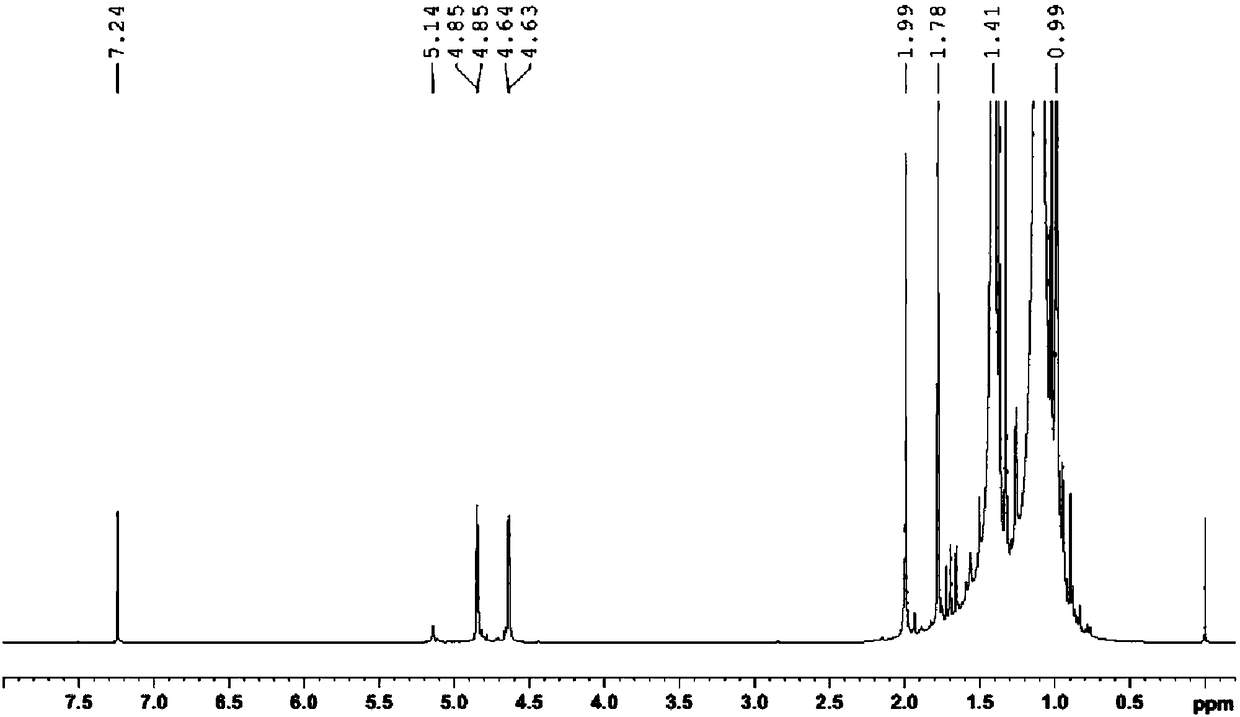
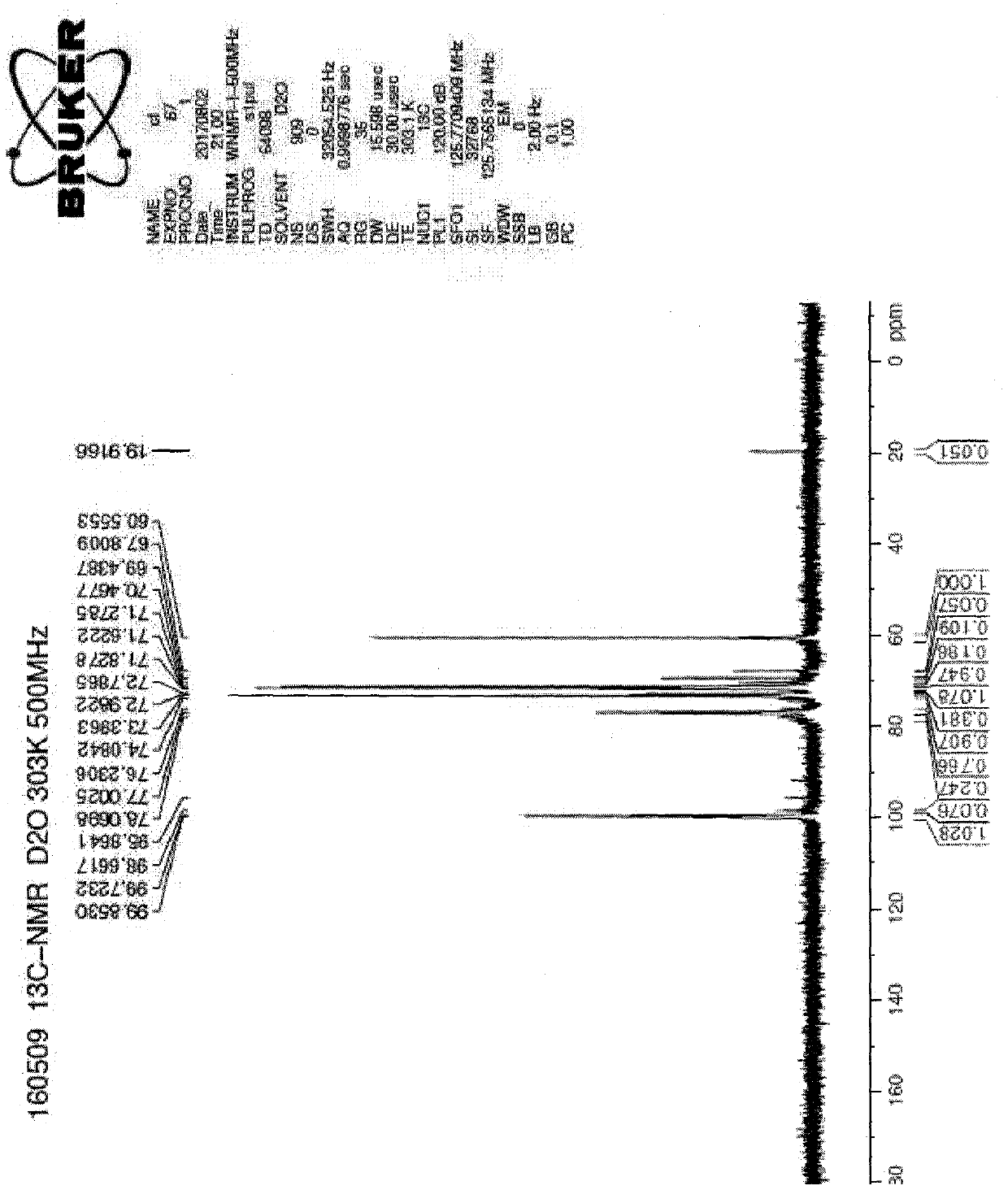
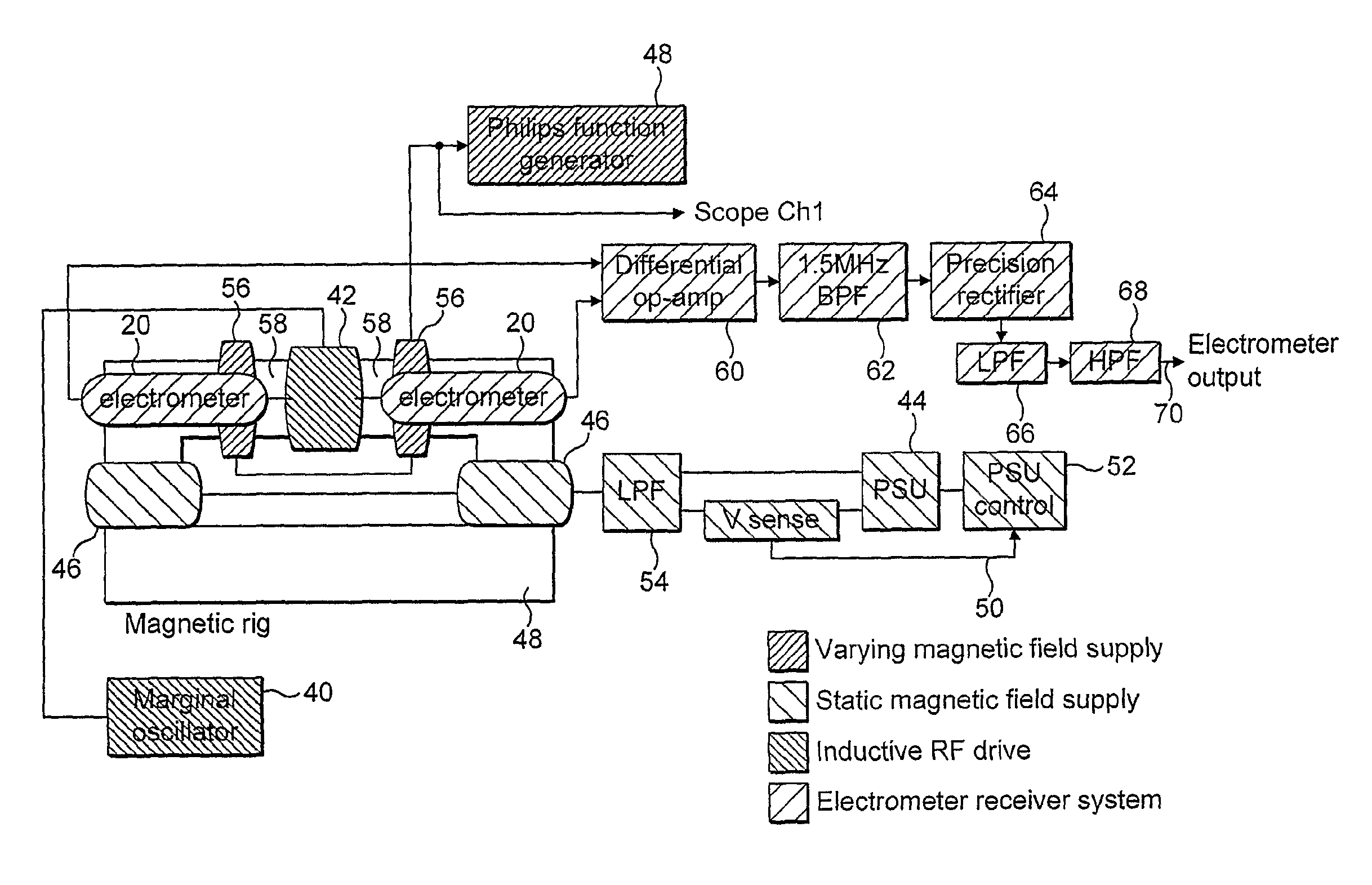
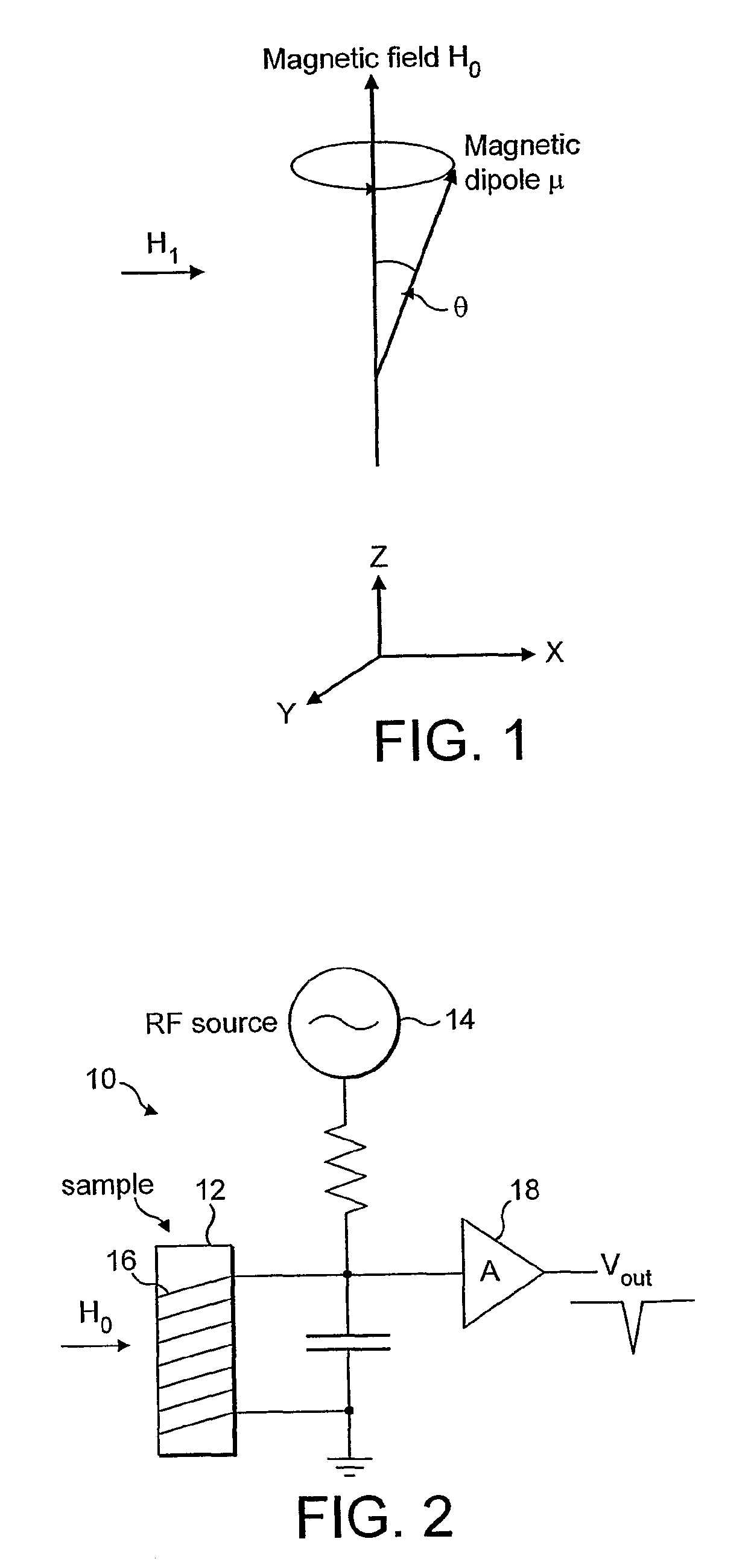
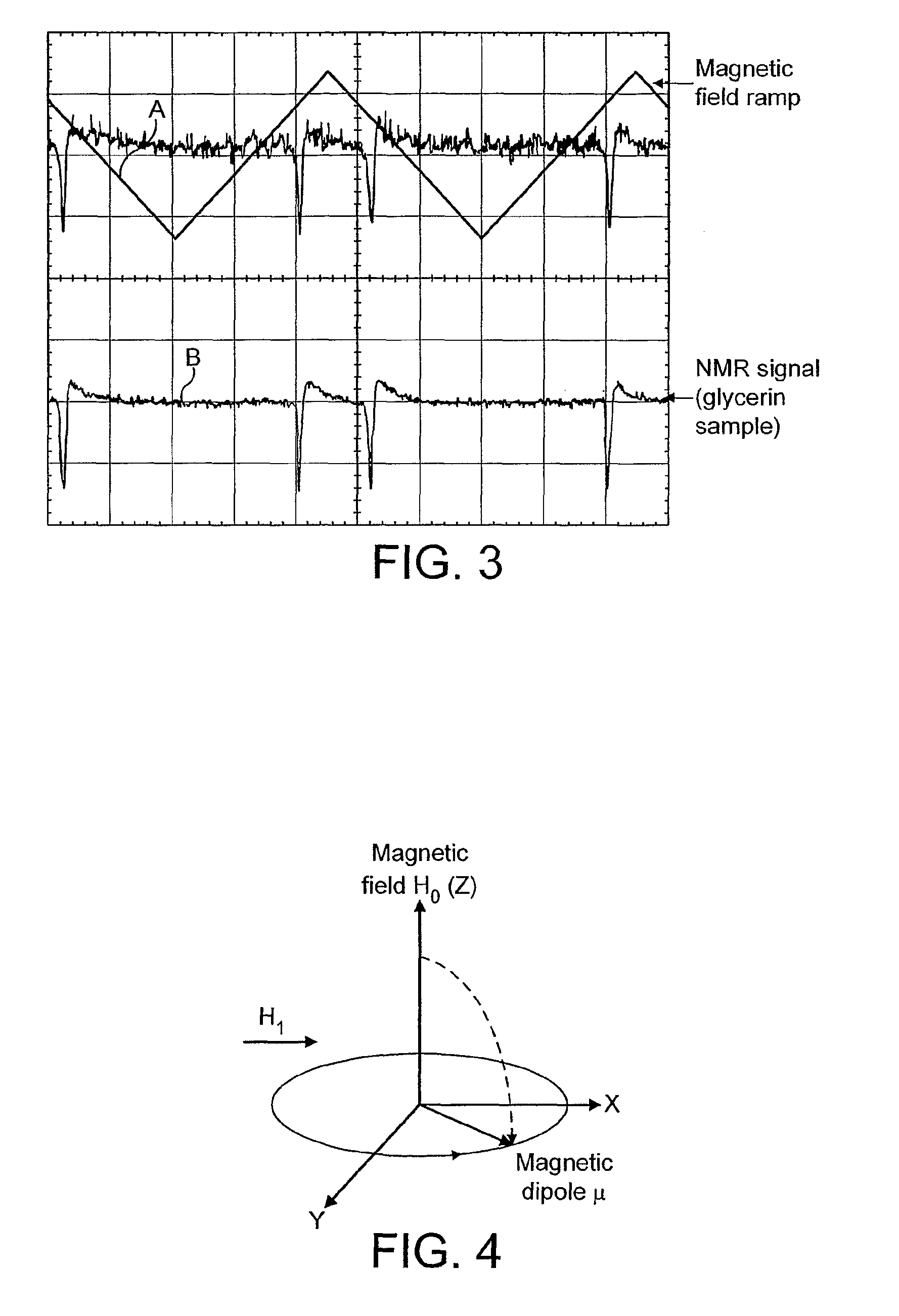
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Nuclear magnetic resonance crystallography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
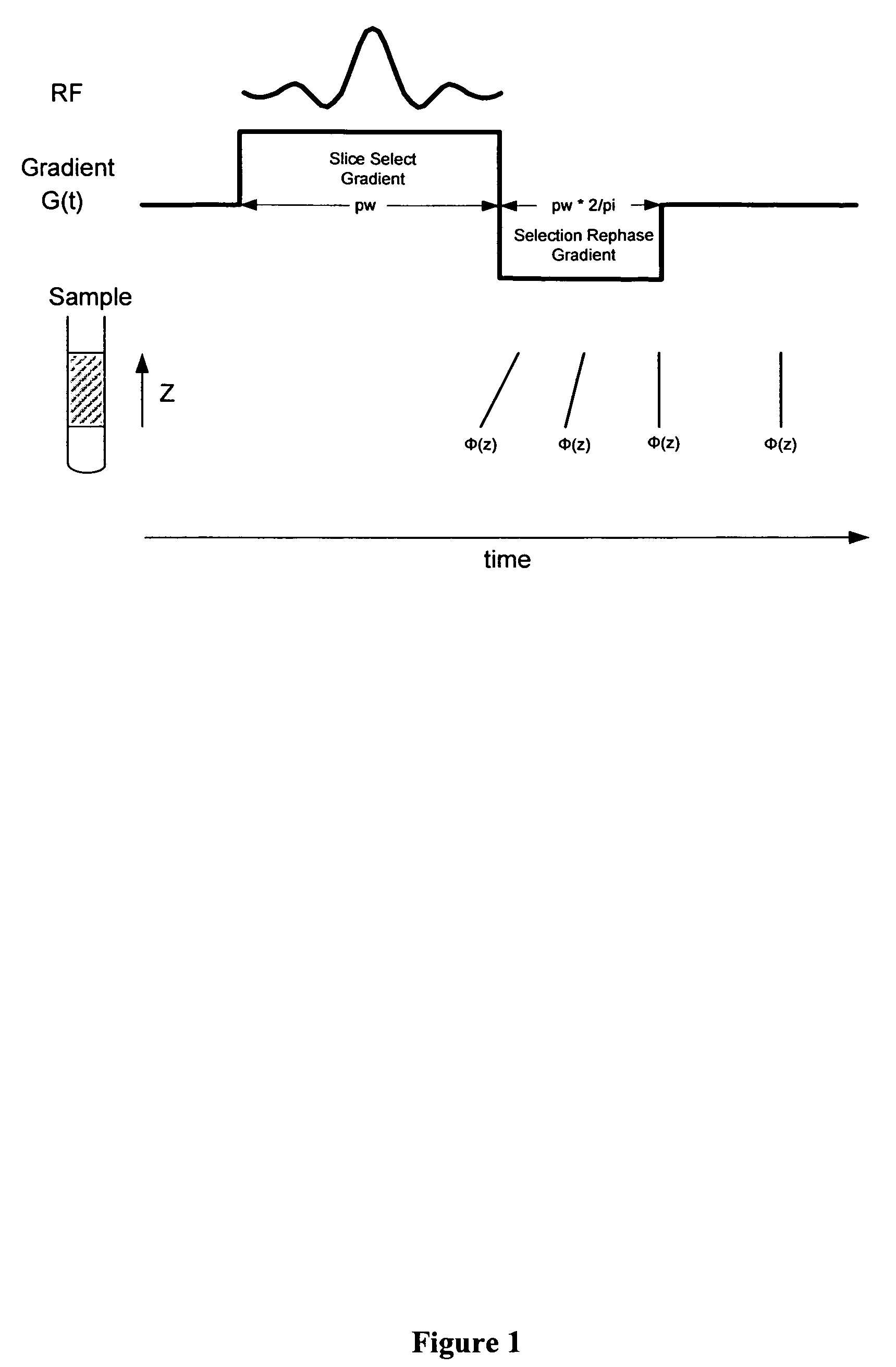
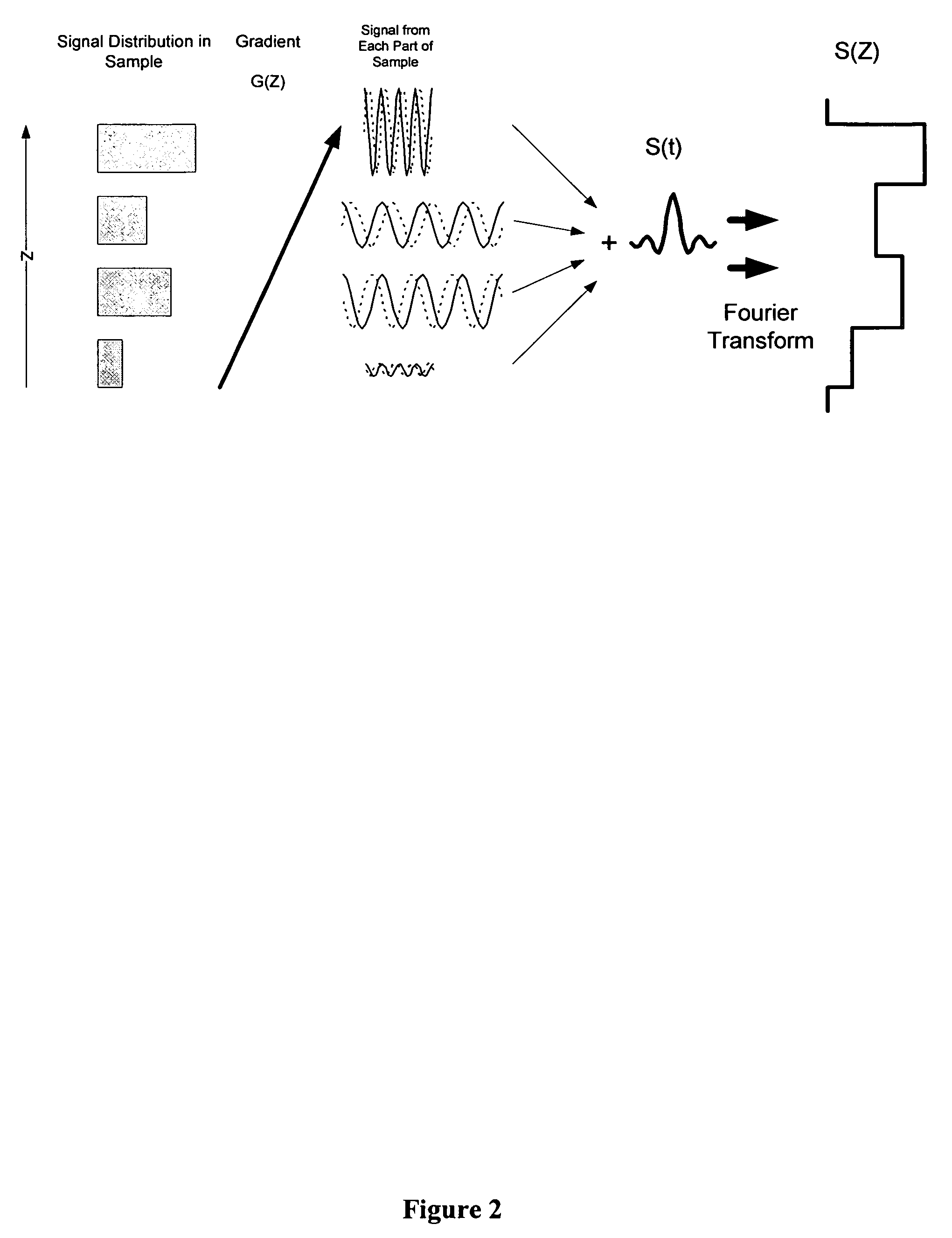
Nuclear magnetic resonance crystallography (NMR crystallography) is a method which utilizes primarily NMR spectroscopy to determine the structure of solid materials on the atomic scale. Thus, solid-state NMR spectroscopy would be used primarily, possibly supplemented by quantum chemistry calculations (e.g. density functional theory), powder diffraction etc. If suitable crystals can be grown, any crystallographic method would generally be preferred to determine the crystal structure comprising in case of organic compounds the molecular structures and molecular packing. The main interest in NMR crystallography is in microcrystalline materials which are amenable to this method but not to X-ray, neutron and electron diffraction. This is largely because interactions of comparably short range are measured in NMR crystallography.
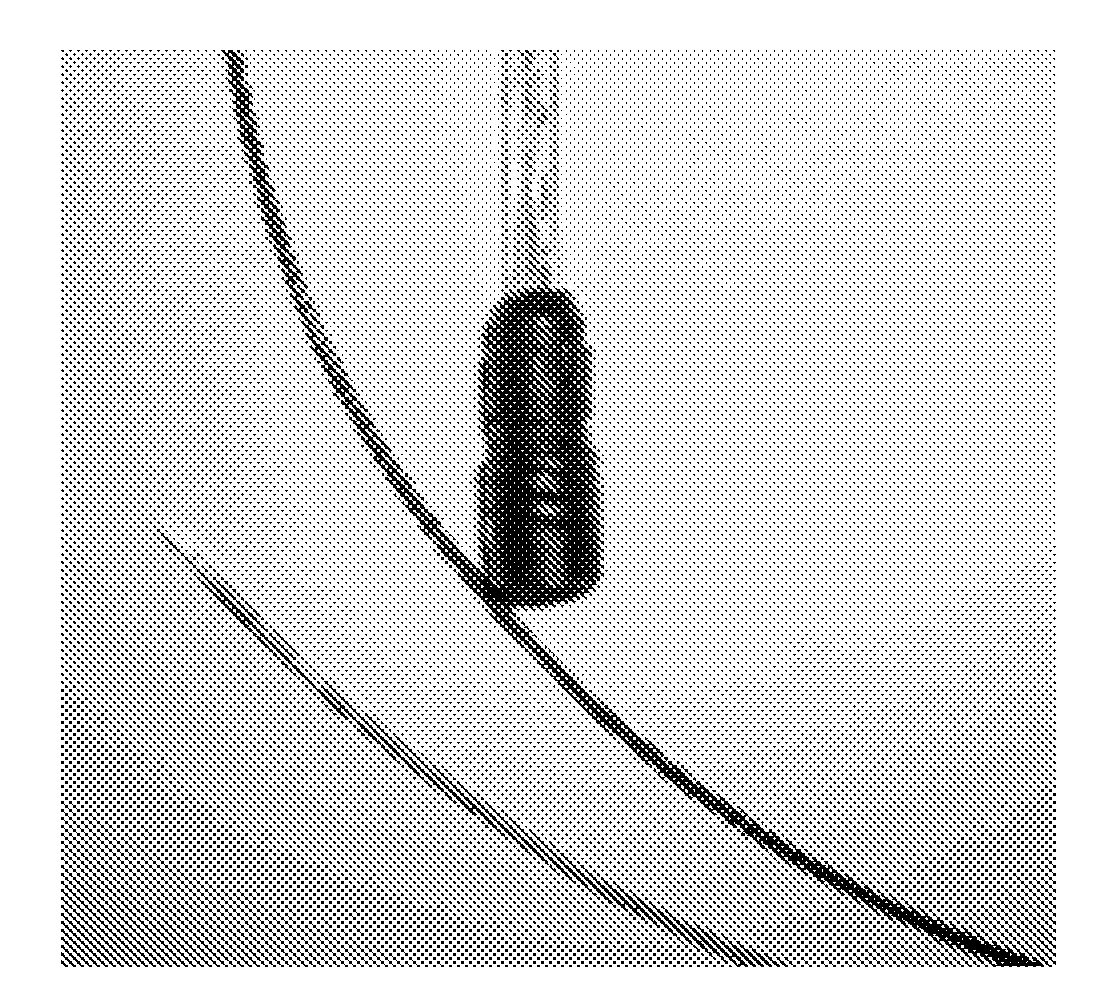
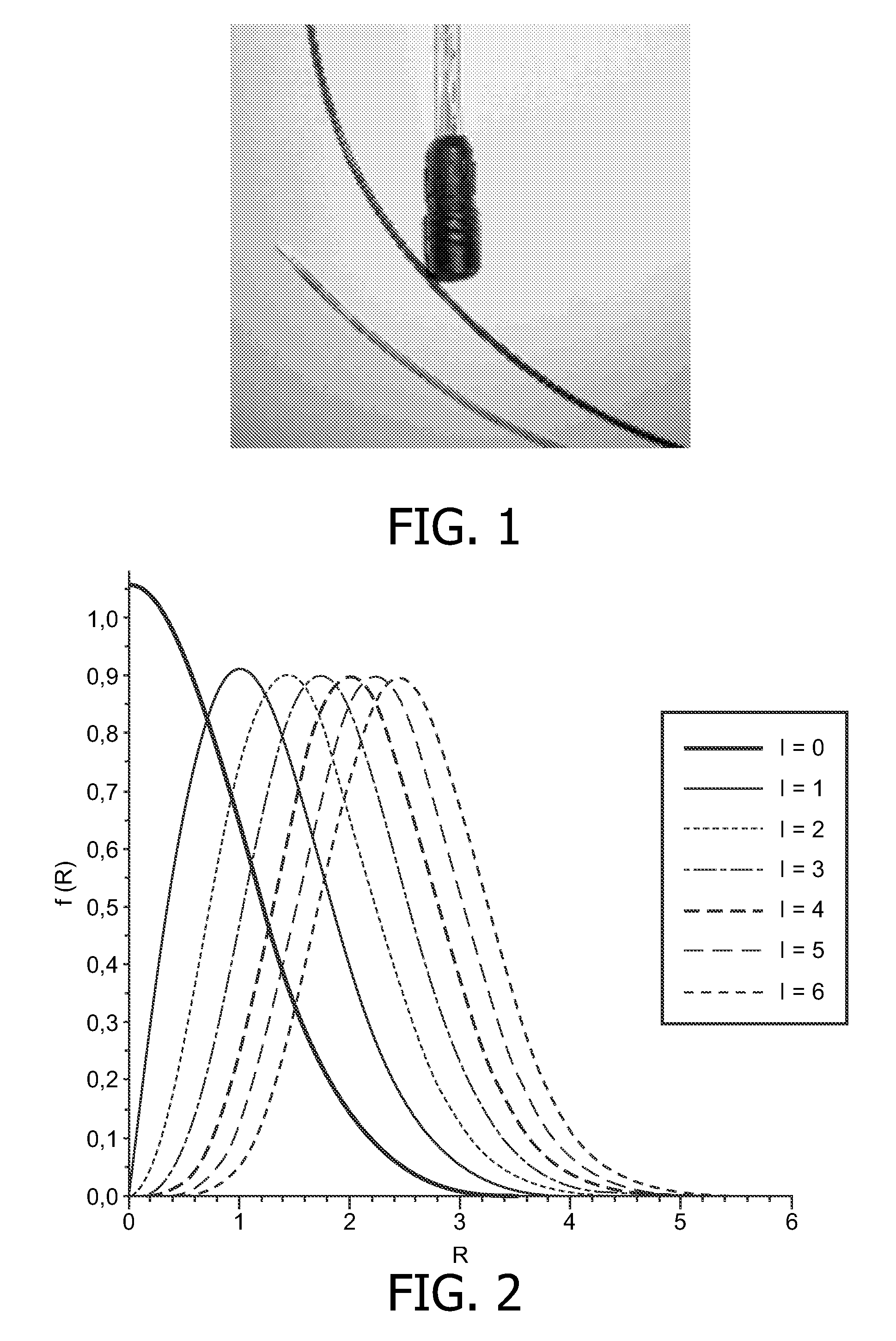
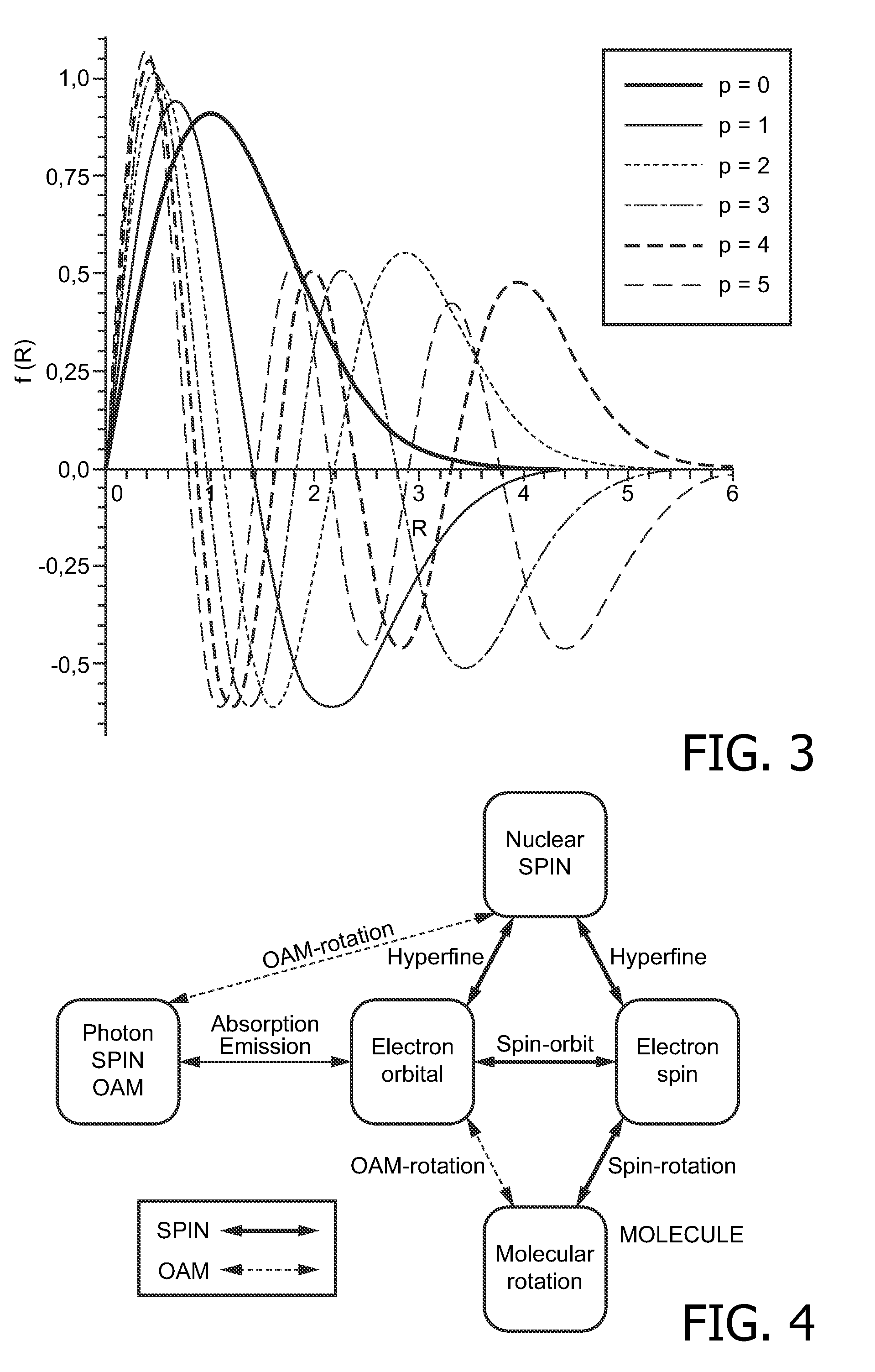
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momemtum
InactiveUS20100327866A1Less noisyHigh resolutionLaser detailsAnalysis using optical pumpingTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
The present invention relates to a device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of a sample, such as fluid, based upon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where the nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentially illuminating the sample with a focused beam of light carrying angular orbital angular momentum (OAM) and possibly momentum (spin). Unlike in usual NMR used for magnetic nuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the invention does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
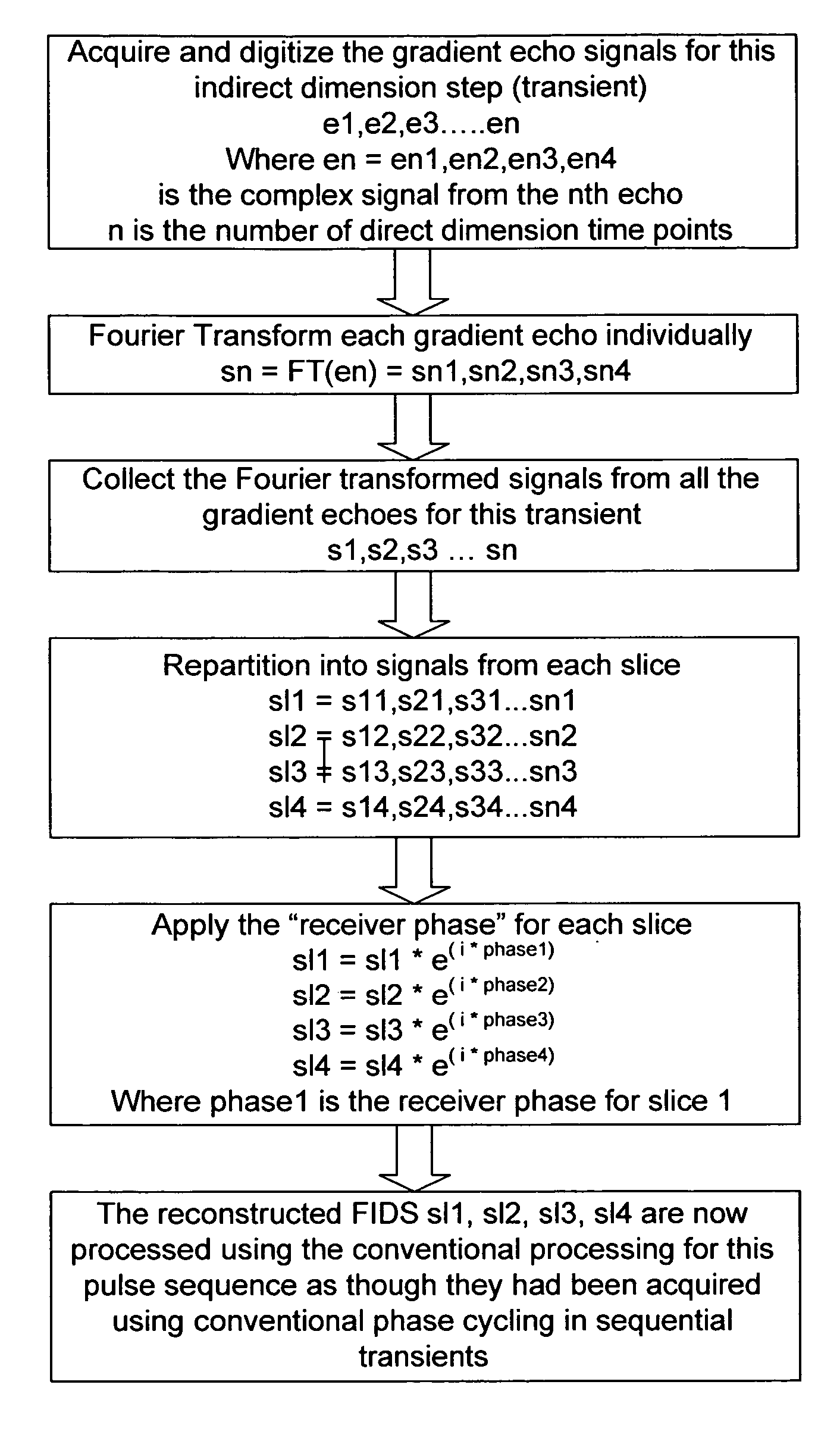
Simultaneous phase cycling for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS7408346B2Less timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyProton NMR
The present invention discloses a method of simultaneously conducting more than one step of a radiofrequency phase cycle in a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiment. The method first involves providing a sample. Next, one or more radiofrequency pulses are applied to a plurality of spatially discrete slices of the sample under conditions effective to simultaneously conduct more than one step of a radiofrequency phase cycle in a single transient. Then, NMR signals generated from the step of applying the radiofrequency pulses are acquired. Finally, the NMR signals are processed to obtain an NMR spectrum.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
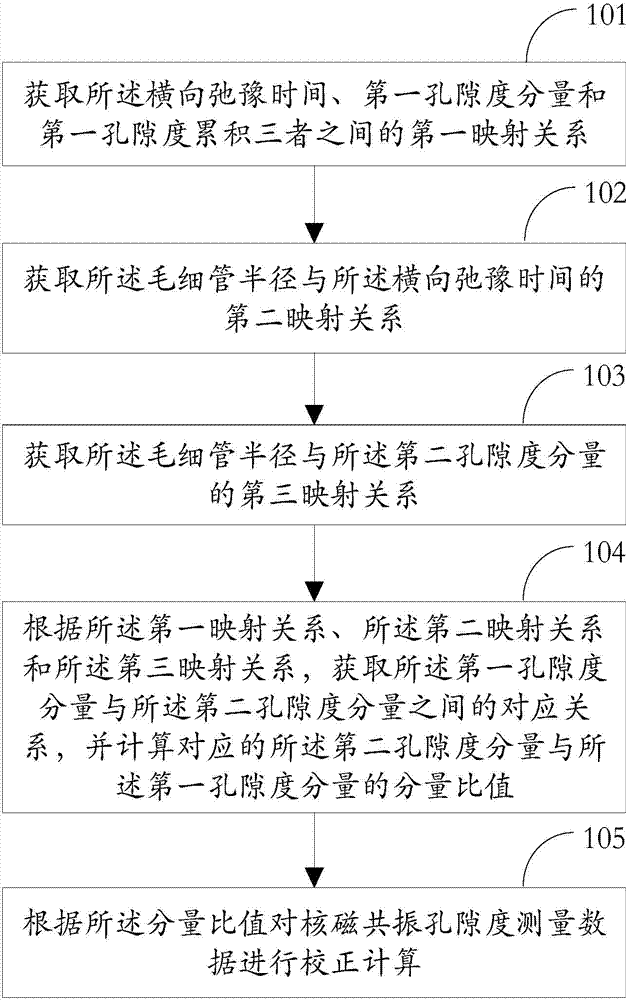
Method, device and system for correcting measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance porosities
ActiveCN103674811AHigh precisionAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisPorosityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
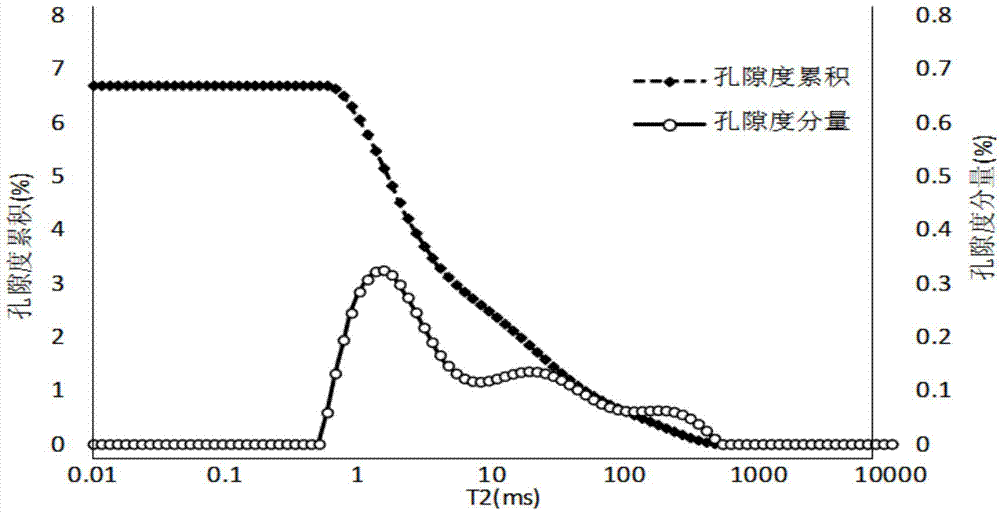
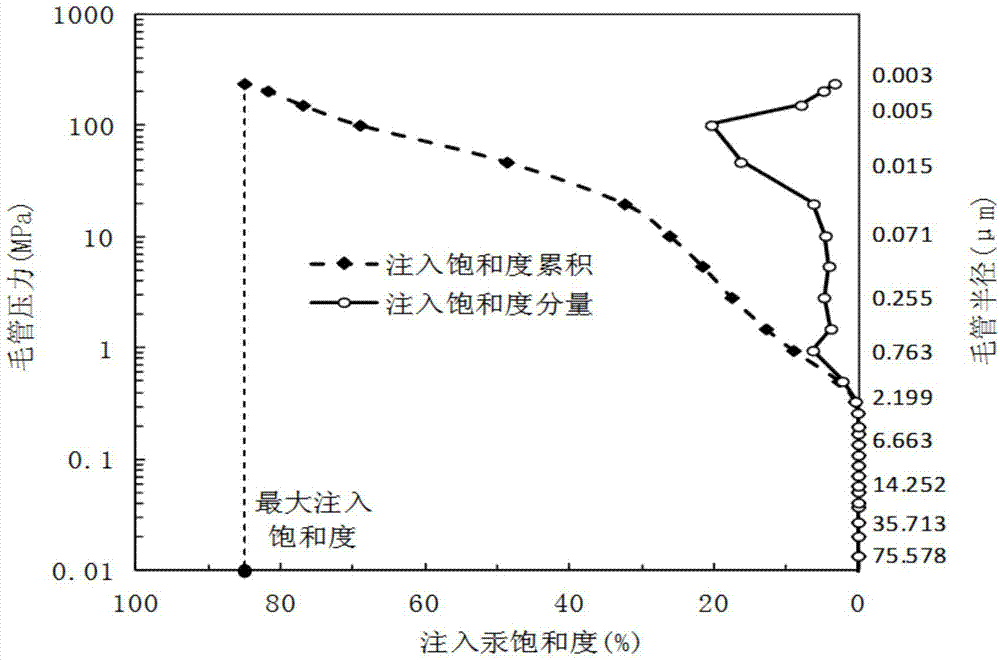
The invention relates to the field of well logging technology and discloses a method, device and system for correcting measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance porosities. A first mapping relation among transverse relaxation time, a first porosity component and first porosity cumulation is obtained, so that a second mapping relation between a capillary radius and the transverse relaxation time is obtained and further a third mapping relation between the capillary radius and a second porosity component is obtained; according to the first mapping relation, the second mapping relation and the third mapping relation, the corresponding relation between the first porosity component and the second porosity component is obtained, and the component ratio of the second porosity component to the first porosity component is calculated; according to the component ratio, the correction computation is performed on the measurement data of nuclear magnetic resonance porosities, so that the accuracy of the existing measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance porosities is improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Nuclear magnetic resonance method for body composition analysis
A method is disclosed for analyzing composition of a body part from nuclear magnetic resonance measurements made on the body part. The method includes exciting a predetermined sequence of nuclear magnetic resonance phenomena in the body part and measuring nuclear magnetic resonance signals from the body part. At least a part of the measured signals are composed into a measurement vector. The mass of the at least one constituent is determined as a predetermined function of the measurement vector. The predetermined function represents the at least one constituent and defines a standard for a range of at least one of compositional variations and temperature variations of the at least one constituent.
Owner:ECHOMRI
Pore measurement method
ActiveCN107014728AQuick testMeet the requirements of porosity testingPermeability/surface area analysisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
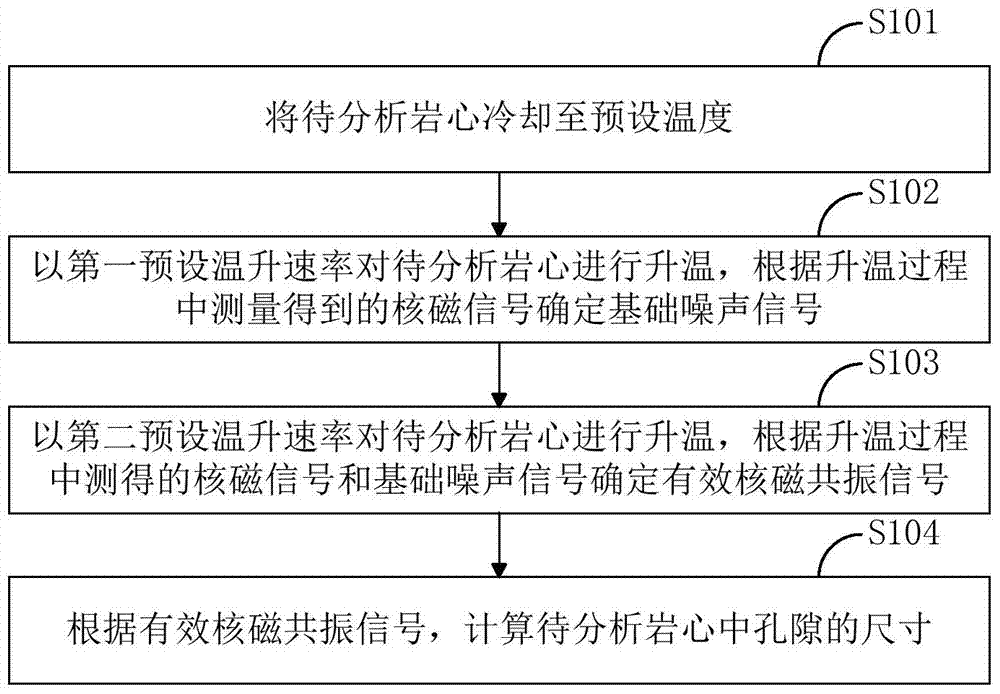
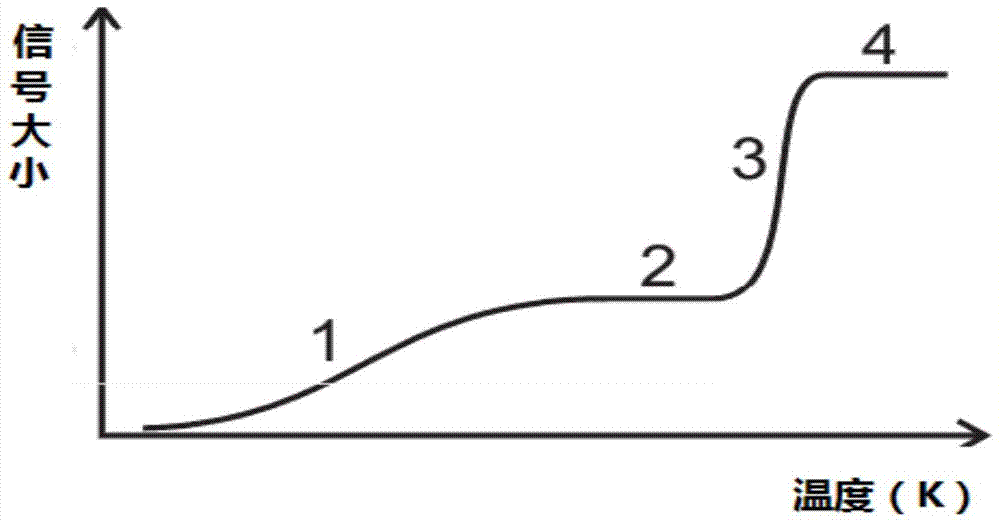
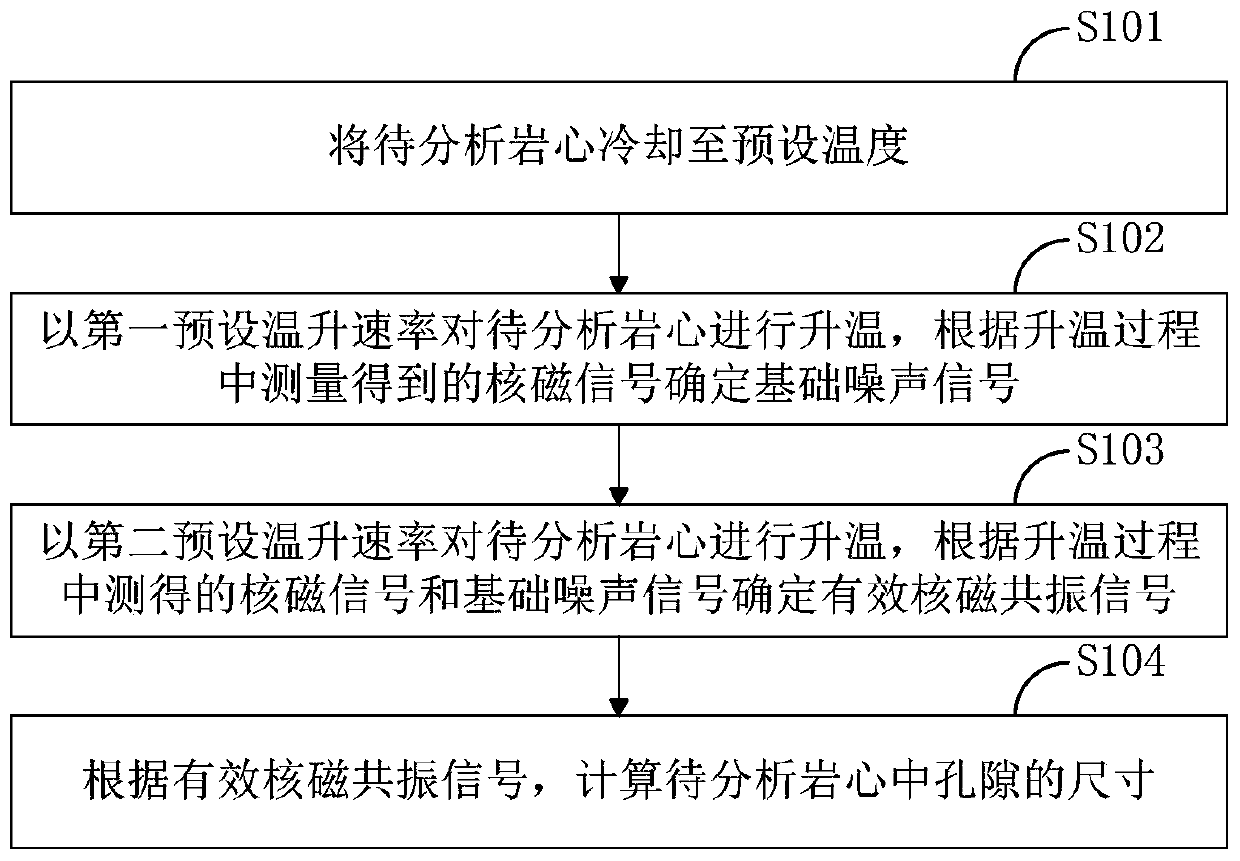
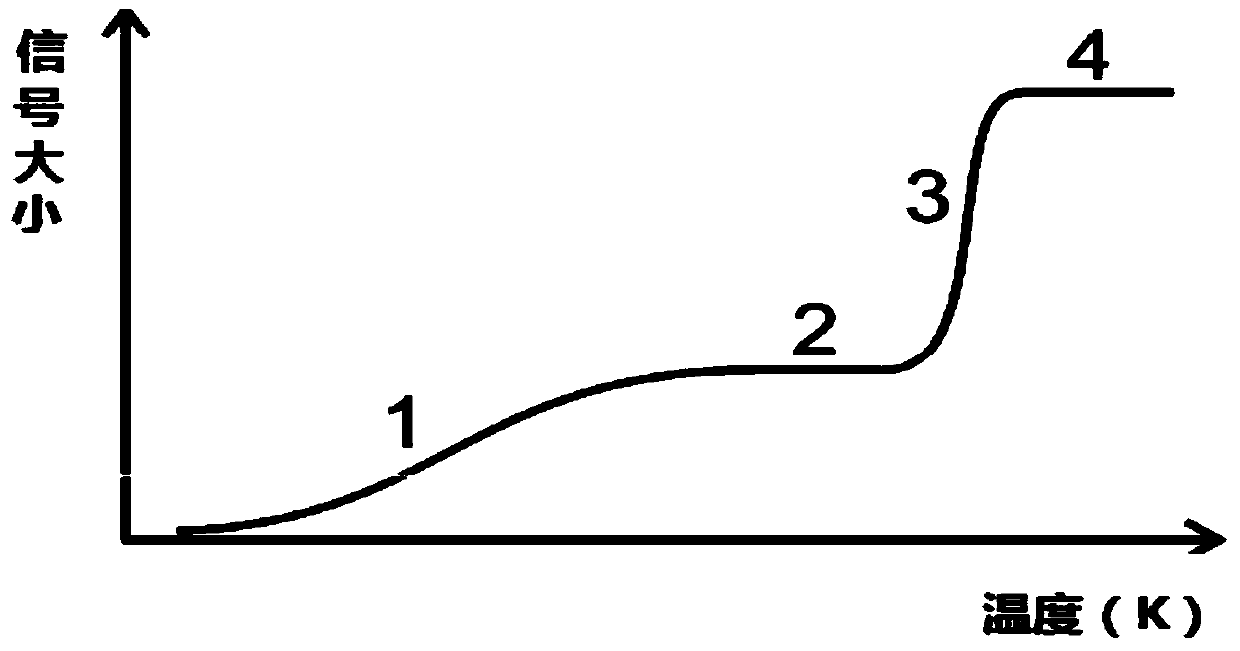
The invention relates to a pore measurement method which comprises the following steps: an effective signal determination step: regulating a temperature of a rock core to be analyzed into a preset temperature, regulating the temperature of the rock core to be analyzed according to a preset temperature change rate, determining a basic noise signal according to a nuclear magnetic resonance signal measured when the rock core to be analyzed is in a crystalline state, and determining an effective nuclear magnetic resonance signal at each temperature according to a nuclear magnetic resonance signal measured when the rock core to be analyzed is in a non-crystalline state and the basic noise signal; and a pore size determination step: determining the size of a pore in the rock core to be analyzed according to the effective nuclear magnetic resonance signal at each temperature. According to the pore measurement method, by adopting nuclear magnetic resonance nondestructive testing means, based on a low-temperature variable entropy nuclear magnetic resonance test technology, a nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrogram of a shale reservoir at different temperatures is tested, and by taking the spectrogram as a test basis, measurement of microscopic pore size distribution in a micro-nanometer magnitude of the shale reservoir is realized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
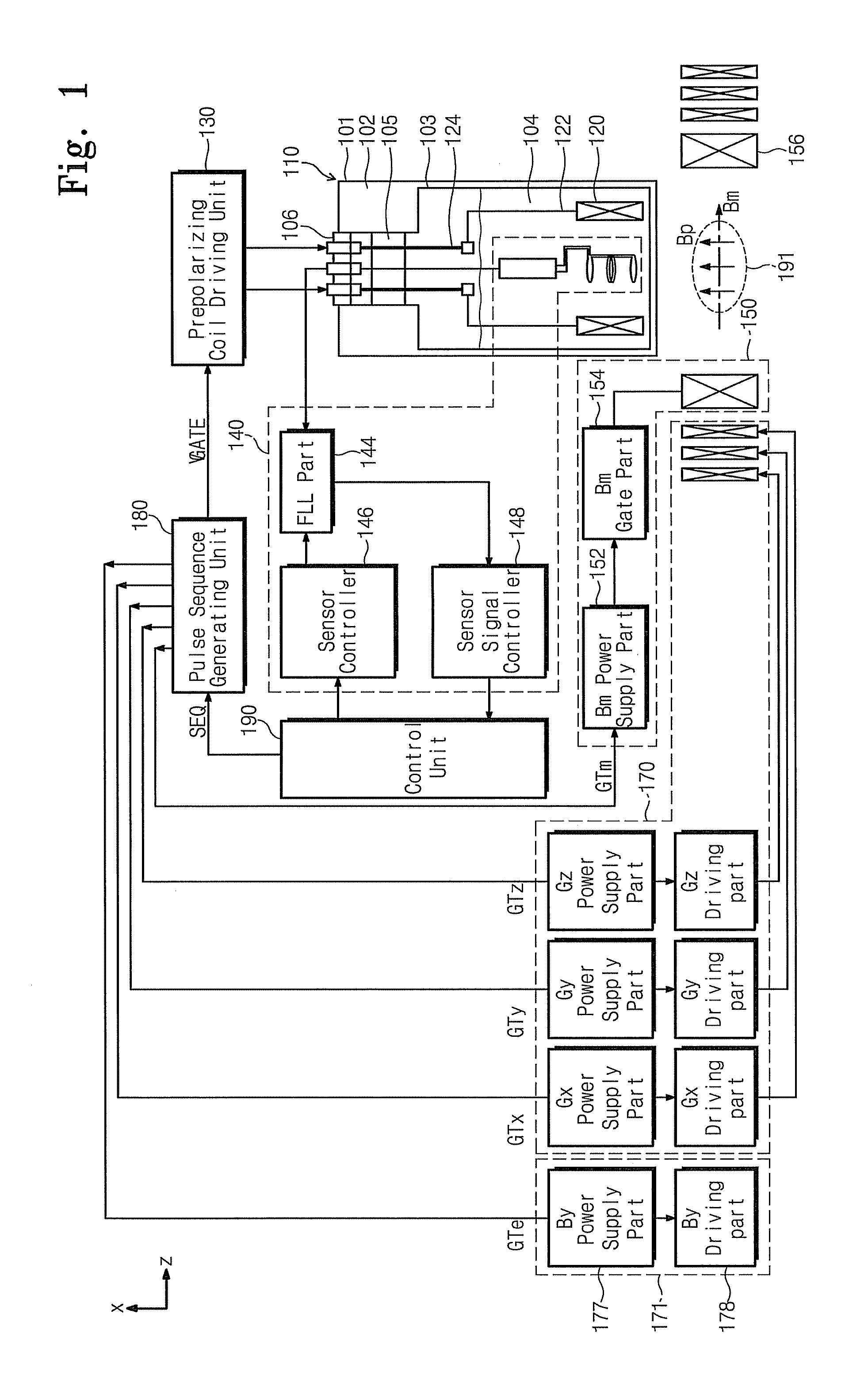
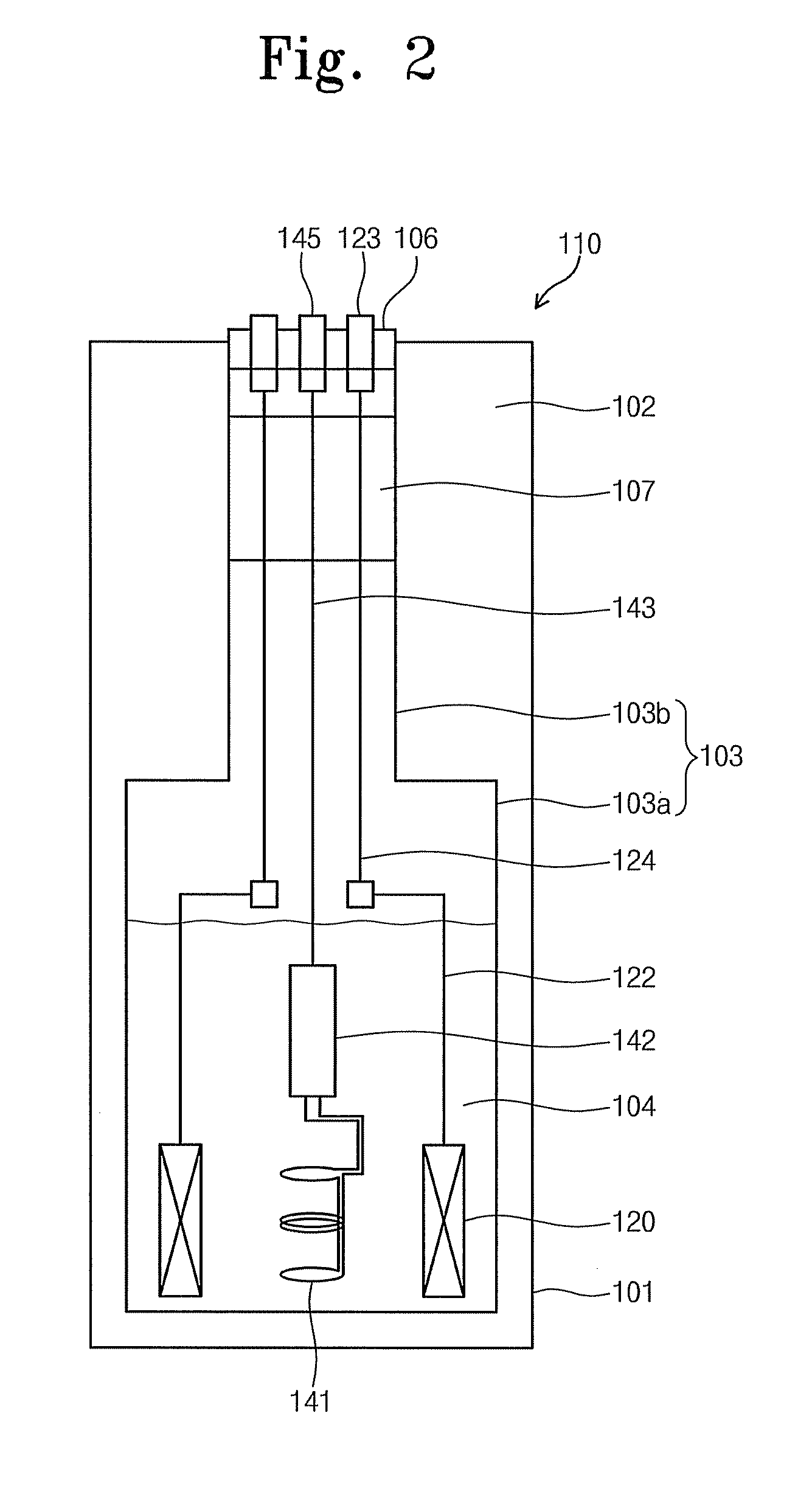
Nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus
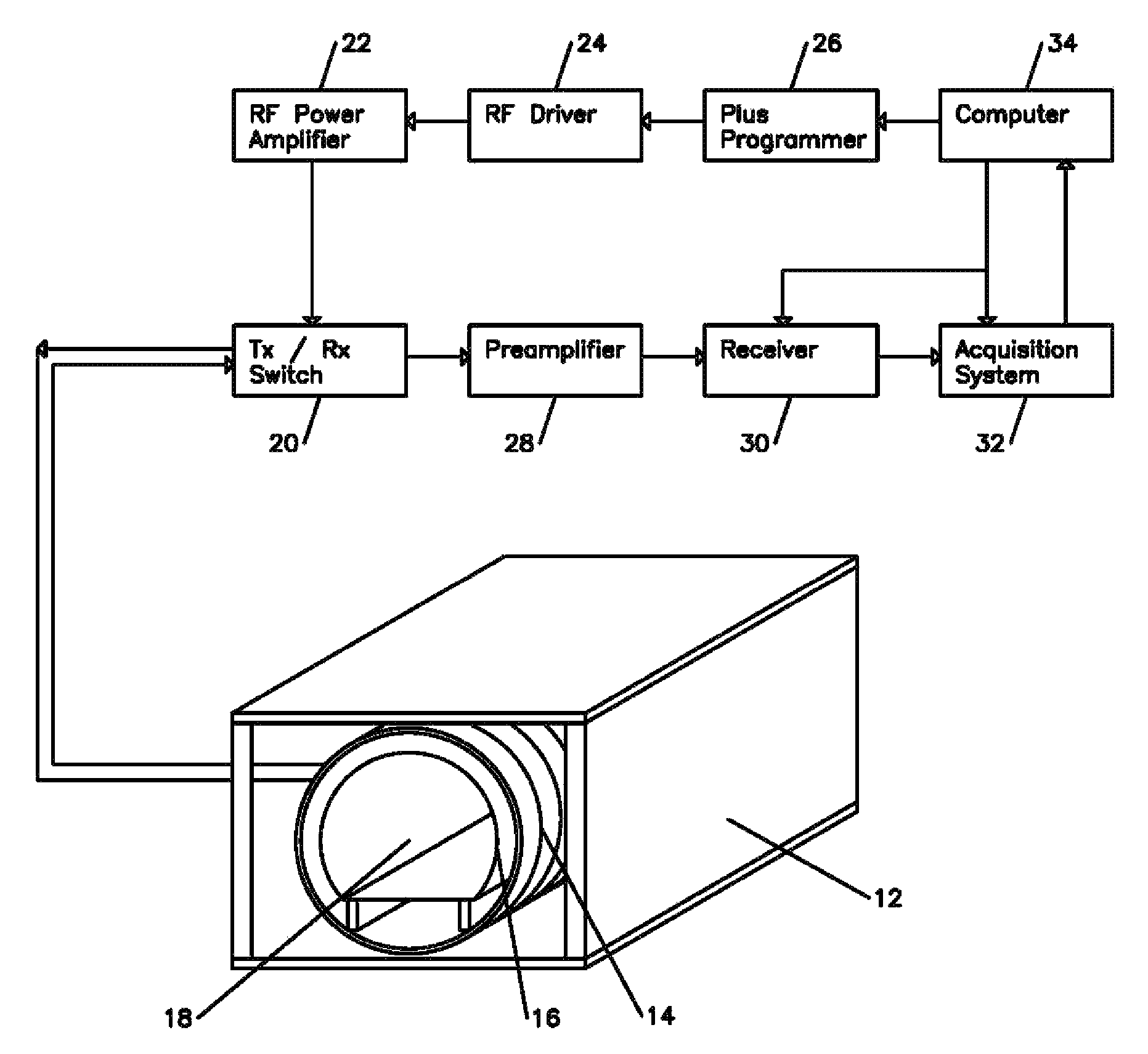
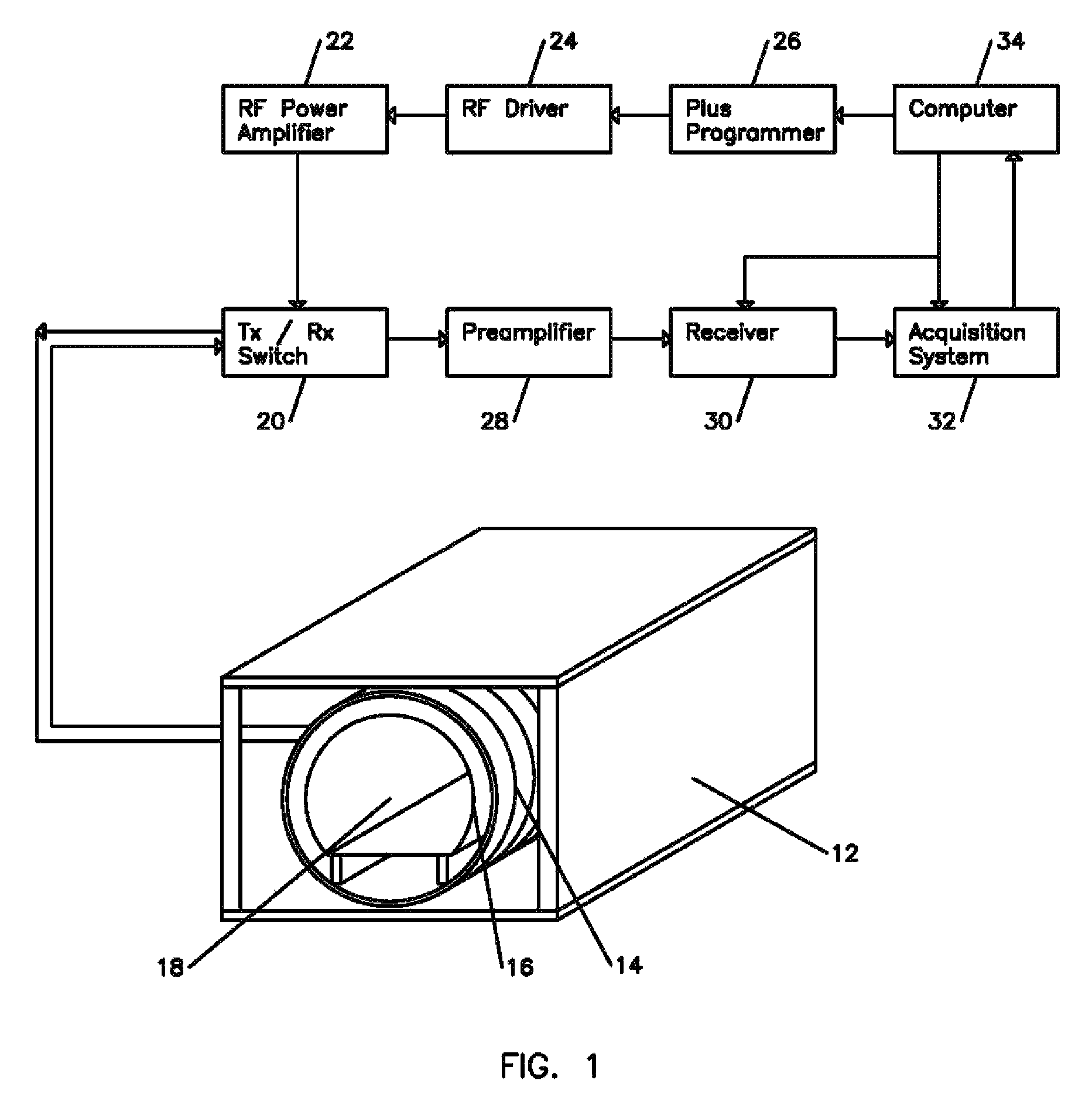
ActiveUS20110068789A1Energy consumption is minimizedHigher prepolarization magnetic fieldDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSuperconducting magnetNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
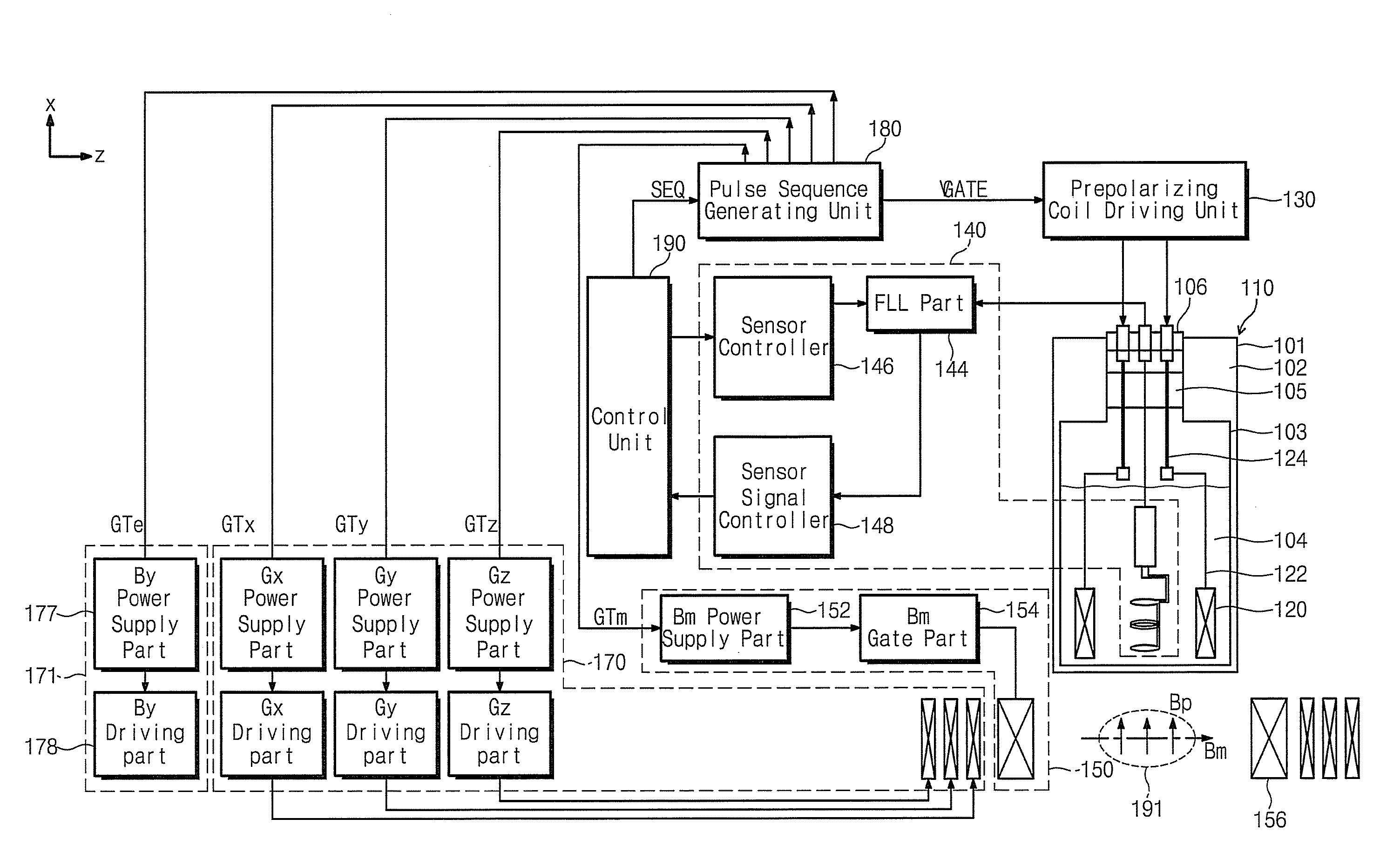
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus includes a dewar containing a low-temperature liquid refrigerant, a prepolarization coil disposed inside the dewar and including a superconducting wire, a prepolarization coil driving unit for intermittent application of current to the prepolarization coil in a capacitor charge / discharge method to generate a prepolarization magnetic field, a sensor unit for measuring a nuclear magnetic resonance signal from a sample to which a prepolarization magnetic field is applied with the prepolarization coil, and a readout magnetic field generation unit for applying a readout magnetic field to the sample.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
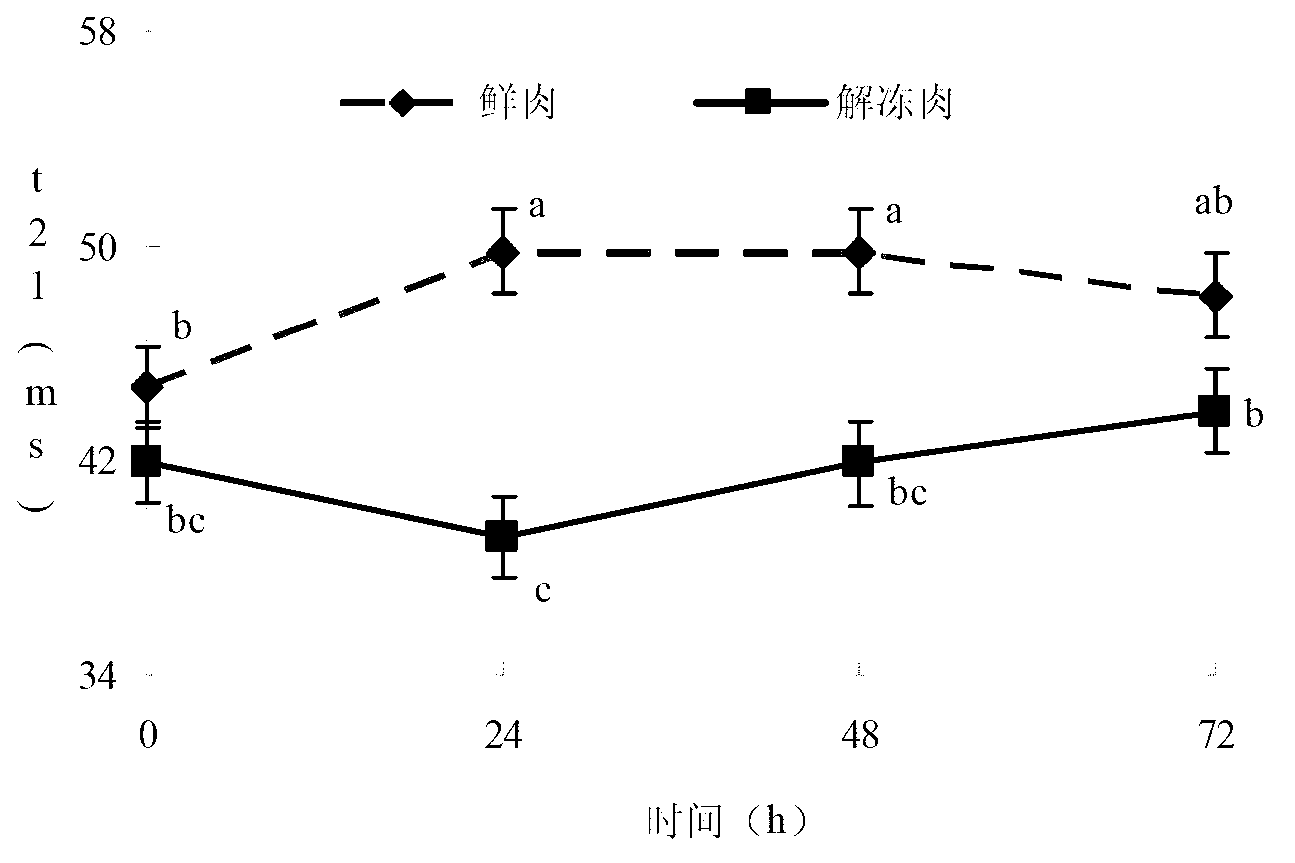
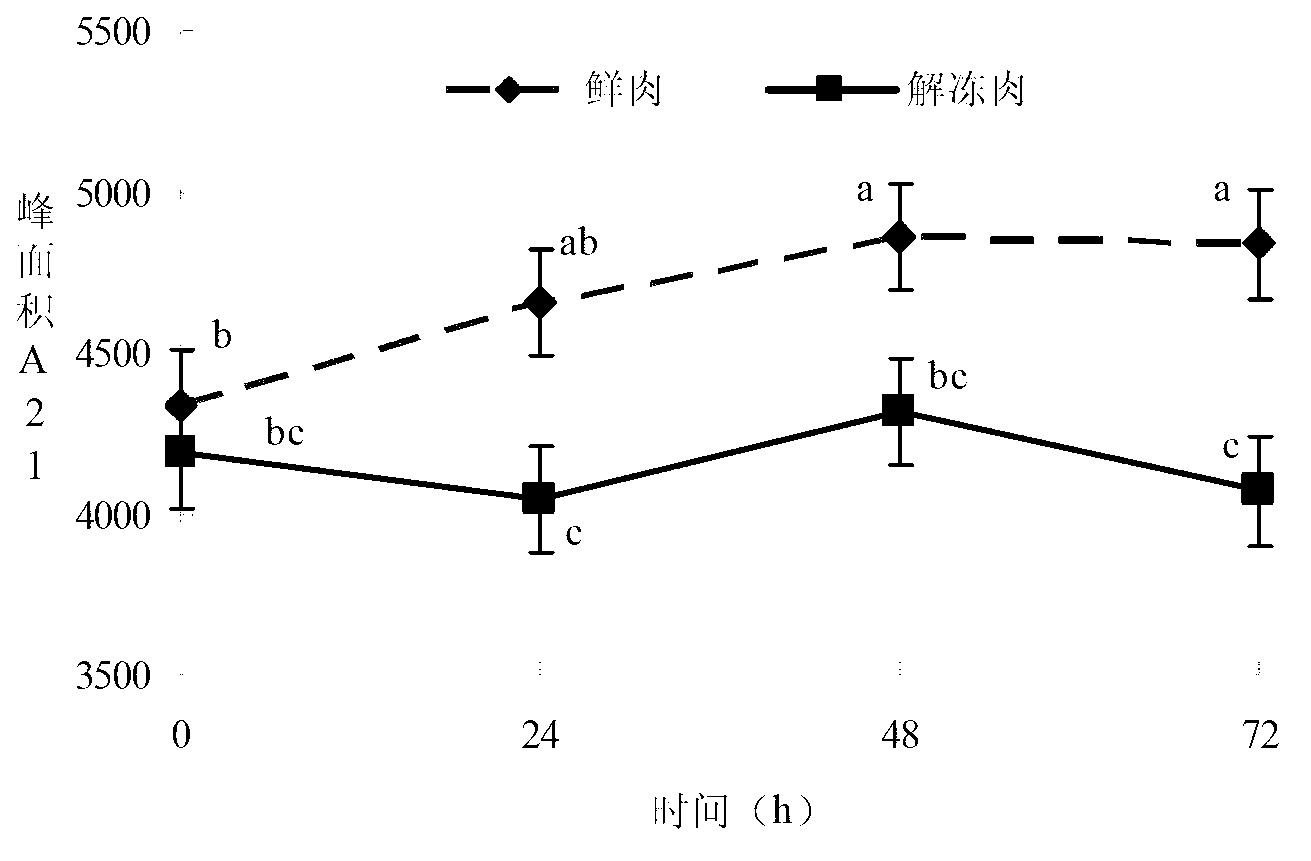
Thawed pork rapid detection indicator screening method based on nuclear magnetic resonance technology
InactiveCN102937601ASolve the rapid detectionStandardization helpsColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceScreening methodLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
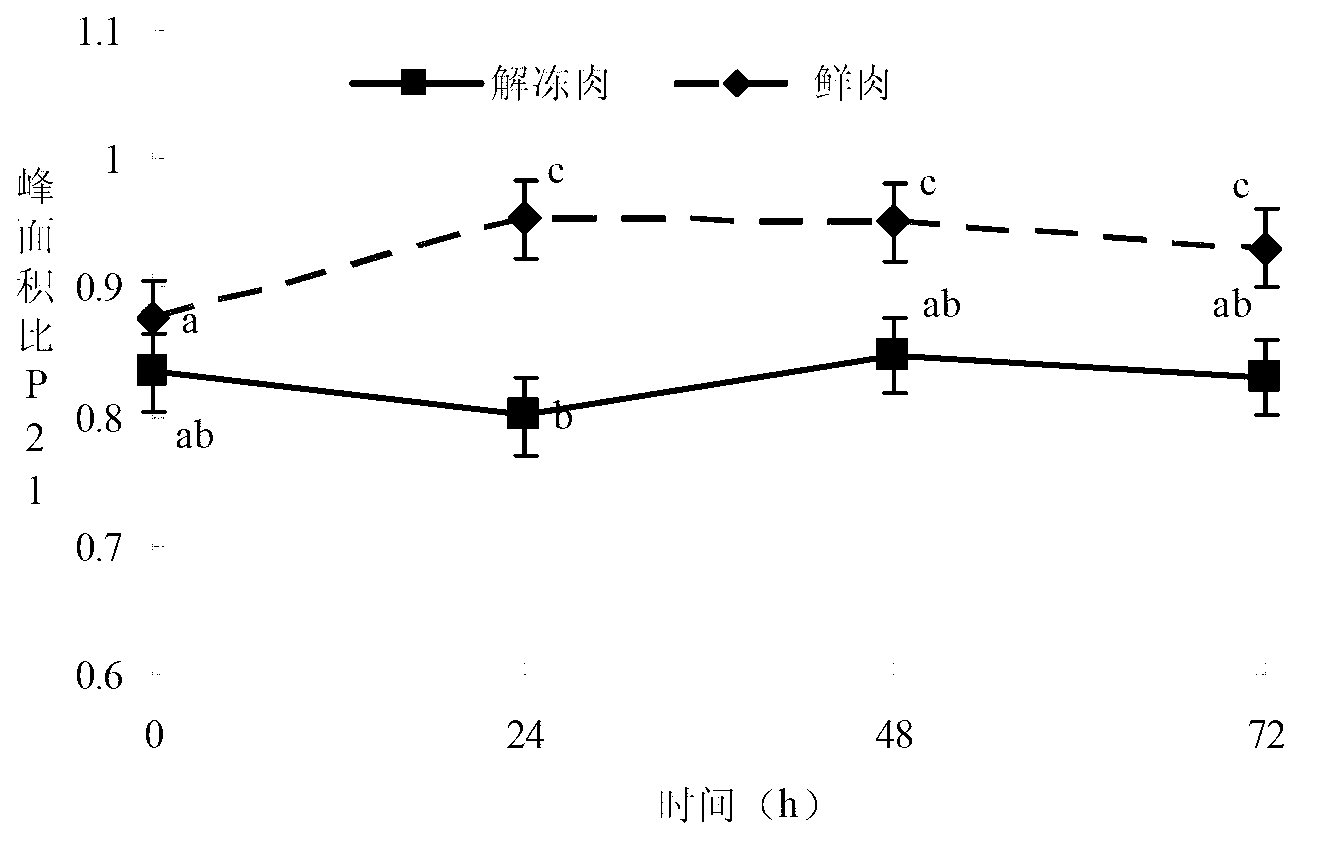
The invention discloses a thawed pork rapid detection indicator screening method based on a nuclear magnetic resonance technology. According to the invention, full bars of pig longissimus muscle obtained after slaughtering within 5h are selected, wherein a pig sample number is no smaller than 10; 8 meat blocks with thicknesses no lower than 2cm are cut along a direction perpendicular to a muscle texture direction; the 8 meat blocks are divided into four groups, wherein one group is blank, and the other three groups are respectively stored for 24h, 48h, and 72h under a temperature of 0-4 DEG C; one meat block of each group is fetched and is frozen and stored for 24h under a temperature of -18 DEG C and is thawed for 6h under a temperature of 0-4 DEG C, and the other meat block of each group is not treated, wherein a repetition number of each treatment combination is no lower than 10; meat color and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2 of each meat block group is respectively determined; peak time t21, peak area A21 and the peak area ratio P21 of the second peak T21 of the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2 image is determined; and the relationships between redness value a* of a chromatic aberration method and thawing and time of thawed pork are determined. Therefore, a standardized operating specification is provided for a thawed pork determination method.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for correcting nuclear magnetic resonance porosity of igneous rock by means of plate
InactiveCN106383365ASolve the problem of small valuesAccurate Correction AccuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonancePorosityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
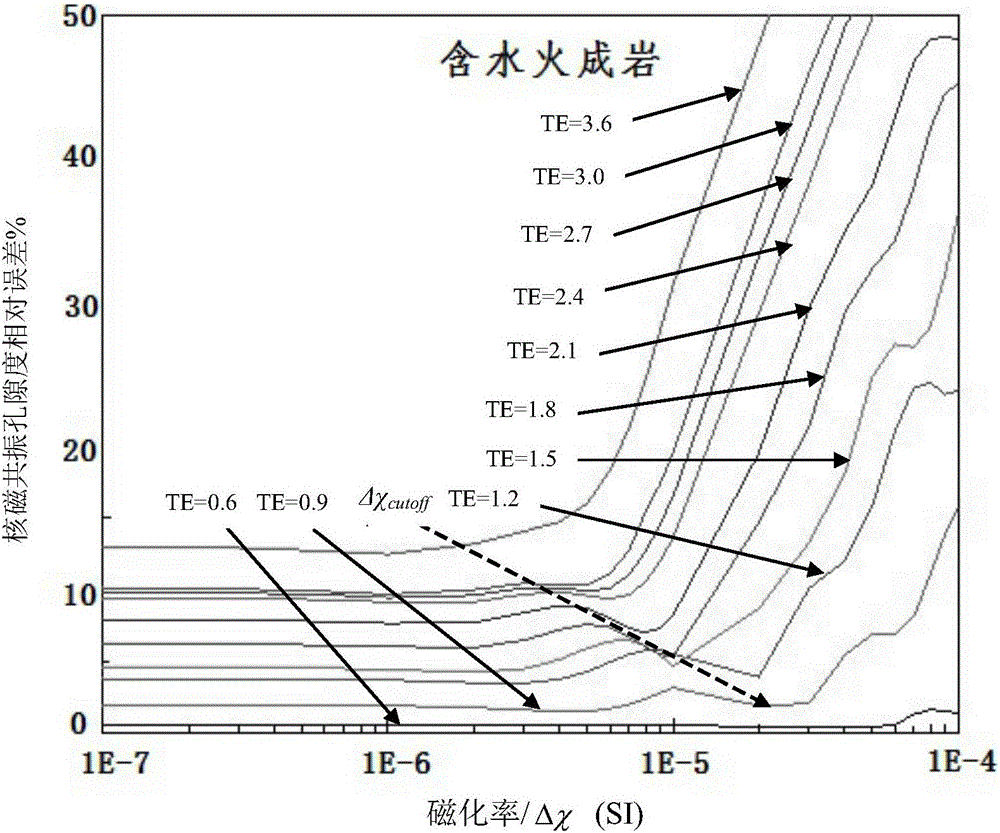
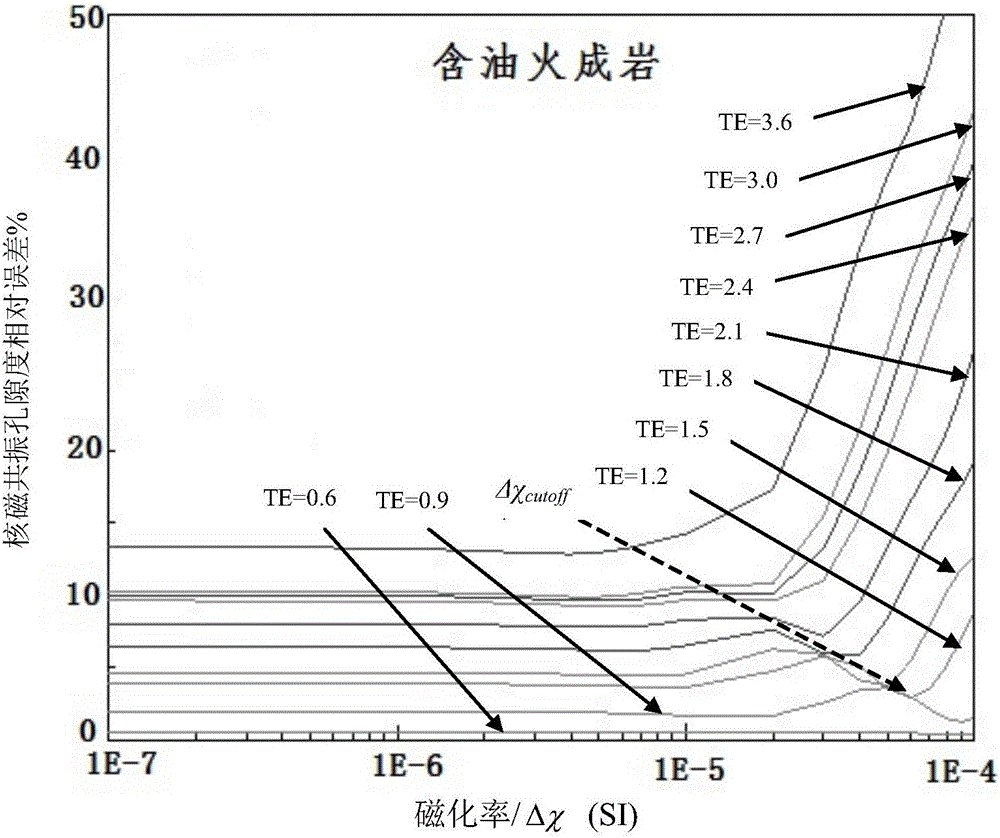
The invention relates to a method for correcting nuclear magnetic resonance porosity of igneous rock by means of a plate. According to the method of the invention, the nuclear magnetic resonance porosity correction plates of different fluid components are obtained through performing analog computation on a large number of values, and a corresponding relative error can be searched by means of the nuclear magnetic resonance porosity correction plates. Under a precondition that fluid property, magnetic susptibility and echo interval in a rock are known, a corresponding relative error can be accurately and quickly obtained through reading the corresponding nuclear magnetic resonance porosity relative error correction plate. Then a nuclear magnetic resonance porosity measurement result is corrected, thereby obtaining the accurate nuclear magnetic resonance porosity. The method settles a problem of relatively small number of the nuclear magnetic resonance porosity and has advantages of high correction accuracy and relatively wide application range. The method supplies important basis for nuclear magnetic resonance logging interpretation of a stratum.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momentum
InactiveCN101939638AHigh sensitivityReduce noiseAnalysis using optical pumpingMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
The present invention relates to a device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of asample, such as fluid, based uponnuclear magneticresonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where the nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentiallyilluminating the sample with a focused beam of lightcarrying angular orbital angular momentum(OAM) and possiblymomentum (spin). Unlike in usual NMR used for (10) magneticnuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the invention does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
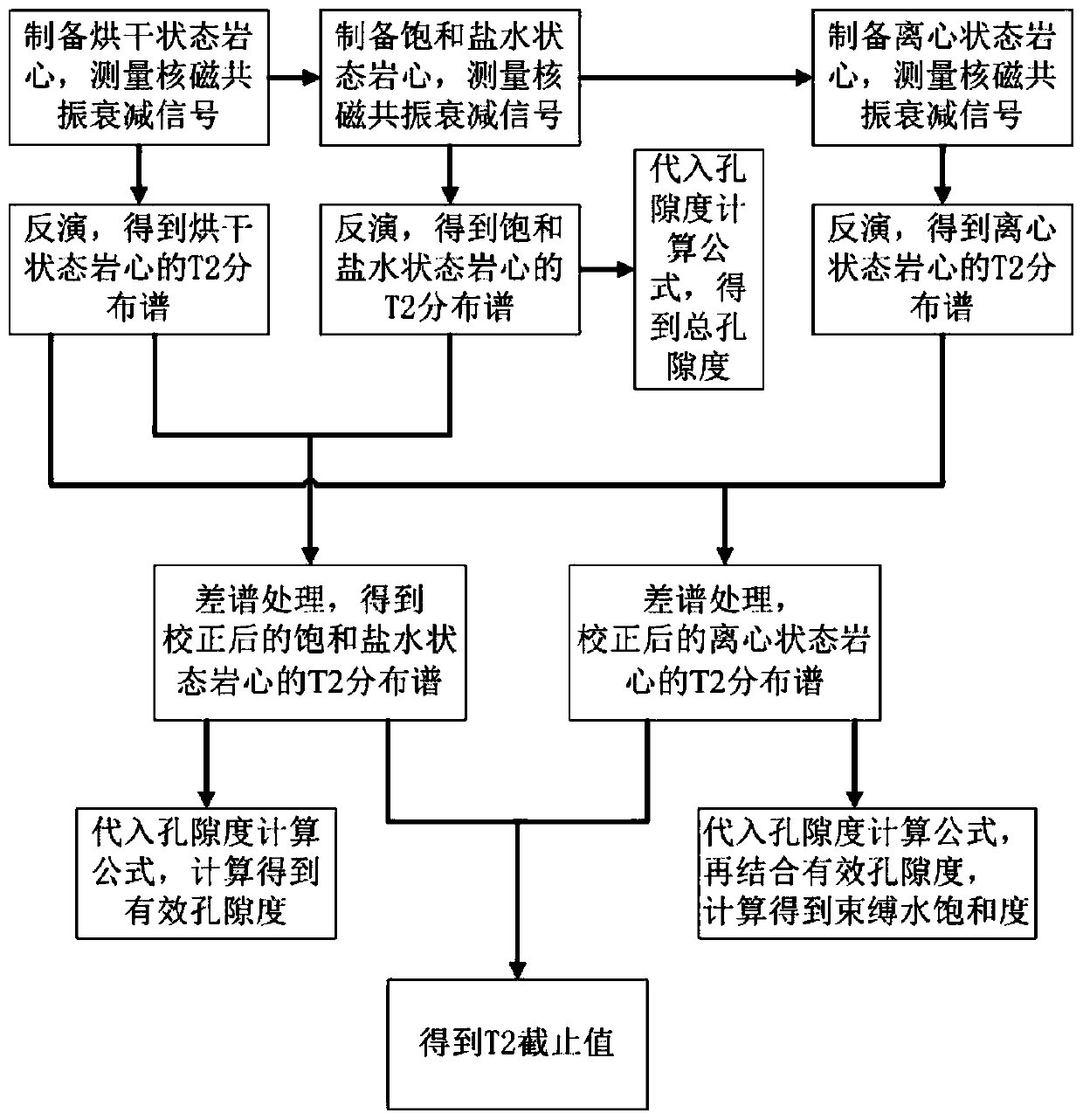
Nuclear magnetic resonance laboratory measuring method for heavy oil and asphaltene cores
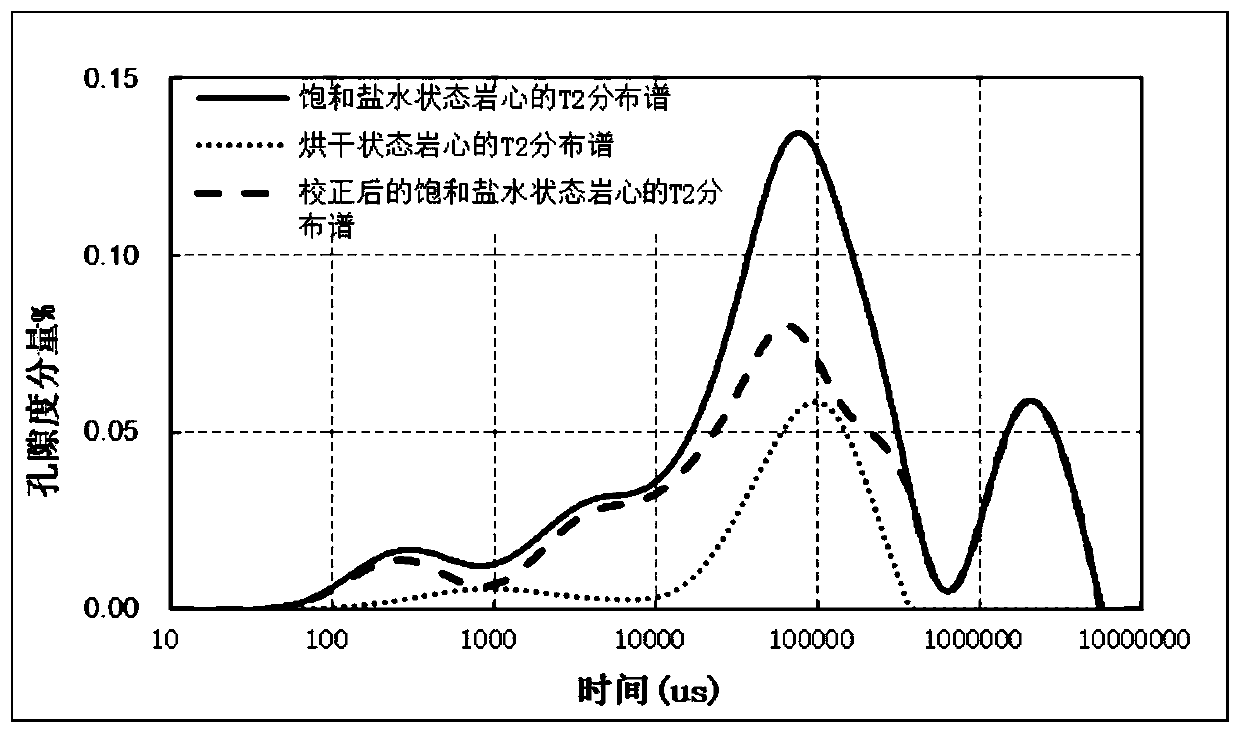
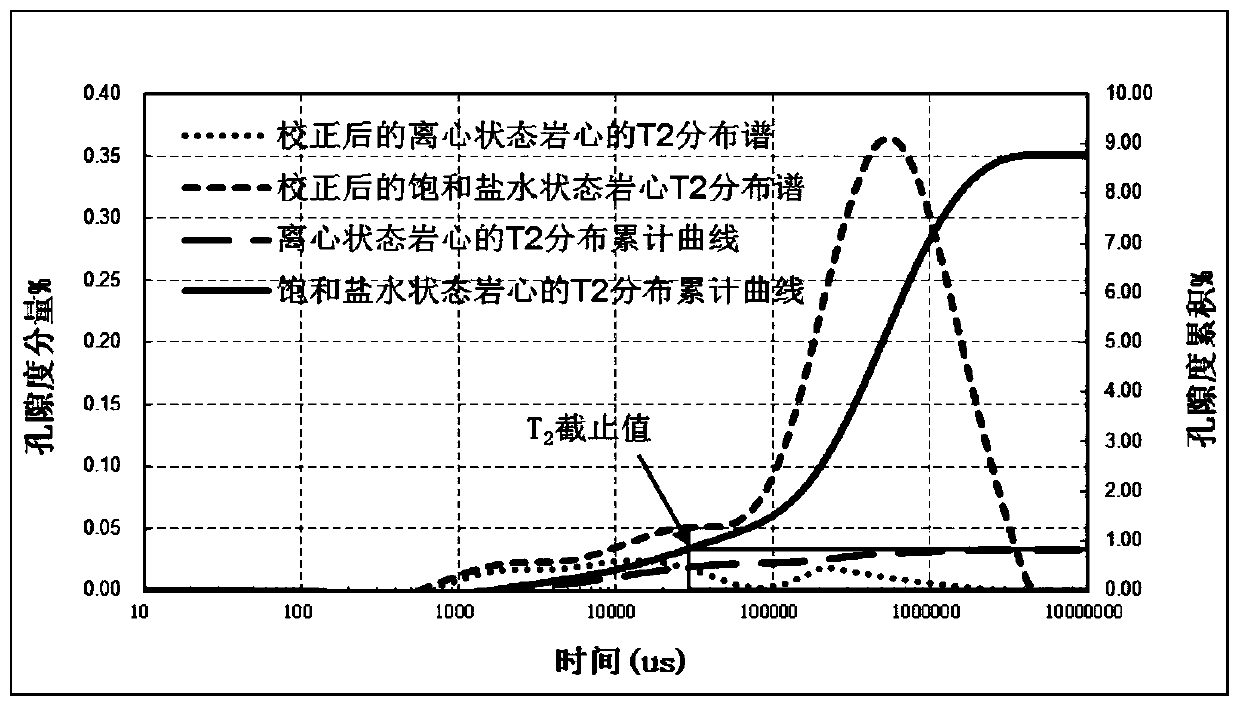
ActiveCN109725016AReduce the impactGuaranteed accuracyWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceAutomatic controlBound water
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance laboratory measuring method for heavy oil and asphaltene cores and belongs to the technical field of automatic control. The method comprises: firstly, measuring the nuclear magnetic resonance attenuation signals of a core in a dry state, a core in a saturated brine state, and a core in a centrifugal state, secondly, obtaining the T2 distributionspectrum of cores in each state by inversion; thirdly, obtaining the corrected T2 distribution spectrum through the difference spectrum processing; further, obtaining a T2 distribution cumulative curve of a core in the saturated brine state and a T2 distribution cumulative curve of a core in the centrifugal state; obtaining total porosity, effective porosity, bound water saturation, and T2 cutoffvalue by calculating the above results. The calculated results are more realistic and accurate, and eliminate the influence of nuclear magnetic resonance attenuation signals in the dry state. The method is specially designed for unconventional cores containing heavy oil and asphaltenes, and has broad application prospects in the field of unconventional oil and gas nuclear magnetic logging.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Reservoir classification method based on nuclear magnetic resonance logging
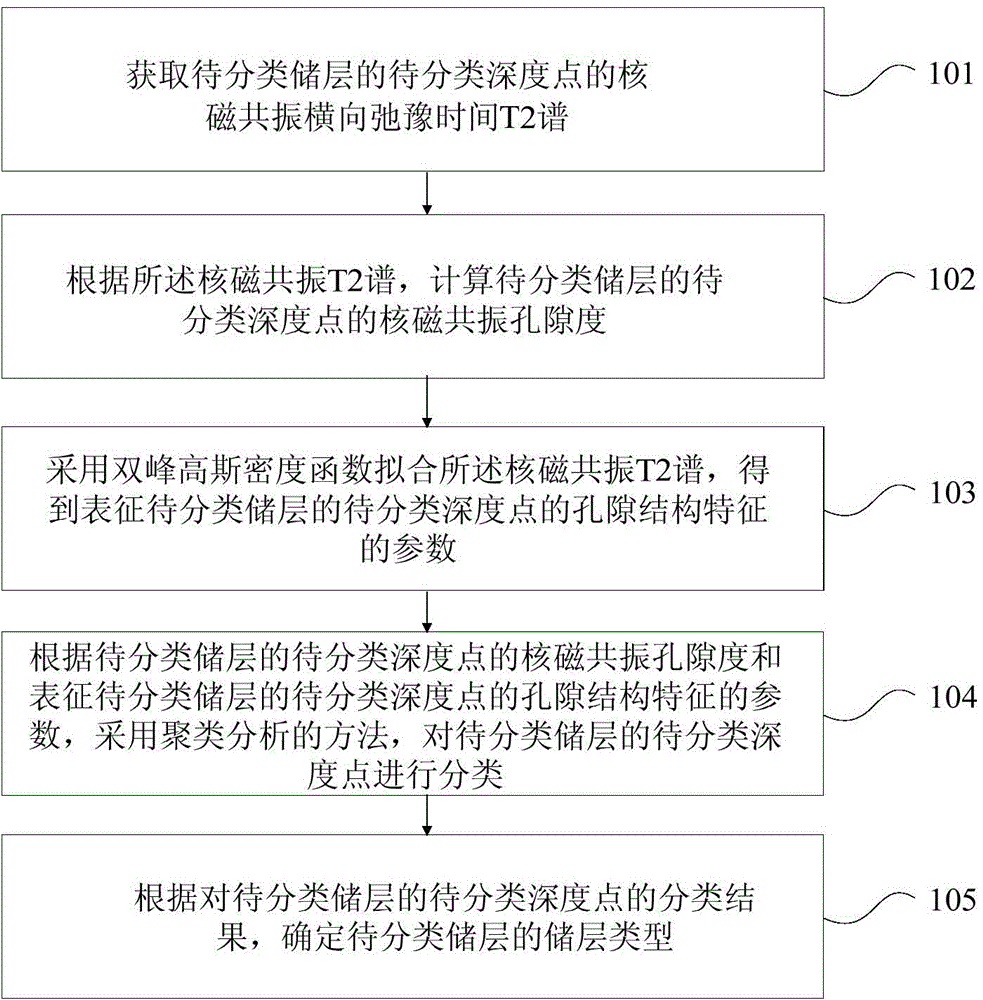
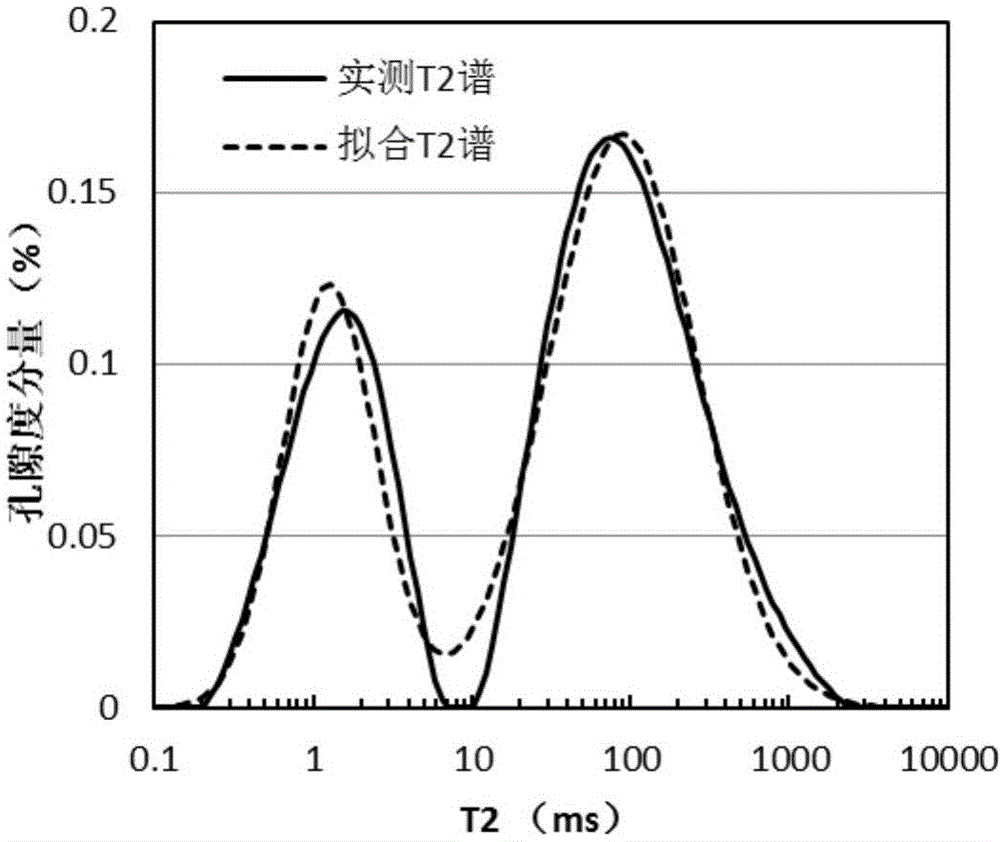
InactiveCN104932027AImprove accuracyElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationPorosityClassification methods
The invention discloses a reservoir classification method based on nuclear magnetic resonance logging, comprising the steps of: obtaining a nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time T2 spectrum of a depth point to be classified of a reservoir to be classified; calculating the nuclear magnetic resonance porosity of the depth point to be classified of a reservoir to be classified in dependence on the nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum; employing a doublet Gaussian density function to fit the nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum to obtain parameters representing pore structure characteristics of the depth point to be classified of a reservoir to be classified; employing a cluster analysis method to clarify the depth point to be classified of a reservoir to be classified in dependence on the nuclear magnetic resonance porosity of the depth point to be classified of a reservoir to be classified and the parameters representing pore structure characteristics of the depth point to be classified of a reservoir to be classified; and determining the reservoir type of the reservoir to be classified in dependence on the classification result of the depth point to be classified of a reservoir to be classified. The technical scheme provides strong technical support for accurate divide and reasonable development of a reservoir type.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Inversion method of nuclear magnetic resonance signals facing multiple relaxation components
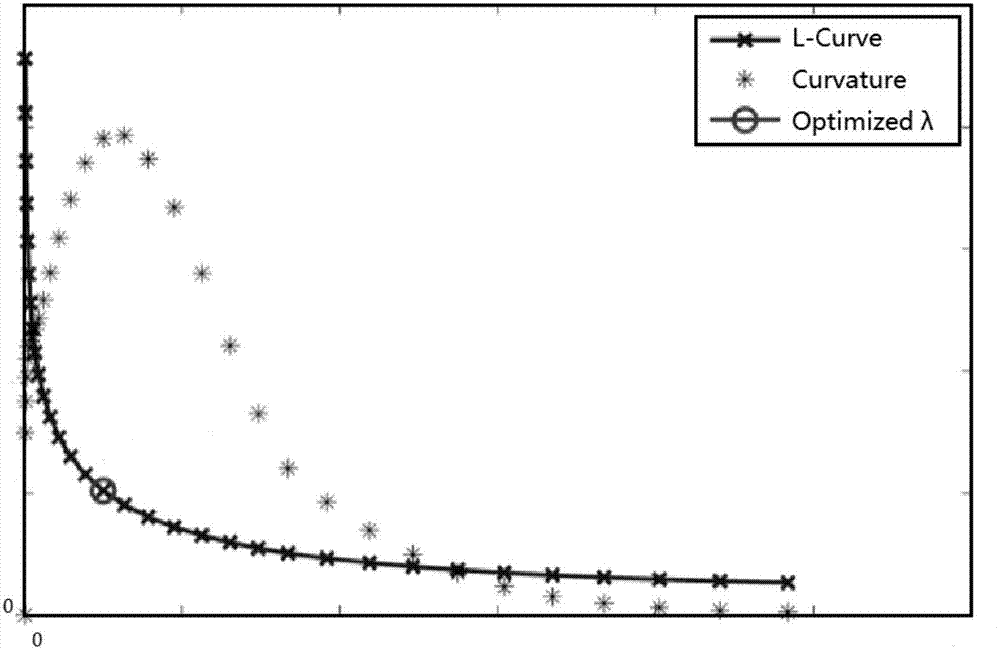
InactiveCN110109037ABest smoothing factorThe solution result is accurateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData compressionInversion methods
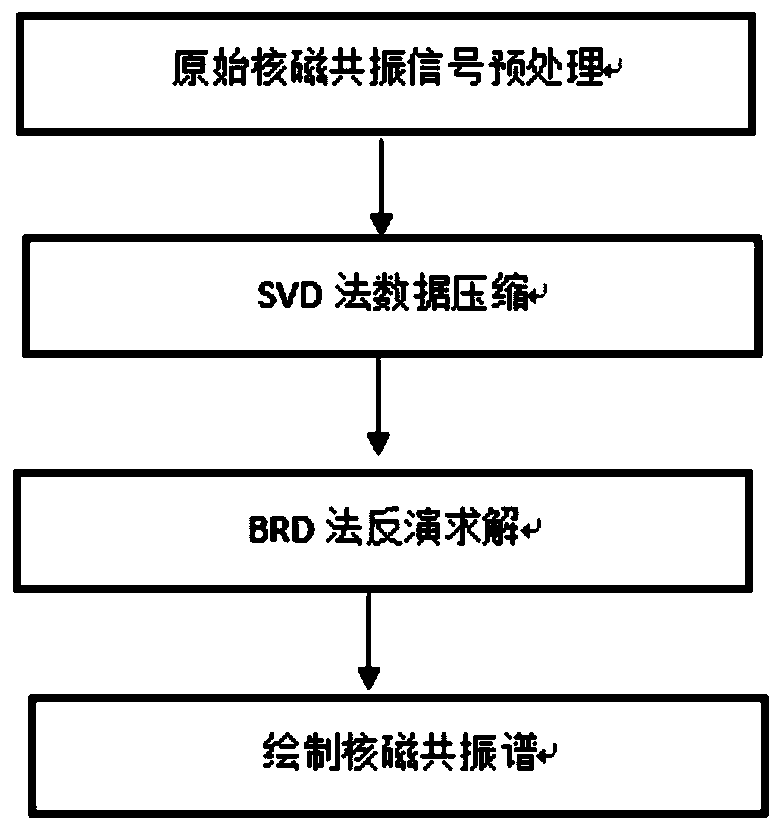
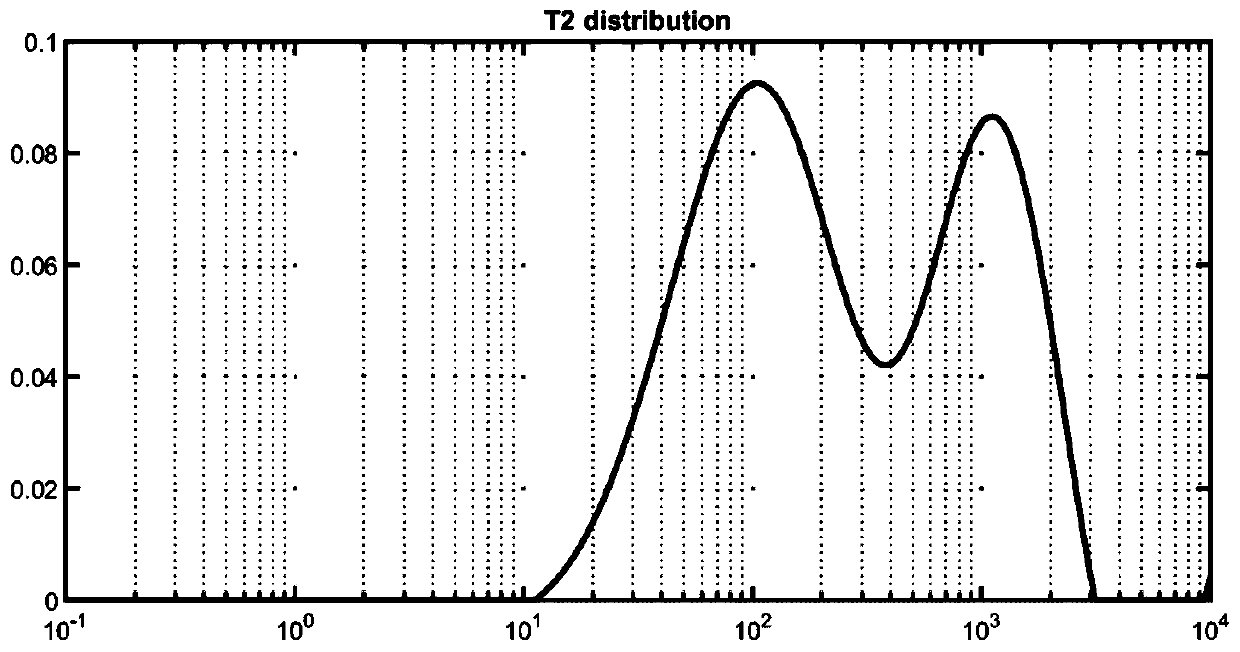
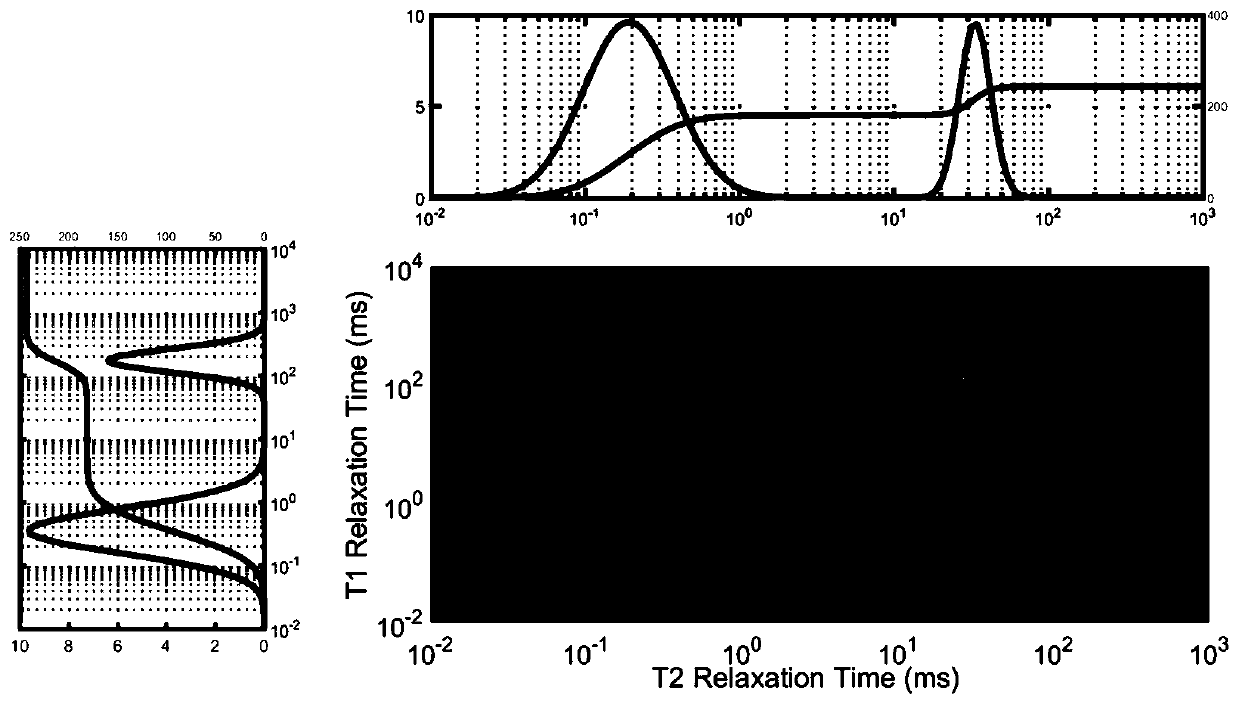
The invention relates to an inversion method of nuclear magnetic resonance signals facing multiple relaxation components. The inversion method of the nuclear magnetic resonance signals facing the multiple relaxation components is characterized by comprising the following steps that (1) original nuclear magnetic resonance signal data are preprocessed, and the signal-to-noise ratio of collected dataand basic parameters of the collected data are obtained; (2) the nuclear magnetic resonance signals are subjected to data compression by an SVD algorithm; (3) an inversion equation of nuclear magnetic resonance is solved based on a BRD algorithm, and obtained solutions are distributed data of transverse relaxation time contained by different relaxation components; and (4) an nuclear magnetic resonance inversion spectrum is drawn, and inversion results are quantificationally evaluated. Compared with an existing nuclear magnetic resonance inversion method, the inversion method of the nuclear magnetic resonance signals facing the multiple relaxation components can process the nuclear magnetic resonance signals with multiple groups of component samples efficiently, can obtain better results under a low signal-to-noise ratio, and has important significance for the aspects of experimental sample identification and quantitative analysis of composition components.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Permanent magnet used for nuclear magnetic resonance imager
ActiveCN103860178AImprove permeabilityHigh saturation magnetic inductionMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)NMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
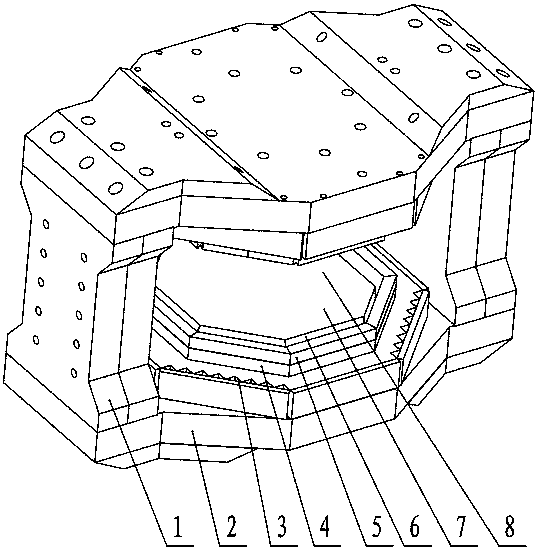
The invention discloses a permanent magnet used for a nuclear magnetic resonance imager. The permanent magnet comprises upper and lower housing caps and double-columns, wherein the upper and lower housing caps and the double-columns are connected through bolts to form a building block-type assembled H-shaped yoke; two steel magnets, two polar plates, two shimming rings, two eddy current discs, gradient coils and transmitting coils are respectively and symmetrically arranged on the upper and lower housing caps in sequence to form testing regions; the upper outer end part of each polar plate is provided with the corresponding shimming ring; the two eddy current discs are respectively arranged in the two shimming rings; the two gradient coils and the two transmitting coils are respectively arranged on the two eddy current discs in the shimming rings; the magnetic field intensity of each imaging region (i.e. sphere region, of which the diameter is 400nm, at the central region of the permanent magnet) is between 4000 gauss to 5500 gauss. The eddy current discs respectively manufactured by splicing amorphous sheets of an iron-based amorphous alloy soft magnetic strip 1K101 is capable of better eliminating or reducing eddy current generated by the polar plates, and therefore, the signal to noise ratio is higher, and imaging is clearer; by adopting the N52-N55 high-performance neodymium-iron-boron steel magnets and the gradient and transmitting integrated coils, the overall dimension reduction and the total weight reduction of the permanent magnet can be realized, and moreover, processing is simple, the structure is changeable and shimming is convenient.
Owner:SHENYANG GENERAL MAGNETIC
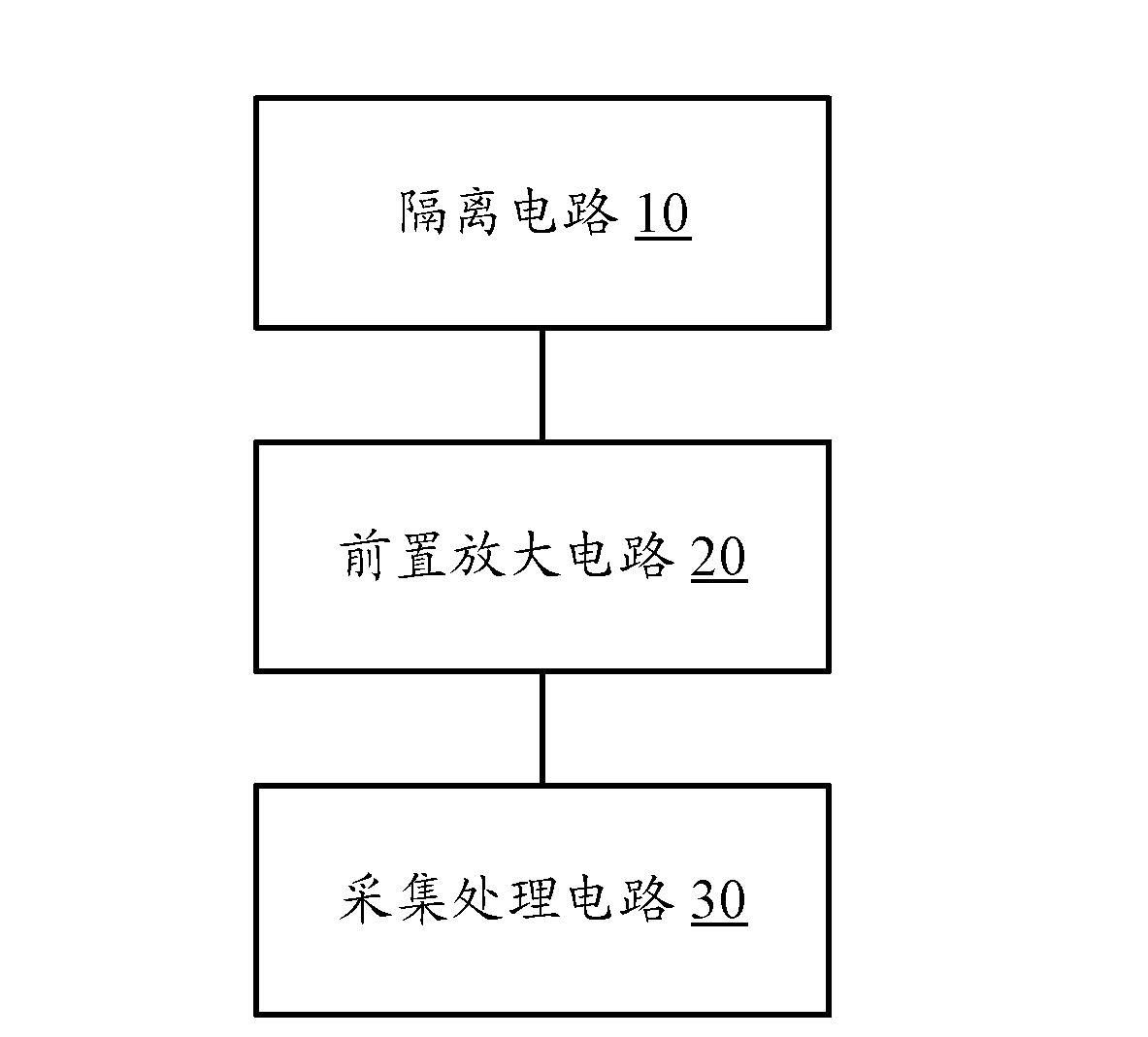
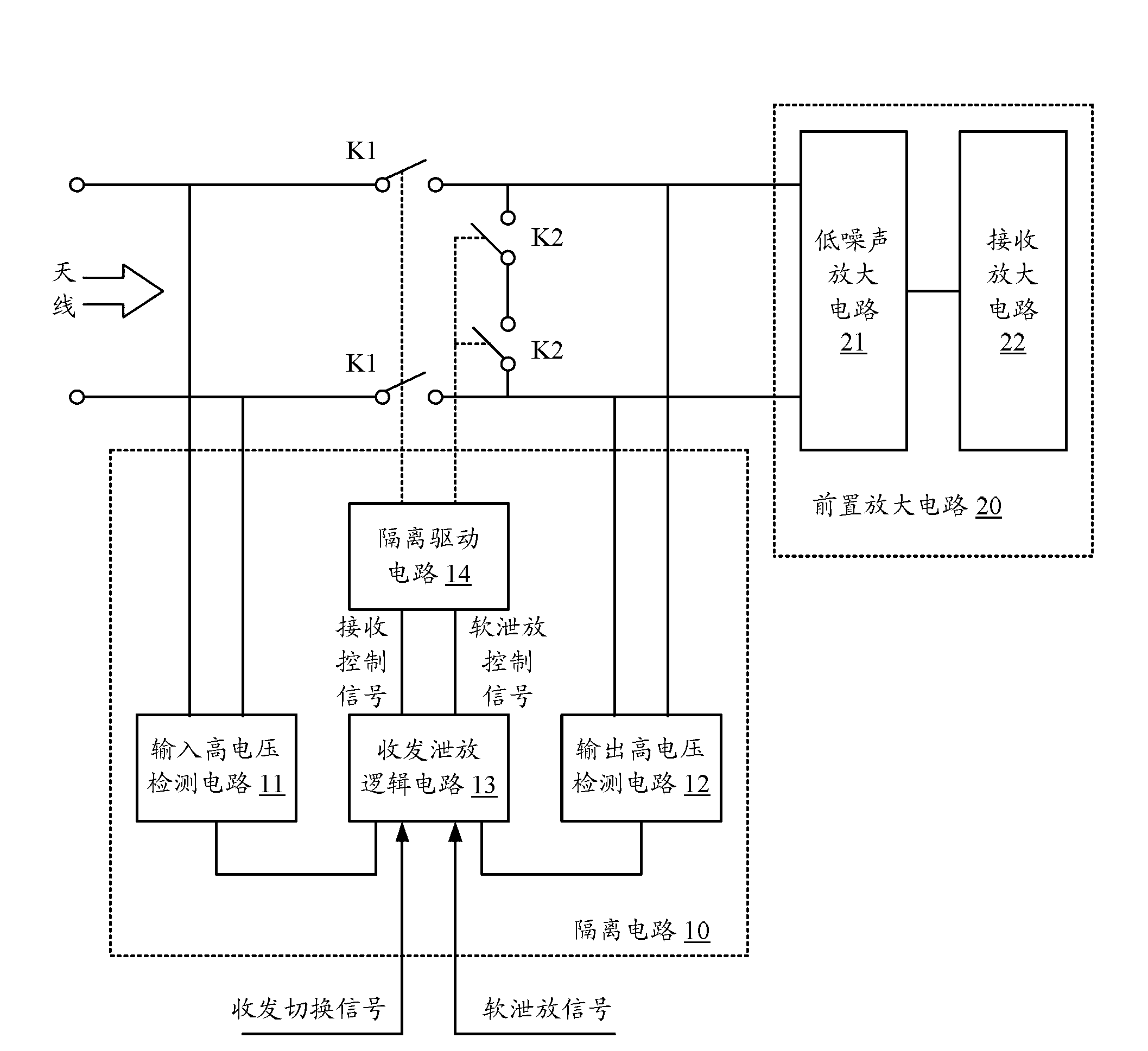
Signal processing device for nuclear magnetic resonance logger
ActiveCN102839965AReduce distanceEliminate signal distortionSurveyNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSignal processing
The invention discloses a signal processing device for a nuclear magnetic resonance logger, and the existing shortcoming that a nuclear magnetic resonance signal enters at the position where a probe and a circuit are connected and causes interference so that distortion happens is overcome. The device is embedded in the probe of the nuclear magnetic resonance logger, and comprises an isolating circuit, a pre-amplification circuit and a collecting and processing circuit, the isolating circuit is used for conduction when an antenna receives a signal, the pre-amplification circuit is used to filter and amplify the signal received by the antenna and output a pre-processed signal which is sent to the collecting and processing circuit, the collecting and processing circuit is used to collect the pre-processed signal to obtain a collected signal and process the collected signal with related digital phase sensitivity detecting (DPSP) or wavelet-type DPSP, and accordingly amplitude value and phase information of a nuclear magnetic resonance echo signal can be obtained. The signal processing device for the nuclear magnetic resonance logger rules out the possibility of signal distortion caused by remote transmission.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Online low-field nuclear magnetic resonance oil-containing seed sorting system
ActiveCN103406287AAccurate measurementLabor savingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSortingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceContact type
The invention discloses an online low-field nuclear magnetic resonance oil-containing seed sorting system. The online low-field nuclear magnetic resonance oil-containing seed sorting system is constructed by integrating a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging analyzer for scientific researches with an automatic sample processing device. The accurate determination on the oil content of grain seeds is realized and a sampling test with large-batch and long-lasting repeated experiments is realized, so that the advantages including no damage and non-contact type detection of a nuclear magnetic resonance technology are expressed to the greatest extent. The online low-field nuclear magnetic resonance oil-containing seed sorting system disclosed by the invention breaks through the technical bottleneck of a grain seed breeding method, so that manpower needed by seed sieving work is saved and the sieving quality is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NIUMAI ELECTRONICS TECH +2
Method for determining conversion rate during p-polyisobutylene phenol synthesis process through quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
ActiveCN108152318AAvoid cumbersomeImprove accuracyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopyPhenol
The invention relates to a method for determining the conversion rate of polyisobutylene, in particular to a method for determining the conversion rate of the polyisobutylene during a process of generating p-polyisobutylene phenol through reaction of the polyisobutylene and excessive phenol through a quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The method comprises the steps of respectively acquiring a polyisobutylene phenol sample, and a polyisobutylene and phenol nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, obtaining chemical shift of the p-polyisobutylene phenol through spectrogram comparison and spectrogram reasoning; determining longitudinal relaxation time T1 of a p-polyisobutylene phenol sample in a deuteration reagent, setting a pulse flip angle and relaxation time of a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer according to the T1, utilizing the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for determining the nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of a solution to be tested, obtaining a peak area of each part of hydrogen through integration, and calculating to obtain the conversion rate of the polyisobutylene through the number of hydrogen actually contained in a target product and raw materials. The method provided by the invention is low in cost, can be used for quickly and accurately evaluating the type and the conversion rate of a synthetic product of the polyisobutylene and the phenol, and provides a powerful evidence for synthesis.
Owner:CHAMBROAD CHEM IND RES INST CO LTD
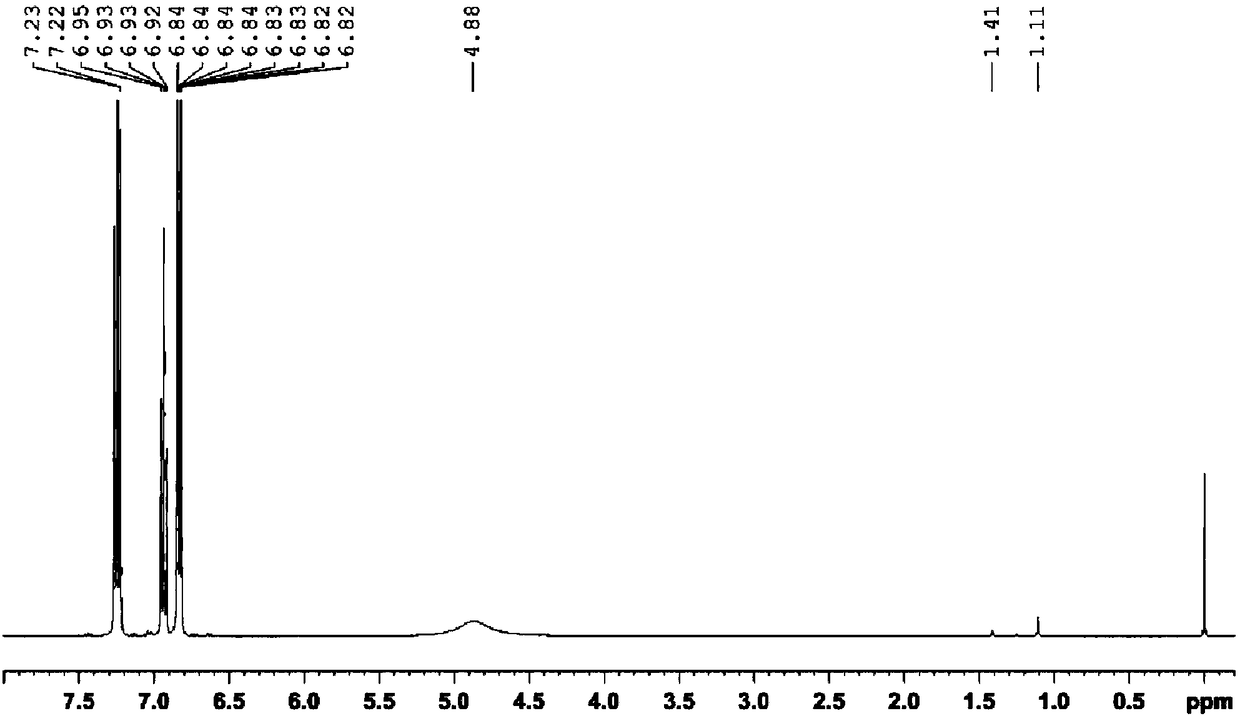
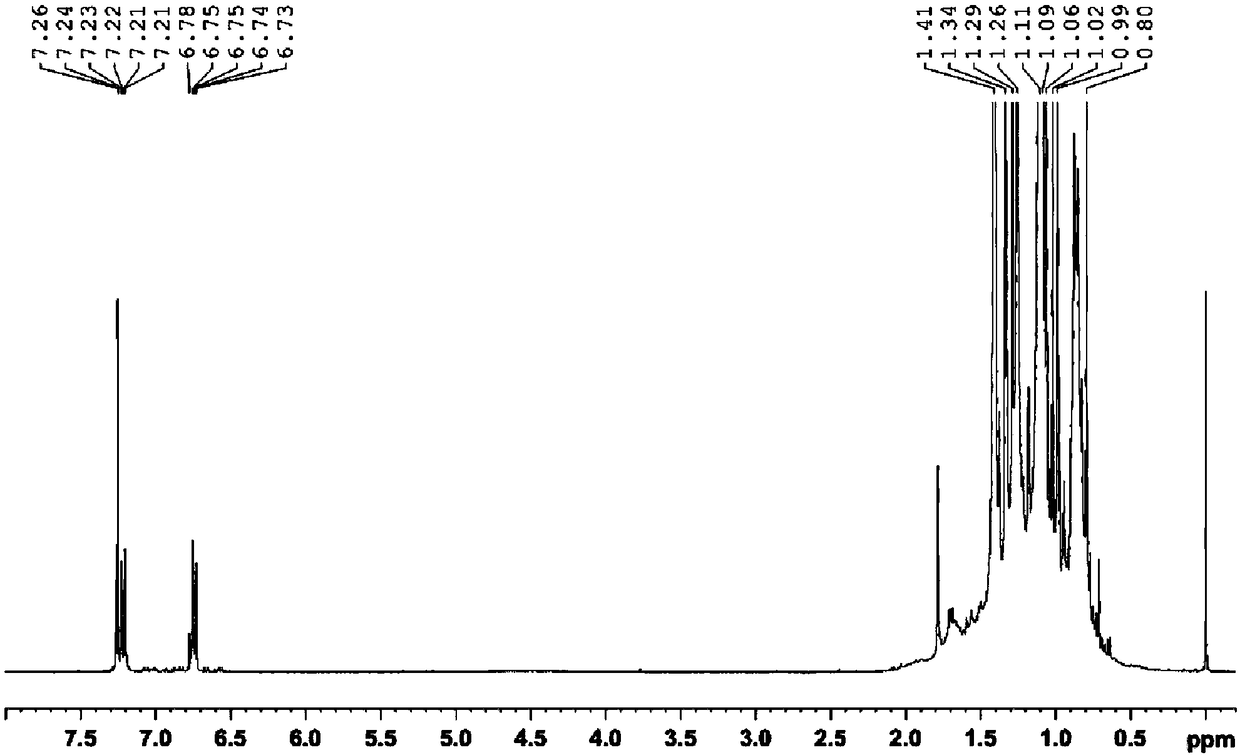
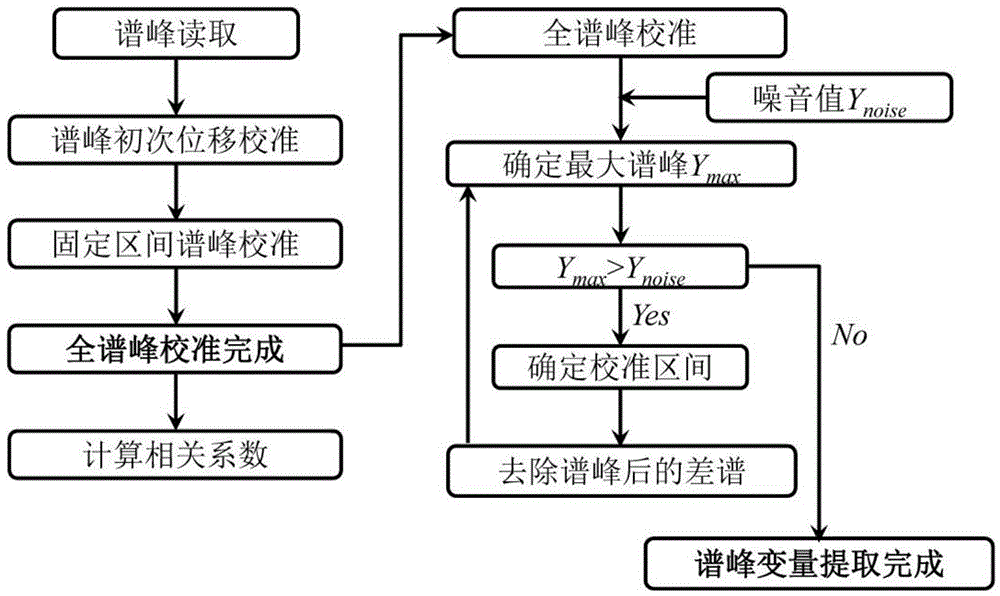
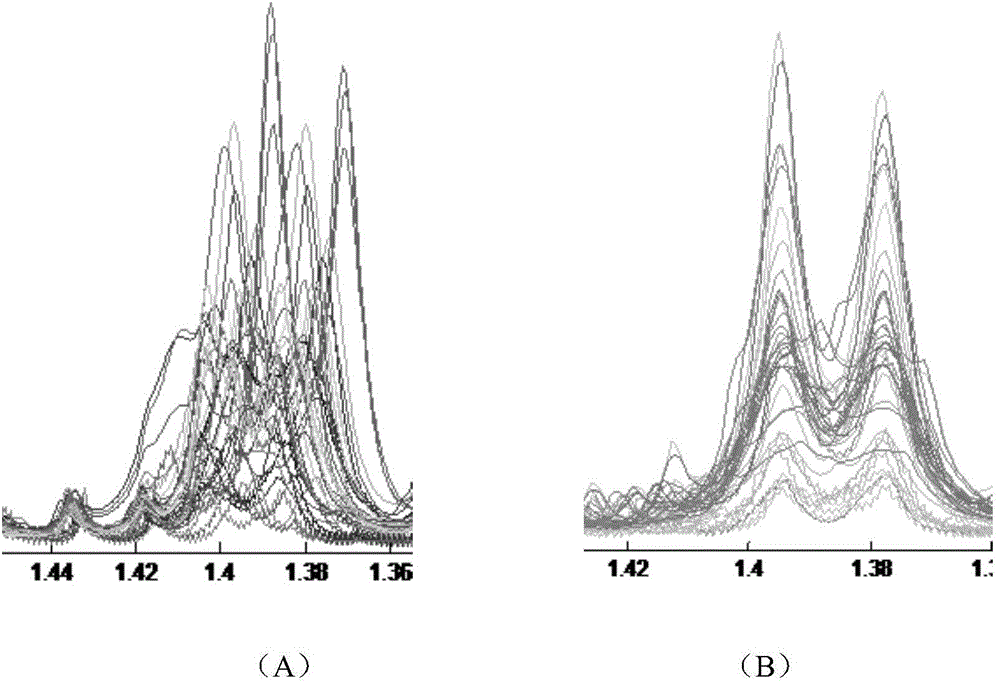
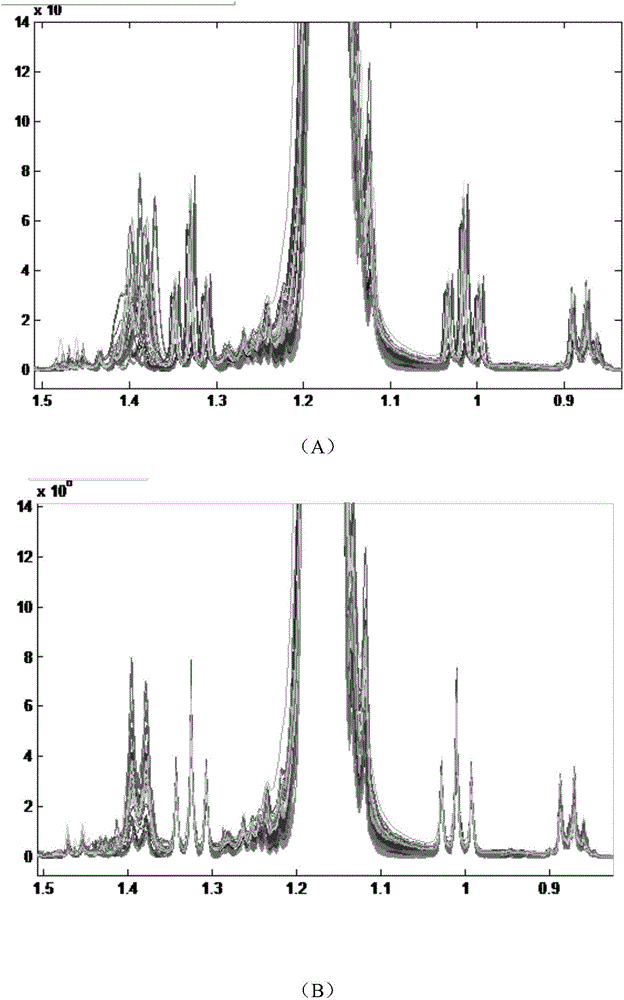
Spectral peak alignment and spectral peak extraction method of nuclear magnetic resonance spectrums
ActiveCN104458785AWide applicabilityWide adaptabilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePeak alignmentNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a spectral peak alignment and spectral peak extraction method of nuclear magnetic resonance spectrums. The method comprises the following steps: reading various nuclear magnetic resonance spectrograms; carrying out preliminary calibration on various nuclear magnetic resonance spectrograms by using spectral peaks with internal standard compounds or characteristic spectral peaks of preset compounds; taking scheduled nuclear magnetic resonance spectrograms as reference spectrograms and dividing into a plurality of fixed intervals; calibrating to-be-calibrated nuclear magnetic resonance spectrograms in various fixed regions; and integrating each nuclear magnetic resonance spectrogram after correcting each nuclear magnetic resonance spectrogram in each fixed region. The spectral peak alignment and spectral peak extraction method is wide in applicability, almost adapts to treatment of all nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum data, and is simple in data treatment and relatively fast in algorithm.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
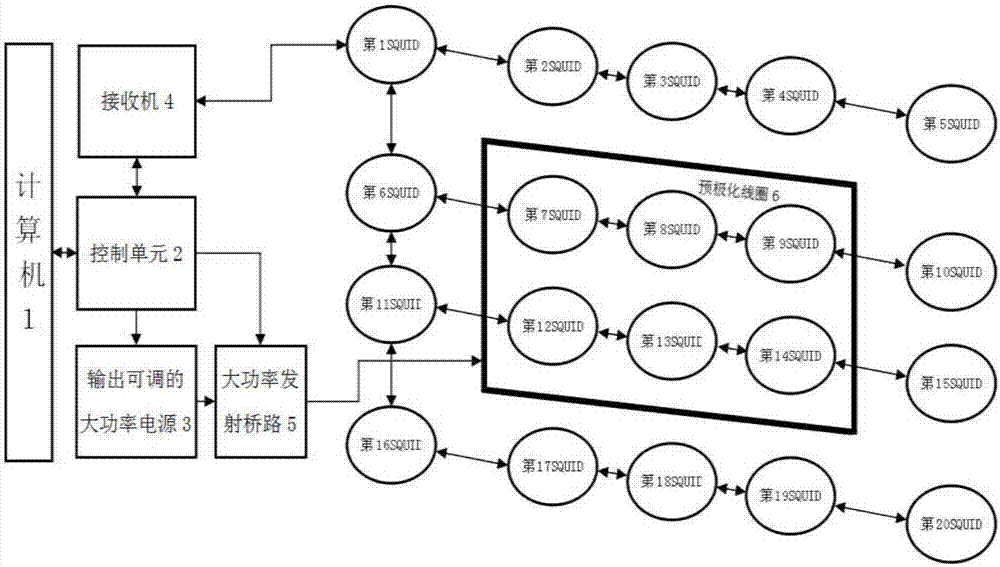
Array SQUID nuclear magnetic resonance groundwater detection device and imaging method
ActiveCN106873044AIncrease the magnetic field strengthAccurate collectionWater resource assessmentDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceWater useMagnetization
The invention relates to an array SQUID nuclear magnetic resonance groundwater detection device and an imaging method. According to the device, a computer is connected with a pre-polarization coil through a control unit, a high power supply and a high-power transmitting bridge circuit, the control unit is connected with a receiver and the high-power transmitting bridge circuit, and the receiver is connected with a 20th SQUID through first to 19th SQUIDs. By polarizing detected water using the pre-polarization coil, the macro magnetization intensity of water is increased. Through an array SQUID receiving mode, extremely weak geo-electrical signals can be detected, greater initial amplitude of a nuclear magnetic resonance signal can be obtained, and an underground nuclear magnetic resonance detection image can be obtained in a strong-noise environment. The problem that a receiver coil is inconvenient to carry and is inconvenient in signal reception in the field is solved, and a reasonable way of receiver layout can be selected according to the topography of a region needing detection. The efficiency of groundwater searching is increased, and the cost of drilling exploration is reduced. The device and the method are conducive to detection of groundwater in a detection area in a complex-topography and strong-noise environment.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
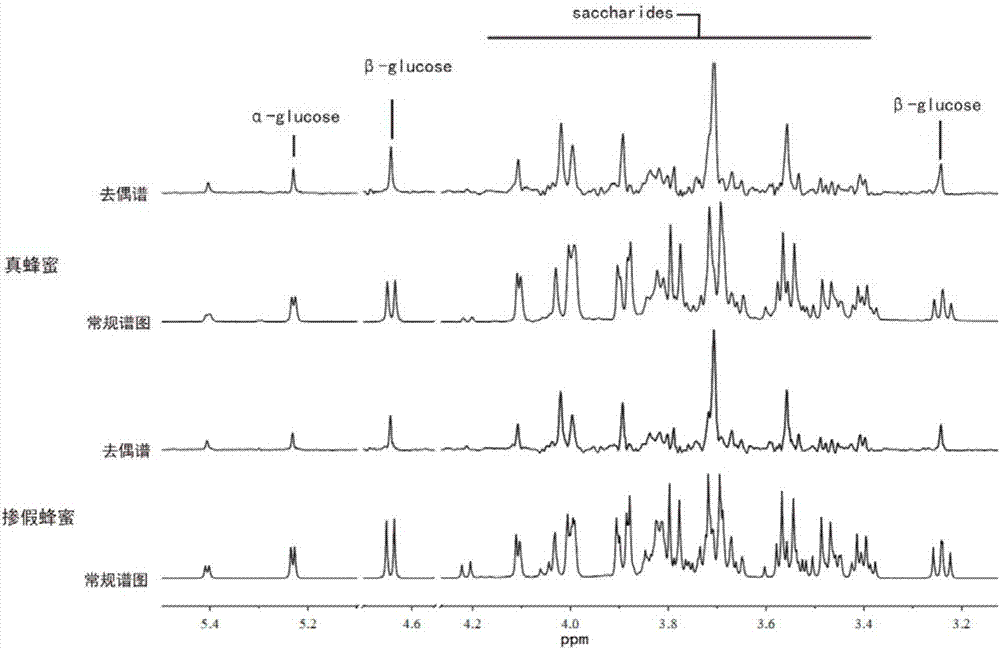
Magnetic resonance imaging decoupling hydrogen spectrum method for identifying true and adulterated honey
ActiveCN107505349ARealize authenticationQuality improvementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceStatistical analysisConfocal
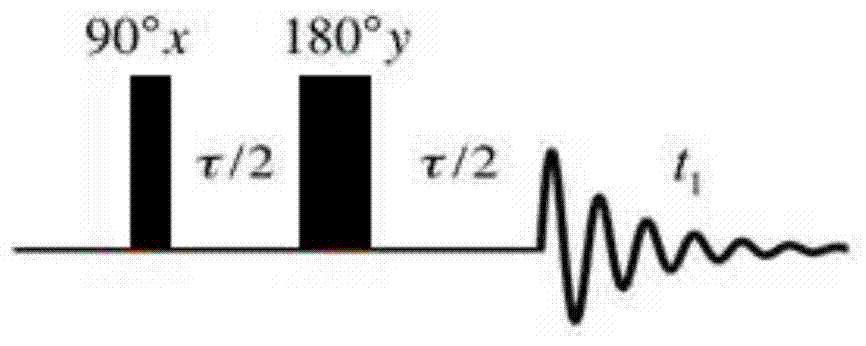
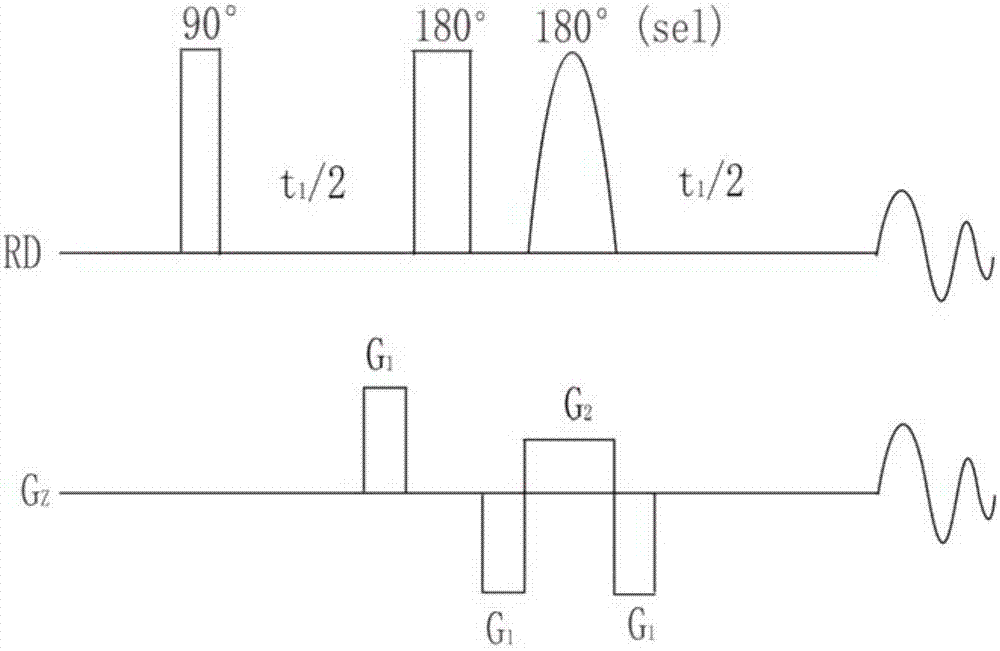
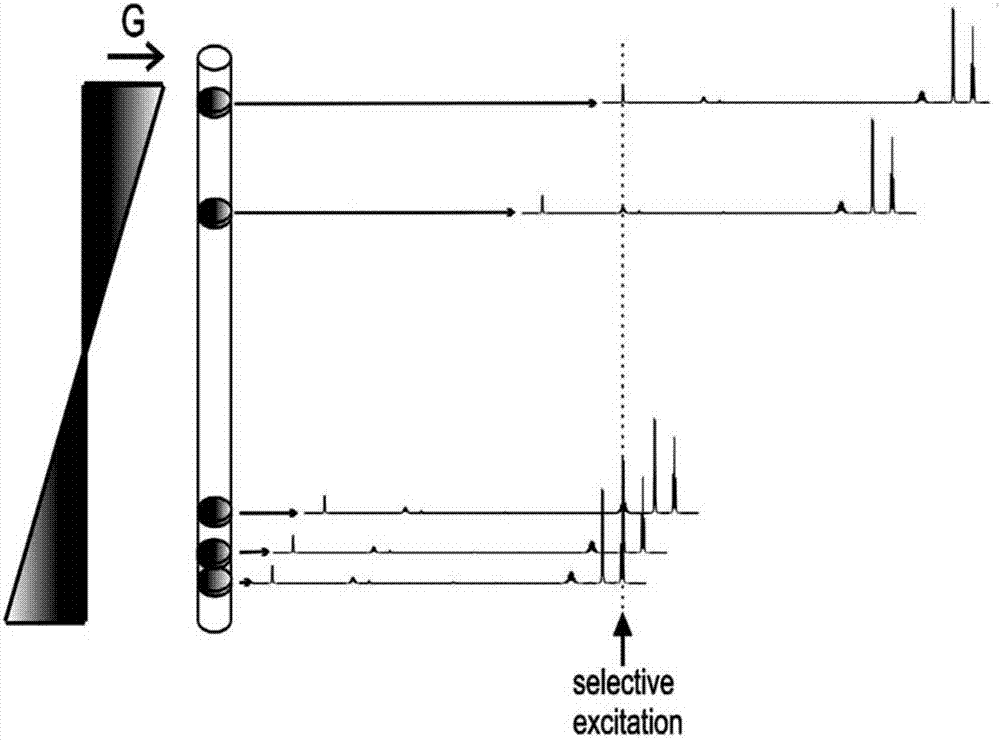
The invention provide a magnetic resonance imaging decoupling hydrogen spectrum method for identifying true and adulterated honey and relates to nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The method comprises the following steps: adding an identified honey sample into a buffer solution, centrifuging the prepared sample, removing supernatant liquid, and transferring the sample into a magnetic resonance resonance tube; importing a precompiled decoupling NMR spectrum pulse sequence into a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; setting pulse sequence parameters and sampling parameters, and collecting data; after the sampling is finished, carrying out relevant data processing so as to obtain a decoupling spectrogram of all samples, and preprocessing corresponding experimental data, so as to obtain subsection integral data of the decoupling spectrogram; and importing the decoupling the subsection integral data into statistical analysis software, carrying out principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least square analysis so as to judge the sizes of inter-group and in-group differences of two groups, analyzing a compound which causes the inter-group differences, and judging an adulteration manner of the adulterated honey. The pulse sequence is homonuclear wide-band decoupling pure chemical displacement spectrum method, and a 1HNMR spectrum with relatively high resolution for eliminating coupled splitting can be obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
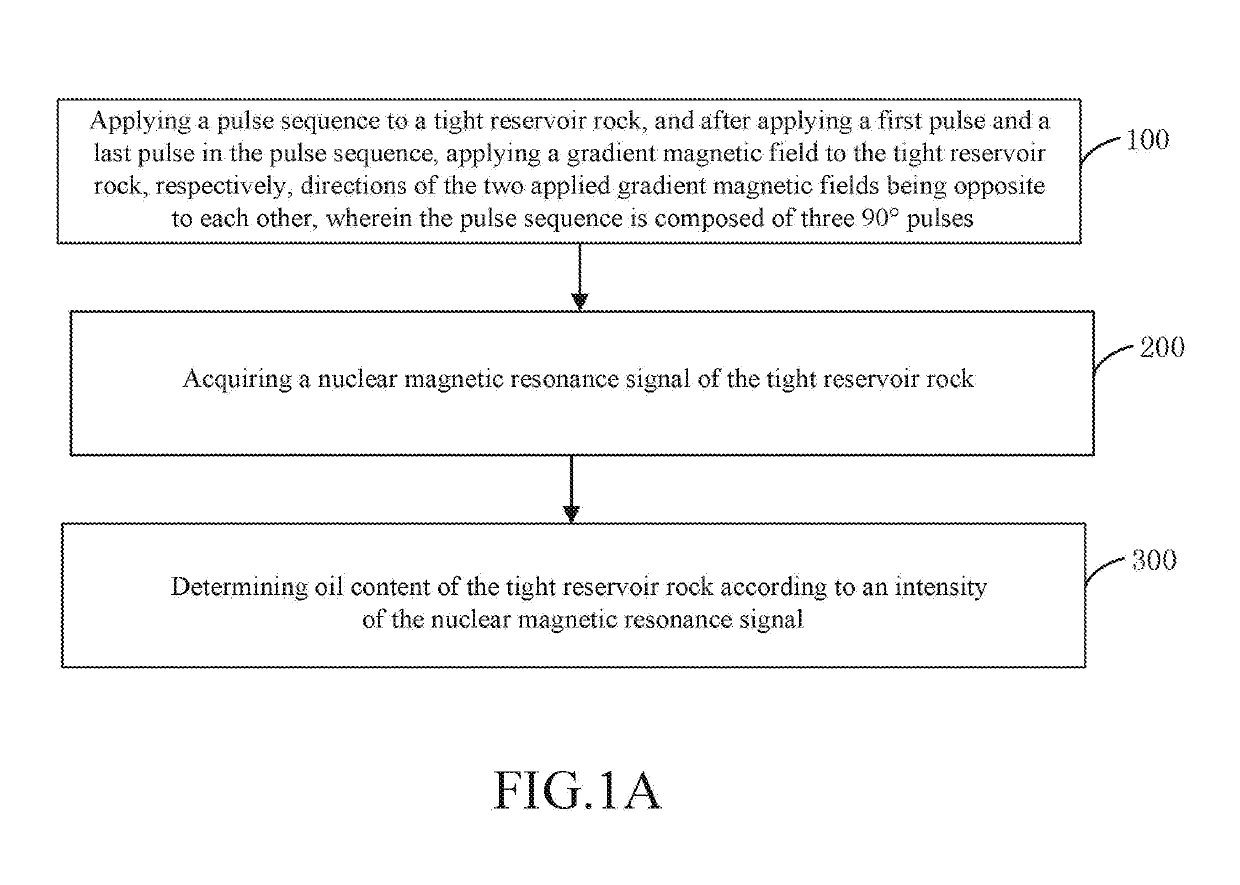
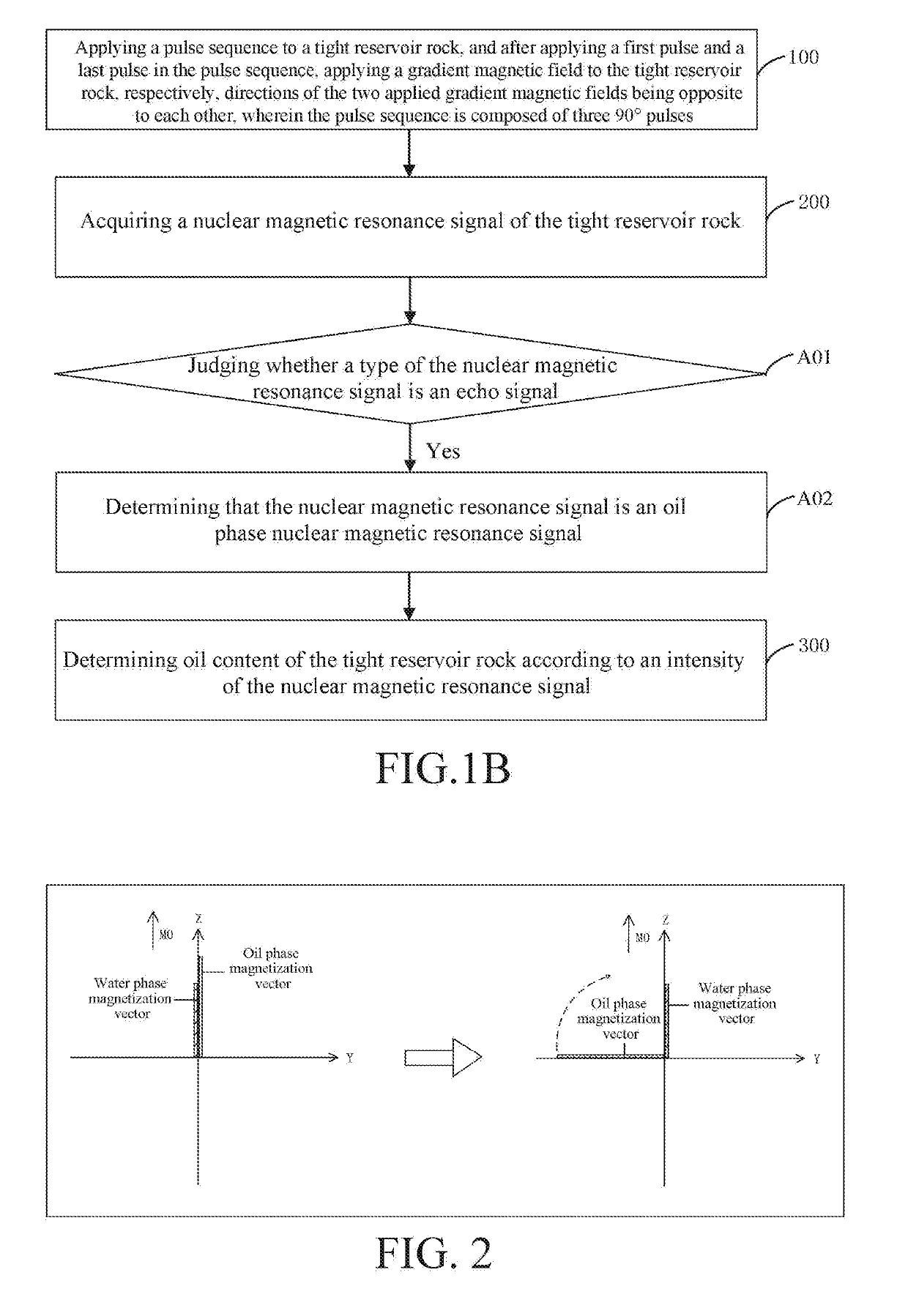
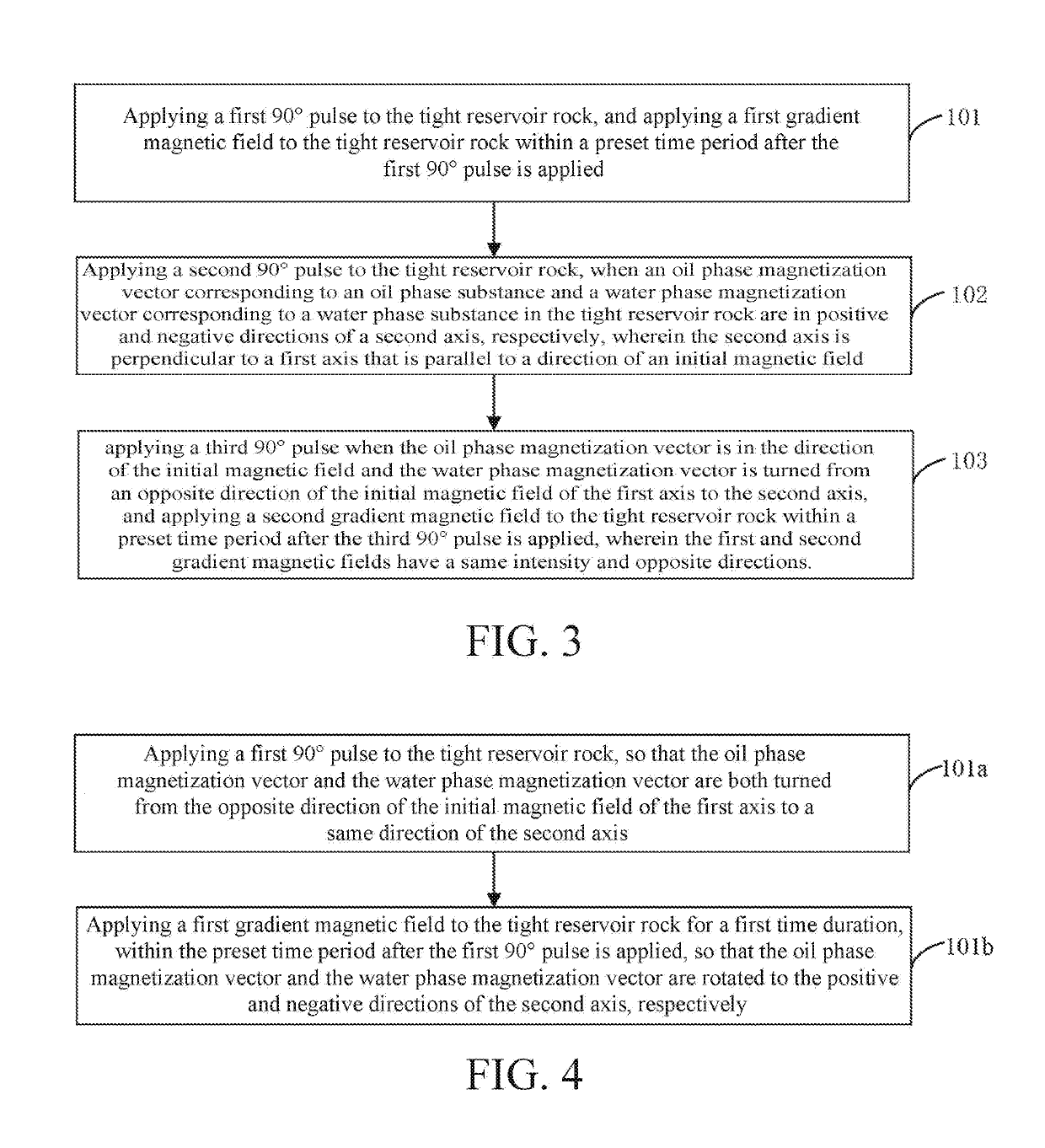
Method and apparatus for measuring oil content of tight reservoir based on nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveUS20190113649A1Improve detection accuracyImprove accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceOil phase
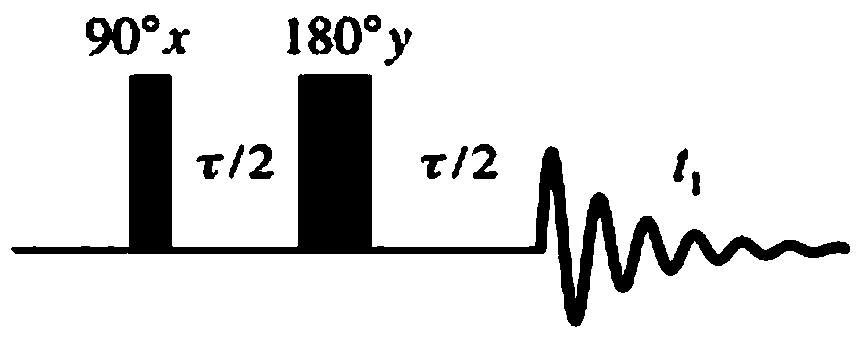
A method and an apparatus for measuring oil content of a tight reservoir based on nuclear magnetic resonance includes applying a pulse sequence to a tight reservoir rock, and after applying a first pulse and a last pulse in the pulse sequence, applying a gradient magnetic field to the tight reservoir rock, respectively, directions of the two applied gradient magnetic fields being opposite to each other, wherein the pulse sequence is composed of three 90° pulses; acquiring a nuclear magnetic resonance signal of the tight reservoir rock; and determining oil content of the tight reservoir rock according to an intensity of the nuclear magnetic resonance signal. The method can accurately distinguish an oil phase nuclear magnetic resonance signal and a water phase nuclear magnetic resonance signal in nanopores of tight reservoir rock, thereby effectively improving the accuracy of the detection result of the oil content of the tight reservoir rock.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
In-situ nuclear magnetic resonance test reactor and detection method thereof
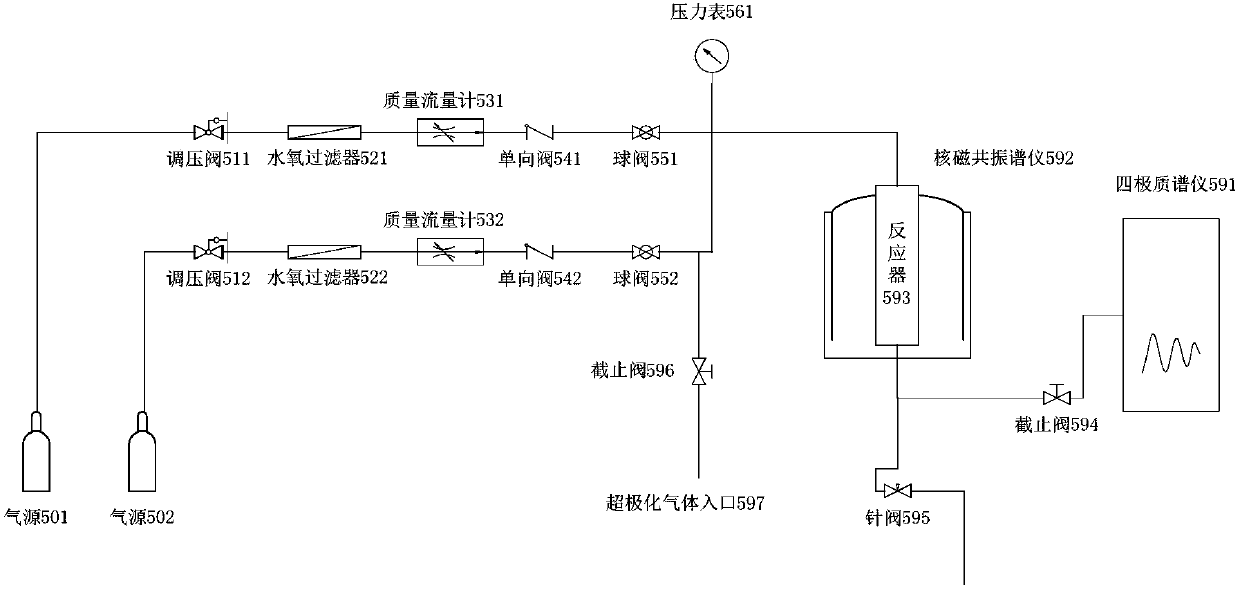
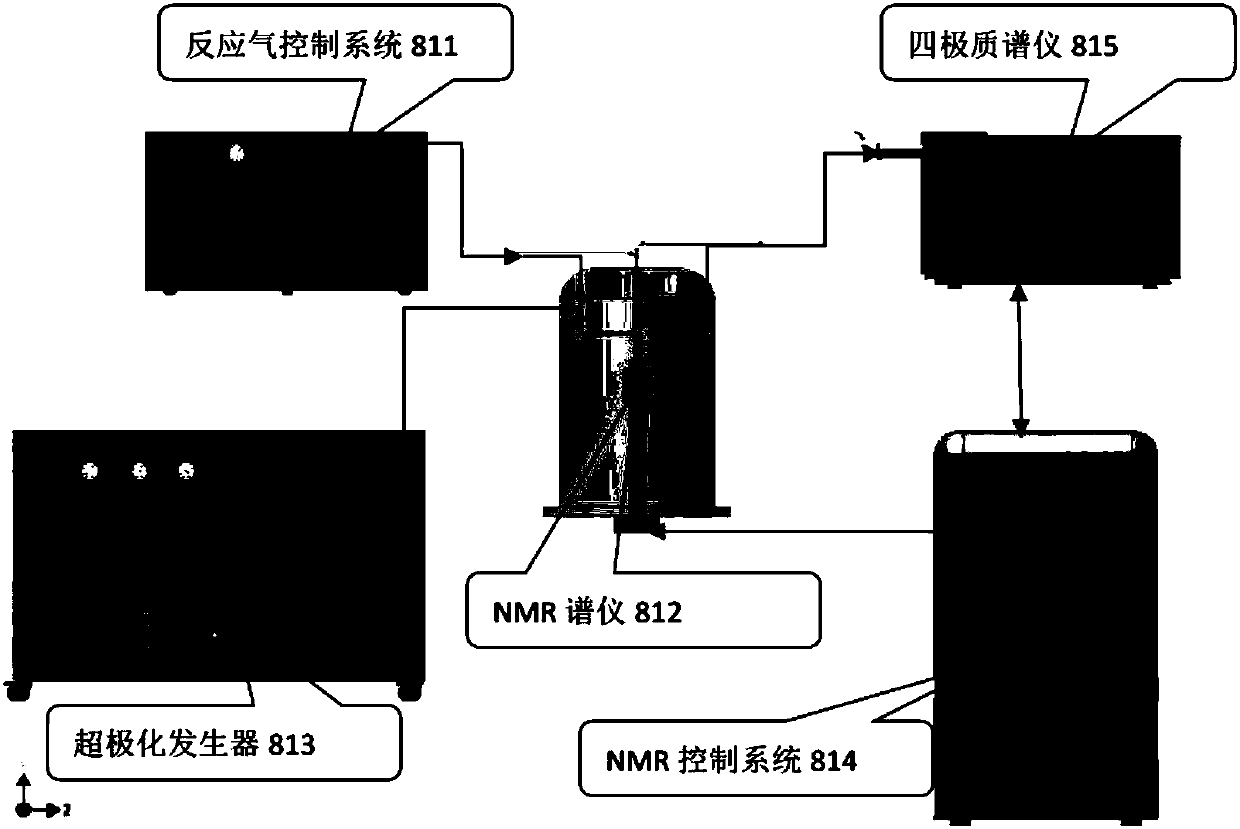
InactiveCN107247063AIngenious designEasy to operateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePhotocatalytic reactionReaction intermediate
The invention relates to an in-situ nuclear magnetic resonance test reactor and a detection method, which can realize the tracking and detection of hydrogen-containing compounds in the real solid-liquid gas photocatalytic reaction process. The in-situ reactor includes: a nuclear magnetic cap that is fixedly connected to the nuclear magnetic tube and the optical fiber and the gas path; the upper and lower holes are opened in the middle of the nuclear magnetic cap, and the hole is covered with a sealing ring, which is respectively connected to the nuclear magnetic tube and the optical fiber; the upper port is used to make the customized optical fiber Go deep into the nuclear magnetic tube, and inject the light into the heterogeneous solid-liquid suspension to be tested; open a hole near the edge above the nuclear magnetic cap, cover the hole with a sealing ring, and connect with the gas circuit; this port is used to pass the gas into the Inside the NMR tube. Using the device of the present invention, the evolution process of hydrogen-containing reactants in the heterogeneous reaction process and their diffusion properties in the liquid can be tracked in situ, the structural information of the reaction intermediate products can be quantitatively analyzed, and the influencing factors and mechanism of the catalytic process can be clarified . This test method can study the reaction performance mechanism in the field of solid-liquid-gas catalysis related to hydrocarbons. The in-situ reactor has ingenious design, simple operation and low cost, and is favorable for popularization and application in other photoreaction and heterogeneous catalytic reaction systems.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Unilateral nuclear magnetic resonance sensor and nuclear magnetic resonance method for measuring soil moisture
ActiveCN106645253ASo as not to damageShort single measurement timeAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMoistureNuclear magnetic resonance logging
The invention relates to a unilateral nuclear magnetic resonance sensor and nuclear magnetic resonance method for measuring soil moisture. The device comprises a housing, a magnet module arranged in the housing, and a radio-frequency coil arranged on the upper surface of the housing, wherein the magnet module is used for generating a static main magnetic field B0; and the radio-frequency coil is used for generating a radio-frequency magnetic field B1 vertical to the static main magnetic field B0, achieving excitation of a soil sample and receiving an echo signal generated by the sample. Hydrogen protons in the soil moisture are directly excited, and an electromagnetic echo released in a relaxation process is detected, so that the nuclear magnetic resonance technology is not affected by the salinity of the soil, the single measurement time is short and the sample is not damaged.
Owner:SHENZHEN ACAD OF AEROSPACE TECH
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momentum
InactiveUS8508222B2Less noisyHigh measurement sensitivityLaser detailsMasersTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
A device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of a sample, such as fluid, is based upon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentially illuminating the sample with a focused beam of light carrying angular orbital angular momentum (OAM) and possibly momentum (spin). Unlike in a typical NMR used for magnetic nuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the present device does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for determining branching degree of glucose polymer by using nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN108020576AHigh measurement accuracySimplify the measurement stepsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSolventProton NMR
The invention relates to a method for determining the branching degree of a glucose polymer, and especially relates to a method for determining the branching degree of the glucose polymer by using nuclear magnetic resonance. The method concretely includes the following steps: dissolving the glucose polymer to be tested in a solvent to form a solution, determining the hydrogen spectrum or carbon spectrum signal integral intensity of the obtained solution by using a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, and analyzing and calculating the branching degree according to the hydrogen spectrum or carbon spectrum signal integral intensity. The method has the following advantages: the structure information can be directly obtained through determining the glucose polymer by a nuclear magnetic resonance technology, so the limitations of traditional chemical methods are broken; and the proton signal integral of glycosides in C1 of a glucose residue in alpha-1,6 linkage is calculated to obtain the branching degree, or the C6 signal integral of the glucose residue in the alpha-1,6 linkage is calculated to obtain the branching degree, so the determination precision is effectively improved, andthe determination step is simplified.
Owner:青岛力腾医药科技有限公司
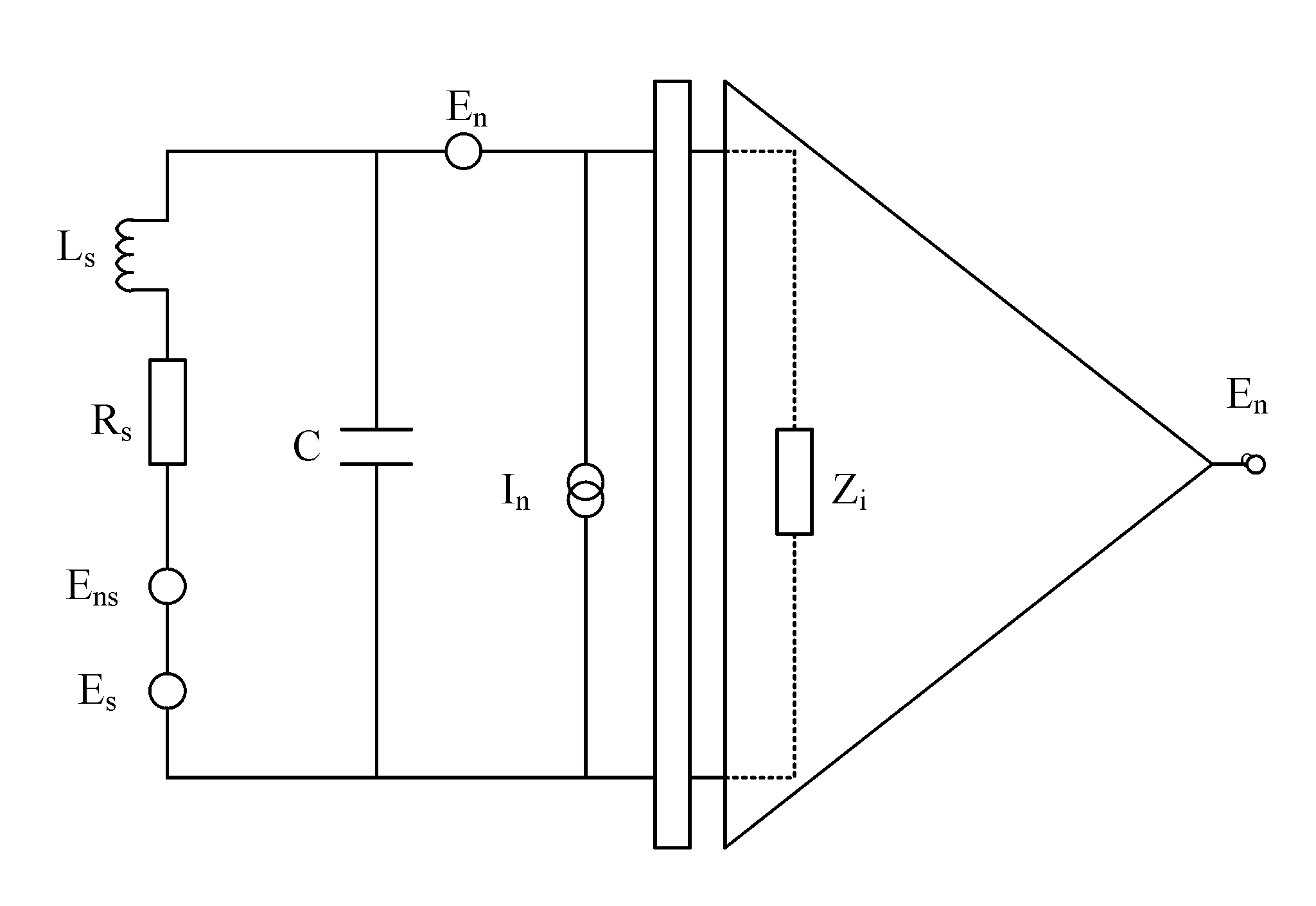
Electric potential sensor for use in the detection of nuclear magnetic resonance signals
InactiveUS7924004B2Reducing recovery and dead timeAvoid couplingMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceCapacitanceElectric potential energy
Owner:THE UNIV OF SUSSEX
In-situ chemical reactor and combined system of in-situ chemical reactor and nuclear magnetic resonance
PendingCN110609053AComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical reactionProton NMR
The invention relates to a device for researching a chemical reaction process in situ. The chemical reaction device is suitable for operation in high-temperature and low-temperature conditions, can provide a chemical reaction process and nuclear magnetic resonance information of a physical structure by being combined with a nuclear magnetic resonance technology, can provide reaction product information, such as quadrupole mass spectrometry and can also achieve dynamic research on millisecond time-resolution reaction. The device is suitable for nuclear magnetic resonance research in the fieldsof chemistry and materials and can also be applied to the fields, such as hyperpolarized atomic magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy testing in the medical field.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic circuit for detecting chip through nuclear magnetic resonance microscope
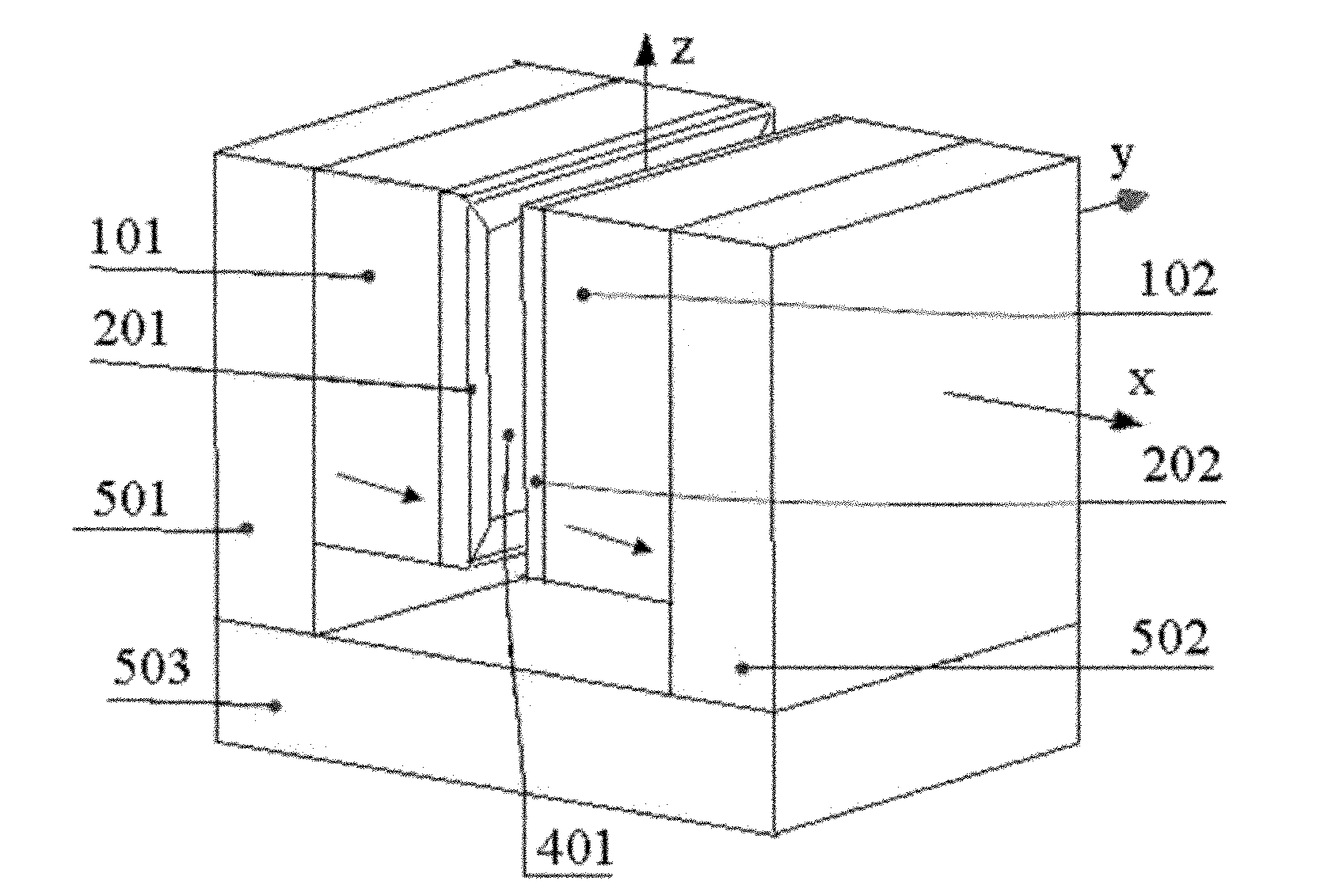
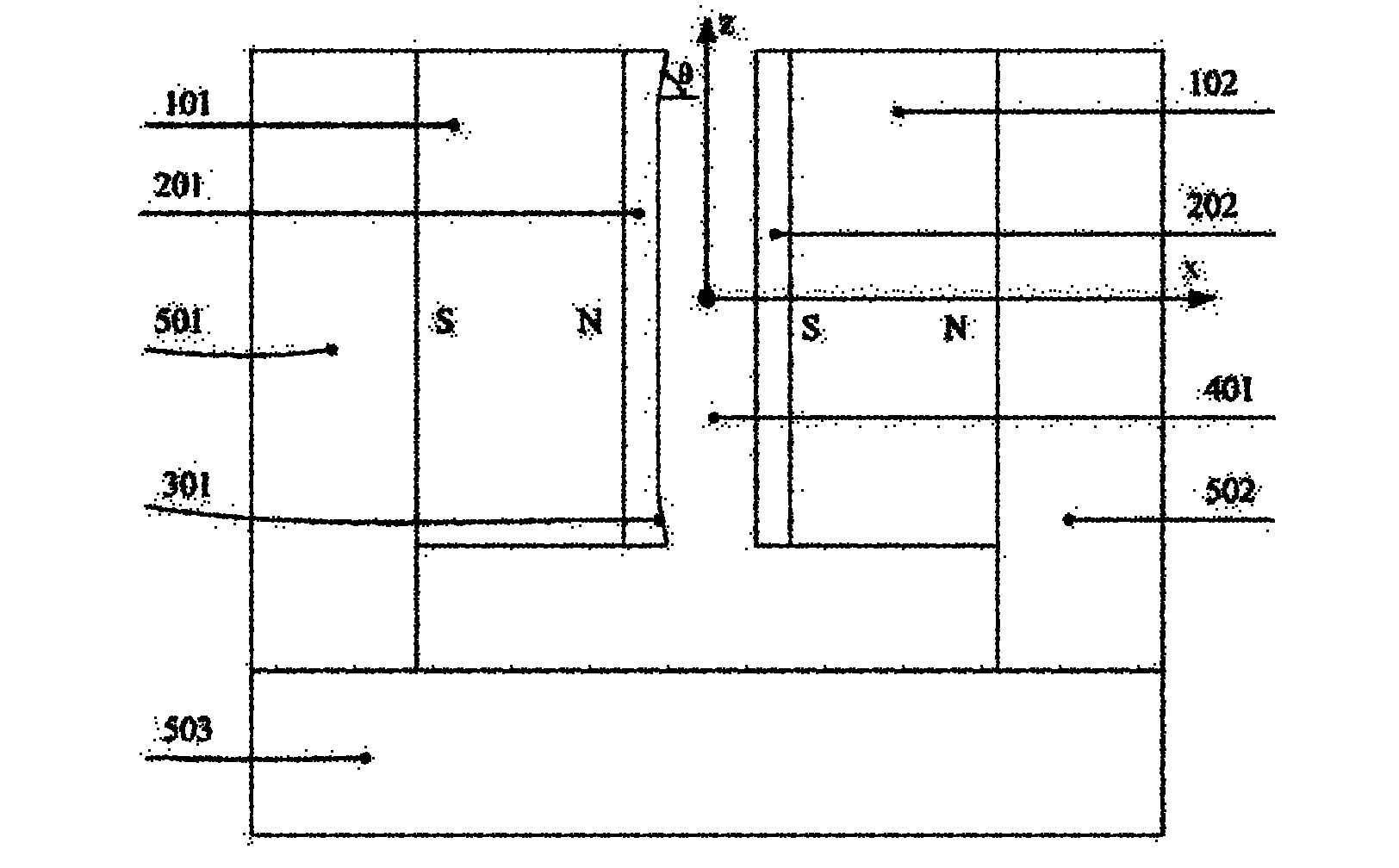
InactiveCN102110513AReduce volumeMeet needsMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic poles
The invention relates to a magnetic circuit for detecting a chip through a nuclear magnetic resonance microscope. The magnetic circuit comprises a first permanent magnet, a first shimming plate, a second shimming plate and a second permanent magnet which are arranged in turn, wherein a gap is reserved between the first shimming plate and the second shimming plate to form a working air gap; and the first permanent magnet and the second permanent magnet have the same magnetic pole direction and are connected with each other through a magnetic conductor. The magnetic circuit has a small volume and is low in manufacturing cost and maintenance cost; a magnetic field which is generated in a working region has high field strength and high magnetic field uniformity; and the requirements for detecting the chip through the nuclear magnetic resonance microscope can be met better.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A kind of porosity measuring method
ActiveCN107014728BQuick testMeet the requirements of porosity testingPermeability/surface area analysisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRock core
The invention relates to a pore measurement method which comprises the following steps: an effective signal determination step: regulating a temperature of a rock core to be analyzed into a preset temperature, regulating the temperature of the rock core to be analyzed according to a preset temperature change rate, determining a basic noise signal according to a nuclear magnetic resonance signal measured when the rock core to be analyzed is in a crystalline state, and determining an effective nuclear magnetic resonance signal at each temperature according to a nuclear magnetic resonance signal measured when the rock core to be analyzed is in a non-crystalline state and the basic noise signal; and a pore size determination step: determining the size of a pore in the rock core to be analyzed according to the effective nuclear magnetic resonance signal at each temperature. According to the pore measurement method, by adopting nuclear magnetic resonance nondestructive testing means, based on a low-temperature variable entropy nuclear magnetic resonance test technology, a nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrogram of a shale reservoir at different temperatures is tested, and by taking the spectrogram as a test basis, measurement of microscopic pore size distribution in a micro-nanometer magnitude of the shale reservoir is realized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
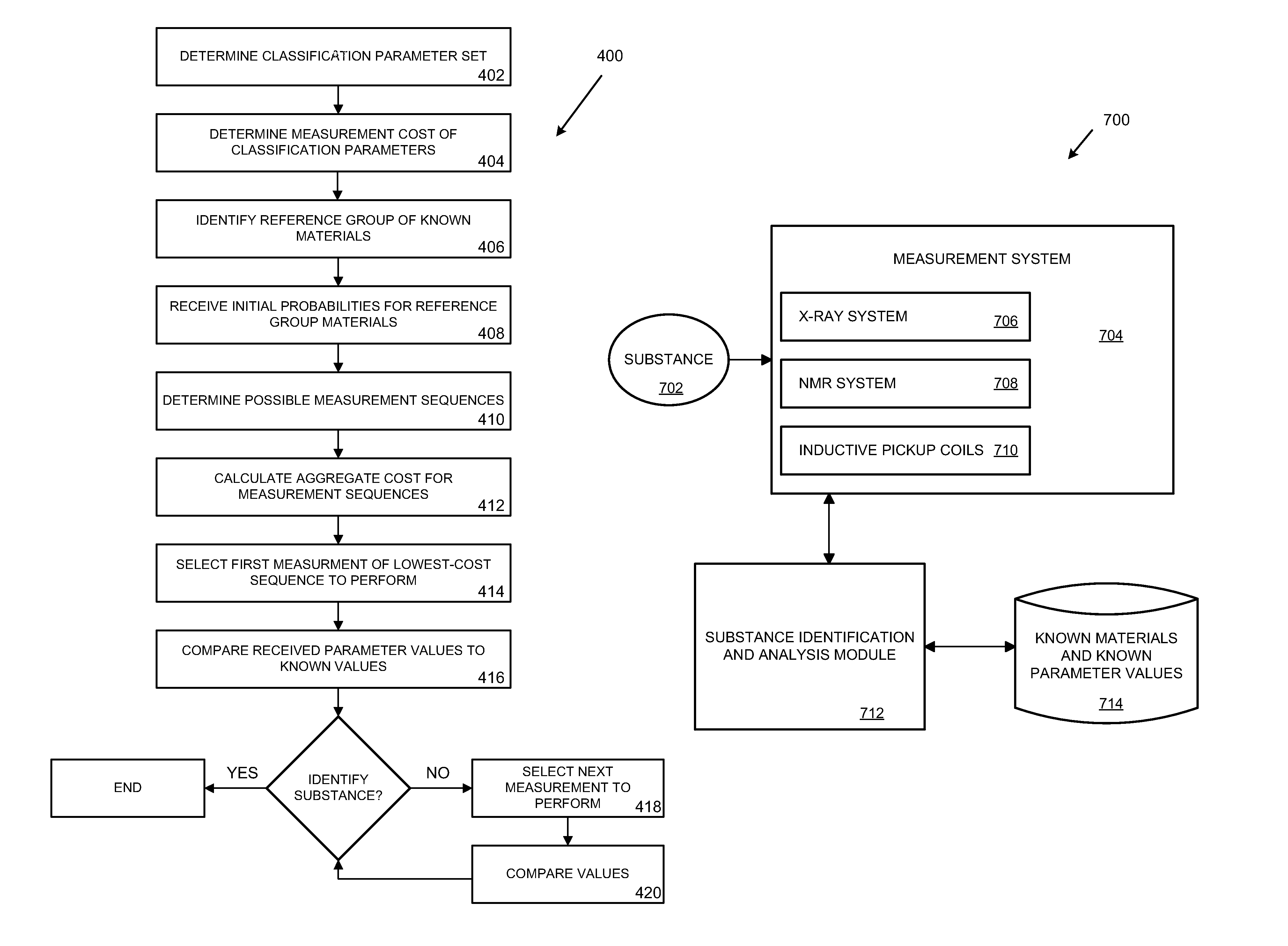
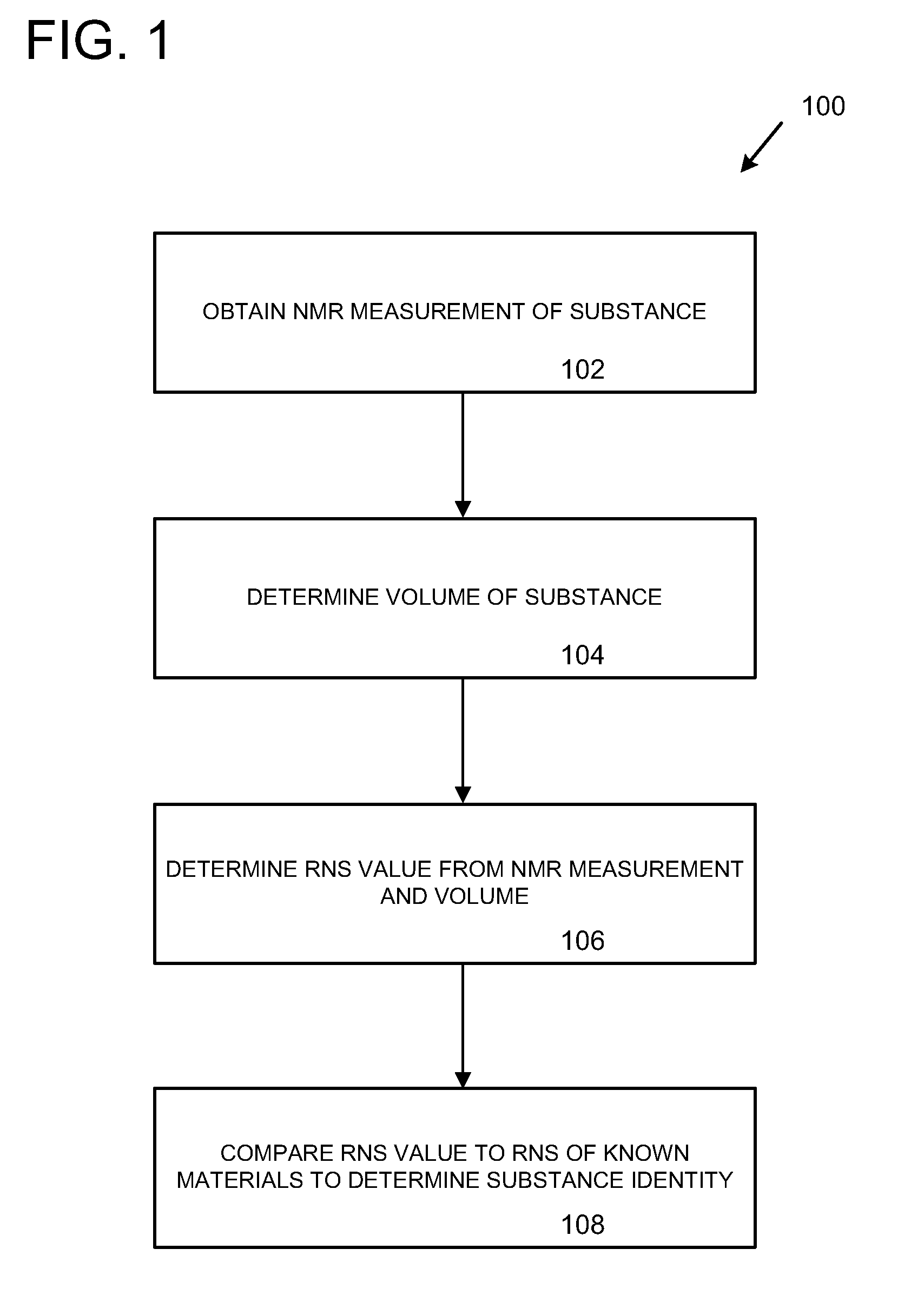
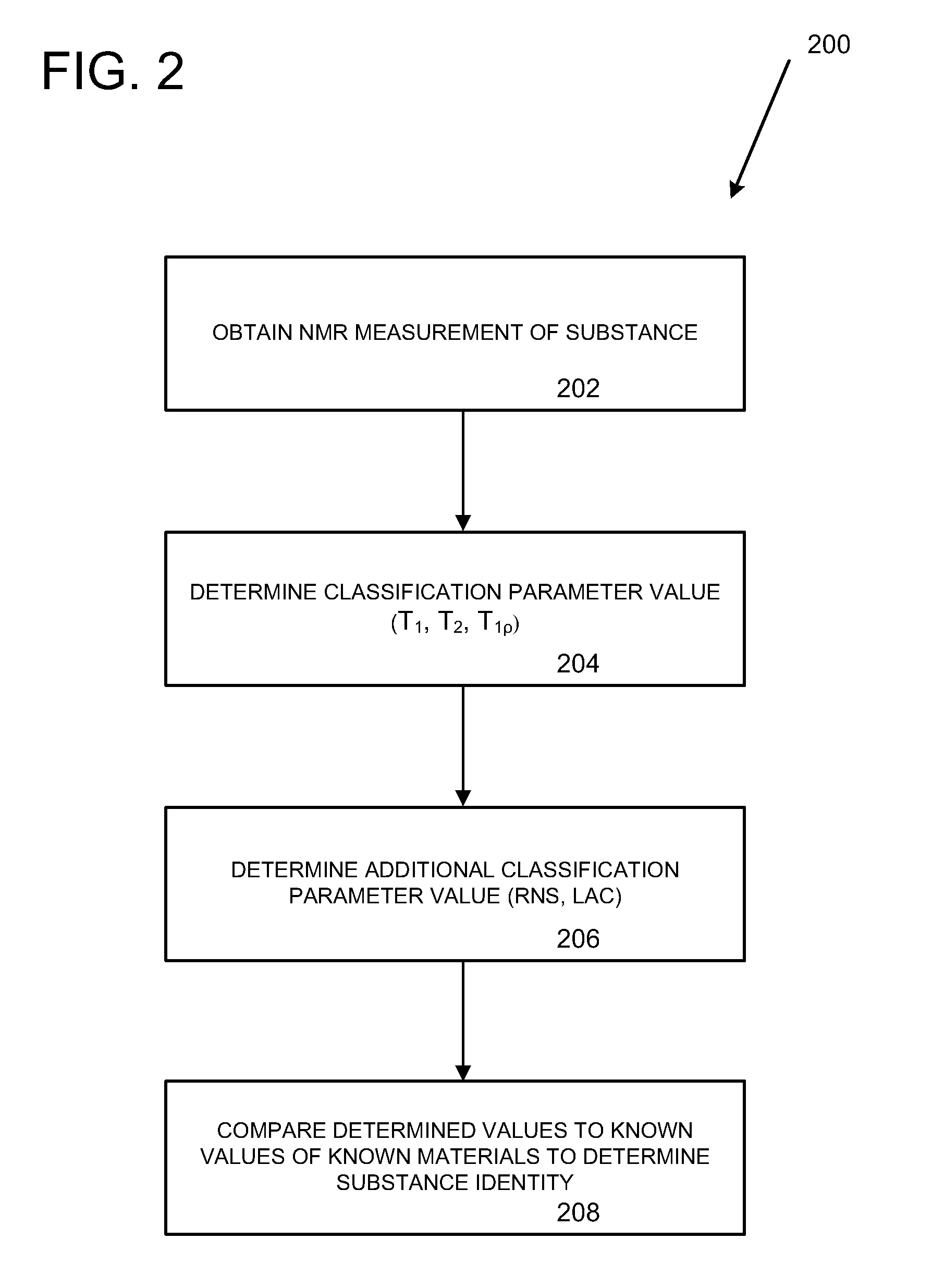
Hypothesis-driven classification of materials using nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry
ActiveUS9411031B2Analysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSpecial data processing applicationsAttenuation coefficientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Technologies related to identification of a substance in an optimized manner are provided. A reference group of known materials is identified. Each known material has known values for several classification parameters. The classification parameters comprise at least one of T1, T2, T1ρ, a relative nuclear susceptibility (RNS) of the substance, and an x-ray linear attenuation coefficient (LAC) of the substance. A measurement sequence is optimized based on at least one of a measurement cost of each of the classification parameters and an initial probability of each of the known materials in the reference group.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momentum
InactiveCN101939638BAnalysis using optical pumpingMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySpectroscopyParamagnetic nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com