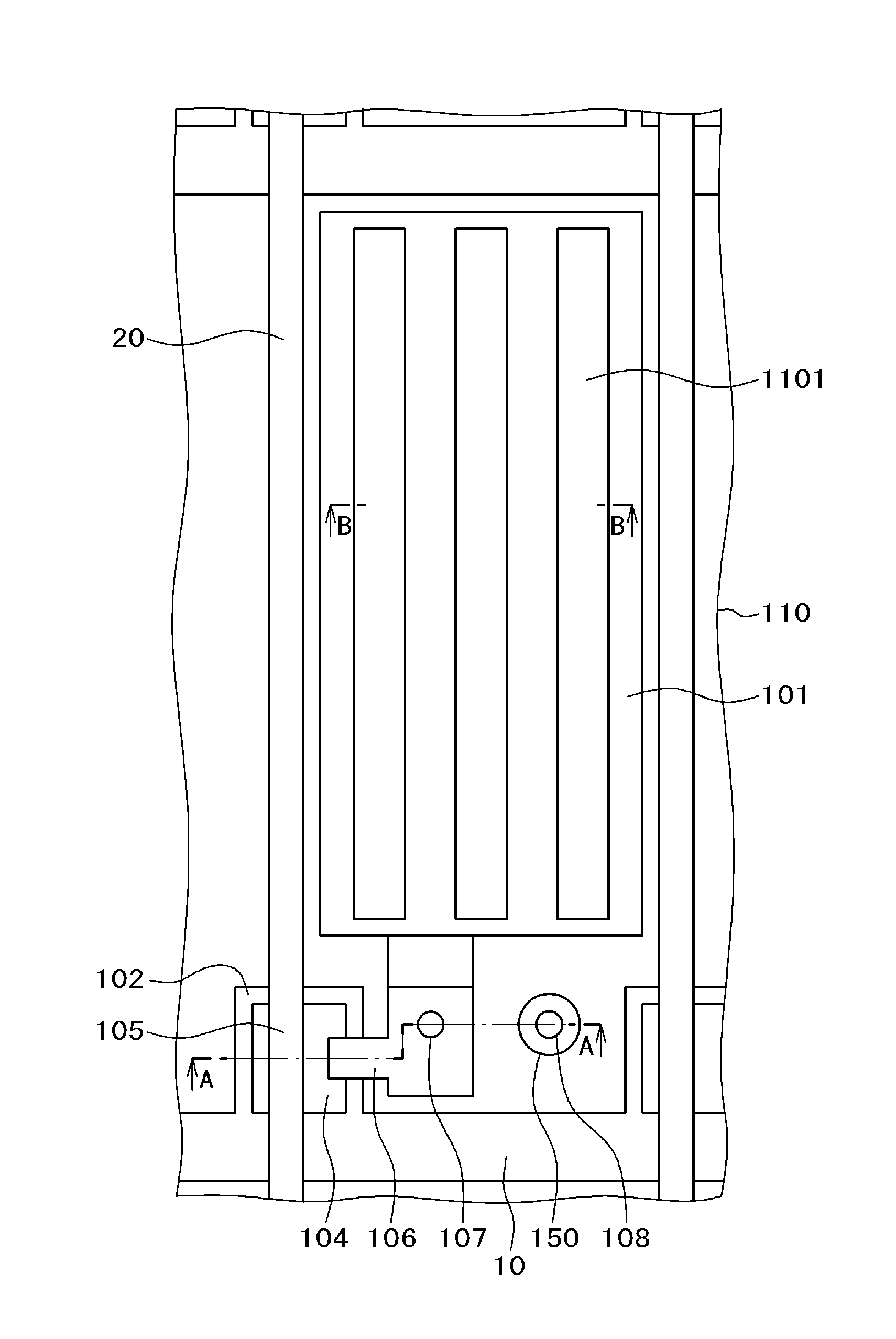
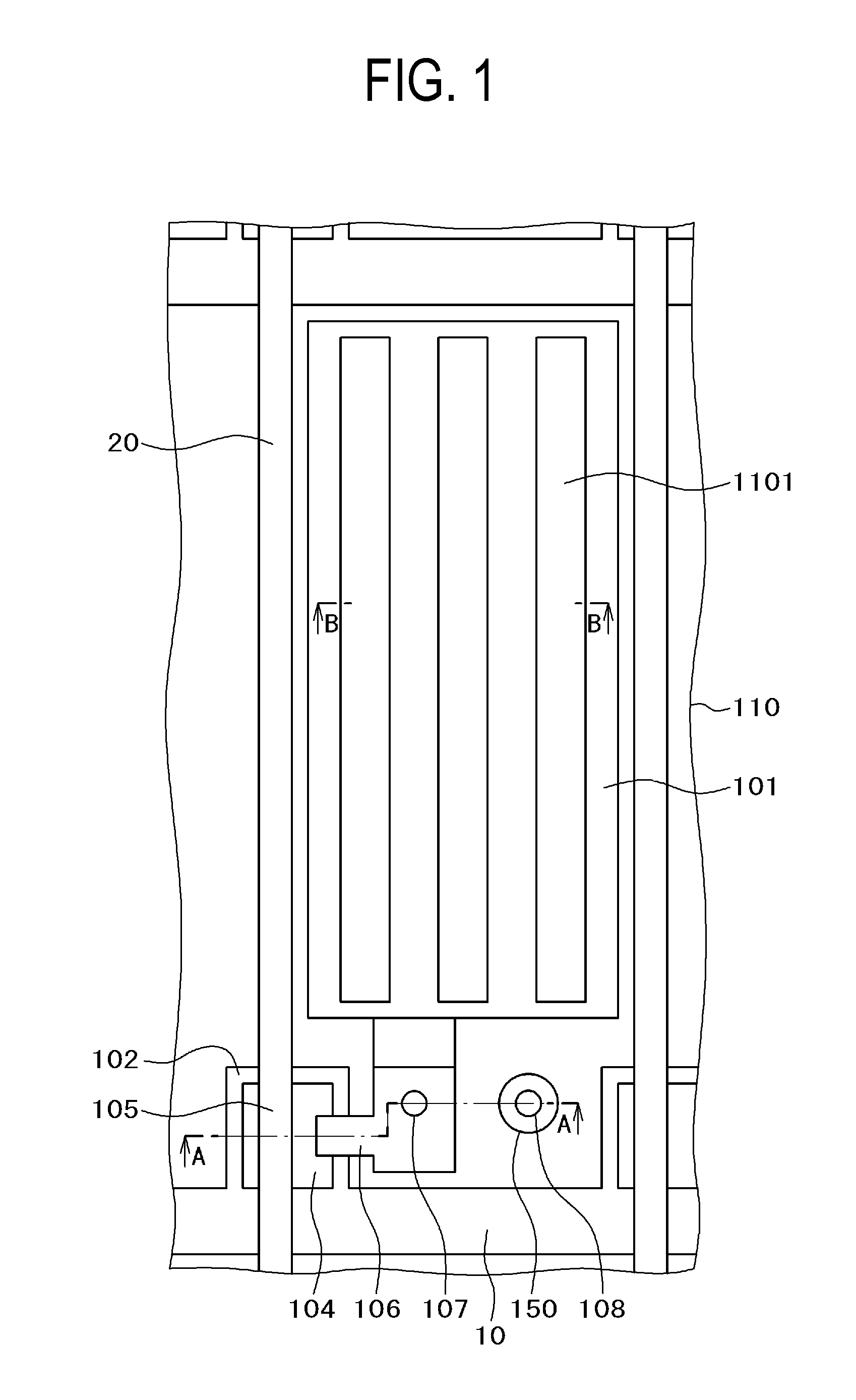
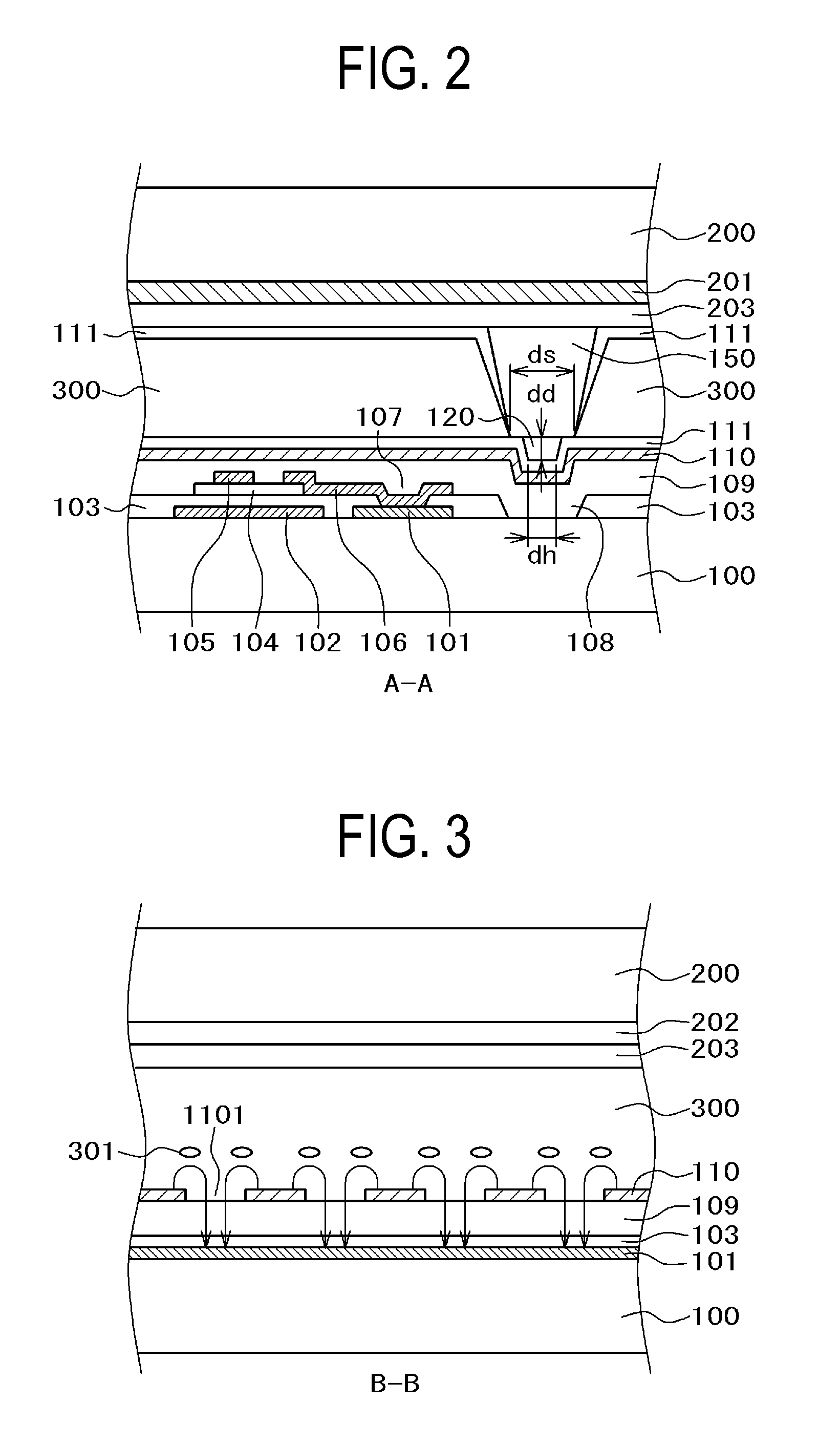
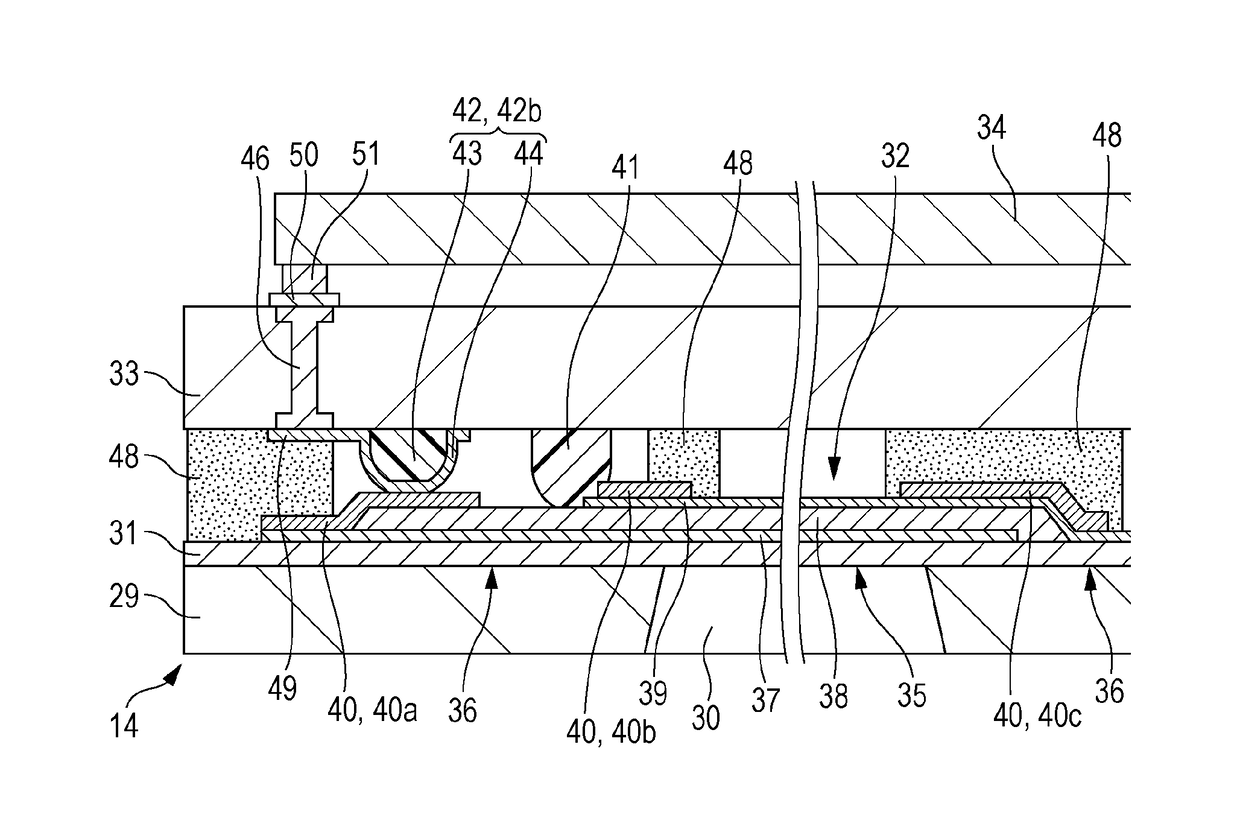
Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Peeling can be suppressed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
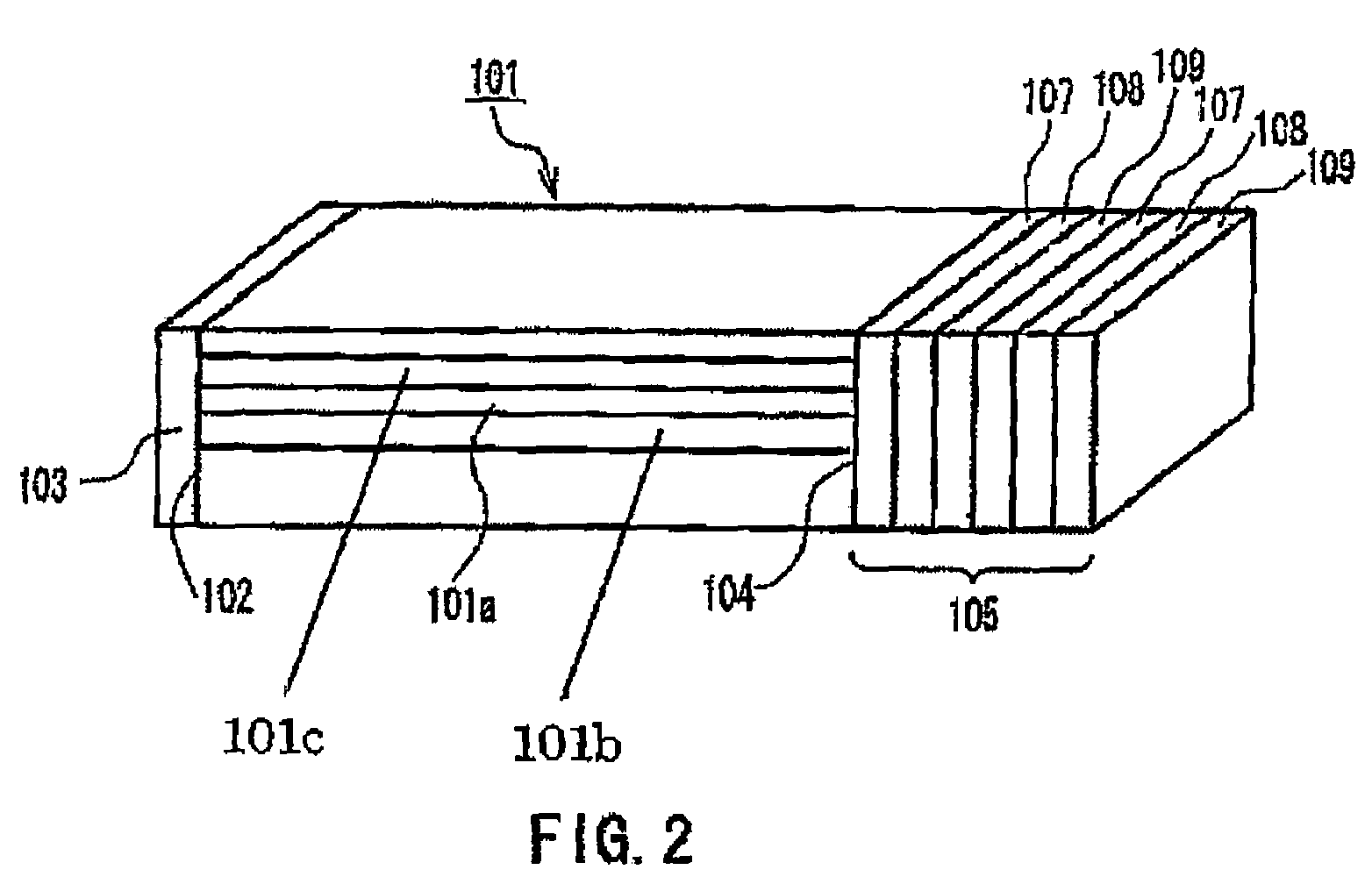
Multilayer coating excellent in wear resistance and heat resistance
InactiveUS7169485B2Improve adhesionImprove the heating effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingInter layerHeat resistance
A multilayer coating according to the present invention comprises an alumina coating formed, directly or through an intermediate layer, on a hard coating composed of a metallic compound formed on the base material, and the Vickers hardness of the hard coating after alumina coating formation being 22 GPa or more. The multilayer coating is excellent in adhesion between a hard coating and an alumina coating and capable of exhibiting excellent wear resistance and heat resistance over a long period.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
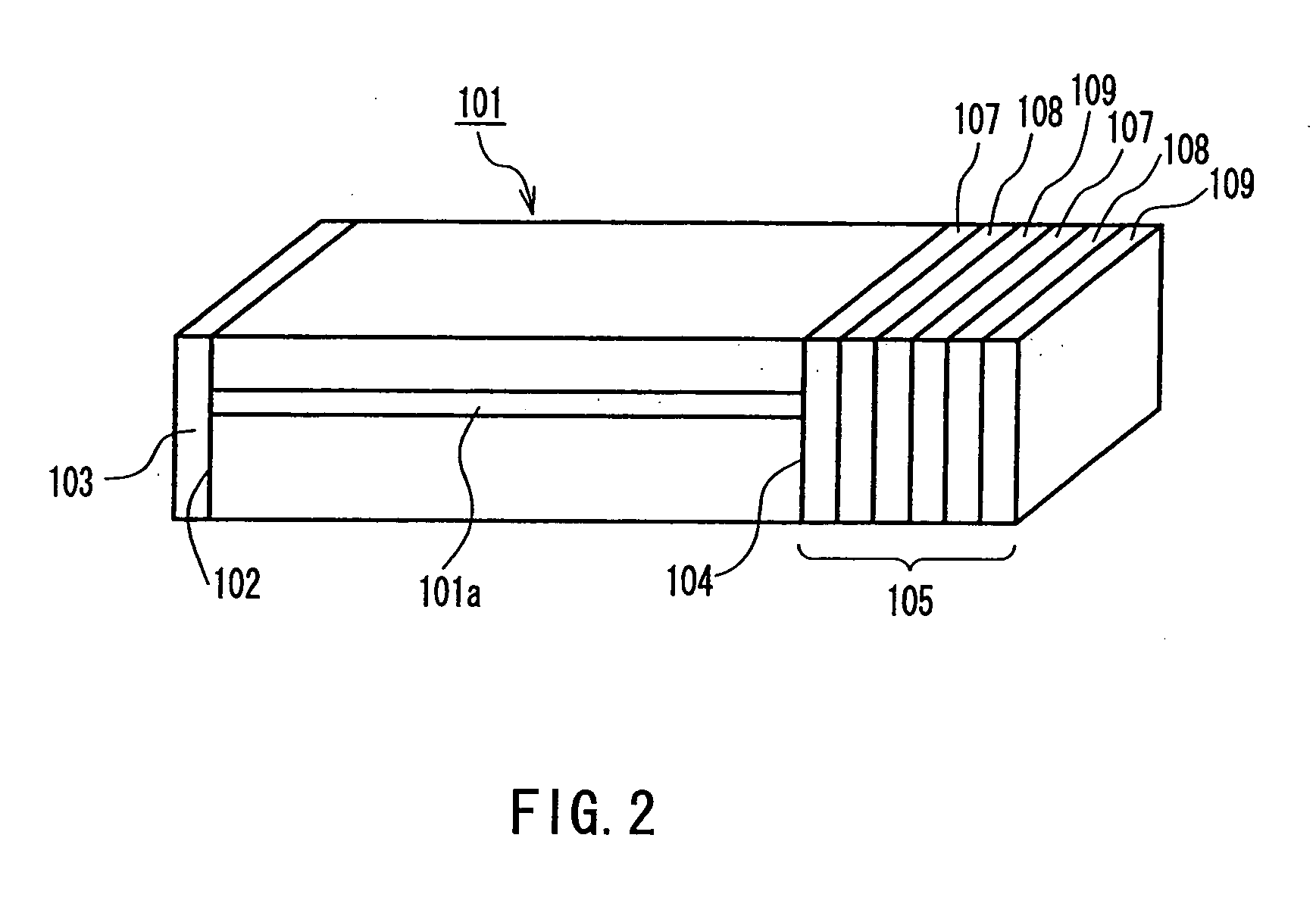
Substrate for use in a liquid crystal display and liquid crystal display using the same
InactiveUS7050137B2Occurrence of crack can be suppressedImprove reliabilityTransistorStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayExternal connection
The invention relates to a substrate for use in a liquid crystal display of a CF-on-TFT structure in which a color filter is formed on the side of an array substrate in which a switching element is formed, and has an object to provide a substrate for use in a liquid crystal display, which enables simplification of a manufacturing process typified by a photolithography process and has high reliability. The substrate for use in the liquid crystal display is constructed to include external connection terminals which include first terminal electrodes electrically connected to gate bus lines led out from a plurality of pixel regions arranged on a glass substrate in a matrix form, second terminal electrodes formed of forming material of a pixel electrode and directly on the glass substrate, and electrode coupling regions for electrically connecting the first and the second terminal electrodes, and which electrically connect an external circuit and the gate bus lines.
Owner:SHARP KK
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080087981A1Avoid crackingPeeling can be suppressedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate formed with at least two element isolation trenches having a first opening width and a second opening width larger than the first opening width, respectively, a non-coating type silicon oxide film formed along an inner surface of each element isolation trench so as to have a film thickness equal to or larger than 23 nm, and a coating type silicon oxide film formed inside the non-coating type silicon oxide film in each element isolation trench.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Fine Carbon Fiber-Metal Composite Material and Method for Production Thereof
InactiveUS20080050589A1Small elastic modulusThermal stressSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic shaping apparatusCarbon layerCarbon fibers
To provide a fine carbon fiber / metal composite material having high mechanical strength, a high thermal conductivity and a low coefficient of thermal expansion and suitable as a substrate for an electronic device. A fine carbon fiber / metal composite material, which is prepared by pressure impregnating a molded product containing fine carbon fibers having a fiber diameter of from 0.5 to 500 nm and a fiber length of at most 1,000 μm, having a multilayer structure wherein cylindrical carbon layers overlap one another, and having a hollow-structured central axis, with aluminum, magnesium, copper or an alloy of such a metal, by molten metal forging.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CORPORATION +1
Substrate for use in a liquid crystal display and liquid crystal display using the same
InactiveUS20060125994A1Improve reliabilitySimple manufacturing processTransistorNon-linear opticsElectricityLiquid-crystal display
Owner:SHARP KK
Solid electrolytic capacitor having carbon layer, containing carbon particles and additive, on solid electrolyte layer, and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS7916456B2InhibitionIncrease resistanceHybrid capacitor electrolytesSolid electrolytic capacitorsCarbon layerElectrical conductor
A carbon layer is formed on a solid electrolyte layer of the solid electrolytic capacitor, and a conductor layer connected to a cathode terminal is further disposed thereon. The carbon layer contains carbon particles, and a first additive or a second additive. The first additive is formed from at least one of those selected from the group consisting of hydrated silica and silicate. The second additive is formed from at least one of those selected from the group consisting of a condensation product of an aromatic sulfonic acid with formaldehyde, a condensation product of an aromatic sulfonate with formaldehyde, polystyrene sulfonic acid, and polystyrene sulfonate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Composite substrate and method of manufacturing composite substrate
ActiveUS20190386640A1Increase resistanceHigh bonding strengthImpedence networksSolid-state devicesWaferingComposite substrate
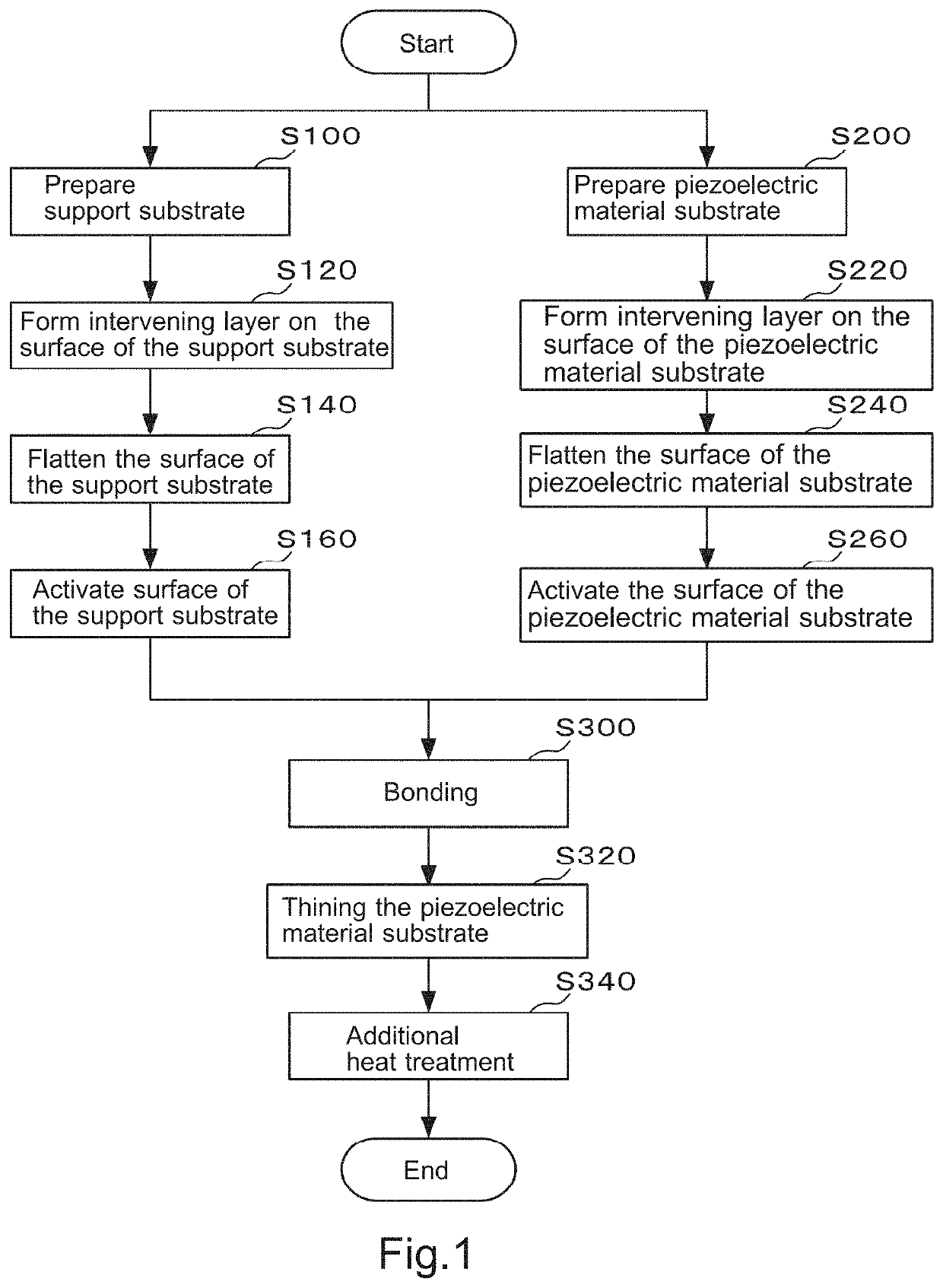
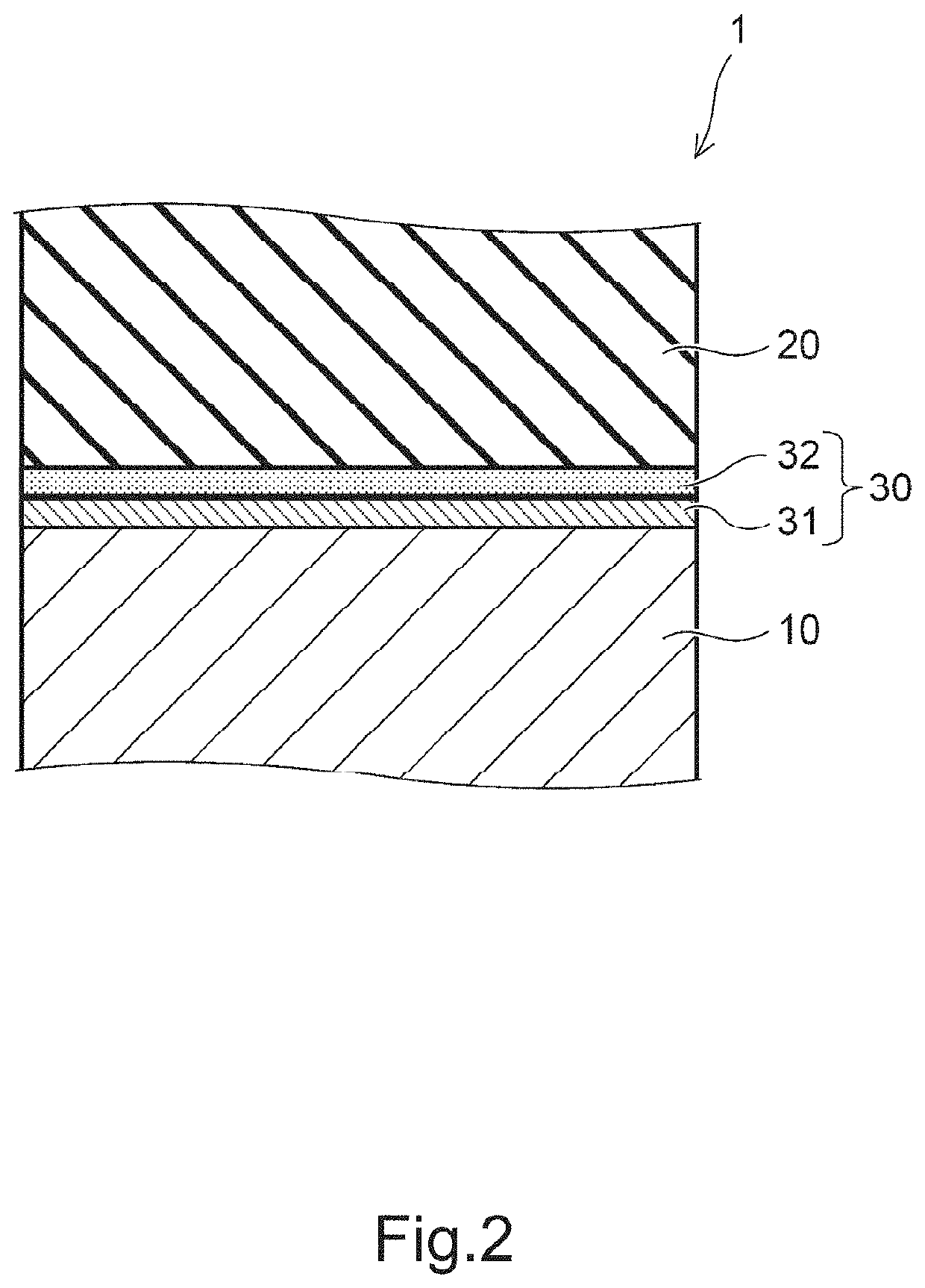
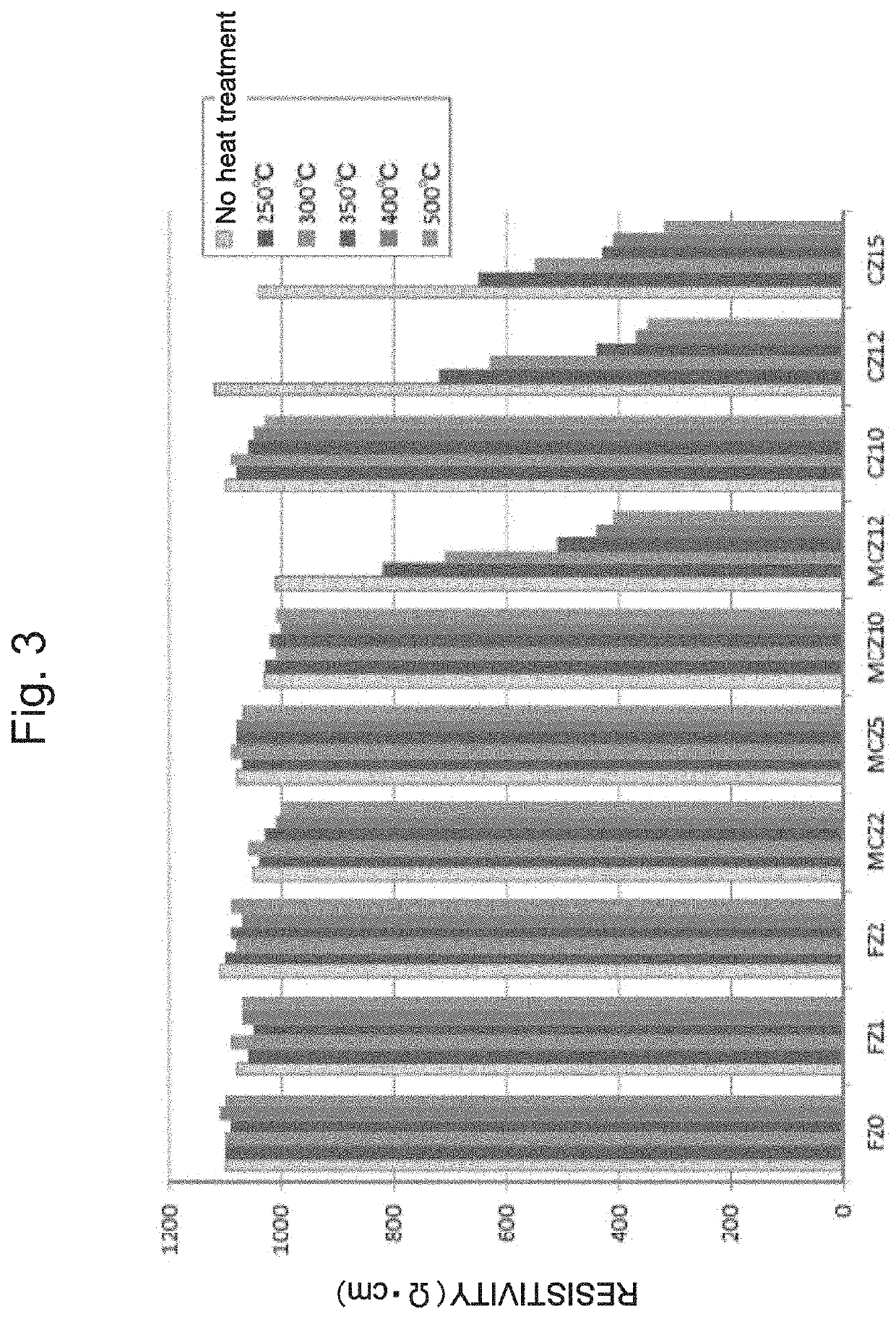
A composite substrate capable of maintaining high resistance after processing at 300° C. and a method of manufacturing the composite substrate are provided. The composite substrate according to the present invention is manufactured by bonding a silicon (Si) wafer having an interstitial oxygen concentration of 2 to 10 ppma to a piezoelectric material substrate as a support substrate, and thinning the piezoelectric material substrate after the bonding. The piezoelectric material substrate is particularly preferably a lithium tantalate wafer (LT) substrate or a lithium niobate (LN) substrate.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
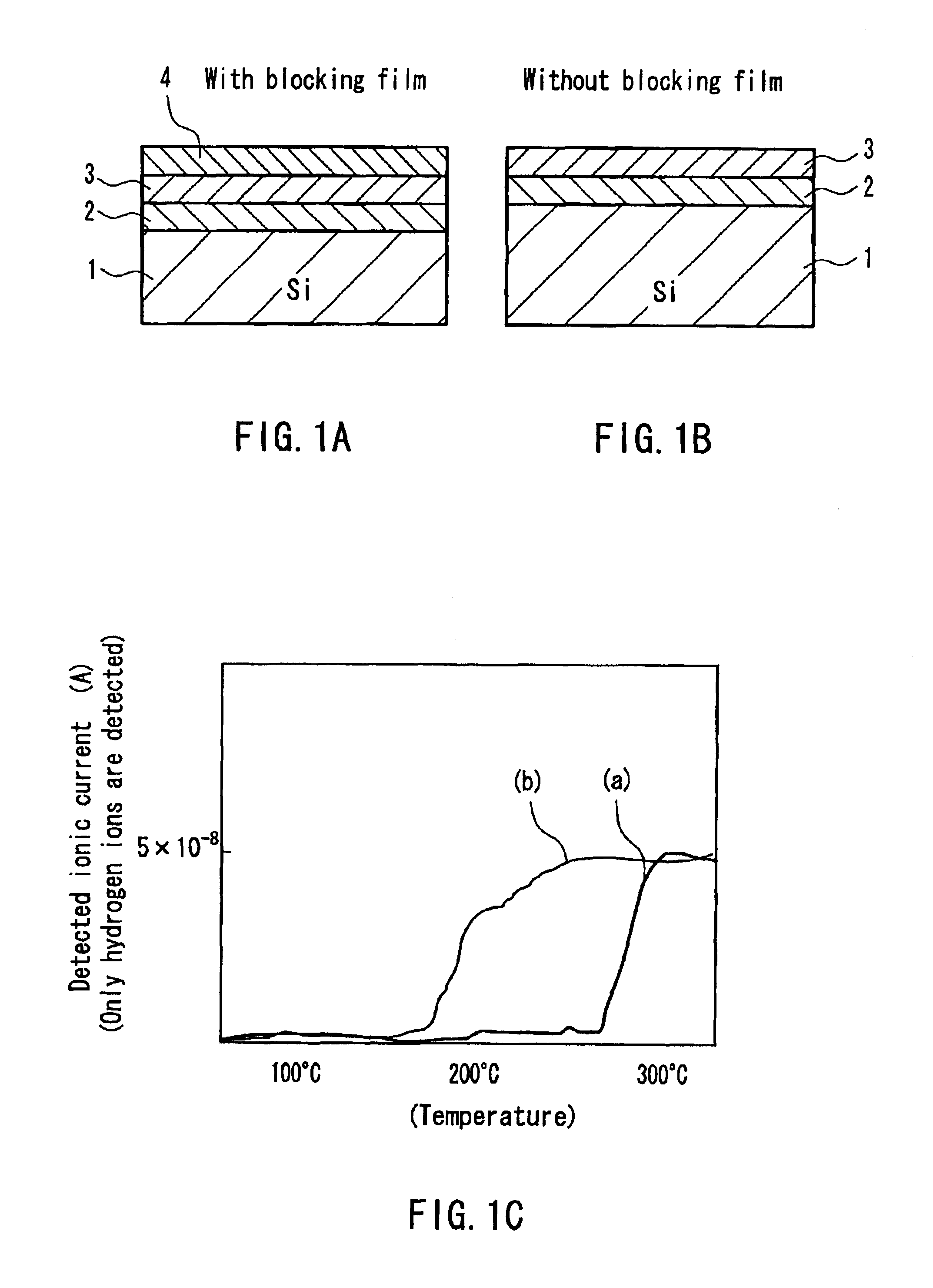
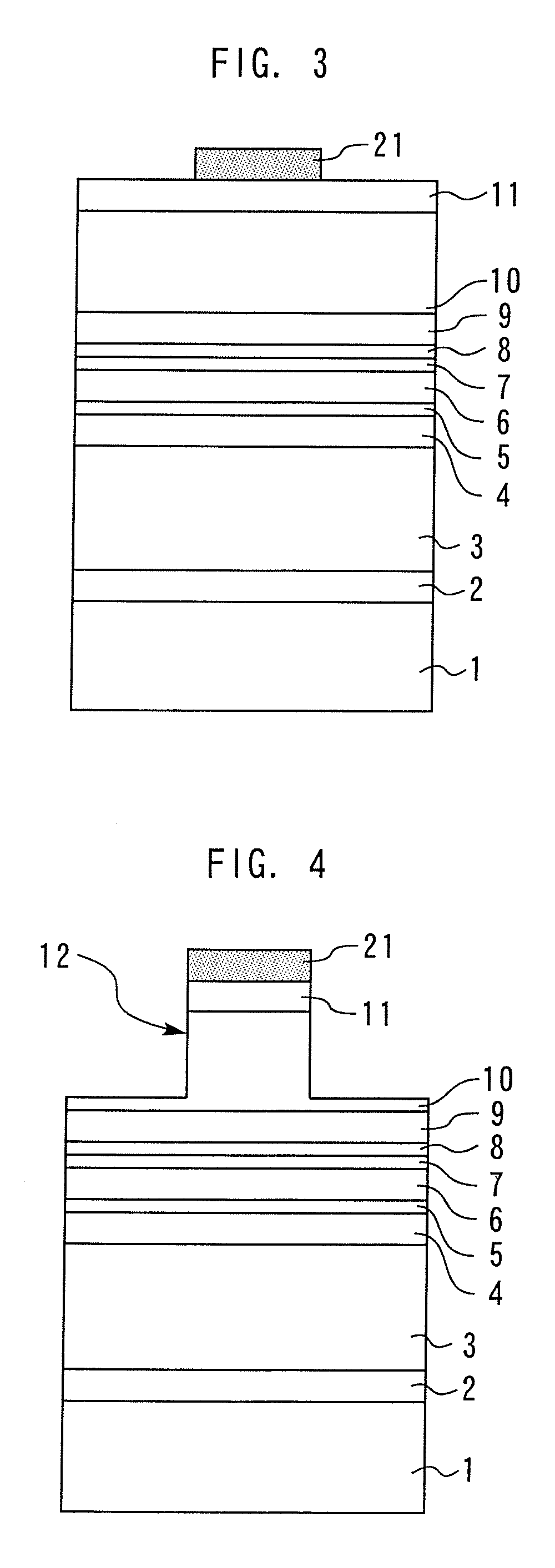
Semiconductor laser and method for manufacturing the same
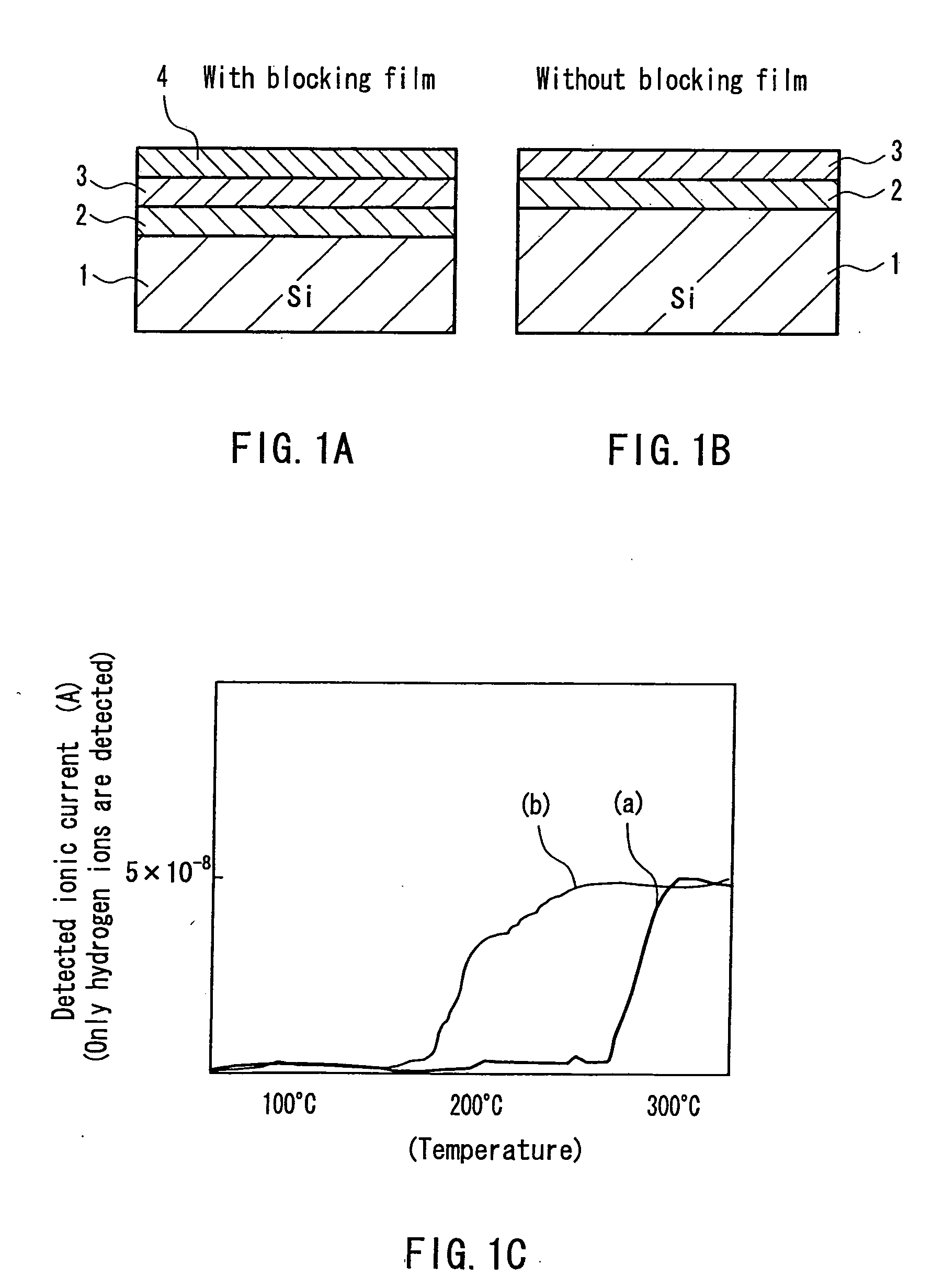
InactiveUS6985504B2Improve heat resistanceCoating can be suppressedSemiconductor lasersLaser cooling arrangementsHydrogenSemiconductor package
A semiconductor laser includes an active layer formed on a substrate and a pair of cladding layers sandwiching the active layer. On at least one of resonator end faces of the semiconductor laser, a first dielectric film with hydrogen added therein is provided. Between the first dielectric film and the resonator end face, a second dielectric film for suppressing the diffusion of hydrogen is provided. Even when a semiconductor laser with an end face coating film including a hydrogen-added film is exposed to high temperatures, peeling of the end face coating film and deterioration of the end face coating film can be suppressed.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing nitride semiconductor light-emitting element
InactiveUS20090130790A1High-output operationLittle time degradationOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOxygenActive layer
A method for manufacturing a nitride semiconductor light-emitting element comprises: forming a semiconductor laminated structure wherein an n-type nitride semiconductor epitaxial layer, an active layer, and a p-type nitride semiconductor epitaxial layer are laminated on a substrate; forming a p-type electrode having a first electrode layer containing Pd and a second electrode layer containing Ta on the p-type nitride semiconductor epitaxial layer; heat treating at a temperature between 400° C. and 600° C. in an ambient containing oxygen after forming the p-type electrode; and forming a pad electrode containing Au on the p-type electrode after the heat treating.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
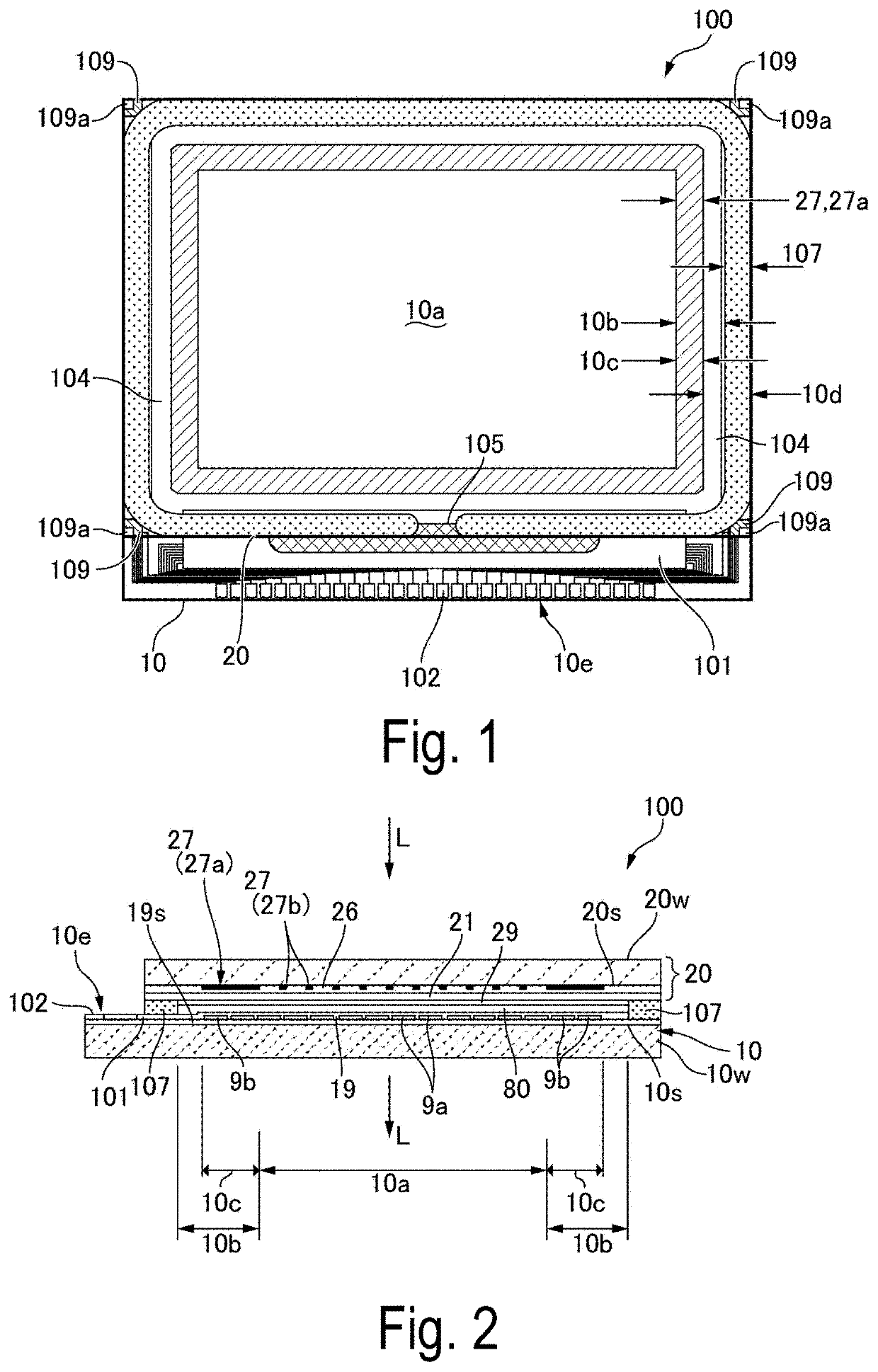
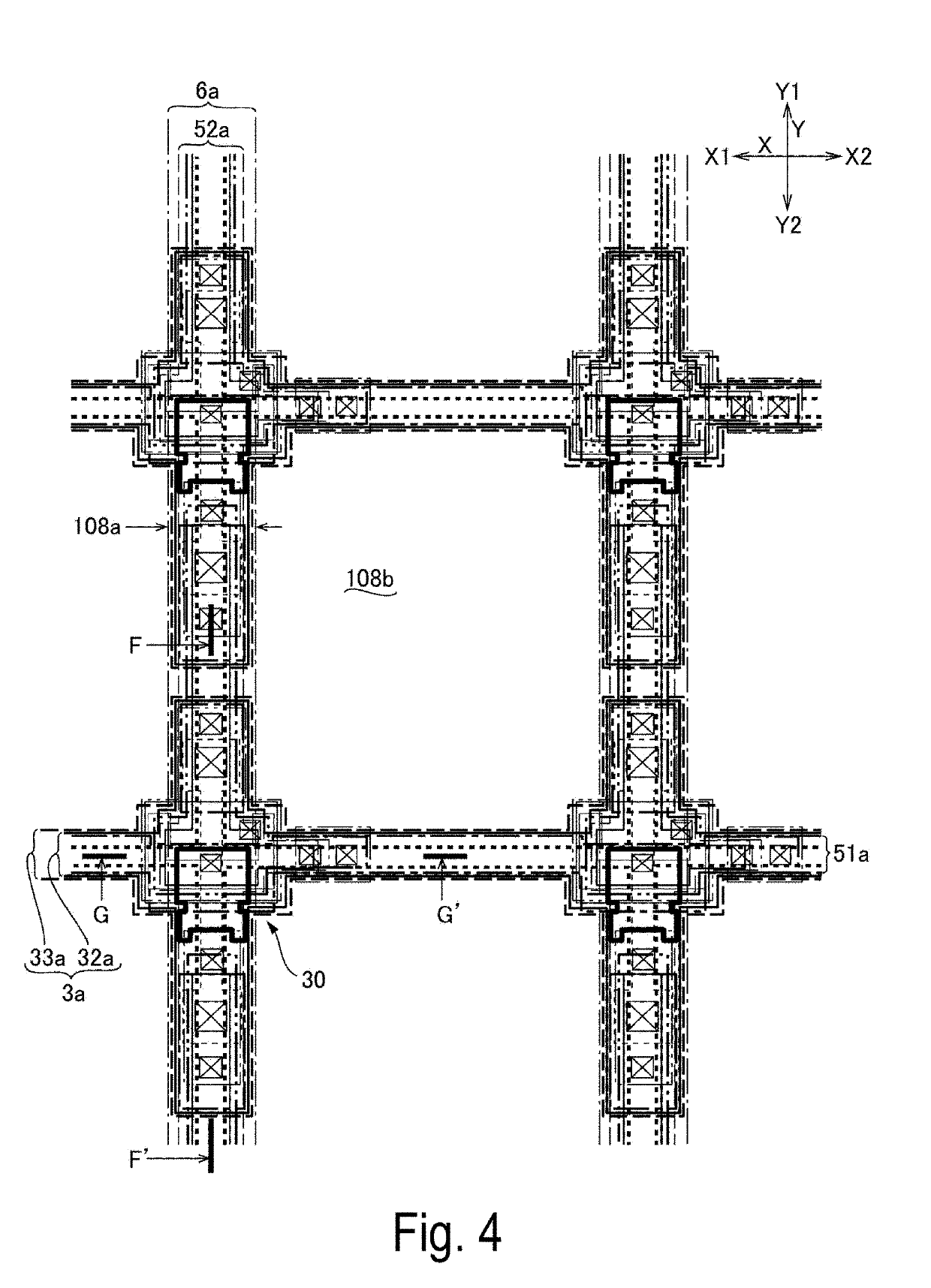
MEMS device, liquid ejecting head, and liquid ejecting apparatus
A MEMS device includes a first substrate in which a first electrode layer, a dielectric layer, and a second electrode layer are stacked on a driving region in this order; and a second substrate which is disposed to face a surface on which the dielectric layer of the first substrate is stacked. The first electrode layer and the dielectric layer extend beyond the second electrode layer toward a non-driving region separated from the driving region, a first resin having elasticity is disposed in a region including an end of the second electrode layer in an extending direction of the dielectric layer, and the first substrate and the second substrate are fixed with an adhesive in a state where the elastically deformed first resin is sandwiched therebetween.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20150153606A1Avoid scratchesImprove reliabilityNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayBright spot
A pixel electrode is formed on a TFT substrate, and a gate insulating film, an inorganic passivation film, a common electrode, and an alignment film are formed in this order thereover. A columnar spacer is formed to the counter substrate and is adapted to define a gap between the TFT substrate and the counter substrate. A through hole is formed in the gate insulating film of the TFT substrate, and the columnar spacer is disposed so as to cover a concave portion formed by the through hole. Since the area of contact between the columnar spacer and the TFT substrate is decreased, it is possible to suppress scraping of the alignment film and thus to prevent occurrence of bright spots.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
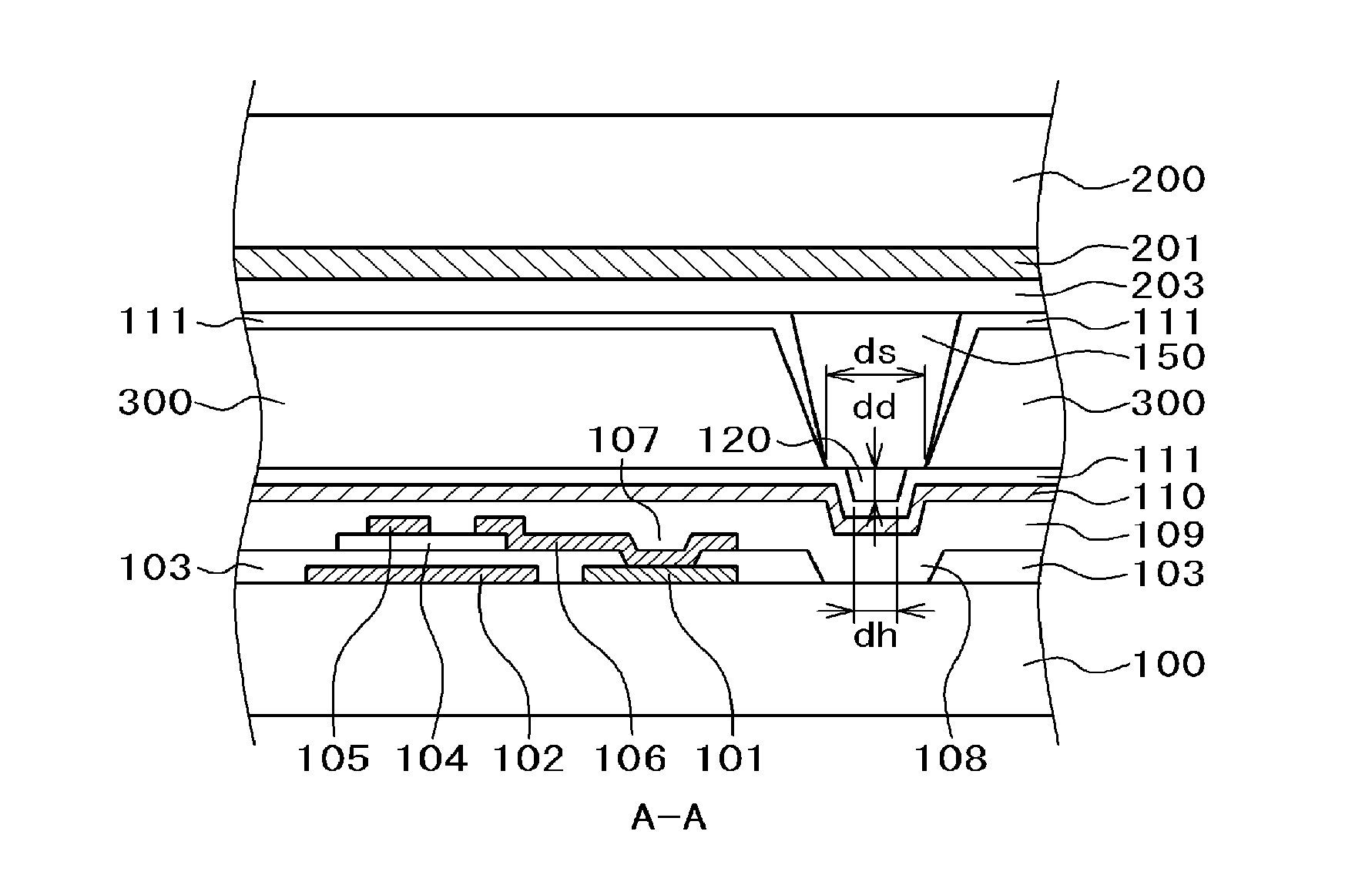
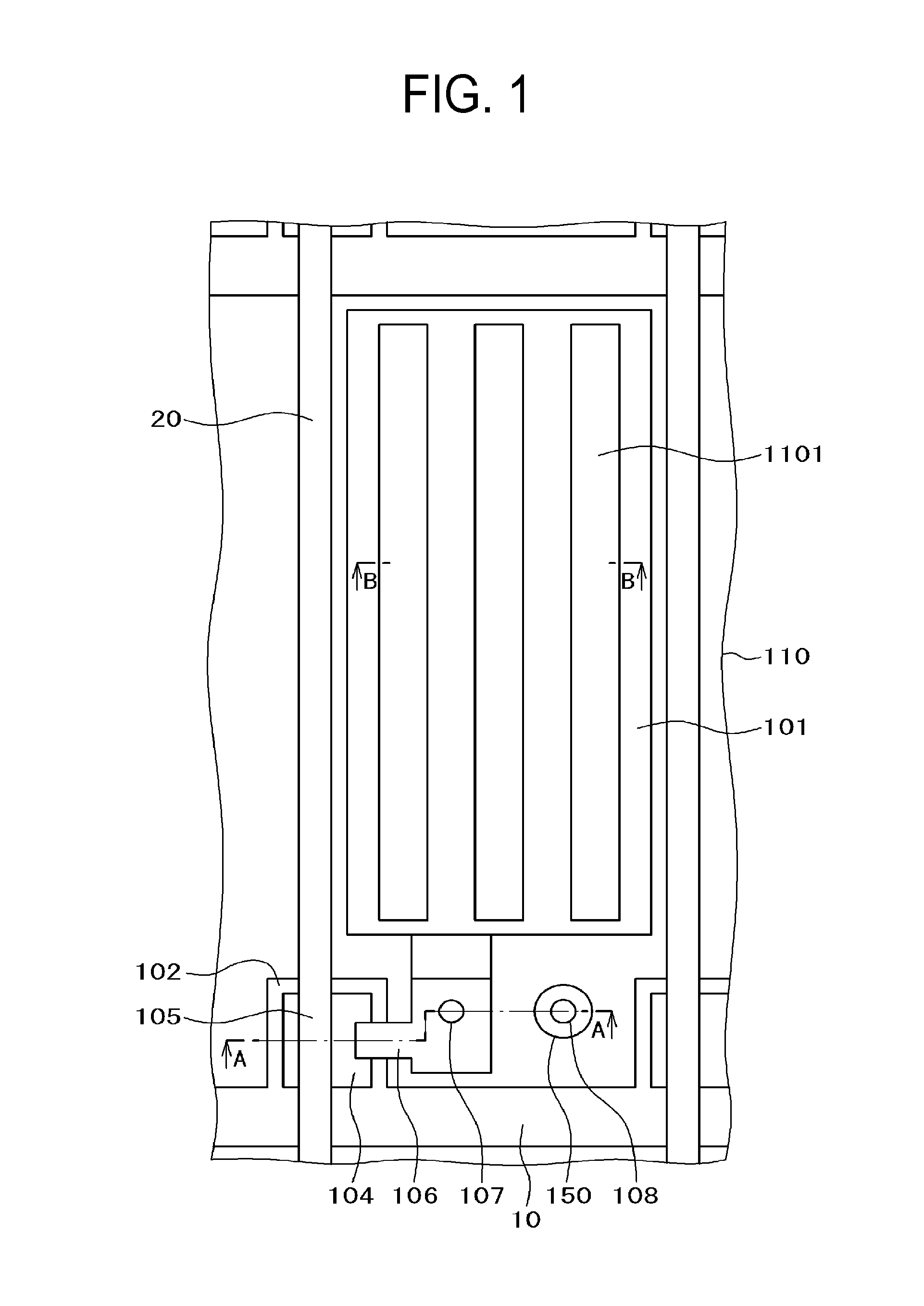
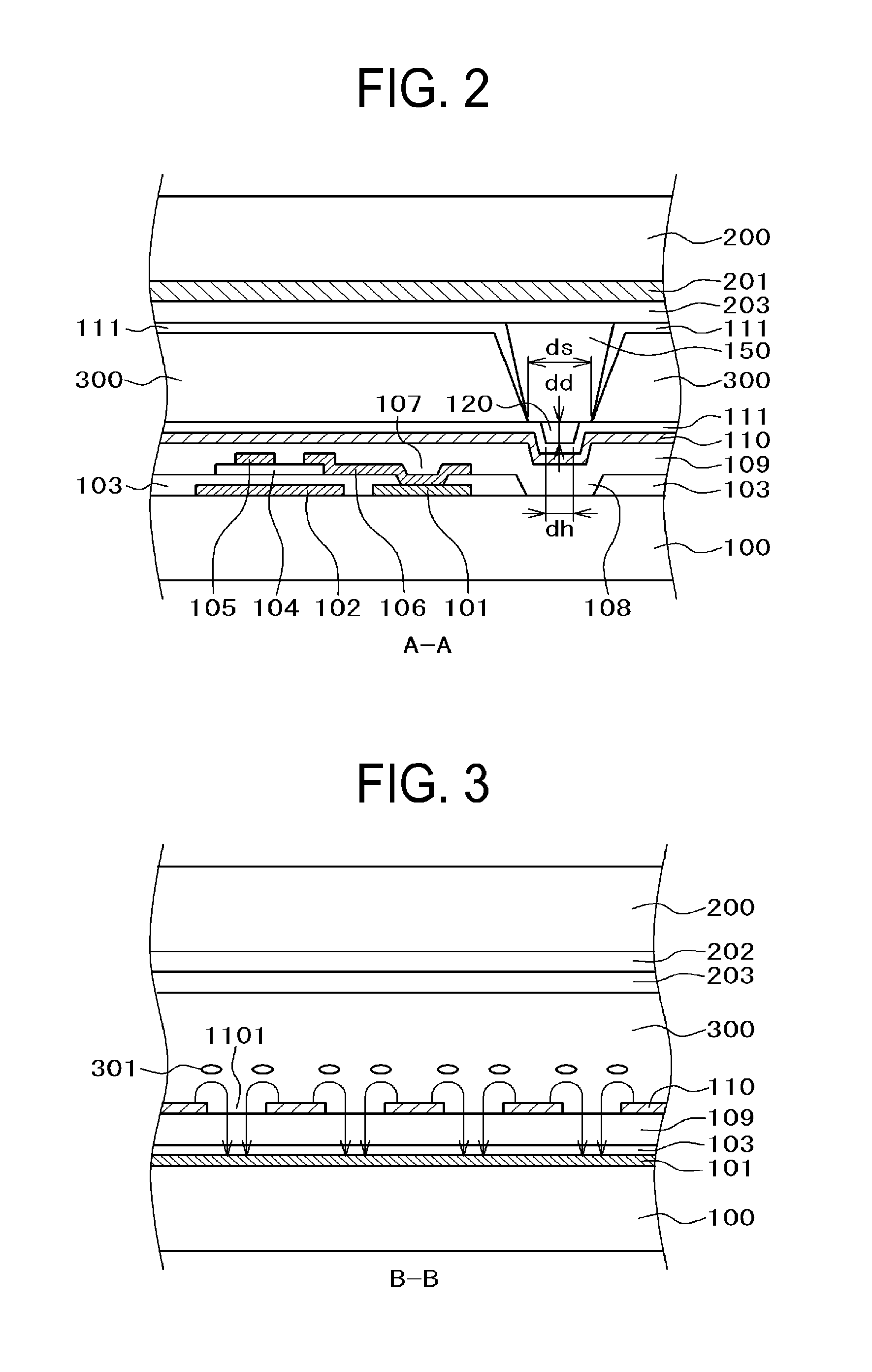
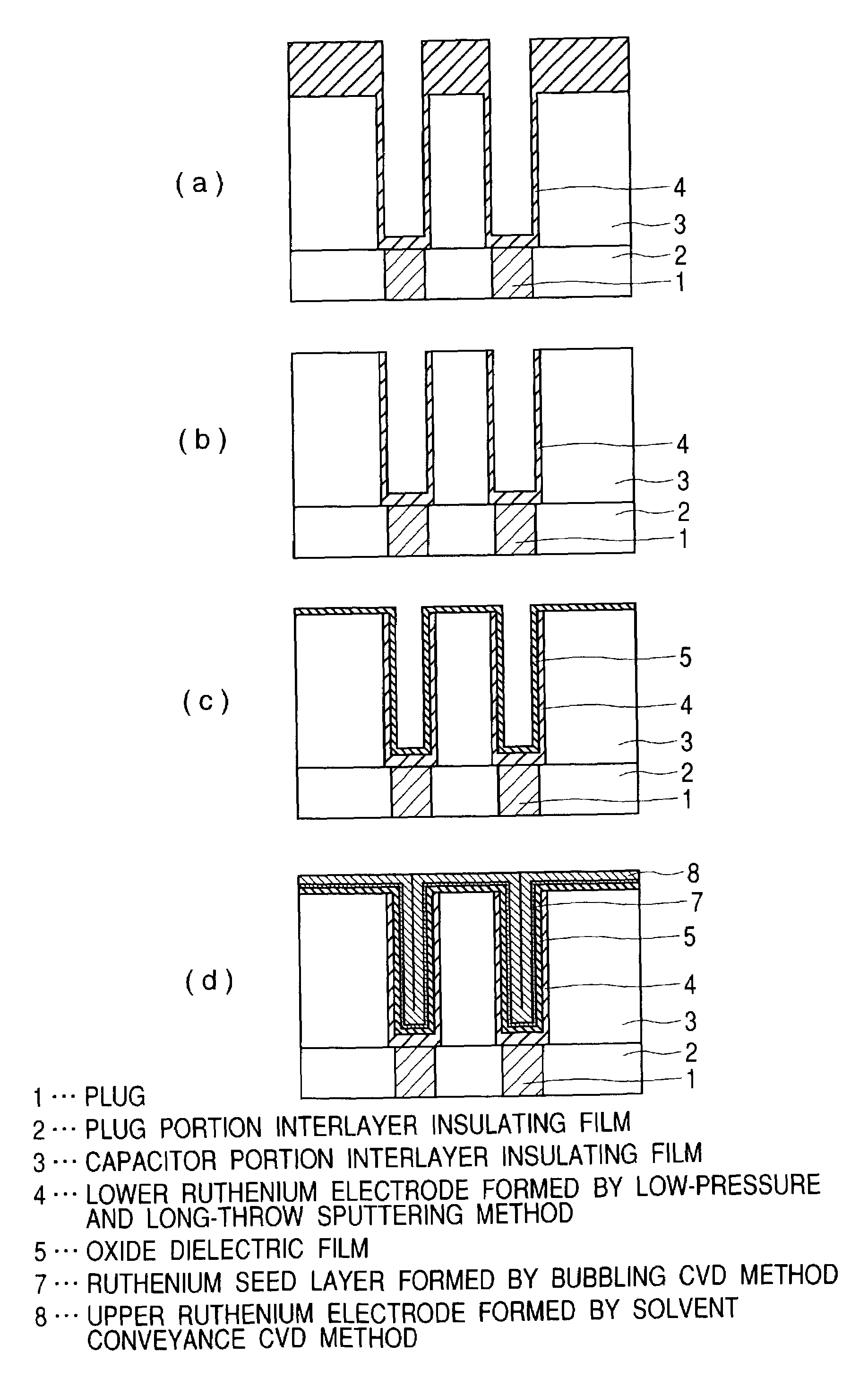
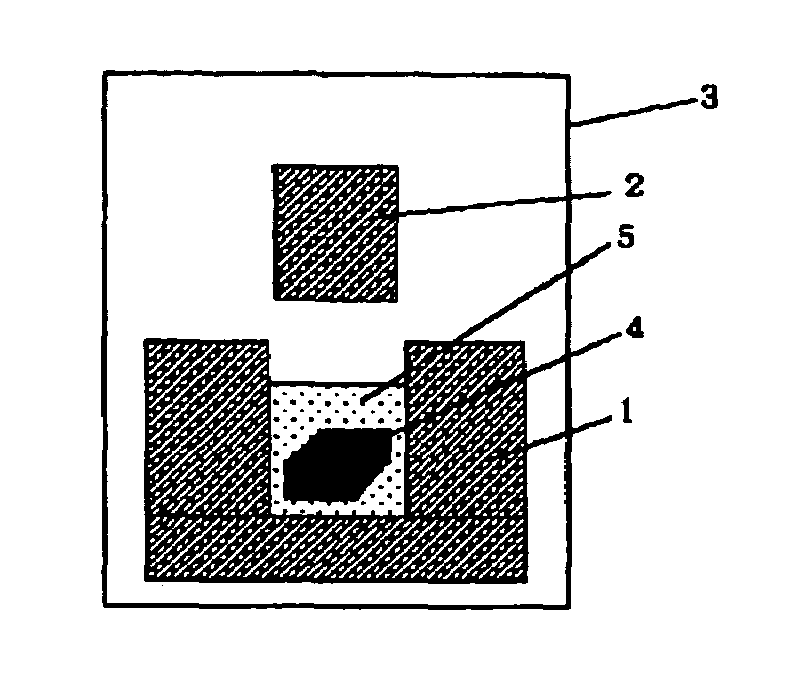
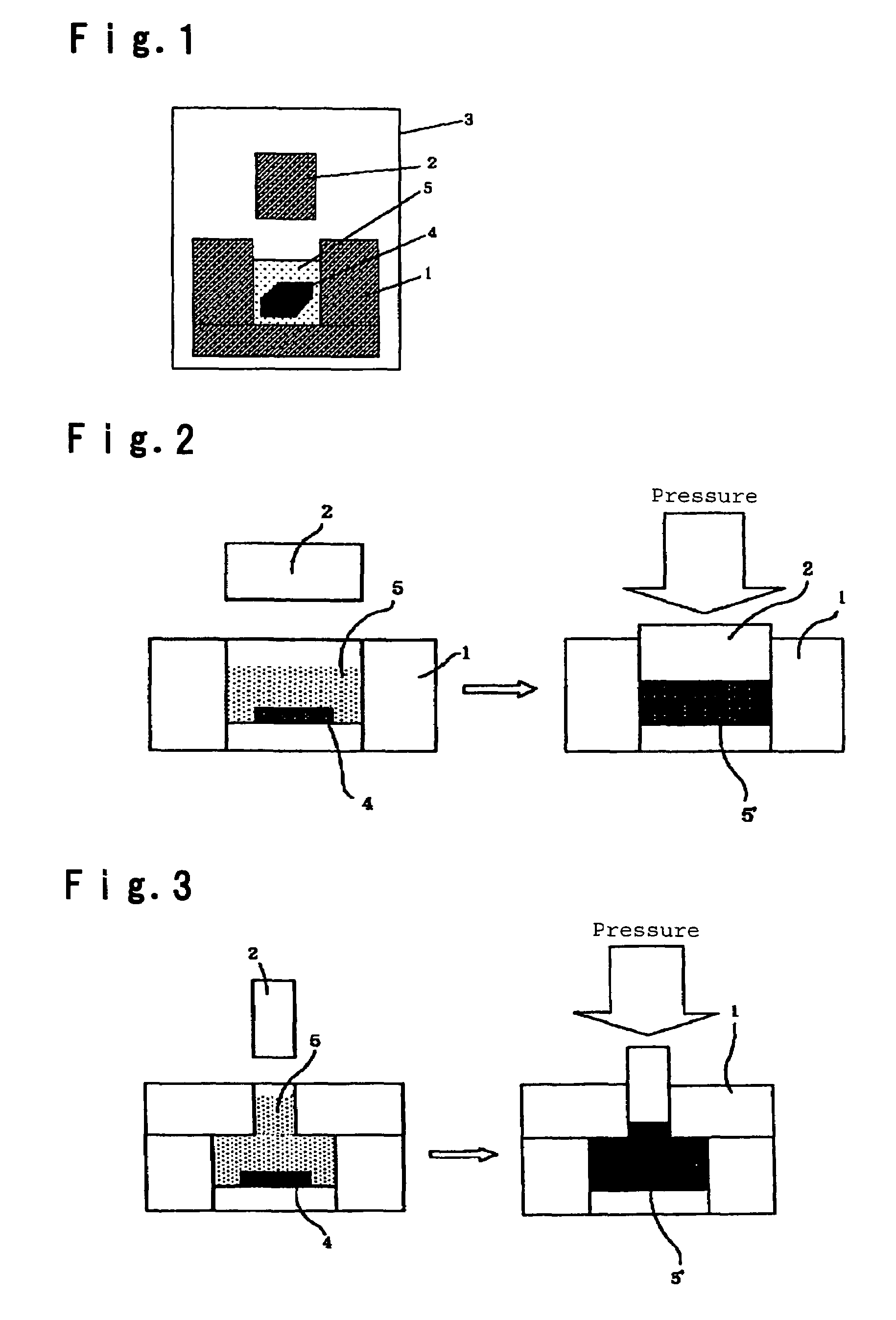
Method for manufacturing a ruthenium film for a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6989304B1Reduce pressureEnhancing straight forwarding propertyTransistorSolid-state devicesGas phaseEngineering
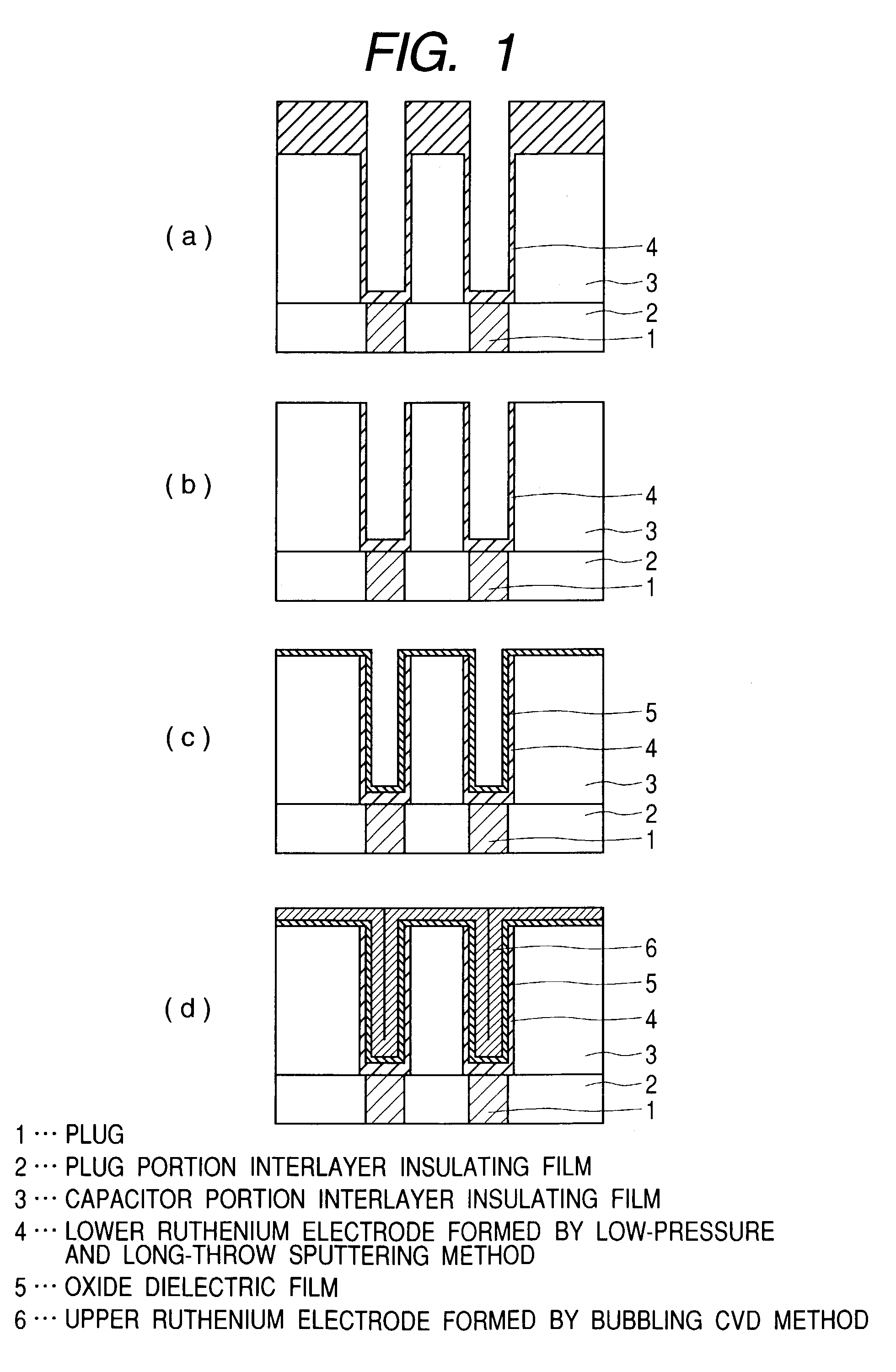
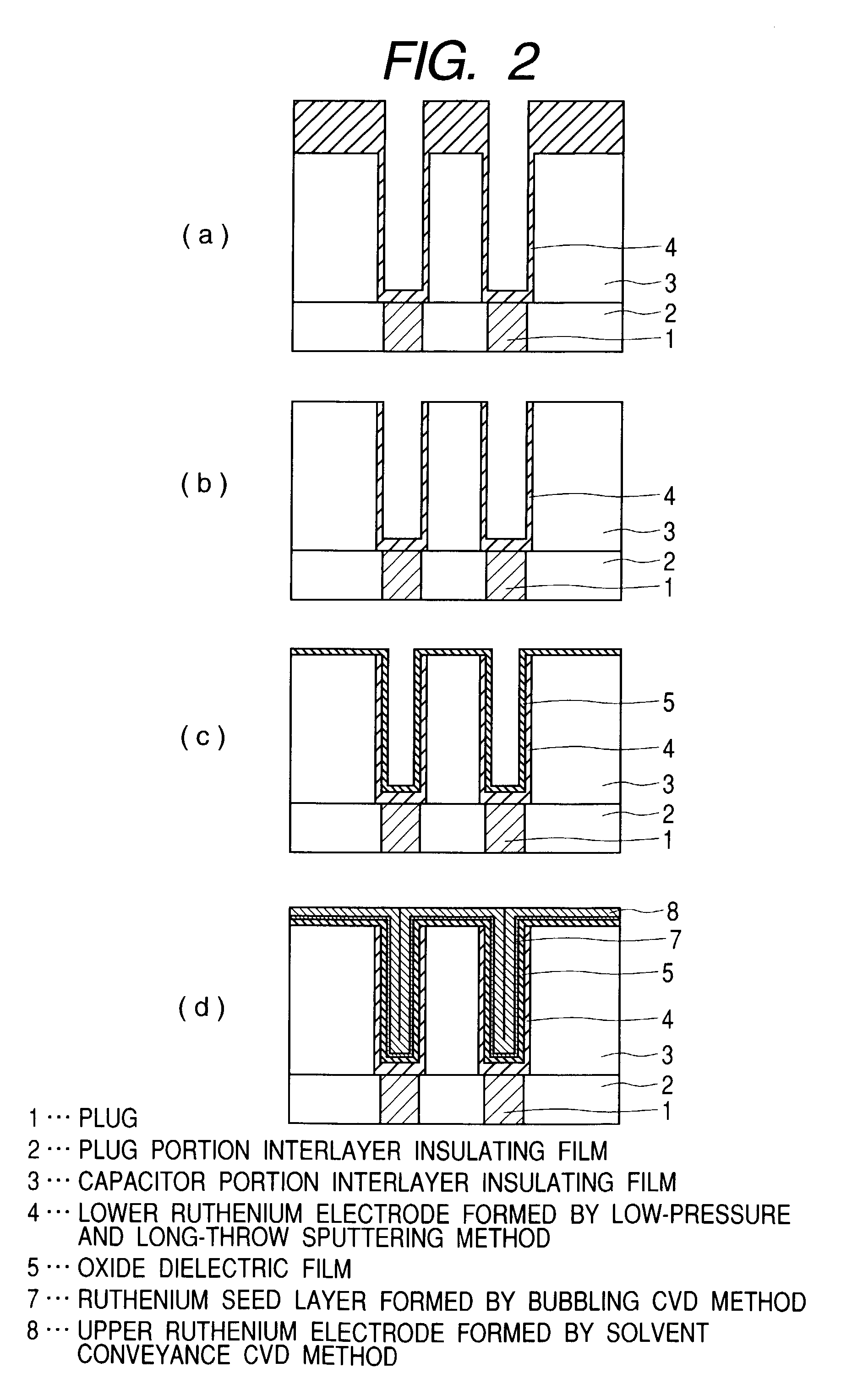
In the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to this invention, when an interlayer insulating film is fabricated such that an opening is cylindrical and low-pressure and long-throw sputtering is used for forming a lower ruthenium electrode, a ruthenium film can be deposited on the side wall of a deep hole. Further, after removing the ruthenium film deposited on the upper surface of the interlayer insulating film, a dielectric material comprising, for example, a tantalum pentoxide film is deposited. Successively, an upper ruthenium electrode is deposited using, for example, Ru(EtCp)2 as a starting material and by chemical vapor deposition of conveying the starting material by bubbling. The upper ruthenium electrode can be formed with good coverage by using conditions that the deposition rate of the ruthenium film depends on the formation temperature (reaction controlling condition). This invention can provide a fine concave type capacitor having a ruthenium electrode.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor laser and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050285135A1Improve heat resistanceCoating can be suppressedLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogenActive layer
A semiconductor laser includes an active layer formed on a substrate and a pair of cladding layers sandwiching the active layer. On at least one of resonator end faces of the semiconductor laser, a first dielectric film with hydrogen added therein is provided. Between the first dielectric film and the resonator end face, a second dielectric film for suppressing the diffusion of hydrogen is provided. Even when a semiconductor laser with an end face coating film including a hydrogen-added film is exposed to high temperatures, peeling of the end face coating film and deterioration of the end face coating film can be suppressed.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Fine carbon fiber-metal composite material and method for production thereof
InactiveUS7563502B2Small elastic modulusReduce interfaceSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic shaping apparatusCarbon layerCarbon fibers
To provide a fine carbon fiber / metal composite material having high mechanical strength, a high thermal conductivity and a low coefficient of thermal expansion and suitable as a substrate for an electronic device.A fine carbon fiber / metal composite material, which is prepared by pressure impregnating a molded product containing fine carbon fibers having a fiber diameter of from 0.5 to 500 nm and a fiber length of at most 1,000 μm, having a multilayer structure wherein cylindrical carbon layers overlap one another, and having a hollow-structured central axis, with aluminum, magnesium, copper or an alloy of such a metal, by molten metal forging.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CORPORATION +1
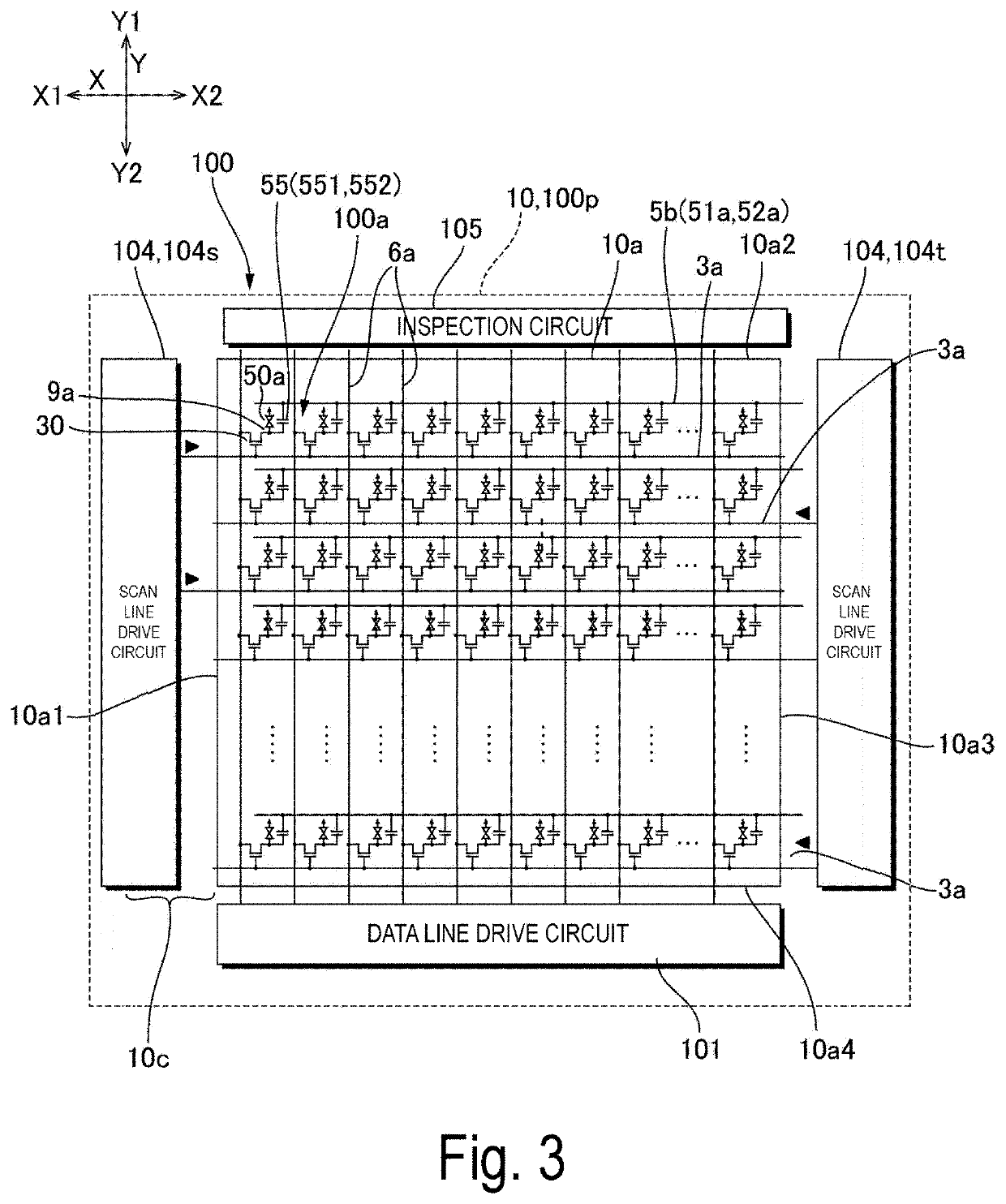
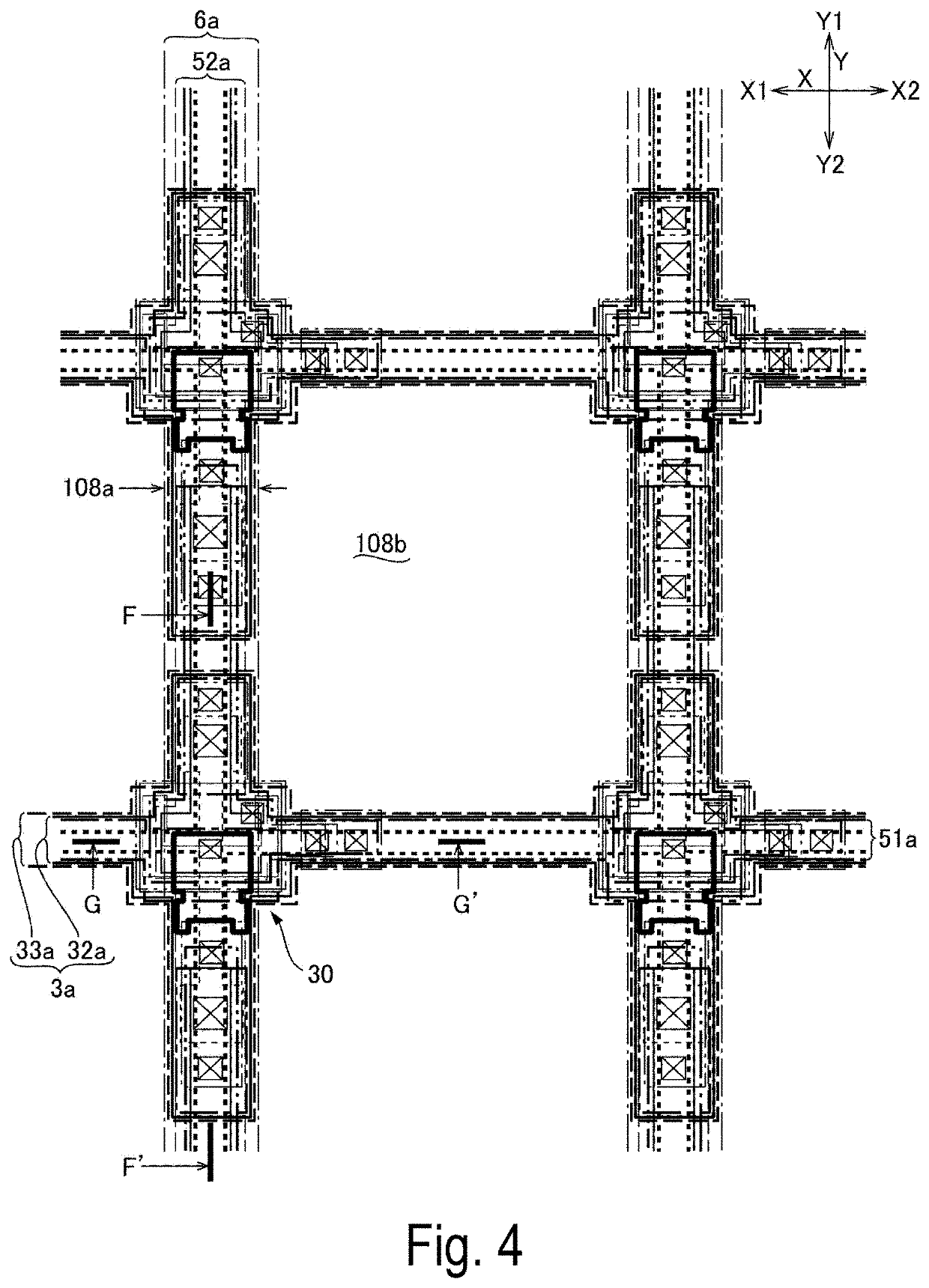
Electro-optical device, manufacturing method for electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
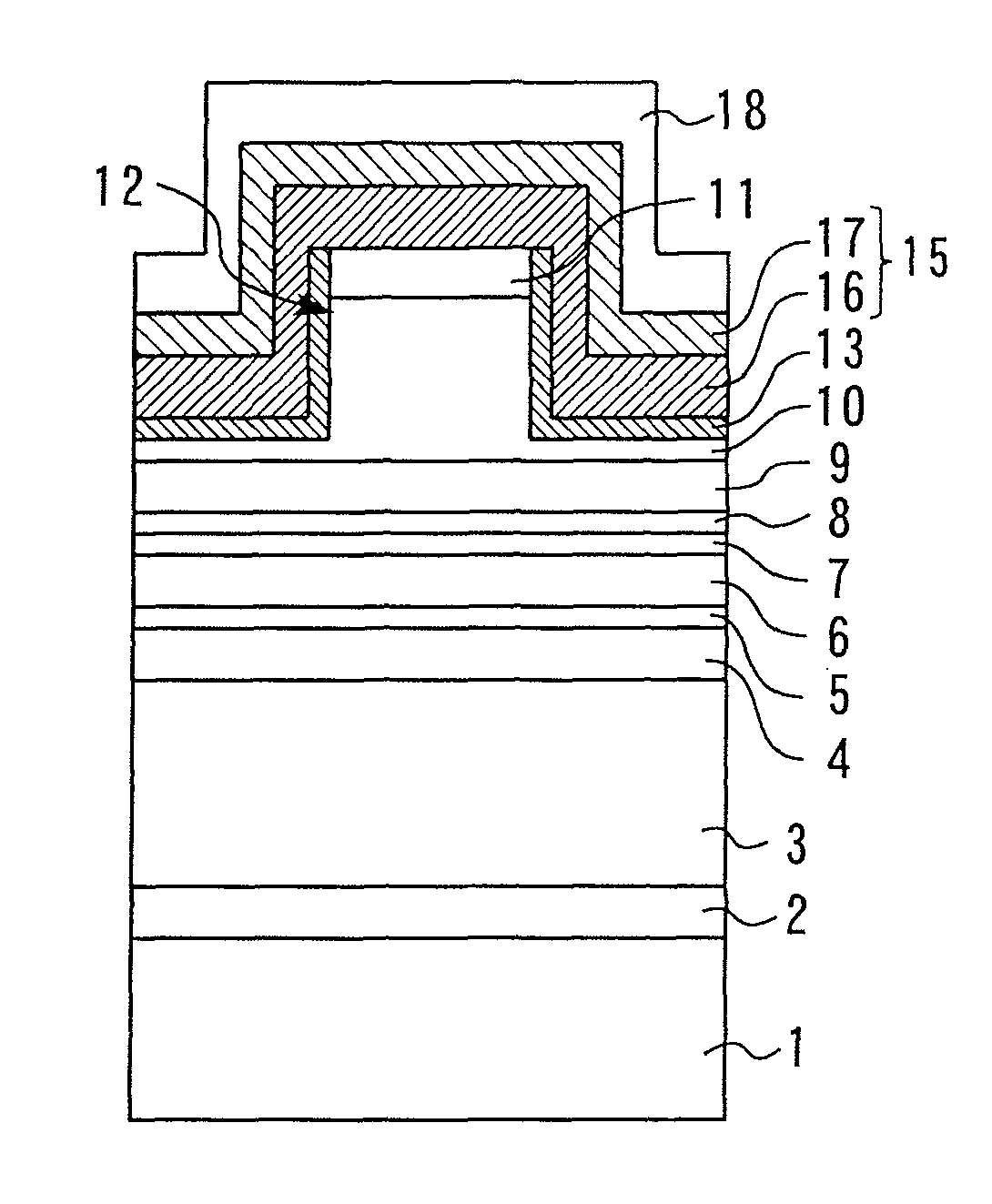
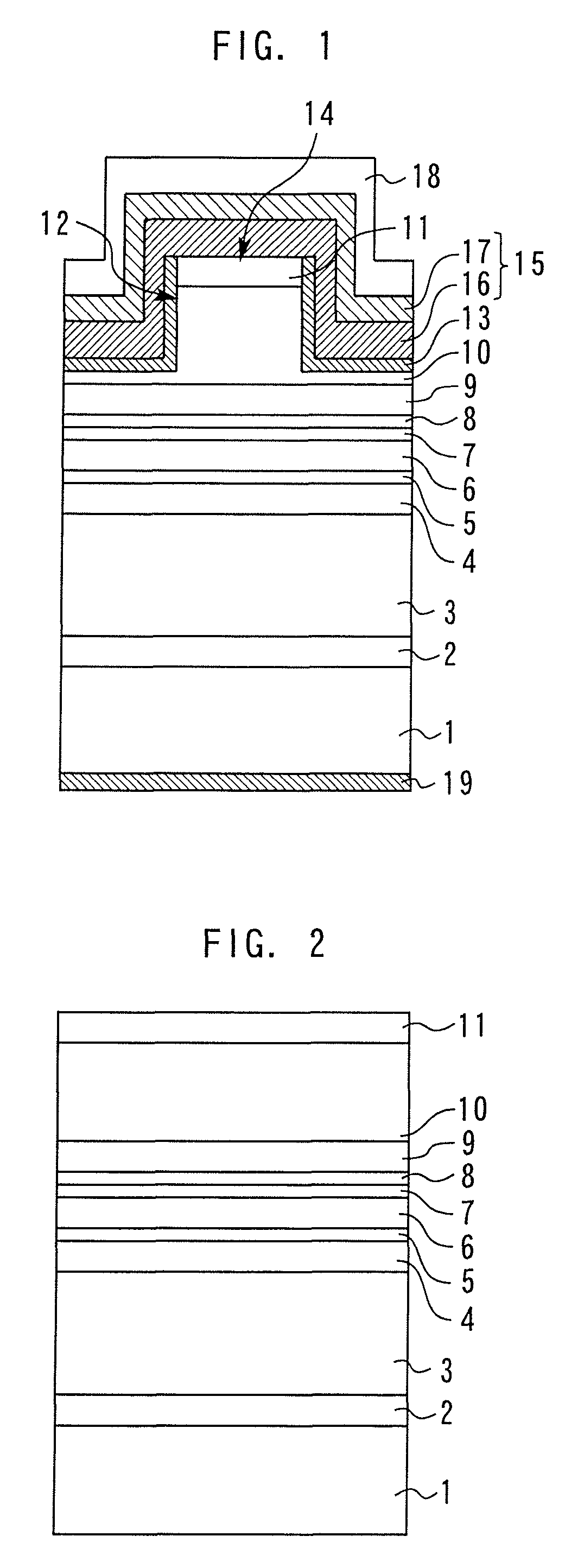
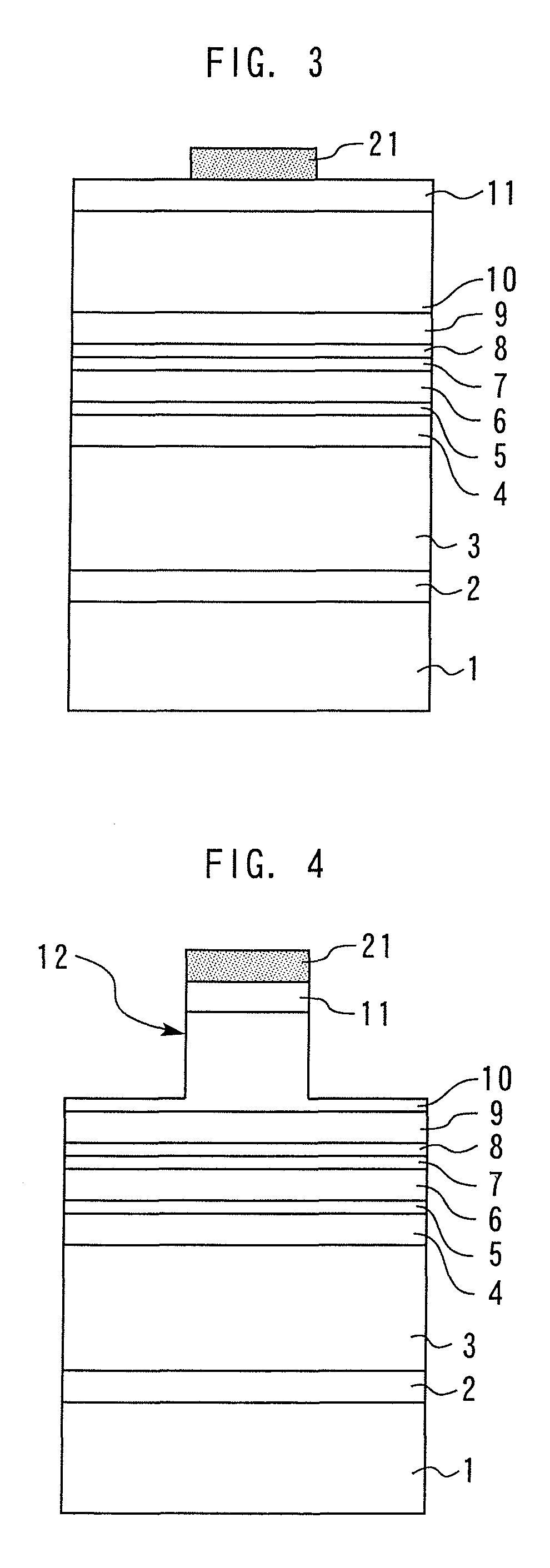
ActiveUS10847741B2Prevent peelingPeeling can be suppressedStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical connectionMaterials science
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Packaging of a semiconductor device with dual sealing materials
ActiveUS11004761B2Peeling can be suppressedReduce thermal stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
The present invention provides a semiconductor device including an insulating layer, a conductive layer bonded to one main surface of the insulating layer, a semiconductor element arranged such that the upper surface of the semiconductor element faces a direction same as the one main surface of the insulating layer, an upper electrode provided on the upper surface of the semiconductor element, a wiring member that has one end electrically bonded to the upper electrode of the semiconductor element and has another end electrically bonded to the conductive layer, and has a hollow portion, a first sealing material, and a second sealing material, in which the first sealing material seals at least part of the semiconductor element so as to be in contact with the semiconductor element, and the second sealing material seals the wiring member so as to be in contact with the wiring member.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for manufacturing nitride semiconductor light-emitting element
InactiveUS7964424B2Reduce contact resistivityHigh-output operationOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOxygenActive layer
A method for manufacturing a nitride semiconductor light-emitting element comprises: forming a semiconductor laminated structure wherein an n-type nitride semiconductor epitaxial layer, an active layer, and a p-type nitride semiconductor epitaxial layer are laminated on a substrate; forming a p-type electrode having a first electrode layer containing Pd and a second electrode layer containing Ta on the p-type nitride semiconductor epitaxial layer; heat treating at a temperature between 400° C. and 600° C. in ambient containing oxygen after forming the p-type electrode; and forming a pad electrode containing Au on the p-type electrode after the heat treating.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
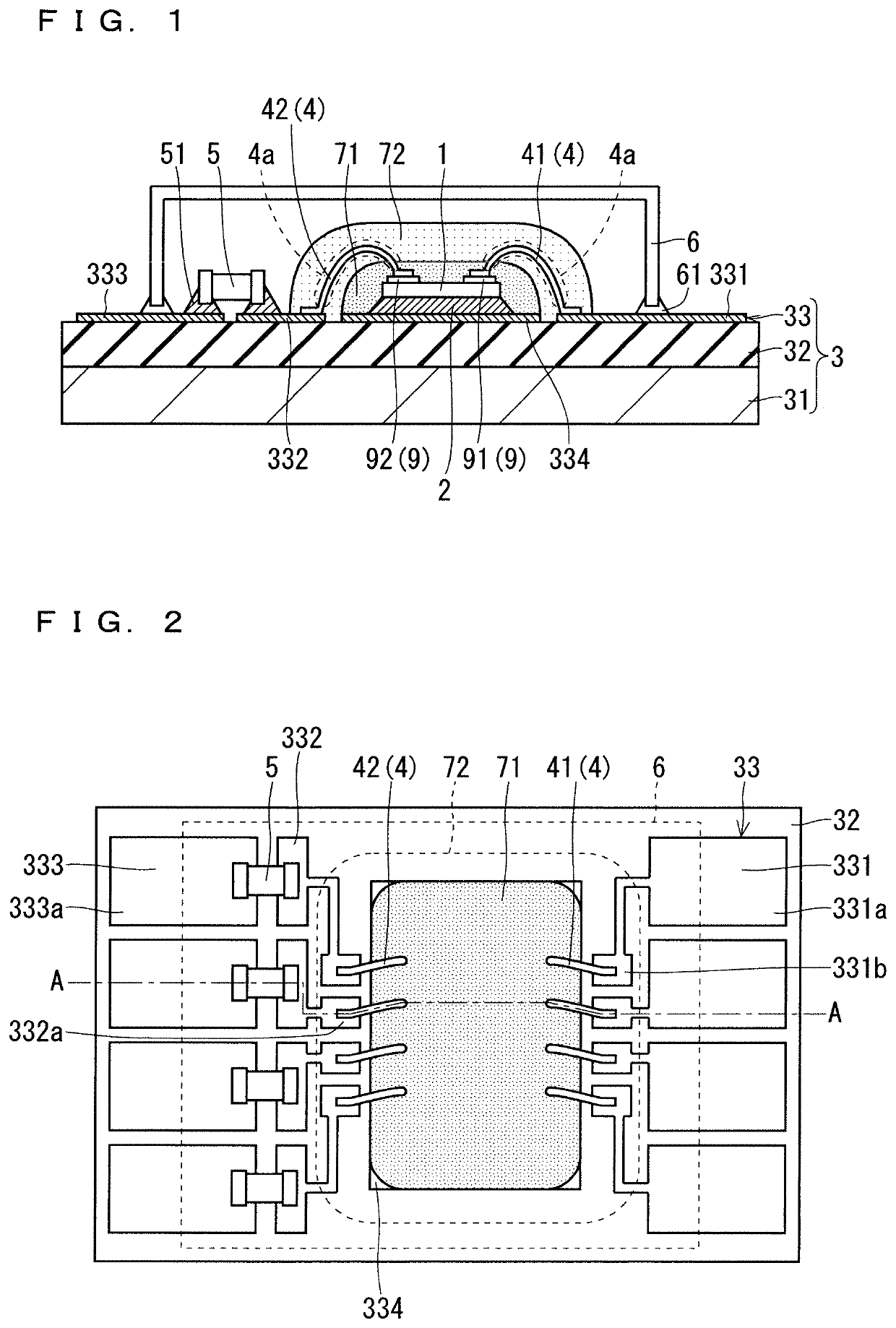
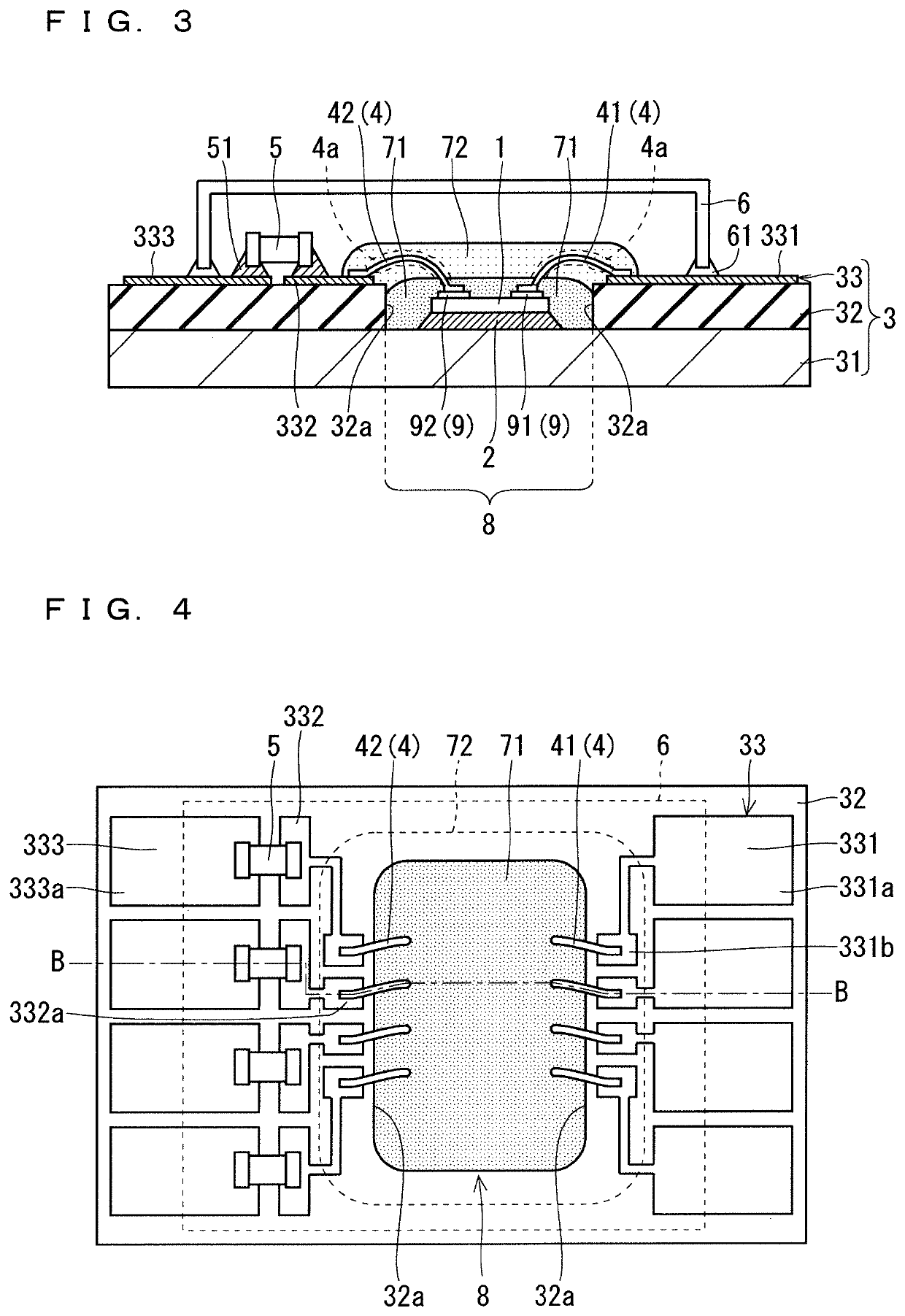
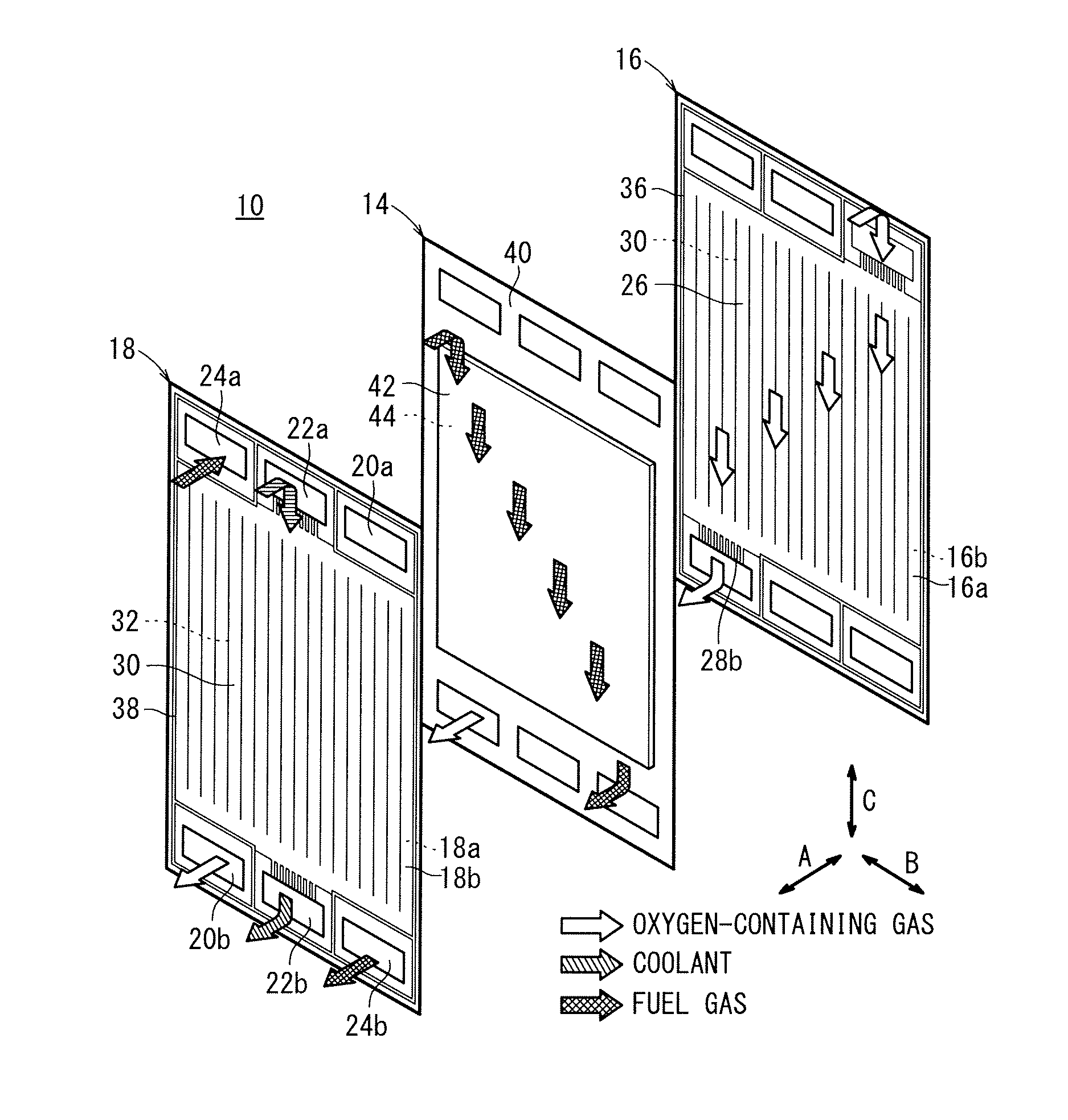
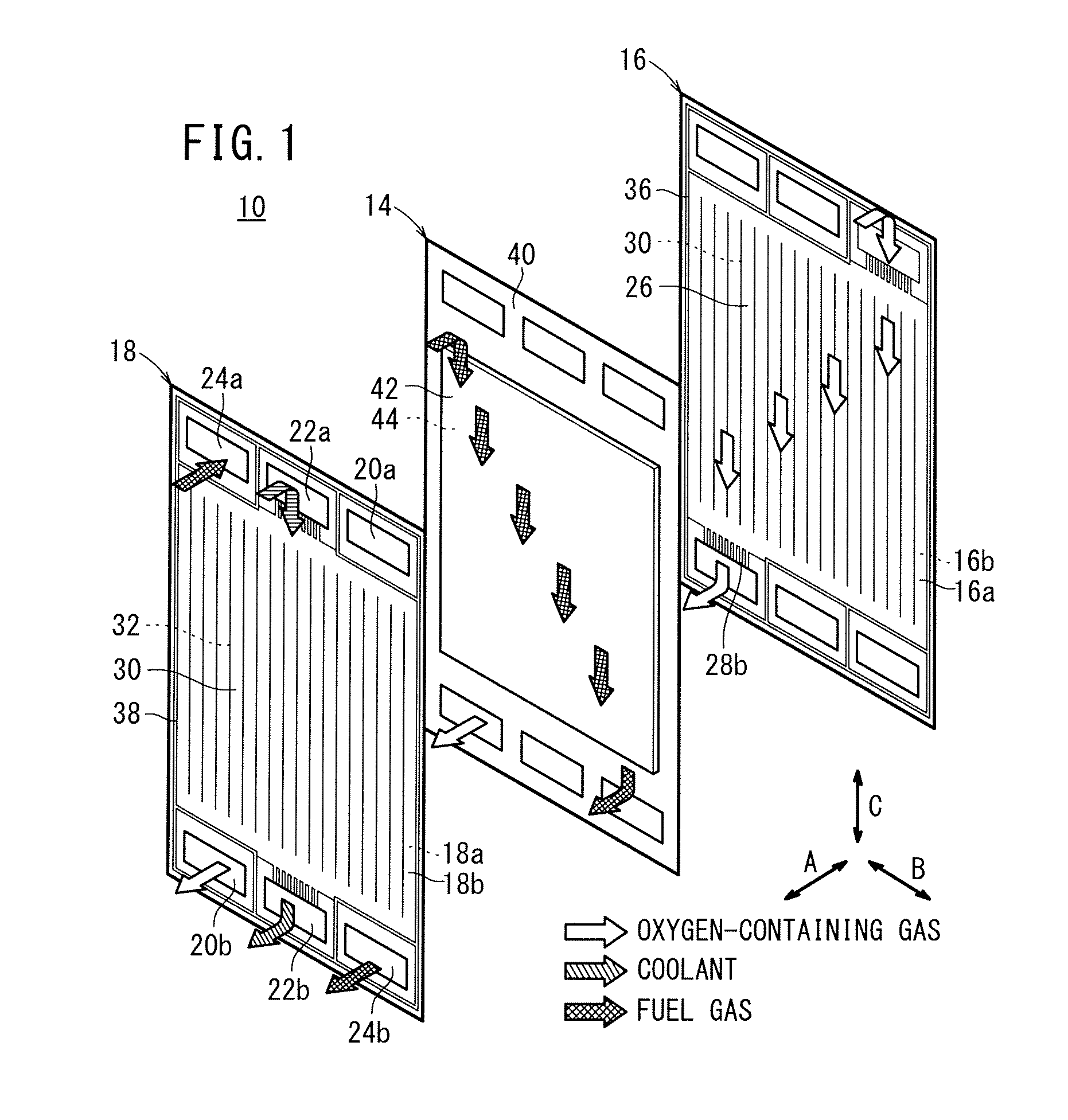
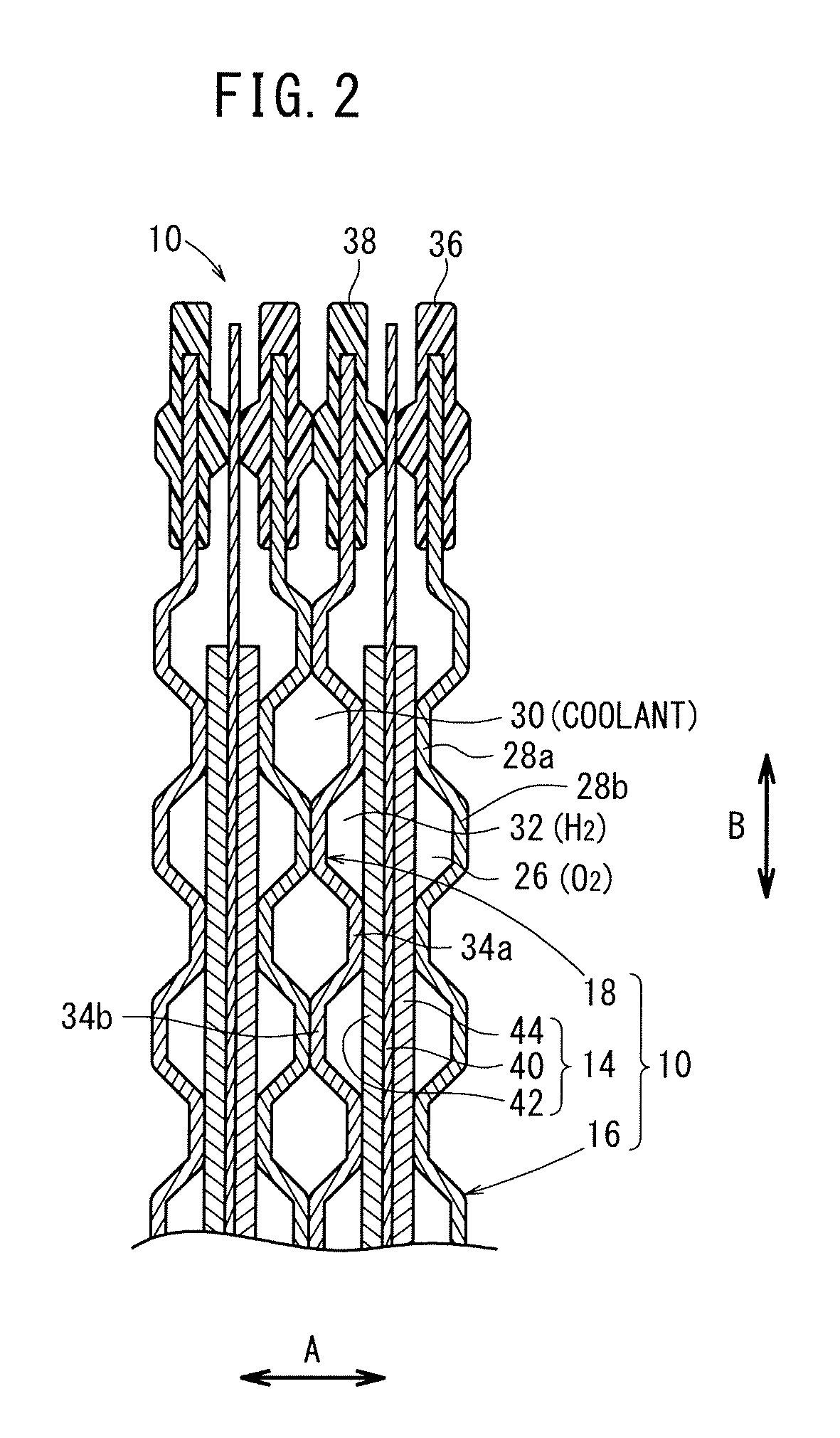
Fuel cell metal separator and noble metal coating method therefor
ActiveUS20120258383A1Peeling can be suppressedImprove conductivityFuel cell auxillariesCell component detailsFuel cellsOxygen
A first metal separator and an electrolyte electrode assembly are stacked in a fuel cell. The first metal separator comprises a convex portion that abuts against the electrolyte electrode assembly, and a concave portion forming an oxygen-containing gas flow channel between the electrolyte electrode assembly and the concave portion. A gold coating layer is formed on the convex portion. The gold coating layer includes a main gold coating portion and a reticulate gold coating portion that extends around the main gold coating portion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Semiconductor device
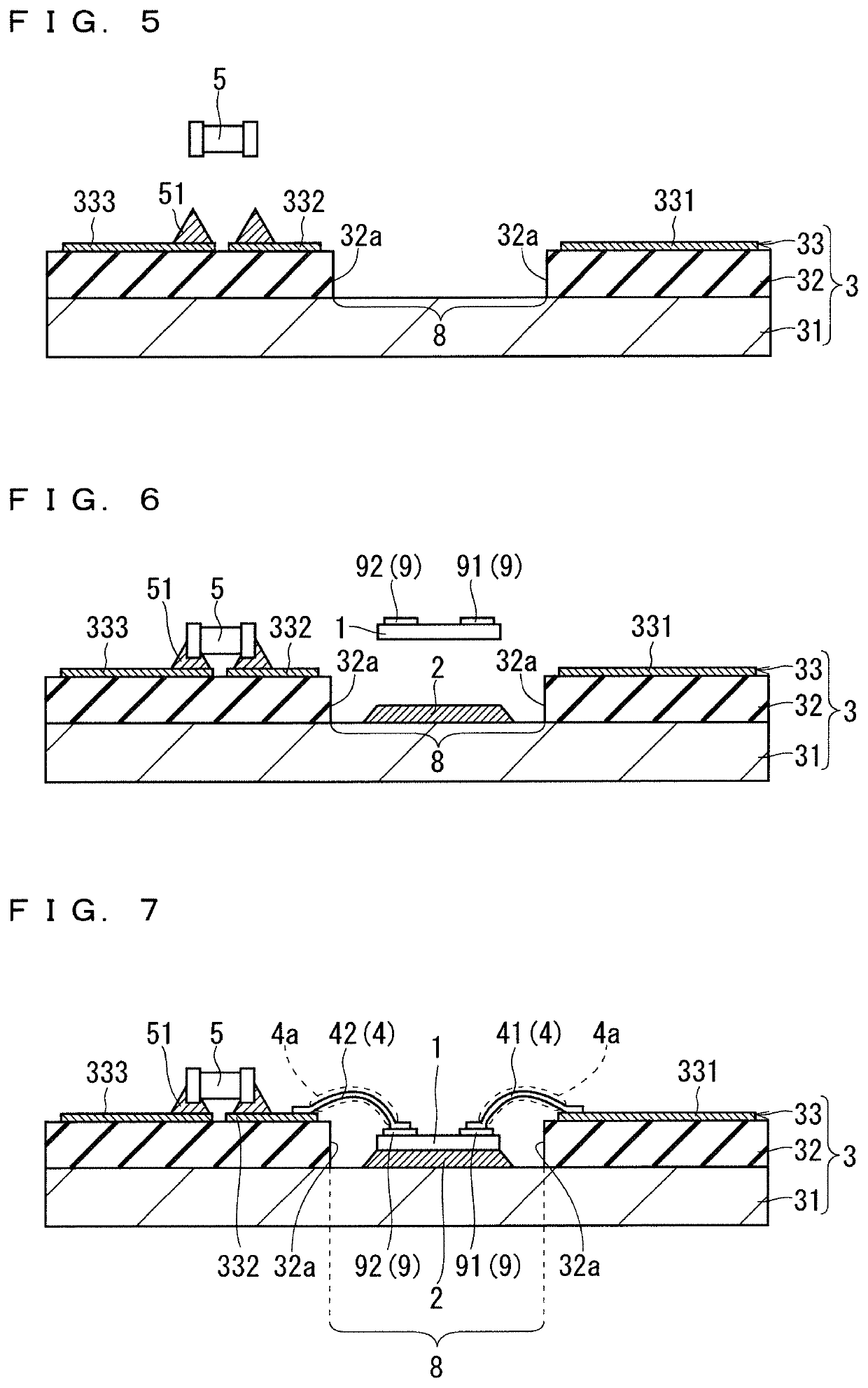
InactiveUS20170207179A1Reduce areaReduce the valueSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialUltrasonic bonding
An object of the present invention is to obtain a semiconductor device having highly reliable bonding portions. The semiconductor device according to the present invention includes an insulating substrate on which a conductive pattern is formed, and an electrode terminal and a semiconductor element which are bonded to the conductive pattern, the electrode terminal and the conductive pattern are bonded by ultrasonic bonding on a bonding face, and the ultrasonic bonding is performed at a plurality of positions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Electro-optical device, manufacturing method for electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20190237696A1Prevent peelingPeeling can be suppressedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityEngineering
A first electrode, a first insulating film, a second electrode, a second insulating film, and a pixel electrode are formed on a one surface side of a first substrate of an electro-optical device. The second electrode is electrically connected [to the first electrode] via a first contact hole that penetrates the first insulating film. The second electrode and the second insulating film configure a continuous flat surface, which is the surface on the opposite side to the first substrate, and the pixel electrode is electrically connected to the second electrode. Of the second insulating film, since an inside section positioned inside a concave portion caused by the first contact hole is connected to an outside section provided on the outside of the concave portion, peeling of the inside section is unlikely to occur
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
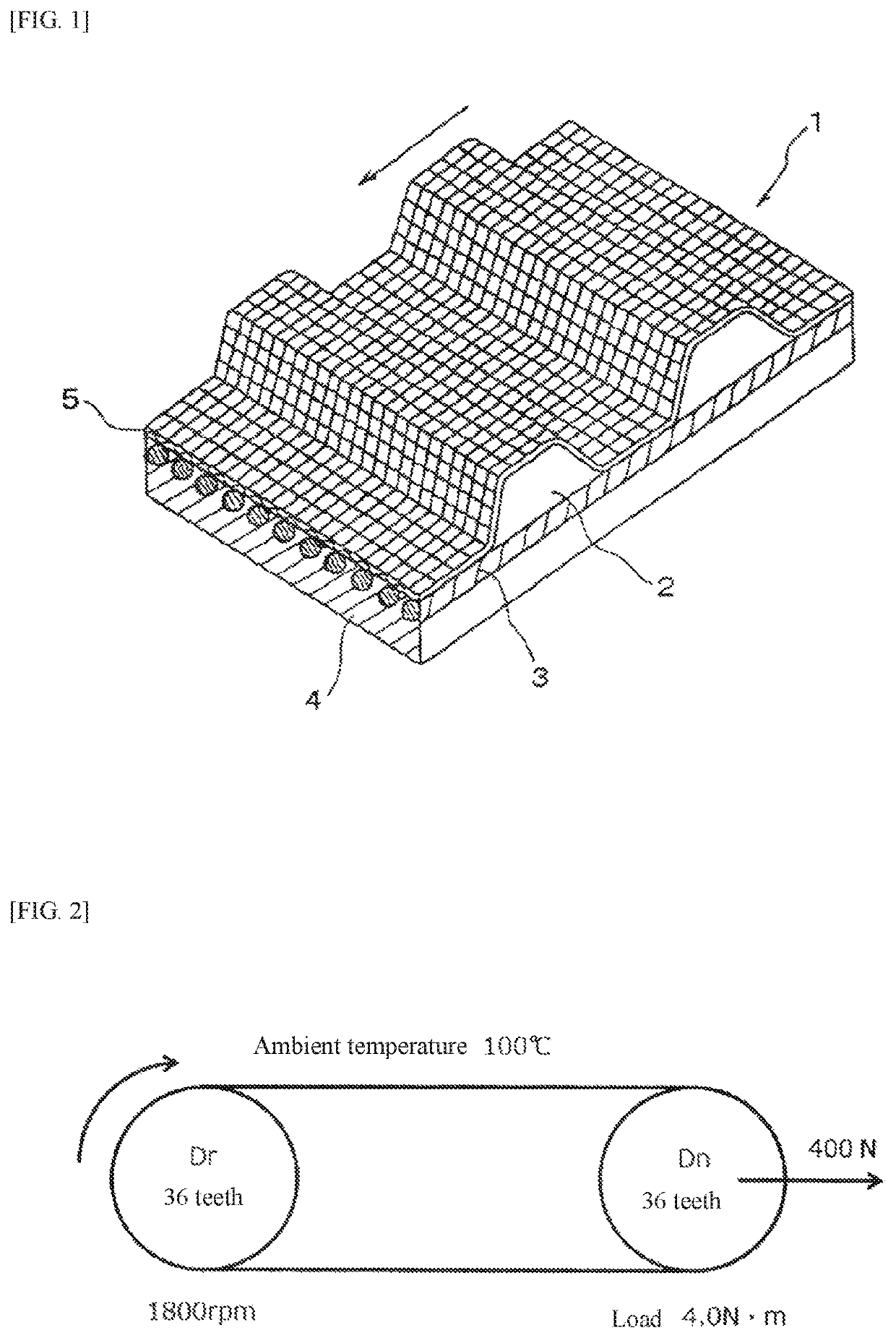
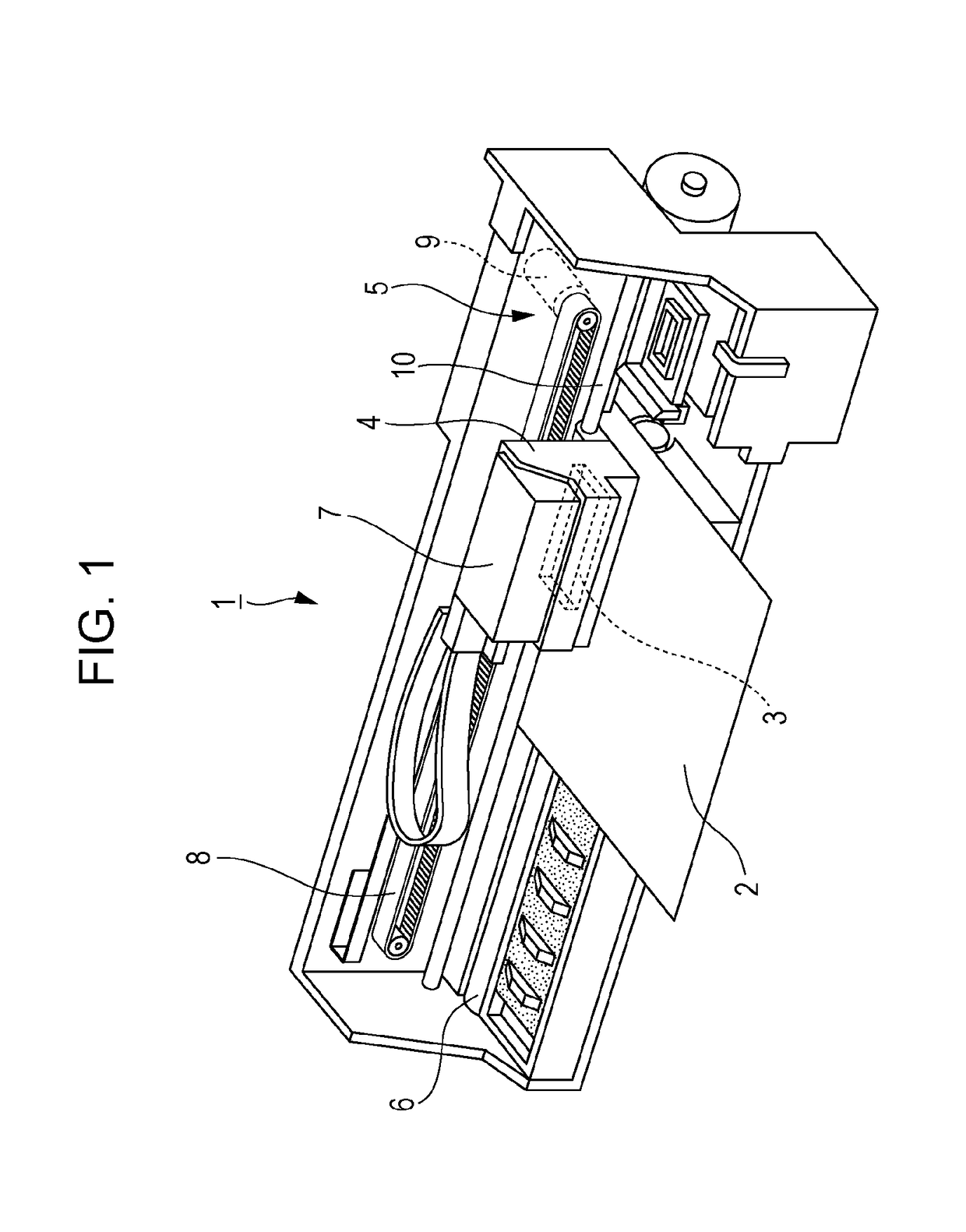
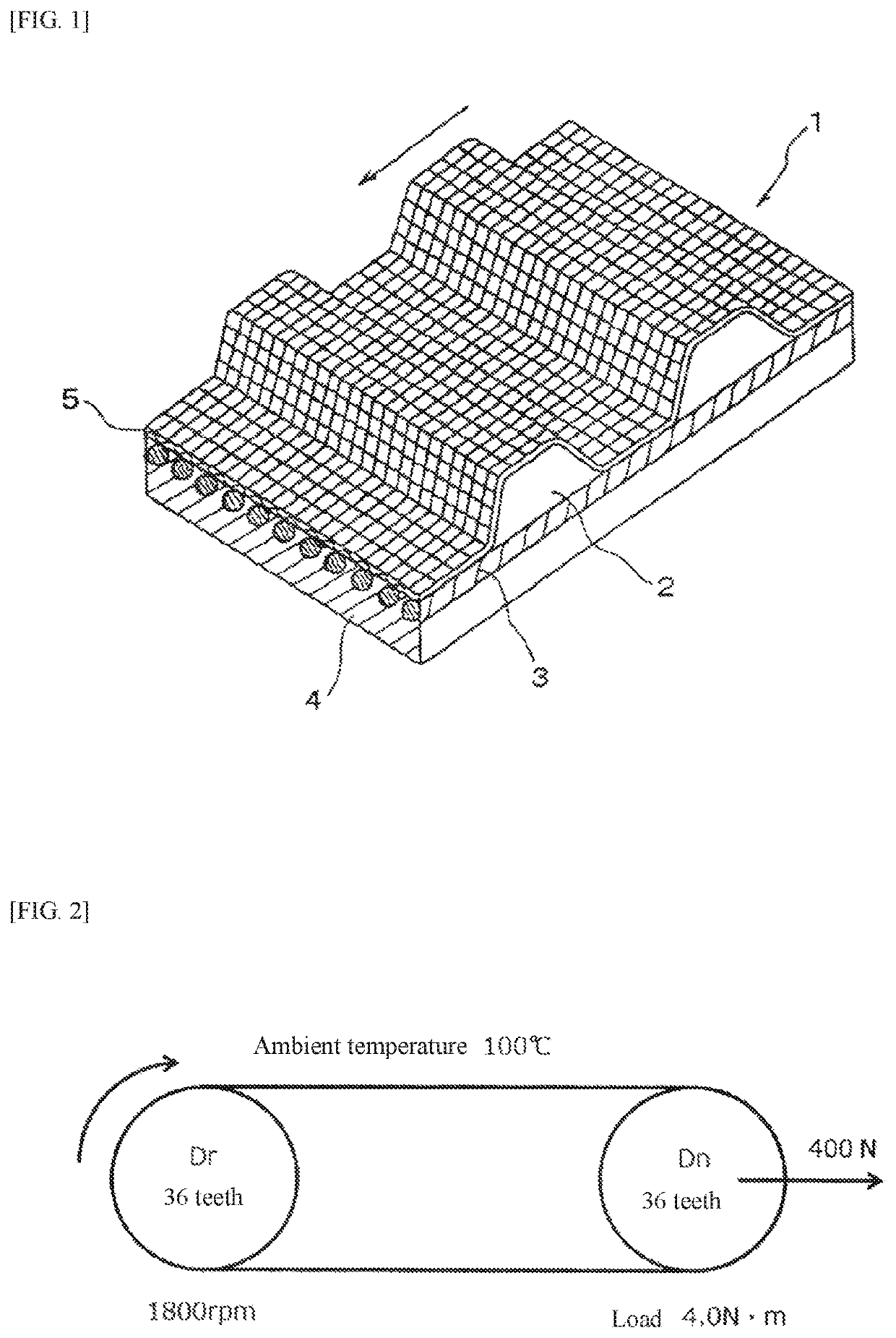
Transmission Belt
ActiveUS20200200232A1Increased durabilityPeeling can be suppressedV-beltsDriving beltsElastomerFiber
The present invention relates to a transmission belt which is provided with: a rubber layer that is formed from a vulcanized product of a rubber composition which contains a rubber component containing an ethylene-α-olefin elastomer, a filler containing silica, a vulcanizing agent containing a sulfur-based vulcanizing agent, and a curable resin containing an amino resin; and a fiber member that is in contact with the rubber layer.
Owner:MITSUBOSHI BELTING LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS6873047B2AdhesionPeeling can be suppressedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device is provided including: a step of forming a solid barrier metal layer on an interlayer insulating film; a removing step of removing at least a part of the solid barrier metal layer located at a place at which a pad opening portion is to be formed; a step of forming a solid second Al alloy film on the interlayer insulating film exposed in the removing step described above and the solid barrier metal layer; a step of patterning the solid second Al alloy film and the solid barrier metal layer so as to form a bonding pad portion on the interlayer insulating film; a step of forming a passivation film on the bonding pad portion and the interlayer insulating film; and a step of forming the pad opening portion in the passivation film at a position located on the bonding pad portion.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
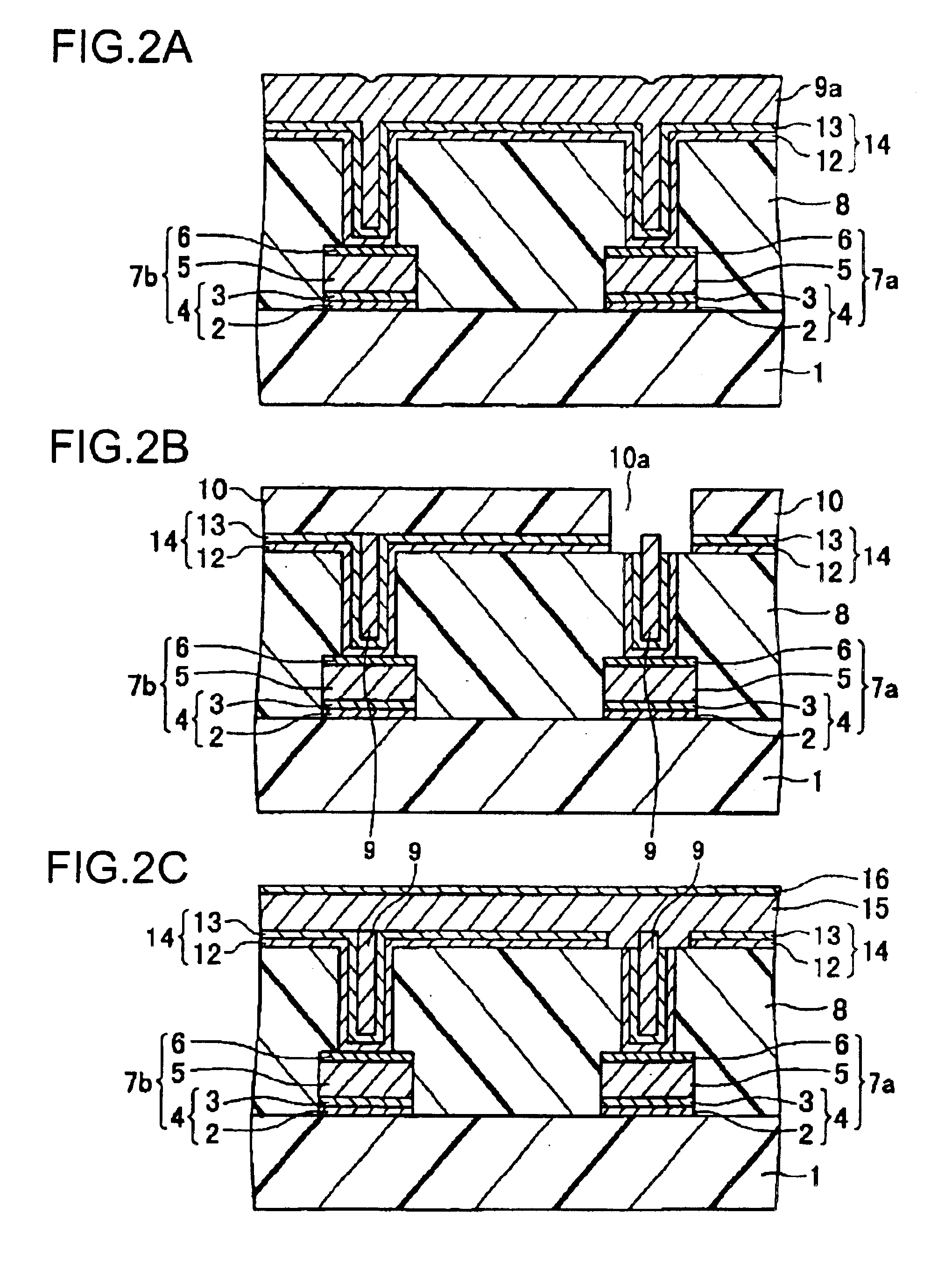
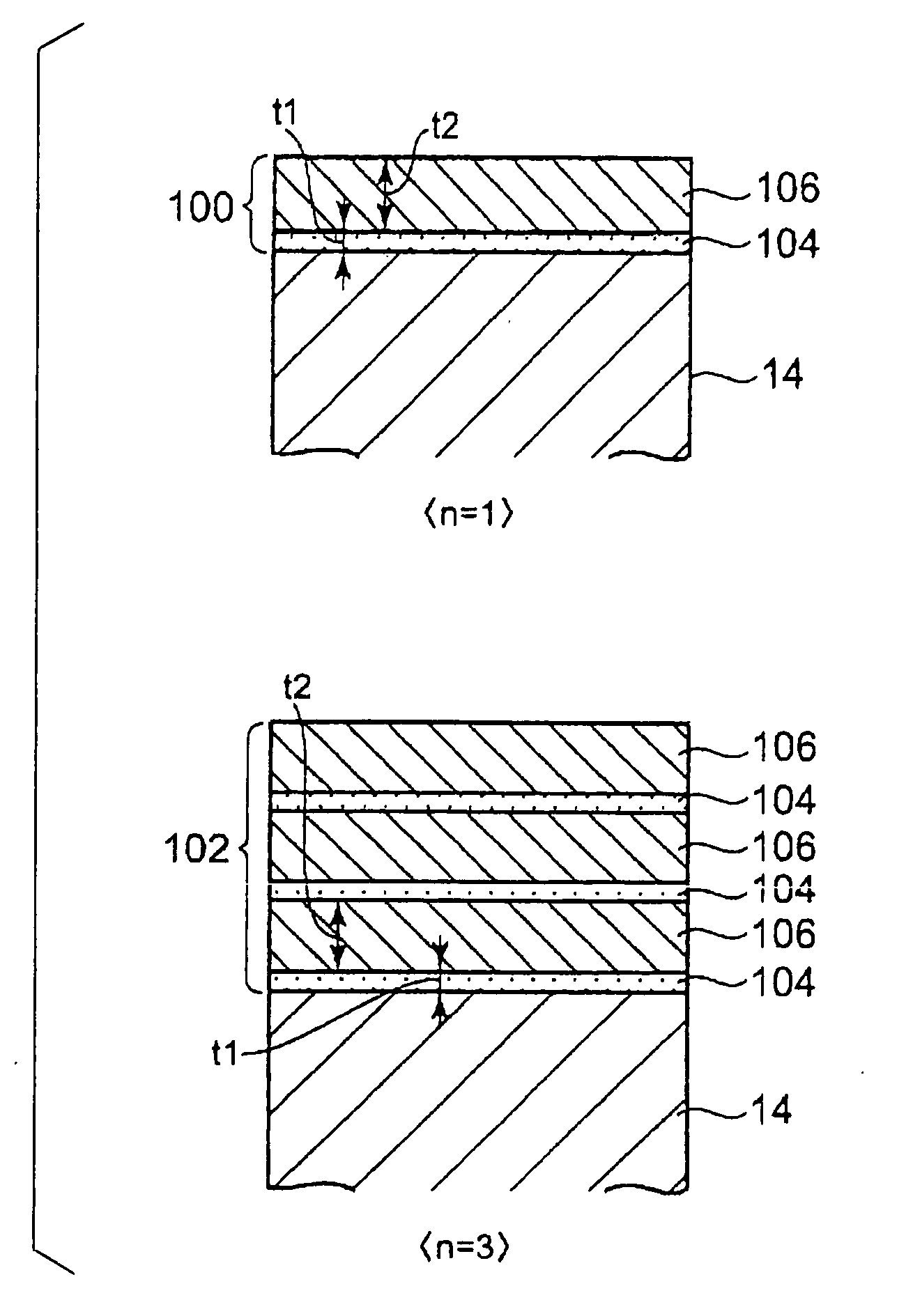
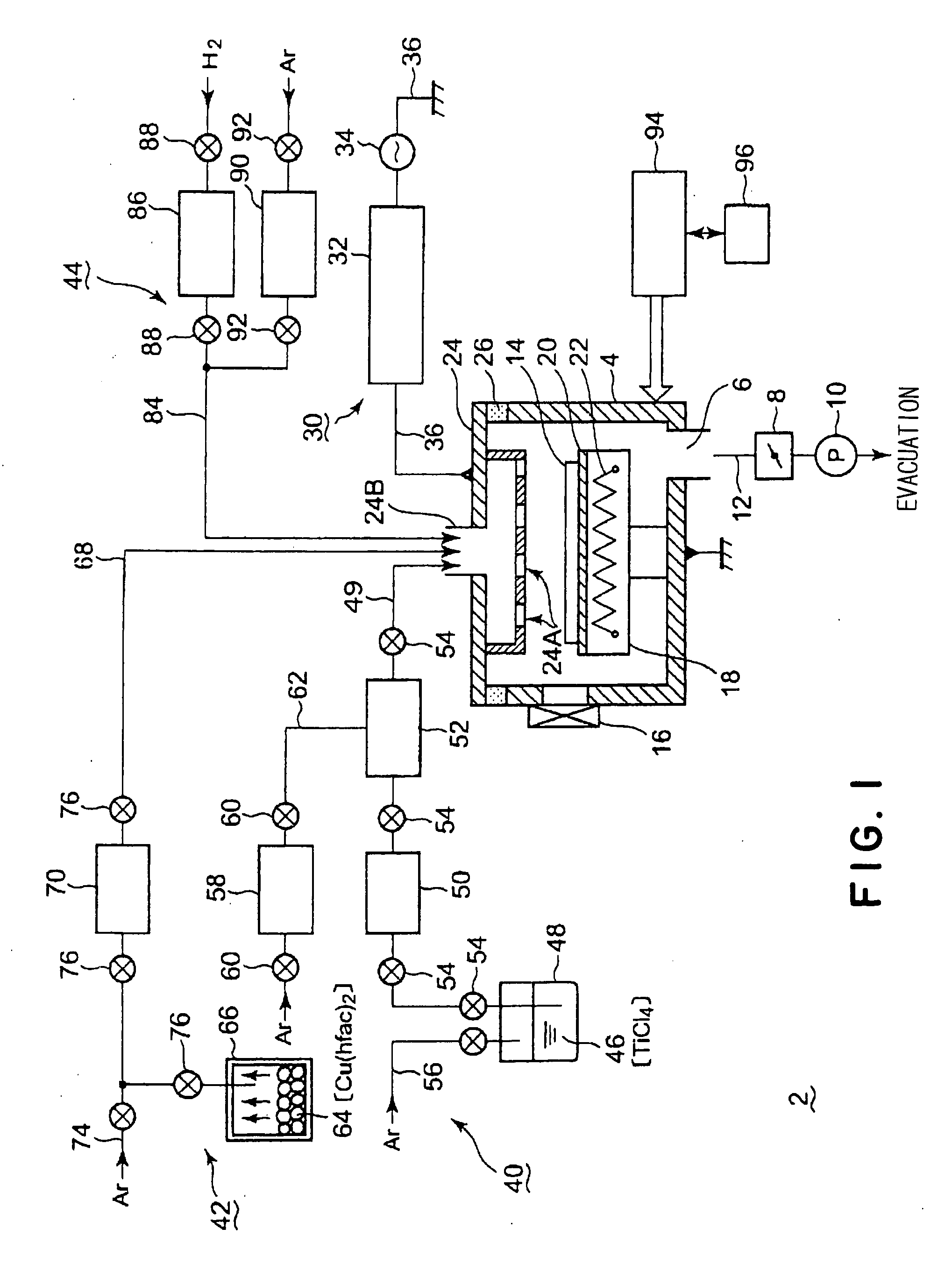
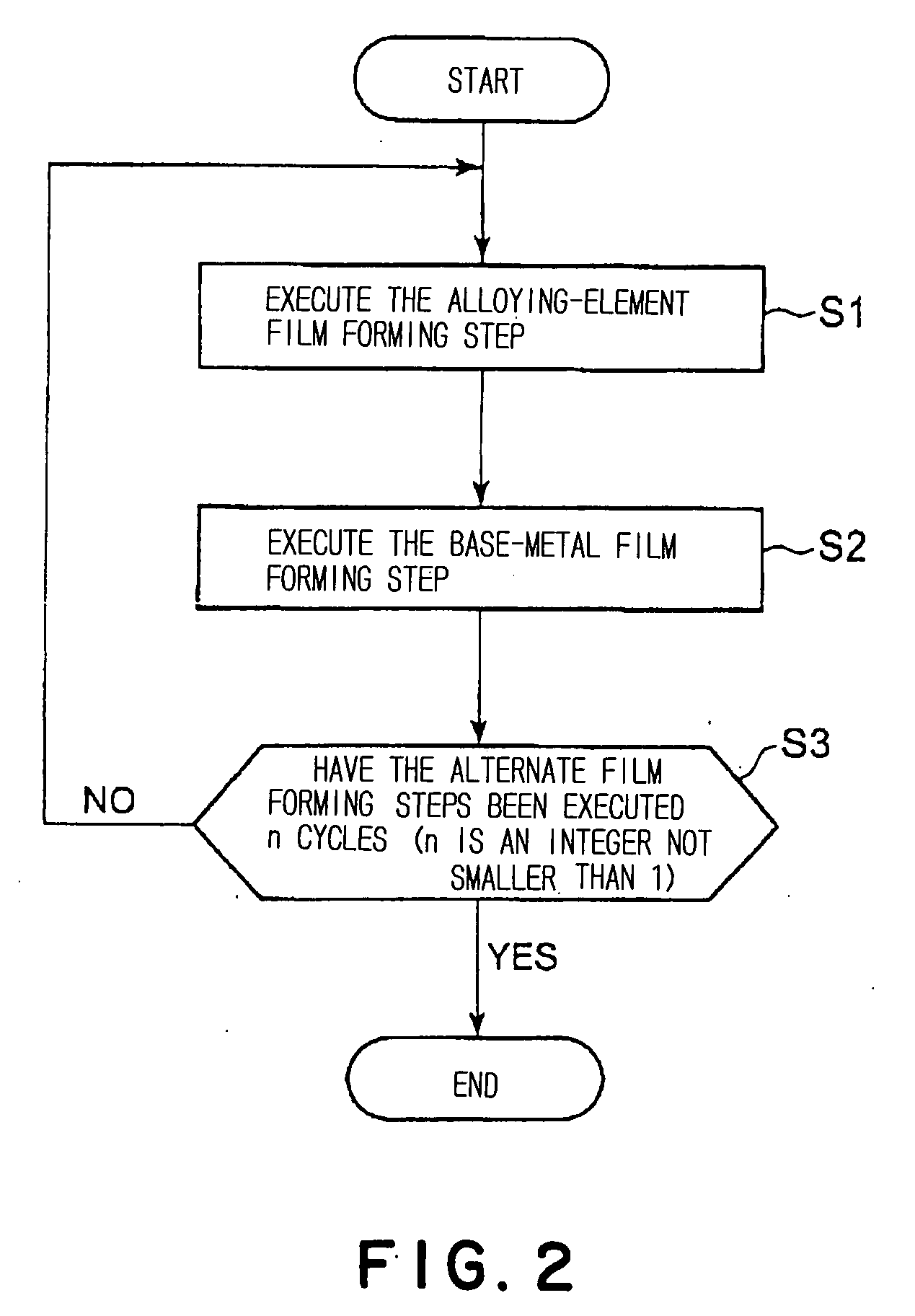
Layered Thin Film Structure, Layered Thin Film Forming Method, Film Forming System and Storage Medium
InactiveUS20080070017A1Satisfactory diffusionImprove adhesionLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMiniaturizationOptoelectronics
There is provided a layered thin film structure forming method capable of forming a layered thin film structure bonded to an underlying layer by high adhesion, of suppressing the peeling of the layered thin film structure off the underlying layer, of achieving satisfactory step coverage even under high miniaturization, and of satisfactorily diffusing an alloying element. A layered thin film structure forming method of forming a layered thin film structure by depositing a plurality of thin films on a surface of a workpiece in a processing vessel capable of being evacuated includes the steps of: forming an alloying-element film 104 of a first metal by using a source gas containing the first metal as an alloying element, and a reducing gas; and forming a base-metal film 106 of a second metal in a thickness greater than that of the alloying-element film by using a source gas containing the second metal, and a reducing gas. At least one cycle of the alternate steps of forming the alloying-element film and forming the base-metal film is executed.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS8982311B2Avoid scratchesImprove reliabilityNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A pixel electrode is formed on a TFT substrate, and a gate insulating film, an inorganic passivation film, a common electrode, and an alignment film are formed in this order thereover. A columnar spacer is formed to the counter substrate and is adapted to define a gap between the TFT substrate and the counter substrate. A through hole is formed in the gate insulating film of the TFT substrate, and the columnar spacer is disposed so as to cover a concave portion formed by the through hole. Since the area of contact between the columnar spacer and the TFT substrate is decreased, it is possible to suppress scraping of the alignment film and thus to prevent occurrence of bright spots.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
MEMS device, liquid ejecting head, and liquid ejecting apparatus
A MEMS device includes a first substrate in which a first electrode layer, a dielectric layer, and a second electrode layer are stacked on a driving region in this order; and a second substrate which is disposed to face a surface on which the dielectric layer of the first substrate is stacked. The first electrode layer and the dielectric layer extend beyond the second electrode layer toward a non-driving region separated from the driving region, a first resin having elasticity is disposed in a region including an end of the second electrode layer in an extending direction of the dielectric layer, and the first substrate and the second substrate are fixed with an adhesive in a state where the elastically deformed first resin is sandwiched therebetween.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Transmission belt
The present invention relates to a transmission belt which is provided with: a rubber layer that is formed from a vulcanized product of a rubber composition which contains a rubber component containing an ethylene-α-olefin elastomer, a filler containing silica, a vulcanizing agent containing a sulfur-based vulcanizing agent, and a curable resin containing an amino resin; and a fiber member that is in contact with the rubber layer.
Owner:MITSUBOSHI BELTING LTD
Photosensitive laminate, transfer material, patterned photosensitive laminate, method for manufacturing the same, touch panel, and image display device
ActiveUS10338470B2Satisfactory patterning propertyPeeling is suppressedPhotomechanical coating apparatusPhotosensitive material processingInorganic particleInorganic particles
An object of the invention is to provide a photosensitive laminate in which two or more layers can be collectively patterned, a transfer material, a patterned photosensitive laminate, a method for manufacturing the patterned photosensitive laminate, a touch panel, and an image display device. According to the invention, there are provided a photosensitive laminate in which a first resin layer, an interlayer, and a second resin layer are laminated on a support in this order, at least one of the first resin layer or the second resin layer includes 20 mass % or greater of inorganic particles, and exposure sensitivity of the second resin layer is higher than that of the first resin layer, a transfer material, a patterned photosensitive laminate, a method for manufacturing the patterned photosensitive laminate, a touch panel, and an image display device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Semiconductor laser
InactiveUS7142576B2Improve heat resistanceCoating can be suppressedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHydrogenActive layer
A semiconductor laser includes an active layer formed on a substrate and a pair of cladding layers sandwiching the active layer. On at least one of resonator end faces of the semiconductor laser, a first dielectric film with hydrogen added therein is provided. Between the first dielectric film and the resonator end face, a second dielectric film for suppressing the diffusion of hydrogen is provided. Even when a semiconductor laser with an end face coating film including a hydrogen-added film is exposed to high temperatures, peeling of the end face coating film and deterioration of the end face coating film can be suppressed.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
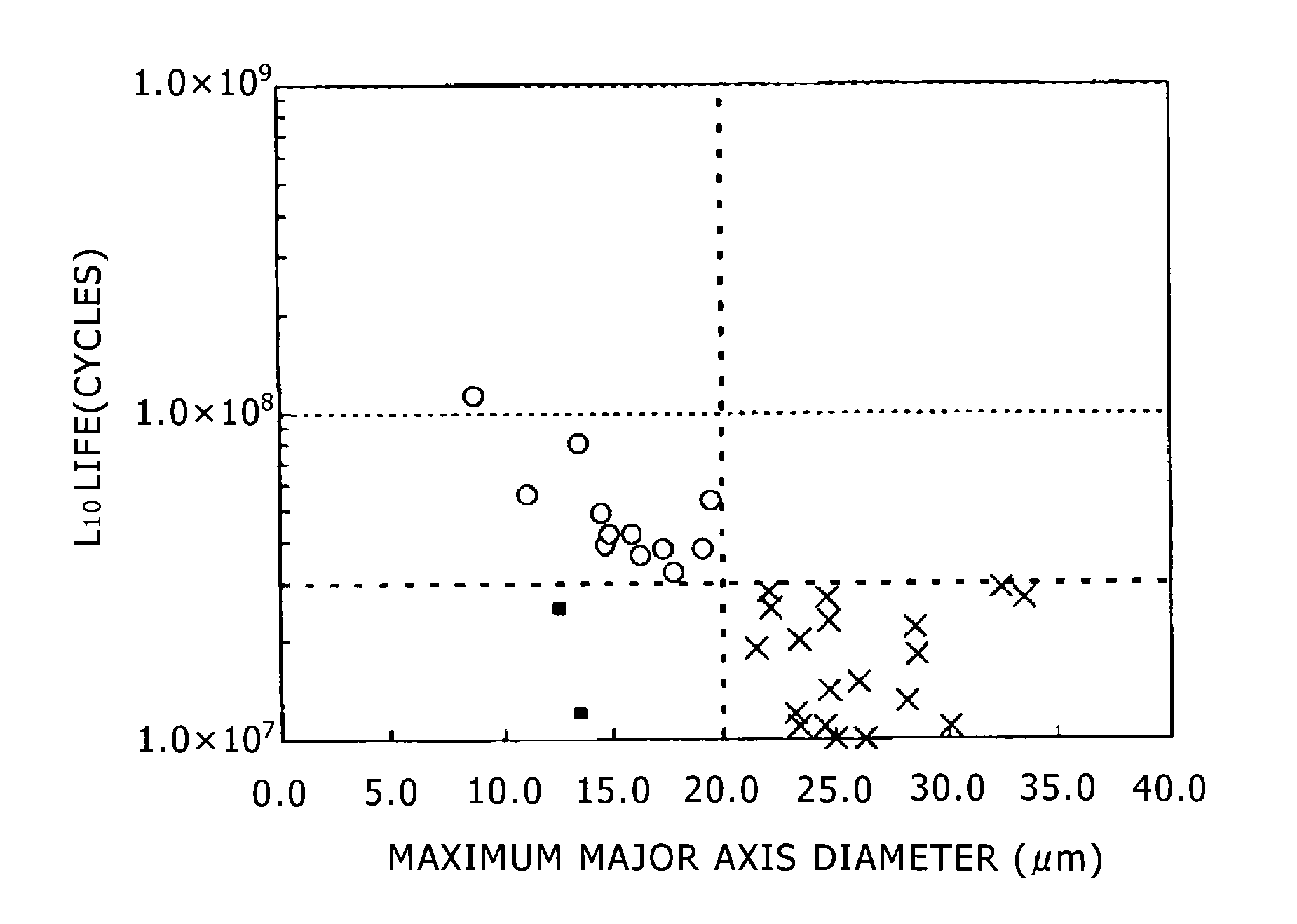
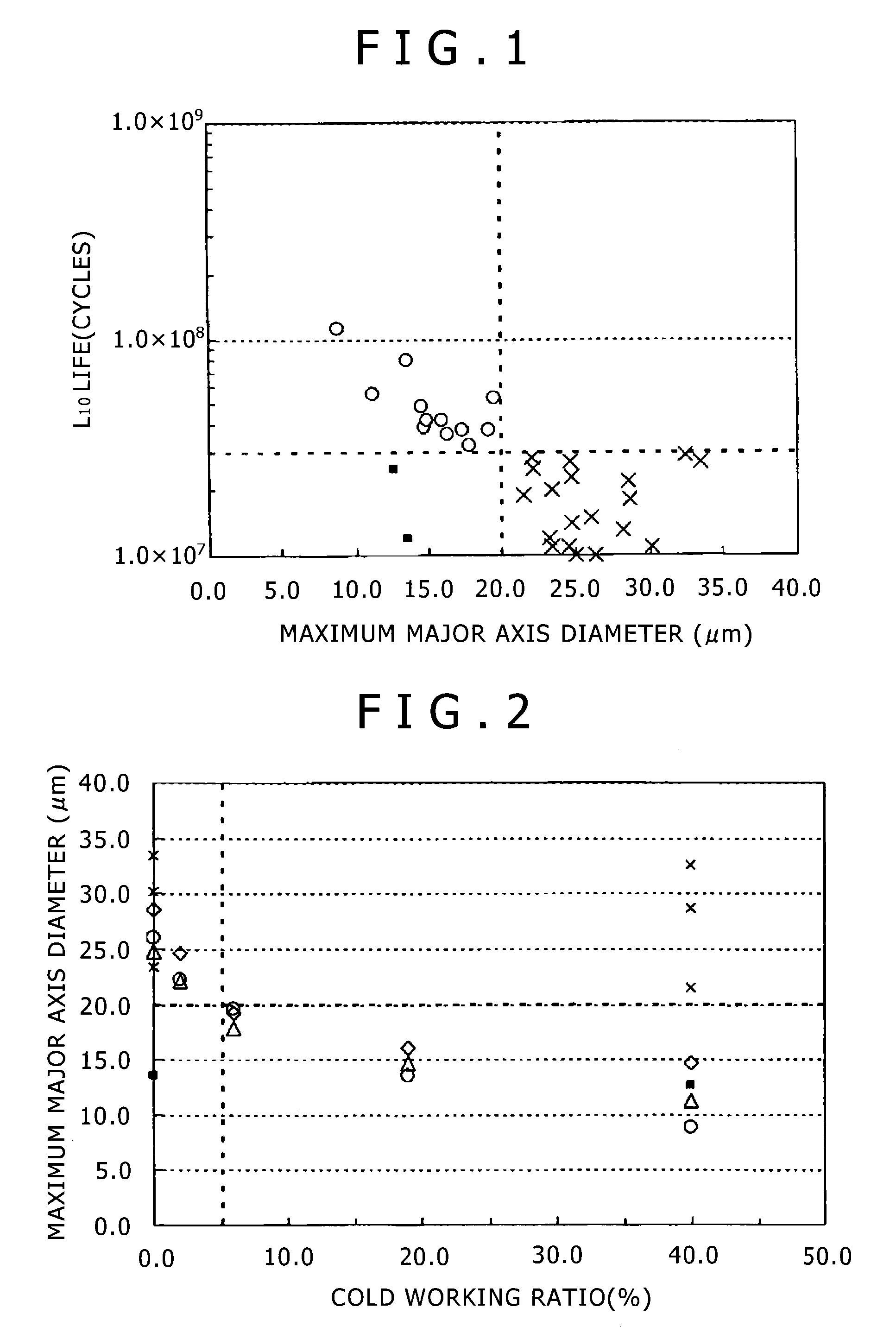
Bearing steel material with excellent rolling contact fatigue properties and a bearing part
ActiveUS9394593B2Improve fatigue performancePeeling can be suppressedFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionRolling contact fatigue
Bearing steel material according to the present invention has: a properly adjusted chemical composition; an average chemical composition of oxide-inclusions which comprises 10 to 45% of CaO, 20 to 45% of Al2O3, 30 to 50% of SiO2, up to 15% (exclusive of 0) of MnO, and 3 to 10% of MgO, with the balance being unavoidable impurities; a maximum major axis diameter of the oxide inclusions in a longitudinal section of the steel material of 20 μm or less; and a spheroidal cementite structure.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Semiconductor device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20190139906A1Reduce areaReduce the valueSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesUltrasonic bondingSemiconductor device fabrication
An object of the present invention is to obtain a semiconductor device having highly reliable bonding portions. The semiconductor device according to the present invention includes an insulating substrate on which a conductive pattern is formed, and an electrode terminal and a semiconductor element which are bonded to the conductive pattern, the electrode terminal and the conductive pattern are bonded by ultrasonic bonding on a bonding face, and the ultrasonic bonding is performed at a plurality of positions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com