Patents
Literature
36 results about "In vivo animal model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In vivo, animal model for expression of hepatitis C virus
Disclosed is a method for expressing hepatitis C virus in an in vivo, animal model. Viable, hepatitis C virus-infected, human hepatocytes are transplanted into a liver parenchyma of a scid / scid mouse host. The scid / scid mouse host is then maintained in a viable state, for up to five days or greater, whereby viable, morphologically intact human hepatocytes persist in the donor tissue and hepatitis C virus is replicated in the persisting human hepatocytes.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
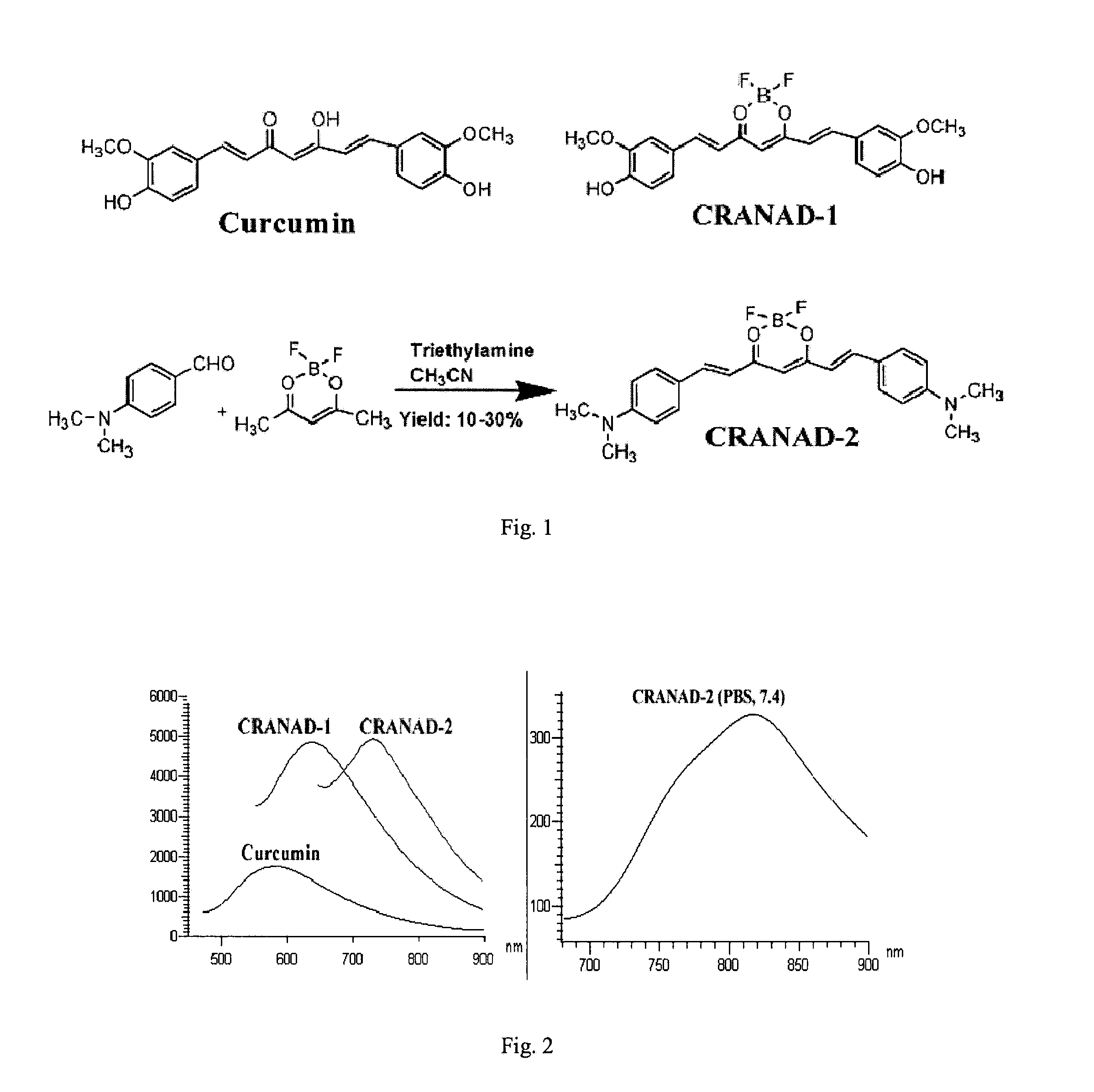
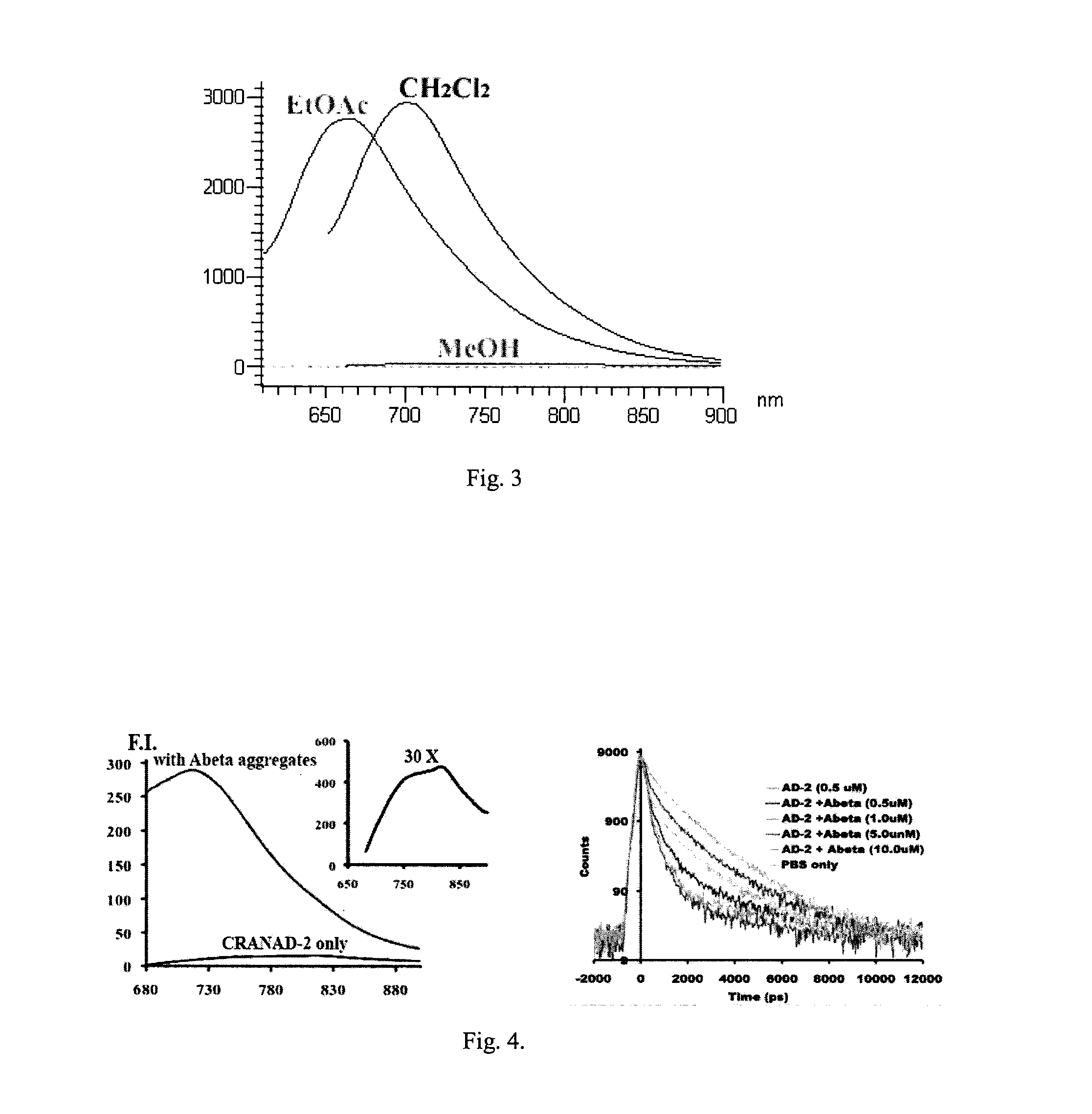
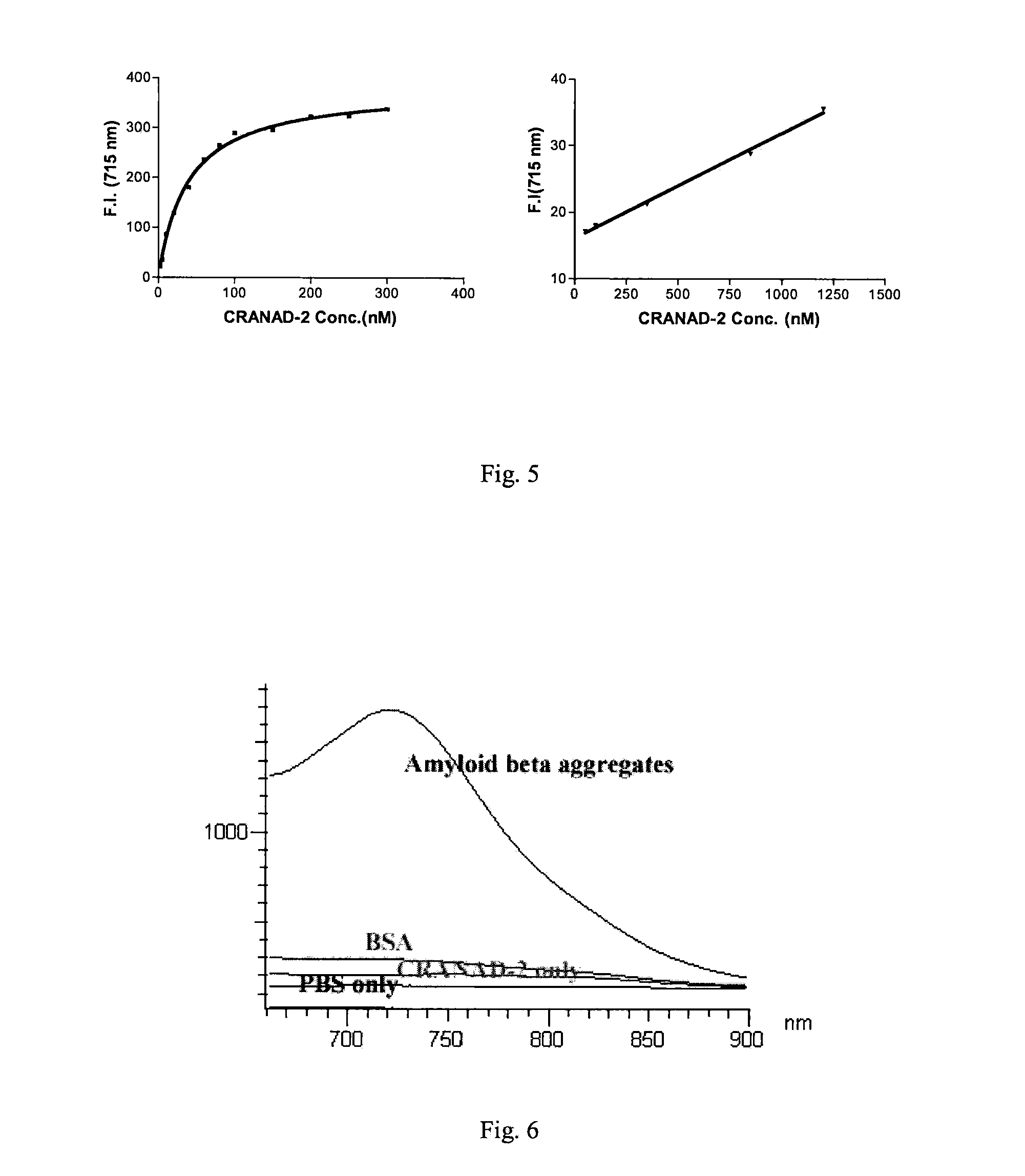
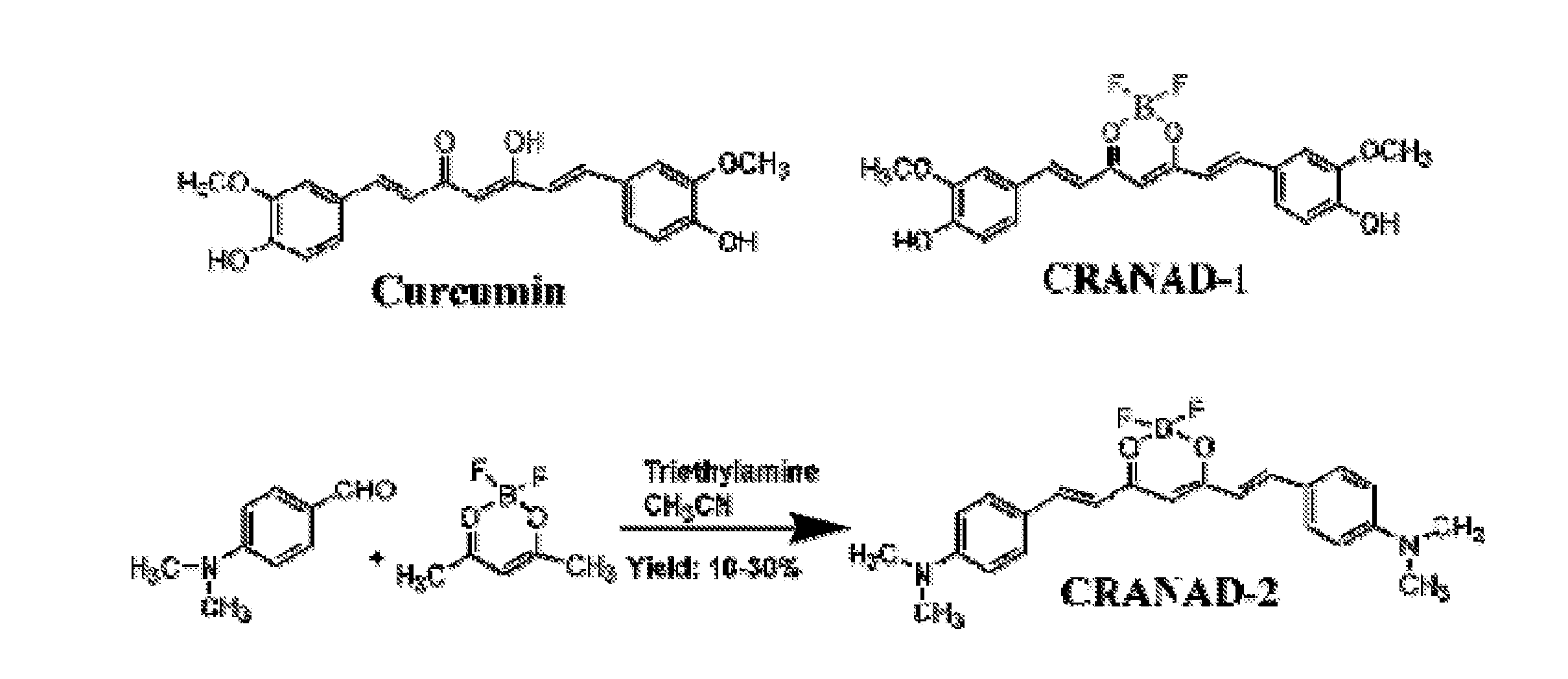
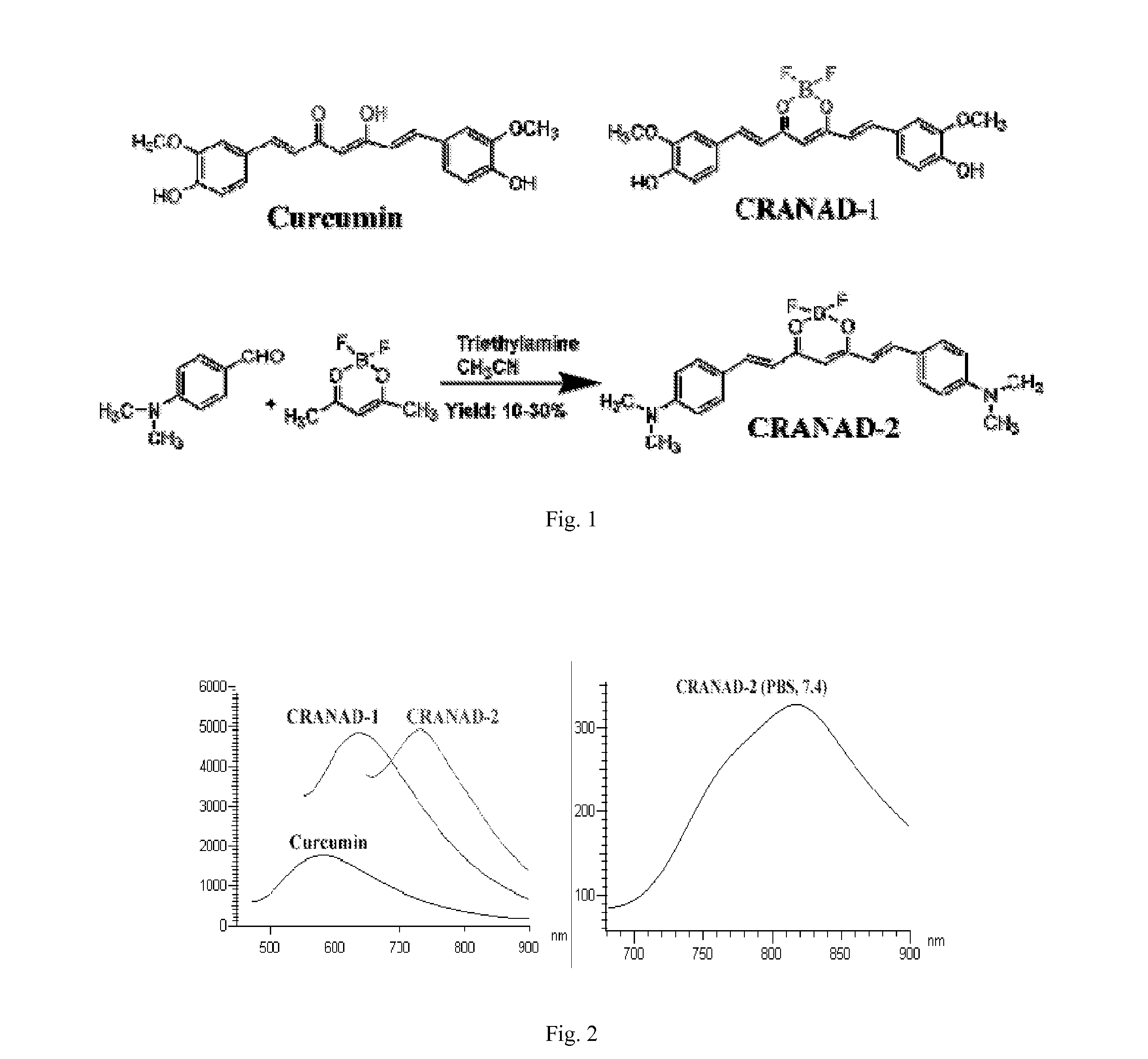
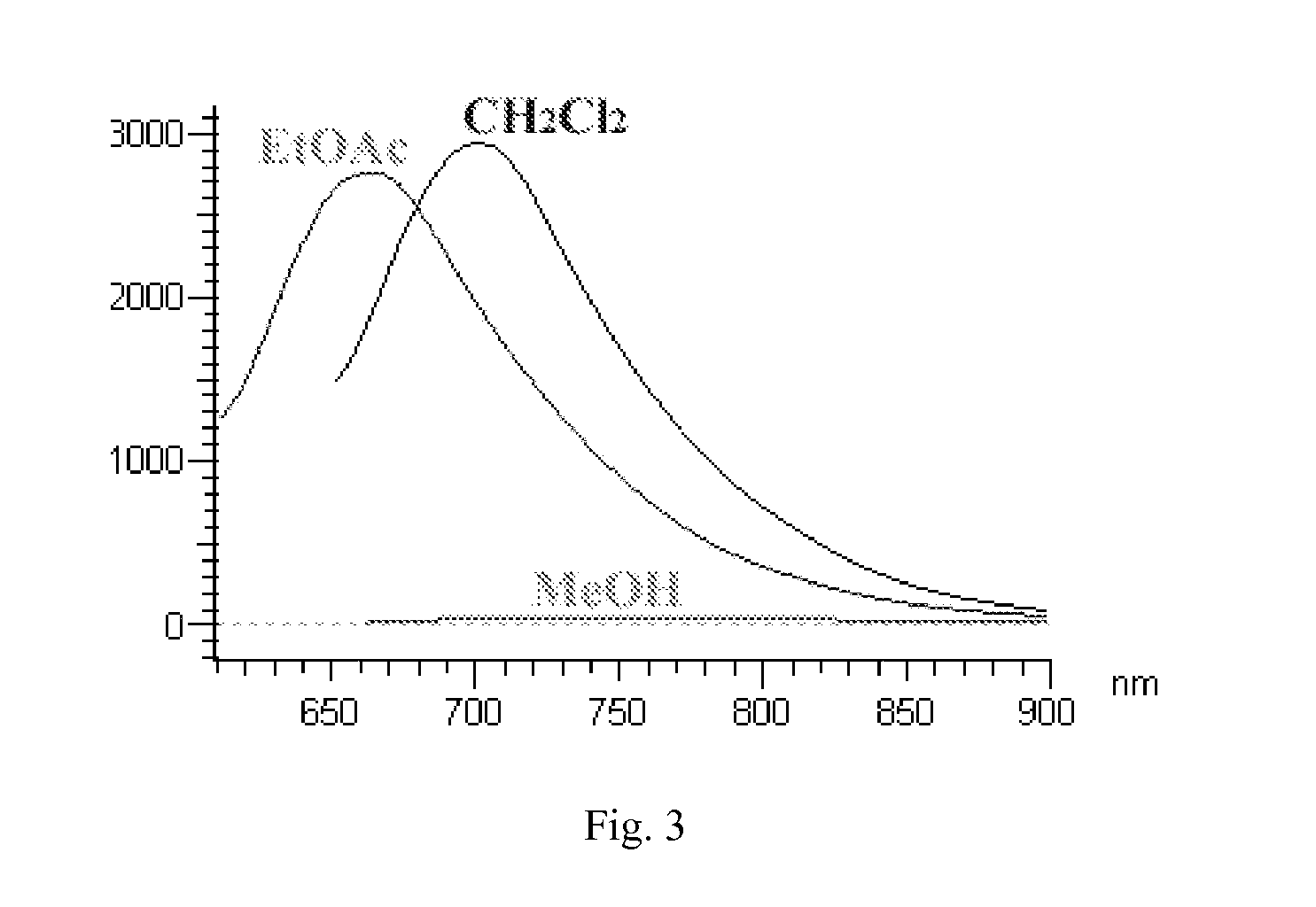
Curcumin Derivatives for Amyloid-Beta Plaque Imaging
InactiveUS20110208064A1Significant fluorescence property changeImprove lipophilicityNervous disorderMagnetic measurementsInfraredAmyloid beta
The present invention provides curcumin-derived near infrared (NIR) imaging probes. Upon interacting with amyloid β aggregates, these probes undergo a range of changes, qualifying them as “smart” probes. The inventors have demonstrated that probes of the invention have the capacity to monitor the progression of Alzheimer's disease in an in vivo animal model. In addition, the present invention encompasses probes useful as PET imaging agents, MRI imaging agents and multimodal imaging agents, as well as related methods of detecting and imaging amyloid β aggregates and plaques.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
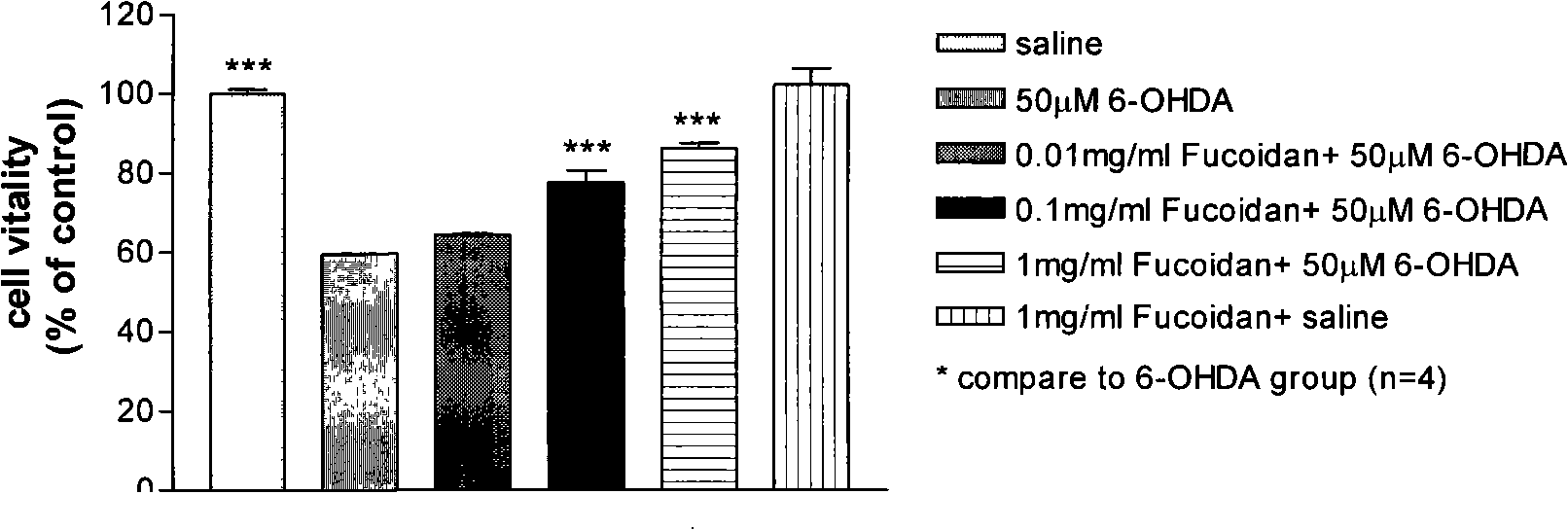
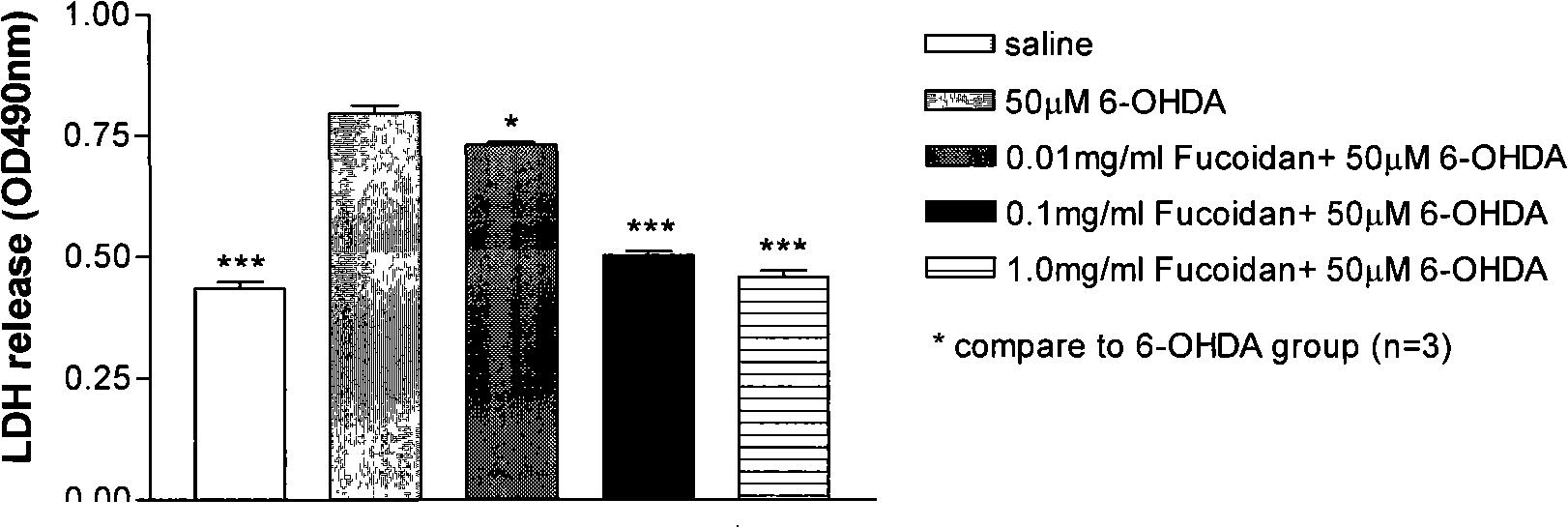
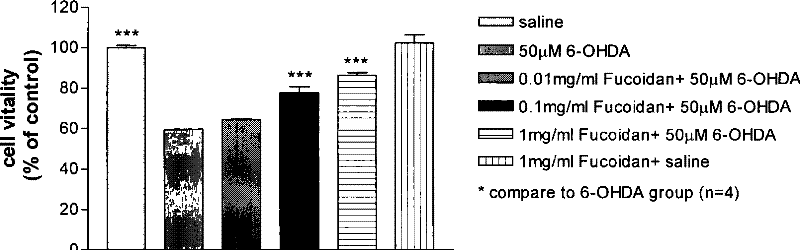
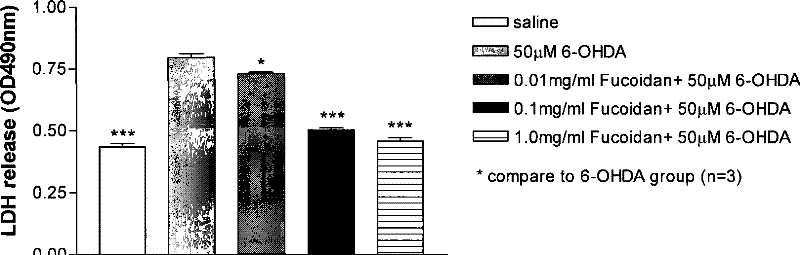
Use of brown alga polysaccharide sulfate in preventing and treating Parkinson's disease
ActiveCN101301310AImprove securityEnsure long-term medication needsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCholinergic cellsSulfated polysaccharides
The invention discloses a novel application of fucoidan sulfate in prevention and cure of a parkinson disease. According to the experiments of an isolated PD cell model and an in vivo animal model, fucoidan sulfate has a certain neuroprotection effect on DA cholinergic neurons of the PD cell model and animal model and can prevent and cure the PD disease. The fucoidan sulfate of the invention can be natural polysaccharide extracts obtained form brown alga such as kelp, focus, bladder wrack, sea-tangle or chorda filum and also can be materials such as low molecular weight SSPSA or oligosaccharide which are obtained through the degradation of fucoidan sulfate.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES +1
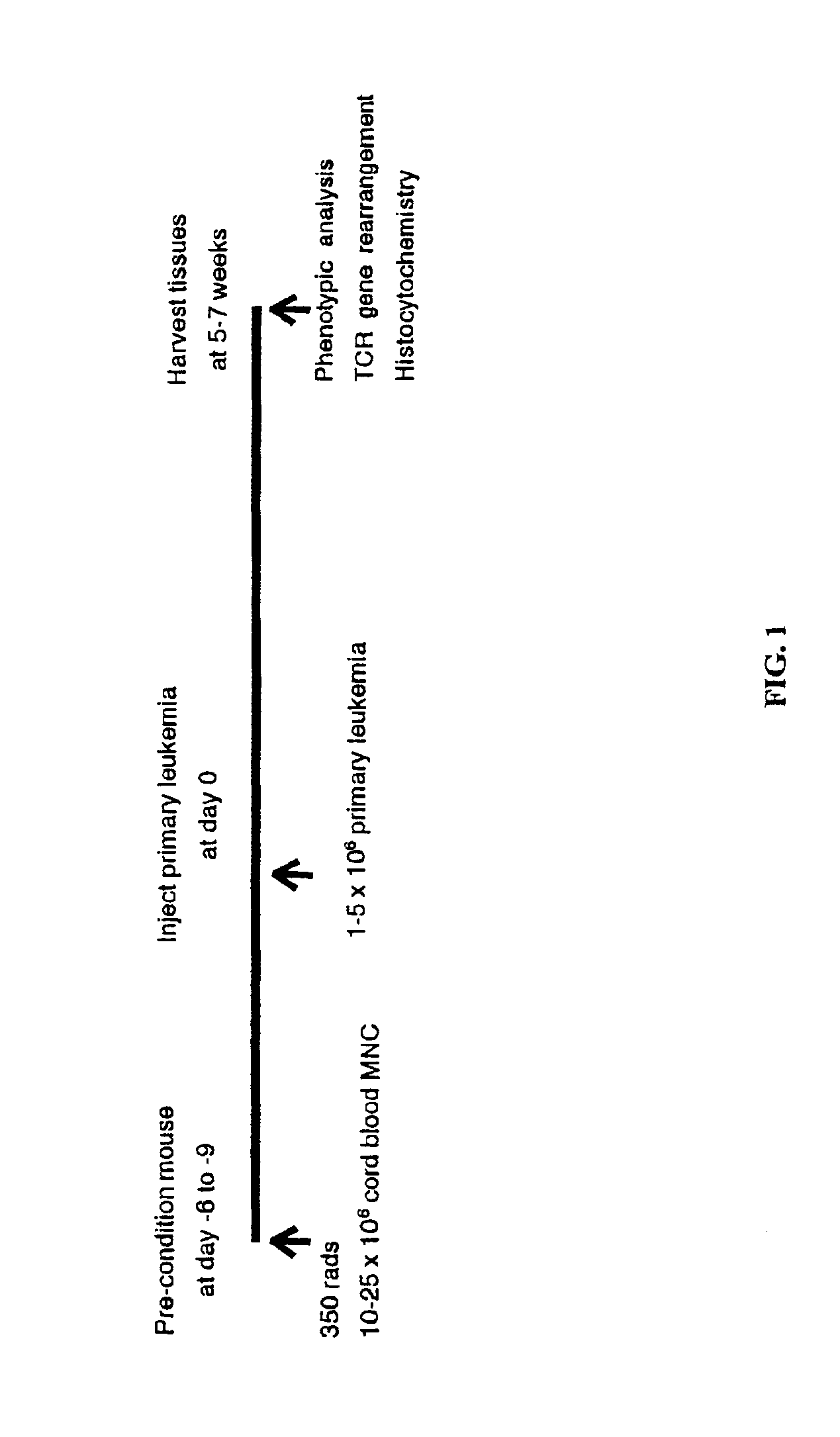
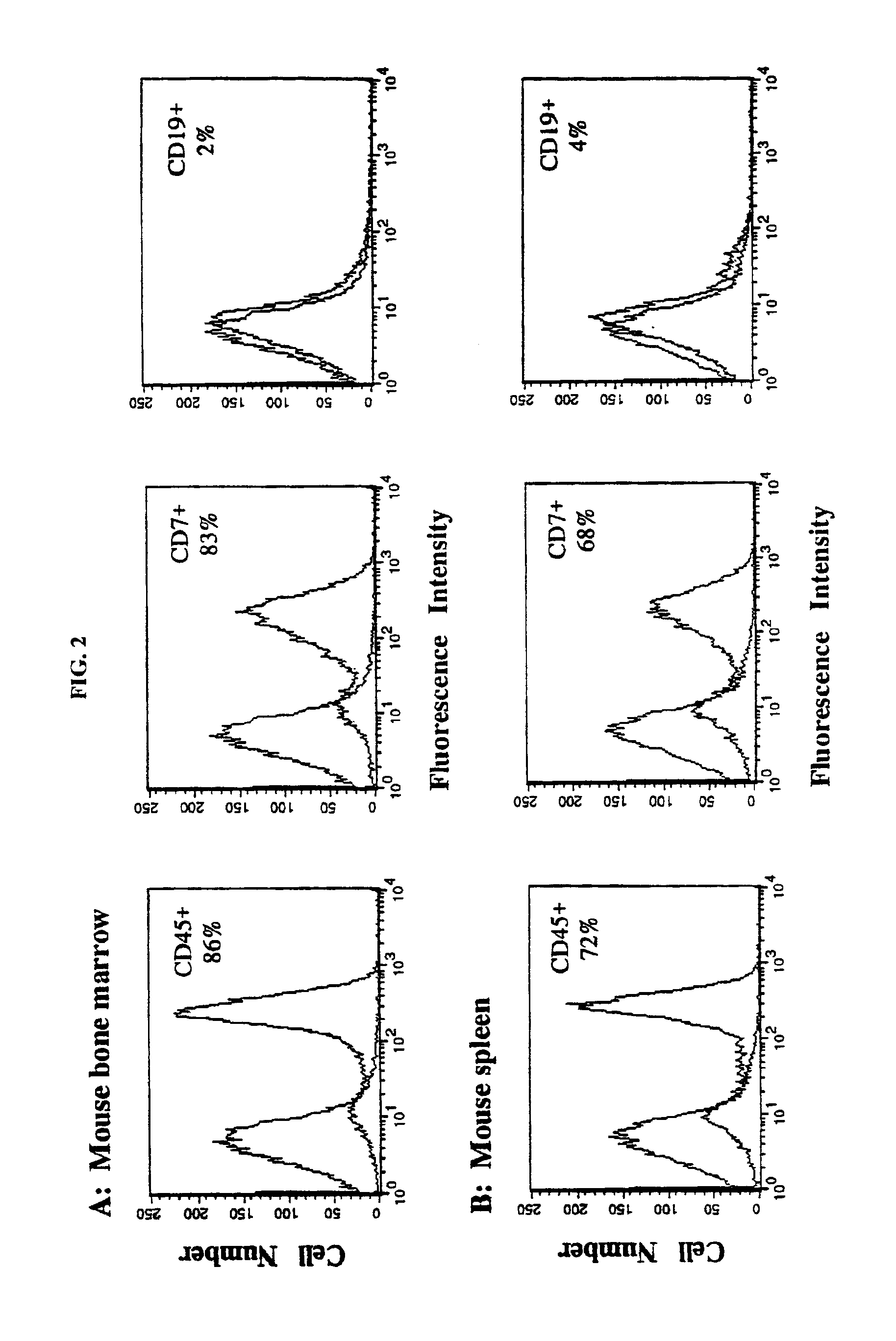
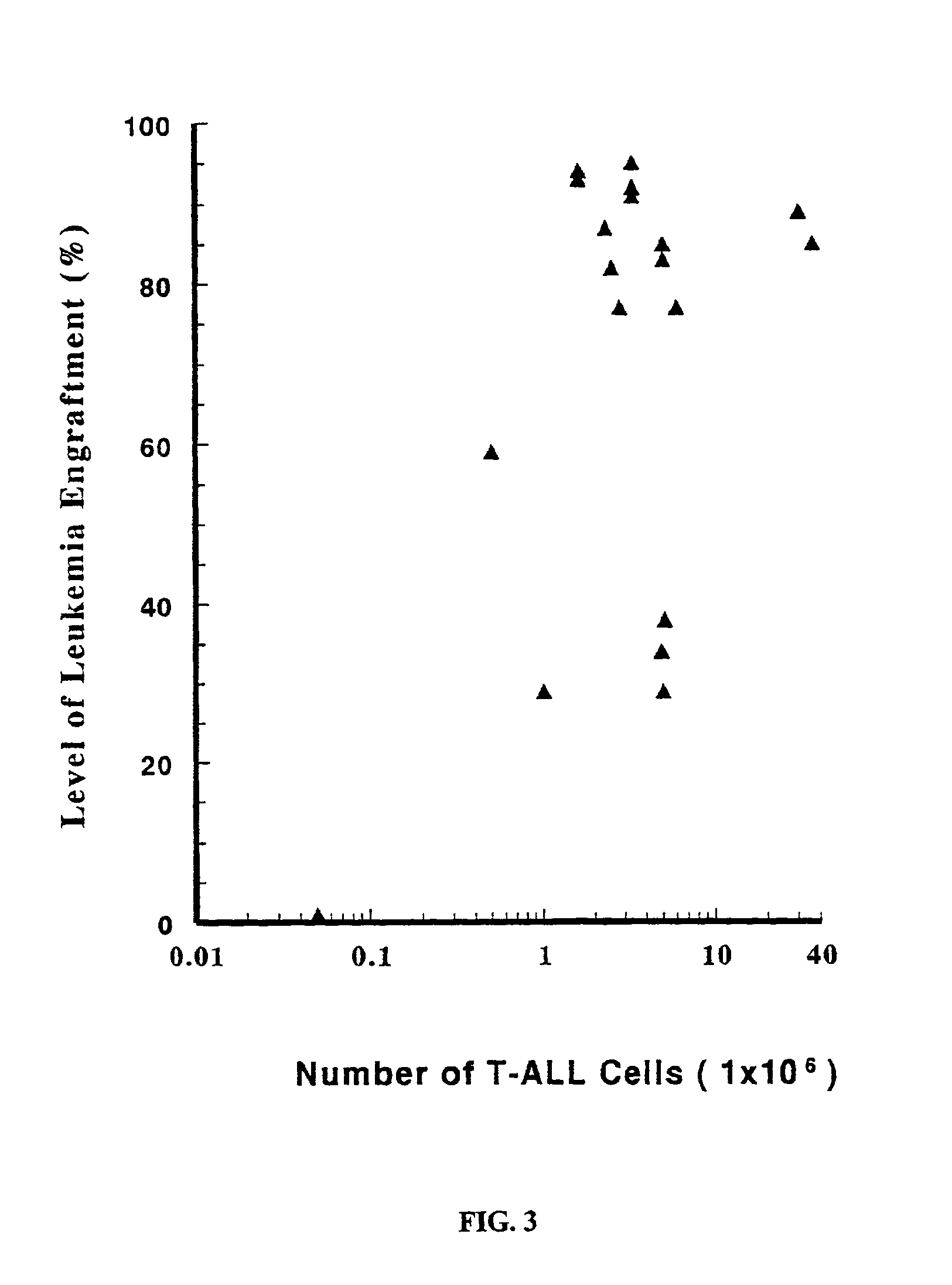
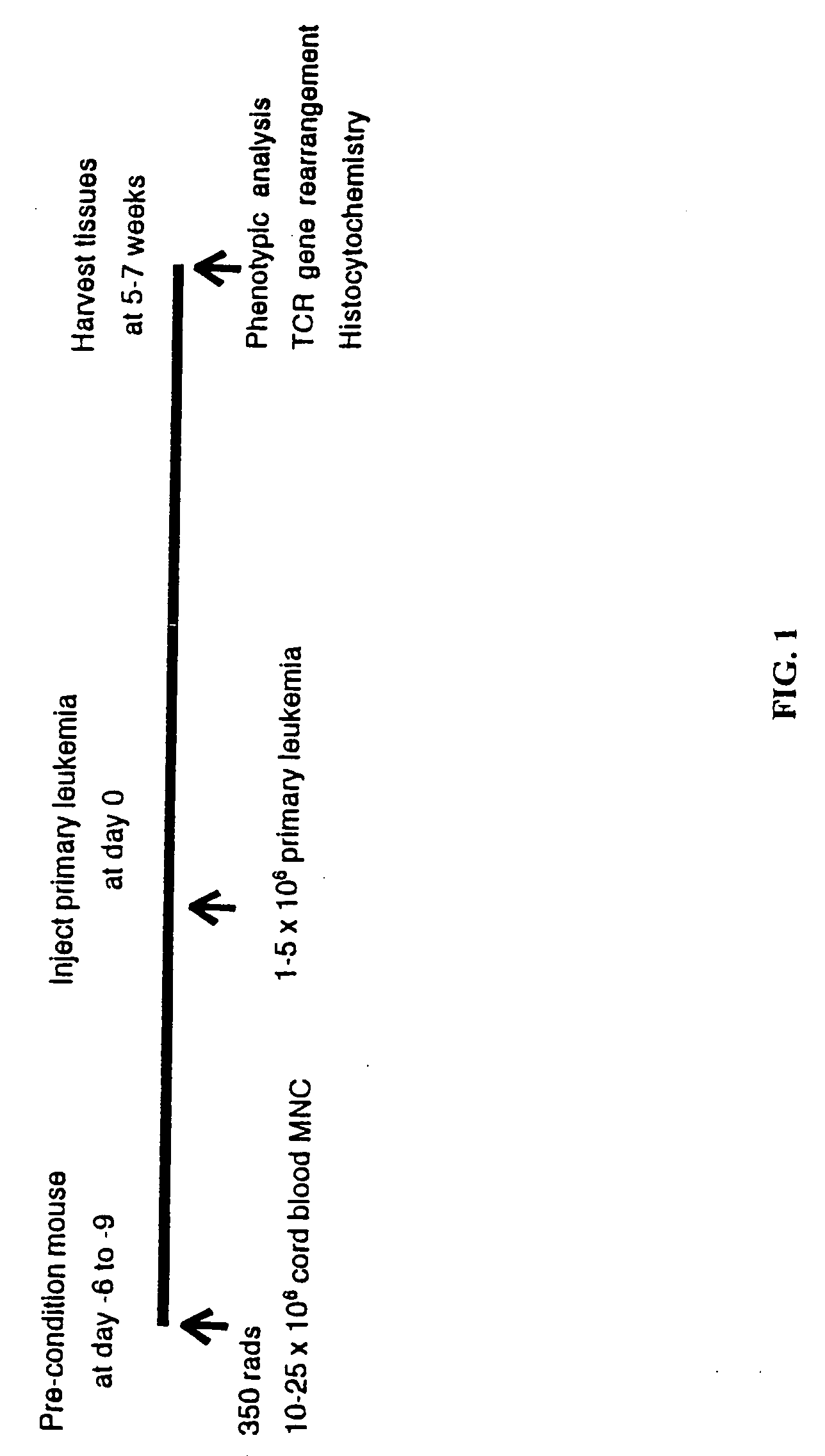
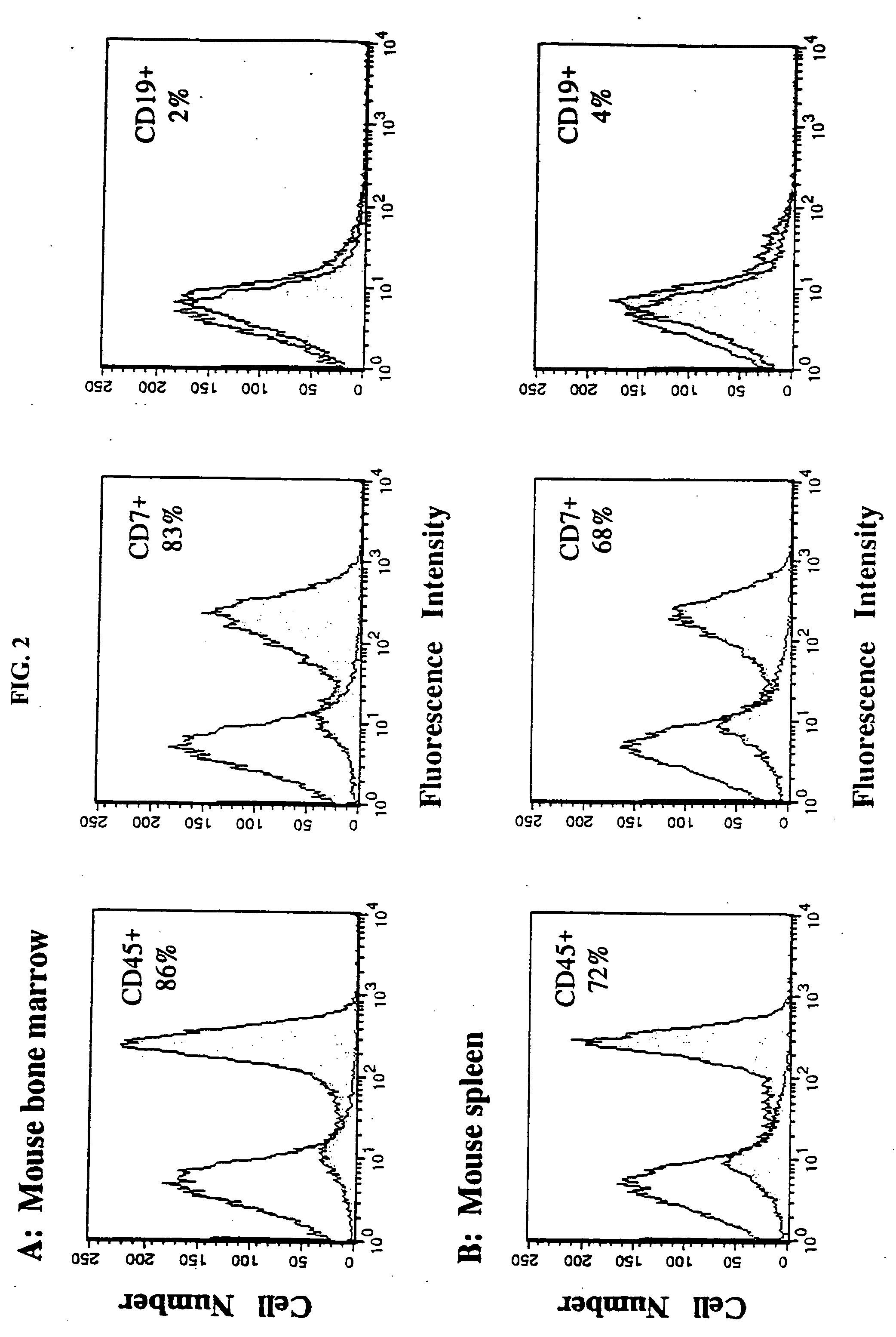
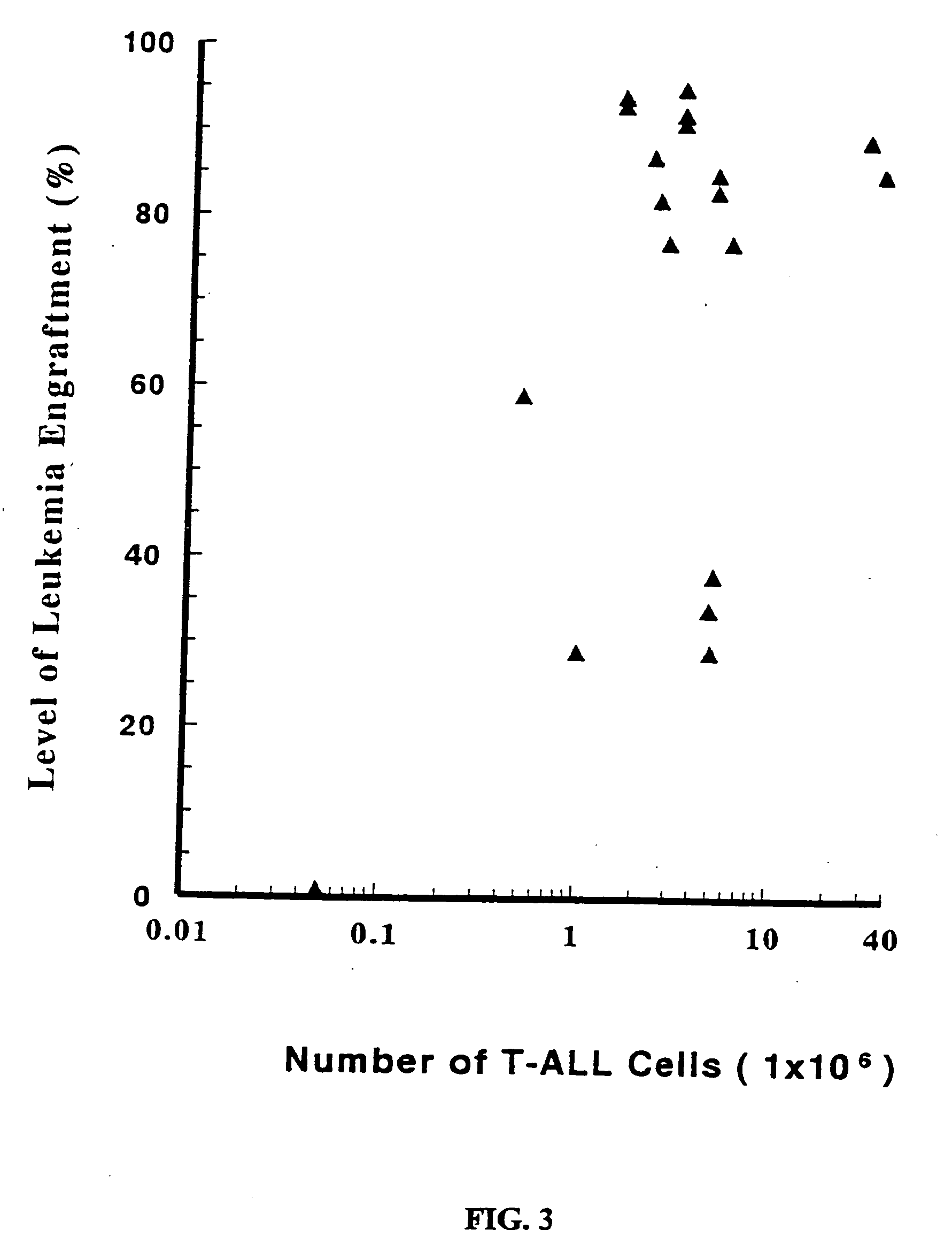
In vivo animal model of human leukemia
InactiveUS6930222B2Improve the level ofIncrease the number ofAnimal husbandryCord blood stem cellHuman leukemia
The present invention provides a process for making an in vivo model of human leukemia. The process includes the steps of: pre-conditioning an immunodeficient rodent by administering to the rodent a sub-lethal dose of irradiation and injecting the rodent with an effective pre-conditioning amount of human fetal cord blood mononuclear cells; maintaining the rodent for from about 5 to 10 days; and injecting the rodent with an effective engrafting amount of primary human leukemia cells. An in vivo and in vitro model of human leukemia are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
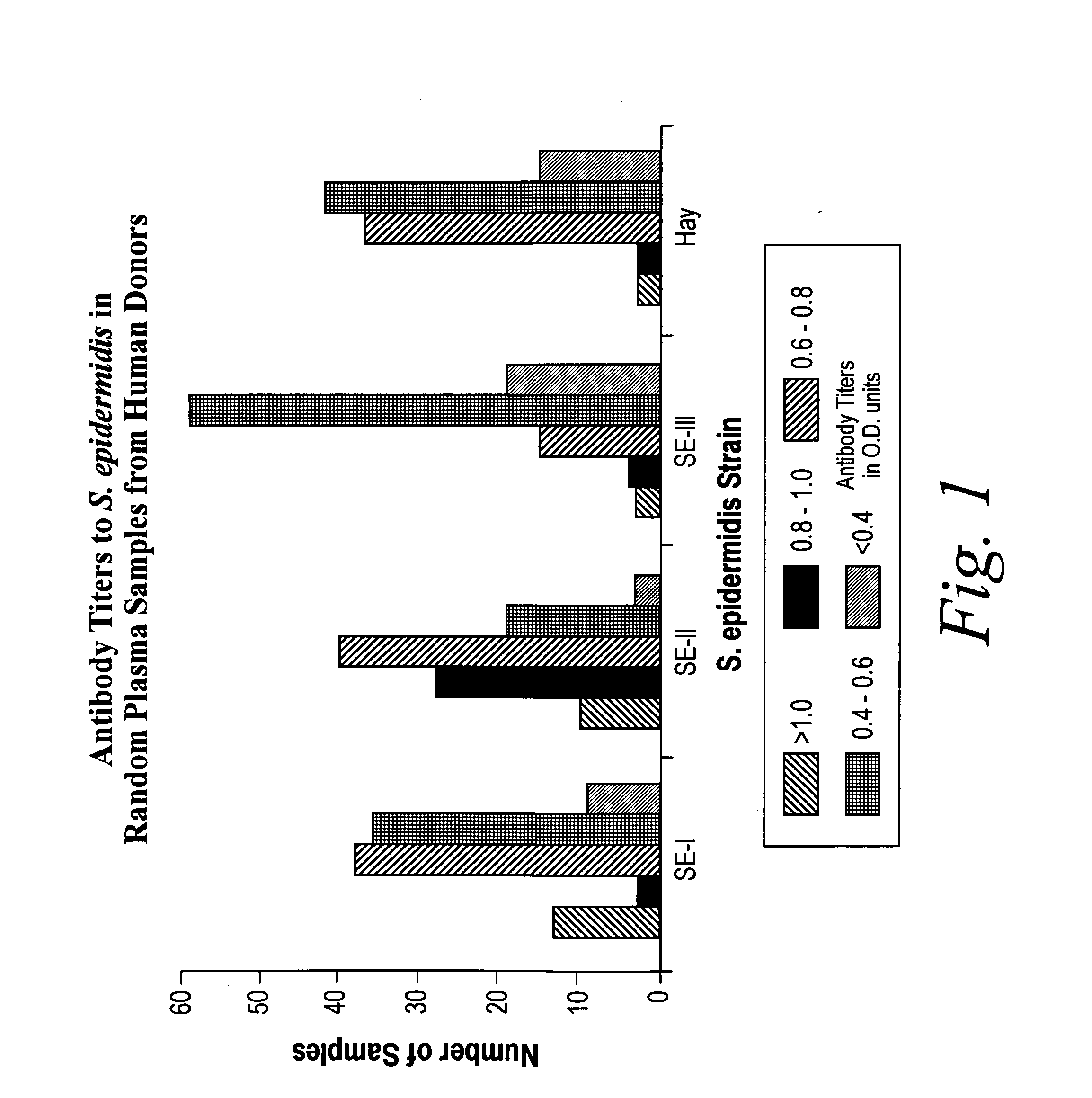
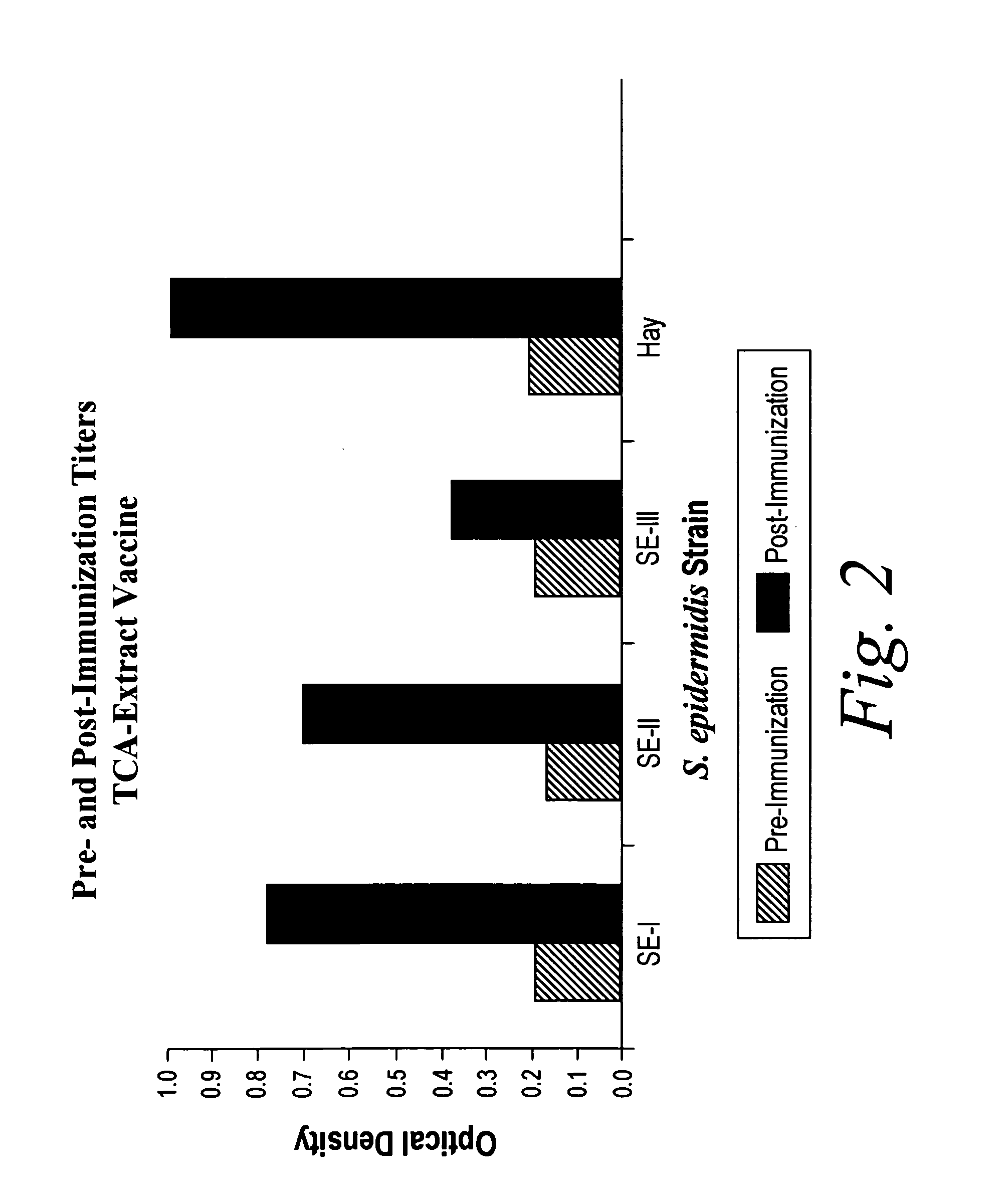
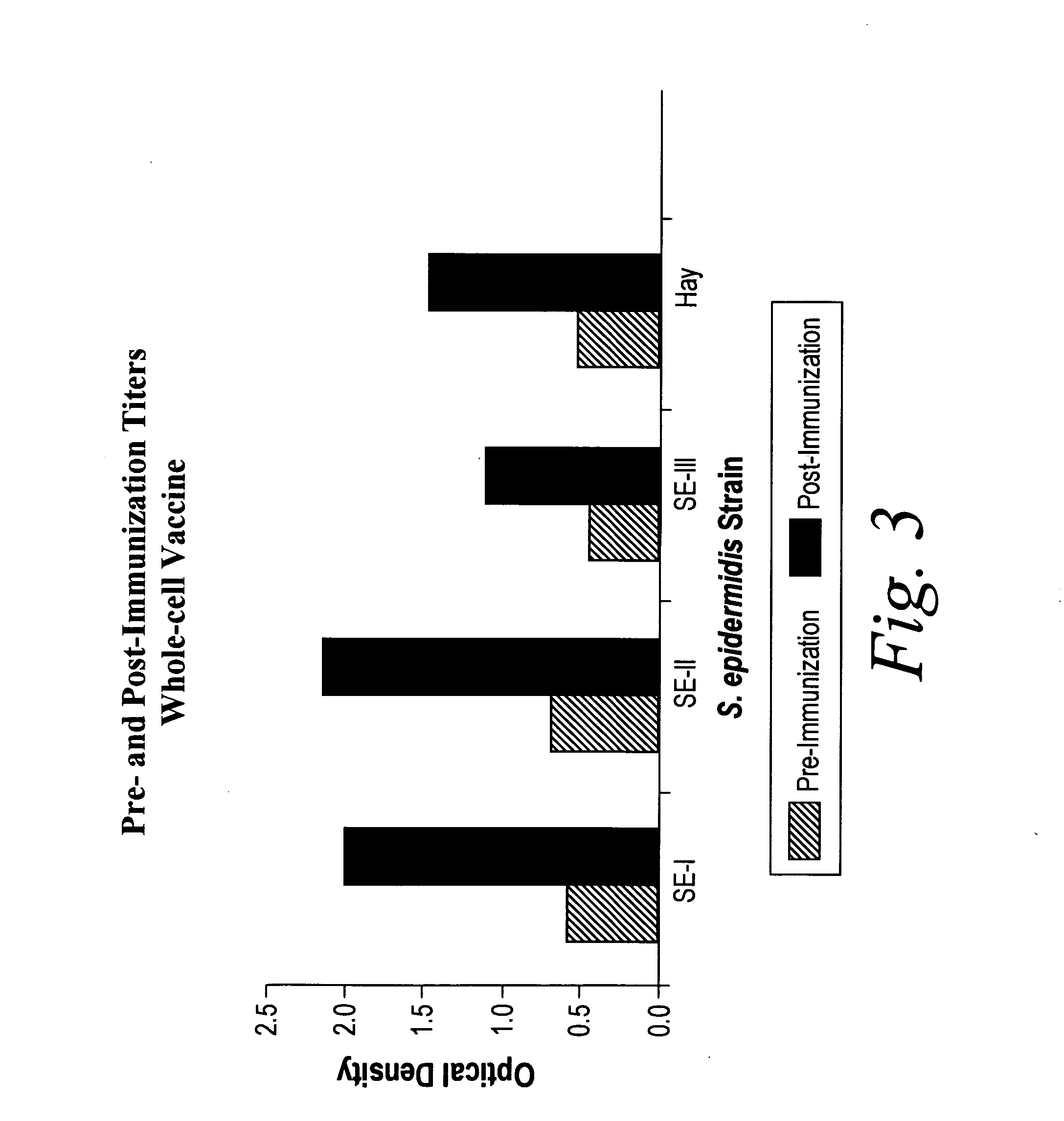
Isolated Broadly Reactive Opsonic Immunoglobulin for Treating a Pathogenic Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Infection
InactiveUS20080139789A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAntigenImmunglobulin e
The invention describes the identification, making, and isolation of immunoglobulin and antigen useful for preventing, diagnosing, and treating staphylococcal infections. The invention further describes an in vivo animal model useful for testing the efficacy of pharmaceutical compositions, including pharmaceutical compositions of immunoglobulin and isolated antigen.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
In vivo screening method of therapeutic agent for memory/learning dysfunctions by schizophrenia
ActiveUS20090176800A1High activityImprove cognitive impairmentCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderPsychosis drugScreening method
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Curcumin derivatives for amyloid-beta plaque imaging
InactiveUS20150087937A1Significant fluorescence property changeImprove lipophilicityNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsInfraredAmyloid beta
The present invention provides curcumin-derived near infrared (NIR) imaging probes. Upon interacting with amyloid β aggregates, these probes undergo a range of changes, qualifying them as “smart” probes. The inventors have demonstrated that probes of the invention have the capacity to monitor the progression of Alzheimer's disease in an in vivo animal model. In addition, the present invention encompasses probes useful as PET imaging agents, MRI imaging agents and multimodal imaging agents, as well as related methods of detecting and imaging amyloid β aggregates and plaques.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method for establishing human bladder transitional cell carcinoma cell line and a mouse model of bladder carcinoma tissue recombination functional reconstruction
InactiveCN106011072AEffective toolEffective meansCell dissociation methodsTumor/cancer cellsCancer cellPrimary cell
The invention discloses a method for establishing a human bladder transitional cell carcinoma cell line and a mouse model of bladder carcinoma tissue recombination functional reconstruction. The method includes the primary cell culture, immortalized cell line identification, tissue reorganization and planting, HE staining, and immunohistochemistry. The invention establishes a novel stable human bladder transitional cell carcinoma cell line, and uses the cell line to construct the mouse model of bladder carcinoma tissue recombination functional reconstruction. The occurrence and development of bladder carcinoma are simulated in mice. The method researches on the biological behavior of bladder carcinoma from in vitro molecular and cell biology and in vivo animal models, and provides an effective tool for the discovery of new biomarkers and therapeutic measures.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Cell cultures from animal models of Alzheimer's disease for screening and testing drug efficacy
InactiveUS20050172344A1Economical and reliable and efficientAnimal cellsBiological testingAmyloid betaToxicology studies
The present invention describes a dissociated cell culture system comprising cells of the hippocampus, one of the brain areas affected by Alzheimer's Disease (AD) or amyloid beta-related diseases. This culture system comprises hippocampal neuronal and glial cells from animal models of AD, particularly, but not limited to, double transgenic mice expressing both the human APP mutation (K670N:M671L) (mAPP), and the human PS1 mutation (M146L) (mPS1), and serves as a powerful tool for the screening and testing of compounds and substances, e.g., drugs, for their ability to affect, treat, or prevent AD or β-amyloid-related diseases. The effects of a test substance on the cells in this culture system can be quantitatively assessed to determine if the test substance affects the cells biochemically and / or electrophysiologically, and / or optically, and / or immunocytochemically. The present in vitro culture system is advantageous for AD drug screening, because it is rapid and efficient. By contrast, even in the fastest animal model of AD, pathology does not start before the end of the second month. If such in vivo animal models are used, it is necessary to wait at least the two month time duration or longer to test for drug efficacy for AD treatment or prevention. At the same time the present invention provides a tool for production of amyloid-beta that can be used for electrophysiological, behavioral, and toxicological studies.
Owner:RES FOUDATION FOR MENTAL HYGIENE INC +1
Application of photochemically-induced cerebral arterial thrombosis model for zebra fish
PendingCN108739556AShort cycleIncrease success rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaVascular endotheliumThrombus
The invention discloses an application of a photochemically-induced cerebral arterial thrombosis model for zebra fish. The cerebrum tissue is taken as an identification index of cerebral arterial thrombosis model for zebra fish. The principle of forming photochemically-induced thrombus is adopted. A rose-bengal solution is injected to abdominal cavities of zebra fish. Therefore, complete local infarction in cortex areas of zebra fish is caused by illumination within short time. Accordingly, an in vivo animal model is established. In the model, blood coagulation is caused by damaging vascular endothelial cells due to singlet oxygen released by the rose-bengal solution under light irradiation. The pathological process of cerebral arterial thrombosis is effectively simulated. According to anexperiment result of an observational index, the cerebrum area tissue of zebra fish has evident loose and infarct phenomena. Swimming behaviors of dysneuria such as whirling and standing upright occurto zebra fish. The method is simple and high in success rate and convenient to promote. Damage sensitivity of cerebrum tissue is high and repeatability is good. The photochemically-induced cerebral arterial thrombosis model for zebra fish can act as a practical tool index for screening medicine, for blood vessel protection after cerebral infarction and thrombolytic therapy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Application of CTRP3 to preparation of drugs for preventing and treating cardiac hypertrophy
InactiveCN108904782AReduce apoptosisImprove heart functionPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderEccentric hypertrophySystole
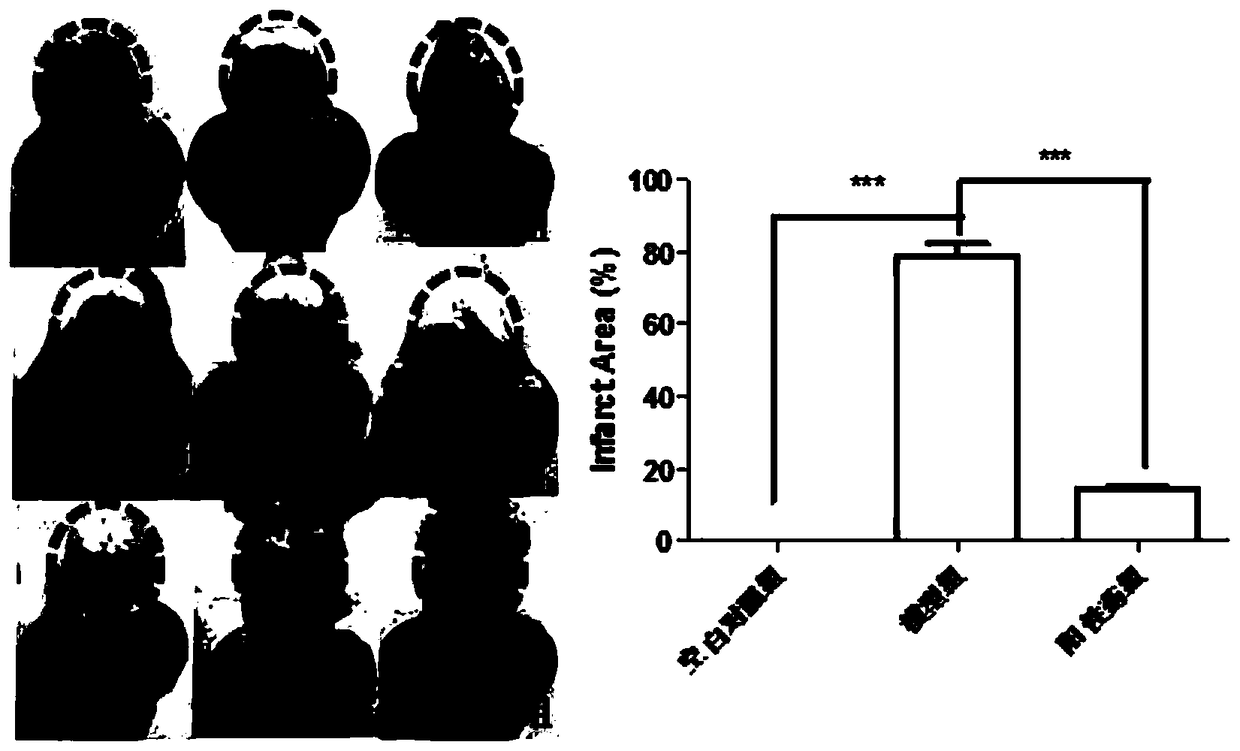
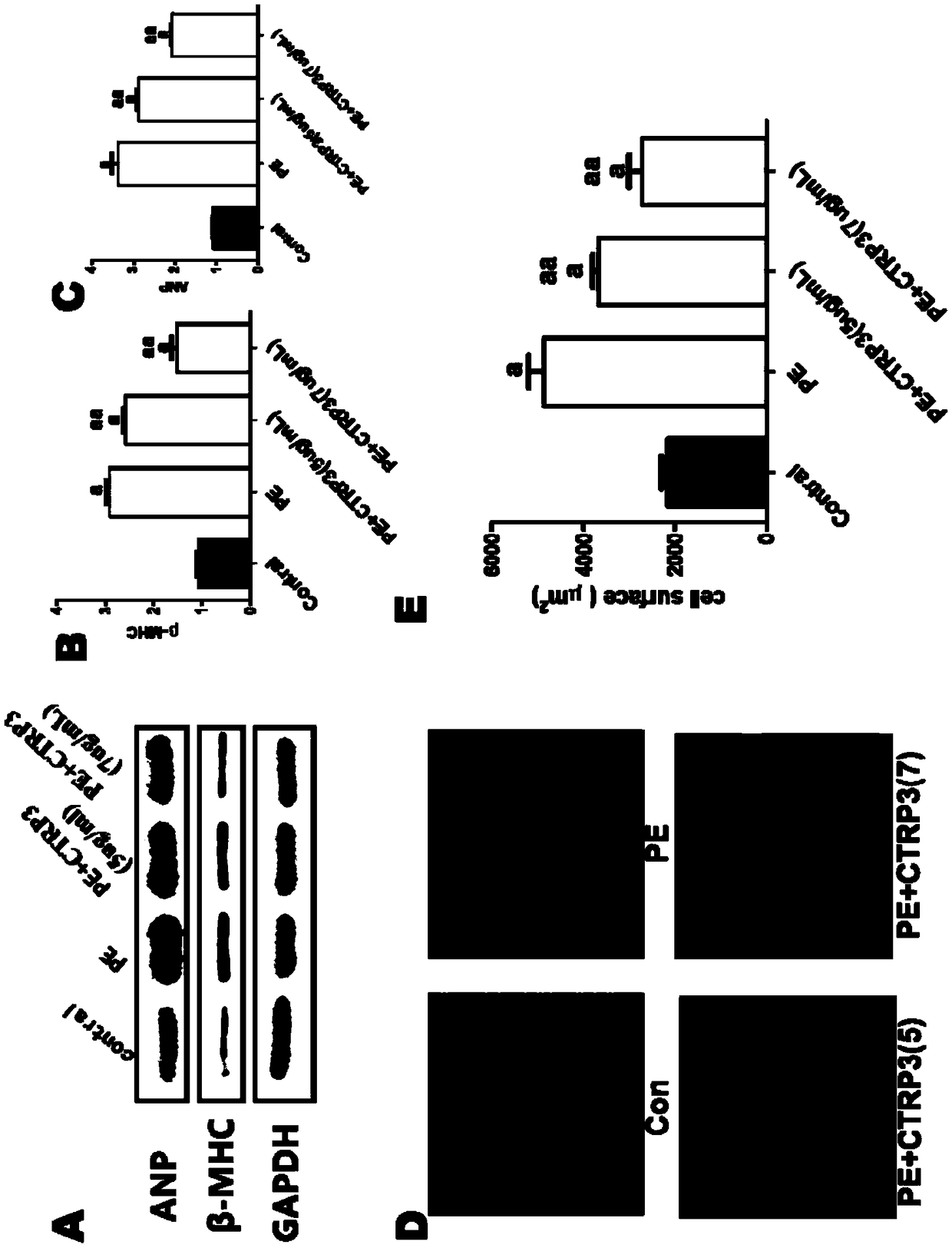
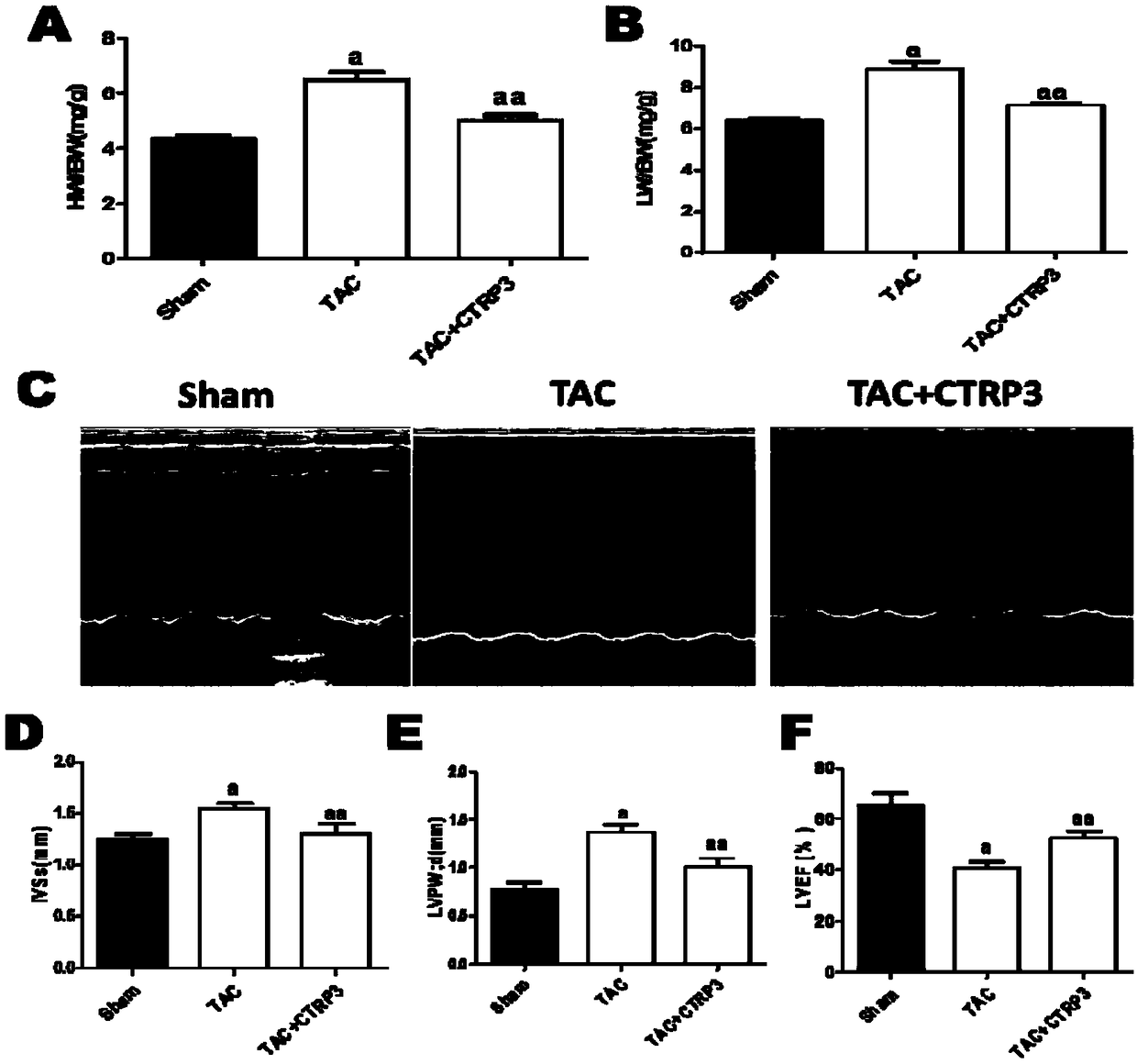
The invention discloses the application of CTRP3 to preparation of drugs for preventing and treating cardiac hypertrophy. A pathologic hypertrophy model of cells is established in the invention, and the pathologic hypertrophy model proves that administration of CTRP3 can lower the expression of cardiac hypertrophy marker molecules and reduce the average surface area of cardiac muscle cells. An in-vivo animal model is also established in the invention, and the in-vivo animal model proves that after administration of CTRP3, the heart-to-body ratio and the lung-to-body ratio of a mouse significantly decrease, the left ventricular systolic function of the heart of the mouse is significantly improved; interventricular septal thickness in a systolic period and left ventricular posterior wall thickness in a diastolic period are significantly reduced; the cross-sectional areas of myocardial cells significantly decrease; the myocardial cells are arranged more closely and regularly; the degreesof myocardial tissue interstitial fibrosis and pericapillary fibrosis are greatly lowered; and thus, it is indicated that CTRP3 has significant prevention effect on pathological cardiac hypertrophy, delays the occurrence of heart failures, and has good clinical application prospects.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
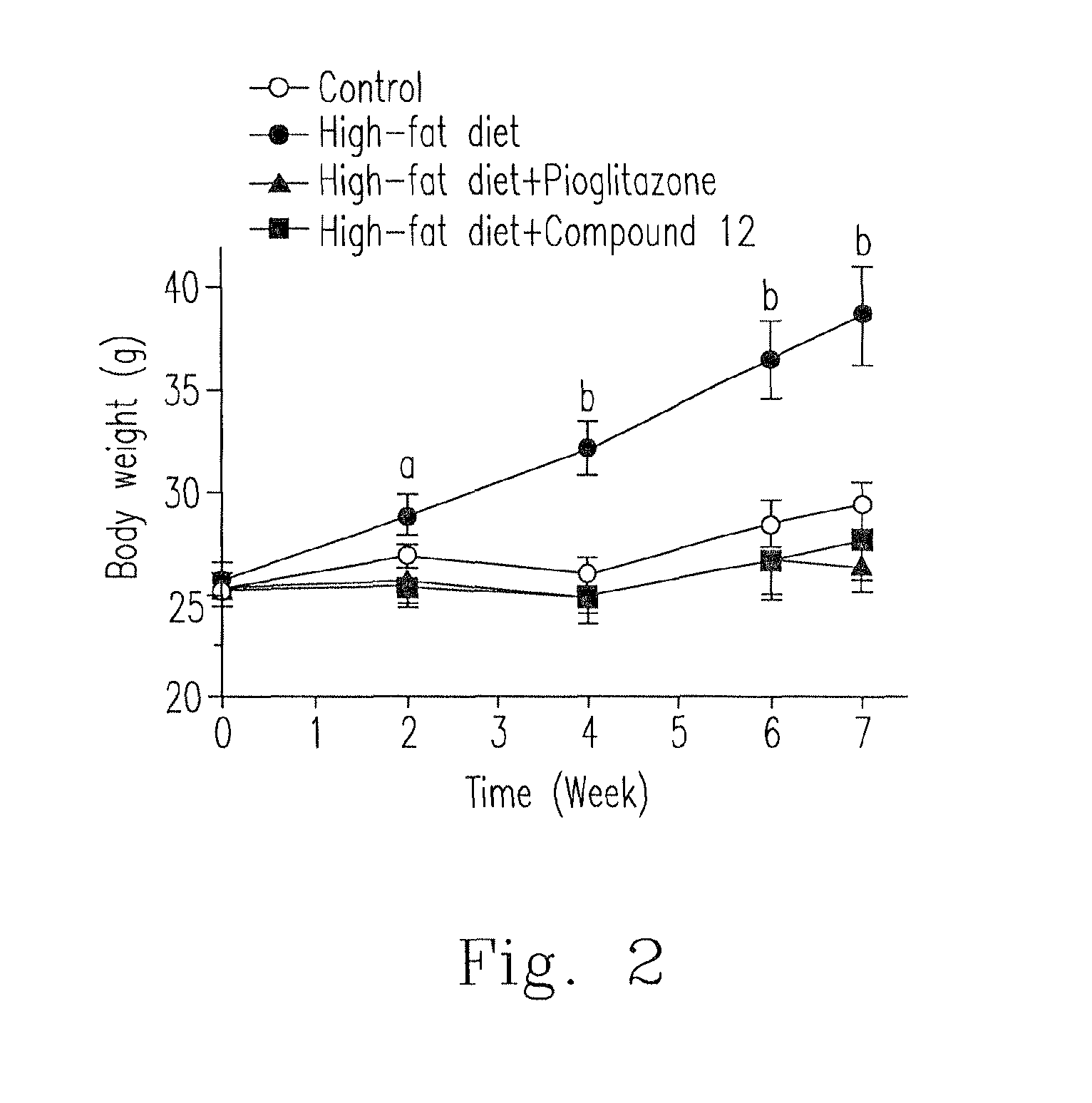
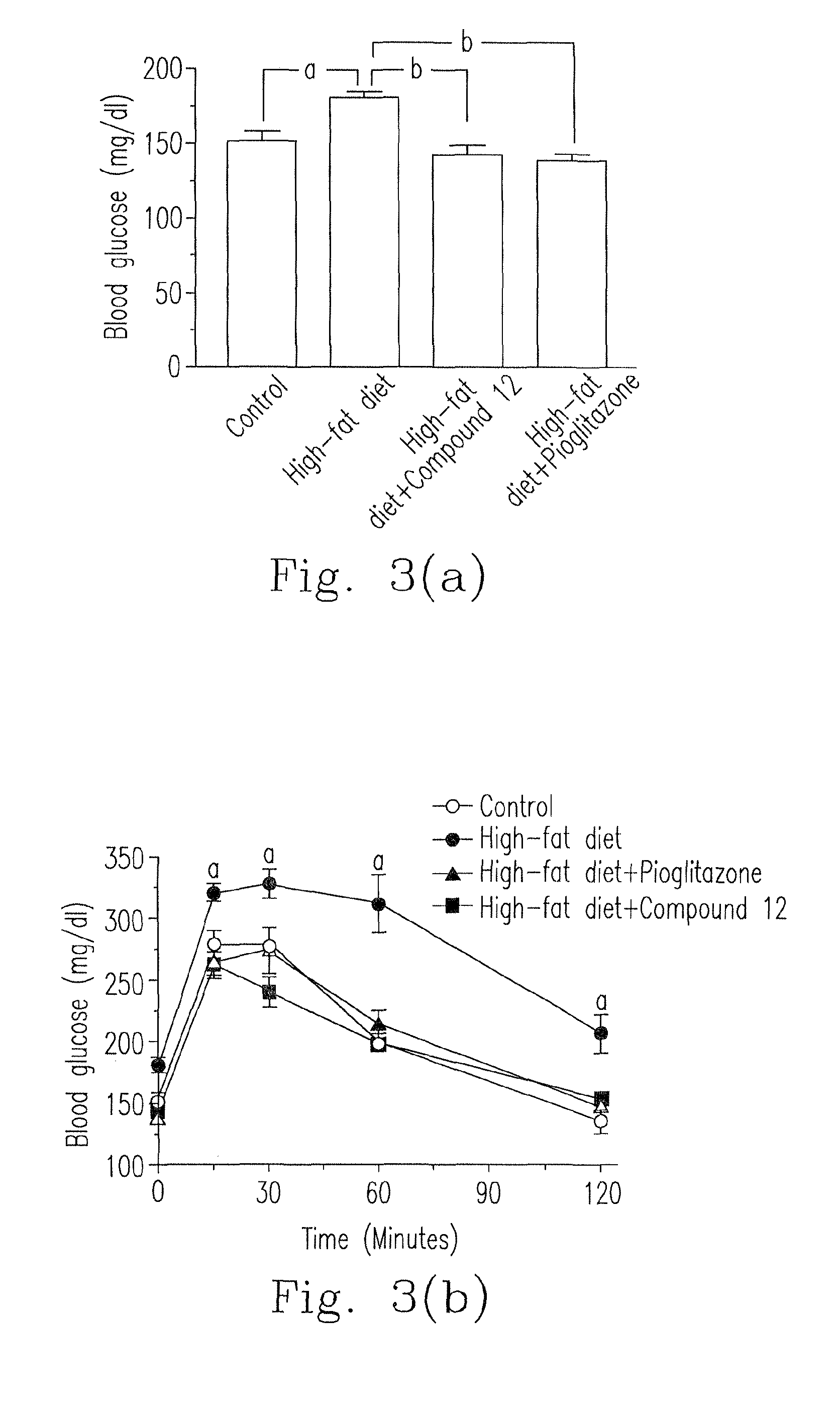
Composition for treating diabetes and metabolic diseases and a preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20140350304A1Inhibiting glycemiaPromote absorptionOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderDiseaseBlood sugar
Disclosed is a chalcone composition for treating diabetes and metabolic syndromes. In particular, the chalcone compound bound with 2-halogen in ring A significantly decreases the blood glucose level in the in vitro anti-diabetic effect experiment. In the in vivo animal model, the leading chalcone compound can prevent the progression of diabetes and control the blood glucose level, and there is no significant difference in the gains in body weight. Throughout the seven-week administration, there are no hepatic or renal toxicity observed.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method of treating memory/learning dysfunctions caused by schizophrenia with lurasidone
ActiveUS8835438B2High activityImprove cognitive impairmentCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderPsychosis drugTypical antipsychotic
A method of evaluating memory / learning functions with the use of a model with glutamic acid N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) type receptor hypofunction as an animal model for schizophrenia and with the use of reference memory task, wherein there has been found concrete means for detecting any differences in activity between typical anti-psychosis drugs and atypical anti-psychosis drugs is found.An in vivo animal model for screening of a therapeutic agent for improving cognitive dysfunction by schizophrenia is provided.
Owner:SUMITOMO PHARMA CO LTD
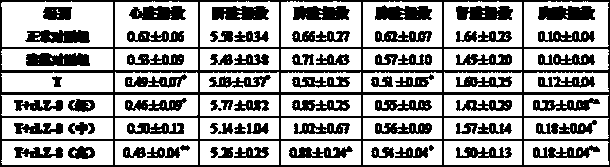
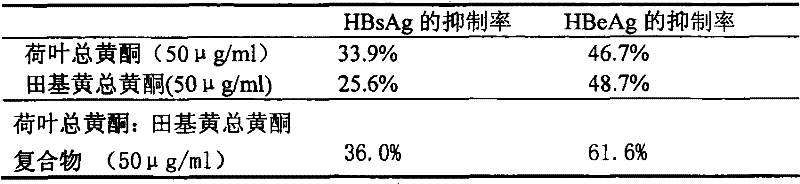
Medicinal composition containing lotus leaves and hypericum japonicum total flavone extraction and use thereof
The invention relates to a medicament complex which is prepared from total flavone extract of lotus leaf and hypericum japonicum thunb, and new usage for preparing anti-hepatitis B virus medicament. The total flavone of lotus leaf and hypericum japonicum thunb of the invention is total flavone extract which is separated and extracted from lotus leaf and hypericum japonicum thunb which grow in China. The complex of lotus leaf and hypericum japonicum thunb is separated and purified, tested by mass spectrum, 13C and 1HNMR, and proved to contain the following chemical components: quercetin, quercetin-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranose, isoquercetin, and kacmpferol and the like. The complex of total flavone extract is tested by in vitro cell model and in vivo animal model and proved to have strong activity of resisting hepatitis B virus and protecting liver. The complex of total flavone extract can be further prepared into anti-hepatitis B virus medicament and dosage forms can be capsules, tablets, granules, and injection and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
In vivo screening method of therapeutic agent for memory/learning dysfunctions by schizophrenia
InactiveUS20070160537A1High activityImprove cognitive impairmentCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderPsychosis drugTypical antipsychotic
A method of evaluating memory / learning functions with the use of a model with glutamic acid N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) type receptor hypofunction as an animal model for schizophrenia and with the use of reference memory task, wherein there has been found concrete means for detecting any differences in activity between typical anti-psychosis drugs and atypical anti-psychosis drugs is found. An in vivo animal model for screening of a therapeutic agent for improving cognitive dysfunction by schizophrenia is provided.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line with high tumorigenic ability and application thereof
InactiveCN107177551AHigh tumorigenic abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesIntrahepatic CholangiocarcinomaMalignant progression
The invention relates to a human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line with high tumorigenic ability and application thereof. The invention discloses a novel human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line which grows stably and has clear quantity of generations and high tumorigenic rate; the human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line can form an adenoid tumor in vivo and can be used for in-vivo and in-vitro research on human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; a foundation is laid for constructing an in-vivo animal model, disclosing a tumor malignant progression mechanism, screening related biomarkers and developing novel intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma resisting medicines.
Owner:HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
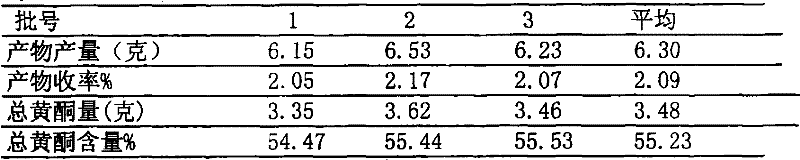
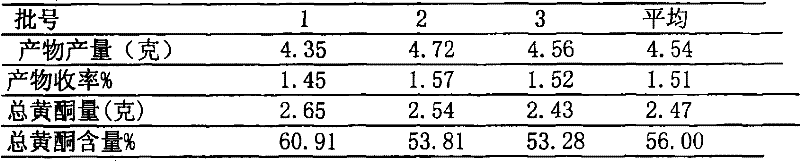
Scutellaria barbata total flavone and its application in preparing influenza virus resisting medicine
The invention relates to total flavone of barbat skullcap and new usage in the preparation of anti-influenza virus drug, belonging to the field of traditional Chinese medicine. The total flavone of barbat skullcap of the invention is total flavone extract which is separated and extracted from the dry aerial part of barbat skullcap which belongs to labiatae scutellaria plant and grows in China. Tested by mass spectrum and 13C, 1H, the total flavone extract of barbat skullcap contains active chemical component 5, 7, 4'-tri-hydroxyl flavone (apigenin) of the above chemical structure. The total flavone extract is tested by in vitro cell model and in vivo animal model and proved to have strong activity of anti-influenza virus. The total flavone extract and active component apigenin can be further prepared into anti-influenza virus drug and the dosage forms can be capsules, tablets, granules, and injection and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
A human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line with high tumorigenic ability and its application
InactiveCN107177551BHigh tumorigenic abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesIntrahepatic CholangiocarcinomaBiomarker (medicine)
The invention relates to a human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line with high tumorigenic ability and application thereof. The invention discloses a novel human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line which grows stably and has clear quantity of generations and high tumorigenic rate; the human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cell line can form an adenoid tumor in vivo and can be used for in-vivo and in-vitro research on human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; a foundation is laid for constructing an in-vivo animal model, disclosing a tumor malignant progression mechanism, screening related biomarkers and developing novel intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma resisting medicines.
Owner:HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
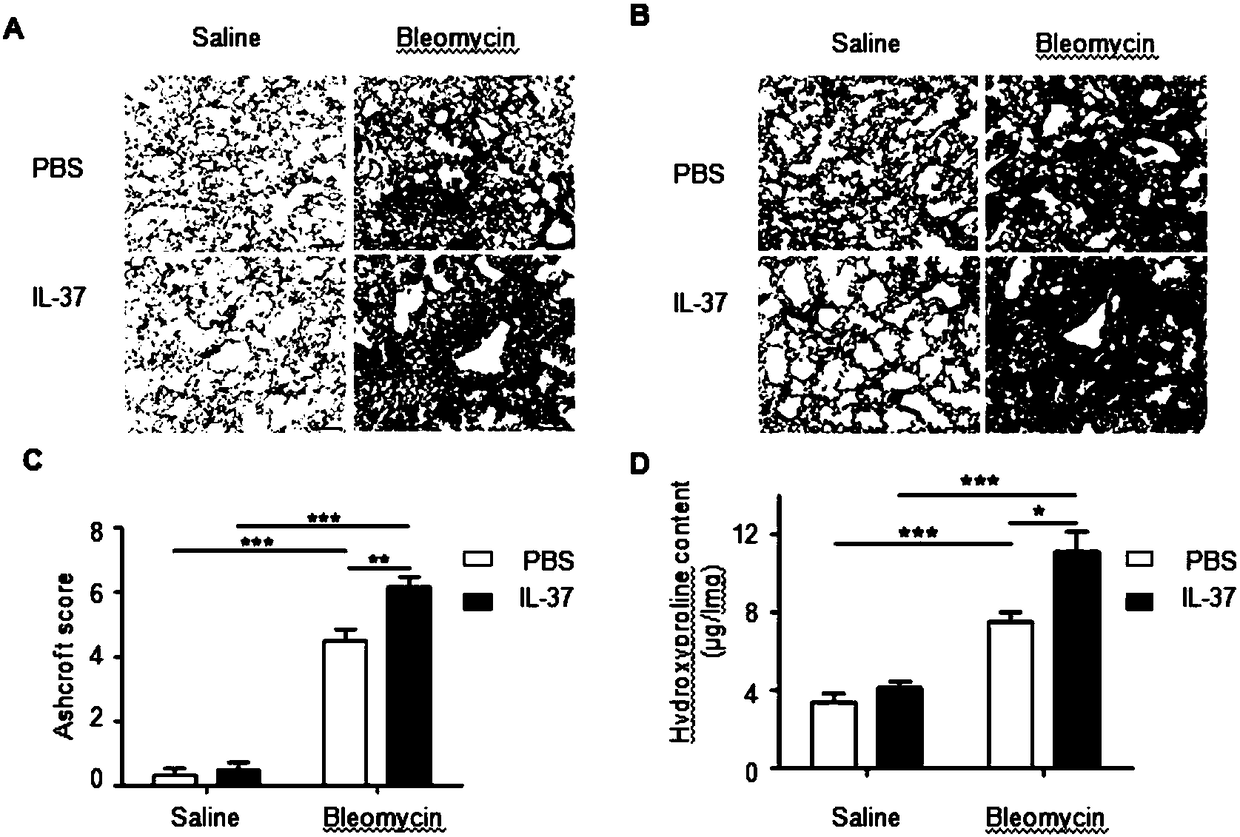
Application of interleukin-37 to controlling fibrosis related diseases
InactiveCN108543068APrevent fibrosisSenses disorderMetabolism disorderWhite blood cellTreatment targets
The invention experimentally proves that IL-37 can obviously enhance pulmonary fibrosis in vitro cell experiments and in vivo animal models. The invention further verifies experimentally that IL-37 promotes fibrosis through TGF-beta-ALK1 access. Therefore, through the discovery of the invention, the TGF-beta signal access can be inhibited by controlling the level of IL-37, and accordingly fibrosisof internal organs can be inhibited. In this way, IL-37 can serve as a treatment target site to treat fibrosis related diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, ischemic heart diseases, viralliver cirrhosis and acute pancreatitis. According to the discovery of the invention, IL-37 has the obvious effect of worsening fibrosis in vitro fibrosis cell culture and in vivo animal models, meanwhile, IL-37 provides a direction for treatment of mice pulmonary fibrosis by serving as a new treatment target site for treating fibrosis related diseases. A more direct, effective and specific methodfor treating fibrosis is provided.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
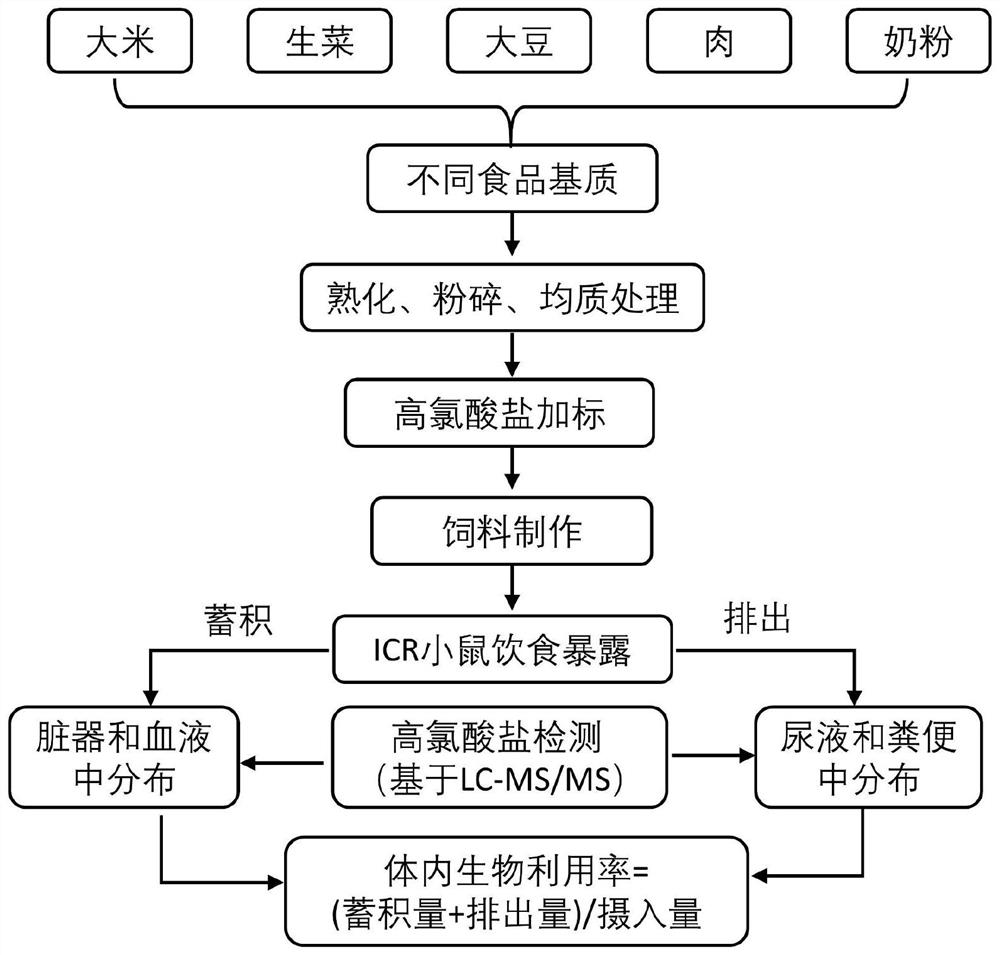
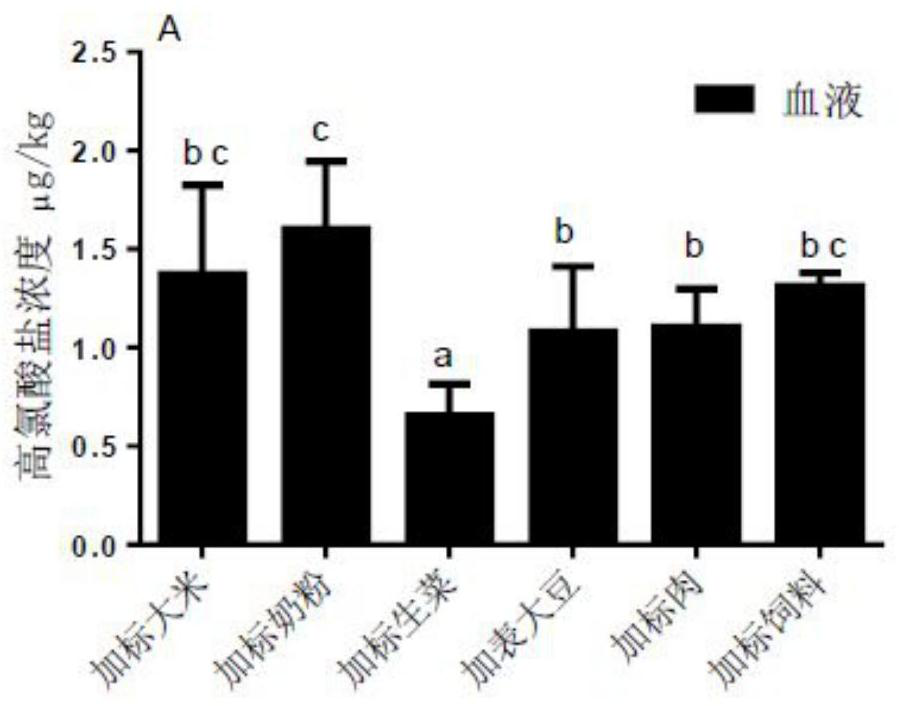
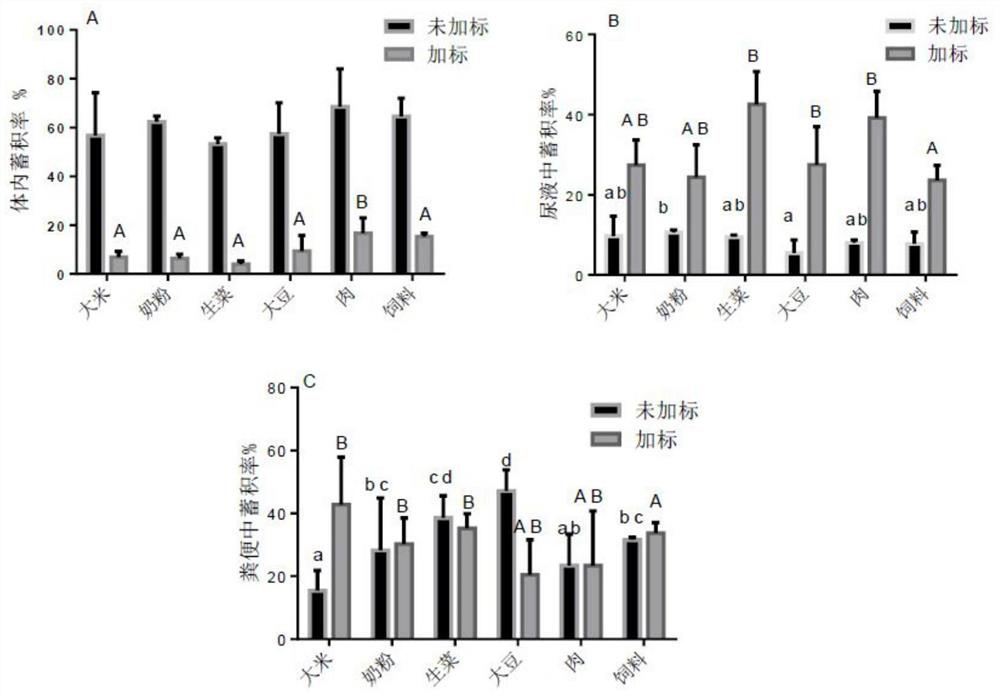
Method for evaluating in-vivo bioavailability of perchlorate in food matrix
The invention provides a method for evaluating the in-vivo bioavailability of a perchlorate in a food matrix. Different food matrixes are used as raw materials; the method comprises steps: adding a standard by adopting a perchlorate solution; preparing different feeds to feed ICR mice, carrying out diet exposure, determining the content of the perchlorate in blood, tissues, organs and urine excrement of the mice in different experimental groups and control groups by using a chromatography-mass spectrometry technology, and calculating the perchlorate in-vivo accumulation rate and the perchlorate bioavailability of the mice. The in-vivo animal model effectively simulates and evaluates the biological utilization rate of perchlorate exposed to human diet, so that the difference caused by the biological utilization rate evaluation of a traditional in-vitro cell model on the body action can be reduced, and technical guidance can be provided for the in-vivo biological utilization rate evaluation of other toxic and harmful pollutants in food.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
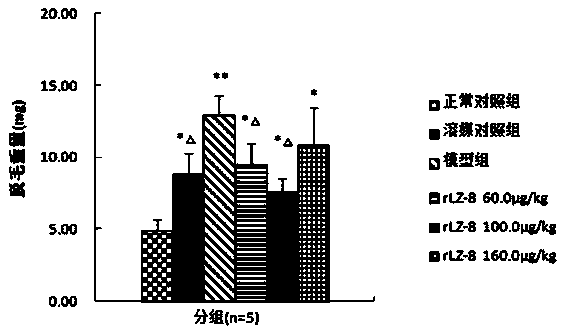
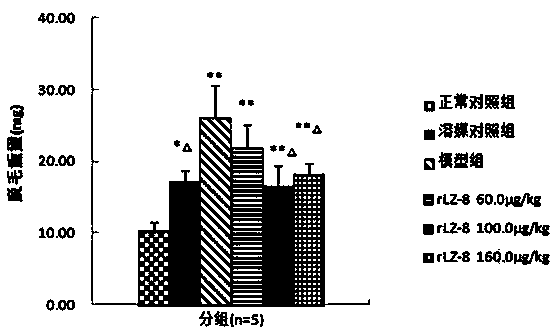
Application of recombinant ganoderma lucidum immunoregulatory protein in preparation of medicine for treating androgenetic alopecia
InactiveCN104001154AEnsure long-term medication needsImprove securityPeptide/protein ingredientsDermatological disorderYeastHormones sex
The invention discloses application of recombinant ganoderma lucidum immunoregulatory protein (rLZ-8) in androgenetic alopecia. In-vivo animal model experiments show that the recombinant ganoderma lucidum immunoregulatory protein is capable of improving depilation of an androgenetic alopecia anomal model and can be used for preventing and treating androgenetic alopecia. The recombinant ganoderma lucidum immunoregulatory protein disclosed by the invention is a high-purity protein substance prepared through a recombination technology and a yeast cell eukaryotic expression system.
Owner:张喜田 +1
Use of medicinal composition containing lotus leaves and hypericum japonicum total flavone extraction in preparing medicine for hepatitis B virus
InactiveCN101167805BOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemHepatitis B virusPharmaceutical Substances
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
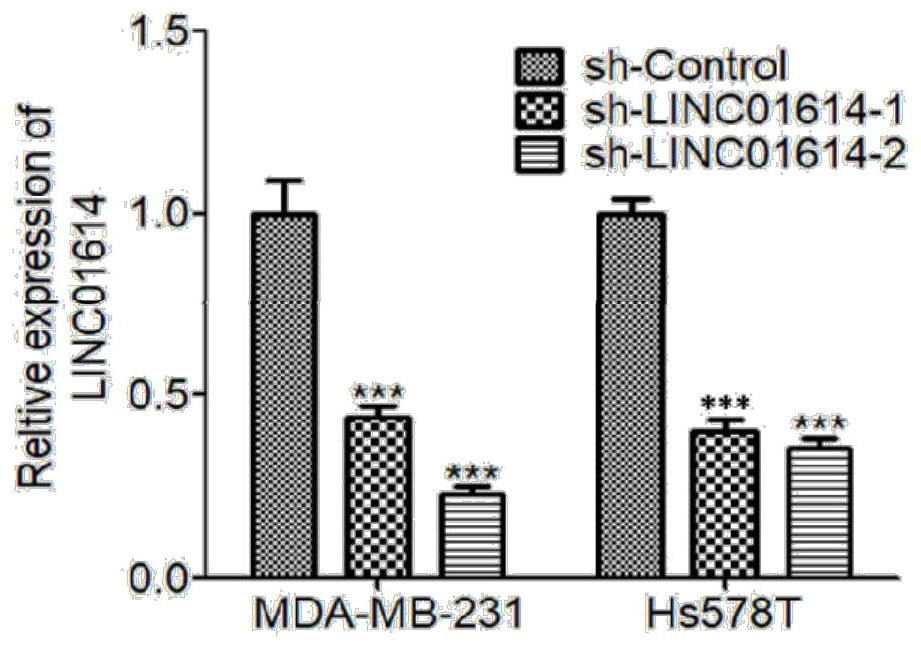
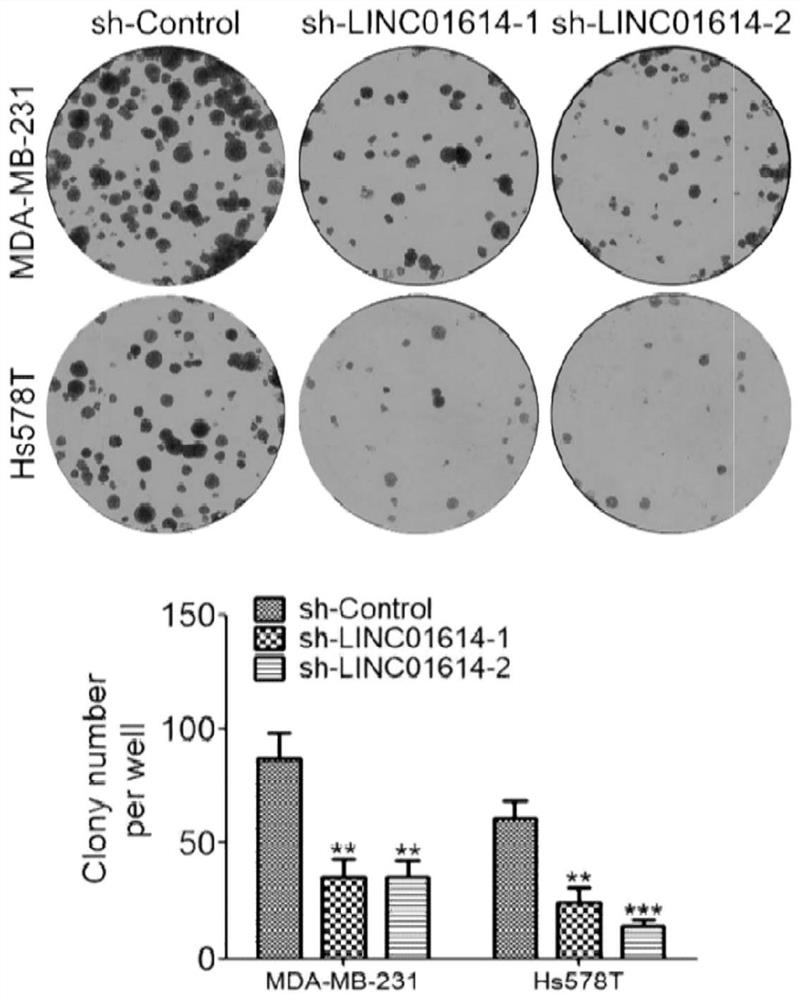
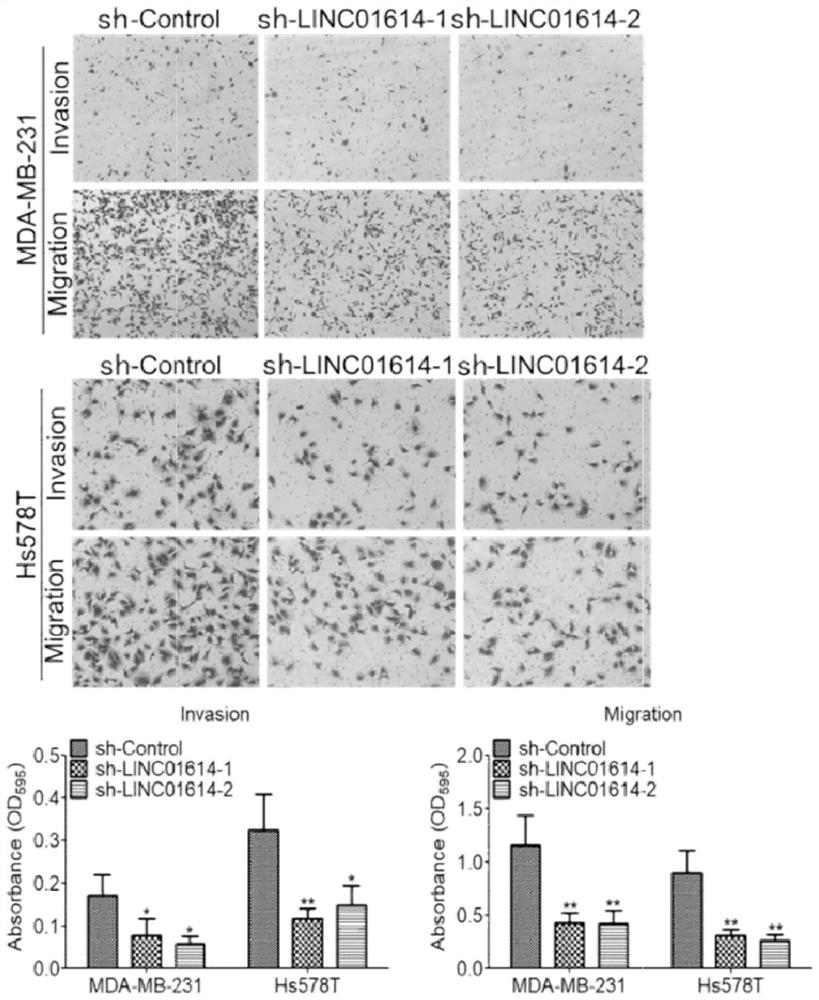
ShRNA molecule for silencing human LINC01614 expression and application thereof
PendingCN114181937AInhibit tumor formationInhibit transferOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryBiomedicineTargeted therapy
The invention discloses a shRNA molecule for silencing human LINC01614 expression and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. On one hand, the invention provides a target gene of the shRNA molecule for silencing human LINC01614 expression, and on the other hand, the shRNA molecule for silencing human LINC01614 expression and application of the shRNA molecule are provided. The obtained shRNA molecule can interfere with LINC01614 expression, so that the migration and invasion ability of tumor cells is reduced, EMT molecule expression is inhibited, and tumor formation and lung metastasis are inhibited in an in-vivo animal model. The invention provides a new scheme for targeted therapy of breast cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Composition for treating diabetes and metabolic diseases and a preparation method thereof
ActiveUS9085520B2Promote absorptionInhibiting glycemiaOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderDiseaseChalcone
Disclosed is a chalcone composition for treating diabetes and metabolic syndromes. In particular, the chalcone compound bound with 2-halogen in ring A significantly decreases the blood glucose level in the in vitro anti-diabetic effect experiment. In the in vivo animal model, the leading chalcone compound can prevent the progression of diabetes and control the blood glucose level, and there is no significant difference in the gains in body weight. Throughout the seven-week administration, there are no hepatic or renal toxicity observed.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Scutellaria barbata total flavone and its application in preparing influenza virus resisting medicine
The invention relates to total flavone of barbat skullcap and new usage in the preparation of anti-influenza virus drug, belonging to the field of traditional Chinese medicine. The total flavone of barbat skullcap of the invention is total flavone extract which is separated and extracted from the dry aerial part of barbat skullcap which belongs to labiatae scutellaria plant and grows in China. Tested by mass spectrum and <13>C, <1>H, the total flavone extract of barbat skullcap contains active chemical component 5, 7, 4'-tri-hydroxyl flavone (apigenin) of the following chemical structure. The total flavone extract is tested by in vitro cell model and in vivo animal model and proved to have strong activity of anti-influenza virus. The total flavone extract and active component apigenin can be further prepared into anti-influenza virus drug and the dosage forms can be capsules, tablets, granules, and injection and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
In vivo animal model of human leukemia
InactiveUS20060015953A1Improve the level ofIncrease the number ofAnimal husbandryHuman leukemiaCord blood stem cell
The present invention provides a process for making an in vivo model of human leukemia. The process includes the steps of: pre-conditioning an immunodeficient rodent by administering to the rodent a sub-lethal dose of irradiation and injecting the rodent with an effective pre-conditioning amount of human fetal cord blood mononuclear cells; maintaining the rodent for from about 5 to 10 days; and injecting the rodent with an effective engrafting amount of primary human leukemia cells. An in vivo and in vitro model of human leukemia are also provided.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
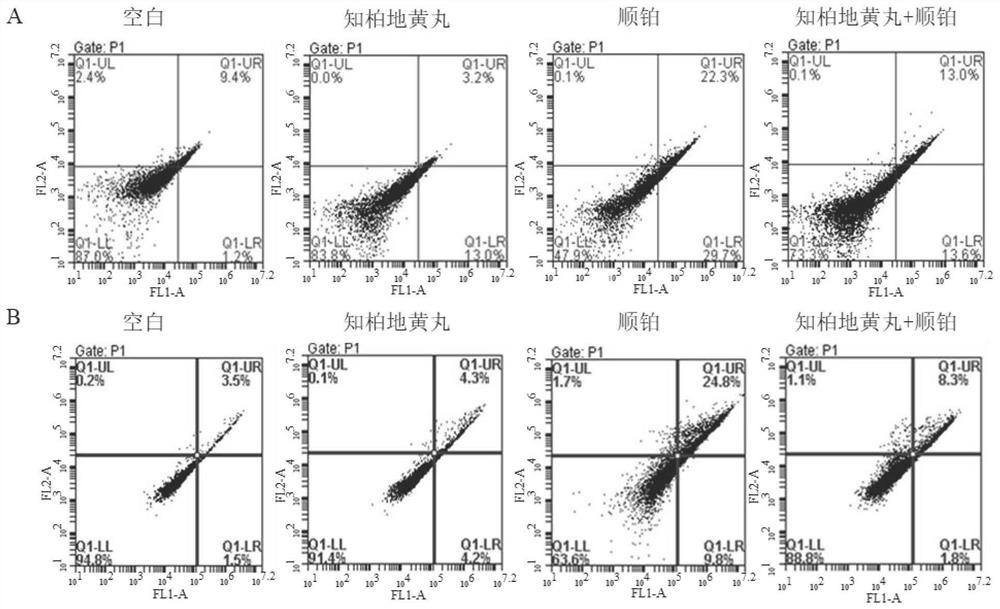
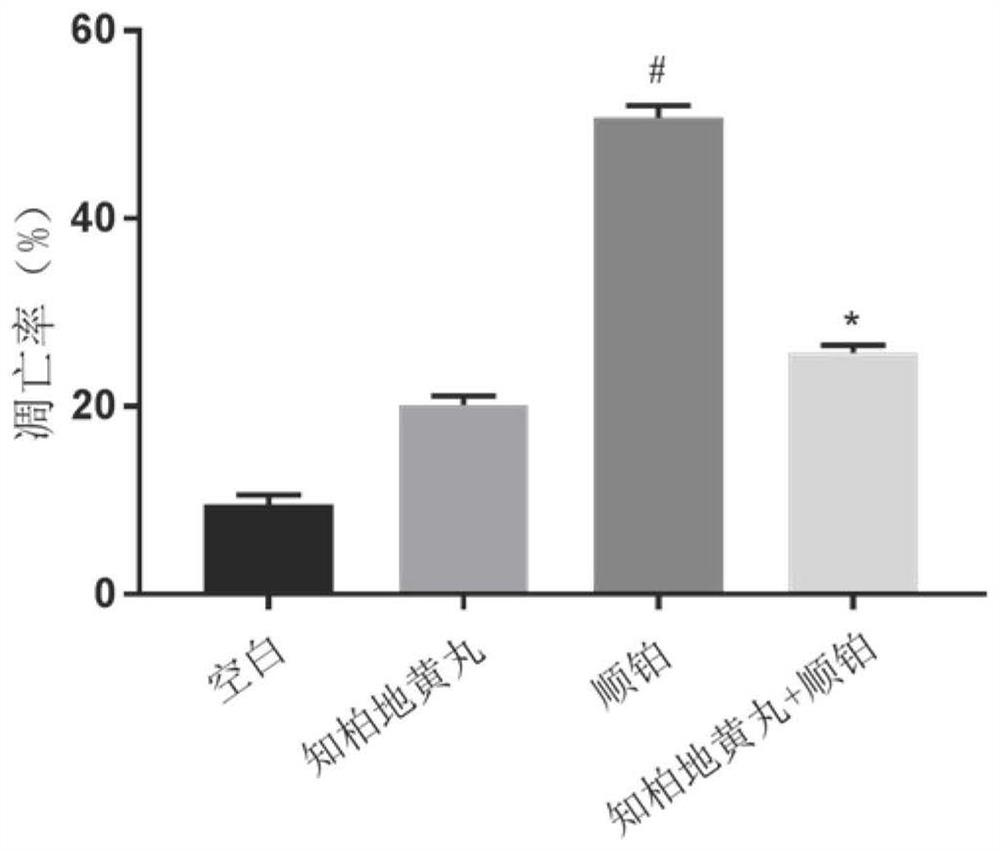
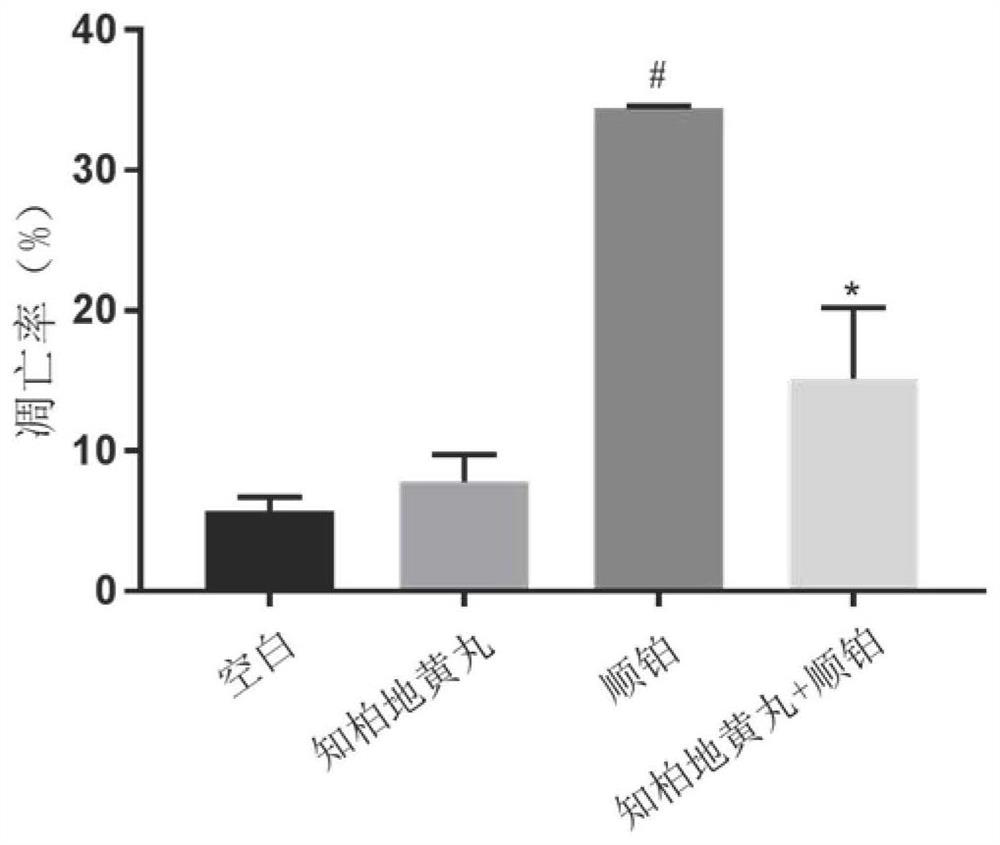
Application of Zhibai Dihuang pill as or in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating cisplatin acute kidney injury
PendingCN114306499AImprovement in acute kidney injuryExpand the scope of treatmentPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsUrinary disorderDiseasePharmacology
The invention discloses an application of Zhibai Dihuang pills as or in preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating cisplatin acute kidney injury. The Zhibai Dihuang pill is used on a cis-platinum-induced acute kidney injury in-vitro cell model and an in-vivo animal model, and the application of the Yin-nourishing and fire-reducing Chinese patent medicine Zhibai Dihuang pill in relieving the cis-platinum-induced acute kidney injury is discussed. The result shows that the acute kidney injury induced by cis-platinum can be obviously improved by using the Zhibai rehmannia pill for intervention treatment on an in-vivo and in-vitro model. The invention develops a new application for the utilization of the Zhibai Dihuang pill, widens the treatment range of the Zhibai Dihuang pill, and opens up a new traditional Chinese medicine treatment method for the cisplatin acute kidney injury.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
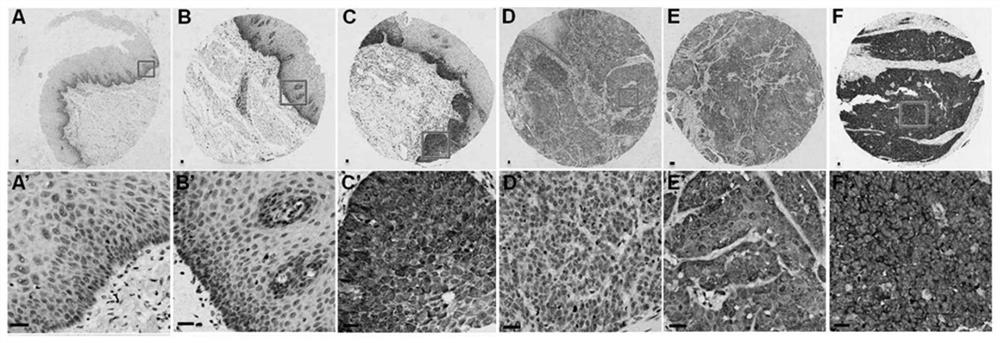
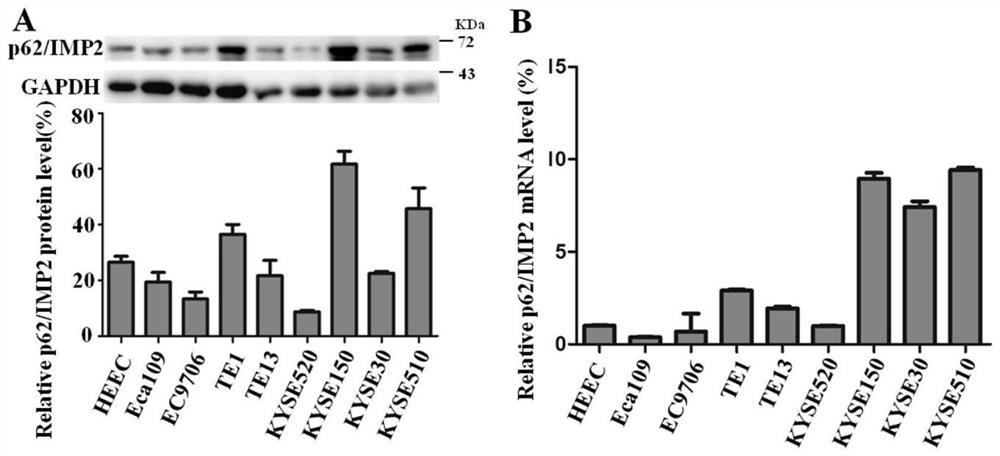
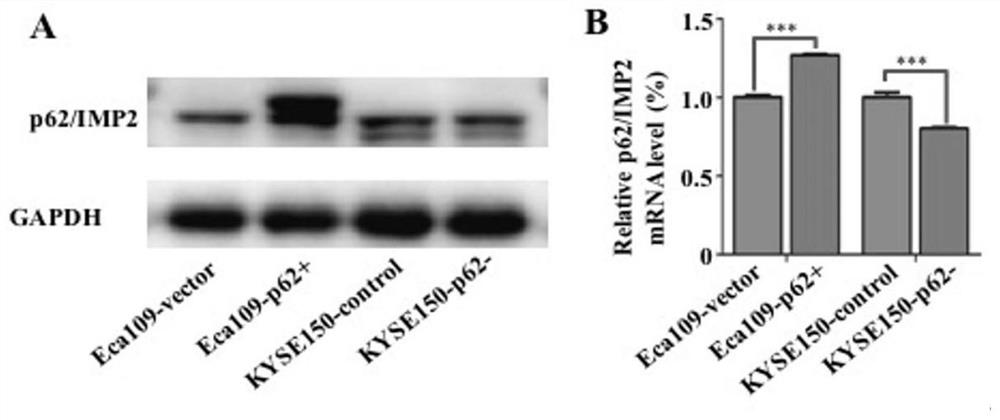
Method for researching influence of tumour-associated antigen p62/IMP2 on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma ESCC
PendingCN112522209APromote conversionIncreased drug resistanceTumor rejection antigen precursorsMicrobiological testing/measurementApoptosisStage I Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The invention discloses a method for researching influence of a tumour-associated antigen p62 / IMP2 on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma ESCC. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, detecting expression characteristics of the p62 / IMP2 in the ESCC; step 2, constructing a stable cell strain for stable over / low expression of the p62 / IMP2; and step 3, observing the effect of the p62 / IMP2 inthe esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Due to the operation of the process steps, an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell model with stable over / low expression of the p62 / IMP2 is constructed in the invention; and cell biology experiments, molecular biology experiments and in-vivo animal models prove that the p62 / IMP2 plays a crucial role in proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis and chemotherapy drug resistance of the ESCC (Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma). An essential basis is provided for deep exploration of an ESCC drug resistance mechanism and gene targeted therapy. According to the invention, the functions and molecular mechanisms of the p62 / IMP2 in ESCC growth, transfer, apoptosis and chemotherapy drug resistance are deeply explored by applying technologies, such as cytobiology function experiments, molecular biology experiments and nude mouse subcutaneous tumorigenesis models; and the correlation between clinical tissue sample analysis and clinical factors is combined.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Use of brown alga polysaccharide sulfate in preventing and treating Parkinson's disease
ActiveCN101301310BImprove securityEnsure long-term medication needsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBiotechnologyCholinergic cells
The invention discloses a novel application of fucoidan sulfate in prevention and cure of a parkinson disease. According to the experiments of an isolated PD cell model and an in vivo animal model, fucoidan sulfate has a certain neuroprotection effect on DA cholinergic neurons of the PD cell model and animal model and can prevent and cure the PD disease. The fucoidan sulfate of the invention can be natural polysaccharide extracts obtained form brown alga such as kelp, focus, bladder wrack, sea-tangle or chorda filum and also can be materials such as low molecular weight SSPSA or oligosaccharide which are obtained through the degradation of fucoidan sulfate.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES +1
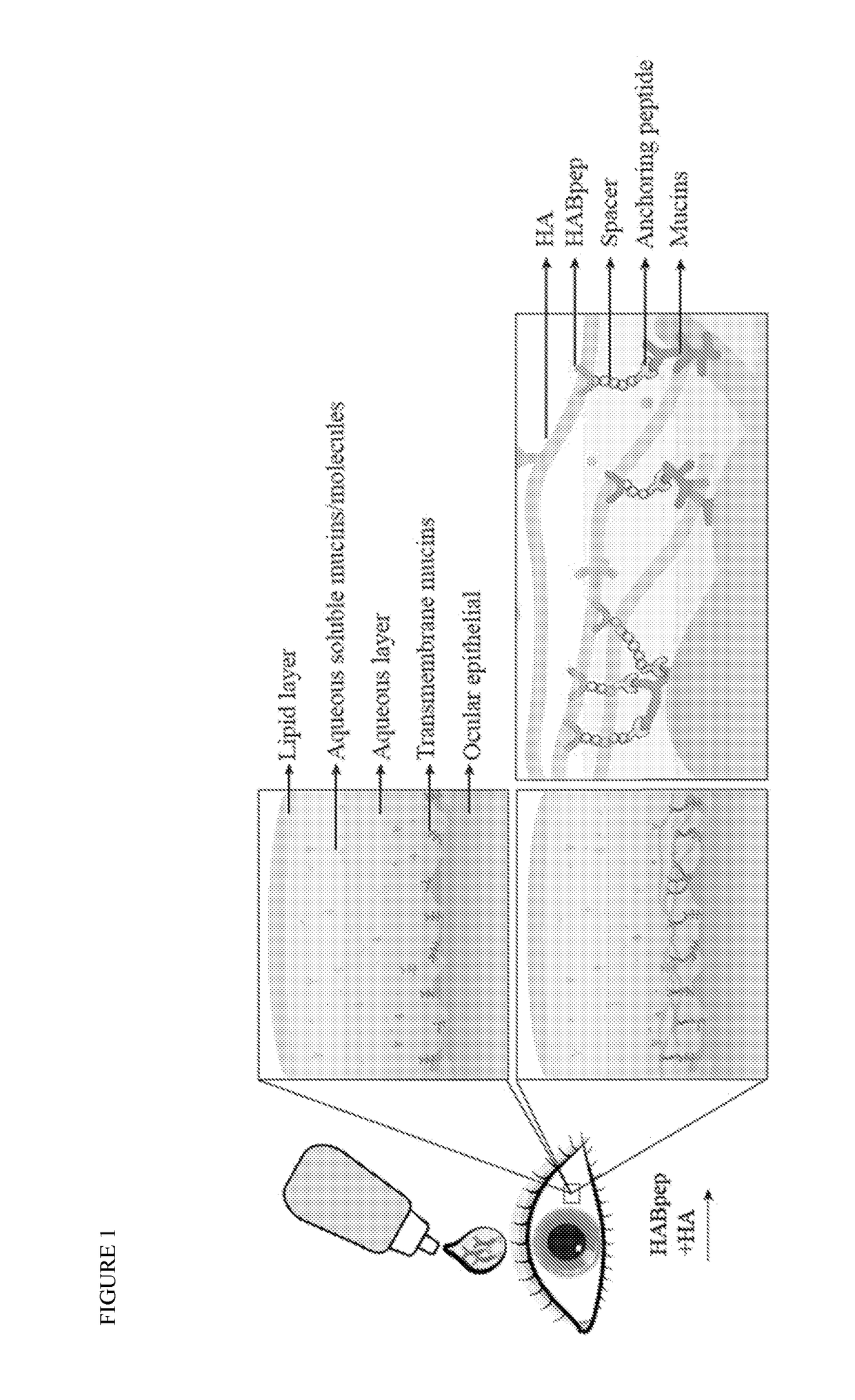
An eye drop solution for enhanced hyaluronic acid retention and delivery
InactiveUS20190000983A1Improve usabilityThin filmOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderBiological materialsOcular disease
The present invention provides biomaterial compositions that can immobilize HA to the ocular surfaces through an HABpep and transmembrane mucins and collagen of ocular tissues can act as anchoring sites. These biomaterial compositions provide prolonged HA binding and retention in both ex vivo and in vivo animal models. HA eye drop solutions with these the inventive biomaterials can prolong the biological and physical benefits to the ocular surface and potentially be more effective in treating eye disorders including dry eye than standard HA-eye drop presently available. Methods of making and use of the compositions are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com