Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Limit profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tricalcium phosphates, their composites, implants incorporating them, and method for their production
InactiveUS20050031704A1Easily controlEnhance packing and densificationBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsChemistryProsthetic implants
Methods for the synthesis of tricalcium phosphates are presented, as well as a series of specific reaction parameters that can be adjusted to tailor, in specific ways, properties in the tricalcium phosphate precursor precipitate. Particulate tricalcium phosphate compositions having an average crystal size of about 250 nm or less are provided. Compositions of the invention can be used as prosthetic implants and coatings for prosthetic implants.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Apparatus and method for preventing brain damage during cardiac arrest, cpr, or severe shock
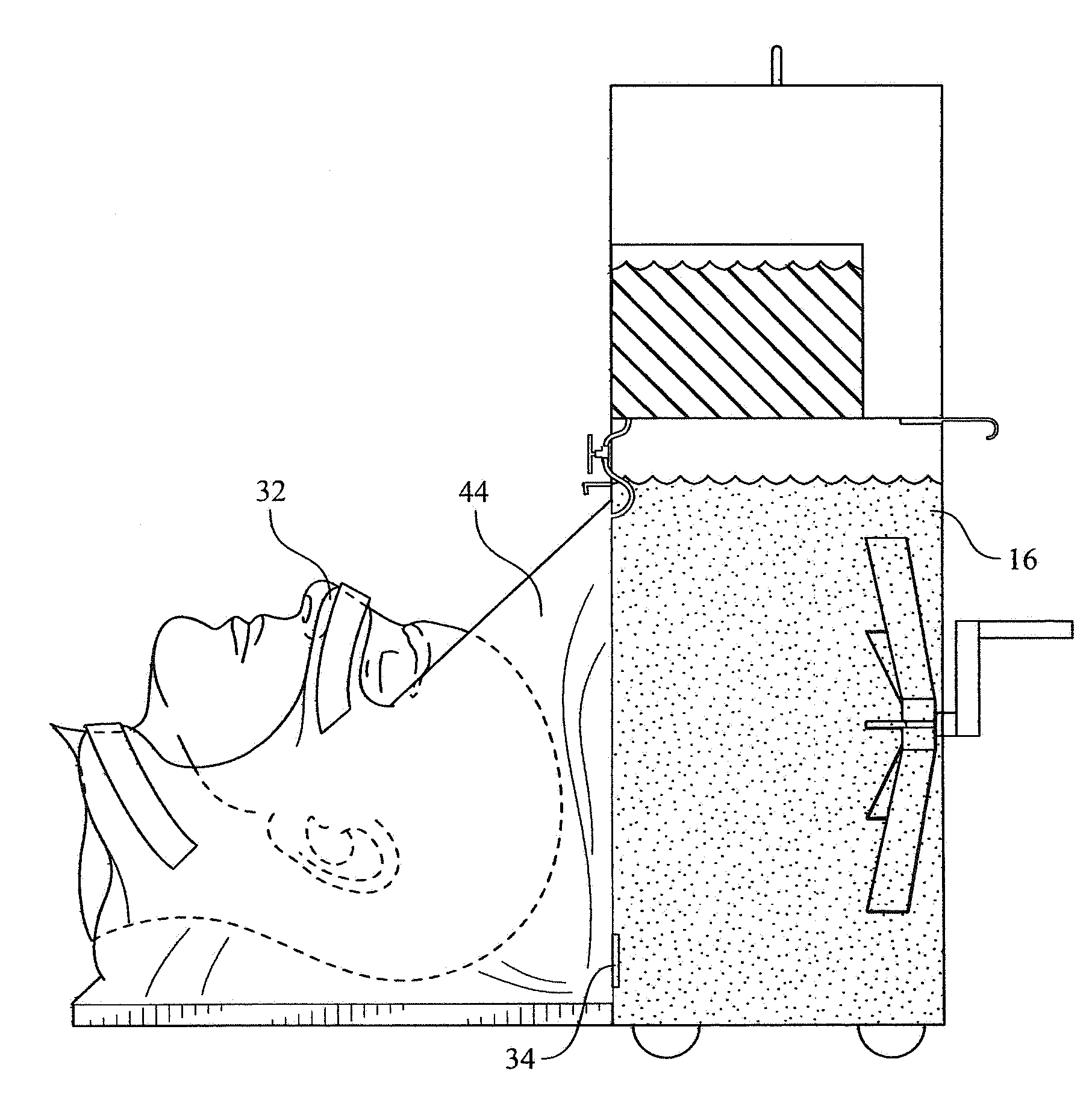
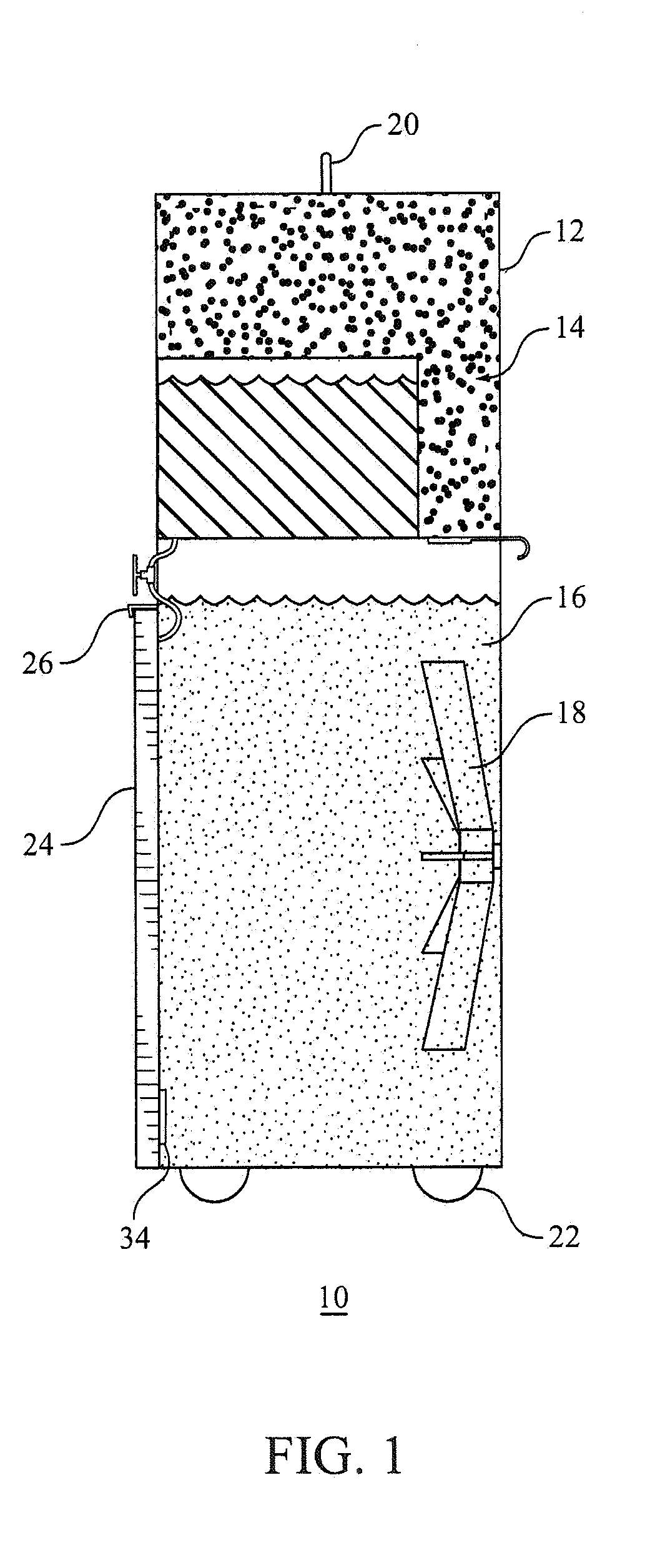
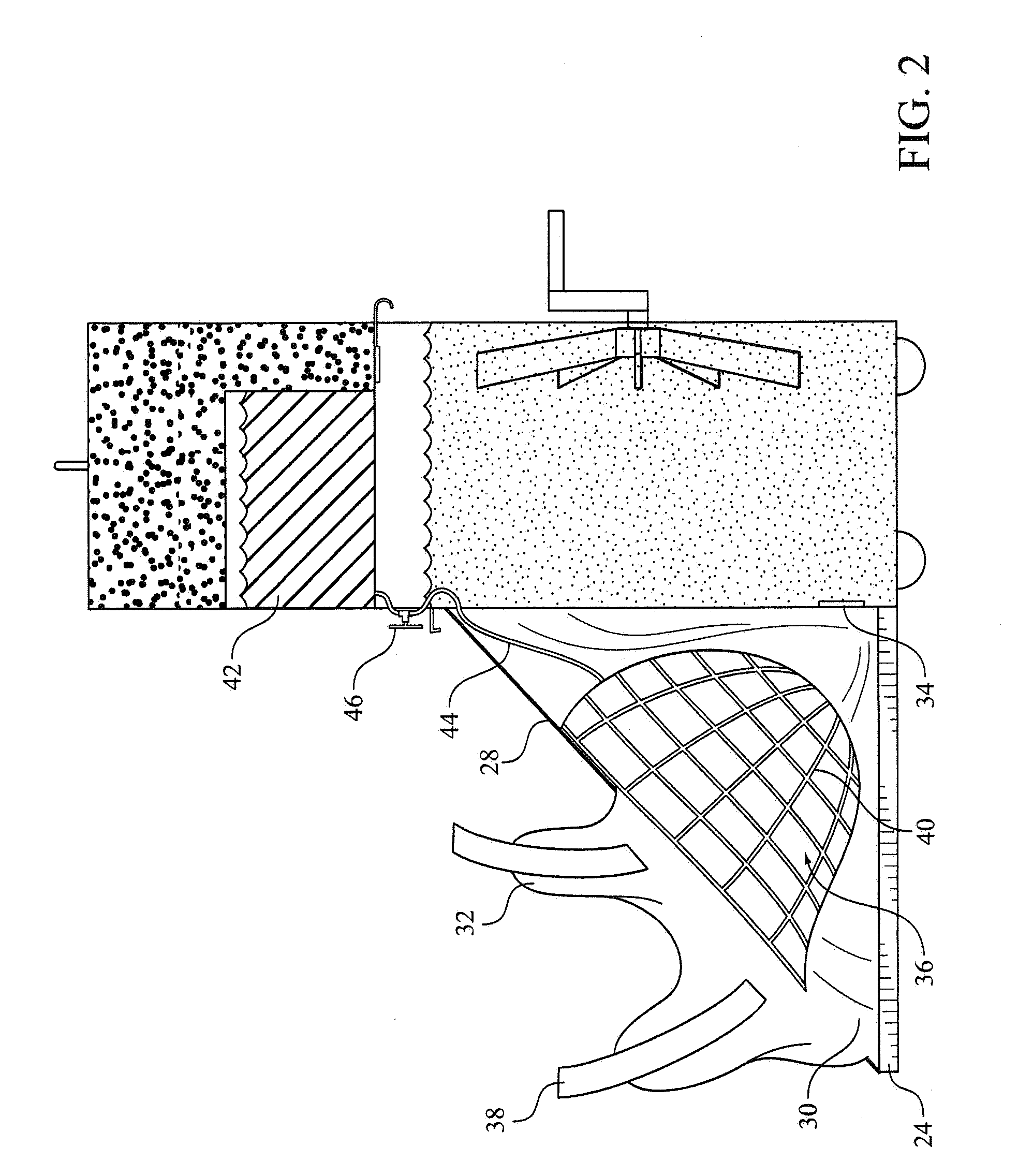
InactiveUS20090276018A1Rapid coolingImprove hypothermiaTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingInjury brainCardiorespiratory arrest
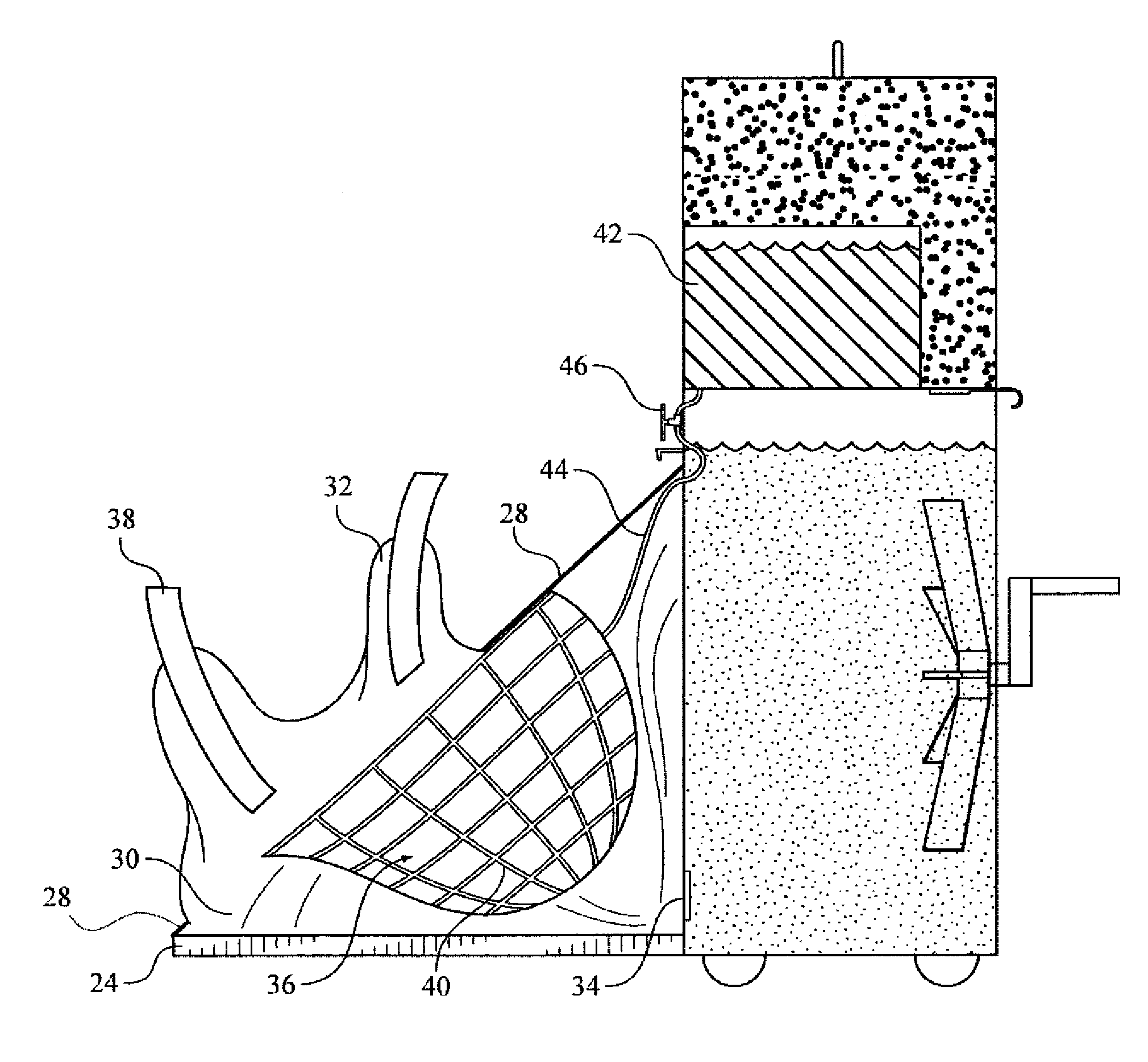
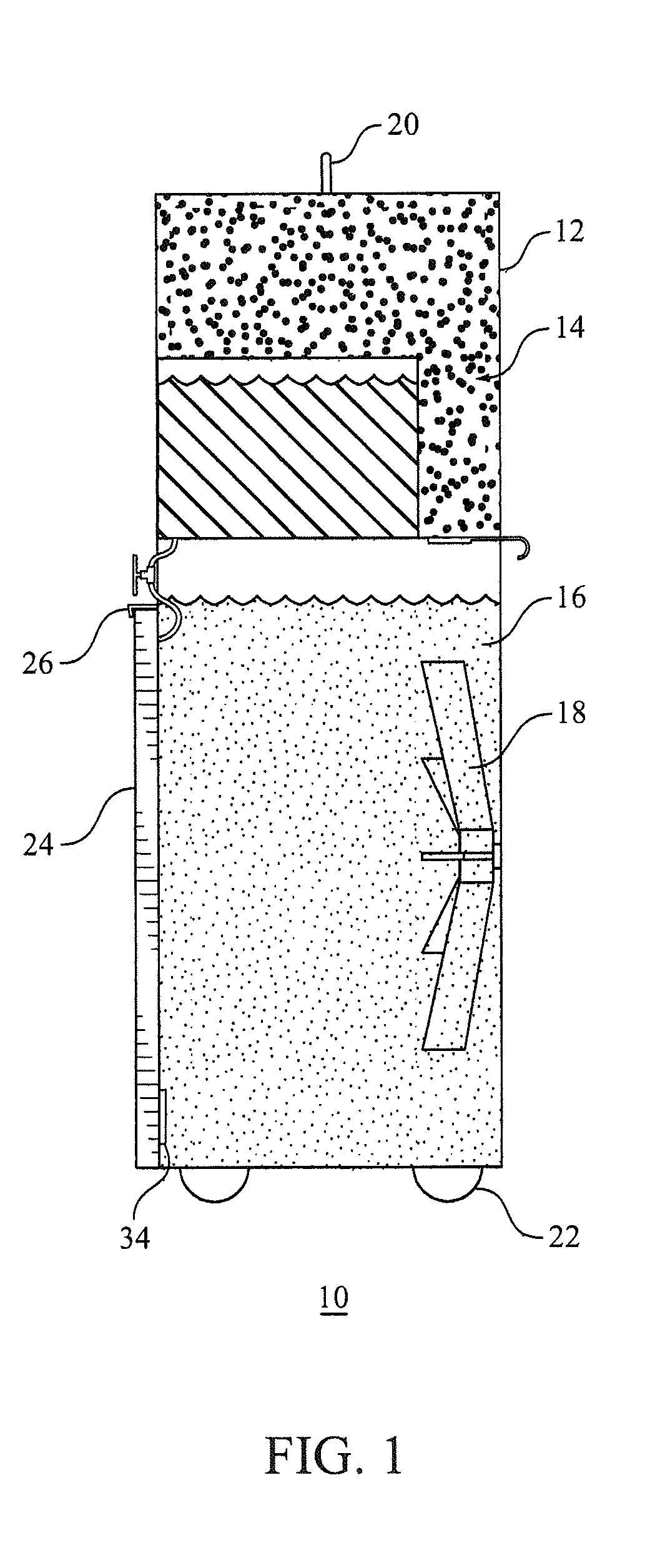
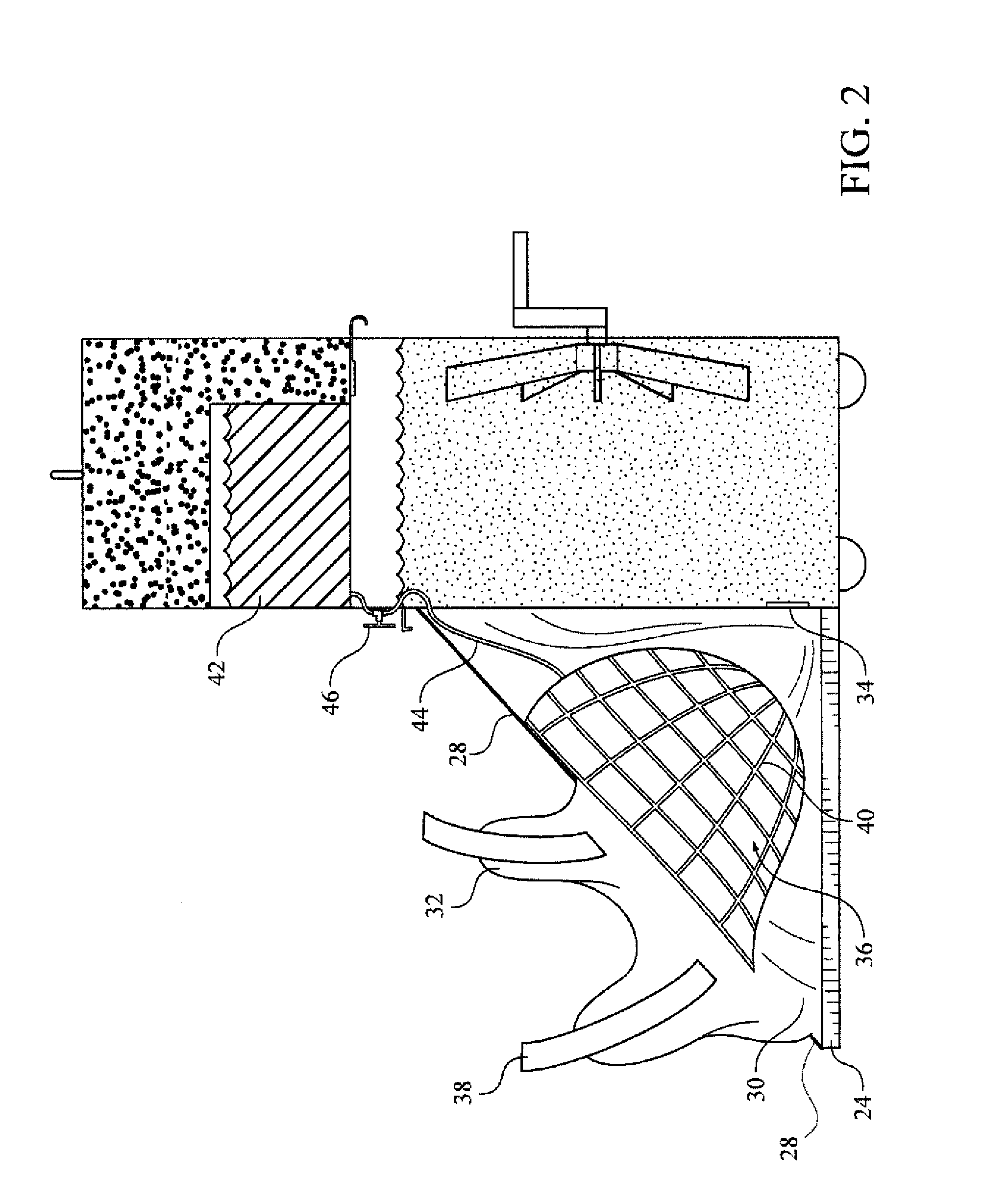
Apparatuses and methods for the cooling of the cranial and extracranial portions of a patient in need thereof. The apparatuses and methods of the present invention preferably employ a head cooling apparatus which includes a watertight shroud for the head and which needs no refrigeration. In certain preferred embodiments, the apparatuses of the present invention are collapsible and possess a reduced profile. In some presently preferred embodiments, the present invention includes a hammock that supports the head. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a shroud that lies behind the head with optional portions that may be drawn over the patient's neck and cranial area. The apparatuses and methods of the present invention also provide an improved mechanism for cooling the cranial and extracranial areas through the use of a novel distribution of endothermic solids (e.g. ammonium nitrate). The present invention provides a novel distribution of ammonium nitrate pellets that preferably includes multiple populations solid ammonium nitrate, preferably including small diameter (e.g., powdered) and larger diameter (e.g., 7 millimeter) ammonium nitrate to allow water initially to be cooled very quickly, thereby facilitating the rapid cooling of the cranial and extracranial areas, while at the same time producing extended hypothermia.
Owner:BRADER ERIC WILLIAM
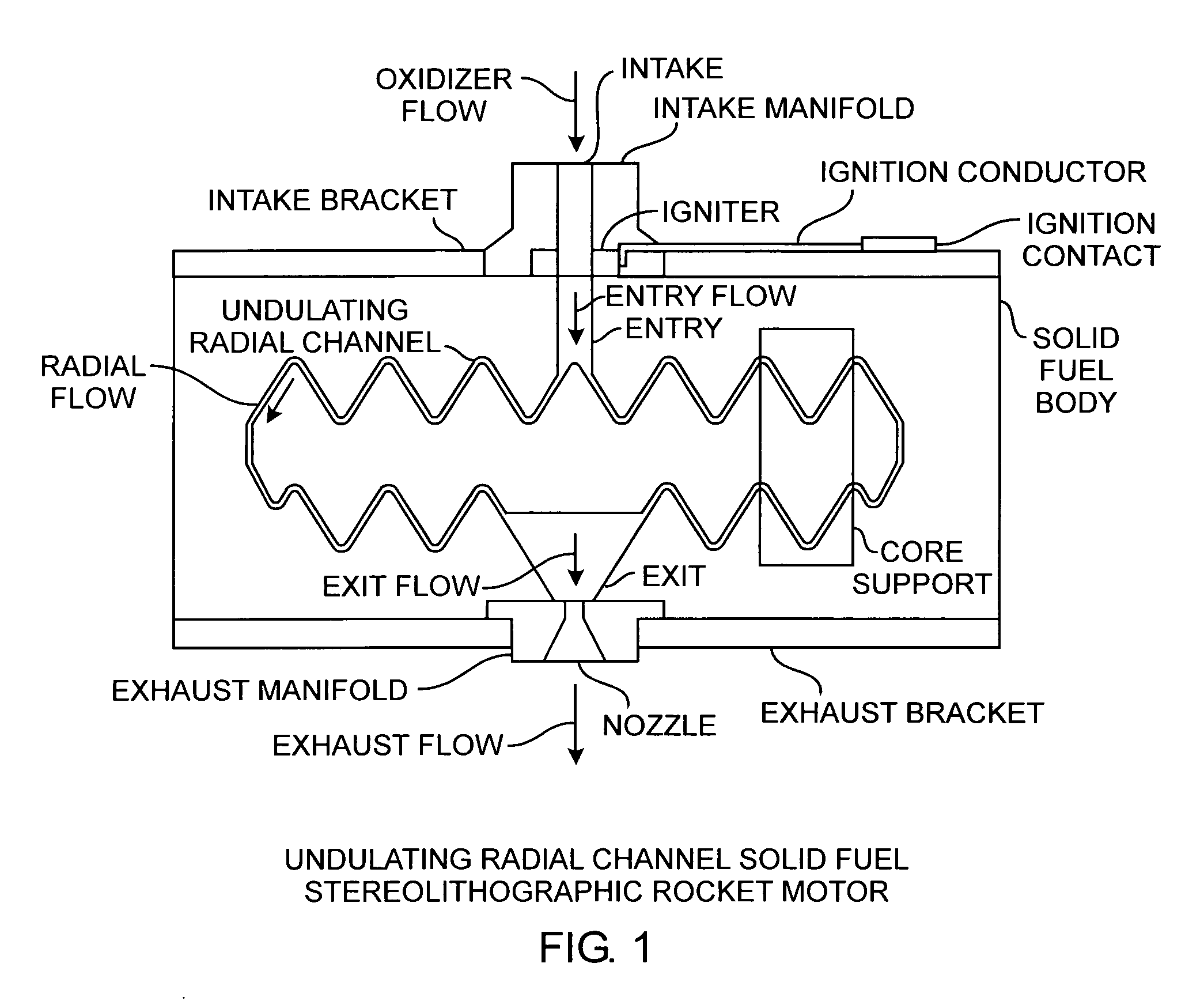
Stereolithographic rocket motor manufacturing method
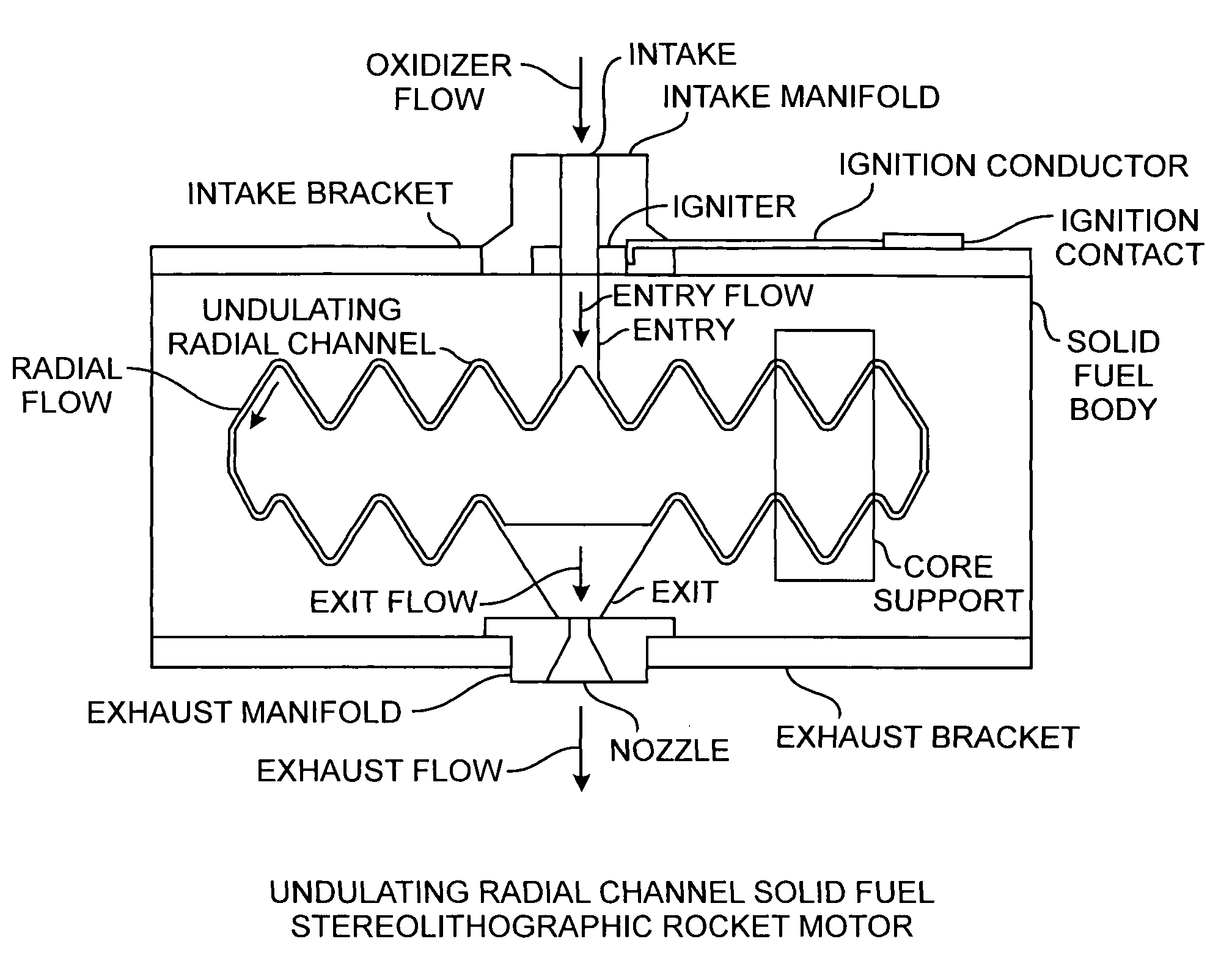
ActiveUS20090217525A1Improve performanceEfficient combustionAdditive manufacturing apparatusWriting implementsSolid fuelStereolithography
A hybrid rocket motor is manufactured by photopolymerizing the solid fuel grain in a stereolithography method, wherein fuel grains in a plastic matrix are deposited in layers for building a solid fuel rocket body in three dimensions for improved performance and for a compact design,
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
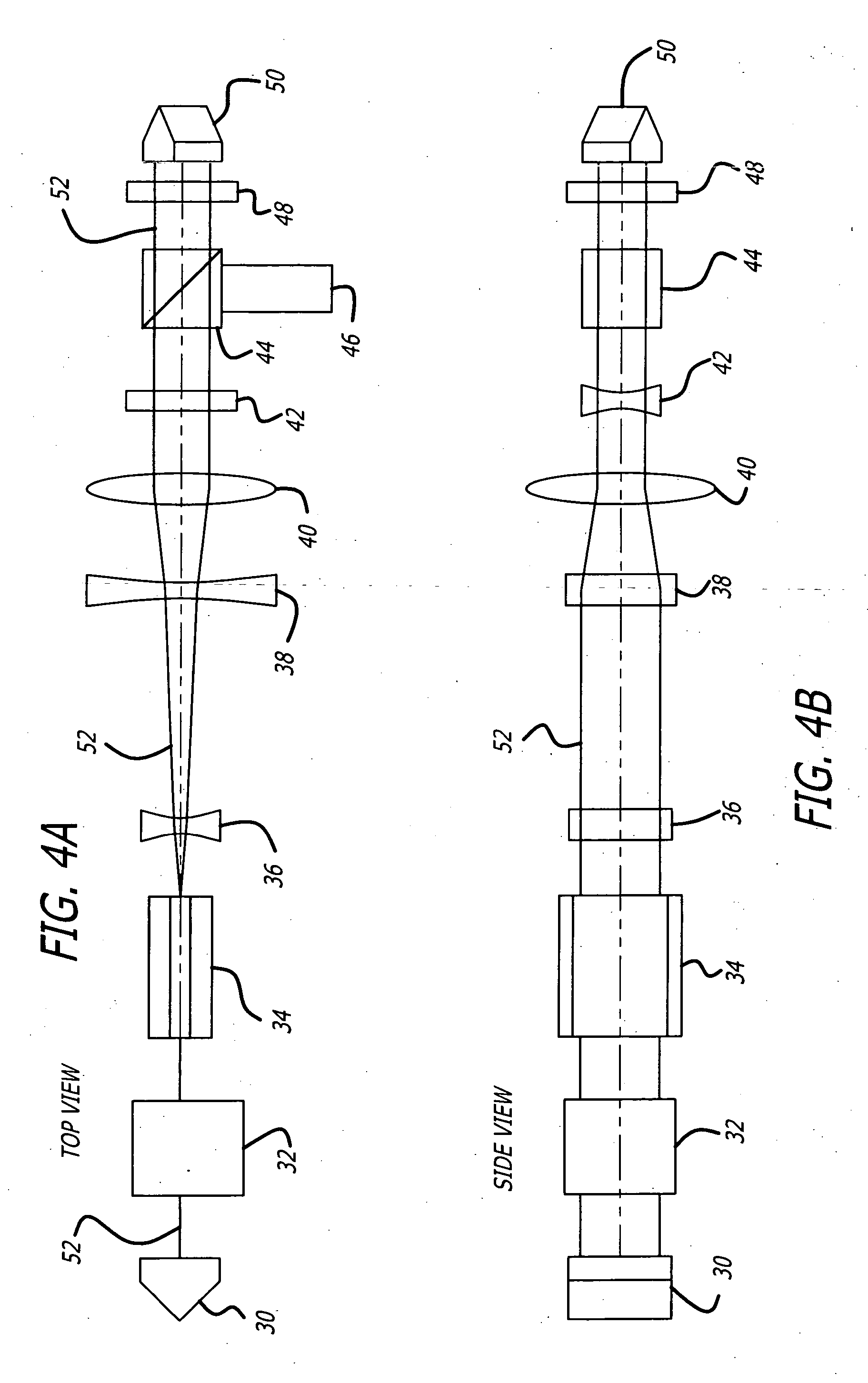
Slab laser and method with improved and directionally homogenized beam quality
ActiveUS20050111496A1Easy dischargeLimit profileOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialTransverse axisTelescope
A laser resonator for generating a laser beam having beam quality along two transverse axes that is determined primarily by the mode discrimination characteristics of one axis. The apparatus including a means for providing a collimated beam of electromagnetic energy with a predetermined orientation with respect to a line of sight thereof, and, a means for rotating the beam such that a transverse mode selection therefor is the same for two orthogonal directions thereof. The first means includes a slab laser having principal axes, and the second means includes a porro prism or a Benson prism. The prism is rotated 45 degrees about the line of sight with respect to the slab axes. The beam is rotated through successive round trip passes through the slab. A telescope, or an anamorphic telescope may be disposed between the slab and the prism. The resonator has a high aspect ratio slab lasing medium with a first and a second end that emit a laser beam. An aperture stop with a narrow transverse dimension and an orthogonal wide transverse dimension defines the laser beam profile. The slab itself may define the aperture stop. A first reflector, is aligned to reflect the laser beam emitted from one end of the slab back into the slab, and thereby define a first end of a resonant cavity. An anamorphic telescope is aligned to receive and reshape the laser beam profile to be substantially symmetrical about its transverse axes. The beam profile of the reshaped laser beam is rotated 90° and reflected, by a second reflector, back into the telescope, defining the second end of the resonator. The reflectors may be porro prisms, mirrors, or Benson prisms. Polarization out-couplers are used in conjunction with electro-optic Q-switches to out-couple-laser energy. The slab may be solid state Yb:YAG.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
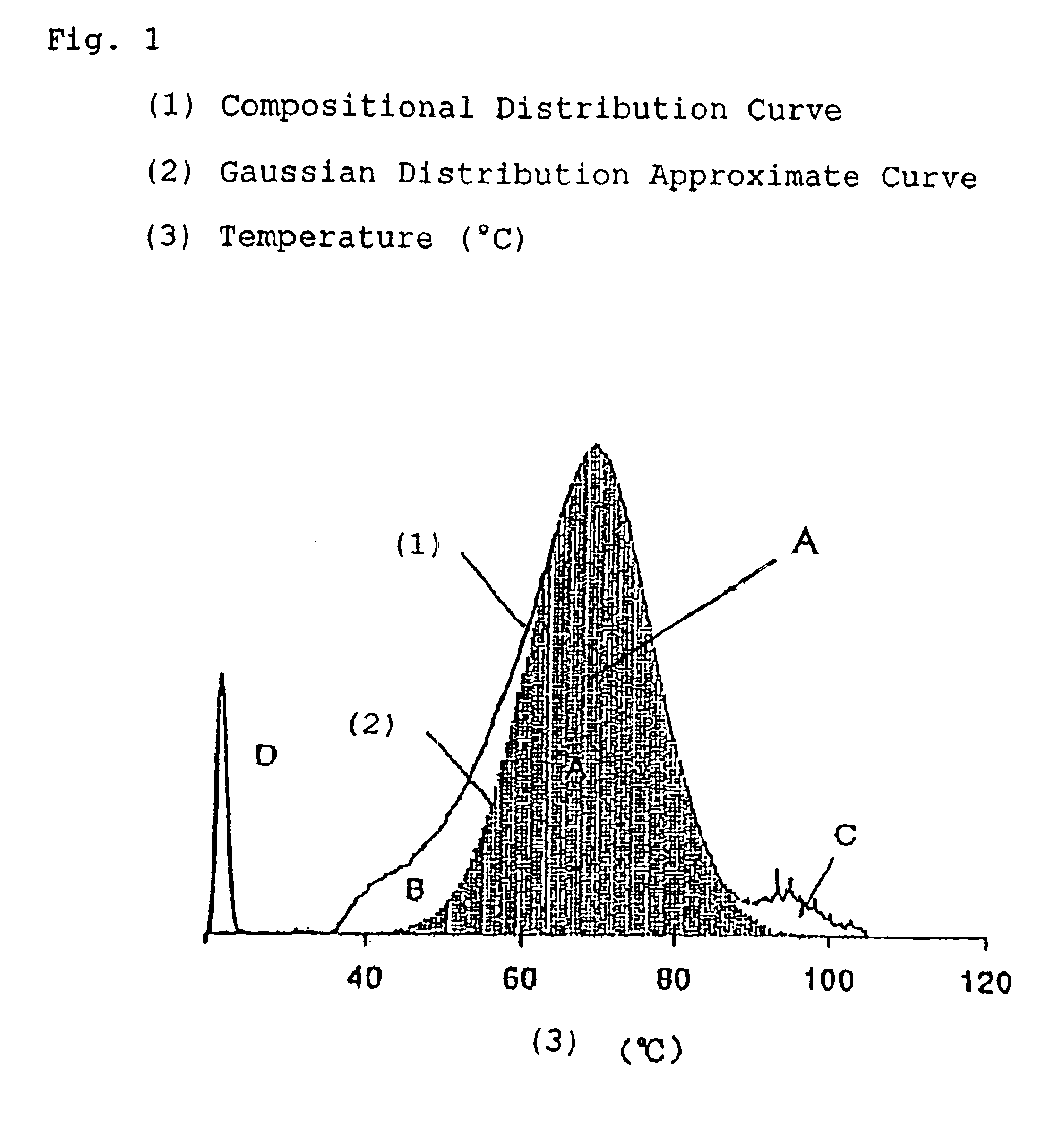
Ethylenic copolymer, composition containing said copolymer, and ethylenic copolymer film
An ethylenic copolymer composition including an ethylenic copolymer having Mw / Mn of 1.5 to 4, Mw of 3,000 to 1,000,000, and a resin density of 0.85 to 0.95 g / cm3. The relationship between the half width at the half maximum [W / 2] of the Gaussian distribution curve, and the average, n, of short-chain branches in the copolymer satisfies the equation,0.704+0.147n=W / 2=−0.055+0.577n. The ethylenic copolymer composition also includes an ethylenic copolymer having an Mw of 3,000 to 1,000,000 and a resin density of 0.85 to 0.95 g / cm3.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
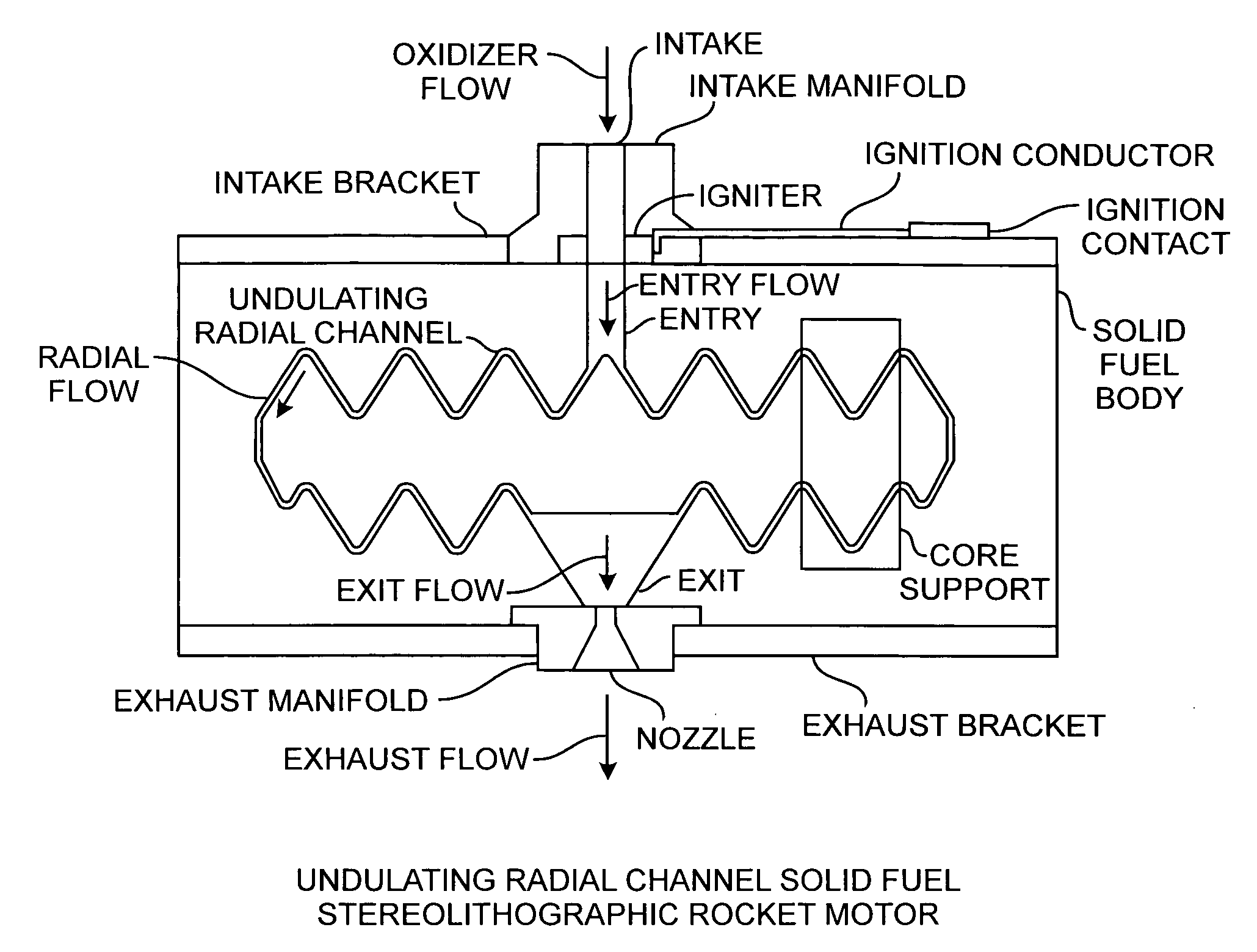
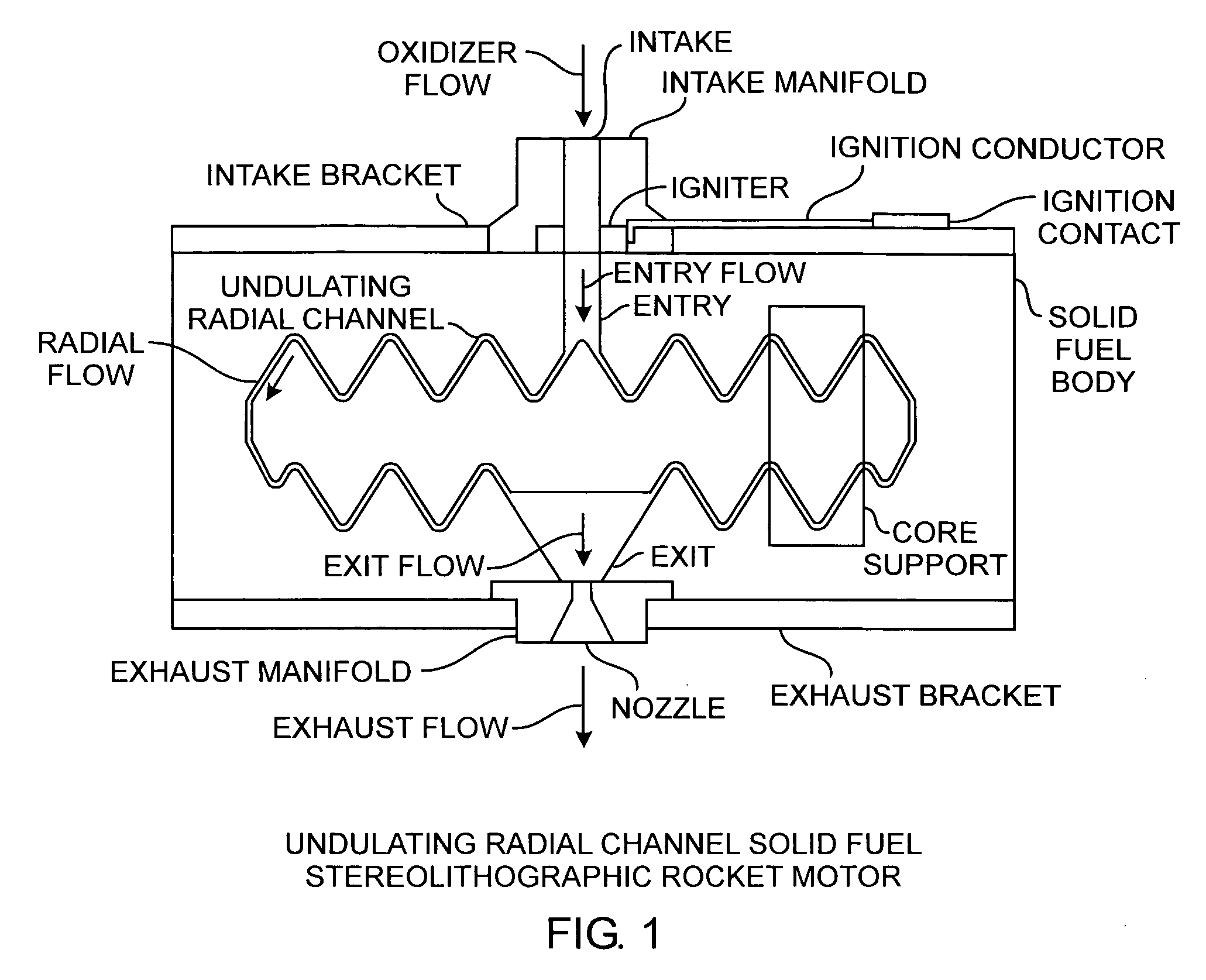
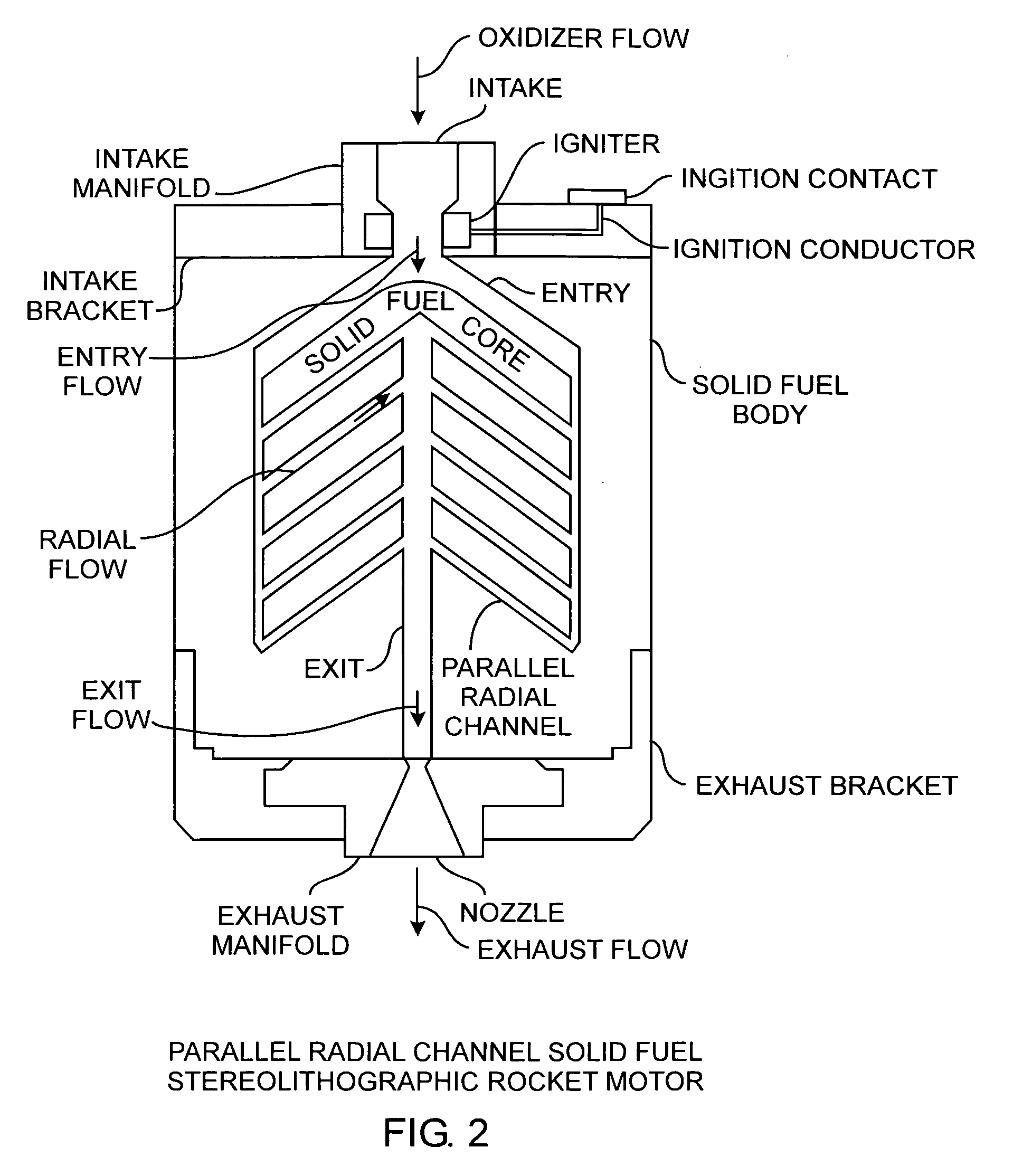
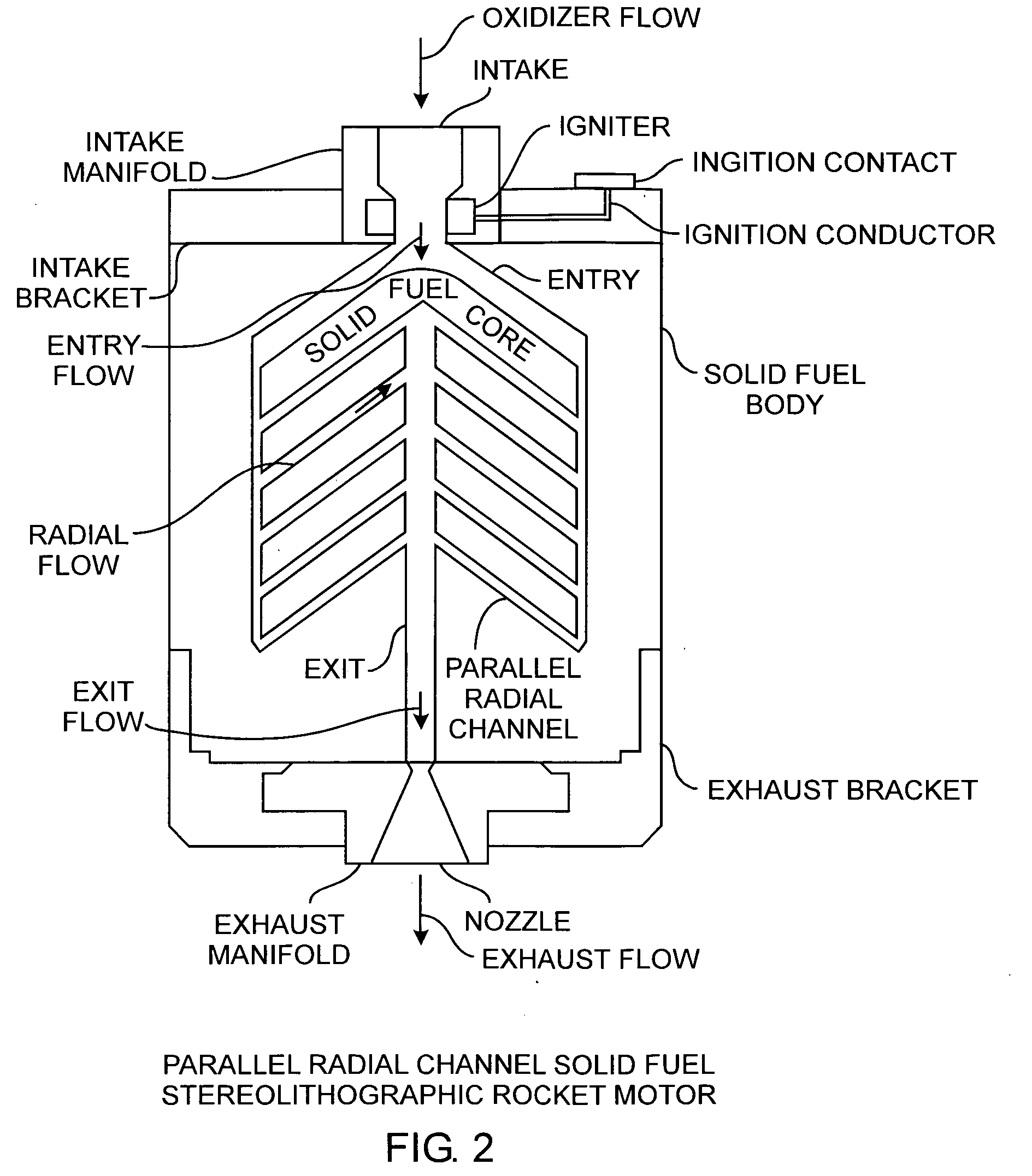
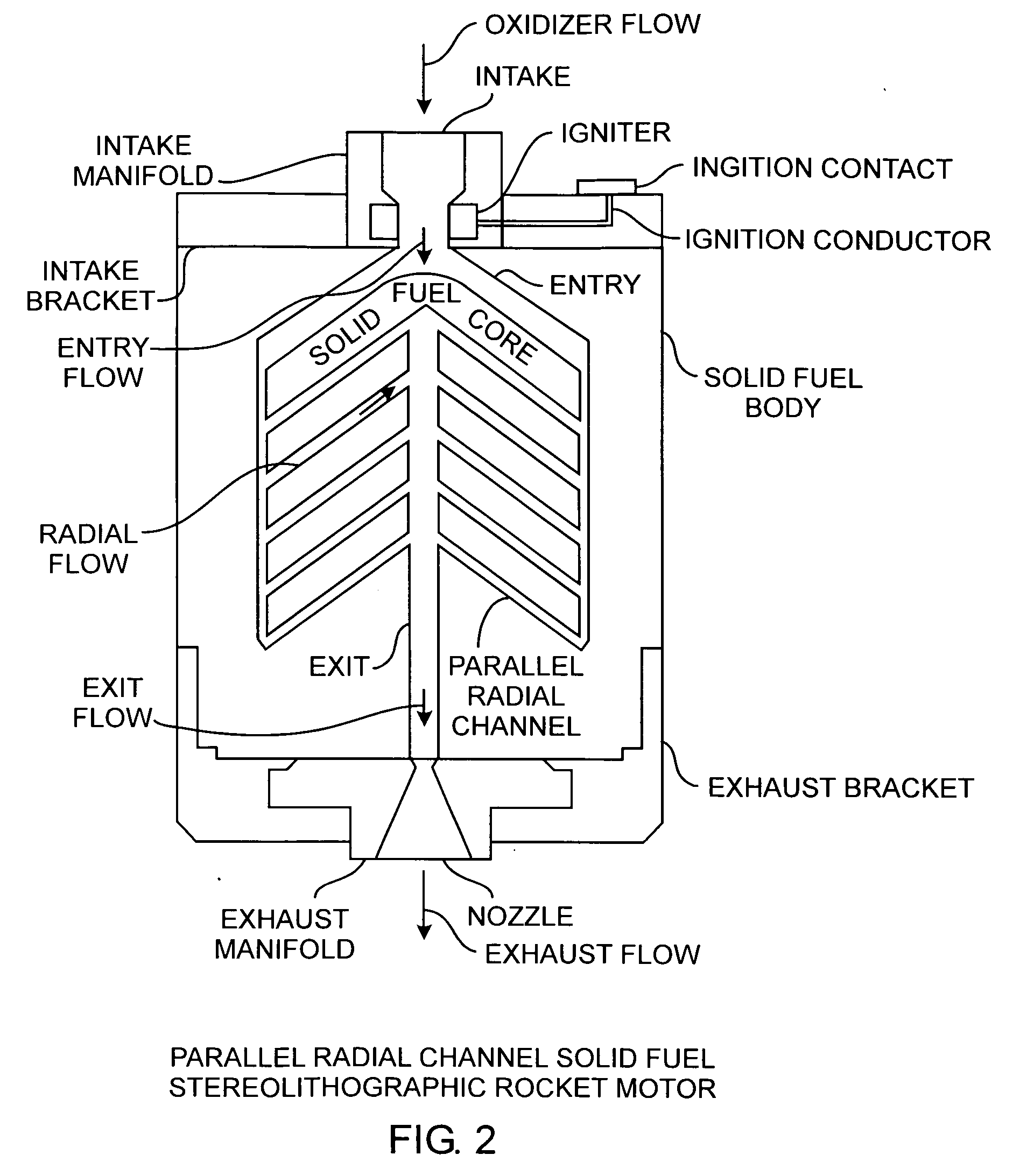
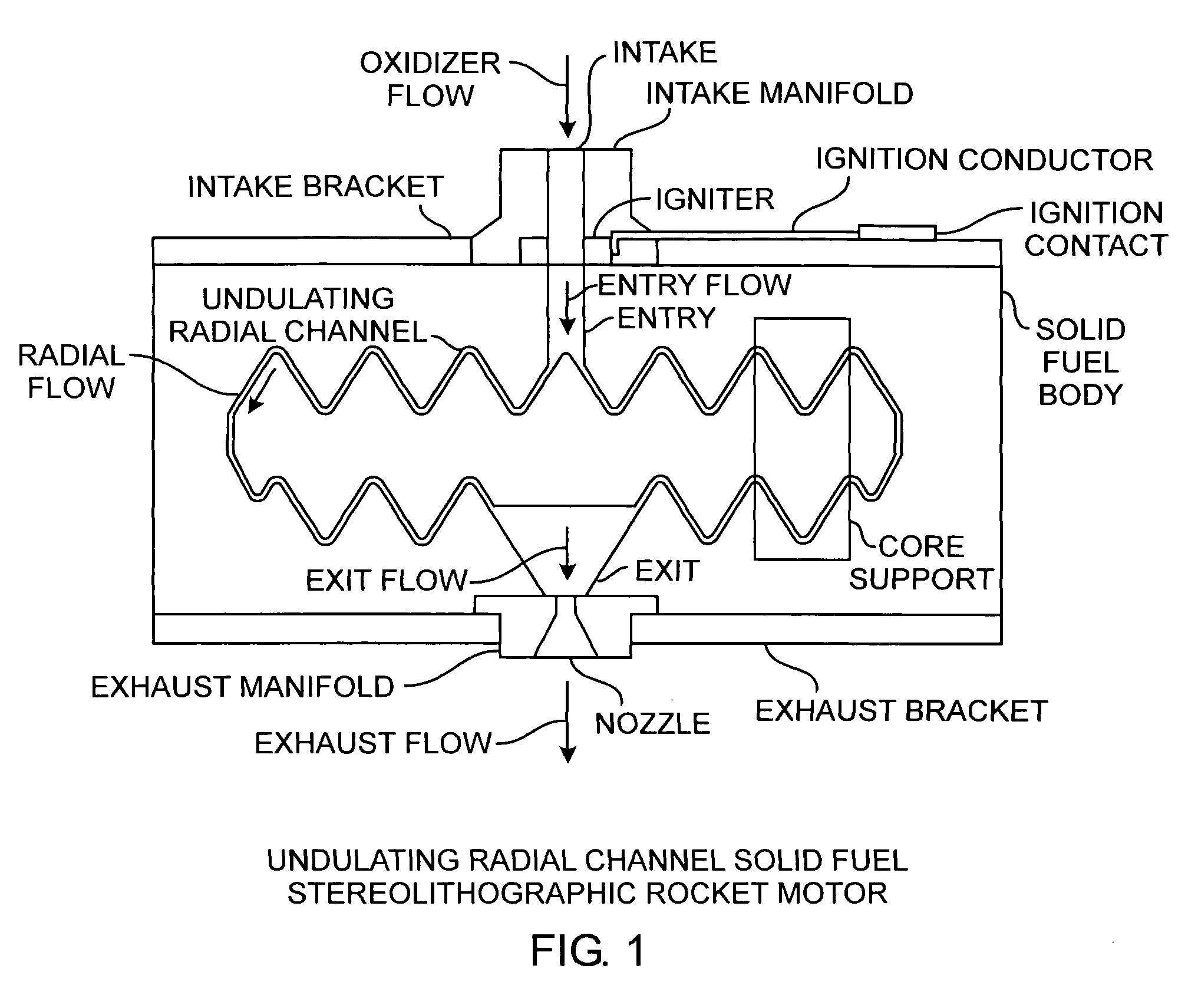
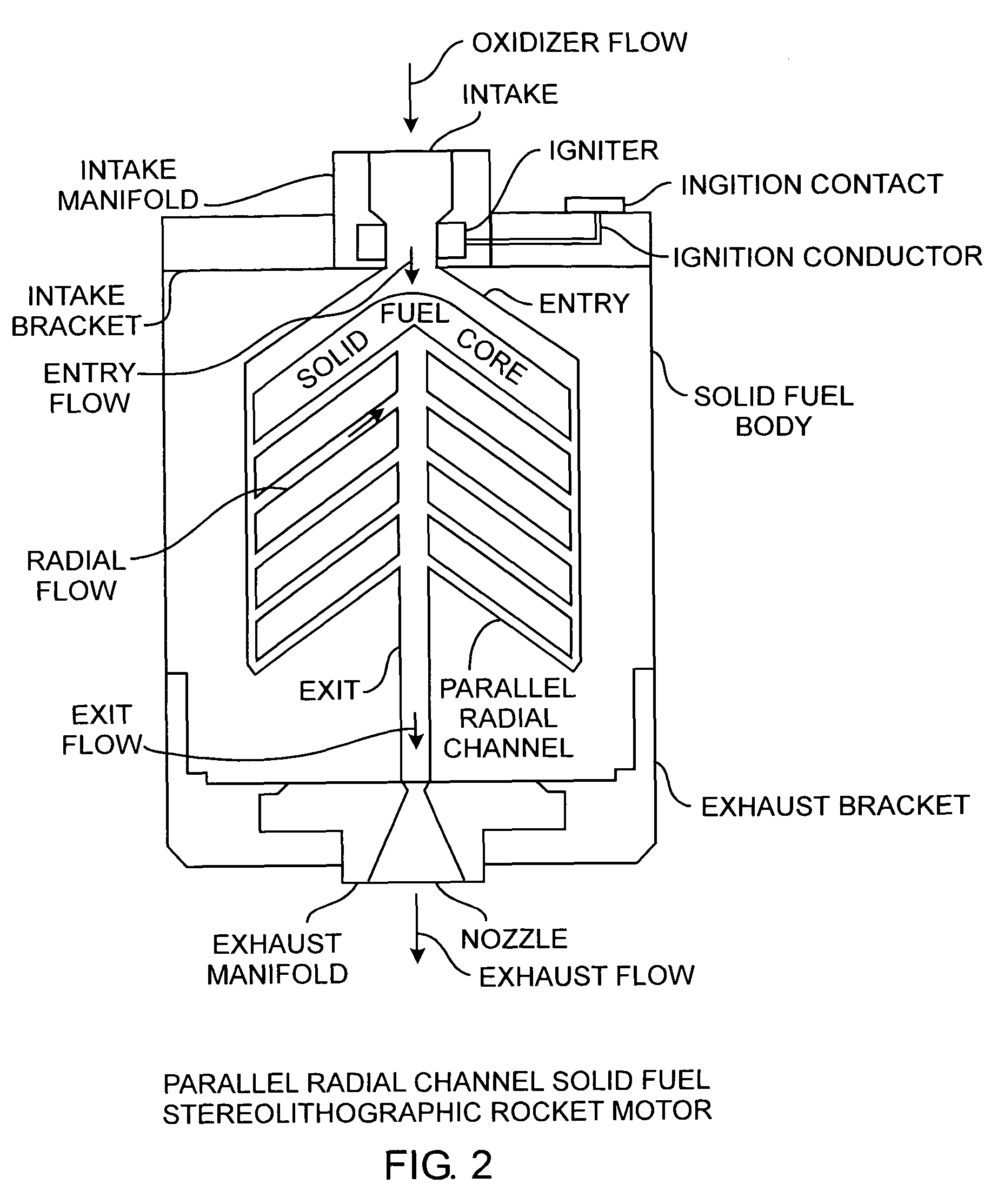
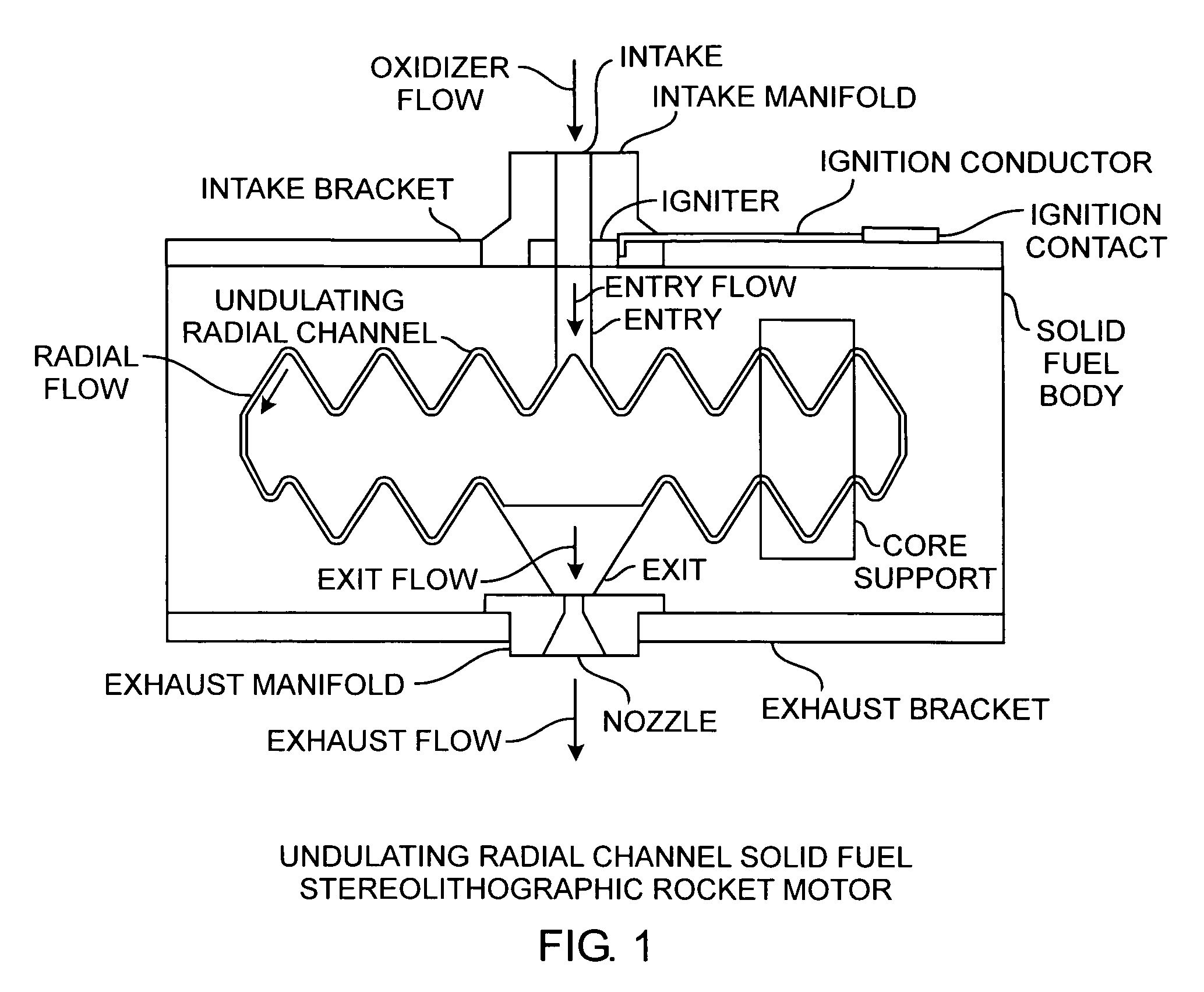
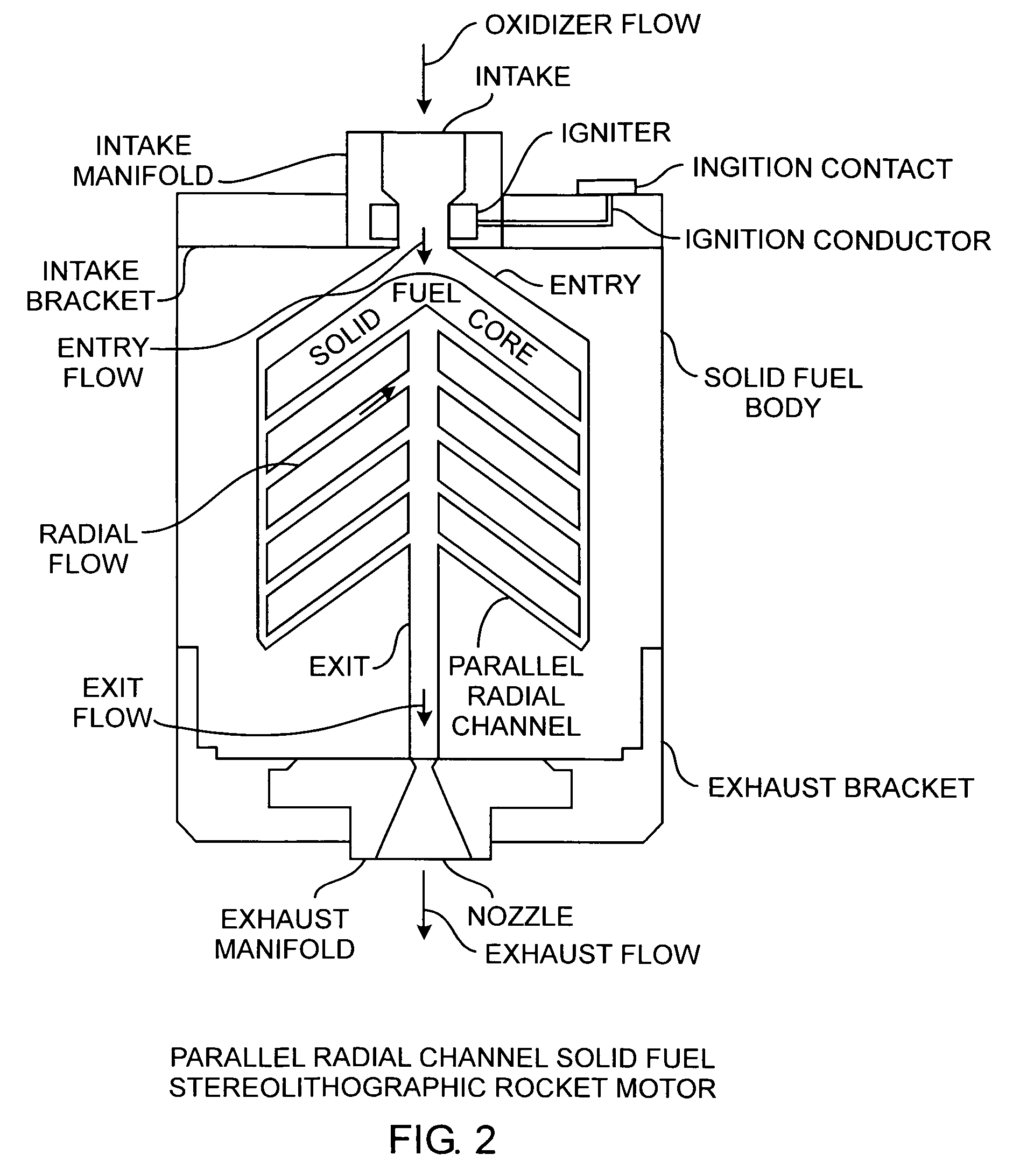
Radial flow stereolithographic rocket motor
ActiveUS20090217642A1Improve performanceEfficient combustionAdditive manufacturing apparatusEngine manufactureSolid fuelStereolithography
A hybrid rocket motor is manufactured by photopolymerizing the solid fuel grain in a stereolithography method, wherein fuel grains in a plastic matrix are deposited in layers for building a solid fuel rocket body in three dimensions for improved performance and for a compact design, the hybrid rocket motor including radial channels for defining a desired burn profile including the oxidizer to fuel burn ratio.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
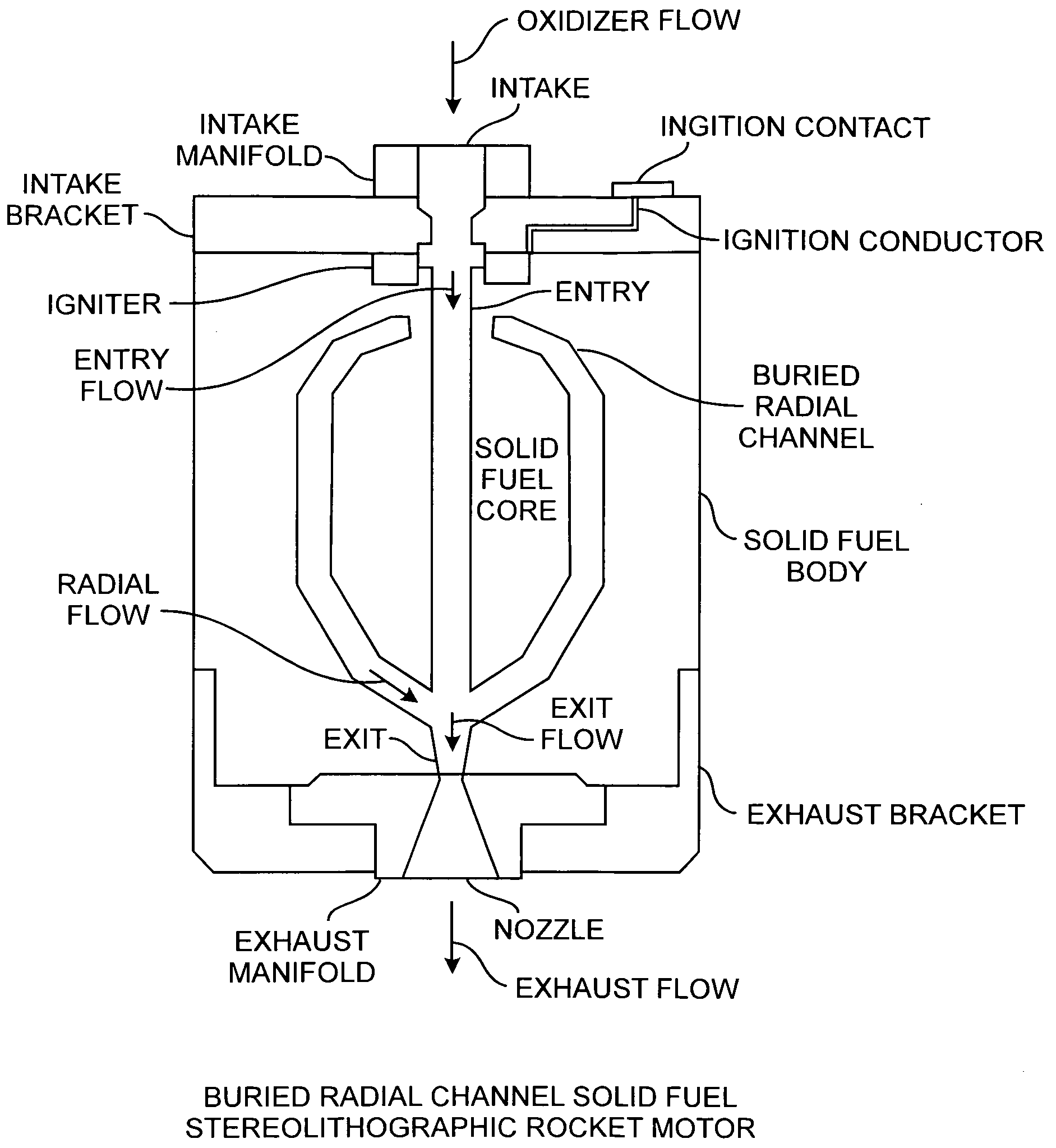
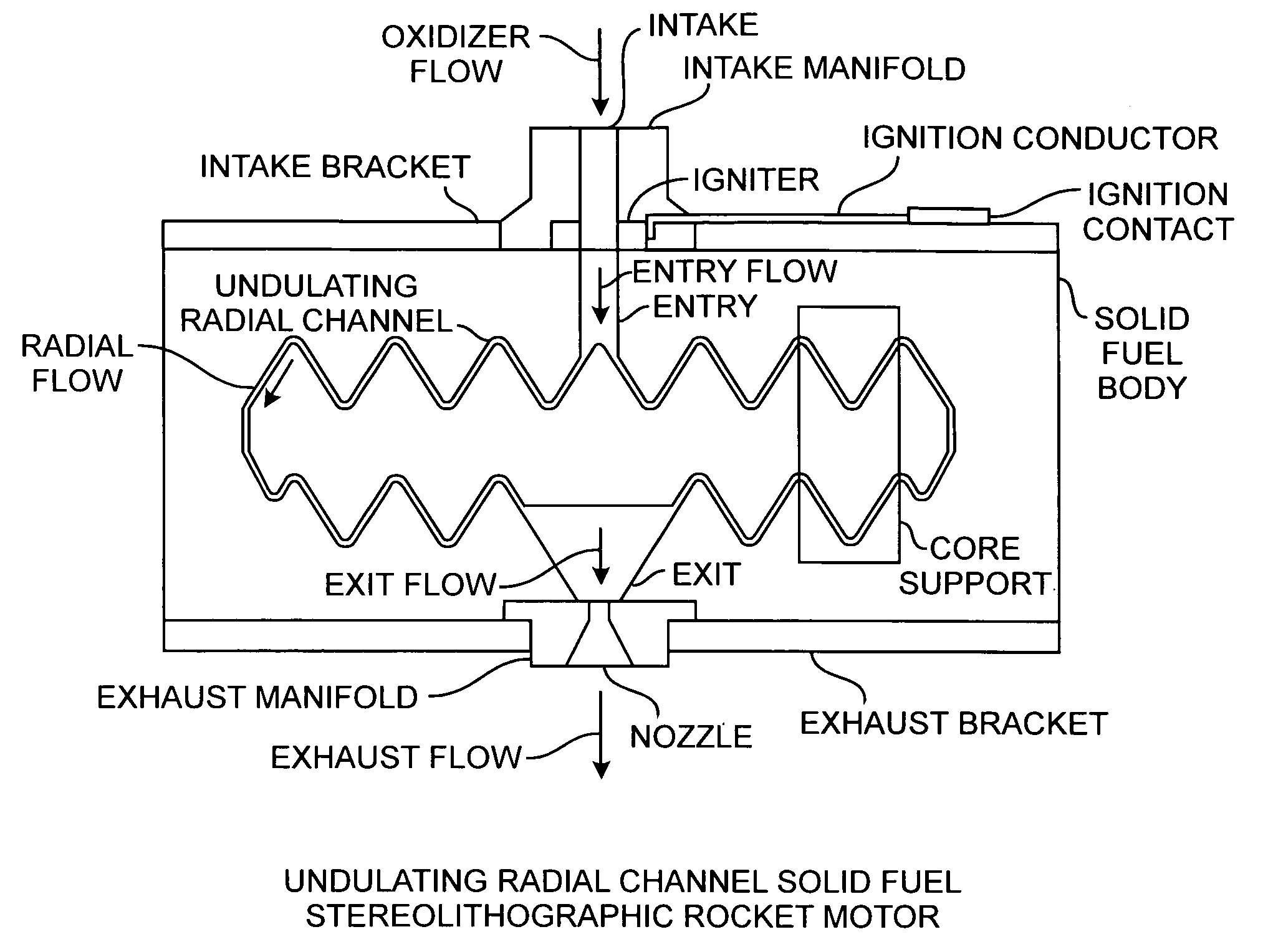
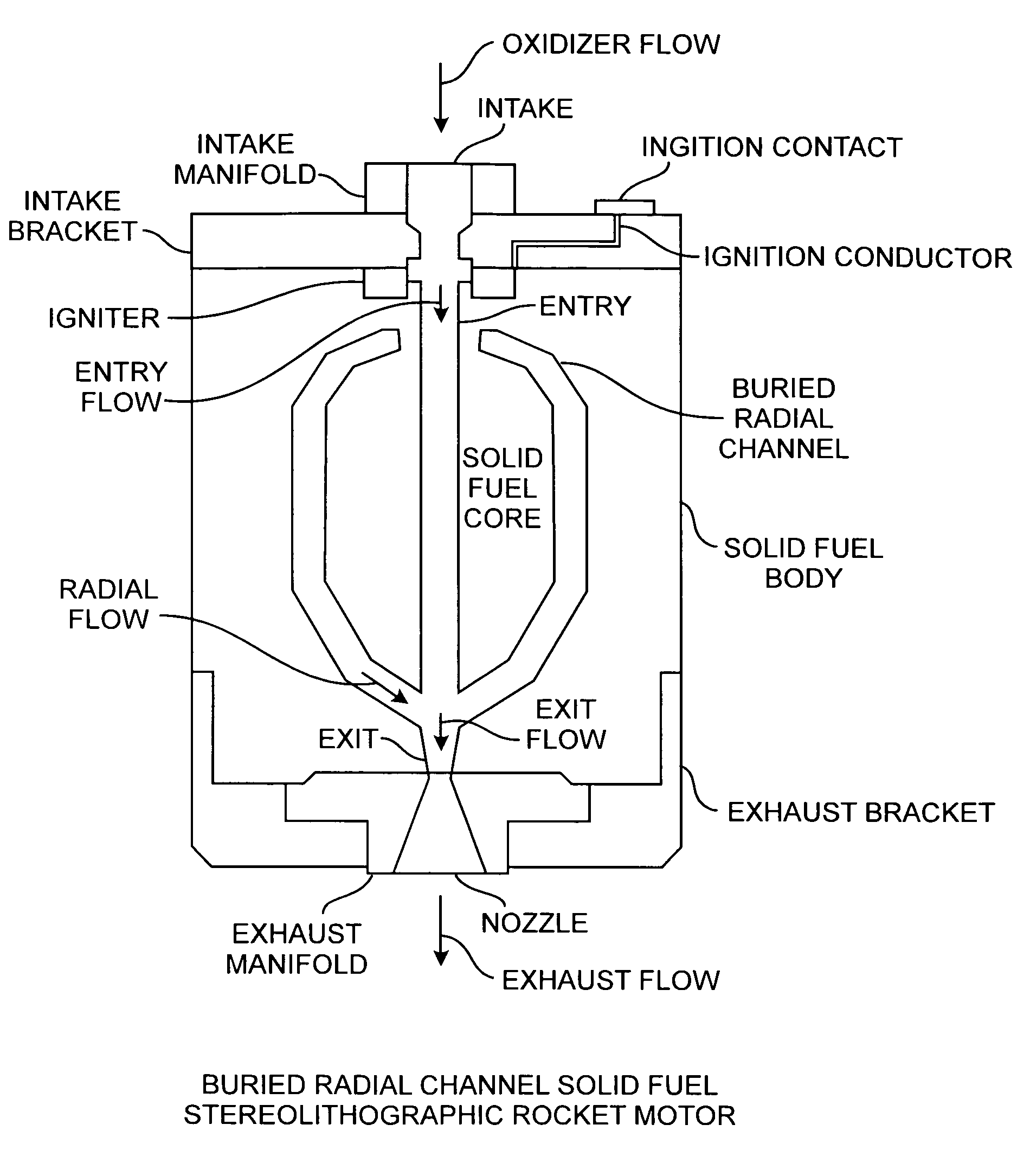
Buried radial flow stereolithographic rocket motor
ActiveUS20100281850A1Improve performanceEfficient combustionAdditive manufacturing apparatusExplosivesSolid fuelStereolithography
A hybrid rocket motor is manufactured by photopolymerizing the solid fuel grain in a stereolithography method, wherein fuel grains in a plastic matrix are deposited in layers for building a solid fuel rocket body in three dimensions for improved performance and for a compact design, the hybrid rocket motor including buried radial channels for defining a desired burn profile including the oxidizer to fuel burn ratio.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
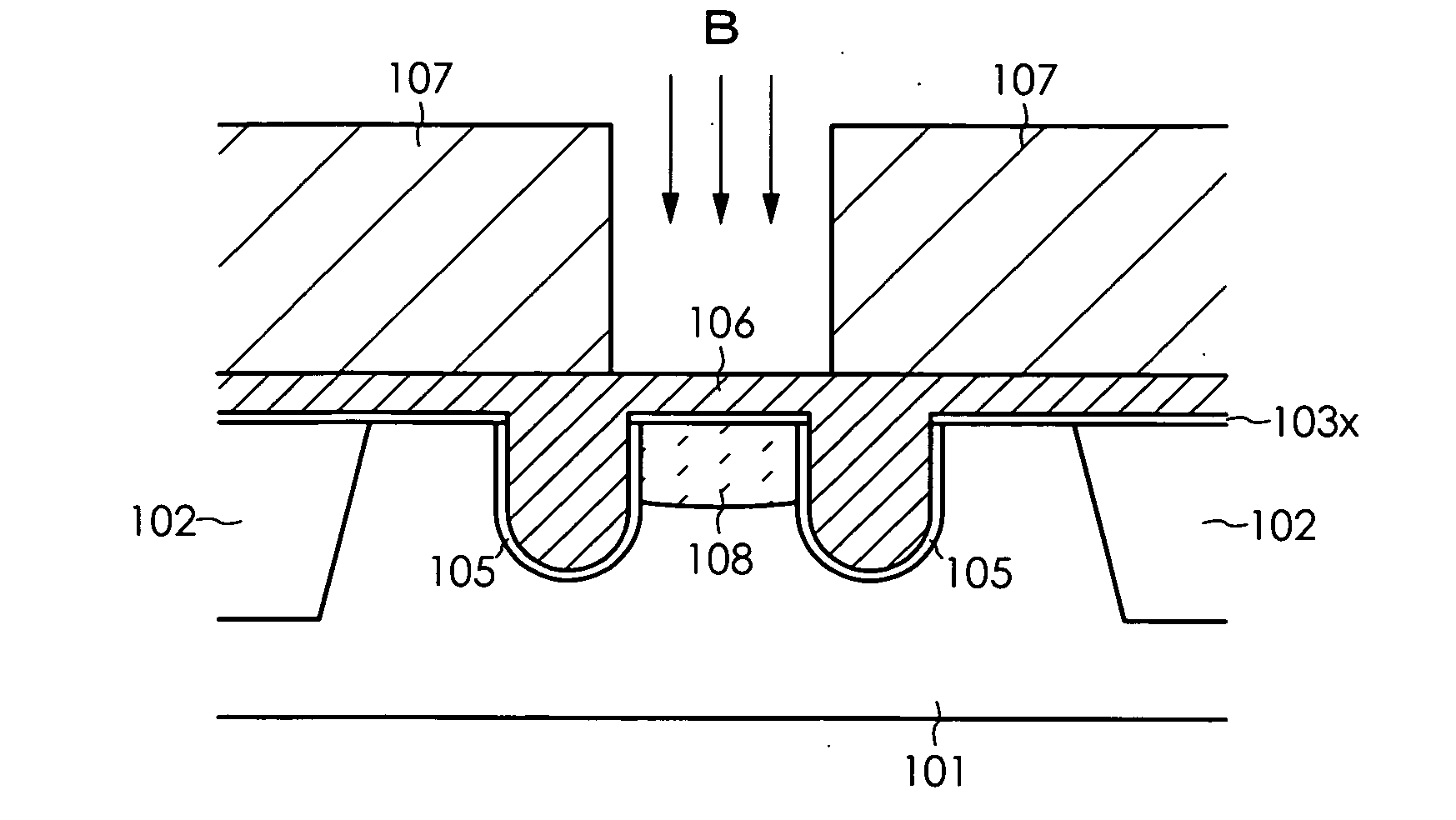
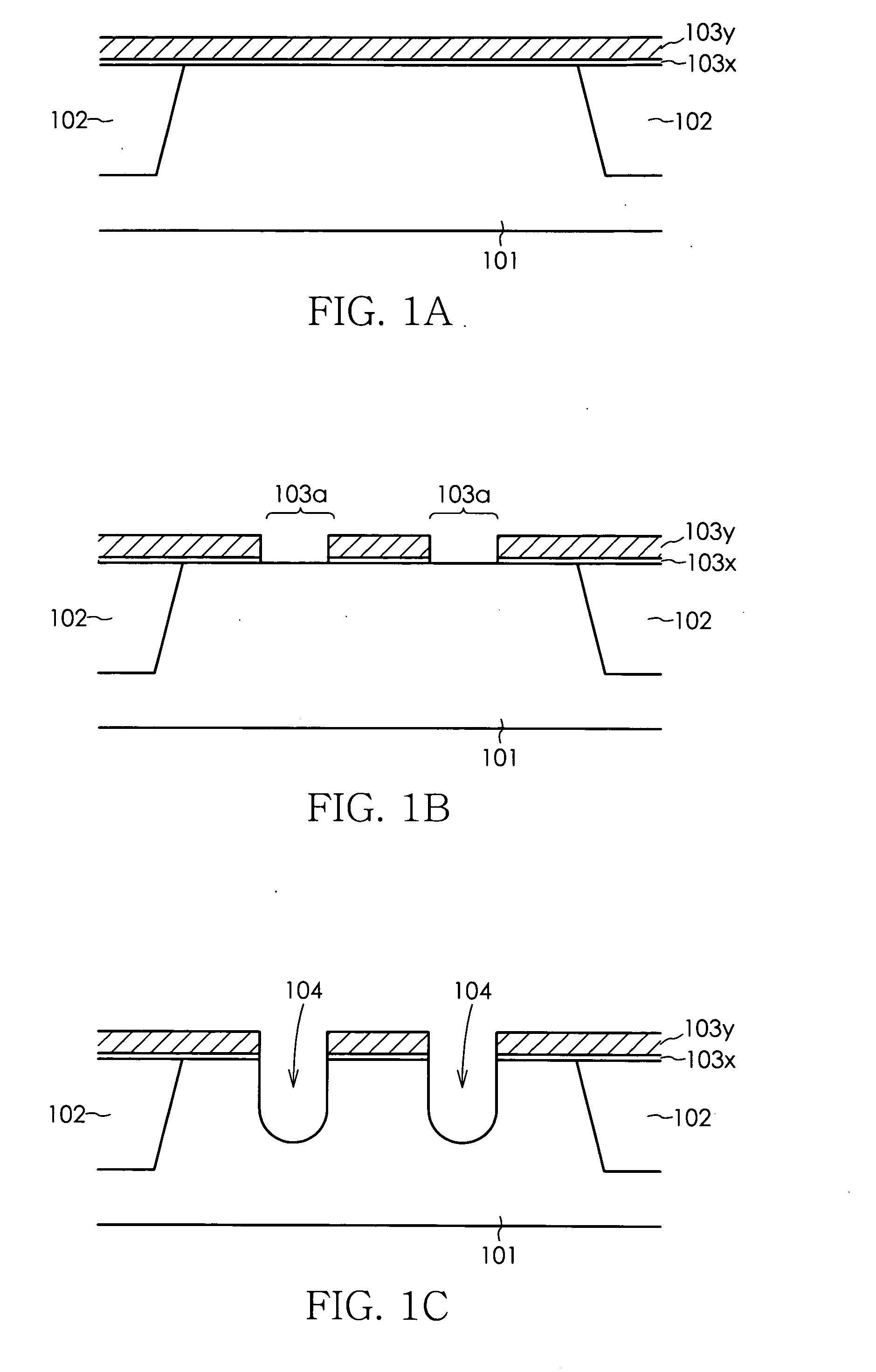
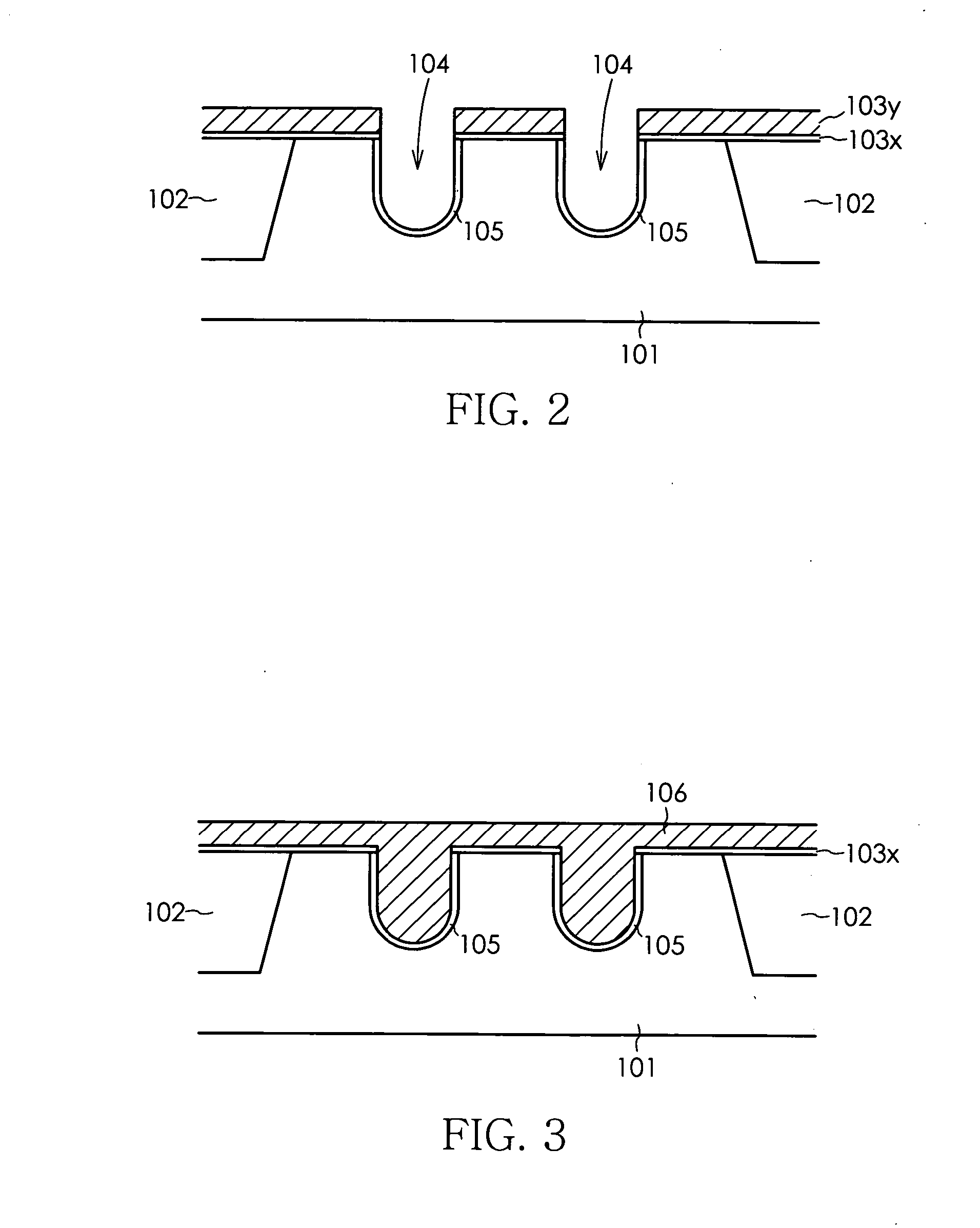
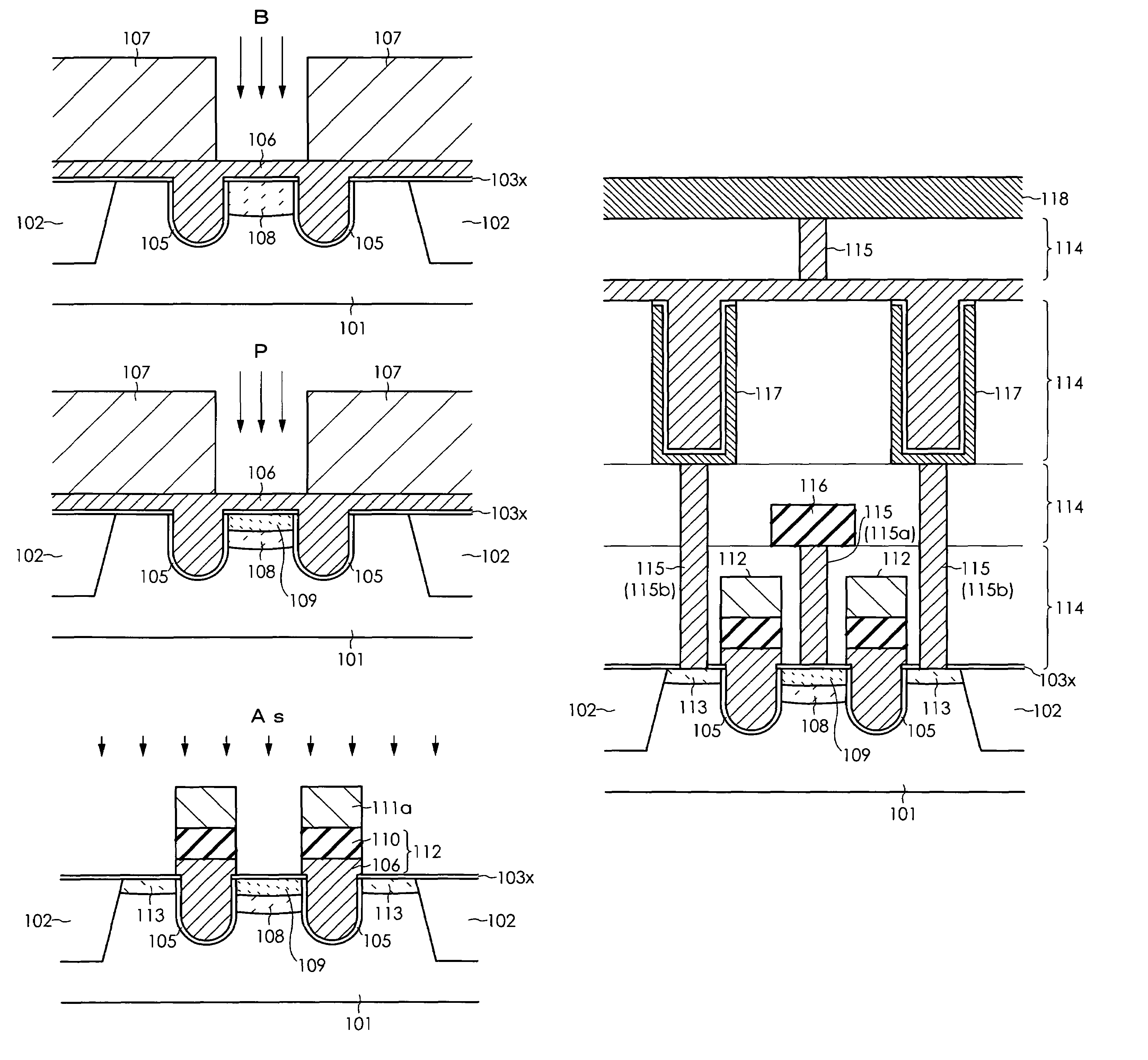
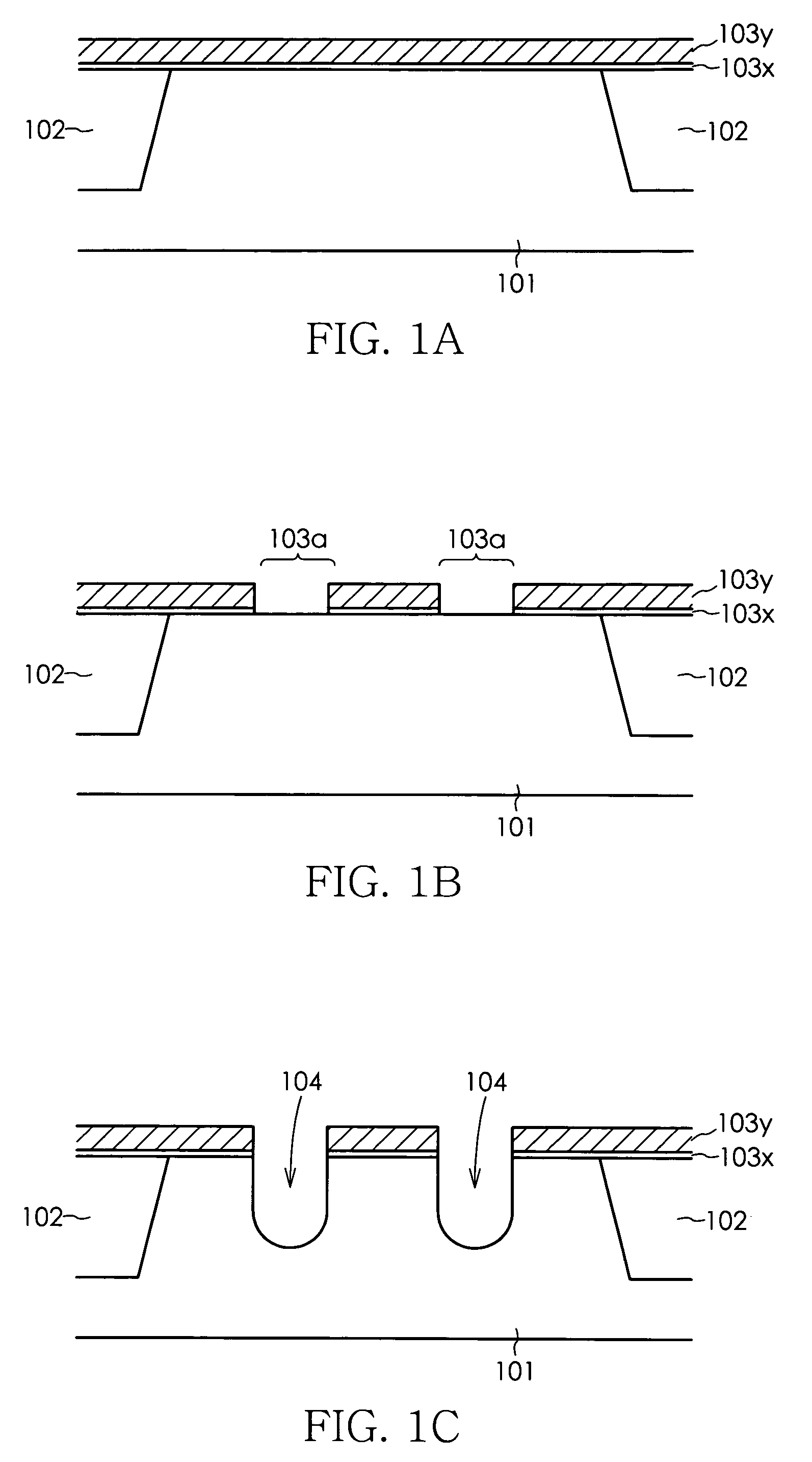
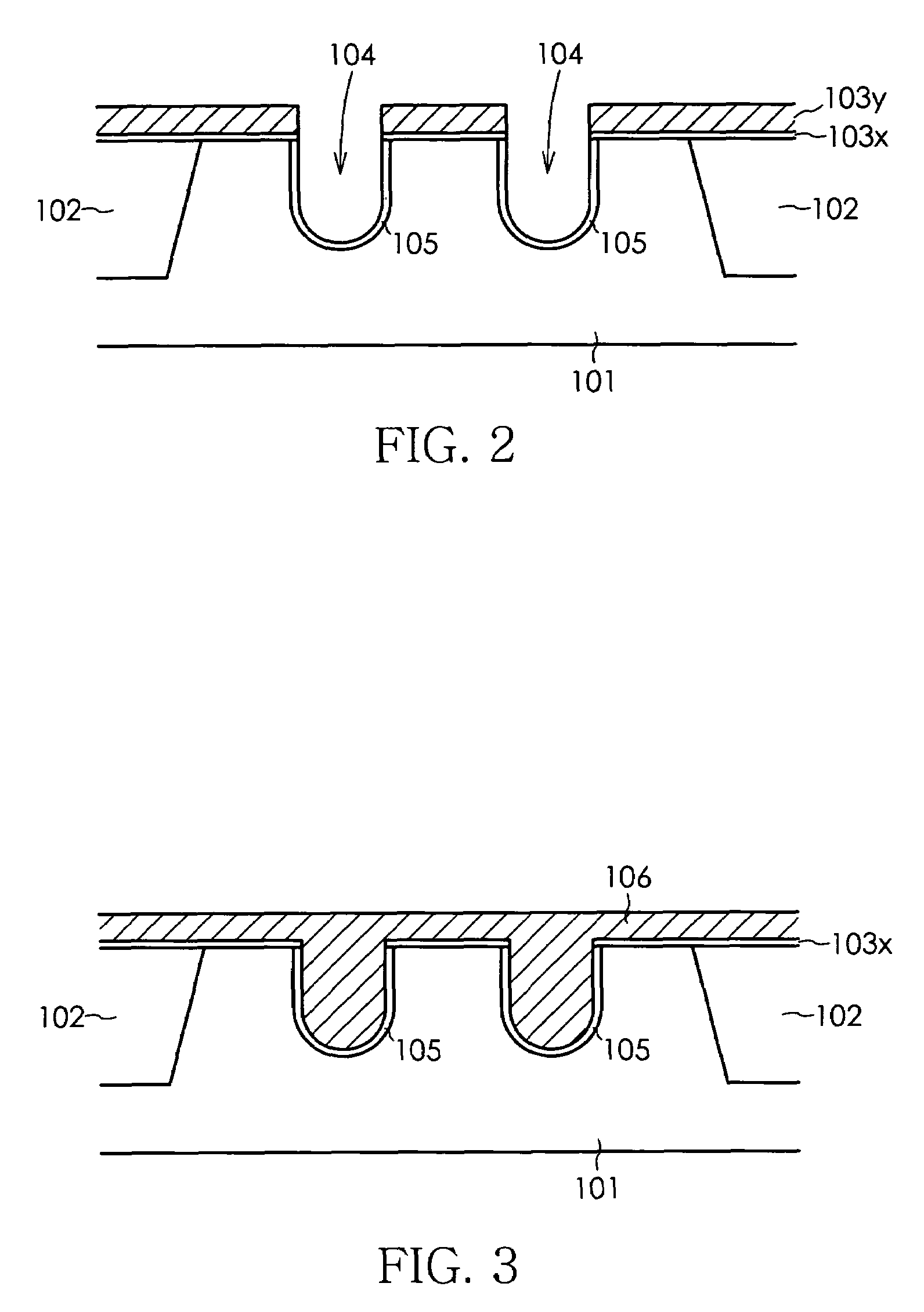
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070072375A1Improve accuracyOvercomes drawbackSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprises the steps of forming a gate trench in a semiconductor substrate, forming a gate insulation film in an inner wall of the gate trench, filling a gate electrode material into at least an inside of the gate trench, forming a gate electrode by patterning the gate electrode material, and selectively forming a punch-through stopper region prior to patterning the gate electrode material, using a mask in a prescribed position of the semiconductor substrate that is adjacent to the gate trench. The step for forming the punch-through stopper region may be performed subsequent to the step for filling the gate electrode material into the gate trench, or may be performed prior to the step for forming the gate trench.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
Profiling Float and Usage of the Profiling Float
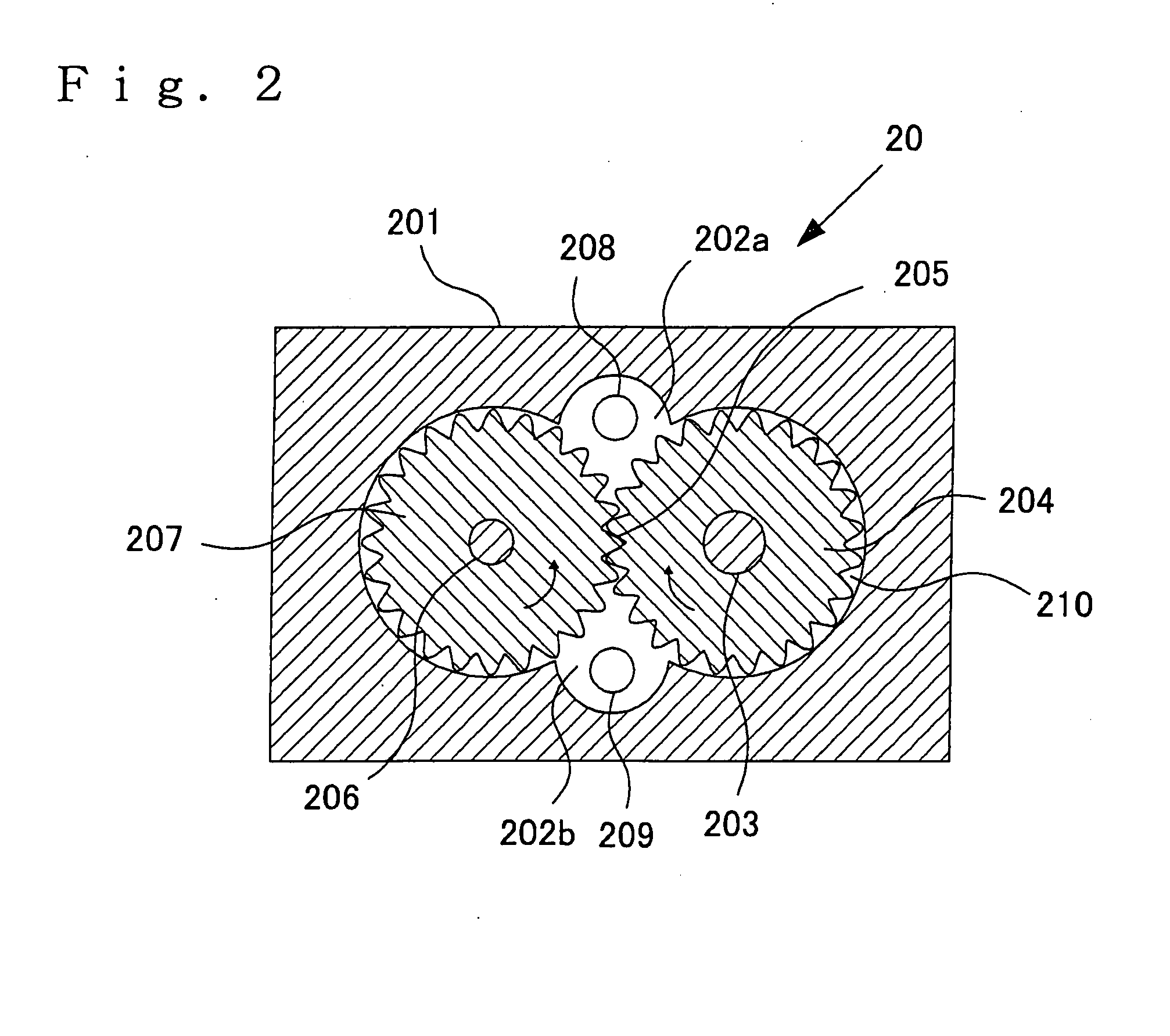
InactiveUS20080087209A1Improve electricity efficiencyEasy to useFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsBuoysGear pumpEngineering
Provided is a profiling float that can minutely and surely control effective buoyancy acting on the float in itself, and usage of the profiling float. The profiling float according to the present invention is equipped with a float chamber forming an airtight internal space, a fluid storage part provided in the float chamber and storing a fluid for control of buoyancy, a bladder provided at the exterior of the float chamber, in the interior of which the fluid for control of buoyancy is filled to change a volume thereof, thereby controlling buoyancy acting on the profiling float, a pump mechanism for transferring the fluid for control of buoyancy between the bladder and the fluid storage part, and a driving source for driving the pump mechanism, wherein the pump mechanism is composed of a gear pump.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
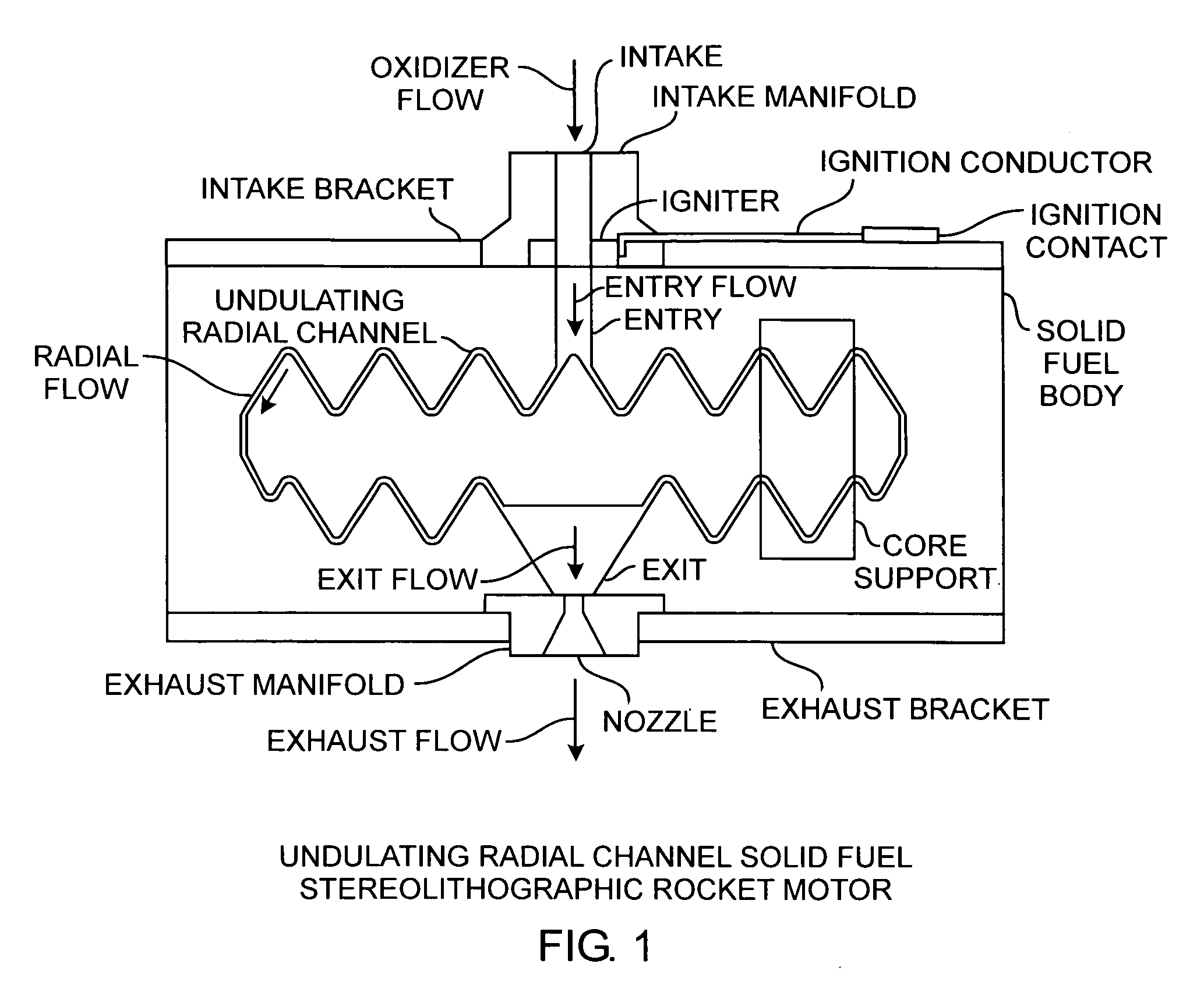
Stereolithographic rocket motor manufacturing method
ActiveUS8225507B2Effective regression rateIncrease surface areaAdditive manufacturing apparatusWriting implementsSolid fuelStereolithography
A hybrid rocket motor is manufactured by photopolymerizing the solid fuel grain in a stereolithography method, wherein fuel grains in a plastic matrix are deposited in layers for building a solid fuel rocket body in three dimensions for improved performance and for a compact design.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
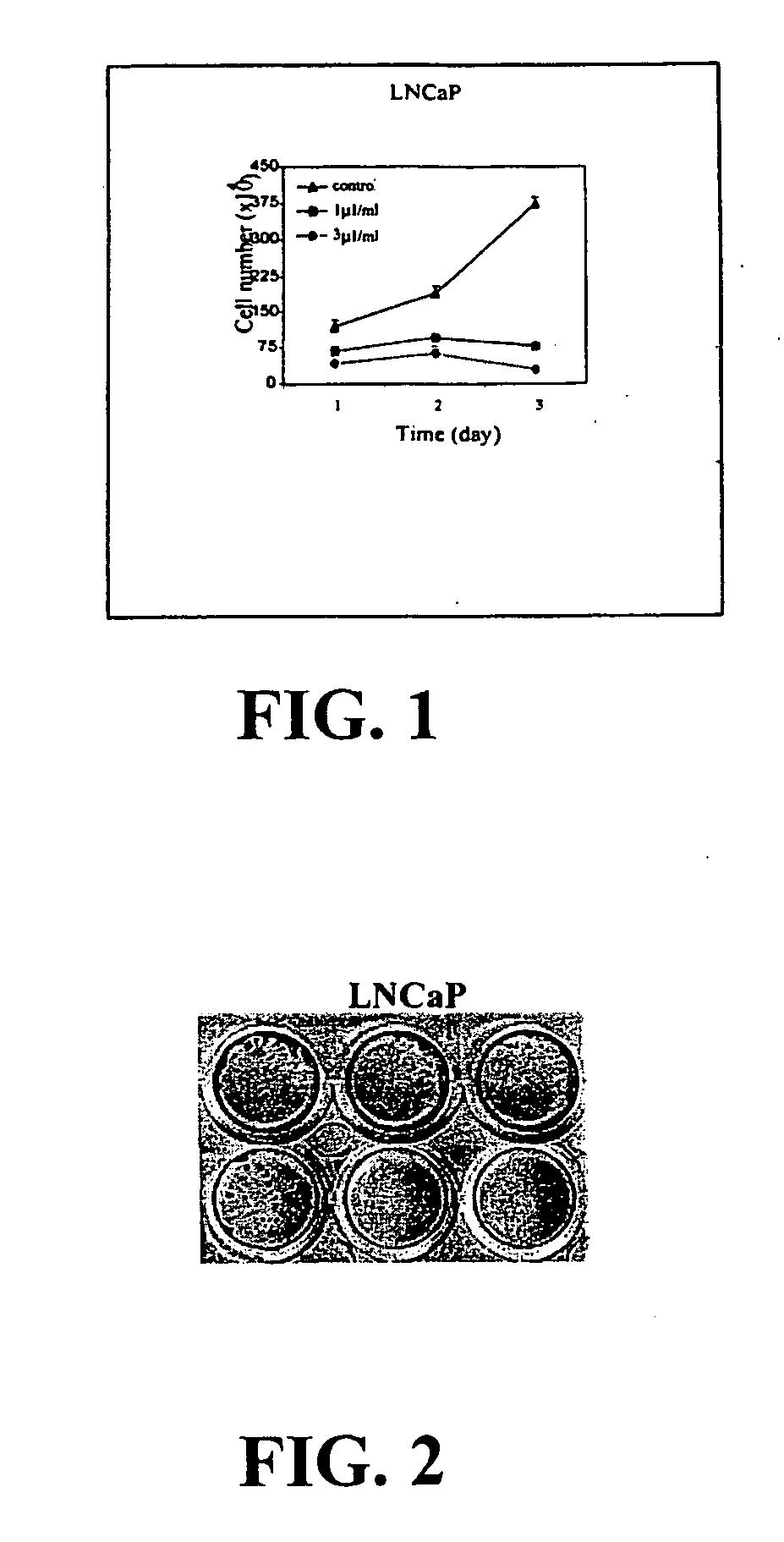
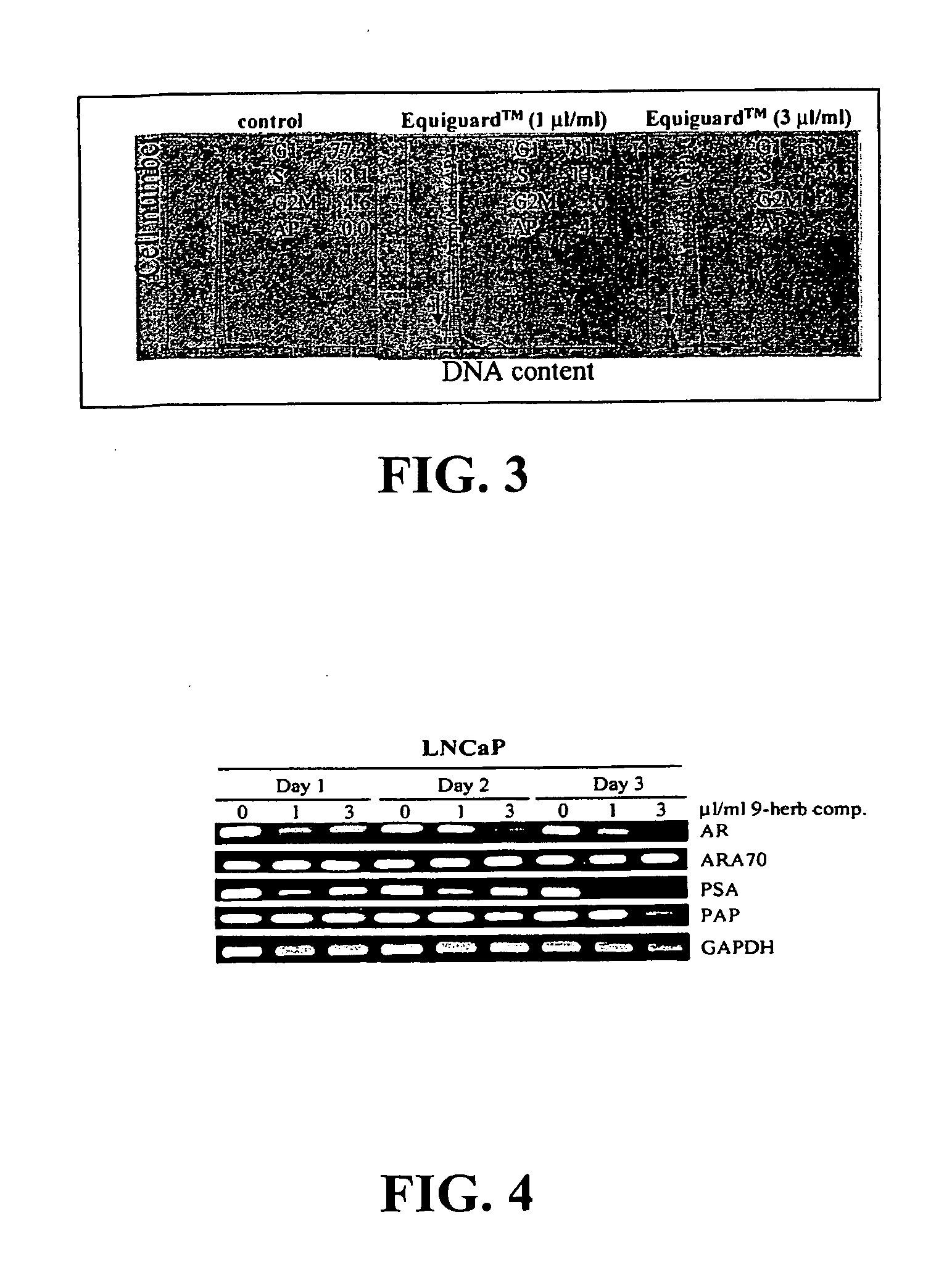
Compositions and methods for prostate and kidney health and disorders, an herbal preparation
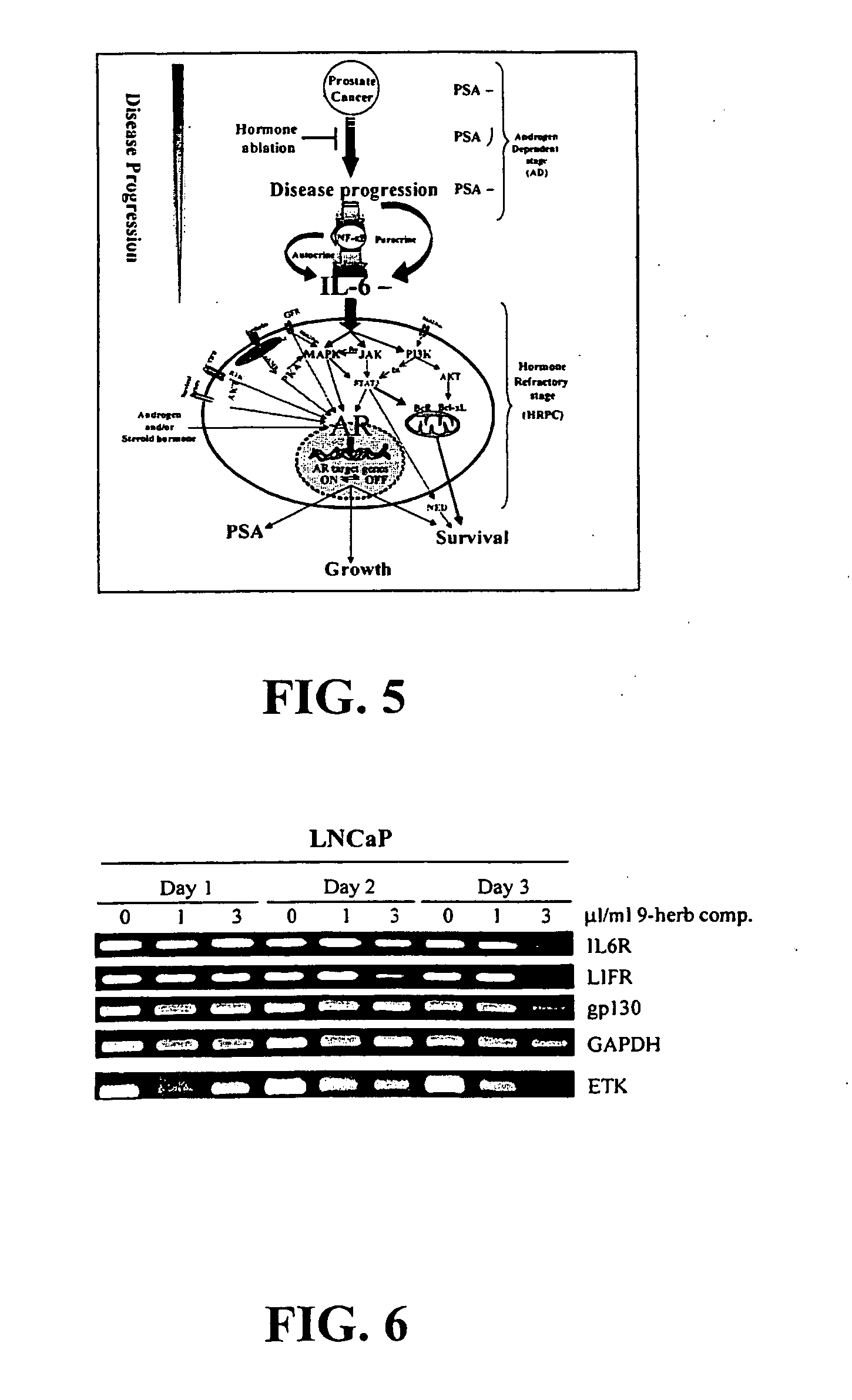
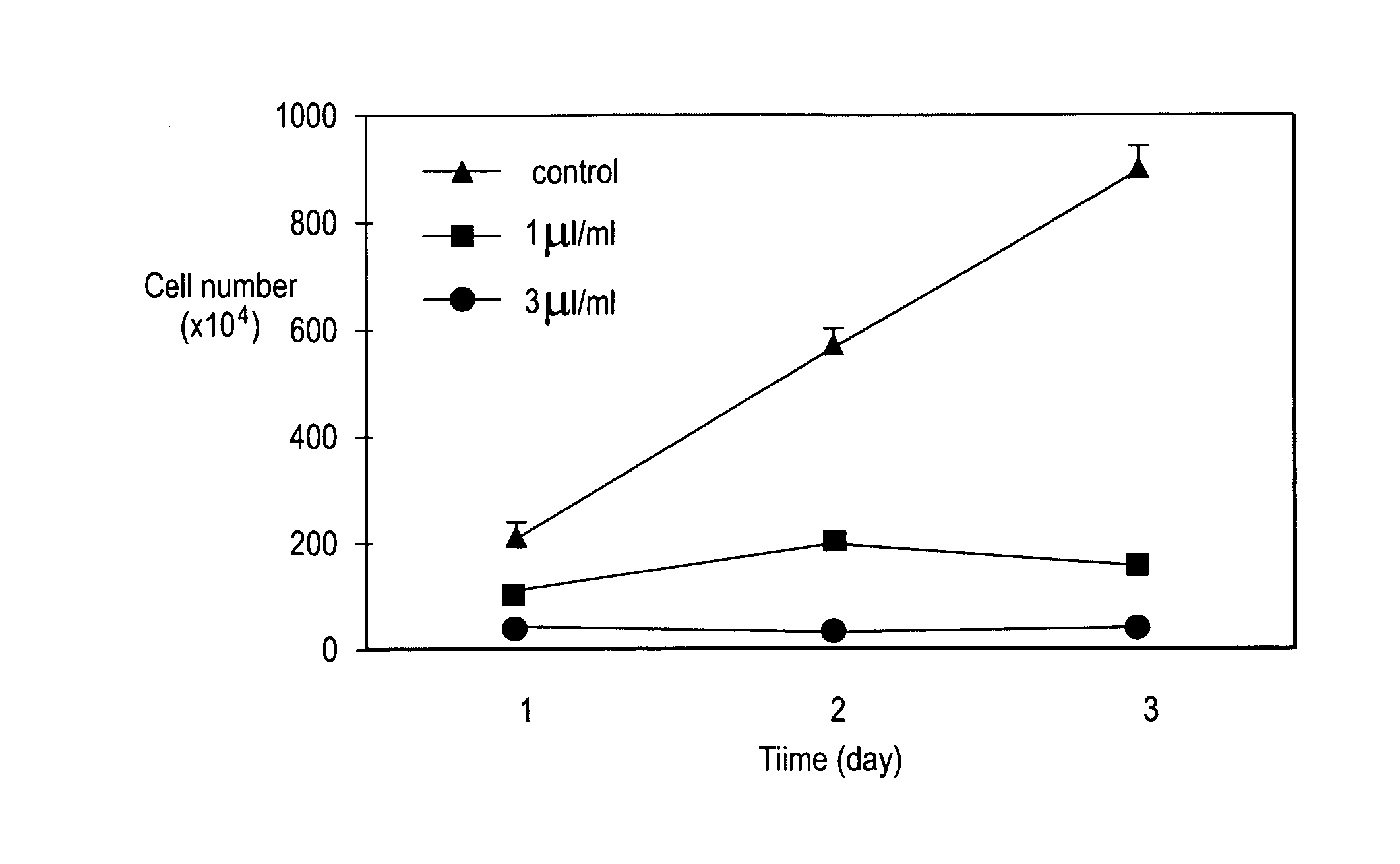
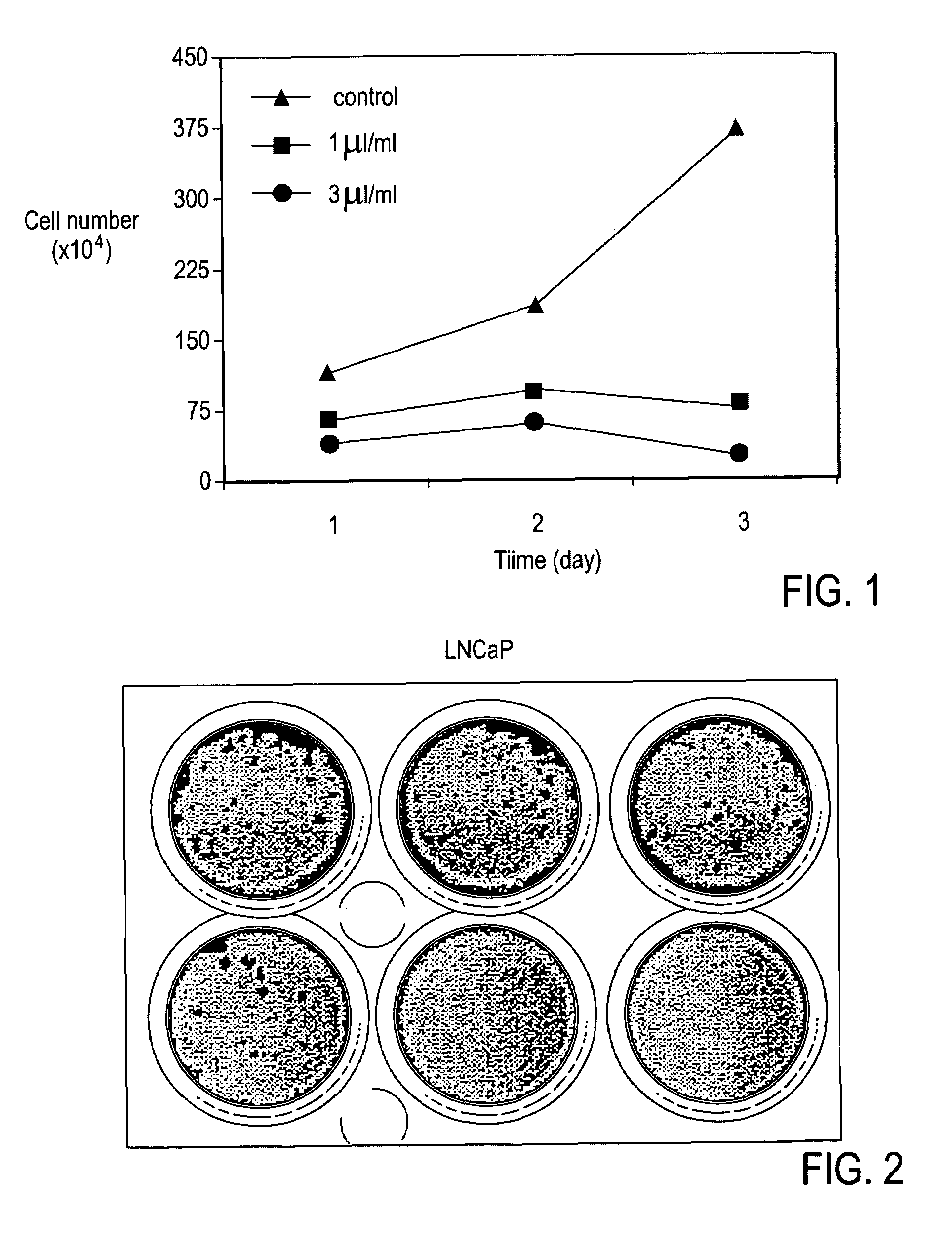
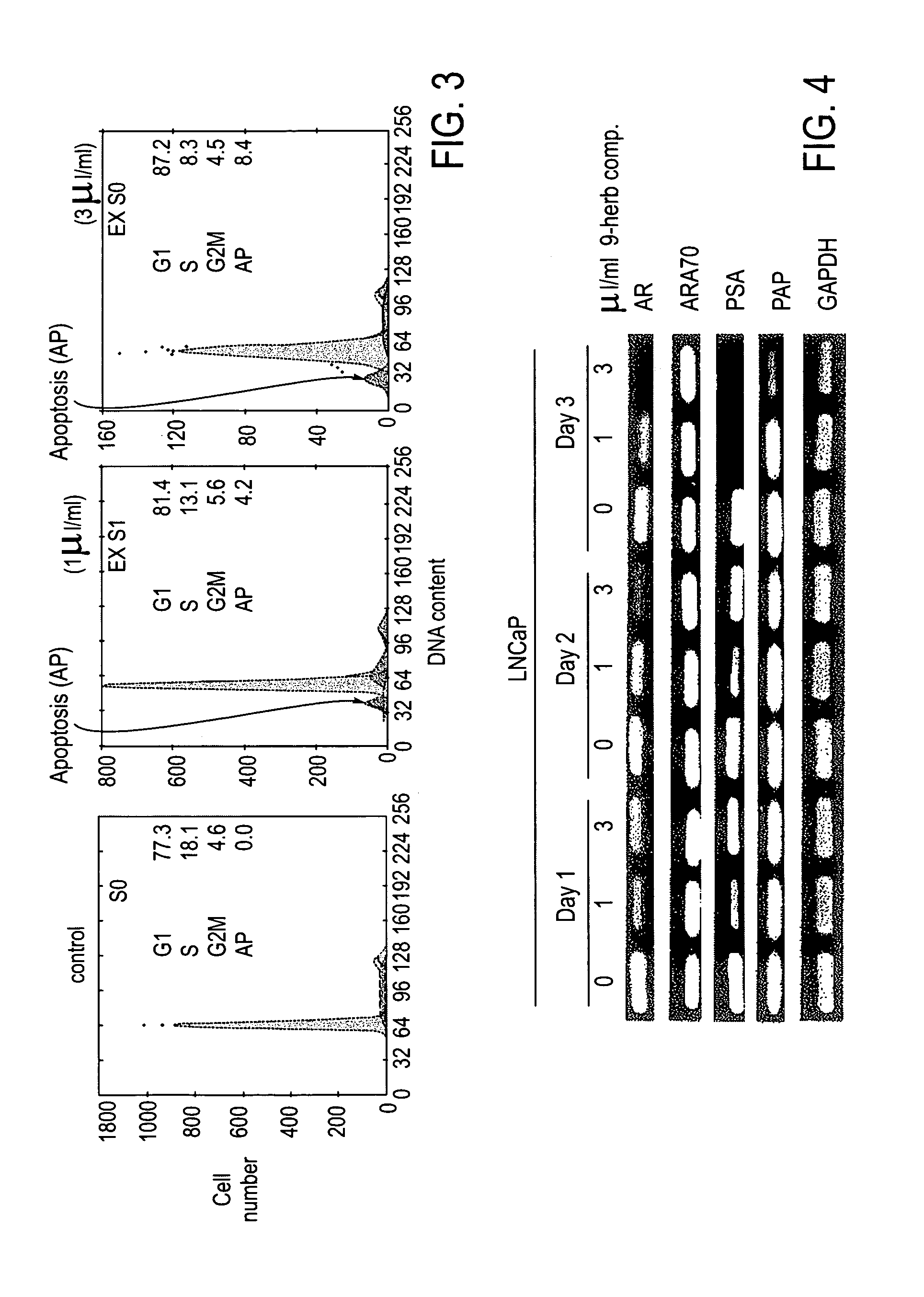
InactiveUS20050136140A1Limit profileAbolish the ability of prostate cancer cells to form coloniesBiocideUnknown materialsDiseaseHerbal preparations
A method including contacting a prostate cell with the composition including an aliquot of the herb Herba Epimedii; and an aliquot of at least three supplemental herbs selected from the group consisting of Fructus Rosae Laevigatae; Fructus Rubi; Fructus Psoralea; Radix Morindae Officinalis; Fructus Schisandrac Chinensis; Fructus Ligustri Lucidi; Semen Cuscutae; and Radix Astragali. A method including identifying a subject with a prostate / kidney disorder; and establishing a regimen for administering a composition including an aliquot of the herb Herba Epimedii, and an aliquot of at least three supplemental herbs selected from the group consisting of Fructus Rosae Laevigatae; Fructus Rubi; Fructus Psoralea; Radix Morindae Officinalis; Fructus Schisandrac Chinensis; Fructus Ligustri Lucidi; Semen Cuscutae; and Radix Astragali.
Owner:SIBONI GRP
Tricalcium phosphates, their composites, implants incorporating them, and methods for their production
InactiveUS8029755B2Easy to controlReduce the temperatureHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocidePhosphoric acidTri calcium phosphate
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Compositions and methods for prostate and kidney health and disorders, an herbal preparation
A composition including an aliquot of the herb Herba Epimedii; and an aliquot of at least three supplemental herbs selected from the group consisting of Fructus Rosae Laevigatae; Fructus Rubi; Fructus Psoralea; Radix Morindae Officinalis; Fructus Schisandrac Chinensis; Fructus Ligustri Lucidi; Semen Cuscutae; and Radix Astragali. A composition including icariin; ursolic acid; ellagic acid; psoralen; deoxyschizandrin; oleanolic acid; quercetin; aslvagaloside; and an extract of the herb Radix Morindae Officinalis. Methods including administering a composition directed at treatment of various kidney disorders or the promotion of kidney health and to the overall health of the kidney, including the use of a composition in the treatment of prostate cancer, prophylatic prostate health, reduction of polyuria, incontinence, proteinuria, as well as for sexual satisfaction.
Owner:SIBONI GRP
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7465637B2Improve accuracyOvercomes drawbackSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprises the steps of forming a gate trench in a semiconductor substrate, forming a gate insulation film in an inner wall of the gate trench, filling a gate electrode material into at least an inside of the gate trench, forming a gate electrode by patterning the gate electrode material, and selectively forming a punch-through stopper region prior to patterning the gate electrode material, using a mask in a prescribed position of the semiconductor substrate that is adjacent to the gate trench. The step for forming the punch-through stopper region may be performed subsequent to the step for filling the gate electrode material into the gate trench, or may be performed prior to the step for forming the gate trench.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
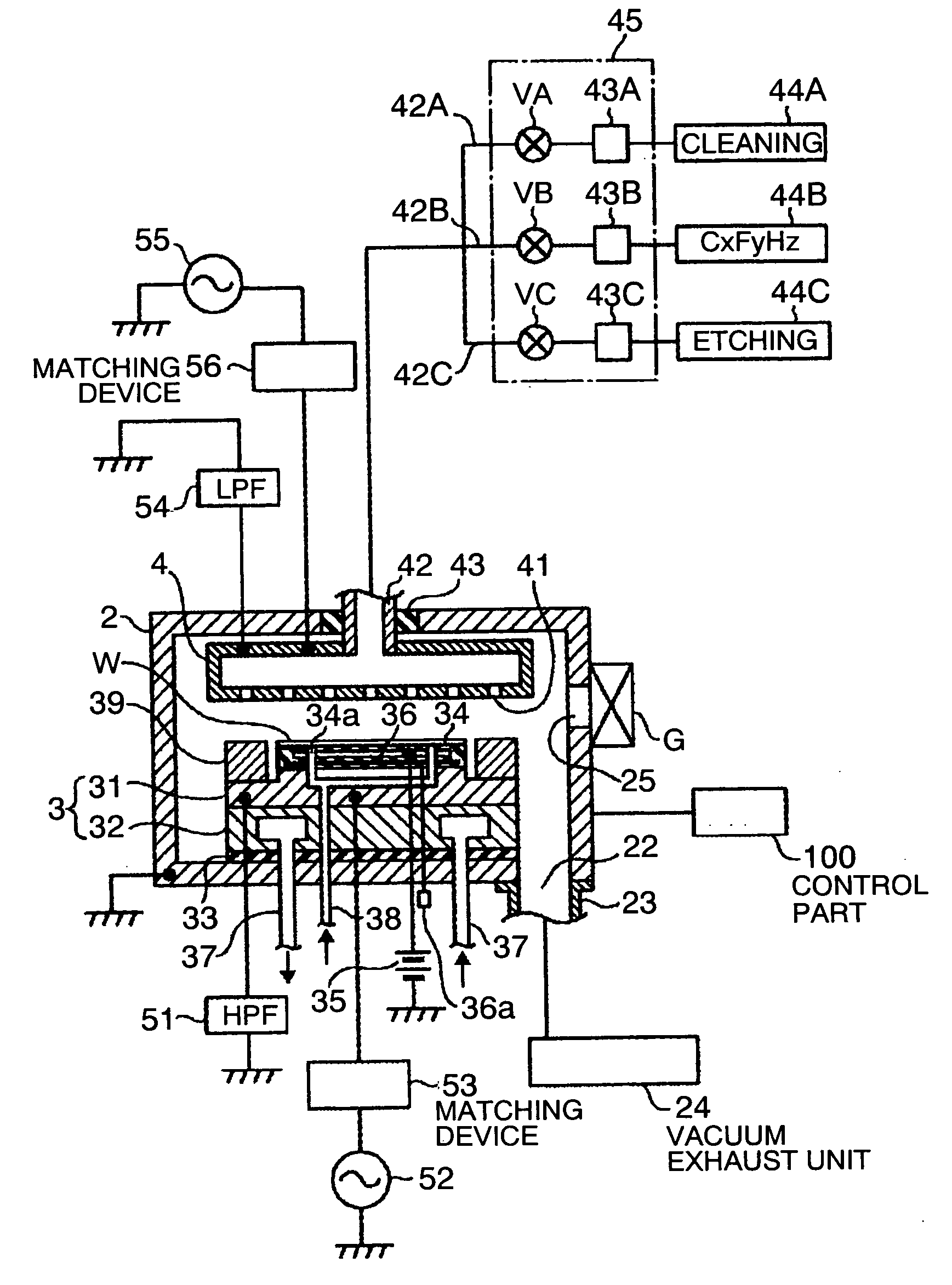
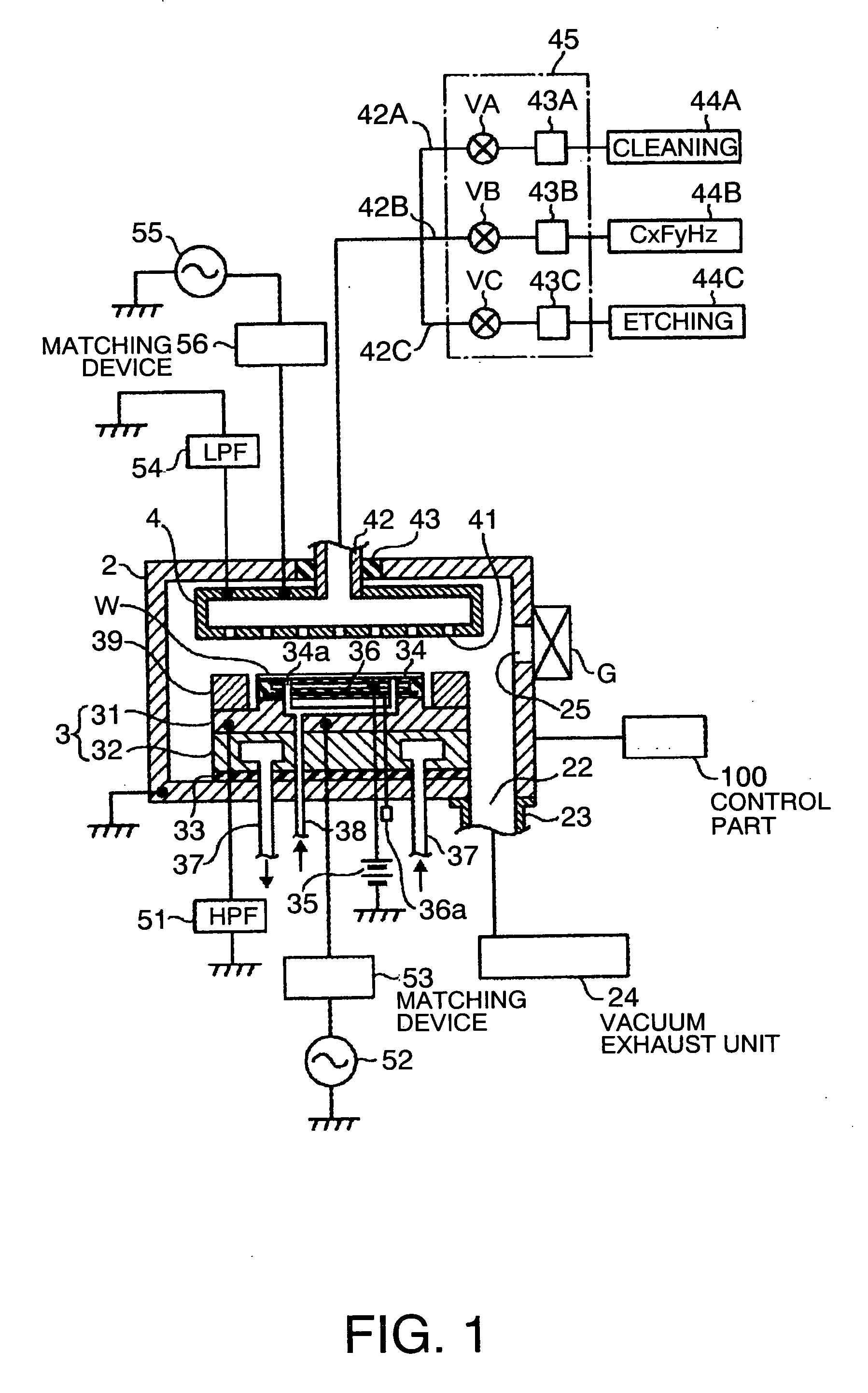
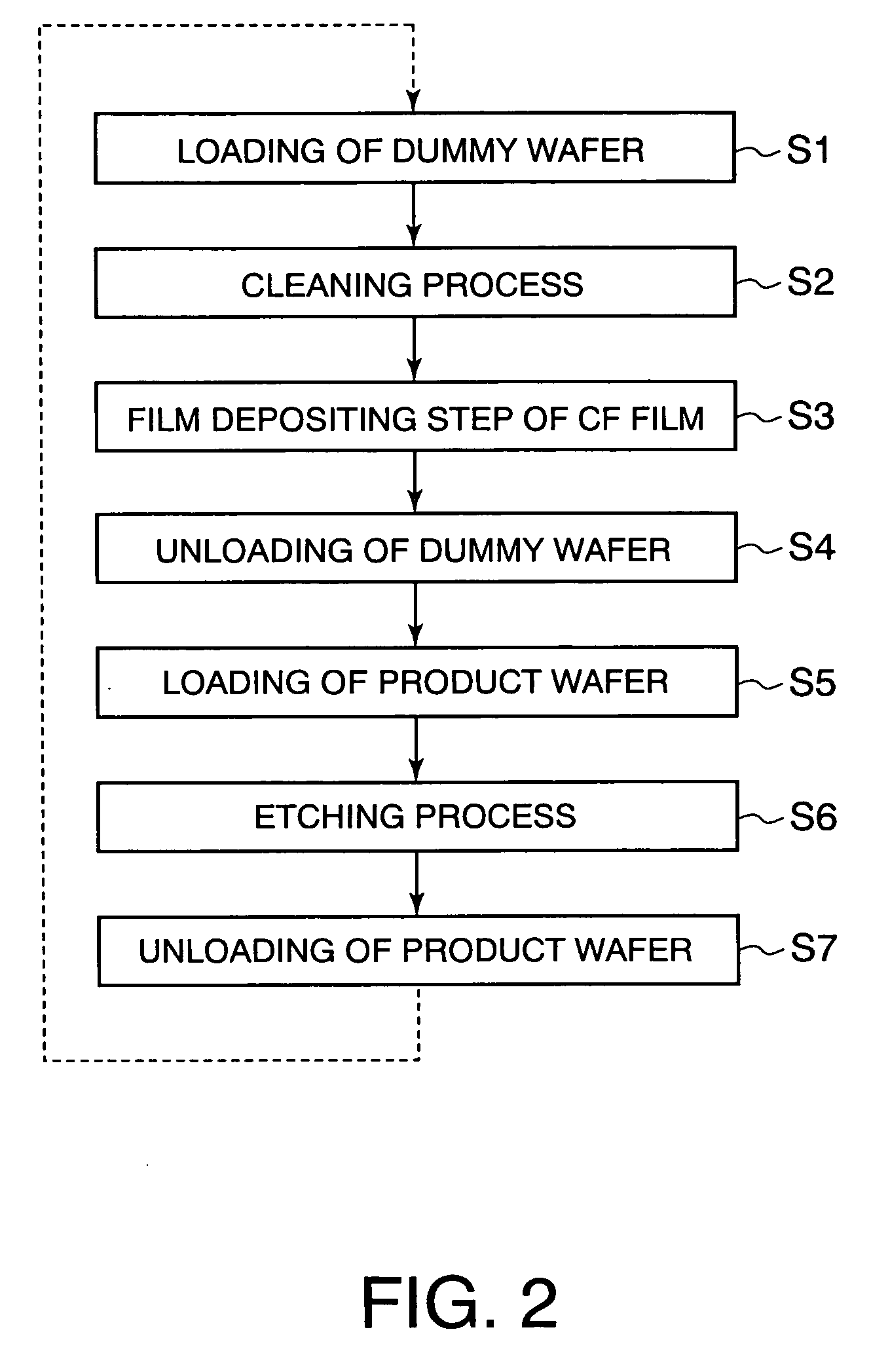
Plasma etchimg method and plasma etching apparatus
ActiveUS20090233450A1Limit profileSmall etching rateGas treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma depositionPlasma etching
The present invention is a plasma etching method comprising: a cleaning step (a) in which a cleaning gas is supplied into a processing vessel and the cleaning gas is made plasma, so that a deposit adhering to an inside of the processing vessel is removed by means of the plasma; a film depositing step (b), succeeding the cleaning step (a), in which a film depositing gas containing carbon and fluorine is supplied into the processing vessel and the film depositing gas is made plasma, so that a film containing carbon and fluorine is deposited on the inside of the processing vessel by means of the plasma; an etching step (c), succeeding the film depositing step (b), in which a substrate is placed on a stage inside the processing vessel, and an etching gas is supplied into the processing vessel and the etching gas is made plasma, so that the substrate is etched by means of the plasma; and an unloading step (d), succeeding the etching step (c), in which the substrate is unloaded from the processing vessel; wherein, after the unloading step (d) has been finished, the cleaning step (a) to the unloading step (d) are repeated again.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
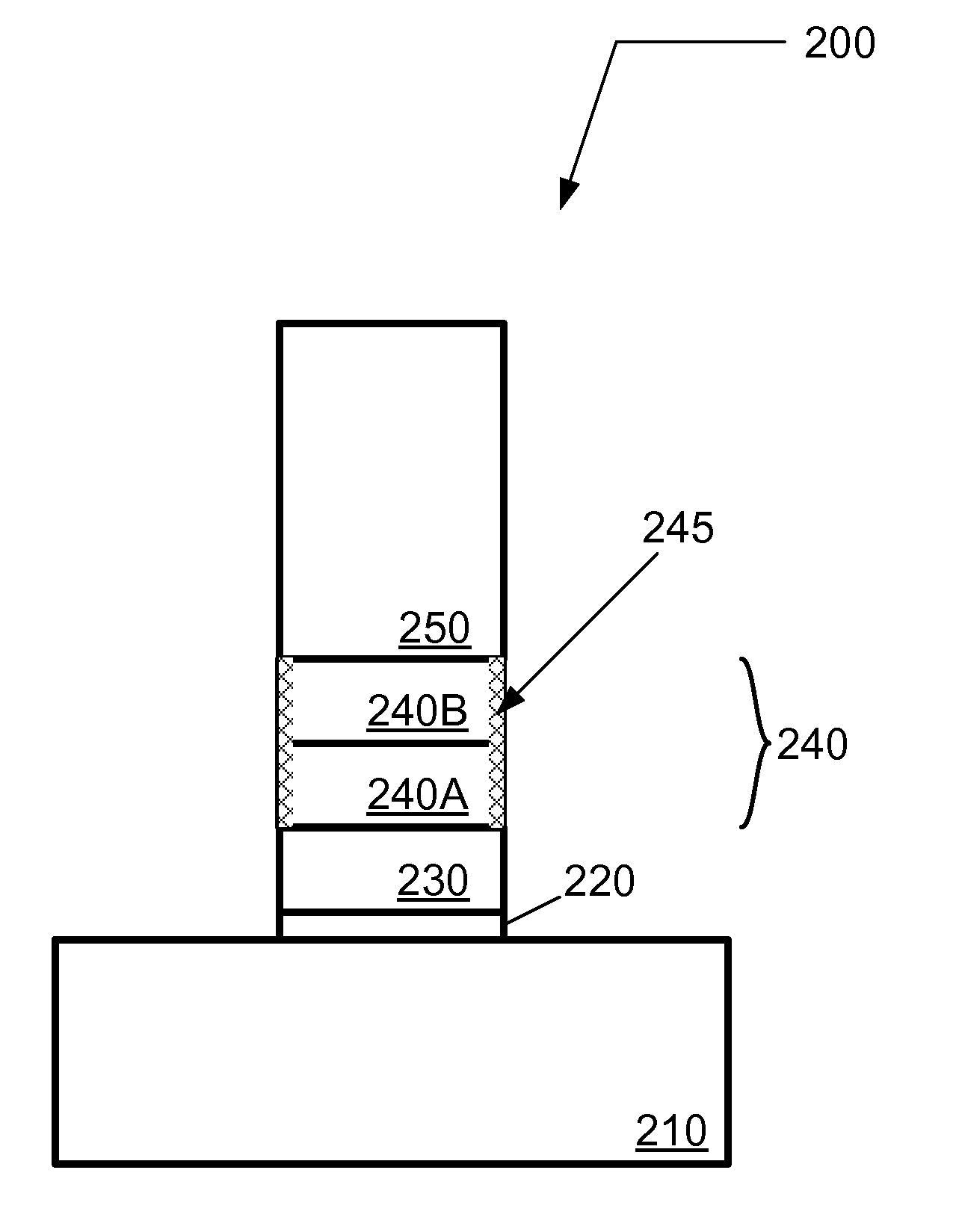
Method for patterning a full metal gate structure
InactiveUS20120244693A1Limit profileReduced under-cuttingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesNitrogenMetal
A method of patterning a gate structure on a substrate is described. The method includes preparing a metal gate structure on a substrate, wherein the metal gate structure includes a high dielectric constant (high-k) layer, a first gate layer formed on the high-k layer, and a second gate layer formed on the first gate layer, and wherein the first gate layer comprises one or more metal-containing layers. The method further includes preparing a mask layer with a pattern overlying the metal gate structure, transferring the pattern to the second gate layer, transferring the pattern to the first gate layer, and transferring the pattern in the first gate layer to the high-k layer, and prior to the transferring of the pattern to the high-k layer, passivating an exposed surface of the first gate layer using a nitrogen-containing and / or carbon-containing environment to reduce under-cutting of the first gate layer relative to the second gate layer, wherein the passivating is performed separately from or in addition to the transferring of the pattern to the first gate layer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
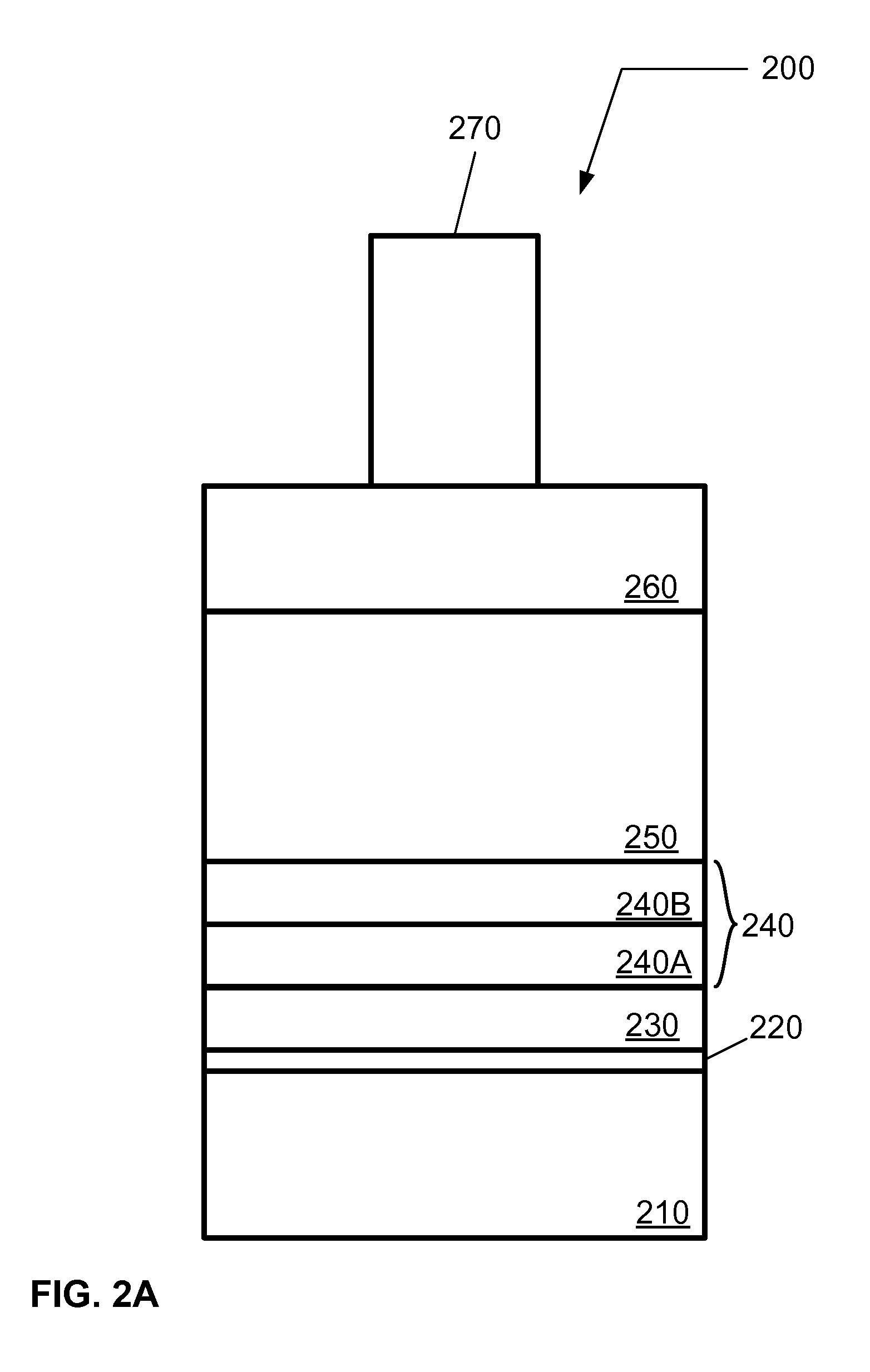
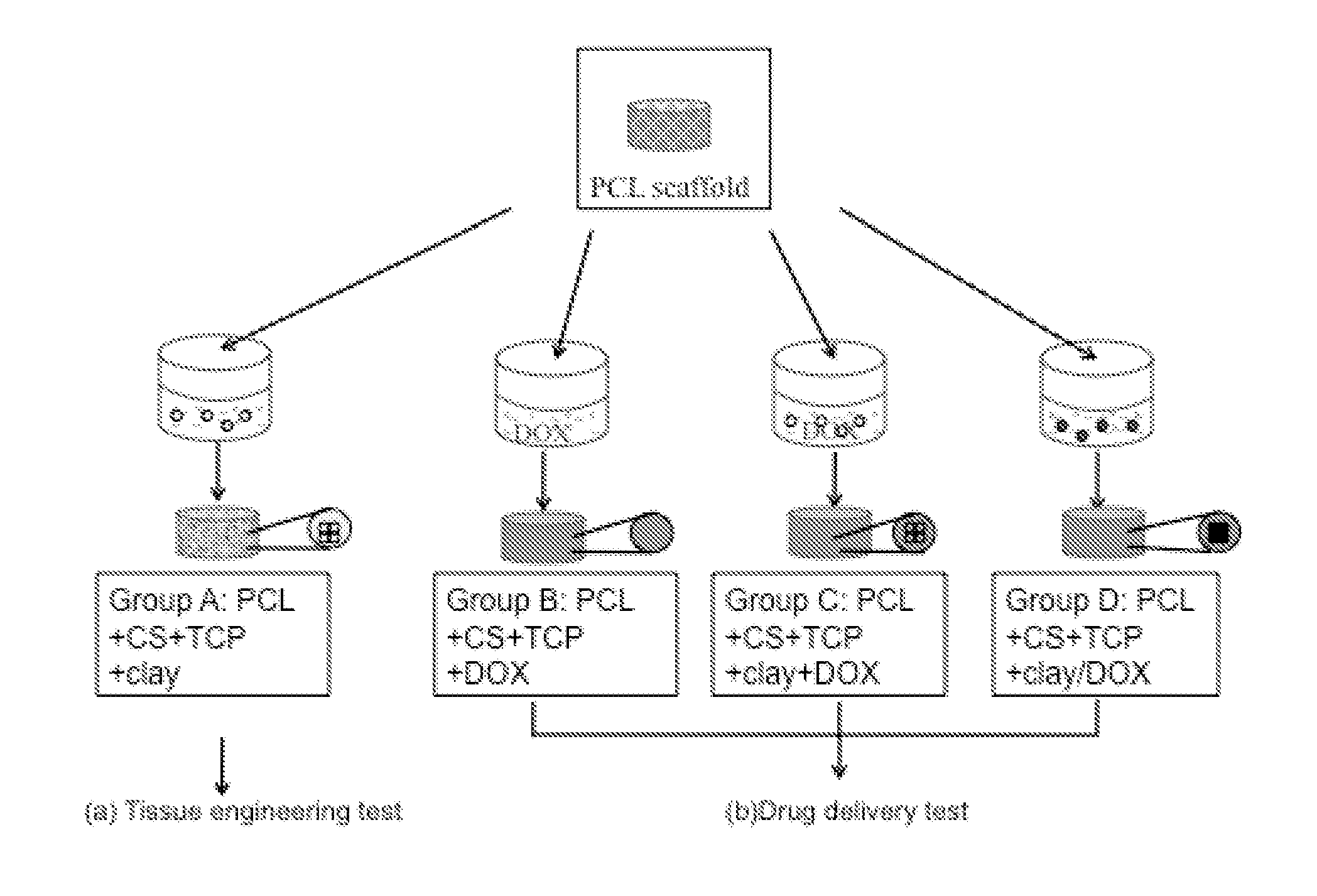
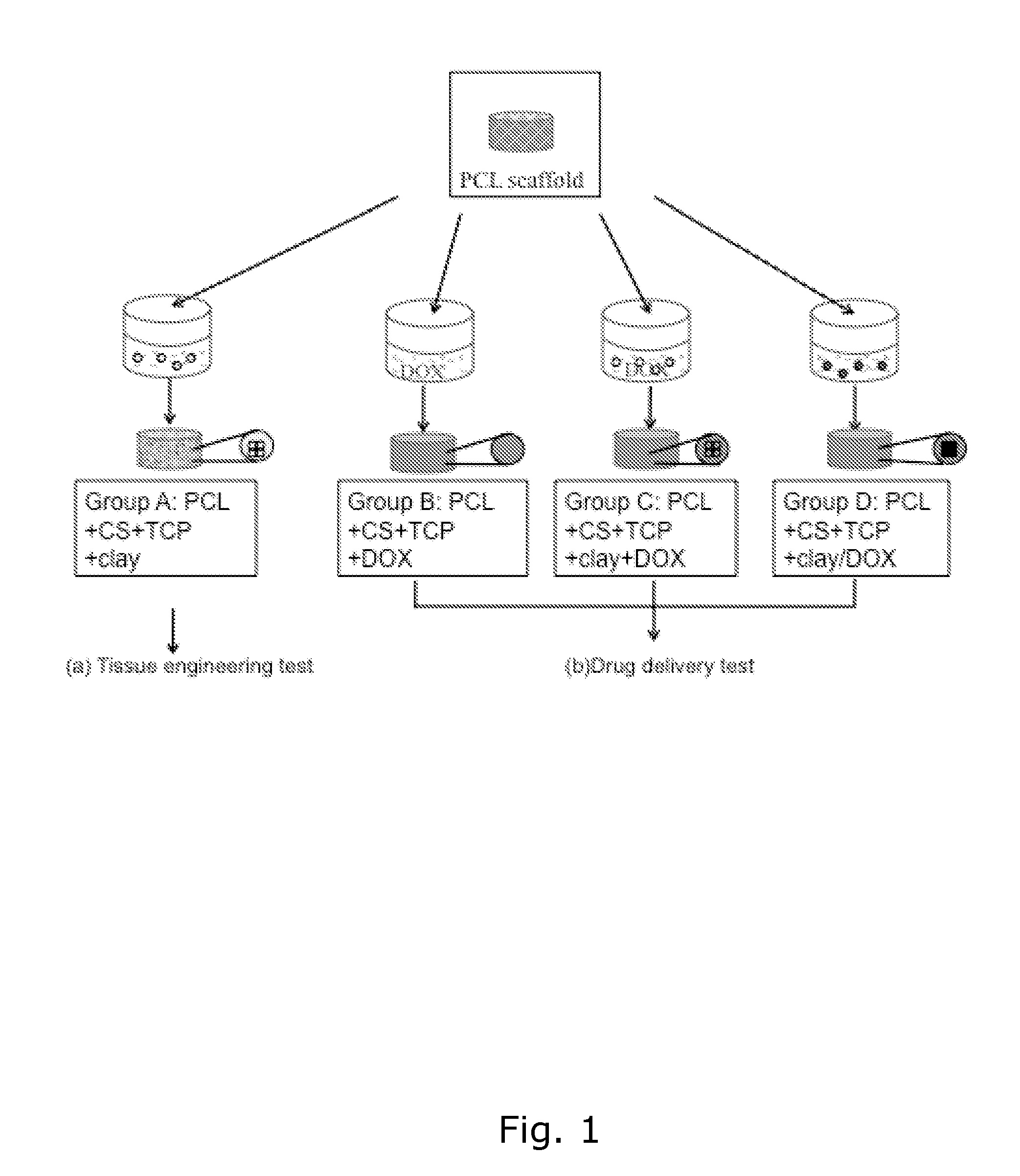
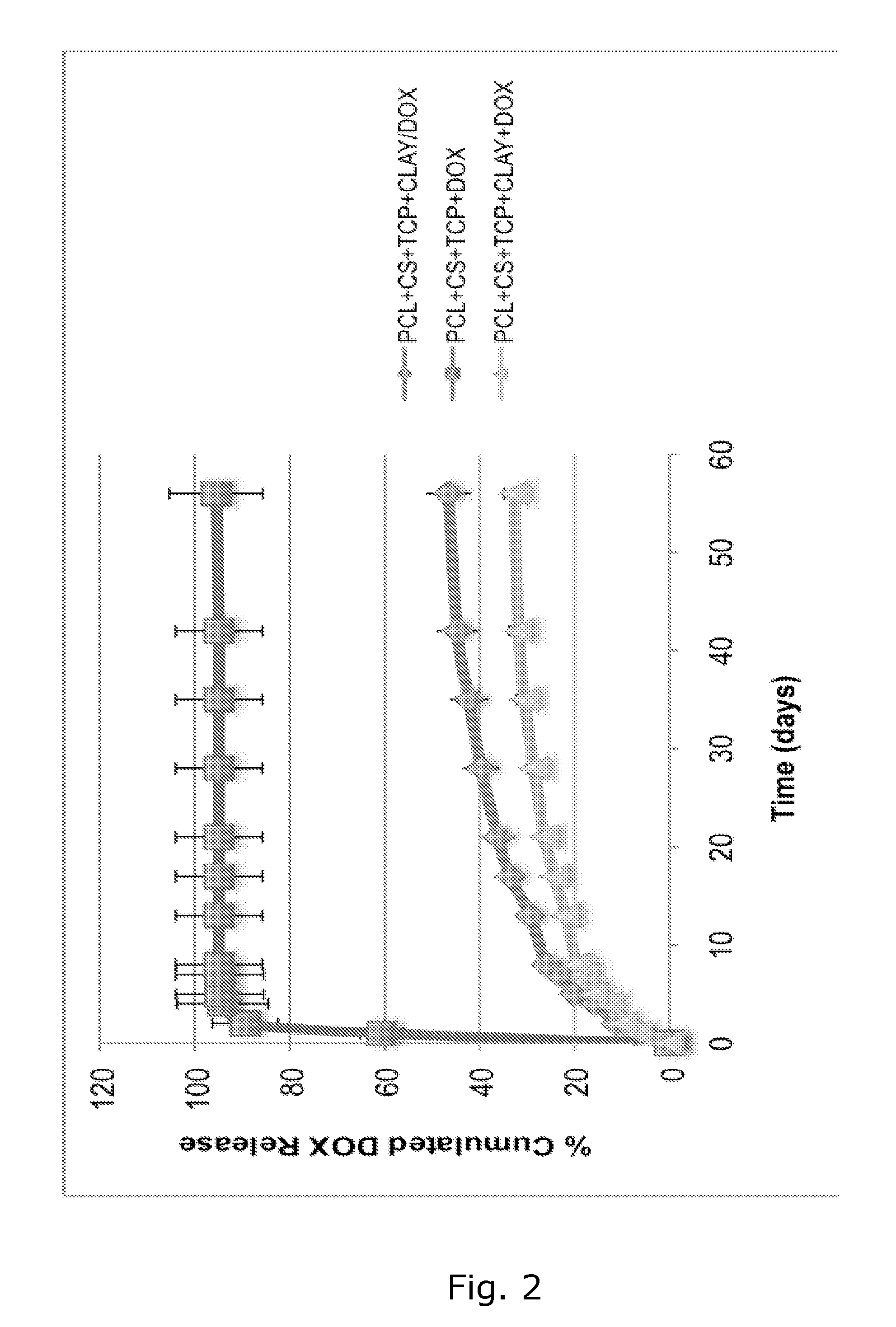
Tissue scaffold with controlled drug release
InactiveUS20130211543A1Promote tissue ingrowthSufficient supportTissue regenerationProsthesisControl releaseIon exchange
A three-dimensional hybrid scaffold capable of supporting cell activities such as growth and differentiation, and capable of controlled release of active pharmaceutical ingredients, characterized in that the scaffold comprises a first and a second biocompatible material, said first material shaped as a framework forming one or more open networks of voids, said second material comprising an ion exchange material, said ion exchange material being loaded with one or more active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Owner:NYGAARD JENS VINGE +5
Buried radial flow rapid prototyping rocket motors
ActiveUS8601790B2Effective regression rateIncrease surface areaAdditive manufacturing apparatusExplosivesSolid fuelRapid prototyping
A hybrid rocket motor is manufactured by photopolymerizing the solid fuel grain in a stereolithography method, wherein fuel grains in a plastic matrix are deposited in layers for building a solid fuel rocket body in three dimensions for improved performance and for a compact design, the hybrid rocket motor including buried radial channels for defining a desired burn profile including the oxidizer to fuel burn ratio.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
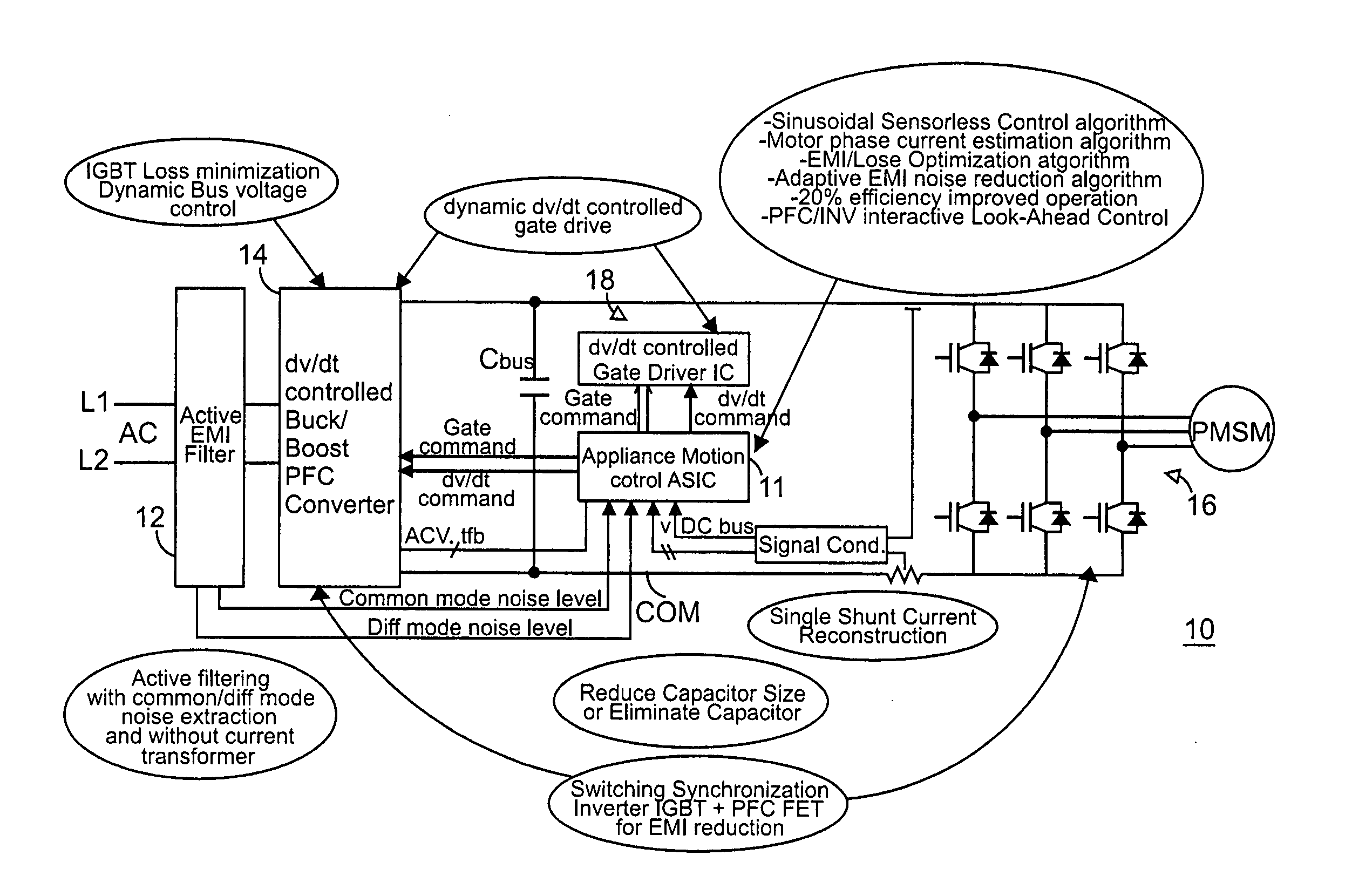
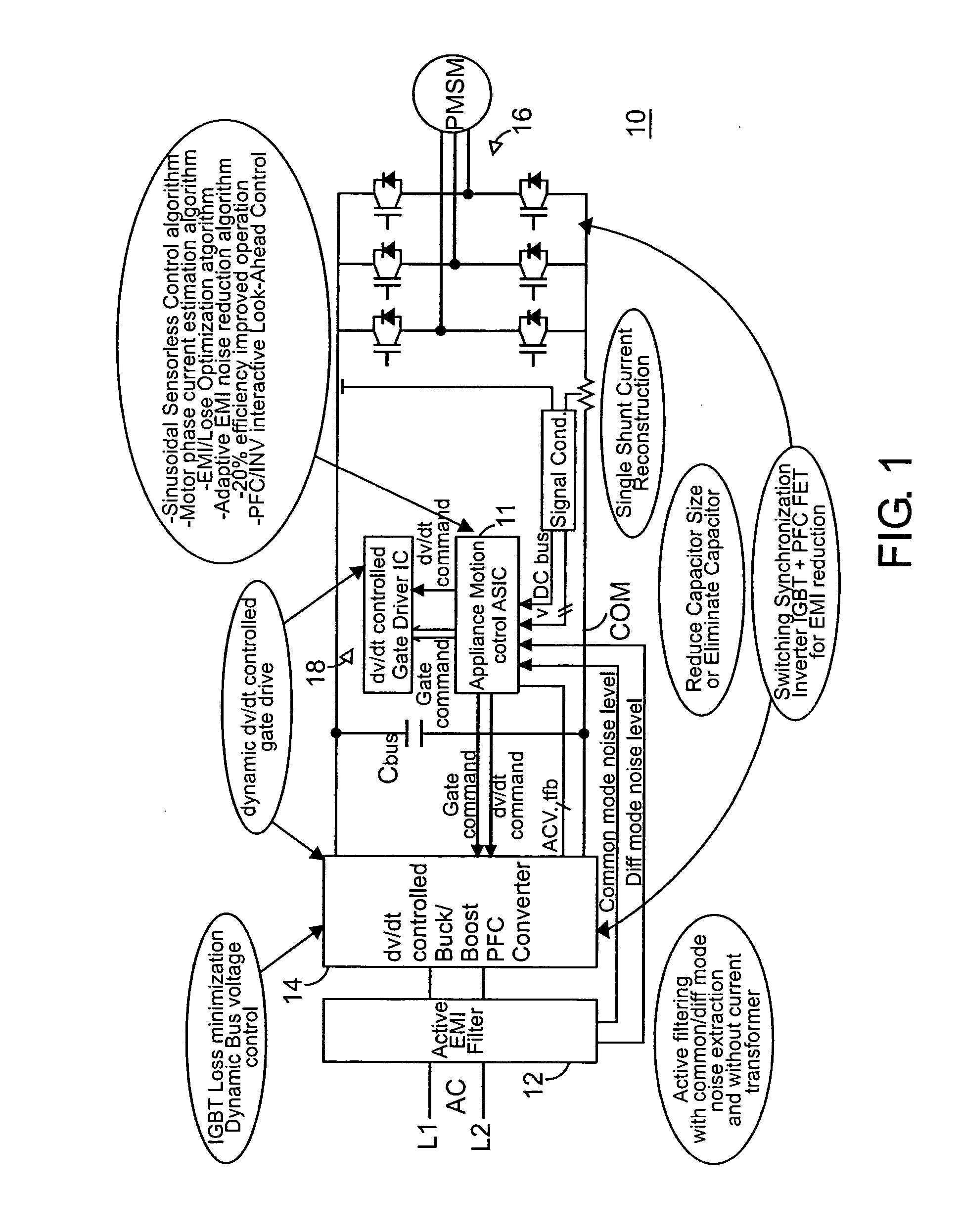
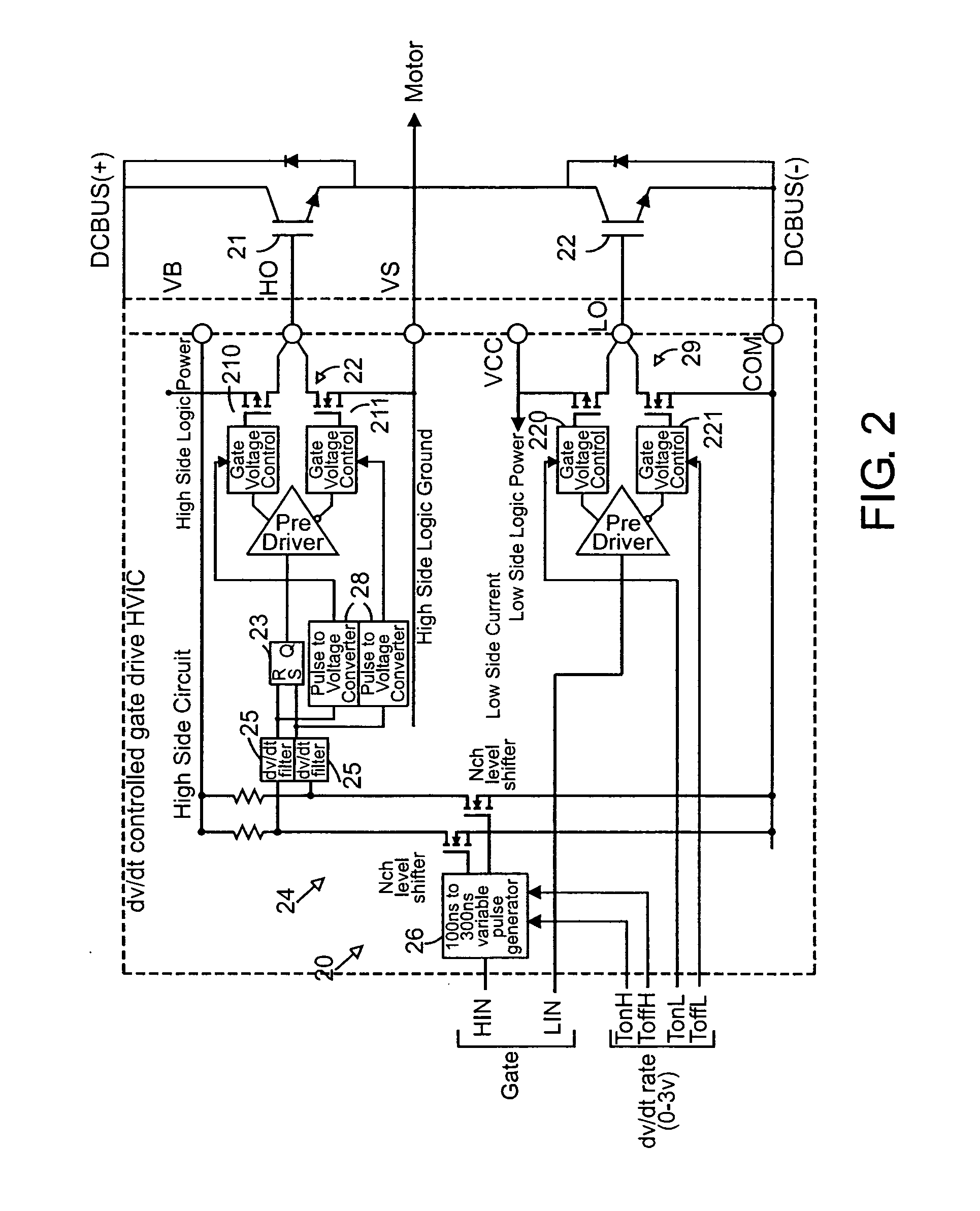
Global closed loop control system with DV/DT control and EMI/switching loss reduction
ActiveUS20060119303A1Common-mode noise can be improvedLimit profileElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPower inverterLevel shifting
A motor drive system control provides global closed loop feedback to cooperatively operate system components to adaptively reduce noise and provide noise cancellation feedback. An active EMI filter reduces differential and common mode noise on an input and provides a noise level indication to a system controller. Power switches in both a power converter and power inverter are cooperatively controlled with dynamic dv / dt control to reduce switching noise according to a profile specified by the controller. The dv / dt control is provided as an analog signal to a high voltage IC and codified as a pulse width for a level shifting circuit supplying control signals to the high voltage gate drive. A noise extraction circuit and technique obtain fast noise sampling to permit noise cancellation and adaptive noise reduction.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS
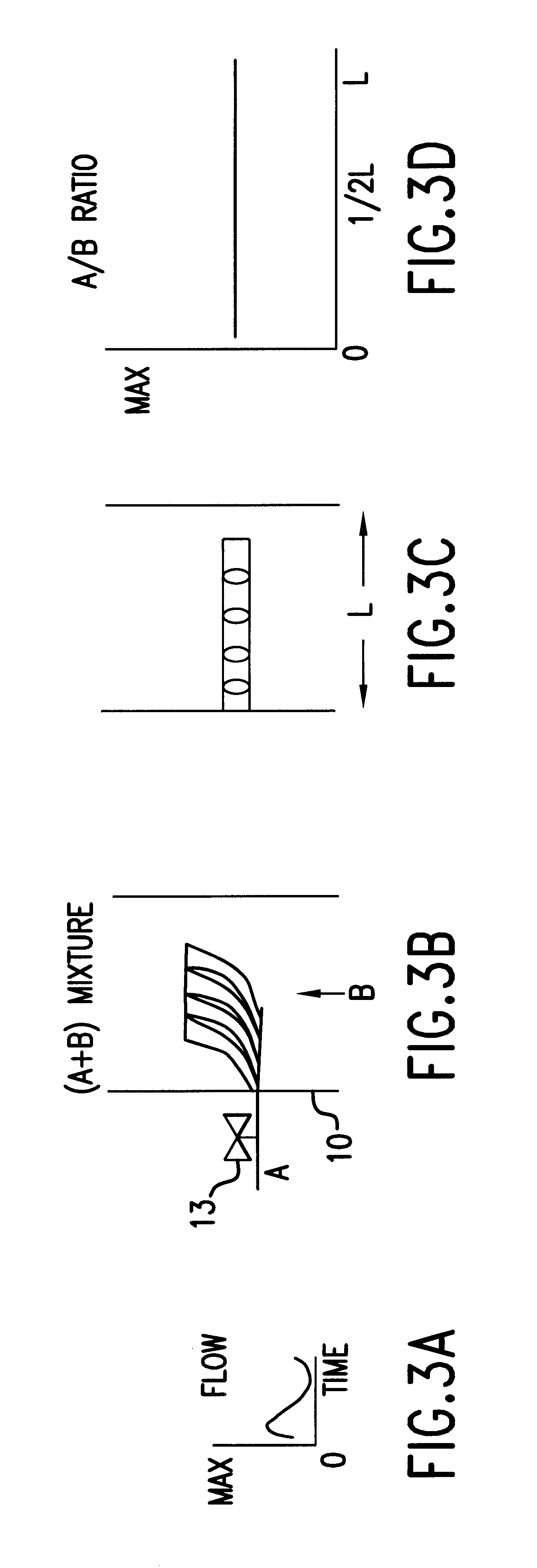
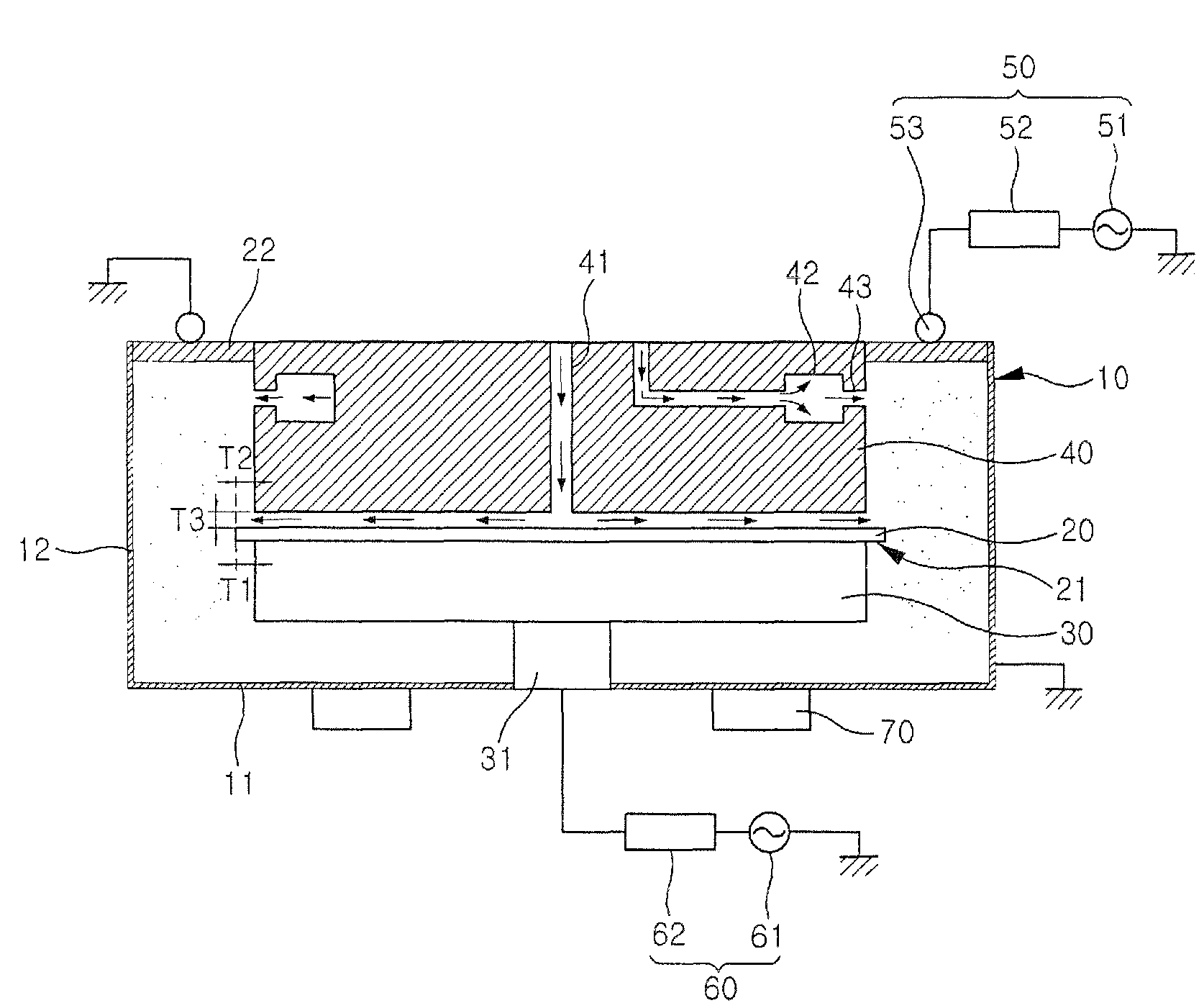
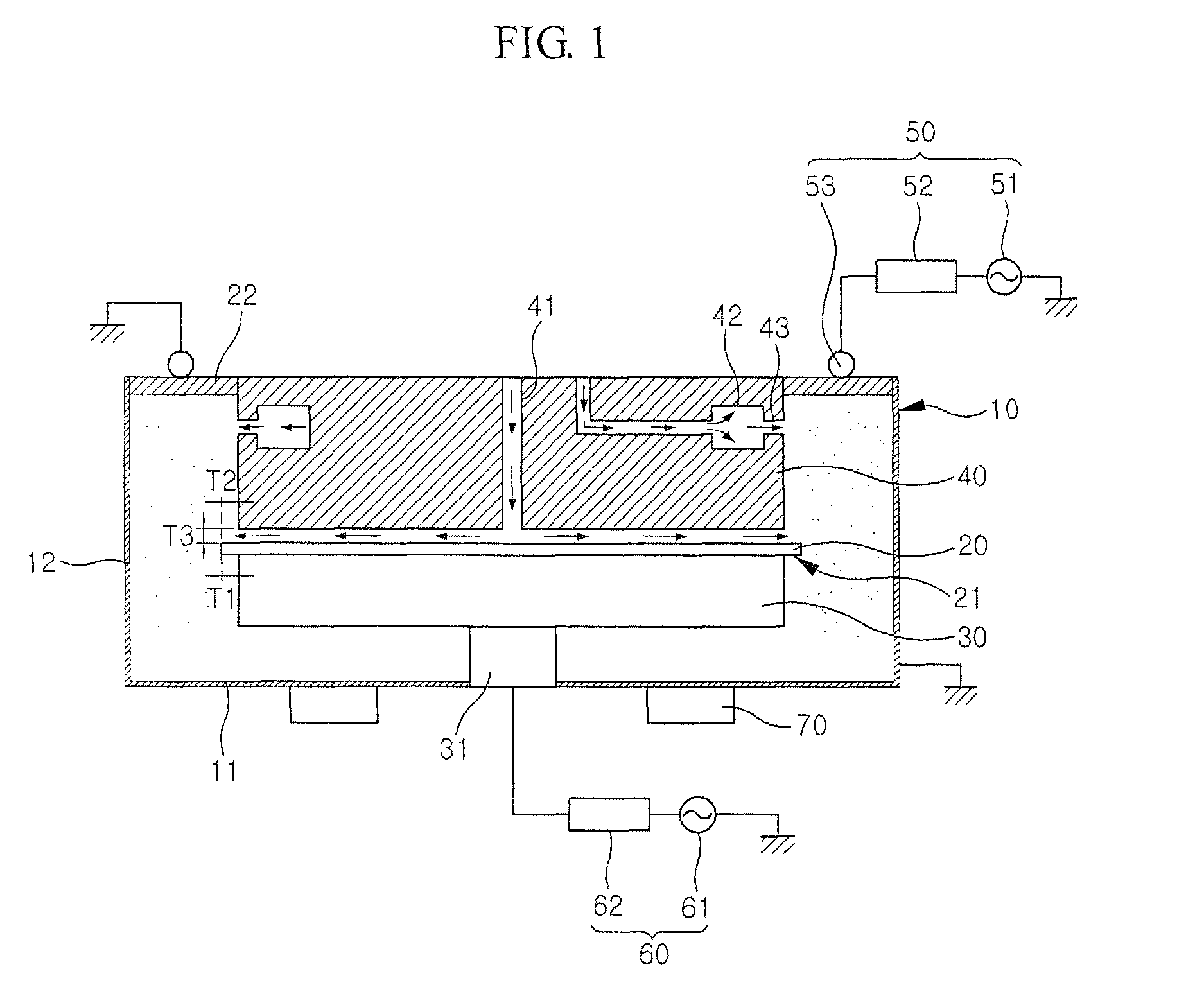
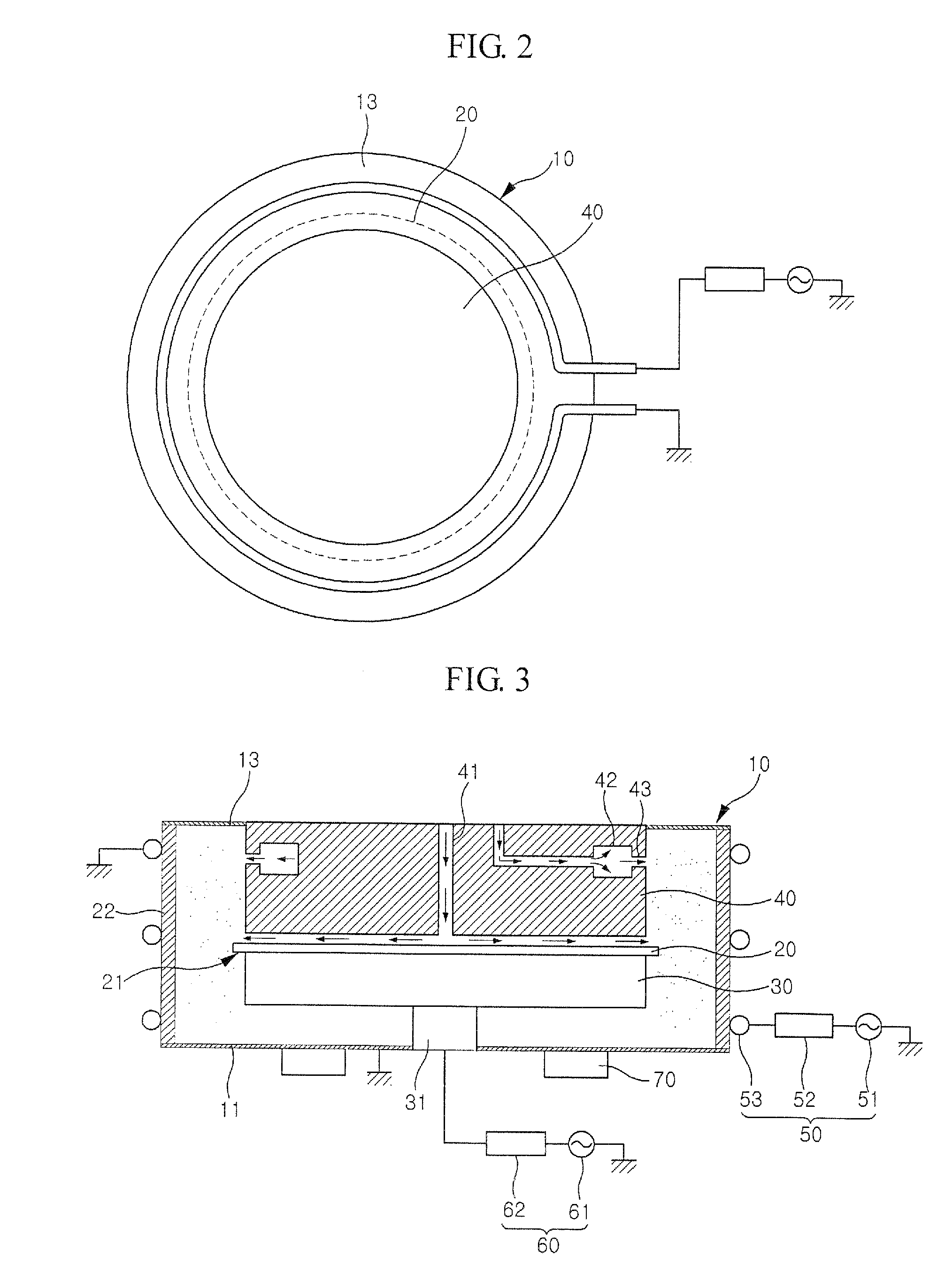
Method and apparatus for controlled mixing of fluids
A method for mixing fluids in which a continuously variable flow rate stream of an injection fluid is introduced into a substantially constant flow rate stream of a primary fluid in a direction substantially transverse with respect to the direction of flow of the substantially constant flow rate stream of the primary fluid.
Owner:INST OF GAS TECH
Plasma etching apparatus
InactiveUS7879187B2Limit profileHigh densityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityEngineering
The present invention relates to a plasma etching apparatus, which comprises a chamber, a substrate support disposed inside the chamber to support a substrate, a shield disposed with a gap on the substrate such that plasma is not generated therein while allowing an edge portion of the substrate to be exposed, an antenna disposed at a position on an outer wall of the chamber to apply plasma-generating power to an area between the edge portion of the substrate and an inner wall of the chamber, and a bias-applying unit for applying bias to the substrate support. According to the present invention, the shield and the substrate support prevent plasma from being generated at other portions of a substrate except an edge portion of the substrate. Inductively coupled plasma is employed to generate plasma with high density, thereby removing a thin film and particles remained at the edge portion of the substrate. In addition, by means of the discharging of inductively coupled plasma, it is possible to improve an etching rate at the edge portion of the substrate and to adjust the profile of an etching process at a low processing pressure.
Owner:JUSUNG ENG
Apparatus and method for preventing brain damage during cardiac arrest, CPR, or severe shock
InactiveUS8449590B2Limit profileEasy to deployTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingCardiorespiratory arrestInjury brain
Apparatuses and methods for the cooling of the cranial and extracranial portions of a patient in need thereof. The apparatuses and methods of the present invention preferably employ a head cooling apparatus which includes a watertight shroud for the head and which needs no refrigeration. In certain preferred embodiments, the apparatuses of the present invention are collapsible and possess a reduced profile. In some presently preferred embodiments, the present invention includes a hammock that supports the head. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a shroud that lies behind the head with optional portions that may be drawn over the patient's neck and cranial area. The apparatuses and methods of the present invention also provide an improved mechanism for cooling the cranial and extracranial areas through the use of a novel distribution of endothermic solids (e.g. ammonium nitrate). The present invention provides a novel distribution of ammonium nitrate pellets that preferably includes multiple populations solid ammonium nitrate, preferably including small diameter (e.g., powdered) and larger diameter (e.g., 7 millimeter) ammonium nitrate to allow water initially to be cooled very quickly, thereby facilitating the rapid cooling of the cranial and extracranial areas, while at the same time producing extended hypothermia.
Owner:BRADER ERIC WILLIAM
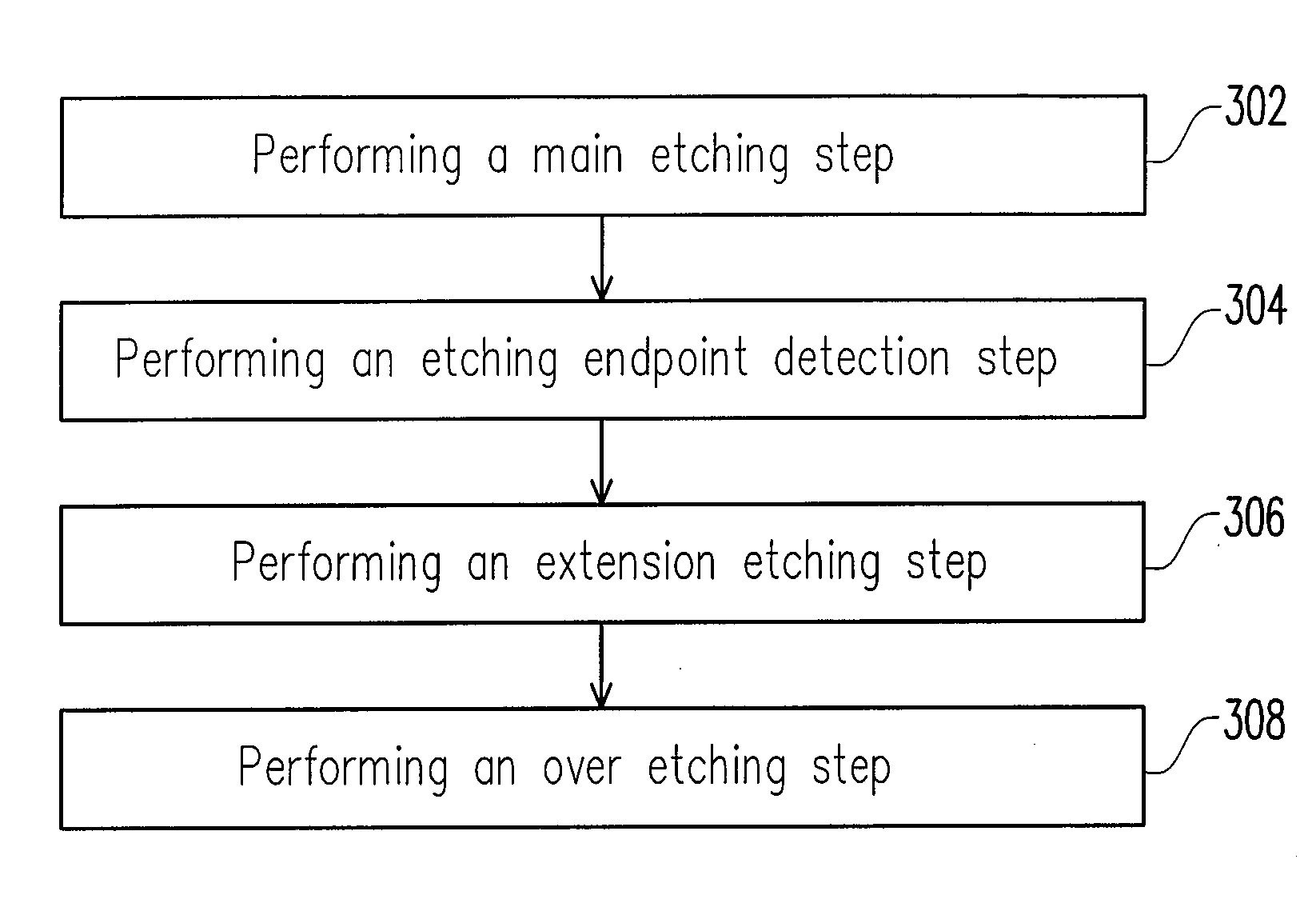
Patterning method
ActiveUS7851370B2Effective controlLimit profileSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer scienceTerminal point
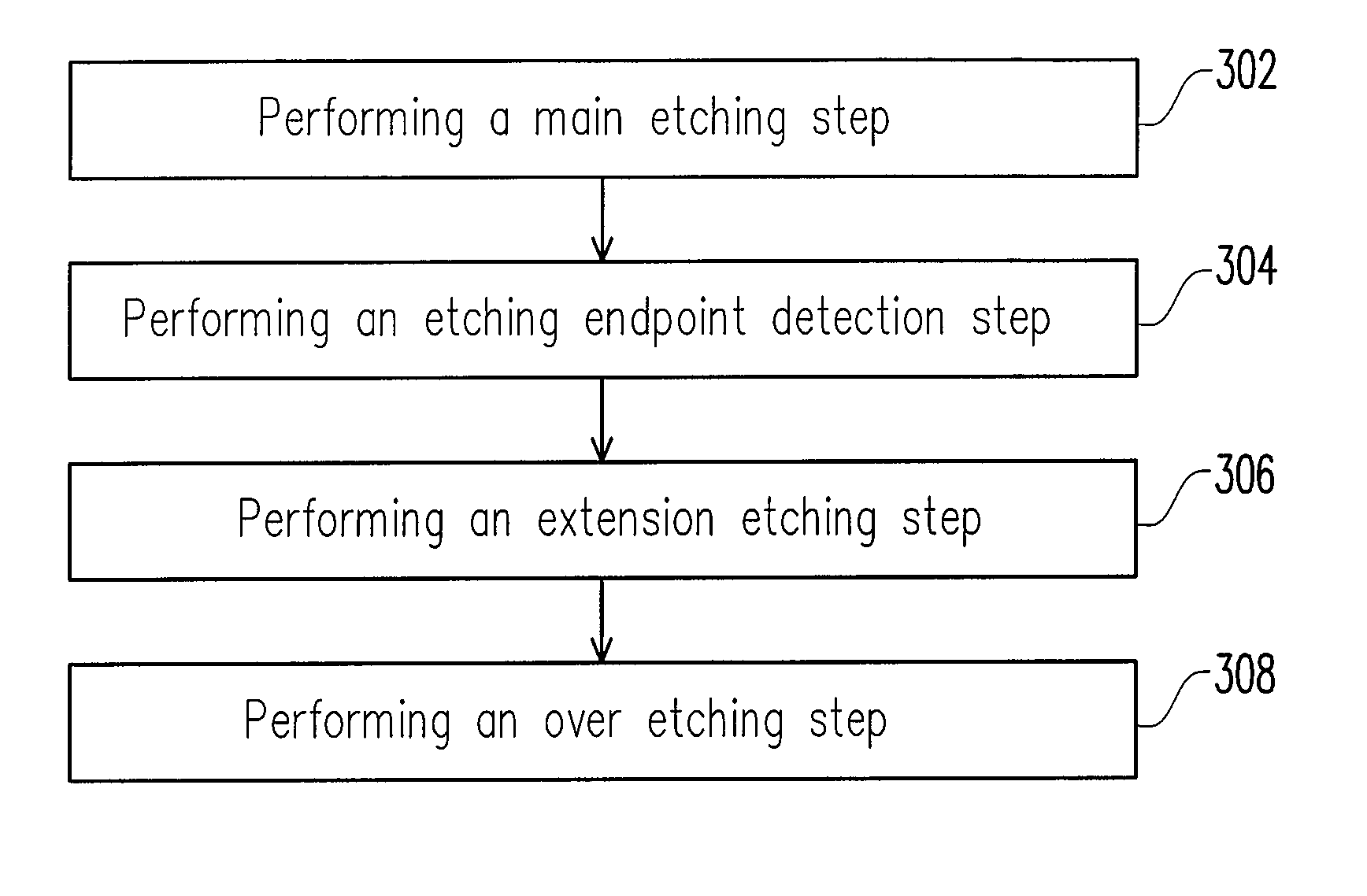
A patterning method is provided. In the patterning method, a film is formed on a substrate and a pre-layer information is measured. Next, an etching process is performed to etch the film. The etching process includes a main etching step, an etching endpoint detection step, an extension etching step and an over etching step. An extension etching time for performing the extension etching step is set within 10 seconds based on a predetermined correlation between an extension etching time and the pre-layer information, so as to achieve a required film profile.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
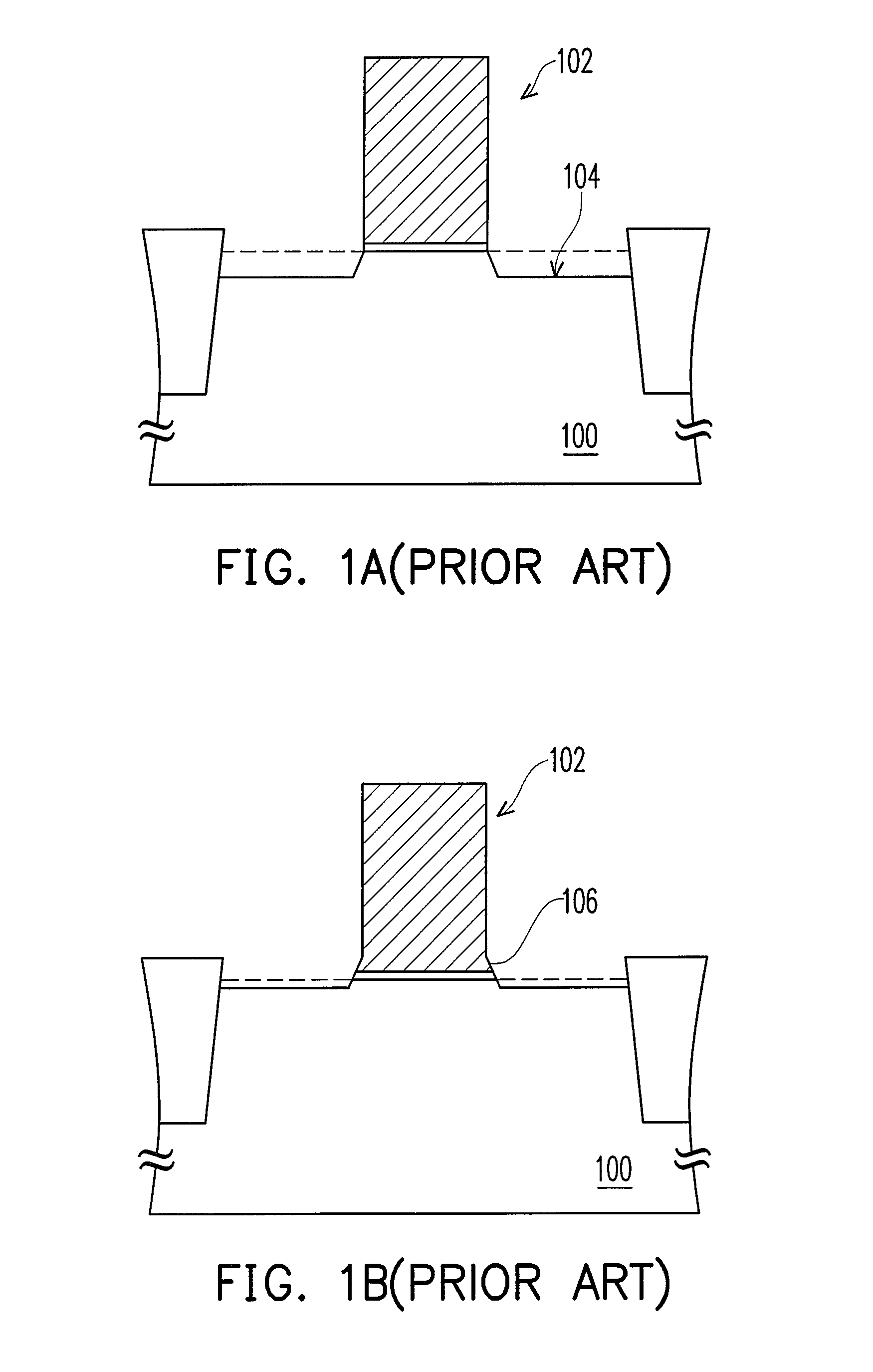
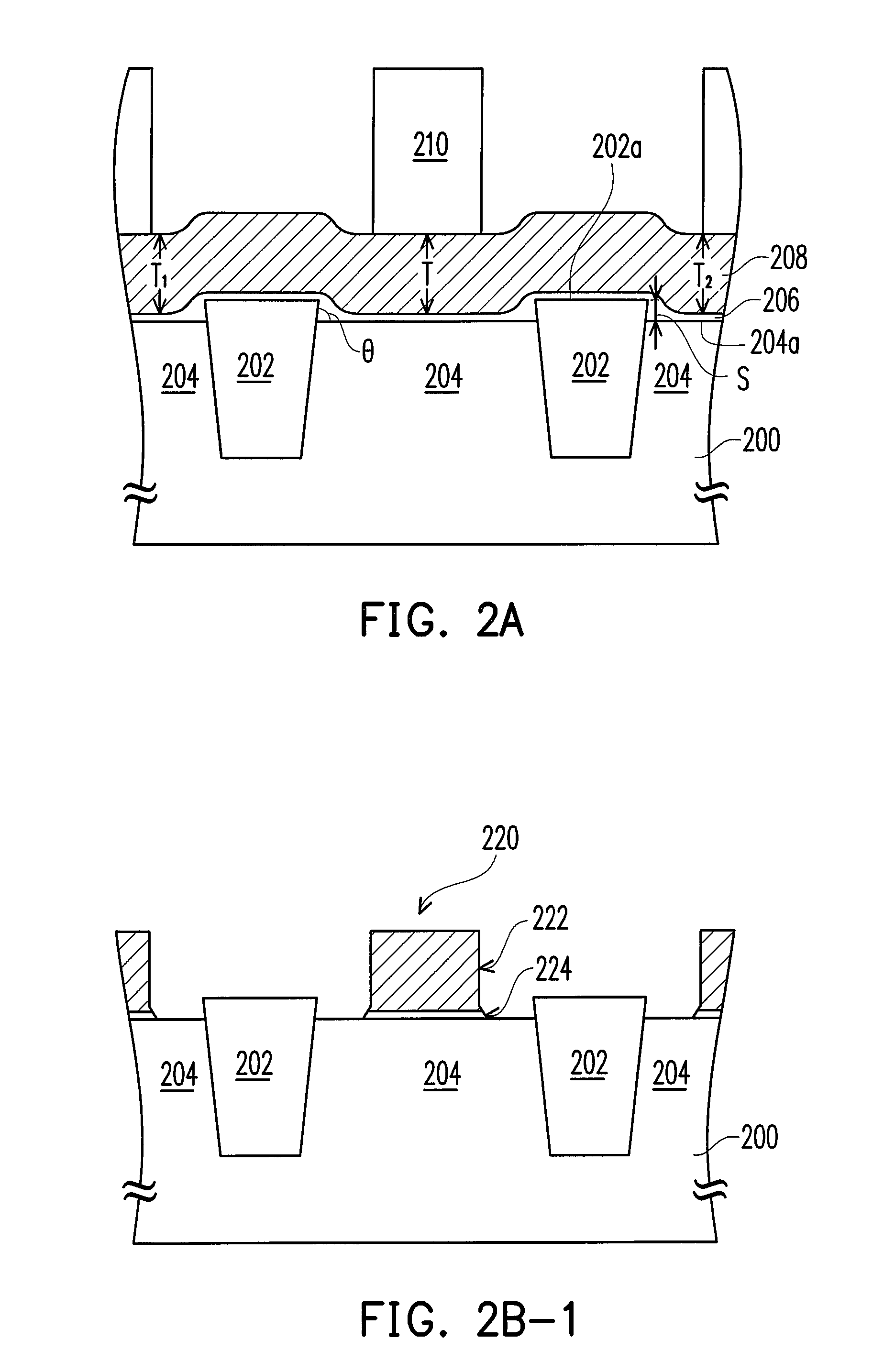
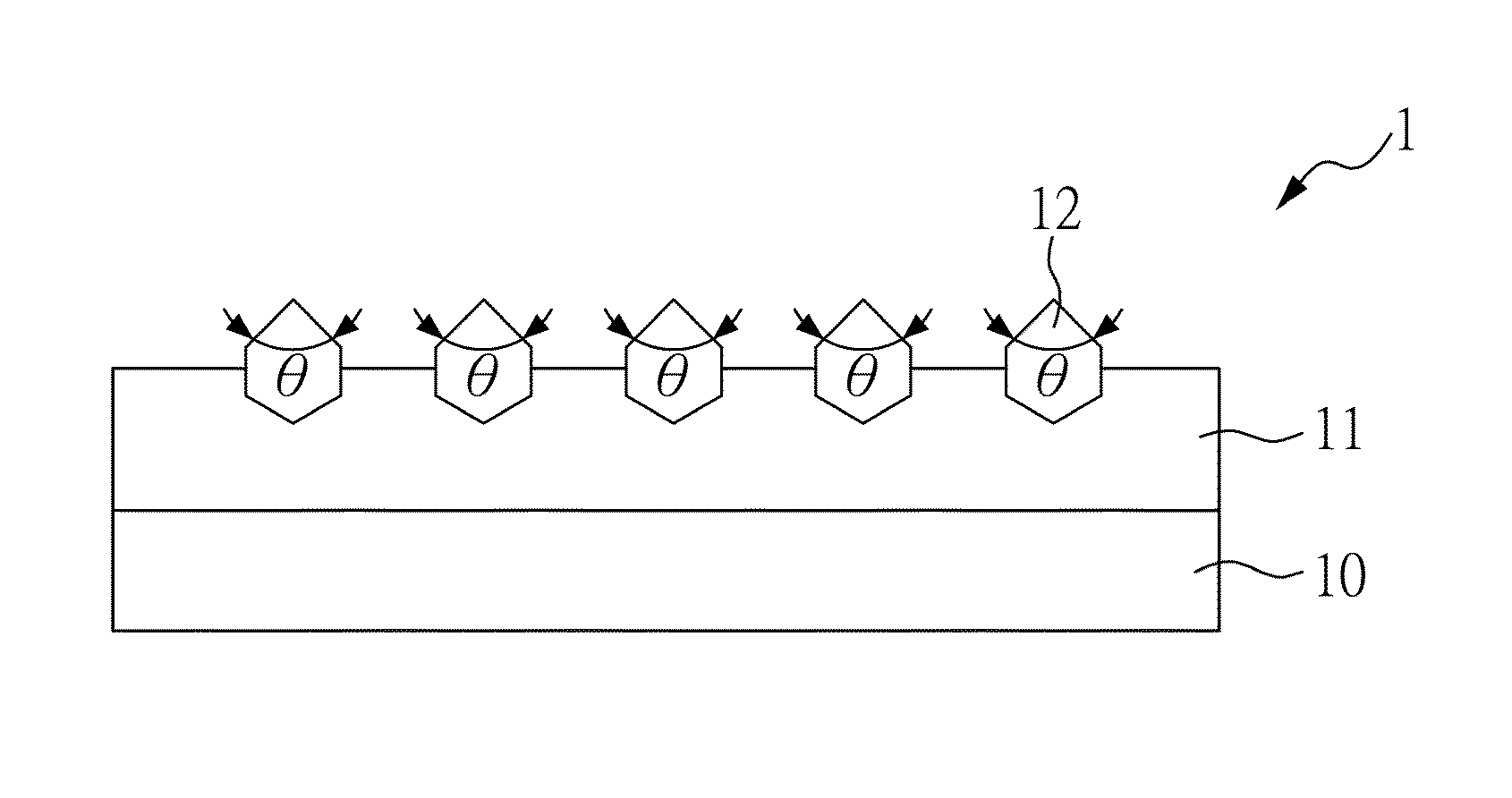
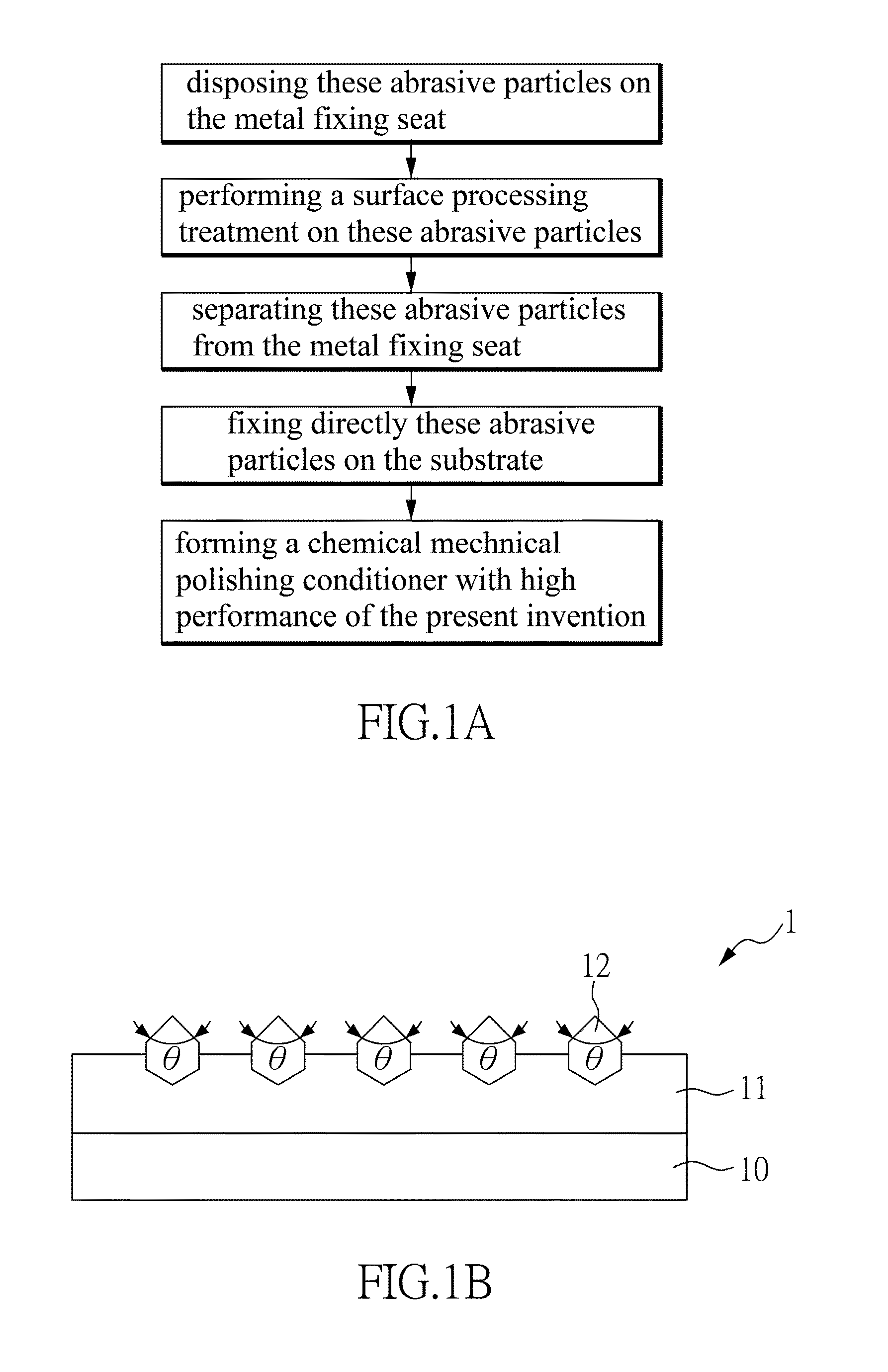
Chemical mechanical polishing conditioner with high performance
InactiveUS20150231759A1Improve performanceImprove cutting effectAbrasion apparatusGrinding devicesCrystal structureEngineering
The present invention relates to a chemical mechanical polishing conditioner with high performance, comprising a substrate; a binding layer disposed on the substrate; and a plurality of abrasive particles fixed directly on the substrate by the binding layer, or each abrasive particle disposed on a metal fixing seat and the substrate have a plurality of blind holes and a plurality of through holes, so that the metal fixing seats are installed into the blind holes or the through holes, and the metal fixing seat fixed on the substrate by the binding layer; wherein the abrasive particles are treated by a surface processing treatment to make the abrasive particles have specific cutting edge angles, crystal structures, tip heights, or tip orientations. Therefore, the present invention can control the profile of each abrasive particle to accomplish the best polishing performance.
Owner:KINIK
Apparatus and process for stacking pieces of material
InactiveUS20080107514A1Limit profileStacked efficiently and effectivelyLoadersWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus for stacking a plurality of pieces of material has an assembly region, one or more platens on a first longitudinal side of the assembly region, and, a plurality of press rams on a second longitudinal side of the assembly region opposite the first longitudinal side. The press rams are movable transversely across the assembly region to immobilize or partially immobilize pieces of material in the assembly region permitting accurate and precise alignment of the pieces relative to each other in the assembly region.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
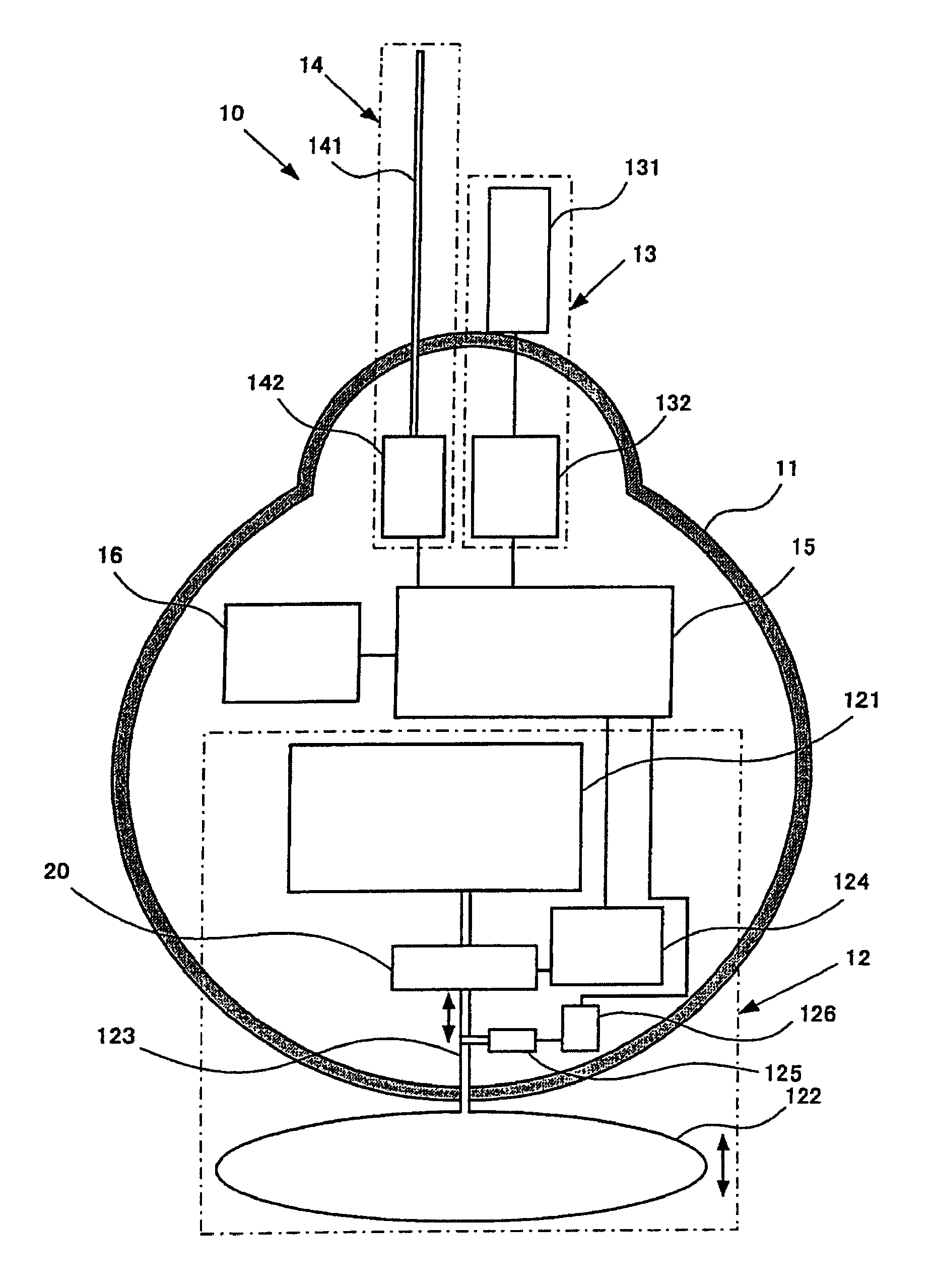
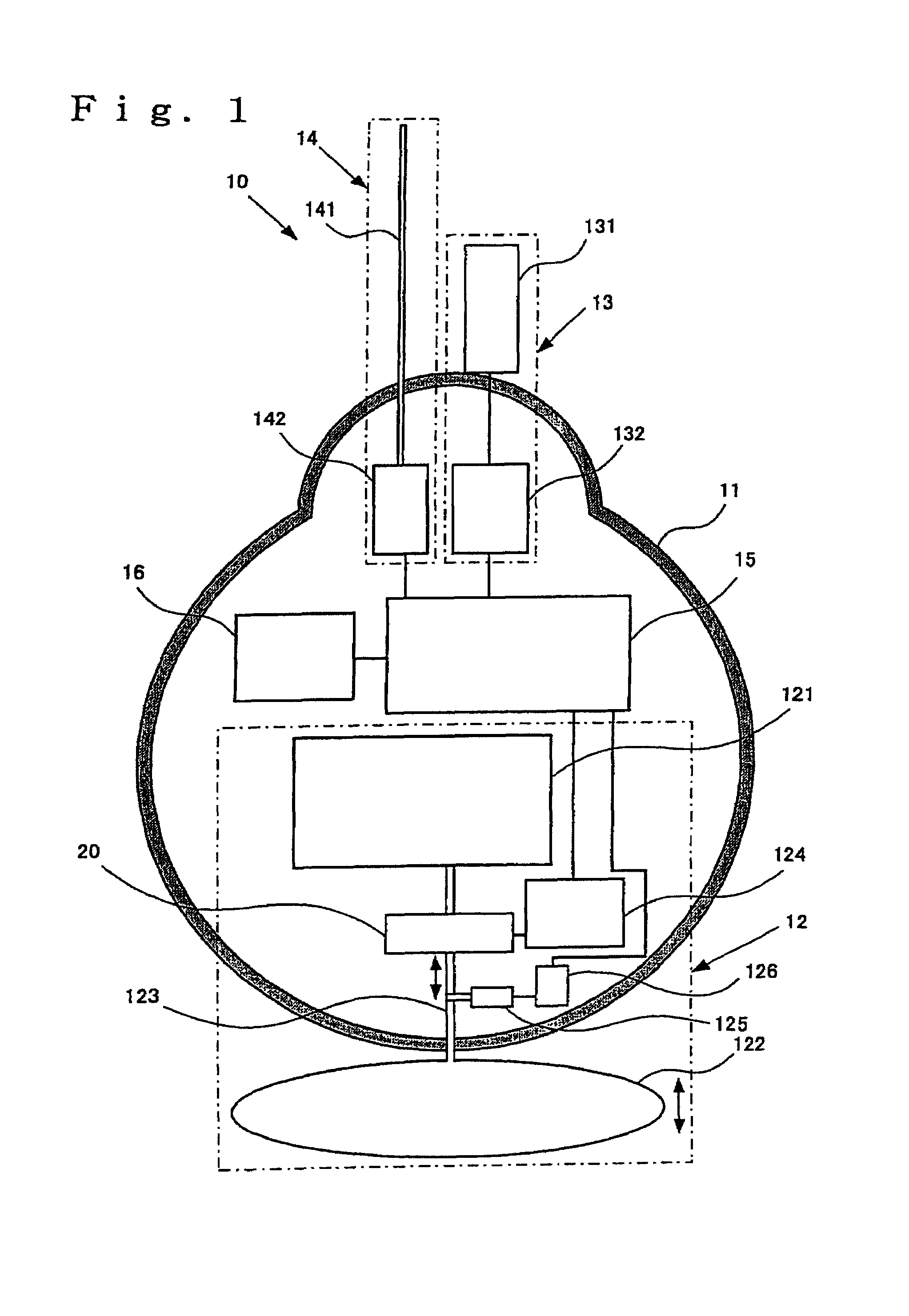
Profiling float and usage of the profiling float
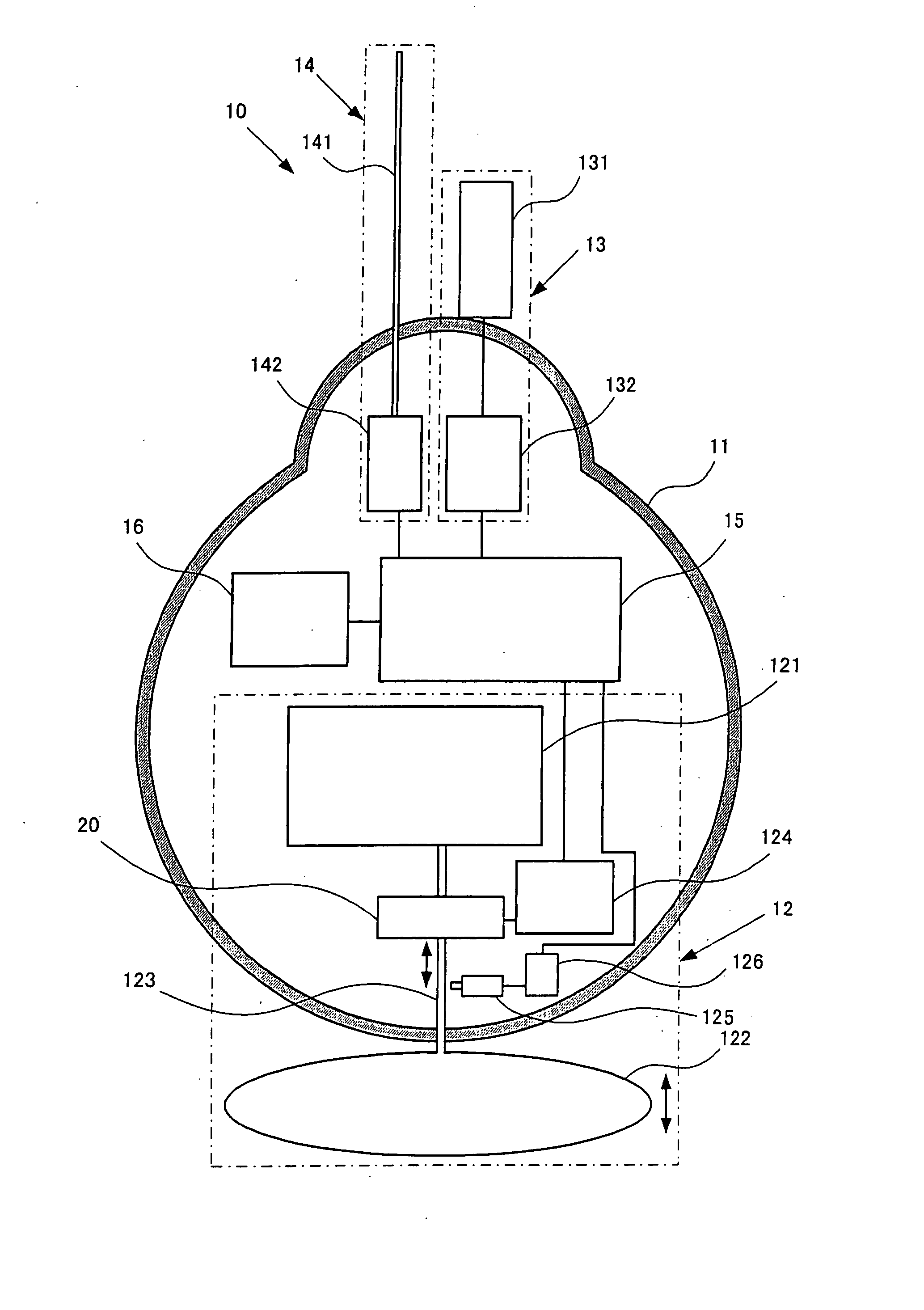
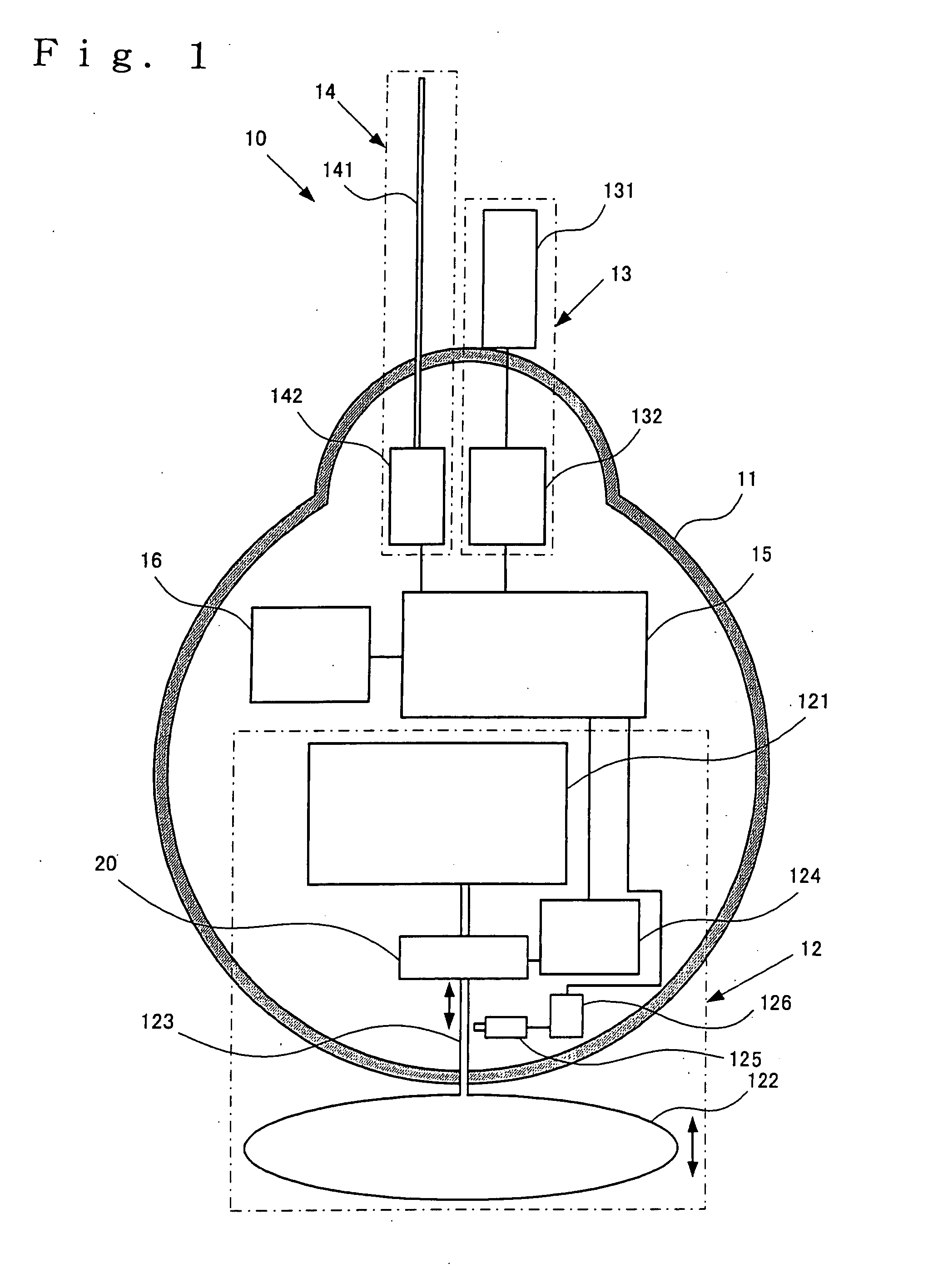
InactiveUS7699677B2Control volumeEasy to controlFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsBuoysGear pumpEngineering
Provided is a profiling float that can minutely and surely control effective buoyancy acting on the float in itself, and usage of the profiling float.The profiling float according to the present invention is equipped with a float chamber forming an airtight internal space, a fluid storage part provided in the float chamber and storing a fluid for control of buoyancy, a bladder provided at the exterior of the float chamber, in the interior of which the fluid for control of buoyancy is filled to change a volume thereof, thereby controlling buoyancy acting on the profiling float, a pump mechanism for transferring the fluid for control of buoyancy between the bladder and the fluid storage part, and a driving source for driving the pump mechanism, wherein the pump mechanism is composed of a gear pump.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Patterning method
ActiveUS20090081817A1Effective controlLimit profileSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer scienceTerminal point
A patterning method is provided. In the patterning method, a film is formed on a substrate and a pre-layer information is measured. Next, an etching process is performed to etch the film. The etching process includes a main etching step, an etching endpoint detection step, an extension etching step and an over etching step. An extension etching time for performing the extension etching step is set within 10 seconds based on a predetermined correlation between an extension etching time and the pre-layer information, so as to achieve a required film profile.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Skateboard with variable-rate elastomeric steering control spring
A skateboard and a variable-rate elastomeric steering control spring include a boardside unitary body formed of an exterior first elastomer having a first durometer on the Shore “A” scale, and an interior second elastomer coupled to the first elastomer and extending at least length of the exterior first elastomer, the second elastomer having a second durometer on the Shore “A” scale and a through hole disposed to receive a kingpin of the skate truck; a roadside unitary body formed of an exterior third elastomer having a third durometer on the Shore “A” scale, and an interior fourth elastomer coupled to the third elastomer and extending at least a length of the exterior third elastomer, the interior fourth elastomer having a fourth durometer on the Shore “A” scale and a through hole disposed to receive the kingpin; and wherein the first, second, third and fourth elastomers comprise at least two durometers on the Shore “A” scale between 65 A and 100 A to enable the boardside unitary body and the roadside unitary body to form the variable-rate elastomeric steering control spring when disposed on the kingpin of the skate truck.
Owner:SOLID DESIGN & MFG CORP LTD
Burner assembly for delivery of specified heat flux profiles in two dimensions
InactiveUS6866501B2Limit profileEnsure maintenanceCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelFuel supplyEngineering
A burner is provided which includes a plurality of burner subunits that each share a single air supply, a single fuel supply and a single control system. Each burner subunit has a plurality of air orifices and a plurality of fuel orifices of sufficient quantity and of a cross-sectional area to control a transverse heat flux profile of the burner. The burner subunits are spaced with respect to one another to control a longitudinal heat flux profile of the burner. The single air supply and said single fuel are adapted to provide an air-fuel mix that ensures the transverse and the longitudinal heat flux profiles are maintained at different fuel and air input rates. A burner of similar design using premixed air and fuel is also disclosed.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Skateboard with variable-rate elastomeric steering control spring
A skateboard and a variable-rate elastomeric steering control spring include a boardside unitary body formed of an exterior first elastomer having a first durometer on the Shore “A” scale, and an interior second elastomer coupled to the first elastomer and extending at least length of the exterior first elastomer, the second elastomer having a second durometer on the Shore “A” scale and a through hole disposed to receive a kingpin of the skate truck; a roadside unitary body formed of an exterior third elastomer having a third durometer on the Shore “A” scale, and an interior fourth elastomer coupled to the third elastomer and extending at least a length of the exterior third elastomer, the interior fourth elastomer having a fourth durometer on the Shore “A” scale and a through hole disposed to receive the kingpin; and wherein the first, second, third and fourth elastomers comprise at least two durometers on the Shore “A” scale between 65 A and 100 A to enable the boardside unitary body and the roadside unitary body to form the variable-rate elastomeric steering control spring when disposed on the kingpin of the skate truck.
Owner:SOLID DESIGN & MFG CORP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com