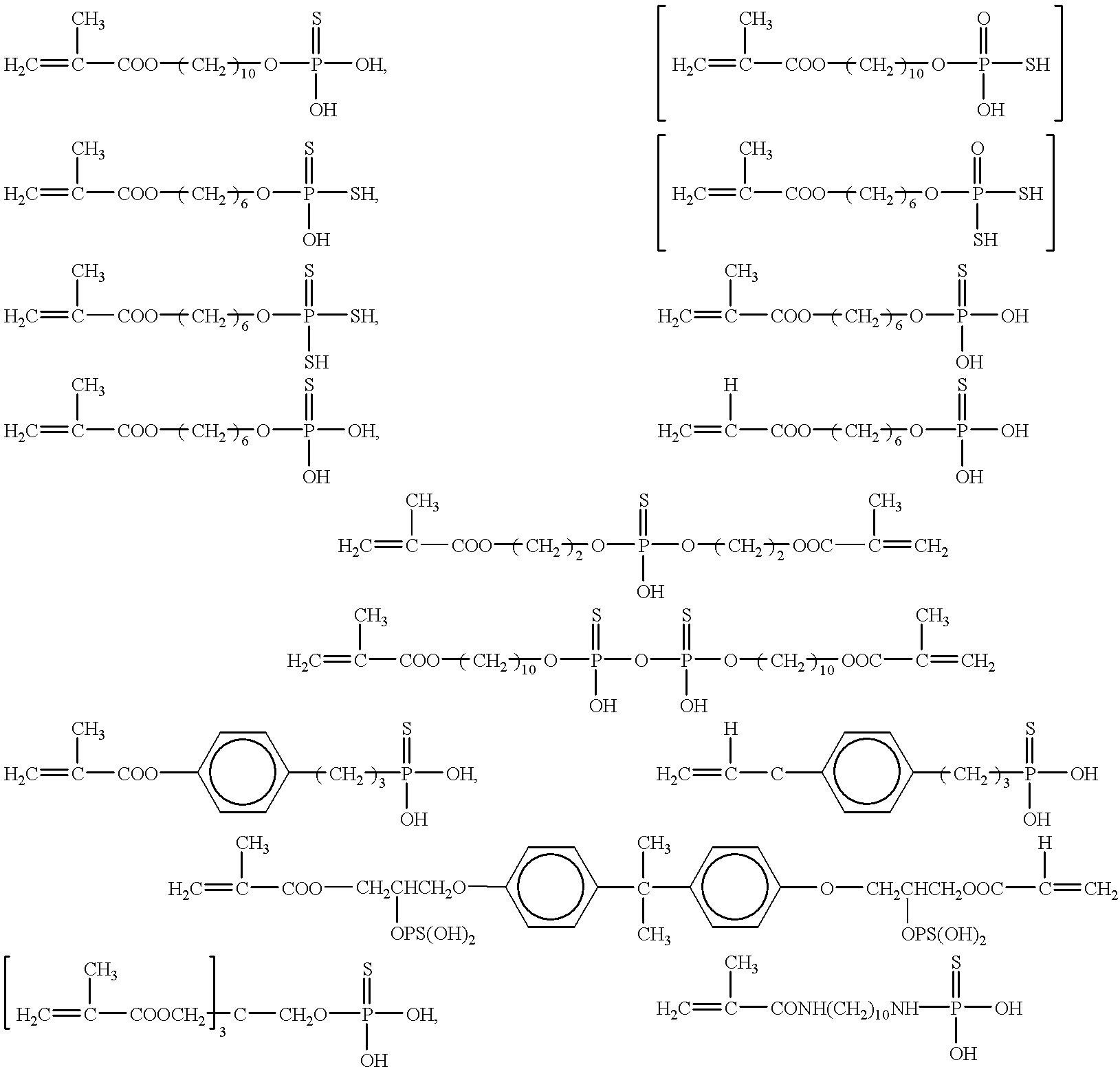
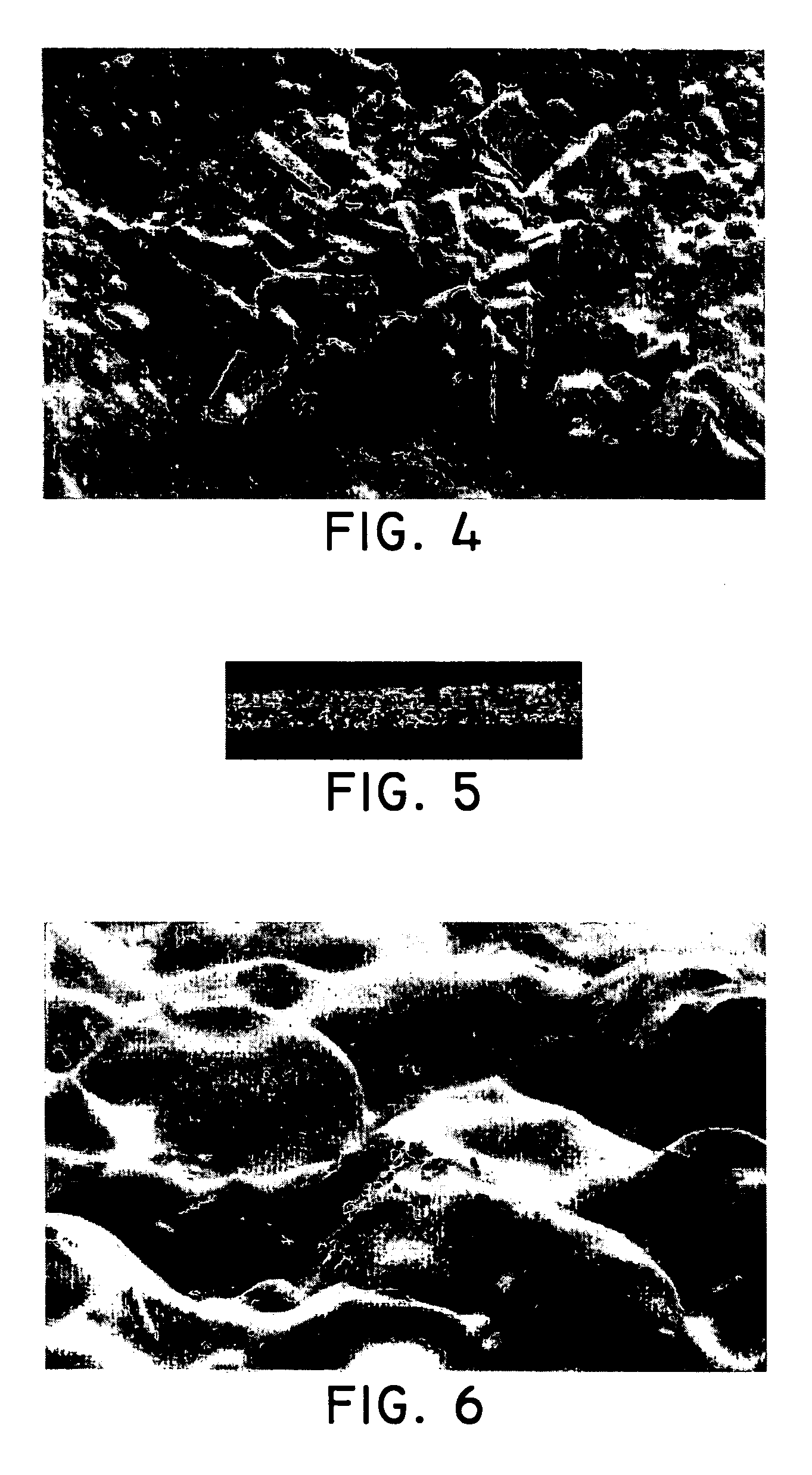
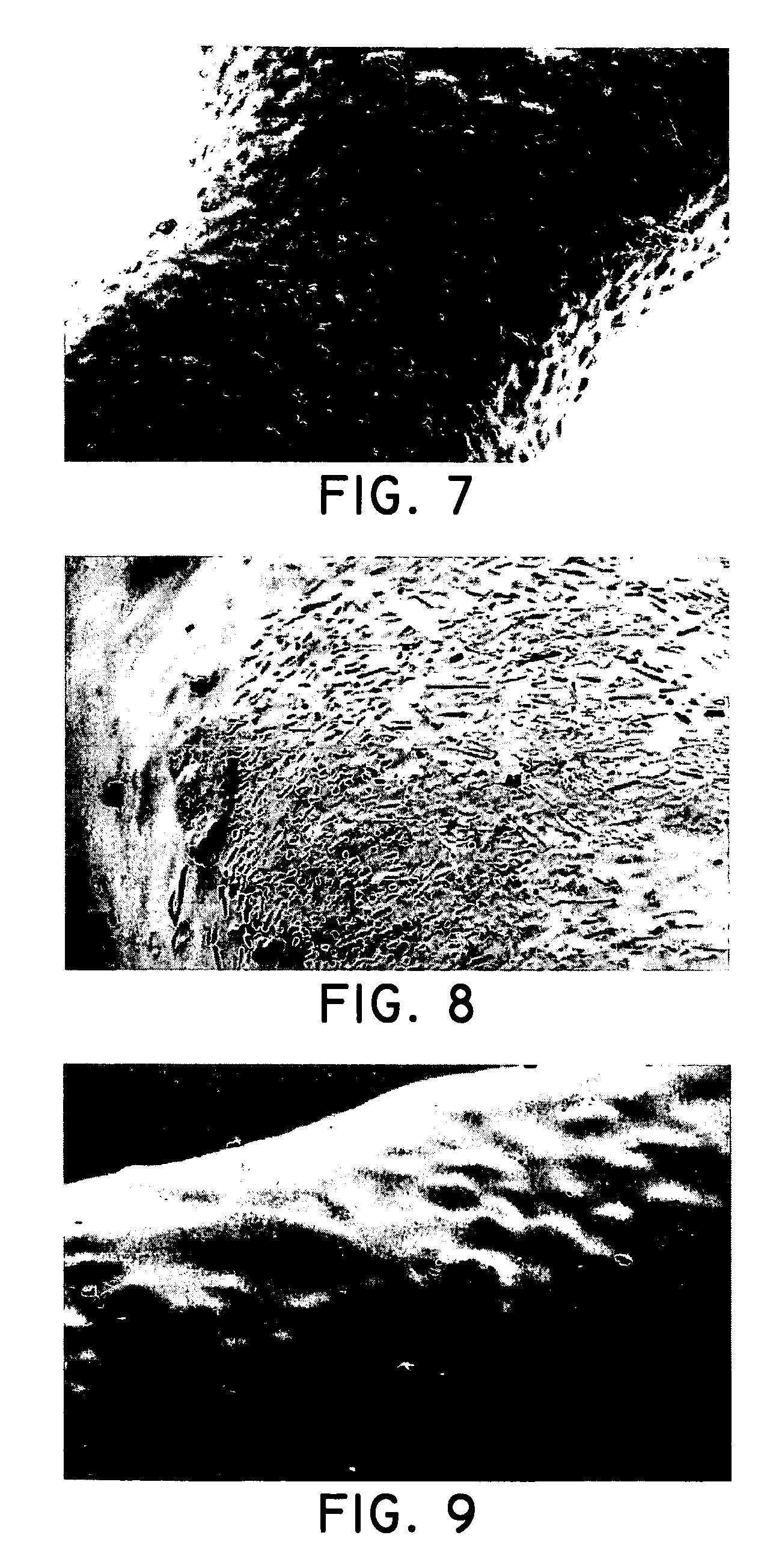
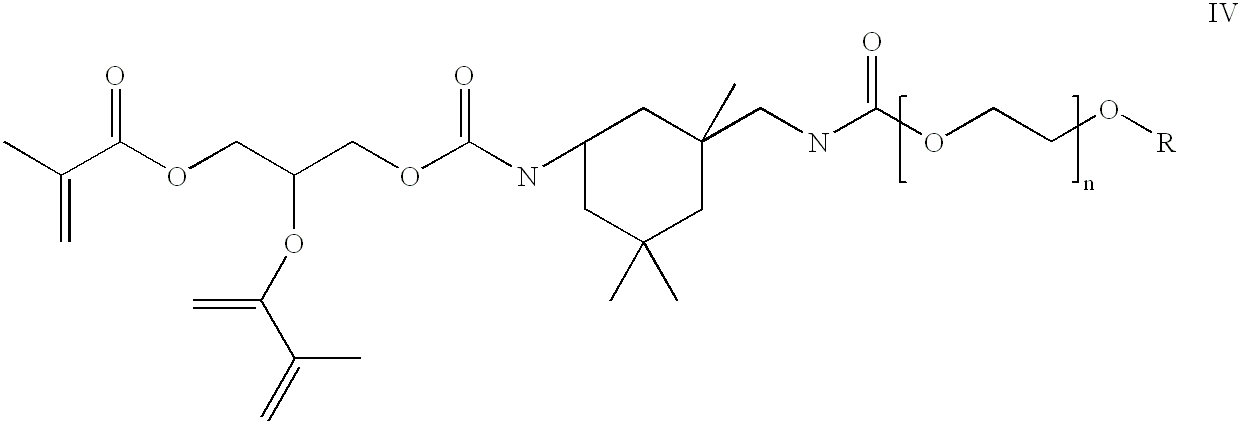
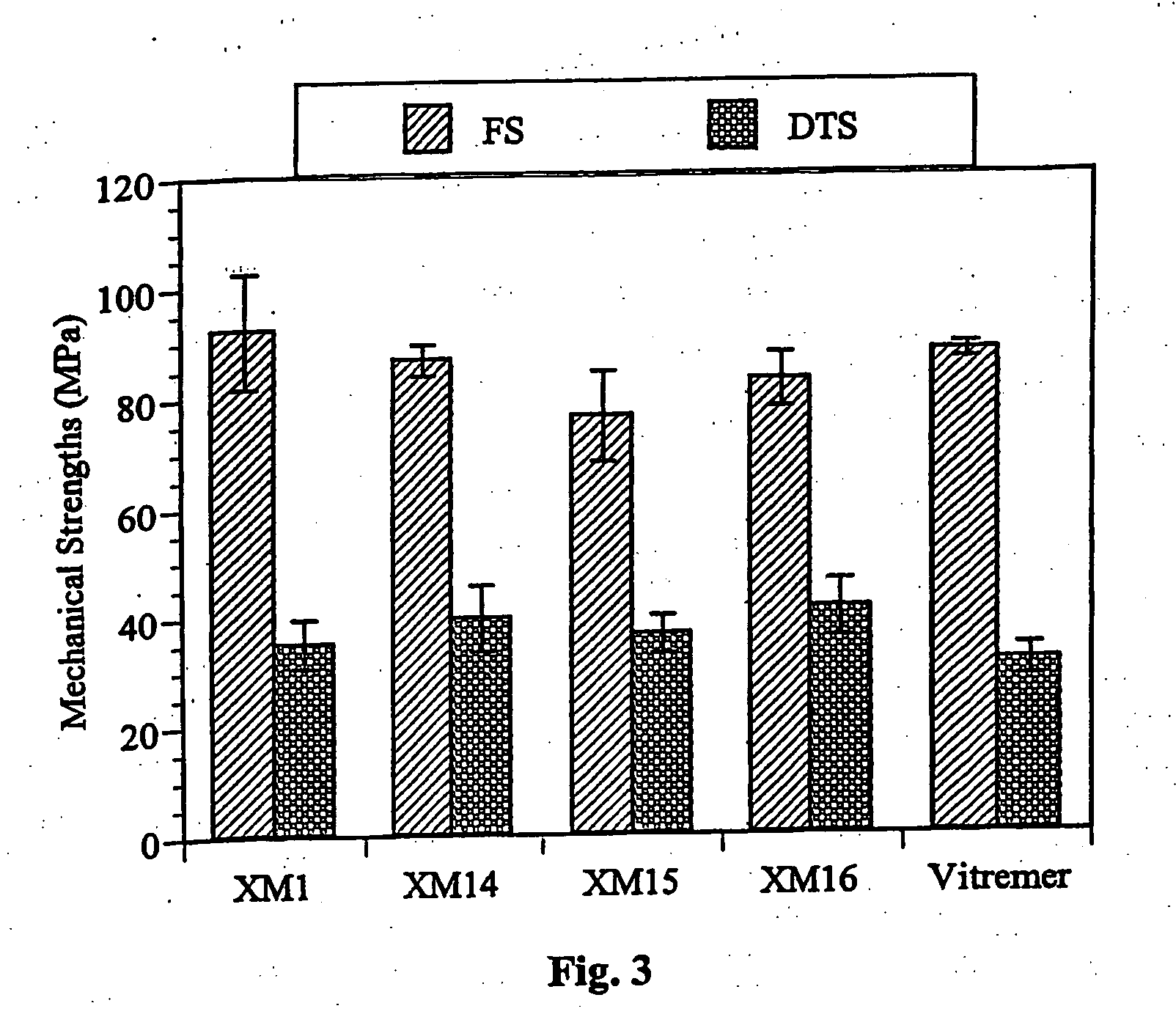
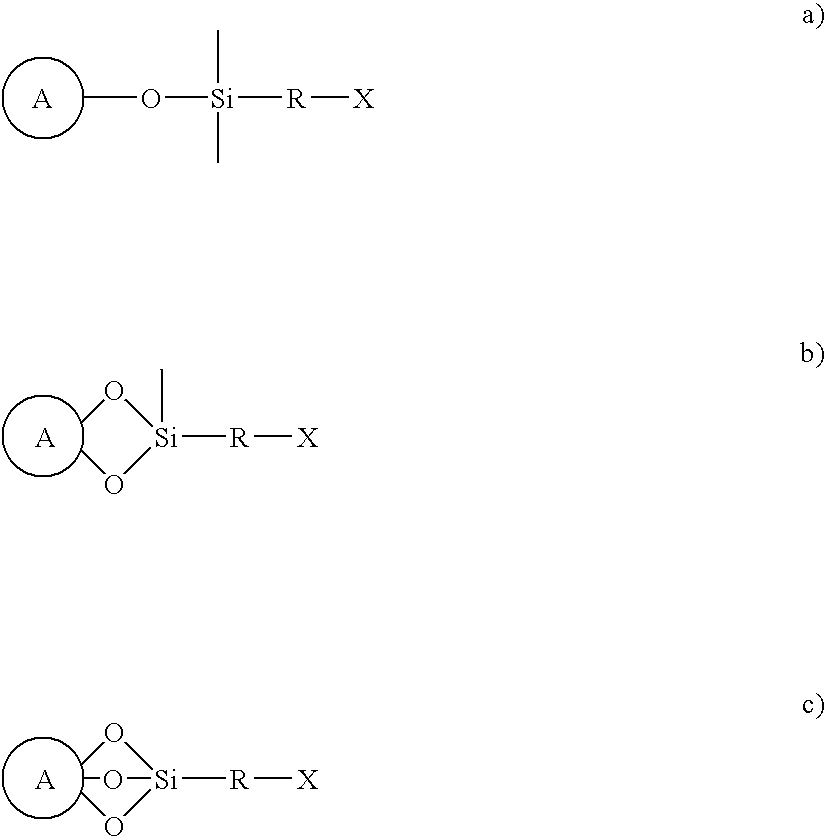
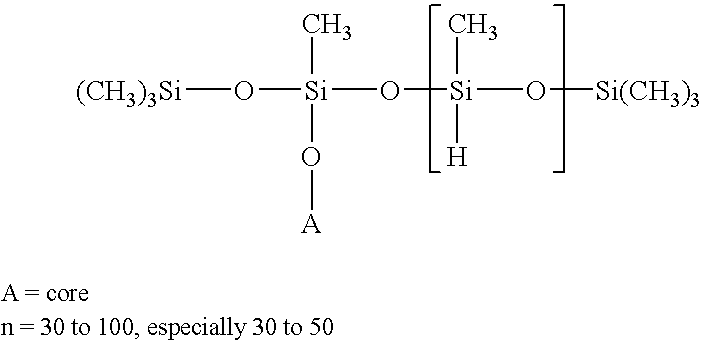
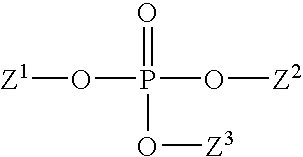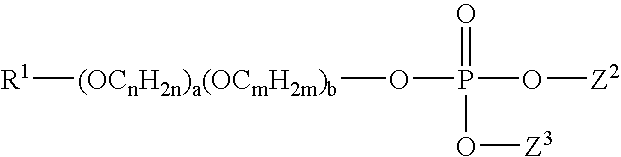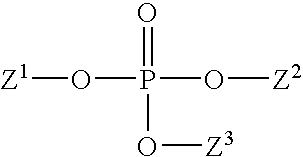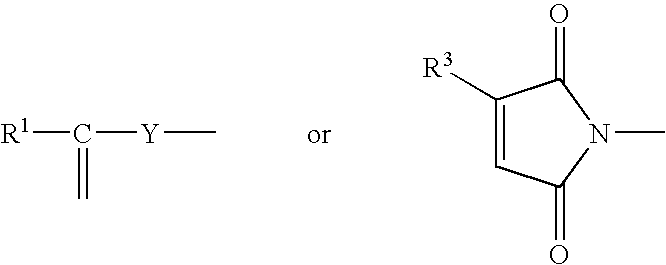Patents
Literature
570results about "Teeth protective coatings" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dental adhesive kit
A kit for dental adhesive comprising a radical polymerizable monomer having an acid group in the molecule, a photosensitizer and / or a peroxide, a water-soluble organic solvent, an organic sulfinic acid and / or a salt thereof or a barbituric acid and / or a derivative thereof, and water. The kit may further comprises a radical polymerizable monomer which has no acid group and is insoluble or hardly soluble in water, an amine compound, a silane coupling agent and a 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-dithion derivative. By using this kit, the adhesive composition can be applied directly to a dentine without conducting a pretreatment.
Owner:SUN MEDICAL
Compositions and Methods for Improving Overall Tooth Health and Appearance
ActiveUS20080247973A1Avoid lostSuperior anticariesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAmmonium compoundsStaining
Disclosed are oral care compositions comprising selected surface-active organophosphate compounds and methods of use to provide protection of teeth from erosion caused by the action of chemicals, such as harsh abrasives and acids. The surface-active organophosphate compounds are substantive to teeth, the phosphate groups binding the calcium in teeth and thus preventing loss of calcium from dissolution when contacted with acids. The organophosphate compound may also deposit a protective surface coating that prevents contact of teeth with erosive challenges. Selected organophosphate compounds contain one or more phosphate groups and are combined in the oral care composition with one or more of a fluoride ion agent, an antimicrobial agent preferably selected from quaternary ammonium compounds and polyvalent metal salts, an anticalculus agent and additional surfactant, to provide benefits including superior anti-erosion, anticaries, antiplaque and anti-staining as demonstrated by enhanced fluoride uptake, remineralization, resistance to acid demineralization and antimicrobial activities, resulting in improved overall tooth health, structural integrity and appearance.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Dental bleaching compositions containing sucralose
Dental bleaching compositions that include sucralose. The bleaching agent is dispersed within a carrier, which is optimally sticky and viscous such as a mixture of propylene glycol and silica fume. Anhydrous propylene glycol and / or anhydrous glycerin are especially useful in order to maintain the desired degree of hydration of the perborate being used. Flavorants may be added to enhance the taste of the dental compositions, since they will be used within a person's mouth. For best results, a flexible, thin-walled, comfortable-fitting, custom dental tray is used with the dental bleaching compositions. The dental compositions are sufficiently sticky and viscous so as to adhere and retain a dental tray against a person's teeth which is designed so as to not exert significant mechanical pressure onto the person's teeth.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
Dental bleaching compositions containing sucralose
InactiveUS6322774B1Effectively disguise the bitter taste of such agents over timeAccurate quantityCosmetic preparationsImpression capsFlavouring agentGlycerol
Dental bleaching compositions that include sucralose as a non-nutritive sweetener. The bleaching agent is dispersed within a carrier, which is optimally sticky and viscous, such as a mixture of a liquid or solvent carrier and a tackifying agent. Propylene glycol and / or glycerin are especially useful liquid or solvent carriers. Flavorants may be added to enhance the taste of the dental compositions, since they will be used within a person's mouth. For best results, a flexible, thin-walled, comfortable-fitting, custom dental tray is used with the dental bleaching compositions. The dental compositions are preferably sufficiently sticky and viscous so as to adhere and retain a dental tray against a person's teeth which is designed so as to not exert significant mechanical pressure onto the person's teeth.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
Non-volatile dental compositions containing multifunctional acrylate compounds and lacking an oxygen-inhibited layer
Dental composite formulations containing an initiator and a multiacrylate compound are disclosed. The formulations lack methyl methacrylate, a volatile, irritating, and potentially hazardous material commonly found in dental formulations. The multiacrylate compound has at least three acrylate functionalities per molecule. The formulations cure to form a surface lacking an oxygen inhibition layer. The formulations can be used as dental sealants, dental coatings, and in fingernail / toenail repair applications.
Owner:BISCO
Methods of using two-part self-adhering dental compositions
ActiveUS20050014861A1High bonding strengthSimple methodImpression capsTooth crownsArylHigh concentration
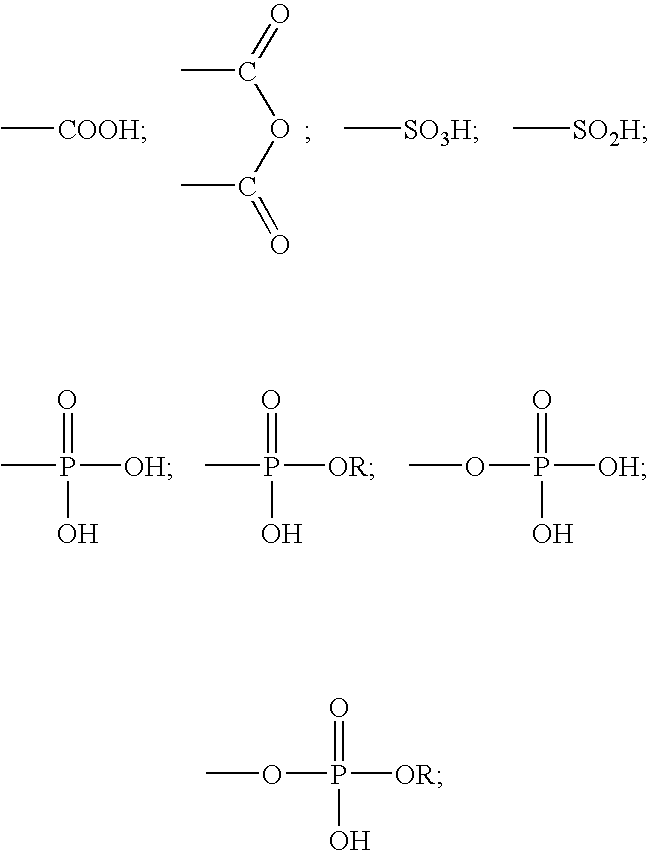
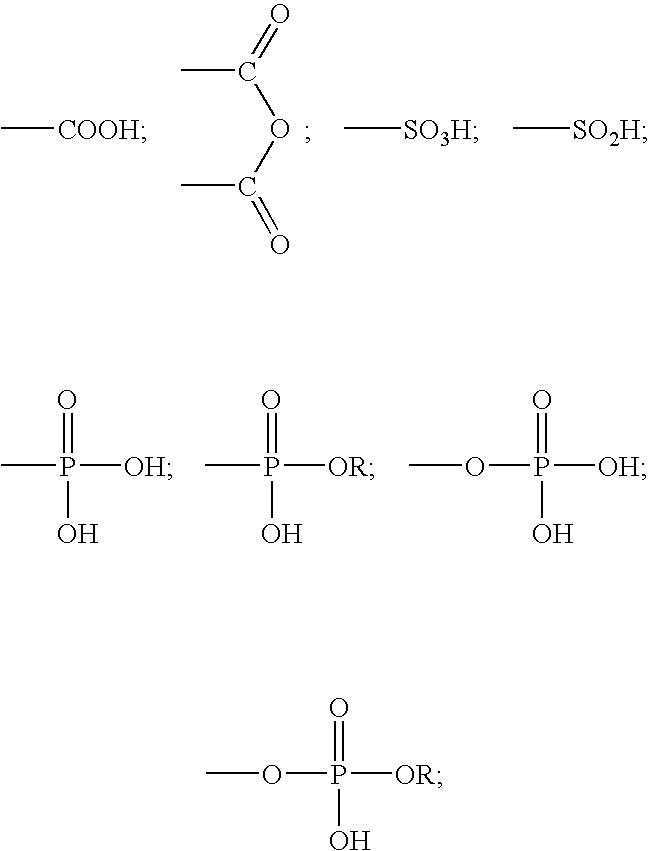
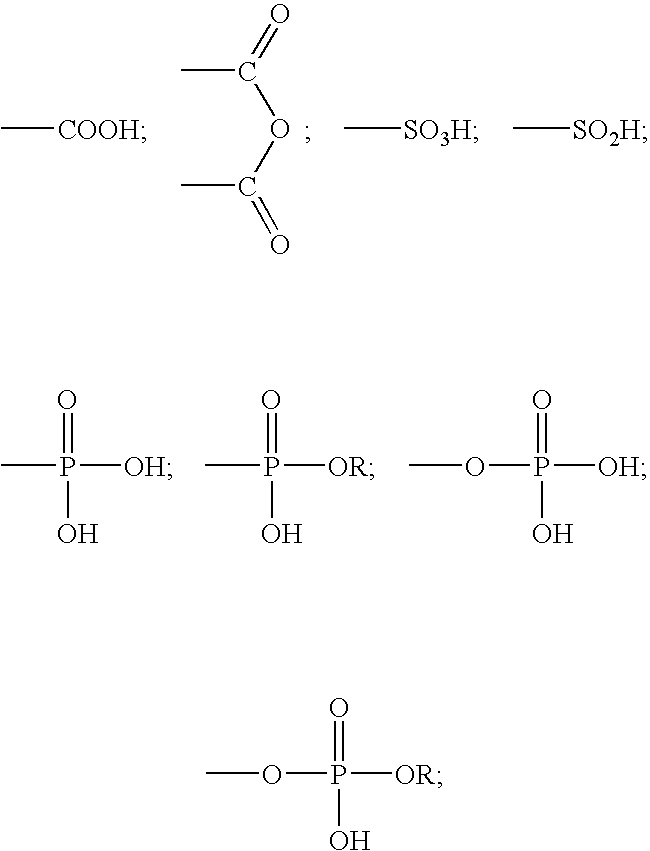
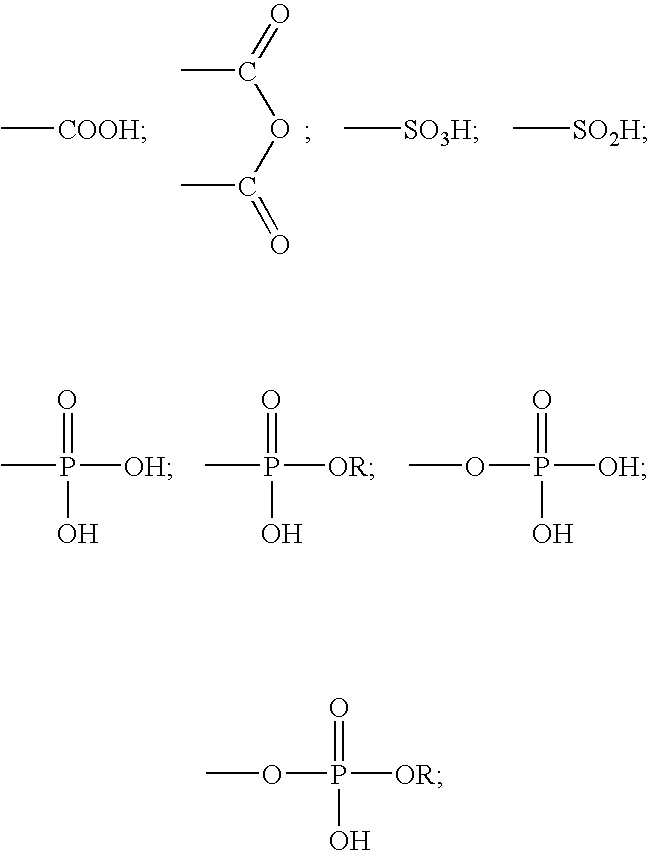
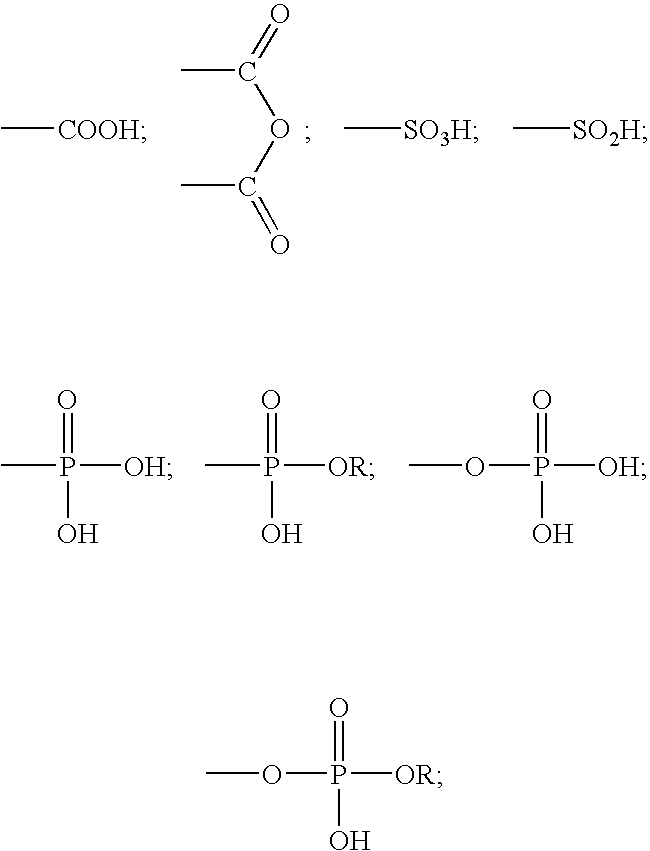
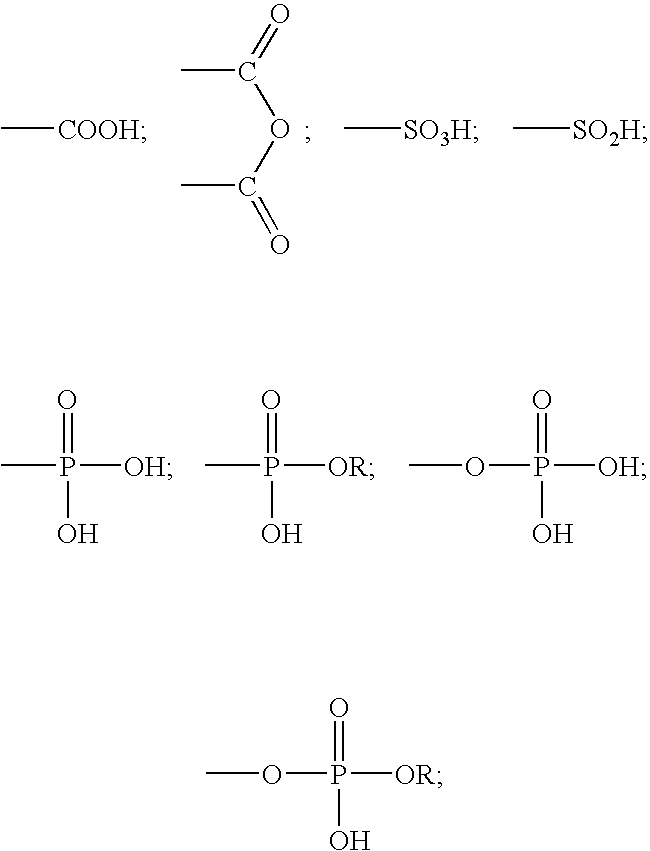
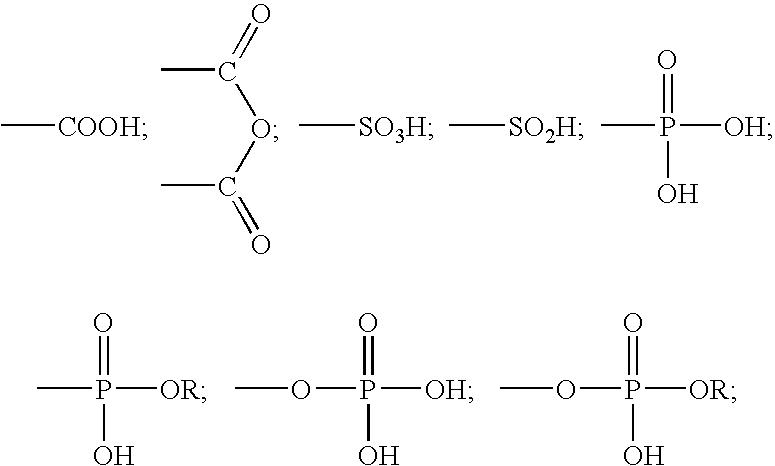
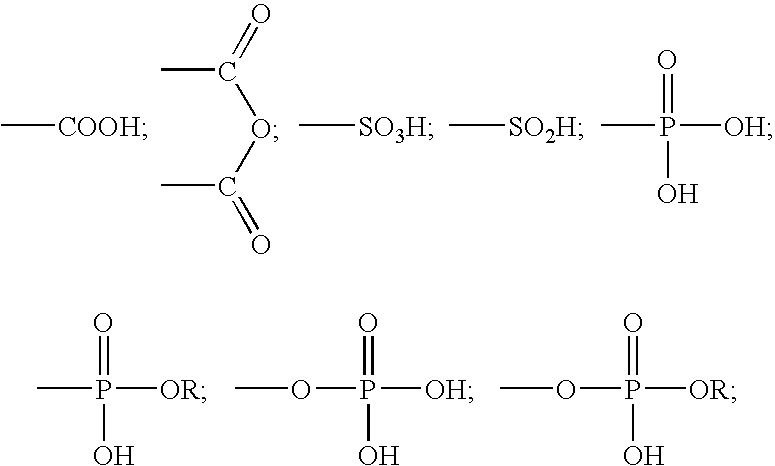
A method for providing a dental composition comprising providing a paste / paste two-part self-adhering dental composition comprising (a) at least one acidic compound containing at least one acidic moiety selected from the group consisting of where R is an alkyl or aryl group; (b) at least one polymerizable monomer without any acidic group where the polymerizable group is selected from the group consisting of an acrylate, a methacrylate and a vinyl group; (c) at least one finely divided filler; (d) a reducing agent; and (e) an oxidizing agent; and providing instructions for mixing the two pastes immediately prior to application where the ratio of a first paste containing (a) or a higher concentration of (a) to a second paste not containing (a) or containing a lower concentration of (a) is greater than 1:1 (by volume). The method also includes mixing the two pastes and applying the mixed composition to a dental substrate.
Owner:THE KERR
Coatings with crystallized active agent(s) and methods
InactiveUS20060134168A1Increased formationIncrease ratingsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMedicineActive agent
The present invention relates to coatings with crystallized active agent(s) and related methods. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method for coating a medical device including selecting a solvent and a polymer, selecting a concentration of an active agent of at least a certain amount of saturation, forming a coating composition having the selected concentration of the active agent, and applying the coating composition to the medical device. In an embodiment, the invention includes an elution control coating disposed on a medical device, the elution control coating including a polymer, and an active agent, wherein the active agent is at least about 80% crystallized within one week of being disposed on the medical device. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method for enhancing the formation of active agent crystals within a coating layer including forming a coating solution and adjusting the concentration of the active agent in the coating solution to reach some percentage of the active agent saturation point. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of enhancing crystallization of an active agent, the method including forming a coating solution comprising a polymer, an active agent, and a solvent; applying the coating solution to a substrate; and increasing the rate of active agent nucleation within the coating.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Methods of using two-part self-adhering dental compositions
ActiveUS7214726B2High bonding strengthSimple methodImpression capsTooth crownsArylHigh concentration
A method for providing a dental composition comprising providing a paste / paste two-part self-adhering dental composition comprising(a) at least one acidic compound containing at least one acidic moiety selected from the group consisting ofwhere R is an alkyl or aryl group;(b) at least one polymerizable monomer without any acidic group where the polymerizable group is selected from the group consisting of an acrylate, a methacrylate and a vinyl group;(c) at least one finely divided filler;(d) a reducing agent; and(e) an oxidizing agent;and providing instructions for mixing the two pastes immediately prior to application where the ratio of a first paste containing (a) or a higher concentration of (a) to a second paste not containing (a) or containing a lower concentration of (a) is greater than 1:1 (by volume). The method also includes mixing the two pastes and applying the mixed composition to a dental substrate.
Owner:THE KERR
Dental compositions and methods with arylsulfinate salts
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
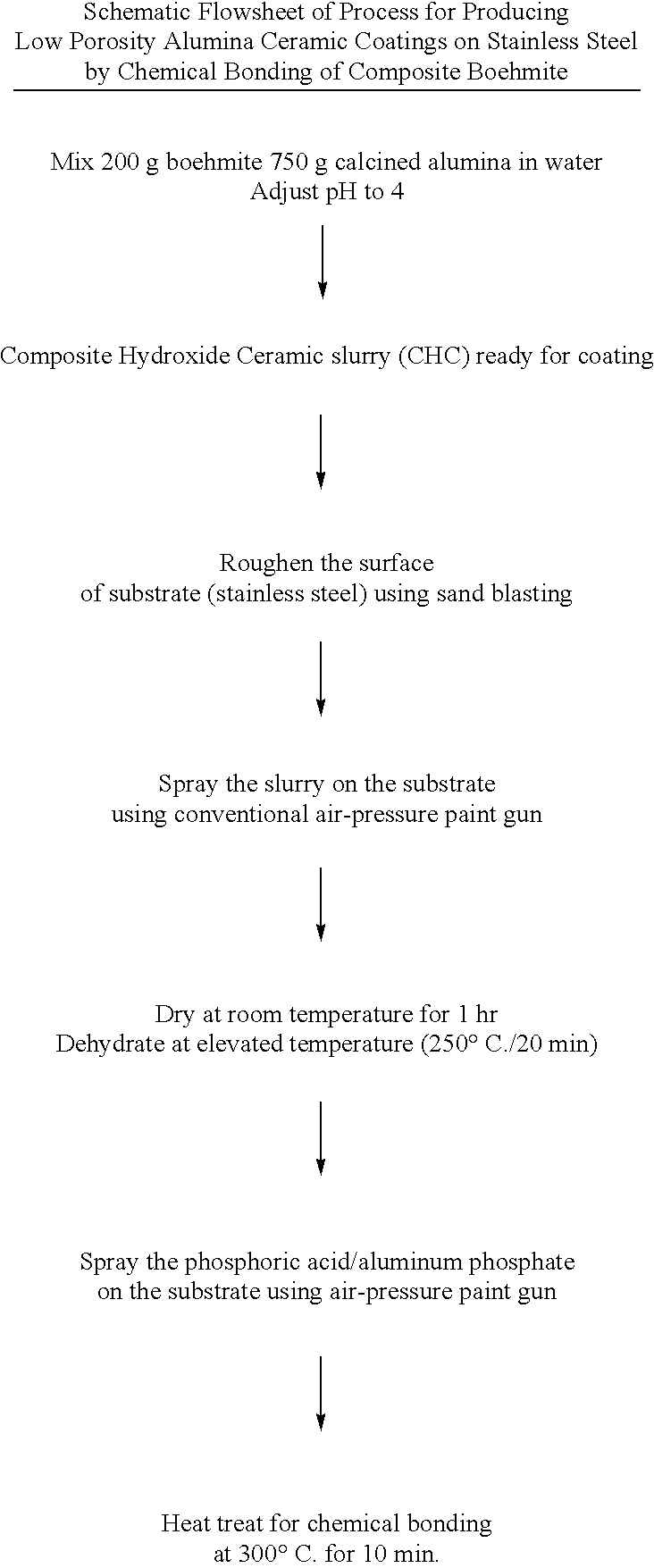
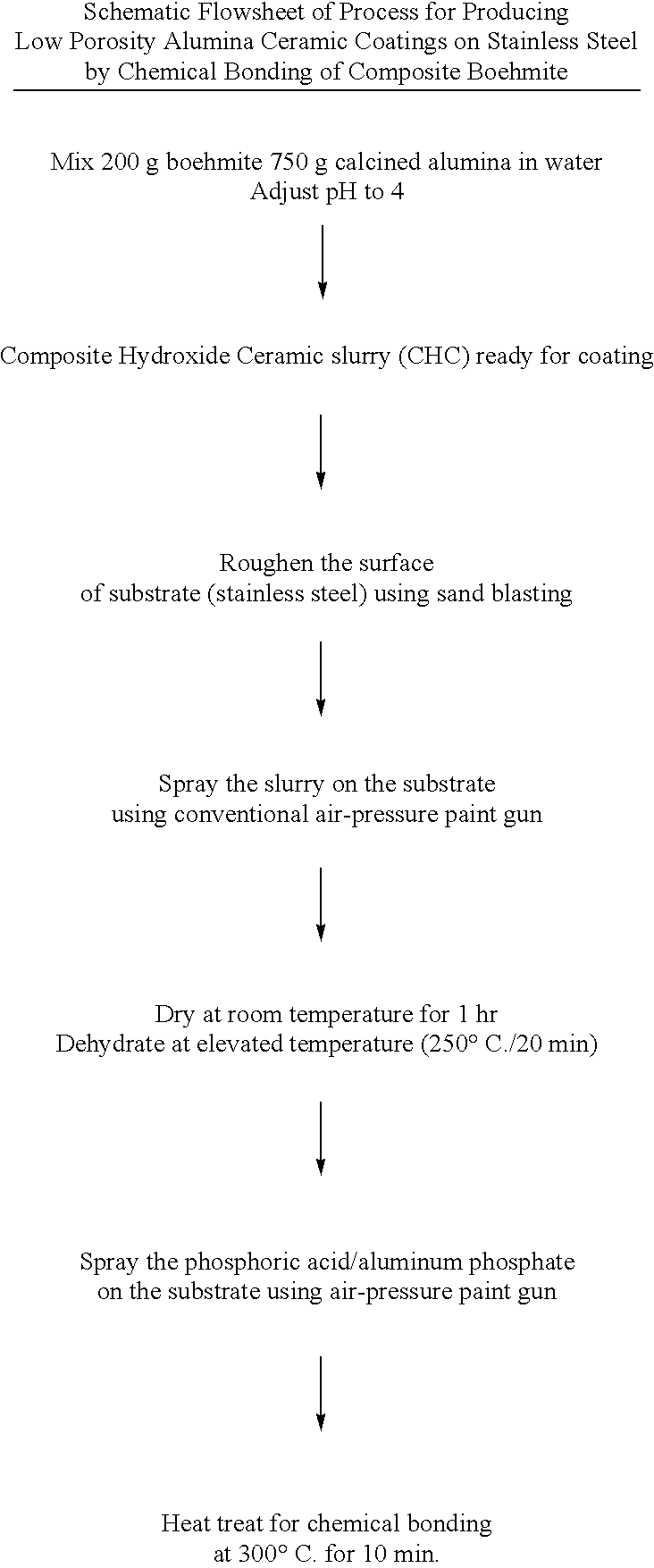
Process for making chemically bonded composite hydroxide ceramics
InactiveUS6770325B2Reduce reactivityMinimizes shrinkageImpression capsPretreated surfacesPhosphateCeramic coating
This invention relates to novel process of preparing chemically bonded composite hydroxide ceramics by exposing a thermally treated hydroxide ceramic to phosphate reagent and subsequent heat treating the resulting system to initiate a rapid chemical bonding reaction. Such combined hydroxide / chemical bonding process can be used to fabricate ceramics or ceramic coatings for a variety of high and low temperature applications, including corrosion protection, wear resistance, dielectric properties, metal reinforced ceramics, ceramic membranes, non-sticky surfaces, bio-active ceramics, thermal barrier ceramics, non-wetted surfaces, and others.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
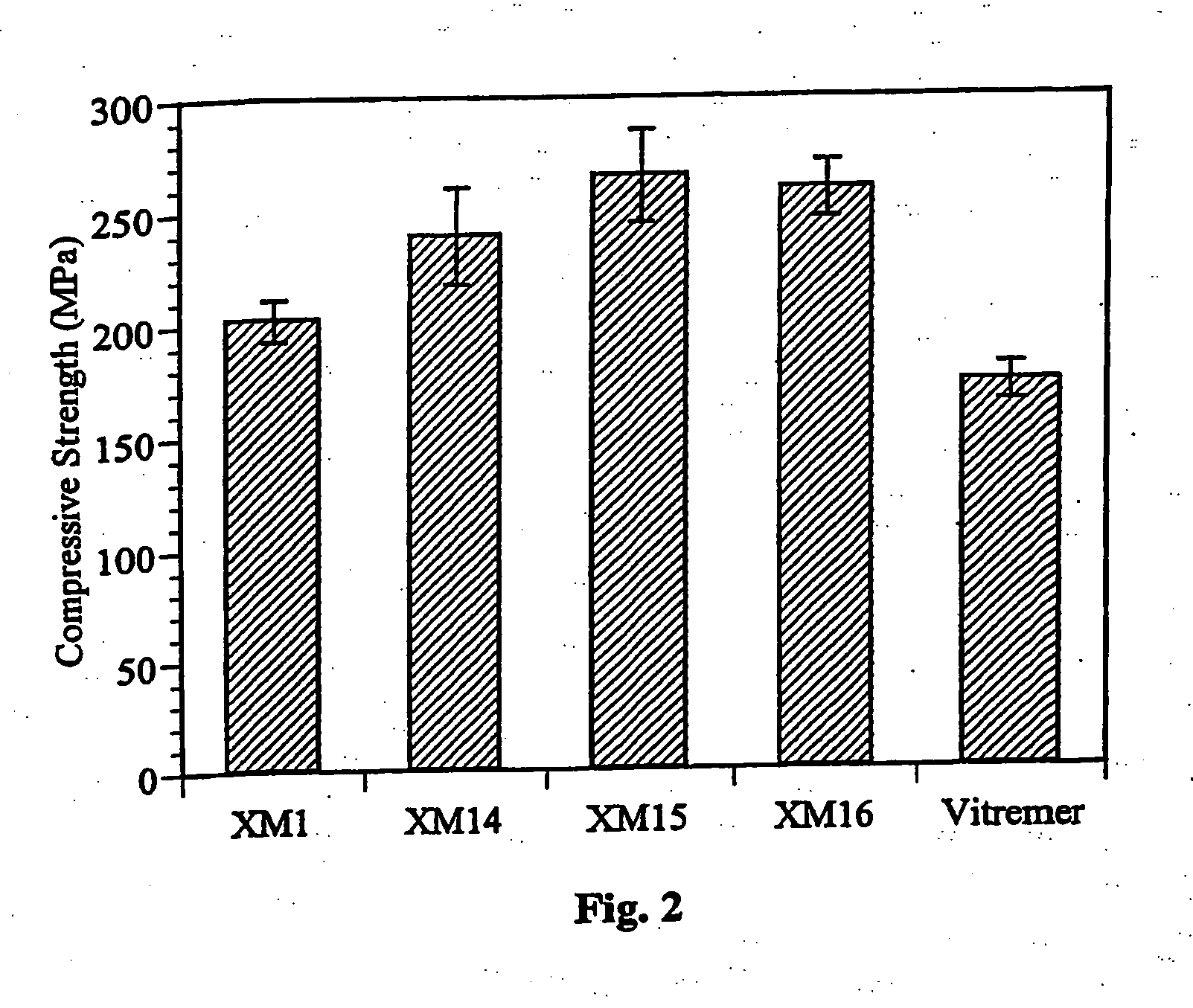
Dental composite materials
A polymerizable dental composition, comprising a polymerizable resin composition; and a filler composition comprising a bound, nanostructured colloidal silica
Owner:PENTRON CLINICAL TECH
Process for making chemically bonded composite hydroxide ceramics
InactiveUS20020107133A1Minimizes shrinkagePromote environmental protectionImpression capsPretreated surfacesPhosphateCeramic coating
This invention relates to novel process of preparing chemically bonded composite hydroxide ceramics by exposing a thermally treated hydroxide ceramic to phosphate reagent and subsequent heat treating the resulting system to initiate a rapid chemical bonding reaction. Such combined hydroxide / chemical bonding process can be used to fabricate ceramics or ceramic coatings for a variety of high and low temperature applications, including corrosion protection, wear resistance, dielectric properties, metal reinforced ceramics, ceramic membranes, non-sticky surfaces, bio-active ceramics, thermal barrier ceramics, non-wetted surfaces, and others.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
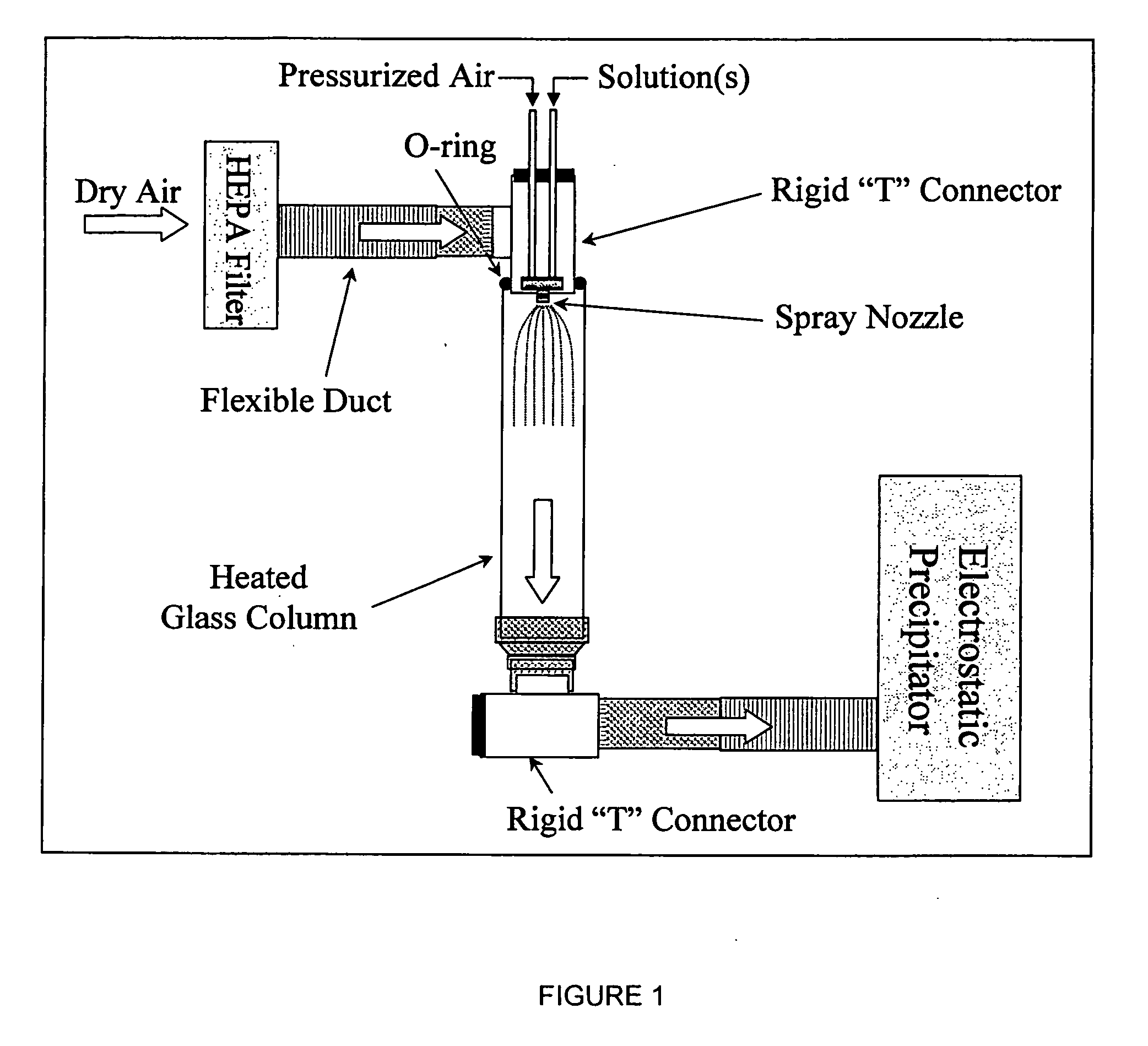
Nanostructured bioactive materials prepared by dual nozzle spray drying techniques
ActiveUS20060110306A1Easy to evaporatePromote formationMagnesium fluoridesImpression capsNanoparticleNanostructure
Nano-particles of calcium and phosphorous compounds are made in a highly pure generally amorphous state by spray drying a weak acid solution of said compound and evaporating the liquid from the atomized spray in a heated colunm followed by collection of the precipitated particles. Hydroxyapatite (HA) particles formed by such apparatus and methods are examples of particle manufacture useful in bone and dental therapies. Dual nozzle spraying etechniques are utilized for generally insoluble compounds.
Owner:ADA FOUND
Self etching adhesive primer composition and polymerizable surfactants
The invention provides a self etching adhesive dental primer composition, a method of use of the primer composition and a product formed from the primer. The dental product is formed from the primer composition which includes water, surfactant and polymerizable material in suspension in the water. The polymerizable material includes monomers which are water immiscible. Preferably the monomers have an average molecular weight less than 1000. The primer composition is used by applying the composition to unetched dental tooth enamel and the polymerizable material is polymerized to form a dental product having adhesion to the enamel of more than 13 MPa. Improved surfactants which contain at least one ethenically unsaturated polymerizable group are provided in accordance with the invention. Surfactants of the present invention copolymerize with and become an integral part of any polymerizable resin matrix in which they are incorporated. This prevents migration of the surfactant through the matrix or slow leaching-out through the interfaces, and brings advantages of biocompatibility and stability of the physical properties of the cured matrix. In addition, the surfactant becomes a permanent part of the matrix, and forms part components of the matrix.
Owner:DENTSPLY DETREY GMBH
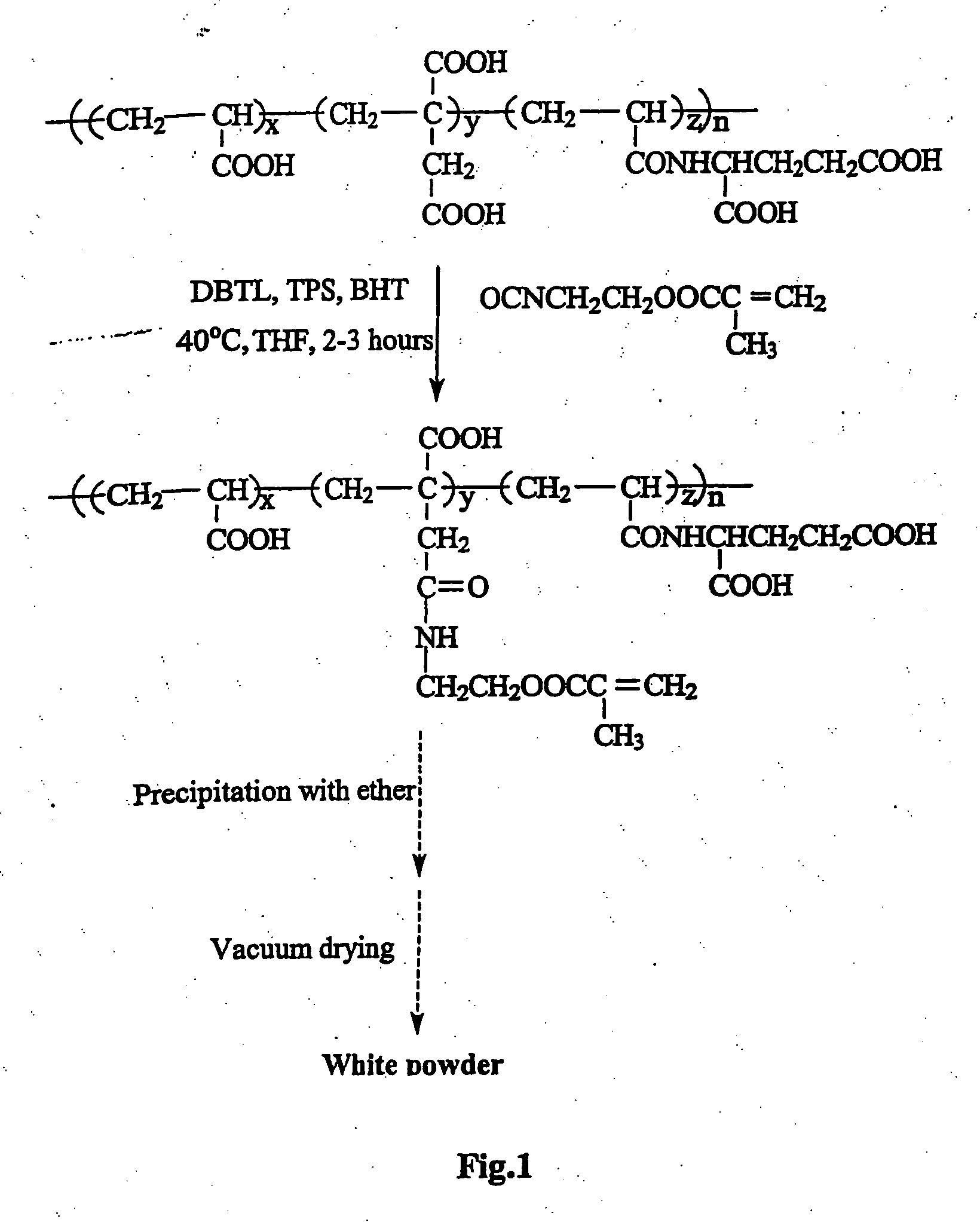
Dental composition containing a polyfunctional (meth)acrylate comprising urethane, urea or amide groups, method of production and use thereof
The invention relates to a dental composition comprising a) a hardenable compound (A1), b) a filler (B1), c) an initiator (C1) being able to initiate curing of compound (A1), compound (A1) having the structure A-(-S1-U-S2-MA)n, with A being a connector element, S1 being a spacergroup comprised of units connected with each other and comprising at least 4 units, S2 being a spacergroup comprised of units connected with each other and comprising at least 4 units, U being an urethane, an amide or an urea group connecting spacergroups S1 and S2, MA being an acrylate or methacrylate group and n being 3 to 6. The invention also relates to a process of producing this dental composition and using the dental composition e.g. as a temporary and / or long term crown and bridge material.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Silver-containing dental composition
InactiveUS20050265931A1Improved color stabilityCosmetic preparationsImpression capsRedoxMechanical property
A dental composition comprising a silver-containing ceramic having antimicrobial and color stabilizing properties and methods for using the composition. The composition comprises a silver-containing glass powder or a silver-containing zeolite powder, at least one monomer having at least one ethylenically unsaturated group, and a polymerization initiator system. Other components, such as a filler, may also be included. The inventive composition possesses antimicrobial properties and exhibits excellent mechanical properties upon curing. Additionally, when the polymerization initiator is a two-part redox initiator system, the composition has improved color stability. The inventive composition can be used as a dental restorative composition, an endodontic composition, an orthodontic composition, and / or a prosthetic composition.
Owner:THE KERR
Two-component initiator system (amine-free) with very good storage stability and particular suitability for acid systems
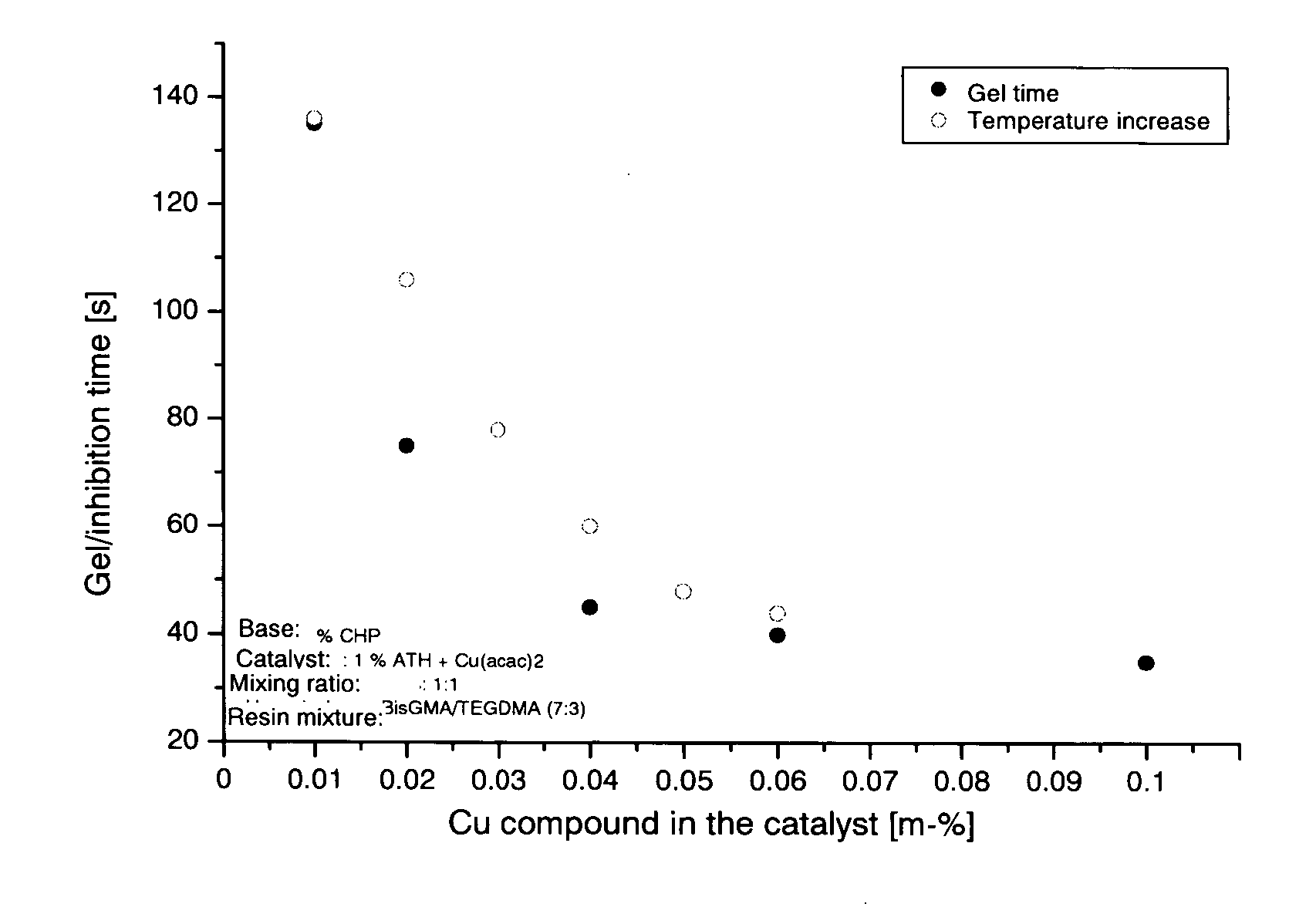
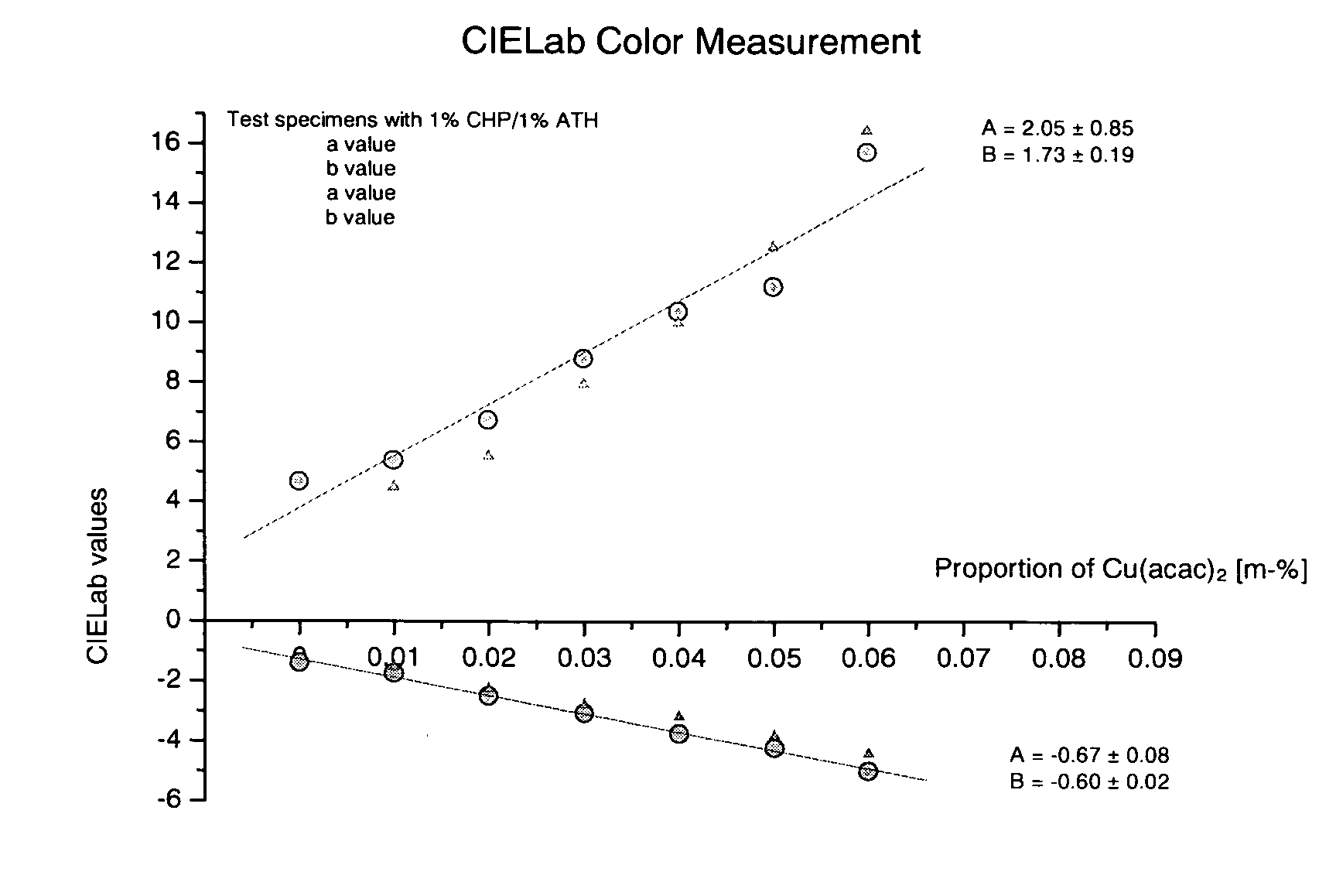
A two-component initiator system having accelerators for curing polymerizable materials comprising the following components: (a) a hydroperoxide compound containing one or more hydroperoxide groups that are bound to a tertiary carbon; (b) a thiourea derivative; and (c) as accelerator, a copper compound which is soluble in the preparation is preferably free of amine and is particularly suited for polymerizable dental compositions.
Owner:HERAEUS KULZER
Glass-ionomer cements containing amino acids
InactiveUS20050165136A1Good biocompatibilityImprove hydrophilicityImpression capsMedical preparationsGlass ionomersMedicine
Disclosed are ionomeric compositions and ionomeric cements containing the compositions. The cements are useful in dental and orthopedic medicine.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
High-temperature resistant polymerizable metal oxide particles
High-temperature resistant polymerizable metal oxide particles having a glass transition temperature of the homopolymerizable >=100° C. and a core A. The core includes an oxide of a metal or semimetal of the third to sixth main group, of the first to eighth subgroup of the periodic table, or of the lanthanides, and has at least one group -(B)w-X bound via the oxygen atom of the oxide or hydroxide, in which B represents a binding link, and X represents a reactive functional group, and w is equal to 0 or 1. The inventive particles are useful, in particular, for producing coating materials, molding materials and adhesives.
Owner:INST FUR OBERFLACHENMODIFIZIERUNG EV +1
Antimicrobial compositions for use in products for petroleum extraction, personal care, wound care and other applications
ActiveUS20140271757A1Improve viabilityProvide benefitsBiocideCosmetic preparationsSolubilityPersonal care
Compositions having antimicrobial activity contain surface functionalized particles comprising an inorganic copper salt which has low water solubility. These types of inorganic salts may also be introduced in porous particles to yield antimicrobial compositions. The compositions may optionally comprise additional antimicrobial agents, salts with high water solubility, organic acids, salts of organic acids and their esters. The compositions may be added to various fluids used in the petroleum extraction industry, or used as coatings on components used in this industry. These antimicrobial materials may be used for reducing both anaerobic and aerobic bacteria and are also useful for reducing corrosion of ferrous components caused by anaerobic bacteria. Although such compositions may be used for any antimicrobial application, and some of the other important uses of these compositions are in wound care, personal care and waste processing.
Owner:AGIENIC
Two-part self-adhering dental compositions
ActiveUS7166651B2Simple procedureSave a lot of timeImpression capsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMethacrylateThiourea
A shelf-stable two-part self-adhering dental composition and method. The composition comprises(a) at least one acidic compound containing at least one acidic moiety selected from the group consisting ofwhere R is an alkyl or aryl group;(b) at least one polymerizable monomer without any acidic group where the polymerizable group is selected from the group consisting of an acrylate, a methacrylate and a vinyl group;(c) a substituted thiourea selected from the group consisting of 1-(2-pyridyl)-2-thiourea and 1-(2-tetrahydrofurfuryl)-2-thiourea; and(d) a hydroperoxide compound with at least one hydroperoxide group attached to a tertiary carbon. The first and second parts are then mixed immediately prior to application, applied to a dental substrate, and hardened. The bond strength of the mixed composition to dentine substrate is at least 3 MPa. The composition has excellent shelf-life and is self-adhering to various dental substrates such as a tooth, metal alloy and porcelain. It can be used as a filling material, a cement, a liner / base, a pit / fissure sealant, a primer or an adhesive.
Owner:THE KERR
Antimicrobial film-forming dental compositions and methods
InactiveUS20060204452A1Improve efficiencyEnhanced levelCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsLipid formationWater dispersible
The present application provides dental compositions, methods of making, and methods of using dental compositions that include an antimicrobial lipid component and a water-dispersible, polymeric film-former.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Curable acrylate polymer compositions featuring improved flexural characteristics
InactiveUS20060035997A1Reducing and eliminating of oxygen-inhibited layerMore flexible and impact-resistantImpression capsSurgical adhesivesMethacrylateAcrylate polymer
The invention describes acrylic and methacrylic acid ester-based polymeric materials containing as flexibilizing and brittleness reducing agents 1-60% of C4-C8 polyalkylene or polyalkyldiene compounds, preferably having a molecular weight of 300-2100, and the use of such materials in dentistry and medicine.
Owner:SCI PHARMA INC
Method of enhancing fluoridation and mineralization of teeth
InactiveUS7387774B2Improve protectionPromote remineralizationCosmetic preparationsImpression capsPresent methodCementum caries
Disclosed are methods of enhancing fluoride incorporation into teeth and mineralization of teeth by use of oral care compositions comprising the combination of one or more fluoride ion sources and specialized phosphonate containing polymers or telomers. The present methods provide enhanced protection of teeth against caries and cavities and increased resistance to acid demineralization associated with caries processes as well as anticalculus (antitartar) benefits.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Therapeutic responsive dental gel composition
InactiveUS20050026107A1High viscosityLong period of timeImpression capsTeeth fillingWater solubleLiquid oral
A liquid oral therapeutic dental composition, that increases in viscosity upon contact with moisture following application to an oral cavity surface, is disclosed. The composition comprises a moisture responsive gel carrier comprising a moisture sensitive polymer complex and a water soluble salt and a therapeutic agent dispersed in the responsive gel carrier. Methods and devices for administering the composition are also disclosed.
Owner:DISCUS DENTAL LLC
Remineralizing dental cements
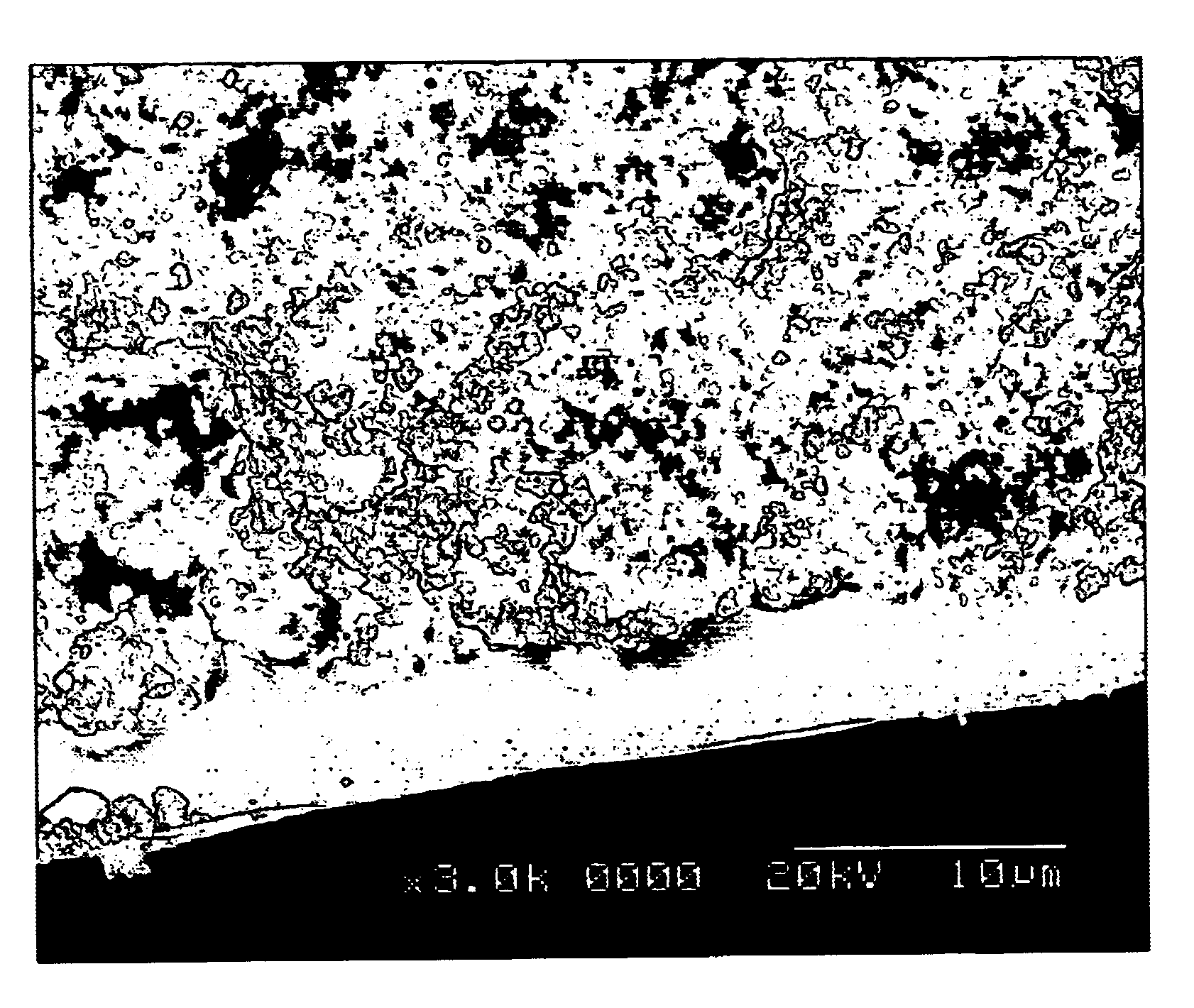
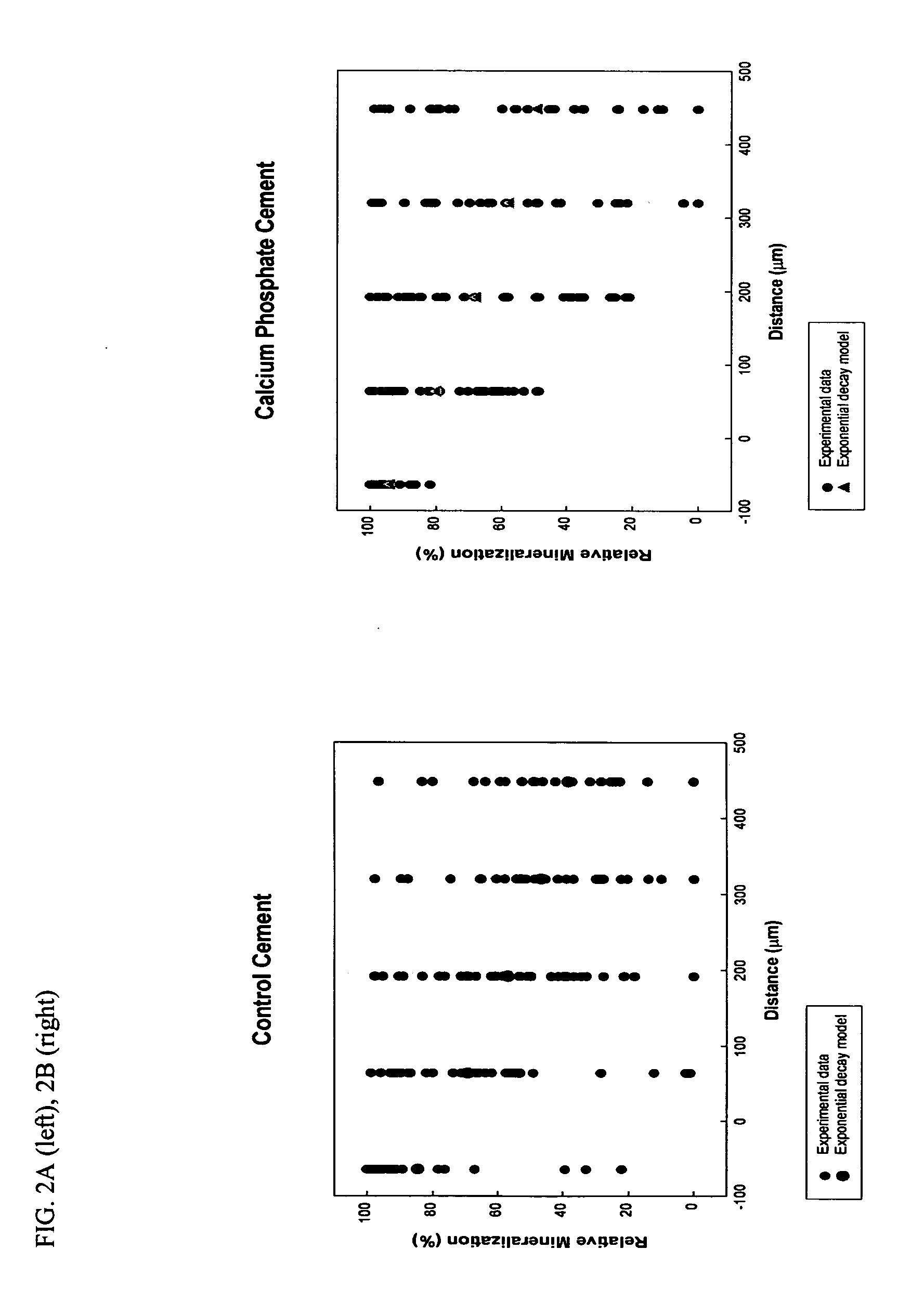
ActiveUS20050020720A1Counteract deleterious effectPromote remineralizationCosmetic preparationsImpression capsPhosphate ionCavity Liner
Remineralizing dental cements contain source(s) of calcium and phosphate ions, adhesive resin monomers, reinforcing base resin monomers, and catalysts able to initiate the polymerization of the adhesive and reinforcing base resin monomers. Such dental cements can be used as orthodontic cements, crown and bridge cements, adhesives, sealants, cavity liners, and protective coatings. The release of calcium and phosphate ions and, optionally, fluoride ions, protects tooth structure from demineralization, a precursor of tooth decay.
Owner:ADA FOUND
Polyimide resin composition and laminate including same
ActiveCN103298855AHigh viscosity elasticGood flexibilityImpression capsElectrolytic capacitorsPolyresinGreek letter alpha
The present invention addresses the problem of providing a resin composition including a polyimide that is soluble in a solvent and from which a resulting film will be highly viscoelastic and flexible at high temperatures. In order to resolve this problem, a polyimide resin composition includes a polyimide including polycondensate units of tetracarboxylic dianhydride and diamine, wherein either the tetracarboxylic dianhydride includes a dianhydride (alpha 1) represented by general formula (1) or the diamine includes an aromatic diamine (beta 1) represented by general formula (2) and the diamine includes an aliphatic diamine (beta 2) represented by general formula (3) or (4), the sum amount of the dianhydride (alpha 1) and aromatic diamine (beta 1) contained therein being 5-49 mol% with respect to the sum of the tetracarboxylic dianhydride and the diamine, and the amine equivalent thereof being 4,000-20,000. In the formula (3), R1 is an aliphatic chain; H2N-R2-NH2... (4), in the formula (4), R2 is an aliphatic chain.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Glass ionomers for enhancing mineralization of hard tissue
The invention relates to glass ionomer for enhancing mineralization of hard tissue of mammals. The glass ionomer comprises, a inert biocompatible ceramic and a bioactive ceramic. The invention also relates to a method for enhancing mineralization of hard tissue of mammals with the aid of said glass ionomer. The invention further relates to the use of said glass ionomer for the preparation of products intended for treatment of defects of soft and hard tissue as well as the use of said glass ionomer for the preparation of a variety of products wherein the ability to enhance mineralization is advantageous.
Owner:NARHI TIMO +4
Antimicrobial compositions for use in wound care products
Compositions having antimicrobial activity contain surface functionalized particles comprising an inorganic copper salt which has low water solubility. These types of inorganic salts may also be introduced in porous particles to yield antimicrobial compositions. The compositions may optionally comprise additional antimicrobial agents, salts with high water solubility, organic acids, salts of organic acids and their esters. The above compositions can be incorporated in a variety of wound care products to provide antimicrobial properties.
Owner:AGIENIC
Ceramic dental restoration
A ceramic restoration based on a leucitic glass-ceramic, which is characterized in that the glass-ceramic includes by way of componentsin that it contains, as sole crystalline phase, leucite in a total proportion from 20 to 45 wt.-%, at least 80% of the theoretically producible quantity of leucite being present, and in that it exhibits a linear coefficient of thermal expansion alpha(20-500° C.) from 12.5.10-6 to 15.5.10-6 K-1. This glass-ceramic is particularly suitable for processing as pressed ceramic and can be advantageously faced with dental ceramic that exhibits a linear coefficient of thermal expansion alpha(20-500° C.) from 13.5.10-6 to 17.0.10-6 K-1.
Owner:DEGUSSA HULS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com