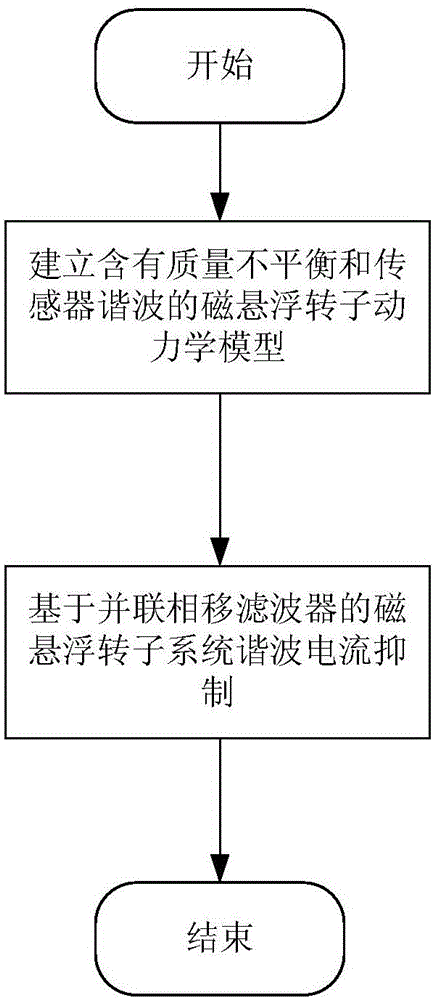
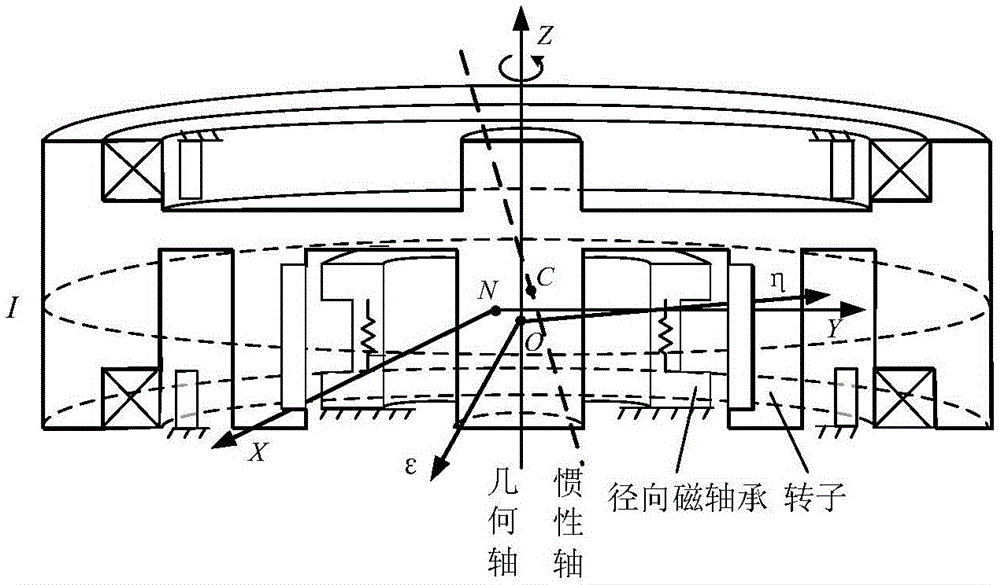
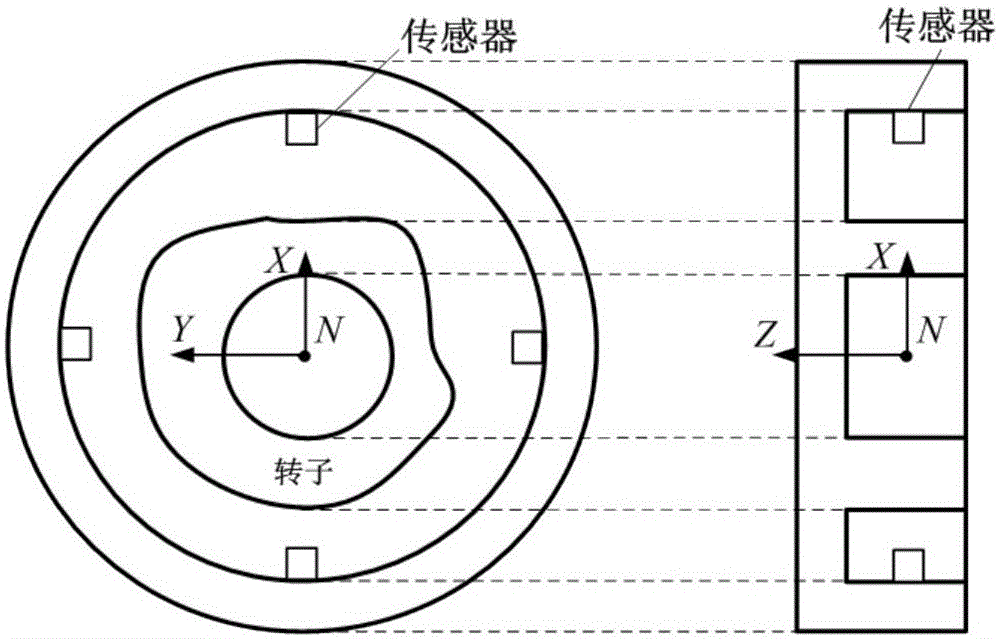
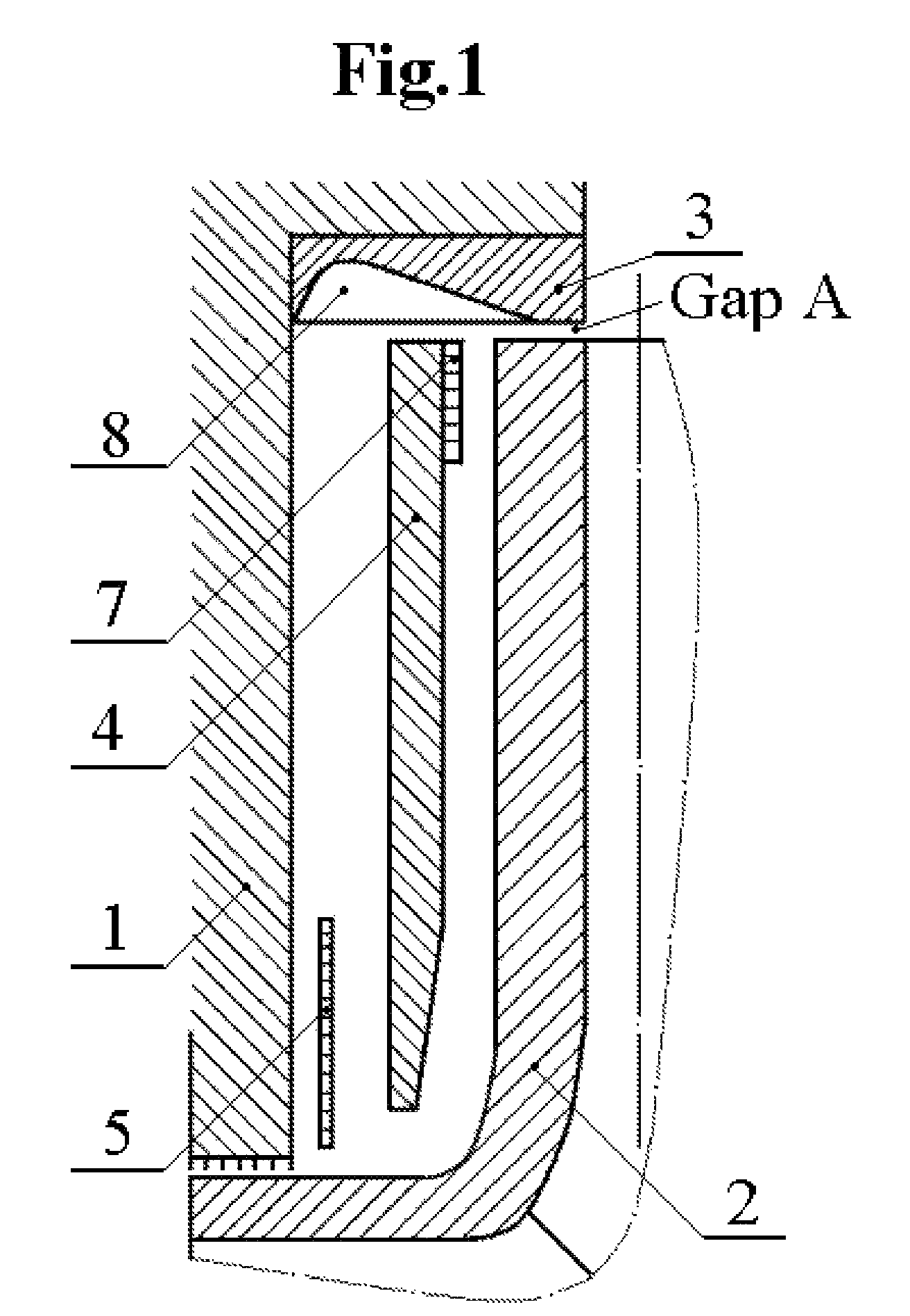
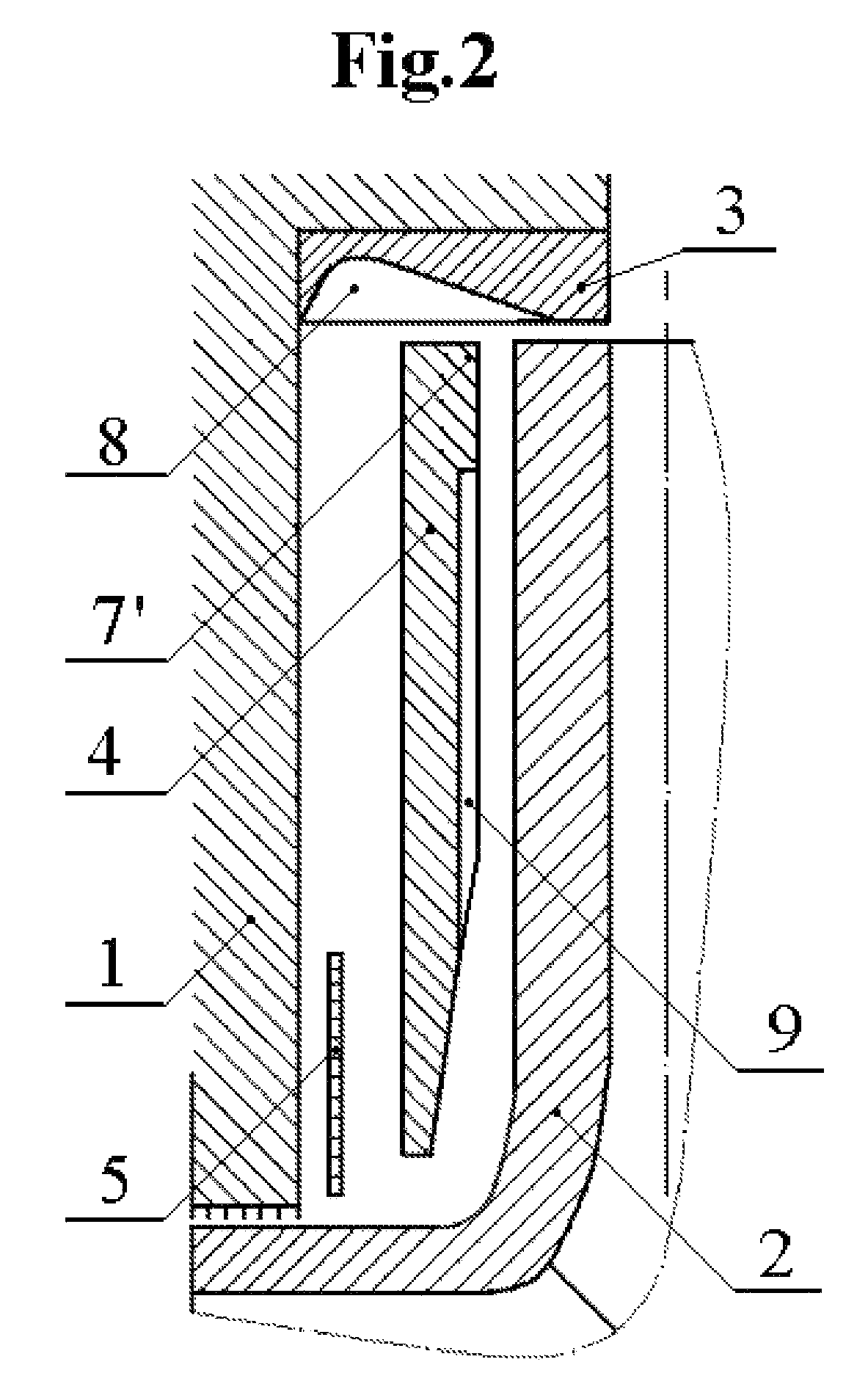
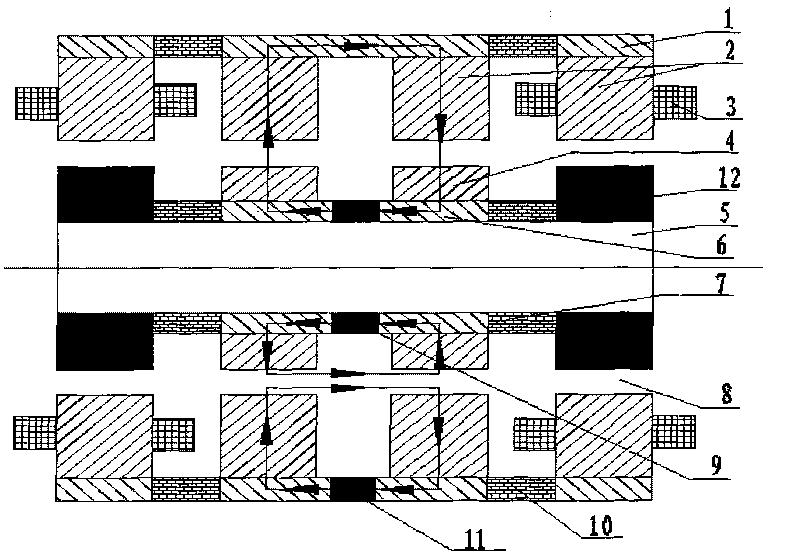
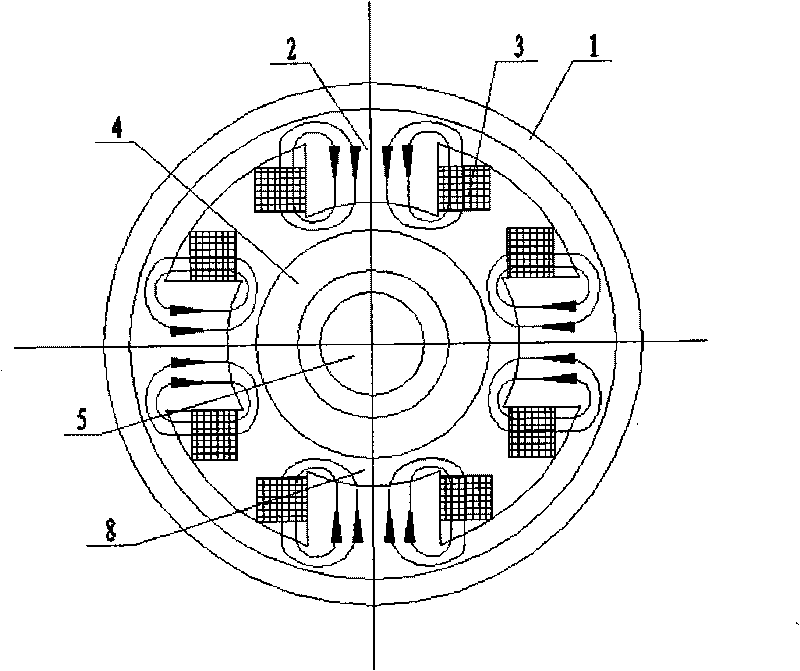
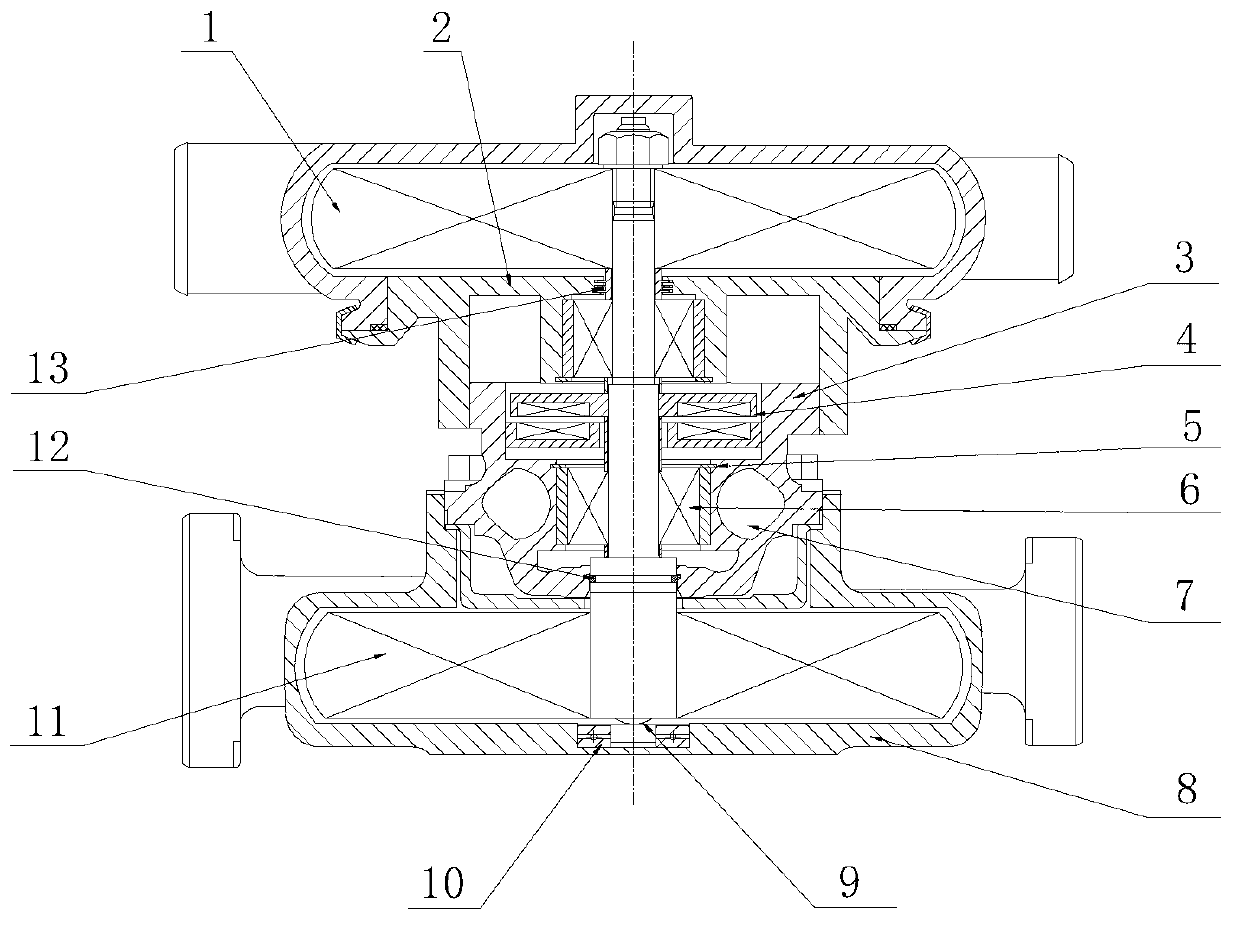
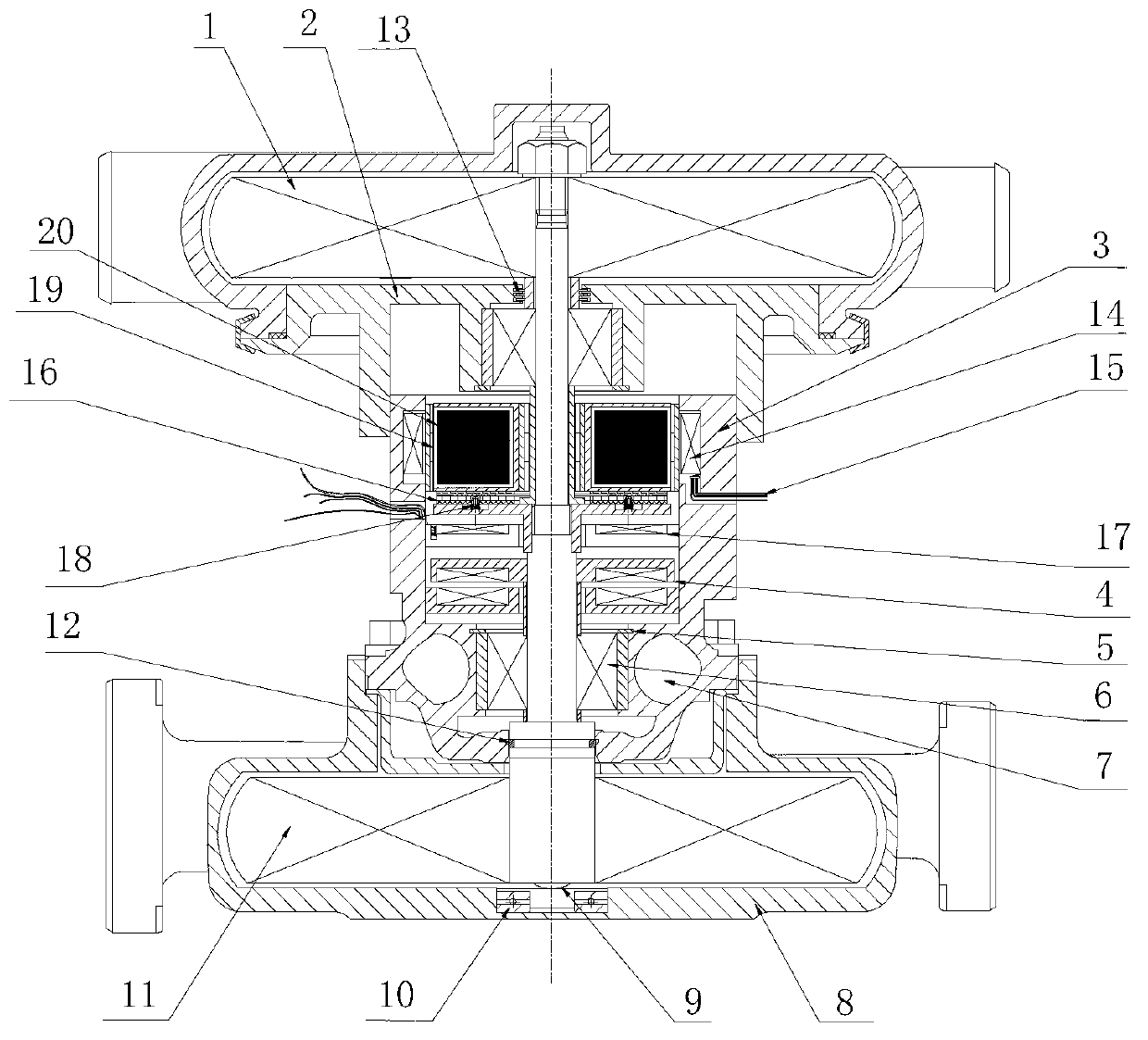
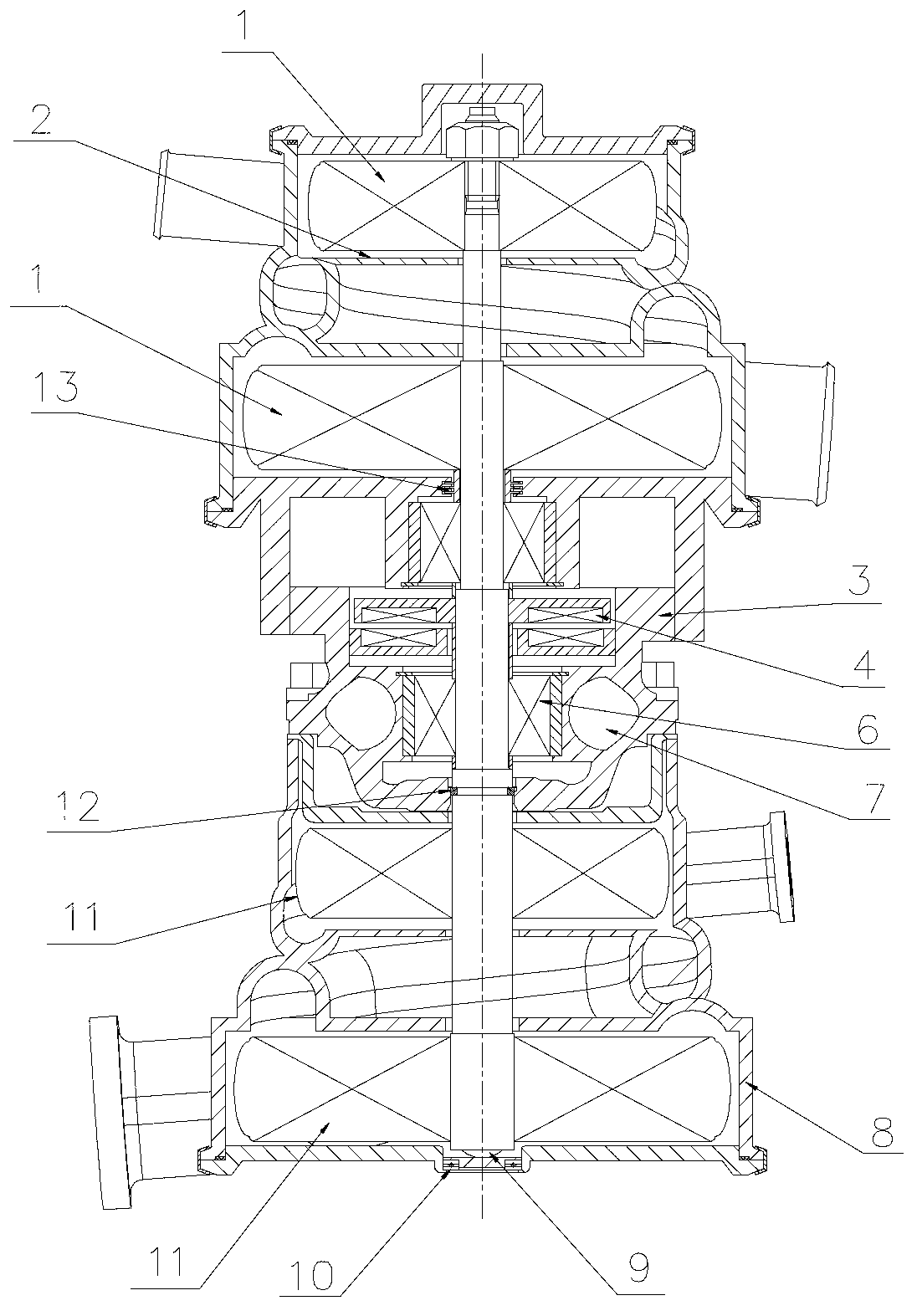
Patents
Literature
161 results about "Rotordynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
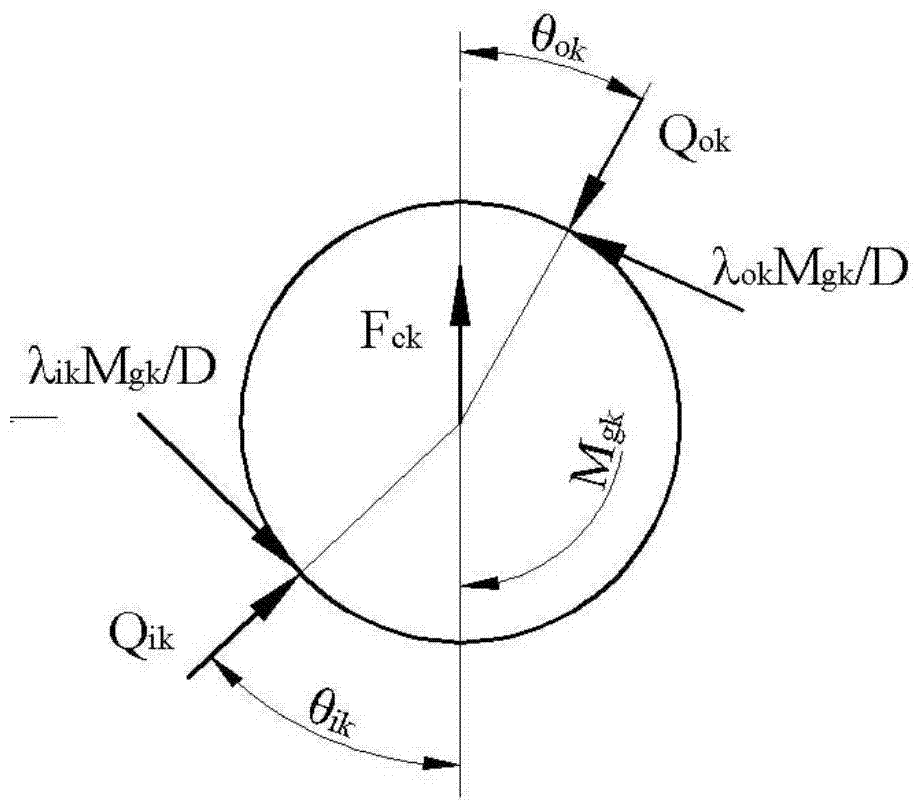
Rotor dynamics is a specialized branch of applied mechanics concerned with the behavior and diagnosis of rotating structures. It is commonly used to analyze the behavior of structures ranging from jet engines and steam turbines to auto engines and computer disk storage. At its most basic level, rotor dynamics is concerned with one or more mechanical structures (rotors) supported by bearings and influenced by internal phenomena that rotate around a single axis. The supporting structure is called a stator. As the speed of rotation increases the amplitude of vibration often passes through a maximum that is called a critical speed. This amplitude is commonly excited by unbalance of the rotating structure; everyday examples include engine balance and tire balance. If the amplitude of vibration at these critical speeds is excessive, then catastrophic failure occurs. In addition to this, turbo machinery often develop instabilities which are related to the internal makeup of turbo machinery, and which must be corrected. This is the chief concern of engineers who design large rotors.
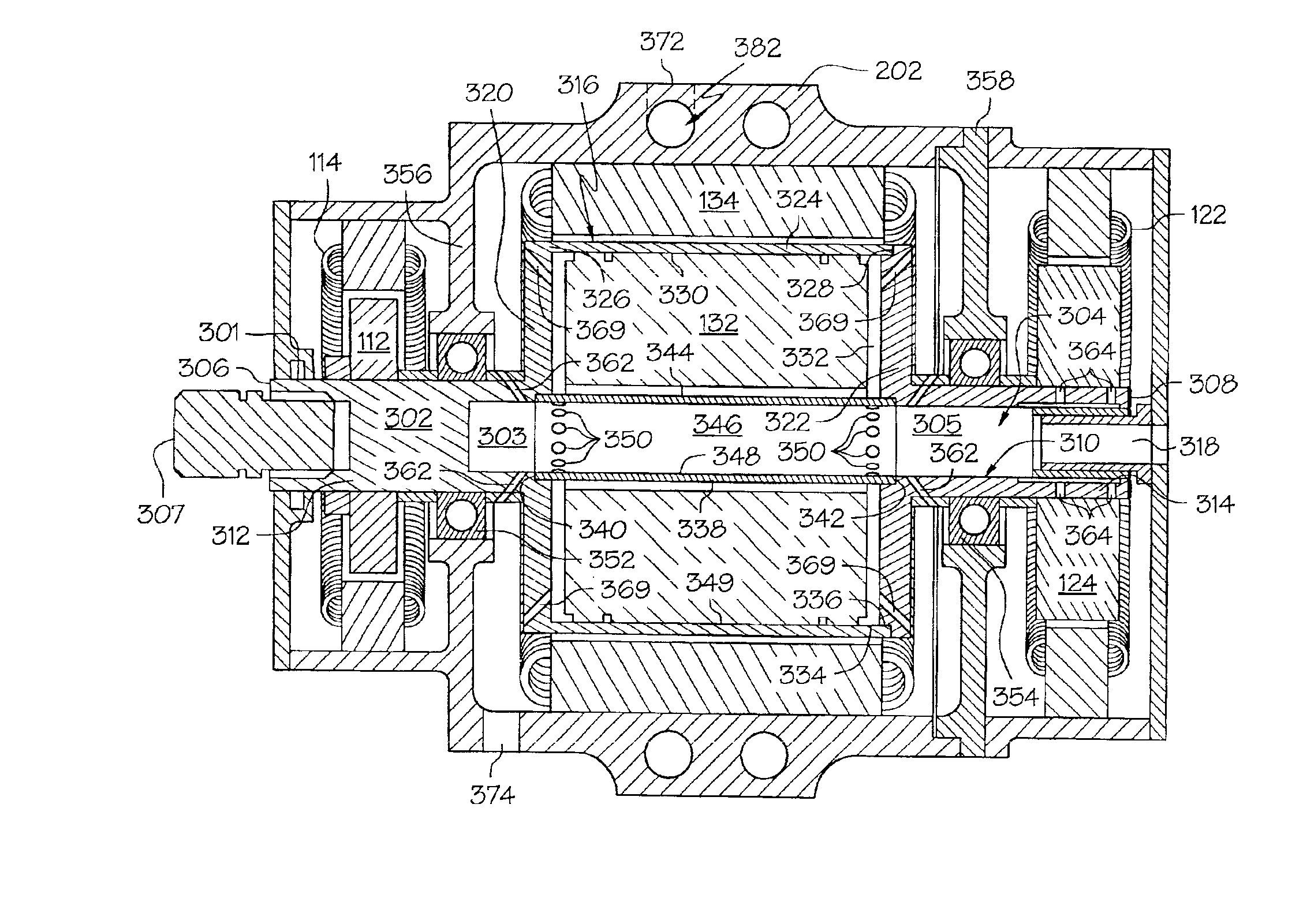
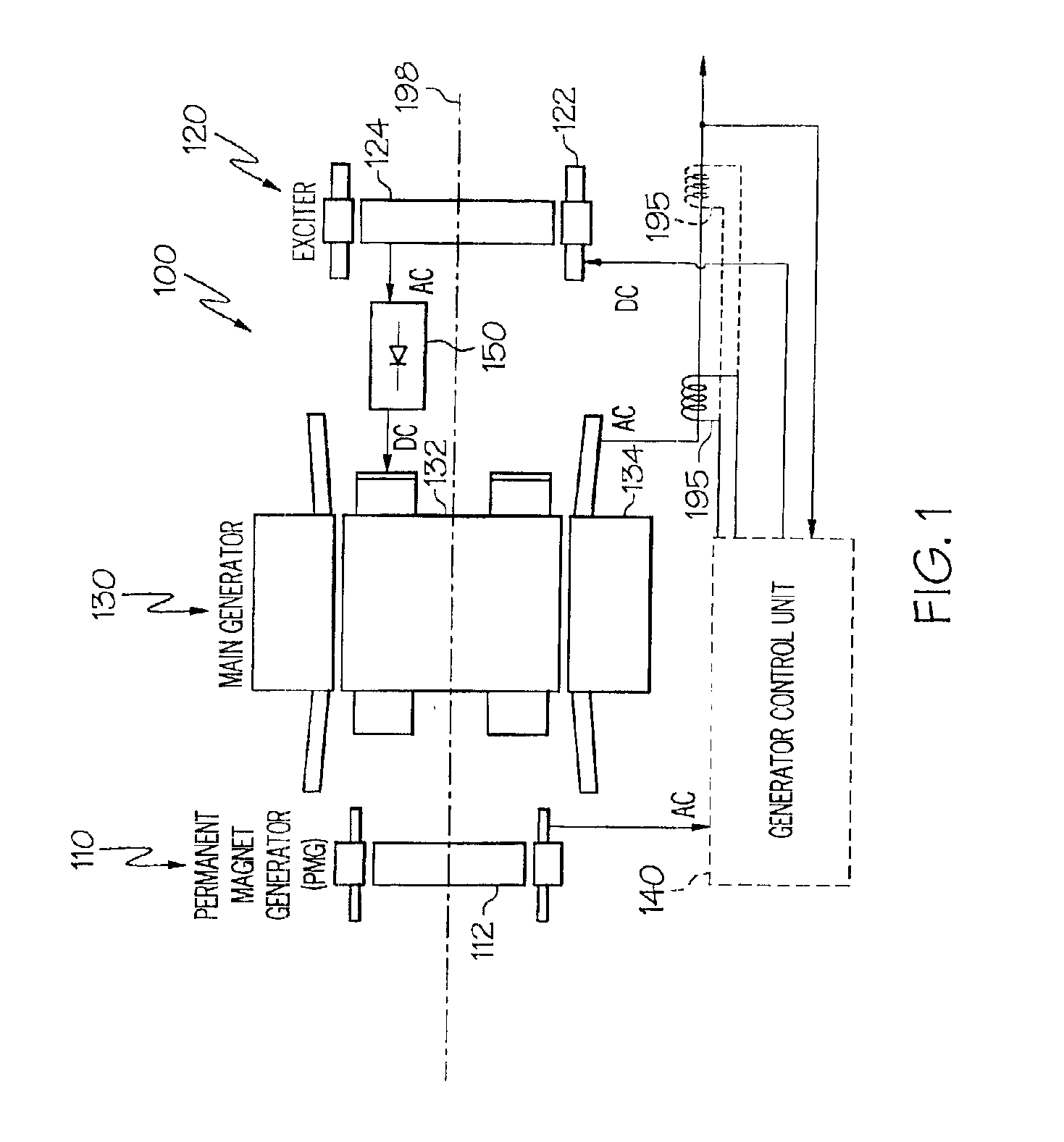
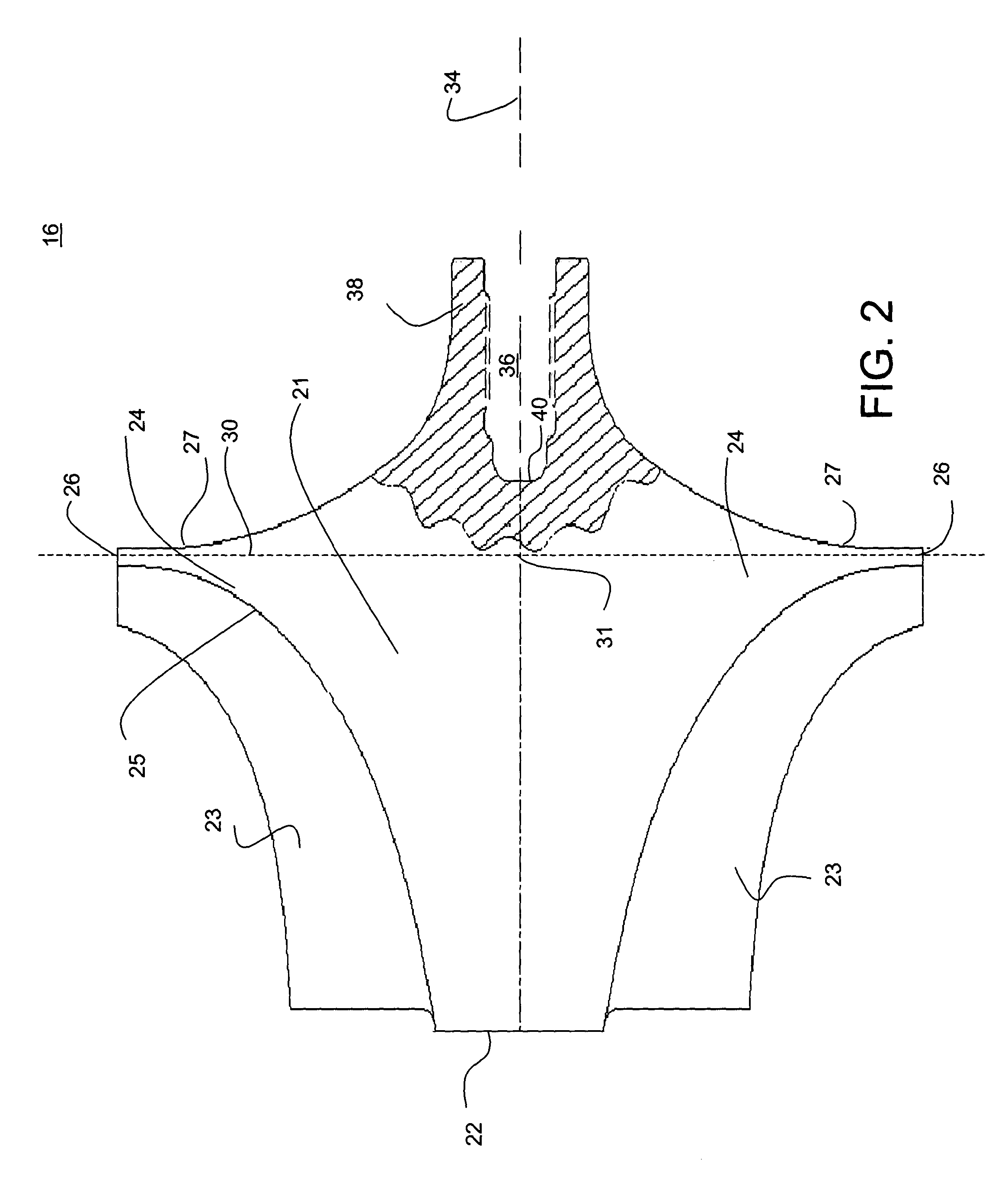
High speed generator with the main rotor housed inside the shaft
InactiveUS6897581B2Improves Structural IntegrityReduce material stressSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsEngineeringTail rotor
A high speed generator has its main rotor located within the main generator shaft assembly. The main rotor is mounted on a substantially hollow rotor shaft, which is also mounted within the main generator shaft assembly. The main stator surrounds at least a portion of the main generator shaft assembly. Main rotor cooling supply orifices extend through the rotor shaft. Main stator cooling supply orifices, which are in fluid communication with the main rotor cooling supply orifices, extend through the main generator shaft assembly. Cooling fluid is directed into the main generator shaft assembly, and flows through the main rotor cooling supply orifices and the main stator cooling supply orifices. The main rotor and main stator cooling supply orifices are configured to supply the main rotor and main stator with a cooling fluid spray. This configuration reduces the rotational fluid mass associated with flood-cooled rotors, which increases structural integrity, lowers material stresses, improves rotor dynamics.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method of Tuning Bending and Torsion Stiffness of Ducted Rotor Core of An Induction Motor
ActiveUS20110074242A1Change stabilityMotor critical vibration speed can be alteredMagnetic circuit rotating partsStatic/dynamic balance measurementInduction motorMotor vibration
Electrodymamic machine rotating mass, including for example induction motor rotors, stiffness tuning methods include selective orientation and compression of modular tie rod assemblies into through bores formed in the rotor lamination core outboard of the rotor shaft during motor manufacture, repair or refurbishment. Stiffness tuning enables a motor manufacturer to tune a rotor's rotordynamic stability, and hence the assembled motor's critical vibration speed. Electrodynamic machine rotating mass tuning can be adjusted in response to machine physical design, operational application and manufacturing variation attributes that impact the assembled machine's critical vibration frequency. Thus the present invention offers a systematic, holistic approach to motor vibration refinement through use of a simple kit of modular tie rod assemblies oriented and tightened in a selected array. Rotor stiffness tuning can be tested virtually on computer work stations. Additional actual rotor stiffness tuning can be performed during manufacture.
Owner:INNOMOTICS LLC
Turbocharger compressor wheel having a counterbore treated for enhanced endurance to stress-induced fatigue and configurable to provide a compact axial length
InactiveUS6994526B2Avoiding and reducing overhangProlong lifePropellersPump componentsImpellerStress induced
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
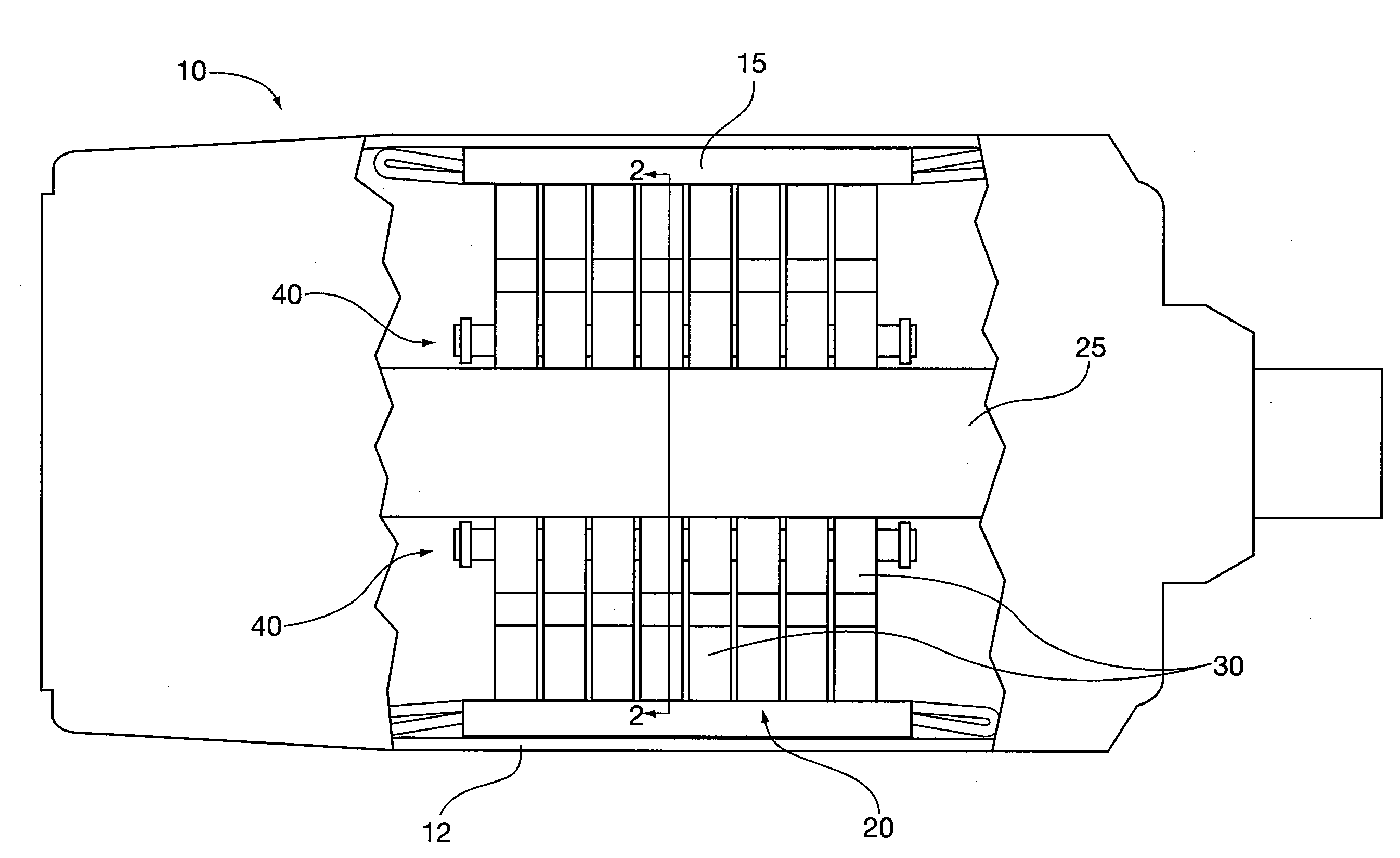
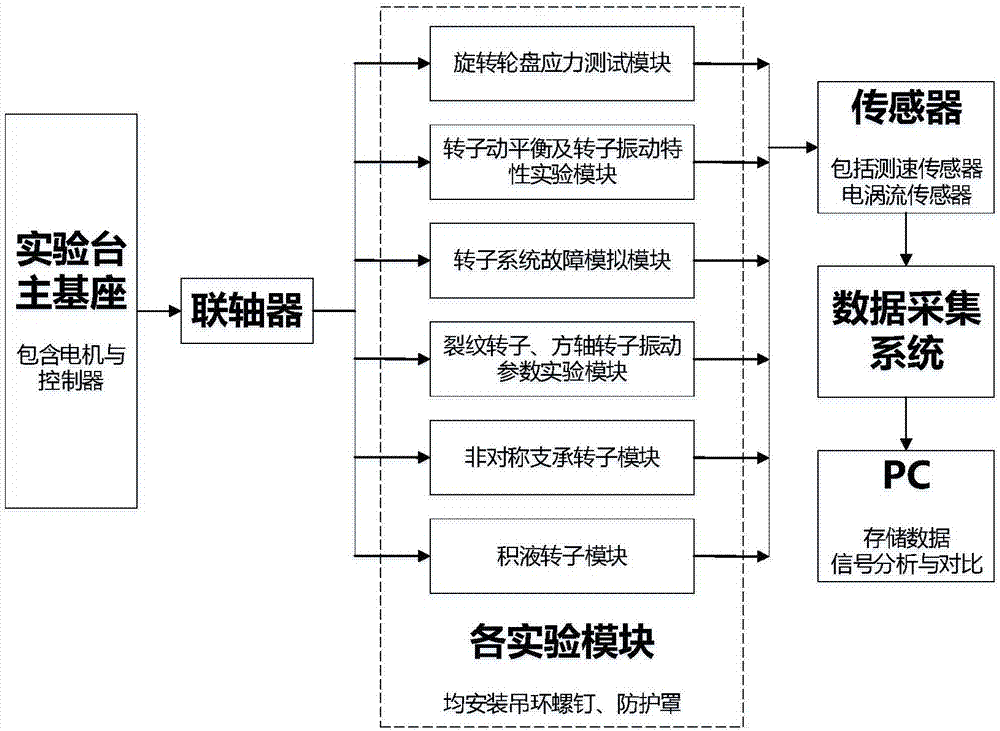
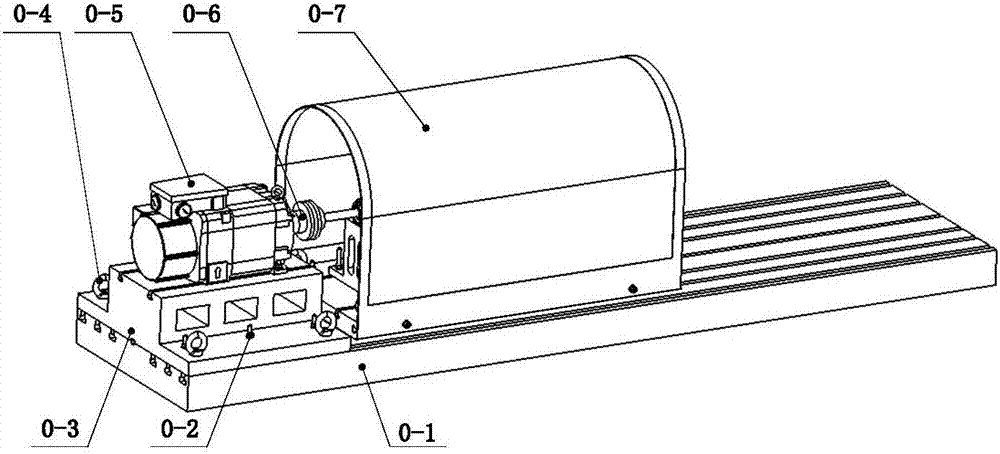
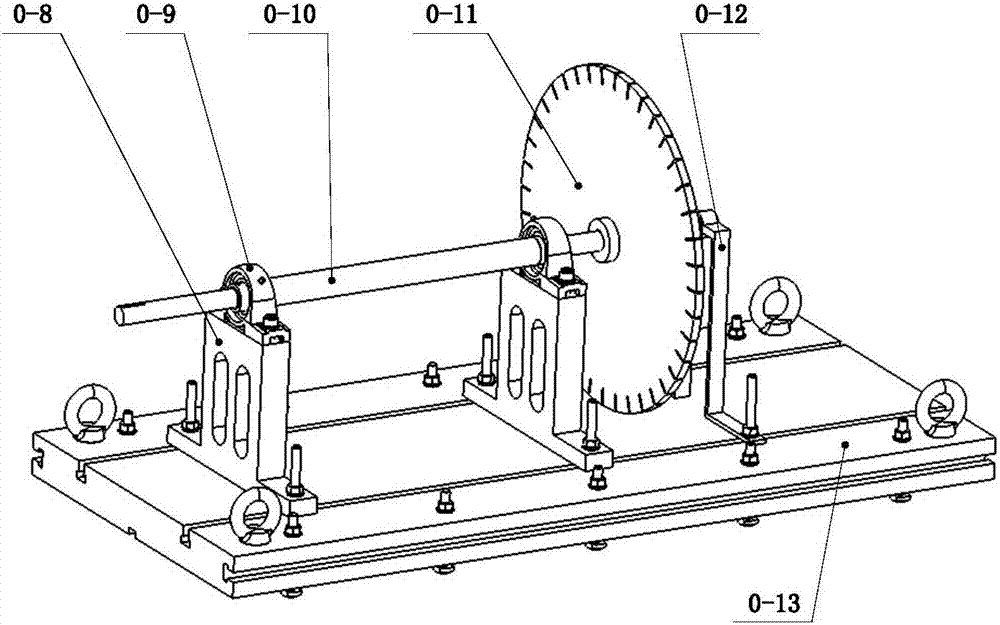
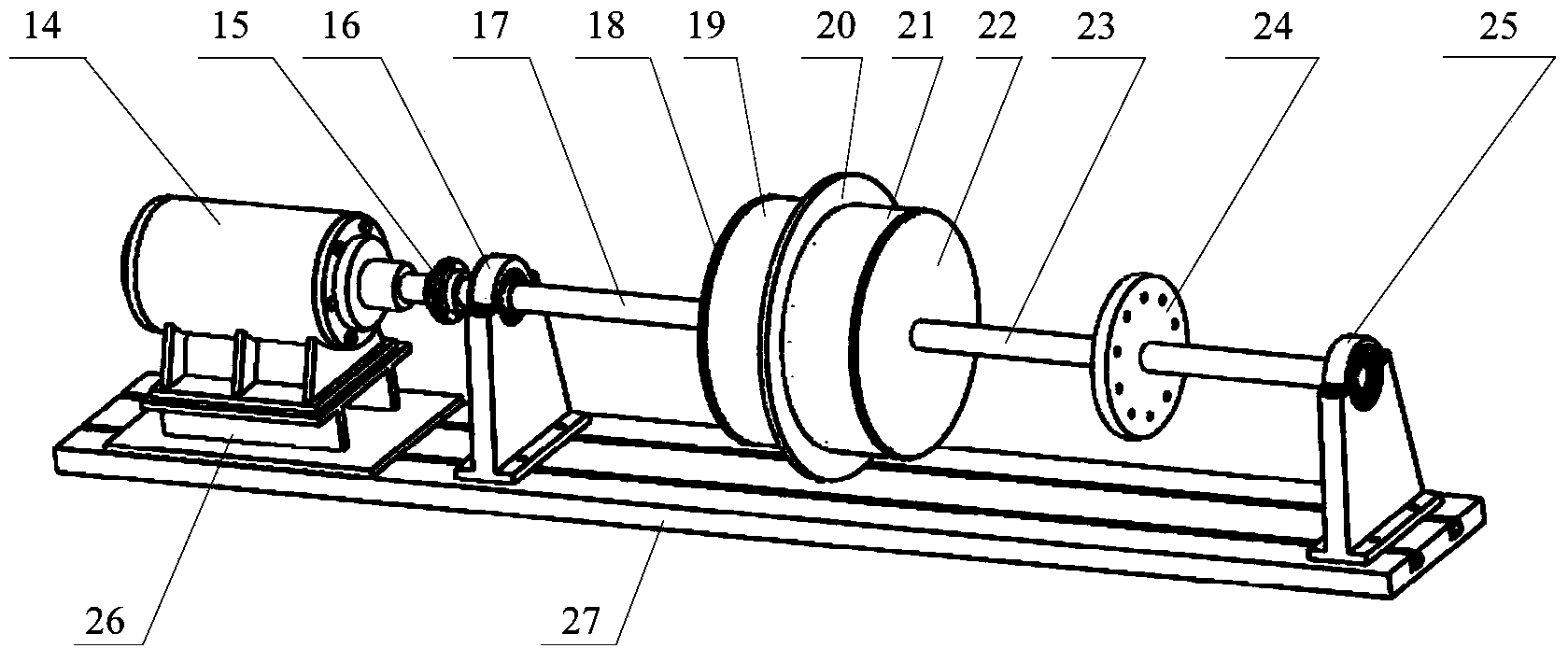
Modularization multifunctional rotor experiment table
The invention provides a modularization multifunctional rotor experiment table. The experiment table comprises an experiment table main substrate, a rotation roulette stress test module, a rotor dynamic balancing and rotor vibration characteristic experiment module, a rotor system fault simulation module, a crack rotor and square shaft rotor vibration parameter experiment module, a non-synchronous support rotor module and a hydrops rotor module. Each module consists of a corresponding module substrate, a rotation shaft, a roulette and a bearing, equipped with a displacement and speed measurement sensor and connected with a data acquisition system and a PC. Each experiment module retains an installation positioning port of the experiment table main substrate towards the outside, and is achieved through a flexible coupling. According to the invention, the experiment table is high universal and interchangeable; the experiment device is convenient to install and disassemble; the rotor system on the experiment table can be timely improved; and the experiment table has multiple functions, is capable of simulating multiple states of rotor operation and can be applied to the field of teaching experiments or scientific research of rotor dynamics and fault diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
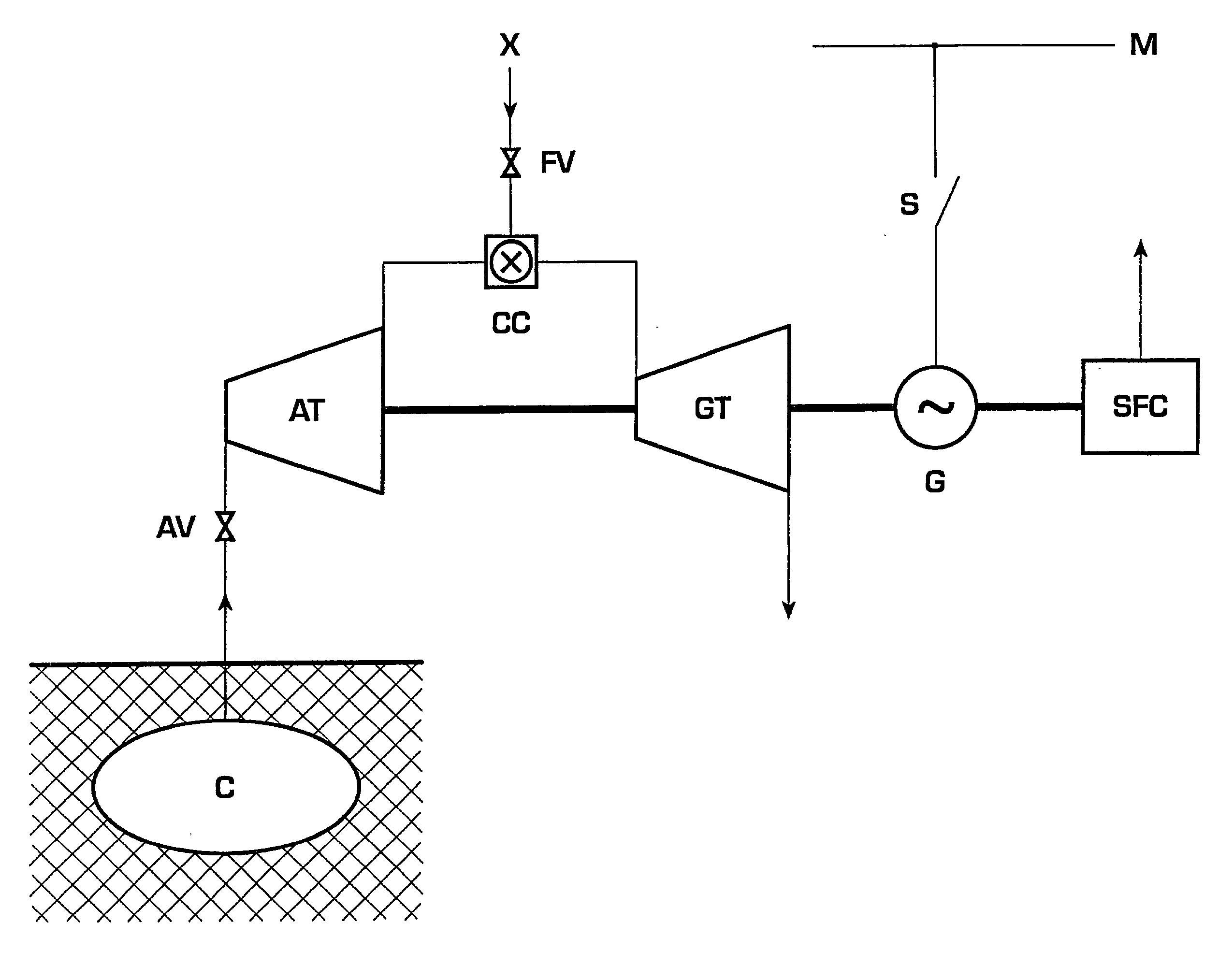
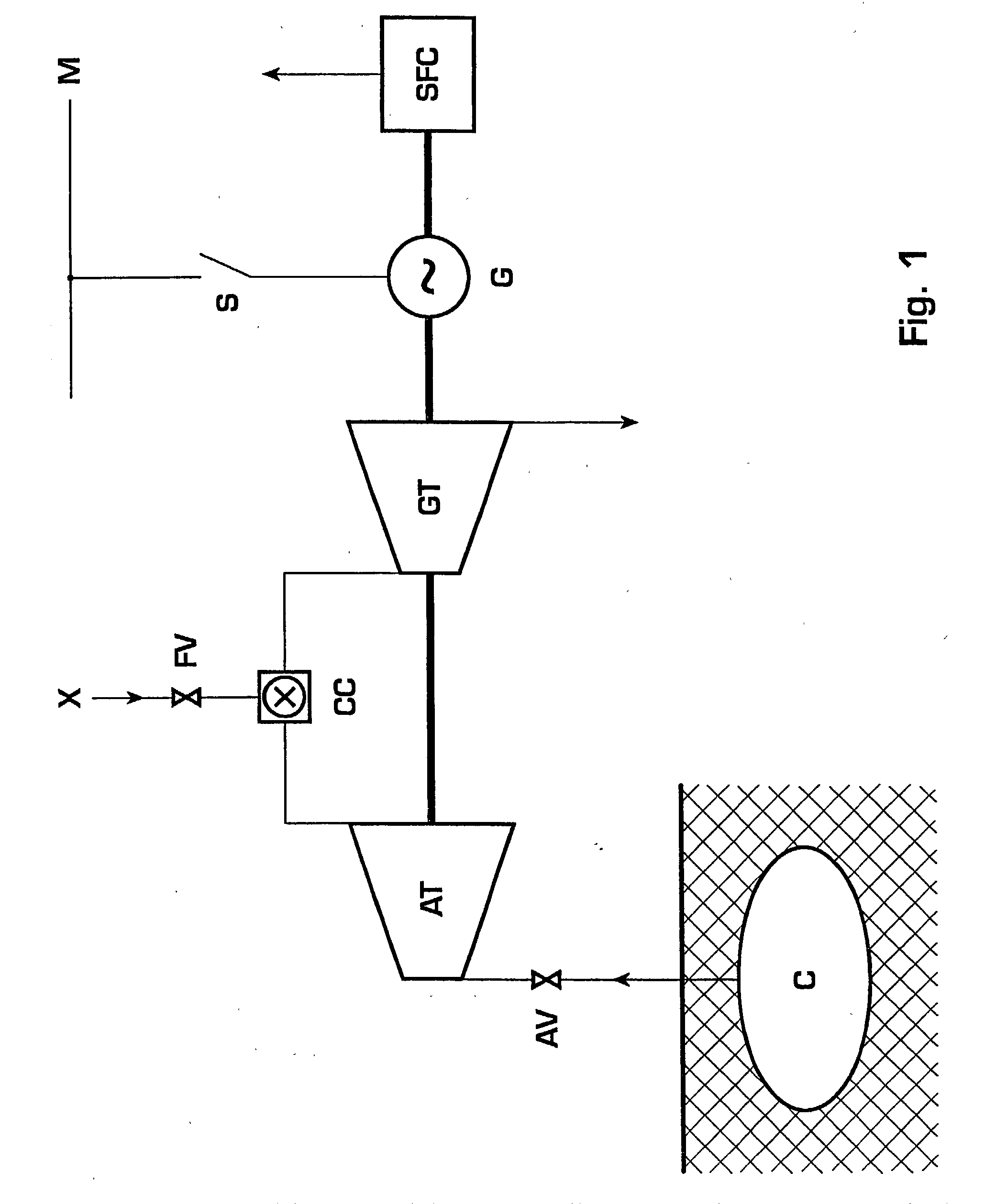
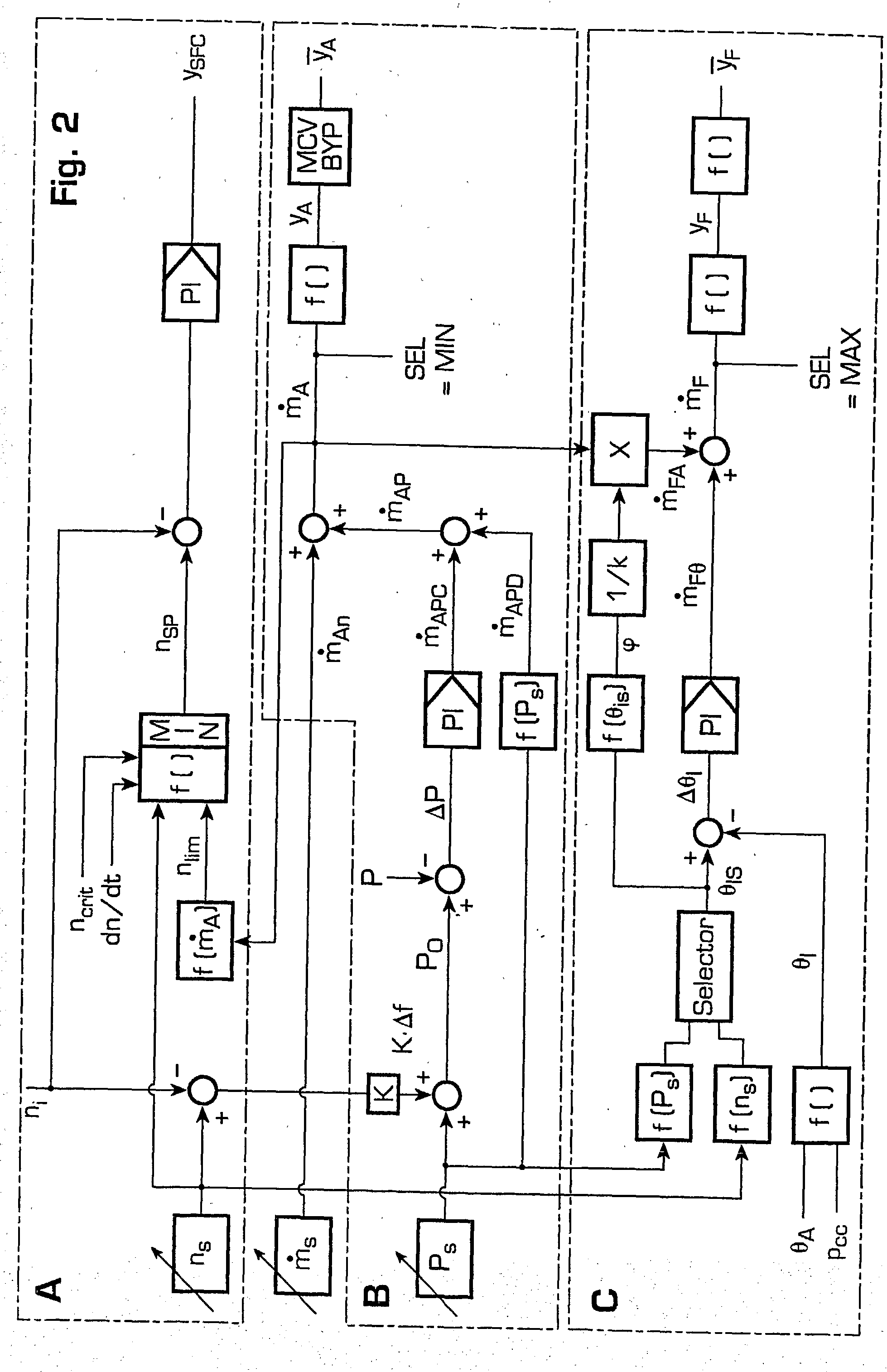
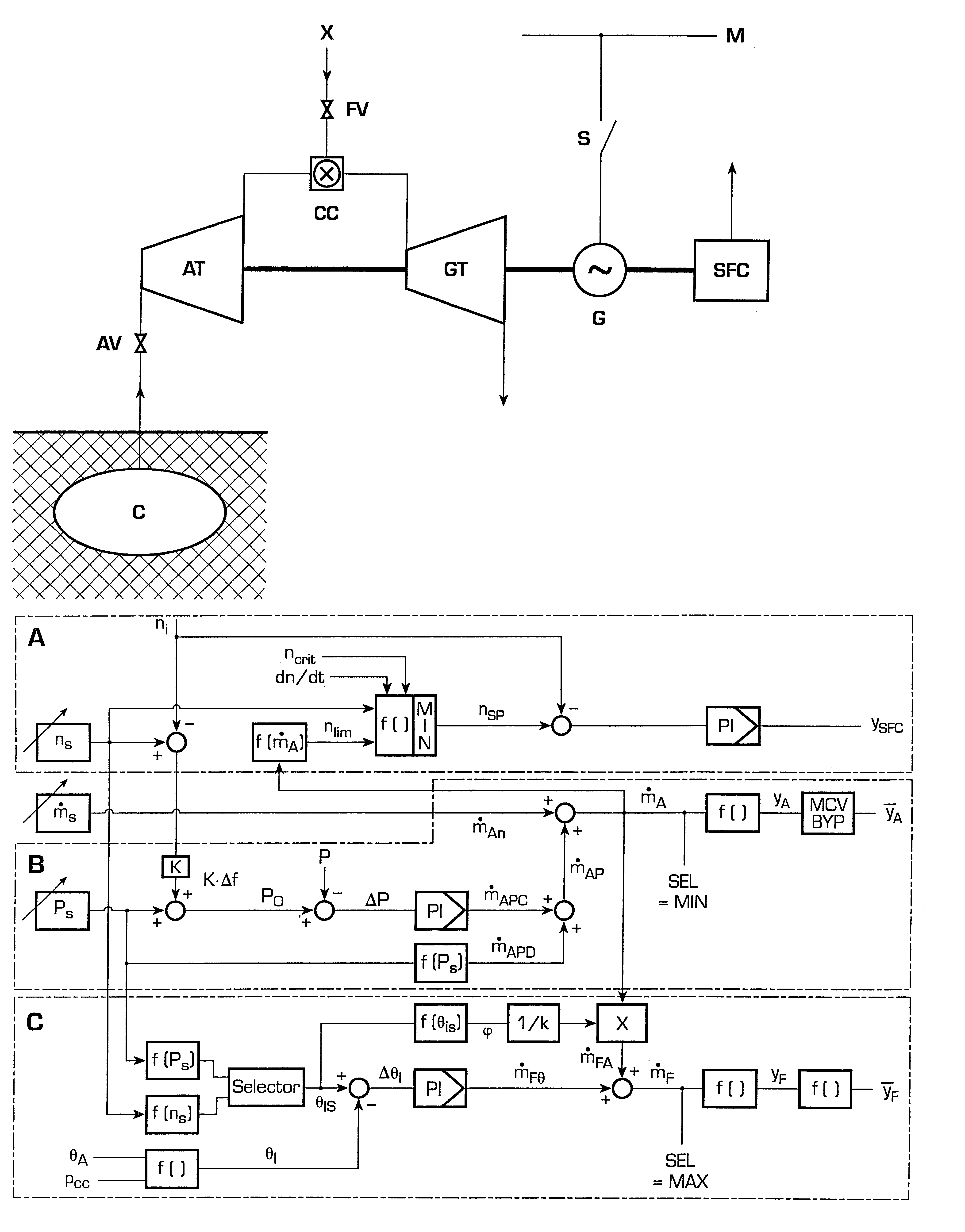
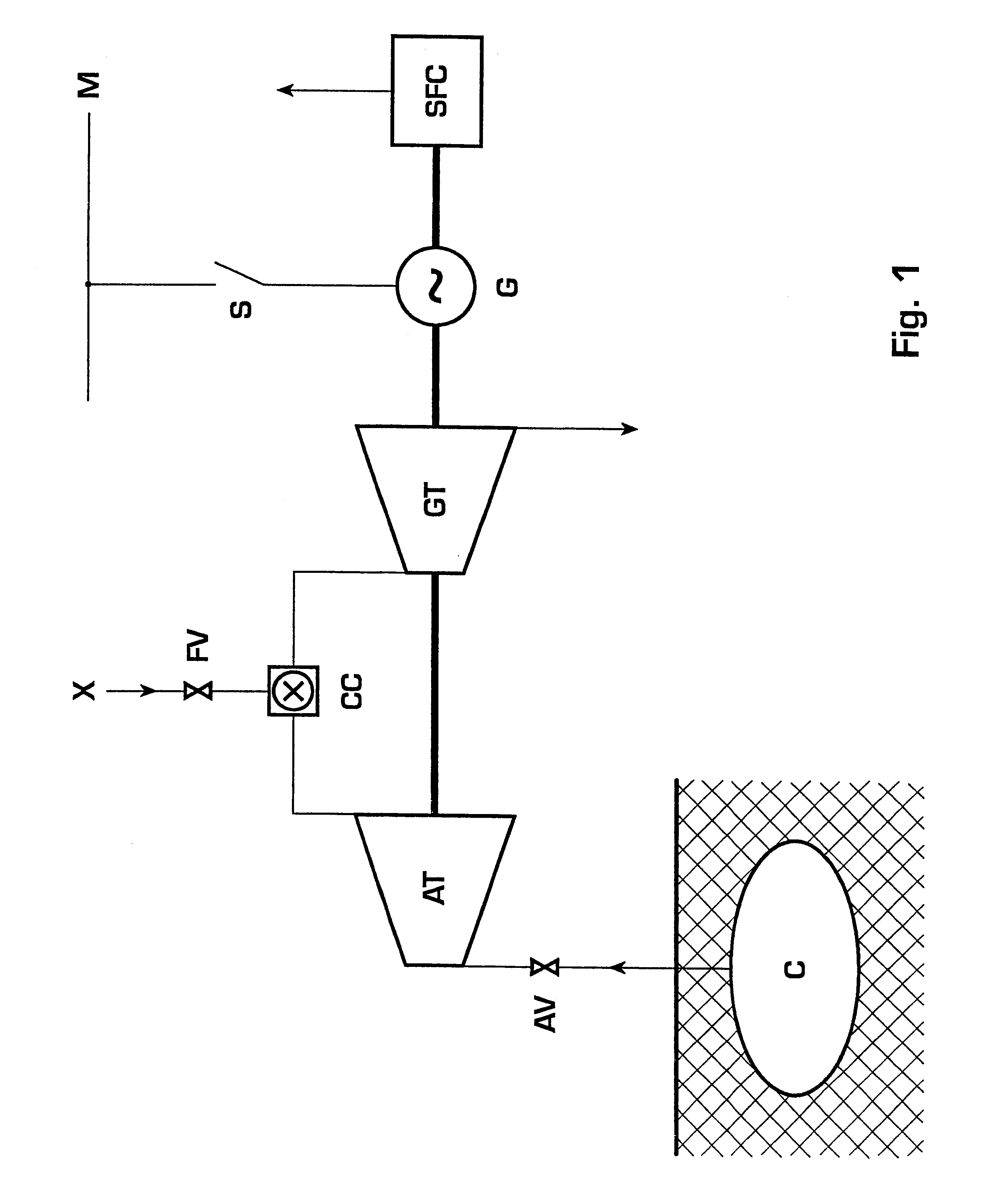
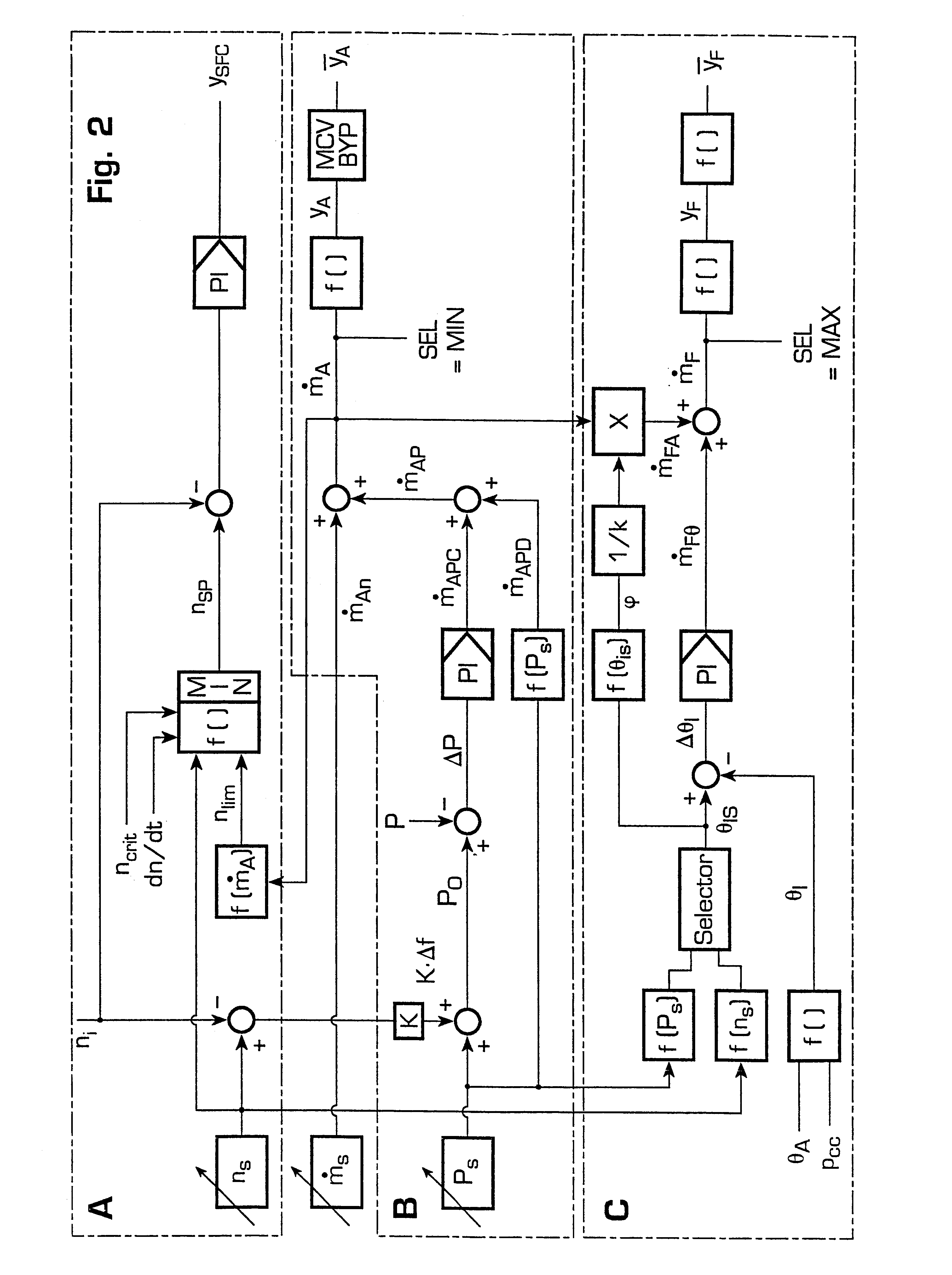
Method for operating a turbine
InactiveUS20030167773A1Prevent speedingInhibition effectTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionTurbine/propulsion engine startersLoop controlClosed loop
A method of operating a turbine arranged in a compressed air energy storage power generation plant comprises an open-loop control of an air mass flow applied within a lower turbine speed range and a closed-loop control of the turbine speed within a higher turbine speed range. The open-loop control comprises the control of the air mass flow by means of air inlet valves and a free development of the turbine speed. The closed-loop control comprises the control of the turbine speed by means of a speed controller, which is acted upon by a speed limiting value determined according to the current air mass flow and a windage calculation. The speed controller activates a static frequency converter in the case that the turbine speed reaches values that are critical with respect to turbine windage or rotor dynamics.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
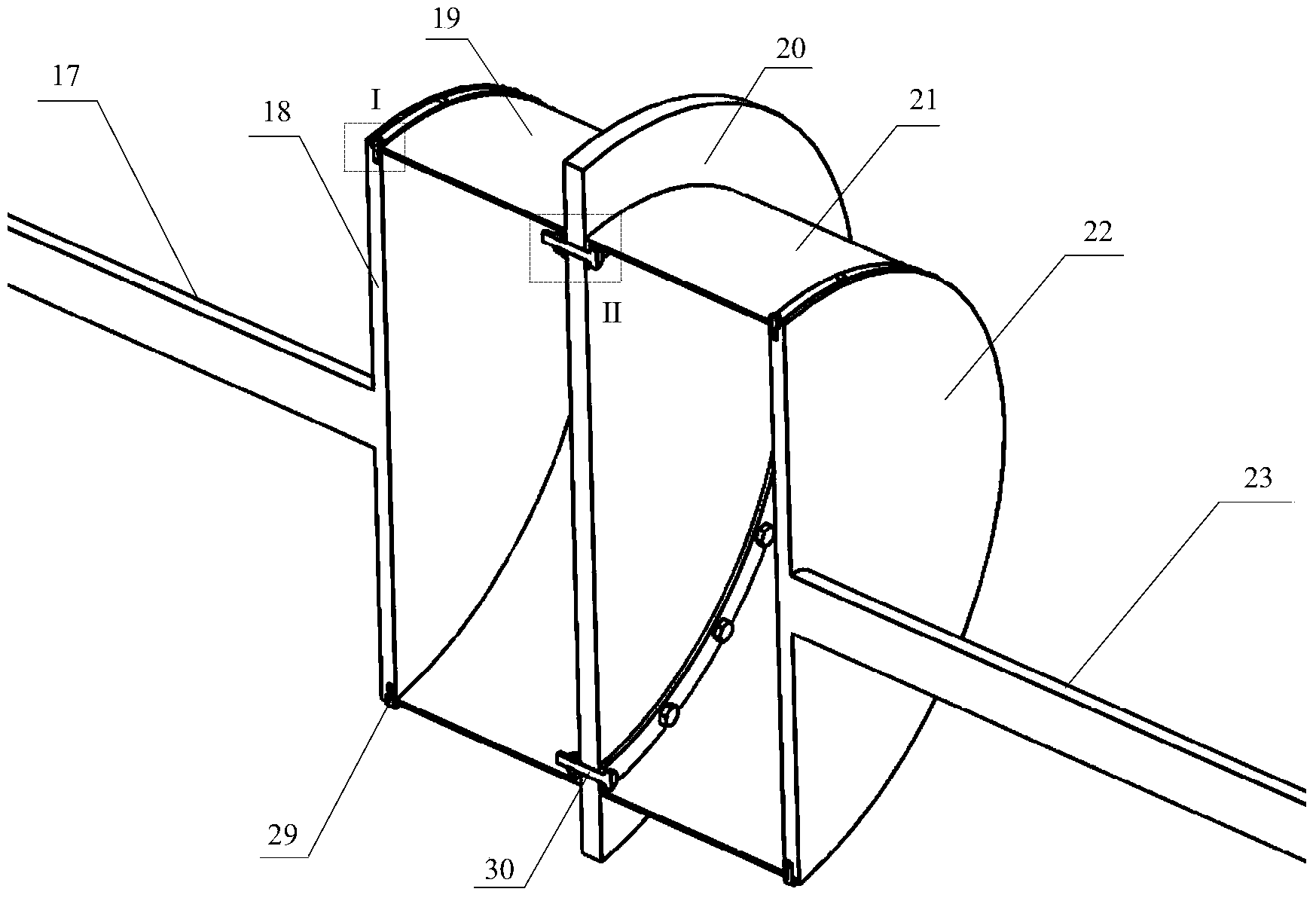
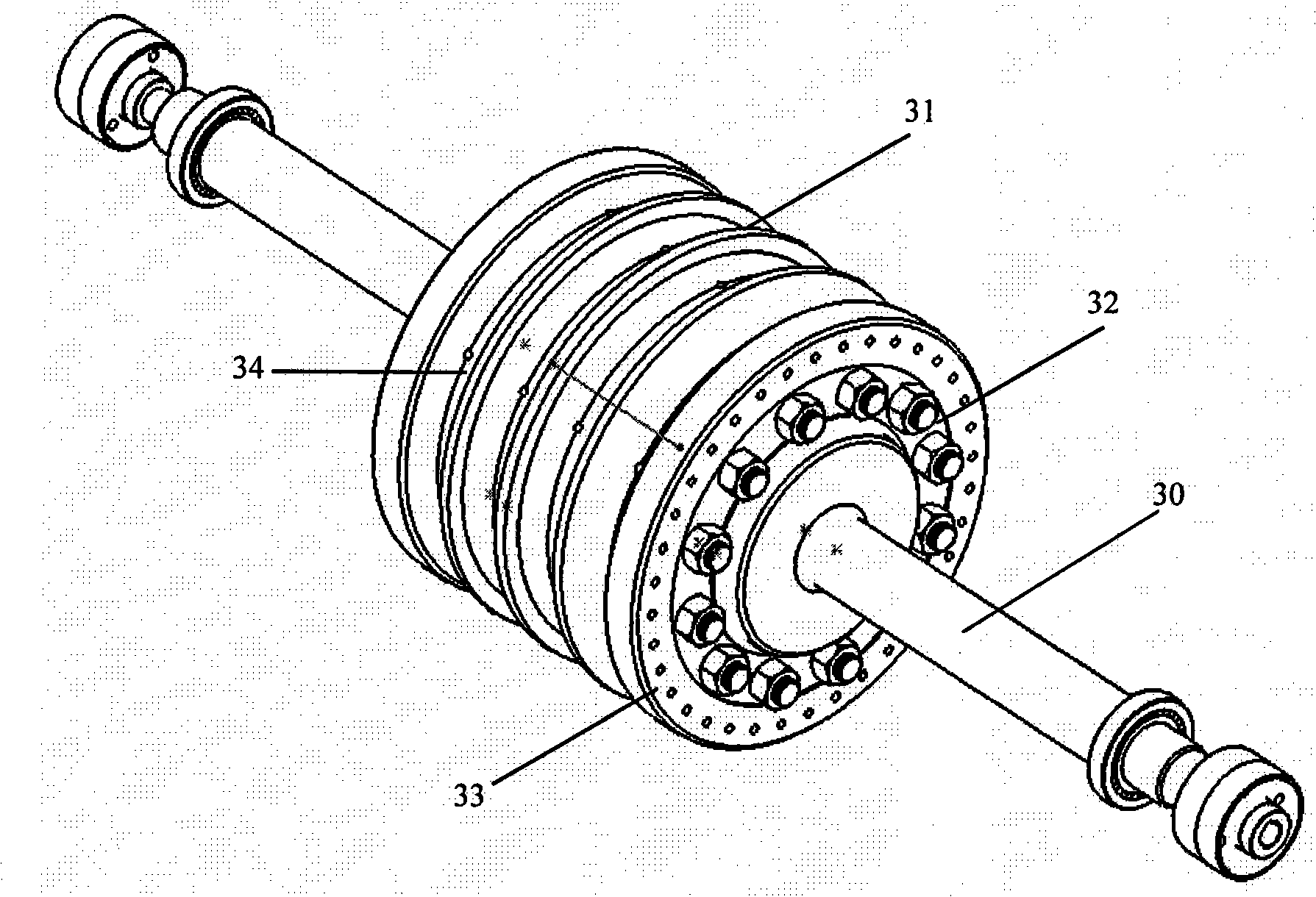
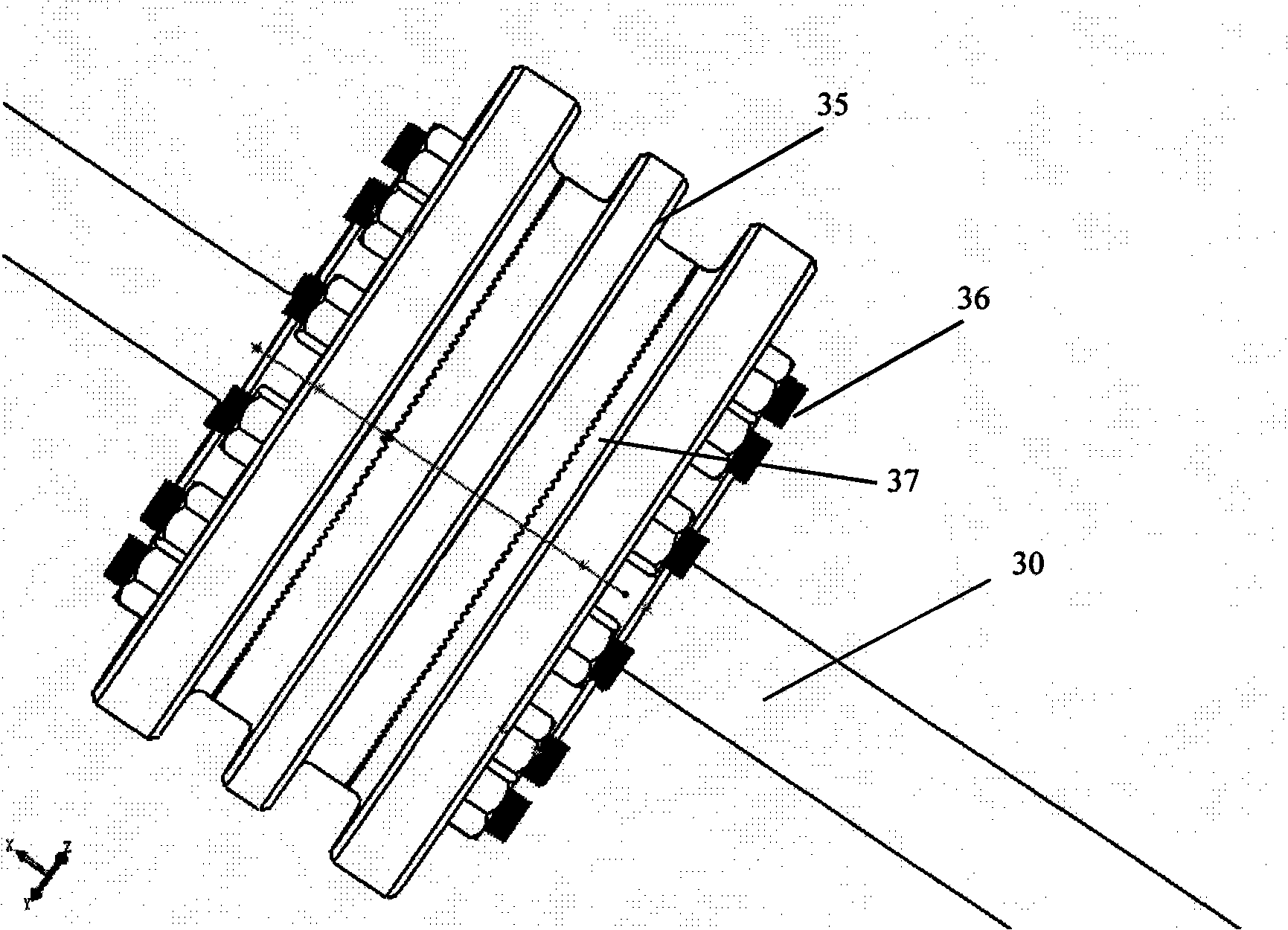
Experimental device for simulating bolt-connected disk-and-drum rotor of aero-engine
ActiveCN103712797AReflect vibration characteristicsMaster transfer propertiesMachine gearing/transmission testingEngine testingCouplingTest bench
The invention discloses an experimental device for simulating a bolt-connected disk-and-drum rotor of an aero-engine, belonging to the technical field of rotor dynamics. The device comprises two bearing seats installed on a test bench base, a disk-and-drum rotor is installed between the two bearing seats, a direct-current motor is arranged on the outer side of the left-side bearing seat, and the direct-current motor is installed on the test bench base through a motor seat and is connected with the disk-and-drum rotor through an elastic coupling. The body of the device is the disk-and-drum rotor which is composed of four wheel disks, two drums and two rotating shafts. The middle large-diameter wheel disk is connected with the drums on the two sides through bolts and inner flanges, the drums on the two sides are respectively in lap joint with the outer edges of the wheel disks on the outer sides, the radial outer sides are compressed tightly by two semi-circular clamps and are fixed by radial screws, the outer sides of the two wheel disks are fixedly connected with two circular-section solid rotating shafts, and the right-end rotating shaft is equipped with one wheel disk. The experimental device can be used for studying the dynamic characteristics of the disk-and-drum rotor and the transmission of vibration load in the disk-and-drum rotor.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
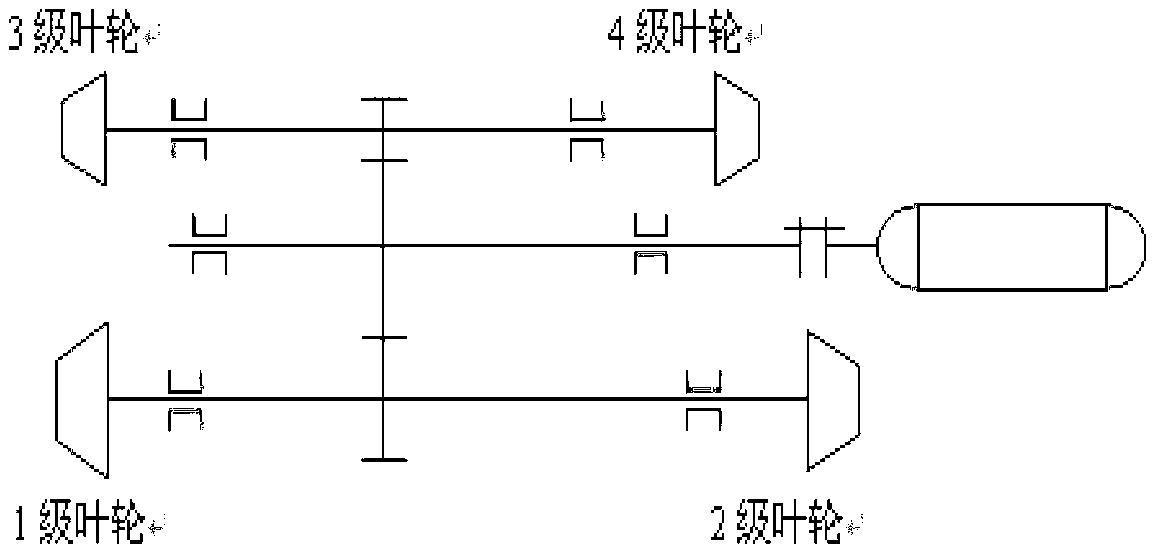
Method for calculating rotor dynamics performance of multi-parallel-axis system
InactiveCN102880796ARealize the combinationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic equationEngineering
The invention relates to a method for calculating rotor dynamics performance of a multi-parallel-axis system. The method comprises the steps specifically as follows: step (1), selecting an analysis object and a calculation type, inputting parameters of a bearing-rotor system, finishing pre-processing operations like discretization of the rotor system; step (2), calling a bearing calculation program, calculating dynamic and static characteristic parameters of each bearing, forming a rotor dynamics equation of a parallel axis system which gives consideration to gear engagement according to the selected analysis object and calculation type; and step (3), calling a solving function to calculate a feature value and a feature vector of a dynamics differential equation, converting the feature value and the feature vector into dynamics characteristic result data through dimension so as to finish calculation and analysis of system stability, critical rotation speed, forced vibration response and vibration mode. According to the method disclosed by the invention, calculation and analysis means for dynamics performance of the multi-parallel-axis system, which can be applied to actual engineering, are developed on the basis of solid theoretical research; the calculated rotor system comprises supports of various types; therefore, combination of bearing calculation and rotor system dynamics analysis is implemented better.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Magnetic bearing system multi-harmonic wave vibration inhibition method based on finite dimensional repetitive control
ActiveCN106873655ASmall amount of calculationOvercoming the influence of vibration suppression accuracyMechanical oscillations controlMagnetic bearingHarmonic
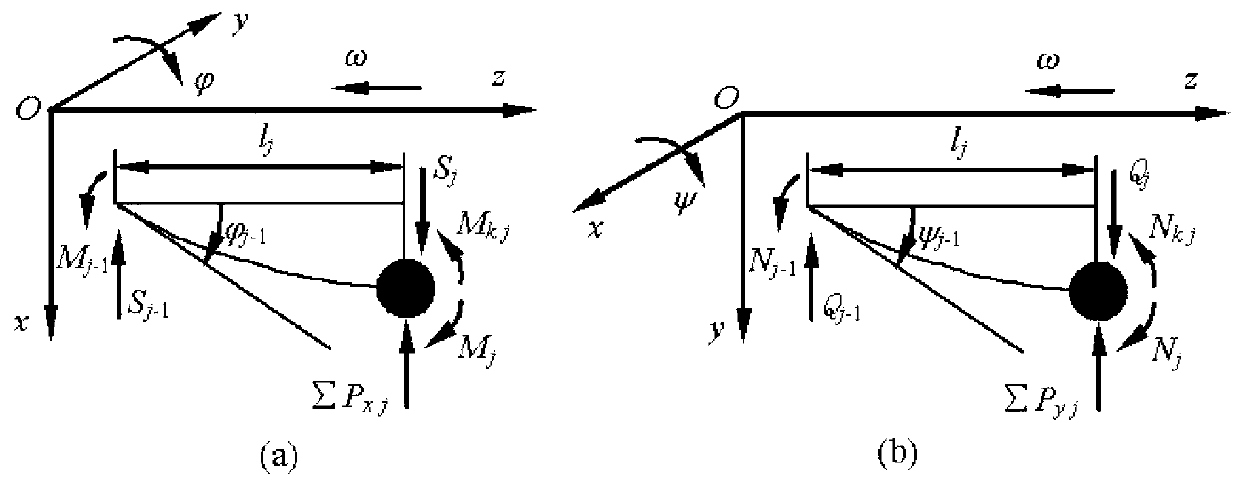
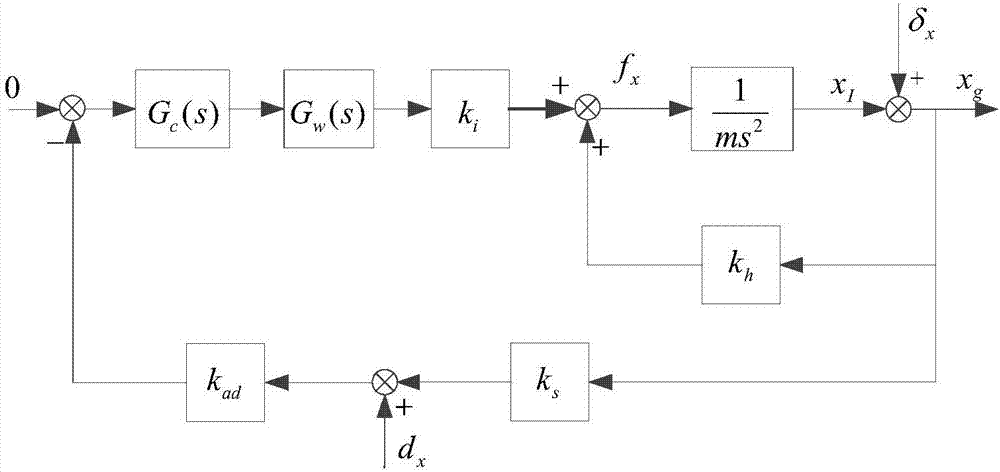
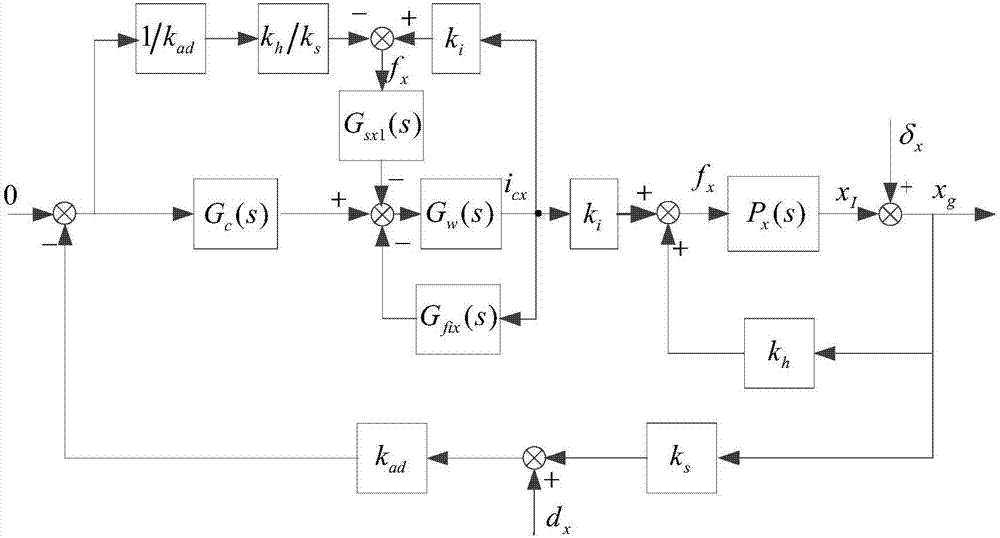
The invention discloses a magnetic bearing system multi-harmonic wave vibration inhibition method based on finite dimensional repetitive control (FDRC). The method comprises following steps of firstly establishing a two-freedom degree magnetic shaft system rotor dynamics model including rotor imbalance and displacement sensor harmonic wave noise Sensor Runout; then, constructing vibration force by use of coil current and a displacement sensor signal and using the vibration force as a controlled variable of the first-order FDRC, thereby achieving same-frequency vibration force inhibition; and designing a parallel type FDRC to achieve high-order subharmonic wave vibration force inhibition, thereby finally achieving two-freedom degree magnetic bearing system harmonic wave vibration inhibition. According to the invention, effects on vibration inhibition precision and system stability caused by a low-pass filter in traditional repetitive control can be overcome; effects on vibration inhibition precision imposed by power amplification low-pass features are overcome; there is no need to additionally design a compensation loop on a power amplification system; and orders of the FDRC can be properly selected according to the vibration force of the system, so calculated quantity is reduced.
Owner:HUACHI KINETIC ENERGY (BEIJING) TECH CO LTD
Magnetic suspension rotor harmonic current suppression method based on parallel phase shift filter
The invention discloses a magnetic suspension rotor harmonic current suppression method based on a parallel phase shift filter. For a magnetic suspension control moment gyro, the method includes that at first, a magnetic suspension rotordynamics model including mass unbalance and sensor harmonic wave is established, the harmonic current suppression method based on the parallel phase shift filter is designed, and different phase shifts are selected based on different rotating speed, so that the system stability is guaranteed. The method can suppress the harmonic component of the magnetic bearing coil current in a magnetic suspension rotor, and is suitable for the harmonic current suppression of a magnetic suspension rotor system including mass unbalance and sensor harmonic wave.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Swirl interruption seal teeth for seal assembly
ActiveUS20140072415A1Reducing steam forceLittle strengthEngine sealsEngine manufactureSpacing toothEngineering
A seal assembly for sealing between a rotating component and a stationary component in a turbomachine. The seal assembly includes a plurality of radially inwardly projecting, axially spaced teeth extending from the stationary component, wherein at least one of the plurality of teeth has at least one axially extending hole therethrough. Axial flow of an operating fluid through the holes acts as an air-curtain to interrupt swirl flow in a seal cavity, therefore reducing steam force that could act to destabilize rotordynamics.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
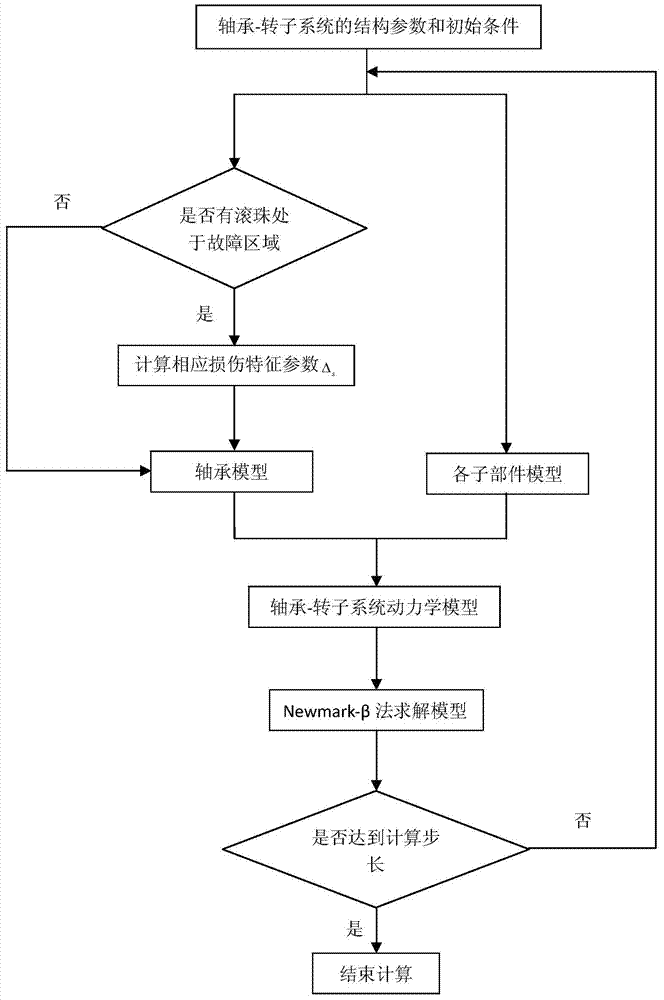
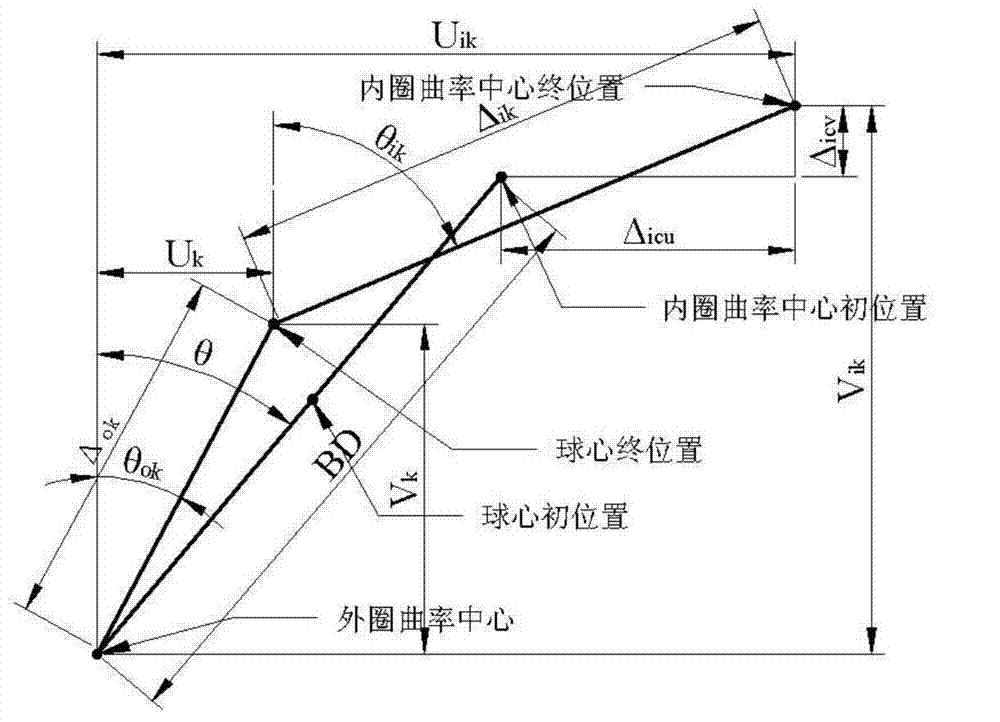
Rolling bearing-rotor system damage vibration response quantitative calculation method
ActiveCN103712785AThe calculation result is accurateMachine bearings testingElement modelDynamic models
The invention discloses a rolling bearing-rotor system damage vibration response quantitative calculation method. The method comprises the steps that the structure parameter and the initial parameter of a bearing-rotor system are acquired; according to the bearing parameters, a five freedom degree bearing model is established, and a bearing stiffness matrix of the bearing-rotor system is acquired; according to the geometric size and the material characteristic parameter of a subcomponent, a finite element model is established, and a rotor stiffness matrix, a rotor gyroscopic matrix, and an equivalent mass matrix caused by a centrifugal force are acquired; a dynamics model of the bearing-rotor system is established; a time-domain integral method is used to solve the bearing-rotor dynamics model, so as to acquire the displacement vibration response of the bearing-rotor system. According to the invention, based on the finite element dynamics model, quantitative calculation can be carried out on vibration response generated by single point or multi-point damage of inner and outer rings of a bearing, and a basis is provided for the analysis and the diagnosis of a fault mechanism of the rotor-bearing system.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
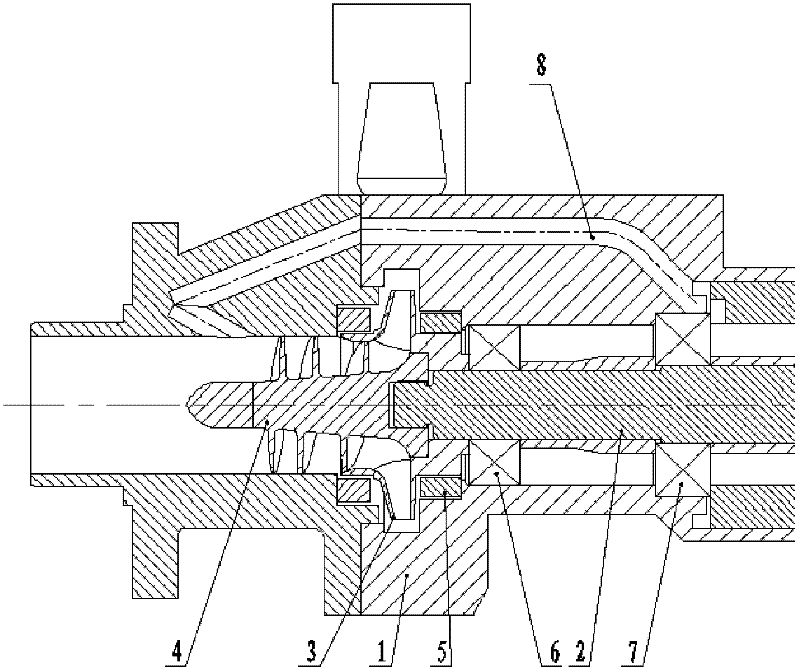
A small high-speed centrifugal pump suitable for wide-range flow regulation
ActiveCN102287398AImprove cavitation resistanceImprove flow stabilityPump componentsPumpsCavitationEngineering
The invention relates to a small-sized high-speed centrifugal pump suitable for flow regulation in a wide range. The centrifugal pump comprises a driving machine, a pump body, a shaft which is arranged in the pump body through bearings, a centrifugal wheel and an inducing wheel, wherein one end of the shaft is connected with the output end of the driving machine, and the other end of the shaft isprovided with the centrifugal wheel and the inducing wheel sequentially; the inducing wheel comprises an inducing wheel hub and inducing wheel blades arranged on the inducing wheel hub; the diameter of the inducing wheel hub is gradually increased from an inlet of the inducing wheel to an outlet; and the pitch of the inducing wheel is gradually increased from the inlet of the inducing wheel to the outlet in a three-section mode, and the inducing wheel is provided with a constant pitch section, a varying pitch section and a constant pitch section sequentially along the axial direction. The technical problems that the centrifugal pump is limited by pump cavitation resistance and rotor dynamics problems in the prior art are solved. The centrifugal pump provided by the invention has the advantages of compact structure, small size, high performance and high cavitation resistance.
Owner:NO 11 INST OF NO 6 ACADEMY OF CHINA AEROSPACE SCI & TECH
Turbocharger compressor wheel having a counterbore treated for enhanced endurance to stress-induced fatigue and configurable to provide a compact axial length
InactiveUS20050056013A1Improve compressor lifeImprove staminaPropellersRotary propellersImpellerStress induced
Compressor wheel and techniques for manufacturing such a wheel are provided. The wheel may include a hub with a counterbore internally treated to impart residual compressive stresses for enhanced endurance to stress-induced fatigue. The surface treatment allows extending the counterbore relatively closer to a plane of typical maximum stress of the wheel. This design flexibility advantageously allows avoiding or reducing overhang of the compressor wheel, thereby improving rotor dynamics and reducing the axial length of the hub, and the overall foot print of the compressor wheel.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Object-oriented nonlinear and non-causal modeling and simulation method for rotor dynamics system
InactiveCN102915388AConvenient analysis methodSpecial data processing applicationsModelicaMulti field
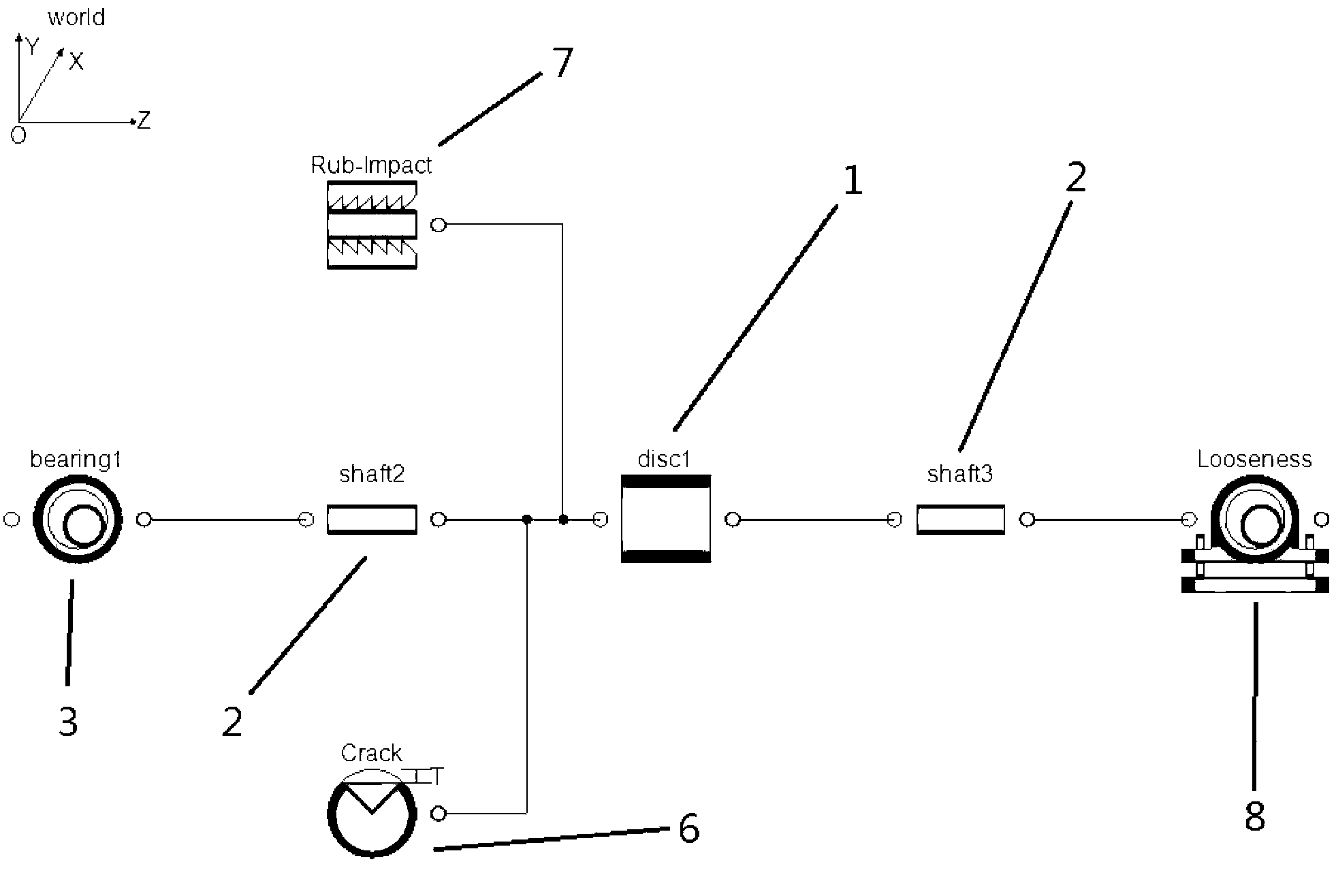
The invention relates to the technical field of simulated modeling of a rotor dynamics system and in particular to an object-oriented nonlinear and non-causal modeling and simulation method for the rotor dynamics system. The modeling and simulation method is based on an object-oriented non-causal multi-field modeling language Modelica; the modeling language Modelica is used for writing the simulated modeling program of the rotor dynamics system; the simulated modeling of the rotor dynamics system is formed by components and faults; the components comprises a turntable component, shaft section components and a bearing component; the turntable component, the shaft section components and the bearing component comprise two connector elements respectively; the faults comprise crack fault, rubbing fault and foundation loosening fault; and by the modeling and simulation method, the rotor dynamics systems with various structures can be modeled, system characteristics and working condition of the rotor dynamics systems can be truly reflected, the faults such as crack, rubbing and foundation loosening can be introduced to perform system analysis, and a convenient analysis measure is provided for engineering technical persons and scientific researchers.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
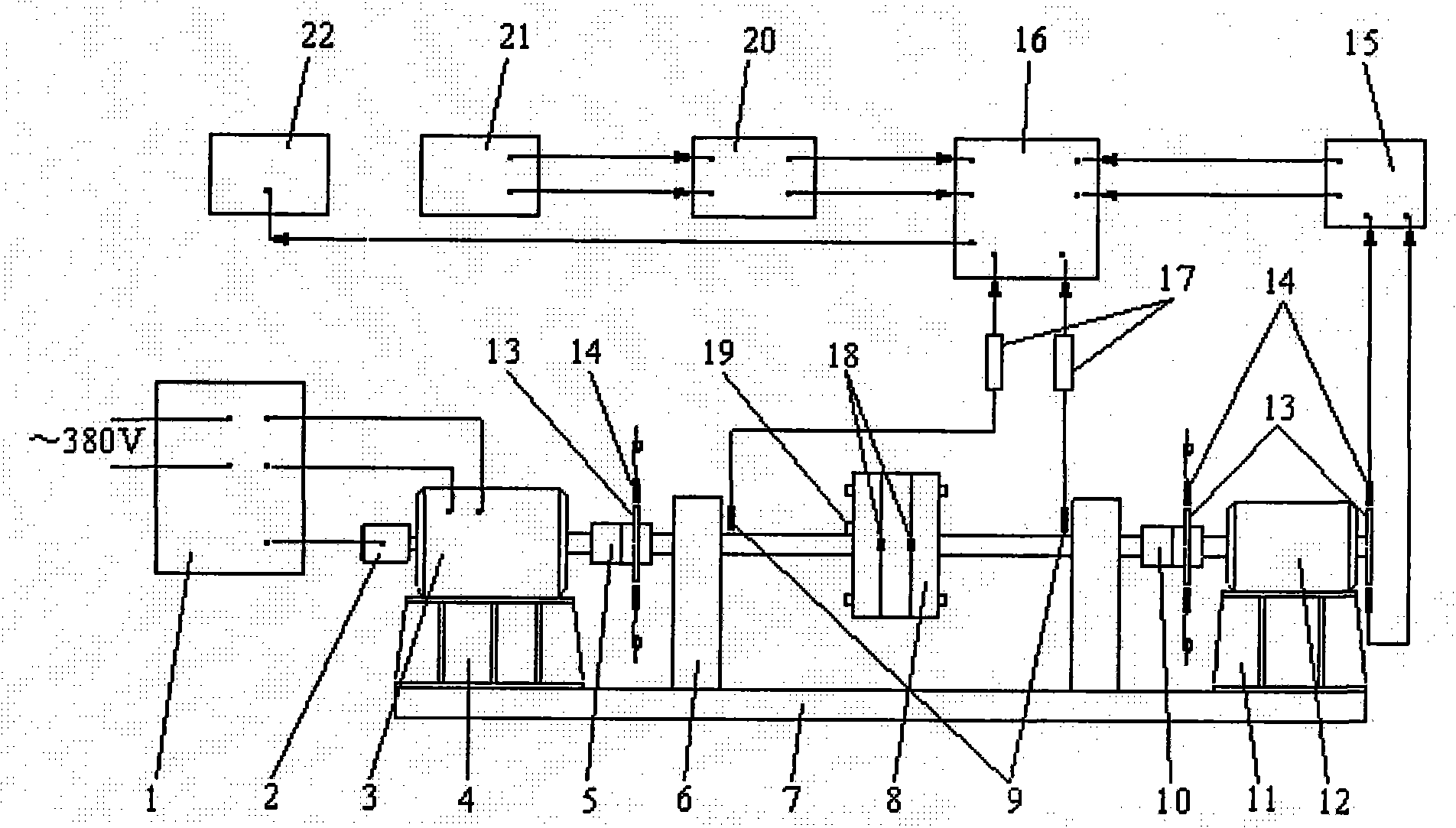
Dynamics characteristic experimental apparatus of heavy type gas turbine pull rod rotor
InactiveCN101329220AImprove the ability of independent design and productionMachine part testingElectricityEngineering
The invention discloses a dynamic property experimental device of a pull rod rotor of a heavy-duty gas turbine, which comprises two bearing blocks that are arranged oppositely on the left and the right on the basis of an experimental platform, a pull rod rotor used for experiment is arranged between the bearing blocks, and a direct current motor is arranged outside the left bearing block, electrically connected with an electric control cabinet and connected with one end of the pull rod motor that extends out of the left bearing block through a first sleeve pipe; an electric generator is arranged outside the right bearing block and connected with the other end of the pull rod motor that extends out of the right bearing block through a second sleeve pipe; an electric eddy current displacement sensor is respectively arranged on shaft necks at the two ends of a rotating shaft of the pull rod motor that are corresponding to the left and the right bearing blocks, and the electric eddy current displacement sensor is connected with a dynamic signal collector that is connected with a computer; a speed measuring gear is respectively arranged at the shaft rear of the electric generator and the first and the second sleeve pipes, a pair of rotating speed sensors are symmetrically arranged along the diameter direction of the gears and connected with a torsional vibrometer, and the torsional vibrometer is connected with the dynamic signal collector by a signal.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
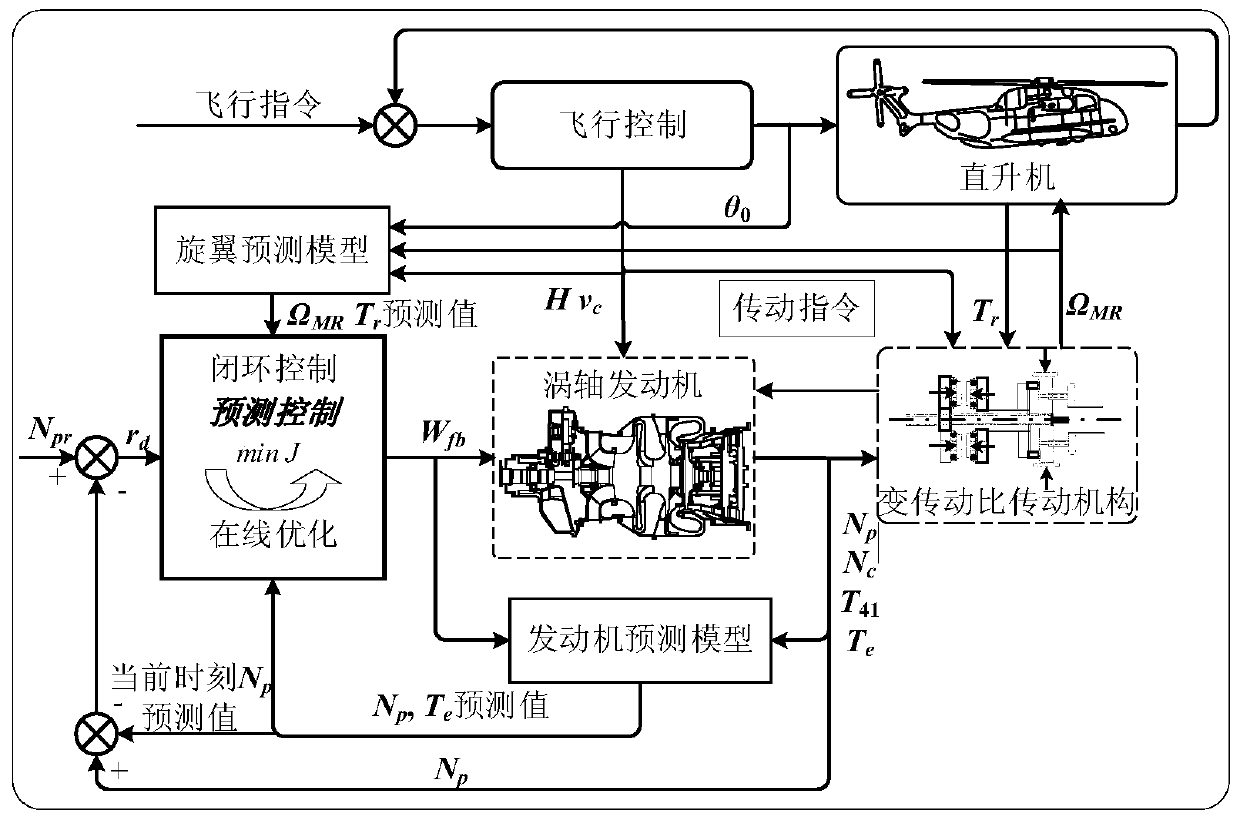
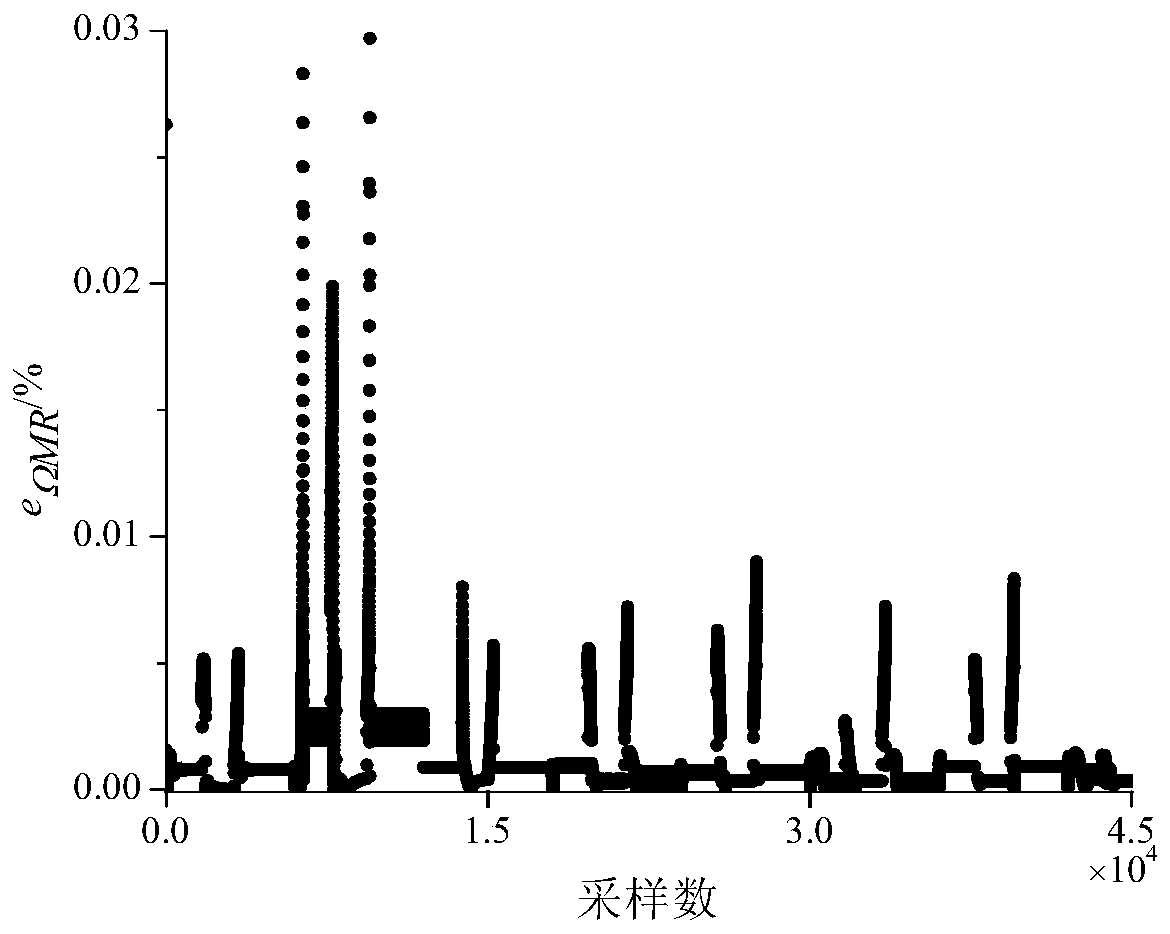
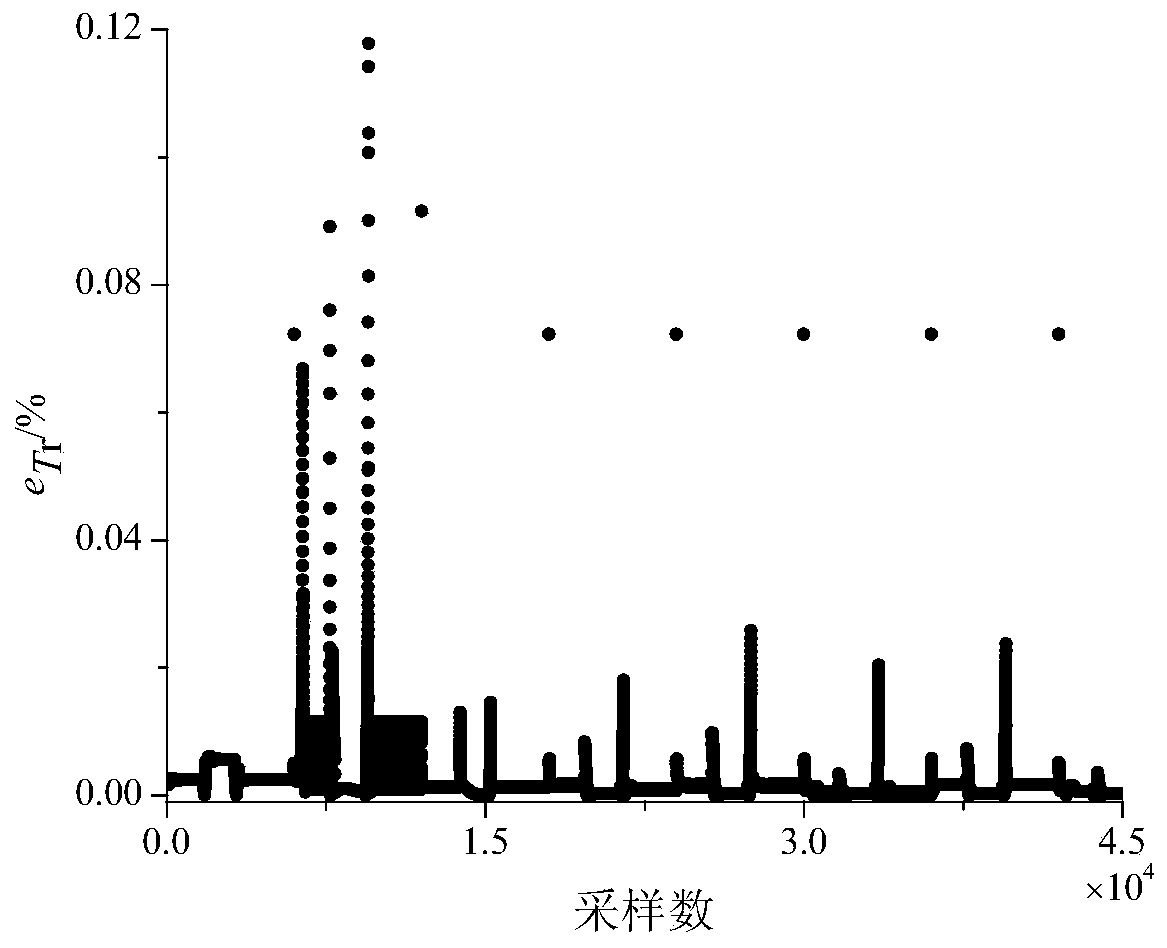
Variable rotor speed helicopter-vortex engine integrated control method and device
InactiveCN109896026AQuick Response ControlExtended service lifeAircraft power plantsSpecial data processing applicationsStatic strengthResponse control
The invention discloses a variable rotor speed helicopter-vortex engine integrated control method. The variable rotor speed helicopter-vortex engine integrated control method is characterized in thaton-line optimization of fuel flow rate of a turboshaft engine is carried out on the basis of comprehensive consideration of a speed control index and rotor dynamic characteristics of matching torque through a variable transmission ratio transmission mechanism; under the conditions of satisfying various restrictions such as compressor speed and engine static strength, speed overshoot and sag of a power turbine in the process of variable rotor speed can be significantly reduced, and not only is fast response control of the turboshaft engine realized, but also the service life of the engine is prolonged. Further disclosed is a variable rotor speed helicopter-vortex engine integrated control device. The variable rotor speed helicopter-vortex engine integrated control method and the device thereof have the advantages of significantly reducing the speed overshoot and sag of the power turbine in the process of the variable rotor speed under the conditions of satisfying the various restrictions such as compressor speed and engine static strength, realizing the fast response control of the turboshaft engine, and prolonging the service life of the engine.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
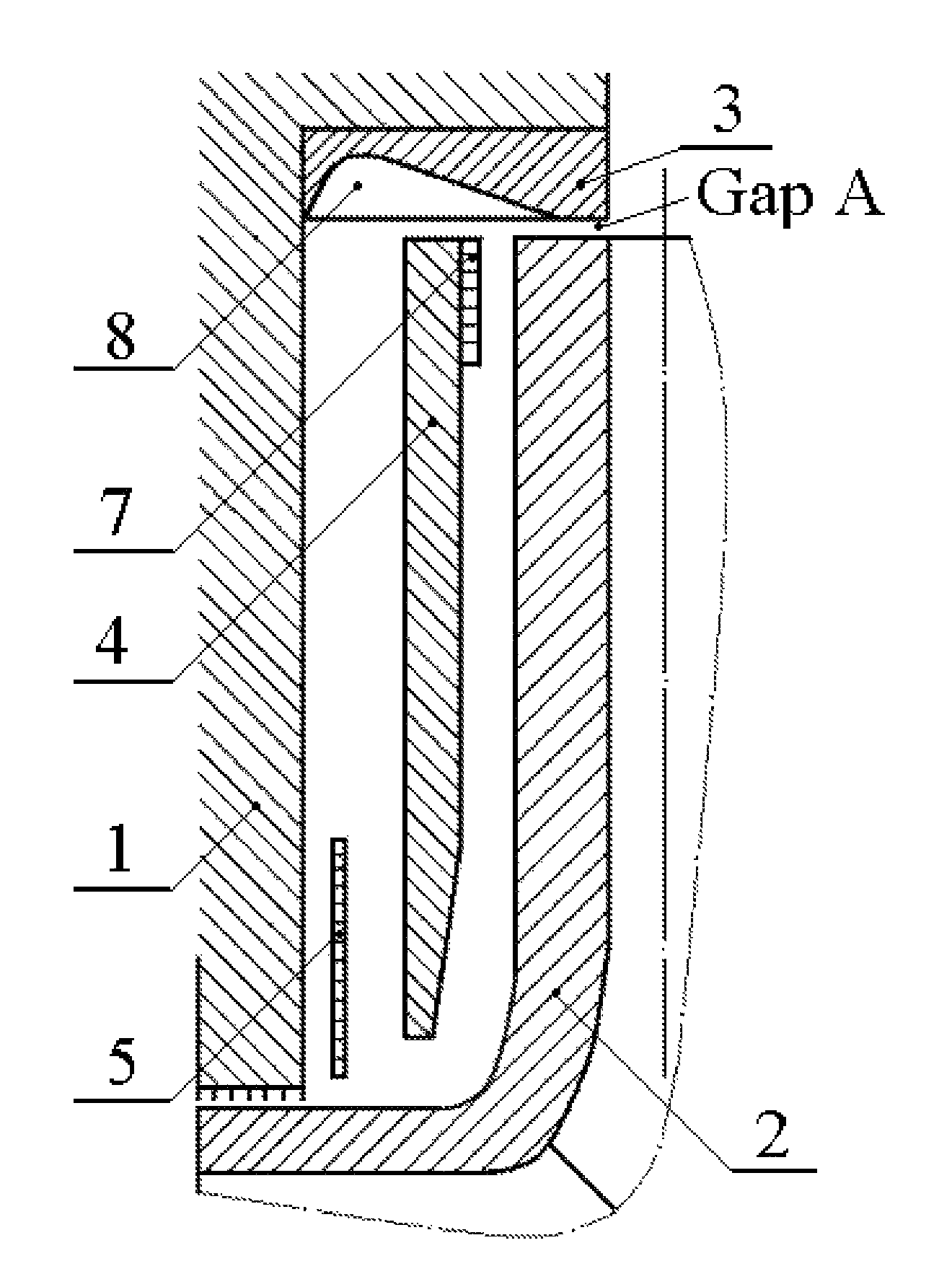
Method and device for reducing axial thrust and radial oscillations and rotary machines using same
A method and apparatus to reduce the axial thrust in rotary machines such as compressors, centrifugal pumps, turbines, etc. includes providing additional peripheral restrictive means (7) attached at the peripheral portion of the disk forming the subdividing means (4) on the side facing the rotating rotor (2). An additional ring element at the periphery of the subdividing means forms additional radial (11) and axial restrictive means (15). Such peripheral restrictive means (7, 11 and 15) function as sealing dams, which combined with the outward flow induced by the rotating impeller, form self-pressurizing hydrodynamic bearings in the axial and radial planes, improving rotordynamic stability. Additionally, a stationary ring element in the center of the cavity forms a seal with the rotor, reducing leakage to suction.
Owner:TECH COMMLIZATION
Monostable radial magnetic bearing with low power consumption and zero gravity action
The invention relates to a monostable radial magnetic bearing with low power consumption and a zero gravity action, which belongs to the field of magnetic suspension bearings and comprises an outer magnetic conduction ring, an outer magnetic isolation ring, an iron core of a stator, an excitation coil, an inner permanent magnetism ring with axial magnetization, an iron core of a rotor, an inner magnetic isolation ring, an inner magnetic conduction ring, inner permanent magnetism rings with radial magnetization, an outer permanent magnetism semiring with axial magnetization, an air gap and a rotor shaft. The iron core of the stator comprises electromagnetic iron cores and permanent-magnetism iron core rings, which form total eight electromagnetic poles at the left end and the right end of the bearing and four semicircular ring type permanent magnetism poles together, wherein the two upper semicircular rings generate attractive force, and the two lower semicircular rings generate repulsive force. In the negative direction of the Y axis of the stator, the outer permanent magnetism semiring with axial magnetization is clamped between the two permanent-magnetism iron core rings of the stator by the outer magnetic conduction ring, the inside of the iron core of the stator is provided with the iron core of the rotor and the inner permanent magnetism rings with radial magnetization, the iron core of the rotor is positioned in the middle, the inner permanent magnetism rings with radial magnetization are positioned at both ends, the middle of the inner magnetic conduction ring is clamped with the inner permanent magnetism ring with axial magnetization, and the air gap is arranged between the inner surface of the stator and the outer surface of the rotor.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and device for reducing axial thrust and radial oscillations and rotary machines using same
ActiveUS20080181762A1Increase pressureReduce thrustPump componentsRotary non-positive displacement pumpsRadial planeAxial thrust
A method and apparatus to reduce the axial thrust in rotary machines such as compressors, centrifugal pumps, turbines, etc. includes providing additional peripheral restrictive means (7) attached at the peripheral portion of the disk forming the subdividing means (4) on the side facing the rotating rotor (2). An additional ring element at the periphery of the subdividing means forms additional radial (11) and axial restrictive means (15). Such peripheral restrictive means (7, 11 and 15) function as sealing dams, which combined with the outward flow induced by the rotating impeller, form self-pressurizing hydrodynamic bearings in the axial and radial planes, improving rotordynamic stability. Additionally, a stationary ring element in the center of the cavity forms a seal with the rotor, reducing leakage to suction.
Owner:TECH COMMLIZATION
Vertical turbocharger
ActiveCN103277184AExtend your lifeImprove reliabilityInternal combustion piston enginesEngine componentsTurbochargerAxial thrust
The invention provides a vertical turbocharger. The vertical turbocharger comprises an air compressor, a middle body, a rotor shaft, a turbine, a sealing ring and a non-liquid oil lubrication bearing, wherein the rotor shaft is perpendicular to the ground, the air compressor and the turbine are arranged at the upper end and the lower end of the rotor shaft respectively, an axial thrust bearing is arranged between the lower end of the rotor shaft and a turbine shell of the turbine, the middle body is arranged between the air compressor and the turbine, the two ends of the middle body are respectively connected with the air compressor and the turbine, the middle body is matched with the rotor shaft through the non-liquid oil lubrication bearing, the sealing ring is arranged between the end, close to the turbine, of the middle body and the rotor shaft, an air inlet of the air compressor and an air inlet of the turbine are both radial air inlets, and an air outlet of the air compressor and an air outlet of the turbine are both radial air outlets. The vertical turbocharger eliminates the influences of the gravity of a rotor on system stability, improves dynamics performance of the turbocharger, and improves the pneumatic efficiency, the pressure ratio and the mechanical efficiency. Compared with a traditional turbocharger, the vertical turbocharger is more compact in structure, and smaller in gas flow loss.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
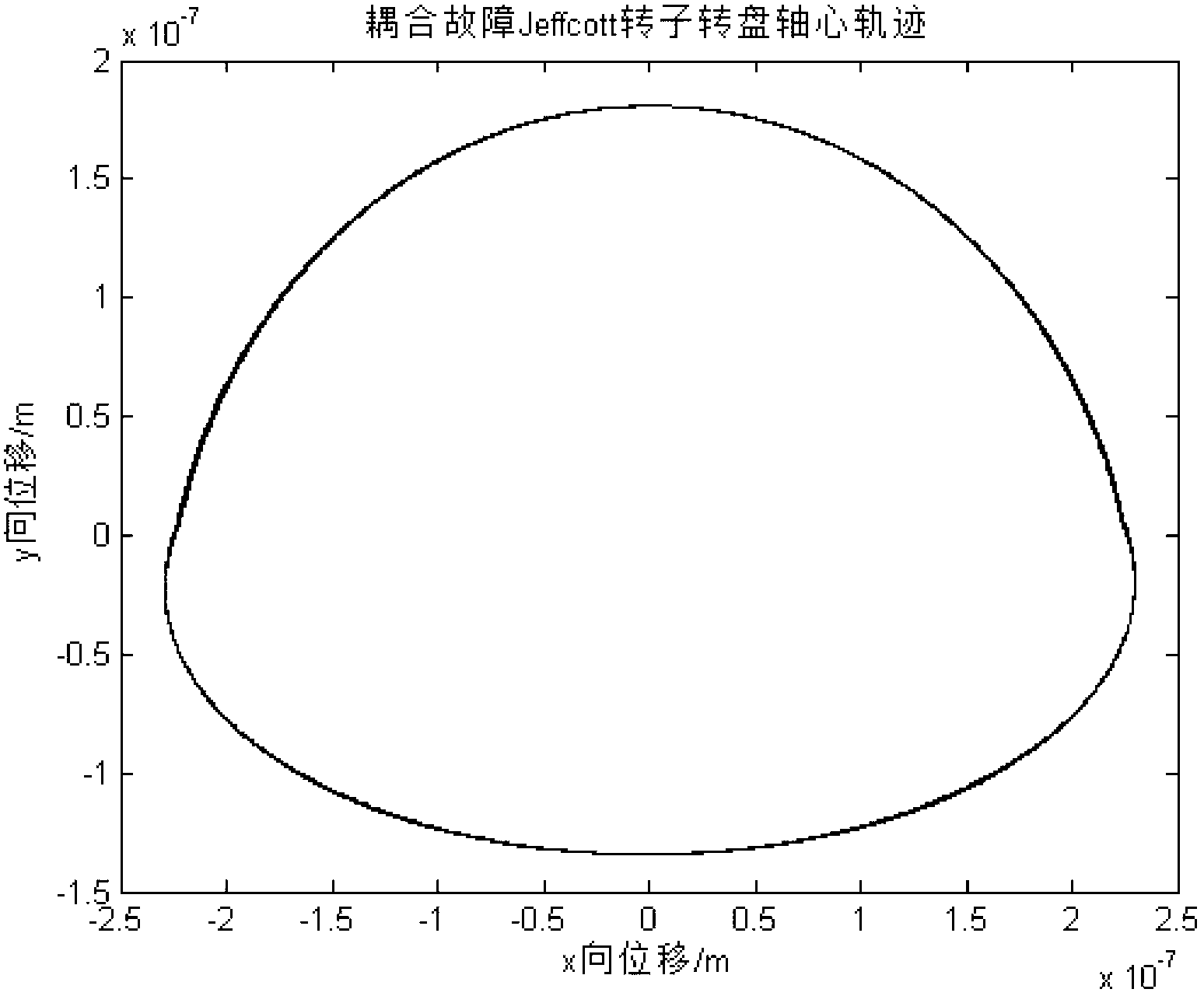
Method for analyzing dynamics of aviation multi-rotor coupling system
InactiveCN102201033AAccurate descriptionHigh precisionMachine gearing/transmission testingEngine testingAviationFinite element method
The invention discloses a method for analyzing dynamics of an aviation multi-rotor coupling system, and belongs to the field of rotor dynamics. By means of an idea of finite element method to solve problems, the method comprises the following steps: separating the aviation multi-rotor coupling system at coupling parts to form independent rotors; taking each rotor as a unit, and taking the coupling force of each coupling part as an external force of the unit of the coupling part to obtain a dynamic differential equation of each unit; analyzing the coupling force of each coupling part ob acquire a coupling matrix and an equation of the coupling force; and leading the dynamic differential equation of each unit and the equation of the coupling force of each unit to be simultaneous to obtain a dynamic differential equation of the aviation multi-rotor coupling system, and solving to acquire the dynamic characteristics of the aviation multi-rotor coupling system. The method is clear in thread, simple and standard in expression, and suitable for analysis on dynamics of the aviation multi-rotor coupling system, can accurately describe the coupling parts, and improves the accuracy of calculation results.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method
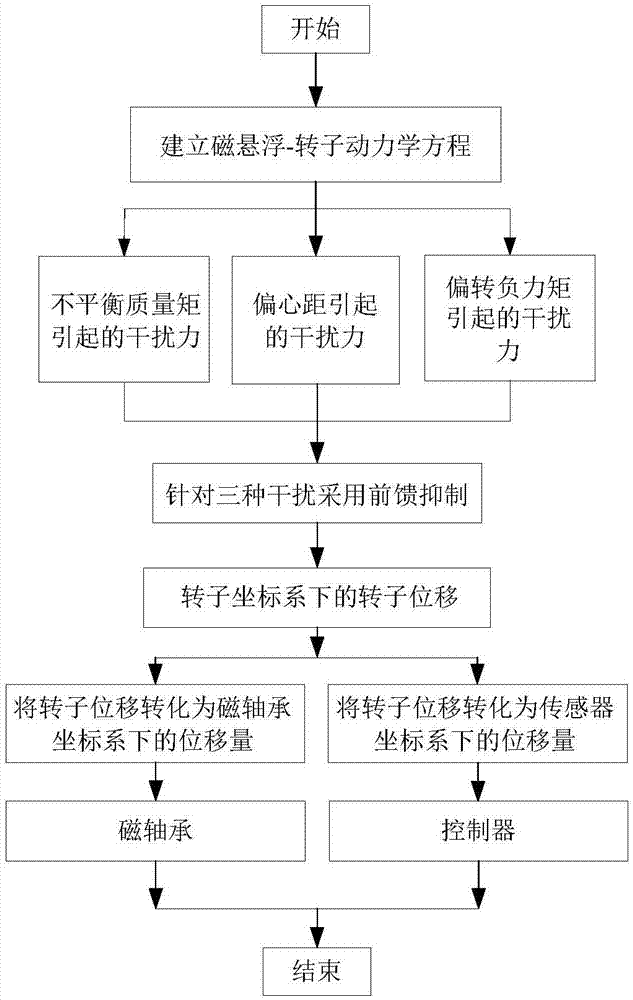
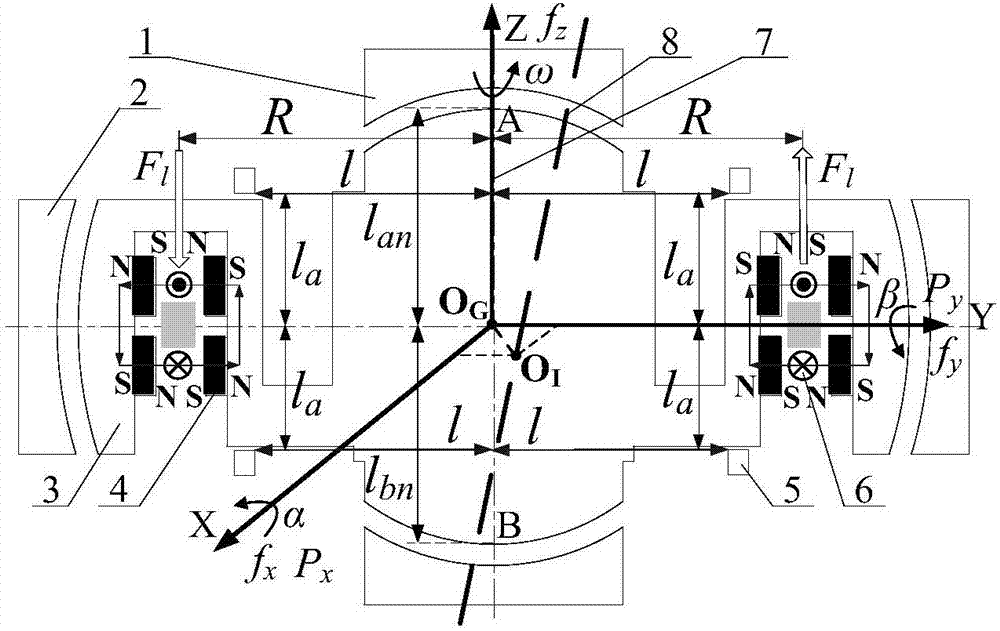
The present invention relates to a magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method. The Newton's second law and the gyro technique equation are employed to establish a magnetic bearing-rotor dynamics equation, based on the D'Alembert's principle, the disturbing force of imbalance mass moment on a rotor caused by deviation of rotor inertial axis from a geometrical axis, the disturbing force of the eccentricity on the rotor caused by the deviation of the rotor mass center from the geometrical axis and the disturbing force of the deflection negative moment on the rotor caused by suspension force passing through the rotor centroid and not passing through the rotor mass center are obtained. Rotor displacement amounts under the three disturbing forces are converted to the displacement amount under a sensor coordinate system and the displacement amount under a magnetic bearing coordinate system through a conversion matrix, the two displacement amounts are respectively acted in the controller and the magnetic bearing, and the feedforward inhibition method is employed to perform inhibition of the three disturbing forces. The magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method can effectively improve the control precision of the imbalance vibration of the magnetic bearing-rotor system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Permanent magnet spherical motor point-to-point motion track planning method based on sine acceleration function and application thereof
ActiveCN106292337AAchieve basic movementPoint to point movement is simpleSimulator controlResearch ObjectDynamic equation
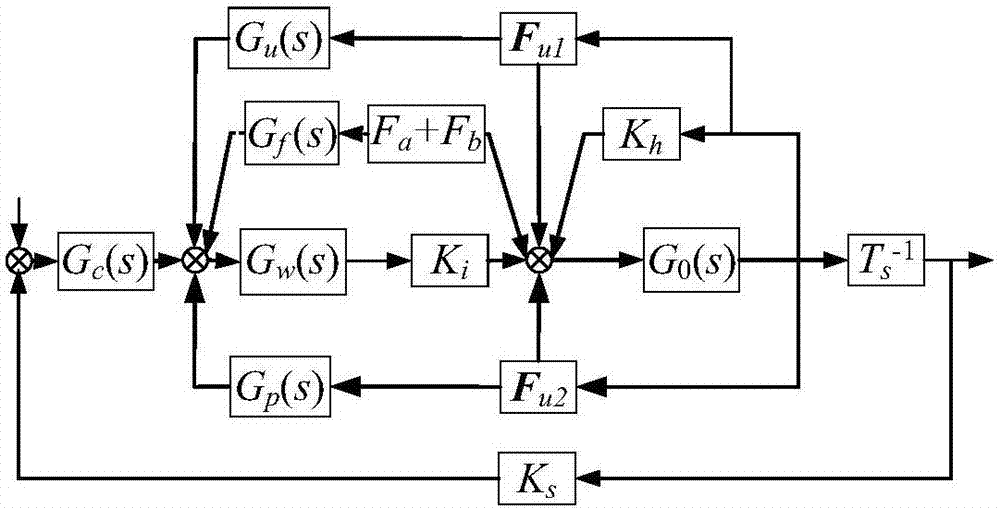
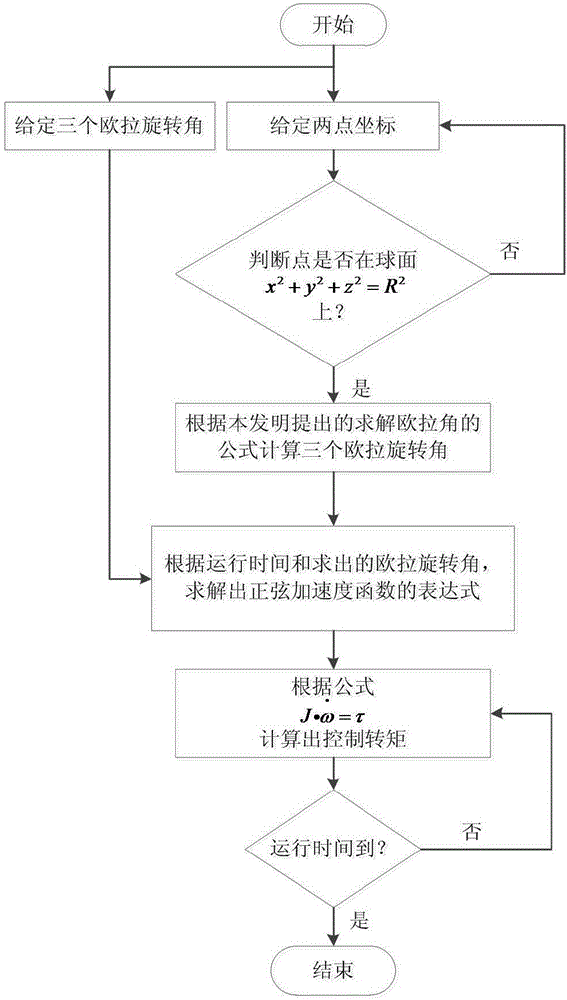
The invention discloses a permanent magnet spherical motor point-to-point motion track planning method based on a sine acceleration function and application thereof. The method is characterized in that a permanent magnet spherical motor rotor is regarded as a research object, firstly a Euler rotation angle or coordinates of two points are given, and the Euler rotation angle is inversely solved by adopting a method of reversely solving the Euler rotation angle according to the coordinates of the two points; then, an expression of the sine acceleration function is solved according to the operating time and initial conditions, and finally a final control torque is obtained according to a rotor dynamics equation. By the adoption of the method, permanent magnet spherical motor point-to-point motion track planning is achieved, the method is applied to complicated and continuous track planning, the adverse influence of input signal impact, non-continuous change and other factors on a control object can be effectively reduced, and accordingly the control accuracy of a control system and the stability of motor operation are improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Rotor structure of magnetic levitation ultra high speed permanent magnet motor
PendingCN106972658AReduce weightReduce maximum stressMagnetic circuit rotating partsMechanical energy handlingUltra high speedMagnetic bearing
The invention relates to a rotor structure of a magnetic levitation ultra high speed permanent magnet motor. The rotor structure comprises a thrust disc shaft, a sheath, a permanent magnet, a shaft, a first magnetic bearing assembly and a second magnetic bearing assembly, wherein the thrust disc shaft comprises a left shaft and a thrust disc, the thrust disc is a solid structure, the portion of the thrust disc shaft contacting with the permanent magnet is a hollow structure, the permanent magnet is a cylindrical structure, and the thrust disc and the left shaft are integrated into body and are prepared from a magnetic conduction metal material with high yield strength. The position corresponding to the thrust disc is must a solid structure, the maximum centrifugation stress can be reduced by half, the portion of the thrust disc shaft contacting with the permanent magnet is must the hollow structure, so the short circuit effect on a permanent magnet magnetic field can be reduced; the other portion of the thrust disc shaft is made to be a hollow structure, so weight of the shaft is reduced; the thrust disc and the partial hollow shaft are the integrated structure, the maximum stress of the center of the thrust disc can be substantially reduced, rotor linear velocity and rotor dynamics characteristics of the magnetic levitation ultra high speed permanent magnet motor are improved, and bearing capability of the magnetic bearing is further reduced.
Owner:天津飞旋高速电机科技有限公司 +1
Vertical combustion gas turbine
ActiveCN103321748AImprove dynamic performanceAvoid stabilityBlade accessoriesGas turbine plantsImpellerAxial compressor
The invention provides a vertical combustion gas turbine. The vertical combustion gas turbine comprises a combustion gas turbine shell, and a gas compressor, a combustion chamber, a gas turbine, a rotary shaft and non-liquid oil lubricating bearings which are located inside the combustion gas turbine shell, wherein the rotary shaft is arranged in a manner of being vertical to the ground; the pressure machine and the gas turbine are respectively mounted at the two ends of the rotary shaft through the non-liquid oil lubricating bearings; the combustion chamber is located between the gas compressor and the gas turbine; air inlets and air outlets of the gas compressor and the gas turbine are radial air inlets and radial air outlets. According to the vertical combustion gas turbine disclosed by the invention, the vertical installation of an impeller mechanical rotor is realized; the rotor dynamic performance of an impeller machine is improved, the service life of the impeller machine is prolonged, and the reliability of the impeller machine is improved; a flowing medium flows through all parts in a manner of radial air feeding and radial air discharging, so as to reduce the gas flowing swerving loss, realize a high pressure ratio and improve the pneumatic efficiency; an axial pneumatic load is not generated and the axial friction loss is relieved; the mechanical efficiency is improved; the non-liquid oil lubricating bearings are adopted so that the structure is simplified and the axial length of the impeller machine is shortened.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Use of spray coatings to achieve non-uniform seal clearances in turbomachinery
The invention provides spray coatings to achieve circumferentially non-uniform seal clearances in turbomachines. In steam and gas turbines it is desirable to assemble the machines with elliptical seal clearances to compensate for expected casing distortion, rotordynamics or phenomena that cause circumferentially non-uniform rotor-stator rubs. The claimed invention allows the casing hardware to be fabricated round, and a spray coating is applied to the radially inner surface such that the coating thickness varies circumferentially, providing the desired non-uniform rotor-stator clearance during assembly.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
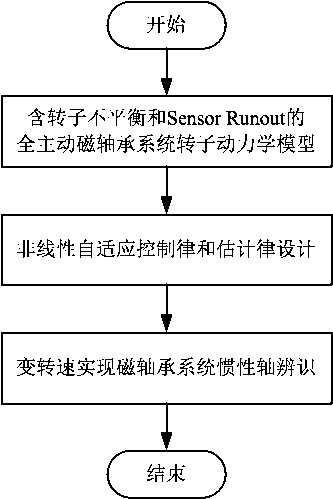
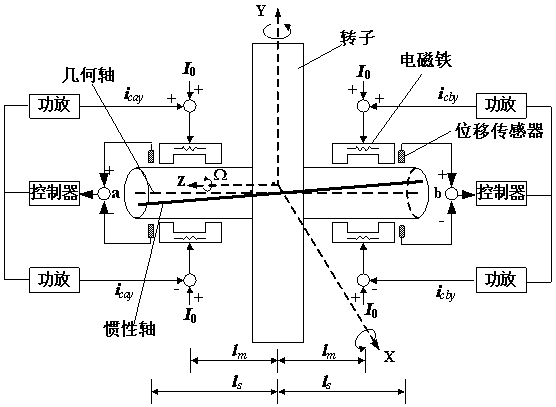
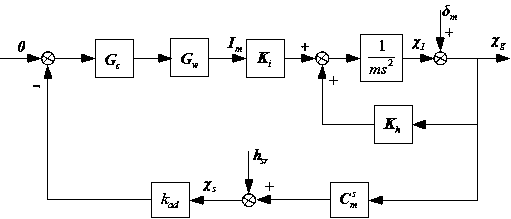
Identifying method for inertia shaft of full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control
InactiveCN107727088AOvercome the disadvantage of large identification errorRealize identificationRotary gyroscopesAdaptive controlMagnetic bearingSystem stability
The invention discloses an identifying method for an inertia shaft of a full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a full-automatic magnetic bearing rotor dynamics model with rotor imbalance and displacement sensor harmonic noise is established; secondarily, a nonlinear self-adaption control rule and estimation rule are provided, the system stability and astringency of estimation parameters are proved, it is guaranteed that a magnetic suspension rotor inertia shaft displacement estimation value is convergent to zero, and meanwhile the high-level harmonic component fourier coefficient of displacement sensor harmonic noise is estimated; then, a variable rotation speed strategy is adopted, the same frequency component of displacement sensor harmonic noise and recognizable degree of rotor imbalance are improved, the fourier coefficient values of two same frequency components are solved, and finallyidentifying for the inertia shaft of the full-automatic magnetic bearing system is achieved. According to the identifying method for the inertia shaft of the full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control, speed raising or speed reduction for one time is only needed, and identifying of the magnetic bearing inertia shaft can be achieved online, so that a magnetic suspension rotor rotates around the inertia shaft.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
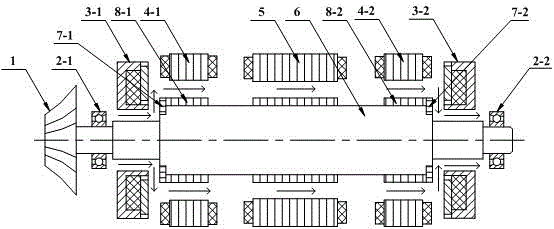
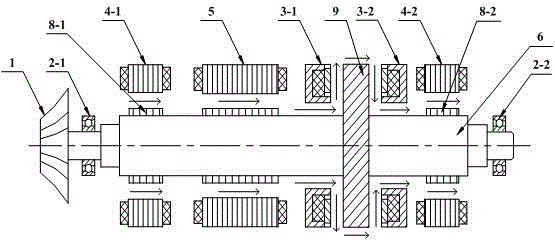
Magnetic suspension motor without thrust disc and work method thereof
ActiveCN106849482ASlow heatingImprove cooling effectMechanical energy handlingCooling/ventillation arrangementRotordynamicsMagnetic levitation
The present invention discloses a magnetic suspension motor without a thrust disc and a work method thereof, and relates to the magnetic suspension motor technology field. The magnetic suspension motor comprises a working machine (1), a left protective bearing (2-1), a left axial direction magnetic suspension bearing (3-1), a left radial direction magnetic suspension bearing (4-1), a high-speed motor (5), a right radial direction magnetic suspension bearing (4-2), a right axial direction magnetic suspension bearing (3-2), a right protective bearing (2-2) and a rotor mandrel (6). The electromagnetic force between the radial direction magnetic suspension bearings and radial direction permeability magnetic materials (8) and the electromagnetic force between the axial direction magnetic suspension bearings and radial direction permeability magnetic materials (7) perform active control of radial direction displacement and axial direction displacement of the rotor mandrel (6). The magnetic suspension motor without a thrust disc and a work method thereof omit a thrust disc (9) to facilitate assembling and cooling of the magnetic suspension motor, and the rotor dynamics performance can satisfy the requirement of high-speed rotation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
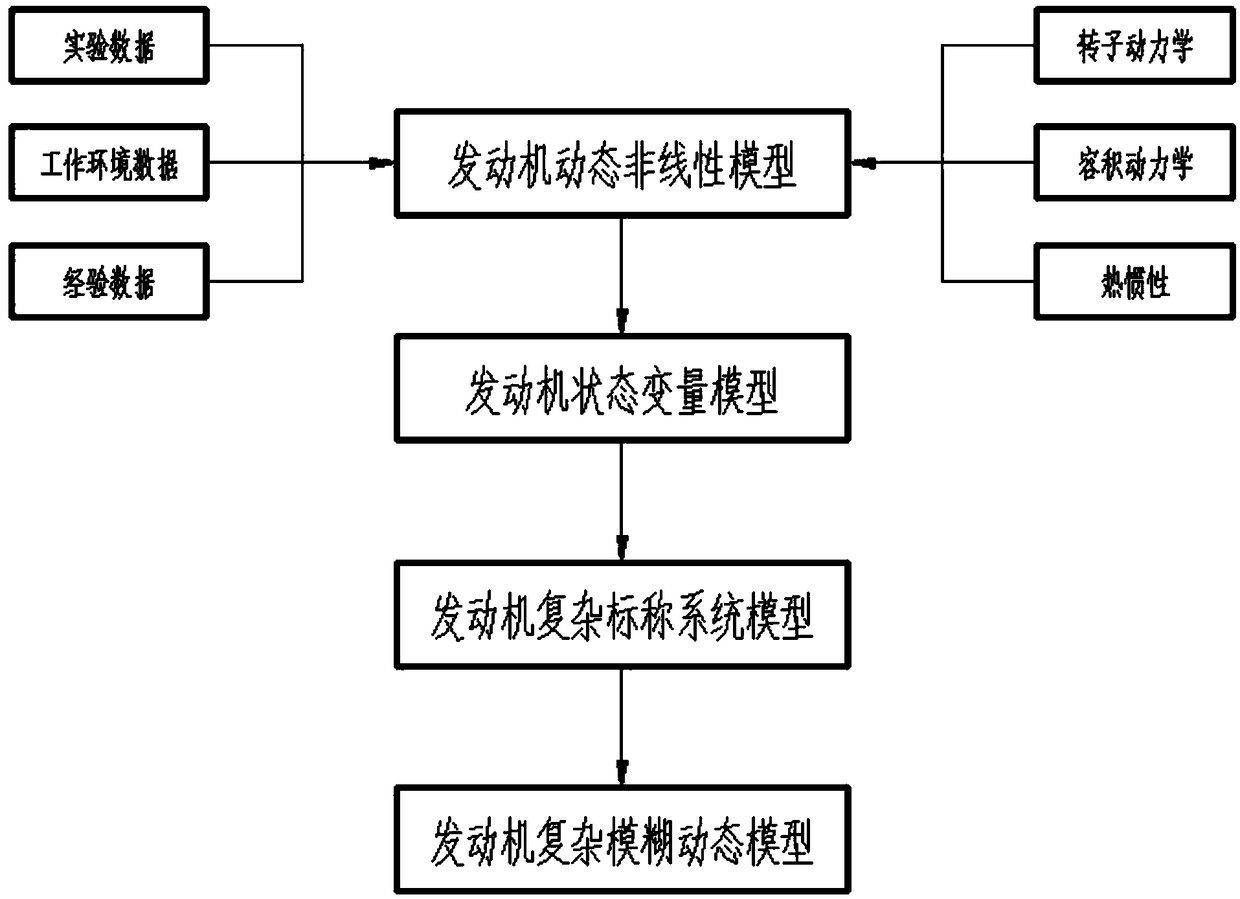
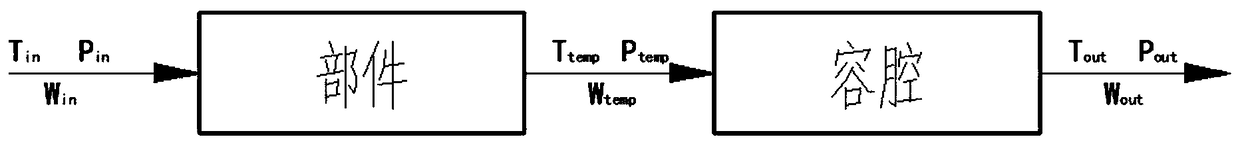
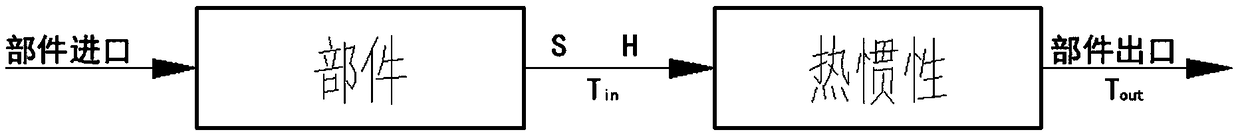
Aero-engine time lag-containing non-determinacy fuzzy dynamic model modeling method
The invention discloses an aero-engine time lag-containing non-determinacy fuzzy dynamic model modeling method comprising the following steps: 1, building an engine multi-dynamics component-level model; 2, building an engine state variable model; 3, building a nominal system model; 4, building an engine fuzzy dynamic model based on a fuzzy theory. The method employs rotordynamics, volume dynamicsand heat transfer theory methods to build an aero-engine nonlinear component-level model; the component-level model modeling method adds the model dynamic information, avoids massive iteration solvingprocess, and improves the model calculation speed and timeliness; the method employs a heredity algorithm to modify design points and non-design points of the aero-engine nonlinear component-level model, and employs the heredity algorithm to modify the aero-engine rotor component flow and an efficiency modification factor, so the design point parameter relative error is kept within 1%, the non-design point parameter relative error is kept within 2%, and the temperature change scope is within 10K.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for operating a turbine
InactiveUS6792760B2Inhibition effectPrevent speedingTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionTurbine/propulsion engine startersLoop controlClosed loop
A method of operating a turbine arranged in a compressed air energy storage power generation plant comprises an open-loop control of an air mass flow applied within a lower turbine speed range and a closed-loop control of the turbine speed within a higher turbine speed range. The open-loop control comprises the control of the air mass flow by means of air inlet valves and a free development of the turbine speed. The closed-loop control comprises the control of the turbine speed by means of a speed controller, which is acted upon by a speed limiting value determined according to the current air mass flow and a windage calculation. The speed controller activates a static frequency converter in the case that the turbine speed reaches values that are critical with respect to turbine windage or rotor dynamics.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com