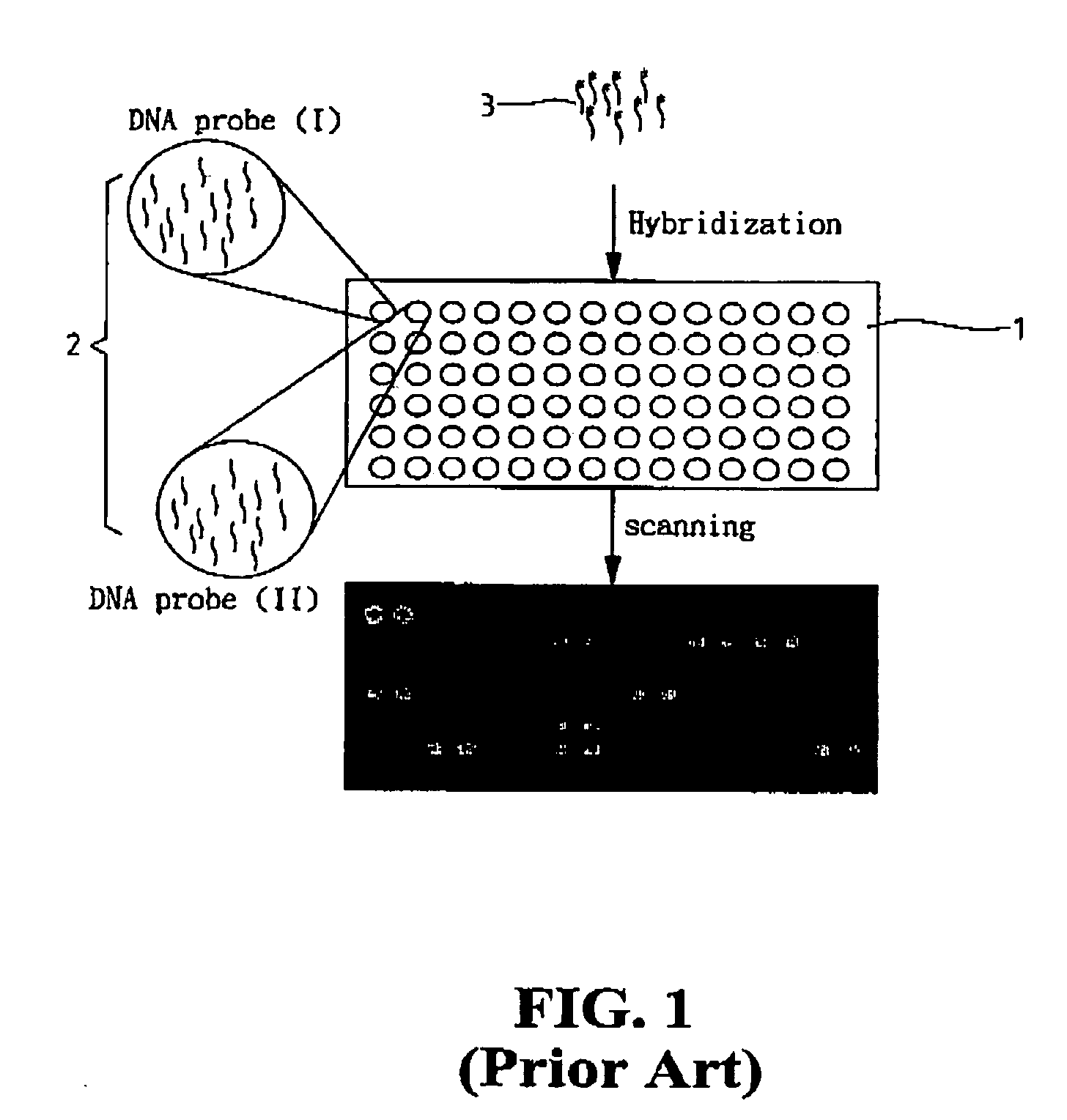
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Charge coupled device camera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Two-dimensional array of semiconductor photosensors capable of detecting and recording images by direct transduction of incident photons into electrical signals; used in a variety of image-processing systems requiring sensitivity, fast linear response, wavelength discrimination, and digital coding.
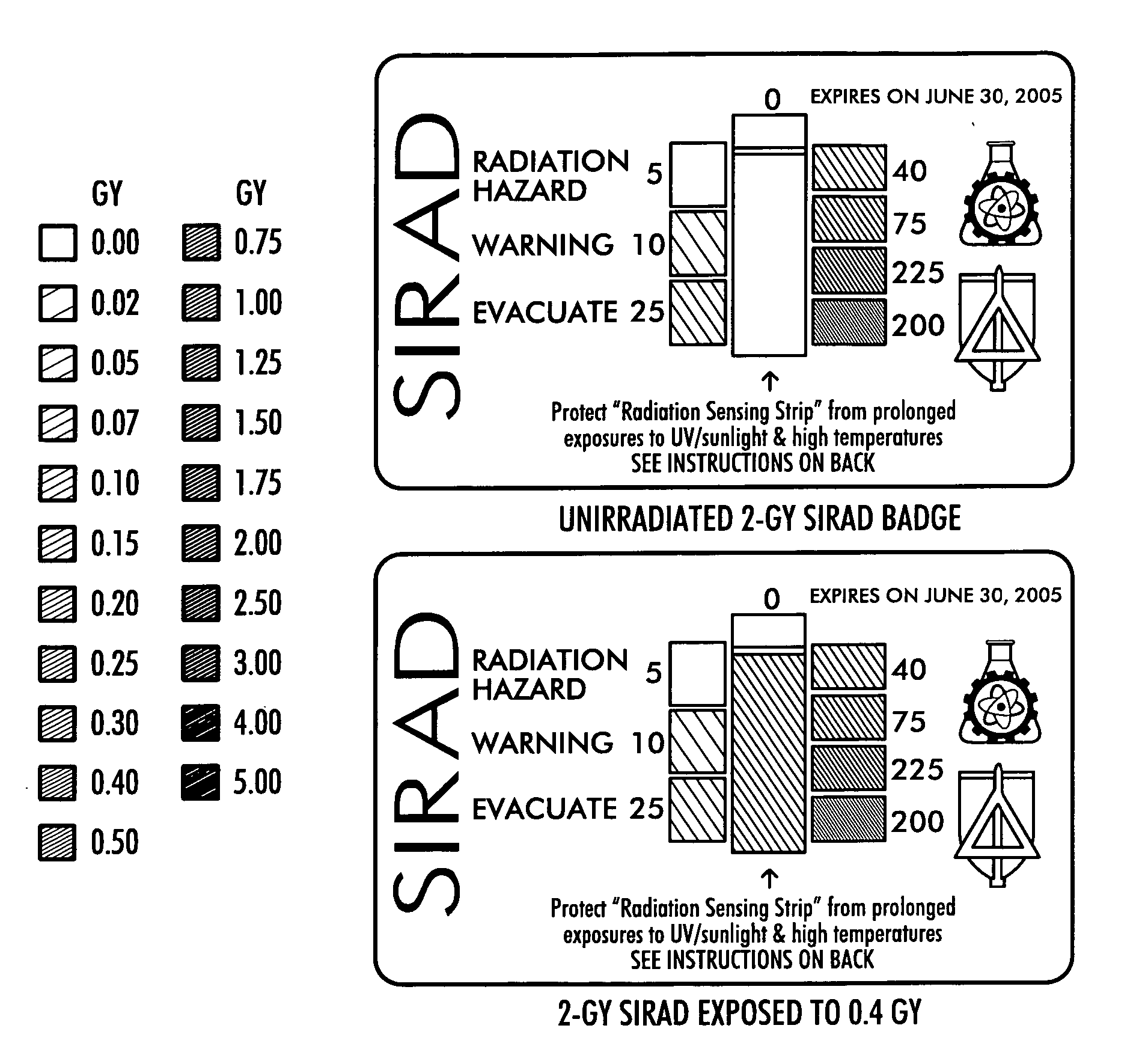
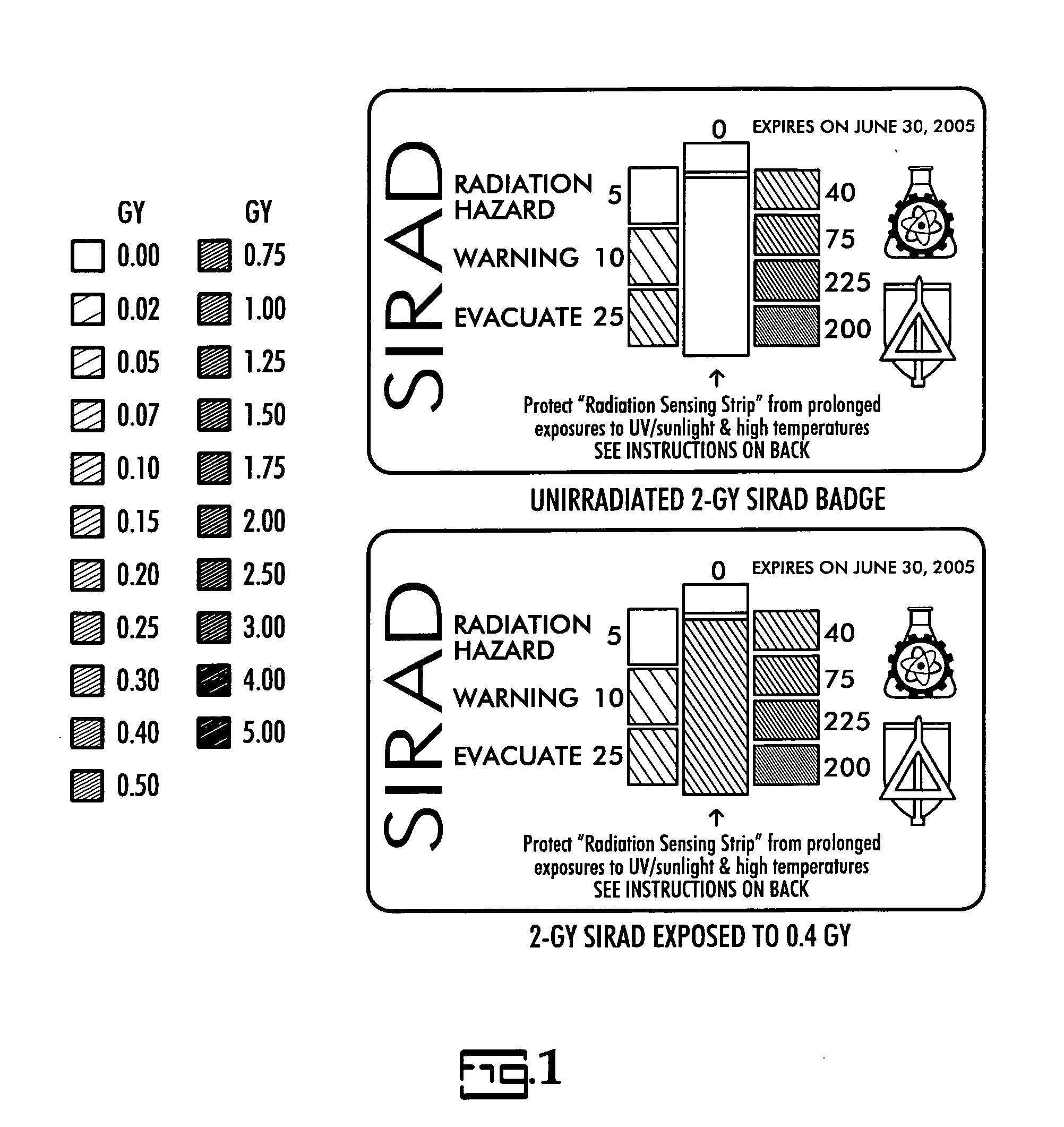
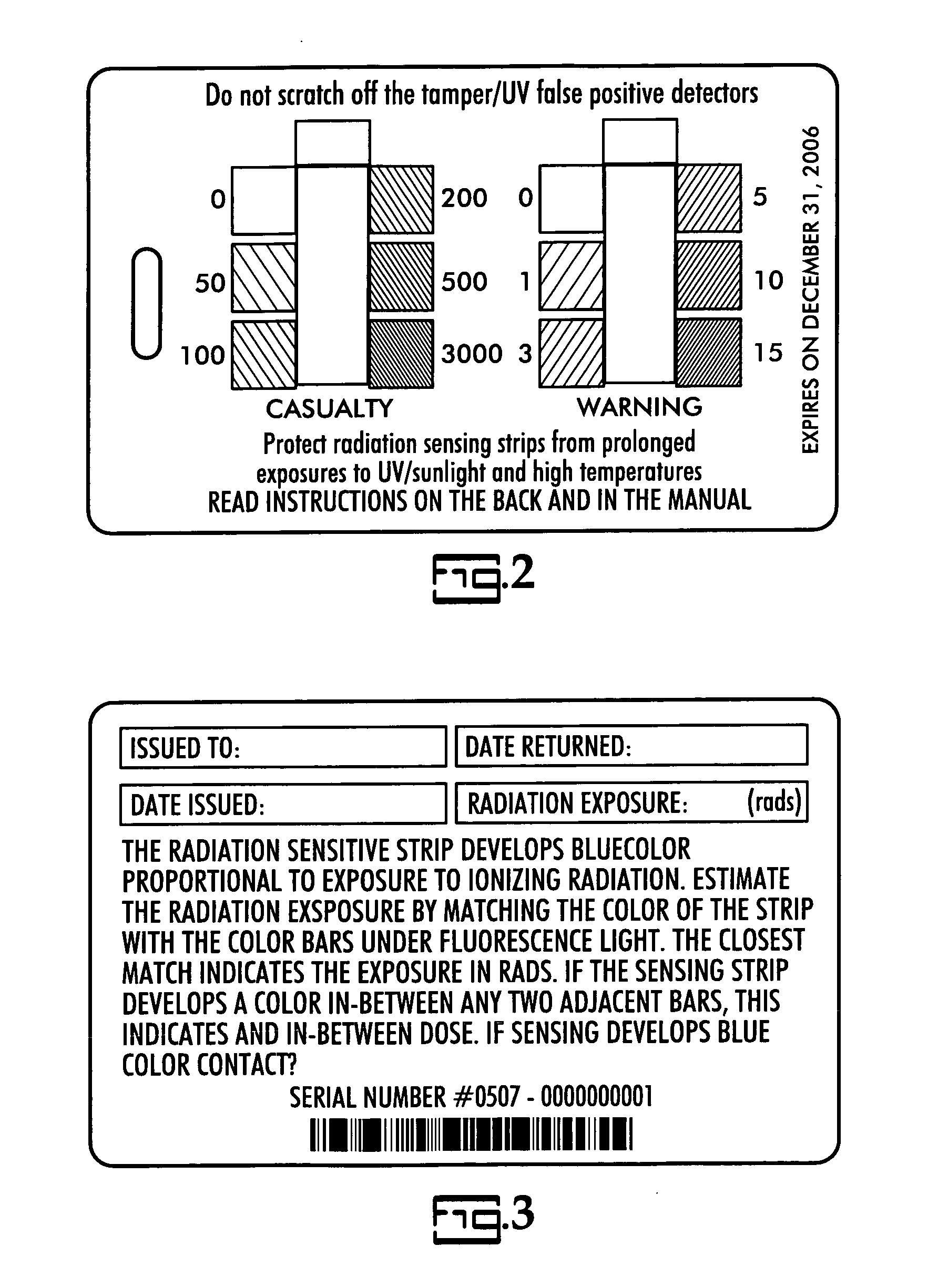
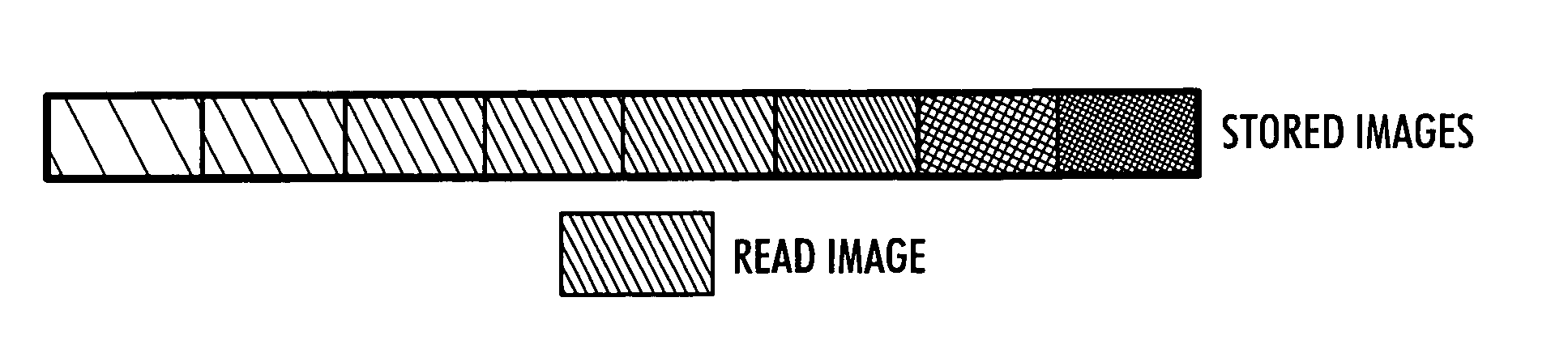
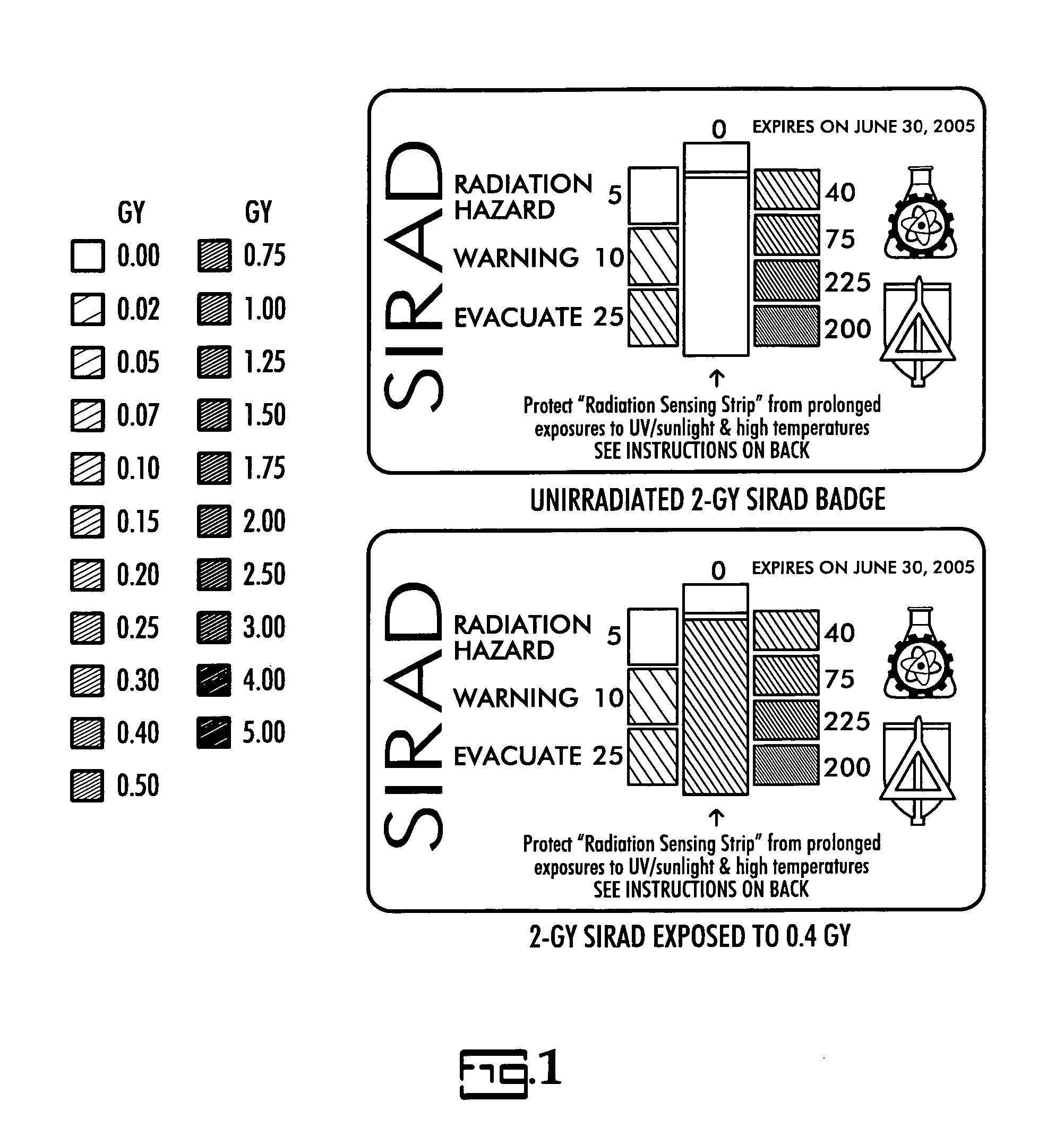
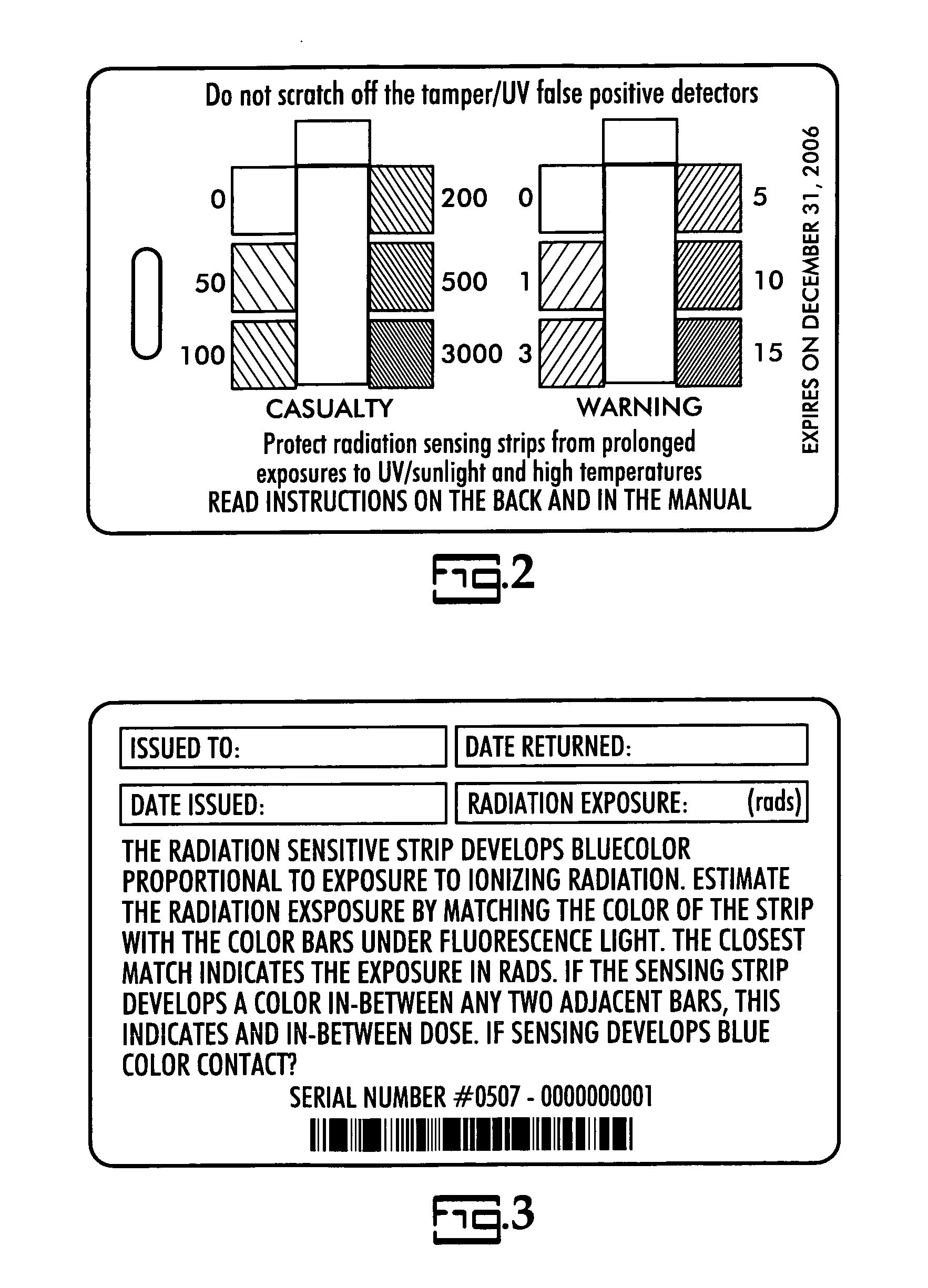
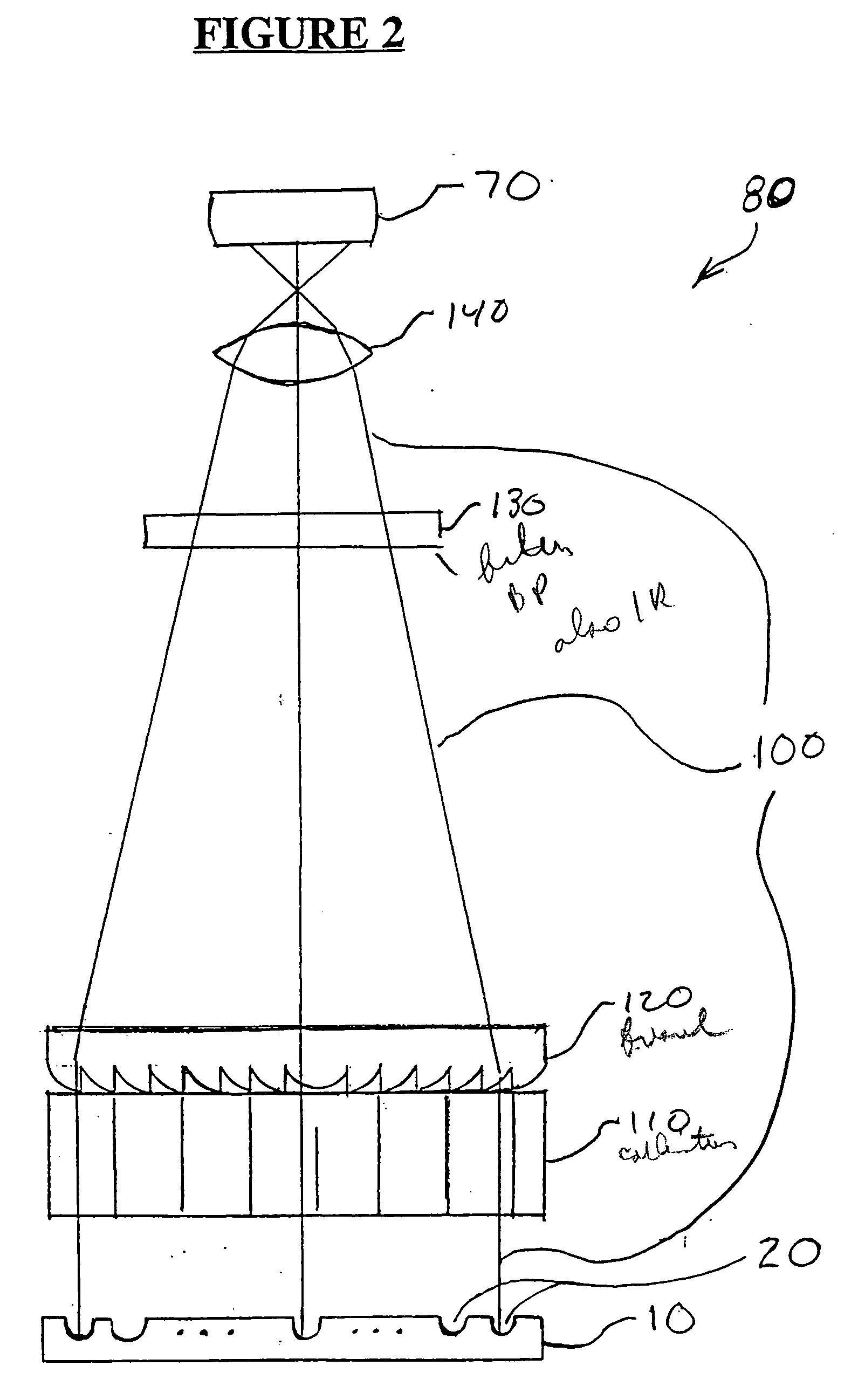
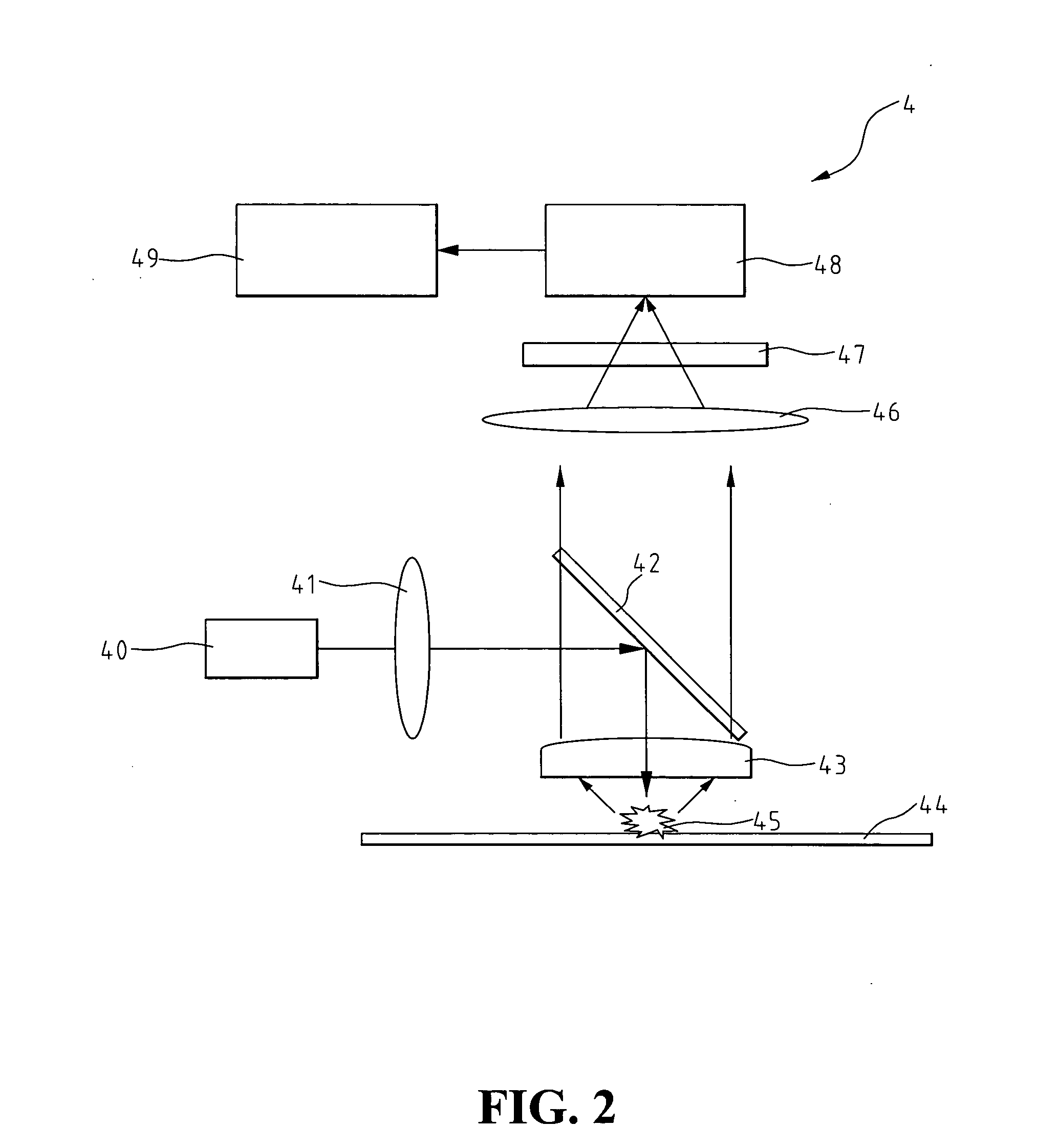
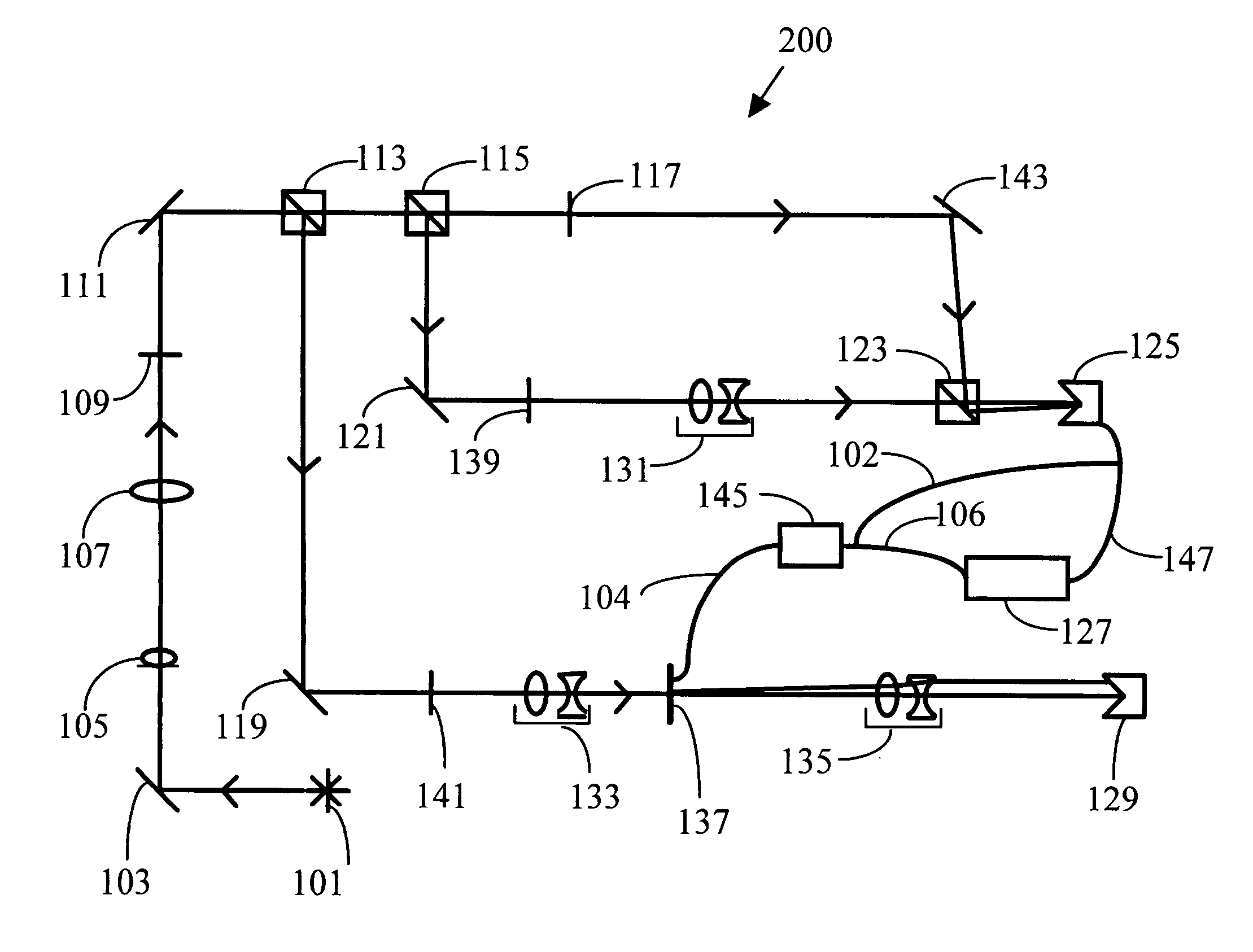
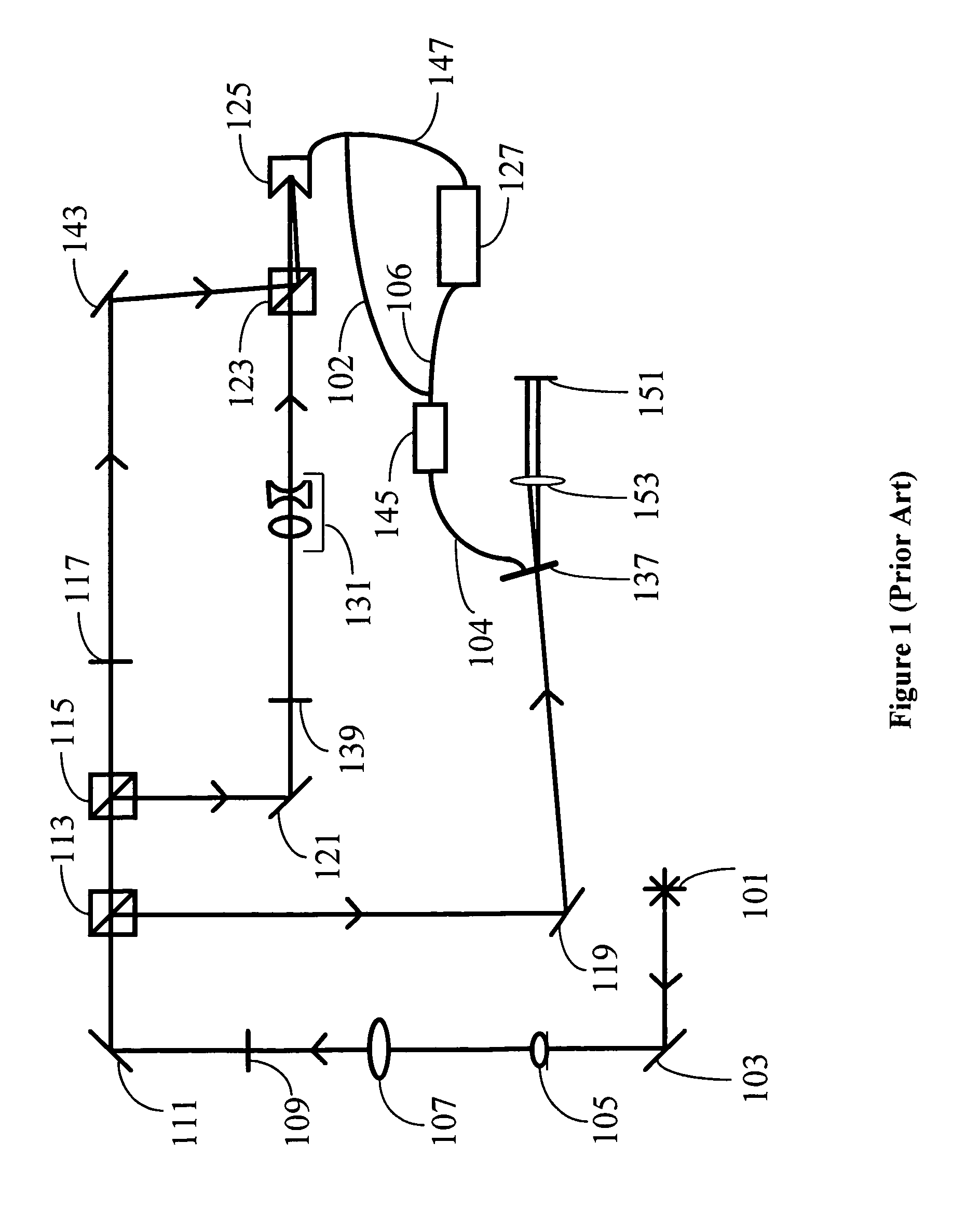
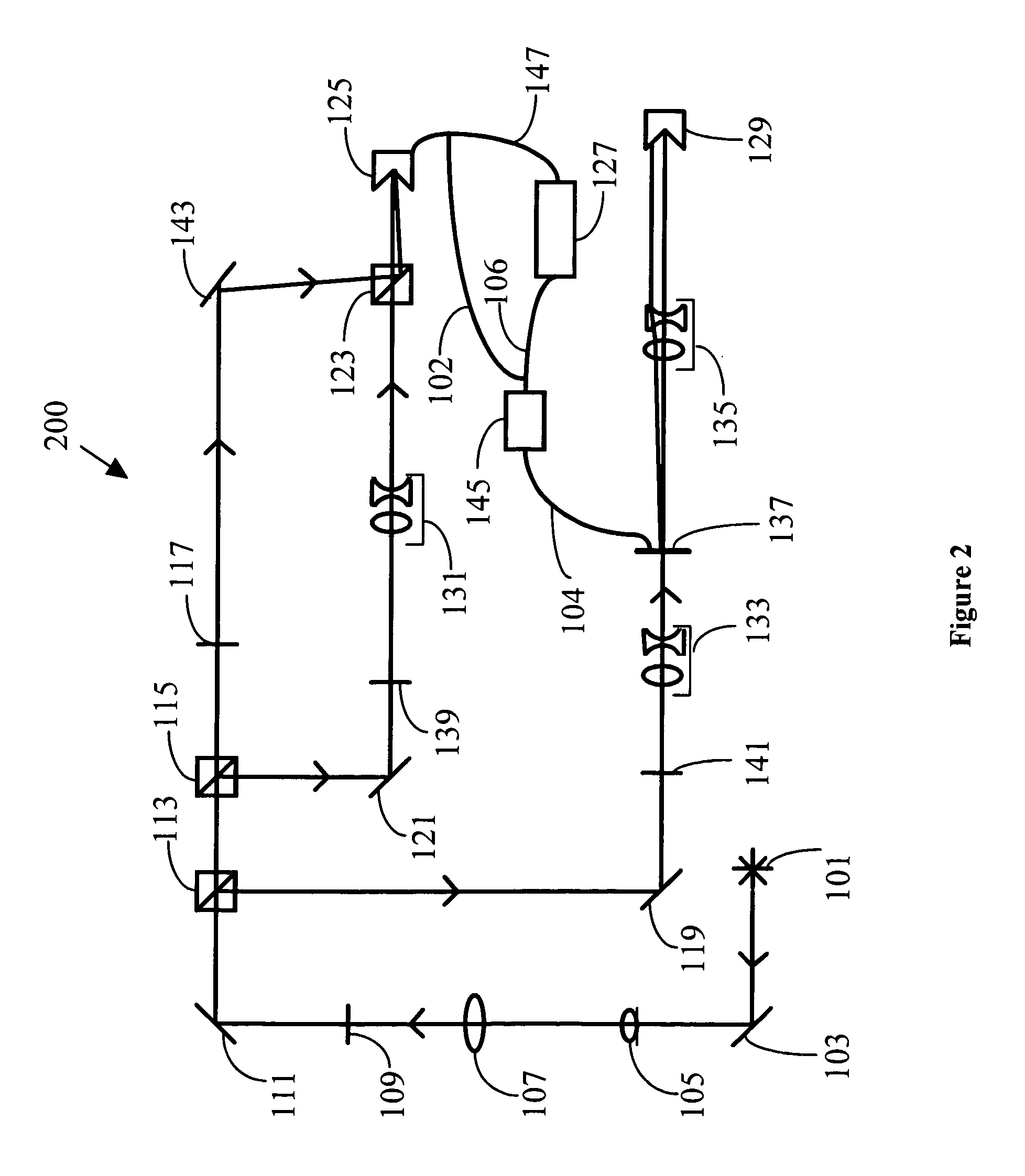
General purpose, high accuracy dosimeter reader
A general purpose high accuracy dosimeter reader, 80, for determination of a treatment condition, based on comparison of an image of treated dosimeter, 111, with a series of images of pre-treated dosimeter, 114, is disclosed. A dosimeter undergoes noticeable changes, such as a color change upon treatment with certain materials, such as toxic gases and processes, such as ionizing radiation and sterilization is pre-treated. The dosimeter is imaged with an imaging device, 115, such as charge-coupled device camera and images of the dosimeter or the changes, e.g., color change, are stored in an information storage device, 118. In order to determine the treatment condition, the treatment dosimeter is imaged and the image is compared with the series of pre-treated images of the dosimeter using software. The closest match of the treated dosimeter with the pre-treated and pre-imaged dosimeter would indicate the treatment conditions. The process and device can be used for almost any indicating device, process and treatment.
Owner:JP LAB INC +1
General purpose, high accuracy dosimeter reader
Owner:JP LAB INC +1
Device and method for the photodynamic diagnosis of tumor tissue
InactiveUS20040082863A1Easy to identifyEasy retrievalLaproscopesRadiation diagnosticsCharge coupled device cameraFungating tumour
An apparatus that includes a surgical telescopic device having a distal end and a proximal end; a camera coupled to the proximal end of the surgical telescopic device; and a holographic notch filter interposed between the camera and the proximal end of the surgical telescopic device. The camera preferably is a charge-coupled-device camera ("CCD camera"). The apparatus may also include a focusing lens or an alternative type of filter such as a long-pass filter or an infrared filter. The surgical telescopic device may be used by illuminating the material with non-white light and detecting the emitted fluorescence, phosphorescence or luminescence.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Imaging system for luminescence assays
InactiveUS6740865B1Good chanceRadiation pyrometryChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFiber bundleFluorescence
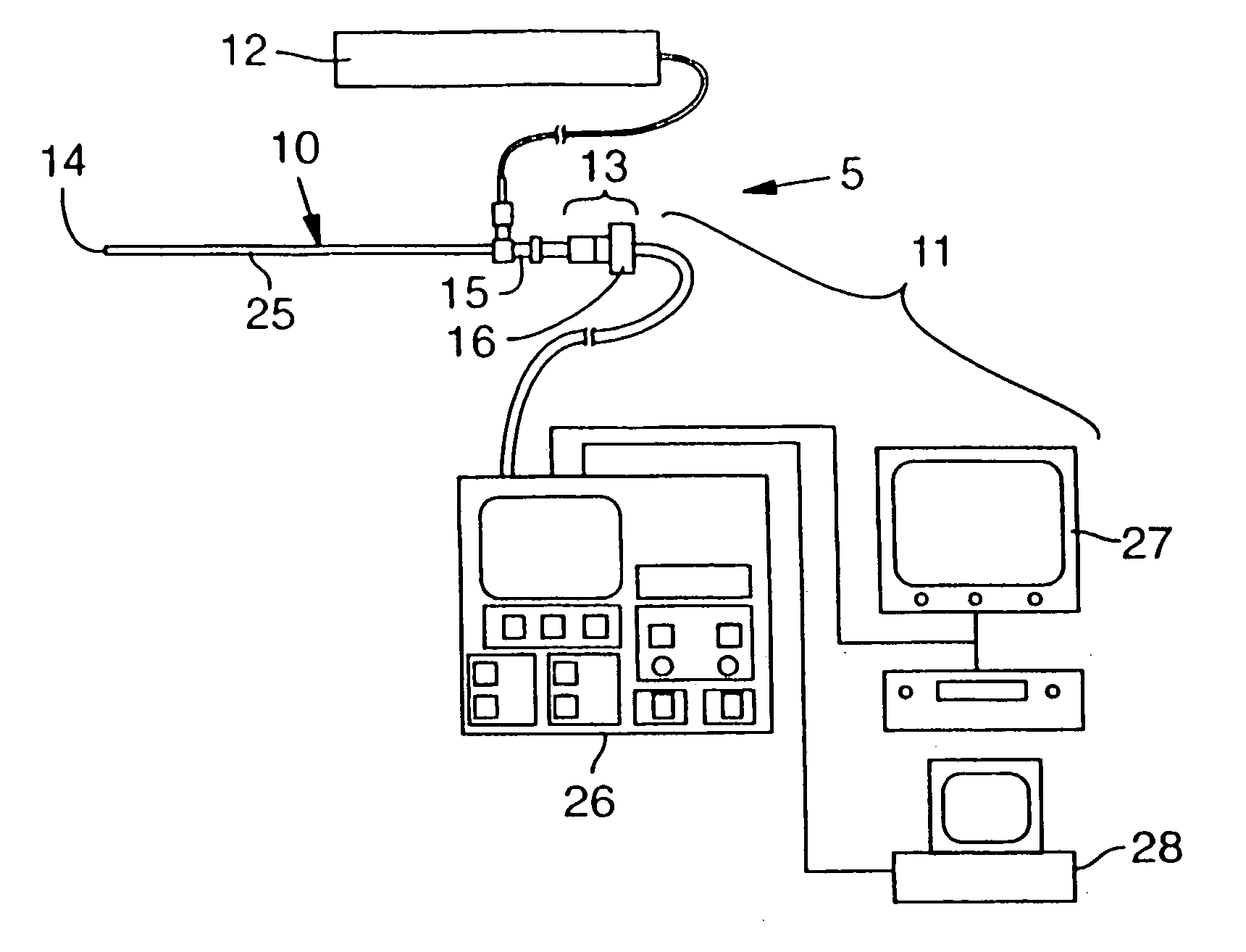
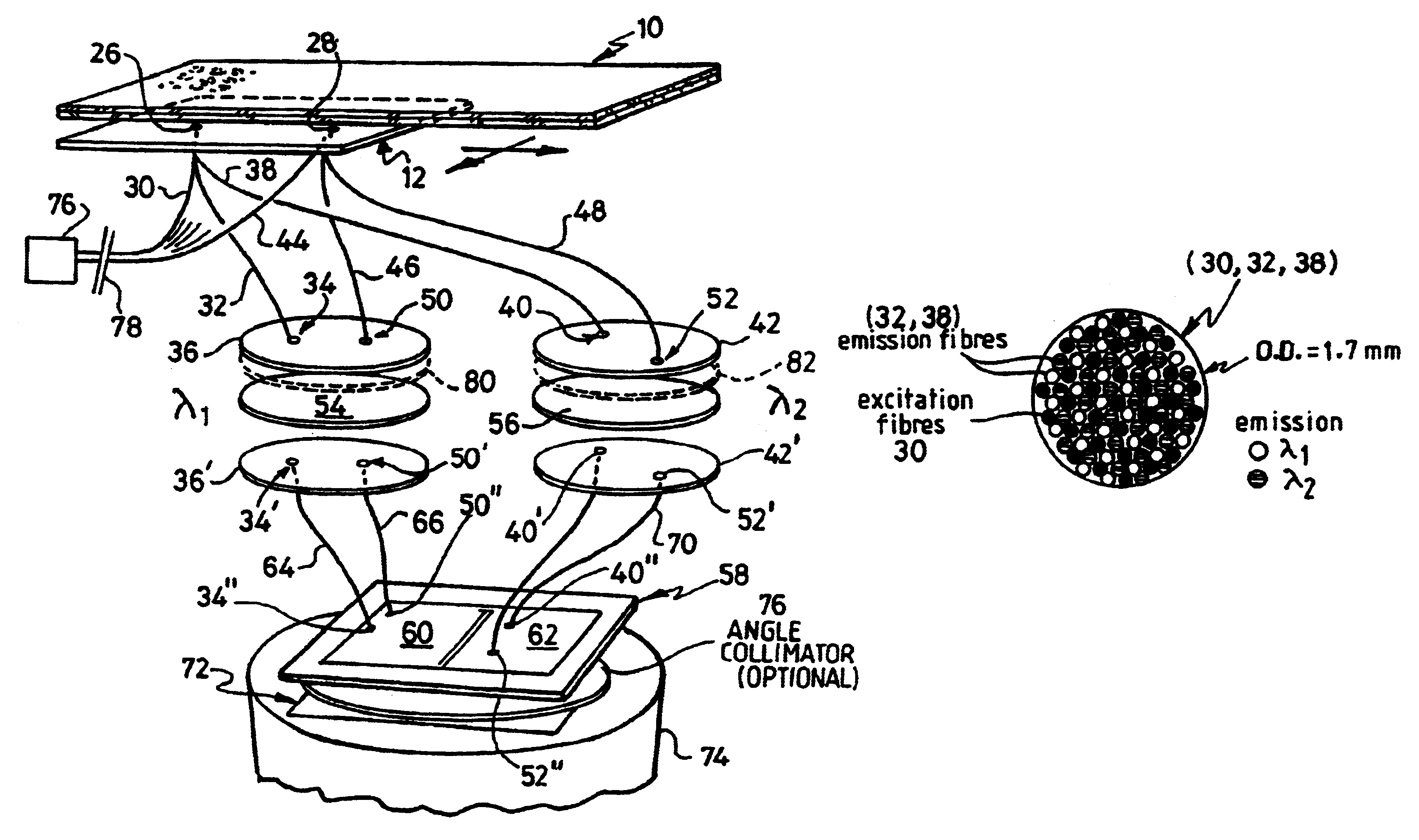
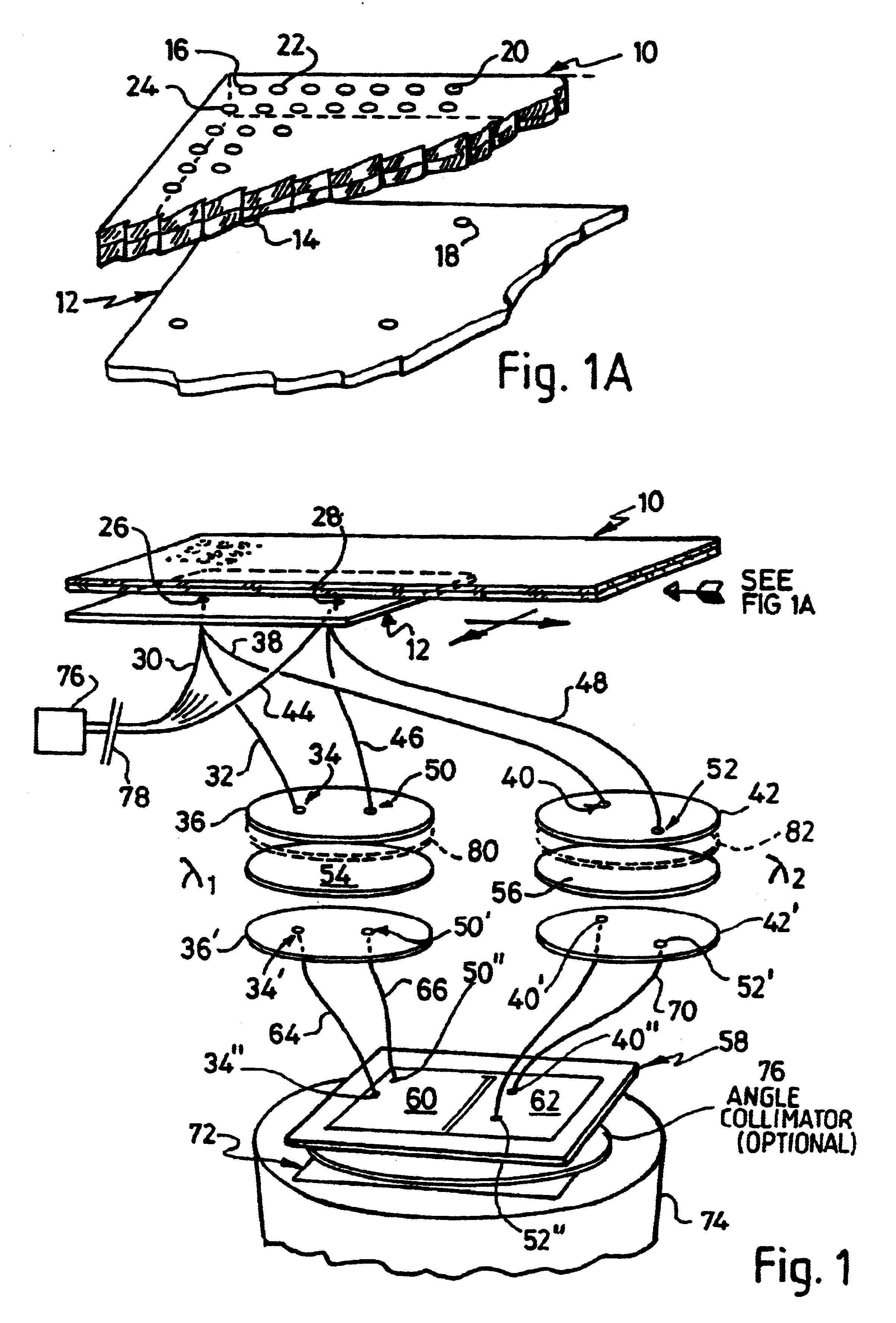
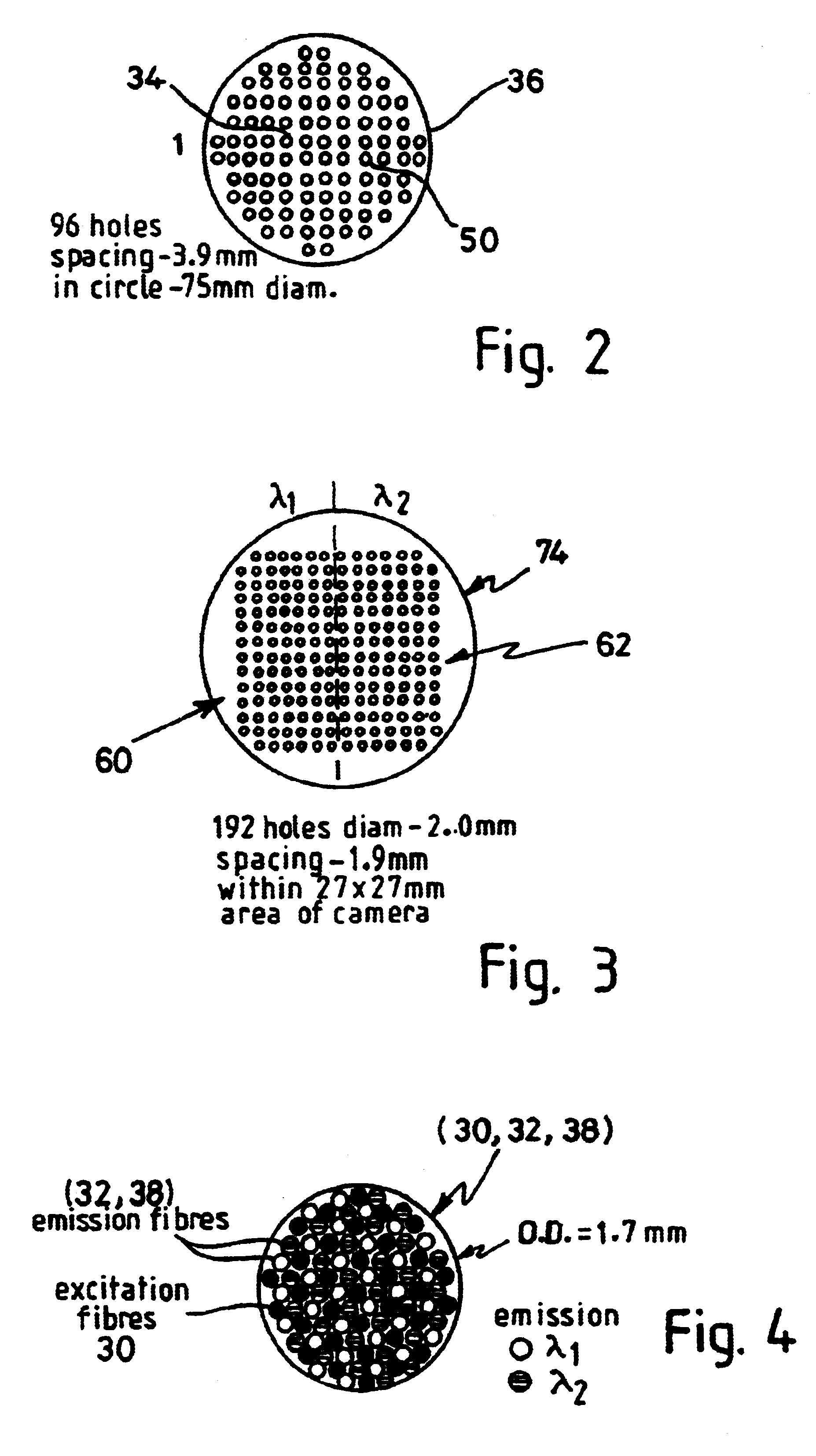
Apparatus for detecting light emitted by assay samples is provided, in which light emitted by the sample is collected for transmission to a charge coupled device camera (74) by an optical fiber bundle. The cross-sectional area of the optical fiber bundle corresponds to the area of the sample, the end of which is located close to the sample for detecting any light emitted therefrom, and selected fibers (30) of those making up the bundle are separated from the remainder and extend to a source of excitation radiation (76) and serve to convey excitation radiation (if required) directly to a corresponding plurality of points distributed over the are of the end face of the bundle and therefore over the area of the sample. The remaining fibers (32, 38) of the bundle serve to collect emitted light (whether generated by fluorescence caused by excitation or otherwise) and provide a light path to the change coupled device camera, wherein the ends of the excitation fibers and the ends of the emitted light collecting fibers area distributed uniformly over the area of the fiber bundle presented to the reaction site.
Owner:PEKINELMER SINGAPORE PTE LTD
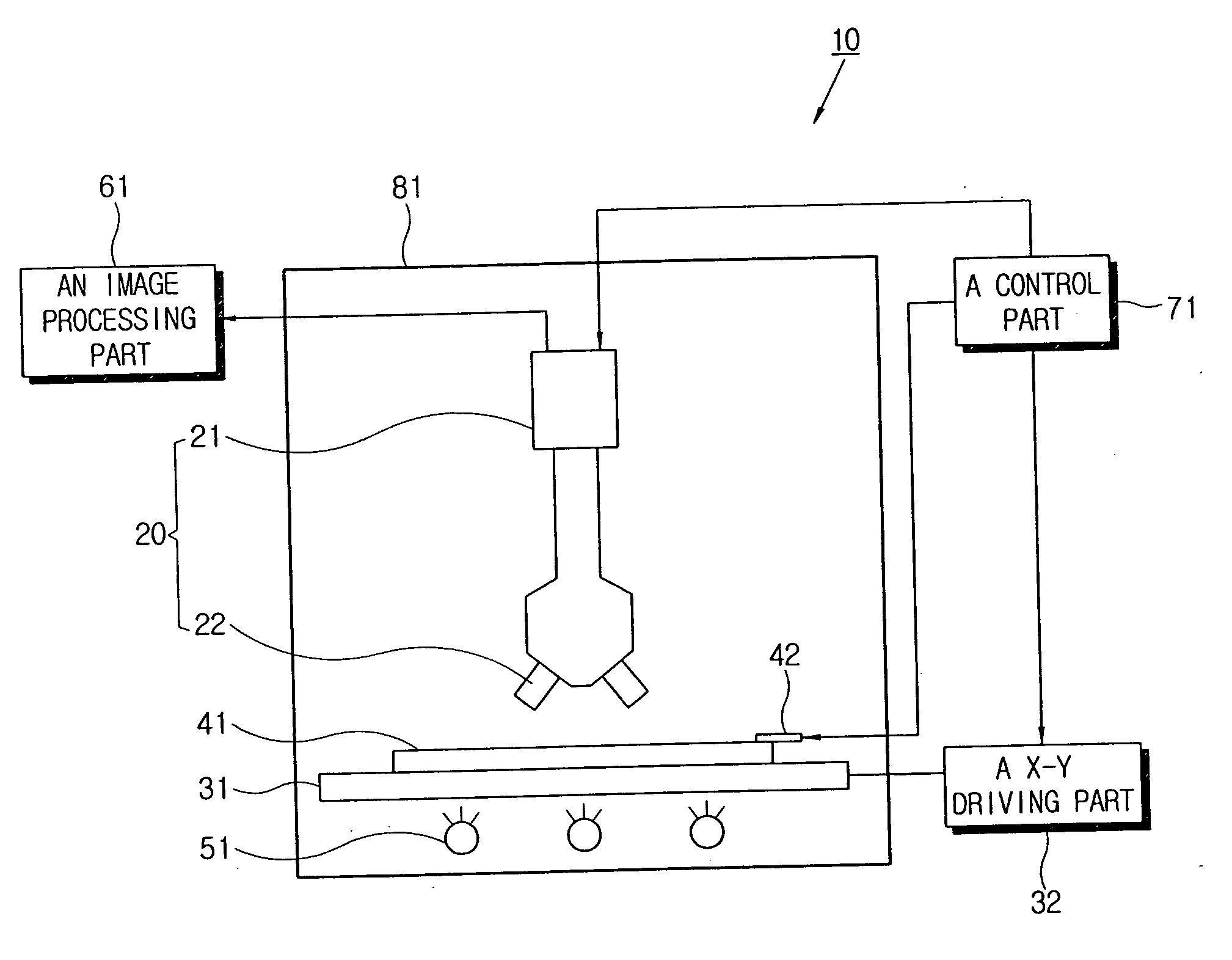
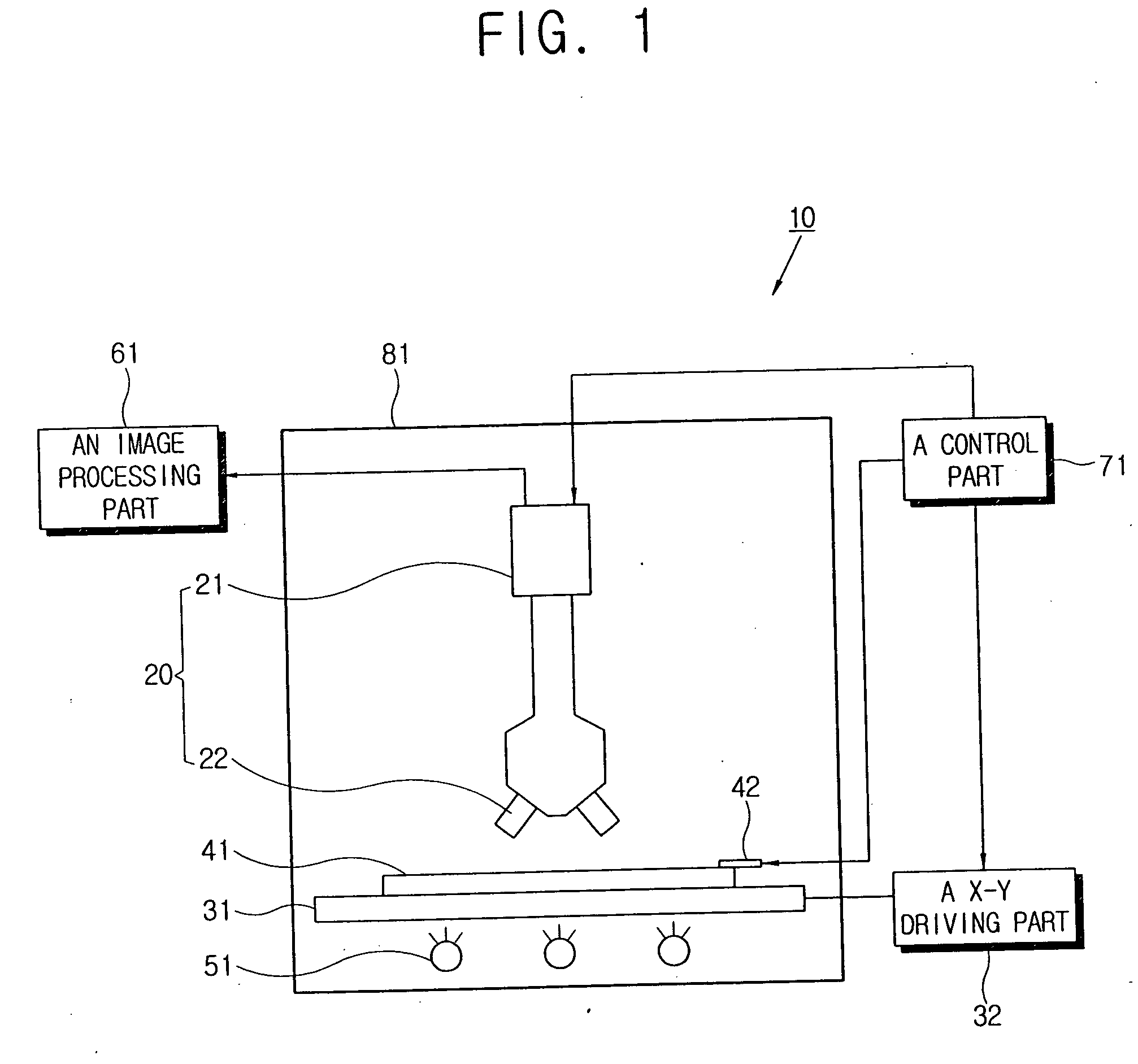
Apparatus for measuring response time and method of measuring response time using the same
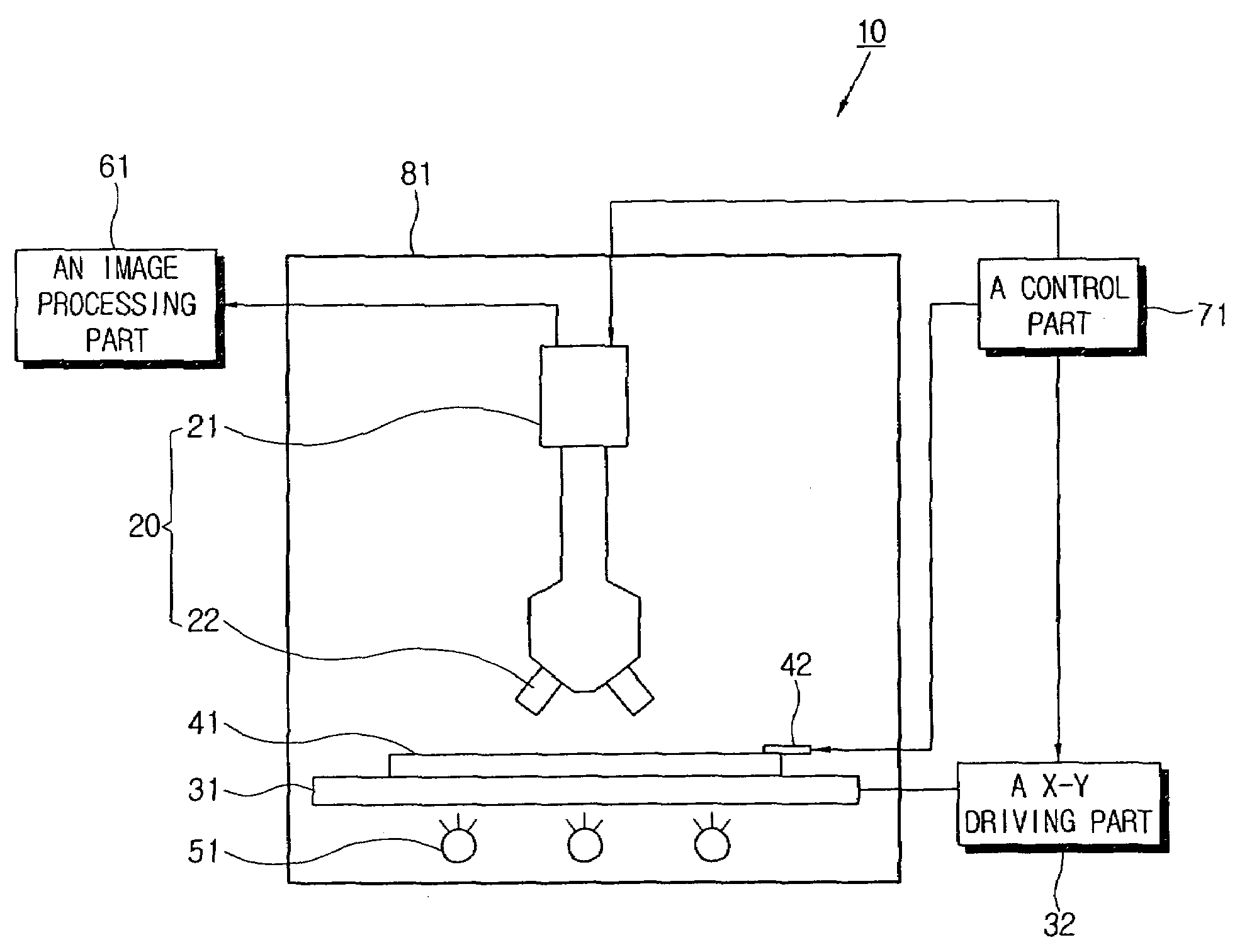
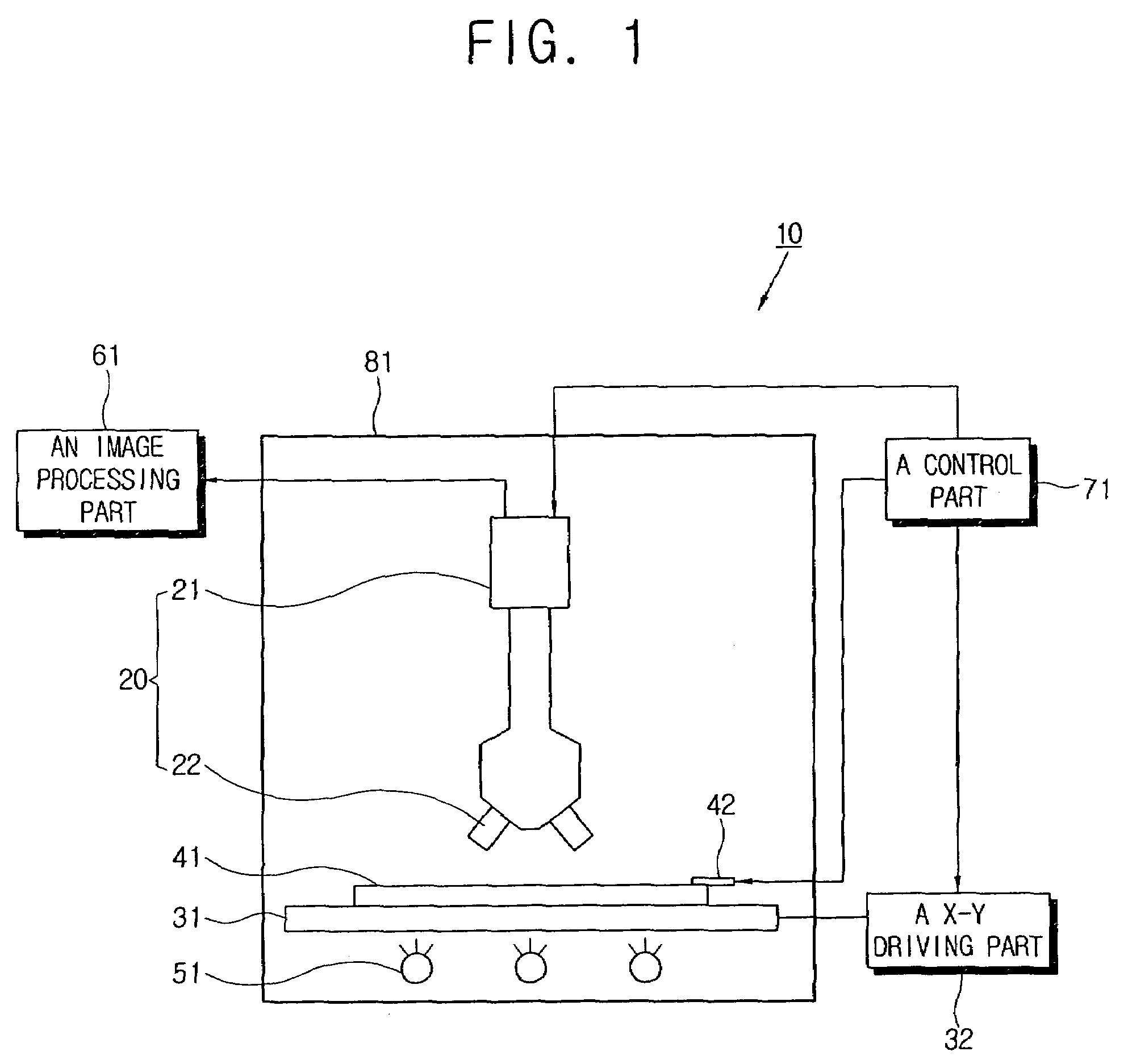
ActiveUS20060139269A1PrintersSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementImaging processingCharge coupled device camera
An apparatus for measuring response time of a display apparatus including a photographing part including a charge coupled device camera and a microscope, an image processing part receiving a picture taken from a photographing part and calculating the response time thereof, and a control part applying a predetermined image signal to the display apparatus and controlling the photographing part to take a picture change of the display apparatus at a predetermined time.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
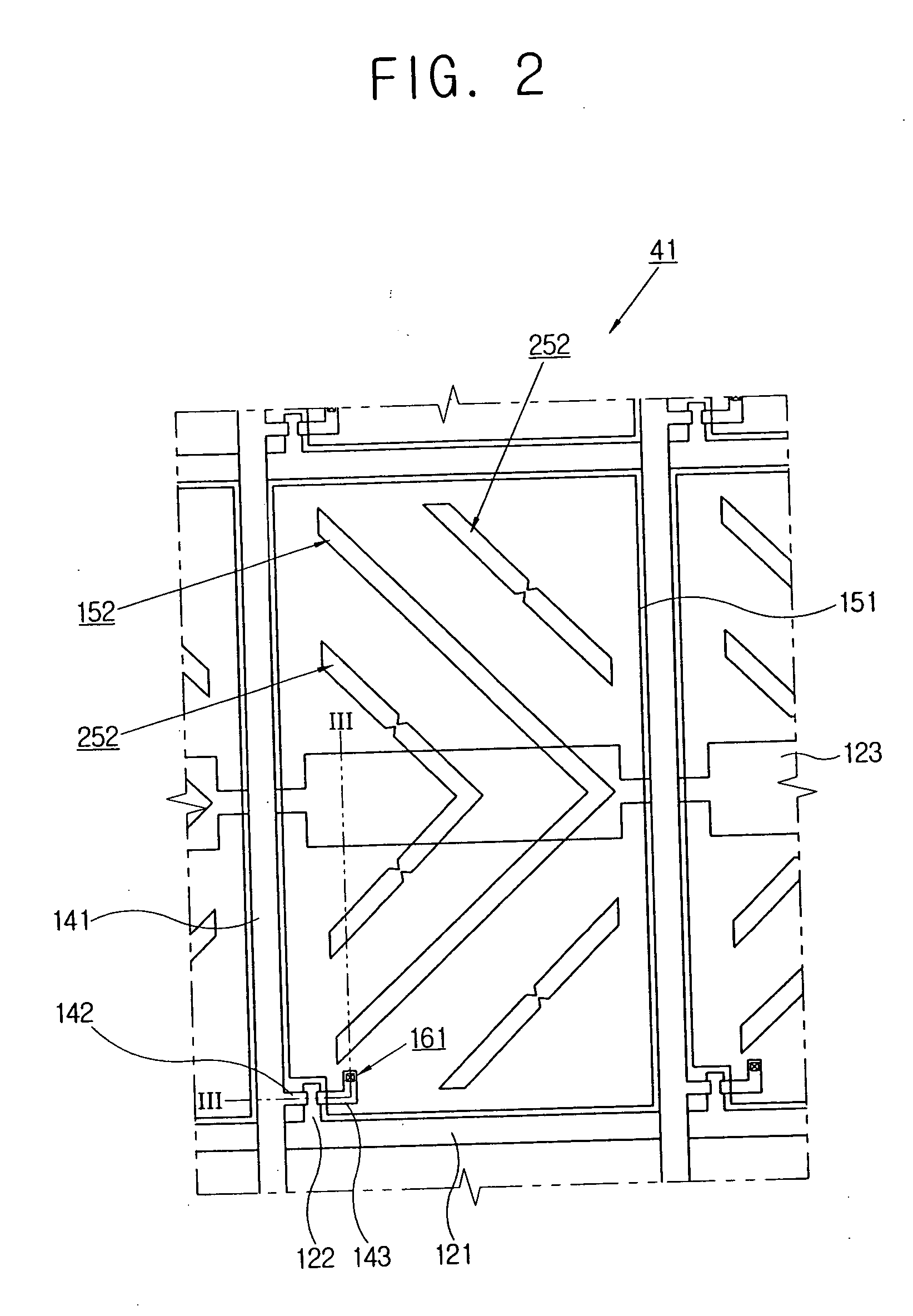
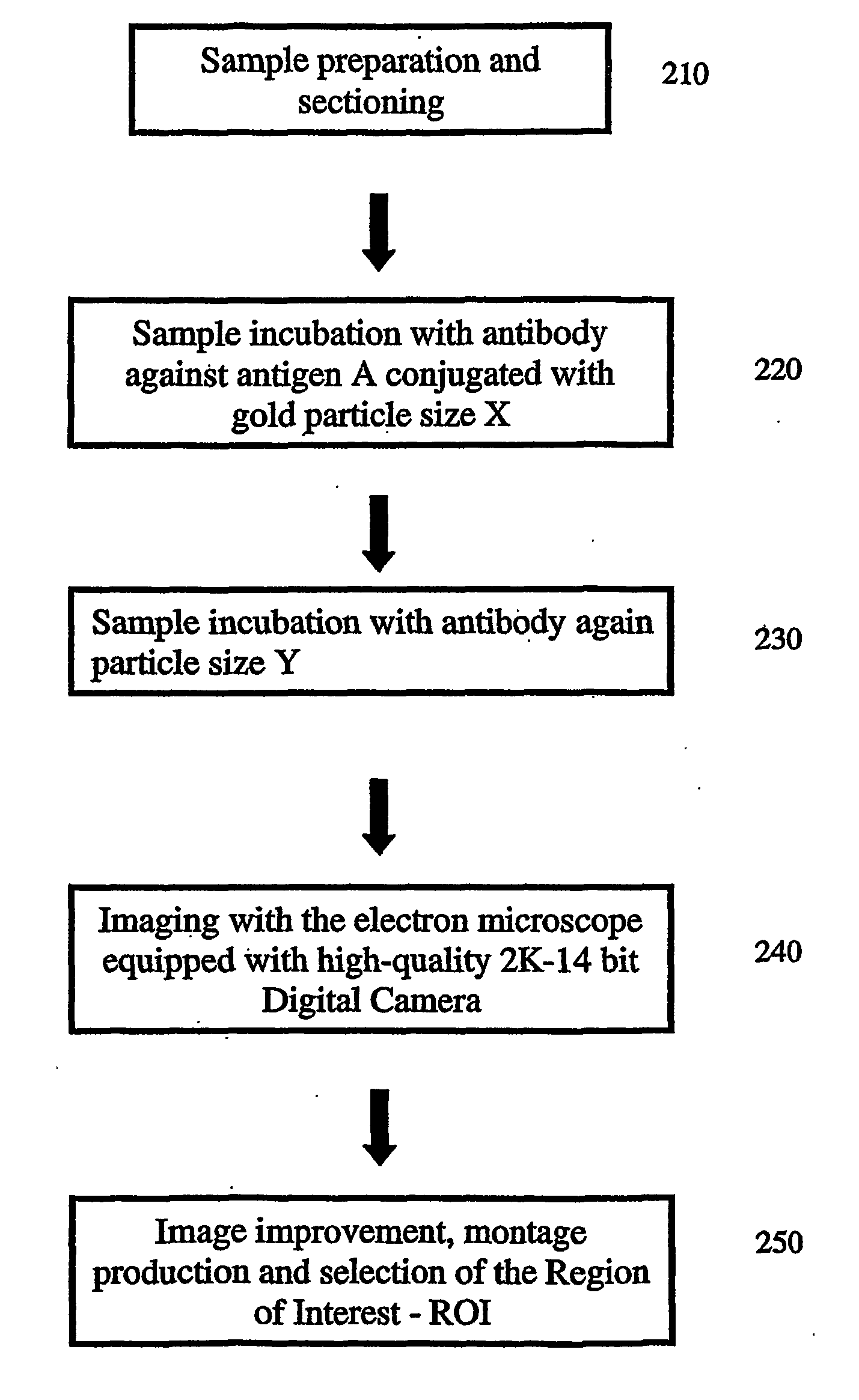
Method and apparatus for multiple labeling detection and evaluation of a plurality of particles
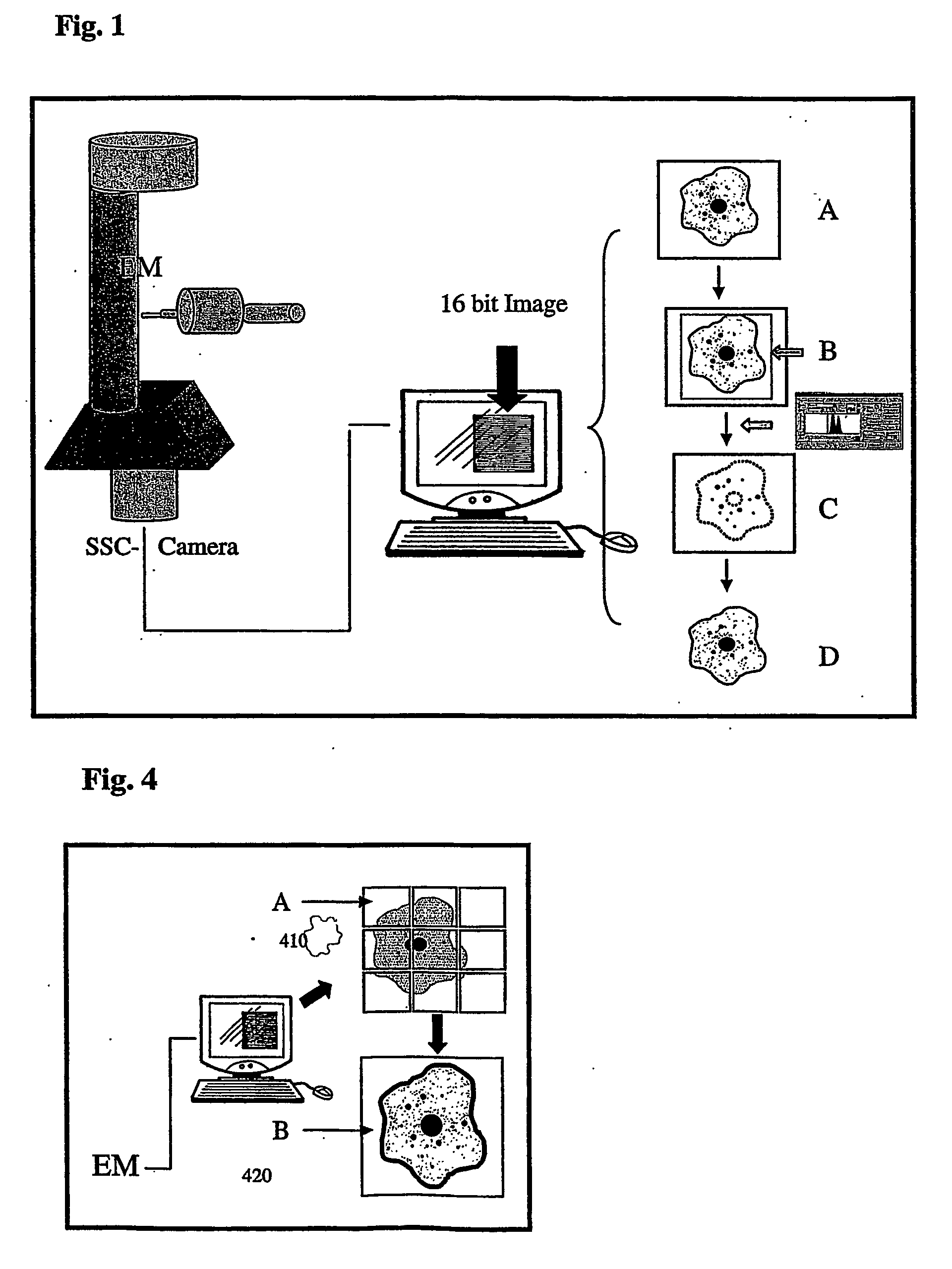
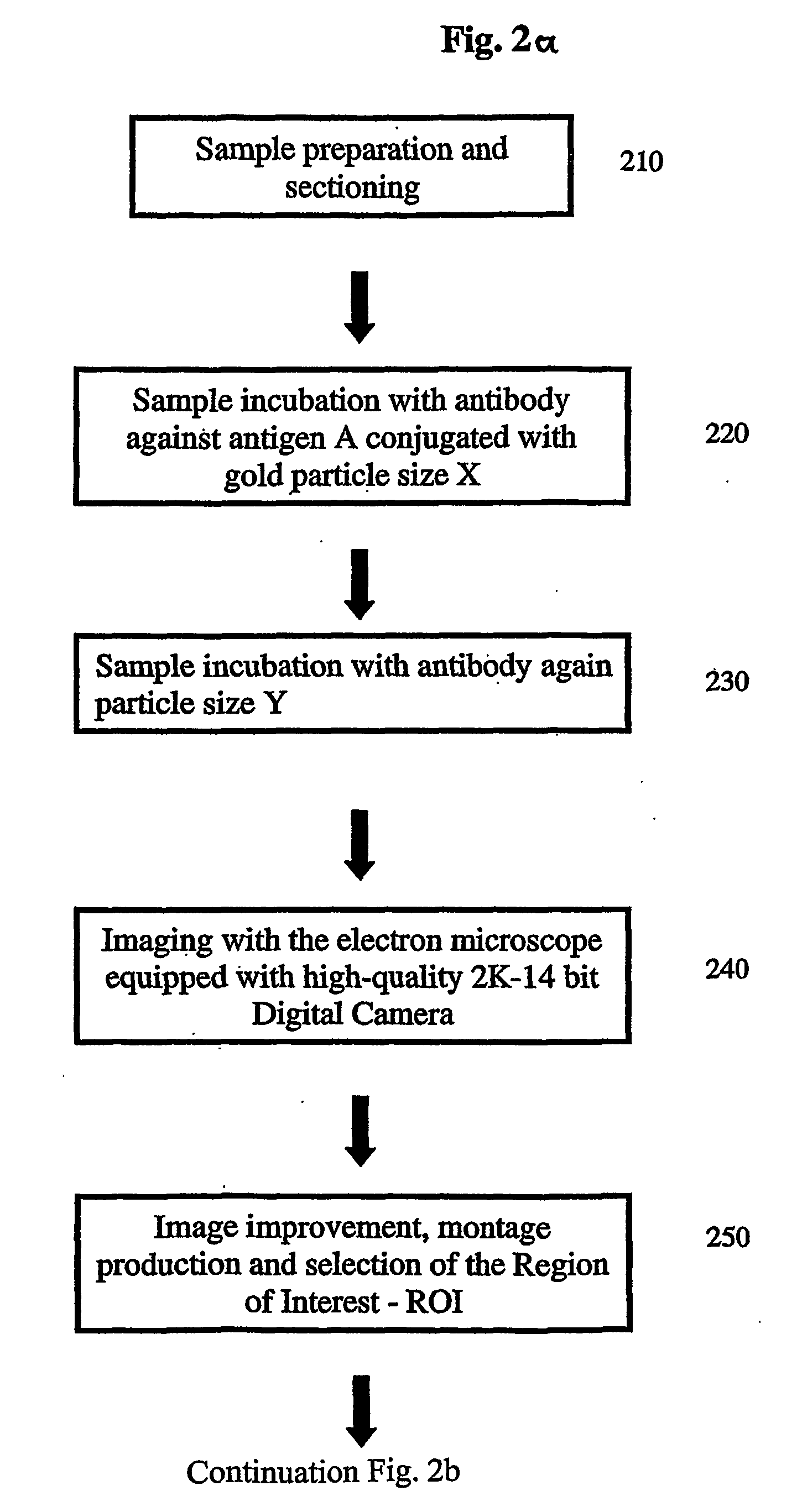
InactiveUS20060210129A1Fast and reliableFast and reliable detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGold particlesImage processing software
The invention relates to a transmission electron microscope equipped with a 2k−2k pixel area Slow Scan Cooled Charge Coupled Device Camera connected to an image processing software for generating an image of a sample. A segmentation of gold particles in the sample is achieved by the separation from specimen structure and background noise. An identification and classification of particle types is carried out according to the shape and size of the detected particles or particle pairs and finally, the gold particle distribution is visualized by the generation of false color overlay images as well as the indication of the numbers in the image.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
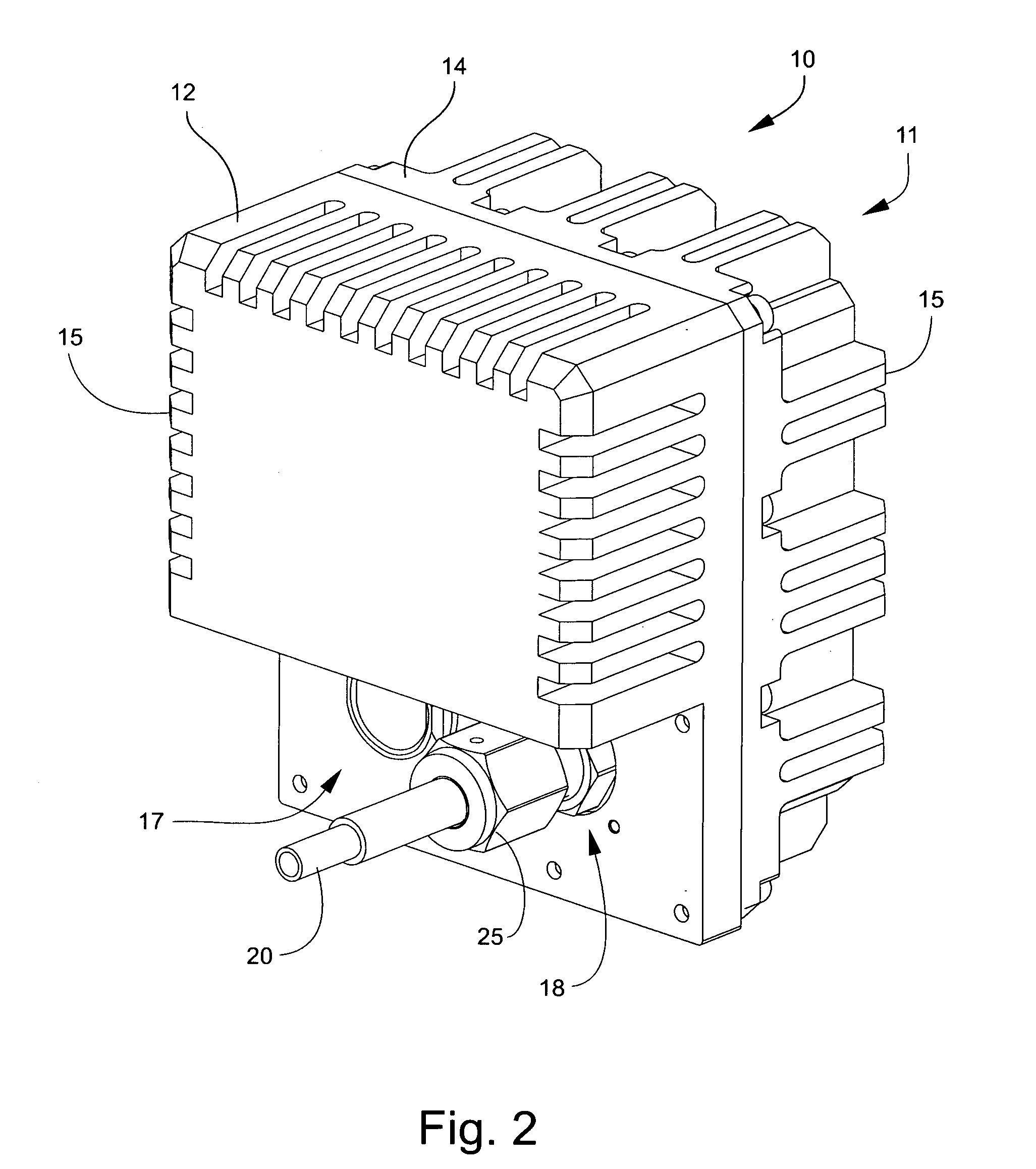
CCD camera architecture and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20130182179A1Improve dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsIndiumCharge coupled device camera
A charge-coupled device camera architecture for improving the dynamic range of the charge-coupled device camera having a charge-coupled device camera contained within a vacuum capable camera case and electrically attached to the outside of the camera case; a thermoelectric cooler thermally attached to a back side of the charge-coupled device camera and electrically attached to the outside of the camera case; a thermal redistribution block thermally attached to the thermoelectric cooler and further thermally attached to the camera case; a pressure measuring mechanism attached to an inside surface of the camera case and electrically connected to the outside of the camera case; a temperature measuring mechanism attached to a surface of the thermal redistribution block and electrically connected to the outside of the camera case; and a vacuum evacuation assembly having an indium lined copper pinch tube.
Owner:PAGE STEPHEN K +1
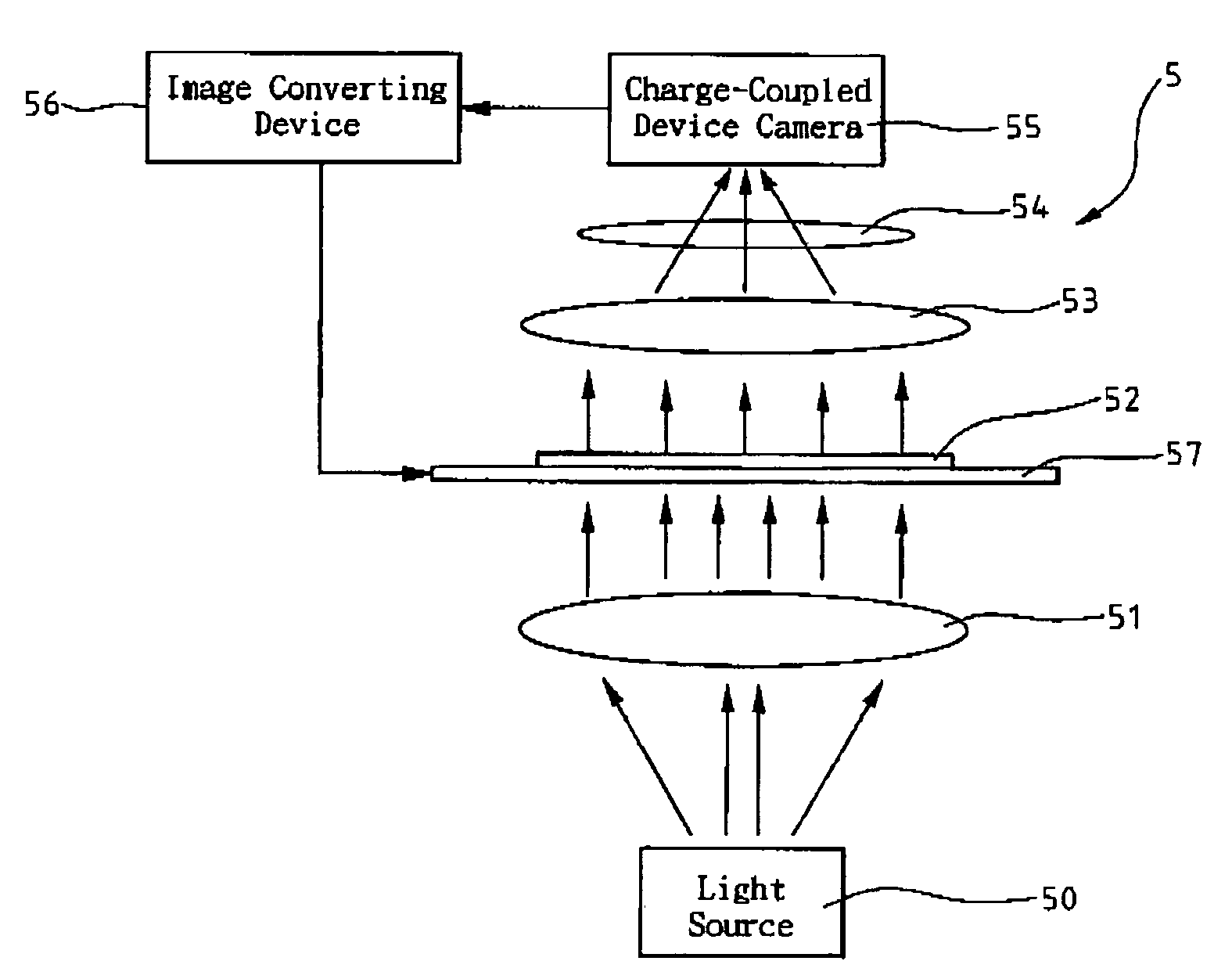
CCD-based biochip reader
InactiveUS7173701B2Efficient and rapid detectionImprove efficiencyPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersDigital dataCharge coupled device camera
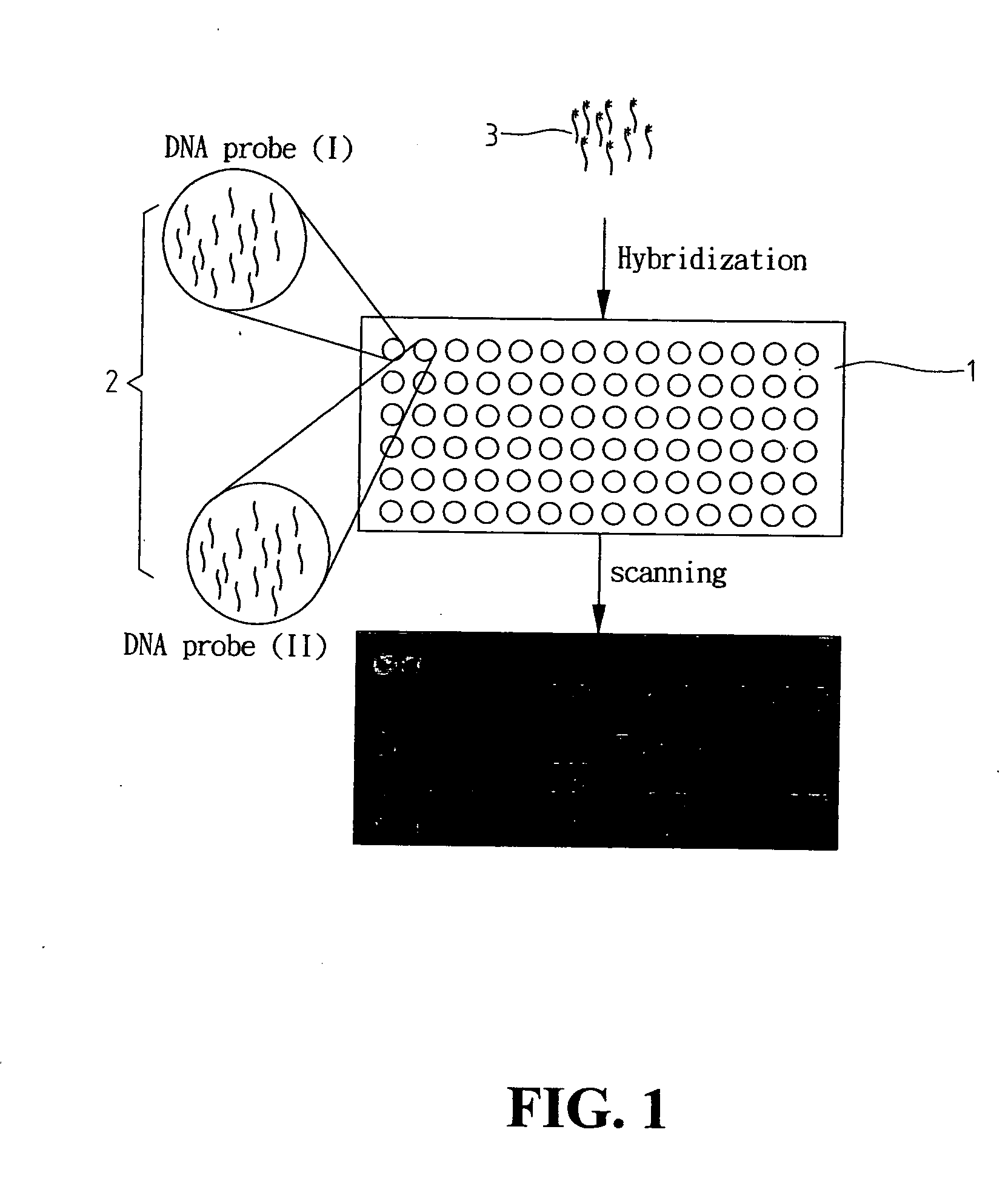
A CCD-based biochip reader includes a light source for emitting light beams, a collimating lens for converting the light beams into wide parallel rays of light, passing said wide parallel rays of light through a biochip and exciting fluorescence from fluorescent targets on the biochip, a focusing lens for focusing the fluorescence, a filter for filtering out said parallel rays of light, and a charge-coupled device camera for generating images from said fluorescence. For recording intensity of the fluorescence from the fluorescent targets, images of the charge-coupled device camera is converted into digital data through an image converting device. Wide parallel laser beams are produced by the laser and through the collimating lens, and excite all samples on the biochip with high efficiency at the same time. In addition, time for analysis is saved when fluorescent images of a large area on biochips are collected and analyzed through the charge-coupled device camera.
Owner:KAIWOOD TECH
Portable electronic apparatus
InactiveCN1346456ACasings/cabinets/drawers detailsDetails for portable computersBusiness cardComputer graphics (images)
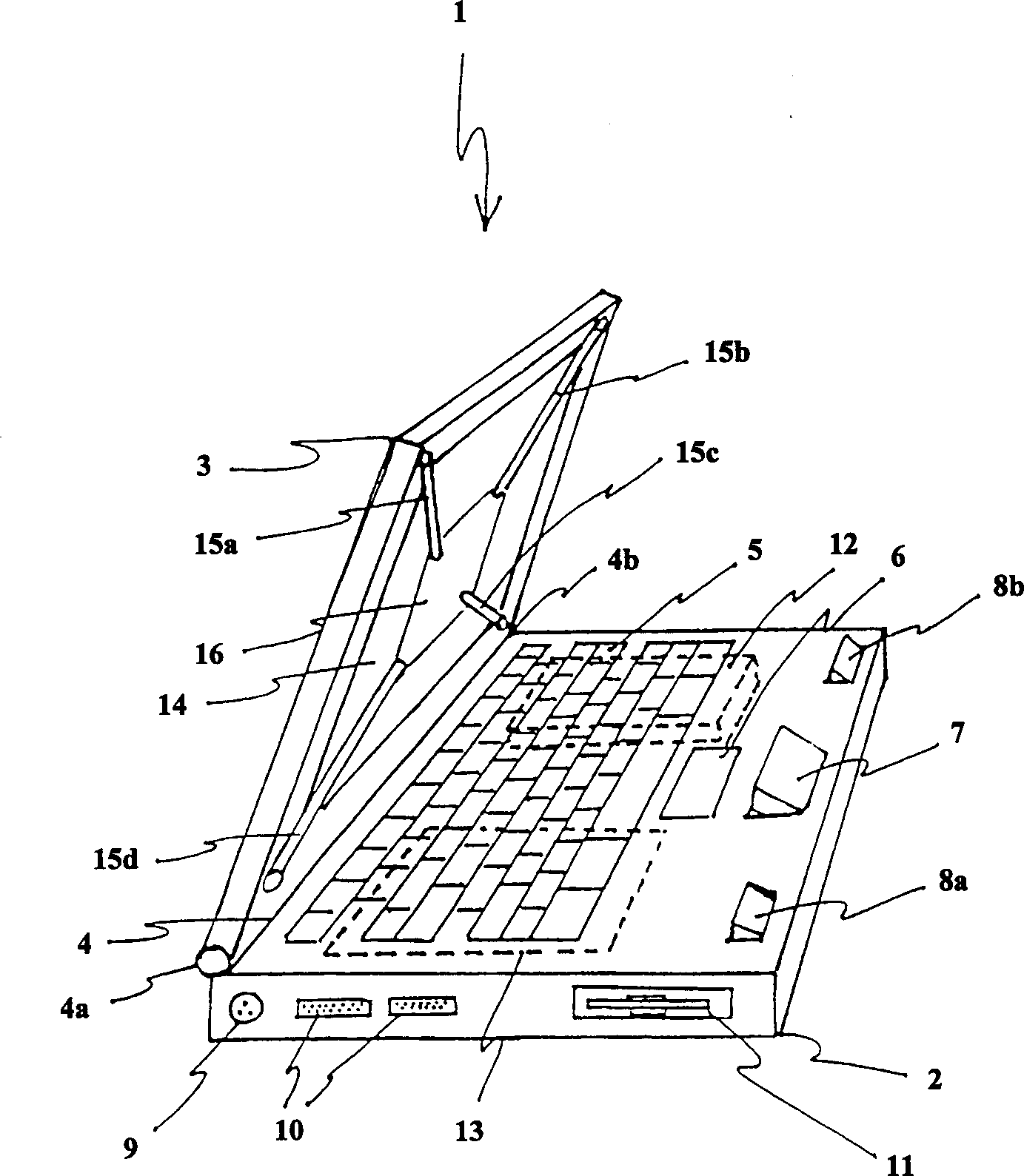
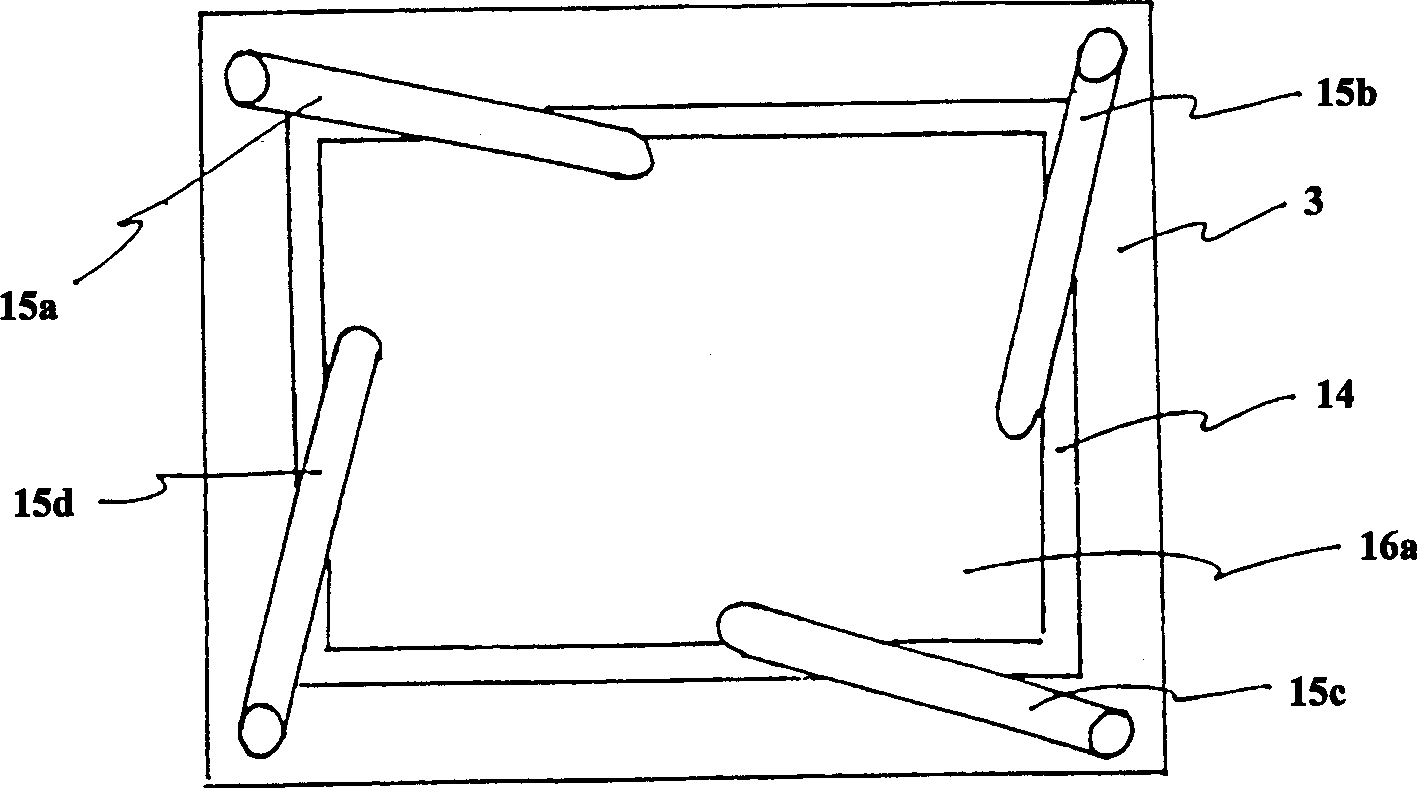
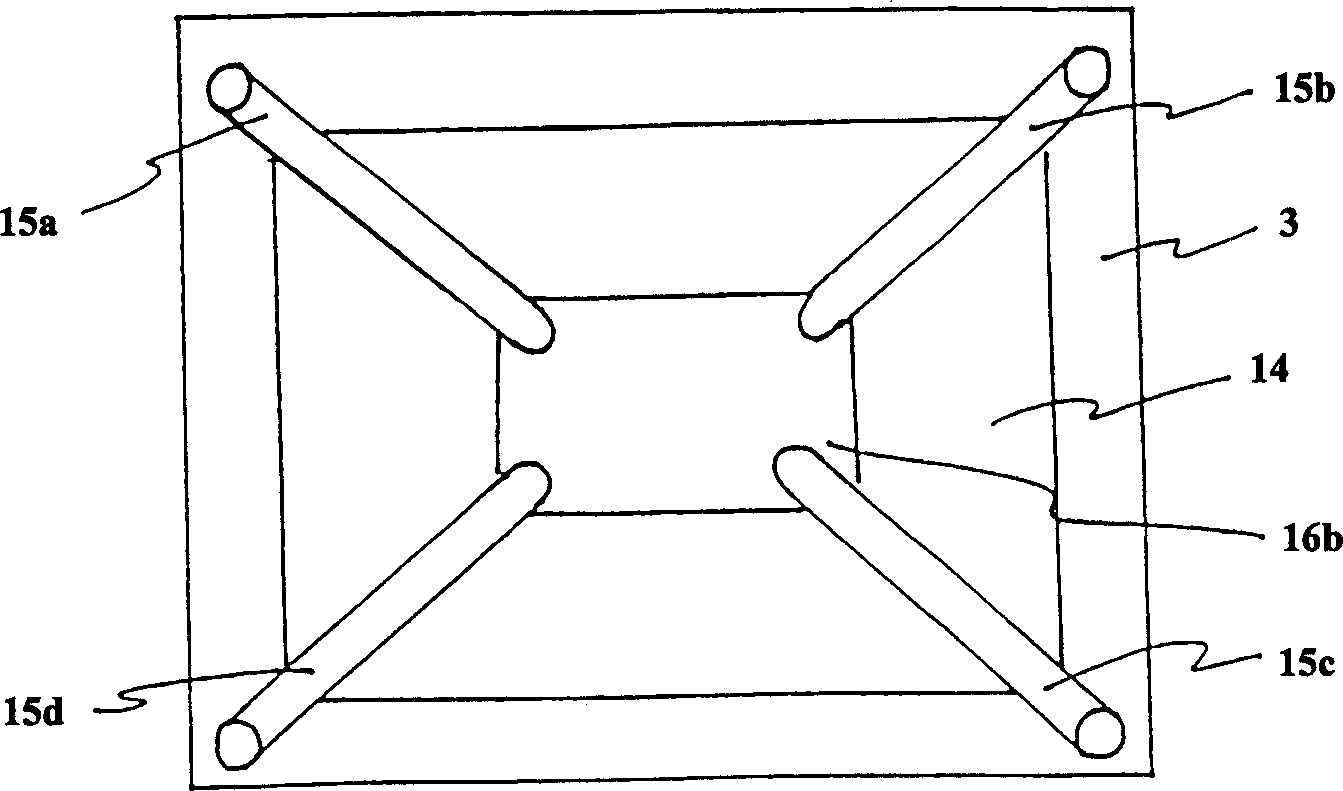
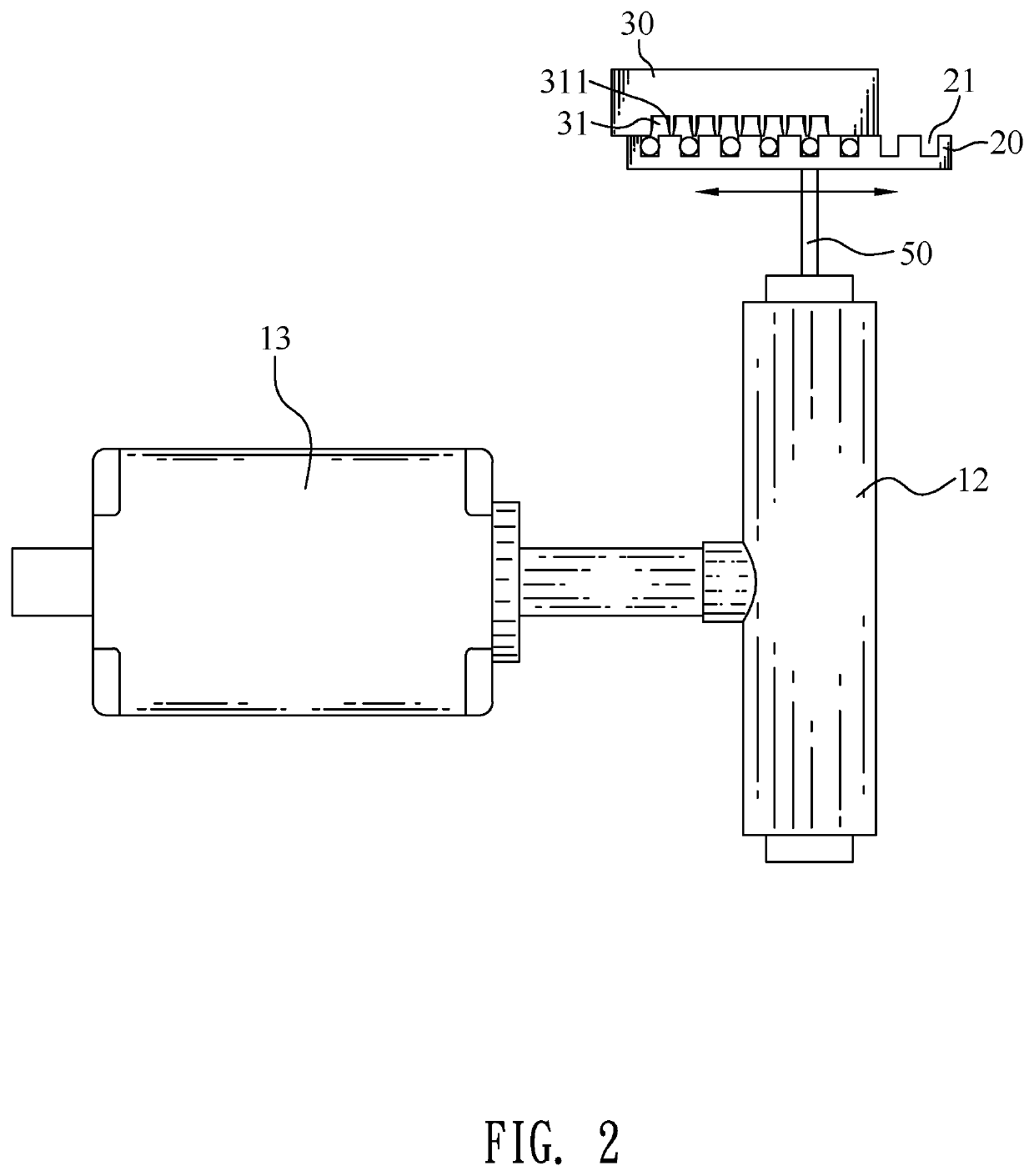
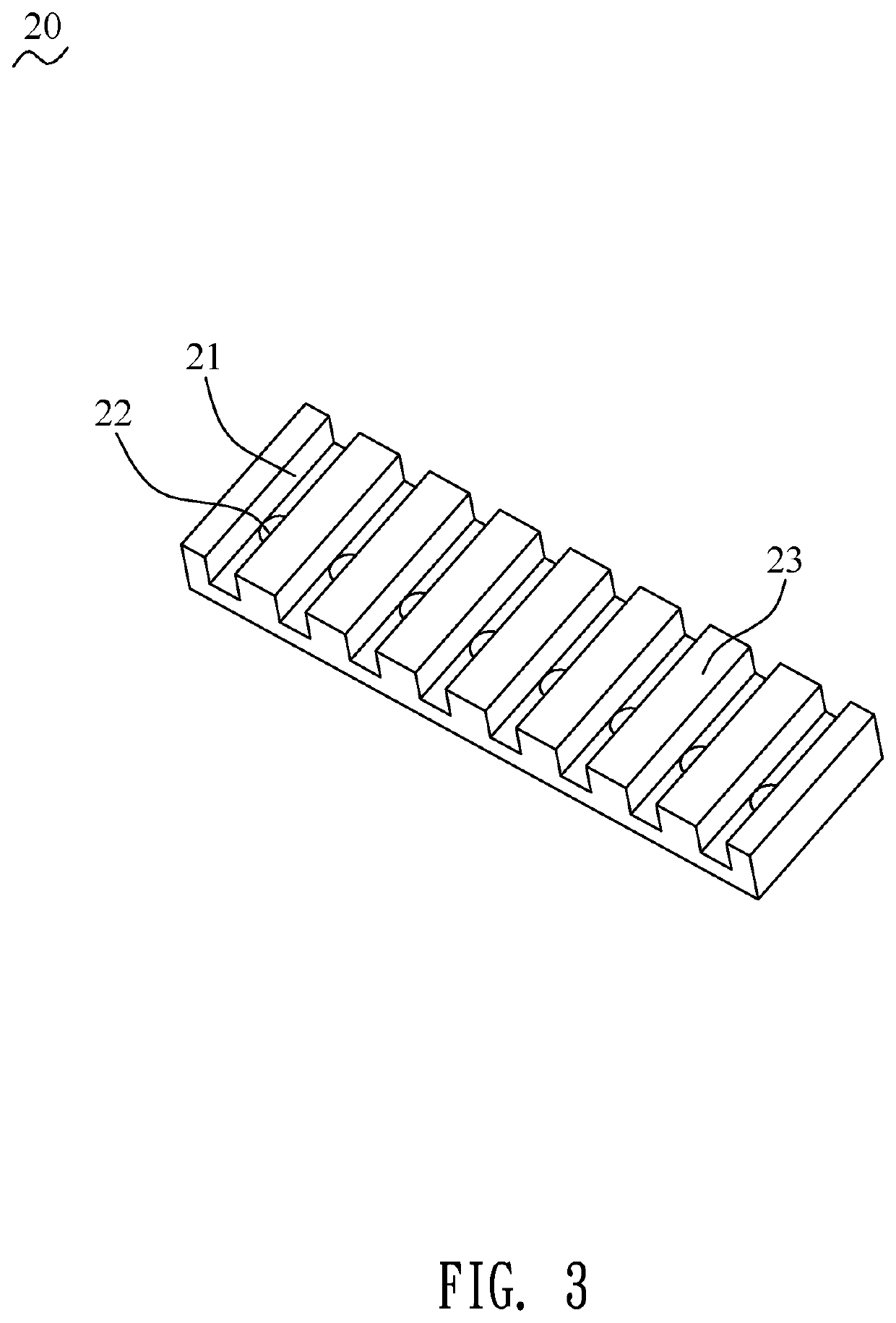
A charge coupled device camera (7) is incorporated into one wing (2) of a portable personal computer (1). A document (16), such as a business card, is placed on the other wing (3), secured by means of clips (15a,15b,15c,15d) or transparent ribbons (125a,125b,125c,125d) and photographed. Blurring of the captured image is reduced because the camera and the document are mounted to the same substrate. Also, optimal positioning of the document is achieved more quickly and easily using this arrangement than using a separate stand to mount the document.
Owner:JOHN QUENTIN PHILLIPPS 30 MOUNT AVENUE EALING LONDON W5 2QJ UK
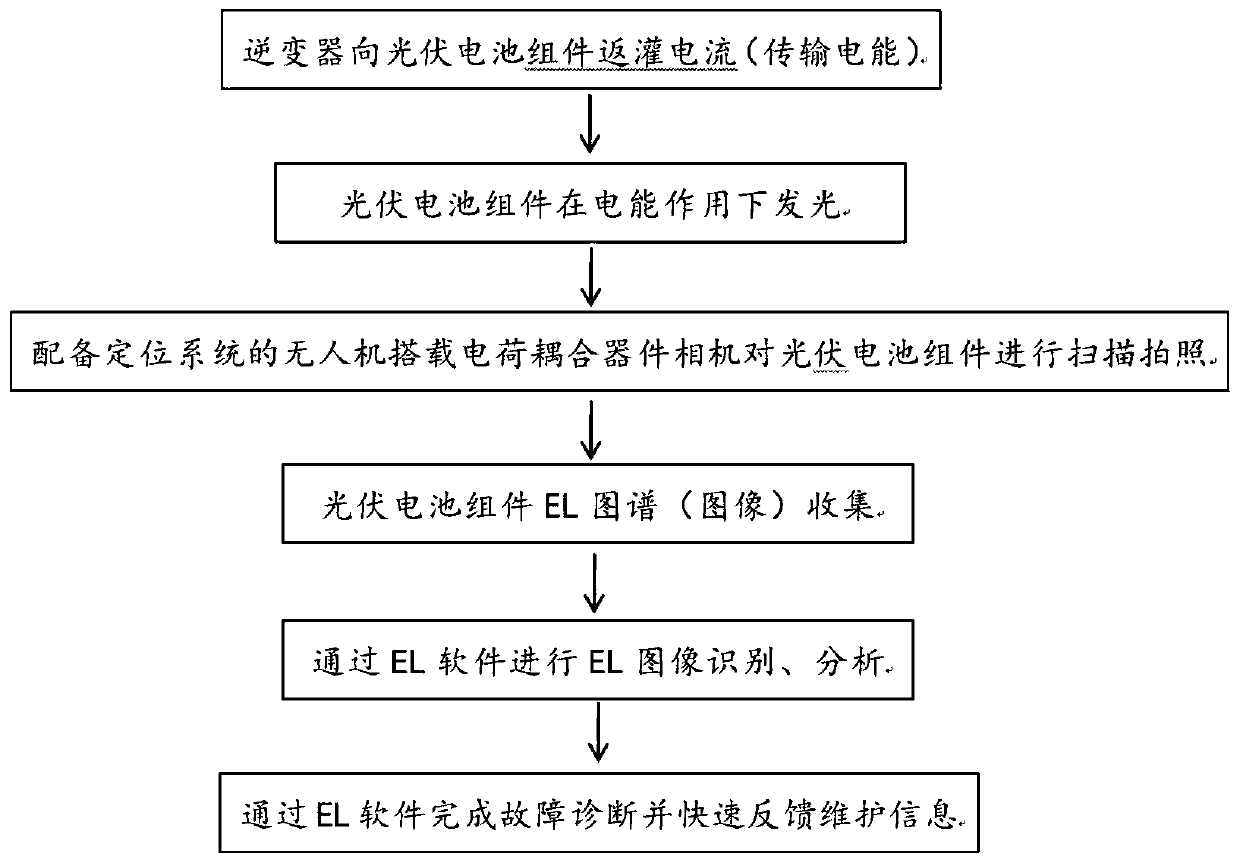
Method for carrying out EL (Electroluminescence) real-time online atlas collection, analysis and diagnosis on photovoltaic cell module by applying unmanned aerial vehicle and backward filling technology of inverter
InactiveCN110277962APhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationCharge coupled device cameraPositioning system
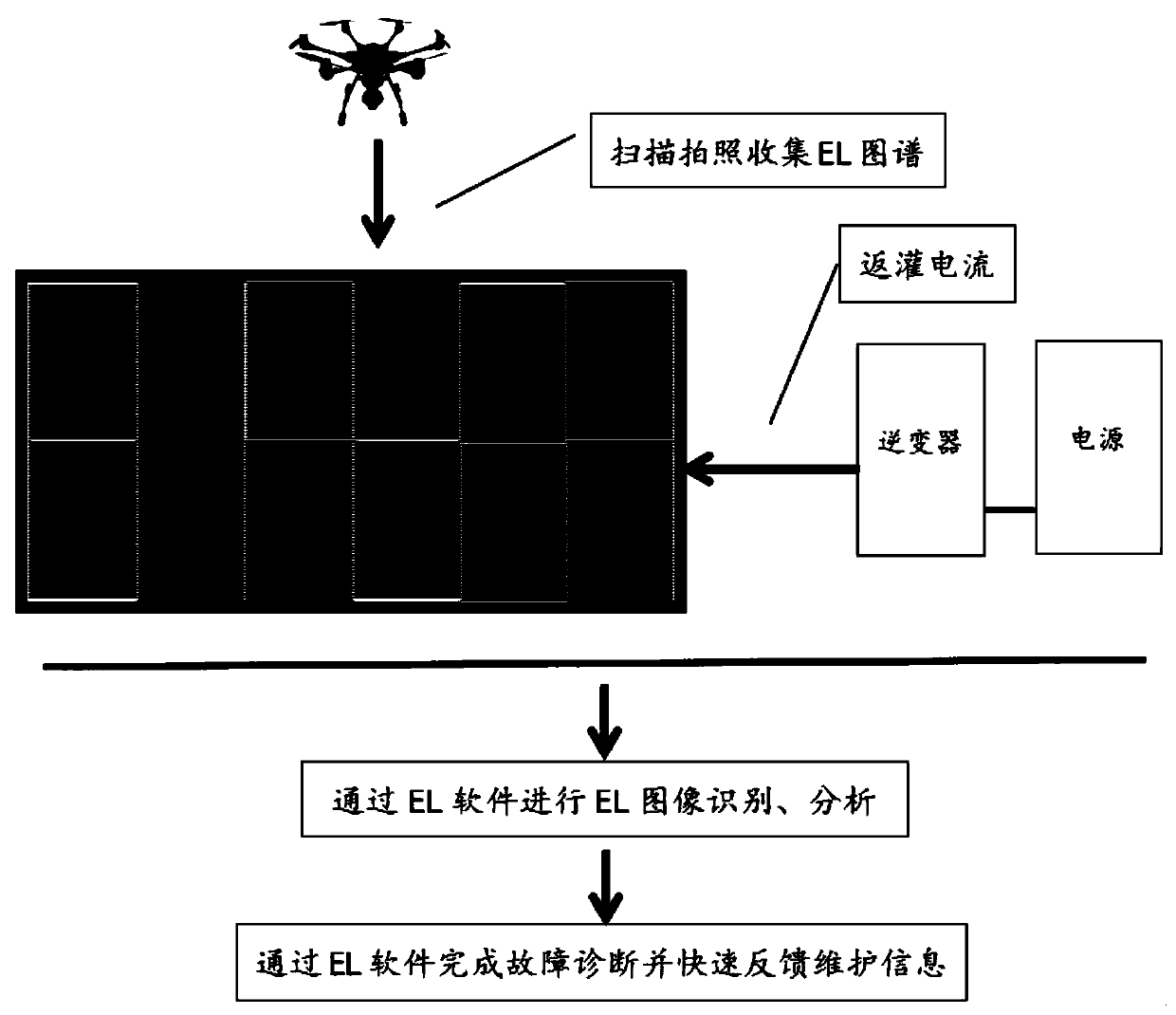
The invention aims to provide a method for carrying out EL (Electroluminescence) real-time online atlas collection, analysis and diagnosis on a photovoltaic cell module by applying an unmanned aerial vehicle and a backward filling technology of an inverter. The EL detection method comprises the steps that the inverter automatically performs backward current filling (electric energy transmission) on the photovoltaic cell module at a constant value; the photovoltaic cell module emits light under the action of the electric energy; the unmanned aerial vehicle equipped with a positioning system carries a charge-coupled device camera to perform scanning and photographing on the photovoltaic cell module in the light emitting state; an EL atlas (image) of the photovoltaic cell module is collected; EL software performs EL image identification and analysis; and the EL software completes fault diagnosis and quickly feeds back maintenance information, thereby achieving the purpose of the invention. The EL detection method provided by the invention can significantly improve the detection efficiency of the photovoltaic cell module.
Owner:NAT ELECTRIC POWER INVESTMENT GRP YELLOW RIVER UPSTREAM HYDROPOWER DEV CO LTD +1
Luminescence detection workstation
InactiveUS20060088444A1Minimize crosstalkChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationCamera lensCharge coupled device camera
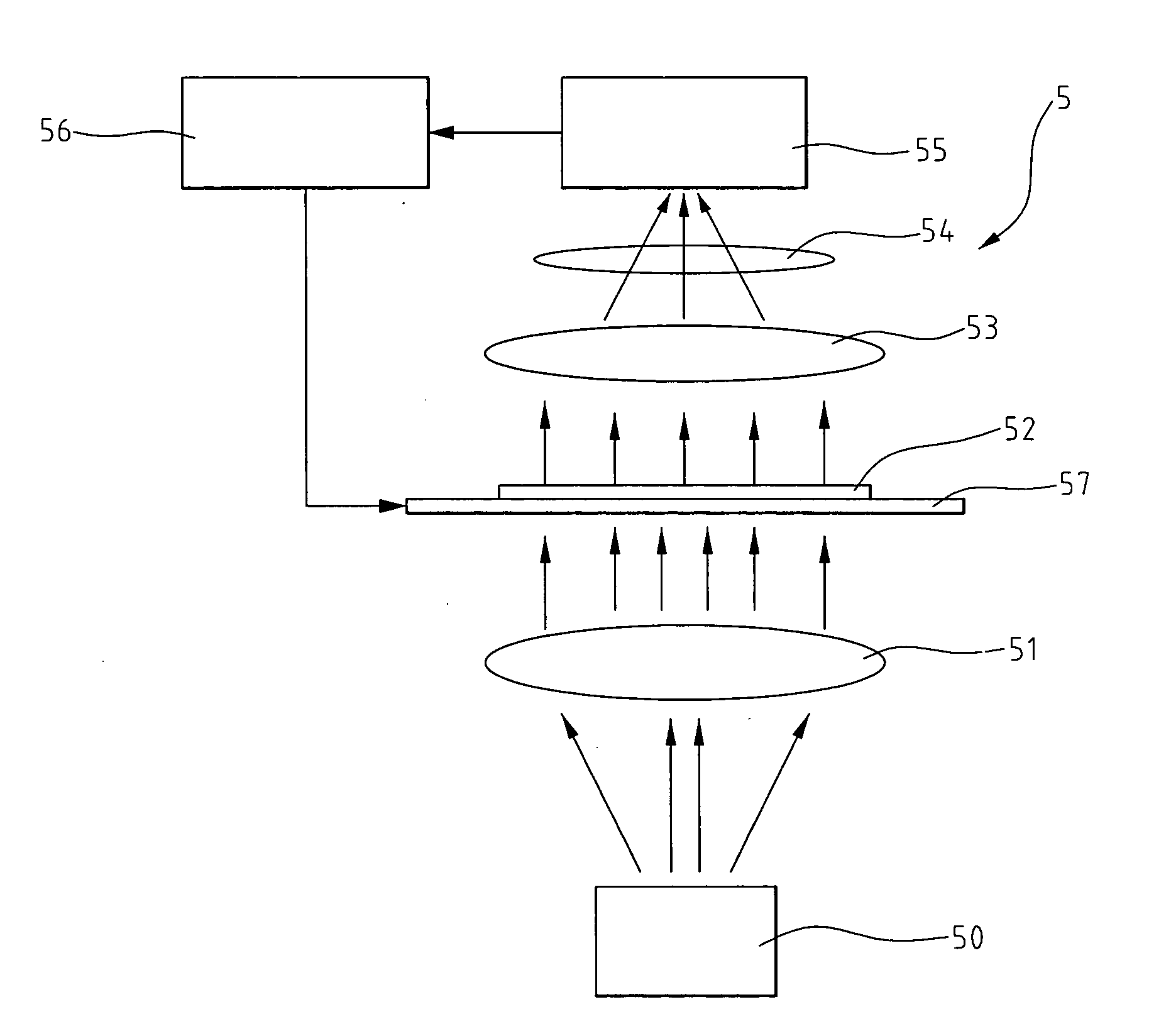
In a luminescence detecting apparatus and method for analyzing luminescent samples, luminescent samples are placed in a plurality of sample wells in a tray, and the tray is placed in a visible-light impervious chamber containing a charge coupled device camera. In the chamber, light from the luminescent samples pass through a collimator, a Fresnel field lens, an infrared filter, and a camera lens, whereupon a focused image is created by the optics on the camera. The use of an infrared filter suppresses stray IR radiation resulting from plate phosphorescence (which can result in abnormally high backgrounds and / or alteration of the image received by the camera).
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
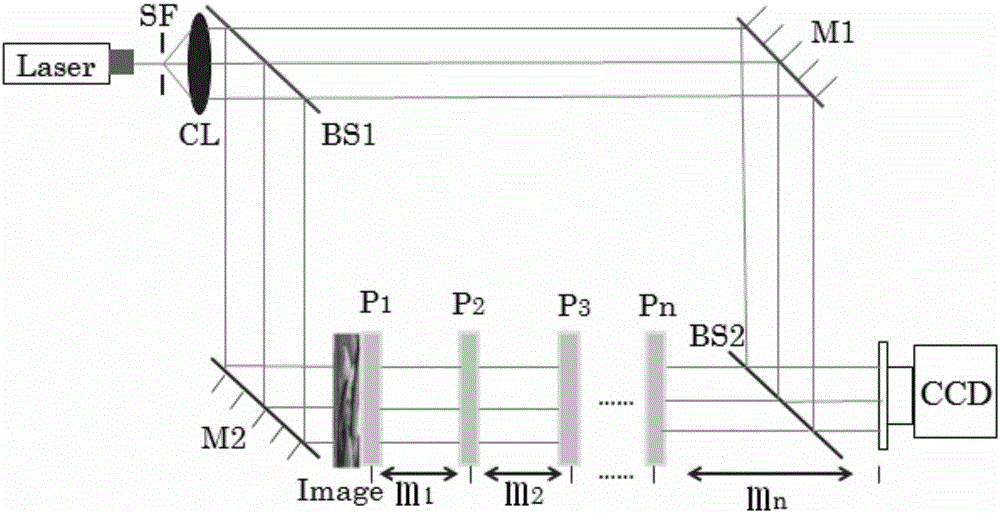
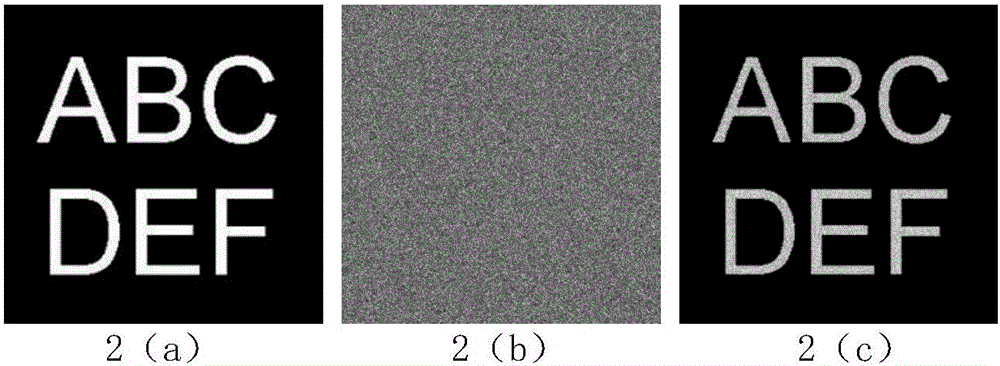
Cascade Fresnel holographic encryption system and method combining two-dimensional chaos and constrained optimization algorithm
PendingCN106447591AEasy to manageEasy transferImage data processing detailsBeam splitterCharge coupled device camera
The invention discloses a cascade Fresnel holographic encryption system and method combining two-dimensional chaos and a constrained optimization algorithm. The system comprises a laser, a spatial filter, a lens, a first beam splitter and a first mirror. A second mirror is arranged on the lower end of the first beam splitter. A second beam splitter is arranged on the lower end of the first mirror. A chaotic random phase mask is arranged between the second mirror and the second beam splitter. A charge coupling device camera is arranged on the other side of the second beam splitter. The method comprises the steps of key generation, image encryption and image decryption. According to the invention, the problem that plural encrypted images are not easily directly recorded is solved from the aspect of an optical system; the problem that a dynamic video cannot be encrypted is solved from the aspect of a recovery algorithm; and key management and transmission are realized from the aspect of a key generation method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
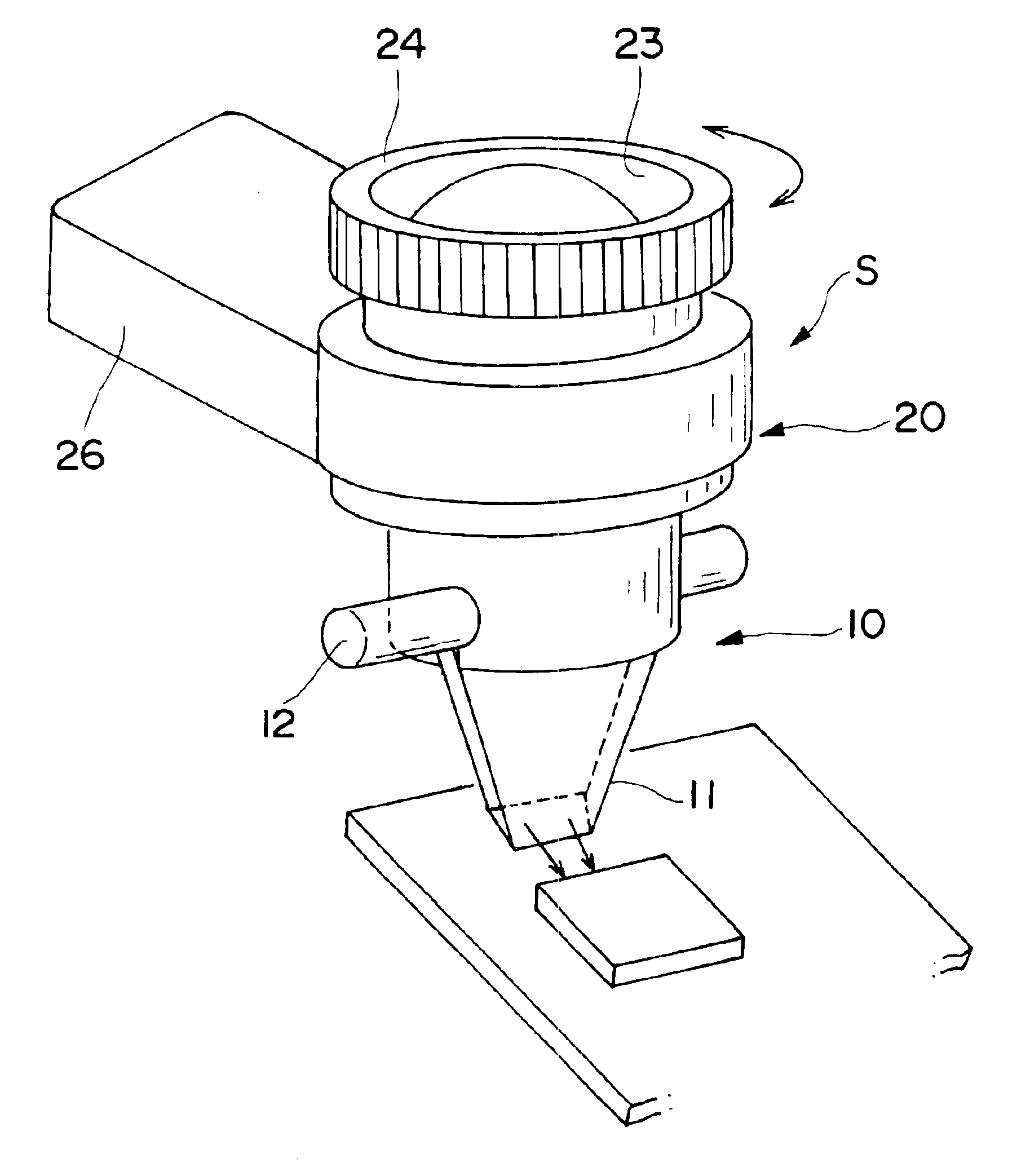
Microscope
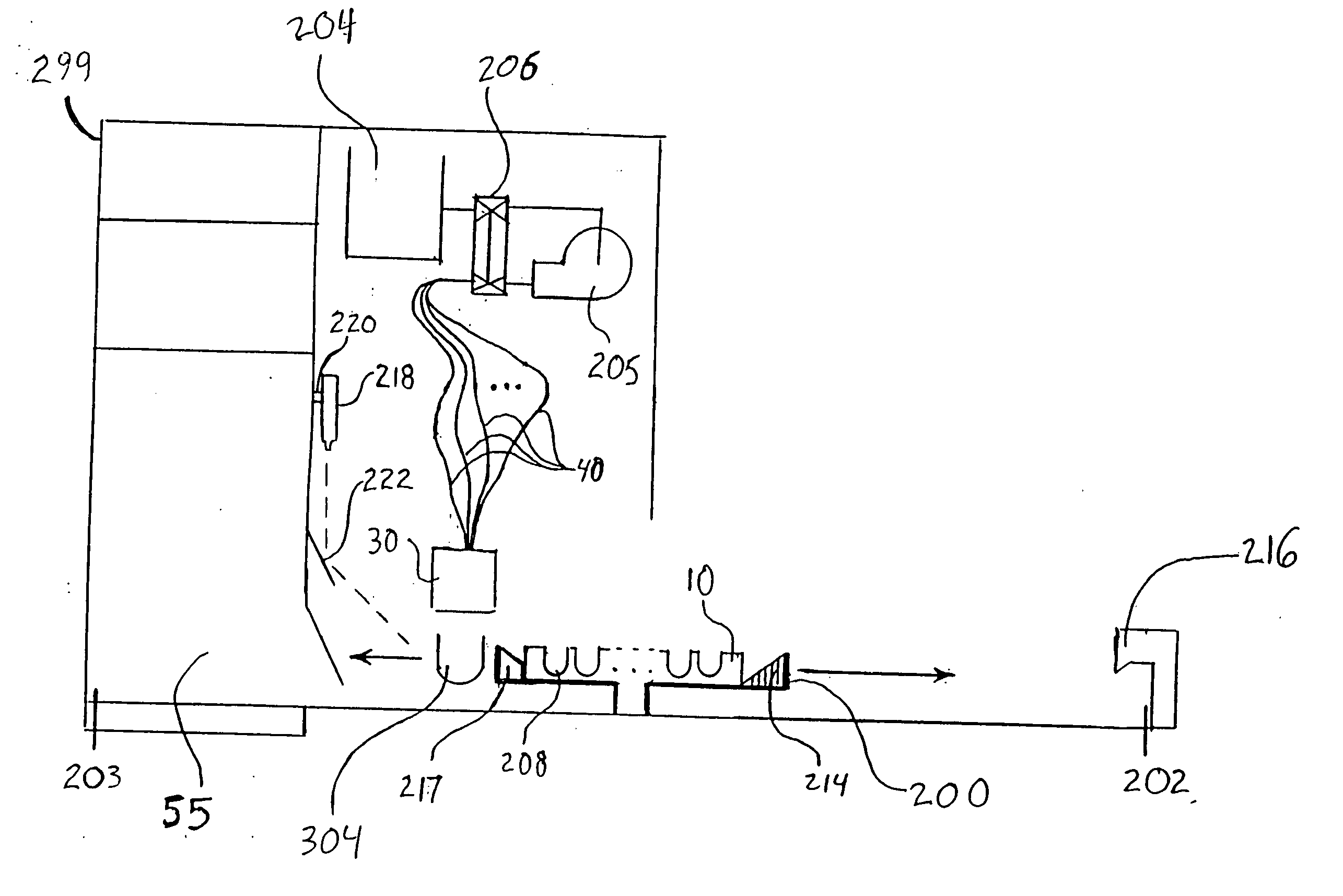
InactiveUS6853482B1Improve lighting efficiencyLight efficiencyMicroscopesTelescopesHorizonCharge coupled device camera
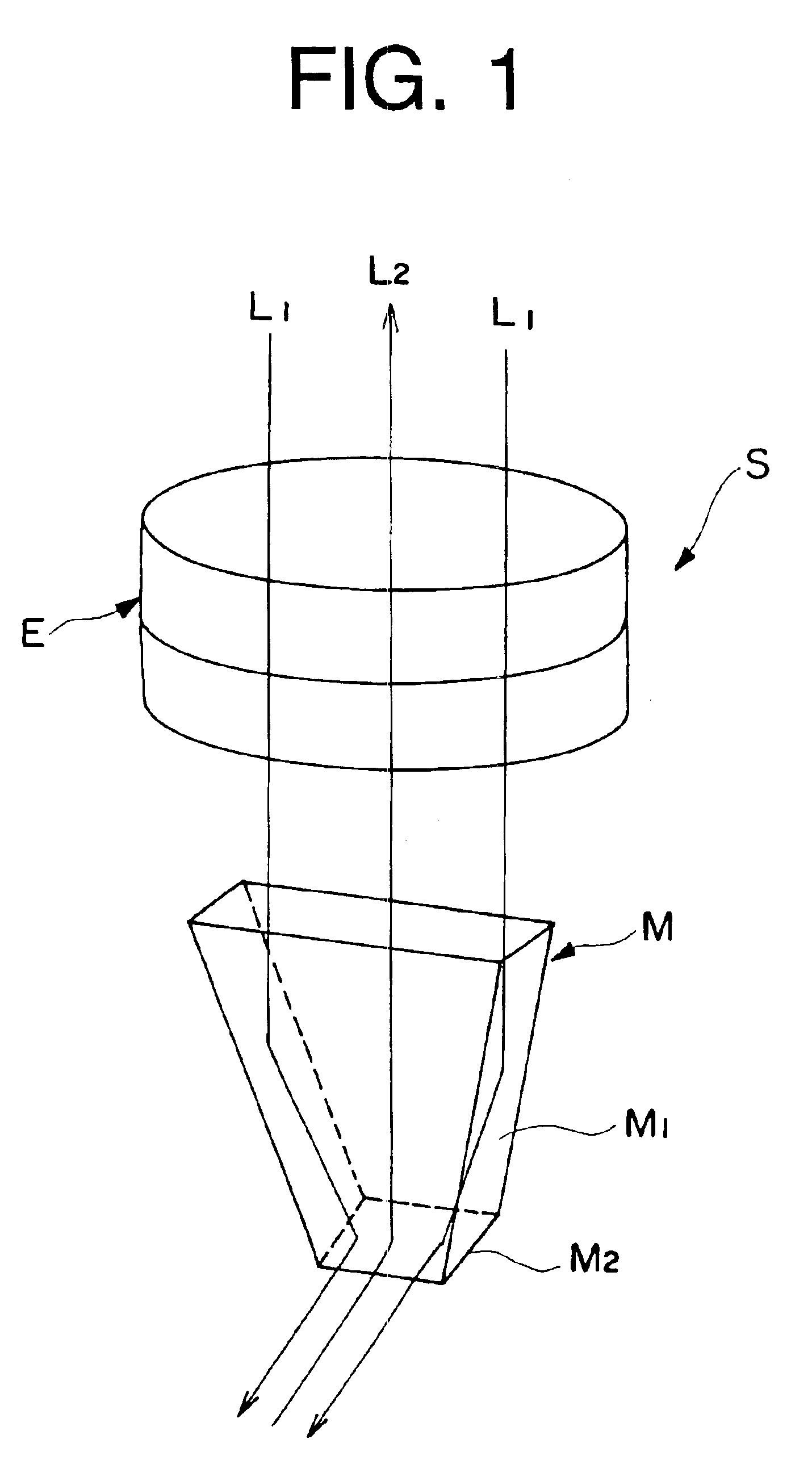
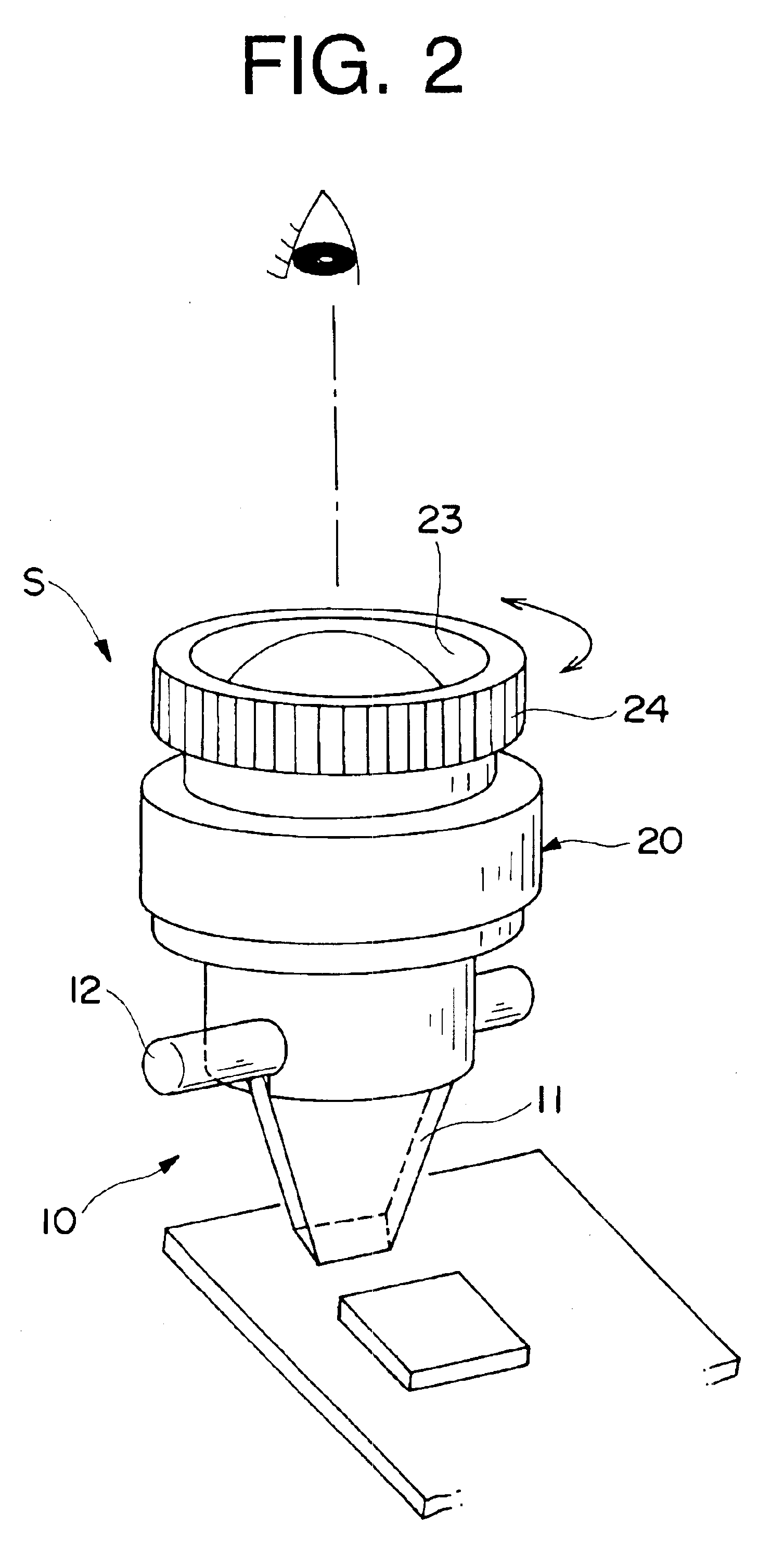
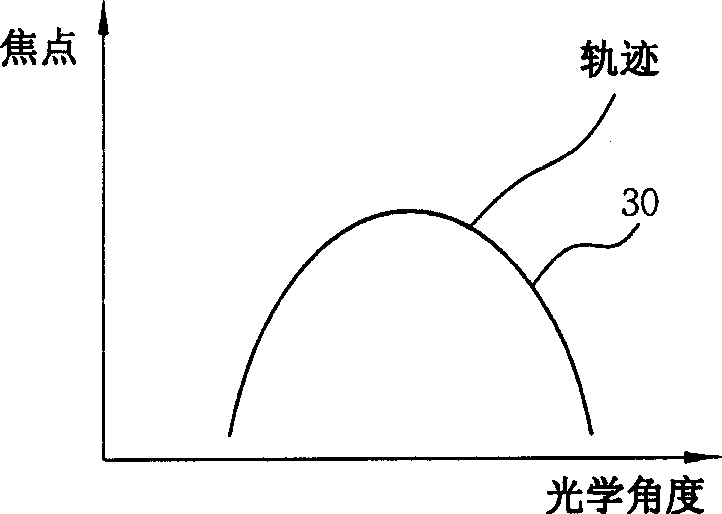
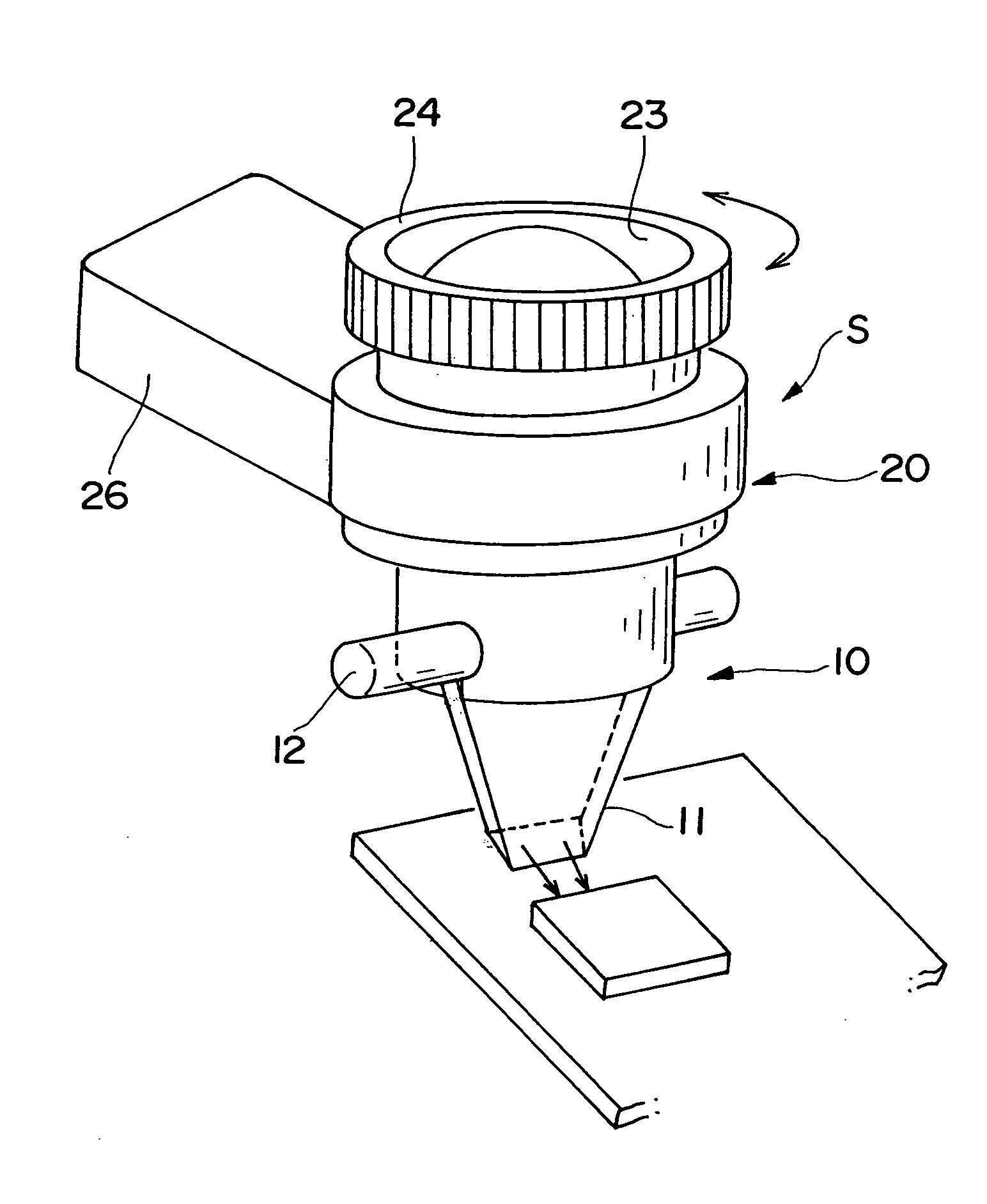
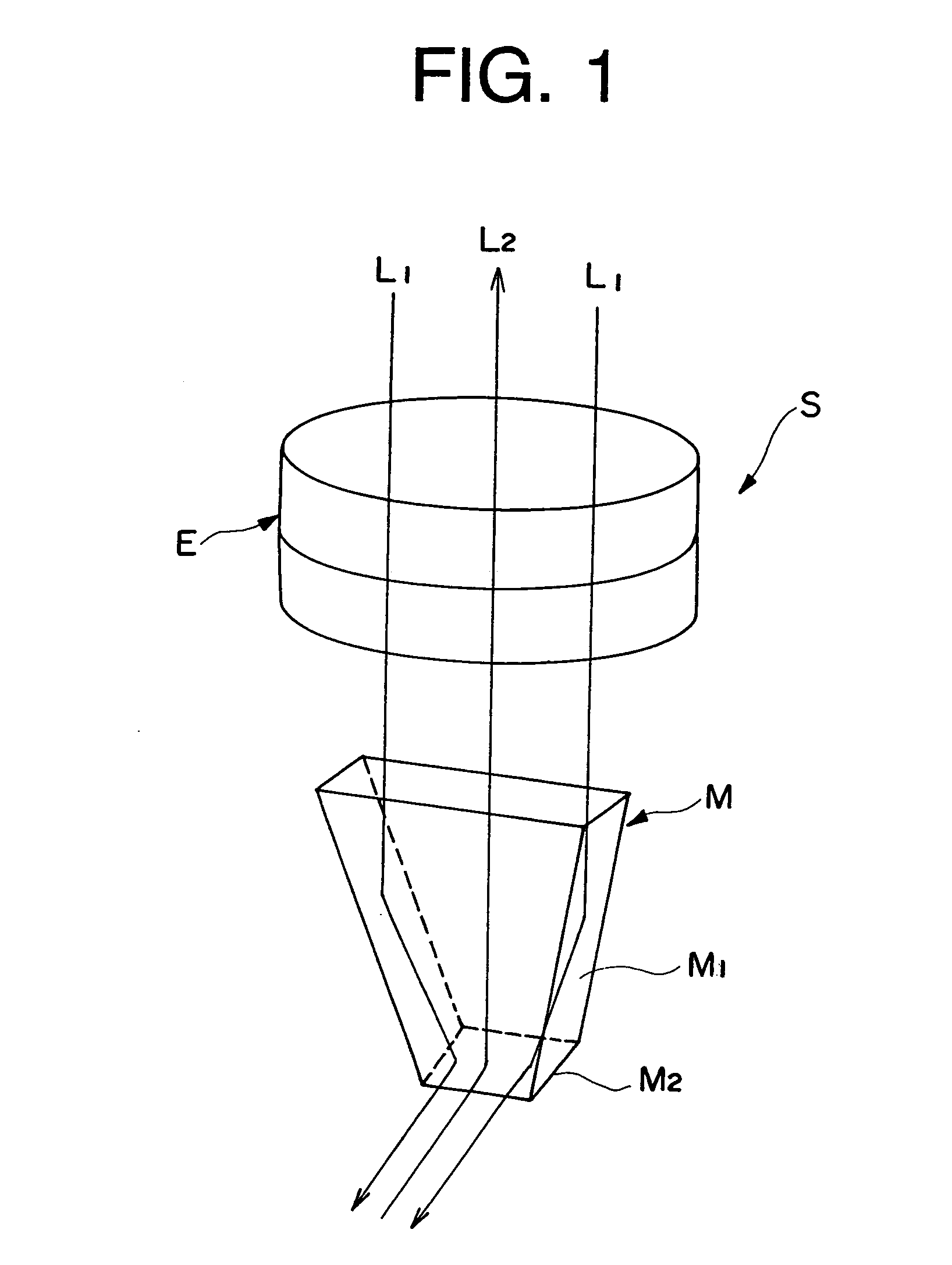
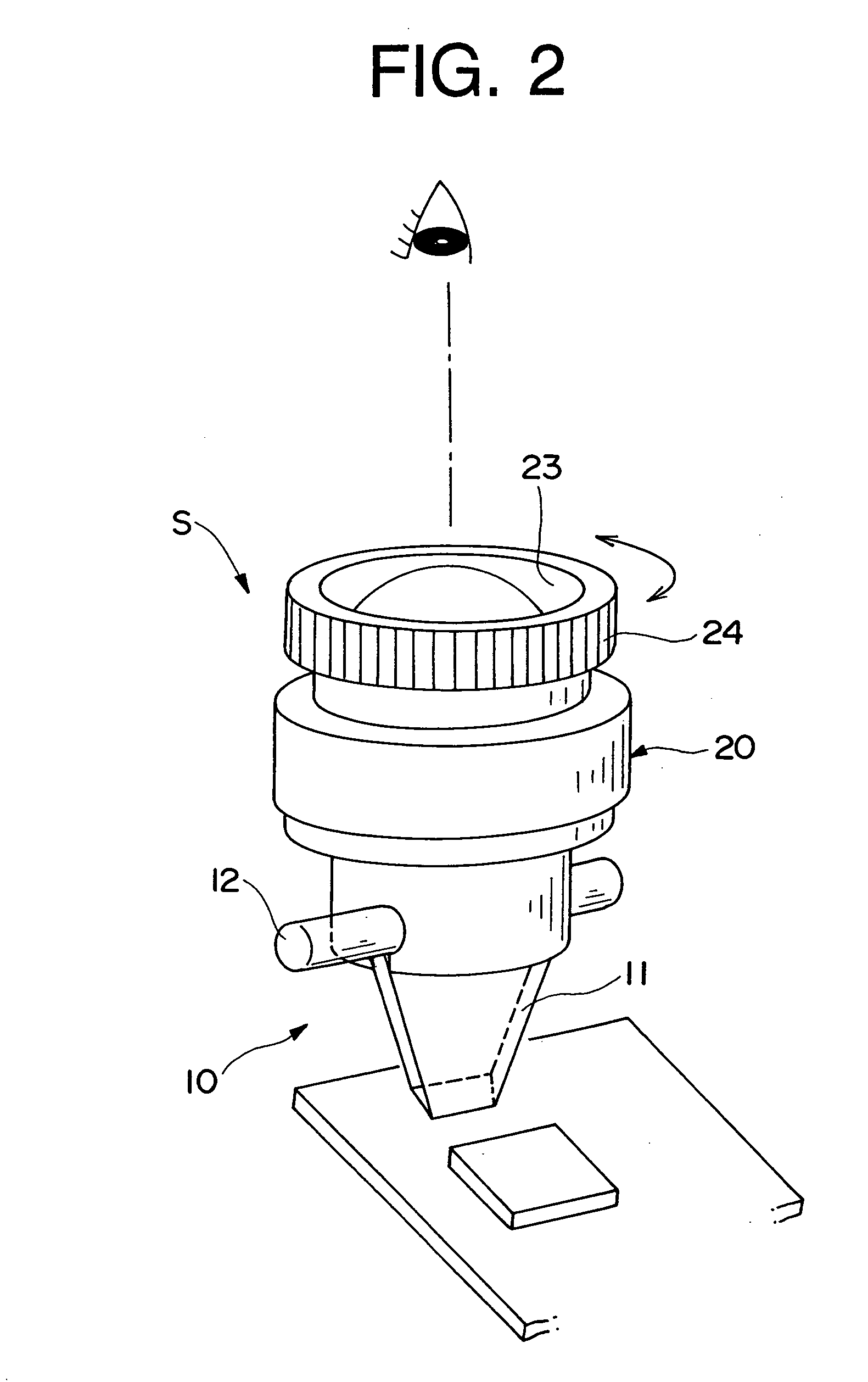
The microscope (S, 100) of the present invention has a hand piece (20, 112), whose tip is mounted with a thin sheet-like mirror unit (M, 10, 130, 220), and around both ends of the base (11c, 131c) thereof is arranged an illuminating light source (32, 117), whereby light is emitted to a target object, image light is lead through the light reception bore (27, 116), to the optical system (114), and is recorded at the CCD camera (111), to obtain video images. The thin sheet-like mirror (M, 11, 131) confines light and navigate it, wherein the width of the mirror can be made narrower like a convergent taper surface (11a, 131a); and it is comprised of a base surface (11c, 131c) where illuminating light comes in and image light goes out, and a mirror surface (11b, 131b) where illuminating light and image light go back and forth, and make the reflection thereof, and the mirror surface (11b, 131b) is slanted to 45 degrees. The microscope may be used as a handy microscope if it is not equipped with a charge-coupled device camera. The microscope can provide a wider horizon, which makes it possible to make a horizontal observation in an extremely narrow space, and can be manufactured at a less expensive price.
Owner:KITAMURA JUN +1
CCD-based biochip reader
InactiveUS20050179900A1Efficient and rapid detectionImprove efficiencyPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersDigital dataLight beam
A CCD-based biochip reader includes a light source for emitting light beams, a collimating lens for converting the light beams into wide parallel rays of light, passing said wide parallel rays of light through a biochip and exciting fluorescence from fluorescent targets on the biochip, a focusing lens for focusing the fluorescence, a filter for filtering out said parallel rays of light, and a charge-coupled device camera for generating images from said fluorescence. For recording intensity of the fluorescence from the fluorescent targets, images of the charge-coupled device camera is converted into digital data through an image converting device. Wide parallel laser beams are produced by the laser and through the collimating lens, and excite all samples on the biochip with high efficiency at the same time. In addition, time for analysis is saved when fluorescent images of a large area on biochips are collected and analyzed through the charge-coupled device camera.
Owner:KAIWOOD TECH
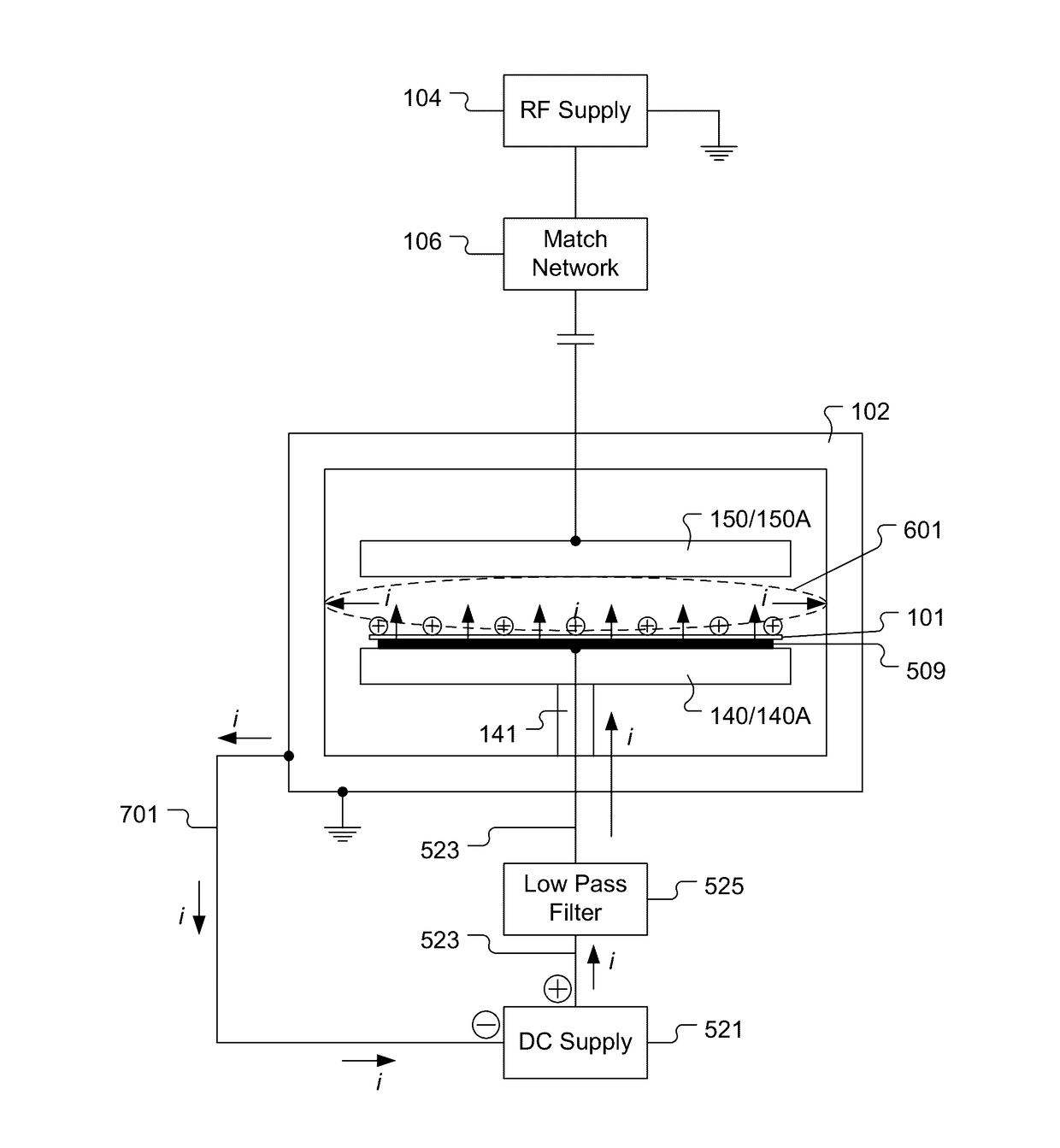
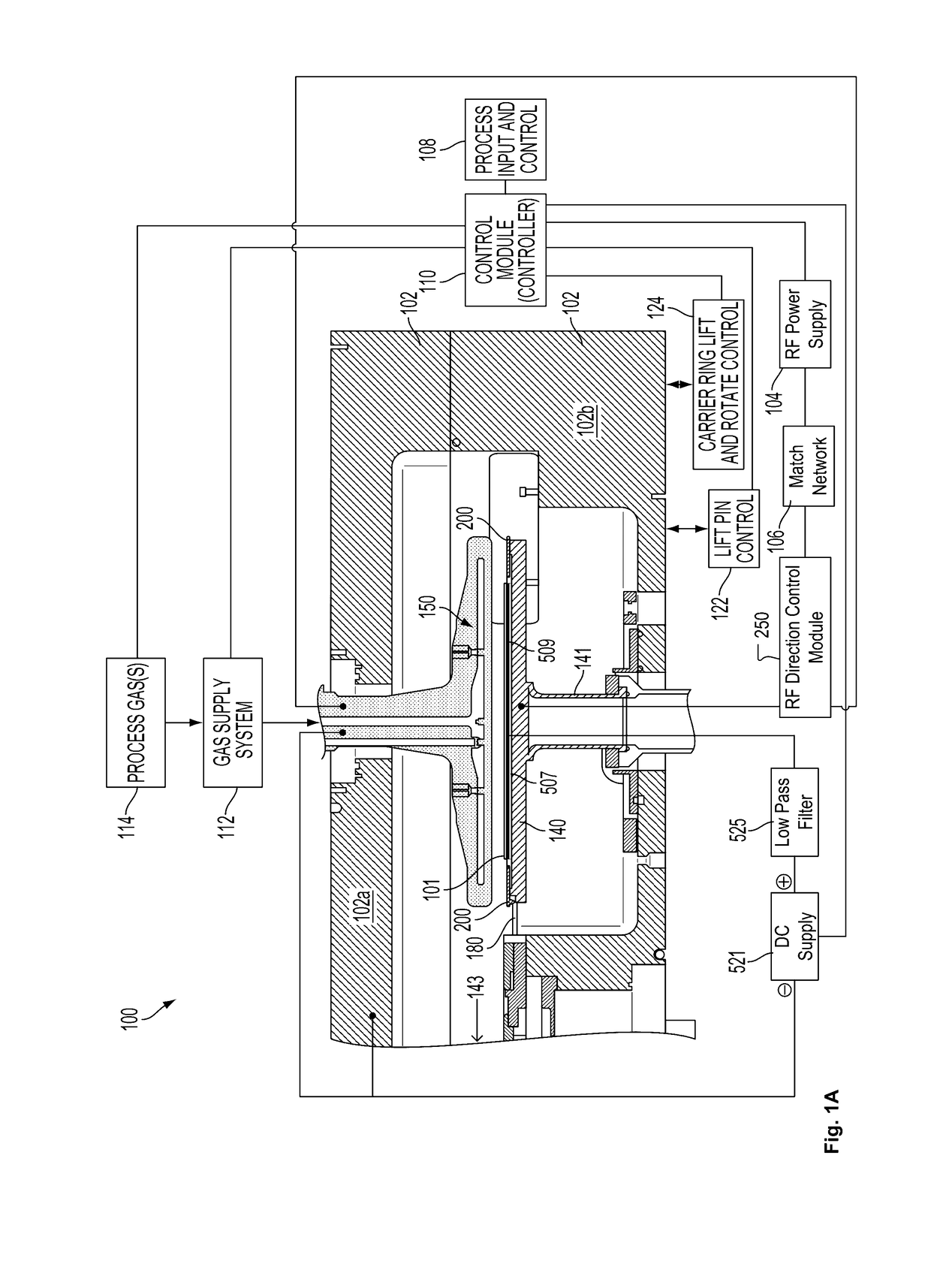
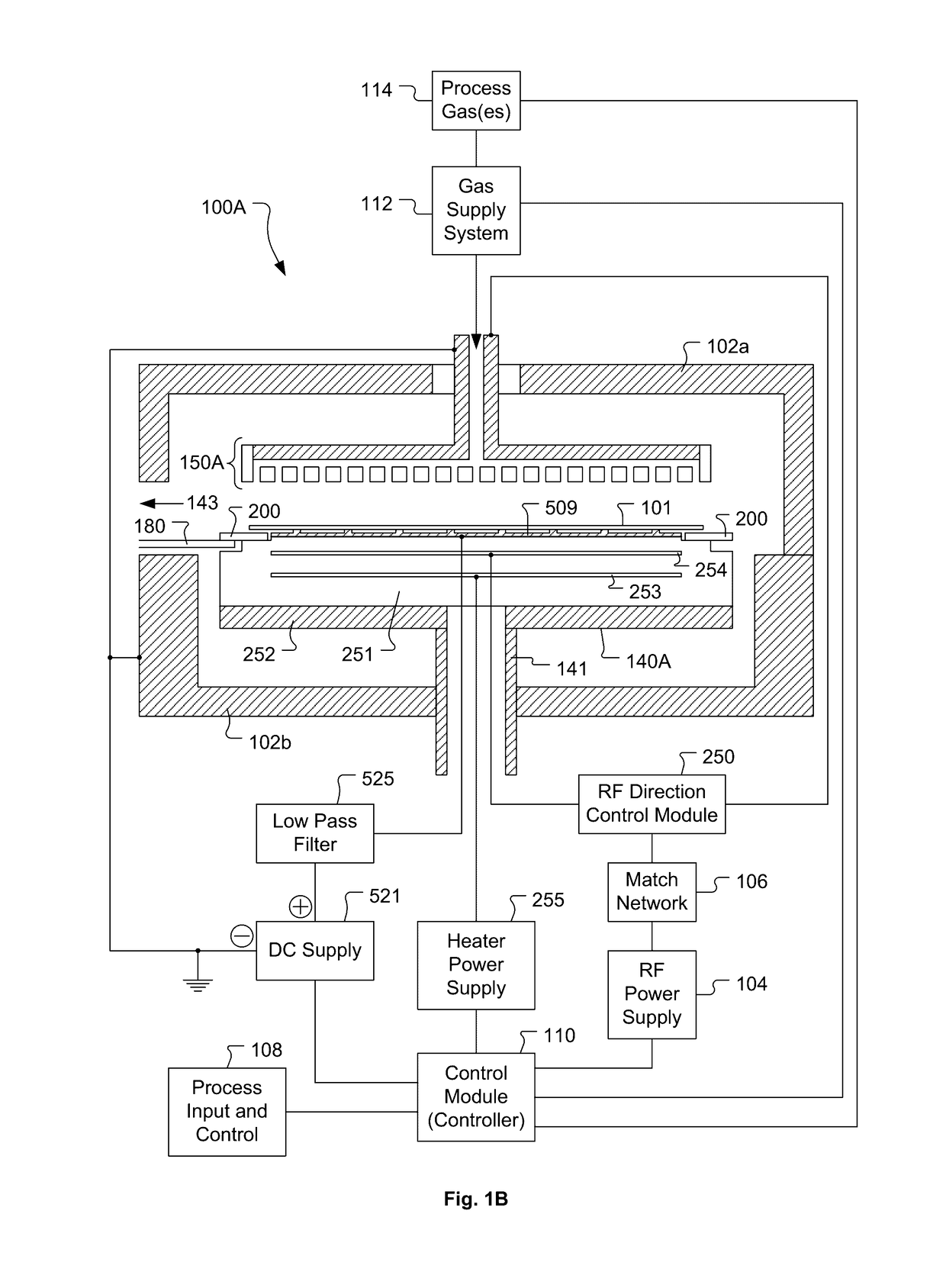
Systems and Methods for Detection of Plasma Instability by Optical Diagnosis
ActiveUS20170141001A1Reduce formationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesPlasma instabilityCharge coupled device camera
A wafer is positioned on a wafer support apparatus beneath an electrode such that a plasma generation region exists between the wafer and the electrode. Radiofrequency power is supplied to the electrode to generate a plasma within the plasma generation region. Optical emissions are collected from the plasma using one or more optical emission collection devices, such as optical fibers, charge coupled device cameras, photodiodes, or the like. The collected optical emissions are analyzed to determine whether or not an optical signature of a plasma instability exists in the collected optical emissions. Upon determining that the optical signature of the plasma instability does exist in the collected optical emissions, at least one plasma generation parameter is adjusted to mitigate formation of the plasma instability.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Method for controlling charge-coupled device camera
A controlling method for a CCD camera in which a photographing area is divided into a number of cell regions, the illumination of each cell regions is detected the photographing mode of a camera is switched to a daytime or nighttime mode on the basis of the detected illumination so that an optimum image is photographed even under conditions where the illumination of a certain position and the total illumination condition in the photographing place changes irregularly.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
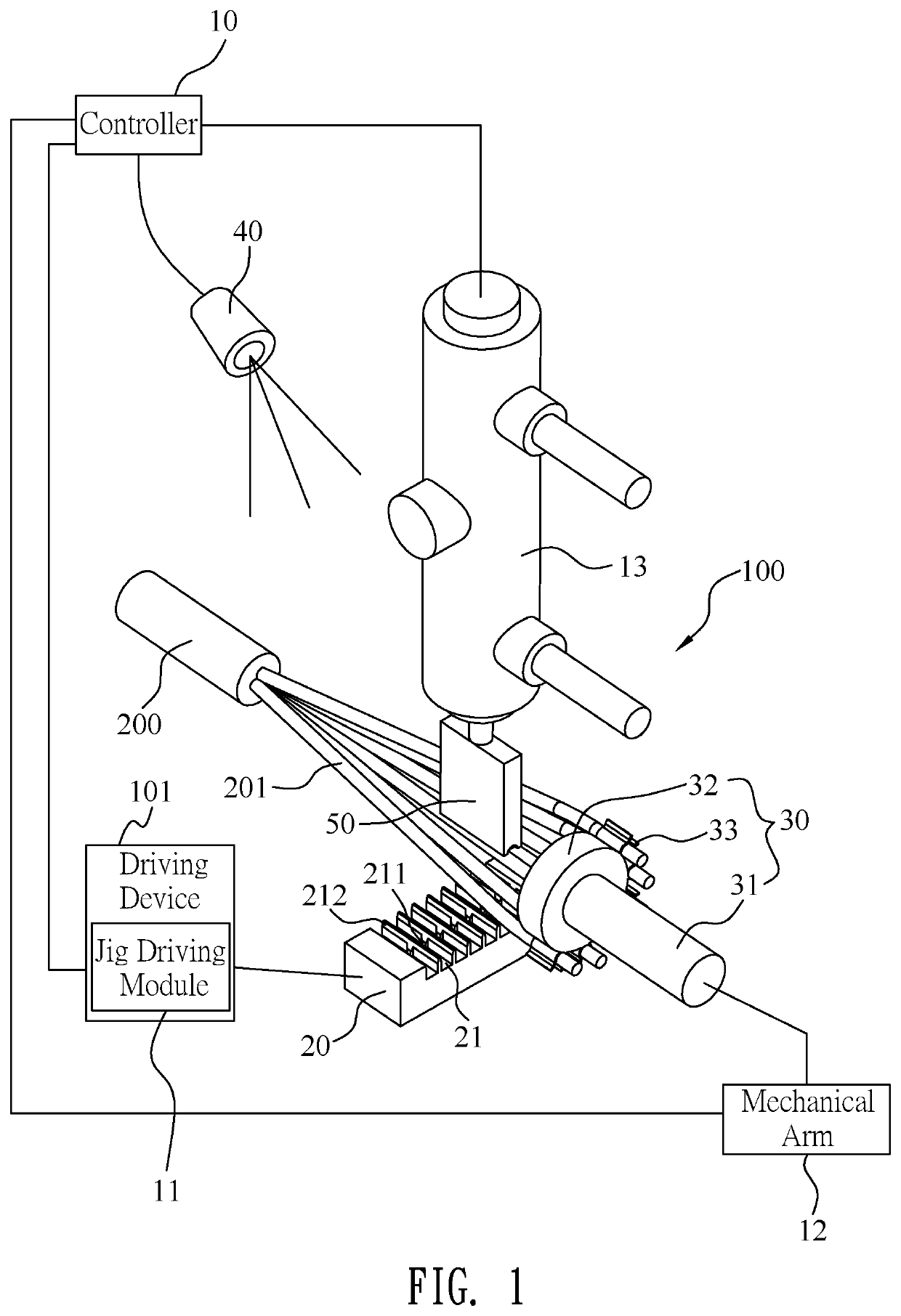
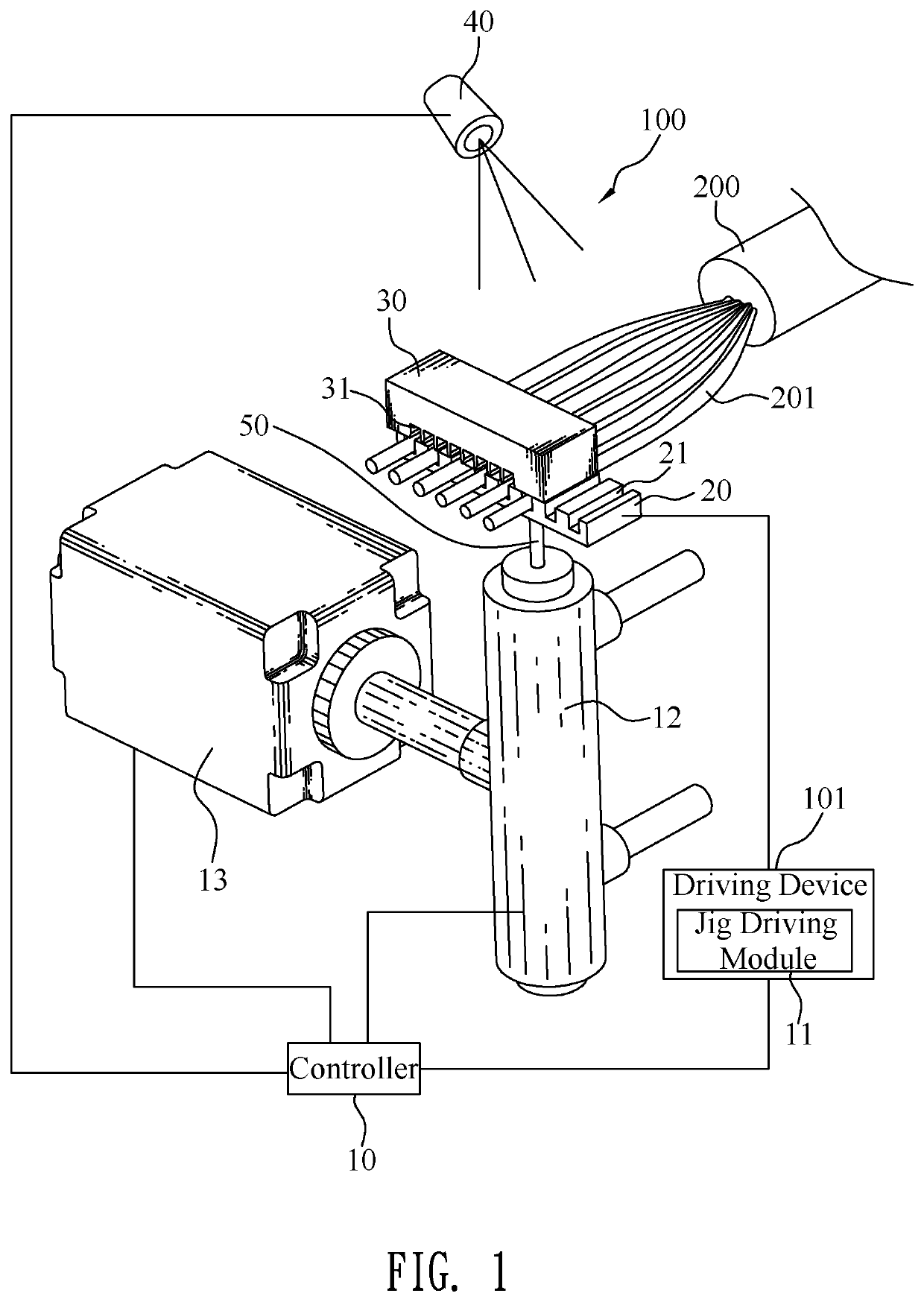
Automatic wire arranging device and automatic wire arranging method applied therein
ActiveUS20190356099A1Save human effortWork lessLine/current collector detailsInsulated cablesCharge coupled device cameraEngineering
An automatic wire arranging device includes a controller, at least one driving device electrically connected with the controller, a wire clamping jig, a wire arranging rotor, at least one charge-coupled device camera and a puncher pin. The wire clamping jig is connected with the at least one driving device. The wire arranging rotor has a spindle, and a cylinder-shaped base portion fastened to a tail end of the spindle. An outer side surface of the base portion is equipped with a plurality of clamping portions. The plurality of the clamping portions are used for clamping a plurality of different characteristic core wires. The wire arranging rotor is connected with the at least one driving device. The at least one charge-coupled device camera faces towards the wire clamping jig and is connected with the controller. The puncher pin is movably disposed above the wire clamping jig.
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
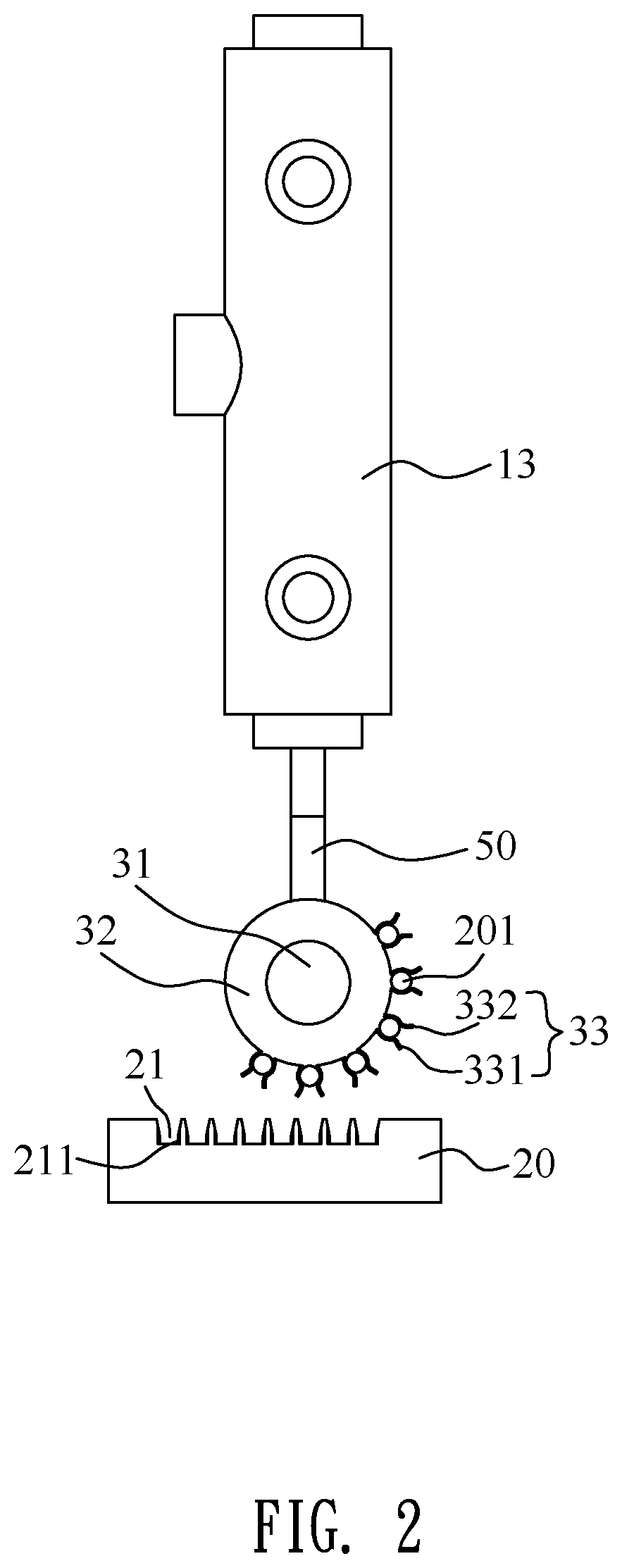
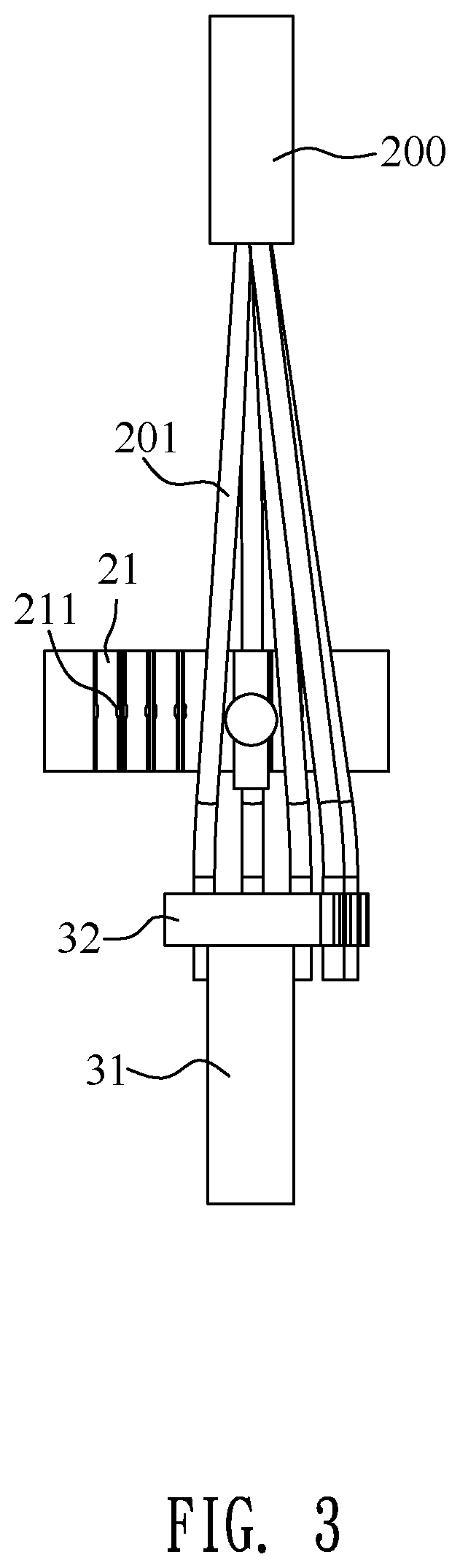
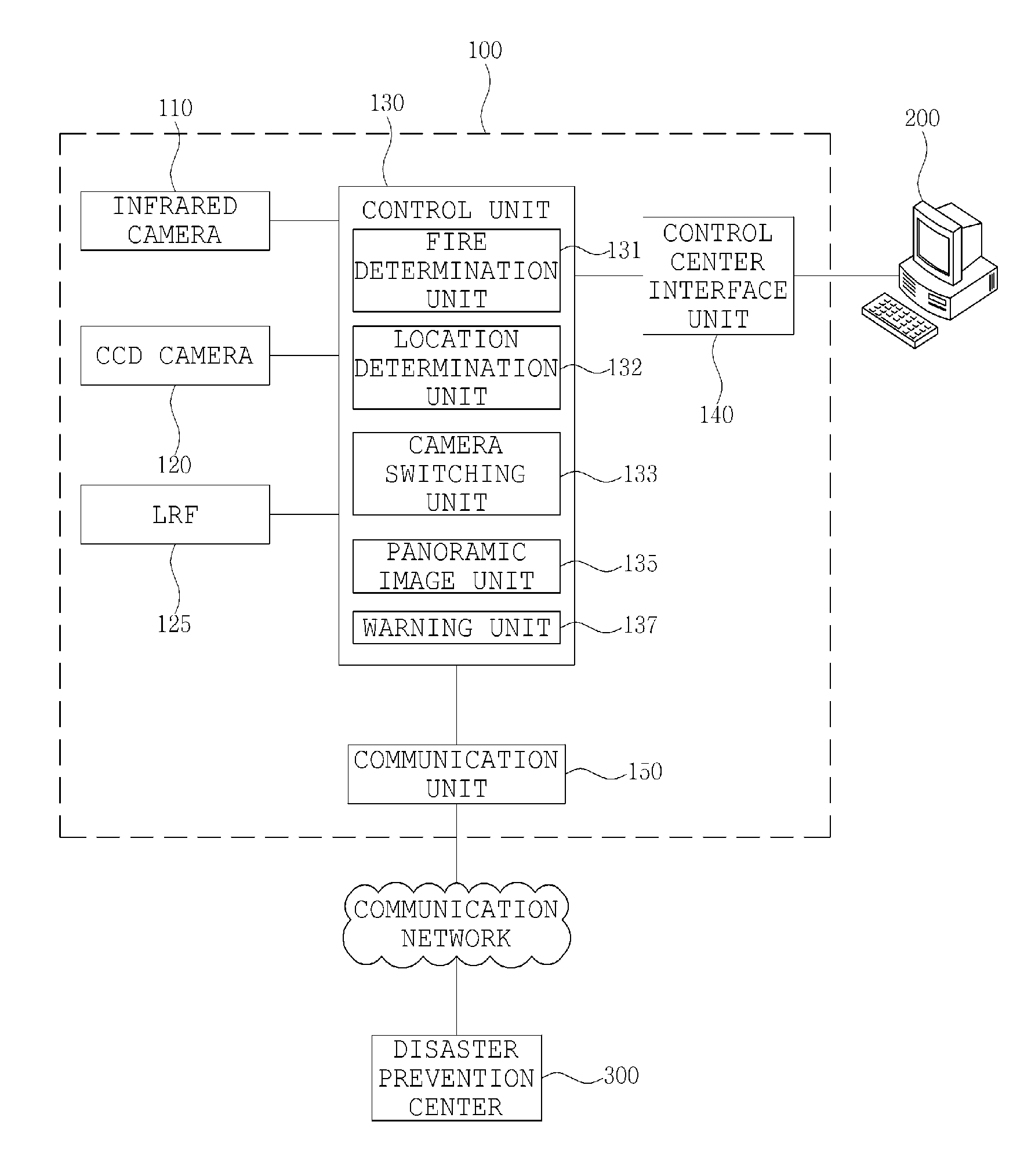
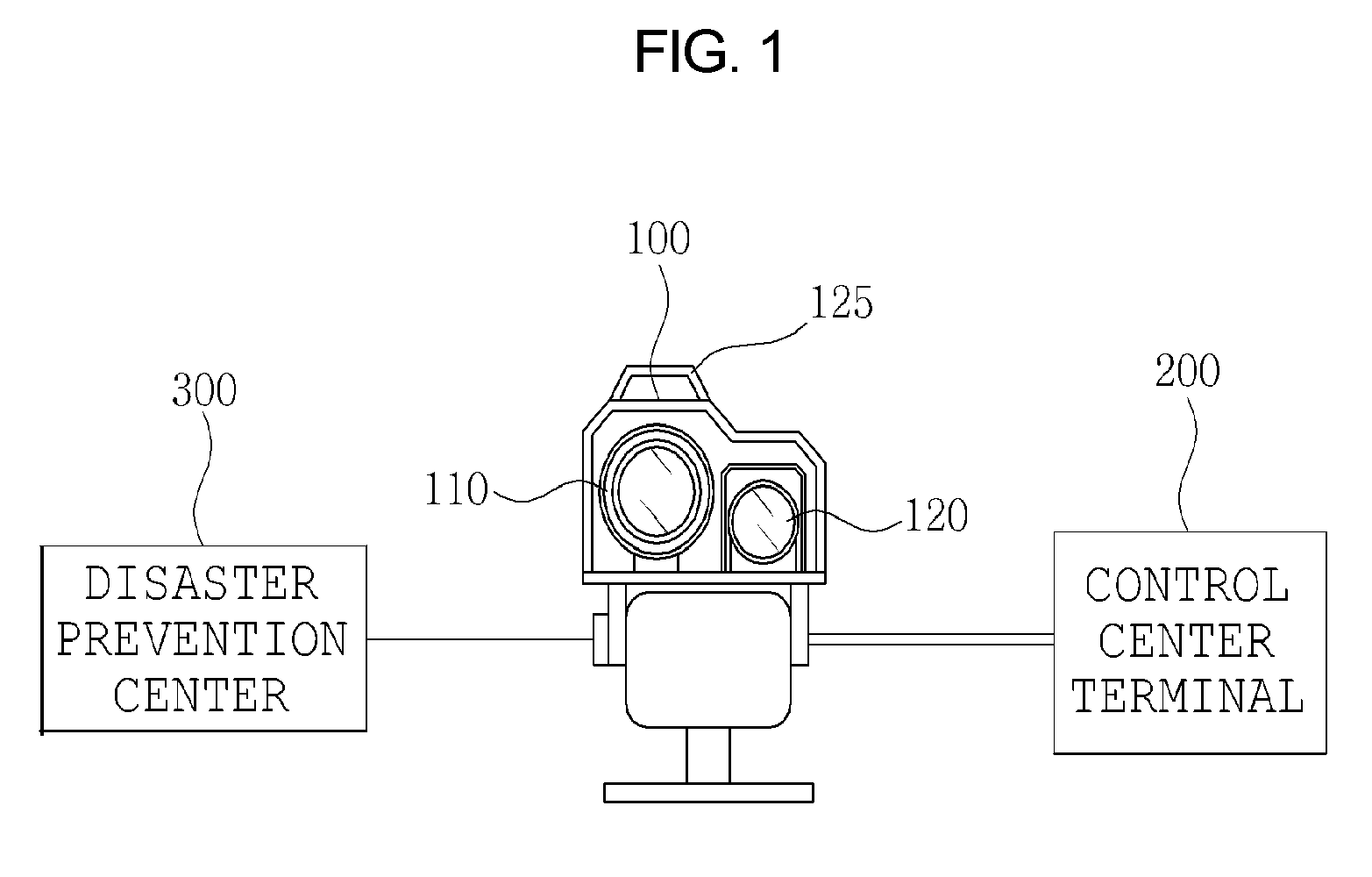
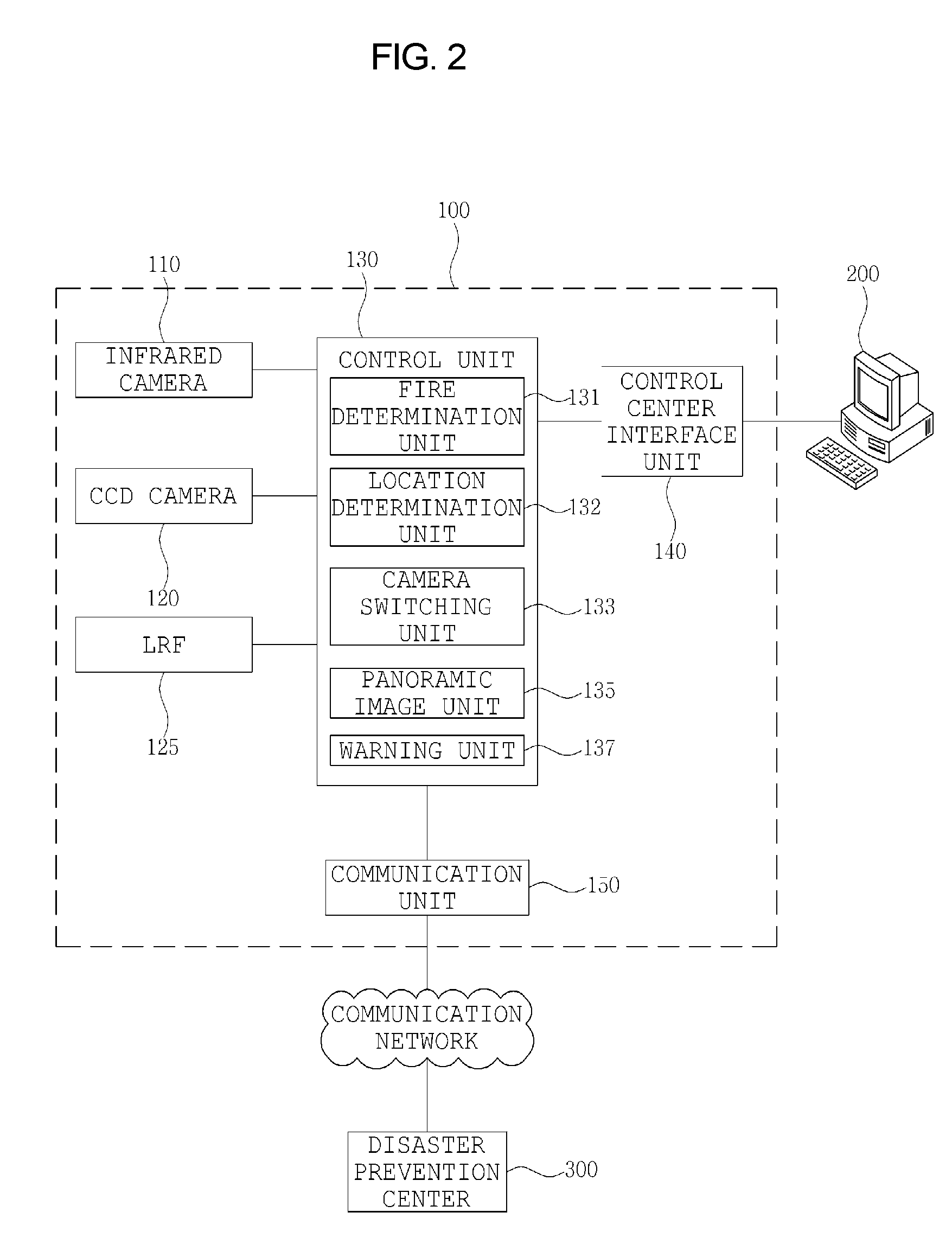
Fire detector using a laser range finder, an infrared camera and a charged coupled device camera
InactiveUS7834771B2Easy to observeTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryFire detectorLaser ranging
A system and method for detecting a fire includes a fire detection device and a control center terminal. The fire detection device includes an LRF for calculating a distance to a location of breakout of a fire using a laser. An infrared camera captures an infrared image and transmits the infrared image to a control unit. A CCD camera captures a CCD image and transmits the CCD image to the control unit. The control unit analyzes the infrared image, determines whether a fire has broken out, performs processing such that the CCD camera captures an area on fire, determines the location of breakout of the fire, performs processing such that the captured image is output to the control center terminal, and controls a function of a warning unit. The warning unit outputs a warning sound or a warning message.
Owner:CHANG SUNG CO LTD
Method for measuring luminescence at a luminescence detection workstation
InactiveUS7670848B2Minimize crosstalkChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationCamera lensCharge coupled device camera
In a luminescence detecting apparatus and method for analyzing luminescent samples, luminescent samples are placed in a plurality of sample wells in a tray, and the tray is placed in a visible-light impervious chamber containing a charge coupled device camera. In the chamber, light from the luminescent samples pass through a collimator, a Fresnel field lens, an infrared filter, and a camera lens, whereupon a focused image is created by the optics on the camera. The use of an infrared filter suppresses stray IR radiation resulting from plate phosphorescence (which can result in abnormally high backgrounds and / or alteration of the image received by the camera).
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Apparatus for measuring response time and method of measuring of response time using the same
ActiveUS7463826B2PrintersSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An apparatus for measuring response time of a display apparatus including a photographing part including a charge coupled device camera and a microscope, an image processing part receiving a picture taken from a photographing part and calculating the response time thereof, and a control part applying a predetermined image signal to the display apparatus and controlling the photographing part to take a picture change of the display apparatus at a predetermined time.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Micro-image examining apparatus
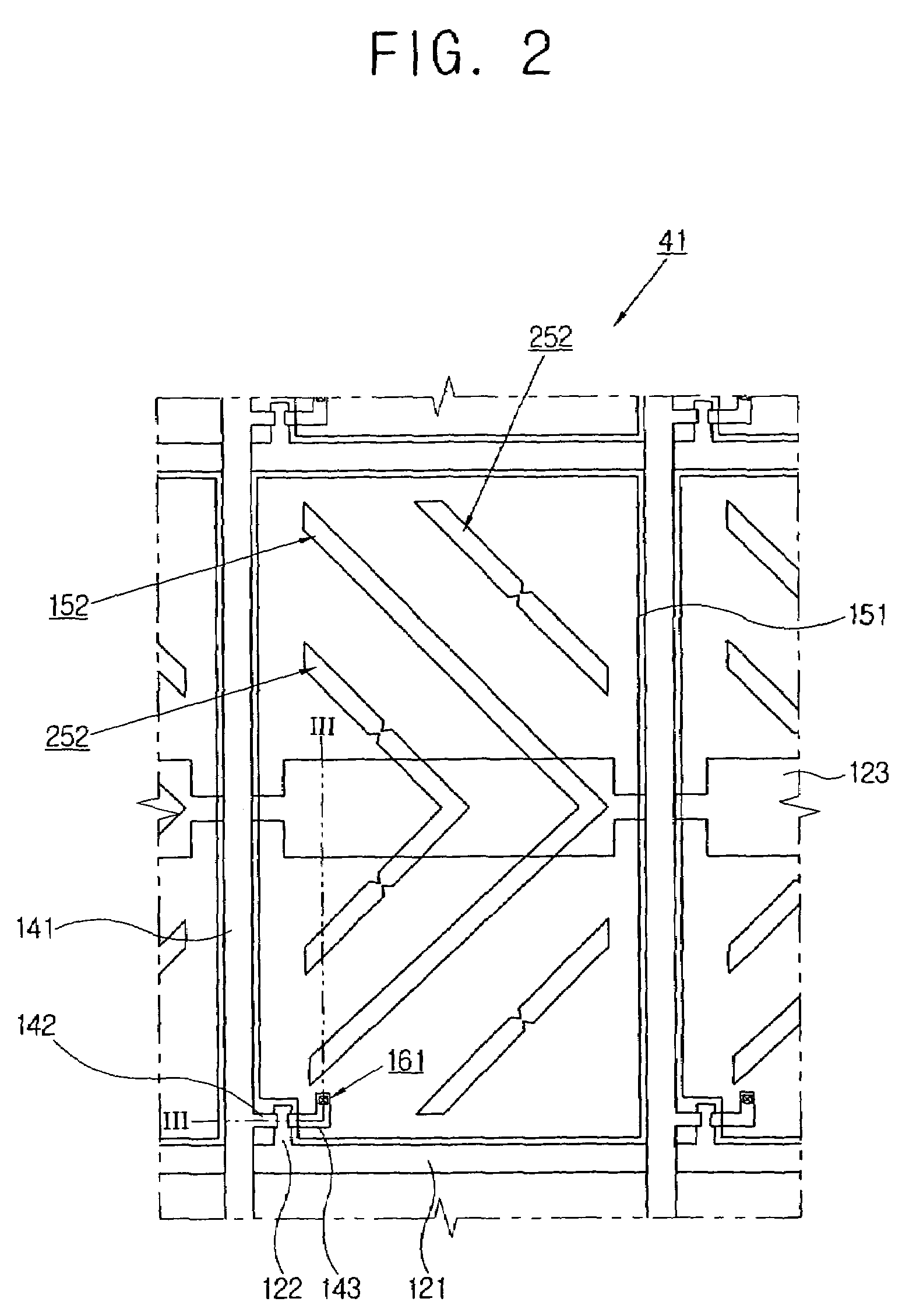
InactiveUS20050244048A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyElectrical testingMaterial analysis by optical meansImage InspectionComputer monitor
A micro-image examining apparatus includes a conveyor belt for moving at least one object to be examined and a microphotographer including a charge-coupled device camera and a lens for acquiring an image of the object on the conveyor belt and for sending the image of the object to a computer monitor. Thus, the objects to be examined are placed on the conveyor belt and moved synchronously. Instead of conventional one-by-one examination by workers, the objects are examined one by one by the microphotographer. The examining efficiency and the examining accuracy are both improved.
Owner:SHANG HANG INT
Method for controlling charge-coupled device camera
InactiveCN1332389ALow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLow-pass filterMiniaturization
In a control method of a CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) camera, control traces for a zoom lens and a focus lens of the camera are adjusted in accordance with pre-stored trace data so as to compensate a focus error in accordance with the use or not of an OLPF (Optical Low Pass Filter) in automatic adjustment of the focus lens and the zoom lens. Accordingly, because a photographing mode can be converted into a daytime mode or a nighttime mode without changing a lens unit, the facility of user can increase, the price can be reduced and miniaturization of a CCD camera can be performed by eliminating a dummy glass for adjusting a refractive index when not using the OLPF.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Microscope
InactiveUS20050111092A1Improve lighting efficiencyClear imagingMirrorsMicroscopesHorizonCharge coupled device camera
The microscope (S, 100) of the present invention has a hand piece (20, 112), whose tip is mounted with a thin sheet-like mirror unit (M, 10, 130, 220), and around both ends of the base (11c, 131c) thereof is arranged an illuminating light source (32, 117), whereby light is emitted to a target object, image light is lead through the light reception bore (27, 116), to the optical system (114), and is recorded at the CCD camera (111), to obtain video images. The thin sheet-like mirror (M, 11, 131) confines light and navigate it, wherein the width of the mirror can be made narrower like a convergent taper surface (11a, 131a); and it is comprised of a base surface (11c, 131c) where illuminating light comes in and image light goes out, and a mirror surface (11b, 131b) where illuminating light and image light go back and forth, and make the reflection thereof, and the mirror surface (11b, 131b) is slanted to 45 degrees. The microscope may be used as a handy microscope if it is not equipped with a charge-coupled device camera. The microscope can provide a wider horizon, which makes it possible to make a horizontal observation in an extremely narrow space, and can be manufactured at a less expensive price.
Owner:KITAMURA JUN +1
Real-time optical correlating system
InactiveUS6999176B1Character and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansLiquid-crystal displayImage resolution
A Real-Time Optical Correlating System produces holograms that contain both amplitude and phase information and have none of the time constraints of the traditional holographic methods. It has been demonstrated to operate at television field rates (60 Hz) employing currently available devices of moderate resolution. Using the System, the holographic matched filter of an input scene is calculated optically as an analog sum, captured by a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera and transmitted directly or through a computer to and displayed on a commercially available liquid crystal display (LCD) device. The correlation plane may be viewed immediately on a suitable screen because there is no film to process or computer calculations to be performed. Concurrently with the creation of the holographic matched filter of the input scene, a Fourier transform of a test scene is produced and both are imaged on another charge-coupled device camera for any correlation between the input and test scenes.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Automatic wire arranging device and automatic wire arranging method applied therein
ActiveUS20190358723A1Low costWork lessCharacter and pattern recognitionWork holdersCharge coupled device cameraEngineering
An automatic wire arranging device includes a controller, at least one driving device electrically connected with the controller, a first wire clamping jig connected with the at least one driving device, a second wire clamping jig disposed to the first wire clamping jig, at least one charge-coupled device camera connected with the controller, and at least one puncher pin connected with the at least one driving device. The first wire clamping jig opens a plurality of first clamping slots. Each of the plurality of the first clamping slots opens a through-hole. The second wire clamping jig opens a plurality of second clamping slots. The at least one puncher pin is capable of penetrating through the through-hole and pushing against a core wire to be away from one of the plurality of the first clamping slots and be blocked in one of the plurality of the second clamping slots.
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Single shot autocorrelator for measuring the duration of an ultrashort pulse in the far field
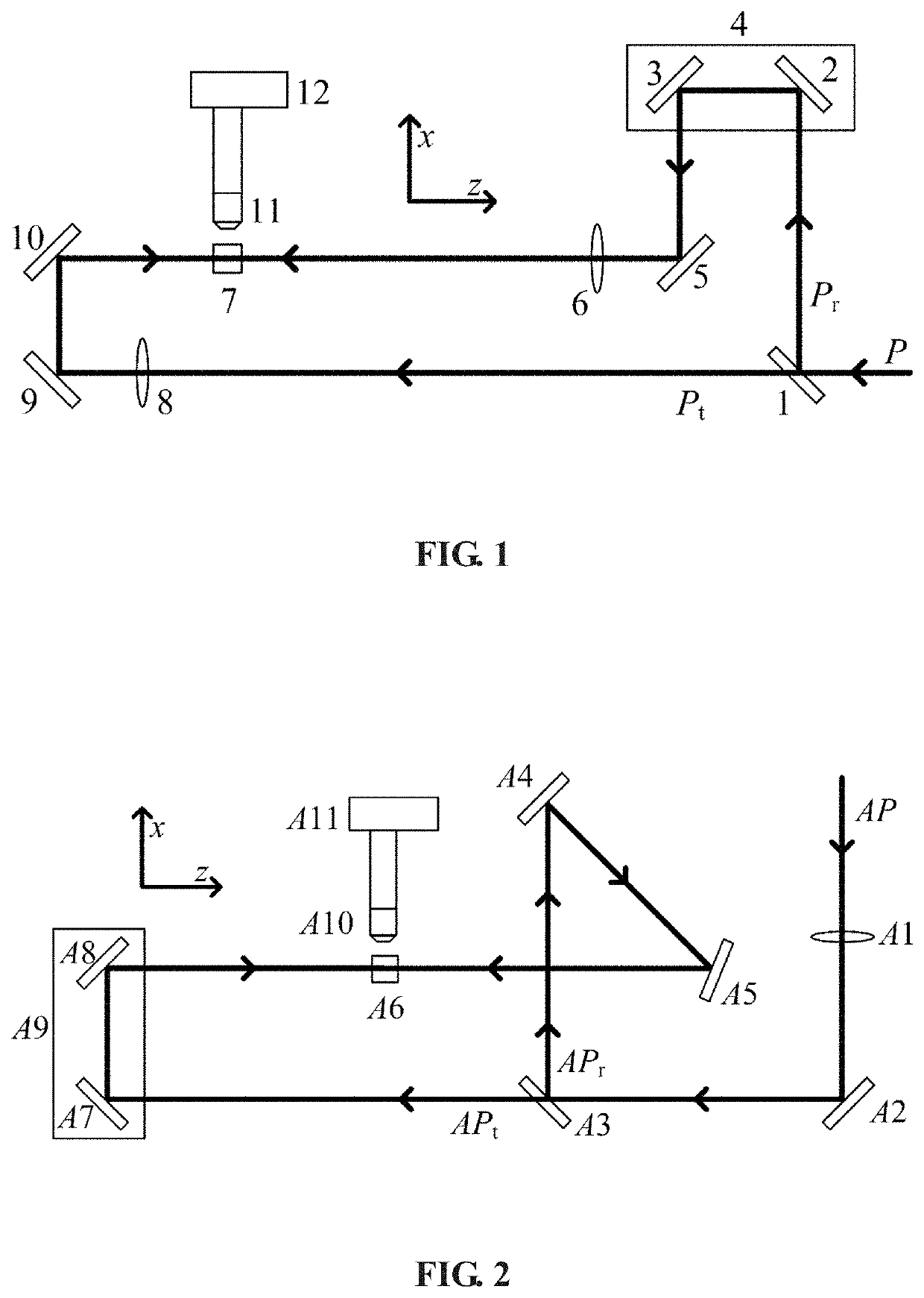
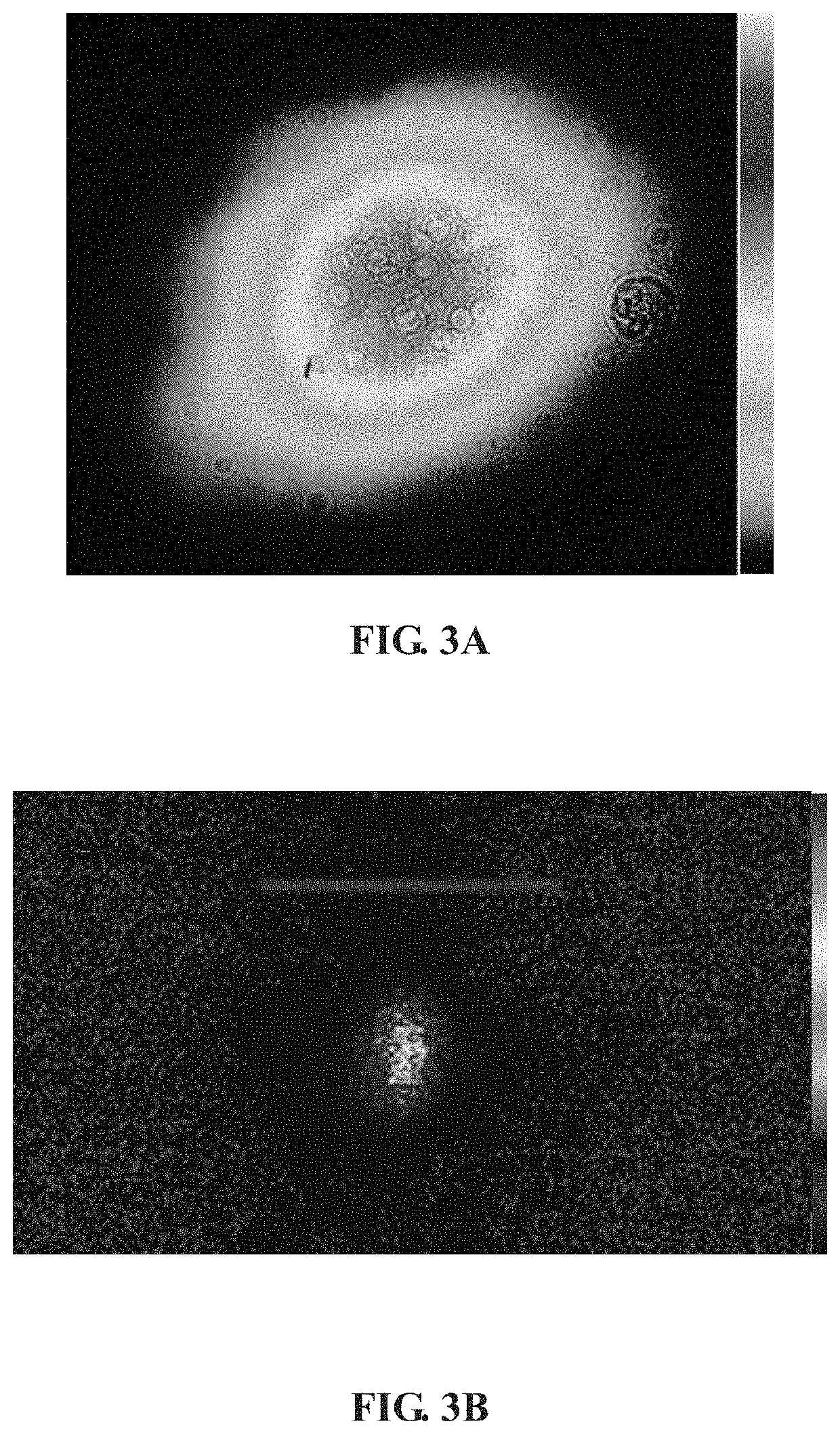
ActiveUS20200292382A1Maintain stable propertiesLow conversionPhotometry using reference valueMicroscopesPulse beamBeam splitter
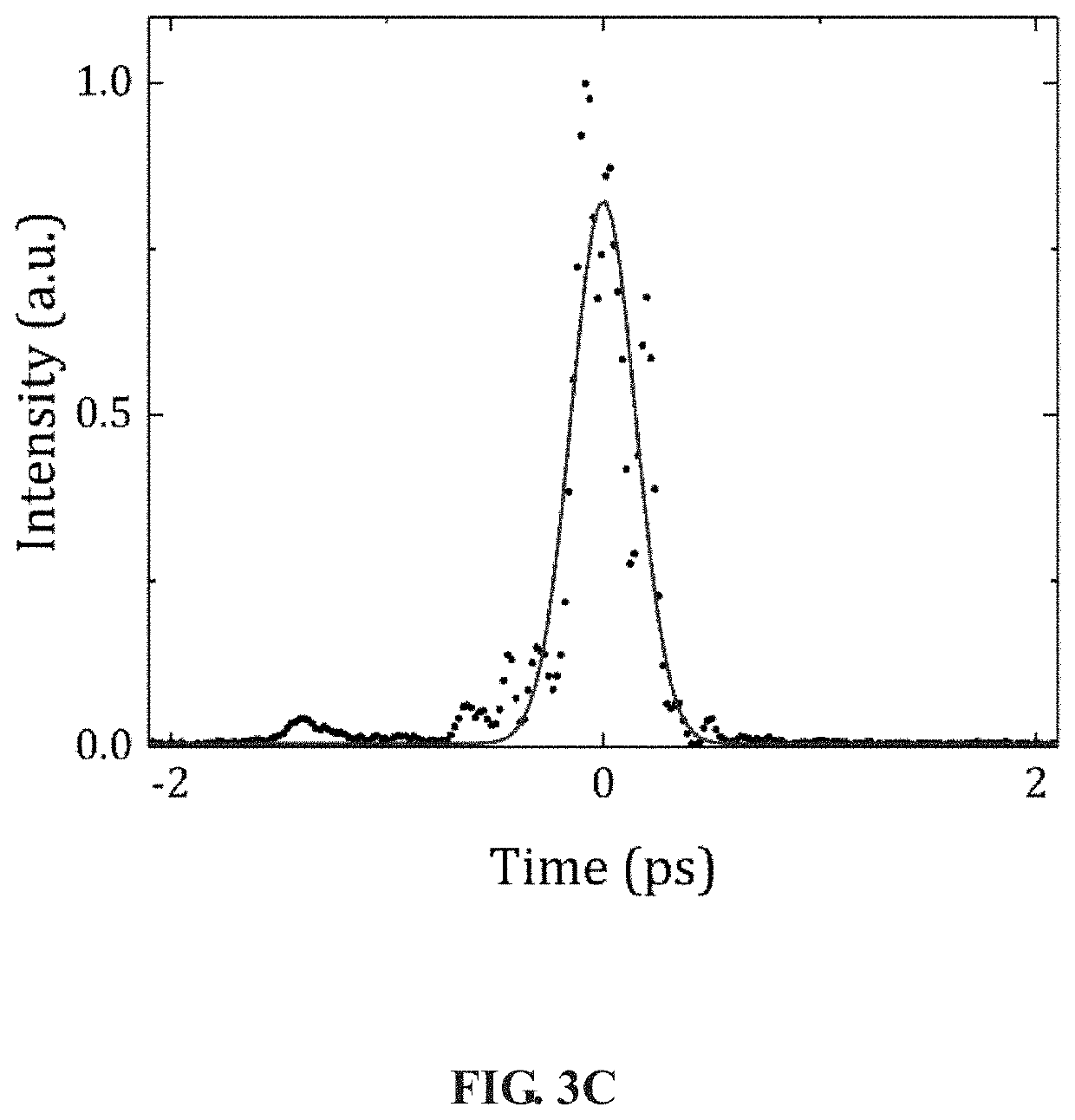
A single shot autocorrelator for measuring duration of an ultrashort laser pulse in the far field, having a beam splitter to form two beams from an input ultrashort pulse: the reflected beam is firstly reflected by two mirrors mounted on a translation stage for adjusting time delay and subsequently a third mirror, and after focused by a spherical convex lens, enters a naturally grown strontium barium niobate crystal along the crystal z axis; the transmitted beam is firstly focused by a spherical convex lens, and after reflected by two mirrors, enters the crystal along the crystal z axis from opposite direction. The crystal is in the common focal regions of two spherical convex lenses and generates the transverse second harmonic pulse beam that is the autocorrelation signal to be recorded, which is imaged with an optical microscope onto a charge coupled device camera mounted perpendicular to the beams.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A magneto-optical trap method and device for laser cooling and trapping
InactiveCN105117774BMeet different experimental parameter requirementsMeet the experimental parameter requirementsComputing modelsNanoinformaticsFluorescenceAlkali metal
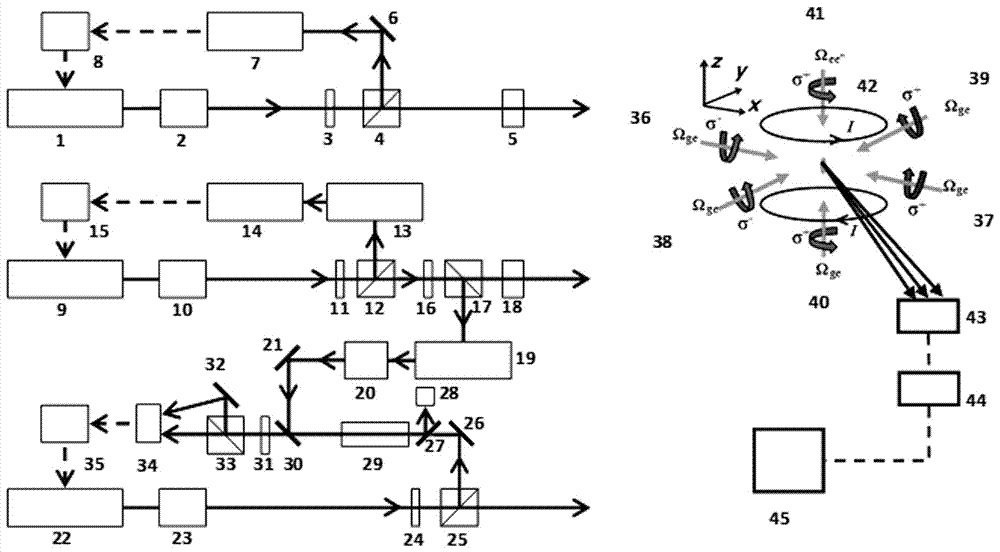
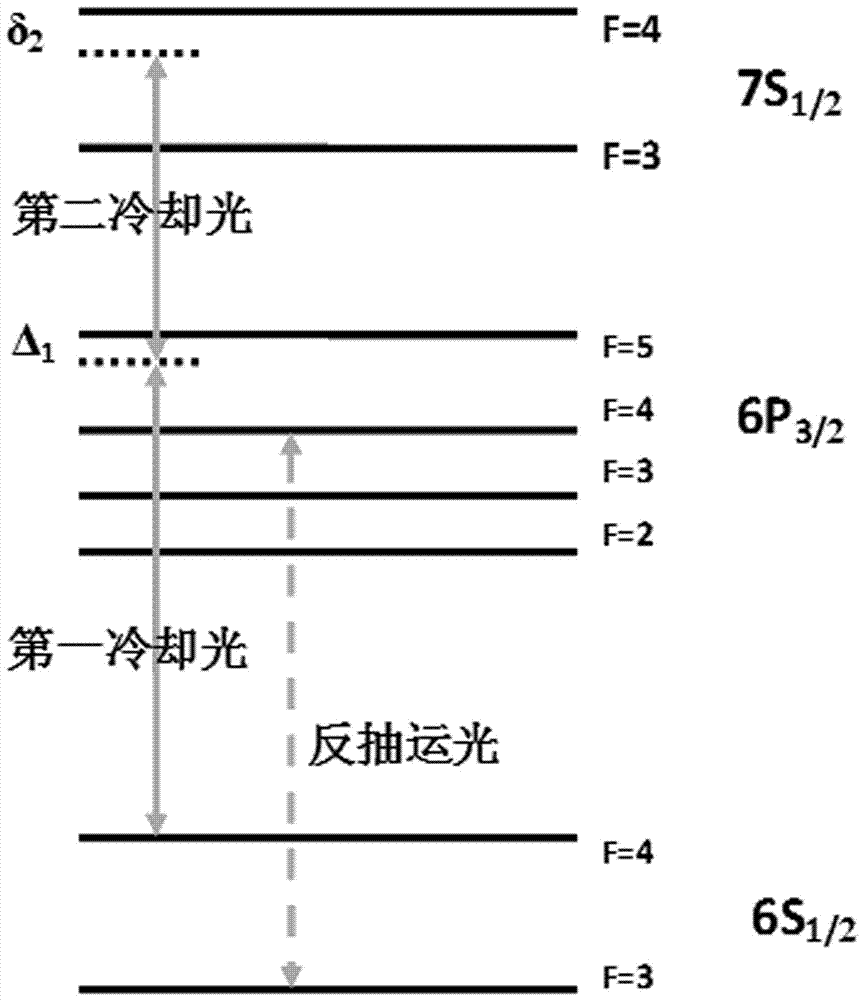
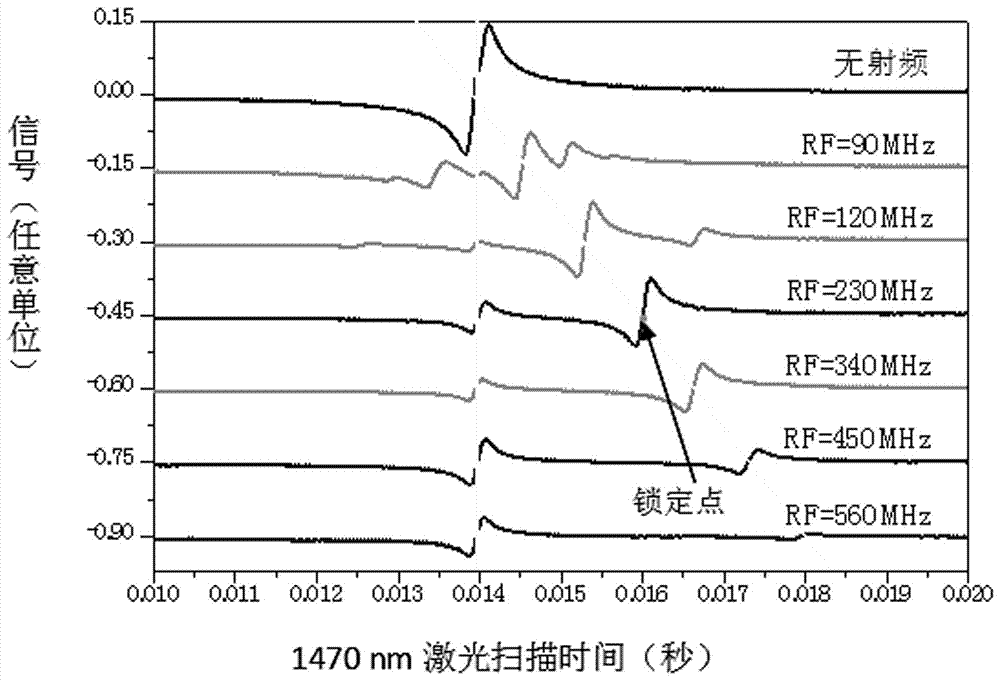
The invention relates to the laser cooling and trapping of step-type energy level alkali metal atoms by lasers of two wavelengths, specifically a magneto-optical trap method for cooling and trapping atoms by using lasers of two wavelengths in the atomic storage band and the optical communication band and device. The method includes the following steps: constructing an atomic vacuum chamber containing a light-transmitting quartz window; constructing the magnetic field part of a magneto-optical trap; constructing the optical path part of the laser working in the ground state and the intermediate excited state of the alkali metal atom; constructing the work in the middle of the alkali metal atom The optical path part of the laser in the excited state and the higher excited state; the detection part of the atomic fluorescence composed of a charge-coupled device camera. The device of the present invention directly cools and captures atoms from a room temperature hot atom vacuum chamber, which can be used for laser cooling and capture of alkali metal atoms with atomic storage band and optical communication band; it can be used for the cooling mechanism of multi-photon cooling atoms And the application research of quantum repeater based on four-wave mixing.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
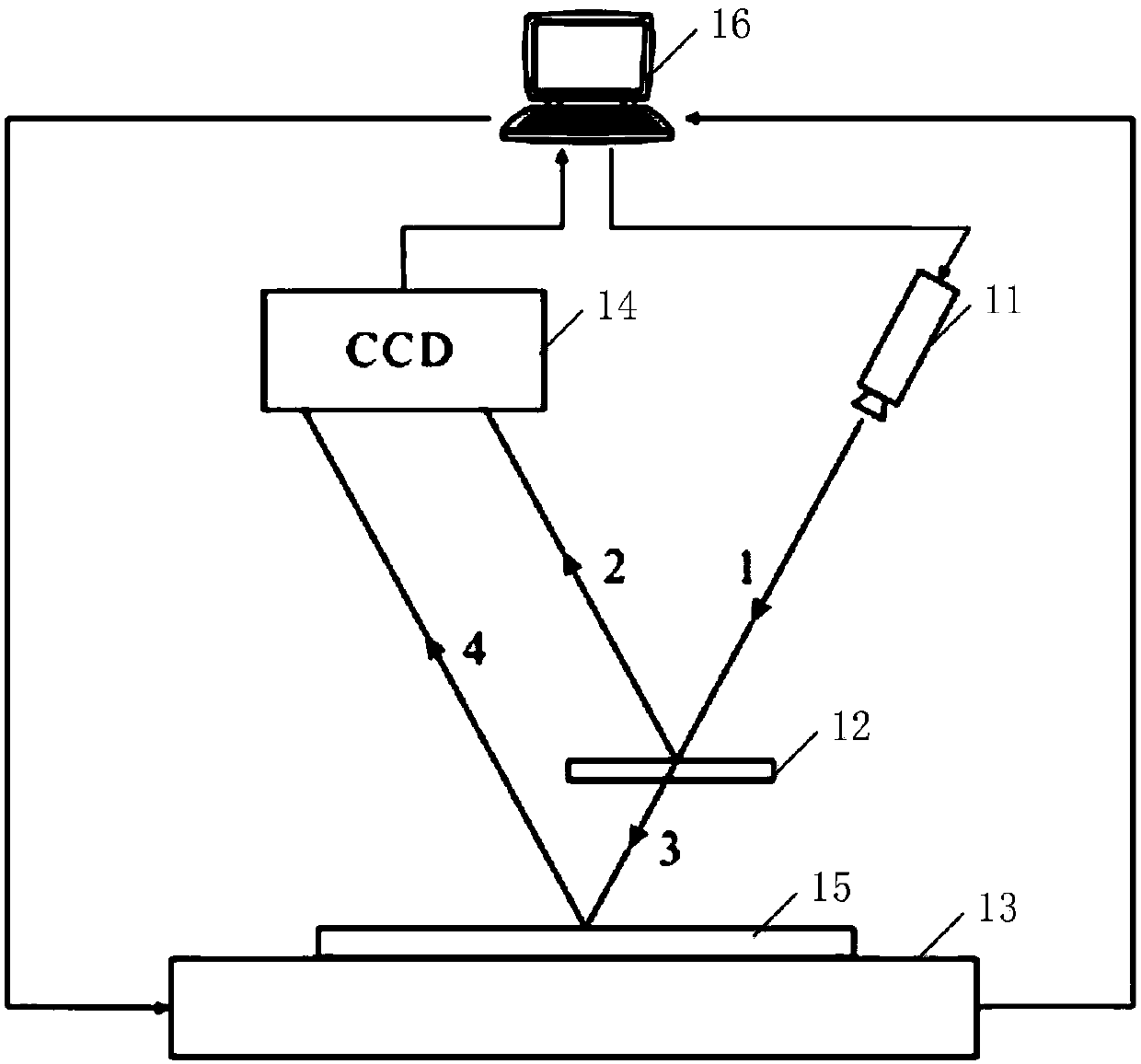
Heat expansion coefficient high-flux detection device and control method thereof
PendingCN107621475AEasy to measureNo damageMaterial thermal coefficient of expansionLaser transmitterHigh flux
The invention relates to a heat expansion coefficient high-flux detection device and a control method thereof. The device comprises a laser emitter, a semi-reflecting lens, a heating table and a charge coupling device camera, wherein a sample to be tested is put on the heating table; the heating table generates heat so as to heat the sample to be tested; the sample to be tested expands; after light rays emitted by the laser emitter reach the semi-reflection lens, reflecting light and transmission light are respectively generated; the reflecting light is reflected into the charge coupling device camera; the transmission light is also reflected into the charge coupling device camera after being reflected on the surface of the sample to be tested. By using the technical scheme provided by theinvention, the detection precision of the heat expansion coefficient can be improved.
Owner:CHENGDU AMPLIFI ENERGY TECH CO LTD
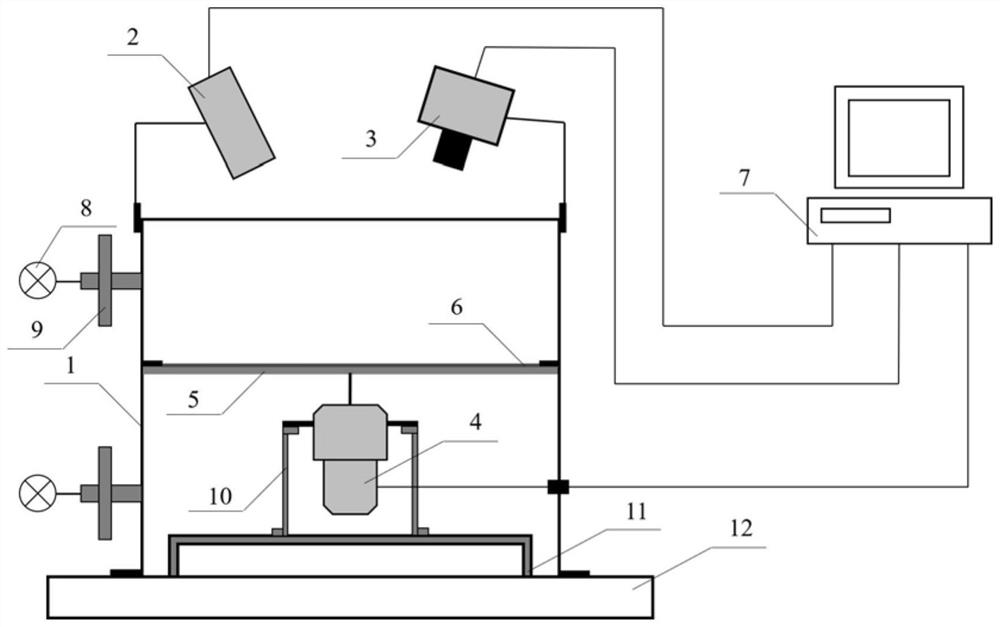
A visualization experiment platform for vibration energy transfer characteristics of thin-wall casing structure
The invention relates to a visualization experiment platform for the vibration energy transfer characteristics of a thin-walled casing structure, which is especially suitable for thin-walled casings of aero-engines, and can realize the global vibration of the thin-walled casing structure under different support conditions, excitation positions and vibration excitation types Experimental study on visualization of energy transfer characteristics. The experimental platform consists of a thin-wall casing structure body coated with optical pressure-sensitive coatings, an optical transparent vacuum box, an exciter, a laser light source, a charge-coupled device (CCD camera), and an image acquisition and control unit. The thin-walled casing structure with optical pressure-sensitive coating is vibrated by the exciter, and the pressure-sensitive coating is excited by the laser light source. In the vacuum environment, the CCD camera captures the sound pressure change on the surface of the thin-walled casing structure and transmits it to the image acquisition. With the control system, the vibration energy transfer vector field diagram of the thin-walled casing structure is obtained, and then the vibration energy transfer characteristics of the thin-walled casing structure are obtained.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
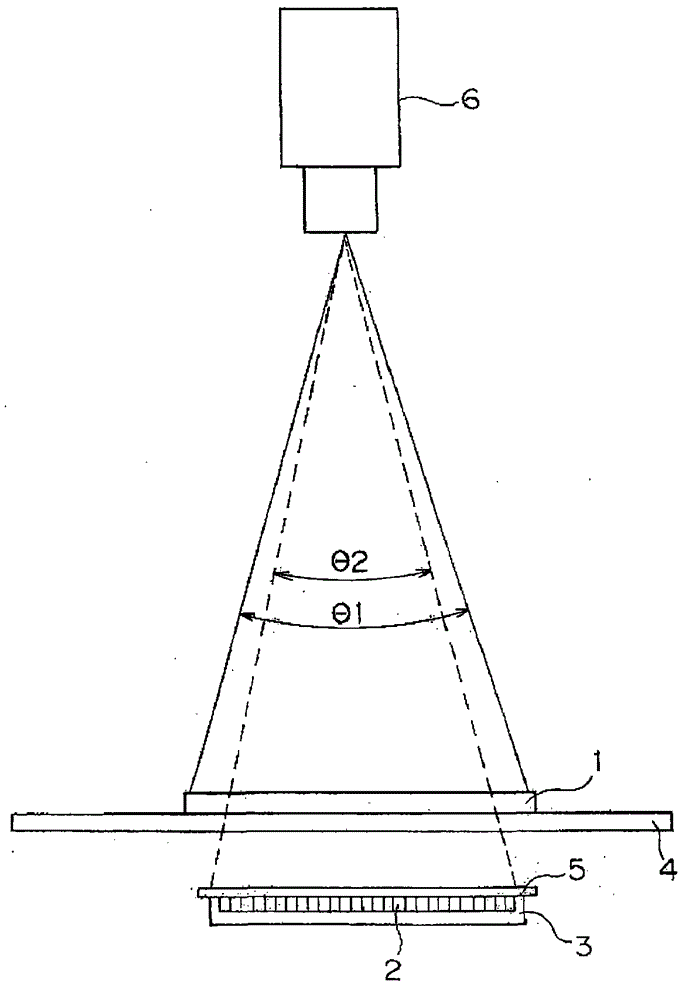
Substrate inspection device and transmission illumination device for substrate inspection device
InactiveCN103543158BWidely used valueAvoid incidenceOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFresnel lensTransmission illumination
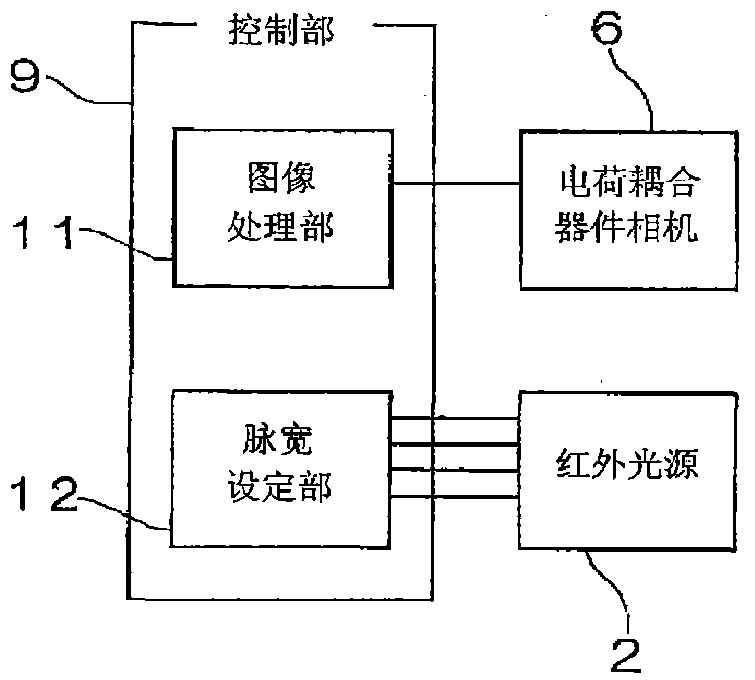
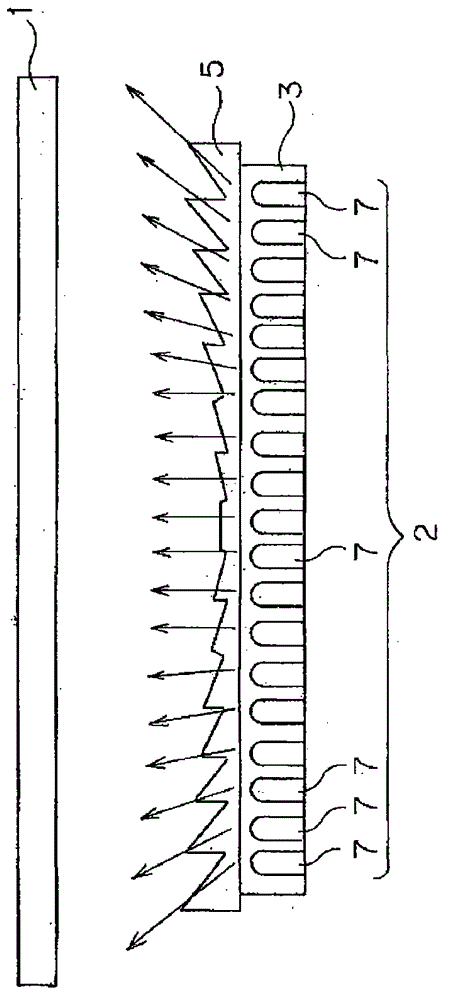
The invention relates to a substrate inspection device and a transmission illuminating device for the substrate inspection device. The substrate inspection device can prevent infrared light from an infrared light source from entering a camera without passing through the substrate, so that the substrate can be accurately inspected. The shape and arrangement of the infrared light source are set so that the field of view of the infrared light source of the charge-coupled device camera is covered by the field of view of the substrate of the charge-coupled device camera. Furthermore, by virtue of the Fresnel lens, the irradiation angle of the infrared light emitted from the light emitting diode element disposed near the edge of the infrared light source is deviated toward the edge direction of the substrate. In addition, the intensity of the infrared light irradiated from the infrared light source to the substrate on the edge region of the substrate is greater than the intensity of the infrared light on the central portion of the substrate.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com