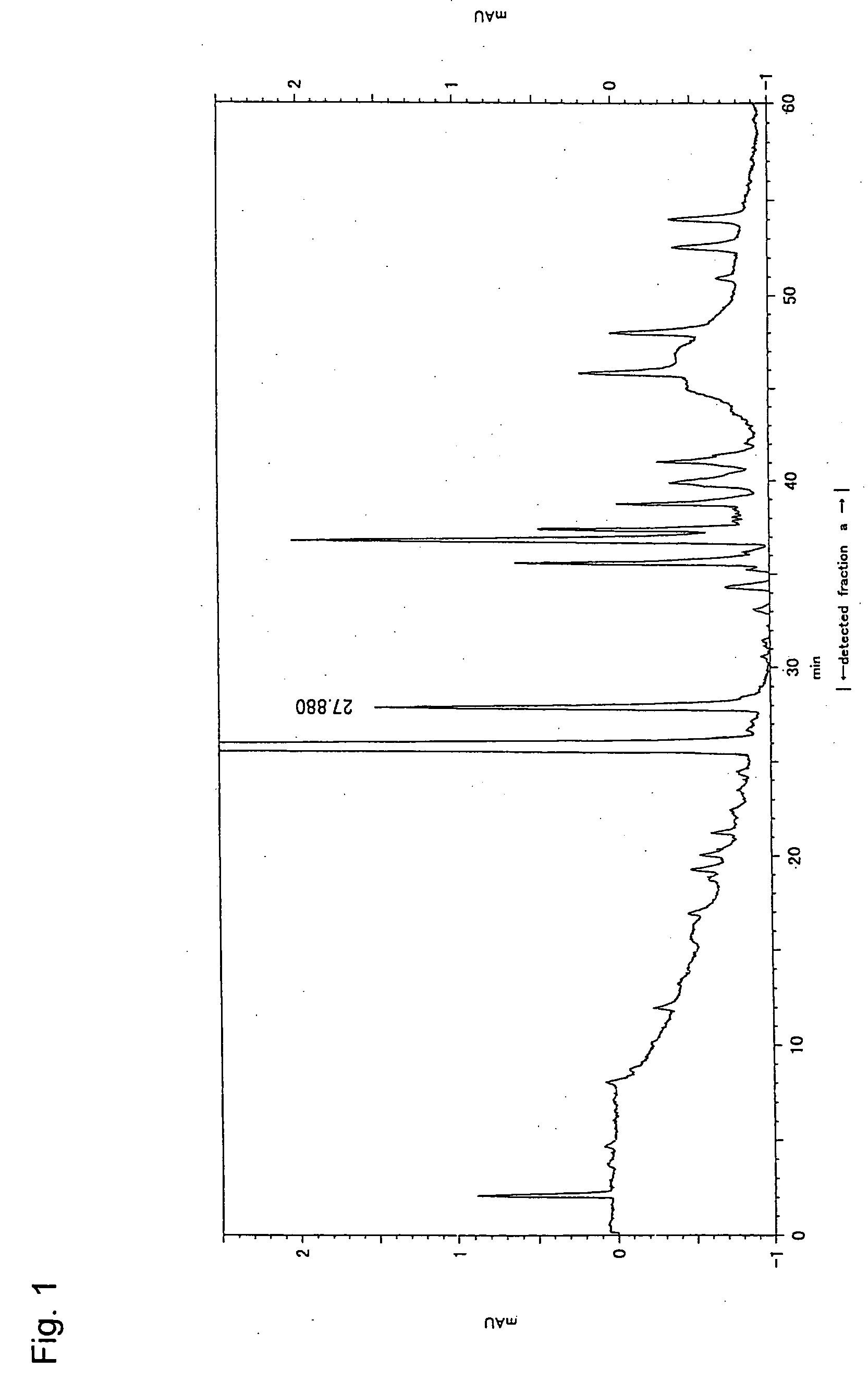
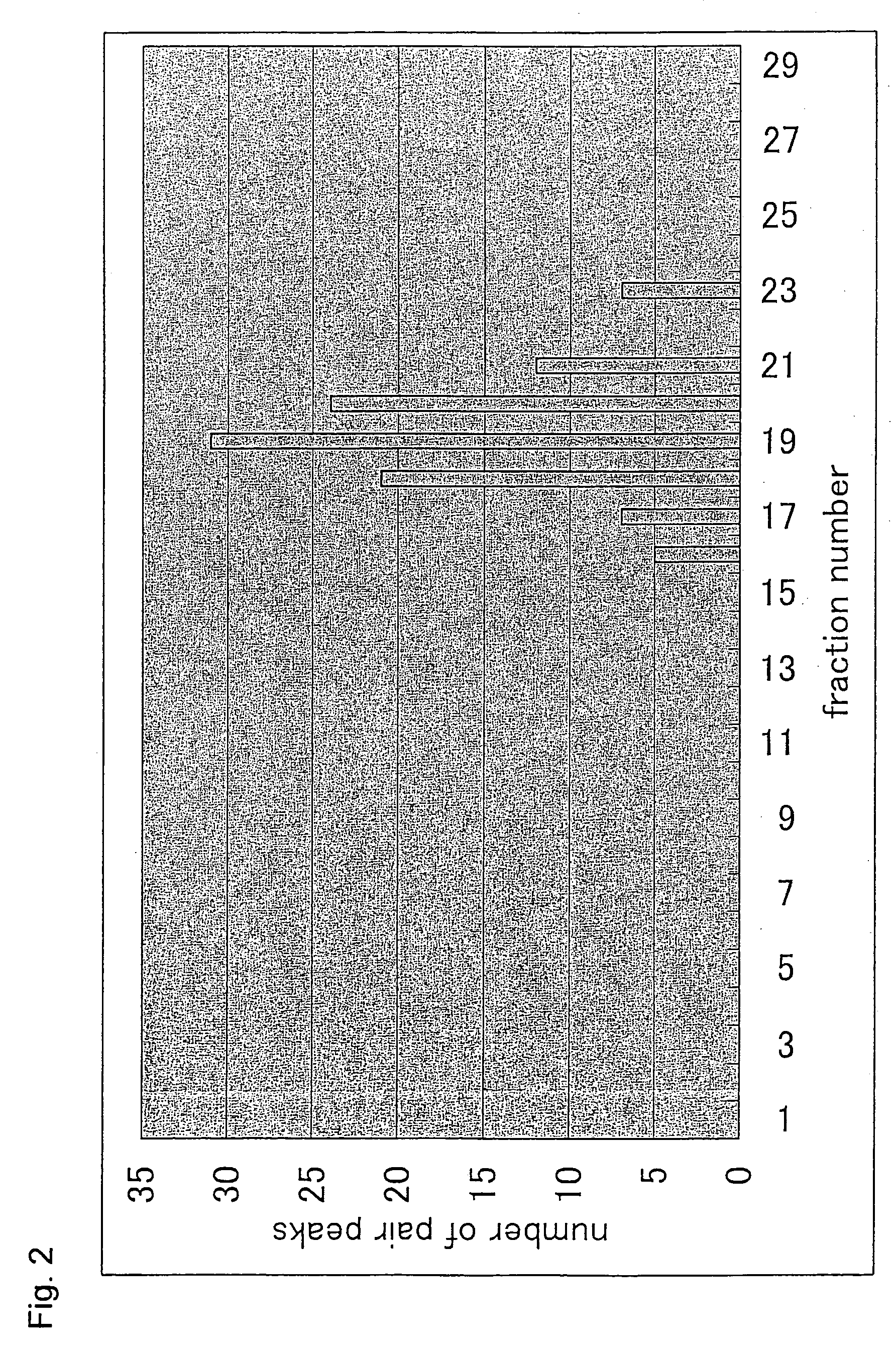
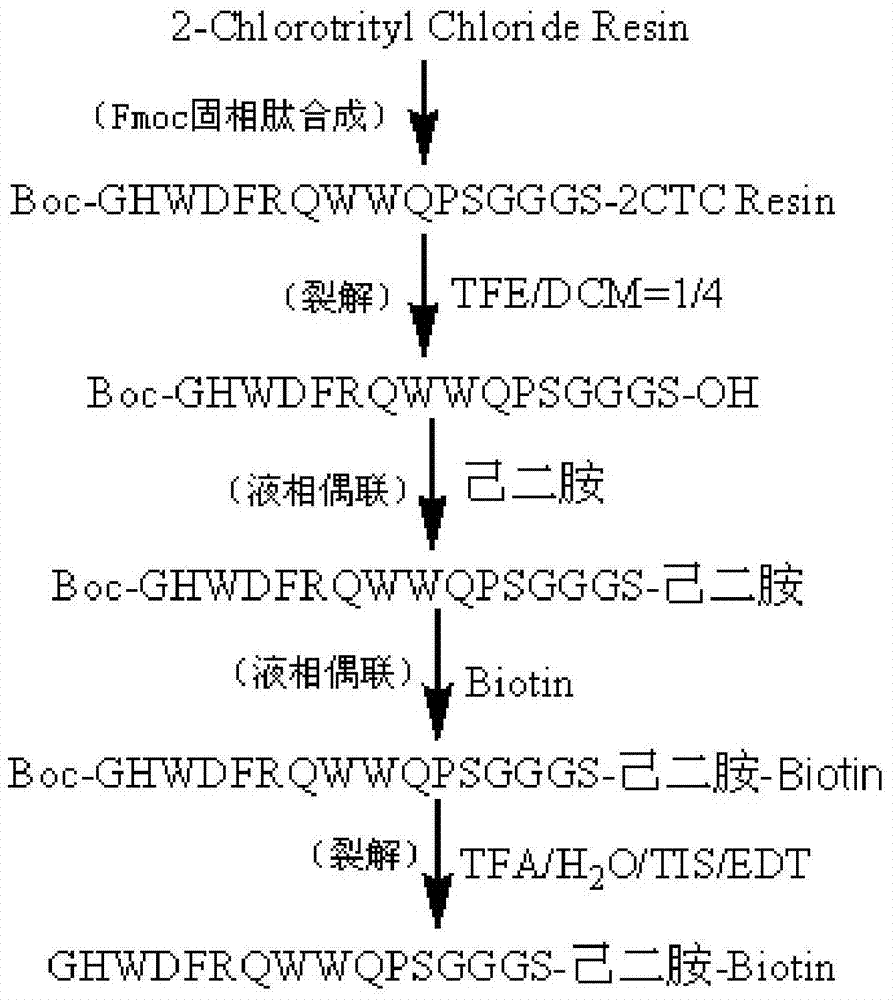
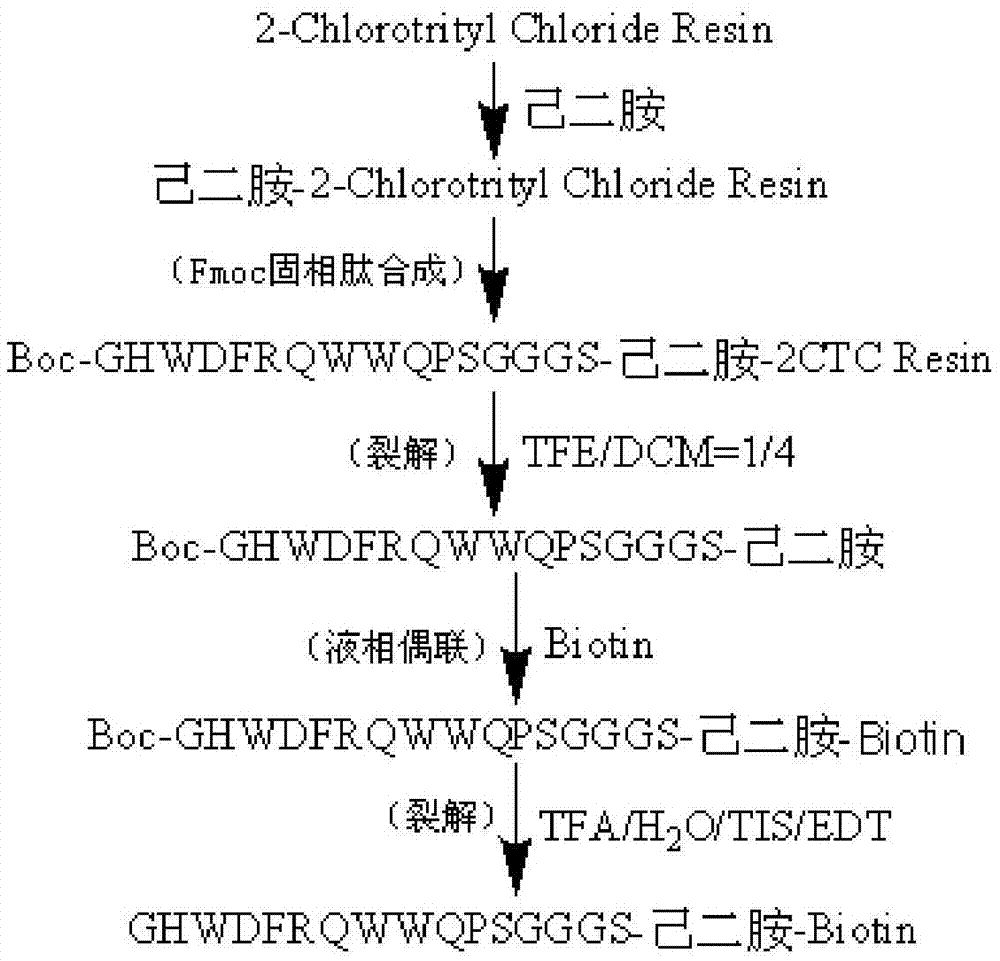
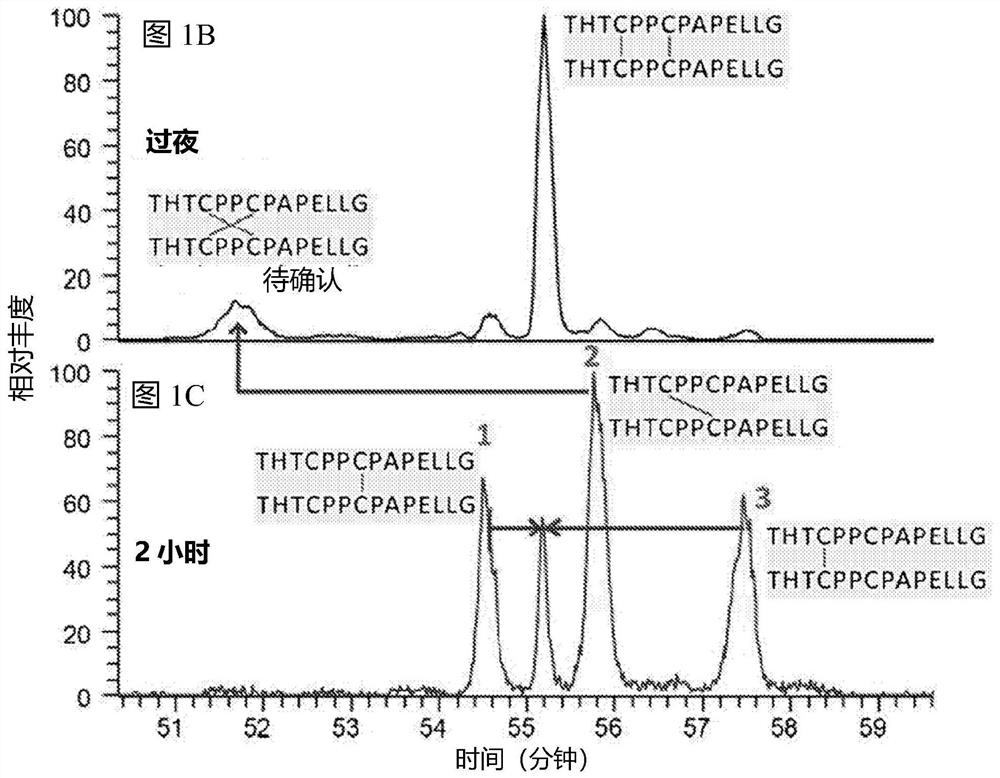
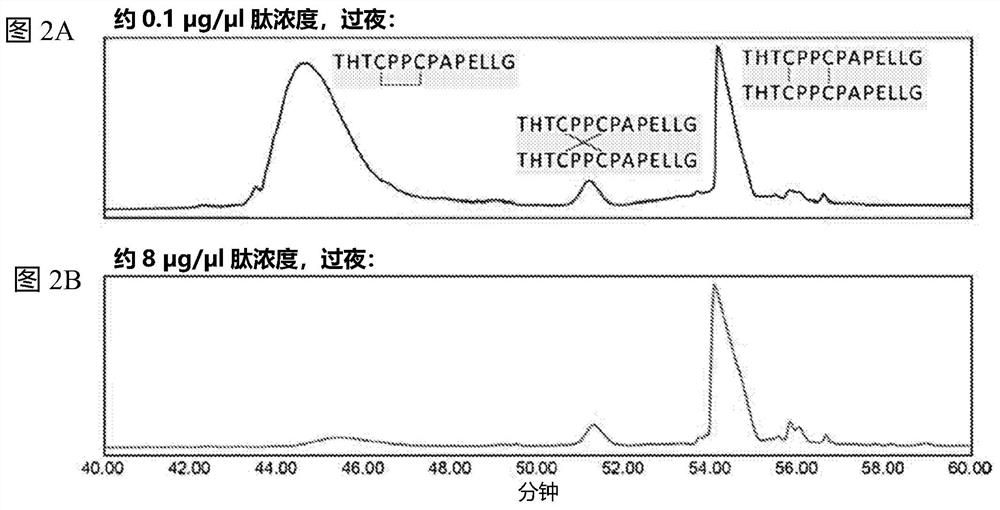
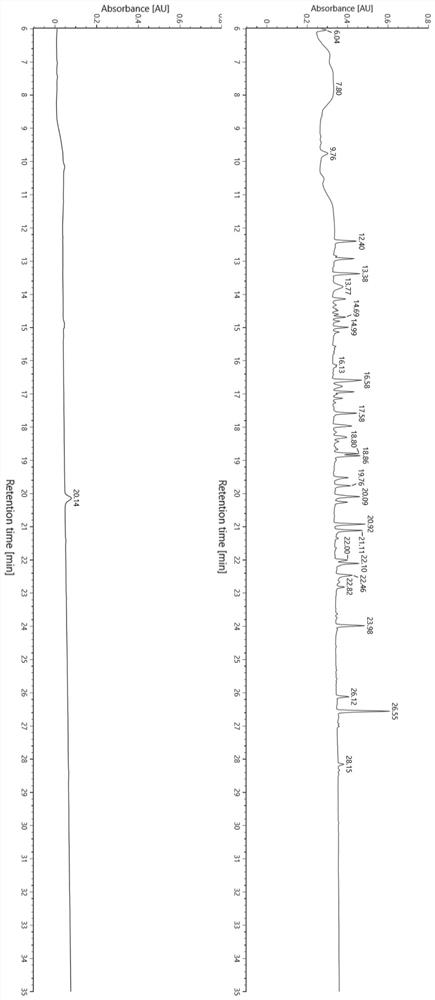
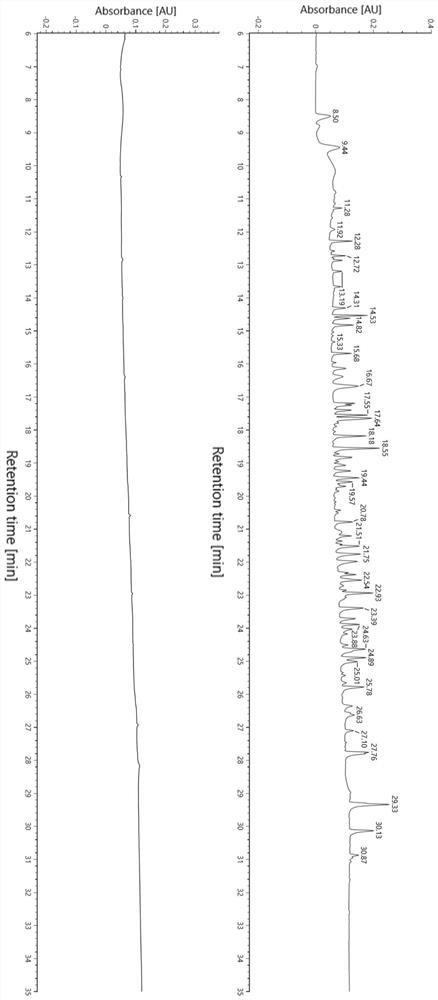
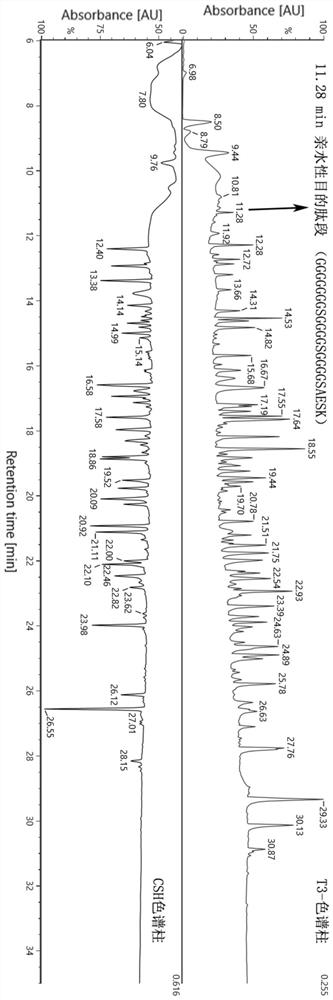
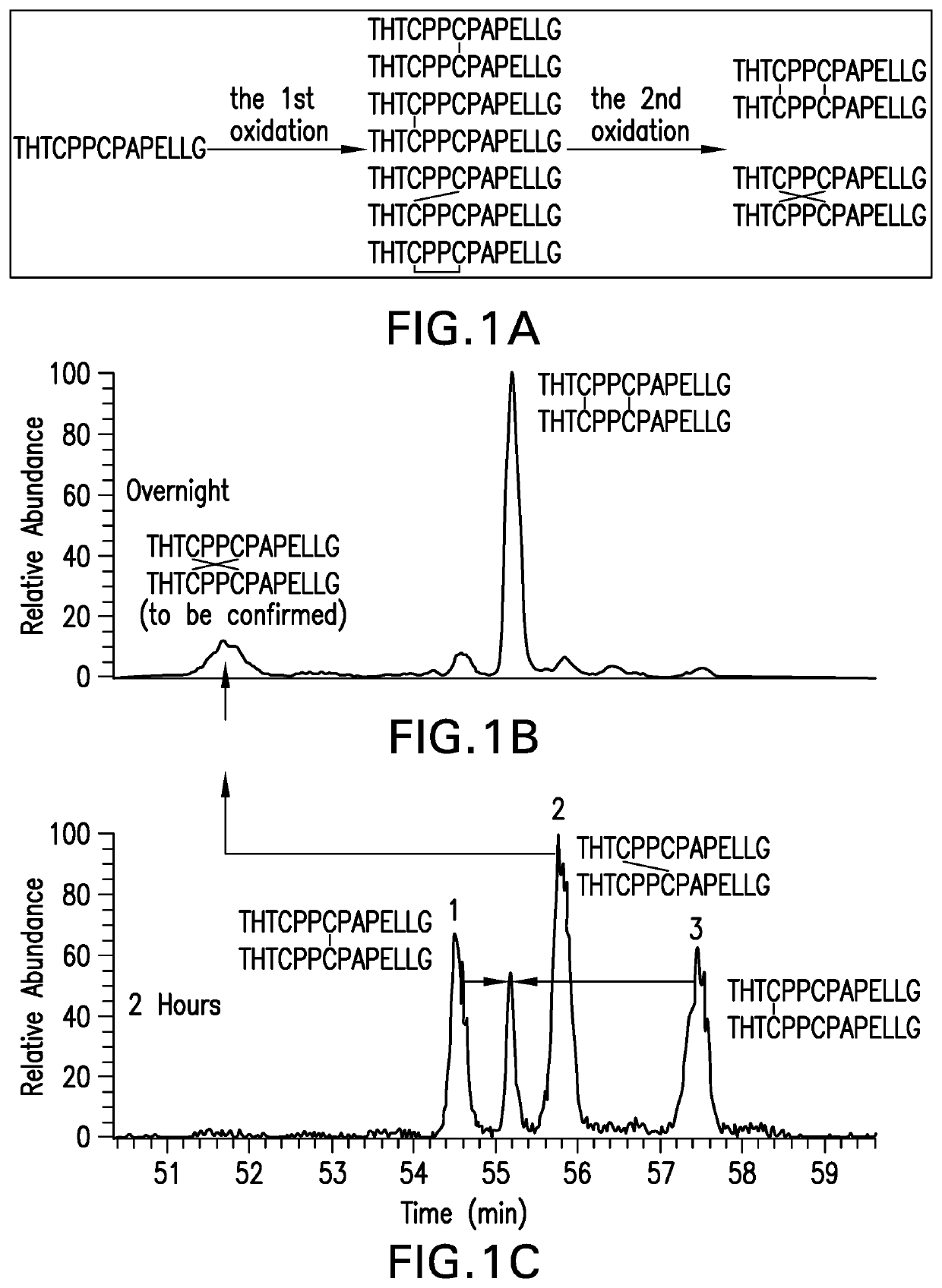
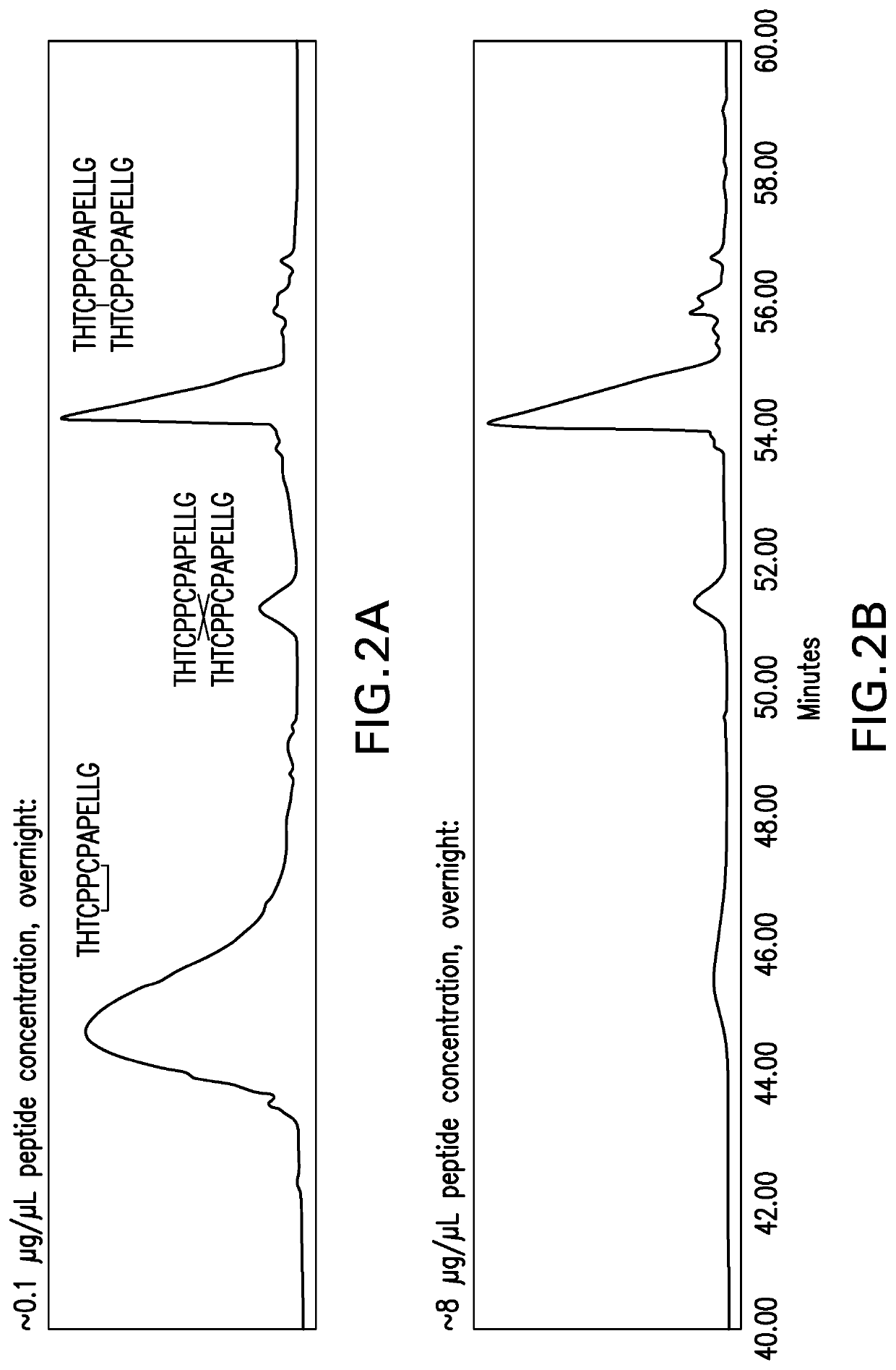
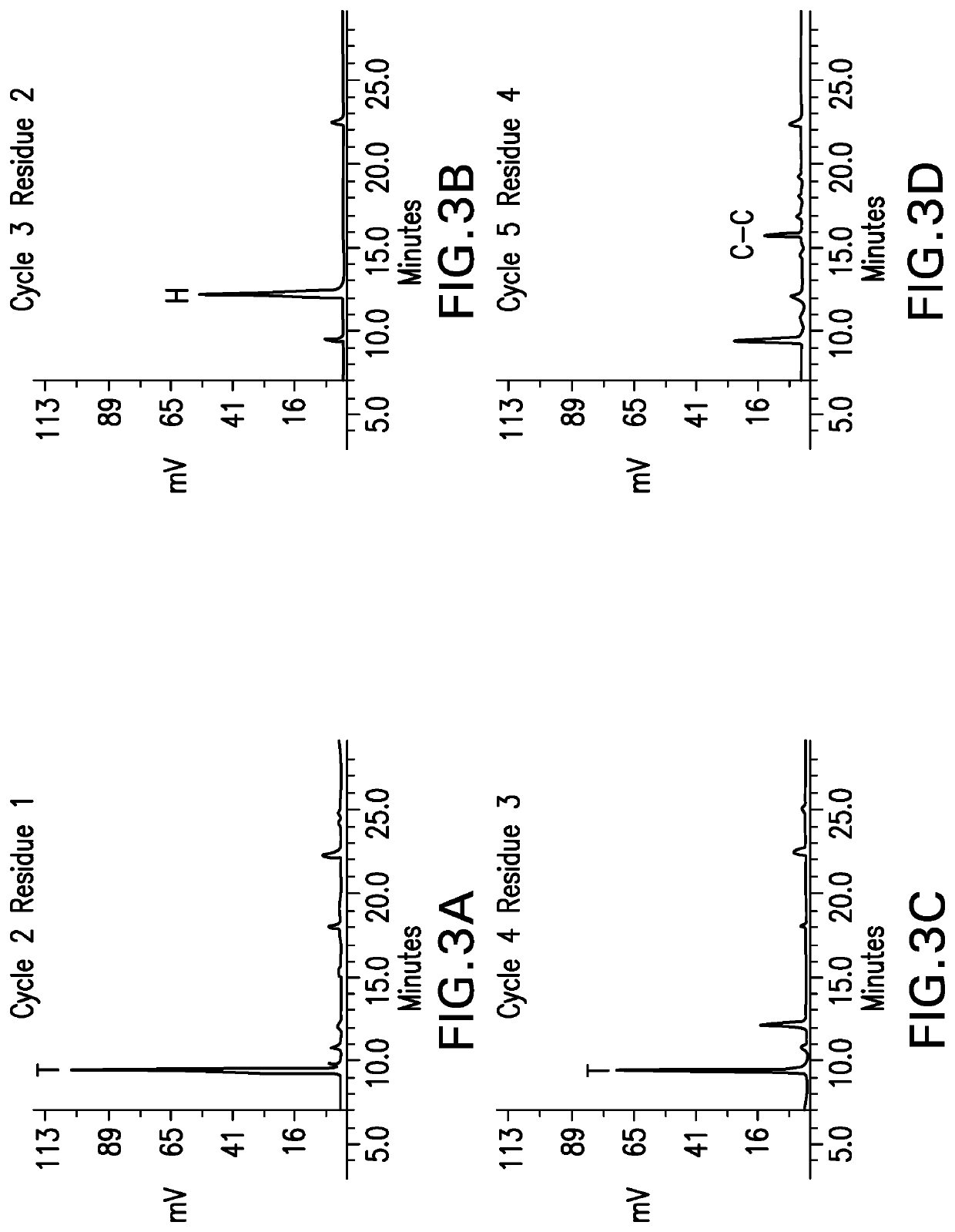
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Peptide analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
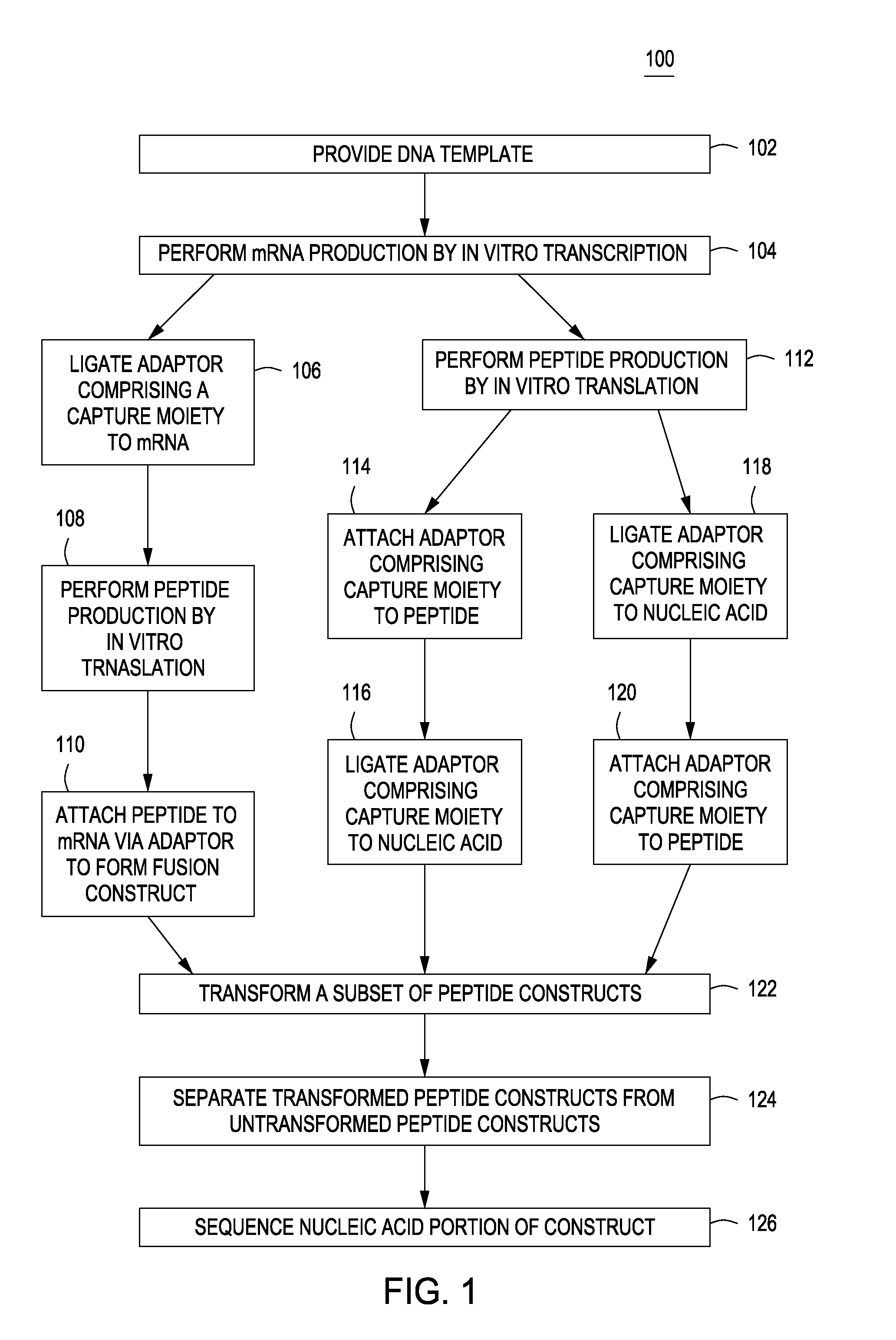
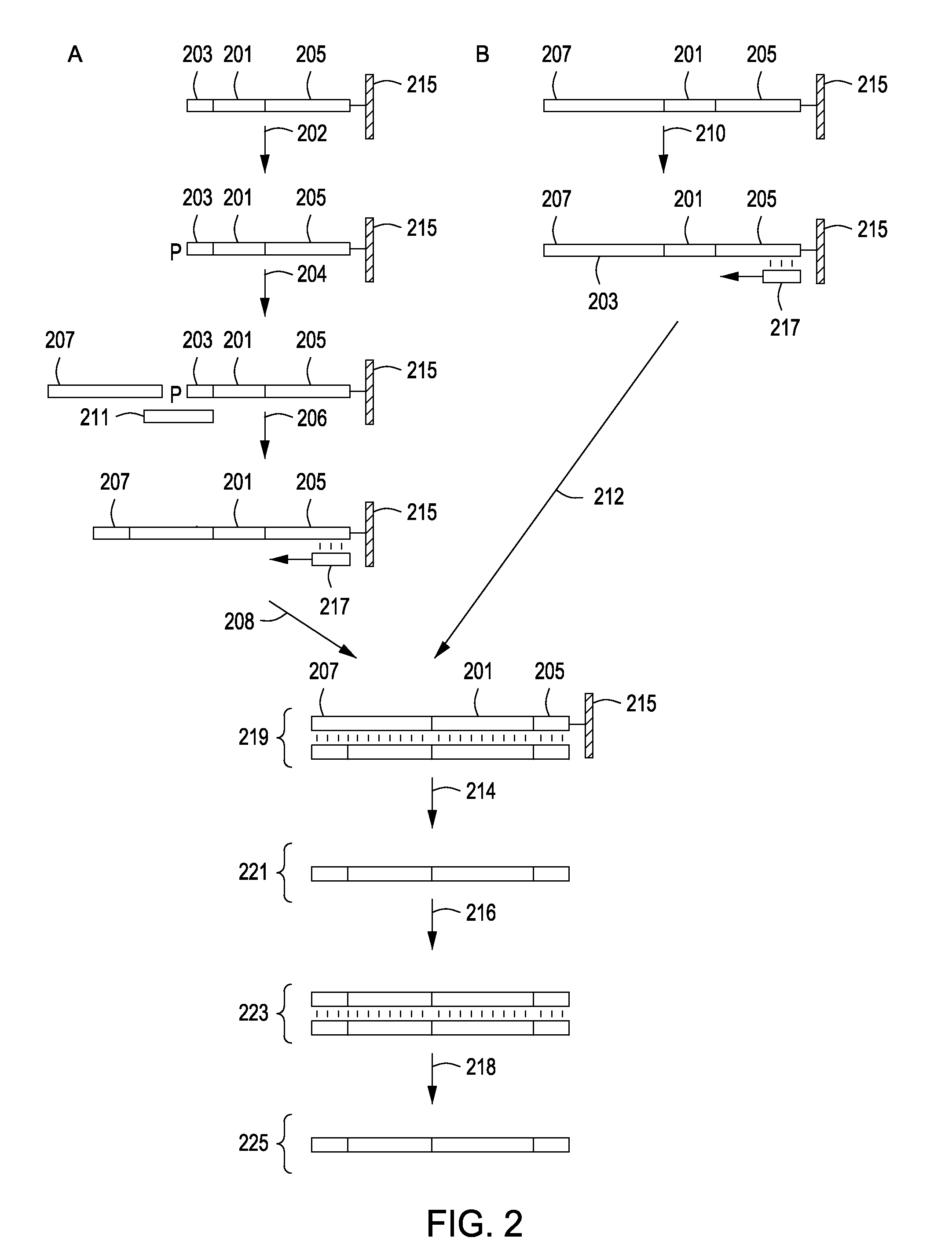
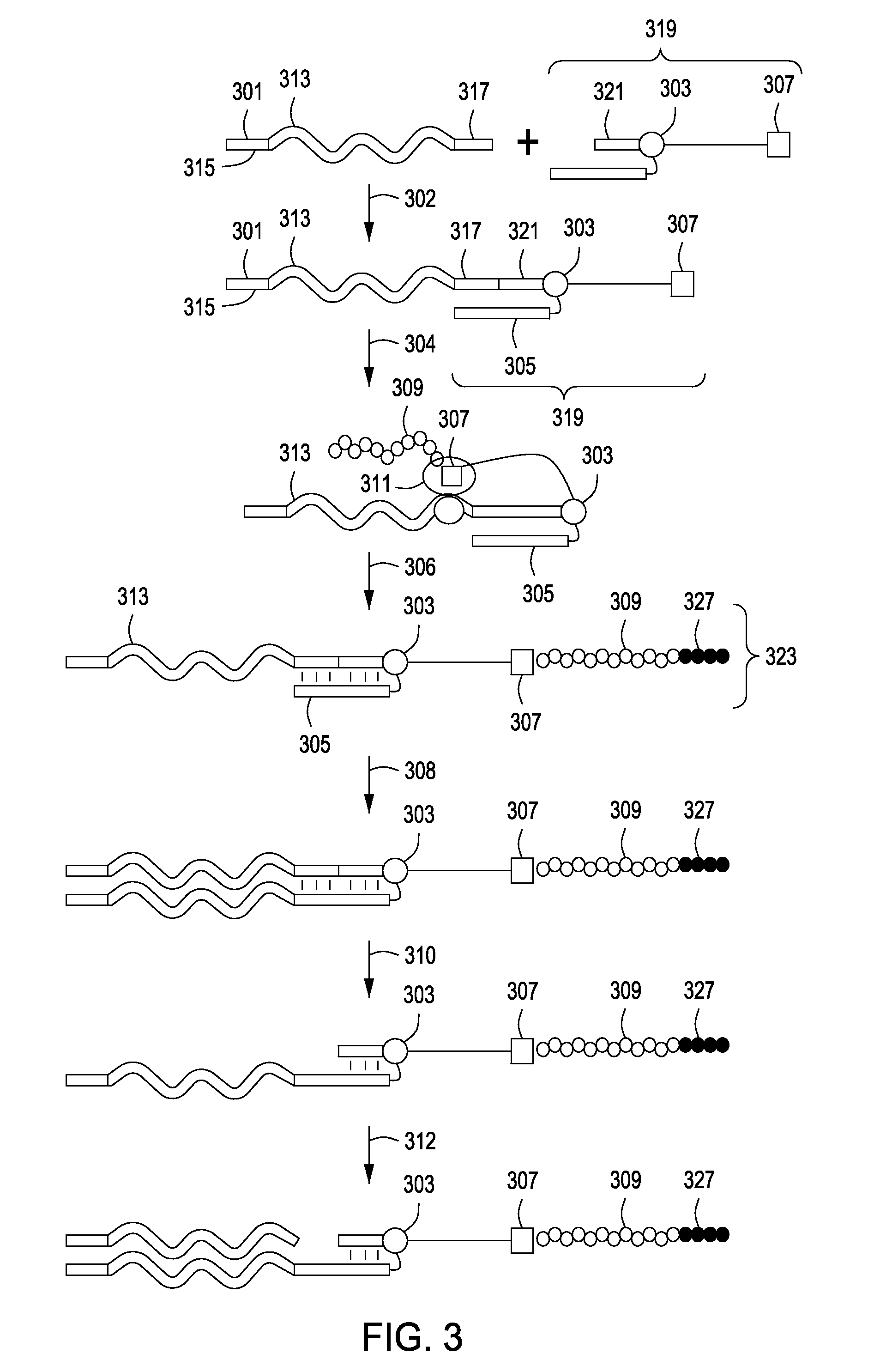
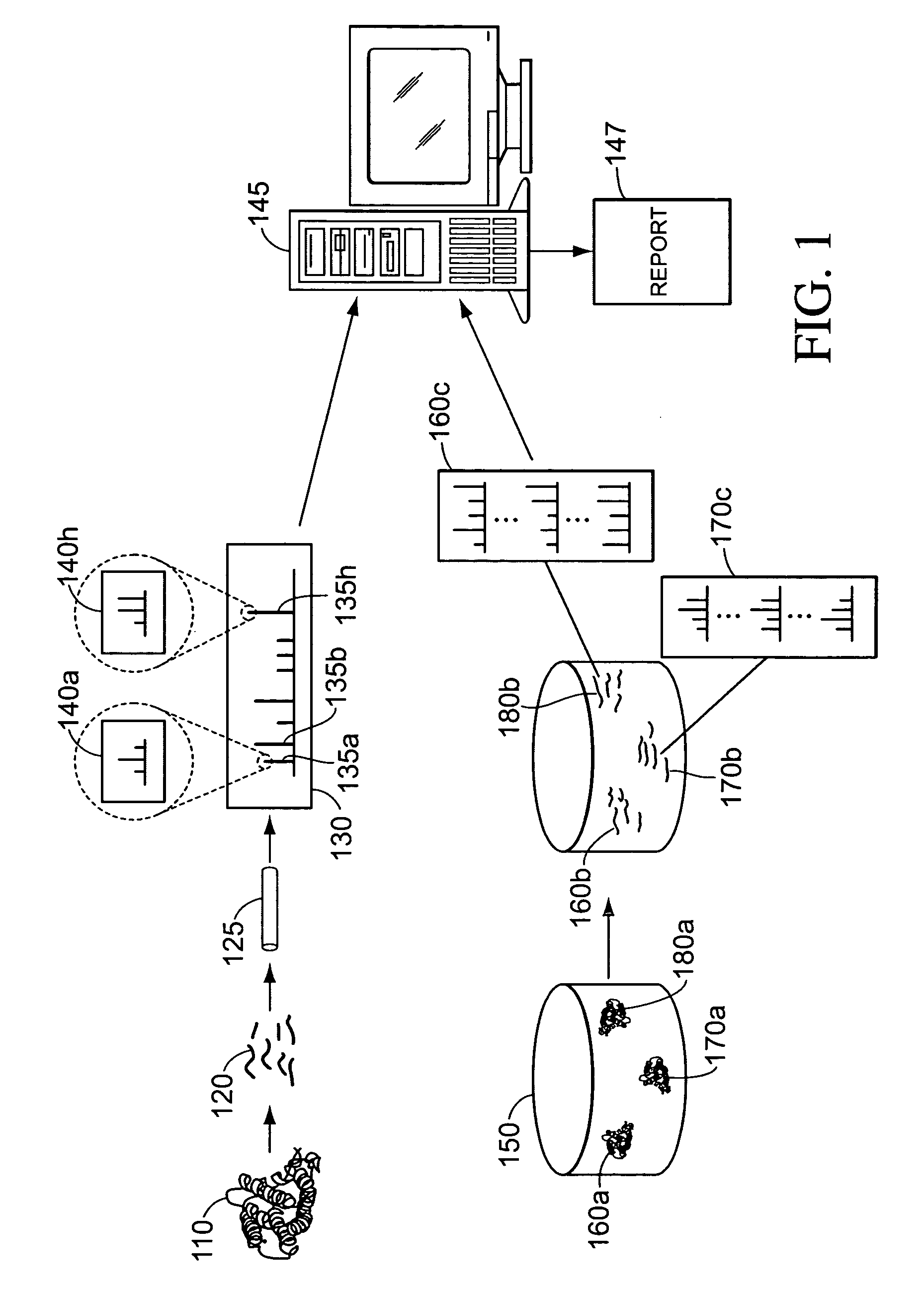
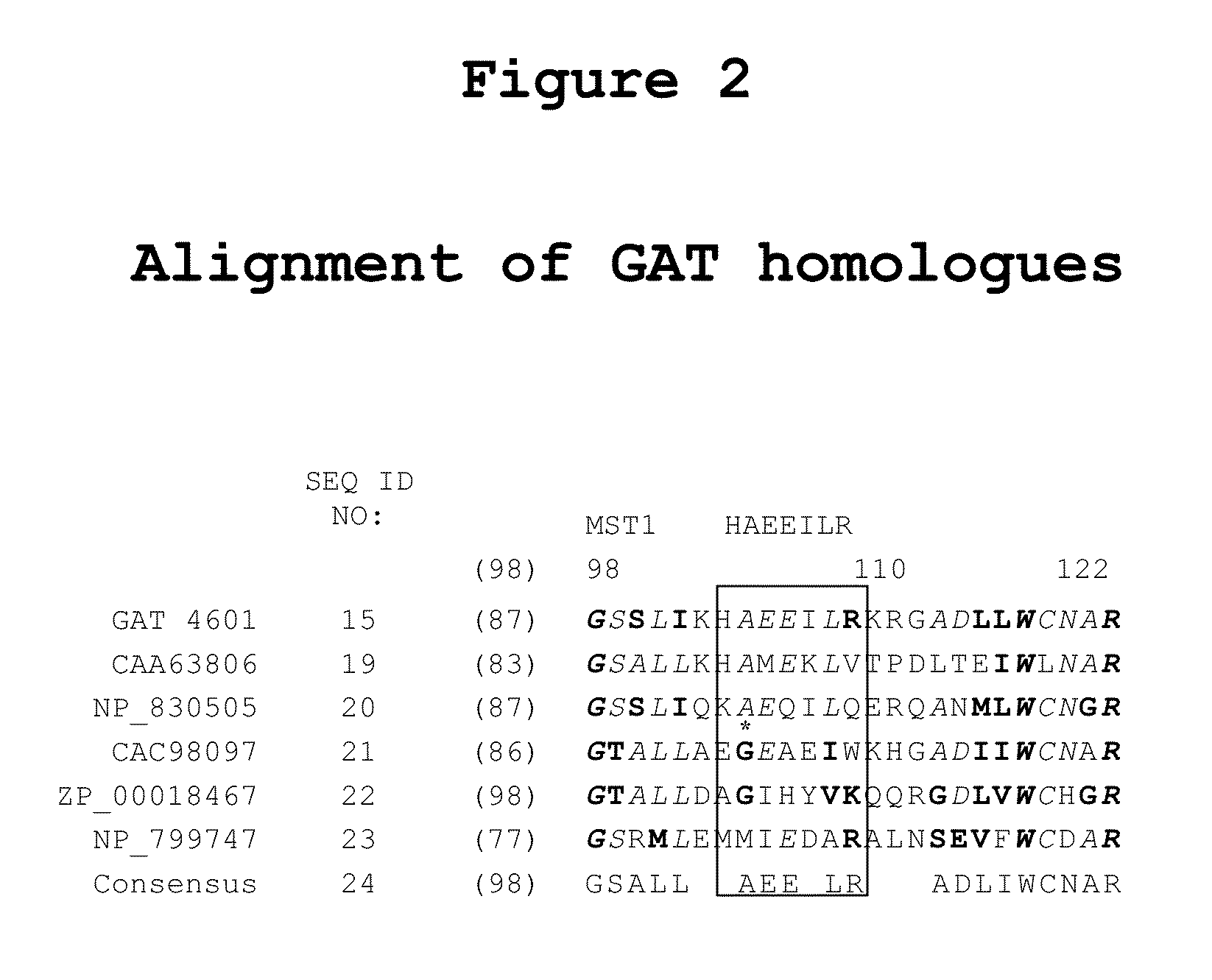
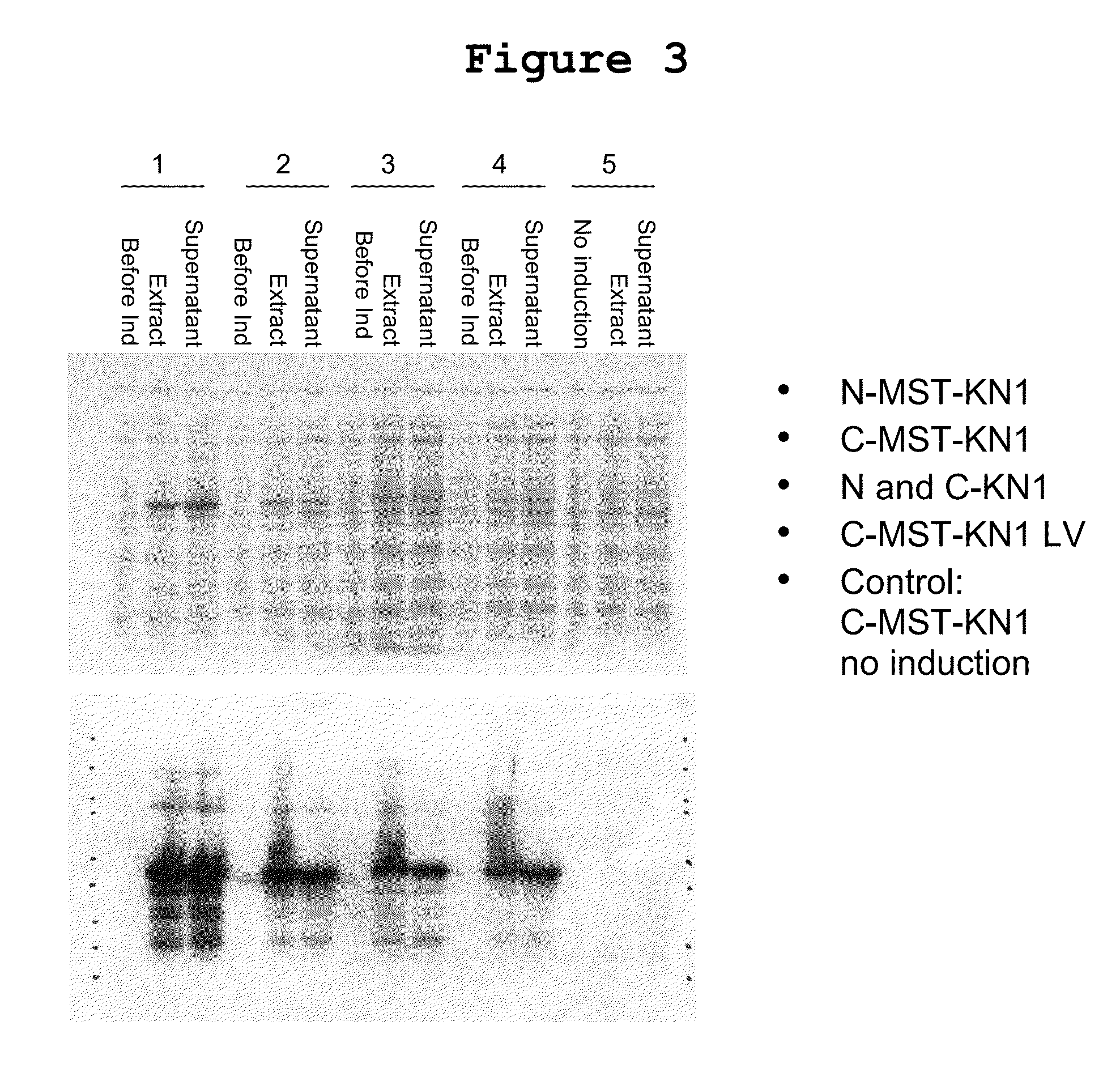
Peptide constructs and assay systems
InactiveUS20120258871A1High throughput screeningMore scalableNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyProteome
The present invention provides methods for constructing peptide construct sets and methods of use of these peptide construct sets in assay systems for peptide analysis, and in particular for use in high throughput peptide analysis. The methods allow for analysis of large sets of peptide constructs in a cost-effective manner, employing molecular biological techniques that are both robust and easily parallelized. Thus, the methods allow for the construction of peptide construct sets encompassing, e.g., the human proteome.
Owner:PROGNOSYS BIOSCI
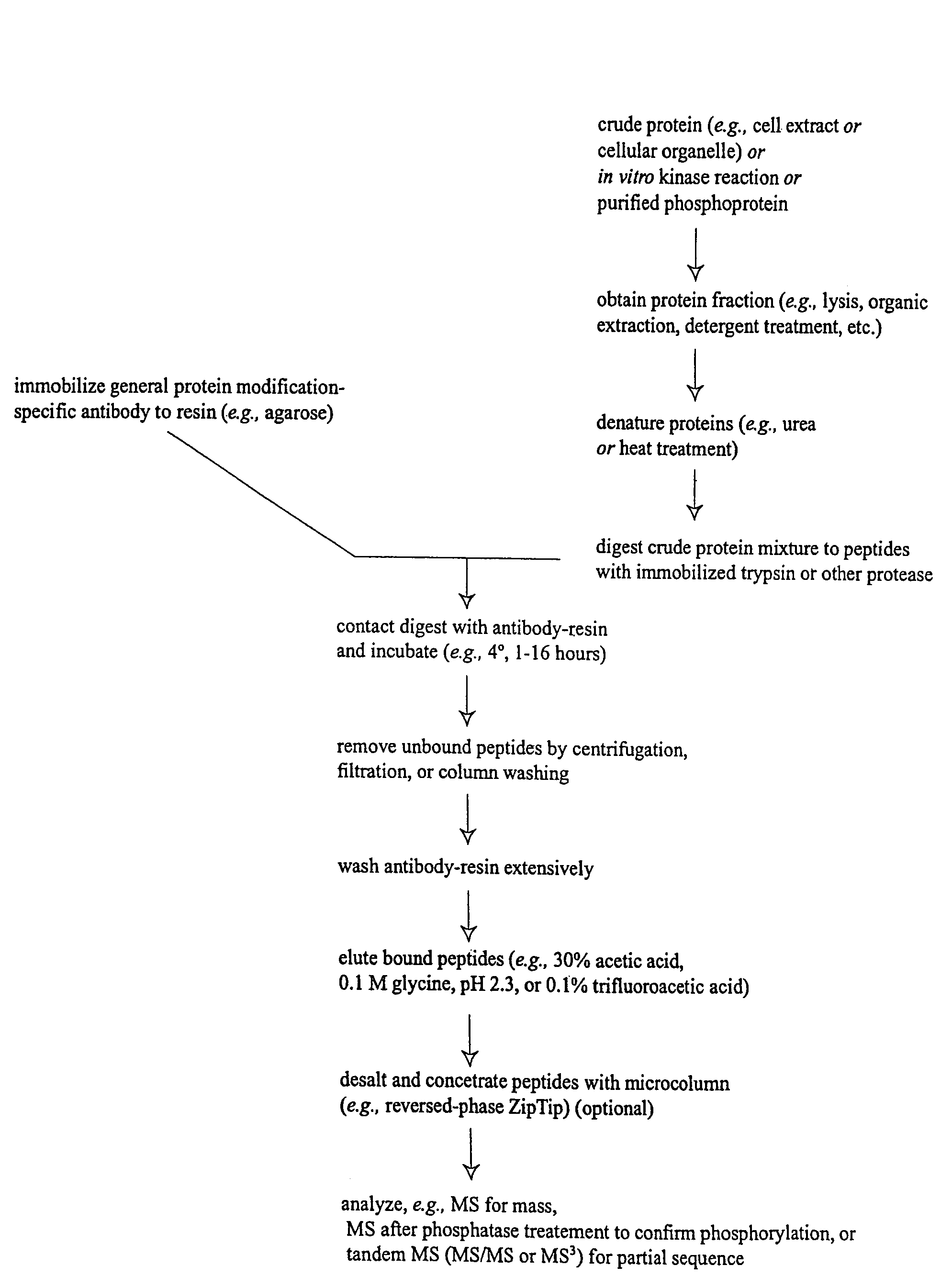
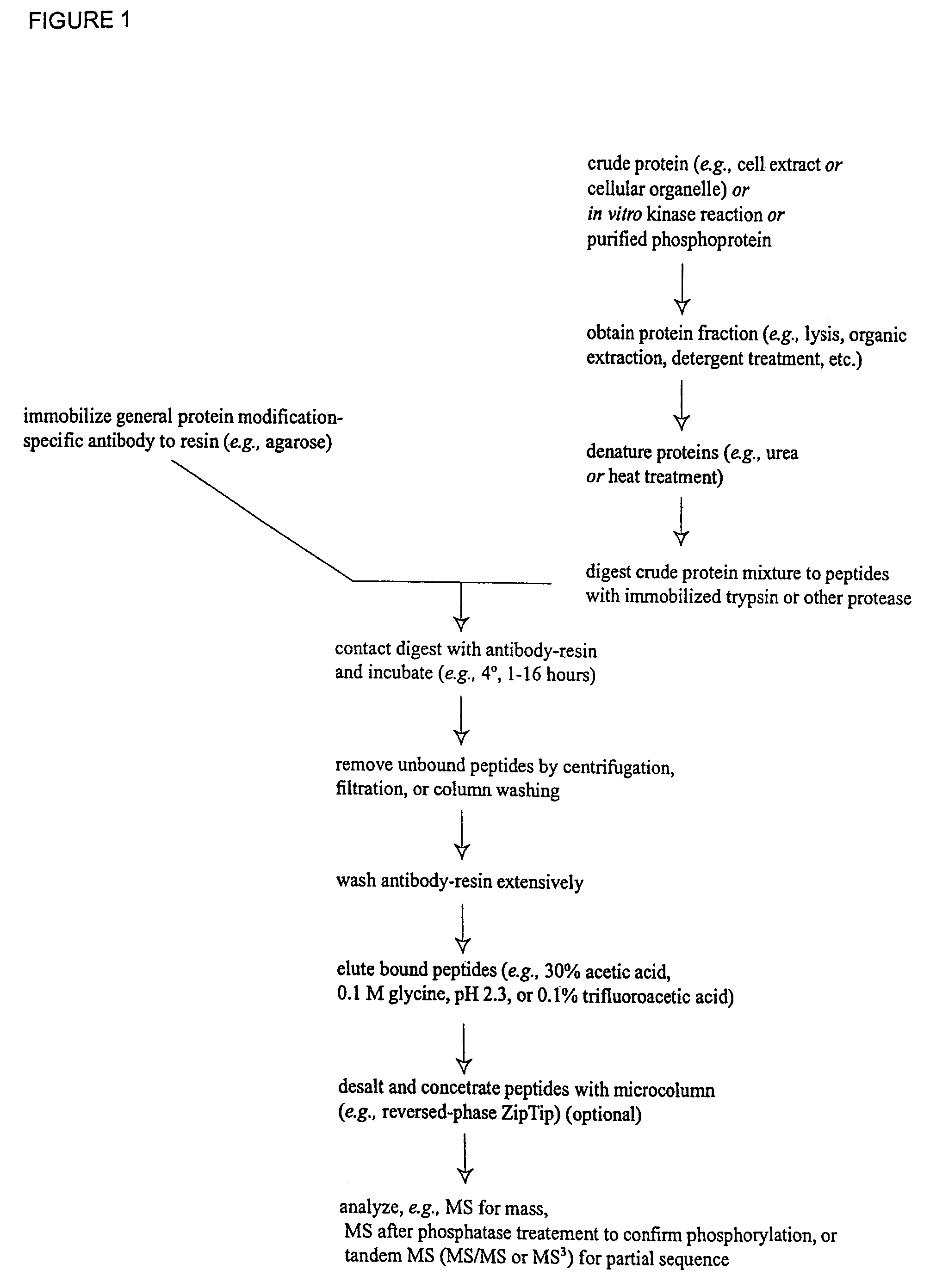
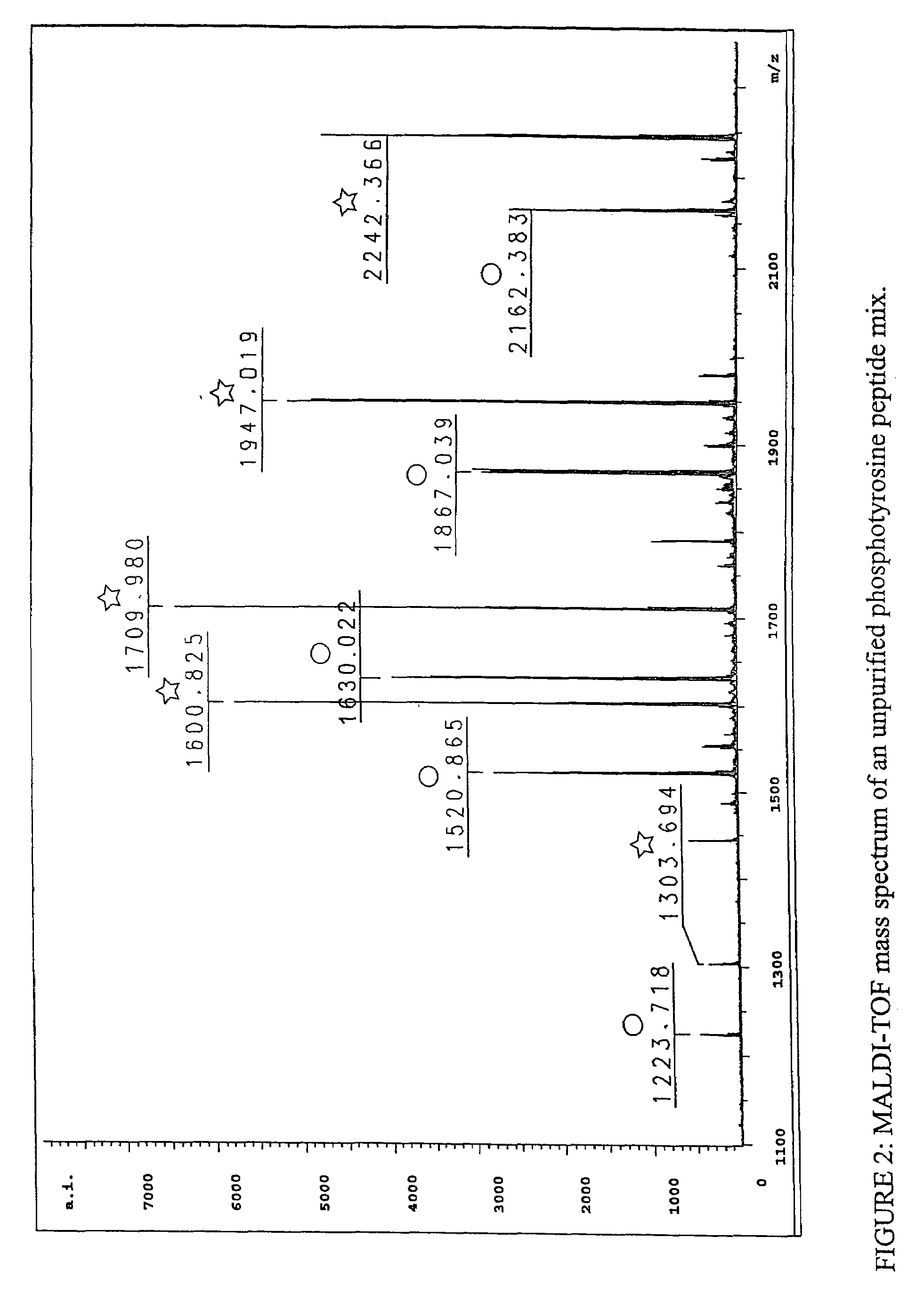
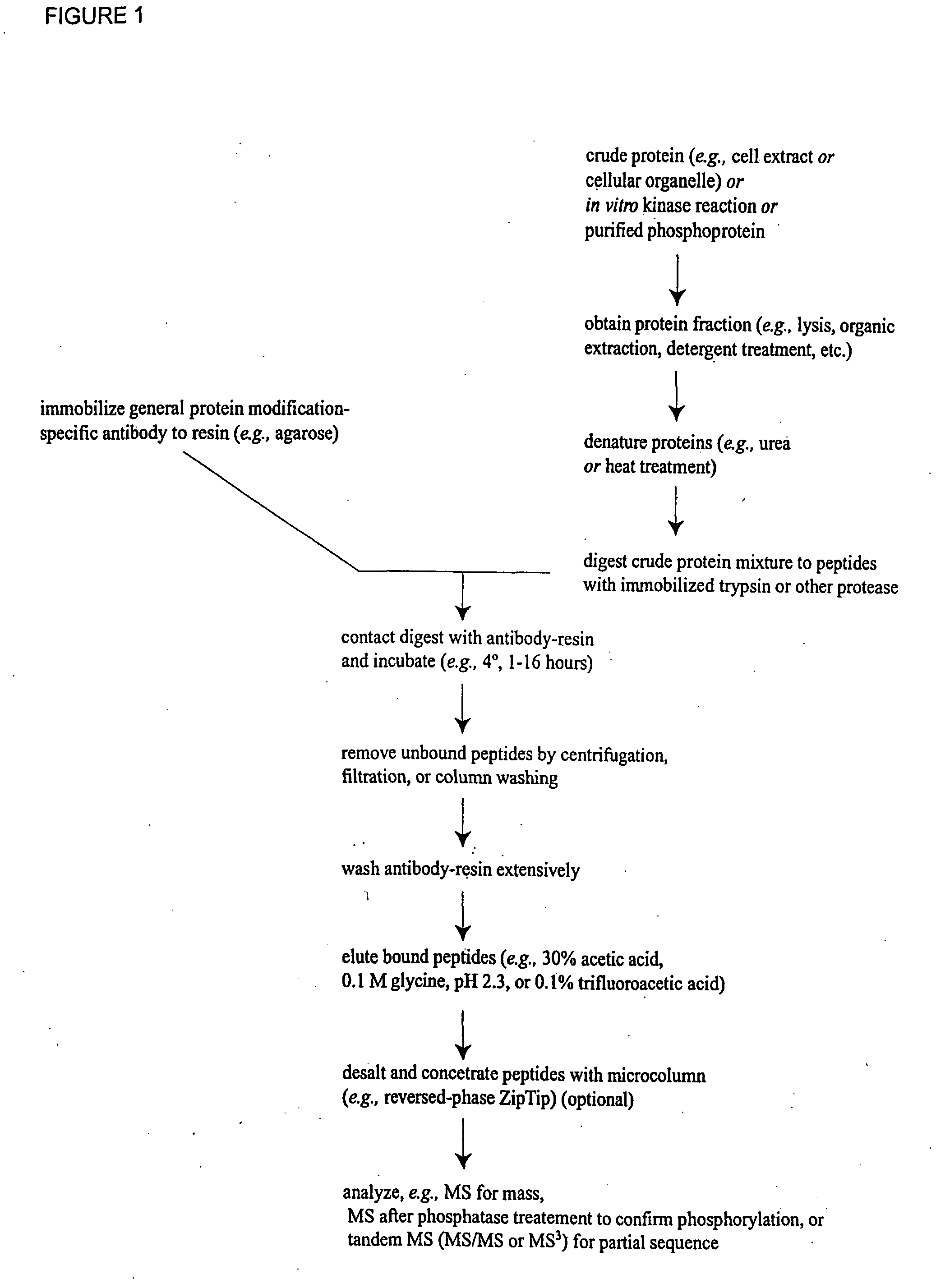
Immunoaffinity isolation of modified peptides from complex mixtures
InactiveUS7300753B2Rapid, efficient, and direct isolation (and subsequent characterization)Improve automationMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological bodyPhosphorylation
The invention provides methods for isolating a modified peptide from a complex mixture of peptides, the method comprising the steps of: (a) obtaining a proteinaceous preparation from an organism, wherein the preparation comprises modified peptides from two or more different proteins; (b) contacting the preparation with at least one immobilized modification-specific antibody; and (c) isolating at least one modified peptide specifically bound by the immobilized modification-specific antibody in step (b). The method may further comprise the step of (d) characterizing the modified peptide isolated in step (c) by mass spectrometry (MS), tandem mass spectrometry (MS—MS), and / or MS3 analysis, or the step of (e) utilizing a search program to substantially match the spectra obtained for the modified peptide during the characterization of step (d) with the spectra for a known peptide sequence, thereby identifying the parent protein(s) of the modified peptide. Also provided are an immunoaffinity isolation device comprising a modification-specific antibody, and antibodies against novel UFD1 and PTN6 phosphorylation sites.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
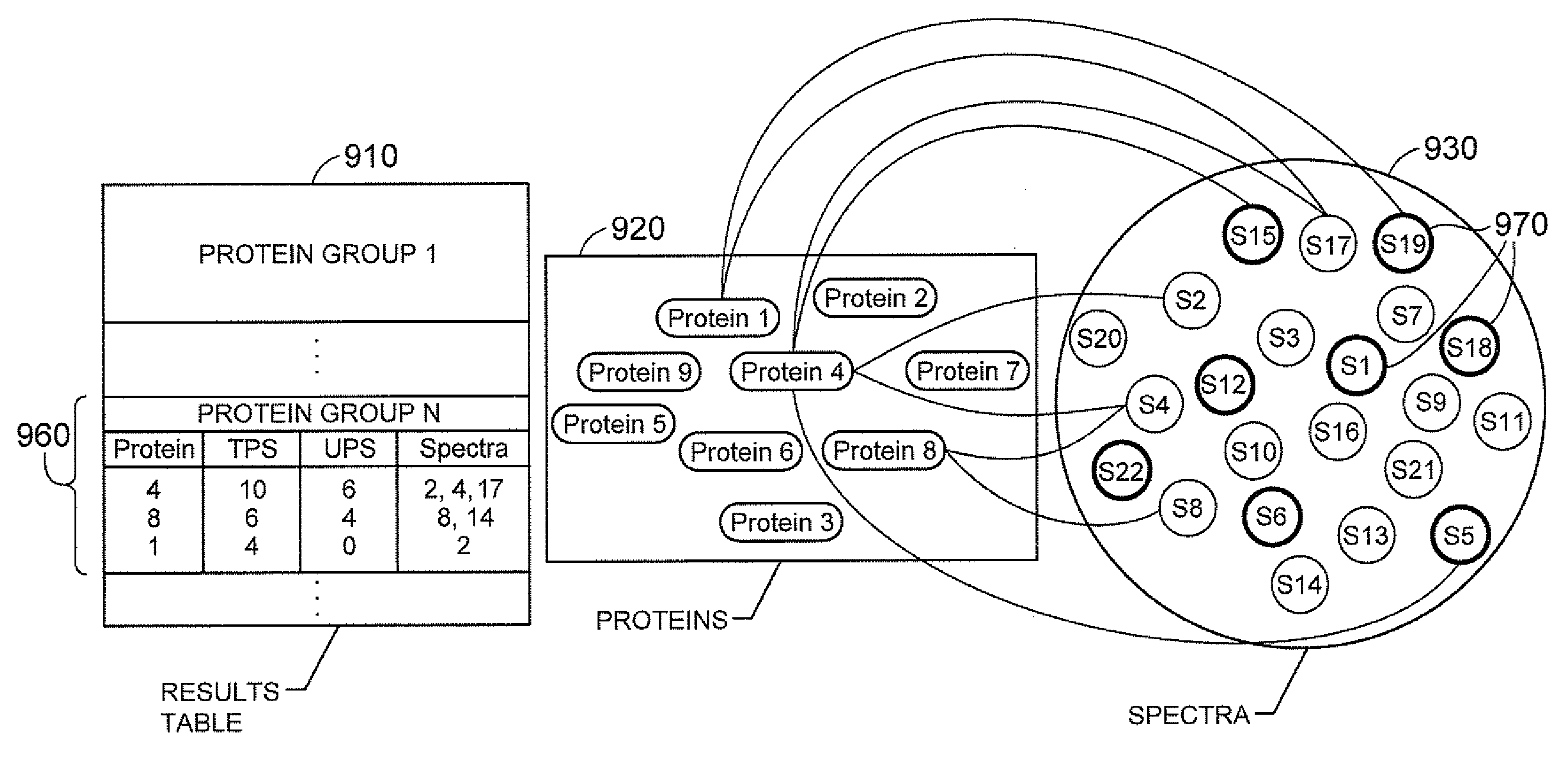
Methods and Systems for Protein and Peptide Evidence Assembly
InactiveUS20090053819A1Reduce manual inspectionTransferrinsAlbumin peptidesProtein insertionMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present teachings provide methods and systems for the identification of proteins via peptide analysis. Some embodiments analyze proteins identified by analysis techniques such as mass spectrometry and build protein groups out of results. Groups can be formed by collecting like proteins and examining the group so as to identify if it is likely that only one form of a protein is present or, if there is enough evidence to support the presence of alternate forms. Various embodiments provide visual reports that can be interactive. These reports can allow a user to visualize relationships between proteins both intra- and inter-group. Methods are also introduced that can reduce the identification of false positives by taking into account a priori information.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
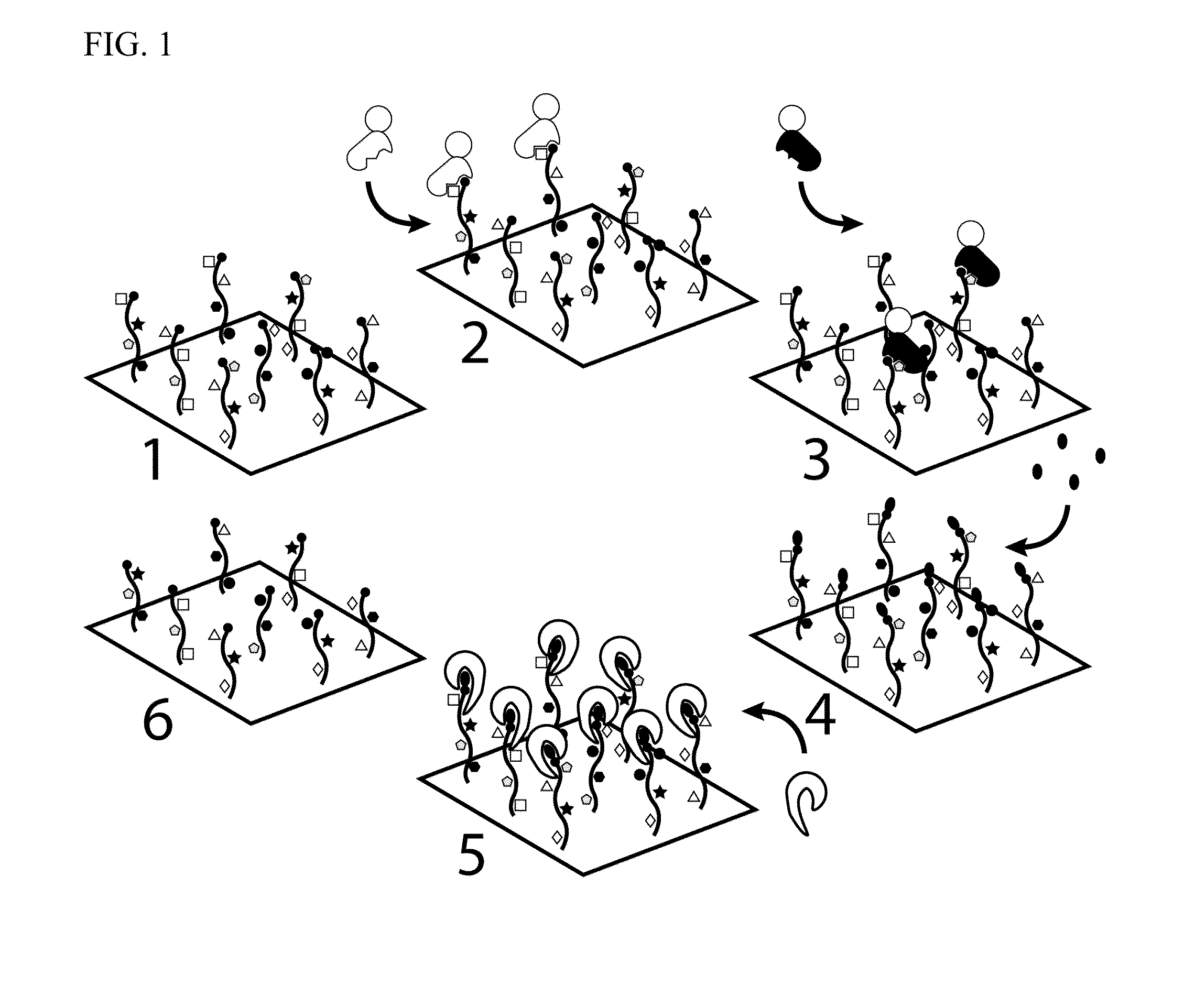
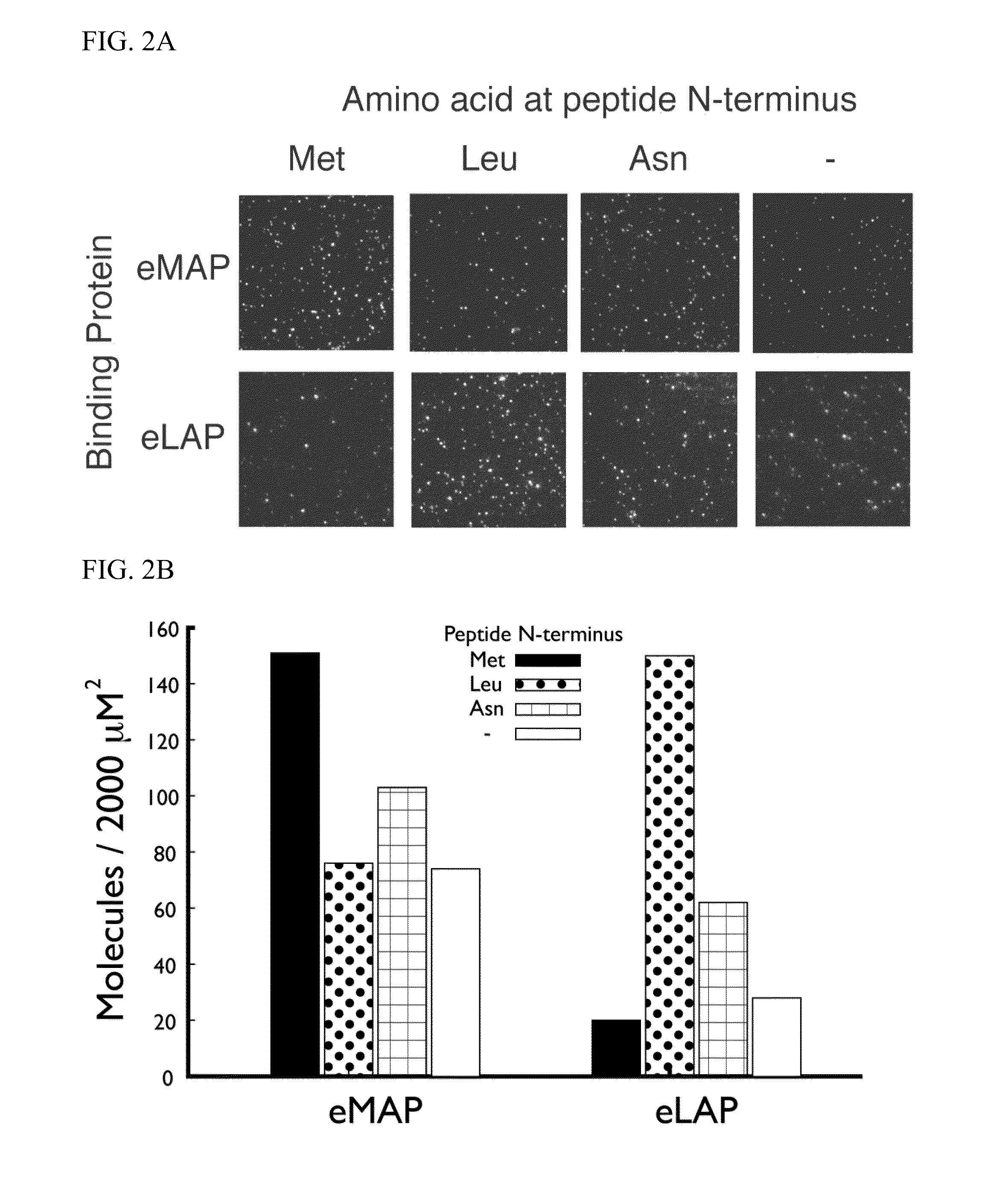
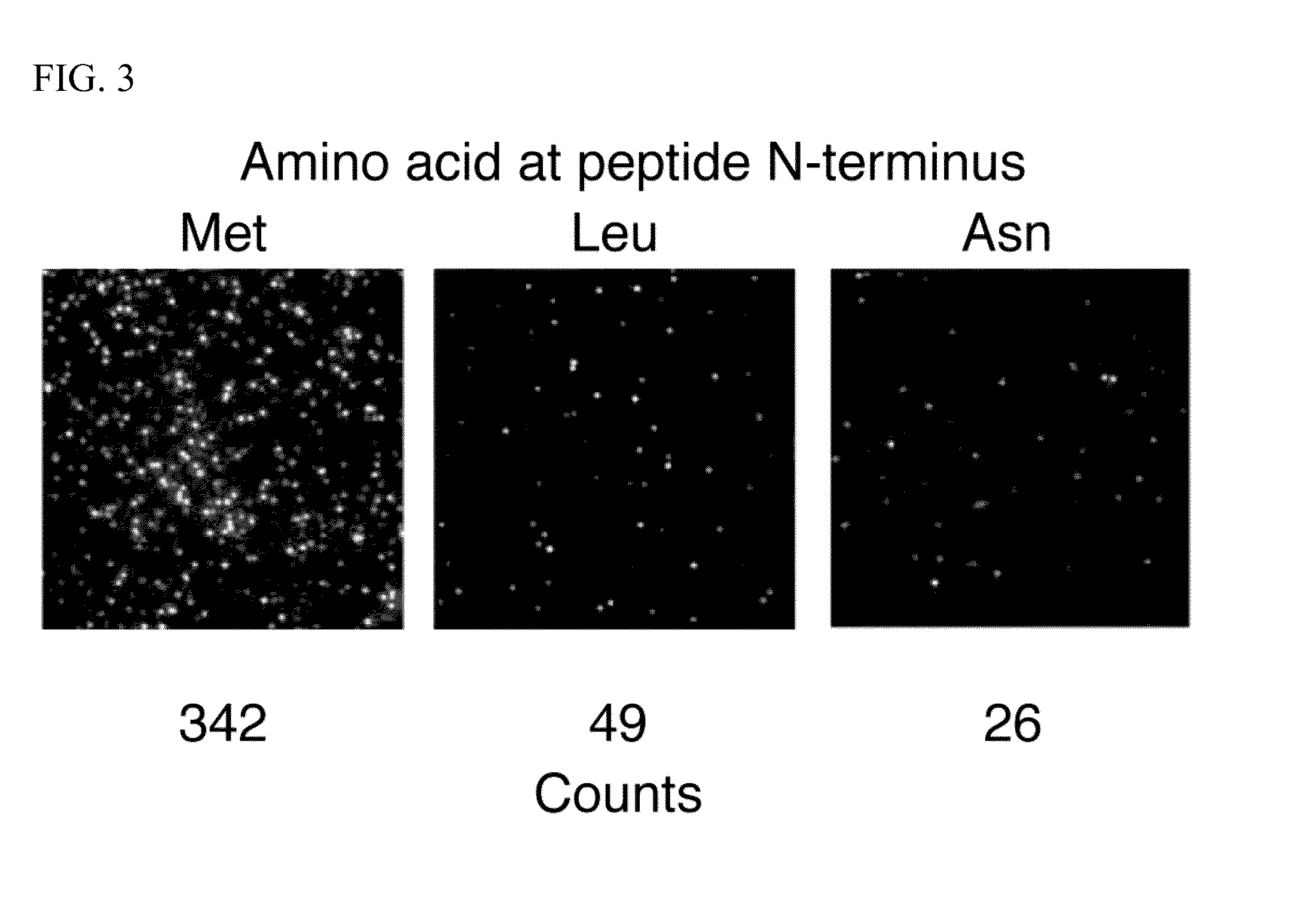
Molecules and methods for iterative polypeptide analysis and processing
Reagents and methods for the digital analysis of proteins or peptides are provided. Specifically provided herein are proteins for identifying the N-terminal amino acid or N-terminal phosphorylated amino acid of a polypeptide. Also, an enzyme for use in the cleavage step of the Edman degradation reaction and a method for using this enzyme are described.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Methods and systems for protein and peptide evidence assembly
InactiveUS20060030053A1Reduce manual inspectionTransferrinsAlbumin peptidesPrior informationTARP Protein
The present teachings provide methods and systems for the identification of proteins via peptide analysis. Some embodiments analyze proteins identified by analysis techniques such as mass spectrometry and build protein groups out of results. Groups can be formed by collecting like proteins and examining the group so as to identify if it is likely that only one form of a protein is present or, if there is enough evidence to support the presence of alternate forms. Various embodiments provide visual reports that can be interactive. These reports can allow a user to visualize relationships between proteins both intra- and inter-group. Methods are also introduced that can reduce the identification of false positives by taking into account a priori information.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Methods for Isolation and Decomposition of Mass Spectrometric Protein Signatures
InactiveUS20150162175A1High selectivityQuality improvementComponent separationParticle spectrometer methodsDecompositionMass analyzer
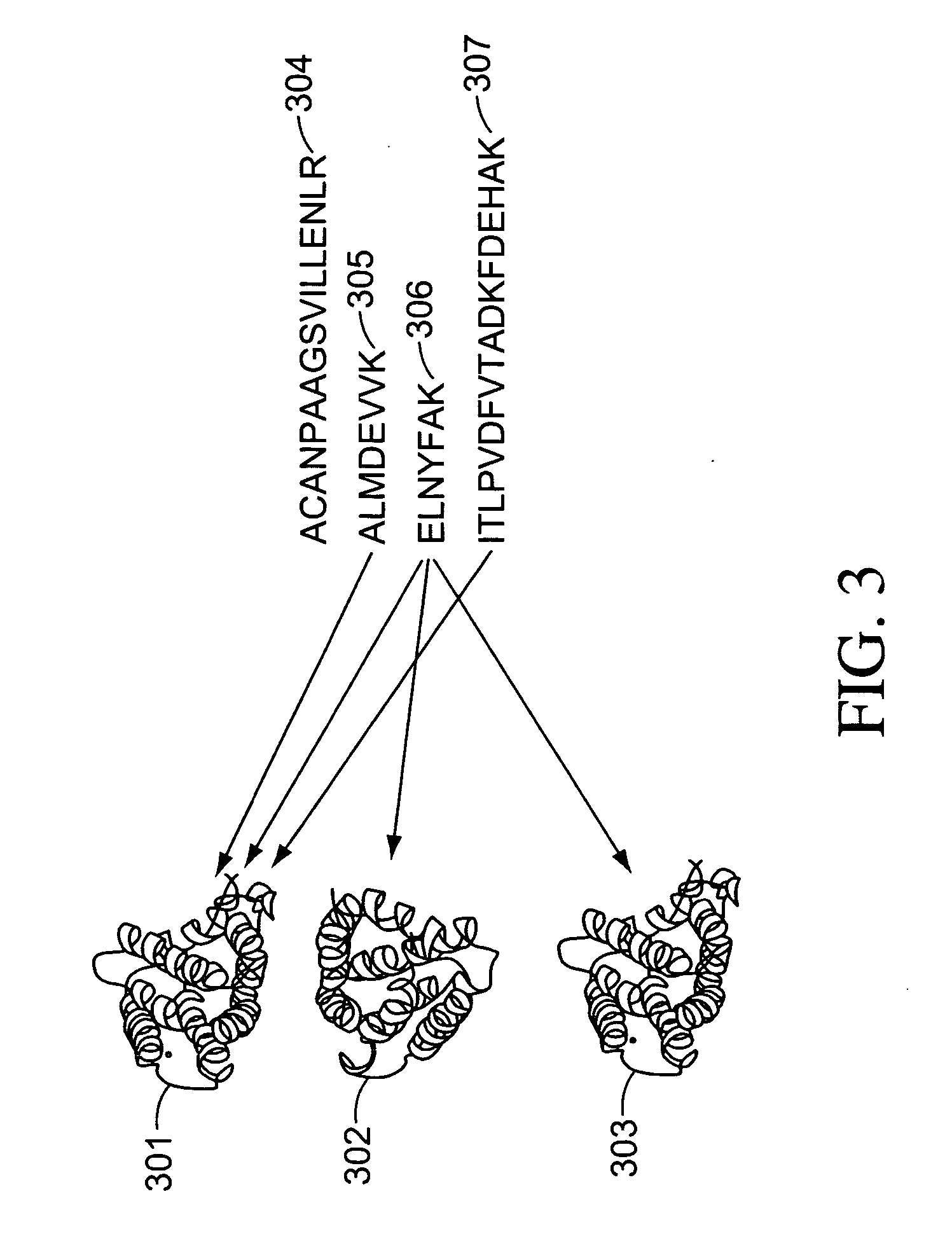
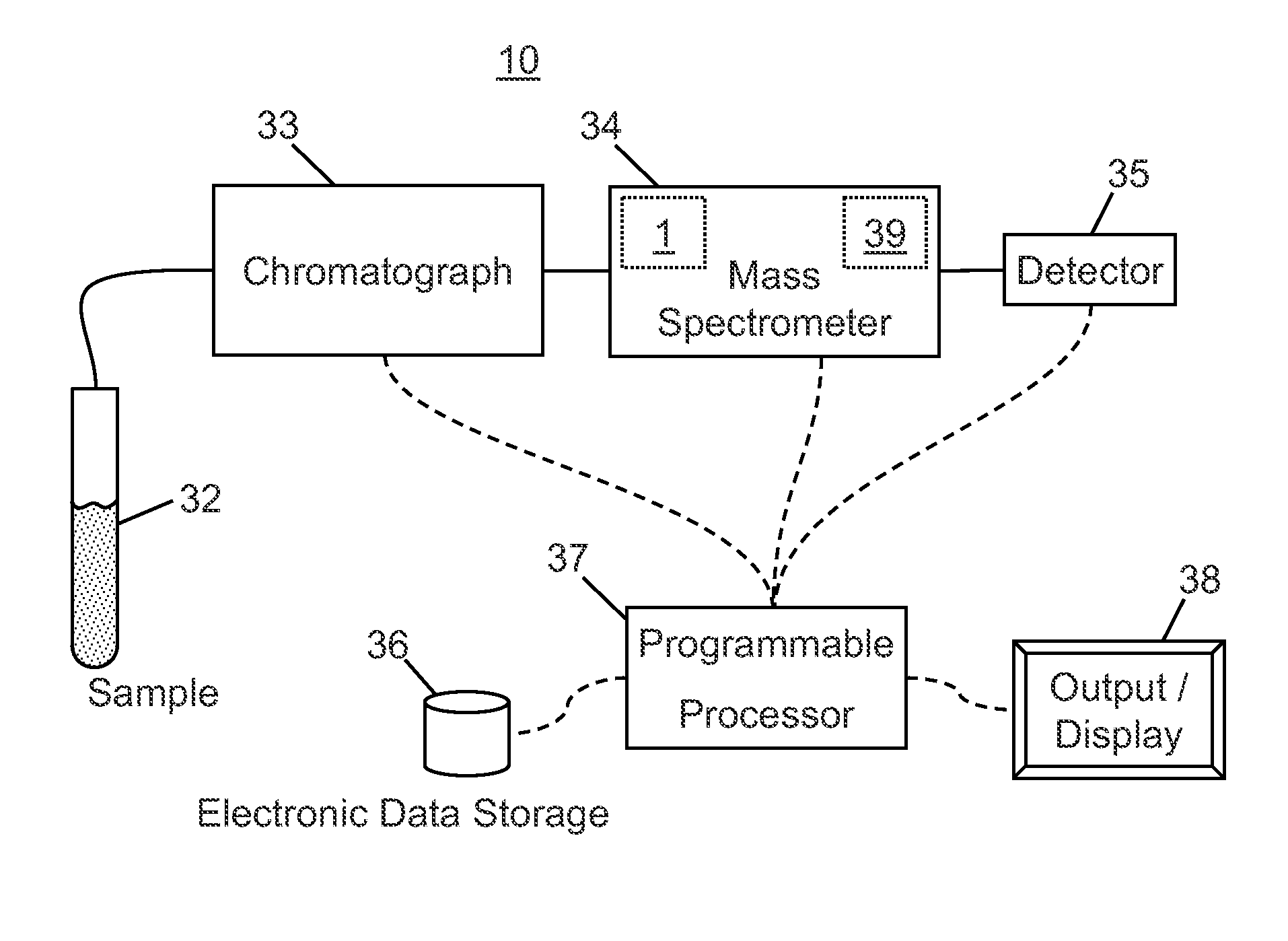
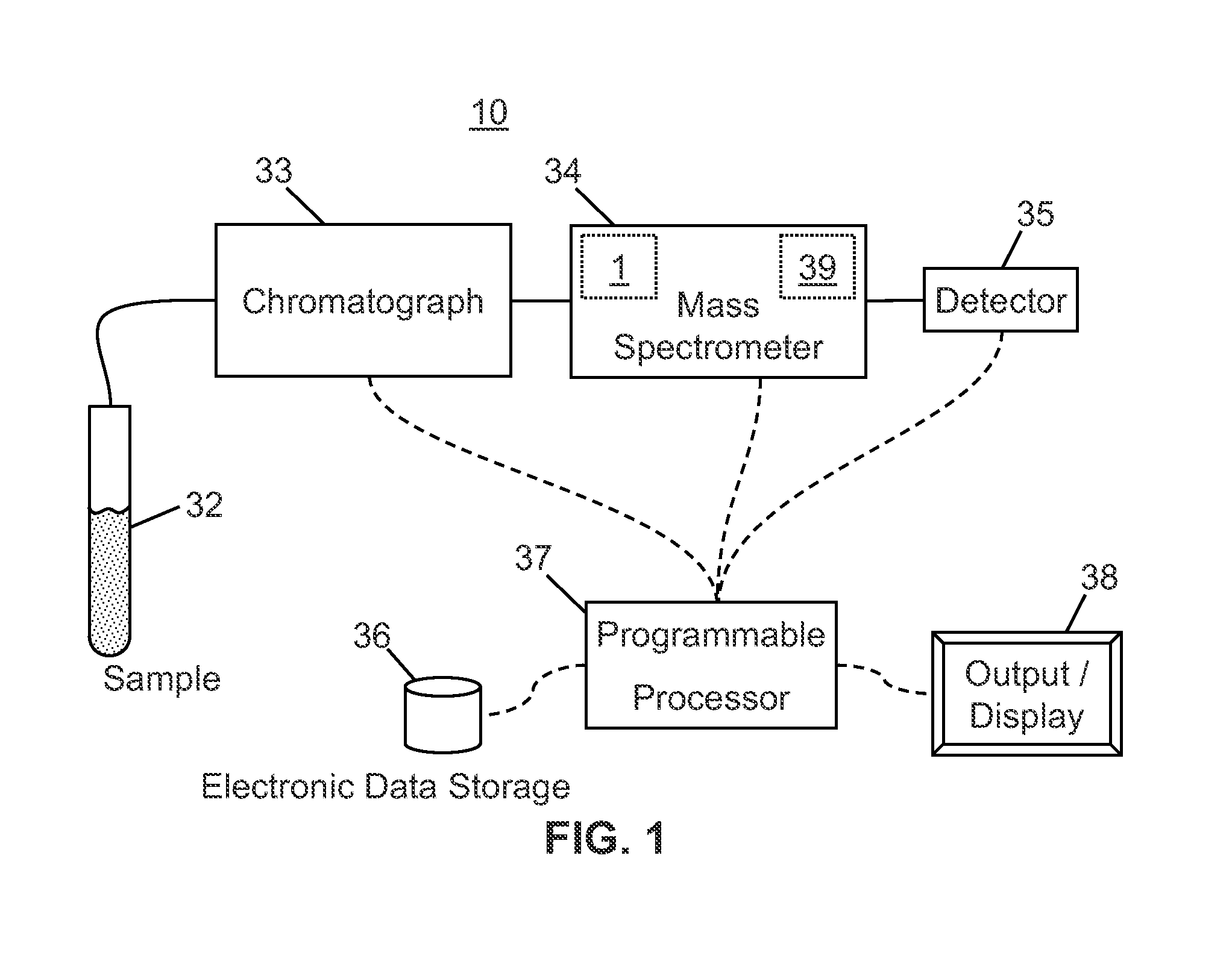
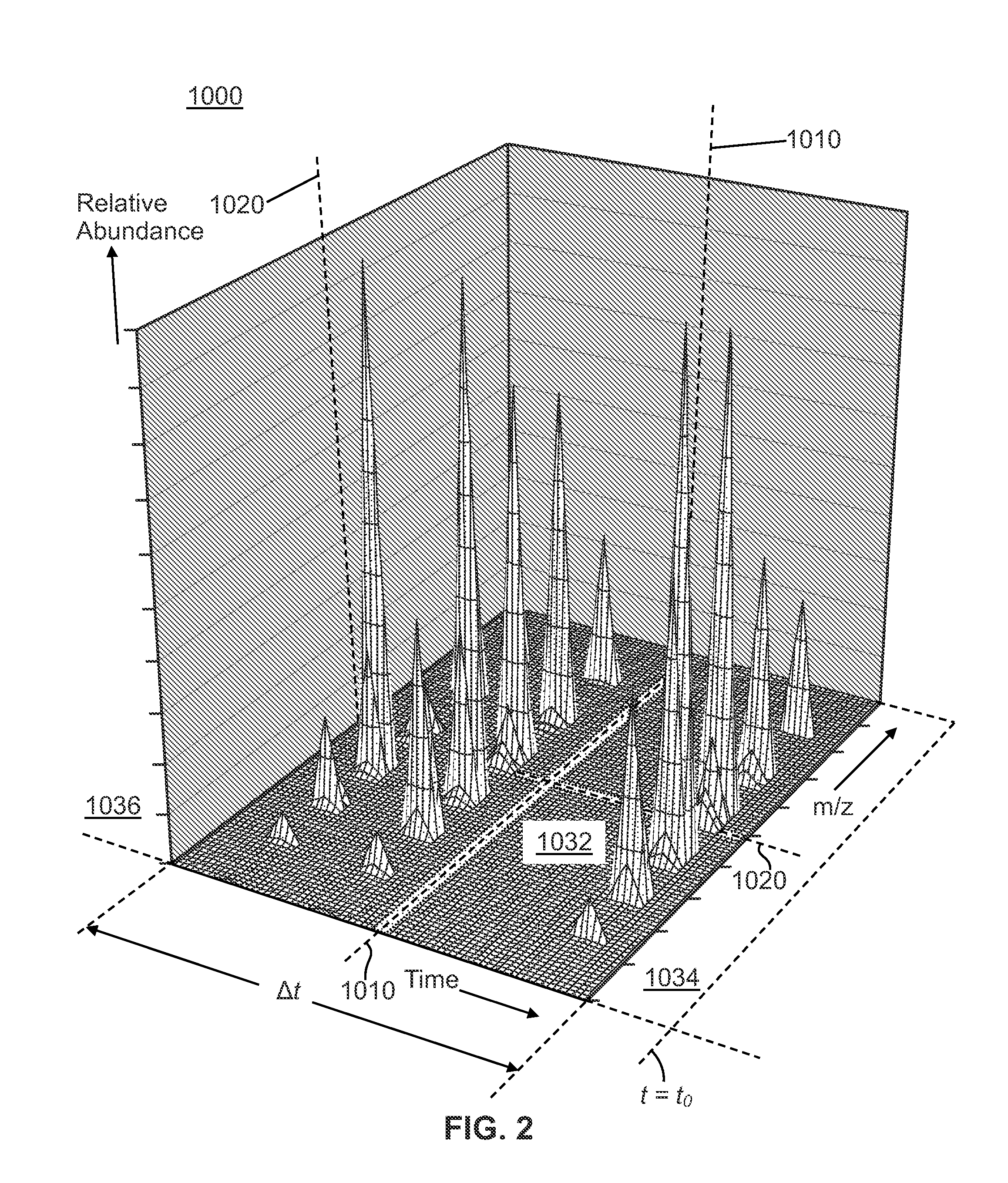
A method of analyzing a liquid mixture comprising protein or peptide molecules mixed with other molecules comprises: passing a portion of the mixture through a liquid chromatograph so as to elute the molecules; transferring the eluted portions of the molecules to an ion source of a mass spectrometer so as to generate ions comprising a plurality of ion species therefrom; transferring the generated ion species to a mass analyzer for detection thereby; generating a respective record of the intensity-versus-time variation of each of a plurality of the detected ion species; identifying and distinguishing a set of ion species corresponding to the ions generated from the eluted portion of the protein or peptide analyte molecules based on the records of the intensity-versus-time variation; and performing at least one additional operation on ions of one or more of the distinguished ion species generated from the protein or peptide analyte molecules.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
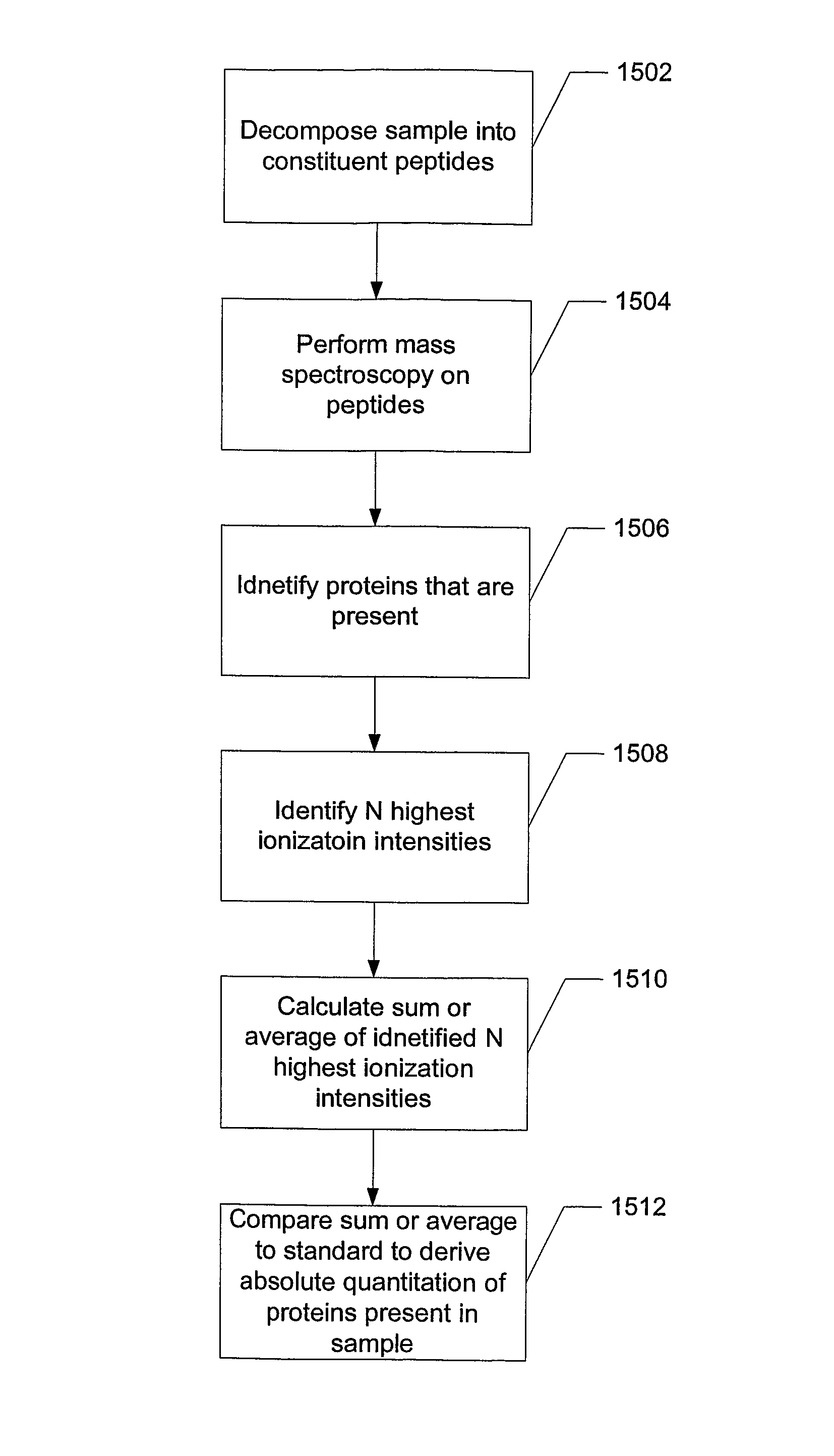
System and method for absolute quantitation of proteins using LC/MS
ActiveUS8271207B2Reduce errorsComponent separationBiological testingConversion factorLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
Absolute quantitation of protein in a sample is provided by comparing a sum or average of the N highest ionization intensities observed for peptides of a particular protein along with a calibration standard. The calibration standard can be in the form of a table generated by prior protein peptide analysis performed using one or more pre-determined proteins. The comparison is used to determine a corresponding absolute quantity of protein based on the observed sum or average of ionization intensities. A simple conversion factor can be applied to the calibration standard value to determine the absolute quantity of protein in the sample.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
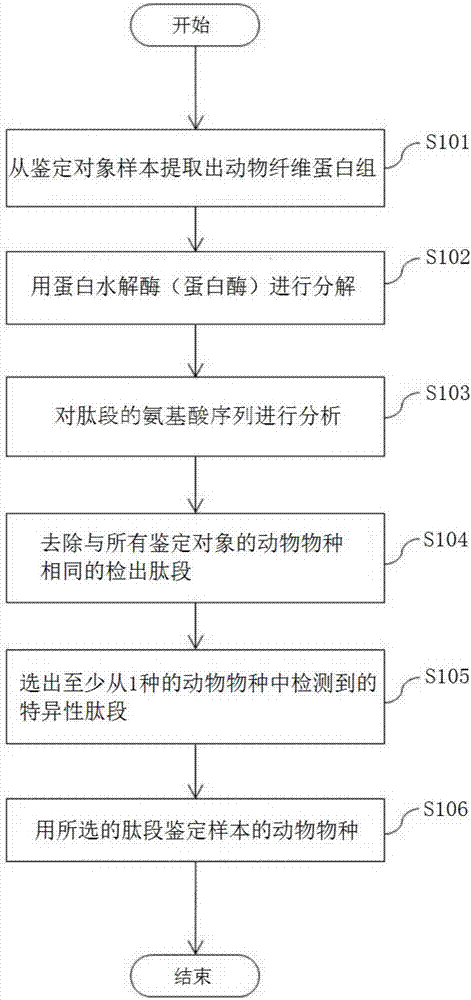
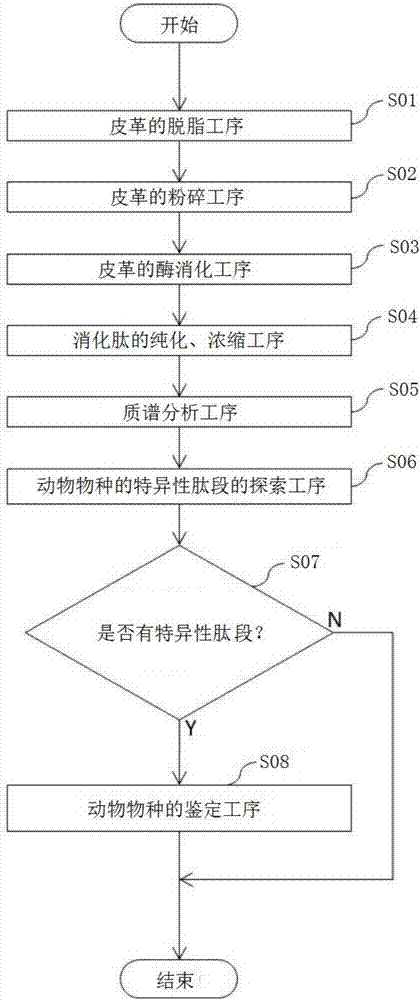
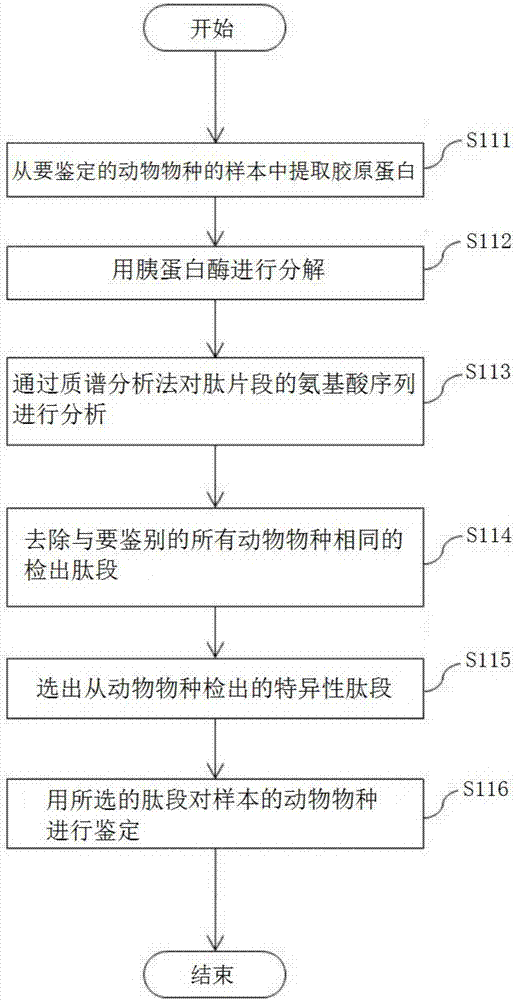
Animal species distinguishing method and device
ActiveCN107532196AEasy to identify accuratelyThe effect of correctly implementing the quality indicationConnective tissue peptidesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAmino acid
[Problem] To provide an objective method and a device for distinguishing animal species by identifying animal species through peptide analysis. [Solution] This method is provided with: a step for, byusing a proteolytic enzyme (protease), cleaving, into peptide fragments, a group of animal fibrous proteins (collagen, etc.) extracted from a distinguishing-subject sample, and analyzing the peptide fragments through amino acid sequencing; a step for removing, from all the analyzed peptide fragments, peptide fragments commonly detected in all animal species to be distinguished, and selecting peptide fragments that are specifically detected in at least one animal species; and a step for distinguishing the animal species of the sample by using the selected peptide fragments. Among the selected peptide fragments, a peptide fragment detected specifically in one particular animal species is used first for distinguishing the animal species of the sample, and, with respect to a sample with whichdistinguishing was unsuccessful, a peptide fragment detected specifically in at least two animal species is used next for distinguishing the animal species.
Owner:KOBE UNIV +1
Fluid micro-flux measuring method
InactiveCN101055201ASimple processLow costVolume/mass flow measurementChemical physicsMeasurement device
The invention which belongs to flow measurement technical field uses microchannel with cross section between 1x10-10 and 1x10-6m2 and obtains the flow data by calculation by measuring the distance of label moves in the microchannel in a certain time. The invention solves the problem of liquid flow measurement of micro / nano liter, the microflow measurement device which is designed with simple process, low costs, high measurement precision can be widely used in the field of biochemical analysis, chiral separation, neural science, protein and peptide analysis using the method of chip laboratory, microcolumn high performance liquid chromatography, etc.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
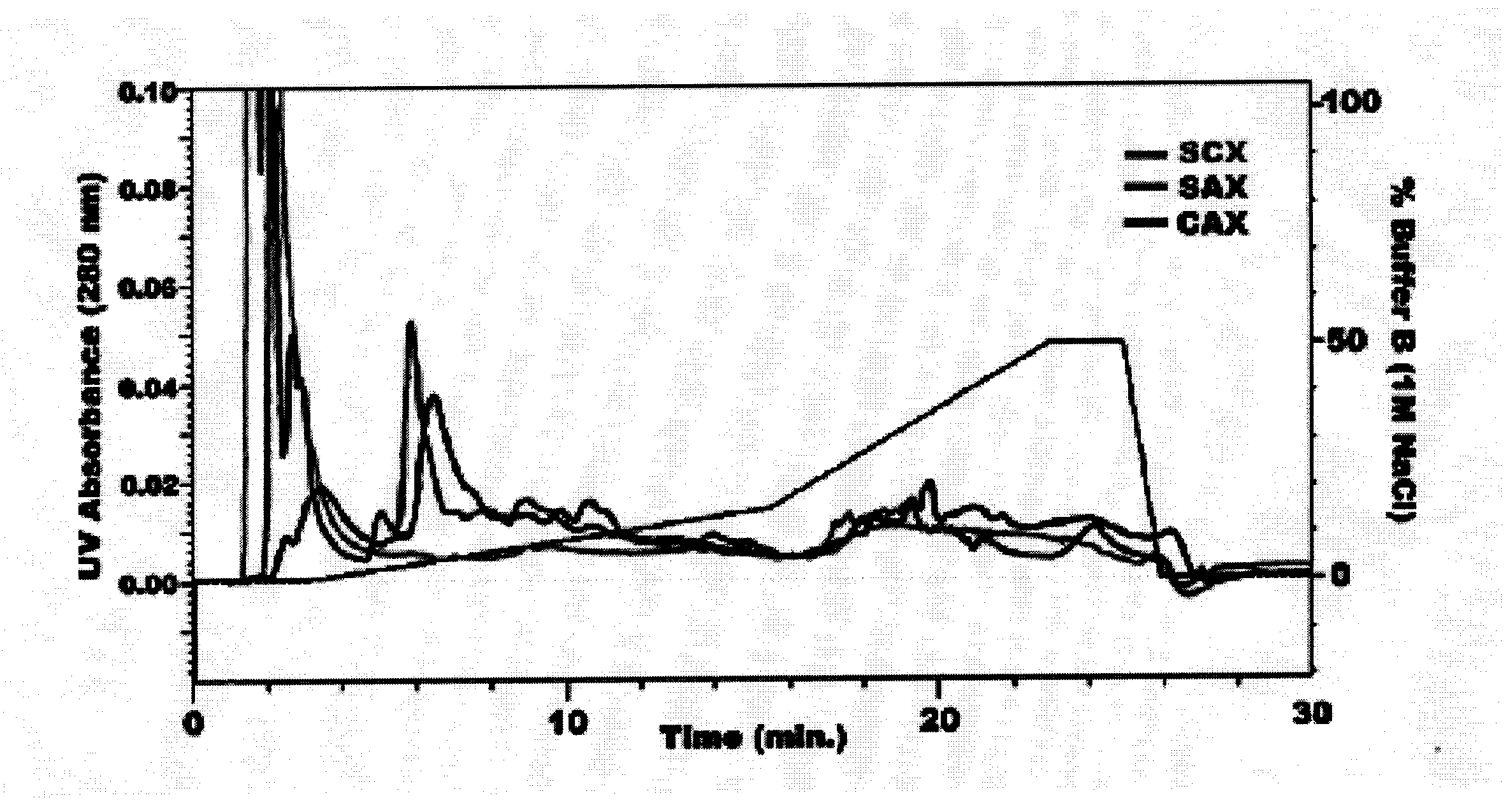
Multidimensional protein separation
InactiveUS20070238864A1Improve visualizationHigh resolutionPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesIon exchangeDifferential analysis
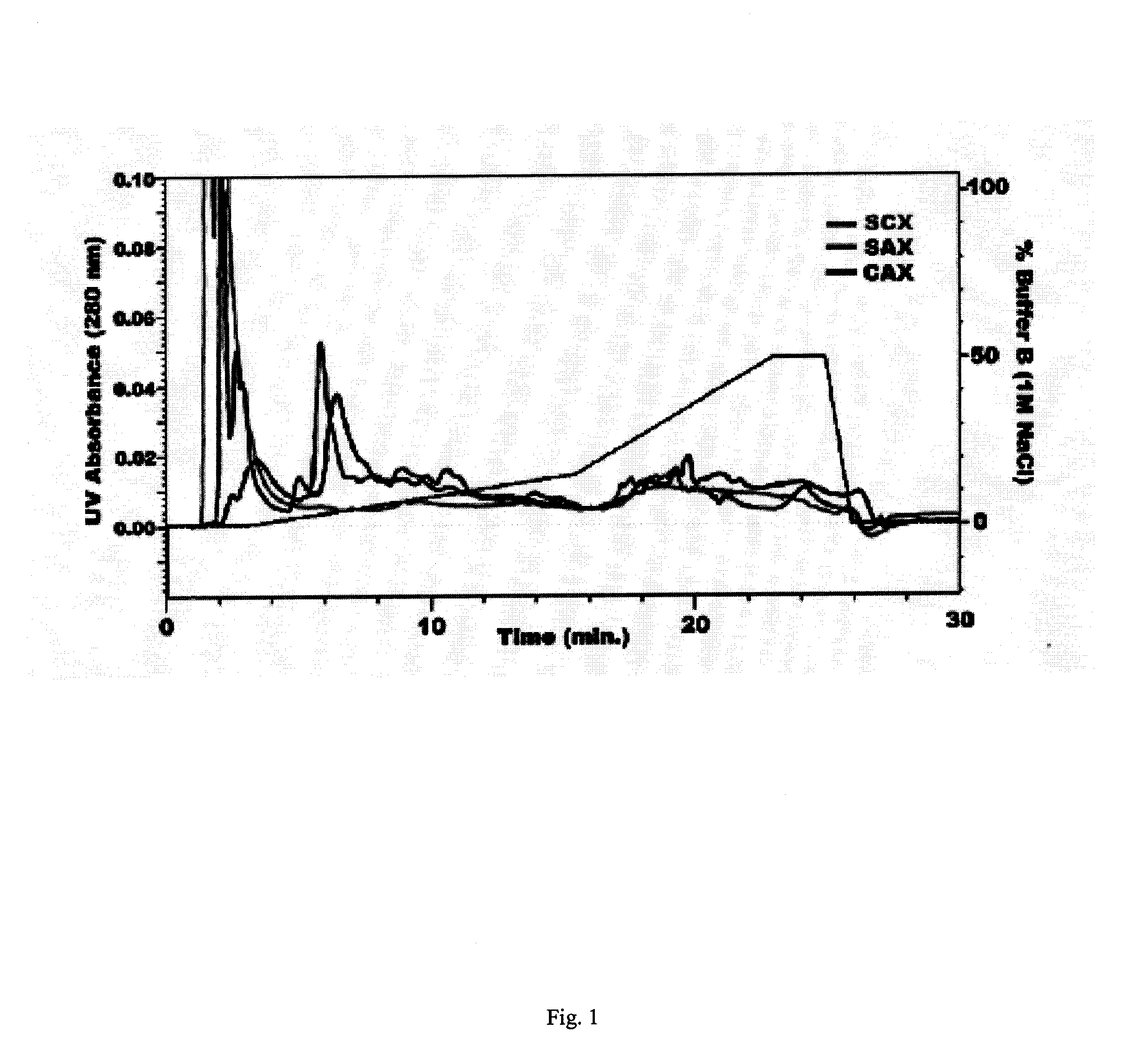
In large scale proteome applications, protein separation is paramount to observing discrete changes and quantitative evaluation must coincide with qualitative protein identification for effective differential analysis. A four dimensional (4D) platform for resolving and differentially analyzing complex biological samples is presented. The system, collectively termed CAX-PAGE / RPLC-MSMS, combines bi-phasic ion-exchange chromatography (1st dimension) and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2nd dimension) for protein separation, quantification and differential band targeting leading toward subsequent capillary reverse phase liquid chromatography (3rd dimension) and data dependant tandem mass spectrometry (4th dimension) for semi-quantitative and qualitative peptide analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Mass Spectrometry of Arginine-Containing Peptides
InactiveUS20080138909A1Simplification of sequence spaceIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProtonationArginine
Peptides can be derivatised such that, when ionised and analysed by mass spectrometry, those containing arginine residues give characteristic peak patterns. Peaks corresponding to arginine-containing peptides can therefore be selected from a mass spectrum in order to simplify and improve peptide analysis. Suitable labels give derivatised peptides that have the ability to form both a stabilised ion species ([P]+) and a protonated ion molecular species ([P+H]+) that differ by one average mass unit. A characteristic peak pattern is seen.
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH IP
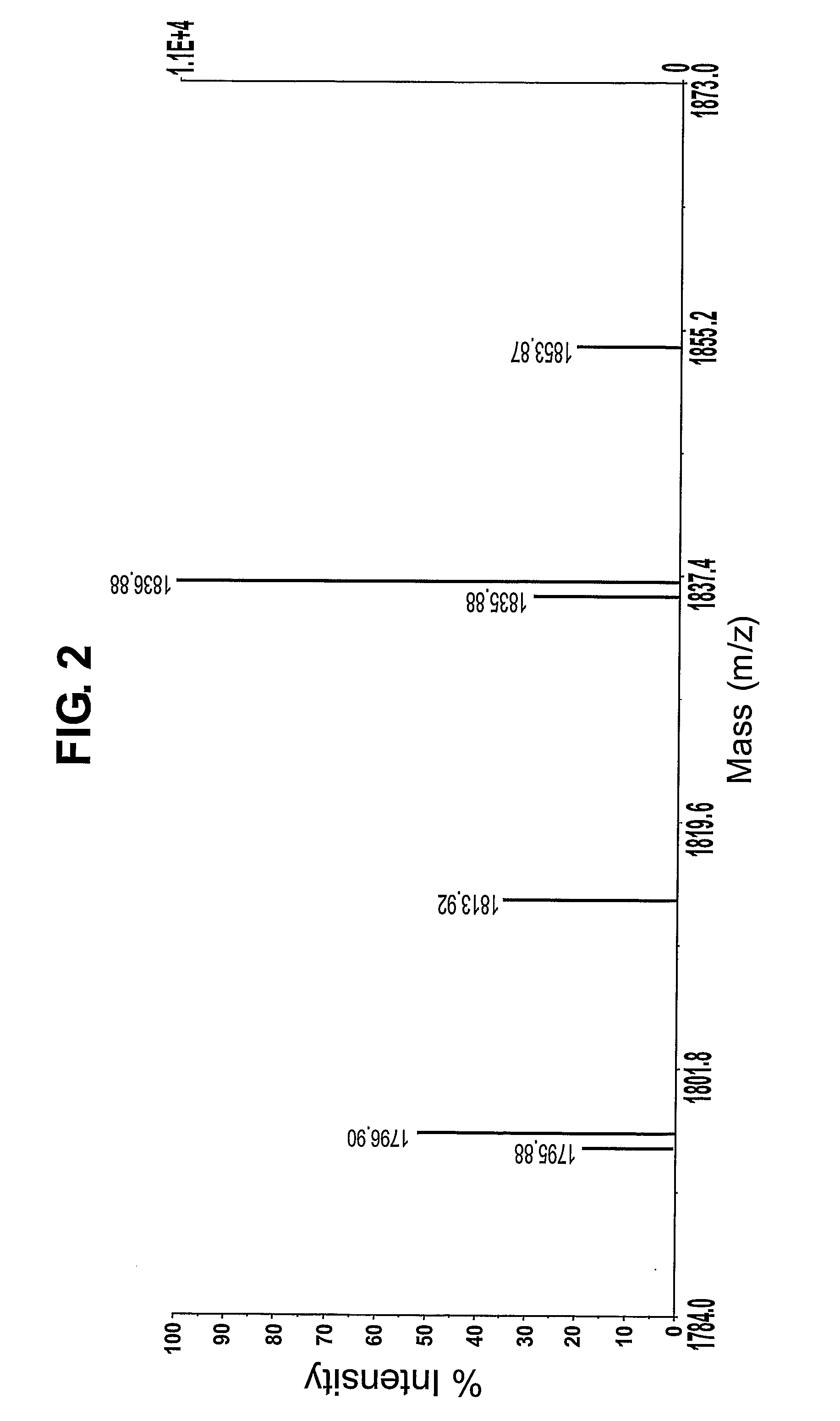
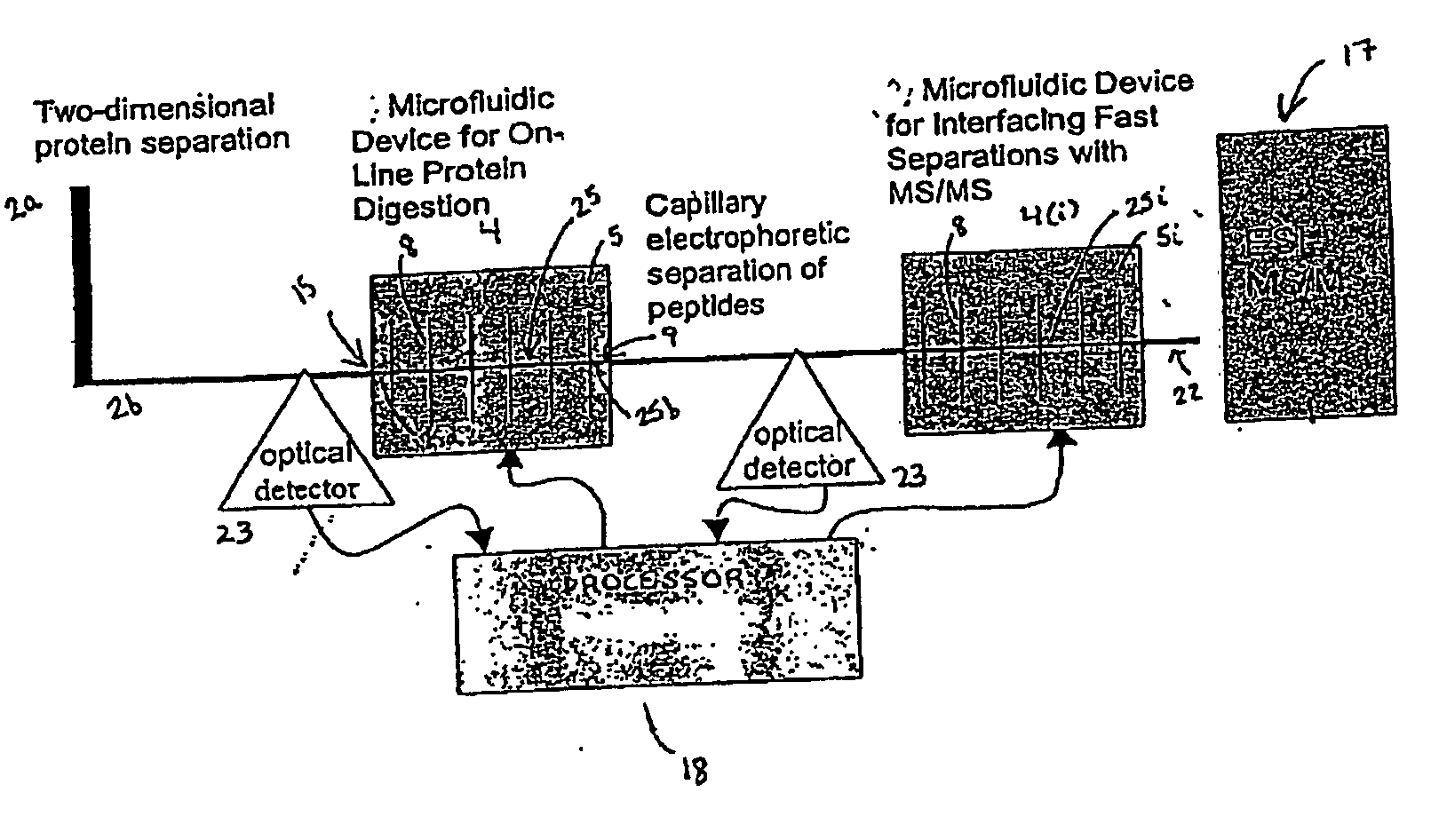
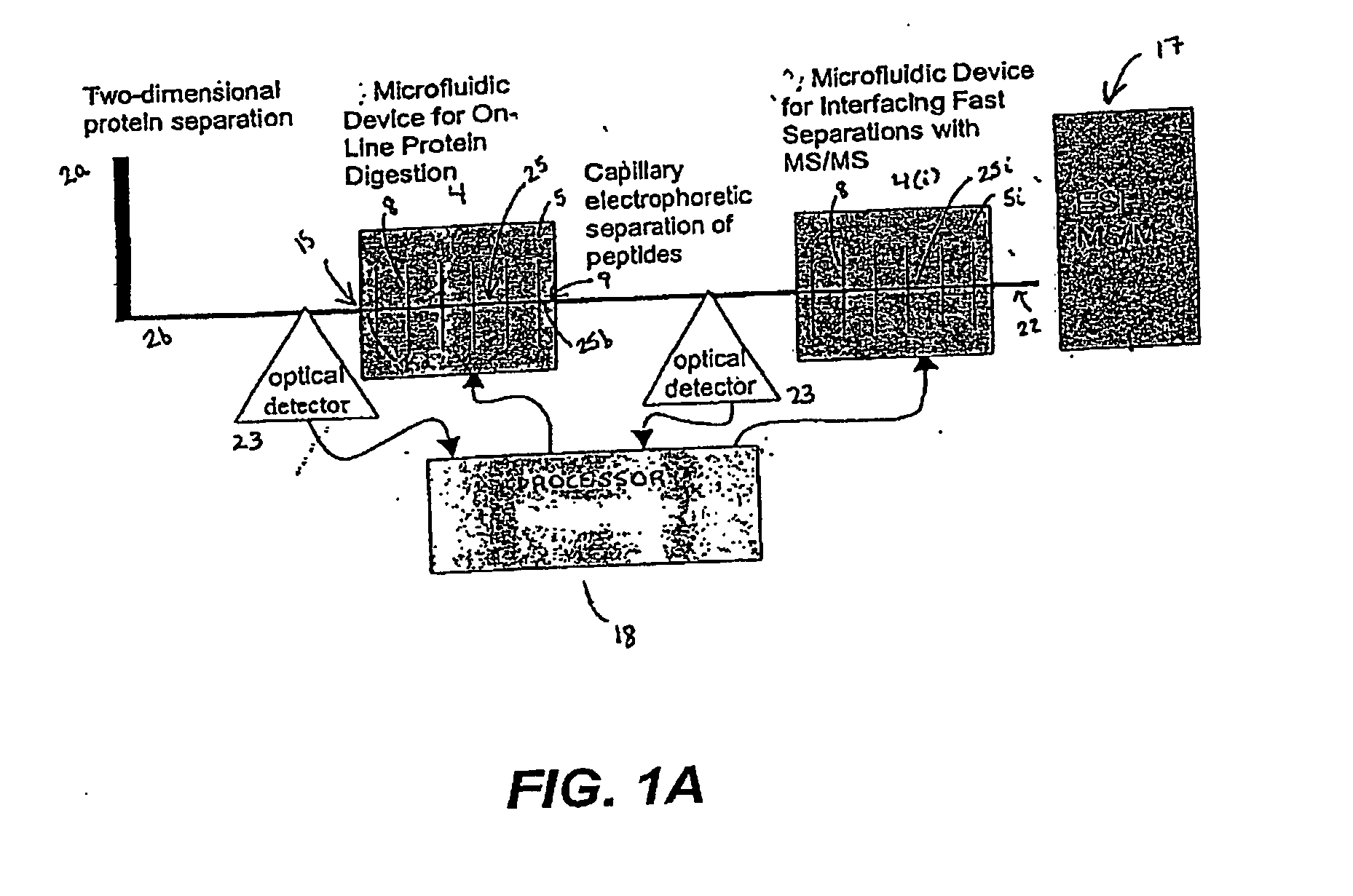
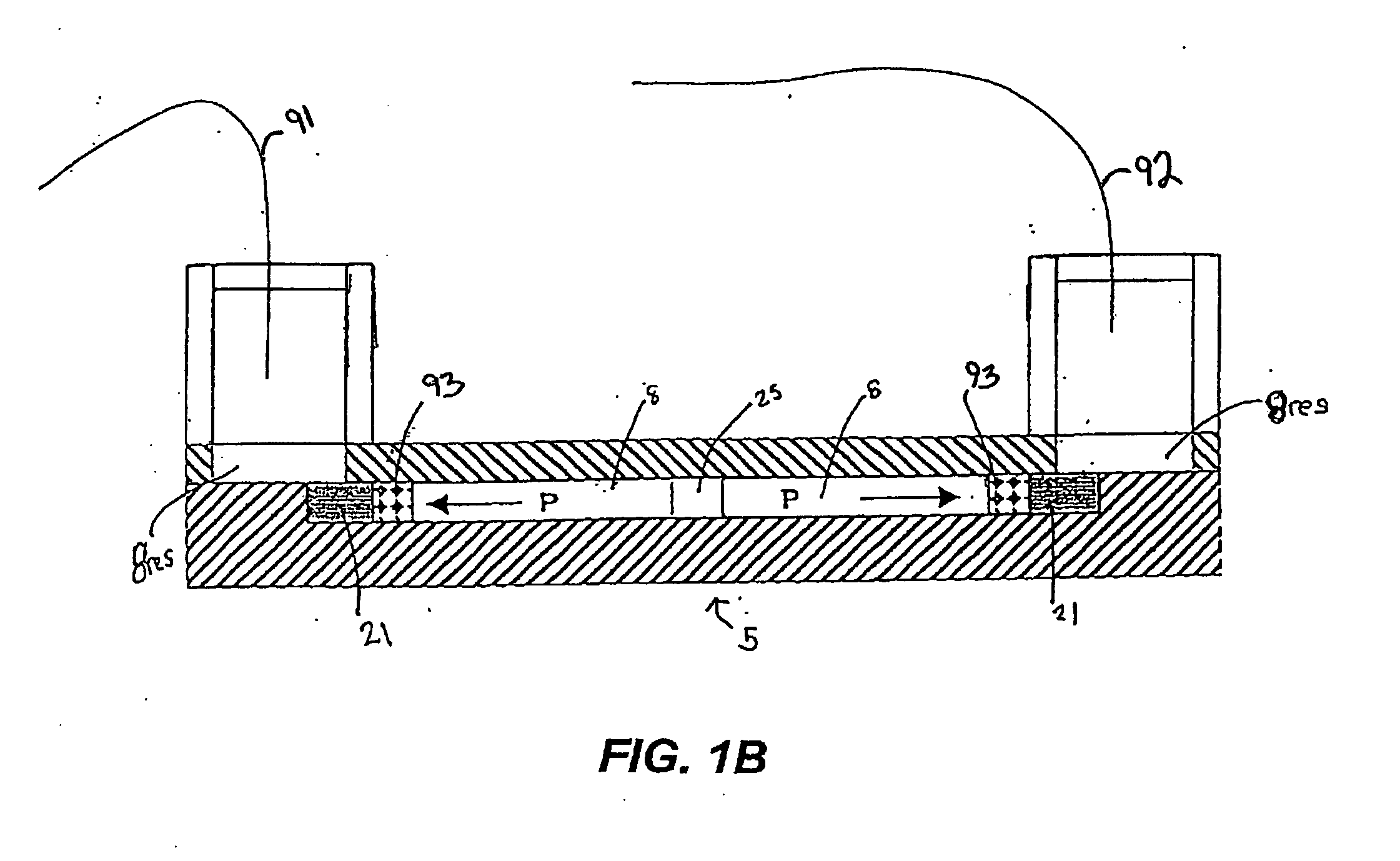
Microfluidic system for proteome analysis
InactiveUS20080076143A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioApparatus sterilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementCell signaling pathwaysMulti dimensional
The invention provides a microfluidic system and method to rapidly analyze large numbers of compounds or complex mixtures of compounds, particularly, low abundance cellular proteins involved in cell signaling pathways. In one aspect, an integrated microfluidic system comprises an upstream separation module (preferably, a multi-dimensional separation device), a microfluidic device for on-device protein digestion of substantially separated proteins received from the upstream separation module, a downstream separation module for separating digestion products of said proteins, a peptide analysis module and a processor for determining the amino acid sequence of said proteins. Preferably, the system comprises an interfacing microfluidic device between the downstream separation module and the peptide analysis module.
Owner:PROTEA BIOSCI
Labeling Agent and Methods for Simultaneous Sequencing and Quantification of Multiple Peptides and Proteins Using the Same
InactiveUS20130183704A1Increase intensityHigh mass valueMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsAnalyteTandem mass spectrometry
The present invention provides a compound that can utilize hydrogen isotope and, at the same time, can quantify multiplexed samples at one time, as well as decreasing the cost for synthesis of the labeling agent. In addition, the present invention provides a novel method for quantitatively analyzing protein and peptide analytes having different quantities form each other using the labeling agent, wherein y-type fragment ions having a high mass which comprises the analyte remained after coupling the labeling agent with the analyte and then removing a part of the labeling agent through tandem mass spectrometry are utilized to conduct the quantitative analysis.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Methods for peptide analysis employing multi-component detection agent and related kits
The present disclosure relates to methods and kits for analysis of peptides, polypeptides and proteins, employing a multi-component detection agent(s). In some embodiments, the method is useful for identifying the terminal amino acid of the peptide. In some embodiments, the multi-component detection agent includes a first detection agent and second detection agent which, when in proximity, is capable of generating a detectable signal.
Owner:ENCODIA INC
System and method for absolute quantitation of proteins using lc/ms
ActiveUS20090306901A1Reduce errorsBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsConversion factorLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
Absolute quantitation of protein in a sample is provided by comparing a sum or average of the N highest ionization intensities observed for peptides of a particular protein along with a calibration standard. The calibration standard can be in the form of a table generated by prior protein peptide analysis performed using one or more pre-determined proteins. The comparison is used to determine a corresponding absolute quantity of protein based on the observed sum or average of ionization intensities. A simple conversion factor can be applied to the calibration standard value to determine the absolute quantity of protein in the sample.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Method and Kit for Peptide Analysis
InactiveUS20080293083A1High resolution and reproducibilityEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryReagent
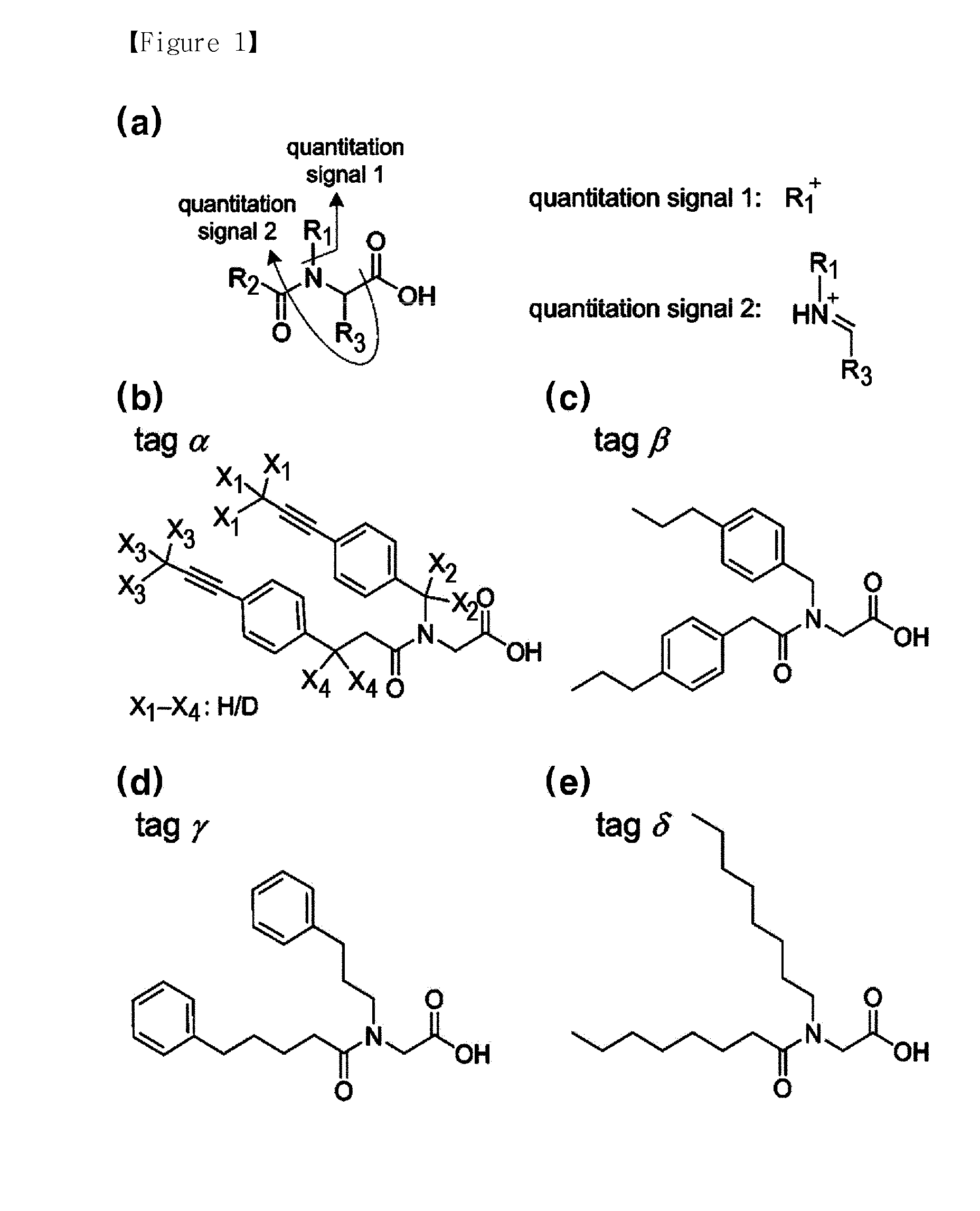
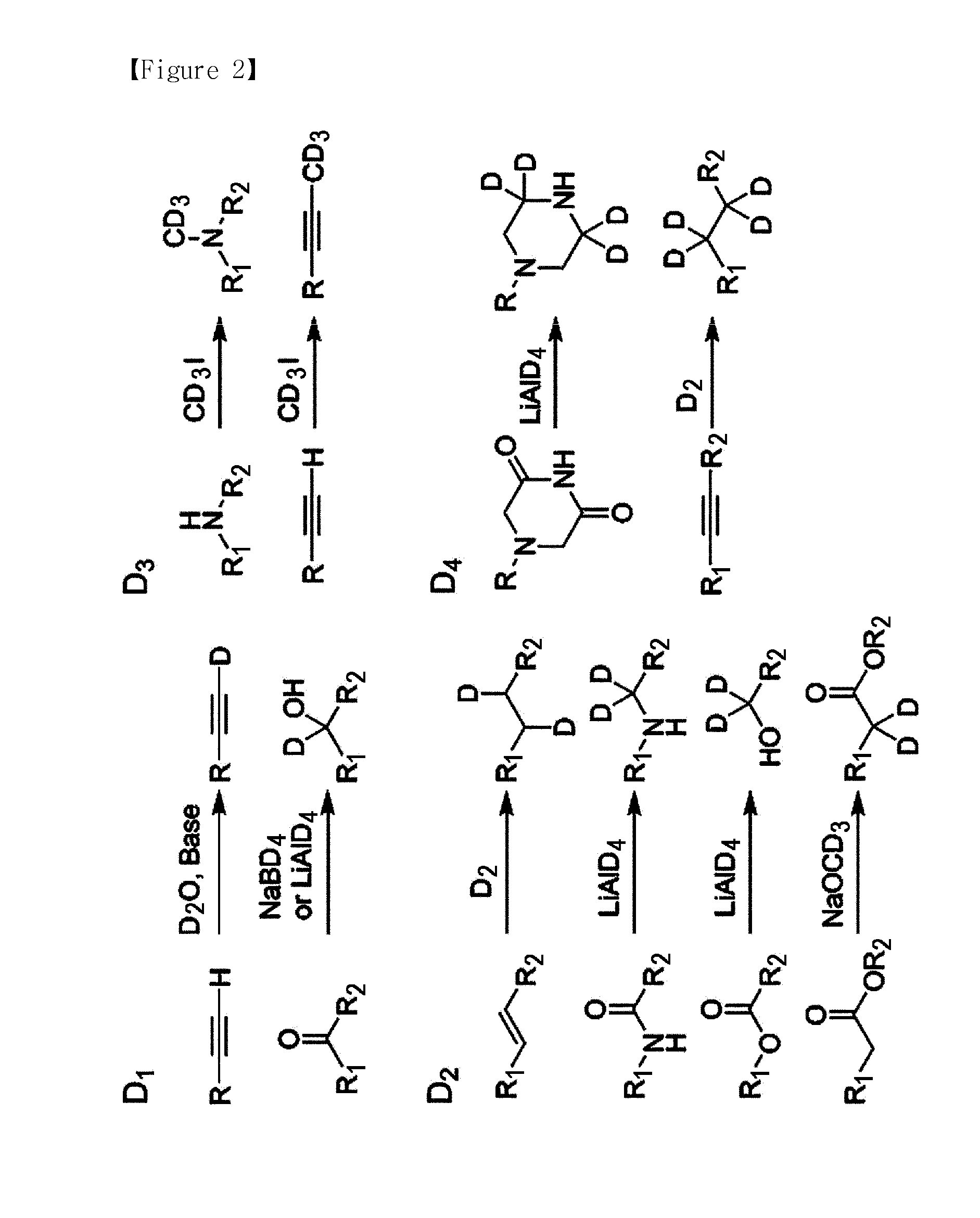
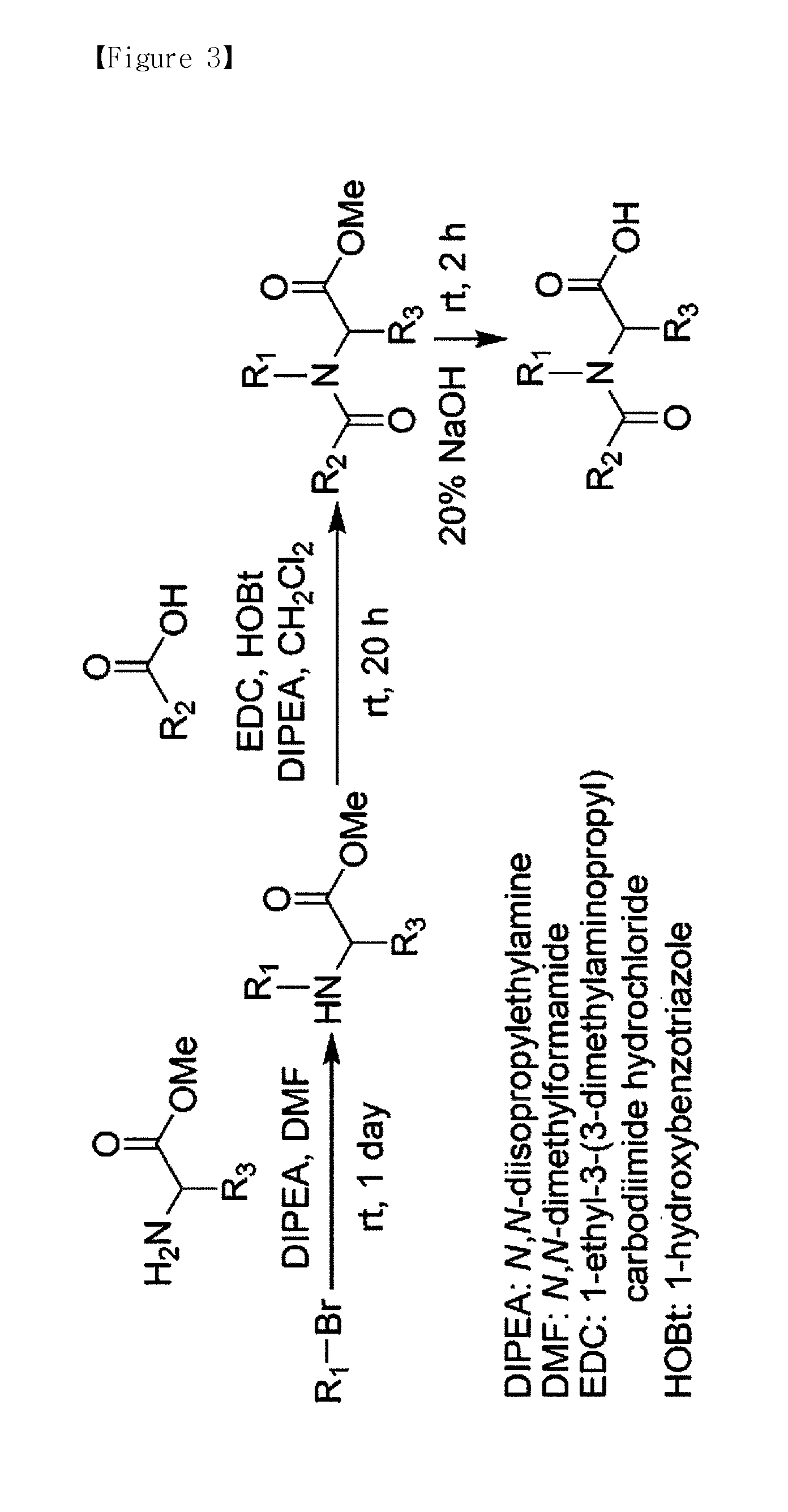
The present invention relates to a method for peptide analysis, comprising the following steps: a) tagging N-terminals of peptides in sample(s) with mass tagging reagent(s) and mass balancing C-terminals of said peptides with mass balancing reagent(s), or vice versa; and b) mass spectrometry analysis of said peptides. The present invention also relates to a kit with global mass tagging reagents and mass balancing reagents for use in said method and a database with specific peptide information.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Sulfenyl compound, labeling reagent, and method of analyzing peptide
InactiveUS20050221413A1High purityImprove hydrophobicityOrganic chemistry methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementLeaving groupIsotopic labeling
A sulfenyl compound represented by the general formula: R—S—X (I)(wherein R represents an organic group having at least one constituent element labeled with an isotope, and X represents a leaving group); a labeling reagent comprising it; and a method of analyzing peptide using the labeling reagent. Preferably the organic group R comprises C, H, and N, and optionally O and / or P as the constituent element, and the isotope is a stable isotope selected from the group consisting of 2H, 13C, 15N, 17O, and 18O.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
C-terminal modification peptide analysis method
ActiveCN106928313AEasy to operateHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionCombinatorial chemistryProtecting group
The invention provides a C-terminal modification peptide analysis method. The method is characterized by including steps: 1) coupling an amino at one end of a diamino compound to solid-phase synthesized resin; 2) adopting an Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis strategy to sequentially couple amino acids to an amino at the other end of the diamino compound so as to obtain fully-protected polypeptide resin; 3) splitting fully-protected polypeptides from resin to obtain the fully-protected polypeptides; 4) removing protecting groups from the fully-protected polypeptides to obtain targeted C-terminal modification peptides; or 5) coupling the fully-protected polypeptides with carboxylic modification groups to obtain the targeted C-terminal modification peptides. The C-terminal modification peptide analysis method has advantages of simplicity in operation, energy saving, environmental friendliness, yield increase and the like.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
Glycopeptide analyzer
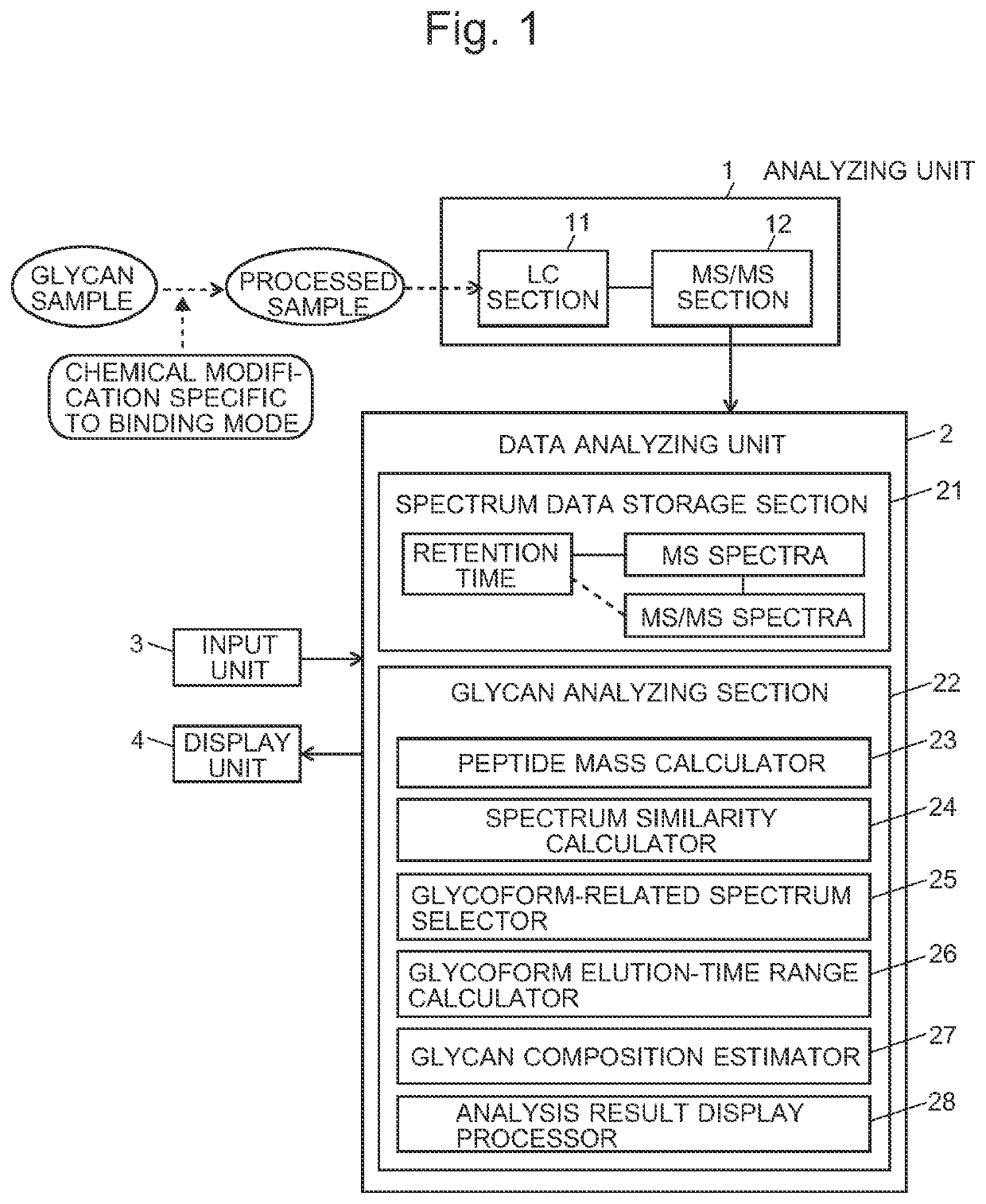
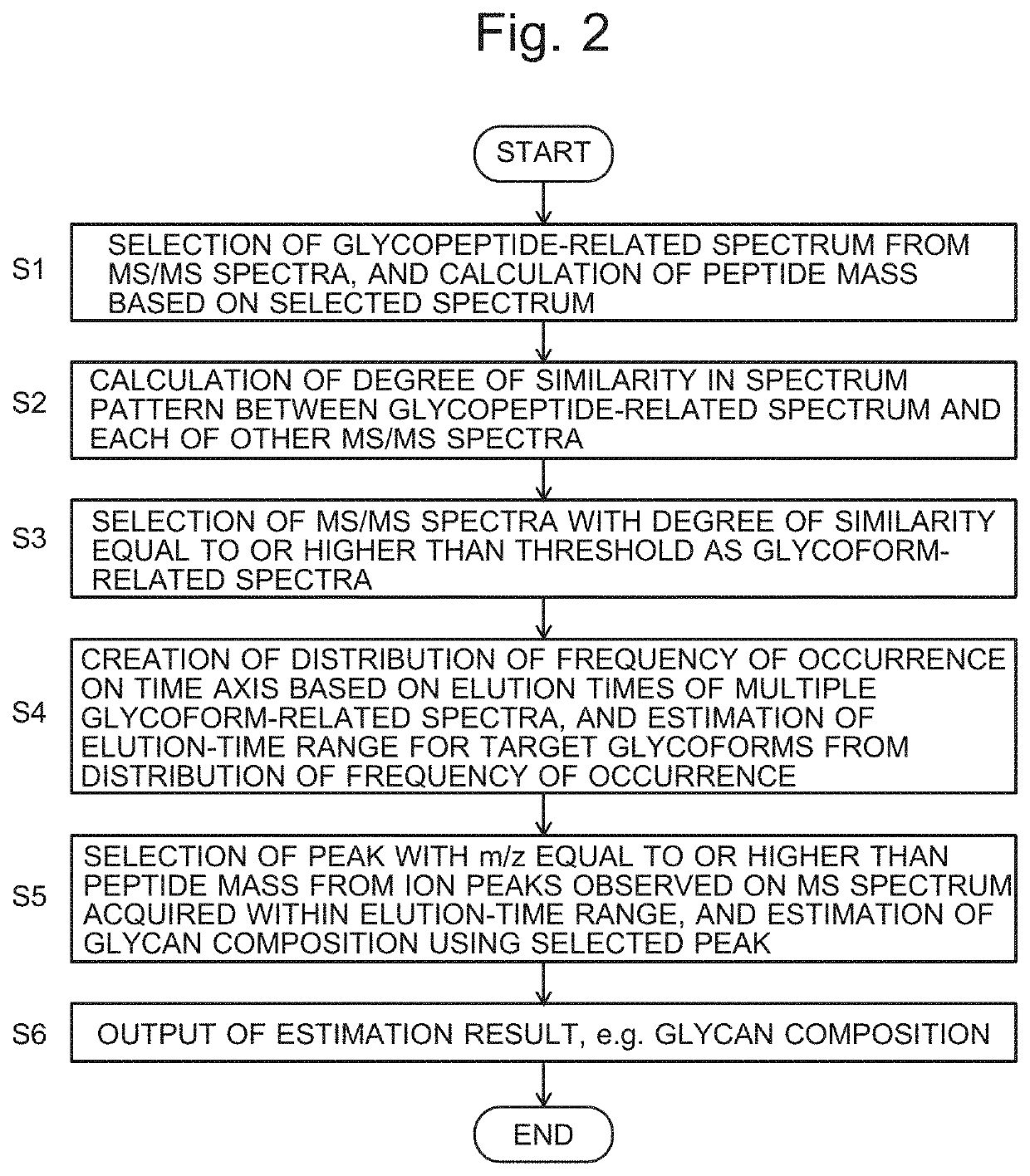
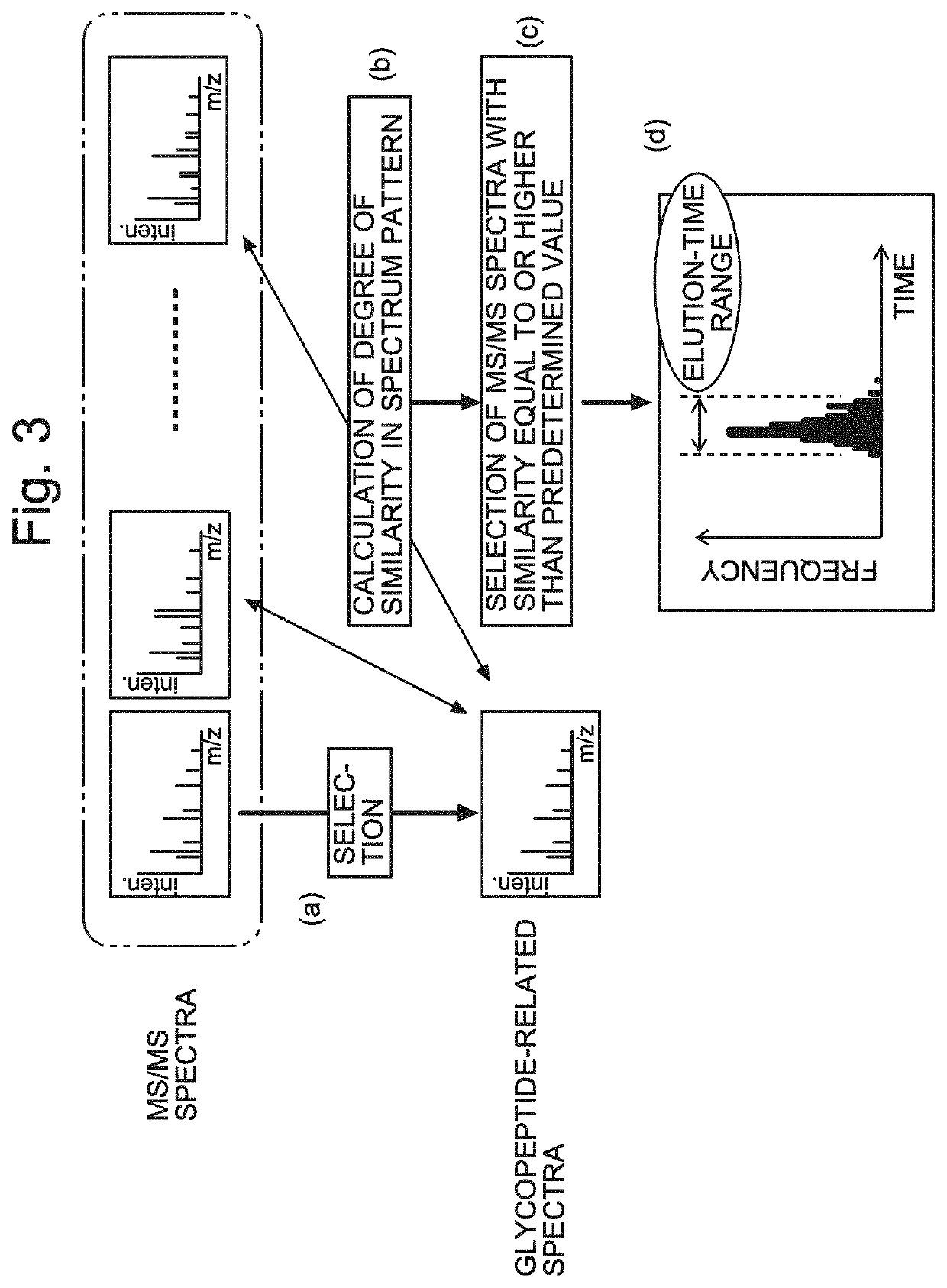
ActiveUS20210208117A1High similarityImprove the level ofComponent separationMass spectrometric analysisStructure analysisGlycan
A glycopeptide analyzer that performs a structural analysis on glycoforms of a glycoprotein, including: a spectrum creator creating an MS / MS spectrum for each elution time based on data acquired by an LC / MS analysis of a sample containing glycopeptides originating from a target glycoprotein; a peptide mass calculator selecting a glycopeptide-related spectrum from a plurality of MS / MS spectra and calculating the mass of a peptide from the selected spectrum; a similarity determiner determining a similarity between the glycopeptide-related spectrum and each of the other MS / MS spectra; an elution-time range estimator estimating an elution-time range based on a distribution of the frequency of occurrence of an MS / MS spectrum for which a high level of similarity has been determined on a time axis; and a glycan composition estimator selecting an ion peak corresponding to a mass equal to or greater than a peptide mass and estimating a glycan composition based on the peak.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Immunoaffinity isolation of modified peptides from complex mixtures
InactiveUS20110053242A1Readily automatableRapid, efficient, and direct isolation (and subsequent characterization)Peptide/protein ingredientsComponent separationTandem mass spectrometryPeptide
The invention provides methods for isolating a modified peptide from a complex mixture of peptides, the method comprising the steps of: (a) obtaining a proteinaceous preparation from an organism, wherein the preparation comprises modified peptides from two or more different proteins; (b) contacting the preparation with at least one immobilized modification-specific antibody; and (c) isolating at least one modified peptide specifically bound by the immobilized modification-specific antibody in step (b). The method may further comprise the step of (d) characterizing the modified peptide isolated in step (c) by mass spectrometry (MS), tandem mass spectrometry (MS-MS), and / or MS3 analysis, or the step of (e) utilizing a search program to substantially match the spectra obtained for the modified peptide during the characterization of step (d) with the spectra for a known peptide sequence, thereby identifying the parent protein(s) of the modified peptide. Also provided are an immunoaffinity isolation device comprising a modification-specific antibody, and antibodies against novel UFD1 and PTN6 phosphorylation sites.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Method for rapidly analyzing protein and strong-polarity long amino acid sequence glycopeptides in biological sample
ActiveCN110441428AHigh enrichment and identification efficiencyHigh enrichment efficiencyComponent separationProtein proteinPeptide
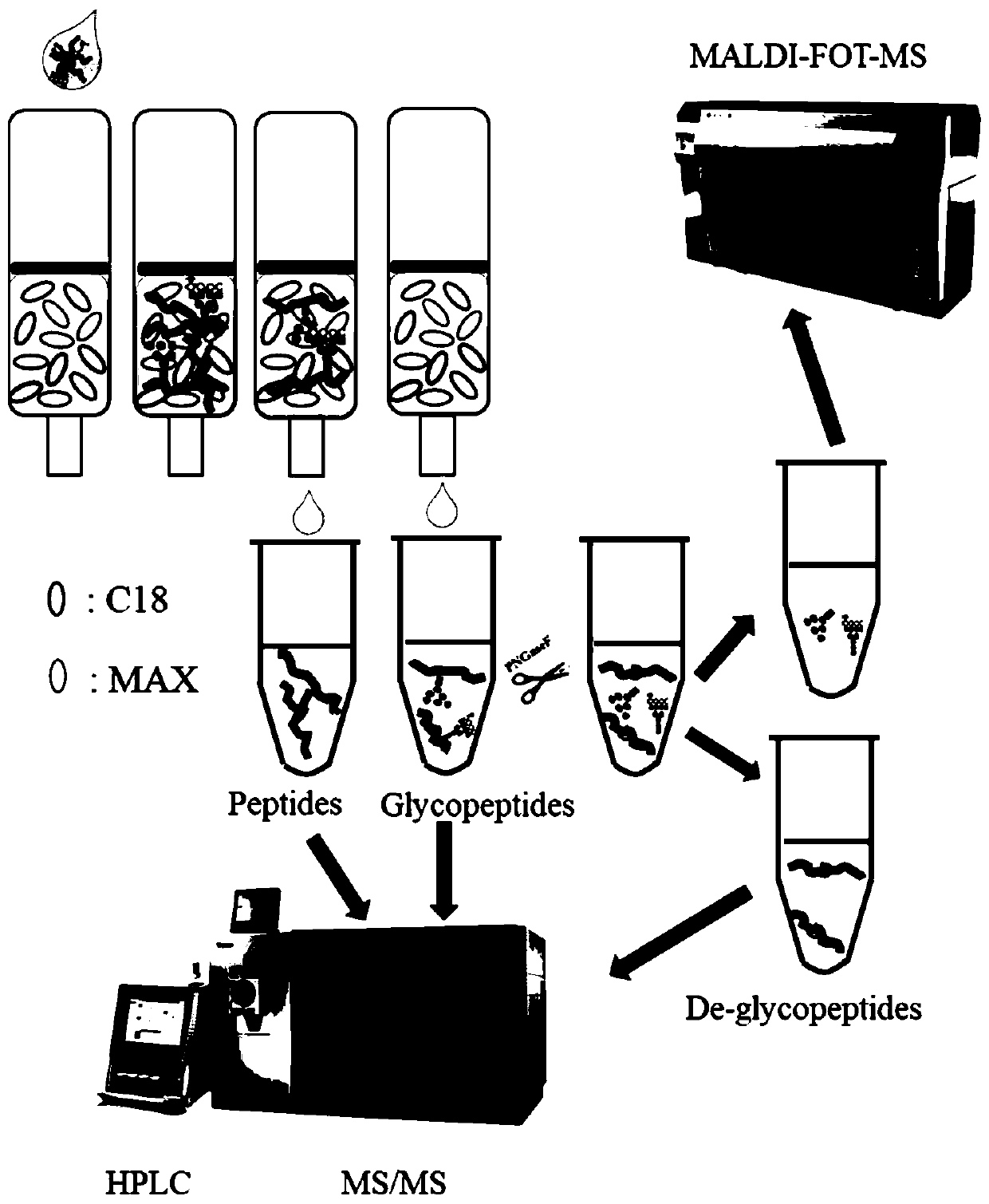
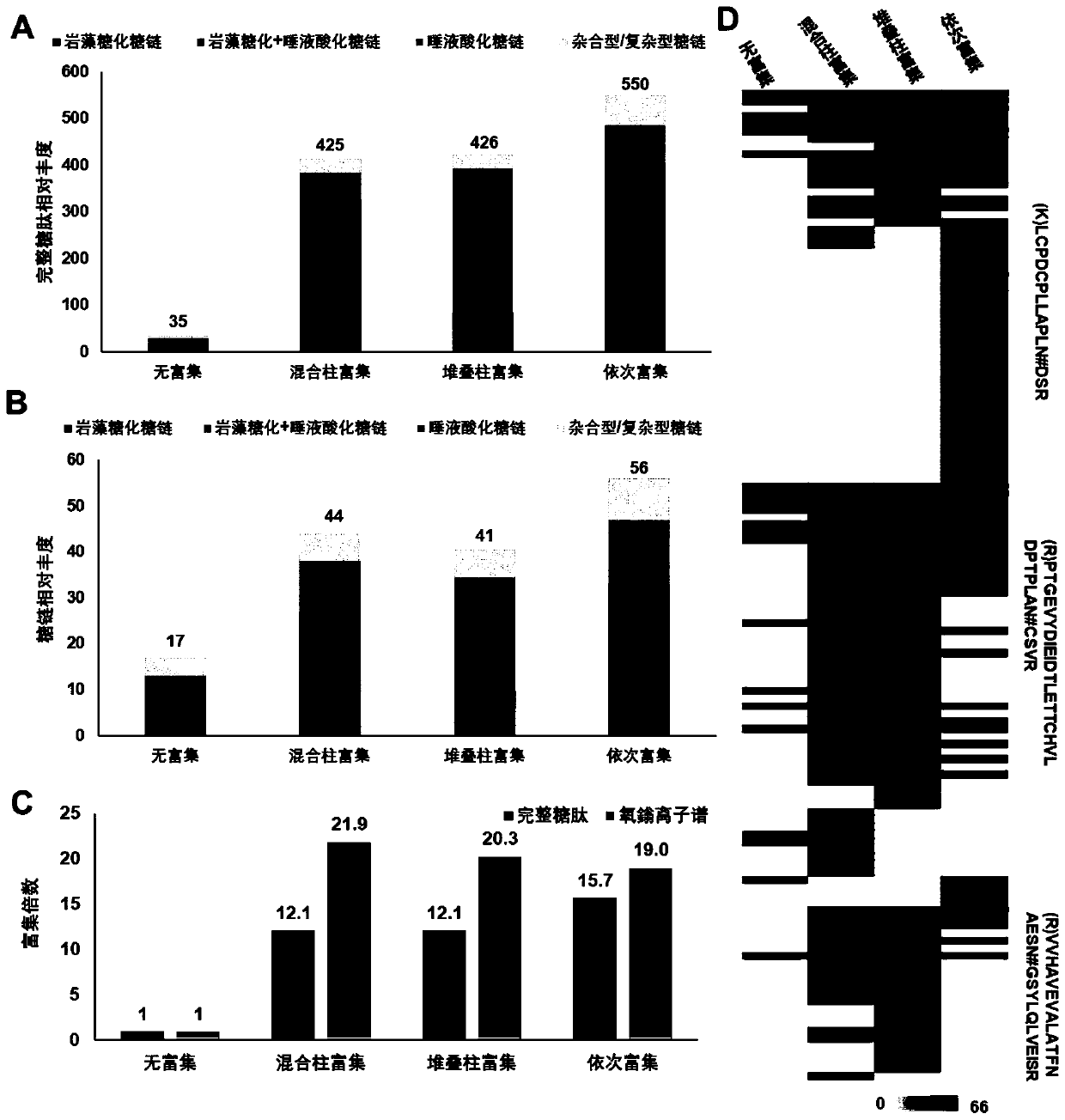
The invention discloses a method for rapidly analyzing protein and strong-polarity long amino acid sequence glycopeptides in a biological sample. The method comprises the following steps of preparingsample protein; preparing a mixed chromatographic column through a one-step enrichment method: mixing C18 and MAX filler to prepare the mixed chromatographic column; carrying out protein digesting; carrying out glycopeptides enriching: enriching glycopeptides by using the mixed chromatographic column; and carrying out LC-MS / MS analysis. According to the one-step enrichment method disclosed by theinvention, the enrichment and identification efficiencies of the glycopeptides with long sequence and stronger polarity are very high; and compared with a traditional sample preparation method, the method disclosed in the invention requires less sample preparation process and time, and only requires less than one hour of the preparation time before mass spectrometry analysis.
Owner:无锡麦迪科思生物科技有限公司
Tandem paired column chemistry for high-throughput proteomic exosome analysis
The present application provides compositions and methods for sample preparation and mass spectrometry analysis of peptide samples obtained from biological samples. The compositions and methods include in-line column systems in which a trapping column is in fluid contact with an analytical column such as, for example, an HPLC column. As the analytes are eluted from the analytical column, they can be passed to a detector (eg, a mass spectrometer) for peptide analysis.
Owner:NX PRENATAL INC
Apparatus and method for multiplexed protein quantification
PendingUS20200408775A1Mass spectrometric analysisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryHydrolase
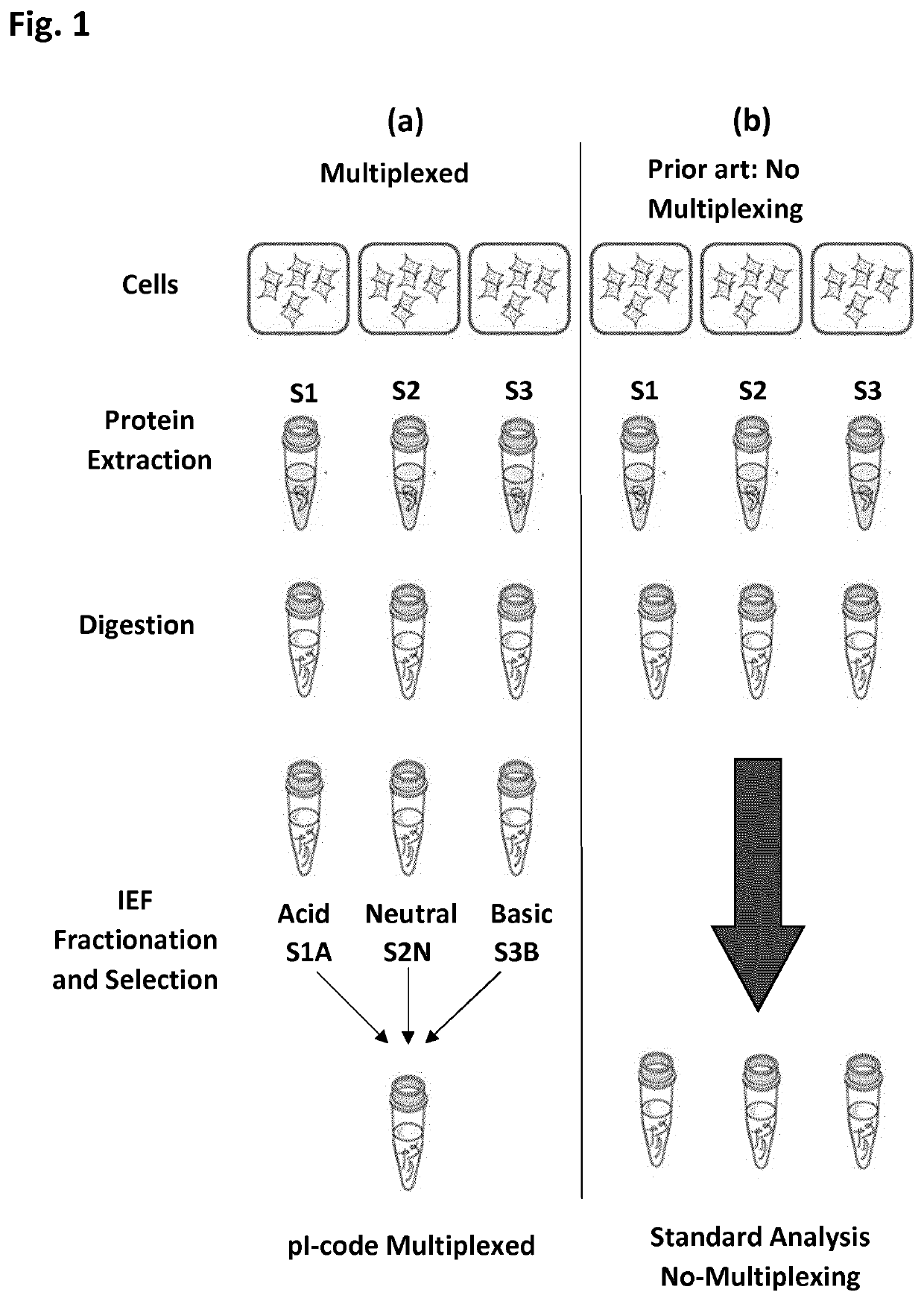
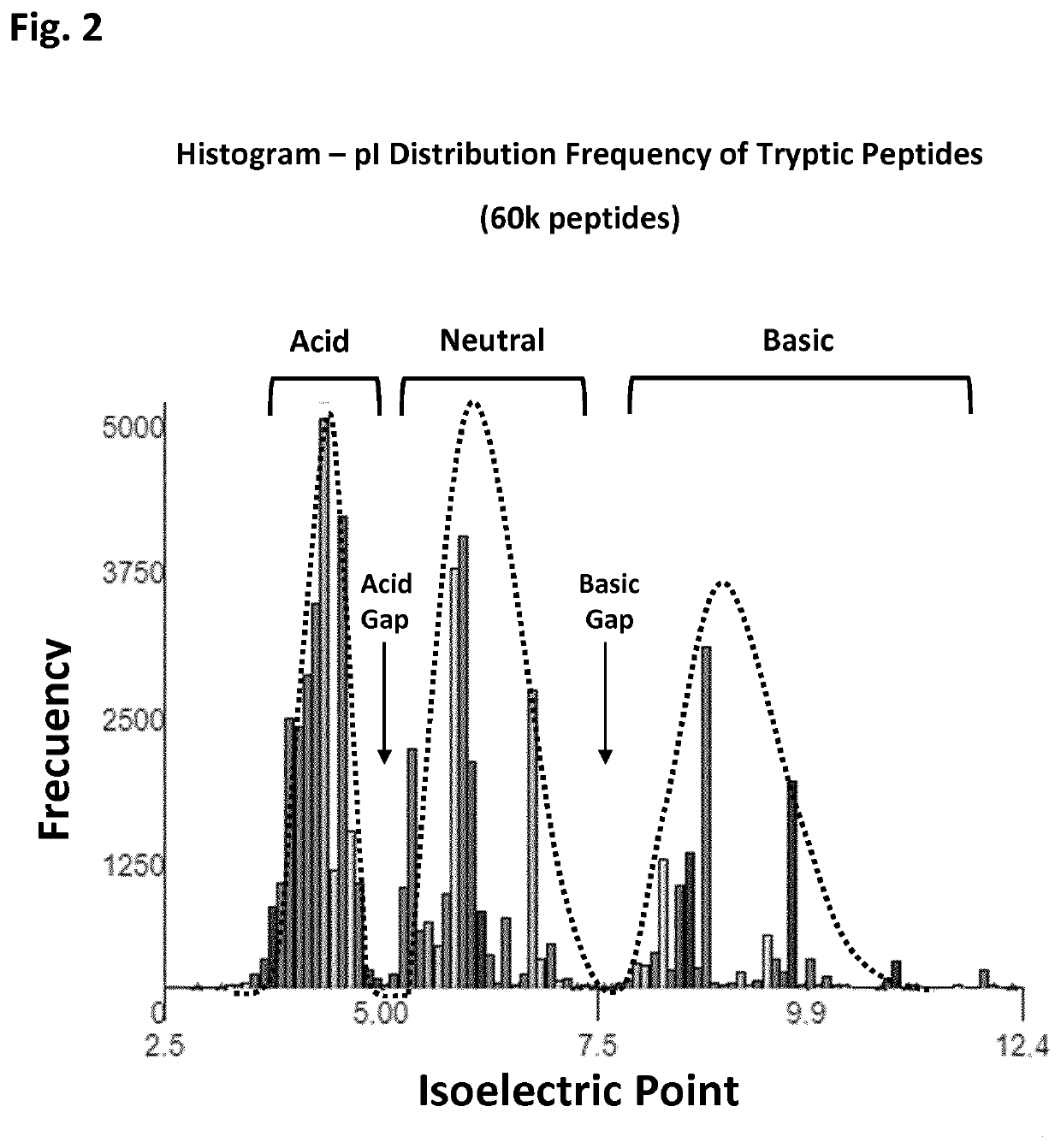
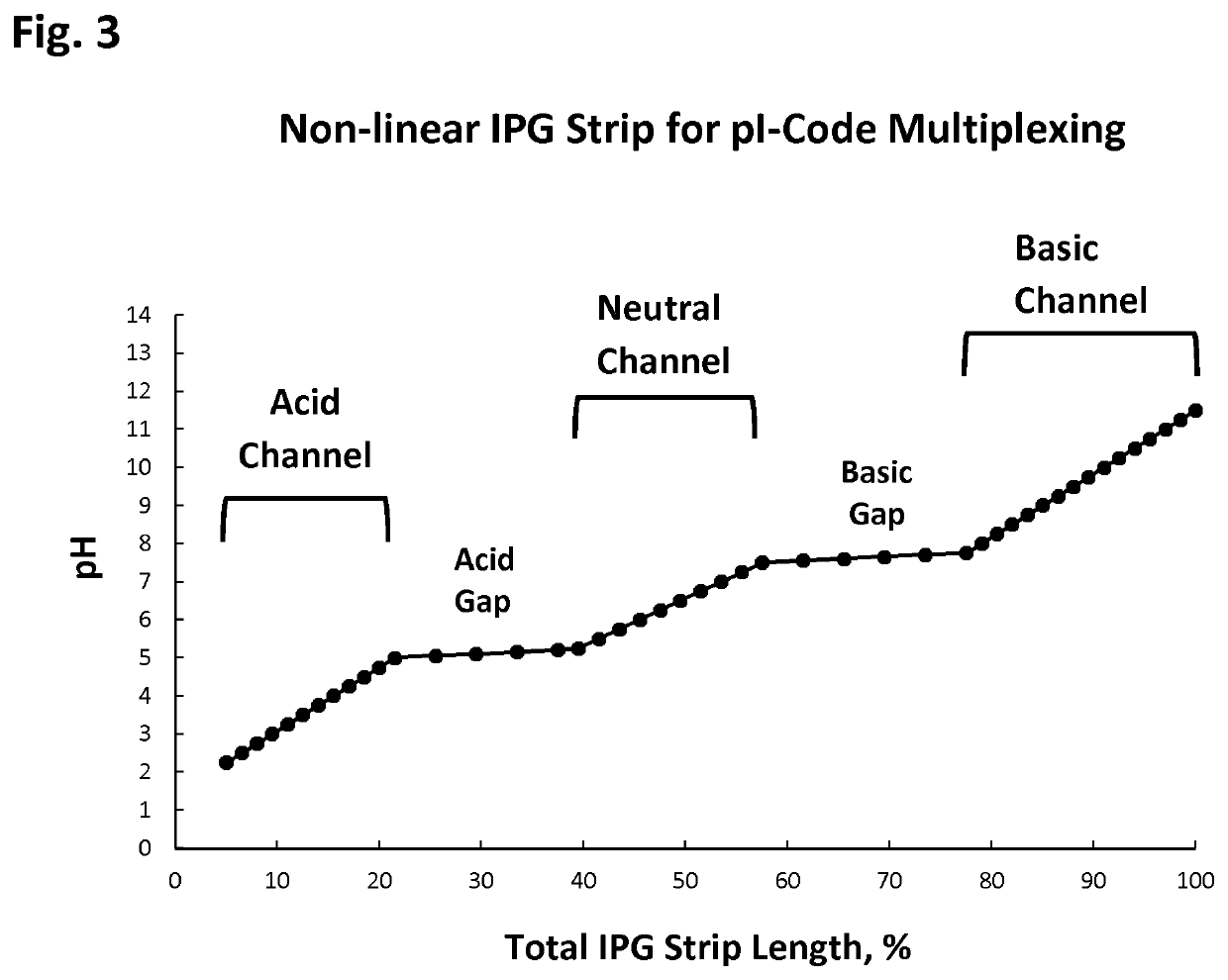
The present disclosure provides a method and apparatus for improvements of sample throughput in proteome analysis by mass spectrometry, by combining multiple non-overlapping isoelectric focusing separations. The method for performing an analysis of a plurality of protein samples, comprises: (a) Adding a proteolytic enzyme of a given specificity to a first protein sample to digest proteins to peptides; (b) Separating the peptides obtained in step (a) by isoelectric focusing; (c) Collecting those peptides which have their isoelectric point value within a first isoelectric point range; (d) Adding a proteolytic enzyme of a given specificity to a second protein sample to digest proteins to peptides; (e) Separating the peptides obtained in step (d) by isoelectric focusing; (f) Collecting those peptides which have their isoelectric point value within a second isoelectric point range, where said second isoelectric point range is different and non-overlapping compared to said first isoelectric point range; (g) Combining the peptides collected in steps (c) and (f) into a single sample and subjecting said sample to mass spectrometry analysis; (h) Deconvoluting signals / data obtained from the mass spectrometry analysis by calculating the isoelectric point of each peptide, and assigning a peptide to the first protein sample if its isoelectric point value matches the isoelectric point range selected in step (c) or to the second protein sample if its isoelectric point value matches the isoelectric point range selected in step (f); and (i) Obtaining quantitative information for proteins of each sample according to magnitude of the signal obtained from each peptide.
Owner:BIOMOTIF
Universal peptide tags for transgene polypeptide analysis by mass spectrometry
Compositions and methods that allow for the rapid detection and accurate quantification of any polypeptides of interest are provided. Compositions include isolated polypeptides comprising at least one universal peptide tag, as well as isolated polynucleotides encoding such polypeptides. The universal peptide tags can be quantified by methods including, but not limited to, mass spectrometry, and can act as surrogates for determining the concentration of the polypeptides comprising the universal peptide tags. Methods provide for the detection and / or quantification of any polypeptides of interest that comprise at least one universal peptide tag, including methods using mass spectroscopy techniques. Methods are also provided for producing hosts, or cells or parts thereof, that comprise polypeptides comprising at least one universal peptide tag. Hosts, or cells, or parts thereof, include mammalian, bacterial, insect, yeast, viral or plant.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
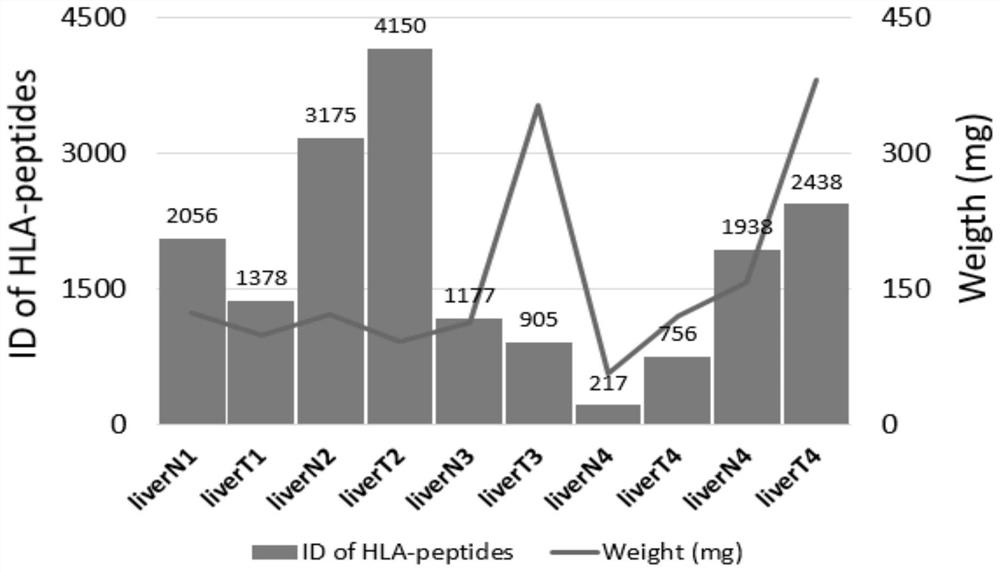
Analysis method for extracting immune polypeptide in biological sample based on immunoprecipitation method
PendingCN113945721AEfficient extractionImprove featuresMass spectrometric analysisBiological testingImmunoprecipitationPeptide fragment
The invention provides an analysis method for extracting immune polypeptide in a biological sample based on an immunoprecipitation method, and belongs to the technical field of immune polypeptide analys. The method comprises the steps that an immunoaffinity column is prepared through a cross-linking reagent, then lysate of the biological sample is subjected to immunoprecipitation, so that an HLA-peptide fragment compound is obtained through enrichment, and then simple two-step elution is conducted through a C18 small column. Impurity removal and desalination of the immune polypeptide can be achieved at the same time through the steps, recovered components can be subjected to mass spectrometric detection after being concentrated, efficient extraction of the immune polypeptide in biological samples such as cells and tissues can be achieved, the sample pretreatment process does not depend on complex instruments, purification and desalination of the immune polypeptide can be completed, and the time required for operation is greatly shortened.
Owner:上海中科新生命生物科技有限公司
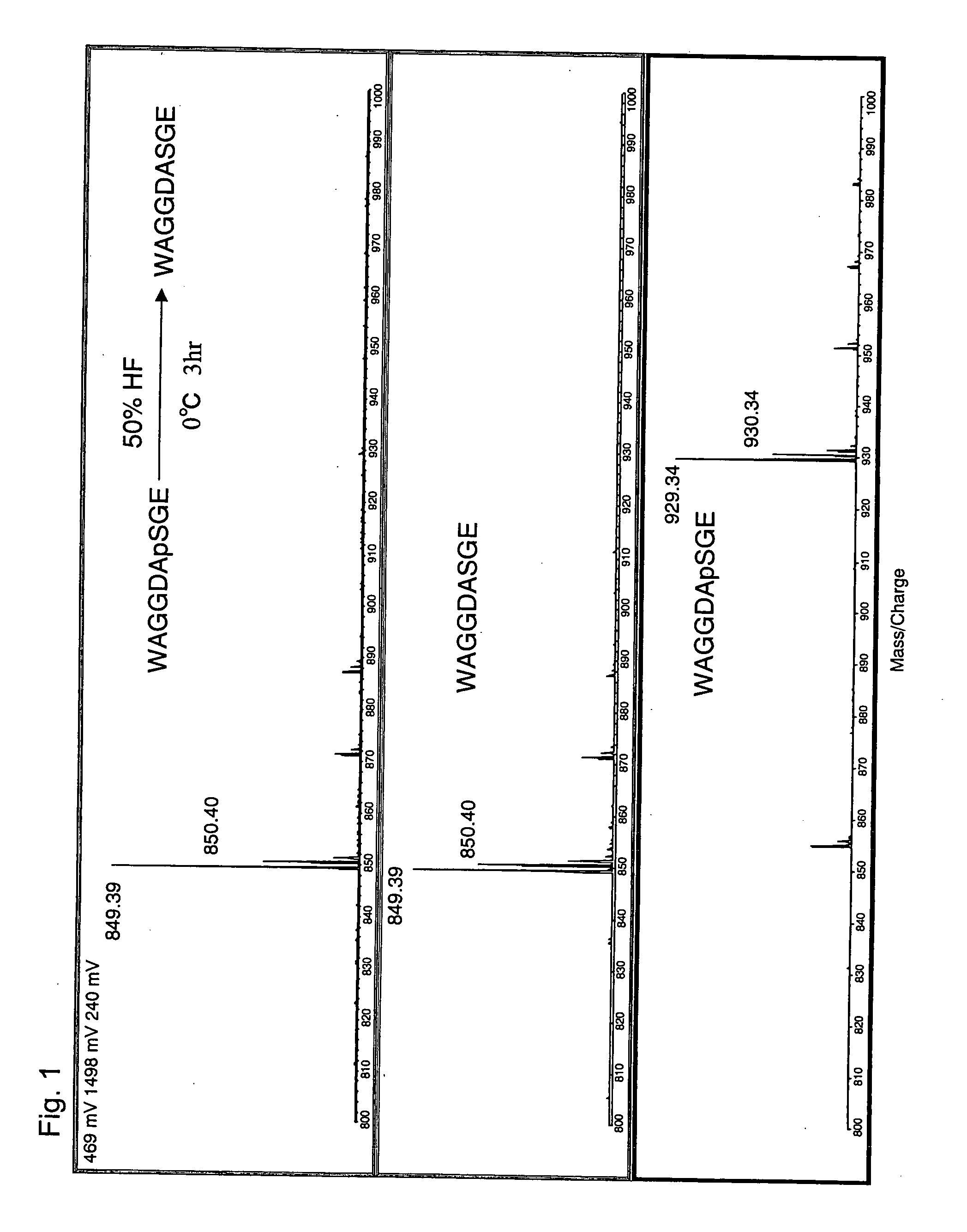
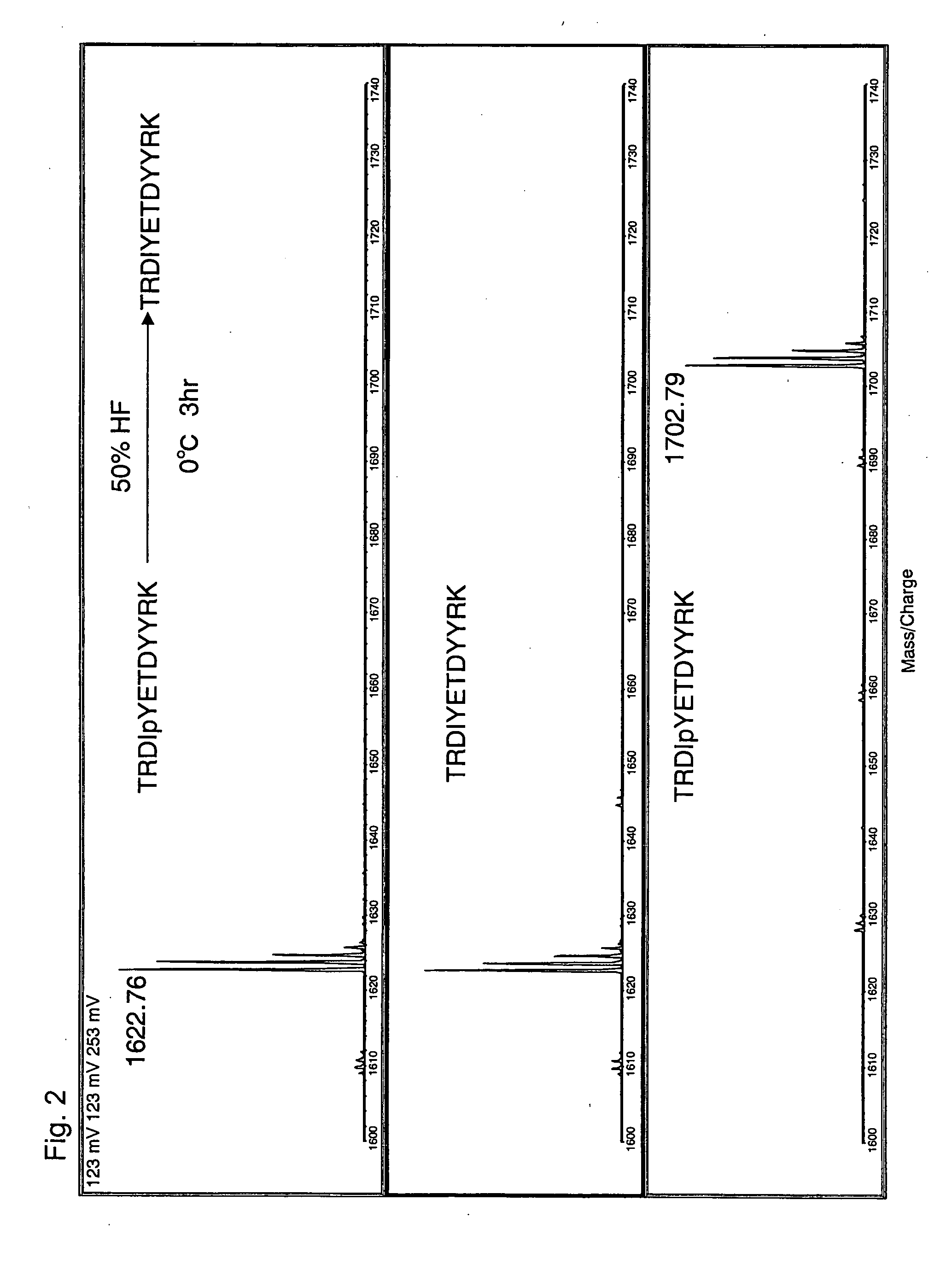
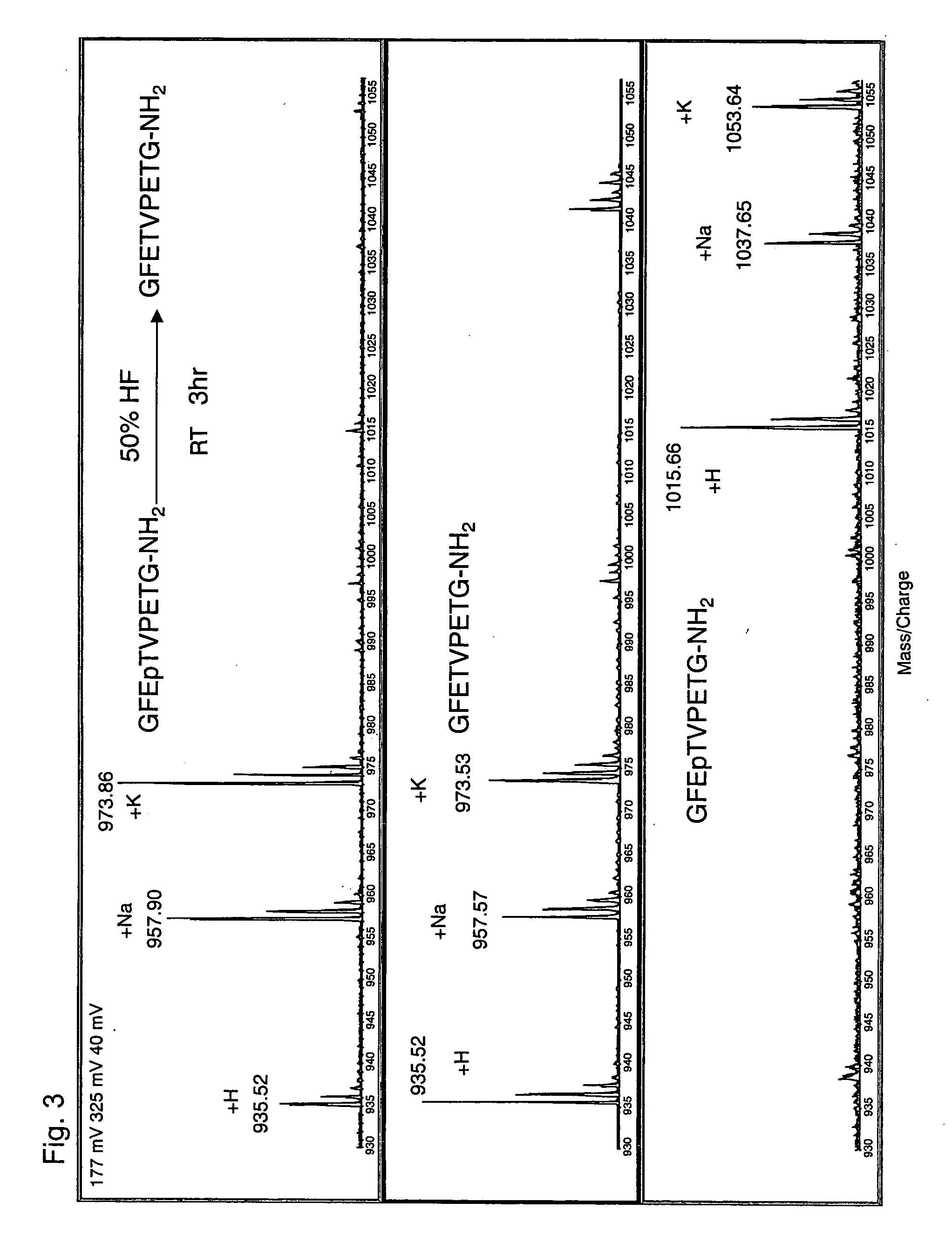
Method of eliminating phosphate group of peptide and method of analyzing peptide
InactiveUS20060046303A1Efficient methodSamplingPeptide preparation methodsHydrofluoric acidHydrogen fluoride
A method for eliminating a phosphate group of a peptide, the method comprising the use of a reagent containing at least one selected from the group consisting of hydrogen fluoride, hydrofluoric acid, and a hydrogen fluoride-containing compound, and a method for peptide analysis that uses such a method. As the hydrogen fluoride-containing compound, hydrogen fluoride-pyridine is preferably used. The elimination of the phosphate group from a peptide may be carried out so that the total amount of the hydrogen fluoride, hydrogen fluoride in the hydrofluoric acid, and hydrogen fluoride in the hydrogen fluoride-containing compound contain in the reagent is 10 to 100 wt % with respect to the reagent, and the temperature for the elimination reaction is −10 to 50° C.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method of synthesizing antagonist peptides for cell growth
ActiveUS10745454B2Improve purification effectImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisMatrigelCompetitive binding
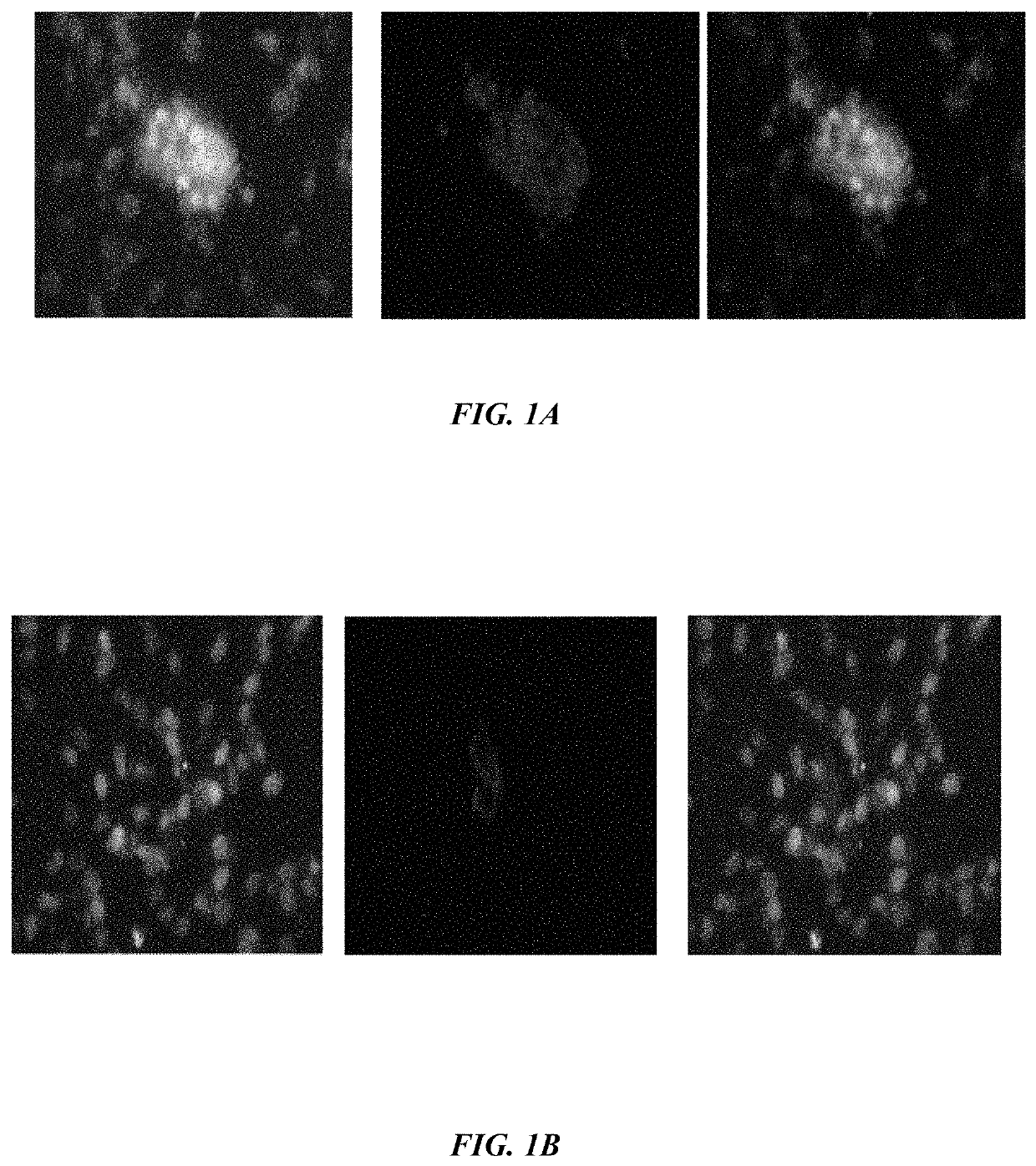
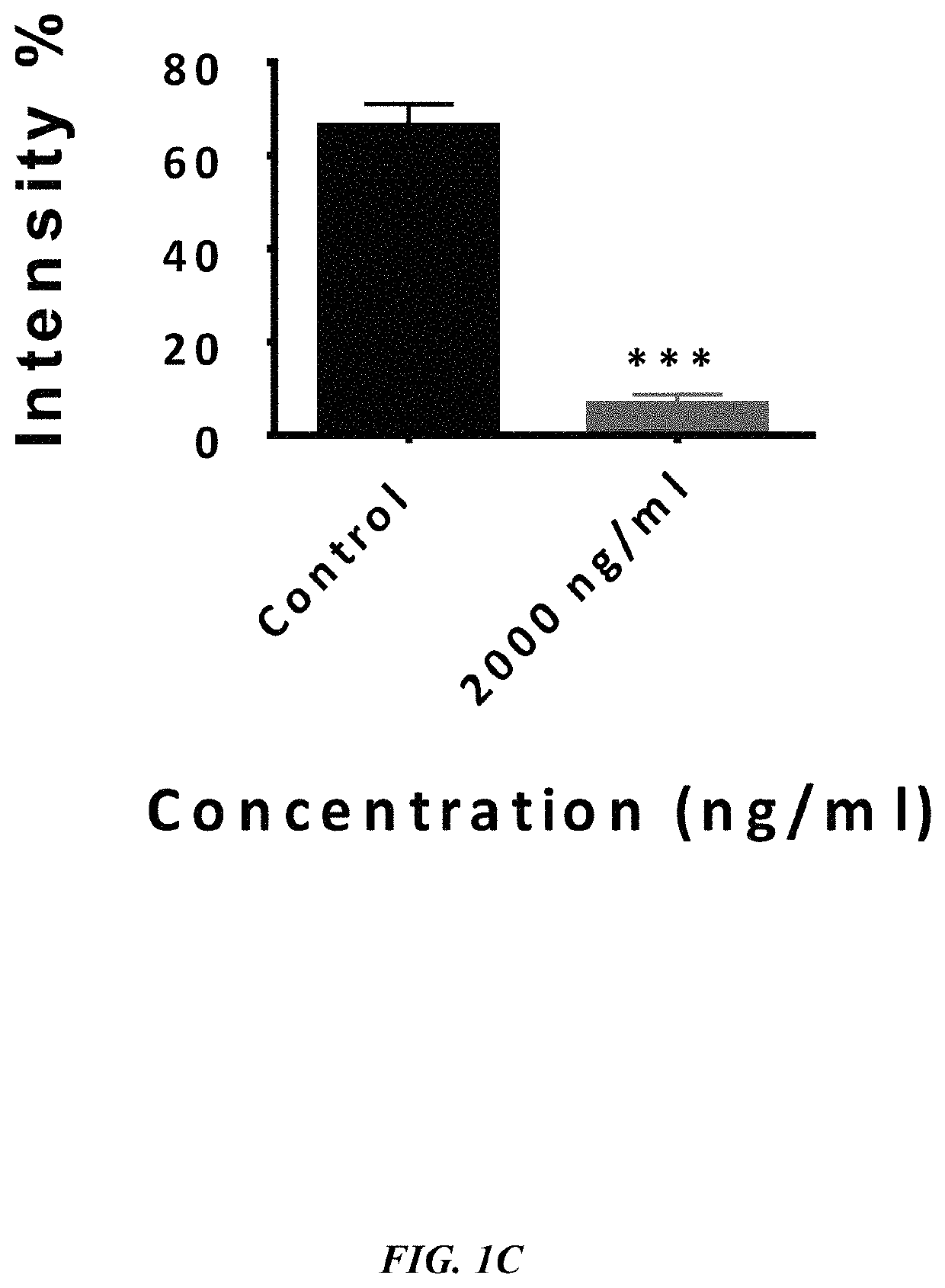
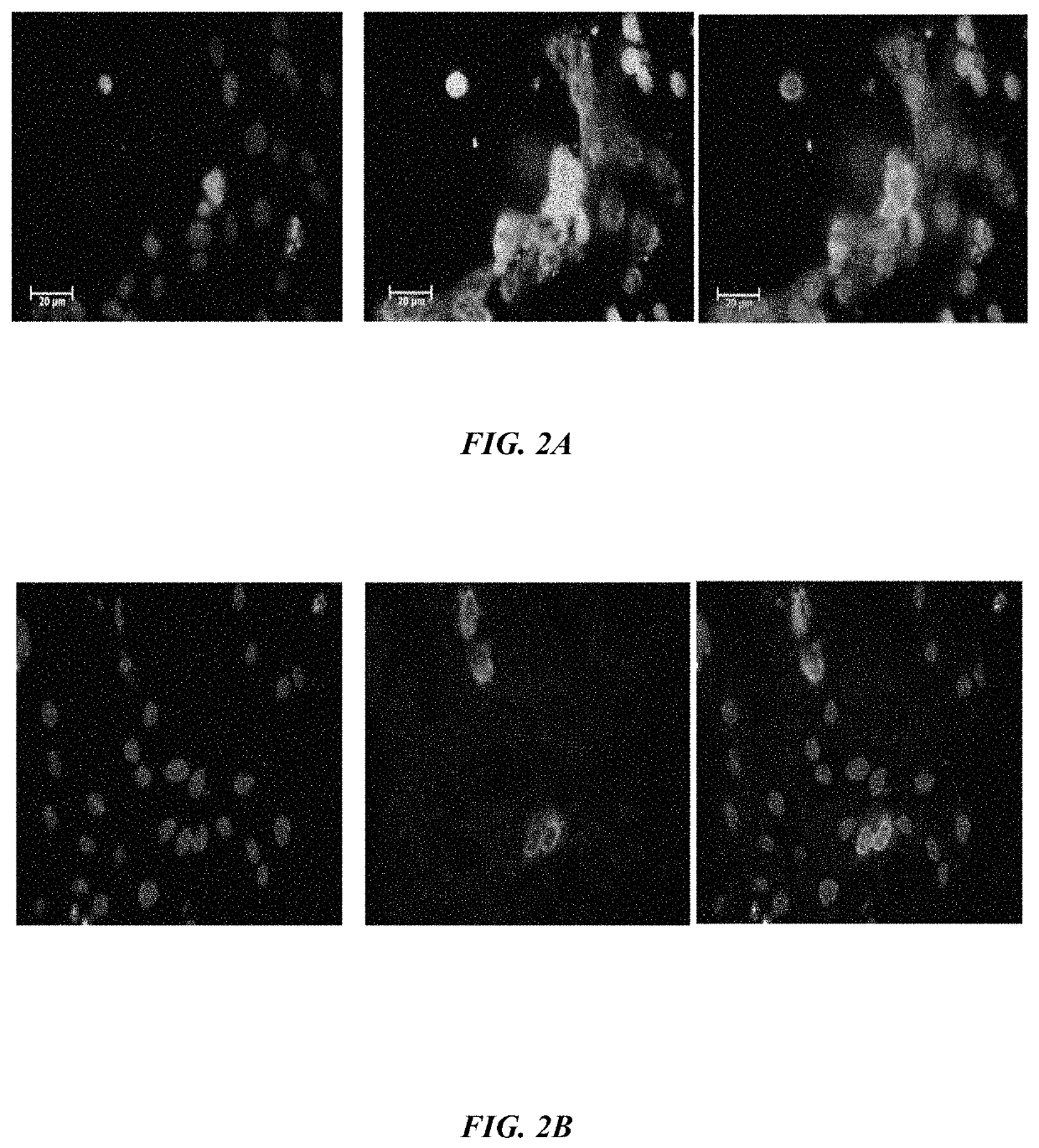
The embodiments herein disclose a method for synthesizing antagonistic peptide VEGF and bFGF. The method comprises synthesizing the antagonistic peptide for VEGF and bFGF and analyzing the purity of peptides. The quality of antagonistic peptide for VEGF and bFGF is analyzed by HPLC chromatogram and Mass spectrometry analysis. The biochemical activity of the antagonistic peptide for VEGF and bFGF is analyzed by competitive binding assay, cell proliferation assay, Matrigel assay for anti-angiogenic activity analysis, histopathological staining and Western blot analysis. The competitive binding assay of antagonistic peptide for VEGF and bFGF illustrate that peptides binds with cell receptors at a concentration of 2000 ng / ml. The cell proliferation assay illustrates that cell growth is arrested when antagonistic peptide for VEGF and bFGF are at a concentration of 2000 ng / ml. The anti-angiogenic activity analysis illustrates that angiogenesis is arrested when the concentration of antagonistic peptide for VEGF and bFGF is 2000 ng / ml.
Owner:ASGHARI SEYED MOHSEN +1
Methods for characterizing disulfide bonds
PendingCN113272650AComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationDisulfide bondingPharmaceutical drug
Compositions and methods for analyzing disulfide bonds are provided. An exemplary method includes preparing peptide standards having no disulfide bonds, scrambled disulfide bond peptide standards, and native disulfide bond peptide standards according to the sequence of the region of the protein drug product that includes the disulfide bond, digesting a sample of protein drug product into peptides, separating the protein drug product peptides, analyzing the protein drug product peptides and the peptide standards, identifying scrambled and native disulfide bond peptides by retention time, and quantifying the level of scrambled disulfide bond peptides.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Peptide mapping method
ActiveCN112763636BEasy to keepUnified approachComponent separationCombinatorial chemistryAqueous solution
The invention discloses a peptide map analysis method, comprising the following steps: performing denatured enzymolysis on a sample to obtain polypeptide fragments; using UPLC-MS to detect the polypeptide fragments, and analyzing the polypeptide according to the collected peptide map data Fragments are assigned; wherein, the mobile phase of the UPLC-MS includes mobile phase A and mobile phase B, the mobile phase A is formic acid aqueous solution, and the mobile phase B is formic acid acetonitrile solution; the UPLC-MS uses ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 column for gradient elution.
Owner:深圳汉腾生物科技有限公司 +3
Methods for characterizing disulfide bonds
ActiveUS20200225243A1Reduce the amount requiredComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationDisulfide bondingPharmaceutical drug
Compositions and methods for analyzing disulfide bonds are provided. An exemplary method includes preparing peptide standards having no disulfide bonds, scrambled disulfide bond peptide standards, and native disulfide bond peptide standards according to the sequence of the region of the protein drug product that includes the disulfide bond, digesting a sample of protein drug product into peptides, separating the protein drug product peptides, analyzing the protein drug product peptides and the peptide standards, identifying scrambled and native disulfide bond peptides by retention time, and quantifying the level of scrambled disulfide bond peptides.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com