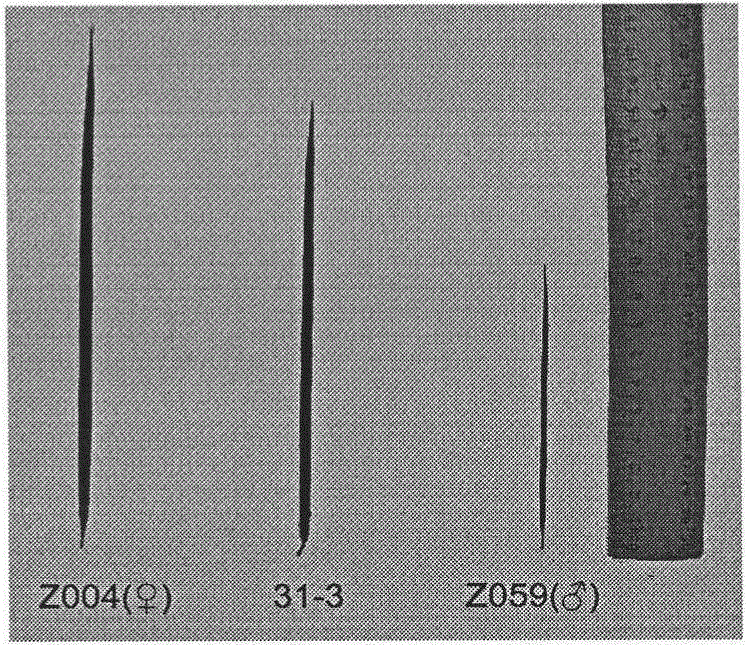
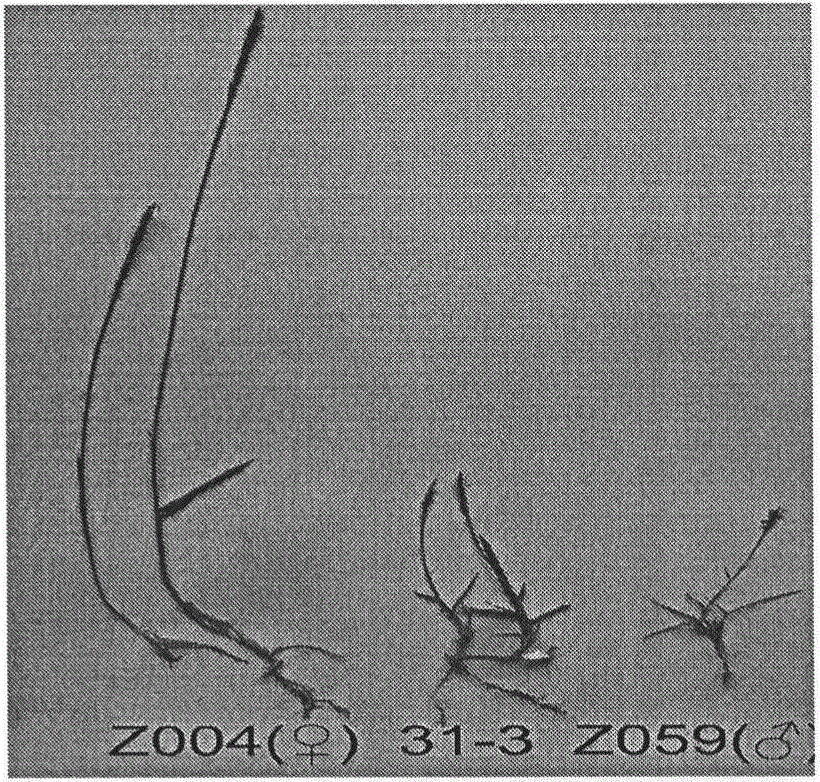
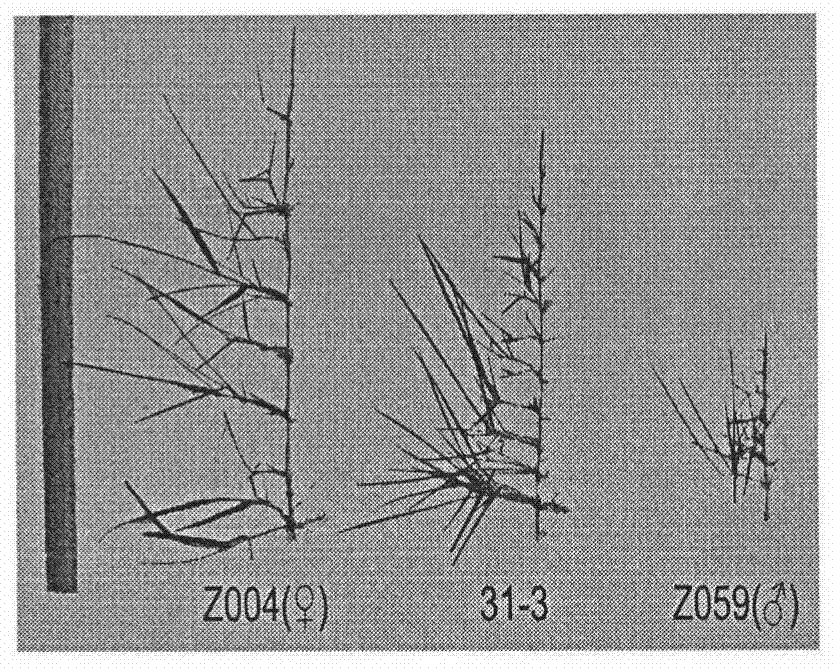
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Zoysia matrella" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zoysia matrella (L.) Merr., commonly known as Manila grass, is a species of mat-forming, perennial grass native to temperate coastal southeastern Asia and northern Australasia, from southern Japan (Ryukyu Islands), Taiwan, and southern China (Guangdong, Hainan) south through Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia and the Philippines to northern Australia (northeast Queensland), and west to the Cocos Islands in the eastern Indian Ocean.
Molecule identification method for Qingdao zoysia japonica and zoysia matrella filial generation authenticity
InactiveCN101240340ALow costHigh polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular identificationF1 generation
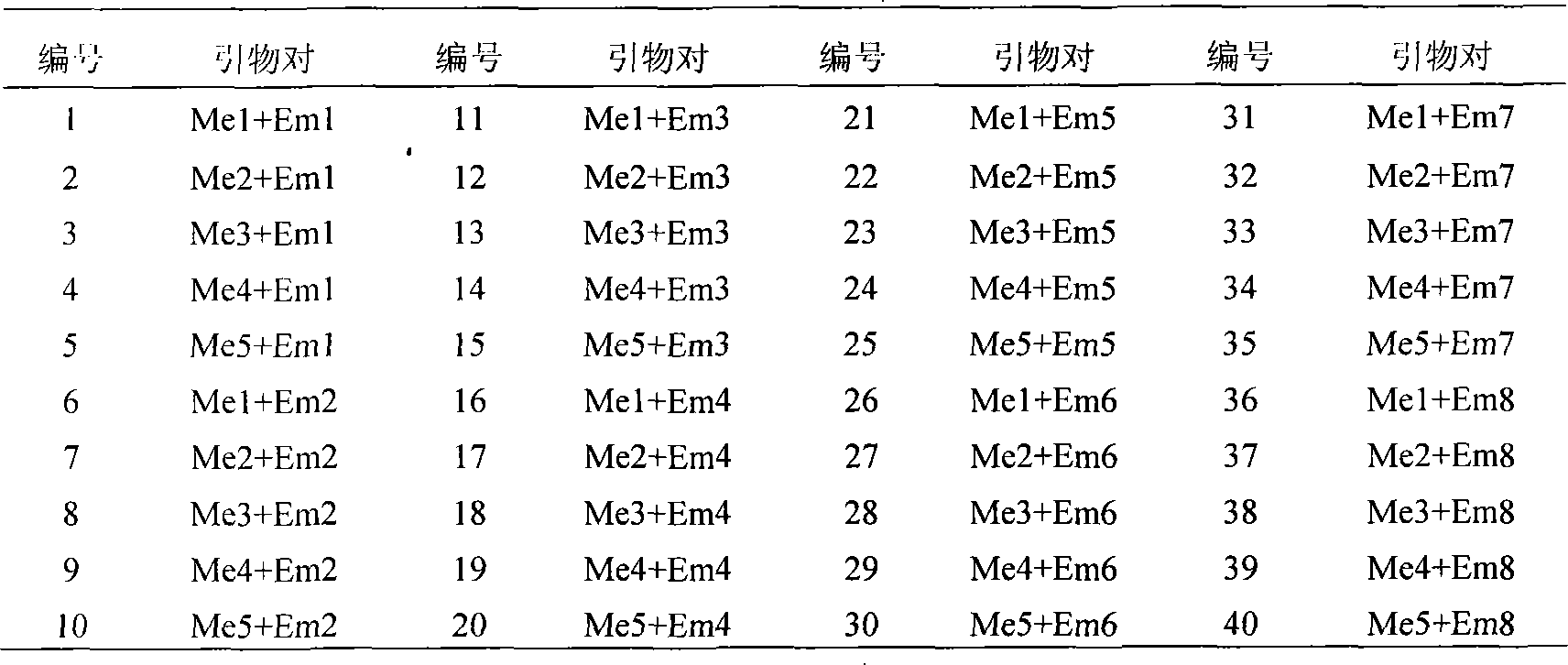
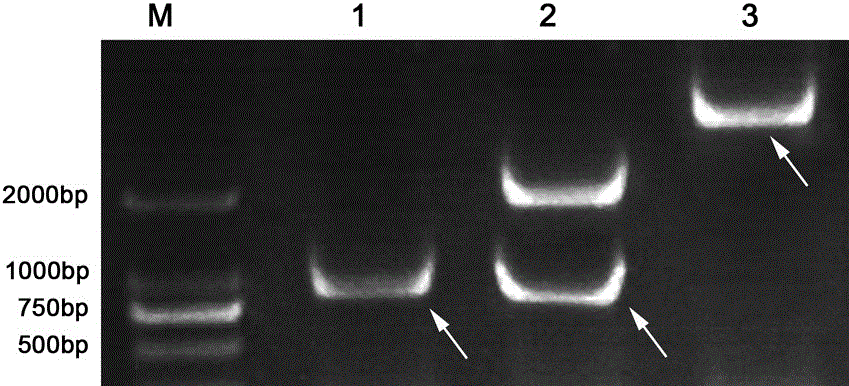
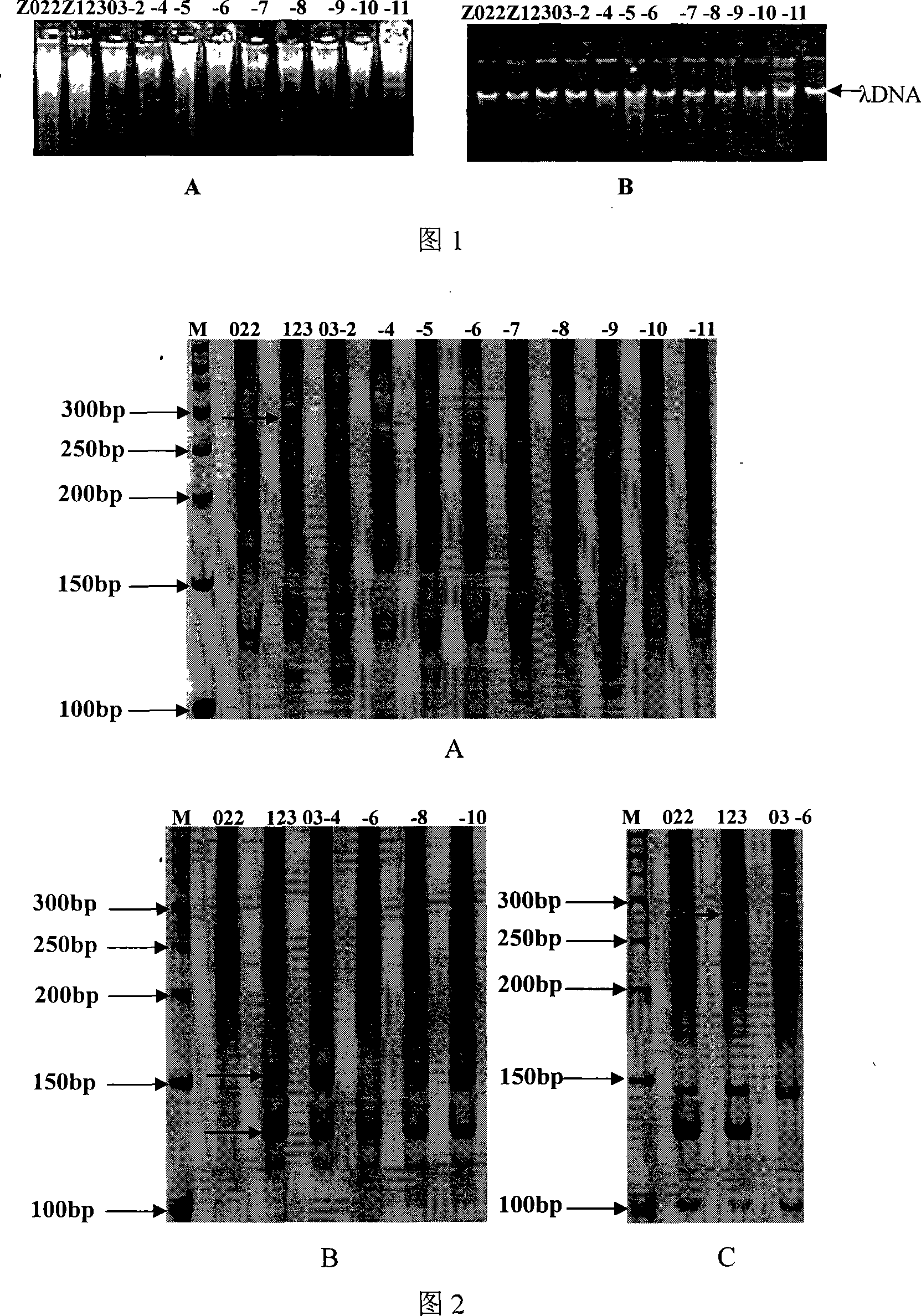
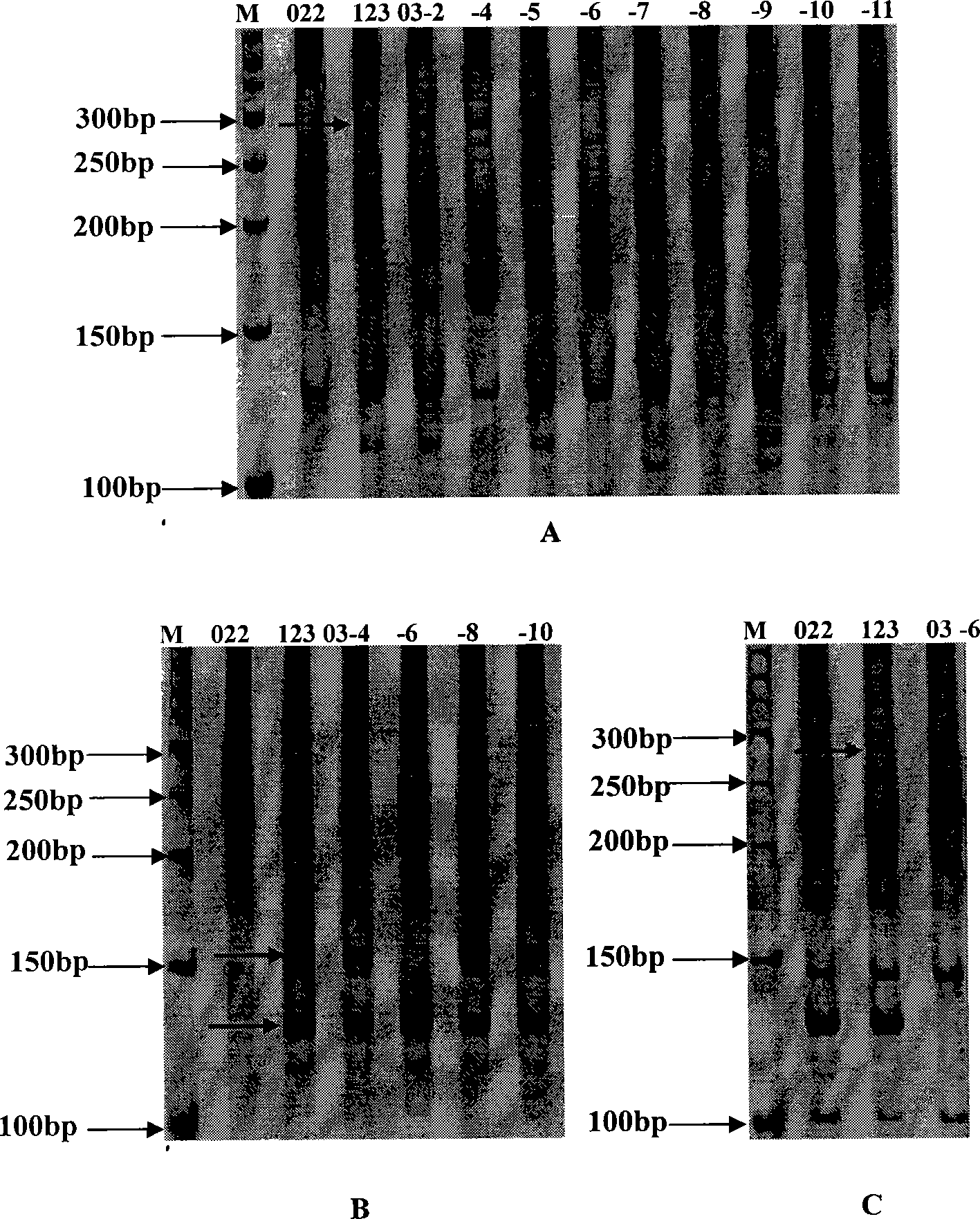
The invention relates to a method for identifying authenticity of filial generation of zoysia and manilagrass, which belongs to the field of biological technology. The invention is specially for rapid and precise identification of authenticity of filial generation of Qingdao zoysia and manilagrass. Using a genome DNA template of nine zoysia filial generations and two parents Qingdao zoysia and manilagrass as the template, select three pairs of SRAP primers, namely primers capable of amplifying specific band not included in female parent on male parent. Perform amplifying and electrophoresis on the male parent, the female parent and the filial generation, and identify according as whether the F1 generation can amplify male parent specific band. The result shows that a filial generation is a real hybrid when each of the nine filial generations has male parent specific band. Thus, a molecular identification system of authenticity of filial generation of Qingdao zoysia and manilagrass is established, by which the authenticity of filial generation of Qingdao zoysia and manilagrass can be quickly identified, the method can also be used for hybrid variety fingerprint map construction and purity identification.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Feed for promoting growth of calves and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104472892APromote digestion and absorptionImprove conversion rateAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceLagenaria
A feed for promoting growth of calves and a preparation method thereof are disclosed. The feed comprises the following raw materials, by weight, 300-400 parts of soyabean protein powder, 200-300 parts of corn bran, 200-300 parts of barley flour, 6-8 parts of soy sauce, 3-4 parts of mature vinegar, 2-3 parts of star aniseed powder, 2-3 parts of chilli sauce, 30-40 parts of pork jelly, 20-30 parts of fish gel, 70-80 parts of coagulated pig blood, 40-50 parts of coagulated duck blood, 20-30 parts of green pepper, 10-20 parts of onion, 10-15 parts of cottonseed oil, 50-60 parts of lagenaria siceria powder, 20-40 parts of mangosteen powder, 3-4 parts of Ligusticum wallichii, 2-3 parts of white peony root, 2-3 parts of Poria cocos, 1-2 parts of cortex lycii, 8-15 parts of coix seed oil, 5-10 parts of aloe freeze-dried powder, 3-5 parts of white carbon black, 50-60 parts of zoysia japonica, 40-50 parts of zoysia matrella, 20-30 parts of Cucurbita pepo L, 10-20 parts of spearmint, 5-10 parts of cypress leaf, 2-4 parts of gynostemma pentaphylla powder, 30-60 parts of rice bran, 20-30 parts of a phagostimulant and a proper amount of water.
Owner:合肥桂和农牧渔发展有限公司
Young turtle fattening feed and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105851683AIncrease appetiteFast appetiteClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffPrawnZoysia japonica
The invention discloses a young turtle fattening feed and a manufacturing method thereof. The young turtle fattening feed is prepared from hoof and horn meal, wool powder, dried locust powder, shrimp meal, coarse corn grains, sorghum, bone meal, green hyacinth beans, grapefruits, corn syrup, whole egg powder, zoysia matrella, nullipore, zoysia japonica, radix ophiopogonis, grist, semen coicis, ginkgo seeds, carrots, bengal waterdropwort herb, california burclover, white pepper, salt, agar, cotton stalks, edible bamboo charcoal powder and the like. The feed solves the problems that a traditional young turtle feed lacks nutrients and is poor in palatability, the manufactured feed is coarse, the young turtle is low in appetite, the weight of the young turtle is increased slowly, and the fattening effect is poor, the obtained feed is rich in nutrient, fine and smooth in taste, fragrant in taste, the appetite of the young turtle can be enhanced, weight increase and meat production are promoted, and the young turtle fed by the feed is high in appetite, rapidly gains weight, is good in fattening effect, can greatly improve economic benefits of young turtle culture and has the quite high popularization value.
Owner:HEFEI NONGTAI AGRI TECH CO LTD
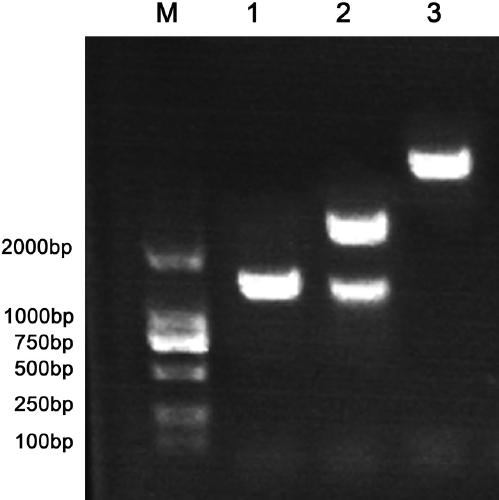
Method for genetic transformation of zoysia matrella mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens
InactiveCN110577966ASimple experimentReduce workloadGenetic engineeringFermentationFunctional genesSkin callus
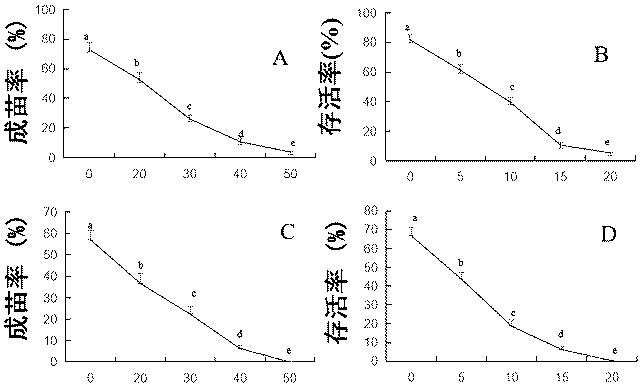
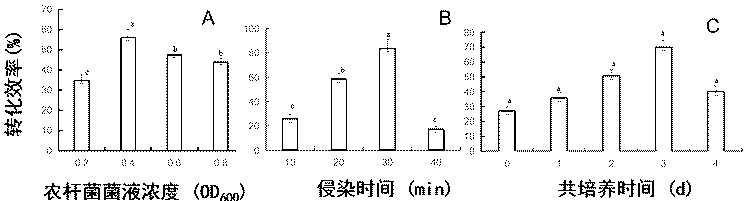
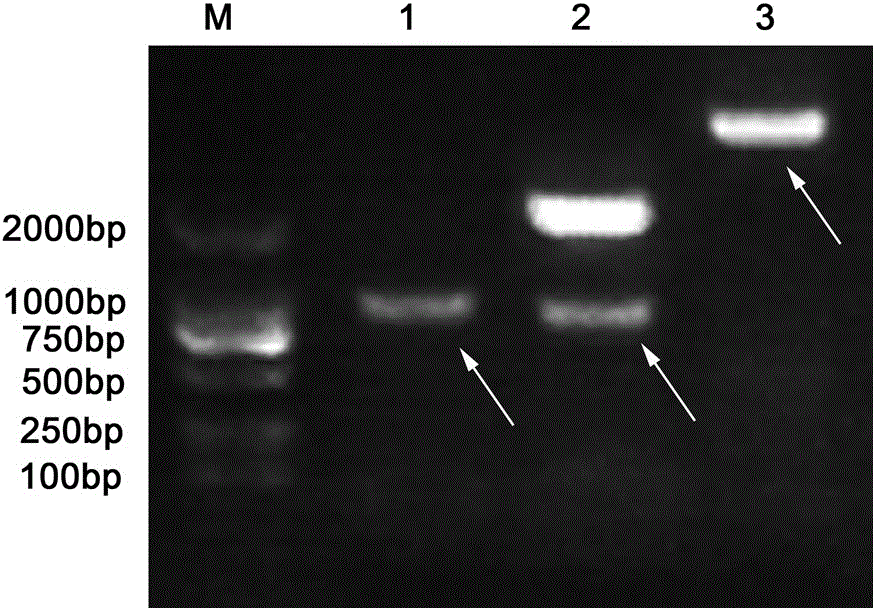
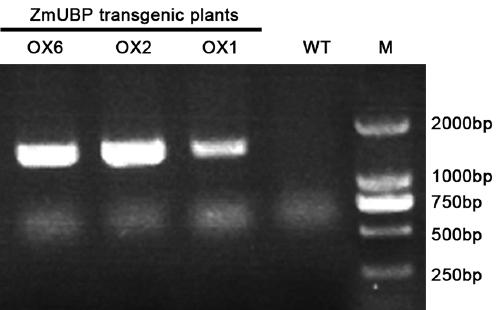
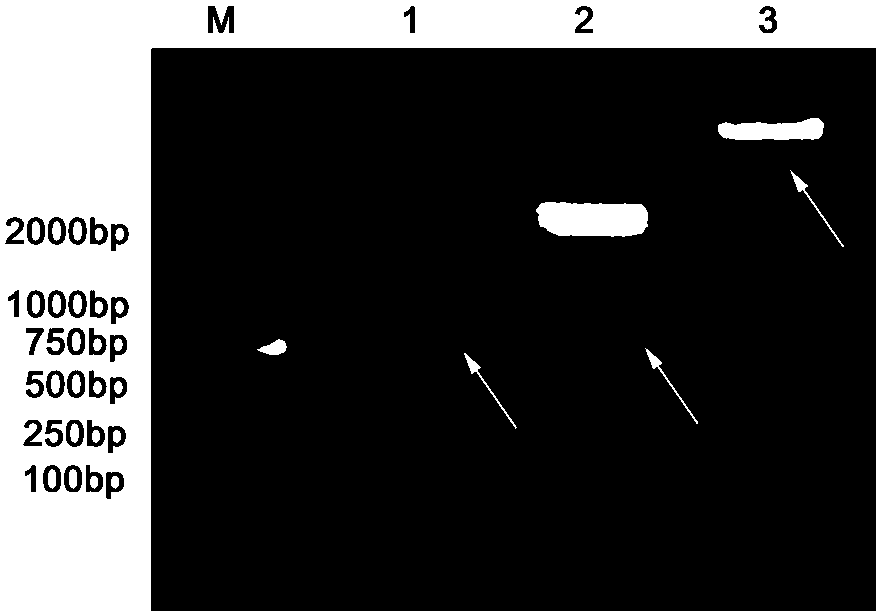
The invention discloses a method for genetic transformation of zoysia matrella mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens. The method includes the steps of the concentration of a bacterial solution, the infection time, the co-culture time, the antibiotic concentration, acclimatization and transplantation, PCR detection of transgenic plants and the like. The method includes the following steps that an optimal genetic transformation system is that an OD600 value of the bacterial solution is 0.4, infection is conducted for 30 min, and selective culture is conducted after co-culture is conducted for 3d; the optimal bacteriostatic concentration of Timentin in a selective culture phase is 250 mg / L, the optimum selection pressure for hygromycin callus screening is 40 mg / L, and the optimum concentration of root taking screening is 15 mg / L; and histochemical analysis and PCR identification of GUS activity show that a target gene is successfully transferred into a genome of the zoysia matrella. Theabove research provides important technical support for gene function research and molecular breeding of the zoysia matrella. The method has the advantages that a stable and high-efficiency zoysia matrella genetic transformation system is obtained, the convenience is provided for genetic improvement of the zoysia matrella, and meanwhile, a key preliminary foundation is laid for verification of functional genes of the zoysia matrella.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for inducing differentiation seedling of manilagrass callus
InactiveCN102630565AHigh regeneration rateSolve the problem of low regeneration rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGene conversionTissue Differentiation
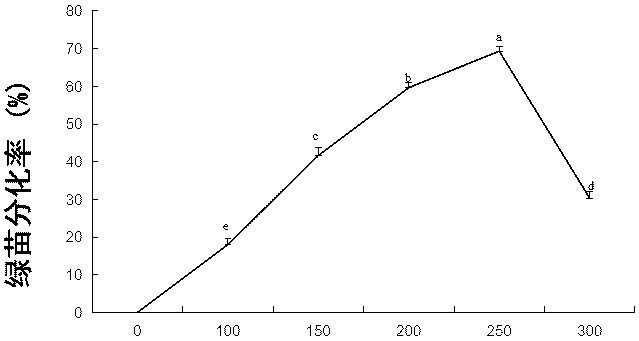
The invention discloses a method for inducing differentiation seedling of manilagrass callus. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting embryonal callus of manilagrass, arranging embryonal callus of manilagrass in a solid medium in which the content of 6-Benzylaminopurine being 0-0.4mg / L and the content of trans-zeatin being 0-0.4mg / L, and growing into seedlings after four weeks. According to the method for inducing the differentiation seedling of the manilagrass callus, disclosed by the invention, a culture medium containing two hormones, namely 6-Benzylaminopurine and trans-zeatin, callus subculturing for a long term is regenerated and cultivated, the regeneration rate of the manilagrass callus subculturing for a long term is remarkably improved, a problem that the regeneration rate of the manilagrass callus subculturing for many years is low is effectively solved, the tissue culture regeneration system of the manilagrass is further modified, and foundation is established for a cell engineering breeding and gene transformation research; and the method is simple to operate and has high efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Planting method for zoysia matrella in green belts on both sides of carriageway
InactiveCN105379522AImprove fertilityHigh activityPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsSoil treatmentCarriageway
The present invention provides a planting method for zoysia matrella in green belts on both sides of a carriageway, and relates to the technical field of urban greening plant cultivation. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of soil treatment, plant immersion, plant fertilization and plant arrangement. The method disclosed by the present invention is reasonable. With the method, zoysia matrella is planted conveniently; sufficient nutrients are ensured; and activity and freezing resistance of plants can be improved.
Owner:HUAIYUAN KONGJINHU AGRI DEV
Cutting propagation method of Zoysia matrella
The present invention provides a cutting propagation method of Zoysia matrella. The cutting propagation method comprises the following steps of: (1) cutting branch selection including the steps of selecting creeping branches to be cut from well-grown turfs formed completely, and pulling the creeping branches out of the soil; (2) cutting branch processing for trimming the creeping branches into a plurality of segments, each segment having 1-2 knots, thereby obtaining to-be-cut branches; (3) cutting substrate selection including the steps of selecting cutting substrate and putting the cutting substrate into a plantation tray with compartments; (4) cutting including the step of inserting the to-be-cut branches obtained by the step (2) into the plantation tray obtained by the step (3) with one branch in each compartment; and (5) management after cutting including the steps of covering each compartment with river sand, compacting the periphery of the branch and completely watering, and then performing daily management. Compared with the prior art, the cutting propagation method of the Zoysia matrella has the advantage of an existing cutting propagation technology, is simple and is low in cost, growth regulating agent is not required, and germination rate and survival rate after transplanting of the Zoysia matrella can be largely increased.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Method for ecological remediation of sea island bare land
ActiveCN106688356AImprove breathabilityFull of nutritionBioloigcal waste fertilisersPlant cultivationFiberSoil properties
The invention relates to a method for ecological remediation of sea island bare land. The method includes steps: (1) shallow excavating of the sea island bare land; (2) replacement soil backfilling; (3) landfill of controlled-release active nutritional packages; (4) sowing of zoysia matrella; (5) cuttage of procumbent juniper. By backfilling of improved mellow soil, a soil base of the sea island bare land can be improved, air permeability of the mellow soil is greatly improved due to addition of fiber materials, and less proneness to caking in long-time use is realized after the mellow soil is backfilled to sea island land; due to organic fertilizers, water retaining agents and soil stabilizing agents, the backfilled mellow soil is rich in nutrition, great in water retaining performance and high in soil property stability and provides sufficient nutrients and moisture for early growth of zoysia matrella and procumbent juniper. The controlled-release active nutritional packages are rich in natural organics and adsorbed and stored trace elements and buried into the improved mellow soil to continuously and slowly release and degrade under rain flushing and natural diffusion, so that nutrient loss can be greatly avoided, and continuous nutrient supply can be provided for later growth of zoysia matrella and procumbent juniper.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
Zoysiagrass plant `TM9`
The present cultivar TM9 (Zoysia matrella Merr.) advantageously has a growing rate of in terms of plant height less than half as compared with existing cultivars and requires mowing every 20 to 40 days during the summer so as to be maintained in fair condition and allows the amount of fertilizer to be reduced to almost less than half.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
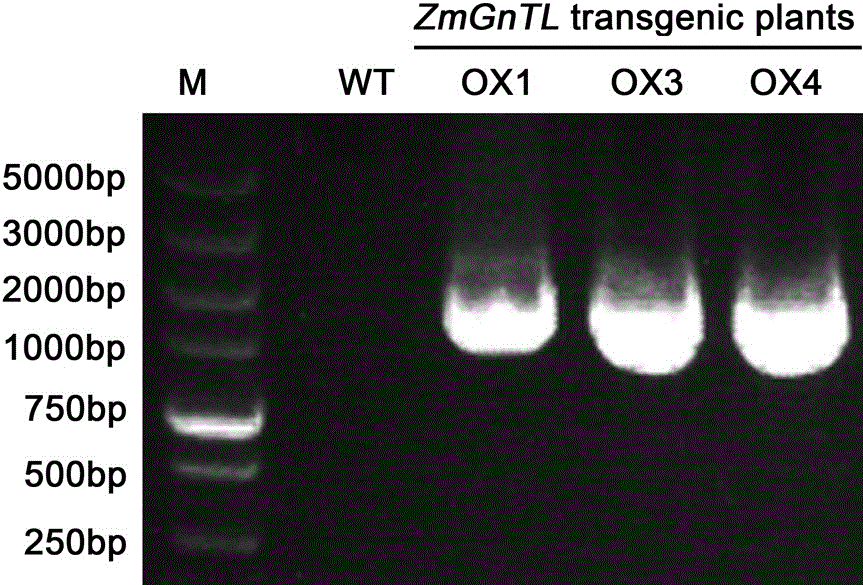
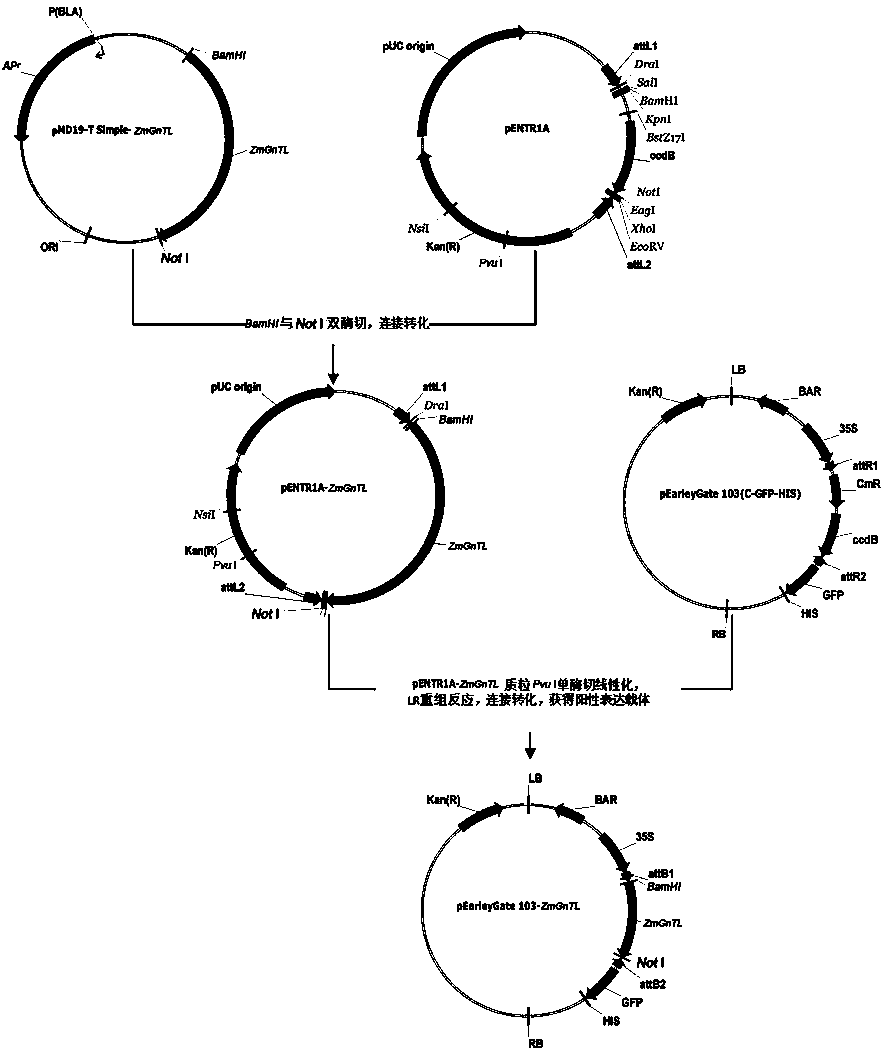
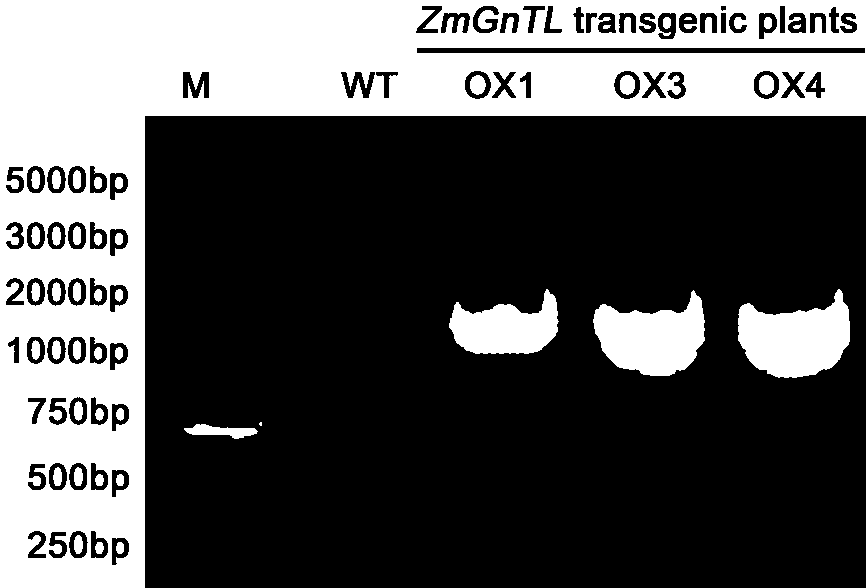
Novel salt-resistant gene ZmGnTl in zoysia matrella and expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN106754996APlant variety improvementImprove salt toleranceEnzymesFermentationHalophyteSalt resistance
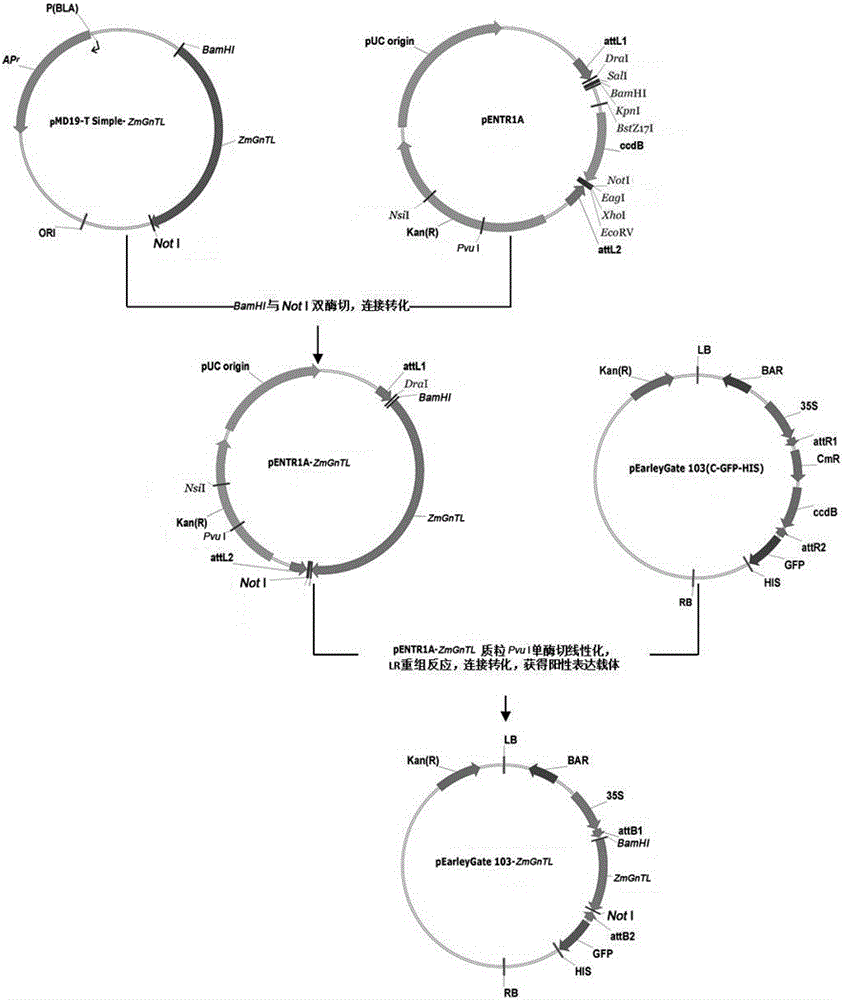
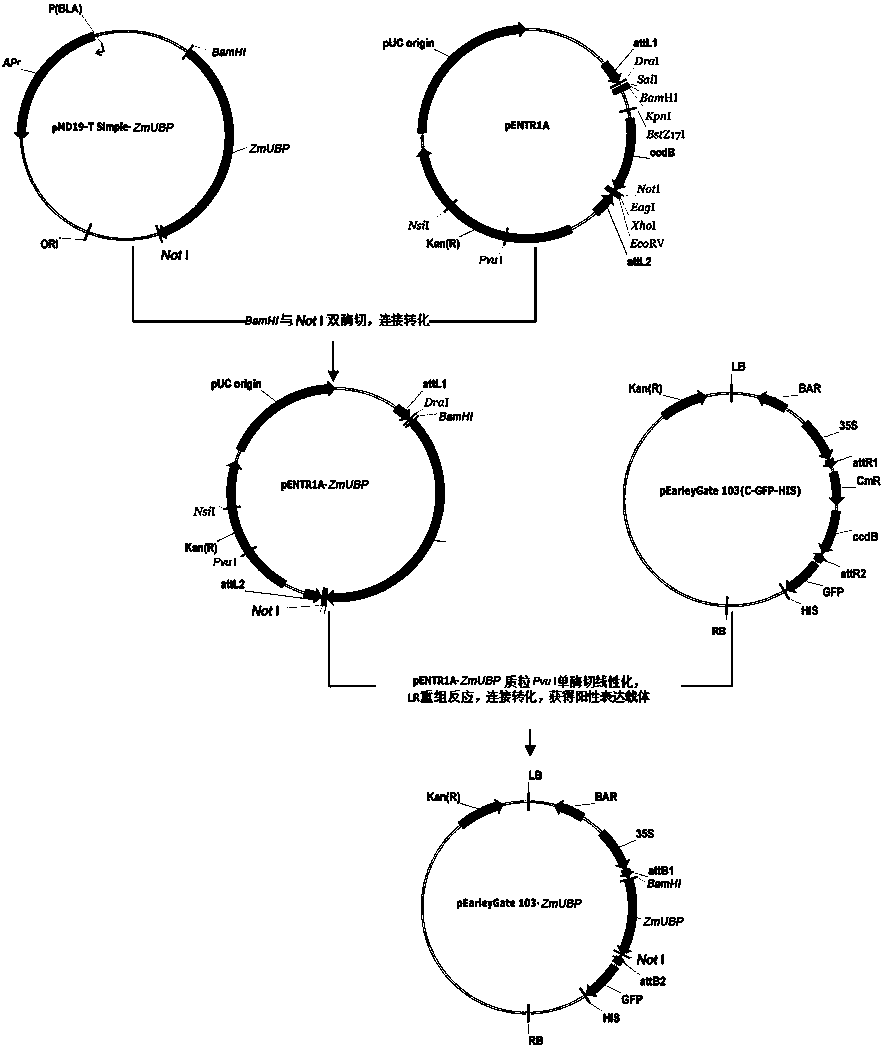
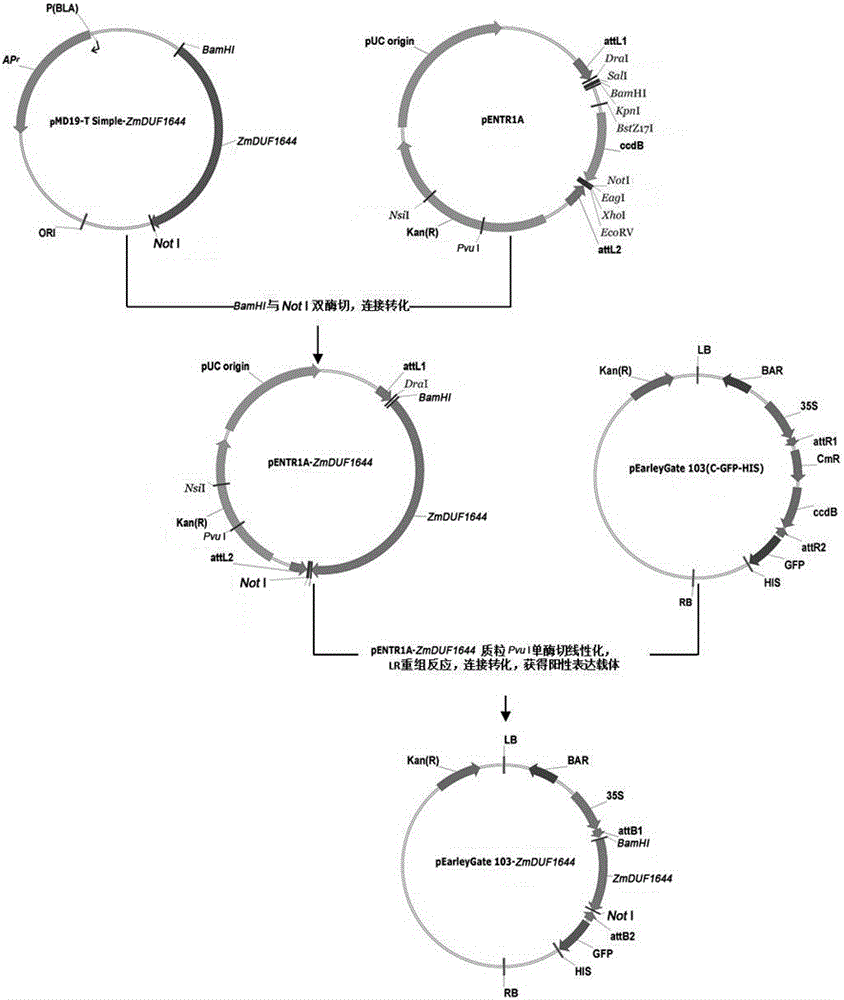
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and discloses a salt-resistant gene ZmGnTL of a halophyte zoysia matrella and an expression vector and an application thereof. The sequence of a novel salt-resistant gene ZmGnTl in zoysia matrella is SEQ ID NO.1. The plant expression vector is obtained by performing a recombination reaction with pEarleyGate103 expression vector plasmids after inserting ZmGnTL after double enzyme digestion of BamHI and NotI into a gateway entry vector pENTR1A. The ZmGnTL of zoysia matrella provided by the invention is the novel salt-resistant gene which can improve the salt resistance of the plant and can be applied to creating salt-resistant novel germplasms and improving plant varieties.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Urban courtyard afforestation configuration mode for reducing PM 2.5
InactiveCN103444422AReduce concentrationStrengthen the position effect of greeningHorticultureZelkovaPosition effect
The invention discloses an urban courtyard afforestation configuration mode for reducing PM 2.5, which comprises the following steps: in the first ten-day period of March, according to the plant configuration standard, digging plant pits and applying cake fertilizer or compound fertilizer in the plant pits; at the front courtyard, adopting the configuration mode of planting zelkova schneiderianas, southern magnolias, sweet-scented osmanthus trees, crape myrtle trees, red maples, pomegranate trees, rhododendron trees, loropetalum chinense var. rubrums and ground cover plants (gardenia and radix ophiopogonis); at the rear courtyard, adopting the configuration mode of planting hackberries, sweet-scented osmanthus trees, Chinese redbud, euonvmus japonicus cv.aureo-ma, camellia and ground cover plants (zephyranthes candida); on the east and west sides of the courtyard, adopting the three-dimensional configuration mode of planting koelreuteria paniculata, banana shrub, loropetalum chinense var. rubrums, pittosporum tobira and ground cover plants (gardenia and zoysia matrella). According to the invention, based on the spatial distribution pattern of urban PM 2.5, the afforestation position effect and the arbor and shrub multi-layer configuration effect of urban communities are strengthened, and the PM 2.5 exhausted by motor vehicles and heavy metal pollutants in the communities are reduced to the greatest degree. With adoption of the urban courtyard afforestation configuration mode disclosed by the invention, the concentration of the PM 2.5 can be decreased for 1.86 times as compared with that of adopting the conventional afforestation mode.
Owner:张冠一
Growth promotion fertilizer for zoysia matrella on greenbelts at two sides of carriageway
The invention discloses growth promotion fertilizer for zoysia matrella on greenbelts at two sides of a carriageway and relates to the technical field of plant plantation fertilizer production. The growth promotion fertilizer comprises, by weight, 50 parts of human excrement and urine, 10 parts of epimedium wushanense particles, 10 parts of corn flour, 8 parts of gelatin, 8 parts of EM inocula, 25 parts of cow dung, 10 parts of a soil conditioner, 8 parts of folium cortex eucommiae powder, 25 parts of clear water, 20 parts of diammonium phosphate, 5 parts of calcium sulfate, 15 parts of zinc nitrate and 28 parts of a modifier. The growth promotion fertilizer has a reasonable ratio, guarantees nutrients, nourishes crops and does not cause environmental pollution.
Owner:HUAIYUAN KONGJINHU AGRI DEV
Nutrition promoting fertilizer of zoysia matrella on green belts on two sides of running lane
InactiveCN105801299ANo pollutionCalcareous fertilisersAgriculture tools and machinesZinc nitrateBiology
The invention provides to a nutrition promoting fertilizer of zoysia matrella on green belts on the two sides of a running lane and relates to the technical field of plant planting fertilizer production.The nutrition promoting fertilizer is characterized by being prepared from, by weight, 50 parts of night soil, 10 parts of Epimedium wushanense granules, 10 parts of corn powder, 8 parts of gelatin, 8 parts of EM fungicide, 25 parts of cow dung, 10 parts of soil amendment, 8 parts of eucommia leaf powder, 25 parts of clean water, 20 parts of diammonium phosphate, 5 parts of calcium sulfate, 15 parts of zinc nitrate and 28 parts of amendment.The nutrition promoting fertilizer is reasonable in matching ratio and capable of guaranteeing nutrition and nourishing crops, and does not pollute the environment.
Owner:BENGBU YUNLIANYUAN LANDSCAPE GARDEN CO LTD
Method for inducing differentiation seedling of manilagrass callus
InactiveCN102630565BHigh regeneration rateSolve the problem of low regeneration rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGene conversionTissue Differentiation
The invention discloses a method for inducing differentiation seedling of manilagrass callus. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting embryonal callus of manilagrass, arranging embryonal callus of manilagrass in a solid medium in which the content of 6-Benzylaminopurine being 0-0.4mg / L and the content of trans-zeatin being 0-0.4mg / L, and growing into seedlings after four weeks. According to the method for inducing the differentiation seedling of the manilagrass callus, disclosed by the invention, a culture medium containing two hormones, namely 6-Benzylaminopurine and trans-zeatin, callus subculturing for a long term is regenerated and cultivated, the regeneration rate of the manilagrass callus subculturing for a long term is remarkably improved, a problem that the regeneration rate of the manilagrass callus subculturing for many years is low is effectively solved, the tissue culture regeneration system of the manilagrass is further modified, and foundation is established for a cell engineering breeding and gene transformation research; and the method is simple to operate and has high efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Zoysiagrass plant 'TM9'
The present culivar TM9 (Zoysia matrella Merr.) advantageously has a growing rate of in terms of plant height less than half as compared with existing cultivars and requires mowing every 20 to 40 days during the summer so as to be maintained in fair condition and allows the amount of fertilizer to be reduced to almost less than half.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for rapidly propagating Zoysia matrella to form lawns in large scale
Owner:句容市后白镇绿草滩花草木专业合作社
A Novel Salt Tolerance Gene zmubp in Zoysia rugosa and Its Expression Vector and Application
InactiveCN106434697BImprove salt tolerancePlant variety improvementPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyHalophyte
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and discloses a salt-tolerant gene ZmPDI in a halophyte zoysia matrella as well as a plant expression vector and application thereof. The sequence of the salt-tolerant gene ZmPDI in the zoysia matrella is SEQ ID NO. 1. The plant expression vector is obtained by carrying out double enzyme digestion on ZmPDI through BamHI and EcoRV, then inserting the ZmPDI into a gateway entry vector pENTR1A, and finally subjecting the ZmPDI and a pEarleyGate103 expression vector plasmid to recombination reaction. The ZmPDI in the zoysia matrella, which is provided by the invention, is a novel salt-tolerant gene; the gene can be used for improving the salt tolerance of a plant, and can be applied to the creation of novel salt-tolerant germplasm and the improvement of a plant variety.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Water tank planting plate cultivation system for zoysia matrella
The invention relates to the technical field of planting plate water planting, and discloses a water tank planting plate cultivation system forzoysia matrella, which comprises a plurality of mutually spliced cultivation units, each cultivation unit comprises an inner shell and an outer shell detachably connected with the outer shell, the inner shell is connected with the outer shell through a plurality of adjusting bolts, the outer shell is connected with the inner shell through a plurality of adjusting bolts, a planting groove used for planting the zoysia matrella is formed in the middle of each inner shell, a plurality of through holes are formed in the side wall of each inner shell, a plurality of protruding blocks are evenly distributed on the outer side of each inner shell, a penetrating hole is formed in each protruding block, each outer shell is movably arranged on the outer side of the corresponding inner shell in a sleeving mode, an annular groove is formed in the top surface of each inner shell along the inner ring, a plurality of spiral connecting bases corresponding to the protruding blocks are distributed at the bottom of each groove, and threaded grooves are formed in the top surfaces of the spiral connecting bases. The water tank planting plate cultivation system is convenient to use for water planting, can completely discharge cultivation soil after the zoysia matrella is mature, and is convenient to use for lawn planting in the later period.
Owner:WEST ANHUI UNIV
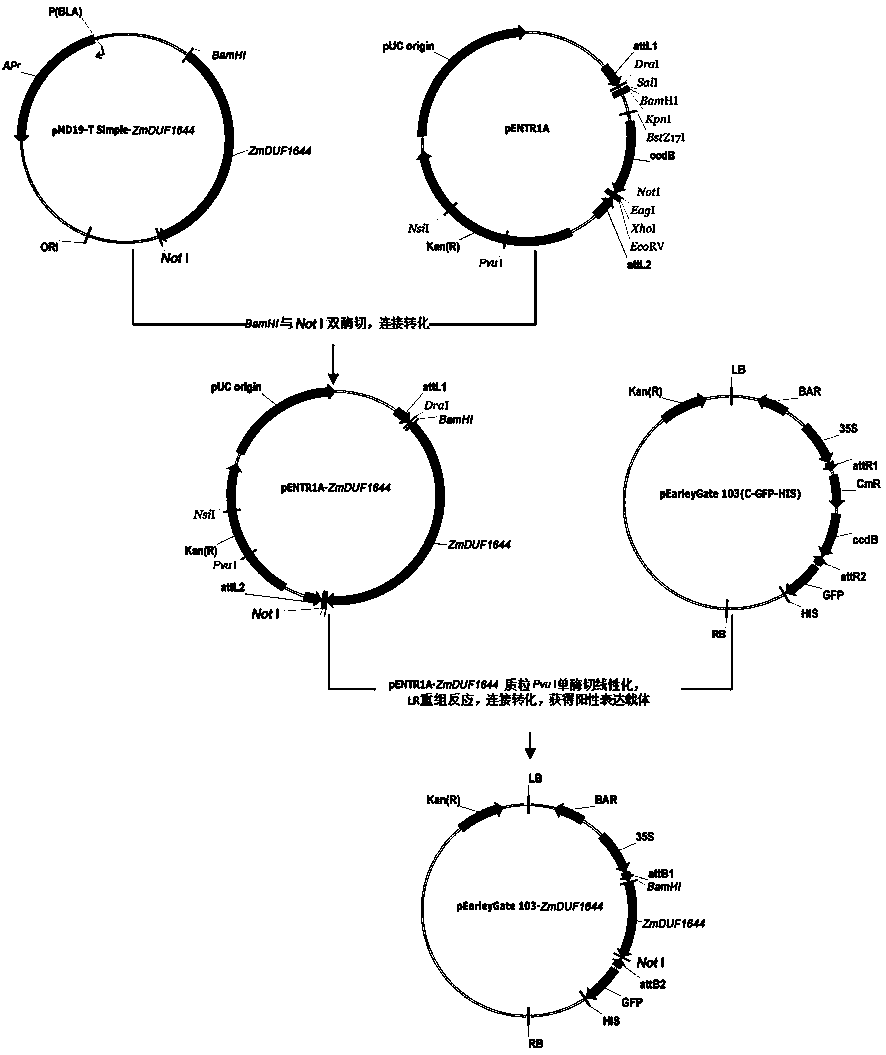
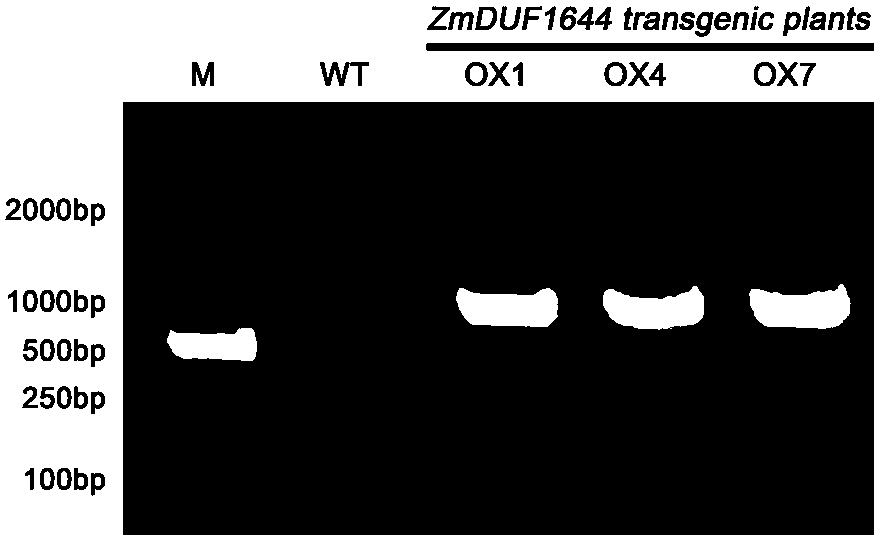
Novel plant salt-resistant gene ZmDUF1644, and expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN106754959APlant variety improvementImprove salt tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationHalophyteSalt resistance
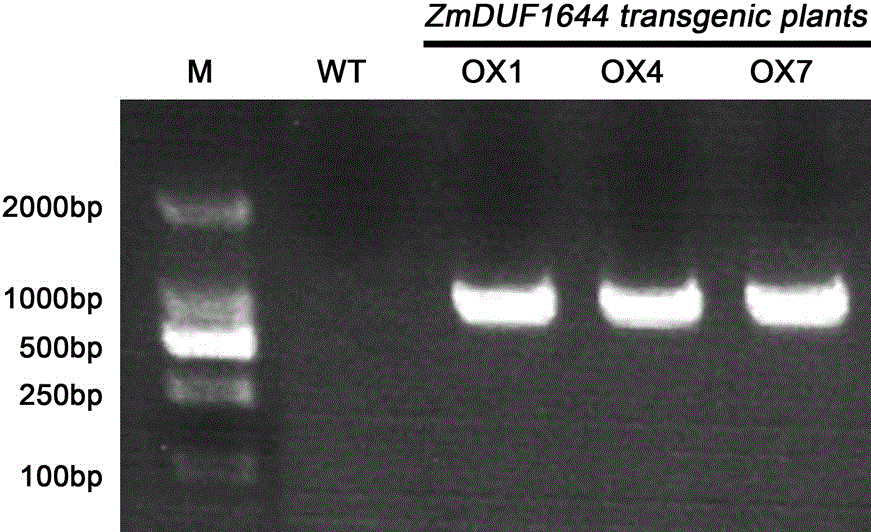
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and discloses a salt-resistant gene ZmDUF1644 of a halophyte zoysia matrella, and an expression vector and an application thereof. The sequence of a novel salt-resistant gene ZmDUF1644 in zoysia matrella is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The plant expression vector is obtained by performing a recombination reaction with pEarleyGate103 expression vector plasmids after inserting ZmDUF1644 subjected to double enzyme digestion of BamHI and NotI into a gateway entry vector pENTR1A. The ZmDUF1644 of zoysia matrella provided by the invention is the novel salt-resistant gene which can improve the salt resistance of the plant and can be applied to creating salt-resistant novel germplasms and improving plant varieties.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Molecule identification method for Qingdao zoysia japonica and zoysia matrella filial generation authenticity
InactiveCN101240340BHigh polymorphismGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular identificationF1 generation
The invention relates to a method for identifying authenticity of filial generation of zoysia and manilagrass, which belongs to the field of biological technology. The invention is specially for rapid and precise identification of authenticity of filial generation of Qingdao zoysia and manilagrass. Using a genome DNA template of nine zoysia filial generations and two parents Qingdao zoysia and manilagrass as the template, select three pairs of SRAP primers, namely primers capable of amplifying specific band not included in female parent on male parent. Perform amplifying and electrophoresis on the male parent, the female parent and the filial generation, and identify according as whether the F1 generation can amplify male parent specific band. The result shows that a filial generation is a real hybrid when each of the nine filial generations has male parent specific band. Thus, a molecular identification system of authenticity of filial generation of Qingdao zoysia and manilagrass is established, by which the authenticity of filial generation of Qingdao zoysia and manilagrass can be quickly identified, the method can also be used for hybrid variety fingerprint map construction andpurity identification.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A Salt Tolerance Gene zmgntl in Zoysia furnosa and Its Expression Vector and Application
InactiveCN106754996BImprove salt tolerancePlant variety improvementEnzymesFermentationBiotechnologyHalophyte
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and discloses a salt-resistant gene ZmGnTL of a halophyte zoysia matrella and an expression vector and an application thereof. The sequence of a novel salt-resistant gene ZmGnTl in zoysia matrella is SEQ ID NO.1. The plant expression vector is obtained by performing a recombination reaction with pEarleyGate103 expression vector plasmids after inserting ZmGnTL after double enzyme digestion of BamHI and NotI into a gateway entry vector pENTR1A. The ZmGnTL of zoysia matrella provided by the invention is the novel salt-resistant gene which can improve the salt resistance of the plant and can be applied to creating salt-resistant novel germplasms and improving plant varieties.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Vegetation restoration method for ecologically fragile areas in northern areas
PendingCN114190236AImprove repair efficiencyPromote growthHops/wine cultivationTurf growingVegetationLight energy
The invention discloses a vegetation restoration method for an ecologically fragile area in the north, and belongs to the field of vegetation restoration. A light-storing noctilucent material is filled between a circular truncated cone cylinder and a light-transmitting rubber film, and one-way perspective films are arranged on the inner wall of the circular truncated cone cylinder and the upper surface of the light-transmitting rubber film; the one-way perspective film is similar to a common mirror, the inner side cannot be seen from the outer side, but the outer side can be clearly seen from the inner side, so that the auxiliary repair device has a relatively strong light reflecting effect in the daytime, the warning effect on the repair subarea can be improved, the manmade accidental damage to the zoysia matrella in the repair subarea is reduced, and the repair efficiency is improved. On the contrary, the outer side cannot be seen from the inner side of the one-way perspective film at night, but the inner side can be clearly seen from the outer side, a certain illumination effect can be achieved at night, light can be absorbed by arranging a light storage type noctilucent material between the circular truncated cone cylinder and the light-transmitting rubber film, and the possibility of loss of stored light energy can be reduced by arranging the one-way perspective film.
Owner:杨莹
Method for planting zoysia matrella on green belts at two sides of traffic lane
InactiveCN105706726AImprove fertilityHigh activityCalcareous fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSoil treatmentNutrient
The invention discloses a method for planting zoysia matrella on green belts at two sides of a traffic lane, relating to the technical field of urban green plant planting. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: soil treatment, plant soaking, plant fertilization and plant clearing. The method is reasonable, the planting is convenient, rich nutrients are ensured, and the activity and freezing resistance of plants can be improved.
Owner:BENGBU YUNLIANYUAN LANDSCAPE GARDEN CO LTD
Interspecific hybridization breeding method for new zoysia plant variety
ActiveCN104429926AGuaranteed purityImprove efficiencyPlant genotype modificationInterspecific hybridizationHabit
The invention discloses an interspecific hybridization breeding method for a new zoysia plant variety and belongs to the technical field of artificial interspecific hybridization breeding of zoysia plants. The method comprises the following steps: with Zoysia japonica and Z.sinica as female parents, and Z.matrella and Z.tenuifolia as male parents, performing artificial hybridization, thereby obtaining the new variety of zoysia plant interspecific hybridization with excellent characters of the parents. The flowering habit of the zoysia plants is fully utilized, namely, when stamens just appear, the anther is not loose, and the stamens are easily removed before the stamens just appear and the anther is loose, so that the purity of filial generations is guaranteed, and the breeding efficiency is improved. The established hybridization breeding system plays an important role in culturing the new zoysia plant variety and promoting the development of lawns in China.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Ecological restoration method of bare land on islands
ActiveCN106688356BImprove breathabilityFull of nutritionBioloigcal waste fertilisersPlant cultivationFiberSoil properties
The invention relates to a method for ecological remediation of sea island bare land. The method includes steps: (1) shallow excavating of the sea island bare land; (2) replacement soil backfilling; (3) landfill of controlled-release active nutritional packages; (4) sowing of zoysia matrella; (5) cuttage of procumbent juniper. By backfilling of improved mellow soil, a soil base of the sea island bare land can be improved, air permeability of the mellow soil is greatly improved due to addition of fiber materials, and less proneness to caking in long-time use is realized after the mellow soil is backfilled to sea island land; due to organic fertilizers, water retaining agents and soil stabilizing agents, the backfilled mellow soil is rich in nutrition, great in water retaining performance and high in soil property stability and provides sufficient nutrients and moisture for early growth of zoysia matrella and procumbent juniper. The controlled-release active nutritional packages are rich in natural organics and adsorbed and stored trace elements and buried into the improved mellow soil to continuously and slowly release and degrade under rain flushing and natural diffusion, so that nutrient loss can be greatly avoided, and continuous nutrient supply can be provided for later growth of zoysia matrella and procumbent juniper.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
Zoysiagrass plant "TMX"
ActiveUS20080282436P1Slow growth ratePromote growthAngiosperms/flowering plantsShade toleranceCultivar
The present culivar TMX (Zoysia matrella Merr.) advantageously has a very slow growing rate in terms of plant height as compared with existing cultivars and requires mowing not more than once a year so as to be maintained in fair condition and allows the amount of fertilizer to be reduced. It also has a high-level of shade tolerance.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
A kind of interspecific hybrid breeding method of new Zoysia plant species
ActiveCN104429926BGuaranteed purityImprove efficiencyPlant genotype modificationInterspecific hybridizationHabit
The invention discloses an interspecific hybridization breeding method for a new zoysia plant variety and belongs to the technical field of artificial interspecific hybridization breeding of zoysia plants. The method comprises the following steps: with Zoysia japonica and Z.sinica as female parents, and Z.matrella and Z.tenuifolia as male parents, performing artificial hybridization, thereby obtaining the new variety of zoysia plant interspecific hybridization with excellent characters of the parents. The flowering habit of the zoysia plants is fully utilized, namely, when stamens just appear, the anther is not loose, and the stamens are easily removed before the stamens just appear and the anther is loose, so that the purity of filial generations is guaranteed, and the breeding efficiency is improved. The established hybridization breeding system plays an important role in culturing the new zoysia plant variety and promoting the development of lawns in China.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A new plant salt tolerance gene zmduf1644 and its expression vector and application
InactiveCN106754959BImprove salt tolerancePlant variety improvementPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyHalophyte
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Zoysiagrass plant `TMX`
The present culivar ‘TMX’ (Zoysia matrella Merr.) advantageously has a very slow growing rate in terms of plant height as compared with existing cultivars and requires mowing not more than once a year so as to be maintained in fair condition and allows the amount of fertilizer to be reduced. It also has a high-level of shade tolerance.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
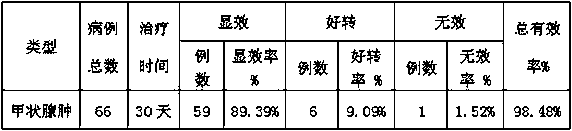
Drug for treatinggoiter and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107648396AEffective treatmentAnthropod material medical ingredientsPteridophyta/filicophyta medical ingredientsLoropetalumVentilago leiocarpa
The invention discloses a drug for treatinggoiter and a preparation method thereof. The drug is mainly prepared from spiny Amarauth herb, goldhair hedyotis herb, wideleaf osbeckia roots, desmodium triquetrum, flos farfarae, scandent hop, kudzu vineroots, stems and leaves of chinese stauntonvine, murraya euchrestifolia, naroow-leaves Sida, stramonium, wild eucommia bark, paniculate swallowwort roots, desmodium triflorum, bark of Chinese catalpa, Chinese loropetalum herb, rauvolfia verticillate, sheathed monochoria herb, pouzolzia zeylanica, henry clematis roots, zoysia matrella, lepidogrammitisdrymoglossoides, ventilago leiocarpa Benth, momordica grosvenori, mole crickets and galium aparine according to a certain weight proportion. The drug has the functions of clearing heat, promoting diuresis, removing toxicity for detumescence, dispelling the wind, reducing phlegm, invigorating the circulation of blood and dispersing blood stasis, is used for treating goiter and is quick to take effect and good in treating effect.
Owner:马雪英
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com