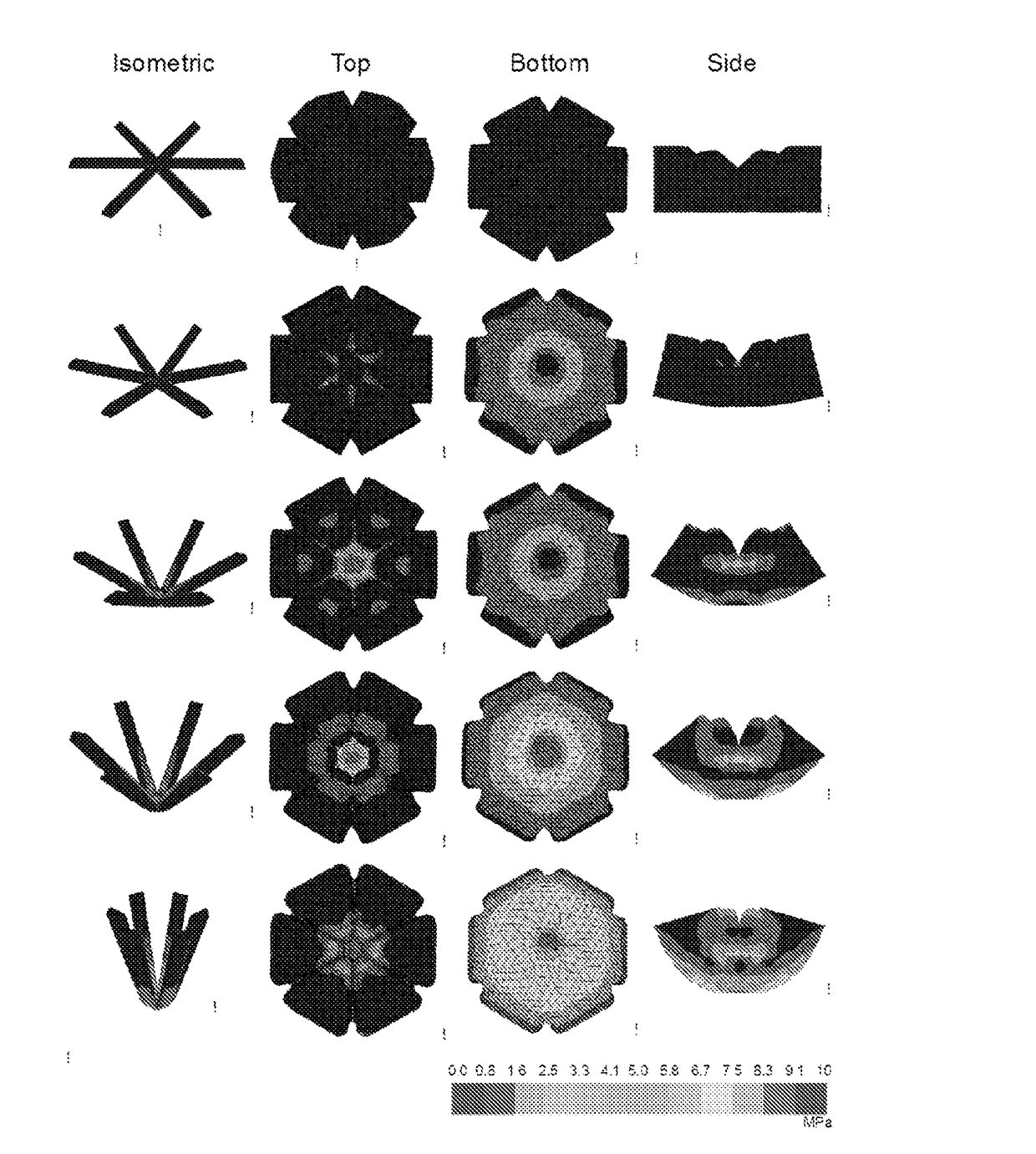
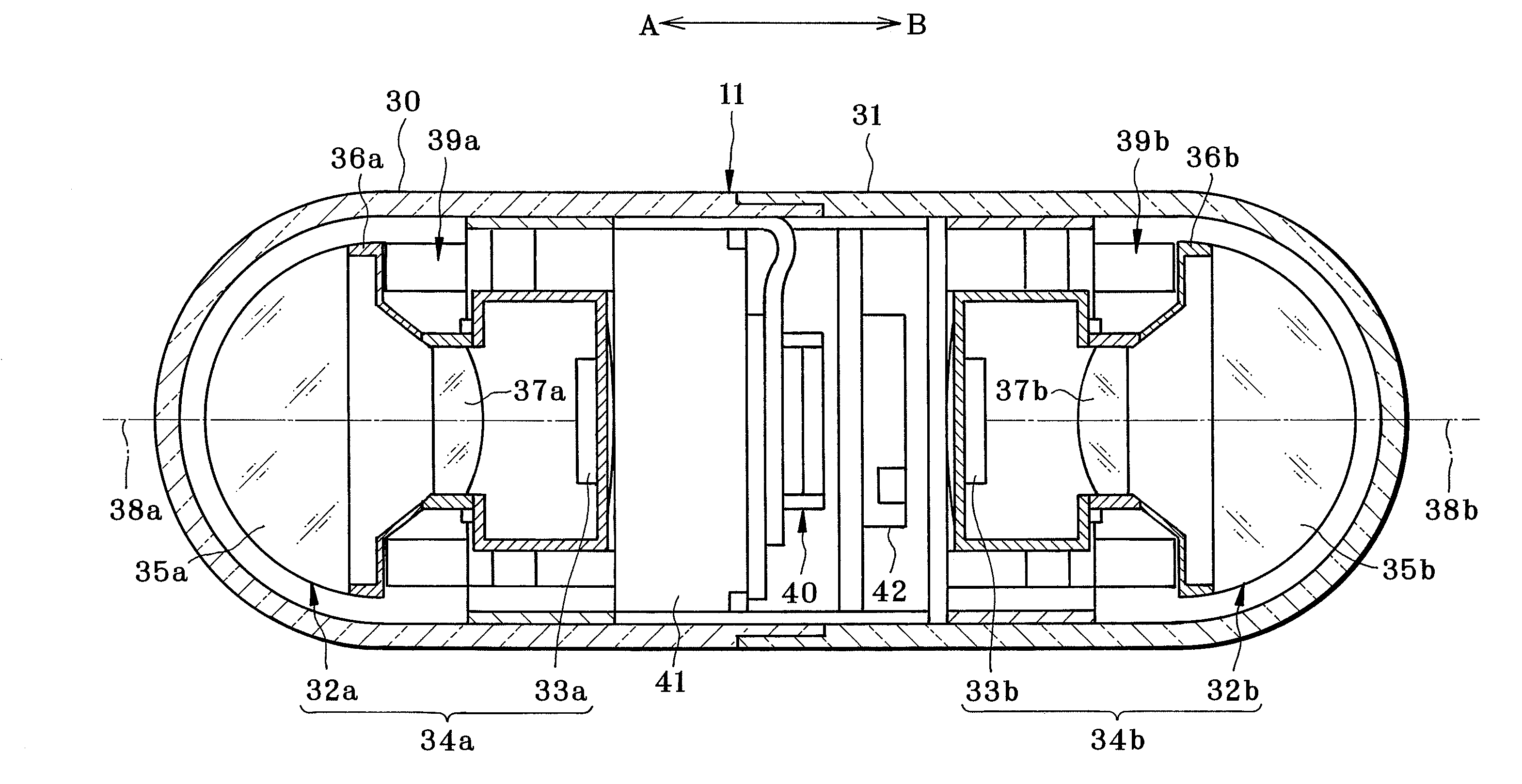
Patents
Literature
113 results about "Via gastrointestinal tract" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
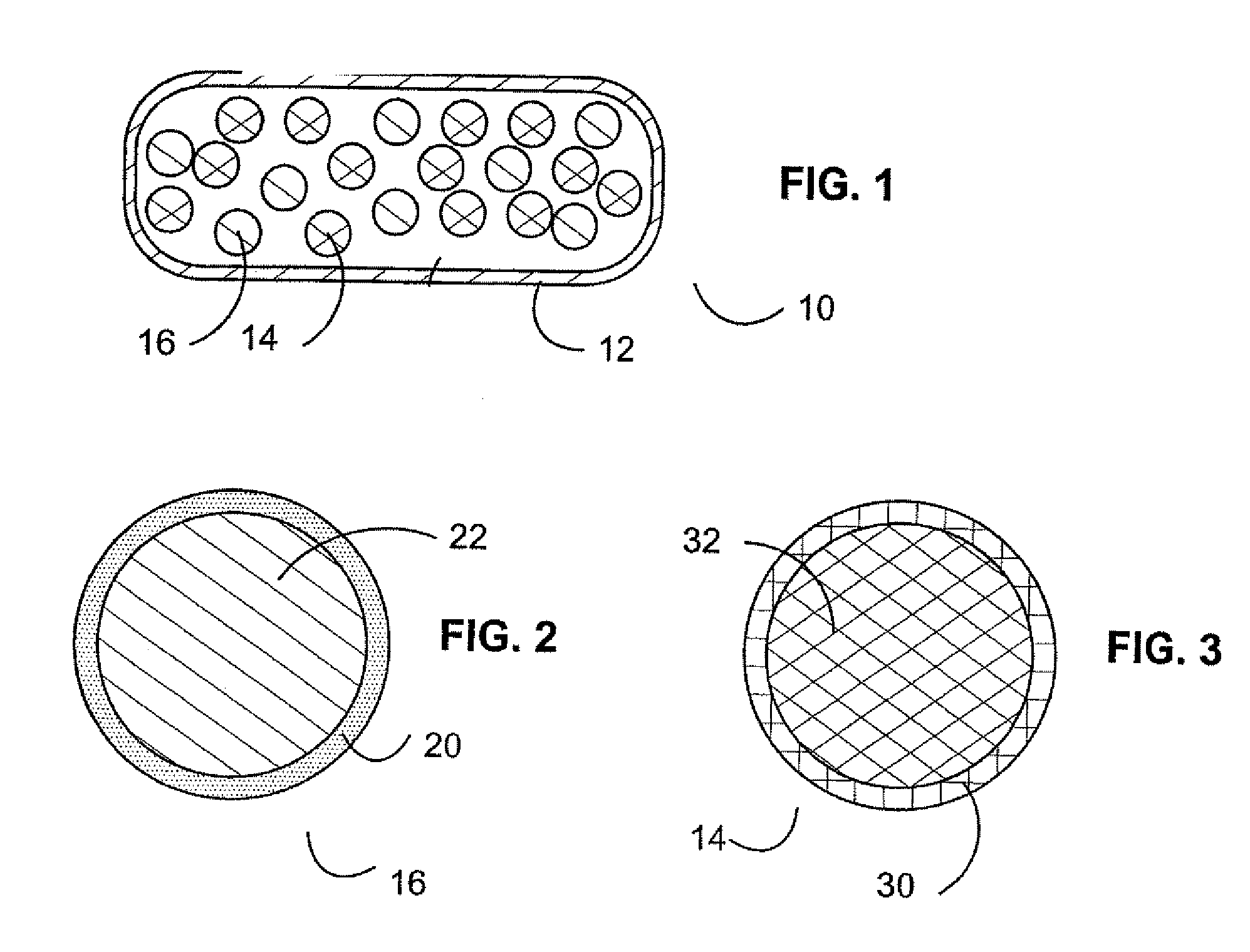
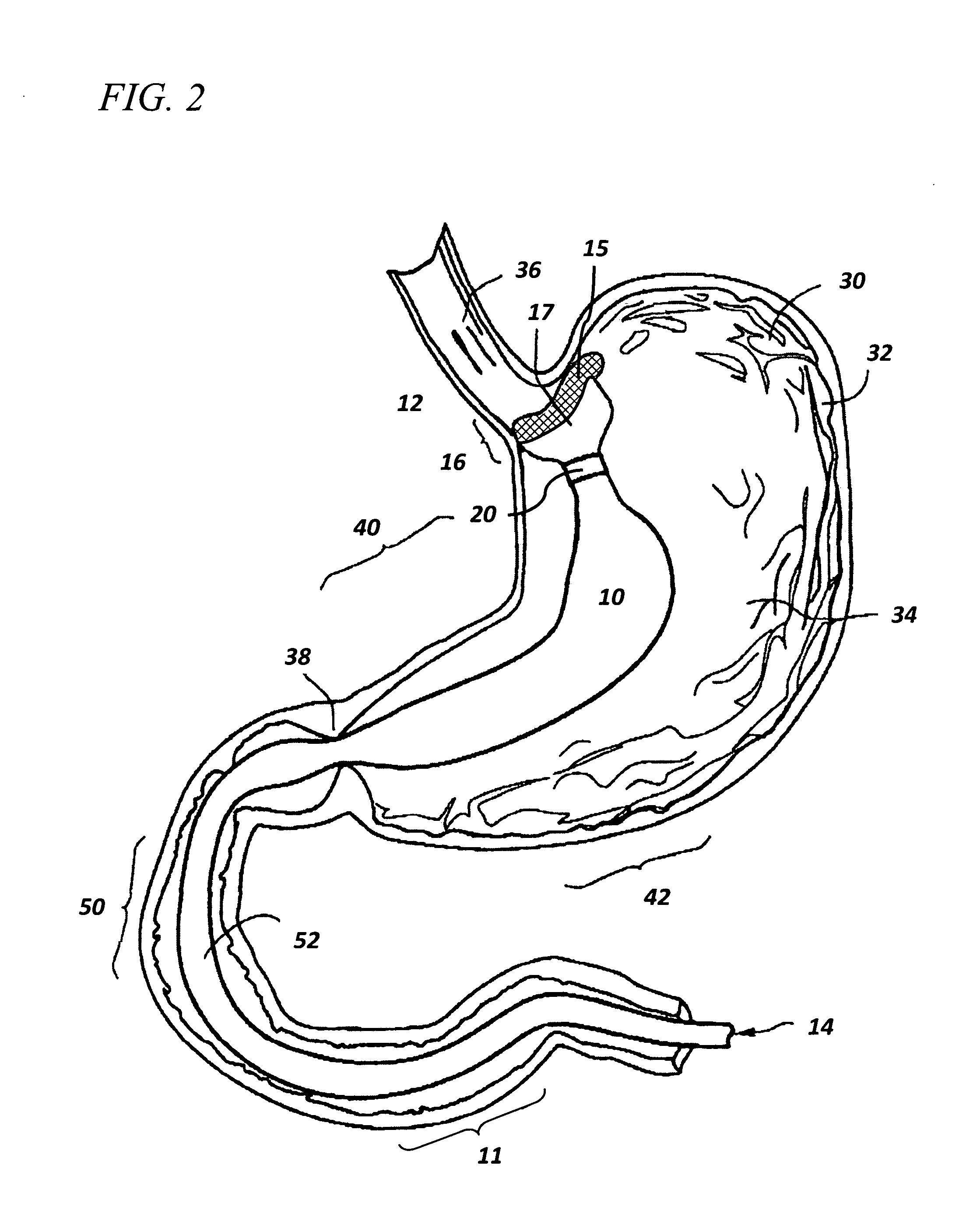
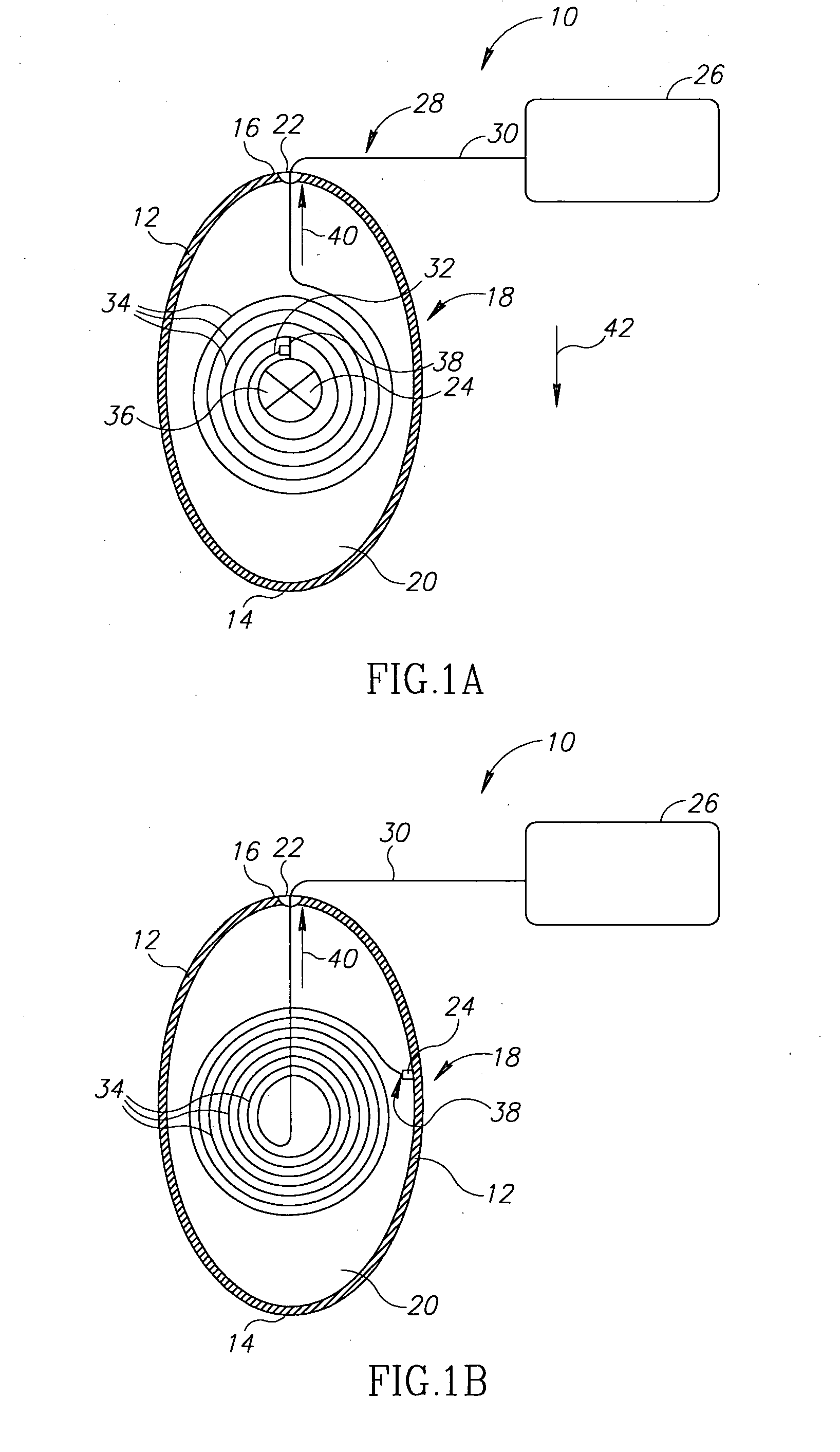
Controlled regional oral delivery
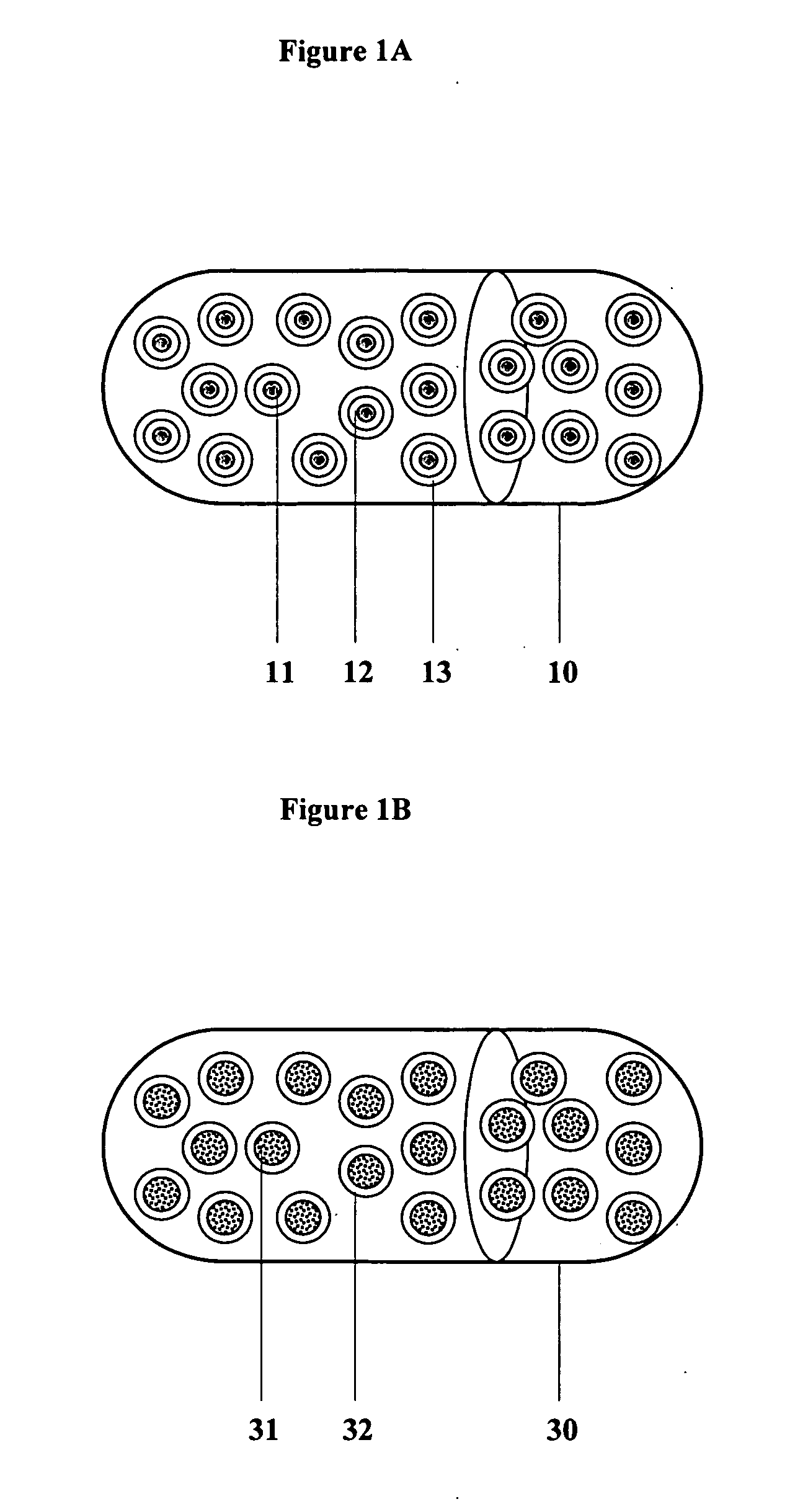
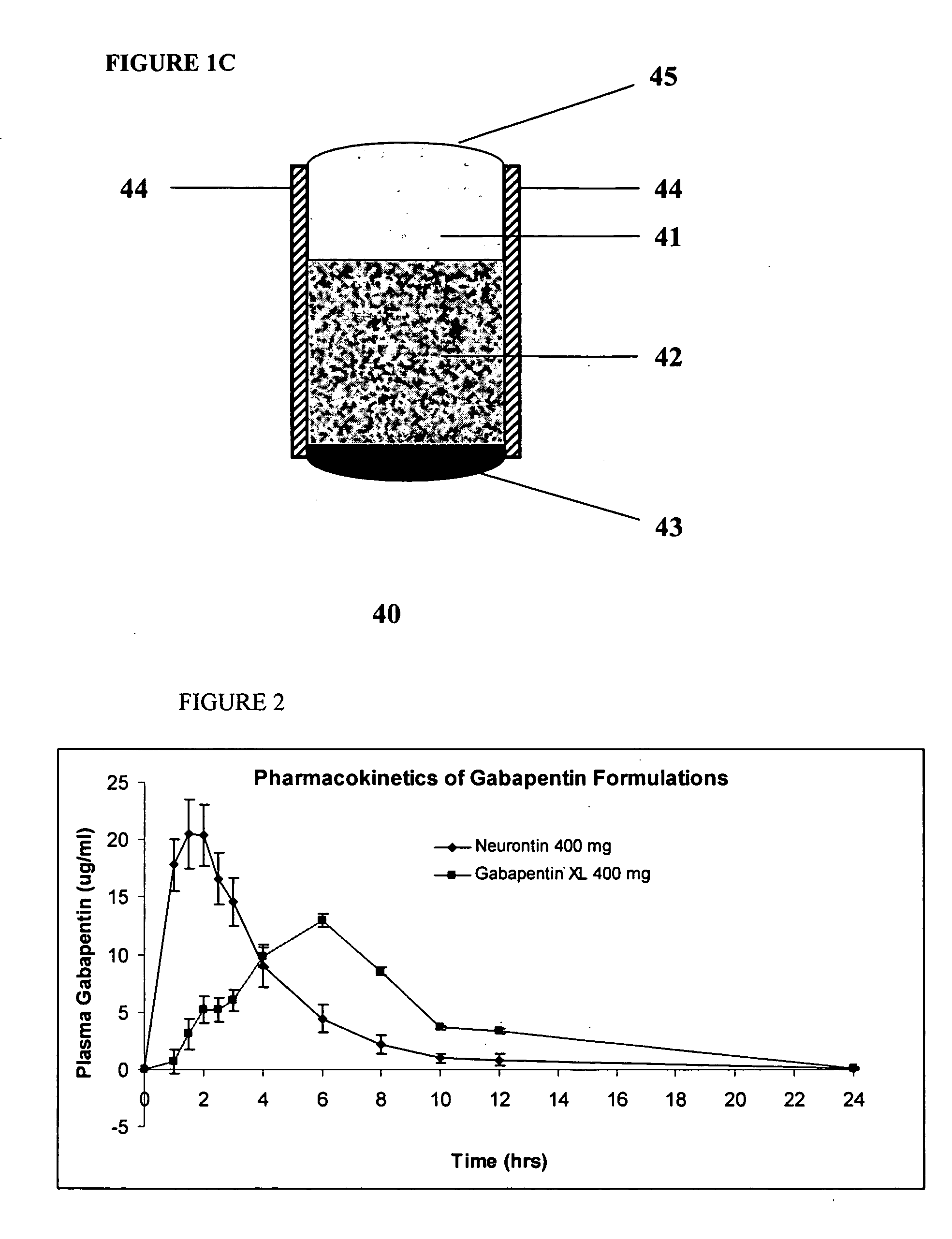
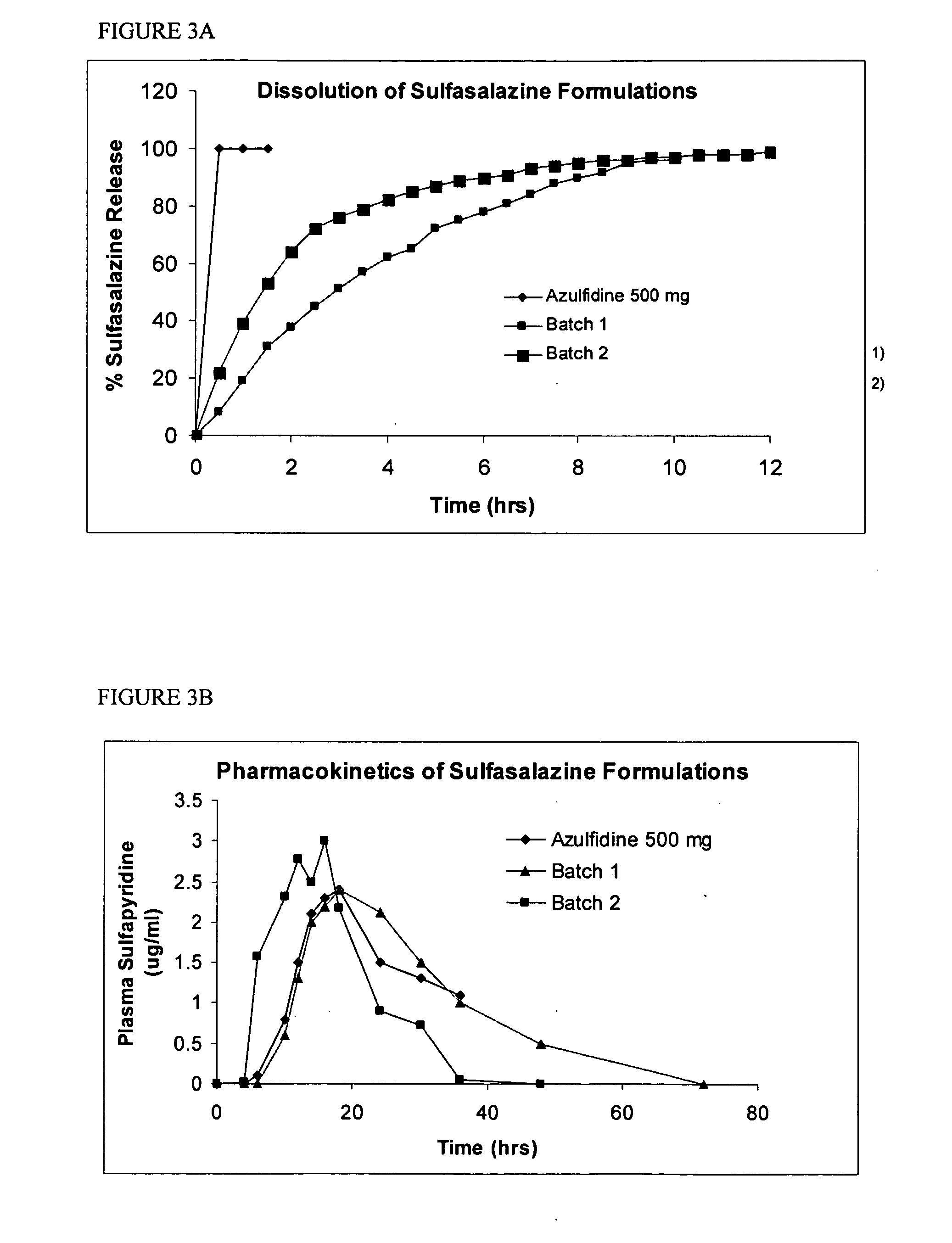
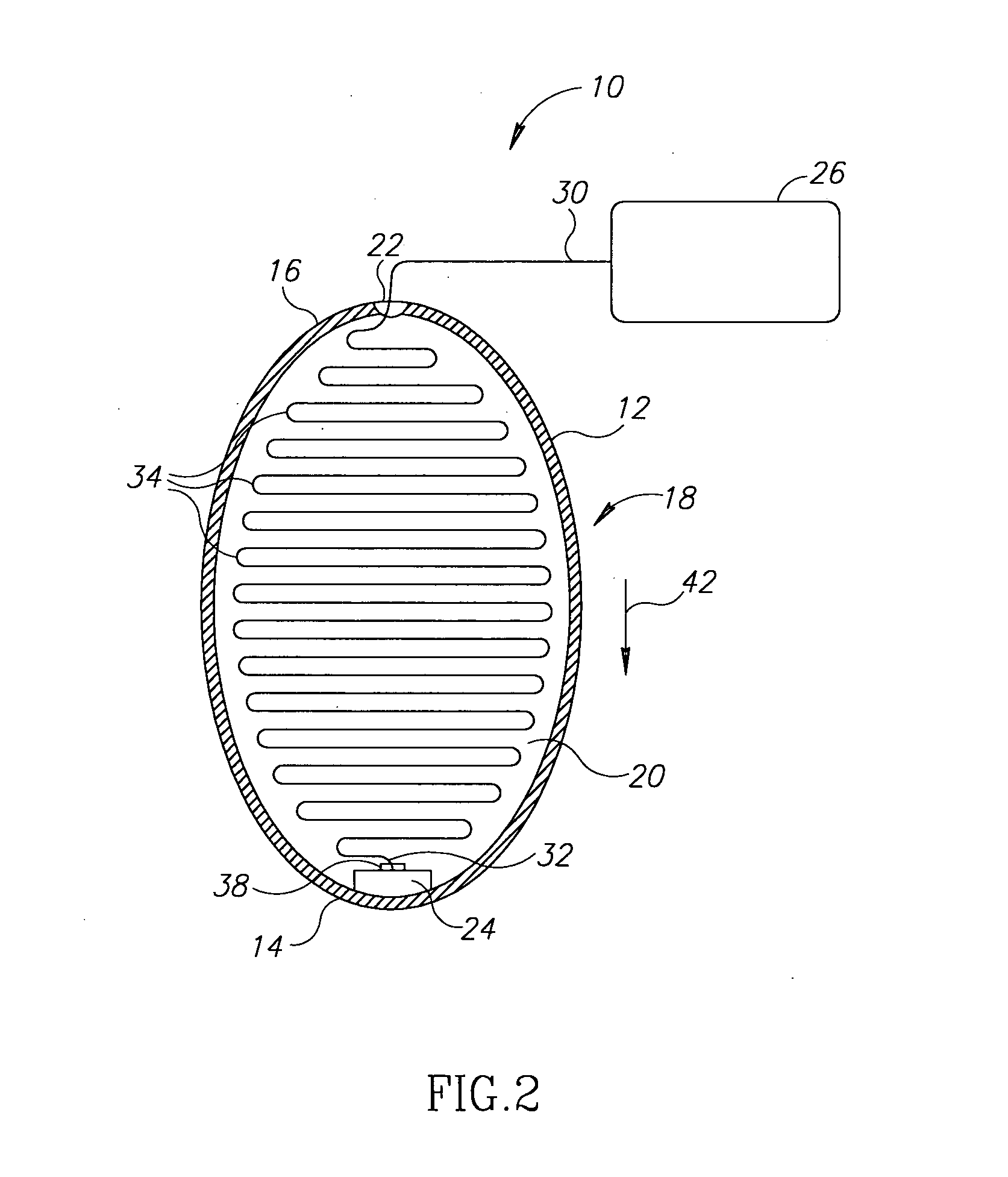
InactiveUS20060045865A1Significant variabilityLow variabilityPill deliveryGranular deliverySolubilityGabapentin
A composite formulation has been developed for selective, high efficacy delivery to specific regions of the mouth and gastrointestinal tract. The formulation is typically in the form of a tablet or capsule, which may include microparticles or beads. The formulation uses bioadhesive and controlled release elements to direct release to specific regions, where the drug is absorbed in enhanced amounts relative to the formulation in the absence of the bioadhesive and / or controlled release elements. This is demonstrated by an example showing delivery of gabapentin with a greater area under the curve (“AUC”) relative to the FDA reference immediate release drug, i.e., the AUC of the composite bioadhesive formulation is greater than 100% of the AUC of the immediate release drug. In the preferred embodiments, the formulation includes drug to be delivered, controlled release elements, and one or more bioadhesive elements. The bioadhesive polymer may be either dispersed in the matrix of the tablet or applied as a direct compressed coating to the solid oral dosage form. The controlled release elements are selected to determine the site of release. The bioadhesive components are selected to provide retention of the formulation at the desired site of uptake and administration. By selecting for both release and retention at a specific site, typically based on time of transit through the gastrointestinal tract, one obtains enhanced efficacy of uptake of the drug. This is particularly useful for drugs with narrow windows of absorption, and drugs with poor solubility such as the BCE class III and class IV drugs.
Owner:VAUNNEX
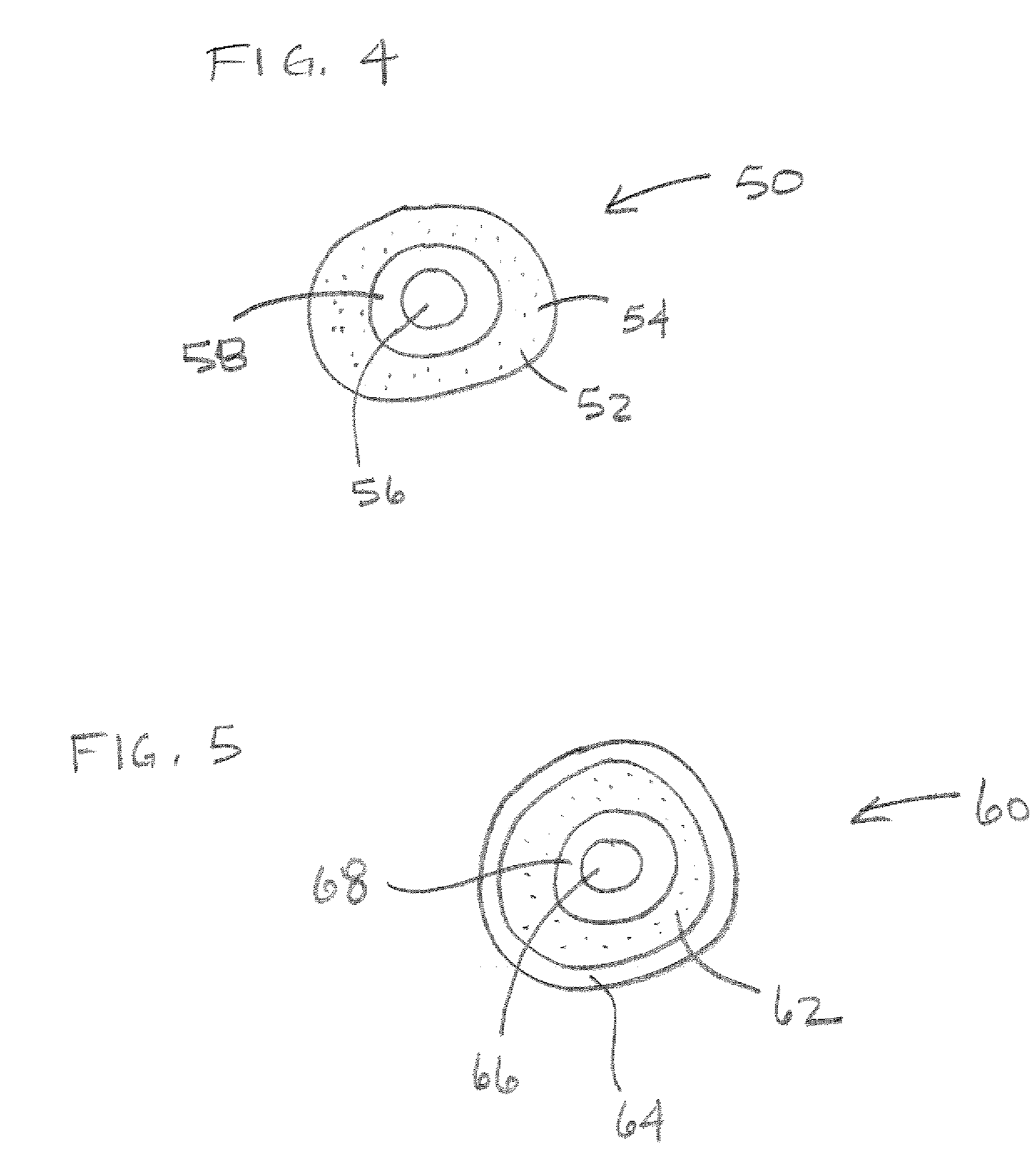
Method for delivering a device to a target location
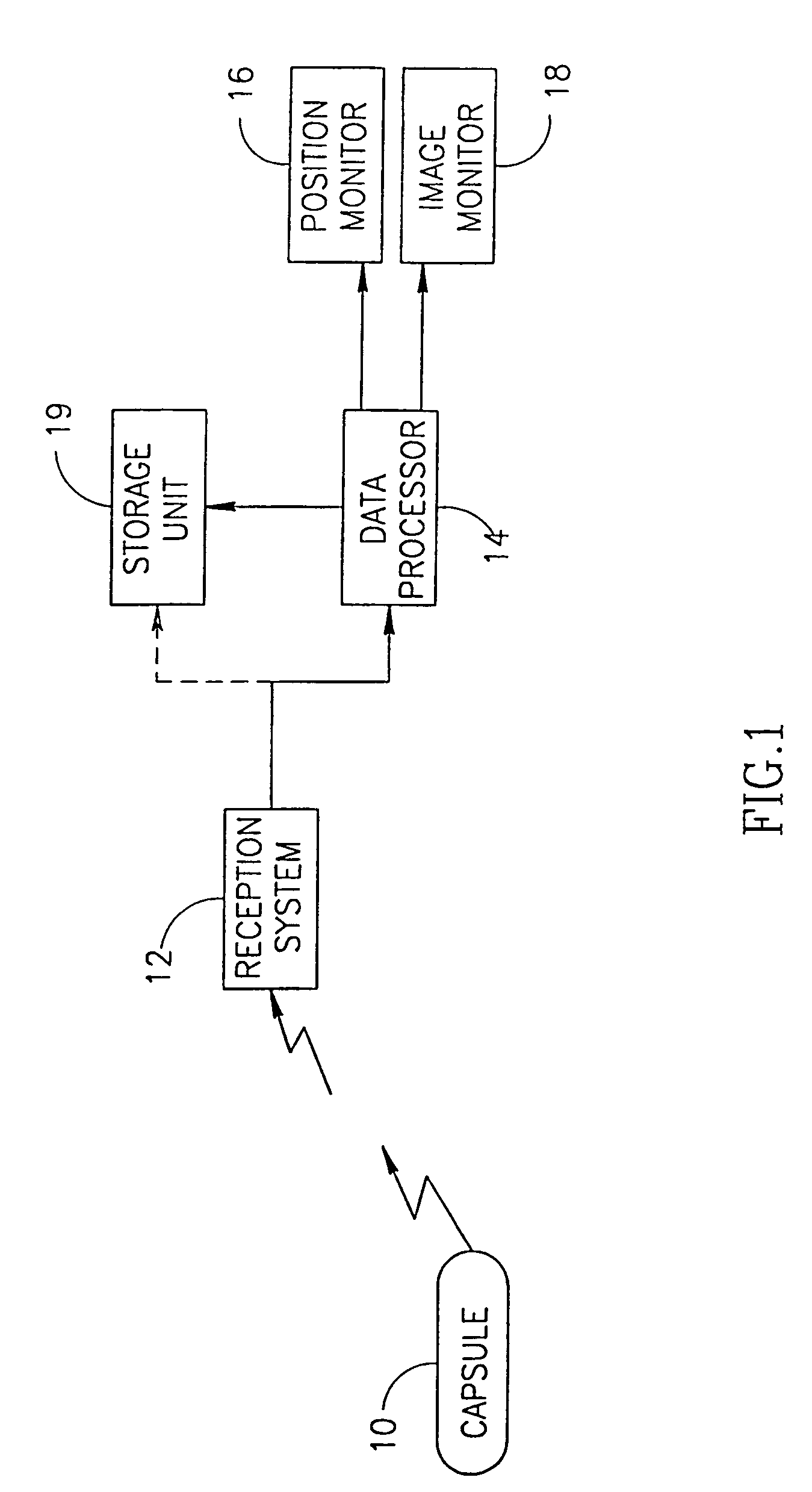
Capsule (60) moves through the gastrointestinal tract (62) in a first pass to generate a map of the gastrointestinal tract, and to identify a location of interest. In its second pass, capsule (60) moves through the gastrointestinal tract, and is controlled to perform a job at the identified location. Repeated localizations generate generate a map of the route taken by the capsule in the gastrointestinal tract (62). images displayed on the image monitor (61) are compared with the generated map displayed on the position monitor (63) to identify the location of a pathology (72).
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Tracking system
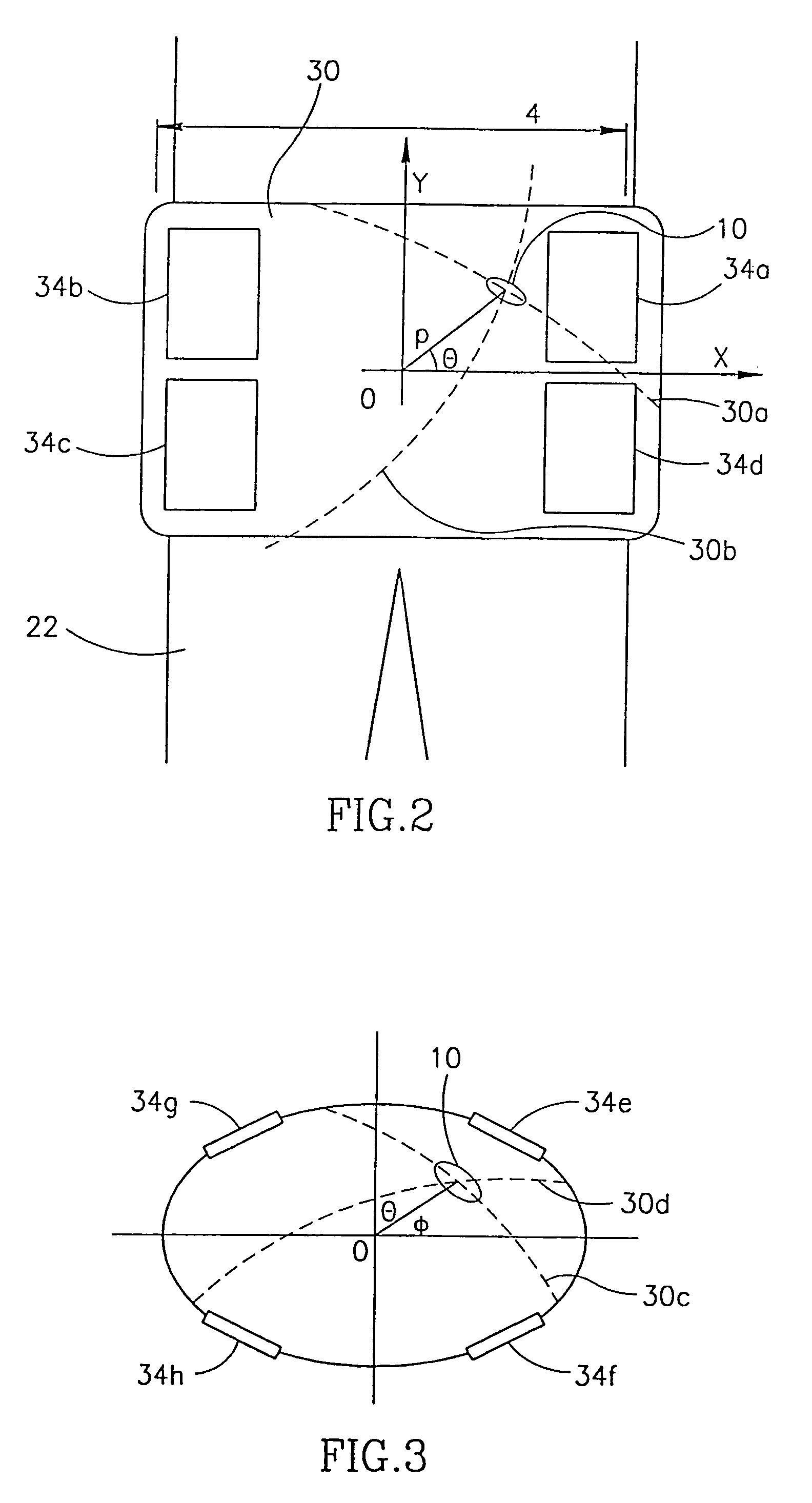
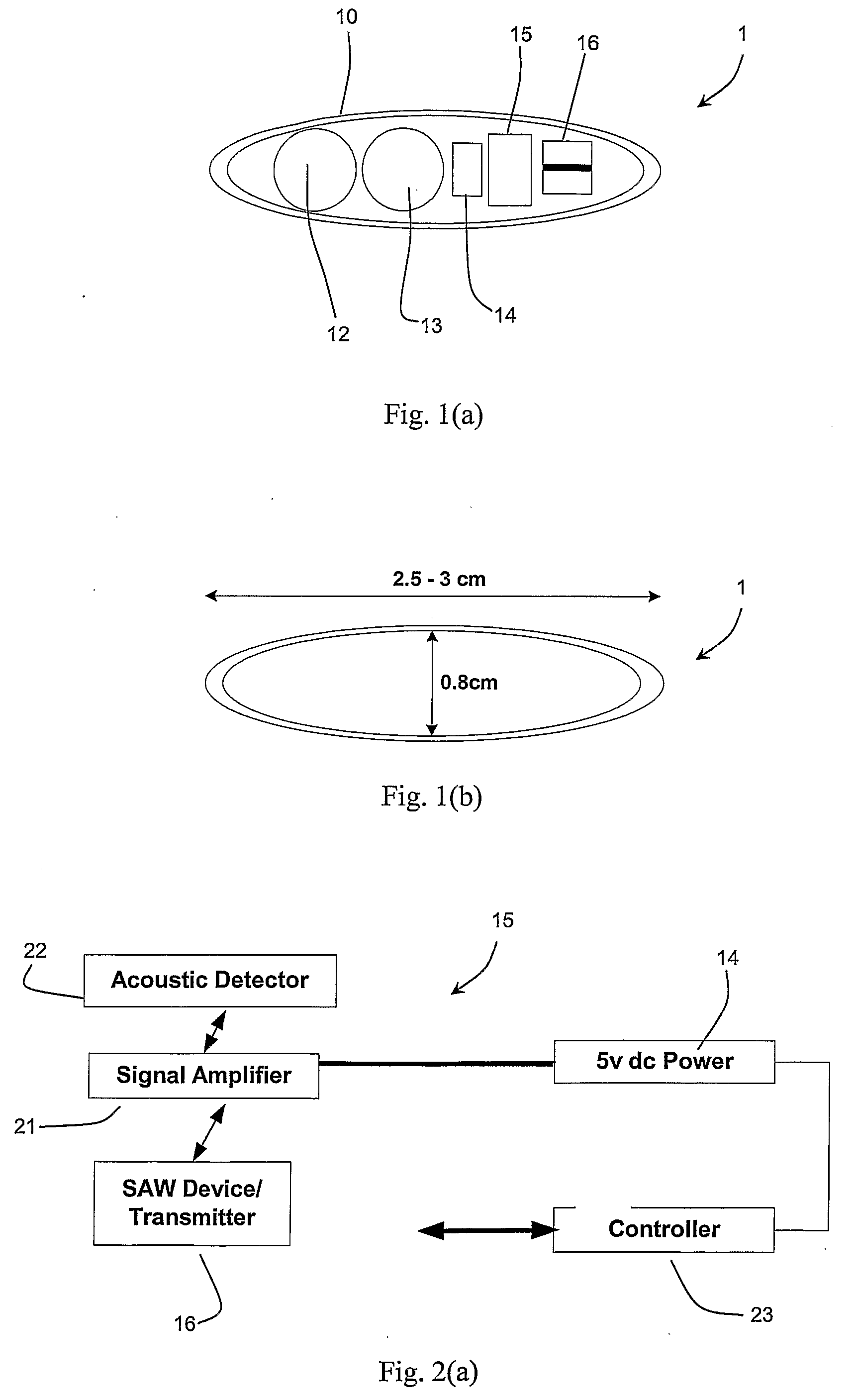
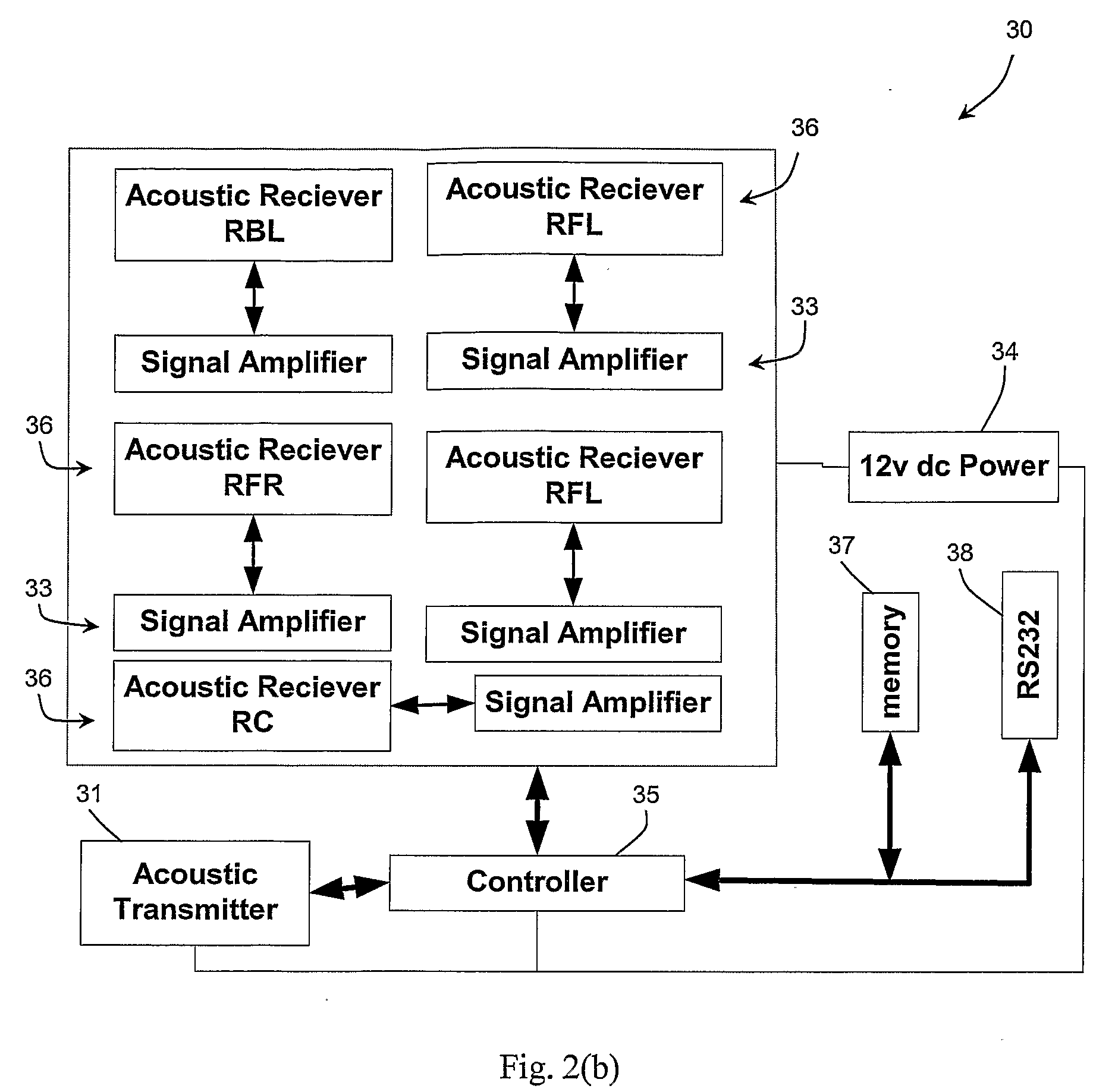
InactiveUS20090124871A1Facilitates acoustic transmissionEasy to receiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryComputer scienceTime of flight
A tracking system of the invention comprises a fixed part (30) and a consumable sensor capsule (1) the location of which is tracked in real time as it moves through the GI tract. The fixed part emits (31) acoustic signals, and the capsule receives these signals and in turn generates, after a set time delay, a response which is received by the fixed part and a computation is made of the distance between the capsule and the fixed part based on the time of flight and the intervening organs as modelled in the system's processor. The response is transmitted after a pre-set time delay and so is a simulated echo. Multiple receivers (36) are located at positions on a belt (40) chosen so that interference by bone is minimised, and so that the tracking procedure is ambulatory. The capsule has sensors (12, 13) which transmit data via an RF antenna incorporated in the capsule casing.
Owner:LIMERICK UNIV OF
Atraumatic delivery devices
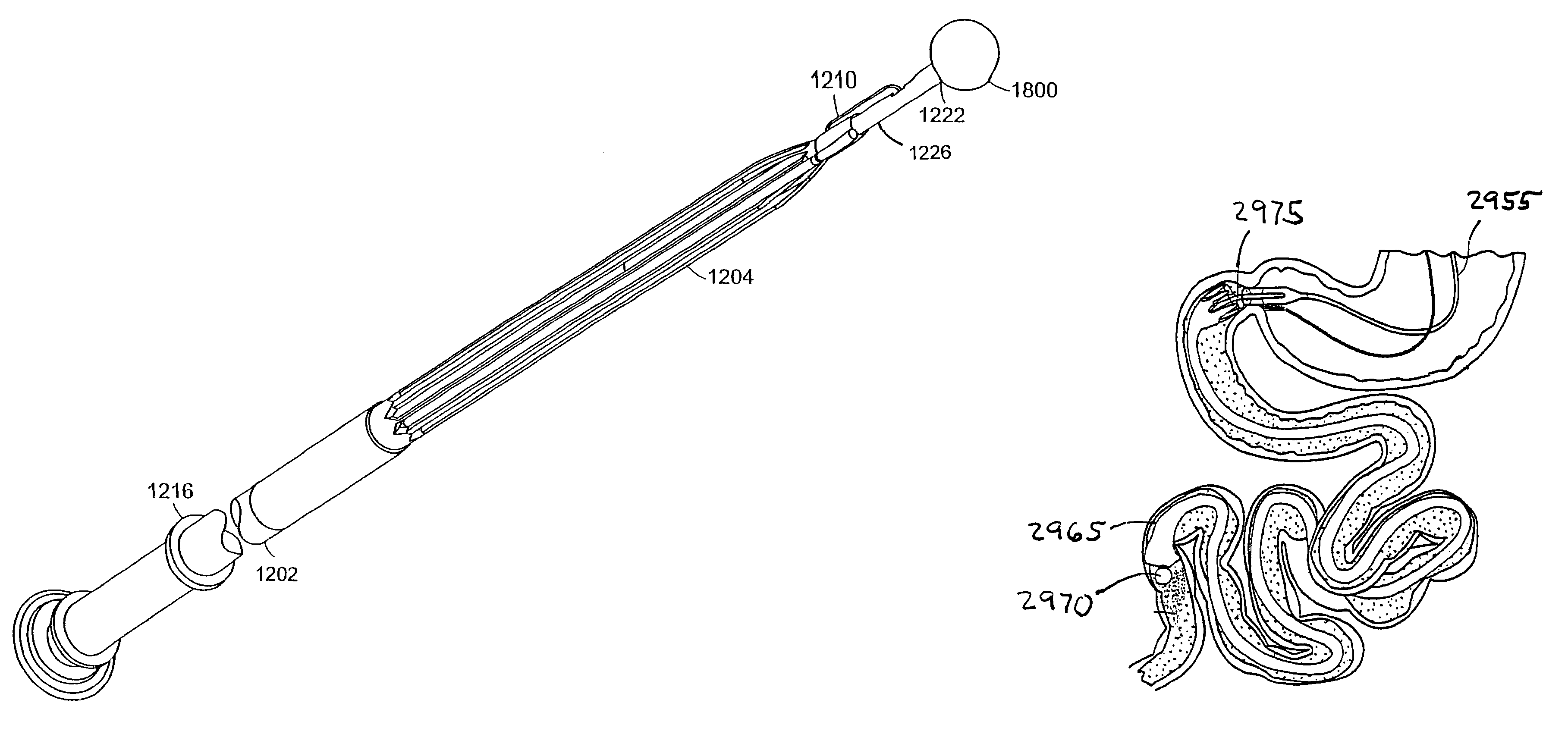
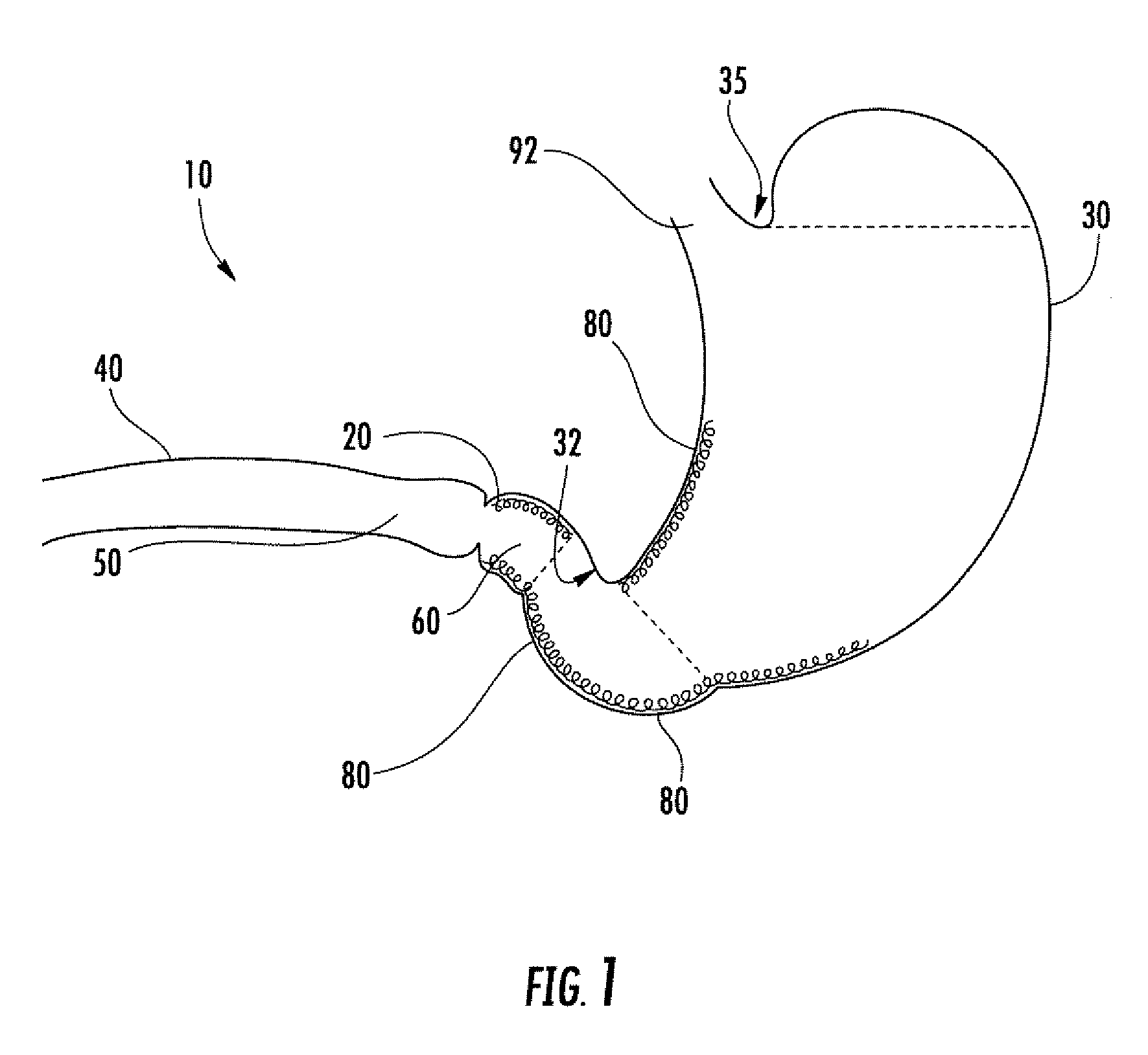
InactiveUS7678068B2Limit absorptionReducing hormone triggersSuture equipmentsStentsImplanted deviceVia gastrointestinal tract
Methods and apparatus for delivering an implant device within the digestive system of an animal are presented. An delivery device includes an outer sheath, or container, for storing a proximal portion of the implant device. The outer sheath is moveable relative to the stored portion of the implant device to release the proximal portion from within the outer sheath. The delivery device also includes an inner sheath defining a lumen therein that extends distal to the outer sheath, a moveable element adapted to secure the distal end of the implant to the inner sheath, and a release mechanism coupled to the moveable element for releasing the distal end of the implant. The device also includes a atraumatic tip, or ball, coupled at its distal end to facilitate guiding the delivery device through the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
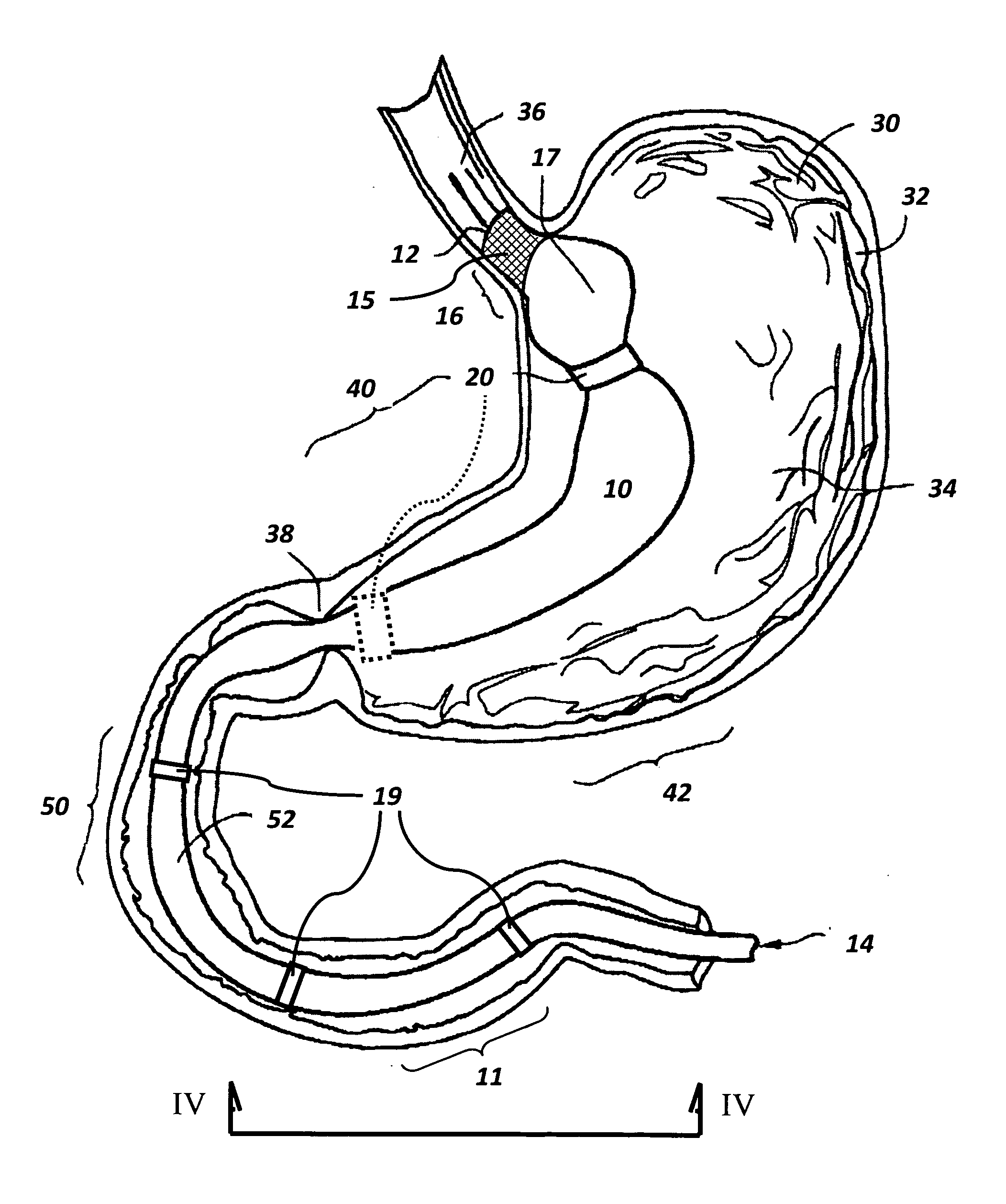
Active Drug Delivery in the Gastrointestinal Tract
InactiveUS20080063703A1Promote absorptionEasy accessInternal electrodesMedical devicesMedicineDrug administration
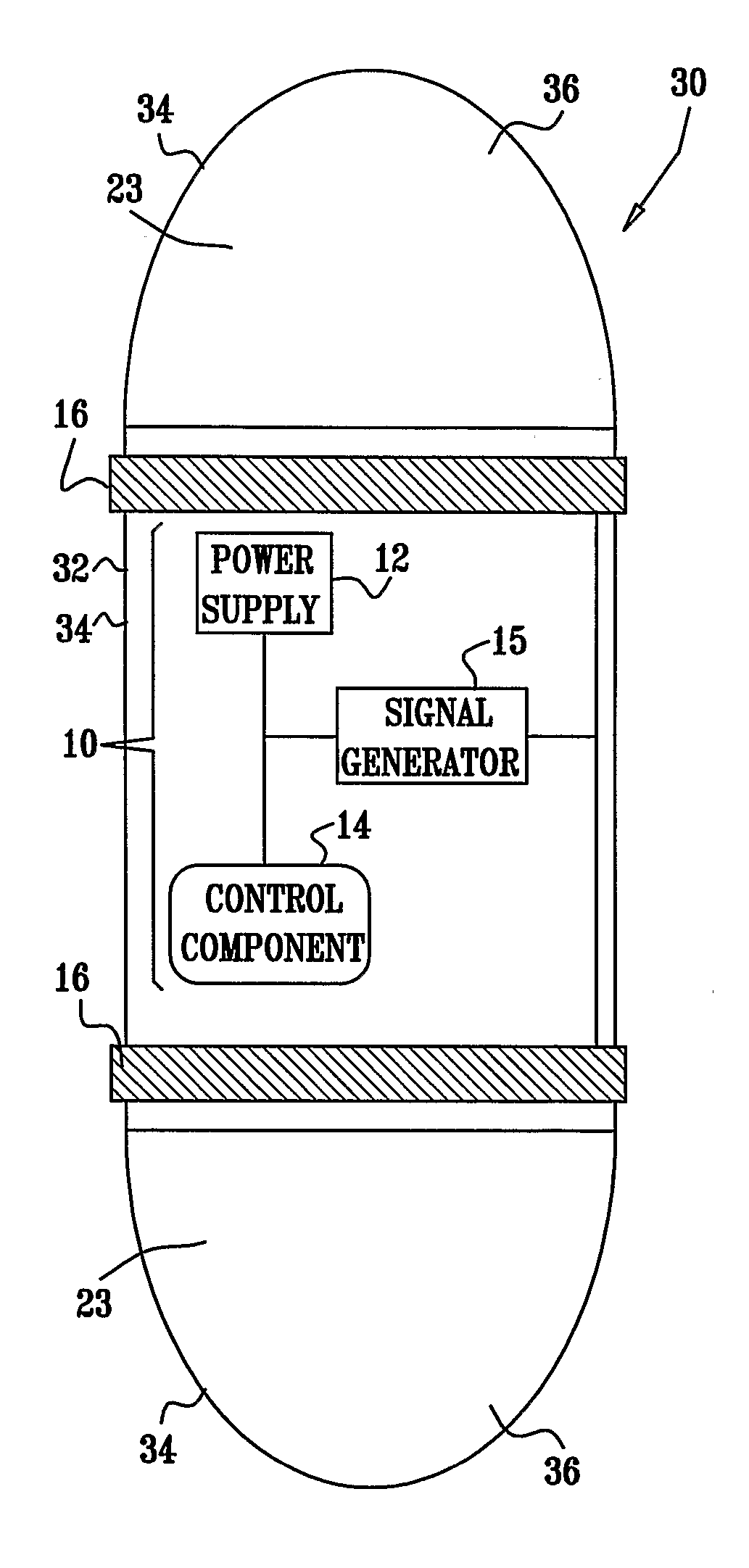
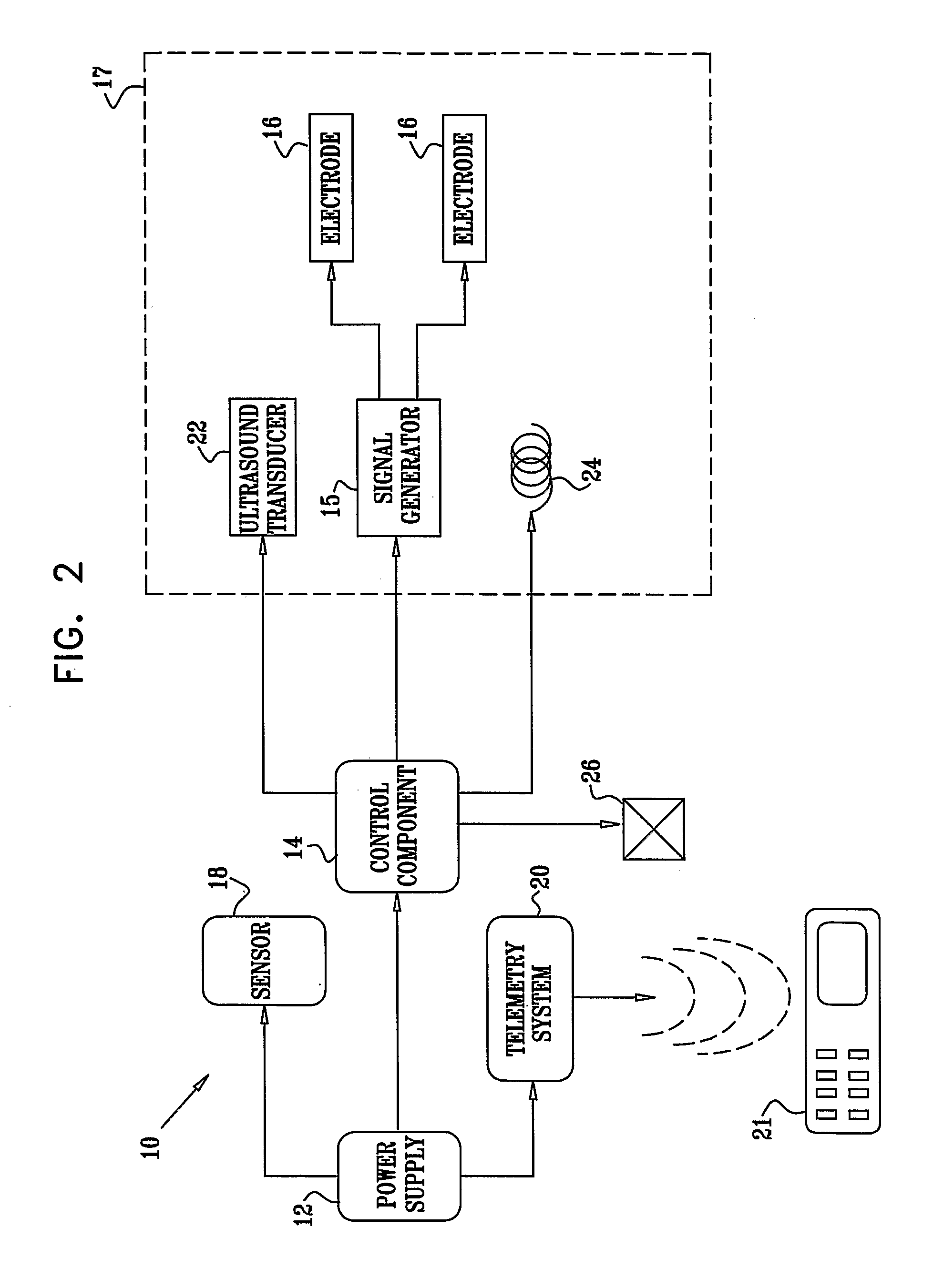
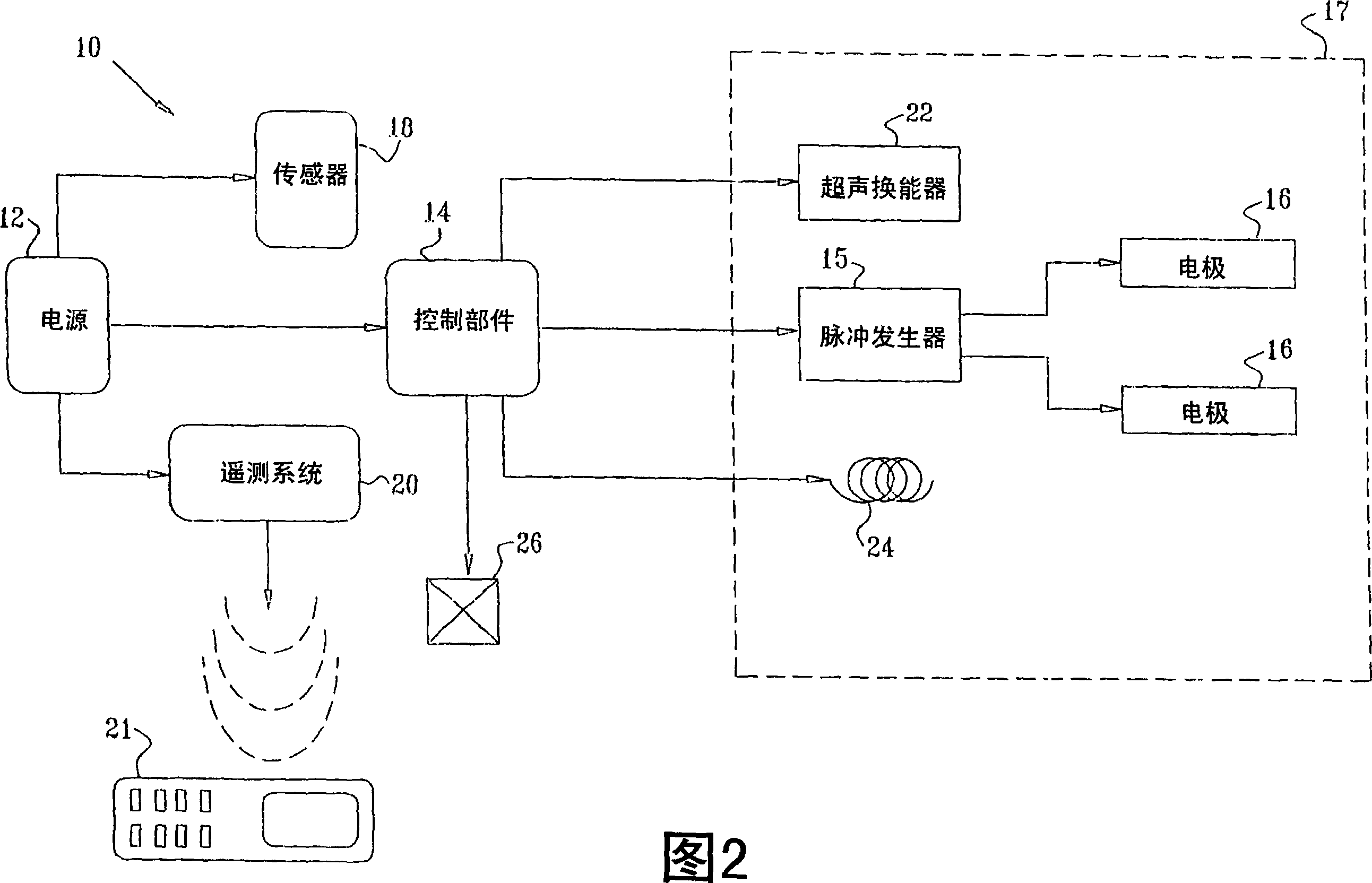
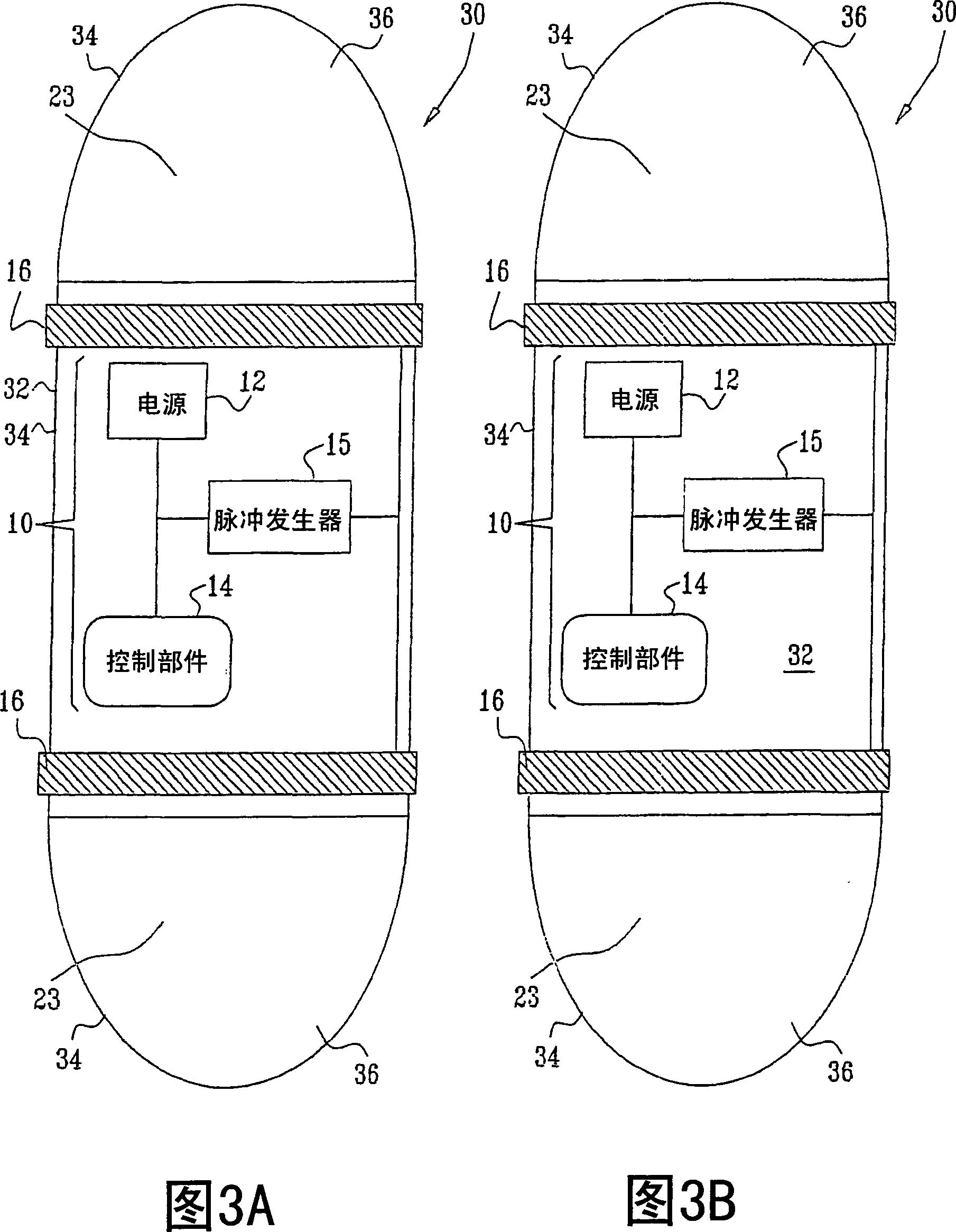
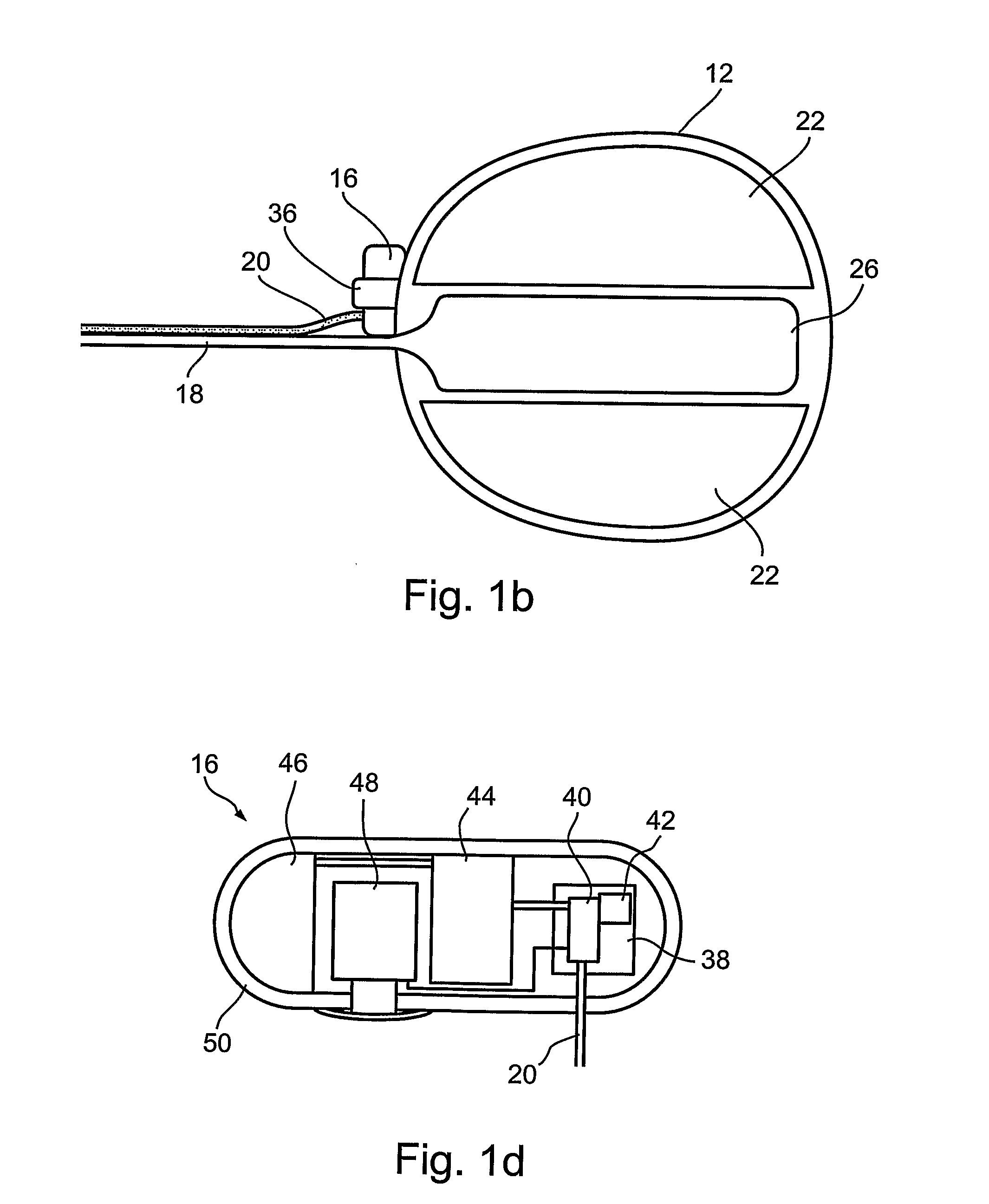
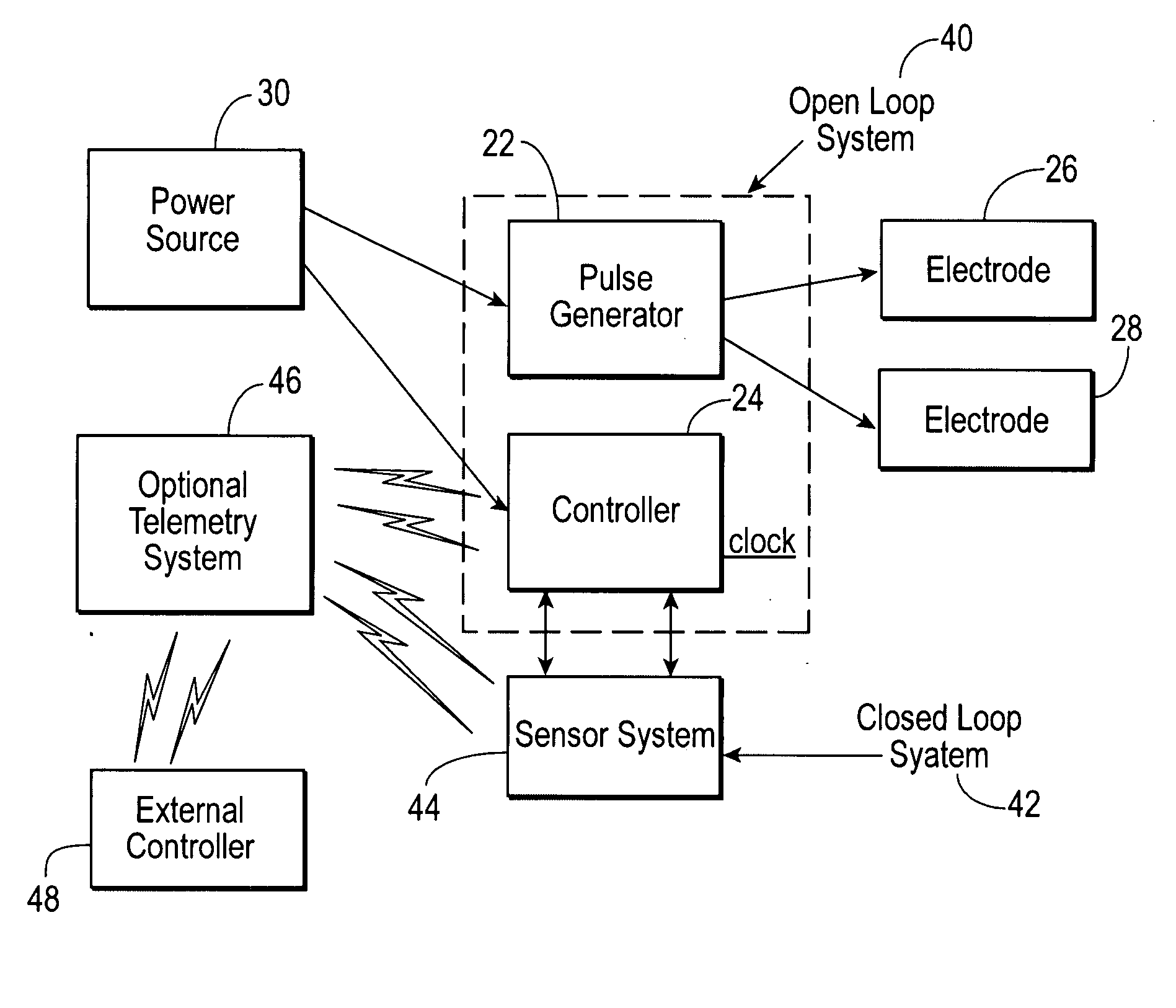
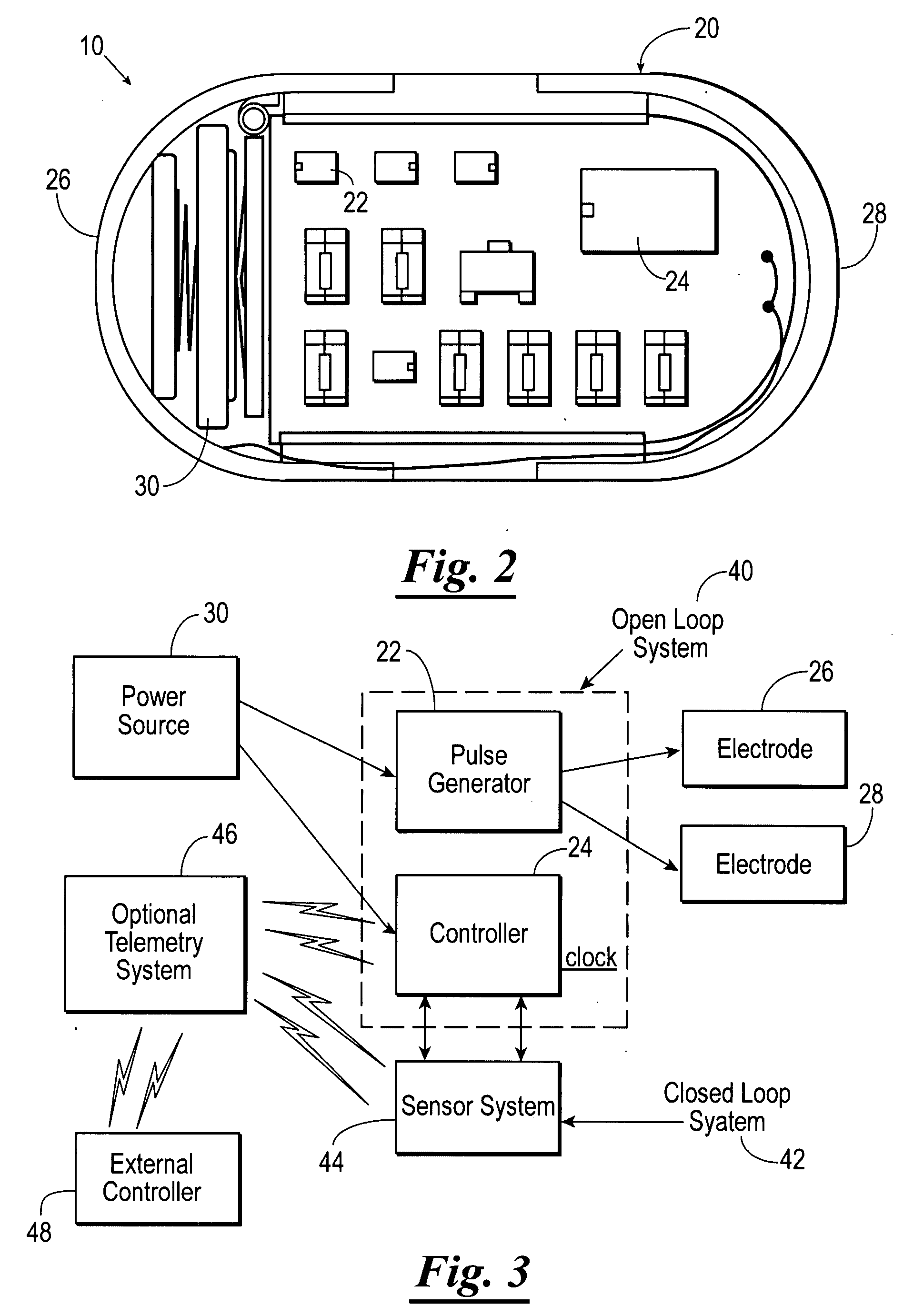
Apparatus (30) for drug administration is provided, including an ingestible capsule (32), which includes a drug (36), stored by the capsule (32), and an environmentally-sensitive mechanism (18), adapted to change a state thereof responsively to a disposition of the capsule (32) within a gastrointestinal (GI) tract (50) of a subject. The capsule (32) further includes first and second electrodes (16), and a control component (14), adapted to facilitate passage of the drug (36), in response to a change of state of the environmentally-sensitive mechanism (18), through an epithelial layer of the GI tract (50) by driving the first and second electrodes (16) to apply a series of pulses at a current of less than about 10 mA, at a frequency of between about 12 Hz and about 24 Hz, and with a pulse duration of between about 0.5 milliseconds and about 3 milliseconds. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:E PILL PHARMA
Compositions and methods for controlling abuse of medications
Pharmaceutical dosage forms are provided for use in deterring abuse of opioids or other medications, which help avoid harm to a patient dependent on the medication. In one case, a pharmaceutical oral dosage form is provided that includes a plurality of microcapsules, each microcapsule of the plurality containing an opioid agonist medication in a controlled release form, and a partial opioid agonist sequestered in the pharmaceutical dosage form, such that upon oral administration of the pharmaceutical oral dosage form the partial opioid agonist will pass through the gastrointestinal tract without uptake by the body.
Owner:PHARMORX THERAPEUTICS
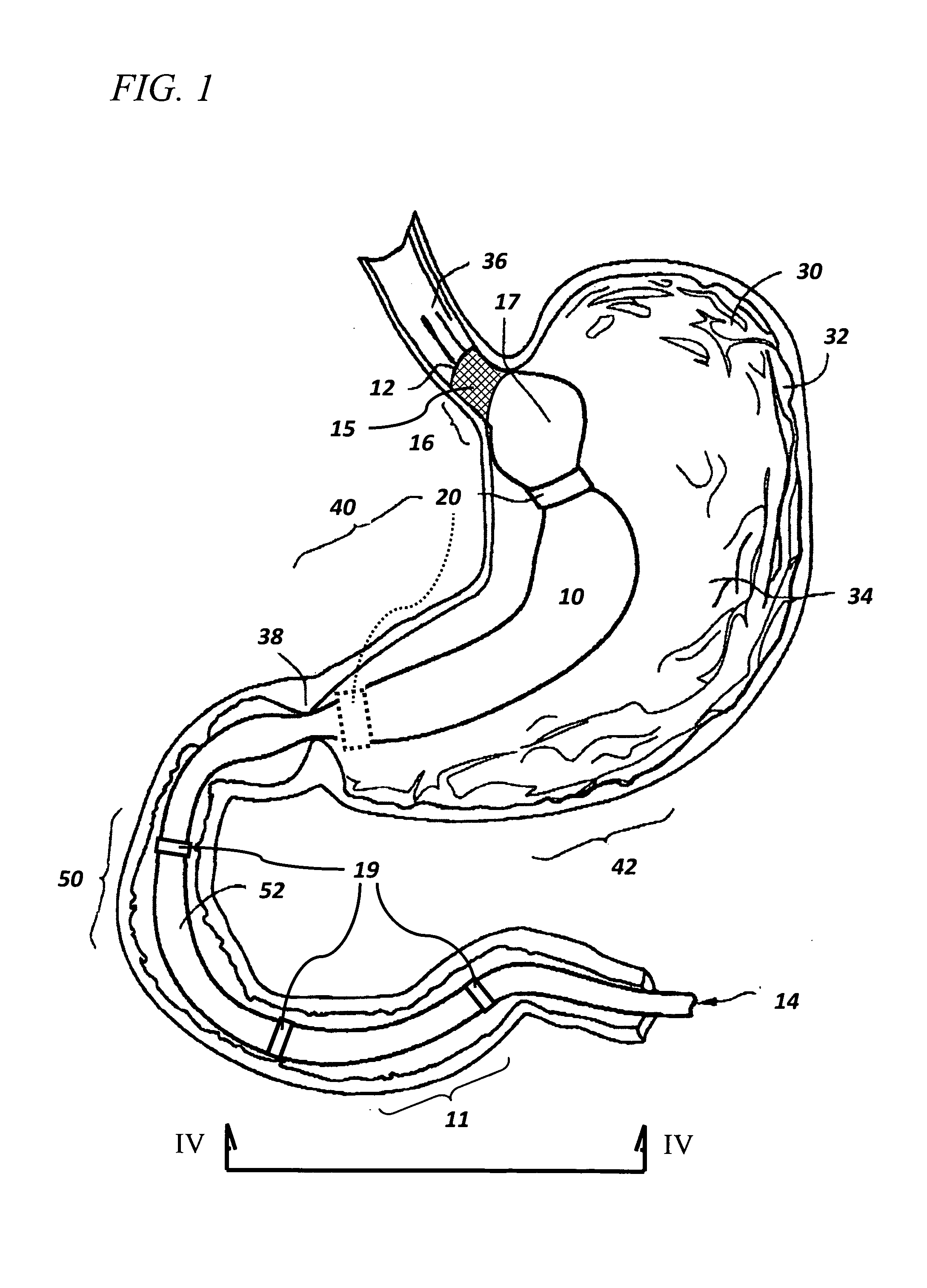
Devices and methods for endolumenal therapy
InactiveUS20090093767A1Promoting tissue in-growthAltering abilityDiagnosticsSurgeryGastrointestinal deviceLower esophagus
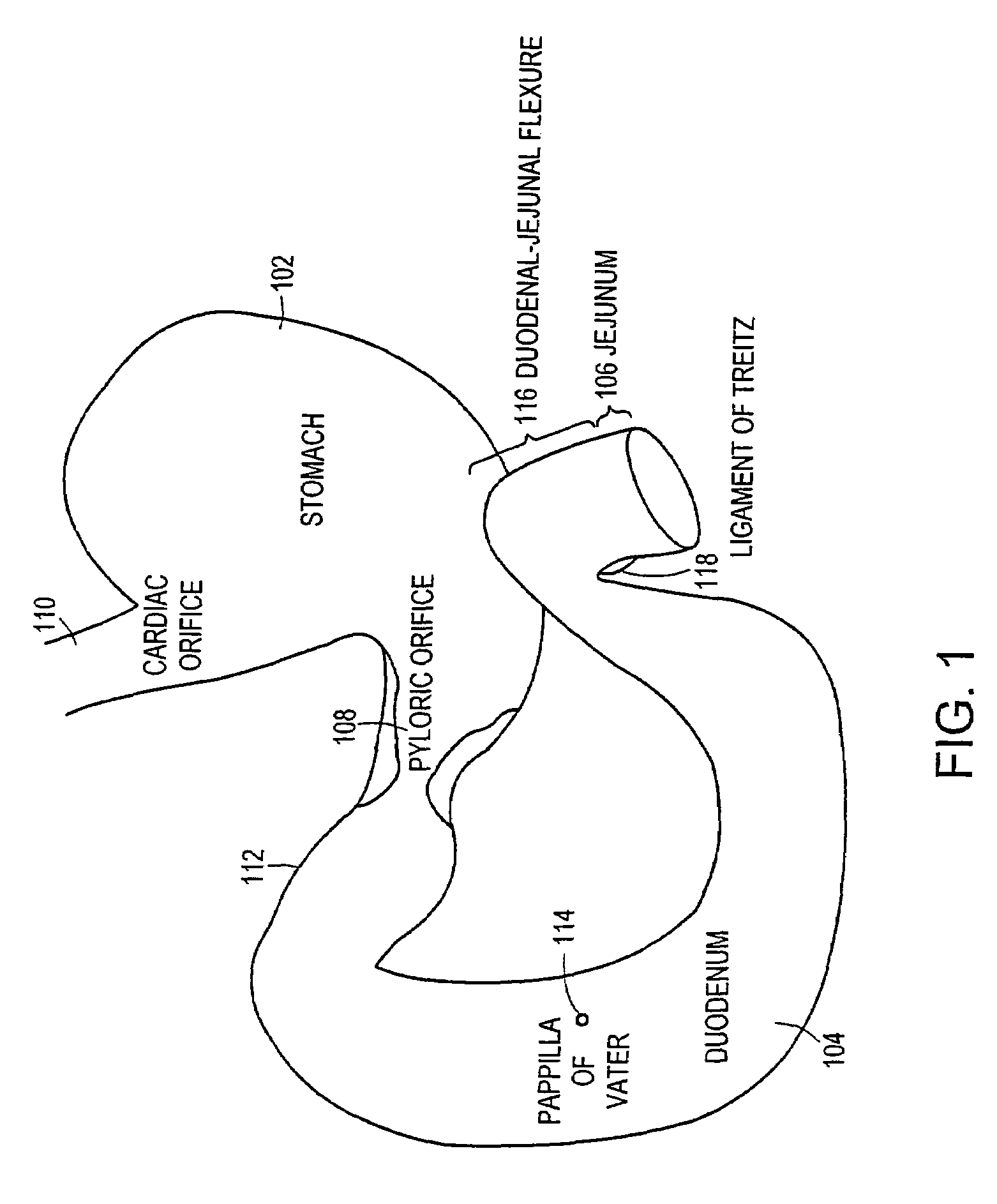
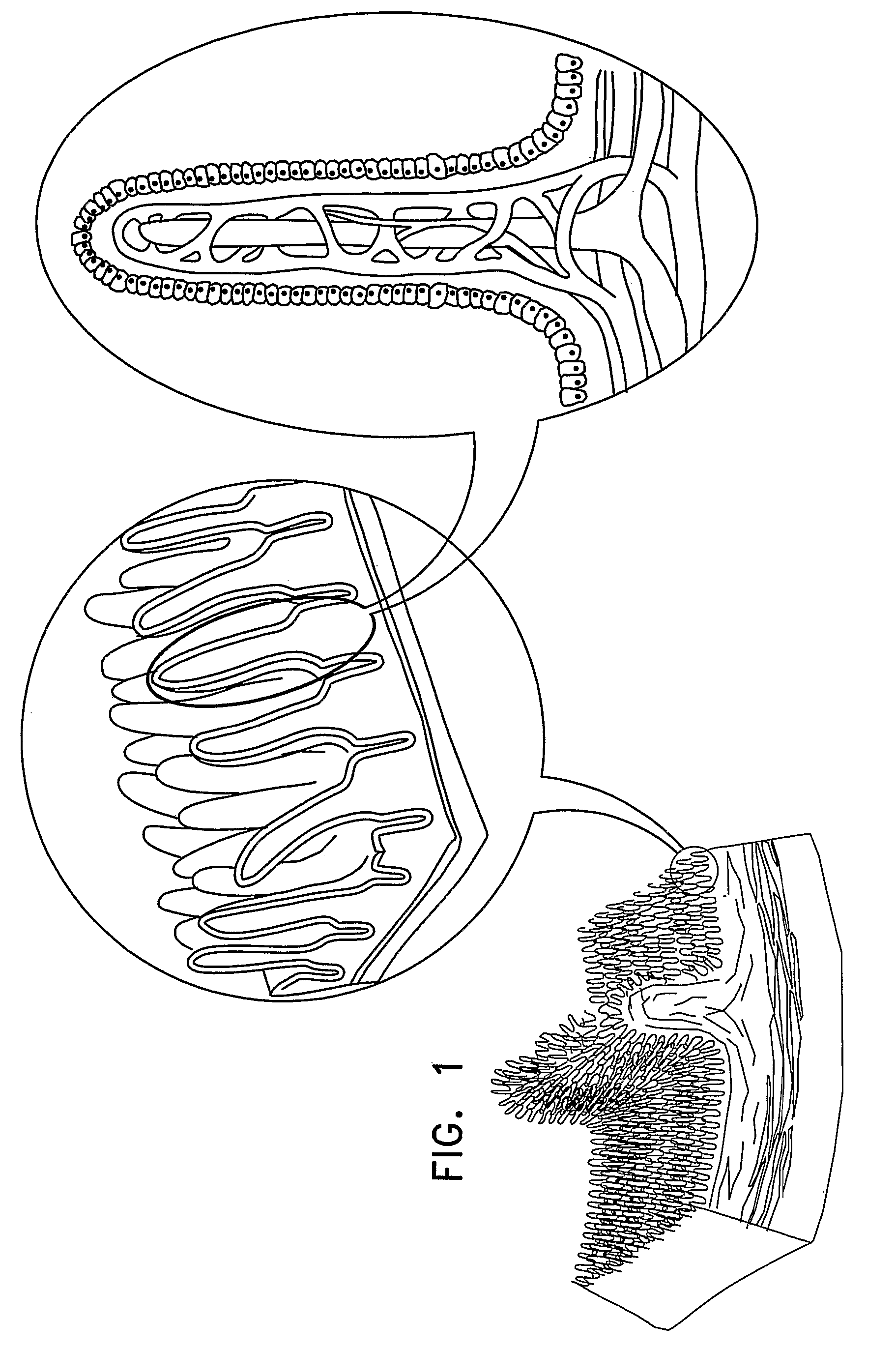
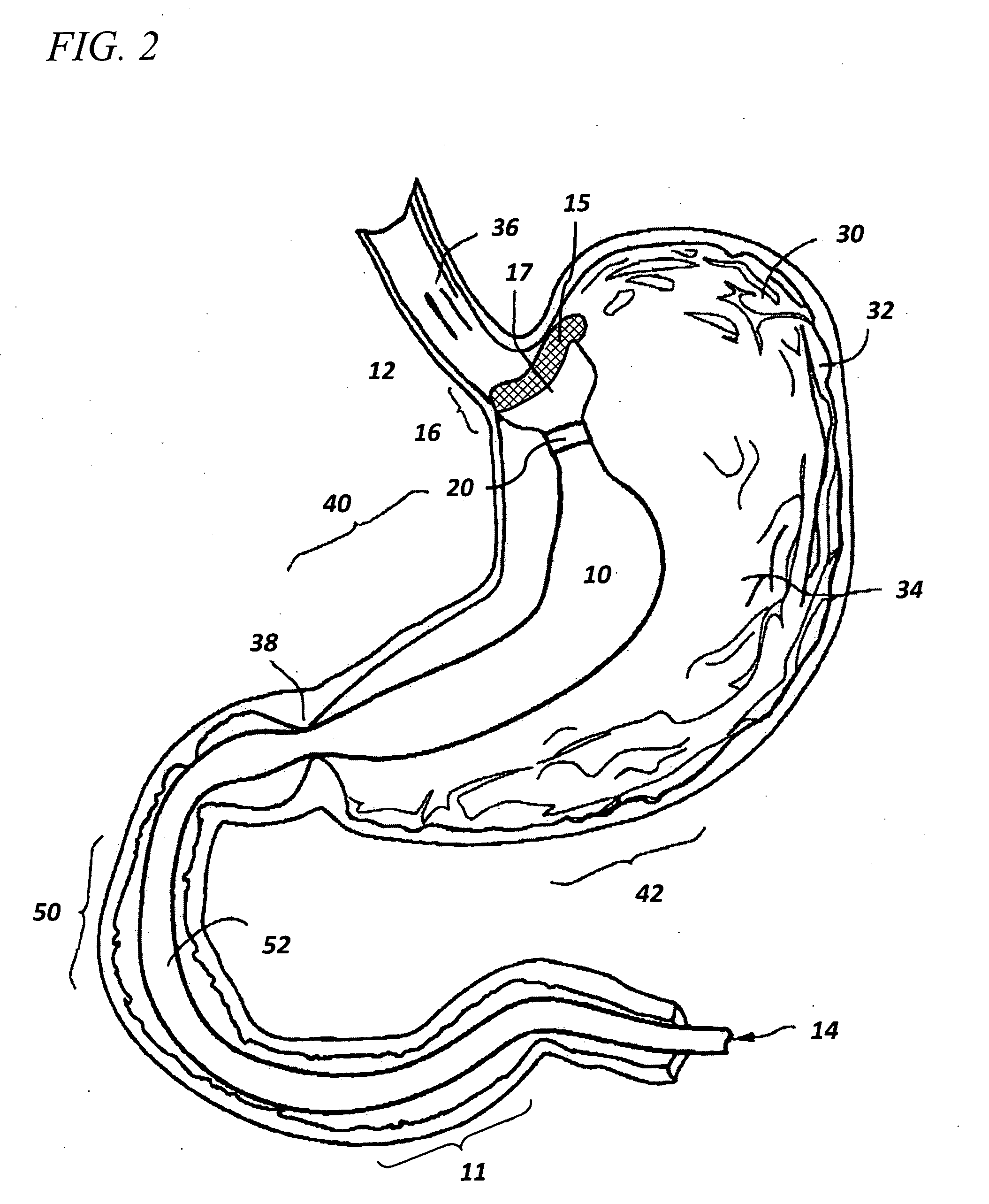
The present invention is directed generically to a means for altering the ability of the mammalian body to absorb nutritive content from ingested foodstuffs, and more specifically to an apparatus and method of use for an endolumenal sleeve (referred to also as an “intragastrointestinal device” or “gastrointestinal device”) positioned in the mammalian gastrointestinal (GI) tract. A suitable endolumenal sleeve is comprised of an anchor element and an opening at a proximal end, an elongate lumen or hollow open-ended tube having a transverse dimension, and a distal orifice. Optionally, an exterior aspect of the elongate lumen may include additional modes of attachment to the tissues walls of the GI tract through the use of one or more means for promoting tissue in-growth. The endolumenal sleeve is retained in the GI tract such that a substantial fraction of the food and liquids passing through the GI tract is channeled into the proximal opening and through an interlumenal space defined within the interior space of the endolumenal sleeve. Within the endolumenal sleeve there may be one or more restrictive means to constrain, impede or otherwise control the operative flow of material through the device. An individual restrictive means can either be of a fixed geometry or such means may include one or more elements which are adjustable in nature or function. The elongate lumen of the endolumenal sleeve is formed of a polymer composition suitable for controlled ingress of biological secretions, egress of certain selected nutritional elements, and may comprise either a single tubular structure or a multi-section (i.e. articulated and / or multiple lumen) assembly. When the endolumenal sleeve is in situ within the mammalian gastro-intestinal system, ingested foodstuffs are conveyed from the proximal end to said distal orifice. In typical applications, the proximal end of the endolumenal sleeve is positioned within the physiological region extending from the lower esophagus to the duodenum and the distal orifice is positioned within the physiological region extending from the upper duodenum to the lower jejunum, though further extension into the lower intestine is possible. Through proper selection of position for the endolumenal sleeve proximal and distal ends, combined by selection of the composition used in the fabrication of the elongate lumen, it is possible to finitely control the degree of nutritive absorption performed by the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:KELLEHER BRIAN
Self-expanding device for the gastrointestinal or urogenital area
InactiveUS20060142794A1Lower the volumeLose weightSurgeryDilatorsIntestinal structureReproductive tract
Devices for treatments of diseases and disorders associated with the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, or urinogenital tract are described herein. Initially, the device is in a temporary form which is suitable for oral or rectal administration. After exposure to a stimulus, such as a temperature or pH change, the device changes shape to a permanent form, which allows it to become mechanically fixed in the stomach, esophagus or intestine. In one embodiment, the device is used to reduce the volume of the stomach, esophagus or intestine without interfering with the flow of the food through the gastrointestinal tract. The device may be used to help overweight patients lose weight and to deliver drugs to treat disorders and diseases in the in the stomach or intestine. The devices are manufactured from a stimuli-sensitive polymeric material, which is biocompatible and primarily adapted to the mechanical properties and geometry in the area to which it is applied. In the preferred embodiment, the material is a shape memory polymer. Depending on the desired application, the polymer may be either biodegradable or non-degradable.
Owner:MINEMOSCIENCE GMBH
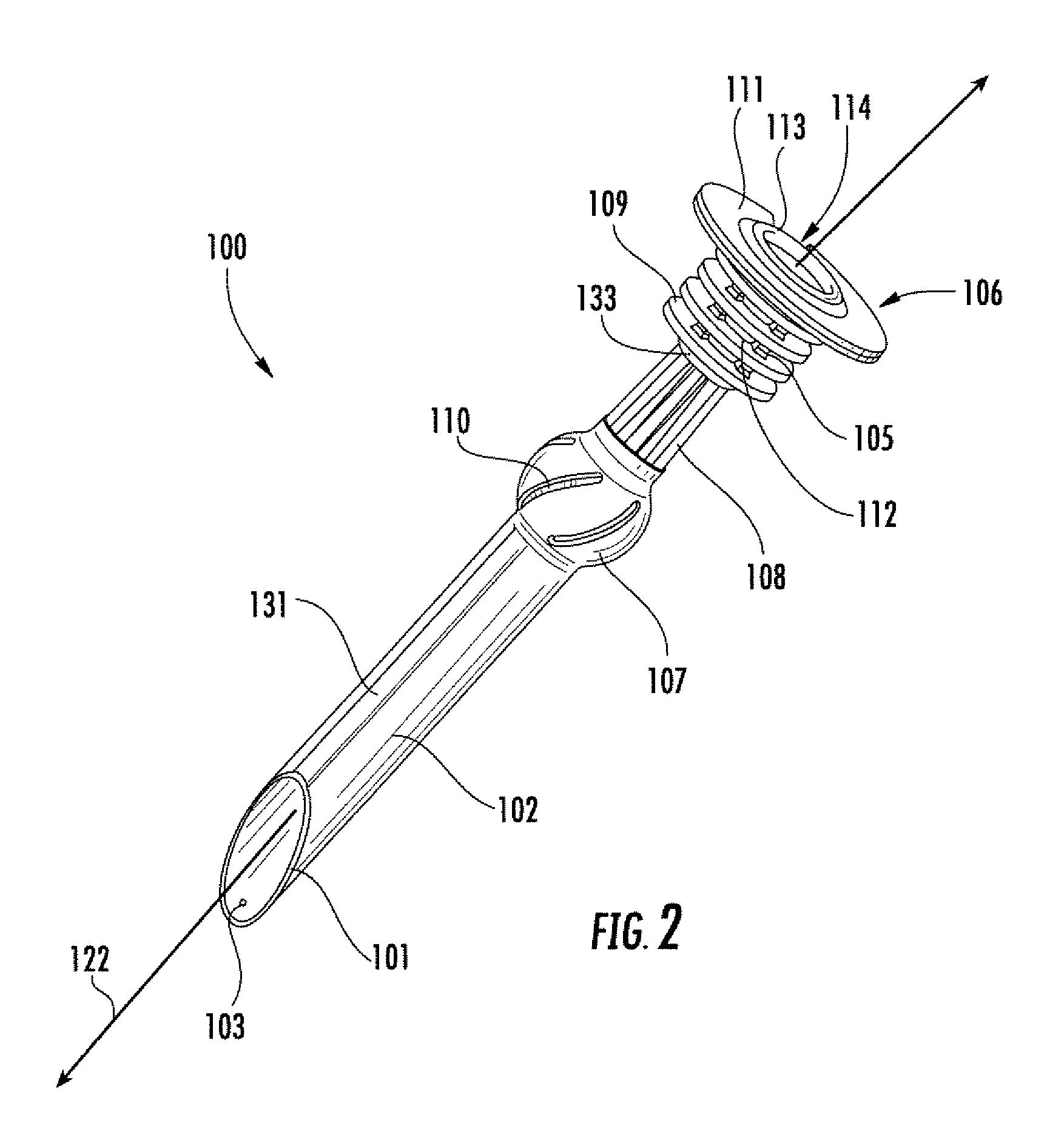
Active drug delivery in the gastrointestinal tract
The invention provides a device (100) for administering a medicament (36, 136) comprising an ingestible capsule (30, 102). The capsule (30, 102) includes a drug (36, 106) stored by the capsule (30, 102). The environmentally sensitive mechanism (eg, coating 104) is adapted to change the state of the capsule (30, 102) in response to its deployment within the subject's gastrointestinal tract. The drive mechanism (eg, drive mechanism 108) is adapted to drive the drug (36, 106) directly through the endothelial layer of the gastrointestinal tract in response to a change in state of the environmentally sensitive mechanism.
Owner:PILL PHARMA E
Devices and methods for augmenting extragastric banding
InactiveUS20090093839A1Promoting tissue in-growthAltering abilitySurgeryDilatorsLower esophagusGastrointestinal device
The present invention is directed generically to a means for altering the ability of the mammalian body to absorb nutritive content from ingested foodstuffs, and more specifically to an apparatus and method of use for an endolumenal sleeve (referred to also as an “intragastrointestinal device” or “gastrointestinal device”) positioned in the mammalian gastrointestinal (GI) tract. A suitable endolumenal sleeve is comprised of an anchor element and an opening at a proximal end, an elongate lumen or hollow open-ended tube having a transverse dimension, and a distal orifice. Optionally, an exterior aspect of the elongate lumen may include additional modes of attachment to the tissues walls of the GI tract through the use of one or more means for promoting tissue in-growth. The endolumenal sleeve is retained in the GI tract such that a substantial fraction of the food and liquids passing through the GI tract is channeled into the proximal opening and through an interlumenal space defined within the interior space of the endolumenal sleeve. Within the endolumenal sleeve there may be one or more restrictive means to constrain, impede or otherwise control the operative flow of material through the device. An individual restrictive means can either be of a fixed geometry or such means may include one or more elements which are adjustable in nature or function. The elongate lumen of the endolumenal sleeve is formed of a polymer composition suitable for controlled ingress of biological secretions, egress of certain selected nutritional elements, and may comprise either a single tubular structure or a multi-section (i.e. articulated and / or multiple lumen) assembly. When the endolumenal sleeve is in situ within the mammalian gastro-intestinal system, ingested foodstuffs are conveyed from the proximal end to said distal orifice. In typical applications, the proximal end of the endolumenal sleeve is positioned within the physiological region extending from the lower esophagus to the duodenum and the distal orifice is positioned within the physiological region extending from the upper duodenum to the lower jejunum, though further extension into the lower intestine is possible. Through proper selection of position for the endolumenal sleeve proximal and distal ends, combined by selection of the composition used in the fabrication of the elongate lumen, it is possible to finitely control the degree of nutritive absorption performed by the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:KELLEHER BRIAN
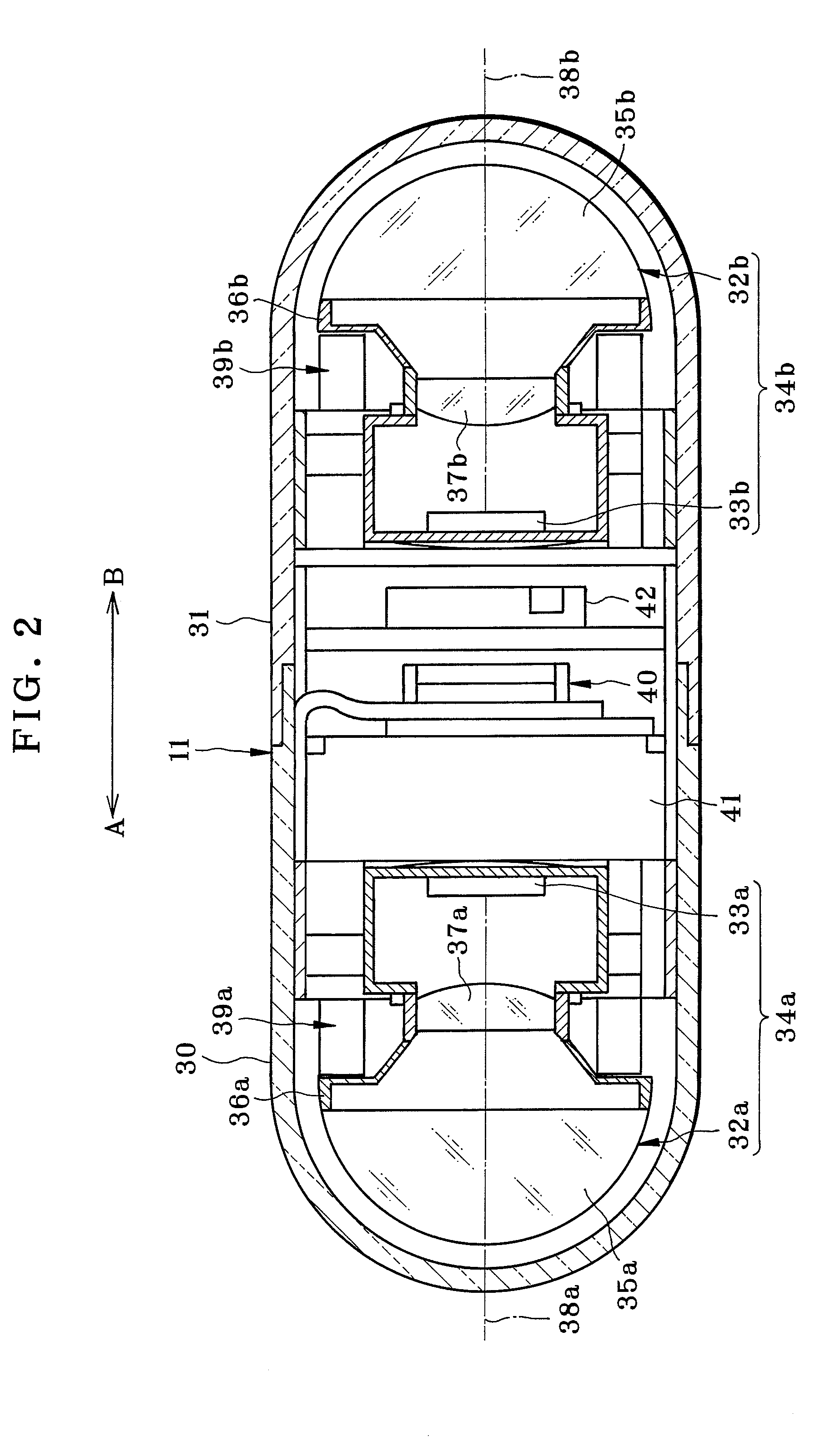
Endoscopic device for locomotion through the gastro-intestinal tract
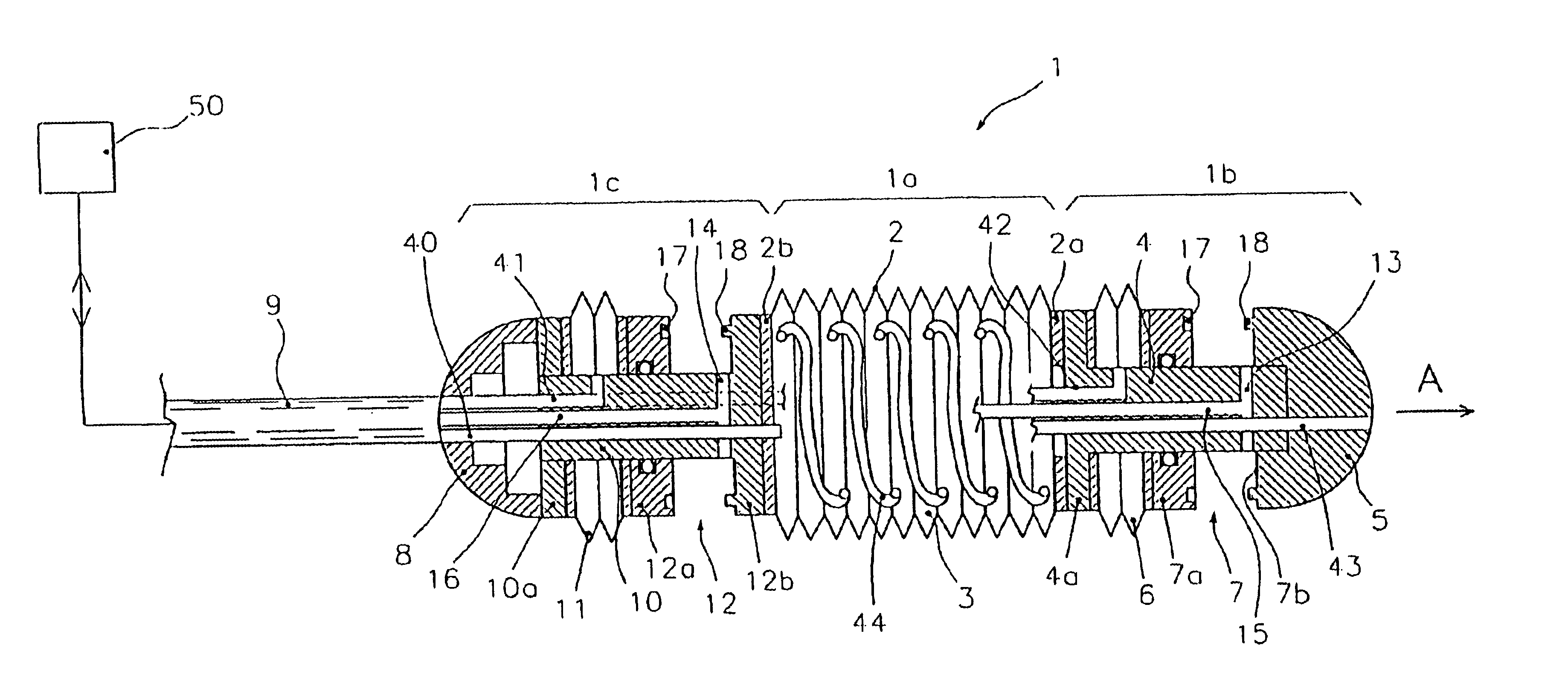
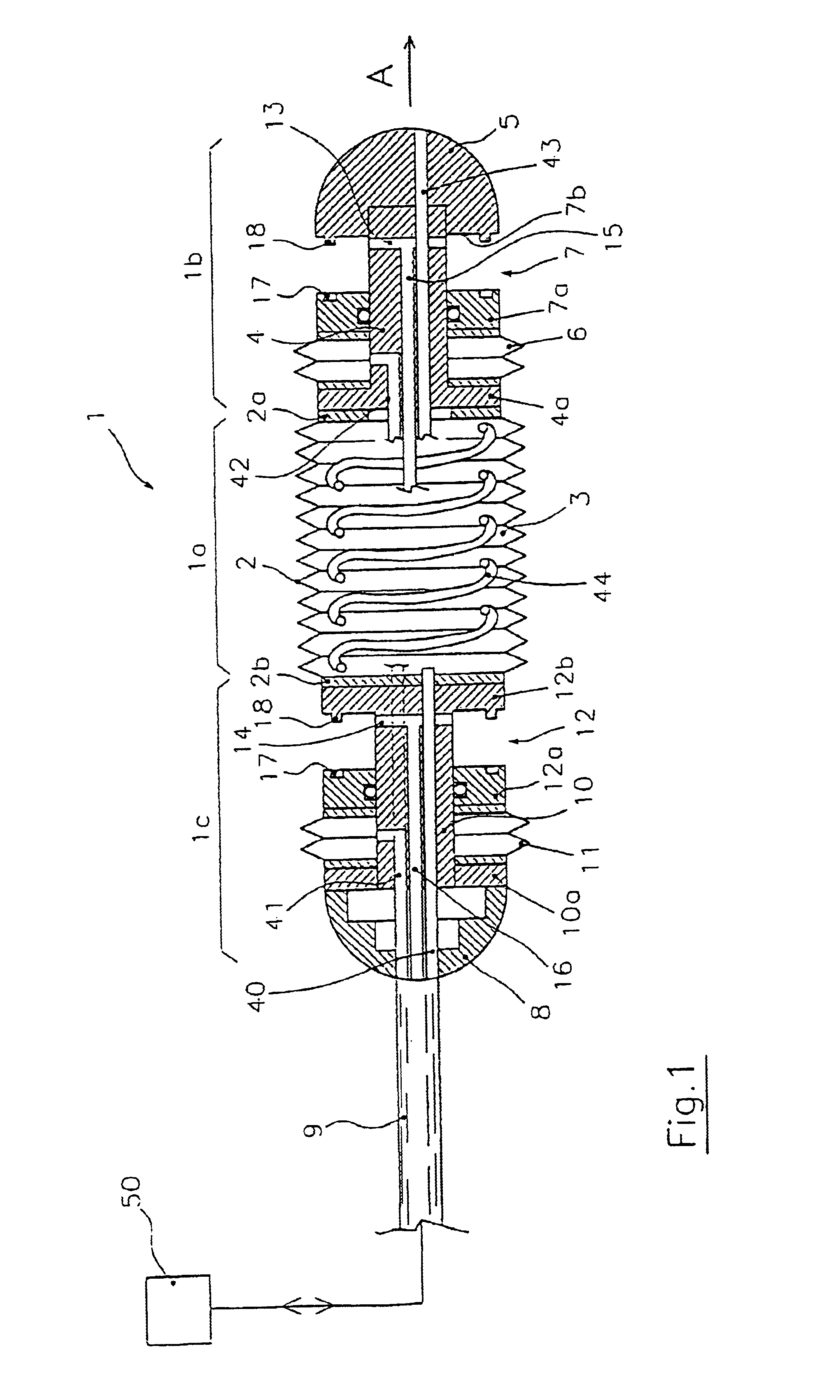
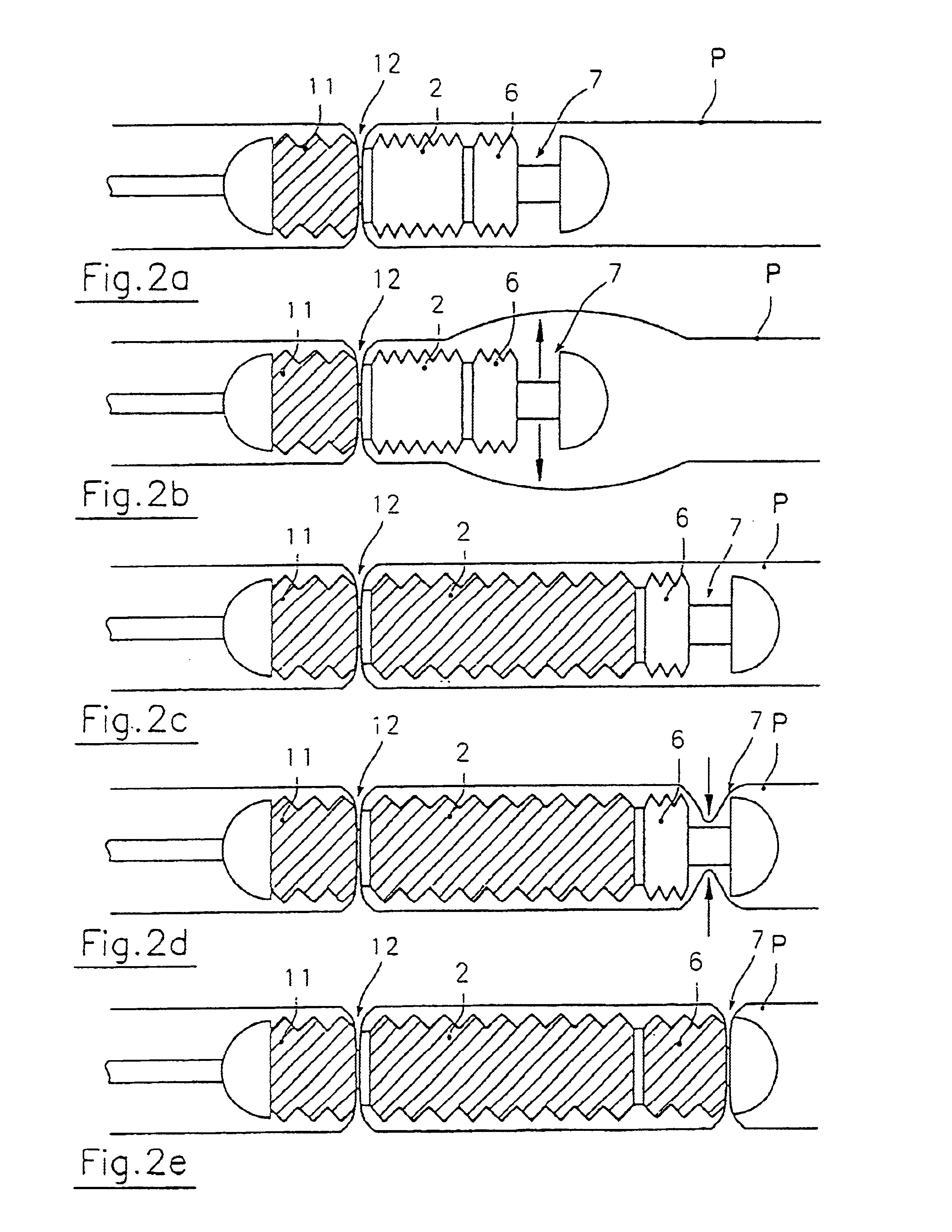
An endoscopic device for locomotion in a body cavity according to a prefixed advancing direction (A) comprising at least a variable length intermediate section (1a, 21a) extending between a front end section (1b, 21b) and a rear end section (1c, 21c). First and second clamping means (7, 12, 27, 32) are integral to the front and rear section, for alternately grasping respective surrounding portions of wall (P) of the body cavity. Sucking means (13, 14, 37, 38) are associated to the first and second clamping means for creating a depression sufficient to cause the body cavity wall portions to collapse within the first and second clamping means while they are in an open condition. Means for actuating alternate extensions and retractions of the intermediate section and actuating means (6, 11, 26, 31) of the first and second clamping means are further provides for synchronous operation to generate a forward motion of the rear end section due to a retraction of the intermediate section, the wall portion (P) surrounding the first clamping means being firmly held therebetween, and to generate a forward motion of the front end section due to an extension of the intermediate section, the wall portion (P) surrounding the second clamping means being firmly held therebetween.
Owner:ERA ENDOSCOPY
Residence structures and related methods
ActiveUS20170106099A1Facilitate dissociationTetracycline active ingredientsMedical devicesStimulantDissolution
Residence structures, systems, and related methods are generally provided. Certain embodiments comprise administering (e.g., orally) a residence structure to a subject (e.g., a patient) such that the residence structure is retained at a location internal to the subject for a particular amount of time (e.g., at least about 24 hours) before being released. The residence structure may be, in some cases, a gastric residence structure. In some embodiments, the structures and systems described herein comprise one or more materials configured for high levels of active substances (e.g., a therapeutic agent) loading, high active substance and / or structure stability in acidic environments, mechanical flexibility and strength in an internal orifice (e.g., gastric cavity), easy passage through the GI tract until delivery to at a desired internal orifice (e.g., gastric cavity), and / or rapid dissolution / degradation in a physiological environment (e.g., intestinal environment) and / or in response to a chemical stimulant (e.g., ingestion of a solution that induces rapid dissolution / degradation). In certain embodiments, the structure has a modular design, combining a material configured for controlled release of therapeutic, diagnostic, and / or enhancement agents with a structural material necessary for gastric residence but configured for controlled and / or tunable degradation / dissolution to determine the time at which retention shape integrity is lost and the structure passes out of the gastric cavity. For example, in certain embodiments, the residence structure comprises a first elastic component, a second component configured to release an active substance (e.g., a therapeutic agent), and, optionally, a linker. In some such embodiments, the linker may be configured to degrade such that the residence structure breaks apart and is released from the location internally of the subject after a predetermined amount of time.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
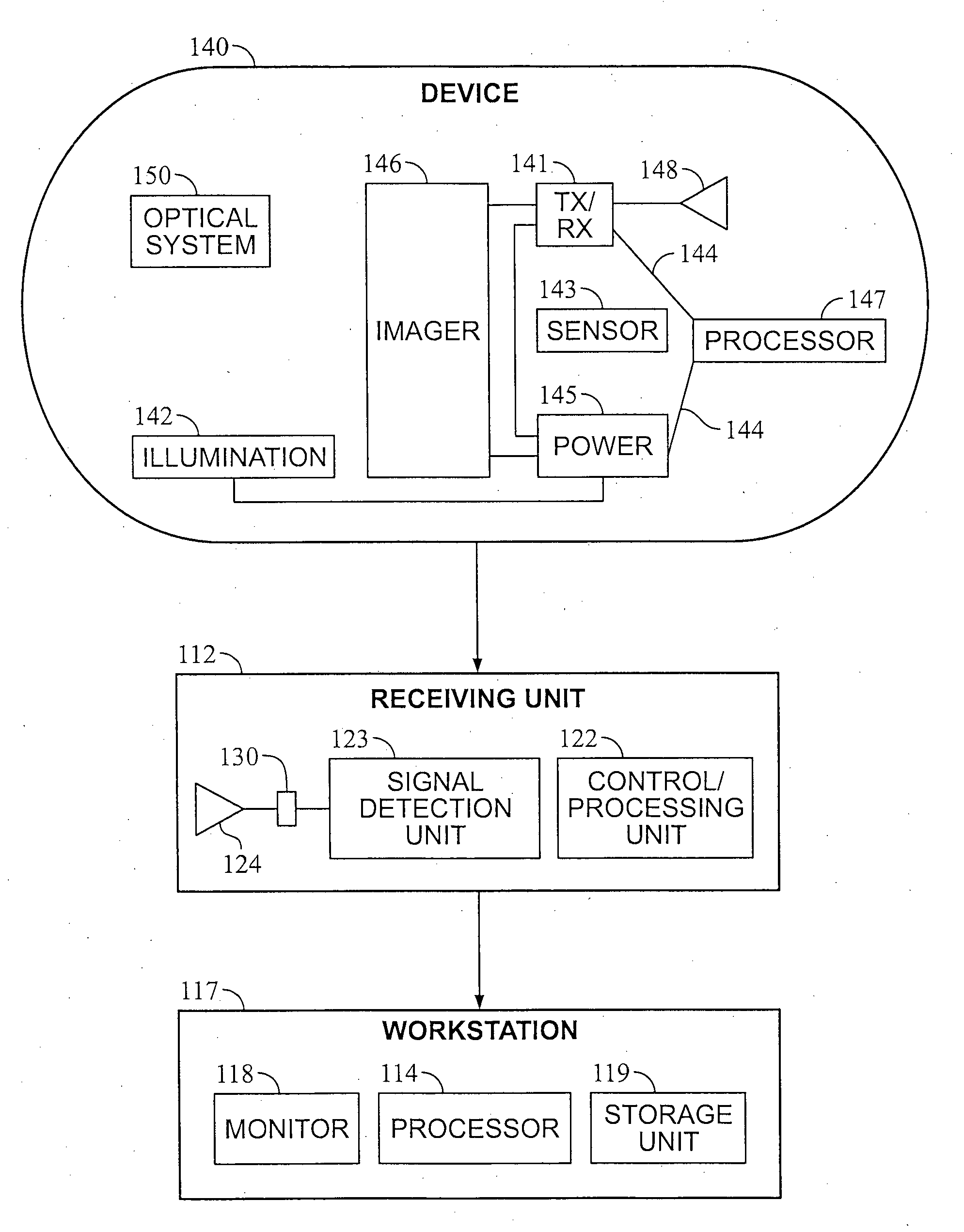
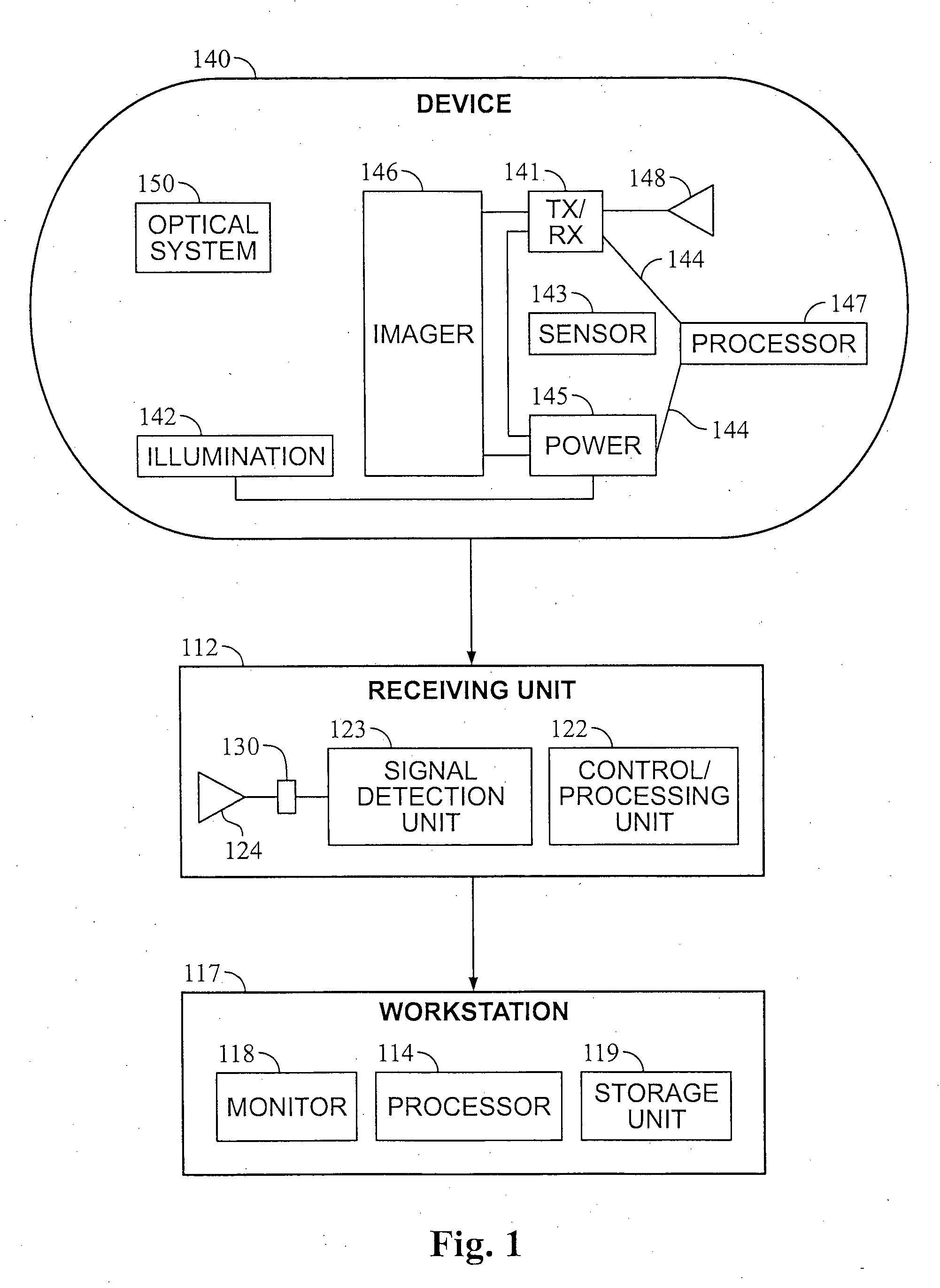
Capsule endoscope, capsule endoscopic system, and endoscope control methood
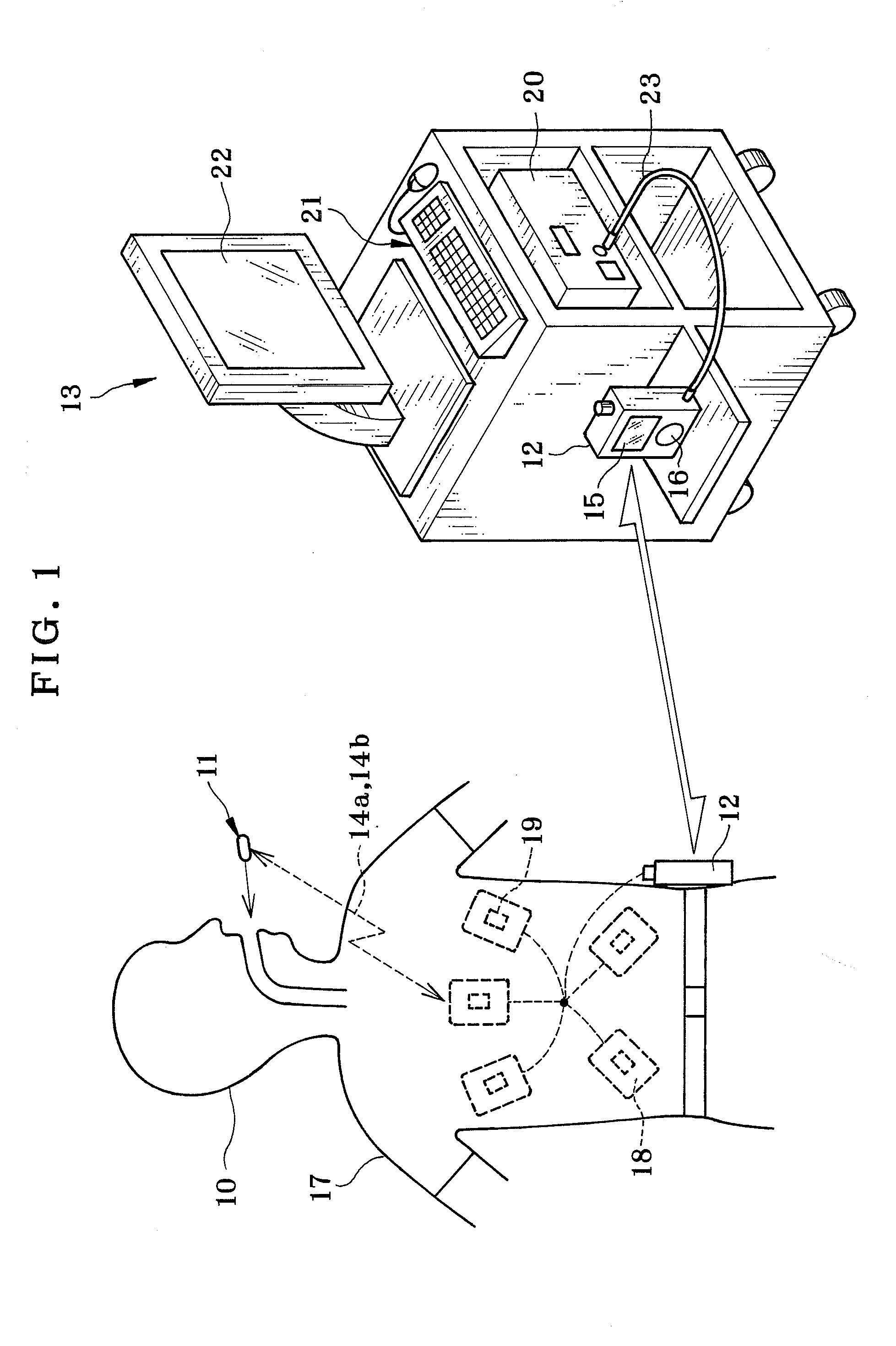
A capsule endoscope system includes a capsule endoscope and a receiver. The capsule endoscope has plural image pickup units for endoscopic imaging by passing a gastrointestinal tract in a body. The receiver for wireless communication with the capsule endoscope receives and stores image data from the capsule endoscope. The receiver includes a data analyzer for retrieving position relationship data expressing a position relationship of the image pickup units to a target region in the gastrointestinal tract. A CPU of the receiver produces a command signal according to the position relationship data for determining a number of frames of imaging per unit time for respectively the plural image pickup units. The capsule endoscope includes a CPU for controlling operation of the plural image pickup units according to the command signal from the receiver.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
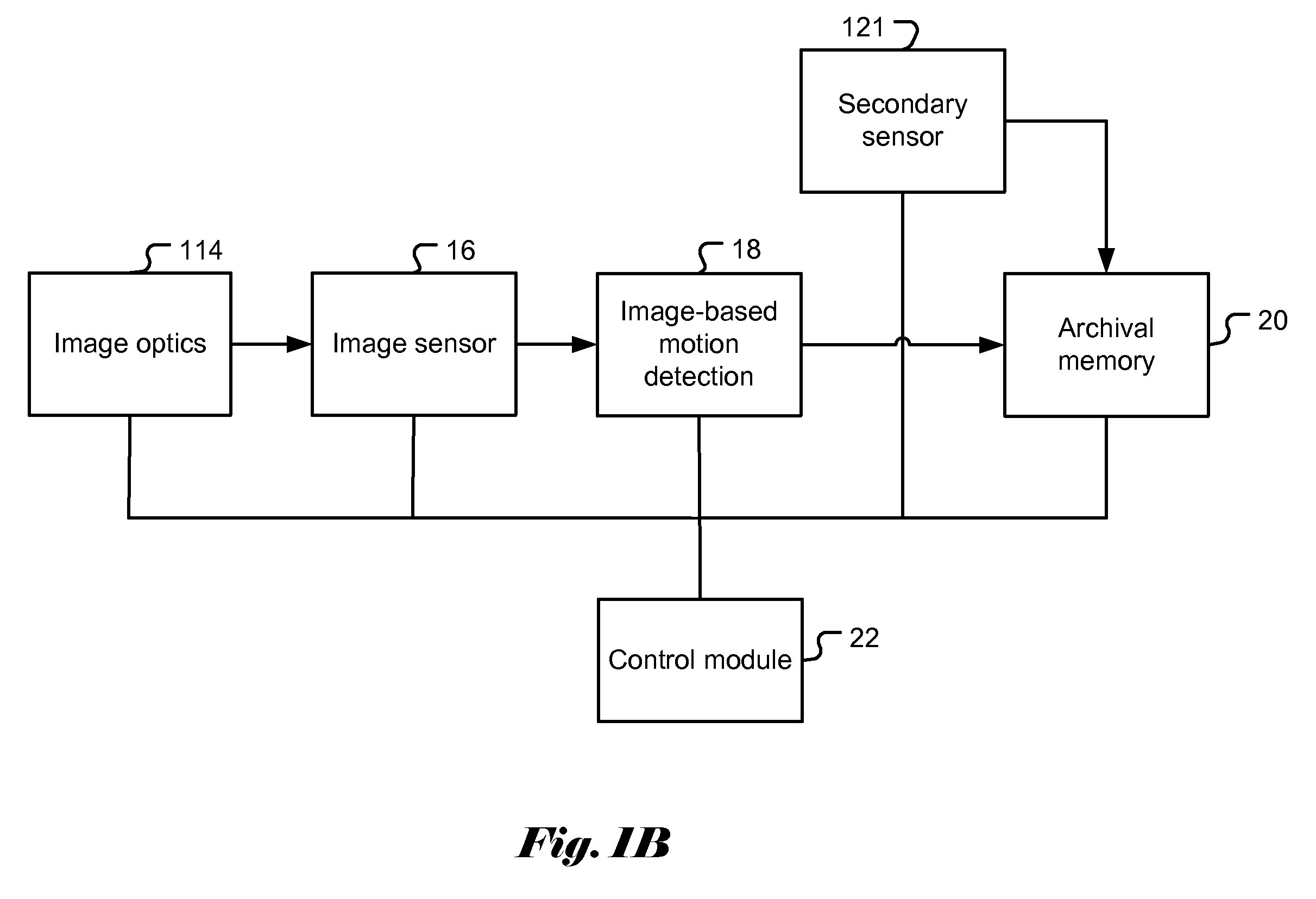
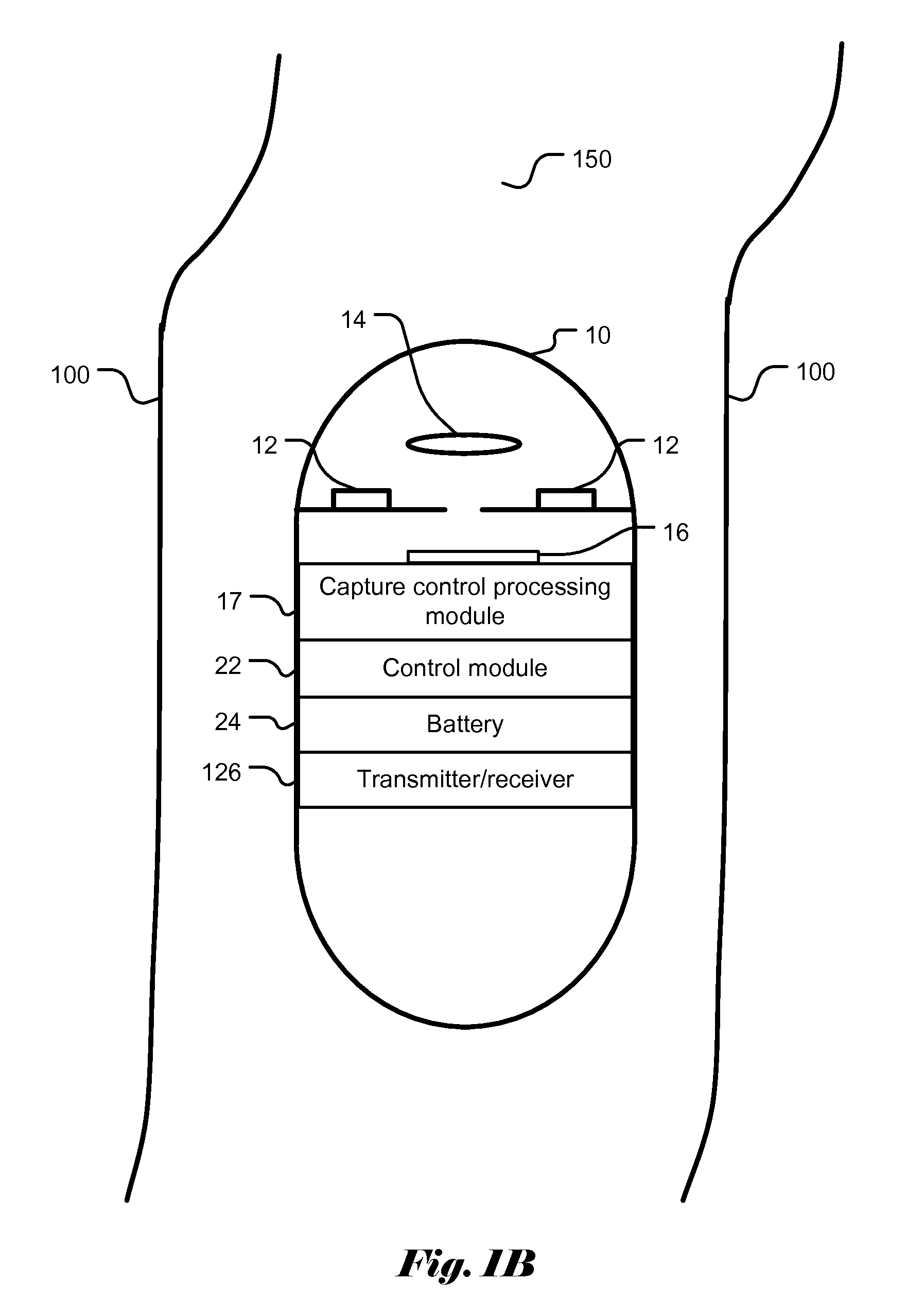
Image capture control for in vivo autonomous camera
ActiveUS20090322865A1Adjustable parametersTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsIntestinal wallsOn board
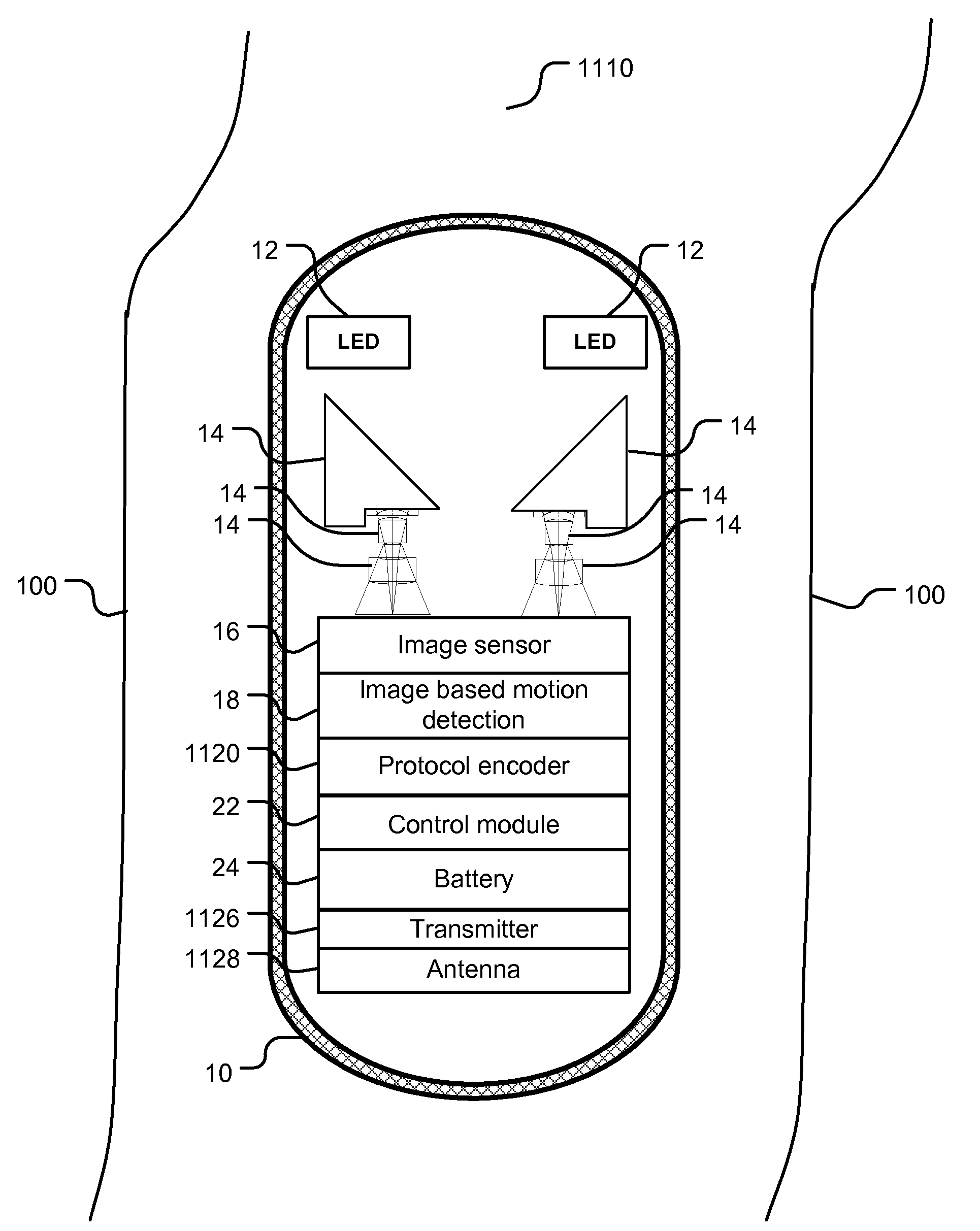
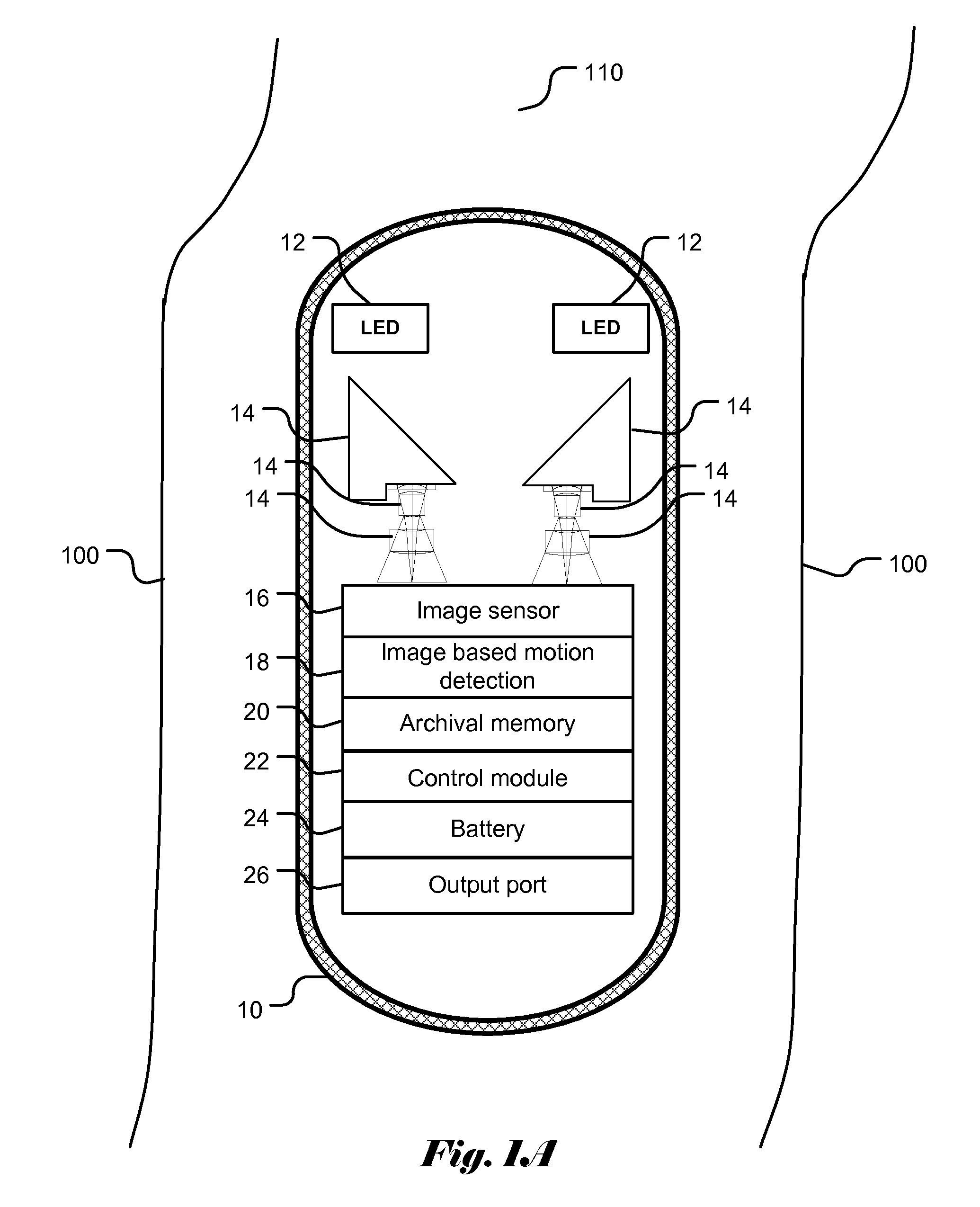
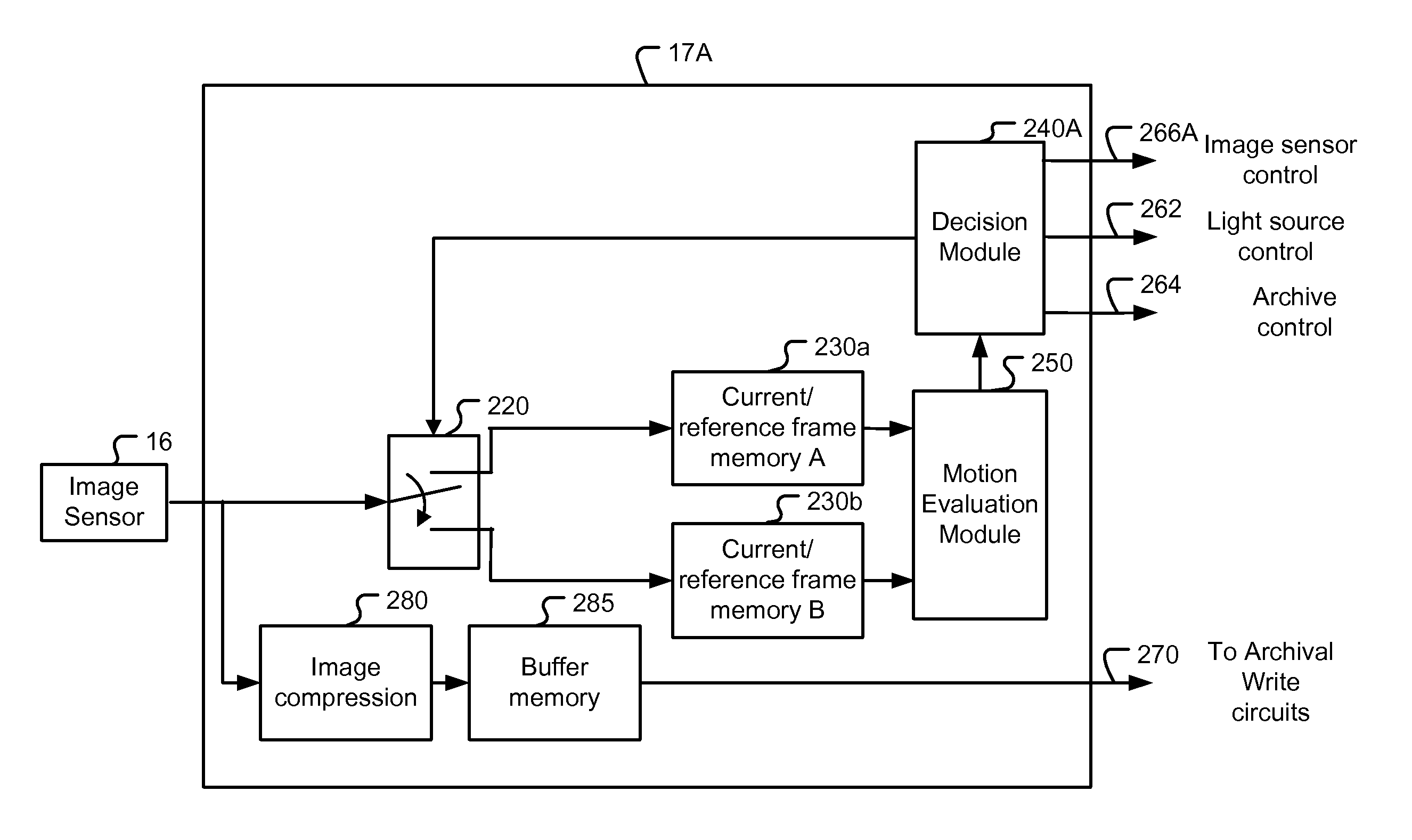
Systems and methods are provided for motion detection and capture control of video data from a capsule camera system having an on-board storage. The capsule camera system moves through the GI tract under the action of peristalsis and records images of the intestinal walls. The capsule's movement is episodic and jerky. The capacity of the on-board storage is limited. In order to avoid unnecessary capture of images when the capsule camera moves very slowly or stalls, motion detection technique is utilized to help control image capture. Furthermore, an adaptive capture control is disclosed that automatically adjusts the threshold level of capture control to maintain proper image capture. The invented capture control also conserves precious battery power by eliminating capture of unnecessary images when the capsule camera moves too slowly or stalls. The present invention of image capture control and threshold update is also applicable to a capsule camera system having a wireless transmitter instead of an on-board storage.
Owner:CAPSO VISION INC
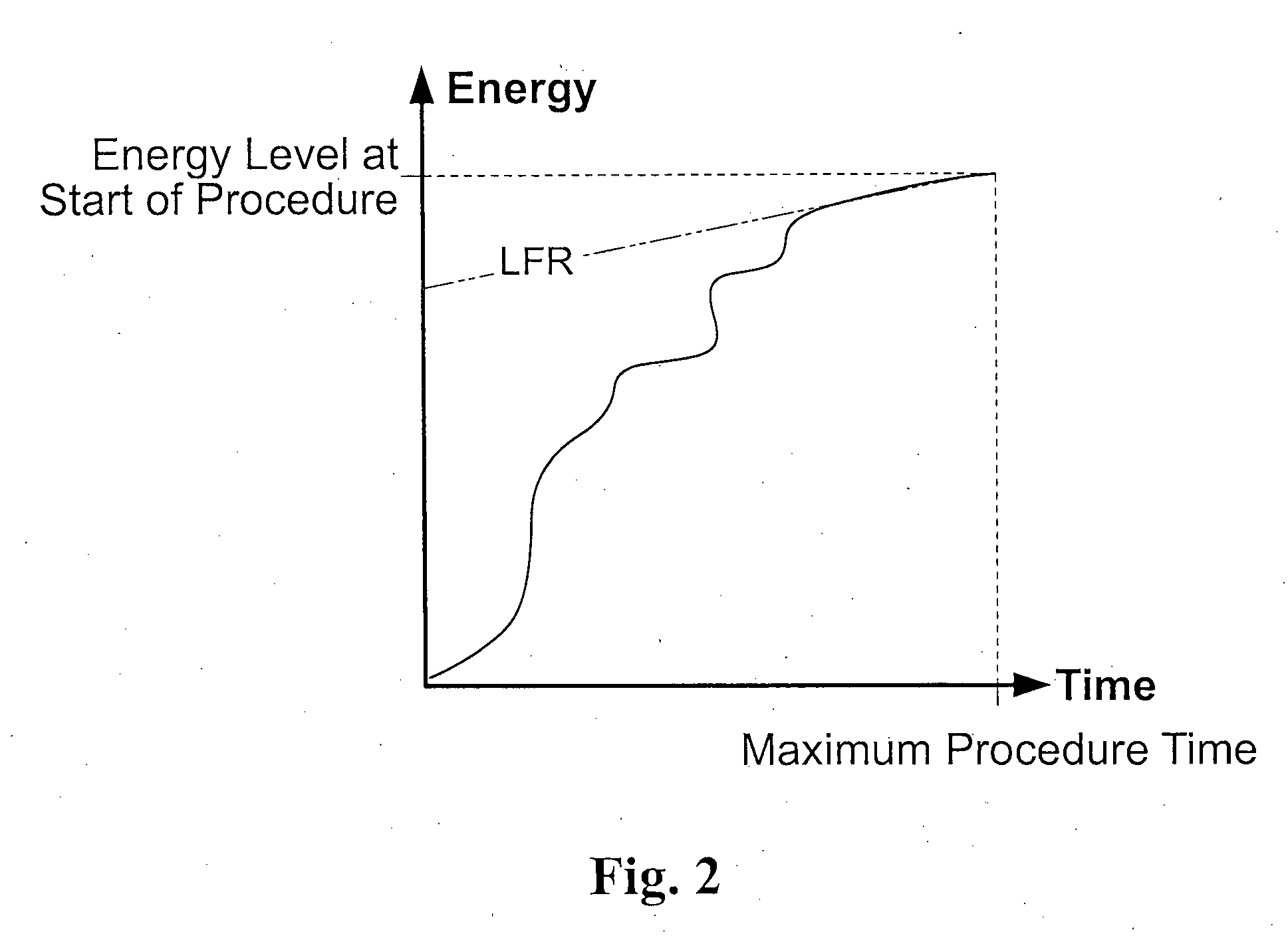
System and method for controlling power consumption of an in vivo device
A method and device may control energy consumption of in an in vivo imaging device by determining or estimating an amount of energy needed to capture images at a frame rate until a complete passage of the device through a predetermined region of the gastrointestinal tract, and alter or limit the frame capture rate accordingly.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
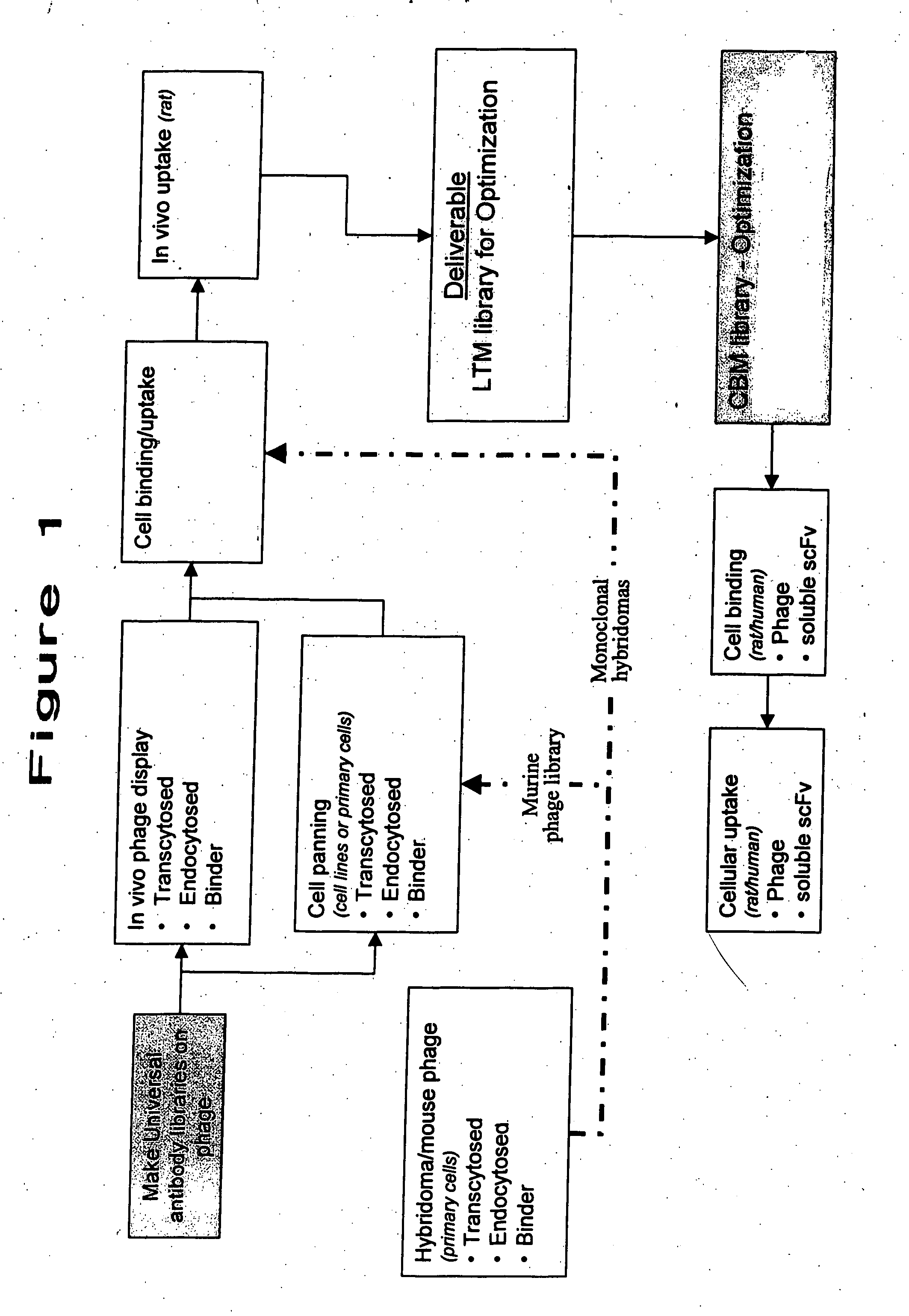
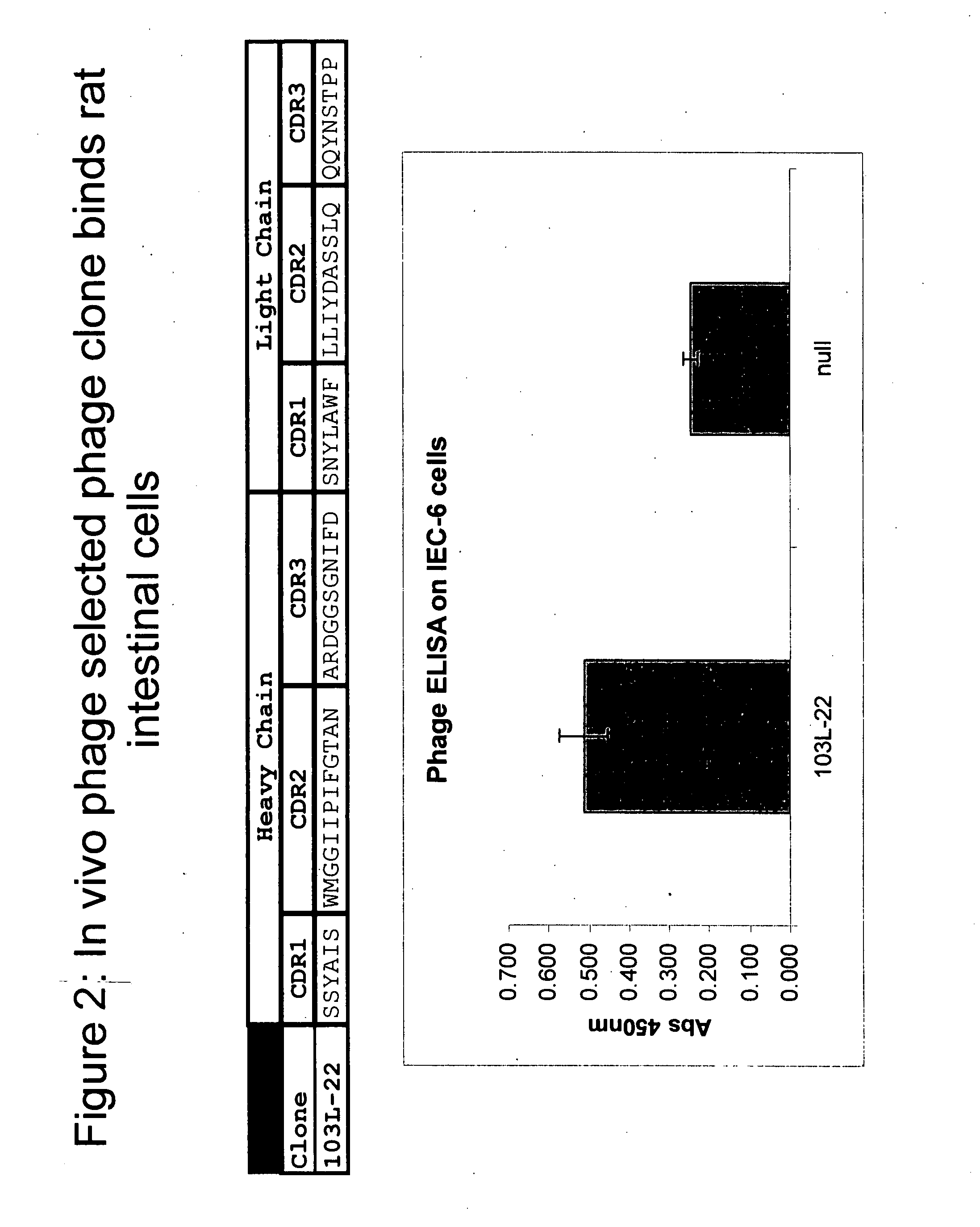
Facilitation of translocation of molecules through the gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS20070224627A1Increase in translocationPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalAntibody fragments
The invention concerns methods and means for facilitating the translocation of molecules through the gastrointestinal tract of mammals. In particular, the invention concerns methods for identifying antibodies, including antibody fragments, capable of translocation from the lumenal side of gastrointestinal tissue into the blood stream or into the lymphatic circulation. The invention further concerns the identification of sequences within or associated with such antibodies facilitating translocation through the gastrointestinal tract. The invention additionally concerns the use of such antibodies and sequences, or other molecules or moieties identified by using such antibodies or sequences, for facilitating oral delivery and absorption of molecules, such as biomolecules (including proteins and nucleic acids), antibodies, peptides, and non-peptide small molecules.
Owner:I2 PHARMA INC
Device, system and method for in vivo light therapy
InactiveUS20130053928A1Increase volumeSlow motionDiagnostics using spectroscopyEndoscopesLight therapyTherapeutic Devices
A swallowable in vivo therapeutic device, and a method for use of a device. The device may include a transparent case and one or more radiation sources, the radiation sources to treat the detected pathological lesions inside the gastrointestinal (GI) tract with light during the passage of the device through the GI tract. A method may include inserting into a patient a device, rotating external magnets in close proximity to the patient, thereby fully controlling the movement of the device inside the GI tract, stopping the device and activating the light radiation in areas of the pathological lesions for a predetermined period of time, and deactivating the light radiation and moving the device further through the GI tract.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Animal Medicine Reminder Tag
ActiveUS20120236690A1Reduced tendency to cause harmStampsMechanical clocksHazardous substanceShock resistance
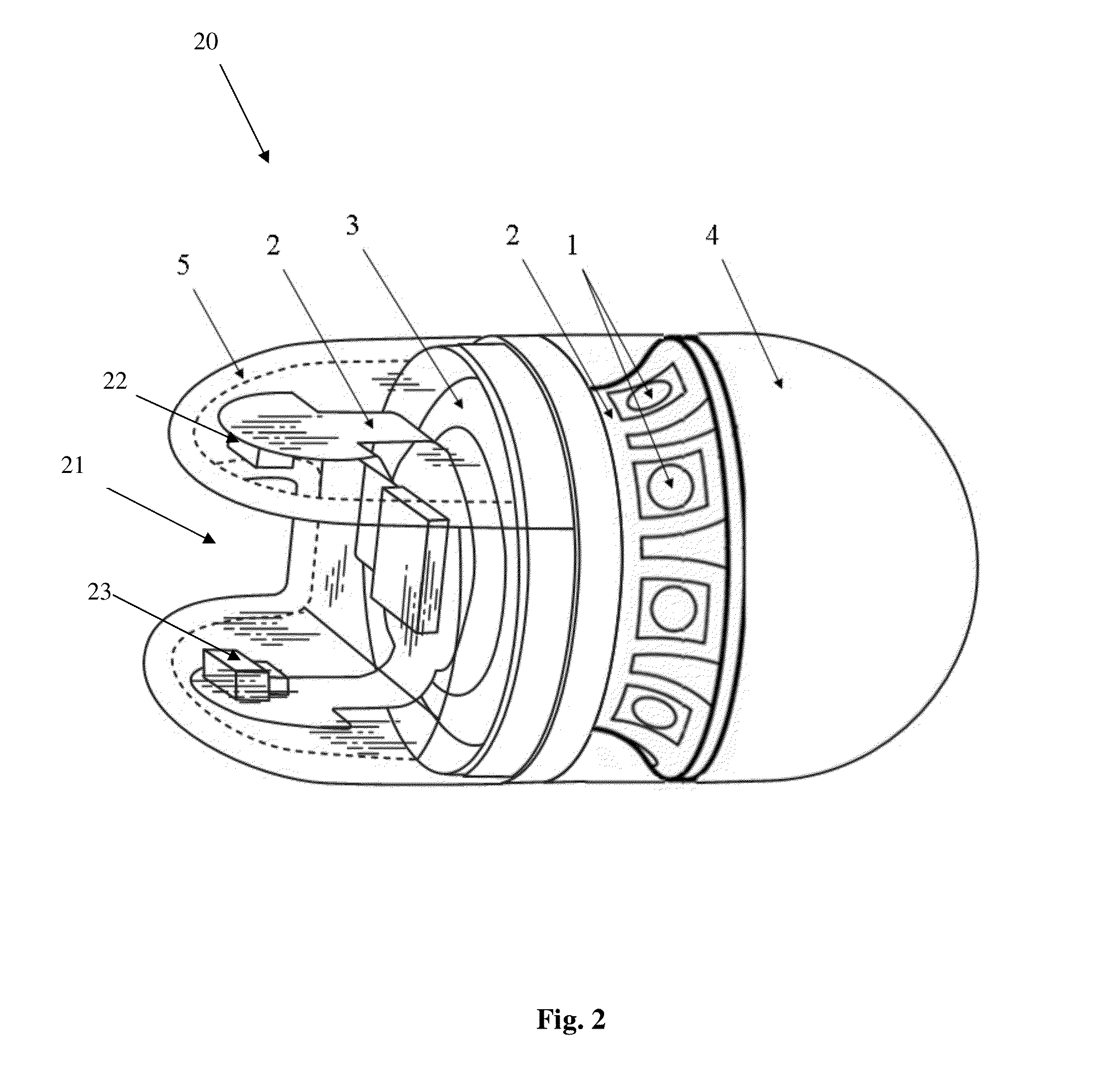
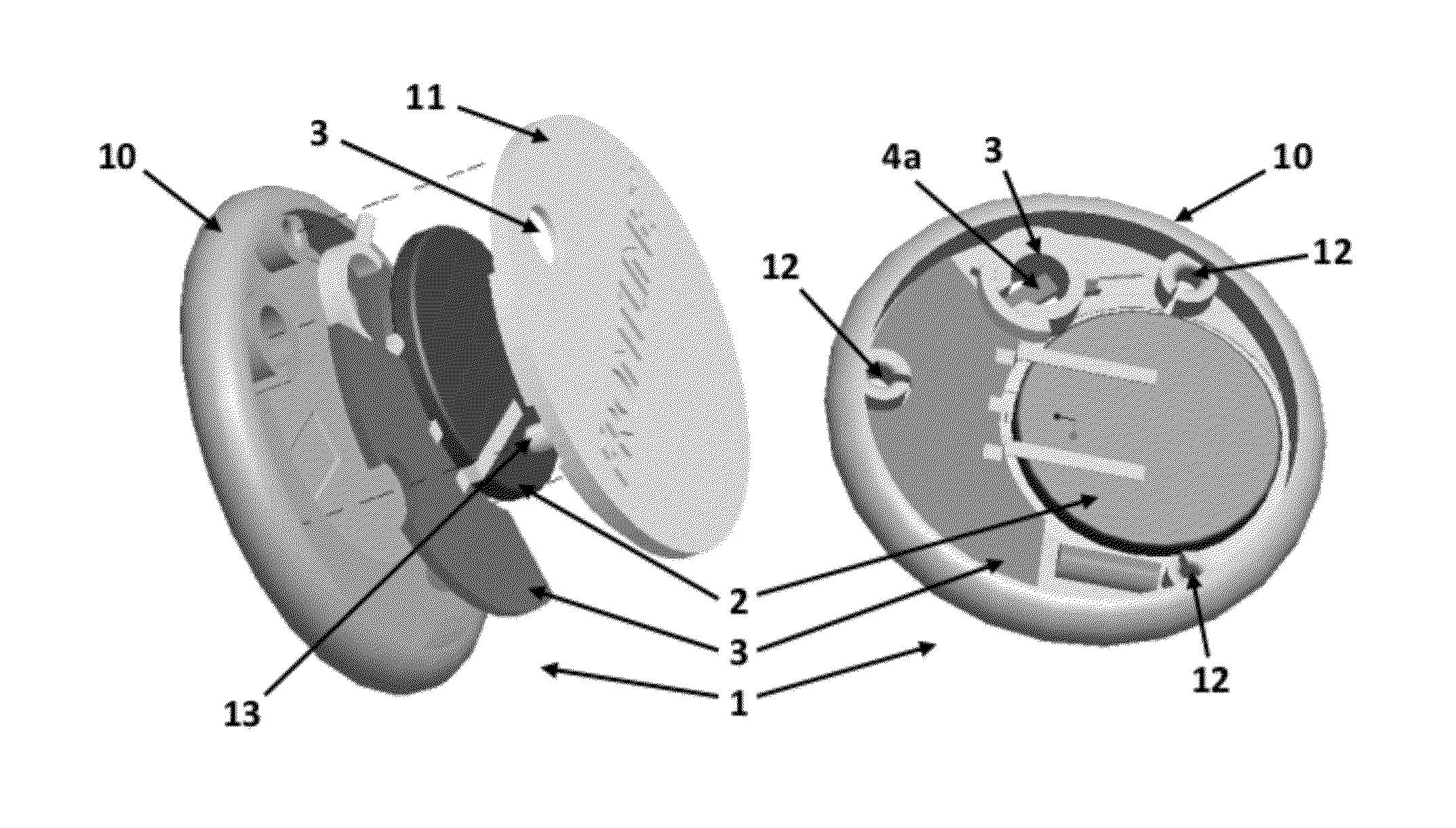
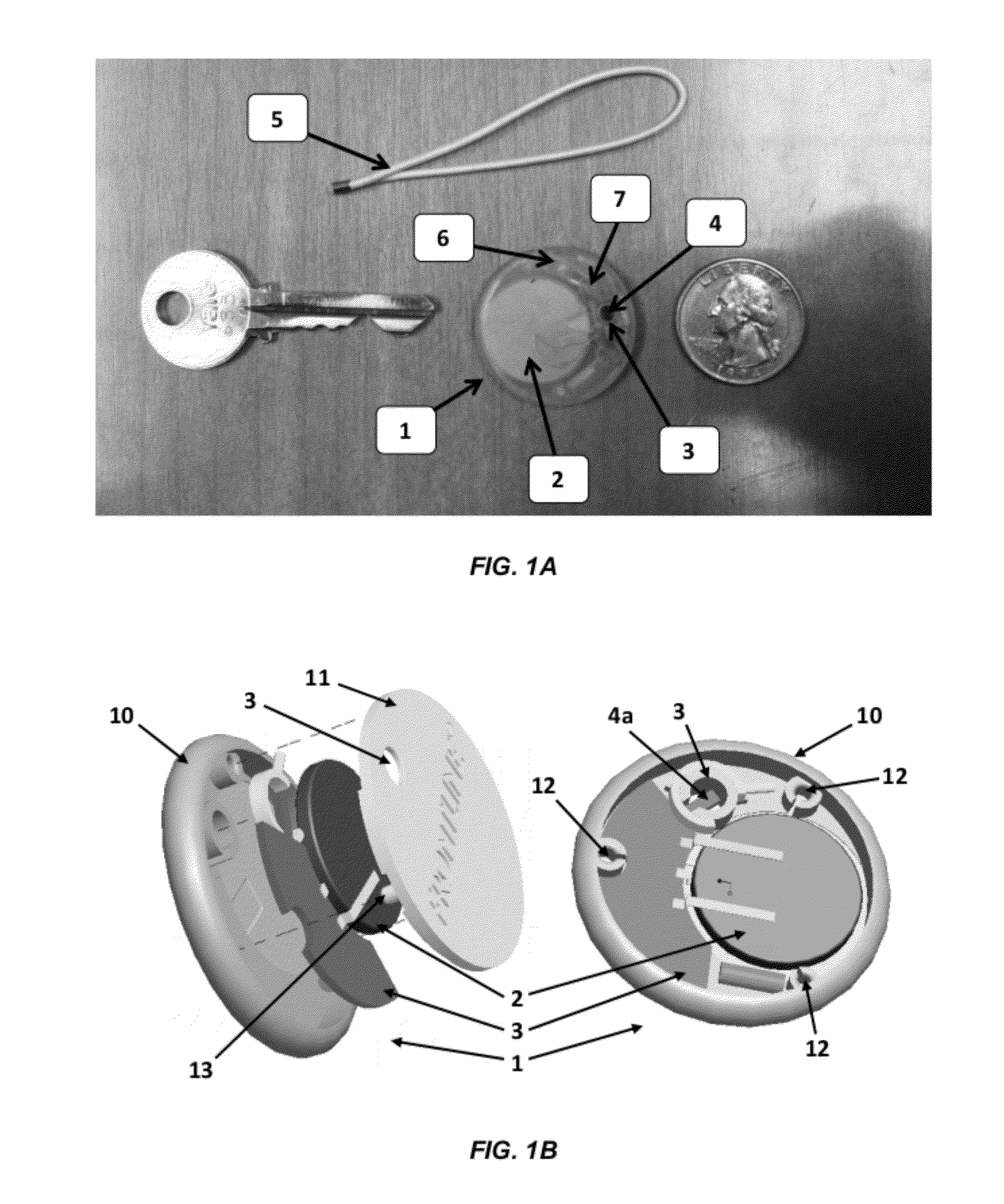
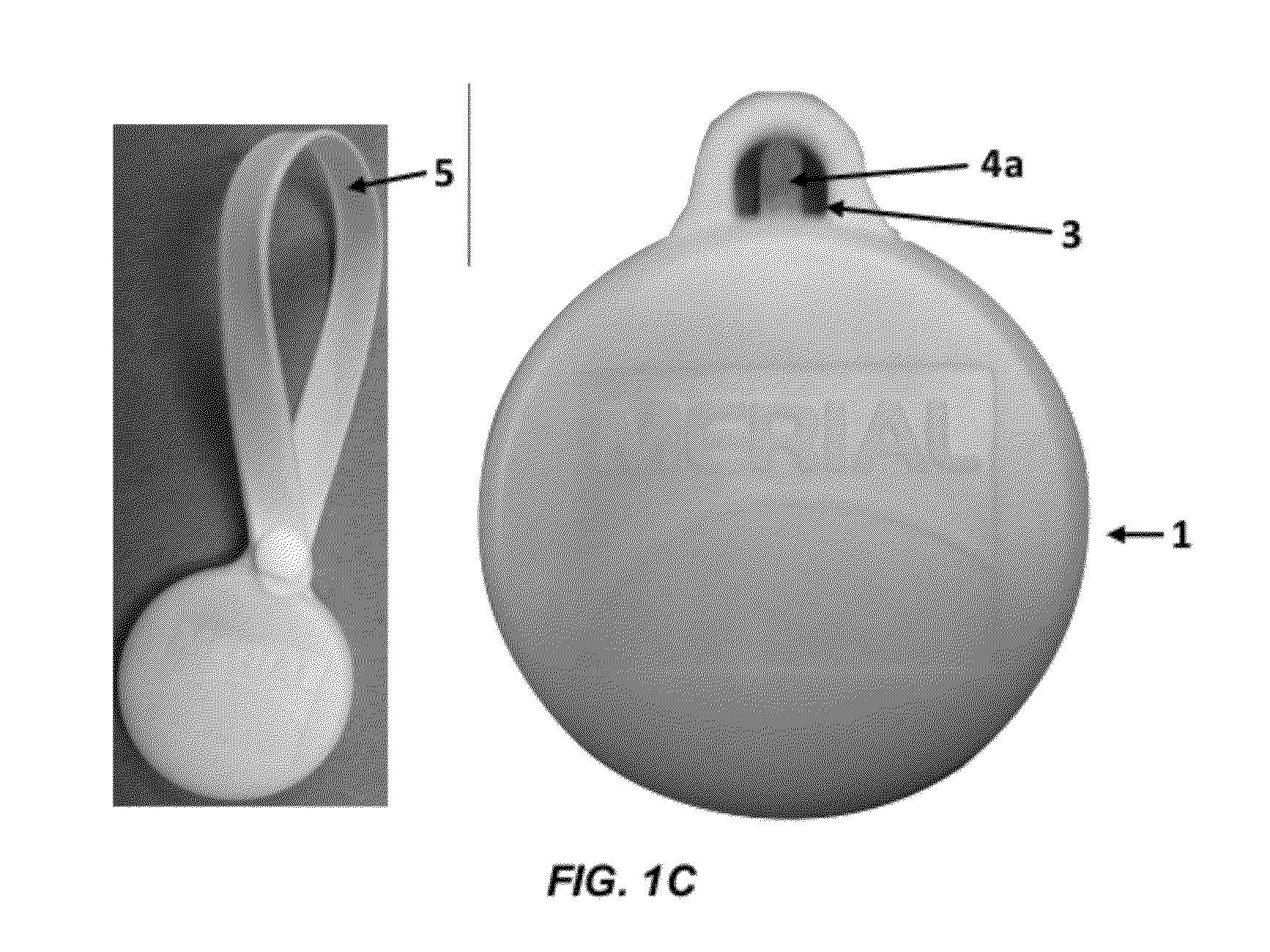
The present invention provides for an animal medicine reminder tag that is non-toxic, water resistant, and shock resistant. The tags described herein are excellent medicine compliance tools as they 1) are automatically activated when attached to the companion animal; 2) produce a persistent reminder after a manufacturer-programmed set period of time; 3) cannot be reset or turned off by the companion animal's caregiver; 4) emit the alarm / signal from both sides; 5) are sealed and non-toxic; and 6) are designed to be minimally harmful if accidentally swallowed, and may even pass safely through the gastro-intestinal tract for sufficiently large animals.
Owner:MERIAL INC
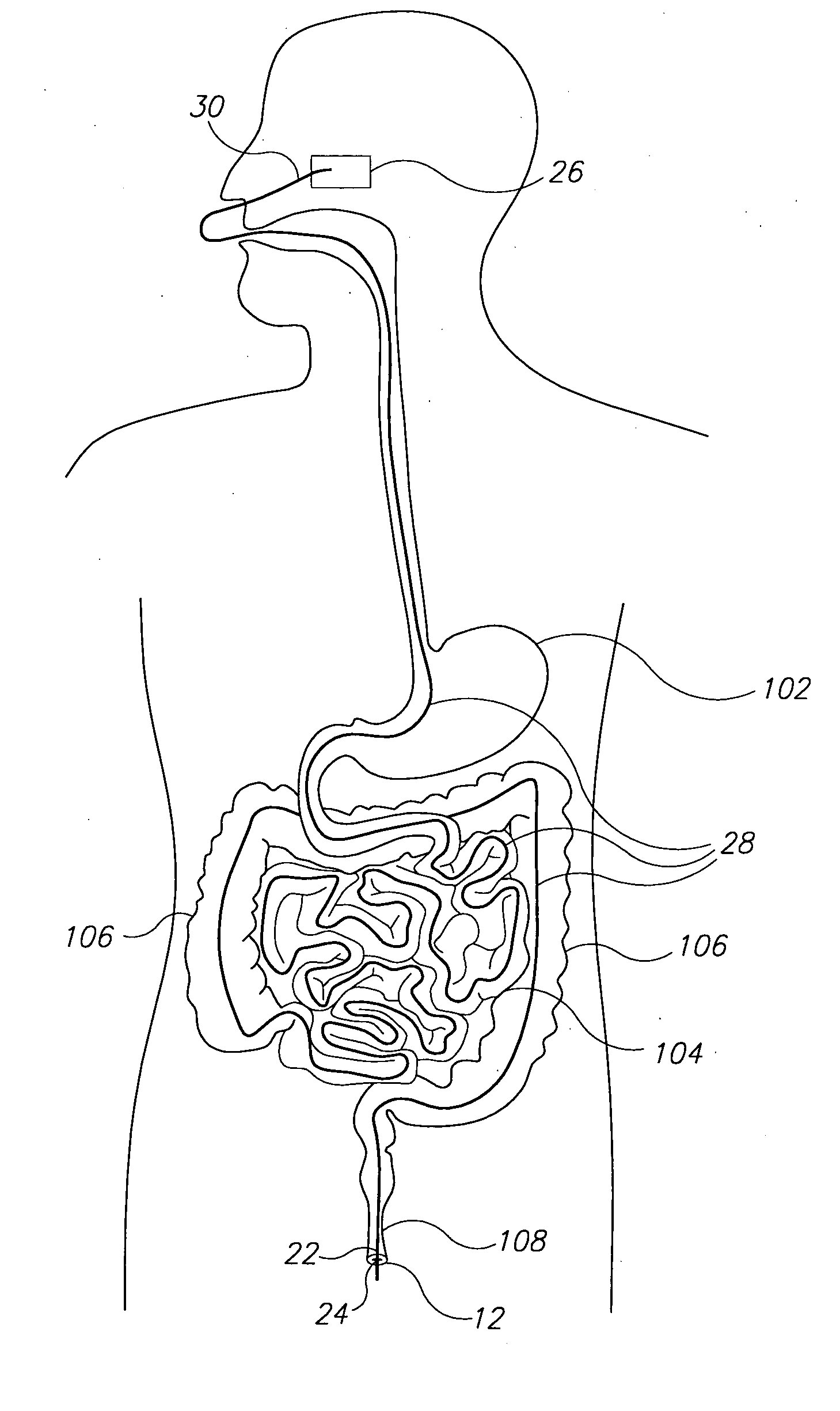
Administration of drugs to a patient
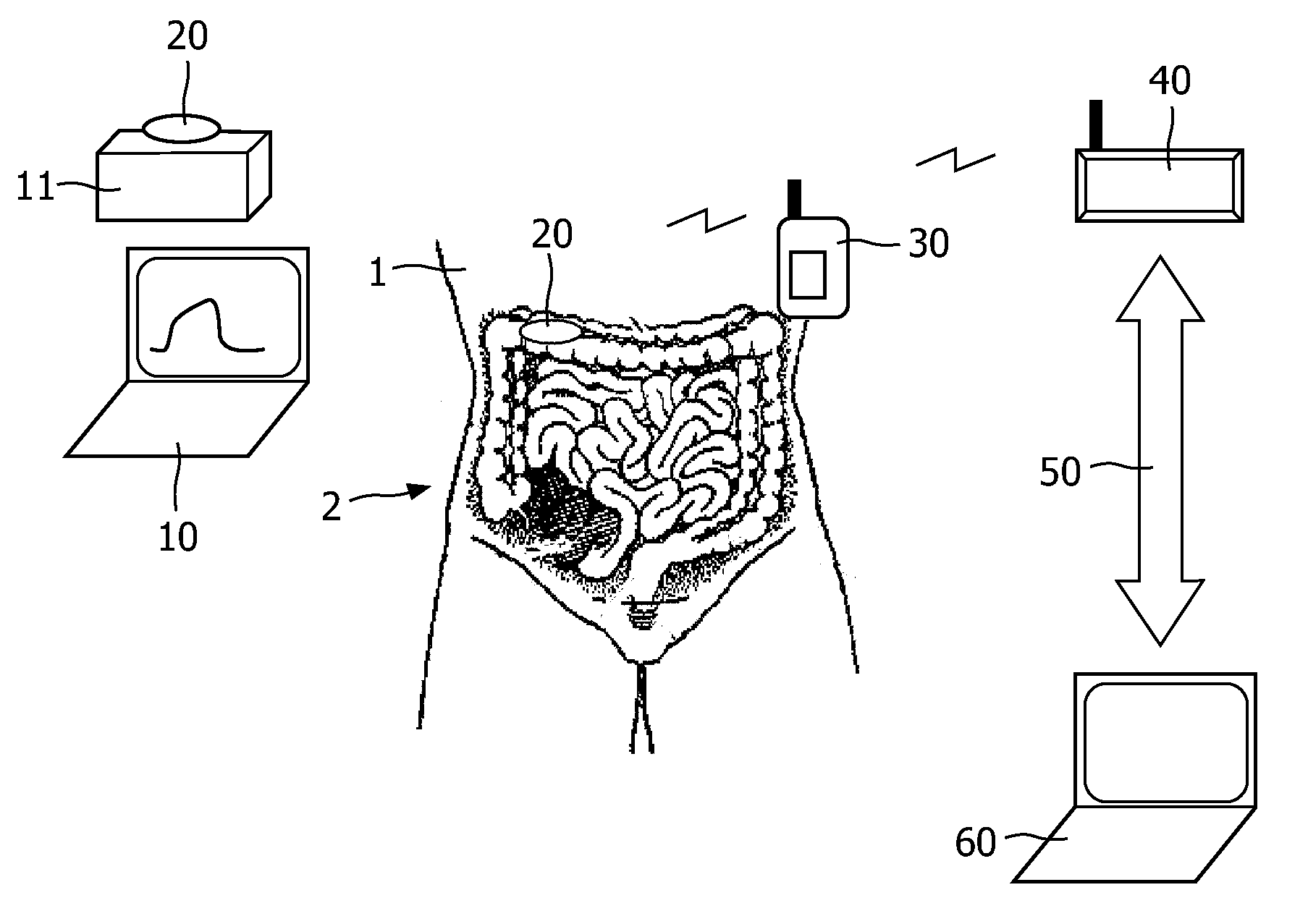
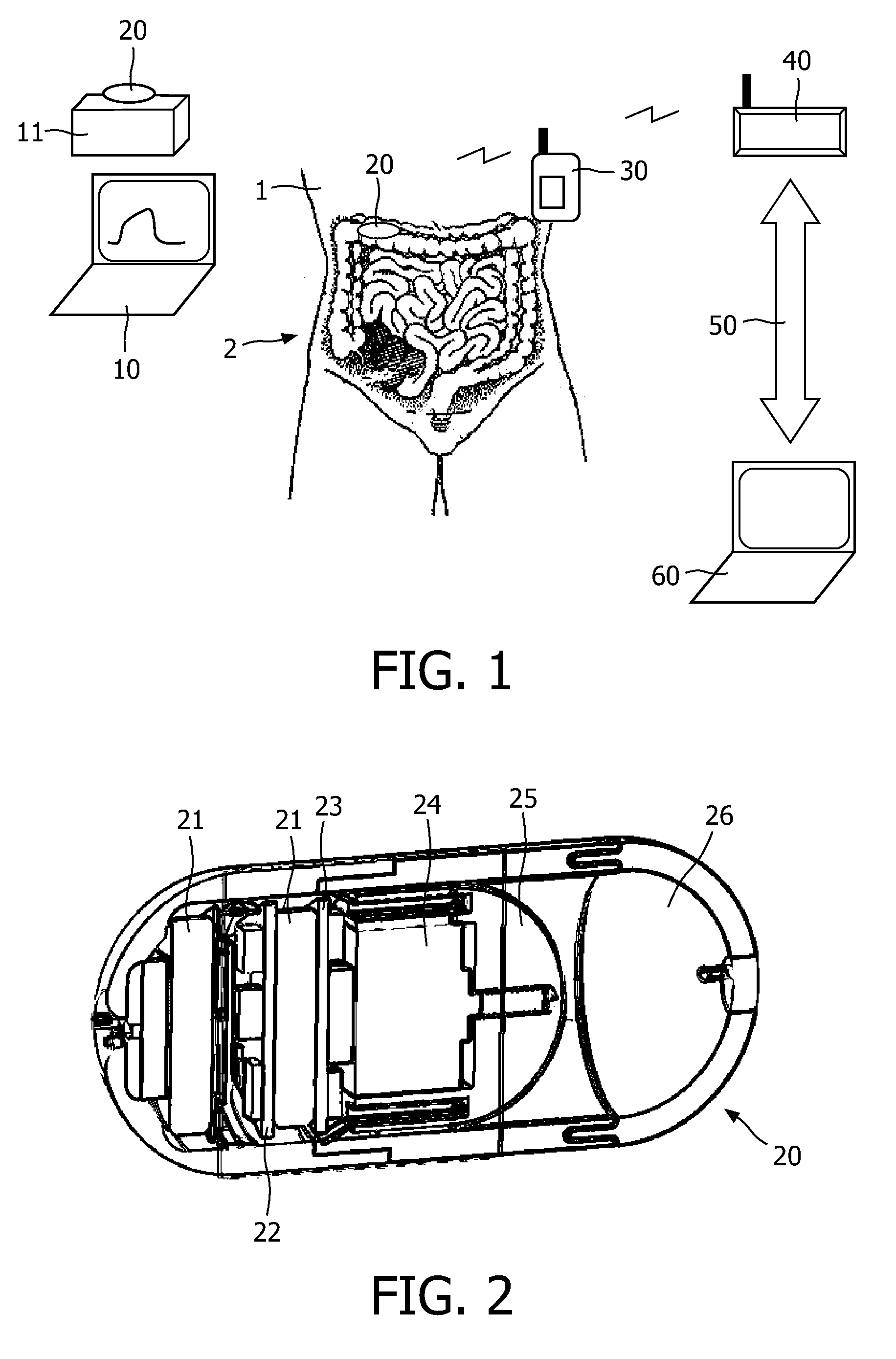
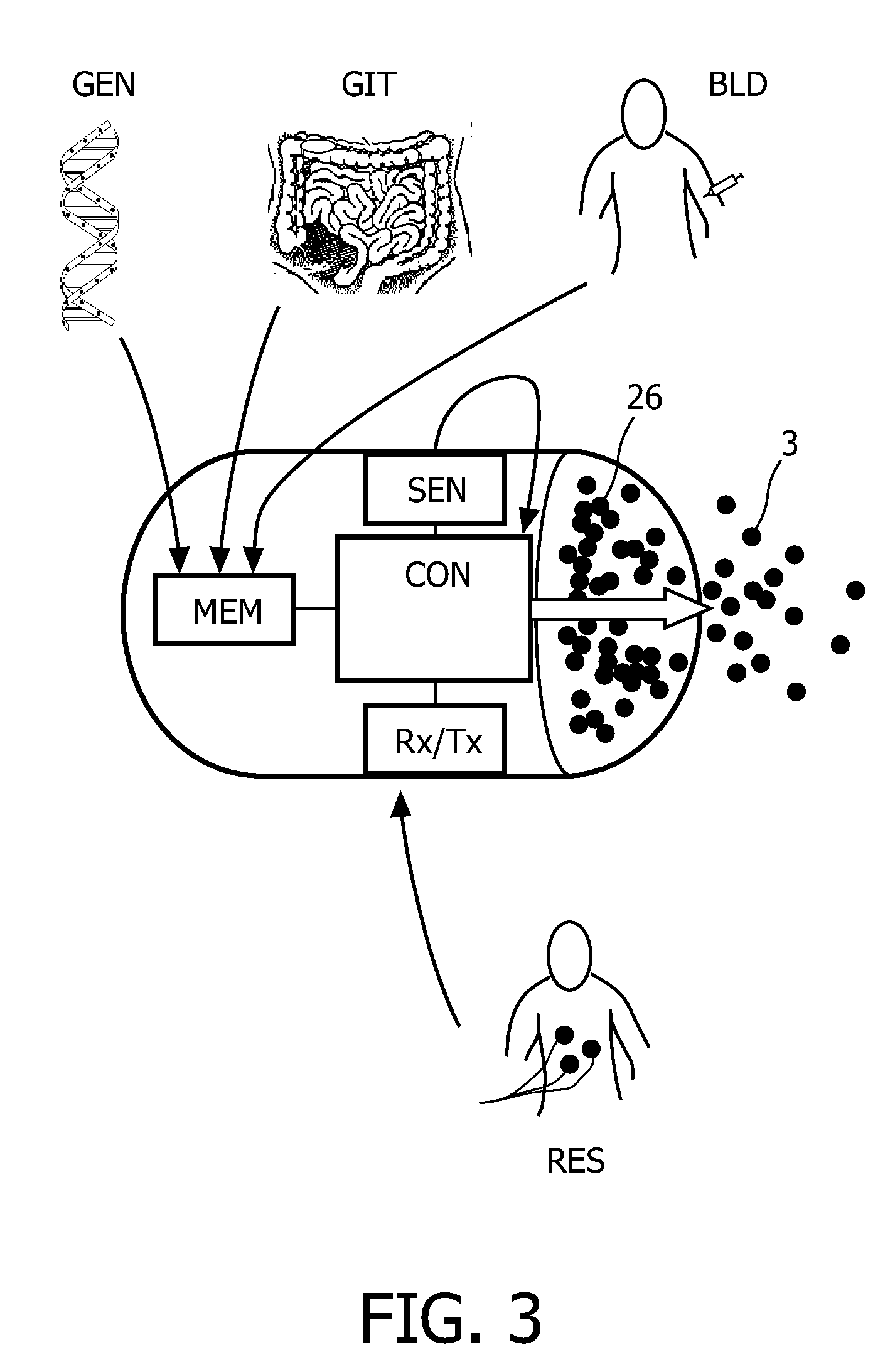
InactiveUS20100331827A1Improve efficiencyImprove securityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedical devicesMedicineVia gastrointestinal tract
The invention relates to a method and an electronic pill (20) for the administration of at least one drug (3) to a patient, wherein the delivery profile of the drug is determined according to at least one individual parameter of the patient. The individual parameter may particularly relate to the genotype (GEN) or phenotype of the patient and for example comprise the distribution of proteins in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Optionally, the individual parameter may be adjusted based on measurements by the electronic pill or external devices during its passage through the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:PROGENITY INC
Residence structures and related methods
InactiveUS20170266112A1Facilitate dissociationTetracycline active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismStimulantDissolution
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Spray administration of compositions including active agents such as peptides to the gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS20100145301A1Delay deploymentIncrease the diameterElectrocardiographyPeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentAdditive ingredient
Methods of administering an active agent such as an active pharmaceutical ingredient by spraying a composition comprising the active agent at a luminal wall of the gastrointestinal tract are disclosed. Also disclosed are devices for administering a composition suitable for implementing the disclosed method. Also disclosed is the use of a peptide as an active agent for the manufacture of a sprayable composition for use in the treatment of a subject by gastrointestinal administration.
Owner:DUOCURE
Gastrointestinal stimulator device for digestive and eating disorders
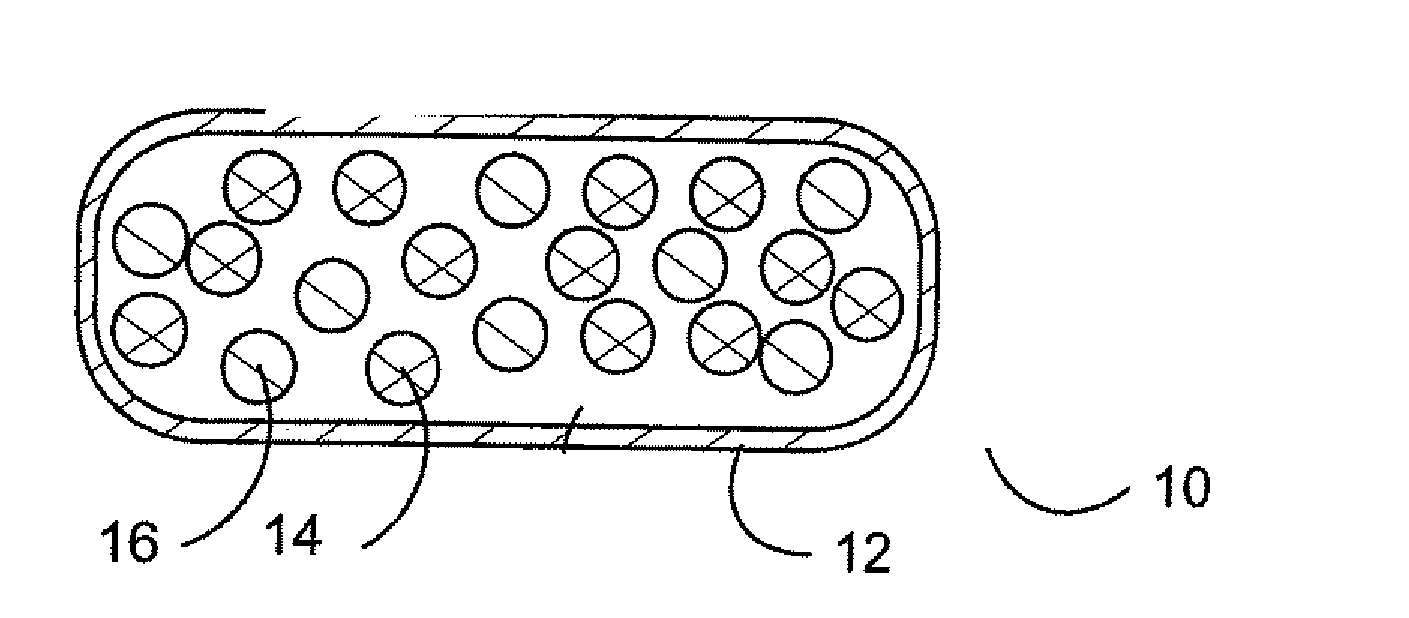
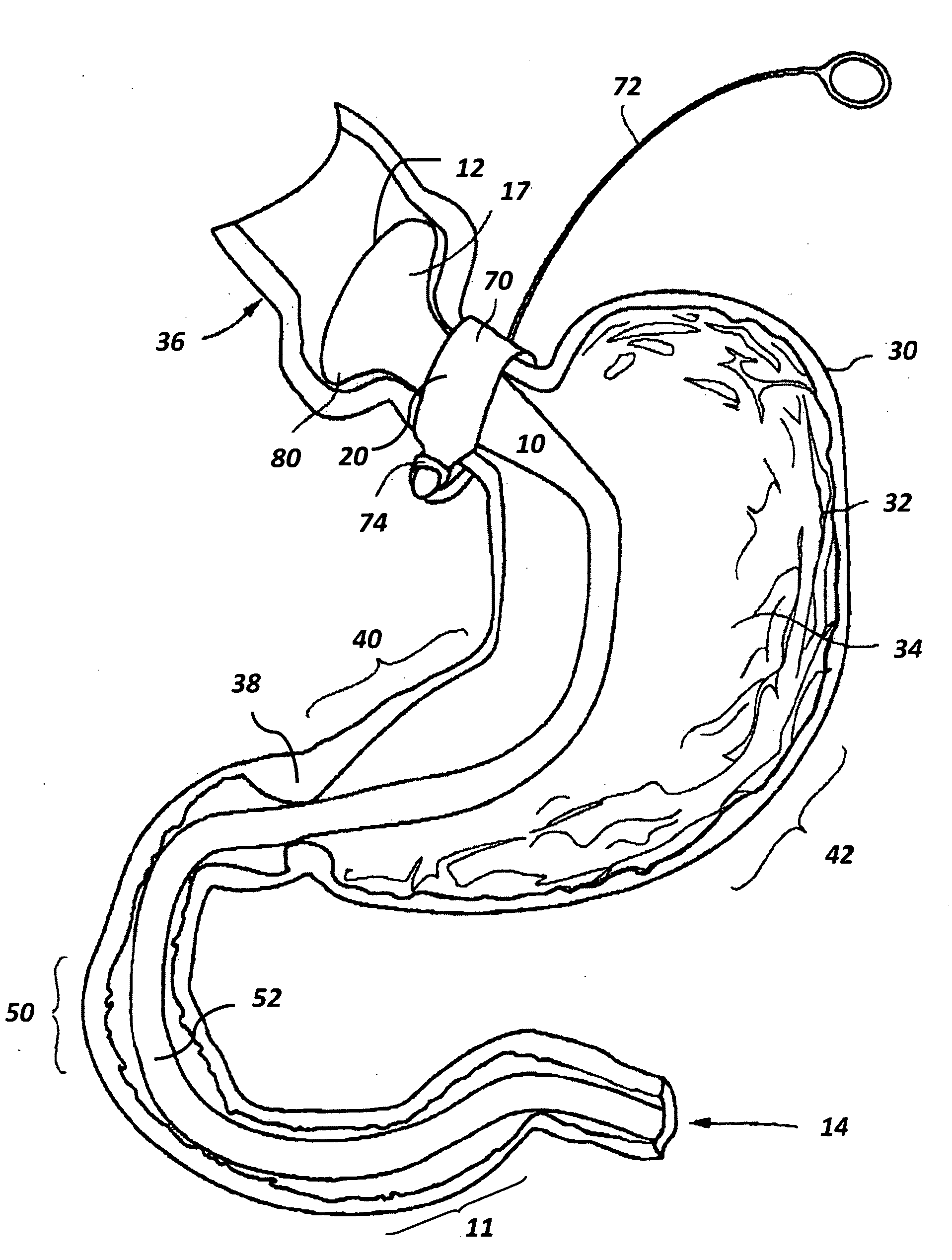
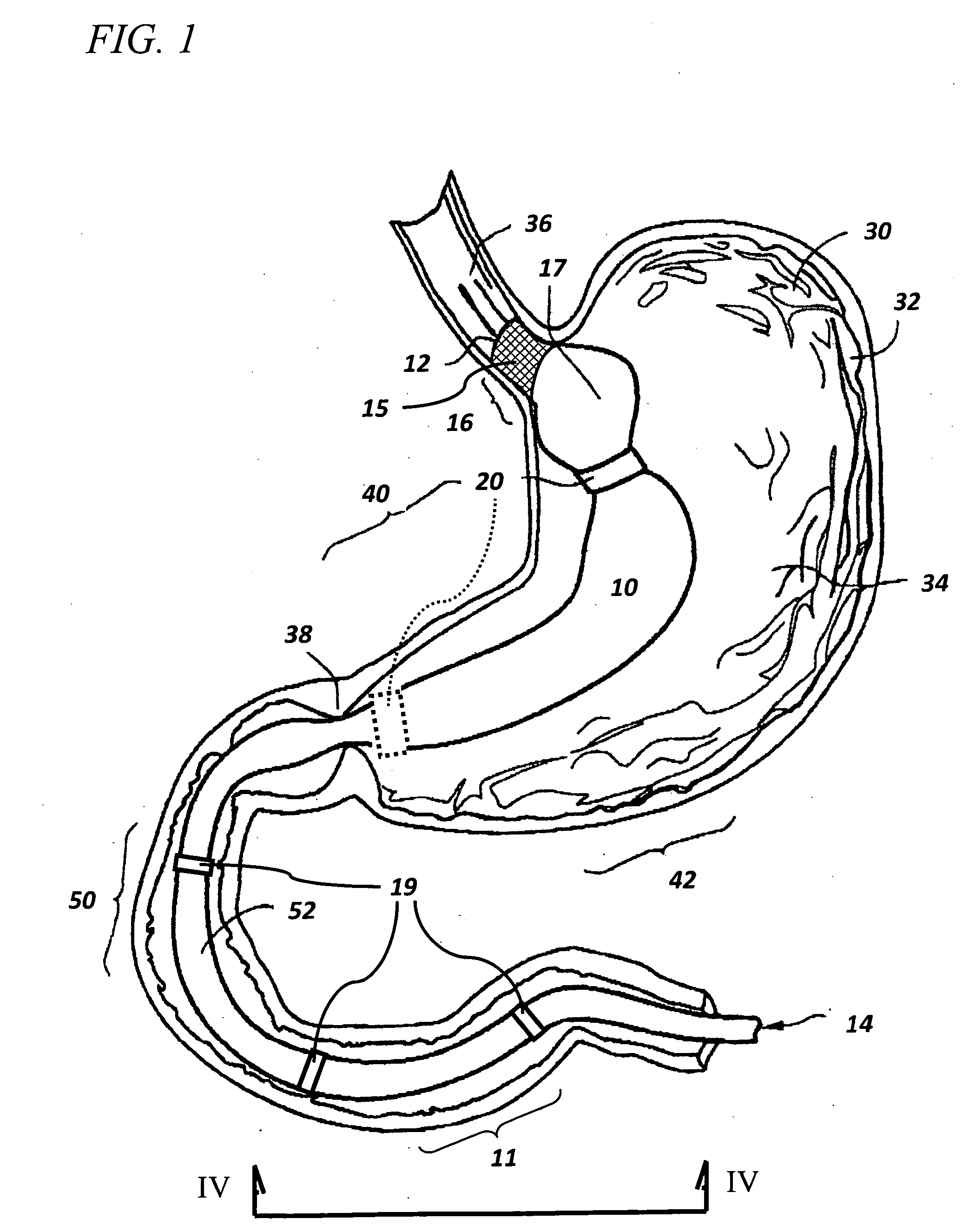
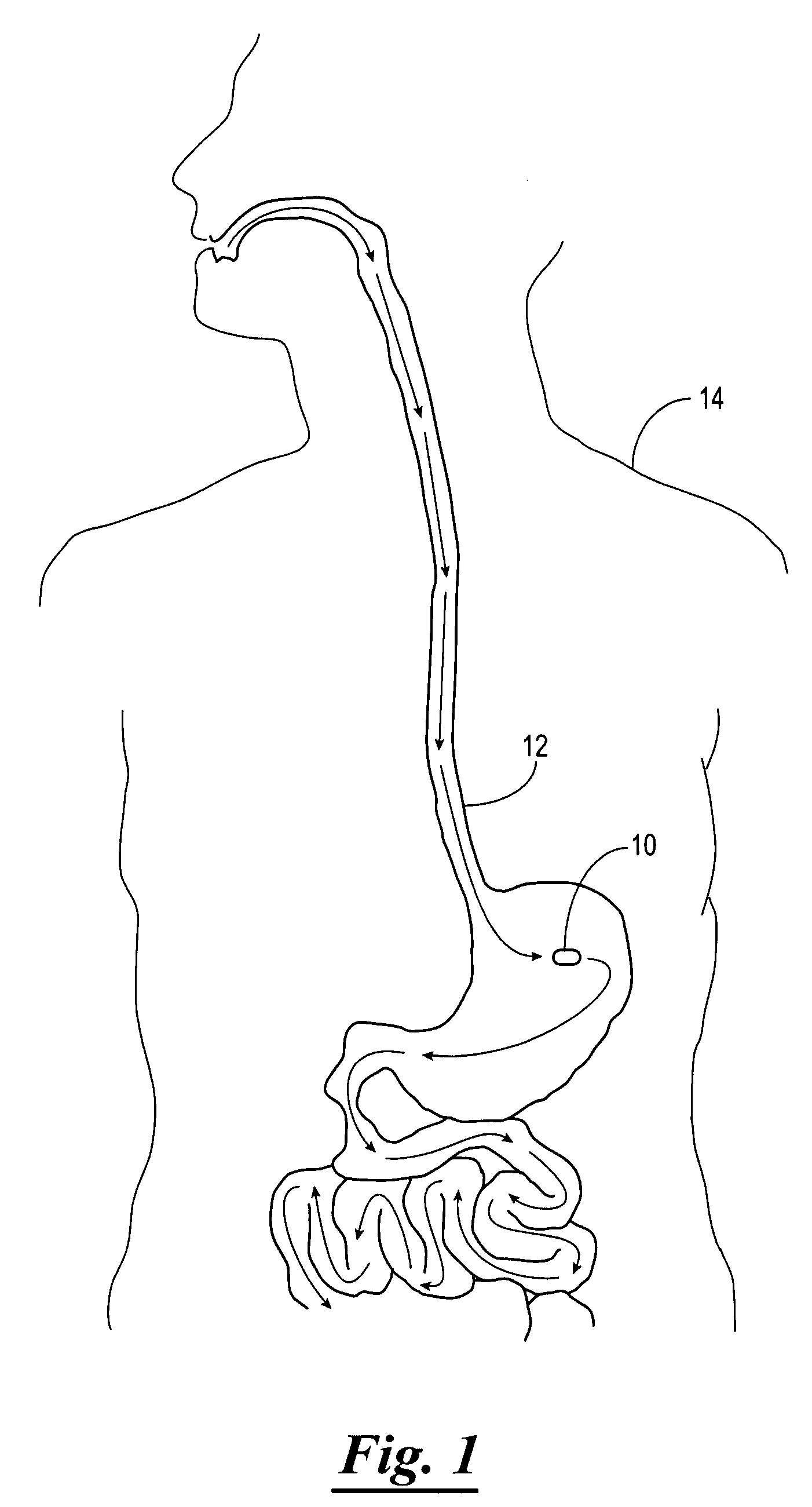
A stimulator device for providing stimulation to the gastrointestinal tract of a user including a housing, at least two electrodes, and a pulse generator. The housing has an exterior surface and an interior surface defining a sealed interior space. The housing is constructed of bio-compatible materials and sized and shaped for transport through the gastrointestinal tract. A portion of the at least two electrodes is disposed on the exterior surface of the housing. The pulse generator is disposed in the interior space of the housing and delivers pulses to the electrodes. Also presented are methods of using a stimulator device in the treatment of: gastrointestinal disorders such as dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux diseases, functional dyspepsia, gastroparesis, postoperative ileus, irritable bowel syndrome, constipation, diarrhea, fecal incontinence, nausea and vomiting; gastrointestinal obstruction or pseudo-obstruction; pain and / or discomfort related to visceral organs; eating disorders, such as obesity, binge eating, bulimia, anorexia, and chemotherapy-induced emesis or emesis of other origin.
Owner:TRANSTIMULATION RES
Solid oral film dosage forms and methods for making same
InactiveUS20110136815A1Dissolve fastGood water solubilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCosmetic ingredientSublingual Absorption
Improved pharmaceutical solid oral film dosage forms for the buccal and / or sublingual delivery of pharmaceutical, nutraceutical or cosmetic ingredients are endowed with instant hydration potential and complete dissolution potentially enabling the active ingredient to become immediately available for enhanced buccal and / or sublingual absorption and / or reduced absorption through the gastrointestinal route. The improved delivery systems for solubilizing and stabilizing pharmaceutically active ingredients exhibit enhanced stability by the use of a combination of crystallization inhibitors, which together can maintain the active ingredient in a desired plurality of particles in an effective size range within a polymeric film matrix.
Owner:INTELGENX CORP
Dipyridamole self-emulsifying medicament administration system and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101780037AHigh dissolution ratePromote absorptionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDipyridamolePeristalsis
The invention discloses a dipyridamole self-emulsifying medicament administration system, which is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by mass: dipyridamole 0.5-10, an oil phase 20-80, a surfactant 10-70 and an auxiliary surfactant 0-50. The system has the advantages that: self-emulsifying capsules prepared by using the dipyridamole, the oil phase, the surfactant and the auxiliary surfactant change into emulsion by slightly stirring after disintegrating in water or spontaneously change into emulsion in vivo under the action of the peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tracts after being delivered by oral taking, wherein the particle size of the emulsion is 10 to 500 nanometers; the dissolution of the dipyridamole is improved greatly; after the system is taken orally, the absorption of the medicament is improved greatly, the bioavailability is improved and the individual difference is reduced; and the preparation process is simple and is suitable for large-scale production of medical enterprises.
Owner:SHENZHEN HEPALINK PHARMA GRP CO LTD
Pyloric valve devices and methods
InactiveUS20090259237A1Avoid flowIntravenous devicesTubular organ implantsLinear configurationEngineering
A pyloric valve is provided for inhibiting the flow of chyme through the pyloric region of the gastrointestinal tract. The pyloric valve includes a blocking portion having a plurality of disc-shaped flanges connected in series. The blocking portion may be disposed in a contracted position wherein the plurality of disc-shaped flanges is disposed in a stacked configuration and a resting position wherein the plurality of disc-shaped flanges is disposed in a linear configuration. The pyloric valve may further include a sleeve that may have a beveled distal end. The pyloric valve may be constructed of silicon. Also provided are methods of inserting and removing the pyloric valve, which each include a step of manipulating the support between its resting and contracted positions. Insertion and removal systems are also provided for use with the pyloric valve.
Owner:E2 LLC DENTONS
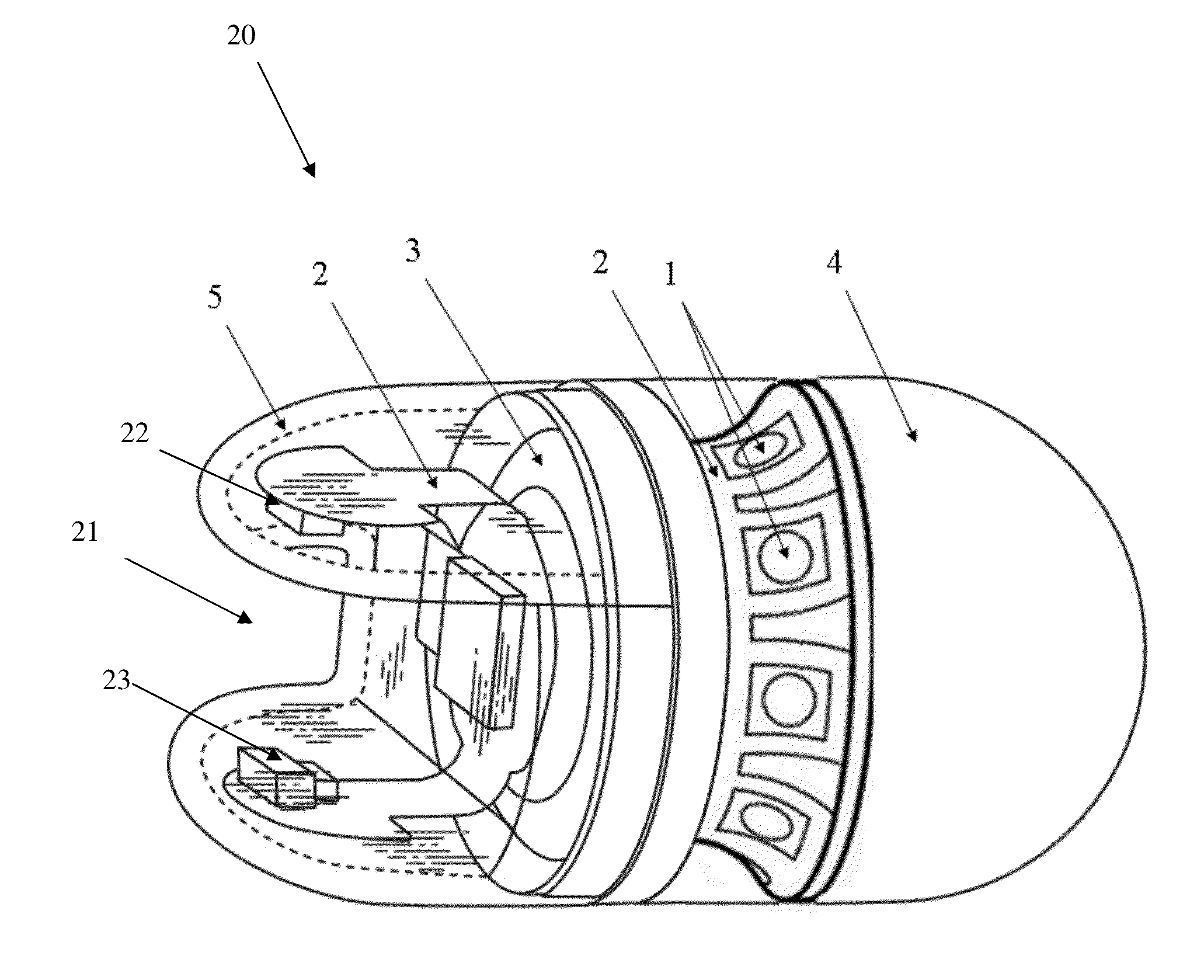
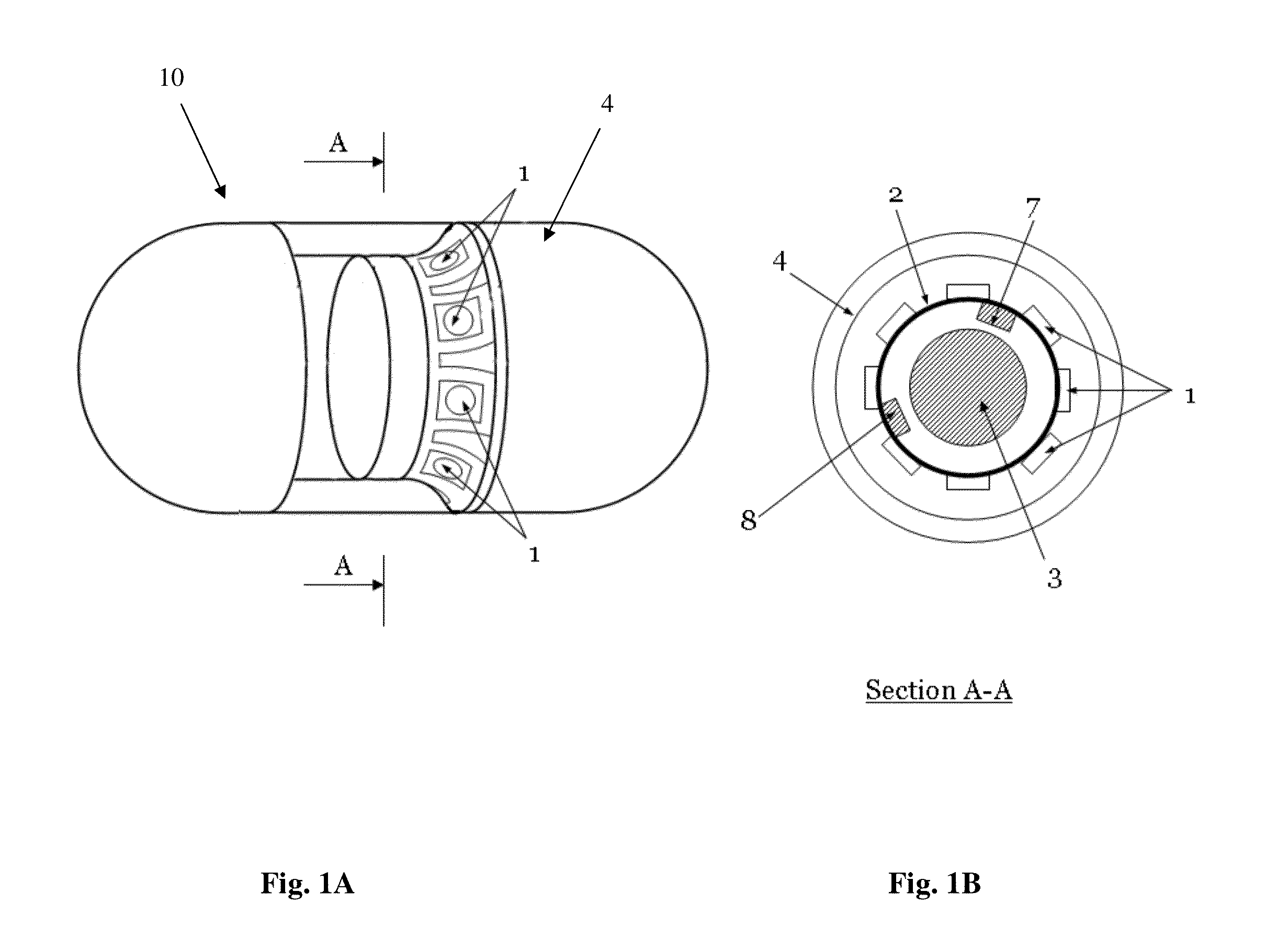
System and method for guiding of gastrointestinal device through the gastrointestinal tract
Systems and methods for guidance of a gastrointestinal device through a gastrointestinal tract are provided. A gastrointestinal guidewire is positioned through the gastrointestinal tract, by introduction of an introducing element into the gastrointestinal tract. One end of the gastrointestinal guidewire is attached to the introducing element, and the other end of the gastrointestinal guidewire is attached to an anchoring element, anchored to a location outside of the gastrointestinal tract. Movement of the introducing element through the gastrointestinal tract results in positioning of the guidewire through the gastrointestinal tract. The guidewire is then used as a scaffold to guide the gastrointestinal device, wherein the gastrointestinal device may be externally controlled. This allows for speeding up, slowing down, reversal and stopping of the gastrointestinal device during its descent through the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:BEN HORIN SHOMRON SILAN
Method for preparing tablet drug composition containing Rosuvastatin calcium
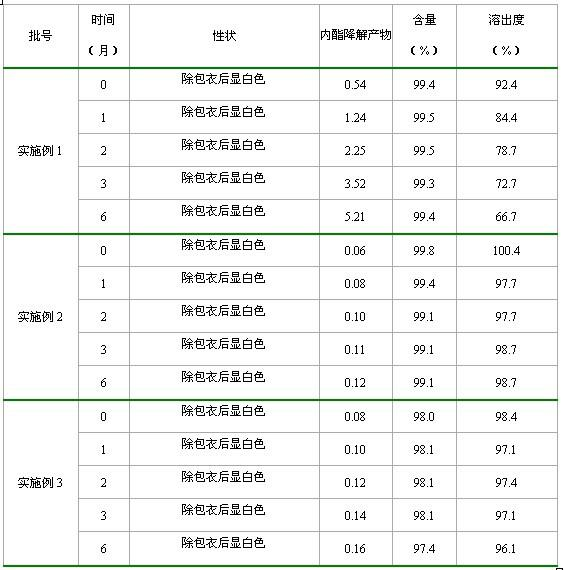
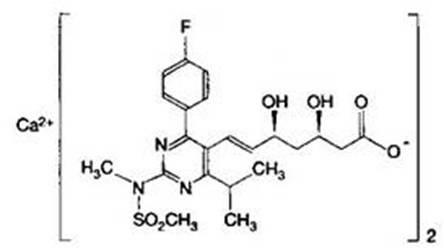
InactiveCN102008477AThe monitoring indicators are qualifiedLow dissolution rateOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCyclodextrinRosuvastatin Calcium
The invention relates to a method for preparing a tablet drug composition containing Rosuvastatin calcium. The preparation forms of the drug composition can be administered to the patients safely and the stability of Rosuvastatin calcium and the absorbability in gastrointestinal tract can be improved. Specifically, the invention relates to a method for preparing the drug composition containing amorphous Rosuvastatin calcium and beta-cyclodextrin. The method is characterized by grinding Rosuvastatin calcium and beta-cyclodextrin under alkaline condition, drying and crashing to obtain (80-100)-mesh fine powder, mixing the fine powder with appropriate auxiliary materials, preparing granules, carrying out tabletting and carrying out coating, thus preparing the drug composition. The in vitro release of the composition is improved to a greater degree, thus improving the bioavailability; and the composition can effectively treat hyperlipidemia, is convenient to take orally, covers the bad taste and is fast to disintegrate and absorb and convenient to carry.
Owner:TIANJIN HANRUI PHARMA
Residence structures and related methods
ActiveUS20190125667A1Facilitate dissociationTetracycline active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismStimulantDissolution
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Capture control for in vivo camera
ActiveUS7940973B2Save resourcesQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsWireless transmissionIntestinal walls
Systems and methods are provided for capture control of video data from a capsule camera system having an on-board storage or wireless transmission. The capsule camera system moves through the GI tract under the action of peristalsis and records images of the intestinal walls. For some periods of time, the capsule camera system may move very slowly and there are little differences in the image data between different frames. These frames can be designated for discard to conserve storage space or conserve power. A capsule control processing unit is incorporated to evaluate motion metric based on image data associated with a current frame and a previous frame. A decision is made based on a profile of the motion metric to select an operation mode from a group comprising Capture Mode and Conservation Mode. The capsule camera system is then operated according to the selected operation mode.
Owner:CAPSO VISION INC
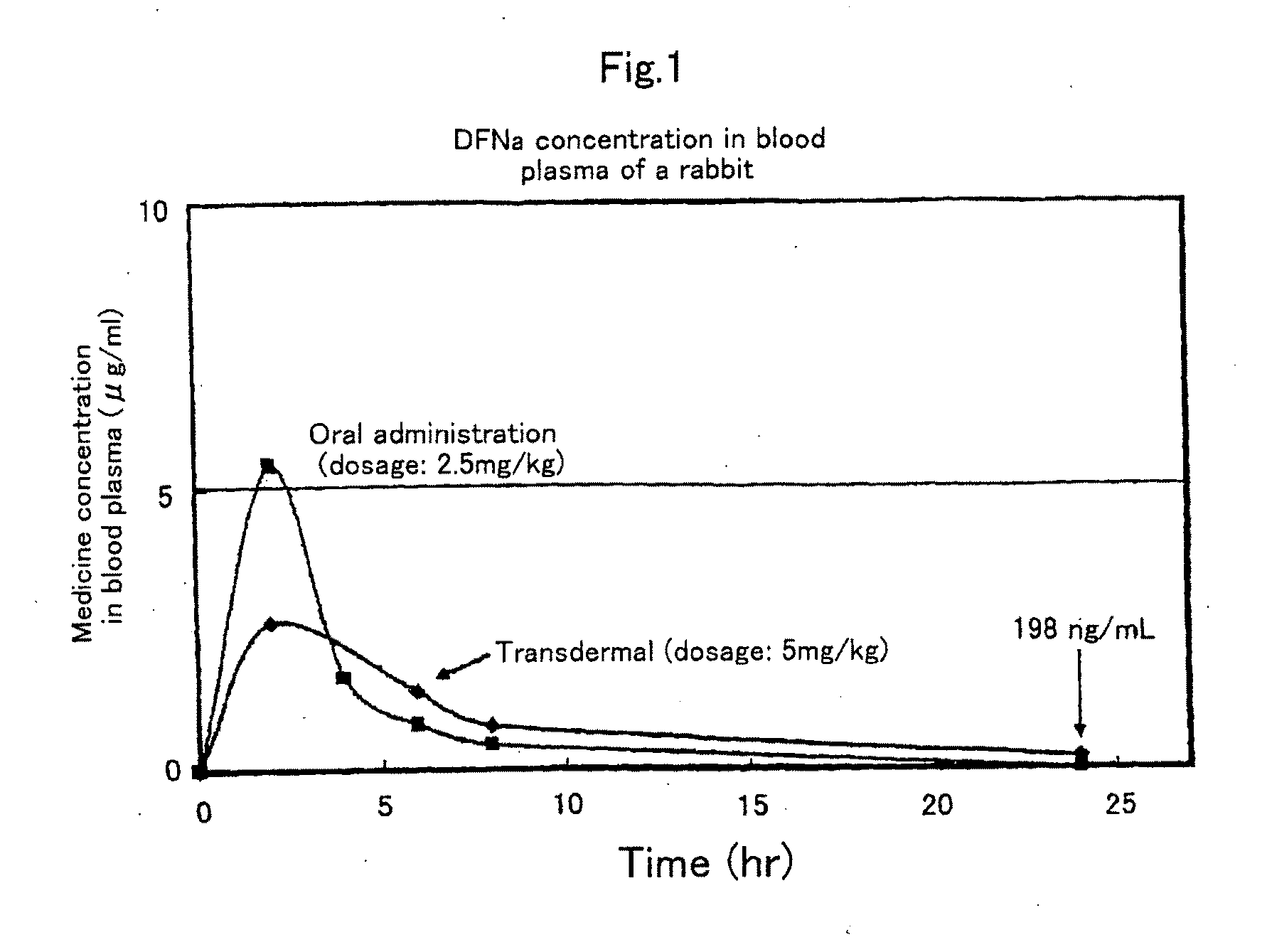
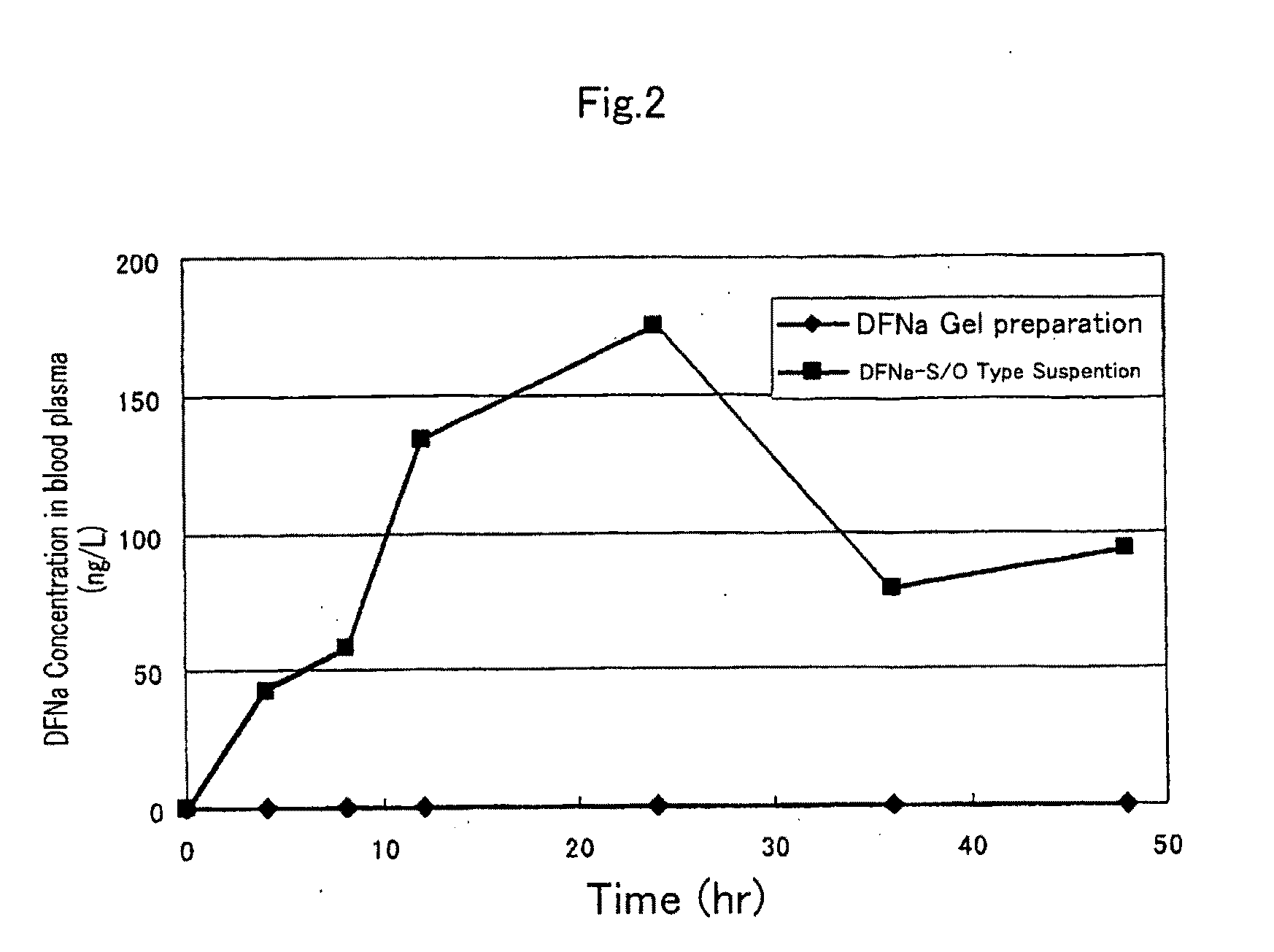
S/O type external preparation
InactiveUS20090238846A1Low rateImprove hydrophilicityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSkin permeabilityOil phase
The present invention provides an external preparation which can improve a skin permeability of a hydrophilic medicine such as NSAID so that the medicine can act directly on a diseased area without passing through gastrointestinal tract or mucosa. The S / O type external preparation external preparation excellent in percutaneous absorbability of the present invention comprises a medicine-containing complex dissolved or dispersed in an oil phase, wherein the complex contains a hydrophilic medicine covered with a surfactant and is in a form of a solid.
Owner:ASPION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com