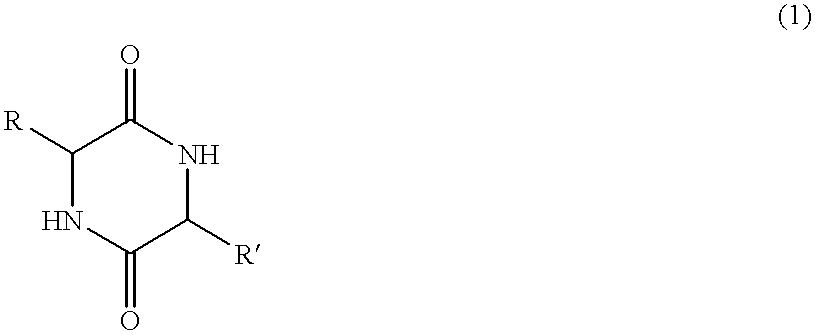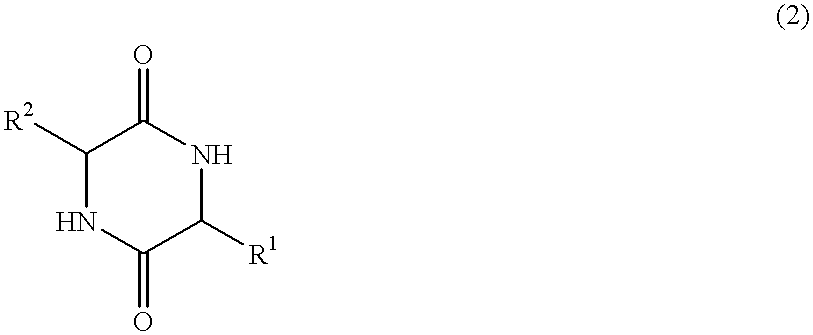Patents
Literature
160 results about "Asn - Asparagine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
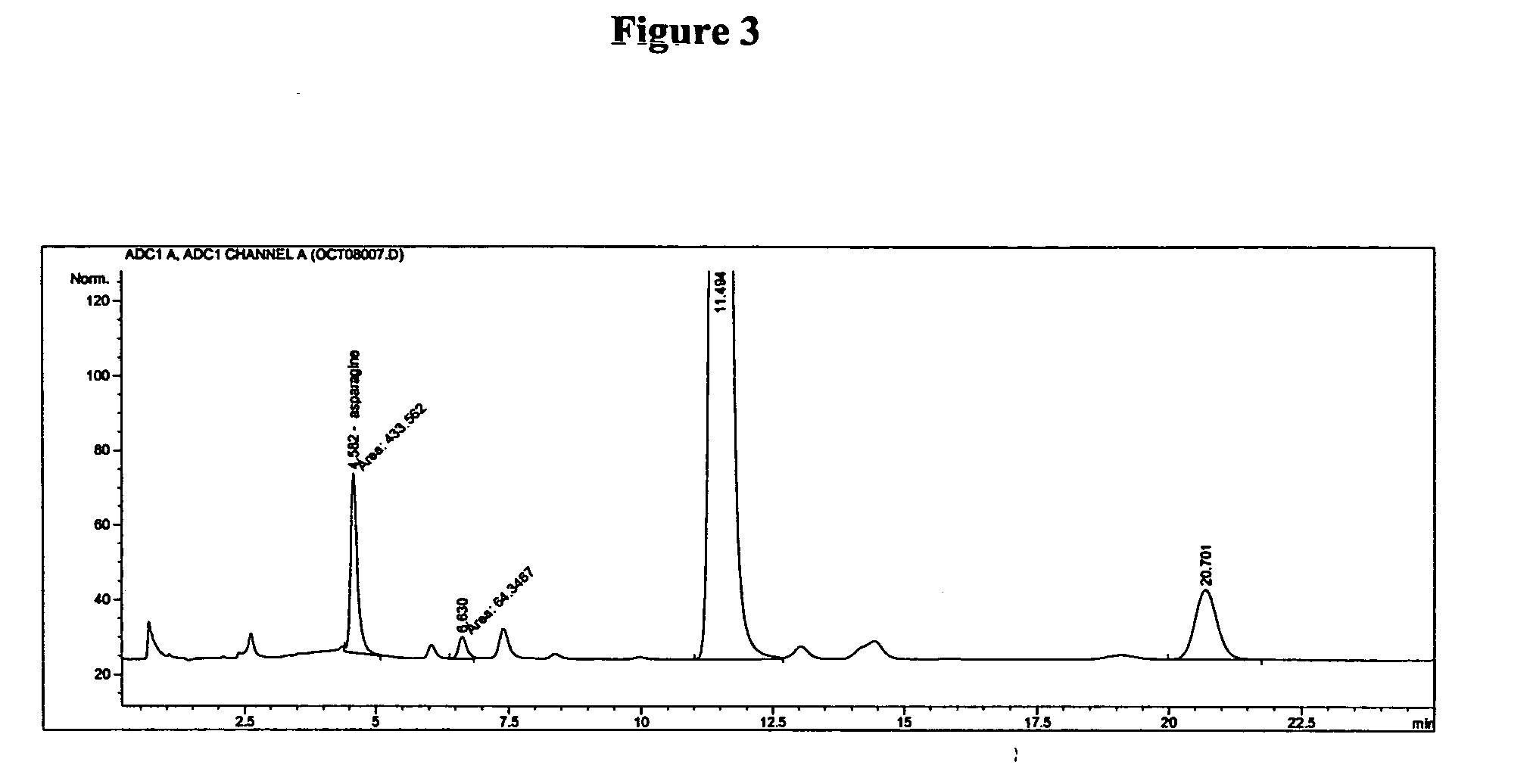
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. 3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain carboxamide, classifying it as a polar (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid.
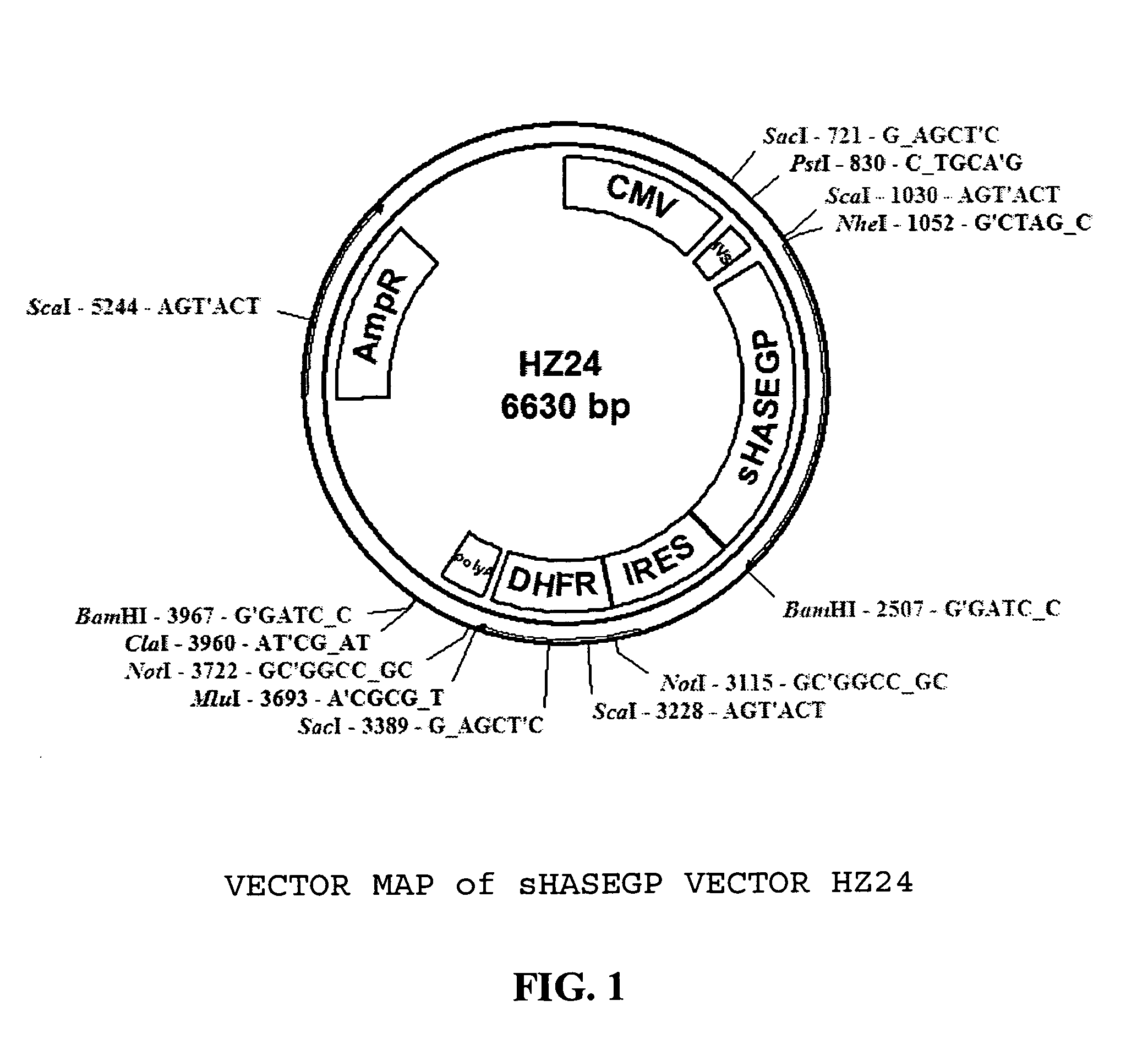
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
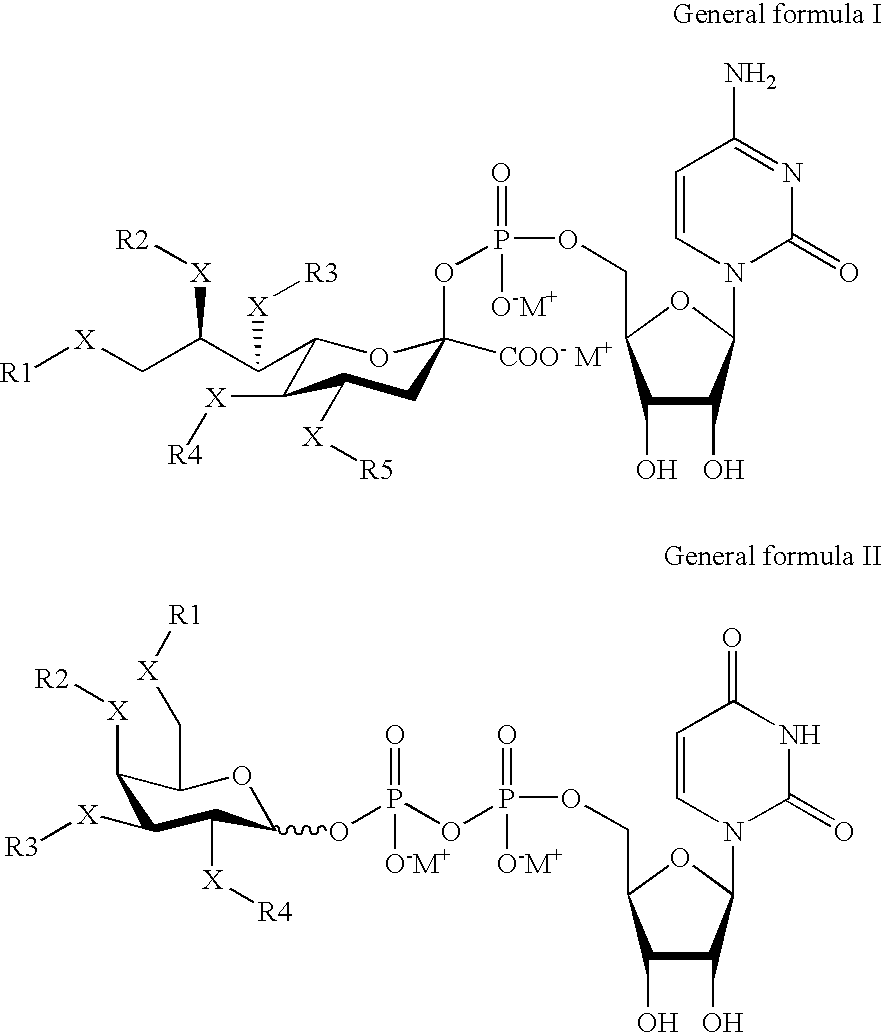
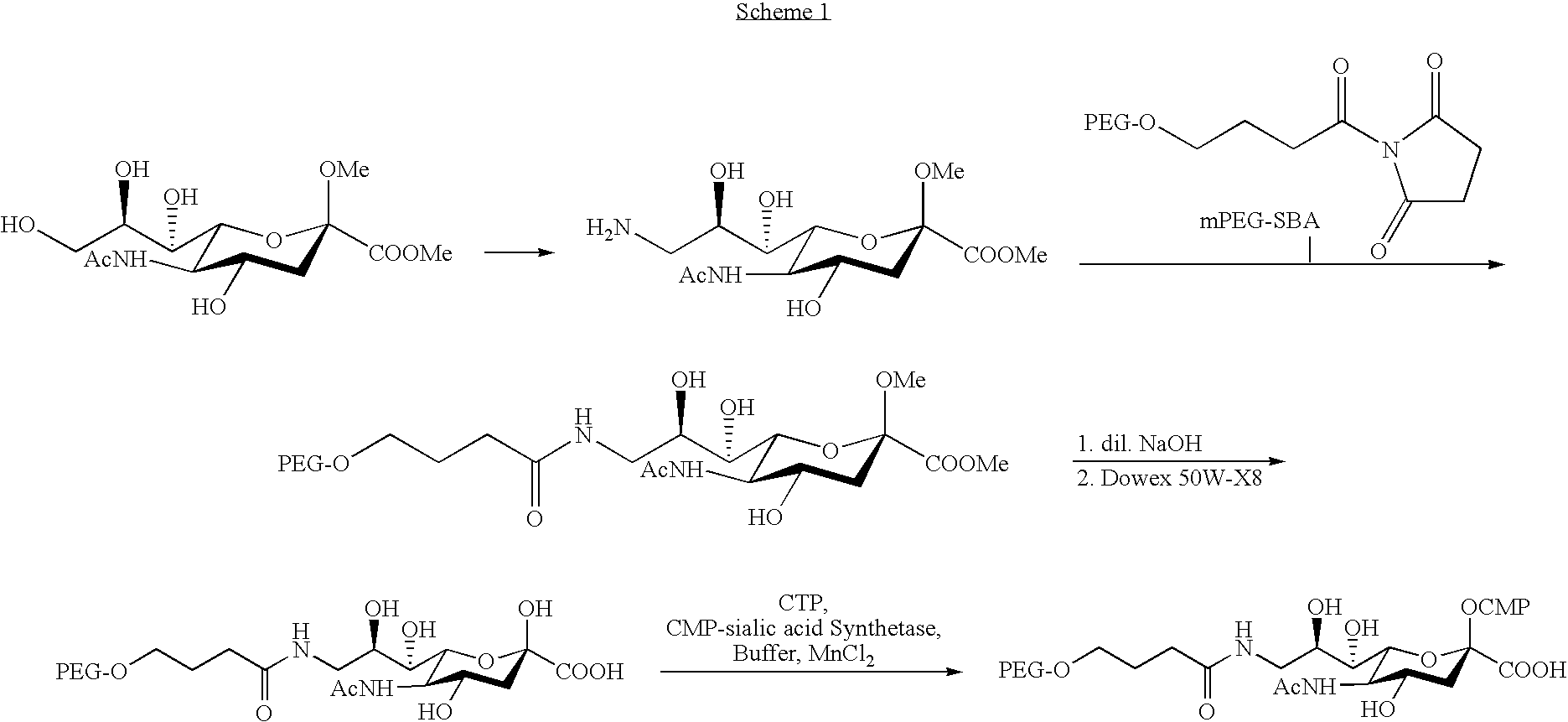
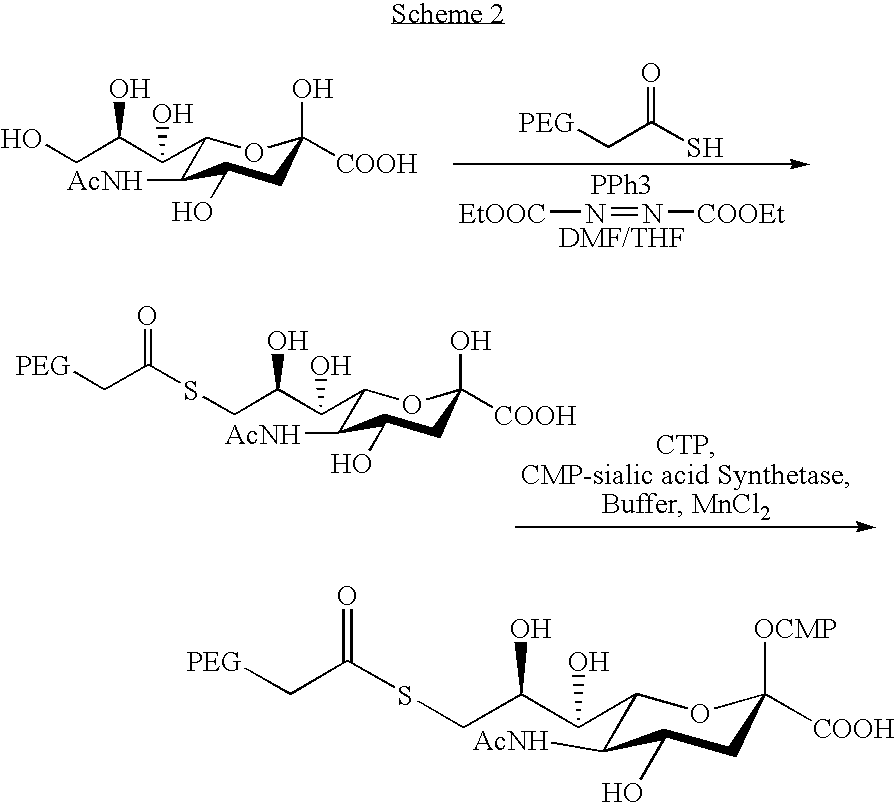
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Peptides from the E2, E6, and E7 proteins of human papilloma viruses 16 and 18 for detecting and/or diagnosing cervical and other human papillomavirus associated cancers
InactiveUS6933123B2Simple and rapid and and more testMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesCysteine thiolateTryptophan
Owner:HU YAO XIONG
Production of polypeptides
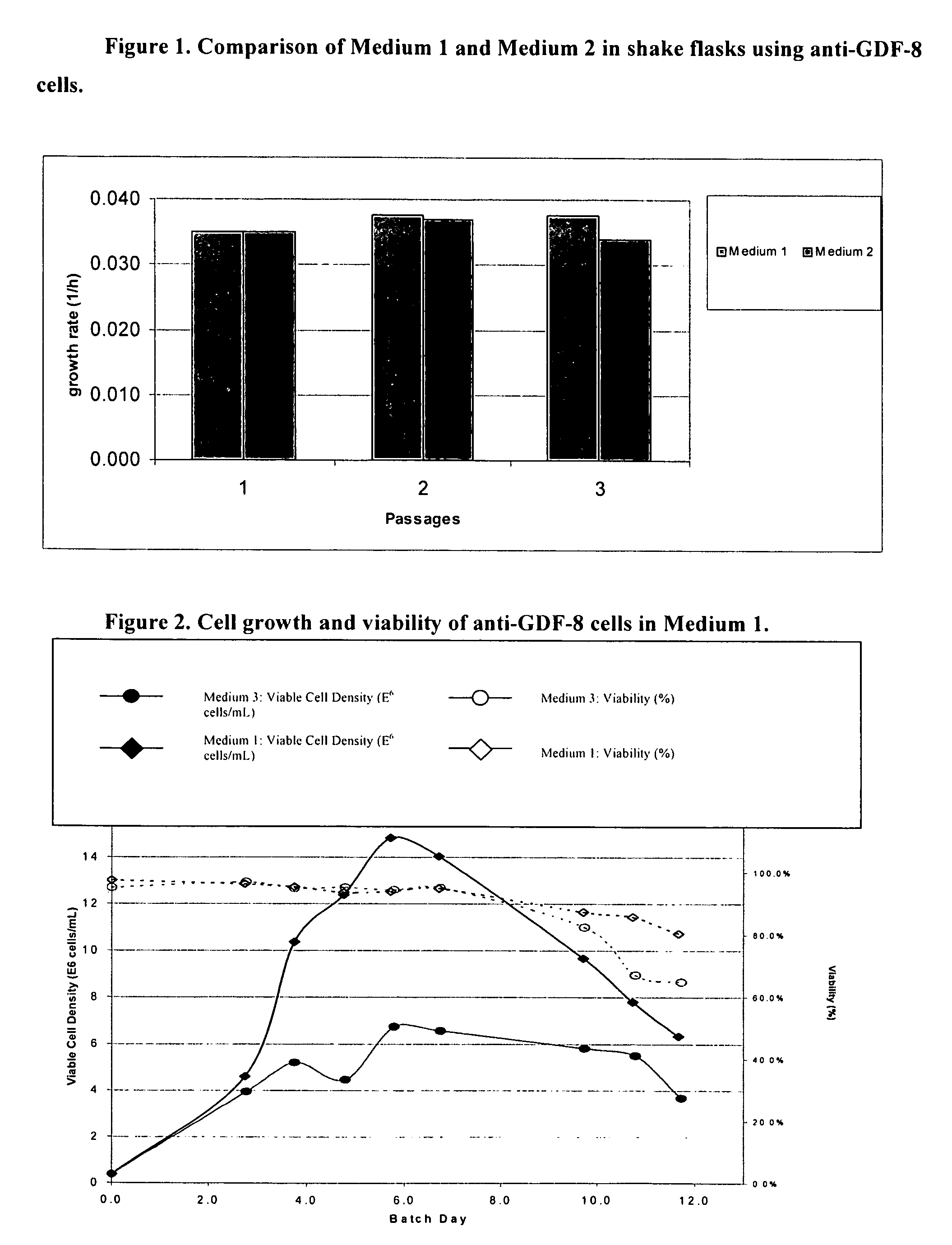
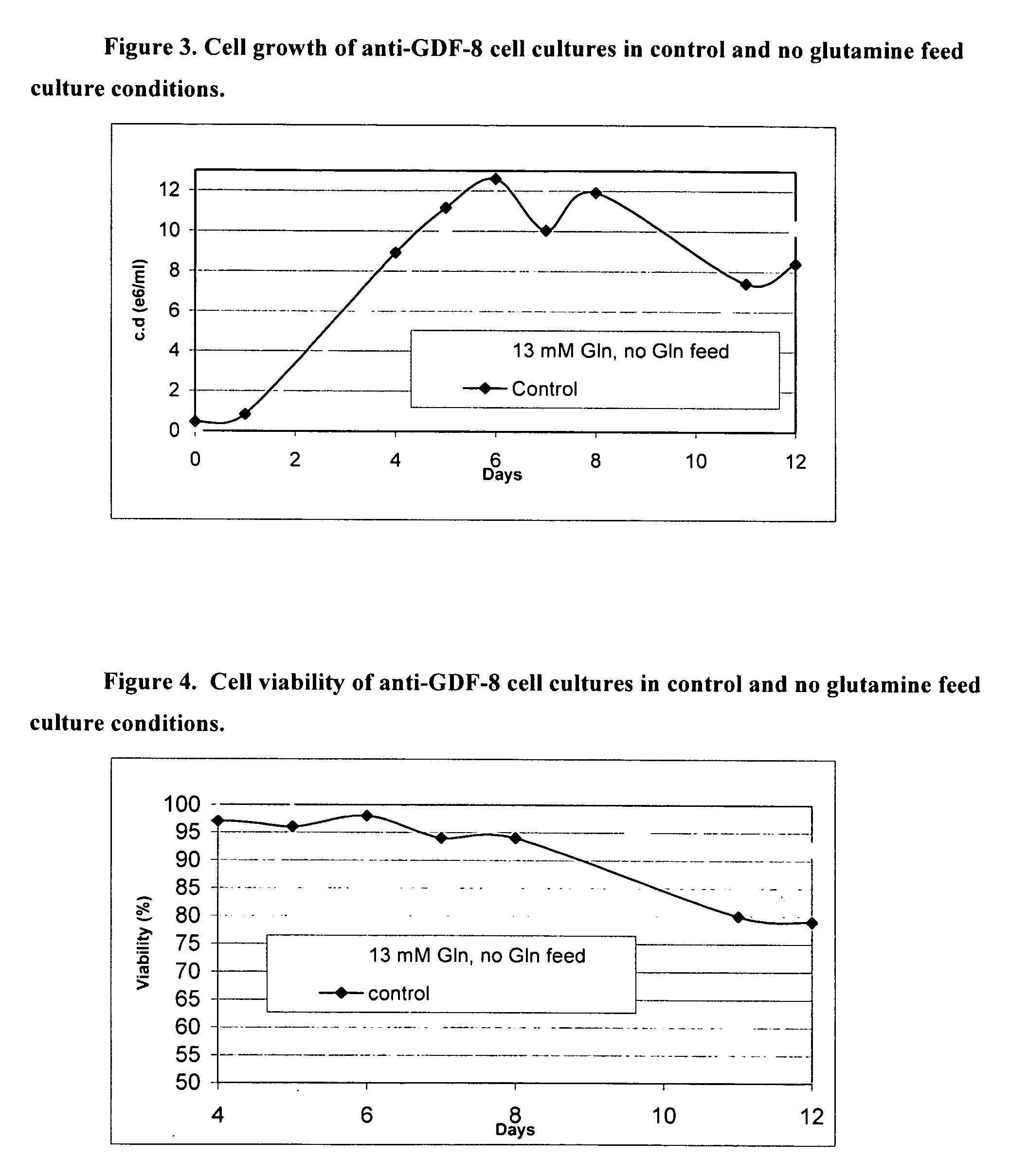
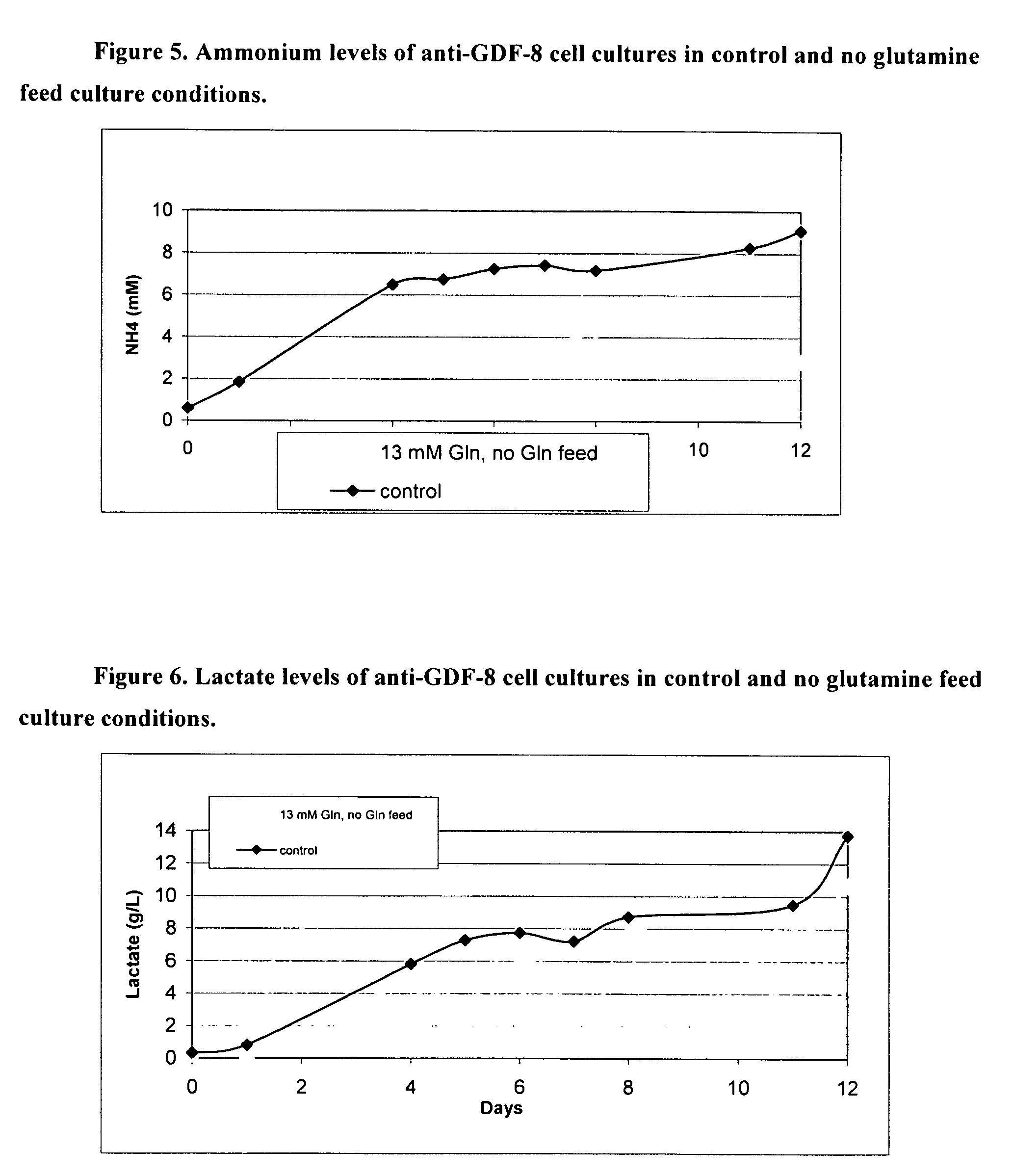
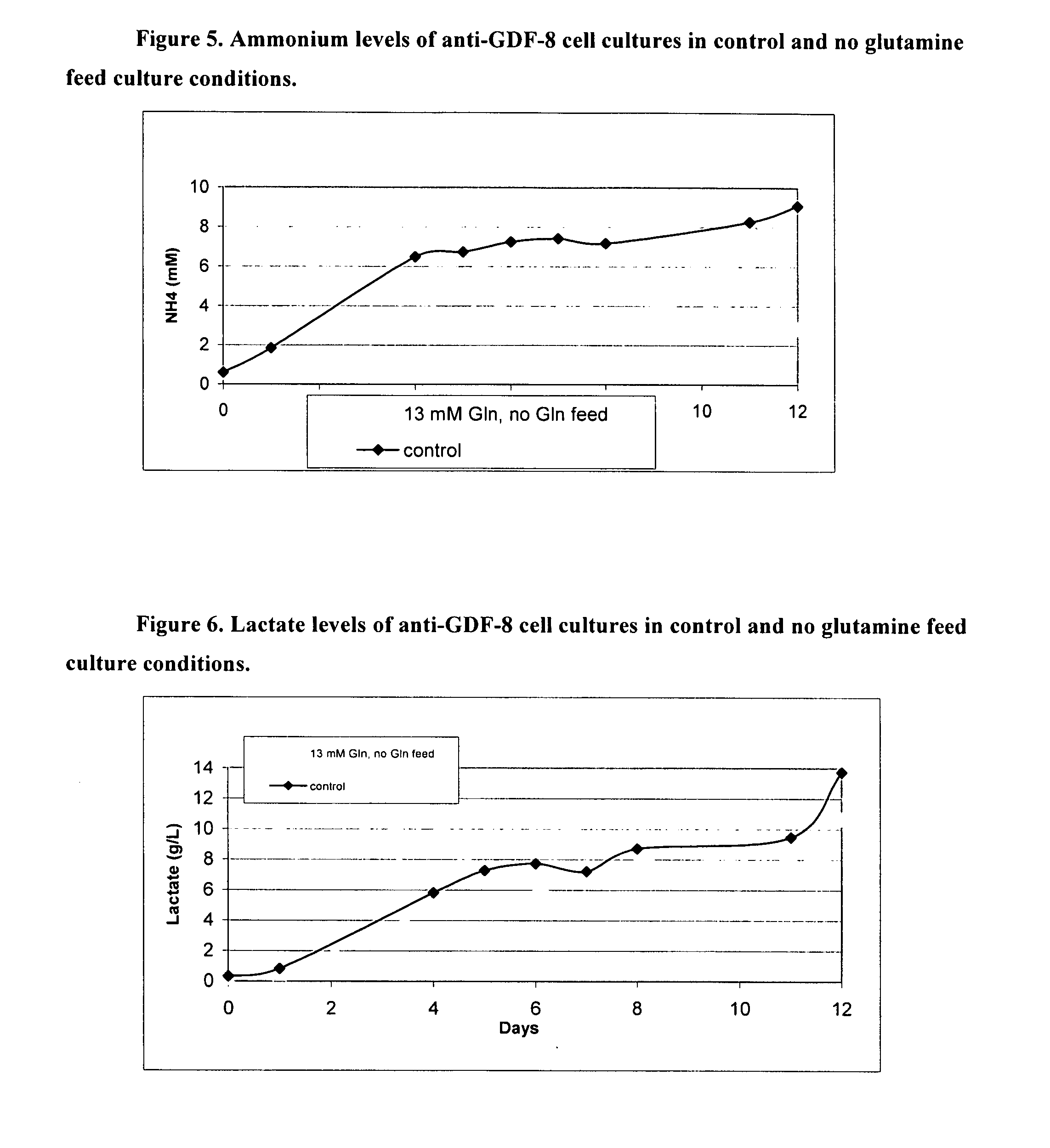
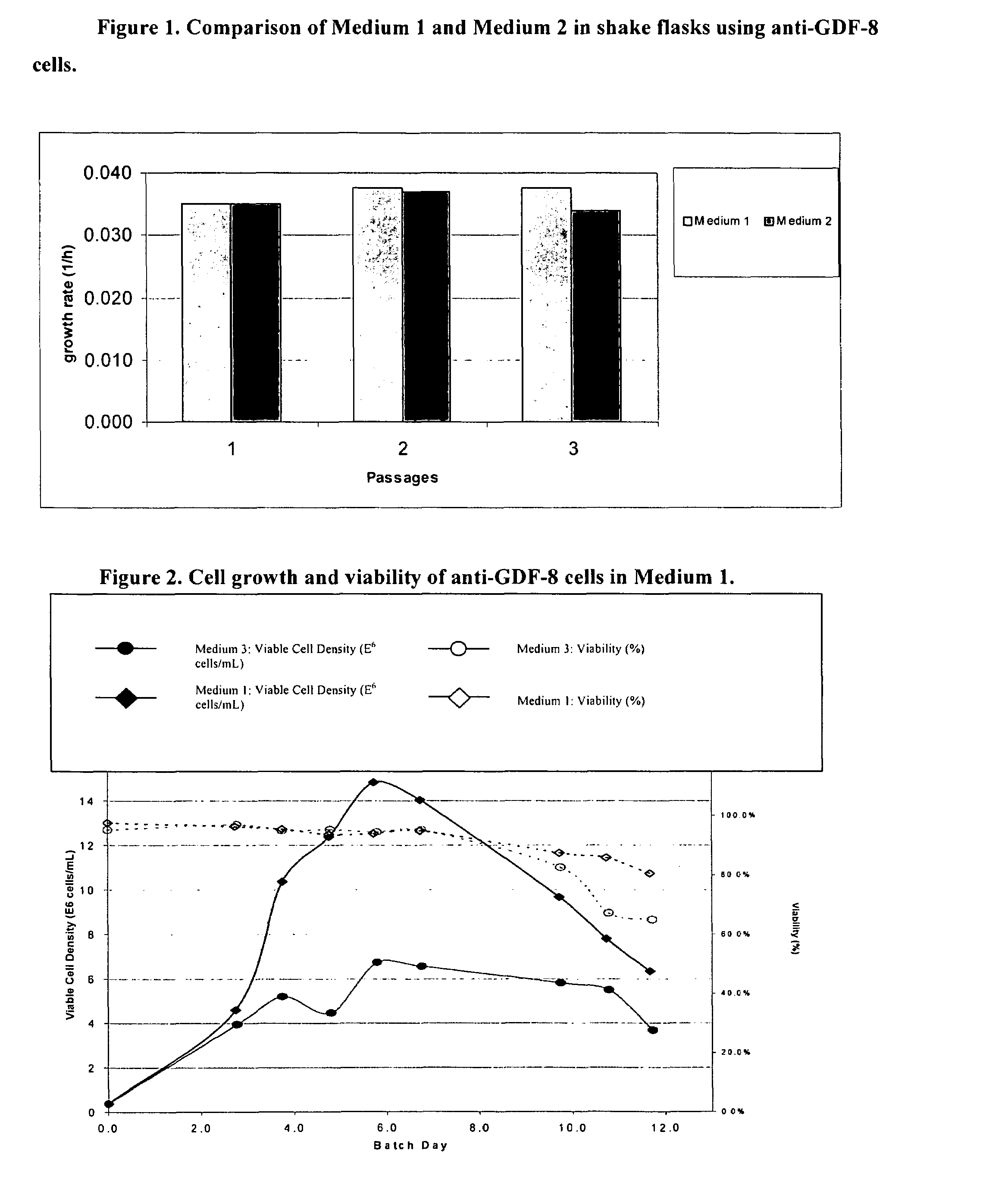
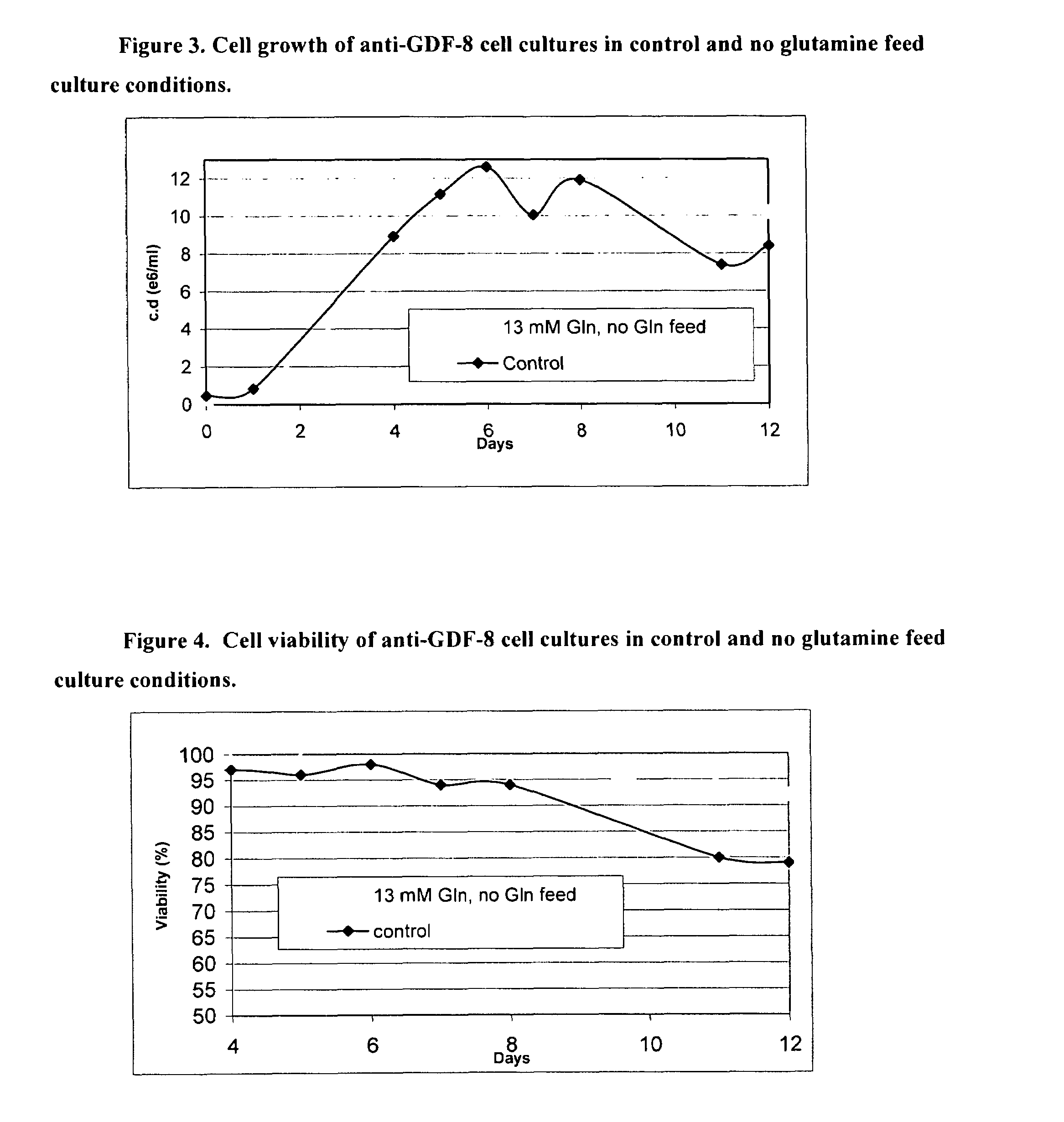
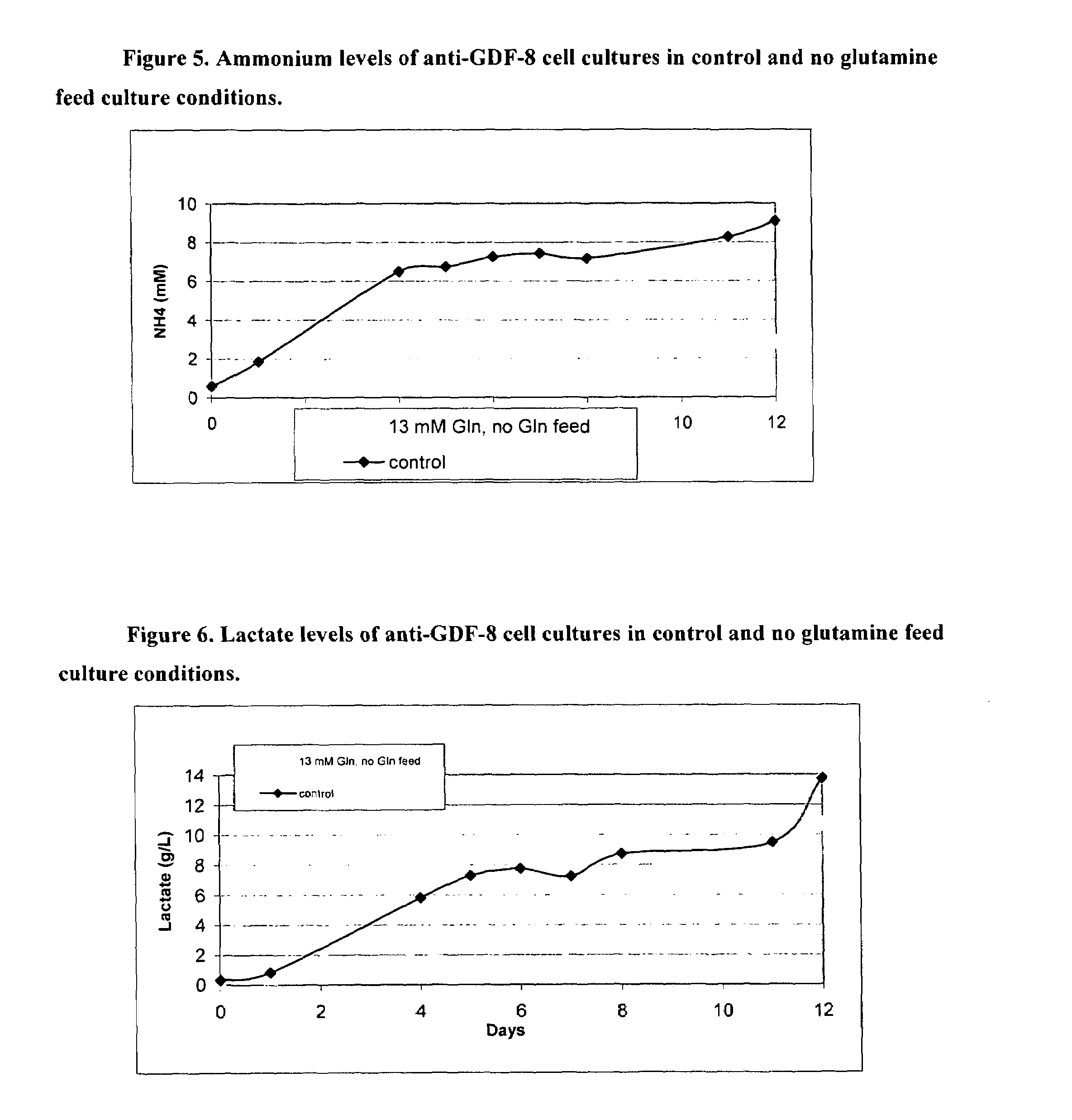
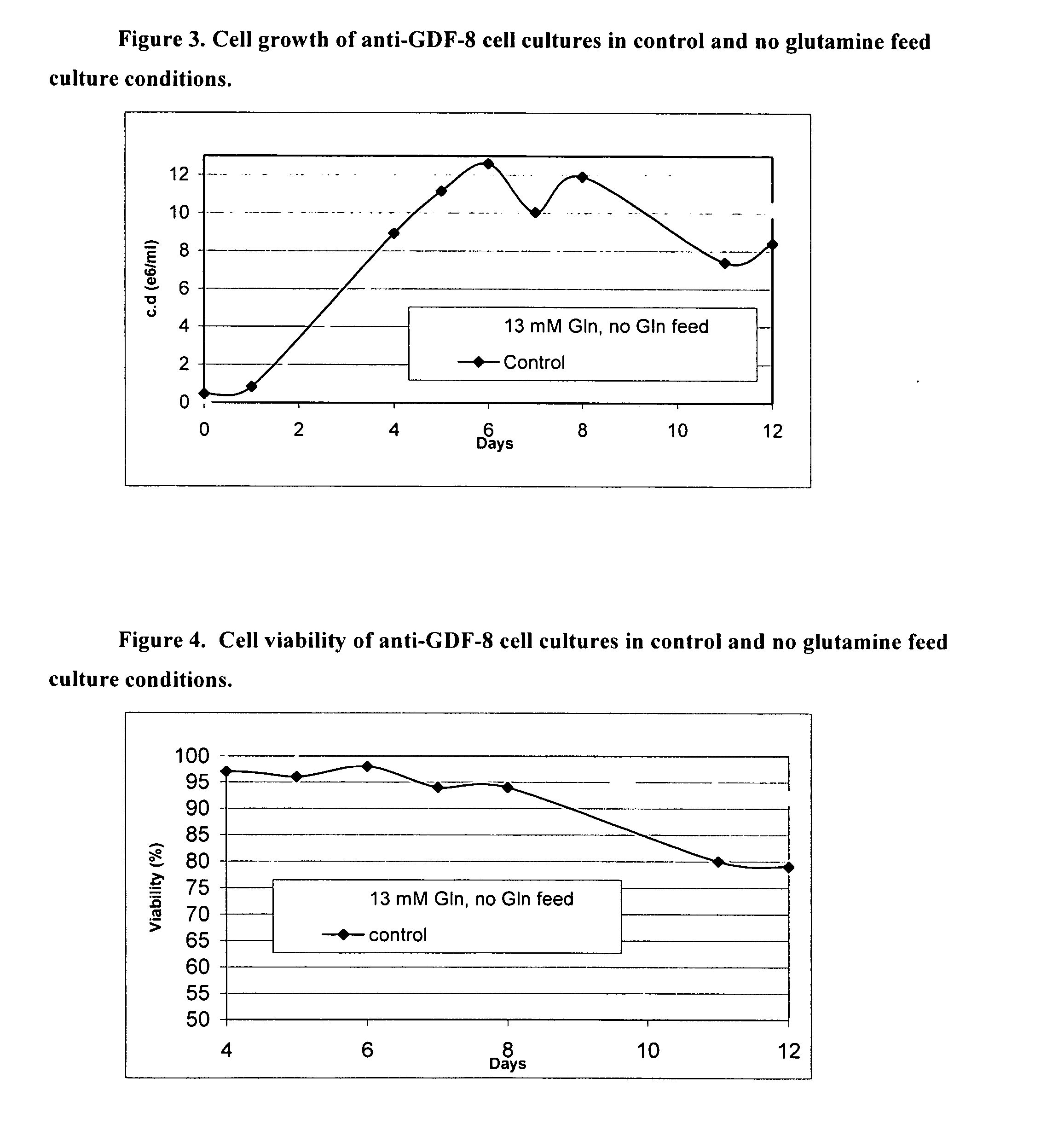
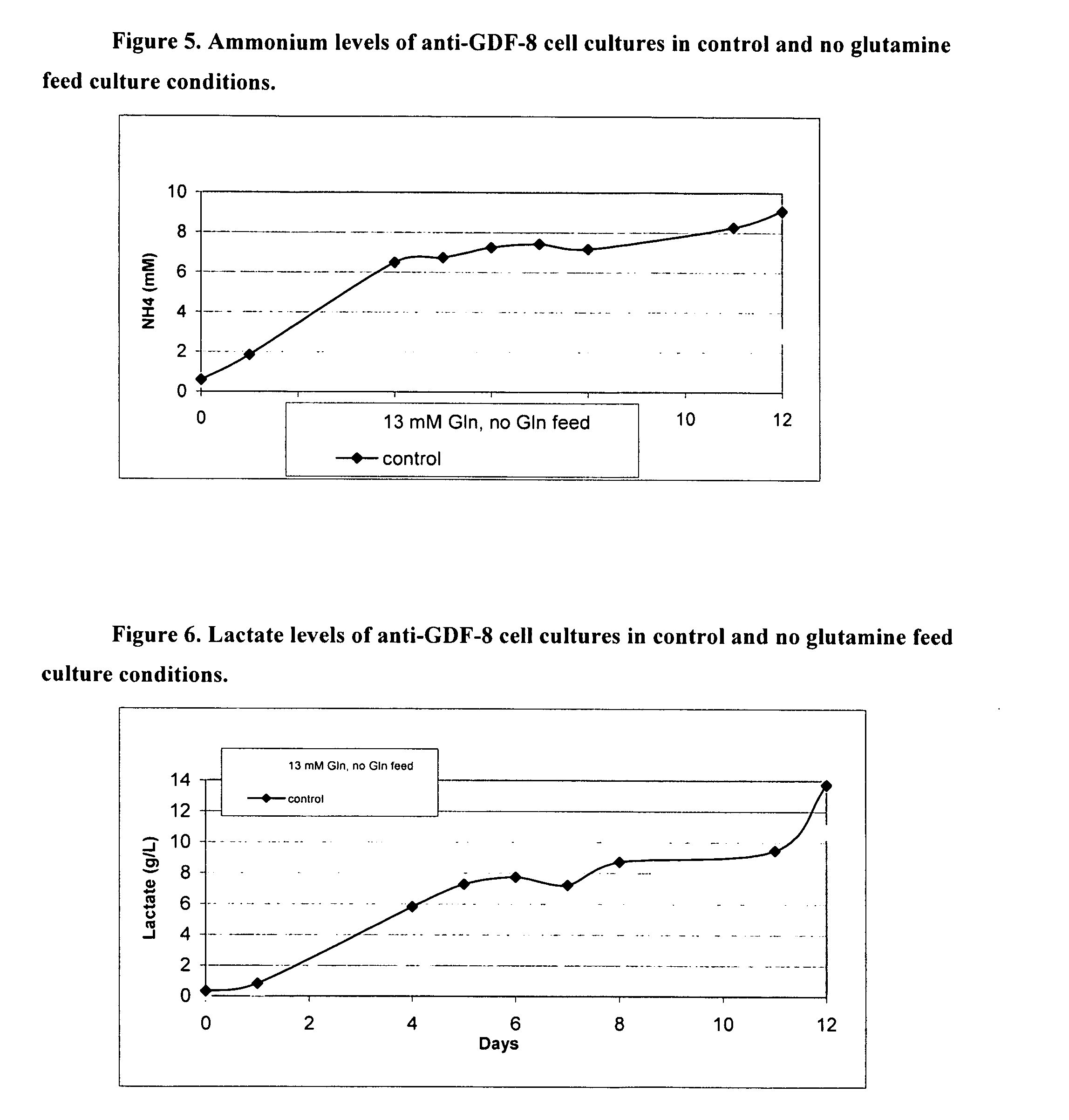
An improved system for large scale production of proteins and / or polypeptides in cell culture, particularly in media characterized by one or more of: i) a cumulative amino acid concentration greater than about 70 mM; ii) a molar cumulative glutamine to cumulative asparagine ratio of less than about 2; iii) a molar cumulative glutamine to cumulative total amino acid ratio of less than about 0.2; iv) a molar cumulative inorganic ion to cumulative total amino acid ratio between about 0.4 to 1; or v) a combined cumulative glutamine and cumulative asparagine concentration between about 16 and 36 mM, is provided. The use of such a system allows high levels of protein production and lessens accumulation of certain undesirable factors such as ammonium and / or lactate. Additionally, culture methods including a temperature shift, typically including a decrease in temperature when the culture has reached about 20-80% of it maximal cell density, are provided. Alternatively or additionally, the present invention provides methods such that, after reaching a peak, lactate and / or ammonium levels in the culture decrease over time.
Owner:PFIZER IRELAND PHARM CORP
Pegylated factor VII glycoforms
InactiveUS20050113565A1Improve functional propertiesFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIIOligosaccharide
The invention concerns a preparation comprising a plurality of Factor VII polypeptides or Factor VII-related polypeptides, wherein the polypeptides comprise asparagine-linked and / or serine-linked oligosaccharide chains, and wherein at least one oligosaccharide group is covalently attached to at least one polymeric group.
Owner:KLAUSEN NIELS +3
Thermal treatment process for tobacco materials
ActiveUS8944072B2Alter natureAlter characterTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentArgininePhenylalanine
A method of preparing a tobacco material for use in a smoking article is provided, including (i) mixing a tobacco material, water, and an additive selected from the group consisting of lysine, glycine, histidine, alanine, methionine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, proline, phenylalanine, valine, arginine, di- and trivalent cations, asparaginase, saccharides, phenolic compounds, reducing agents, compounds having a free thiol group, oxidizing agents, oxidation catalysts, plant extracts, and combinations thereof; (ii) heating the mixture; and (iii) incorporating the heat-treated mixture into a smoking article as a smokable material. A smoking article in the form of a cigarette is also provided that includes a tobacco material pre-treated to inhibit reaction of asparagine to form acrylamide in mainstream smoke. Upon smoking, the smoking article is characterized by an acrylamide content of mainstream smoke that is reduced relative to an untreated control smoking article.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Soluble hyaluronidase glycoprotein (sHASEGP), process for preparing the same, uses and pharmaceutical compositions comprising thereof
ActiveUS20090181032A1Extended half-lifeImprove distributionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGP's), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
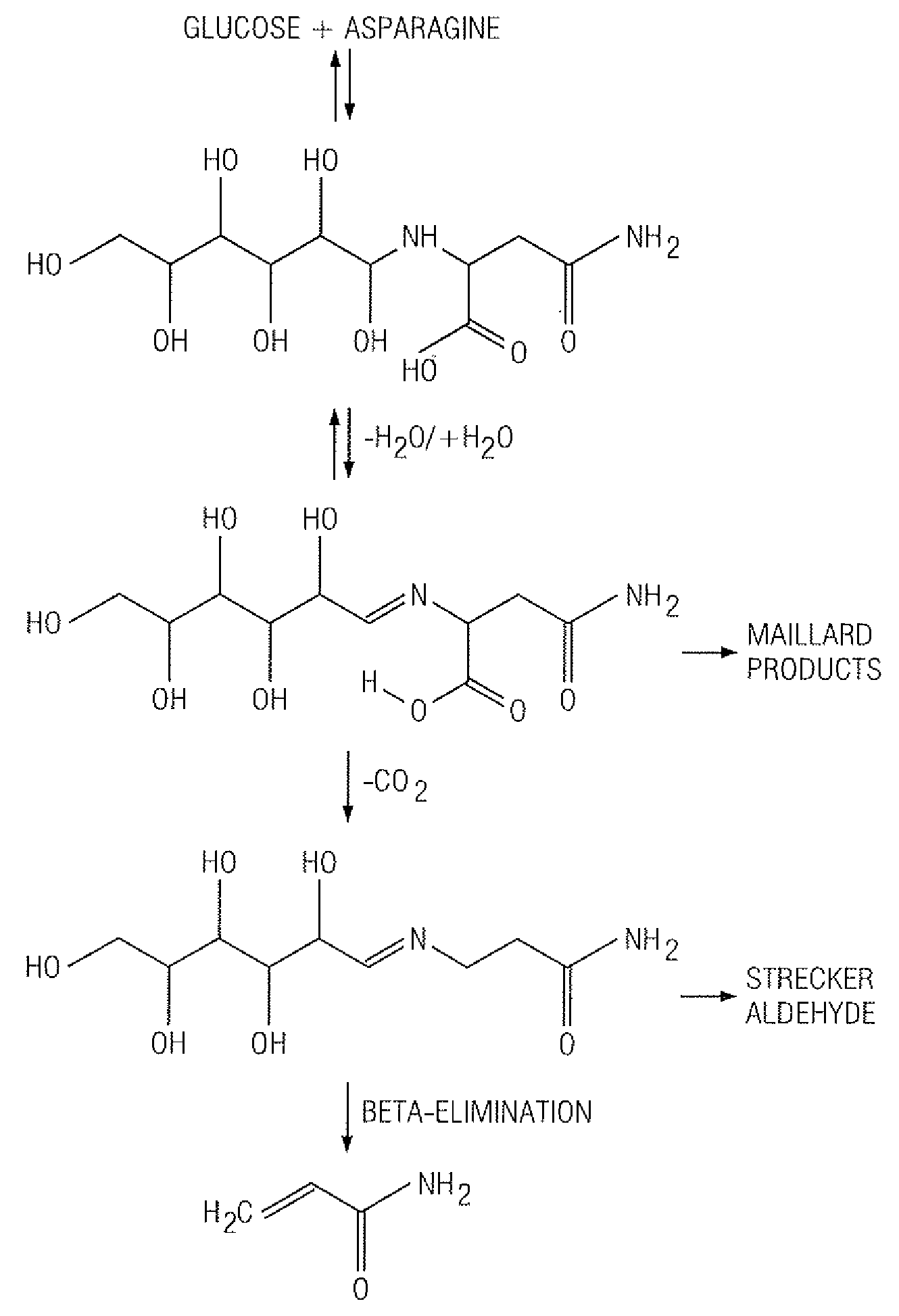
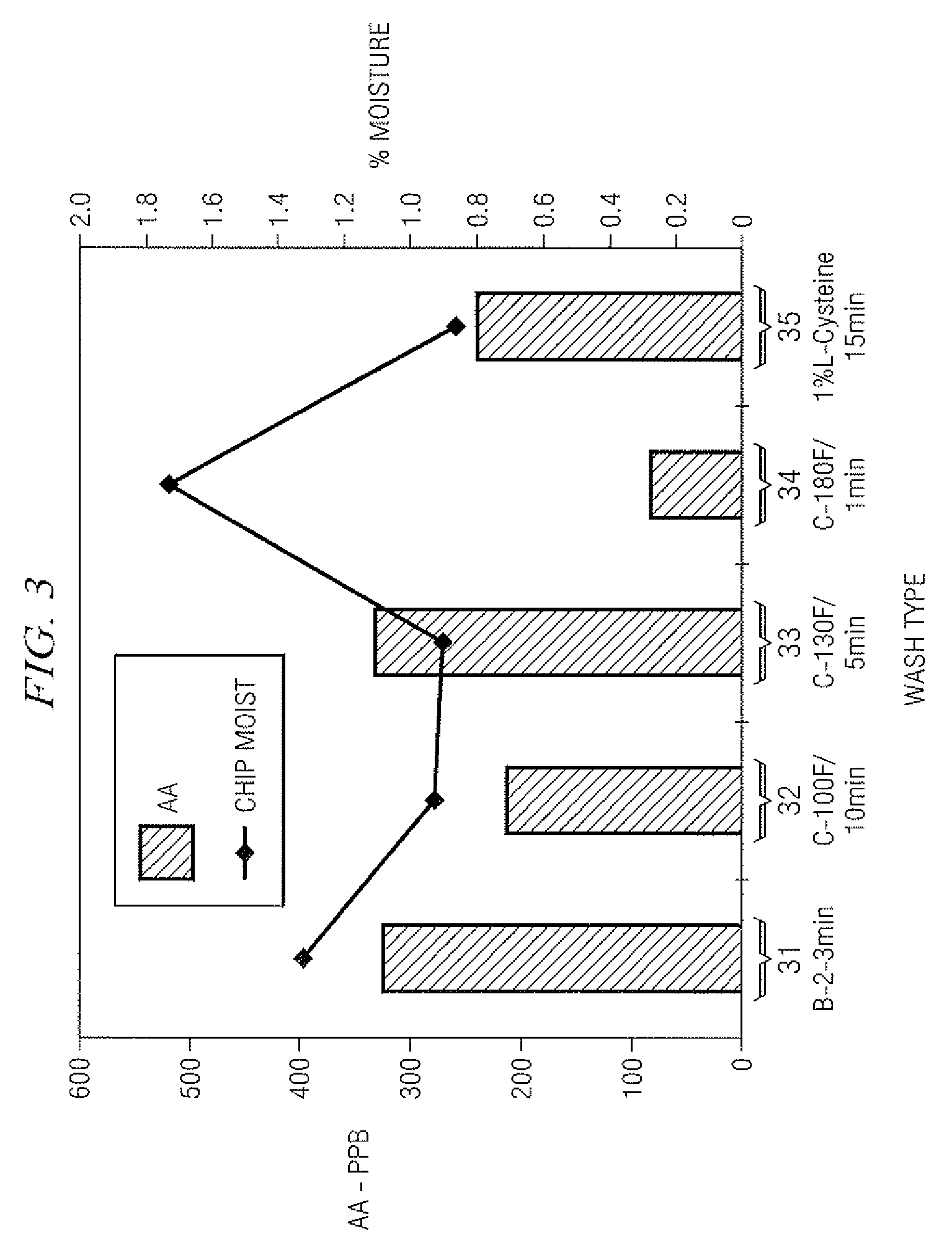
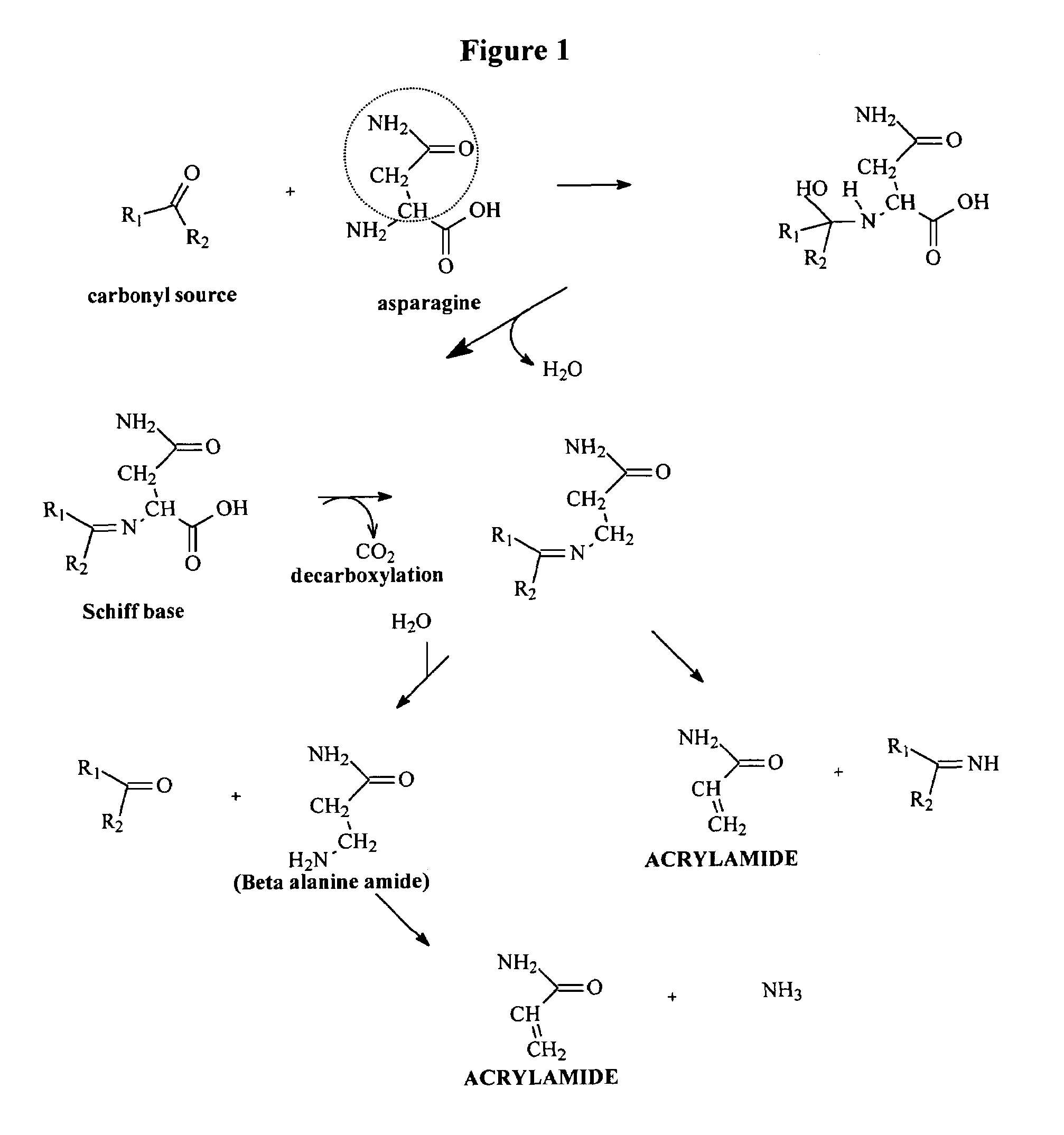
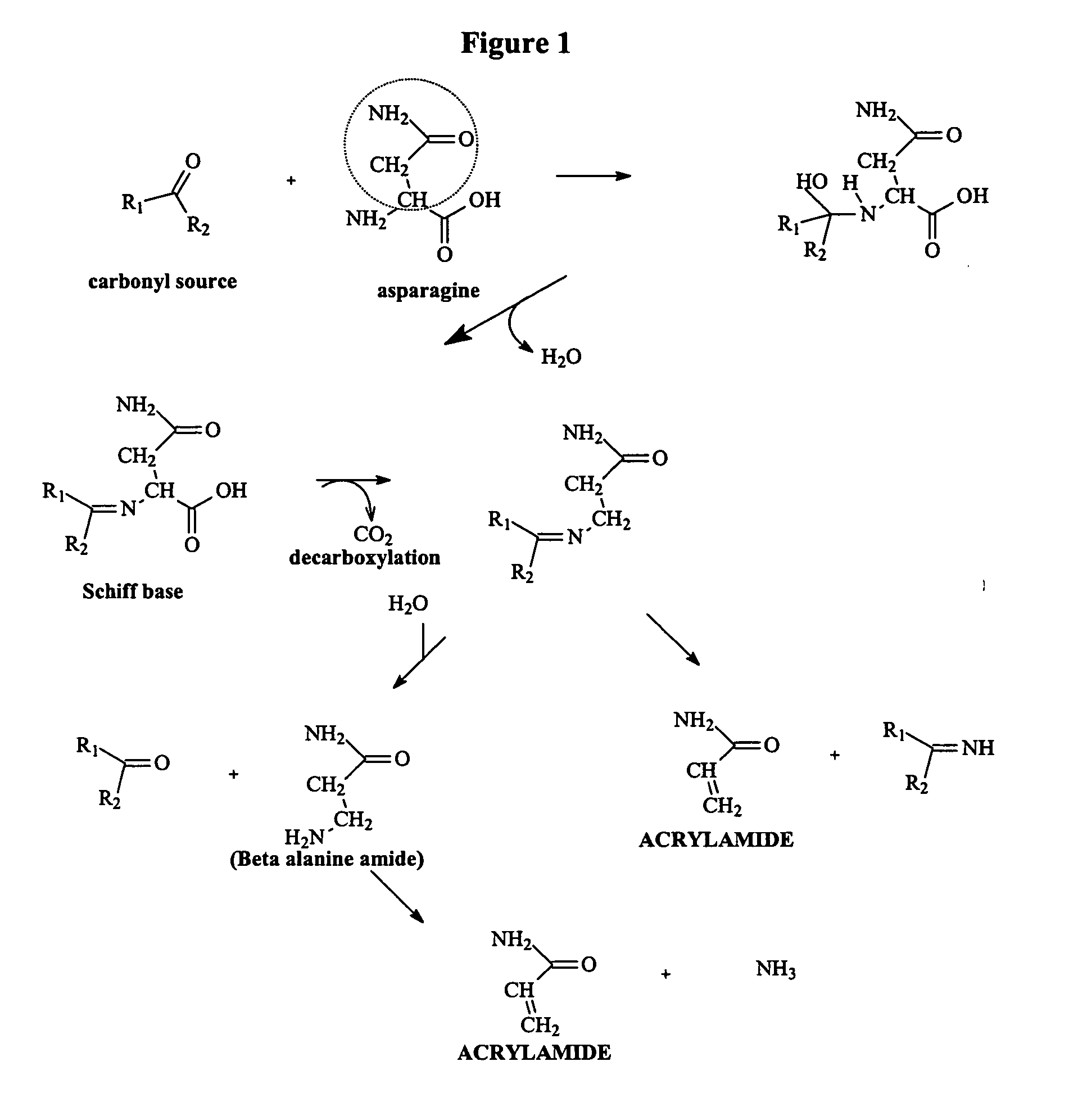
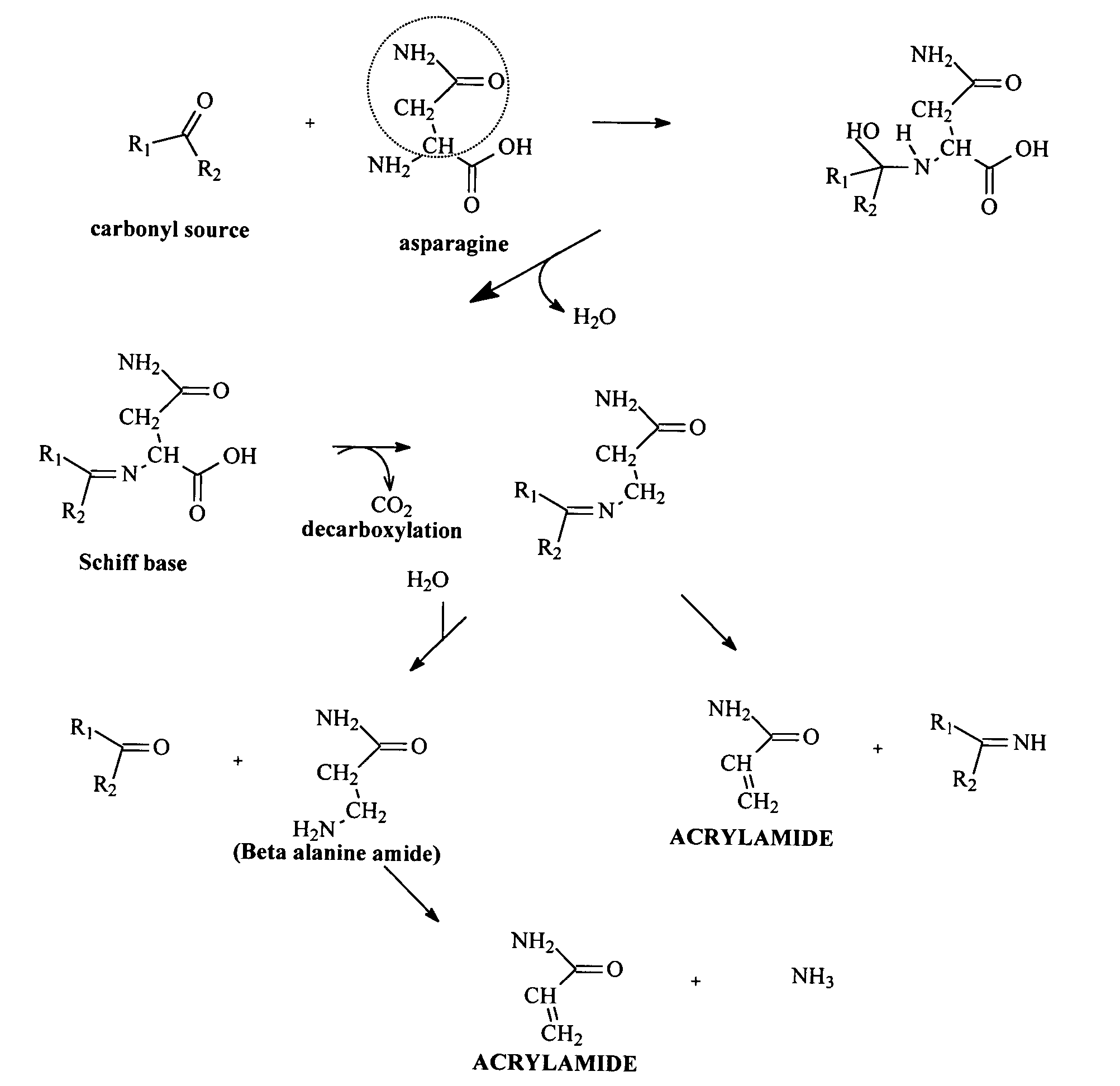
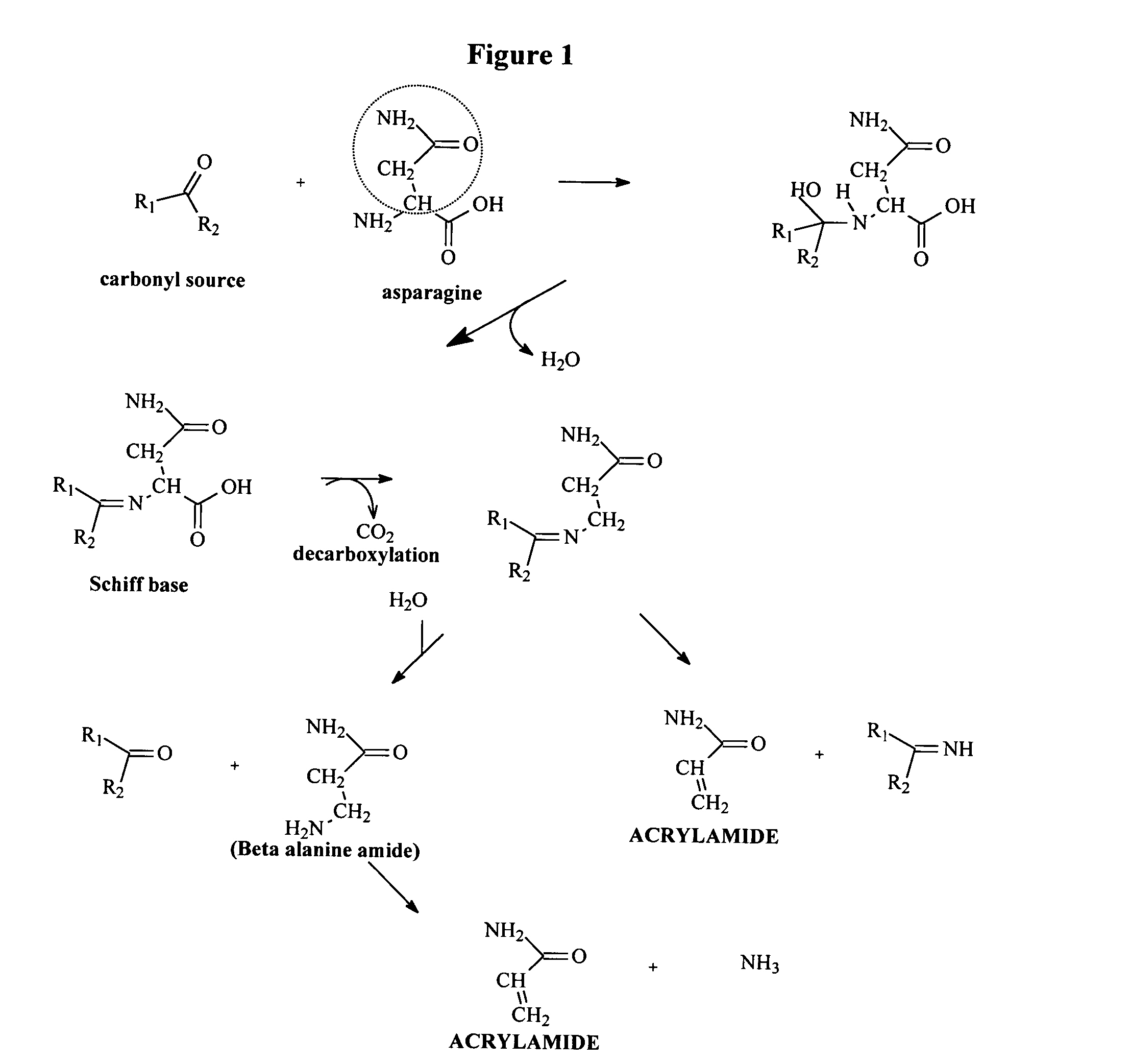
Method for Reducing Acrylamide Formation in Thermally Processed Foods
InactiveUS20070141227A1Reduce the amount requiredFood preparationHops treatmentIngested foodAsn - Asparagine
A method for reducing the amount of asparagine, a pre-cursor of acrylamide, in food products that are thermally processed. This invention permits the production of foods having significantly reduced levels of acrylamide. The method relies on contacting a potato feed such as potato slices containing asparagine, an acrylamide pre-cursor, with a leaching solution to extract asparagine out of the potato feed. Thermally processing the leached potatoes will result in a potato product having a lower level of acrylamide than a non-leached, thermally processed potato product.
Owner:FRITO LAY NORTH AMERICA INC
Pegylated Factor VII Glycoforms
InactiveUS20080039373A1Improve functional propertiesFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIIOligosaccharide
The invention concerns a preparation comprising a plurality of Factor VII polypeptides or Factor VII-related polypeptides, wherein the polypeptides comprise asparagine-linked and / or serine-linked oligosaccharide chains, and wherein at least one oligosaccharide group is covalently attached to at least one polymeric group.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Method for reduction of acrylamide in roasted coffee beans, roasted coffee beans having reduced levels of acrylamide, and article of commerce
InactiveUS7220440B2Reduce acrylamide contentReduced and low level of acrylamideHydrolasesTea extractionEnzymeAsn - Asparagine
Roasted coffee beans having reduced levels of acrylamide, coffee beans having reduced levels of asparagine, and an article of commerce. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for reducing the level of acrylamide in roasted coffee beans comprising reducing the level of asparagine in coffee beans. In another aspect, the invention provides a method for reducing the level of asparagine in coffee beans comprising adding an asparagine-reducing enzyme to coffee beans. In still another aspect, an article of commerce communicates to the consumer that the roasted coffee beans, coffee beans, product comprising roasted coffee beans or coffee beans, and / or article of commerce has reduced or low levels of asparagine and / or acrylamide.
Owner:KELLOGG NORTH AMERICA
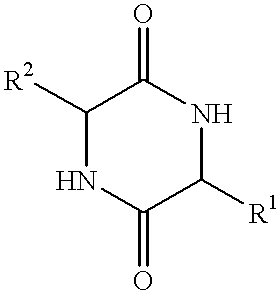
Method of synthesizing diketopiperazines
InactiveUS6967202B2Prevent unwanted side reactionInhibit side effectsOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsSide chainTyrosine
The invention provides a method of synthesizing a diketopiperazine of the formula: wherein:R1 is —CH2COR3, or —CH2CH2COR3;R2 is the side chain of an amino acid selected from the group consisting of glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, serine, threonine, aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid, glutamine, lysine, hydroxylysine, histidine, arginine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan, thyroxine, cysteine, methionine, norvaline and ornithine;R3 is —OH, —NH2, —OR4, —NHR4, or —NR4R4; andeach R4 is independently an alkyl, aryl, alkylaryl, or arylalkyl.
Owner:AMPIO PHARMA
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20100196423A1Reduce sensitivityGreater serum half-livesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated form of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Production of alpha-ABeta
InactiveUS20060160180A1Reduce accumulationHigh level of proteinAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsTotal amino acidsInorganic ions
An improved system for large scale production of proteins and / or polypeptides in cell culture, particularly in media characterized by one or more of: i) a cumulative amino acid concentration greater than about 70 mM; ii) a molar cumulative glutamine to cumulative asparagine ratio of less than about 2; iii) a molar cumulative glutamine to cumulative total amino acid ratio of less than about 0.2; iv) a molar cumulative inorganic ion to cumulative total amino acid ratio between about 0.4 to 1; or v) a combined cumulative glutamine and cumulative asparagine concentration between about 16 and 36 mM, is provided. The use of such a system allows high levels of protein production and lessens accumulation of certain undesirable factors such as ammonium and / or lactate. Additionally, culture methods including a temperature shift, typically including a decrease in temperature when the culture has reached about 20-80% of it maximal cell density, are provided. Alternatively or additionally, the present invention provides methods such that, after reaching a peak, lactate and / or ammonium levels in the culture decrease over time.
Owner:PFIZER IRELAND PHARM CORP
Production of TNFR-Ig
An improved system for large scale production of proteins and / or polypeptides in cell culture, particularly in media characterized by one or more of: i) a cumulative amino acid concentration greater than about 70 mM; ii) a molar cumulative glutamine to cumulative asparagine ratio of less than about 2; iii) a molar cumulative glutamine to cumulative total amino acid ratio of less than about 0.2; iv) a molar cumulative inorganic ion to cumulative total amino acid ratio between about 0.4 to 1; or v) a combined cumulative glutamine and cumulative asparagine concentration between about 16 and 36 mM, is provided. The use of such a system allows high levels of protein production and lessens accumulation of certain undesirable factors such as ammonium and / or lactate. Additionally, culture methods including a temperature shift, typically including a decrease in temperature when the culture has reached about 20-80% of it maximal cell density, are provided. Alternatively or additionally, the present invention provides methods such that, after reaching a peak, lactate and / or ammonium levels in the culture decrease over time.
Owner:PFIZER IRELAND PHARM CORP
Production of proteins in glutamine-free cell culture media
ActiveUS8512983B2Increased longevityIncrease productivityAnimal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammalCell culture media
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
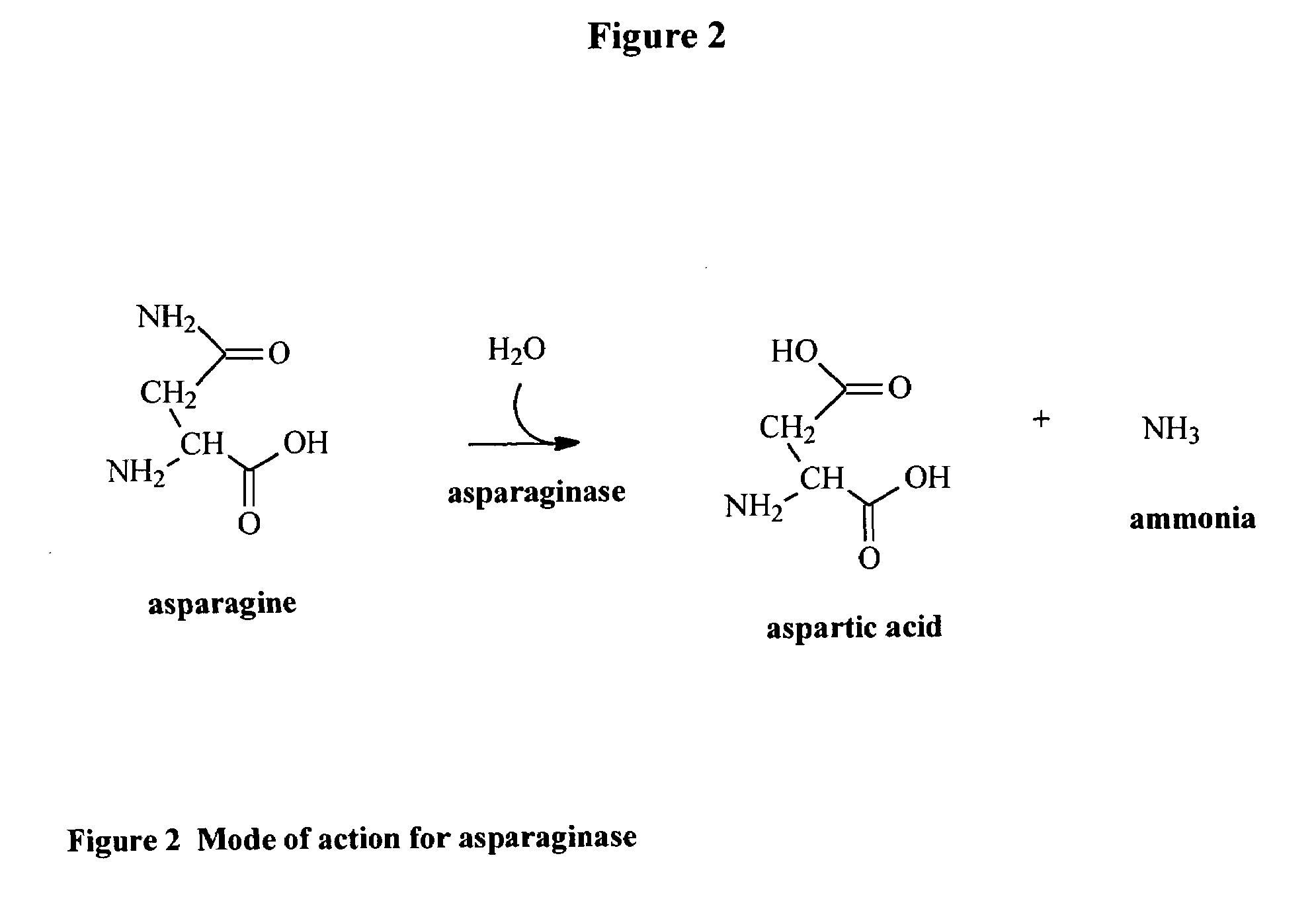
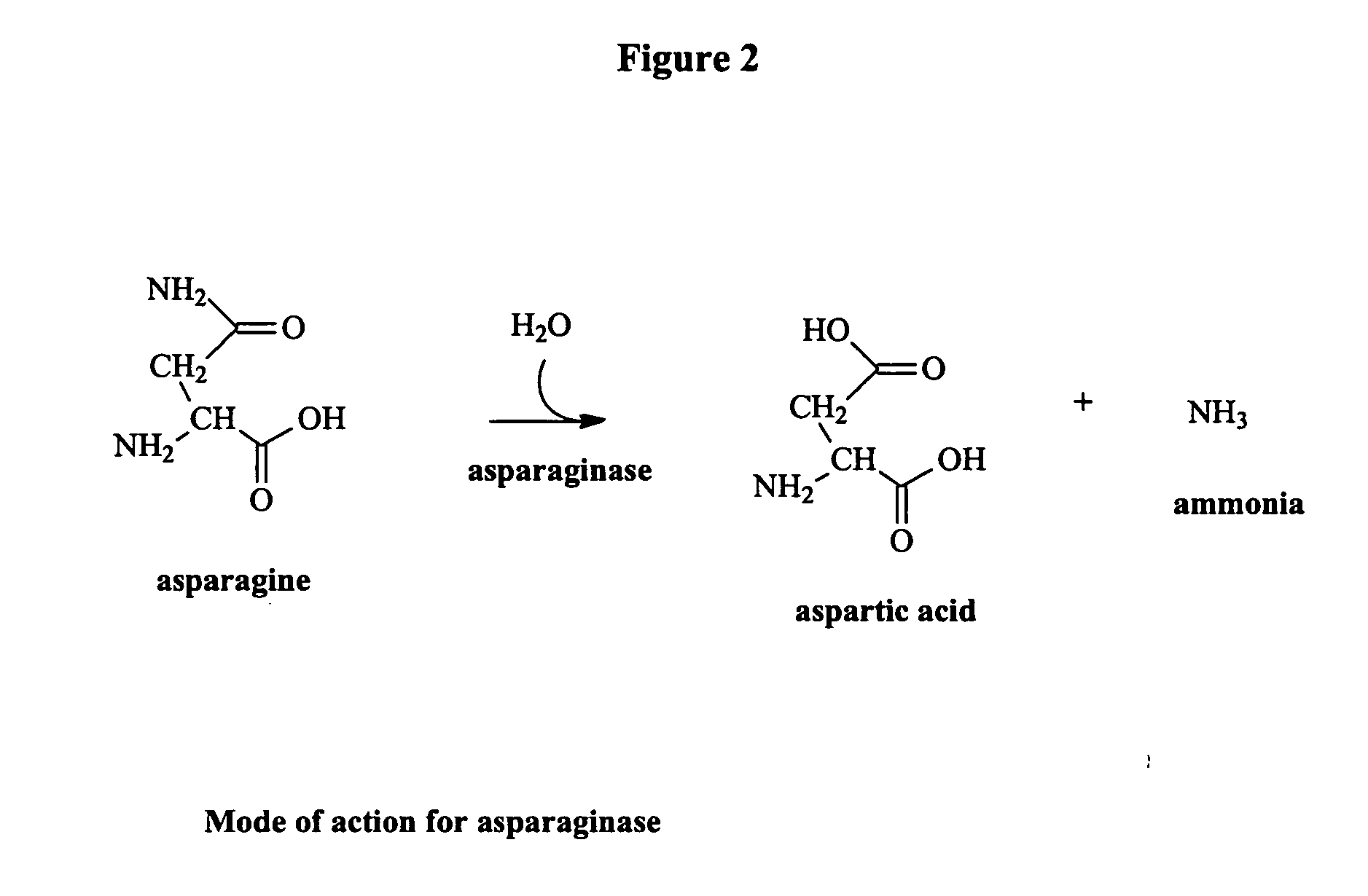
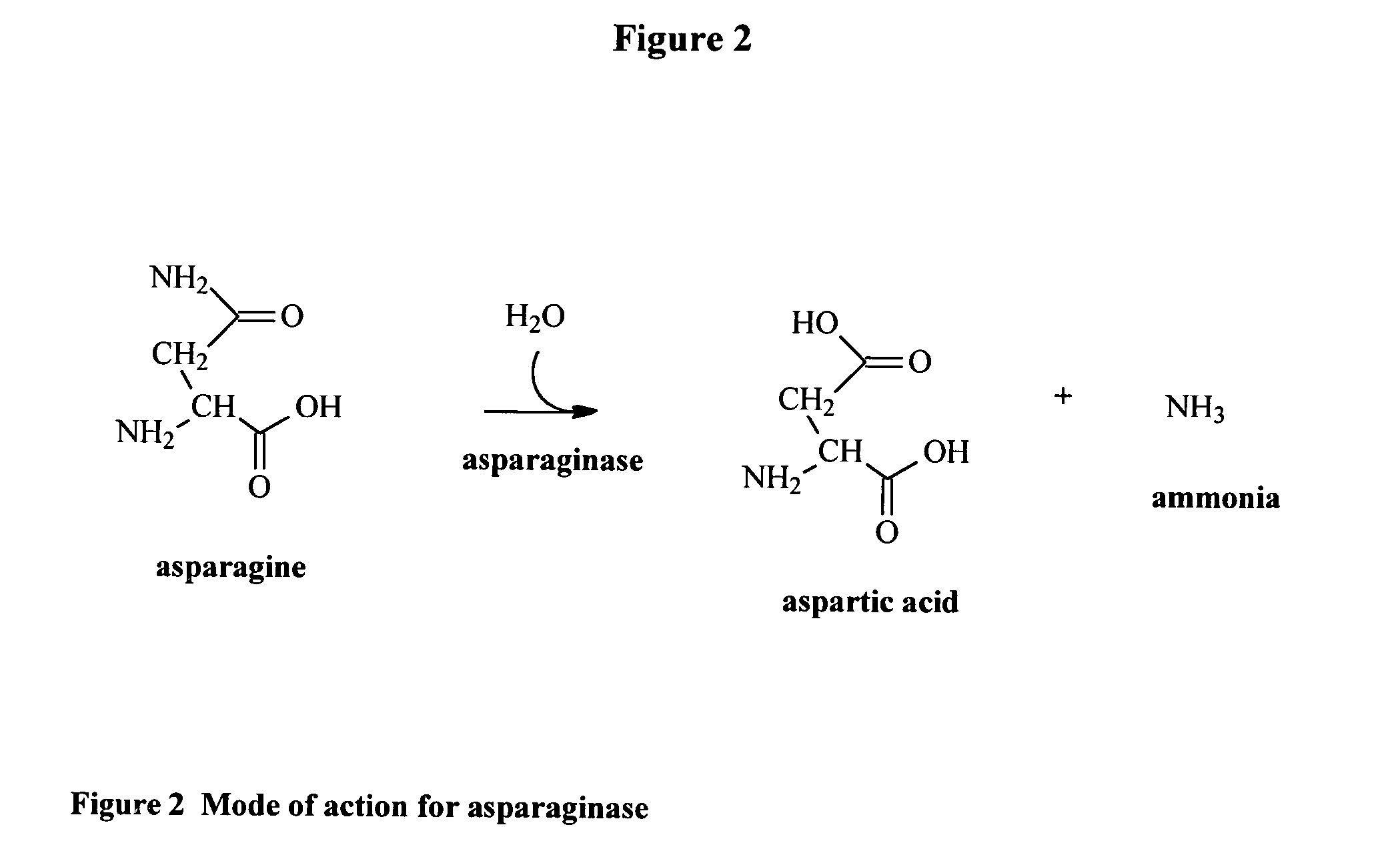
Utilization of Wolinella succinogenes asparaginase to treat diseases associated with asparagine dependence
InactiveUS6251388B1Highly efficaciousLess immunosuppressive activitySugar derivativesBacteriaHomotetramerAutoimmune condition
Described herein are methods for producing recombinant forms of asparaginase derived from Wolinella succinogenes. In addition, methods for covalent modification of proteins, including asparaginases, by acylation are also provided. Certain embodiments provide for epitopic-labeling of the amino terminus of W. succinogenes asparaginase. Additional embodiments concern methods for the therapeutic utilization of the native, homotetrameric form of W. succinogenes asparaginase, as well as the use of epitopically-labeled or non-epitopically-labeled recombinant W. succinogenes asparaginase (or a covalently modified analog thereof) in the therapeutic treatment of malignant and non-malignant hematological disease and other diseases where asparagine depletion or deprivation would be efficacious or which respond to asparagine depletion or deprivation, as well as their potential utilization in the therapeutic treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, AIDS, and SLE.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES
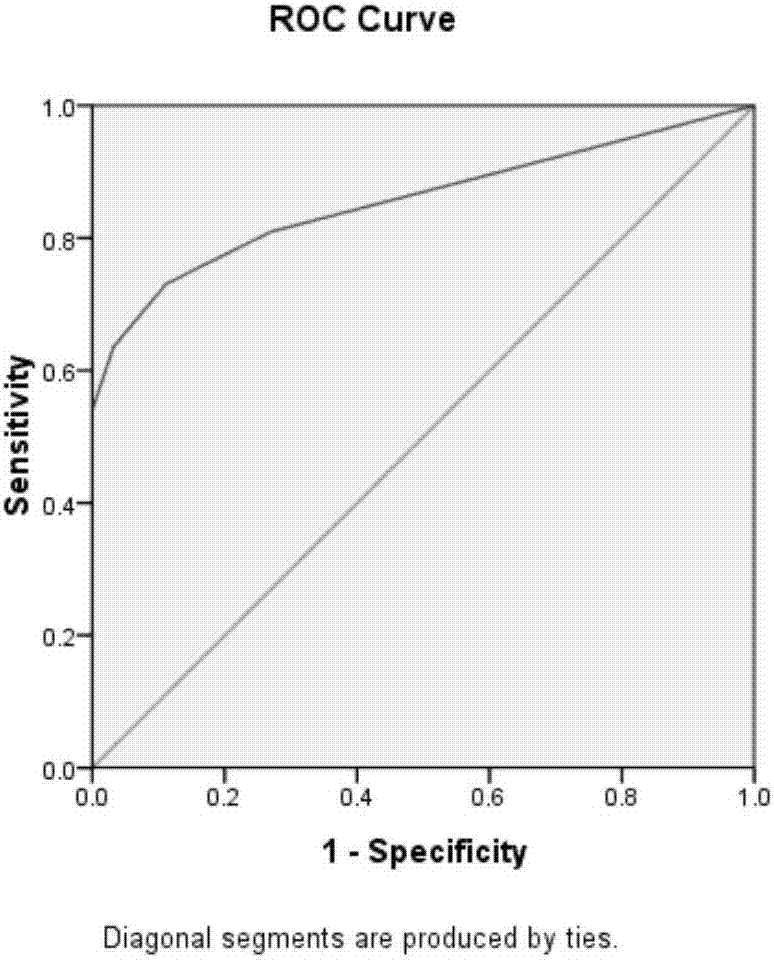
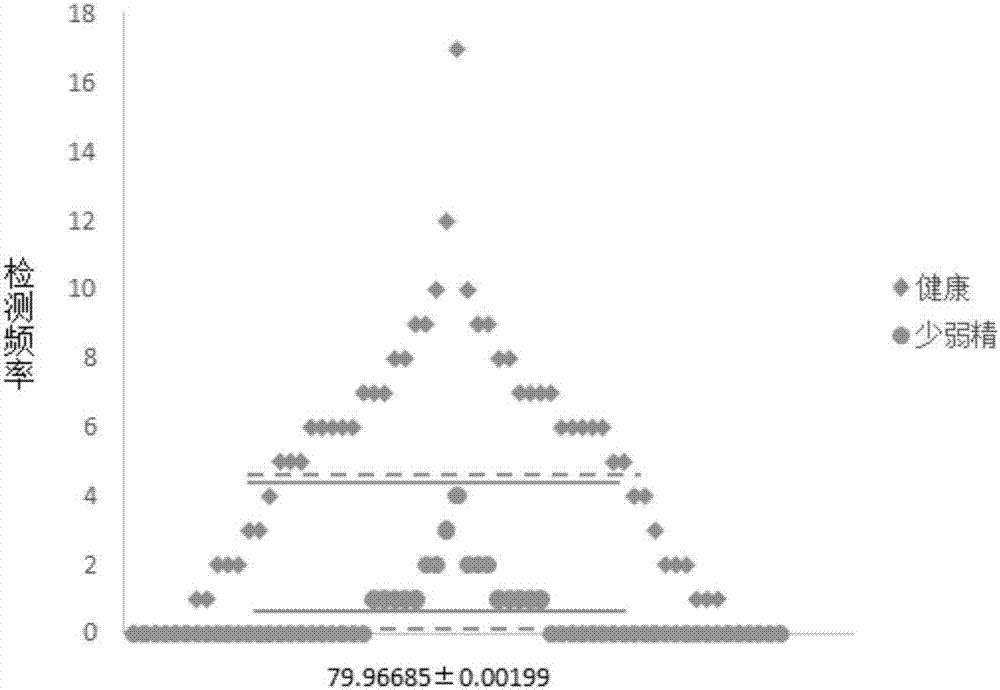
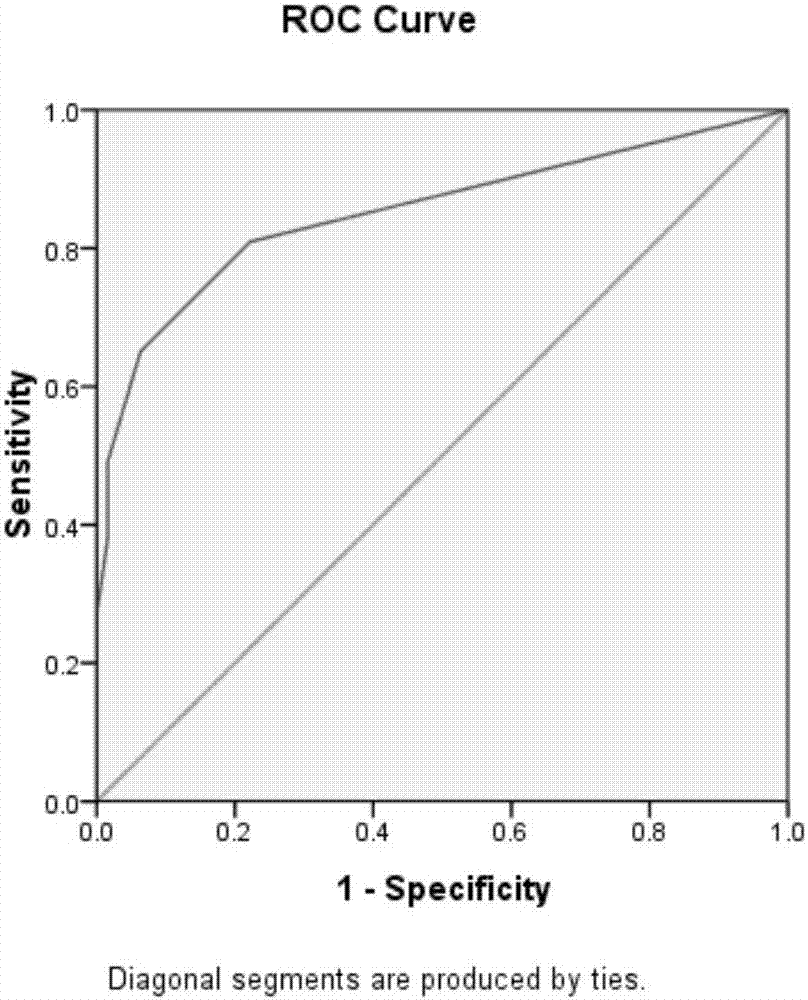
Application of AKAP4 protein with 186th-site N-114.04278 in preparing reagent for diagnosing severe oligoasthenospermia
The invention discloses application of asparagine with AKAP4 protein 186th-site generating mass shift -114.04278 as a biological marker in preparing a reagent for diagnosing severe oligoasthenospermia. The fact that the detection frequency of the AKAP4 protein 186th-site generating mass shift -114.04278 can be used for diagnosing the severe oligoasthenospermia is found, so that a new diagnosis and treatment target is provided for the severe oligoasthenospermia.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Production of TNFR-lg
ActiveUS20060121569A1Reduce accumulationHigh level of proteinAnimal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTotal amino acidsInorganic ions
An improved system for large scale production of proteins and / or polypeptides in cell culture, particularly in media characterized by one or more of: i) a cumulative amino acid concentration greater than about 70 mM; ii) a molar cumulative glutamine to cumulative asparagine ratio of less than about 2; iii) a molar cumulative glutamine to cumulative total amino acid ratio of less than about 0.2; iv) a molar cumulative inorganic ion to cumulative total amino acid ratio between about 0.4 to 1; or v) a combined cumulative glutamine and cumulative asparagine concentration between about 16 and 36 mM, is provided. The use of such a system allows high levels of protein production and lessens accumulation of certain undesirable factors such as ammonium and / or lactate. Additionally, culture methods including a temperature shift, typically including a decrease in temperature when the culture has reached about 20-80% of it maximal cell density, are provided. Alternatively or additionally, the present invention provides methods such that, after reaching a peak, lactate and / or ammonium levels in the culture decrease over time.
Owner:PFIZER IRELAND PHARM CORP
Method for reducing acrylamide in foods, foods having reduced levels of acrylamide and article of commerce
ActiveUS20050202153A1Reduce acrylamide contentLower Level RequirementsMilk preparationDough treatmentFood materialEnzyme
A method for the reduction of acrylamide in food products, food products having reduced levels of acrylamide, and an article of commerce. In one aspect, the method comprises reducing the level of asparagine in a food material before final heating (e.g., cooling). In another aspect, the method comprises adding to a food material an enzyme capable of hydrolyzing the amide group of free asparagine. In yet another aspect, an article of commerce communicates to the consumer that a food product has reduced or low levels of acrylamide or asparagine.
Owner:KELLOGG NORTH AMERICA
Plating solution of palladium alloy and method for plating using the same
InactiveUS20080073218A1Increased durabilityImprove hydrogen permeabilityMembranesSemi-permeable membranesNeutral Amino AcidsThreonine
The present invention relates to a plating solution of palladium alloy and has an object to provide a plating solution of palladium alloy highly stable and capable of stably forming a plated film of a given alloy composition. The present invention relates to a plating solution of palladium alloy containing a palladium complex and a metal salt, wherein the palladium complex is coordinated with at least one neutral amino acid selected from the group consisting of glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine and tyrosine as a ligand.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
Method for reducing acrylamide in corn-based foods, corn-based foods having reduced levels of acrylamide, and article of commerce
InactiveUS7527815B2Reduce acrylamide contentLower Level RequirementsMilk preparationDough treatmentFood materialEnzyme
A method for the reduction of acrylamide in corn-based food products, corn-based food products having reduced levels of acrylamide, and an article of commerce. In one aspect, the method comprises reducing the level of asparagine in a corn-based food material before final heating (e.g., cooking). In another aspect, the method comprises adding to a corn-based food material an enzyme capable of hydrolyzing the amide group of free asparagine. In yet another aspect, an article of commerce communicates to the consumer that a corn-based food product has reduced or low levels of acrylamide or asparagine.
Owner:KELLOGG NORTH AMERICA
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS20150080554A1Optimize purification stepsInhibition formationOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationThreonineHistidine
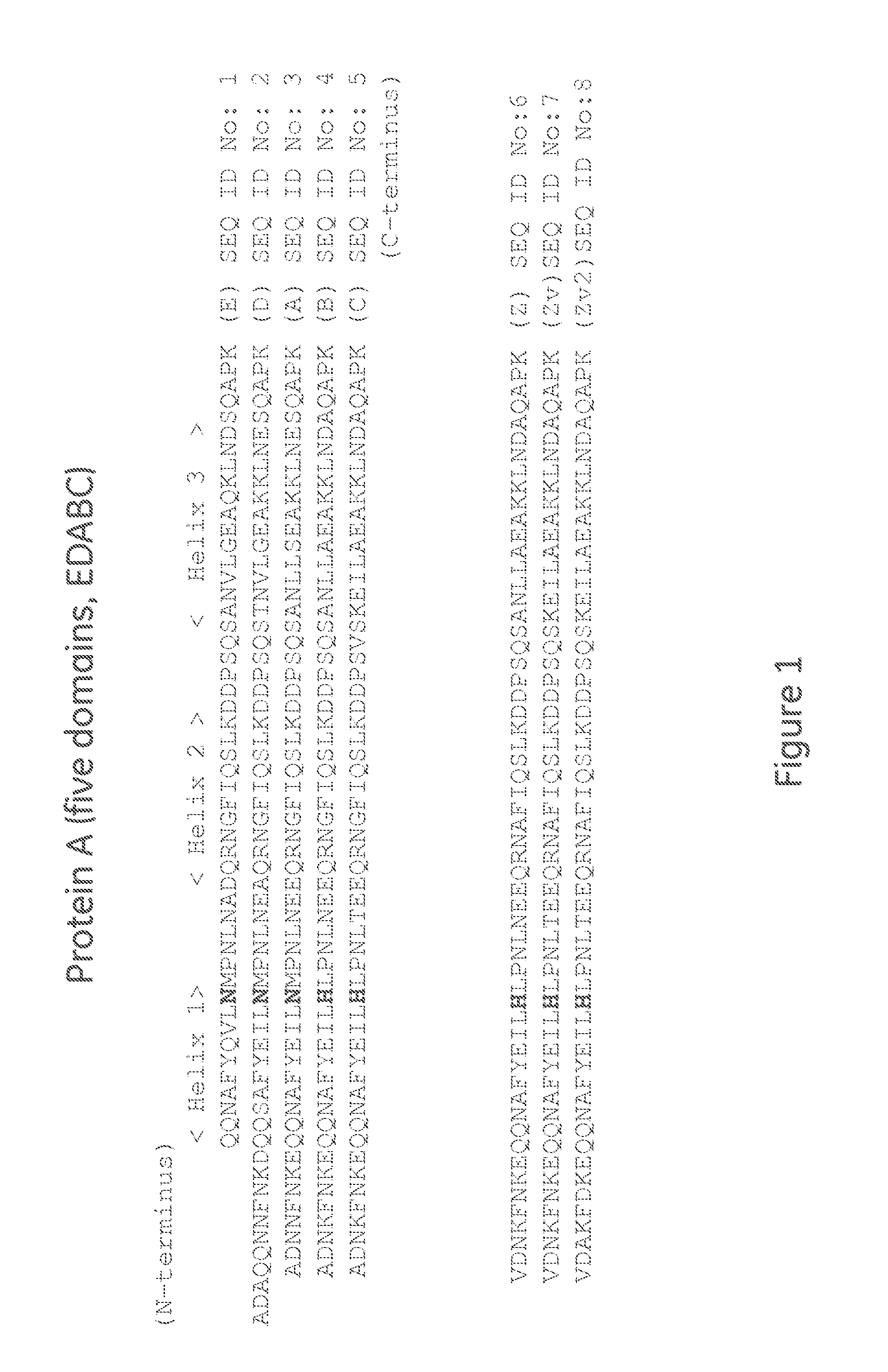
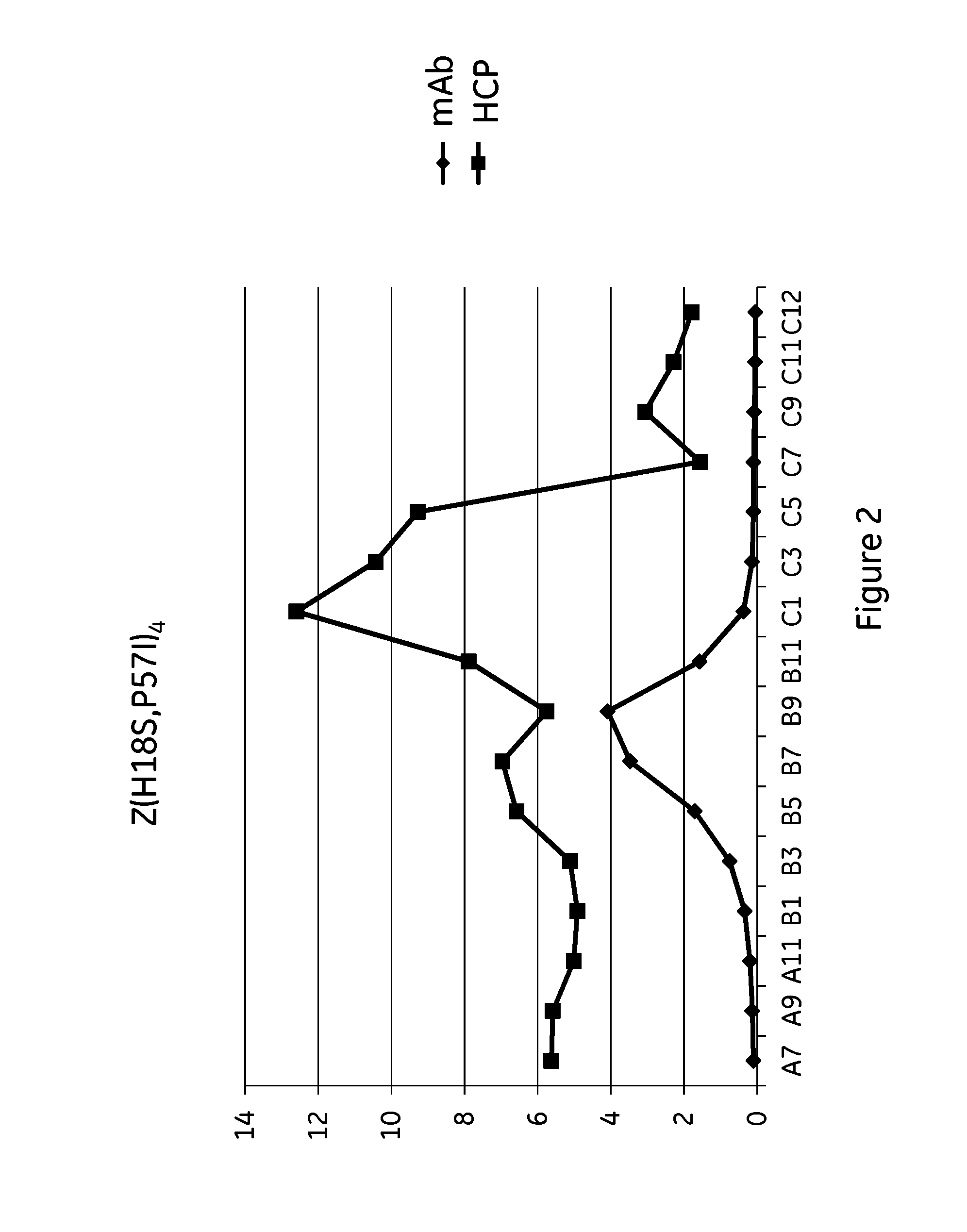
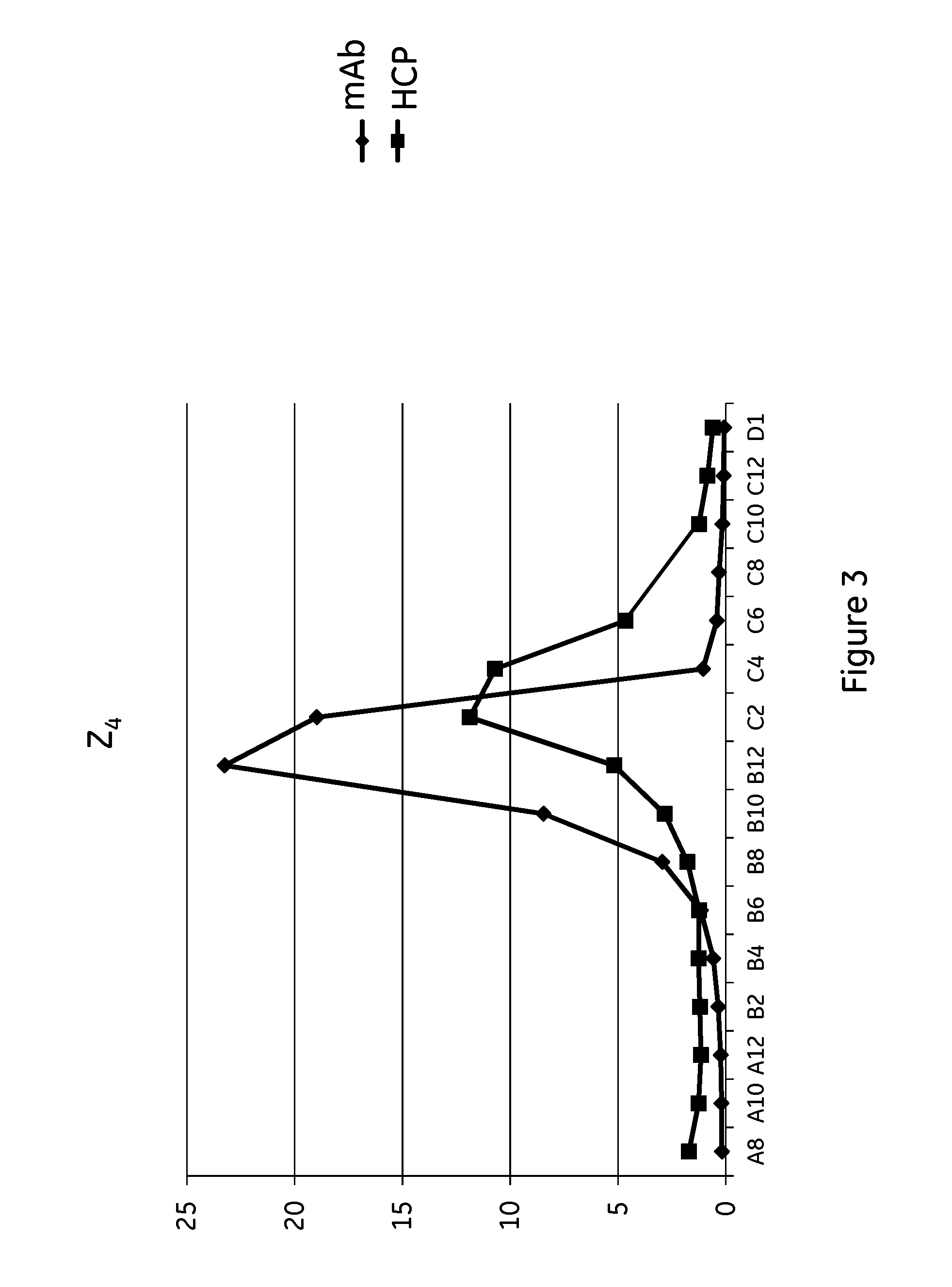
The invention discloses an immunoglobulin-binding protein comprising one or more mutated immunoglobulin-binding domains (monomers) of staphylococcal Protein A (E, D, A, B, C) or protein Z or a functional variant thereof, wherein in at least one of the one or more mutated monomers, the asparagine or histidine at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of Protein A or of Protein Z has been deleted or substituted with a first amino acid residue which is not proline or asparagine and wherein, if the amino acid residue at position 57 is proline and the amino acid residue at position 28 is asparagine, then the amino acid residue at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of protein A or of protein Z is not serine, threonine or lysine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Artificial nutrient medium for Phellinus linteus fluid culture and method for fermentation of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide
InactiveCN101348803APromote growthIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhellinus igniariusTryptophan
The invention provides a synthetic medium for culturing a phellinus igniarius liquid. The synthetic medium takes glucose as a carbon source and 20 kinds of amino acid as a nitrogen source, and consists of inorganic salt and vitamin. The ratio of carbon to nitrogen is designed as 50 to 1; and the specific concentration g / l is as follows: the glucose: 30 to 80 grams; glutamic acid: 0.1 to 1.5 grams; glutamine: 0.1 to 1.5 grams; aspartic acid: 0.1 to 1.5 grams; asparagines: 0.1 to 1.5 grams; glutamic acid: 0.01 to 0.1 gram; tryptophan: 0.01 to 0.1 gram; valine: 0.01 to 0.1 gram; alanine: 0.01 to 0.1 gram; etc. During the whole culture process of the synthetic medium, phellinus igniarius mycelium is quick in growth; the yield of the phellinus igniarius mycelium can reach 20 grams per liter to the highest degree; simultaneously no agricultural and sideline product is introduced as the carbon source and the nitrogen source; substances such as proteins in the medium, medium compositions and so on are not carried; phellinus igniarius exopolysaccharide produced through fermentation has high purity and stable quality; and the yield of phellinus igniarius polysaccharide can reach 0.198 gram per liter to the highest degree. The synthetic medium has the advantages of clear compositions, stable quality and so on, and can be used for mass culture of the phellinus igniarius liquid and research of the regulation and control rule of polysaccharide anabolism.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
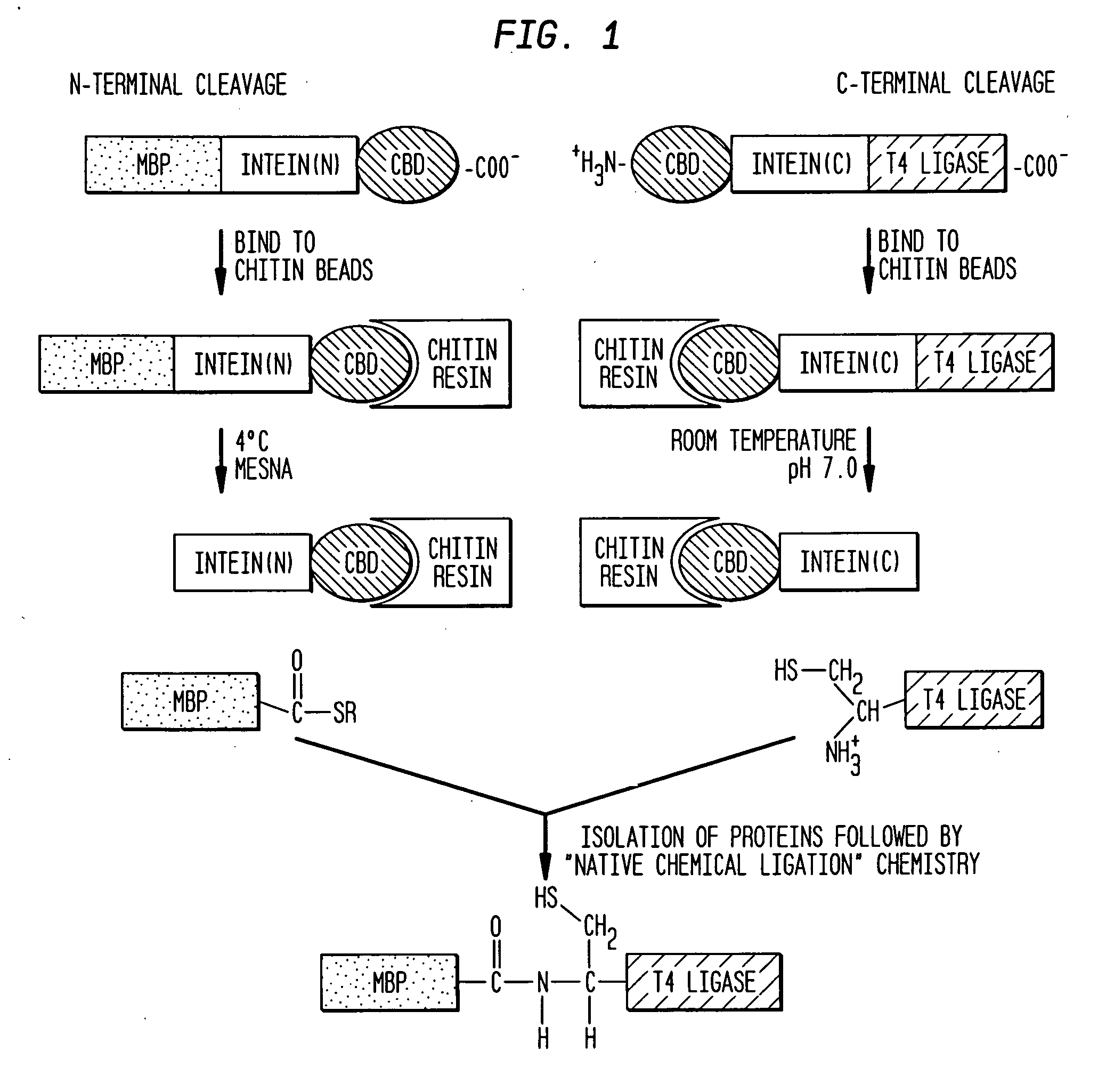
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum , is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:EVANS THOMAS +2
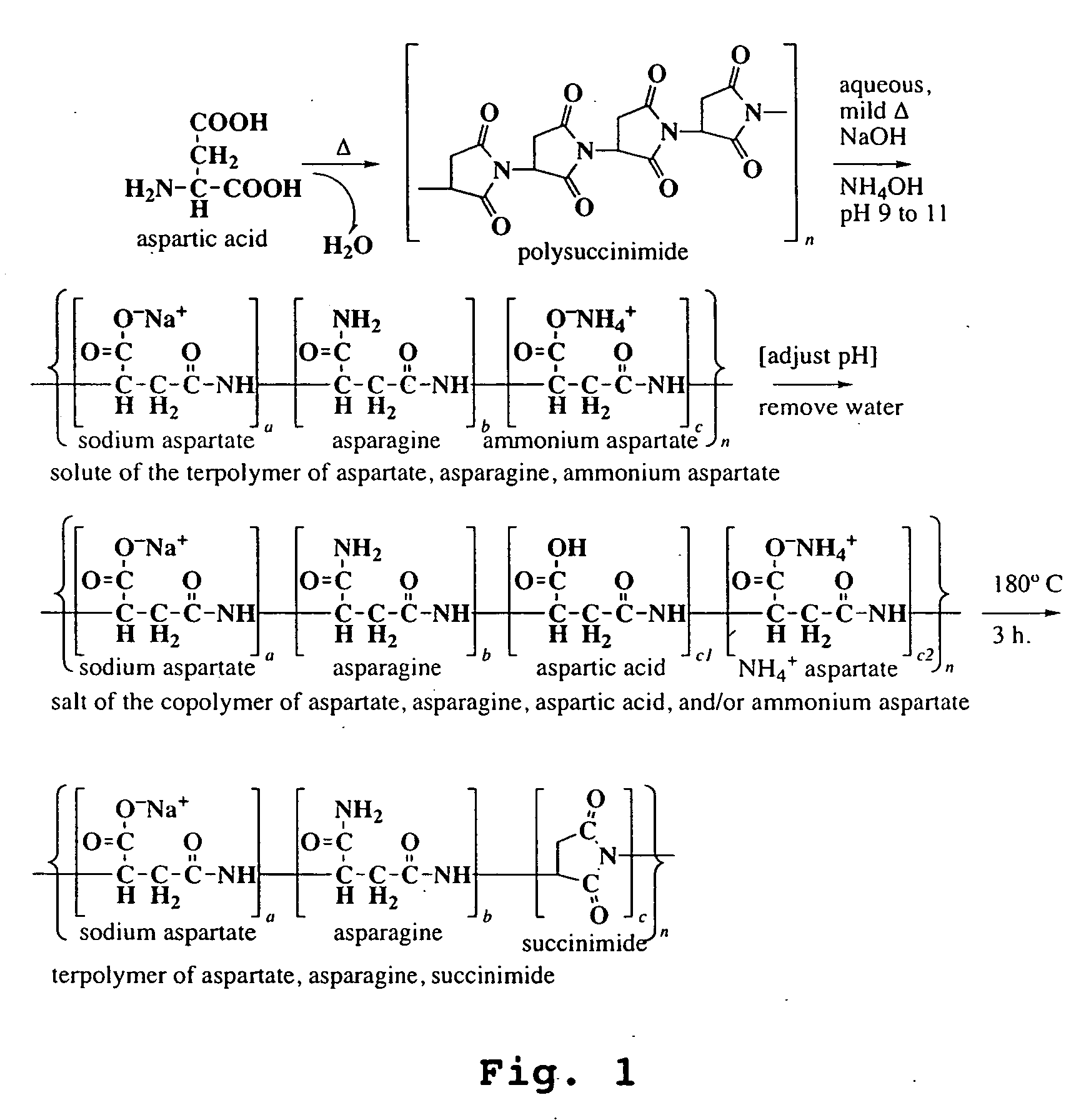
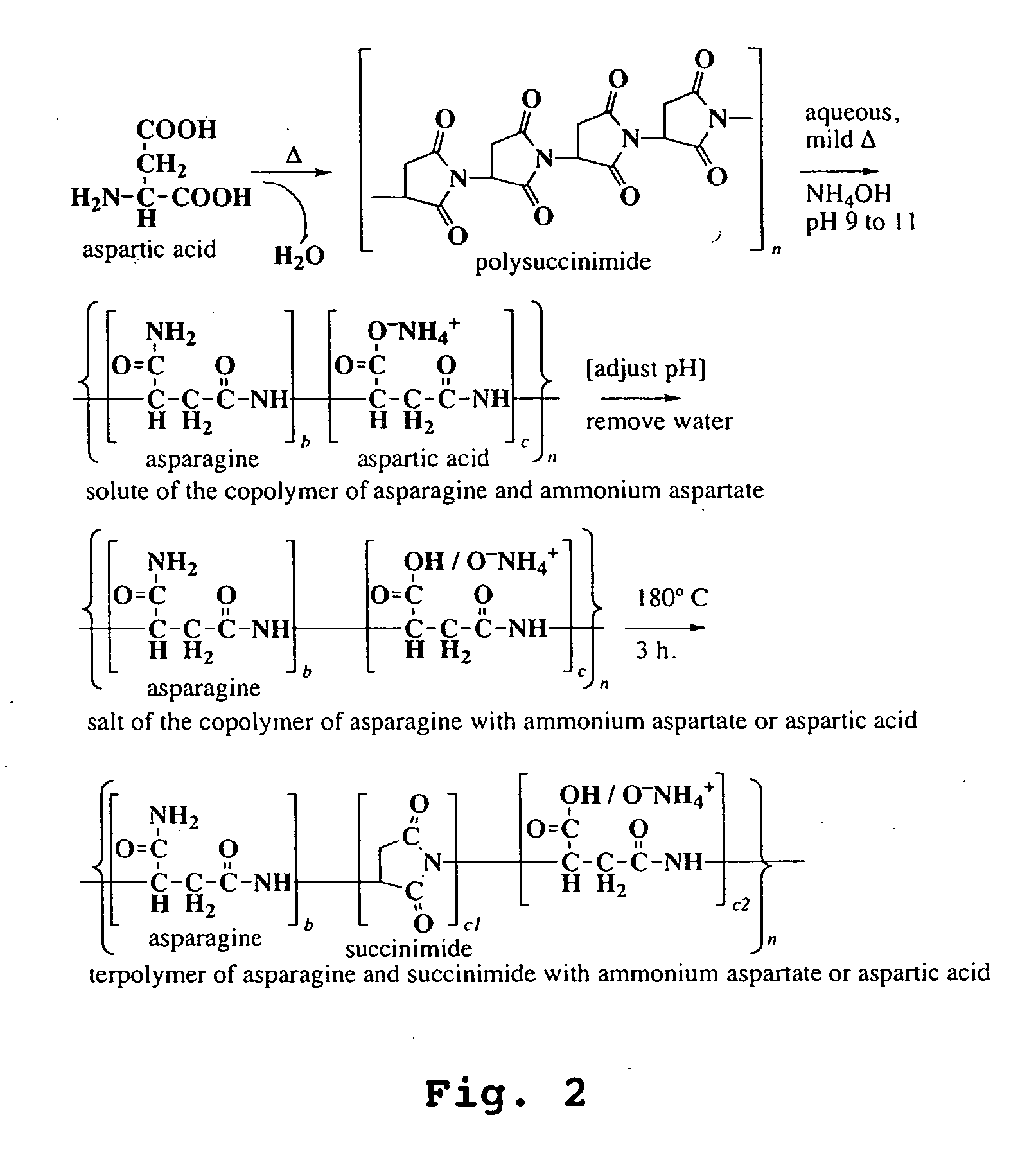
Copolymers of amino acids and methods of their production
InactiveUS20050065316A1Lower levelImprove the level ofAgriculture tools and machinesCoatingsWater solubleAsn - Asparagine
Disclosed are copolymers based on aspartic acid or its precursor molecules and methods of their production. The copolymers are water-soluble over a wide range of composition and molecular weight. Their preparation involves conversion of a polysuccinimide to copolymers of defined composition, containing aspartate and succinimide residues and / or residues of asparagine. In particular, the copolymers include water-soluble terpolymers of aspartate, asparagine, and succinimide.
Owner:AQUERO
Physiologically active complex
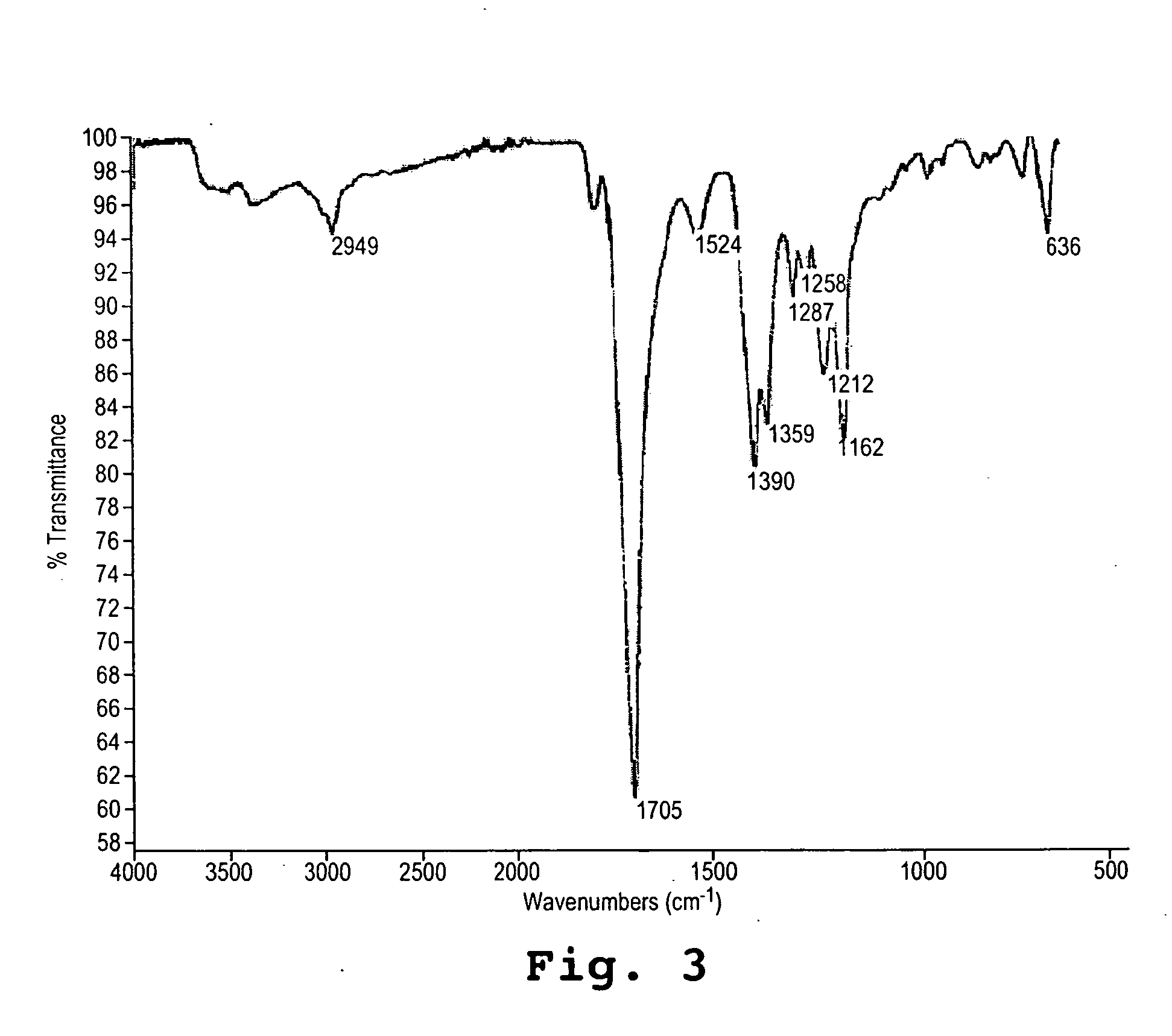
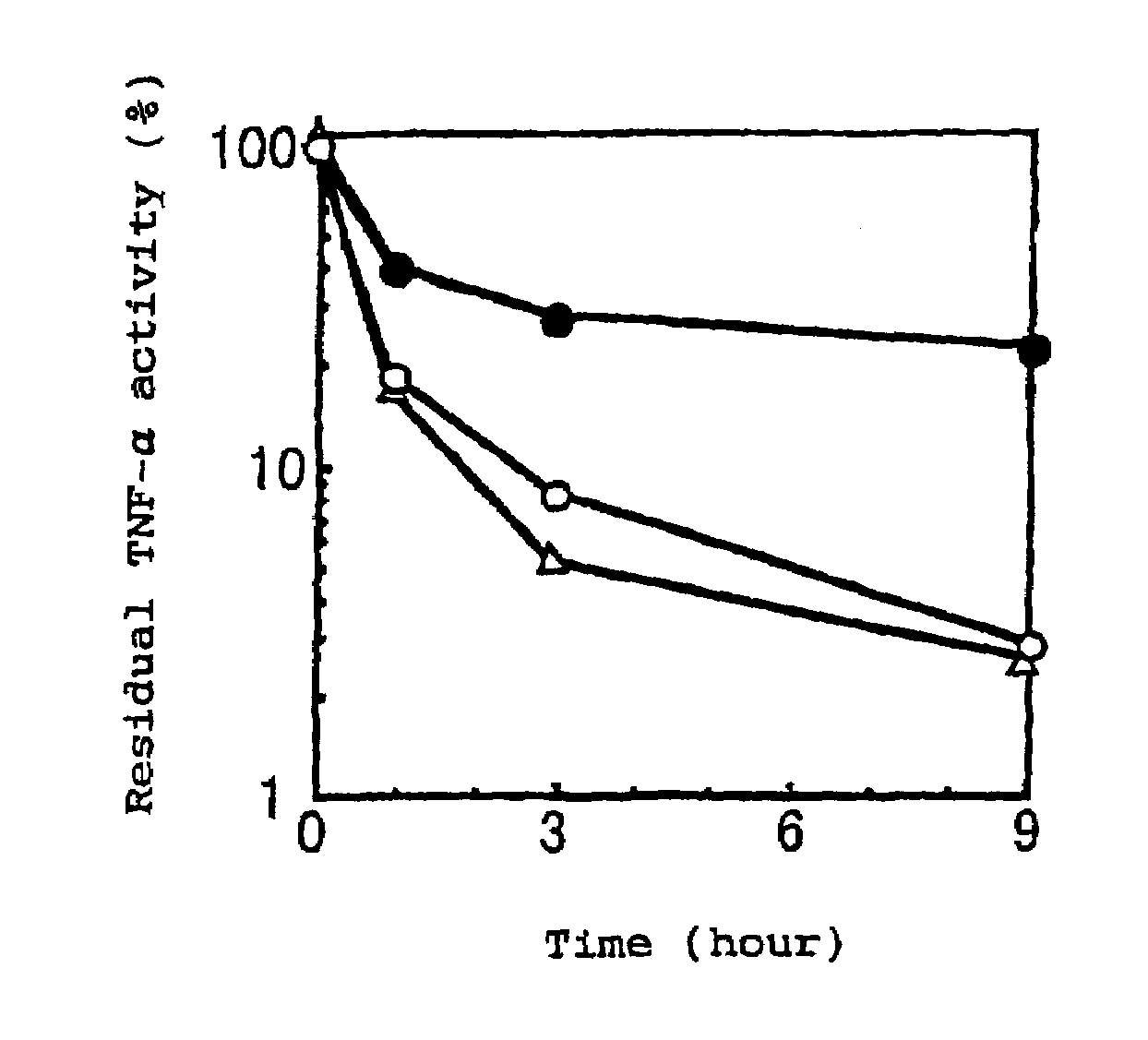
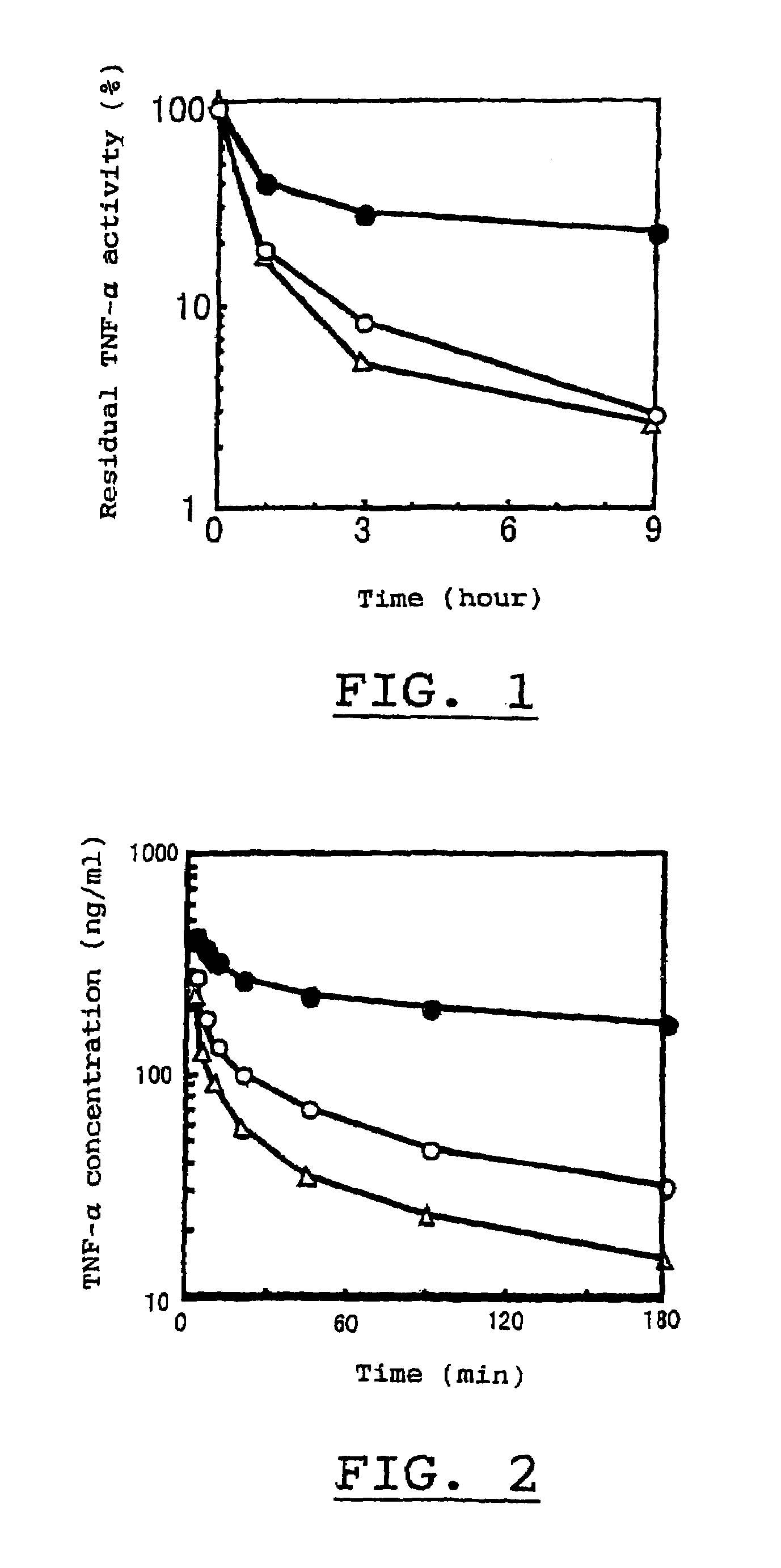
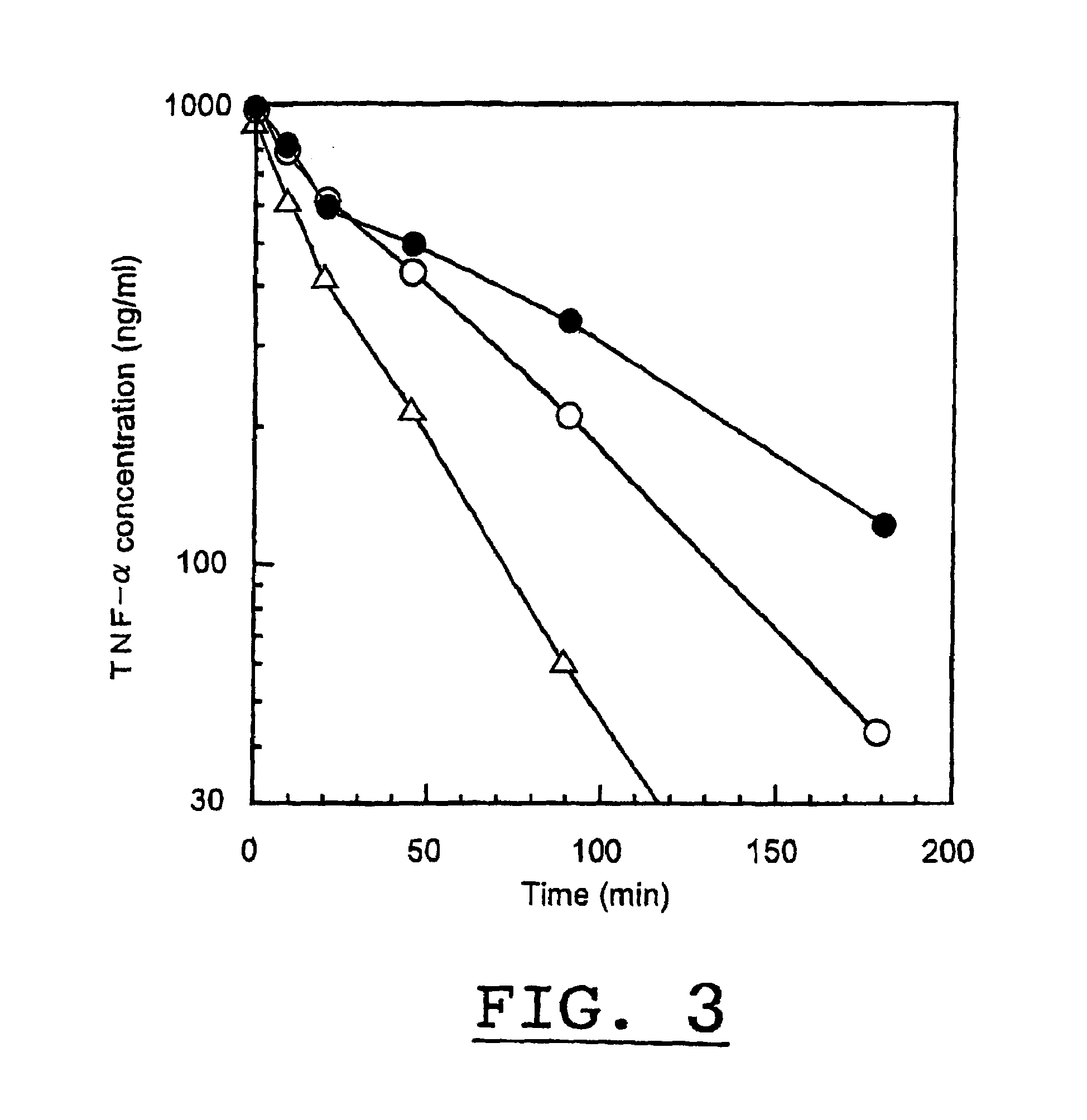
Disclosed is a physiologically active complex which comprises a proteinaceous part with TNF activity and a high molecular part bound artificially to the N-terminus of the proteinaceous part. The proteinaceous part in the complex has the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:2 where Xaa is a member selected from the group consisting of asparagine, alanine, arginine, serine, threonine, proline, methionine, and leucine; while the high molecular part in the complex is a homopolymer of polyethylene glycol, copolymer of polyethylene glycol, or a derivative thereof.
Owner:MAYUMI TADANORI +3
Plant nutrient solution
InactiveCN105967871APromote growthRaw materials are easy to getMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSodium iodideInsect pest
The invention discloses a plant nutrient solution. The plant nutrient solution is prepared from the following components: potassium nitrate, urea, ammonium nitrate, magnesium sulfate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, calcium nitrate, manganese sulfate, zinc sulfate, ferric citrate, boric acid, sodium molybdate, sodium iodide, folic acid, asparagine, glucose, amino acid, multiple vitamins, collagen, pepper water and deionzed water. The plant nutrient solution disclosed by the invention is easy to obtain raw materials, simple in preparation, low in cost, green and safe, and rich in nutrients, the needed nutrients for each stage of plant growth are met, the growth is promoted, insect pests are effectively prevented, and the plant nutrient solution is beneficial for the plant growth by using the plant nutrient solution for a long time.
Owner:马鞍山纽盟知识产权管理服务有限公司
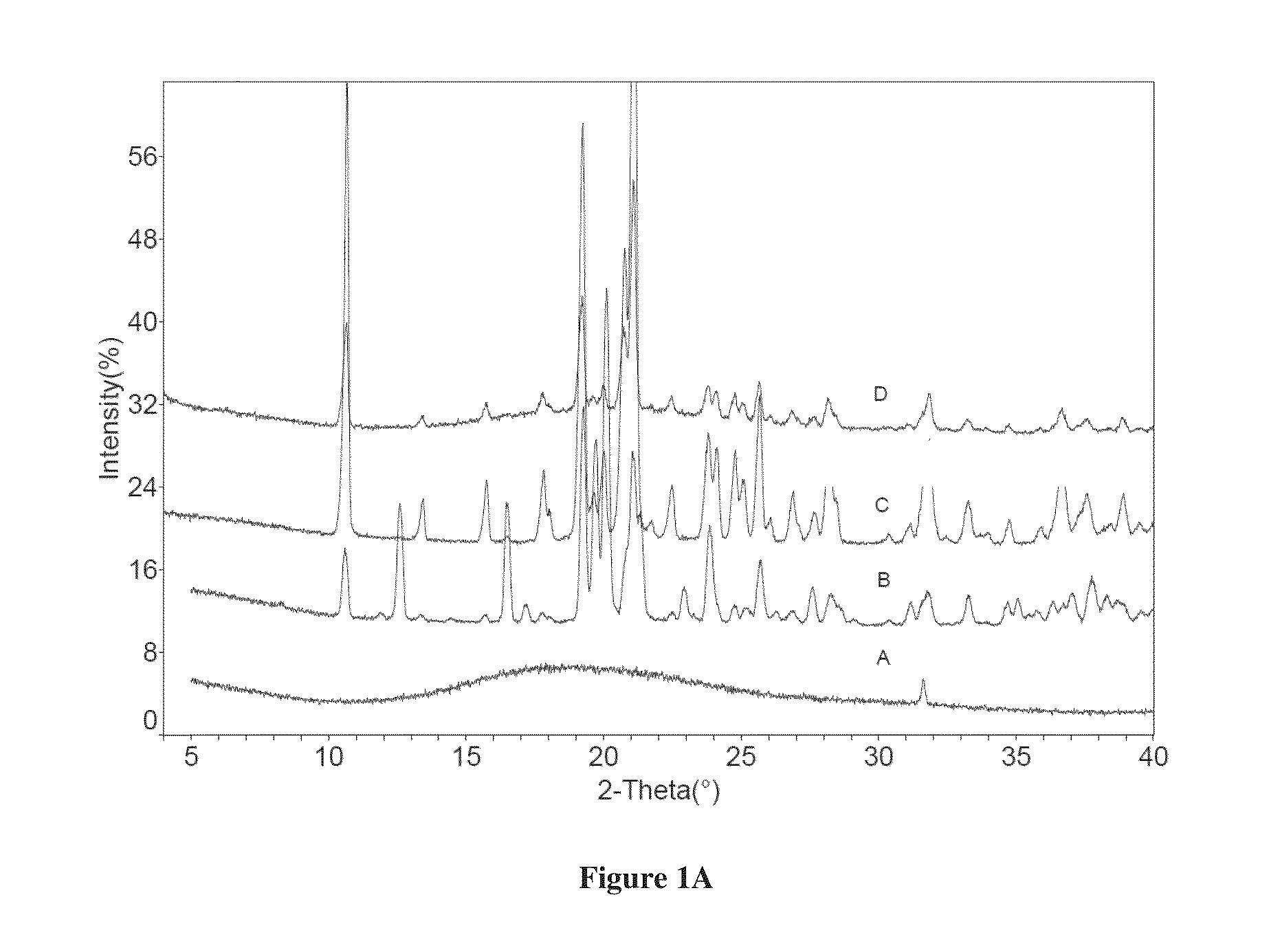
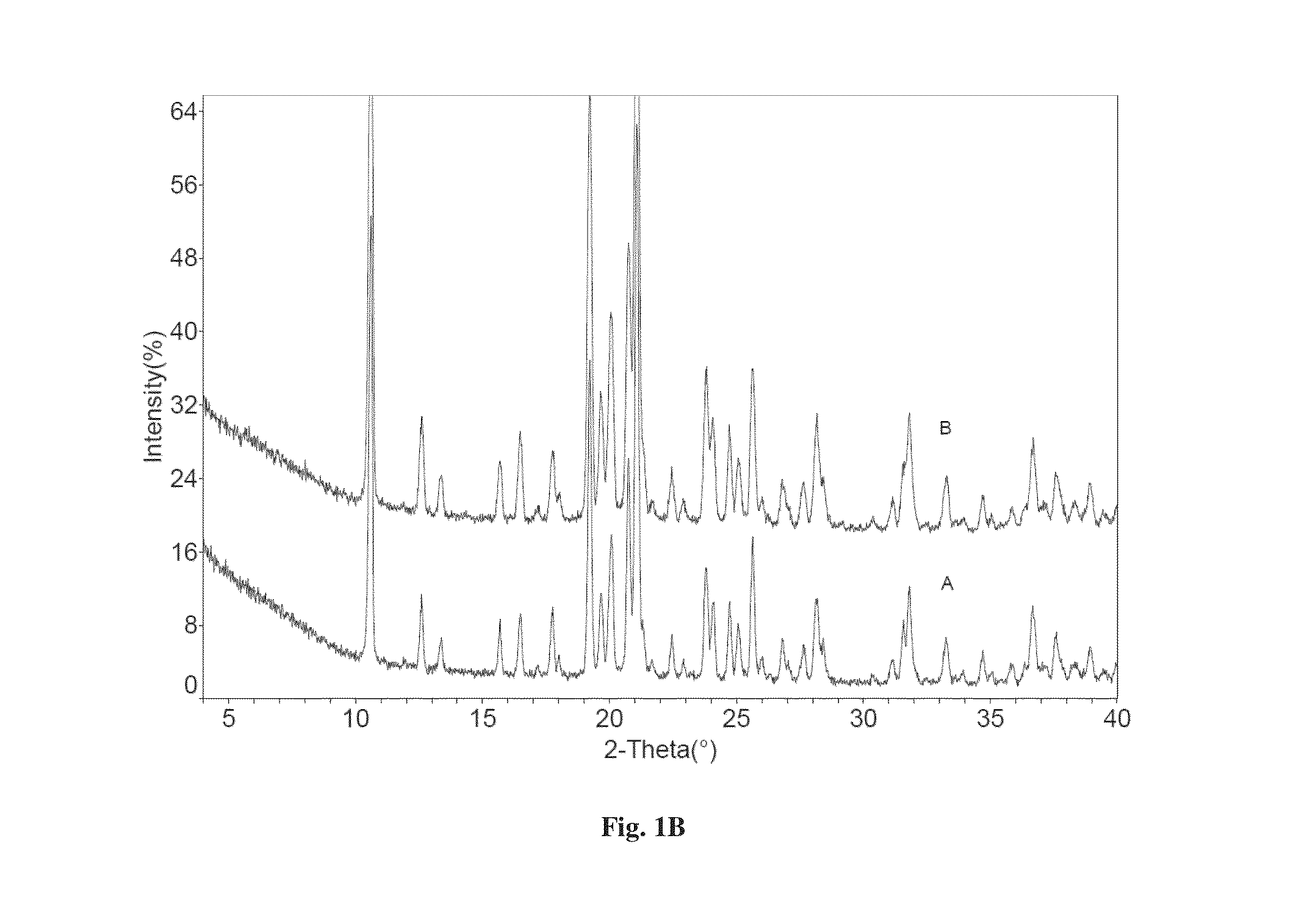
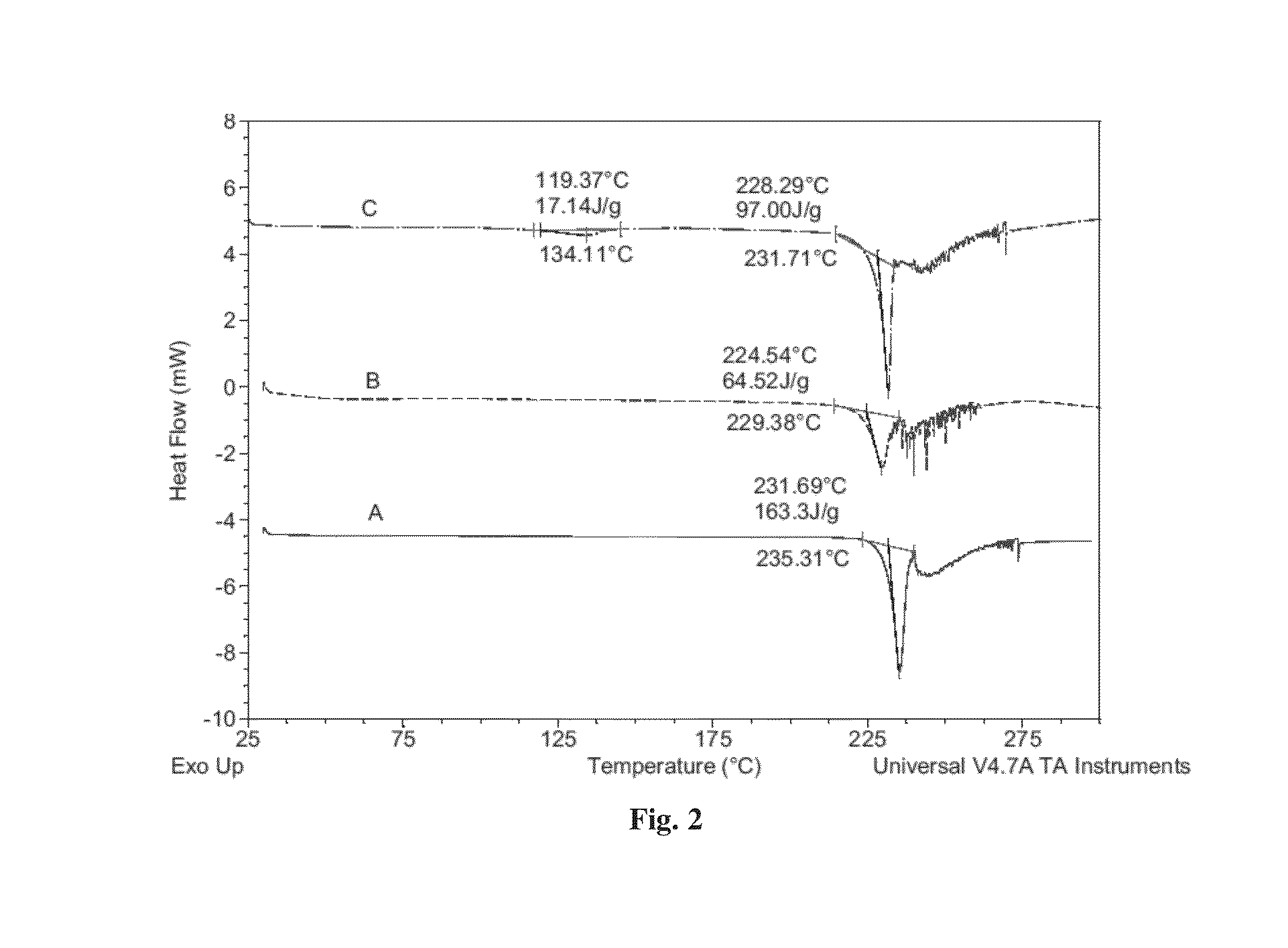
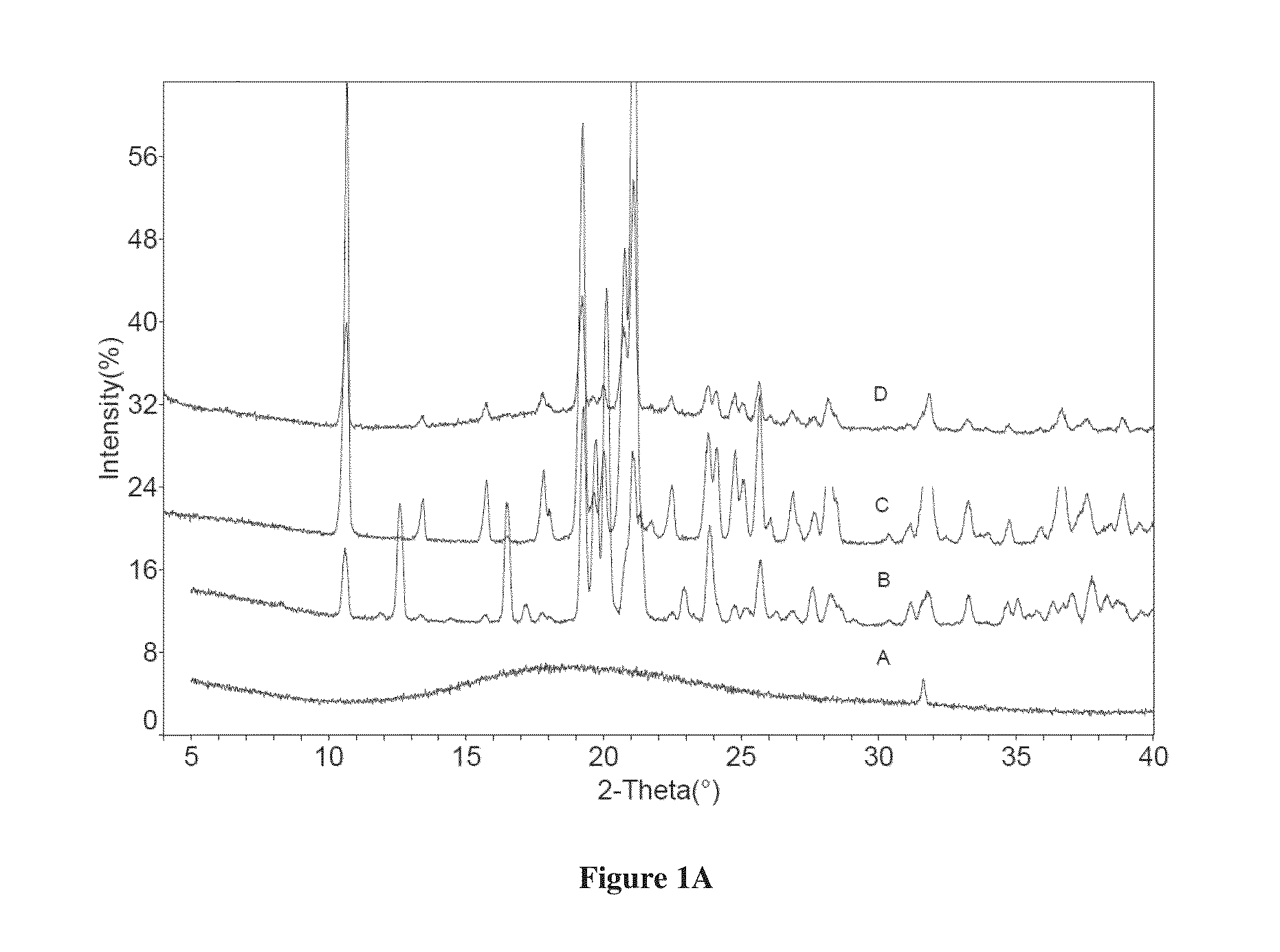
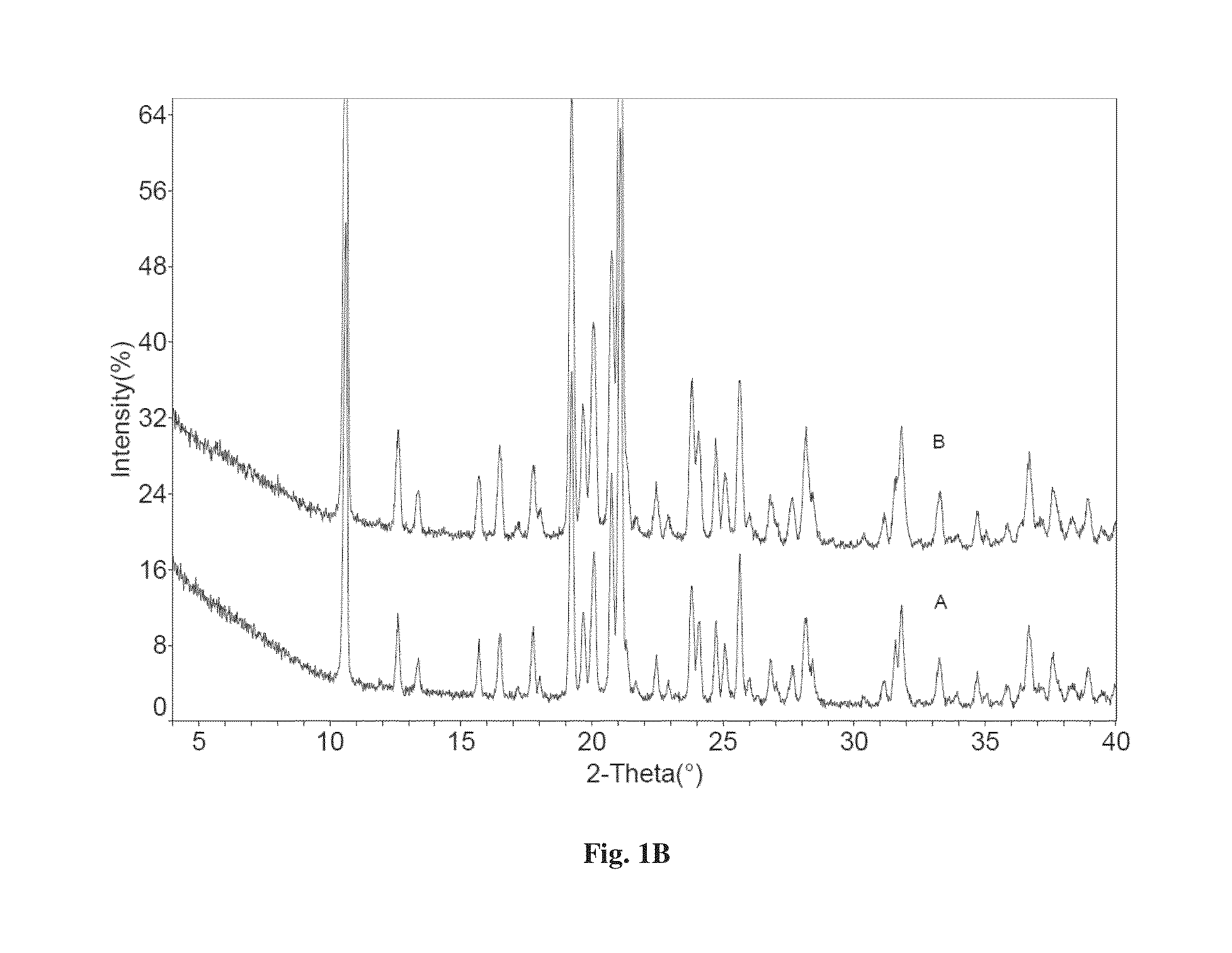
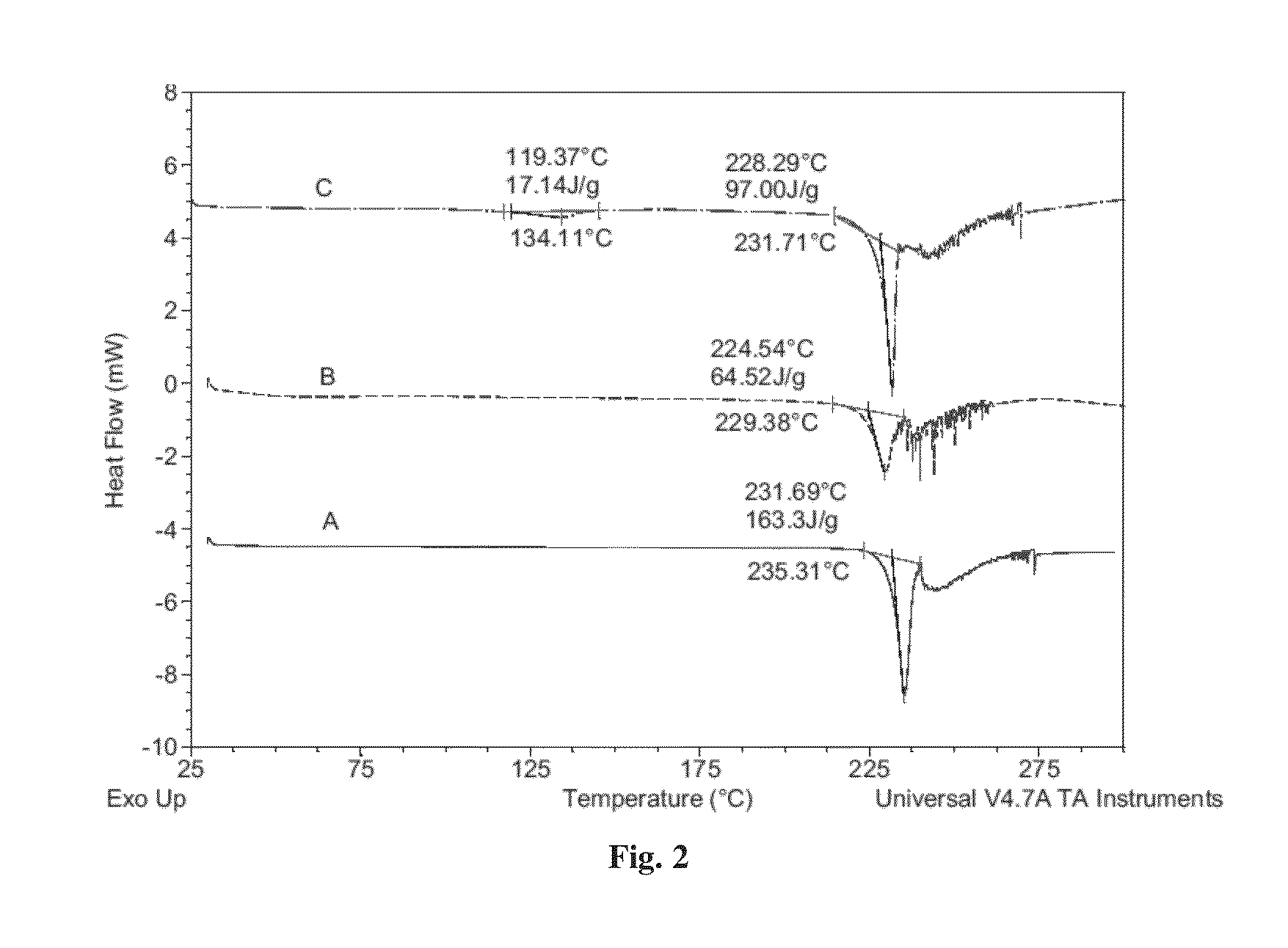
Co-crystals of dapagliflozin
ActiveUS20140343010A1Adequate stability characteristicBetter physicochemical propertyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLactosePharmacology
The present invention provides novel co-crystal forms of dapagliflozin, namely a dapagliflozin lactose co-crystal and a dapagliflozin asparagine co-crystal, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising same, methods for their preparation and uses thereof for treating type 2 diabetes.
Owner:MAPI PHARMA
Co-crystals of dapagliflozin
ActiveUS9006188B2Adequate stability characteristicMaintain good propertiesPowder deliveryBiocideLactosePharmacology
The present invention provides novel co-crystal forms of dapagliflozin, namely a dapagliflozin lactose co-crystal and a dapagliflozin asparagine co-crystal, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising same, methods for their preparation and uses thereof for treating type 2 diabetes.
Owner:MAPI PHARMA
Asparagine containing elastin peptide analogs
InactiveUS6794362B1Increase skin elasticityImprove skin appearanceBiocideCosmetic preparationsElastin peptidesElastin tissue
The present invention is directed to a composition which is used to enhance the elasticity and / or appearance of tissue. Specifically, the present invention is directed to a composition formulated from peptides or peptide-like compounds having low molecular weights and which substantially correspond to sequences found in elastin. The present composition specifically includes chemical modification of the peptides described herein, specifically carboxy and amino modification including the addition of amino acids to either end of the peptide fragments.
Owner:CONNECTIVE TISSUE IMAGINEERING
High-performing electrophoresis gels with extended shelf lives
ActiveUS20100187114A1Short runtimeLoss of resolutionElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisHydroxymethyl
Polyacrylamide gels that offer high resolution as electrophoretic media for protein separations and an improved resistance to hydrolysis upon storage are made by including either taurine, asparagine, or both as an ampholyte, in combination with either tris(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane or bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino-tris(hydroxymethyl)methane as a buffer, plus other conventional components.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com