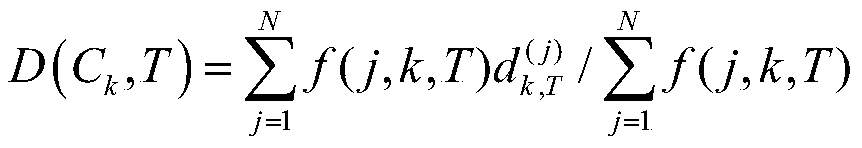Patents
Literature
40 results about "Docking (molecular)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the field of molecular modeling, docking is a method which predicts the preferred orientation of one molecule to a second when bound to each other to form a stable complex. Knowledge of the preferred orientation in turn may be used to predict the strength of association or binding affinity between two molecules using, for example, scoring functions.
Drug-protein interaction prediction model based on convolutional neural network
PendingCN113593633APredict interactionHigh computational complexityBiostatisticsDrug referencesProtein targetBinding site
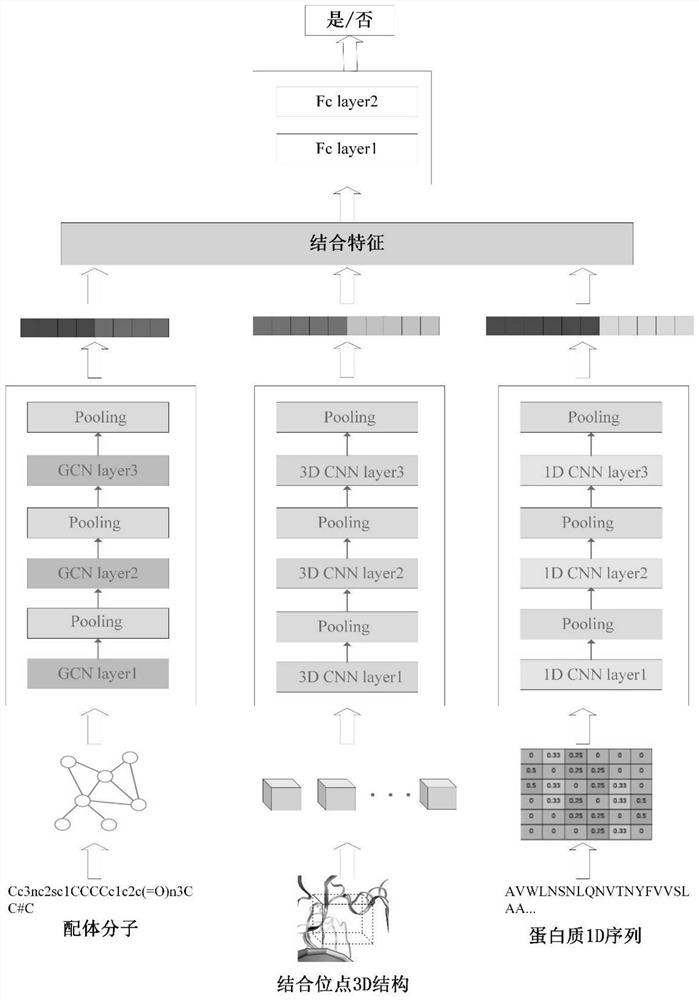
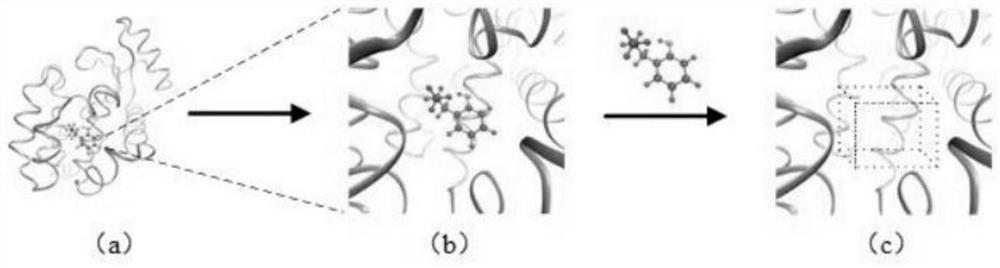
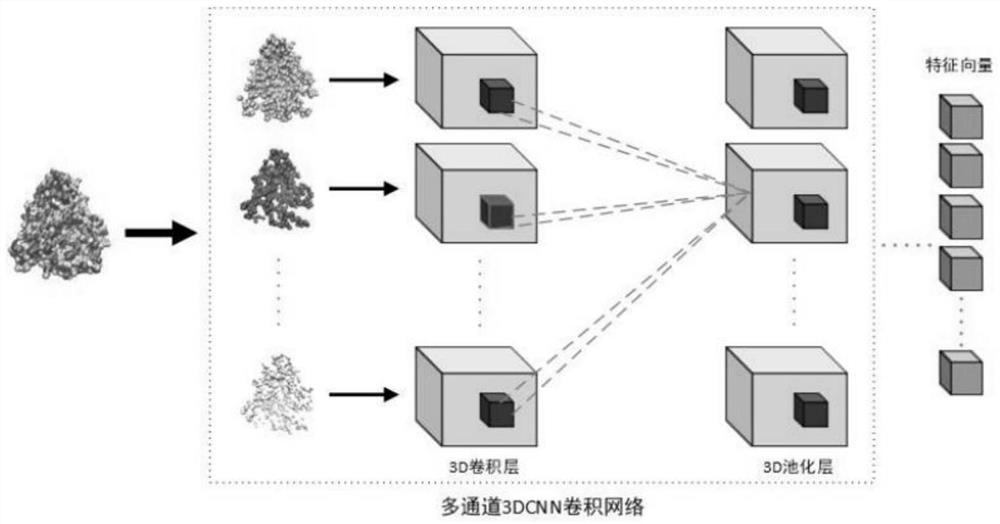
The invention provides a drug-protein interaction prediction model based on a convolutional neural network, and the construction method of the prediction model comprises the following steps: 1, constructing a bounding box descriptor for a binding site of a target protein, and extracting the spatial structure characteristics of the multi-channel binding site by using a three-layer 3D convolutional neural network; 2, based on the amino acid sequence of the target protein, extracting amino acid composition characteristics of the protein by using a three-layer 1D convolutional neural network; 3, constructing a molecular map for to-be-screened drug molecules, and extracting drug molecule features by using a three-layer map convolutional neural network; and 4, combining all the obtained features to obtain an overall feature, and inputting the overall feature into the two-layer full-connection network to predict drug-protein interaction, so that the method not only considers local features of binding sites closely related to the docking process, but also considers global features of protein, and the characteristics are used for predicting the compound-protein interaction.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Multi-source information medicine screening method based on knowledge graph
ActiveCN110851617AExtensive sources of dataImprove accuracyMolecular designSpecial data processing applicationsPharmacy medicineTheoretical computer science
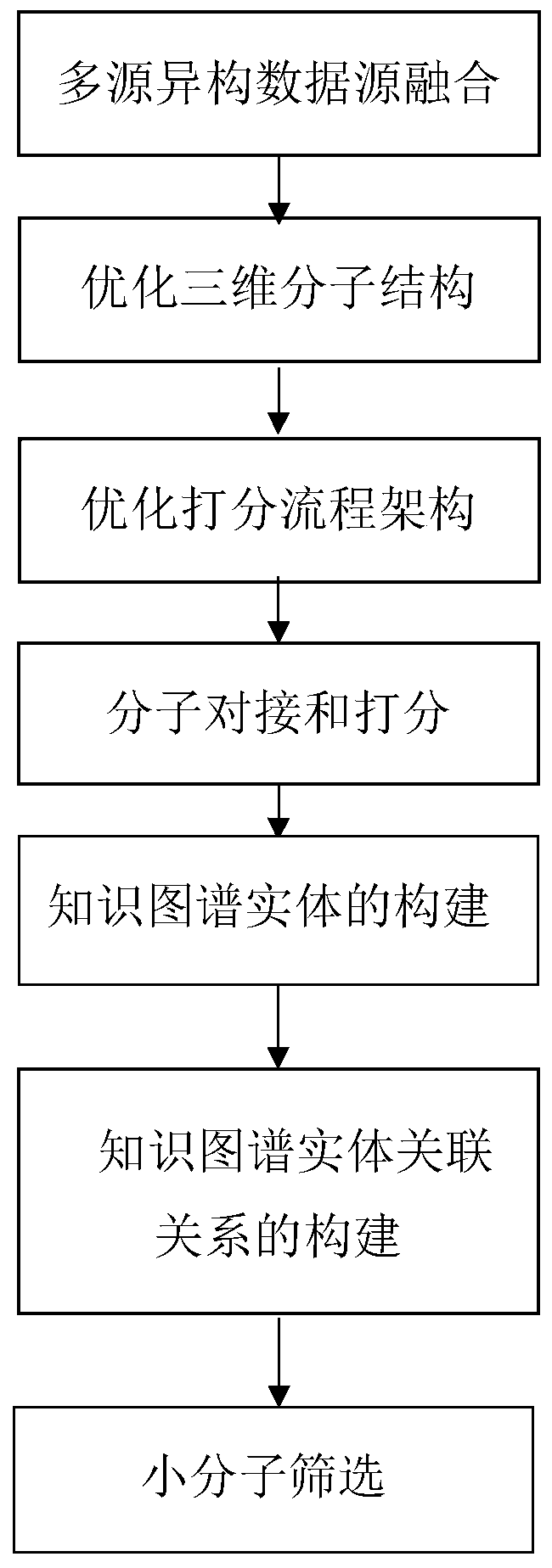
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine screening, and discloses a multi-source information medicine screening method based on a knowledge graph, which comprises the following steps of: fusing multisource heterogeneous data sources; optimizing a molecular structure; optimizing a scoring process architecture; carrying out molecular docking and scoring; constructing a knowledge graph entity; constructing a knowledge graph entity association relationship; screening retrieval. According to the method, optimized three-dimensional molecular structures, scored and screened molecularinformation and other information are organized into the knowledge graph, and loop retrieval is performed in the knowledge graph, so that drug screening is more efficient and higher in accuracy.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method of predicting protein-ligand docking structure based on quantum mechanical scoring
ActiveUS20110246166A1Accurately carry-outAccurately and quickly explainChemical property predictionAnalogue computers for chemical processesProtein–ligand dockingBiology
Provided is a protein-ligand docking prediction method based on quantum mechanical scoring. The method includes evaluating a protein-ligand docking structure by using a molecular mechanical energy-based scoring function and reevaluating the protein-ligand docking structure by using a rescoring function obtained by combining a quantum mechanical factor with the molecular mechanical energy-based scoring function. In accordance with the method using the quantum mechanical scoring, it is possible to more accurately carry out modeling than conventional force field-based methods.
Owner:QUANTUM BIO SOLUTIONS
Screening method of TTR (transthyretin) small-molecule inhibitors
InactiveCN103425859AImprove reliabilityShorten the development and research cycleSpecial data processing applicationsDiseasePharmacophore
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for screening pharmaceutically active compounds from traditional Chinese medicines and acting agent
PendingCN112063708AImprove screening efficiencyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseDrug target
The invention provides a method for screening pharmaceutically active compounds from traditional Chinese medicines and an acting agent. The method comprises the following steps: determining a key signal pathway related to diseases, enabling different traditional Chinese medicine extracts to act on cell lines related to the diseases, and quantitatively analyzing the change condition of a transcription spectrum in cells based on a characteristic gene expression profile, so as to determine the adjusting effect of the different traditional Chinese medicine extracts on the key signal pathway, and selecting traditional Chinese medicines which have effects on the key signal pathway related to the diseases; collecting component compounds of the traditional Chinese medicines from different traditional Chinese medicine databases, and screening potential active compounds from the component compounds according to oral bioavailability and medicine similarity; screening a medicine target which can be used as a medicine effect in the key signal pathway; and further screening the potential active compounds by utilizing the medicine target to obtain the pharmaceutically active compounds. The methodprovided by the invention is a method for screening medicines or small molecular compounds on a large scale on a transcription level by combining a high-throughput medicine screening platform and a second-generation sequencing technology with molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation, is high in screening efficiency, and provides a new idea for medicine screening.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
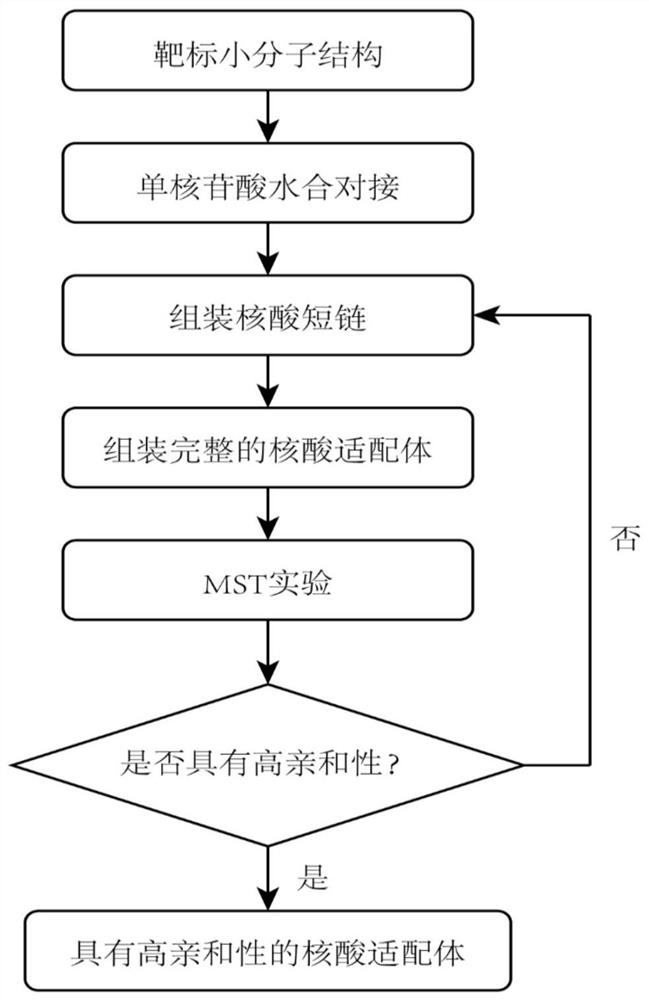
Aptamer design method based on single-nucleotide molecular docking
ActiveCN112210587AConformational stabilityThe experiment cycle is longMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerNucleotide
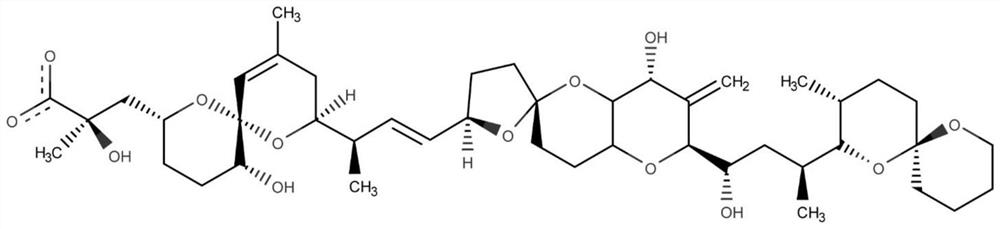
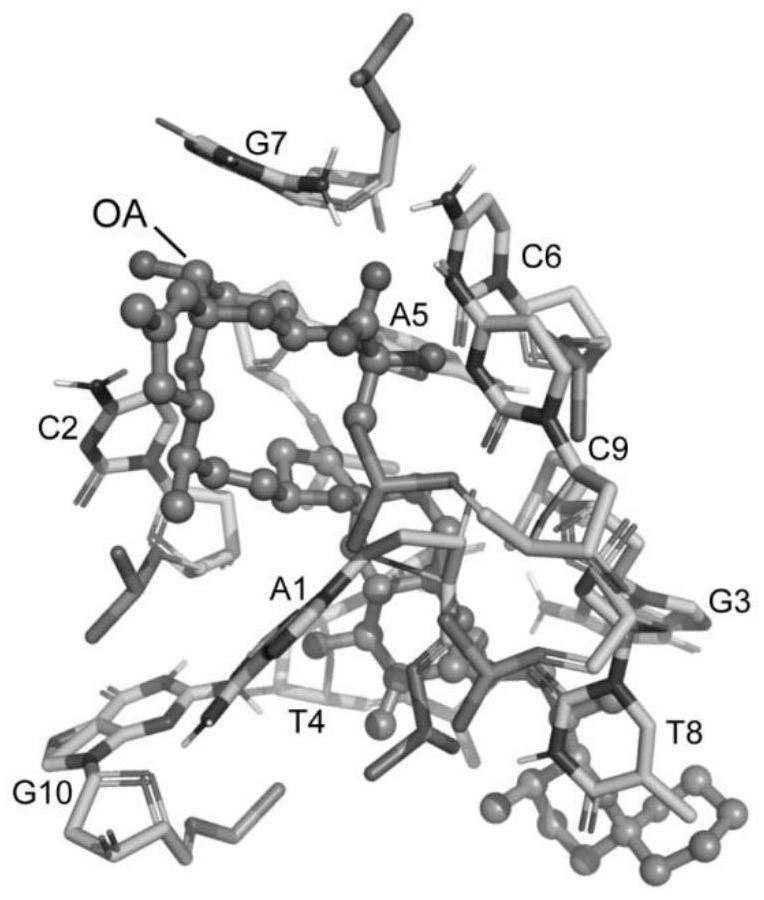
The invention belongs to the technical field of aptamer design, and particularly relates to an aptamer design method based on single-nucleotide molecular docking. Starting from an experimental structure of a target small molecule, positions of nucleotides combined around the target small molecule are obtained through hydration docking; then, the discrete nucleotides are assembled into a complete aptamer; and finally, the binding capacity of the designed aptamer and the target small molecule is detected by adopting an MST experiment. The aptamer design method in the invention has been used in the design of aptamers of toxin small molecule okadaic acid (OA); the toxin is a widely distributed marine biological toxin, and can cause diarrhea type shellfish poisoning, so that the detection of OAin marine products is of great significance to food safety; an aptamer OA-D1 targeting OA is obtained by design through a calculation method; the MST experiment verifies that the equilibrium dissociation constant of the aptamer and OA is 75.6 nM; and therefore, the calculation design method is reasonable and effective.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Machine learning and molecular simulation based methods for enhancing binding and activity prediction
Systems and methods for molecular simulation in accordance with embodiments of the invention are illustrated. One embodiment includes a method for predicting a relationship between a ligand and a receptor. The method includes steps for identifying a plurality of conformations of a receptor, computing docking scores for each of the plurality of conformations and a set of one or more ligands, and predicting a relationship between the set of one or more ligands and the plurality of conformations of the receptor.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
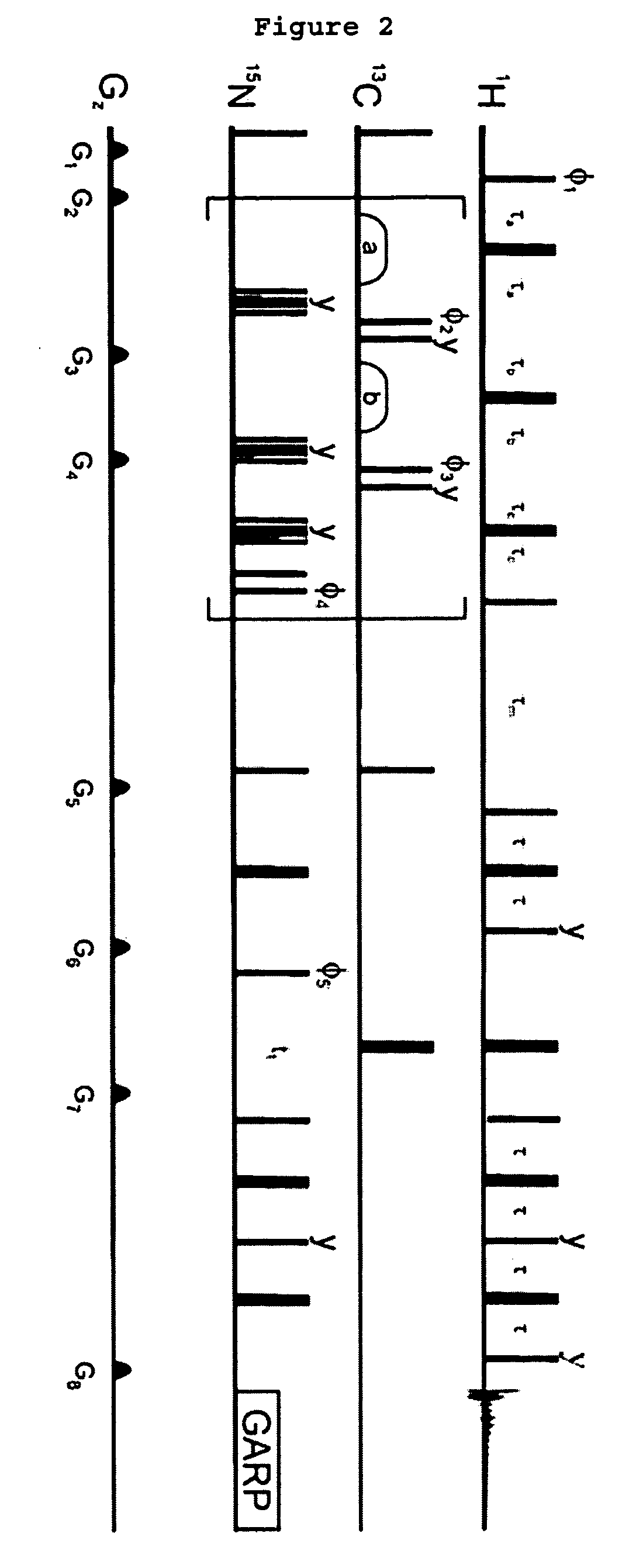
Methods and devices for characterizing macromolecular complexes using isotope labeling techniques
InactiveUS20060183157A1Reduces H densityMagnetic measurementsBiological testingIsotopic labelingSpectroscopy
A method for characterizing interactions in macromolecular complexes, such as protein-protein or protein-ligand complexes, by selective isotopic labeling of the target molecule to reduce the 1H density in a selected spectral region; by irradiating the target; and by monitoring the polarization using filtered nuclear Overhauser spectroscopy (NOESY) and / or by performing selective saturation transfer experiments to determine the docking potential of the macromolecular complex.
Owner:COWBURN DAVID +3
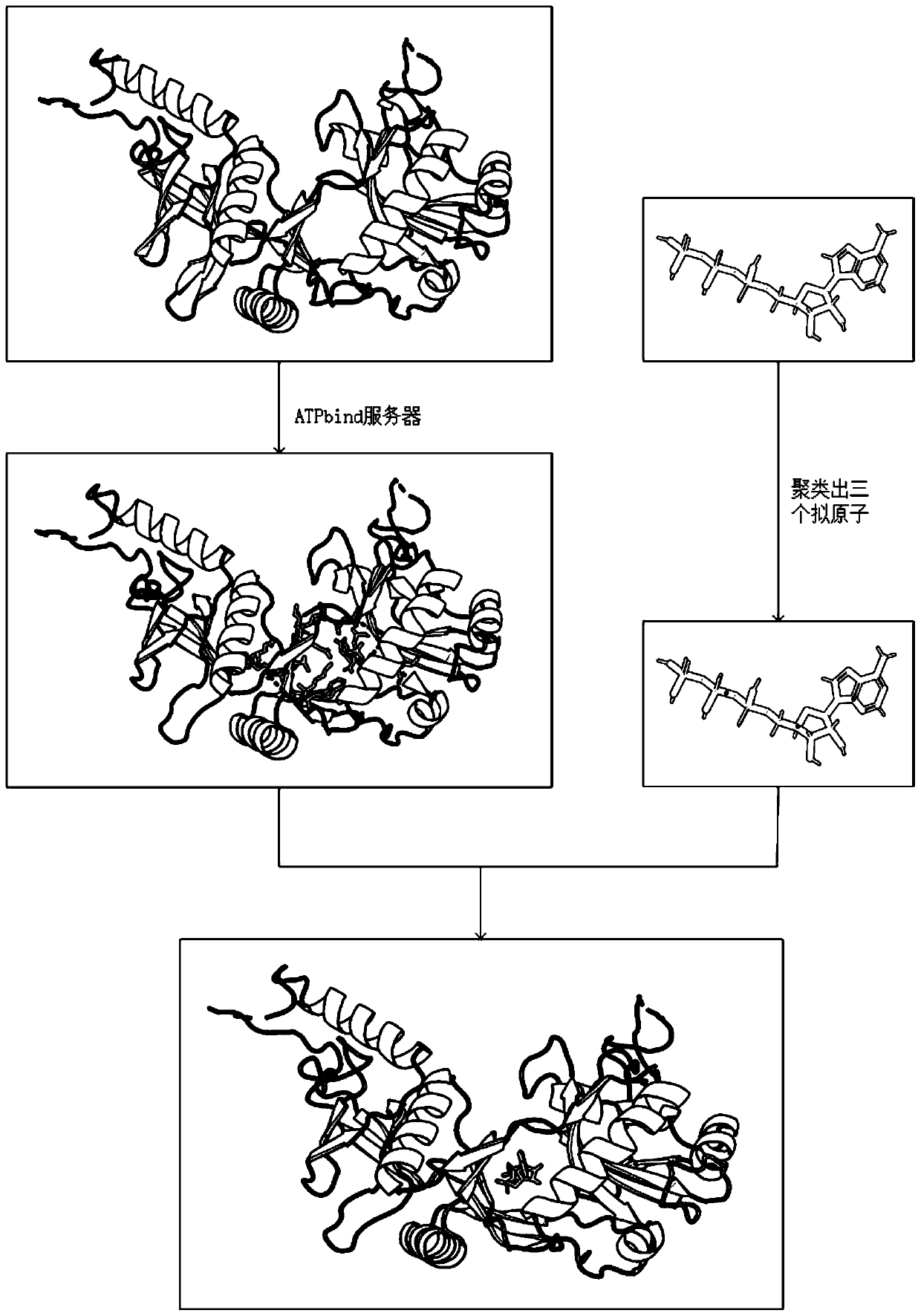
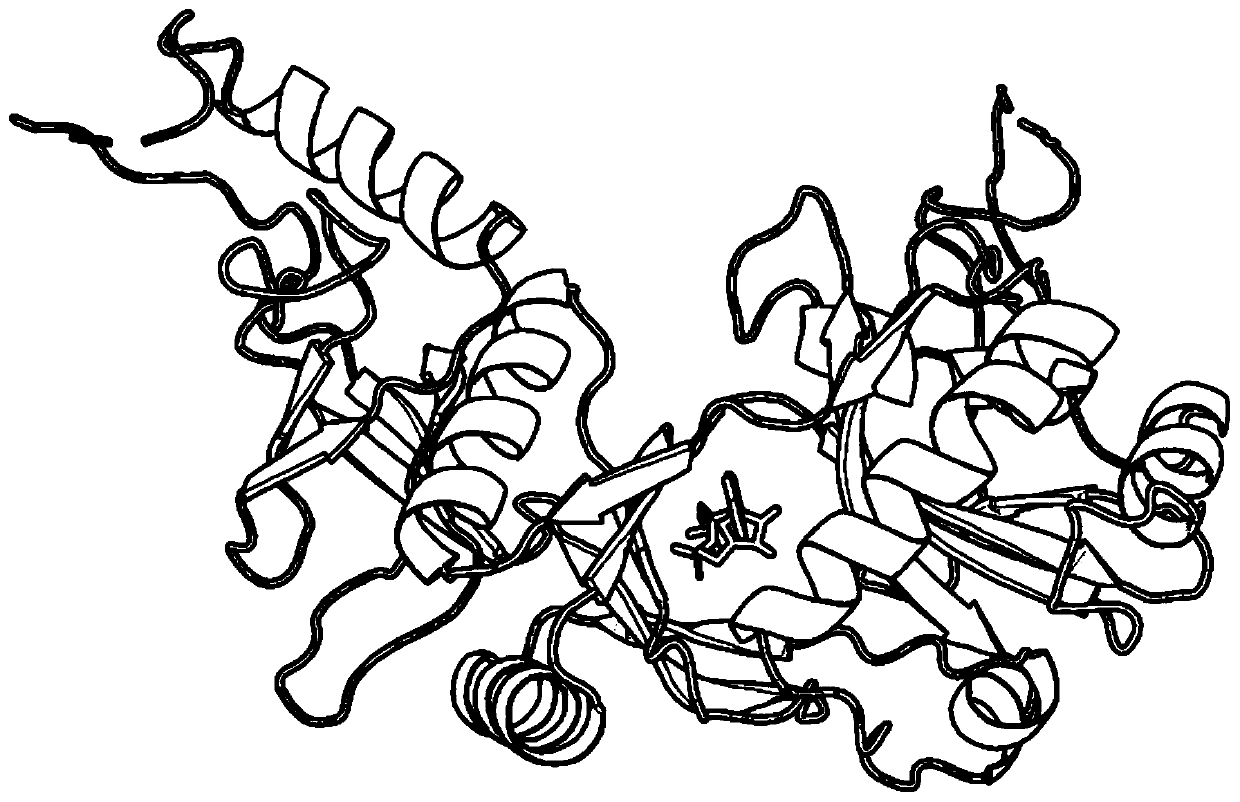
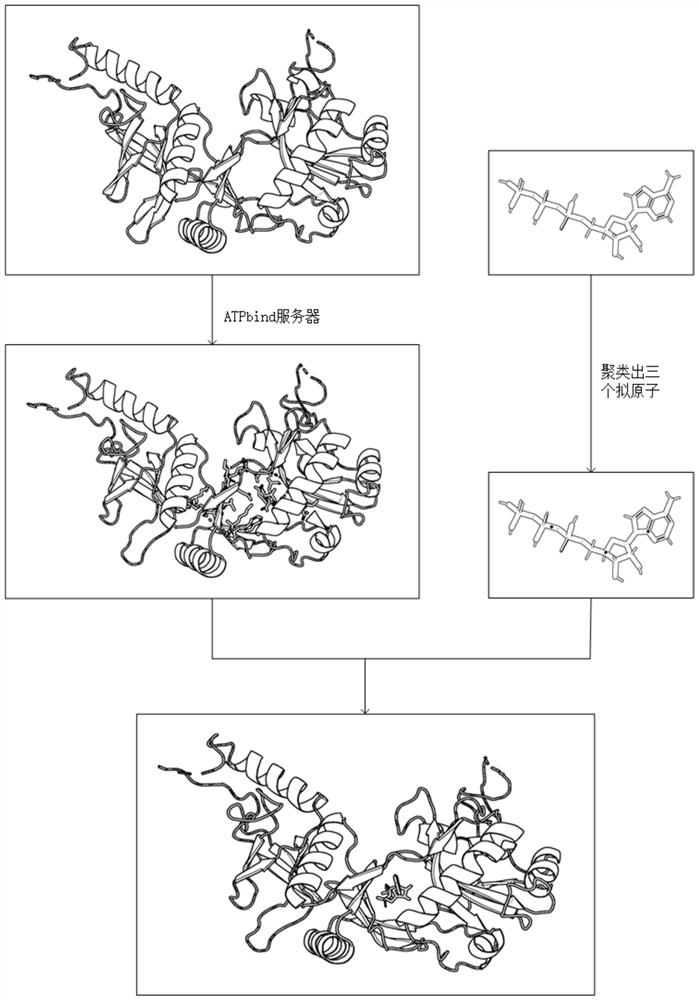
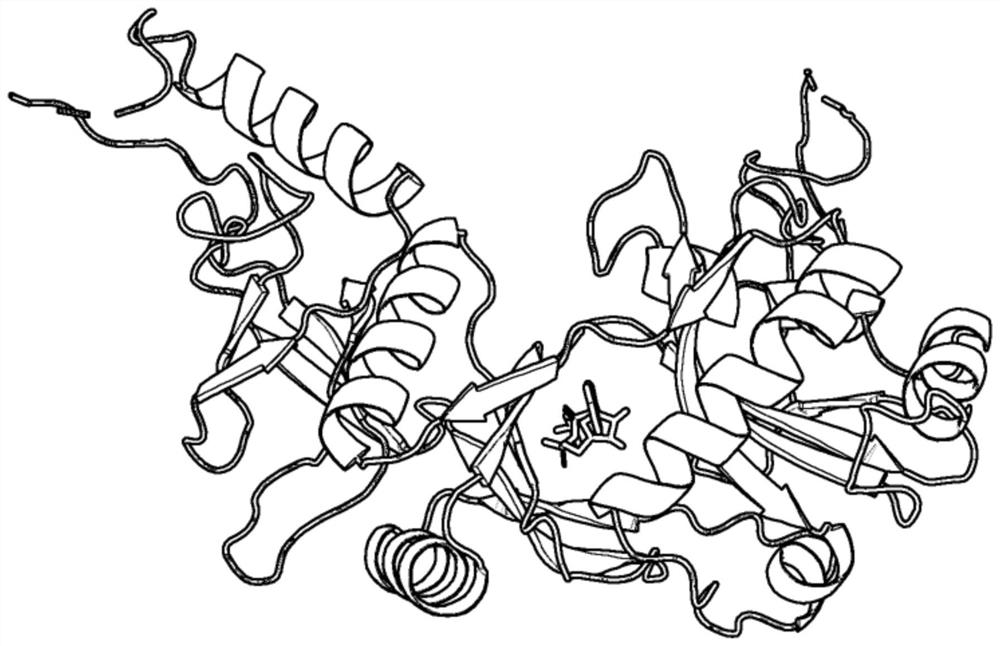
Differential evolution-based protein ATP docking method
ActiveCN110197700AImprove forecast accuracyReduce computational costBiostatisticsArtificial lifeSpatial structureComputer science
Disclosed is a differential evolution-based protein ATP docking method. First, an ATPbind server is used to predict protein-ATP binding residue information, which improves the prediction accuracy of acomplex molecular spatial structure. Then, the original protein-ATP structure prediction problem is transformed into an optimal problem of searching for the optimal individual through the design of the individual population, which reduces the computational cost. Finally, by the differential evolution algorithm is used to search for the optimal individual, which improves the prediction accuracy ofthe protein-ATP complex structure. The invention provides a differential evolution-based protein ATP docking method with low computational cost and high search efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
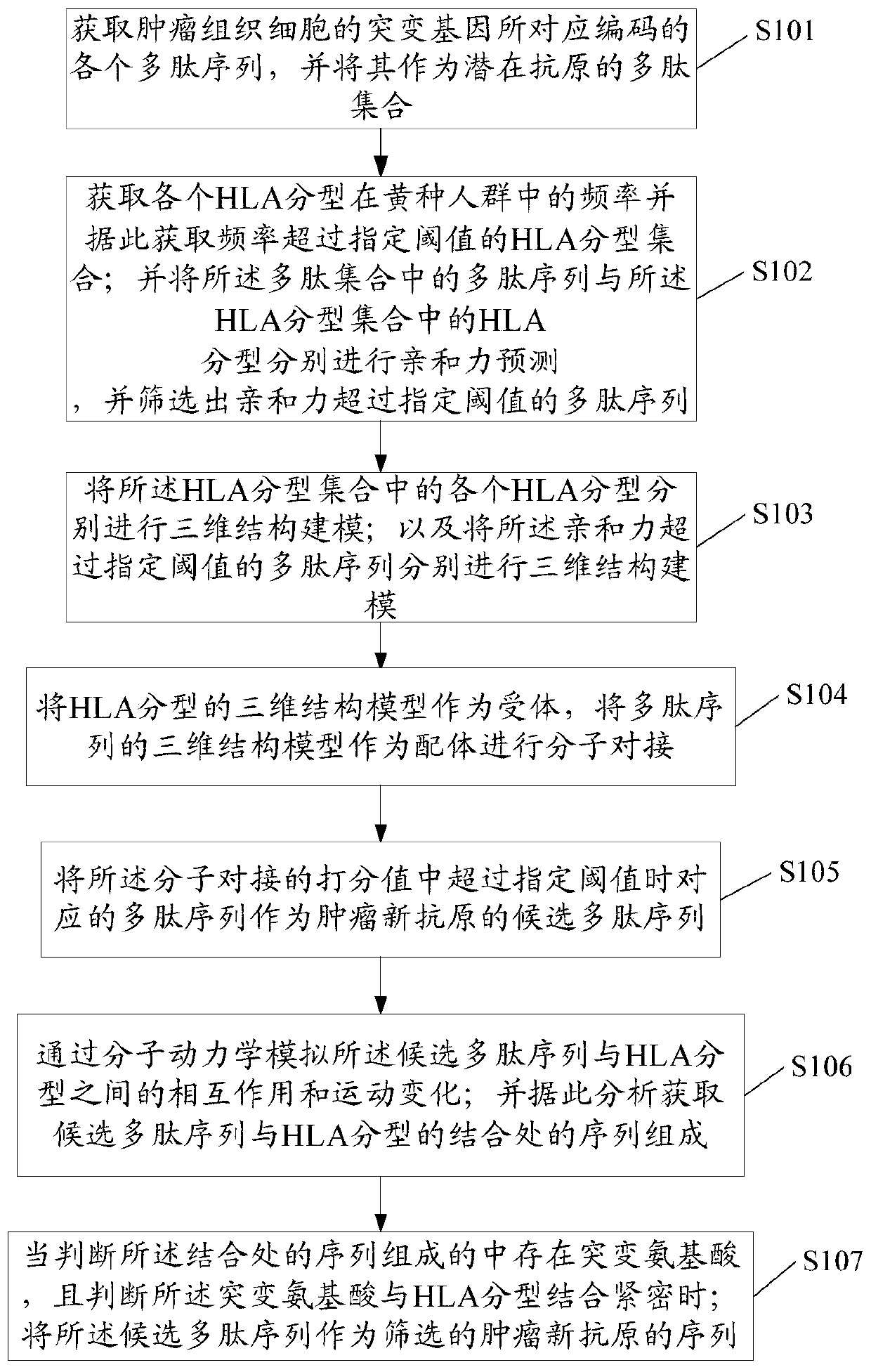
Method for screening tumor neoantigen based on HLA typing and structure
ActiveCN110675913AReduce the number of experimentsSave moneyInstrumentsMolecular structuresAntigenReceptor
The invention provides a method for screening a tumor neoantigen based on HLA typing and structure, including: A, obtaining an encoded polypeptide sequence corresponding to a mutant gene of a tumor tissue cell and using the same as a polypeptide collection of a potential antigen; B, obtaining an HLA typing collection whose HLA typing frequency in the yellow population exceeds a specified threshold; performing affinity prediction on the polypeptide collection and the HLA typing collection, and selecting out a polypeptide sequence with an affinity exceeding the specified threshold; C, 3D structurally modeling the HLA in the HLA typing collection and 3D structurally modeling the polypeptide sequence; D, performing molecular docking by using the HLA as a receptor and using the polypeptide sequence as a ligand; E, using the polypeptide sequence corresponding to a score exceeding the specified threshold as a candidate polypeptide sequence of a tumor neoantigen. The screening method of the present application facilitates subsequent targeted experiments based on this, can greatly reduce the number of experiments, and saves time, labor, and cost.
Owner:BETA PHARM SUZHOU LTD
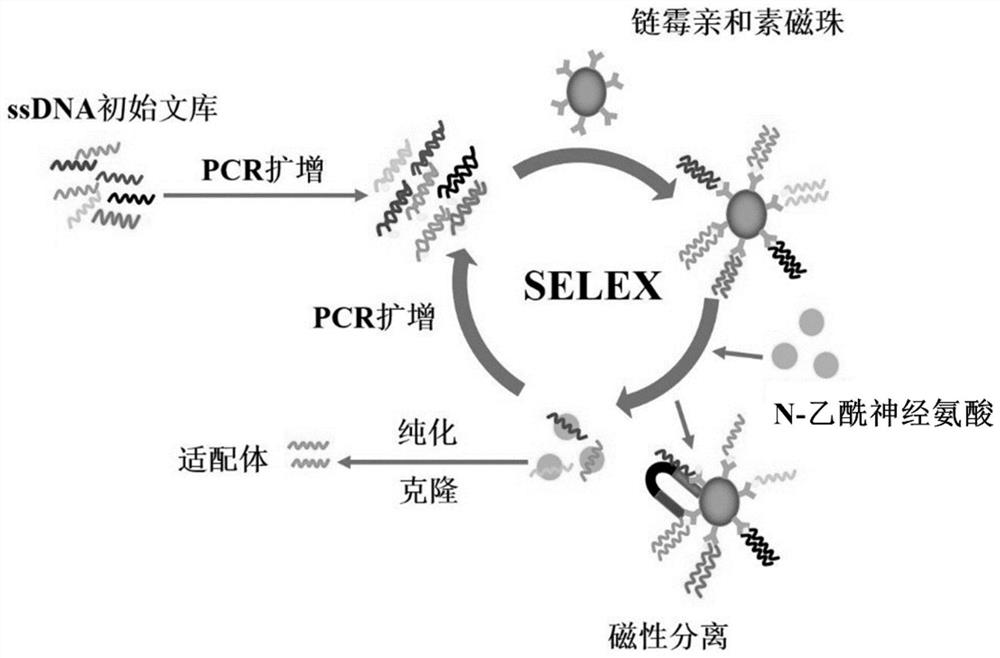
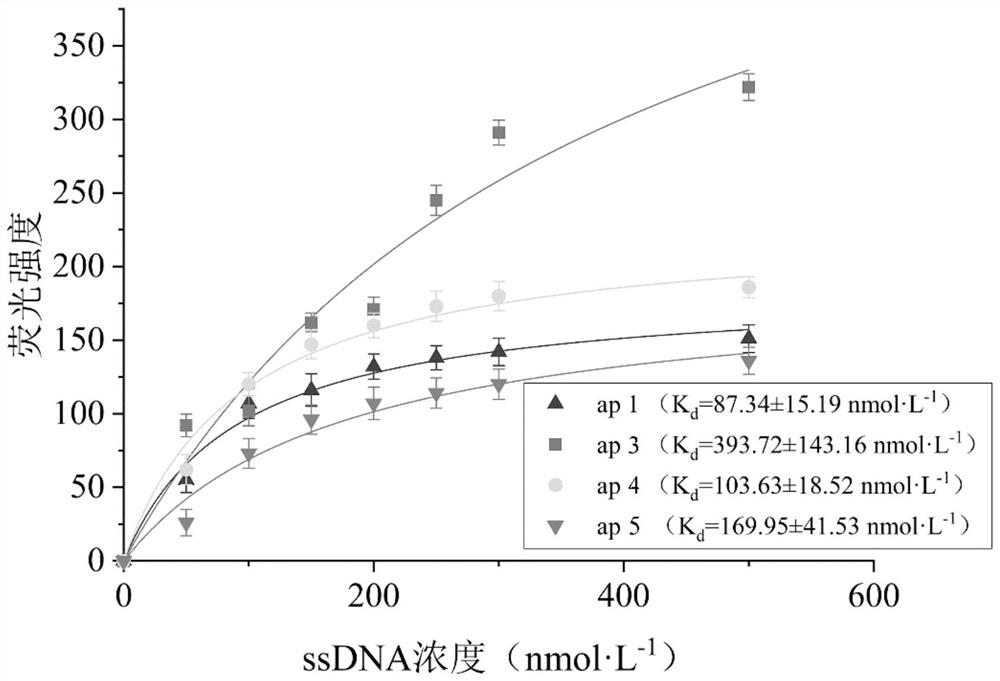
ssDNA aptamer capable of specifically recognizing N-acetylneuraminic acid and application thereof
ActiveCN113151283AImprove stabilityHigh affinityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerMagnetic Bead Technology
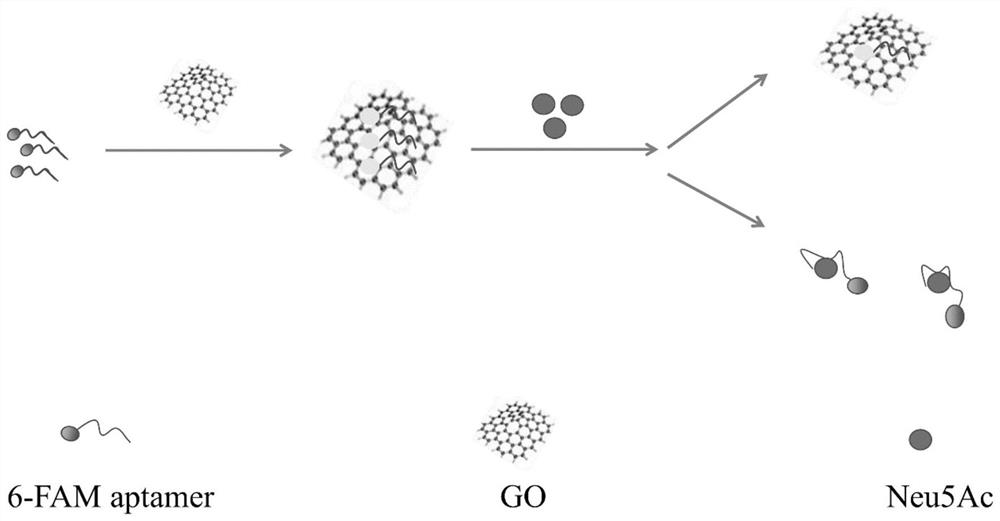
The invention relates to an ssDNA aptamer capable of specifically recognizing N-acetylneuraminic acid and application thereof. According to the invention, 4 ssDNA aptamer sequences capable of being highly specifically combined with Neu5Ac are obtained through screening of a magnetic bead-SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment) technology, and sequence ap1 has the highest affinity and specificity; and moreover, sequence ap1 is stable in structure. On the basis of sequence ap1, the sequence is truncated according to a secondary structure and a molecular simulation docking result to obtain one aptamer ap2 with the sequence length of 21nt, and the affinity is improved compared with that before truncation. The ssDNA aptamer disclosed by the invention is relatively high in binding specificity and affinity with Neu5Ac, and is high in sensitivity when being applied to Neu5Ac detection.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for predicting ligand-protein interaction based on quantum calculation
ActiveCN114446383AAvoid difficultiesOvercoming the inability to train for large problemsQuantum computersMolecular designProtein moleculesBinding site
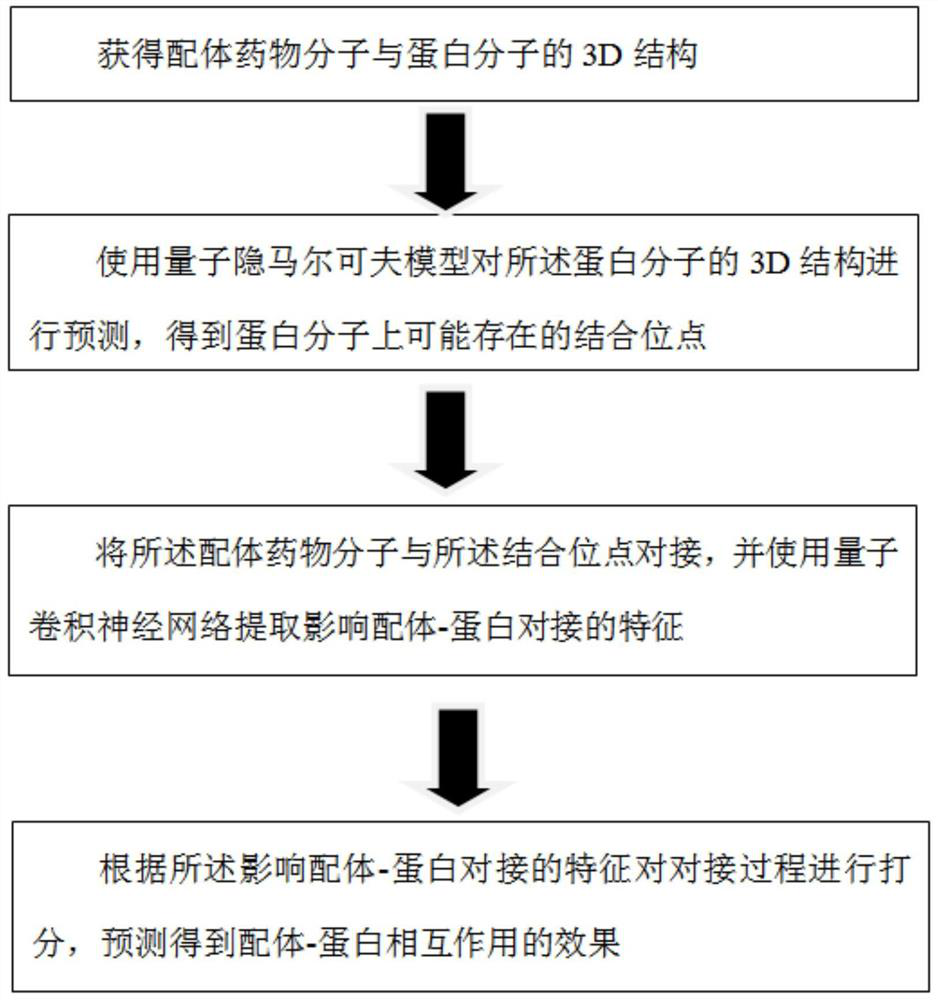
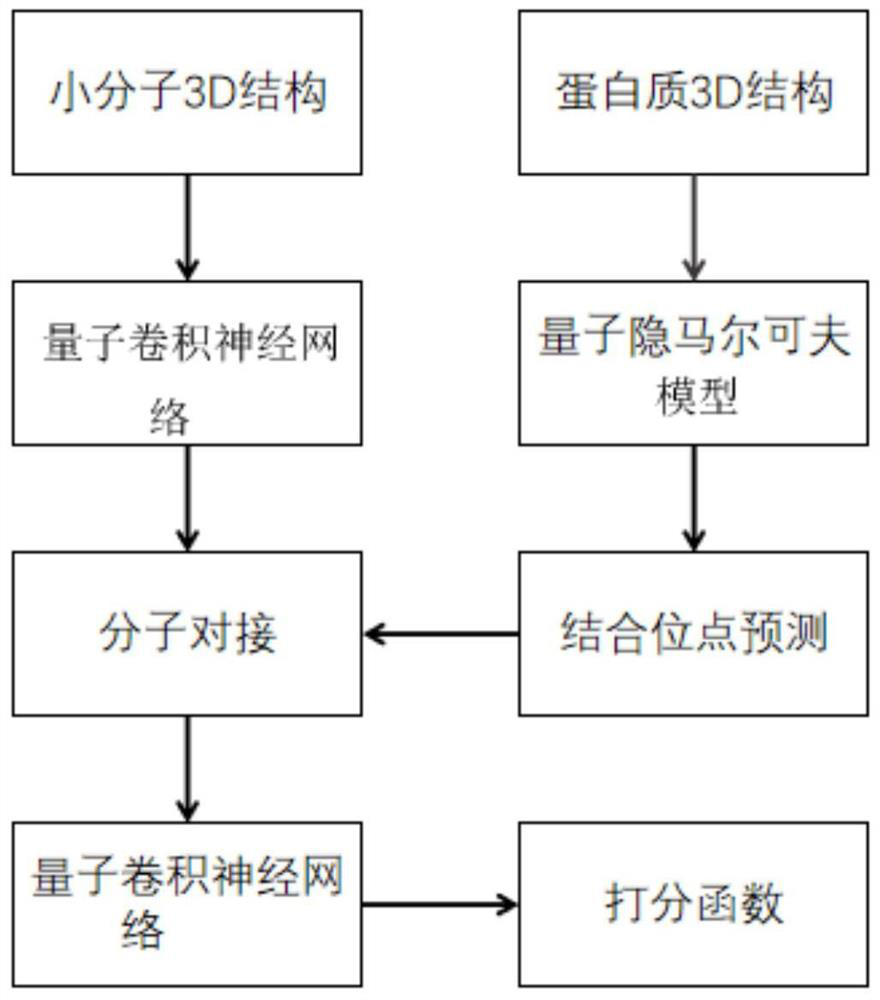
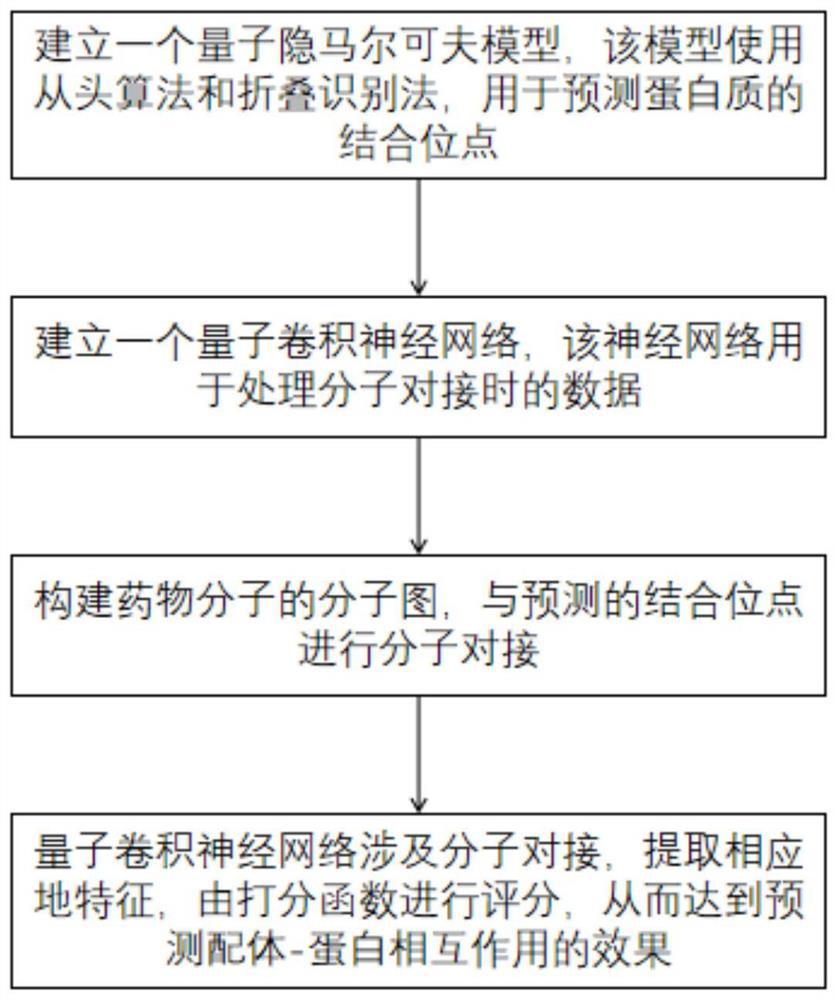
The invention discloses a ligand-protein interaction prediction method based on quantum computing, and belongs to the field of quantum computing and computational biology, and the ligand-protein interaction prediction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a 3D structure of a ligand drug molecule and a protein molecule; predicting the 3D structure of the protein molecule by using a quantum hidden Markov model to obtain a binding site possibly existing on the protein molecule; docking ligand drug molecules with binding sites, and extracting characteristics affecting ligand-protein docking by using a quantum convolutional neural network; the docking process is scored according to the characteristics affecting ligand-protein docking, and the ligand-protein interaction effect is obtained through prediction. Related information of molecular docking is described based on the quantum convolutional neural network, the quantum hidden Markov model is used for predicting binding sites possibly existing on receptor protein, synchronous prediction of molecular docking and protein structures is achieved, meanwhile, quantum calculation is combined with the field of biological medicine, and the difficulty of protein 3D structure prediction is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Drug virtual screening method and system based on receptor and ligand
PendingCN113808683AImprove training accuracyImprove accuracyComputational theoretical chemistryChemical machine learningVirtual screeningReceptor
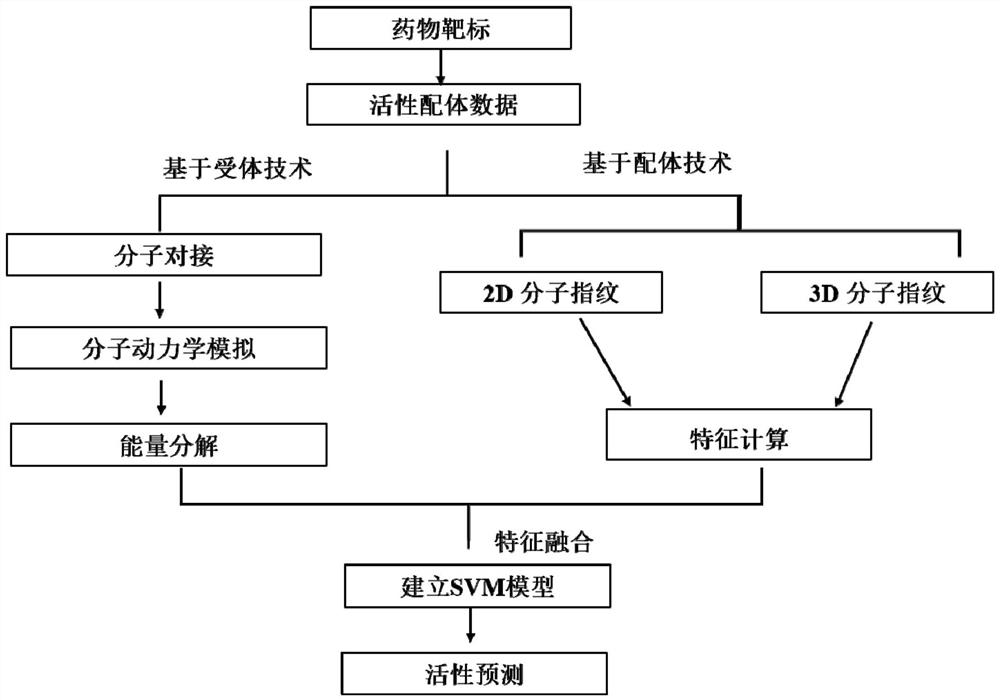
The invention relates to a drug virtual screening method and system based on receptors and ligands. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining activity data of a target receptor, the activity data of the receptor being used for molecular docking; (2) obtaining ligands of the target receptor and activity data of the ligands to construct a ligand structure library; (3) processing the activity data of the ligands in the ligand structure library to obtain molecular fingerprints of the ligands; (4) carrying out molecular docking on the target receptor and ligands in the ligand structure library, then carrying out molecular dynamics simulation, and then carrying out energy decomposition to obtain an energy decomposition value; (5) selecting the molecular fingerprints and the energy decomposition values in proportion for feature fusion, and establishing a model according to a machine learning algorithm; and (6) performing virtual drug screening by using the model. The drug screening method and system are low in cost and high in efficiency, and have wide application prospects in the fields of drug activity prediction, structure optimization and design.
Owner:深圳市绿航星际太空科技研究院
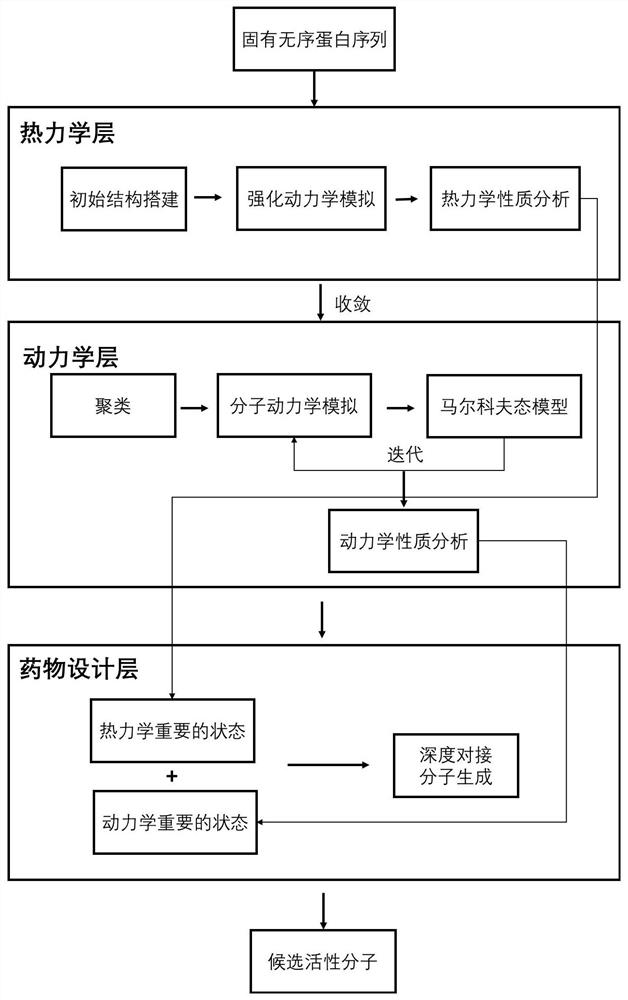
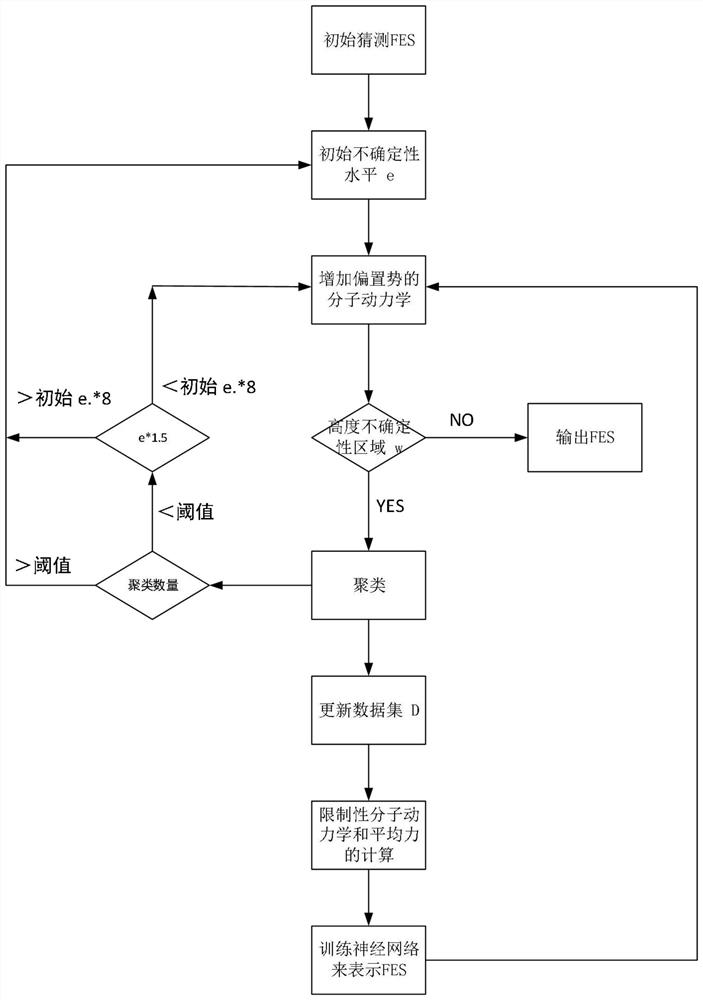
Drug molecule design method and device for inherent disordered protein
ActiveCN113990401AImprove sampling efficiencyIncrease spaceMolecular designComputational theoretical chemistryAmino acidMolecular dynamics
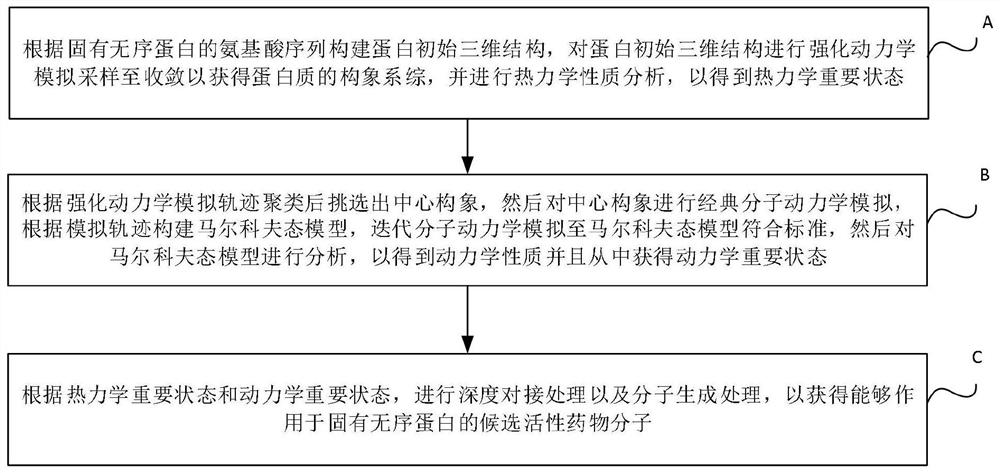
The invention discloses a drug molecule design method and device for inherent disordered protein. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a protein initial three-dimensional structure according to an amino acid sequence of inherent disordered protein, performing enhanced dynamic simulation sampling on the protein initial three-dimensional structure until convergence to obtain a conformation ensemble of the protein, and performing thermodynamic property analysis to obtain a thermodynamic important state; selecting a central conformation after intensified dynamics simulation trajectory clustering, then carrying out classical molecular dynamics simulation on the central conformation, constructing a Markov state model according to a simulation trajectory, carrying out iterative molecular dynamics simulation until the Markov state model meets a standard, and then analyzing the Markov state model, obtaining kinetic properties and kinetic important states therefrom; and performing deep docking treatment and molecular generation treatment according to the thermodynamic important state and the dynamic important state, so as to obtain candidate active drug molecules capable of acting on the inherent disordered protein.
Owner:北京深势科技有限公司
Sensitivity analysis algorithm for computer-aided pilot drug optimization design
InactiveCN111415703AThe result is accurateNot easy to make mistakesMolecular designCheminformatics data warehousingSensitive analysisAlgorithm
The invention discloses a sensitivity analysis algorithm for computer-aided pilot drug optimization design. The method comprises receptor-based drug design and ligand-based drug design; the receptor-based drug design comprises molecular docking, and is a virtual operation of recognizing, adapting and combining a small molecular compound ligand to a biomacromolecule receptor; the design aims at discovering small molecule compounds matched with receptor binding sites, screening seedling heads and lead compounds from a virtual library, mutually recognizing receptors and drug molecules through space matching and energy matching to form molecular complexes, and predicting the operation process of the structure of the complexes. The computer-aided drug design is utilized, a computer serves as anoperation interface and an auxiliary means, the technologies of computational chemistry, molecular graphics, statistics, databases and the like are utilized, interaction between drugs and receptors is studied, new bioactive molecules are found and designed, and convenience is provided for finding and optimizing synthesis of lead compounds.
Owner:杭州憶盛医疗科技有限公司
A kind of method for screening chitinase ofcht I inhibitor
ActiveCN107832577BEasy to prepareStrong inhibitory activityMolecular designChemical structure searchPharmacophoreReceptor
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Application of anthocyanin screened based on molecular simulation technology in inhibiting malignant biological behaviors of colon cancer cells
PendingCN111445961AInhibit malignant biological behaviorReduce SOD activityMolecular designMicrobiological testing/measurementColon cancer cellMalignancy
The invention relates to an application of anthocyanin screened based on the molecular simulation technology in inhibiting malignant biological behaviors of colon cancer cells. On the basis of computer simulation, a large amount of anthocyanin with an outstanding docking effect is screened, cancer cells are taken as a model, and the influence of anthocyanin on malignant biological behaviors of thecancer cells is inspected, so that the anthocyanin is proved to have the capacity of promoting cancer cell apoptosis and can be applied to anti-cancer treatment research.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Construction method for distinguishing model of activity effect of PBDEs derivatives on enoyl-ACP reductase
ActiveCN112233730AAccurate calculation of activity effectsChemical property predictionHydrolasesReceptorReductase
The invention discloses a construction method for distinguishing a model of the activity effect of PBDEs derivatives on enoyl-ACP reductase. The construction method comprises the steps of receptor andligand modeling, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. The calculation result of the model is consistent with the result of an in-vitro binding activity determination experiment, and the result shows that the construction method of the model can accurately calculate the activity effect of the PBDEs derivatives on the enoyl-ACP reductase.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Ribosome inactivated protein attenuated modification method for blocking receptor binding
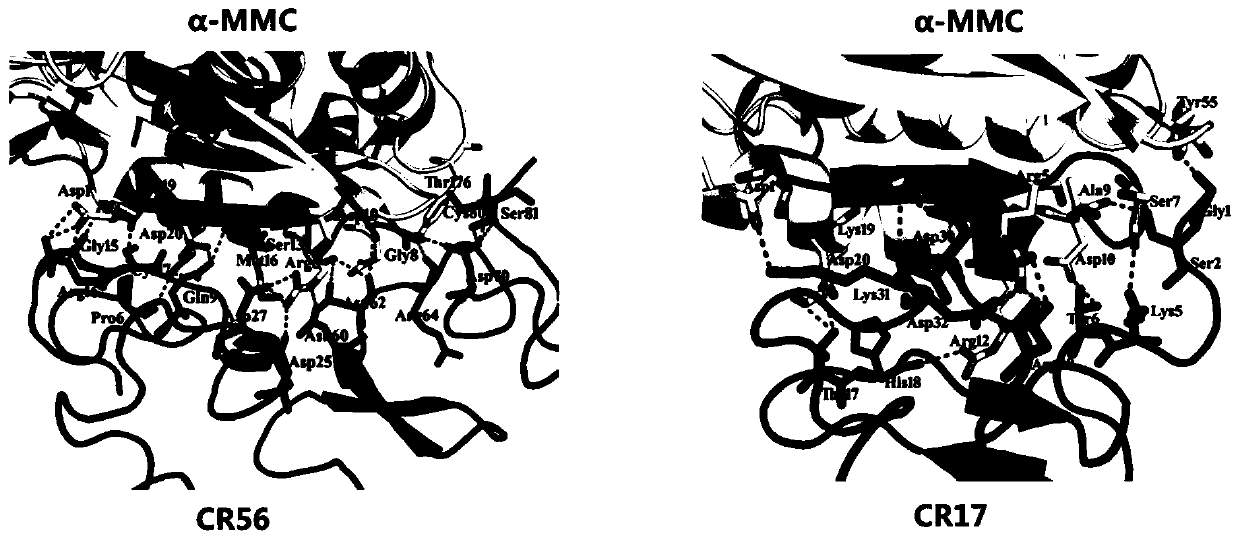
ActiveCN111500611ANo apparent cytotoxicityStrong cytotoxicityFluorescence/phosphorescenceVector-based foreign material introductionBinding siteReceptor
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly discloses a ribosome inactivated protein attenuated transformation method for blocking receptor binding, which comprises the following steps of: A, predicting a binding site, namely predicting a part where ribosome inactivated protein is bound with a receptor and the binding site by using molecular docking software; b, performing mutation transformation on the amino acid residues of the binding sites according to the prediction result in the step A; c, performing codon optimization according to the mutant gene obtained in the step B; d, synthesizing the whole gene of the target mutant optimized in the step C, and constructing an expression vector; and E, detection: detecting the target mutant gene protein constructed in the step D, detecting whether the target mutant gene protein enters cells or not through a toxicity test and a fluorescence test, and detecting whether the target mutant gene protein is expressed or not. The structural modification mode of the mutation binding site amino acid residues created by the scheme can significantly block alpha-MMC from entering cells and causing cytotoxicity thereof, thereby achieving a significant attenuation effect.
Owner:成都富岱生物医药有限公司
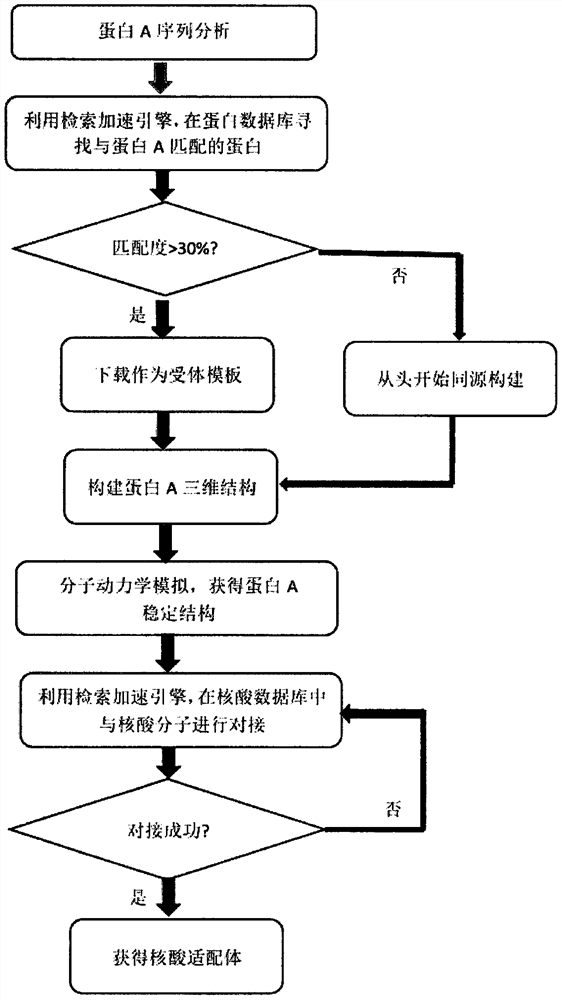
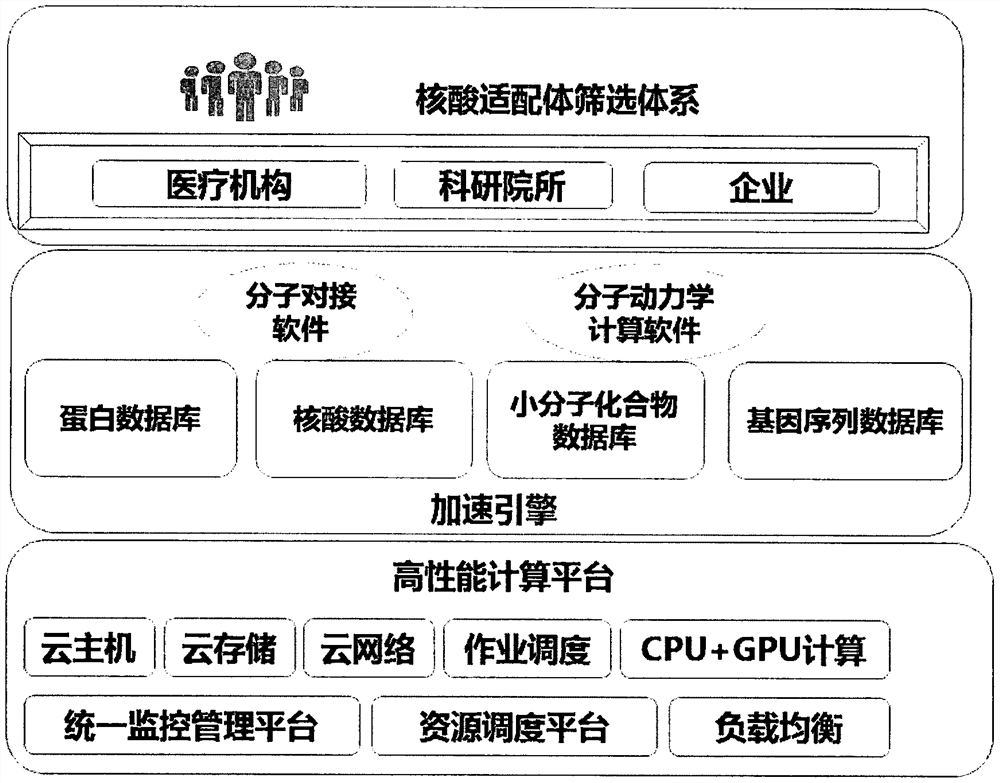
A high-performance computing platform-based computer-aided screening method for nucleic acid aptamers and nucleic acid aptamers
ActiveCN110111849BReduce the number of experimentsImprove screening efficiencySequence analysisInstrumentsAptamerProtein target
The invention provides a nucleic acid adapter computer-aided screening method based on a high-performance calculating platform, wherein the method relates to the field of molecular biology detecting technology. According to a matching principle, whether a protein structure which matches a target protein exists in a database system which is integrated in a screening platform is determined through searching; if yes, the protein structure is used as an acceptor template; and otherwise, homologous construction is performed. A primary selected nucleic acid adaptor is obtained through modular dynamics simulation and molecular docking screening as a nucleic acid adaptor candidate. The method and the nucleic acid adapter have advantages of high efficiency, high speed and high accuracy. The screening method can be combined with wet-method experiments, thereby reducing the number of the wet-method experiments, saving experiment cost and improving screening success rate. Through computer-aided simulation analysis, information such as chemical reaction mechanism between the protein and nucleic acid molecule in an adaption process is obtained. Furthermore the data are displayed on a terminal. Furthermore a data support is supplied at an aspect of disclosing a possible interaction mechanism between a corresponding biomaterial and the nucleic acid molecule. Therefore the method and the nucleic acid adapter have an important researching meaning and high use value.
Owner:BEIJING COMPUTING CENT +1
Application of virtually screened compound in preparation of antitumor drug and antitumor drug
PendingCN112250637AGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPharmacophorePharmaceutical drug
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Computer-aided screening method for small molecule target nucleic acid aptamers based on high-performance computing platform and small molecule target nucleic acid aptamers
ActiveCN110246538BReduce the number of experimentsReduce work intensityProteomicsGenomicsAptamerStructure analysis
The invention provides a computer-aided screening method for small molecule target nucleic acid aptamers based on a high-performance computing platform, and relates to the technical field of molecular biology. Firstly, analyze the structure of the small molecule target, and then screen in the small molecule compound library. If the matching principle is met, it will be used as the target small molecule target for molecular docking with nucleic acid molecules. If the matching principle is not met, the molecular structure can be constructed. , the small molecule target after molecular structure construction is used as the target small molecule target, and molecular docking is carried out with the nucleic acid molecule. If the docking is successful, the nucleic acid molecule is the primary nucleic acid aptamer, which solves the binding site between the small molecule target and the nucleic acid molecule Small molecular weight, weak affinity, difficulty in grasping nucleic acid molecules, many consumables, small differences in size, mass, and charge properties between the complex formed by the small molecule target and the nucleic acid itself, and the difficulty in separating the two.
Owner:BEIJING COMPUTING CENT
Rapid screening method for hepatotoxic compounds in polygonum multiflorum based on MRP2/3
PendingCN113380342AEfficient screeningShorten the timeChemical property predictionMolecular entity identificationChemical structureChemical compound
The invention relates to a method for screening hepatotoxic compounds in polygonum multiflorum based on a computer molecular docking technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a three-dimensional chemical structure of at least one compound to be detected in the polygonum multiflorum; (2) obtaining protein homologous modeling structures of the MRP2 and the MRP3, and respectively determining active sites of the MRP2 and the MRP3; (3) respectively carrying out computer molecular docking on the compound to be detected, a positive compound 1 with an MRP2 inhibition effect and a positive compound 2 with an MRP3 inhibition effect with the active sites to obtain docking scores; and (4) judging the to-be-detected compound as the hepatotoxic compound under the condition that the docking score of the to-be-detected compound reaches a docking judgment value. The screening method disclosed by the invention is rapid, economical and simple to operate, and can realize high-throughput screening of numerous compounds.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
A method for protein ATP docking based on differential evolution
ActiveCN110197700BImprove forecast accuracyReduce computational costBiostatisticsArtificial lifeProtein-protein complexProtein pair
A differential evolution-based protein ATP docking method. First, the ATPbind server is used to predict the protein-ATP binding residue information, which improves the prediction accuracy of the molecular spatial structure of the complex; then, the original protein-ATP is designed by population individuals. The ATP structure prediction problem is transformed into an optimization problem of searching for the optimal individual, which reduces the computational cost. Finally, by using the differential evolution algorithm to search for the optimal individual, the prediction accuracy of the protein-ATP complex structure is improved. The invention provides a protein ATP docking method based on differential evolution with low computational cost and high search efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A molecular modification design method for improving the catalytic efficiency of prolyl endopeptidase
ActiveCN111540404BHigh catalytic activitySequence analysisSystems biologyRecombinaseProlyl endopeptidase
The rational design method of the present invention to transform prolyl endopeptidase to improve its catalytic efficiency is mainly to obtain Sphaerobacter thermophiles prolyl endopeptidase through homology modeling, and obtain enzyme-substrate complex by molecular docking Structure, MD simulation stabilizes the structure, virtual saturation mutation of enzyme residues near the substrate, constrained MD simulation puts the enzyme in a perfect catalytic "near-offensive" conformation, uses MM / GBSA method to calculate binding free energy for virtual screening Mutant enzymes with improved potential catalytic efficiency were obtained. The enzyme was expressed by an Escherichia coli expression system, purified by a nickel column, and the enzyme activity and kinetic parameters of the recombinant enzyme for the nonapeptide substrate were determined by HPLC. The results show that the molecular transformation design method of the present invention can rapidly and effectively improve the catalytic activity of prolyl endopeptidase, which shows that the enzyme transformation method of the present invention is reliable.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Methods and systems for assessing drug development outcomes
PendingUS20220319634A1Level of interactionChemical property predictionMolecular designProtein structureEngineering
Systems and methods are disclosed herein for computer-aided method utilizing machine learning, artificial intelligence and automated docking for developing, customizing, discovery and maintaining the process of drug development pipeline finding of compounds containing Boron and Nitrogen, symmetric, aromatic, heteroaromatic, cyclic, heterocyclic compounds for drugs. The proposed method uses and identifies Boron Nitrogen Organic Compounds as a drug candidate for drugs through the use of software. The system works by automatically processing data to identify potential compounds containing Boron Nitrogen organic compounds as drug candidates using machine learning. The system further provides molecular data as smiles / inchi / calculates properties and predicts the pharmaceutical activity with machine learning algorithms. It further provides functionality of automated docking to novel 3D protein structures and automated structure generation using RNN (recurrent neural networks) or LSTM (long short-term memory). The system can present neural networks and LSTM (long short-term memory) networks to the user.
Owner:M KLEBER JULIAN
Computer screening method for small molecular covalent inhibitors and application of method to screening of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase covalent inhibitors
ActiveCN106407739AEasy to operateGood effectSpecial data processing applicationsMolecular structuresScreening methodComputer-aided
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine and particularly relates to a computer screening method for small molecular covalent inhibitors and an application of the method to the screening of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase covalent inhibitors. According to the method, in computer-aided screening and design processes of covalent inhibitors, steric hindrance of a protein receptor is reduced or eliminated first and then the protein receptor is used for screening, design and modification of the covalent inhibitors or covalent binding molecules. According to the application of the method to the screening of the S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase covalent inhibitors, pyruvoyl 68 residues in an S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase crystal structure are removed and optimization is performed in Rosetta software to obtain an optimized protein crystal structure; docking calculation is performed on small molecules to obtain docking calculation results; and the calculation results are screened to obtain the small molecular covalent inhibitors. According to the method and the application thereof, the perfect docking calculation method for numerous non-covalent inhibitors can be widely used, so that the screening, optimization and discovery of the covalent inhibitors can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Experimental method for screening FASN inhibitor in peony seed meal monomeric compound based on computer simulation
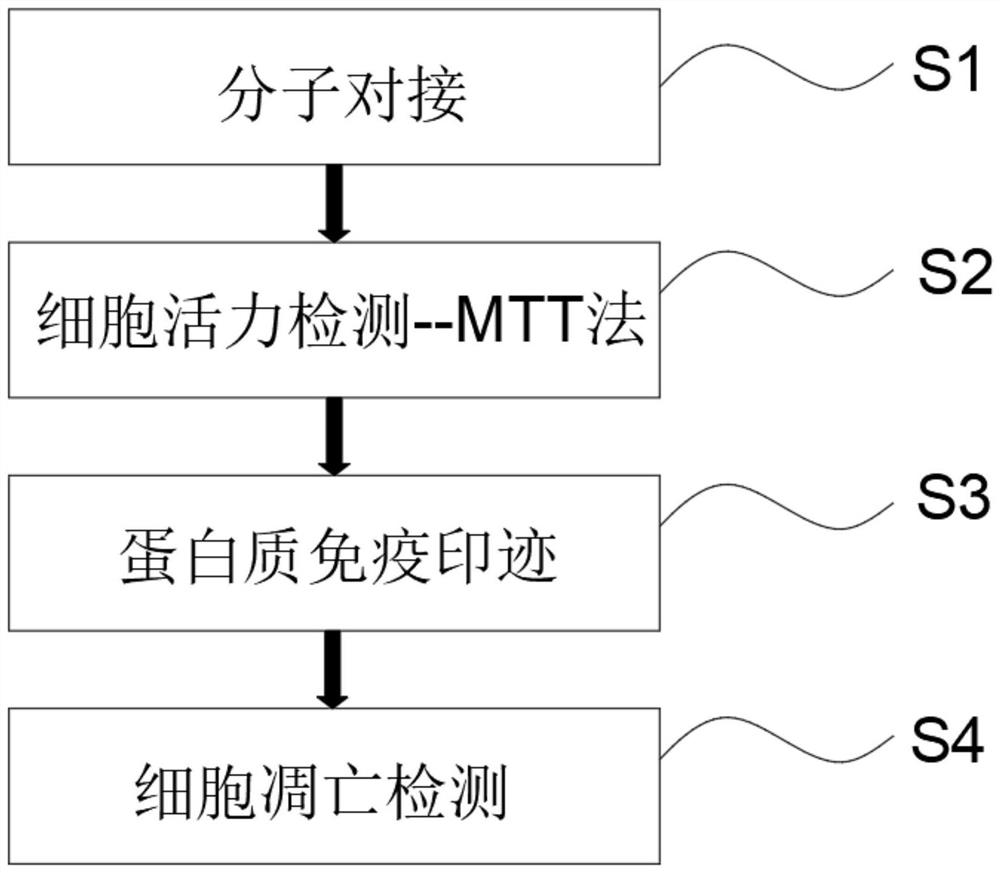
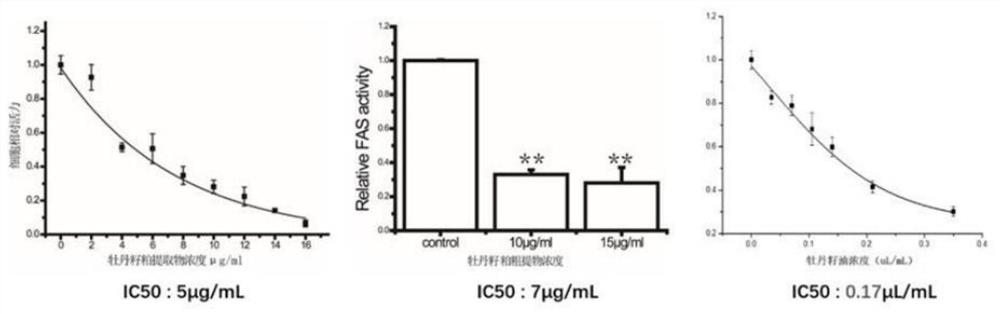
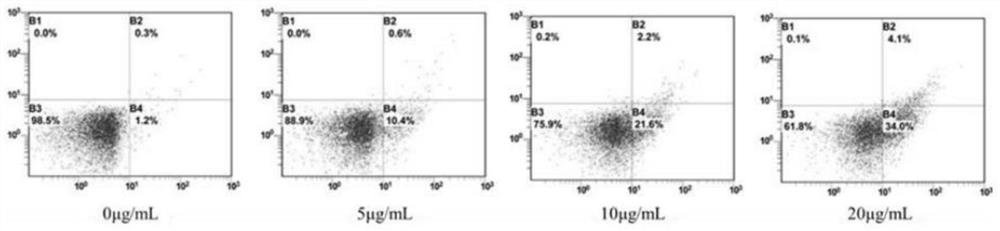
PendingCN114107427AImprove fidelityEffective understandingCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDimerApoptosis
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical analysis, and discloses an experimental method for screening a fatty acid synthase (FASN) inhibitor in a peony seed meal monomeric compound based on computer simulation, and the experimental method for screening the FASN inhibitor in the peony seed meal monomeric compound based on computer simulation comprises the following specific operation steps: S1, molecular docking; s2, cell activity detection; s3, performing protein immunoblotting; and S4, cell apoptosis detection. Whether four monomeric compounds in the peony seed meal extract have anti-tumor activity caused by inhibition of FASN activity and expression or not is screened by means of a molecular docking method, a homologous modeling means is tried to construct a whole enzyme dimer structure of FASN, and a new thought and a new method are provided for screening of the FASN inhibitor. A large number of invalid experiments can be effectively avoided, the success rate of experiment operation is improved, and the experiment operation cost is reduced.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method to distinguish between peroxidase-activated proliferator receptor gamma full agonist, partial agonist, and antagonist activity
ActiveCN110426512BReduce usageReduce workloadMolecular designPeptide preparation methodsExperimental laboratoryPharmacophore
The invention discloses a method for distinguishing the activities of peroxidase-activated proliferation receptor gamma full agonists, partial agonists and antagonists, including receptor and ligand modeling; molecular docking; traditional molecular dynamics simulation; Well-Tempered Meta ‑dynamic molecular dynamics simulation; pharmacophore construction. The method of the present invention can quickly distinguish the PPARγ activity of compounds with different structures, greatly reduces the use of chemicals and cells in the traditional toxicology experiment process in the laboratory, reduces the workload of the laboratory, and saves laboratory funds; thereby distinguishing compounds before QSAR modeling The activity of PPARγ makes the results of QSAR model closer to reality, so that traditional QSAR can be more widely used.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for rapidly evaluating neurotoxicity of bisphenol compound
PendingCN114863996ARapid neurotoxicitySave human effortBiostatisticsDesign optimisation/simulationPhospholipidBackbone chain
The invention discloses a method for rapidly evaluating neurotoxicity of bisphenol compounds, which comprises the following steps: selecting a G protein coupled estrogen receptor which possibly mediates novel bisphenol to play a stronger estrogen effect as a target spot, constructing a GPER-phospholipid membrane model, and carrying out molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation to obtain the neurotoxicity of the bisphenol compounds. Comparing the structure-effect relationship of BPs and G1 in a GPER binding bag from molecular and atomic levels, including: analyzing RMSD, RMSF, the strength of interaction energy of binding of BPs and GPER and the occupancy rate of formed hydrogen bonds in the simulation process; and comparing high-frequency conformations of the combination of the BPs and G1 with the GPER and the characteristics of the dynamic change of the main chain atoms of the GPER to comprehensively analyze the potential of the BPs as the GPER agonist to cause the neurotoxic effect. In-vitro cell experiments prove that the GPER indeed mediates the neurotoxic reaction of the BPs compound, which indicates that the method provided by the invention is feasible.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com