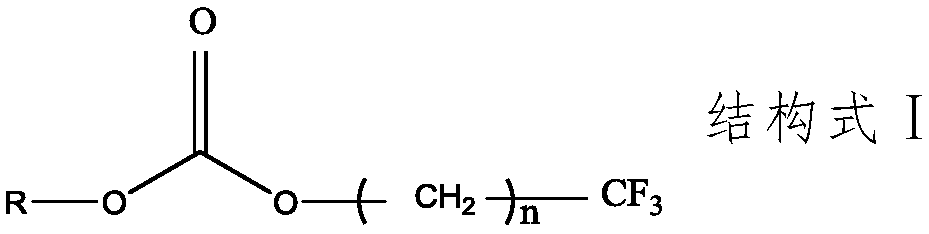Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Positive response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
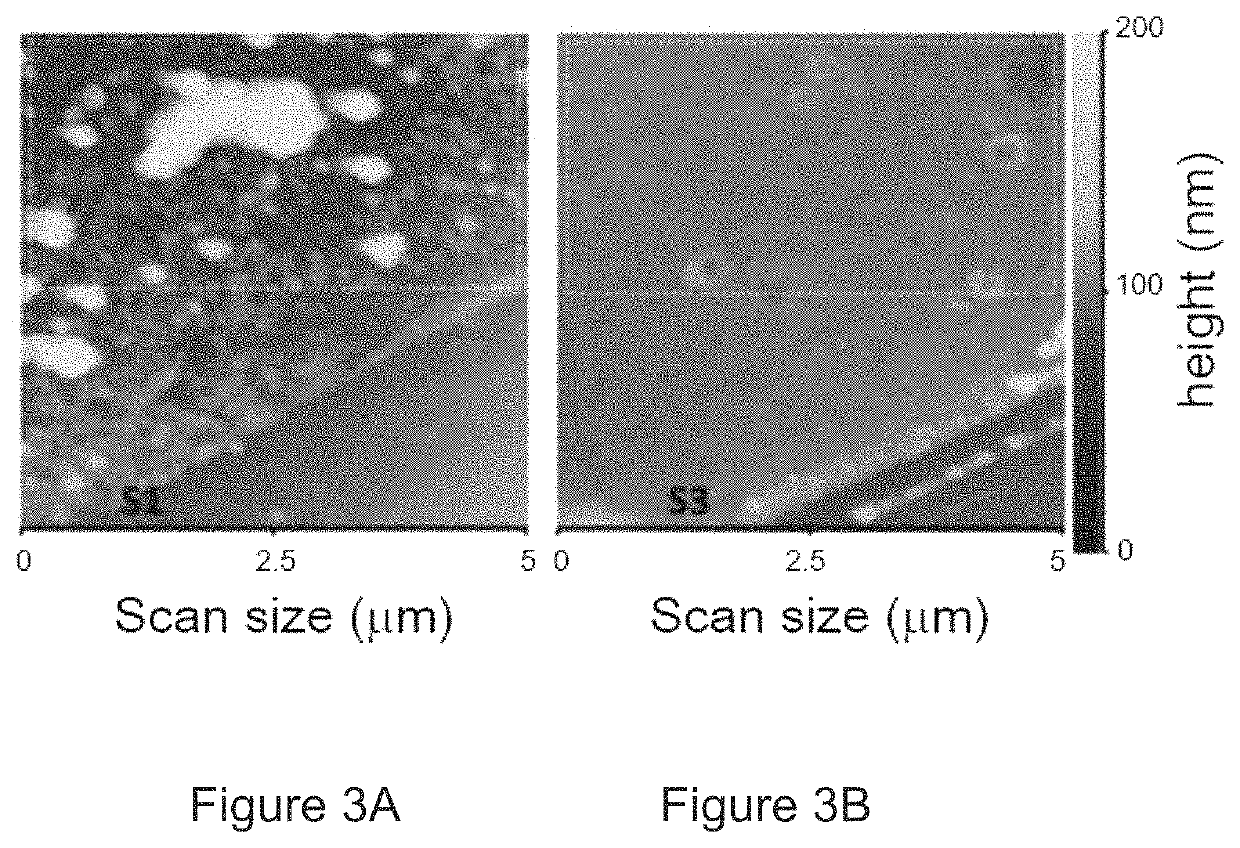
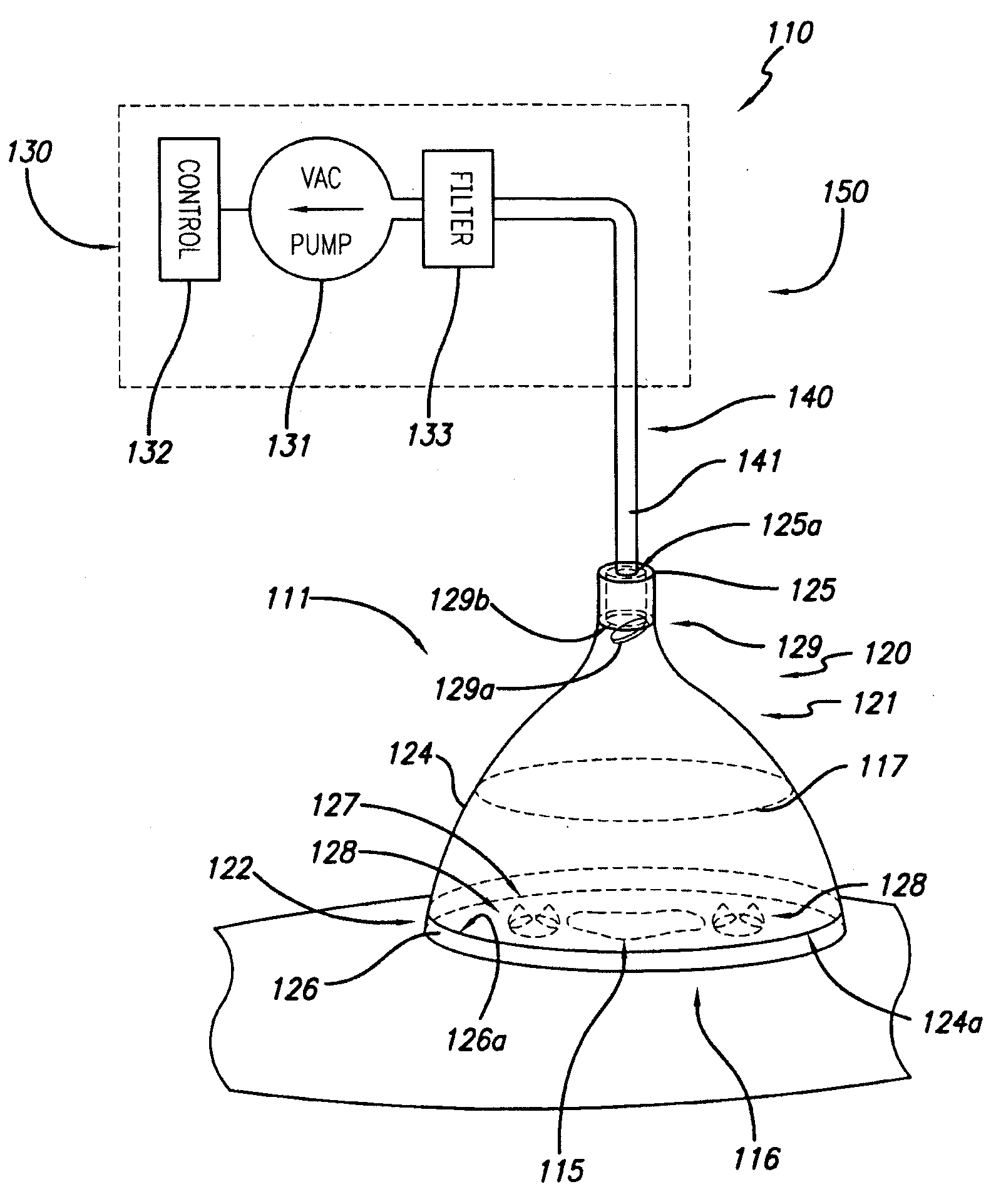
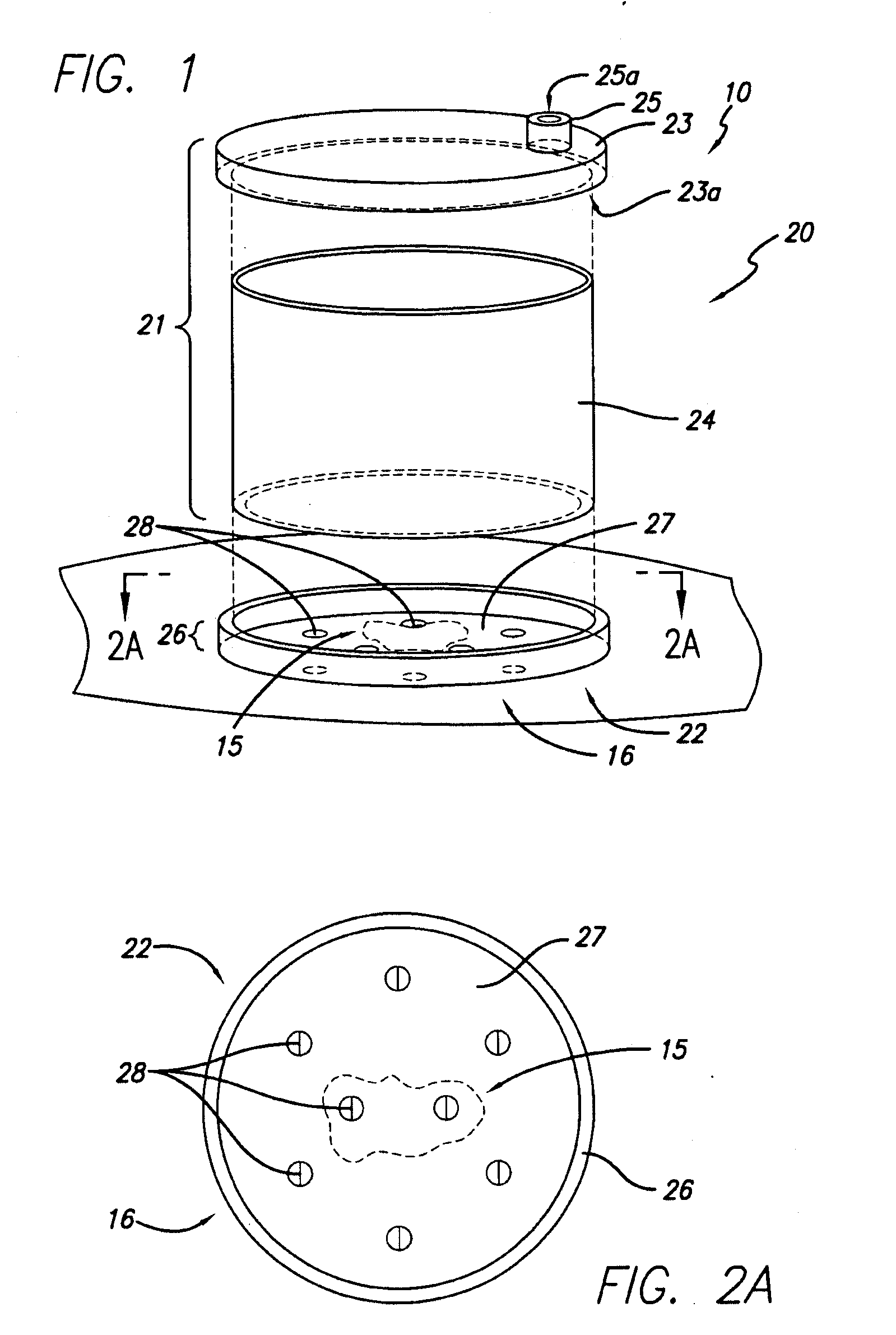
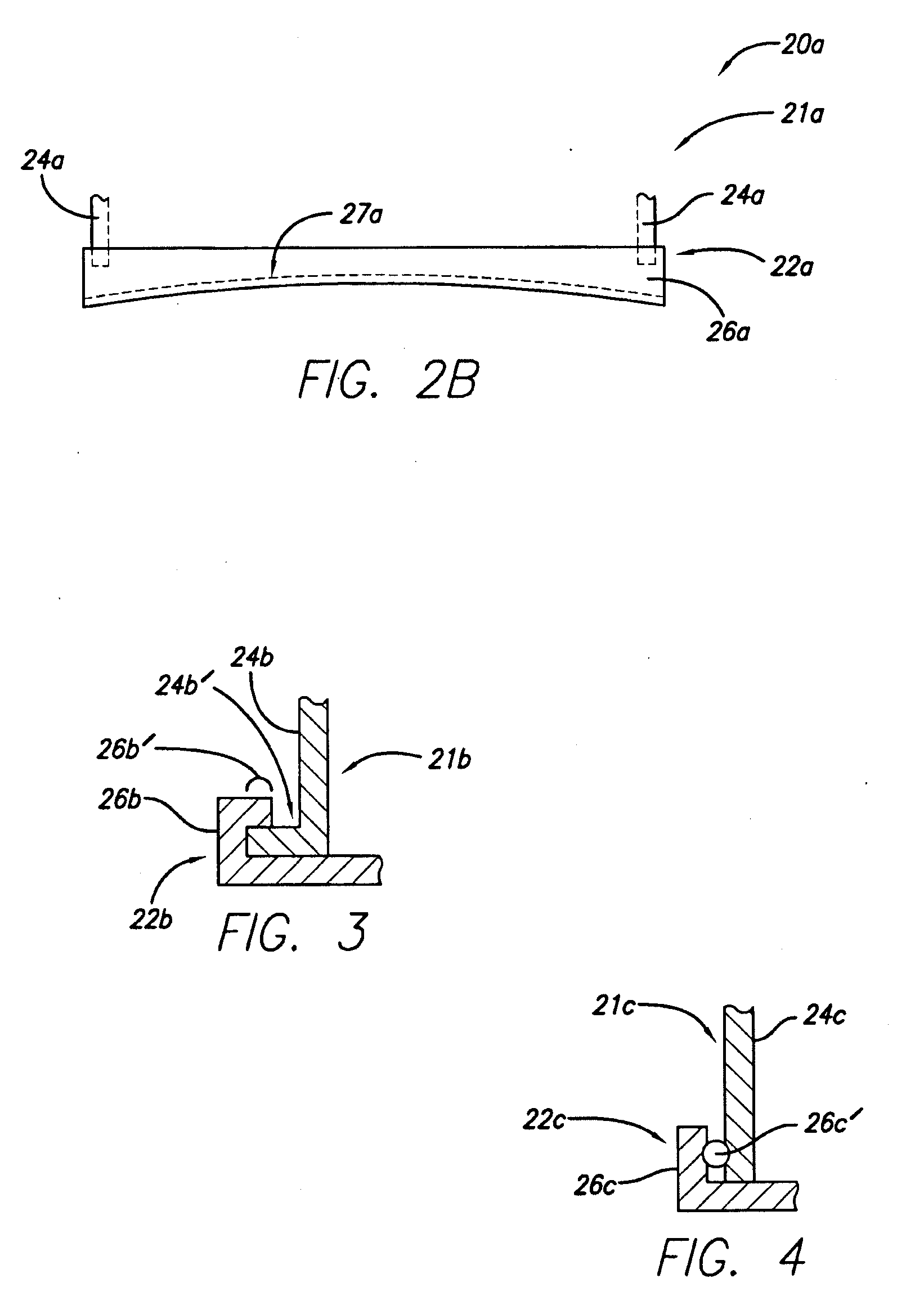
Reduced pressure wound treatment system
ActiveUS20100160879A1Heal fastIncreased formationMedical devicesIntravenous devicesPhysical woundWound site
A reduced pressure treatment appliance is provided for treating a wound on the body of a patient. In some embodiments, the appliance comprises a cover, which can have a top cup member and an interface member. The interface member can have flow control means, configured to permit exudate from the wound to flow through the flow control means into the volume under the cover, but not in the opposite direction. Also, in some embodiments, the top cup member can have a lid member, a cup body member, and lid attachment means to removably attach the lid member to the cup body member. In some embodiments, the cover can be configured to facilitate access to the wound for monitoring, treatment and other purposes without removing the cover from the body. The wound treatment appliance can have a vacuum system to supply reduced pressure to the site of the wound in the volume under the cover. A suction bulb can be used to provide a source of reduced pressure to the cover. Additionally, methods are provided for using various embodiments of the treatment appliance.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Morphology engineering of conductive metallic nanoparticles capped with an organic coating
ActiveUS20130171733A1Broaden spectrumPositive responseComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesVolatile organic compoundMetal
The present invention is directed to a sensor having continuous and discontinuous regions of conductive metallic nanoparticles capped with an organic coating which enables the detection of volatile organic compounds and / or water vapor.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Photo-imageable Hardmask with Positive Tone for Microphotolithography
ActiveUS20100261097A1Positive responseReadily dispersiblePhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColor toneChemistry
Disclosed are the deactivation mechanism and chemistry platforms that make high-silicon hardmask films photo-imageable like positive-tone photoresist for microphotolithography. The deactivation mechanism requires a catalyst to promote crosslinking reactions, and a photoacid generator to deactivate the catalyst. The initial hardmask films are soluble in developers. If not radiated, films become insoluble in developers due to crosslinking reactions promoted by catalyst. If radiated, films remain soluble in developers due to deactivation of catalyst by photoacid generator. Compositions of positive-tone photo-imageable hardmask based on the chemistry of polysiloxane and polysilsesquioxanes are disclosed as well. Also disclosed is a method of modifying polysiloxane and polysilsesquioxane films for controlled diffusion of catalysts, photoacid generators, and quenchers. Further disclosed are processes of using photo-imageable hardmasks to create precursor structures on semiconductor substrates with or without an intermediate layer.
Owner:SUN SAM XUNYUN
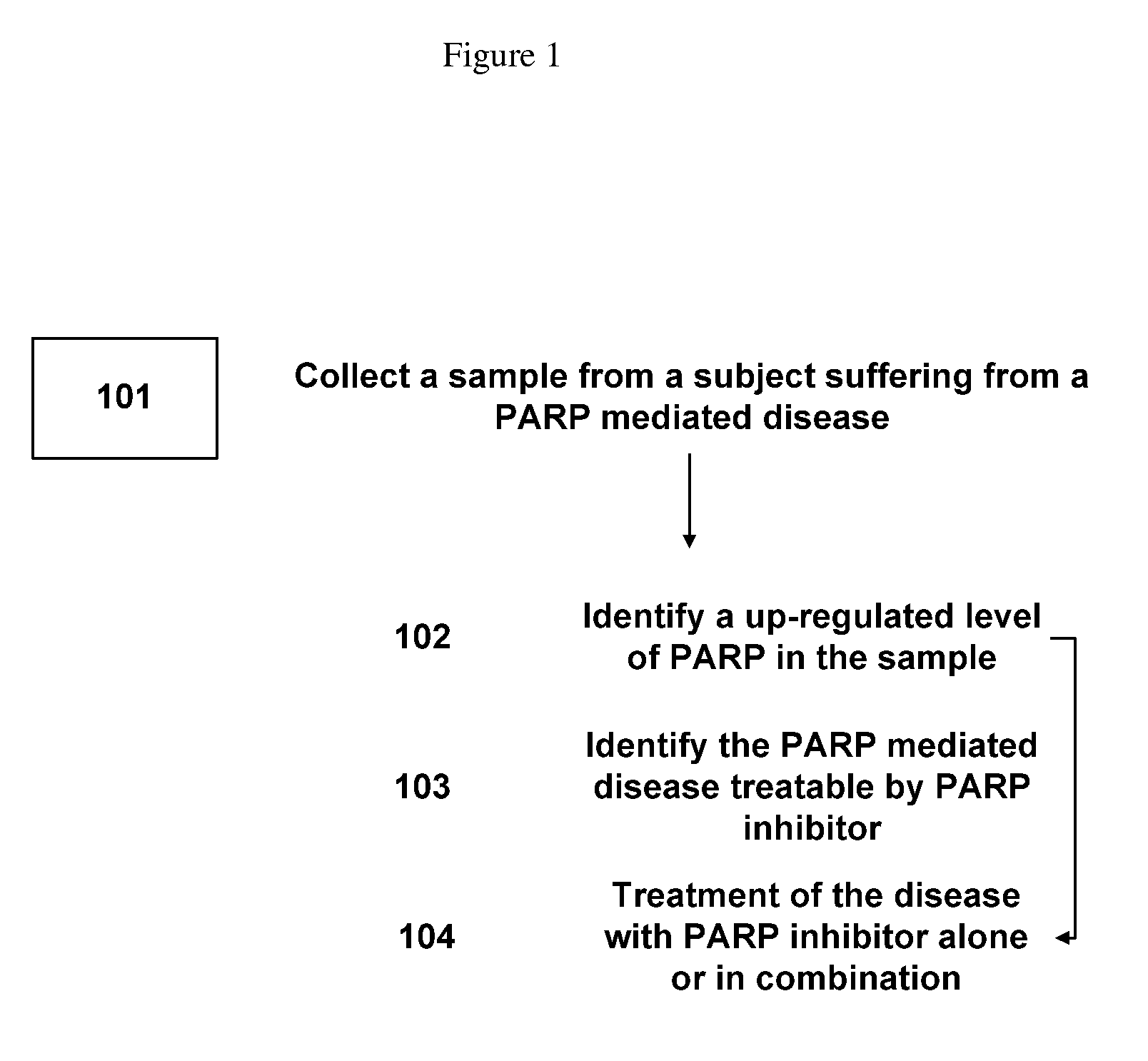
Method of treating diseases with parp inhibitors
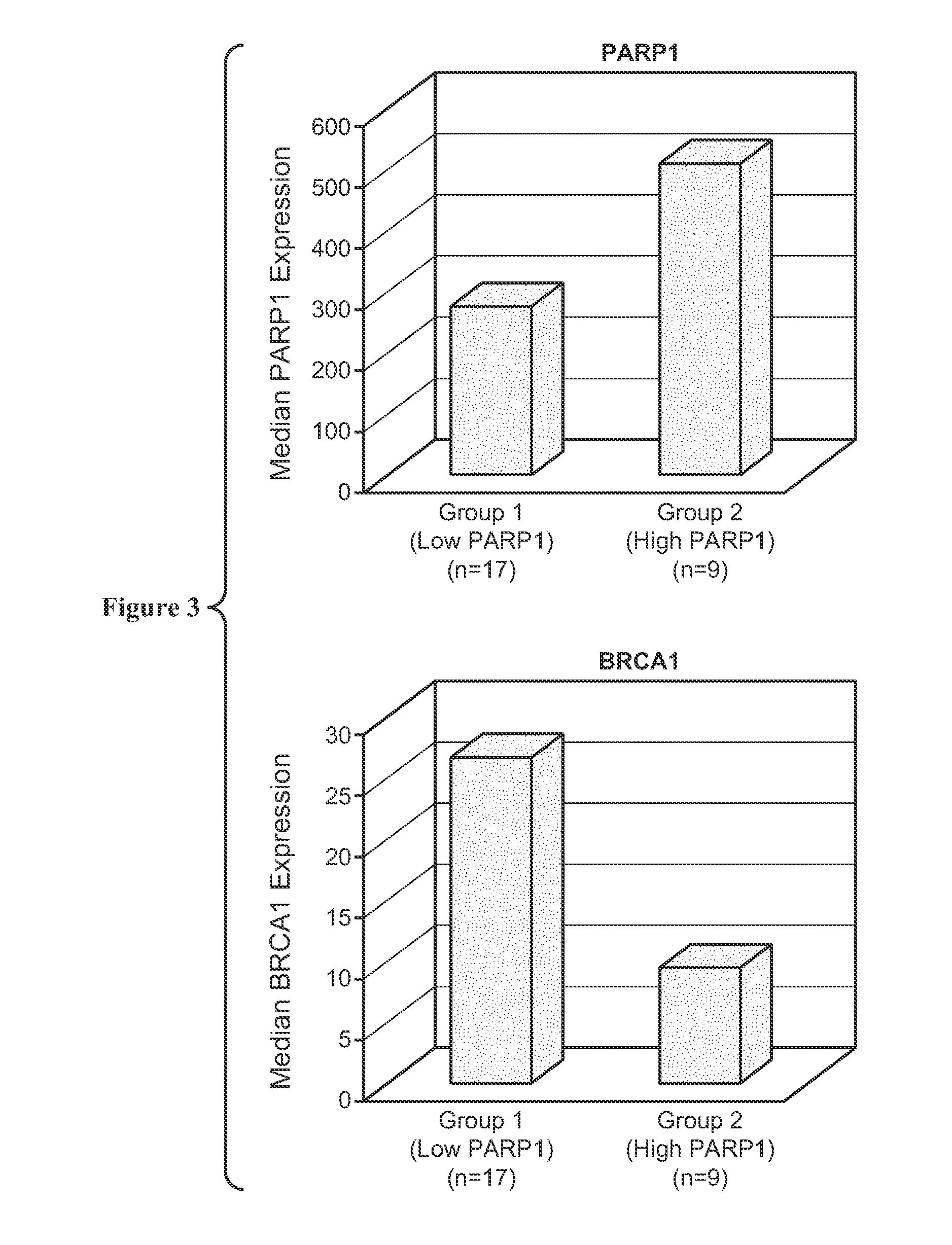
InactiveUS20100279327A1Positive responseOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePopulationReproductive system
The present invention relates to methods of identifying a disease treatable with PARP modulators by identifying a level of PARP in a sample of a subject, making a decision regarding identifying the disease treatable by the PARP modulators wherein the decision is made based on the level of PARP. The method further comprises of treating the disease in the subject with the PARP modulators. The methods relate to identifying up-regulated PARP in a disease and making a decision regarding the treatment of the disease with PARP inhibitors. The extent of PARP up-regulation in a disease can also help in determining the efficacy of the treatment with PARP inhibitors. The present invention also relates to methods of identifying a disease treatable with PARP modulators by identifying a level of PARP in a plurality of samples from a population, making a decision regarding identifying the disease treatable by the PARP modulators wherein the decision is made based on the level of PARP. The method further comprises of treating the disease in a subject population with the PARP modulators. The methods relate to identifying up-regulated PARP in a disease and making a decision regarding the treatment of the disease with PARP inhibitors. The extent of PARP up-regulation in a disease can also help in determining the efficacy of the treatment with PARP inhibitors.The present invention discloses various diseases that have up-regulated or down-regulated PARP and can be treated with PARP inhibitors or PARP activators, respectively. The examples of the diseases include cancer, inflammation, metabolic disease, CVS disease, CNS disease, disorder of hematolymphoid system, disorder of endocrine and neuroendocrine, disorder of urinary tract, disorder of respiratory system, disorder of female reproductive system, and disorder of male reproductive system.
Owner:BIPAR SCI INC
Method and system of controlling promotional call-ins
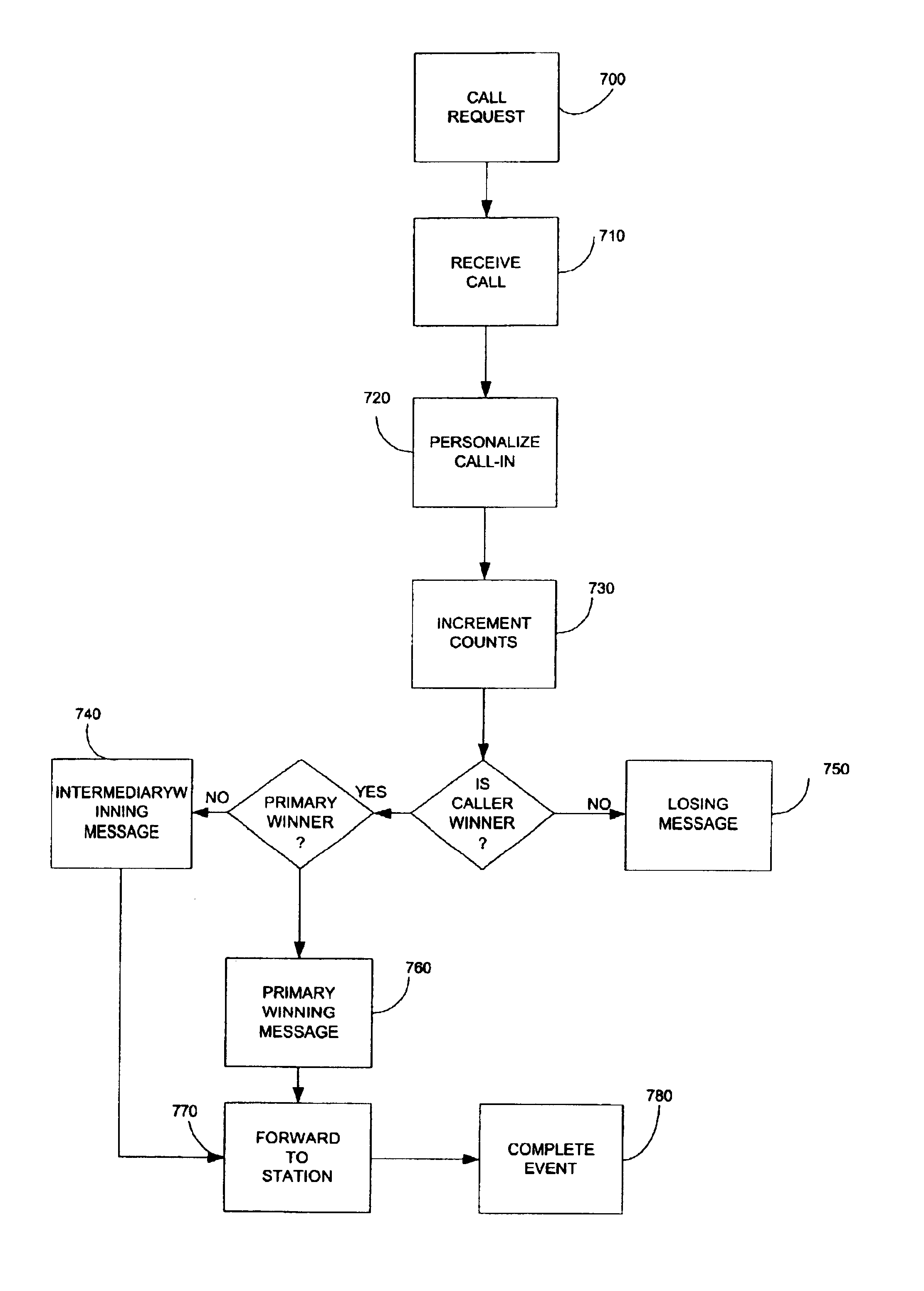
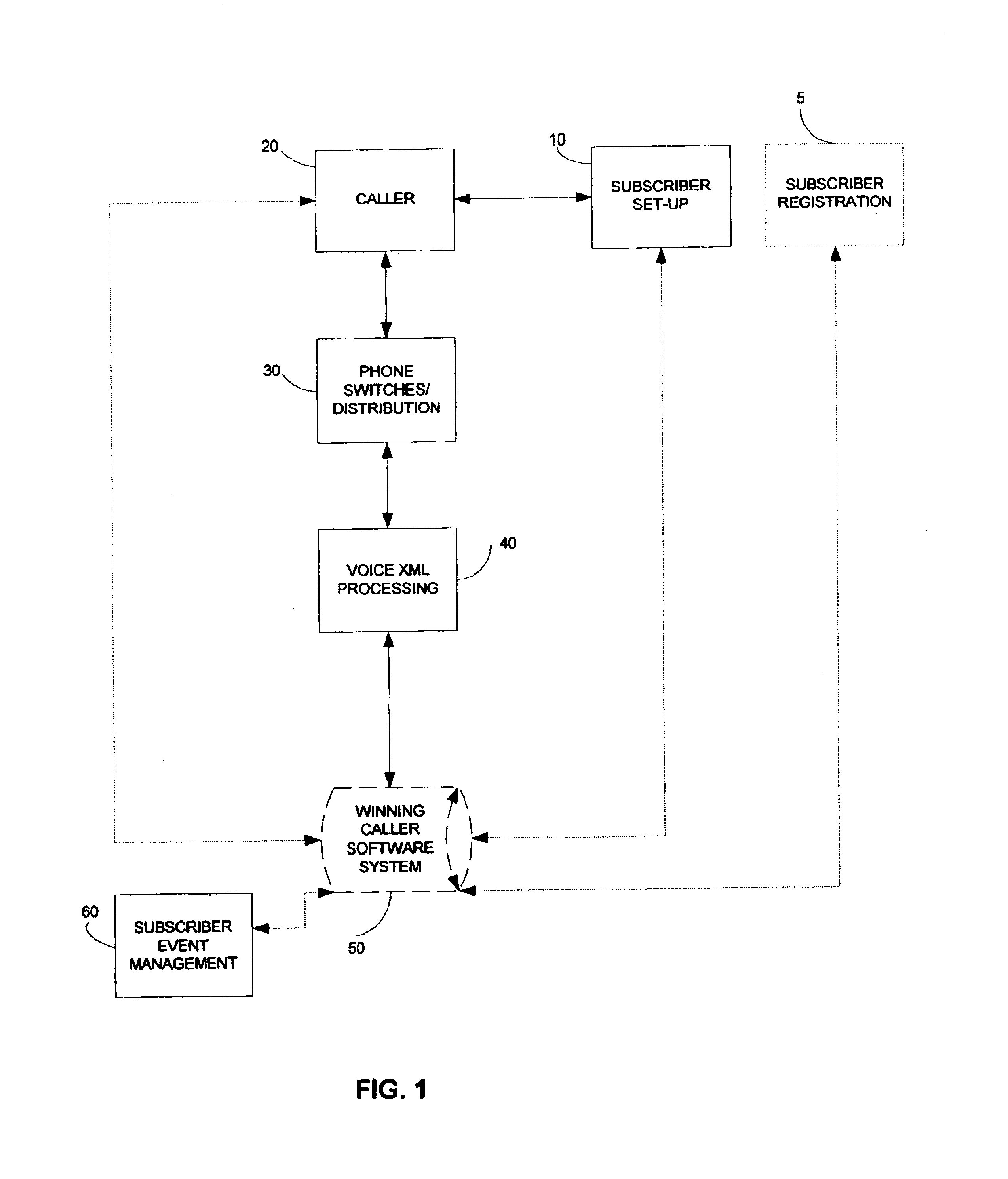
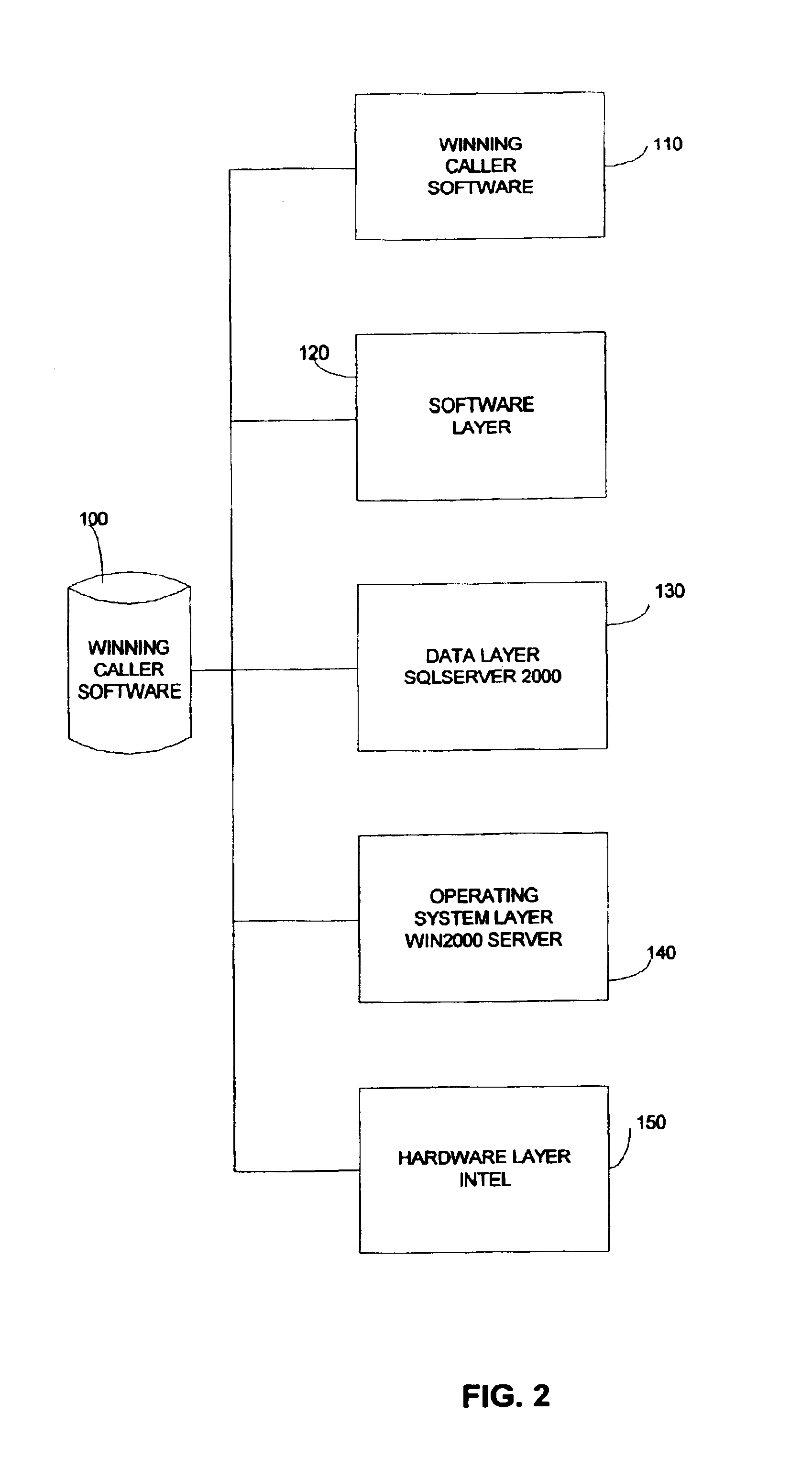
A method and system for receiving, logging, answering, controlling, and forwarding calls from radio or other promoter call-in contestants, wherein said method provides an efficient means for controlling call-in contests. Radio call-in contests are the most typical, but the method applies to other types of promotions, such as direct mail, store banners and print ads. The system consists of a voice vendor, web server, database, telecommunications, and application software to control and count the calls and to provide administrative functions. Every caller receives a positive response, acknowledgement and notification of the caller number, and an opportunity to obtain other benefits, such as discounted items. Only the winning caller is forwarded to the radio station. The radio station only needs to answer to the winning caller. All other callers, including those callers after the winning caller is determined, receive a response on the first try, without needing to repeatedly redial to get through on the telephone line.
Owner:CIAVOLINO MARCO
Photo-imageable hardmask with positive tone for microphotolithography
ActiveUS8911932B2Positive responseReadily dispersiblePhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoacid generatorSilsesquioxane
Disclosed are the deactivation mechanism and chemistry platforms that make high-silicon hardmask films photo-imageable like positive-tone photoresist for microphotolithography. The deactivation mechanism requires a catalyst to promote crosslinking reactions, and a photoacid generator to deactivate the catalyst. The initial hardmask films are soluble in developers. If not radiated, films become insoluble in developers due to crosslinking reactions promoted by catalyst. If radiated, films remain soluble in developers due to deactivation of catalyst by photoacid generator. Compositions of positive-tone photo-imageable hardmask based on the chemistry of polysiloxane and polysilsesquioxanes are disclosed as well. Also disclosed is a method of modifying polysiloxane and polysilsesquioxane films for controlled diffusion of catalysts, photoacid generators, and quenchers. Further disclosed are processes of using photo-imageable hardmasks to create precursor structures on semiconductor substrates with or without an intermediate layer.
Owner:SUN SAM XUNYUN
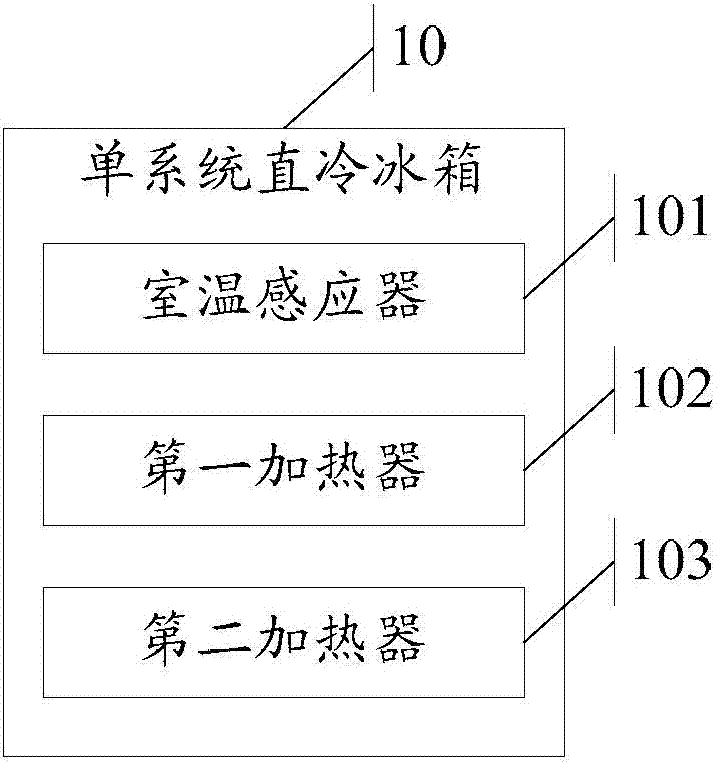
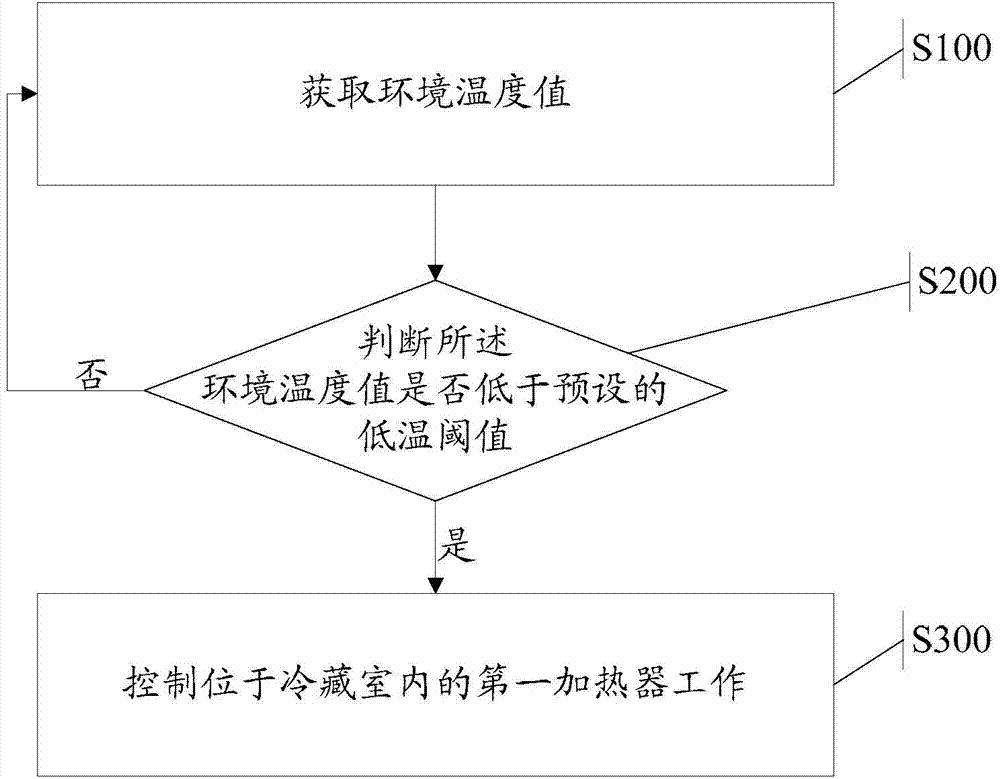
Single-system direct-cooling refrigerator and auxiliary temperature control method for single-system direct-cooling refrigerator
ActiveCN104729231ARoom temperature improvementEasy to produceLighting and heating apparatusCooling fluid circulationTemperature controlEngineering
The invention discloses a single-system direct-cooling refrigerator and an auxiliary temperature control method for the single-system direct-cooling refrigerator. The single-system direct-cooling refrigerator comprises an indoor temperature sensor and a first heater, wherein the indoor temperature sensor is used for judging whether the refrigeration function needs to be started by acquiring the indoor temperature value in a refrigerating chamber, and the first heater is used for heating air at the position of the indoor temperature sensor. The auxiliary temperature control method for the single-system direct-cooling refrigerator comprises the steps that the environment temperature value is obtained, and whether the environment temperature value is lower than a preset low-temperature threshold value is judged; when the environment temperature value is lower than the preset low-temperature threshold value, the first heater is controlled to work. The single-system direct-cooling refrigerator and the auxiliary temperature control method for the single-system direct-cooling refrigerator have the advantages that the temperature of the refrigerating chamber is prevented from being too low, and the temperature of a variable-temperature chamber is prevented from being too high.
Owner:HEFEI MIDEA REFRIGERATOR CO LTD +1
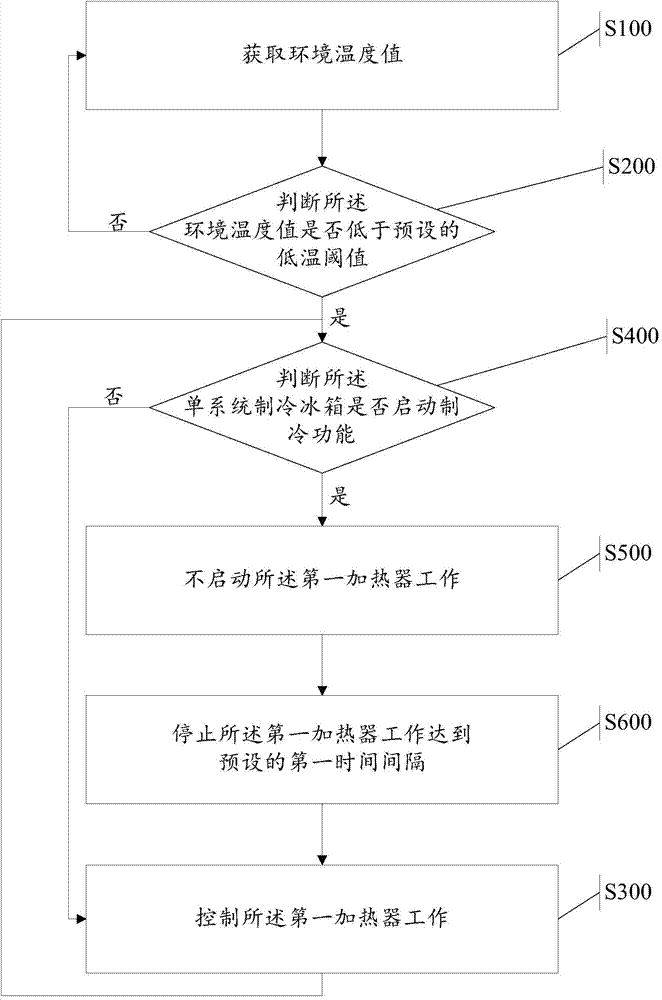
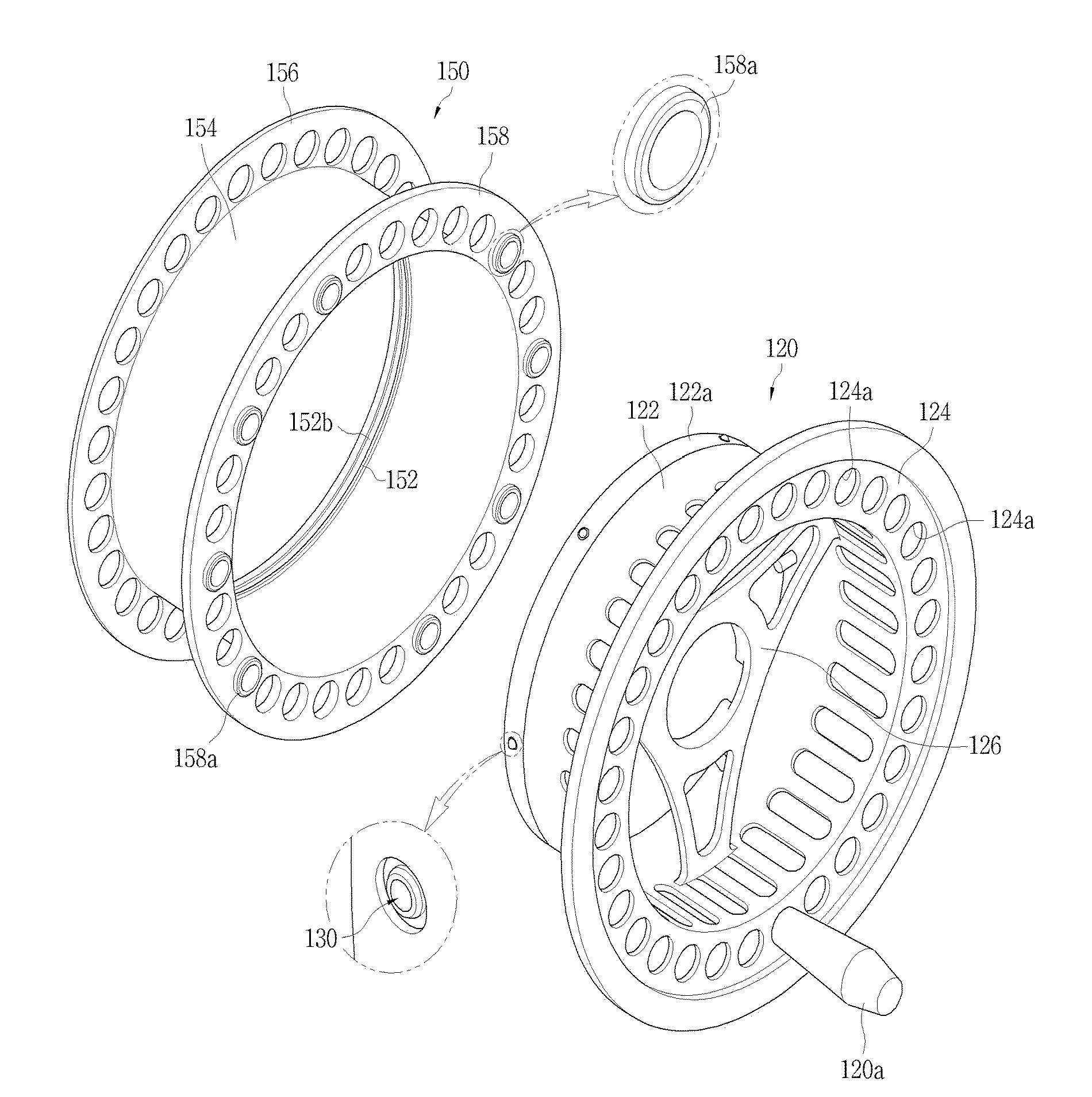
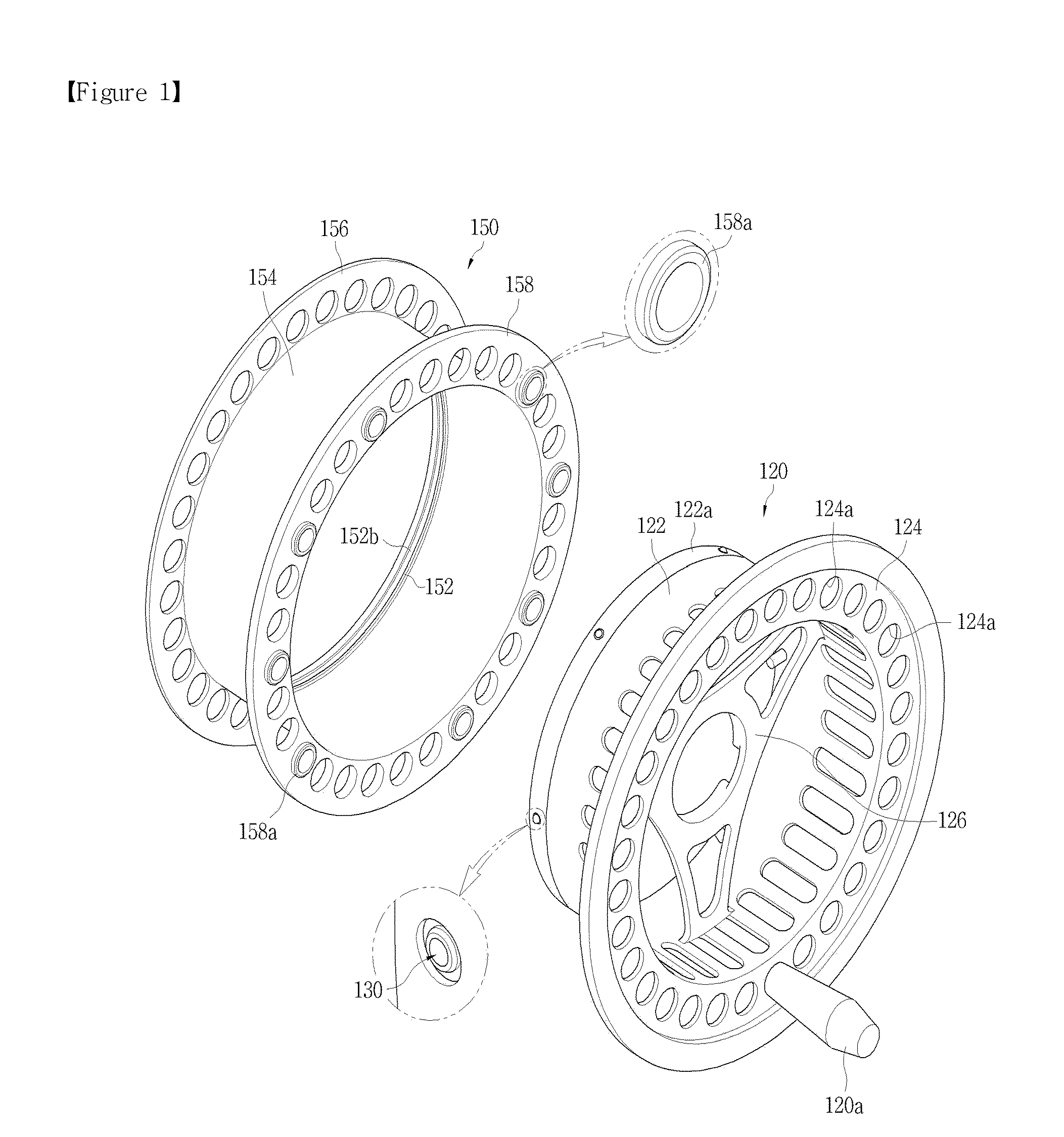
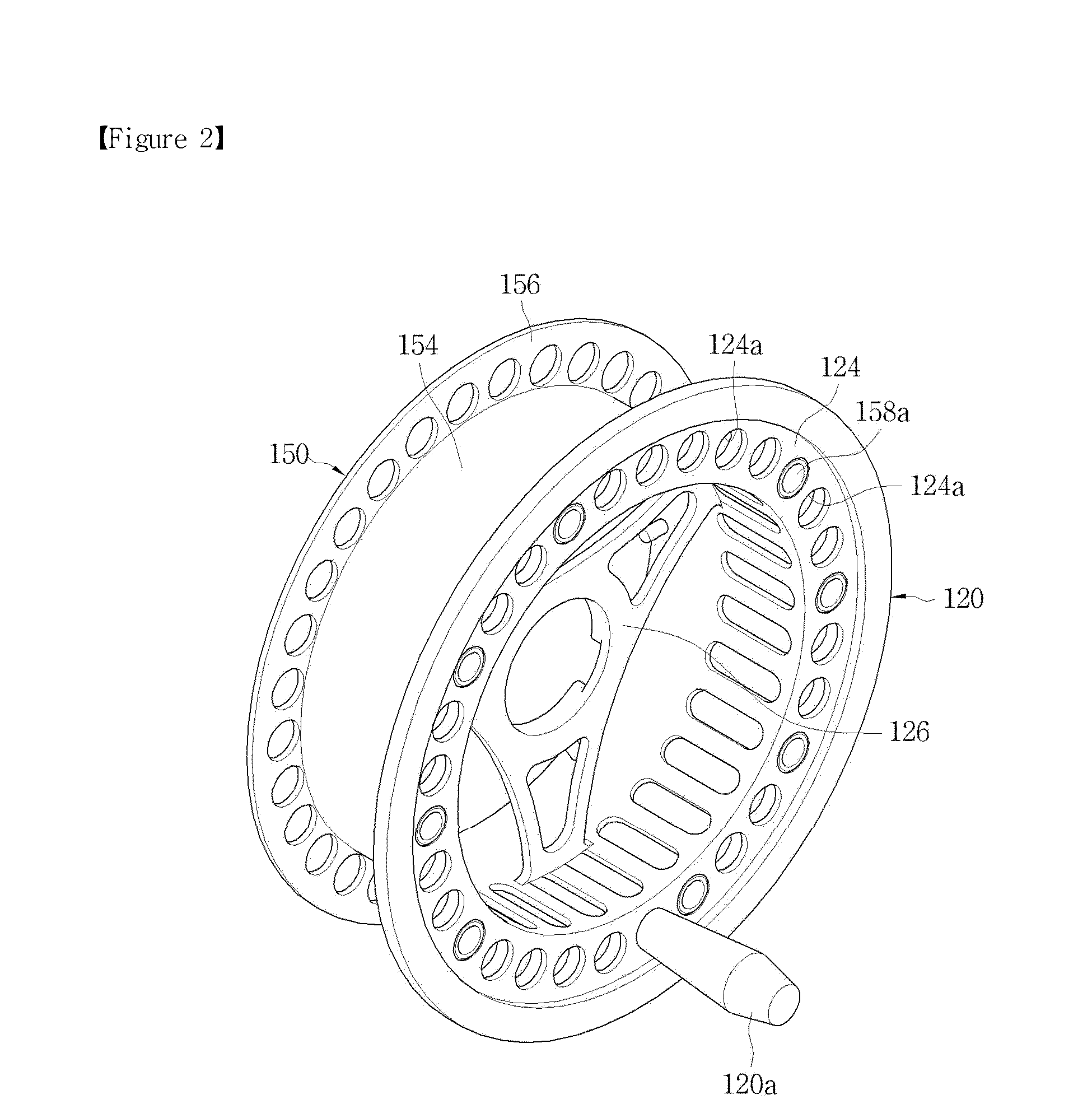
Fly reel spool
A fly reel spool rotatably coupled with a frame mounted on a fishing rod to wind a fish line includes a rotary frame rotatably coupled inside the frame; a winding drum having a ball-catching protrusion on an inner circumference coupling with the rotary frame, the winding drum configured such that the fish line is wound on or unwound from an outer circumference; a locking ball installed in an outer circumference of the rotary frame to protrude from and retract into the rotary frame; elastic means for elastically holding the locking ball so that it protrudes from the outer circumference of the rotary frame, whereby the locking ball is caught by one touch on the ball-catching protrusion on the inner circumference of the winding drum when the rotary frame is coupled with the winding drum, and stopping means for supporting the winding drum and the rotary frame to rotate together.
Owner:KANG SEOK WOON +1
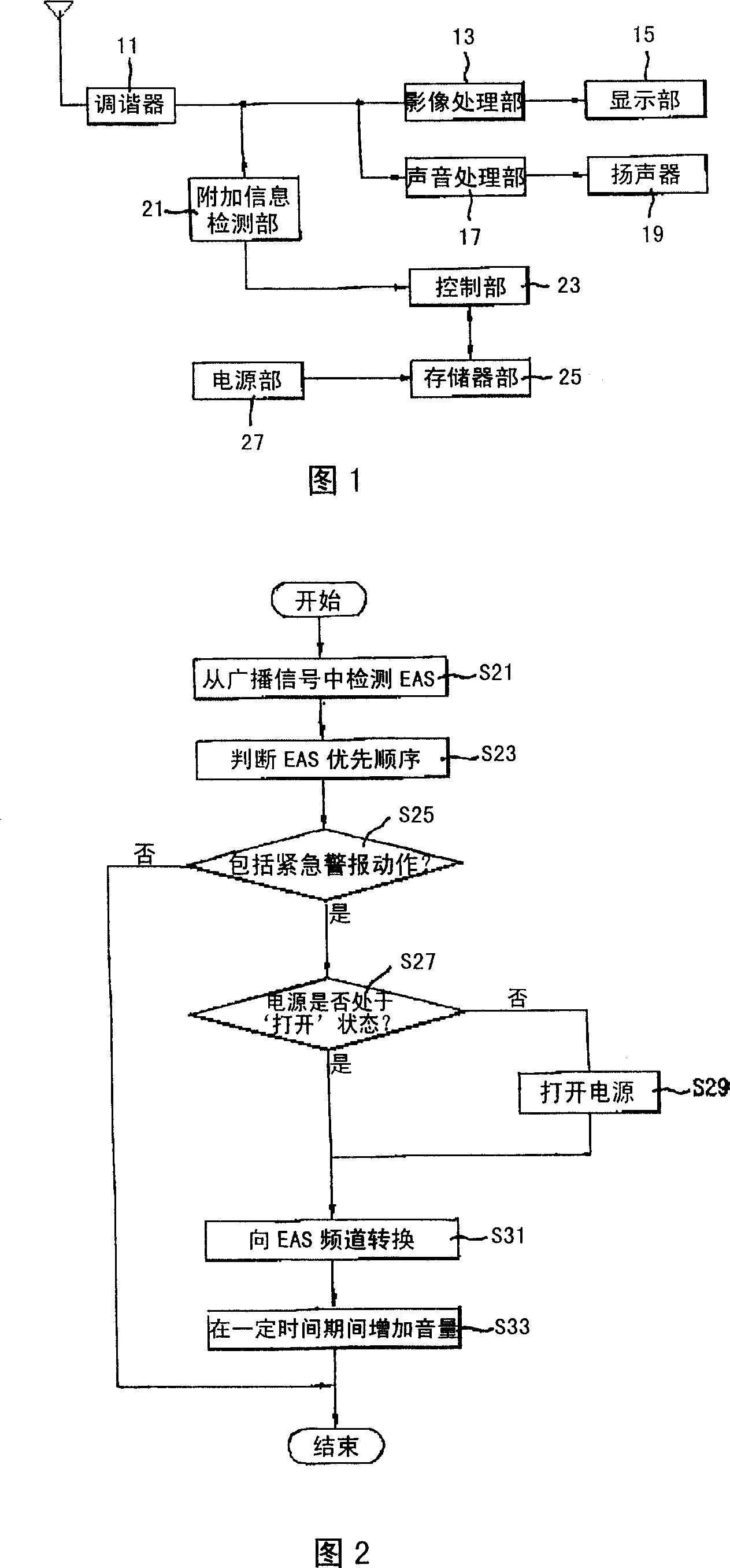
Information processing device and method of image equipment emergency alarm system
InactiveCN101001352AQuick and accurate identificationIncrease volumeSimultaneous/sequential multiple television signal transmissionInformation processingMethod of images
This invention relates to an information process device and a method for red alert system of image devices, in which, the device is composed of the following parts: an additional information test part testing EAS information from broadcast signals and a control part judging if it carries out the red alert operation based on the test EAS information, turning on the supply of the device if so to convert it to the channel appointed by the EAS information and increase volume, the process method includes: 1, searching for the EAS information from broadcast signals, 2, judging if it carries out red alert operation based on the EAS information, 3, turning on the device supply to convert it to the channel appointed by the EAS information if so.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS(NANJING) PLASMA CO LTD
Method for monitoring early treatment response
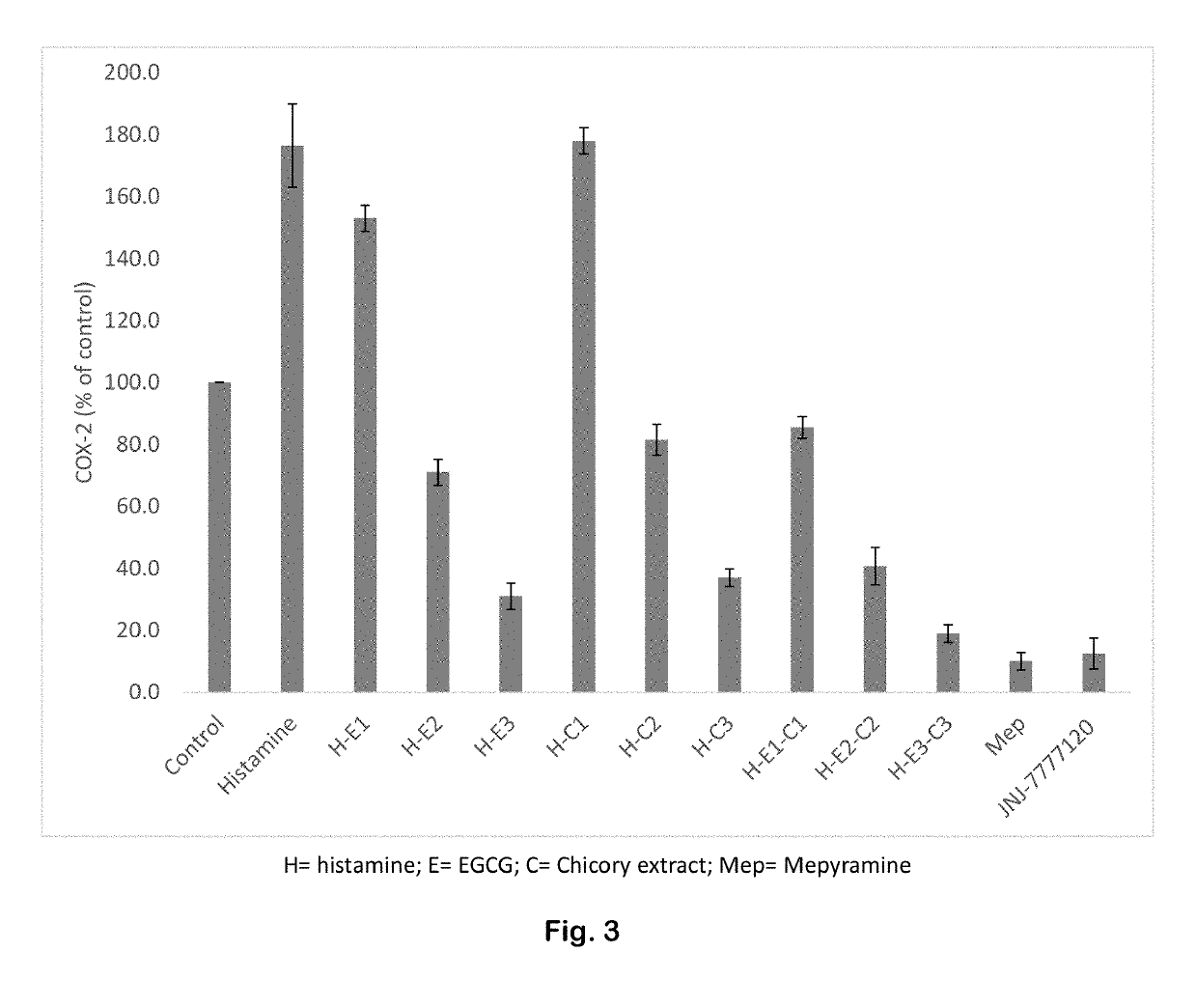
InactiveUS20060222591A1Decrease in amountPositive responseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic chemistryTreatment responseMagnetic resonance spectroscopic
Disclosed is a method for monitoring early treatment response of a cancer treatment comprising measuring by magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), for example, proton MRS, the amount of Choline present in the endomembranes of the cancerous tissue before and after treatment; the treatment comprises administration of a cytotoxic therapy, whereby a decrease in the amount of Choline after treatment is indicative of a positive response. The decrease in the amount of Choline represents the decrease in the internal cell membrane as a result of down regulation of the organelles and their secretory granules and their transport vesicles. Disclosed also is a method for determining effectiveness of a cytotoxic treatment of cancer. In addition, a method for monitoring protein translation related to the cytotoxic treatment of cancer is disclosed.
Owner:RECEPTOMON LLC
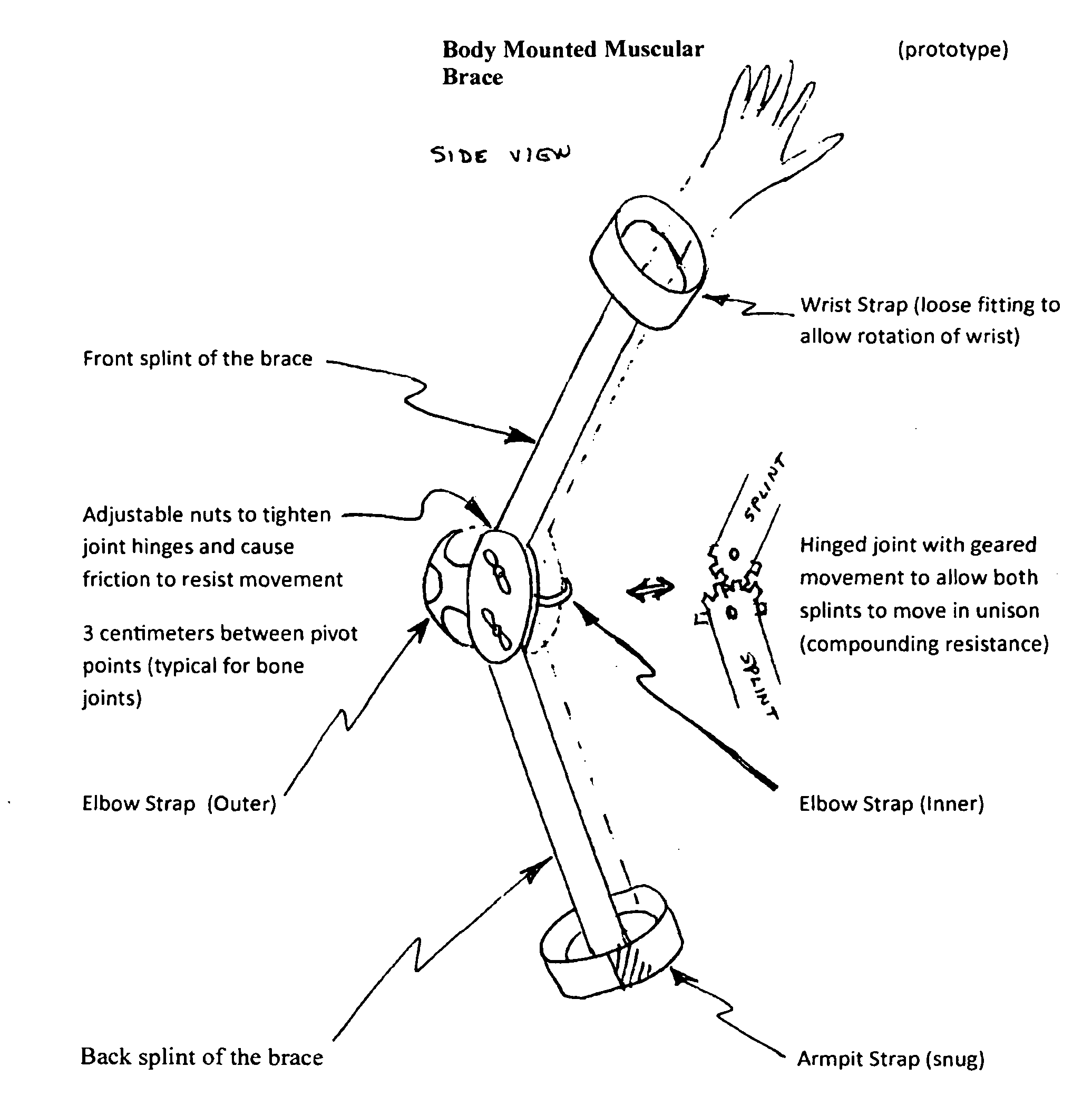
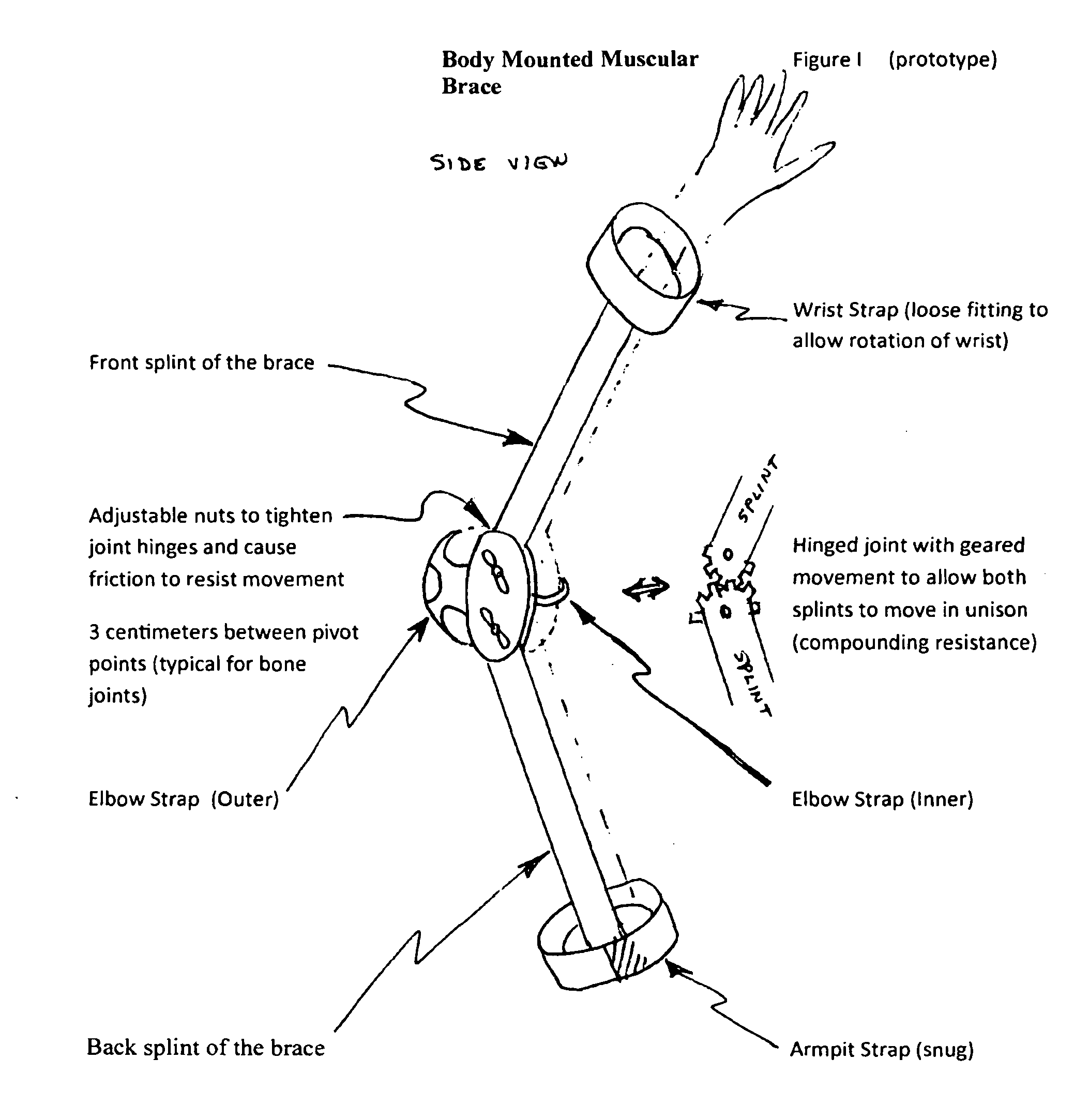
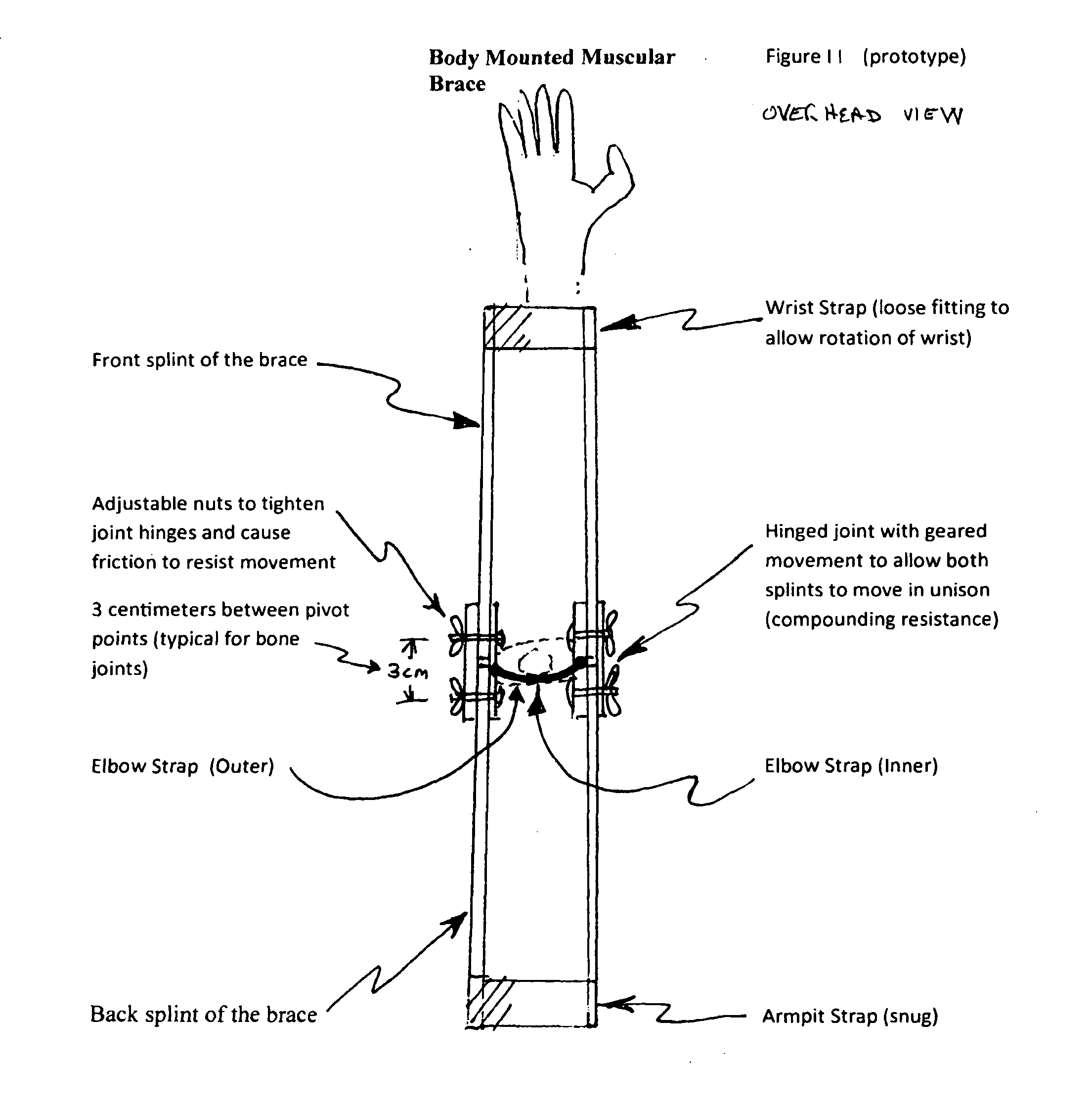
Body Mounted Muscular Brace
InactiveUS20110065553A1Easy to useEasy to removeFrictional force resistorsSacroiliac jointEngineering
A portable, easily body-mounted, light-weight hinged brace to build muscle groups by adding adjustable resistance at the joint
Owner:CERSONSKY STEVEN M
Methods and kits for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer
ActiveUS20160348182A1Accurate diagnosisDetermine the likelihood of developing PDACMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicinePhases of clinical research
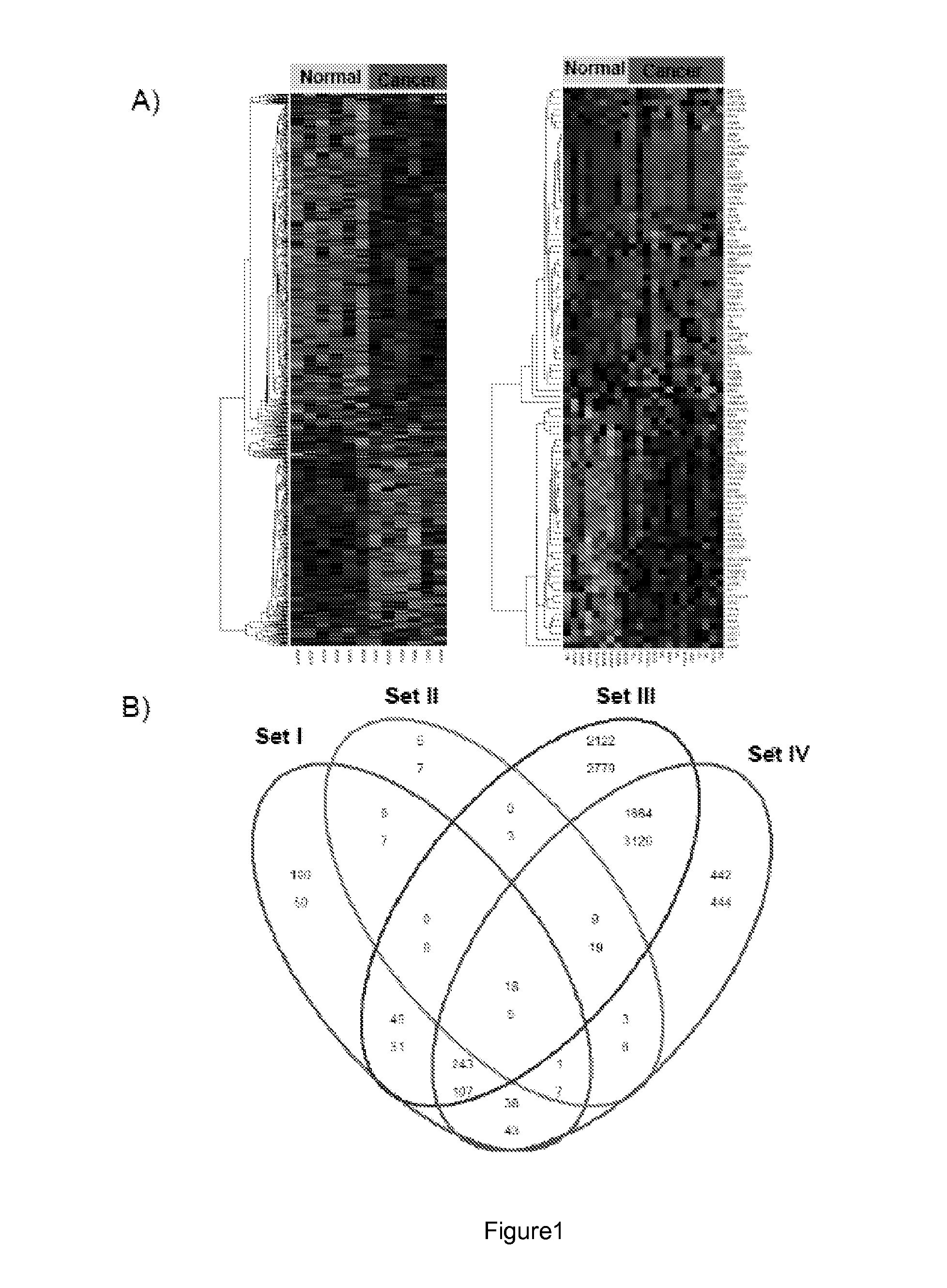
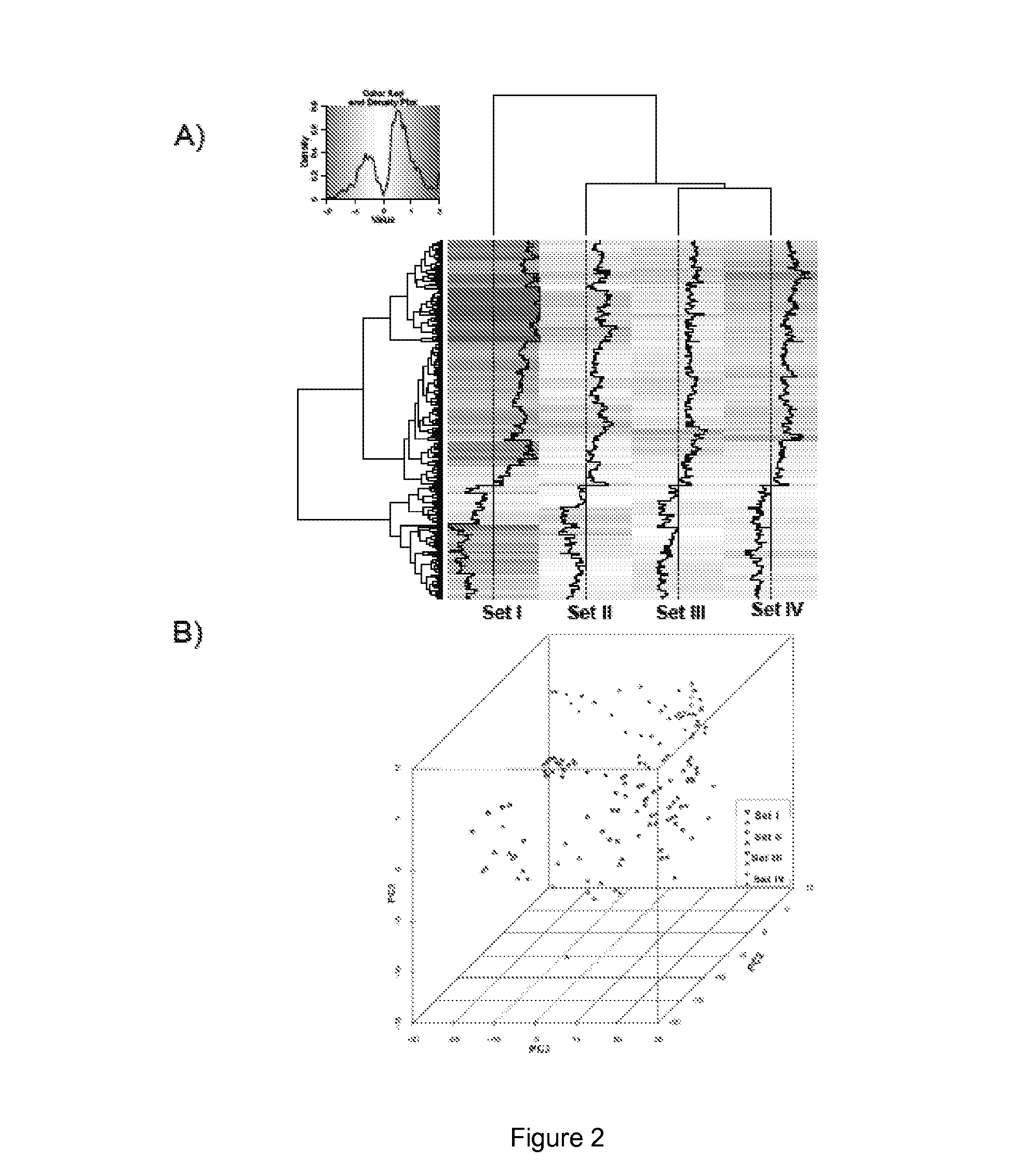
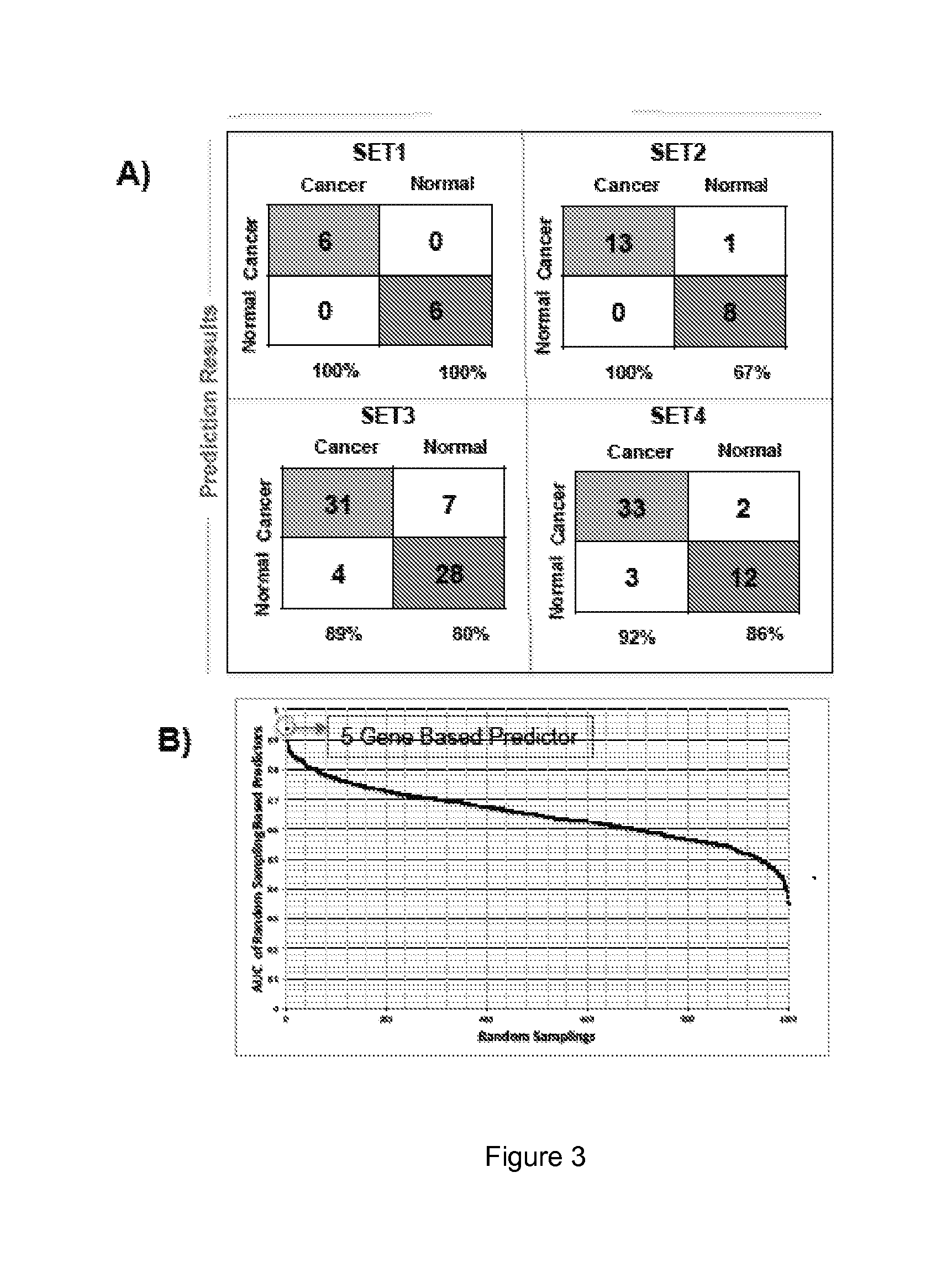
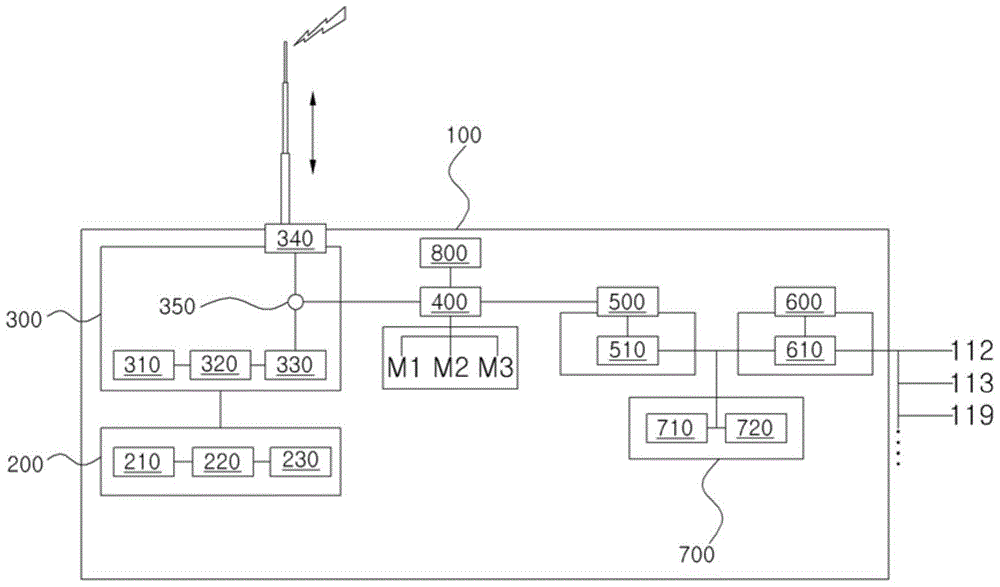
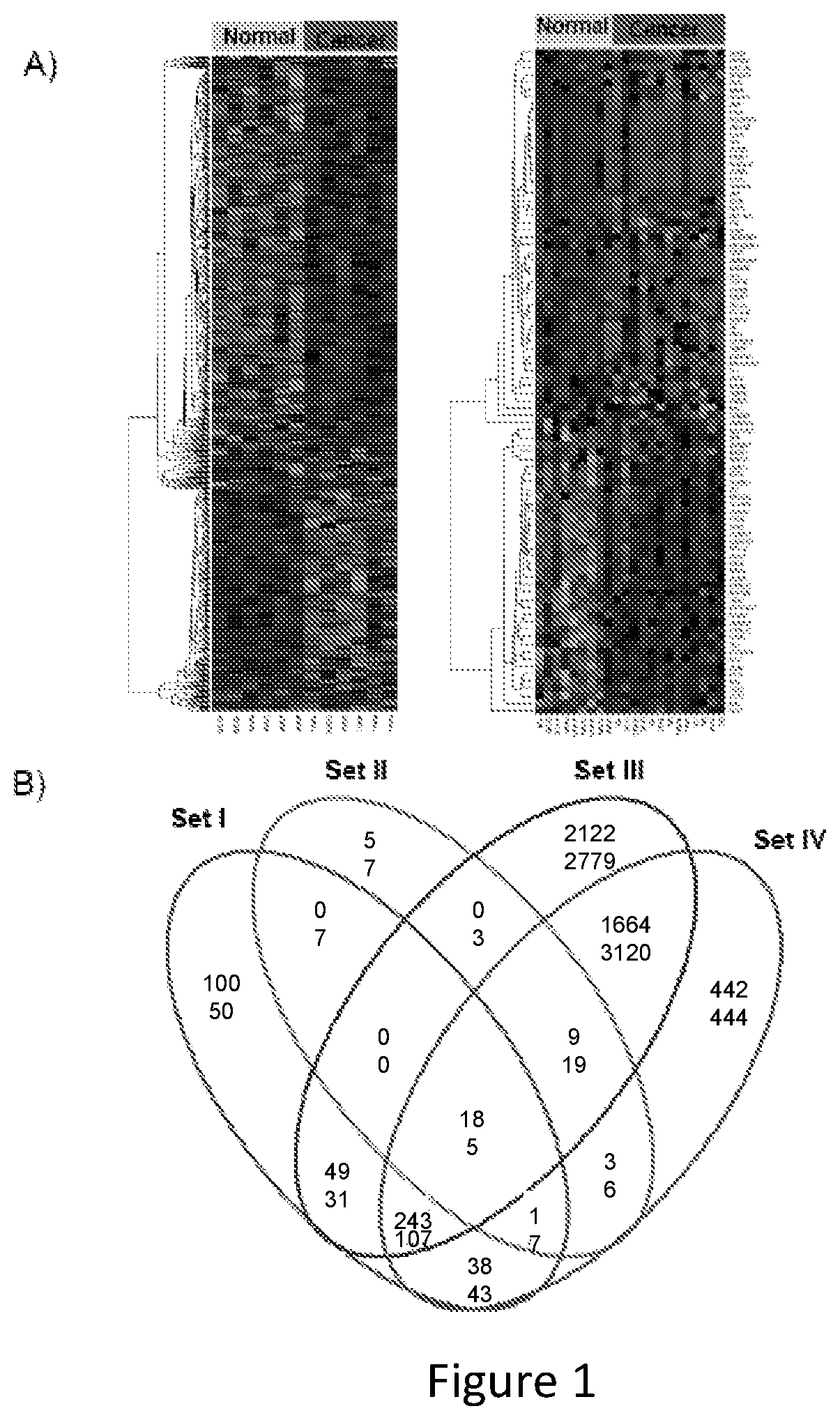
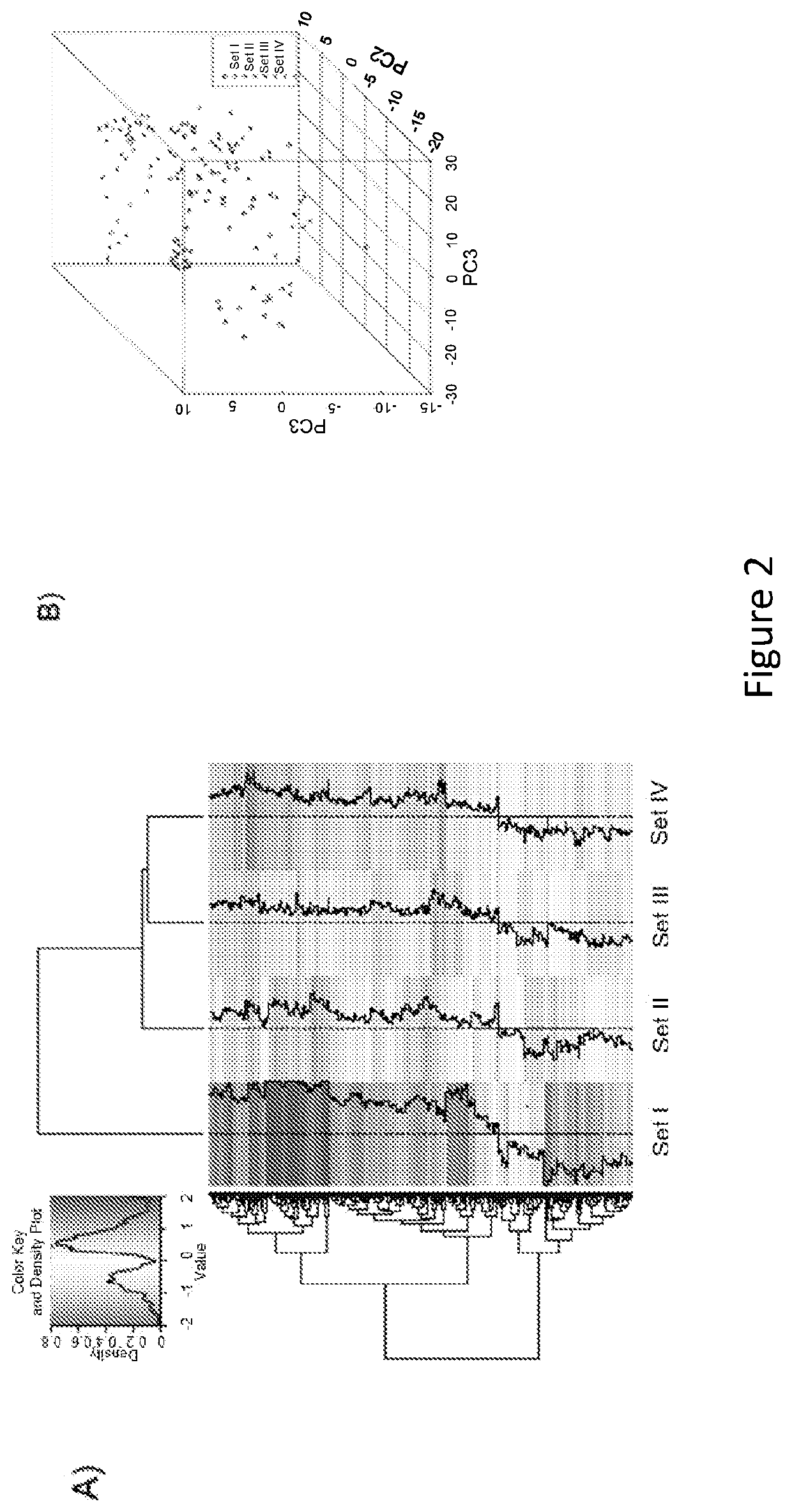
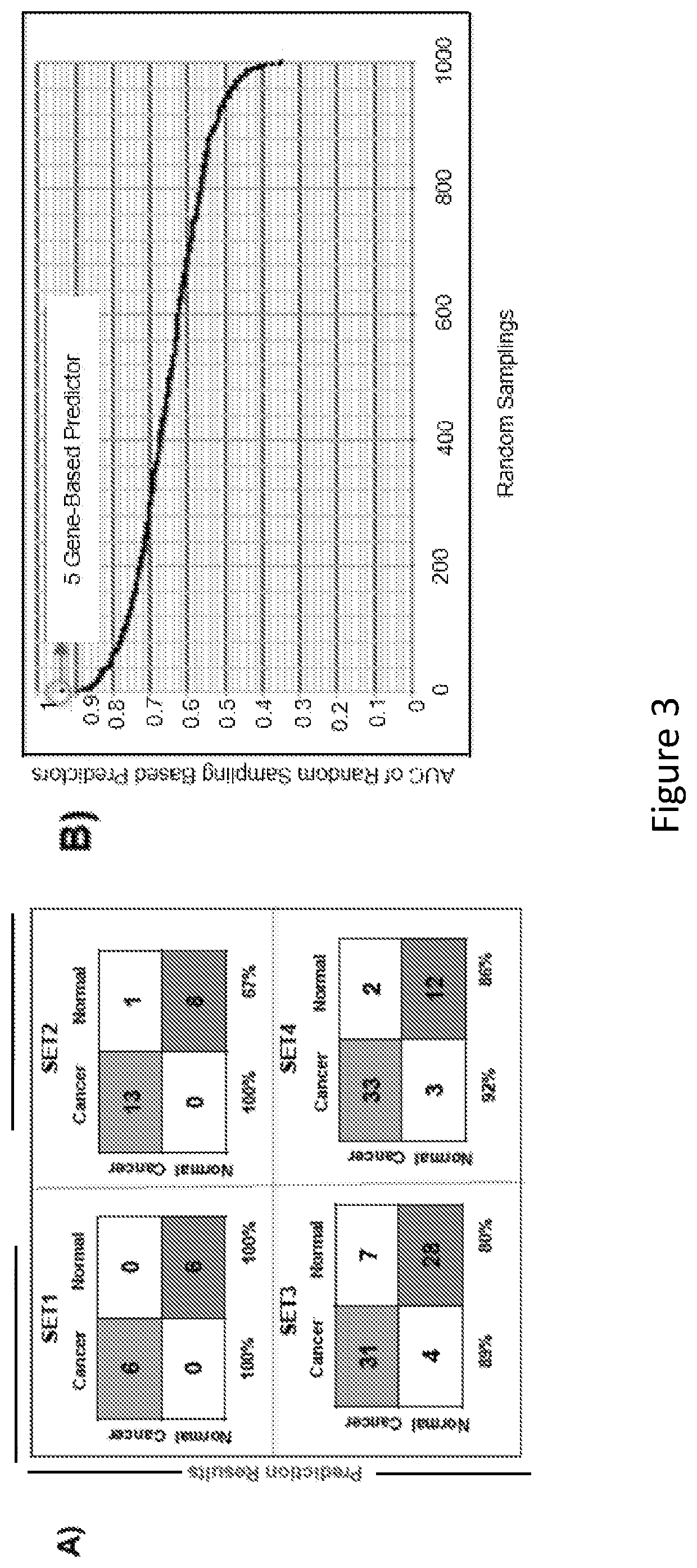
The present disclosure relates to the identification of genes and gene combinations that are correlated with patients having or being predisposed to developing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). In some instances, methods herein utilize panels of 5 or 10 genes to accurately diagnose PDAC, determine the likelihood of developing PDAC, or determine the severity / stages of PDAC. These panels may be used in a molecular diagnostic test.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Refrigerator with fault information leading function
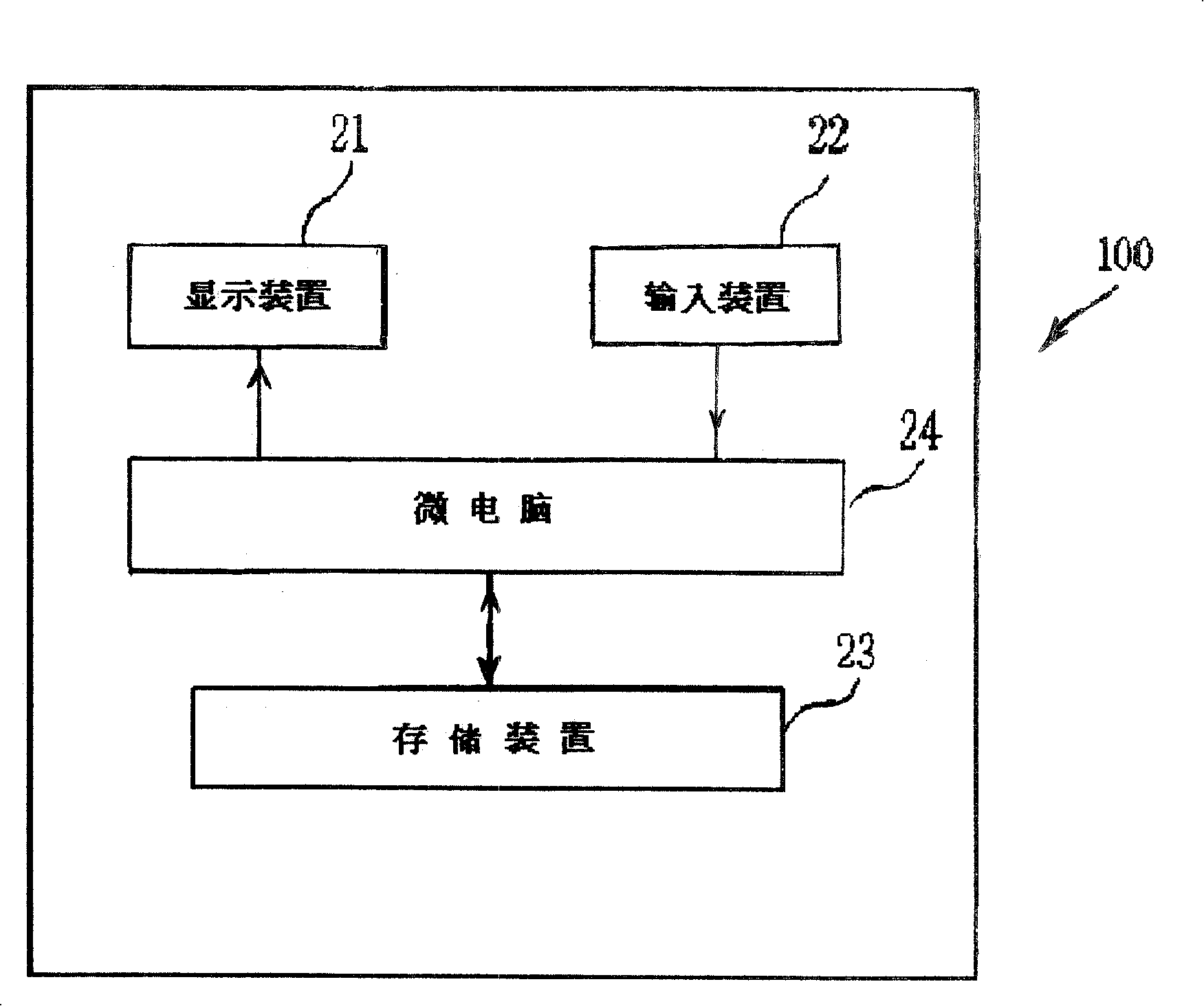
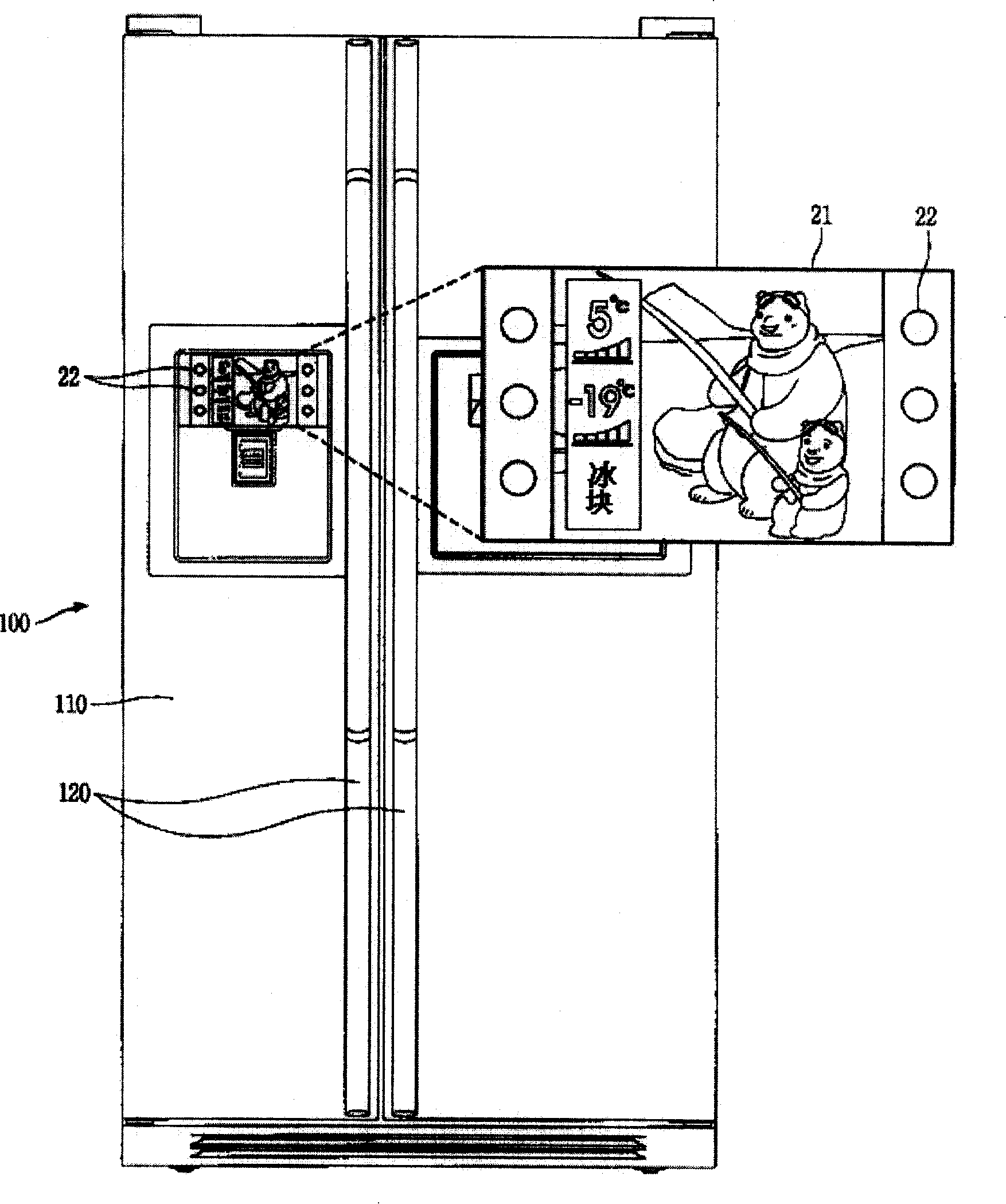
ActiveCN101210756APositive responseFast and correctLighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsDisplay deviceEngineering
The invention relates to a refrigerator with fault information guide function, which can display fault information to a user according to the working condition of the refrigerator, and a refrigerator fault information guide method. The refrigerator comprises a storage device for storing the fault information, a display device for displaying the fault information, and a control device for reading the fault information correspondent to the working condition of the refrigerator from the storage device and then inputting the fault information to the display device for display. The refrigerator fault information guide method comprises of the following steps of: judging the working condition of the refrigerator, judging the fault information correspondent to the working condition of the refrigerator, and displaying the fault information. The invention can display the fault information to the user according to the working condition of the refrigerator; and can allow the user to directly and actively handle the fault information, to accurately and rapidly handle the relevant problems of the refrigerator, and to easily know the functions of the refrigerator.
Owner:TAIZHOU LG ELECTRONICS REFRIGERATOR CO LTD
Electrolyte additive, lithium battery electrolyte and lithium ion battery
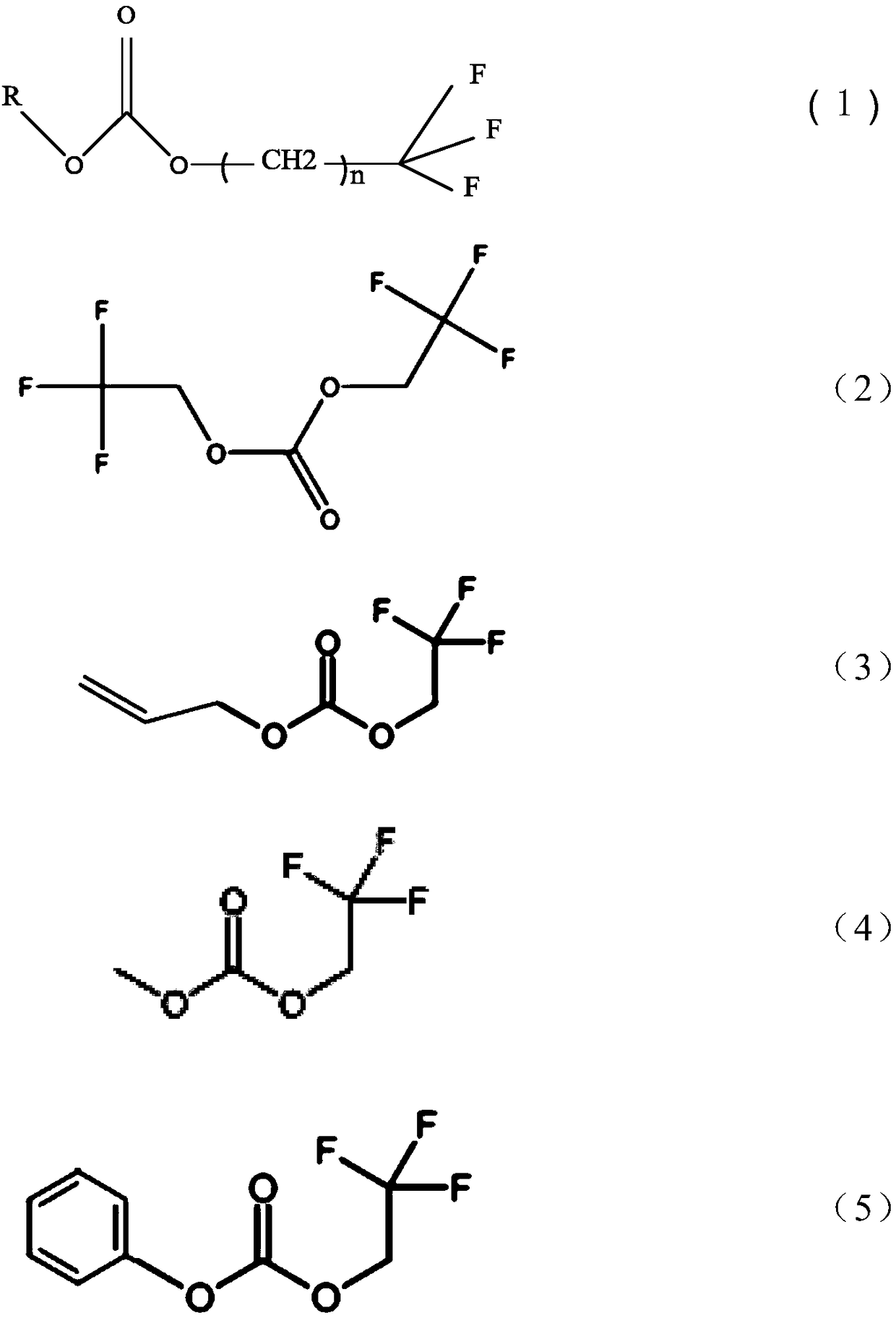
InactiveCN108767315AEnhanced electrochemical stability windowIncrease working voltageSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceOrganic electrolytesDissolutionStructural formula
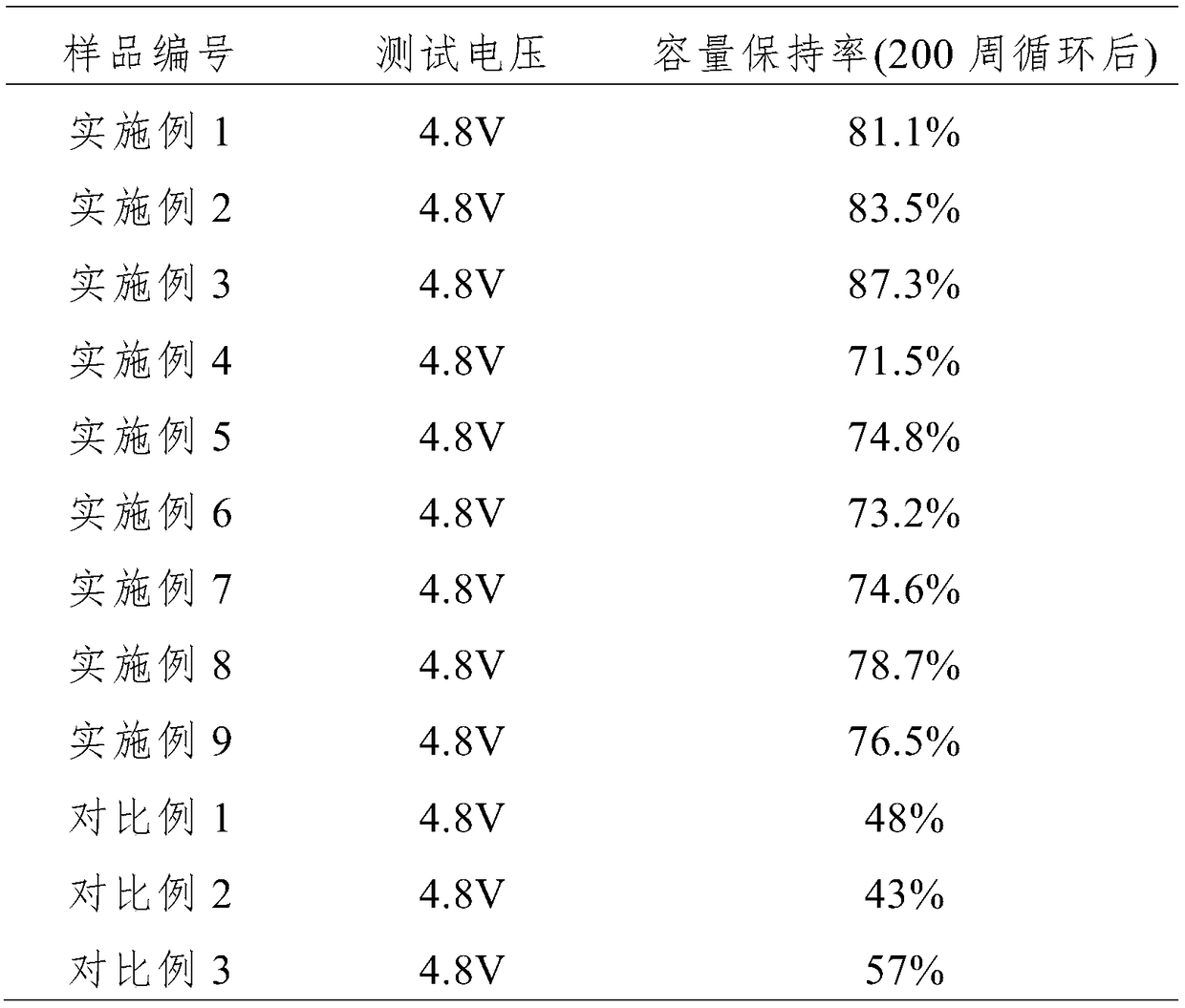
The invention relates to an electrolyte additive, an electrolyte and a lithium battery, and belongs to the technical field of lithium batteries. The electrolyte additive comprises at least one of thecompounds shown in the structural formula I: a formula which is as shown in the specification, wherein R in the structural formula I is one of a fluorine group, a phenyl group, an alkyl group, and analkenyl group, wherein n is an integer of 1 to 5. According to the electrolyte additive, the electrolyte additive is subjected to a decomposition reaction in the electrolyte, and the obtained productgenerates a protective film on the surface of a positive electrode, so that a passivation effect is achieved, dissolution of a metal element in a positive electrode material and the collapse of the positive electrode material structure are inhibited, the electrochemical stability window of the electrolyte is improved, the working voltage range of the electrolyte is widened, and the cycling efficiency of the battery under a high voltage (for example 4.2-5.0V) can be effectively improved.
Owner:桑德新能源技术开发有限公司 +1
GVU shielding box
InactiveCN104989560ACompact and simplified layoutOptimize layoutInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusEngineeringPneumatic valve
The invention discloses a GVU shielding box. The GVU shielding box comprises a shielding box body, shielding box end covers, a gas detecting sensor interface flange, a gas outlet flange, a gas inlet flange, a scavenging port flange and a pneumatic valve gas inlet and feedback interface, wherein openings are formed in the two ends of the shielding box body, the shielding box end covers cover the openings of the two ends of the shielding box body to form a containing space for containing a gas valve, the gas detecting sensor interface flange is used for installing a gas detecting sensor, the gas outlet flange and the gas inlet flange are used for connecting the GVU shielding box with an engine and a gas station, a valve in the GVU shielding box and gas in a pipeline can be connected with the outer side of a cabin through the scavenging port flange, and the pneumatic valve gas inlet and feedback interface conducts control and control feedback on the valve in the shielding box body. The GVU shielding box is high in integrity and compact and attractive in structure, makes the gas valve of the engine compactly and simply arranged, makes a gas supply system pipeline simply arranged, is attractive in overall appearance and reduces potential sealing leakage hazards.
Owner:GUANGXI YUCHAI MASCH CO LTD
Composition and Method for Improving Sleep Duration and Quality
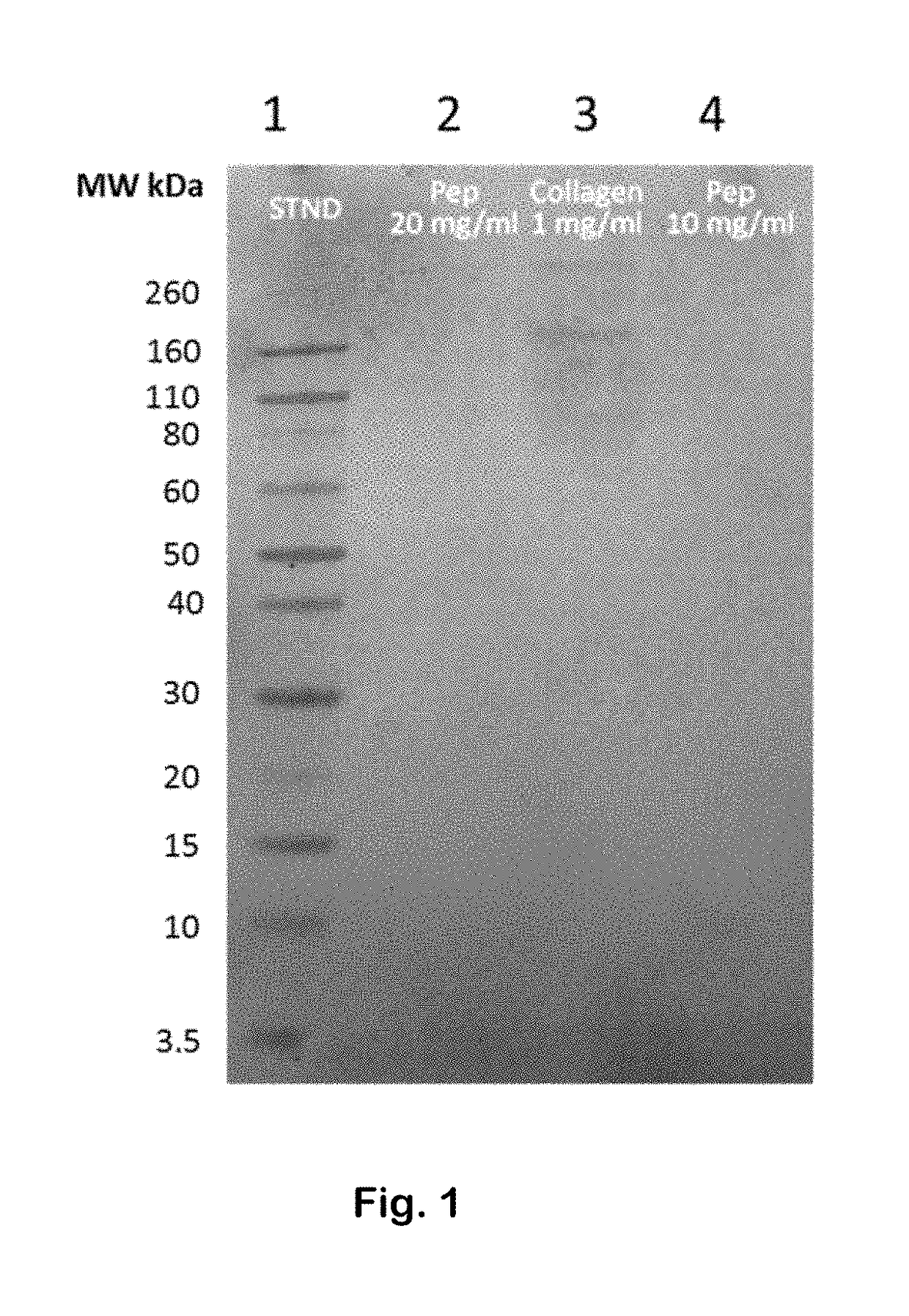
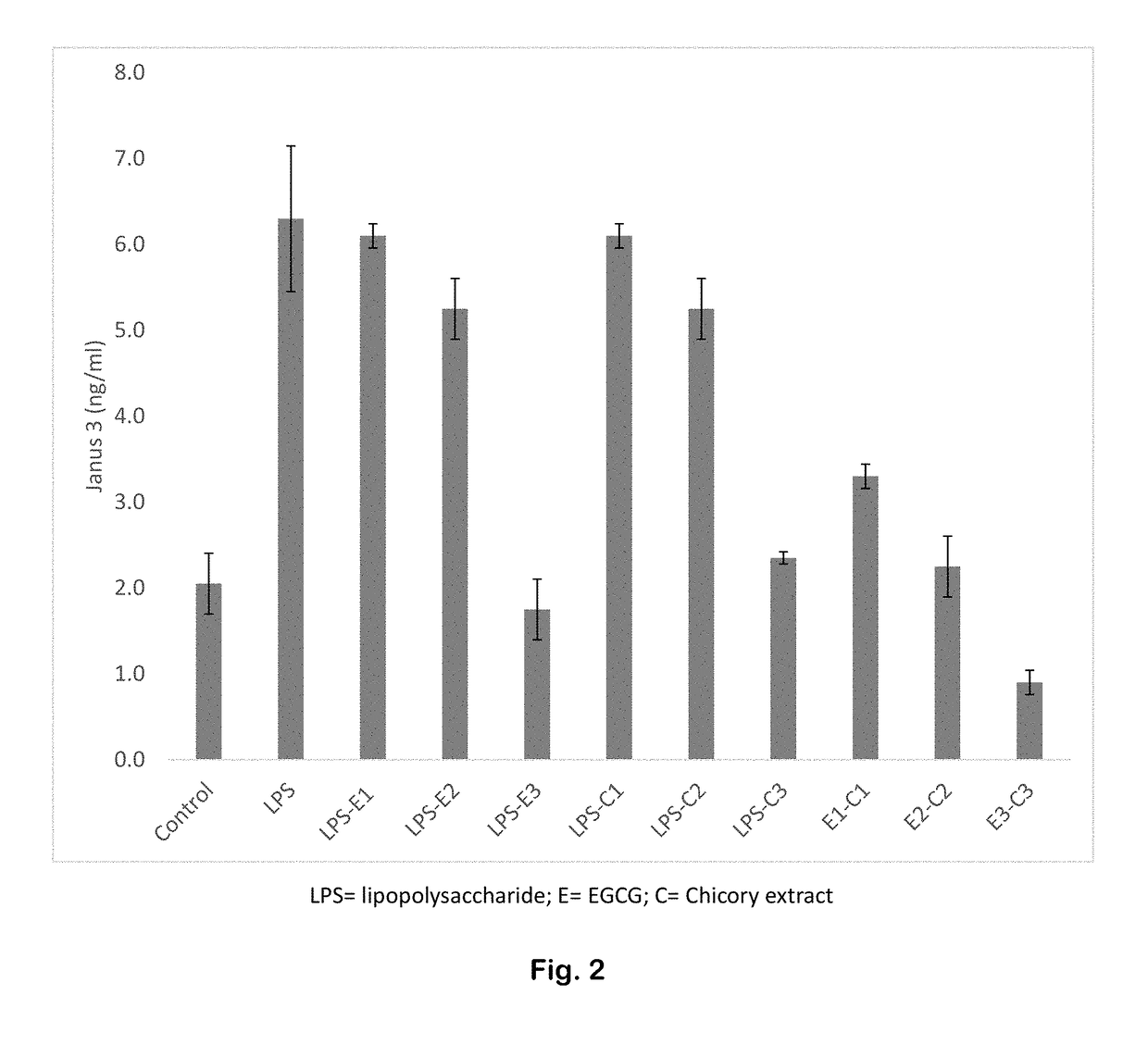
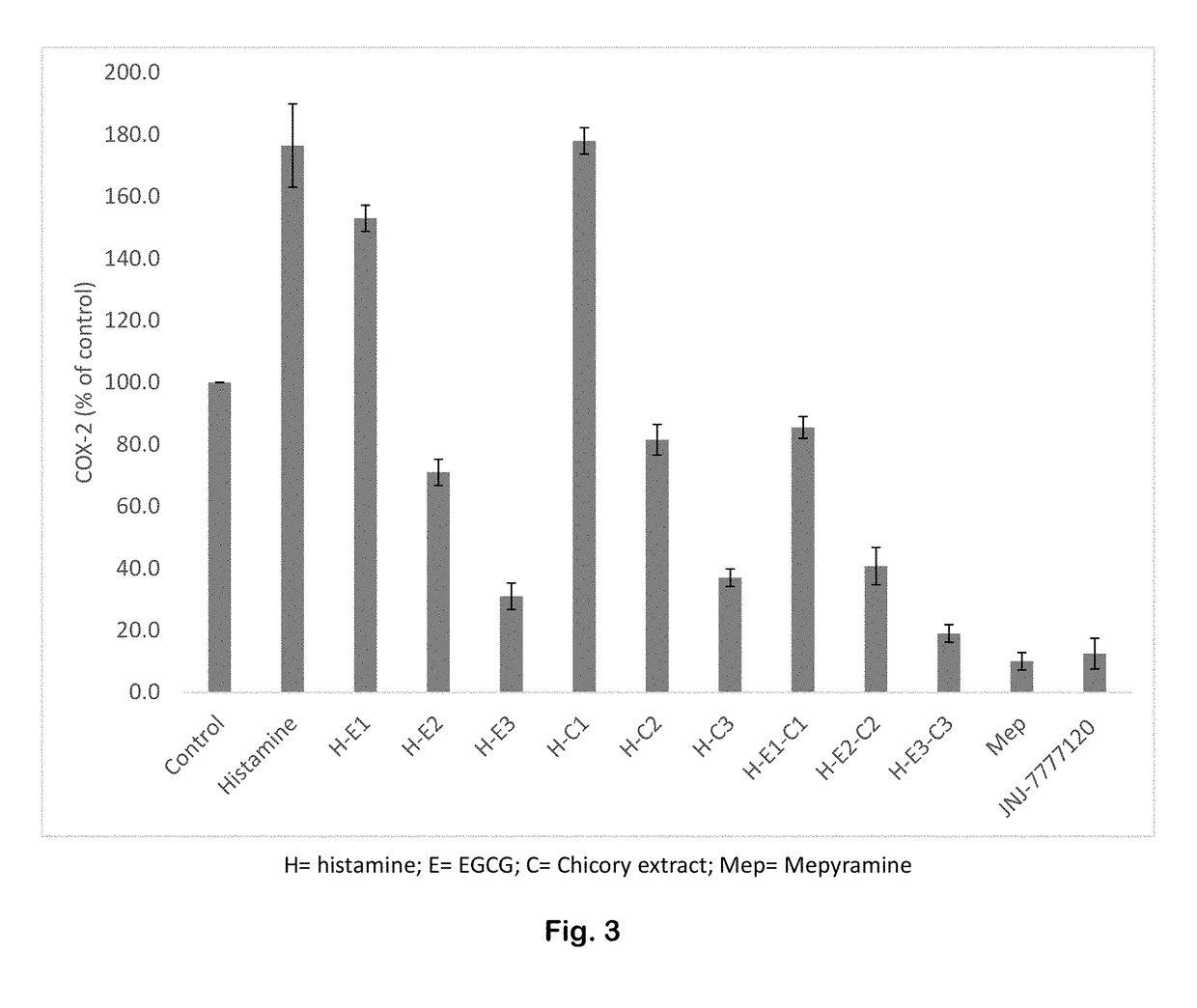
ActiveUS20180021411A1Large dropout ratePoor responsePeptide/protein ingredientsHeavy metal compound active ingredientsSide effectPhysiology
An intervention for sleep disorders comprises: collagen, a gelatin peptide, or the amino acid glycine; L-theanine; lactucopicrin, deoxylactucopicrin, or another lactucopicrin derivative; hyaluronic acid; epigallocatechin gallate; and quinic acid. The intervention helps regulate pro-inflammatory biomarkers that are often associated with insomnia development and progression. These biomarkers include cytokines and enzymes associated with tryptophan degradation. Inhibition of these enzymes and cytokines improves tryptophan availability and sleep quality, and allows individuals to sleep better with fewer side effects. The composition promotes high-quality, deep sleep.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Case of personal terminal device with electric shocking function
InactiveCN104767842AProtection from external shocksPositive responseTelephone set constructionsTerminal equipmentElectric power
The invention discloses a case of personal terminal device with an electric shocking function. The case comprises a case main body wrapping a personal terminal, a shocking part, an operation part, a multimedia part and a communication part. The shocking part is used for storing, allowing the case main body to be protruding, and receiving and amplifying electric power from a power supplying part of the case main body so as to allow the power supplying part to generate strong current. The operation part connects the power supplying part, the shocking part and a cell phone terminal and allows the shocking part to perform accelerated movement in a dangerous occasion. The multimedia part is arranged on one side of the case main body so as to collect sound or images of the scene according to the accelerated movement. The communication part connects the shocking part, the operation part, the power supplying part and the personal terminal with power and transmits the sound and the images collected by the multimedia part, and the current positions to a specific mechanism during the accelerated movement of the shocking part. The case has a function of protecting the personal terminal against external shocking. In addition, during the dangerous occasion, a terminal owner can protect and defend herself or himself with the case.
Owner:李和贞 +1
Morphology engineering of conductive metallic nanoparticles capped with an organic coating
ActiveUS10663420B2Broaden spectrumPositive responseWithdrawing sample devicesNanosensorsWater vaporNanoparti cles
The present invention is directed to a sensor having continuous and discontinuous regions of conductive metallic nanoparticles capped with an organic coating which enables the detection of volatile organic compounds and / or water vapor. Continuous regions may exhibit a positive response upon exposure to volatile organic compounds and to water vapor, while discontinuous regions exhibit a negative response upon exposure to water vapor larger than the positive response of the continuous region.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
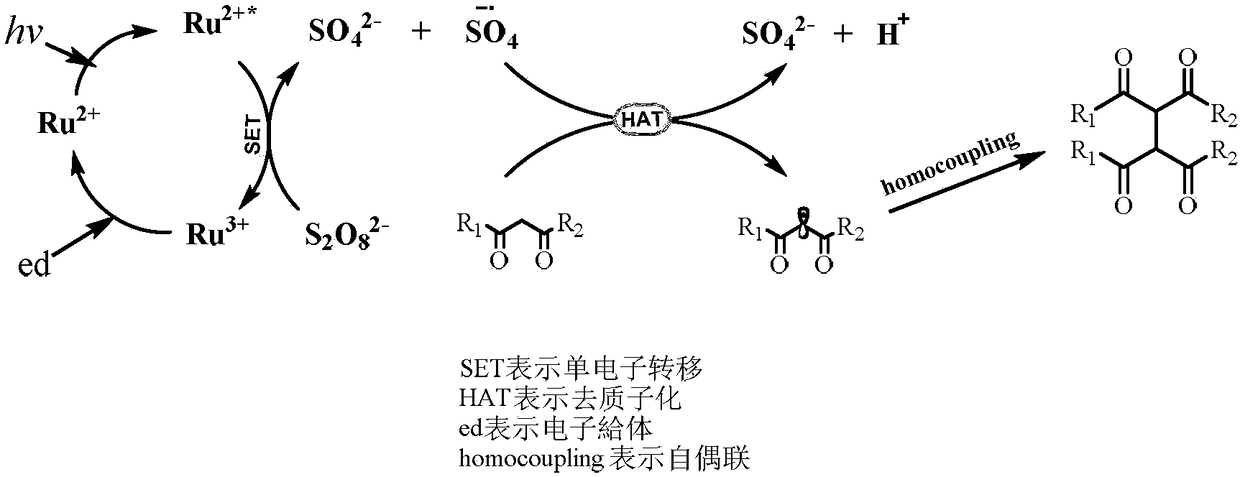
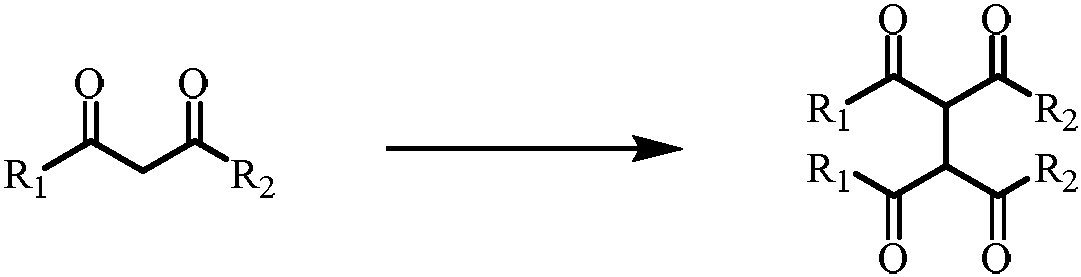
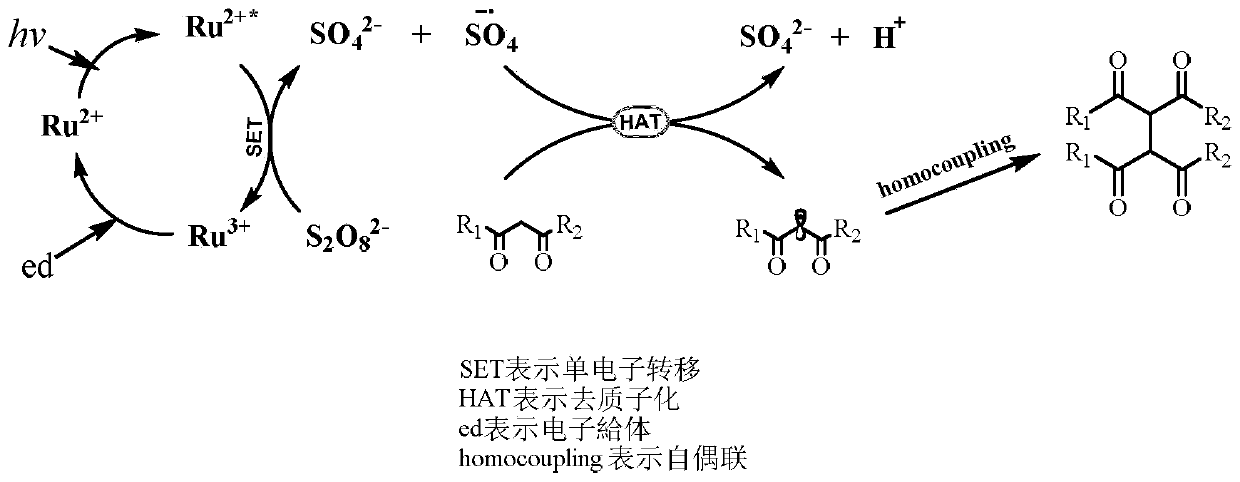
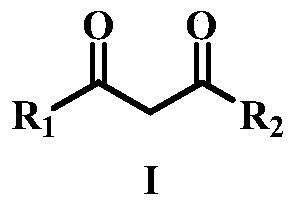
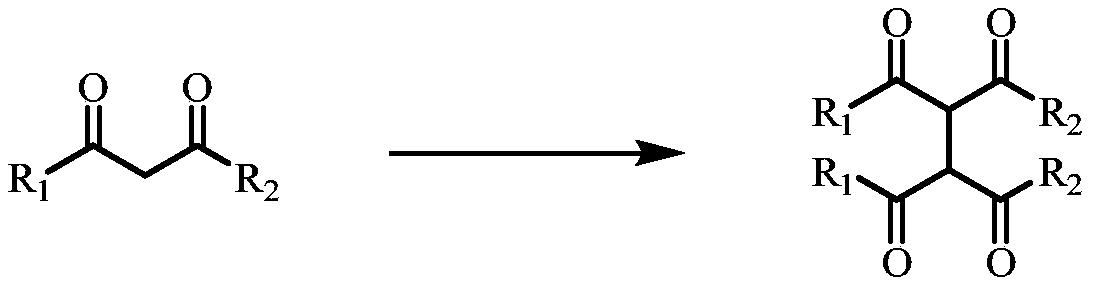
Method of dehydrogenation self-coupling of 1,3-dicarbonyl compound with visible light catalysis
ActiveCN108440291ARealize the coupling reactionHigh hydrogen abstraction efficiencyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCouplingDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a method of dehydrogenation self-coupling of a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound with visible light catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of (1) dissolving a photocatalyst,a peroxide and the 1,3-dicarbonyl compound into a solvent, and adding 1,4-dioxane to obtain a reaction solution; and (2) illuminating the reaction solution obtained in the step (1) with visible light, and performing separation after reaction is finished to obtain a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound dehydrogenation self-coupling product. By adopting the method provided by the invention, adopted visible light catalysis realizes coupling reaction of a dicarbonyl compound under the relatively mild conditions and responds current green chemical idea, and coupling of the dicarbonyl compound is finished witha more scientific and environment-friendly method.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
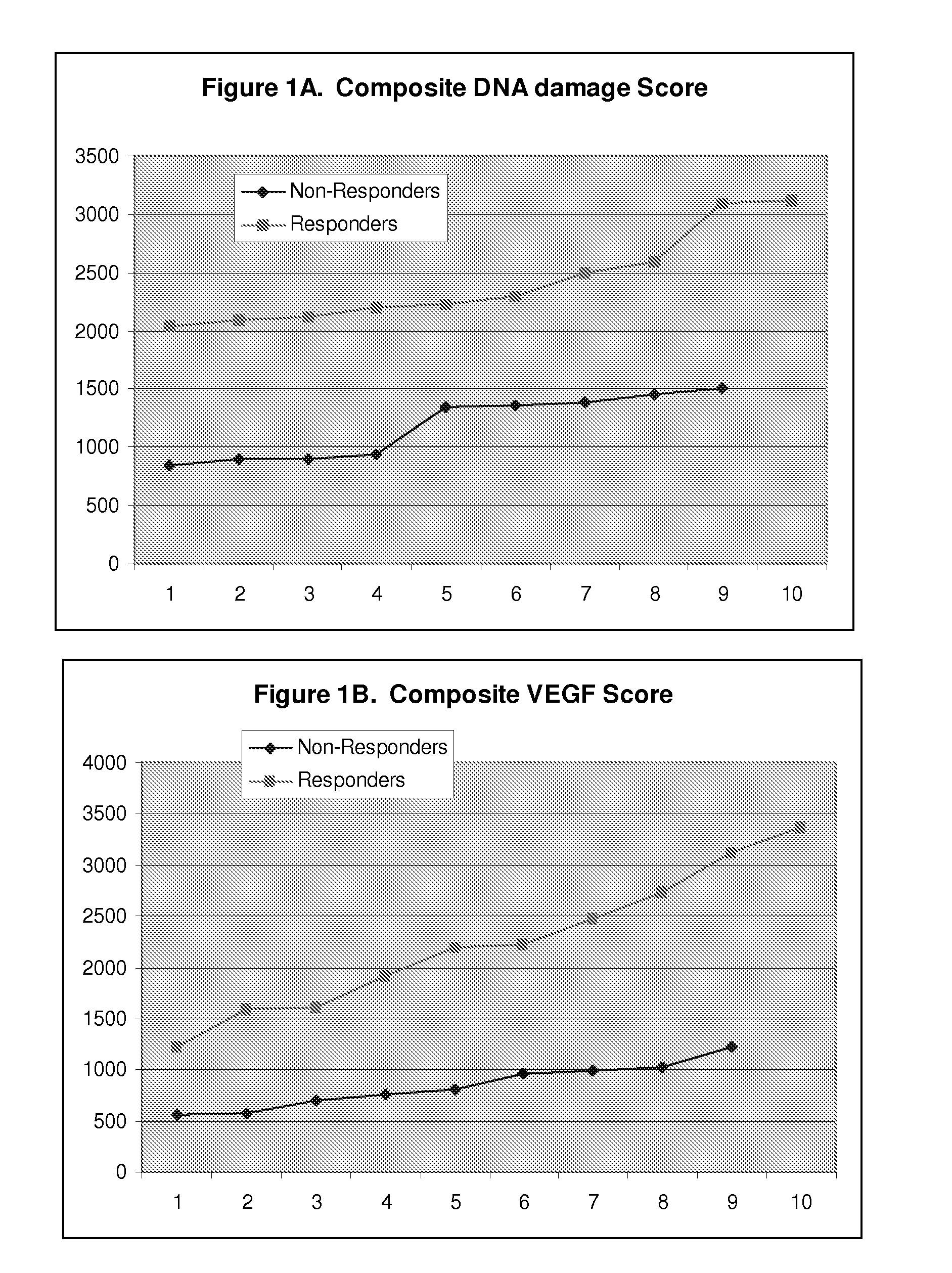
Methods for predicting survival in metastatic melanoma patients
InactiveUS9410205B2Prolong survival timeStimulate immune responseMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDifferential survivalAbnormal tissue growth
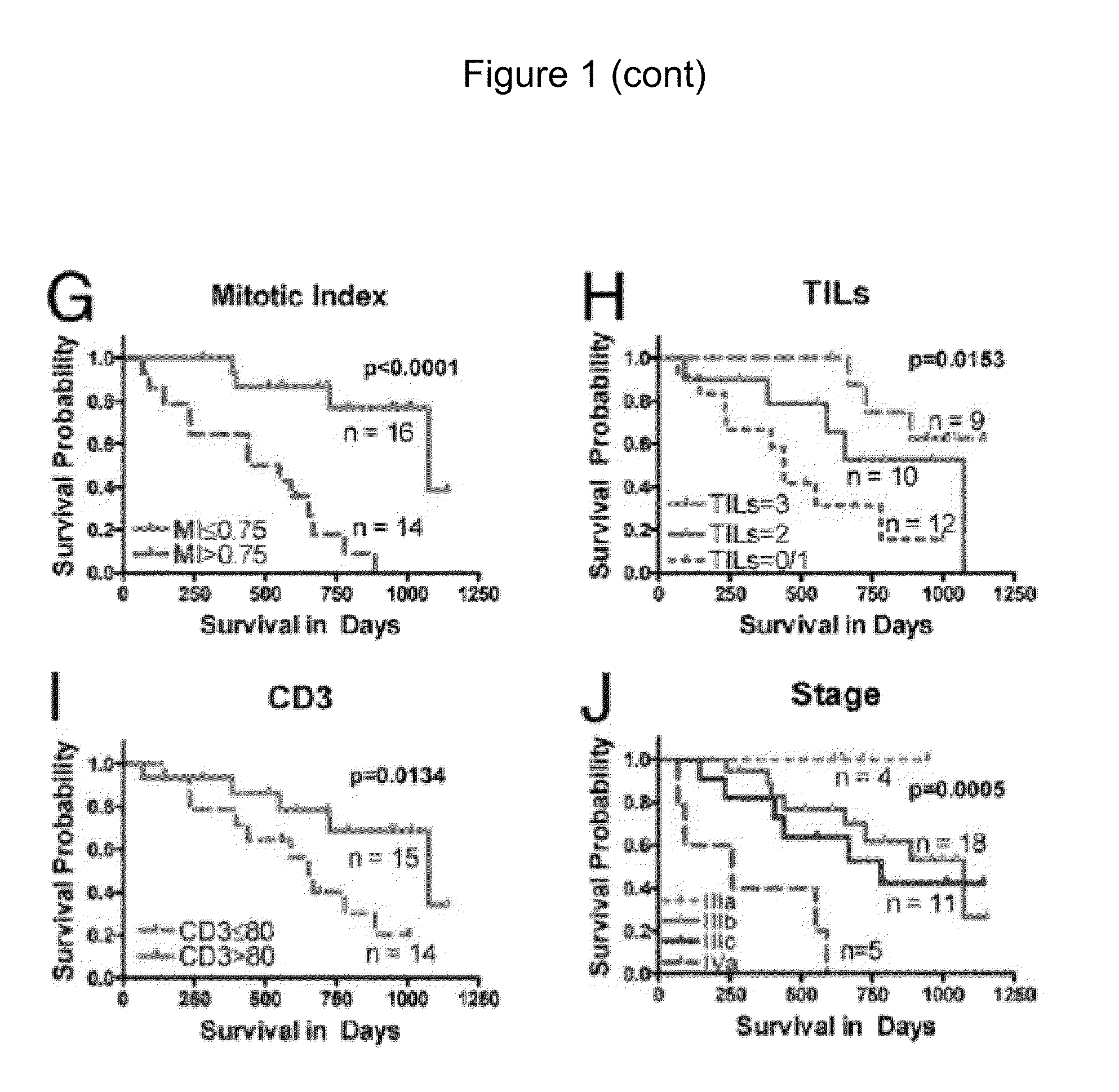
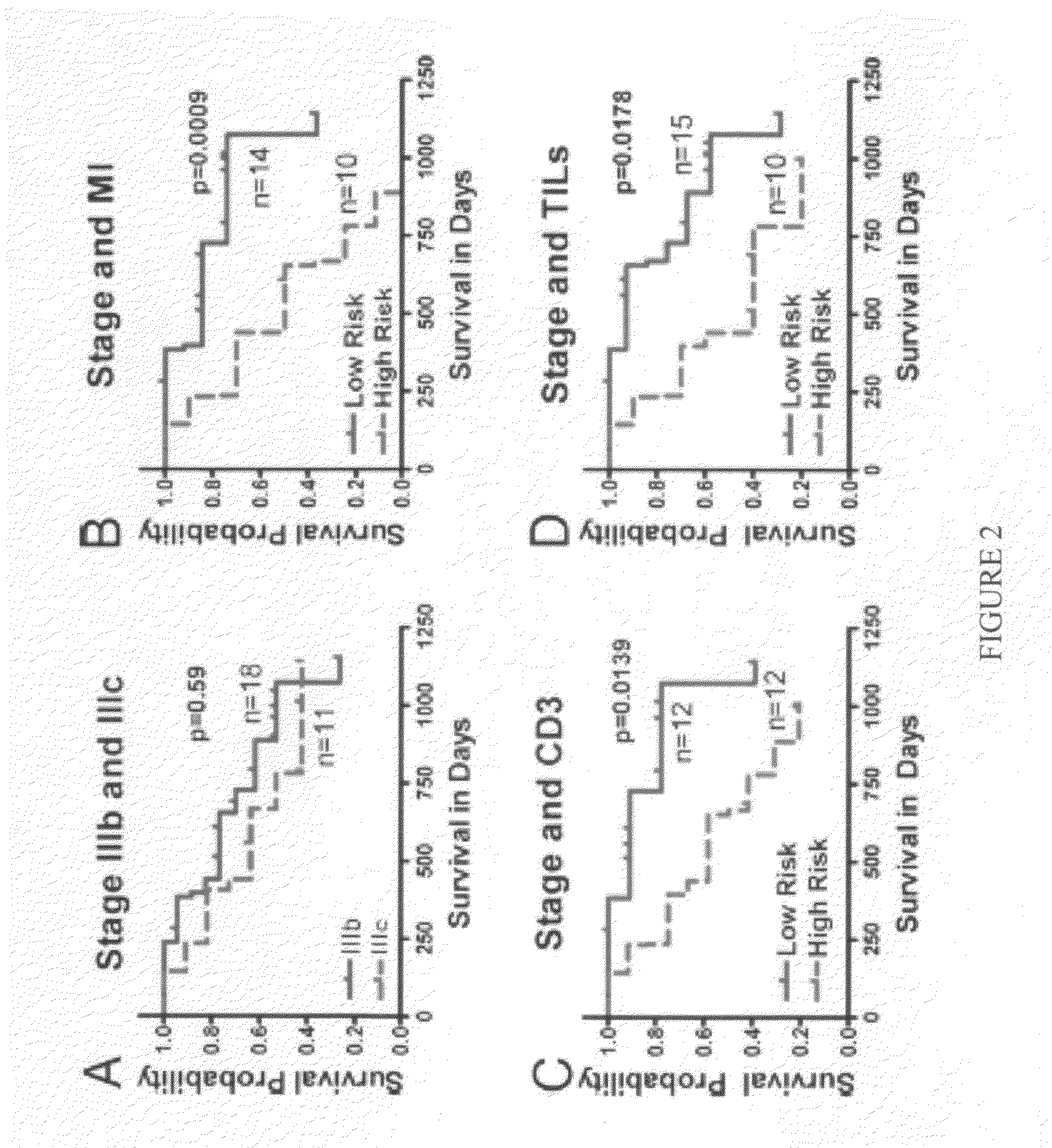
Cellular and genetic signatures and methods of using same for subcategorizing stage III melanoma tumors are described herein. The signatures and methods are particularly useful with regard to establishing more distinct criteria on which basis to differentiate stage IIIB and IIIC melanoma patients. Assessment of the cellular and genetic signatures of a melanoma sample using methods described herein yields information on which basis differential survival duration and sensitivity to various cancer therapies can be predicted for a Stage IIIB or Stage IIIC melanoma patients. As described herein, gene expression profiling, determination of mitotic index (MI), and quantification of tumor infiltrating leukocytes (TILs) and CD3+ cells in metastatic lesions may be utilized to predict or assess drug response, drug sensitivity, and clinical outcome in metastatic melanoma patients.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Portable terminal case having electric shock function with additional fingerprint recognition
InactiveCN105873465APositive responseElectric shock equipmentsOther accessoriesBiological activationElectric shock
The present invention relates to a portable terminal case having an electric shock function with additional fingerprint recognition, wherein the case is adapted not only to effect the intrinsic function of a case of protecting a portable terminal from external shocks but also to positively protect and defend the user of the portable terminal from risk factors during an emergency situation. The case is characterized in that it comprises: a shock unit which is provided so as to be able to be housed in and project from one side of a main body of the case for housing the main body of a portable terminal, and which generates a high current by amplifying a supply of electrical energy received from a power-supply unit provided in the main body of the case; an operating unit which activates the shock unit during an emergency situation; a multimedia unit which is provided on one side of the main body of the case, and which either directly collects sound or an image(s) of the situation when the shock unit is activated by means of the operating unit, or uses a microphone and a camera incorporated in the portable terminal so as to effect control in such a way as to collect sound or an image(s) of the situation when the shock unit is activated by means of the operating unit; and a communication unit for sending, to a specific institution, the current location of the portable terminal together with the sound or image(s) collected by the multimedia unit during activation of the shock unit.
Owner:李和贞
Methods and kits for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer
ActiveUS10604809B2Accurate diagnosisDetermine the likelihood of developing PDACMicrobiological testing/measurementAdenocarcinomaPancreas
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
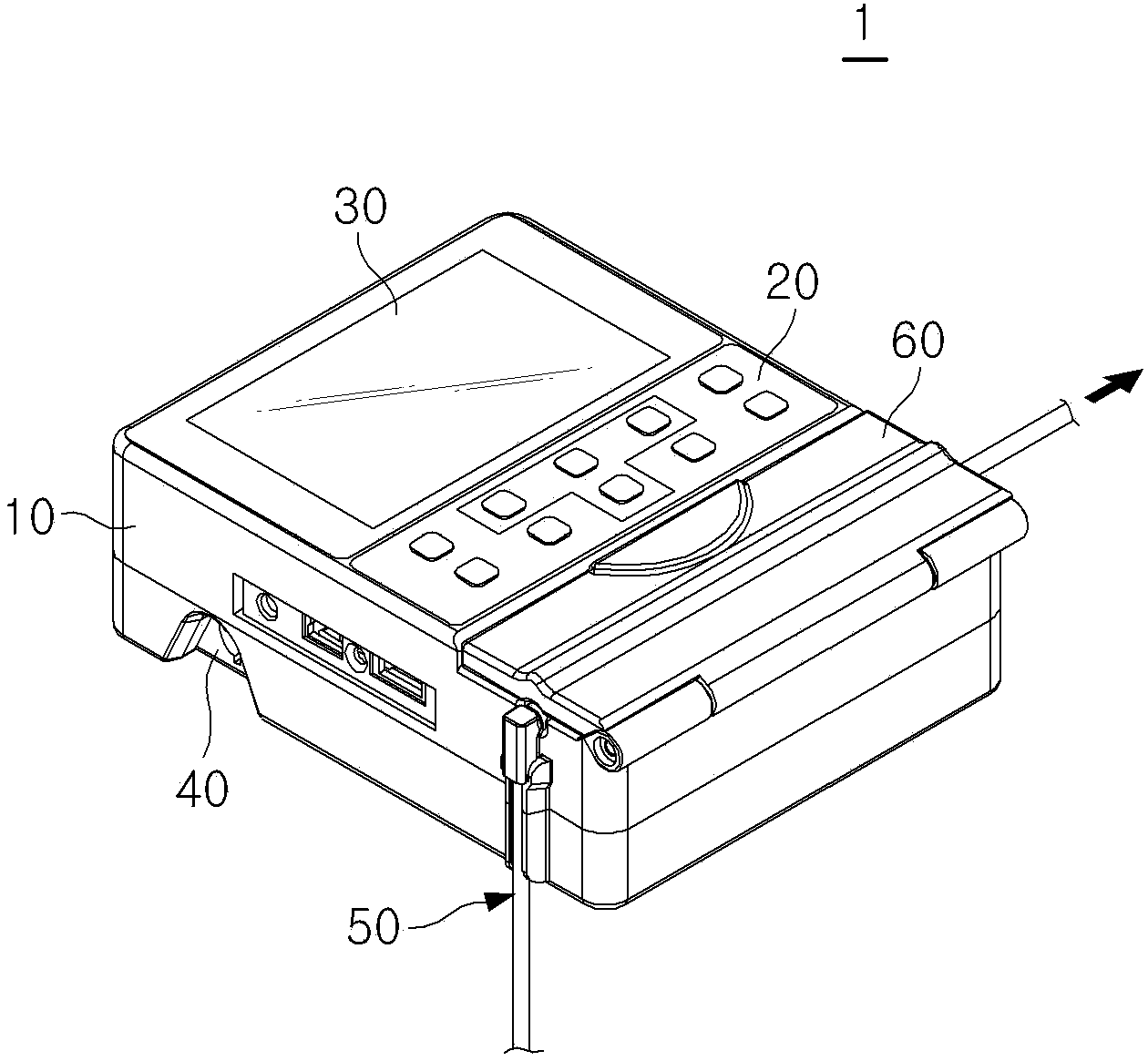
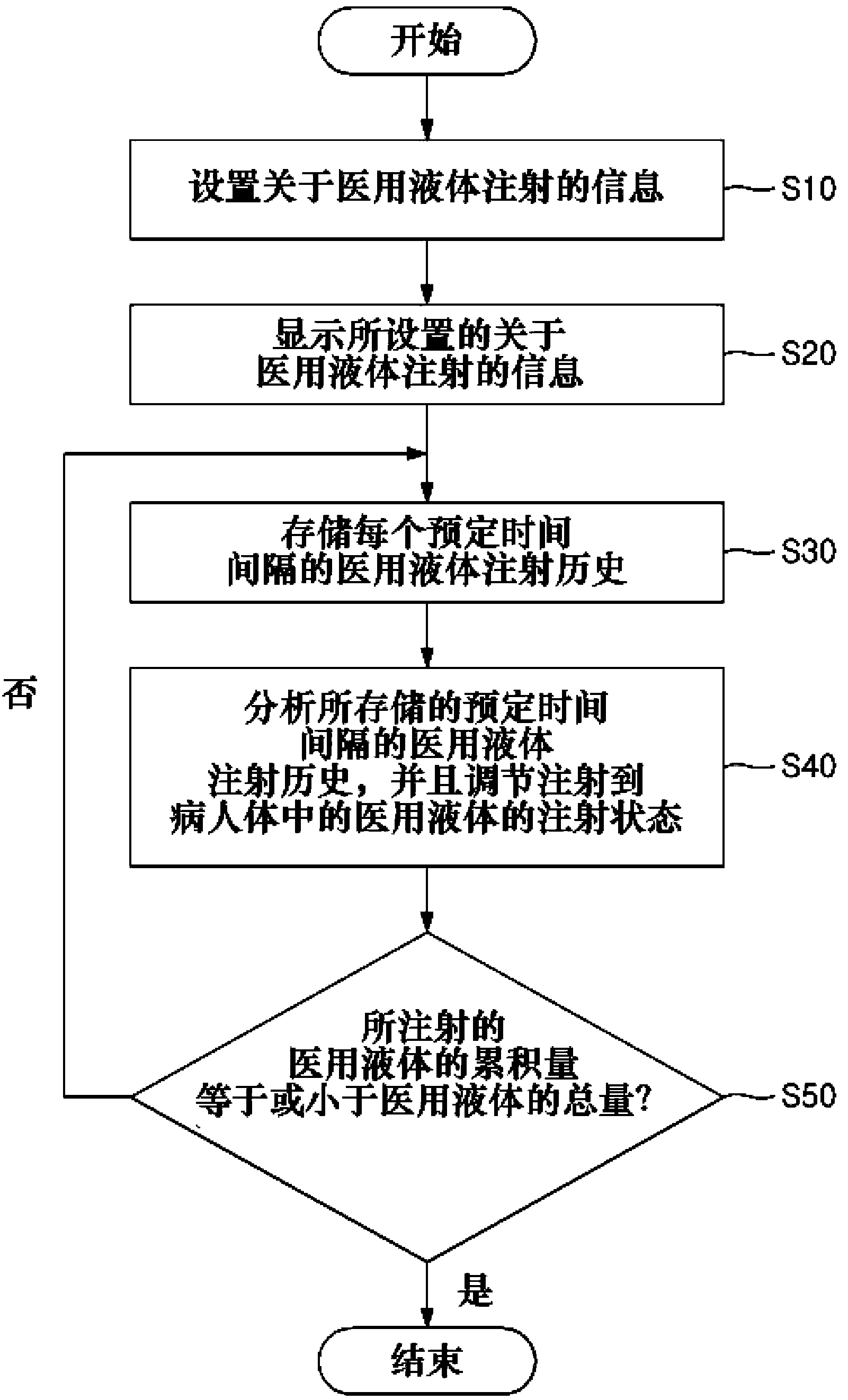
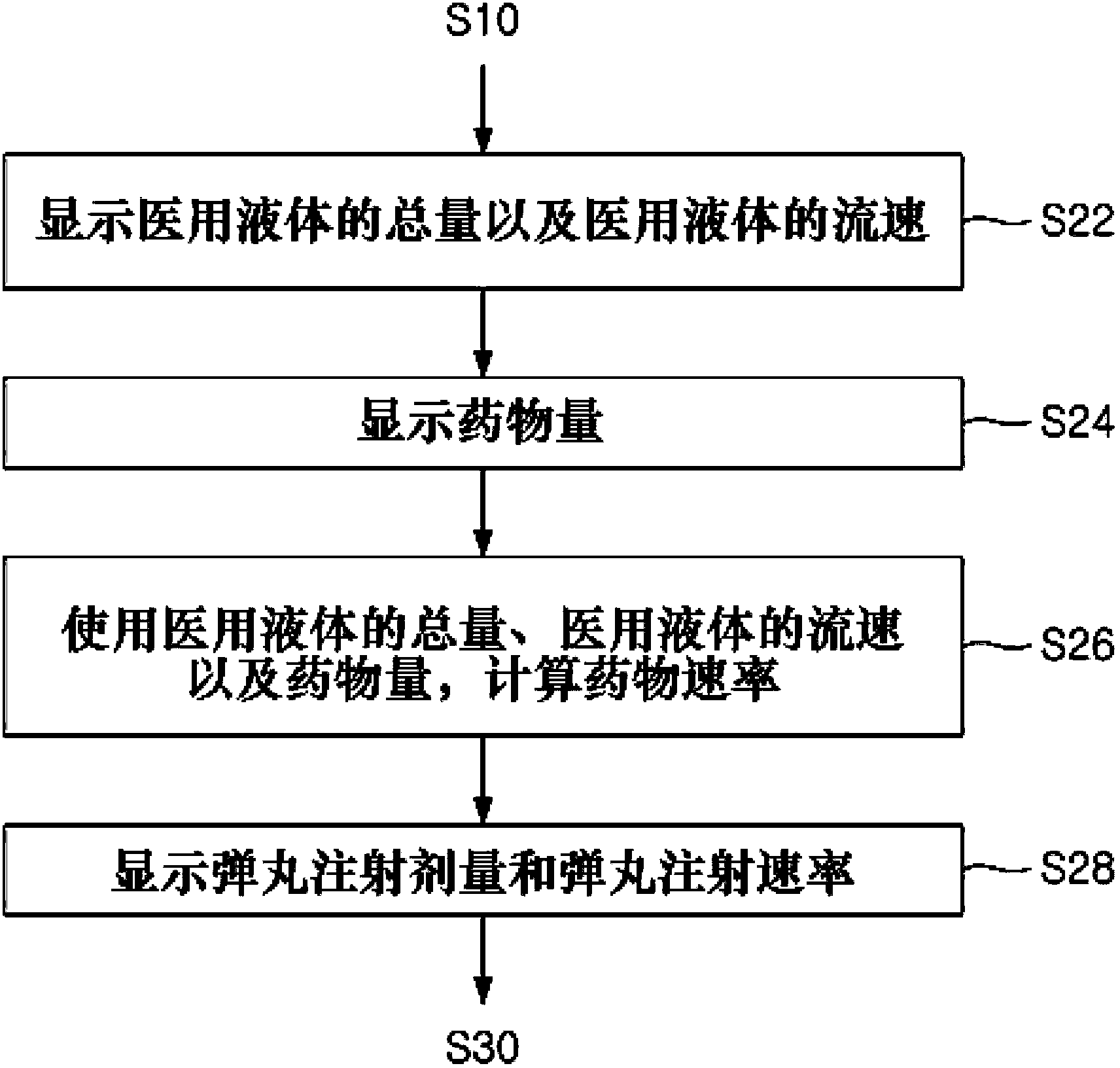
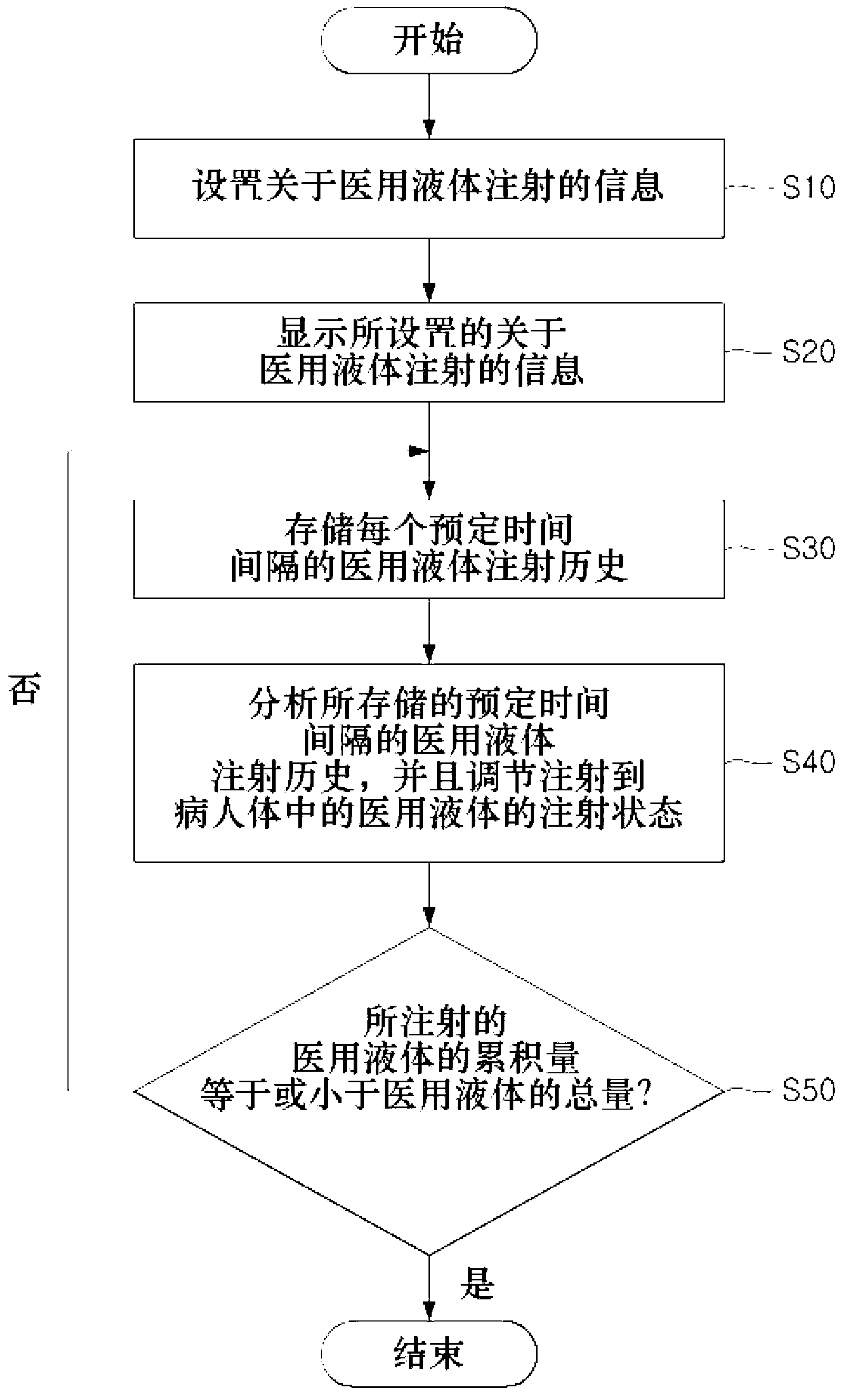
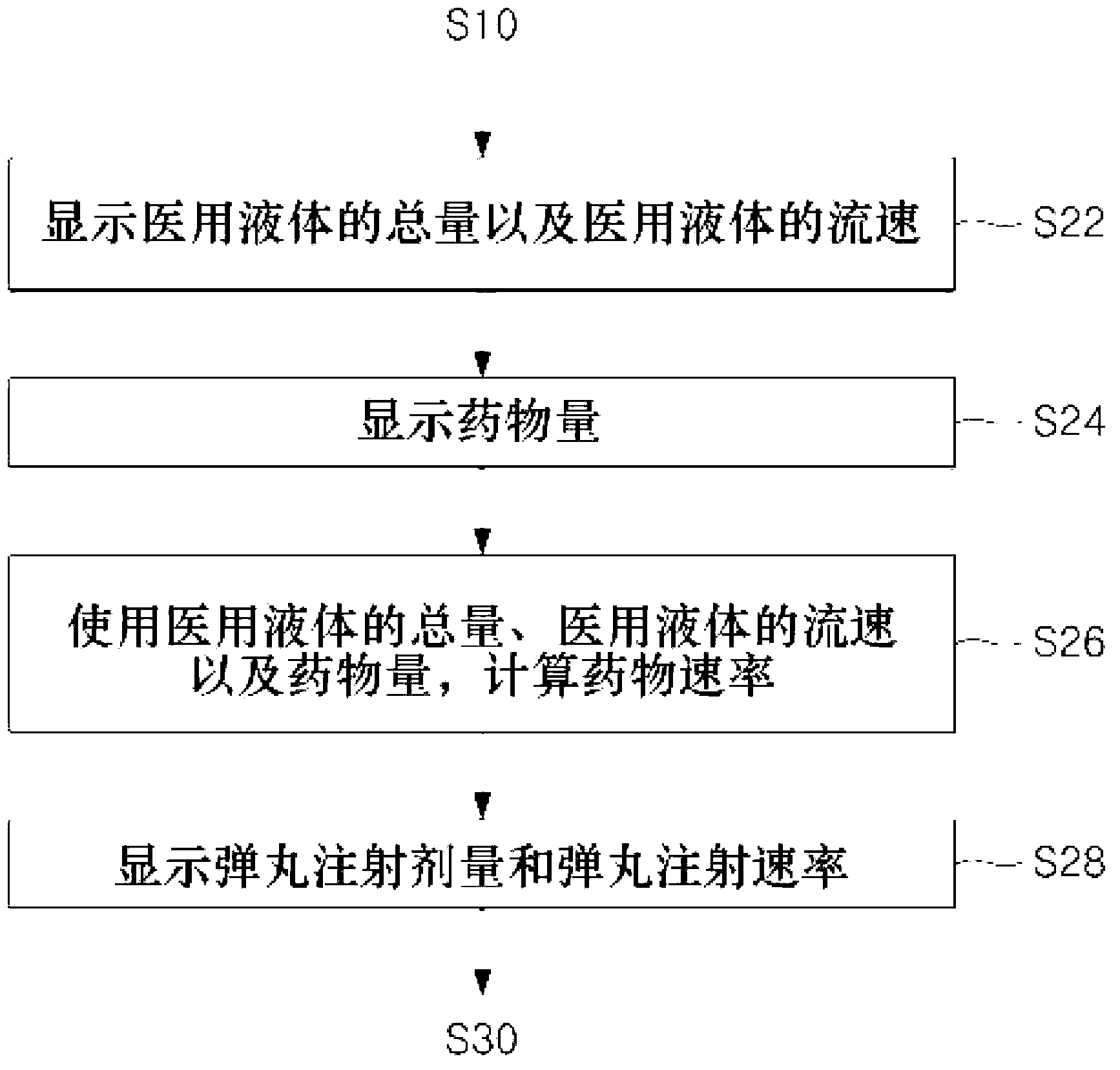
Method for managing history of liquid medicine injections
The present invention relates to a method of managing the injection history of medical fluids. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of managing the injection history of a medical fluid capable of managing the injection history of a medical fluid in a device for injecting a medical fluid that automatically injects a predetermined amount of the medical fluid into a patient in the vein or epidural space to manage the patient's pain.
Owner:WOO YOUNG MEDICAL CO LTD
A method for the dehydrogenation self-coupling of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds catalyzed by visible light
ActiveCN108440291BRealize the coupling reactionHigh hydrogen abstraction efficiencyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationDehydrogenationCarbonylation
The invention discloses a method of dehydrogenation self-coupling of a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound with visible light catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of (1) dissolving a photocatalyst,a peroxide and the 1,3-dicarbonyl compound into a solvent, and adding 1,4-dioxane to obtain a reaction solution; and (2) illuminating the reaction solution obtained in the step (1) with visible light, and performing separation after reaction is finished to obtain a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound dehydrogenation self-coupling product. By adopting the method provided by the invention, adopted visible light catalysis realizes coupling reaction of a dicarbonyl compound under the relatively mild conditions and responds current green chemical idea, and coupling of the dicarbonyl compound is finished witha more scientific and environment-friendly method.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Composition and method for improving sleep duration and quality
ActiveUS10376566B2Large dropout ratePoor responsePeptide/protein ingredientsHeavy metal compound active ingredientsSide effectPhysiology
An intervention for sleep disorders comprises: collagen, a gelatin peptide, or the amino acid glycine; L-theanine; lactucopicrin, deoxylactucopicrin, or another lactucopicrin derivative; hyaluronic acid; epigallocatechin gallate; and quinic acid. The intervention helps regulate pro-inflammatory biomarkers that are often associated with insomnia development and progression. These biomarkers include cytokines and enzymes associated with tryptophan degradation. Inhibition of these enzymes and cytokines improves tryptophan availability and sleep quality, and allows individuals to sleep better with fewer side effects. The composition promotes high-quality, deep sleep.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Assembling equipment for rotatable inductive probe
ActiveCN110948225AReduce the loss rateExtended service lifeAssembly machinesPositioning apparatusStructural engineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:深圳市鑫康医疗器械有限公司
Industrial network integrated cloud management system
PendingCN113189946AImplement security managementRealize real-time monitoringTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlCloud processingData information
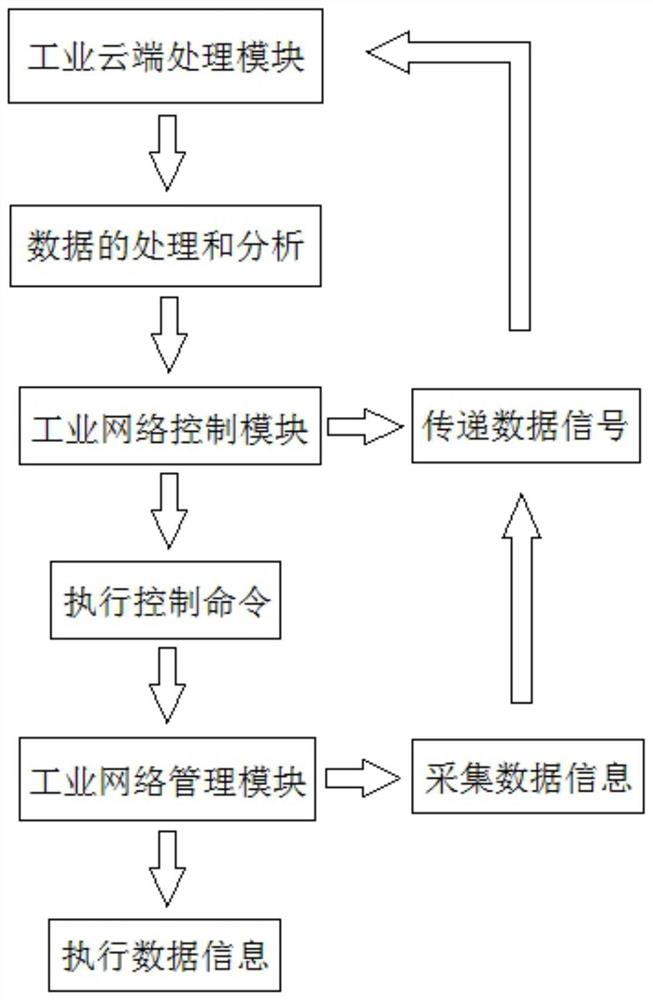
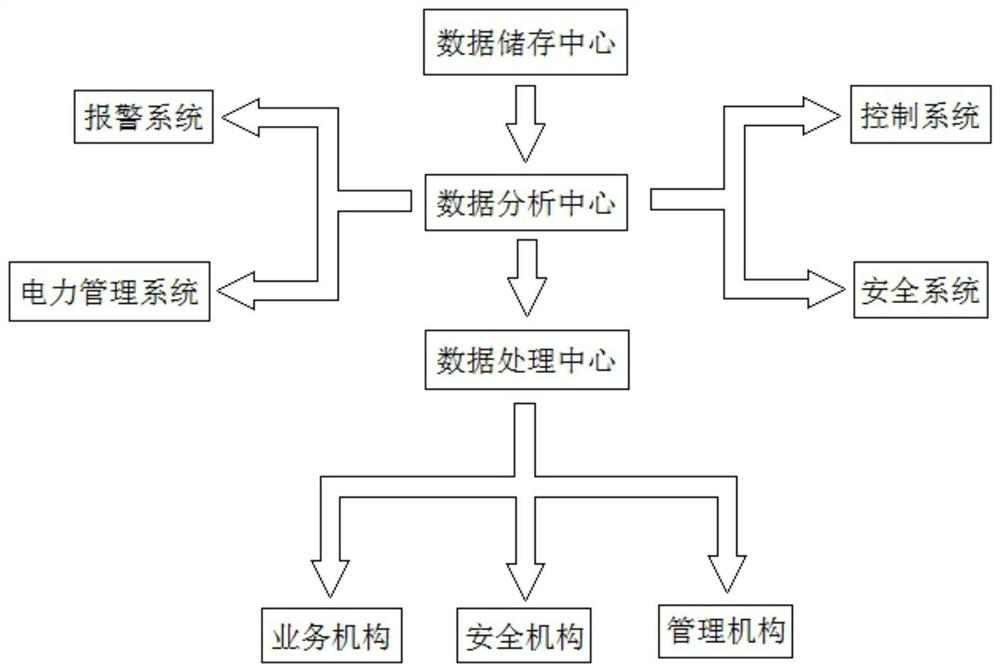
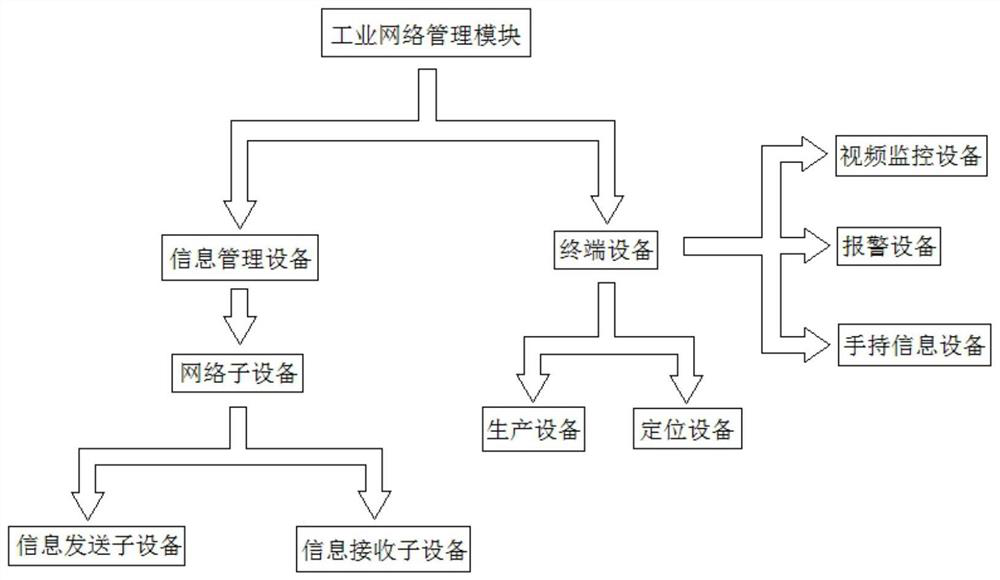
The invention discloses an industrial network integrated cloud management system which comprises an industrial cloud processing module, an industrial network control module and an industrial network management module. The industrial cloud processing module is connected with the industrial network control module, the industrial network control module is connected with the industrial network management module, the industrial cloud processing module is responsible for processing, storing and analyzing data, and the industrial network control module is responsible for executing a control command and transmitting a data signal. The industrial network management module is responsible for collecting and executing data information. The system has the advantages that all the modules are clear in division of labor, the modules are relatively independent in industrial production management, the data processing speed and accuracy are improved, the data processing functions of different modules can be adjusted in time according to the actual requirements of different enterprises, the situation that the whole management system is reset due to data adjustment is avoided, and therefore, the system is suitable for managing different types of enterprises.
Owner:江苏中安智信通信科技股份有限公司
Method for managing history of liquid medicine injections
InactiveCN102883760APositivePositive responseDrug and medicationsMedical devicesInternal medicineEpidural space
The present invention relates to a method for managing the history of liquid medicine injections. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for managing the history of liquid medicine injections, capable of managing the liquid medicine injection records of a liquid medicine injection apparatus which automatically injects a constant dosage of liquid medicine with the aim of managing the pain of a patient.
Owner:WOO YOUNG MEDICAL CO LTD
Method of Predicting Non-Response to First Line Chemotherapy
InactiveUS20100184065A1Positive responseGood prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGood prognosisChemotherapy regimen
The invention provides a method for determining a prognosis of colorectal cancer in a colorectal cancer patient, comprising classifying said patient as having a good prognosis or a poor prognosis using measurements of a plurality of gene products in a cell sample taken from said patient, said gene products being respectively products of at least 1 of the genes listed in Table 1, or respective functional equivalents thereof, wherein said good prognosis predicts a positive response to standard chemotherapy regimens, and said poor prognosis predicts non-responsiveness. Provided herein, the invention includes a gene signature to predict which patients will to benefit from standard colon cancer therapy; alternatively, patients who are classified as non-responders may be more likely to benefit from a novel agent such as a Notch inhibitor.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC +1
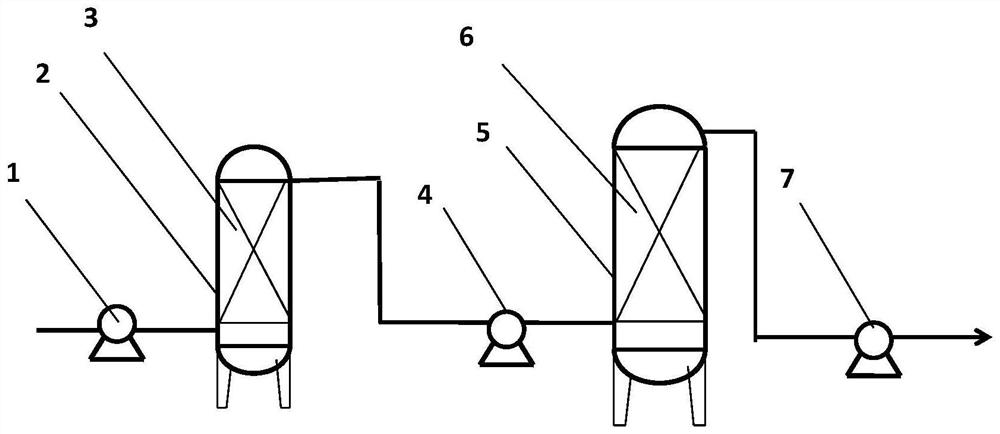
System and method for removing COD and calcium ions in cold rolling dilute alkali reverse osmosis concentrated water
ActiveCN112010385AEfficient removalEconomic treatment processWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processActivated carbonWater treatment system
The invention discloses a cold rolling dilute alkali reverse osmosis concentrated water treatment system. The system comprises a water inlet pump and a reaction tower, the water inlet pump is connected with a modified chitosan adsorption reaction tower, a modified chitosan-activated carbon mixed filler is arranged in the modified chitosan adsorption reaction tower, and the modified chitosan adsorption reaction tower is sequentially connected with a lifting pump, a modified resin adsorption tower and a water outlet pump; and modified chloromethylated polystyrene chelate resin is arranged in themodified resin adsorption tower. The invention further provides a method for removing COD and calcium ions in the cold-rolled dilute alkali reverse osmosis concentrated water. The economical and efficient pollutant treatment process is developed according to the water quality and water quantity conditions of the cold rolling reverse osmosis concentrated water, cyclic utilization, energy conservation and emission reduction are taken as main tasks, environmental pollution is reduced, and increasingly strict environmental protection laws and regulations can be actively coped with.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com