Patents
Literature
74 results about "Finite element method analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for controlling machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN104077442AReduce machining accuracyShorten the processing cycleSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisMachining deformation
The invention discloses a method for controlling the machining accuracy of large integrated thin-walled parts based on finite element analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, extracting local structural features of the large integrated thin-walled part; 2, performing finite element simulative analysis on local structural features to obtain an optimized cutting technology; 3, numerically modeling a large integrated workblank, and loading an initial internal stress; 4, protocoling a tool path, namely protocoling the machining sequence of the feature structures; 5, performing simulative analysis on the integrated structure to obtain a predicted deformation result under the condition of process technology; 6, regulating and optimizing a clamp scheme to control machining deformation. The method adopts finite element simulation, can analyze and predict in advance before the actual machining of the parts, and thereby corresponding machining strategy is adjusted, machining deformation is effectively controlled, production cycle of the parts is shortened, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING CHENGUANG GRP +1
Probabilistic finite element method (PFEM)-based steel-bridge fatigue reliability evaluation method
ActiveCN102384856ALow costShorten the evaluation cycleStructural/machines measurementStatistical analysisElement analysis
The invention relates to a probabilistic finite element method (PFEM)-based steel-bride fatigue reliability evaluation method, in particular to a fatigue reliability evaluation method by combining dynamic weighing data (WIM) of a car and the analysis of the PFEM, which aims at solving the problems that the bridge structure health monitoring cost is higher and the stress measuring point distribution is limited, and utilizes the real WIM data to statistically analyze car load and establishes a probabilistic distribution model of a car type, road distribution, axle weight and wheel-base. Finite element method analysis software is used for establishing a numeric model of a bridge. A probabilistic finite element program is compiled, stress amplitude and stress cyclic quantity of a key part under the random car load effect are extracted through the sampling, loading and finite element analysis to be statistically counted. The fatigue reliability calculation is performed according to the statistical result, and the reliability attenuation trend of the evaluated part in the subsequent application process is predicted. By adopting the method, a feasible analysis tool is provided for the fine fatigue evaluation of complicated steel-bridge details.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
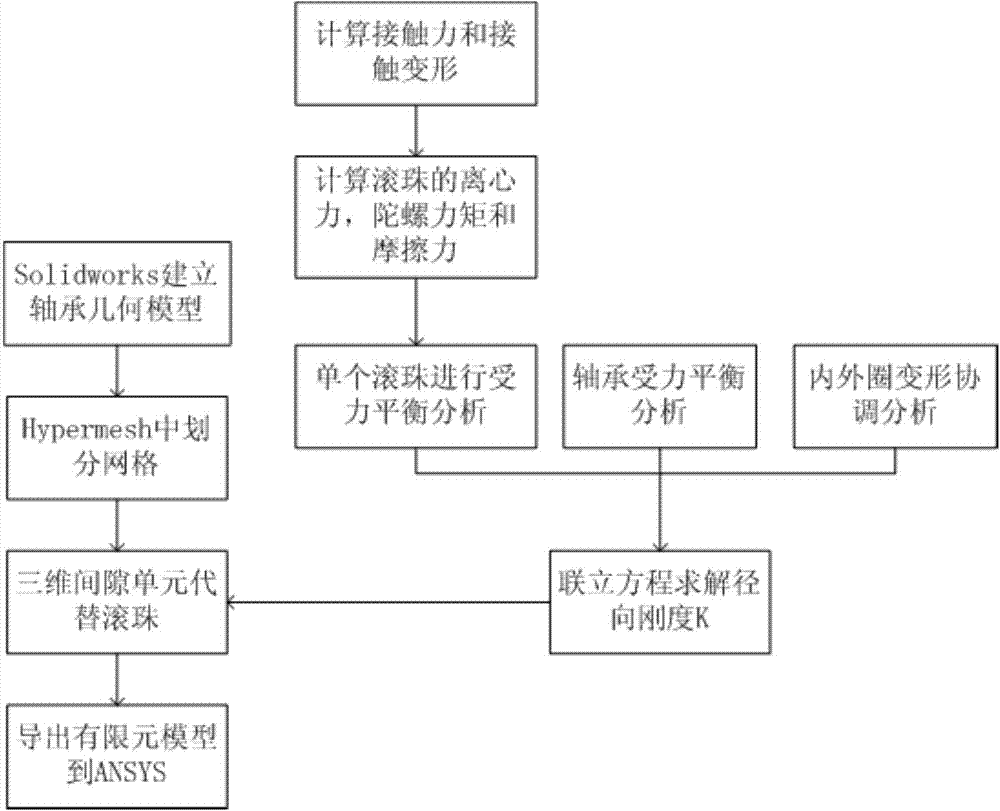
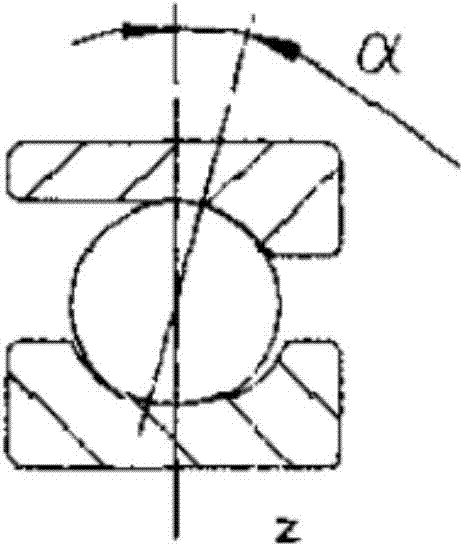
Bearing simplifying method in finite element simulation analysis
InactiveCN104239654AThe result is close to the realSimple calculationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelElement analysis
The invention discloses a bearing simplifying method in finite element simulation analysis. According to the method, a three-dimensional gap unit is used for simplifying finite element analysis of an angular contact bearing, and a three-dimensional model of the bearing is drawn in three-dimensional mapping software solidworks. The bearing model is imported into finite element pre-processing software Hypermesh. An outer ring and an inner ring of the bearing are divided into hexahedral meshes. The outer ring and the inner ring of the bearing are connected through the three-dimensional gap unit. The spring stiffness K in the gap unit is worked out through a bearing radial stiffness calculation program. The finite element model is exported from the Hypermesh, then the finite element model is imported into engineering simulation software ANSYS, and mechanical calculation is conducted. According to the method, the calculation amount of finite element analysis can be simplified, the efficiency can be increased, and the calculation accuracy cannot be damaged.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reconstruction of parameterization model of quadrilateral finite element grid model
InactiveCN105787226AHigh expressionReduce in quantityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALReconstruction algorithm
The invention provides a parameterization reconstruction algorithm of a quadrilateral finite element grid model. By taking a quadrilateral grid model obtained by finite element analysis software as the basis, a unit number and a node coordinate of the quadrilateral grid model are used as input information for reconstructing a topological relation between quadrilateral grid units; merging operation including unit grid standard merging, block domain self-adaptive merging and the like are carried out according to obtained topological information, so that the quantity of block domains is reduced and merged sub-domains are obtained; characteristic points on boundaries of the sub-domains obtained by merging are remained and are connected to form a certain quantity of quadrilateral final sub-domains; and finally, a body parameterization model is obtained by carrying out construction, adjustment and optimization of a body parameter model according to the boundaries of the obtained final sub-domains. The algorithm can be used for carrying out parameterization reconstruction on the quadrilateral grid model of structures including a porous plate and the like, and the obtained body parameterization model is applicable to isogeometric analysis; and the algorithm has the advantages of simplicity in expression, whole-domain smoothing and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
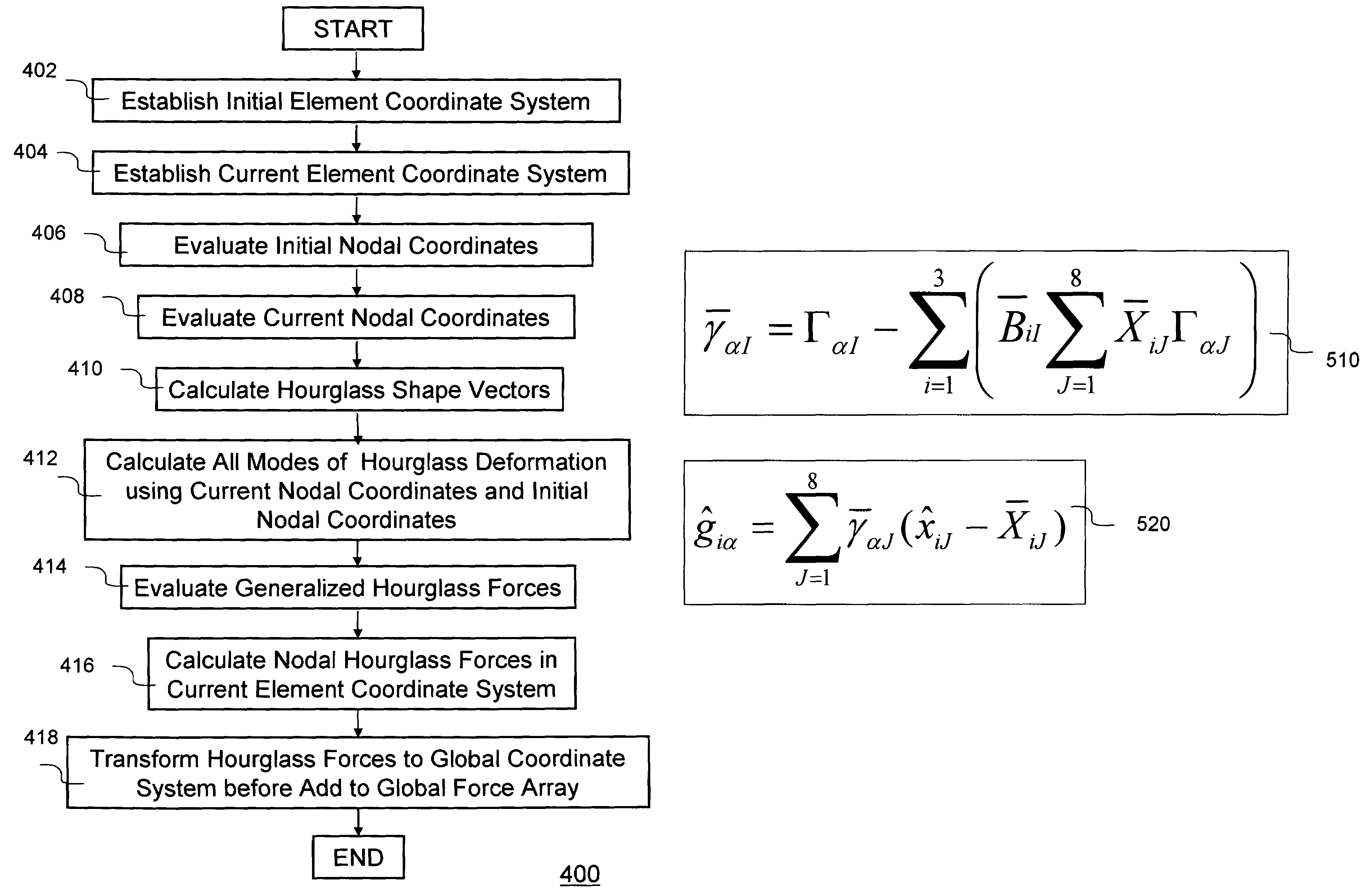
Method and system for controlling hourglass deformations of solid elements in finite element analysis
ActiveUS7392163B1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationNODALElement analysis
Hourglass deformations due to zero-energy or hourglass modes in rank-deficient solid elements must be effectively controlled, or the deformations may grow large and produce an unrealistic deformed geometry. Traditional methods of hourglass control allow error to accumulate by measuring hourglass deformation with incremental terms throughout a solution, which may produce inaccurate results due to unrealistic hourglass deformations. The present invention discloses a new method to control hourglass deformation without any incremental accumulations. Instead the nodal forces to resist hourglass deformations are calculated basing on the initial nodal coordinates and current nodal coordinates at each cycle. The present invention is implemented in a finite element software product.
Owner:ANSYS
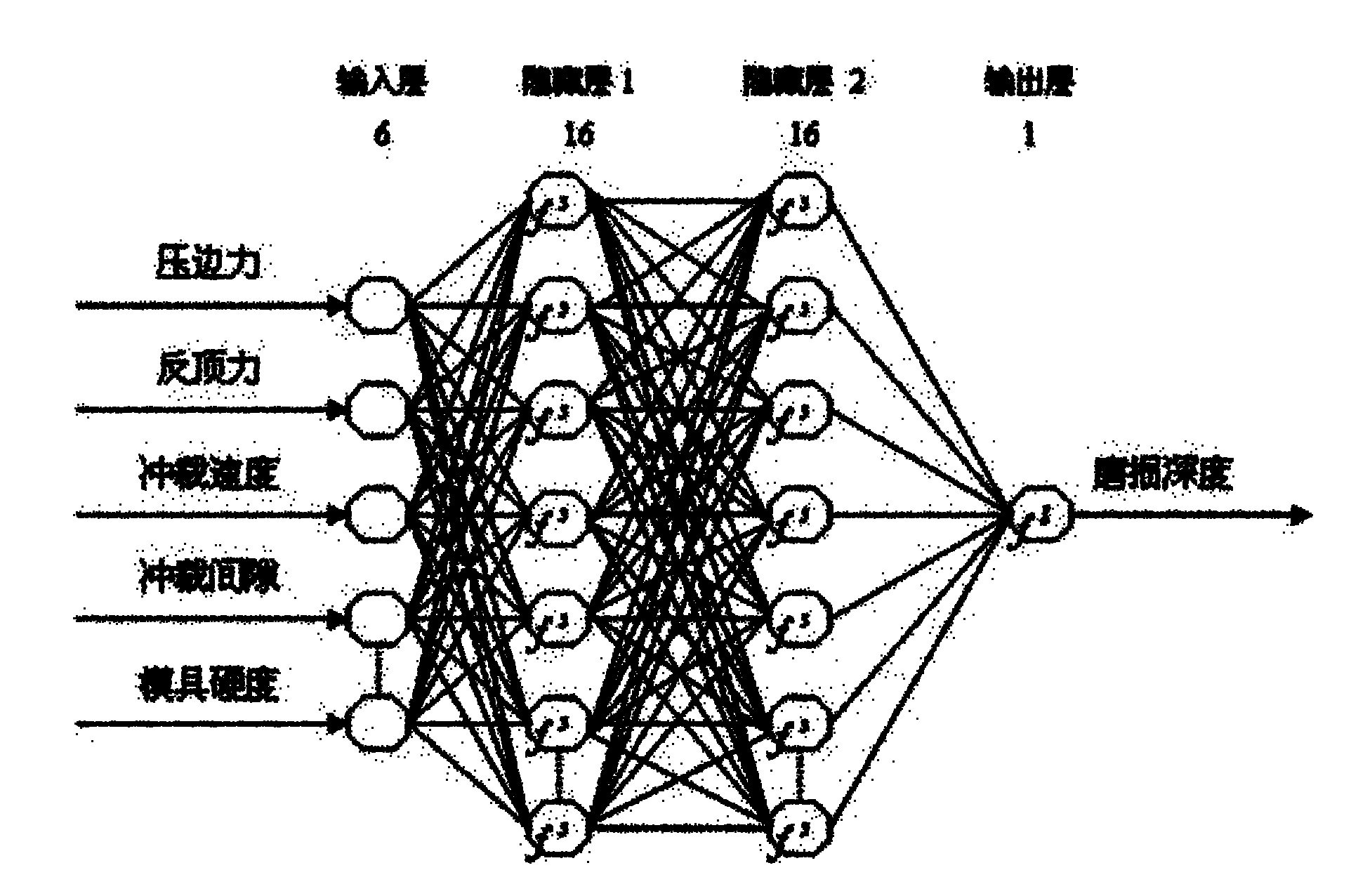
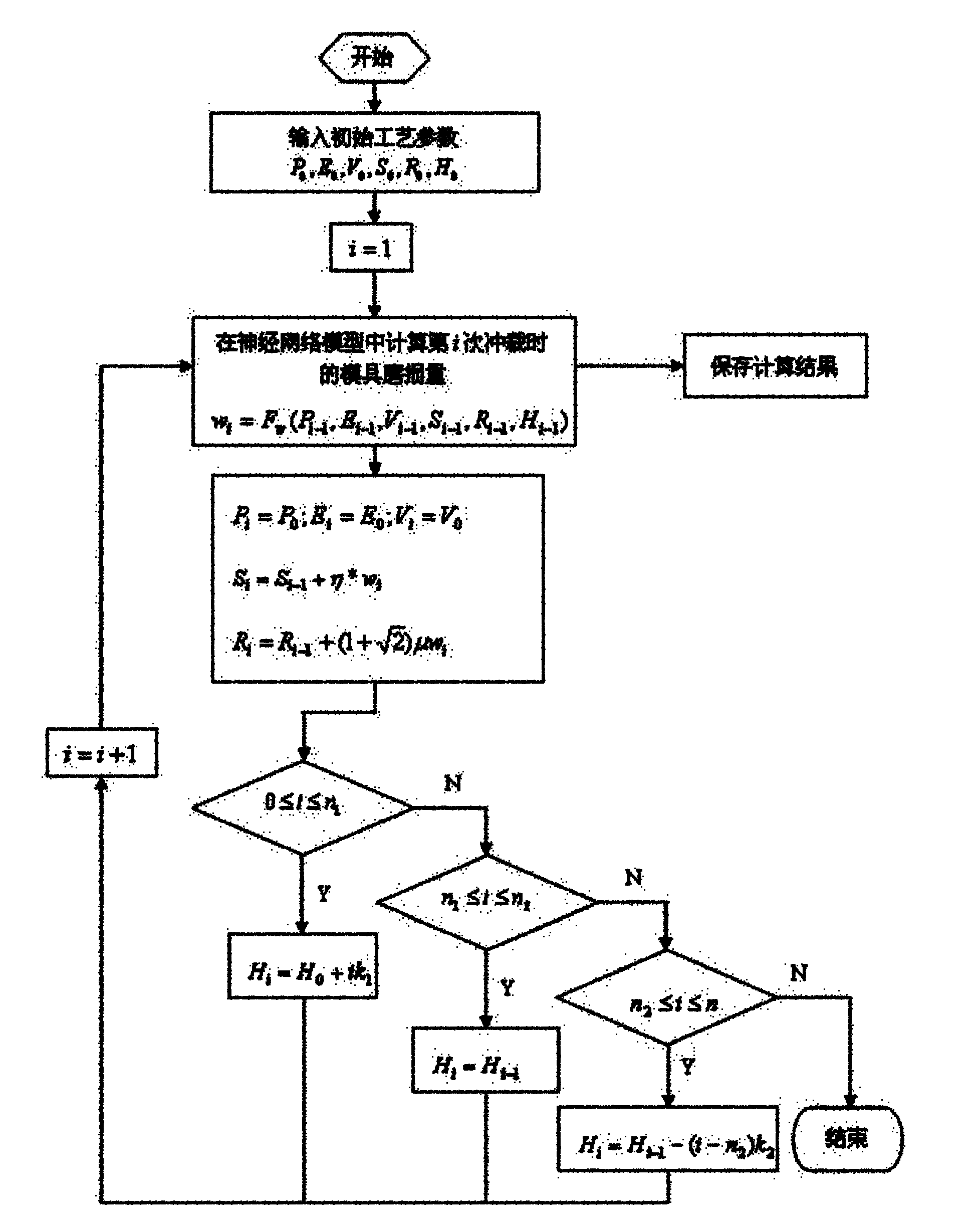
Wear prediction method for fine blanking dies based on finite-element technique and artificial neural network
ActiveCN102103646AImprove forecast accuracyQuick responseBiological neural network modelsSpecial data processing applicationsFinite element techniqueElement analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of fine blanking, in particular relates to a wear prediction method for fine blanking dies based on a finite-element technique and an artificial neural network. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: building a finite-element analysis model, namely, simulating a fine blanking process on a finite-element analysis and calculation platform, and calculating the wear extent of a fine blanking die in the fine blanking process by using an Archard wear model; building a neural network model, namely, training a designed neural network model by using a finite-element analysis result guided by an orthogonal experimental design so as to obtain a functional relation between the wear extent of the fine blanking die and fine blanking parameters; obtaining the fine blanking parameters, namely, obtaining the functional relations between the fine blanking parameters and the wear extent, blanking time, and the like of the fine blanking die according to geometrical relationships and production practices; and building and simulating a fine blanking wear prediction model. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high prediction precision, fast response speed and strong operability.
Owner:武汉客车制造股份有限公司
Finite element analysis method for formula racing car frames
InactiveCN108170972ASolve problems that cannot be solved by manual calculation in experimentsImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelVehicle frame
The invention provides a finite element analysis method for formula racing car frames, belongs to the technical field of computer aided engineering, and aims at solving the problem that existing racing car frame optimization and analysis are bad in correctness and long in design period. The finite element analysis method comprises the following steps of: A, constructing a three-dimensional model and carrying out meshing to convert the three-dimensional model into a finite element model; B, applying boundary conditions according to each working condition, carrying out finite element analysis and calculation on frame bending rigidity under each working condition, and comparing the analysis result with material bending strength to carry out structure optimization; C, respectively applying forced displacement in opposite directions on two sides of the car frame, carrying out finite element analysis and calculation to obtain torsional rigidity of the car frame, and carrying out structure optimization according to the analysis result; and D, analyzing and comparing whether a fixed frequency of each order modal of the car frame is different from an external main excitation frequency or not, and carrying out structure optimization according to the result. According to the method, the correctness of optimization and analysis is improved, the expenditure is decreased and the design period is shortened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIRUN AUTOMOBILE +2
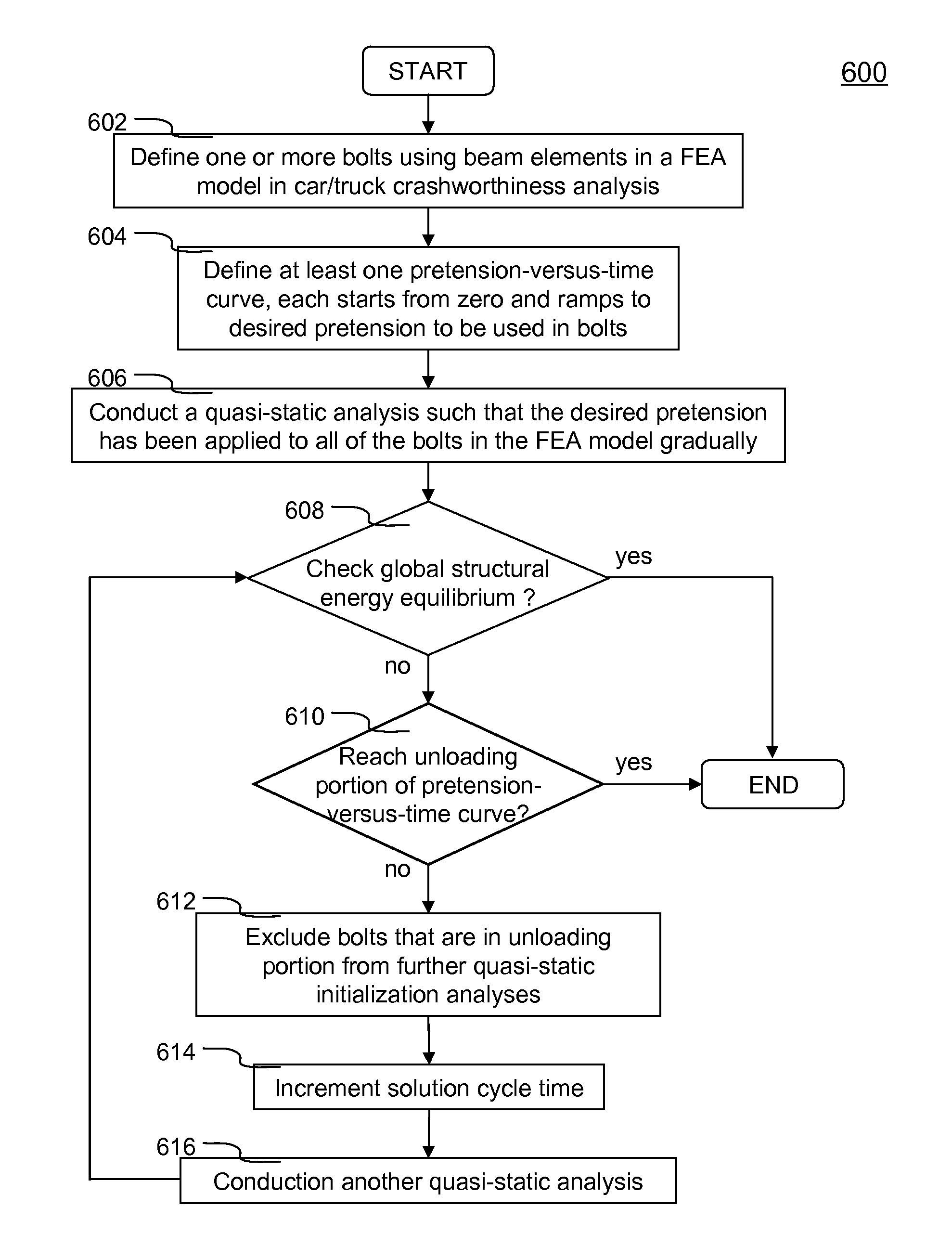
Method of initializing bolt pretension in a finite element analysis
ActiveUS20100076739A1Small incrementAvoid the needAnalogue computers for vehiclesDesign optimisation/simulationElement analysisMechanical engineering
In one aspect of the invention, each bolt is modeled using a beam element in a FEA model. To apply desired pretension to one or more bolts, at least one pretension-versus-time curve is specified. Each pretension-versus-time curve includes ramp portion, desired pretension portion and optional unloading portion. Duration_of the pretension-versus-time curve generally covers first 0.5-1% of total simulation time of a car crashworthiness analysis. Ramp portion starts from zero to desired pretension in a substantially linear manner, and hence being configured for applying desired pretension to a bolt gradually with smaller increments. Desired pretension portion is configured for ensuring the desired pretension can actually be applied to the beam element during an initialization process—a series of quasi-static analyses. Since the method is independent of the deformation of the beam, the method completely avoids the need to iteratively determine an axial strain or displacement that gives the desired pretension.
Owner:ANSYS
Roughness predication and control method for belt steel produced by electric spark textured working roller
ActiveCN104624669ACalculation speedImprove forecast accuracyMeasuring devicesTension/compression control deviceSurface roughnessStrip steel
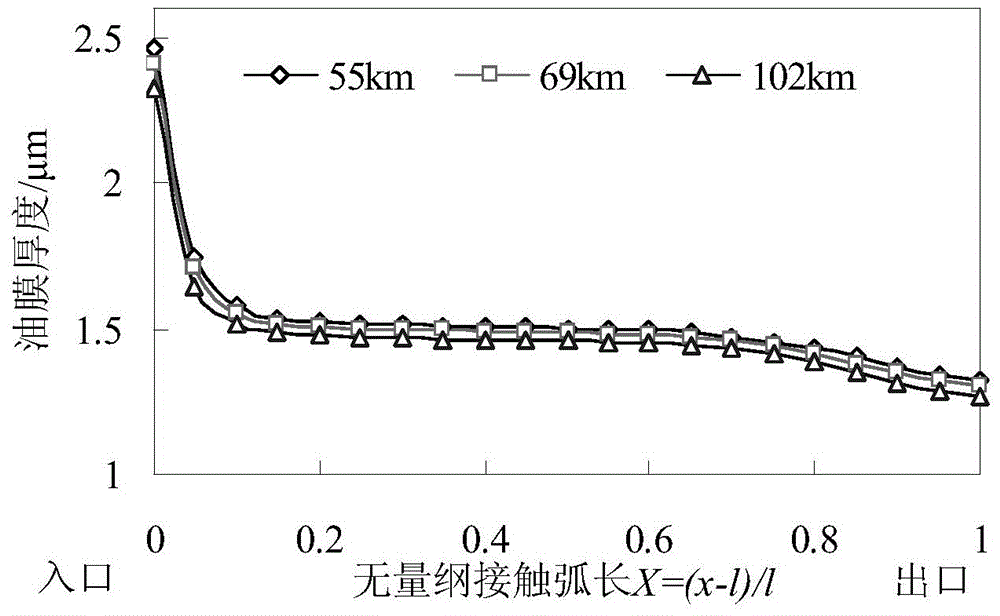
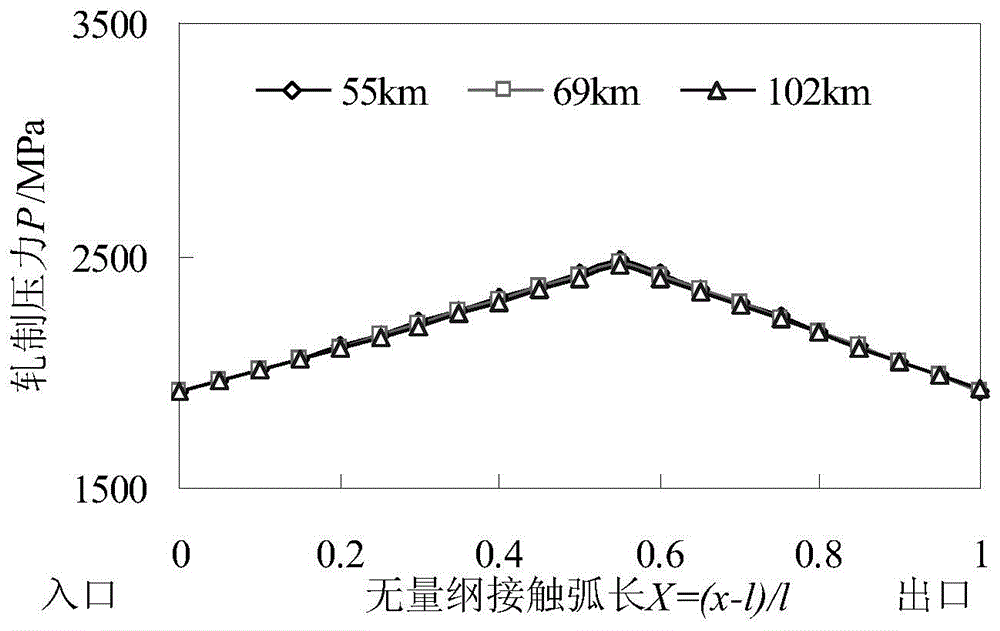
The invention discloses a roughness predication and control method for belt steel produced by an electric spark textured working roller. On the basis of inter-interface minimum oil film thickness, electric spark textured working roller surface abrasion depth and abrasion surface roughness are obtained by the method, a relation of interface minimum oil film thickness, working roller abrasion depth and belt steel surface roughness provided by the invention can be used for predicating the surface roughness of the cold-rolled belt steel produced by the electric spark textured working roller; a belt steel surface roughness target interval and a roughness predication value are compared; if the roughness predication value is not in the belt steel surface roughness target interval, the rolling speed and the pressing rate are adjusted. Compared with finite element method analysis and an empirical equation obtained by tracking and measuring the belt steel surface roughness, the method has the characteristics of rapid calculation speed and wide applicable range; the method considers the influences on a working roller surface abrasion and roughness copying process by inter-interface oil film distribution in a cold rolling process, and has higher predication precision.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
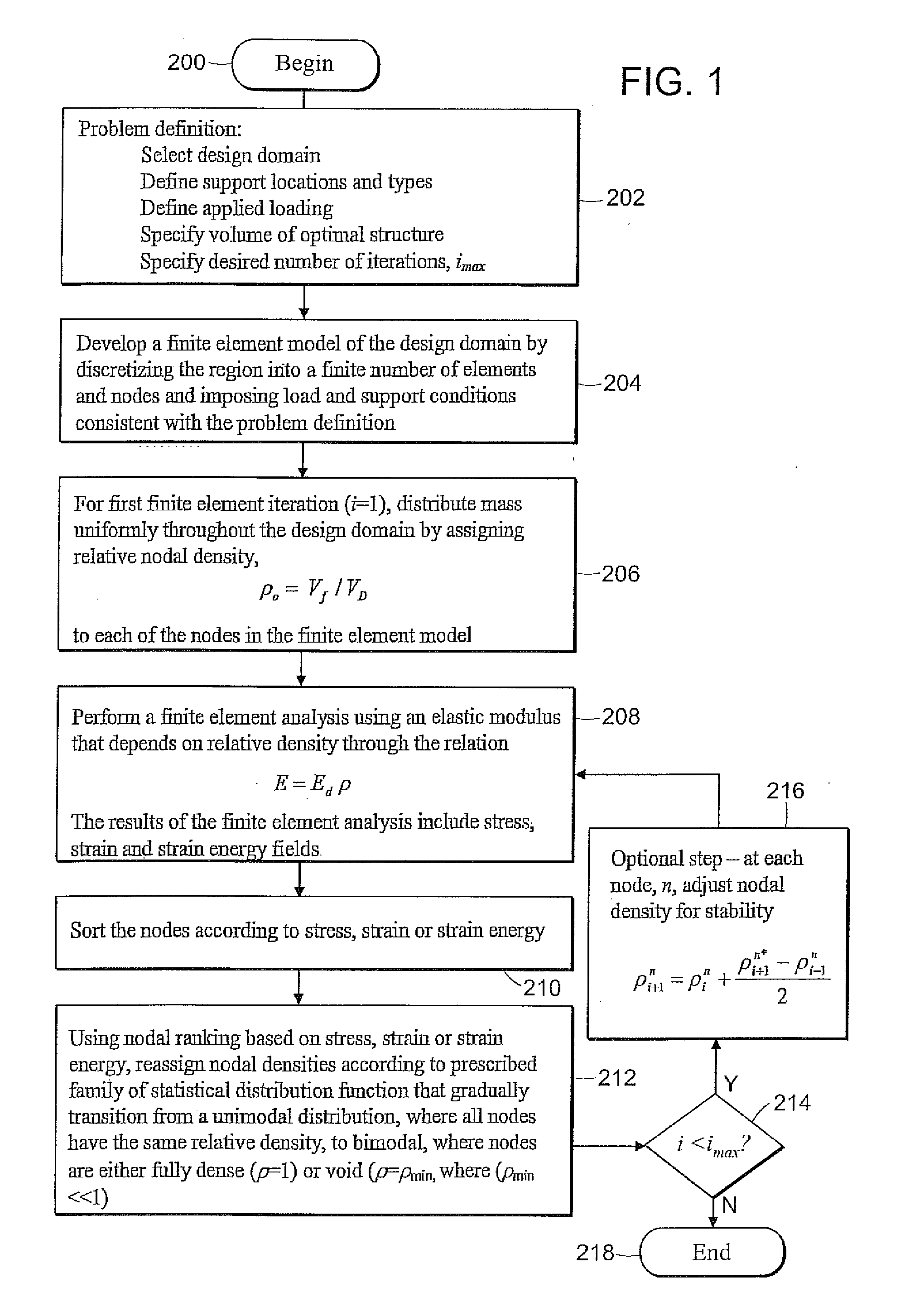
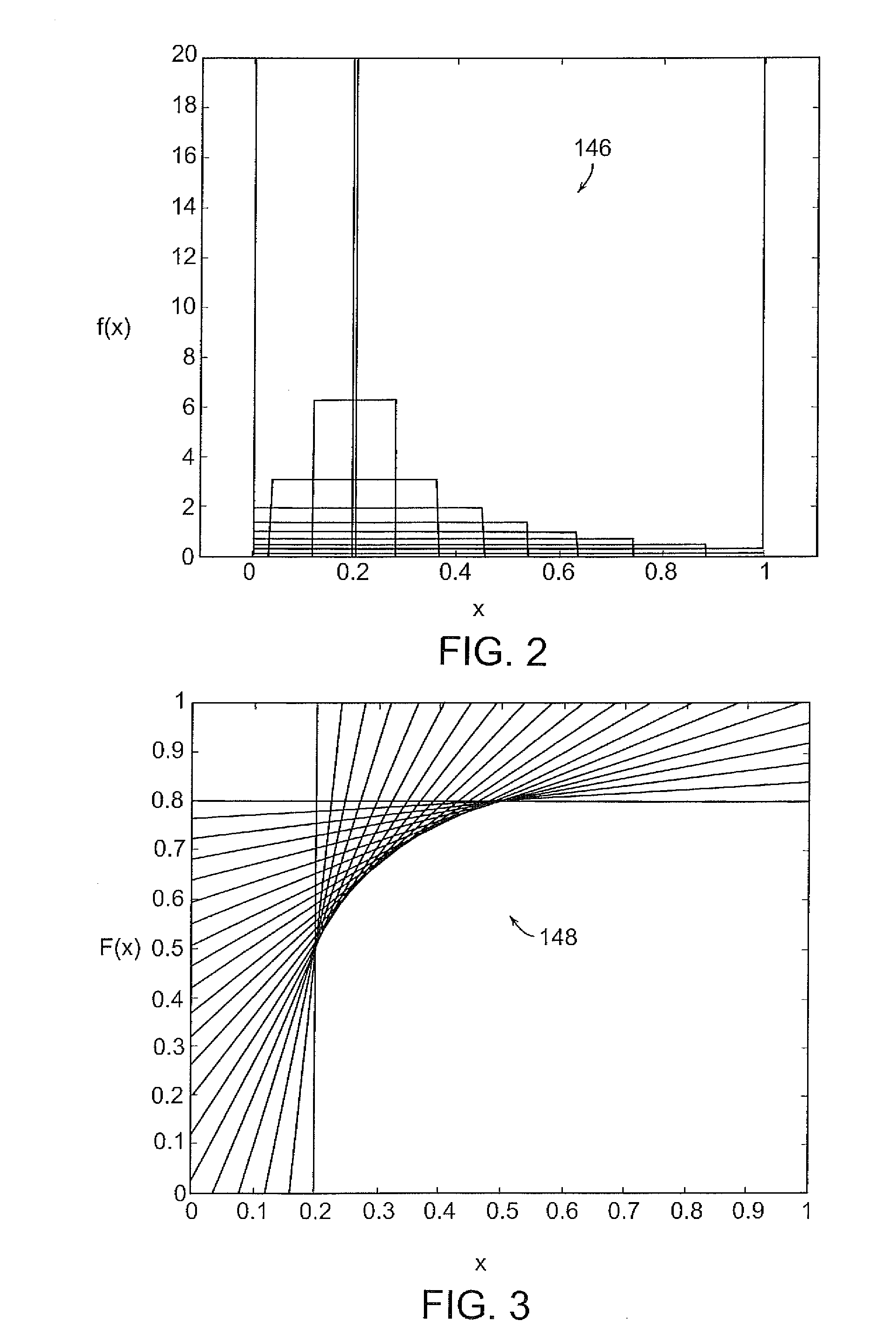
Systems and methods for finite element based topology optimization
InactiveUS20110166833A1Optimize topologyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationNODALElement analysis
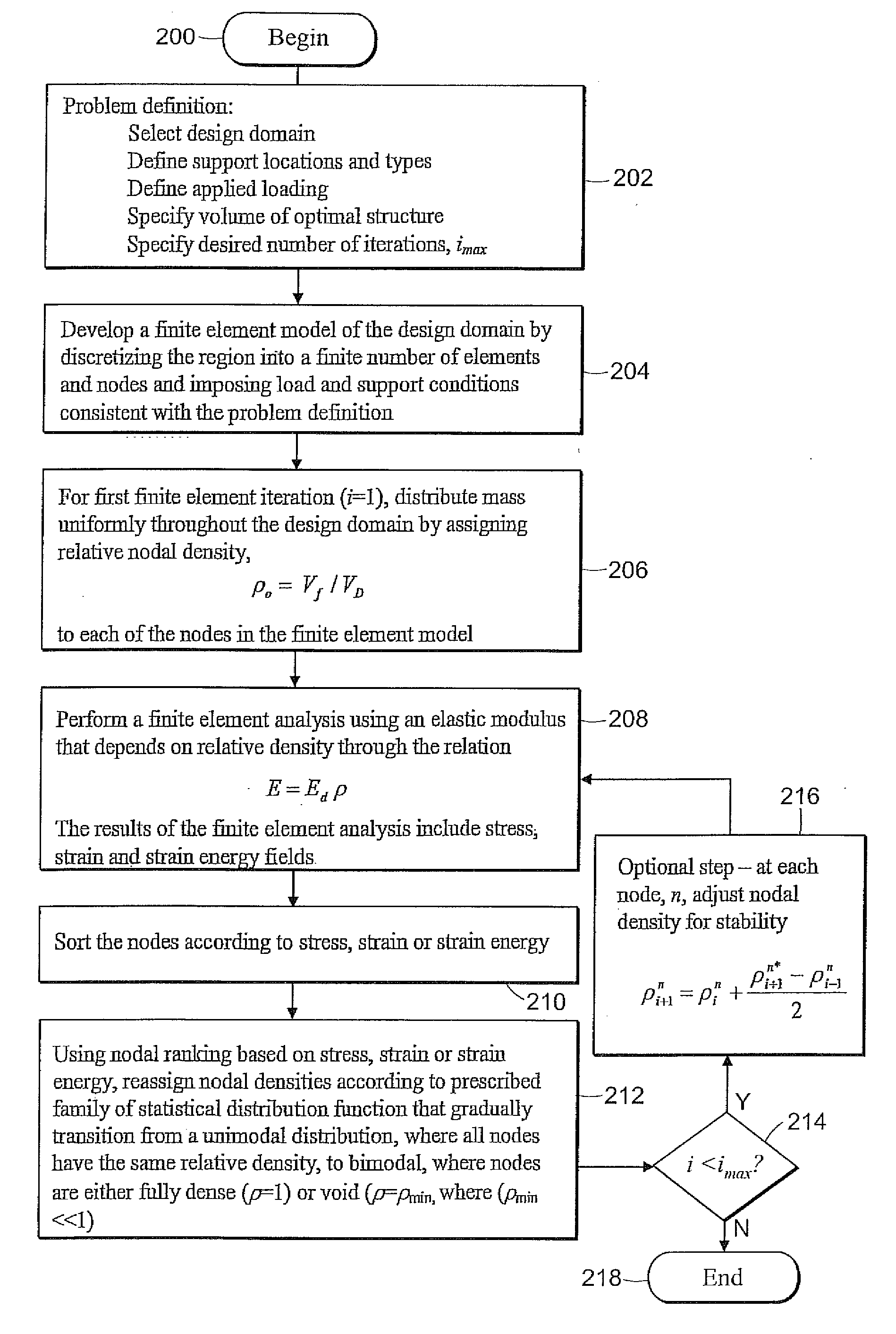
A method is disclosed of providing an optimal minimum mass topology for a structure based on a set of design criteria including at least one support point and at least one force to be applied to the structure. The method includes the steps of: identifying a plurality of nodes within a structure design domain, and assigning an initial density value to said plurality of nodes; conducting a finite element analysis on the nodes; determining one of a stress intensity or strain energy values for each node; ranking the nodes by relative stress intensity or strain energy values; adjusting the density value for each node; and repeating the steps of conducting a finite element analysis on said nodes, wherein the step of adjusting each density value for each node is performed according to a family of statistical distribution functions that gradually transition to a bimodal distribution wherein nodes are either fully dense or effectively void thereby providing an optimal topology.
Owner:BOARD OF GOVERNORS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION STATE OF RHODE ISLAND & PROVIDENCE PLANTATIONS
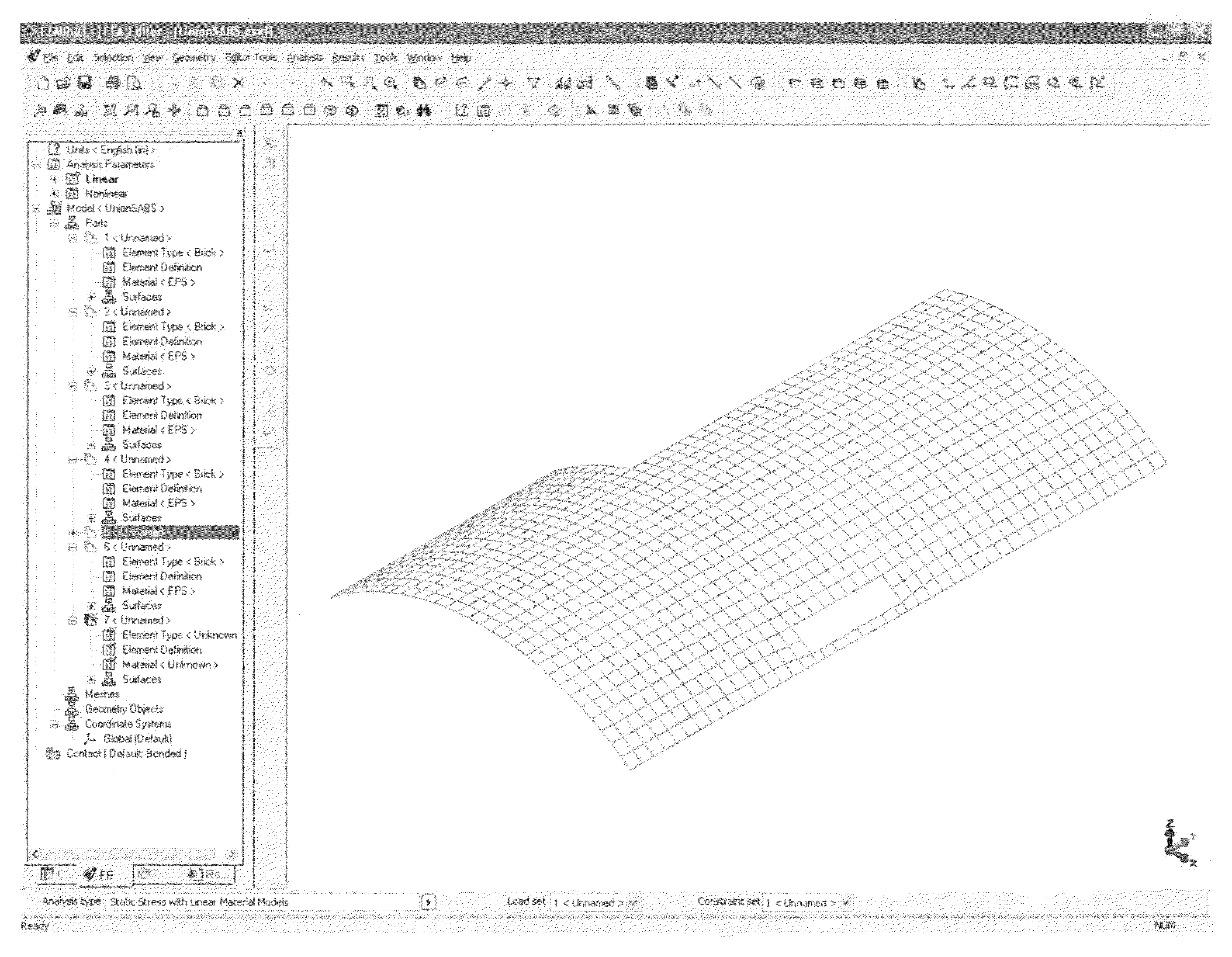
Method of performing a finite element analysis of a composite structure
The invention provides a method of analyzing a building made from Expanded Poly Styrene (EPS) which is coated on the inside and outside with Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC) or other strengthening coating. The building is designed in a CAD program. Then, the building is divided up into small volumes in the CAD program or in a Finite Element Analysis program using an automeshing program. Plates are added to the inner and outer surfaces of the volumes using copying and automeshing commands. Appropriate characteristics of the EPS and GFRC are assigned to the volumes and plates. A FEA analysis can then be run.
Owner:SAEBI NASSER
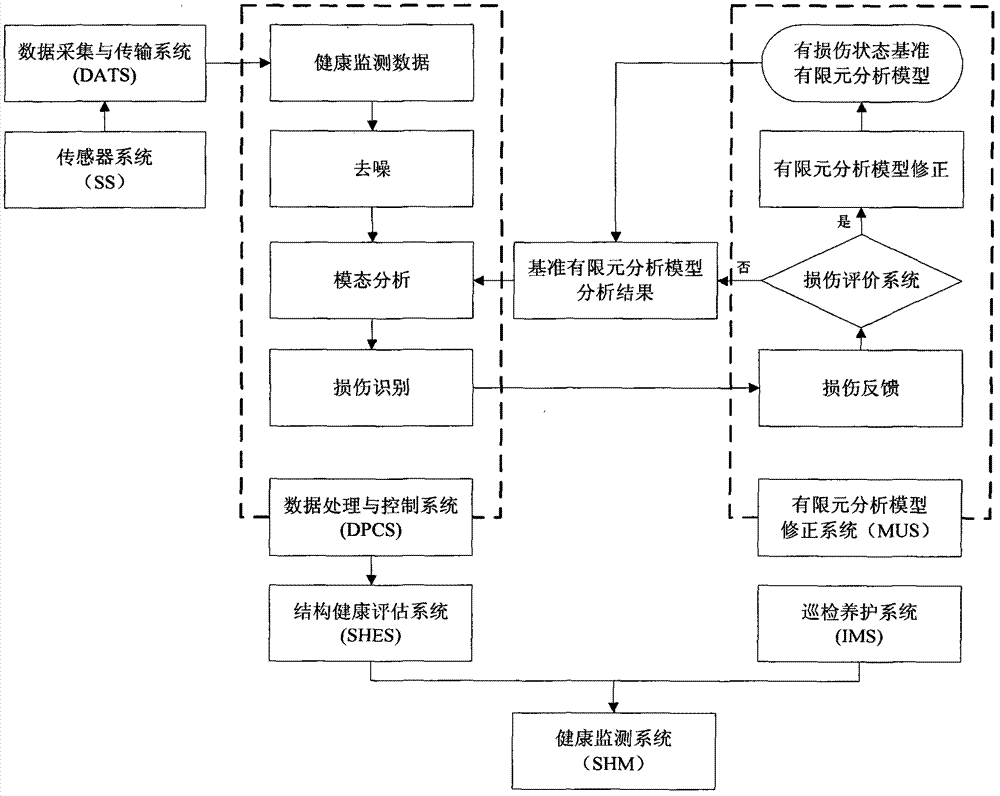
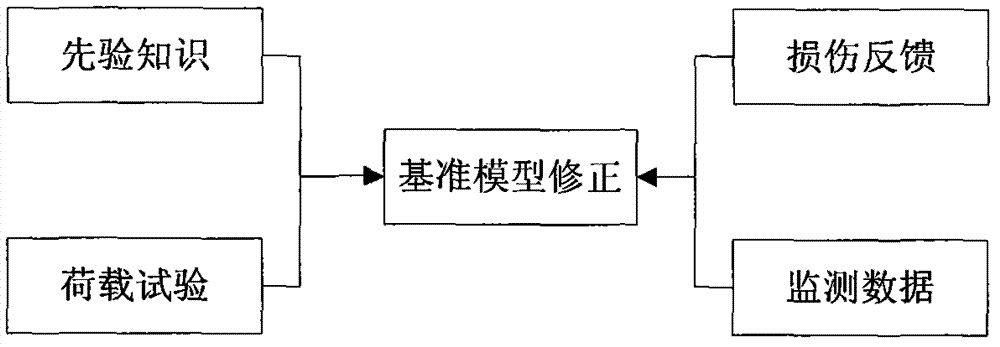
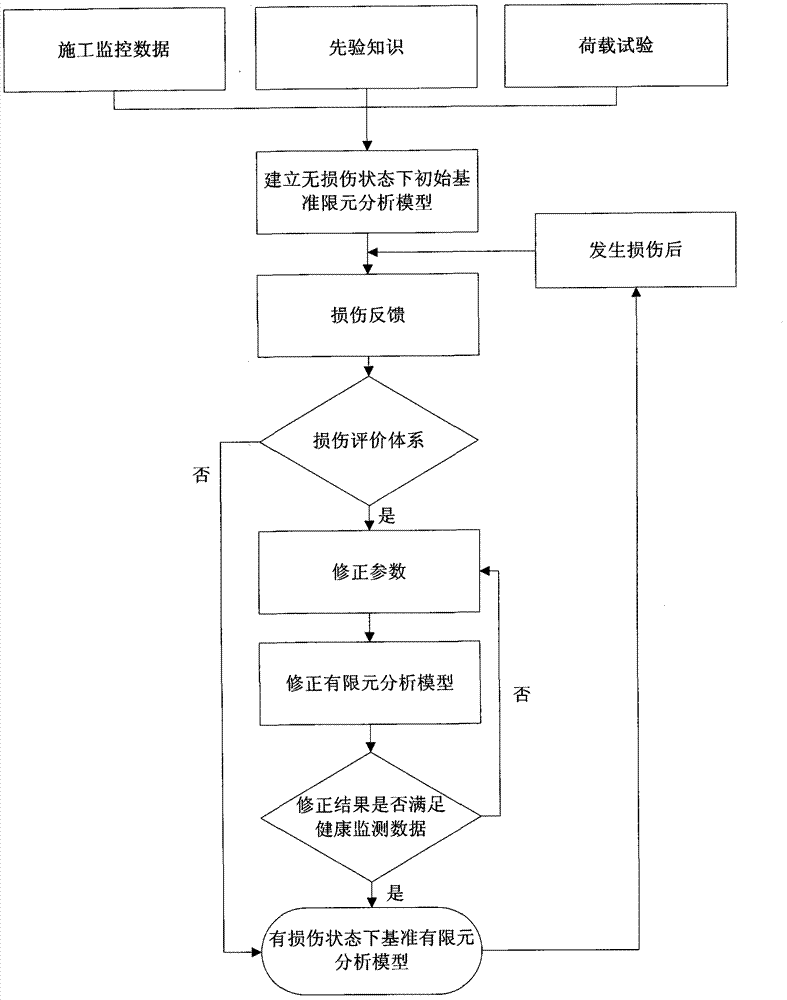
Health monitoring system integrating finite element analysis model updating technology
The invention discloses a health monitoring system integrating the finite element analysis model updating technology. The system consists of six parts including an SS (sensor system), a DATS (data acquisition and transmission system), a DPCS (data processing and control system), an SHES (structure health evaluation system), an IMS (inspection maintenance system) and a finite element analysis MUS (model updating system). The finite element analysis MUS consists of two major parts including a finite element analysis model for establishing the initial standard and an updated finite element analysis model. The finite element analysis model updating function can be carried out by the health monitoring system under the condition without traffic closing, and the accurate and reliable finite element model analysis results can be provided.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
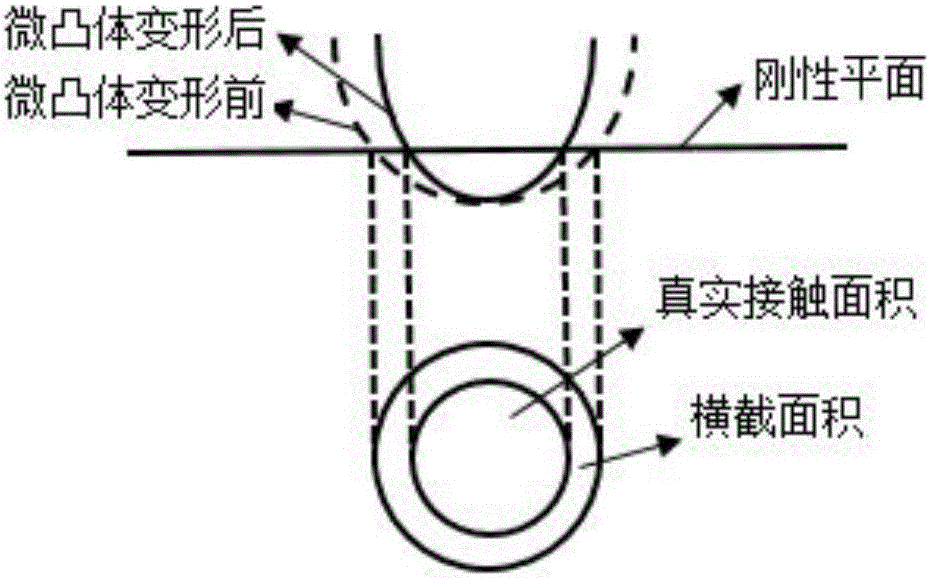
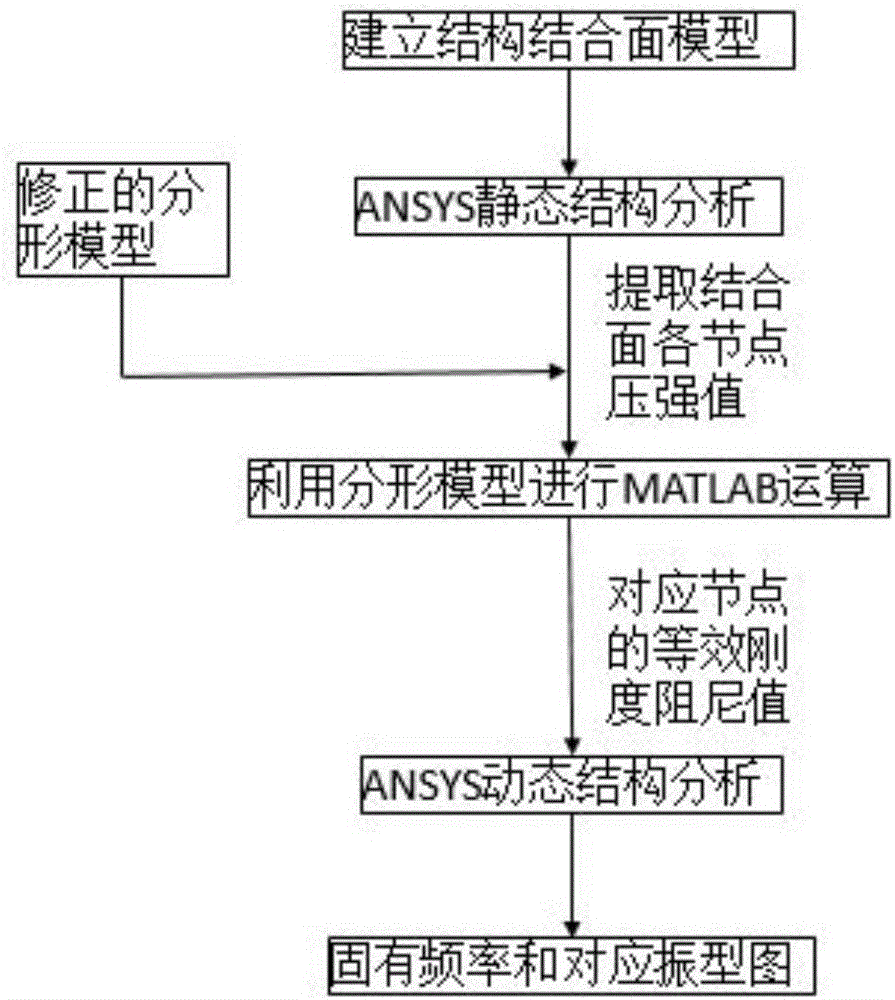
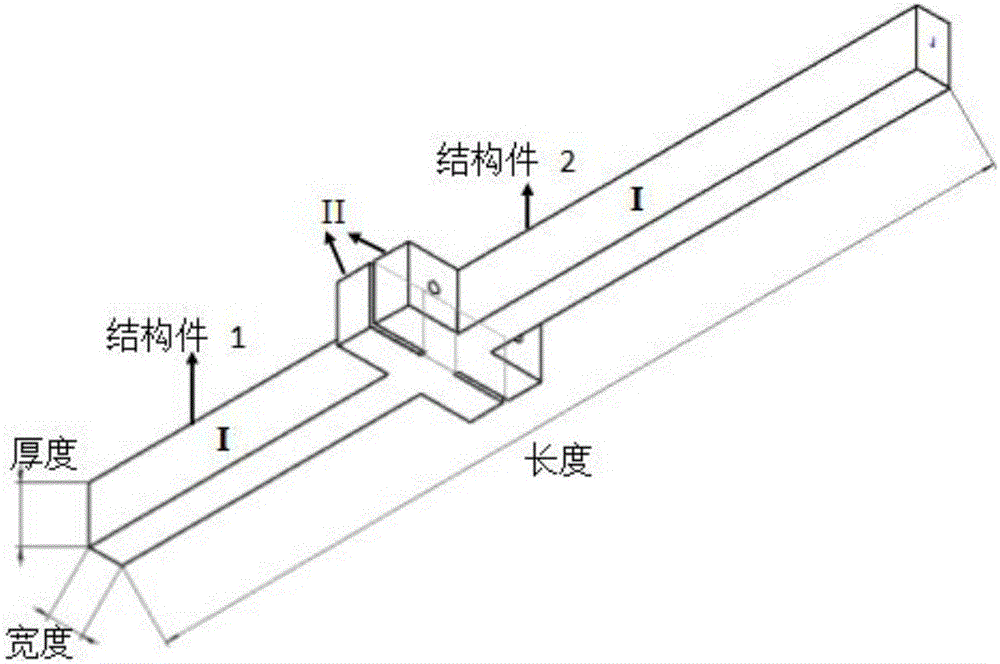
Method for analyzing dynamic characteristics of bolted structure based on three-dimensional fractal theory
InactiveCN106529035AAchieving accurate estimatesGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationFinite element analysis softwareMATLAB
The invention relates to a method for analyzing dynamic characteristics of a bolted structure based on a three-dimensional fractal theory. Modern industries rapidly develop; therefore, requirements on the machining precision of a machine tool are also increasingly high; but, the contact quality of a joint part between machine tool parts has a great influence on the machining precision of the machine tool; researches show that 60-80% of the total rigidity and 90% of the total damping of the machine tool come from the joint part; but, the integral rigidity and damping of the machine tool determine the machining precision of the machine tool; and thus, the theoretical basis can be provided for researching the integral dynamic performance of the machine tool by accurately estimating the contact rigidity and damping of the joint part. For a bolted joint surface, in combination with MATLAB numerical value simulation software and ANSYS finite element analysis software, a method for estimating the dynamic performance of the bolted joint surface is provided based on a three-dimensional fractal surface and a contact rigidity and damping model built by considering the influence of an elastoplastic deformation stage simultaneously.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
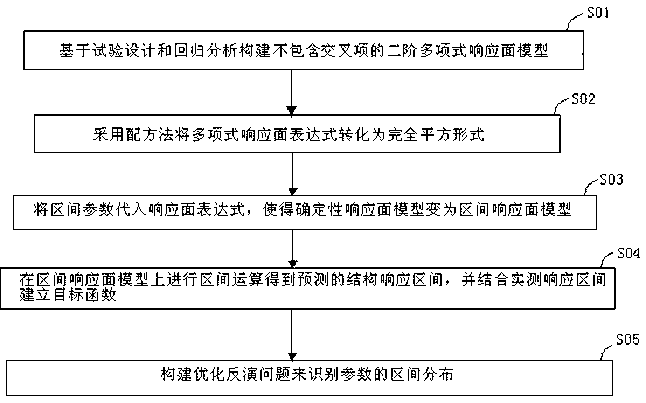
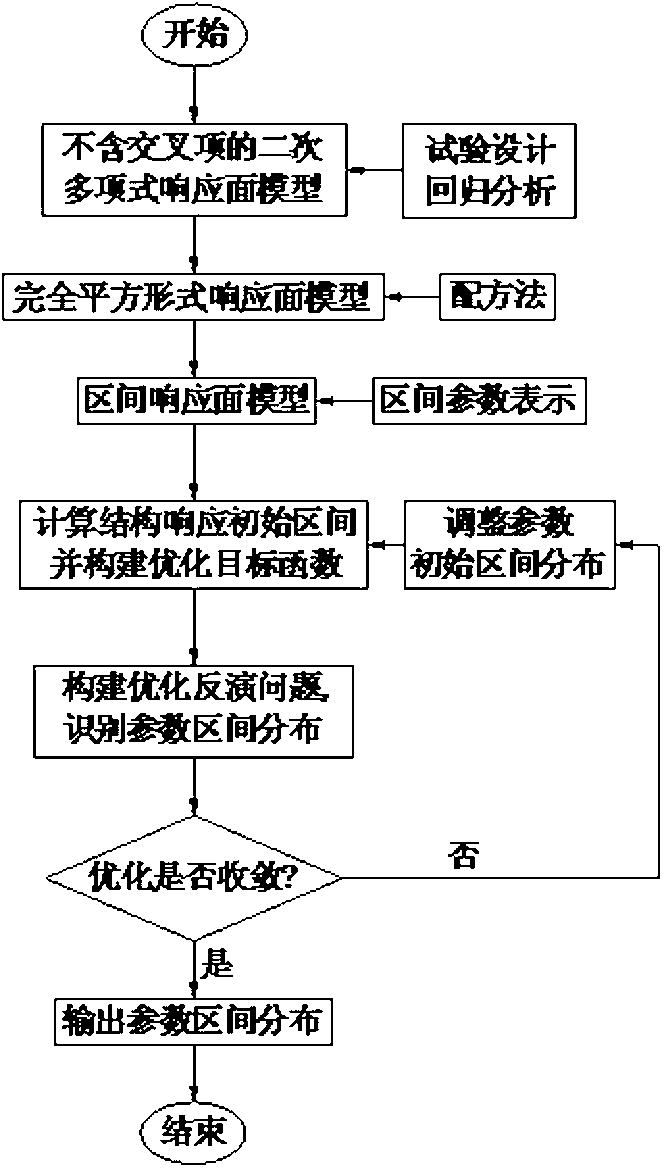
Random model updating method based on interval response surface model
ActiveCN103324798AImprove correction efficiencyGuaranteed calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsRegression analysisComputer science
The invention relates to random model updating method based on an interval response surface model. The method is characterized by including the steps of firstly, building a second-order polynomial response surface model without cross terms according to experiment design and regression analysis; secondly, using a square completing method to convert a polynomial response surface expression into perfect square; thirdly, substituting interval parameters into the response surface expression to allow the definite response surface model to be changed into the interval response surface model; fourthly, performing interval calculation on the interval response surface model to obtain predicted structural response intervals, and combining the predicted structural response intervals with actual response intervals to build a target function; fifthly, building a optimization inversion problem to identify interval distribution of parameters. By the method, the expansion problem of interval calculation is avoided, fast calculation of structural response intervals is considered, finite element analyzing calculation and sensitivity matrix building during (interval) random model updating are avoided, a large amount of calculation time and cost is saved, and ill-conditioned optimization is avoided as much as possible.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
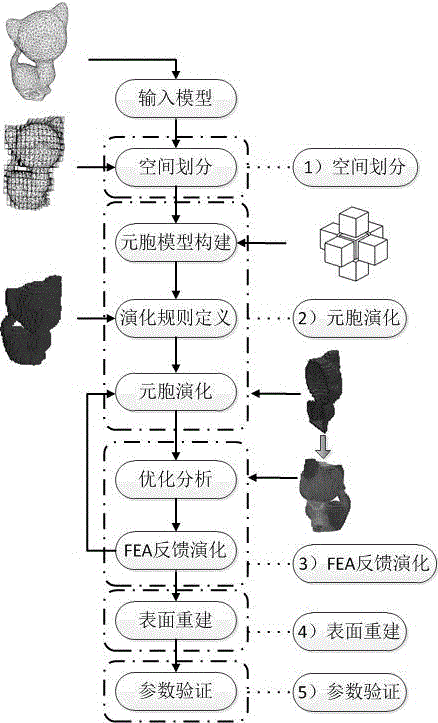
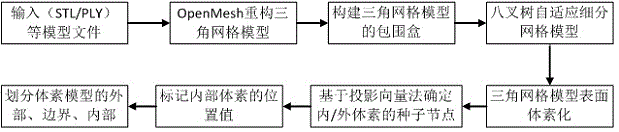
Three-dimensional cellular automaton based lightweight model and optimizing method
InactiveCN105528494AWith lightweight performanceReduce consumptionDesign optimisation/simulationMulti-objective optimisationCellular automationElement analysis
The invention relates to a three-dimensional cellular automaton based lightweight model and optimizing method, comprising operation steps: firstly, performing space dividing on an input network model with an octree, then according to design demands, establishing neighborhood information based cellular evolution, then, defining the relation that a neighborhood information based cellular automaton combines with FEA feedback information based finite element analysis, establishing FEA analysis feedback evolution, and generating a lightweight structure based on two evolution rules. A feedback based optimizing strategy is established, simulated information can be fed back to a design flow, and a drive structure is optimized to change macro attributes of a design target. Finally, the generated lightweight model is subjected to surface recreating and related parameters verifying, and an experiment proves that the invention is very suitable for establishing a 3D (three-dimensional) printing lightweight model.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
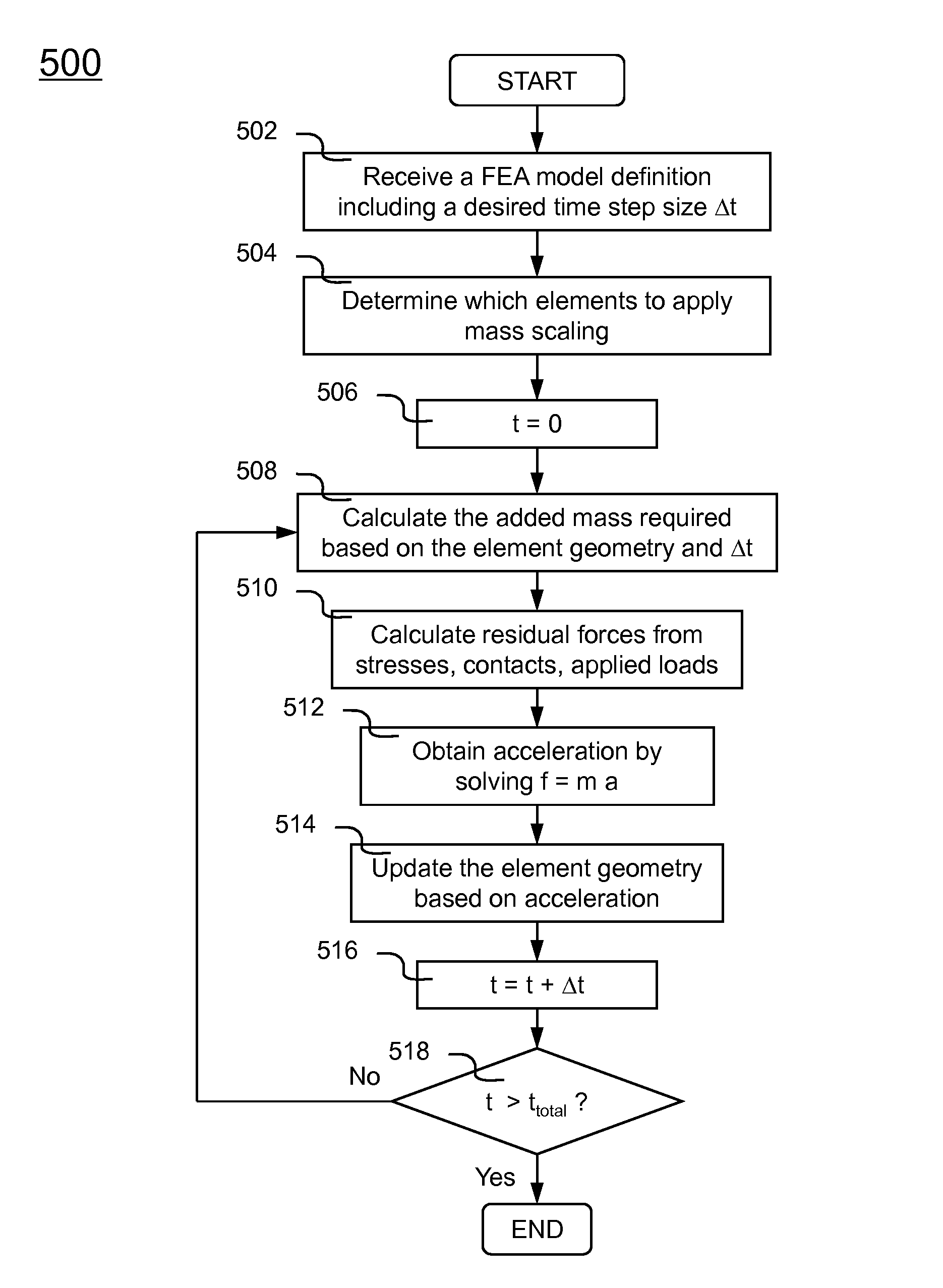
Methods and systems for applying mass scaling in finite element analysis
InactiveUS20120323536A1Reduce the impactIncrease mass densityDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingComputational scienceElement analysis
Methods and systems for applying mass scaling in finite element analysis is described. Elements with a critical time step smaller than a user desired time step are identified. Out of these elements, elements located in a particular region requiring realistic simulated dynamic responses are processed with selective mass scaling and the rest are processed with regular mass scaling. Selective mass scaling requires more computation but can better preserve dynamic structural characteristics. The aforementioned method is referred to as a mixed mode mass scaling. Mixed mode mass scaling allows engineering simulation to be conducted within a reasonable turnaround time, because only a portion of the FEA model is subjected to more computation intensive selective mass scaling. Selective mass scaling technique includes reducing effects caused in three translational and three rotational rigid body modes of shell element.
Owner:LIVERMORE SOFTWARE TECH
Fast three-dimensional visualization method based on preprocessing result of finite-element analysis
InactiveCN101982837AReduce redundancyReduce complexity3D-image rendering3D modellingElement analysisCombined use
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Random finite element analysis based infrared-decoy-projectile pneumatic feature modeling method
InactiveCN106485035ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAerodynamic dragElement analysis
The invention discloses a random finite element analysis based infrared-decoy-projectile pneumatic feature modeling method. The pneumatic feature modeling method includes the steps of analysis and simplification of infrared-decoy-projectile working field, finite element subdivision of the decoy projectile working field, determination of unit interpolation based function, analysis of finite units, establishment of overall-random finite element equation, establishment and simulation of decoy projectile motion equation and the like. A temperature flow field distribution and random air-resistance movement feature model of a decoy projectile is provided on the basis of a finite analysis method by analyzing working mechanism and operating status of the decoy projectile; basis is provided for design of the infrared decoy projectile and research on an infrared guidance algorithm, and important guiding significance is achieved for establishment of an infrared visual simulation system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Automatic grid density generation method applicable to finite element analysis during forging process
ActiveCN102222134AOptimize reasonable density distributionImprove analysis efficiencySpecial data processing applications2D geometric modelGrid density
The invention relates to an automatic grid density generation method applicable to finite element analysis during a forging process. According to the boundary curvature, geometric property, the distribution of field variables (such as stress, strain, strain rate and temperature and the like) and requirement for the number of division units of a geometric model as well as a user-designated density window, the method is capable of automatically generating optimized and reasonable grid density distribution and a gird model, effectively controlling the number of the grid units generated eventually and combing various grid generation methods so as to generate an adaptive finite-element grid model and greatly improve the analysis efficiency and precision of numerical analysis methods such as like a finite element method. The method is applicable to the automatic gird density generation of not only 2D geometric models but also 3D geometric models. In addition, the method is applicable to not only finite-element grid density generation but also cases that initial grid division and grid re-division are needed when finite volume and finite difference are used to analyze other engineering problems.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for extracting flatness errors of mechanical structural plane based on finite element analysis
ActiveCN103267507AShorten the development cycleImprove economyMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsNODALElement analysis
The invention provides a method for extracting the flatness errors of a mechanical structural plane based on finite element analysis. First, a three-dimensional solid model of a valve is built with the CAD technology, and simulated analysis under composite working conditions is carried out on the three-dimensional solid model through finite element software to measure and obtain the coordinates of all nodes of a deformed valve seat plane; space analytic geometry knowledge is utilized and a certain assessment method is combined to determine the position of an assessment basal plane (namely an ideal plane) of the valve seat plane so as to enable the maximum variations from all the nodes of the valve seat plane to the assessment basal plane to be smallest; the distance from each node of the valve seat plane to the assessment basal plane is calculated to obtain a high pole and a low pole and finally obtain the flatness errors. The method for extracting the flatness errors of the mechanical structural plane based on the finite element analysis has the advantages that the flatness errors can be extracted from the result of the finite element analysis of mechanical products including the valve and the like, whether the flatness errors meet requirements of graph paper is detected so as to judge out effects on performance such as sealing performance caused by deformation of the valve under the composite working conditions.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Systems and methods of performing vibro-acoustic analysis of a structure
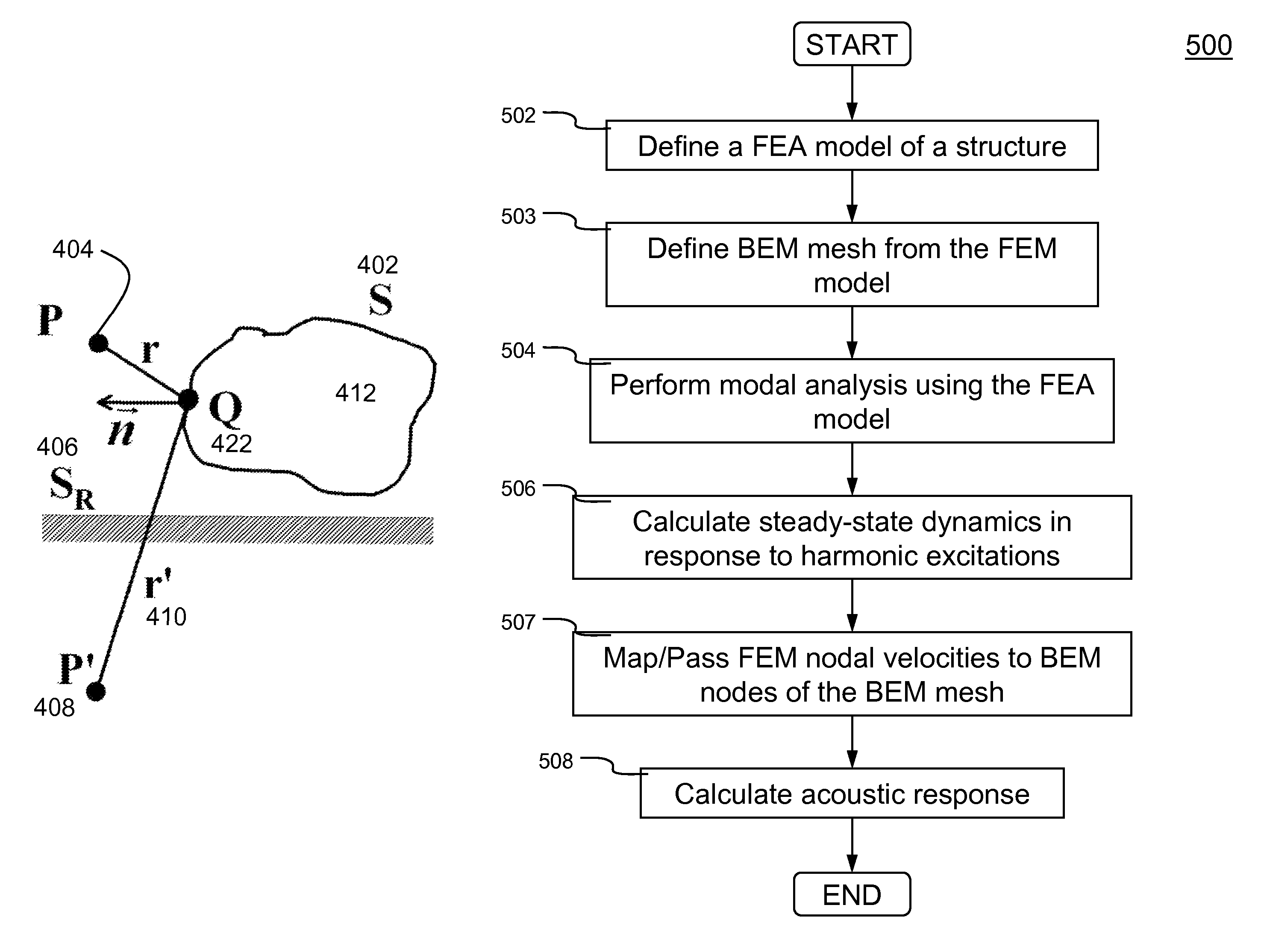
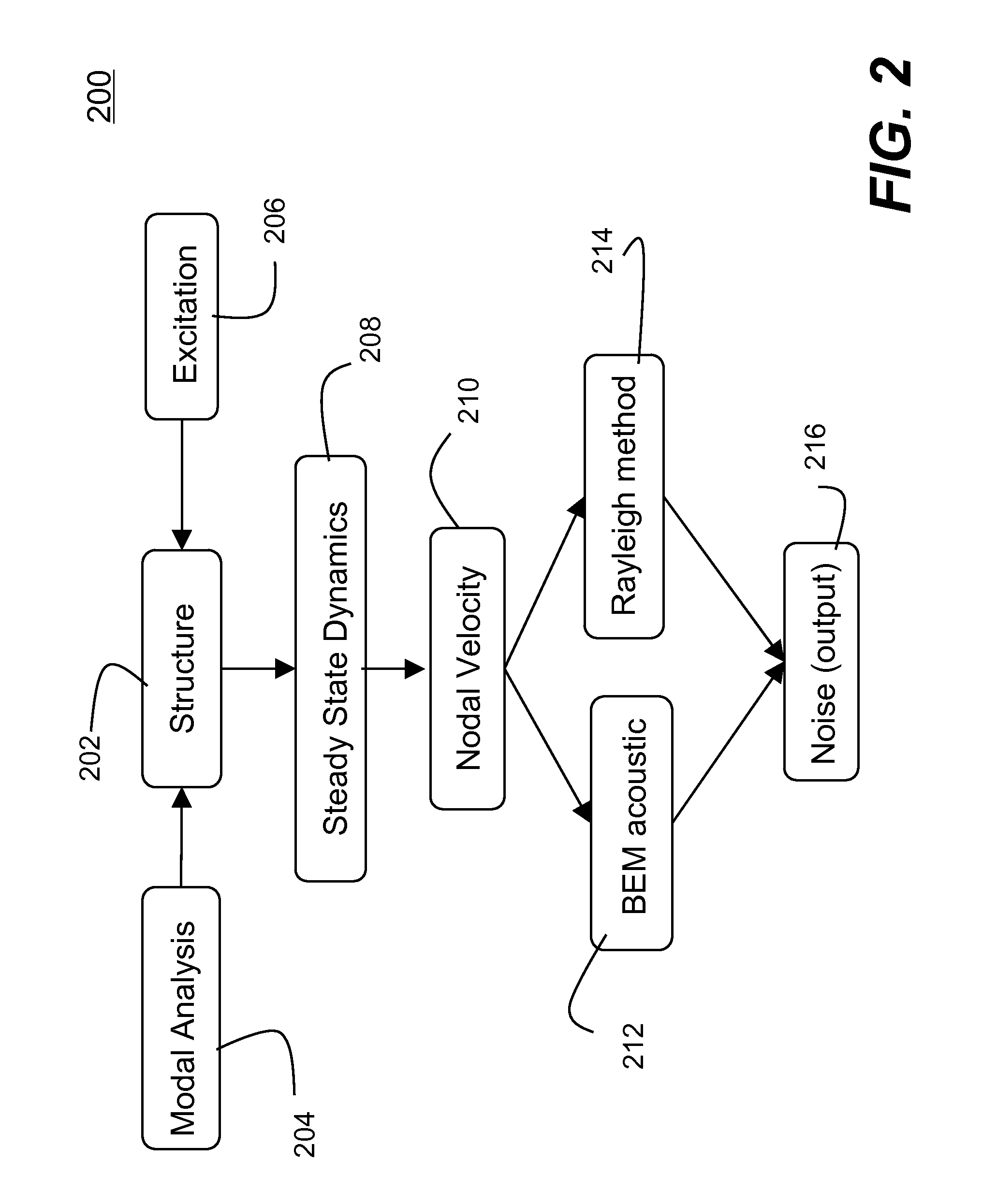
ActiveUS8306793B2Match real world resultFast convergenceFlow propertiesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusNODALElement analysis
Methods and systems for simulating acoustic field resulted from particular excitations by performing vibro-acoustic analysis of a structure are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, vibro-acoustic analysis of a structure is performed in two stages. First, steady state dynamic (SSD) responses are obtained using a finite element analysis model of a structure subject to harmonic excitations (e.g., external nodal loads, pressures, or enforced motions (e.g., ground motions), etc.). The steady state responses are the results (e.g., nodal velocities at desired locations of the structure) obtained in a finite element analysis in frequency-domain. Second, an acoustic analysis is conducted according to Helmholtz equation using the nodal velocities obtained at desired locations on the structure as a boundary condition. The acoustic analysis can be performed in a number of procedures (e.g., boundary element method, Rayleigh approximation method, etc.).
Owner:ANSYS
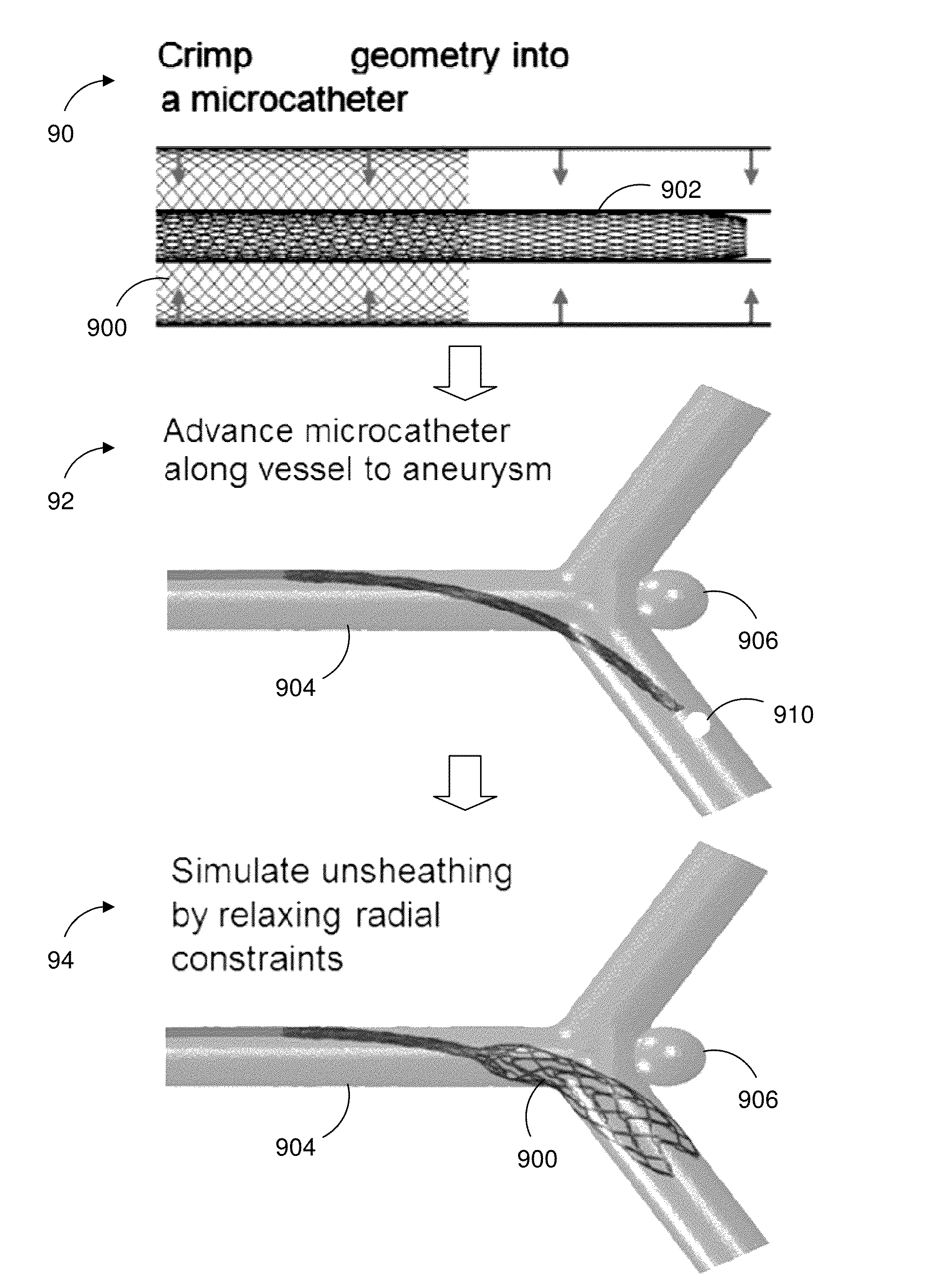
Device specific finite element models for simulating endovascular treatment
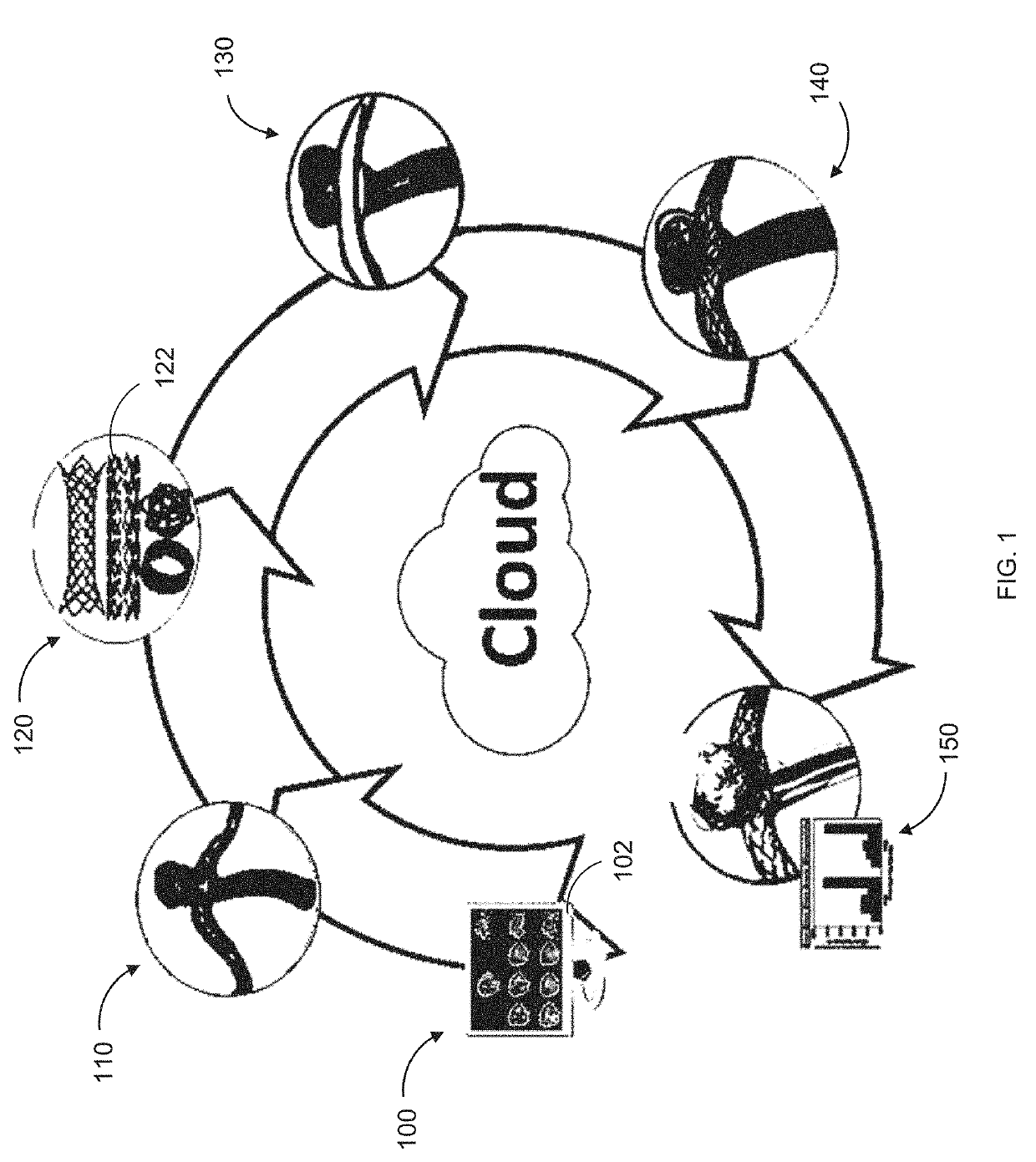
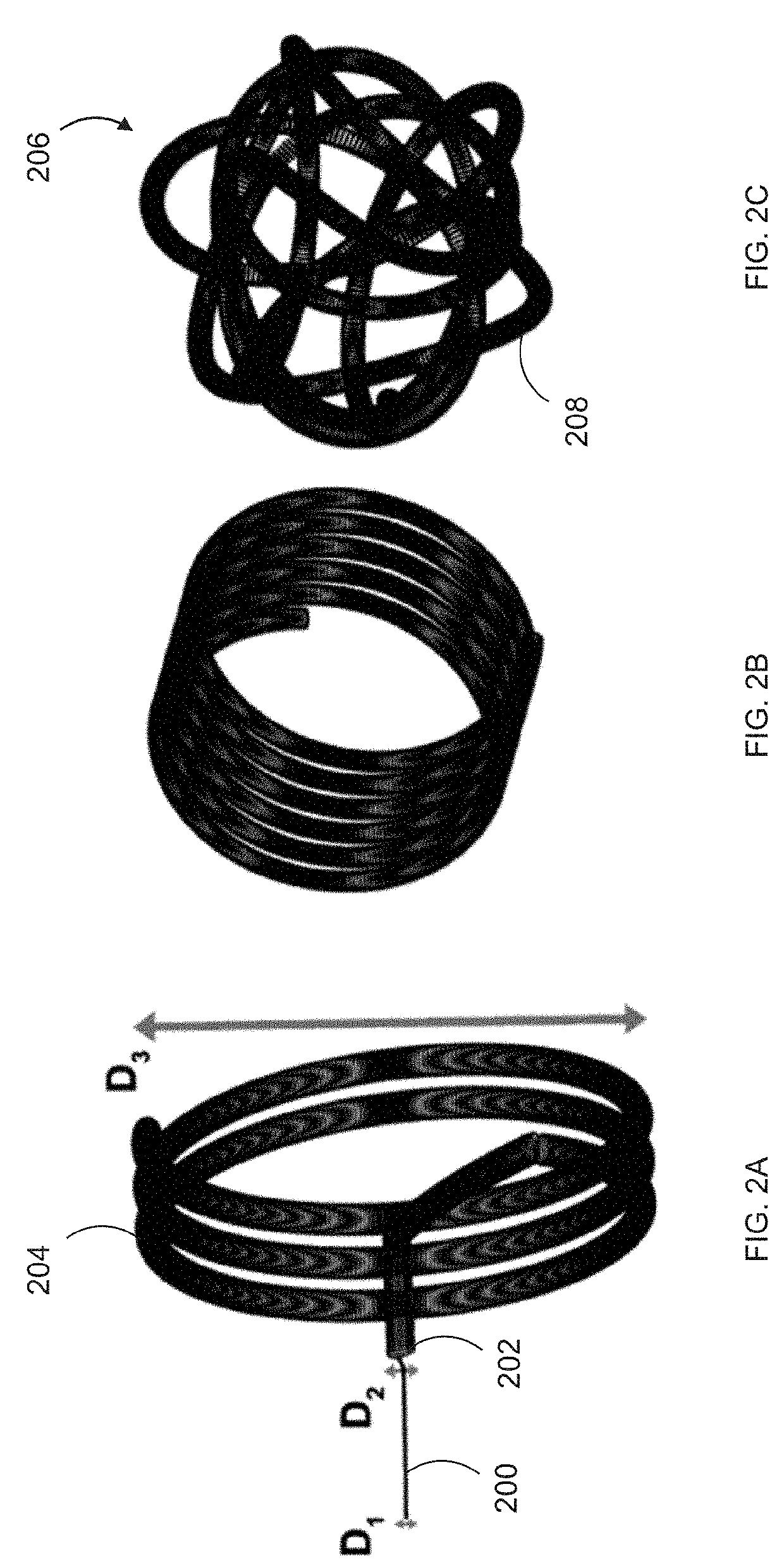
ActiveUS20150235569A1Educational modelsElectrical appliancesAnatomical structuresEndovascular treatment
Systems and methods provide a novel computational approach to planning the endovascular treatment of cardiovascular diseases. In particular, the invention simulates medical device deployment and hemodynamic outcomes using a virtual patient-specific anatomical model of the area to be treated, high-fidelity finite element medical device models and computational fluid dynamics (CFD). In an embodiment, the described approach investigates the effects of coil packing density, coil shape, aneurysmal neck size and parent vessel flow rate on aneurysmal hemodynamics. A processor may receive patient clinical data used to construct the relevant anatomical structure model. The processor may access medical device models constructed using finite element analysis and three dimensional beam analysis, and simulates the deployment of selected medical devices in the anatomical structure model. The selected medical device models and the anatomical structure model mesh, allowing the processor to simulate hemodynamic outcomes using computational fluid dynamics.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
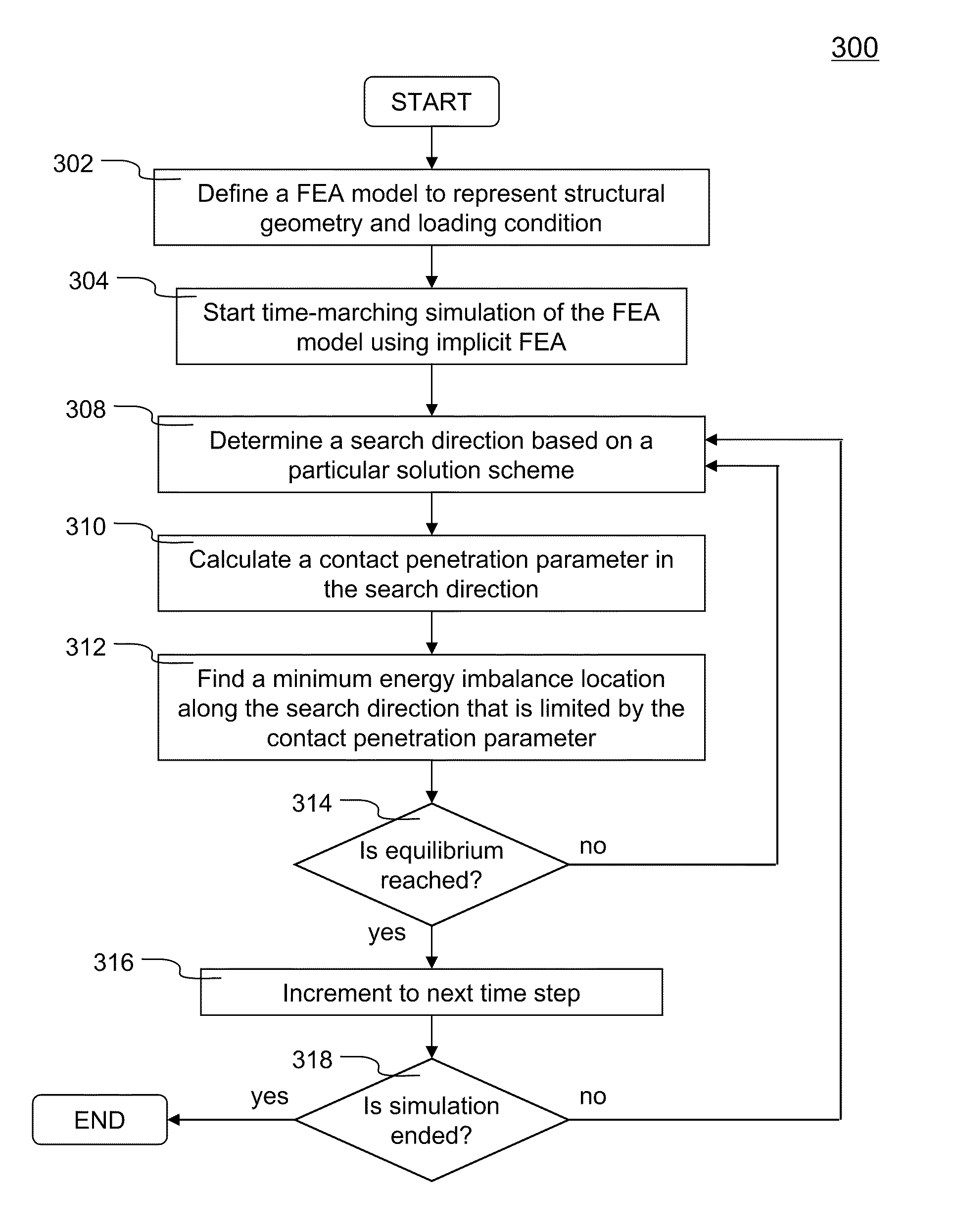
Systems and methods of limiting contact penetration in numerical simulation of non-linear structure response
ActiveUS7953578B2Analogue computers for chemical processesComputation using non-denominational number representationNODALElement analysis
Owner:ANSYS
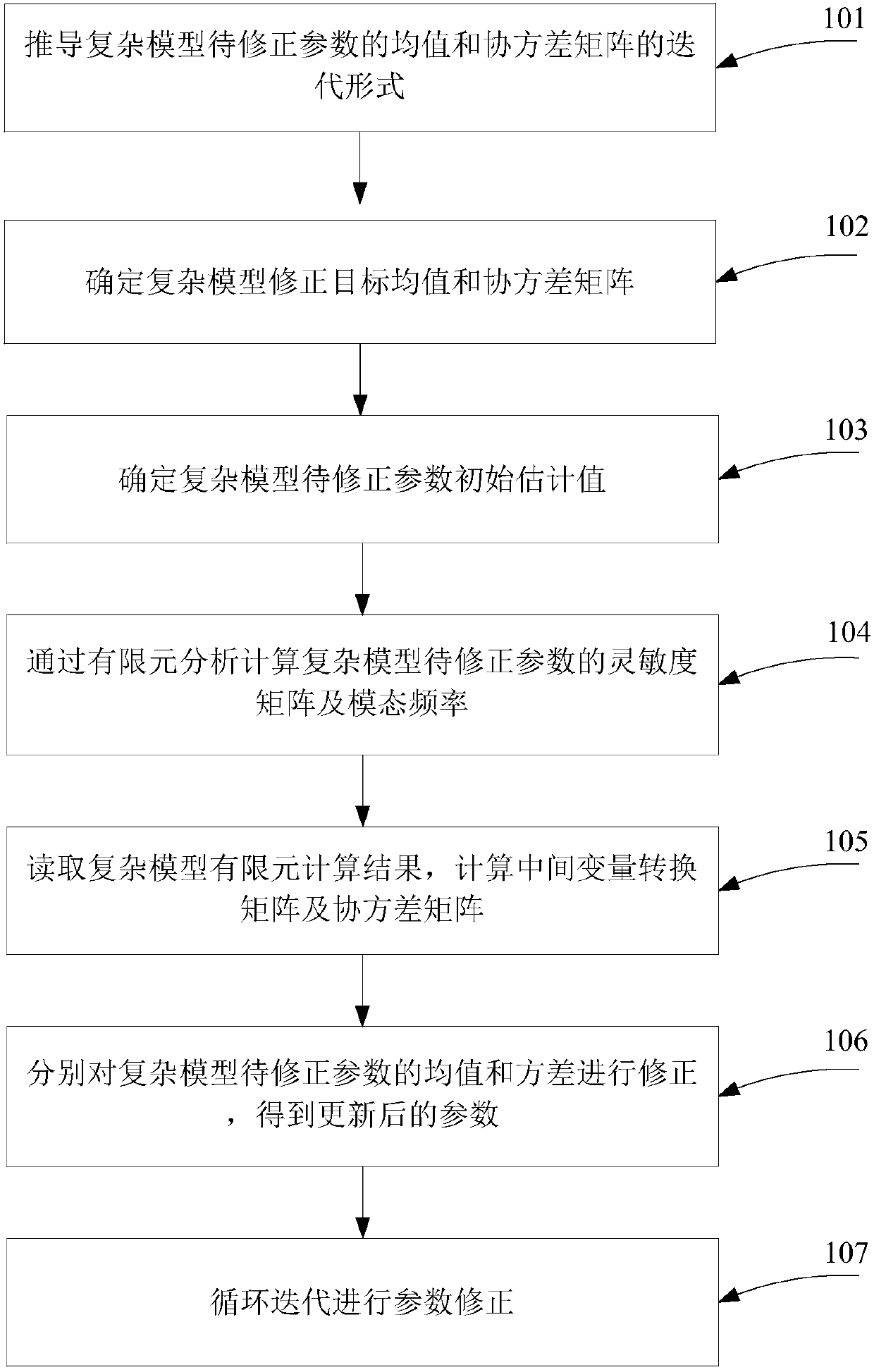
Finite element model correction method based on perturbation method for complex model under uncertainty
InactiveCN108334670AImprove correction accuracyFast convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelElement analysis
The invention provides a finite element model correction method based on the perturbation method for a complex model under uncertainty, comprising: deducing an iteration form for average and covariance matrixes for under-correction parameters of the complex model; determining complex model correction target average and covariance matrixes; determining initial estimated values of the under-correction parameters of the complex model; calculating a sensitivity matrix and modal frequencies for the under-correction parameters of the complex model through finite element analysis; reading finite element calculation results of the complex model, and calculating an intermediate variable conversion matrix and the covariance matrix; correcting an average and covariance of the under-correction parameters of the complex model to obtain updated parameters; performing cyclic iteration to carry out parameter correction. File reading-writing and data transmission channels are established based on the commercial mathematical software MATLAB and the finite element simulation software NASTRAN; the method is suitable for solving model correction problems where both system parameters of a complex modeland test data present uncertainty, and corrected parameters have high average precision.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Seismic destructive force evaluation method and device based on dynamic elastoplasticity and ground motion
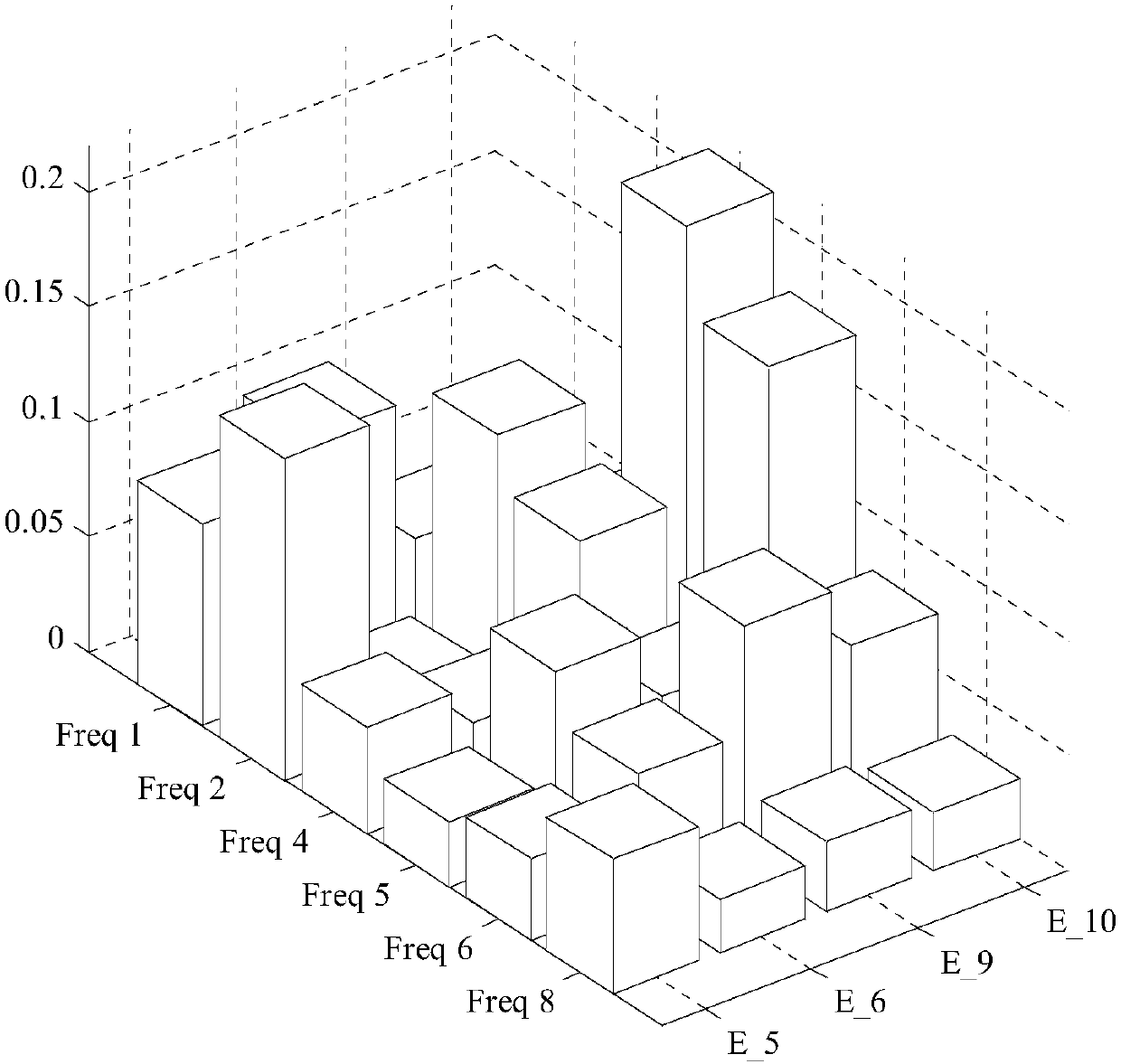
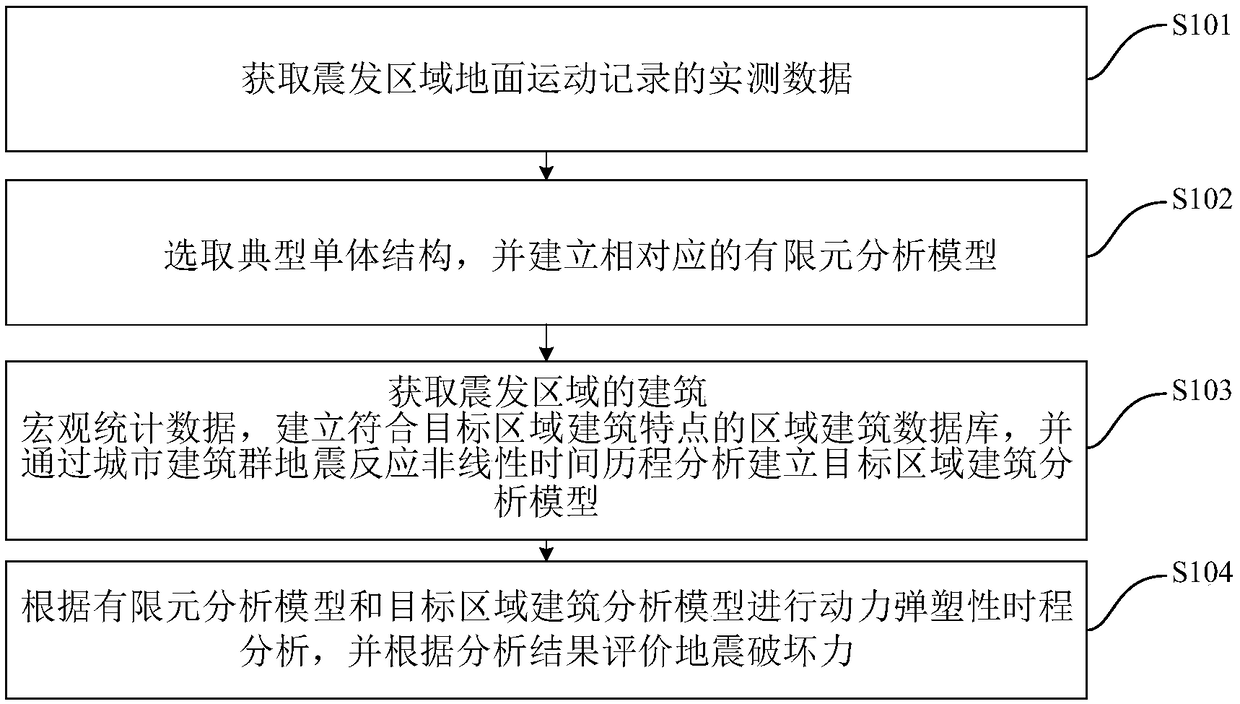
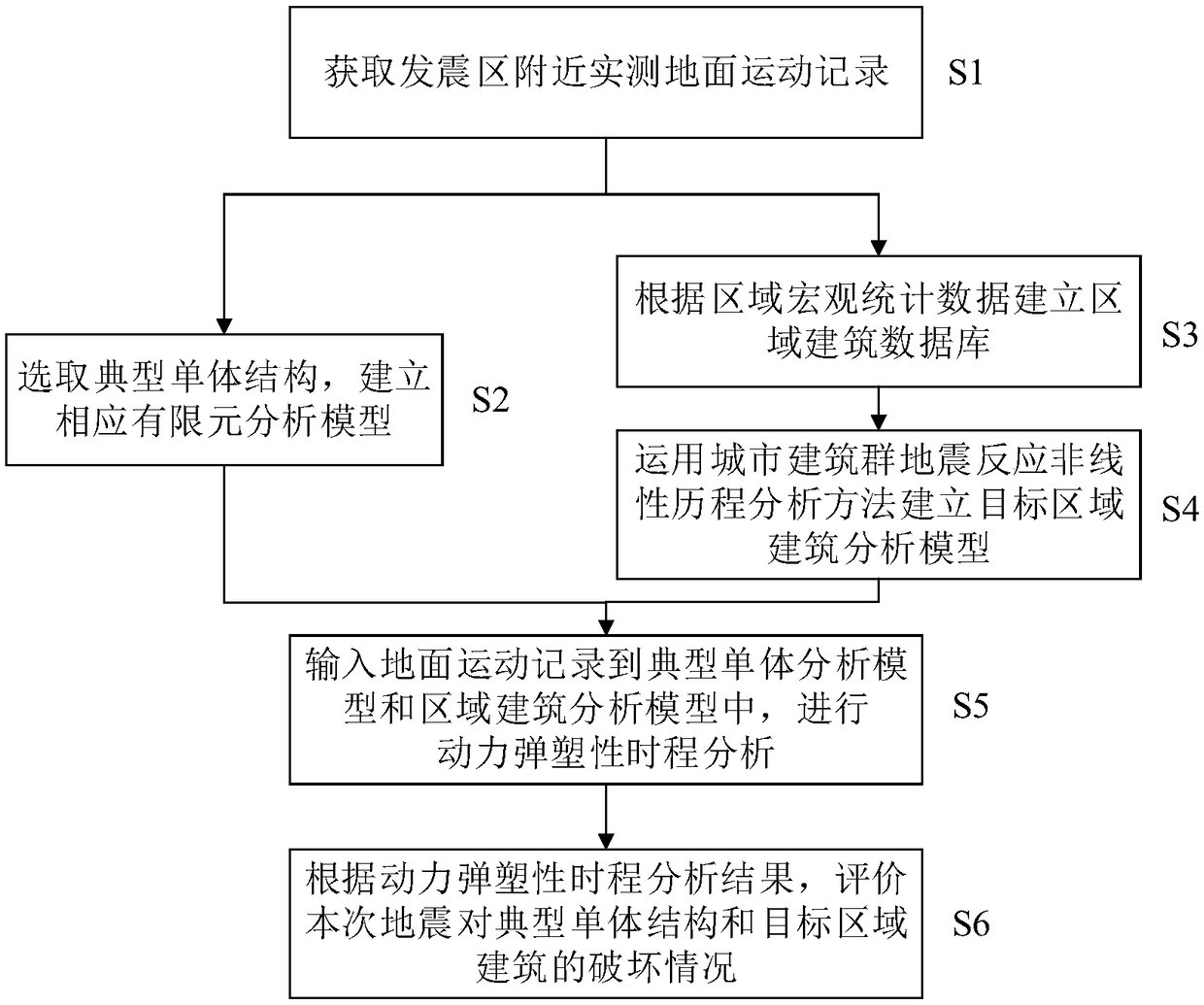
PendingCN109063327AAccurate and fast evaluationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement analysisComputer science
The invention discloses a method and a device for evaluating earthquake destructive force based on dynamic elastoplasticity and ground motion, wherein, the method comprises the following steps: obtaining measured data of ground motion records in earthquake occurrence area; the typical monomer structure is selected and the corresponding finite element analysis model is established. Obtain the macroscopic statistical data of the buildings in the earthquake-stricken area, establish the regional building database which accords with the characteristics of the buildings in the target area, and establish the analysis model of the buildings in the target area through the nonlinear time history analysis of the earthquake response of the urban buildings; The dynamic elastoplastic time history analysis is carried out according to the finite element analysis model and the target area building analysis model, and the earthquake destructive power is evaluated according to the analysis results. Thismethod can evaluate the earthquake destructive power accurately and quickly, and provide strong support for the disaster relief work after the earthquake.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of soft-rock slope stability
InactiveCN107908890ASolving slope stability problemsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMechanical modelsElement analysis
The invention discloses a finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of soft-rock slope stability. The method includes the following steps: step one, obtaining rock slope failure types, slope stability influence factors and slope reinforcement support measures by induction, establishing a mechanical model of engineering geology simulation analysis under the action of the different influence factors, and analyzing a dominant factor controlling the soft-rock slope stability and a potential mode thereof; and step two, using an approximate equivalent physical model, which is formed bya plurality of mutually associated unit bodies, by a finite-element analysis method of the slope stability to replace actual structures or continua, and establishing equations, which characterize force and displacement relationships, through basic principles of structure and continuum mechanics and physical characteristics of units. The finite-element analysis, monitoring and support method of thesoft-rock slope stability uses the finite-element method to analyze the stability thereof, carries out support and treatment on places where danger may further occur, and has certain guiding significance for solving slope stability problems.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Device specific finite element models for simulating endovascular treatment
PendingUS20190251866A1Medical simulationEducational modelsEndovascular treatmentAnatomical structures
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Method for researching electric field shielding of power transmission line based on tree electrical characteristics
InactiveCN111273090AResistance/reactance/impedenceElectromagentic field characteristicsLarchElectrical impedance tomography
The invention relates to comprehensive and deep understanding of the shielding effect of trees on an electric field of a power transmission line so as to prevent high electromagnetic radiation from harming a human body. The method comprises the following steps: selecting Xing'an larch and poplar as research objects to measure the resistivity of the tree at different heights by using a PiCUS tree electrical impedance tomography imaging instrument; using an HI-3604 power frequency electromagnetic field measuring instrument for measuring the electric field intensity around two trees under a powertransmission line; and establishing a model in combination with the measurement result of the trees resistivity, calculating the electric field intensity around the trees by using finite element analysis software, and verifying and comparing the calculation result with actual measurement data, so that the feasibility of finite element method analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for selecting packing for roll bending of integral panel based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN103530448AShorten the design cycleReduce design costSpecial data processing applicationsSocial benefitsLS-DYNA
The invention discloses a method for selecting packing for roll bending of an integral panel based on finite element analysis. ANSYS / LS-DYNA calculation software is used in the method, and the method comprises the following steps of defining material models of rollers, panels and the packing, establishing and segmenting geometric models, dividing lattices on the geometric models, applying restrictions and speed load to an upper roller and a lower roller, carrying out solving, and analyzing and comparing the straightness, the residual stress and the unit strain obtained through post-processing results to obtain a preferred packing variety. According to the method, the optimized packing variety is obtained by selecting different varieties of packing to carry out comparison through the method of the finite element, the method can be directly used for guiding the selection of the packing in actual production, therefore, the design period is shortened greatly, design cost is reduced, and design efficiency is improved. Meanwhile, the method is an environment-friendly production mode, and large amount of economy, environment and social benefit can be generated for enterprises and the society.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
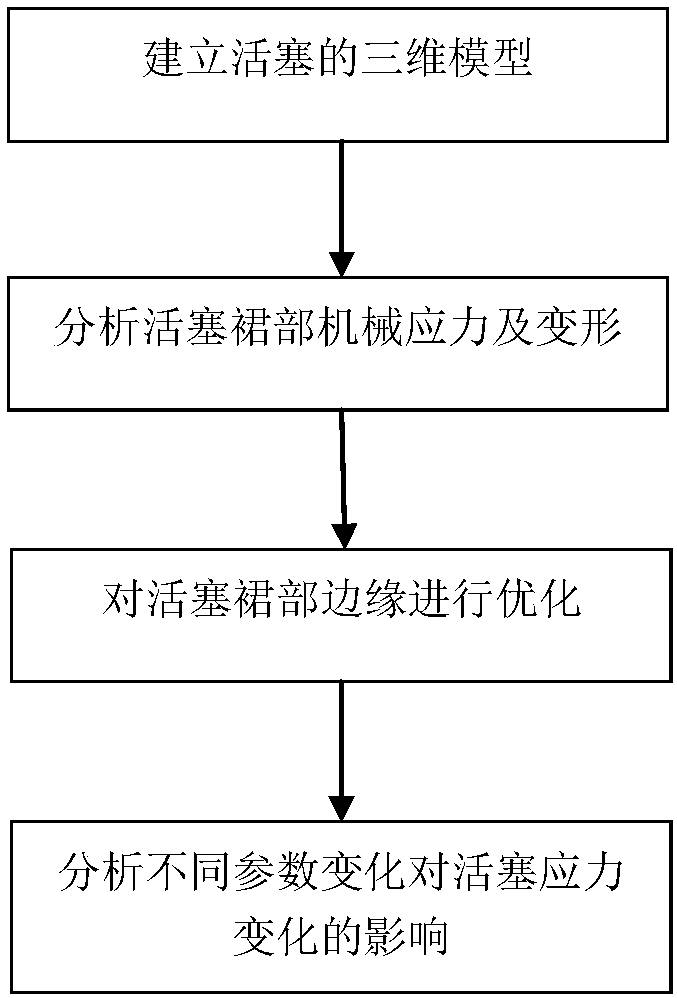
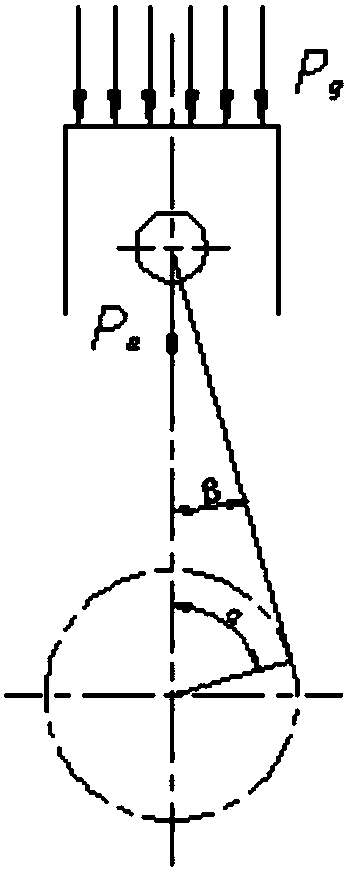
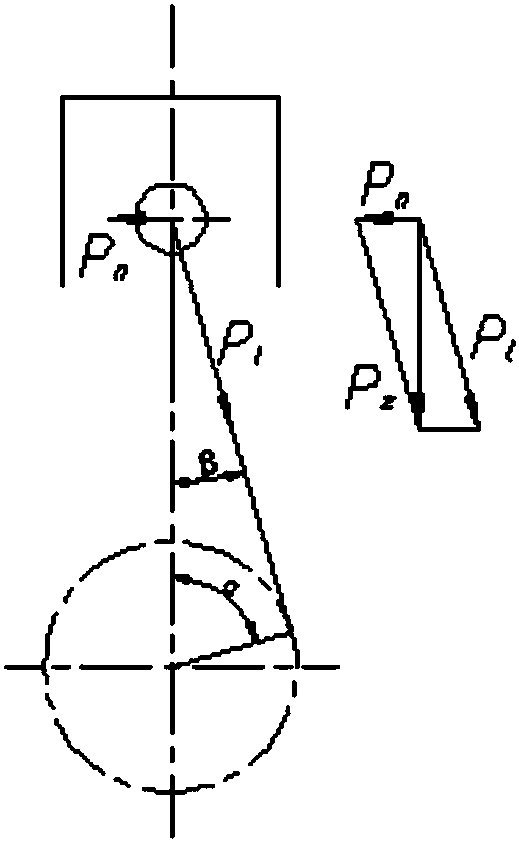
Piston skirt optimization method based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN107679346AExcellent stress modeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a piston skirt optimization method based on finite element analysis. The problems that in the prior art, the load of a piston is too large and the stress on a piston skirt cannot be effectively analyzed are solved. The method has the advantages that stress analysis is conducted on the piston skirt, and the piston can better meet work requirements by changing skirt parameters to optimize the piston skirt. According to the technical scheme, the method includes the following steps that a three-dimensional model of the piston is established, piston parameters are set, and grids are divided; the mechanical stress and deformation of the piston skirt are analyzed to obtain the maximum stress position of the piston skirt; the edge of the piston skirt is optimized to obtaina skirt optimization result.
Owner:山东云内动力有限责任公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com