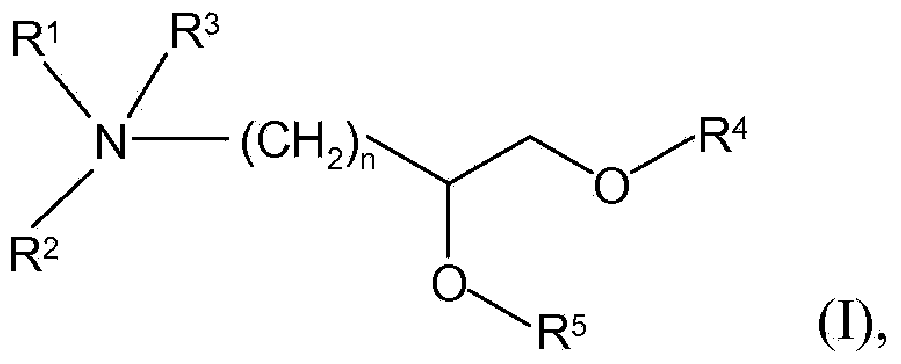
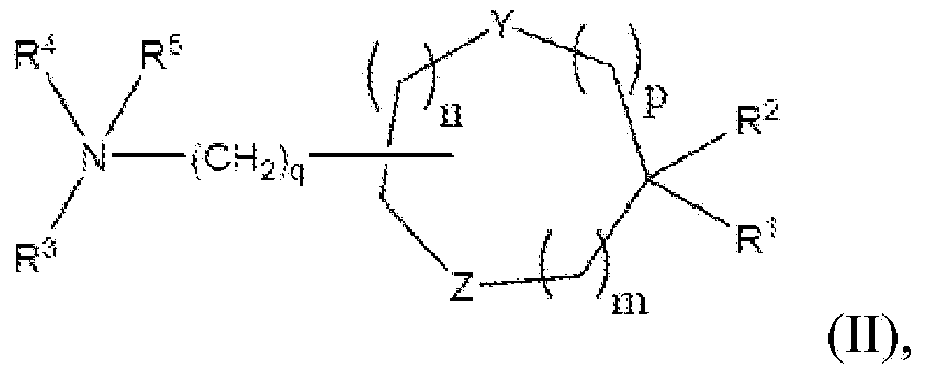
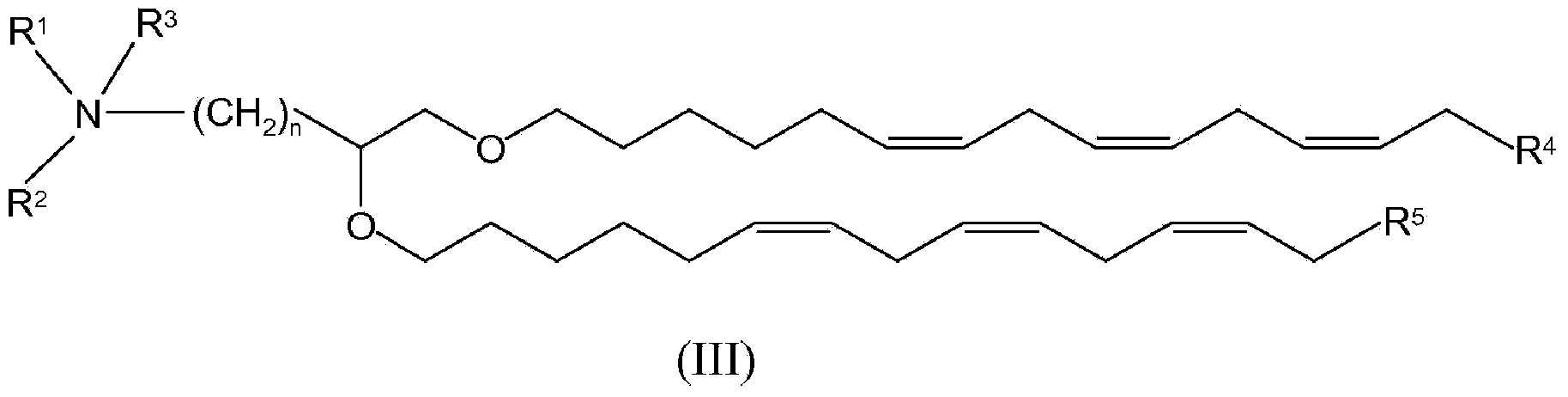
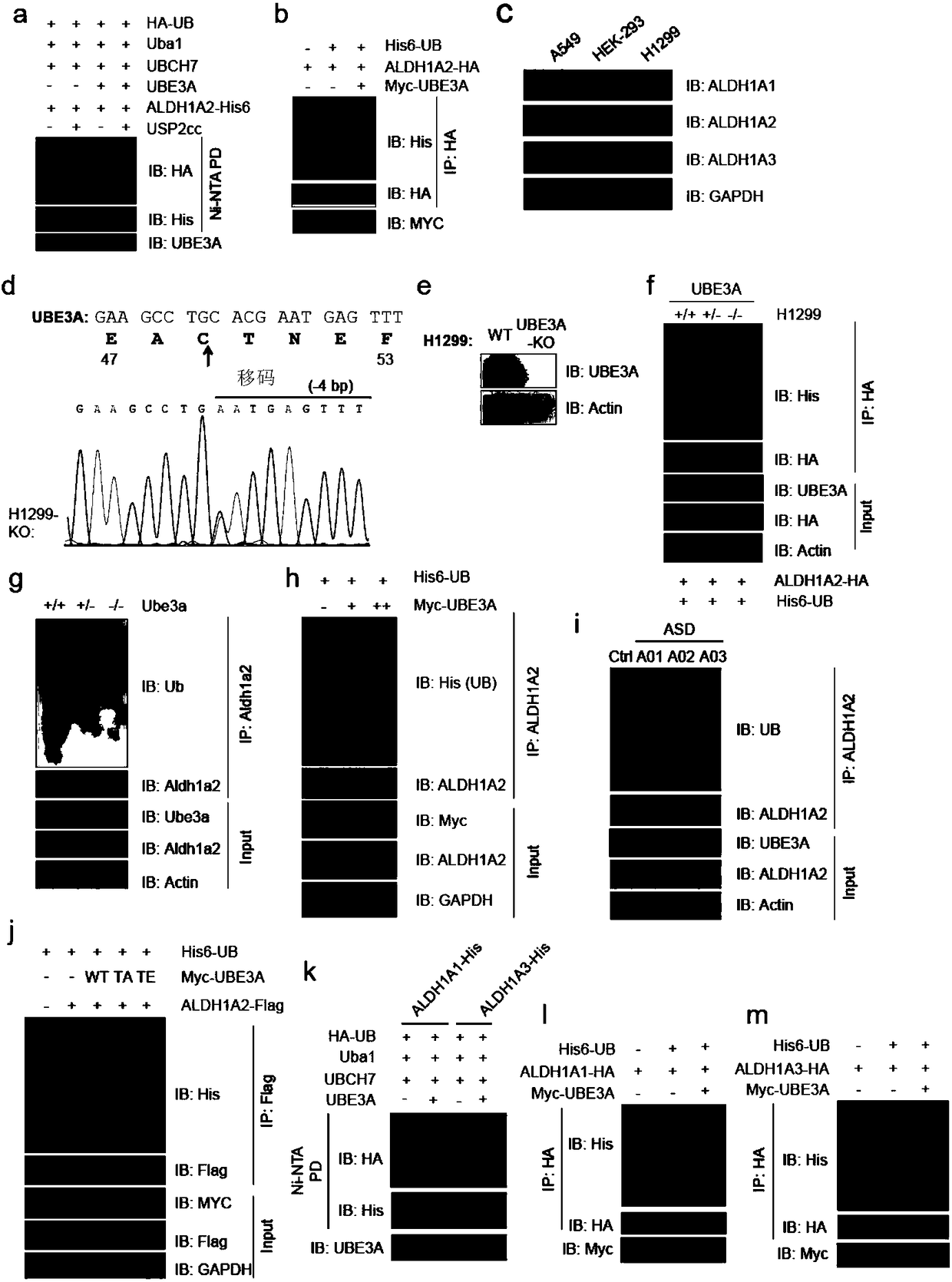
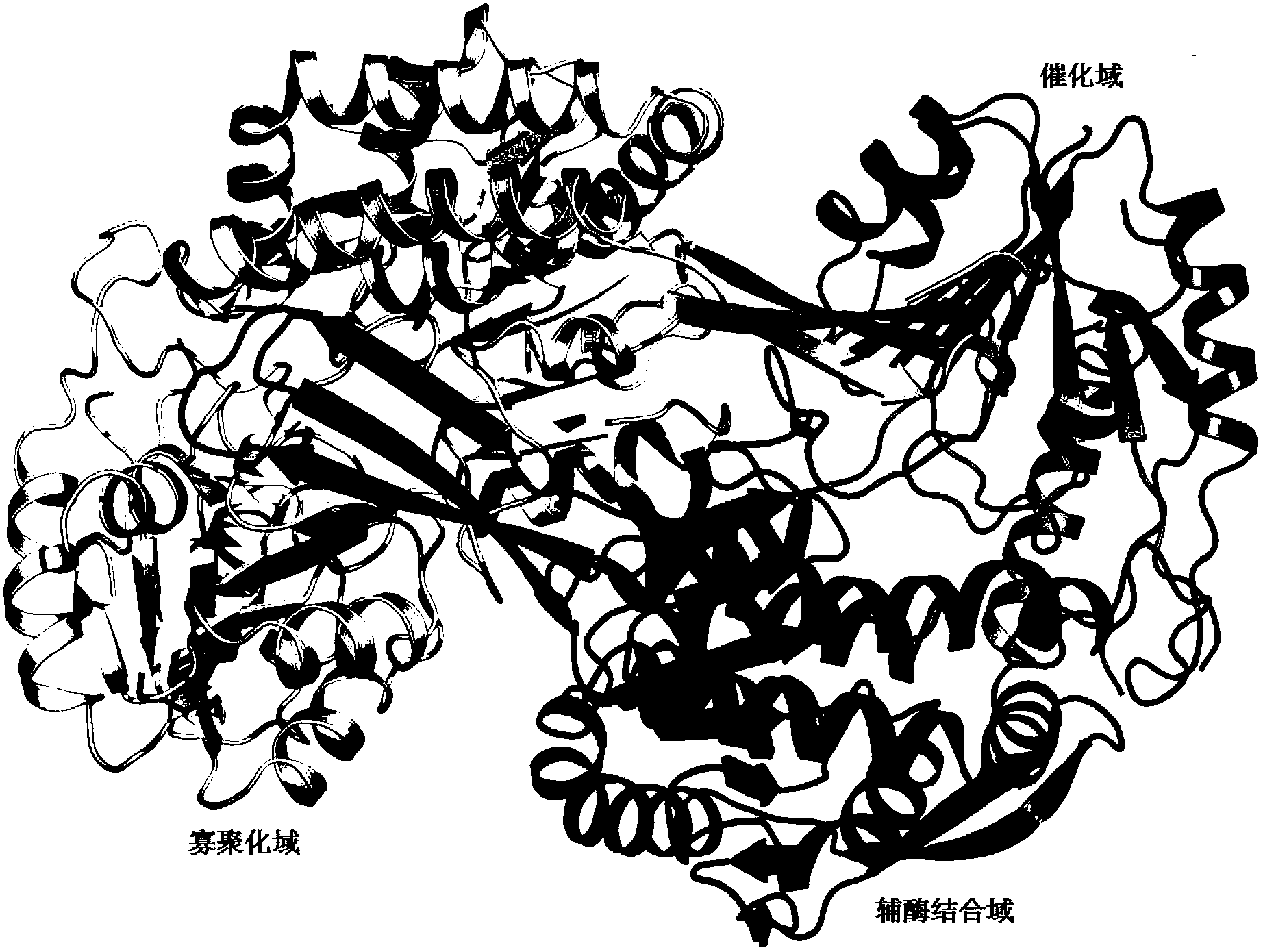
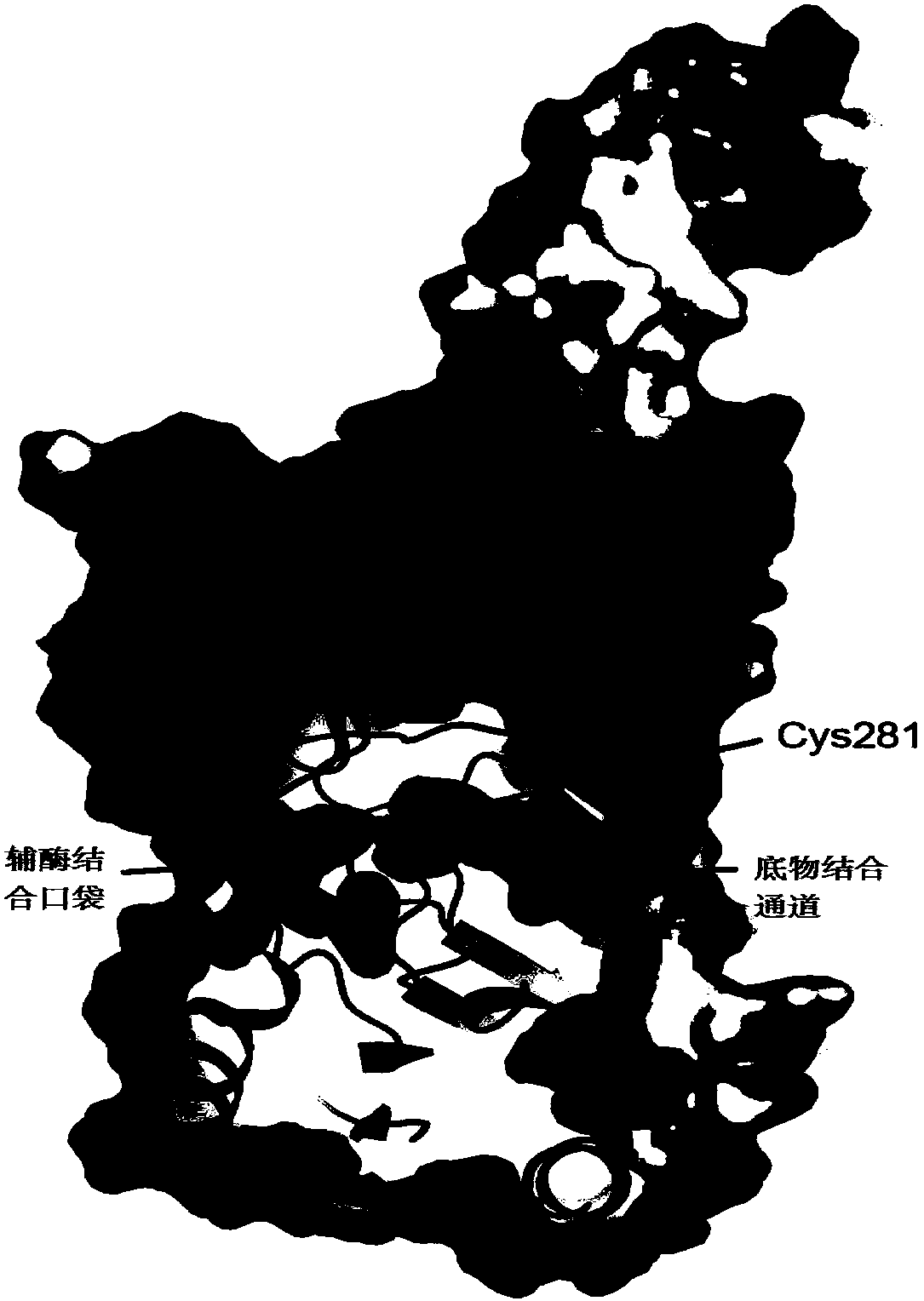
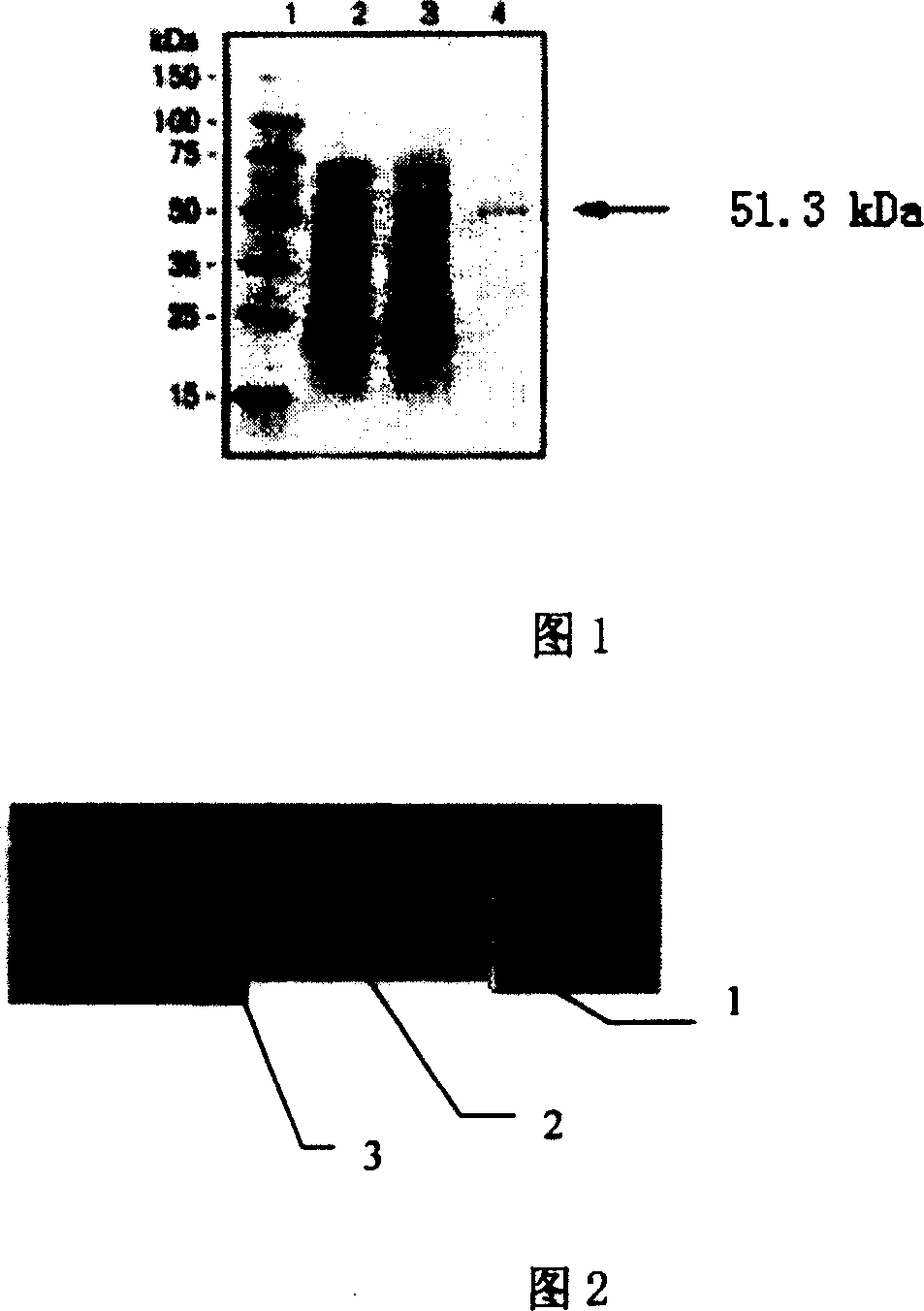
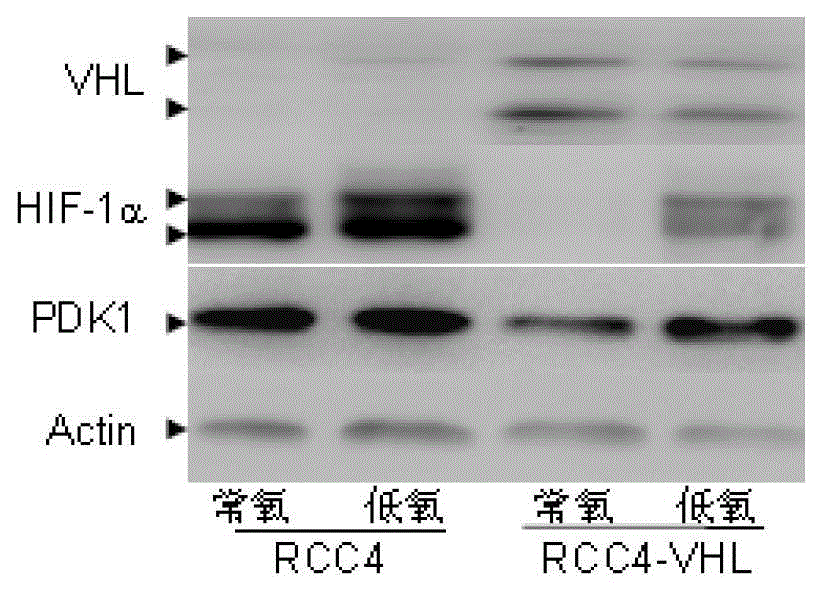
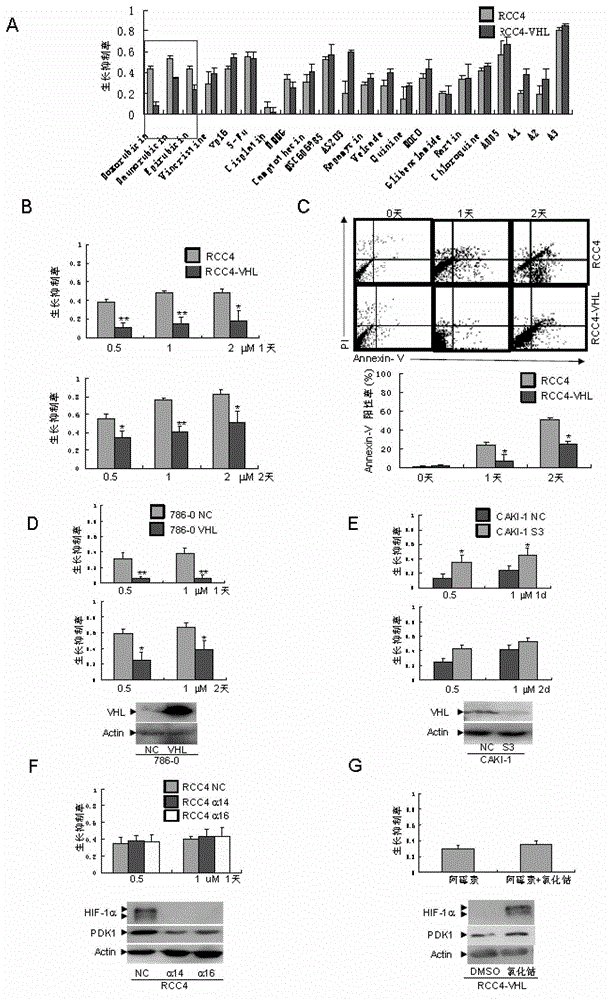
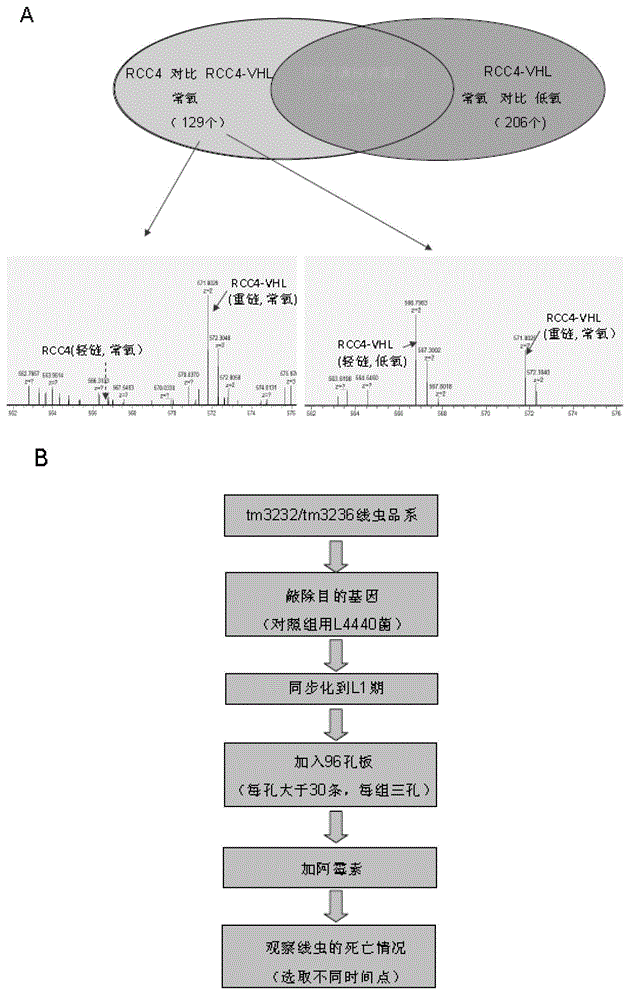
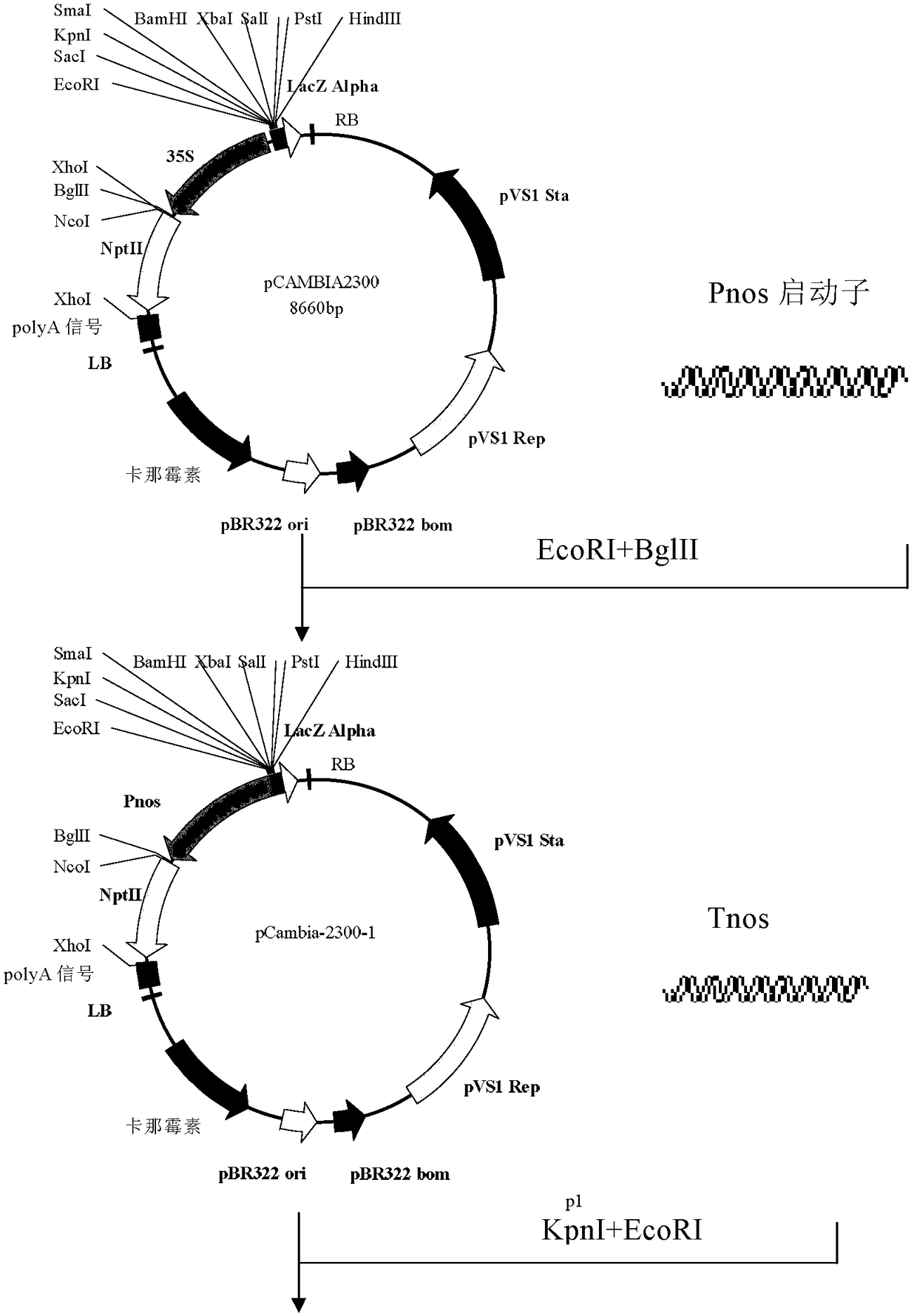
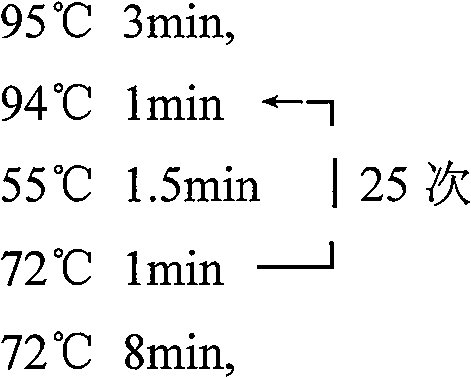Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
32 results about "Betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, a betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction betaine aldehyde + NAD⁺ + H₂O ⇌ betaine + NADH + 2 H⁺ The 3 substrates of this enzyme are betaine aldehyde, NAD⁺, and H₂O, whereas its 3 products are betaine, NADH, and H⁺. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor.
Compositions and methods for silencing aldehyde dehydrogenase
InactiveUS8999950B2Increasing the amount of acetaldehydeIntensifying the adverse effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcoholismsLipid formation
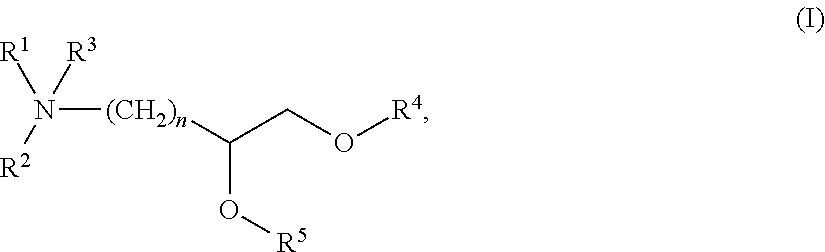
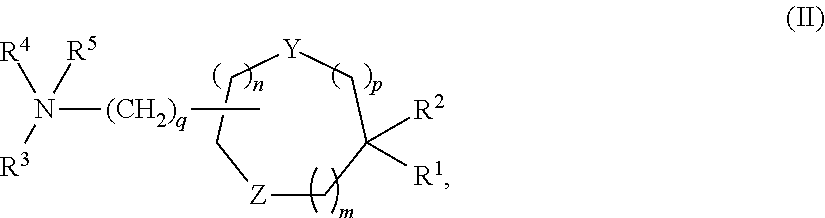
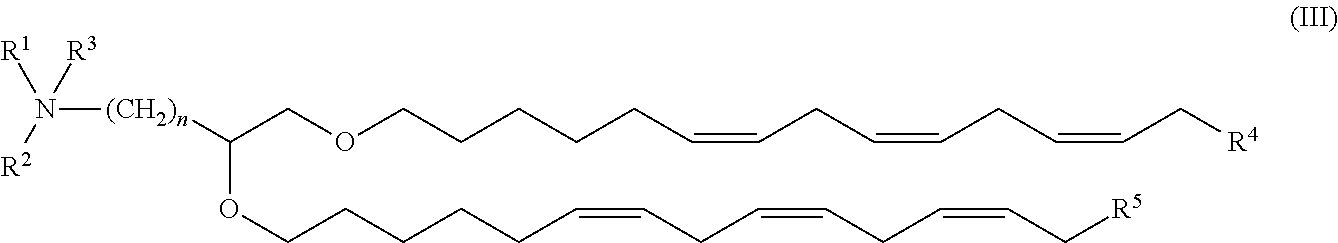
The present invention provides compositions comprising therapeutic nucleic acids such as interfering RNA (e.g., dsRNA such as siRNA) that target aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene expression, lipid particles comprising one or more (e.g., a cocktail) of the therapeutic nucleic acids, methods of making the lipid particles, and methods of delivering and / or administering the lipid particles (e.g., for treating alcoholism in humans).
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Method for creating fragrant rice by knocking out BADH2 (betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase) gene by utilizing CRISPR/Cas9 system
InactiveCN108913714ASuccessful knockoutRapid creationVectorsPlant peptidesBetaine2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline
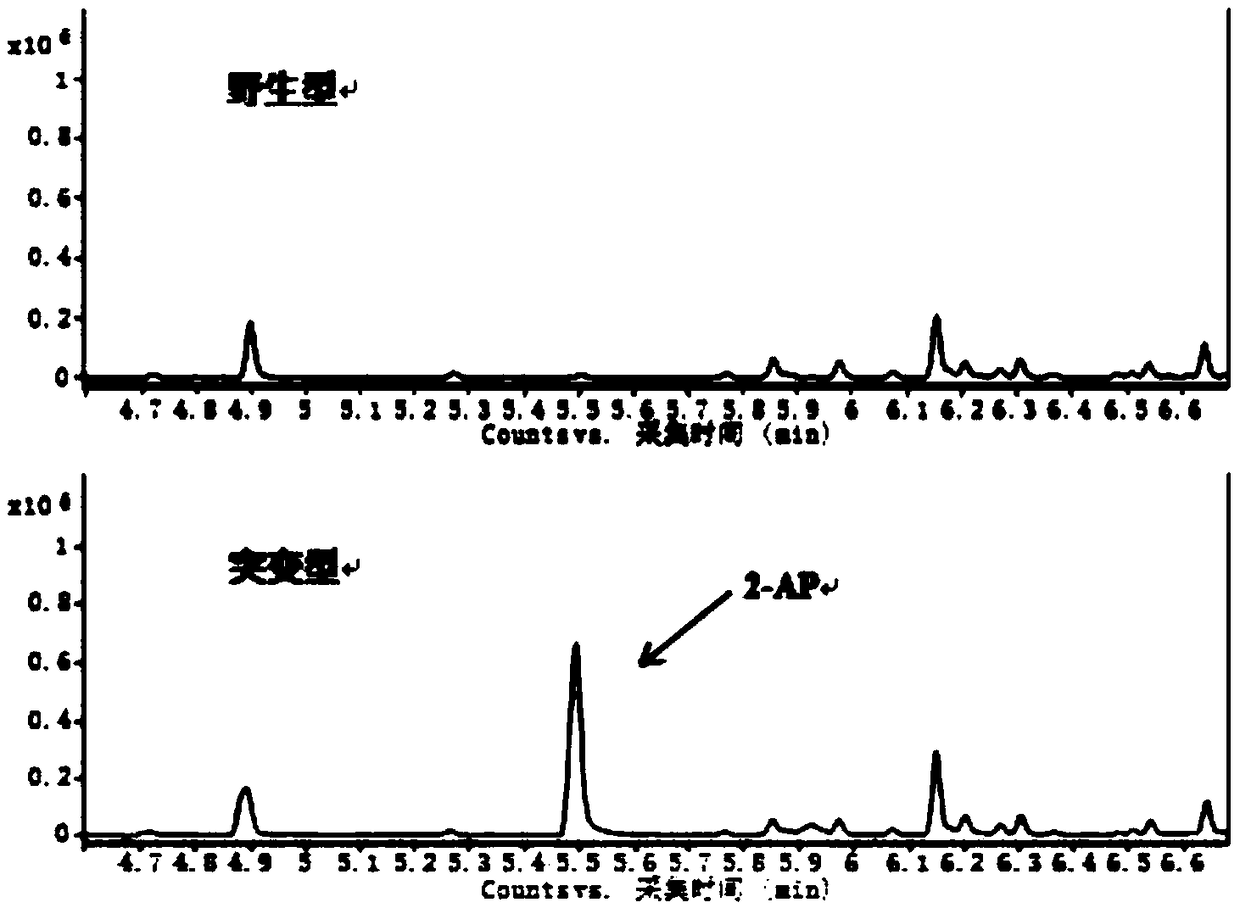
The invention discloses a method for creating fragrant rice by knocking out a BADH2 (betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase) gene by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas9 system, belongs to the technical field of rice breeding, and relates to a method for creating fragrant rice by applying the rice betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH2) gene. According to the method, in the fragrant rice, the function of the BADH2 (betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase) gene is lost, so that a chemical substance of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline(2-AP) is accumulated so as to generate the fragrance, and a sgRNA guide sequence adopted by the CRISPR / Cas9 system is any one of the sequences which are as as shown in the SEQ ID NO.2 or the SEQ ID NO.3 in the figure 1 in the specification. The method has the advantages that the BADH2 (betaine aldehydedehydrogenase) gene can be successfully knocked out, so that the fragrant rice can be quickly created; and the operation is simple, time and labor are saved, and the breeding life of the fragrant riceis shortened.
Owner:江西省超级水稻研究发展中心
Aroma gene in rice and functional marker thereof
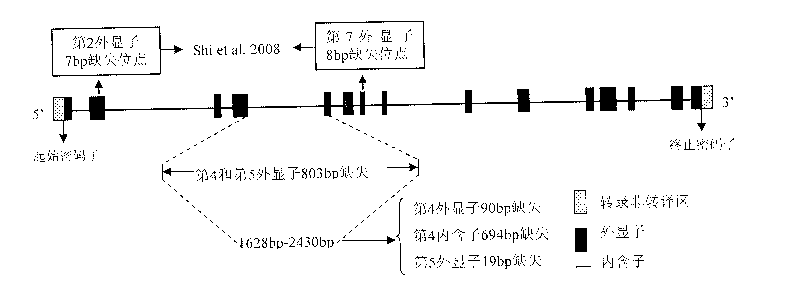
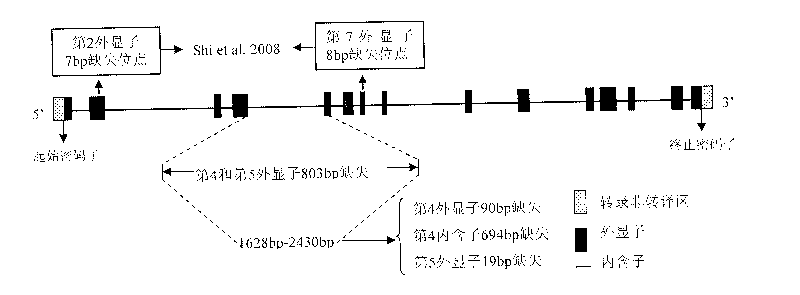
An aroma gene in rice and a functional marker thereof belong to the biotechnology field. The aroma gene is characterized in that the aroma gene is allelic to a coded betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase gene Badh2 on chromosome 8; compared with the normal Badh2, in the aroma gene, 803bp is deleted between the fourth exon and the fifth exon; the deleted base is positioned between downstream 1628bp and 2430bp of a transcription initiator codon of the gene; and the 803bp deleted base corresponds to the fourth exon 90bp, the fourth intron 694bp and the fifth exon 19bp. The functional marker FMbadh2-E4-5 of the aroma gene is designed according to the aroma gene in rice. By the method, the aroma gene can be transplanted to the non-aroma rice varieties with target, thus greatly promoting cultivation of new high-quality aromatic rice varieties.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 fragrance gene in paddy rice, primer of molecular marker and screening method
InactiveCN103525840AMeet needsOvercome biasMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
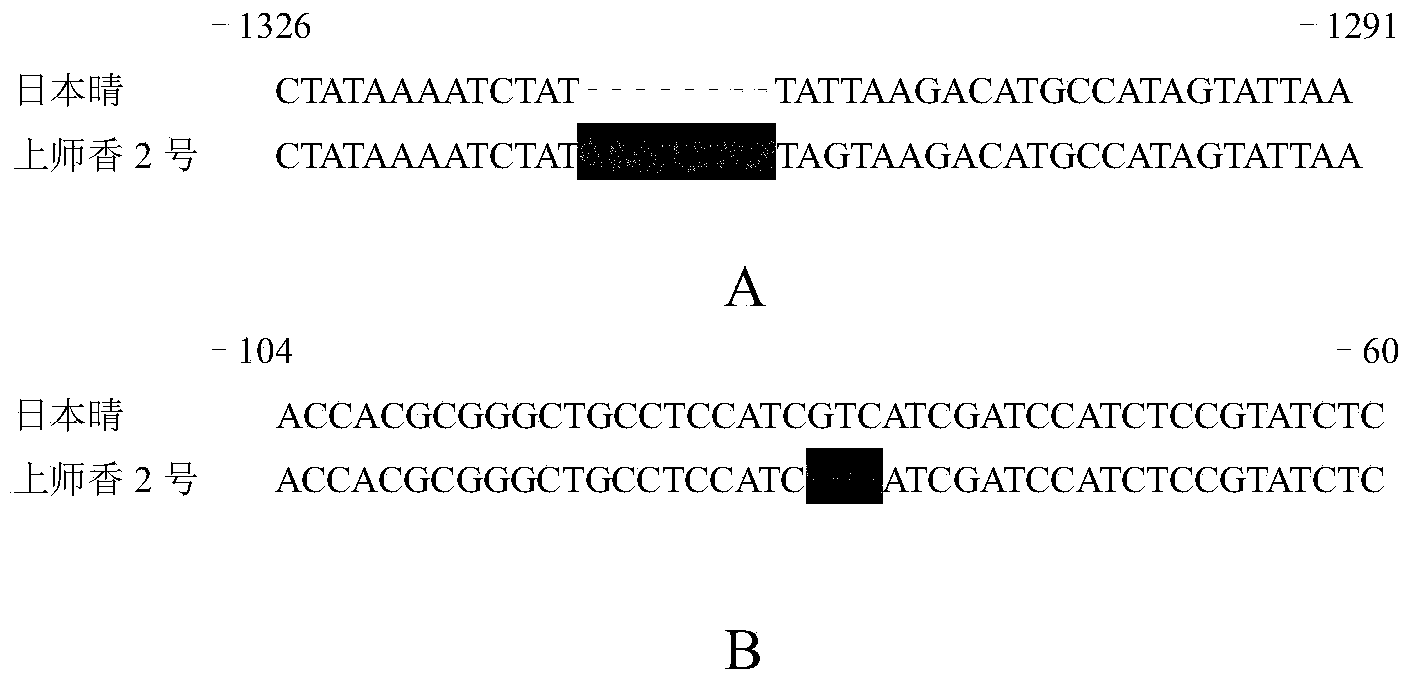
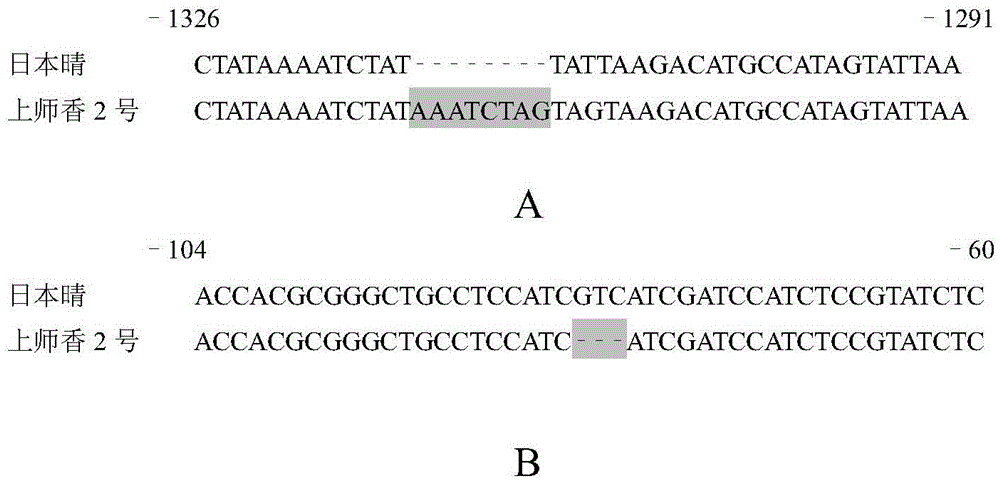
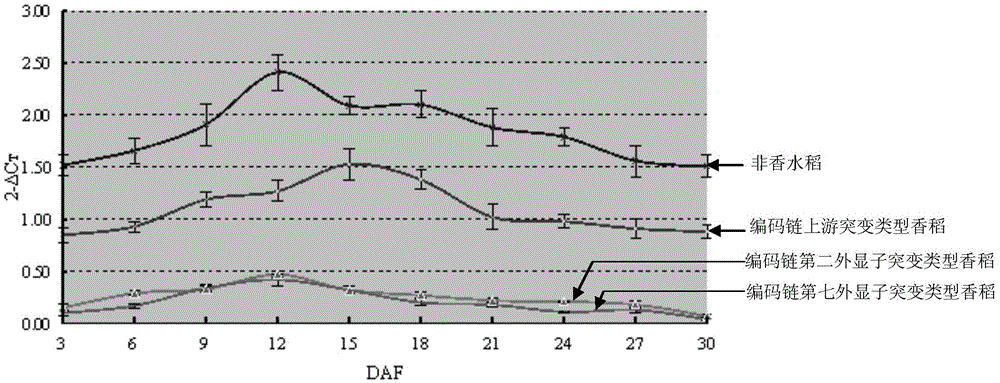
The invention discloses a new betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene enabling paddy rice to have the characteristic of light fragrance, and compared with non-fragrant paddy rice nipponbare, the mutation site is not located in coding strand but belongs to the mutation-type betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene at the upstream of the coding strand. Three nucleotides are lost at the -81 site at the upstream of the first nucleotide of the initiation codon of the coding strand, and eight nucleotides are inserted into the -1314 site. A new light-fragrance type paddy rice species is cultivated once homozygous progeny is obtained by transferring the gene into non-fragrant paddy rice via hybridization. The invention also discloses a method for screening the paddy rice possessing the light-fragrance type characteristic and a primer of a molecular marker. The new gene is provided for cultivation of the light-fragrance type paddy rice; also the betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 fragrance gene in paddy rice, the primer of molecular marker and the screening method help to perform assistant selection on plants containing light-fragrance gene, are beneficial to improve selection effect, and also help to identify whether the inbred progeny light-fragrance gene formed at the later stage of breeding is in a homozygous state, so that the breeding target can be realized rapidly and effectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Aldehyde dehydrogenase gene, vector, engineering bacteria and application thereof
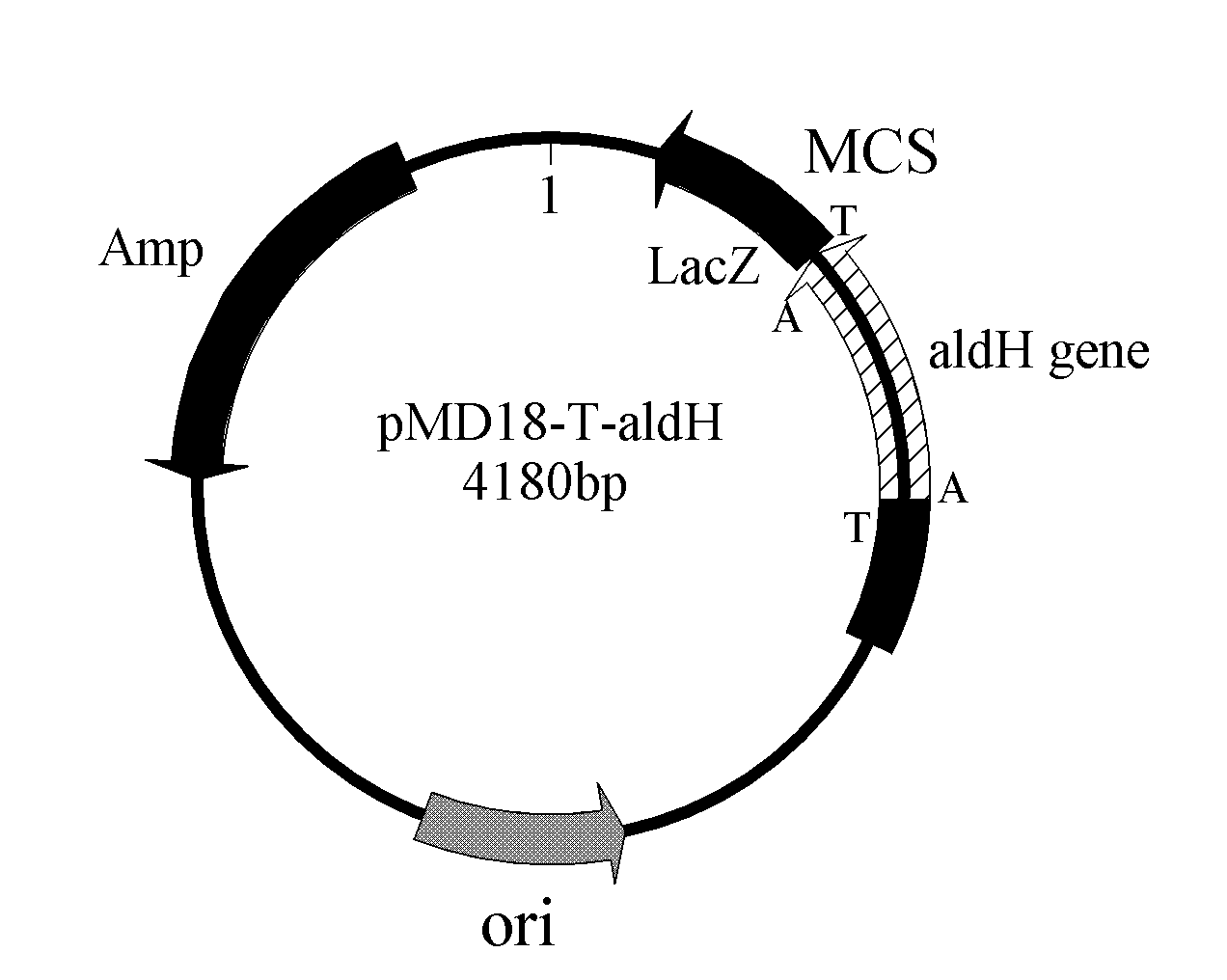
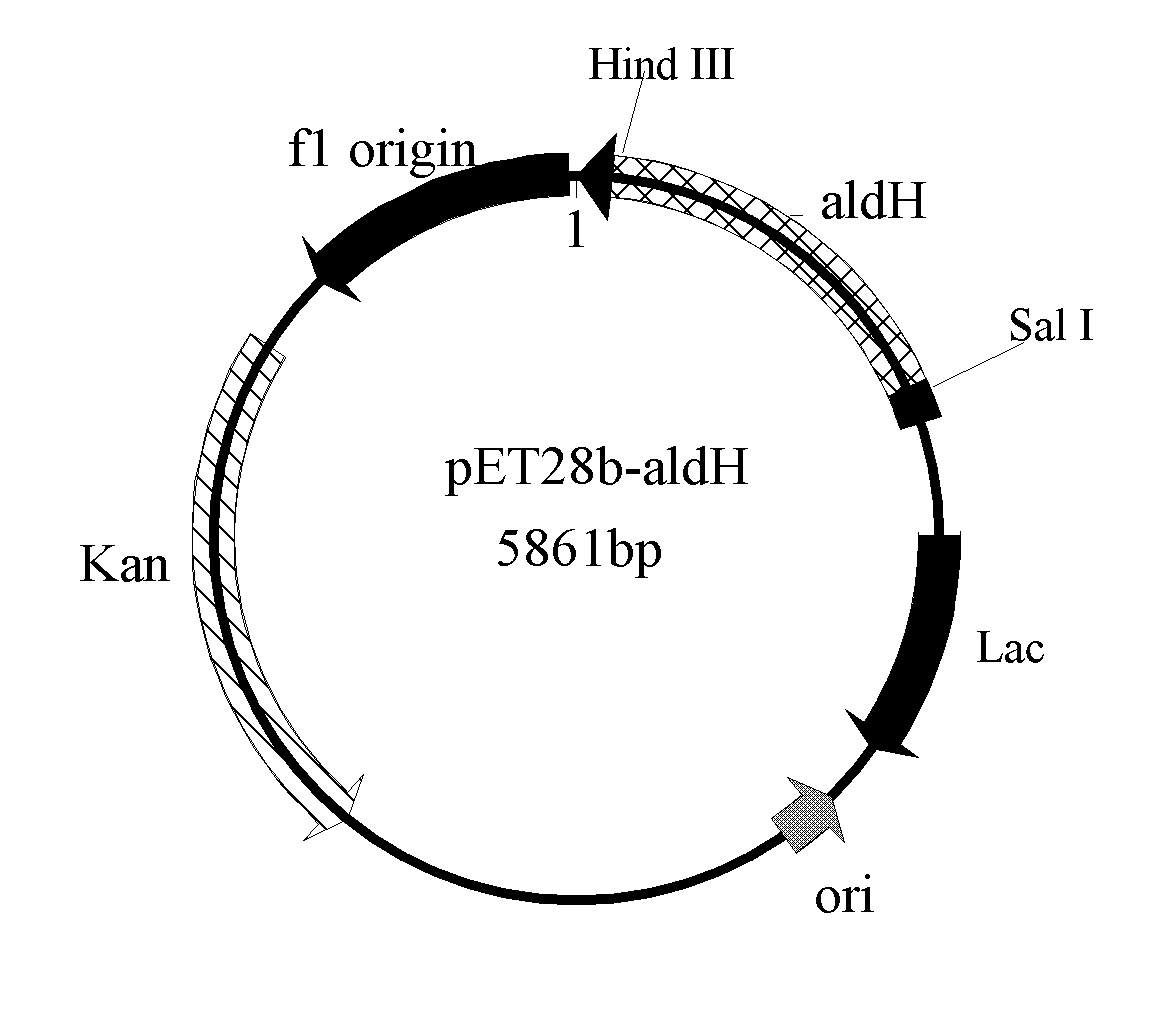
The invention provides an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae strains, a recombination expression vector, engineering bacteria thereof, and applications thereof in preparing the recombination aldehyde dehydrogenase. The invention provides an aldehyde dehydrogenase gene nucleotide sequence derived from the saccharomyces cerevisiae strains, connects and constructs the gene and the expression vector into an expression recombination plasmid pET28b-aldH containing the gene, and transforms the expression recombination plasmid pET28b-aldH to colibacillus BL21 to obtain the recombination colibacillus BL21 / pET28b-aldH containing the expression recombination plasmid pET28b-aldH; and the recombination colibacillus constructed by the invention can be applied to carry out biocatalysis and transformation, thus acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde or 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde are transformed into corresponding acetic acid, propionic acid or 3-hydroxypropionic acid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
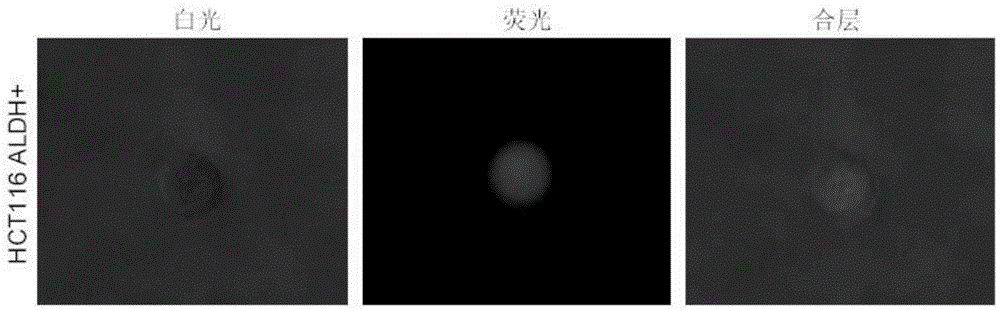
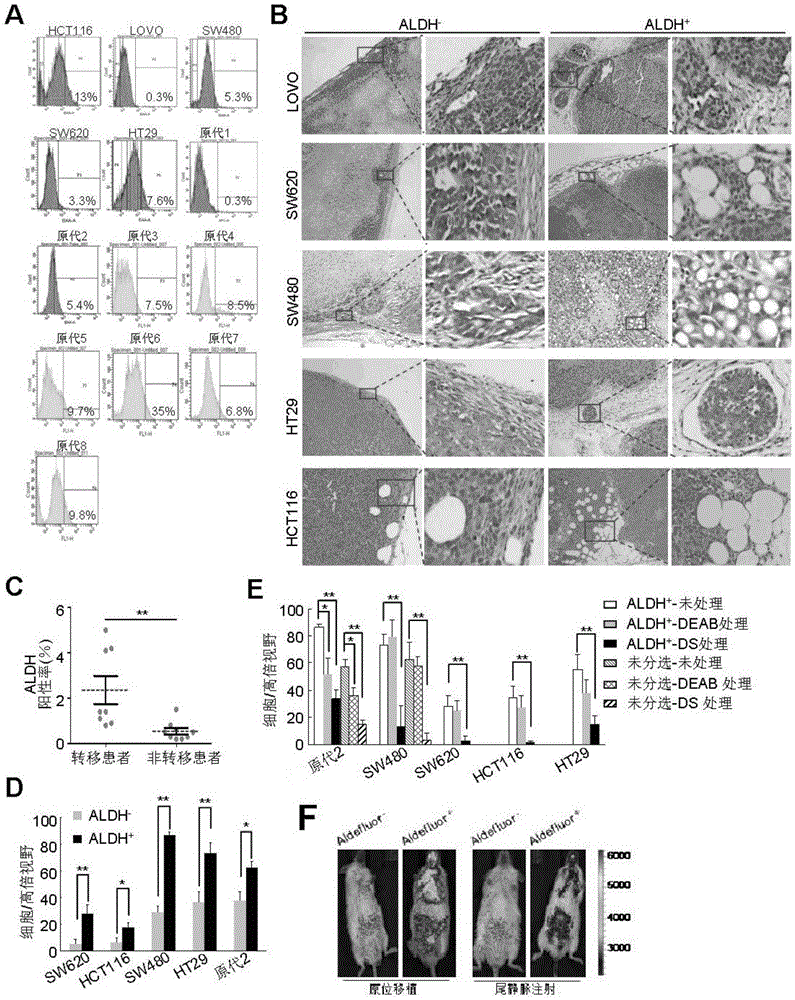
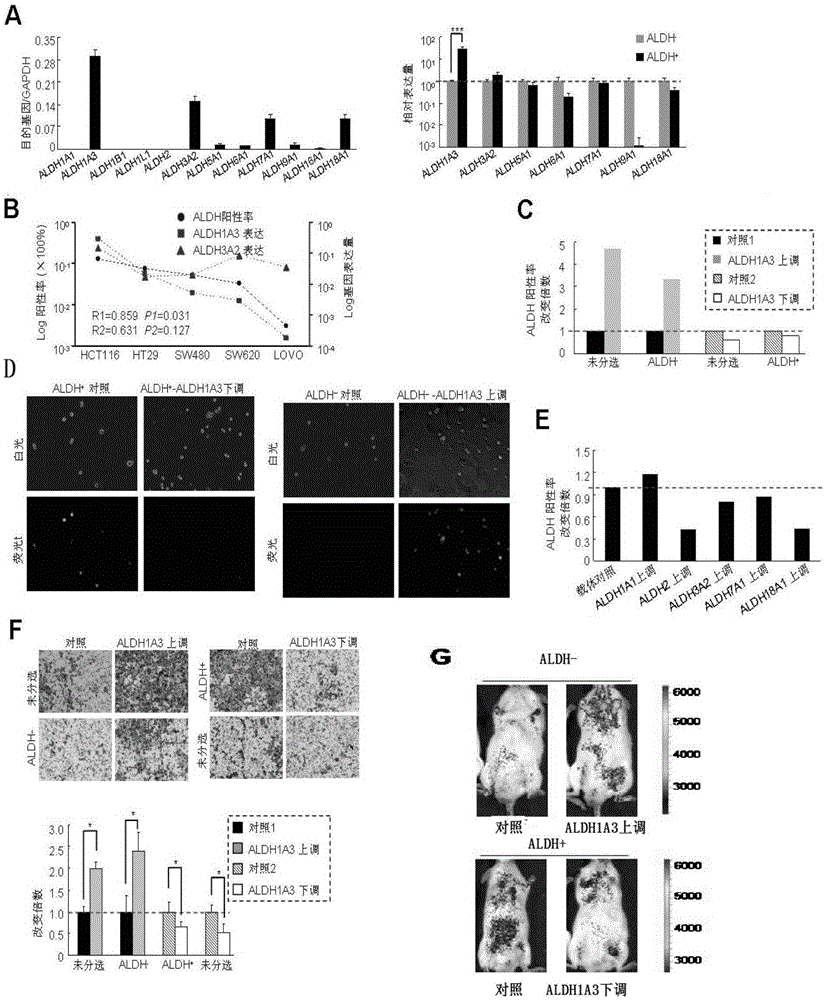
Application of aldehyde dehydrogenases 1A3 and encoding gene thereof as target for preventing and treating invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer
InactiveCN105734121AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFhit geneCancer research
The invention discloses applications of aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDH) 1A3 and an encoding gene thereof as a target for preventing and treating invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer and as an independent prognostic determination factor for the colorectal cancer, and also an application of an expression down-regulation agent, an activity inhibitor and an over-expression effect inhibitor of the ALDH 1A3 in preparation of medicines for reversing the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer. The applications have important significance of preventing and treating the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer and prognostic determination of the colorectal cancer.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
ALDH2 (aldehyde dehydrogenase 2) Gene polymorphism detection kit
InactiveCN108265113AFast startupFast catalytic speedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPoint of careFluorescence
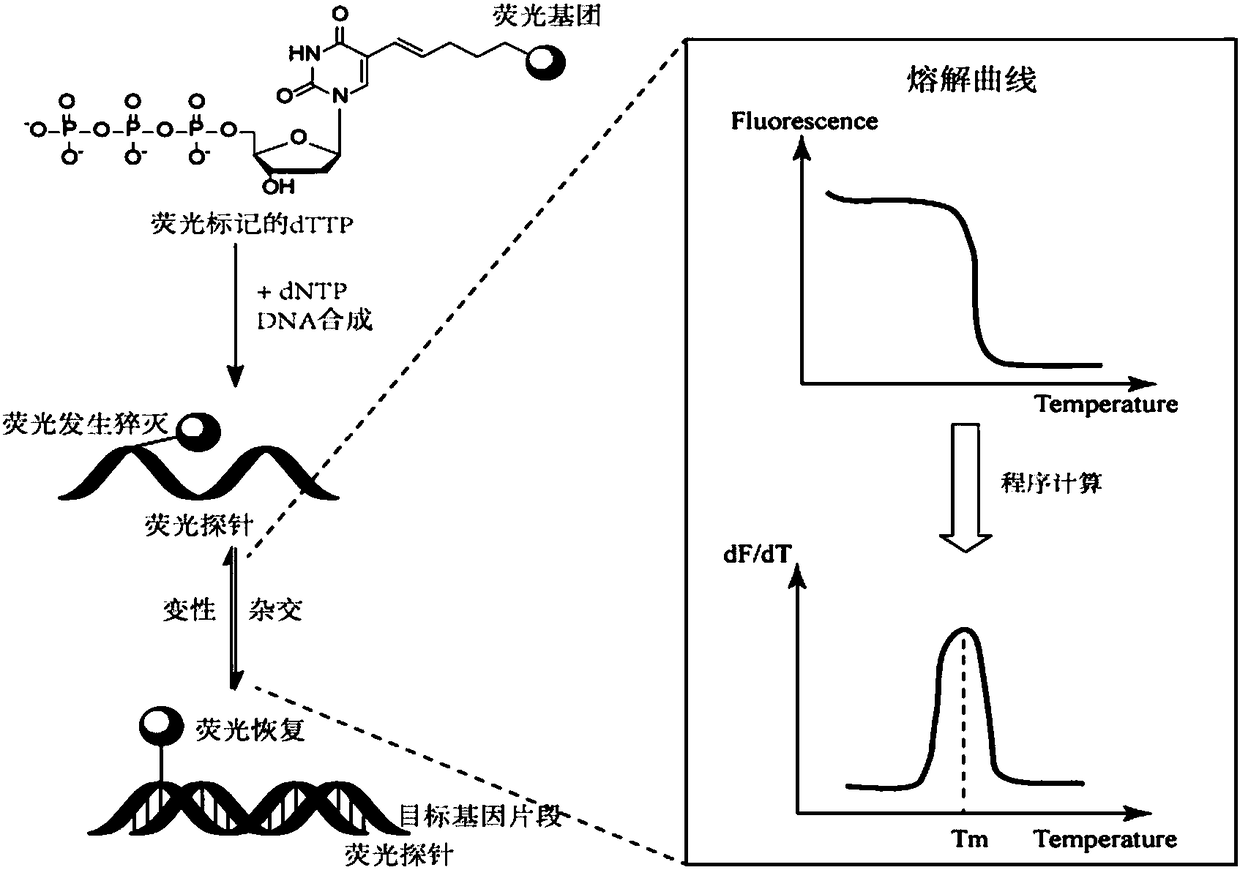
The invention discloses an ALDH2 (aldehyde dehydrogenase 2) Gene polymorphism detection kit, having the advantages that detection sensitivity is high, the lowest detection limit is 7.8 pg DNA; the kitis simple to operate and allows point-of-care test without professional knowledge; the detection time is short, down to 45 min; the detection specificity is high, and the detection accuracy is very high since a specific fluorescent probe is used; nucleic acid extraction is not required, low-melting-point agarose is added, and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is greatly avoided. When used with ParaDNA gene amplification detectors to carry out POCT (point-of-care test), the kit can be used to clinically provide guidance on the administration of nitroglycerin and the notification on the risk of alcohol drinking.
Owner:滨江华康(北京)生物科技有限公司
Synthetic pathways for biofuel synthesis
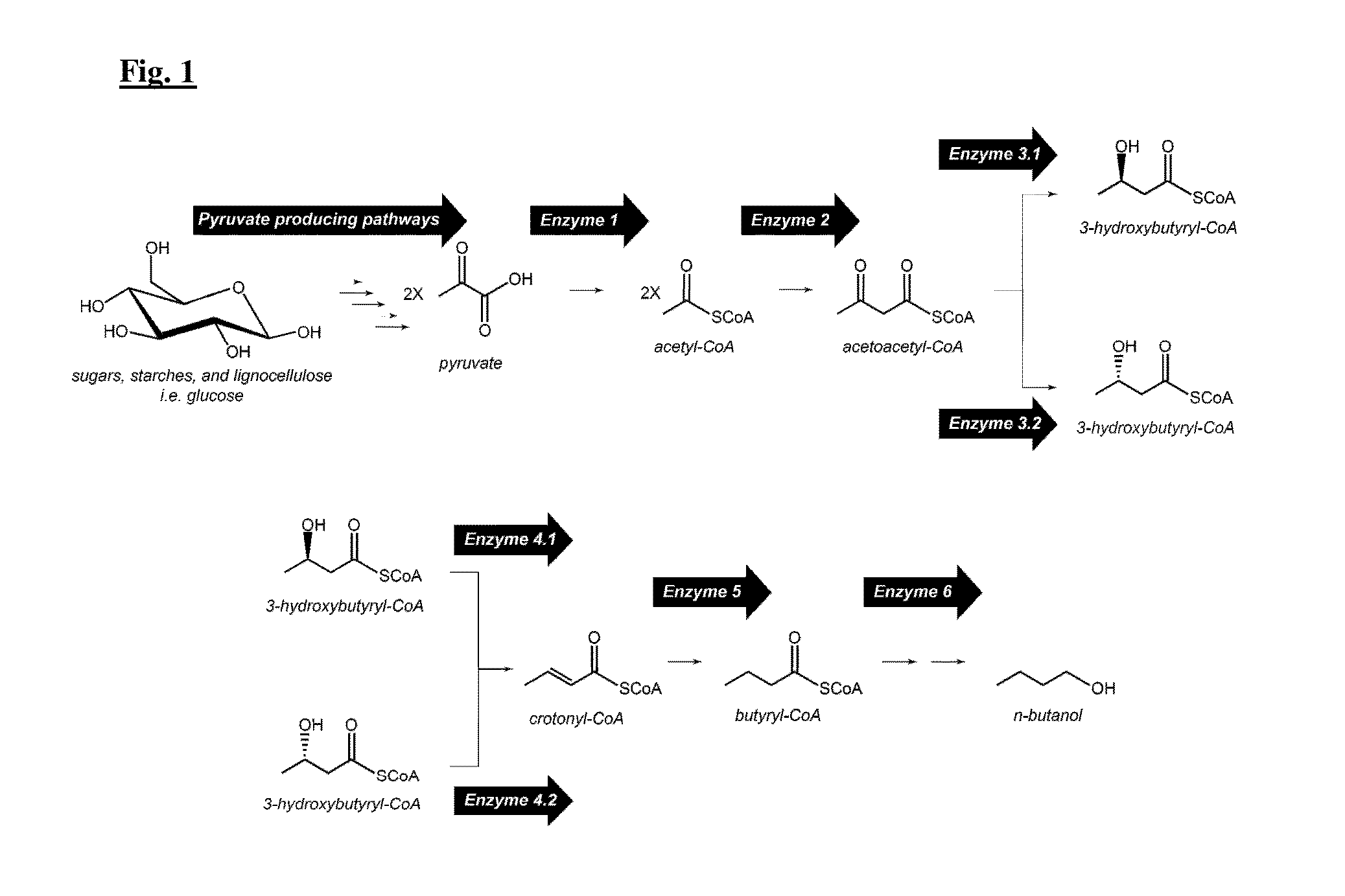
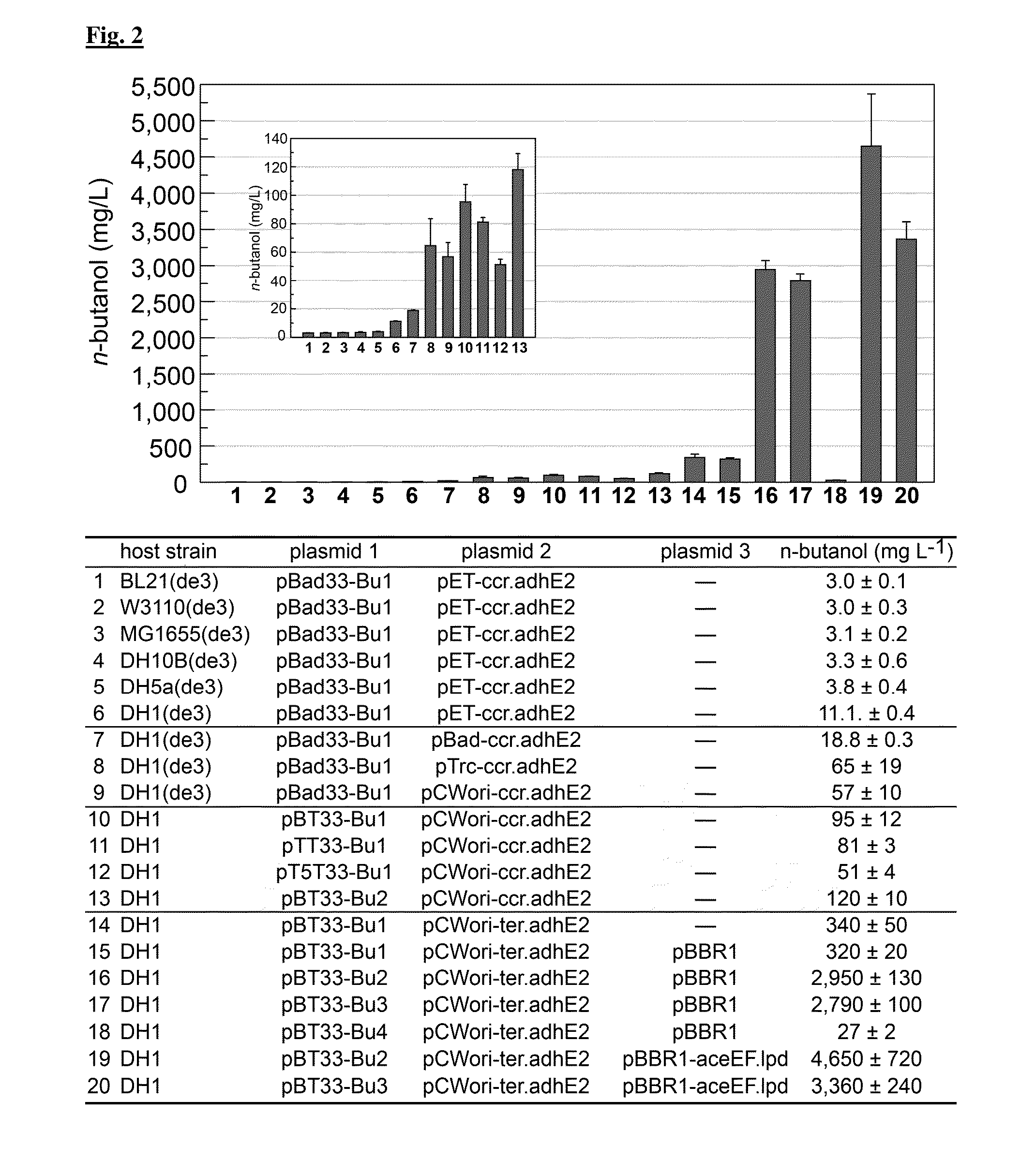
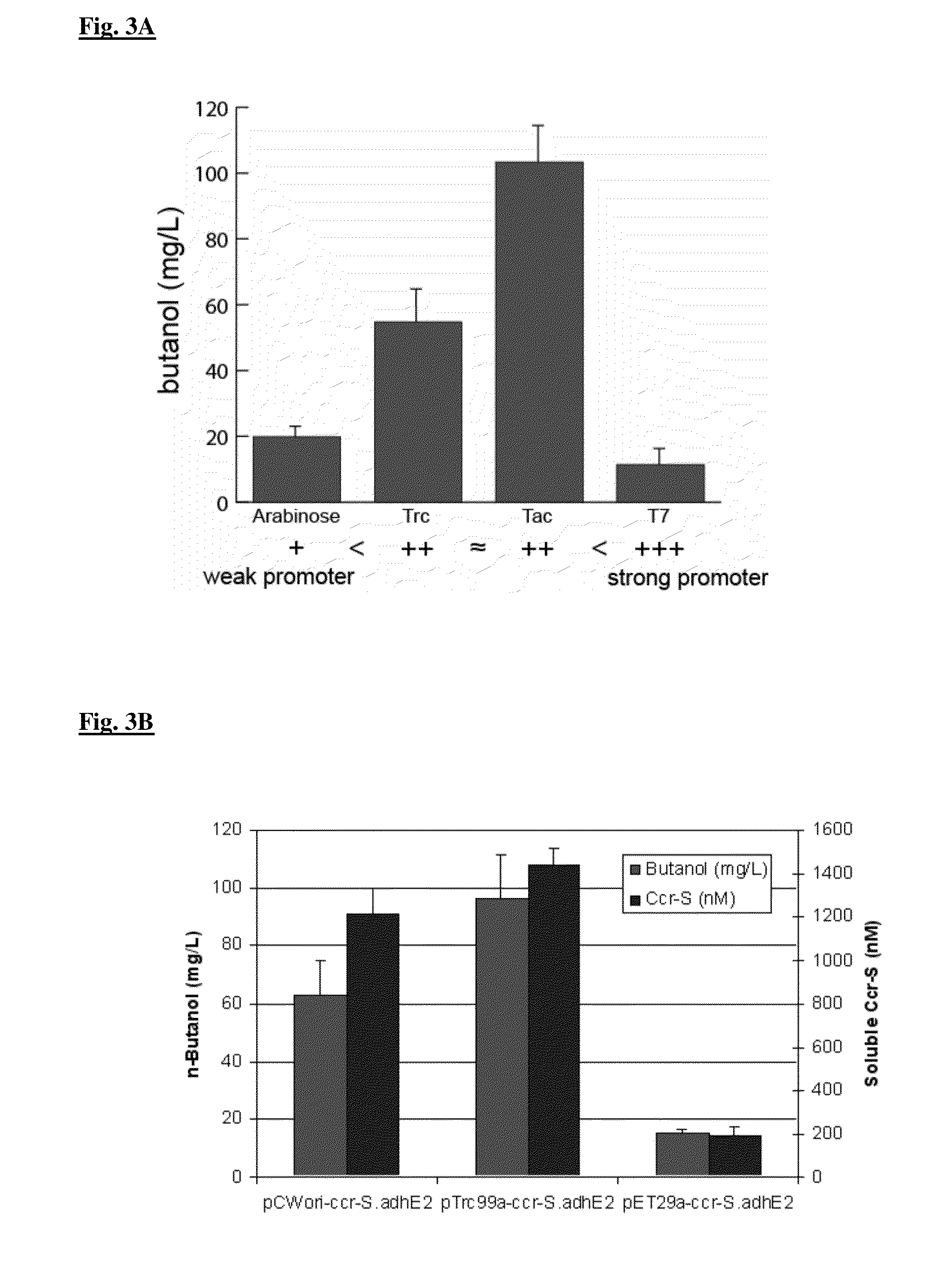
The present disclosure provides optimized recombinant cells for the production of n-butanol. Methods for the use of these cells are also provided. Specifically, the utility of acylating aldehyde dehydrogenases and pyruvate:flavodoxin / ferredoxin-oxidoreductase for the improvement of n-butanol yields from recombinant cells is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for silencing aldehyde dehydrogenase
InactiveUS20140248338A1Inhibit expressionIncreasing the amount of acetaldehydeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAlcoholismsLipid particle
The present invention provides compositions comprising therapeutic nucleic acids such as interfering RNA (e.g., dsRNA such as siRNA) that target aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene expression, lipid particles comprising one or more (e.g., a cocktail) of the therapeutic nucleic acids, methods of making the lipid particles, and methods of delivering and / or administering the lipid particles (e.g., for treating alcoholism in humans).
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Thermophilic long-chain alkyl aldehyde dehydrogenase and crystal structure thereof
ActiveCN102676464AThermally stableImprove thermal stabilityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesAlkaneEscherichia coli
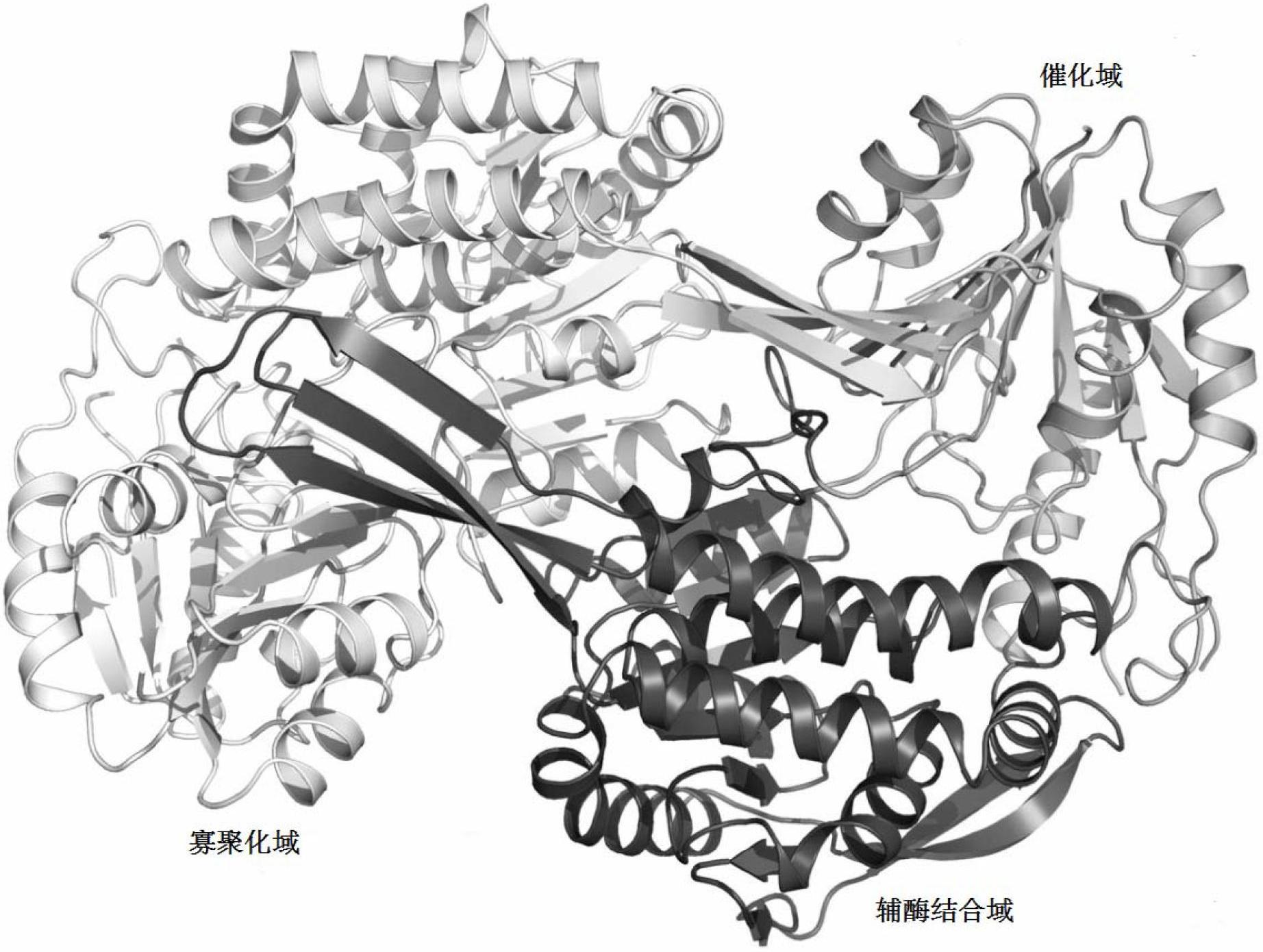
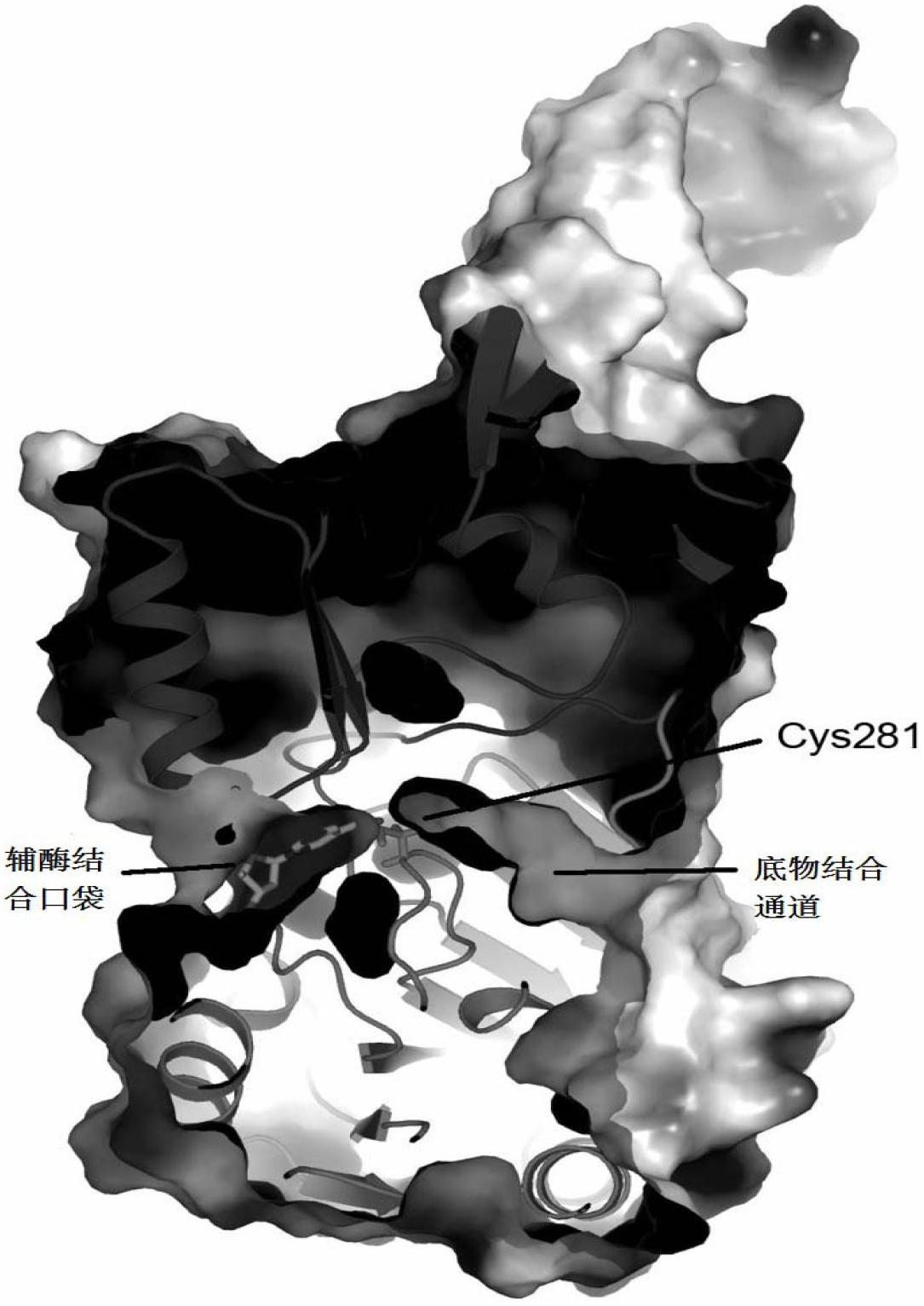
The invention relates to thermophilic long-chain alkyl aldehyde dehydrogenase in an n-alkane end degradation process of thermophilic denitrified bacillus and a crystal structure thereof. A molecular clone method is utilized, so that a target gene is cloned into escherichia coli (E. coli) so as to be heterologously expressed. A purified product of aldehyde dehydrogenase is obtained through a protein purification method. A crystal of the aldehyde dehydrogenase, which is suitable for diffraction, is obtained through a hanging droplet crystallization method. The crystal structure of the aldehyde dehydrogenase is analyzed by utilizing an X-ray diffraction method. The results show that the aldehyde dehydrogenase contains a characteristic ALDH fold which is formed by three structural domains. Site-specific mutagenesis is carried out on conserved residues on an enzyme activity part, and the influence of the conserved residues on enzyme activity is proved through wild type of the enzyme and enzyme activity experiment of the mutant thereof. The results can comprehensively reflect space conformation of the enzyme, and provide theoretical guidance for further researching relation between structures and functions of the aldehyde dehydrogenase, and improving the degradation activity of the enzyme.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 sequence designed according to preferred codon of pichia pastoris
InactiveCN101649323AHangover hasLiver protection hasMicroorganism based processesFermentationBetaine-aldehyde dehydrogenaseYeast
The invention relates to a gene sequence, in particular to a human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 sequence designed according to a preferred codon of pichia pastoris. The sequence is characterized in that aDNA molecule is designed according to the preference of the pichia pastoris, and a code of the molecule has the same nucleotide sequence as a protein coded by a human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene ID217 on an amino acid level. The human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene sequence designed according to the preferred codon of pichia pastoris is realized by the following steps: on the basis of a human ALDH2 gene (gene ID 217), UTR and signal peptide are deleted; enzyme cutting sites of an incision enzyme EcoR I and an incision enzyme Not I are added; a codon GCG for coding Ala is replaced by GCU according to the use method of the pichia pastoris codon, and codons CGC and CGG for coding Arg are replaced by AGA, AGG, CGU and CGA; and altogether 28 bases are modified to obtain a target sequence ALDH2. The gene sequence can express with high efficiency in the pichia pastoris, can be applied to preventing alcoholism and protecting livers and has the effects of preventing alcoholism and protecting livers.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for generating frangrance flavor through inactivation or reduction functional protein with betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH) activity
The invention relates to methods of increasing production of fragrance by an organism capable of expressing a functional protein having an amino acid sequence that is at least 30% identical to the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, comprising reducing or eliminating the activity of the functional protein in the organism. The invention also relates to methods of establishing whether an organism is capable of producing a fragrance, and to methods of producing organisms which produce fragrance.
Owner:GRAIN FOODS CRC
Compositions and methods for silencing aldehyde dehydrogenase
The present invention provides compositions comprising therapeutic nucleic acids such as interfering RNA (e.g., dsRNA such as siRNA) that target aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene expression, lipid particles comprising one or more (e.g., a cocktail) of the therapeutic nucleic acids, methods of making the lipid particles, and methods of delivering and / or administering the lipid particles (e.g., for treating alcoholism in humans).
Owner:PROTIVA BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Microorganism having novel acrylic acid synthesis pathway having enhanced activity of coa acylating aldehyde dehydrogenase and method of producing acrylic acid using the same
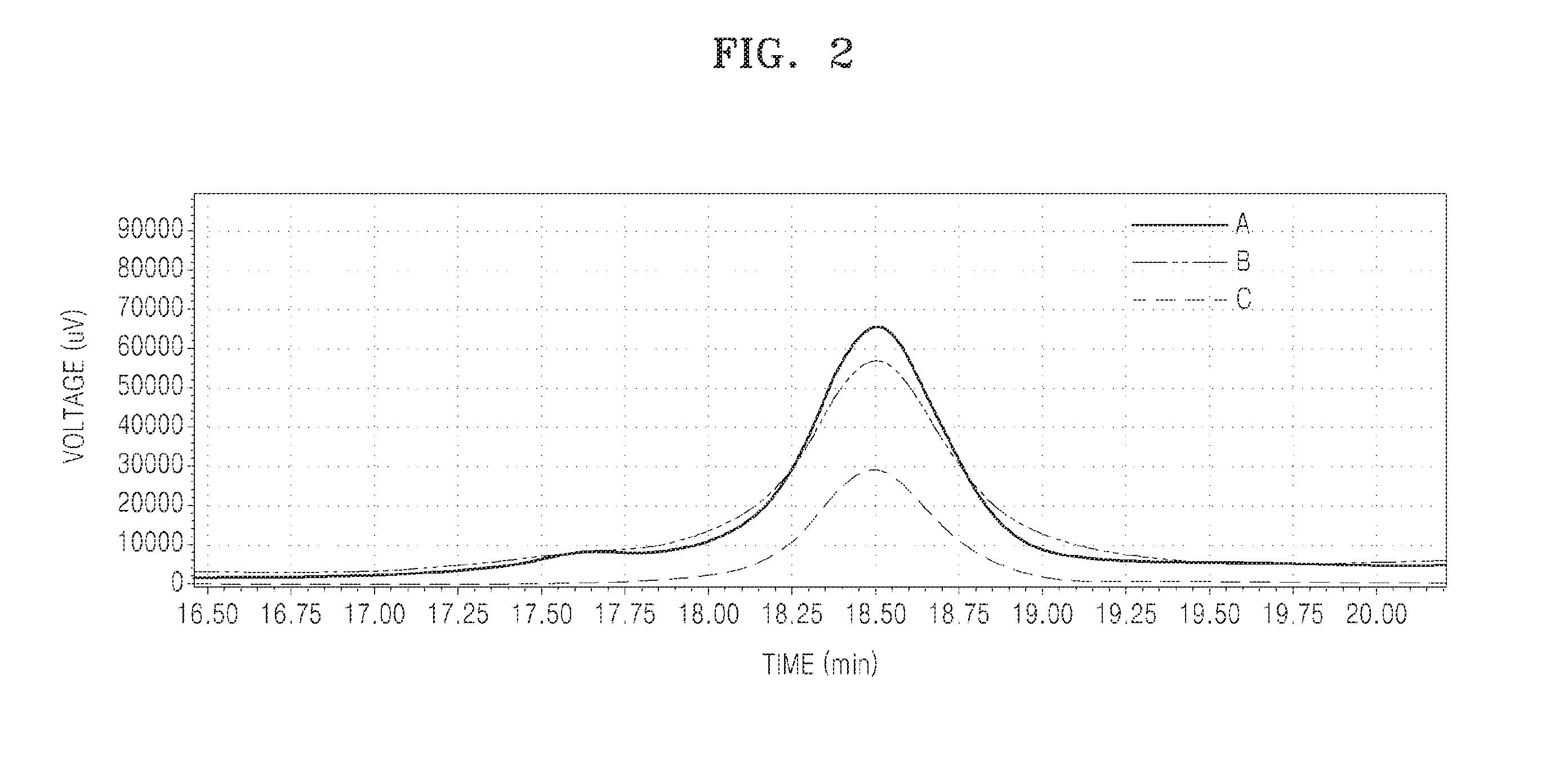
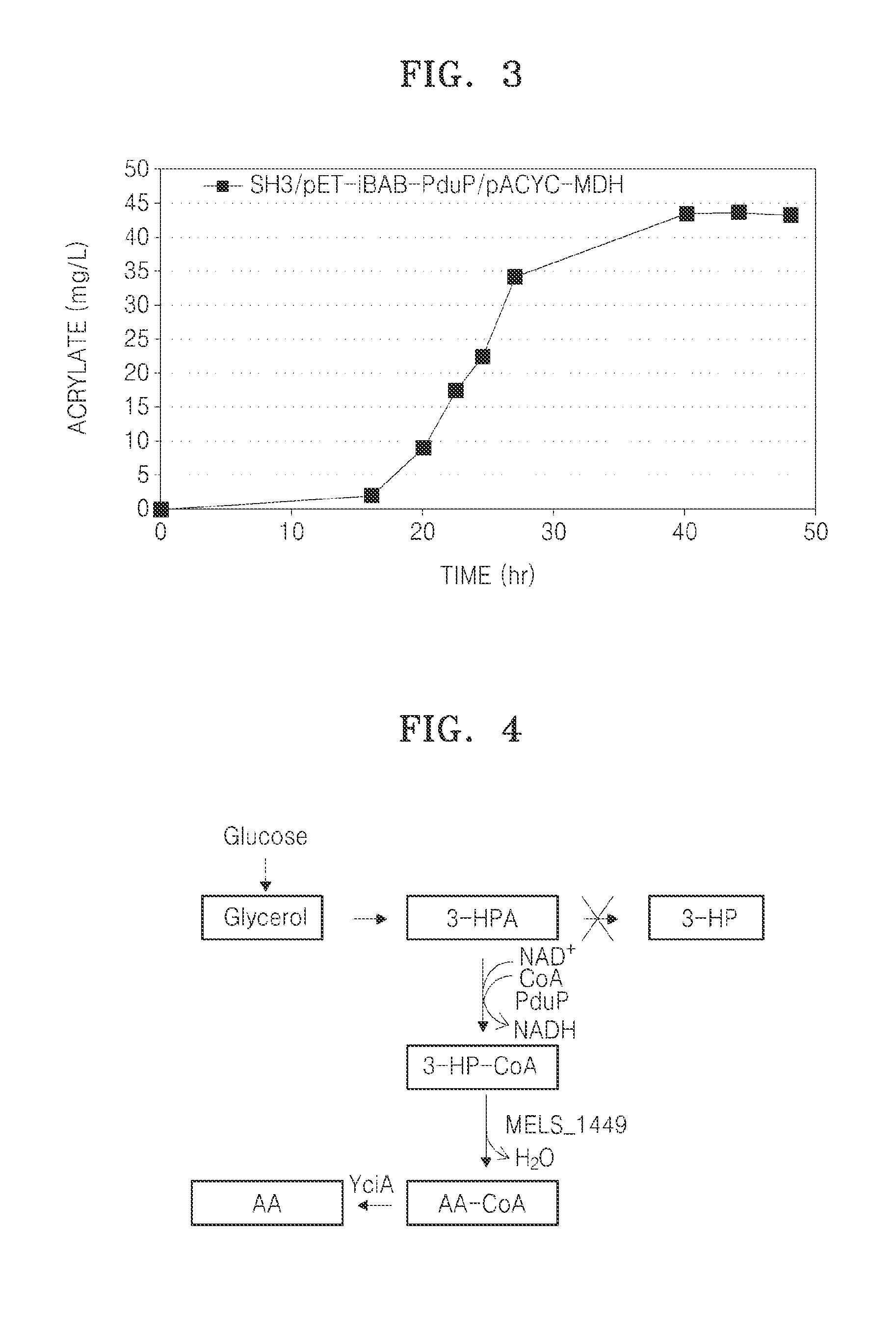
A microorganism capable of producing acrylic acid, comprising a genetic modification that increases activity of CoA acylating aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) catalyzing conversion of 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde (3-HPA) to 3-hydroxy propionyl-CoA (3-HP-CoA) and a genetic modification that increases activity of 3-HP-CoA dehydratase catalyzing conversion of 3-HP-CoA to acrylyl-CoA in the microorganism in comparison with a cell that is not genetically engineered; as well as a method of producing the microorganism, and a method of producing acrylic acid using the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Rice aroma gene of paddy rice and constructing process and use of expression vector including the rice aroma gene
InactiveCN1810974ABreed fastFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionStart codonBac clone
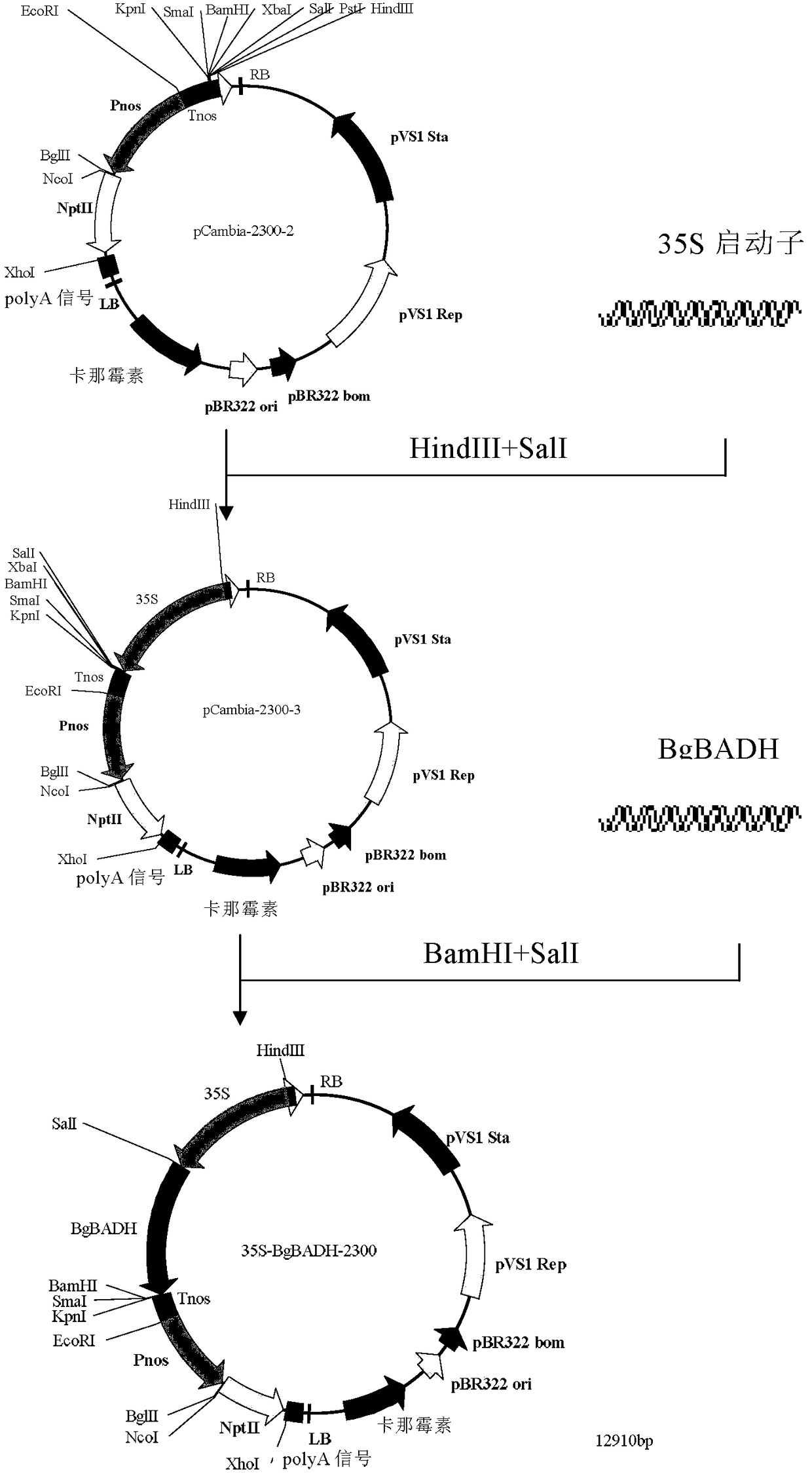
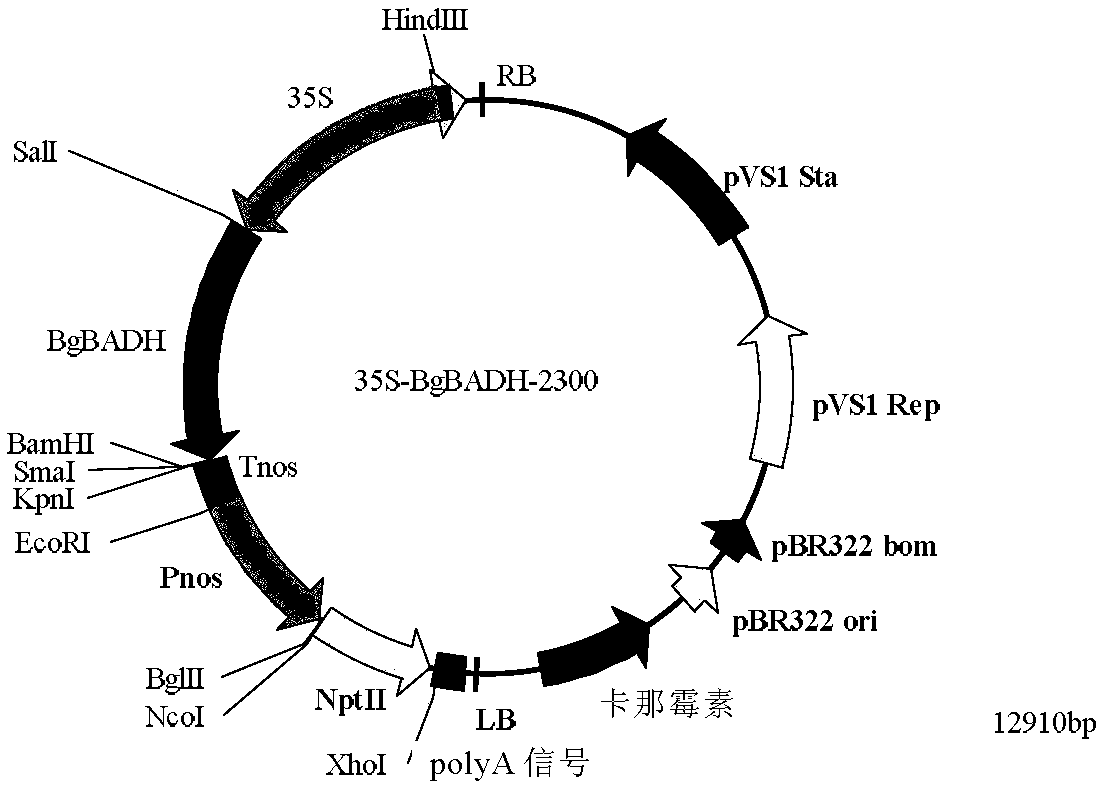
The present invention relates to rice breeding gene technology in biotechnology field, and is rice aroma gene of paddy rice and the constructing process and use of expression vector including the rice aroma gene. The rice aroma gene of paddy rice has nucleotide of total length of 9066 bases and including 1242 bases in start codon ATG upstream, 5859 bases in the gene region and 1965 bases in the termination codon TAA downstream, coding area comprising 15 exons, and gene sequence as changed betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase coding gene Badh with an 8 base deletion in the 7-th exon. Through cutting the integral rice aroma gene of paddy rice of the positive BAC clone with the limiting cleavage sites HindIII on two sides of the rice aroma gene of paddy rice Badh and cloning to expression vector pCAMBIA1302, the expression vector of rice aroma gene of paddy rice may be obtained and may be used in breeding excellent rice variety.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Ammonia ion diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and ammonia ion concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464346AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsEnzymatic ColorimetryPyrophosphate
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring ammonia (ions) by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of ammonia (ions), and belongs to the technical field of medical / food / environmental inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, glutamic acid, adenyl pyrophosphate, acetyl phosphate, glutamine synthetase, acetokinase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the concentration of ammonia (ions).
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
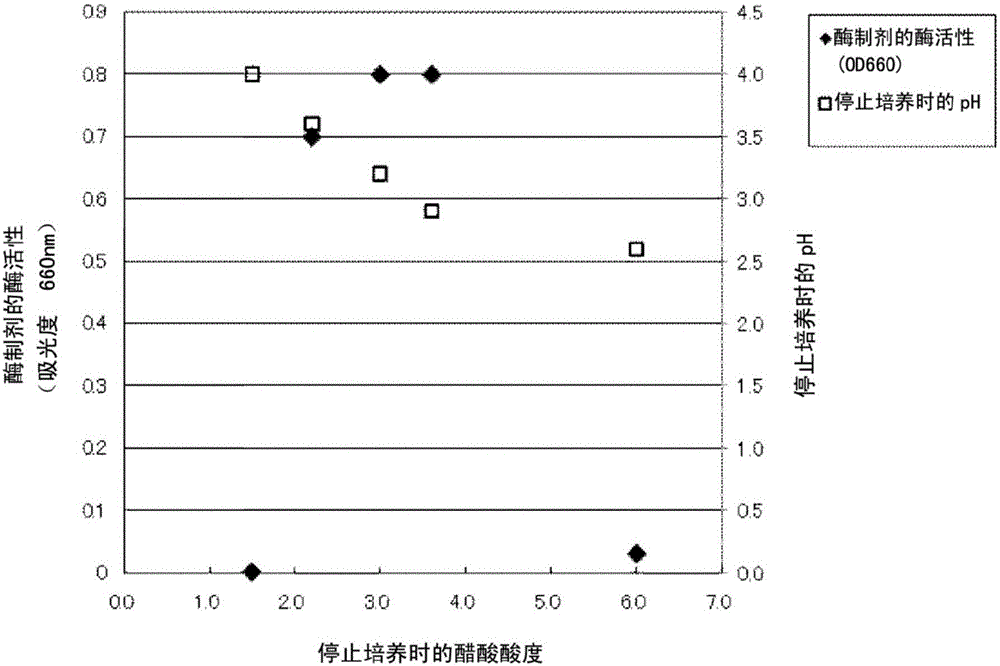
Enzyme agent
ActiveCN106133134AEfficient removalEasy to useEnzyme stabilisationOxidoreductasesPotassium ferricyanideCell membrane
Provided is an enzyme agent with which C1-10 aldehydes can be effectively removed. This enzyme agent contains, as an effective ingredient, a composite of an aldehyde dehydrogenase produced by an acetobactor belonging to the genus Gluconacetobacter with cell membranes with which the aldehyde dehydrogenase has combined. The enzyme agent has a pH of 4-7, and the aldehyde dehydrogenase activity thereof per 0.006 mg of the proteins derived from the acetobactor is 0.05-3 in terms of the absorbance (660 nm) of an aqueous solution (3.9 mL) of ferric ferrocyanide which is yielded from potassium ferricyanide as acetoaldehyde is oxidized with the enzyme agent.
Owner:Q P CORP
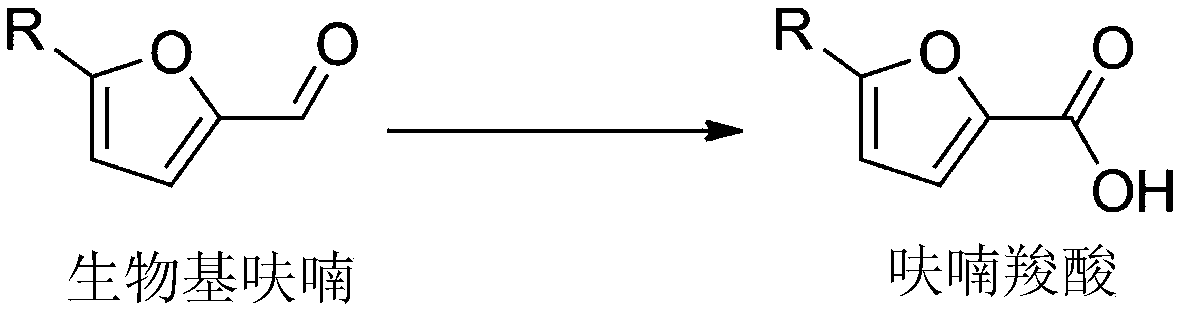
Aldehyde dehydrogenases, gene thereof, construction of recombinant strain and application of recombinant strain in synthesis of furancarboxylic acid
ActiveCN109536466AEfficient selective oxidation synthesisEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFuranGenetic engineering
The present invention relates to the fields of genetic engineering technology and biocatalysis, and discloses aldehyde dehydrogenases, a gene thereof, construction of a recombinant strain and an application of the recombinant strain in synthesis of furancarboxylic acid. A gene mining technology is used to screen five aldehyde dehydrogenases from comamonas testosteroni SC1588, and amino acid sequences of the aldehyde dehydrogenases are shown in SEQ ID. 1, SEQ ID. 2, SEQ ID. 3, SEQ ID. 4 or SEQ ID. 5. The five aldehyde dehydrogenases can all efficiently catalyze a bio-based furan selective oxidation to synthetize the corresponding furancarboxylic acid. The yield of a target product is up to about 90%, the highest yield can even reach 100%, and a space-time yield is up to 1.9 g.L<-1>.h<-1>. The production process is simple, production conditions are mild and production efficiency is high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
ALDH1A (aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A), agonist and catalysate of ALDH1A, application of inhibitor
The invention discloses ALDH1A (aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A), an agonist and a catalysate of the ALDH1A, and an application of an inhibitor. Particularly, the invention discloses the application of theALDH1A or the agonist or the catalysate, the ALDH1A is used to prepare a pharmaceutical composition or preparation, and the pharmaceutical composition or preparation is used to treat and / or prevent infantile autism.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Primer and method for detecting molecular marker of rice aroma allele
InactiveCN103484556BAchieve breeding goalsSimplify pre-operation stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAromatic riceEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a primer and a detection method which can detect a screened molecular marker aiming at aromatic rice with multiple types of aroma genes and amplify a molecular marker of multiple types of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase genes 2 (Badh2 / badh2) which are directly related to rice aroma formation. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting total DNAs of the rice as a template, and adding the primer for performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification; (2) performing restriction endonuclease Alu I digestion on a PCR product; (3) performing gel electrophoresis detection on an enzyme-digested product. The situation that only a mutation type of the aroma allele can be identified in the process of detecting a molecular marker of aroma genes in the past is broken, plants containing different types of the aroma genes can be selected in an assisted mode, a mutation type of the aroma allele of a parent aromatic rice variety is not required to determined before the operation of performing novel aromatic rice variety breeding on the molecular marker in an assisted mode, and pre-operation steps of molecular marker-assisted breeding are simplified, so that a breeding objective for breeding a novel aromatic rice variety is rapidly and effectively realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Use of aldehyde dehydrogenase as biomarker for beta-cell dysfunction and loss
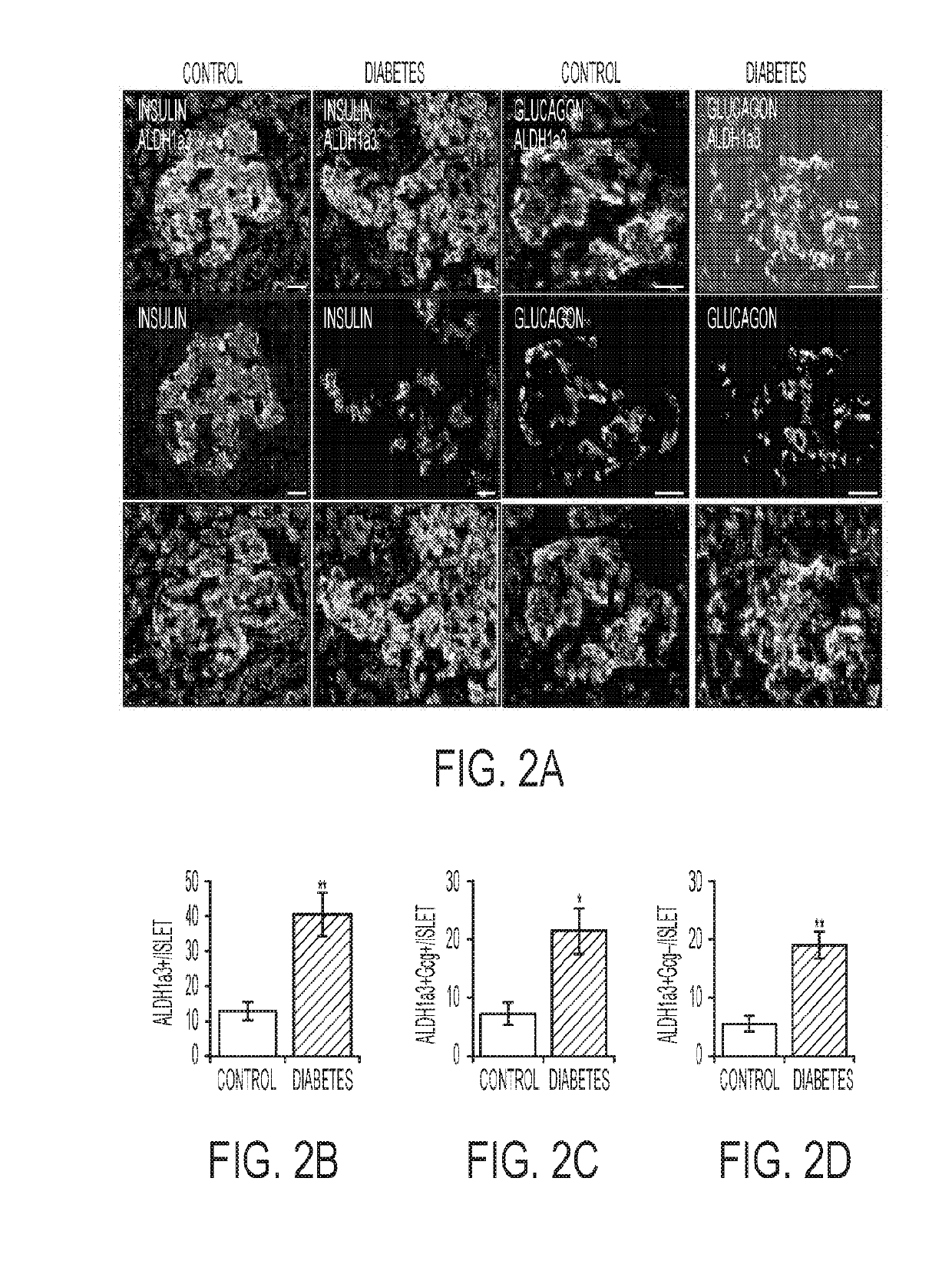
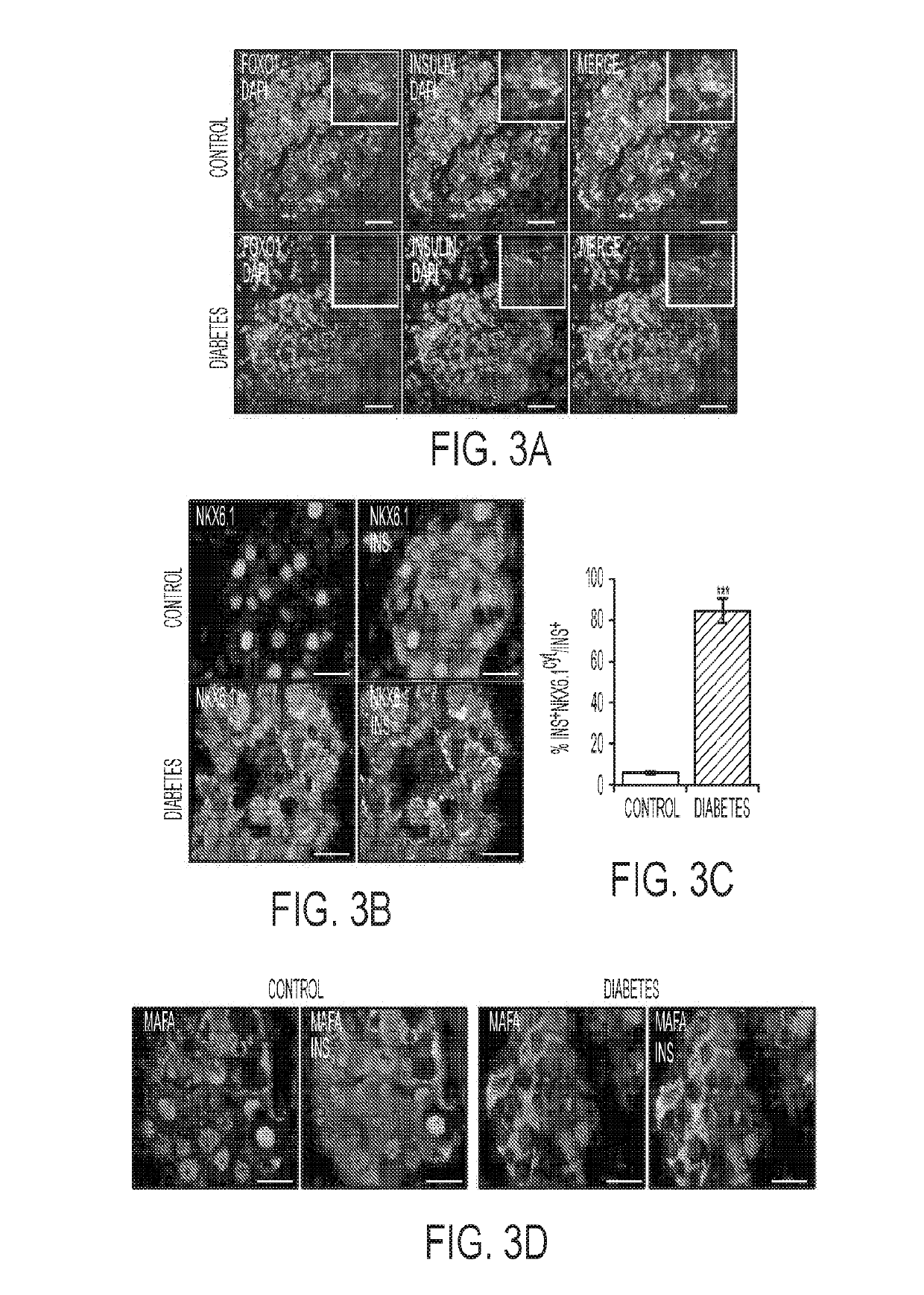
ActiveUS20190265229A1Promote mitochondrial dysfunction-theFunction increaseGenetically modified cellsPancreatic cellsLow insulinBiomarker (petroleum)
Methods are provided for obtaining a sample of β cells from an isolated donor pancreas or isolated pancreatic islets and analyzing the sample using flow cytometry to determine the percentage of β cells in the sample that express detectable levels of ALDH1 A3. If the percentage of ALDH1 A3-expressing β cells in the sample is about 3% or lower, then it is possible to determine that the pancreas or islets are healthy enough for implantation into a subject, and implanting the pancreas or islets. If the percentage of ALDH1 A3-expressing cells is above about 5%, then it is determined that the pancreas or islets are not suitable for implantation into the subject and discarding the pancreas or islets. Isolated non-insulin-producing or low-insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells are also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Rice aroma gene of paddy rice and constructing process and use of expression vector including the rice aroma gene
The present invention relates to rice breeding gene technology in biotechnology field, and is rice aroma gene of paddy rice and the constructing process and use of expression vector including the rice aroma gene. The rice aroma gene of paddy rice has nucleotide of total length of 9066 bases and including 1242 bases in start codon ATG upstream, 5859 bases in the gene region and 1965 bases in the termination codon TAA downstream, coding area comprising 15 exons, and gene sequence as changed betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase coding gene Badh with an 8 base deletion in the 7-th exon. Through cutting the integral rice aroma gene of paddy rice of the positive BAC clone with the limiting cleavage sites HindIII on two sides of the rice aroma gene of paddy rice Badh and cloning to expression vector pCAMBIA1302, the expression vector of rice aroma gene of paddy rice may be obtained and may be used in breeding excellent rice variety.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Kalium ion diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and kalium ion concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464403AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPotassiumEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring kalium (ions) by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of kalium (ions), and belongs to the technical field of medical / food / environmental inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, adenosine diphosphate, enolphosphopyruvate, ferricytochrome b1, pyruvate kinase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the velocity of the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the concentration of kalium (ions).
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for designing human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 sequence according to preferred codon of pichia pastoris
InactiveCN101649323BHangover hasLiver protection hasMicroorganism based processesGenetic engineeringAlcoholismsSequence signal
The invention relates to a method for designing gene sequences, in particular to a human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 sequence designed according to a preferred codon of pichia pastoris. The sequence is characterized in that a DNA molecule is designed according to the preference of the pichia pastoris, and a code of the molecule has the same nucleotide sequence as a protein coded by a human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene ID 217 on an amino acid level. The human aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene sequence designed according to the preferred codon of pichia pastoris is realized by the following steps: on the basis of a human ALDH2 gene (gene ID 217), UTR and signal peptide are deleted; enzyme cutting sites of an incision enzyme EcoR I and an incision enzyme Not I are added; a codon GCG for coding Ala is replaced by GCU according to the use method of the pichia pastoris codon, and codons CGC and CGG for coding Arg are replaced by AGA, AGG, CGU and CGA; and altogether 28 bases are modified to obtain a target sequence ALDH2. The gene sequence can express with high efficiency in the pichia pastoris, can be applied to preventing alcoholism and protecting livers and has the effects of preventing alcoholism and protecting livers.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Thermophilic long-chain alkyl aldehyde dehydrogenase and crystal structure thereof
ActiveCN102676464BThermally stableImprove thermal stabilityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention relates to thermophilic long-chain alkyl aldehyde dehydrogenase in an n-alkane end degradation process of thermophilic denitrified bacillus and a crystal structure thereof. A molecular clone method is utilized, so that a target gene is cloned into escherichia coli (E. coli) so as to be heterologously expressed. A purified product of aldehyde dehydrogenase is obtained through a protein purification method. A crystal of the aldehyde dehydrogenase, which is suitable for diffraction, is obtained through a hanging droplet crystallization method. The crystal structure of the aldehyde dehydrogenase is analyzed by utilizing an X-ray diffraction method. The results show that the aldehyde dehydrogenase contains a characteristic ALDH fold which is formed by three structural domains. Site-specific mutagenesis is carried out on conserved residues on an enzyme activity part, and the influence of the conserved residues on enzyme activity is proved through wild type of the enzyme and enzyme activity experiment of the mutant thereof. The results can comprehensively reflect space conformation of the enzyme, and provide theoretical guidance for further researching relation between structures and functions of the aldehyde dehydrogenase, and improving the degradation activity of the enzyme.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
I type aldehyde dehydrogenase of clonorchis sinensis, its coding nucleic acid and application
InactiveCN100360665CToxic reductionAvoid enteringPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsClonorchis sinensisPolynucleotide
The invention discloses new genes for encoding clonorchis sinensis type I aldehyde dehydrogenase, polypeptides encoded by the genes, and antibody of the polypeptides. The invention also discloses the depressor of the polypeptides for screening clonorchis sinensis type I aldehyde dehydrogenase, the use of polynucleotides as primer or as probe, in particular the use of the polypeptide and polynucleotide as diagnosis reagent kit, and vaccine.
Owner:佛山顺德智研生物科技有限公司
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 as a drug target in treatment of tumor cells with anthracycline chemotherapy drugs
InactiveCN103784465BOvercome the shortcomings of only relying on surgical treatmentIncrease lethalityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellDrug target
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
A kind of olive betaine dehydrogenase badh and its coding gene and application
A betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH) derived from bruguiear gymnorrhiza, coding gene thereof, and application of the coding gene in cultivating improved salt-tolerant and drought-tolerant transgenic plants.
Owner:BIOCENTURY TRANSGENE CHINA
Plant transgenic selection system using betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH) as marker gene and use thereof
InactiveCN102304506AReduce cost inputAvoid Biosecurity ConcernsRecombinant DNA-technologyAngiosperms/flowering plantsSelect agentGene selection
The invention discloses a plant transgenic selection system using betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase (BADH) as a marker gene and use thereof and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. In the system, BADH is used as a marker gene of an exogenous gene and NaCl is used as a selecting agent. The use comprises the following steps: (1) determining NaCl concentration which can just inhibit plant tissue differentiation; (2) transferring the exogenous gene which contains the BADH marker gene into a plant cell or tissue; and (3) culturing the transgenic tissue or cell into which the BADH marker gene is transferred on a culture medium in which the NaCl concentration determined by the step (1), obtaining the transgenic tissue or cell into which the BADH marker gene is transferred into if the transgenic tissue or cell can grow, and confirming by molecular detection. The invention has the advantages of greatly lowering the cost investment in a transgenic test, solving the safety problem of transgenic organisms, and providing low cost selection for the construction of a safe and effective selection system for plant genetic transformation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
A rice betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 fragrance gene, primers for molecular markers and screening method
InactiveCN103525840BMeet needsOvercome biasMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention discloses a new betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene that can make rice show a light-flavored characteristic. Compared with the non-perfume rice "Nipponbare", the mutation site is not located on the coding chain, but belongs to the upstream mutation of the coding chain. Types of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 genes. There was a deletion of 3 nucleotides at position -81 upstream of the first nucleotide of the initiation codon of the coding strand, and an insertion of 8 nucleotides at -1314. By crossing this gene into non-perfume rice and obtaining homozygous offspring, a new light-scented rice variety can be bred. The invention also discloses a method for screening rice with the light-scented characteristic gene and molecular marker primers. The invention provides new genes for cultivating light-scented rice, and can also assist in selecting plants containing light-scented genes, which is conducive to improving the selection effect, and can also determine whether the light-scented genes of self-bred offspring formed in the later stage of the breeding process are in a homozygous state Identification to achieve breeding goals quickly and efficiently.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com