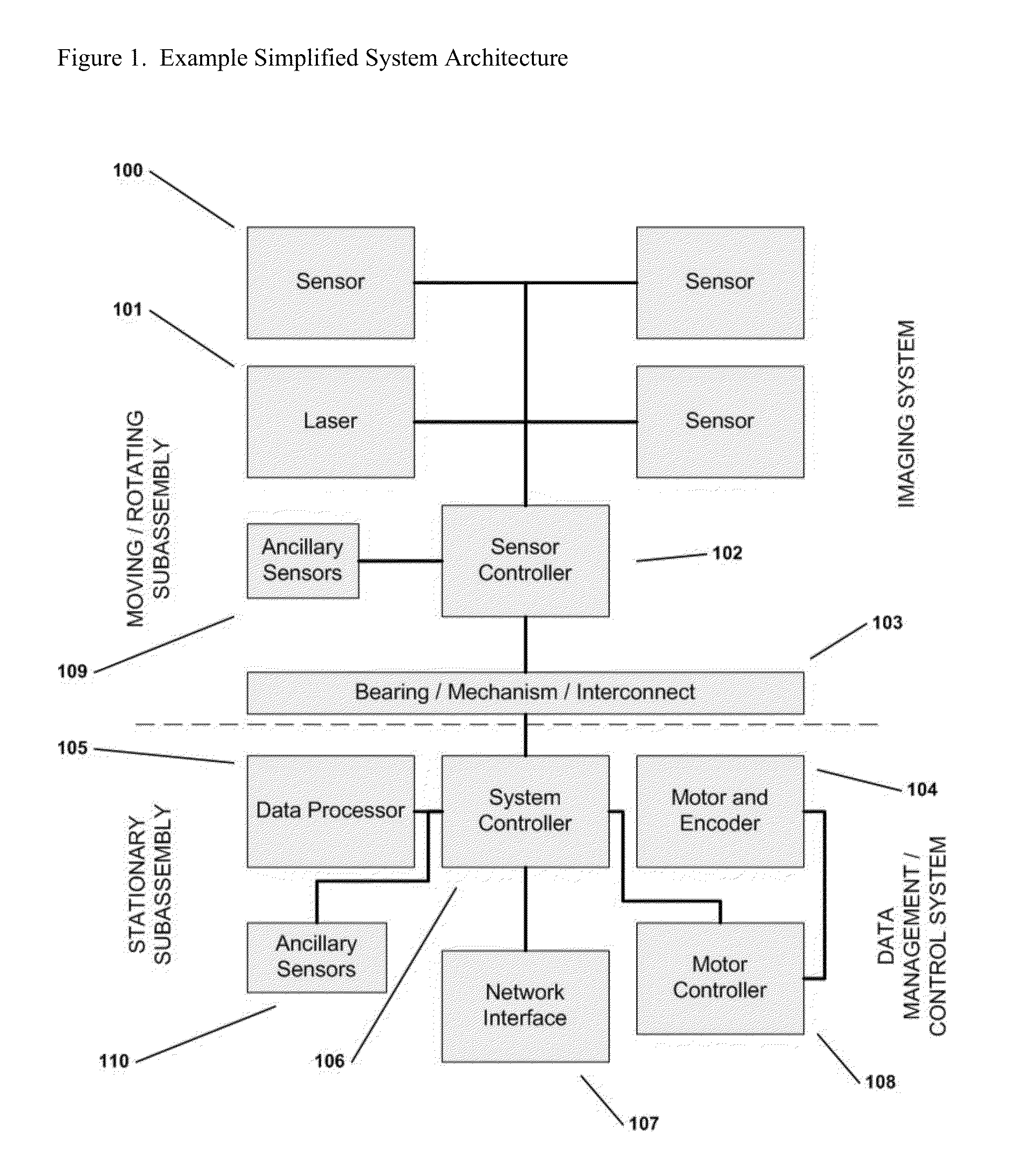
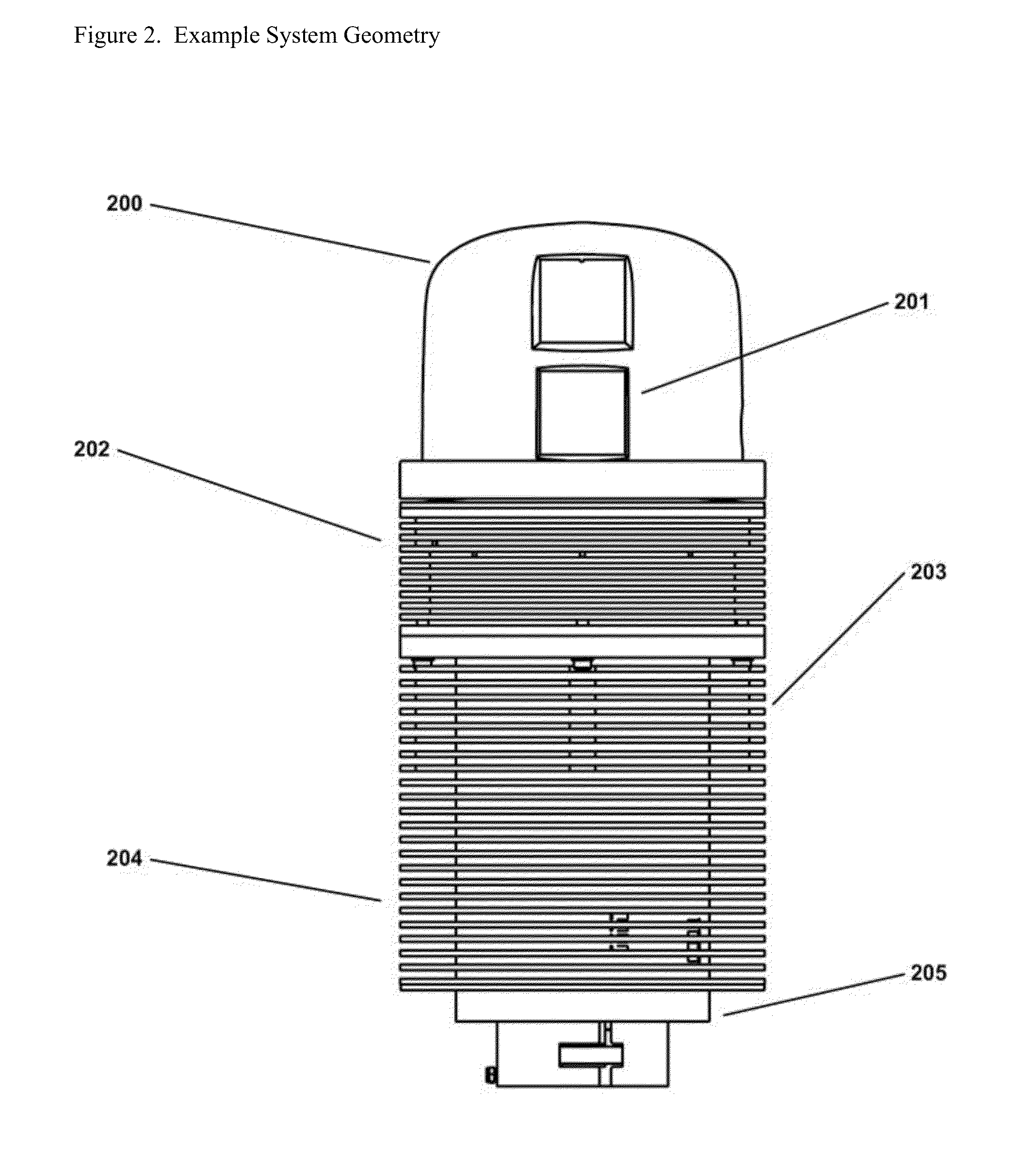
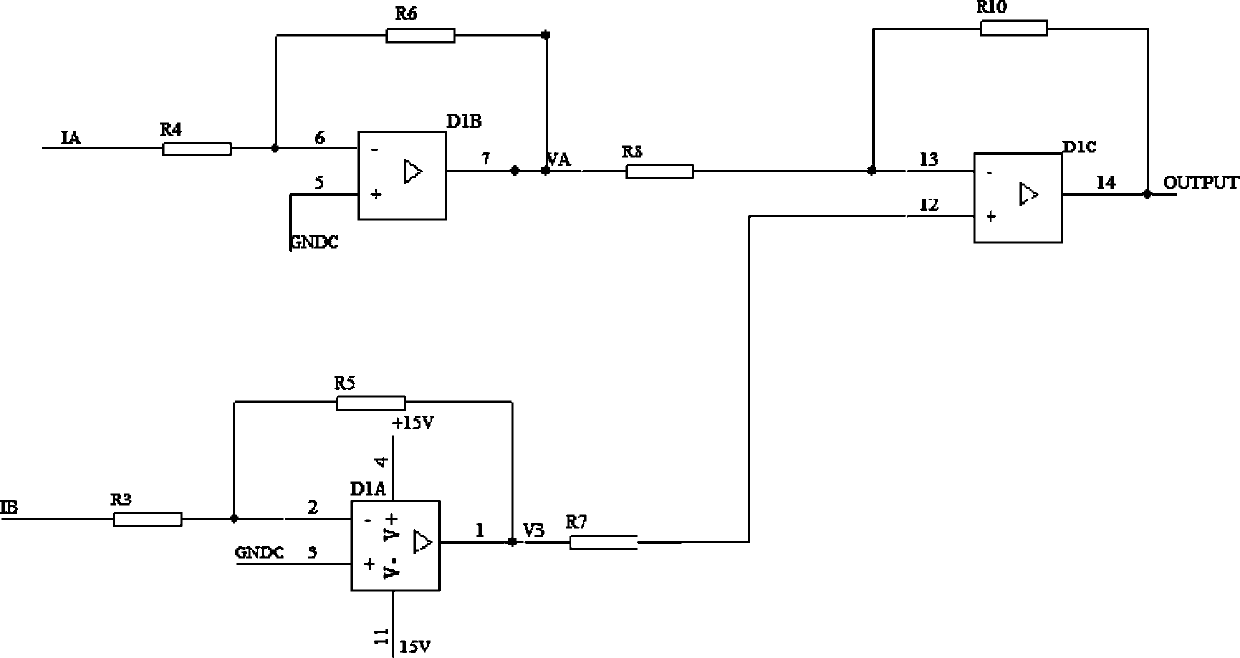
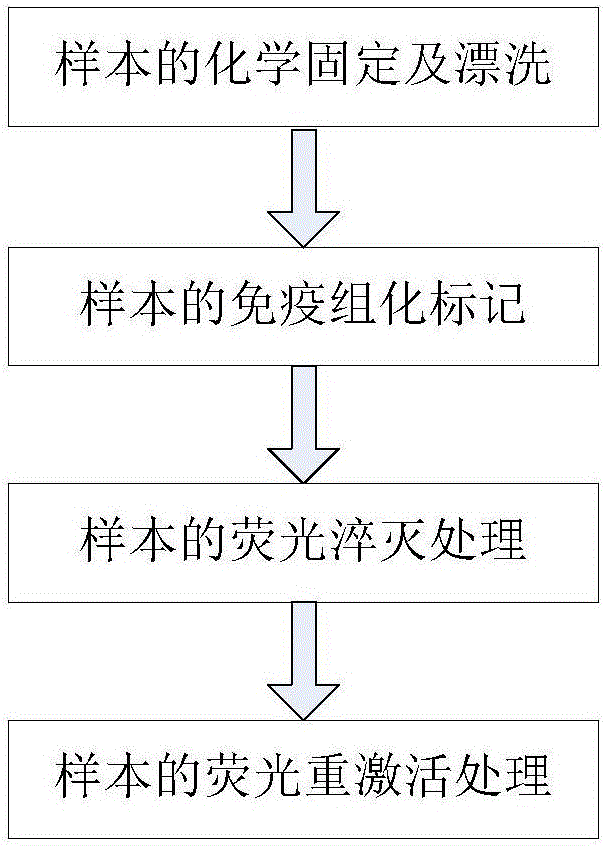
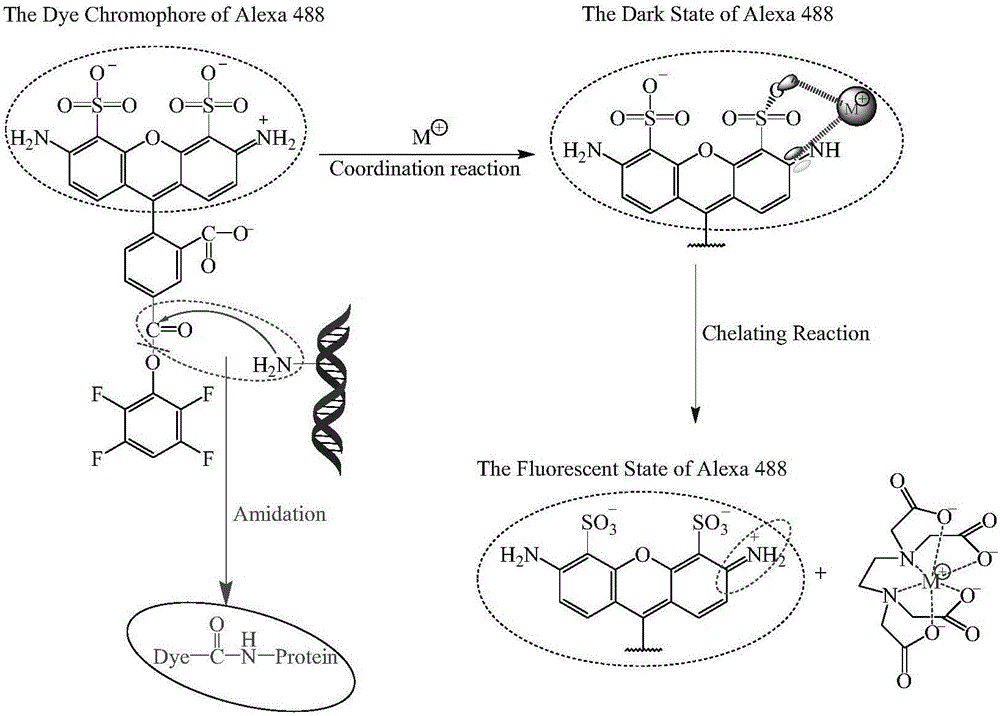
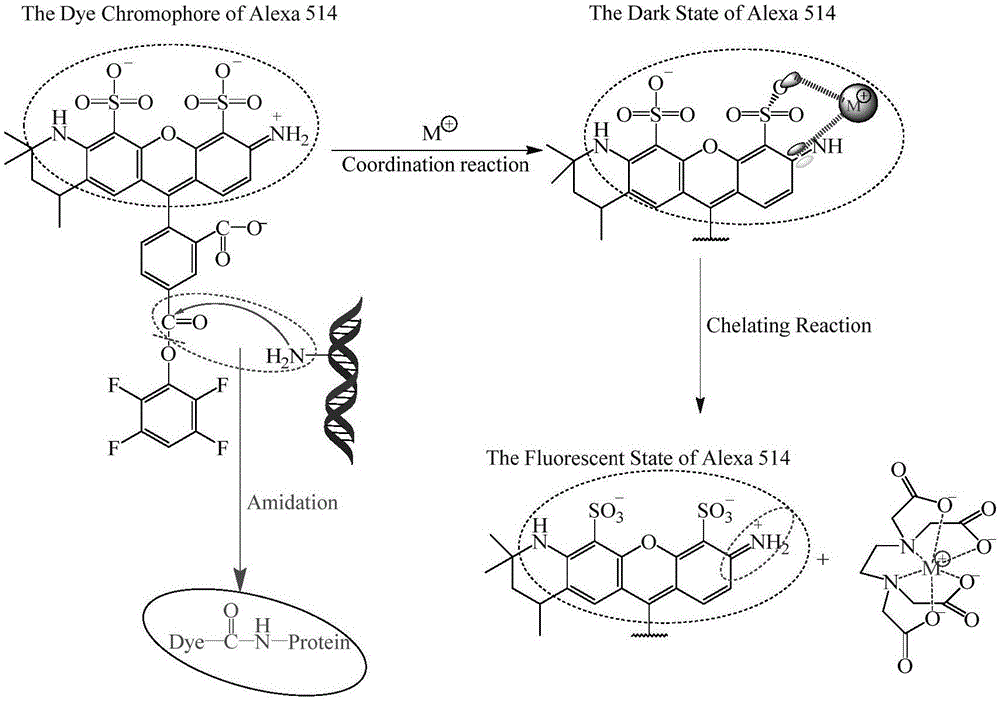
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Wide field imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
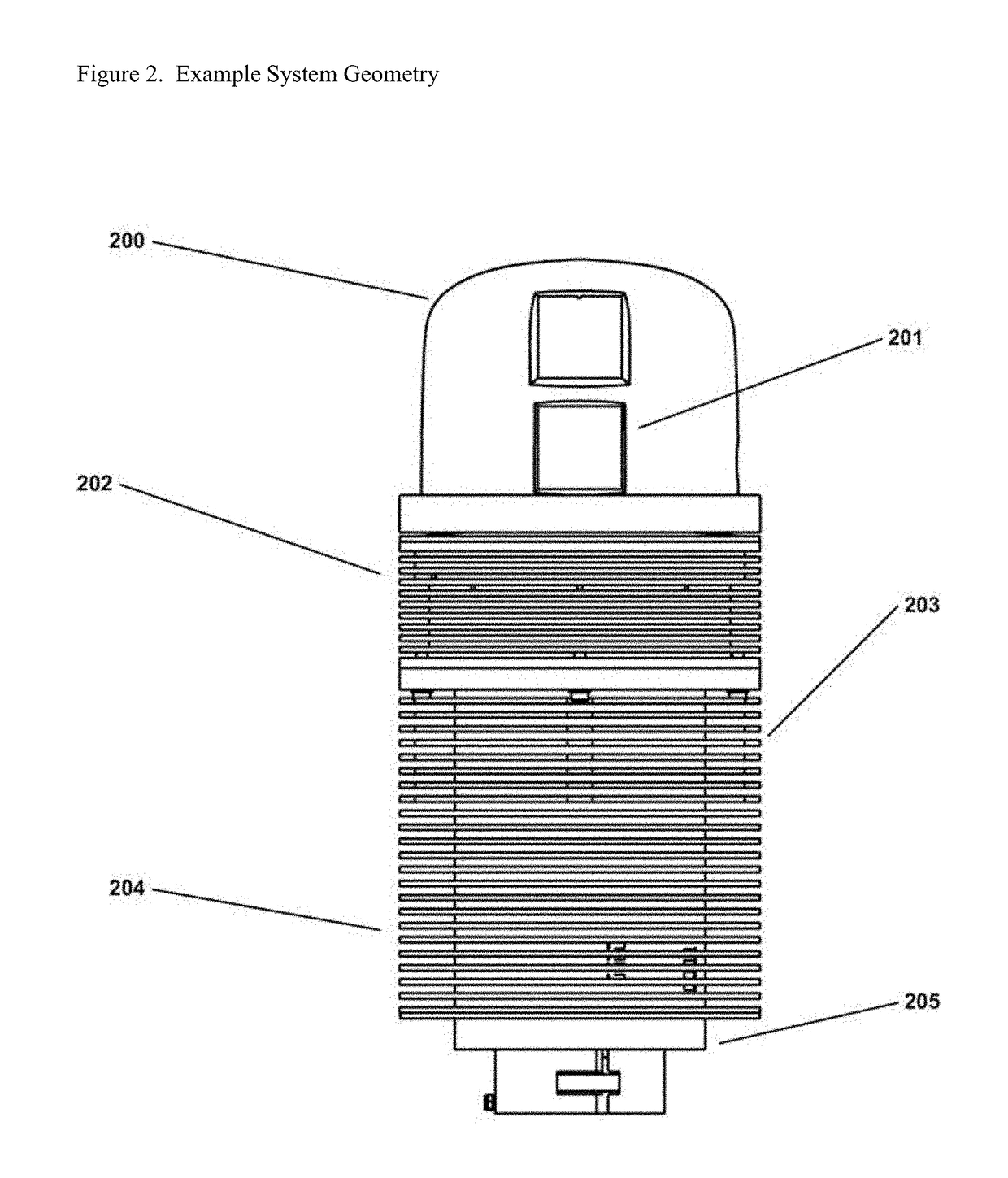
Wide field imaging (WFI) and ultra wide field imaging (UWFI) are now increasingly popular. WFI refers to imaging beyond 50 degrees field area. UWFI systems can image upto 200 degrees. They are well capable of imaging over 80% of the retinal surface area. The peripheral retina can be photographed with small pupils in...
Extended depth of field imaging system using chromatic aberration
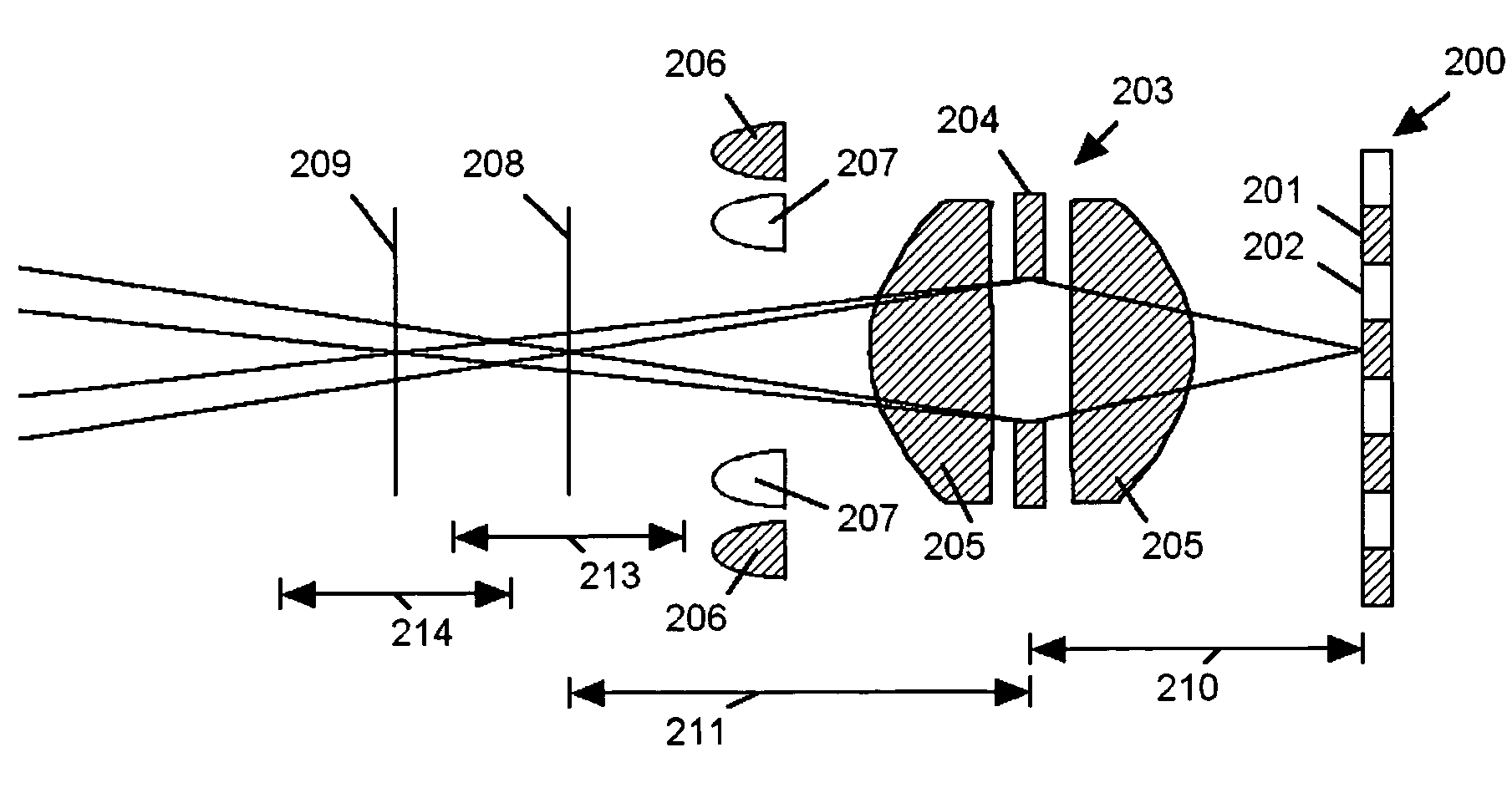
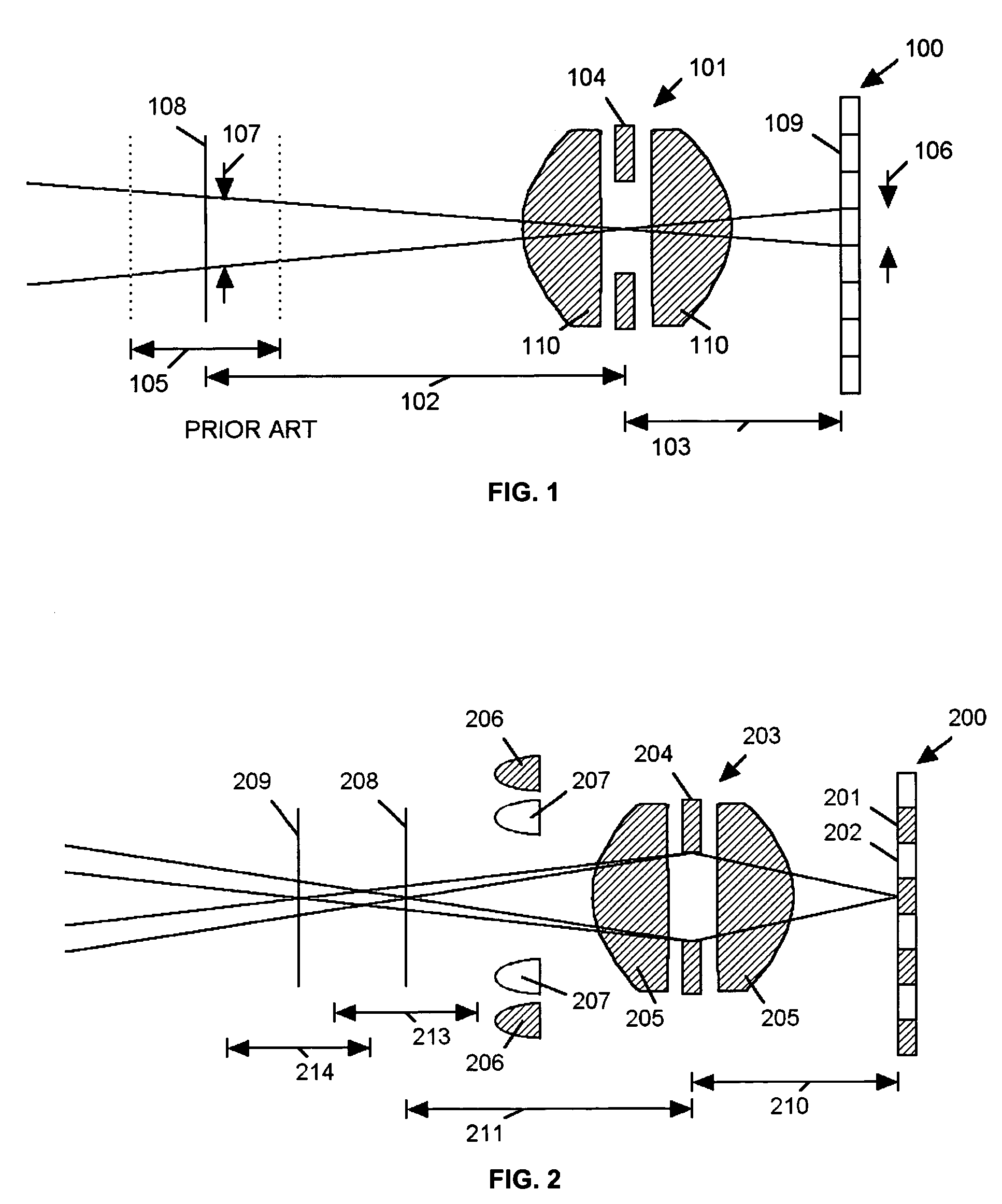
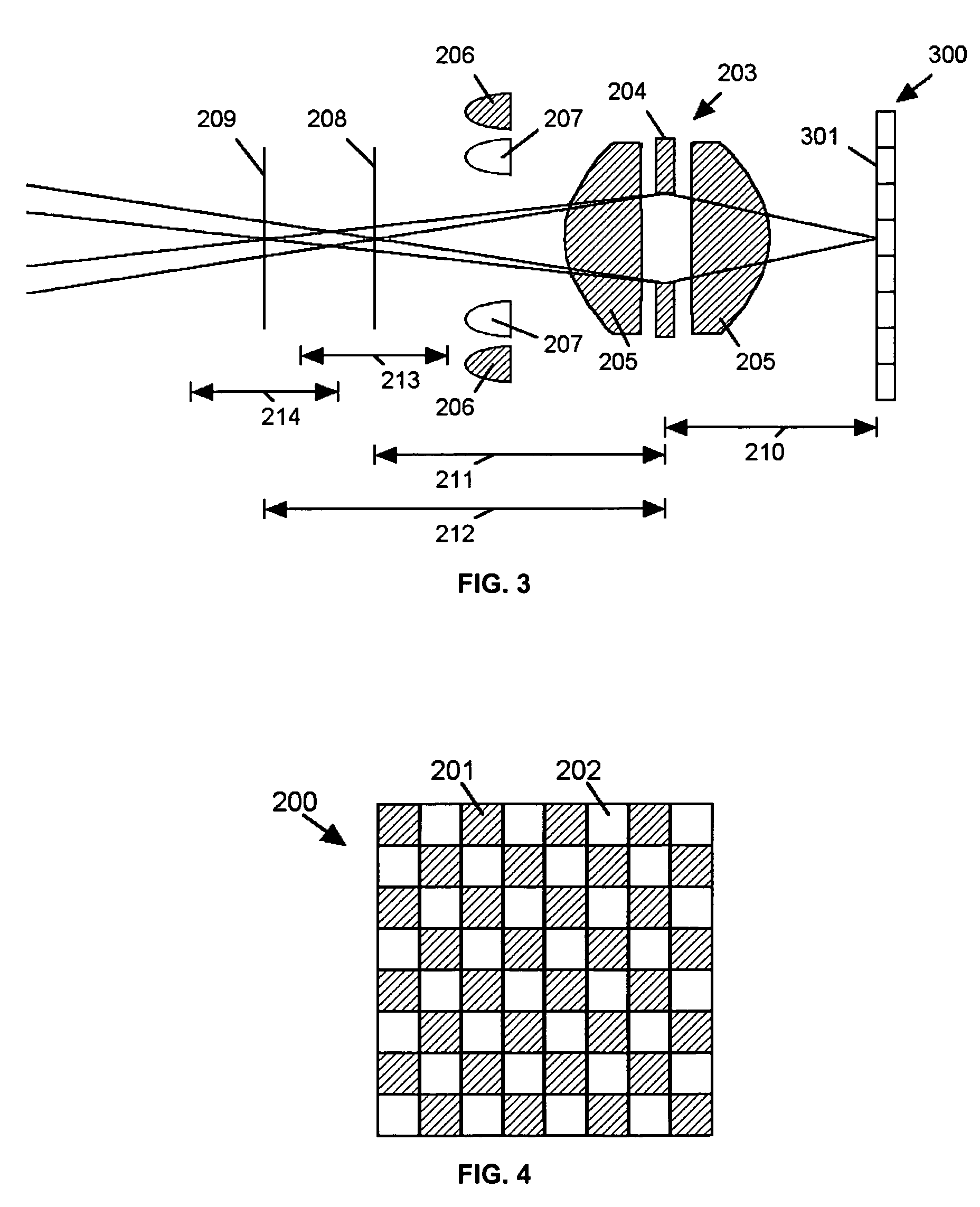
ActiveUS7224540B2Lower optical magnificationHigh intensity illuminationRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFocal positionDepth of field
An imaging system (FIG. 3) is disclosed that has a wavelength dependent focal shift caused by longitudinal chromatic aberration in a lens assembly (203) that provides extended depth of field imaging due to focal shift (213,214) and increased resolution due to reduced lens system magnification. In use, multiple wavelengths of quasi-monochromatic illumination, from different wavelength LEDs (206,207) or the like, illuminate the target, either sequentially, or in parallel in conjunction with an imager (200) with wavelength selective (colored) filters. Images are captured with different wavelengths of illumination that have different focus positions (208,209), either sequentially or by processing the color planes of a color imager separately. Extended depth of field, plus high resolution are achieved. Additionally, information about the range to the target can be determined by analyzing the degree of focus of the various colored images.
Owner:PSC SCANNING INC
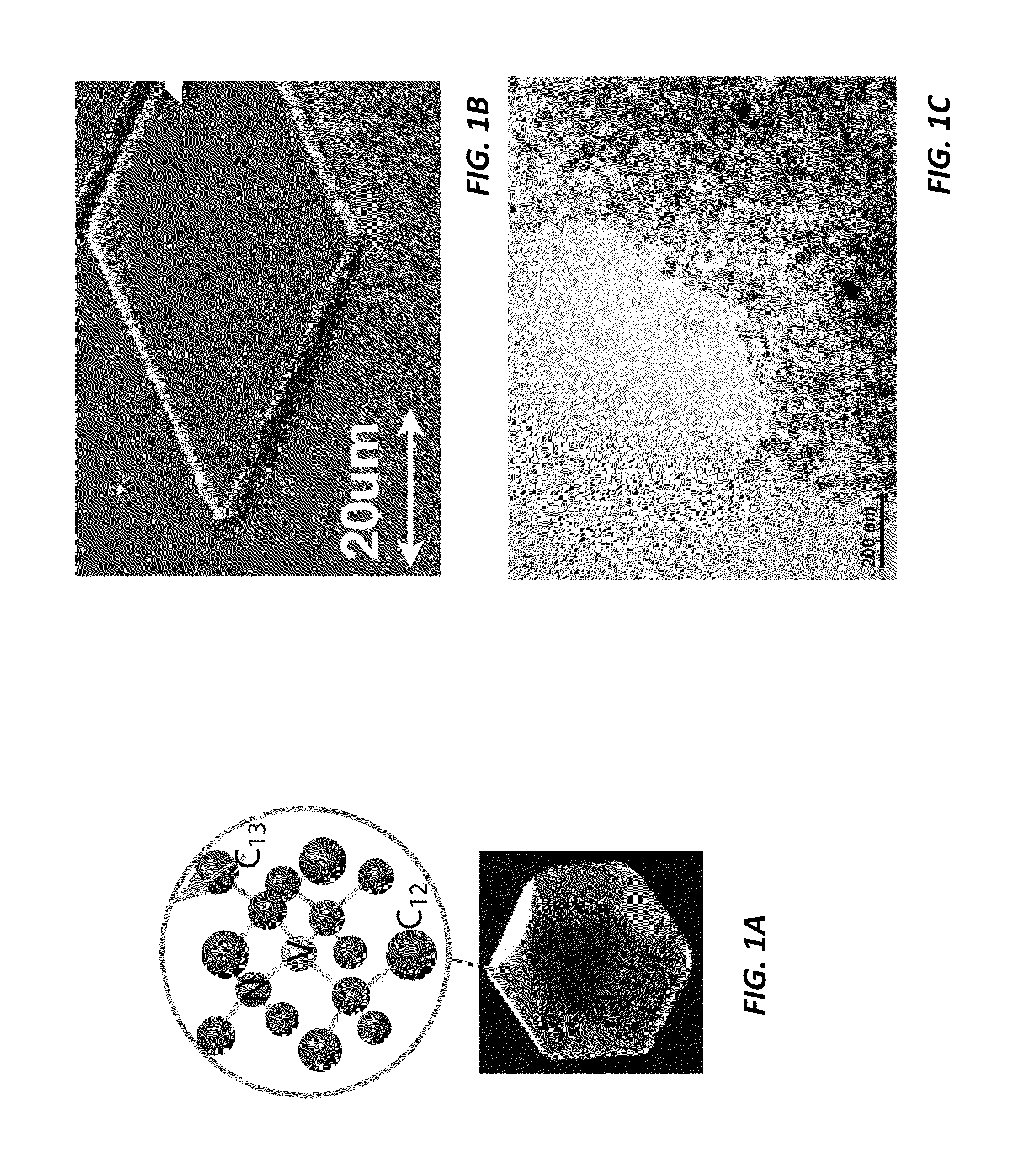
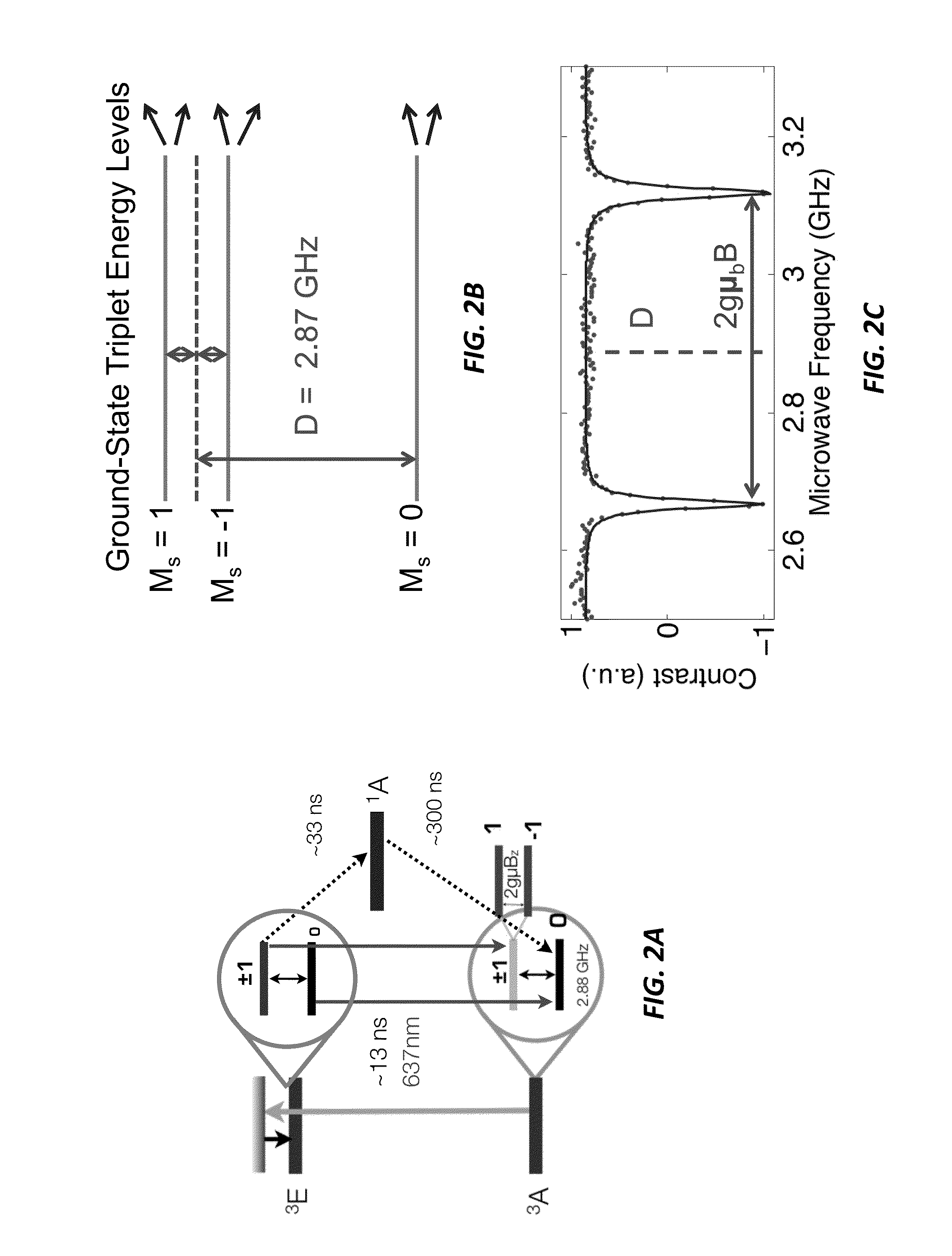
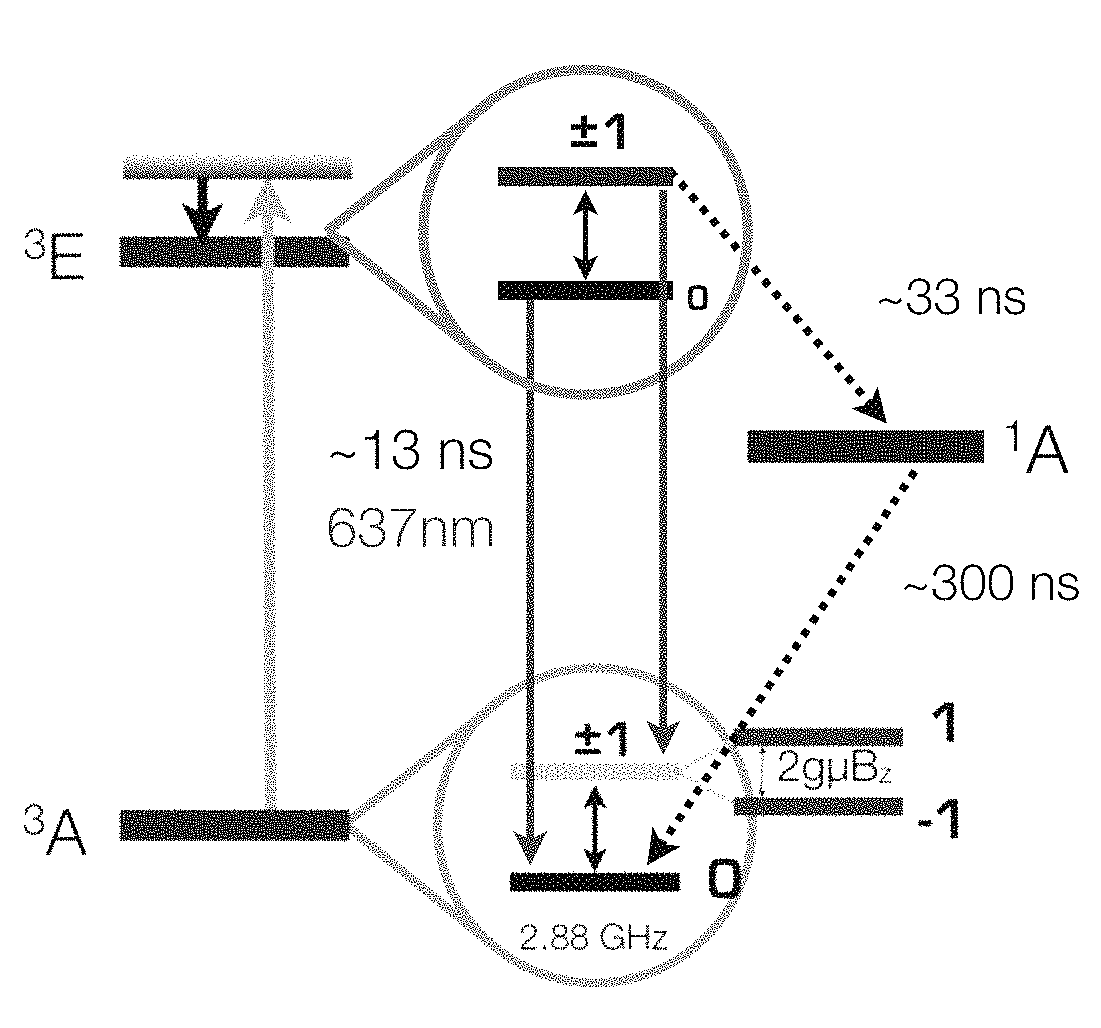
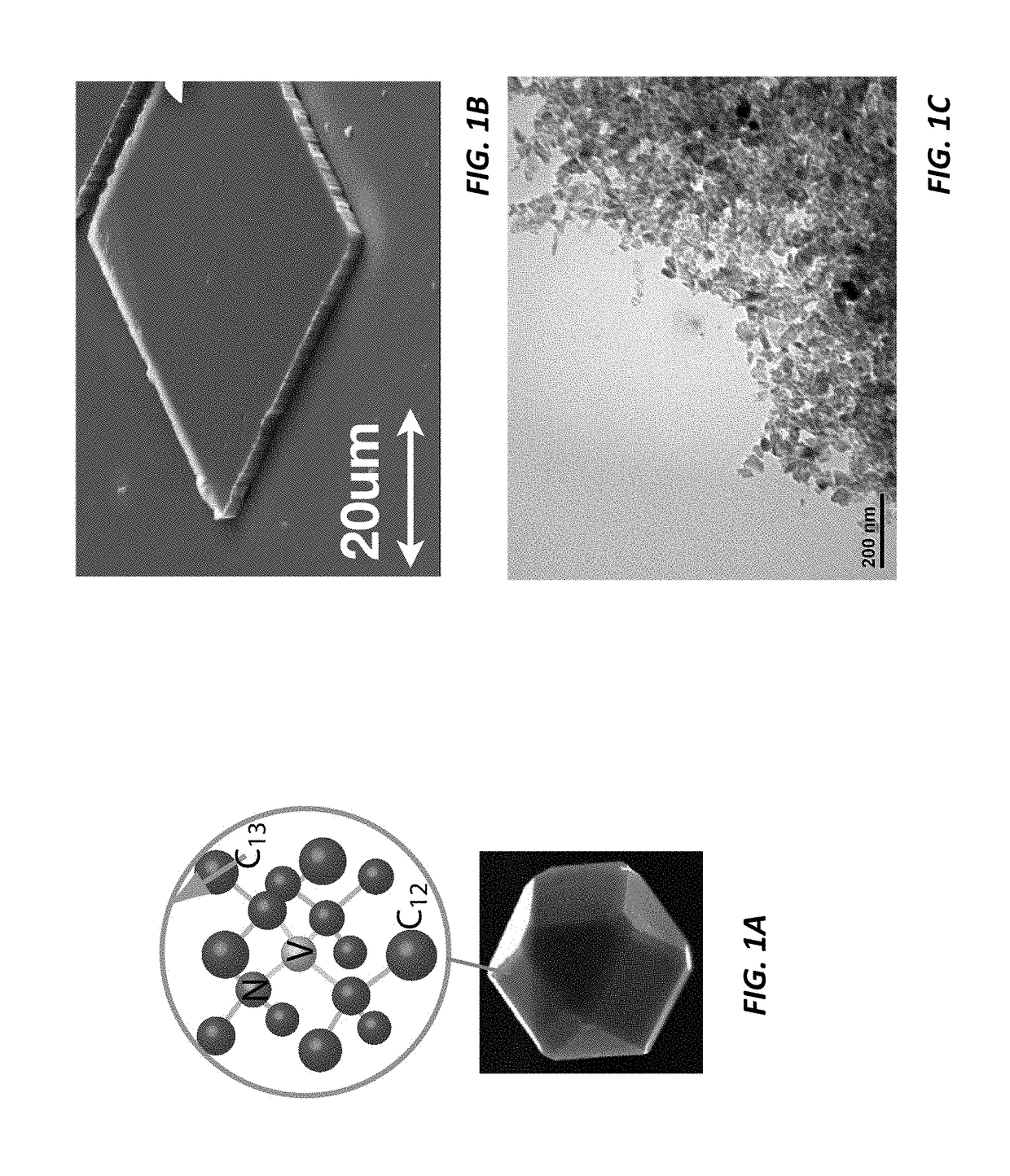
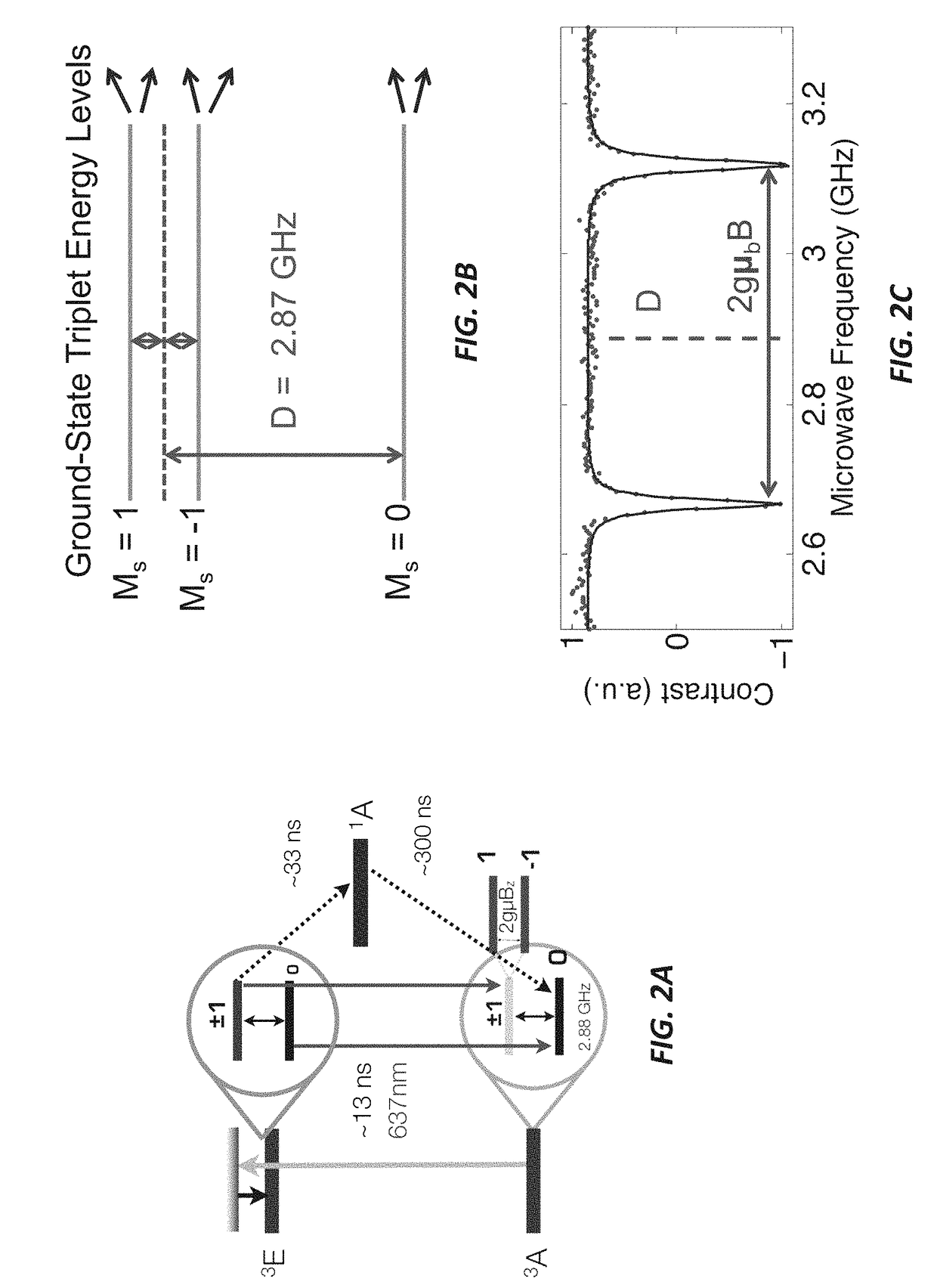
Wide-field imaging using nitrogen vacancies
Nitrogen vacancies in bulk diamonds and nanodiamonds can be used to sense temperature, pressure, electromagnetic fields, and pH. Unfortunately, conventional sensing techniques use gated detection and confocal imaging, limiting the measurement sensitivity and precluding wide-field imaging. Conversely, the present sensing techniques do not require gated detection or confocal imaging and can therefore be used to image temperature, pressure, electromagnetic fields, and pH over wide fields of view. In some cases, wide-field imaging supports spatial localization of the NVs to precisions at or below the diffraction limit. Moreover, the measurement range can extend over extremely wide dynamic range at very high sensitivity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for high resolution spatially modulated fluorescence imaging and tomography
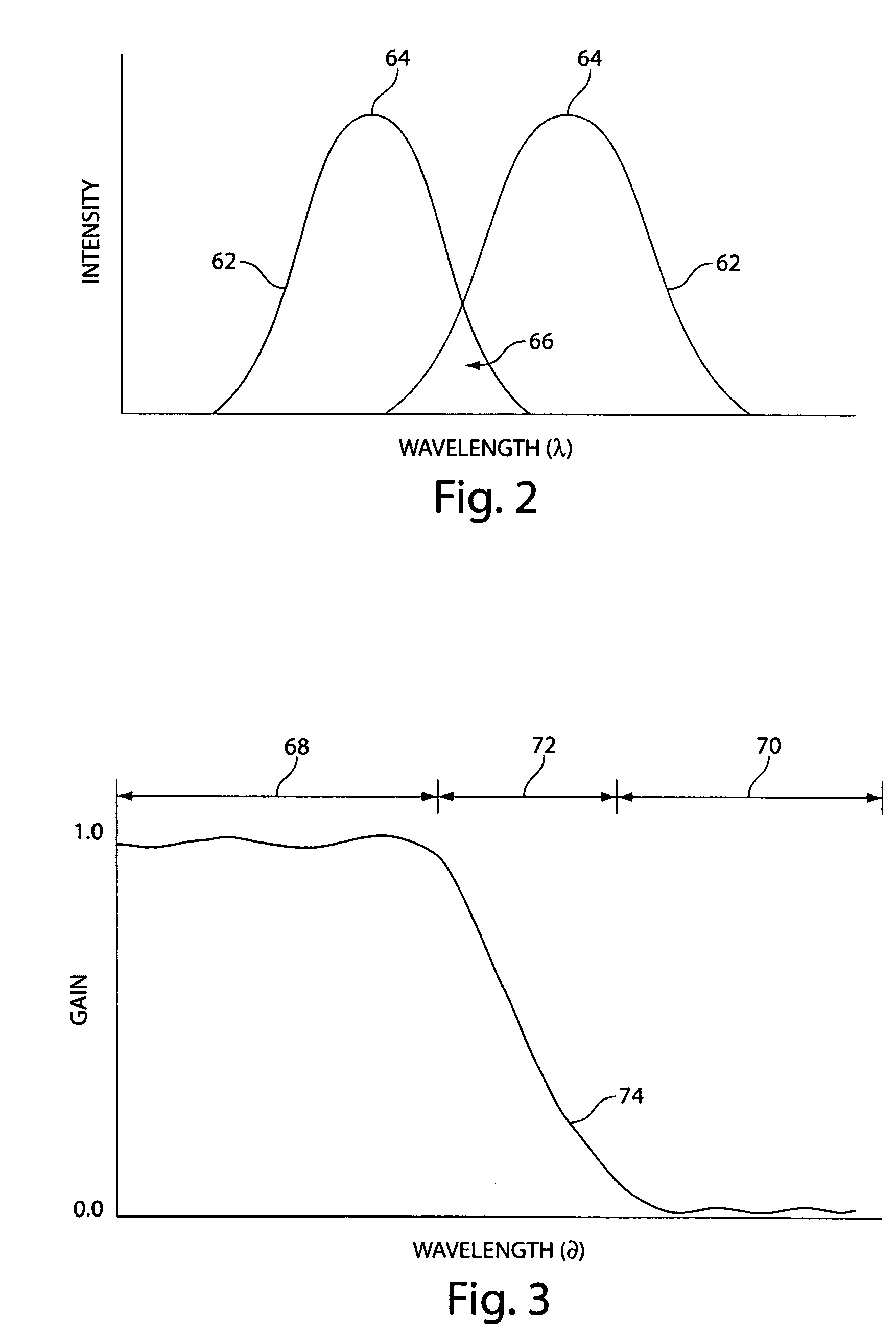
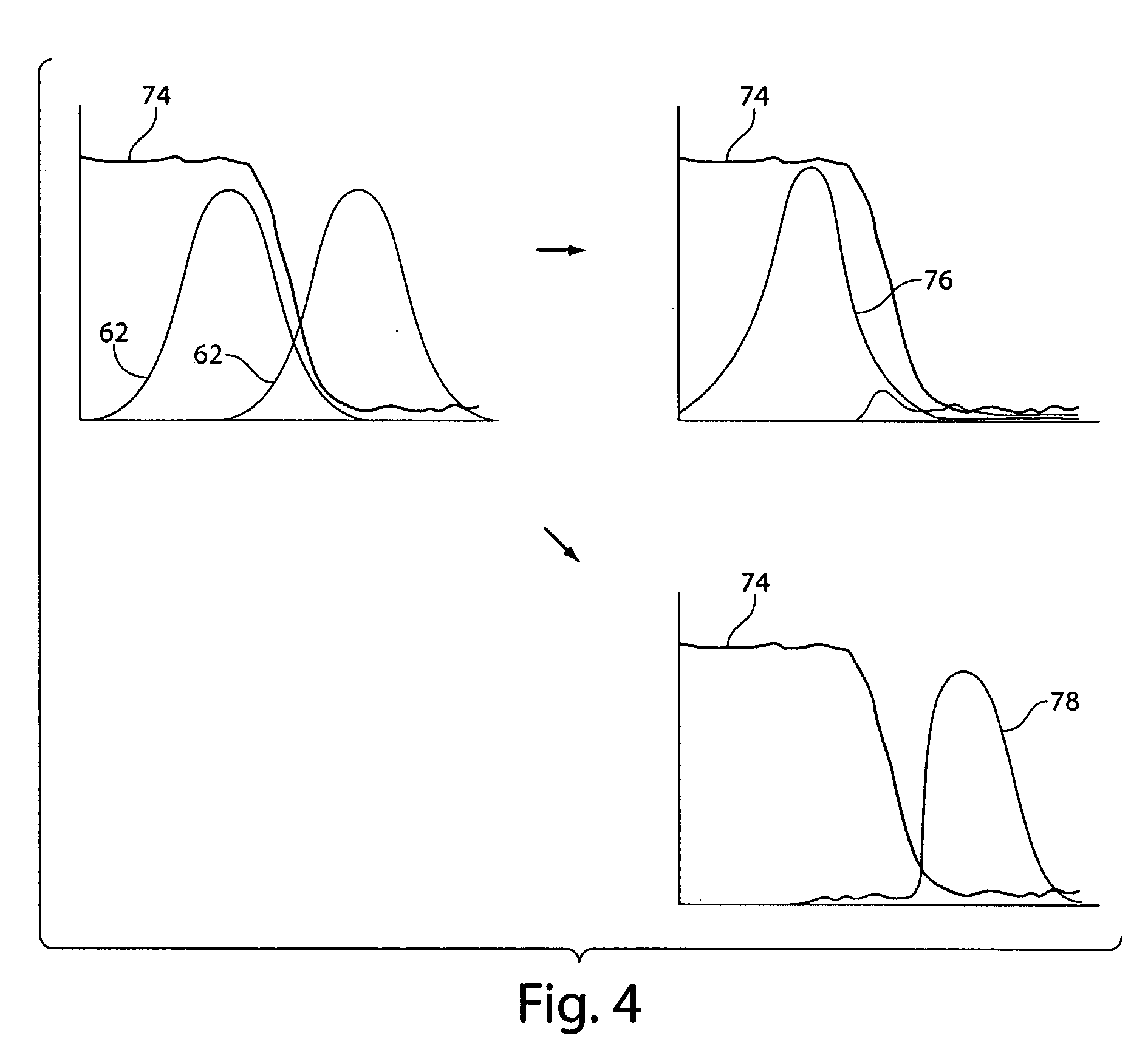
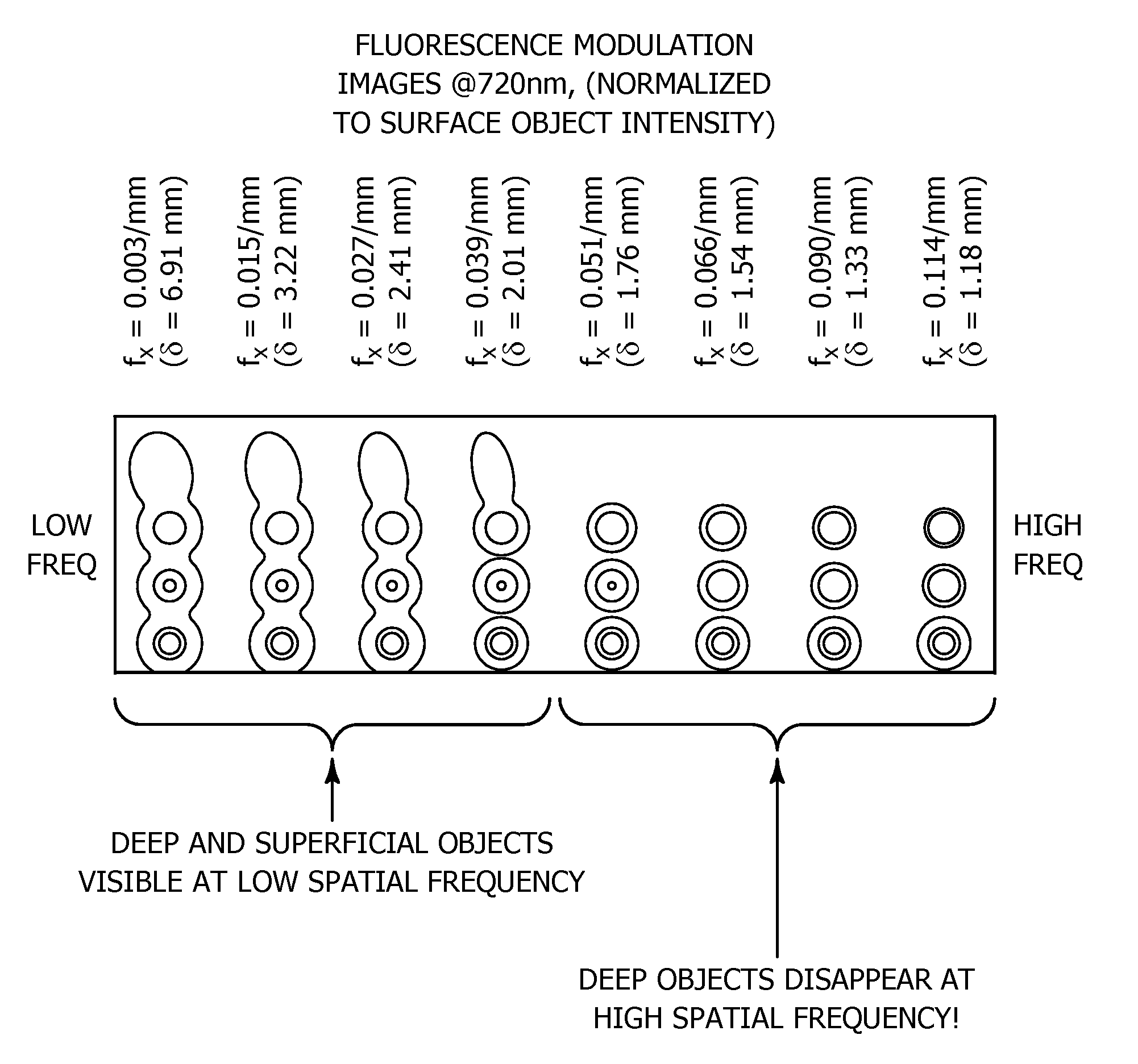
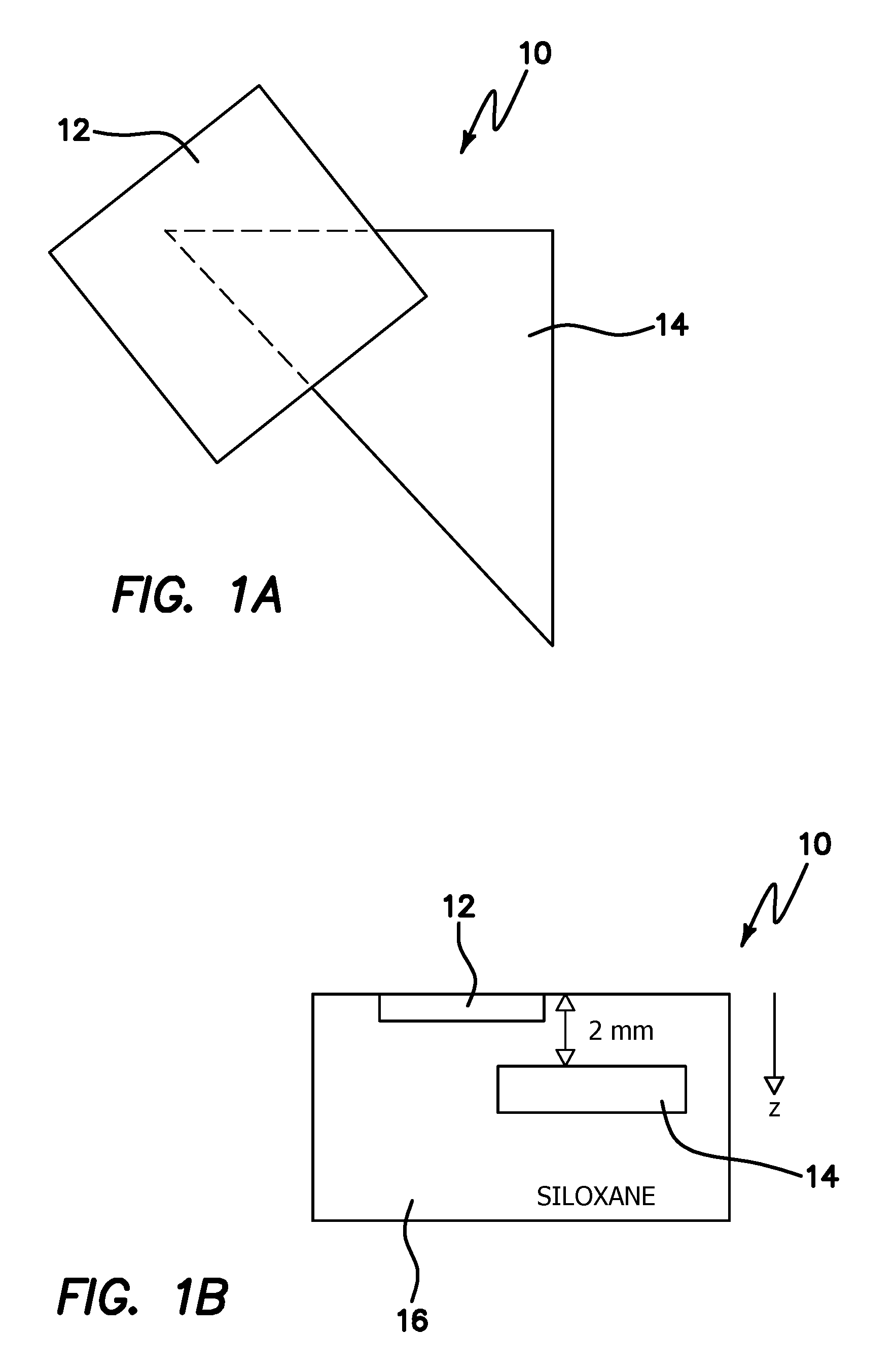
An improvement in a method for quantitative modulated imaging to perform depth sectioned reflectance or transmission imaging in a turbid medium, such as human or animal tissue is directed to the steps of encoding periodic pattern of illumination preferably with a fluorescent excitation wavelength when exposing a turbid medium to the periodic pattern to provide depth-resolved discrimination of structures within the turbid medium; and reconstructing a non-contact three dimensional image of the structure within a turbid medium. As a result, wide field imaging, separation of the average background optical properties from the heterogeneity components from a single image, separation of superficial features from deep features based on selection of spatial frequency of illumination, or qualitative and quantitative structure, function and composition information is extracted from spatially encoded data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Large depth-of-field imaging system and iris recogniton system
InactiveUS20100110275A1High transfer functionTelevision system detailsImage analysisDepth of fieldDigital image processing
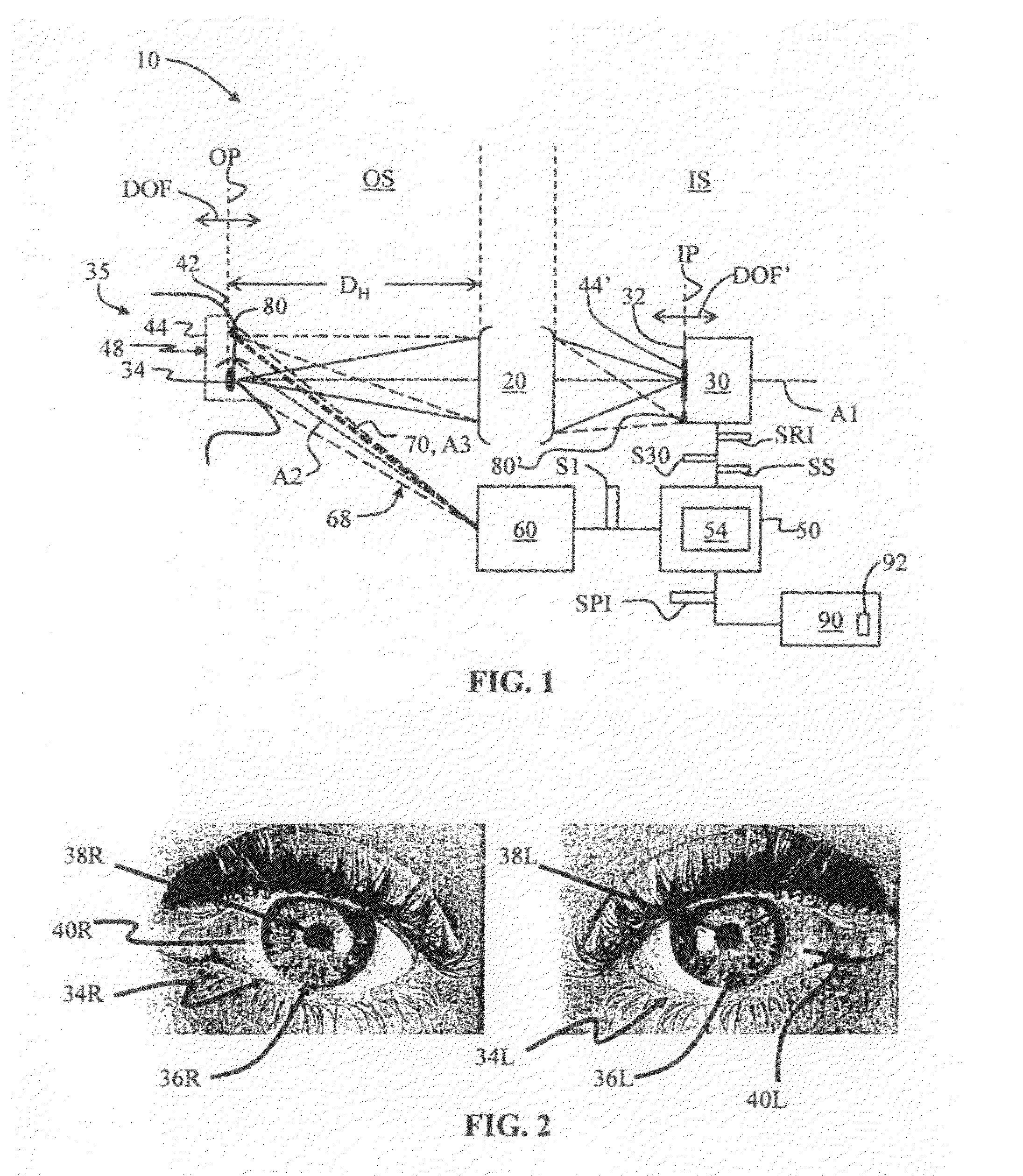
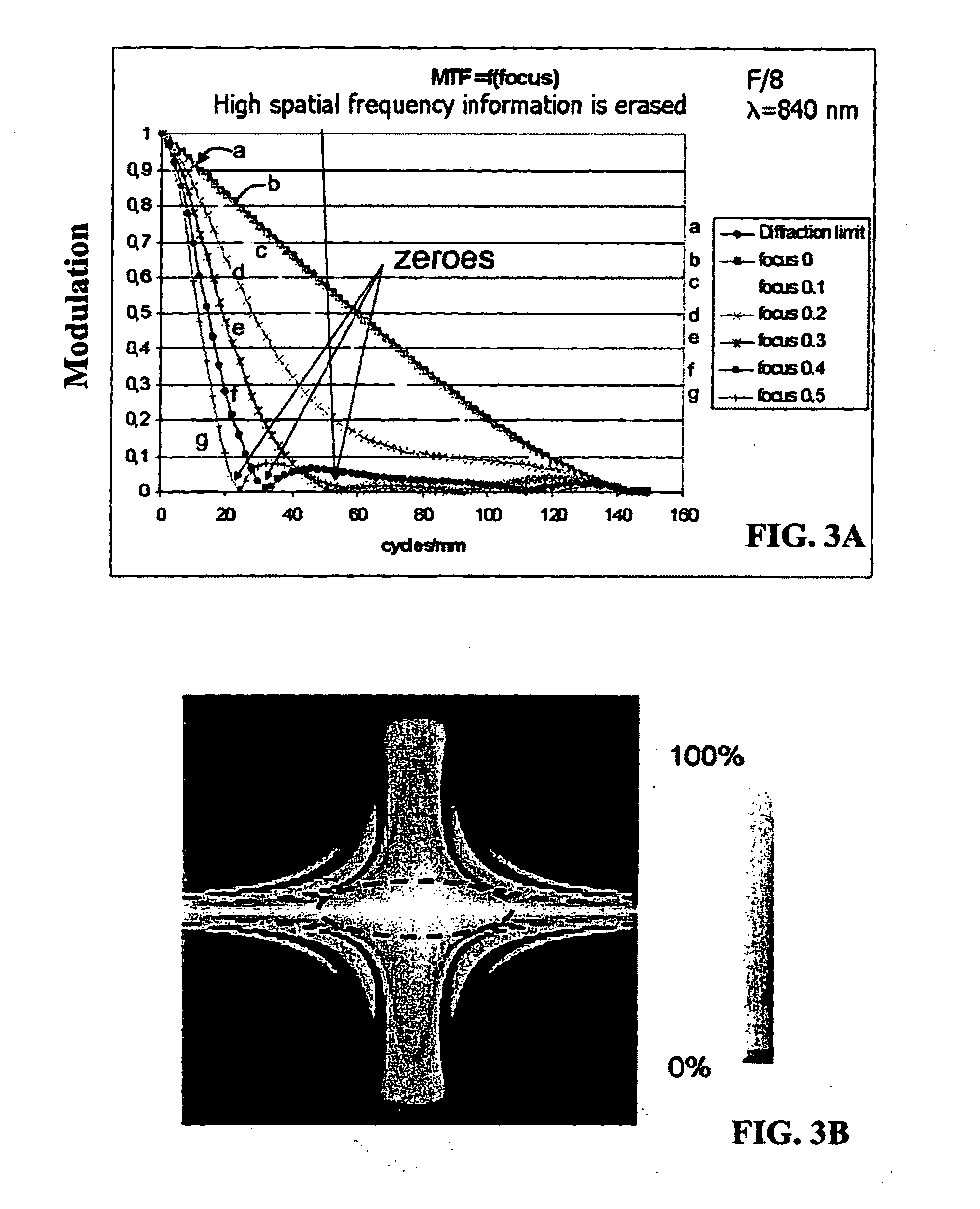
(A2) An extended depth of field (DOF) imaging system (10) is disclosed that has a corresponding extended depth of focus (DOF′) by virtue of its optical system (20) having a select amount of spherical aberration. The imaging system has an image processing unit (54) adapted to process the raw images and perform contrast enhancement to form processed images. The image processing includes restoring the defocused modulation transfer functions (MTFs) using a gain function (G) and the amount of defocus. The imaging system can include an illumination system (60) that illuminates the object being imaged to establish a distance (DH) between the optical system and the object, where distance DH is used in the restoring of the MTF. An iris-recognition (I-R) system based on the enhanced DOF imaging system is also disclosed.; Optical system embodiments for use in the DOF imaging system that can provide select amounts of spherical aberration—and thus select increases in DOF—without increasing the adverse impact of other aberrations on image formation are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBAL BIONIC OPTICS PTY LTD
Systems and methods for detecting and analyzing polymers
InactiveUS7351538B2Easy to detectEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWide fieldLinear arrays
A detection system and methods for improving the ability of the detection system to recognize labels that are disposed on a polymer. Embodiments of the invention include schemes for selecting emitters and labels used within the system in a manner that allows an increase in the number of distinct labels that can be used together in a system. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods are directed to identifying portions of a detection signal that may be associated with extra labels residing within a detection zone. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods relate to using wide field imaging detectors while reducing out of focus noise contributions to detection signals of the system. Still, other embodiments relate to the use of linear array detectors to detect labels.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Systems and methods for detecting and analyzing polymers
InactiveUS20060078915A1Easy to detectEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWide fieldSystem identification
A detection system and methods for improving the ability of the detection system to recognize labels that are disposed on a polymer. Embodiments of the invention include schemes for selecting emitters and labels used within the system in a manner that allows an increase in the number of distinct labels that can be used together in a system. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods are directed to identifying portions of a detection signal that may be associated with extra labels residing within a detection zone. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods relate to using wide field imaging detectors while reducing out of focus noise contributions to detection signals of the system. Still, other embodiments relate to the use of linear array detectors to detect labels
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Method and apparatus for high resolution spatially modulated fluorescence imaging and tomography
An improvement in a method for quantitative modulated imaging to perform depth sectioned reflectance or transmission imaging in a turbid medium, such as human or animal tissue is directed to the steps of encoding periodic pattern of illumination preferably with a fluorescent excitation wavelength when exposing a turbid medium to the periodic pattern to provide depth-resolved discrimination of structures within the turbid medium; and reconstructing a non-contact three dimensional image of the structure within a turbid medium. As a result, wide field imaging, separation of the average background optical properties from the heterogeneity components from a single image, separation of superficial features from deep features based on selection of spatial frequency of illumination, or qualitative and quantitative structure, function and composition information is extracted from spatially encoded data.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Systems and methods for detecting and analyzing polymers
InactiveUS20060228747A1Easy to detectEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWide fieldSystem identification
A detection system and methods for improving the ability of the detection system to recognize labels that are disposed on a polymer. Embodiments of the invention include schemes for selecting emitters and labels used within the system in a manner that allows an increase in the number of distinct labels that can be used together in a system. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods are directed to identifying portions of a detection signal that may be associated with extra labels residing within a detection zone. In other embodiments, the detection system and methods relate to using wide field imaging detectors while reducing out of focus noise contributions to detection signals of the system. Still, other embodiments relate to the use of linear array detectors to detect labels
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
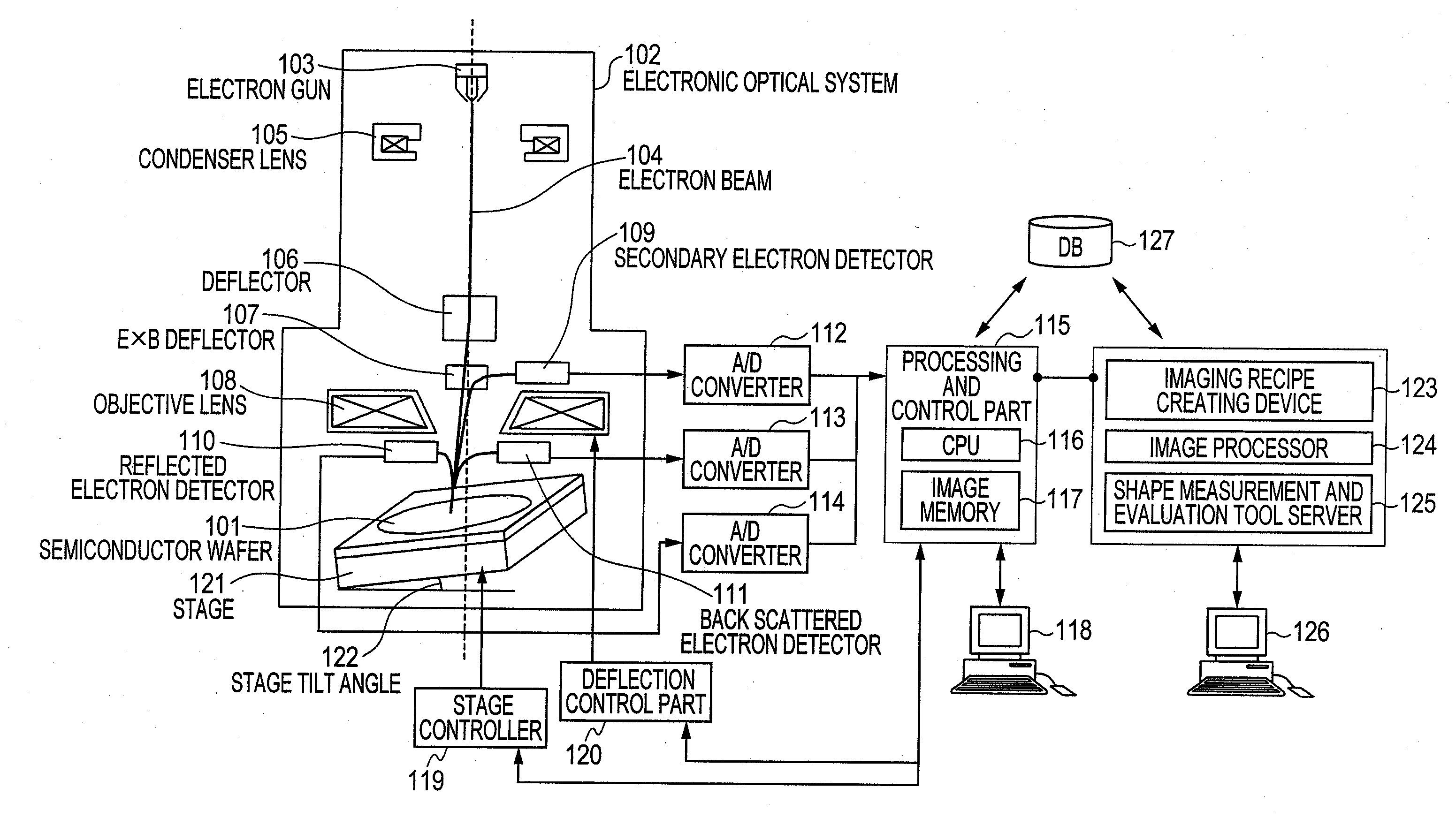
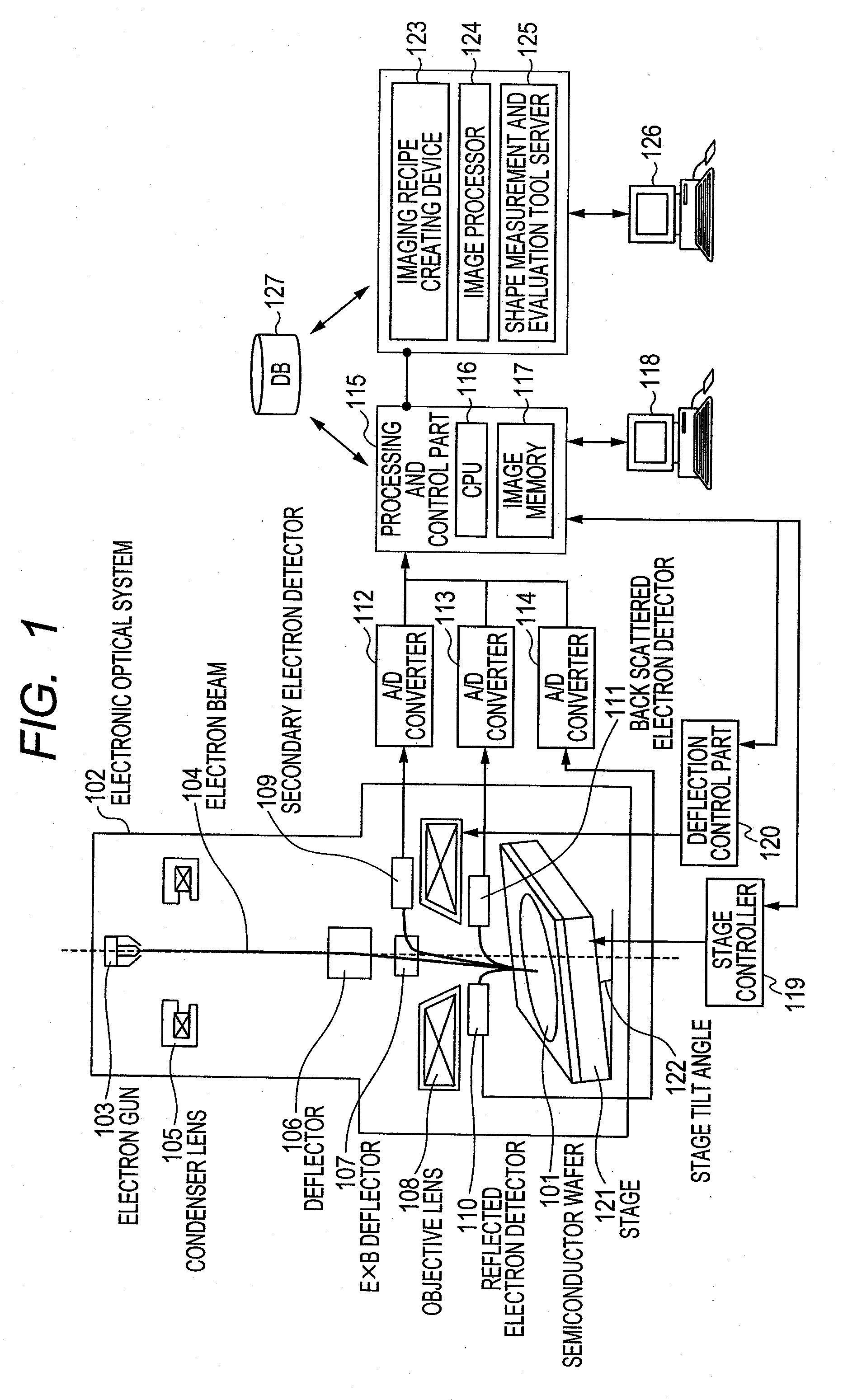
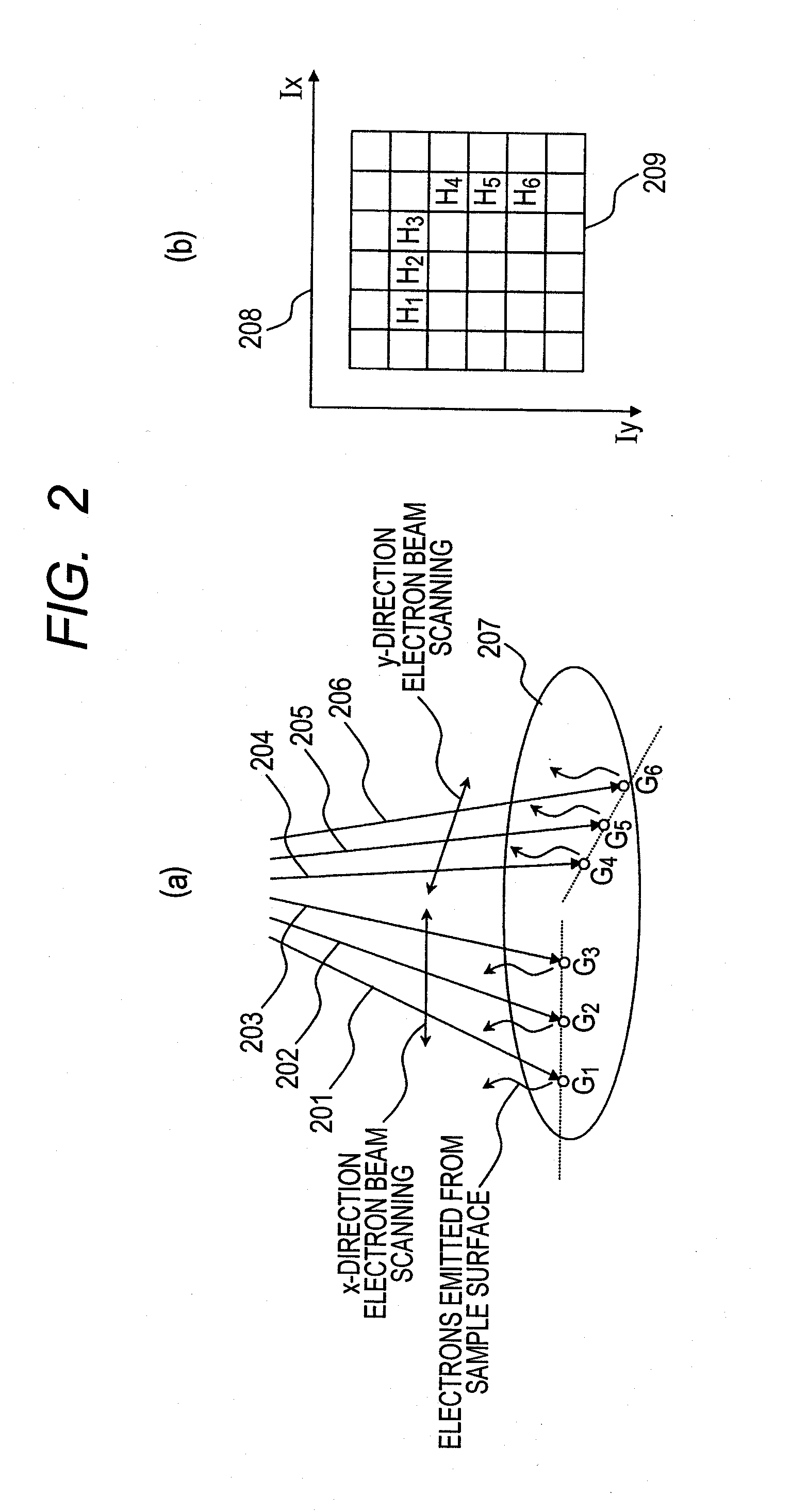
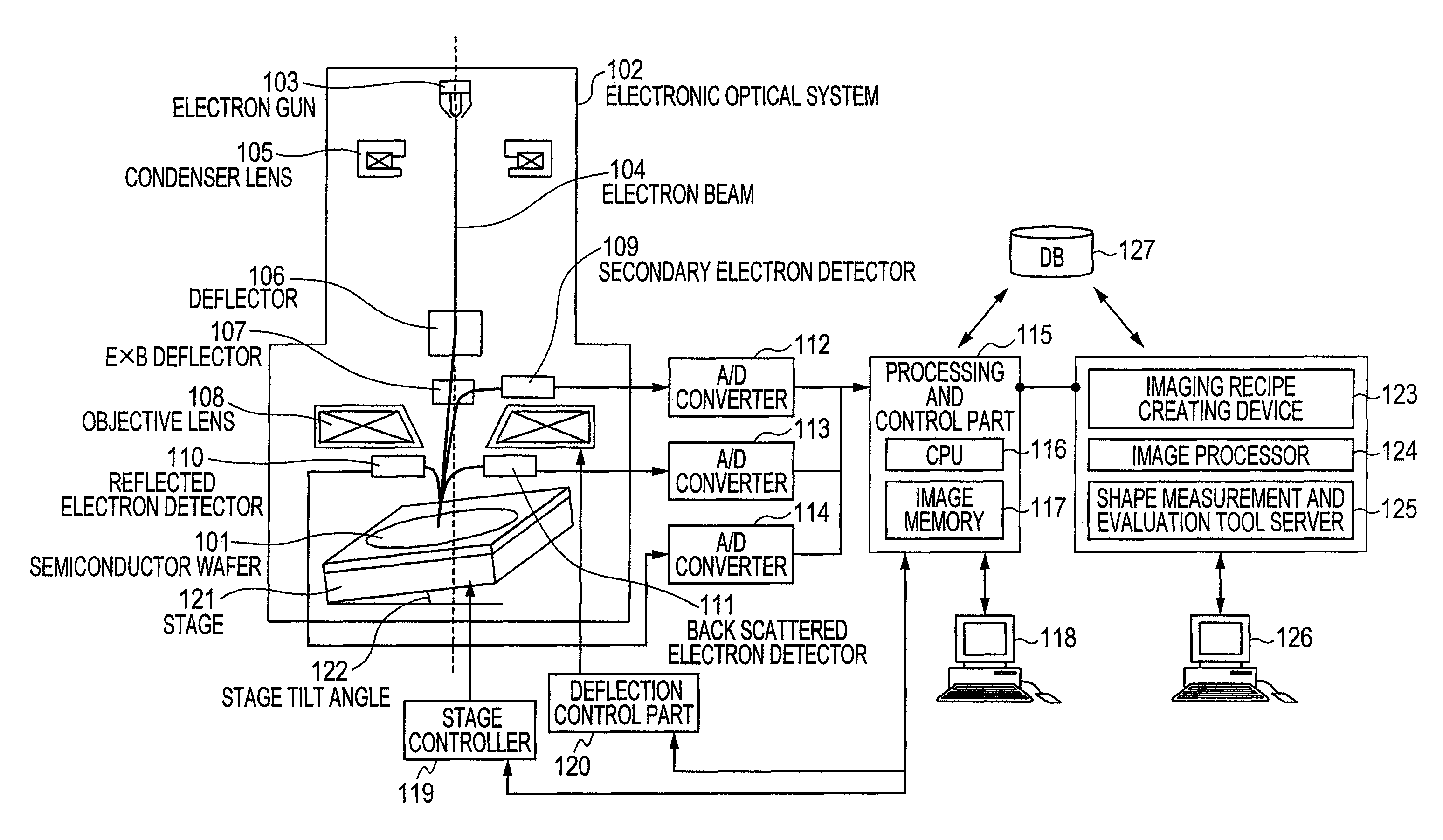
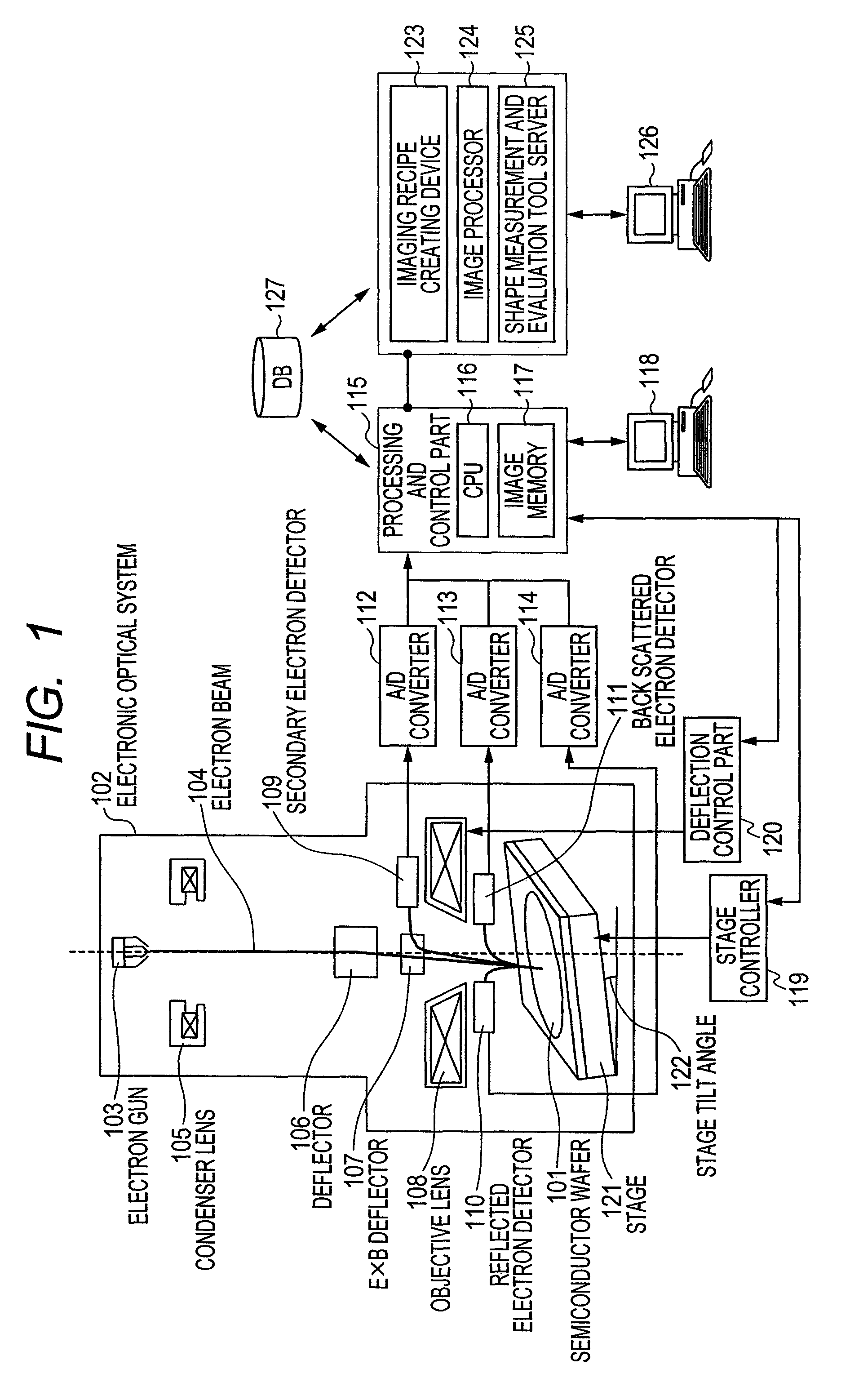
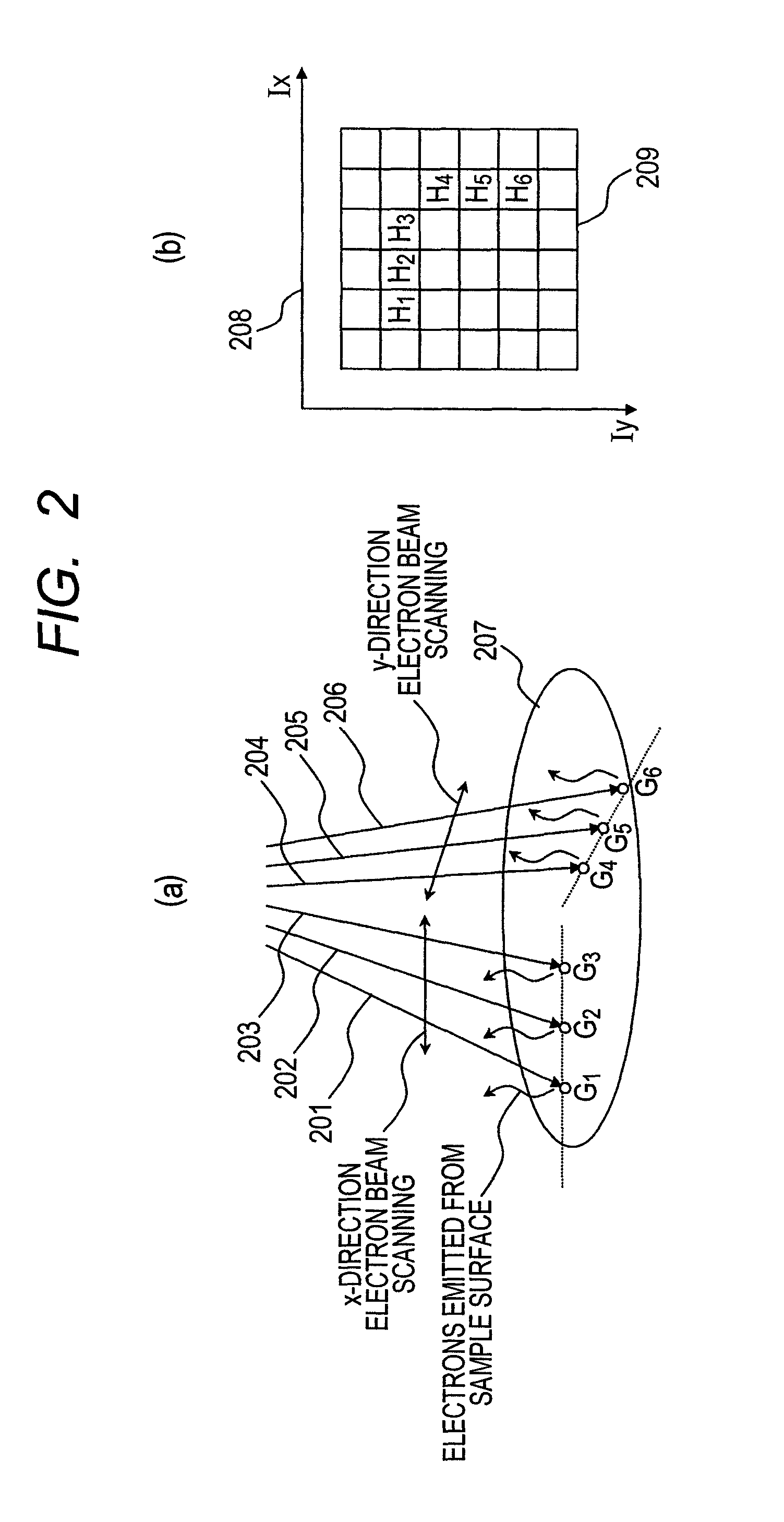
Method and device for synthesizing panorama image using scanning charged-particle microscope
ActiveUS20110181688A1High resolutionElectric discharge tubesTelevision systemsComputer scienceSemiconductor
Provided is a panorama image synthesis technique using a scanning charged-particle microscope and capable of obtaining a panorama image synthesis that is robust against contamination and the imaging shift and distortion of an image in a wide-field imaging region (EP) for semiconductor fine patterns. The panorama image synthesis technique in the wide-field imaging region (EP) using the scanning charged-particle microscope is characterized in that the layout of each adjustment point, each local imaging region, and an imaging sequence comprising the imaging order of the each adjustment point are optimized and created as an imaging recipe.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
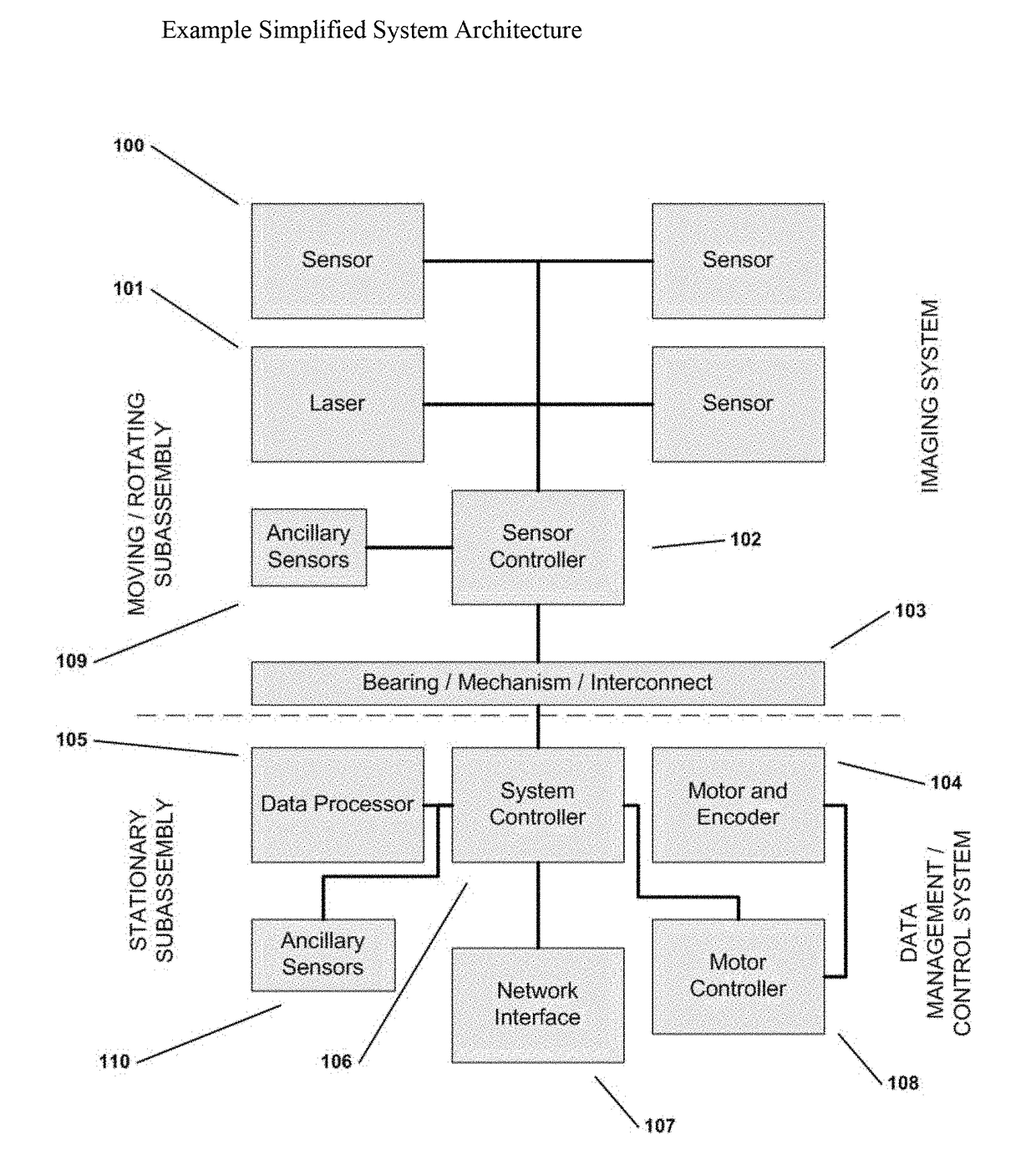
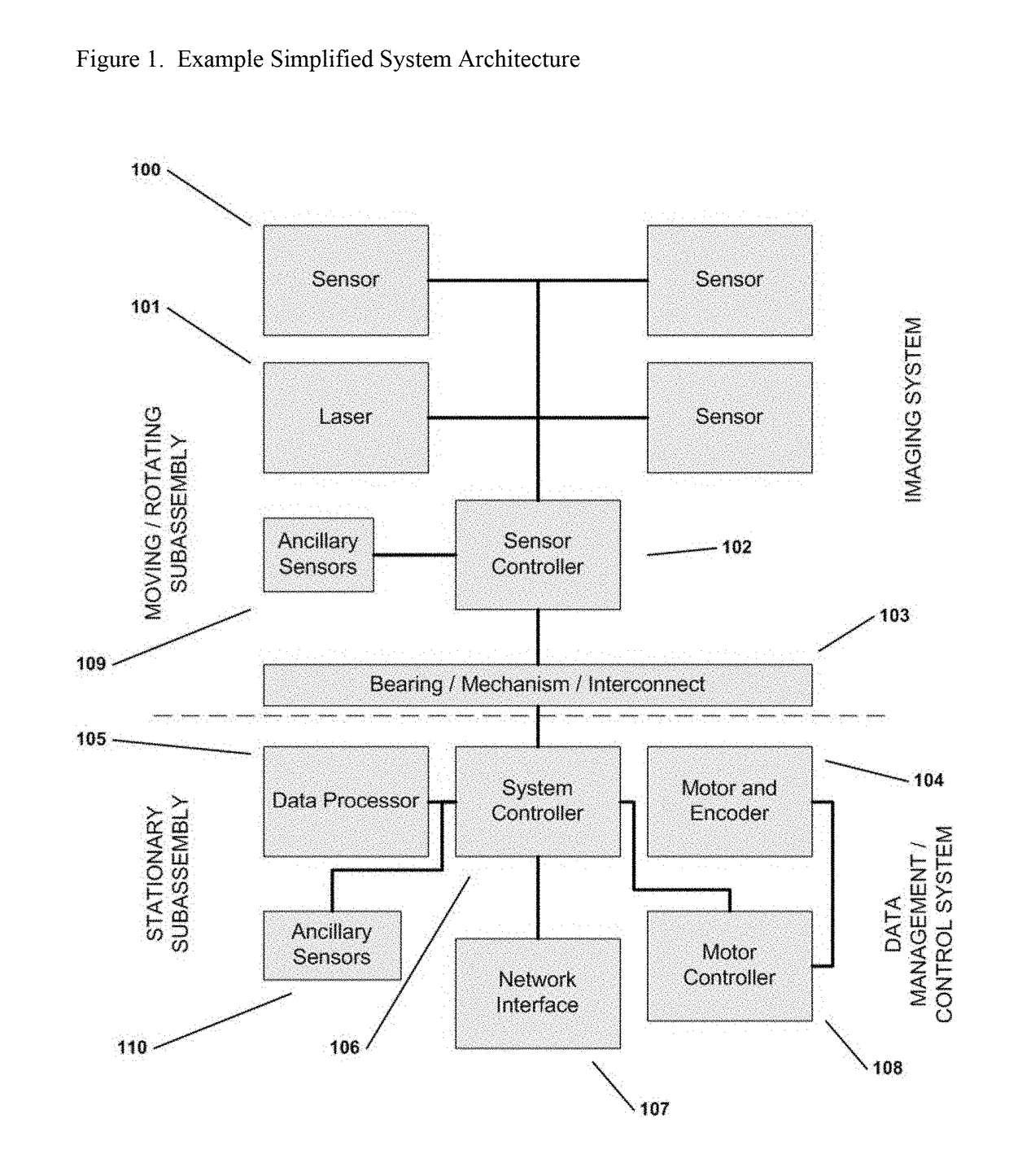
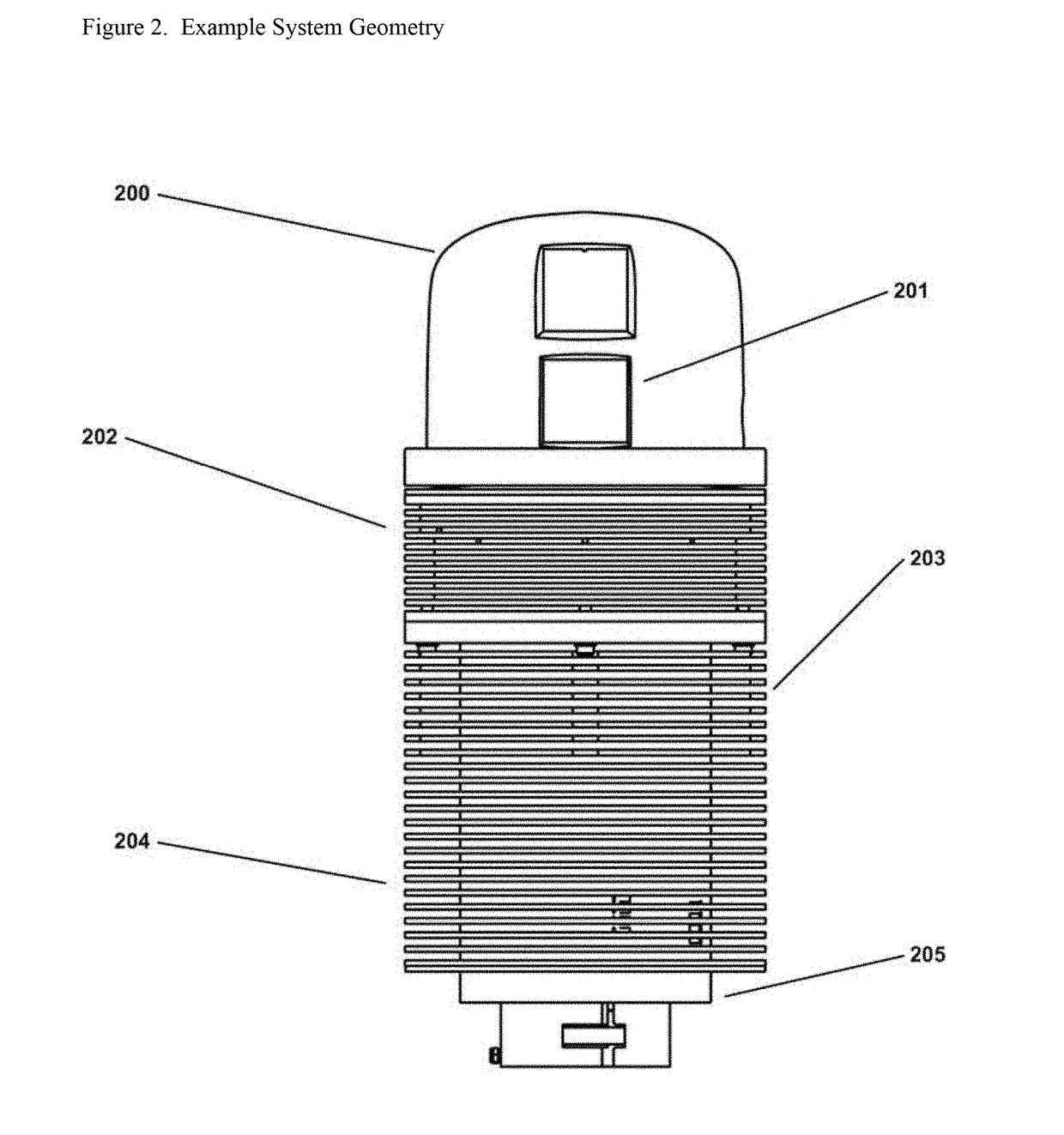
Wide Area Imaging System and Method
ActiveUS20140247323A1Low costOvercome limitationsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsWide areaImage field
The present invention provides a new and useful paradigm in wide area imaging, in which wide area imaging is provided by a step / dwell / image capture process and system to capture images and produce from the captured images a wide area image. The image capture is by a sensor that has a predetermined image field and provides image capture at a predetermined frame capture rate, and by a motorized step and dwell sequence of the sensor, where image capture is during a dwell, and the step and dwell sequence of the sensor is synchronized with the image capture rate of the sensor.
Owner:DIVERSIFIED INNOVATIONS FUND LLLP
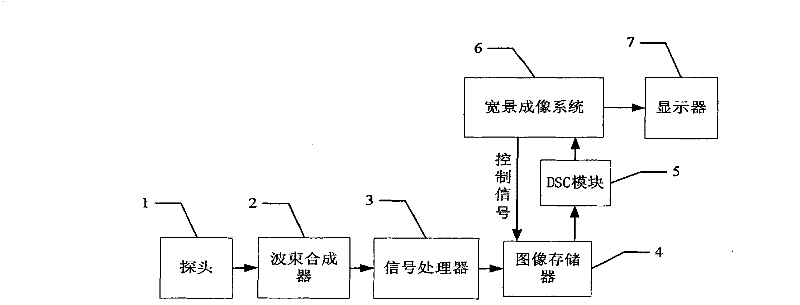
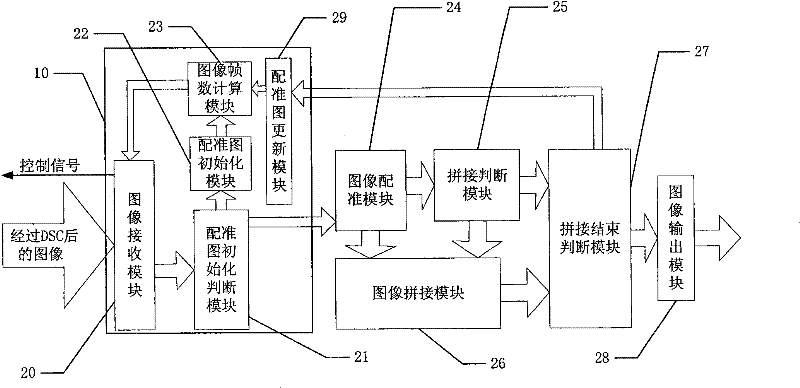
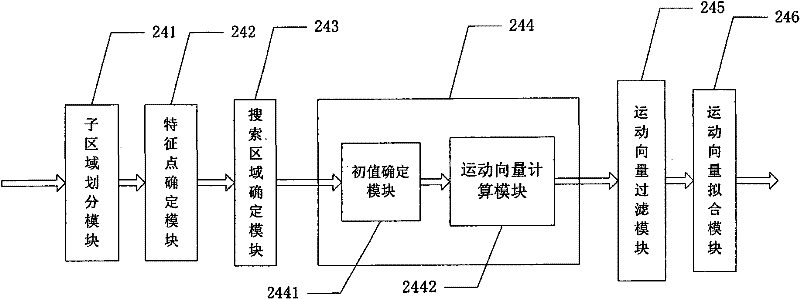
Image registration method, wide-field imaging method, ultrasonic imaging method and system thereof
ActiveCN102274042AQuick calculationQuick registrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementMotion vectorUltrasonic imaging
The invention discloses an image registration method, a panoramic imaging method, an ultrasonic imaging method and systems thereof. All the methods comprise the following basic steps: determining a floating chart and a registration chart; dividing out a plurality of subregions in the floating chart; determining a characteristic point in each subregion; determining the search region of each characteristic point in the registration chart; calculating the motion vector of each characteristic point relative to the registration chart; carrying out fitting on the motion vector to obtain the transformation coefficient of floating chart relative to the registration chart; and splicing to obtain a panoramic image through the transformation coefficient. The methods disclosed by the invention can accurately and rapidly conduct image registration to form the panoramic image.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
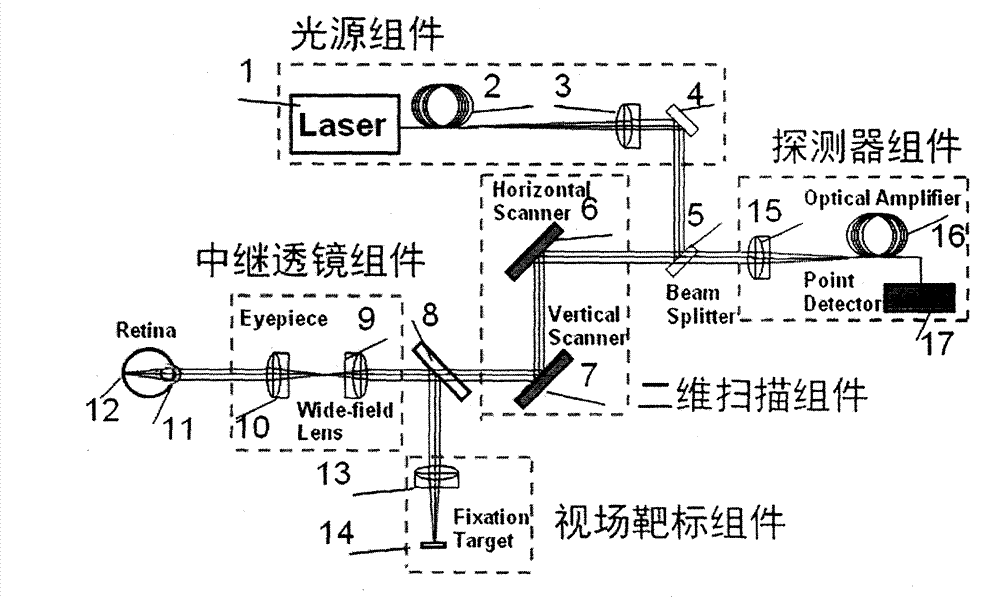
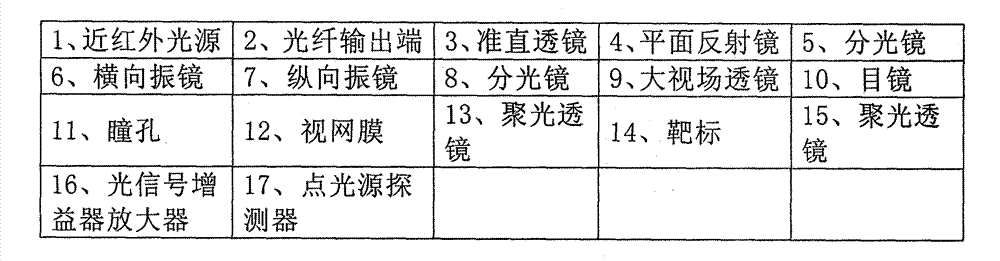
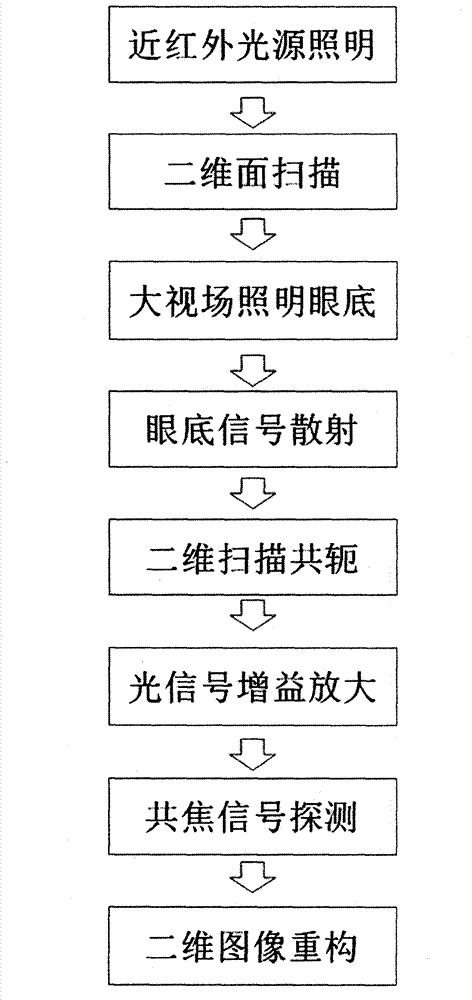
Fundus imaging equipment for clinical diagnosis
InactiveCN102885612AOvercome only single shotOvercoming the inability to obtain video fundus imagesOthalmoscopesDiseaseEyepiece
The invention discloses fundus imaging equipment for clinical diagnosis. The fundus imaging equipment for the clinical diagnosis consists of a light source component, a two-dimensional scanning component, a relay lens component, a detector component and a field-of-view target component. According to the fundus imaging equipment for the clinical diagnosis, an observation direction of a patient is fixed by utilizing the field-of-view target component, a retina of a human eye is scanned by using the two-dimensional scanning component, the detector component and an optical amplifier of the detector component optically enlarge a signal reflected by the retina to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio of an image, and a high-resolution image of the retina is acquired through the detection of a confocal signal; according to the fundus imaging equipment for the clinical diagnosis, the influence of field curvature and aberration in an imaging view field is reduced by the special design of a wide-field lens of the relay lens component, and the wide-field imaging of 30 to 60 degrees is realized by adjusting an eyepiece; high-resolution fundus imaging equipment which is compact is design and is applicable to the clinical diagnosis is fulfilled by the schemes of light source fiber input and optical signal fiber output, so that the imaging quality of the traditional fundus photography system is greatly improved, the imaging view field is greatly increased, and the clinical operability of equipment is strengthened; and the fundus imaging equipment for the clinical diagnosis particularly can acquire high-resolution images of retinas of human eyes under the condition that the retinas reflect weak signal light, and is used for the clinical diagnosis of fundus diseases.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
Wide-field imaging using nitrogen vacancies
Nitrogen vacancies in bulk diamonds and nanodiamonds can be used to sense temperature, pressure, electromagnetic fields, and pH. Unfortunately, conventional sensing techniques use gated detection and confocal imaging, limiting the measurement sensitivity and precluding wide-field imaging. Conversely, the present sensing techniques do not require gated detection or confocal imaging and can therefore be used to image temperature, pressure, electromagnetic fields, and pH over wide fields of view. In some cases, wide-field imaging supports spatial localization of the NVs to precisions at or below the diffraction limit. Moreover, the measurement range can extend over extremely wide dynamic range at very high sensitivity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and device for synthesizing panorama image using scanning charged-particle microscope
ActiveUS8767038B2High resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesComputer scienceDistortion
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Wide area imaging system and method
ActiveUS9813618B2Low costOvercome limitationsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsWide areaImage field
The present invention provides a new and useful paradigm in wide area imaging, in which wide area imaging is provided by a step / dwell / image capture process and system to capture images and produce from the captured images a wide area image. The image capture is by a sensor that has a predetermined image field and provides image capture at a predetermined frame capture rate, and by a motorized step and dwell sequence of the sensor, where image capture is during a dwell, and the step and dwell sequence of the sensor is synchronized with the image capture rate of the sensor.
Owner:DIVERSIFIED INNOVATIONS FUND LLLP
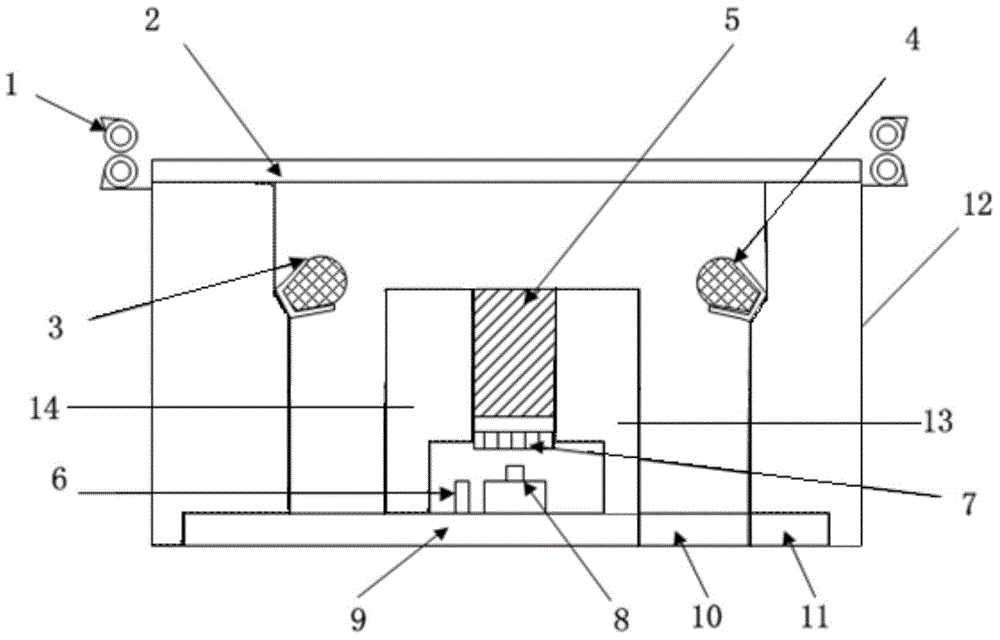
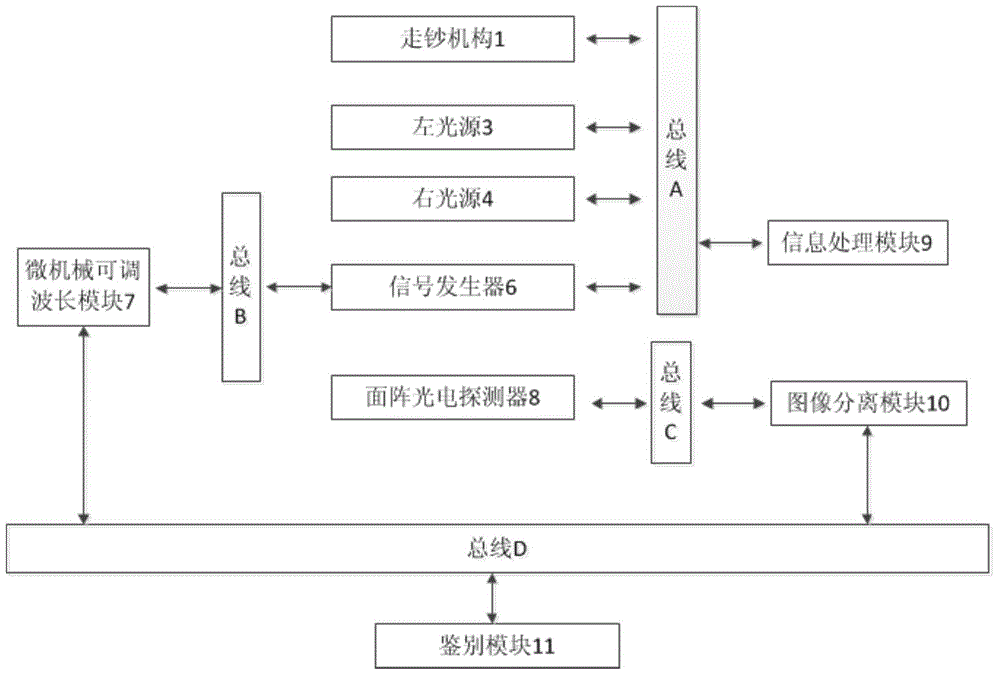
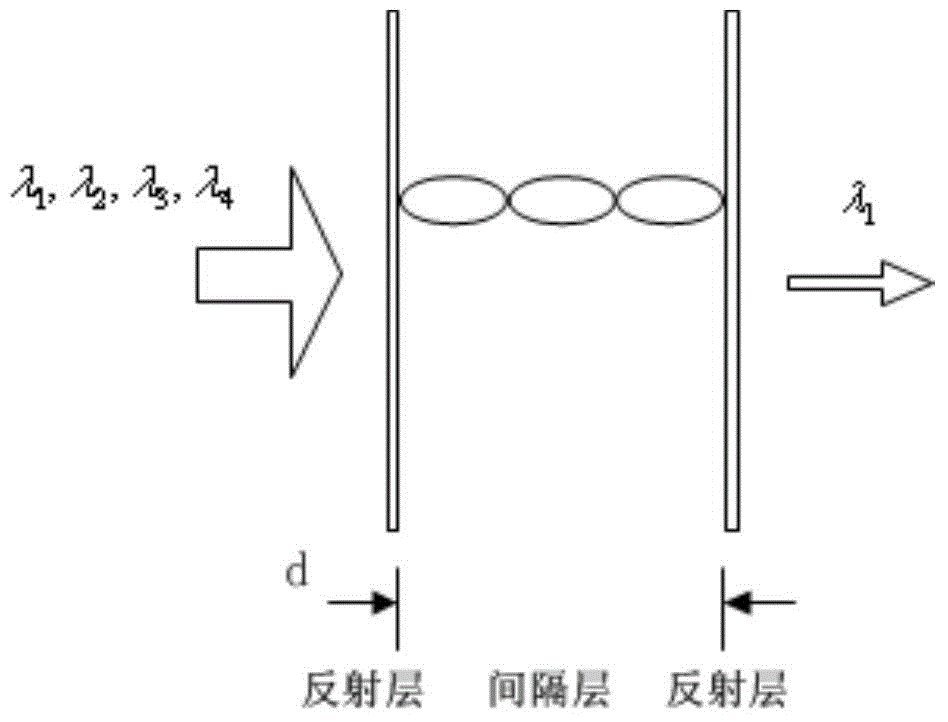
Multi-spectral recognition device and multi-spectral recognition method for banknotes
InactiveCN104916036AImprove identification accuracyPaper-money testing devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionWide fieldLength wave
The embodiment of the invention provides a multi-spectral recognition device for banknotes, which is used for acquiring images of a banknote in each optical spectrum section, comparing the images with preset conditions and improving the recognition accuracy. The technical scheme is that the multi-spectral recognition device for banknotes provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises a wide field imaging module, a wavelength adjusting module, a photoelectric detection module and an identification module; the wide field imaging module is used for acquiring a reflection image of the banknote to be detected; the wavelength adjusting module is used for extracting n reflection sub-images of the reflection image under n optical spectrum sections, wherein the n is a natural number which is greater than 2; the photoelectric detection module is used for carrying out photoelectric signal conversion on the n reflection sub-images, and acquiring n converted images corresponding to the n reflection sub-images; and the identification module is used for recognizing the authenticity of the banknote to be detected through the n converted images.
Owner:GRG BAKING EQUIP CO LTD
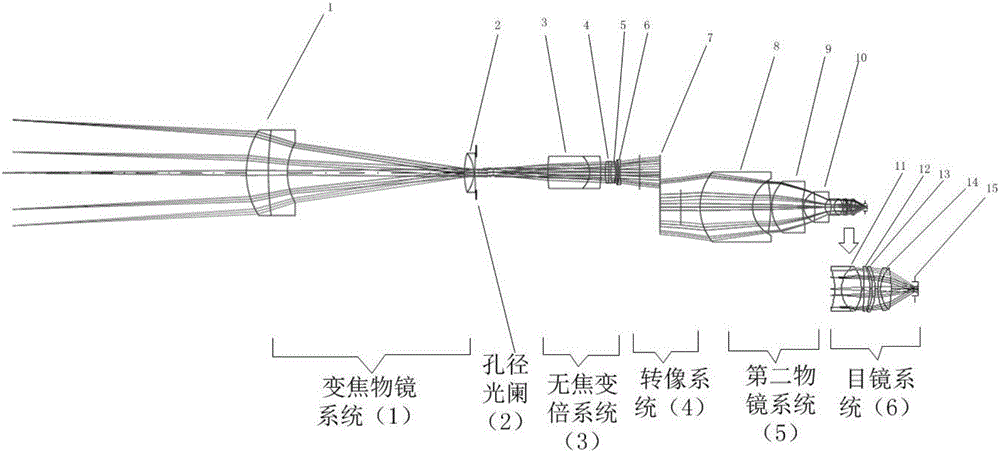
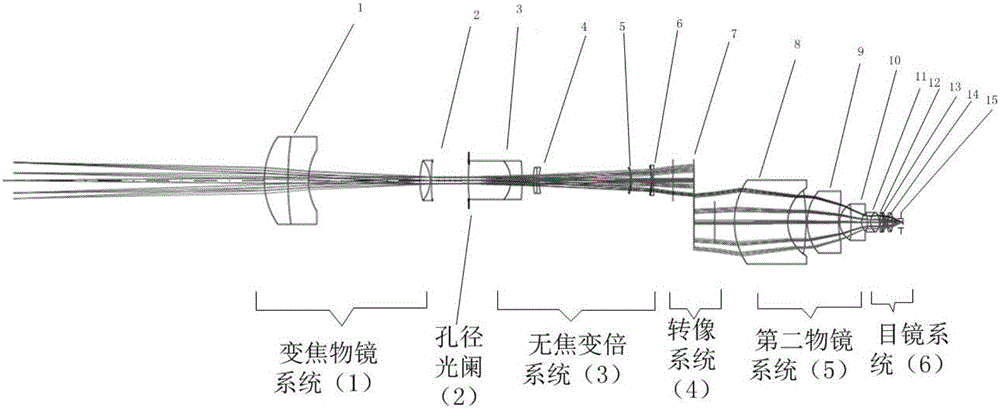
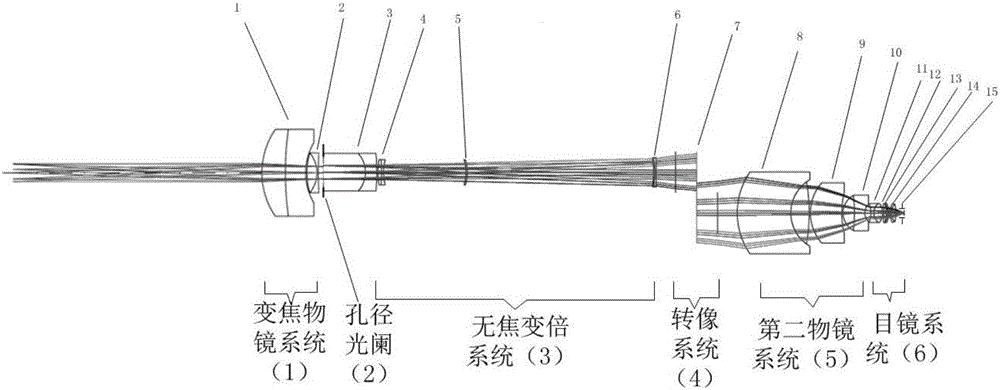
Wide-field and long-working-distance continuous zooming operating microscope optical system
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical instruments, and especially relates to a wide-field and long-working-distance continuous zooming operating microscope optical system. The system comprises a variable-focus objective system (1), an aperture diaphragm (2), an unfocused zooming system (3), an image rotation system (4), a second objective system (5), and an eyepiece system (6). Optical aberration needing correction of all parts of the system is distributed reasonably, two aspheric surfaces are introduced to correct advanced optical aberration caused by wide-field imaging, and thus, good wide-field microscopic imaging is achieved. As the components between and inside the variable-focus objective system and the unfocused zooming system do complex motion according to different rules, the magnifying power changes continuously, and the position of the image plane is fixed. Long working distance is realized through 'positive and negative' focal power distribution. The system of the invention meets the demand of clinical application, has the advantages of wide field, variable focus, and long working distance, and is particularly applicable to the field of neurosurgery operation or free flap transplant operation demanding a wide field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
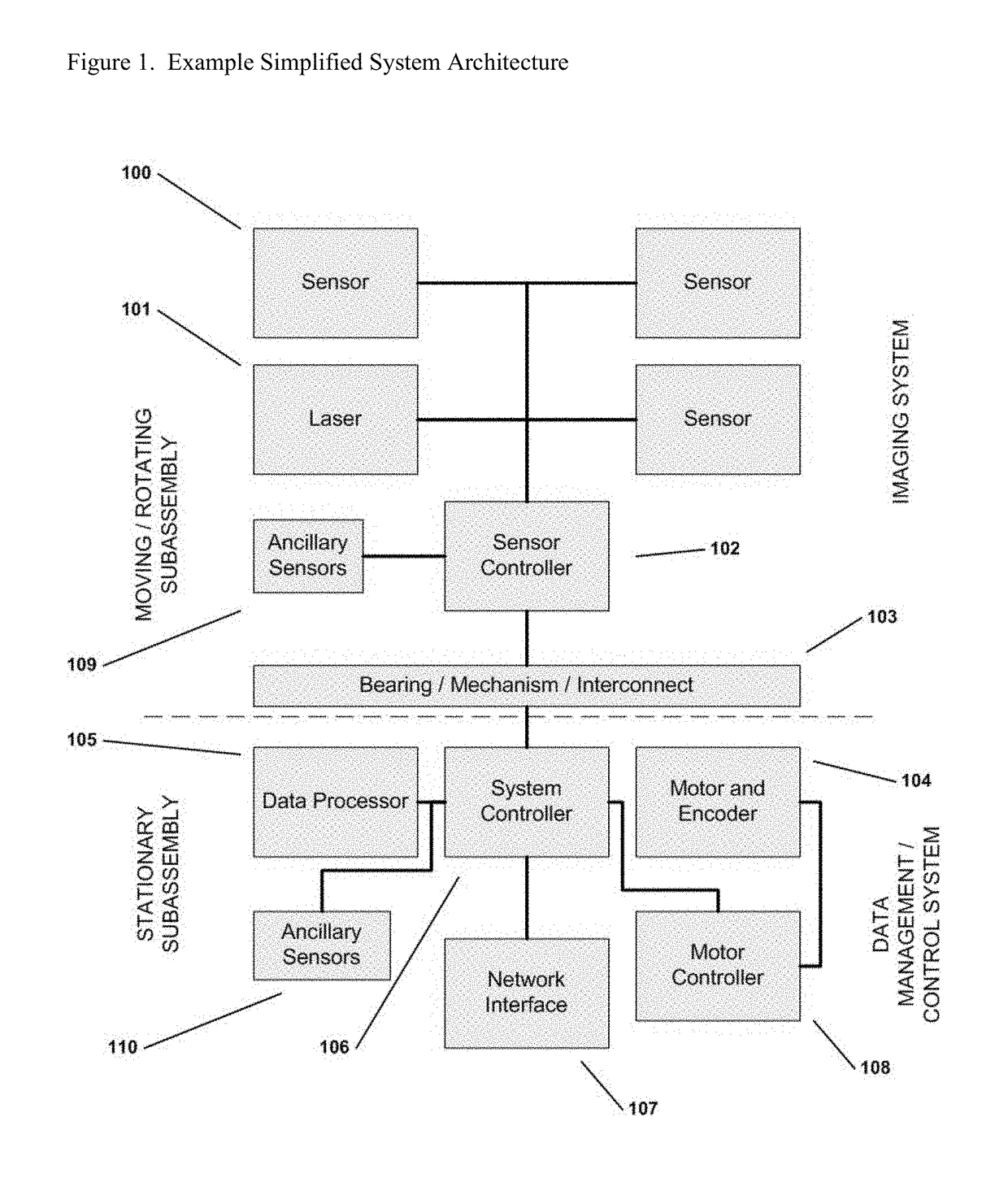
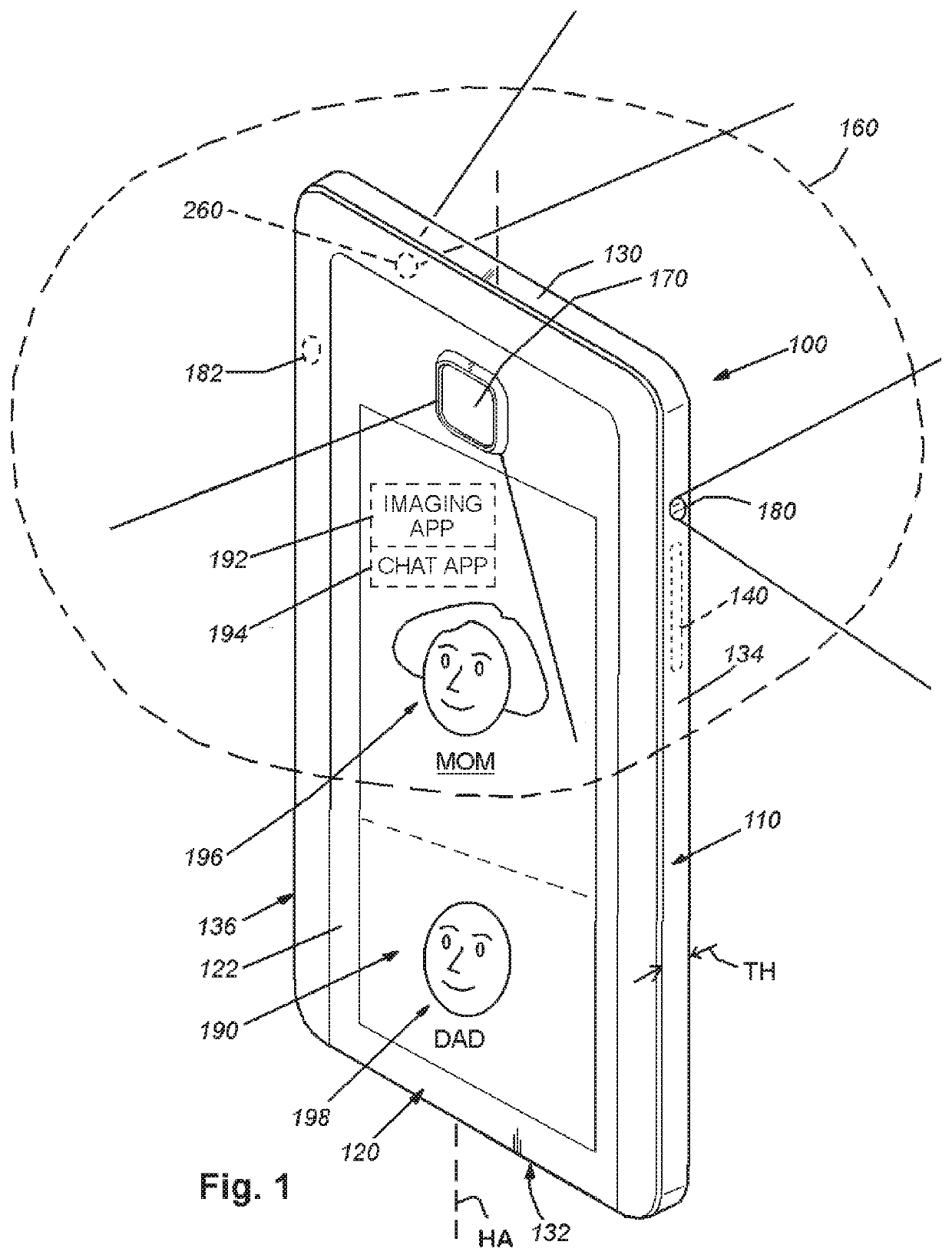
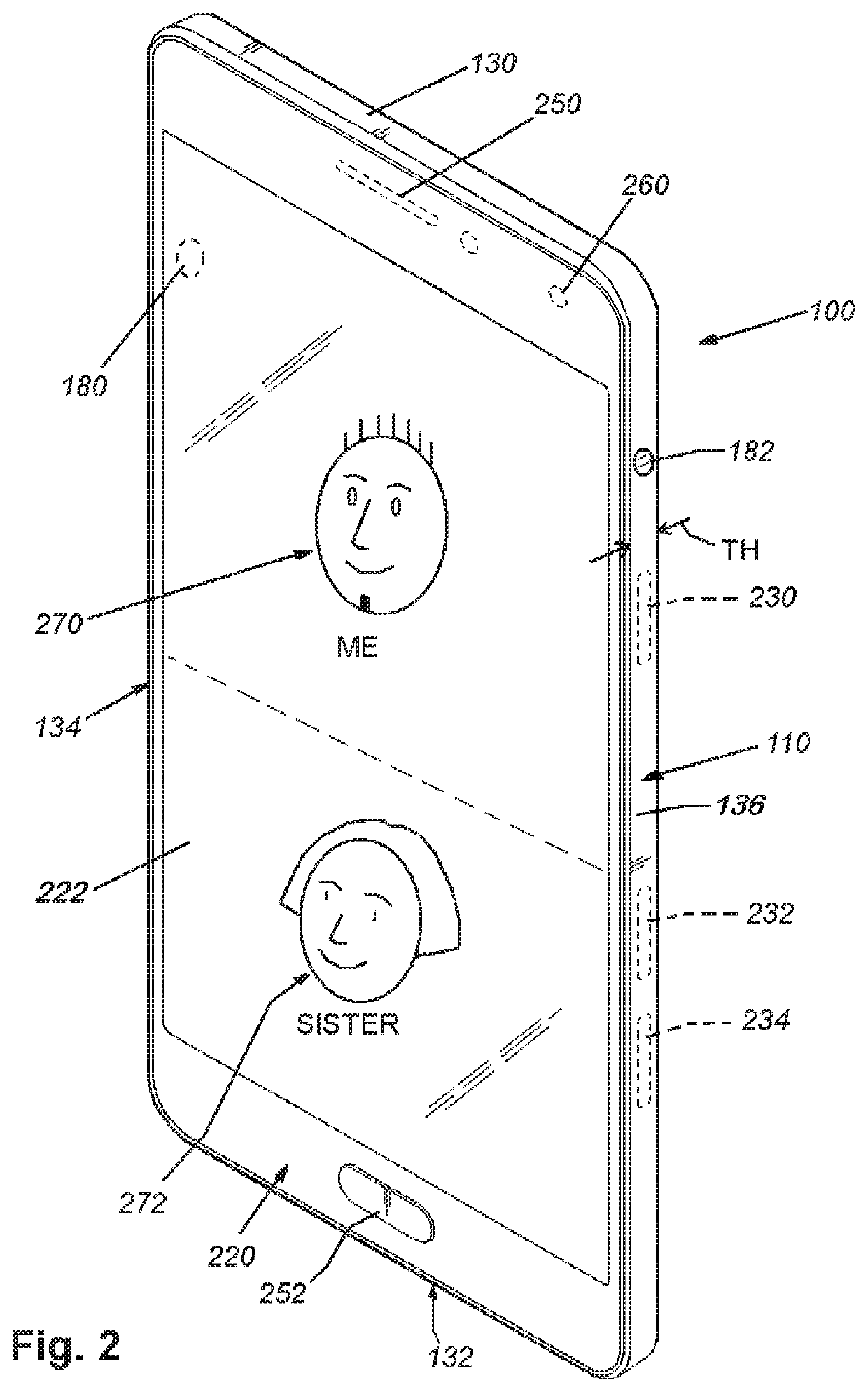
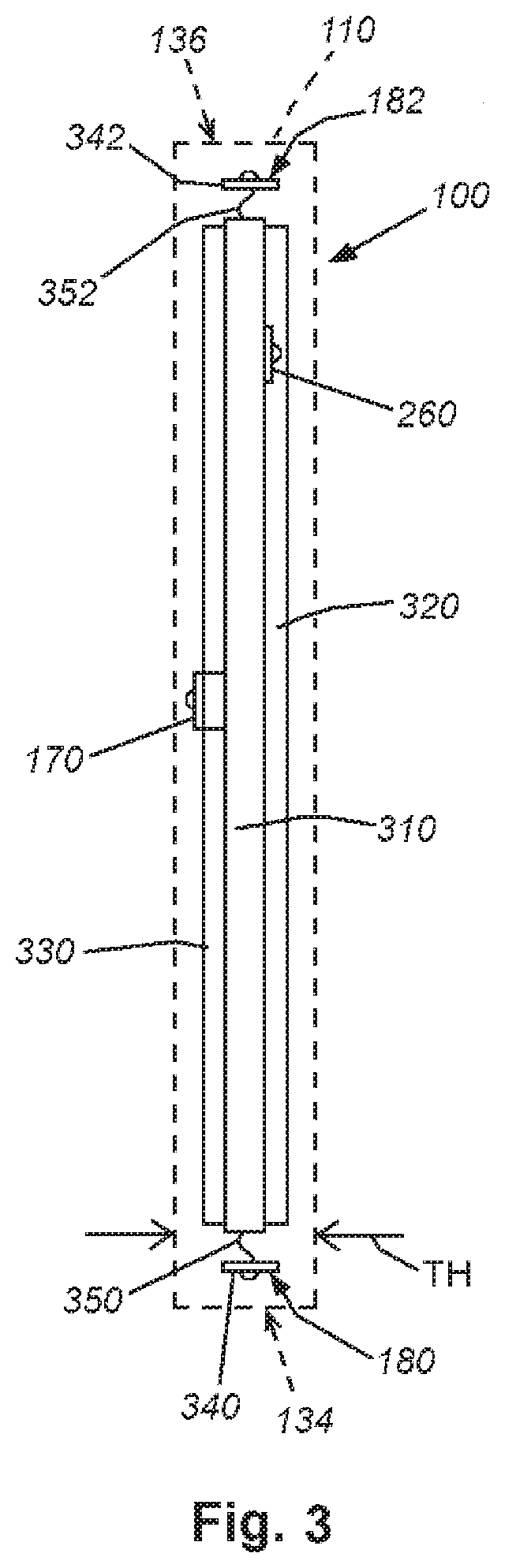
System and method for providing wide-area imaging and communications capability to a handheld device
ActiveUS20200260049A1Avoids inconvenient finger placementOvercome disadvantagesTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsProjection imageWide field imaging
This invention provides a system and method for utilizing a wireless, handheld communication device to image a scene in multiple directions, so as to include multiple parties in addition to the user, and also, optionally, to project images on a plurality of display screens—for example a user-facing screen on the front face of the phone and an opposing screen on the rear / back face of the phone that faces (e.g.) a chat participant other than the user (an audience). The housing of the smartphone is adapted to provide a multi-camera and multi-screen arrangement. More particularly, the housing of the smartphone is adapted to include (at least) a front-directed camera and a rear-directed camera on respective front and rear faces, and openings along the left and right side edges for small-scale cameras and associated protective windows that are directed to image the left and right areas adjacent to the phone.
Owner:ERNA SALVATORE
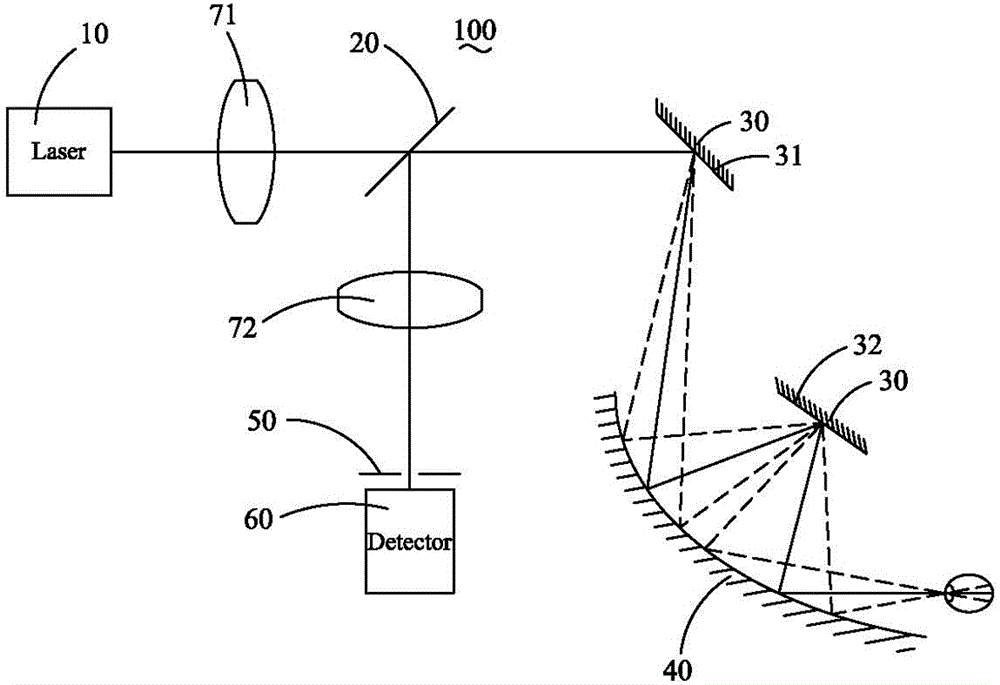
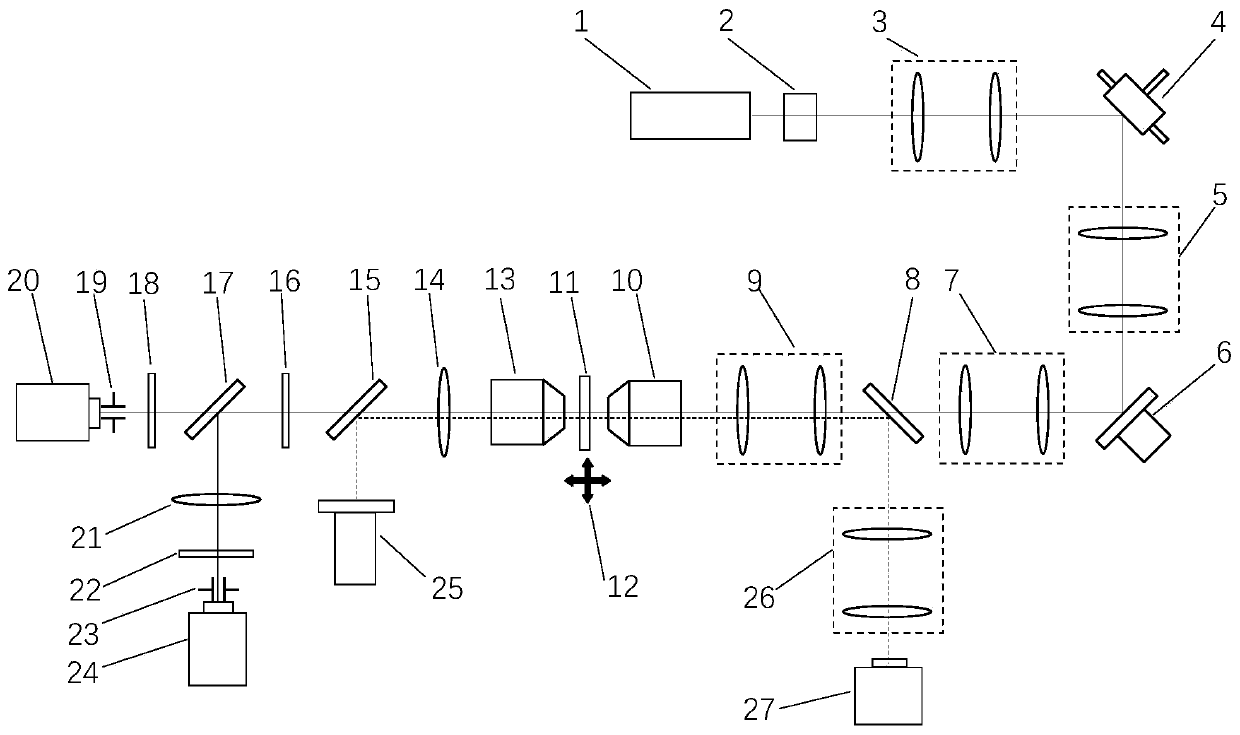
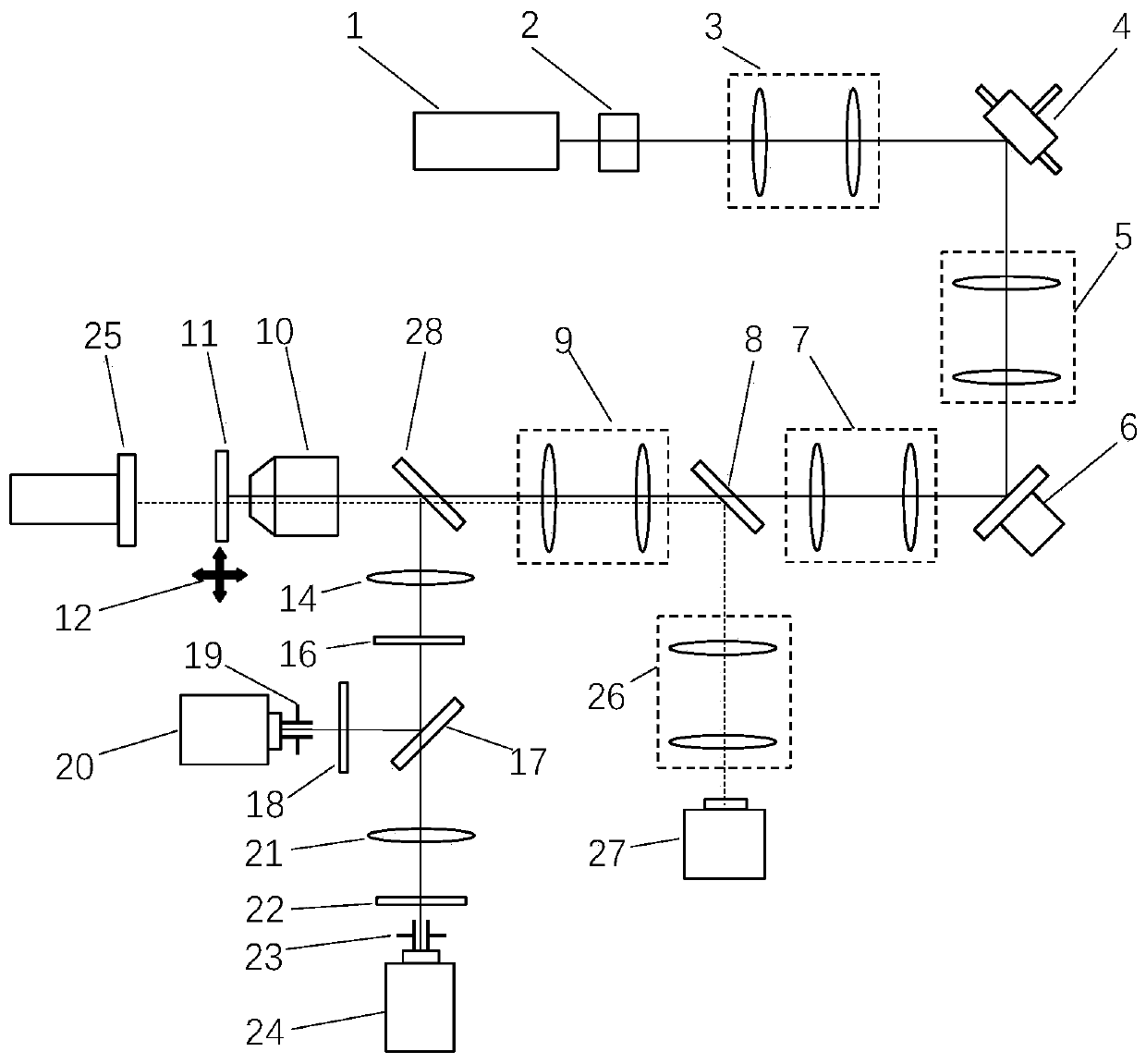
Ultra-wide field fundus imaging system
ActiveCN106388765ARealize large field of view imagingAvoid ghost imagesMirrorsRefractometersAngle of incidenceUltra wide field
The invention discloses an ultra-wide field fundus imaging system which comprises a light source, an optical splitter, a scanning assembly, a curved reflector, a detection pinhole and an imaging assembly, wherein the scanning assembly comprises a first scanning mirror and a second scanning mirror, the first scanning mirror scans in the first direction, and the second scanning mirror scans in the second direction; light emitted by the light source is reflected by the first scanning mirror, the curved reflector, the second scanning mirror and the curved reflector respectively after passing by the optical splitter and then enters the fundus; the light entering the fundus returns to the optical splitter along the same route after being reflected by the retina, penetrates through the detection pinhole and enters the imaging assembly. Compared with the prior art, the ultra-wide field fundus imaging system realizes fundus imaging by total reflection, and ghost images brought by imaging of a lens module are effectively avoided. Because the curvature of the curved reflector changes gradually, the light reflected by the curved reflector can enter the fundus at larger angle of incidence, and large view field imaging is realized.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
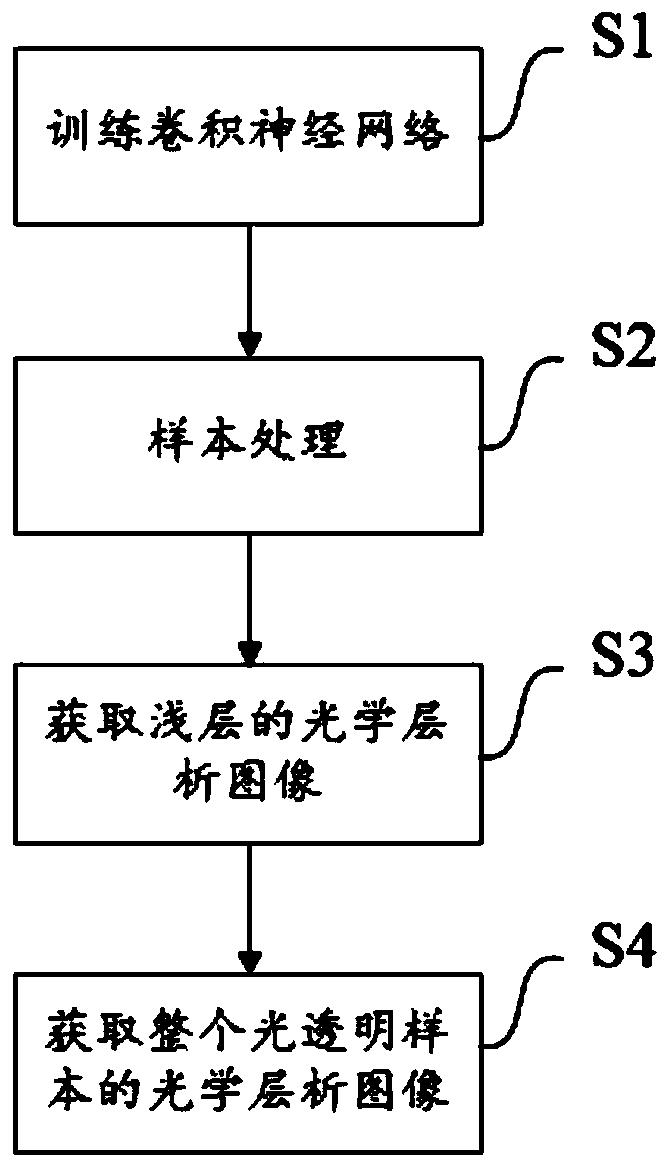
Rapid three-dimensional imaging method applicable to optical transparent sample
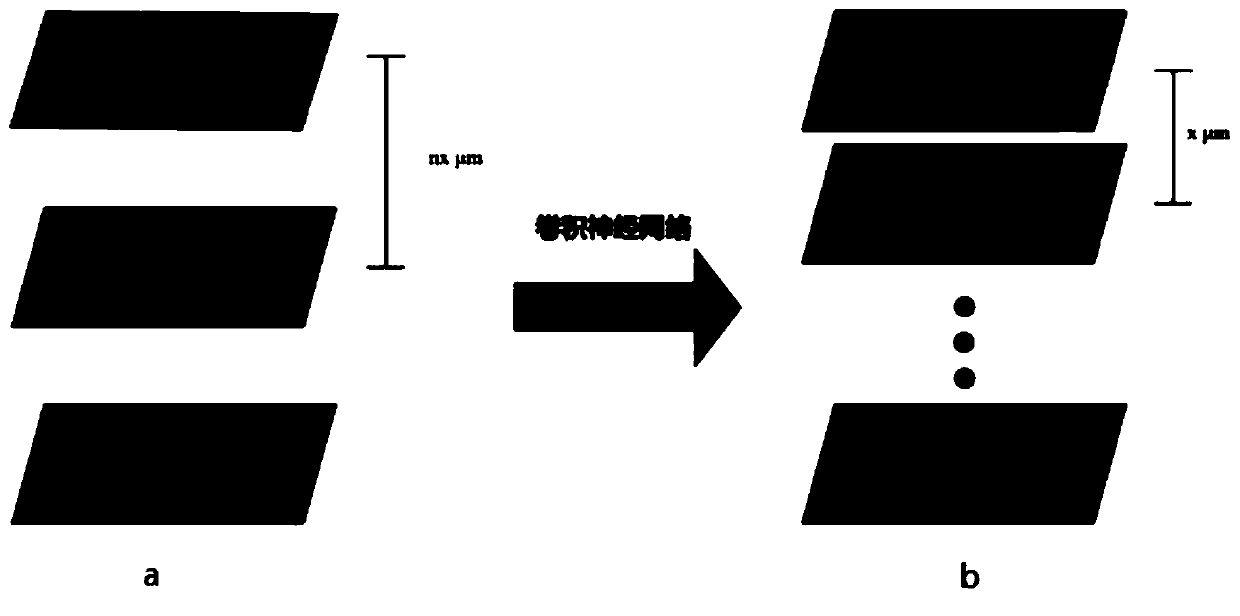
ActiveCN110243827AReconstruction from projectionPreparing sample for investigationWide fieldHigh flux
The invention provides a rapid three-dimensional imaging method applicable to an optical transparent sample. The method comprises the steps of S1, training a convolution neural network; S2, processing a sample, in which a to-be-imaged sample is fixed after optical transparent processing; S3, acquiring an optical chromatography image of a shallow, in which wide-field images of the shallow layer are acquired and are input to the convolution neural network of which training is completed, and optical chromatography images which are same in numbers and sizes of the wide-field images are obtained; and S4, acquiring the optical chromatography image of the whole optical transparent sample. According to the method, a three-dimensional image of the sample is obtained by high-flux wide-field imaging and rapid axial scanning, and finally, a clear and complete three-dimensional image is restored by the convolution neural network; and by the method, the image shooting speed is remarkably increased, and a photobleaching effect is reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Wide area imaging system and method
ActiveUS20180176466A1Low costOvercome limitationsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsWide areaImage field
The present invention provides a new and useful paradigm in wide area imaging, in which wide area imaging is provided by a step / dwell / image capture process and system to capture images and produce from the captured images a wide area image. The image capture is by a sensor that has a predetermined image field and provides image capture at a predetermined frame capture rate, and by a motorized step and dwell sequence of the sensor, where image capture is during a dwell, and the step and dwell sequence of the sensor is synchronized with the image capture rate of the sensor.
Owner:DIVERSIFIED INNOVATIONS FUND LLLP
Self-adaptive second and third harmonic combined detection microimaging method and device
InactiveCN110623641AStrong complementarityImprove imaging depthDiagnostics using lightSensorsMicro imagingImaging quality
The invention relates to a self-adaptive second and third harmonic combined detection microimaging method and device, and belongs to the technical field of optical microimaging. Second and third harmonic signal detection modules are simultaneously arranged on a detection path of a conventional harmonic microscope device; the separation and wave filtering of second harmonic signals and third harmonic signals are realized by using a dichroscope and a light filter; an independent photoelectric detector is used for respectively detecting the second and third harmonic signals; and a self-adaptive aberration correcting device is introduced into a system, and is used for correcting aberration existing during great-depth detection on a sample. The device provided by the invention comprises a laserscanning system, a self-adaptive aberration correcting system, a harmonic signal exciting system, a harmonic signal detection system, a wide-field imaging system and an image rebuilding and data processing system. The combined detection of the second and third harmonic signals and the complementation of sample structure information are realized; and the imaging quality is maintained during great-depth detection.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
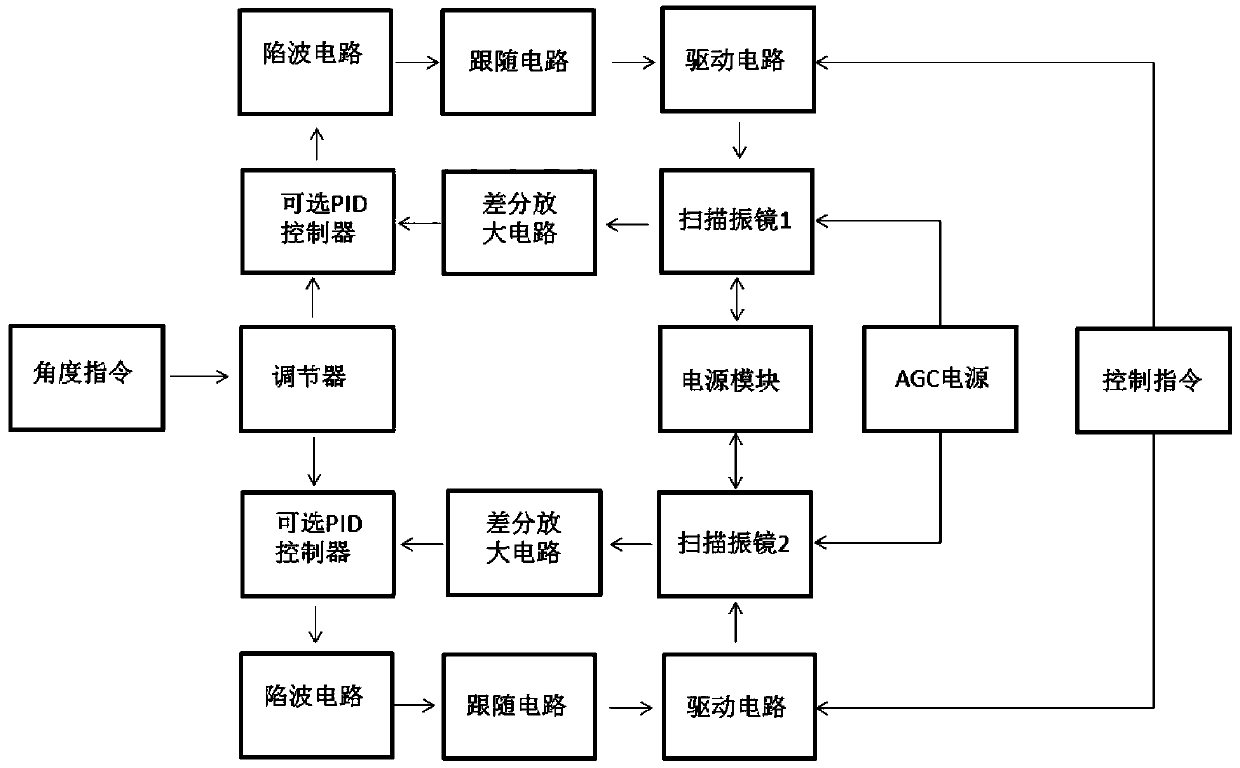
Scanning galvanometer control system for area array infrared wide-area imaging
ActiveCN109060146AImprove adaptabilityReduce overheadProgramme controlRadiation pyrometryWide areaGyroscope
The invention discloses a scanning galvanometer control system for area array infrared wide-area imaging. The scanning galvanometer control system comprises an interface module, a control module, a drive module and an interface unit. All the modules are integrated in an area array thermal imager. The interface module obtains an instruction of the control end of a wide-area imaging system through two paths of data lines and converts the instruction into parallel data to be sent to the control module. The control module analyzes the instruction and can further independently solve encoder and gyroscope information to obtain angle compensation information. The drive module is connected with the control module to drive a single-shaft galvanometer or a double-shaft galvanometer to conduct scanning motion. According to the scanning galvanometer control system for area array infrared wide-area imaging, the imaging blurring problem caused by motion of the area array thermal imager in area arrayinfrared wide-area imaging systems for weekly scanning, reciprocating scanning or two-dimensional scanning and the like is solved, the motion in integral imaging of an area array detector can be compensated by adopting the technical scheme, thus clear imaging is achieved when the thermal imager makes motion, and then clear wide-area images are spliced in the imaging system.
Owner:HUBEI JIUZHIYANG INFRARED SYST CO LTD
Fluorescence control method used in labeling biological tissues with organic fluorescent dye molecules
ActiveCN106568753AReduced conjugated π electron densityQuenching is reversiblePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceLarge sizeMetal ion sequestering
The invention discloses a fluorescence control method used in labeling biological tissues with organic fluorescent dye molecules. According to the fluorescence control method, hexatomic rings are formed via combination of metal ions with the organic fluorescent dye molecules, and quenching of the fluorescence of the organic fluorescent dye molecules is realized; coordination bonds are formed by a metal ion chelating agent with metal ions, combination of the metal ions with the organic fluorescent dye molecules is destroyed, and reactivation of the fluorescence of the organic fluorescent dye molecules is realized. The fluorescence control method is capable of realizing complete fluorescence quenching, and convenient and controllable reactivation. The fluorescence control method used in labeling biological tissues with organic fluorescent dye molecules is combined with a wide-field imaging system, so that chemical chromatography imaging of samples labeled with the fluorescent dye molecules is realized, and rapid chemical chromatography imaging of large-size biological tissues labeled with organic fluorescent molecules is realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Imaging Apparatus
InactiveUS20080030879A1Avoid crackingReduce device sizeTelevision system detailsPanoramic photographyParallaxWide area
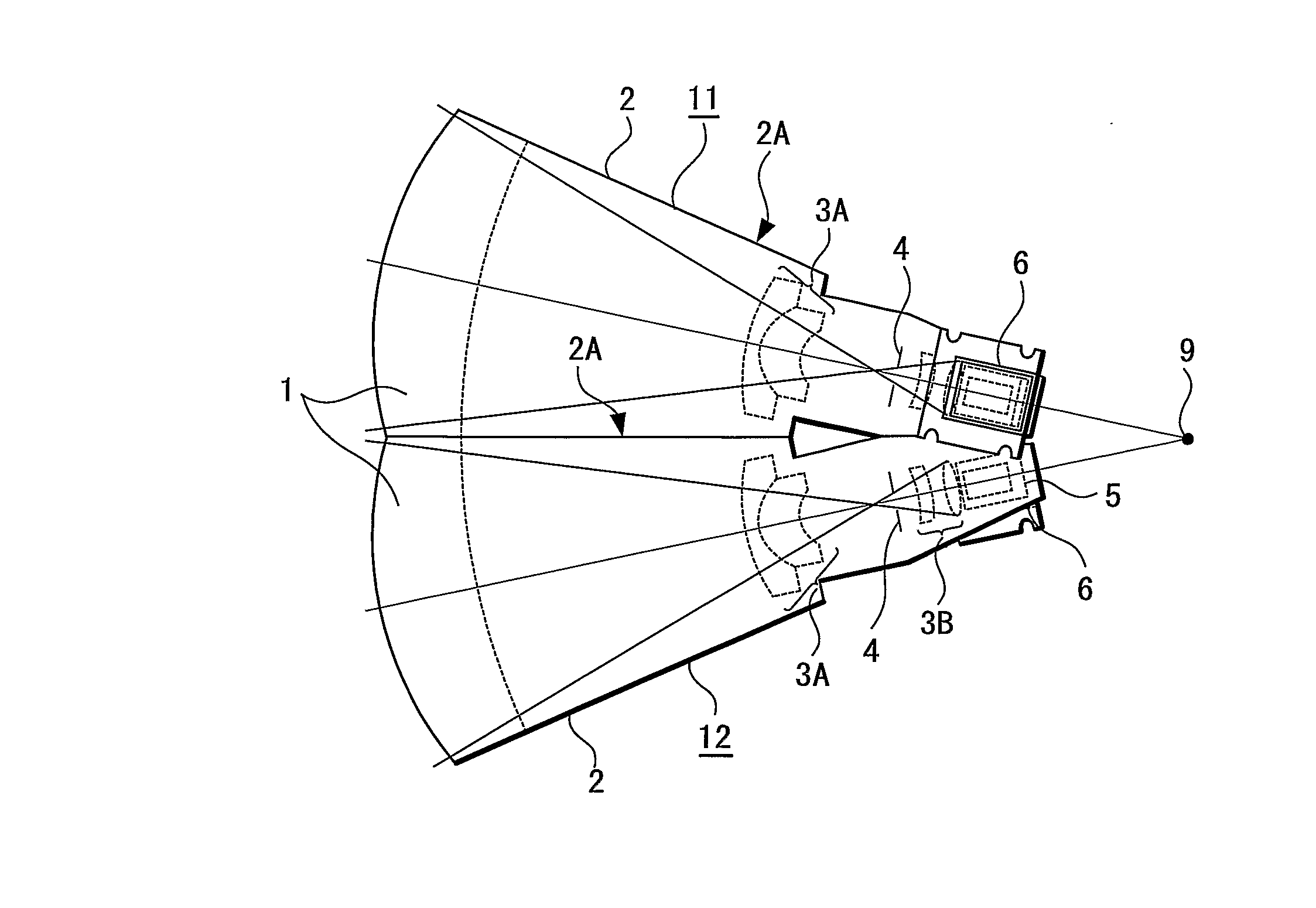
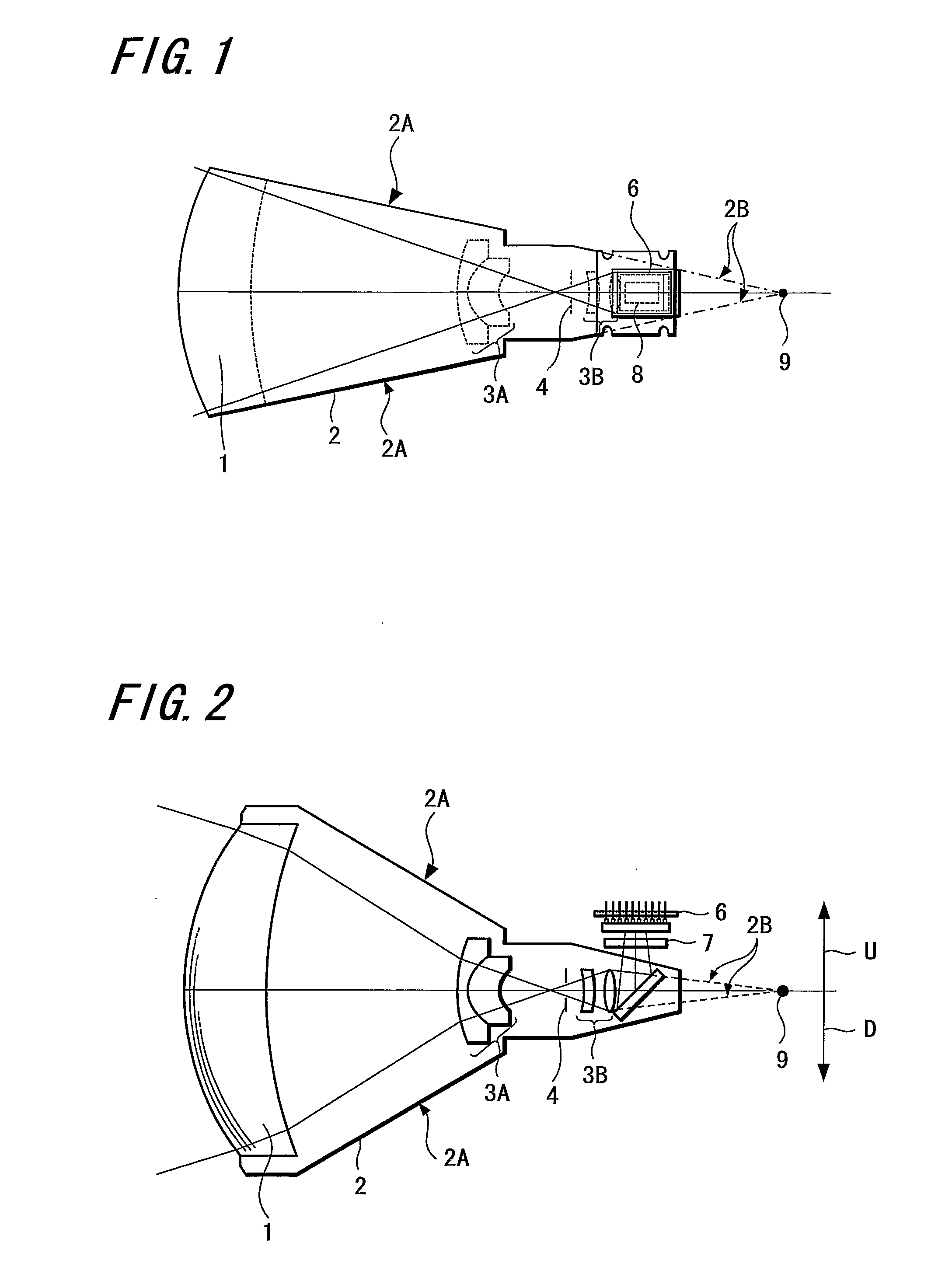
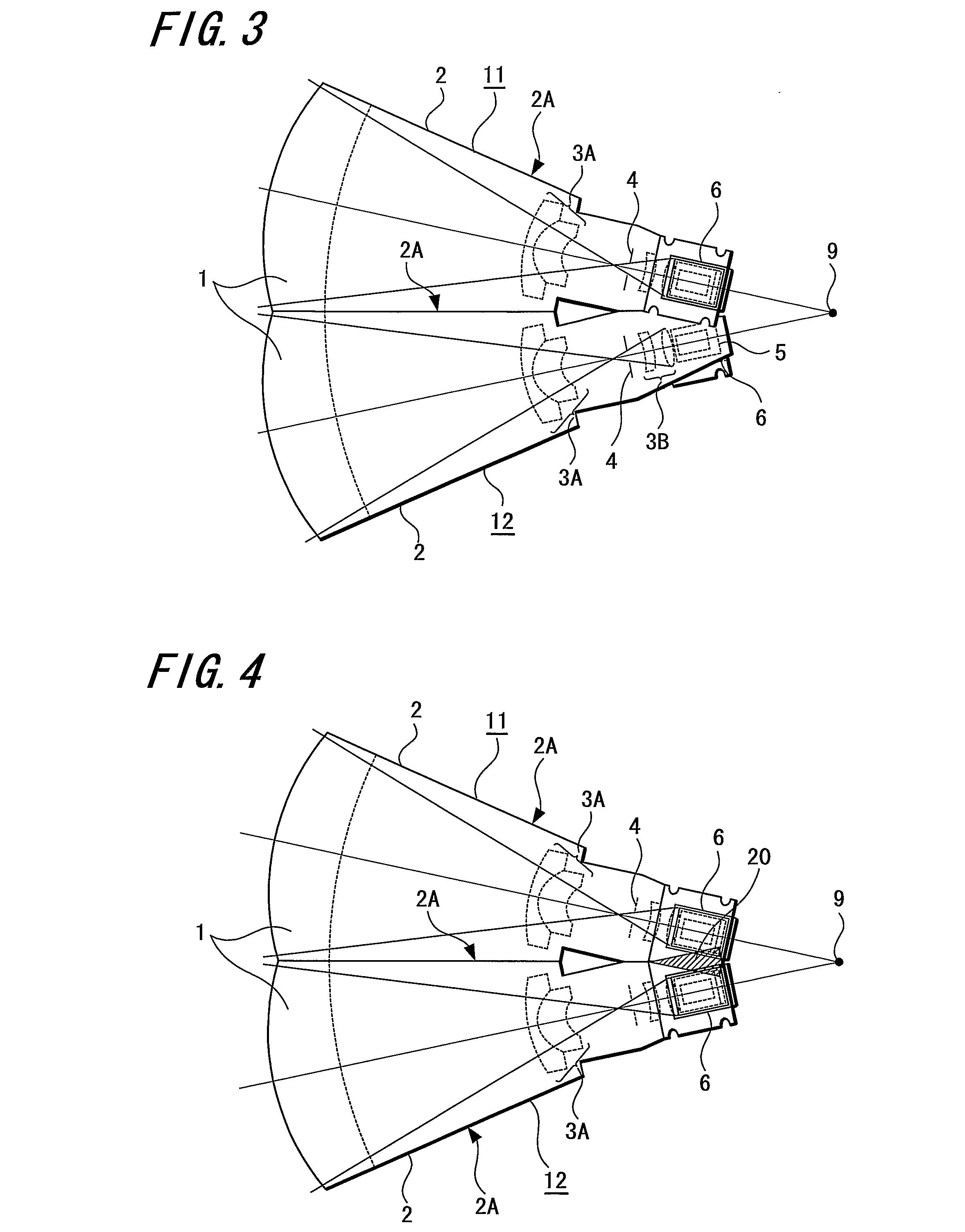
The present invention provides an imaging apparatus capable of imaging a wide area, controlling parallax to achieve an excellent image quality, and utilizing an imaging element with a relatively large package. The imaging apparatus for imaging a wide area as a subject by dividing the subject into a plurality of subject portions and respectively imaging the subject portions using a plurality of imaging means 11, 12 is configured such that the imaging means 11, 12 include lenses 1, 3A, 3B, and imaging element 6; respective NP points 9 of the a plurality of imaging means 11, 12 are concentrated within a minute radius region based on one of the NP points as a center; an optical element 5 having a reflection function is arranged behind a refraction surface of the lens 1 located at the nearest position from the subject in each of the imaging means 11, 12; the imaging element 6 is arranged behind the optical element 5 having the reflection function and outside of a space formed by straight lines which pass from the NP point 9 to circumferential portions in respective directions of the lens 1; and light beams bent by the optical element 5 having the reflection function are detected by the imaging element 6.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for real-time data analysis of infectious department
ActiveCN110310730AImprove automation management levelImplement cleanupCharacter and pattern recognitionHealthcare resources and facilitiesVisual field lossWide field
The invention relates to an apparatus for real-time data analysis of the infectious department. The apparatus comprises: a signal triggering device used for activating a connected dust collector whenreceiving a first control instruction in order to achieve the removal of dusts and ash in the infectious department and turning off the connected dust collector when receiving a second control instruction in order to stop the removal of the dusts and ash in the infectious department; and a dome camera located at the roof of the infectious department and used for performing wide-field imaging operation on the scene below the dome camera to obtain and output a corresponding wide-field imaging image, wherein the wide field is a visual field range of above 120 DEG. The invention also relates to amethod for real-time data analysis of the infectious department. The apparatus and the method for real-time data analysis of the infectious department have a reliable principle, and can be widely used. Targeted detection of the dust concentration of the overall environment of the infectious department and the adoption of an automatic control mode improve the efficiency and speed of environmental maintenance of the infectious department.
Owner:梁山县人民医院
Super-resolution wide-area imaging method for airborne battlefield monitoring radar of unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN104076361AHigh resolutionImprove resolutionSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWide areaEstimation methods
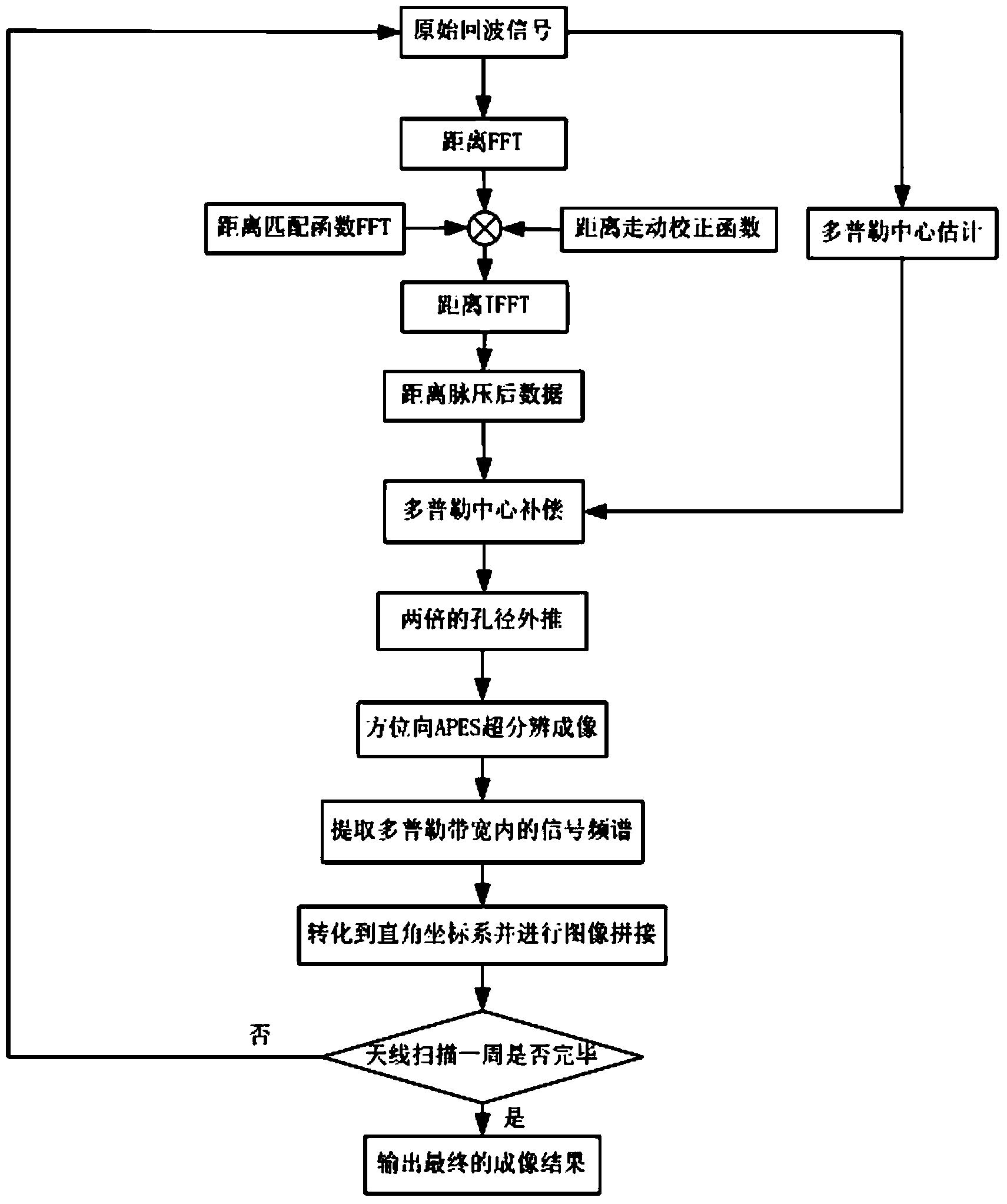
The invention belongs to the technical field of super-resolution wide-area imaging for radars and in particular relates to a super-resolution wide-area imaging method for an airborne battlefield monitoring radar for an unmanned aerial vehicle. The super-resolution wide-area imaging method for the airborne battlefield monitoring radar for the unmanned aerial vehicle comprises the following step of combining ground monitoring images of all irradiation areas of the battlefield monitoring radar into a wide-area ground monitoring image. Generating the ground monitoring images of the irradiation areas of the battlefield monitoring radar comprises the following steps of preprocessing corresponding original echo data through the battlefield monitoring radar to obtain corresponding central post-compensation data, carrying out aperture extrapolation on the corresponding central post-compensation data in the azimuth to obtain corresponding aperture post-extrapolation data, carrying out amplitude phase estimation method super-resolution processing on the corresponding aperture post-extrapolation data in the azimuth to obtain corresponding azimuth super-resolution processed data and obtaining corresponding sub images according to the corresponding azimuth super-resolution processed data.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
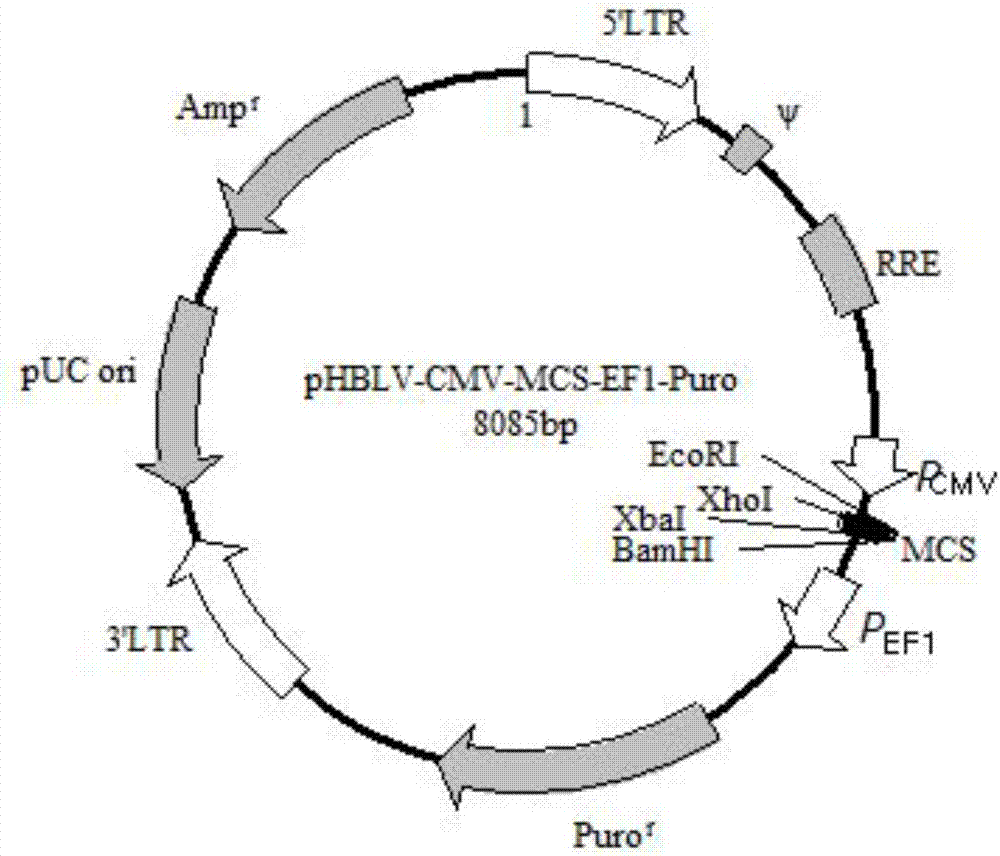
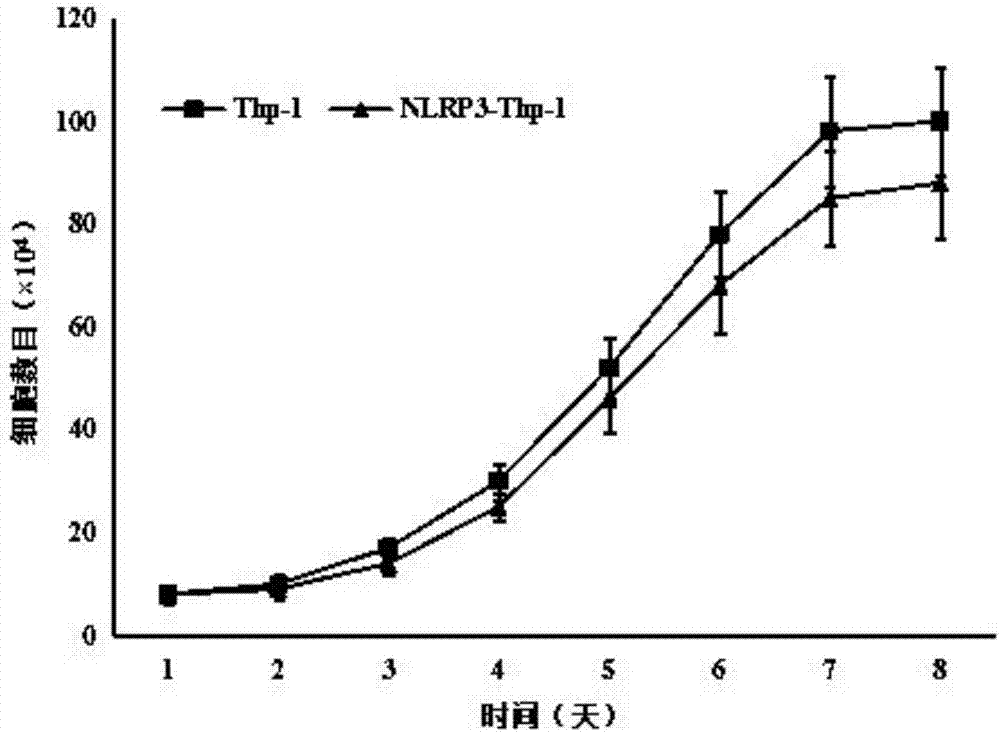
Fluorescent cell sensor for screening inflammasome NLRP3 activators and inhibitors
ActiveCN107190023AEfficient discoveryImprove the efficiency of drug screeningCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsShootBiological activation
The invention discloses a fluorescent cell sensor for screening inflammasome NLRP3 activators and inhibitors, and belongs to the technical field of drug screening. The cell fluorescence sensor is constructed by transgenic means. An NLRP3 promoter core region and a ZSGREEN gene are inserted into a plasmid vector and is transferred into Thp-1 cells to obtain a stable cell line; the stable cell line emits green fluorescence after receiving the stimulus of an NLRP3 inflammasome, and wide-field imaging high content is used for capturing fluorescent cells. The fluorescence sensor can achieve two goals, first, substances causing high expression of NLRP3 can be discovered rapidly and efficiently, and second, in the role of an NLRP3 activator, substances inhibiting NLRP3 activation can be quickly and efficiently found. The wide-field imaging high content can be used for shoot fluorescent images in a high-throughput mode, and the efficiency of screening medicines is greatly improved. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for primarily screening of drugs with the NLRP3 inflammasome as a target, and can also be used for the scientific study of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
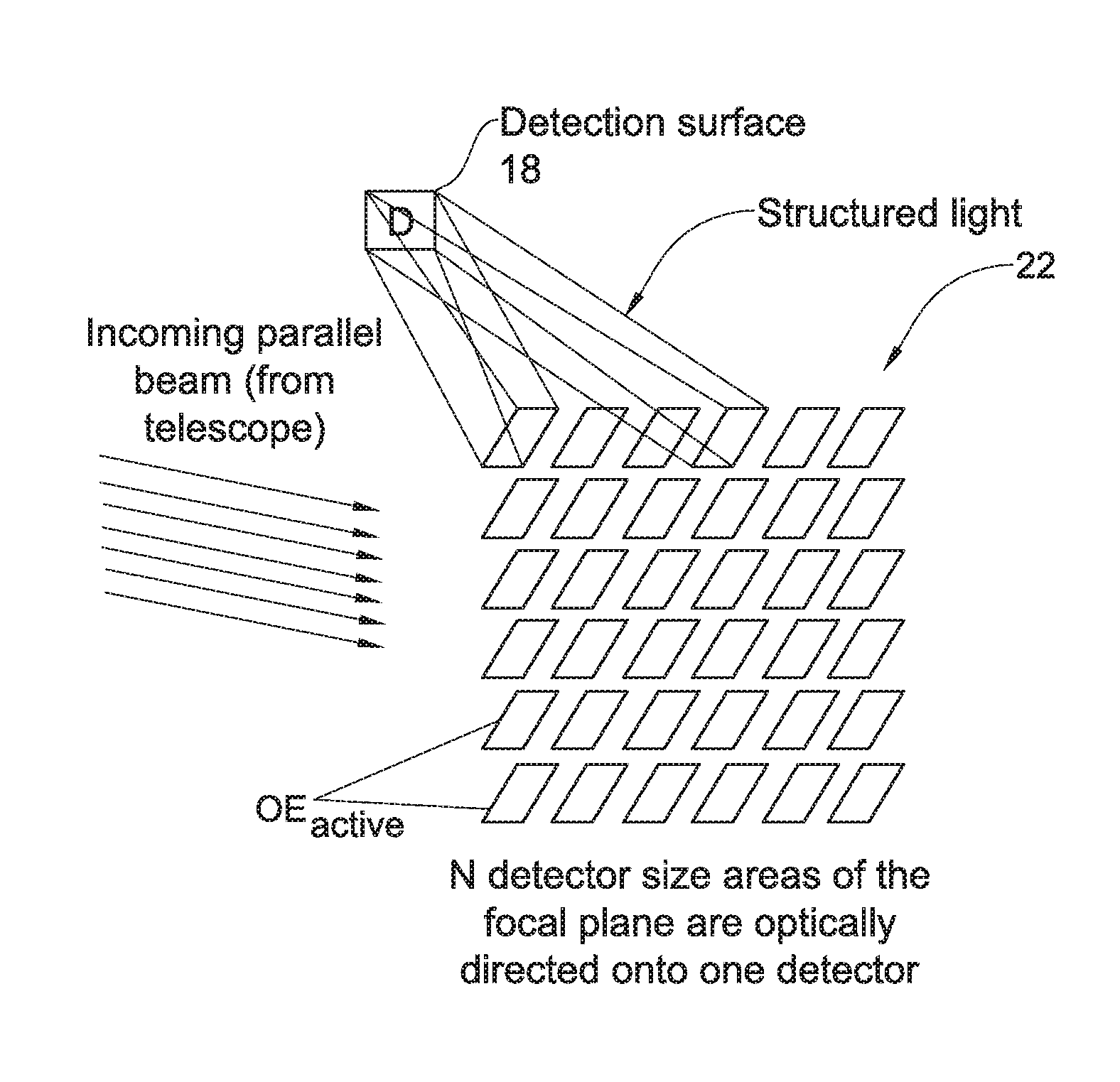
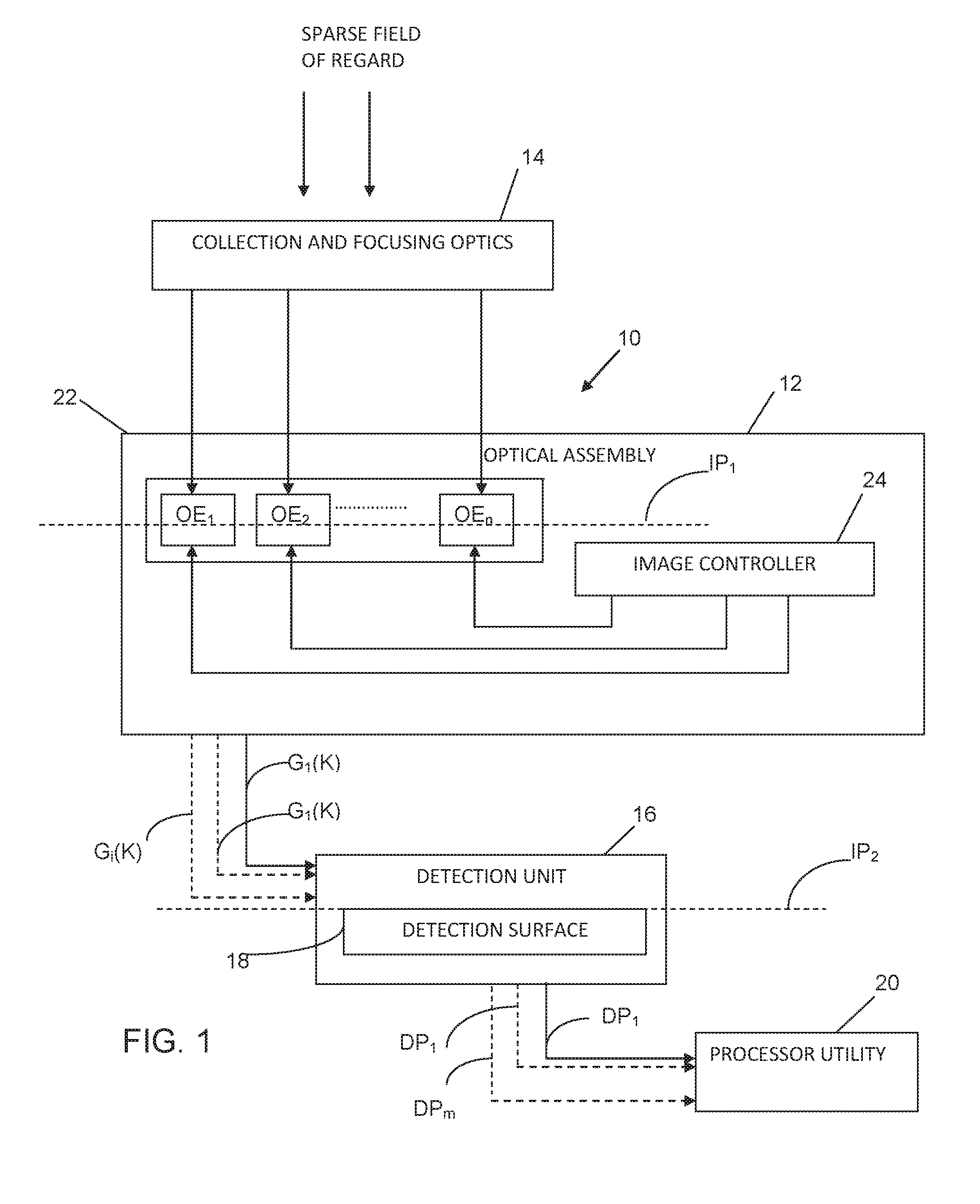
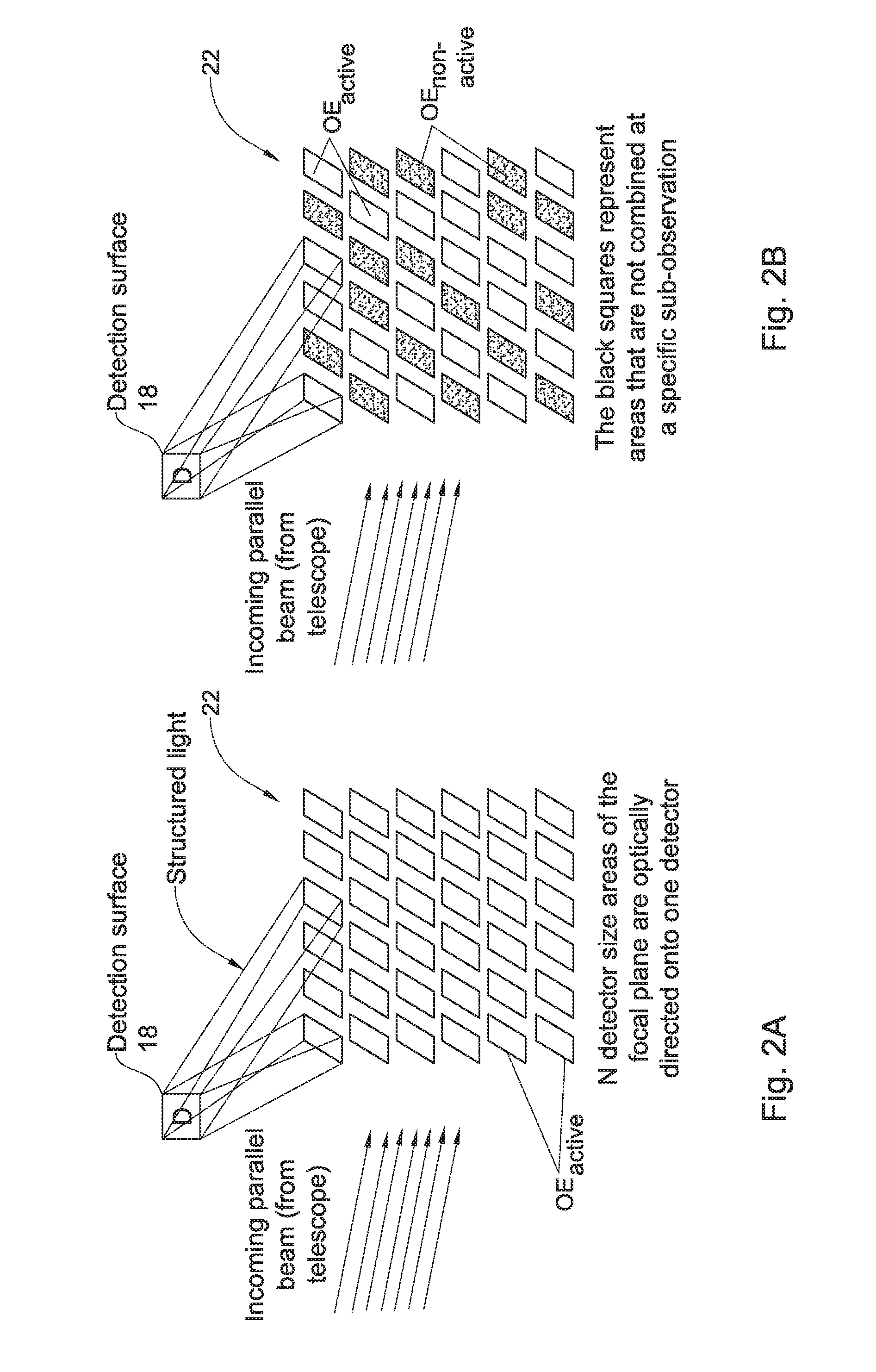
Wide field imaging using physically small detectors
InactiveUS20150362737A1Improve spatial resolutionSmall pixel sizeTelevision system detailsImage analysisWide fieldImage resolution
An imaging method and system are provided, being particularly useful for imaging a relatively wide field of regard on a relatively small detection surface with high spatial resolution. The method comprises: creating a segmented image of a field of regard in an effective object plane, said image being formed by an array of N image parts of the field of regard; and projecting a selected number M≧1 of patterns of structured light onto a detection surface, which is located in a plane conjugate to the effective object plane and has geometry and size substantially of the image part, each of the M patterns being formed by selected K light components of said N image parts concurrently projected onto the entire detection surface forming a superposition of the K image parts, thereby enabling reconstruction of the image of the field of regard from detected number M of patterns of the structured light.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
A Method for Acquiring Microscopic Motion Information Under Shear Field Using Fluorescence Wide-field Imaging
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com