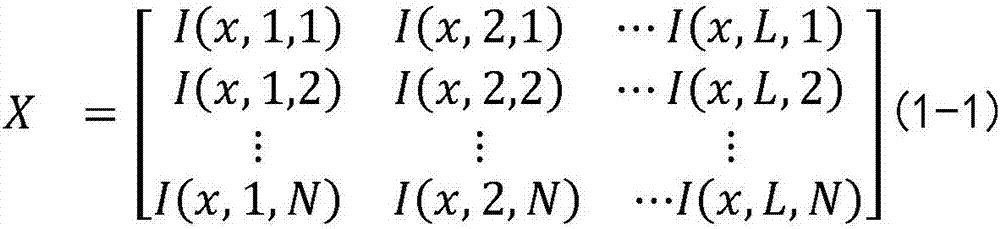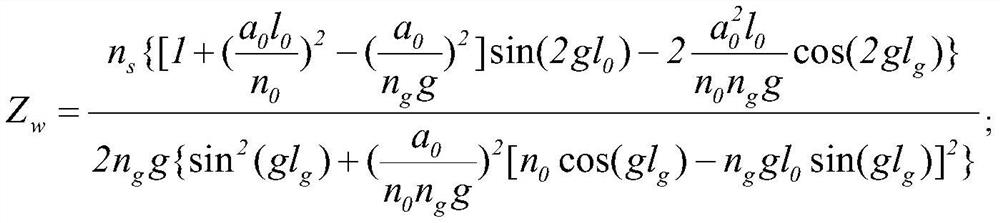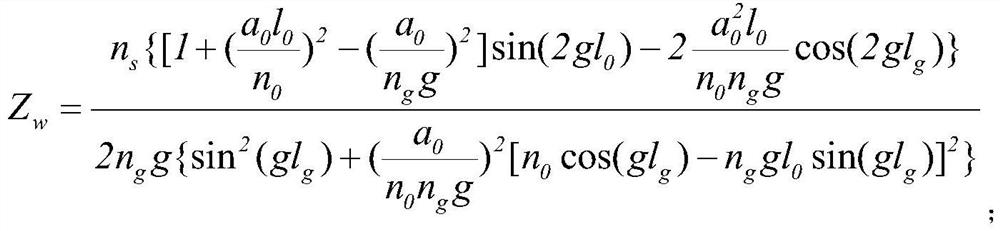Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Enable high-resolution imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
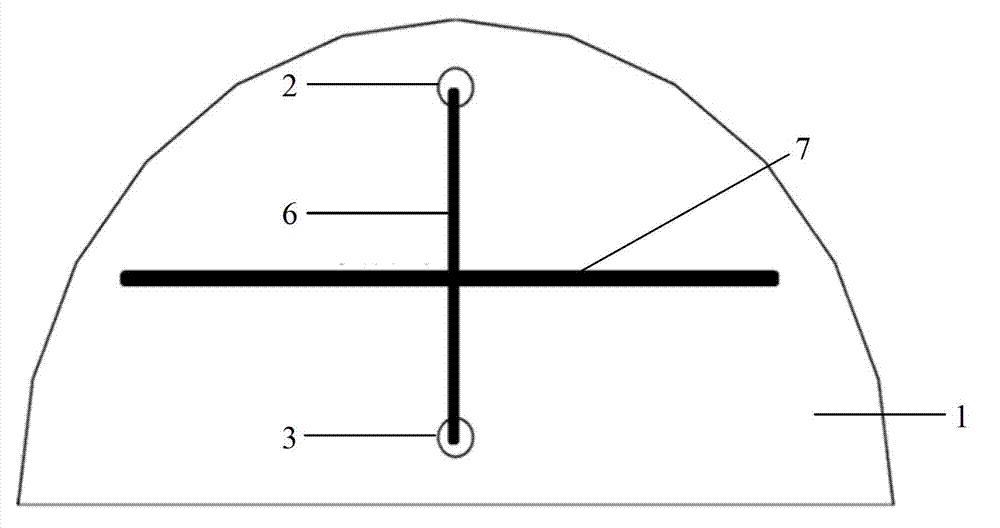
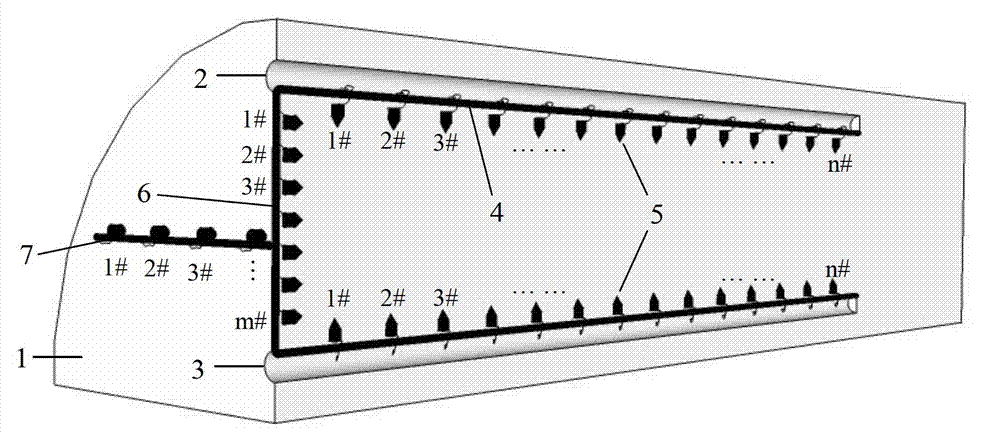
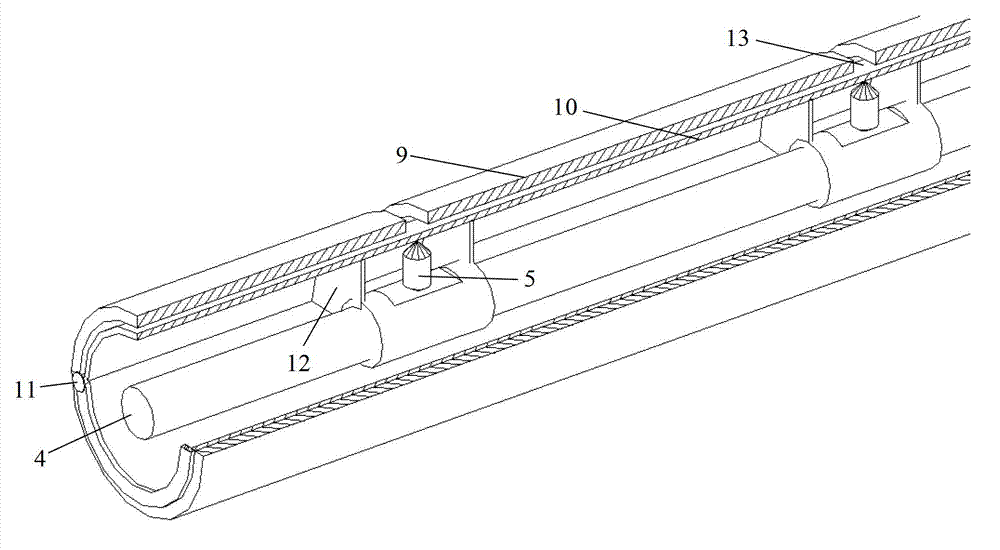
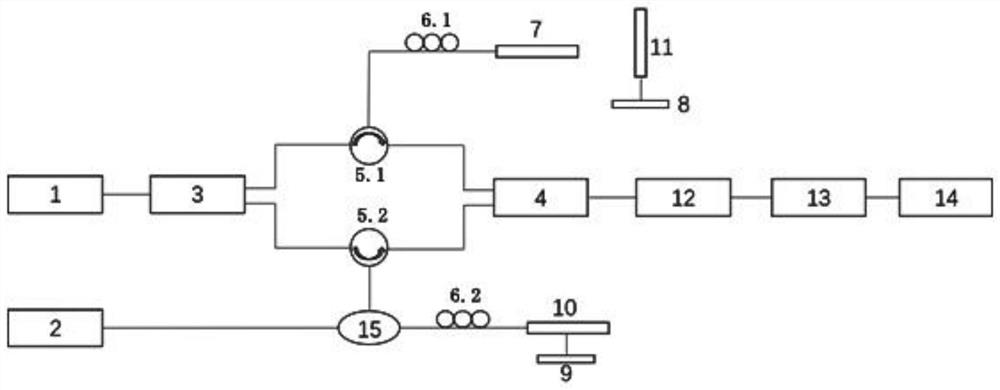
High-resolution three-dimensional resistivity CT (Computed Tomography) imaging advanced prediction system and method of underground engineering
ActiveCN102759751AEffectively provenCompensation accuracyElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationFine structureGeomorphology
The invention discloses a high-resolution three-dimensional resistivity CT (Computed Tomography) imaging advanced prediction system and method of underground engineering. According to the system and the method, a three-dimensional measuring mode of parallel double drilled holes and orthogonal measuring liens is designed; a multiple-coverage, fully automatic and fully combined free data acquisition mode is adopted; the conventional electrical process data acquisition mode is improved, so that richer data quantity can be achieved; a three-dimensional total space resistivity data inversion interception method is performed, so that a more accurate three-dimensional imaging effect can be obtained, a three-dimensional resistivity fine structure of a geologic body in a certain range in front of a working face is obtained, and high-resolution accurate imaging of an abnormal geologic body can be realized; and particularly, the resolution of a deep part is obviously improved, the bottleneck that only a local region can be detected by advanced bore is broken through, the defects of low accuracy and resolution of the conventional advanced prediction geophysical exploitation method are overcome, and a feasible approach is provided for realizing high-resolution accurate advanced prediction of construction of the underground engineering.
Owner:山东百廿慧通工程科技有限公司
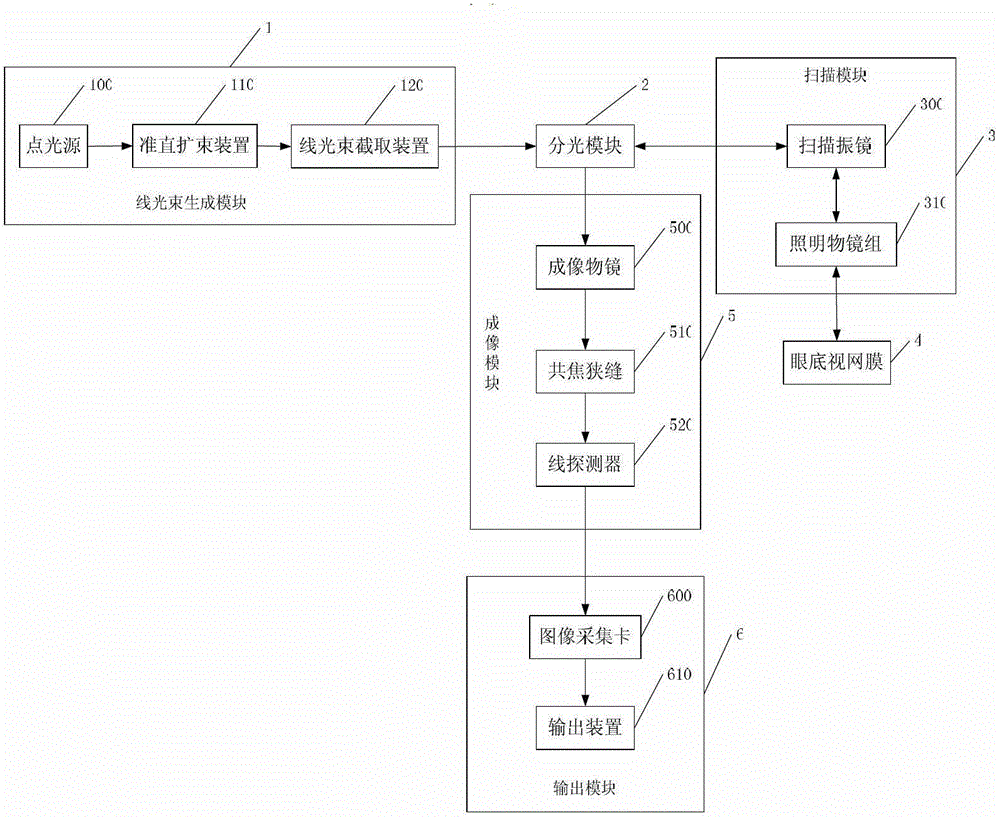
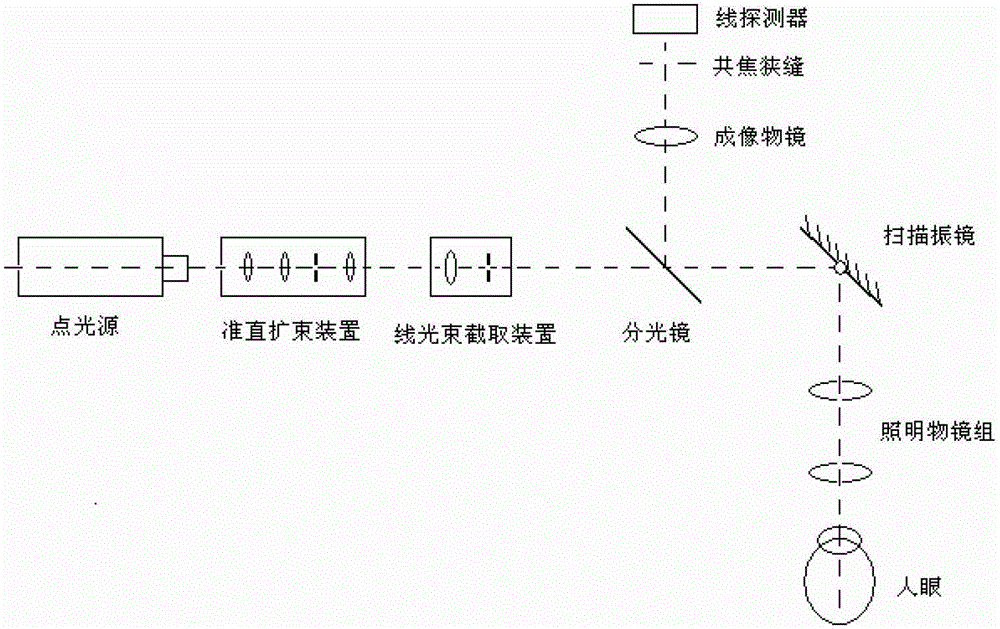
Line scanning confocal imaging image guidance-based self-adaption confocal scanning retina imaging method and device
ActiveCN102860815APrecise positioningEnable high-resolution imagingOthalmoscopesVisual field lossHigh resolution imaging
The invention relates to a line scanning confocal imaging image guidance-based self-adaption confocal scanning retina imaging method and device. By adopting the method, on the basis that one-dimensional scanning is performed on fundus retinae by a line scanning confocal imaging unit to obtain large-visual field imaging of the retinae, local small region positions of the retinae can be randomly selected and are marked from large-visual field imaged images, and a self-adaption confocal scanning retina imaging unit can be used for realizing accurate positioning on the small regions of the retinae and performing high-resolution imaging on the small regions. According to the line scanning confocal imaging image guidance-based self-adaption confocal scanning retina imaging method and device, the large-visual field imaging of the line scanning confocal fundus retinae and the accurate high-resolution imaging of the small region positions of the self-adaption confocal scanning fundus retinae can be obtained at the same time. Under the image guidance of the fundus retinae large-visual field imaging acquired by the line scanning confocal imaging unit, the accurate positioning can be realized on the local small regions by the self-adaption confocal scanning retinae imaging unit, and meanwhile, the high-resolution imaging is realized on the small region positions.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
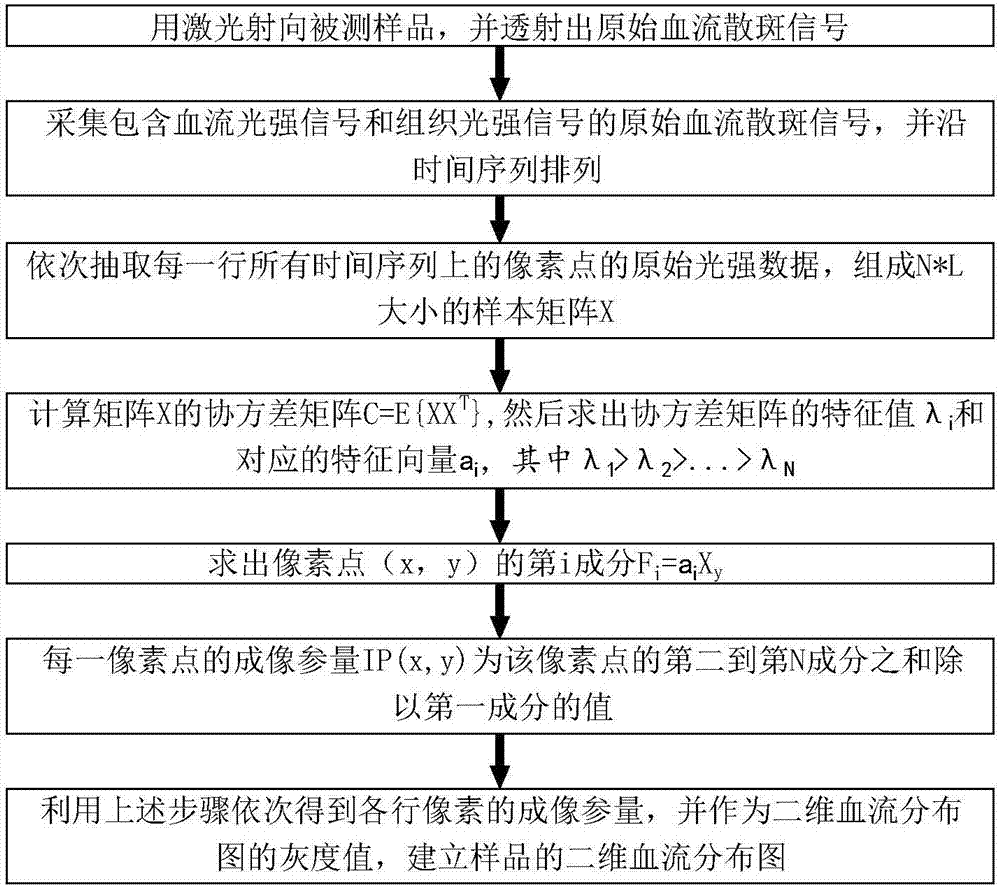
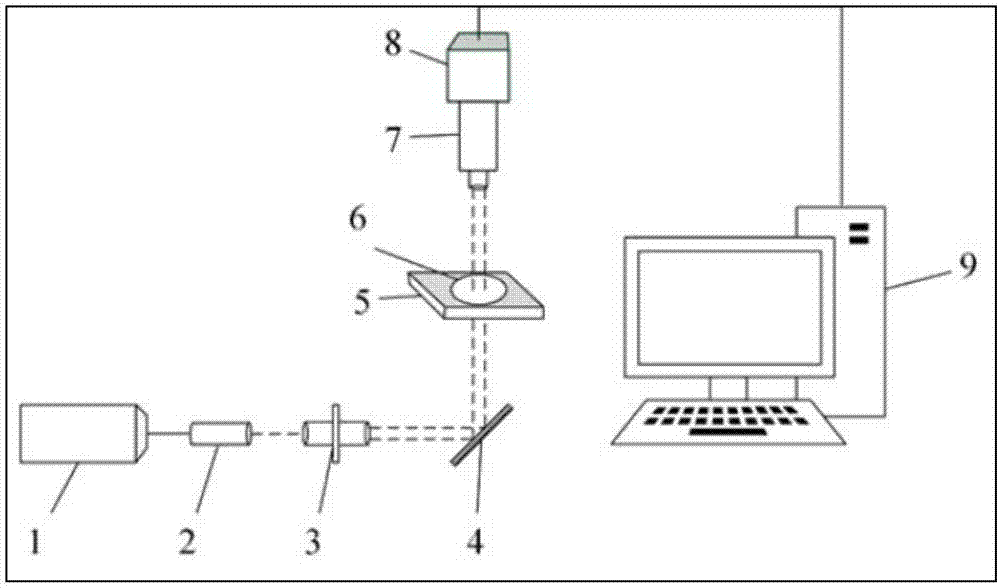
Speckle blood flow imaging method and device based on component analysis
ActiveCN107485383ANo injection requiredHigh spatio-temporal resolutionDiagnostic signal processing2D-image generationDiseaseDepth of field
The invention discloses a speckle blood flow imaging method and device based on component analysis. The method comprises the steps of performing component analysis on an original blood flow speckle signal, separating out a blood flow light intensity signal and a tissue light intensity signal, calculating out an imaging parameter, utilizing the imaging parameter as a gray value of a two-dimensional blood flow distribution diagram and establishing a two-dimensional blood flow distribution diagram of a sample. The method has the advantages of no invasion, no contrast medium injection, no damage and the like; the method can be applied to living small animal samples like blood flow imaging of mice, fish embryo and the like; the method has great application prospect in pathology diagnosis and analysis of a part of blood flow diseases. The device has the advantages of low cost, no damage to samples, ability in quickly achieving blood flow imaging, high imaging accuracy and application to blood flow monitoring; a transmission type imaging system is utilized, so that a deeper imaging depth is obtained; a long-focus telecentric lens is introduced into, so that blood flow at a deep position is in a focus depth range, a camera can collect clear images, and a higher spatial resolution is obtained.
Owner:佳维斯(武汉)生物医药有限公司
Method for synthesizing rare earth metal compound nano cluster and application thereof
ActiveCN103143037AEnable high-resolution imagingStrong targetingEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsX-ray constrast preparationsRare earth metal compoundsSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a rare earth metal compound nano cluster and application of the rare earth metal compound nano cluster in the aspects of target imaging of diseased regions such as tumor and contrast medium preparation. The rare earth metal compound nano cluster prepared by the method has a small particle size, good permeability, high fluorescent stability, high sensibility and strong targeting, so that the tumor can be accurately positioned; the rare earth metal compound nano cluster is directly synthesized by biological tumor cells and has good biocompatibility; and the method is convenient to operate and intuitive in result, synchronous analysis and detection in multiple states and multiple modes can be carried out, and the method has a wide medical application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
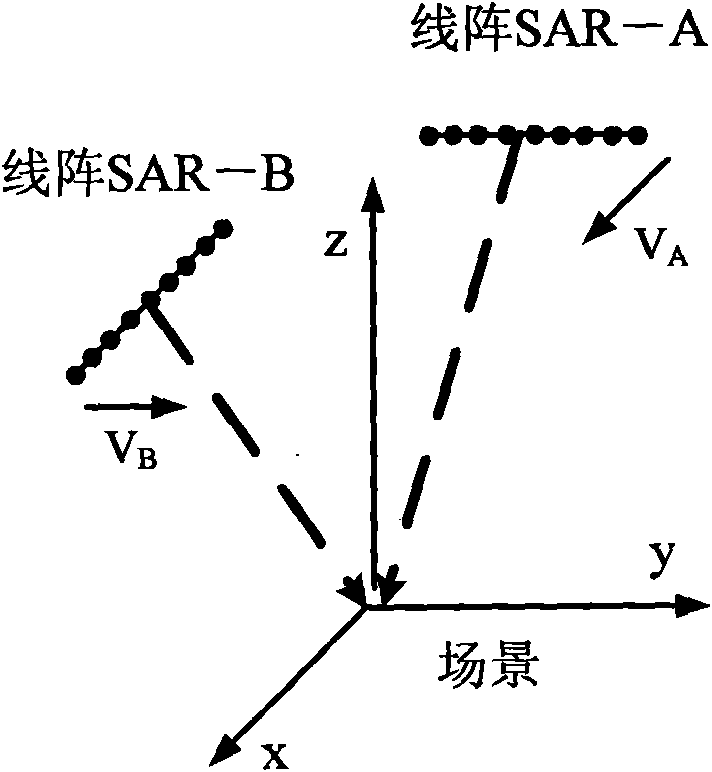
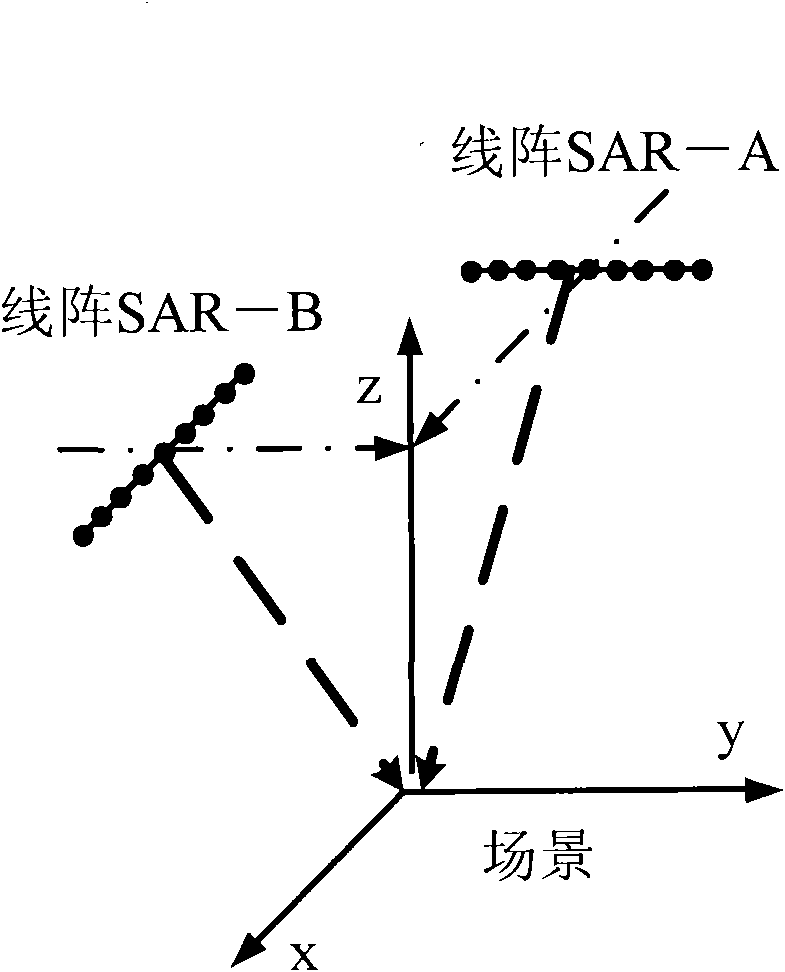
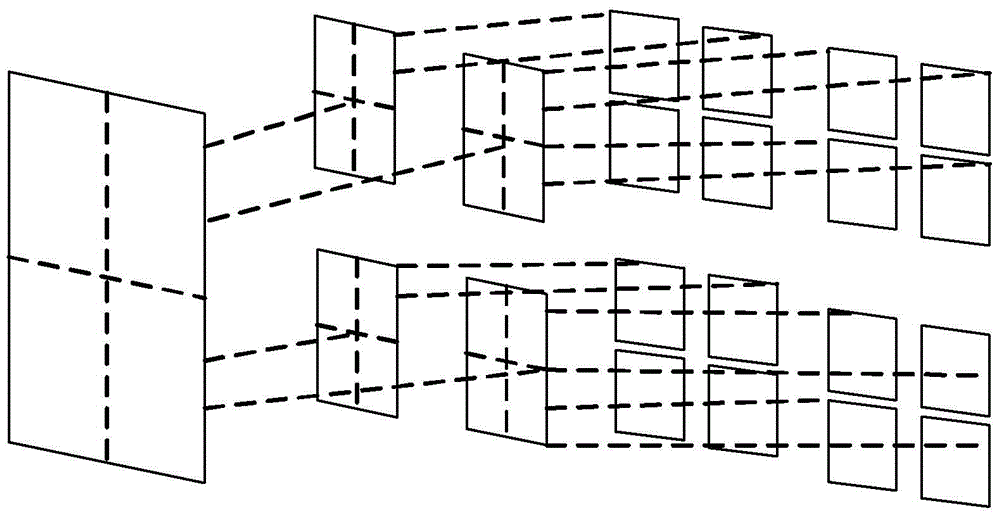
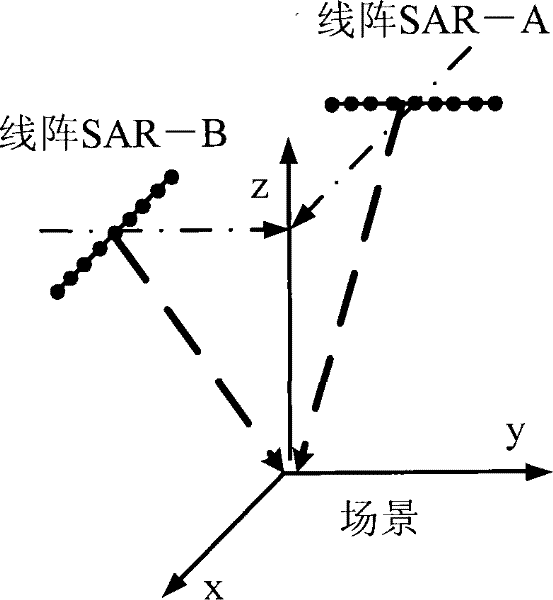
Method for improving resolution of linear-array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars
ActiveCN101666879AEnable high-resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingImage resolution
The invention provides a method for improving the resolution of linear-array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars. The method adopts two linear-array three-dimensional imaging syntheticaperture radars with orthogonal motion tracks for imaging of the same region, and then blends two acquired images by discrete wavelet transform technology so as to obtain a linear-array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar image with high resolution. The invention has the following advantages of realizing high-resolution imaging of the linear-array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars by using a relatively short array antenna and solving the problem of relatively low tangential track resolution of images acquired by the linear-array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars. The method can be widely applied in the fields such as synthetic aperture radar imaging, earth remote sensing and geological mapping.
Owner:四川电子科技大学教育发展基金会
High-orbit sub-aperture ISAR imaging method for ship target
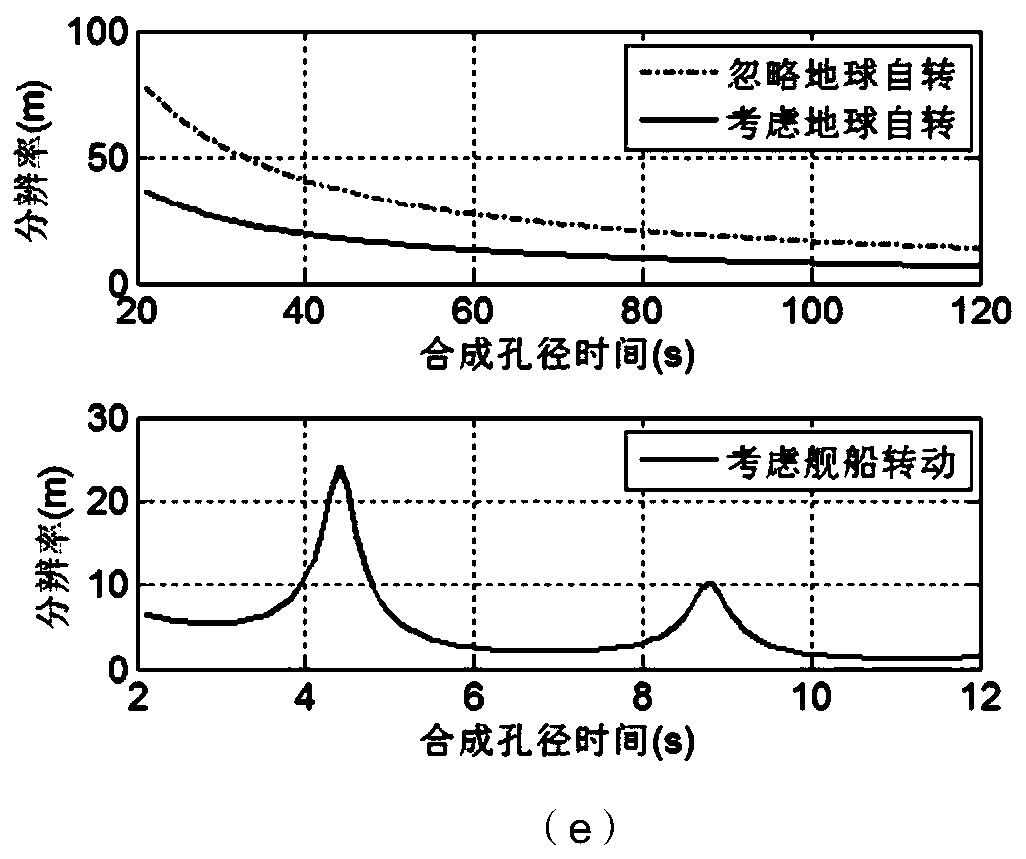
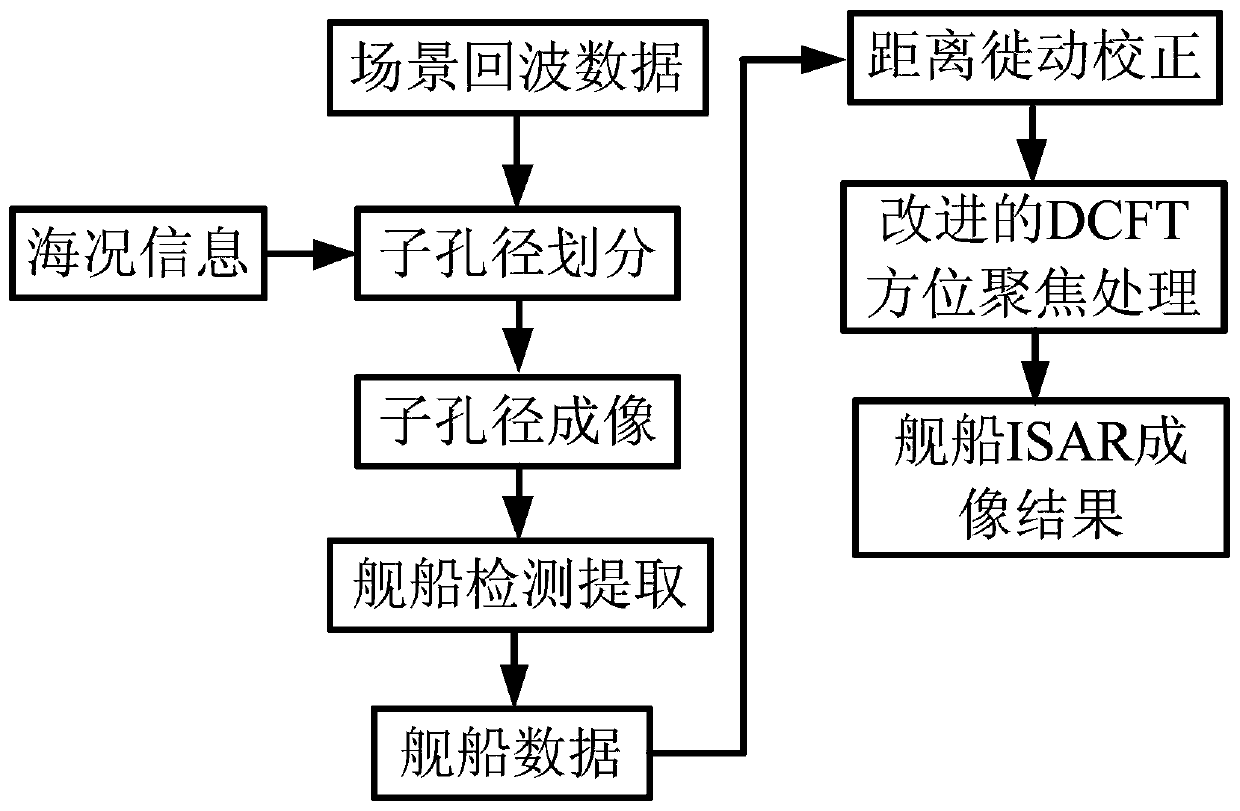
ActiveCN110515077AApplicable scoutingSuitable for applications such as monitoringRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingMarine engineering
The invention discloses a high-orbit sub-aperture ISAR imaging method for a ship target, and aims at solving the problems of image defocusing and difficulty in improving the resolution due to the factthat a ship moves in long synthetic aperture time, as long as hundreds of thousands of seconds, required by high resolution imaging of a high-orbit satellite with a high orbit but relatively low running speed. On one hand, the sub-aperture synthetic aperture time is short, and influence of ship motion on imaging is reduced, and on the other hand, the rotation angle generated by ship swing is alsobeneficial to realizing high-resolution ISAR imaging. Traditional understanding that ship motion is regarded as a motion error is broken through, high-resolution ISAR imaging is carried out by utilizing the ship motion, the problem of contradiction between high-orbit long synthetic aperture time and the ship motion is solved, and the method can be applied to the fields of high-orbit ship target detection, identification and imaging.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Method for merging resolutions of linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars
ActiveCN101614810AEnable high-resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingImage resolution
The invention provides a method for merging resolutions of linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars. The method adopts two linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars of which the motion trails are orthogonal to image the same region and then adopts an orthogonal spatial projection matrix technology to merge two obtained images, thereby generating a high-resolution linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar image. The method solves the problem that the cross track resolution of the linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar image is lower than the long track resolution of the linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar image. The method has the advantages of realizing the linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar high-resolution imaging by using a short array antenna and can be used in the fields of synthetic aperture radar imaging, earth remote sensing and the like.
Owner:四川电子科技大学教育发展基金会
Photoacoustic microimaging adaptive scanning system and method
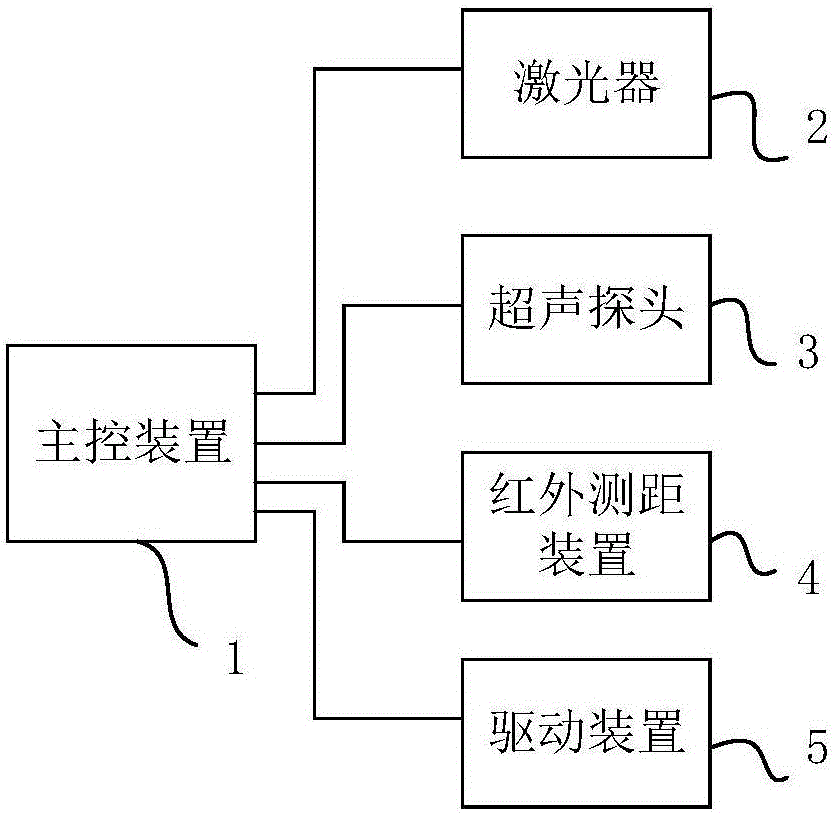
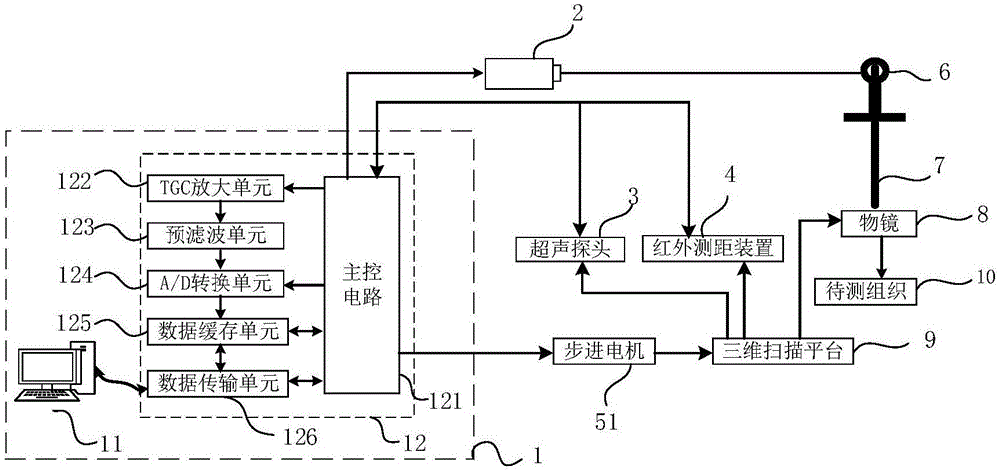
InactiveCN106691377AAutomatic distance adjustmentEnable high-resolution imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsControl setHigh resolution imaging
The invention relates to a photoacoustic microimaging adaptive scanning system and method. The photoacoustic microimaging adaptive scanning system comprises a master control set, a laser, an ultrasonic probe, an infrared ranging device and a drive unit; the infrared ranging device detects first vertical distance between the ultrasonic probe and a first position point of to-be-detected tissue; the infrared ranging device detects second vertical distance between the ultrasonic probe and a second position point of the to-be-detected tissue; the master control set controls the drive unit to drive the ultrasonic probe to move to the position above the second position point according to the first vertical distance and the second vertical distance, and the distance between the ultrasonic probe and the second position point is enabled to be equal to the first vertical distance; the ultrasonic probe collects photoacoustic signals generated from the first position point and the second position point. By the arrangement, the distance between the ultrasonic probe and the to-be-detected tissue can be automatically adjusted when materials or biological tissue lower in flatness are subjected to imaging, real-time focusing is guaranteed, and high-resolution imaging of photoacoustic images is realized.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
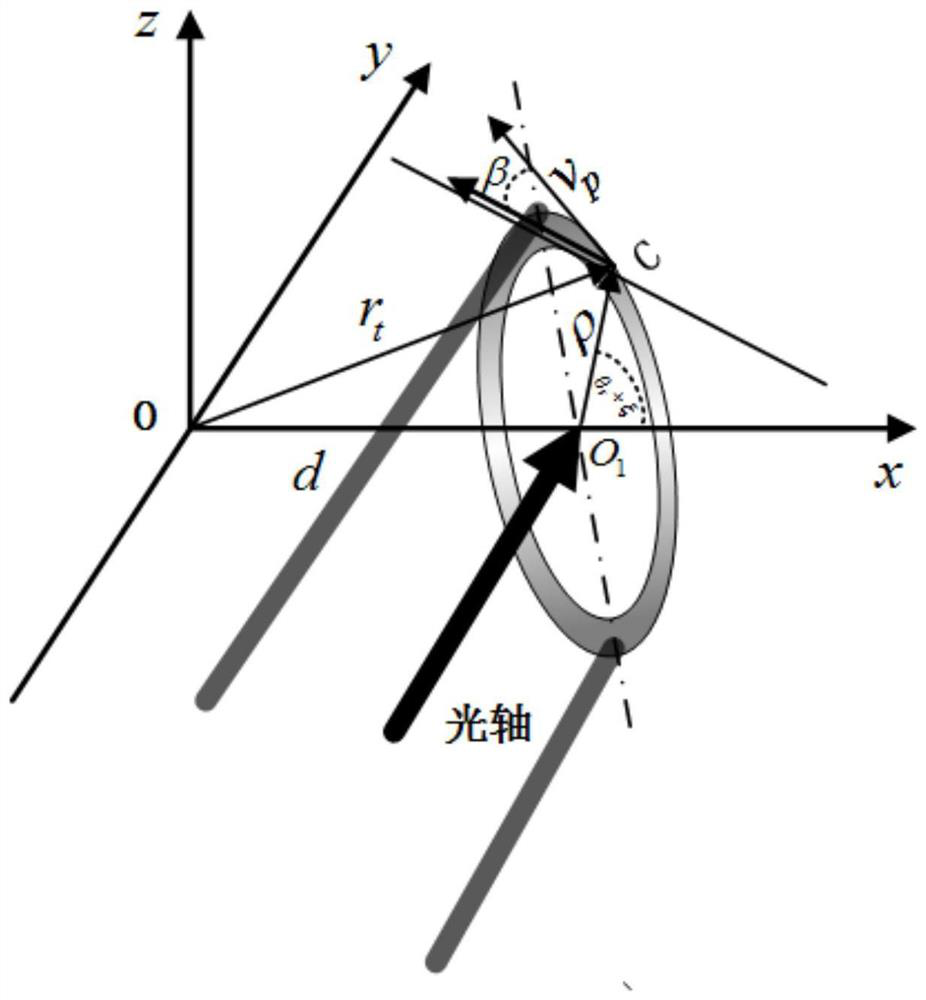
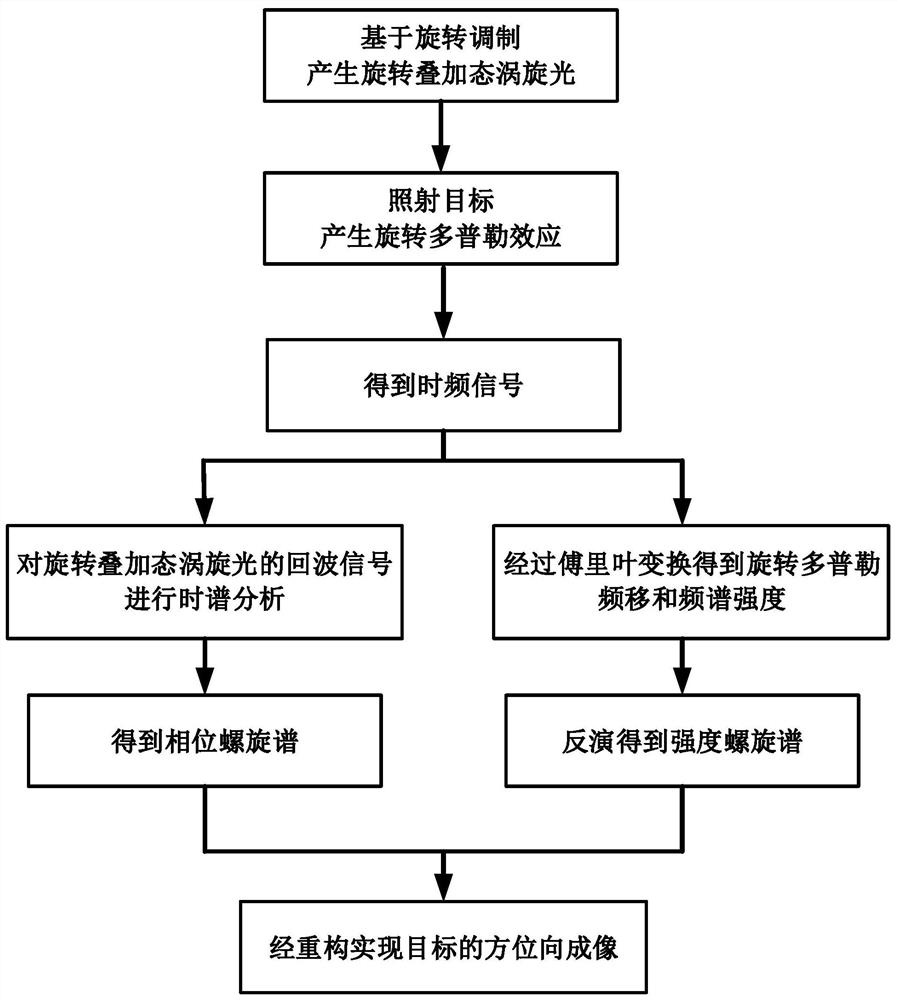
Target azimuth imaging method based on superimposed vortex light
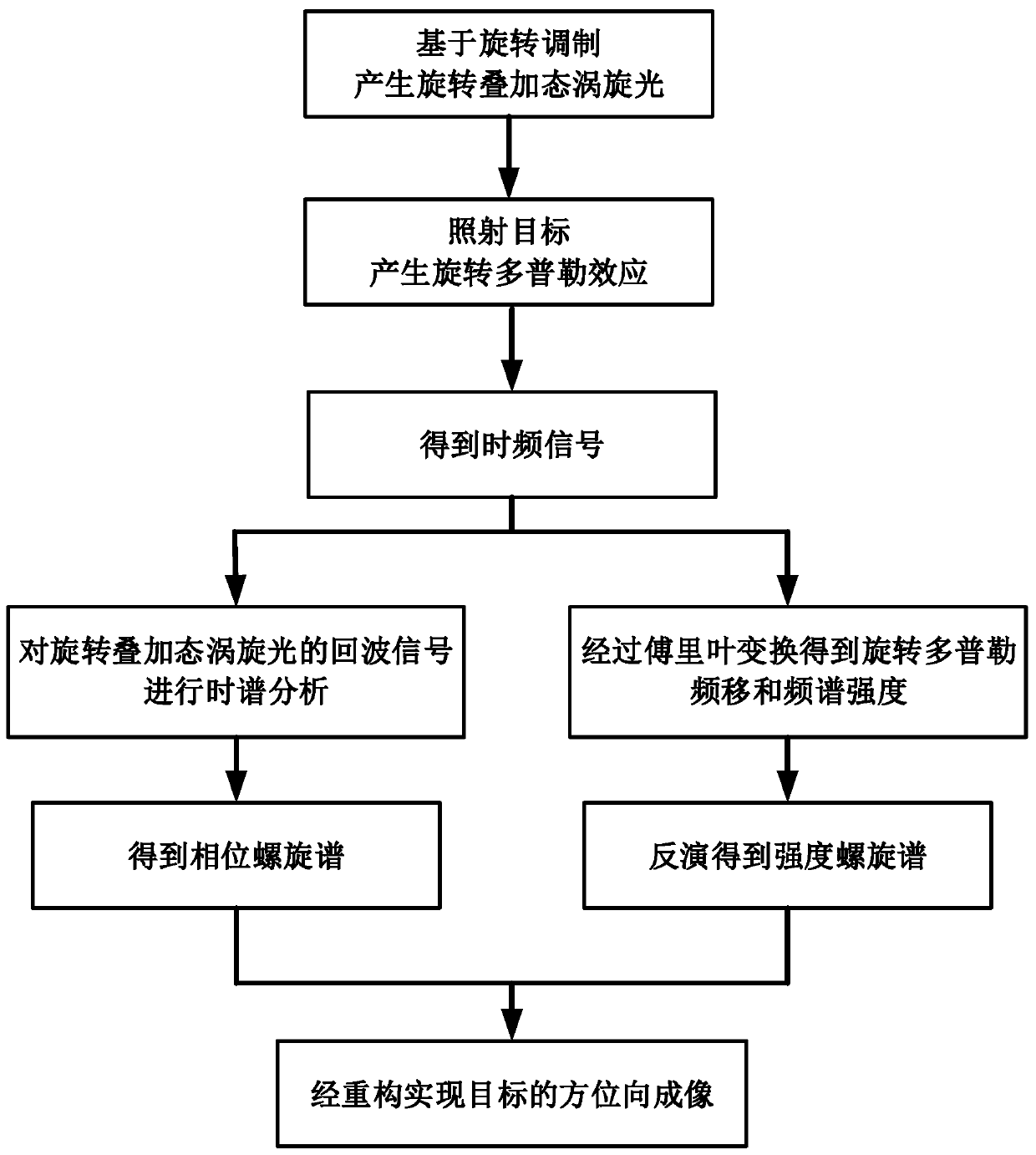
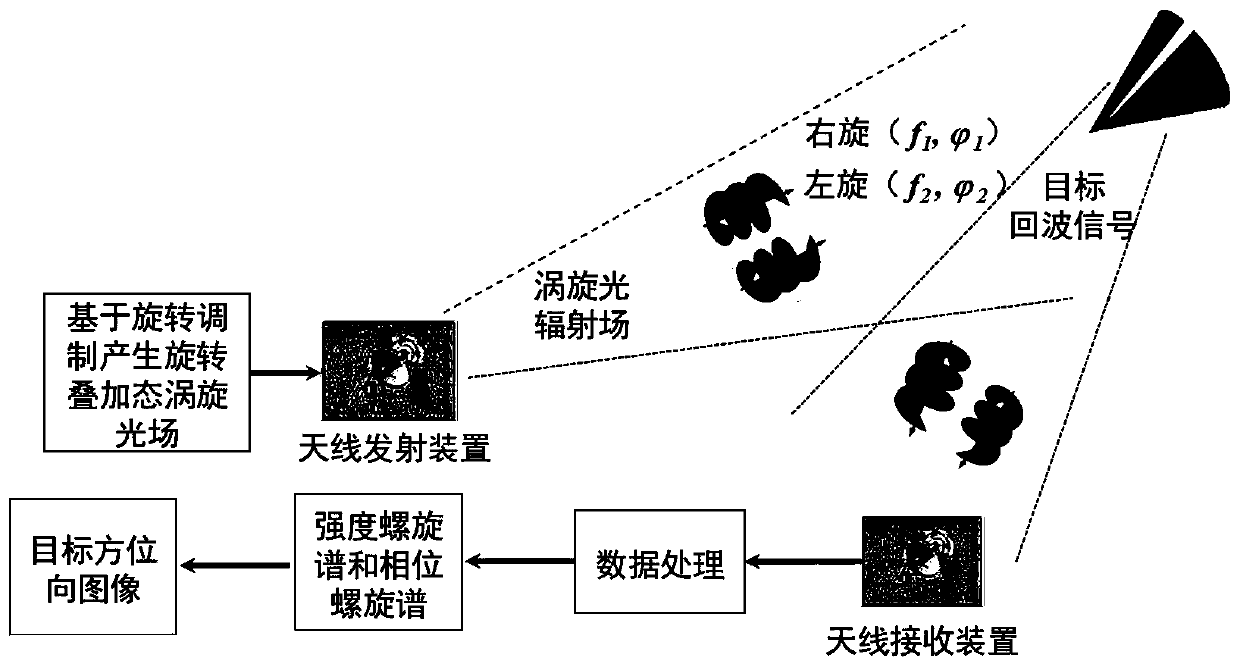
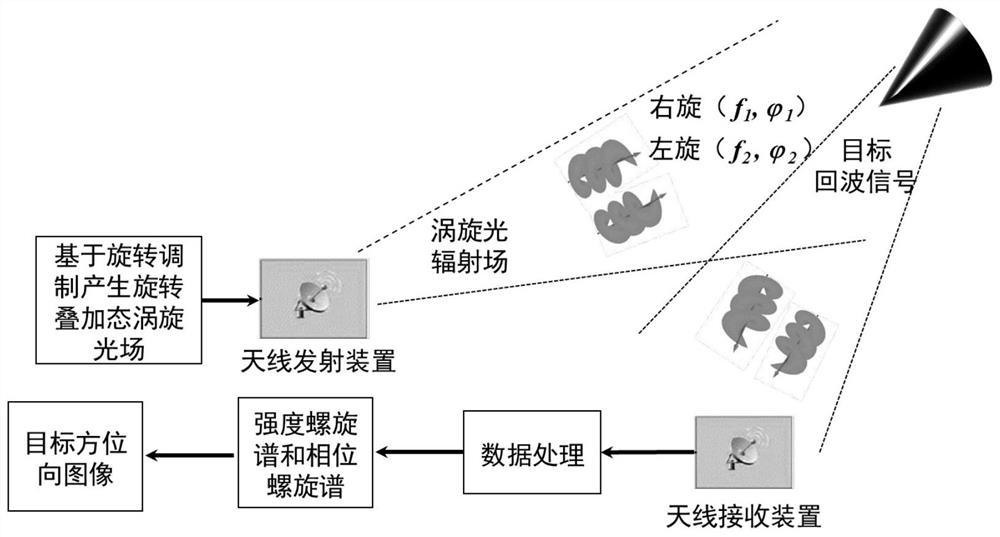
ActiveCN111474558ANovel methodAchieving Rotational Doppler EffectElectromagnetic wave reradiationImaging conditionImage resolution
The invention relates to a target azimuth imaging method based on superimposed vortex light. The method comprises the steps: generating a rotation superposition state vortex light irradiation target with different time-varying phase differences based on rotation modulation; generating rotation Doppler effect, performing fourier transform on the target echo signal to obtain a time-frequency signal;obtaining an intensity spiral spectrum of the rotation superposition state vortex light by utilizing a space-time inversion relationship between the rotation Doppler frequency shift signal and the intensity spiral spectrum, and carrying out time spectrum analysis on echo signals of the rotation superposition state vortex light with different time-varying phase differences to obtain a phase spiralspectrum of the rotation superposition state vortex light; and finally, realizing azimuth imaging of the target through reconstruction by superposition of the intensity spiral spectrum and the phasespiral spectrum of the vortex light in the rotation superposition state. The method has high imaging resolution under the foresight / staring imaging condition, and imaging is achieved without dependingon motion and benefited by motion.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Onboard inverse synthetic aperture laser radar micro-motion imaging method under sparse sampling
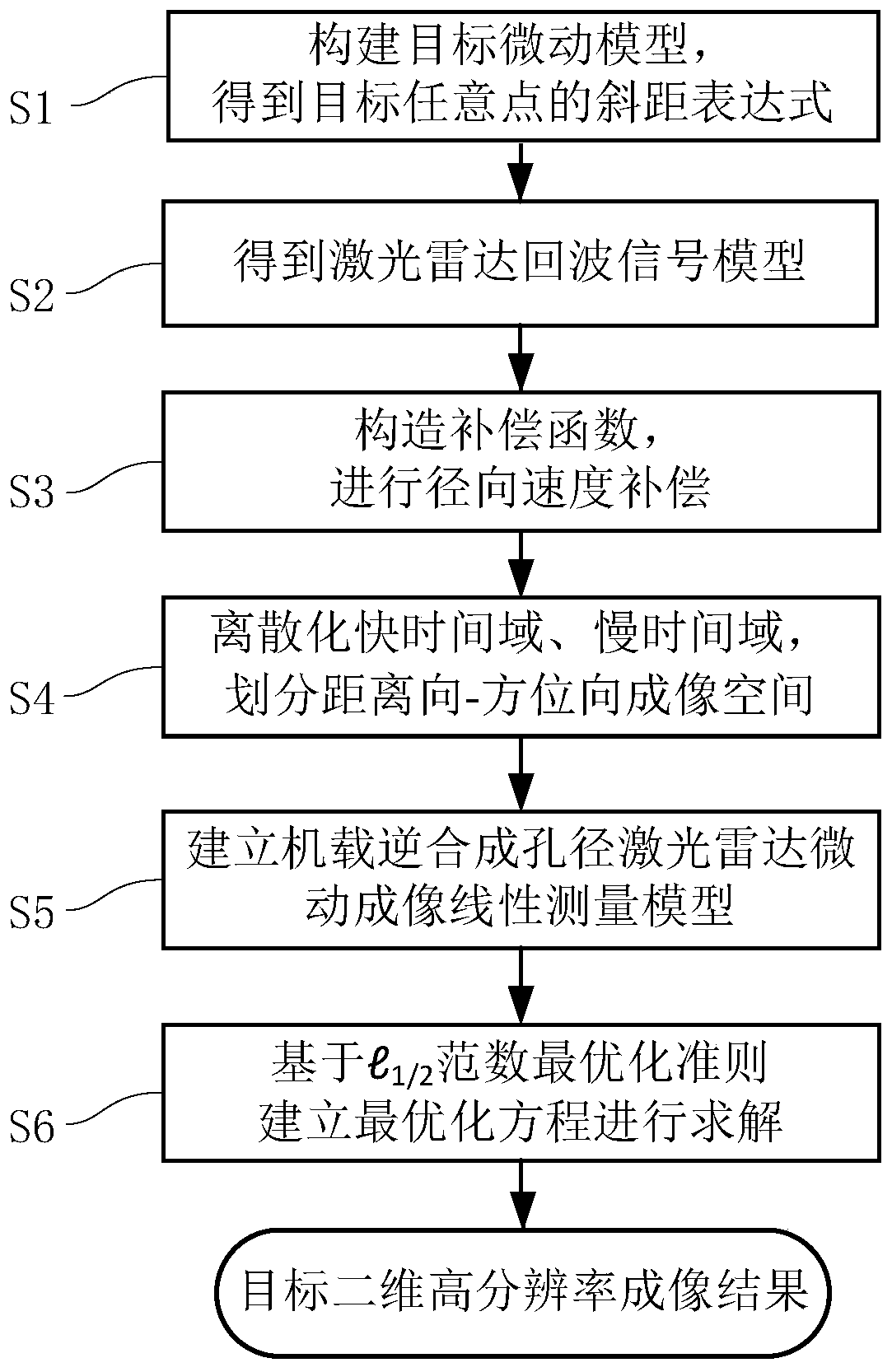
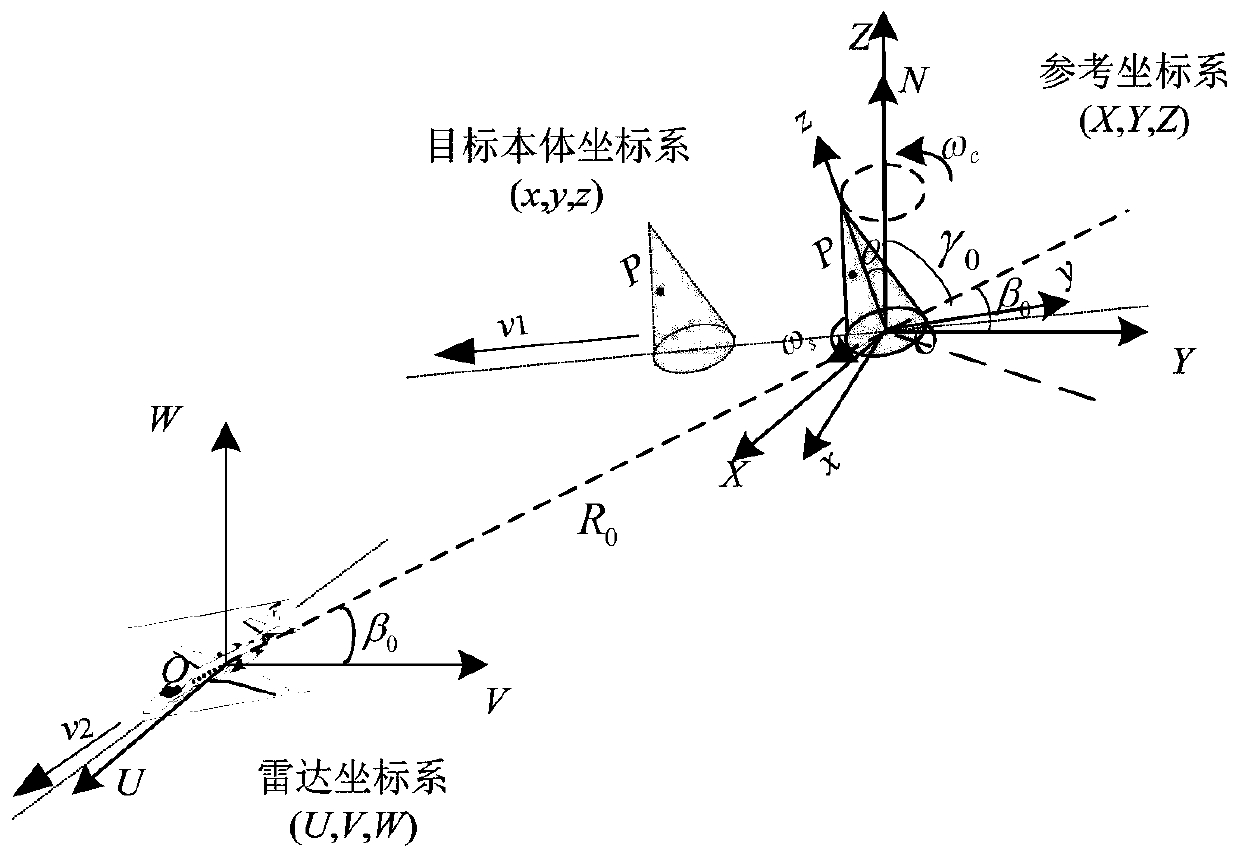
ActiveCN110632616AEnable high-resolution imagingReduce azimuth data rate requirementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh resolution imagingImaging quality
The invention relates to an onboard inverse synthetic aperture laser radar micro-motion imaging method under sparse sampling. The method comprises the following steps: specific to a micro-motion target in the air, building a target motion model, and obtaining a slant-range expression of any point on the target; obtaining a laser radar echo signal model; by estimating a radial speed of the target,constructing a compensation function, and performing radial speed compensation on an echo signal; expressing a fast time domain and a slow time domain in a discretization manner, and dividing a distance direction-azimuth imaging space into N*M grids; specific to the divided distance direction-azimuth imaging space, building an onboard inverse synthetic aperature laser radar micro-motion imaging linear measurement model; and by utilizing a compressive sensing theory, establishing an optimization equation based on an l1 / 2 norm optimization criterion, and solving, thus obtaining an image reconstruction result under the sparse sampling. The method provided by the invention is specific to laser radar detection and can realize high-resolution imaging on the target at a high sparse sampling rate,the azimuth data rate requirement is effectively lowered, and the laser radar imaging quality is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
Millimeter wave and terahertz multi-band radar detection imaging system and method
PendingCN113325417AReduce bandwidth requirementsQuality improvementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti bandLow noise
The invention discloses a millimeter wave and terahertz multi-band radar detection imaging system and method. The method is composed of a system method composed of a low-frequency-band radar signal generator, a millimeter wave and terahertz multi-frequency-band frequency multiplication link and amplification module, a millimeter wave and terahertz multi-frequency-band combiner, a millimeter wave and terahertz transmitting / receiving antenna, a millimeter wave and terahertz frequency band frequency divider, a millimeter wave and terahertz multi-frequency-band low-noise power amplifier and receiving link, an intermediate-frequency signal processing and acquisition module, a radar signal storage and image processor and the like, and a corresponding multi-frequency-band radar detection imaging algorithm module. Millimeter wave and terahertz multi-band combined emission and shunt receiving are adopted in the system method, and multi-band signal splicing and related processing methods are adopted in the signal processing and detection imaging algorithm level, so that the requirements of millimeter wave and terahertz band broadband signal generation, amplification and receiving on high-band devices are reduced, high-power, high-quality and flexible broadband millimeter wave and terahertz frequency band detection imaging can be realized, and a new realization way is provided for wide application of millimeter wave and terahertz frequency band refined detection imaging.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
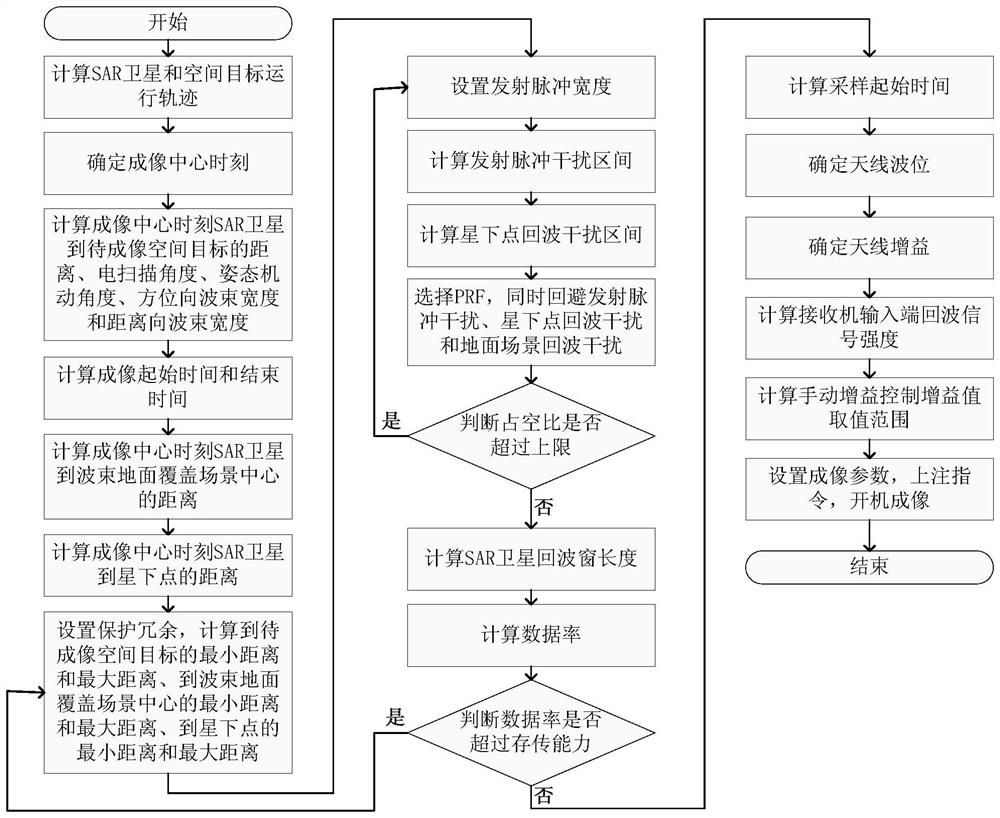
Method for imaging space target by on-orbit SAR satellite
ActiveCN112505694AMeans of economic realizationFeasible means of realizationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRelative motionComputer science
The invention relates to a method for imaging a space target by an on-orbit SAR satellite, which fully considers the high-speed relative motion characteristics of the on-orbit SAR satellite and the space target to be imaged and the system limitation, and combines STK software to solve the problems that the relative motion of the SAR satellite and the space target is complex, the geometrical relationship is difficult to determine and the imaging parameter precision requirement is high in the space target imaging process. By selecting a proper pulse repetition frequency, effective reception of the echo of the space target to be imaged is ensured, and interference of emission pulse, sub-satellite point echo, ground scene echo and the like is avoided at the same time. Through the mode of combining satellite attitude maneuver and antenna electric scanning, the beam pointing required by the SAR satellite for space target imaging is realized, the implementation cost and complexity are reduced, and the application range of the on-orbit SAR satellite is expanded.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
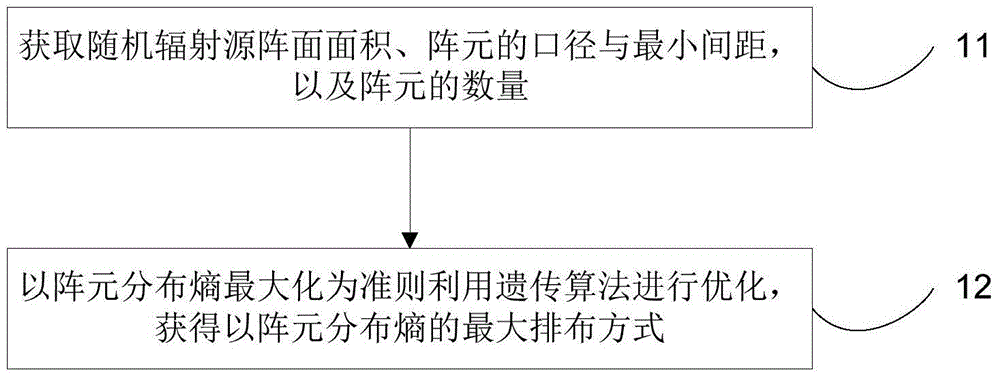
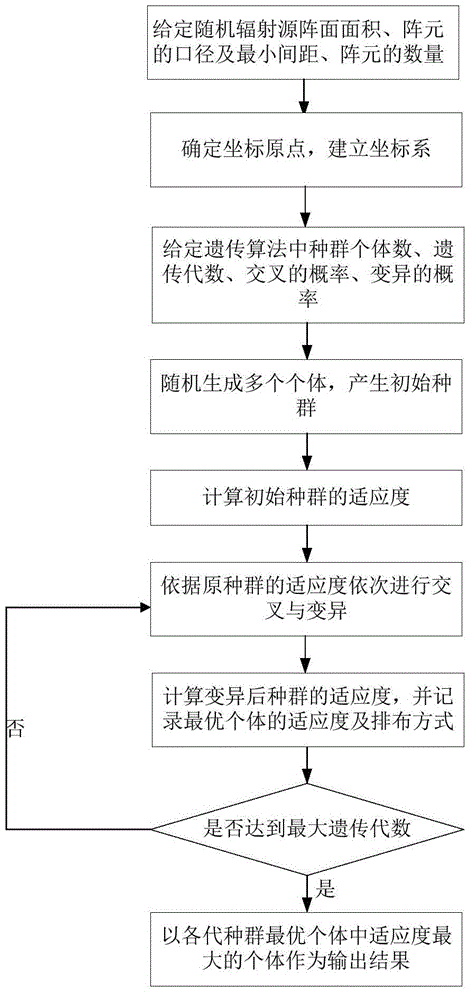
Microwave staring correlated imaging random radiation array element spatial arrangement optimization method
ActiveCN104597445AIncrease randomnessEnable high-resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionStaringRadiation field
The invention discloses a microwave staring correlated imaging random radiation array element spatial arrangement optimization method. The method includes acquiring the random radiation array area and the minimum distances, diameters and numbers of the array elements; performing optimization by adopting the rule of array element arrangement entropy maximization by the genetic algorithm, and acquiring the maximum arrangement manner of the array element arrangement entropy. By the aid of the method, the randomness of the radiation field can be improved, and the high-resolution imaging is implemented.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
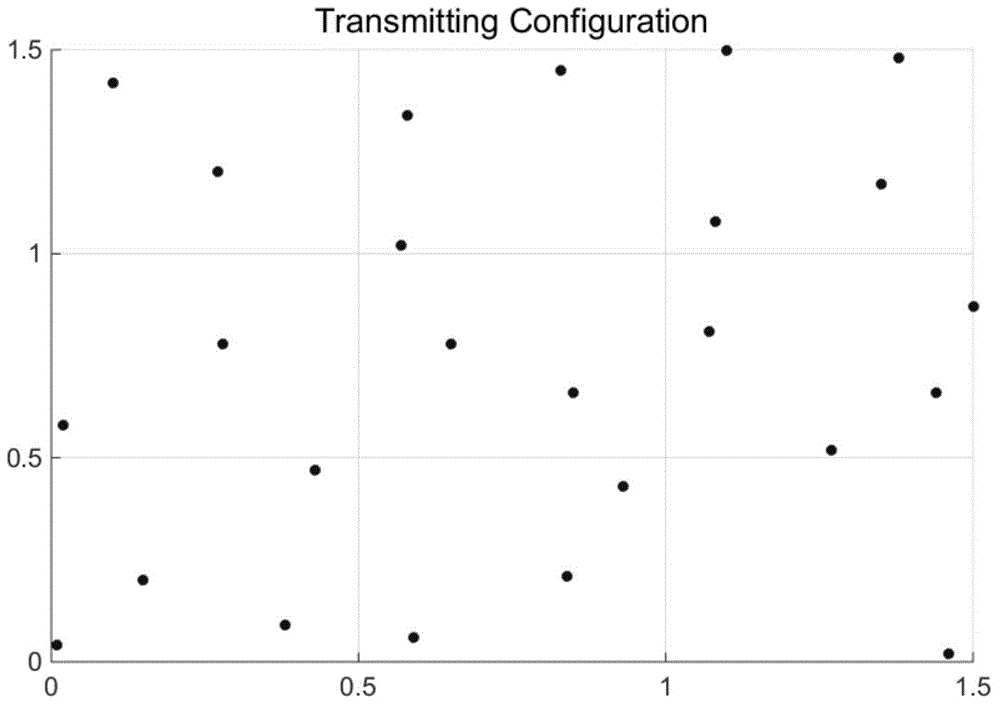
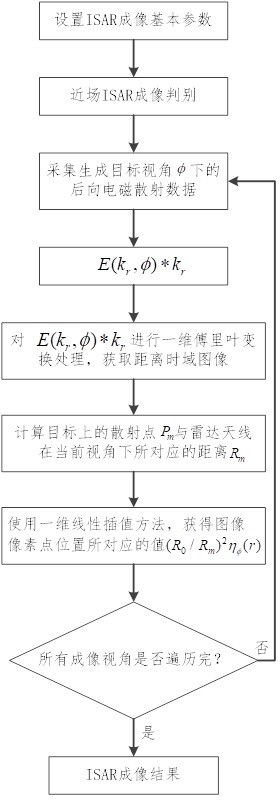
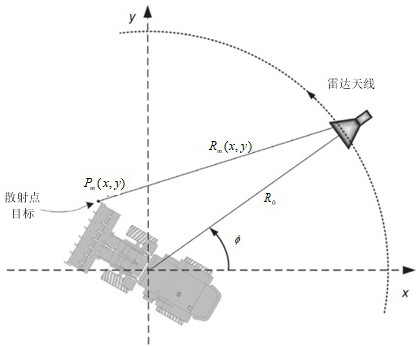
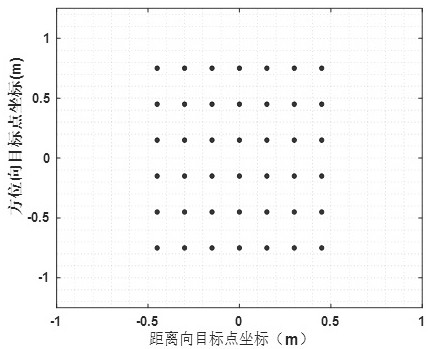
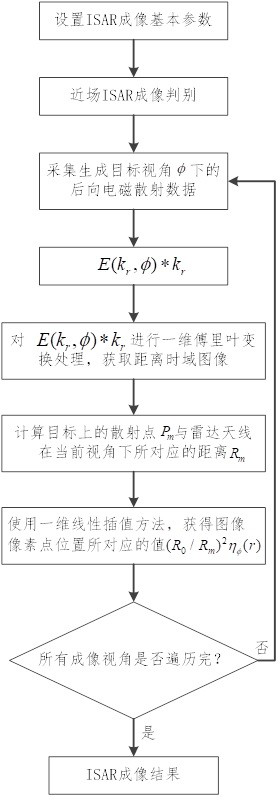
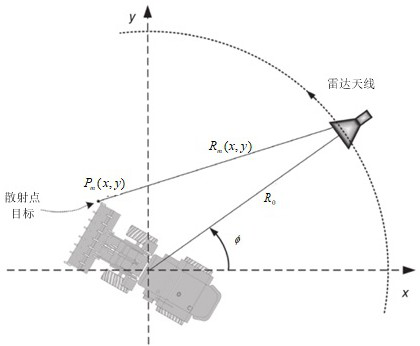
Efficient near-field large-size and small-size target ISAR imaging method based on backward projection
ActiveCN114488152AReduce the number of transformationsImaging steps are simpleRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar antennasTime domain
The invention discloses an efficient near-field large-size and small-size target ISAR imaging method based on backward projection. The method comprises the steps that an image data matrix is initialized; acquiring a distance time domain image by using a target backward electromagnetic scattering echo signal corresponding to the azimuth view angle; based on the distance from the radar antenna to the central scattering point of the target, the distance between any scattering point on the target except the central scattering point and the radar antenna, the distance time domain image and the image data matrix, obtaining an imaging result under the current visual angle; and superposing imaging results under all visual angles to obtain a near-field ISAR imaging result. According to the method, near-field ISAR fine imaging of targets with large and small sizes can be realized, the operand is reduced, and the target detection, recognition and resolution capabilities are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
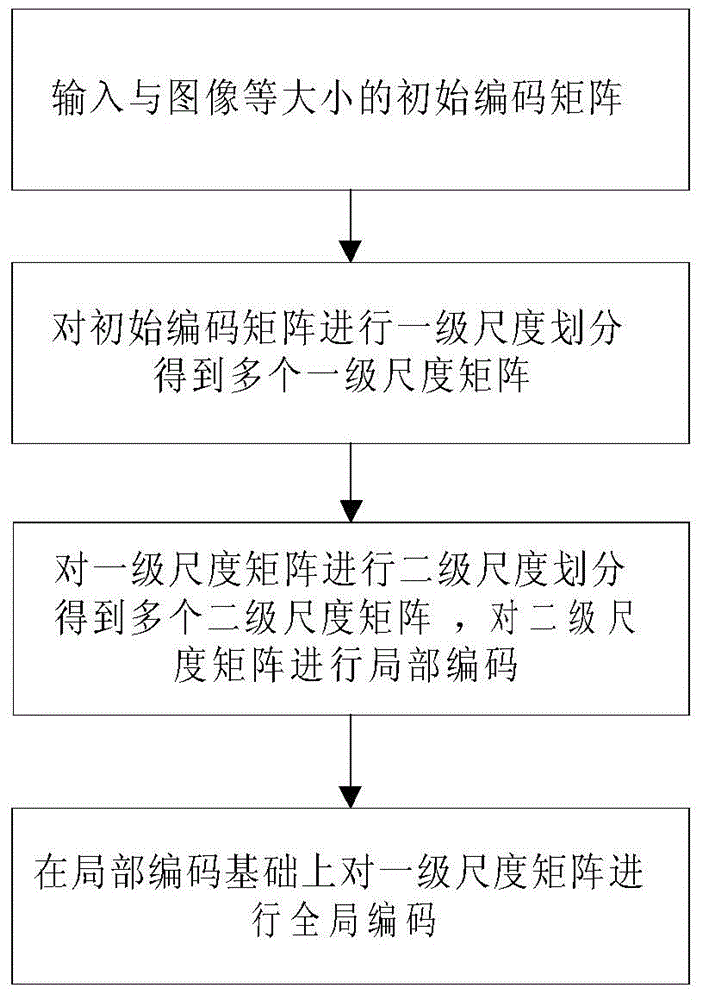
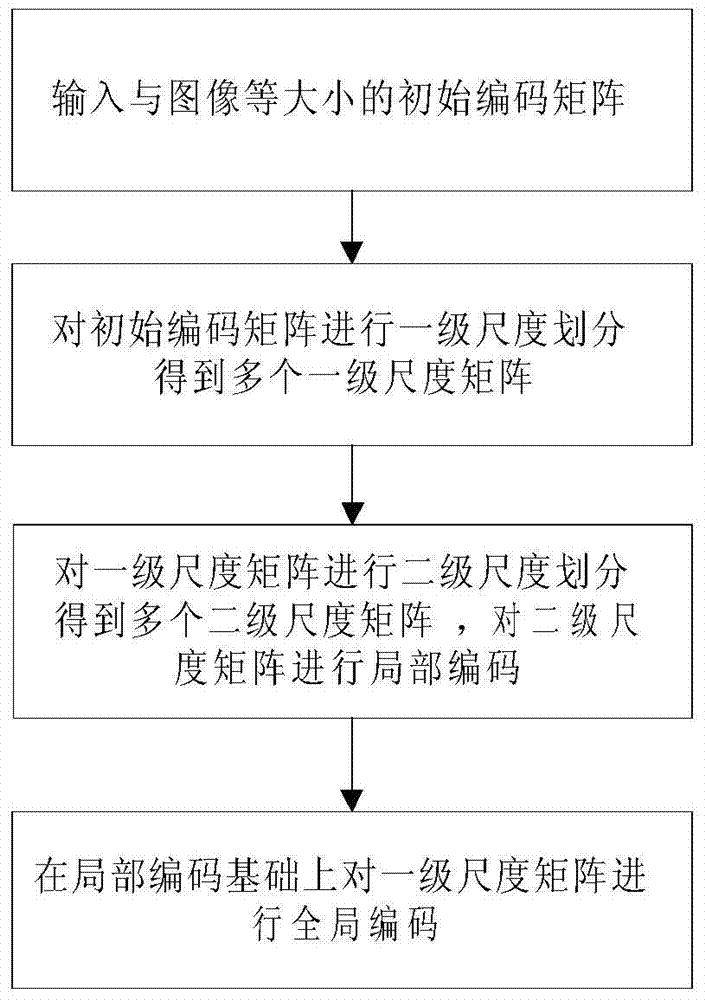
Multi-scale matrix coding method
ActiveCN104992456ALow comprehensive costGood refactoringImage codingCompressed sensingMatrix encoding
The invention discloses a multi-scale matrix coding method. The multi-scale matrix coding method comprises the following steps: inputting an initial coding matrix in the same size as an image, performing first-stage scale division on the initial matrix to obtain a plurality of first-stage scale matrixes, performing second-stage scale division on the first-stage matrixes to obtain a plurality of second-stage scale matrixes, performing local coding on the second-stage scale matrixes, and performing global coding on the first-stage scale matrixes on the basis of the local coding. Based on a block segmentation compressed sensing technology, the further division is performed on the basis of a segmented block, the coding matrixes obtaining more information of the segmented block can be designed according to dependencies between pixels, and, compared with an existing coding matrix, the coding matrix provided in the invention has the better reconstruction effect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
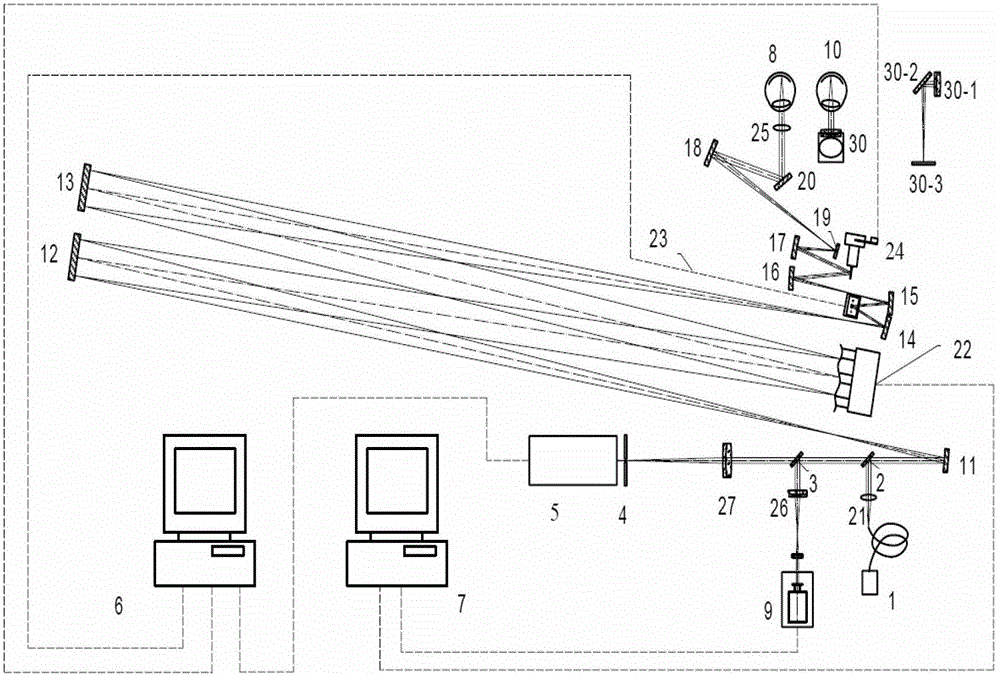
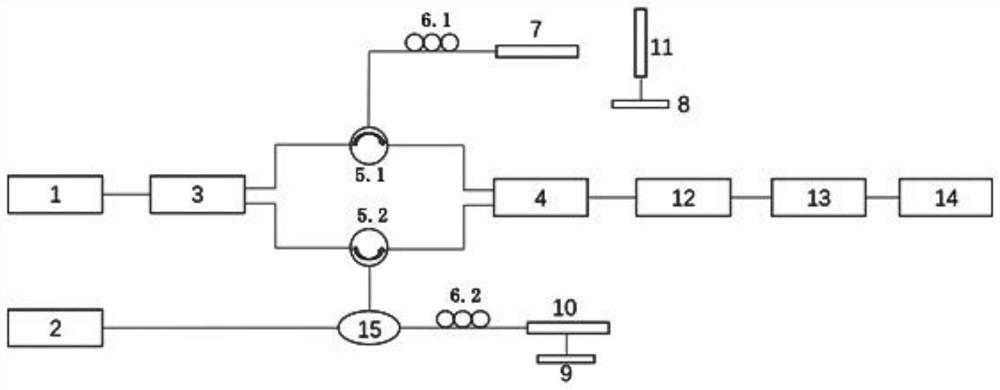
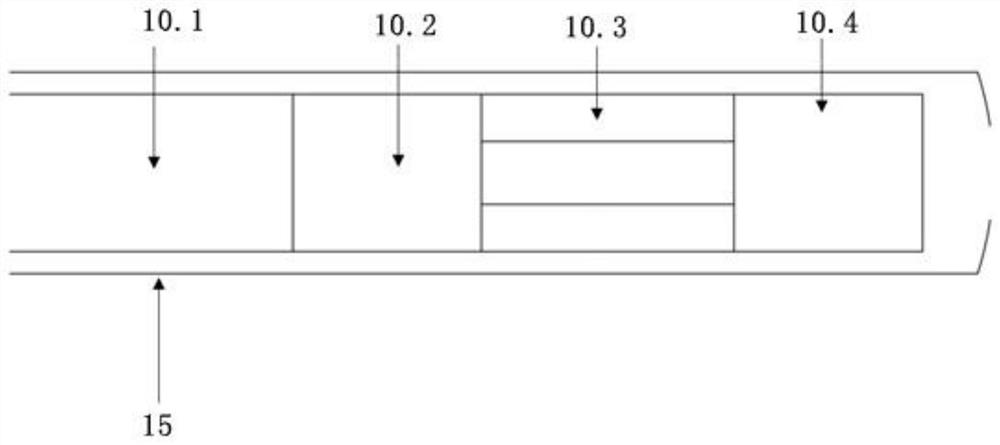
Optical fiber probe and length-adjustable variable-focus optical fiber OCT device based on beam expanding
ActiveCN112426128AWith adjustable focus positionEnable high-resolution imagingSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyHigh resolution imagingBeam source
The invention provides an optical fiber probe and a length-adjustable variable-focus optical fiber OCT device based on beam expanding. The OCT device comprises a broadband light source, a laser lightsource, a first coupler, a reference arm light path structure, a sample arm light path structure and a spectral analysis component; the broadband light source is used for emitting a source light beam,and the source light beam is divided into a first light beam and a second light beam by the first coupler; the laser light source is used for emitting pump light; the first light beam enters the reference arm light path structure, and the second light beam is coupled with the pump light emitted by the laser light source and enters the optical fiber probe of the sample arm light path structure, sothat the focus of the optical fiber OCT device is adjustable; and the spectral analysis component is used for receiving and analyzing the first light beam reflected back from the reference arm lightpath structure and the second light beam reflected back from the sample arm light path structure. The variable-focus optical fiber OCT device adopts an all-fiber probe structure as a sample arm, is small and exquisite, is easy to package, has the characteristic of adjustable focus, and can realize high-resolution imaging beyond the fixed depth-of-field range of a traditional probe.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
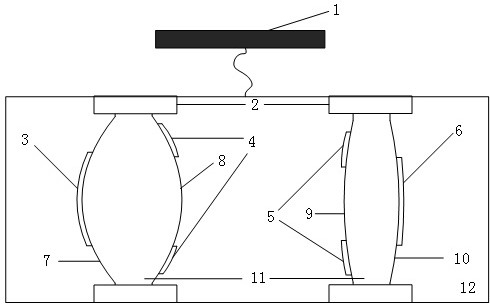
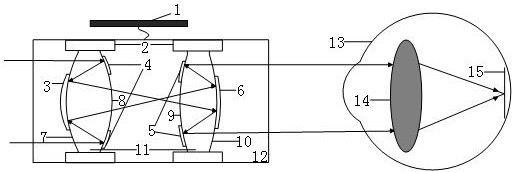
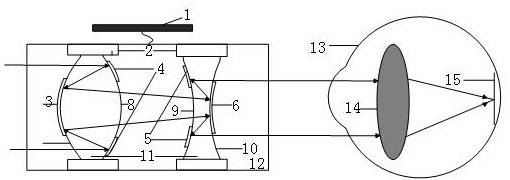
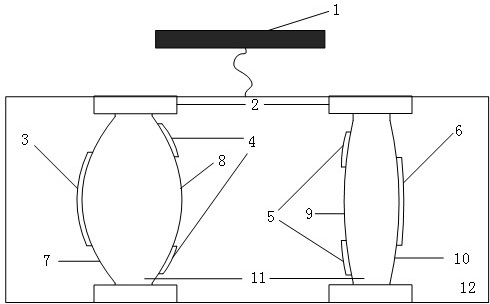
Large-aperture large-target-surface high-resolution half-group compensation focusing lens and working method thereof
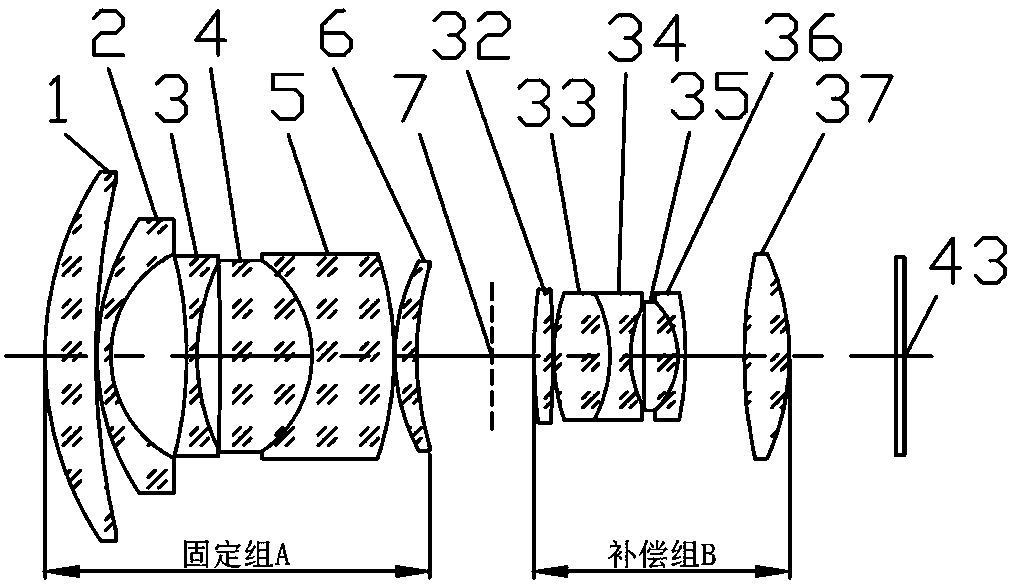
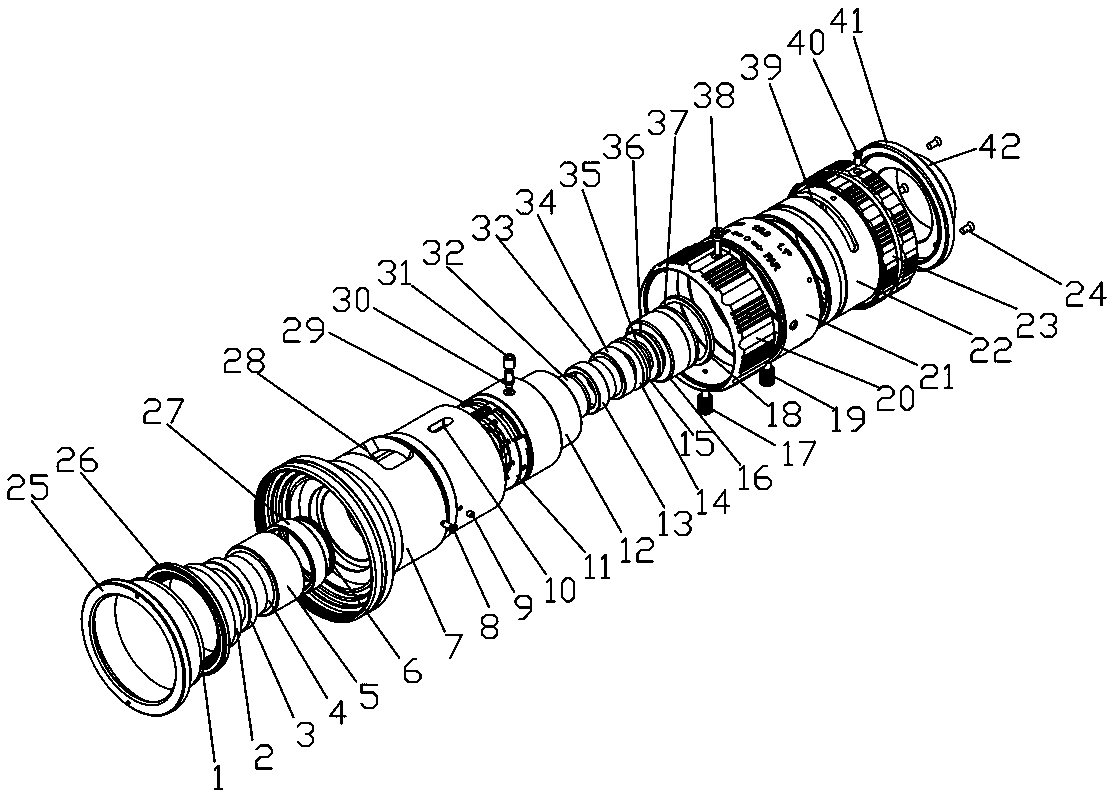
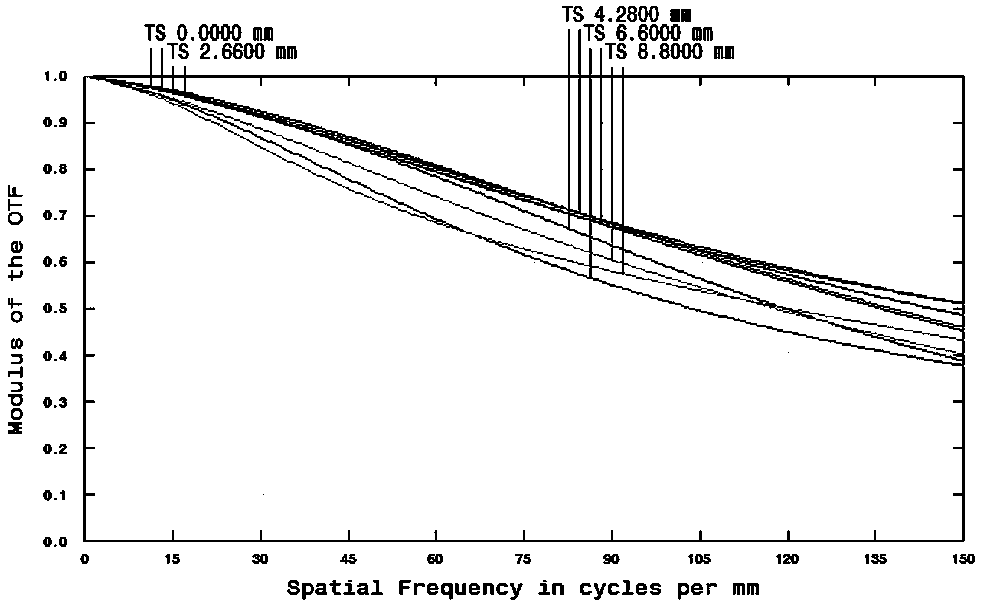
The invention relates to a large-aperture large-target-surface high-resolution half-group compensation focusing lens and a working method thereof. An optical system of the lens comprises a fixed groupA, a diaphragm 7 and a compensation group B which are sequentially arranged from front to back along an incident light path, wherein the fixed group A comprises a positive meniscus lens (1), a negative meniscus lens (2), a biconcave lens (3), a first gluing group formed by tightly gluing a positive meniscus lens (4) and a negative meniscus lens (5), and a positive meniscus lens (6); and the compensation group B comprises a biconvex lens (32), a second gluing group formed by tightly gluing the biconvex lens (33) and the biconcave lens (34), a third gluing group formed by tightly gluing a biconvex lens (35) and a negative meniscus lens (36), and a biconvex lens (37). The lens realizes the characteristics of large light transmission, large target surface and high resolution of the optical system, and adopts a half-group compensation mode for focusing, i.e., the focusing is completed by adjusting the compensation group B to move back and forth in the optical axis direction, thereby realizing close-range detection high-resolution imaging.
Owner:FUJIAN FUGUANG TIANTONG OPTICS
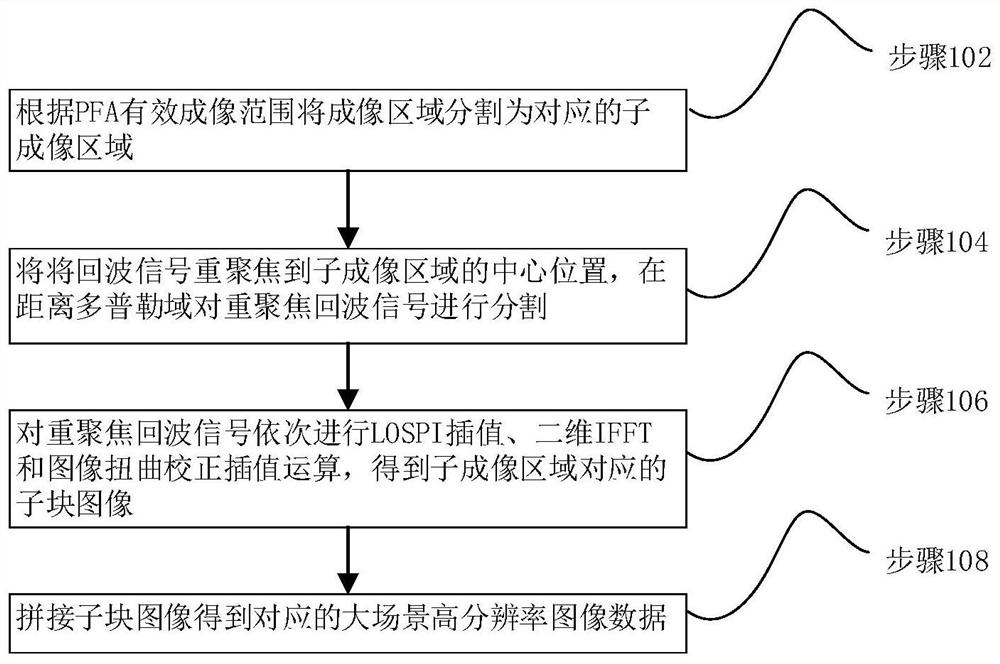
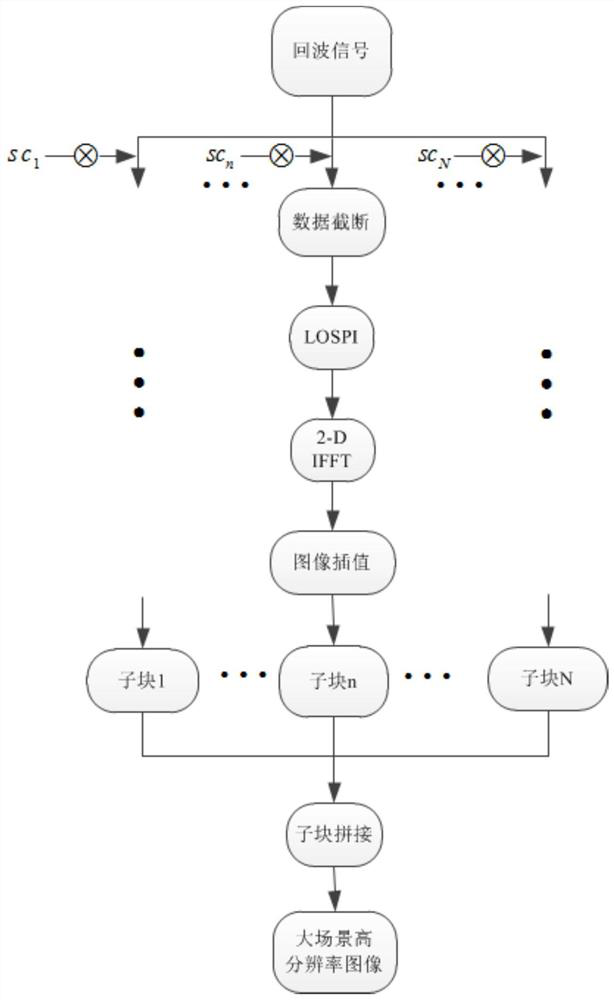
Large-scene high-resolution imaging method and device based on block imaging
PendingCN113093186ASolve the problem of large amount of calculation and long operation timeSolve the problem of small depth of focusRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhysicsNuclear medicine
The invention relates to a large-scene high-resolution imaging method and device based on block imaging. The method comprises the following steps of: segmenting an imaging area into corresponding sub-imaging areas according to an effective imaging range of a PFA, refocusing echo signals corresponding to the sub-imaging areas to the central positions of the sub-imaging areas, obtaining refocused echo signals corresponding to the sub-imaging regions in a distance Doppler domain, sequentially carrying out lOSPI interpolation, two-dimensional IFFT and image distortion correction interpolation operation on the refocused echo signals to obtain sub-block images corresponding to the sub-imaging areas, and splicing the sub-block images to obtain corresponding large-scene high-resolution image data. The block imaging algorithm provided by the invention solves the problem that the focusing depth of a traditional PFA algorithm is small, does not depend on a radar track, solves the defects that the calculation amount is large and the operation time is long in the traditional block imaging algorithm, and can achieve high-resolution imaging of a large scene.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
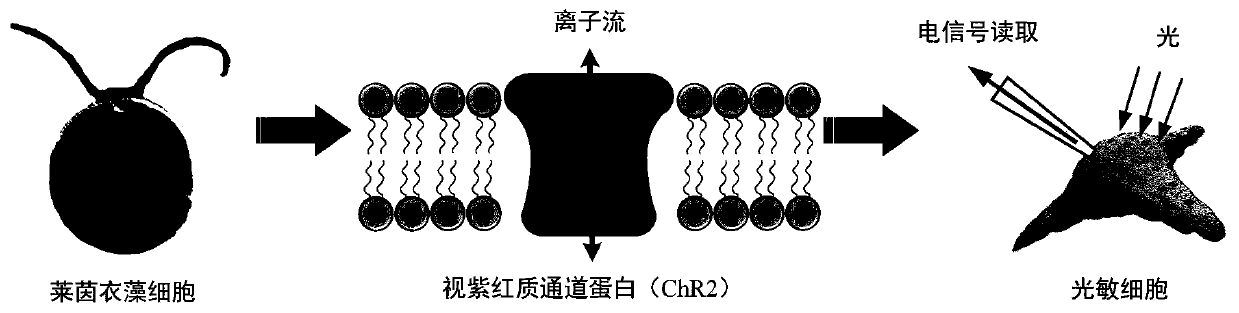
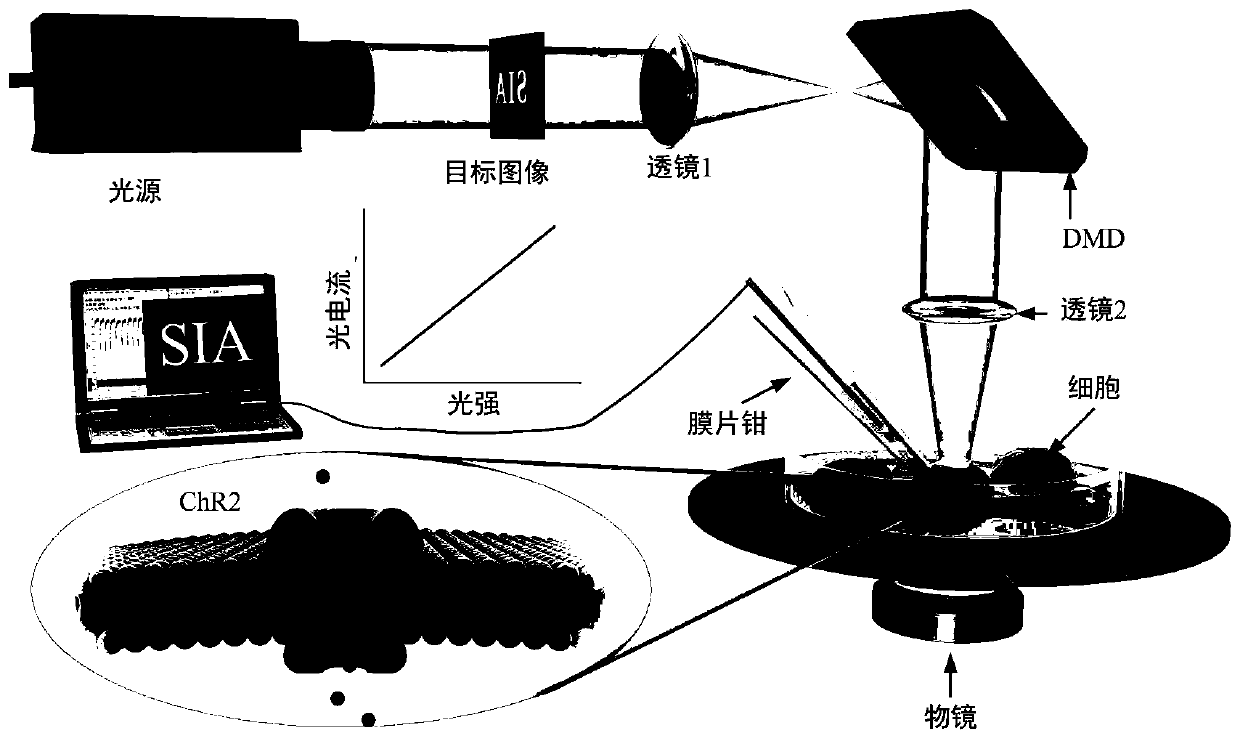
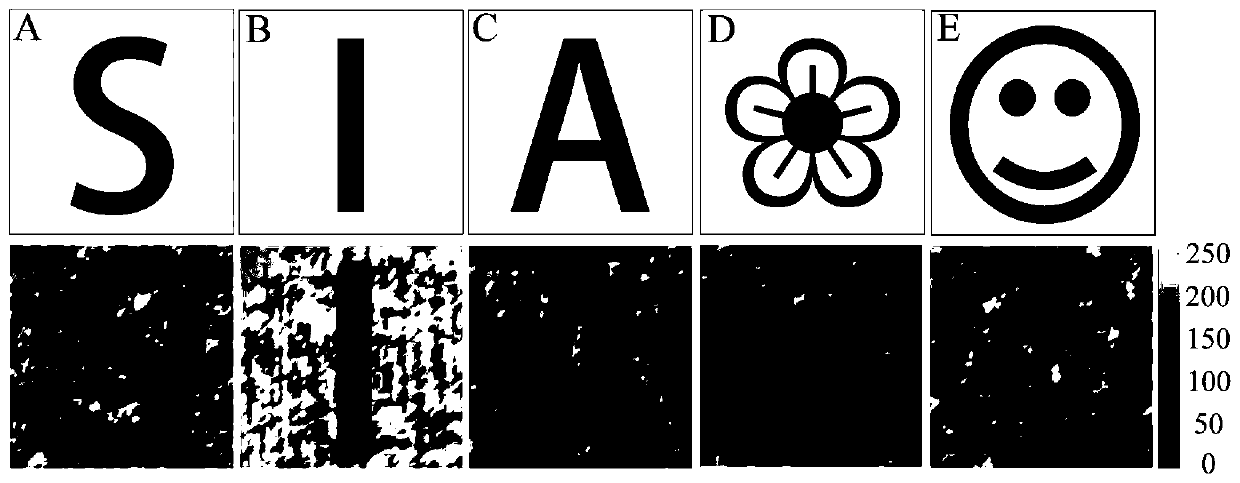
Manufacturing method of cell fusion photoelectric sensor and working method of imaging system thereof
InactiveCN111263086AGood light adaptabilityHigh saturationTelevision system detailsGenetically modified cellsChlamydomonas reinhardtiiLight perception
The invention discloses a cell fusion photoelectric sensor and a working method of an imaging system of the cell fusion photoelectric sensor. The manufacturing method of the cell fusion photoelectricsensor comprises the following steps: rhodopsin channel protein (ChR2) extracted from a chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell eye spot is transfected into a human embryonic kidney 293 (Hek293) cell; finally,the expression of the ChR2 plasmid in the cell is observed through a fluorescence microscope, and the cell expression result is further verified through photostimulation by using a patch clamp technology; the Hek293 cell expressing ChR2 is used as a sensitive material of a photoelectric sensor, optical signals absorbed by a device are converted into an ionic current by the Hek293 cell, and a patch clamp technology is used as a signal acquisition and processing unit of the photoelectric sensor; and the cell is combined with patch clamp detection equipment to form the cell fusion photoelectricsensor. The biological fusion photoelectric device has the beneficial effects that the biological fusion photoelectric device can fully utilize the advantages of organisms in light perception or vision, so that a novel device with better performance than a pure artificial device is generated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-resolution imaging camera for large-F-number diffraction real-time correction based on pixel coding
PendingCN113393380ASmall distortionReduce processing costsGeometric image transformationImaging qualityImaging lens
The invention provides a high-resolution imaging camera for large-F-number diffraction real-time correction based on pixel coding. The high-resolution imaging camera solves the problem that an existing traditional imaging camera needs to adopt a long focal length and a large aperture to achieve high-resolution imaging. The high-resolution imaging camera comprises an imaging lens, a detector and a data processing module, the imaging lens is a large-F-number and large-Q-value imaging lens and is used for collecting imaging light of a measured target; the detector is a low-noise detector and is used for converting the imaging light acquired by the imaging lens into an image; the data processing module comprises a computer program, a pixel coding algorithm is realized when the computer program is executed, and diffraction real-time correction is performed by using the pixel coding algorithm to obtain a high-resolution image; the large-F-number imaging camera is small in aperture, the equivalent Nyquist MTF is low (the F number is 25, and the MTF is about 0.02), the resolution is improved by introducing a pixel coding algorithm, and the large-F-number imaging camera has the advantages of being small in aperture, long in focal length, high in resolution, light in weight, high in image quality and the like.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Design method of Fermat spiral Greek ladder photon sieve and its imaging optical path
The point spread function determines the imaging properties of the optical system, and different point spread functions can achieve different imaging results. By introducing the Fermat helix into the Greek ladder photon sieve, the Fermat helix modulates the distribution positions of the sieve holes in the Greek ladder photon sieve to obtain the Fermat helix Greek ladder photon sieve. Through the imaging optical path based on the Fermat spiral Greek ladder photon sieve to generate multiple focal points in the axial direction, the function of different point spread functions of the multi-focal plane of a single device is realized, including anisotropic Airy disk and vortex focus, which can be applied to coherence Focusing and imaging from X-ray to terahertz band in light field. The first and third focuses are anisotropic Airy disks, which can achieve different resolutions in different directions for the input object, which helps to improve the resolution of the object's interested direction; the second focus is the vortex focus, The vortex focus can be used for optical trapping. In addition, when used for imaging, the radial Hilbert transform can be realized based on the helical phase filter, and the edge enhancement of the amplitude and phase objects can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
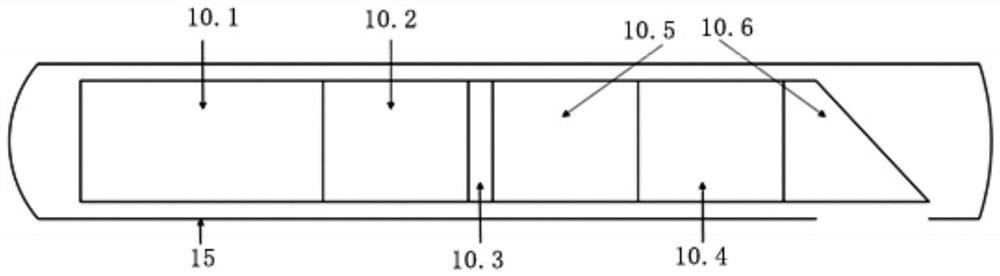
Porous film observation window
PendingCN108169234AEnable high-resolution imagingFast and effective observation and positioningMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionHigh resolution imagingOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a porous film observation window. The window comprises a substrate and thin films with preset thickness; the substrate comprises a first surface and a second surface which areoppositely arranged; the thin films with the preset thickness are arranged on the first surface and the second surface, and the shapes and sizes of the thin films are conform to the shape and size ofthe substrate; observation grooves penetrating through the first surface and the second surface are formed in the substrate, and the observation grooves also penetrate through the thin film located onthe first surface or the second surface; a plurality of through holes penetrating through the thin films which are not penetrated by the observation grooves are formed in the thin films which are notpenetrated by the observation grooves at intervals, and the through holes correspond to the observation grooves so that samples can be observed through the through holes. According to the window, part of the samples extending out of the through holes or arranged above the through holes can be observed through the arranged through holes to achieve high-definition imaging of the samples.
Owner:SUZHOU IN SITU CHIP TECH CO LTD
A target azimuth imaging method based on superposition vortex light
ActiveCN111474558BNovel methodAchieving Rotational Doppler EffectElectromagnetic wave reradiationImaging conditionPhase difference
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Method for synthesizing rare earth metal compound nano cluster and application thereof
ActiveCN103143037BEnable high-resolution imagingStrong targetingEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsX-ray constrast preparationsRare earth metal compoundsSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a rare earth metal compound nano cluster and application of the rare earth metal compound nano cluster in the aspects of target imaging of diseased regions such as tumor and contrast medium preparation. The rare earth metal compound nano cluster prepared by the method has a small particle size, good permeability, high fluorescent stability, high sensibility and strong targeting, so that the tumor can be accurately positioned; the rare earth metal compound nano cluster is directly synthesized by biological tumor cells and has good biocompatibility; and the method is convenient to operate and intuitive in result, synchronous analysis and detection in multiple states and multiple modes can be carried out, and the method has a wide medical application prospect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Multiscale Matrix Coding Method
The invention discloses a multi-scale matrix encoding method, comprising the following steps: inputting an initial encoding matrix of the same size as an image; dividing the initial encoding matrix into a first-level scale matrix to obtain multiple first-level scale matrices; The first-level scale matrix is divided into multiple second-level scale matrices, and the second-level scale matrix is locally encoded; the first-level scale matrix is globally encoded on the basis of local encoding. The present invention is based on the block-based compressed sensing technology, further divides the blocks, and according to the dependencies between pixels, can design a coding matrix that obtains more information about the block. Compared with the existing coding matrix, the structure is better.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
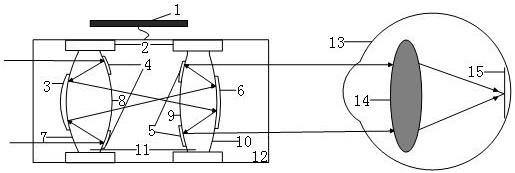
A kind of lightweight zoom telescopic glasses
ActiveCN111897122BFilling the void in telephotoEnable high-resolution imagingTelescopesLensEyepieceHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a lightweight zooming telescope, comprising: a drive control device, a driver, a circular reflective film on the incident surface of an objective lens, a circular reflective film on the exit surface of the objective lens, a circular reflective film on the incident surface of the eyepiece, and a circular reflective film on the exit surface of the eyepiece film, zoom surface Ⅰ, zoom surface Ⅱ, zoom surface Ⅲ, zoom surface Ⅳ, medium Ⅰ and medium Ⅱ; the technical point of this invention is: the curvature of the zoom surface used in the system can be changed when the drive device is working, not only can realize the The high-resolution imaging of long-distance objects can also continuously zoom to quickly identify the tiny details of the object; the present invention adopts a catadioptric hybrid structure, and the zoom surface is coated with a reflective film. When light is incident on the lens, the reflection on the zoom surface of the lens The film makes the light path reflect multiple times in the lens, which reduces the radial size of the telescope. Compared with traditional telescopes, the system is more compact and lightweight, filling the vacancy of zoom glasses in terms of telephoto.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for merging resolutions of linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars
ActiveCN101614810BEnable high-resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarImage resolution
The invention provides a method for merging resolutions of linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars. The method adopts two linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radars of which the motion trails are orthogonal to image the same region and then adopts an orthogonal spatial projection matrix technology to merge two obtained images, thereby generating a high-resolution linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar image. The method solves the problem that the cross track resolution of the linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar image is lower than the long track resolution of the linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar image. The method has the advantages of realizing the linear array three-dimensional imaging synthetic aperture radar high-resolution imaging by using a short array antenna and can be used in the fields of synthetic aperture radar imaging, earth remote sensing and the like.
Owner:四川电子科技大学教育发展基金会
Optical fiber probe and variable-focus optical fiber OCT device based on adjustable mode field area
ActiveCN112426129AReduce regulation costReduce the difficulty of optimizationSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyOptical pathBroadband light source
The invention provides an optical fiber probe and a variable-focus optical fiber OCT device based on an adjustable mode field area. The OCT device comprises a broadband light source, a laser light source, a first coupler, a reference arm light path structure, a sample arm light path structure and a spectral analysis component; the source light beam is divided into a first light beam and a second light beam by a coupler I; the sample arm light path structure adopts an optical fiber probe as a sample arm; the first light beam enters the reference arm light path structure, and the second light beam is coupled with pump light emitted by the laser light source and enters an optical fiber probe of the sample arm light path structure, so that the focus of the optical fiber OCT device is adjustable; and the spectral analysis component is used for receiving and analyzing the first light beam reflected back from the reference arm light path structure and the second light beam reflected back fromthe sample arm light path structure. The variable-focus optical fiber OCT device adopts an all-fiber probe structure as a sample arm, is small and exquisite, is easy to package, and has the characteristic of adjustable focus; and meanwhile, the variable-focus optical fiber OCT device can be used for endoscopy, and achieves high-resolution imaging beyond the depth-of-field range.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
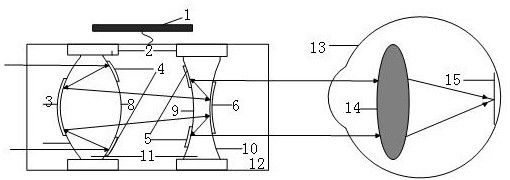
Light-weight zoom telescopic glasses
ActiveCN111897122AFilling the void in telephotoEnable high-resolution imagingTelescopesLensEyepieceHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses light-weight zoom telescopic glasses, which comprise a driving control device, a driver, an objective lens incident surface circular reflecting film, an objective lens emergentsurface annular reflecting film, an eyepiece incident surface annular reflecting film, an eyepiece emergent surface circular reflecting film, a zoom surface I, a zoom surface II, a zoom surface III,a zoom surface IV, a medium I and a medium II. The technical key points of the invention are as follows: the curvature of the zoom surfaces used by the system can be changed when a driving device works, so that high-resolution imaging of a long-distance object can be realized, and tiny details of the object can be quickly identified through continuous zooming; a catadioptric hybrid structure is adopted, the zoom surfaces are plated with the reflecting films, when light enters the lens, the reflecting films on the zoom surfaces of the lens enable a light path to be reflected for multiple timesin the lens, so that the radial size of the telescope is reduced; and compared with a traditional telescope, the light-weight zoom telescopic glasses are more compact and lighter, and the vacancy of zoom glasses in the aspect of telescoping is filled up.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Efficient near-field size target isar imaging method based on back projection
ActiveCN114488152BReduce the number of transformationsImaging steps are simpleRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar antennasTime domain
The invention discloses an efficient near-field size target ISAR imaging method based on back projection, comprising: initializing an image data matrix; using the target back electromagnetic scattering echo signal corresponding to the azimuth viewing angle to obtain a distance time domain image; The distance from the radar antenna to the center scattering point of the target, the distance between any scattering point on the target and the radar antenna except the center scattering point, the distance time domain image, and the image data matrix, the imaging results under the current viewing angle are obtained; the imaging results under all viewing angles Superposition is performed to obtain near-field ISAR imaging results. The present invention can realize near-field ISAR fine imaging of large and small targets, reduce the calculation amount, and improve the target detection, recognition and resolution capabilities.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com