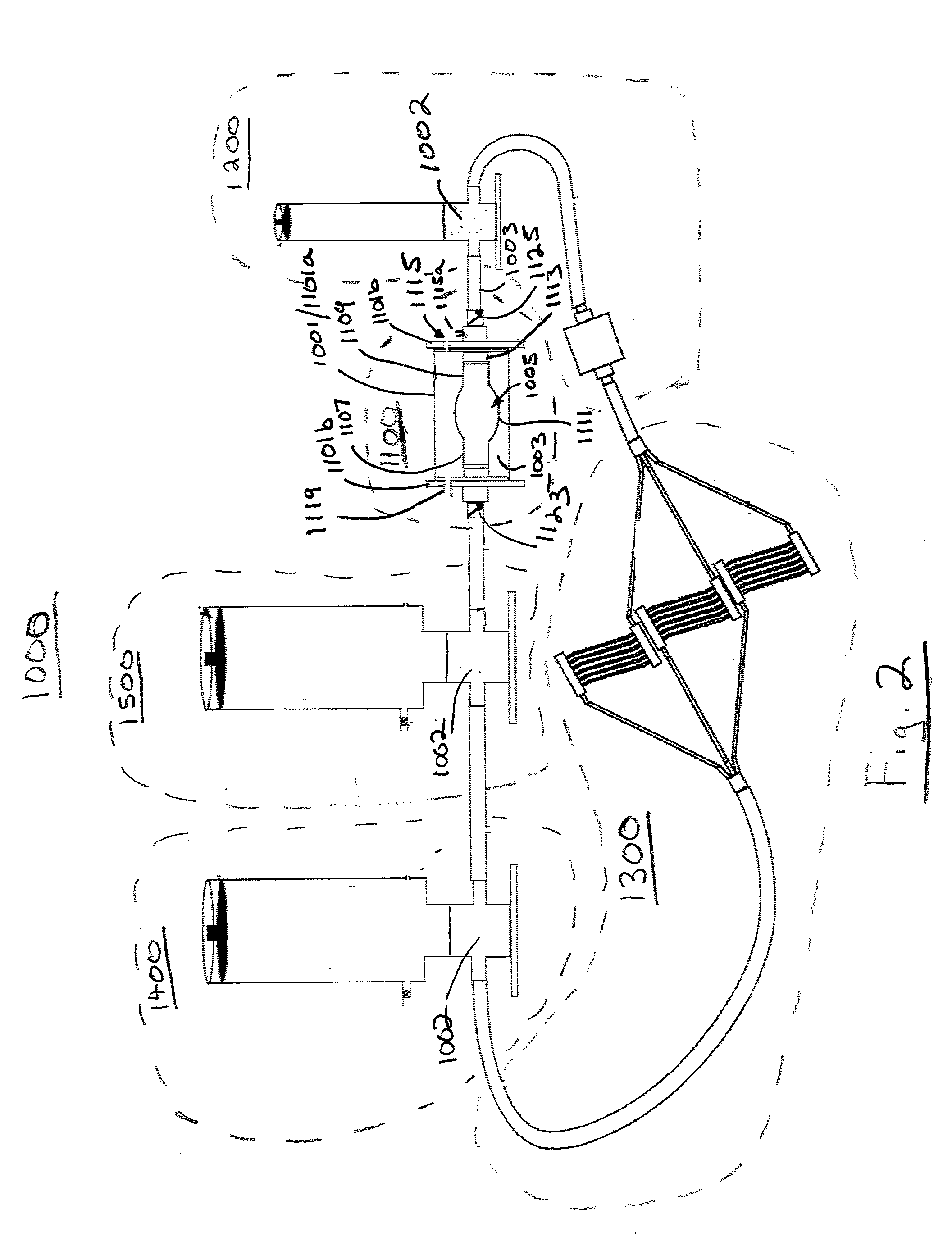
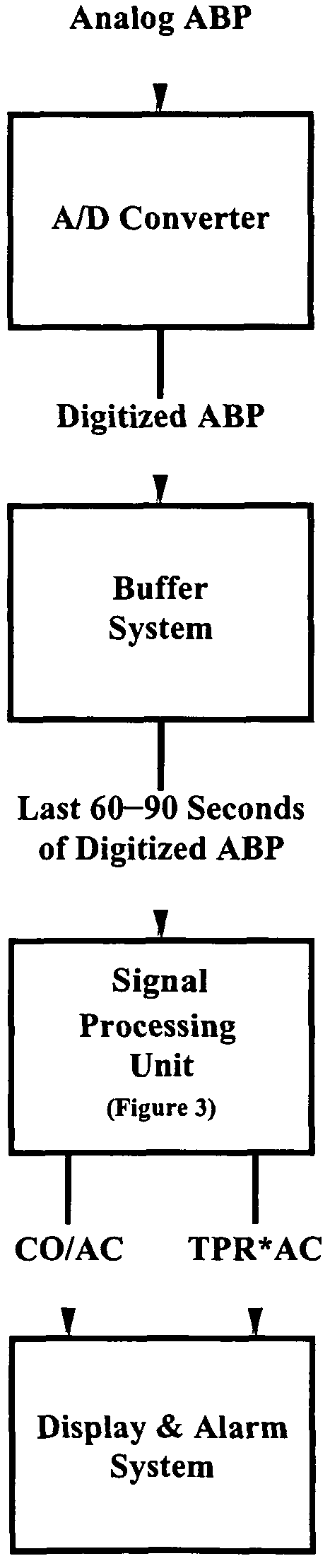
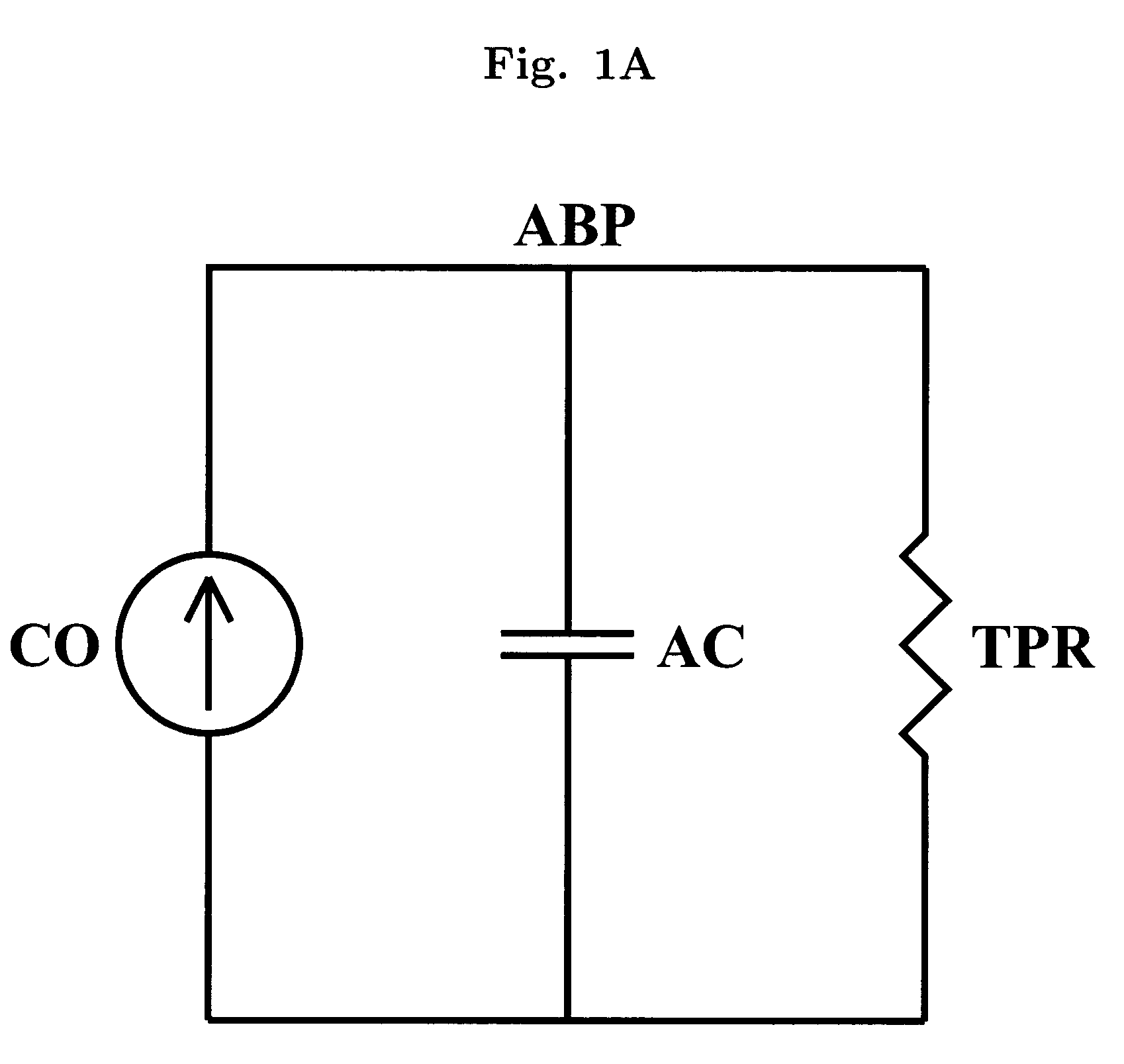
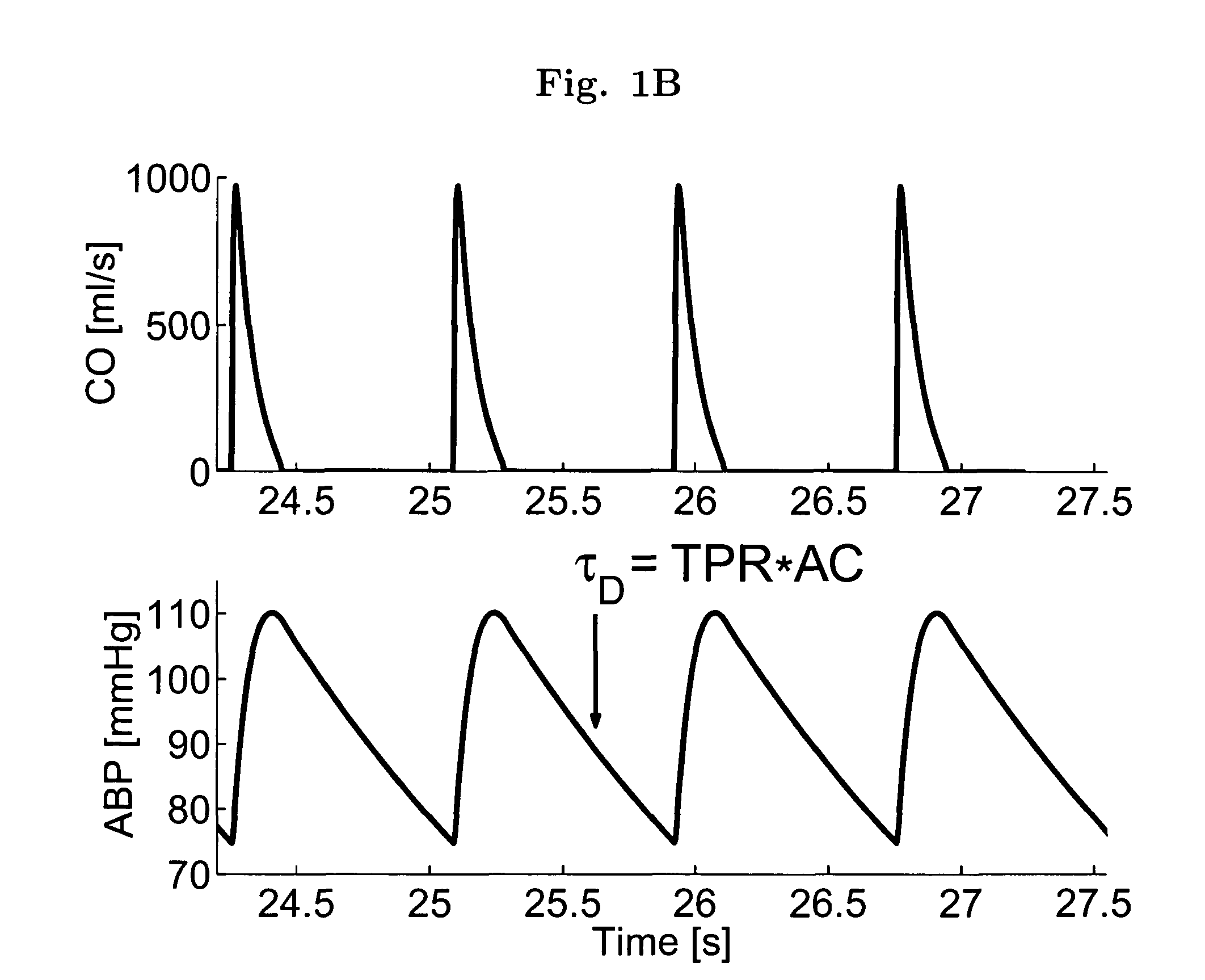
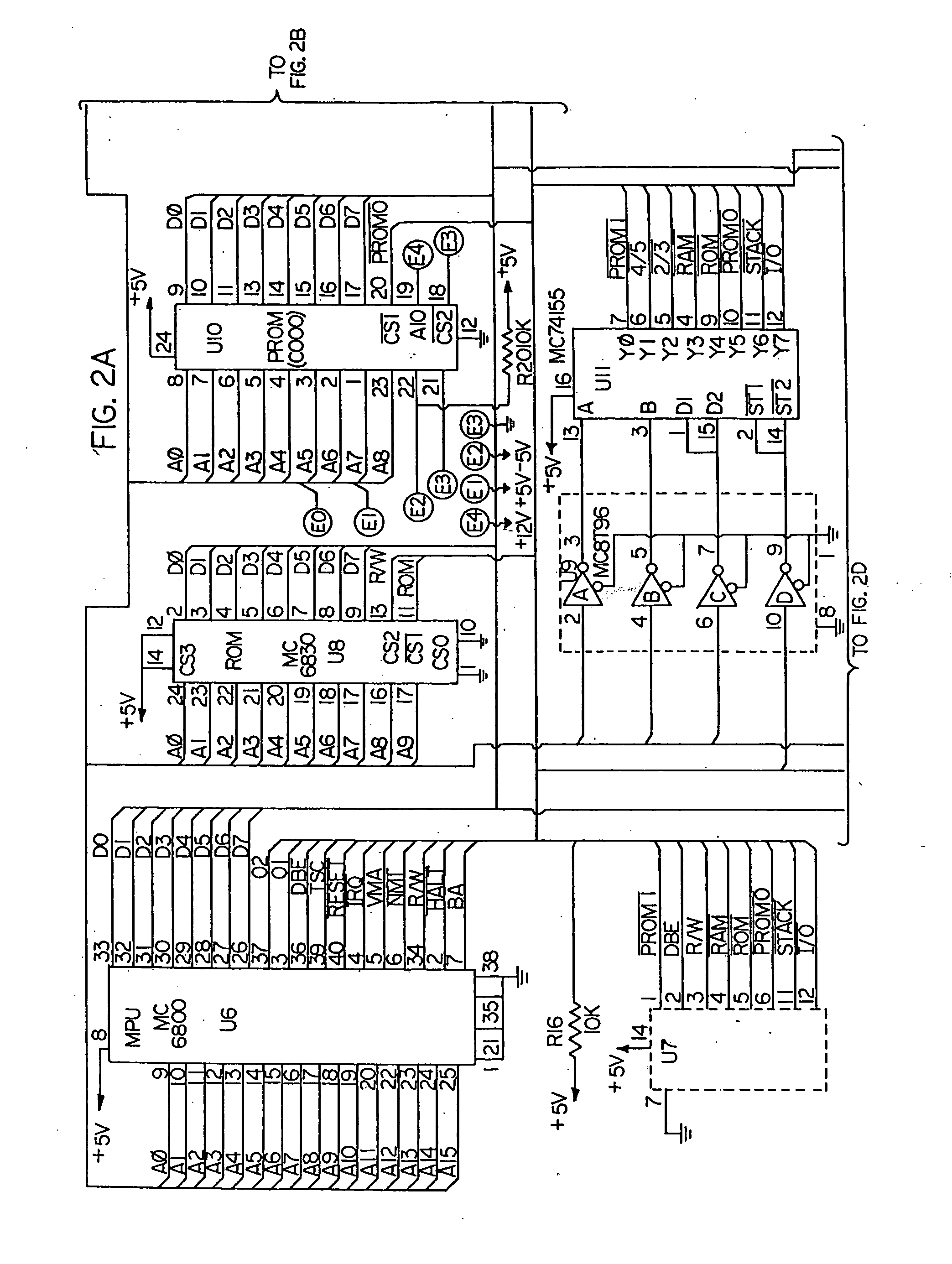
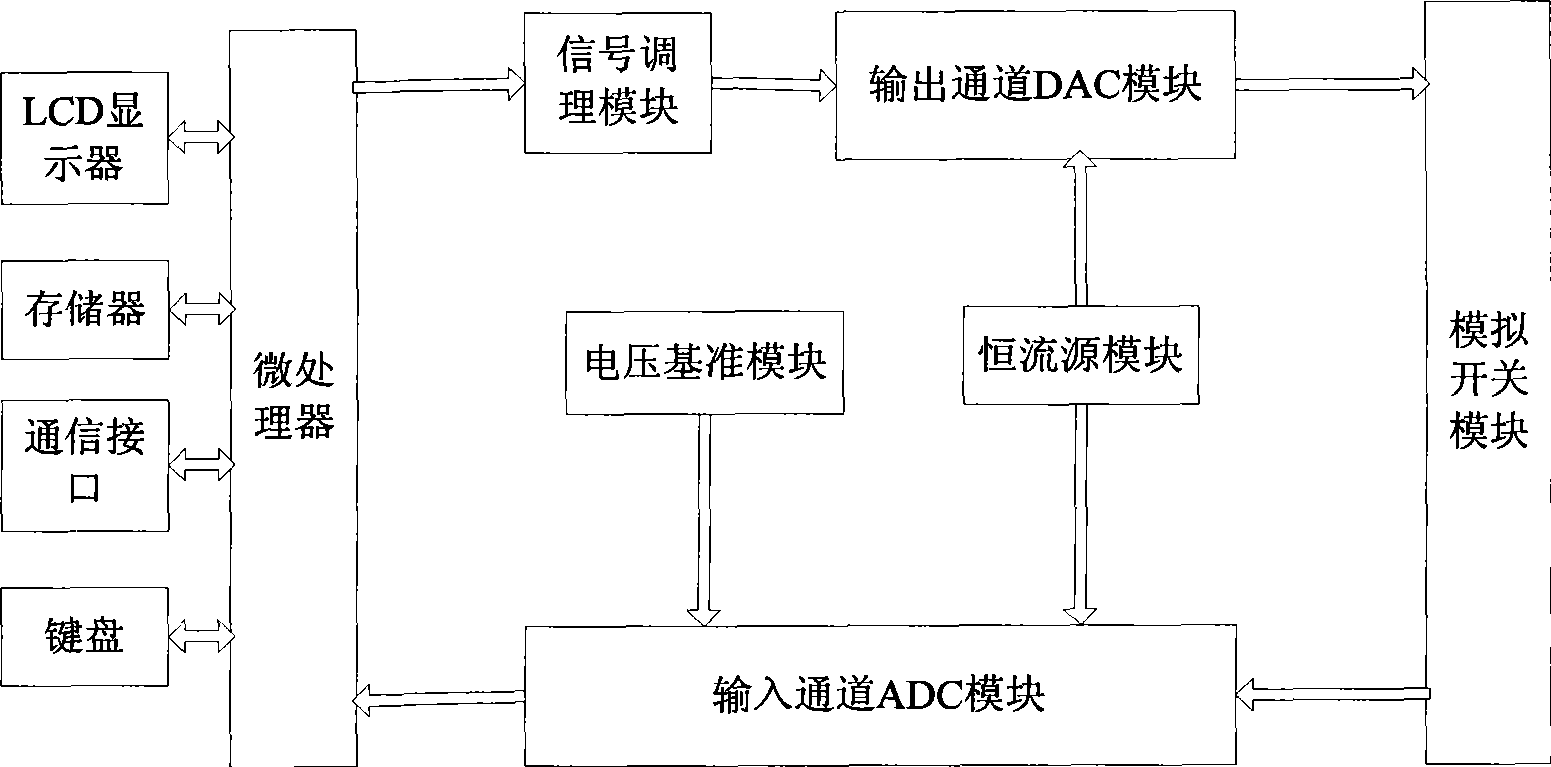
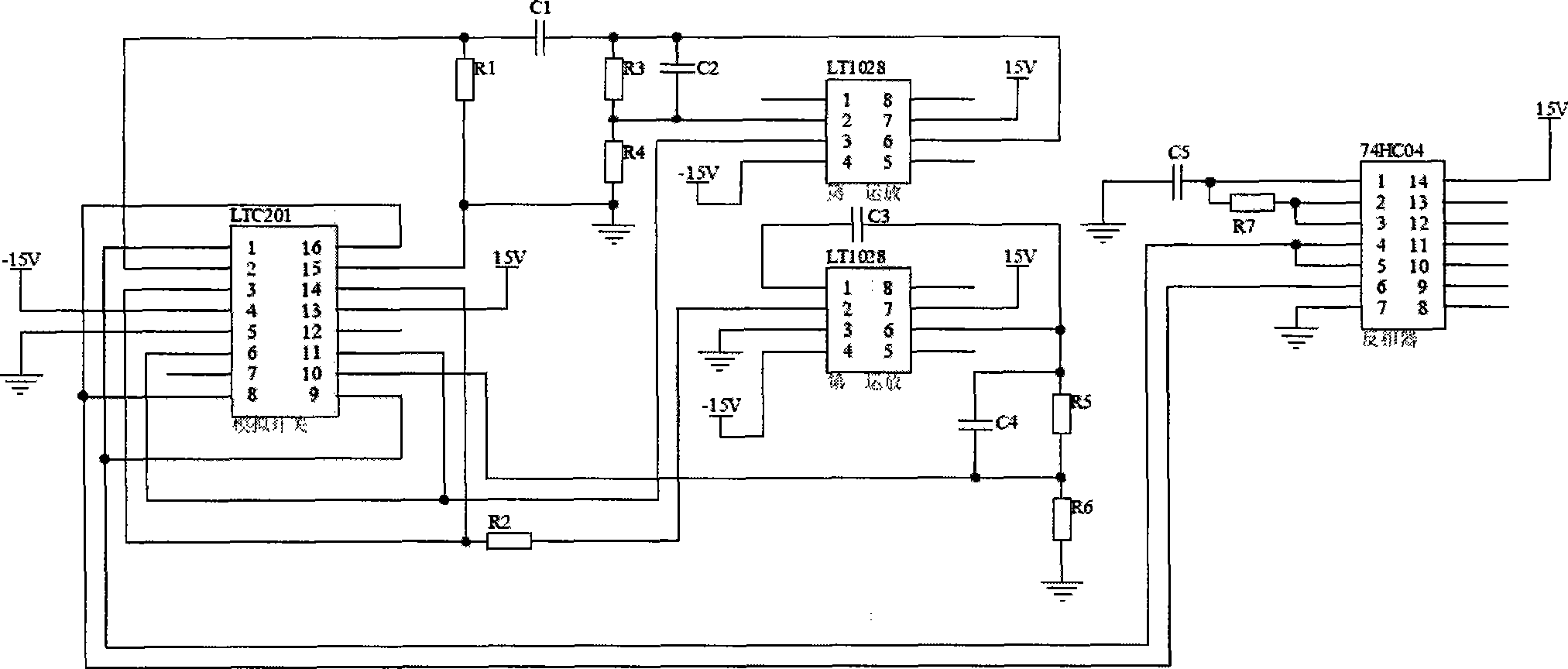
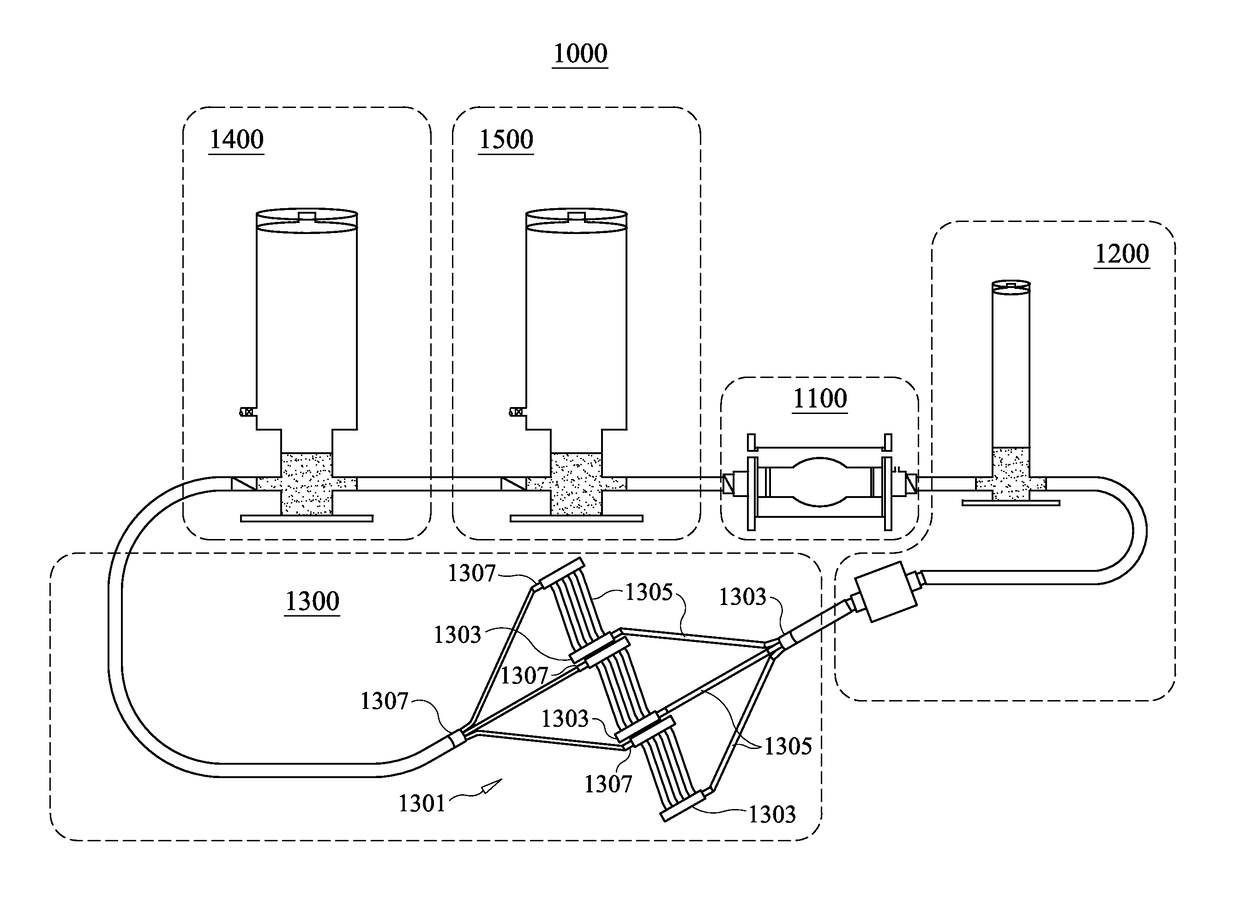
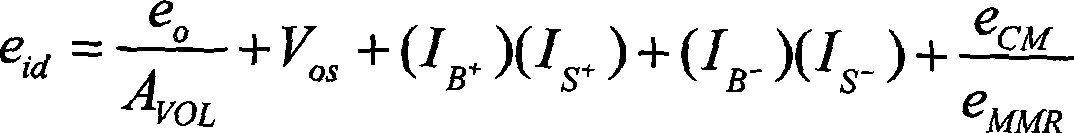Patents
Literature
76 results about "Peripheral resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
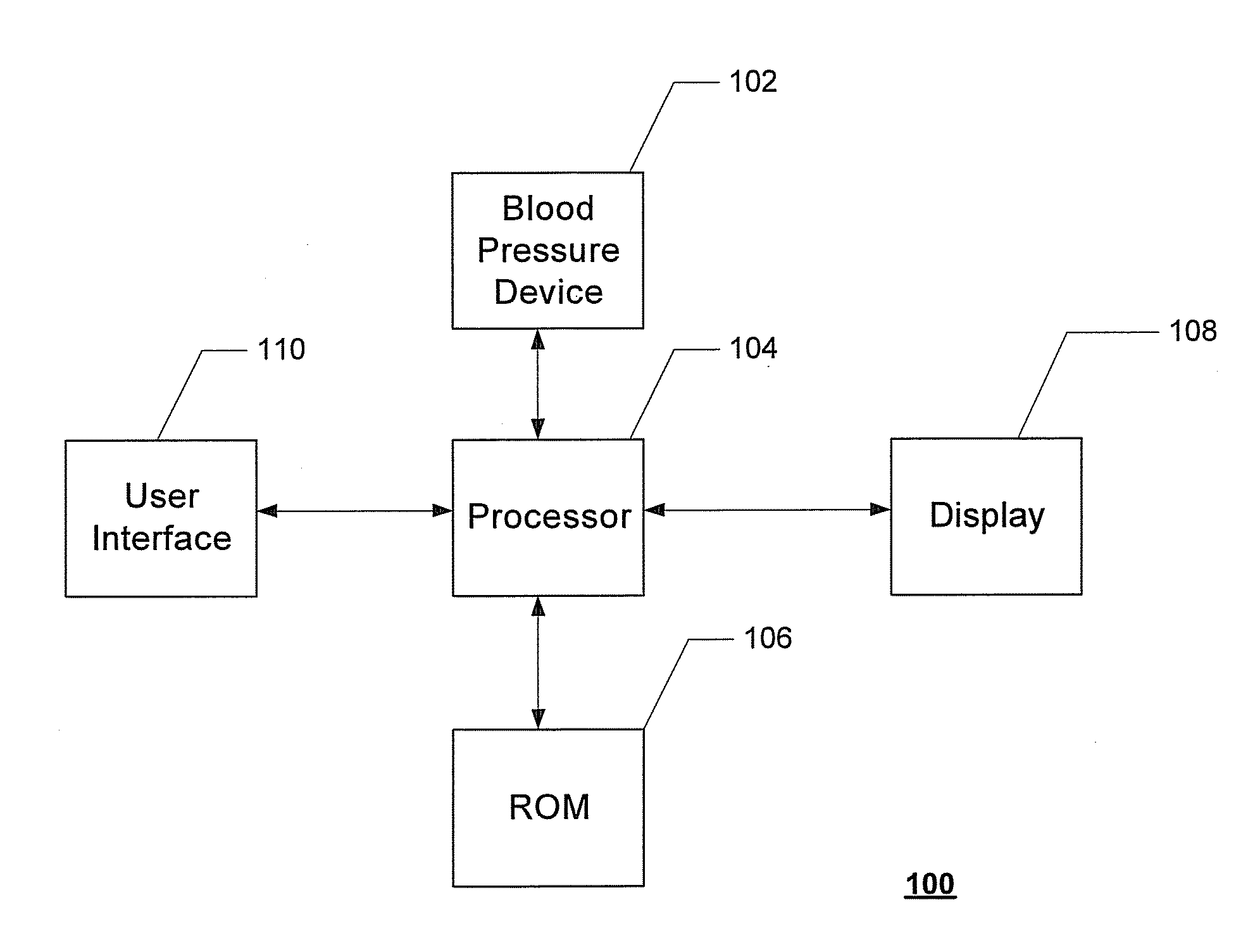
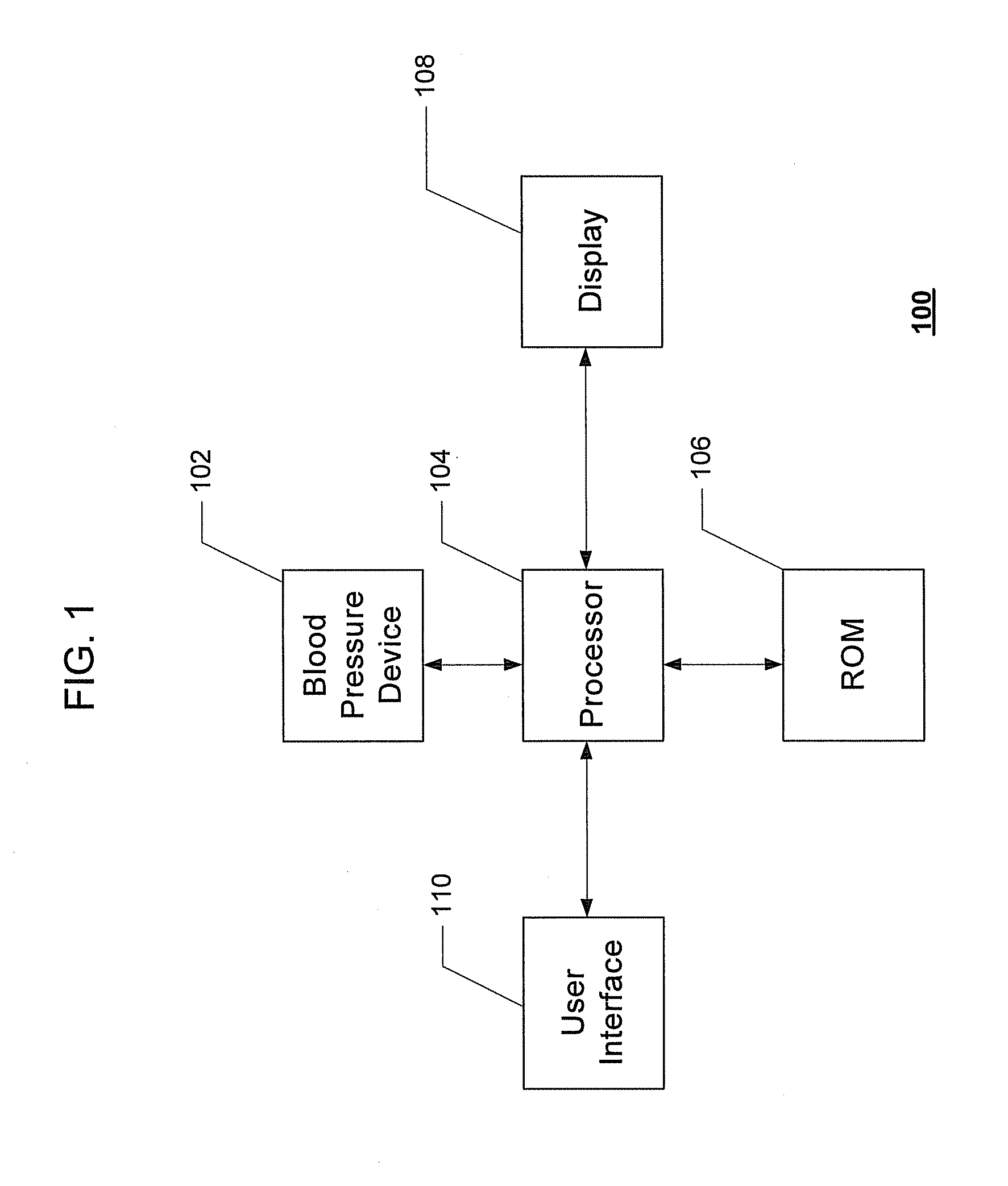
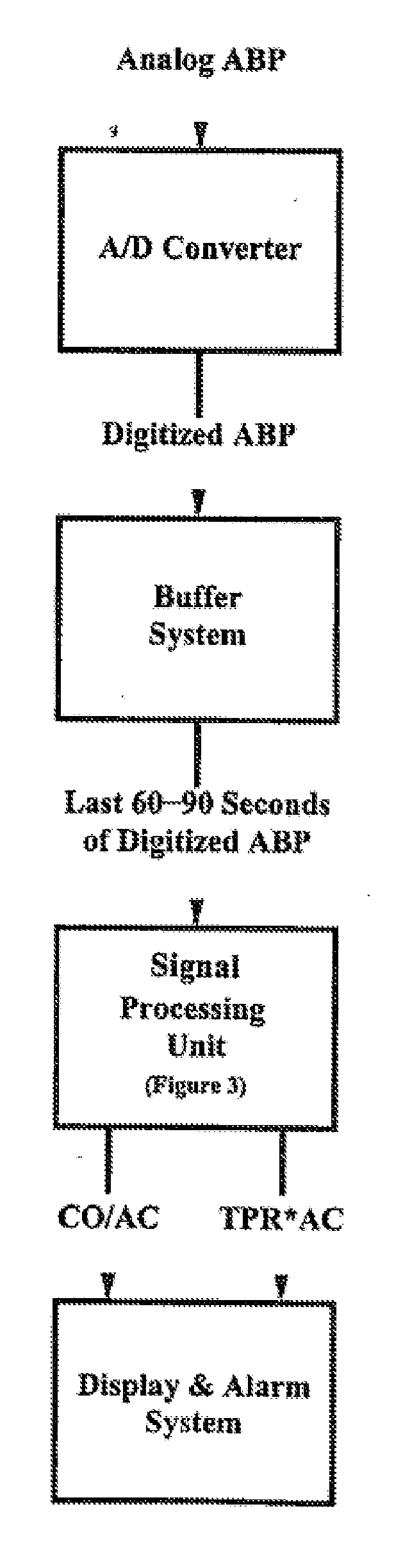
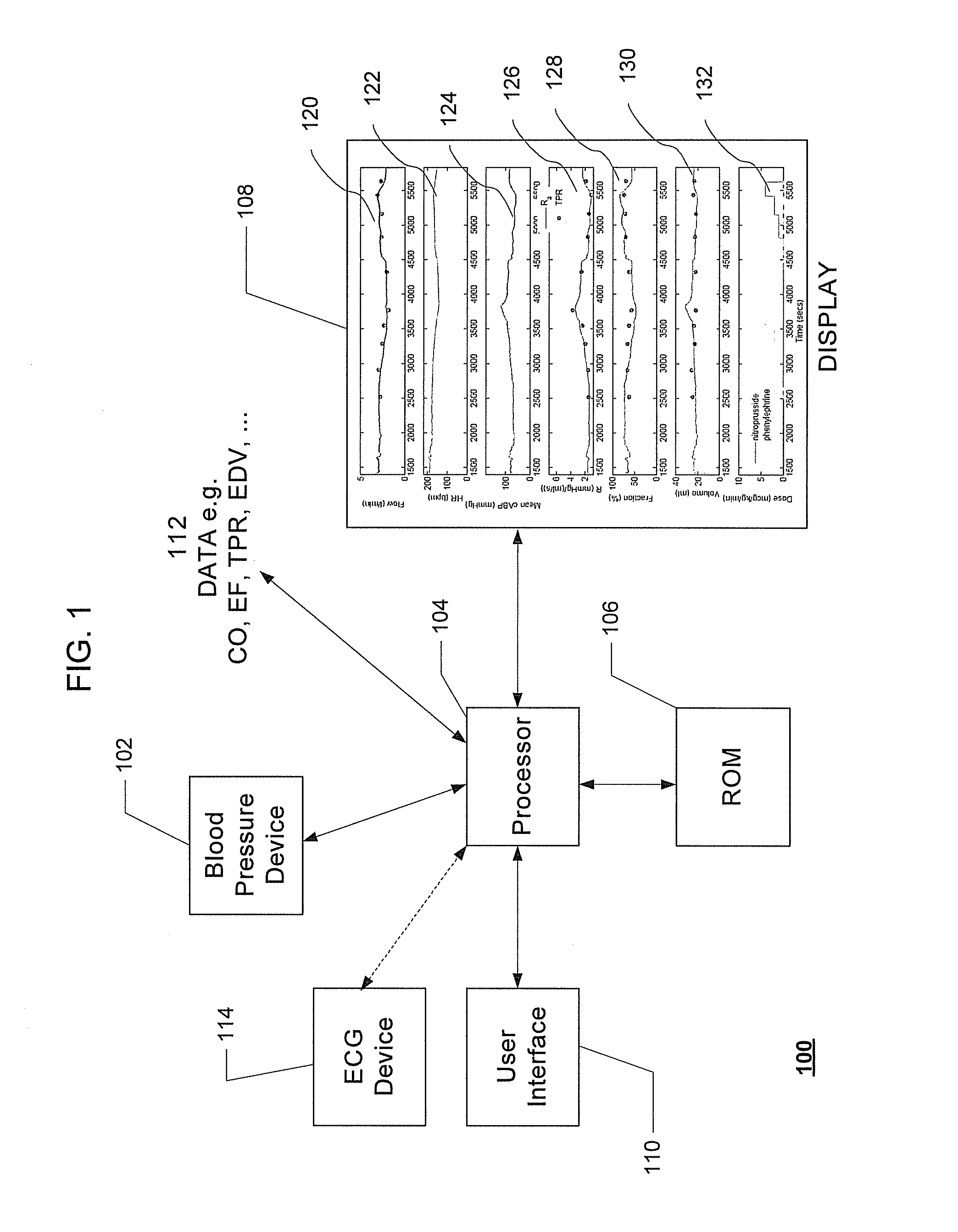
Systems and Methods for Model-Based Estimation of Cardiac Output and Total Peripheral Resistance
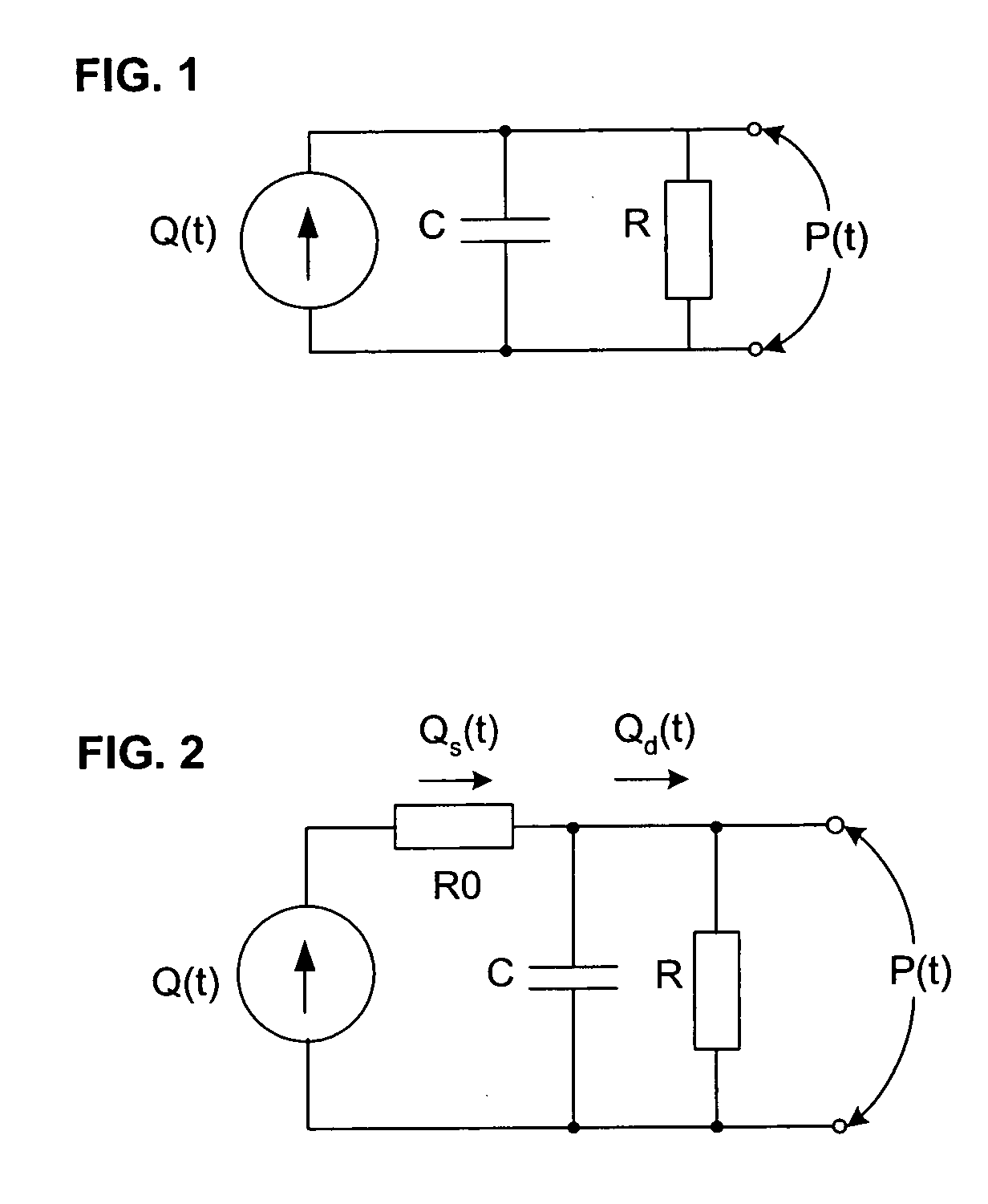
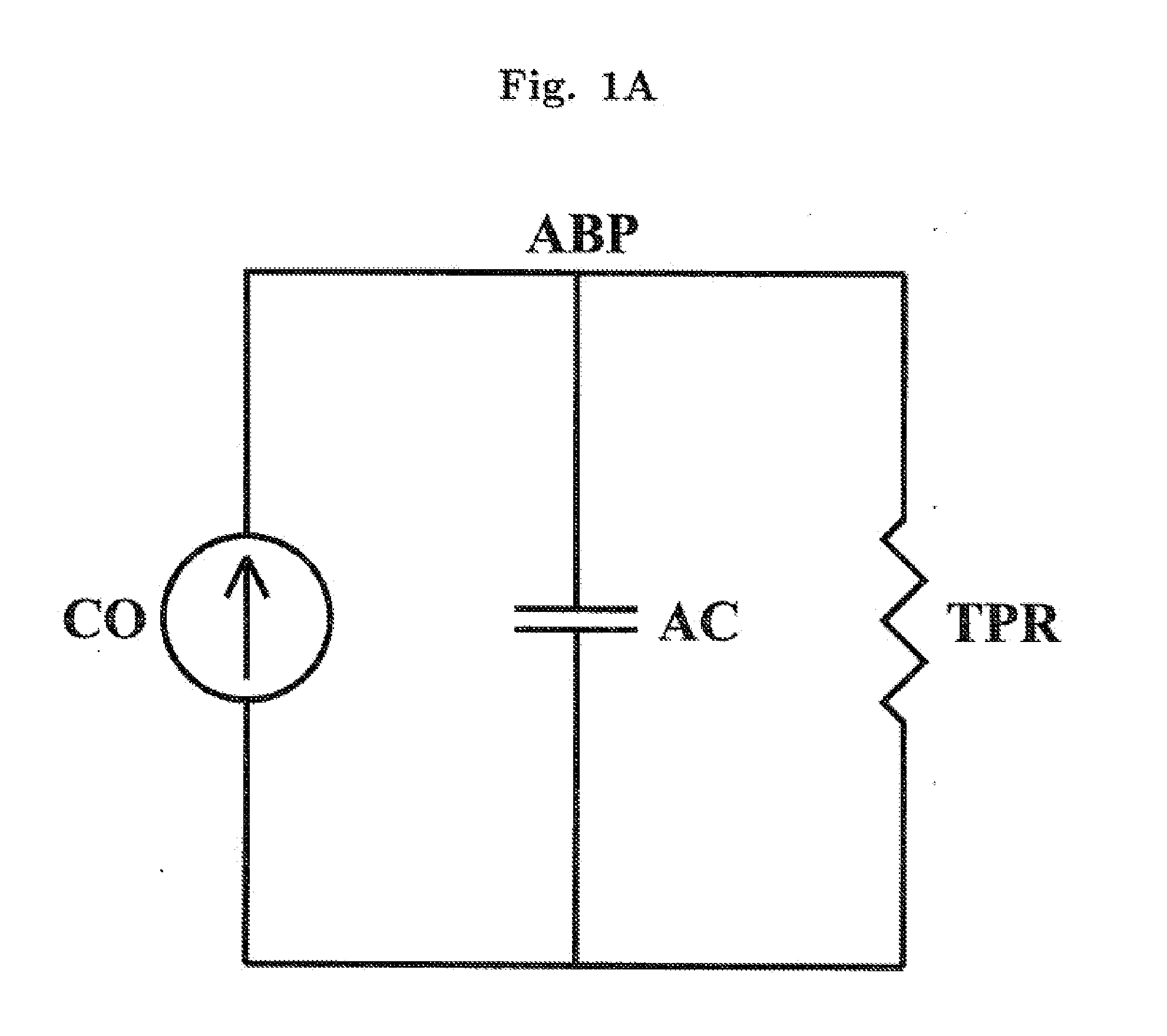
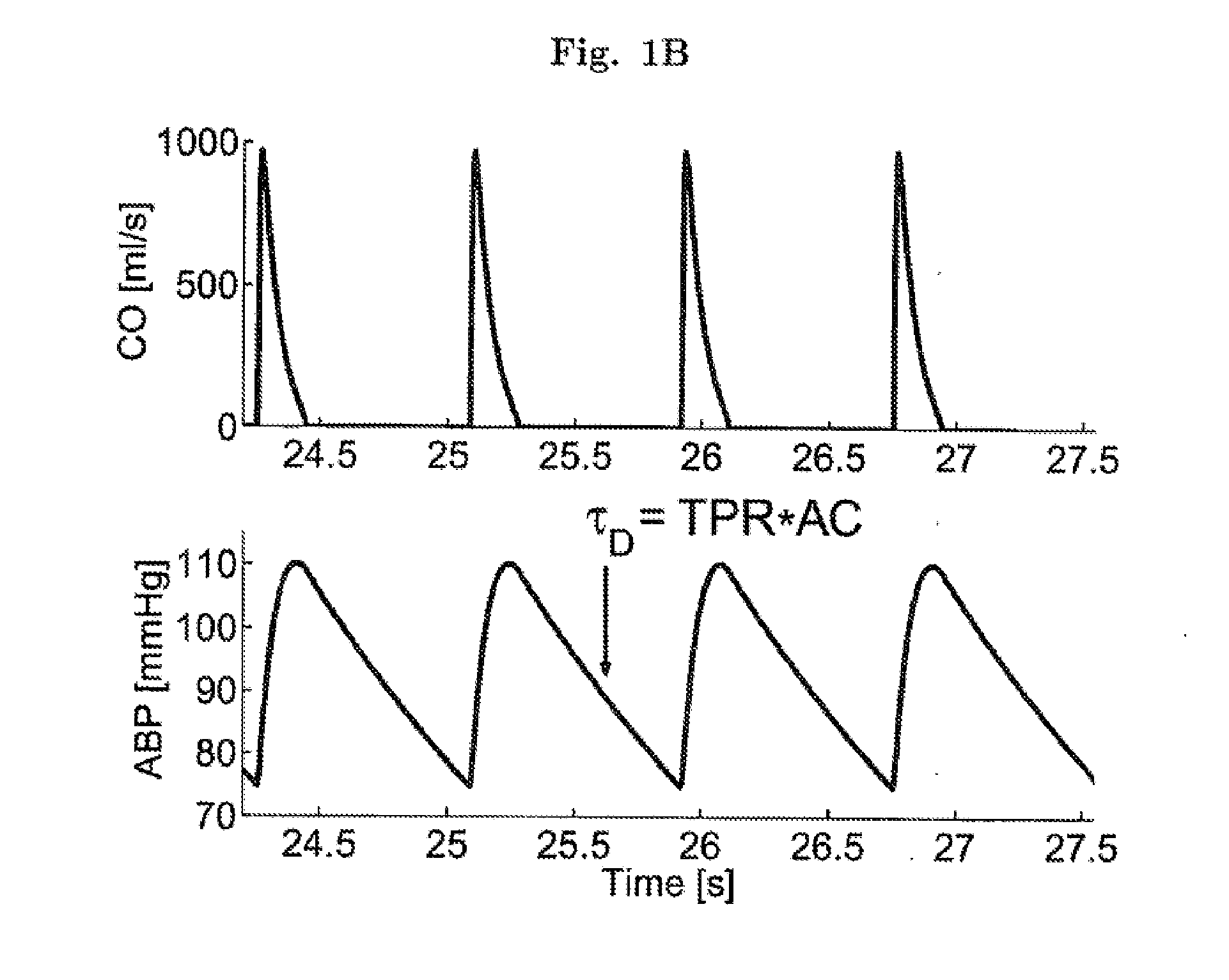
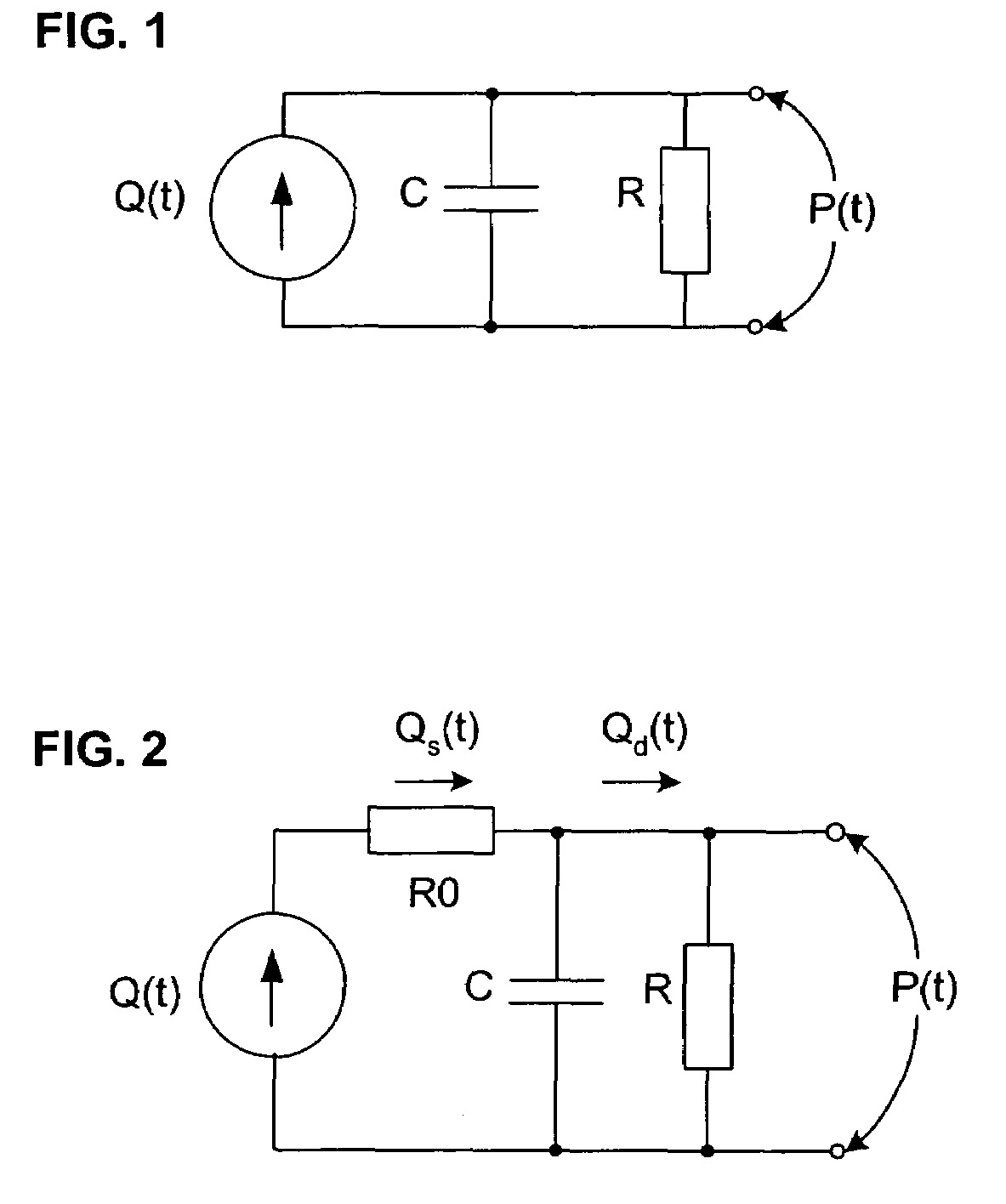
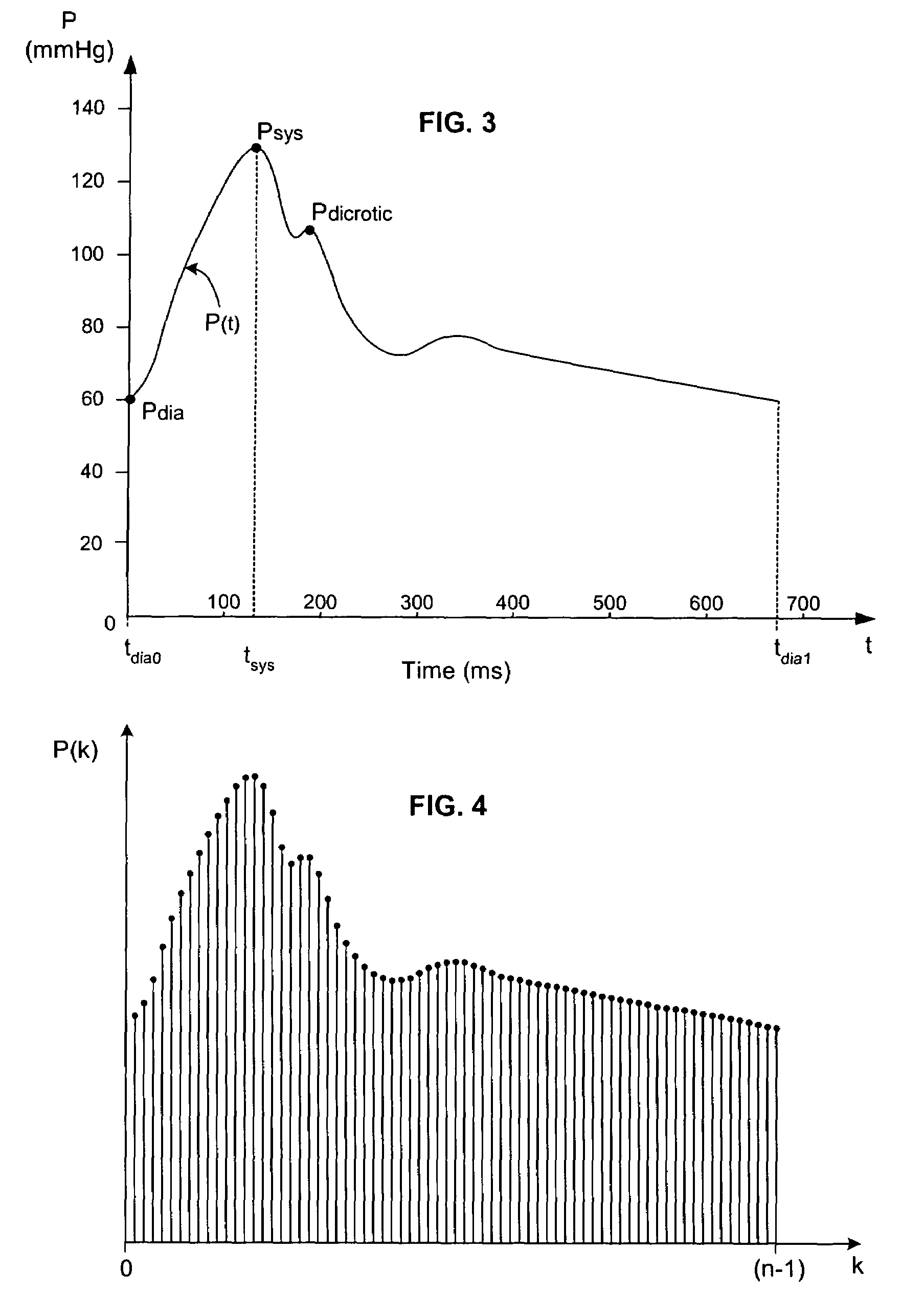
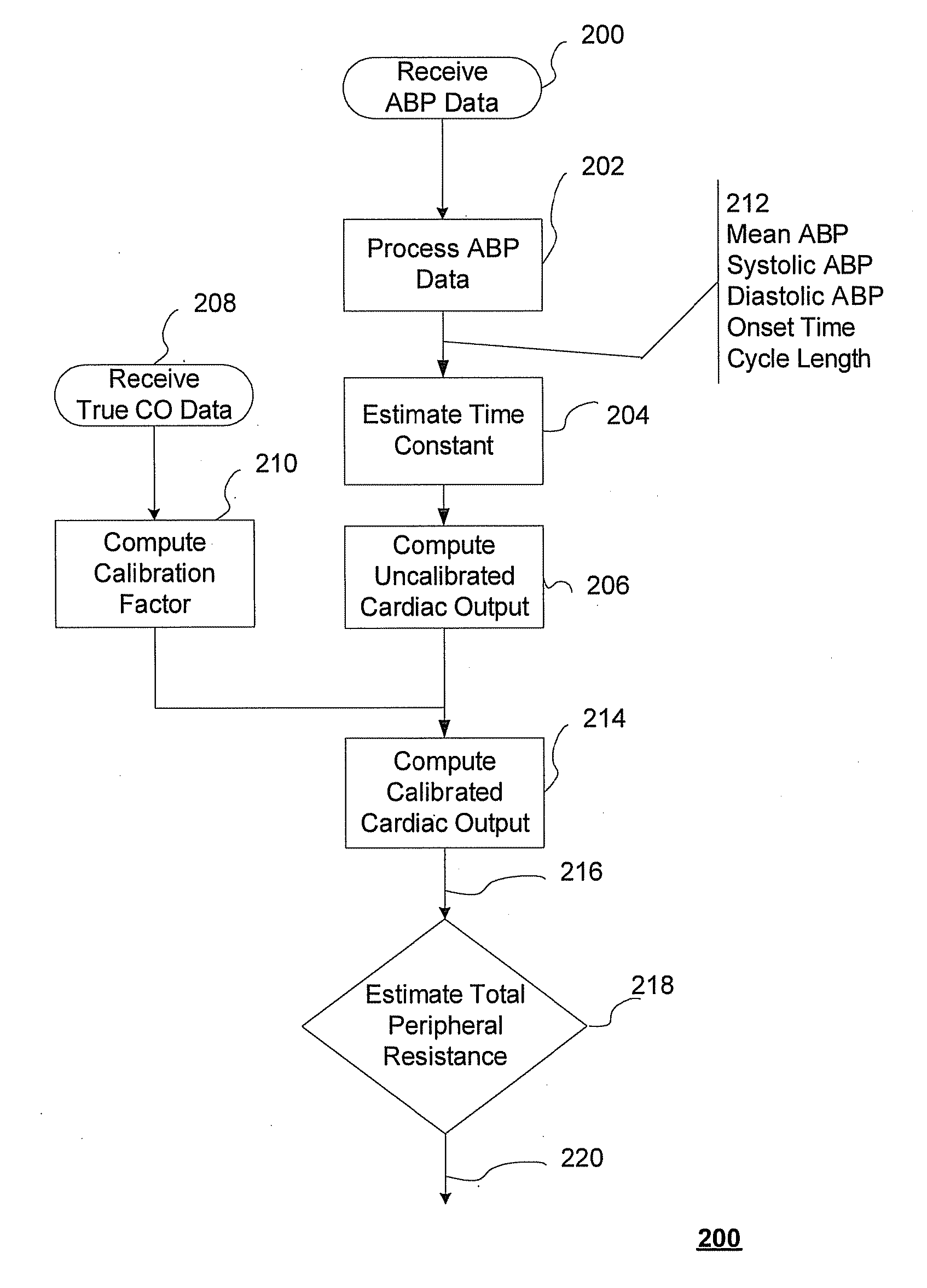
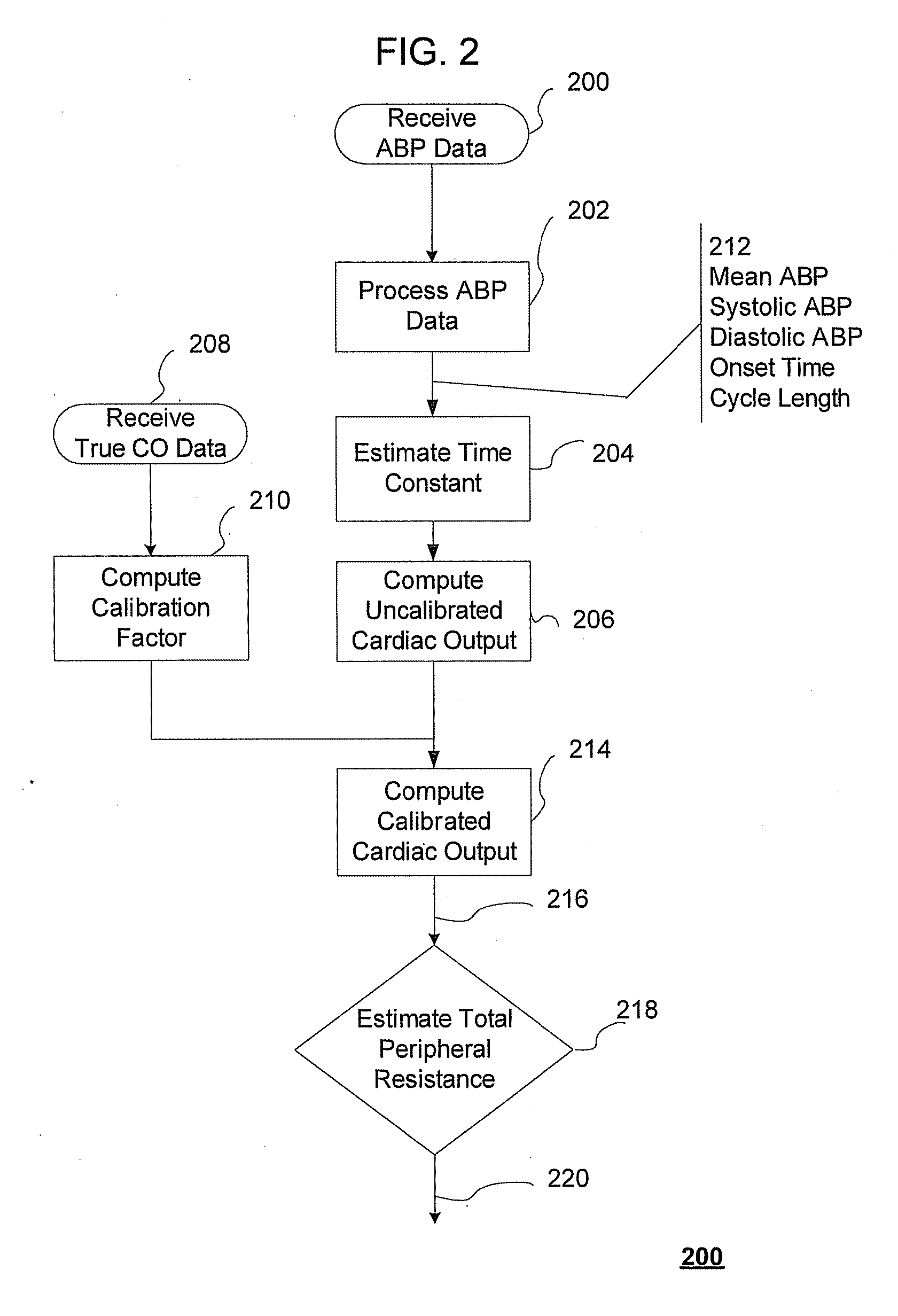
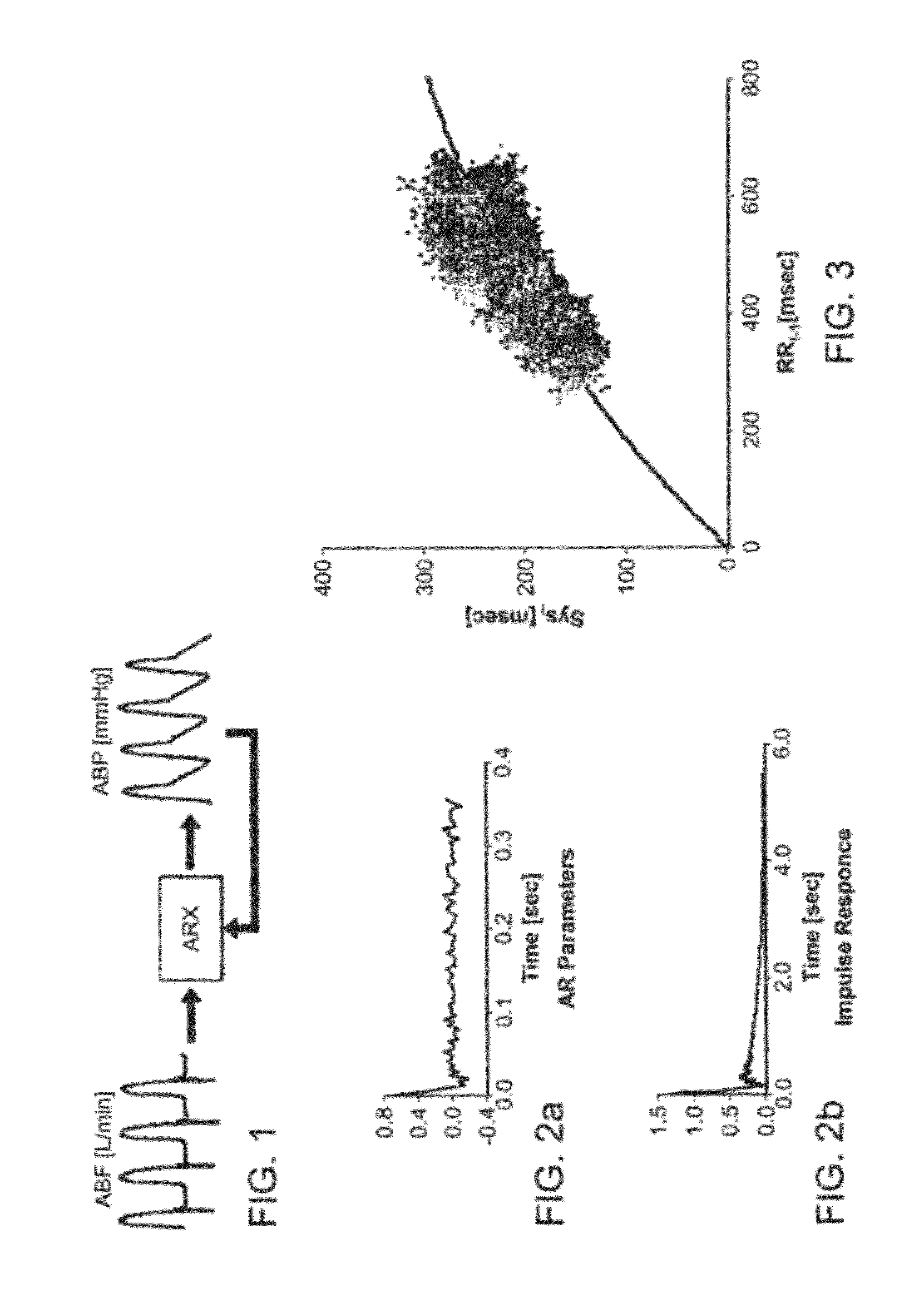
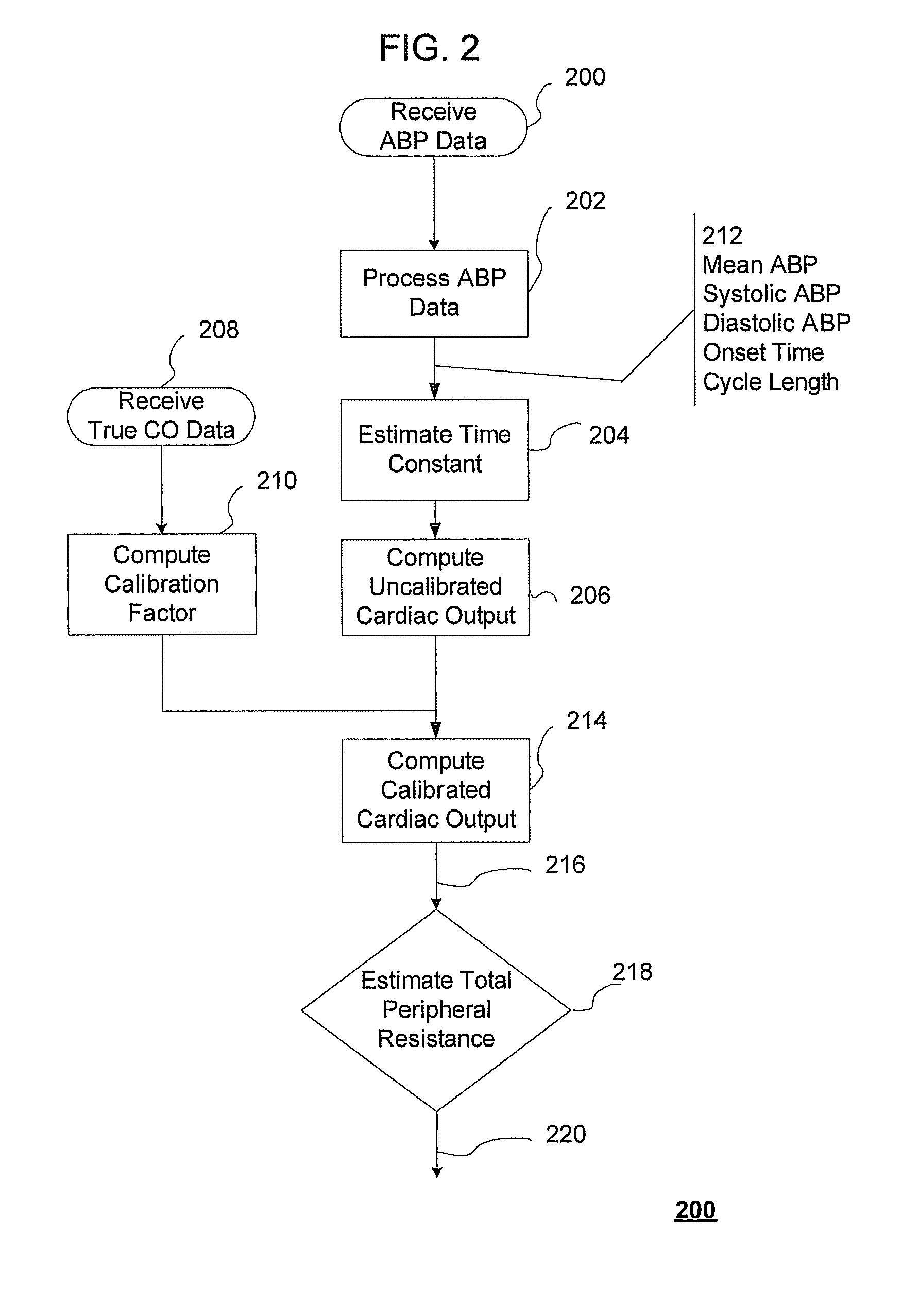
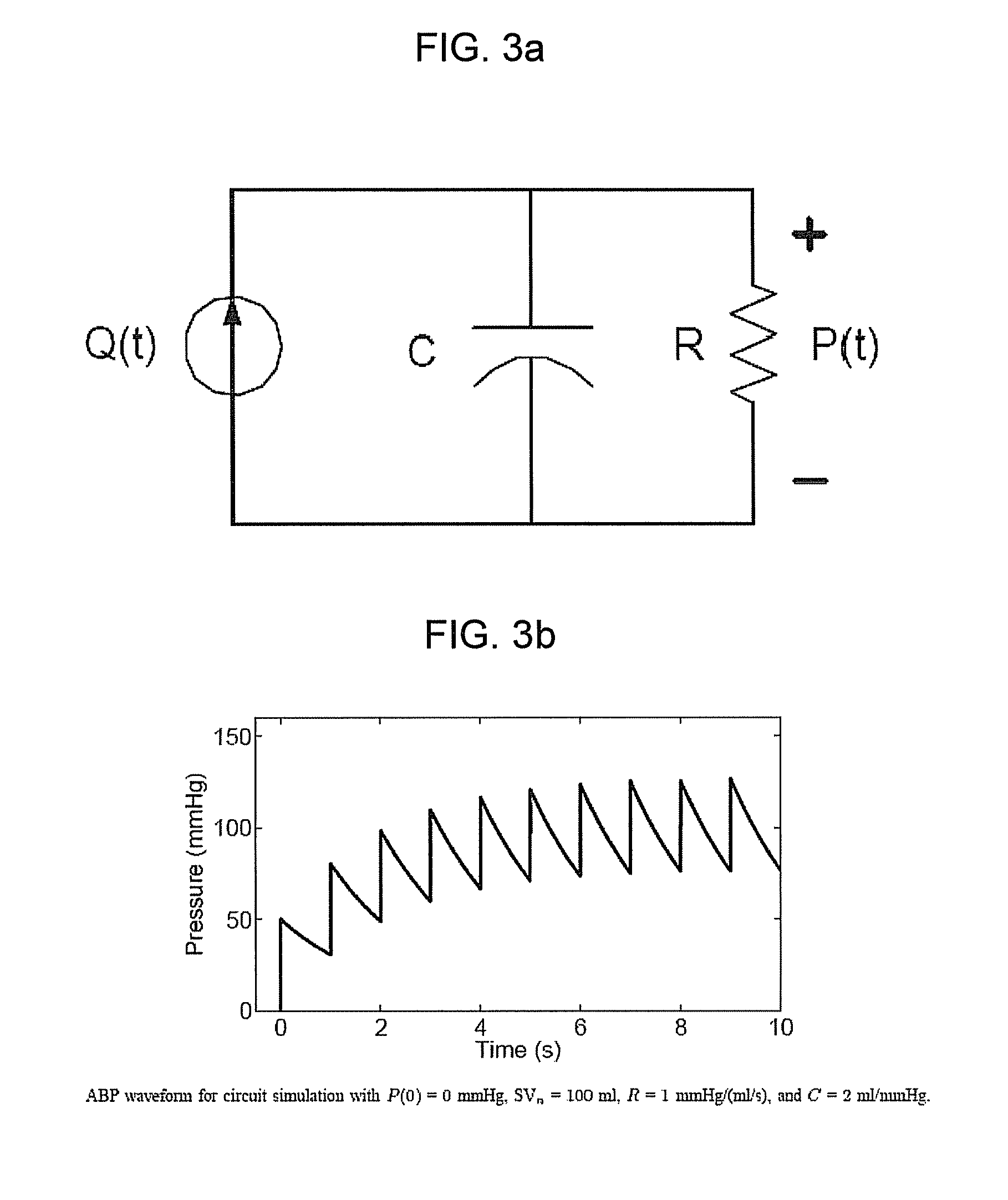
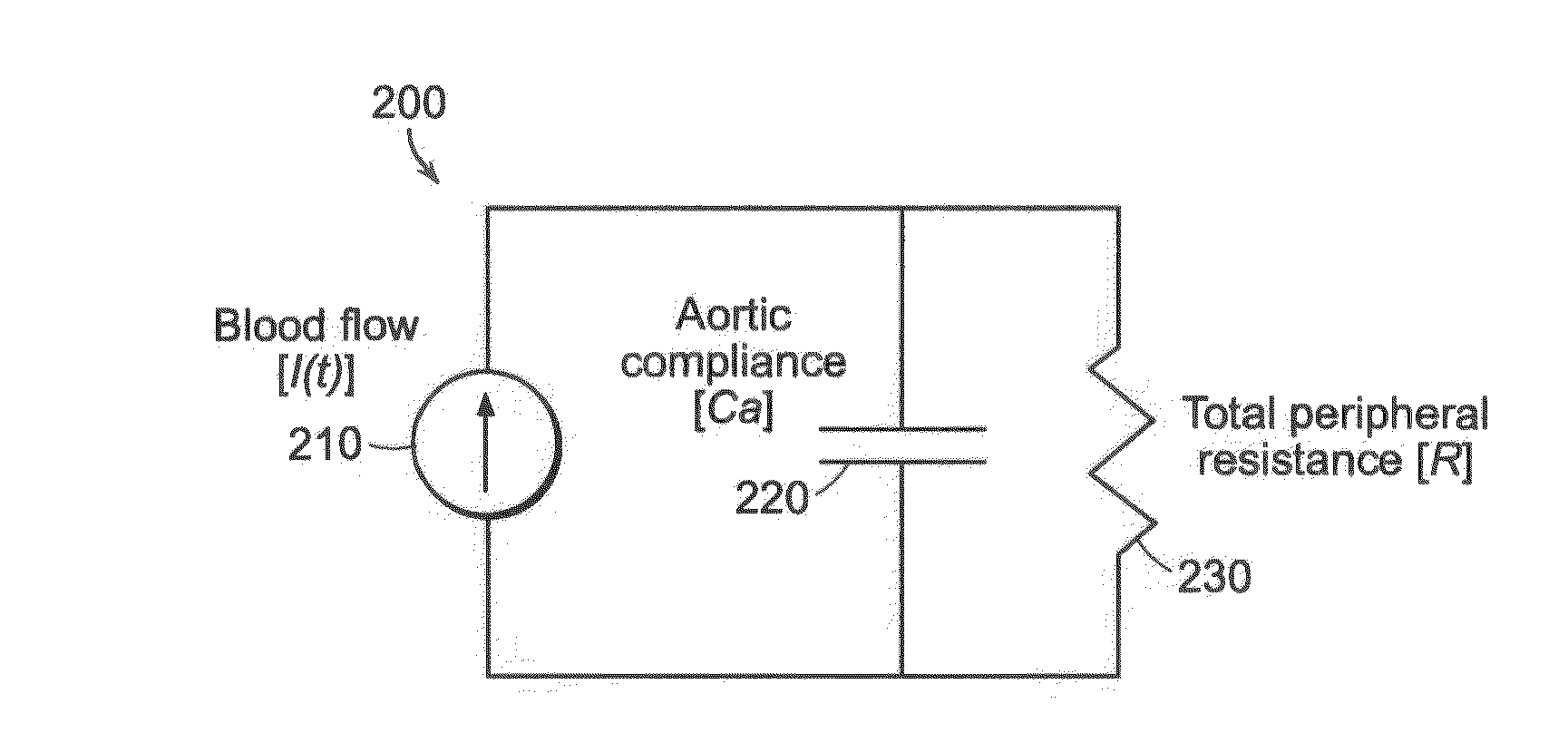
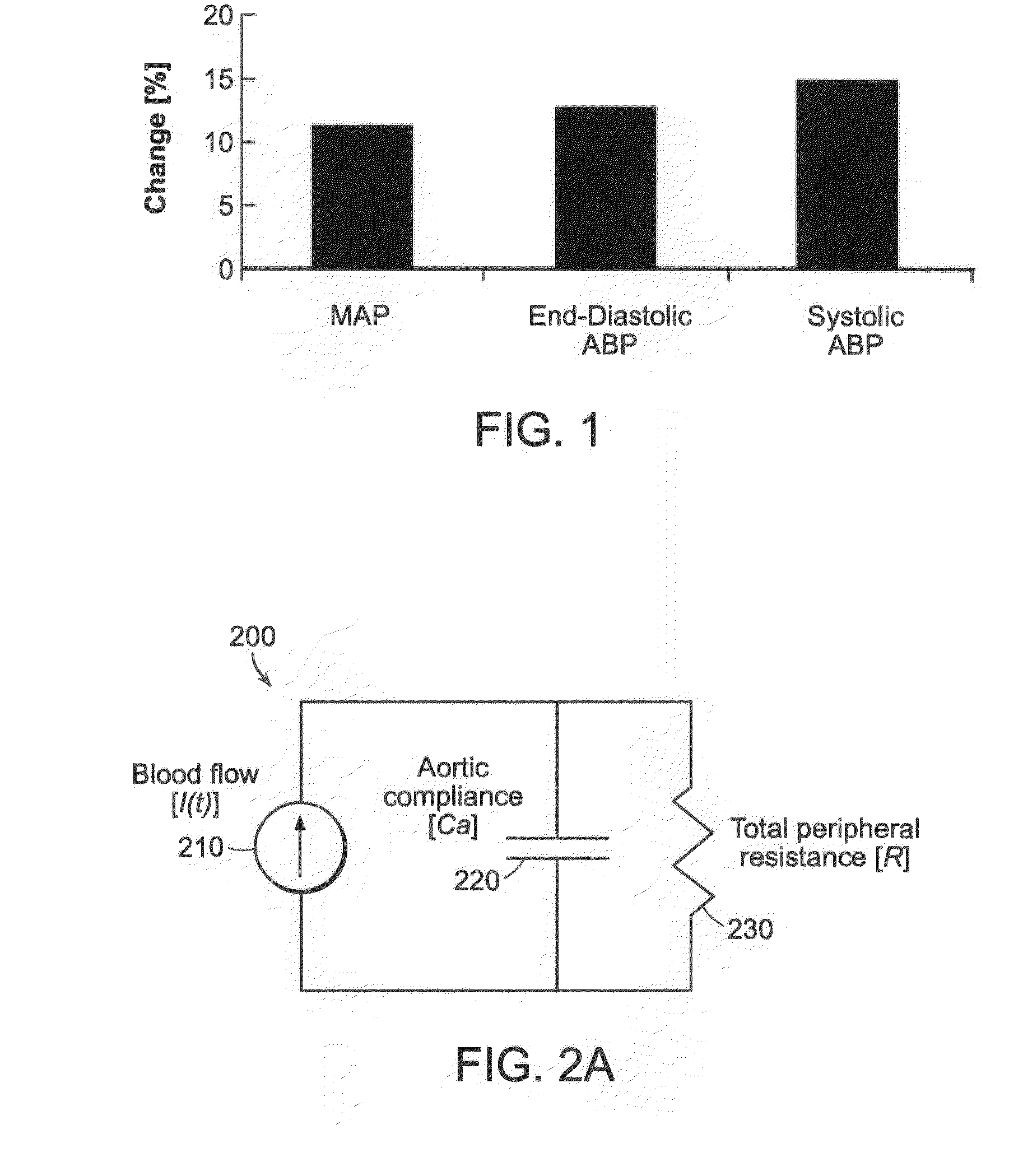
The methods and systems for estimating cardiac output and total peripheral resistance include observing arterial blood pressure waveforms to determine intra-beat and inter-beat variability in arterial blood pressure and estimating from the variability a time constant for a lumped parameter beat-to-beat averaged Windkessel model of the arterial tree. Uncalibrated cardiac output and uncalibrated total peripheral resistance may then be calculated from the time constant. Calibrated cardiac output and calibrated total peripheral resistance may be computed using calibration data, assuming an arterial compliance that is either constant or dependent on mean arterial blood pressure. The parameters of the arterial compliance may be estimated in a least-squares manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Pulse contour method and apparatus for continuous assessment of a cardiovascular parameter
ActiveUS20060235323A1Benefit of the square-root error dependenceCatheterSensorsElectrical resistance and conductanceData set
A cardiovascular parameter such as cardiac output is estimated from a current pressure waveform data set without needing to directly measure blood flow or arterial compliance. The general shape of an input flow waveform over one beat-to-beat cycle is assumed (or computed), and then the parameters of a flow-to-pressure model, if not pre-determined, are determined using system identification techniques. In one embodiment, the parameters thus determined are used to estimate a current peripheral resistance, which is used not only to compute an estimate of the cardiovascular parameter, but also to adjust the shape of the input flow waveform assumed during at least one subsequent beat-to-beat cycle. Another embodiment does not require computation of the peripheral resistance and still another embodiment computes a flow estimate from an optimized identification of the parameters defining the assumed input flow waveform.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Wrist and forearm exercising apparatus
InactiveUS7094182B1Creating frictionIncrease frictional resistanceFrictional force resistorsForearm muscleEngineering
Apparatus for exercising the forearm muscles responsible for movement of the hand at the wrist. The apparatus comprises two rigid rings adjoined by, and allowed to rotate about, the axis of a central, cylindrical variable resistance mechanism. The rigid rings each support a handgrip that is allowed to rotate about the inner circumference of each ring at variable resistance settings set with a peripheral resistance mechanism including an externally threaded terminal end of each handgrip, a knurled sleeve with internal threads at one end and external threads at the other. The knurled sleeve can be rotated about the axis of each handgrip, through internal threads of the inner ring, into the inner surface of the outer ring thereby creating a desired frictional resistance. The desired resistance can be preset and returned to through the incorporation of click-stops.
Owner:HOLTEN WILLIAM S
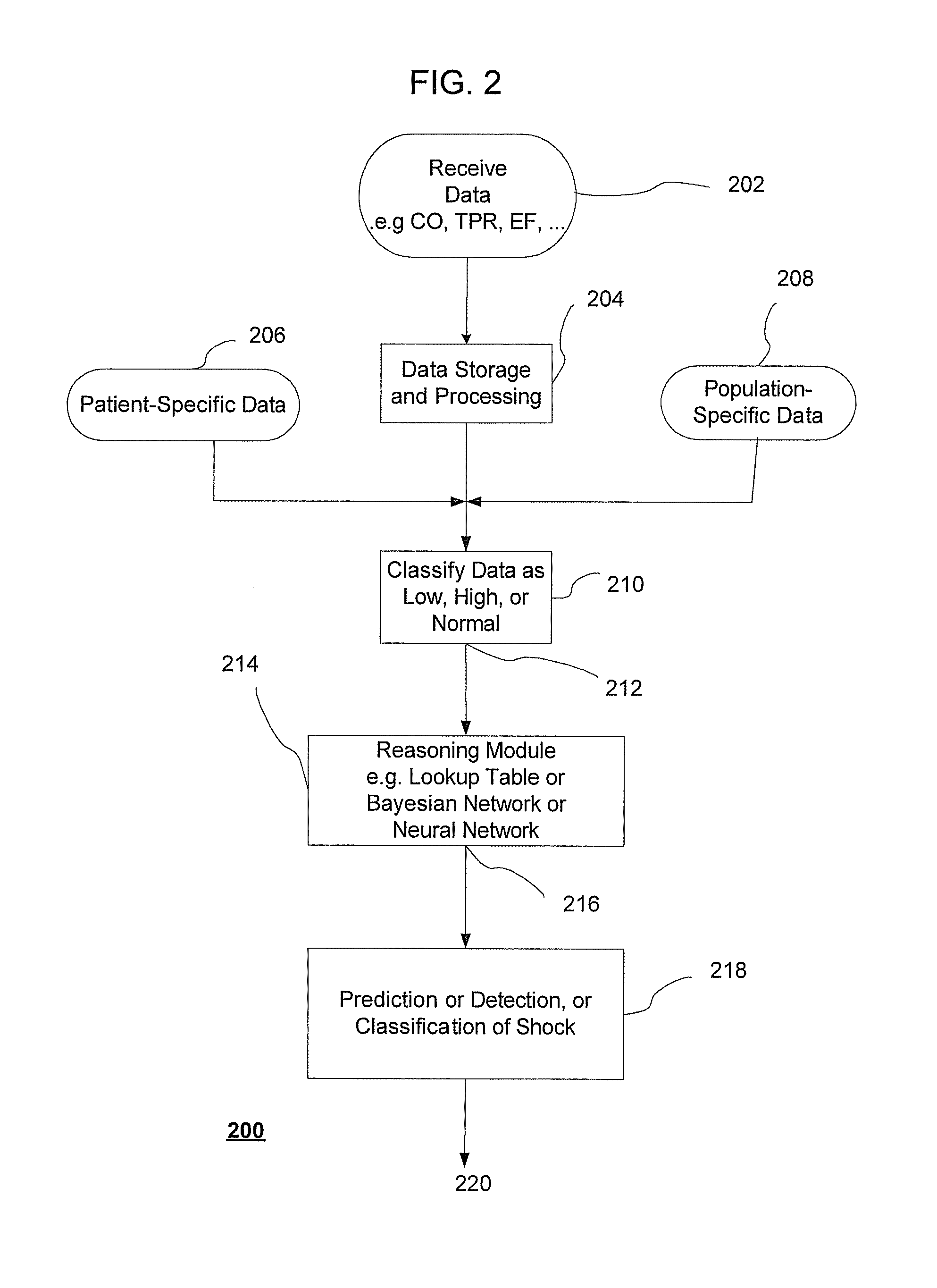
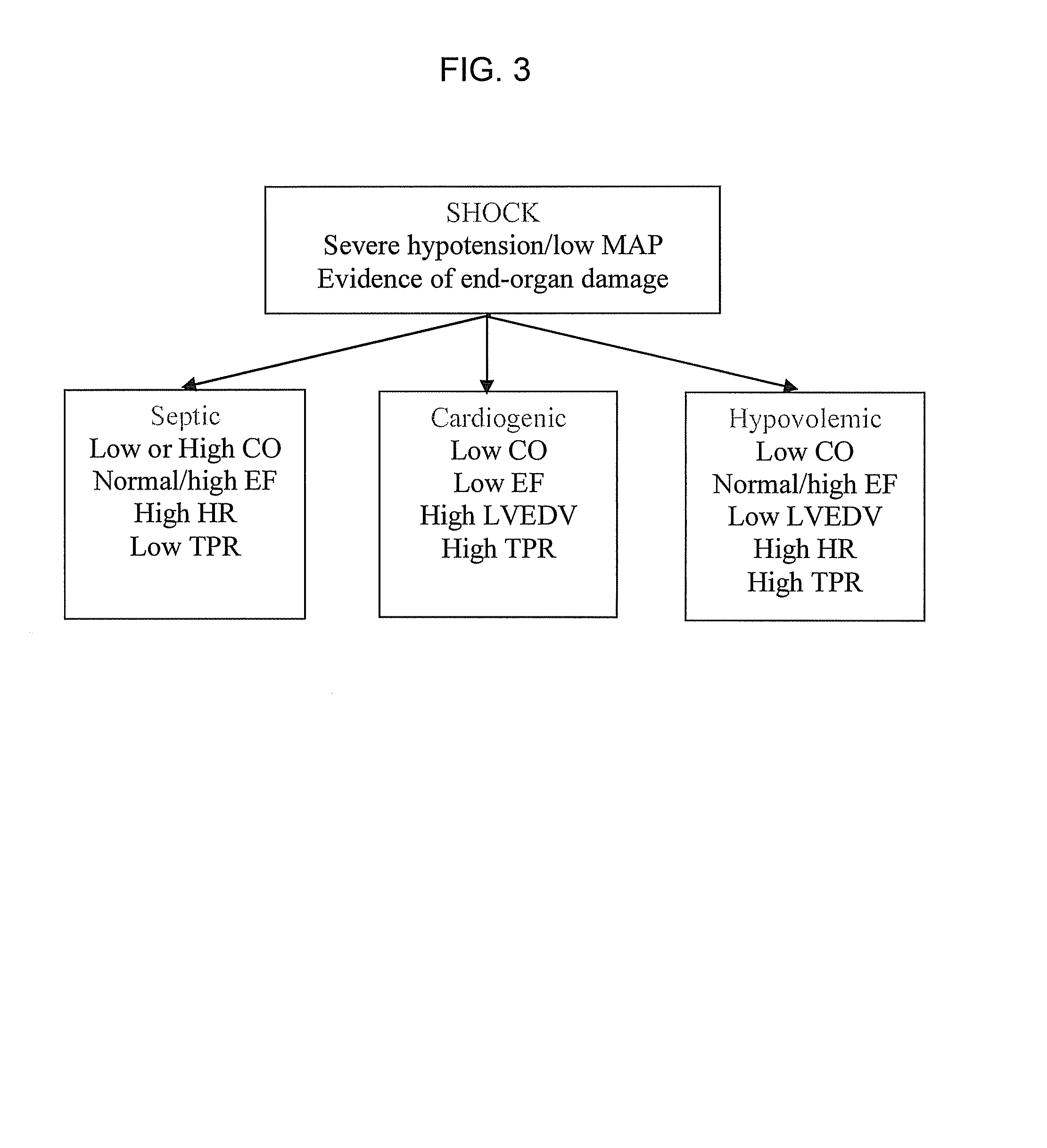
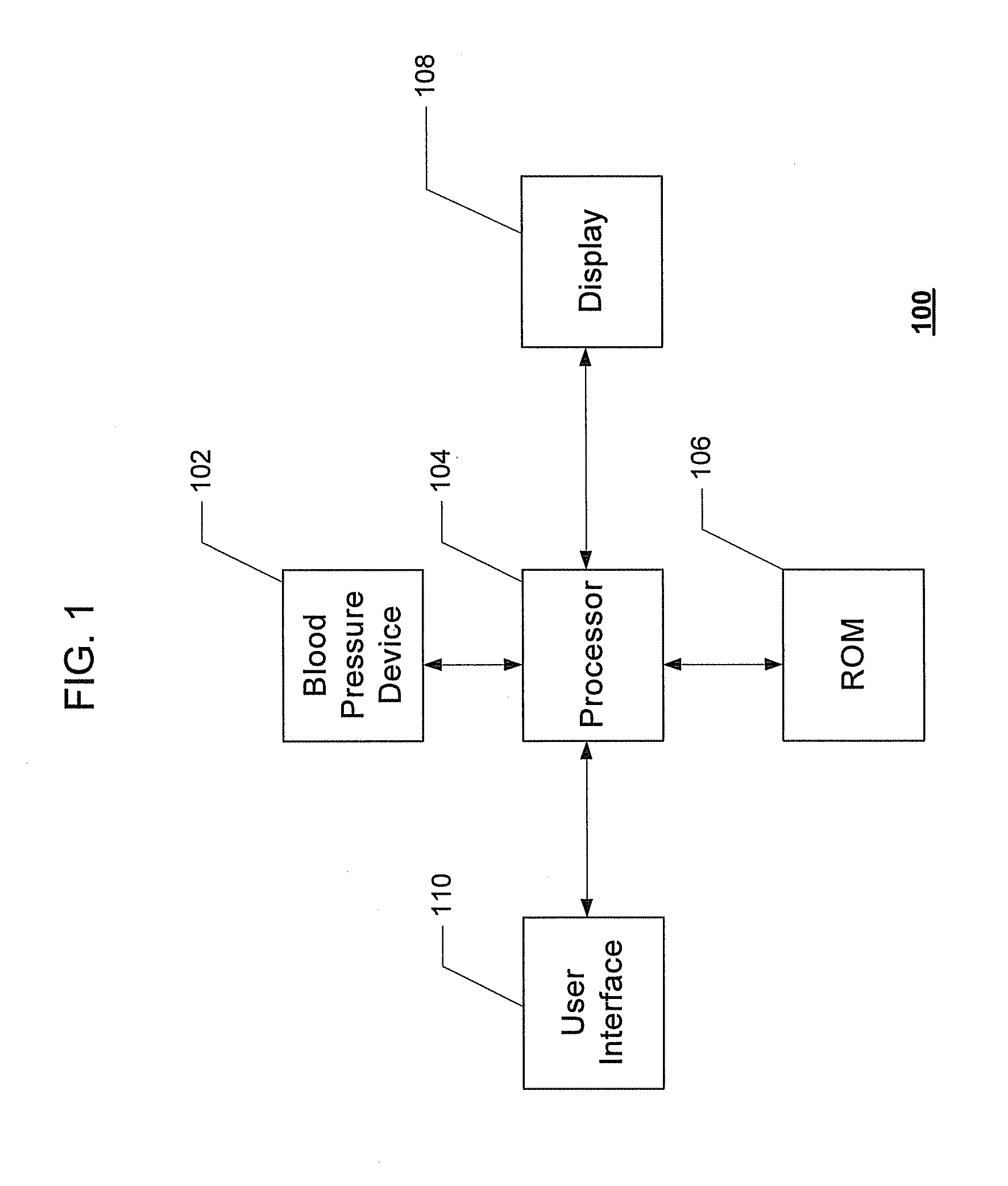
System and method for prediction and detection of circulatory shock
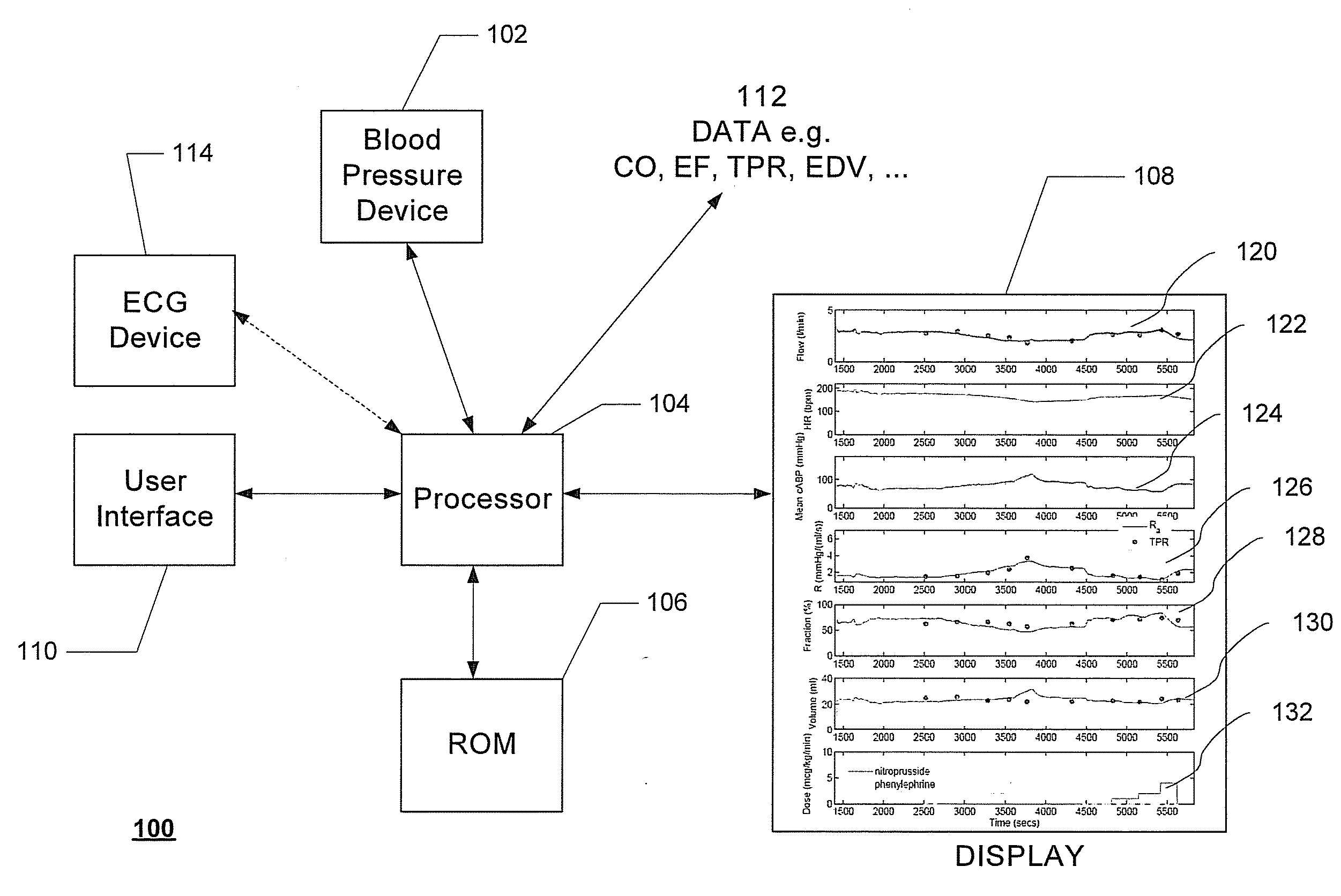
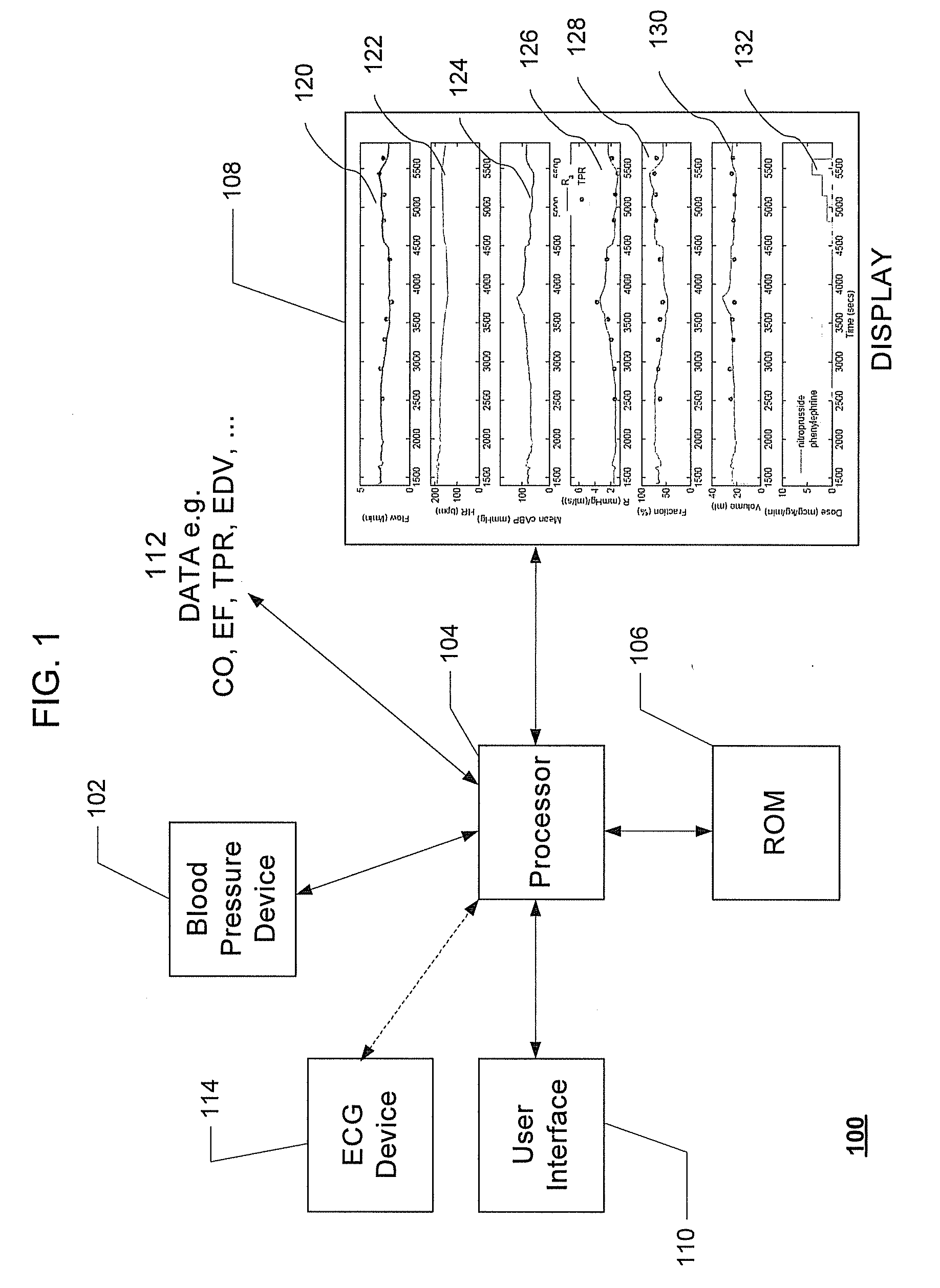
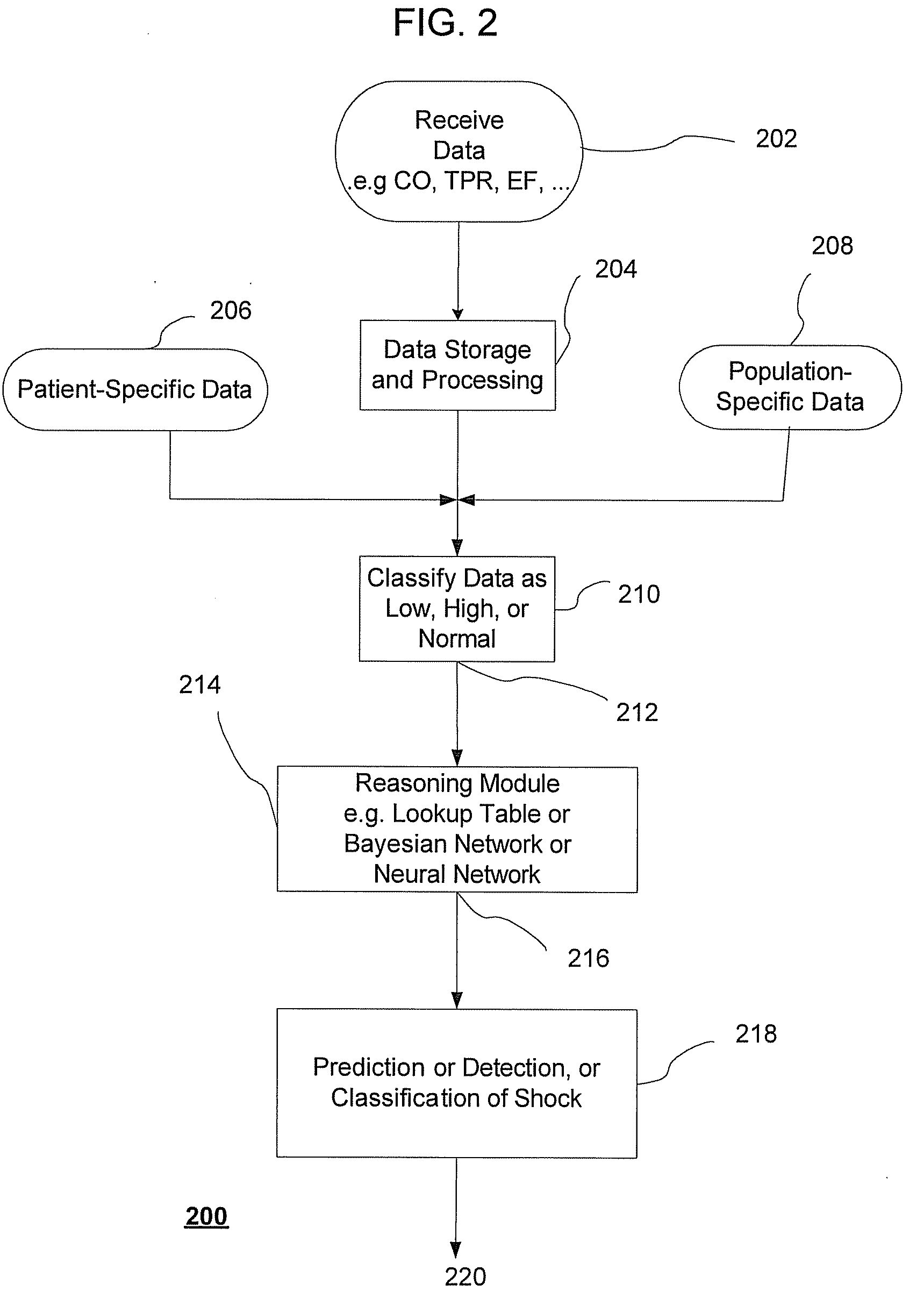
Systems and methods for prediction and detection of circulatory shock using estimates or measurements of arterial blood pressure, heart rate, stroke volume, cardiac output, total peripheral resistance, cardiac ejection fraction, cardiac contractility and ventricular end-diastolic volume are provided. These estimates and measurements are used to determine a type of circulatory shock. In some embodiments, the type of circulatory shock is determined to be one of septic shock, hypovolemic shock, anaphylactic shock, hemorrhagic shock, and cardiogenic shock.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
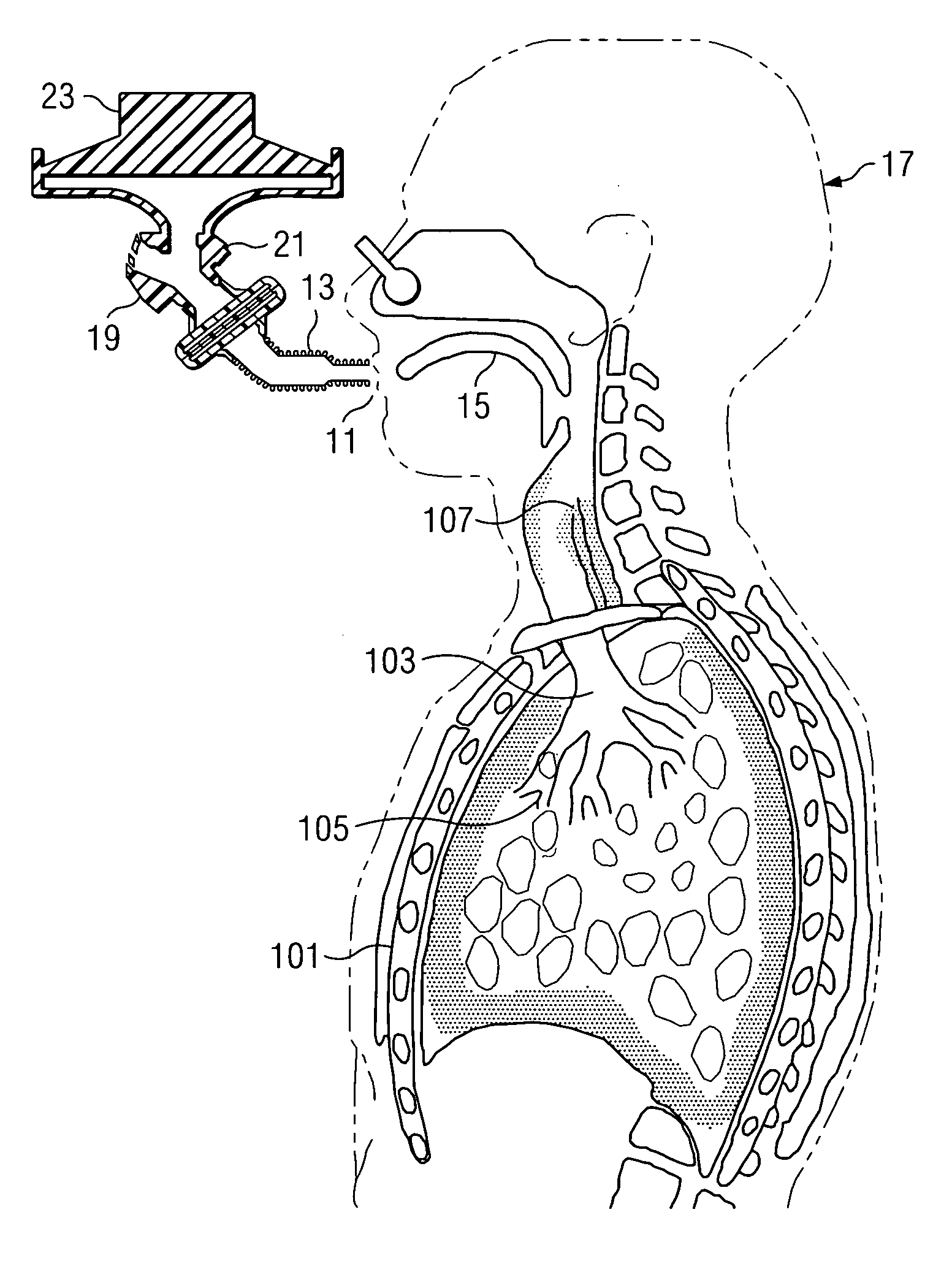
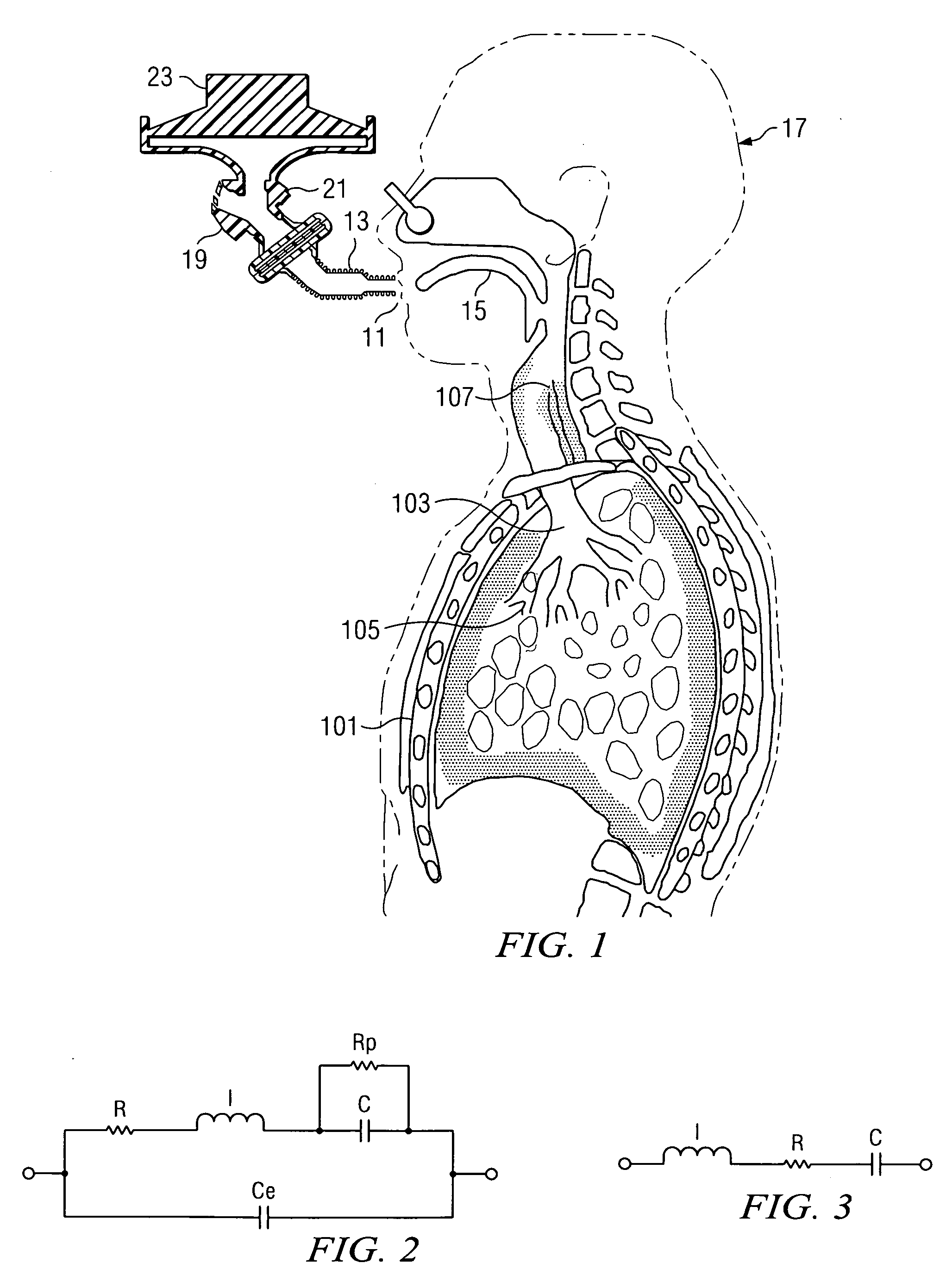
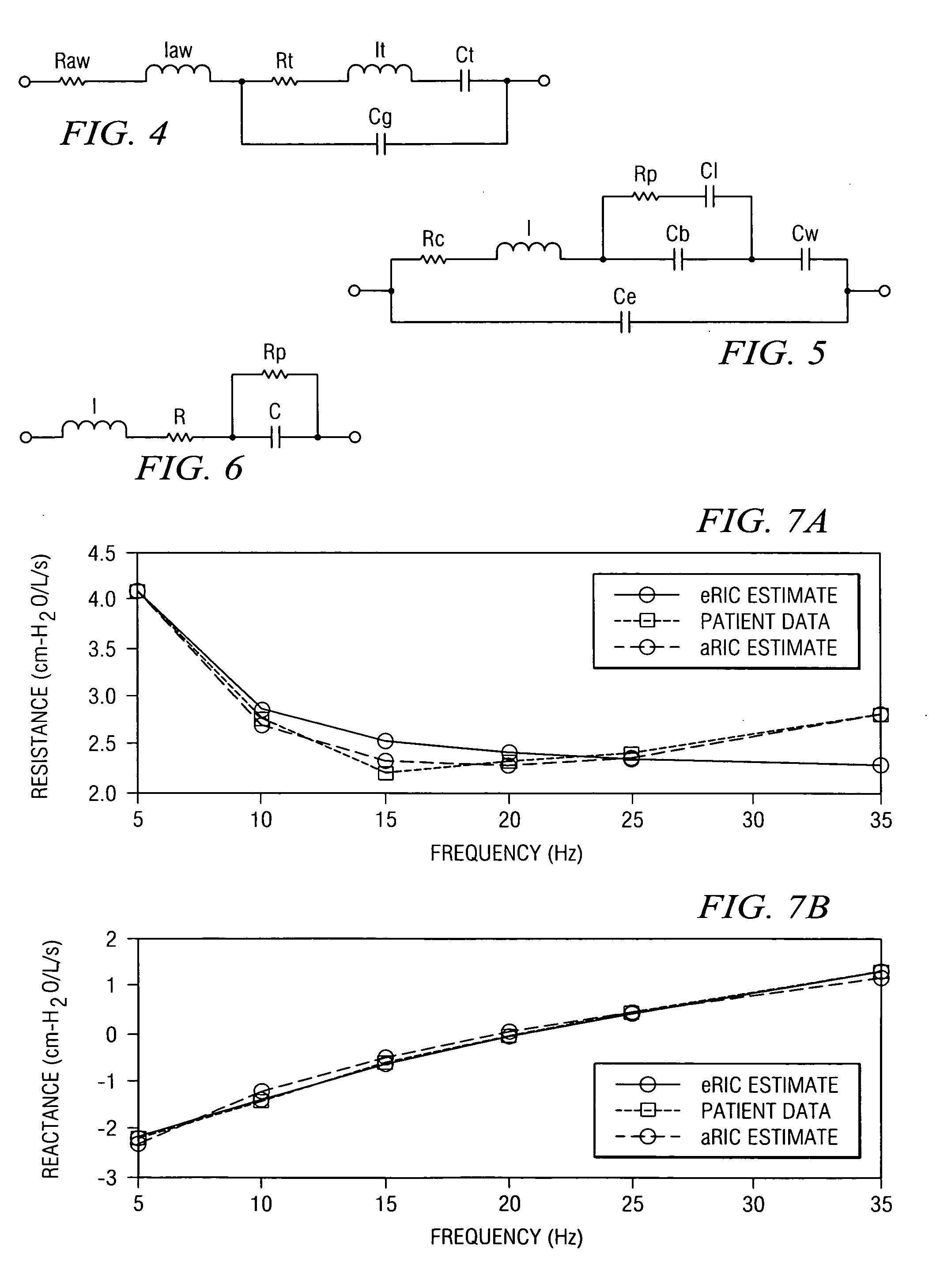
Augmented RIC model of respiratory systems
The present invention generally relates to an apparatus and method analyzing the respiratory characteristics of a human respiratory system from impulse oscillometry data, through the use of a linear network of electrical components. The present invention offers an improved alternative to the RIC respiratory circuit model, with an addition of a peripheral resistance to account for the resistance presented by the respiratory system's small airways and of a capacitor to account for extrathoracic compliance. After air pressure and air flow measurements are obtained from the subject by performing Impulse Oscillometry System testing, a graphical representation of a mechanical impedance characteristic may be derived. This allows for the estimation and adjustment of parameter values of the linear network whose components correlate to the resistances, compliances and inertances inherent in the respiratory system. Additionally, the linear network of electrical components may be configured as a virtual network represented in graphical form wherein the parameter values are estimated and adjusted according to program instructions operating on a computer system. The linear network of electrical components serves to provide parametric means for detection, diagnosis and treatment of various pathologies in the human respiratory system.
Owner:TEXAS CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Methods and apparatus for determining cardiac output
ActiveUS20110034813A1Ease of evaluationElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsWhole bodyCardiac cycle
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for determining a dynamical property of the systemic or pulmonary arterial tree using long time scale information, i.e., information obtained from measurements over time scales greater than a single cardiac cycle. In one aspect, the invention provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cardiac output (CO) from a single blood pressure signal measurement obtained at any site in the systemic or pulmonary arterial tree or from any related measurement including, for example, fingertip photoplethysmography.According to the method the time constant of the arterial tree, defined to be the product of the total peripheral resistance (TPR) and the nearly constant arterial compliance, is determined by analyzing the long time scale variations (greater than a single cardiac cycle) in any of these blood pressure signals. Then, according to Ohm's law, a value proportional to CO may be determined from the ratio of the blood pressure signal to the estimated time constant. The proportional CO values derived from this method may be calibrated to absolute CO, if desired, with a single, absolute measure of CO (e.g., thermodilution). The present invention may be applied to invasive radial arterial blood pressure or pulmonary arterial blood pressure signals which are routinely measured in intensive care units and surgical suites or to noninvasively measured peripheral arterial blood pressure signals or related noninvasively measured signals in order to facilitate the clinical monitoring of CO as well as TPR.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV +1
Systems and methods for using physiological information
Systems and methods using a database of physiological information for the design, development, testing and use of therapeutics. In one aspect, the physiological information can include at least one of: hemodynamic monitoring information, pulmonary arterial pressure, cardiac output, heart rate, respiratory rate, peripheral vascular resistance, total peripheral resistance or dicrotic notch information. Optionally, the cardiovascular physiology information can include ambulatory physiological information.
Owner:CARDIOMEMS
Method and System for Non-Invasive Measurement of Cardiac Parameters
ActiveUS20100049071A1Reduction in arterial wall distensibilityImprove applicabilityElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsElectricityData selection
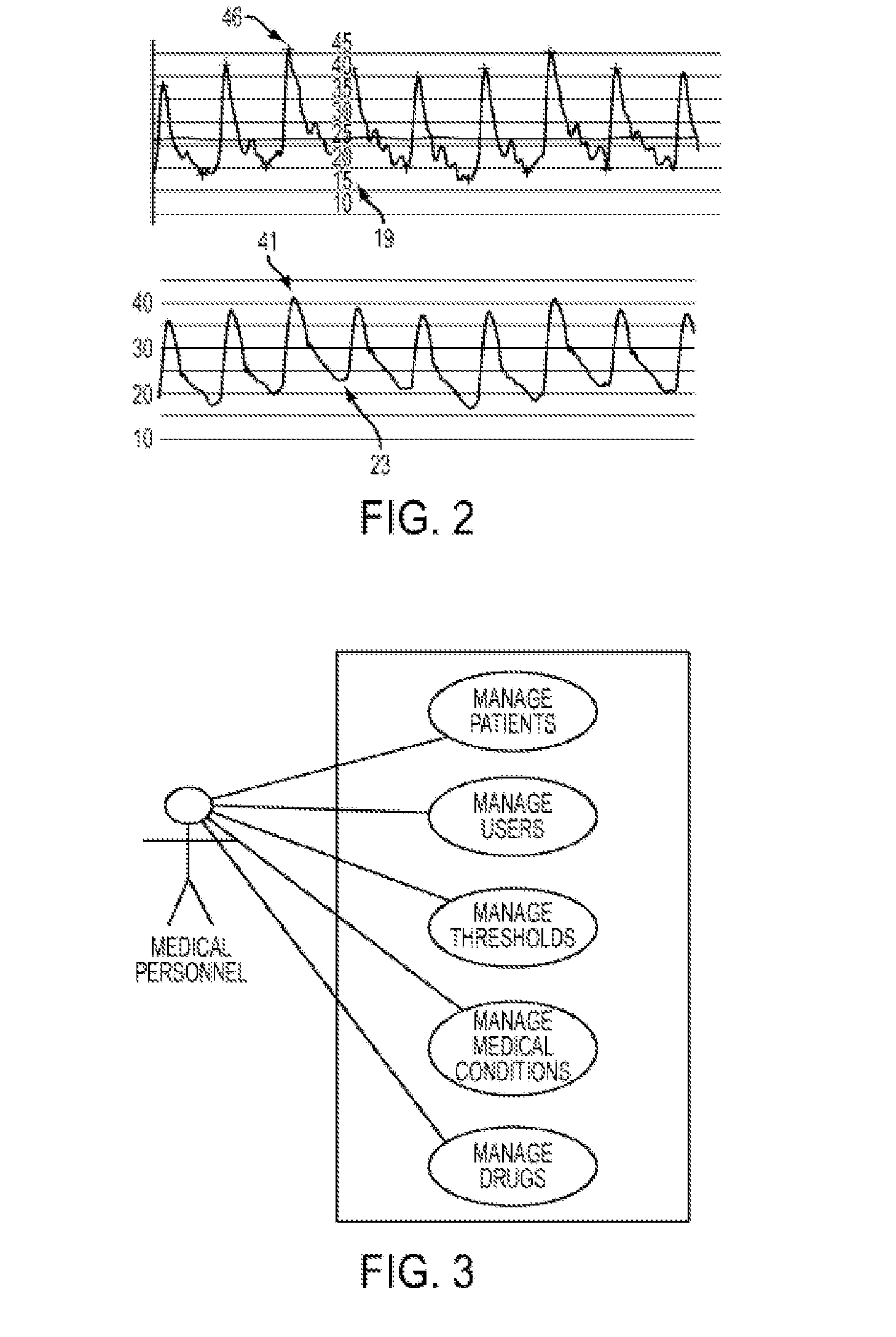
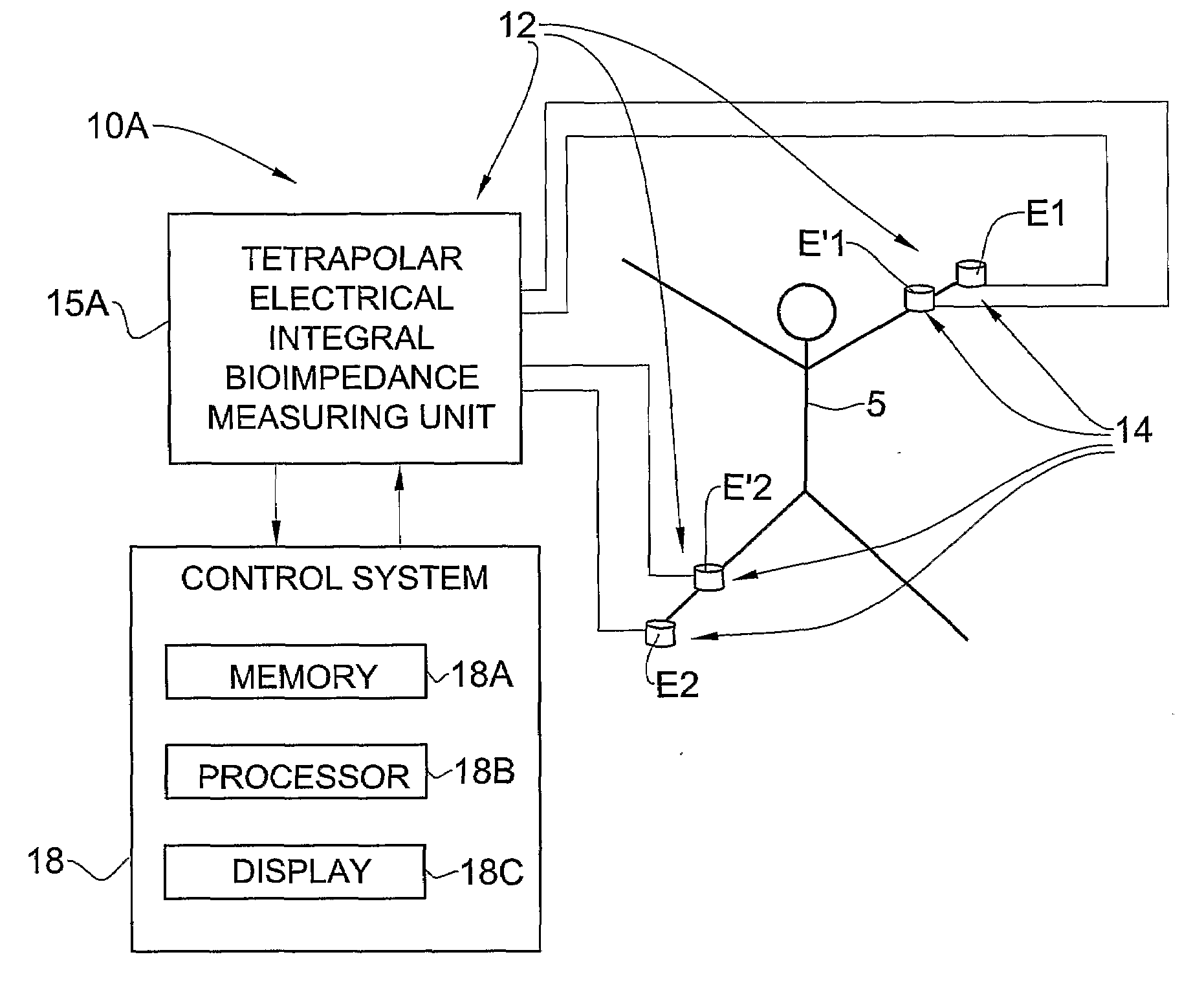
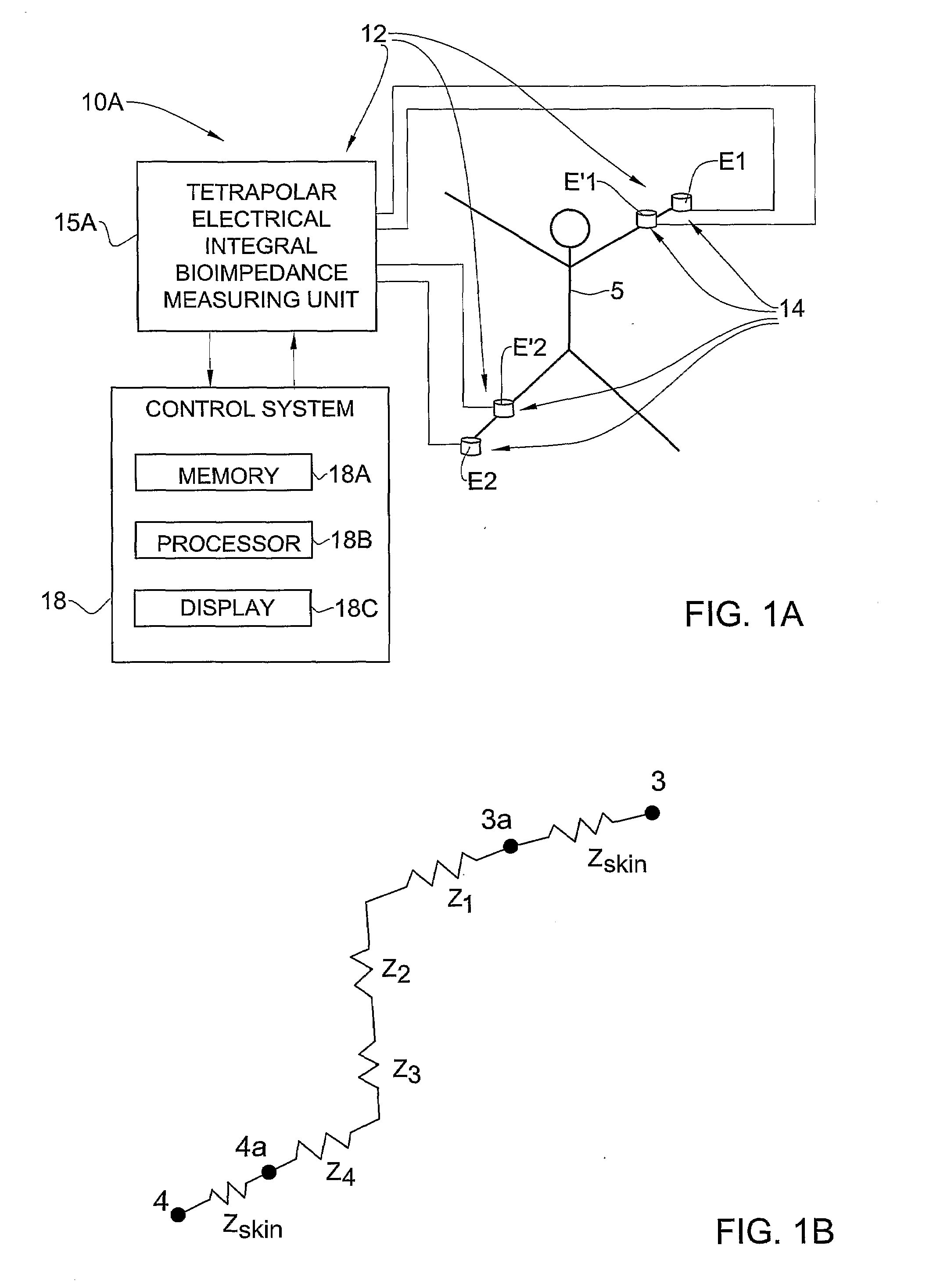
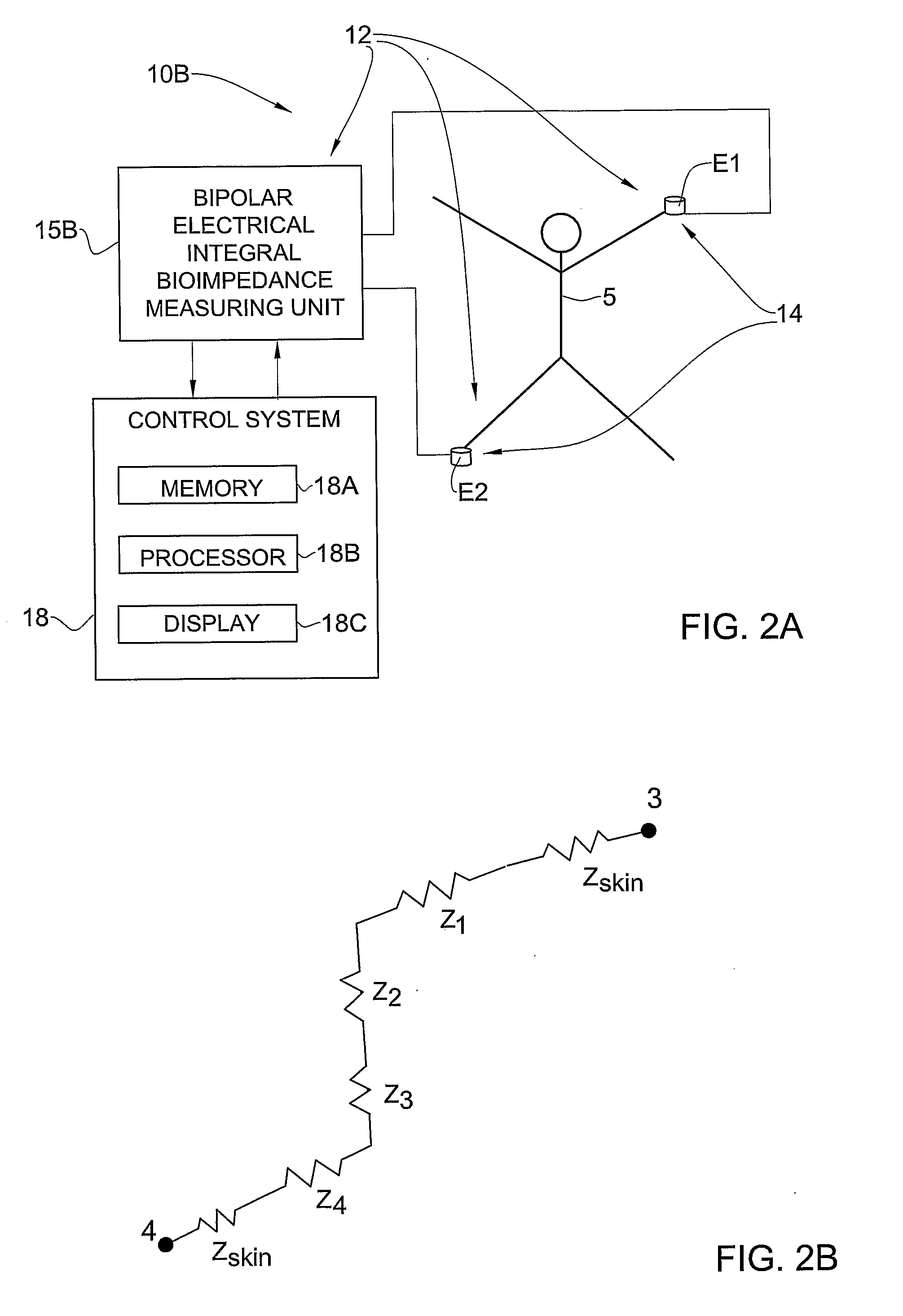
A method and system are presented for use in assessment of at least one cardiac parameter of an individual. An electrodes arrangement is applied to an individual's body, for applying an electrical field to the body and providing an electrical output indicative of a systolic impedance change and of a velocity of said change during a cardiac cycle. Also provided is additional data indicative of at least of the following conditions of the individual: a value of total peripheral resistance (TPR), a value of cardiac index (CI), and existence of the AHF condition. Data corresponding to these condition is analyzed to determine whether the TPR satisfies a first predetermined condition and / or the CI satisfies a predetermined second condition and / or whether the acute heart failure (AHF) condition is identified, to thereby use the data indicative of the measured electrical output and selectively calculate said at least one cardiac parameter based on either the systolic impedance change data or on said data of the velocity of the impedance change.
Owner:NEW N I MEDICAL 2011
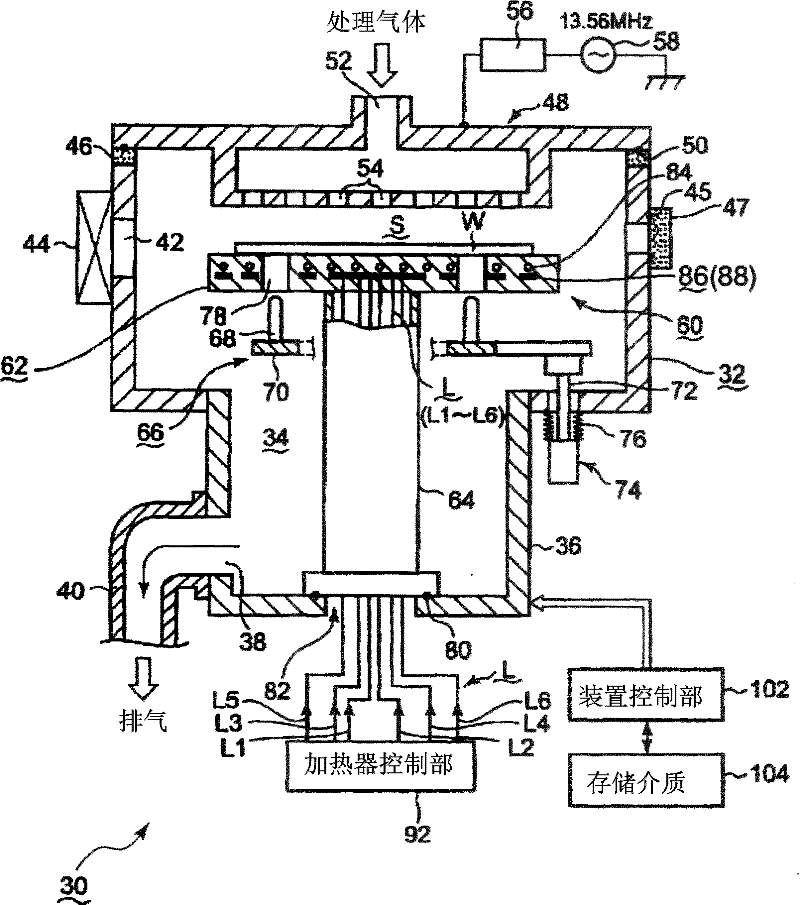
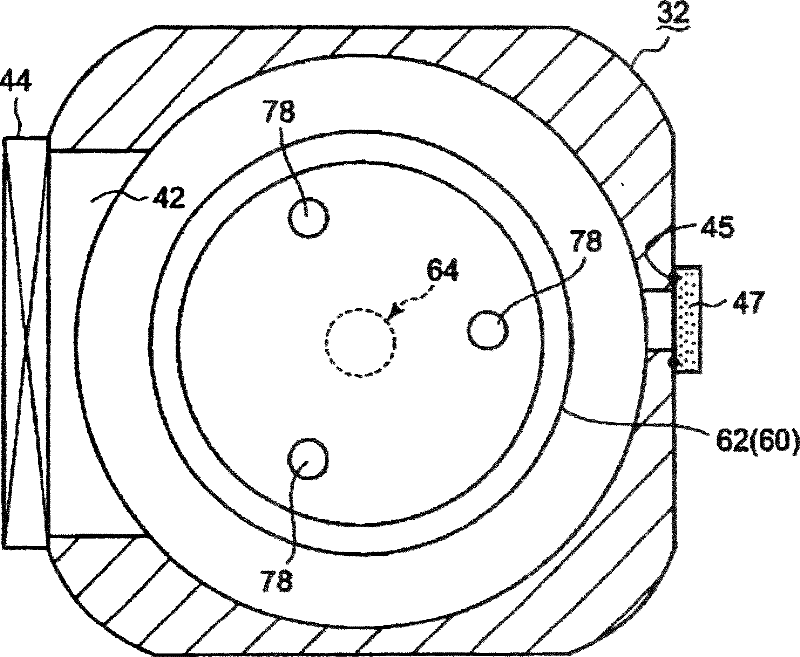
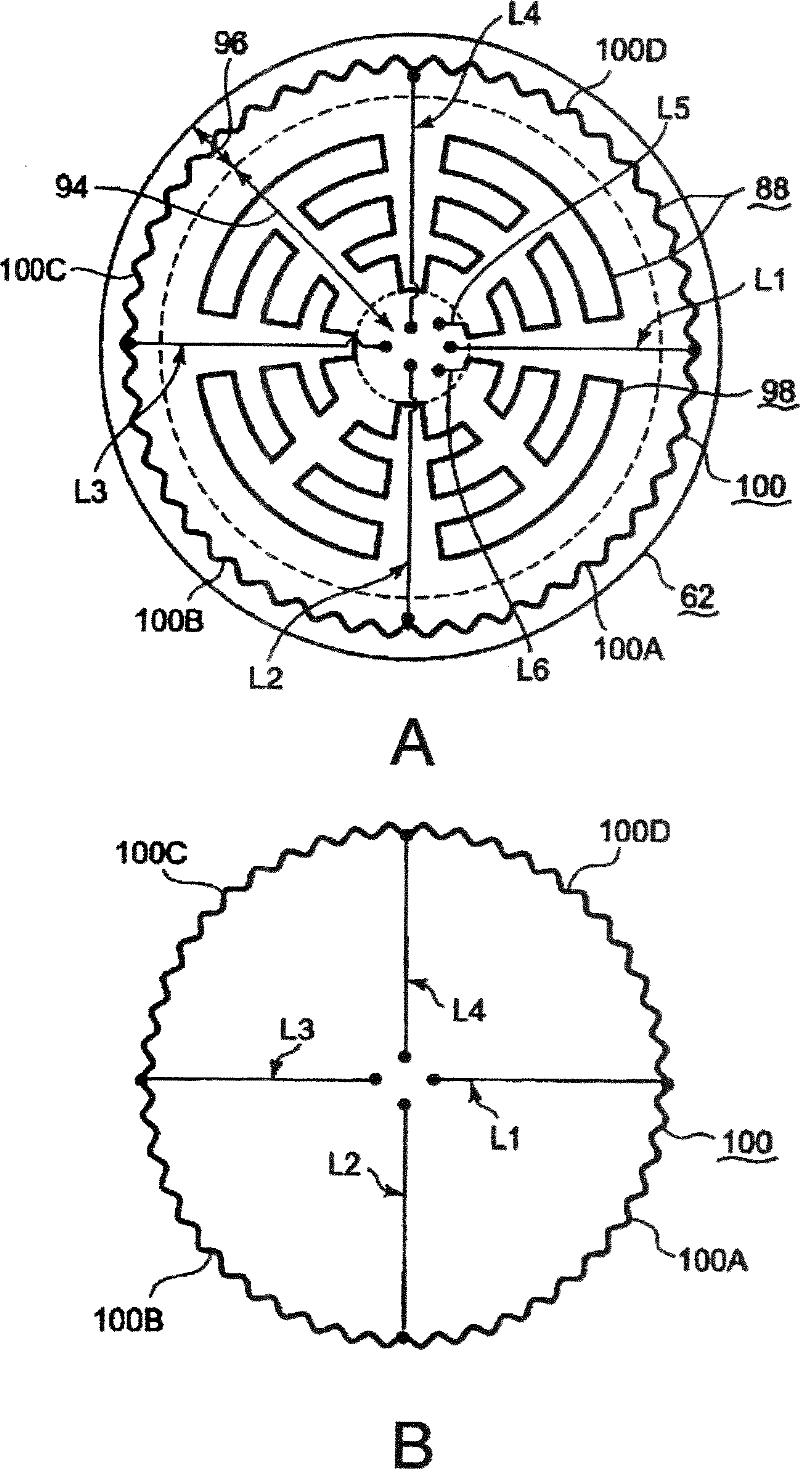
Mounting table structure and treatment device
InactiveCN102362332AElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Pulse contour method and apparatus for continuous assessment of a cardiovascular parameter
ActiveUS7651466B2Benefit of the square-root error dependenceCatheterSensorsElectrical resistance and conductanceData set
A cardiovascular parameter such as cardiac output is estimated from a current pressure waveform data set without needing to directly measure blood flow or arterial compliance. The general shape of an input flow waveform over one beat-to-beat cycle is assumed (or computed), and then the parameters of a flow-to-pressure model, if not pre-determined, are determined using system identification techniques. In one embodiment, the parameters thus determined are used to estimate a current peripheral resistance, which is used not only to compute an estimate of the cardiovascular parameter, but also to adjust the shape of the input flow waveform assumed during at least one subsequent beat-to-beat cycle. Another embodiment does not require computation of the peripheral resistance and still another embodiment computes a flow estimate from an optimized identification of the parameters defining the assumed input flow waveform.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
High common mode rejection ratio preamplifier
InactiveCN1414701AHigh Differential Mode GainHigh Common Mode Rejection Ratio PerformanceDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesInstrumentation amplifierResistance capacitance
A preamplifier with high common-mode suppression ratio includes connect output end of parallel dual mode instrumentation amplifier with coupling circuit of two groups of resistance-capacitance separately, the circuits of two groups of resistance-capacitance connected with the input end of integrated instrumentation amplifier in next stage amplifier separately, the common-mode signal sampling circuit connected with outupt end of parallel dual mode instrumentation amplifier separately and the coupling circuit of two groups of resistance-capacitance also connected with common-mode signal sampling circuit so that it is made to have the advatnages as follows: the common-mode suppression ratio being infinite, the output being output signal of dual end differential action and no relationship to the matching of its peripheral resistance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for converting high-precision single-chip digital signal into shaft angle signal
ActiveCN102589584AHigh precisionImprove conversion accuracyUsing electrical meansConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyAxis–angle representationTransformer
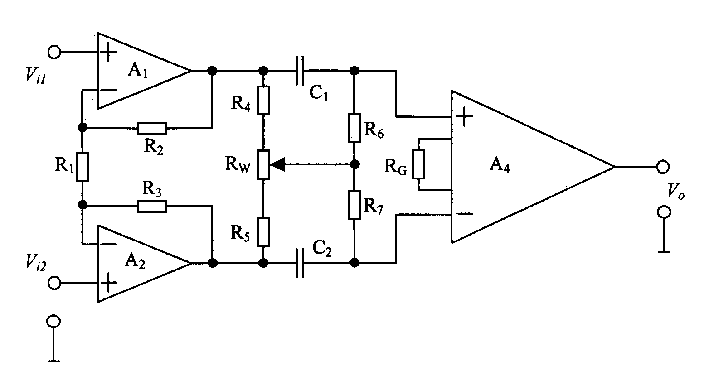
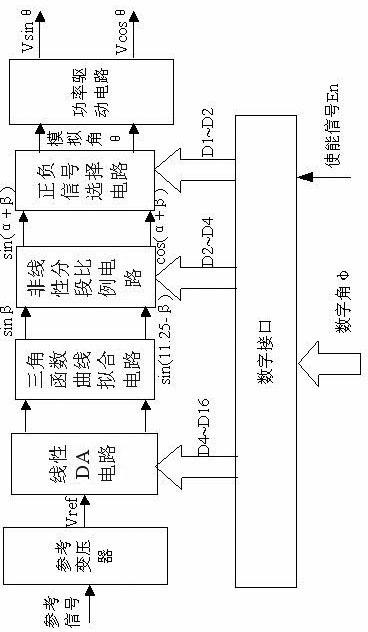
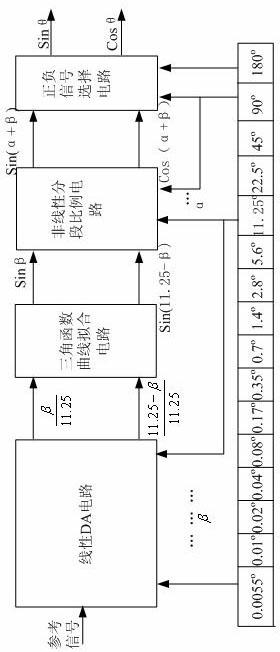
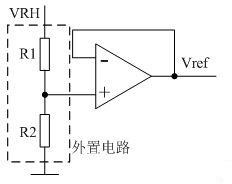
The invention discloses a method for converting a high-precision single-chip digital signal into a shaft angle signal. A circuit for realizing the method is composed of a reference transformer, a linear DA (Direct-Alternating) circuit, a trigonometric function curve fitting circuit, a non-linear segmented proportional circuit, a negative and positive signal selection circuit, a power driving circuit and a digital interface circuit, wherein the circuits are integrated on a single chip by the compatible multivoltage high-voltage CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductors) technology; the linear DA circuit is composed of high-precision 12-bit weighted resistance network D / A conversion circuits; the trigonometric function curve fitting circuit and the non-linear segmented proportional circuit are composed of precise resistance networks; and the reference transformer and the power driving circuit are composed of an operational amplifier and an adjustable peripheral resistance circuit. The method for converting a high-precision single-chip digital signal into a shaft angle signal has the advantages of small circuit volume, good reliability, high integration degree, high conversion precision and strong expandability, a system element can be installed with high precision, and the high-precision single-chip digital signal can be effectively converted into the shaft angle signal.
Owner:连云港杰瑞电子有限公司
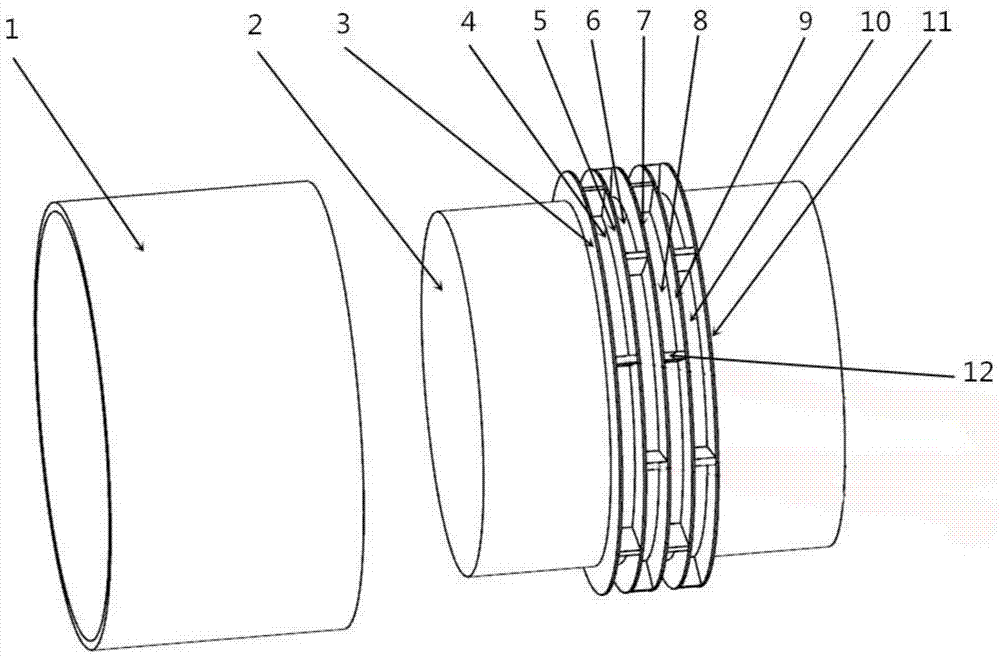
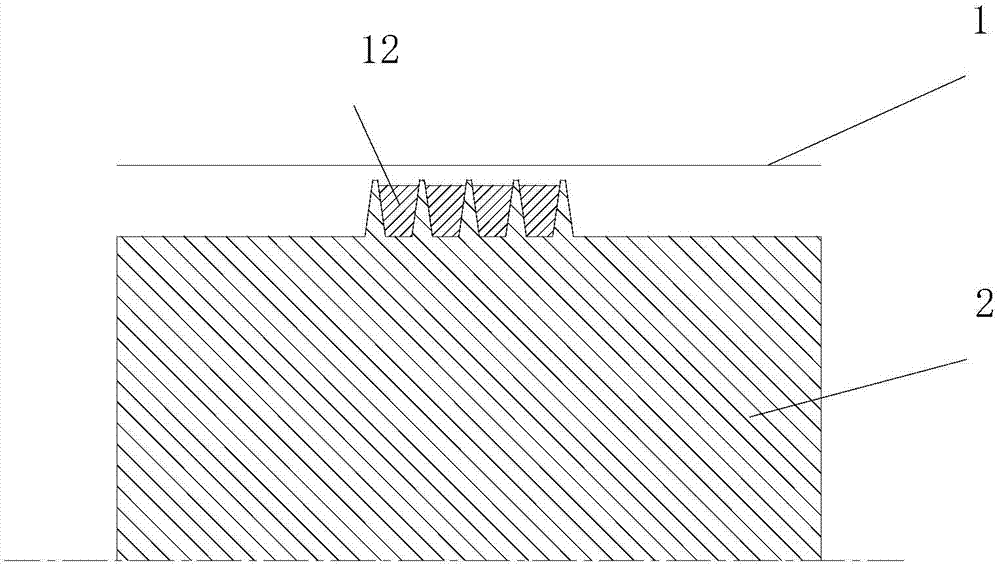
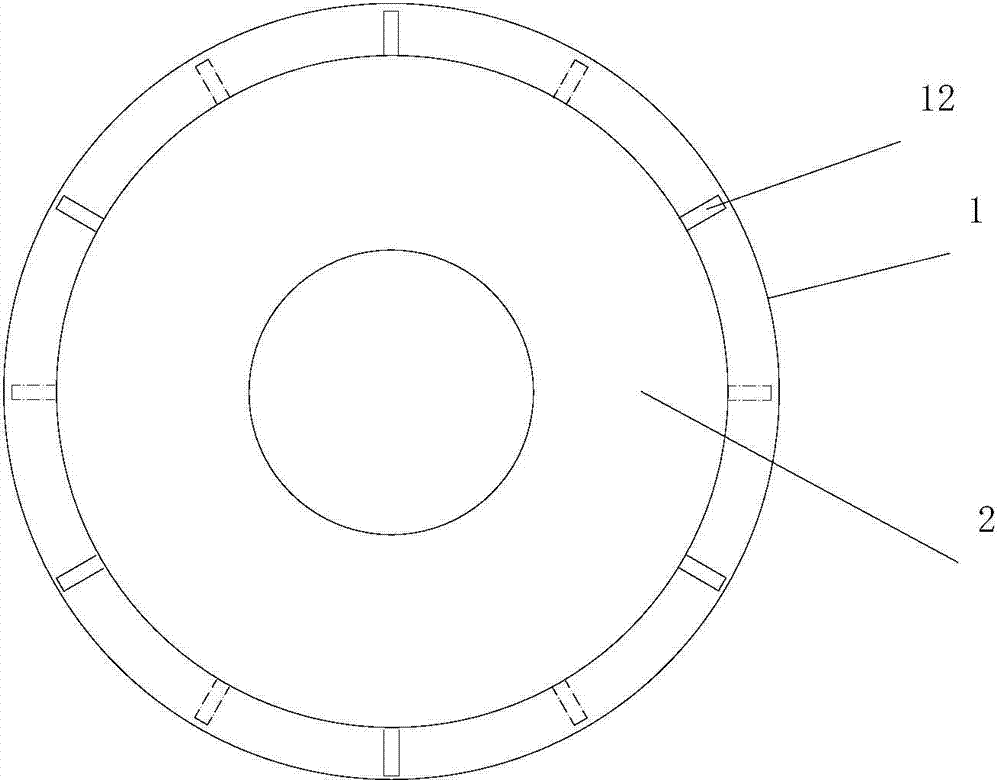
Aero-engine labyrinth tight-sealing structure
ActiveCN104514582AReduce circumferential flowReduce leakageLeakage preventionMachines/enginesPeripheral resistanceAero engine
Provided is a labyrinth tight-sealing structure for increasing inner peripheral resistance of an aero-engine labyrinth cavity. The total flow reducing purpose is achieved by decreasing peripheral flowing of air flows. According to the specific technical scheme, the aero-engine labyrinth tight-sealing structure comprises a tight-sealing lining, a rotary shaft and a plurality of labyrinths arranged on the peripheral surface of the rotary shaft, wherein a labyrinth cavity is formed between every two adjacent labyrinths, and the tight-sealing lining is installed on the rotary shaft through a labyrinth structure. The aero-engine labyrinth tight-sealing structure is characterized in that labyrinth cavity partition plates are distributed in the labyrinth cavities in the peripheral direction and divide smooth annular flowing channels of the labyrinth cavities to form continuous peripheral cavity regions. By utilizing the throttling effect of the partition plates and eddy inside the cavities, peripherally-flowing air flows can flow up and down, fluid flowing resistance can be increased, the peripheral flowing of the labyrinth cavities can be reduced, and fluid leakage amount can be reduced.
Owner:南京亿贤奇信息科技有限公司
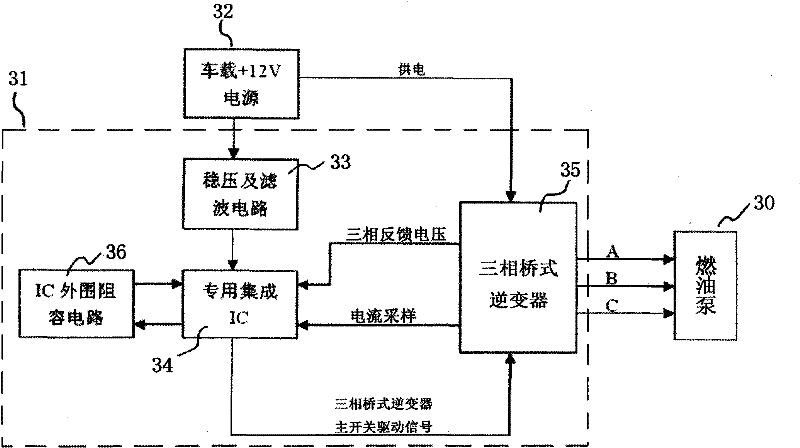
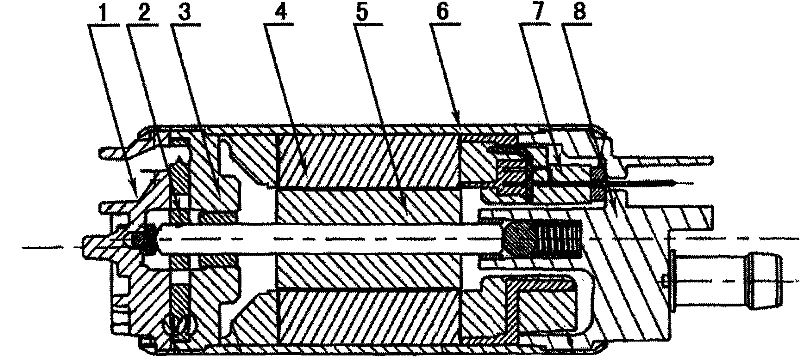
Novel brushless motor fuel pump
InactiveCN102207050AEffective corrosionEfficient conductionMachines/enginesLiquid fuel feedersCapacitanceBrushless motors
The invention relates to a novel brushless motor fuel pump. In the technical scheme, a brushless motor controller is connected outside the fuel pump, namely one end of an electronic plug-in part is connected with a fuel pump motor stator, and the other end of the electronic plug-in part is connected with the brushless motor controller; a vehicle-mounted power supply is connected outside and an integrated circuit is connected inside a voltage-stabilizing and filtering circuit in the brushless motor controller; the integrated circuit is respectively connected with a peripheral resistance-capacitance circuit and a three-phase bridge inverter; and a starting circuit and three-phase feedback voltage in the integrated circuit are connected with a phase locked logic phase change circuit respectively. The defects that a position sensor has low sealing property, ages quickly, is corroded, and the like are overcome. By a counter potential reversing technology, the pump can effectively resist fuel corrosion and fuel electric conduction, can be suitable for various liquid fuels such as gasoline, methanol, ethanol and the like, has high reliability, small volume, long service life and low price, is convenient to install, reduces a motor gap, and improves motor output and motor efficiency, and the volume of a pump body is reduced.
Owner:周铁
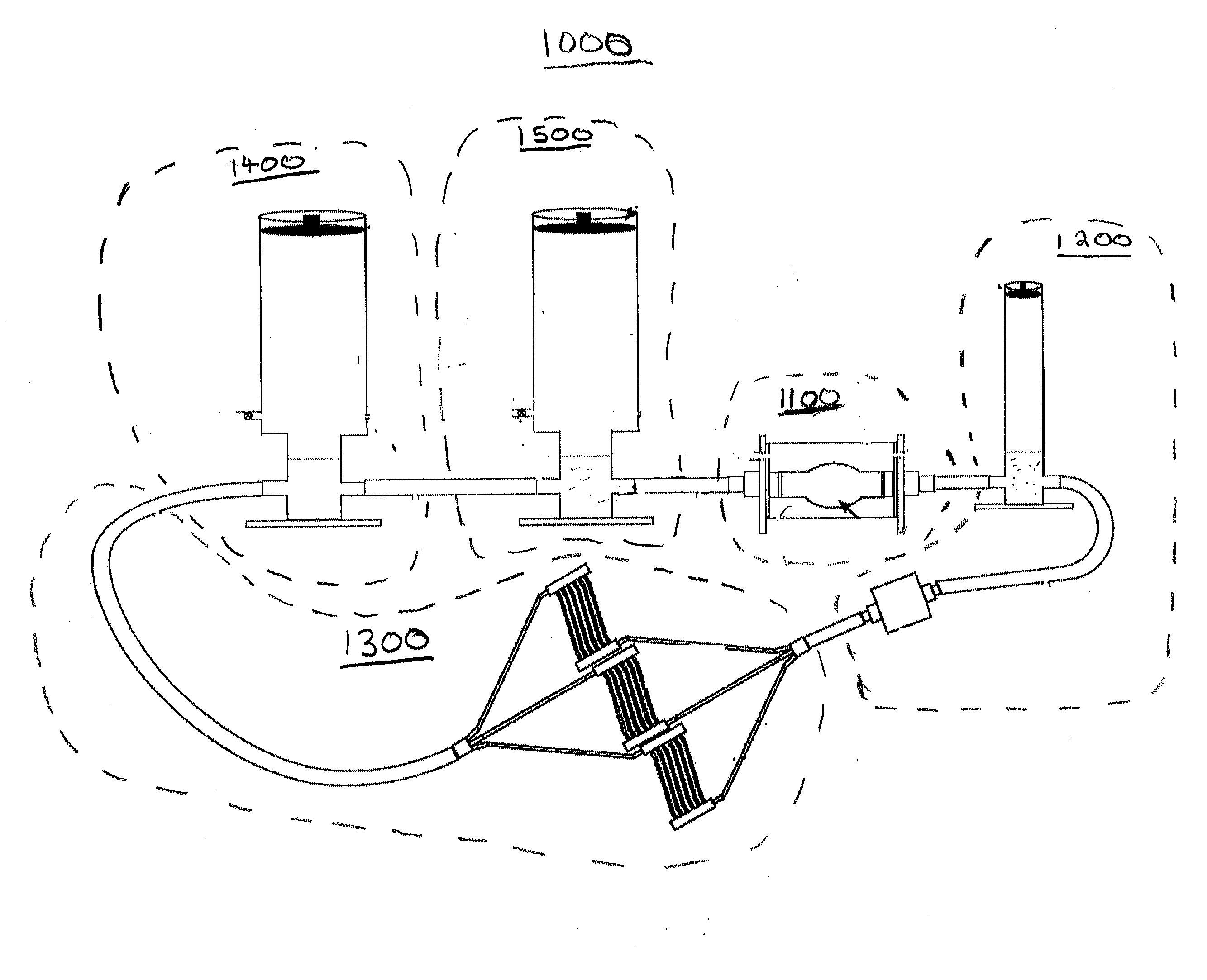
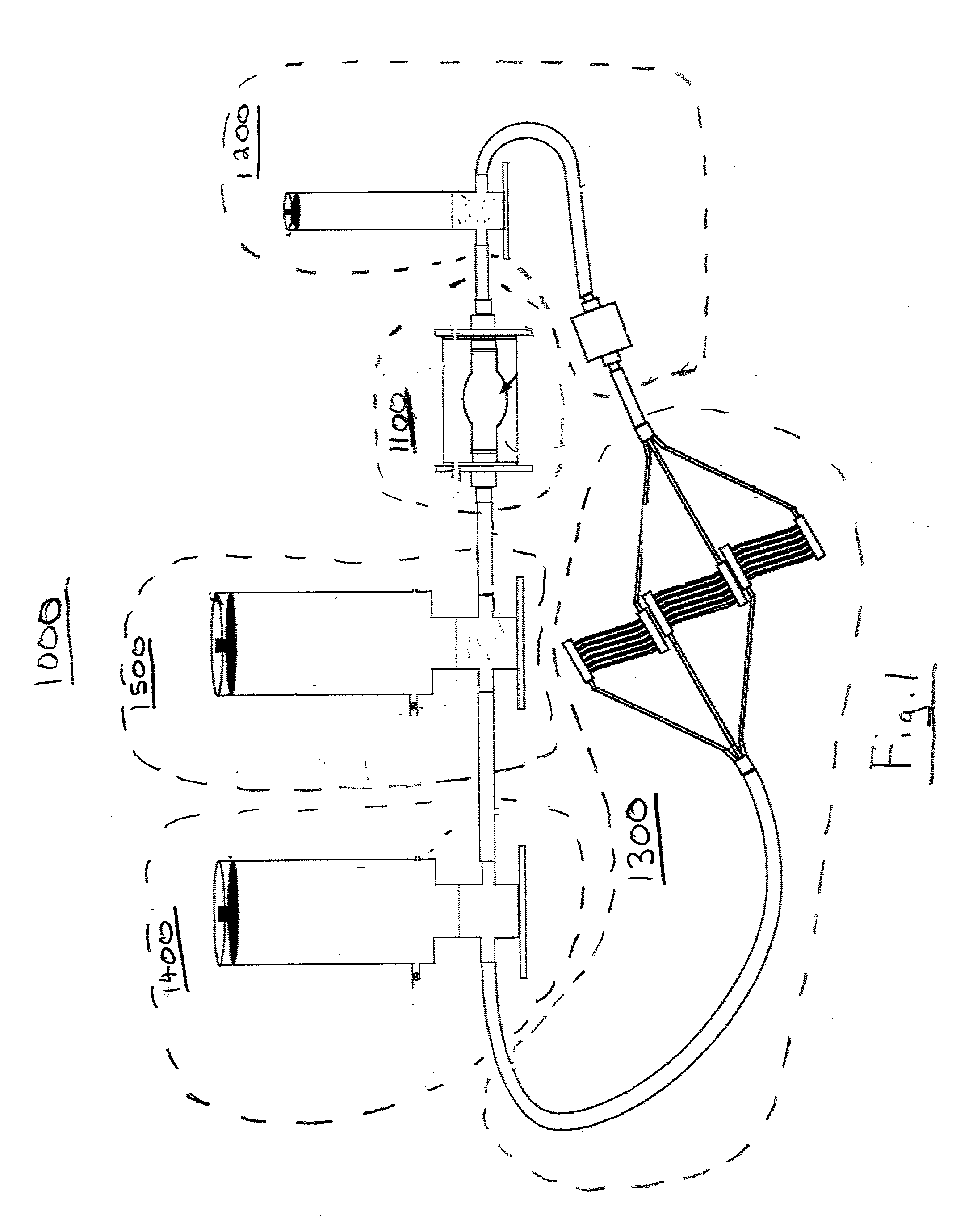
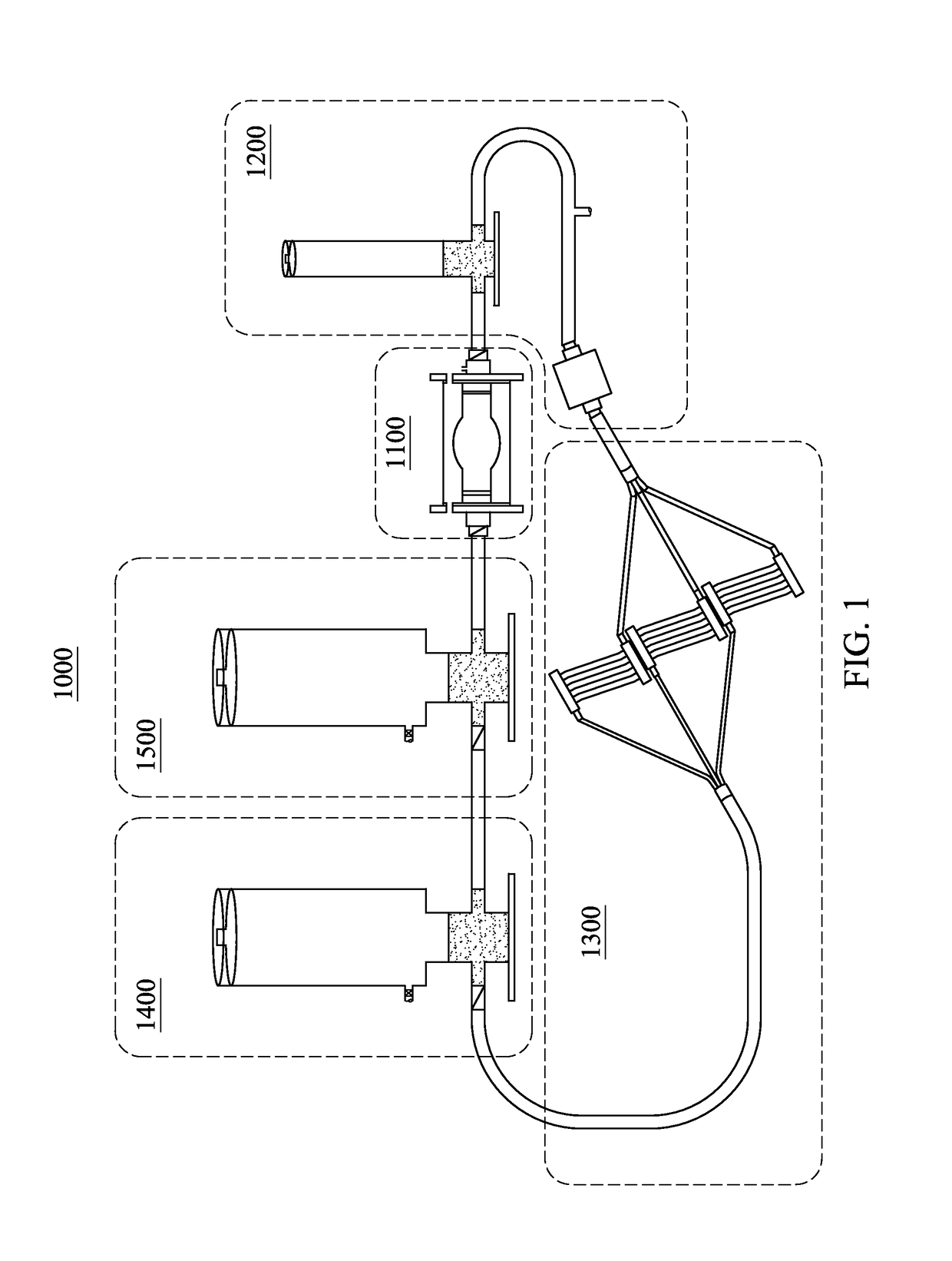
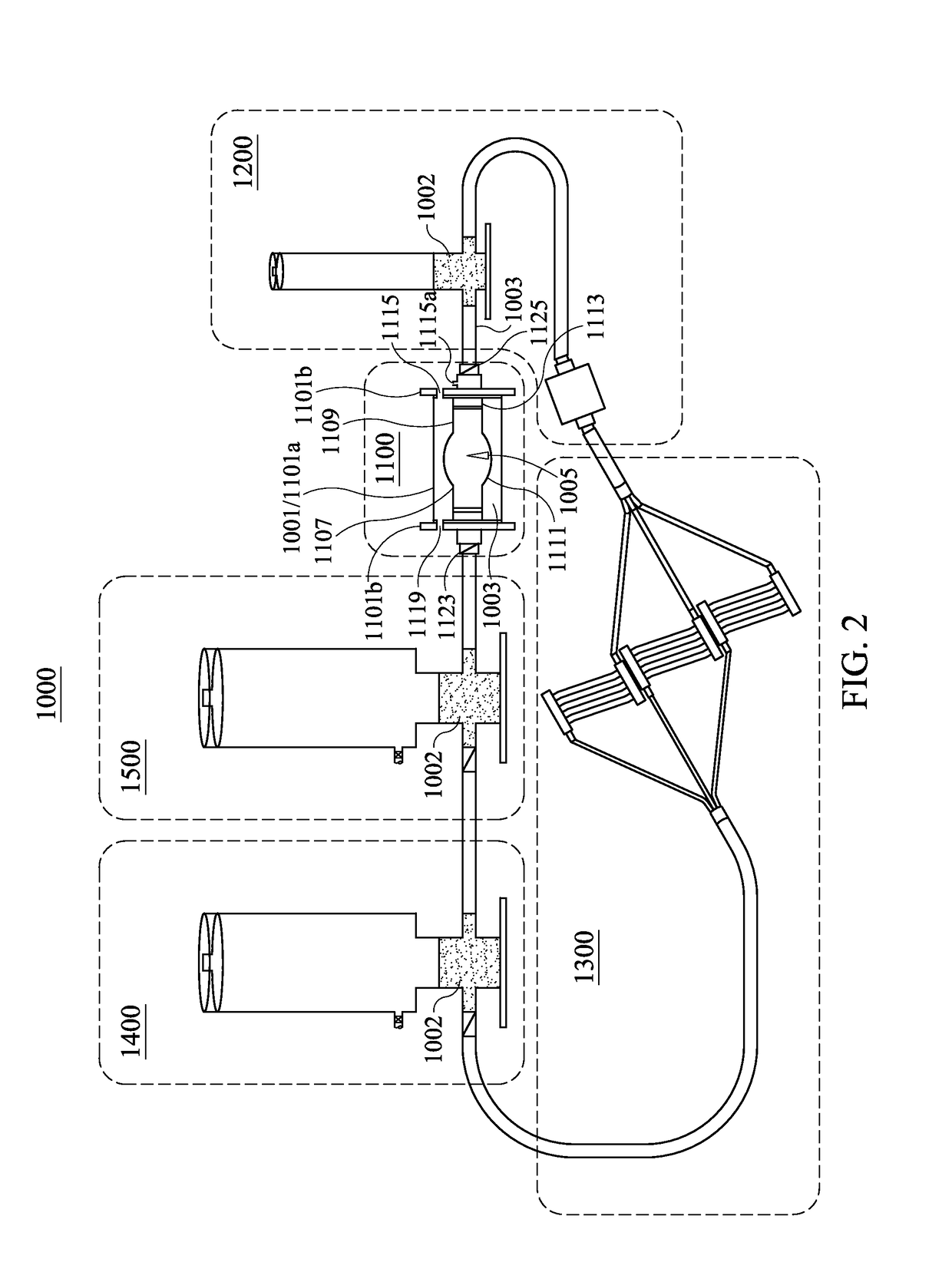
Mechanical Model of the Cardiovascular System and Method of Demonstrating the Physiology of the Cardiovascular System
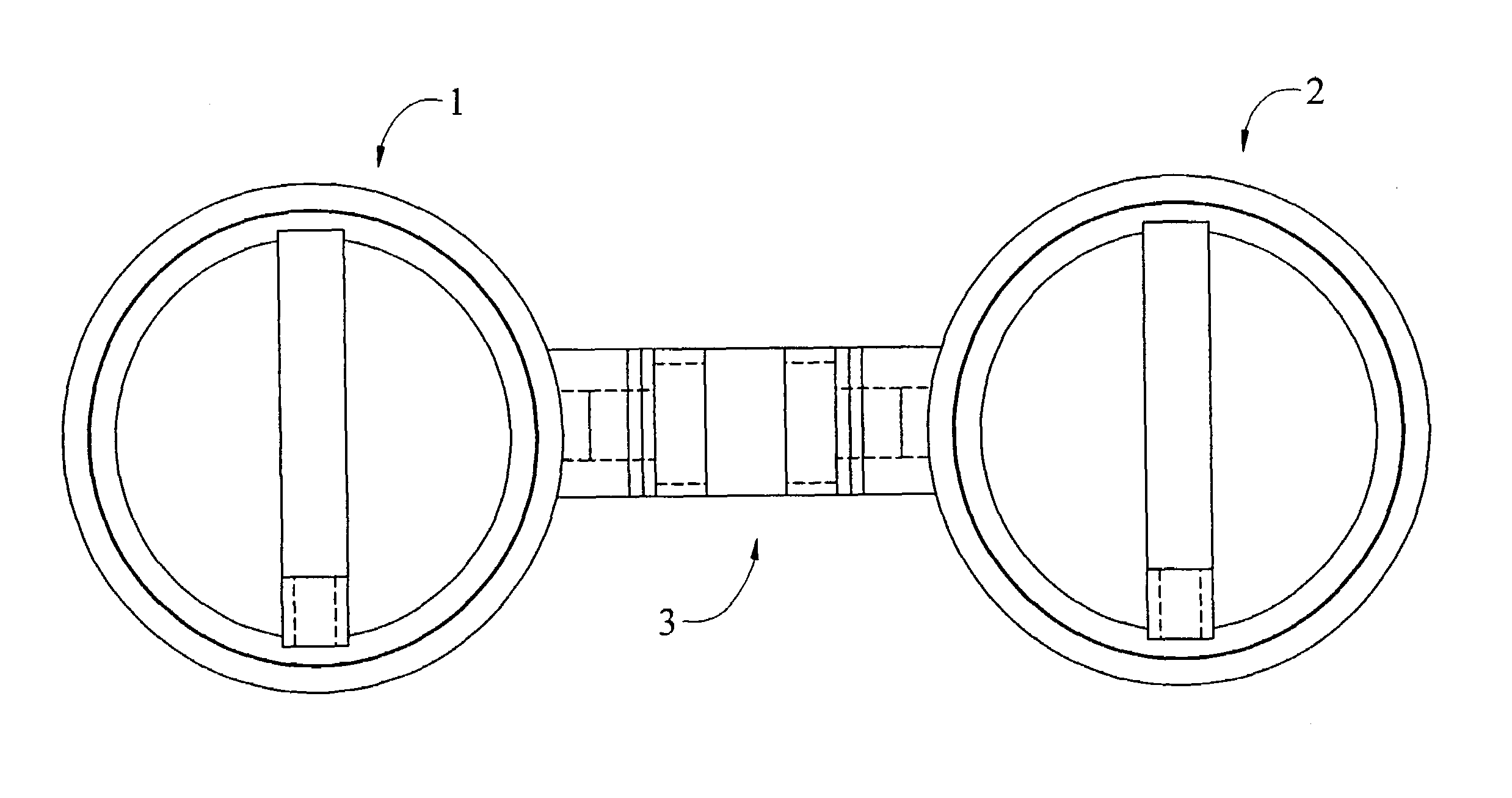
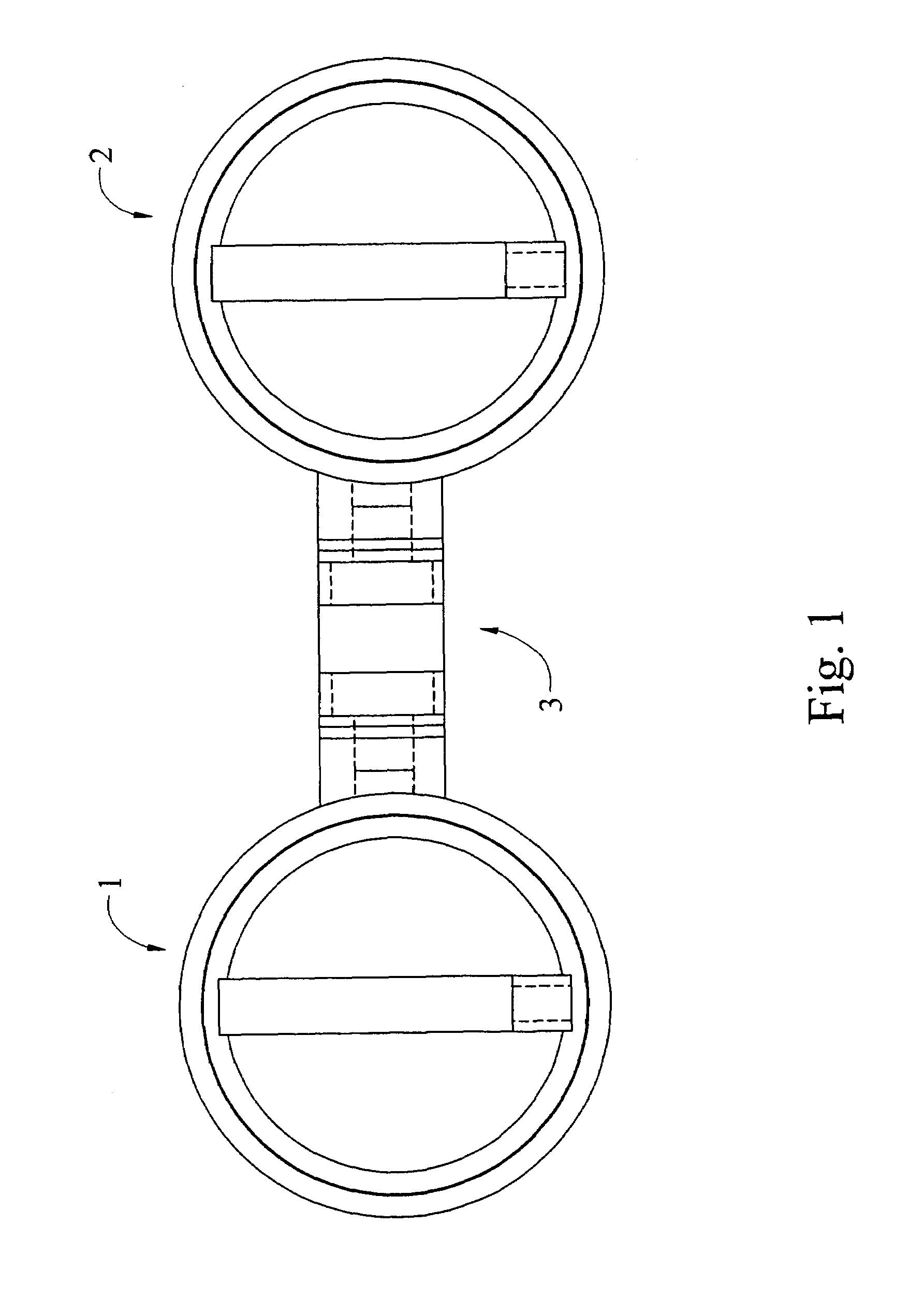
A hydraulic model of the cardiovascular system for illustrating a plurality of physiological concepts and relationships including arterial compliance, venous compliance, and peripheral resistance, said model comprising: a.) a cardiac subsystem for moving a fluid in a singular direction in a closed hydraulic system; b.) an arterial subsystem for modeling arterial compliance, the arterial subsystem fluidically coupled with the cardiac subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the cardiac subsystem; c.) a peripheral resistance subsystem for modeling peripheral resistance, the peripheral resistance subsystem fluidically coupled with the arterial subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from arterial subsystem; d.) a peripheral venous (PV) subsystem for modeling peripheral venous compliance and for modeling a peripheral venous pump (PVP), the peripheral venous subsystem fluidically coupled with the peripheral resistance subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the at least one downstream conduit; and e.) a central venous (CV) subsystem for modeling central venous compliance and for modeling a thoracic pump (TP), the CV subsystem fluidically coupled with the PV subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the PV subsystem and to pass the fluid to the cardiac subsystem to complete the cardiovascular cycle.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SCRANTON
Methods and apparatus for determining cardiac output
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for determining a dynamical property of the systemic or pulmonary arterial tree using long time scale information, i.e., information obtained from measurements over time scales greater than a single cardiac cycle. In one aspect, the invention provides a method and apparatus for monitoring cardiac output (CO) from a single blood pressure signal measurement obtained at any site in the systemic or pulmonary arterial tree or from any related measurement including, for example, fingertip photoplethysmography.According to the method the time constant of the arterial tree, defined to be the product of the total peripheral resistance (TPR) and the nearly constant arterial compliance, is determined by analyzing the long time scale variations (greater than a single cardiac cycle) in any of these blood pressure signals. Then, according to Ohm's law, a value proportional to CO may be determined from the ratio of the blood pressure signal to the estimated time constant. The proportional CO values derived from this method may be calibrated to absolute CO, if desired, with a single, absolute measure of CO (e.g., thermodilution). The present invention may be applied to invasive radial arterial blood pressure or pulmonary arterial blood pressure signals which are routinely measured in intensive care units and surgical suites or to noninvasively measured peripheral arterial blood pressure signals or related noninvasively measured signals in order to facilitate the clinical monitoring of CO as well as TPR.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV +1
Systems and methods for model-based estimation of cardiac output and total peripheral resistance
The methods and systems for estimating cardiac output and total peripheral resistance include observing arterial blood pressure waveforms to determine intra-beat and inter-beat variability in arterial blood pressure and estimating from the variability a time constant for a lumped parameter beat-to-beat averaged Windkessel model of the arterial tree. Uncalibrated cardiac output and uncalibrated total peripheral resistance may then be calculated from the time constant. Calibrated cardiac output and calibrated total peripheral resistance may be computed using calibration data, assuming an arterial compliance that is either constant or dependent on mean arterial blood pressure. The parameters of the arterial compliance may be estimated in a least-squares manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
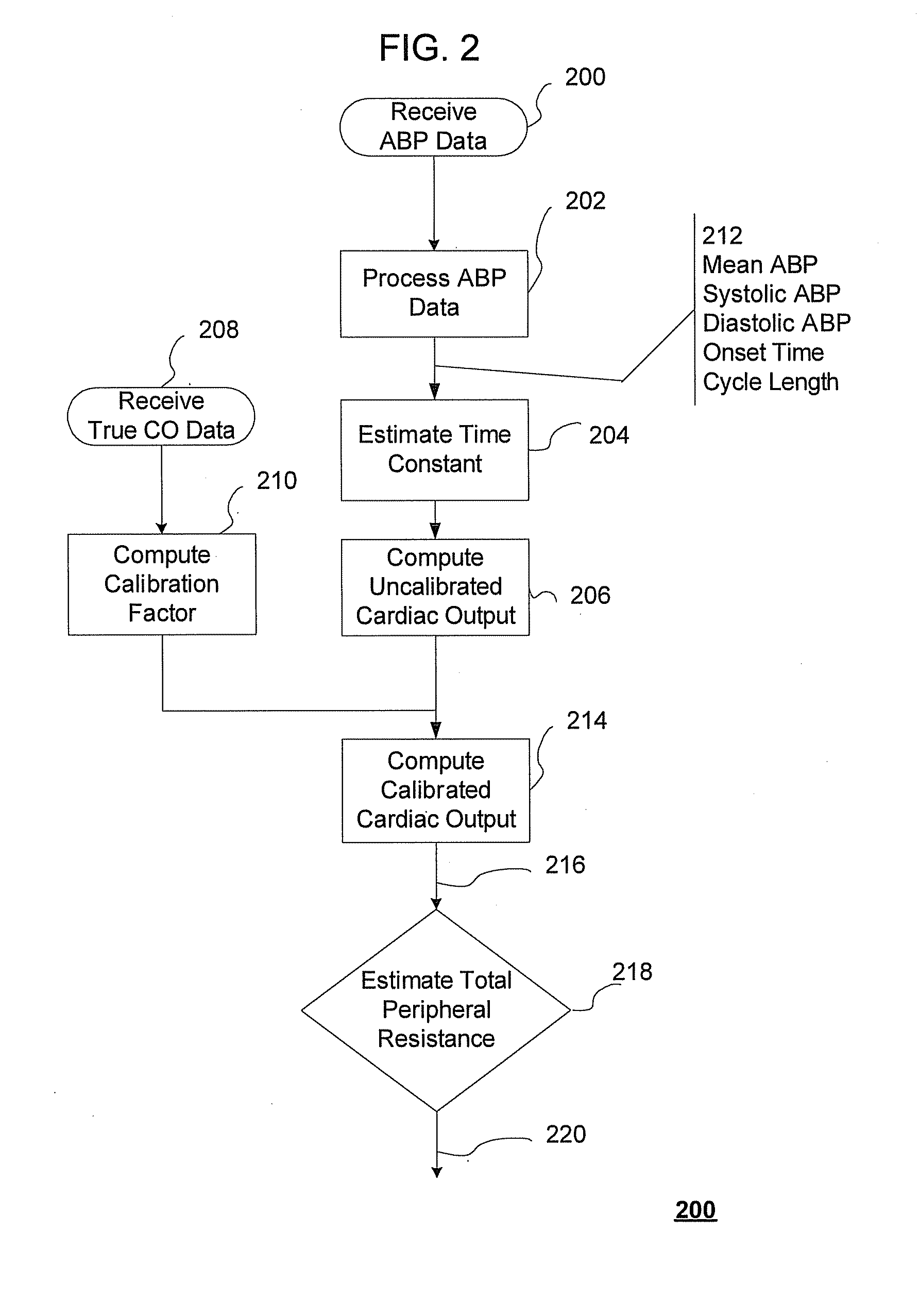
Cardiovascular index estimation methods
InactiveUS20120259189A1Reduce estimated instantaneous aortic blood flowUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEvaluation of blood vesselsEstimation methodsPulse pressure
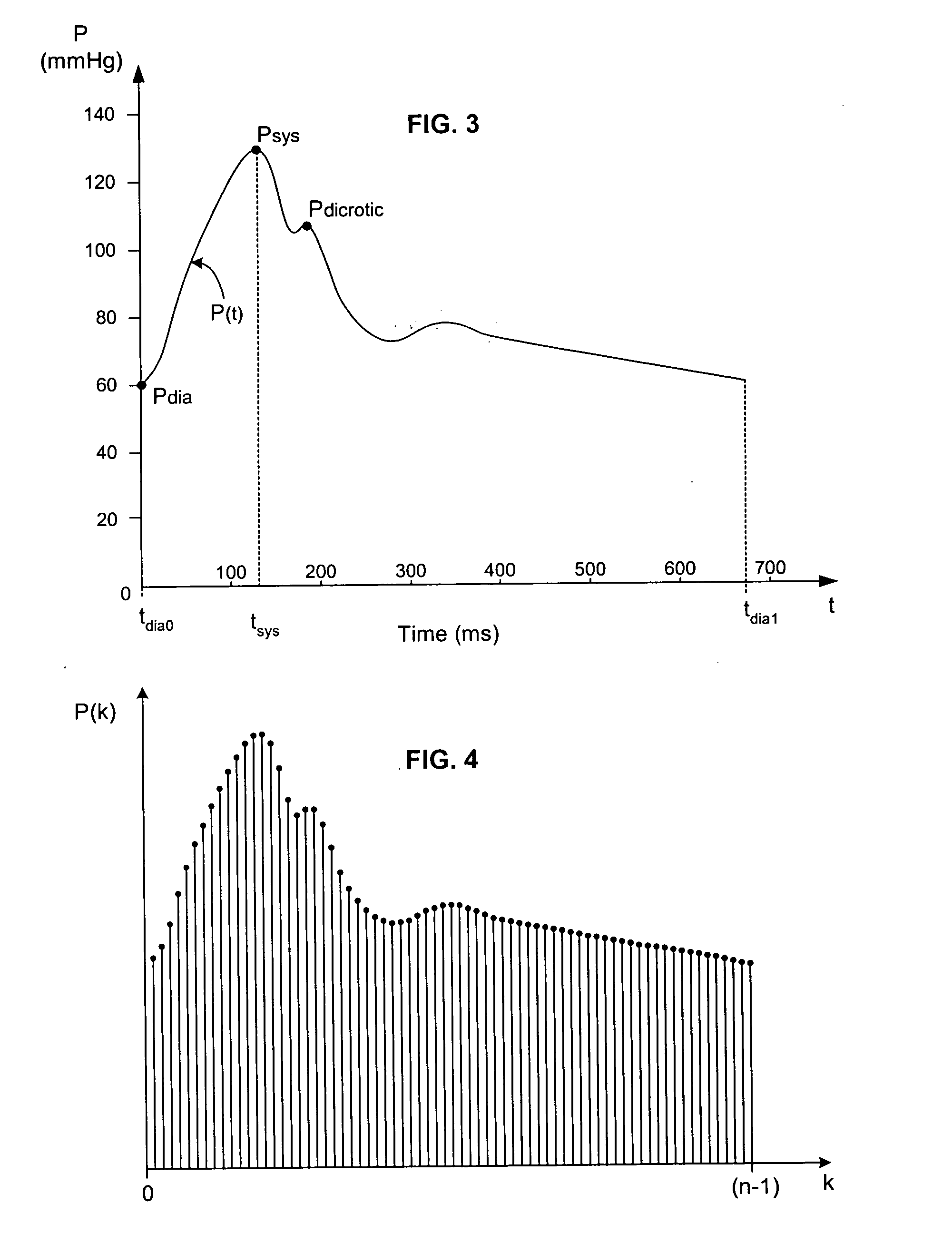
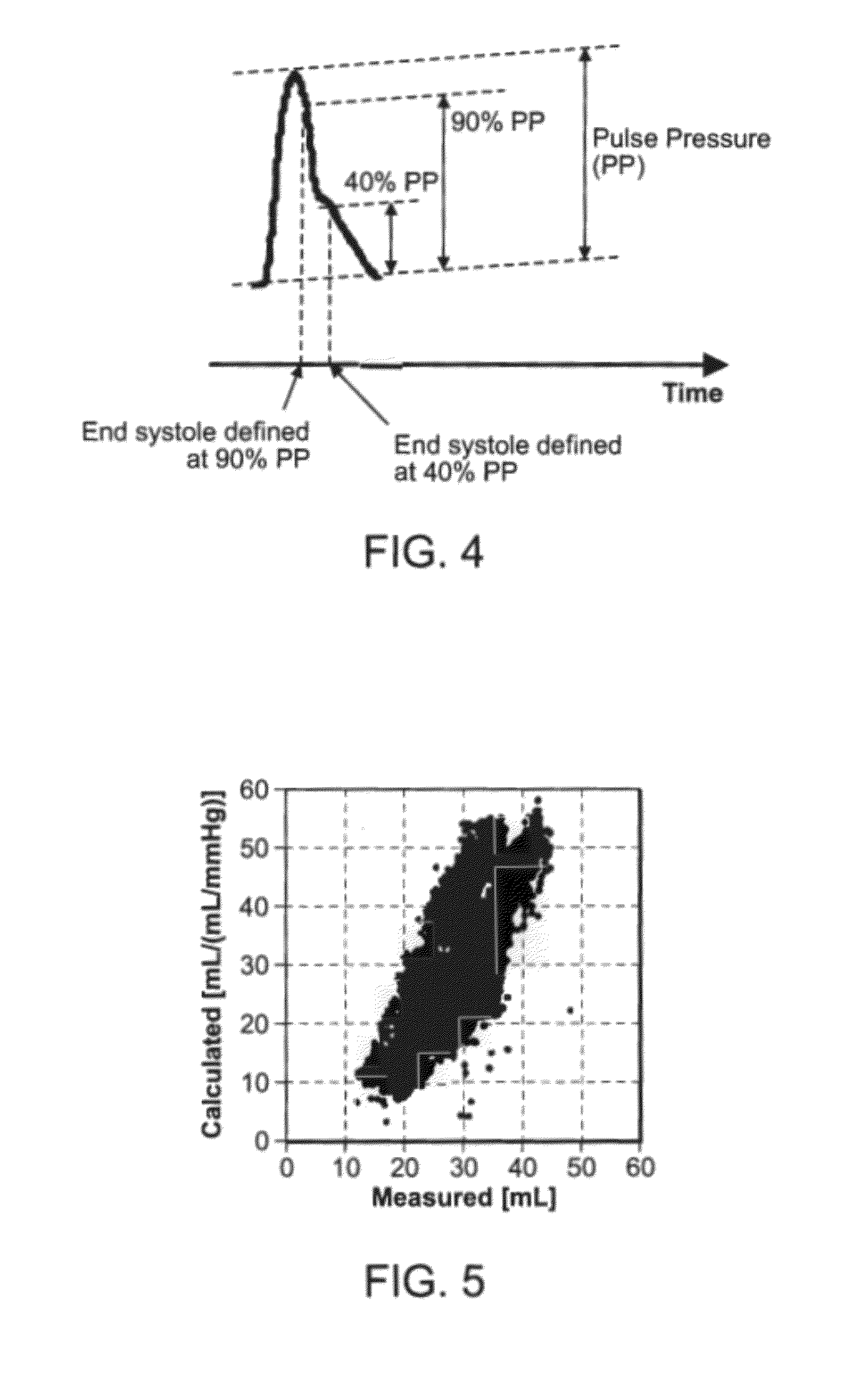
New algorithms to estimate cardiovascular indices by analysis of the arterial blood pressure (ABP) signal. The invention comprises recording and identification of cardiovascular descriptors (including ABP signal, diastolic pressure, systolic pressure, pulse pressure, and end systole), calculation of cardiovascular system parameters, and calculation of aortic blood flow, stroke volume, cardiac output, total peripheral resistance, and characteristic time constant.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for using physiological information
InactiveUS20120064006A1Improve indication effectReduce the impactPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticHaemodynamic monitoringCardiovascular physiology
Systems and methods using a database of physiological information for the design, development, testing and use of therapeutics. In one aspect, the physiological information can include at least one of: hemodynamic monitoring information, pulmonary arterial pressure, cardiac output, heart rate, respiratory rate, peripheral vascular resistance, total peripheral resistance or dicrotic notch information. Optionally, the cardiovascular physiology information can include ambulatory physiological information.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
Precise constant flow source based on differential amplifier and feedback buffer
PendingCN108508955AHigh input impedanceImprove consistencyElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a precise constant flow source based on a differential amplifier and a feedback buffer. The precise constant flow source comprises an amplifier, an input resistor-feedback resistor integrated differential amplifier, a feedback buffer, a triode T2, a resistor Rref and a resistor Rload, wherein a reference voltage output circuit is connected to a positive input end of the differential amplifier, a negative input end of the differential amplifier is connected to the ground, an output end of the differential amplifier is connected to a base electrode of a triode T2, an emitting electrode of the triode T2 is connected with a SENSE wiring end of the differential amplifier, is sequentially connected to the resistor Rref and the resistor Rload and is connected to the ground, an voltage feedback input end of the differential amplifier is connected with an output end and negative input end of the feedback buffer, and a node between the resistor Rref and the resistor Rloadis connected with a positive input end of the feedback buffer. According to the precise constant flow source, the coherence of peripheral resistances is improved by virtue of the differential amplifier, and a current output loop and a voltage feedback circuit are isolated by virtue of the feedback buffer, so that the input impedance relative to outside of the differential amplifier is increased,and the current of the constant flow source is more accurate.
Owner:INST OF CHEM MATERIAL CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
System and method for prediction and detection of circulatory shock
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for model-based estimation of cardiac output and total peripheral resistance
The methods and systems for estimating cardiac output and total peripheral resistance include observing arterial blood pressure waveforms to determine intra-beat and inter-beat variability in arterial blood pressure and estimating from the variability a time constant for a lumped parameter beat-to-beat averaged Windkessel model of the arterial tree. Uncalibrated cardiac output and uncalibrated total peripheral resistance may then be calculated from the time constant. Calibrated cardiac output and calibrated total peripheral resistance may be computed using calibration data, assuming an arterial compliance that is either constant or dependent on mean arterial blood pressure. The parameters of the arterial compliance may be estimated in a least-squares manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Hair growth inducer
InactiveCN106138058AReduces symptoms associated with shedding diseaseImprove regenerative abilityOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsDiseaseTofacitinib
The invention discloses a hair growth inducer, which comprises an active ingredient composed of tofacitinib and minoxidil with a mass percentage of 0.1:99.9-99.9:0.1. The hair growth inducing agent provided by the invention, its active ingredient comprises tofacitinib and minoxidil, wherein tofacitinib is a kind of JAK inhibitor, can interact with target cells (such as dermis, epidermis, dermal papilla cells or hair follicles) Cell) specific protein active site selectively binds, inhibits the transmission of cell pathway signals and the synthesis of characteristic cytokines, thereby reducing the symptoms associated with hair loss diseases; Minoxidil is a potassium ion channel opener that can directly relax Vascular smooth muscle has a powerful dilation effect on small arteries, reduces peripheral resistance, promotes the growth of hair follicle cells, and thus regenerates hair; the combination of these two substances synergistically acts on the target protein of target cells and vascular smooth muscle, and inhibits cytokines Synthesis and accelerated blood circulation, in order to achieve a significant effect of promoting hair regeneration.
Owner:颜晓丽
Portable physiological parameter monitor
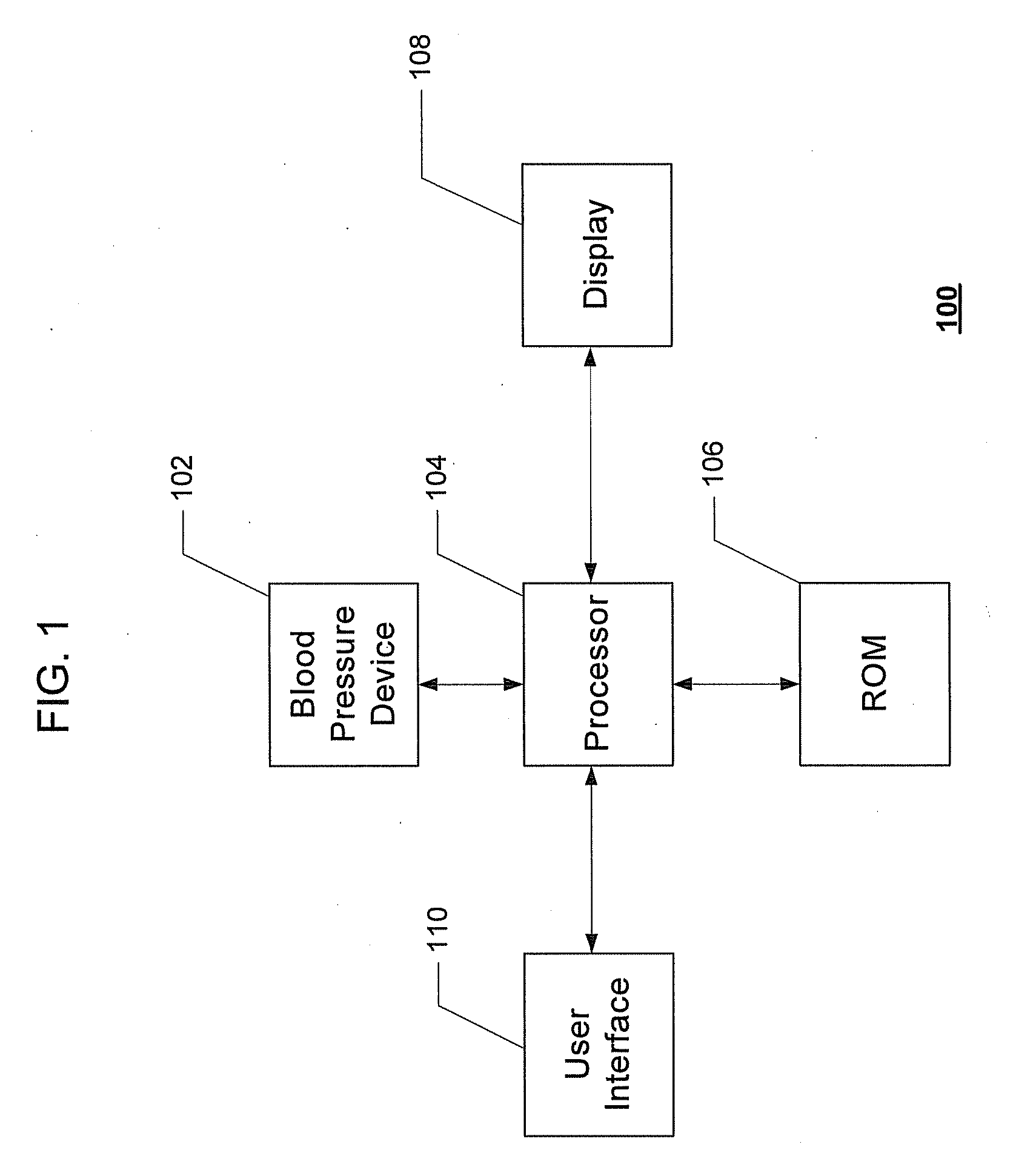
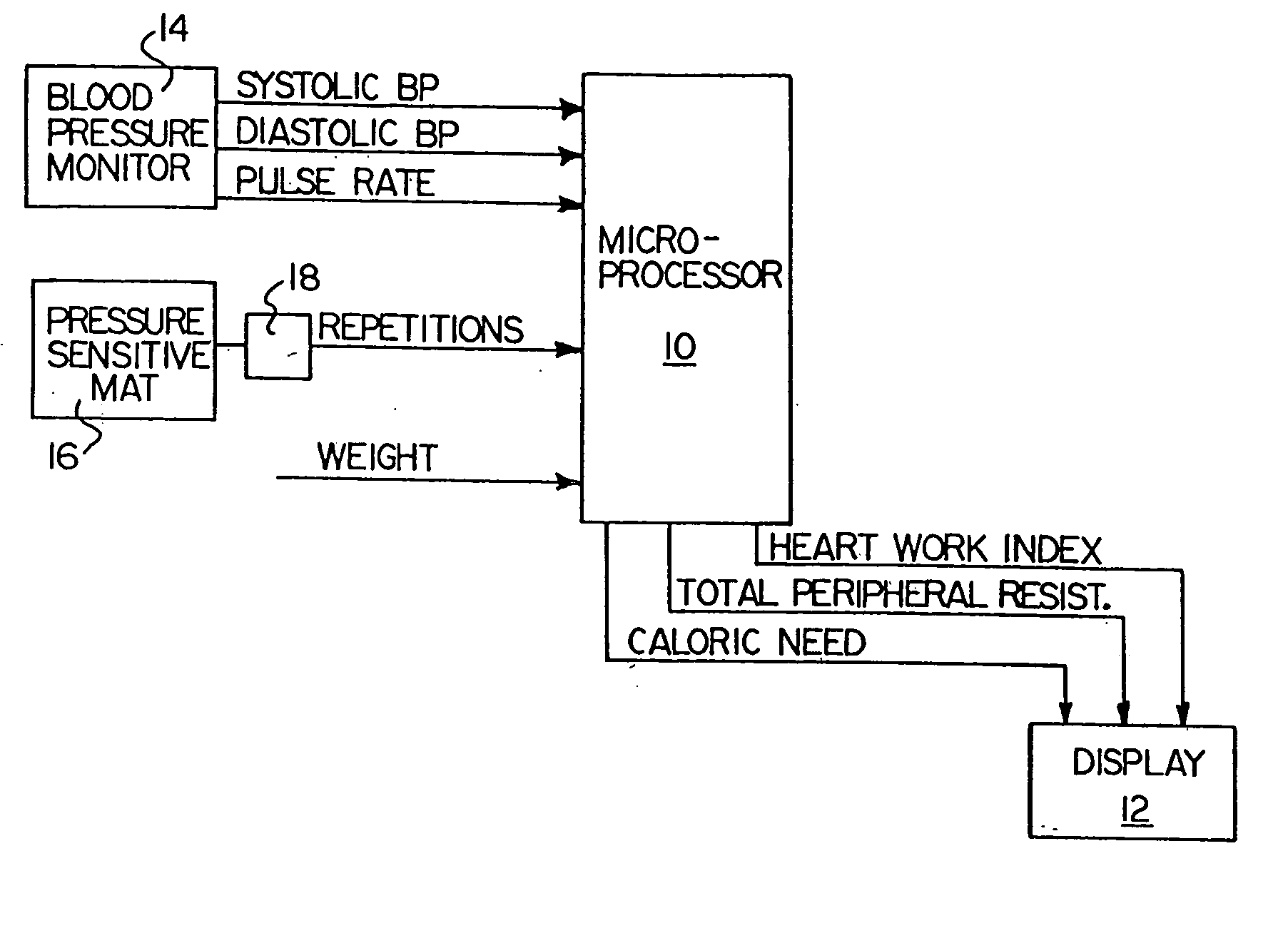
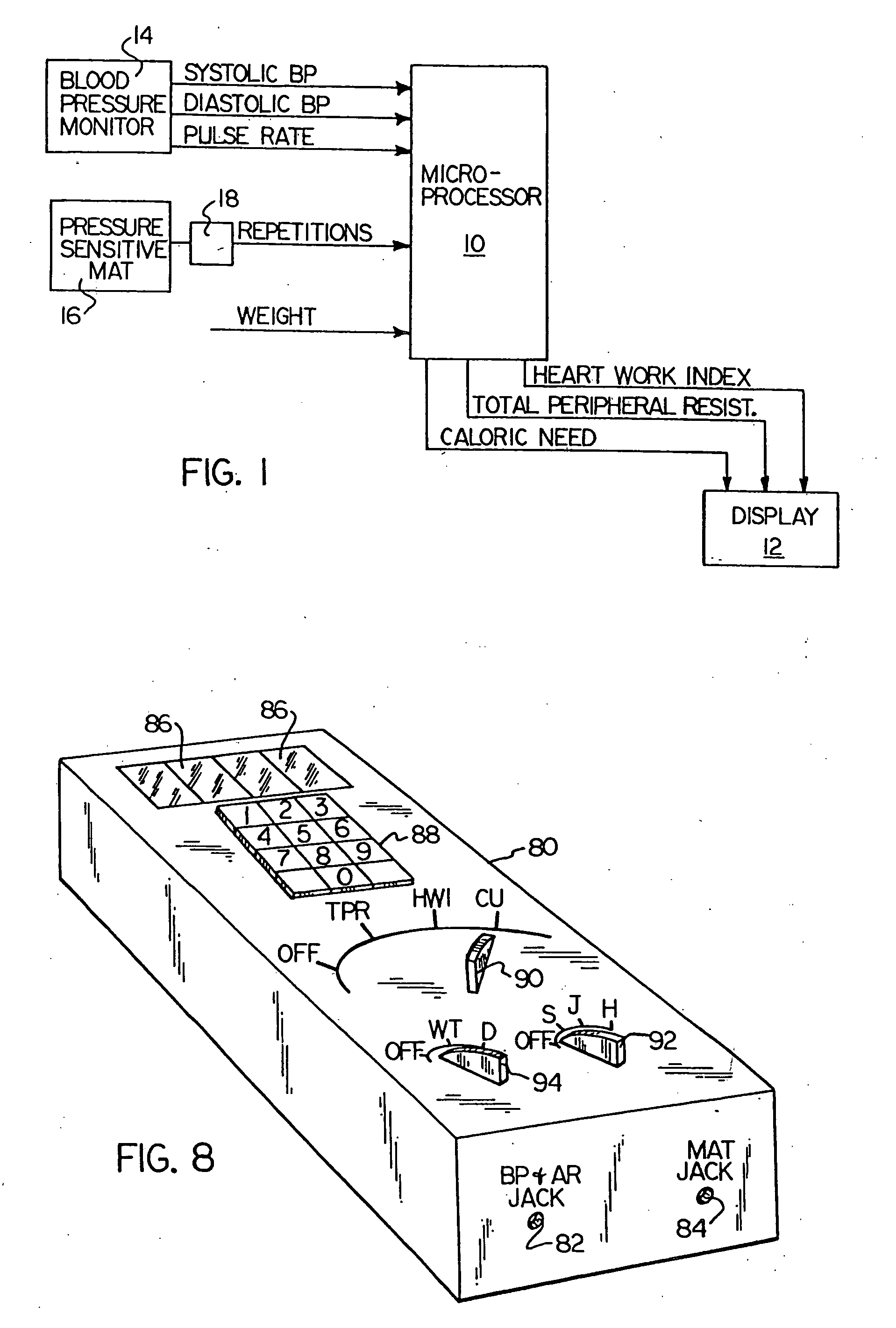
InactiveUS20070156052A1Person identificationEvaluation of blood vesselsSphygmomanometerDisplay device
A microprocessor unit receives input data from a work measuring station, a sphygmomanometer, and a heart rate sensor and combines such data to provide output signals to a display device indicative of various physiological parameters relating to cardiovascular fitness such as heart work index, total peripheral resistance to blood flow, and caloric need. A carrying case for the aforesaid equipment converts into an exercise stool by means of folding or removable legs.
Owner:MOORE ROY D
Mechanical model of the cardiovascular system and method of demonstrating the physiology of the cardiovascular system
A hydraulic model of the cardiovascular system for illustrating a plurality of physiological concepts and relationships including arterial compliance, venous compliance, and peripheral resistance, said model comprising: a.) a cardiac subsystem for moving a fluid in a singular direction in a closed hydraulic system; b.) an arterial subsystem for modeling arterial compliance, the arterial subsystem fluidically coupled with the cardiac subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the cardiac subsystem; c.) a peripheral resistance subsystem for modeling peripheral resistance, the peripheral resistance subsystem fluidically coupled with the arterial subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from arterial subsystem; d.) a peripheral venous (PV) subsystem for modeling peripheral venous compliance and for modeling a peripheral venous pump (PVP), the peripheral venous subsystem fluidically coupled with the peripheral resistance subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the at least one downstream conduit; and e.) a central venous (CV) subsystem for modeling central venous compliance and for modeling a thoracic pump (TP), the CV subsystem fluidically coupled with the PV subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the PV subsystem and to pass the fluid to the cardiac subsystem to complete the cardiovascular cycle.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SCRANTON
Nifedipine medicine composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102370644AHigh dissolution ratePromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChronic stable anginaPeripheral resistance
The invention discloses a nifedipine medicine composition and a preparation method thereof. The nifedipine medicine composition contains nifedipine, hydroxymethyl propyl cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose. The hydroxymethyl propyl cellulose is used as slow-releasing framework material; the weight ratio of the nifedipine and the hydroxymethyl propyl cellulose is 2:1-1:1; and the weight ratio of the nifedipine and the microcrystalline cellulose is 1:4-1:3; and lactose, starch, calcium hydrophosphate and glucose can be also added. The method for preparing the nifedipine medicine composition comprises the following steps of: (1) crushing and screening; (2) drying; and (3) tabletting. According to the invention, the dissolution rate of the nifedipine in the water can be increased, the coronary arteries in the normal blood supply area and the ischemic area are relaxed while the absorption rate of the nifedipine in the body is increased so that coronarospasm and is released and prevented and myocardial contraction is inhibited; myocardial oxygen consumption is reduced; the peripheral resistance is released; after load of heart is reduced; sinus node function and atrioventricular conduction of the isolated heart are slowed down; and the nifedipine medicine composition is applicable to variant angina pectoris, unstable angina pectoris and chronic stable angina pectoris.
Owner:JILIN AODONG GROUP DALIAN PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Signal conditioning circuit for high precision measuring uV level voltage
InactiveCN101413969AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityCurrent/voltage measurementAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a signal conditioning circuit for high-precision measurement of mu V-level voltage. The conditioning circuit comprises three parts of a two-phase square-wave generator, a signal amplification circuit which is based on the principles of chopper modulation and demodulation and a closed-loop feedback compensation circuit. The square-wave generator is composed of three inverters and a peripheral resistance capacitance element, the signal amplification circuit is composed of two general-purpose operational amplifiers, four analog switches and the peripheral resistance capacitance element, each two analog switches constitute one group and are used as input and output analog switches to be respectively controlled by two output signals of the square-wave generator; the chopper modulation by the input analog switches, the amplification by the first operational amplifier, the synchronous demodulation by the output analog switches and the second amplification treatment by the second operational amplifier are carried out on a signal to be measured; a conditioning signal which is output by the second operational amplifier is fed back to a signal input end after the voltage division by the resistance, thereby constituting the closed-loop feedback compensation circuit. The technical specifications of the signal conditioning circuit are as follows by the test: noise is less than 40nV at 0.1-10Hz, offset voltage is less than 1uV, and offset drift is less than 0,01uV per DEG C, thereby fully meeting the requirements on the high-precision measurement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Mechanical model of the cardiovascular system and method of demonstrating the physiology of the cardiovascular system
A hydraulic model of the cardiovascular system for illustrating a plurality of physiological concepts and relationships including arterial compliance, venous compliance, and peripheral resistance, said model comprising: a.) a cardiac subsystem for moving a fluid in a singular direction in a closed hydraulic system; b.) an arterial subsystem for modeling arterial compliance, the arterial subsystem fluidically coupled with the cardiac subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the cardiac subsystem; c.) a peripheral resistance subsystem for modeling peripheral resistance, the peripheral resistance subsystem fluidically coupled with the arterial subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from arterial subsystem; d.) a peripheral venous (PV) subsystem for modeling peripheral venous compliance and for modeling a peripheral venous pump (PVP), the peripheral venous subsystem fluidically coupled with the peripheral resistance subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the at least one downstream conduit; and e.) a central venous (CV) subsystem for modeling central venous compliance and for modeling a thoracic pump (TP), the CV subsystem fluidically coupled with the PV subsystem to receive the fluid discharged from the PV subsystem and to pass the fluid to the cardiac subsystem to complete the cardiovascular cycle.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SCRANTON
Health care product for diabetes
InactiveCN105395706ANo side effectsSignificant effectDispersion deliveryPre-extraction tea treatmentSide effectBitter gourd
The invention discloses a health care product for diabetes. The health care product is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3-6 parts of American ginseng, 13-17 parts of folium mori, 8-12 parts of bitter gourd, 8-12 parts of radix puerariae, 6-10 parts of fruit of Chinese wolfberry, 6-10 parts of lemon, 6-10 parts of black beans, 6-10 parts of walnut kernel, 6-10 parts of black sesame, 8-12 parts of green tea, 3-6 parts of dried orange peel and 3-6 parts of liquorice root. The health care product can develop an effect on promoting the secretion of endogenous insulin, and can reduce peripheral resistance of exogenous insulin, improve bioactivity, promote glycometabolism, lower blood glucose and blood lipid and improve microcirculation, so as to recover the blood glucose value of a patient to be normal. The health care product disclosed by the invention, which belongs to a medicine free from chemical ingredients, is suitable for long-term taking, and the health care product is free from toxic and side effects; the health care product has the advantages of being significant in curative effect, rapid to take effect, low in cost, free from side effects, free from drug resistance and capable of effectively controlling the blood glucose value; and the health care product is significant in curative effect on patients at various ages.
Owner:CHONGQING HONGYANG BIOTECH CO LTD
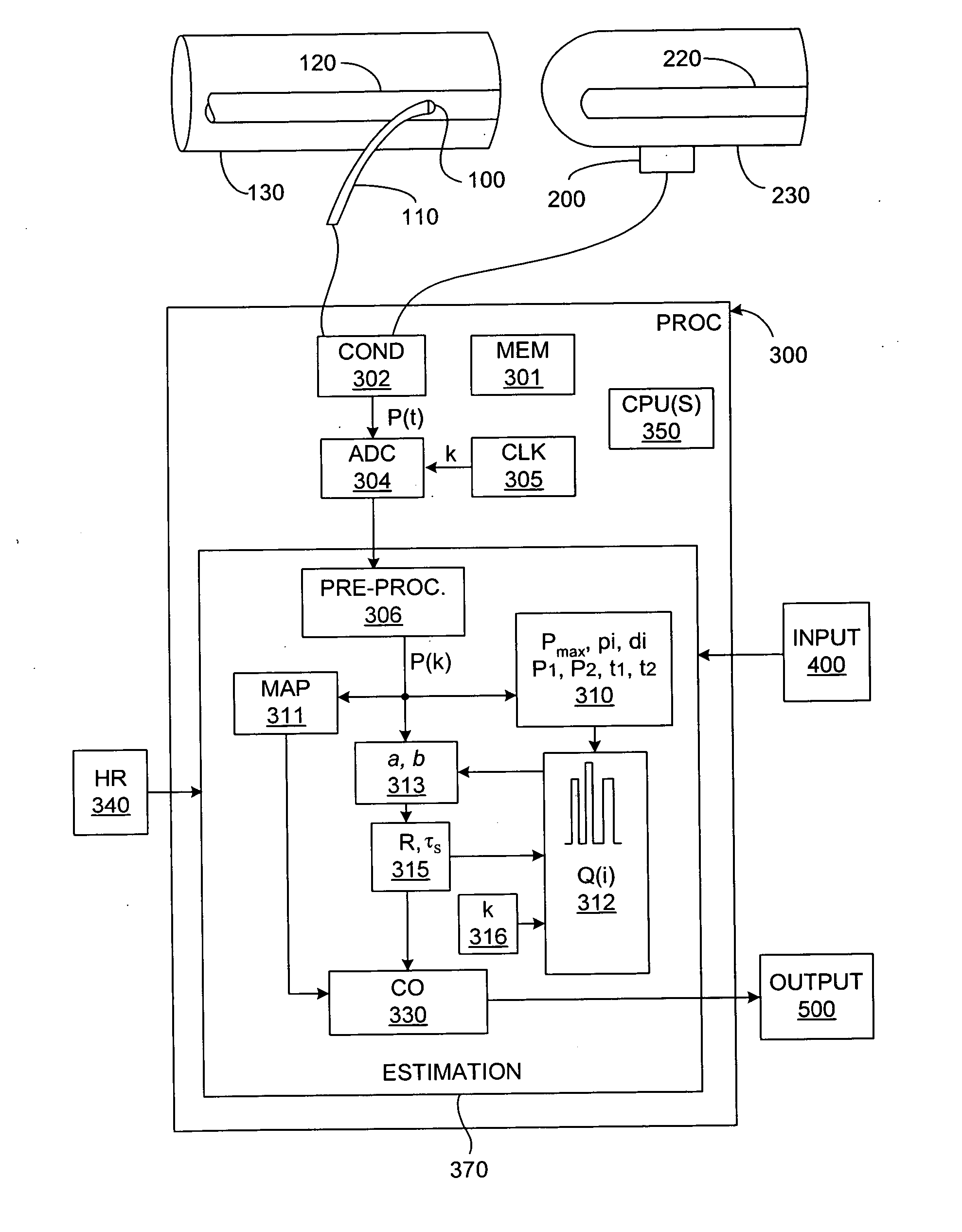
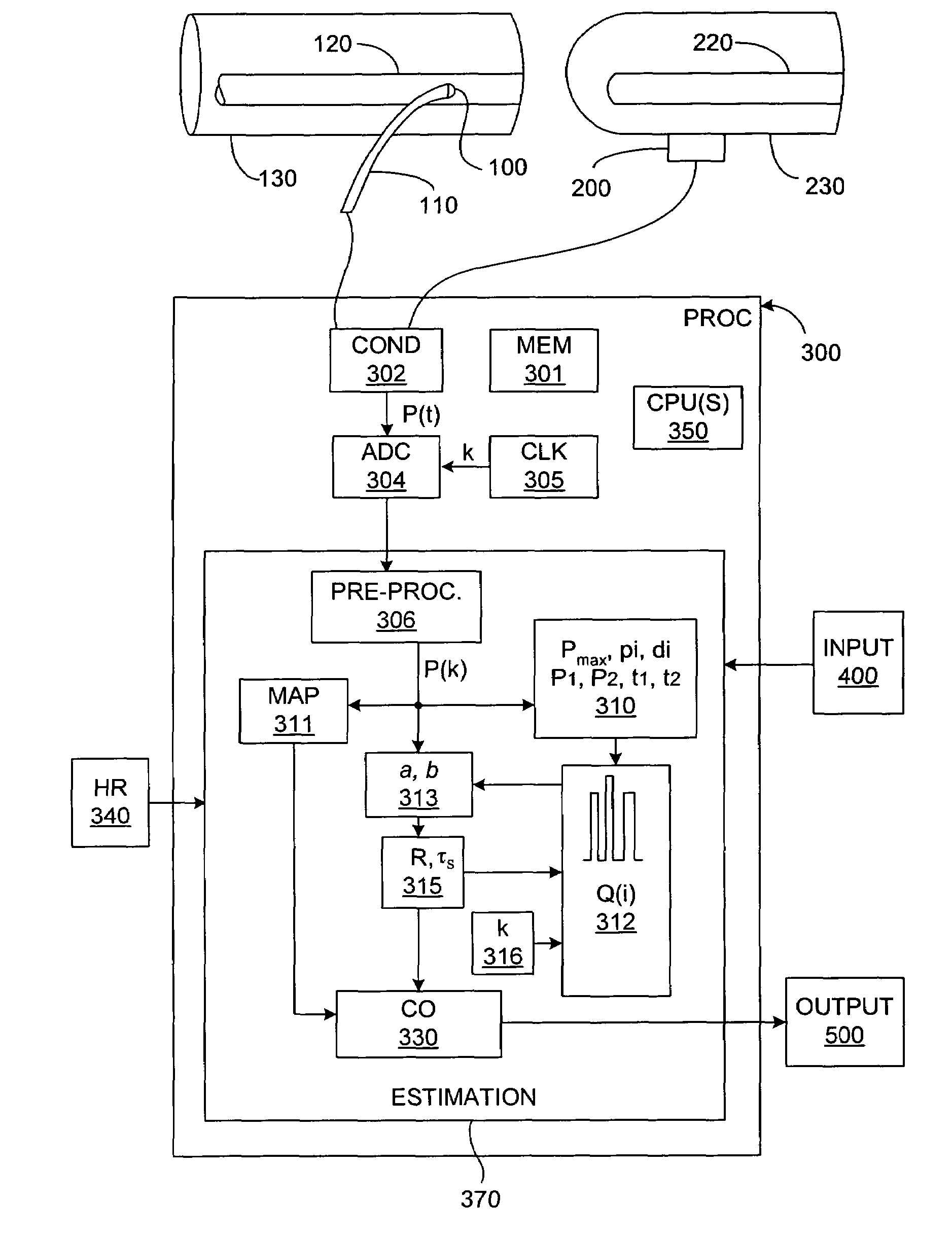
Method for estimating changes of cardiovascular indices using peripheal arterial blood pressure waveform
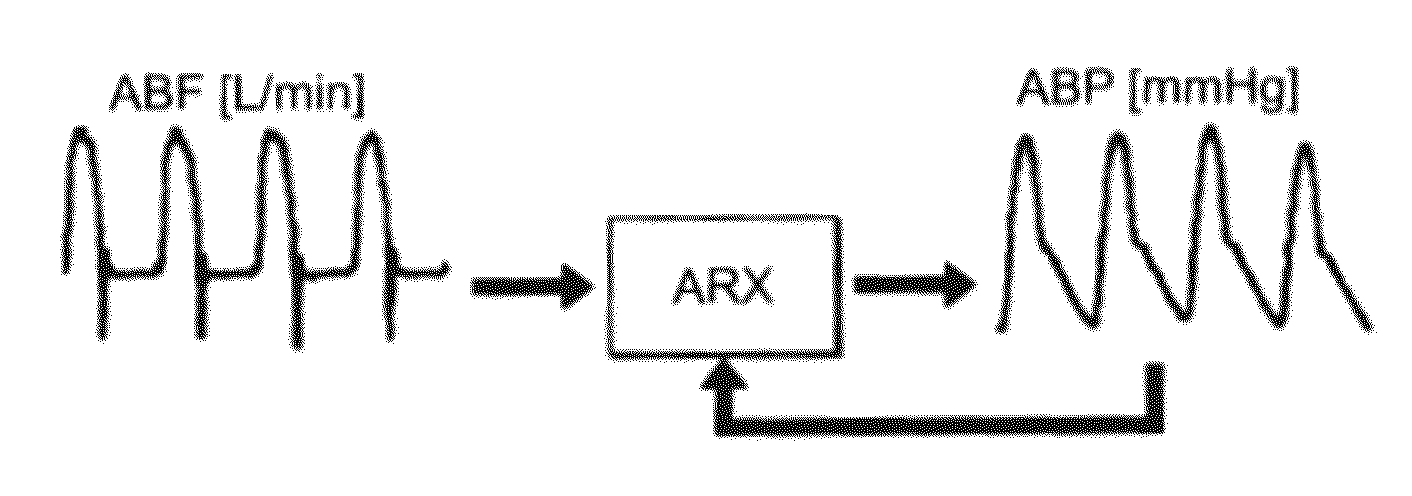
ActiveUS20140358015A1Estimates are accurate and reliableEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterArterial treeBlood arterial
The systems and methods described herein enable reliable estimation of cardiovascular indices on real-time, non-invasive or minimally-invasive, and heat-to-beat basis. Cardiovascular indices which can be estimated include: stroke volume (SV), which being limited to, cardiac output (CO) and total peripheral resistance (TPR). In various embodiments, one or more of these indices are estimated continuously, on a beat-to-beat basis, using peripheral arterial blood pressure (ABP) waveforms and certain parameters derived from the peripheral ABP waveforms. The derived parameters are substantially insensitive to distortions of the ABP waveform arising from tapered arterial branches throughout the arterial tree. The methods describe herein can provide a more accurate and reliable estimate of hemodynarnic parameters than existing techniques.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com