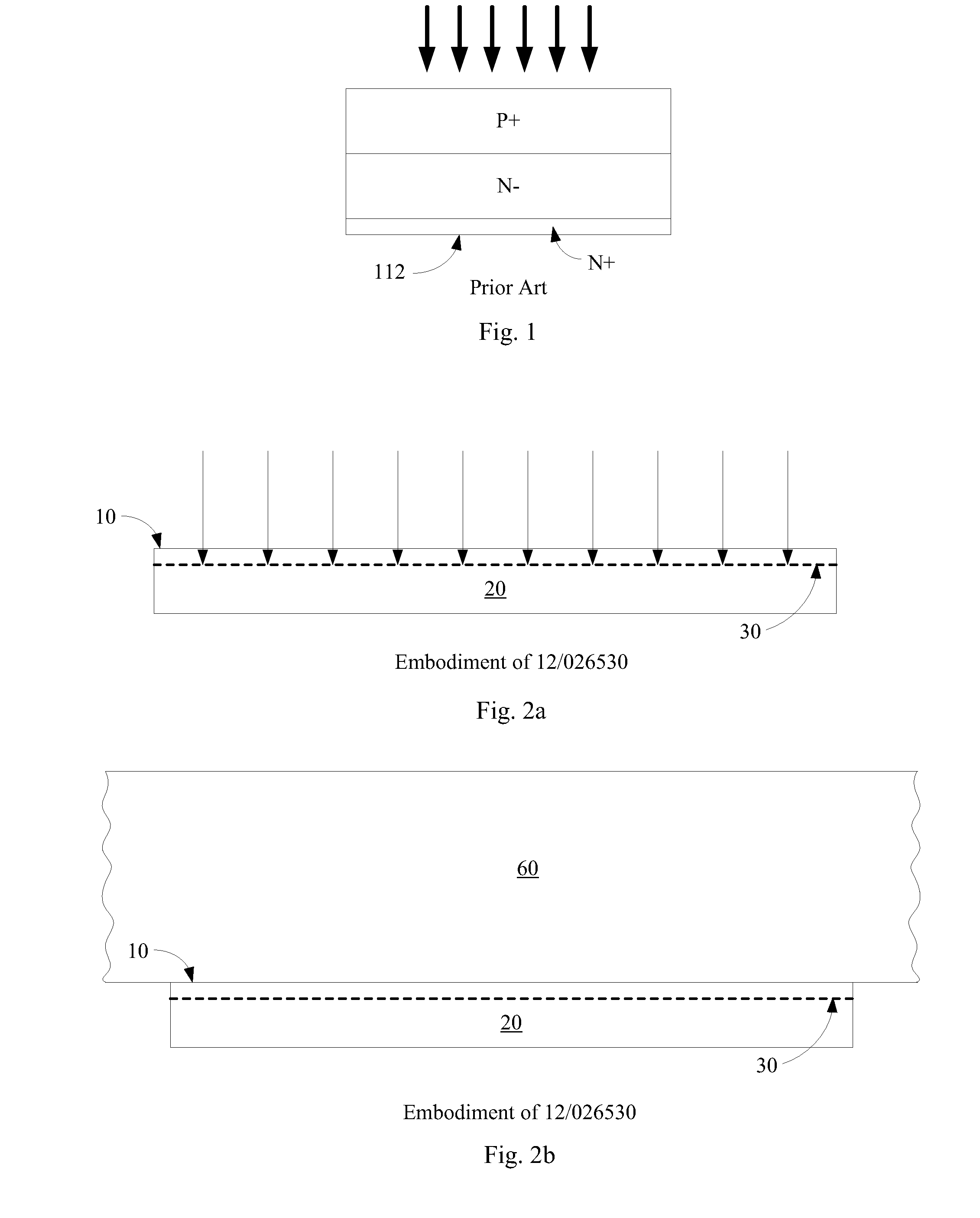
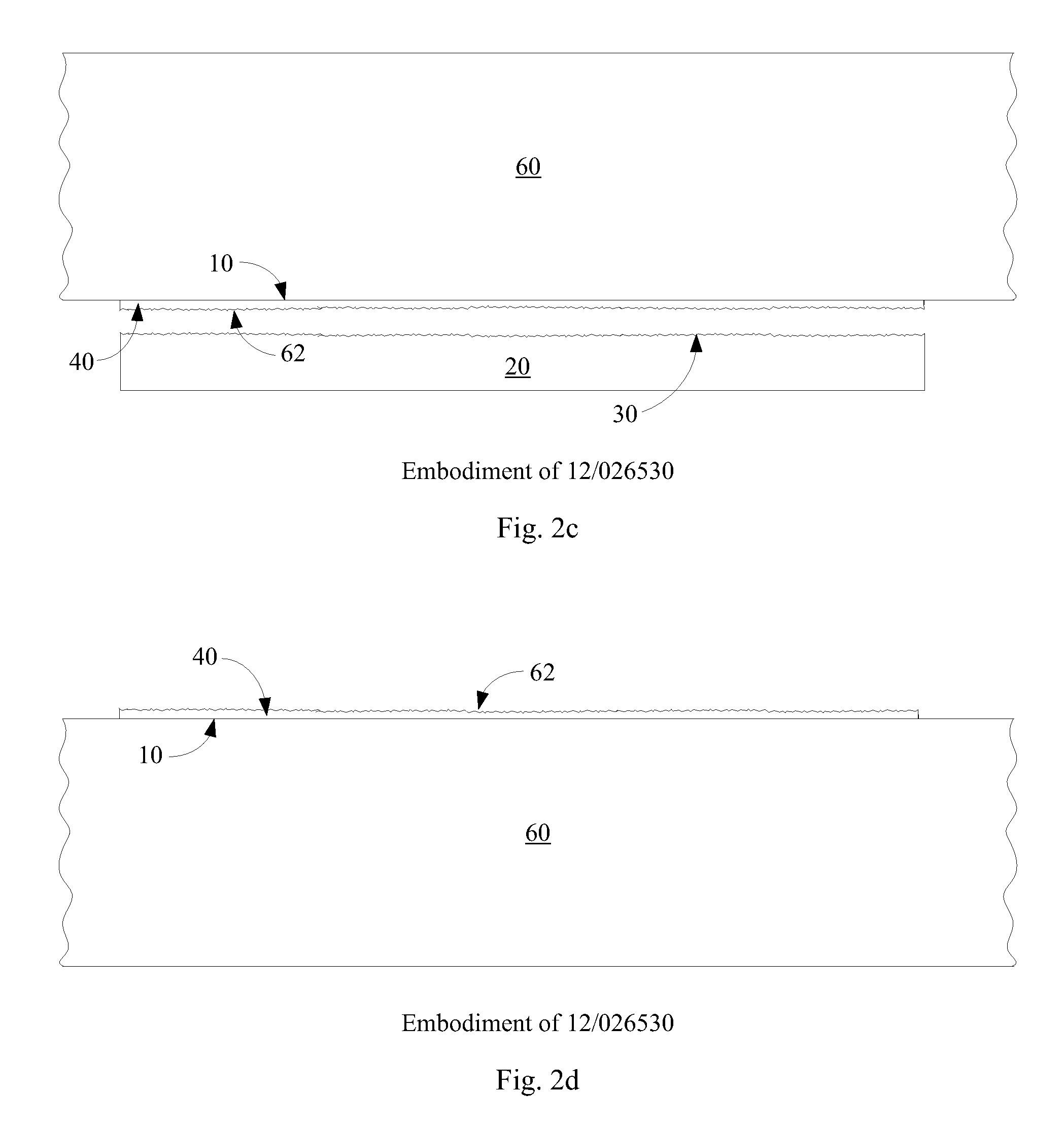
This article provides a more detailed explanation of p–n diode behavior than that found in the articles p–n junction or diode. A p–n diode is a type of semiconductor diode based upon the p–n junction. The diode conducts current in only one direction, and it is made by joining a p-type semiconducting layer to an n-type semiconducting layer. Semiconductor diodes have multiple uses including rectification of alternating current to direct current, detection of radio signals, emitting light and detecting light.
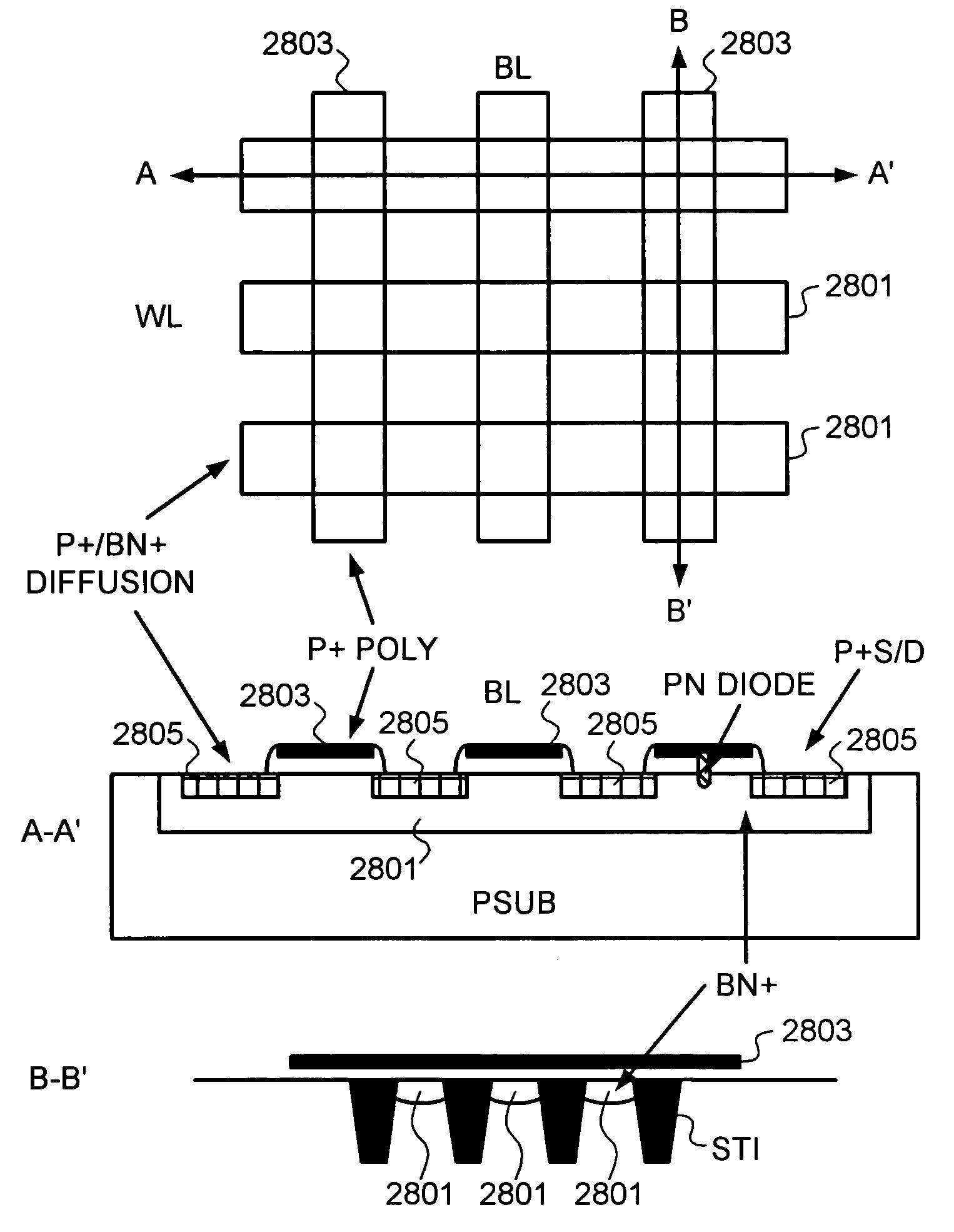
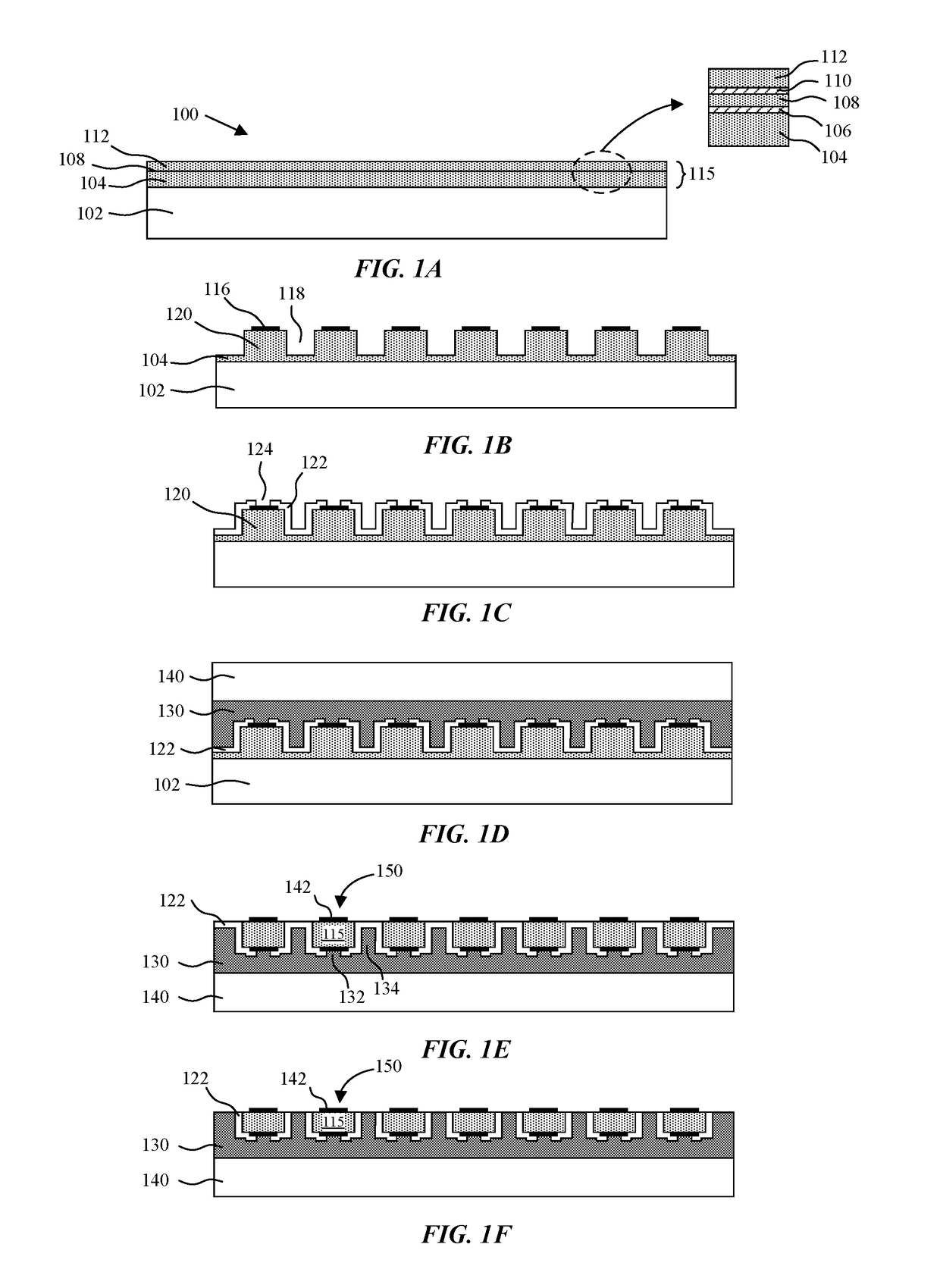
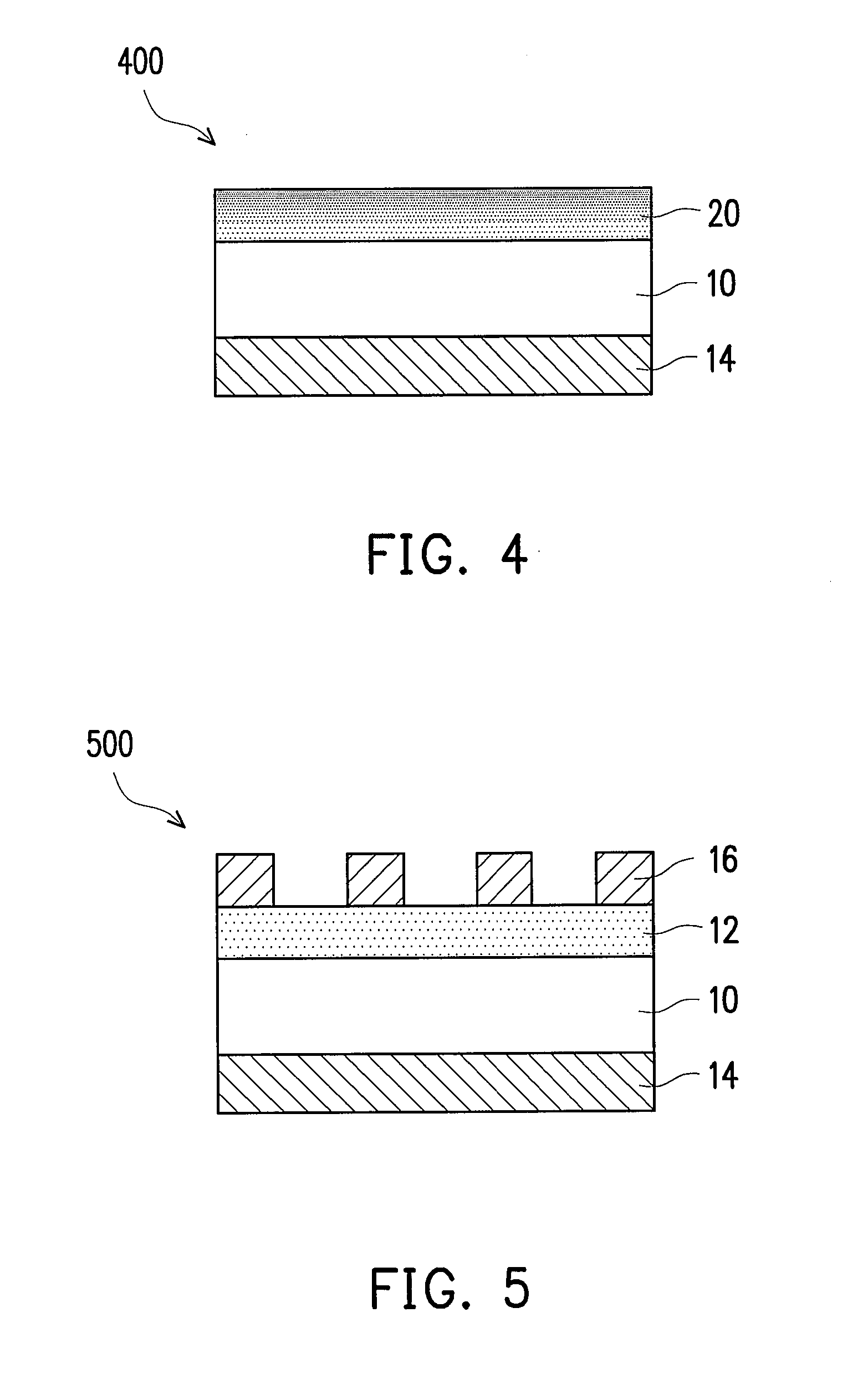
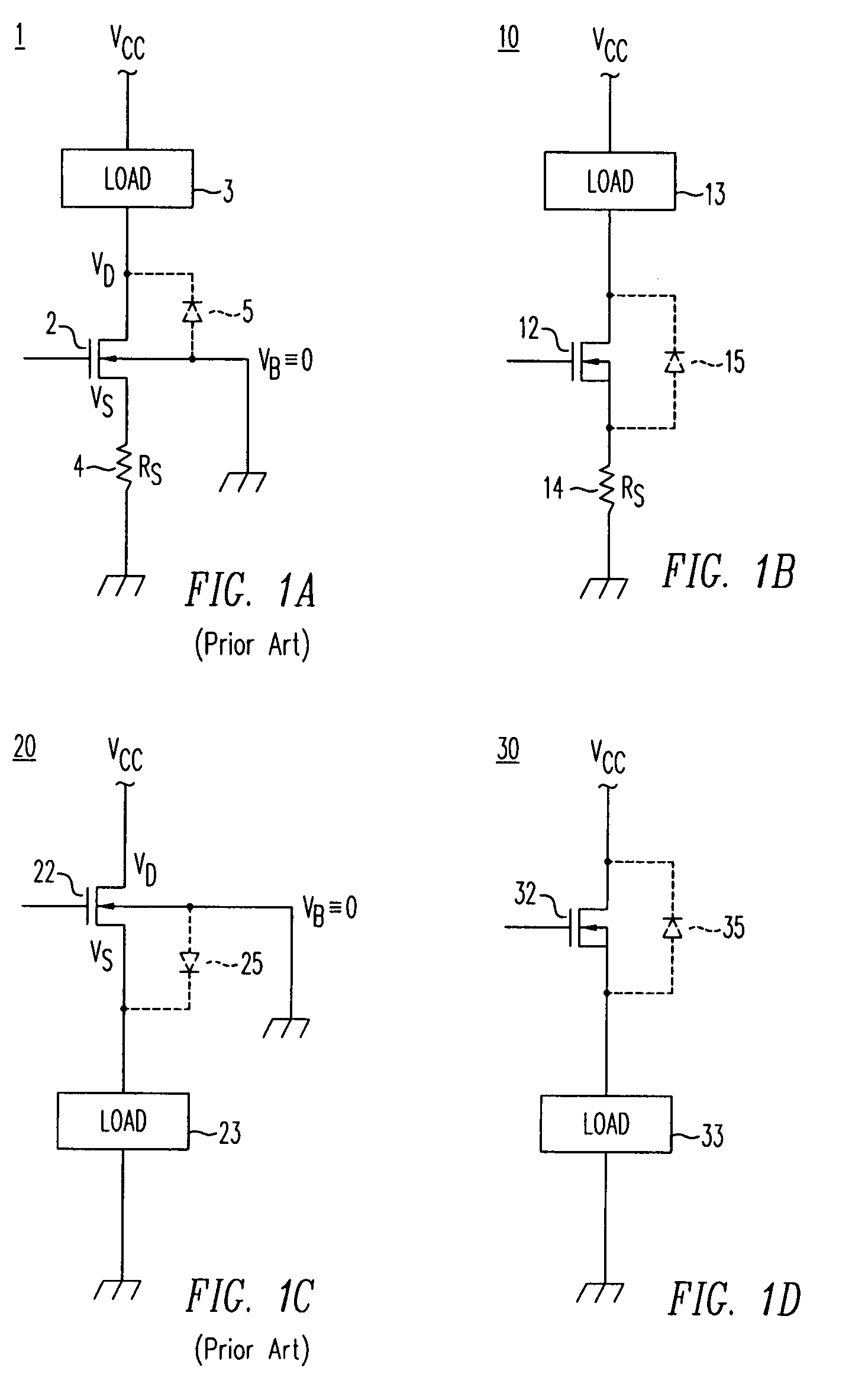
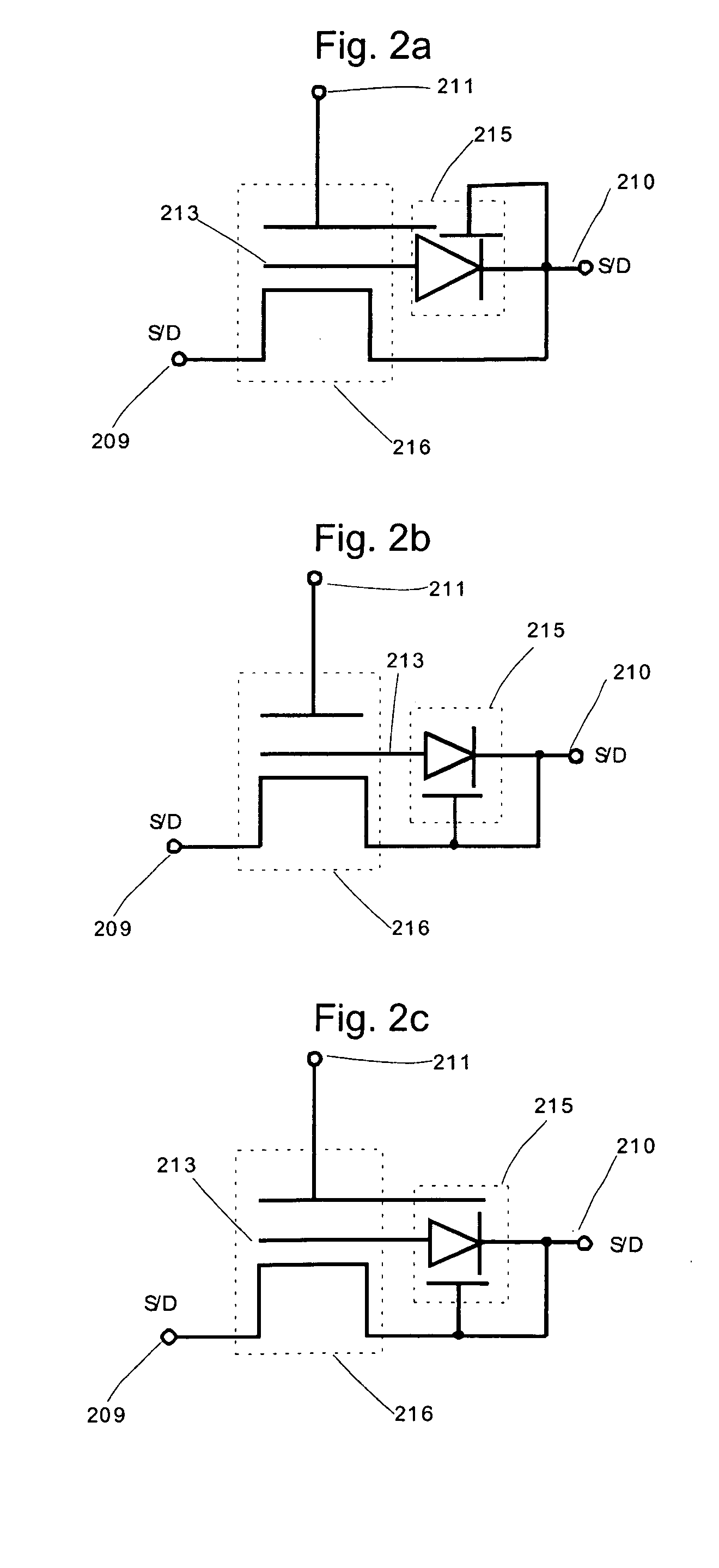
High density semiconductor memory cell and memory array using a single transistor and having counter-doped poly and buried diffusion wordline
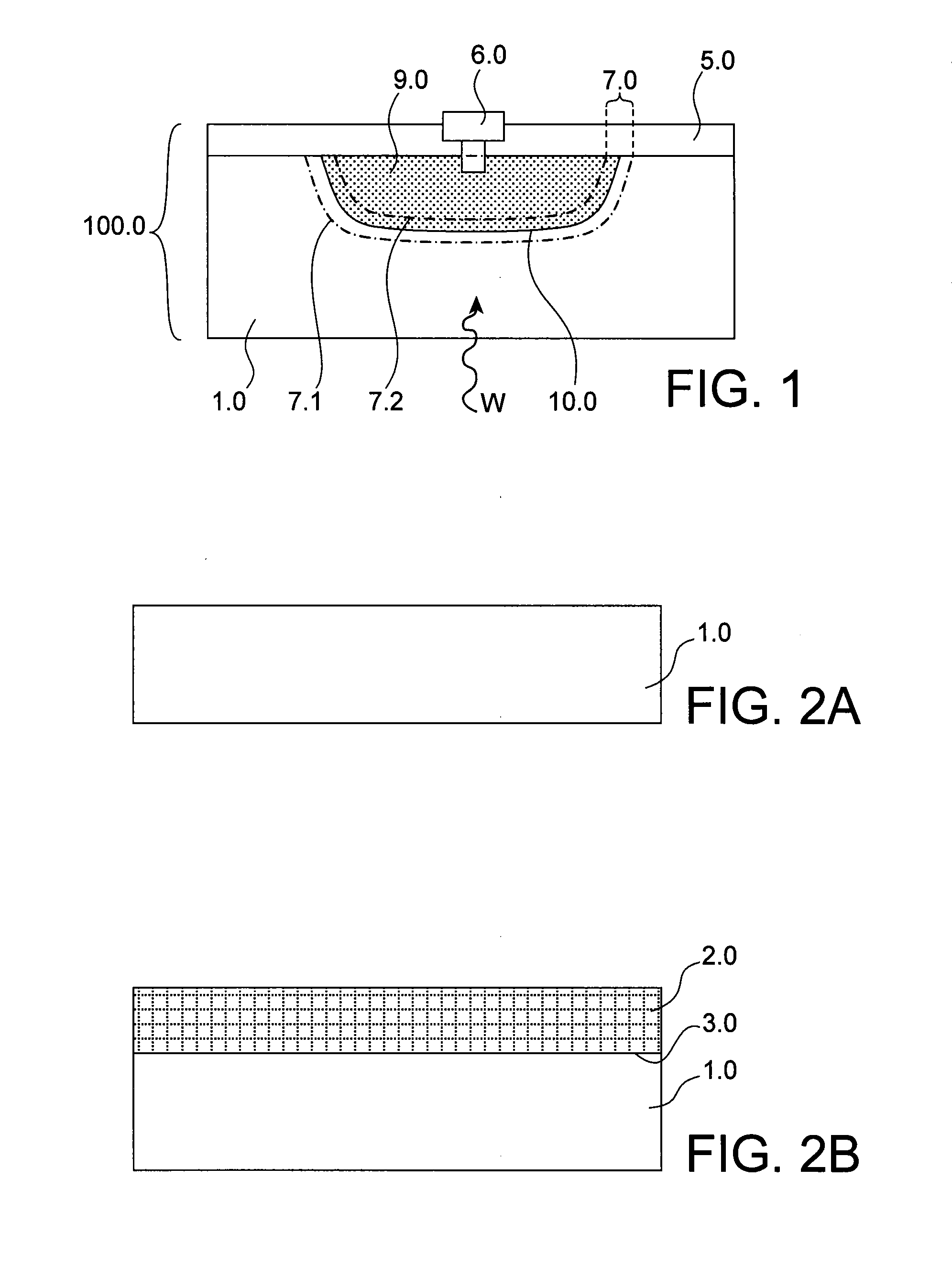
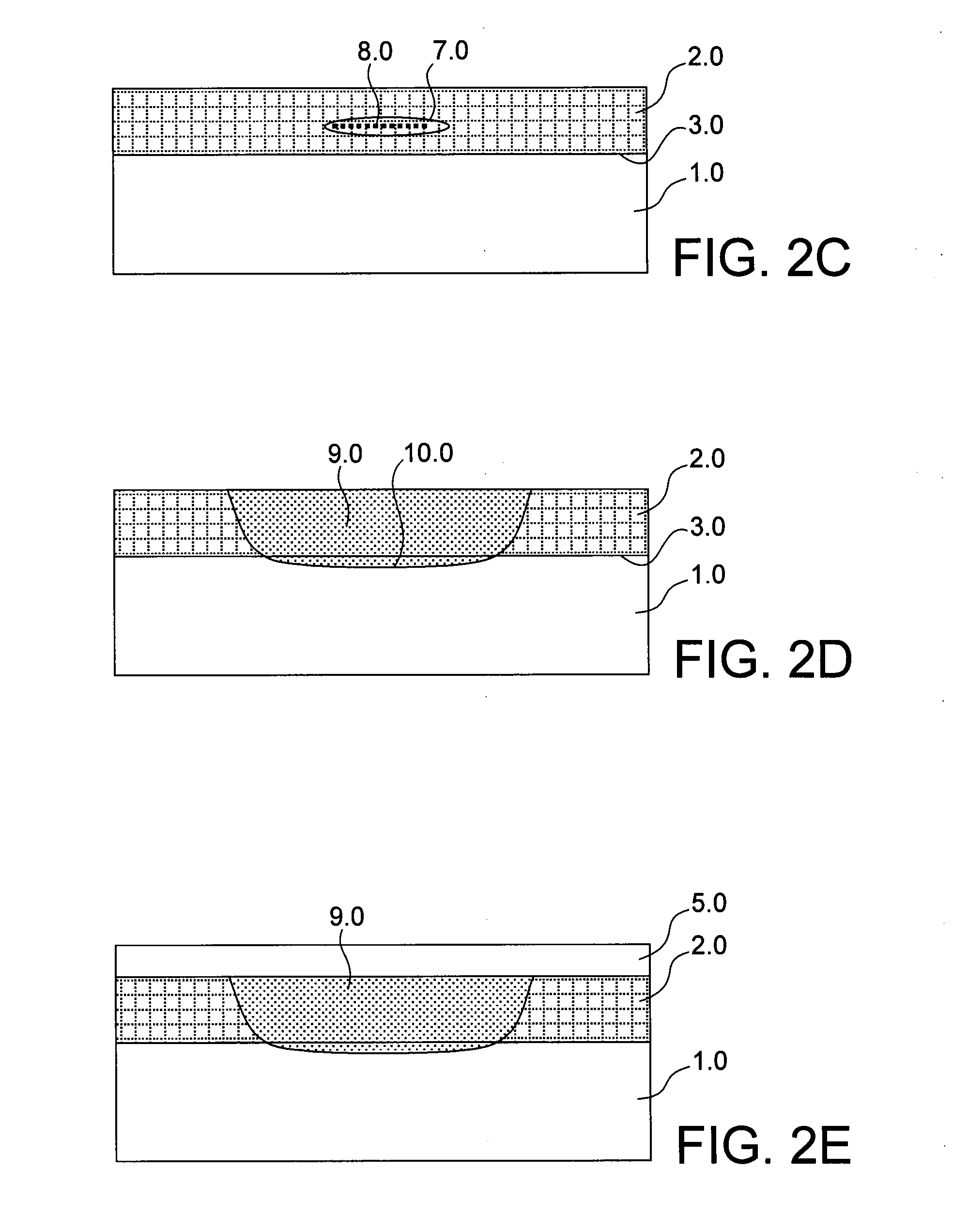
A programmable memory cell comprised of a transistor located at the crosspoint of a column bitline and a row wordline is disclosed. The transistor has its gate formed from the column bitline and its source connected to the row wordline. The memory cell is programmed by applying a voltage potential between the column bitline and the row wordline to produce a programmed p+ region to form a p-n diode in the substrate underlying the gate of the transistor. Further, the wordline is formed from a buried diffusion N+ layer while the column bitline is formed from a counterdoped polysilicon layer.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
High-voltage bipolar-CMOS-DMOS integrated circuit devices and modular methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20070278568A1Eliminate needReduce seizuresTransistorSolid-state devicesCMOSDevice material
All low-temperature processes are used to fabricate a variety of semiconductor devices in a substrate the does not include an epitaxial layer. The devices include a non-isolated lateral DMOS, a non-isolated extended drain or drifted MOS device, a lateral trench DMOS, an isolated lateral DMOS, JFET and depletion-mode devices, and P-N diode clamps and rectifiers and junction terminations. Since the processes eliminate the need for high temperature processing and employ “as-implanted” dopant profiles, they constitute a modular architecture which allows devices to be added or omitted to the IC without the necessity of altering the processes used to produce the remaining devices.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED +1
Solar Cell Devices
InactiveUS20100006143A1Improve photovoltaic conversion efficiencyReduce manufacturing costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum wellQuantum dot
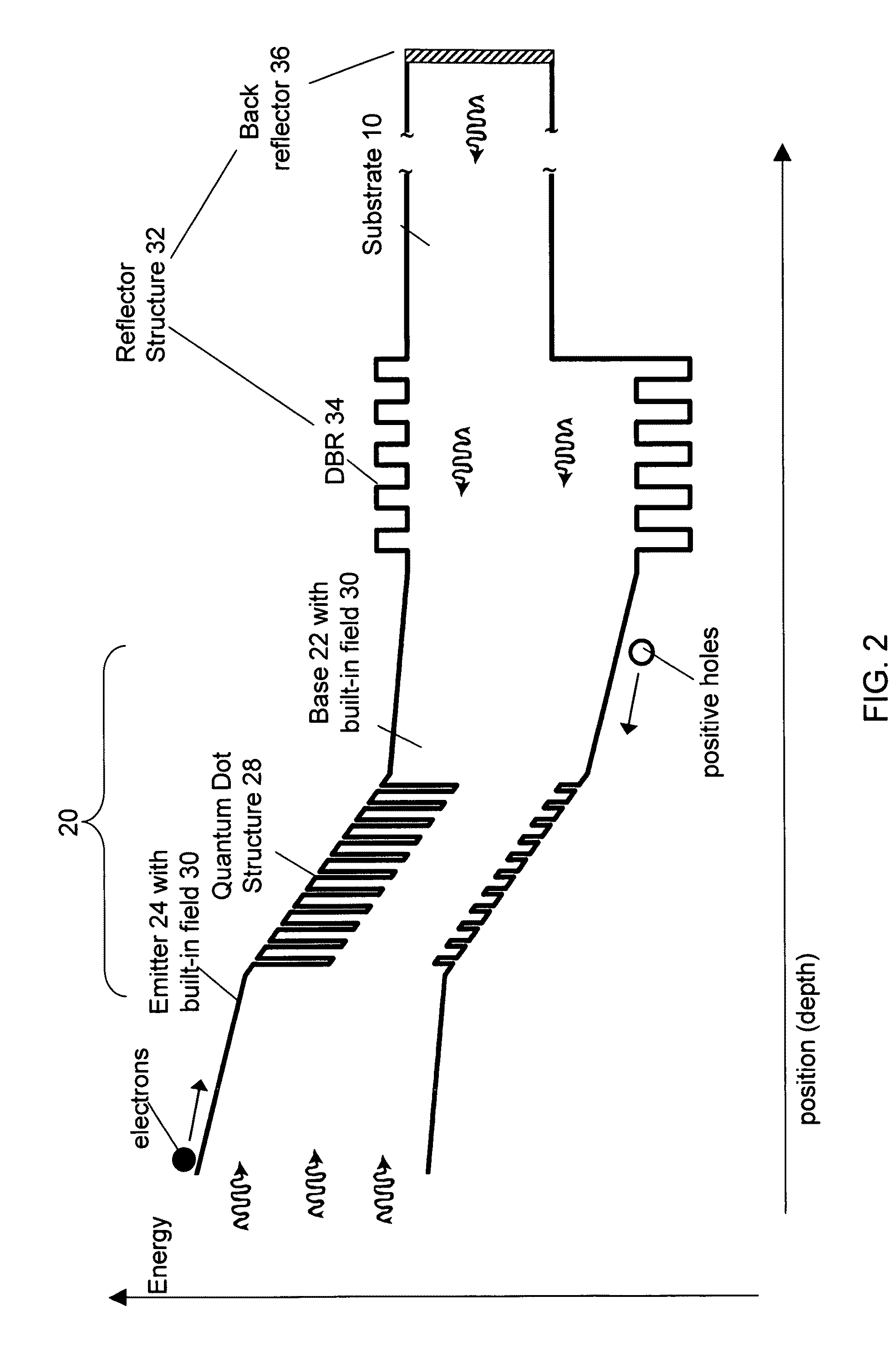
A solar cell device includes a p-n diode component over a substrate, the p-n diode component including at least one subcell, each subcell including an n-type semiconductor layer and a p-type semiconductor layer to form a p-n junction. The solar cell device further includes at least two features selected from: i) a nano-structured region between at the p-n junction of at least one subcell; ii) an n-type and / or a p-type layer of at least one subcell that includes a built-in quasi-electric field; and iii) a photon reflector structure. Alternatively, the solar cell device includes at least two subcells, and further includes a nano-structured region at the p-n junction of at least one of the subcells, wherein the subcells of the solar cell device are connected in parallel to each other by the p-type or the n-type semiconductor layer of each subcell. Alternatively, the solar cell device further includes a nano-structured region at the p-n junction of at least one subcell, wherein the nano-structured region includes i) a plurality of quantum dots or quantum wells that include InN or InGaN, the quantum dots or quantum wells embedded within a wide band gap matrix that includes InGaN, GaN, or AlGaN, or ii) a plurality of quantum dots or quantum wells that include InAs, GaAs or InGaAs, the quantum dots or quantum wells embedded within a wide band gap matrix that includes InGaP, GaAsP, AlGaAs, AlGaInAs or AlGaInP.
Owner:KOPIN CORPORATION
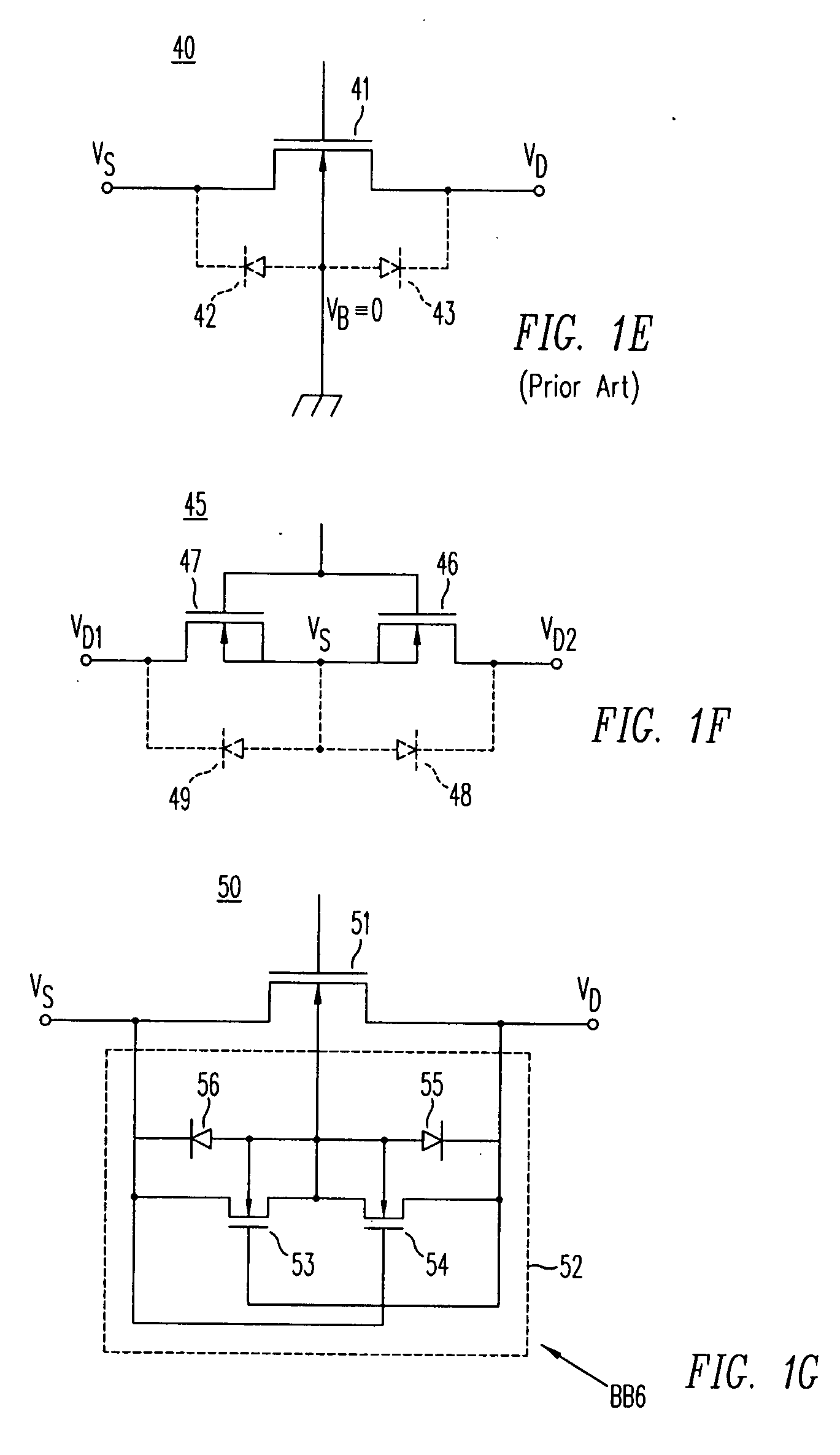
Structure and method for latchup suppression utilizing trench and masked sub-collector implantation
InactiveUS6956266B1Improve latchup robustnessImprove robustnessTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringP–n diode
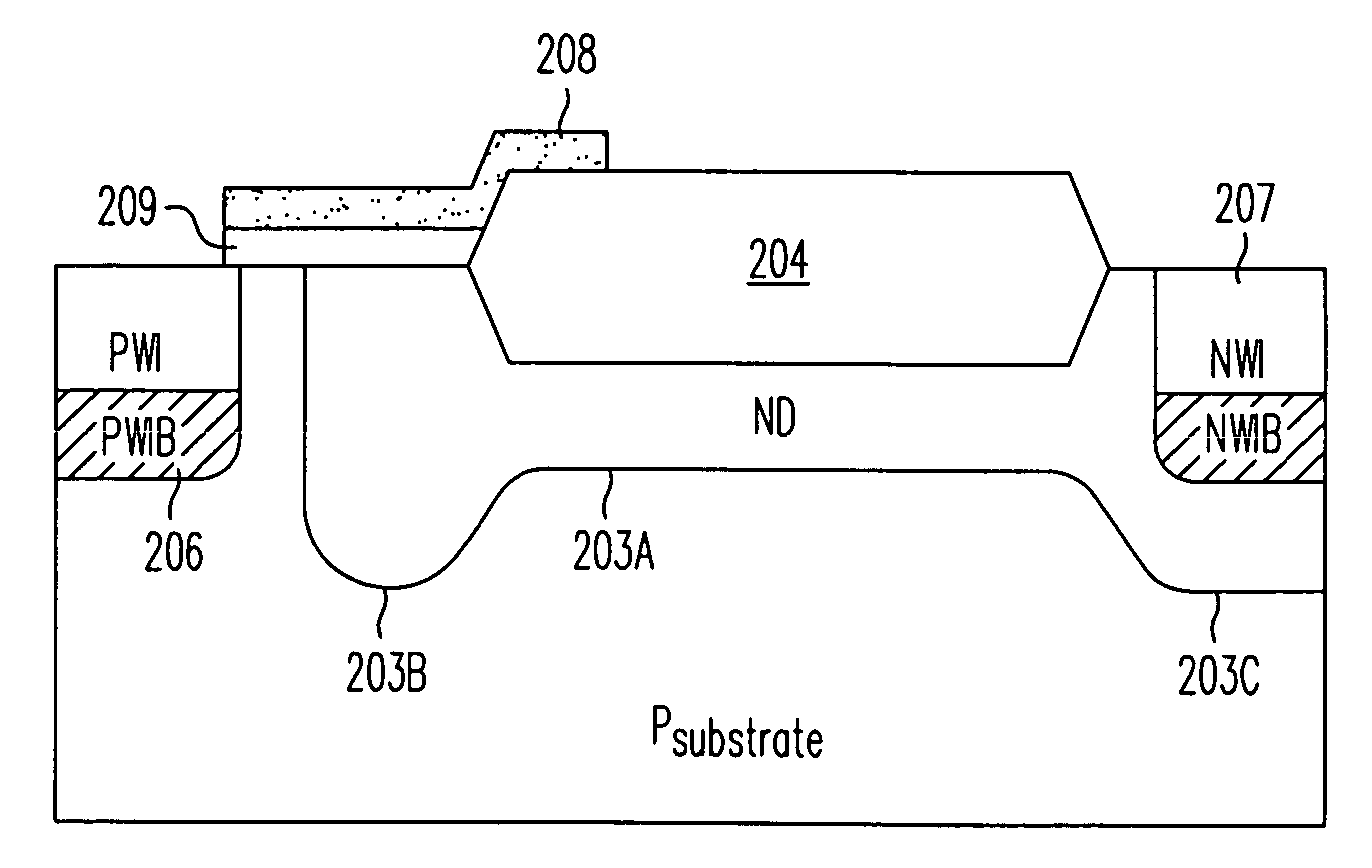
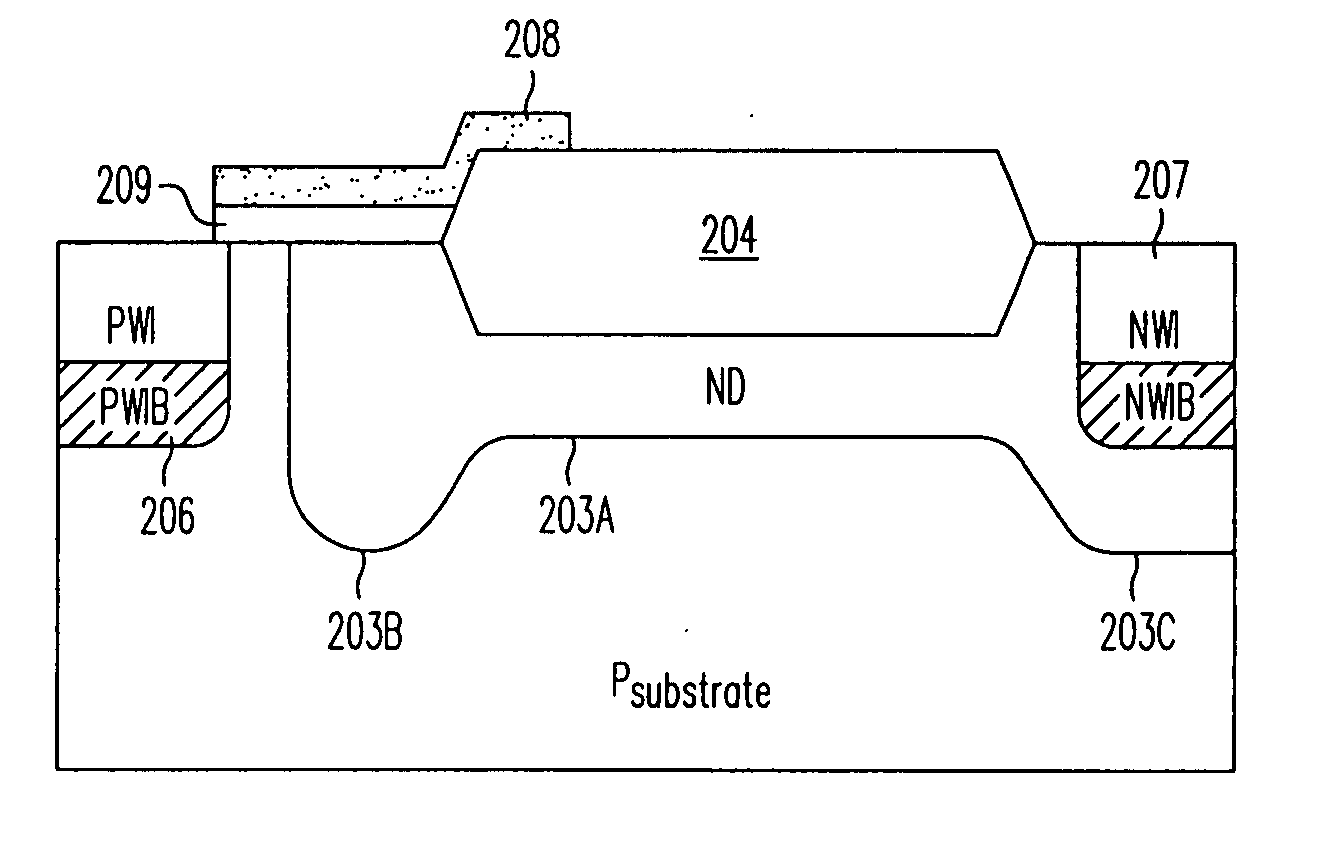
A method and structure for an integrated circuit comprising a substrate of a first polarity; a trench structure in the substrate; a well region of a second polarity abutting the trench structure; and a heavily doped region of the second polarity abutting the trench structure, wherein the heavily doped region is adapted to suppress latch-up in the integrated circuit, wherein the heavily doped region comprises a sub-collector region, and wherein the trench structure comprises a deep trench structure or a trench isolation structure. The integrated circuit further comprises a p+ anode in the well region and a n+ cathode in the well region, wherein the integrated circuit is configured as a latchup robust p-n diode. In another embodiment, the integrated circuit further comprises a p+ anode in the well region; a n+ cathode in the well region; and a gate structure over the p+ anode and n+ cathode.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High-voltage bipolar-CMOS-DMOS integrated circuit devices and modular methods of forming the same
All low-temperature processes are used to fabricate a variety of semiconductor devices in a substrate the does not include an epitaxial layer. The devices include a non-isolated lateral DMOS, a non-isolated extended drain or drifted MOS device, a lateral trench DMOS, an isolated lateral DMOS, JFET and depletion-mode devices, and P-N diode clamps and rectifiers and junction terminations. Since the processes eliminate the need for high temperature processing and employ “as-implanted” dopant profiles, they constitute a modular architecture which allows devices to be added or omitted to the IC without the necessity of altering the processes used to produce the remaining devices.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
LED structures for reduced non-radiative sidewall recombination
LED structures are disclosed to reduce non-radiative sidewall recombination along sidewalls of vertical LEDs including p-n diode sidewalls that span a top current spreading layer, bottom current spreading layer, and active layer between the top current spreading layer and bottom current spreading layer.
Owner:APPLE INC
High performance optoelectronic device
InactiveUS20090283138A1Low production costSimple processPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsP–n diode
Owner:TATUNG COMPANY +1
Micro LED with dielectric side mirror
InactiveUS20160181476A1High melting temperatureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesP–n diodeDielectric mirror
LEDs and an electronic device are disclosed. In an embodiment an LED includes a p-n diode and a dielectric mirror spanning along a lateral sidewall of the p-n diode and directly underneath the p-n diode. An opening is formed in the dielectric mirror directly underneath the p-n diode, and a bottom conductive contact is on the dielectric mirror directly underneath the p-n diode and within the opening in the dielectric mirror.
Owner:APPLE INC
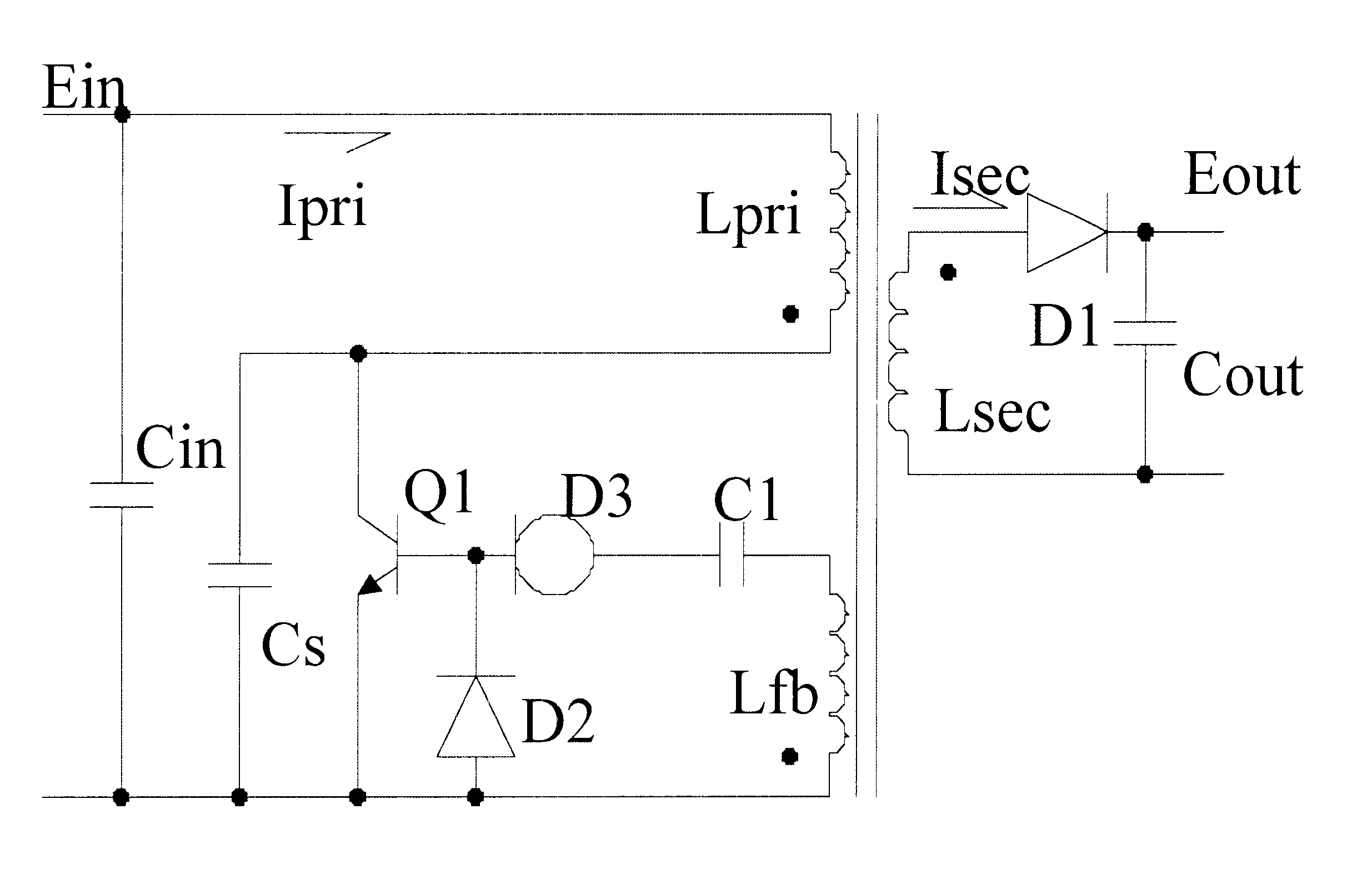
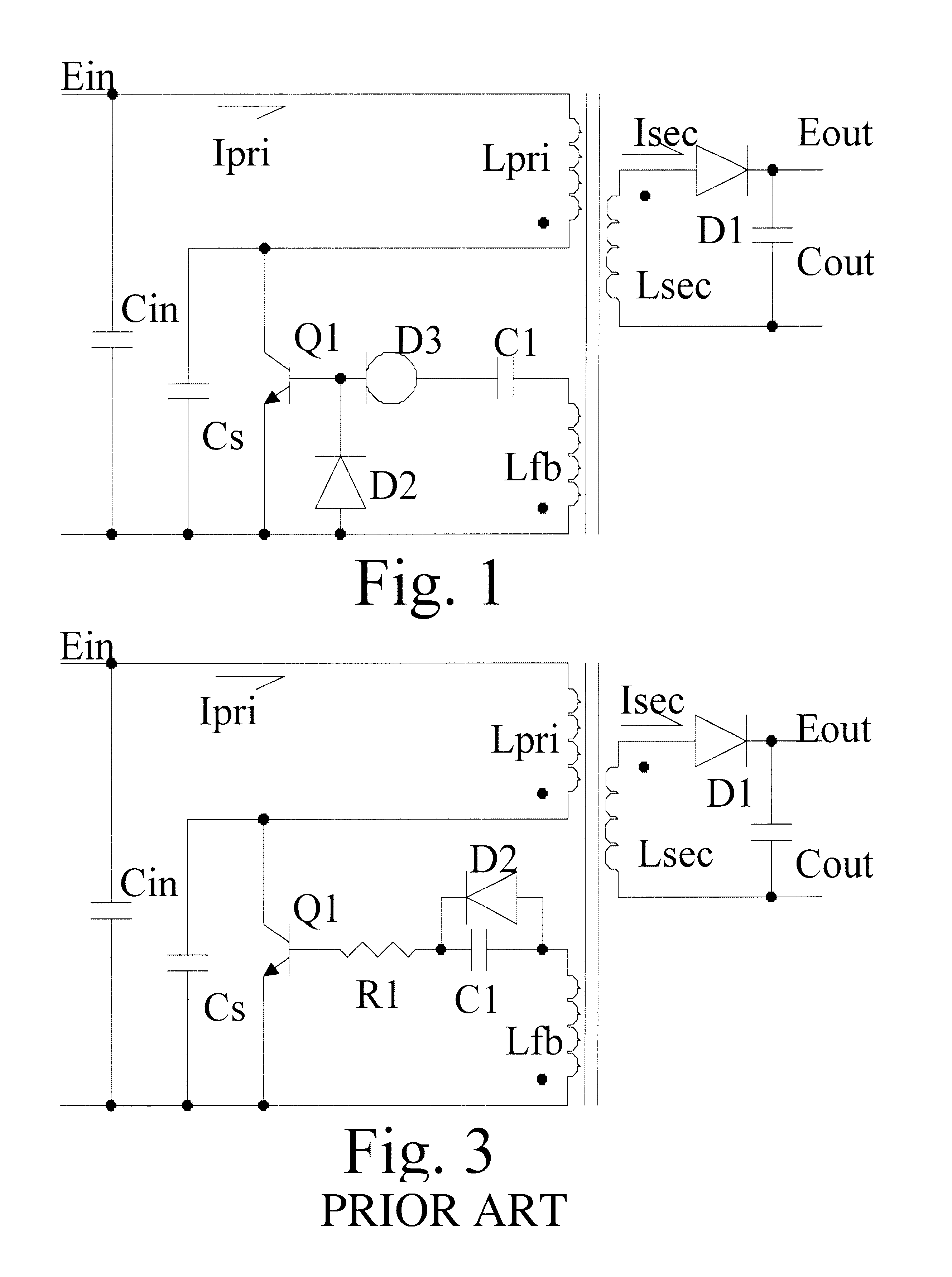
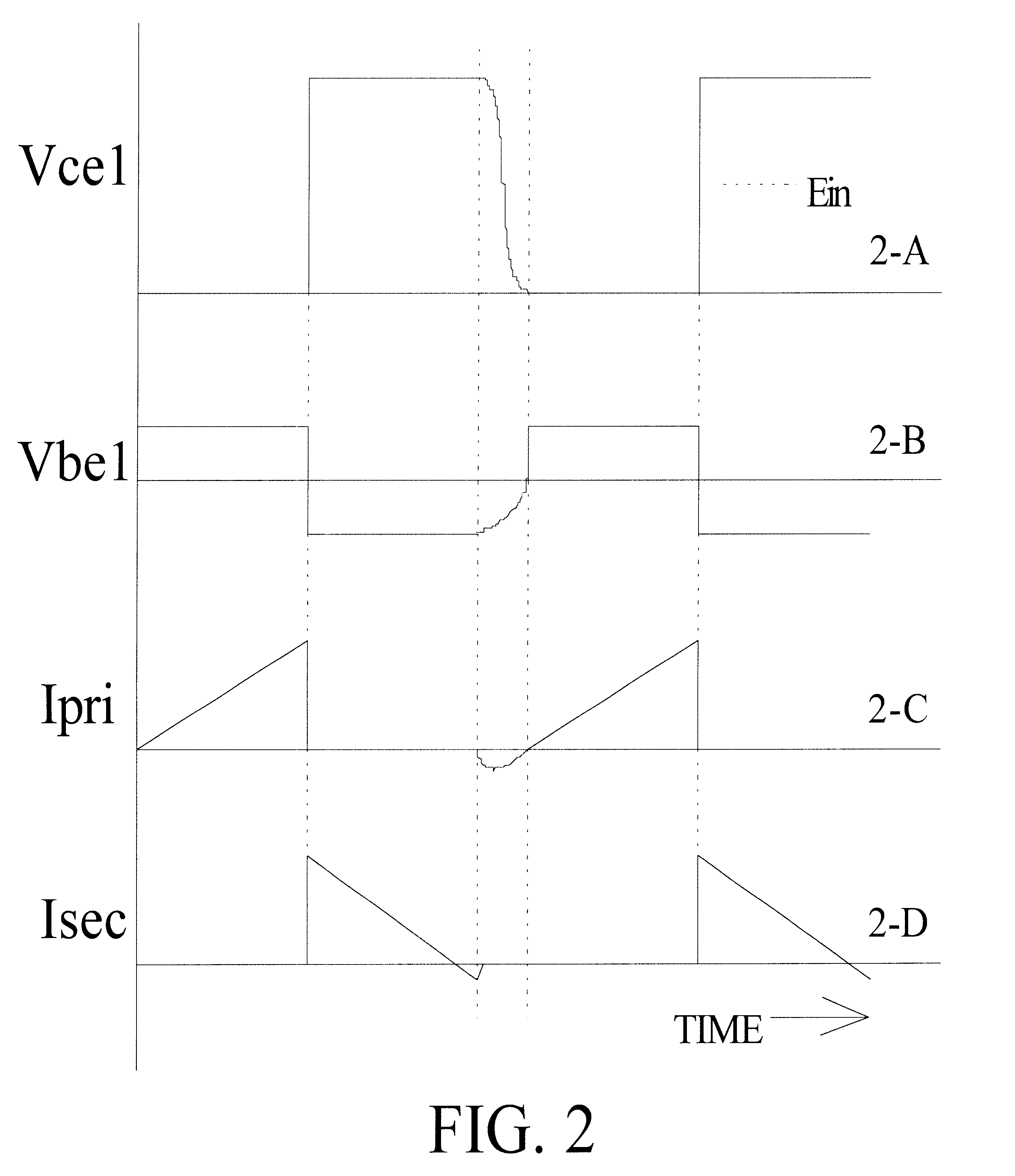
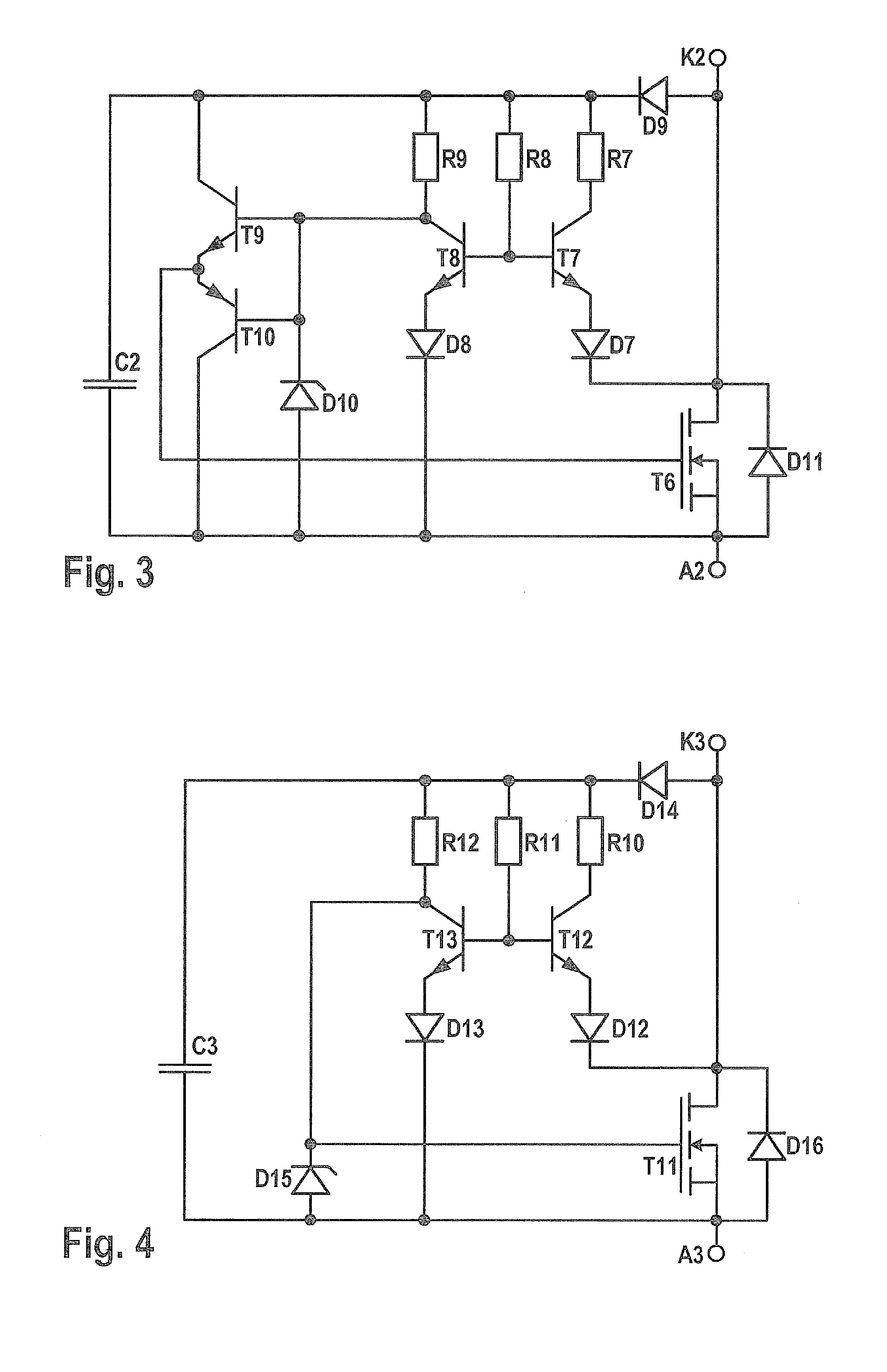
Self-oscillation type resonant flyback converter utilizing charge stored effect of the P-N diode
InactiveUS6404654B1Increase powerEasy to switchEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSelf-oscillationConductor Coil
A self-oscillation type resonant flyback converter includes a series combination of a primary winding and a switching transistor. A secondary winding is connected to a power diode and to an output capacitor. A feedback winding is connected to a delay driving circuit comprising a delay diode, a constant-current diode and a capacitor. The delay driving circuit is provided to delay a positive feedback signal from said feedback winding, so that when said power diode becomes non-conducting, said delay diode becomes in the reverse conduction state, starting a free resonance period that concludes when the said delay diode becomes non-conducting and the switching transistor is achieved at zero voltage switching.
Owner:INTEGRATED PROGRAMMABLE COMM
High-voltage bipolar-CMOS-DMOS integrated circuit devices and modular methods of forming the same
All low-temperature processes are used to fabricate a variety of semiconductor devices in a substrate the does not include an epitaxial layer. The devices include a non-isolated lateral DMOS, a non-isolated extended drain or drifted MOS device, a lateral trench DMOS, an isolated lateral DMOS, JFET and depletion-mode devices, and P-N diode clamps and rectifiers and junction terminations. Since the processes eliminate the need for high temperature processing and employ “as-implanted” dopant profiles, they constitute a modular architecture which allows devices to be added or omitted to the IC without the necessity of altering the processes used to produce the remaining devices.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
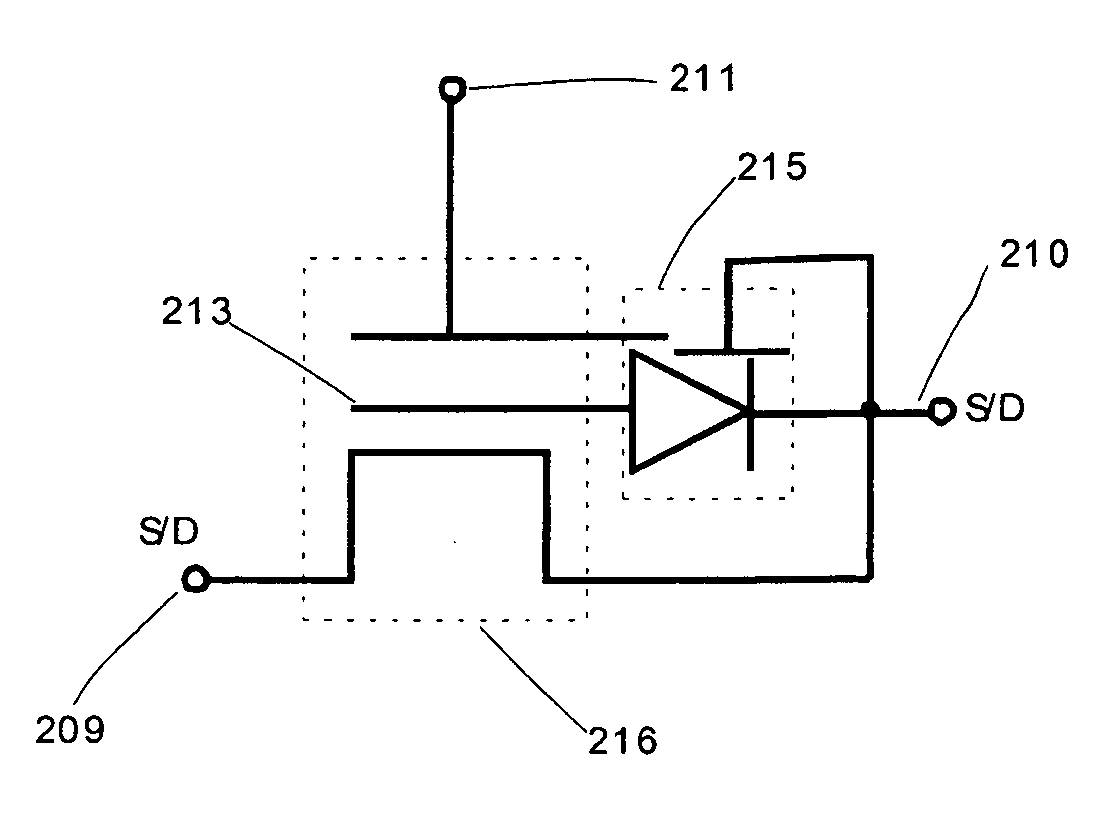
Semiconductor memory device and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20090185426A1Shorter read and write timesIncrease in sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesP–n diodeSemiconductor
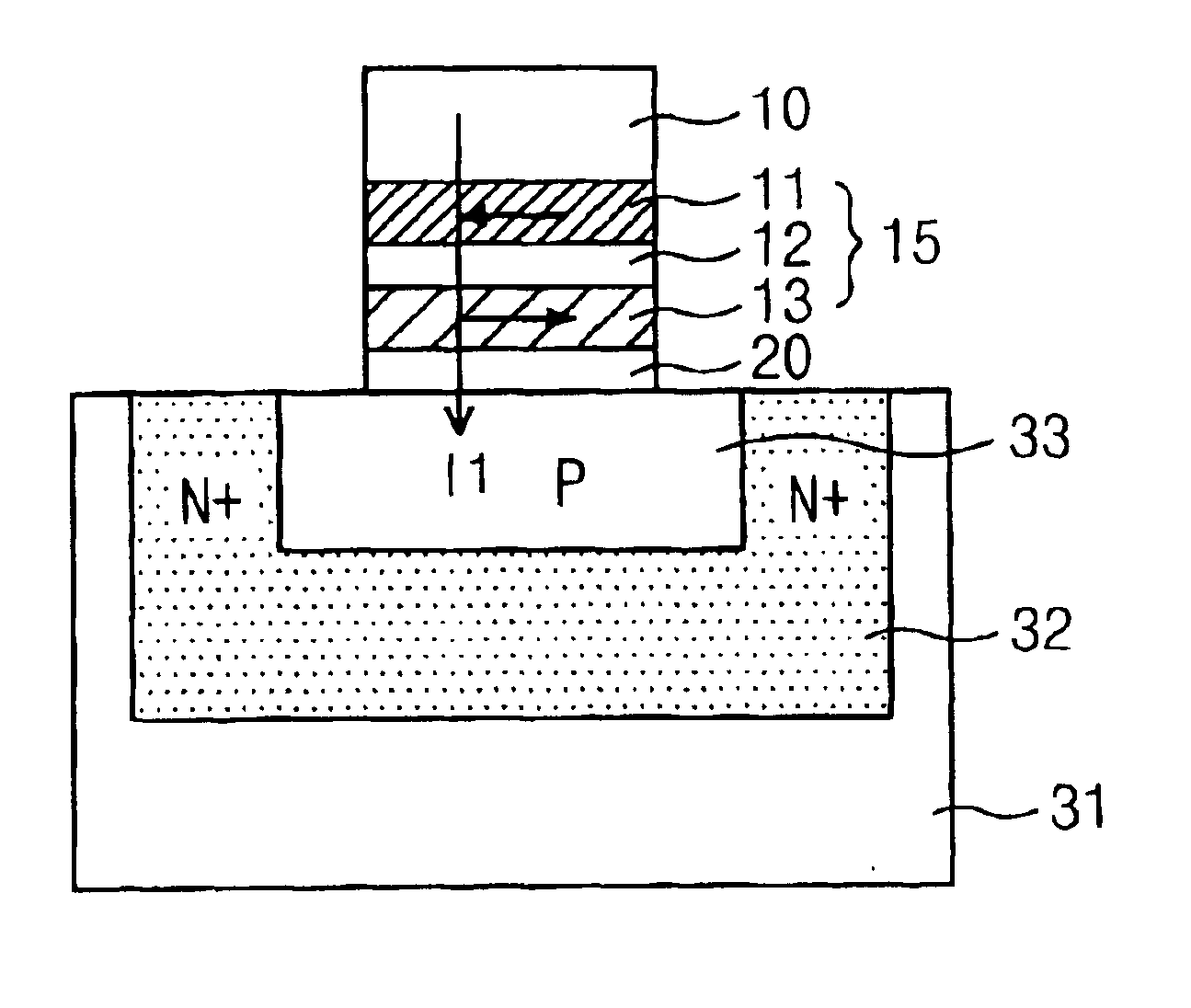
The present invention discloses a semiconductor memory device comprising a source, a drain, a floating gate, a control gate, a recess channel and a gated p-n diode. The said p-n diode connects said floating gate and said drain. The said floating gate is for charge storage purpose, it can be electrically charged or discharged by current flowing through the gated p-n diode. An array of memory cells formed by the disclosed semiconductor memory device is proposed. Furthermore, an operating method and a method for producing the disclosed semiconductor memory device and array are described.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIENTAL SEMICONDUCTOR CO LTD
High-voltage bipolar-CMOS-DMOS integrated circuit devices and modular methods of forming the same
All low-temperature processes are used to fabricate a variety of semiconductor devices in a substrate the does not include an epitaxial layer. The devices include a non-isolated lateral DMOS, a non-isolated extended drain or drifted MOS device, a lateral trench DMOS, an isolated lateral DMOS, JFET and depletion-mode devices, and P-N diode clamps and rectifiers and junction terminations. Since the processes eliminate the need for high temperature processing and employ “as-implanted” dopant profiles, they constitute a modular architecture which allows devices to be added or omitted to the IC without the necessity of altering the processes used to produce the remaining devices.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Liquid crystal display
The invention provides a liquid crystal display. The liquid crystal display comprises a liquid crystal module, a backlight module, a driving and detecting module and a plurality of light sensors, wherein the liquid crystal module consists of a polarizer, a glass substrate, liquid crystal, a color filter, a thin film transistor, a black matrix, a plurality of conductive wires and the like; the backlight module comprises a light source, a light guide plate, a diffuser sheet and the like; the driving and detecting module comprises a data driver, a gate driver, a light sensor driver, a light sensing detector and the like; the plurality of light sensors consist of P-N diodes or thin film transistors; one light sensor is arranged on each pixel unit respectively; and the plurality of light sensors are used for sensing red and infrared radiation which is transmitted by the light source, passes through the liquid crystal module and is then reflected back by touch fingers of a light touch liquid crystal user and passes through the color filter, so that a sense signal is output for judging a finger touch position.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
LED structures for reduced non-radiative sidewall recombination
LED structures are disclosed to reduce non-radiative sidewall recombination along sidewalls of vertical LEDs including p-n diode sidewalls that span a top current spreading layer, bottom current spreading layer, and active layer between the top current spreading layer and bottom current spreading layer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Rectifier circuit
ActiveUS20100244559A1Reduce power lossReduce expenditureTransistorAc-dc conversion without reversalEngineeringP–n diode
Rectifier circuits which are usable, instead of diodes, for rectifying alternating voltages, and which, like diodes, form two-terminal networks having a cathode terminal and an anode terminal. The power loss of these rectifier circuits is clearly less that the power loss of silicon p-n diodes. These rectifier circuits also include voltage clamping functions.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
Nanotube array electronic and opto-electronic devices
InactiveUS20090189143A1Reduce contact resistanceMinimized contact resistanceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyPhotonics
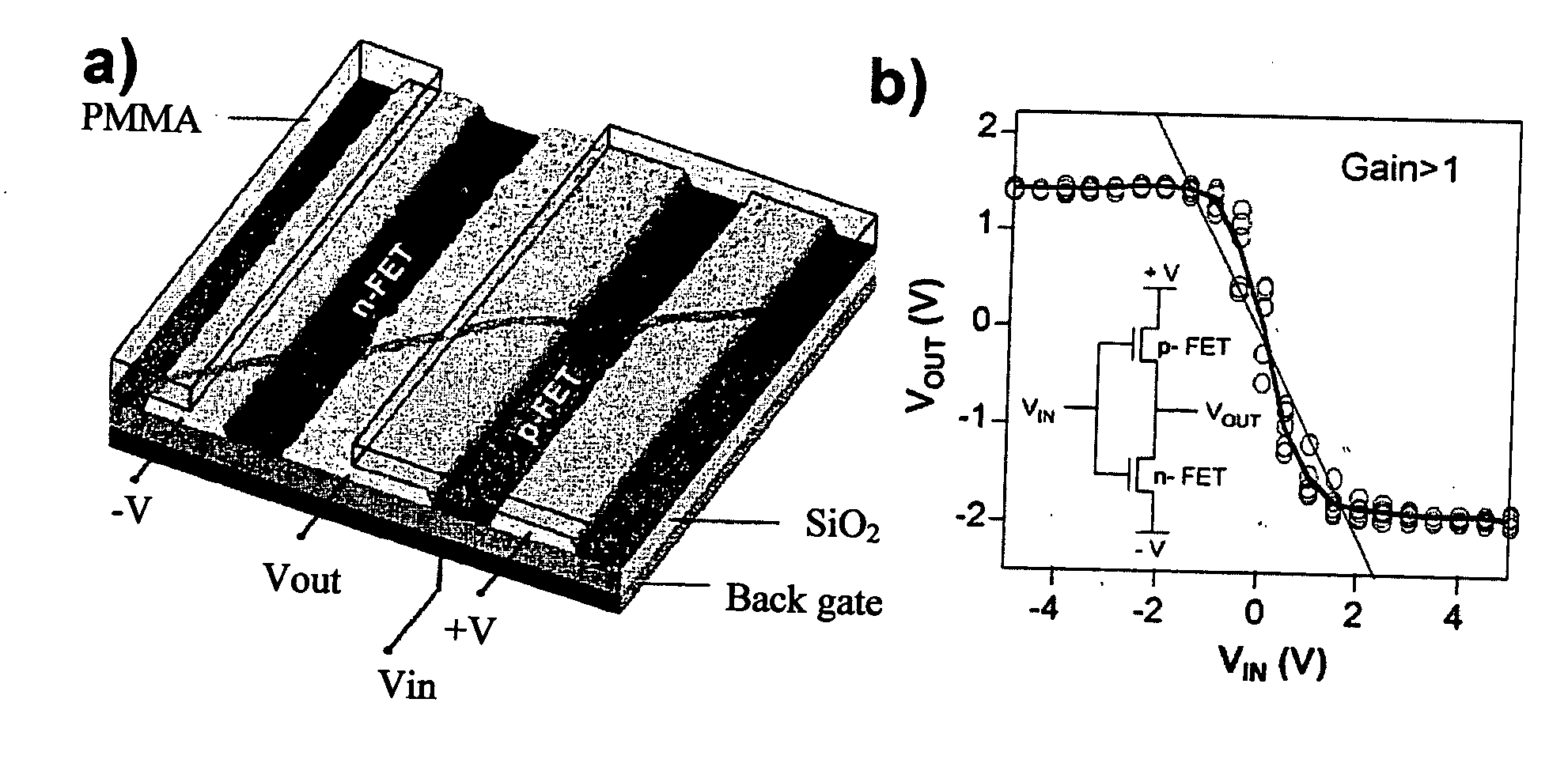
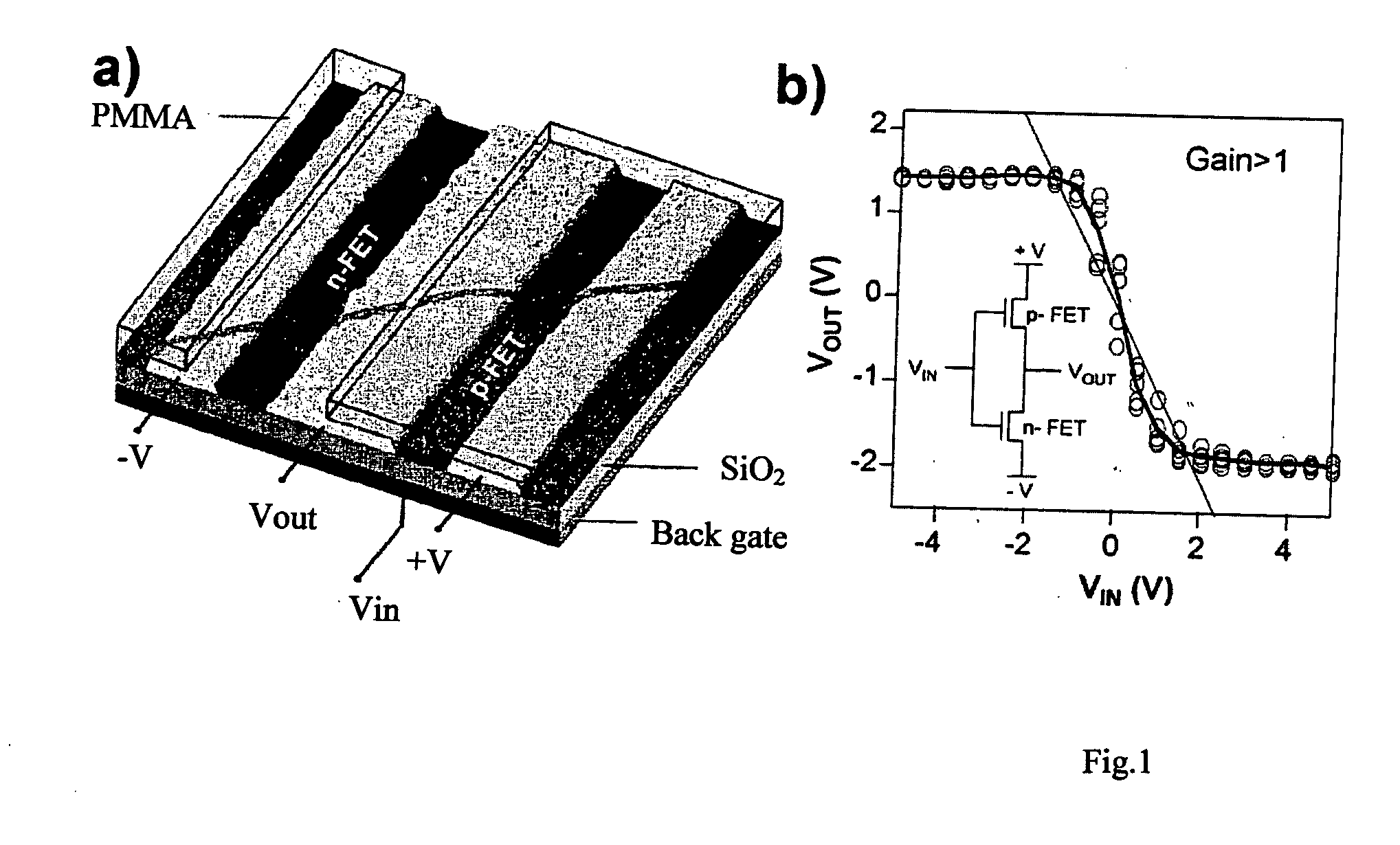
Carbon nanotube (CNT)-based devices and technology for their fabrication are disclosed. The discussed electronic and photonic devices and circuits rely on the nanotube arrays grown on a variety of substrates, such as glass or Si wafer. The planar, multiple layer deposition technique and simple methods of change of the nanotube conductivity type during the device processing are utilized to provide a simple and cost effective technology for a large scale circuit integration. Such devices as p-n diode, CMOS-like circuit, bipolar transistor, light emitting diode and laser are disclosed, all of them are expected to have superior performance then their semiconductor-based counterparts due to excellent CNT electrical and optical properties. When fabricated on Si-wafers, the CNT-based devices can be combined with the Si circuit elements, thus producing hybrid Si-CNT devices and circuits.
Owner:NANO ELECTRONICS & PHOTONIC DEVICES & CIRCUITS
High voltage switching devices and process for forming same
ActiveUS20050167697A1Increase concentrationReduce concentrationPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh pressureP–n diode
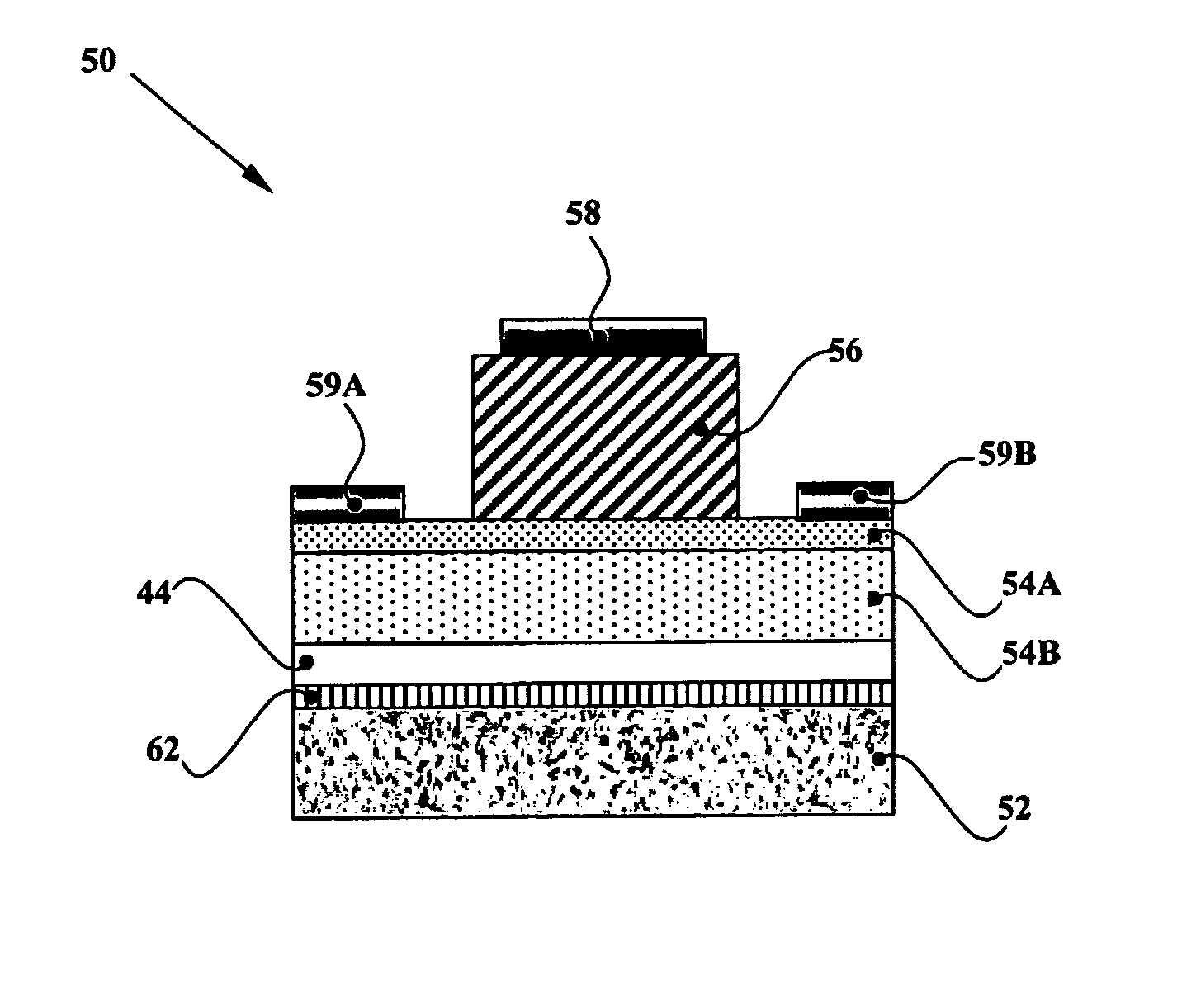
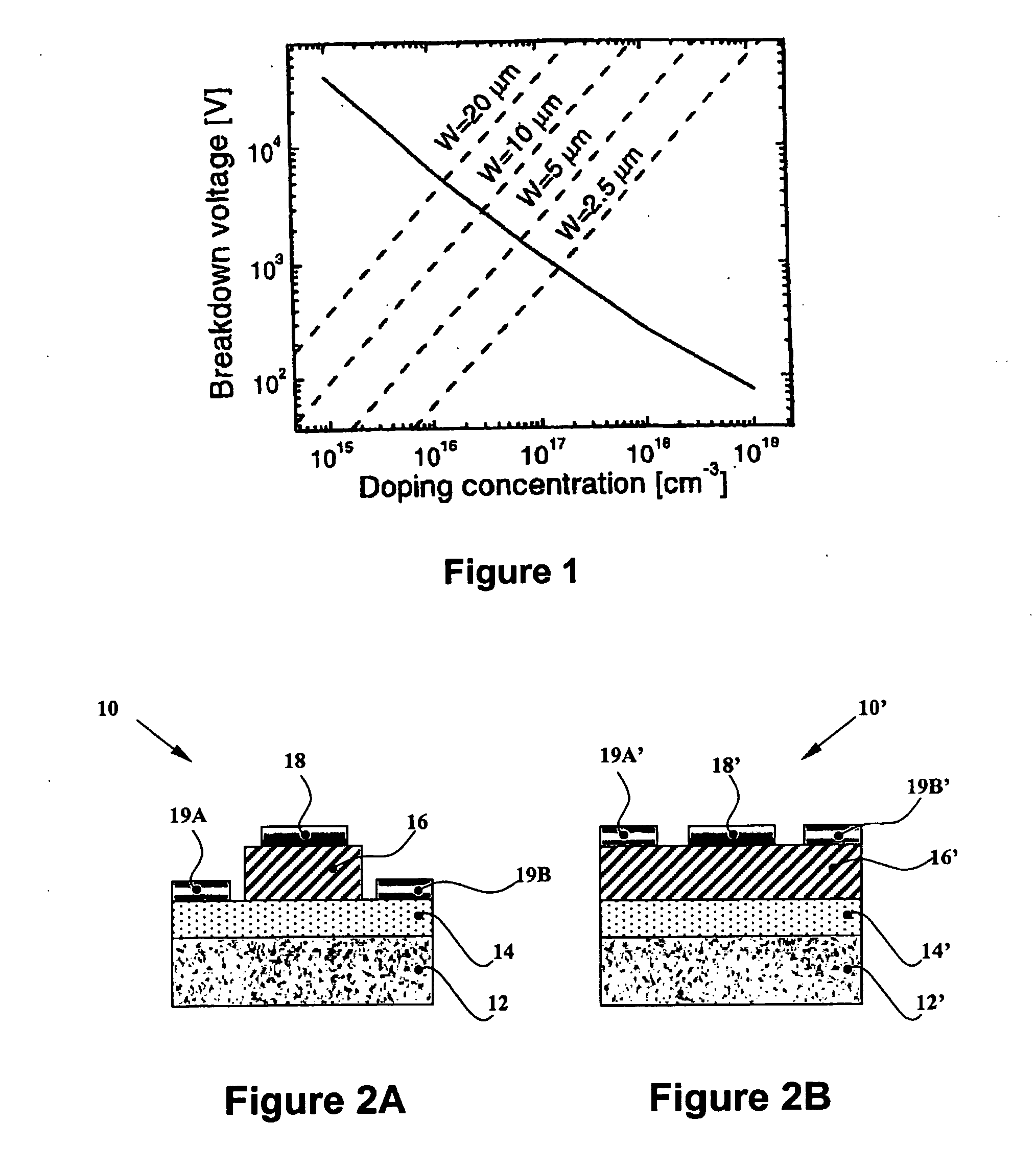
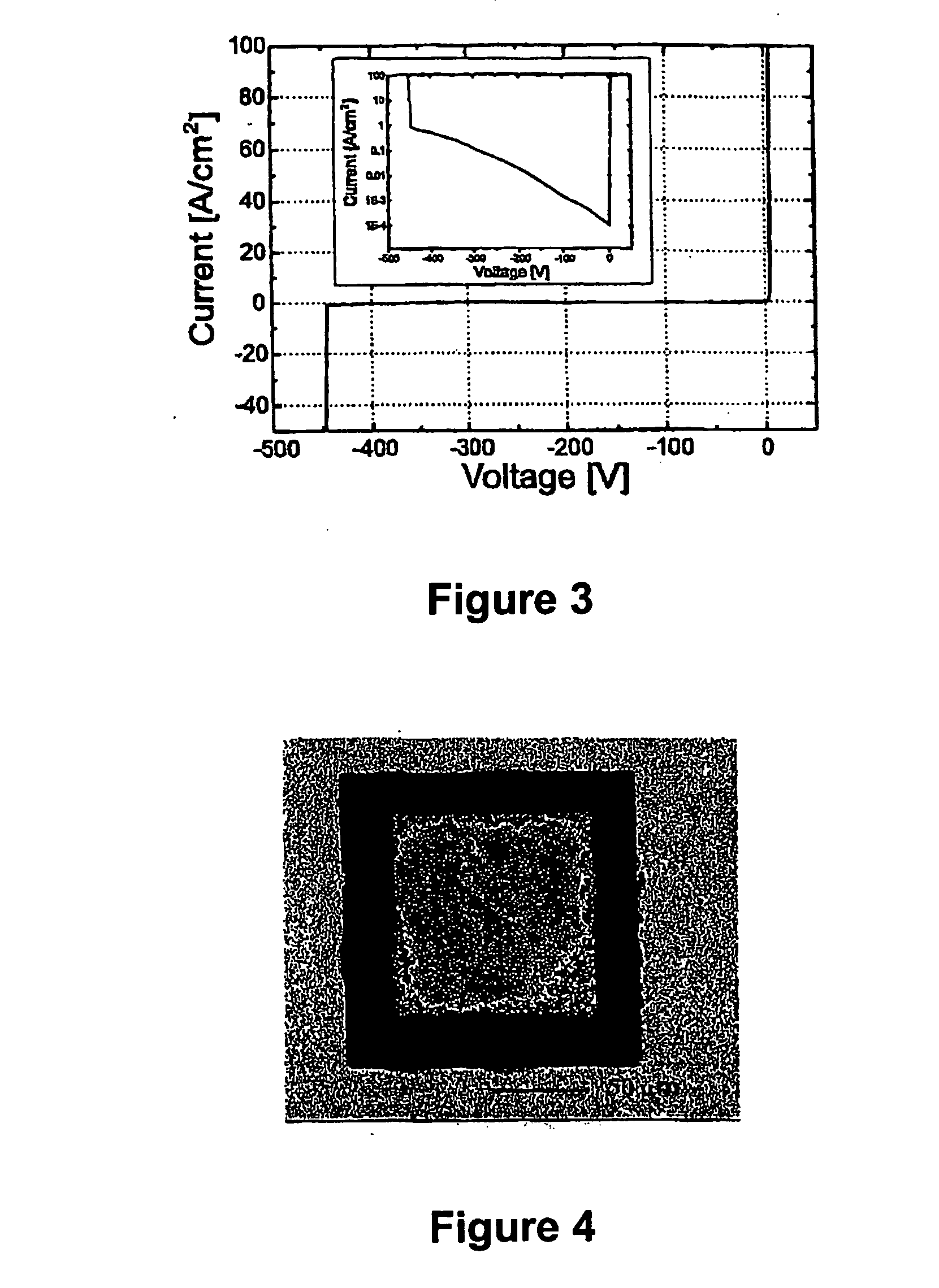
The present invention relates to various switching device structures including Schottky diode (10), P-N diode, and P-I-N diode, which are characterized by low defect density, low crack density, low pit density and sufficient thickness (>2.5 um) GaN layers (16) of low dopant concentration (<1E16 cm−3) grown on a conductive GaN layer (14). The devices enable substantially higher breakdown voltage on hetero-epitaxial substrates (<2 KV) and extremely high breakdown voltage on homo-epitaxial substrates (>2 KV).
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Photodiode Assembly With Improved Electrostatic Discharge Damage Threshold
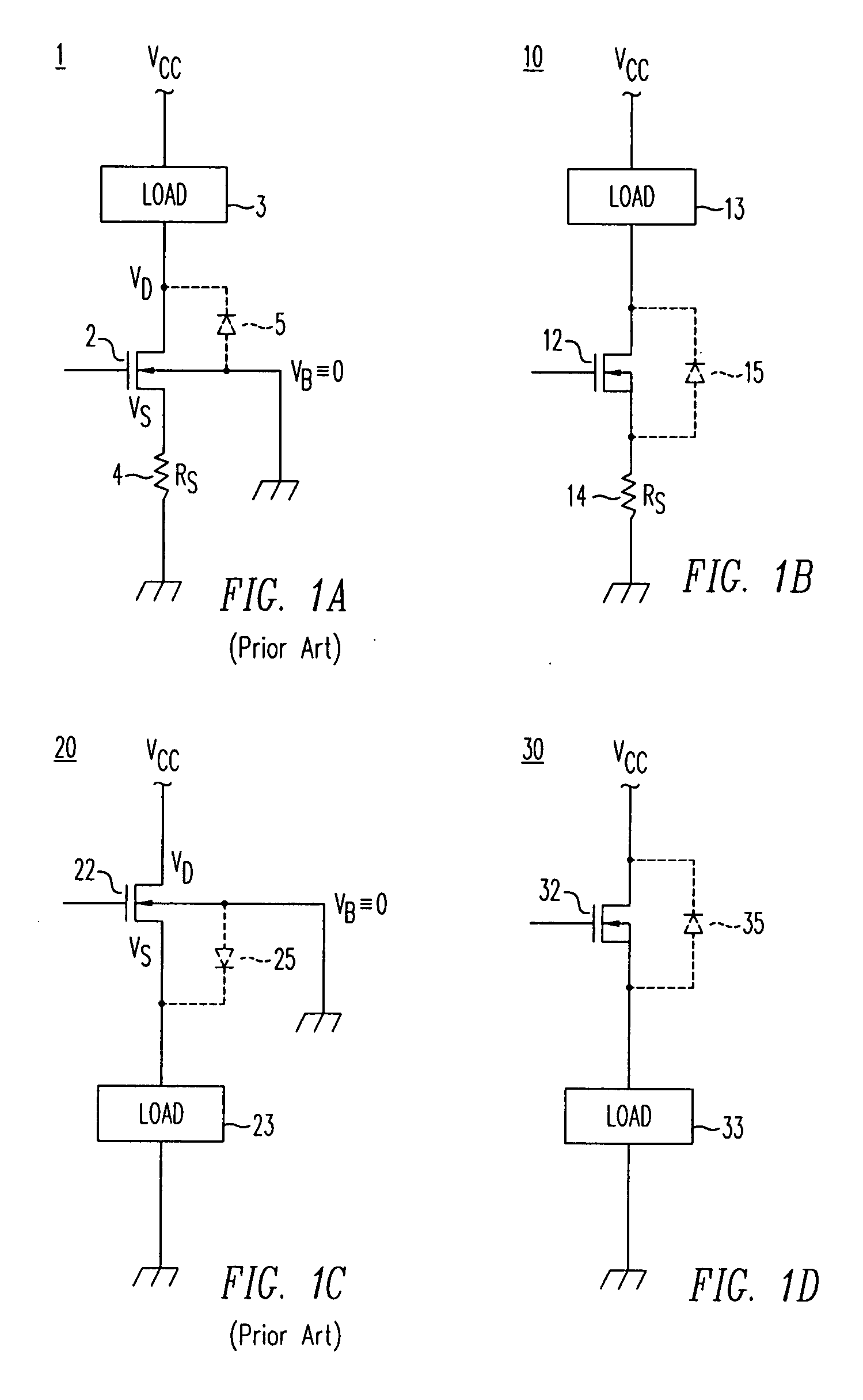
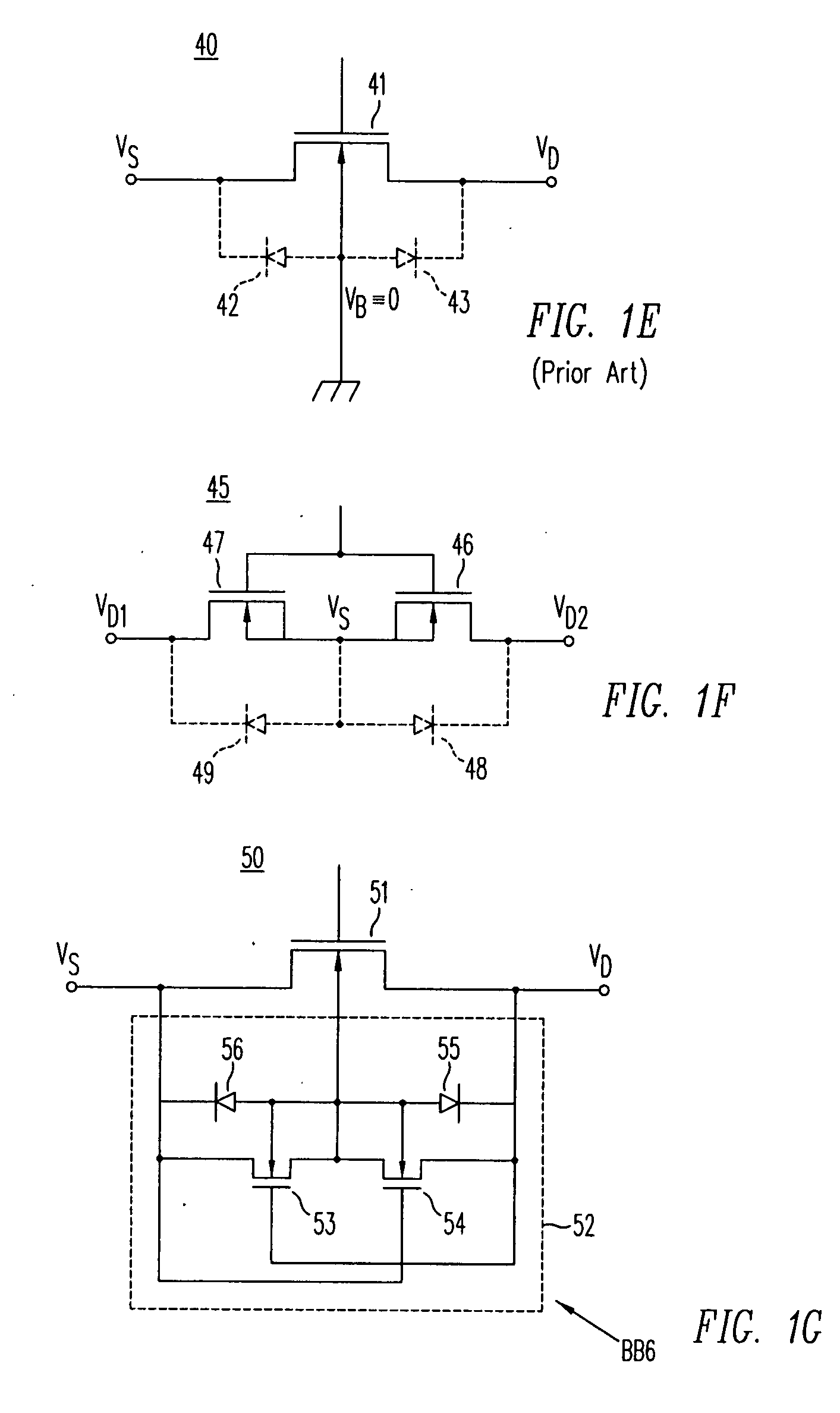
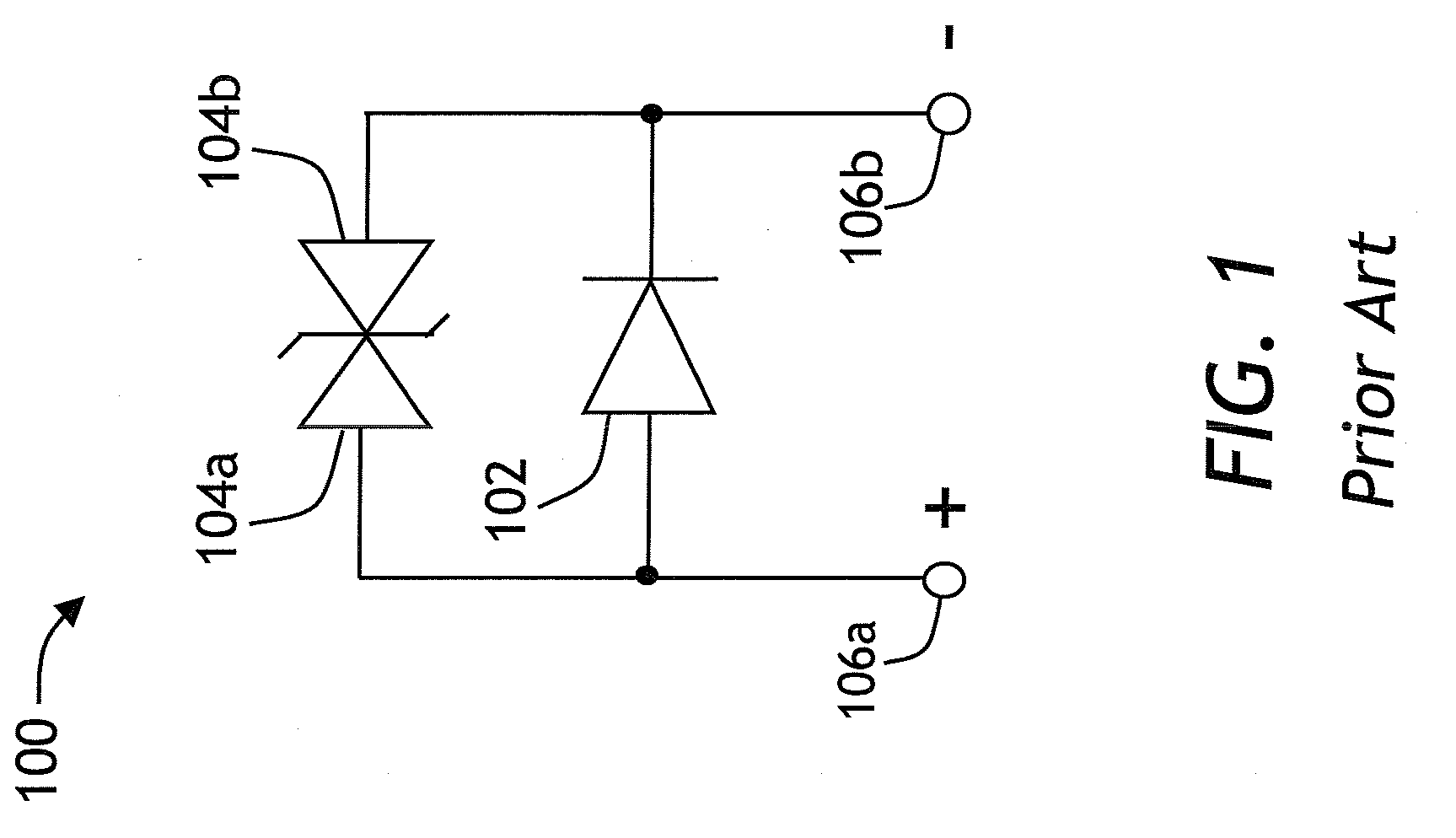
A photodiode with an improved electrostatic damage threshold is disclosed. A Zener or an avalanche diode is connected in parallel to a photodiode. Both diodes are integrated into the same photodiode housing. The diodes can be mounted on a common header or onto each other. An avalanche photodiode and an avalanche diode can be fabricated on a common semiconductor substrate. A regular p-n diode connected in series, cathode-to-cathode or anode-to-anode, to a Zener diode, forms a protection circuit which, when connected in parallel to a photodiode, provides a smaller electrical capacity increase as compared to a simpler circuit consisting just of a Zener or an avalanche diode.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
LED structures for reduced non-radiative sidewall recombination
LED structures are disclosed to reduce non-radiative sidewall recombination along sidewalls of vertical LEDs including p-n diode sidewalls that span a top current spreading layer, bottom current spreading layer, and active layer between the top current spreading layer and bottom current spreading layer.
Owner:APPLE INC
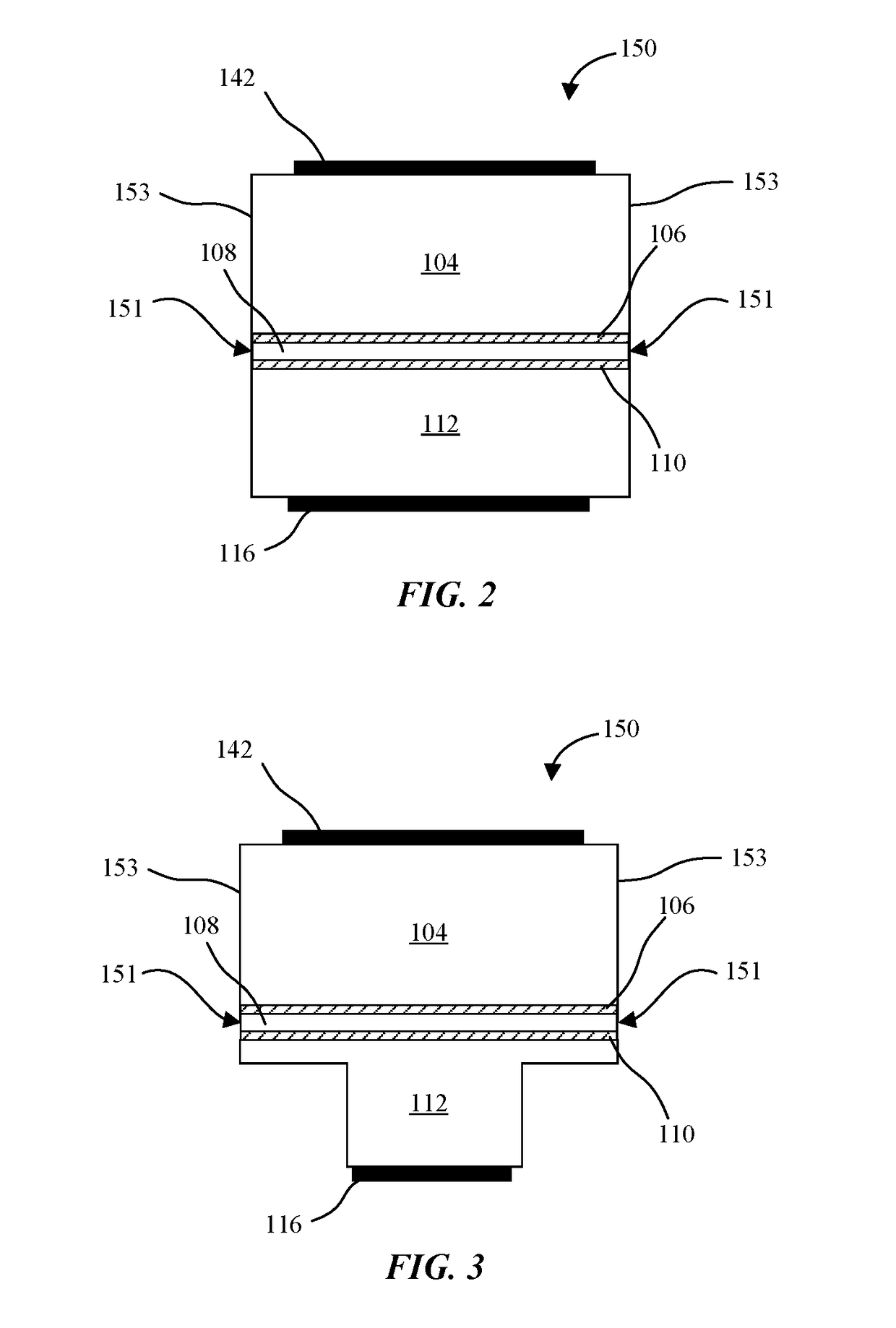
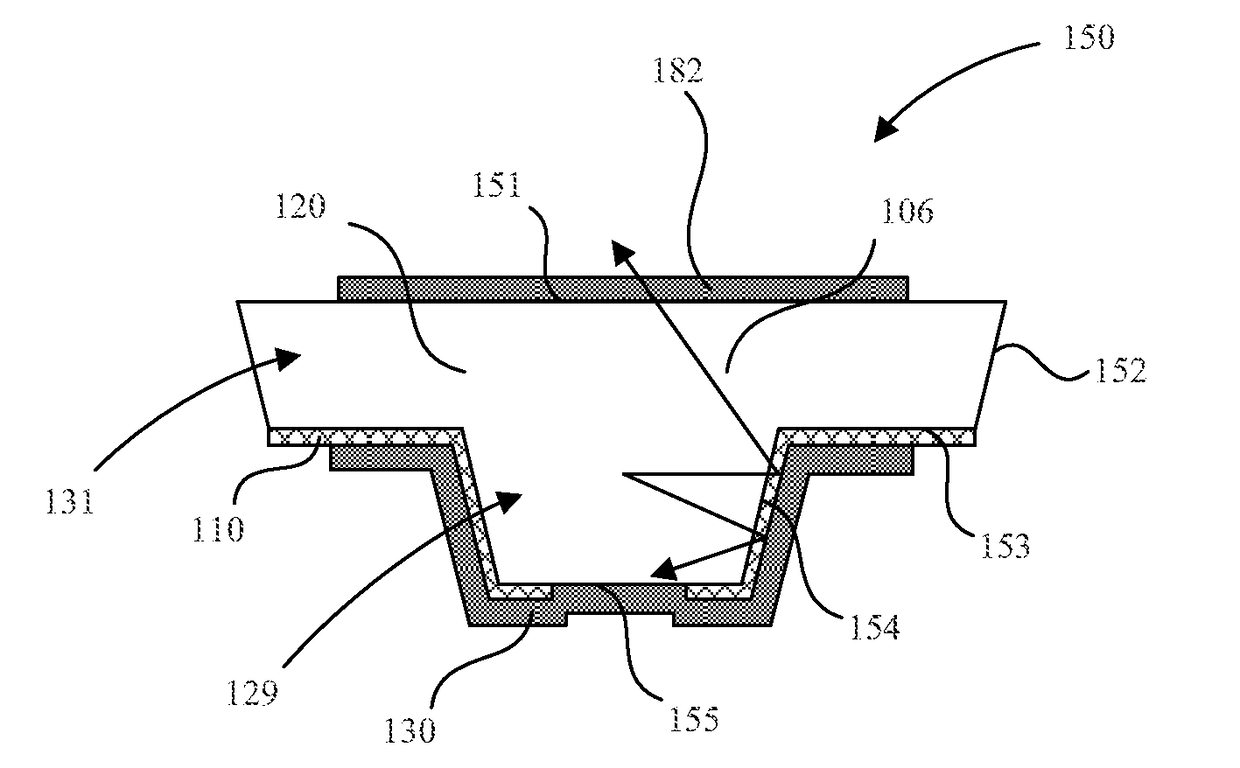
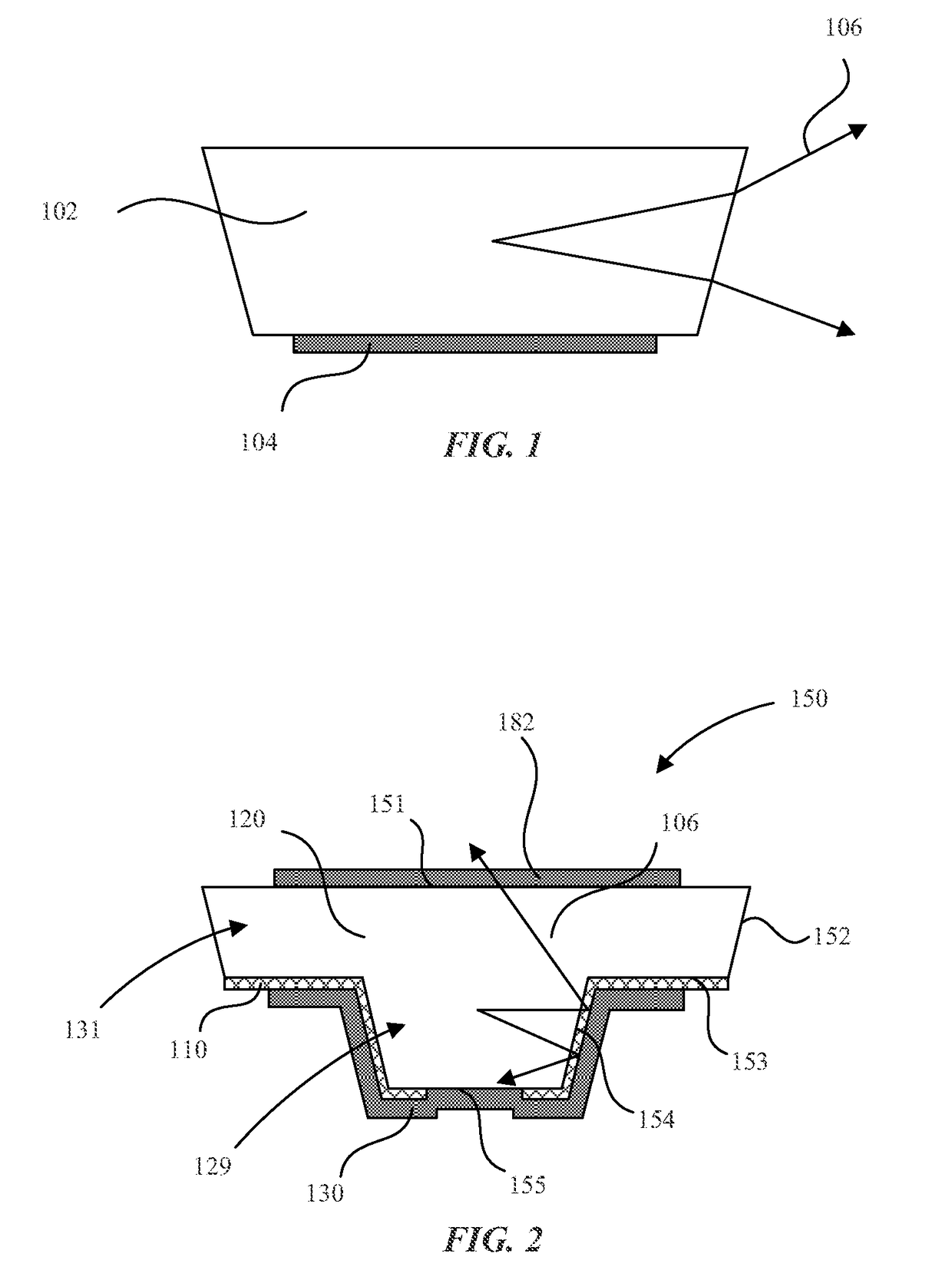
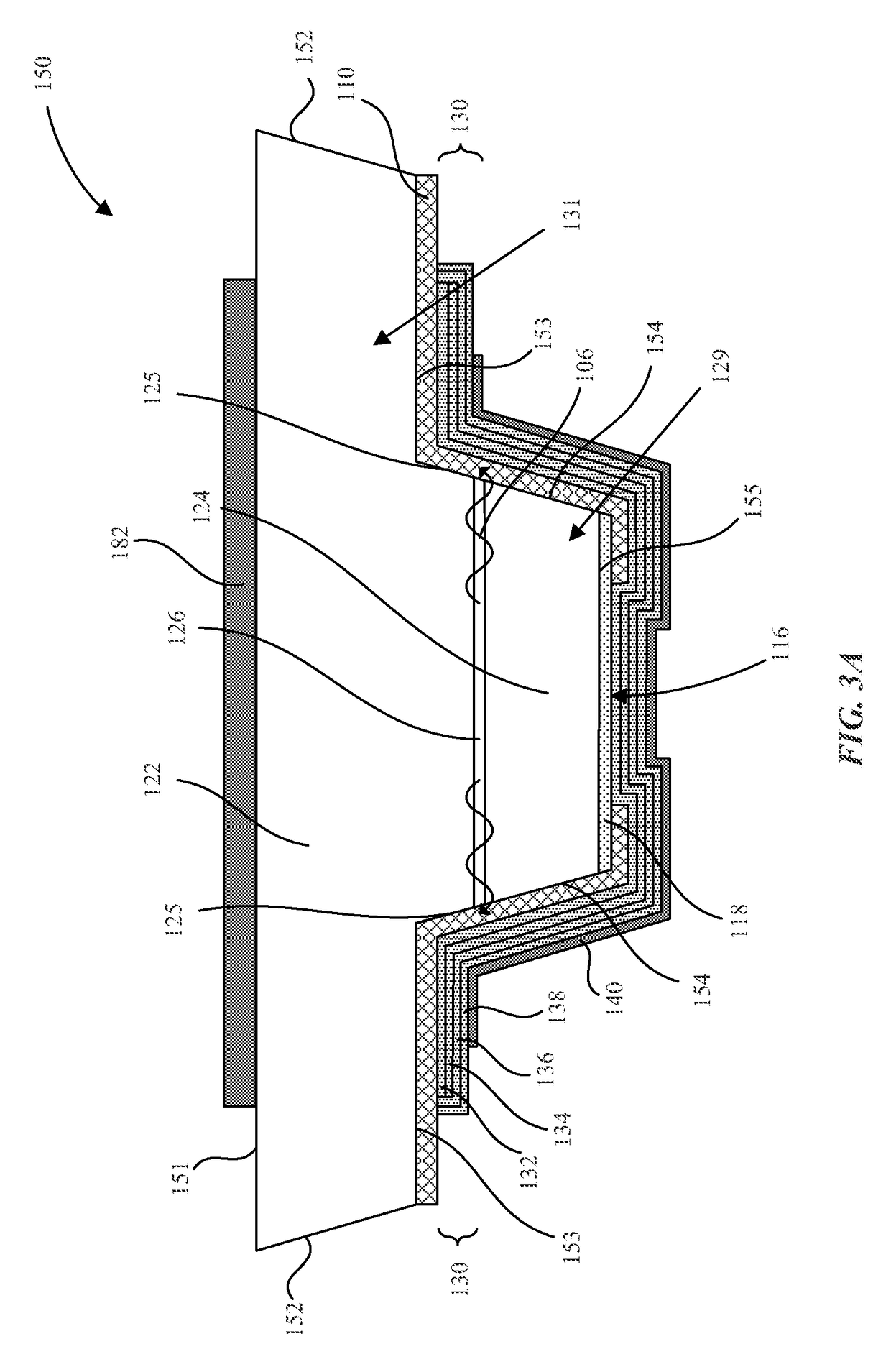
Micro-light emitting diode with metal side mirror
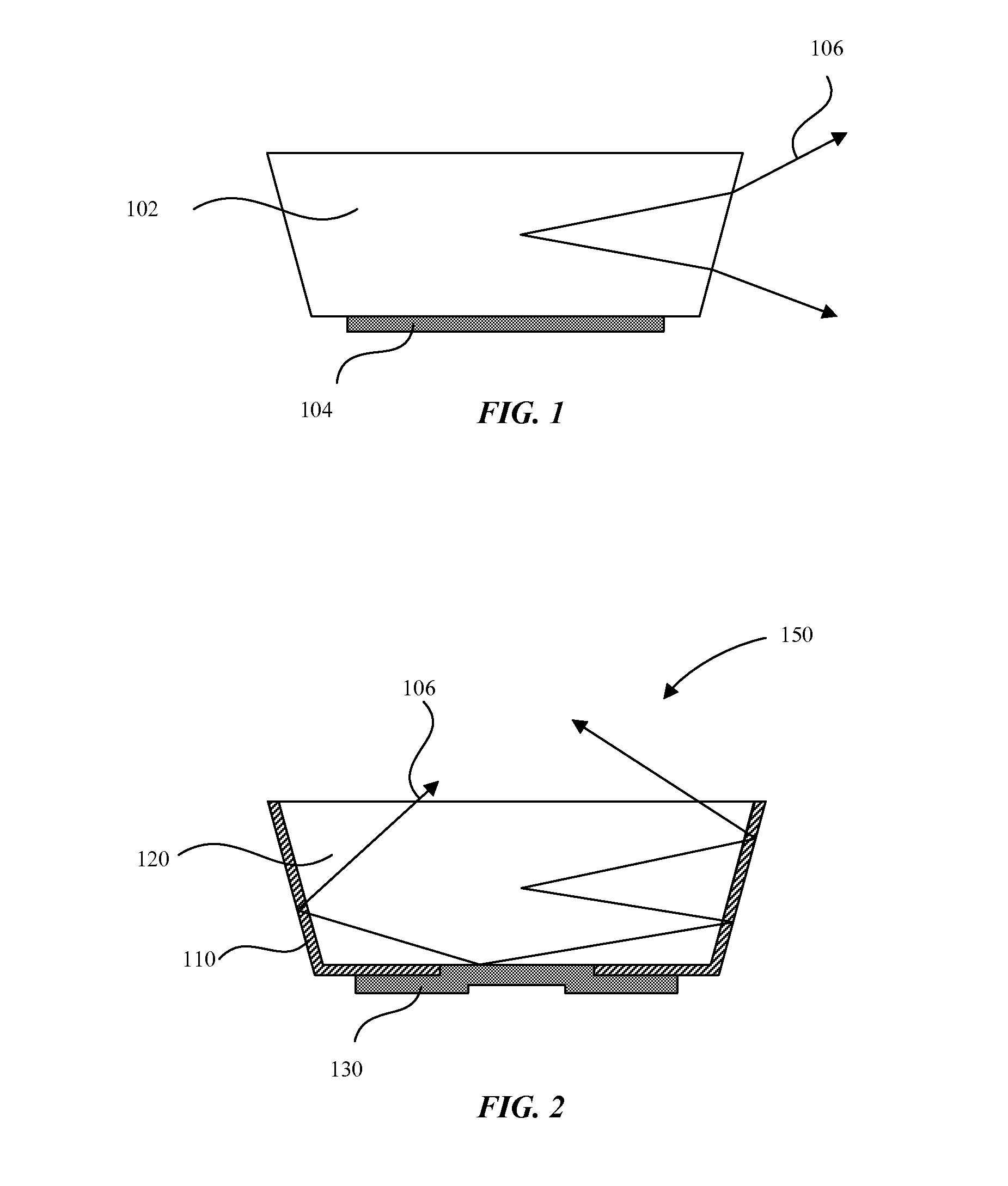
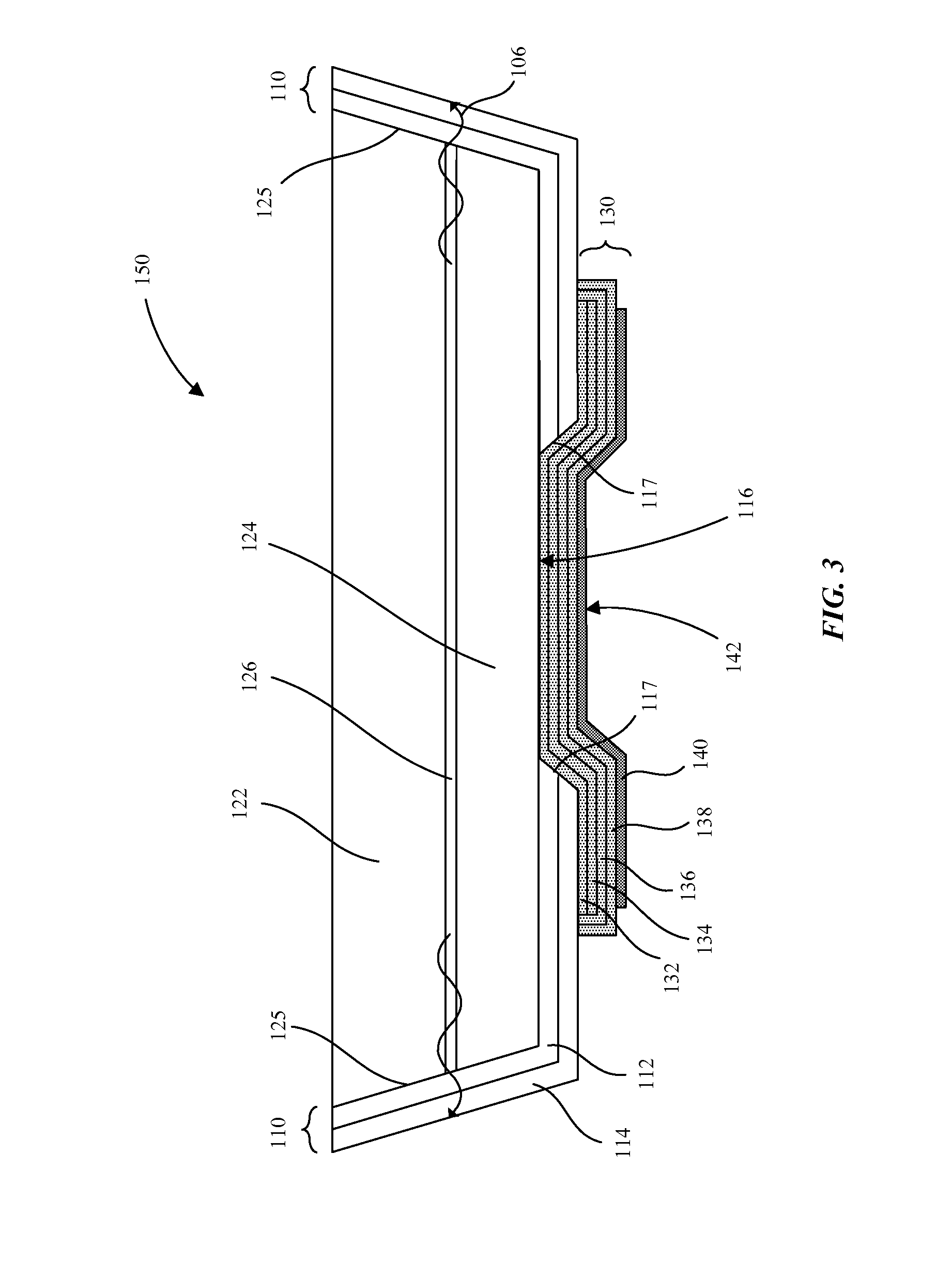
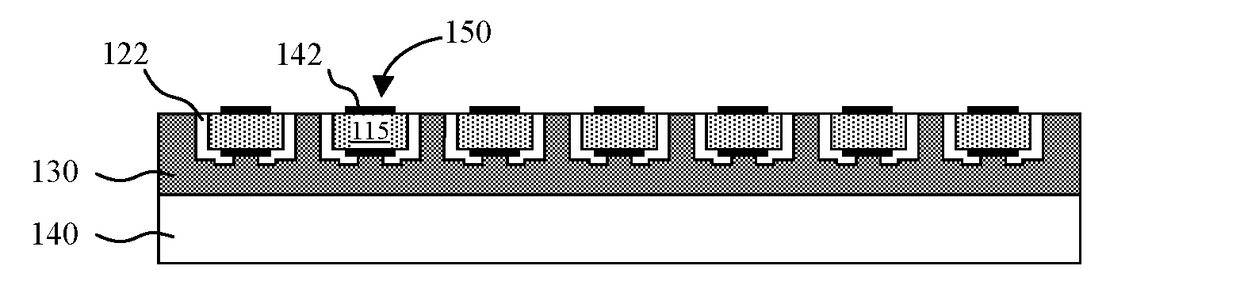
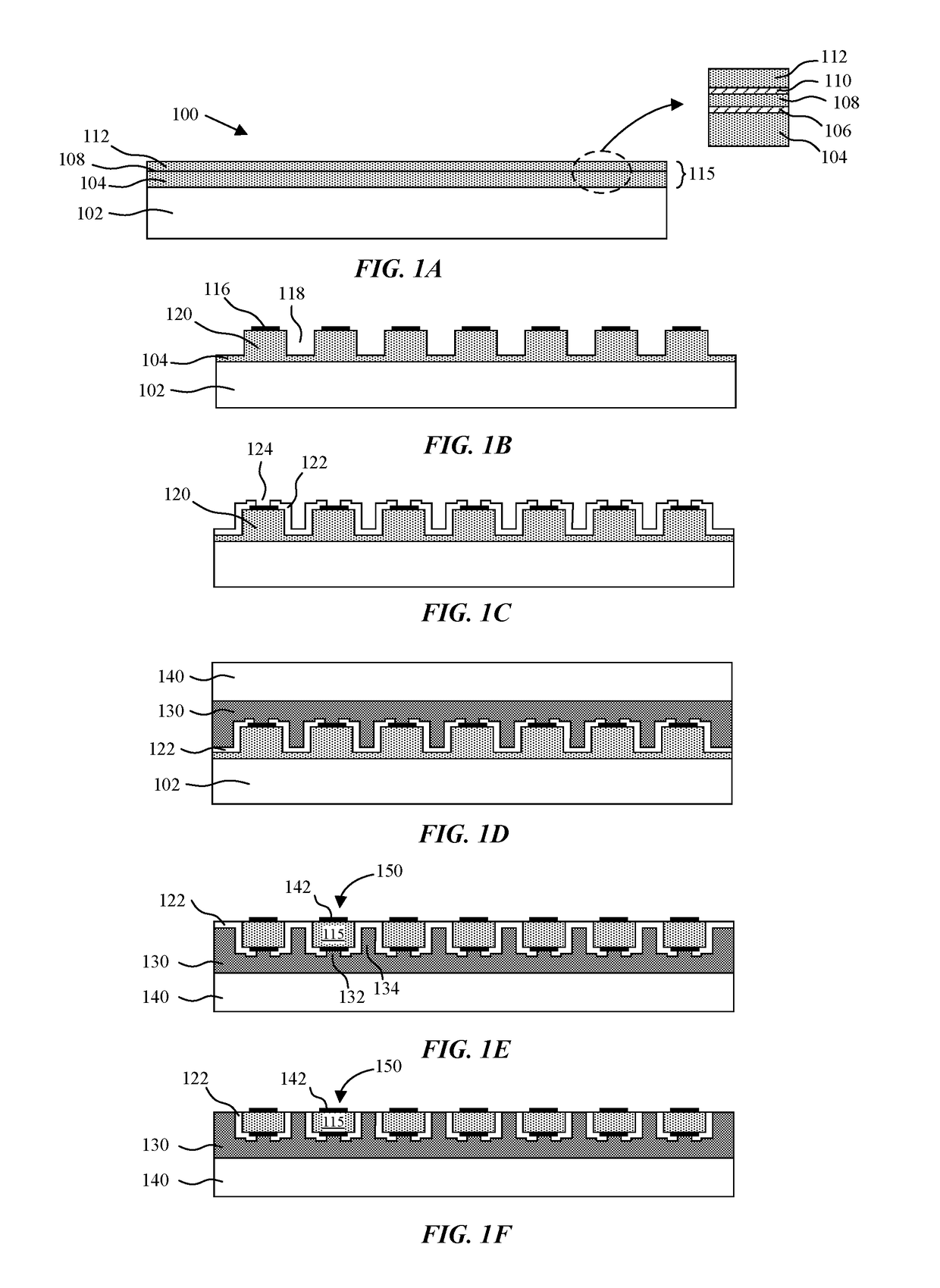
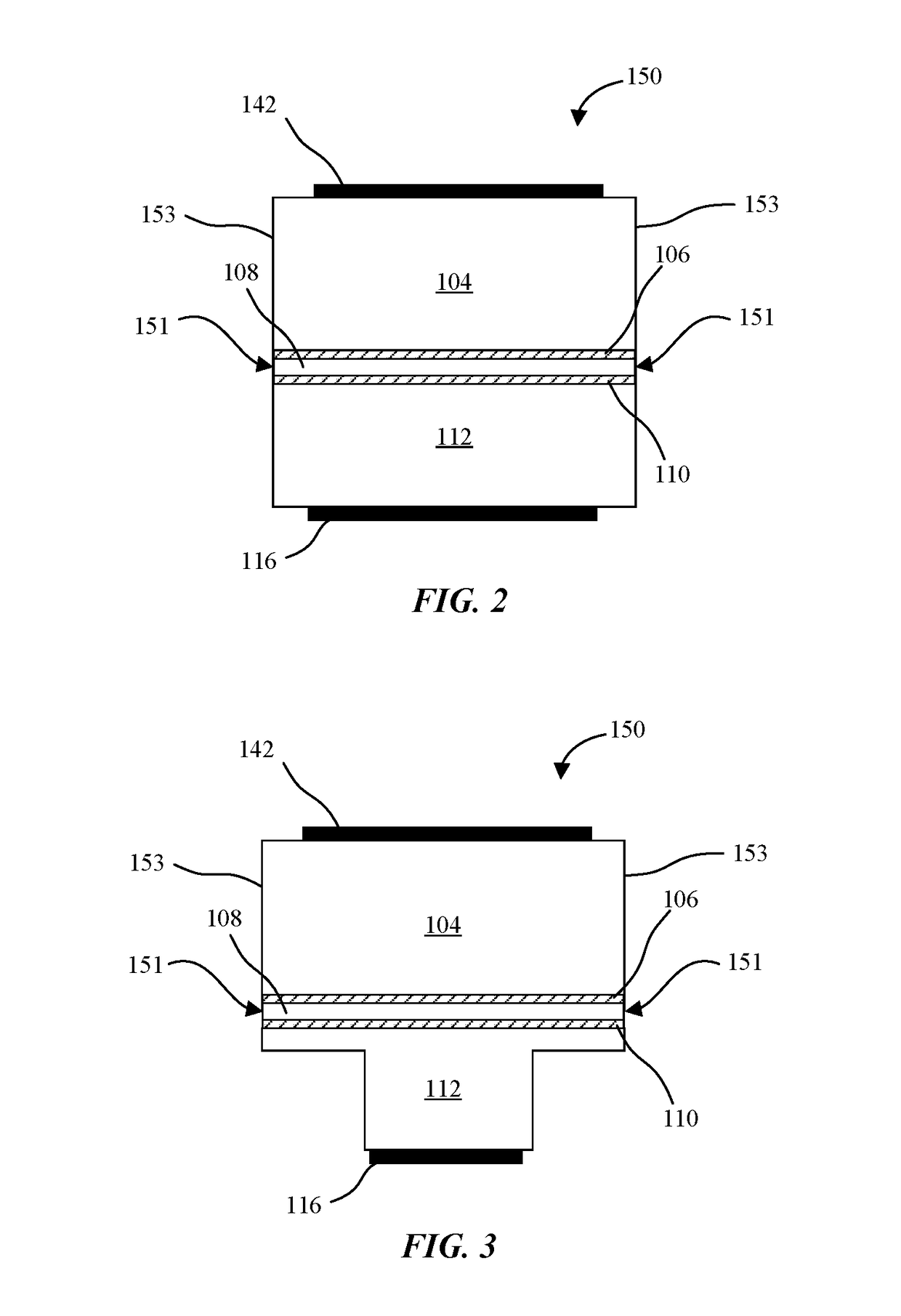
Light emitting diodes and display systems are disclosed. In an embodiment a light emitting diode (150) includes a p-n diode (120) including a mesa structure (129) that protrudes from a base structure (131). A reflective metallization (130) laterally surrounds the mesa structure, which also includes a quantum well layer of the p-n diode.
Owner:APPLE INC
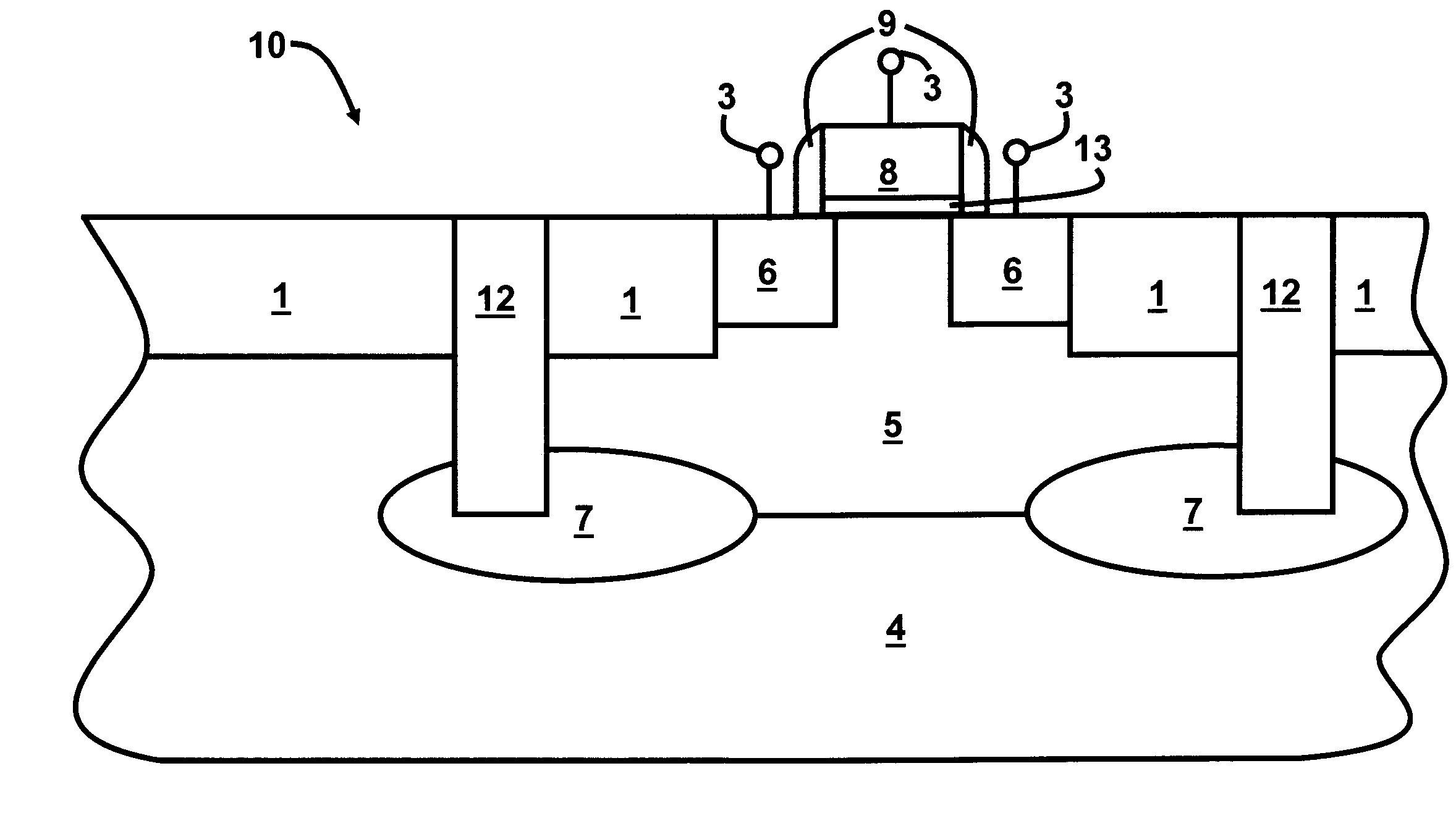
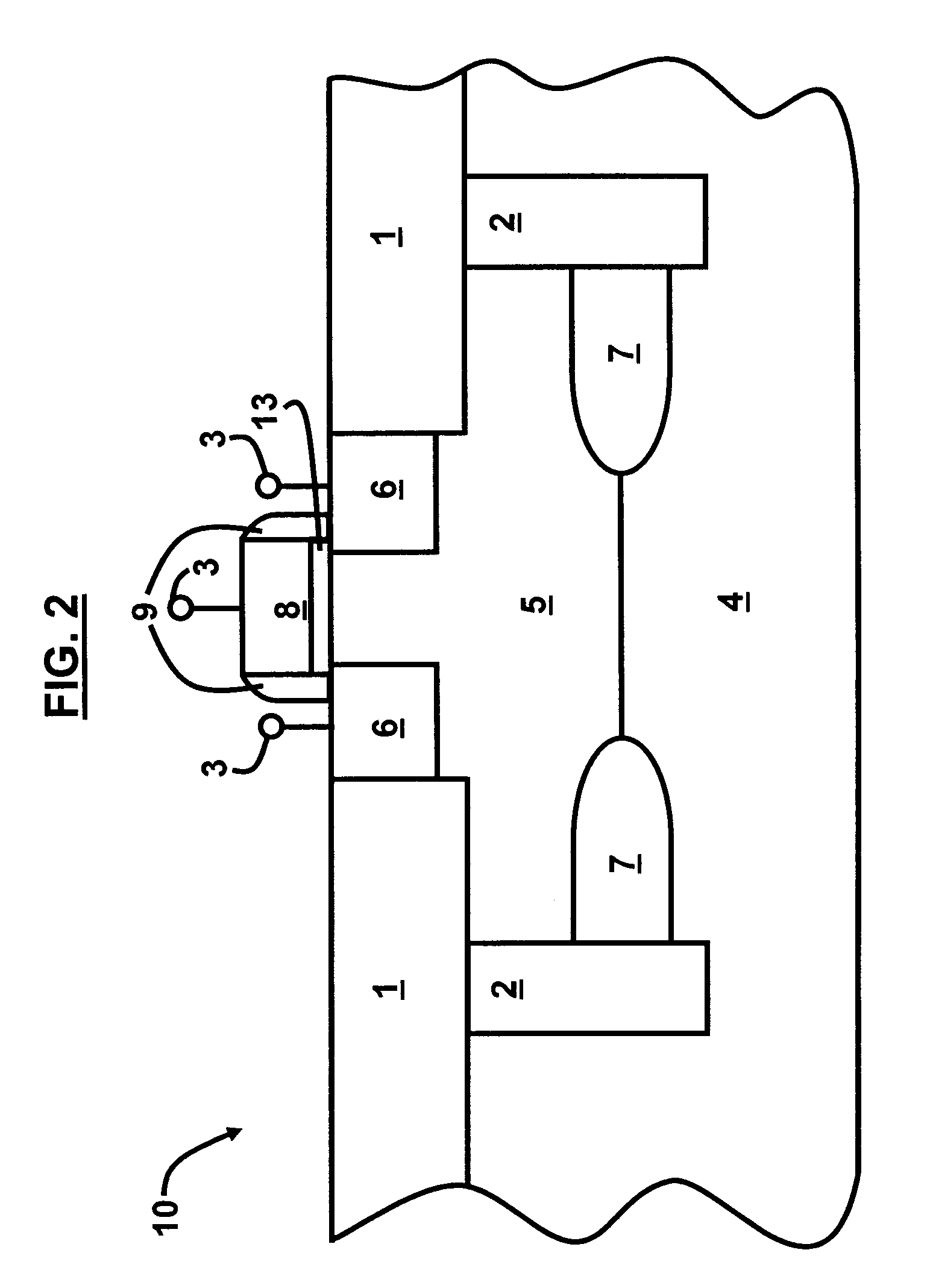
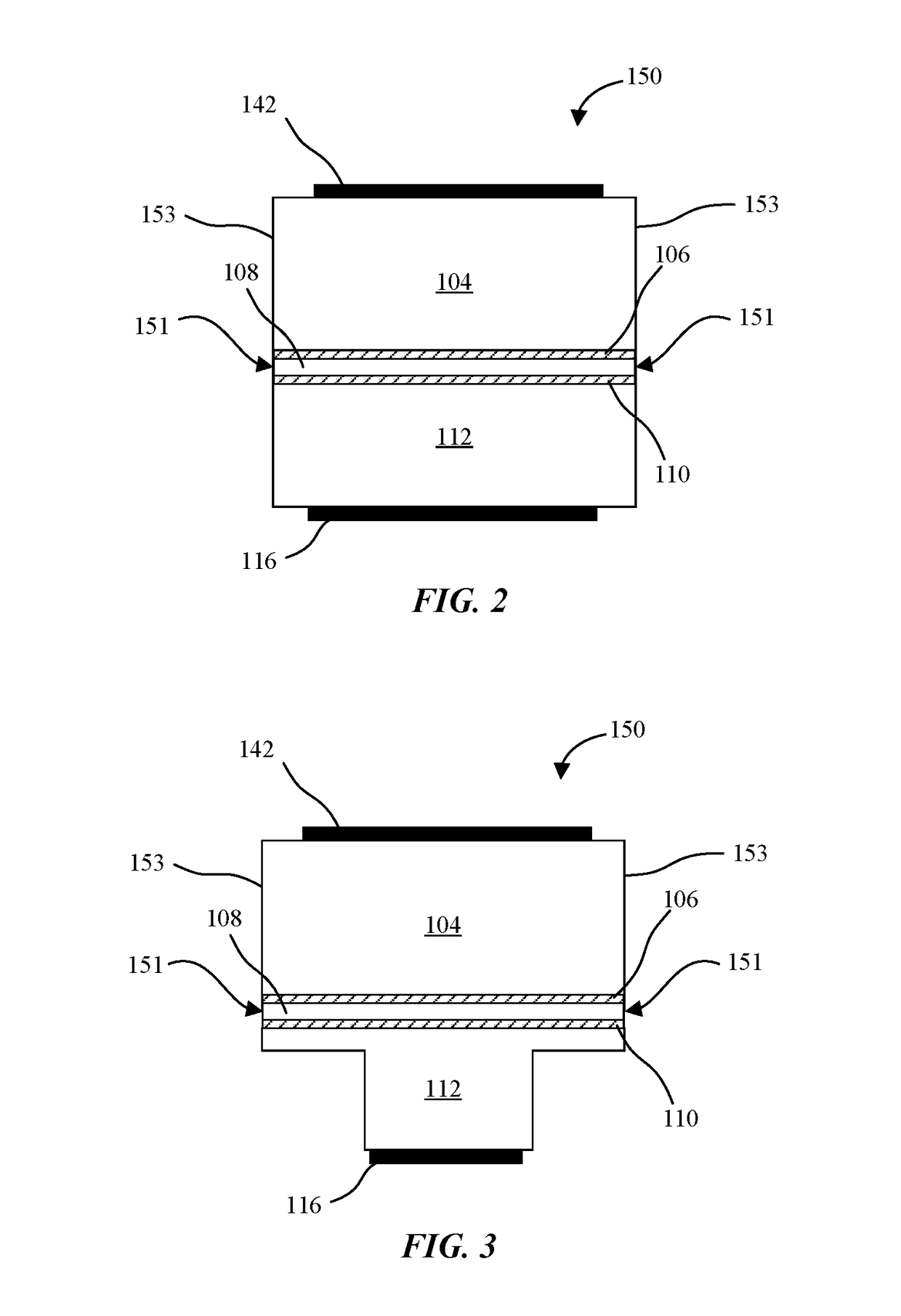
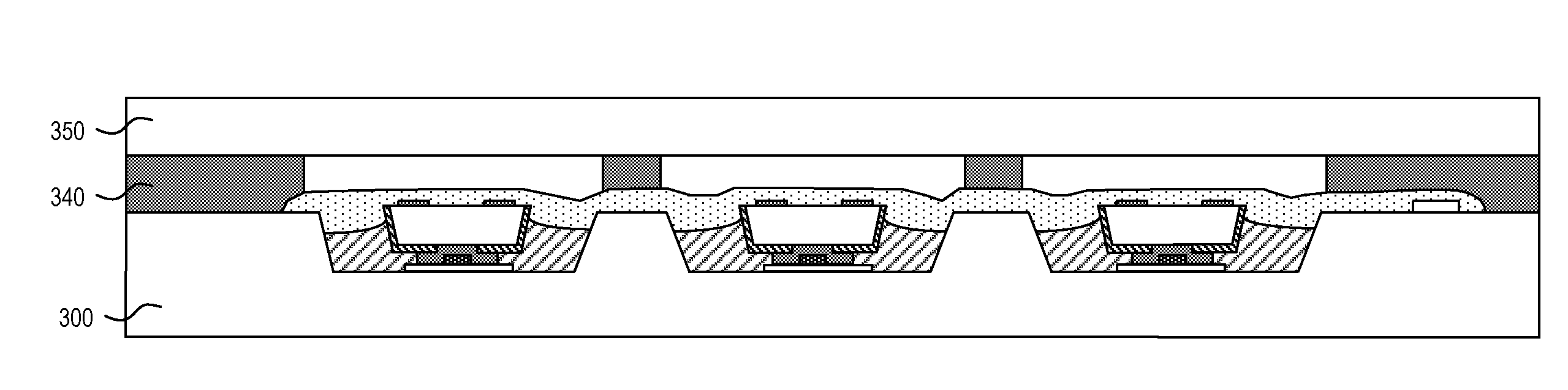
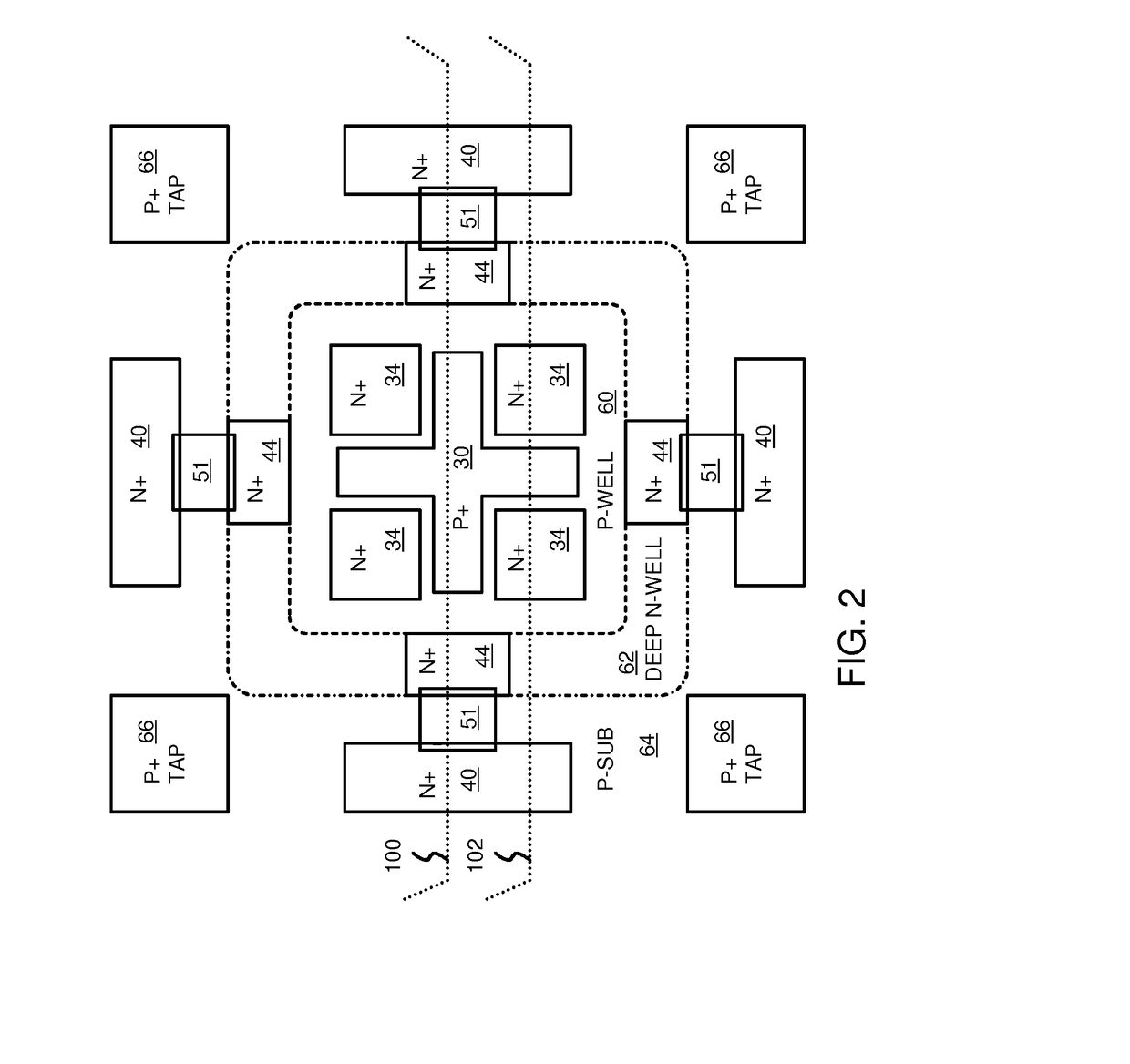
Lateral-Diode, Vertical-SCR Hybrid Structure for High-Level ESD Protection
A lateral p-n diode in the center of and surrounded by a vertical Silicon-Controlled Rectifier (SCR) forms an Electro-Static-Discharge (ESD) protection structure. The lateral p-n diode has a cross-shaped P+ diode tap with four rectangles of N+ diode regions in each corner of the cross. A P-well under the P+ diode tap is also an anode of a vertical PNPN SCR that has a deep N-well in a P-substrate. The deep N-well surrounds the lateral diode. Triggering MOS transistors are formed just beyond the four ends of the cross shaped P+ diode tap. Each triggering MOS transistor has N+ regions at the edge of the deep N-well and in the P-substrate that act as the cathode terminals. A deep P+ implant region under the N+ region at the edge of the deep N-well decreases a trigger voltage of the vertical SCR.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Nano-tubes semiconductor device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101924137AImprove charge balance effectUniform doping concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringField-effect transistor
The invention relates to a semiconductor device and a preparation method thereof. A nano-tubes area is produced by adopting the thin epitaxial layer formed on the channel sidewall of the semiconductor body. The thin epitaxial layer possesses an even and consistent dosage concentration. A first thin epitaxial layer in the same conducting type as the semiconductor body is formed on the channel sidewall of the semiconductor body. A second thin expitaxial layer in the opposite conducting type with the semiconductor body is formed on a first expitaxial layer. The first and the second expitaxial layer possess an even and consistent dosage concentration. An electric charge balance is achieved by choosing an appropriate first and second expitaxial layer and appropriate thickness and dosage concentration of the semiconductor body. The semiconductor body is a P-shaped substrate with light dosage. By adopting the N-expitaxial layer / P-expitaxial layer nano-tubes structure of the same type, a metal oxide field effect tube with a vertical channel, a insulated gate dipole transistor, a Schottky diode and a P-N diode can be produced.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INT LP
Device and method for transient voltage suppressor
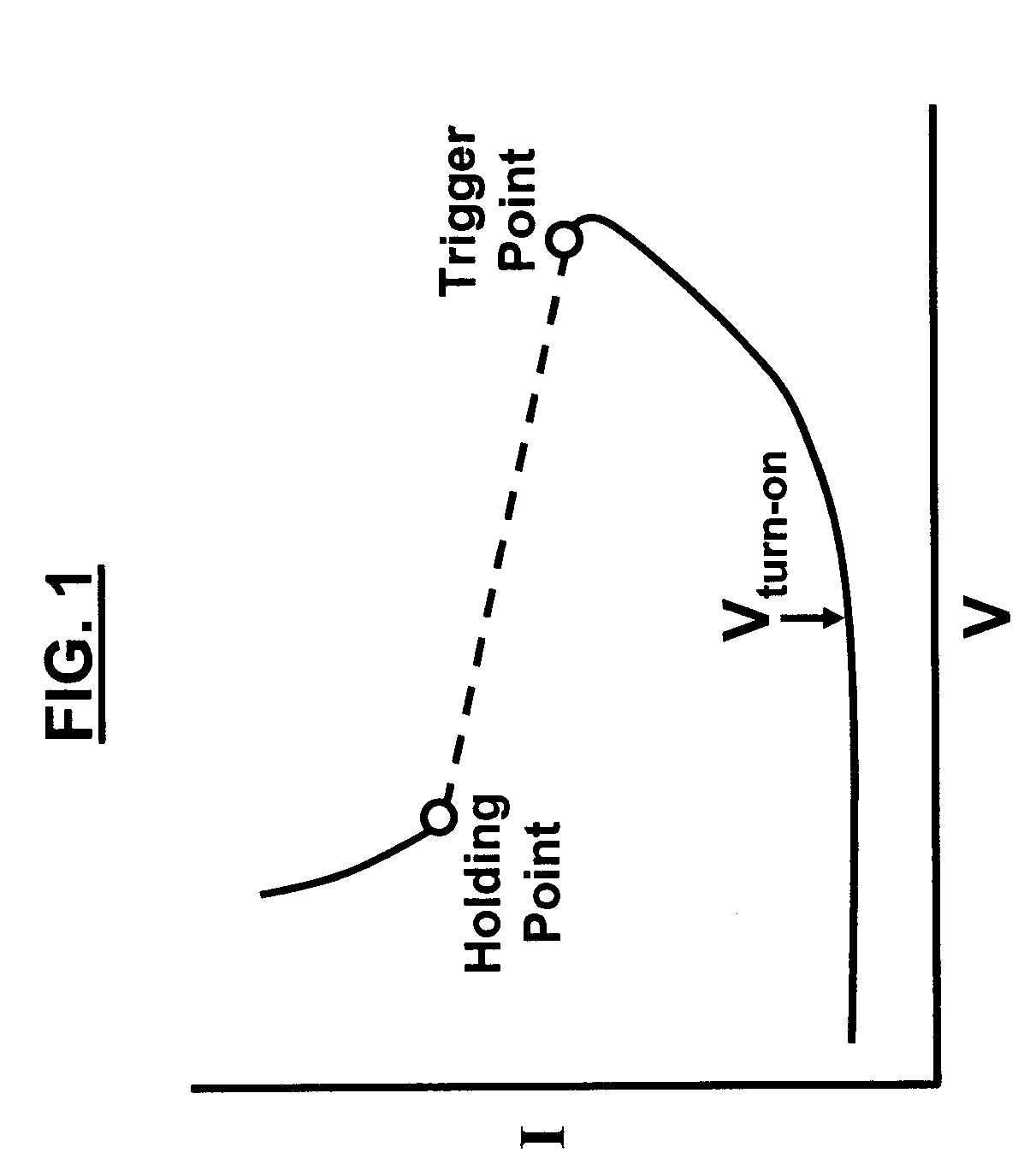
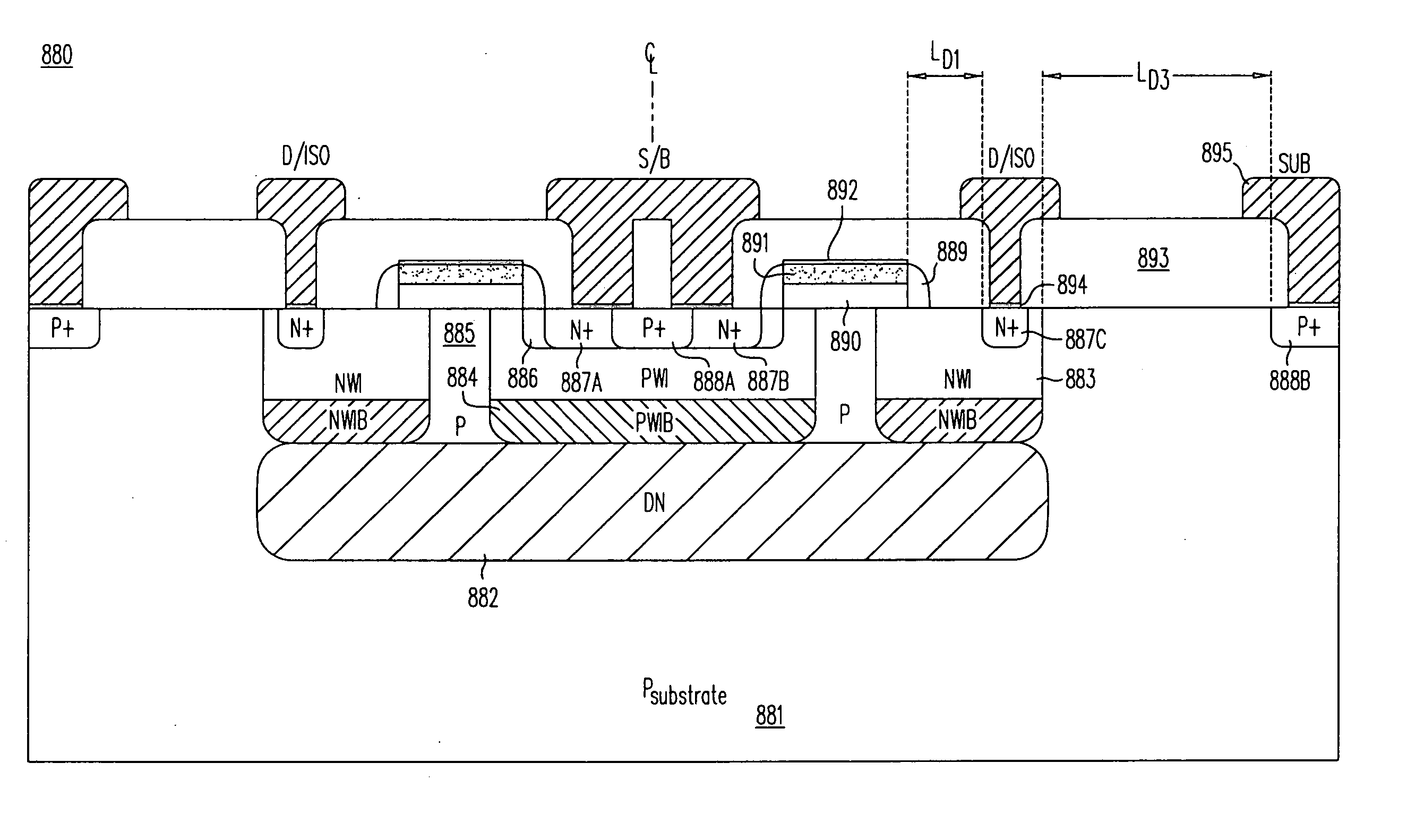
ActiveUS20110266592A1Control associated clamping voltageProcess is complicated and expensiveSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFilling materialsTransient voltage suppressor
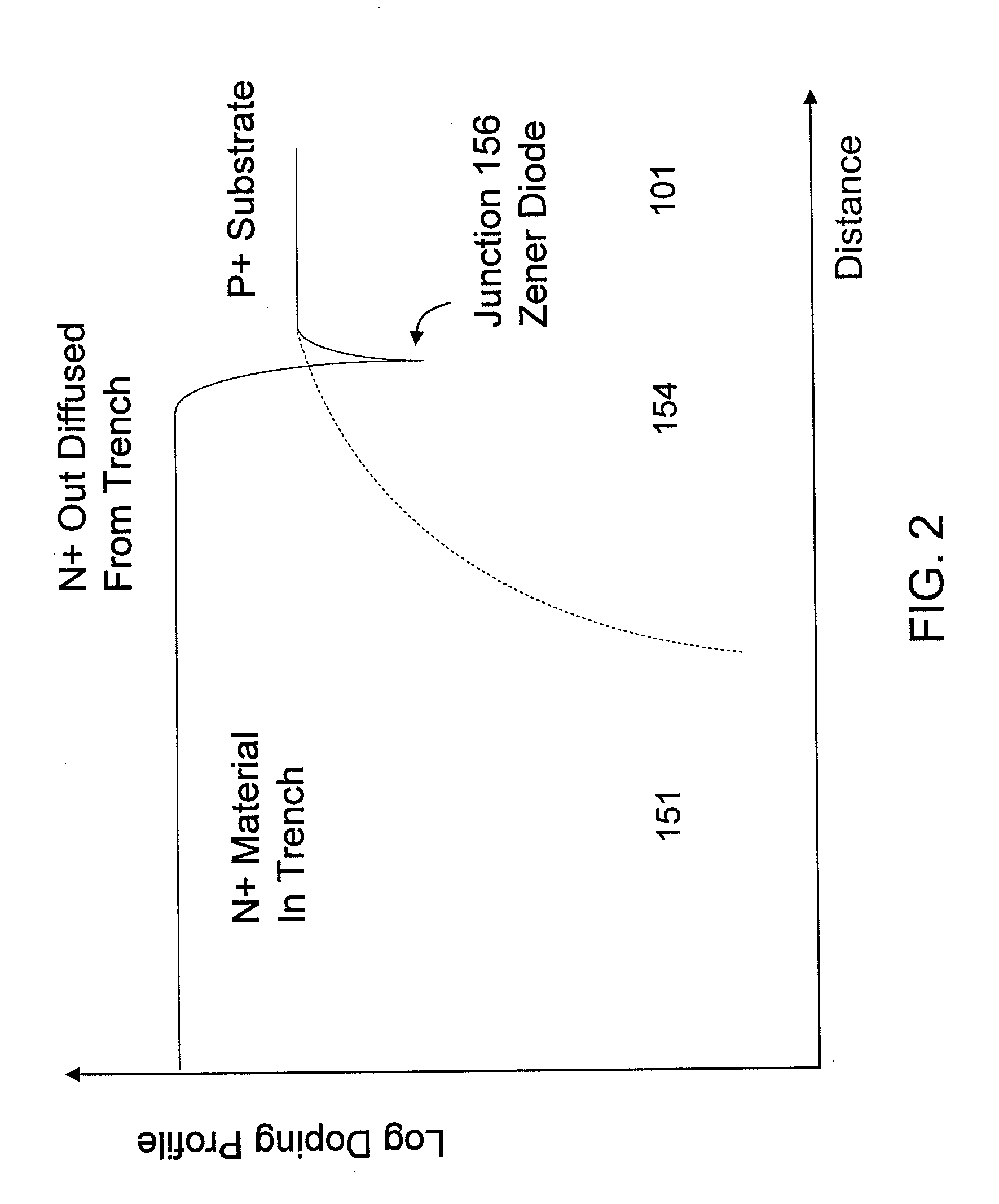
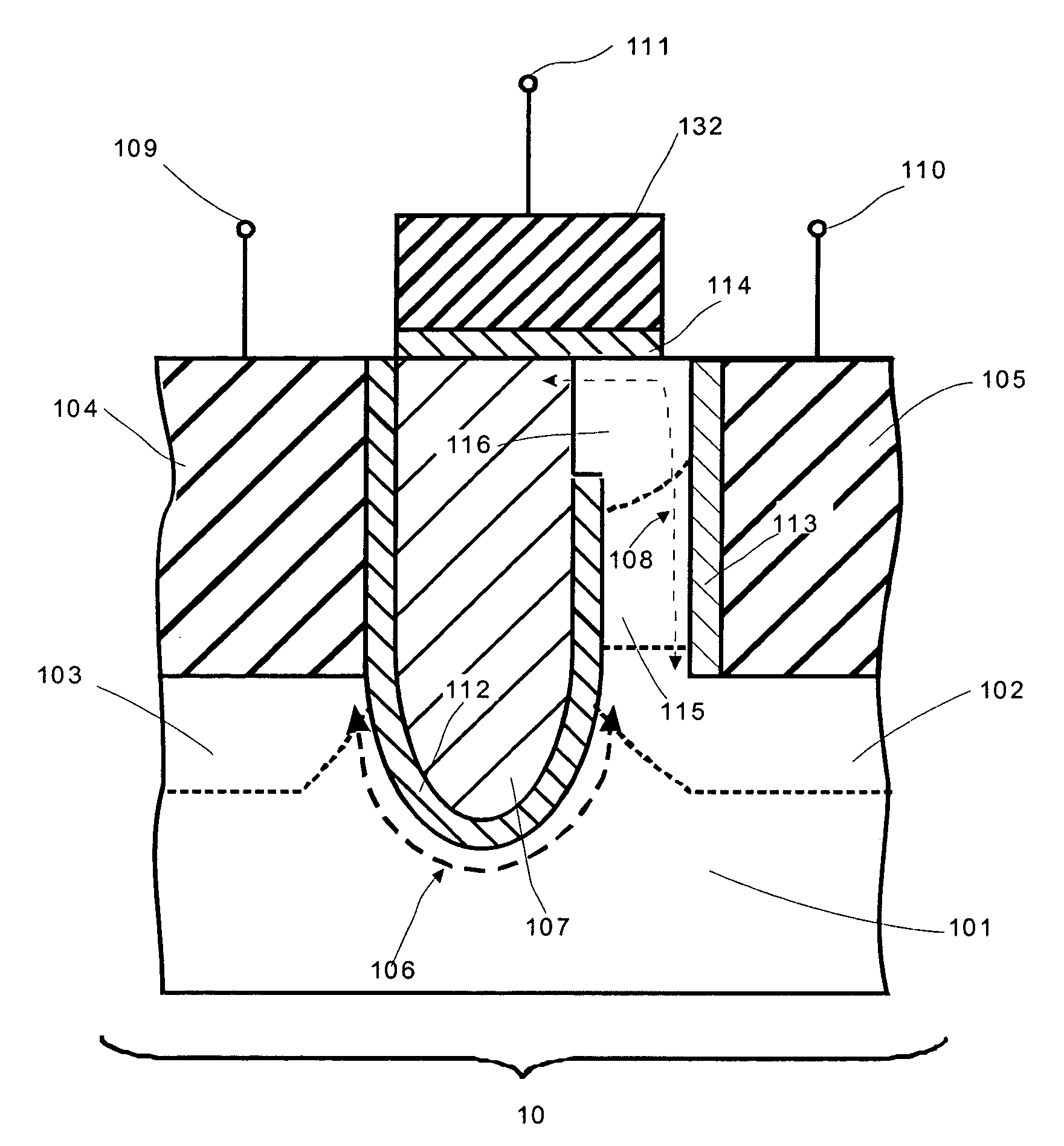
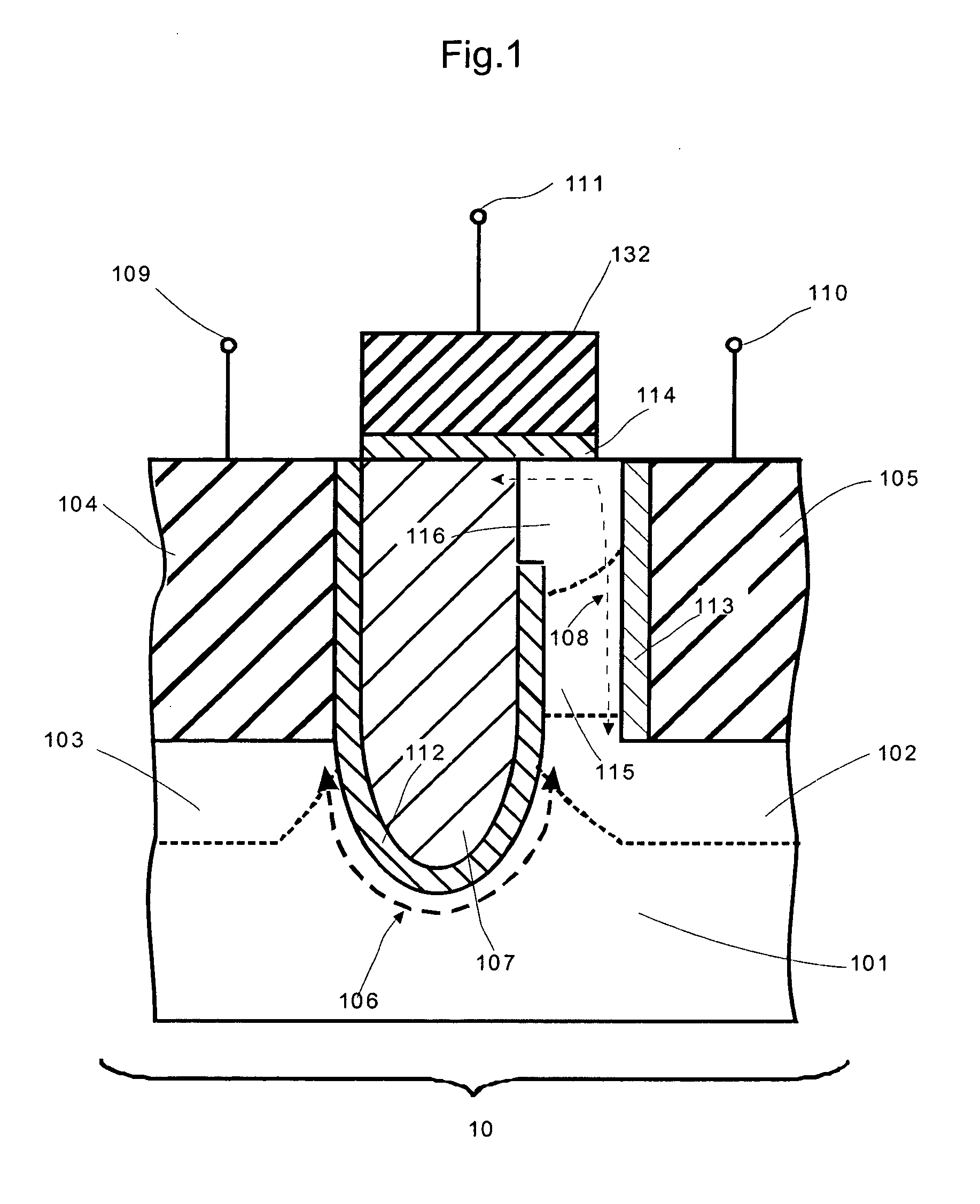
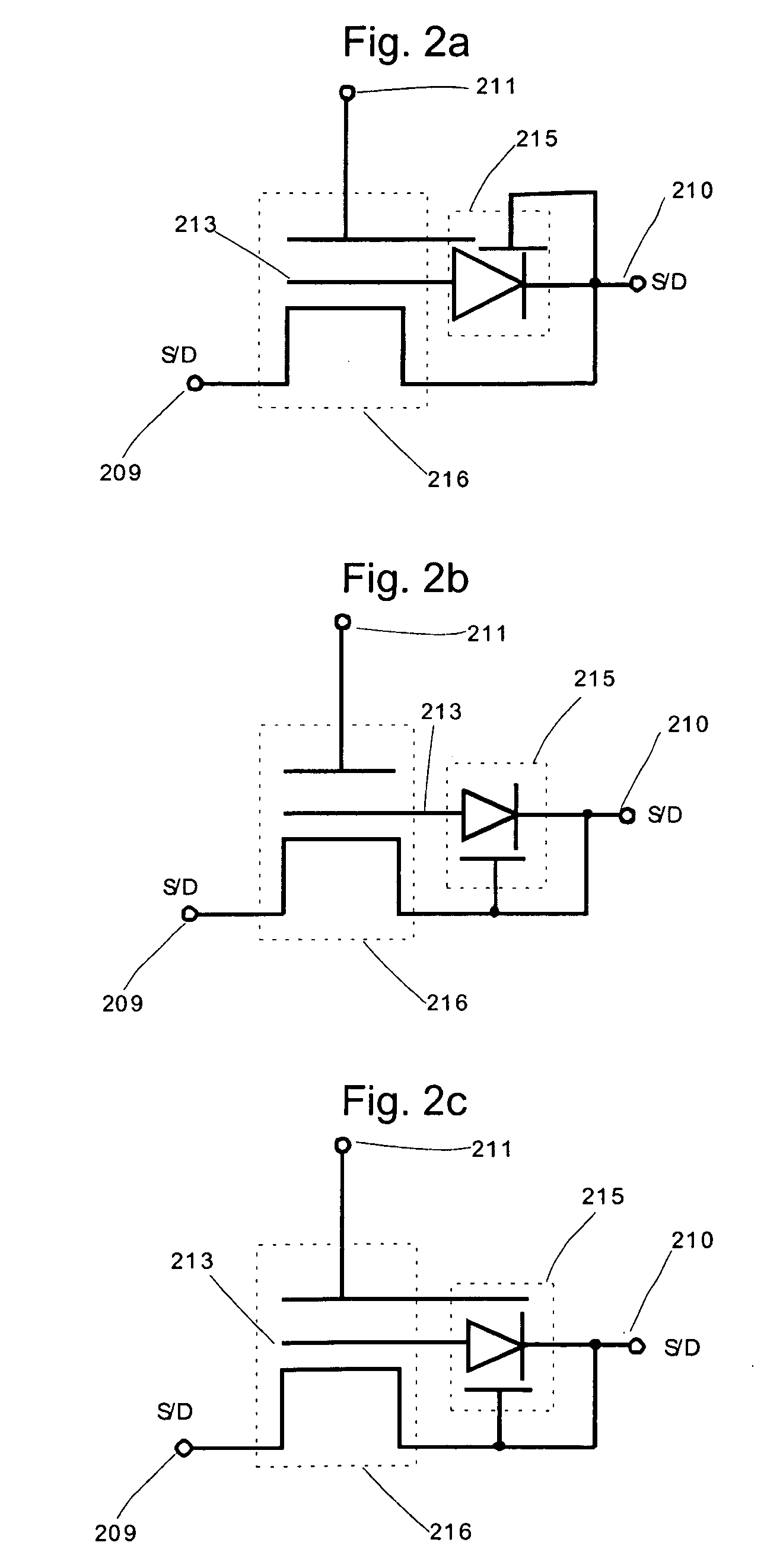
A transient voltage suppressor (TVS) device includes a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type, and a first and a second semiconductor regions of a second conductivity type overlying the semiconductor substrate. A semiconductor layer of the second conductivity type overlies the first and the second semiconductor regions. The TVS device has a first trench extending through the semiconductor layer and the first semiconductor region and into the semiconductor substrate, and a fill material of the second conductivity type disposed in the first trench. A clamping diode in the TVS device has a junction between an out-diffused region from the fill material and a portion of the semiconductor substrate. The TVS device also includes a first P-N diode formed in a first portion of the semiconductor layer, and a second P-N diode having a junction between the second semiconductor region and the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device and method of forming the same
ActiveUS8089801B2Shorter read and write timesIncrease in sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesP–n diodeSemiconductor
The present invention discloses a semiconductor memory device comprising a source, a drain, a floating gate, a control gate, a recess channel and a gated p-n diode. The said p-n diode connects said floating gate and said drain. The said floating gate is for charge storage purpose, it can be electrically charged or discharged by current flowing through the gated p-n diode. An array of memory cells formed by the disclosed semiconductor memory device is proposed. Furthermore, an operating method and a method for producing the disclosed semiconductor memory device and array are described.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIENTAL SEMICONDUCTOR CO LTD
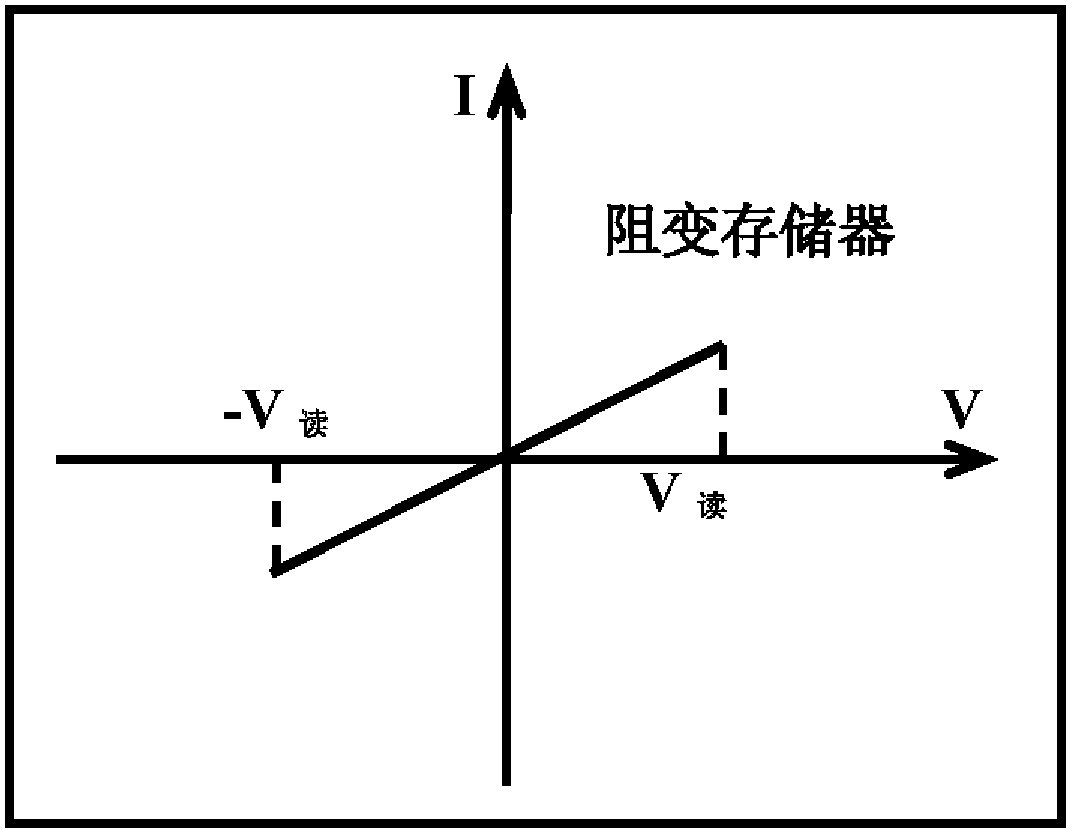
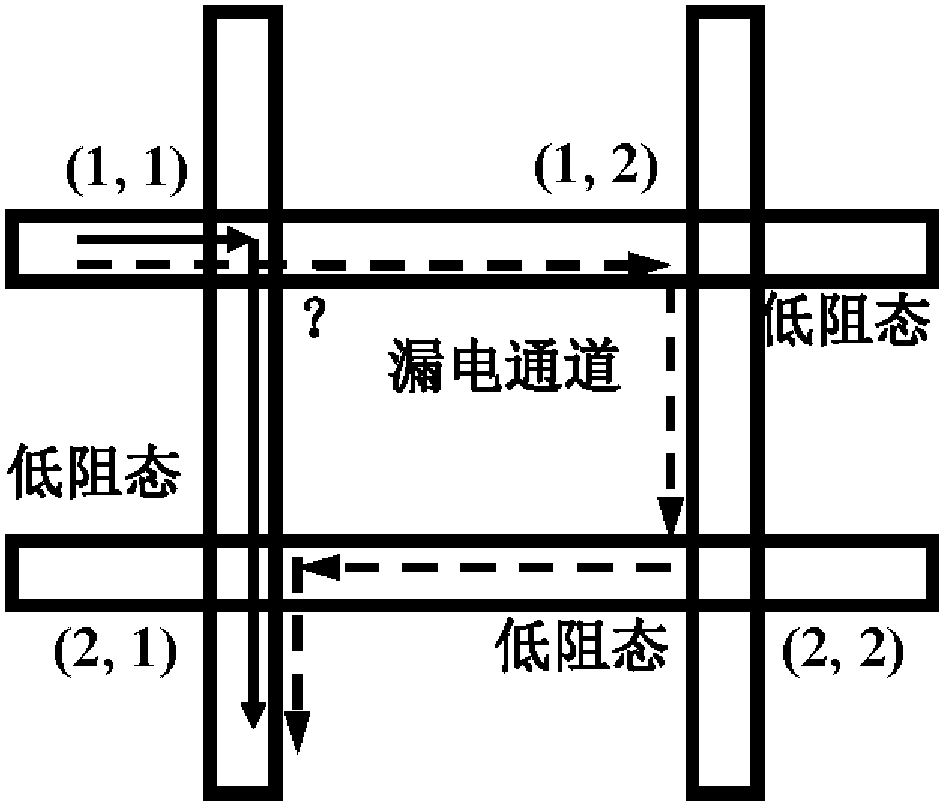
Strobing device unit used for cross array integration way of double-pole type resistance change storage
InactiveCN103137646AReduce read crosstalk problemsIncrease the on-currentSolid-state devicesDigital storageRectifier diodesElectrical polarity
The invention discloses a strobing device unit used for a cross array integration way of a double-pole type resistance change storage. The strobing device unit used for the cross array integration way of the double-pole type resistance change storage is characterized in that the strobing device unit comprises an n-p diode and a p-n diode. Polarity of the n-p diode and polarity of the p-n diode are opposite. The polarity of the n-p diode is in parallel connection with polarity of the p-n diode. The strobing device unit is has the feature of the two-way rectification. The strobing device unit used for the cross array integration way of the double-pole type resistance change storage has the feature of the two-way rectification. High electric current density can be provided of the random voltage polarity in the brakeover-state. Rectification ratio (RV2 / RV) is provided in the read-voltage. The phenomenon of read-interference in the double-pole type resistance change storage cross array structure can be restrained. Misreading is avoided. The problem that the common rectification diode is only suitable for the single-pole type resistance change storage cross array is solved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
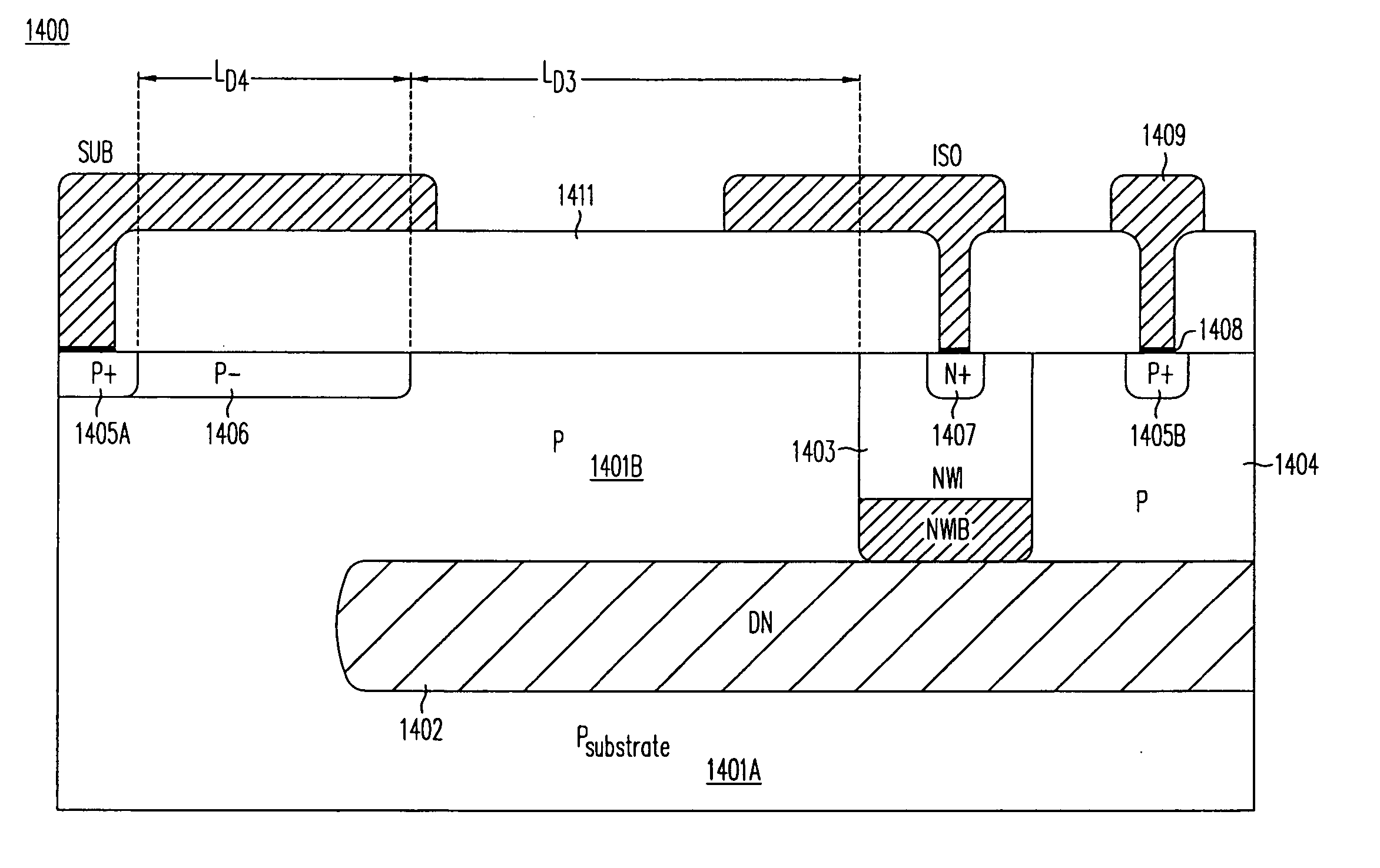
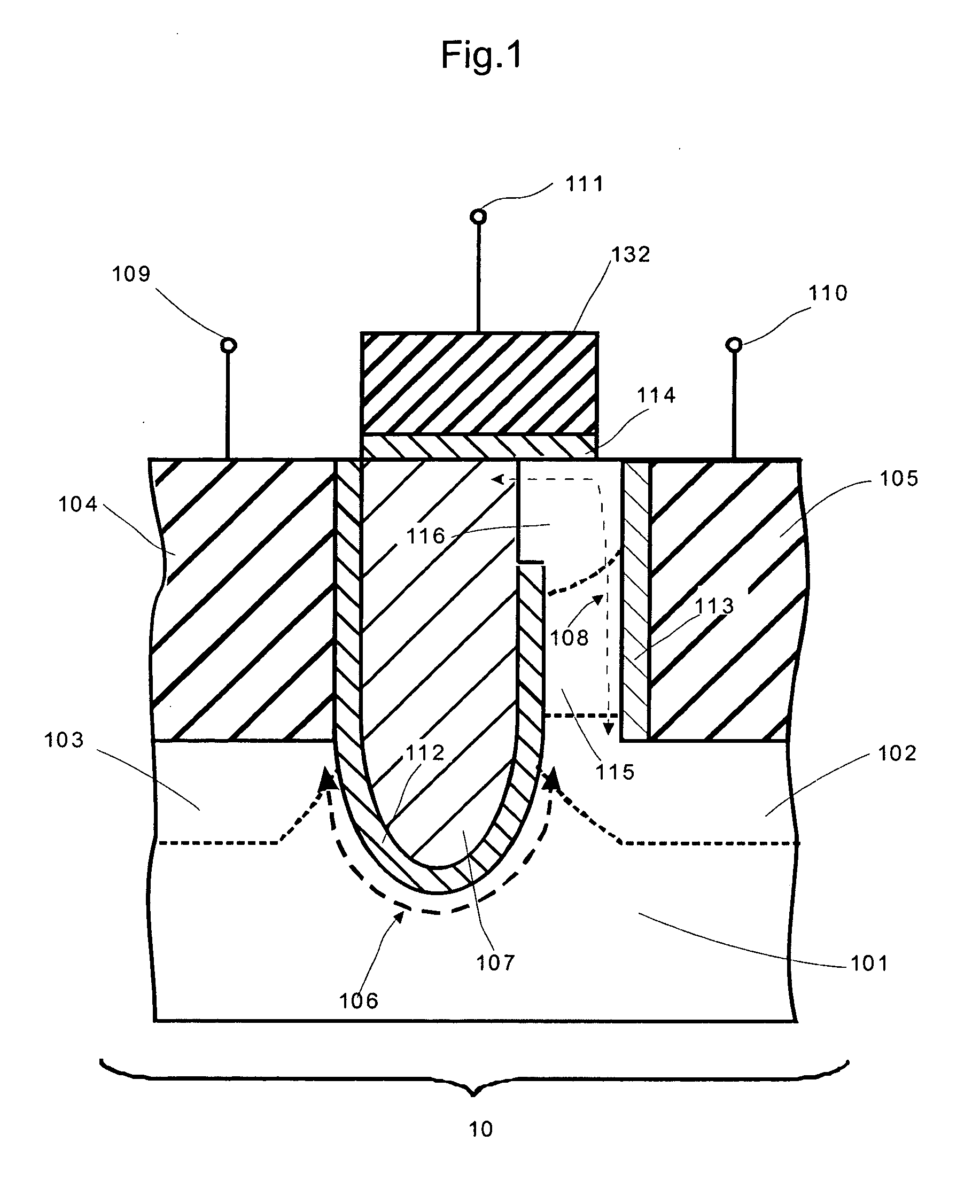
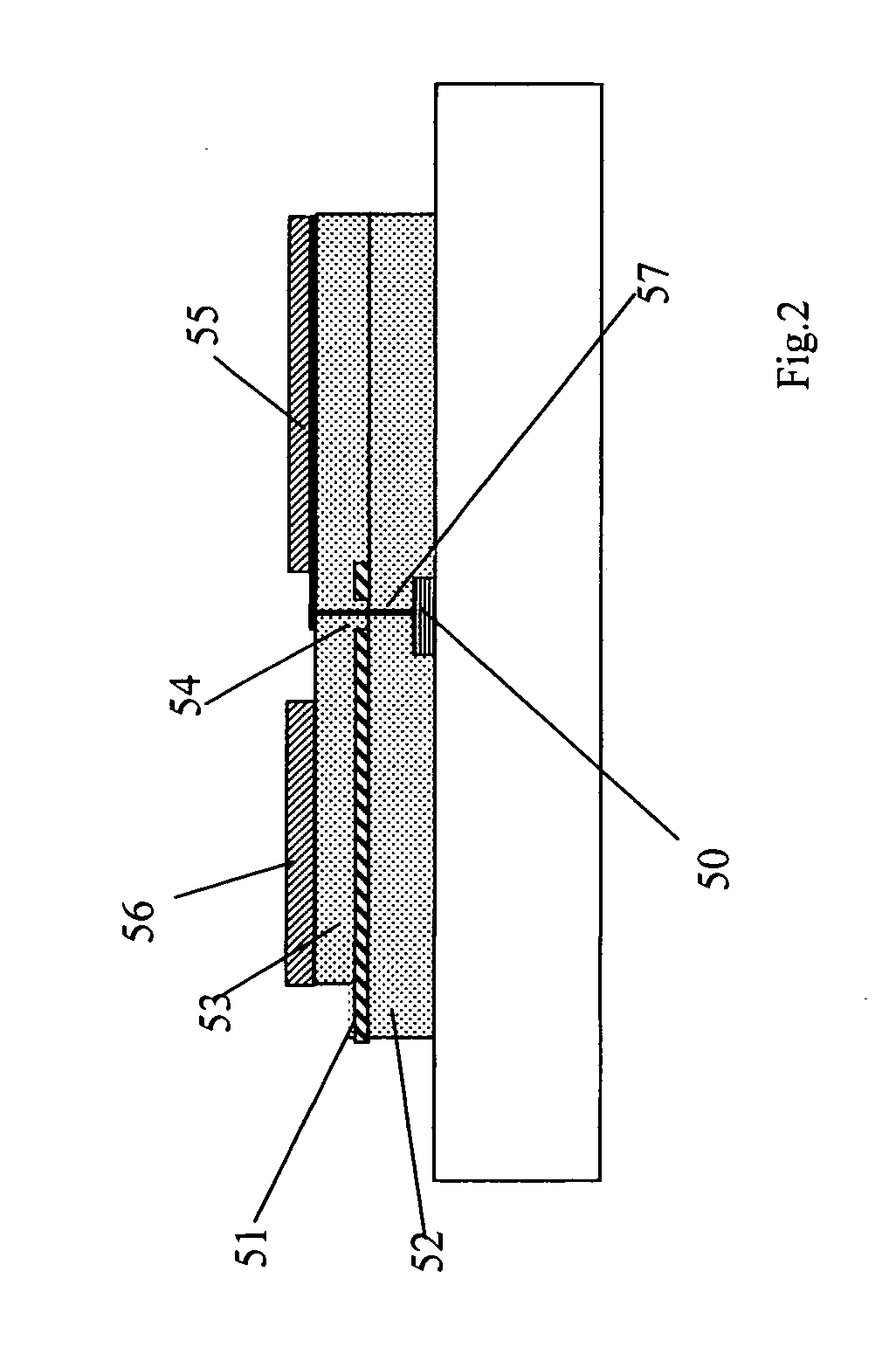
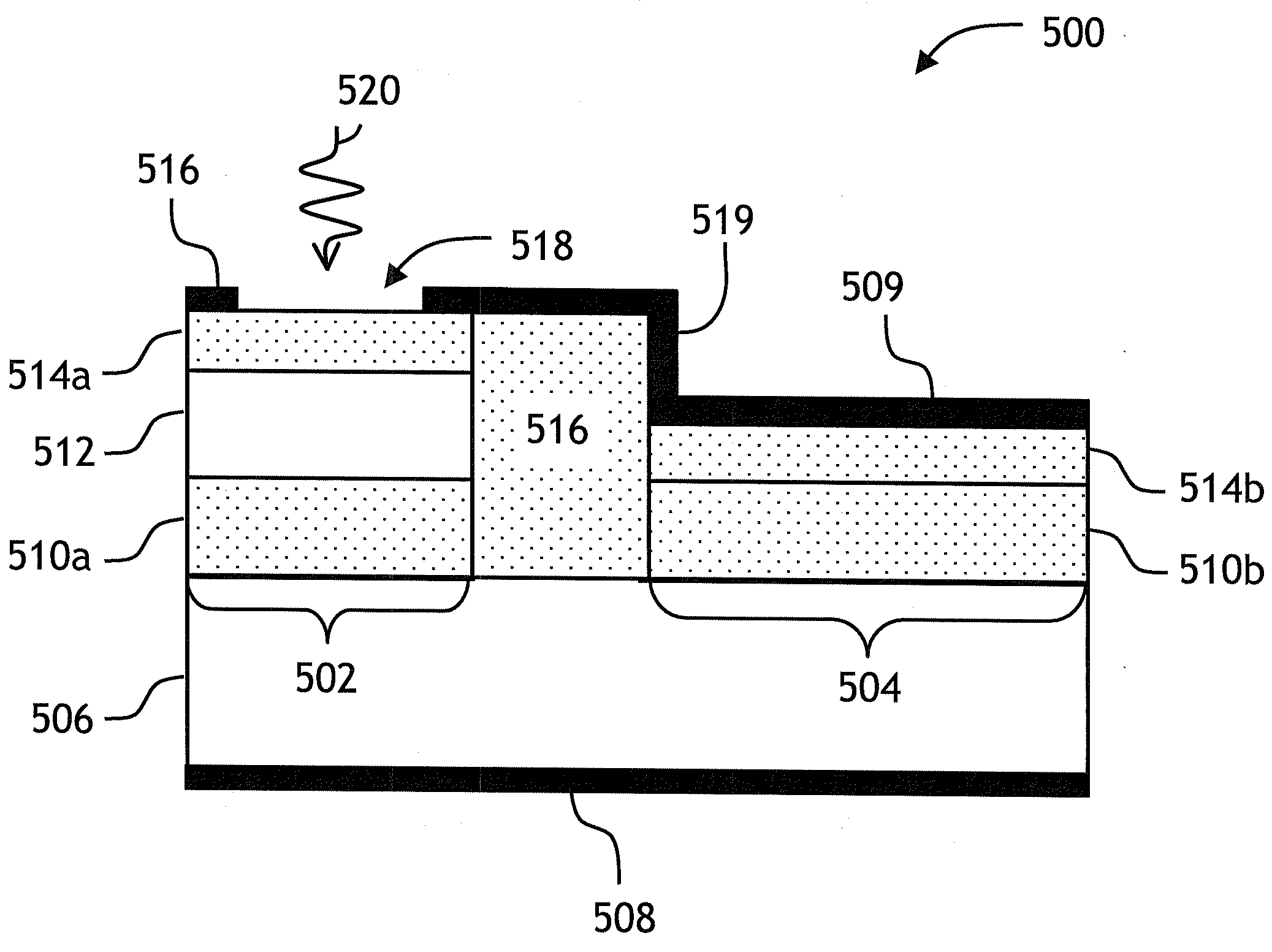
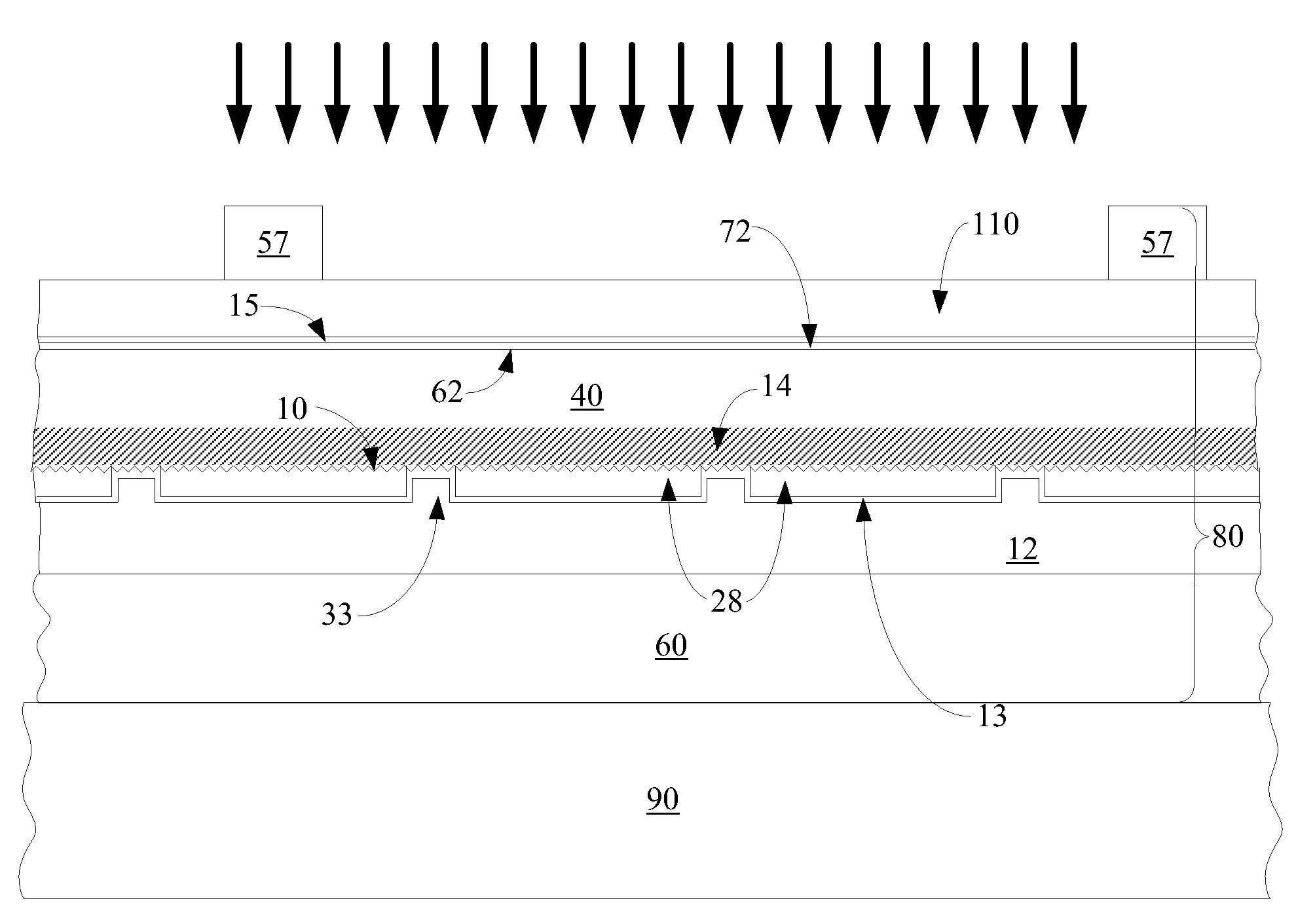
P-n diode having a controlled heterostructure self-positioned on hgcdte, for infrared imagers
ActiveUS20140319580A1Reduce impactQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesP–n diodeChemistry
A device including at least one heterostructure p / n diode, including a substrate based on HgCdTe including for each diode: a first part having a first cadmium concentration; a concentrated part, having a second cadmium concentration, greater than the first concentration, forming a heterostructure with the first part; a p+ doped zone situated in the concentrated part and extending into the first part, forming a p / n junction with an n-doped position of the first part, or a base plate; and the concentrated part is only located in the p+ doped zone and forms a substantially constant cadmium concentration well.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
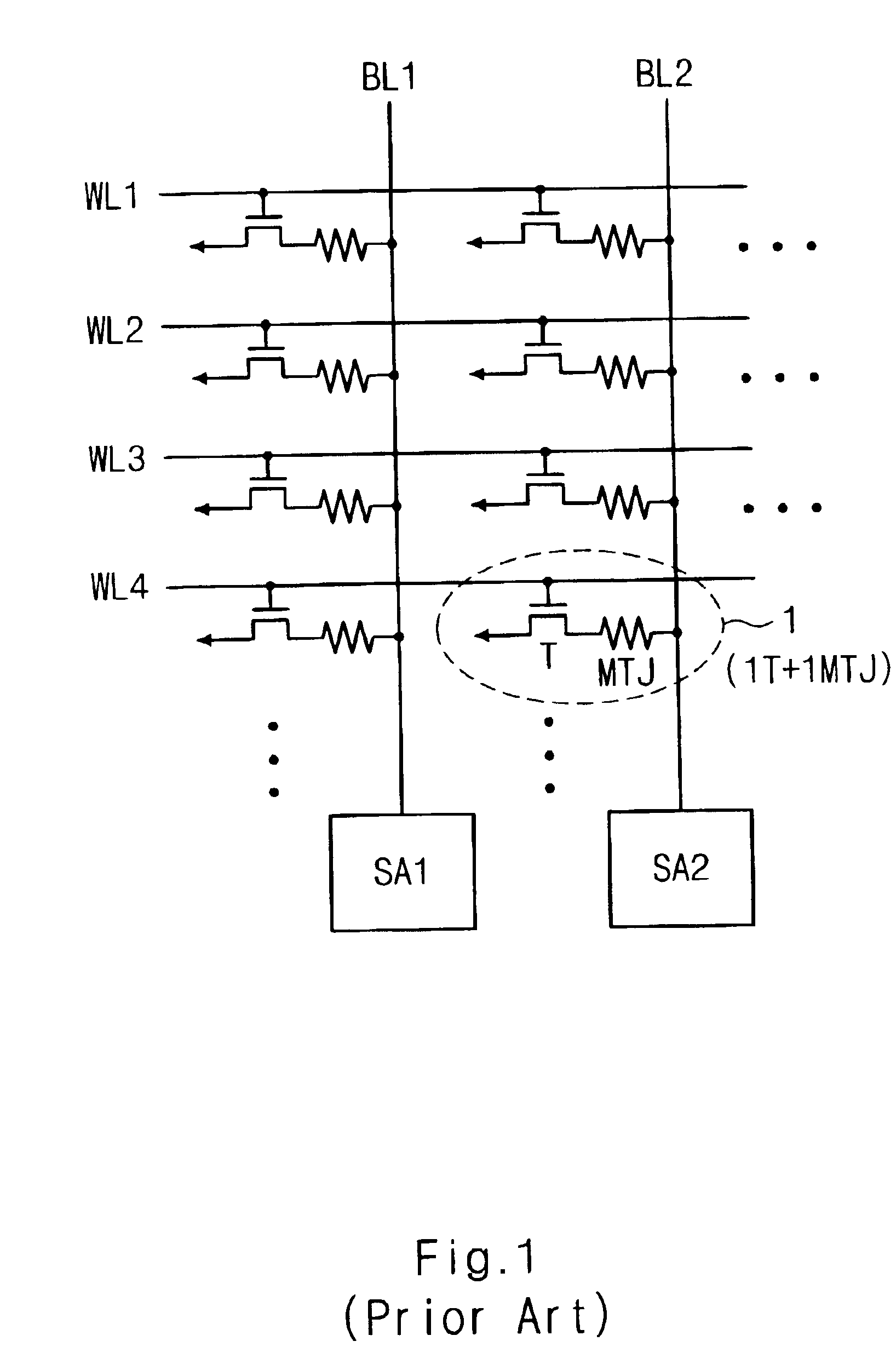
Magnetic random access memory
InactiveUS6868003B2Simple structureSmall cell sizeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Integration of an electrical diode within a fuel cell
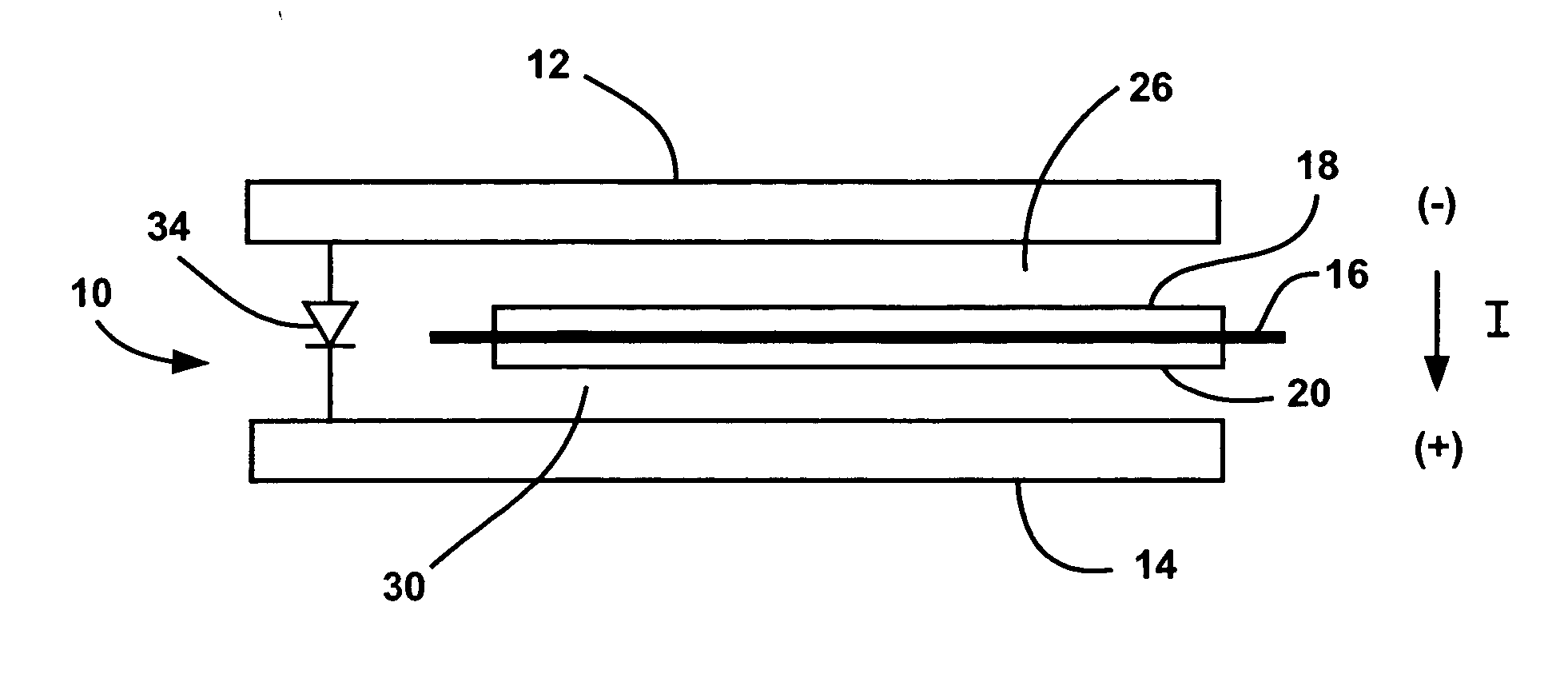
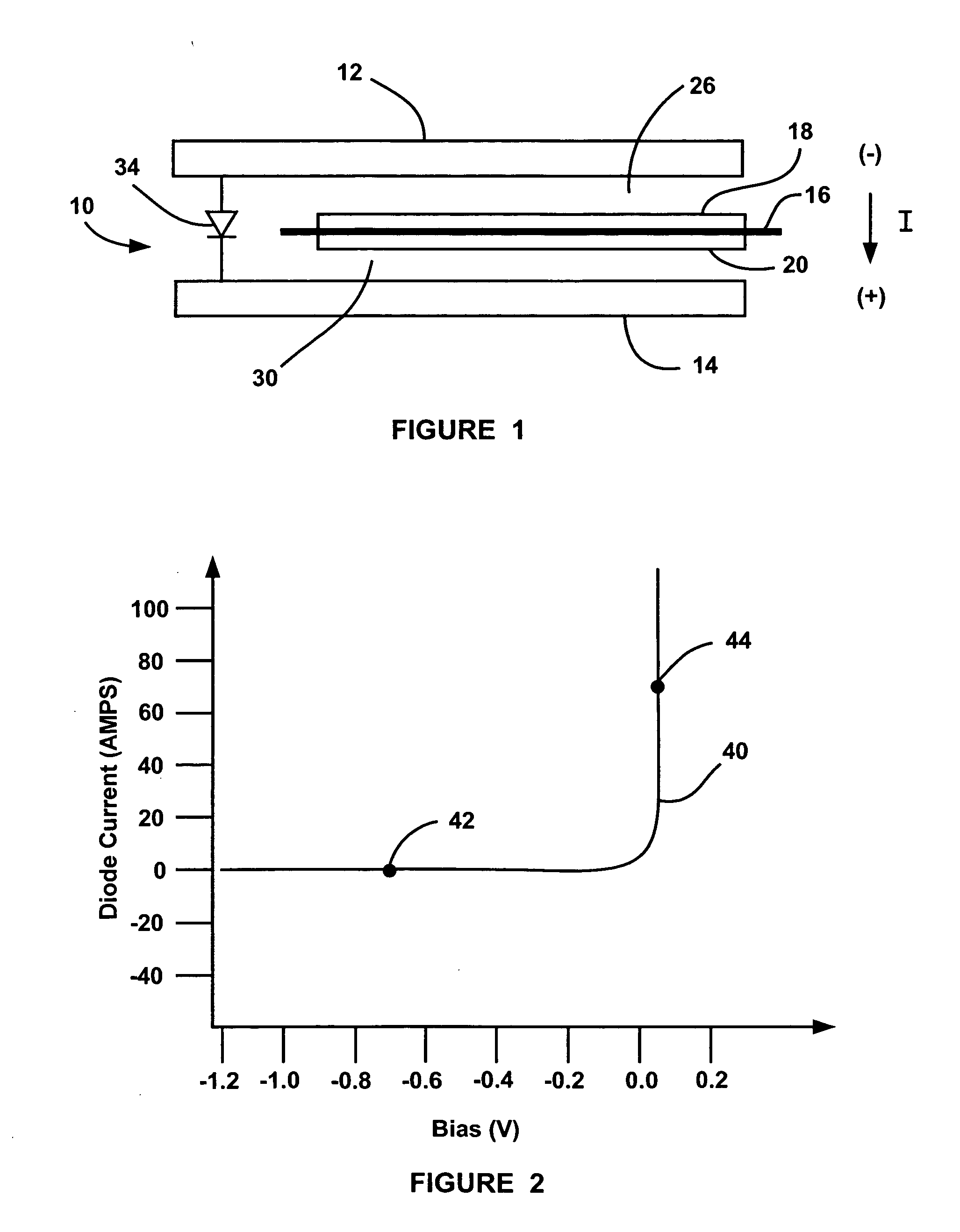
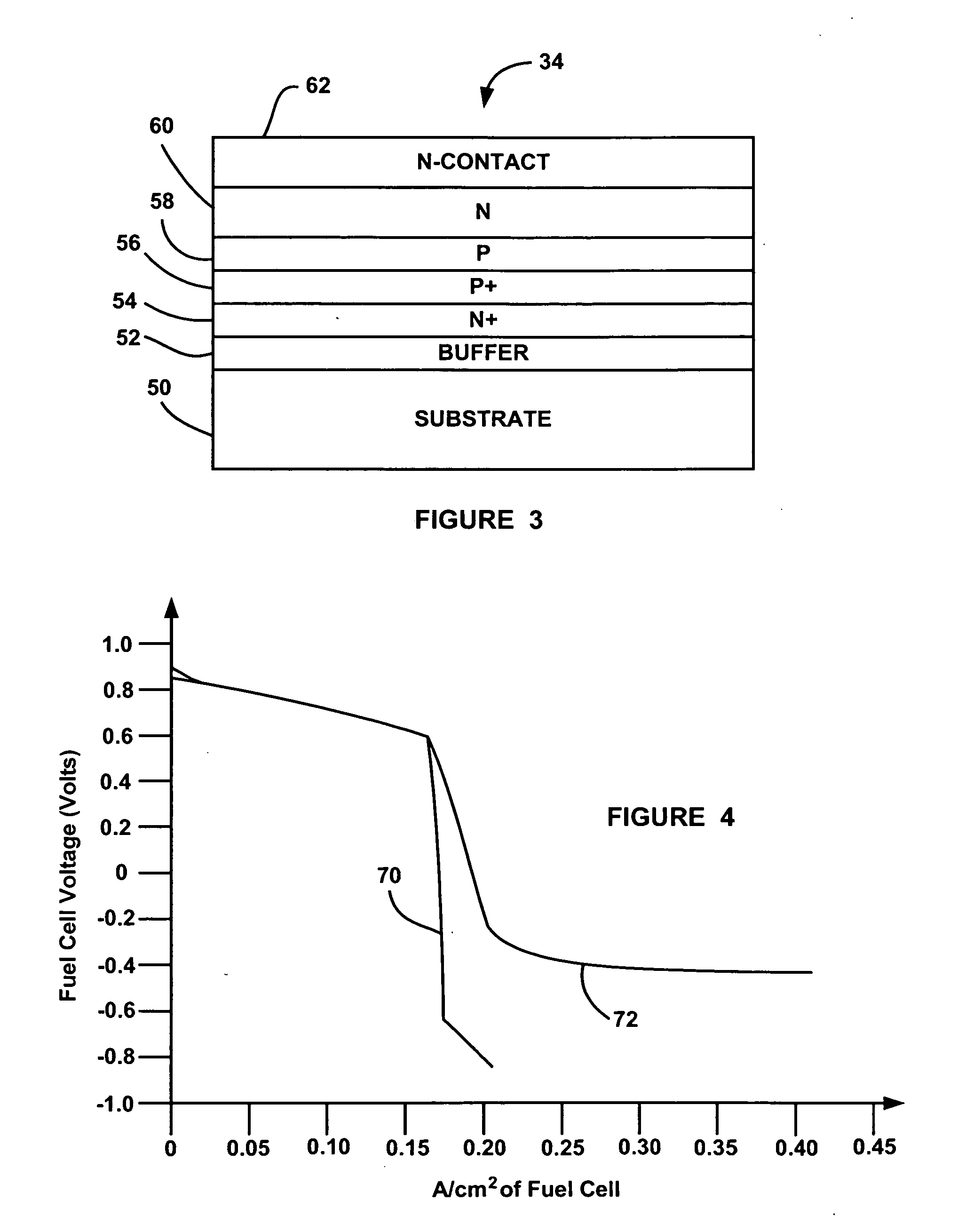
InactiveUS20060147769A1Reduce thicknessFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesElectricityFuel cells
A fuel cell system that employs a diode electrically coupled between bipolar plates in a fuel cell of a fuel cell stack for preventing the fuel cell between the plates from reversing its polarity. The diode is a thin-sheet p-n diode including doped semiconductor layers and has a thickness relative to the thickness of the MEA in the fuel cell so that the overall stack thickness does not increase. When the fuel cell is operating properly the diode does not conduct and all of the current through the fuel cell goes through the MEA. If the electric load on the stack increases to a level beyond the capability of the fuel cell, where the potential across the fuel cell goes significantly below zero, the diode will begin to conduct so that any current that cannot travel through the MEA with the cell voltage less than one negative forward diode voltage drop is able to go around the MEA through the diode.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
LED structures for reduced non-radiative sidewall recombination
LED structures are disclosed to reduce non-radiative sidewall recombination along sidewalls of vertical LEDs including p-n diode sidewalls that span a top current spreading layer, bottom current spreading layer, and active layer between the top current spreading layer and bottom current spreading layer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Photovoltaic cell comprising an mis-type tunnel diode
InactiveUS20100224238A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationTunnel diodeWafer dicing
A photovoltaic cell comprising a thin semiconductor lamina is described; the lamina is formed by cleaving from a donor wafer while the wafer is bonded to a receiver element which provides mechanical support. Thus fabrication steps performed following cleaving are advantageously performed at temperatures that will not damage the receiver element. By fabricating a cell comprising an MIS-type tunnel diode, rather than a conventional p-n diode, a high-temperature doping step may be avoided.
Owner:GTAT CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com