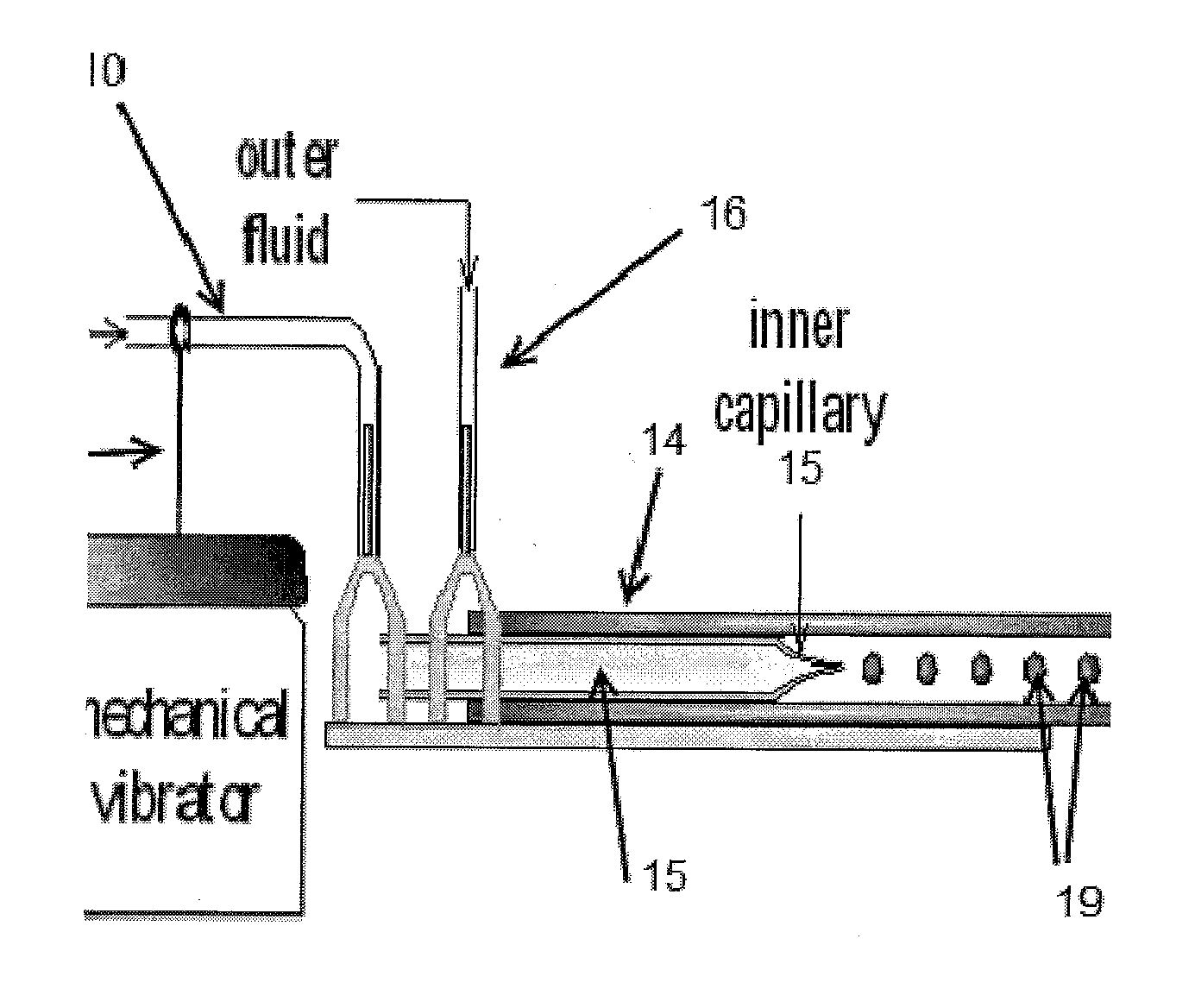
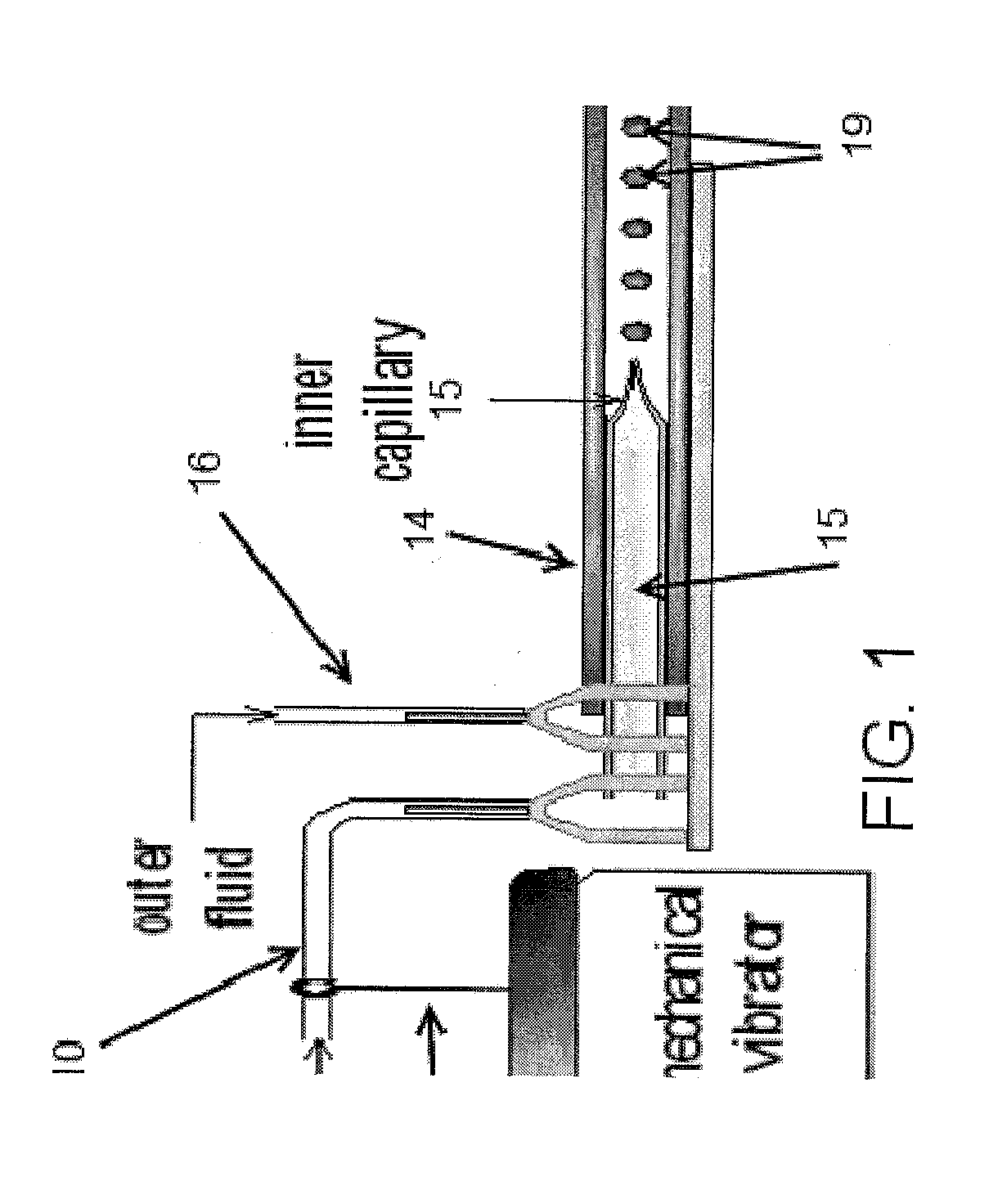
Patents
Literature
151 results about "Large droplet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
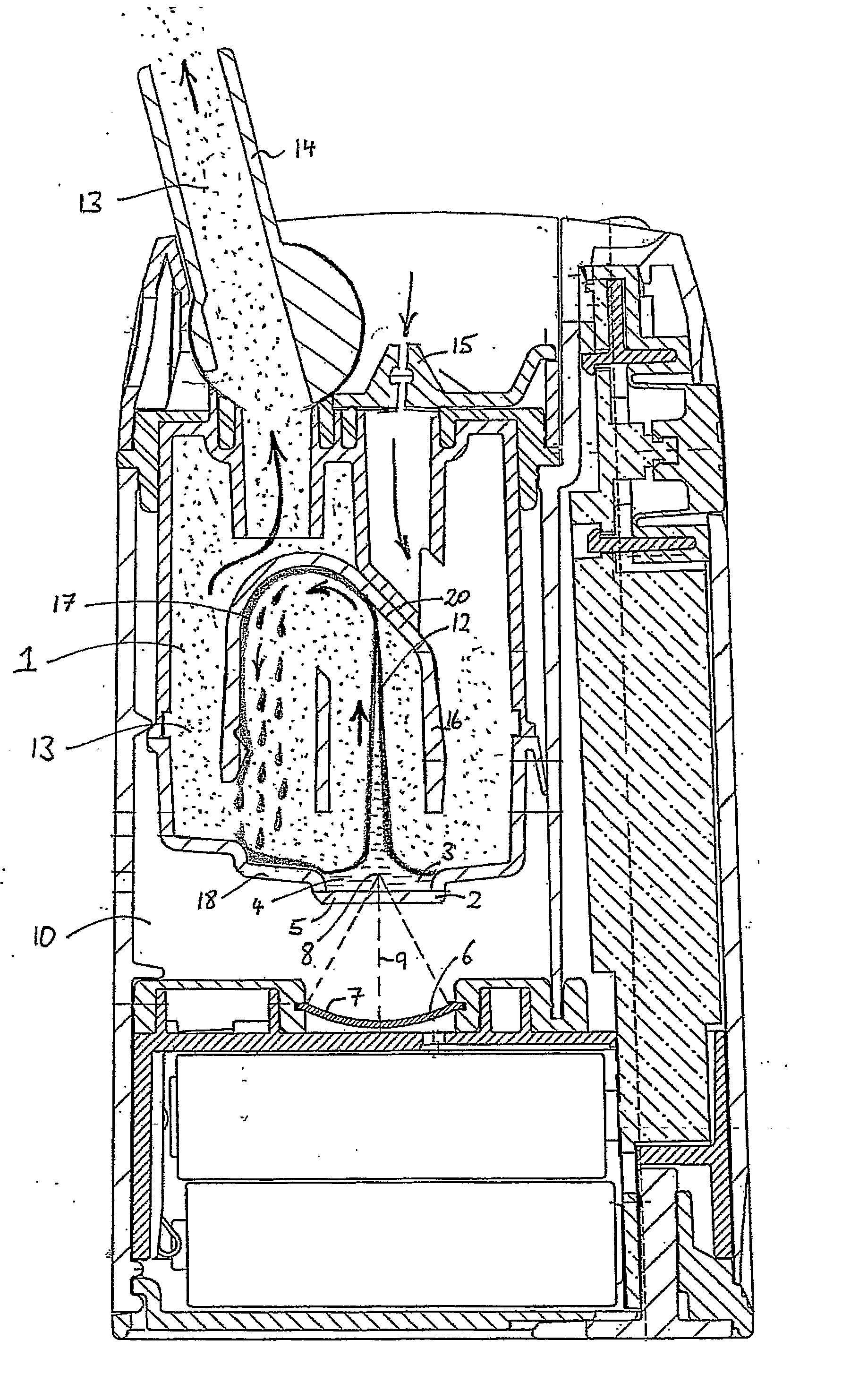
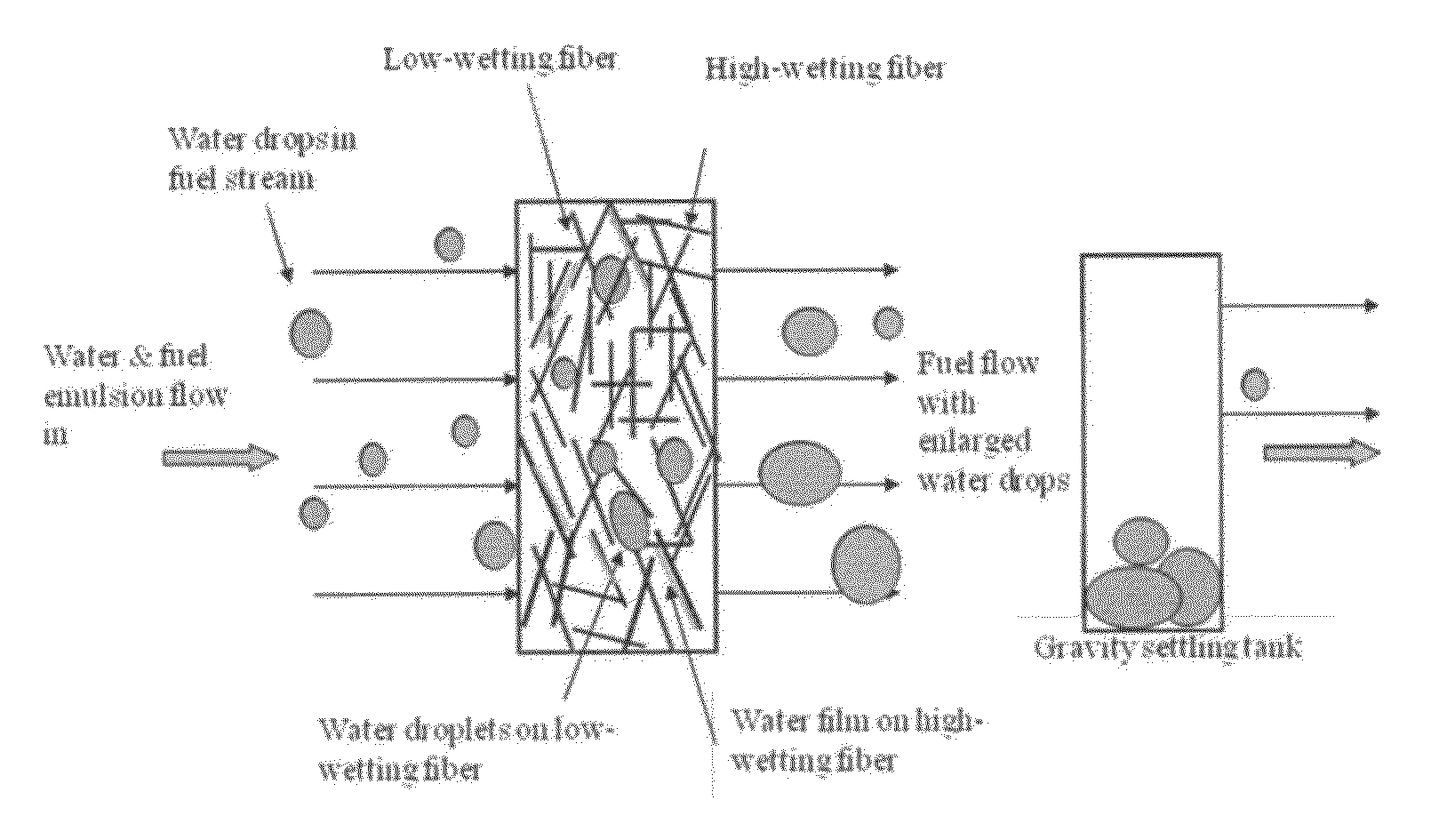
Mixed hydrophilic/hydrophobic fiber media for liquid-liquid coalescence
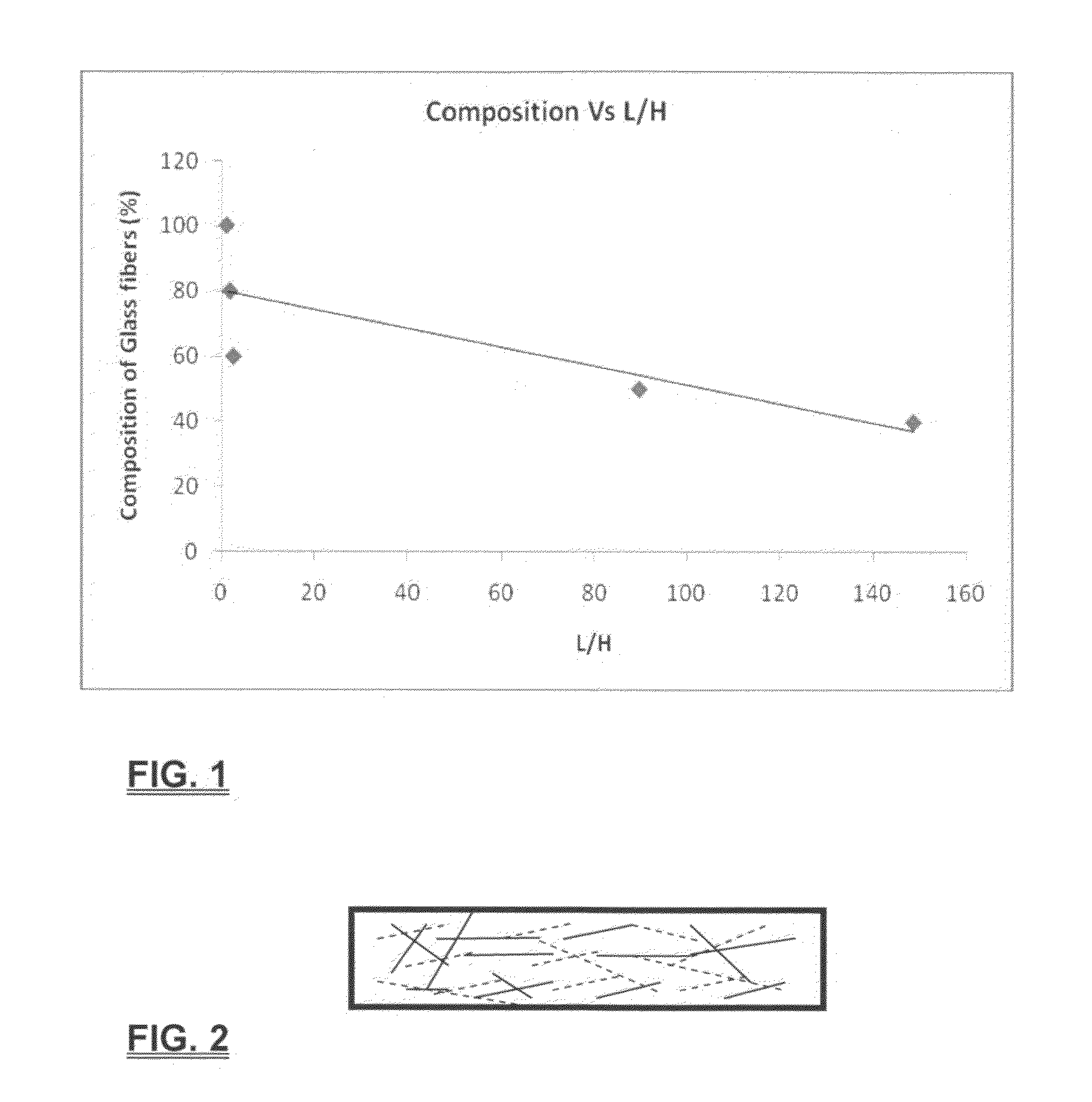
ActiveUS20100200512A1Liquid suspension thickening by filtrationWater/sewage treatmentWashburn's equationFiber
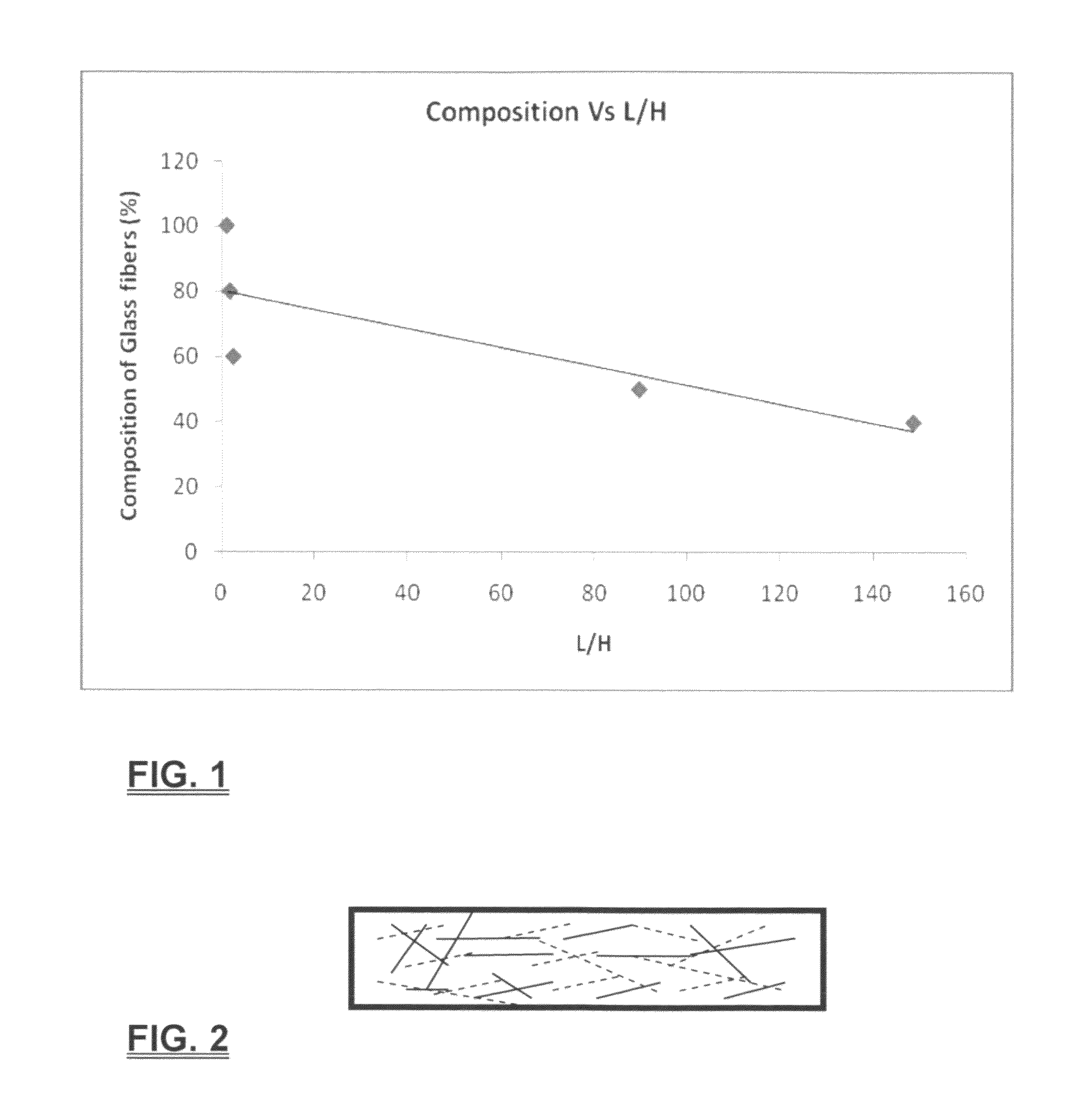
An immiscible lipophilic or hydrophilic liquid phase separated respectively from a continuous hydrophilic phase or a lipophilic phase liquid. Fibers having hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties are mixed, layered, etc., and formed into a filter. The separation mechanism involves capture of small droplets of the immiscible phase, coalescence of the small droplets into larger droplets as the immiscible liquid flows through the fiber filter, and release of the large immiscible droplets from the filter. With respect to separation of a hydrophilic immiscible fluid such as water in a lipophilic continuous fluid such as oil, the hydrophobic fibers will cause small water droplets to migrate towards the hydrophilic fibers whereby large droplets are formed on hydrophilic surface. The large droplets stay on hydrophilic fiber surface for extended periods of time and continue to coalescence until they are so large that they can no longer be maintained by the hydrophilic fibers and are released and drained off of the filter. In designing such filter, wettability of the filter media is an important parameter. The filter media can be designed by mixing hydrophilic and hydrophobic fibers in various proportions to achieve an optimum wettability range for separation of the immiscible liquid from the continuous phase liquid. The wettability of filter media can be characterized by a modified Washburn Equation.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Fill material for direct-contact heat/mass exchangers
InactiveUS20150048528A1Reduced dysfunctionSmall sizeAdditive manufacturing apparatusUsing liquid separation agentFilling materialsLinear element
Fill material for a direct contact heat exchanger wherein the fill material has flow pathways bounded by an array of linear elements, namely a mesh. The invention intentionally uses surface tension and capillary action to anchor the fluid / fluid interface in a desired location. The heat exchanger is wick or collector in direct contact with the fill material (matrix) to extract fluid without formation of large droplets. The mesh is made from a neutrally wetting material.
Owner:BARTON SEAN ANDERSON
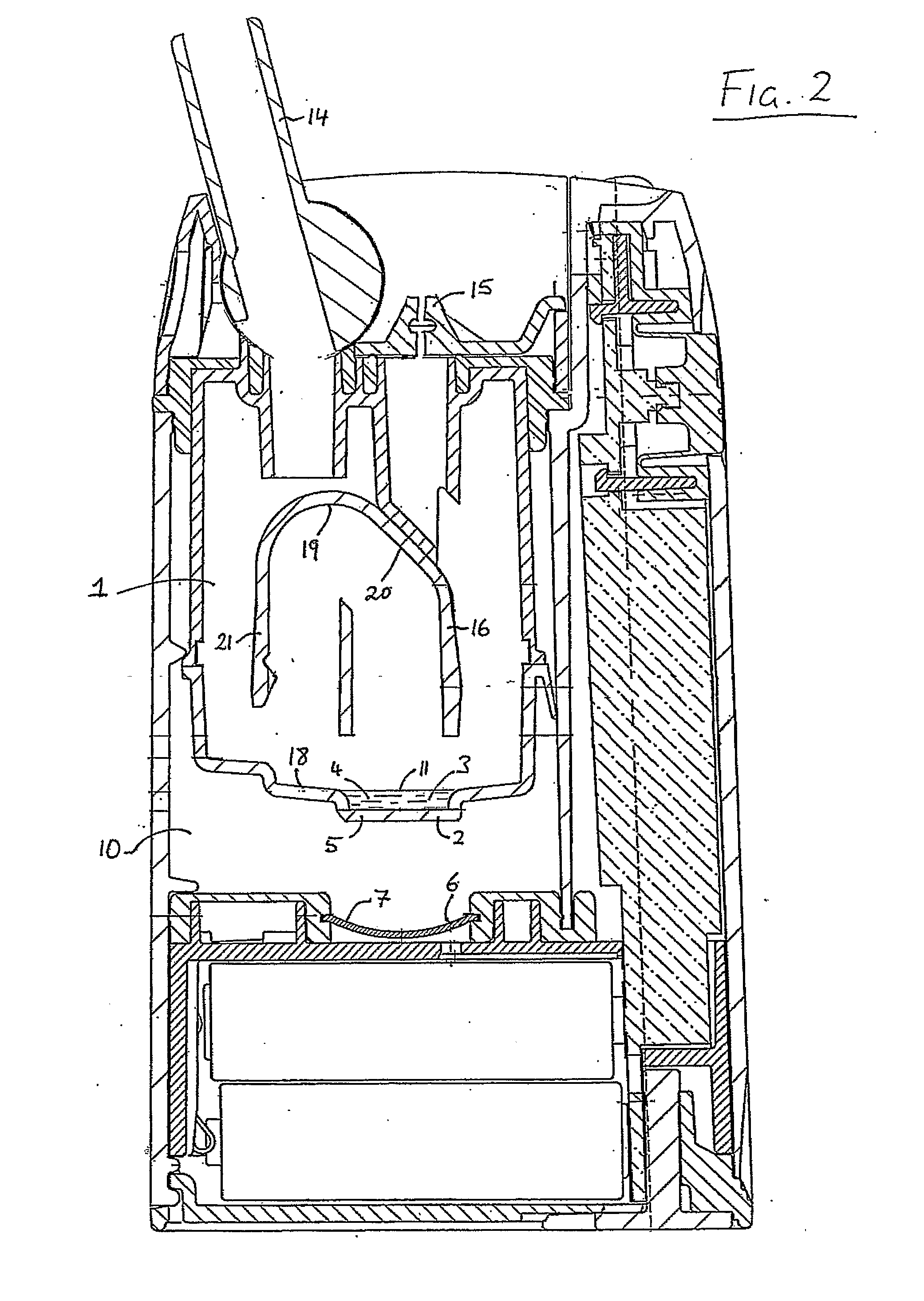
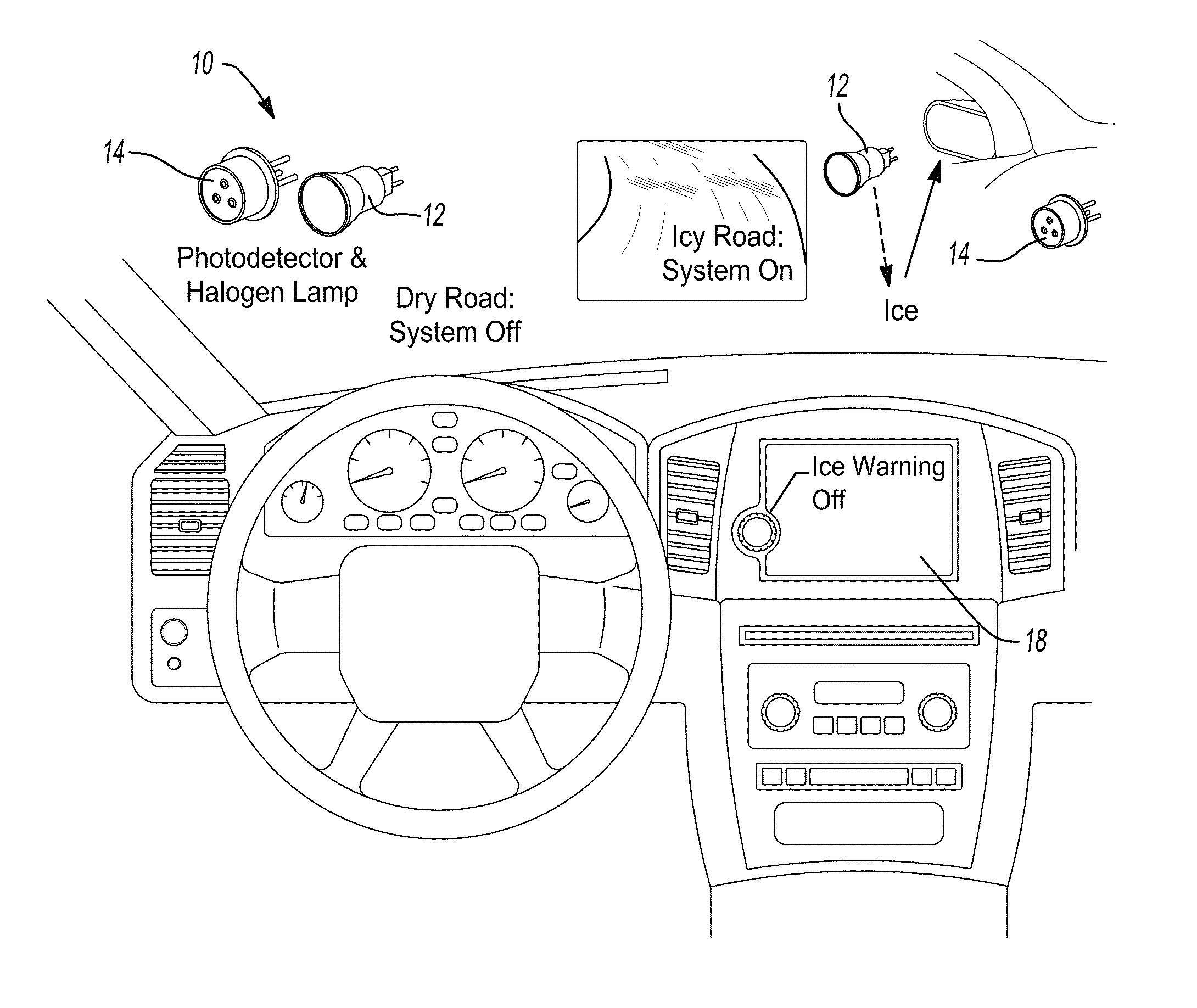
Apparatus and method for detecting aircraft icing conditions
ActiveUS20120274938A1De-icing equipmentsColor/spectral properties measurementsBeam splitterLiquid state
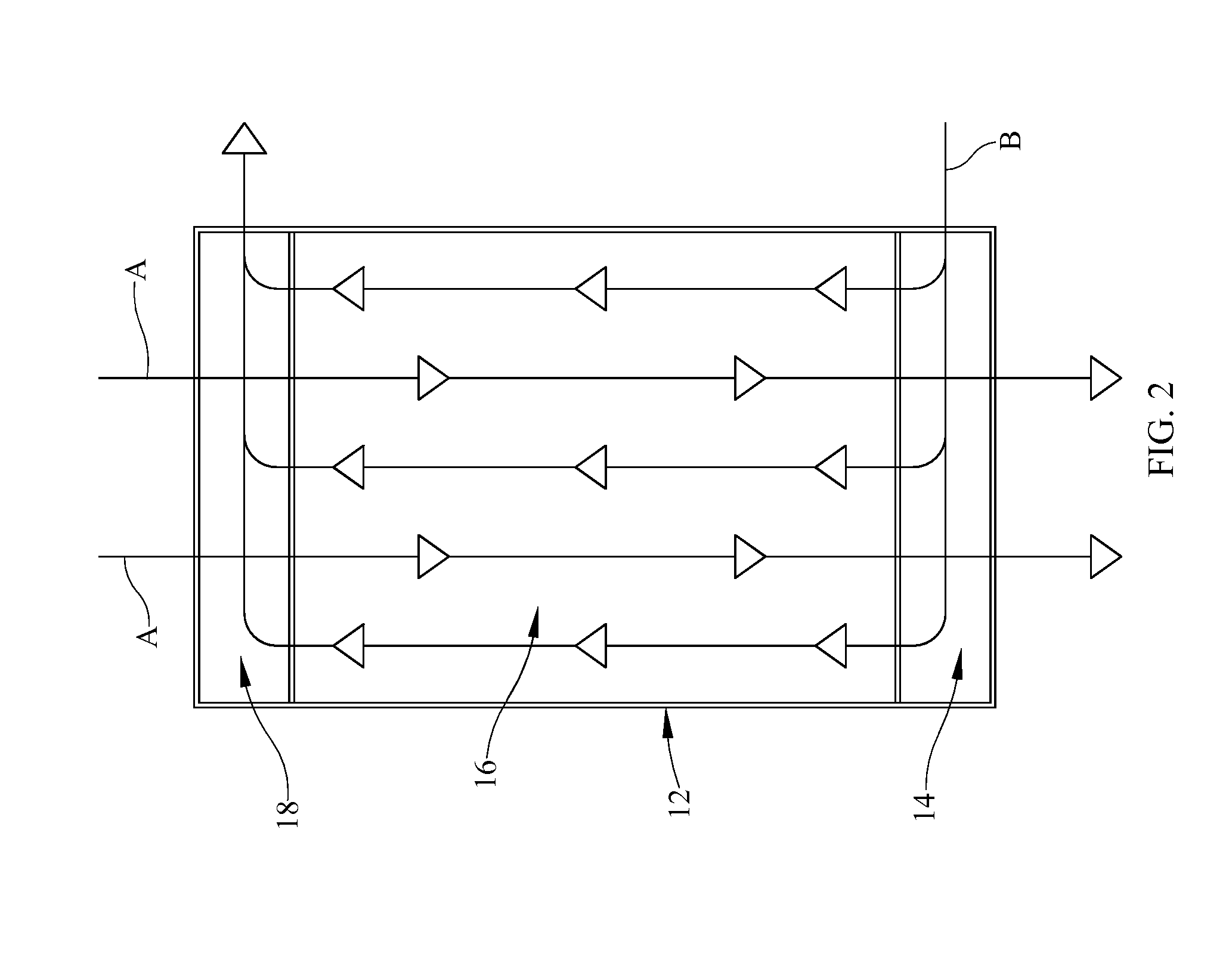
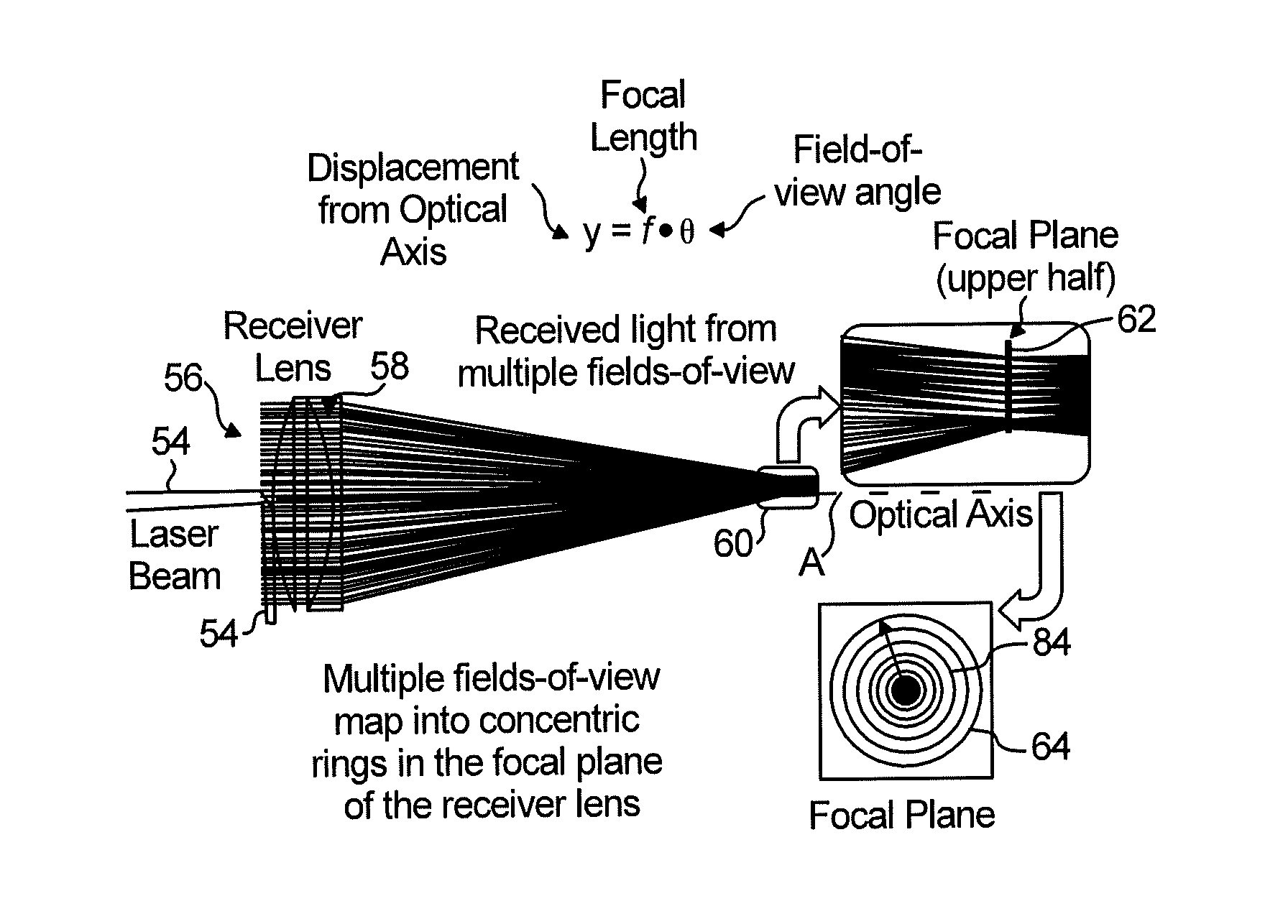
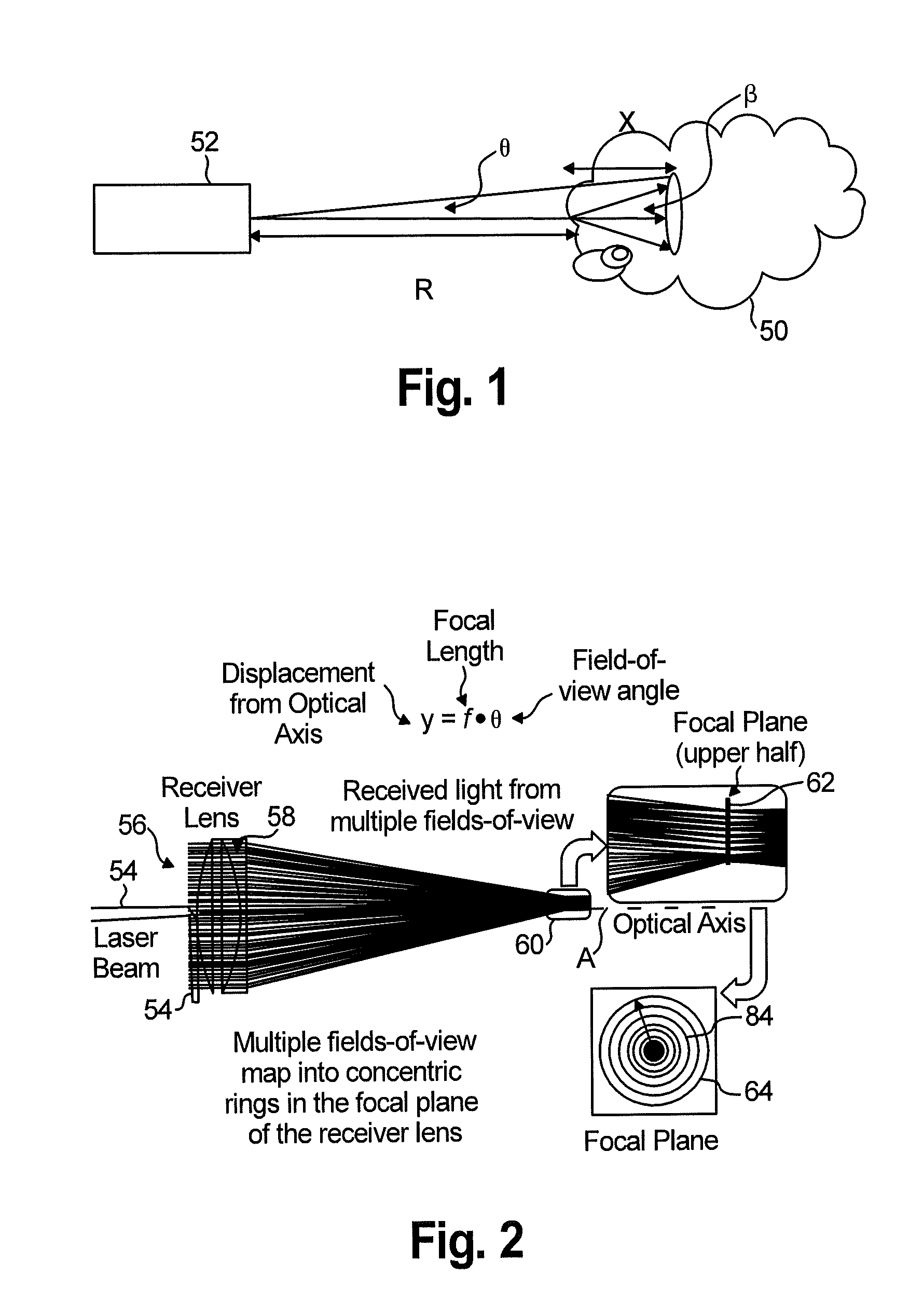
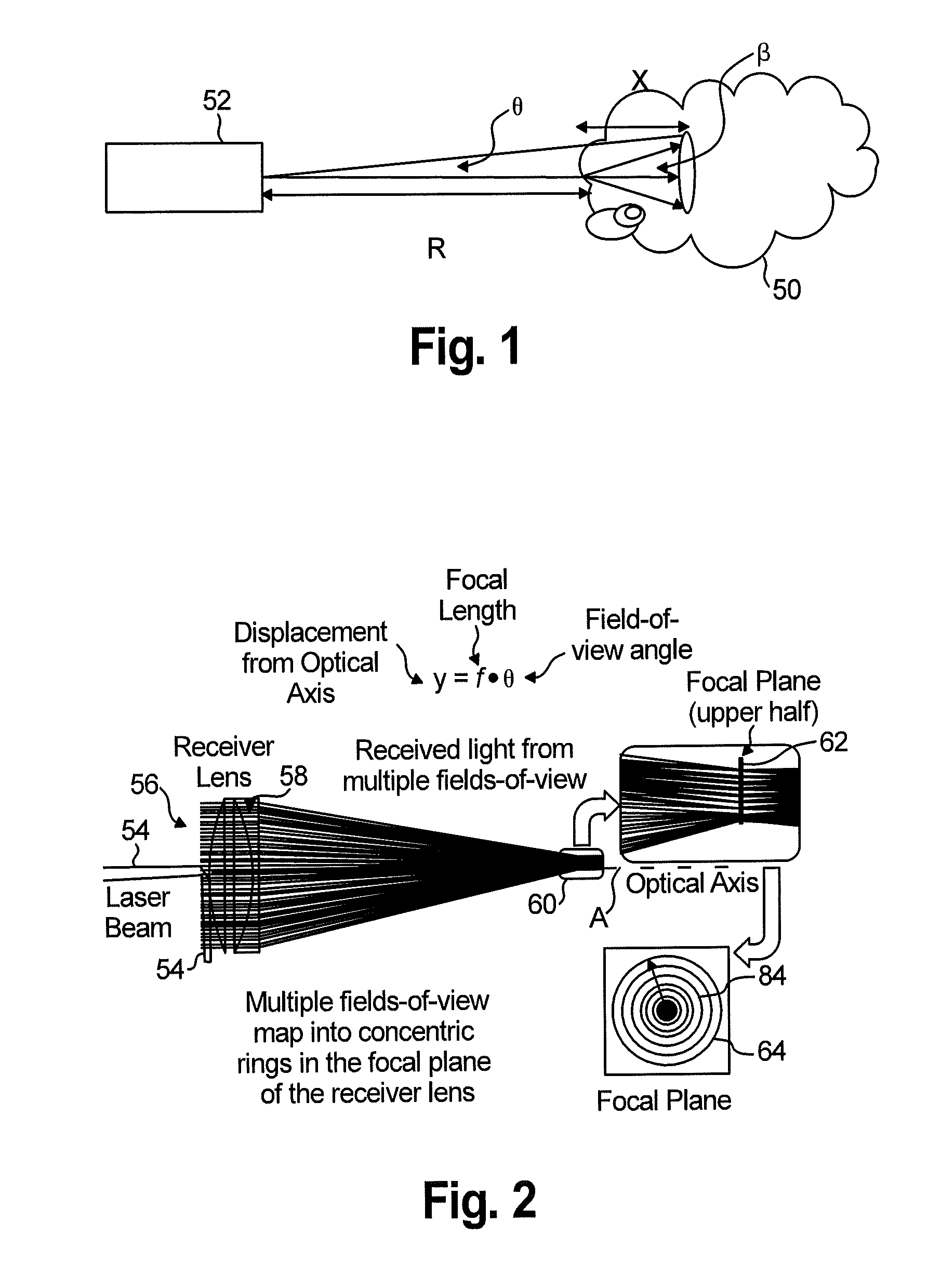
An apparatus for detecting icing conditions on an aircraft includes a laser system configured to direct a light signal into a cloud, a lens component configured to collect echo signals from a cloud caused by the light signal directed into the cloud, a beam splitter component configured to redirect signals received and passing through the lens component into at least first and second paths and a supercooled large droplet (SLD) detector to receive the redirected signals. The SLD includes a first signal detector component configured to perform a first color measurement on the first redirected signal, and a second signal detector component configured to perform a second color measurement on the second redirected signal. The SLD detector is configured to use the first and second color measurements to determine liquid water content and droplet diameter distribution for the cloud.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
Detecting device for detecting icing by image and detecting method thereof
InactiveUS20130113926A1Avoid and reduce mistakeAccurate identificationImage enhancementImage analysisSuper coolingImaging processing
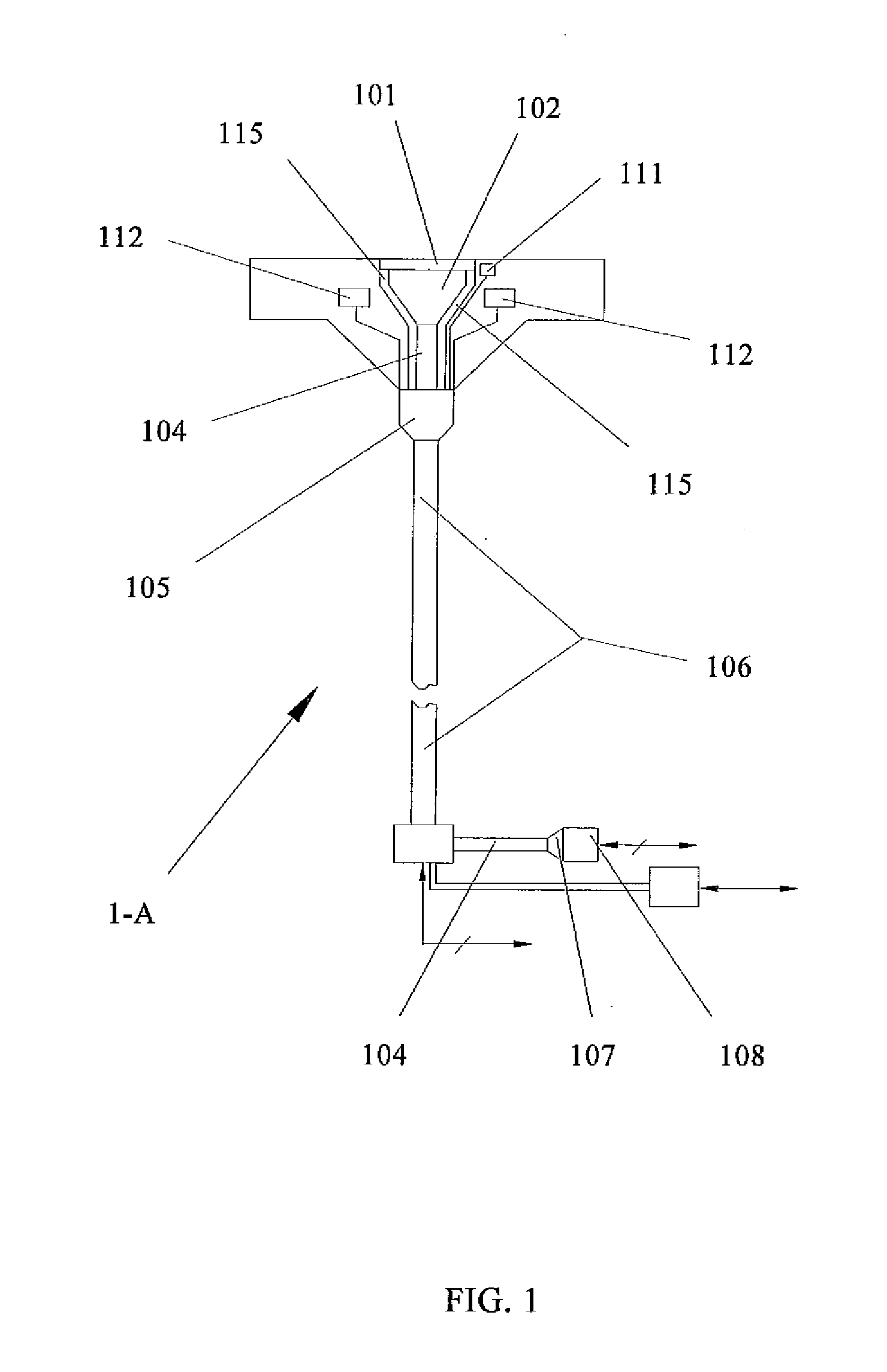
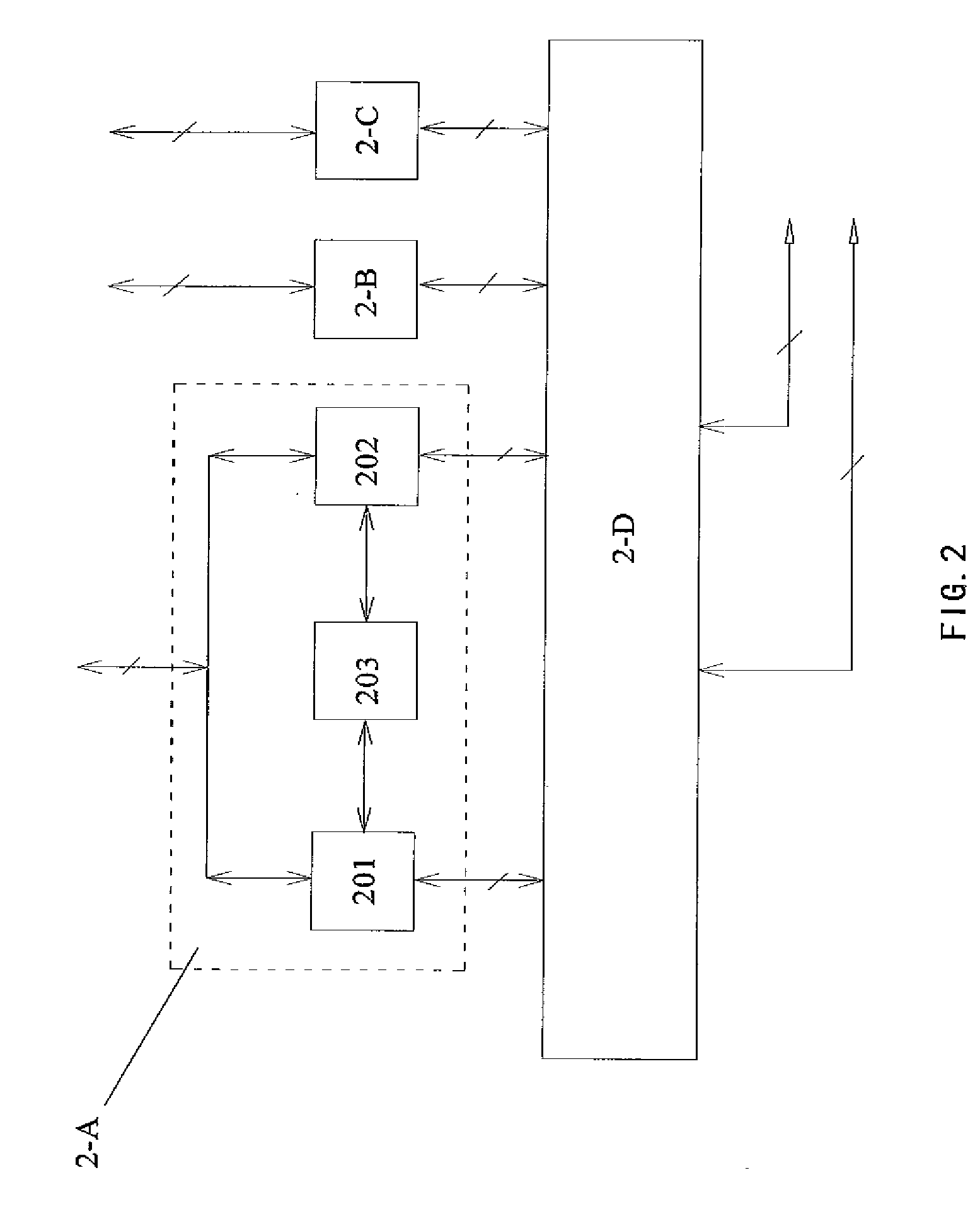
A detecting device for detecting icing by an image includes an image acquiring system (1-A) and an image processing system (2-A). The image acquiring system (1-A) can acquire an image of an object's surface. The image processing system (2-A) can analyze the image and obtain an icing condition of the object's surface. The detecting device is simple and reliable. It can identify the category of the icing effectively. So, it can improve the accurateness of the icing detection significantly and can accomplish the detection of the object's whole surface. Furthermore, it can detect an icing condition of a super-cooled large droplet. A method for detecting an icing condition of an object's surface using the detecting device is also provided.
Owner:COMAC +2
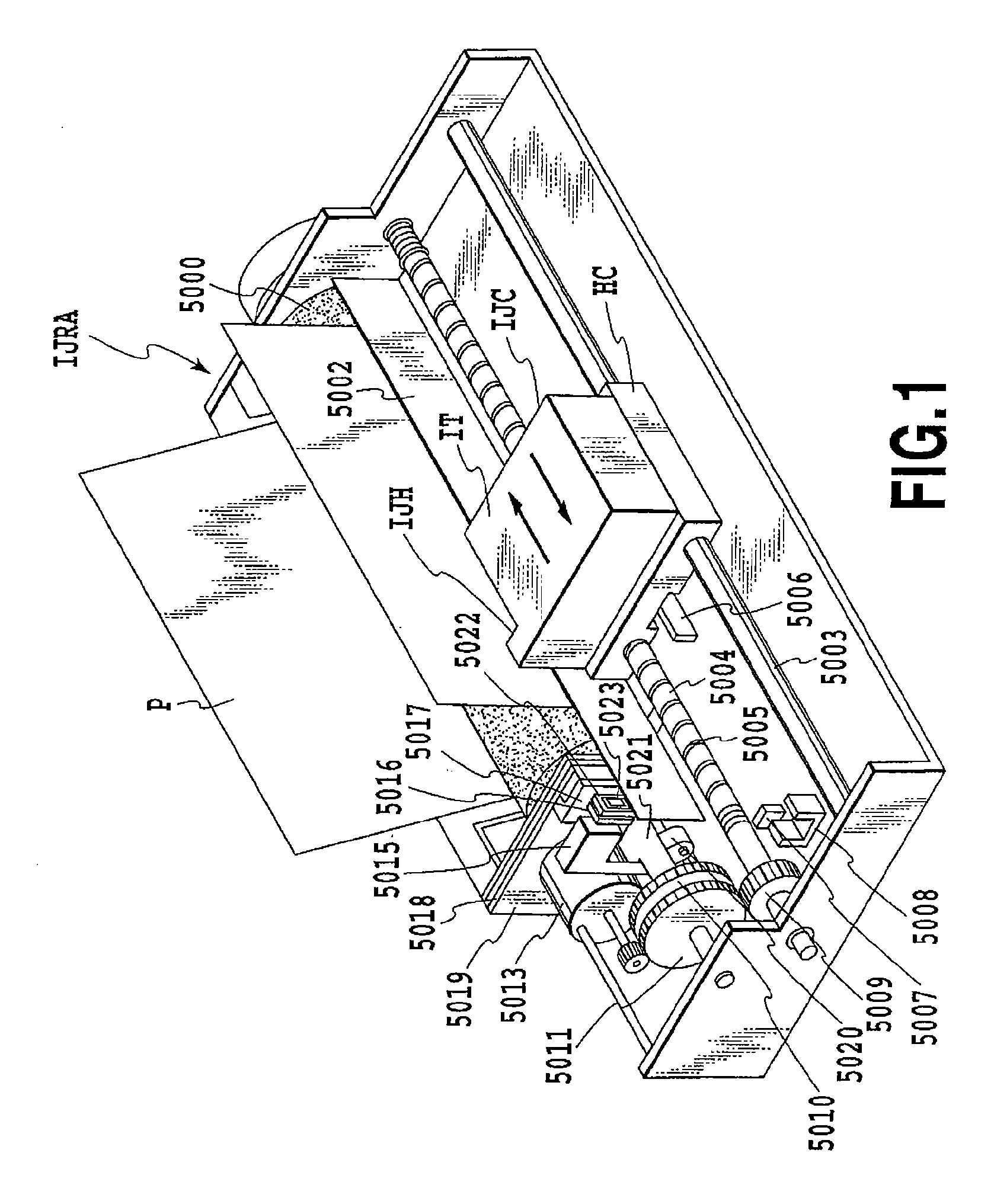
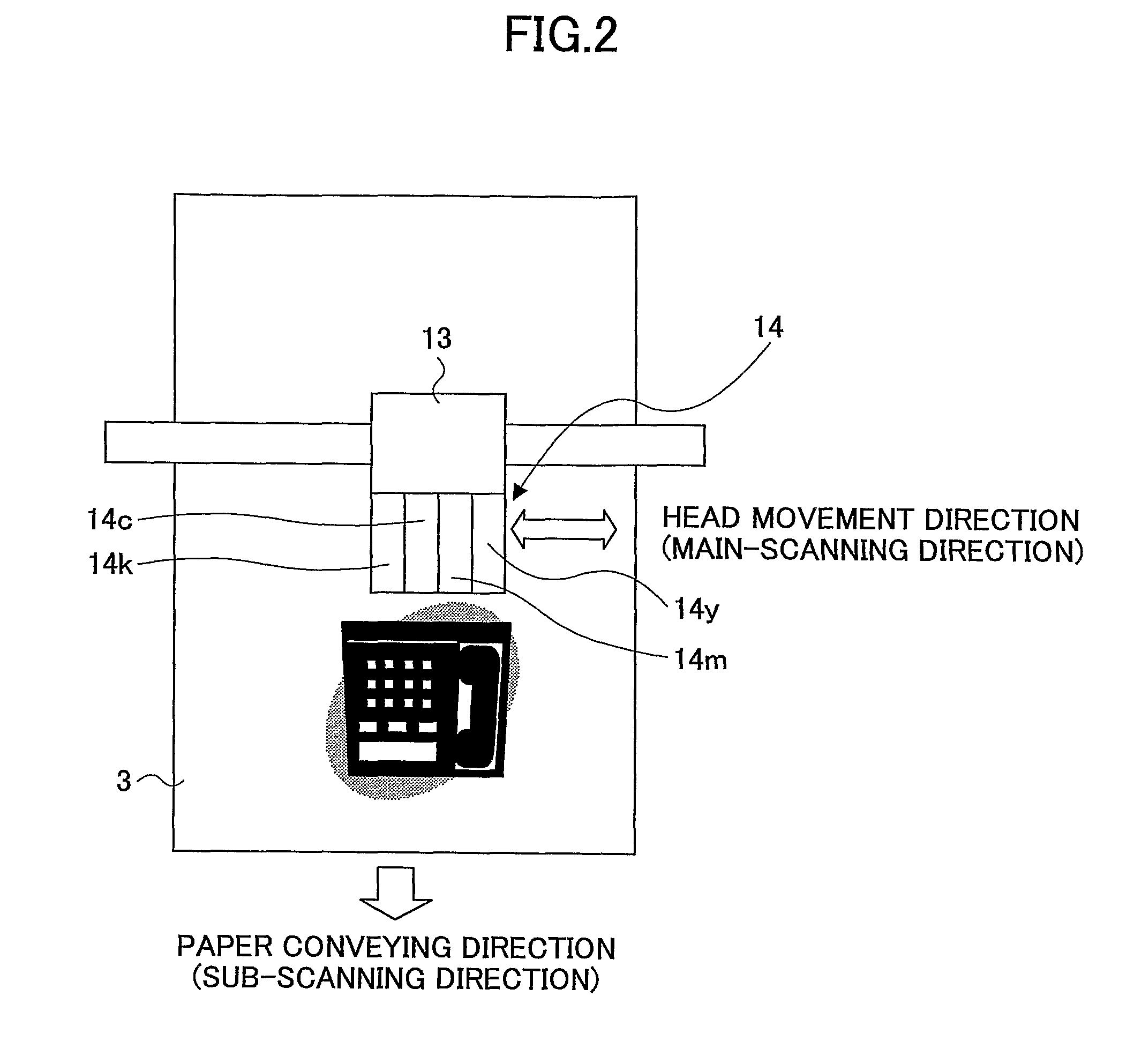
Ink jet recording head and ink jet recording apparatus
InactiveUS20080143786A1High image quality recordingRecording unevennessInking apparatusSmall dropletImaging quality
An ink jet recording head and an ink jet recording apparatus are provided to prevent occurrence of a white line or recording unevenness due to a head tilt, and realize a high image quality recording. For this purpose, in a recording head provided with nozzles ejecting three types of droplets, a large droplet, medium droplet and small droplet, nozzles are configured such that any nozzles are not arranged on the same line at the centers thereof in the main scanning direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Nebuliser
InactiveUS20080245362A1Minimized volumeMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesNebulizerUltrasonic sensor
The present invention relates to a nebuliser and method of nebulising a liquid. The nebuliser includes a nebulisation chamber (1) having a well (2) adapted to contain a liquid (3) to be nebulised. An energy source in the form of an ultrasonic transducer (6) has as a curved energy transmission surface (7). This curved energy transmission surface defines a focal point (8) and a focal length (9). The energy source is spaced from the well such that the distance between the focal point and the energy source intrudes into the well not greater than 50% of the focal length. Preferably the well is shaped such that during nebulisation the level of the liquid in the well remains within a predetermined focal length range to thereby provide a substantially constant flowrateut of nebulised liquid. The nebuliser may also include a deflector baffle or fountain diverter (16) which acts to deflect the nebulised liquid fountain rising from the well. In order to reduce large droplets leaving the nebulisation chamber a circuitous or labyrinthine path is also provided between the well and the exit (13) of the nebulisation chamber
Owner:INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH
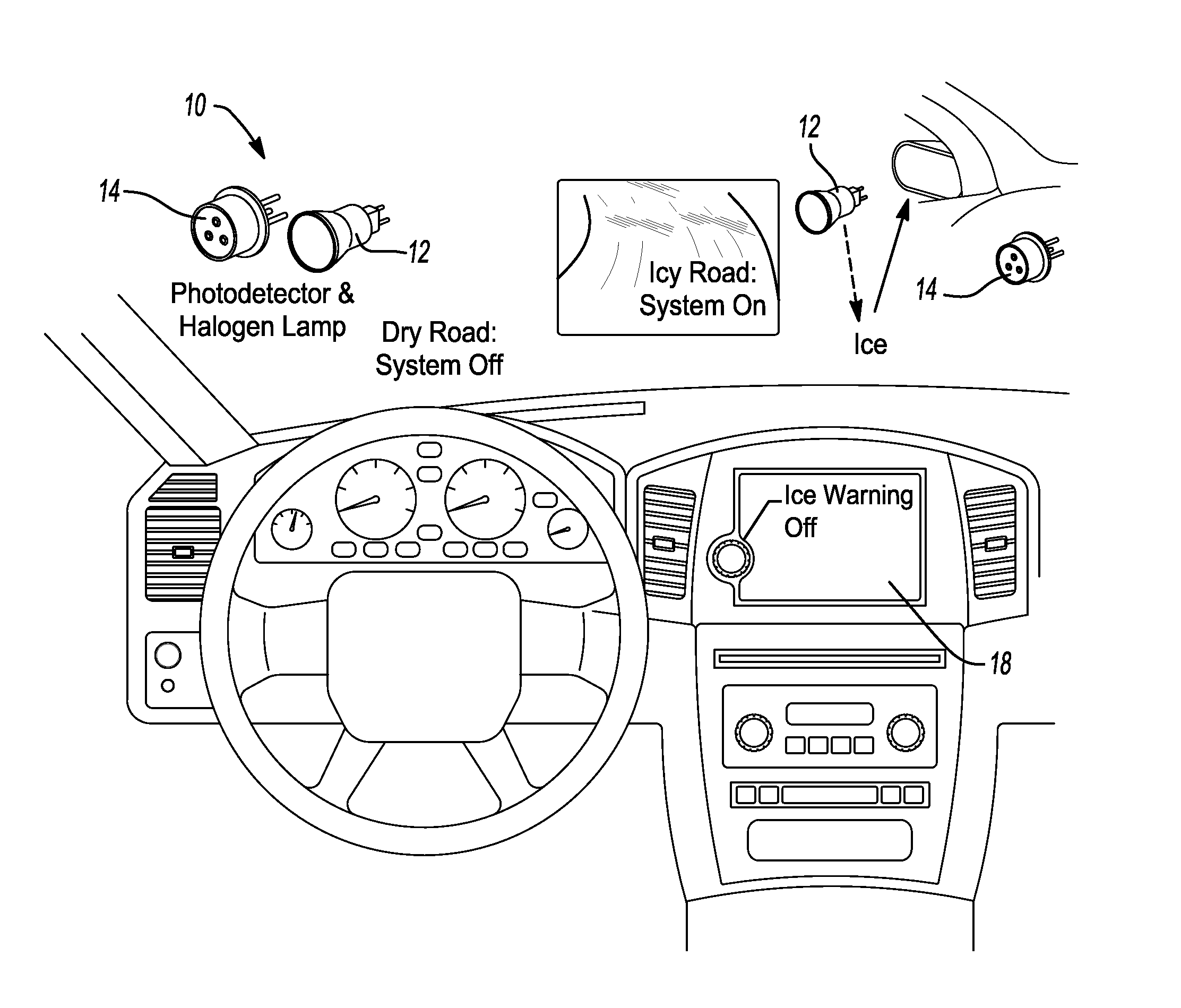
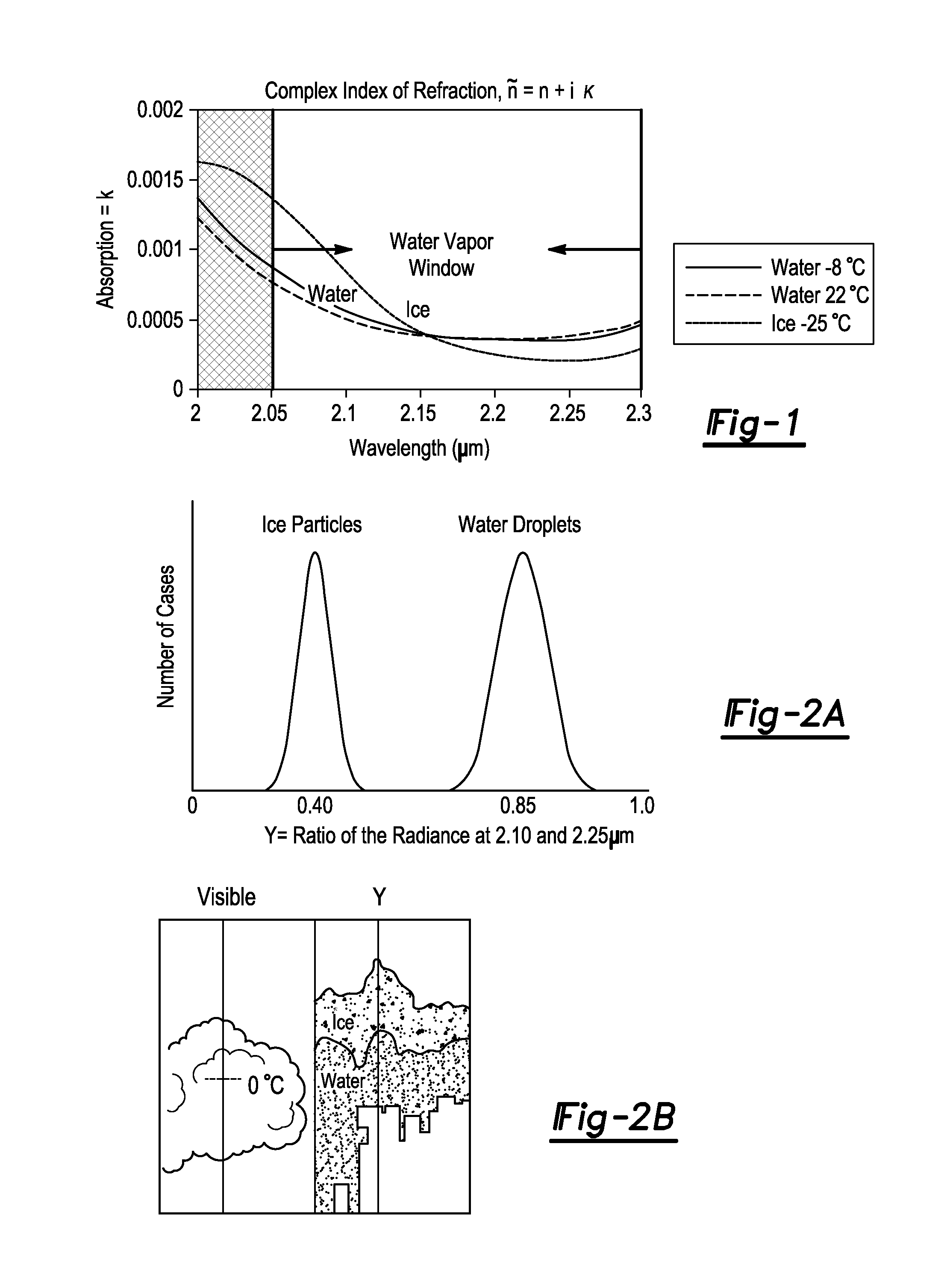
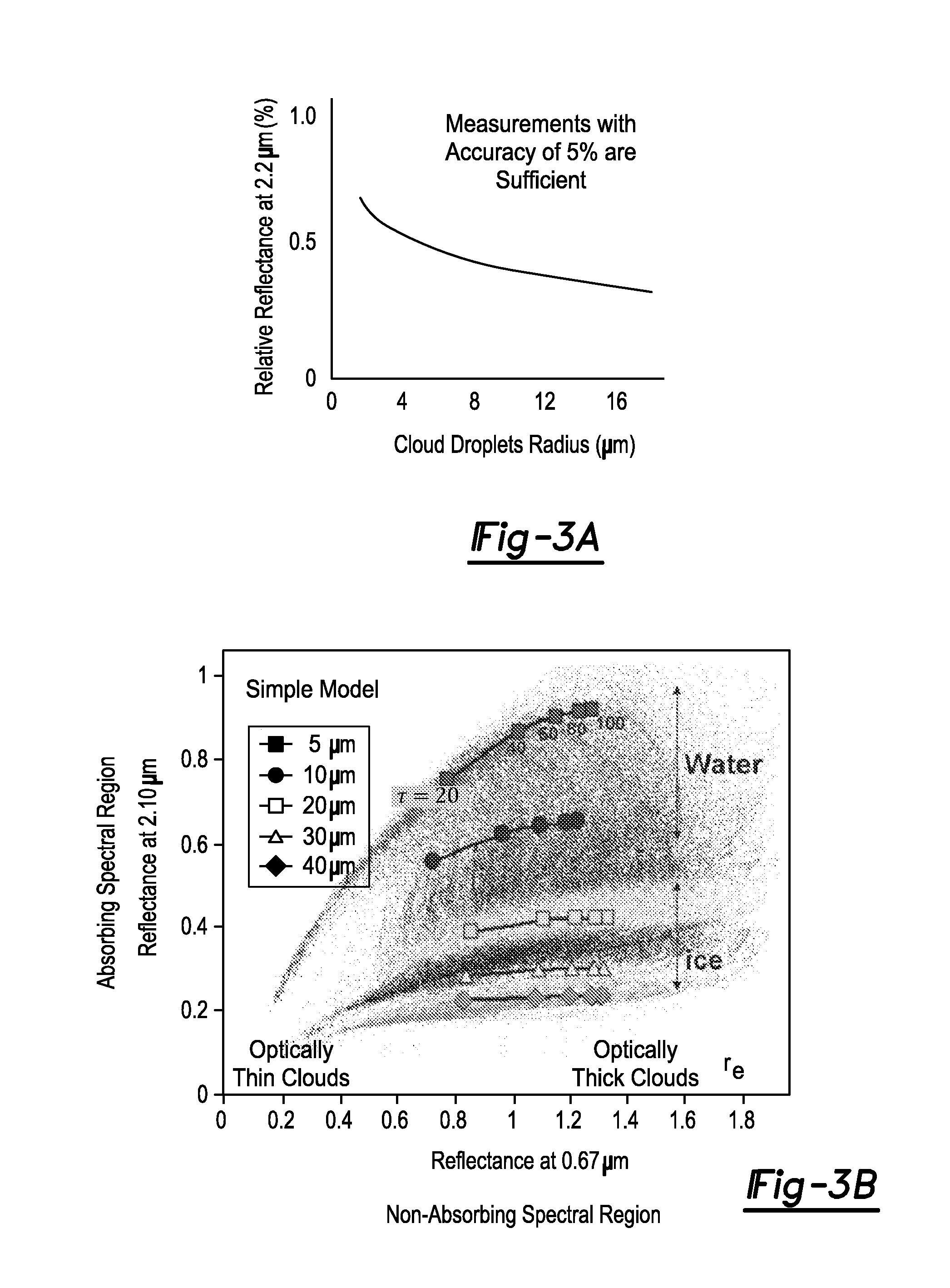
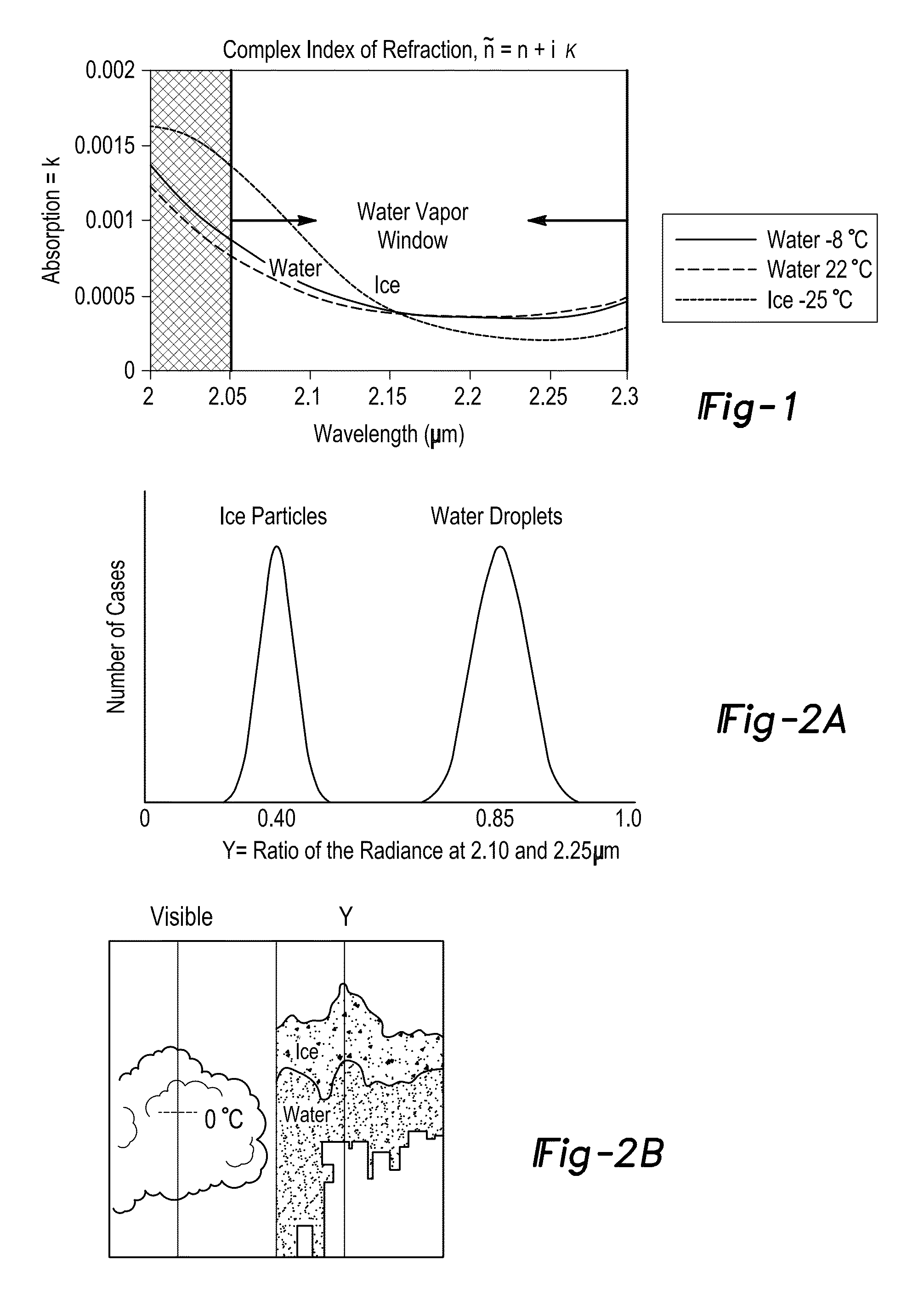
Ice and supercooled water detection system
ActiveUS20150120092A1Maximize safetyIncrease incidenceAnalogue computers for trafficScattering properties measurementsRadianceLarge droplet
A system for detecting ice or supercooled large droplets within an area of interest having a detection system measuring radiance or reflectance of the area of interest when exposed to shortwave infrared radiation having a wavelength in the range of about 2.05 μm to about 2.30 μm. The detection system measures the radiance or reflectance in a first band having a wavelength in the range of about 2.05 μm to about 2.15 μm and outputting a first band signal, and further measures the radiance or reflectance in a second band having a wavelength in the range of about 2.15 μm to about 2.30 μm and outputting a second band signal. A processing unit determines a ratio of the first band signal and the second band signal and compares the ratio to a predetermined critical ratio and outputs a determination signal indicating presence of ice or supercooled water droplets.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
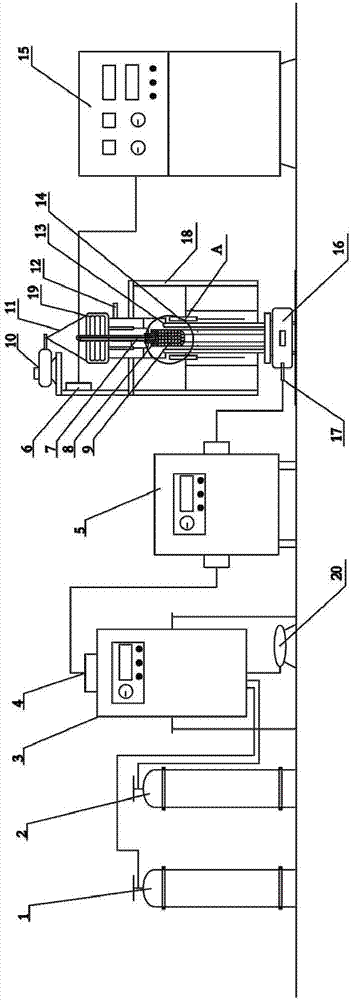
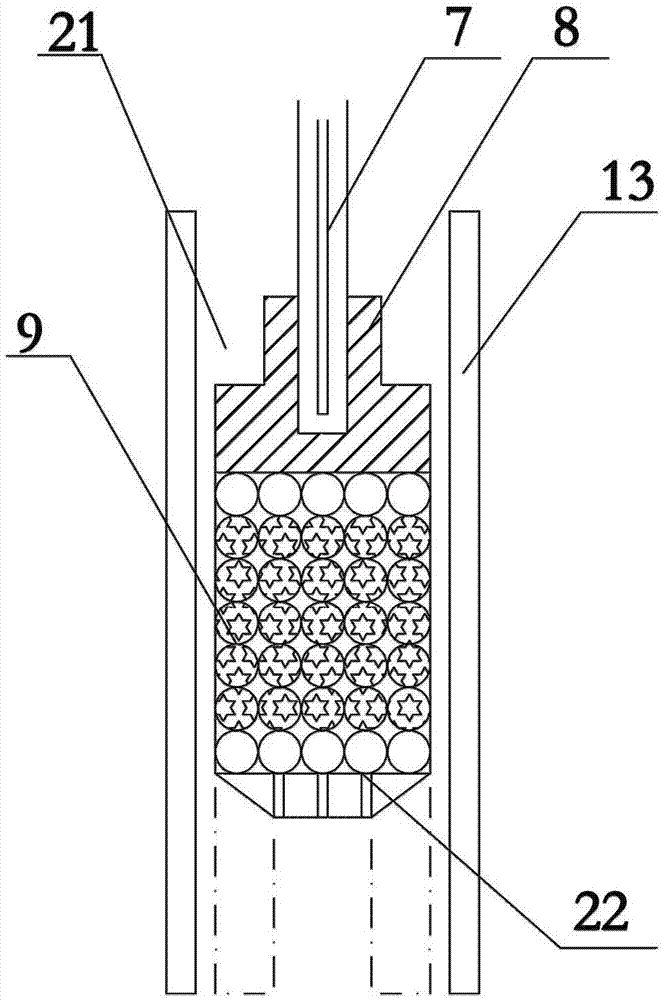
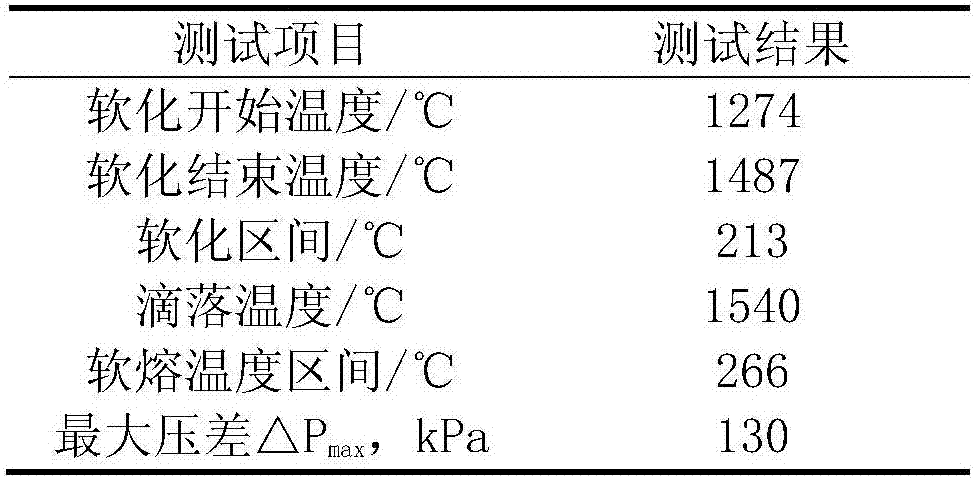
Device for testing soft-melting and dropping characteristics of ferruginous burden of blast furnace and method
PendingCN107543777AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityFlow propertiesInvestigating phase/state changeAutomatic controlGraphite
The invention relates to a device for testing soft-melting and dropping characteristics of ferruginous burden of a blast furnace and a method. The device comprises a melting and dropping furnace, a heating device, a graphite pressure lever, a thermocouple, a sampling box, reductive gas and an automatic control device and is characterized by further comprising a supporting framework, a lifting mechanism, a load, a displacement sensor and a gas supplying system. The graphite pressure lever is a piston type graphite pressure lever, one end of the load is fixedly connected with the piston type graphite pressure lever, the other end of the load is fixedly connected with a hoisting steel wire rope, and a lifting motor of the lifting mechanism, the gas supplying system and the heating device areall electrically connected with the automatic control device. The device and the method have the advantages that through carrying out testing by a 2kg-grade large-sized melting and dropping furnace and assisting the melting and dropping furnace with the heated reductive gas, the soft-melting and dropping characteristics of iron ore can be more accurately tested, and a reference foundation is provided for actual raw material regulation, technical research and the like of blast furnace production. The accuracy and reliability of test results can be greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
Apparatus and method for detecting aircraft icing conditions
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
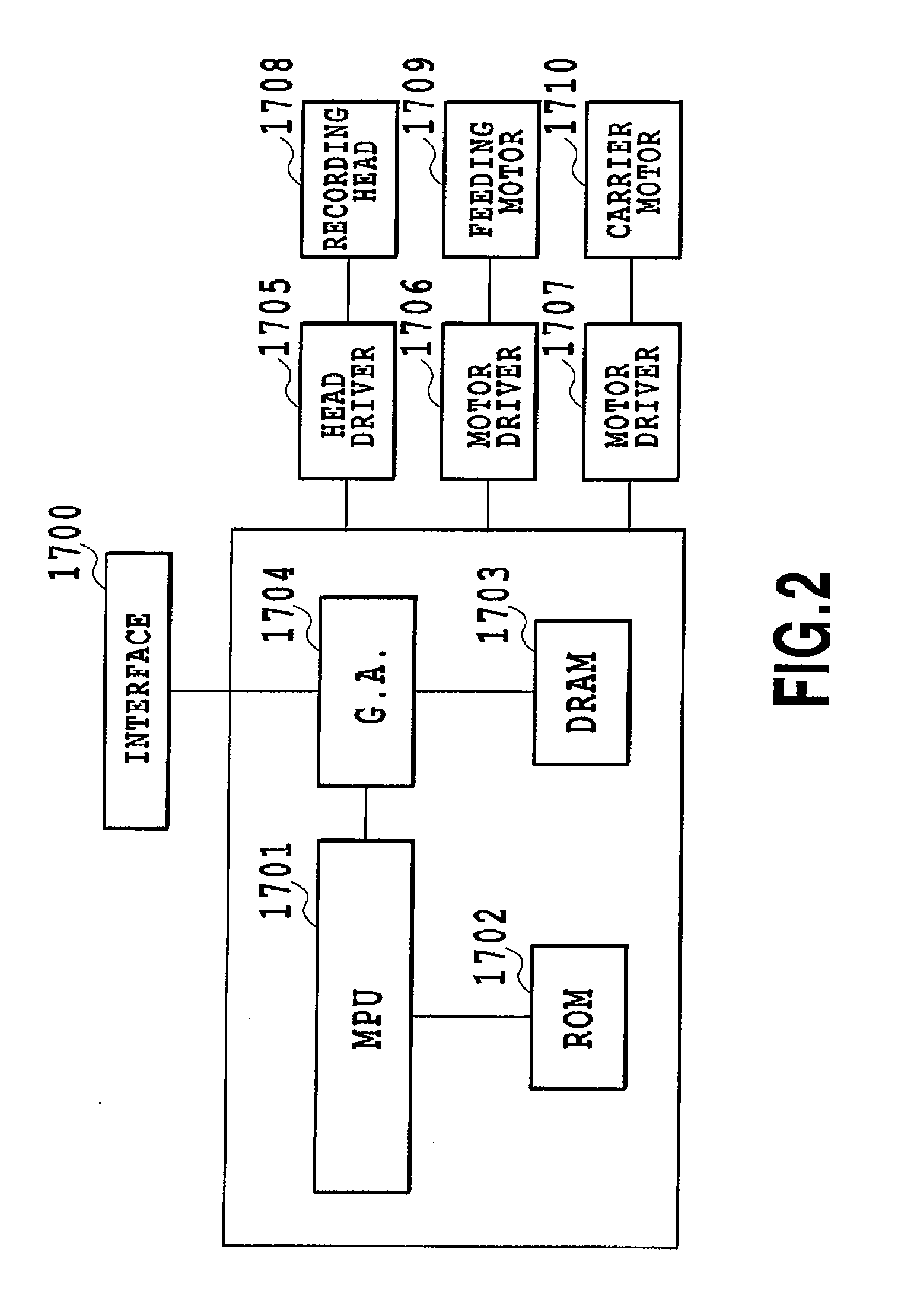
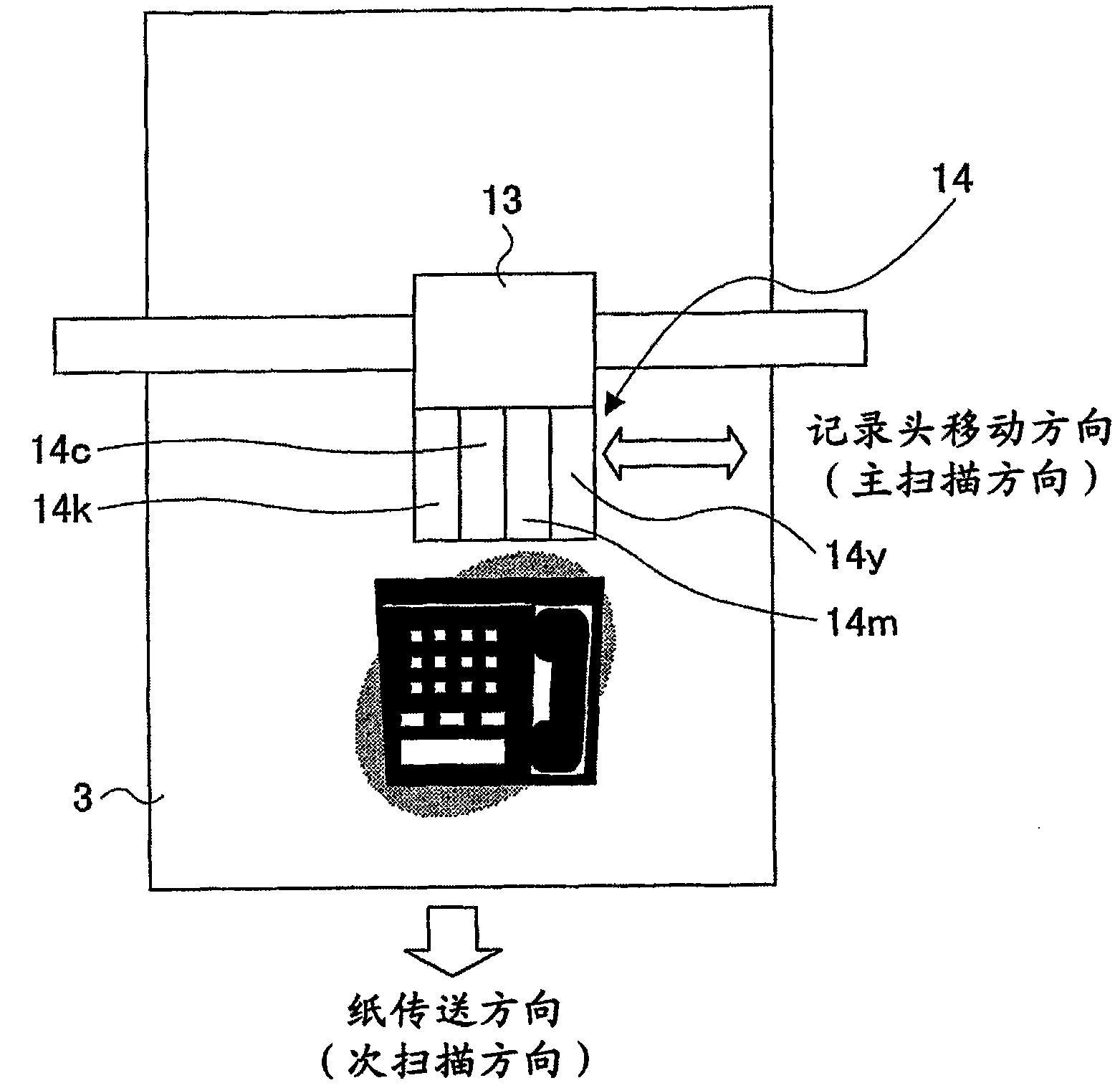
Image forming apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070211101A1Improve visibilityReduce load concentrationOther printing apparatusSmall dropletImage formation
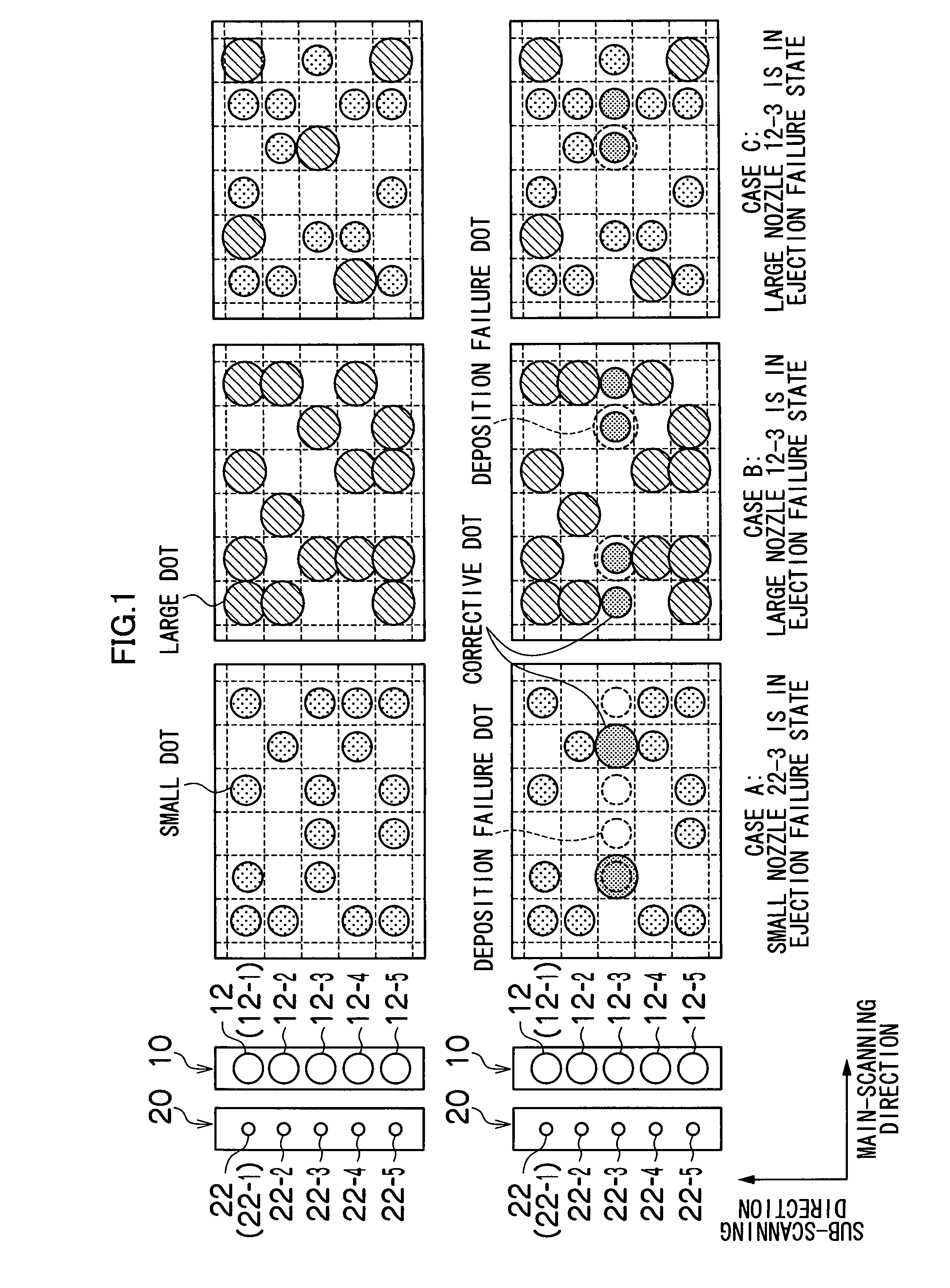
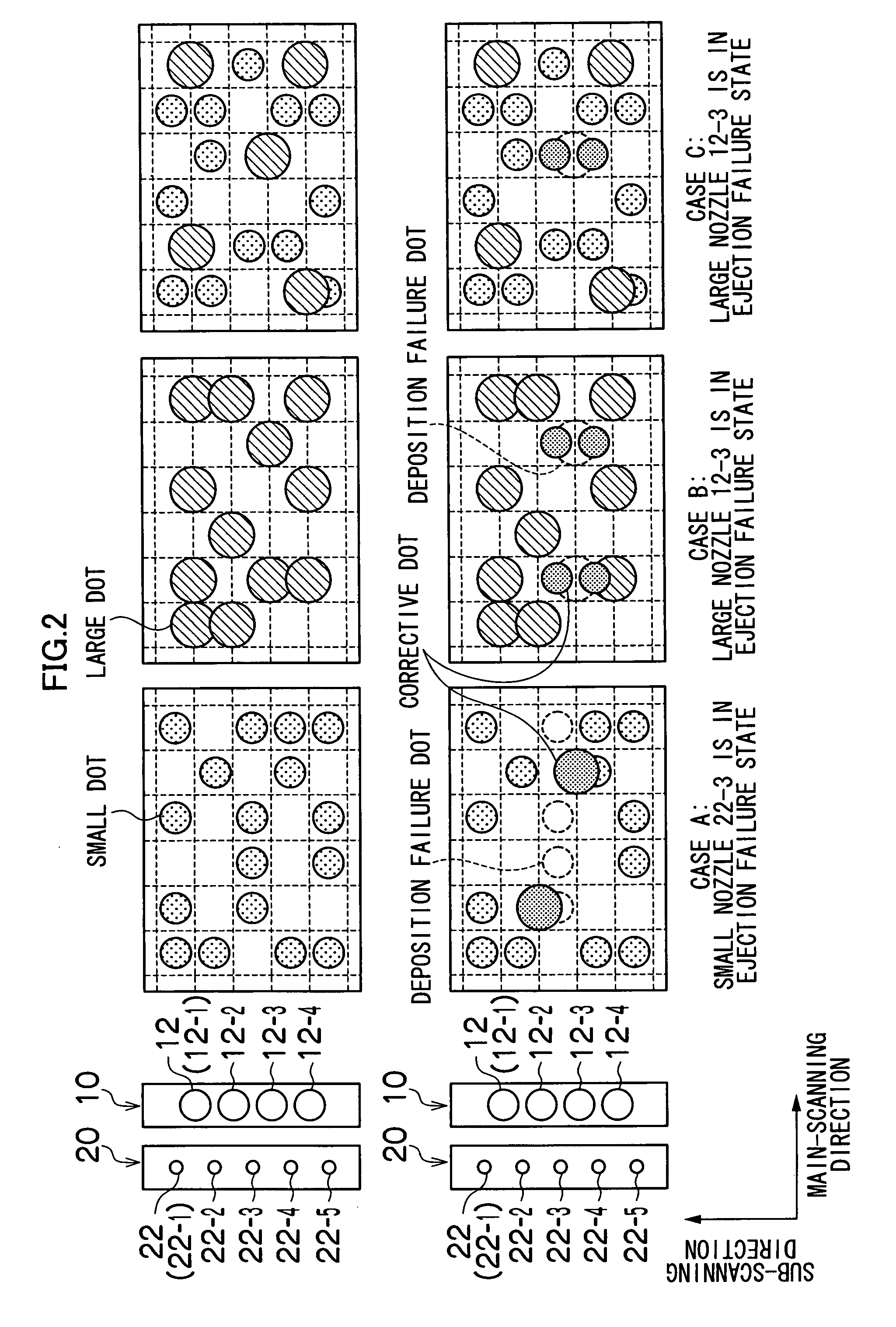
The image forming apparatus includes: a first group of large nozzles which eject large droplets of liquid for a color; a second group of small nozzles which eject small droplets of the liquid for the color, the small droplets having volume smaller than the large droplets; a dot data creation device which creates dot data according to input image data; a dot data correction device which corrects the dot data if there is an abnormal nozzle in one of the first and second groups, in such a manner that a corrective nozzle is selected from the other of the first and second groups, and droplet ejection performed by the corrective nozzle substitutes for droplet ejection that is originally to be performed by the abnormal nozzle; and a driving device which drives the large and small nozzles to eject the large and small droplets according to the corrected dot data.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
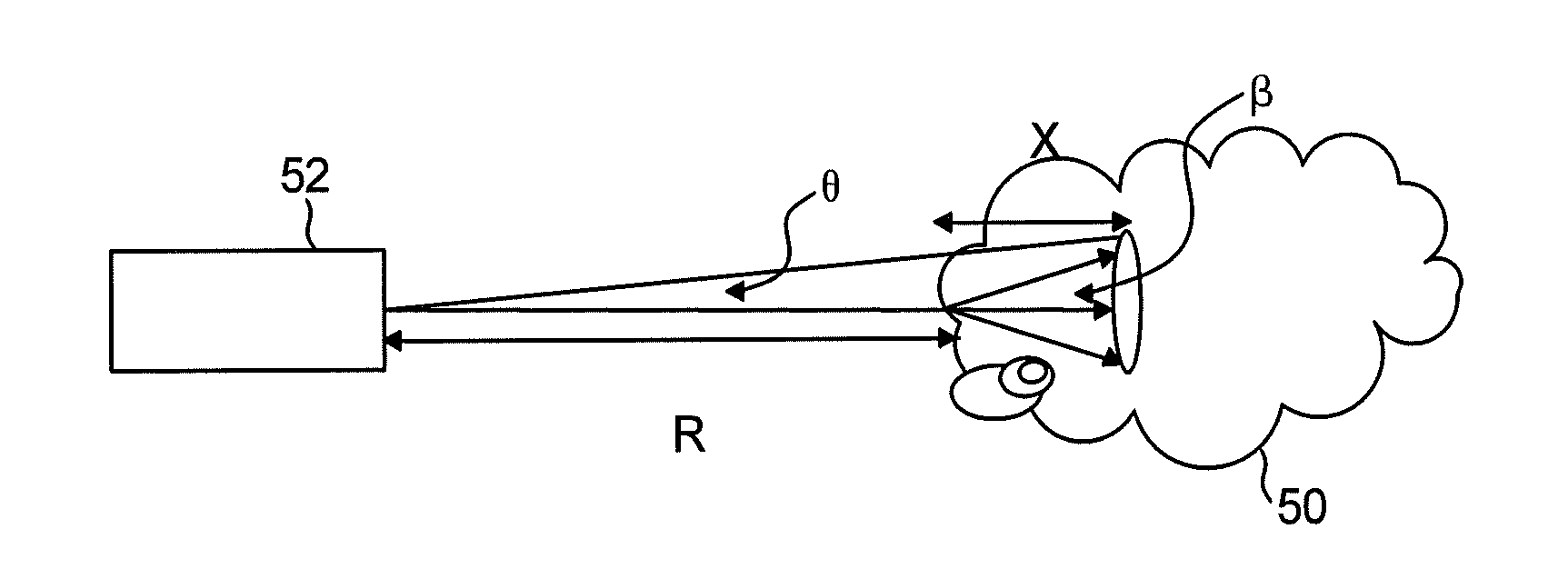
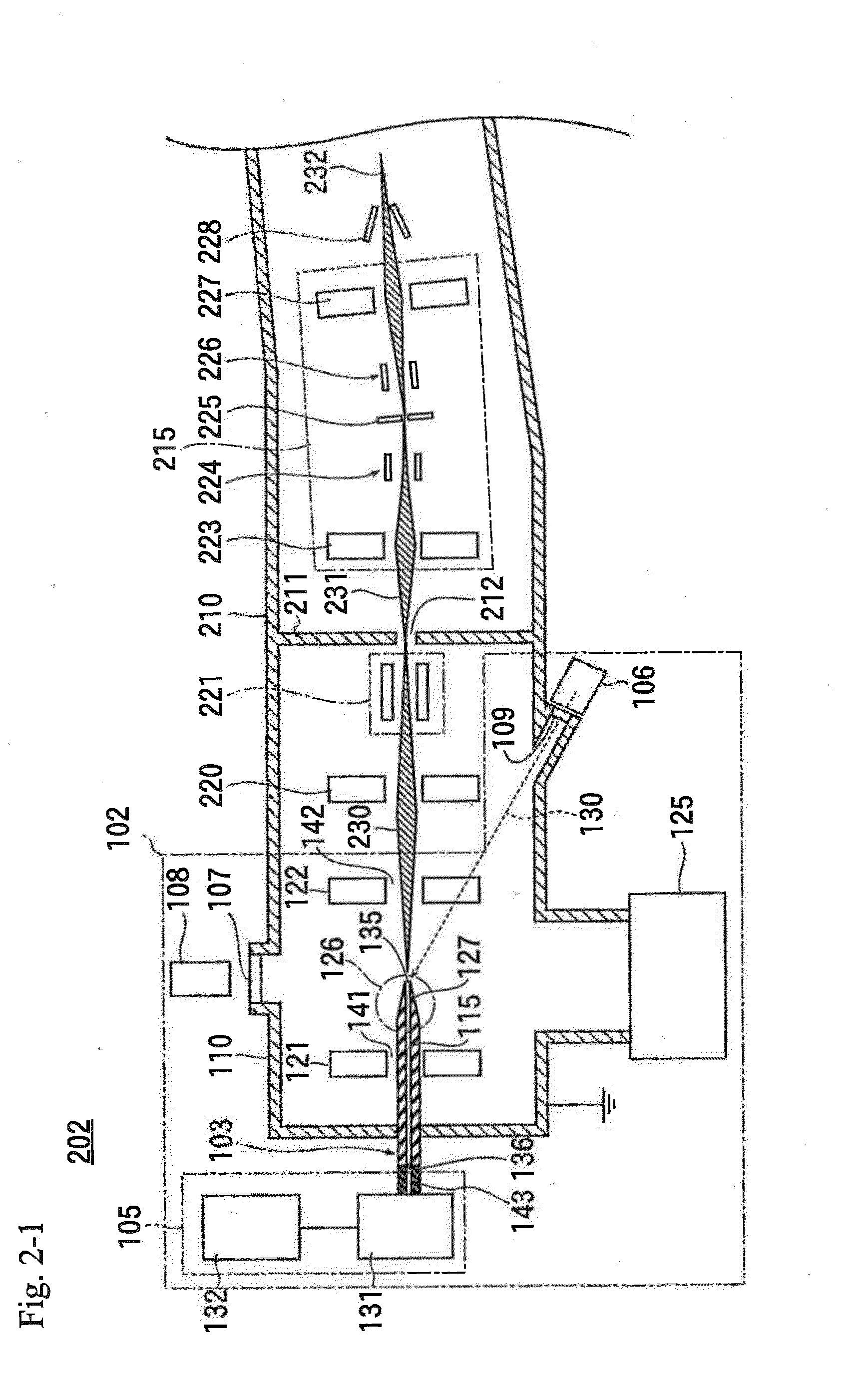
Computing method of model parameters in icing wind tunnel experiment under supercooled large droplet condition
InactiveCN104268399AMeet the similarity requirementsSpecial data processing applicationsJet aeroplaneScale model
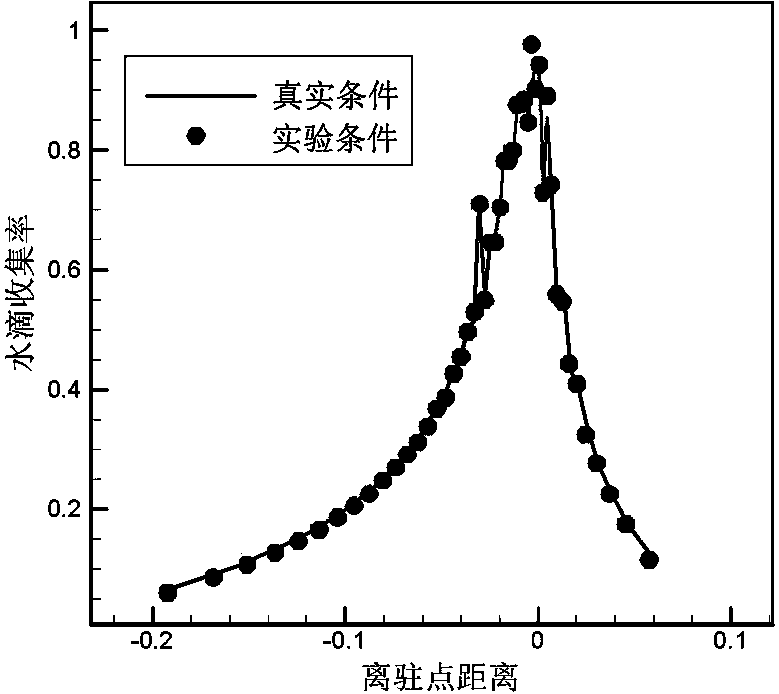
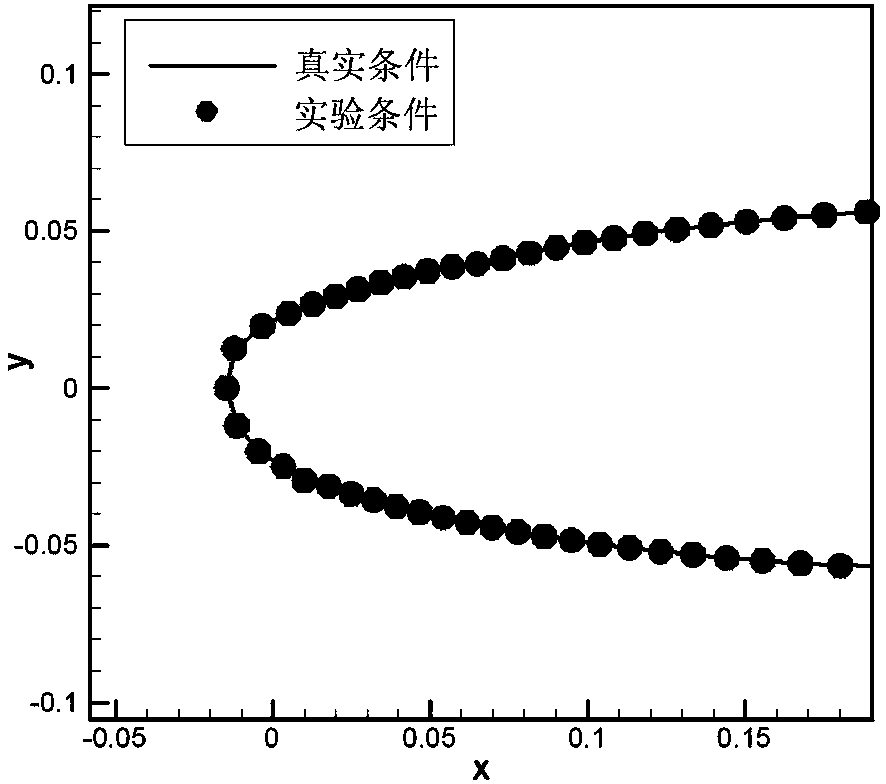
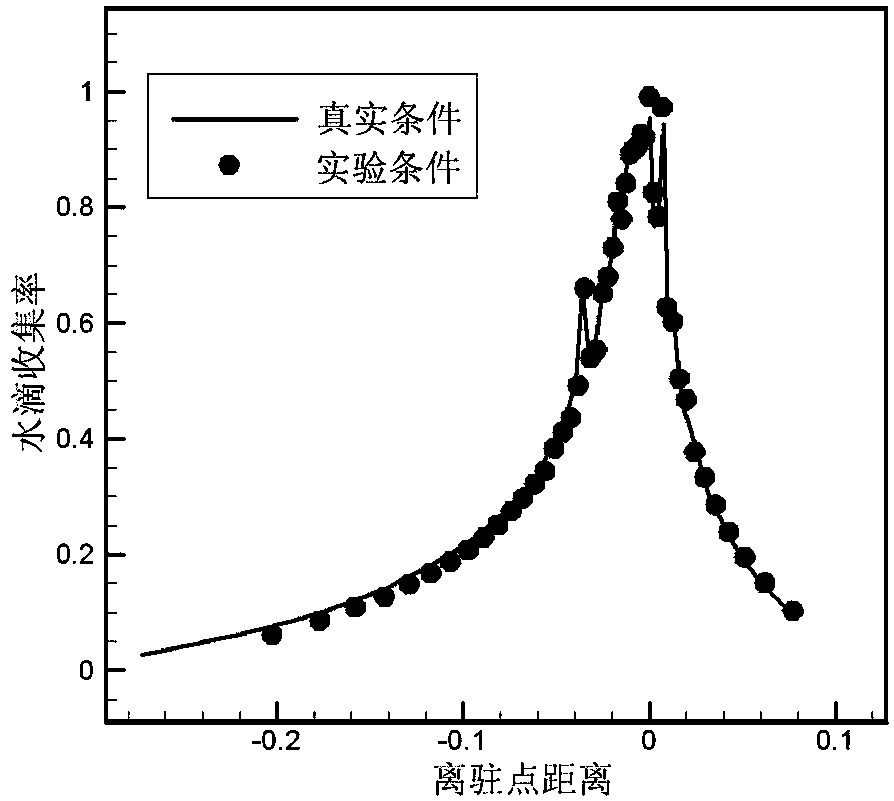
The invention discloses a computing method of model parameters in an icing wind tunnel experiment under a supercooled large droplet condition and aims at solving the problems that an existing parameter selecting method for a supercooled small droplet icing experiment does not function well if being applied to a supercooled large droplet icing experiment and that the real icing condition cannot be reflected by icing on a scale model of the airplane. The computing method of the model parameters in the icing wind tunnel experiment under the supercooled large droplet condition is capable of orderly giving the experimental parameters of a wind tunnel test section such as air velocity, average droplet grain diameter, air pressure, liquid water content, icing time and low supercooled water temperature corresponding to real icing flying conditions by use of a theoretical derivation and numerical computation method after determining the scale relation of the model and the real airplane. An aircraft icing wind tunnel experiment is performed according to the converted test parameters, and the experimental result and the real result are capable of meeting the similarity requirement on the major characteristics of the icing process. As a result, the computing method of the model parameters in the icing wind tunnel experiment under the supercooled large droplet condition is capable of obtaining the model parameters for the icing wind tunnel experiment; the corresponding parameters are capable of reflecting the real icing condition in the icing wind tunnel experiment.
Owner:AERODYNAMICS NAT KEY LAB
Method for spray-forming melts of glass and glass-ceramic compositions
The invention relates to a process and apparatus for forming a particulate composition, especially a particle glass composition, through the use of shock waves. A nozzle element is utilized having inlets for introduction of cold and heated gas and a delivery tube for introducing molten material. Through the introduction of the cold and heated gases, droplets are formed from a molten stream, a cone-shaped standing shock wave is formed, and shock waves are formed via a modified Hartmann-Sprenger chamber, the shock waves impinging on the droplet stream to break up the larger droplets.
Owner:SCHOTT CORP
Method and Apparatus For Three-Dimensional Digital Printing
Techniques are presented for digital ink jet printing upon a substrate with a significant third dimension. Droplets in the range of 120 pL to 200 pL have been found suitable for substrates with variability, in the third dimension, of up to approximately 4 cm. A larger droplet can be generated by utilizing a plurality of drive pulses, each of which generates a smaller droplet, and having the plurality of smaller droplets combine in mid-air. The data to be printed can be derived from a 3D model and such 3D model can also be used to guide shaping of the substrate. The 3D model can be produced from 2D image data. If the 2D image data is a two-dimensional portrait photograph, a result, of using the present invention, can be a realistic portrait in the form of a bas-relief sculpture.
Owner:3DPHOTOWORKS
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, image forming system, and storage medium
InactiveUS20110090276A1Small droplet sizeSolve or reduce one or more problemsOther printing apparatusPictoral communicationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing method includes converting multilevel data of an image into a dot pattern using a multilevel error diffusion process. The conversion includes determining a pixel corresponding to an abnormal nozzle based on abnormal nozzle information provided for each of droplet sizes supported by nozzles of an image forming apparatus; preventing jetting of a droplet onto the determined pixel; distributing a quantization error of the determined pixel calculated in the multilevel error diffusion process to neighboring pixels; and if extra-large droplets with a droplet size greater than the droplet size of a full-size droplet capable of filling a pixel are to be formed in the neighboring pixels as a result of distributing the quantization error, removing one or more of the extra-large droplets or reducing the droplet size of one or more of the extra-large droplets.
Owner:RICOH KK
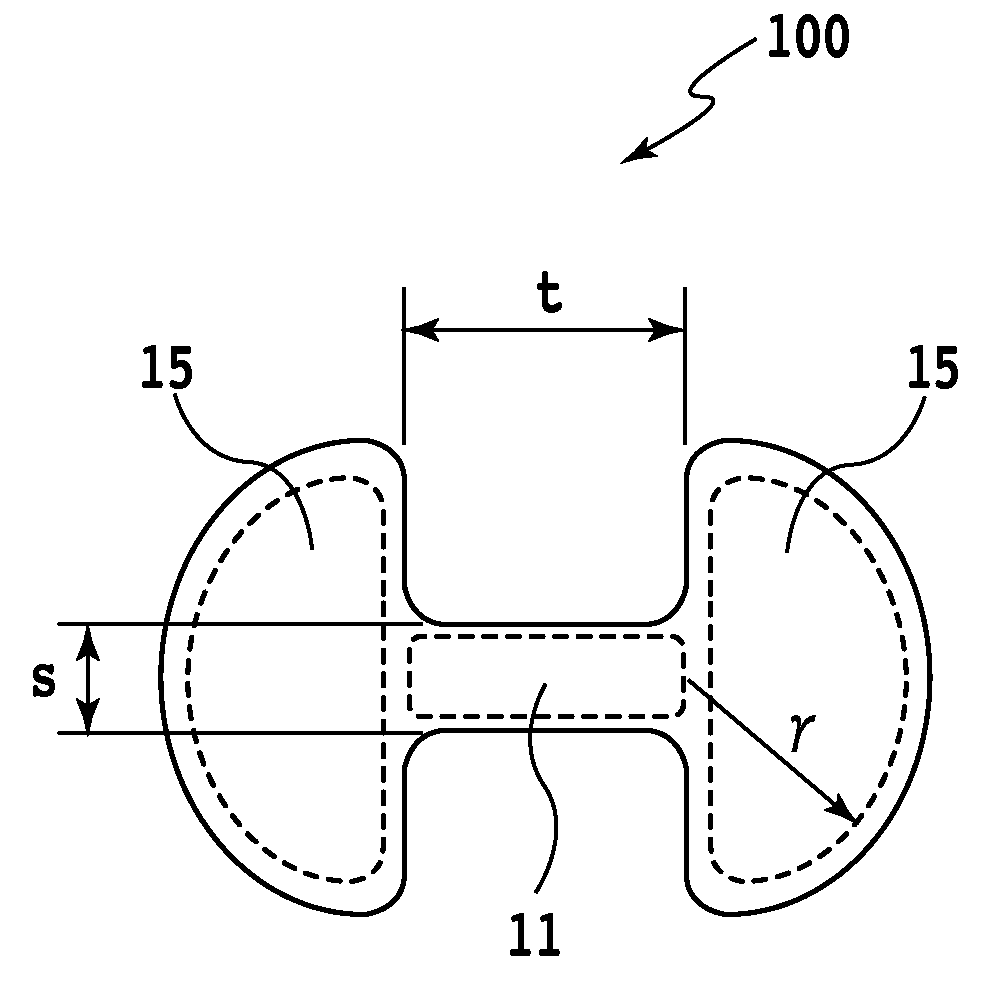
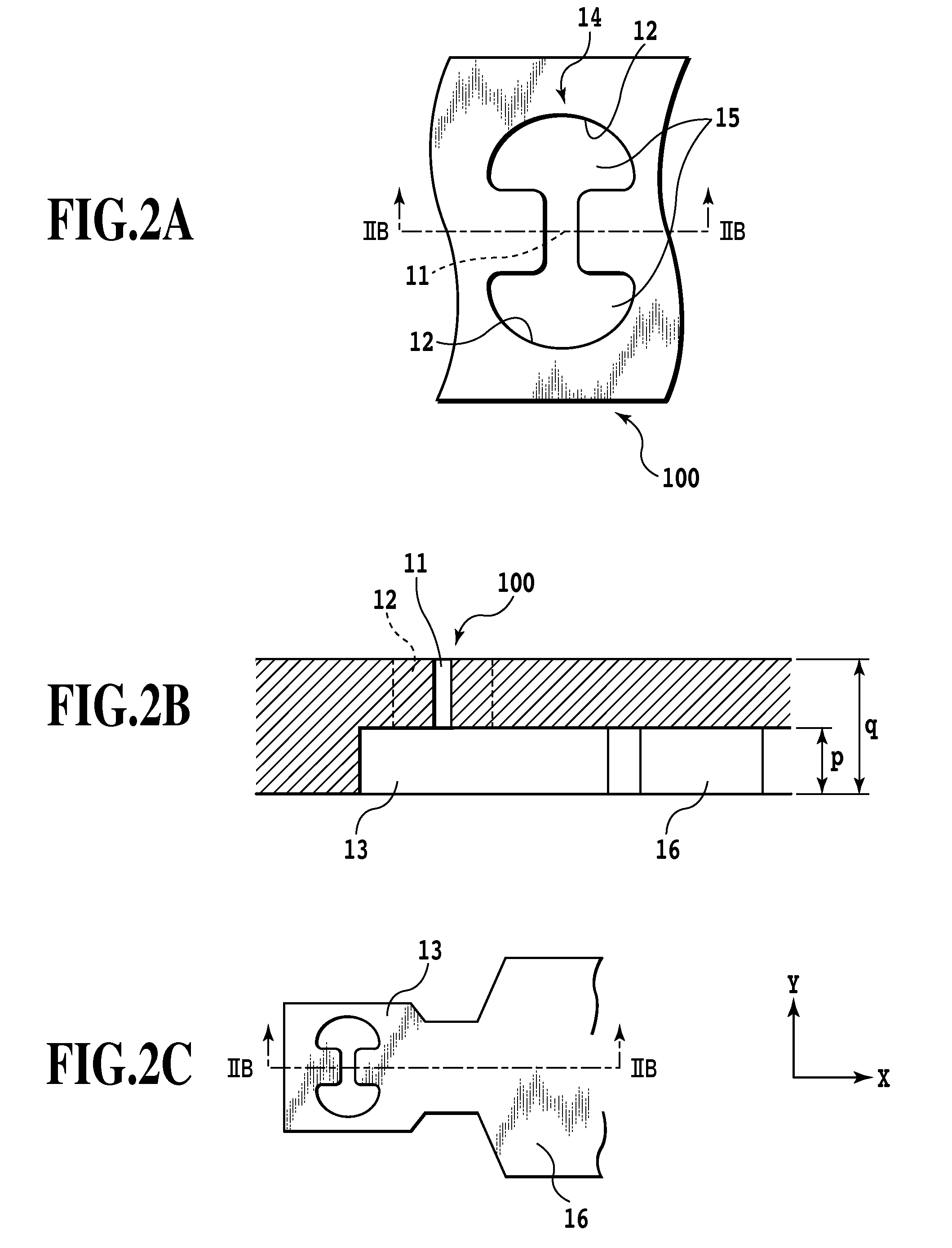
Liquid ejection head and liquid ejection method
ActiveUS20080291244A1Little dot landing position deviationLittle dot landing position deviationsInking apparatusLarge dropletElectrical and Electronics engineering
A liquid ejection method is provided which ejects small-volume droplets from ejection openings and causes them to reliably combine together on the fly into a large droplet that is less susceptible to influences of air flows, thus realizing a printing with reduced droplet landing position deviations. To that end, each of the ejection openings is constructed of two openings spaced apart and a slit-like constricted connection portion that connects the two openings together.
Owner:CANON KK
Static contact angle calculation method
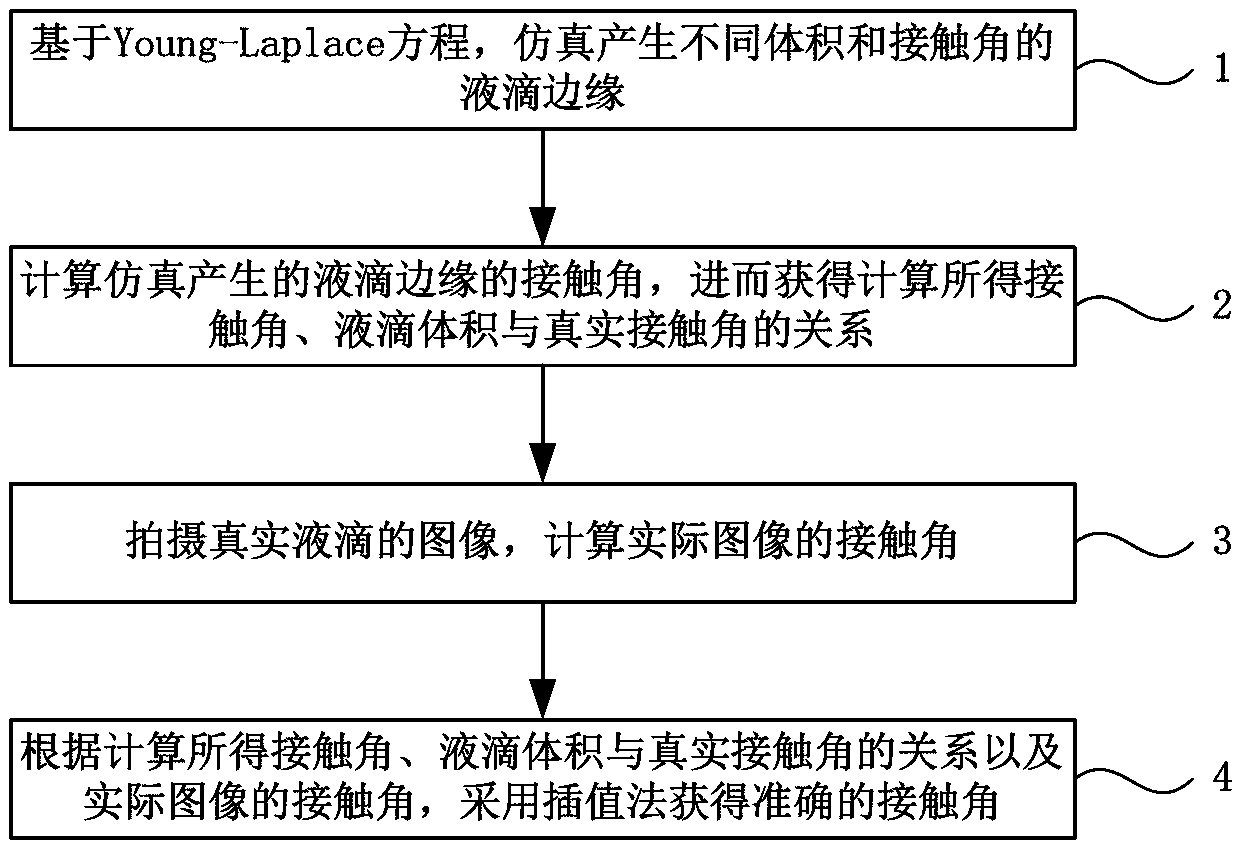
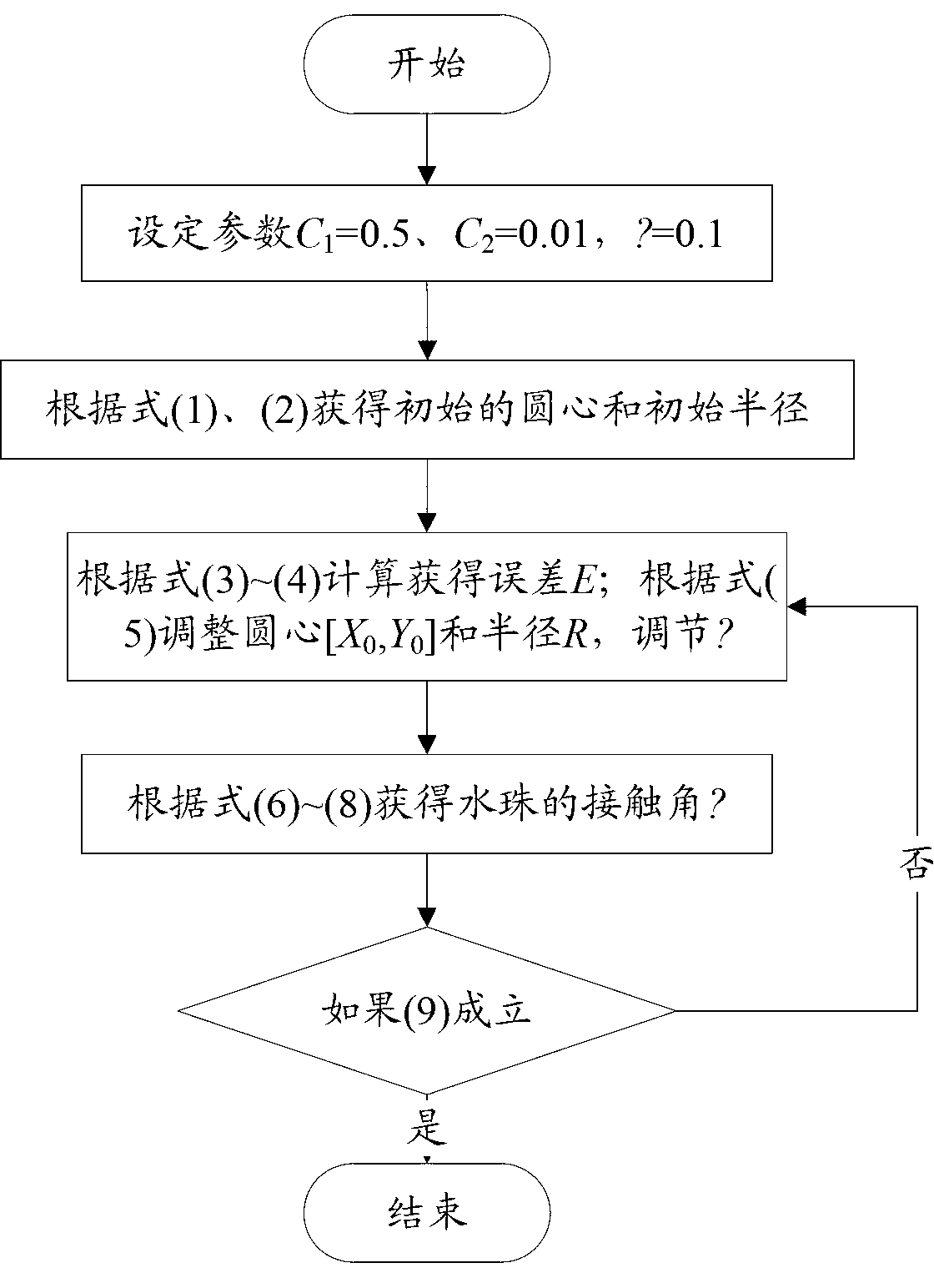
InactiveCN103017689AReduce mistakesAvoid computational complexitySurface/boundary effectUsing optical meansLarge dropletYoung–Laplace equation
The invention discloses a static contact angle calculation method in the technical field of material performance test. The method includes: simulating to generate droplet margins of different sizes and contact angles on the basis of the Young-Laplace equation; calculating the contact angles of the droplet margins generated by simulation to obtain relation among the calculated contact angles, the droplet sizes and the real contact angles; taking a picture of a real droplet image and calculating the contact angle of the image; and using the interpolation or similar methods to obtain accurate contact angles according to the contact angle of the actual image and the relation among the calculated contact angles, the droplet sizes and the real contact angles. Errors brought by large droplet sizes and contact angles to the circle fitting method and theta / 2 method can be effectively reduced, calculation efficiency is improved, and programming difficulty is lowered.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Mixed hydrophilic/hydrophobic fiber media for liquid-liquid coalescence
ActiveUS8409448B2Liquid suspension thickening by filtrationWater/sewage treatmentWashburn's equationFiber
An immiscible lipophilic or hydrophilic liquid phase separated respectively from a continuous hydrophilic phase or a lipophilic phase liquid. Fibers having hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties are mixed, layered, etc., and formed into a filter. The separation mechanism involves capture of small droplets of the immiscible phase, coalescence of the small droplets into larger droplets as the immiscible liquid flows through the fiber filter, and release of the large immiscible droplets from the filter. With respect to separation of a hydrophilic immiscible fluid such as water in a lipophilic continuous fluid such as oil, the hydrophobic fibers will cause small water droplets to migrate towards the hydrophilic fibers whereby large droplets are formed on hydrophilic surface. The large droplets stay on hydrophilic fiber surface for extended periods of time and continue to coalescence until they are so large that they can no longer be maintained by the hydrophilic fibers and are released and drained off of the filter. In designing such filter, wettability of the filter media is an important parameter. The filter media can be designed by mixing hydrophilic and hydrophobic fibers in various proportions to achieve an optimum wettability range for separation of the immiscible liquid from the continuous phase liquid. The wettability of filter media can be characterized by a modified Washburn Equation.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
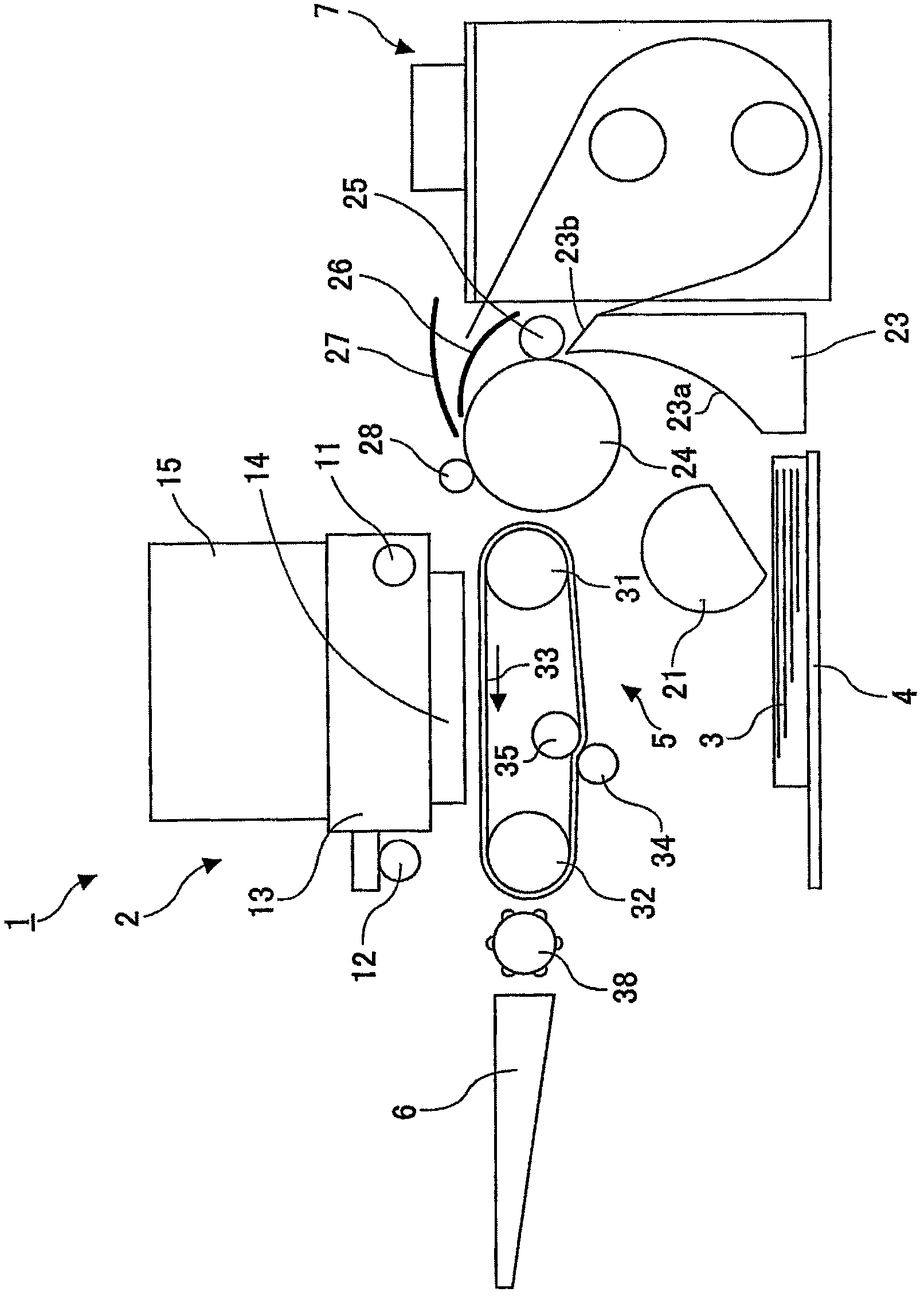
Liquid ejection recording head
A compact liquid ejection recording head capable of forming high-quality images at high speed includes large nozzles for ejecting large droplets, medium nozzles for ejecting medium droplets, and small nozzles for ejecting small droplets. The large nozzles are arranged on one side of an ink supply port, while the small nozzles and the medium nozzles are arranged on the other side of the ink supply port. The number of the small nozzles is larger than that of the medium nozzles, and that of the large nozzles. This allows high-quality and high-speed printing using the small nozzles, high-speed photo printing using the medium and small nozzles, and high-speed printing using the large nozzles.
Owner:CANON KK
Liquid recording head
InactiveUS20080136872A1Leveling precisionSimply and inexpensively an ink jet recording headPrintingSmall dropletLarge droplet
A liquid recording head for effecting recording by ejecting droplets from a plurality of ejection outlets formed on a substrate is provided. The liquid recording head includes a plurality of large droplet ejection outlets each having a relatively large ejection amount, a plurality of small droplet ejection outlets each having in a relatively small ejection amount, energy generating elements for generating energy for ejecting the droplets from the plurality of large droplet ejection outlets and the plurality of small droplet ejection outlets, a liquid chamber for retaining liquid to be ejected from the plurality of large droplet ejection outlets or the plurality of small droplet ejection outlets, at least two first flow passages for establishing communication between the liquid chamber and each of first ejection outlets; and a second flow passage for establishing communication between the liquid chamber and at least two second ejection outlets.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method for generation of emulsions with low interfacial tension and measuring frequency vibrations in the system
ActiveUS20130274353A1Reduce interfacial tensionVibration measurement in solidsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSmall dropletBreakup
A method and apparatus for generating droplets with a high level of uniformity in liquid systems that present a low interfacial tension. This method and apparatus utilize the breakup of the dispersed phase in a controlled fashion by periodically varying the pressure that drives the fluids so as to successfully generate emulsions with a good control over the size. The method and apparatus can be used for the formation of simple emulsion or double emulsion where a larger droplet contains one or more smaller droplets.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
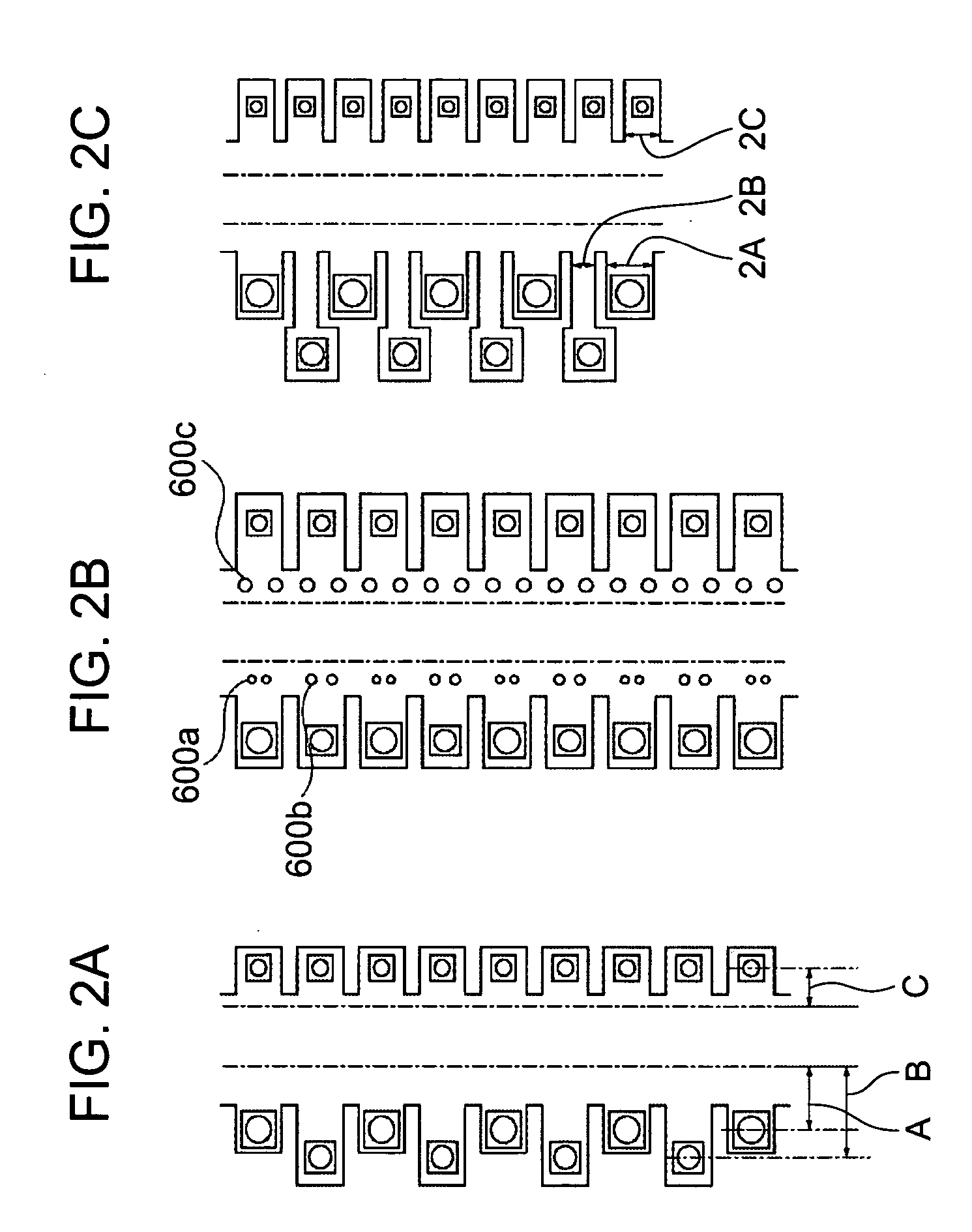
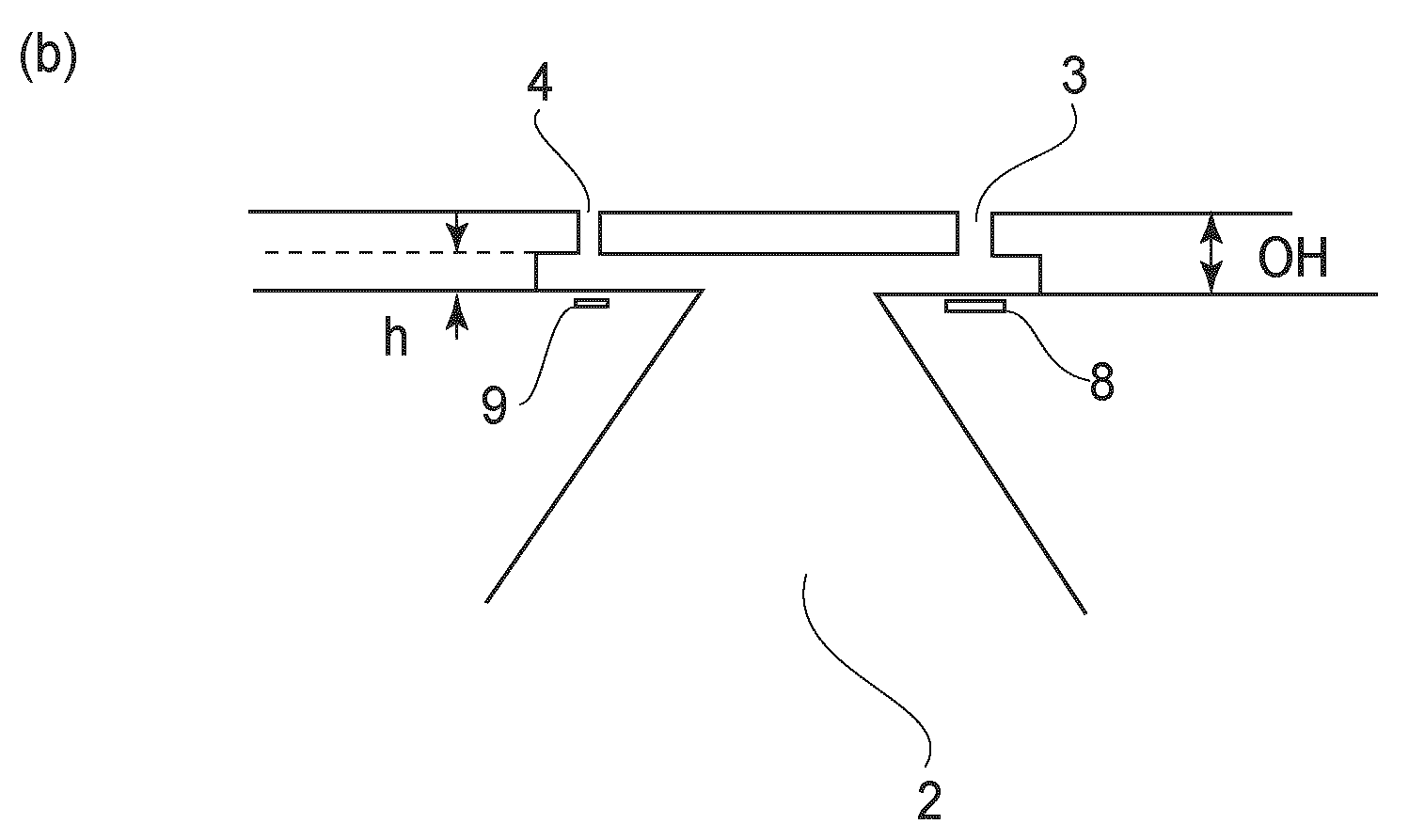
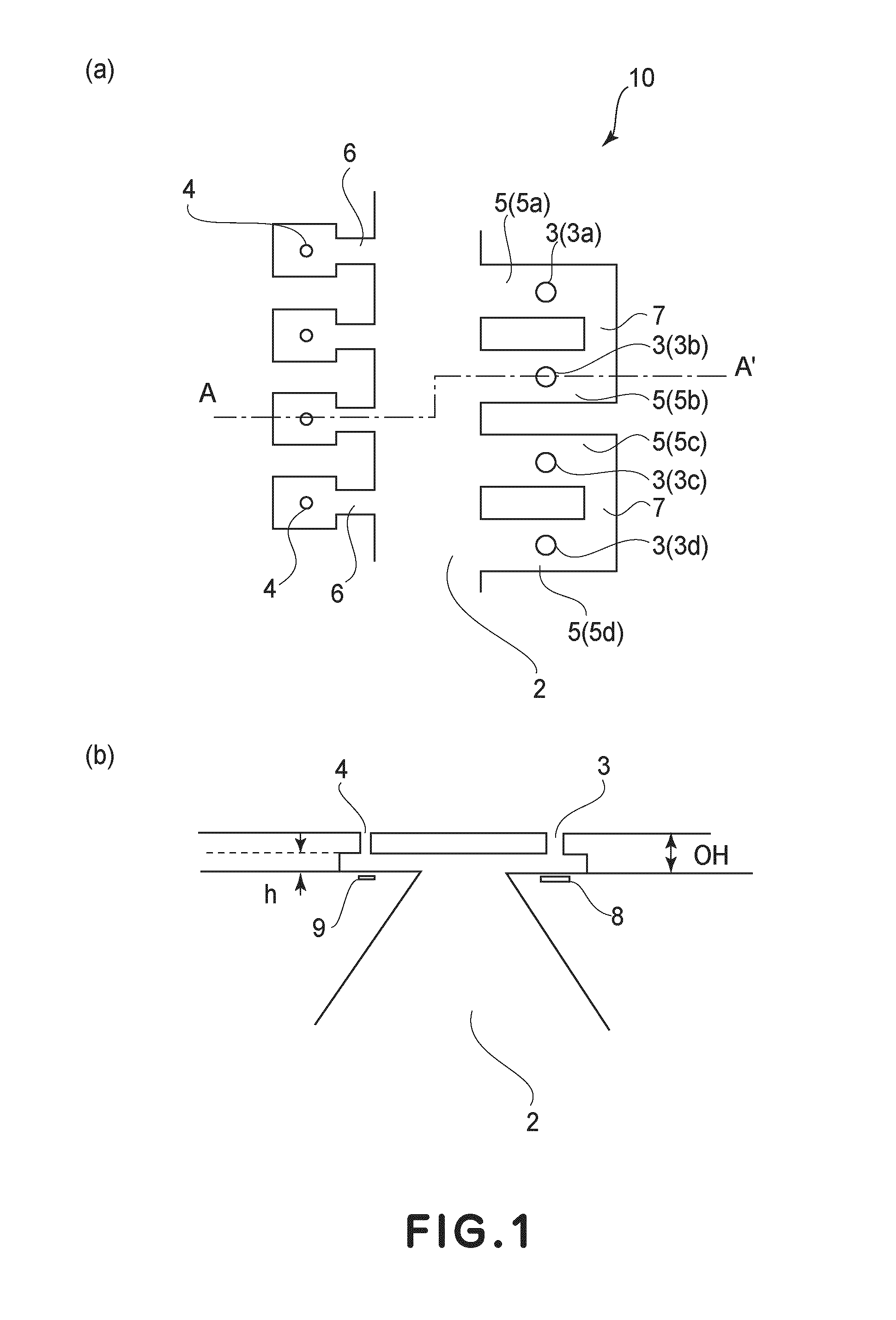
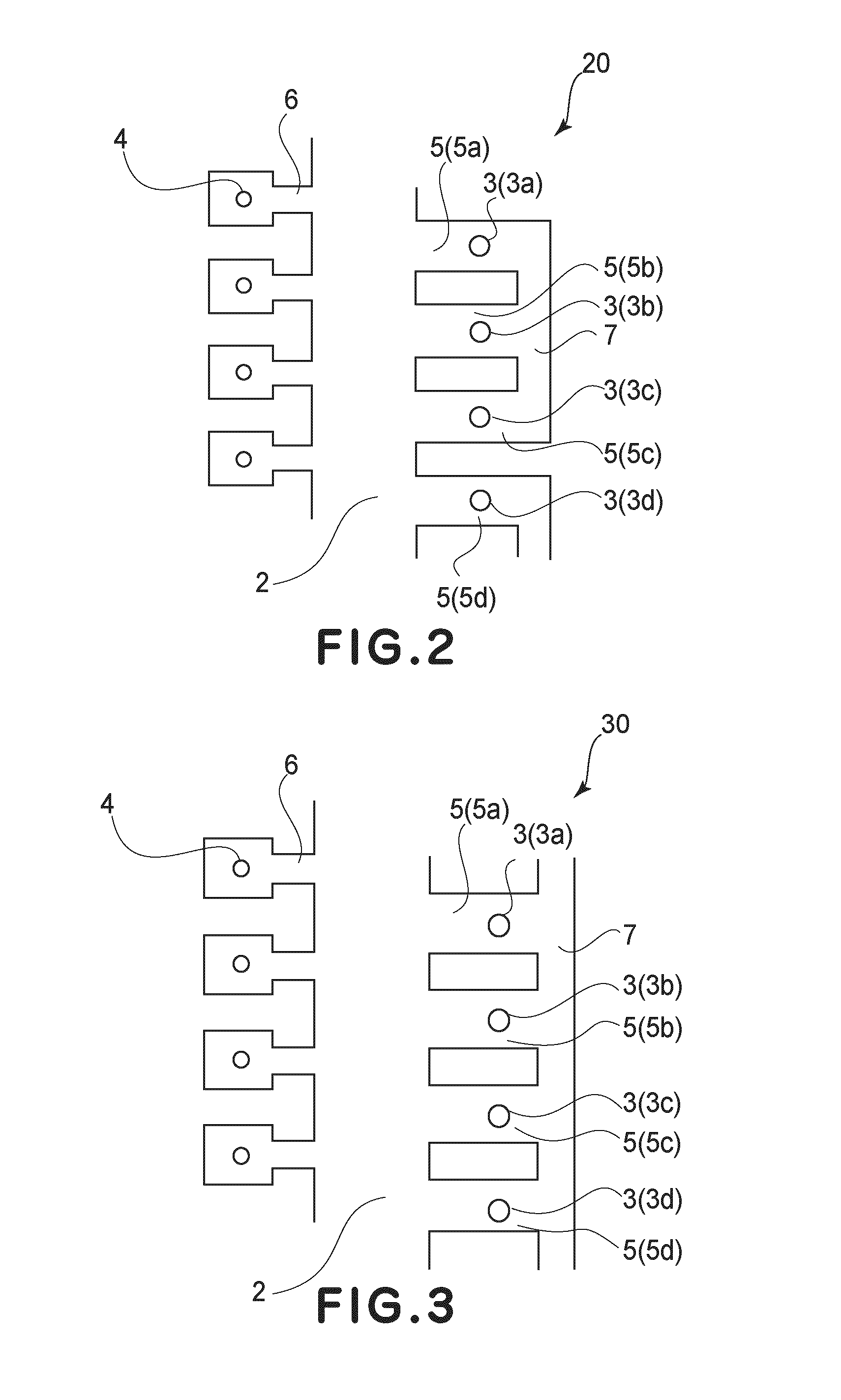
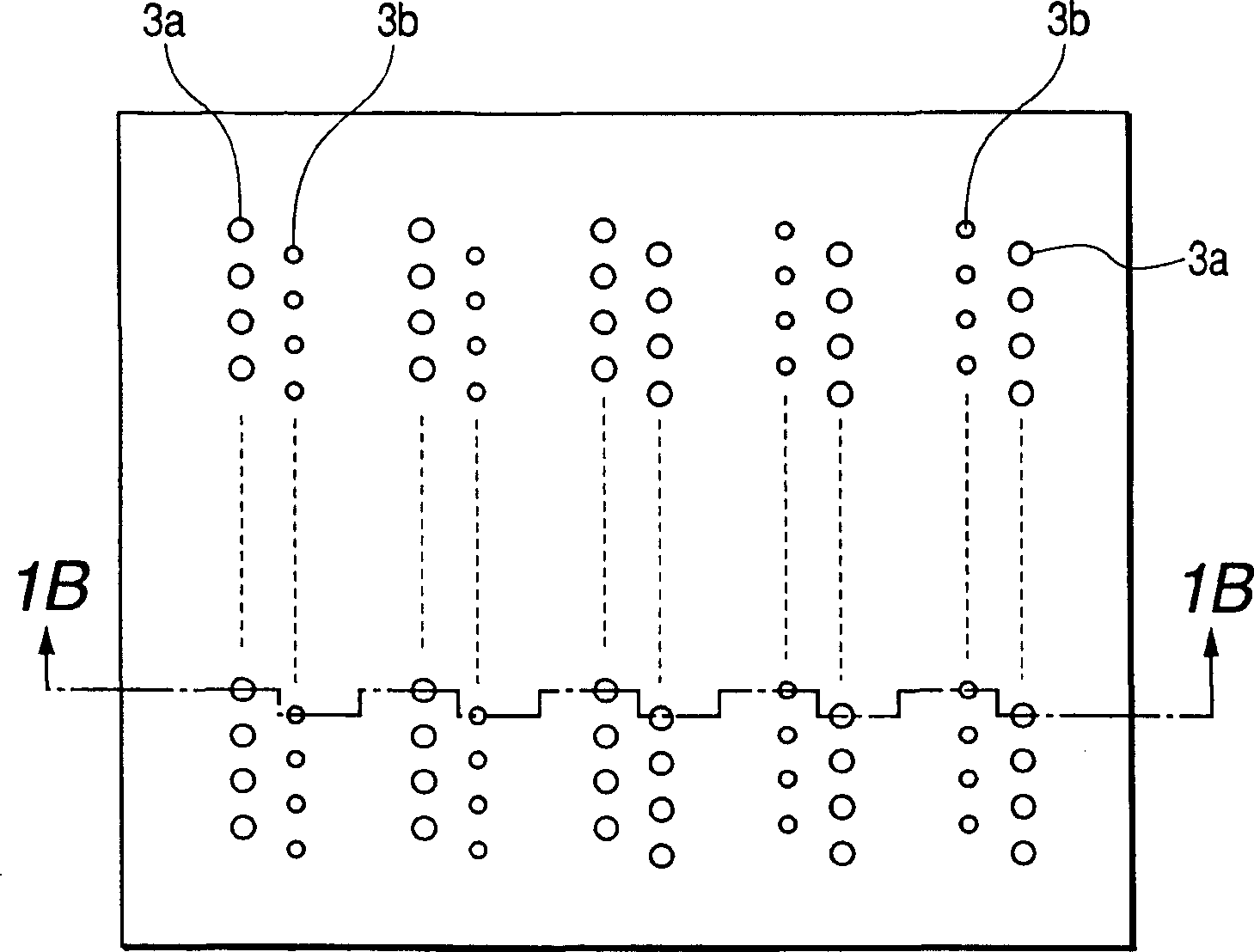
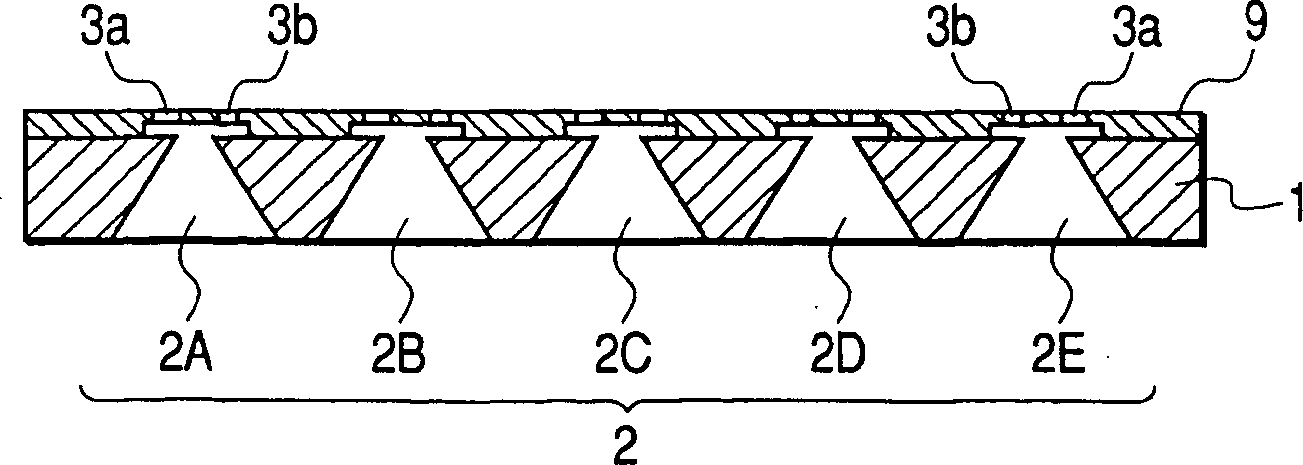
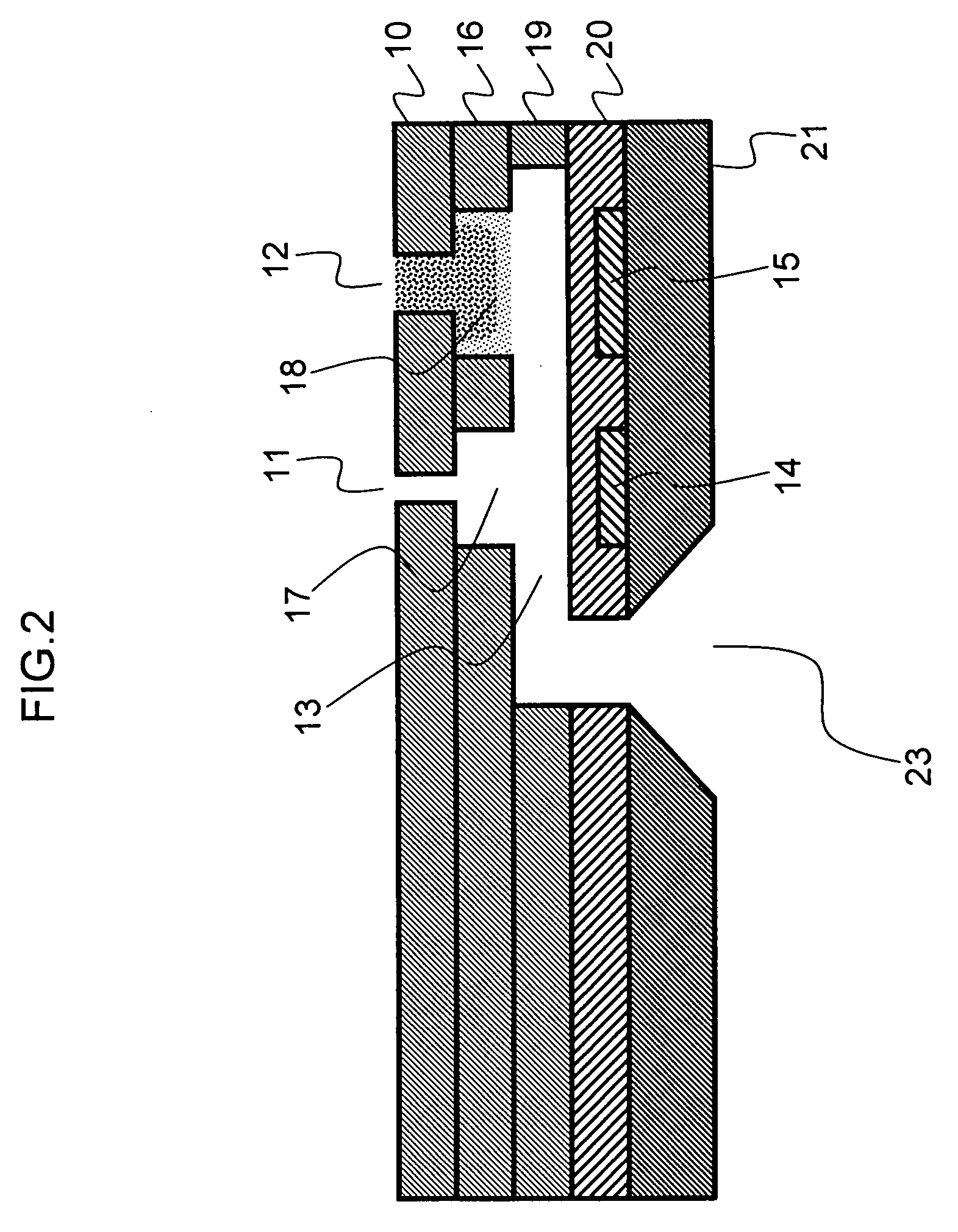
Ink-jet recording head
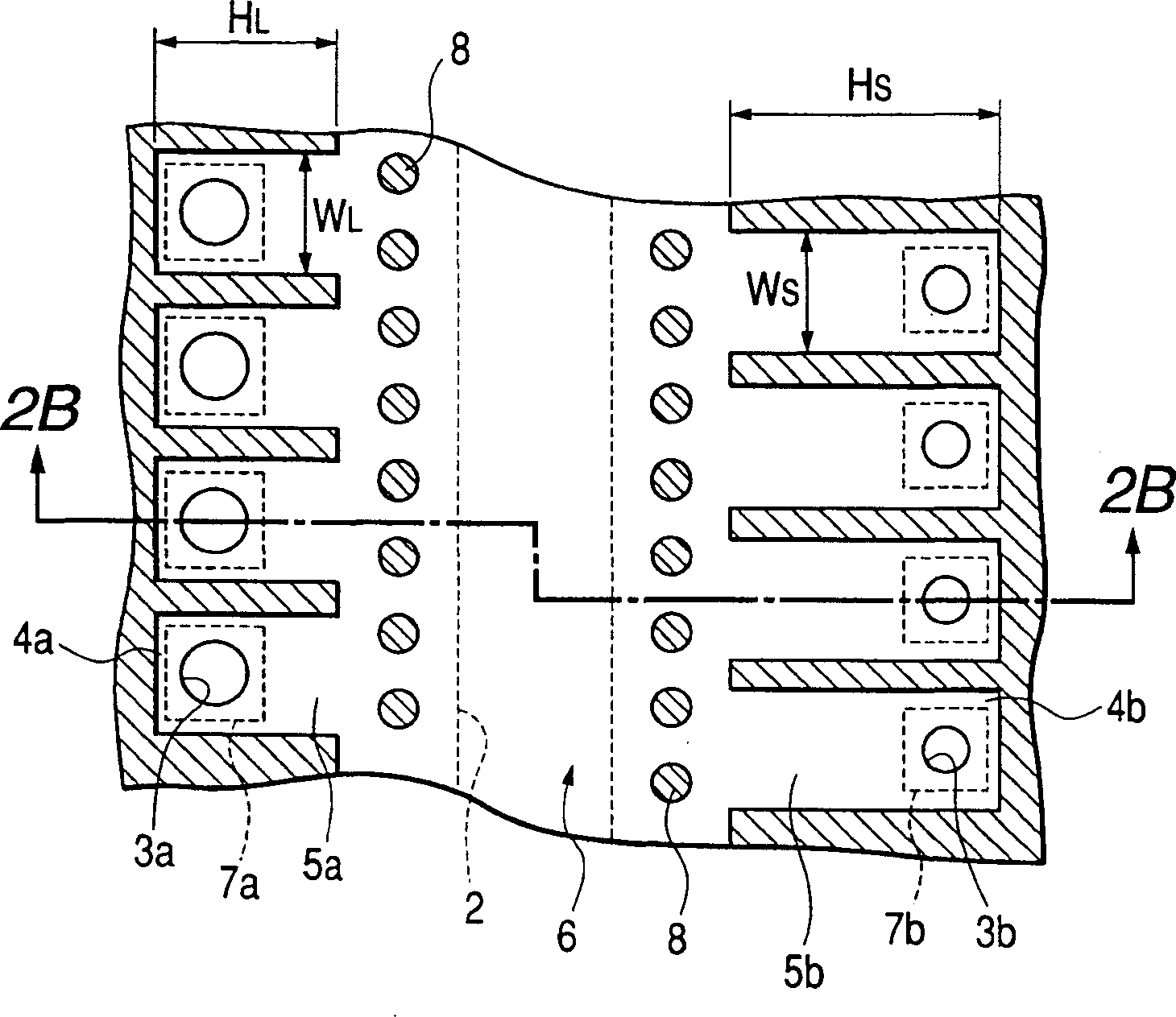
The invention discloses an inkjet recording head, which can eject small droplets and large droplets. It passes from a common liquid chamber (6) through an ink flow channel (5a, 5b) and a pressure chamber (4a, 4b), and is connected to the inkjet recording head. The outlets (3a, 3b) use the thermal energy of the heaters (7a, 7b) to eject ink droplets from the ejection ports (3a, 3b). The width of the ink flow passage (5a, 5b) is narrower than the width of the pressure chamber (4a, 4b), and the ink flow passage (5a, 5b) serves as a throttling portion. If the cross-sectional area of the ink flow path for small droplets is SS, the cross-sectional area of the small droplet pressure chamber is SRS, the cross-sectional area of the ink flow path for large droplets is SL, and the cross-sectional area of the large droplet pressure chamber is SRL, then SS / SRS<SL / SRL. According to the structure of the present invention, losses can be reduced and energy efficiency can be improved even in nozzles that eject small ink droplets.
Owner:CANON KK
An electronic cigarette atomizer
The invention discloses an electronic cigarette atomizer, which comprises an oil bin, a capillary tube and a suction nozzle. The oil inlet end of the capillary tube is communicated with the oil bin inner cavity, and the oil outlet end of the capillary tube is communicated with the suction nozzle. The oil bin is provided with an air vent which communicates the oil bin inner cavity and the atmosphere, and also comprises a key assembly which can open or close the air vent. A circuit board and a circuit switch assembly for controlling whether a circuit key switch on the circuit board is turned onare also included. The key assembly and the circuit switch assembly are linked, and when the key assembly controls the air vent to open, the circuit switch assembly controls the circuit key switch toturn on; when the key assembly controls the vent to close, the circuit switch assembly controls the key switch to open. As that smoke oil can be quickly and timely supply to the heating component through the capillary tube for atomization, the us is not easy to suck large droplets, the atomization is sufficient, the smoke particles are fine and exquisite, the smoke mouthfeel is good, the smoke amount is large, the oral cavity is not scalded, and the user experience is good.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HUNAN INDAL CORP +1
Nebulizer for Charged Aerosol Detection (CAD) System
A nebulizer for a charged aerosol detection (CAD) system is disclosed. The nebulizer is provided with a spray emitter for generating a spray of droplets within a central region of a spray chamber. The central region is separated from an upper region by a horizontally projecting rib, which defines a passageway between the central and upper regions. The major direction of droplet travel within the upper region is substantially reversed with respect to the major direction of droplet travel within the central region. Larger droplets are unable to negotiate the turn from the central to upper regions and impinge on a rear surface of the spray chamber. Removal of larger droplets has the advantageous effect of enabling the detector to sense a smaller range of particle sizes, which establishes a relatively steady electrical current at the detector.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
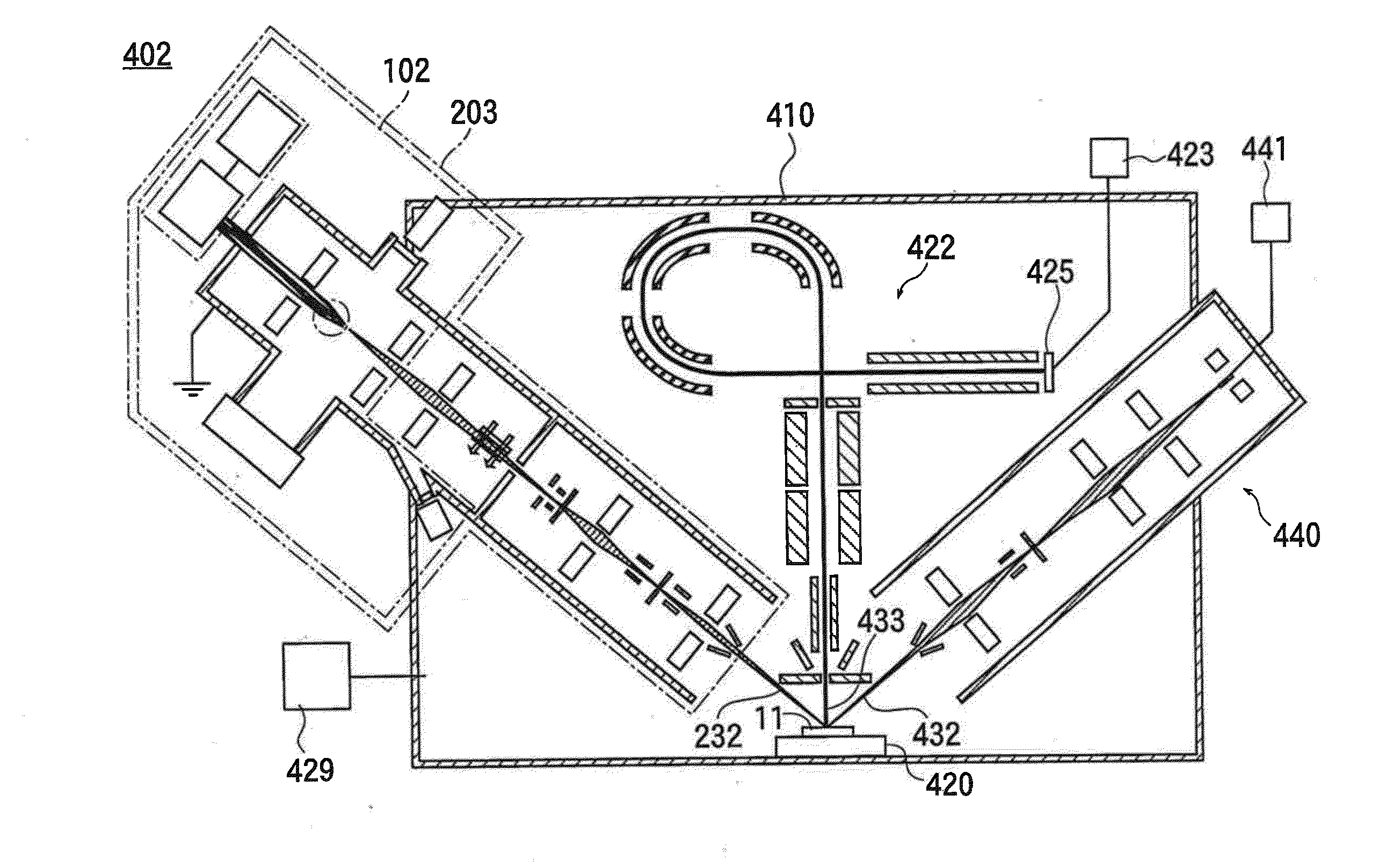
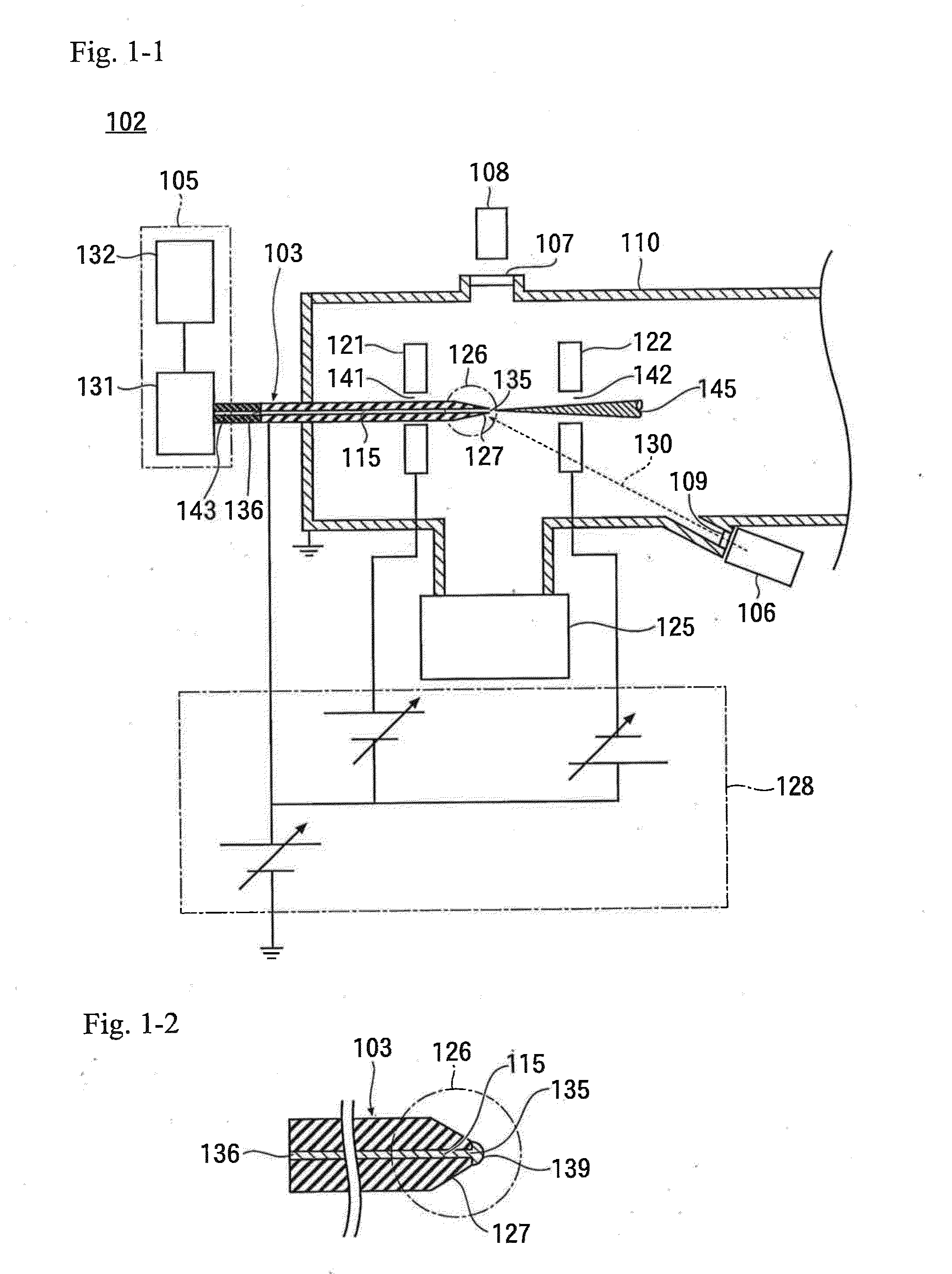
Ion source, ion gun, and analysis instrument
ActiveUS20150206732A1Suppressing damage to a acceptable levelLow yieldStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSpectroscopyMass spectrometry
Provided are an ion source, an ion gun, and an analysis instrument, which are capable of performing sputtering without damage to a surface of a sample and improving detection sensitivity in mass spectroscopy. In the ion source, an emission opening to which ionization liquid is supplied is disposed in an electric field formed in vacuum environment by an extracting electrode so that super large droplet cluster ions are generated from the emission opening. When the sample is irradiated with a super large droplet cluster ion beam, the sample surface is subjected to sputtering without damage, so as to remove contamination substances or to expose a new surface of the sample. In mass spectroscopy, detection sensitivity is improved.
Owner:ULVAC PHI INC
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, image forming system, and storage medium
ActiveCN102083628APrevent sprayingSize removes one or more oversized ink drops or reducesPrintingPictoral communicationImaging processingImage formation
The present invention provides an image processing method including a conversion step of converting multilevel data of an image into a dot pattern using a multilevel error diffusion process. The conversion step includes the steps of determining a pixel corresponding to an abnormal nozzle based on abnormal nozzle information provided for each of droplet sizes supported by nozzles of an image forming apparatus; preventing jetting of a droplet onto the determined pixel; distributing a quantization error of the determined pixel calculated in the multilevel error diffusion process to neighboring pixels; and if extra- large droplets with a droplet size greater than the droplet size of a full-size droplet capable of filling a pixel are to be formed in the neighboring pixels as a result of distributing the quantization error, removing one or more of the extra-large droplets or reducing the droplet size of one or more of the extra-large droplets.
Owner:RICOH KK
Liquid ejection recording head
A compact liquid ejection recording head capable of forming high-quality images at high speed includes large nozzles for ejecting large droplets, medium nozzles for ejecting medium droplets, and small nozzles for ejecting small droplets. The large nozzles are arranged on one side of an ink supply port, while the small nozzles and the medium nozzles are arranged on the other side of the ink supply port. The number of the small nozzles is larger than that of the medium nozzles, and that of the large nozzles. This allows high-quality and high-speed printing using the small nozzles, high-speed photo printing using the medium and small nozzles, and high-speed printing using the large nozzles.
Owner:CANON KK
Liquid ejection head and image forming apparatus including liquid ejection head
InactiveUS20070195126A1Low running costReduce maintenance frequencyInking apparatusLiquid jetThermal energy
The liquid ejection head includes: a large nozzle which ejects a large droplet of liquid; a small nozzle which has a smaller nozzle diameter than the large nozzle and ejects a small droplet of the liquid which has a smaller volume than the large droplet; a first heat generating element and a second heat generating element which are provided opposite to the large nozzle and the small nozzle respectively, and apply thermal energy to the liquid in at least one individual flow channel that supplies the liquid to the large nozzle and the small nozzle in such a manner that a bubble causing the large droplet of the liquid to be ejected from the large nozzle and a bubble causing the small droplet of the liquid to be ejected from the small nozzle respectively; a first liquid chamber which is provided between the large nozzle and the at least one individual flow channel and between the large nozzle and the first heat generating element corresponding to the large nozzle.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Liquid atomising device and its uses as drug addict device
InactiveCN1803307AGuaranteed accuracyAvoid landingLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid spraying apparatusAutomatic controlSprayer
The invention discloses a liquid atomized device and usage as suction toxicant exposure device, which comprises the following parts: accumulator, catheter, liquid adjustment valve, sprayer, air compression pump and air compressor conduit, wherein the big droplet collection cup is set in front of sprayer, whose bottom connects the big droplet reflux pipe to build a specific liquid foggy environment; the spray sensor can be set in the spray chamber, which accomplishes the self-control of liquid foggy quantity through connecting the signal amplifier with adjustment valve controller. The invention can be an experimental device to test animal suction toxicant exposure or other exposures, which collects large droplet in the accumulator to circulate.
Owner:广东省职业病防治院
Subsea production system
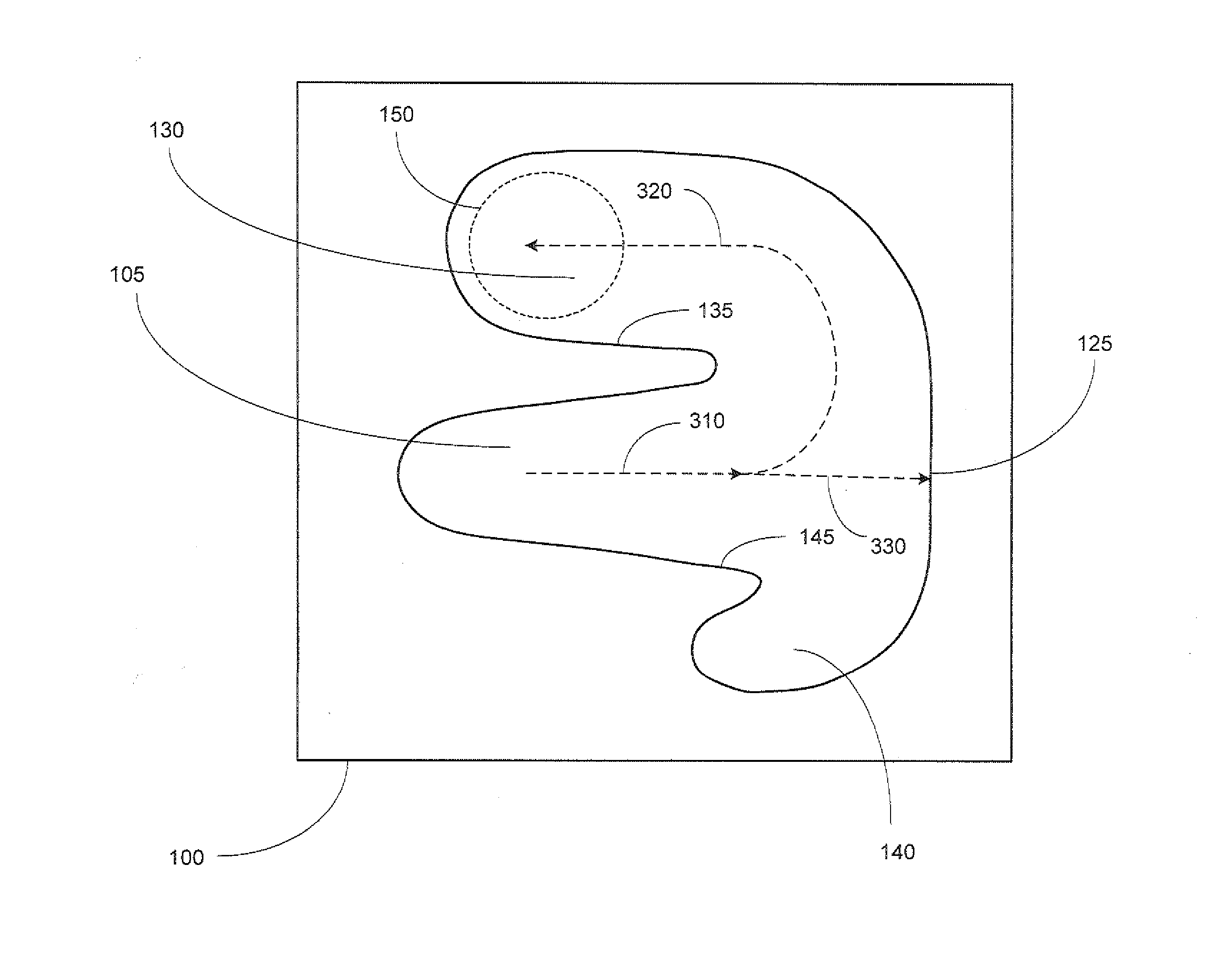
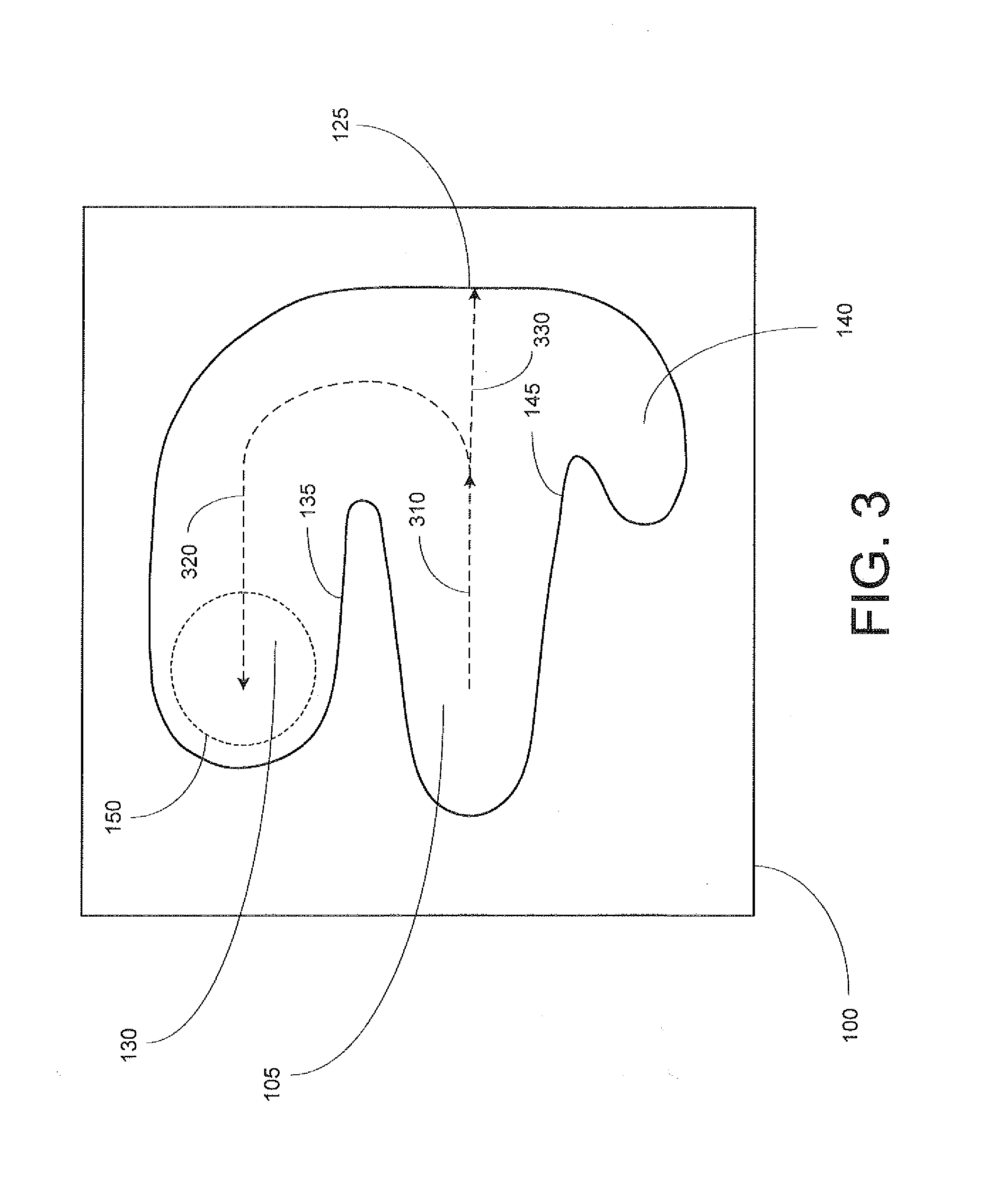
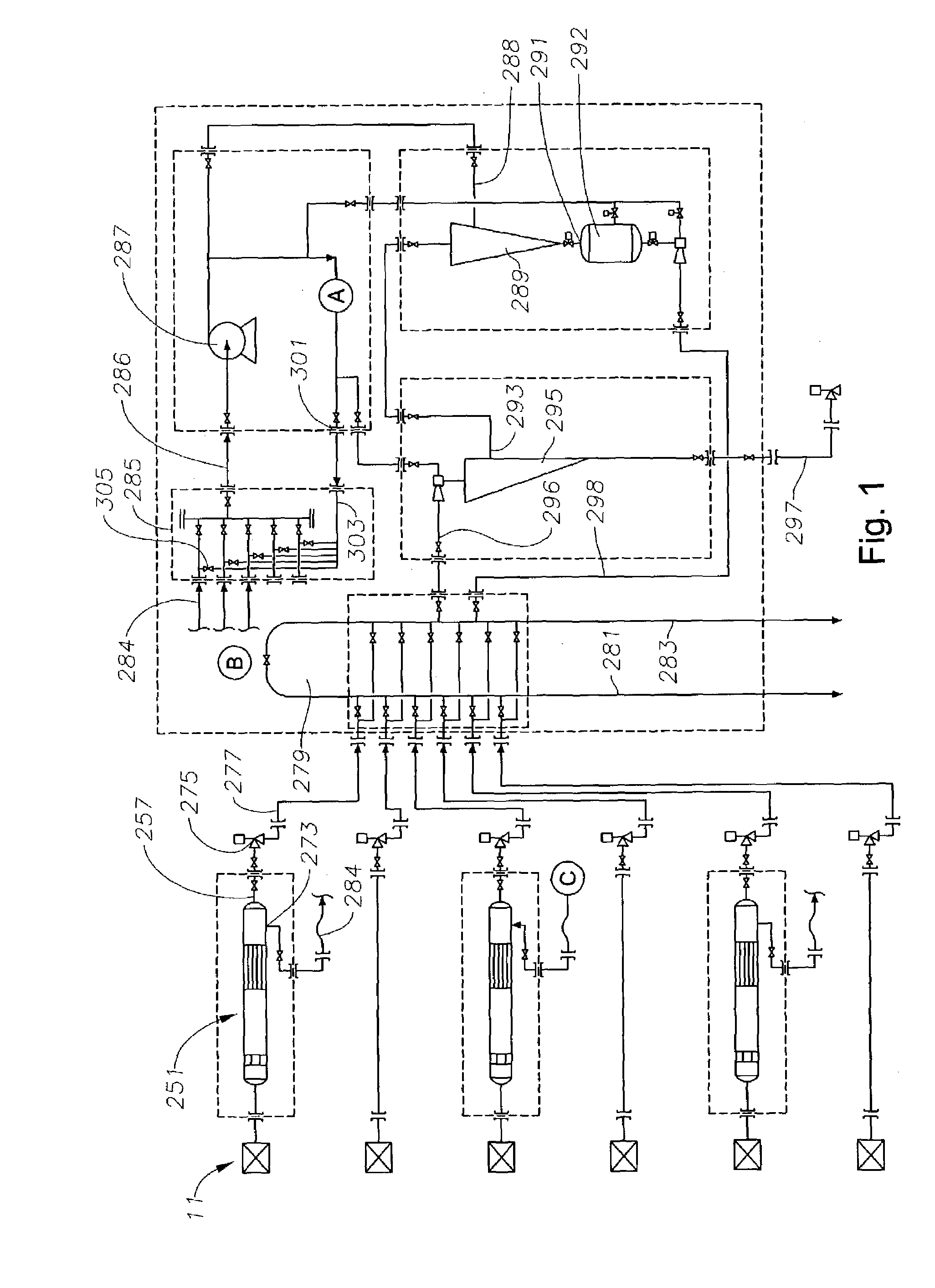
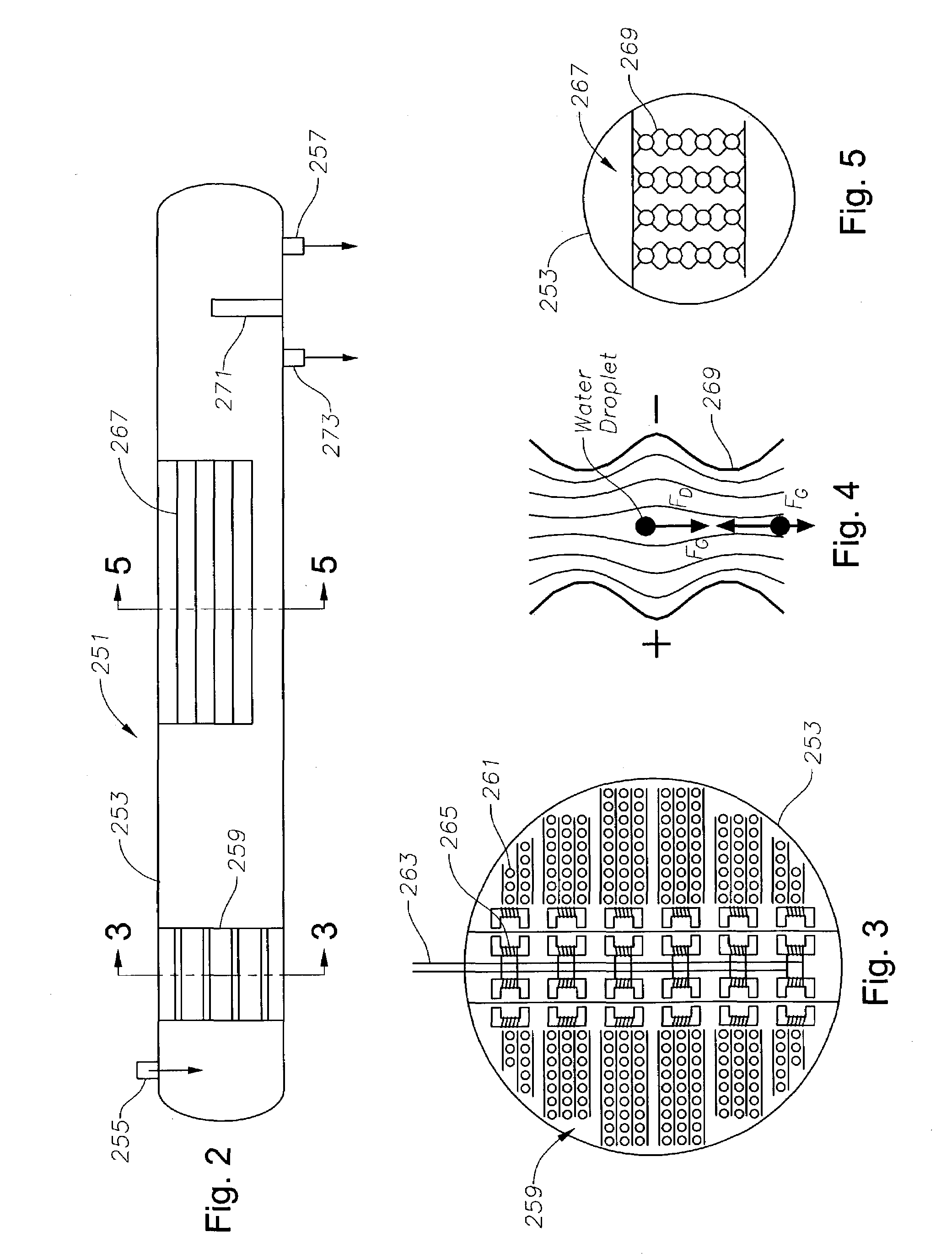
ActiveUS7175748B2Easy to separateHigh work pressureWaste water treatment from quariesLiquid separation auxillary apparatusOcean bottomDielectrophoresis
A subsea well fluid processing system has a separator for separating heavier and lighter components of well fluid flowing from a subsea well and directing the lighter components to flow to a surface processing facility. A choke is located downstream of the separator for limiting the flow rate of well fluid. The separator has a cylindrical chamber having a length at least ten times its diameter. A coalescing unit located in the chamber causes water droplets in the well fluid to coalesce into larger droplets. A dielectrophoresis unit having undulating sheets spaced close to each other is also located in the chamber. The sheets of the unit are supplied with an electrical potential to force the water droplets into predetermined passage portions to form high water content sections of liquid. Bypass valves allow backflushing of one of the separators while others continue to operate.
Owner:VETCO GRAY SCANDINAVIA
Ice and supercooled water detection system
ActiveUS9297755B2Maximize safetyIncrease incidenceDe-icing equipmentsScattering properties measurementsRadianceLength wave
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com