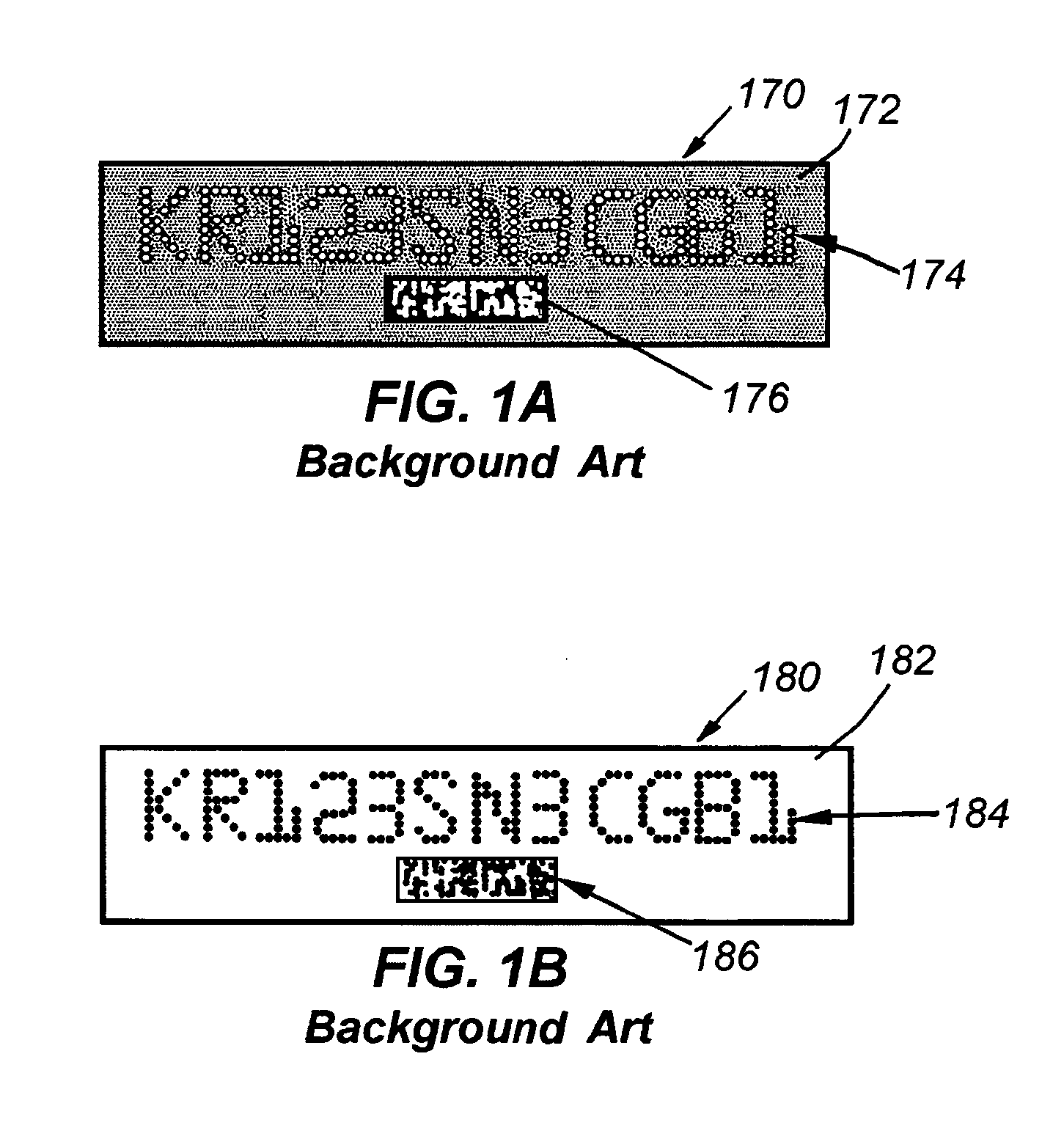
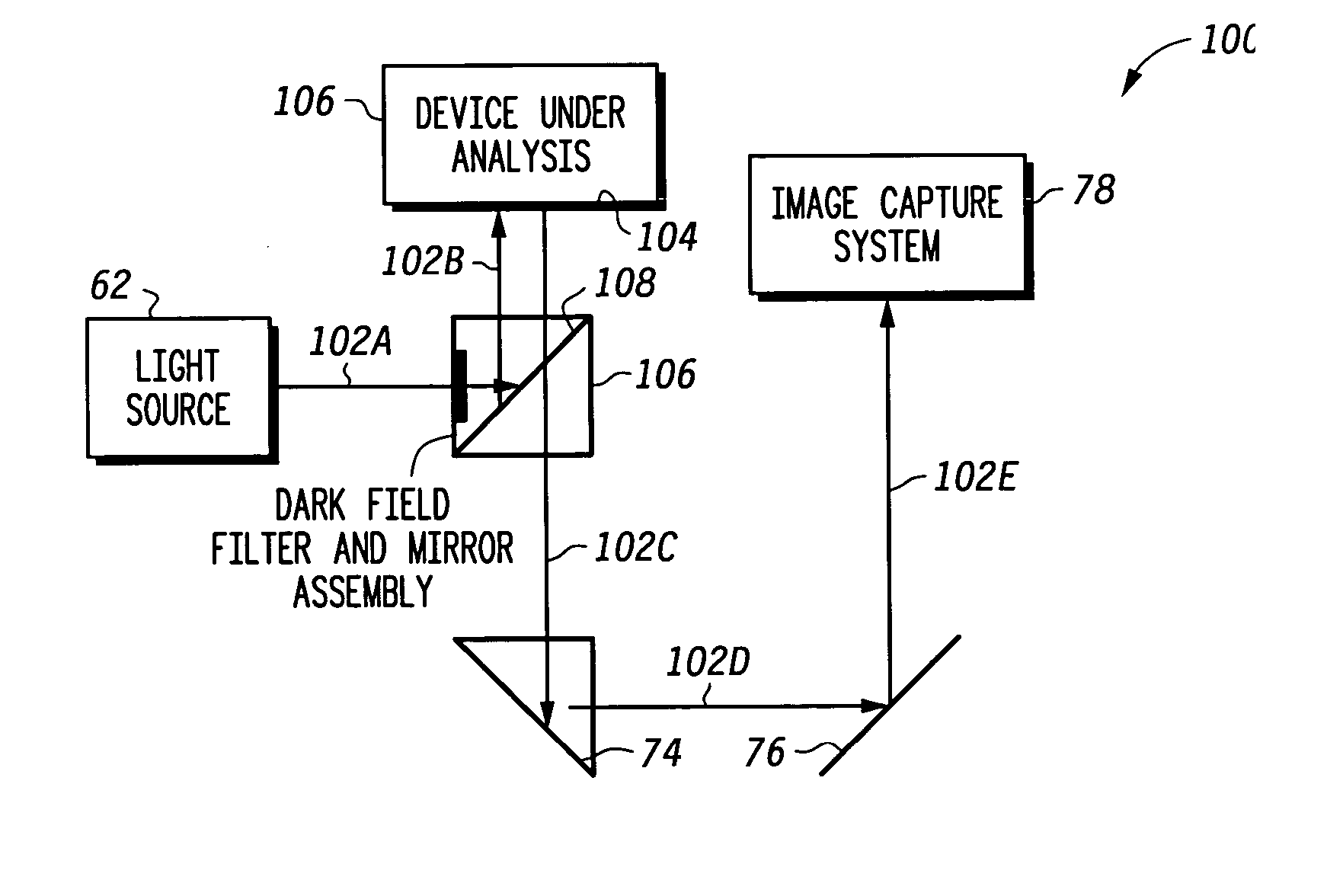
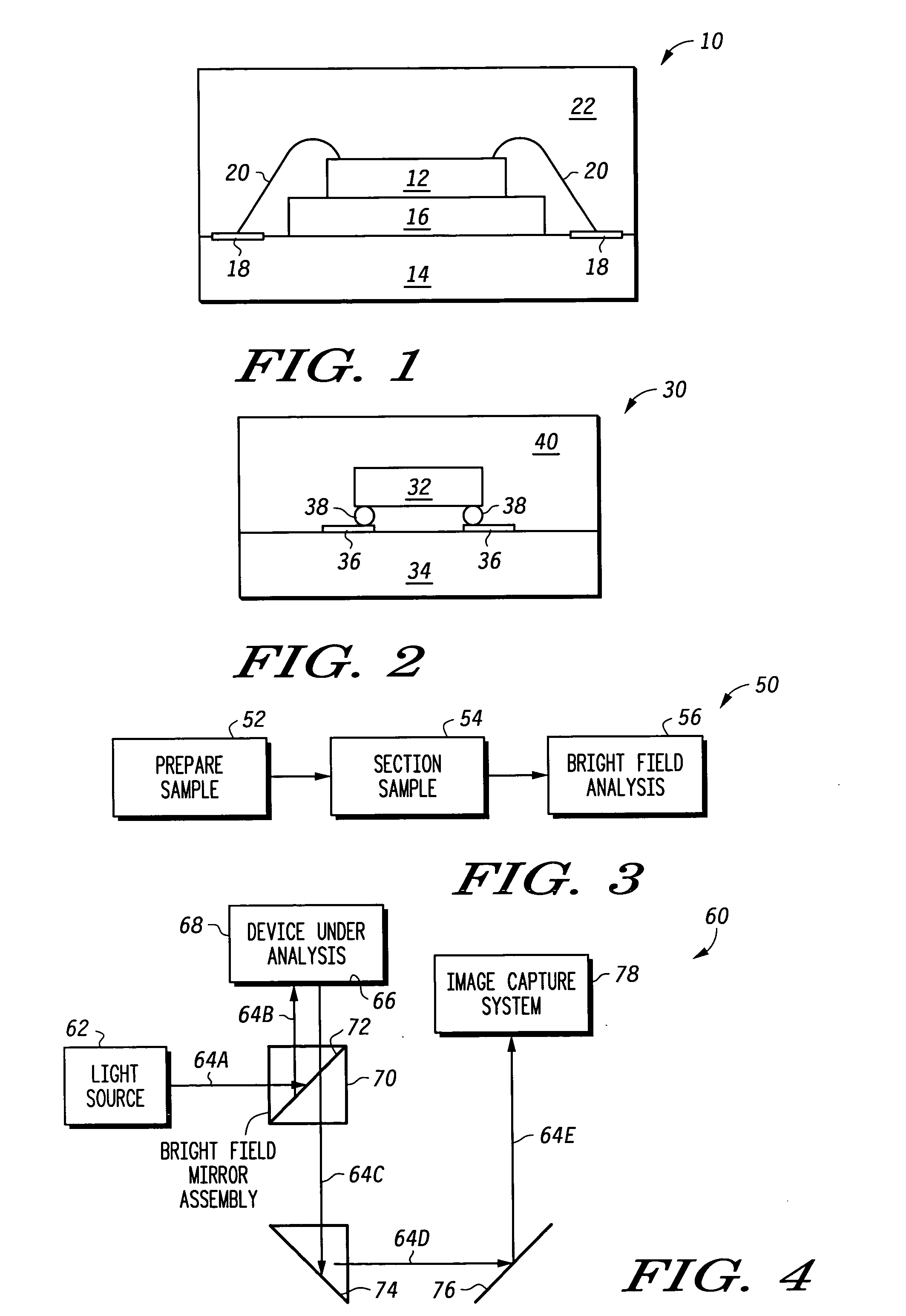
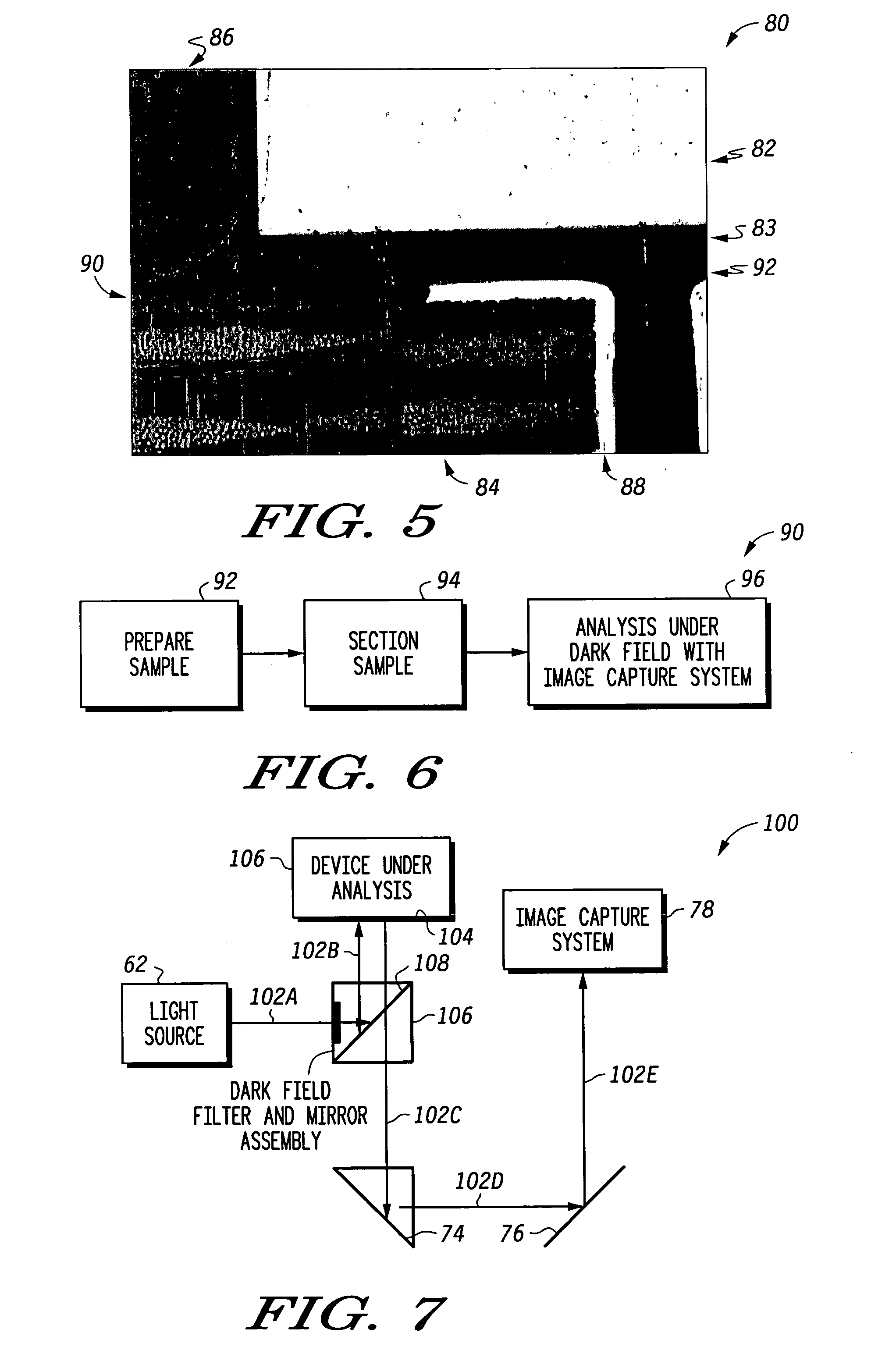
Patents
Literature
106 results about "Darkfield illumination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
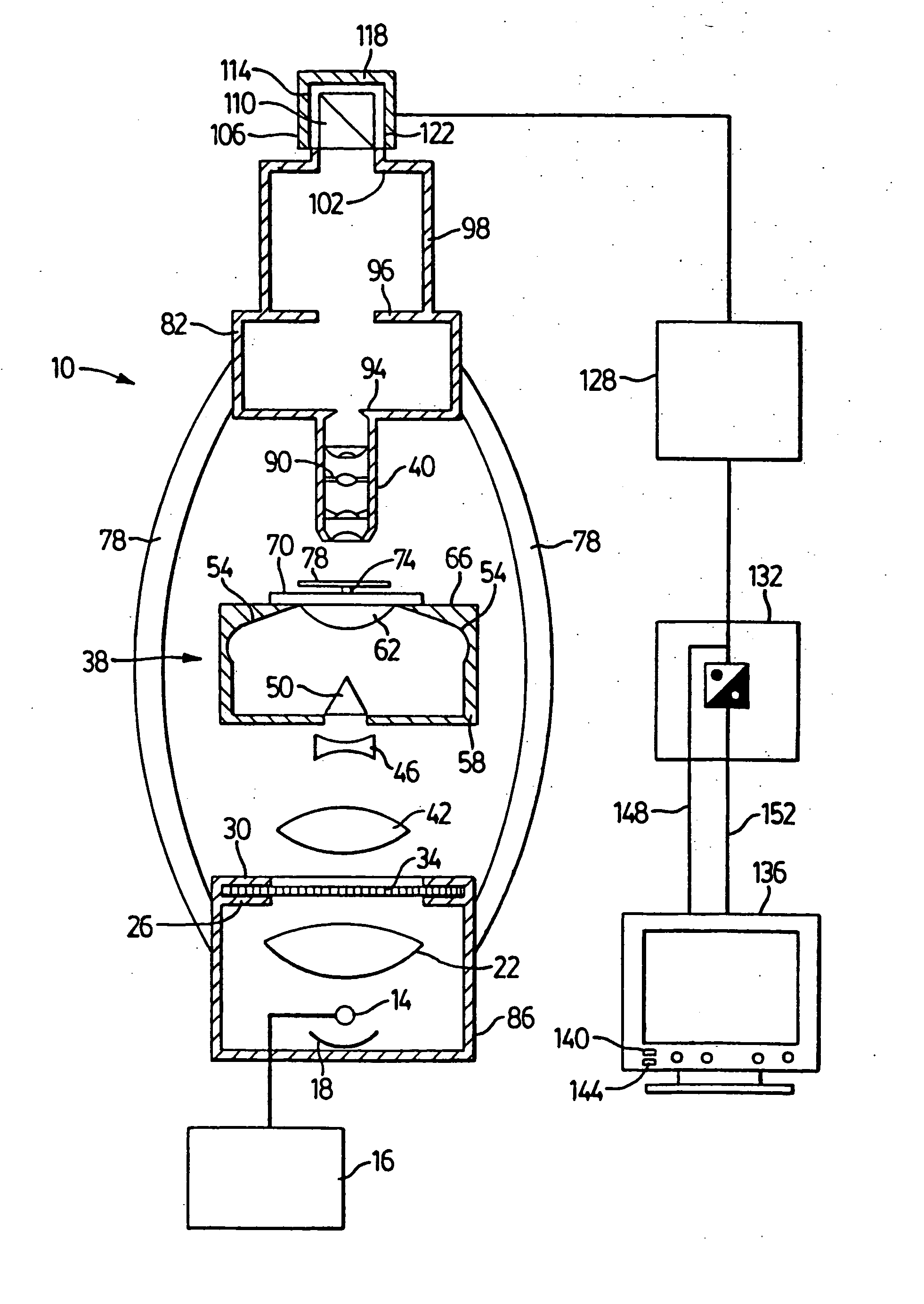
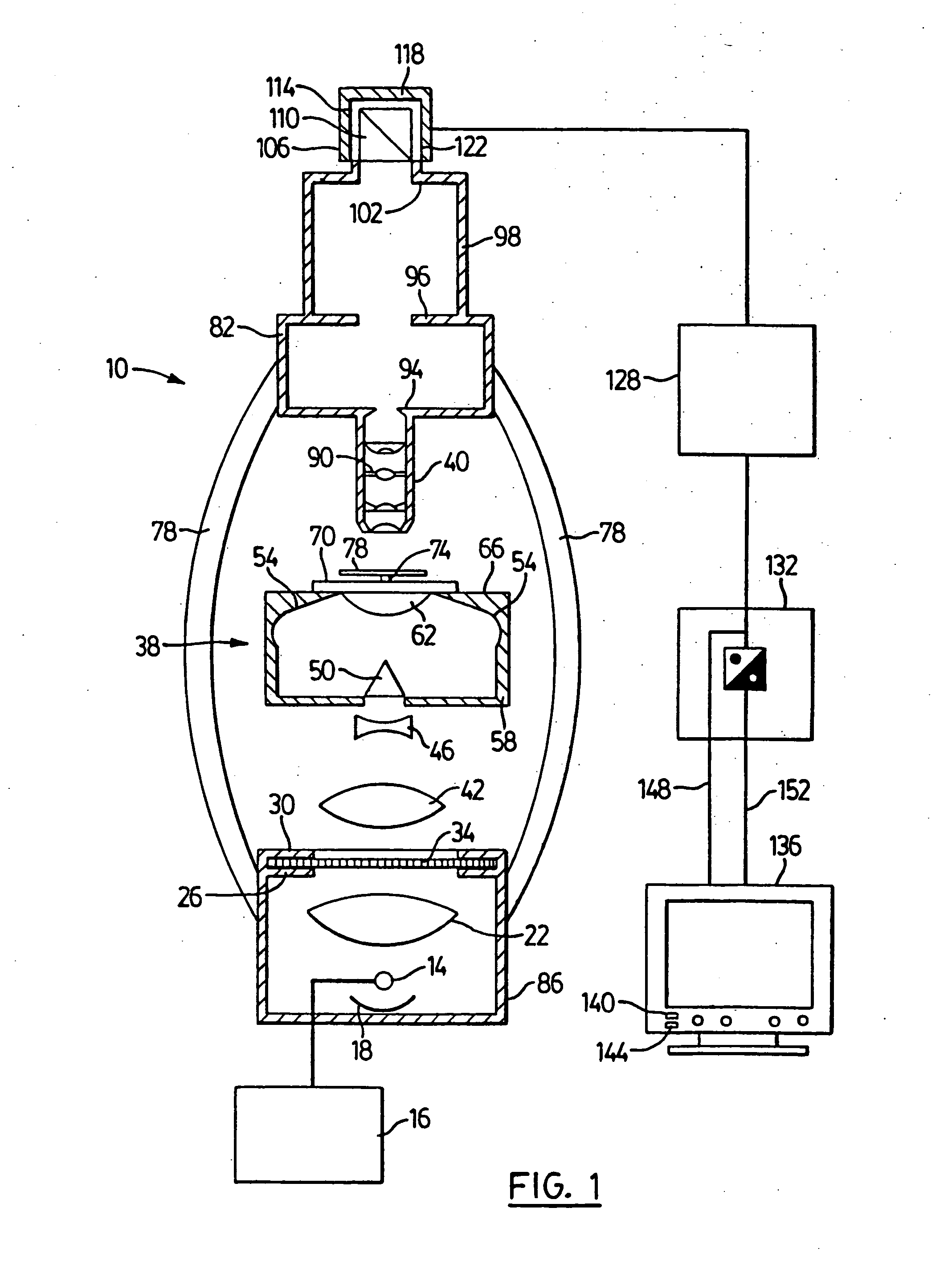
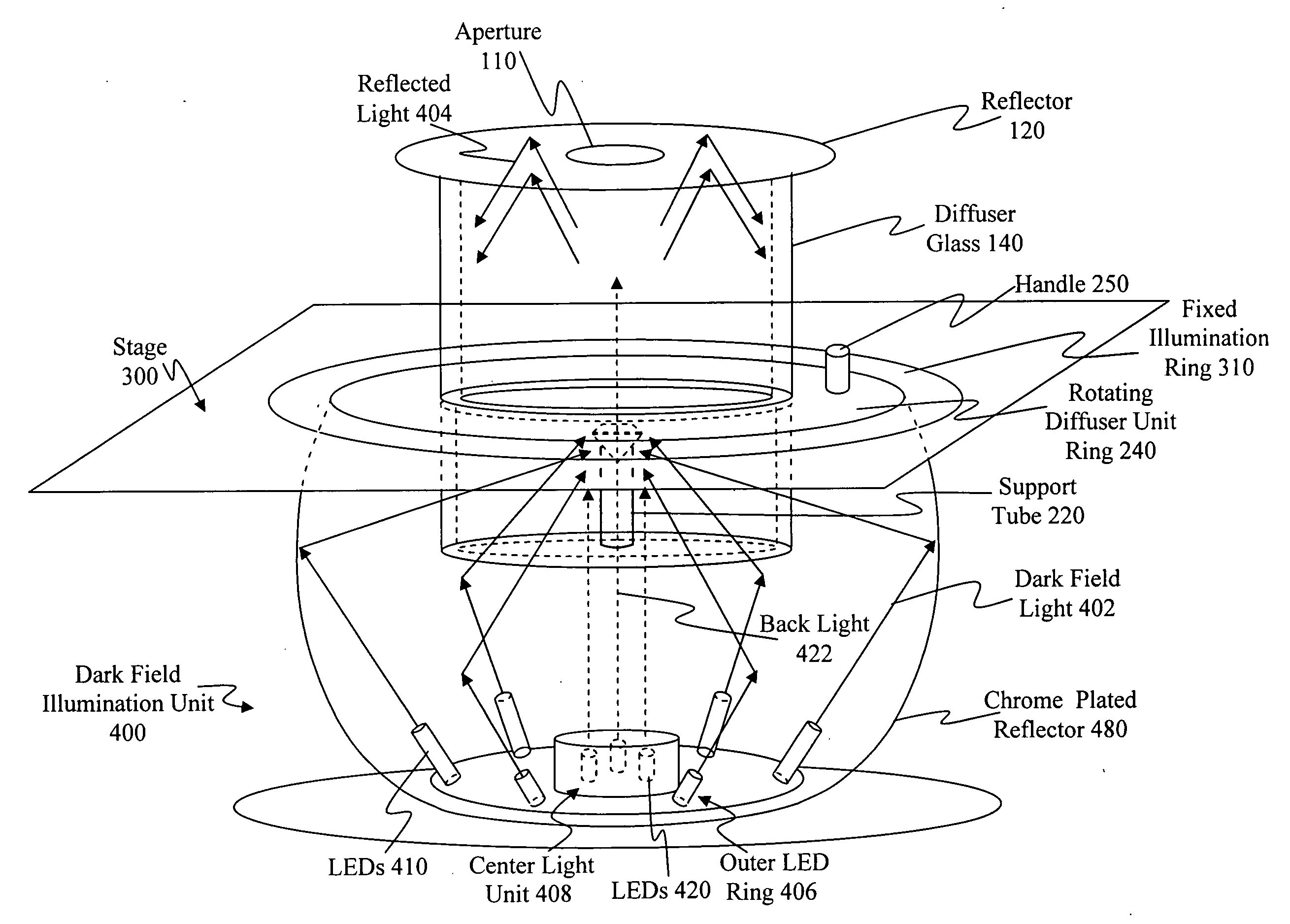
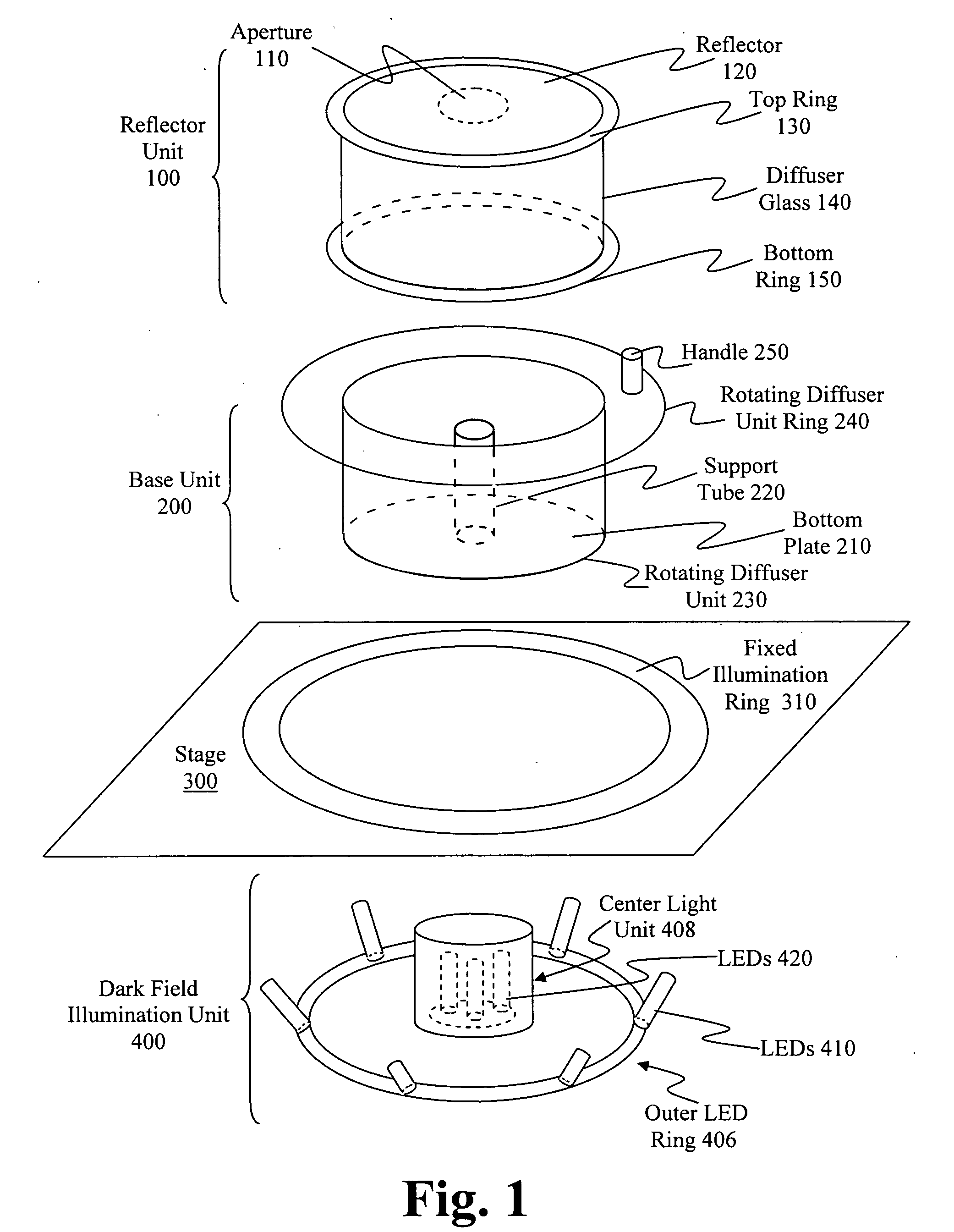
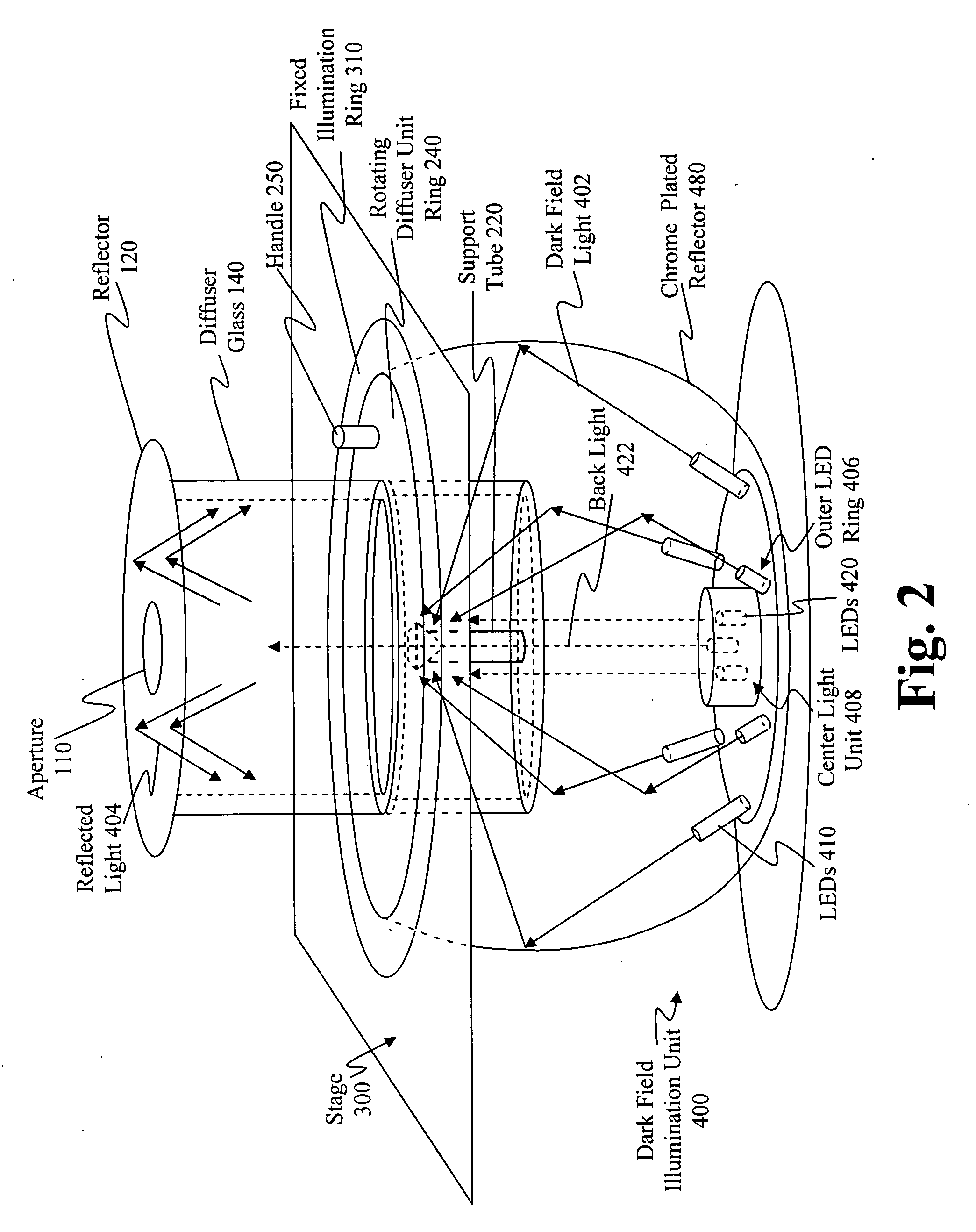
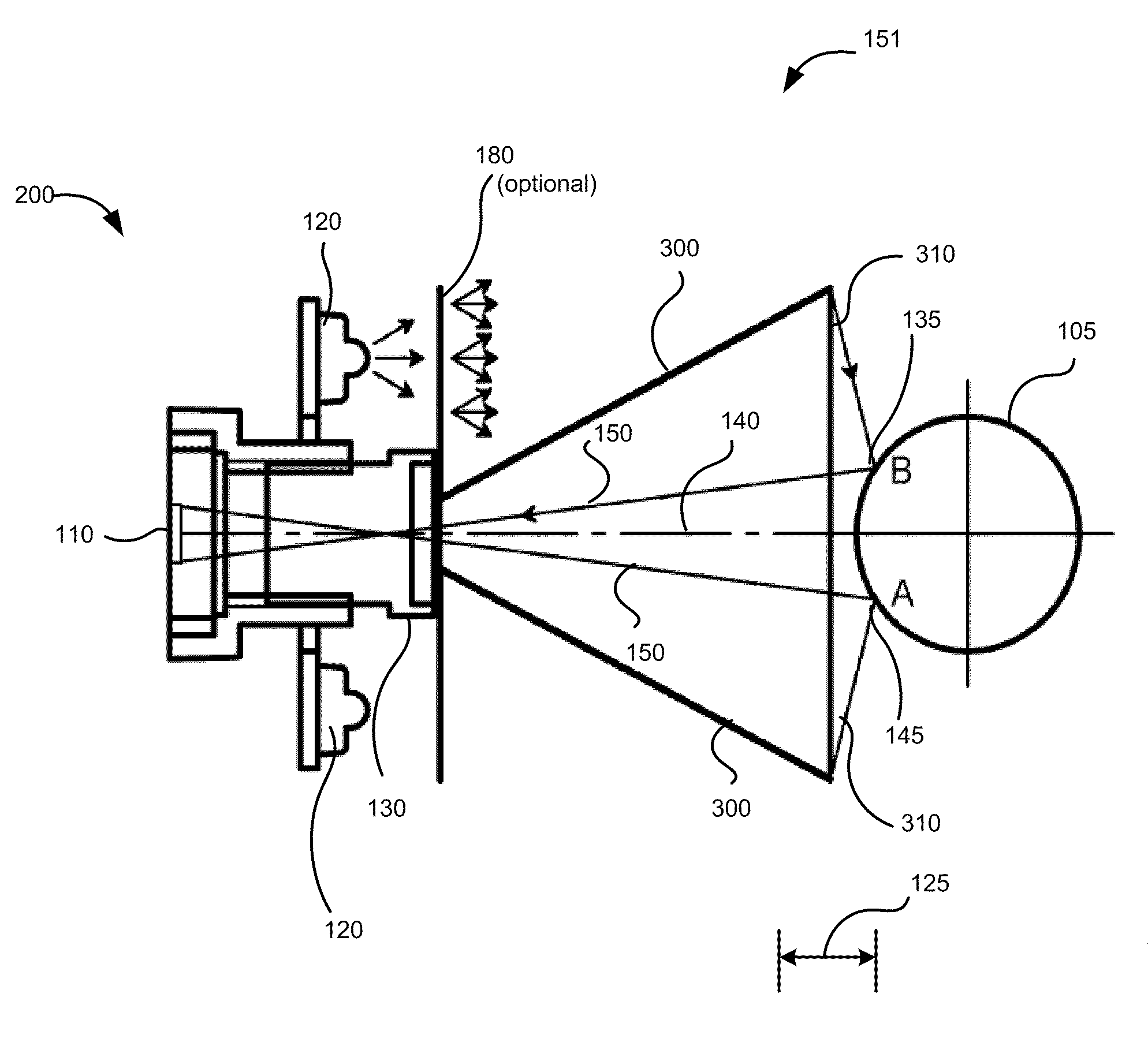
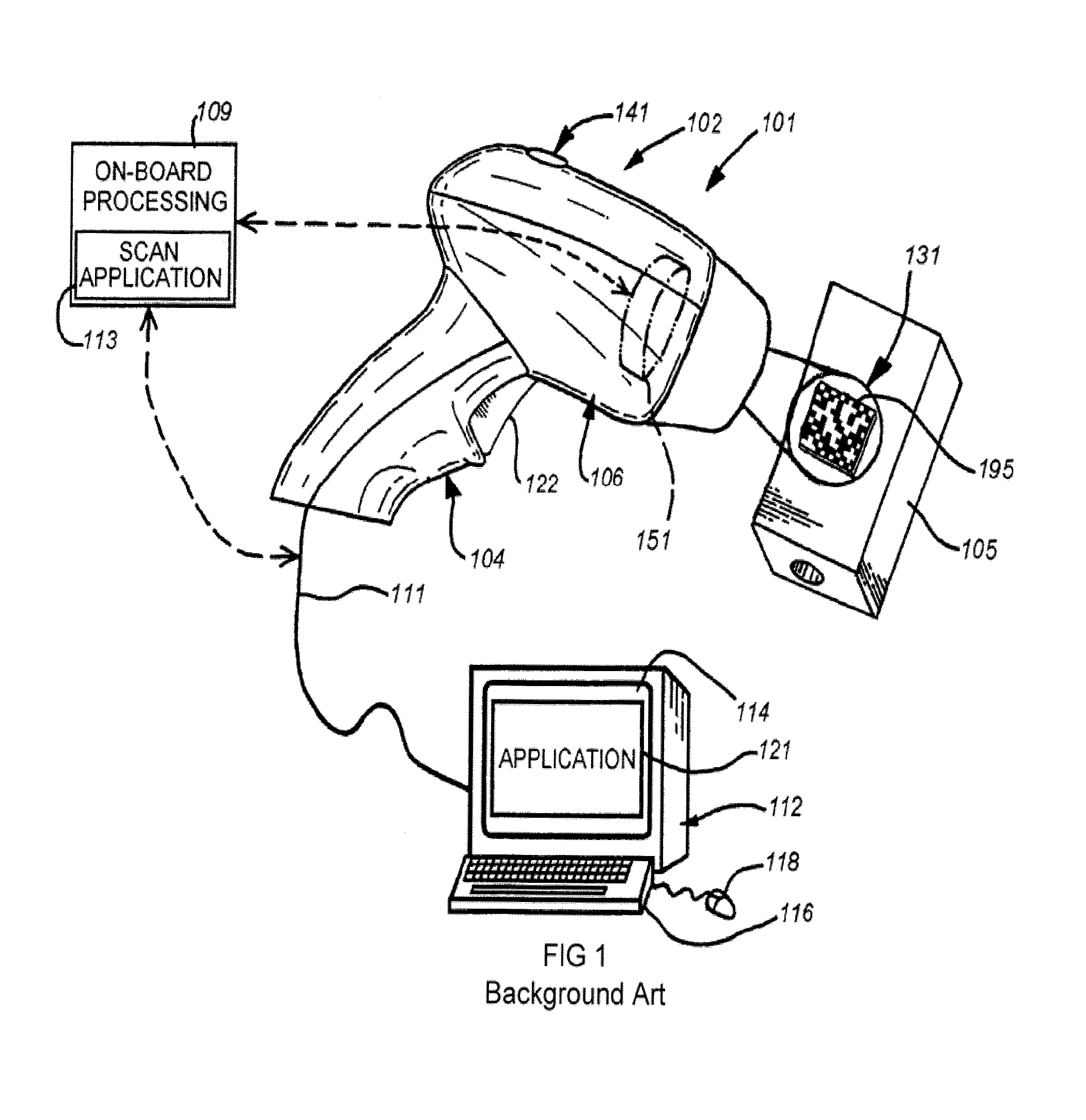
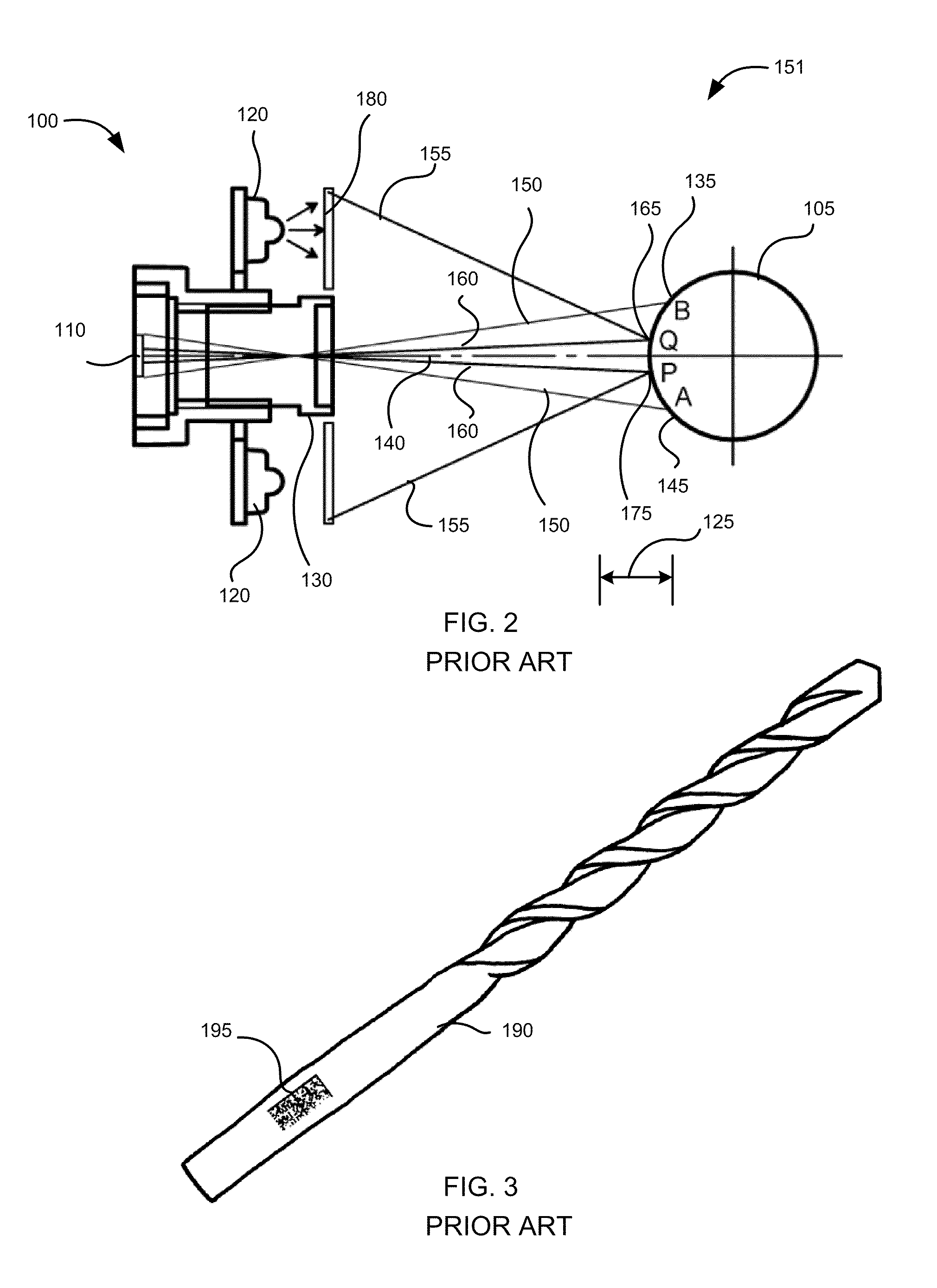
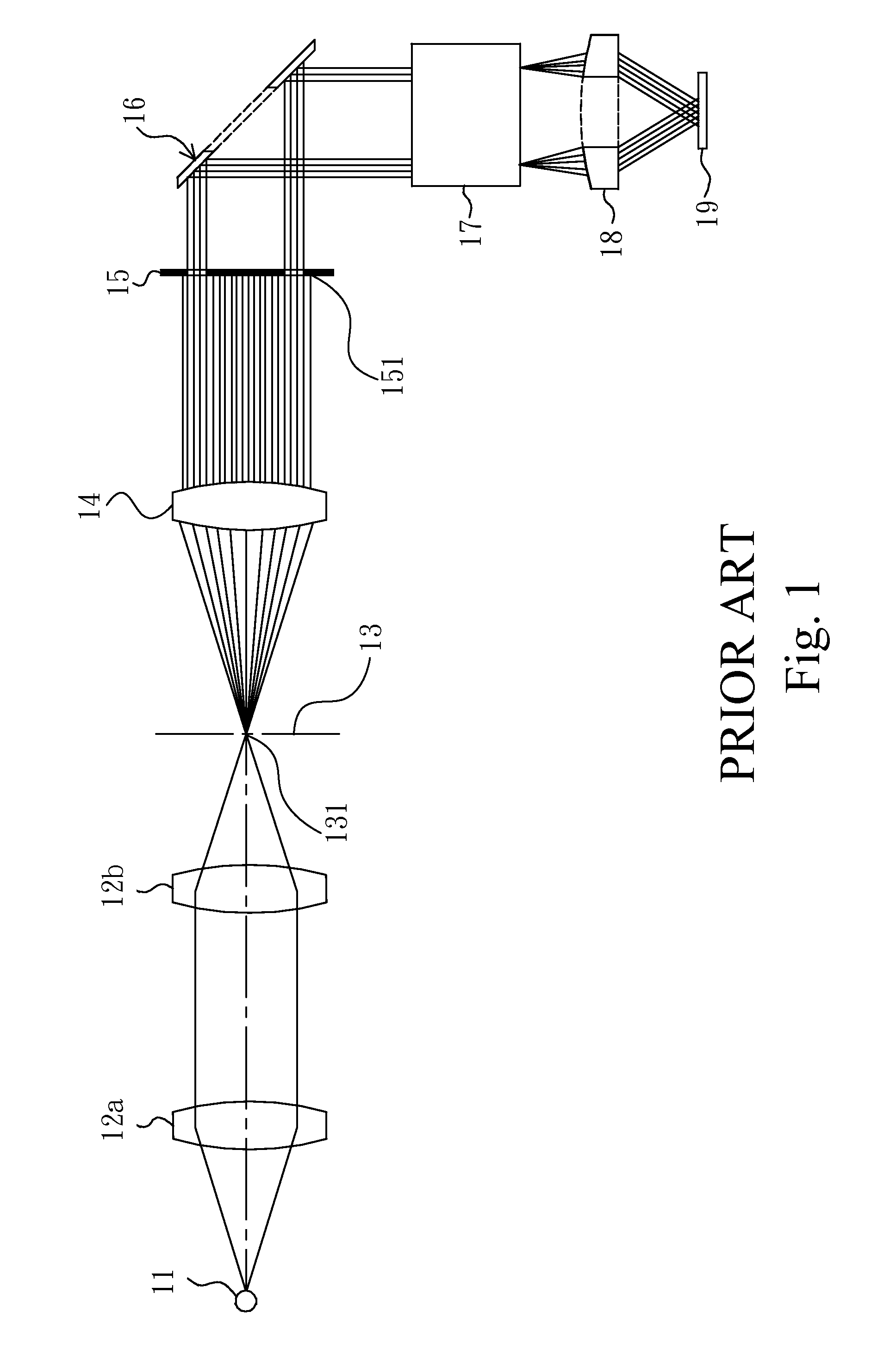
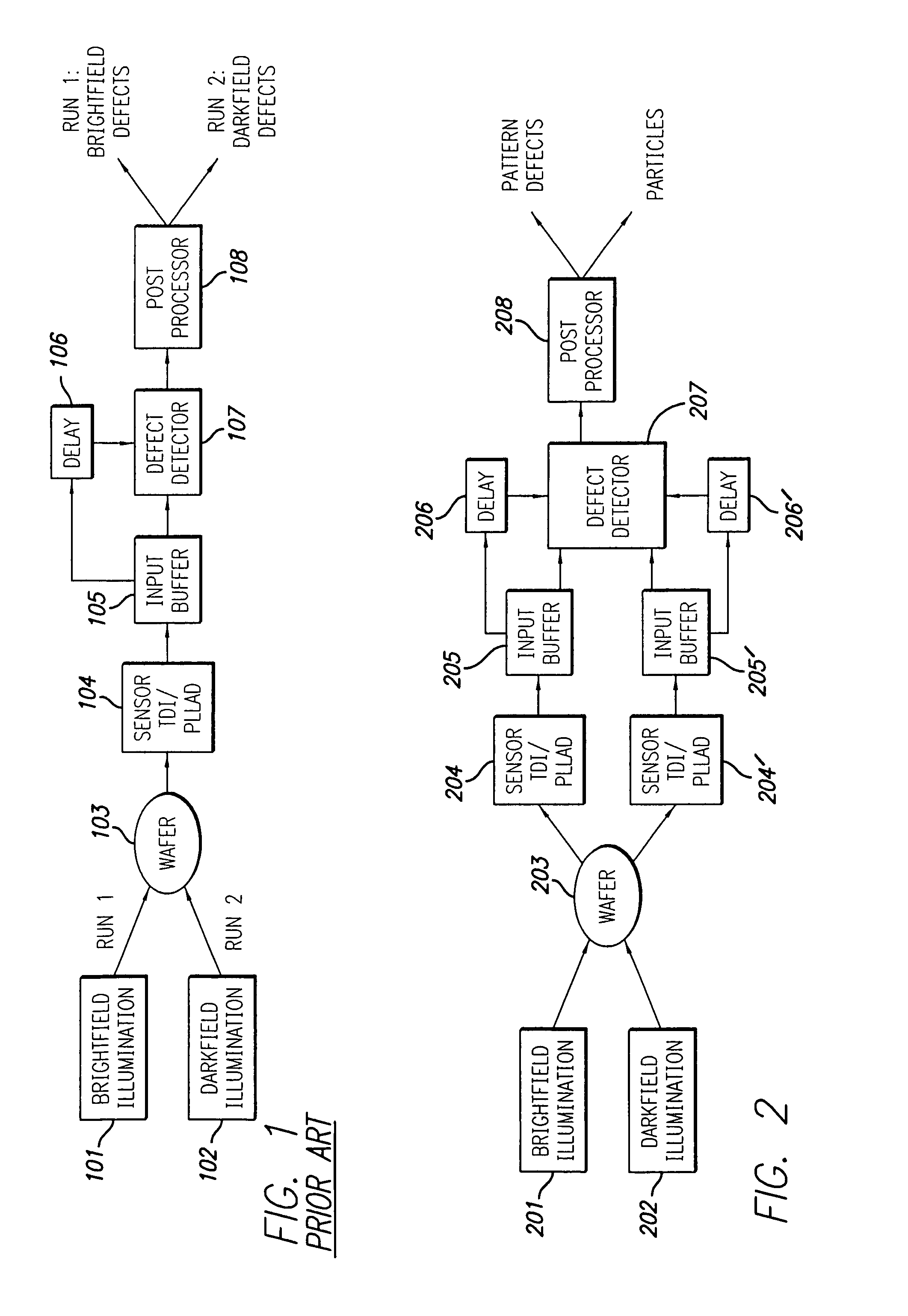
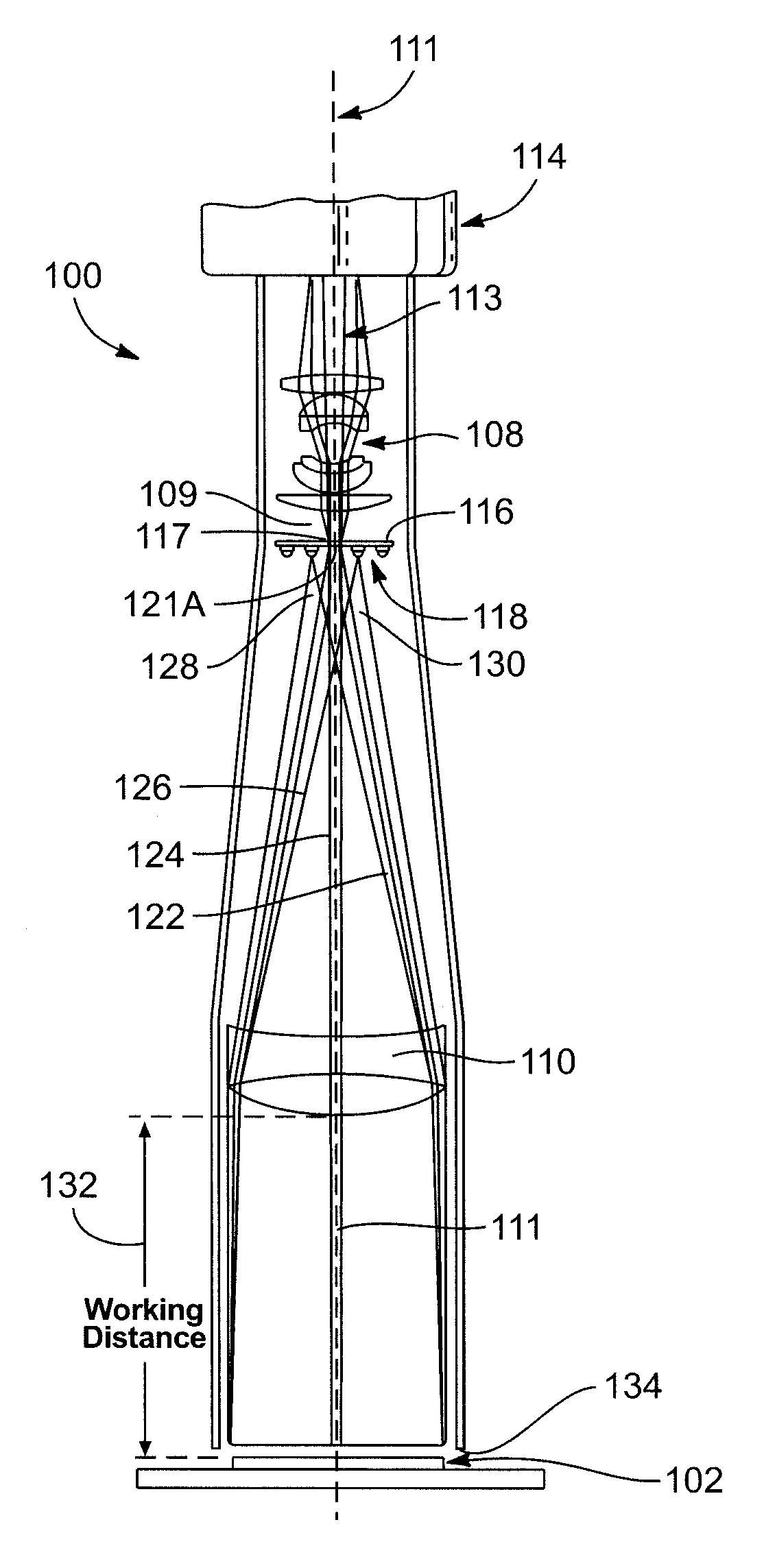
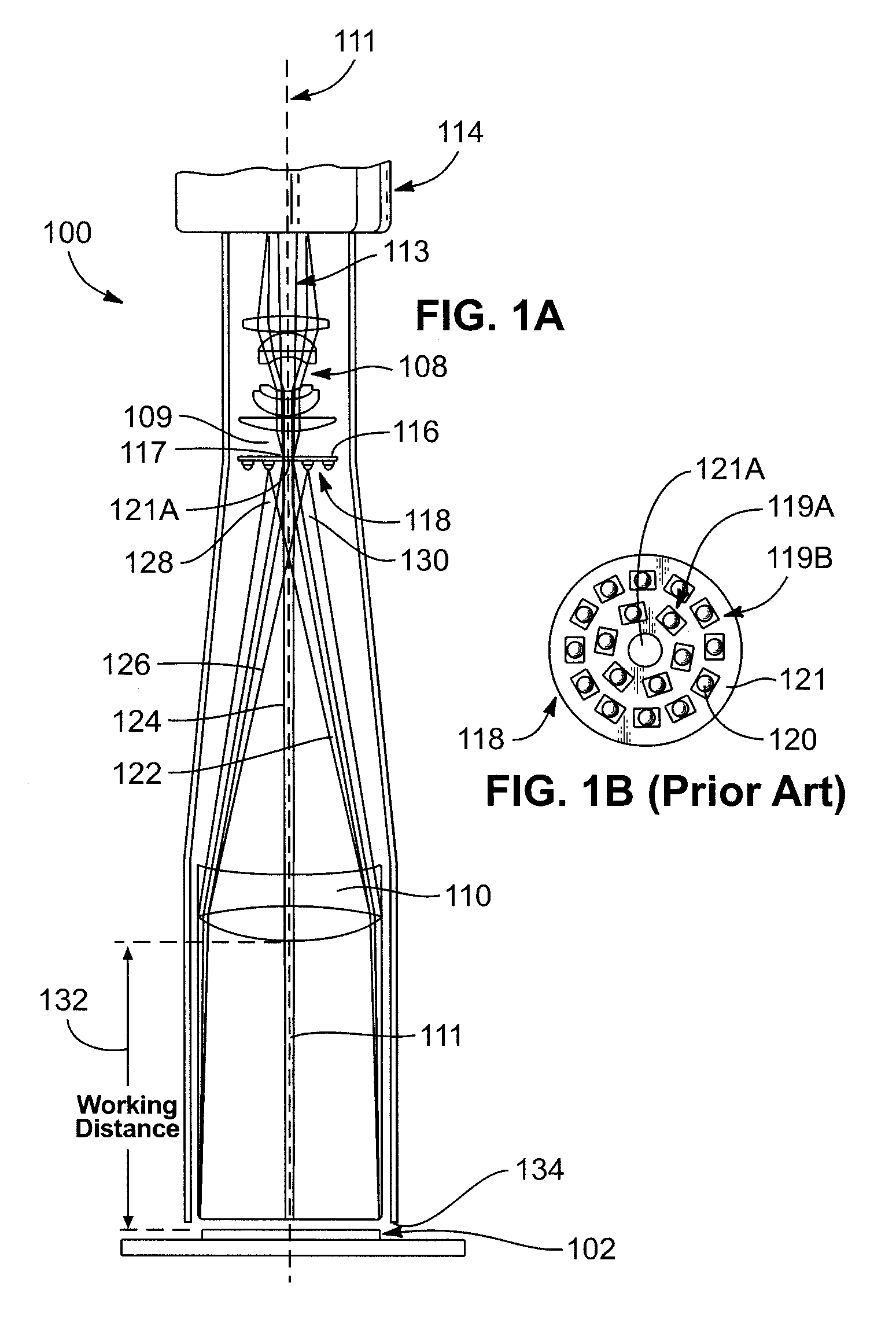
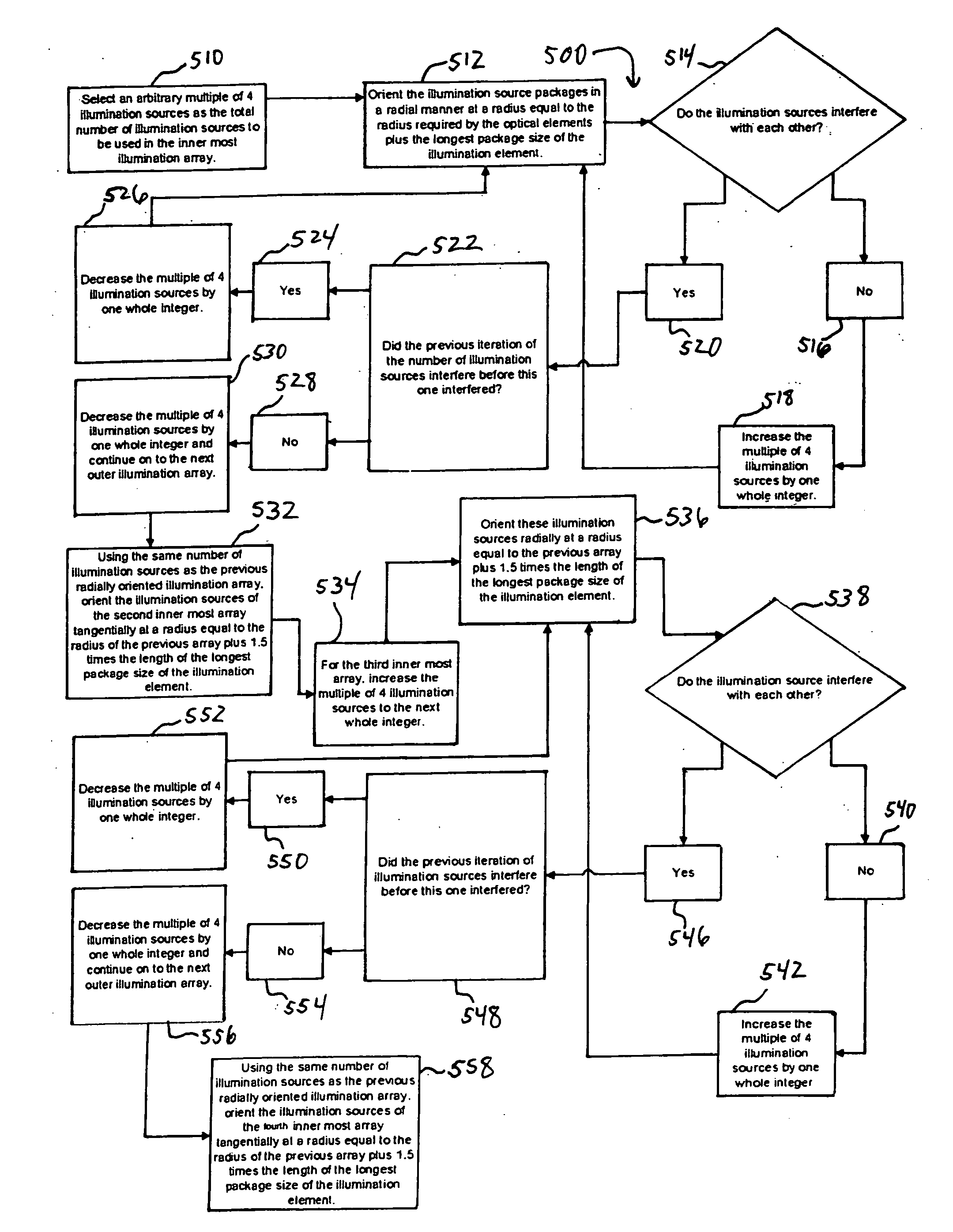
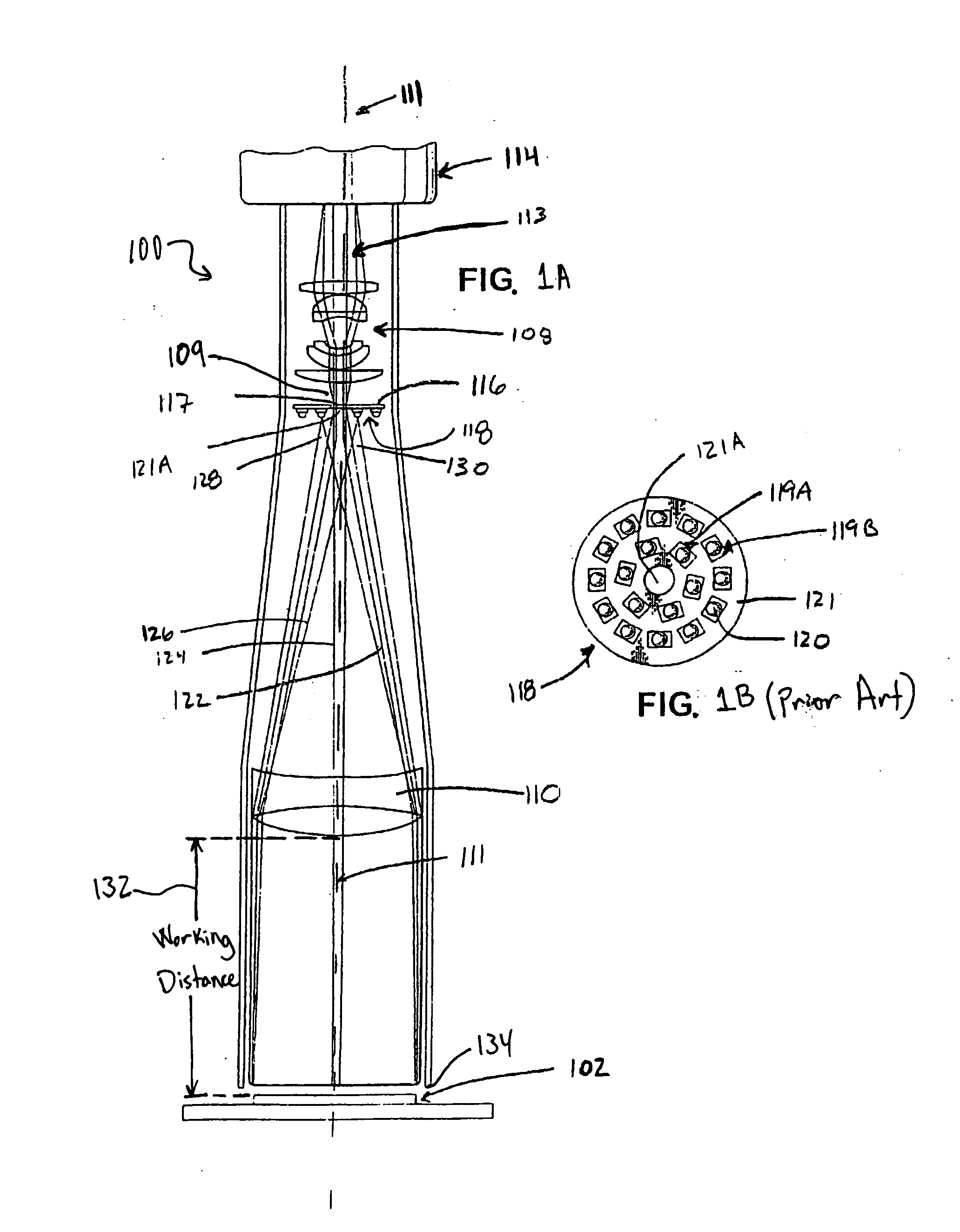
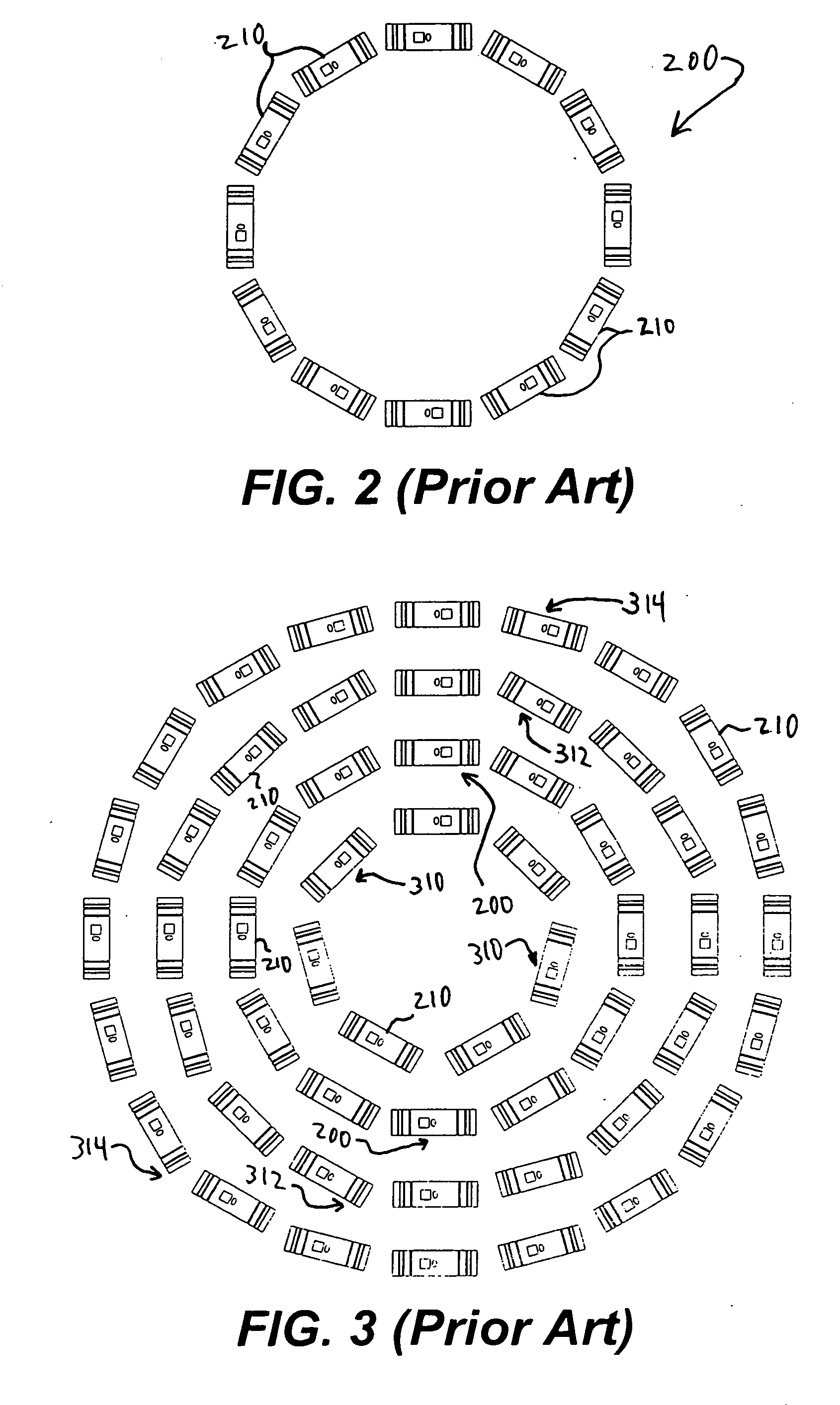
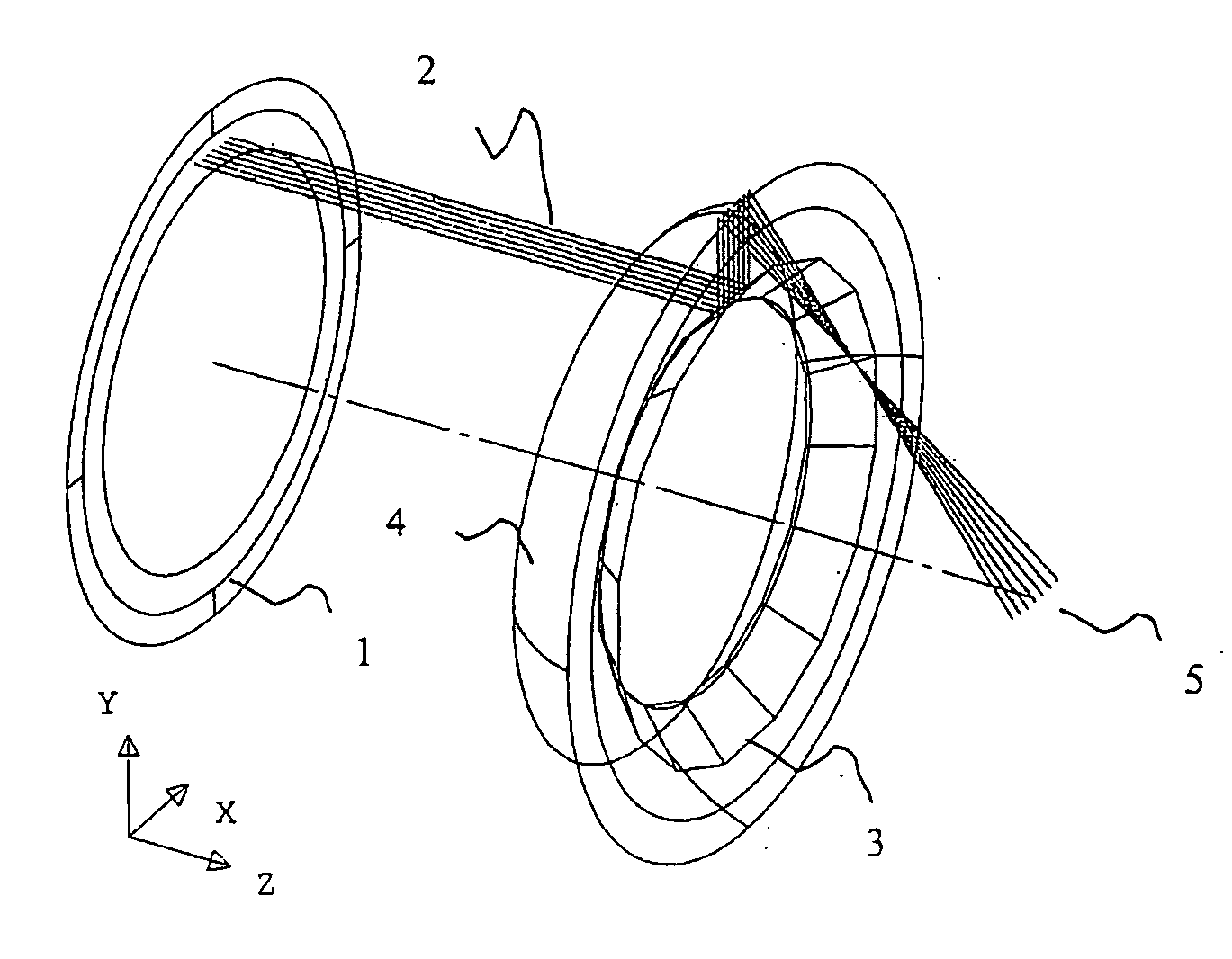
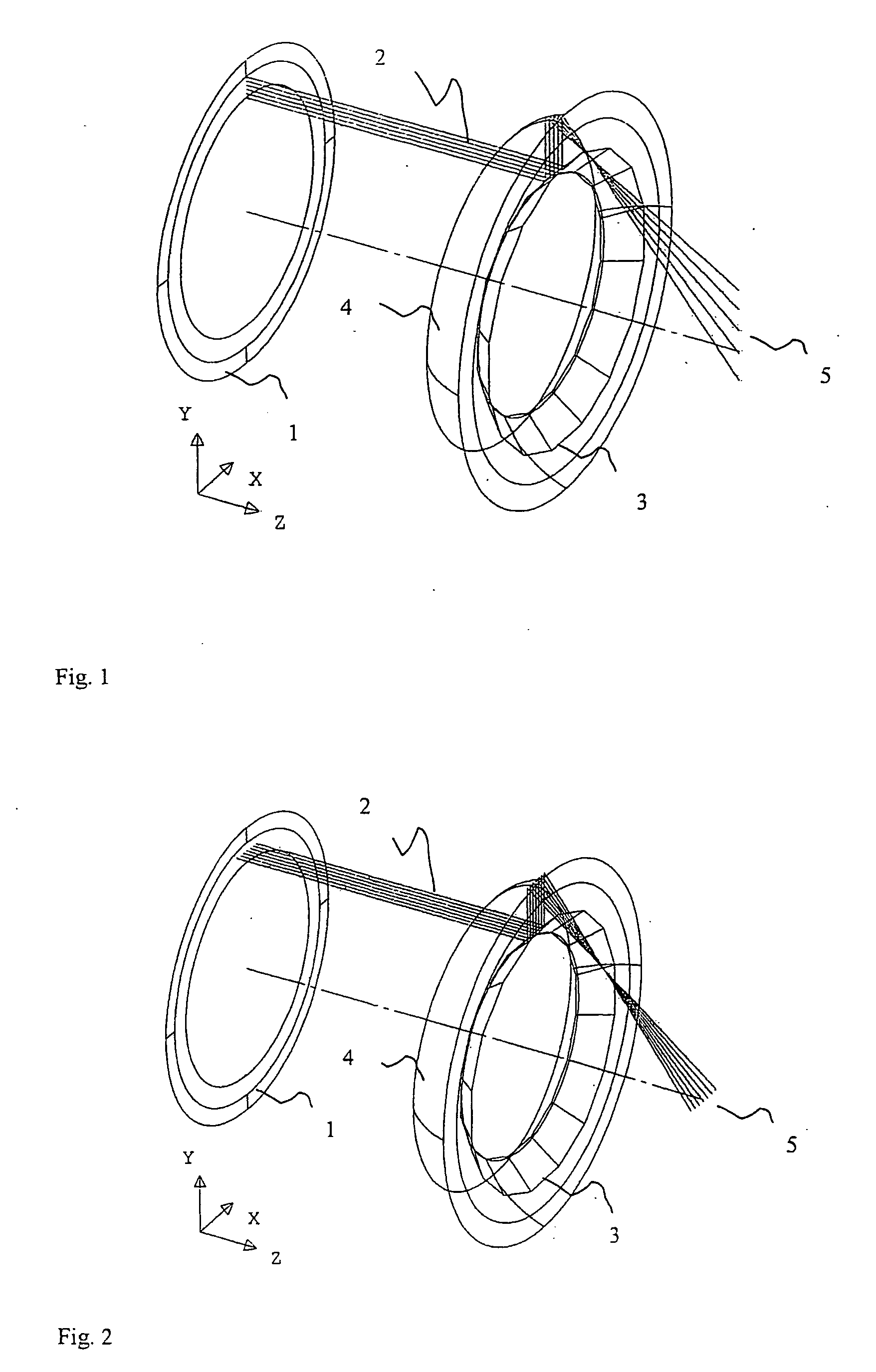
The principal elements of darkfield illumination are the same for both stereomicroscopes and more conventional compound microscopes, which often are equipped with complex multi-lens condenser systems or condensers having specialized internal mirrors containing reflecting surfaces oriented at specific geometries.
Light pipe illumination system and method
InactiveUS20050087601A1Easy to aimOvercome disadvantagesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical axisLight pipe
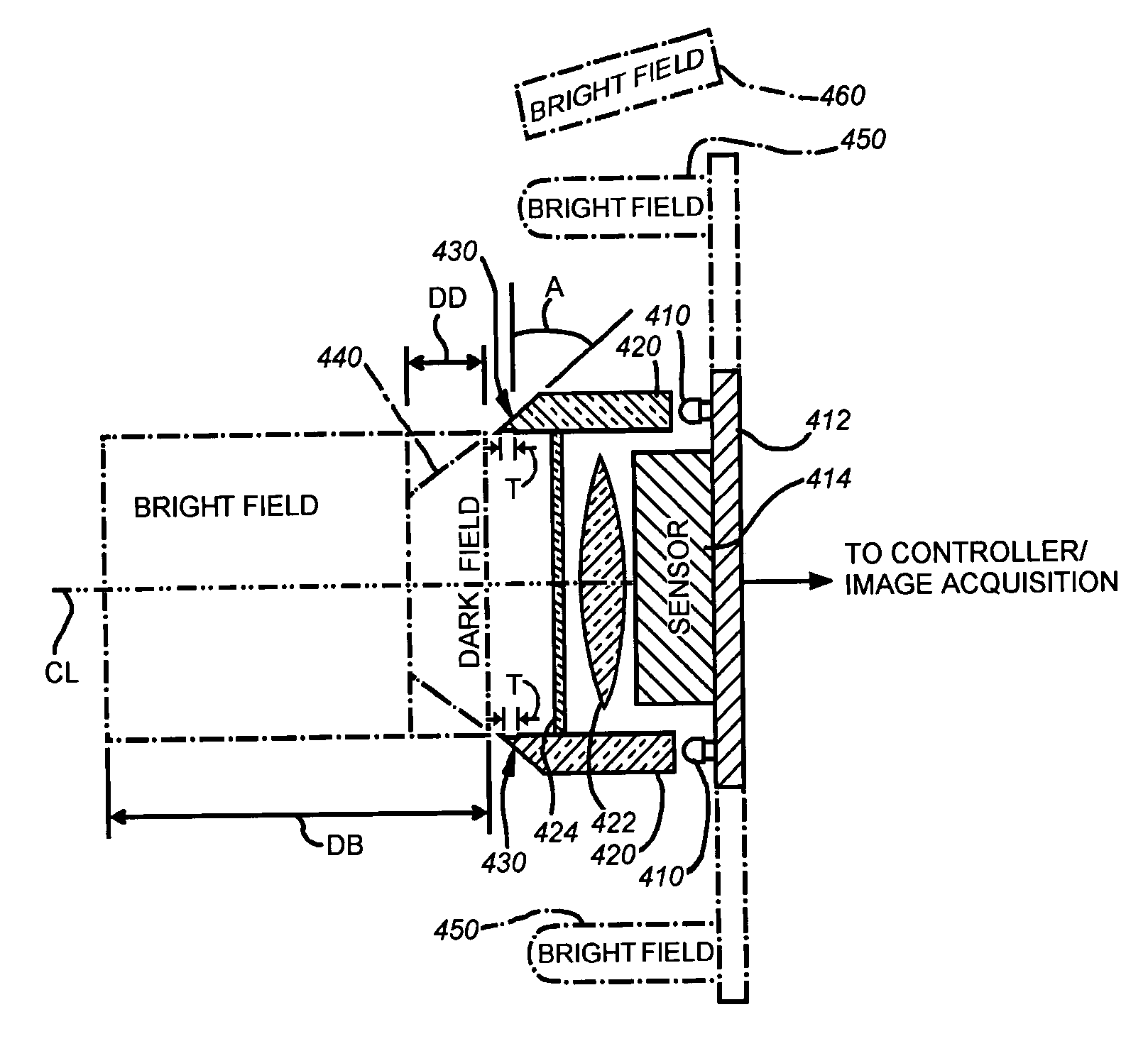
A system and method is provided for illuminating a subject using a light pipe that transmits light from a source, such as an LED ring illuminator to an outlet that directs the light appropriately as either bright field illumination, dark field illumination or both. The light pipe can include concentric cylinders, typically with a bright field illuminator nested within a dark field illuminator. The tip of the dark field illuminator may be angled so as to internally reflect light inwardly toward the central optical axis of a camera at a low angle. The tip can be located near the focal plane of the camera for the desired field of view. The field of view of the camera sensor can be modified to reject data outside of a illumination field of a particular shape. This illumination field can be created by shaping the light pipe in a predetermined form that projects the modified illumination field. Likewise, a set of aiming illuminators (in, for example, a noticeable color) can be provided around the perimeter of the light pipe to delineate outer boundaries of the illumination field or area of interest. These approaches facilitate better aiming of the sensor into the desired area of interest so that it is illuminated and / or acquired most-fully.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
Hand held symbology reader illumination diffuser
ActiveUS20060133757A1High contrast imageCoupling light guidesSensing record carriersDiffuse illuminationHand held
A hand held industrial identification symbol reader projects diffuse illumination onto a region of interest to produce high contrast images of symbols. The diffuse illumination is particularly well suited for producing images of symbols that are marked directly on objects. The diffuse illumination is created through the use of an optically translucent diffuser having a generally tapered shape that distributes diffuse illumination throughout the field of view of the reader. The diffuse illumination can be supplemented with dark field illumination using selectively actuated illumination sources.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
Control unit for mixed light illumination, especially for microscopy
InactiveUS7273298B2The way is simple and fastReduce brightnessLighting elementsFire alarmsImaging processingControl signal
A control unit for a microscope, a stereomicroscope, or an industrial image processing machine is described, to which at least three lighting units, e.g. for incident light-bright field illumination, incident light-dark field illumination, and for transmitted light illumination, are connected. Respective lighting units are simultaneously controlled according to user commands, e.g. for interval control to simulate a moving light source. The user commands can be input by function keys and / or a foot switch and / or stored in a memory provided in the control unit. Alternatively or in addition, the control unit can receive command statements from an external computer connected via an interface or control signals from an external camera. The control unit detects temperatures of the lighting units and shuts off a lighting unit or generates a warning signal when its temperature becomes excessive.
Owner:SCHOTT AG +1
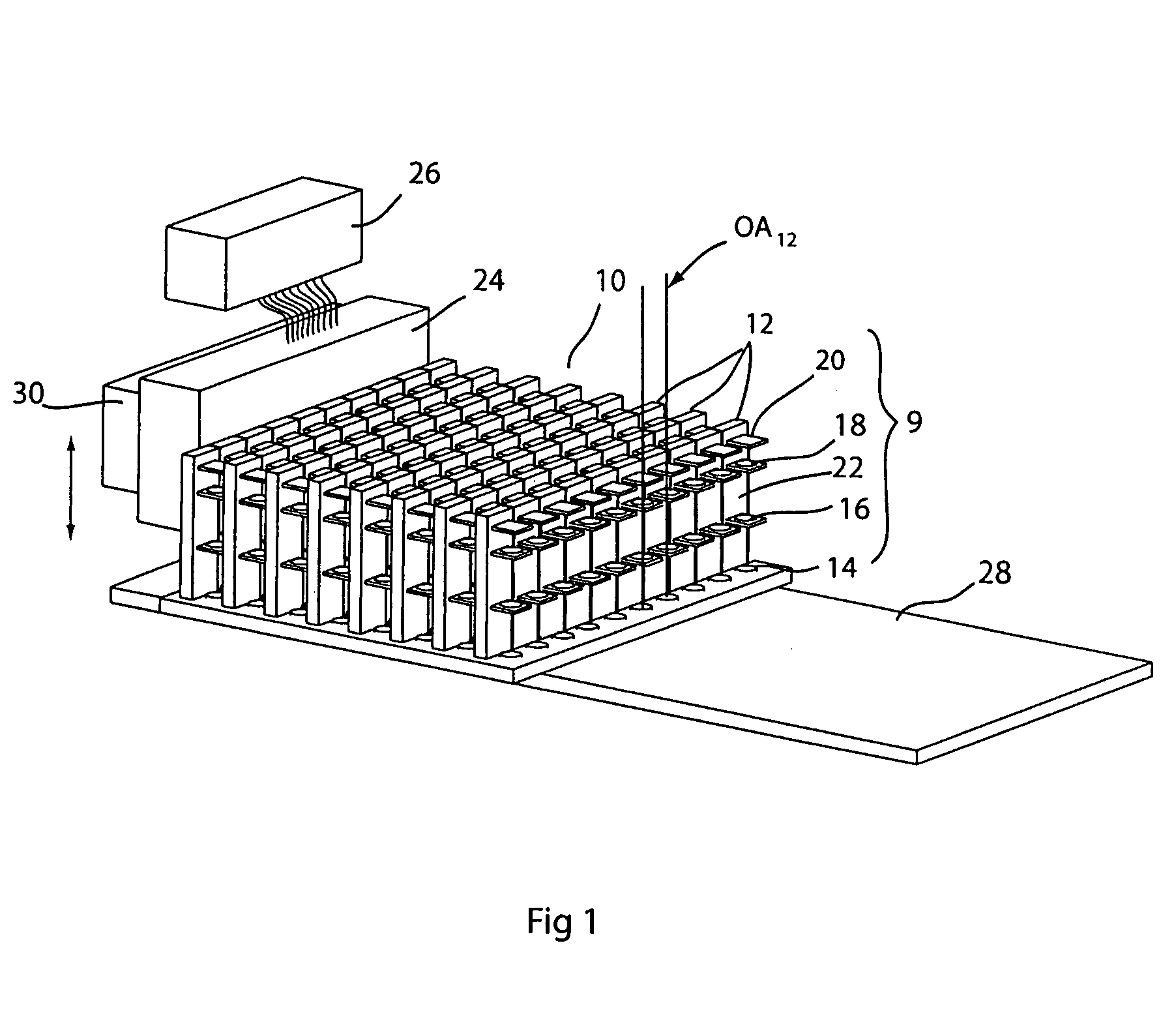
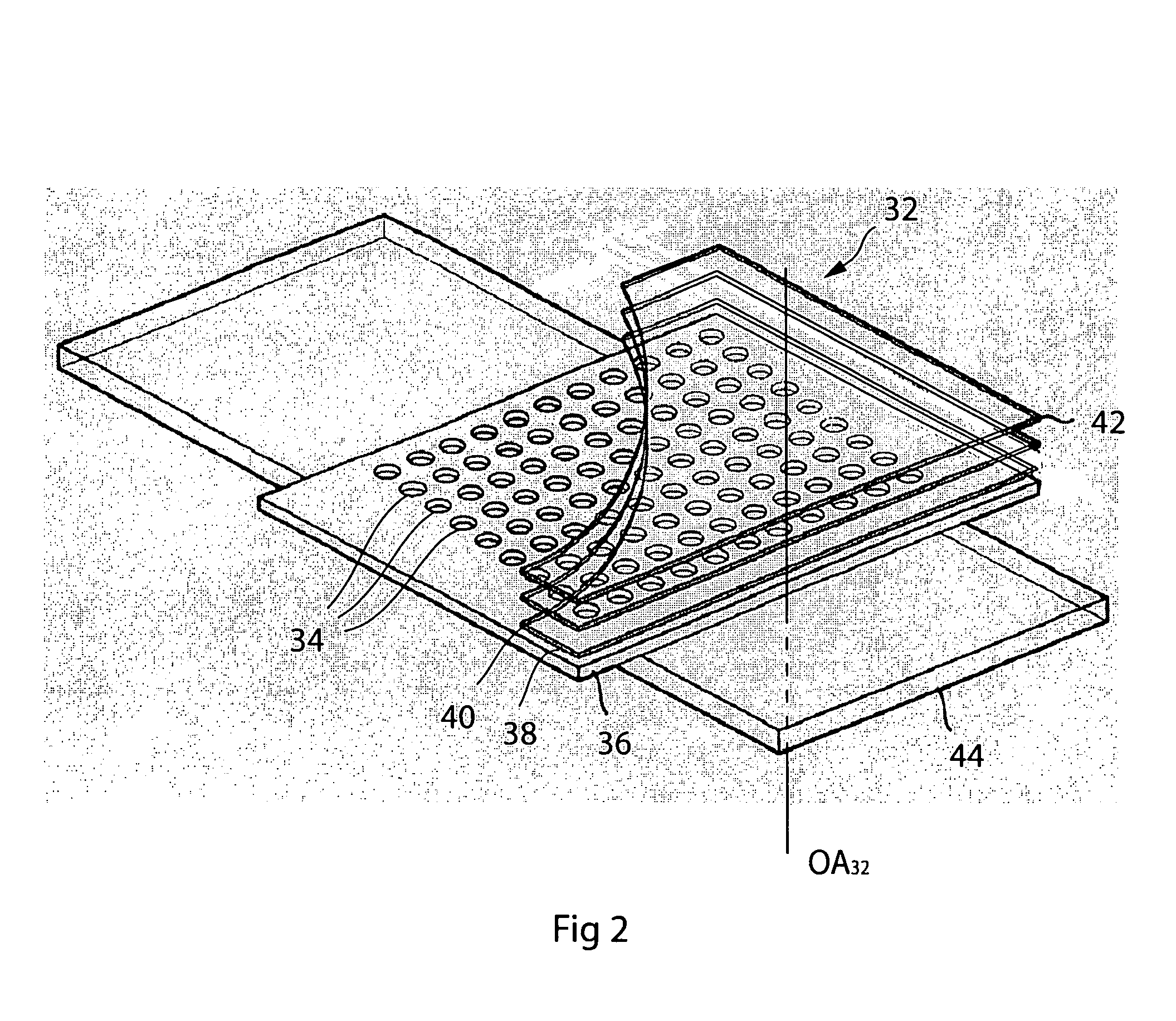
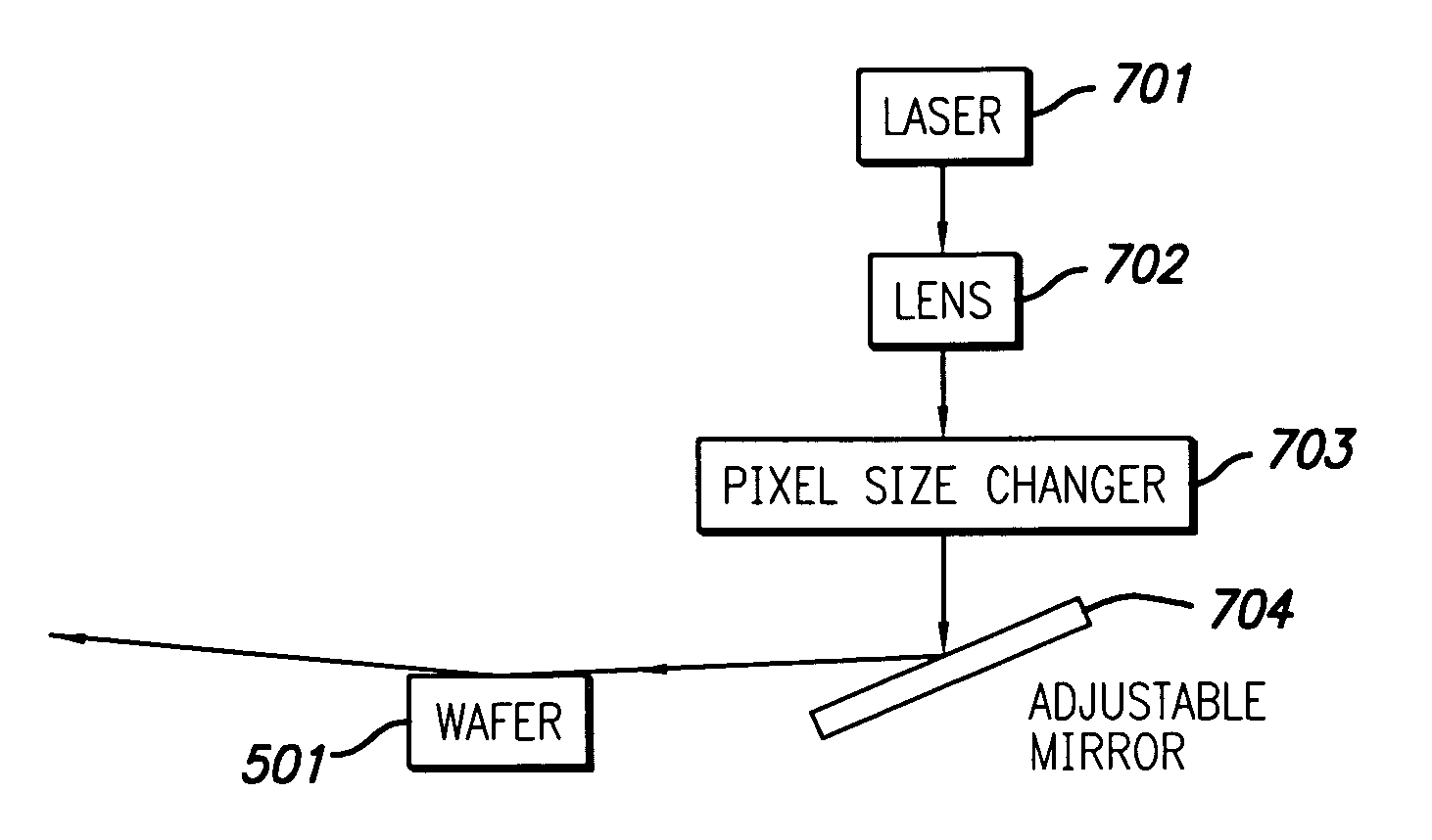
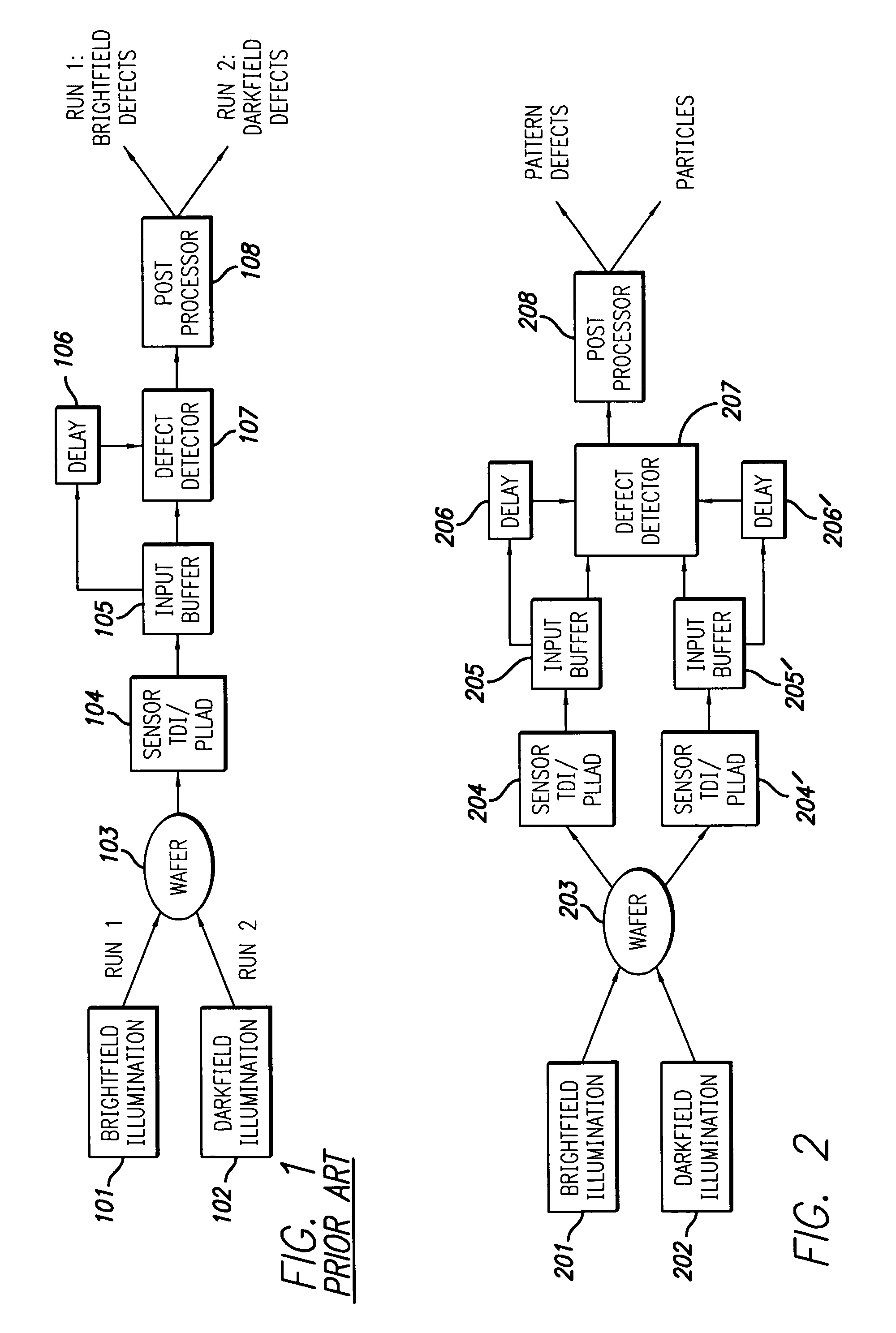
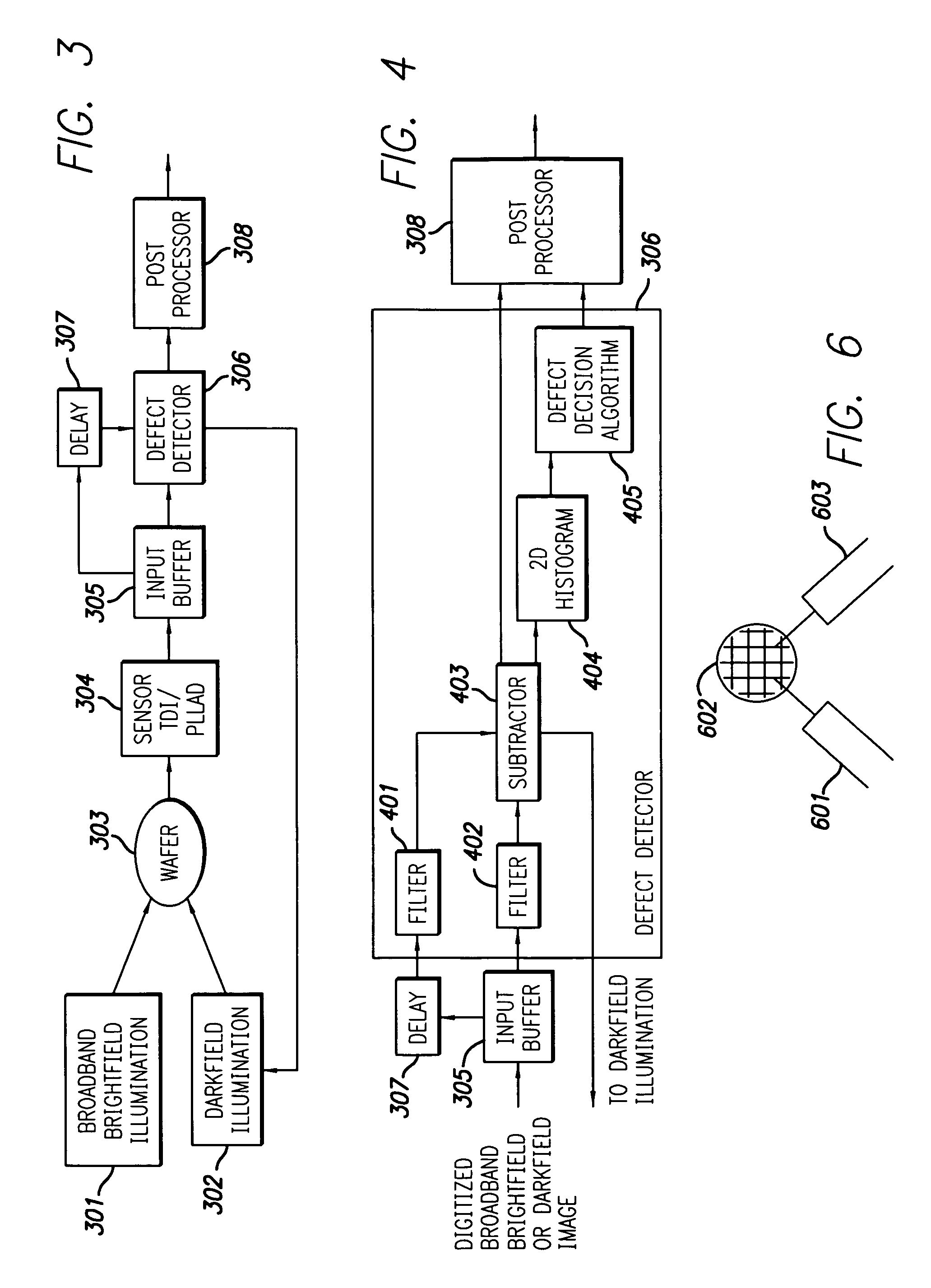
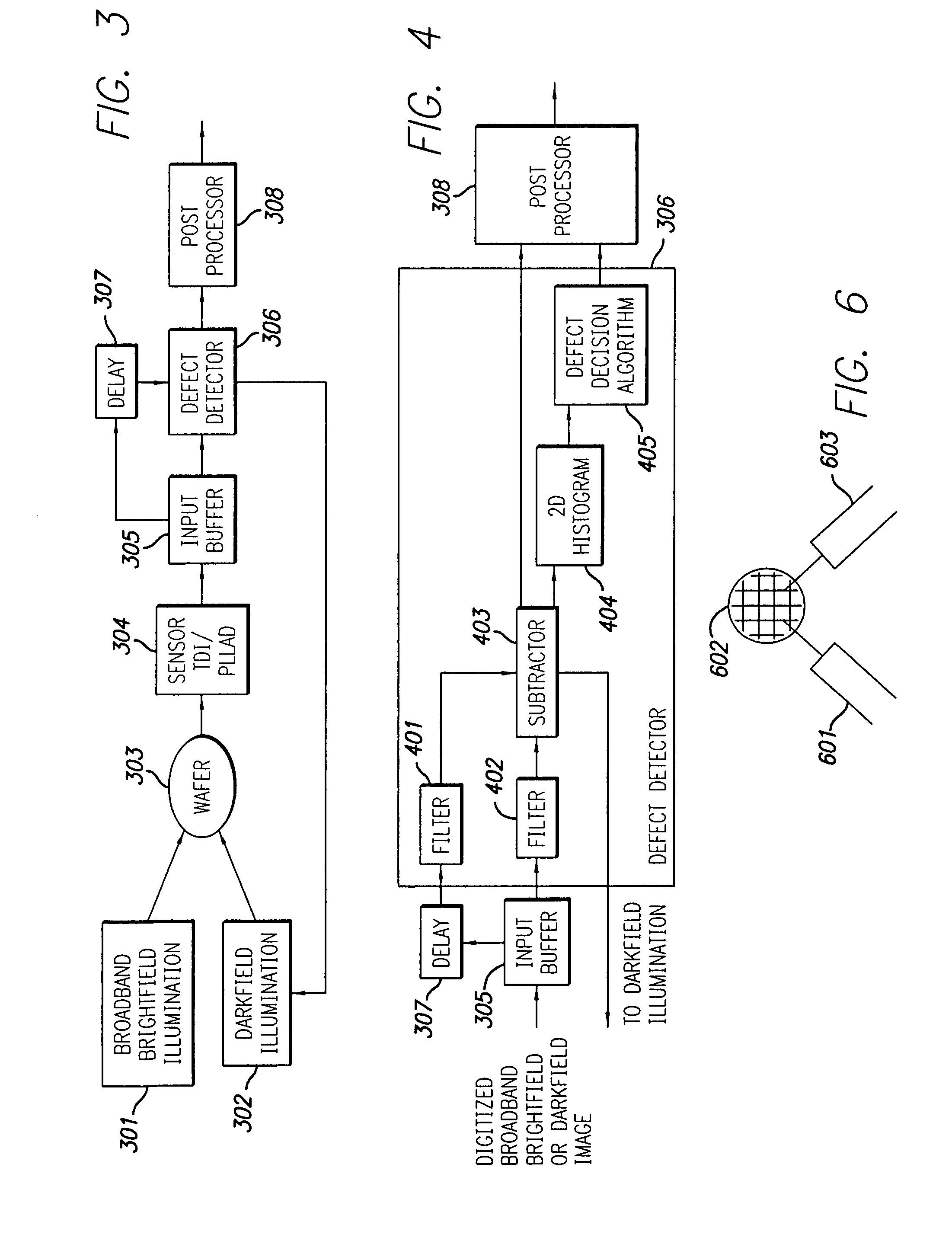
High throughput brightfield/darkfield wafer inspection system using advanced optical techiques
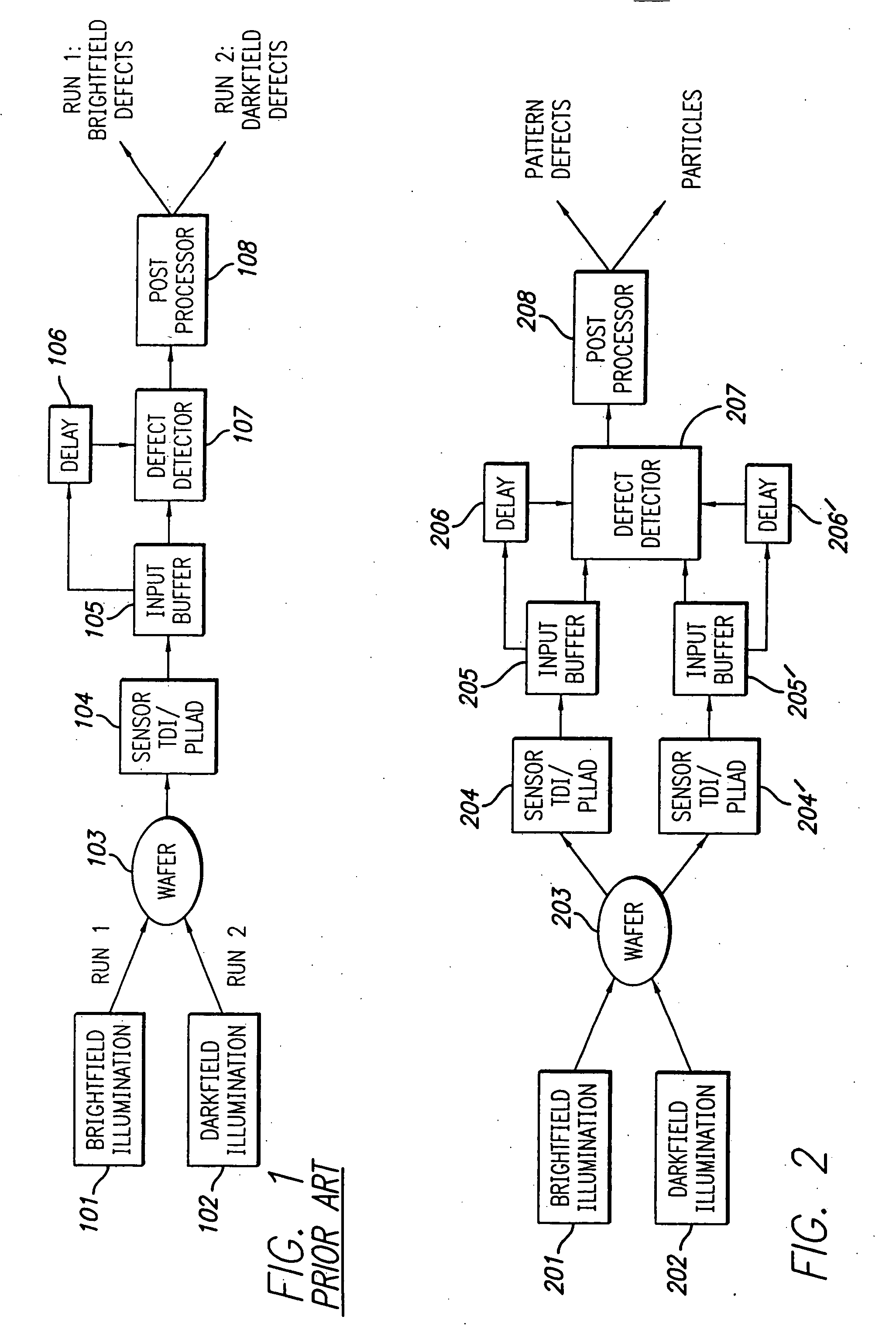
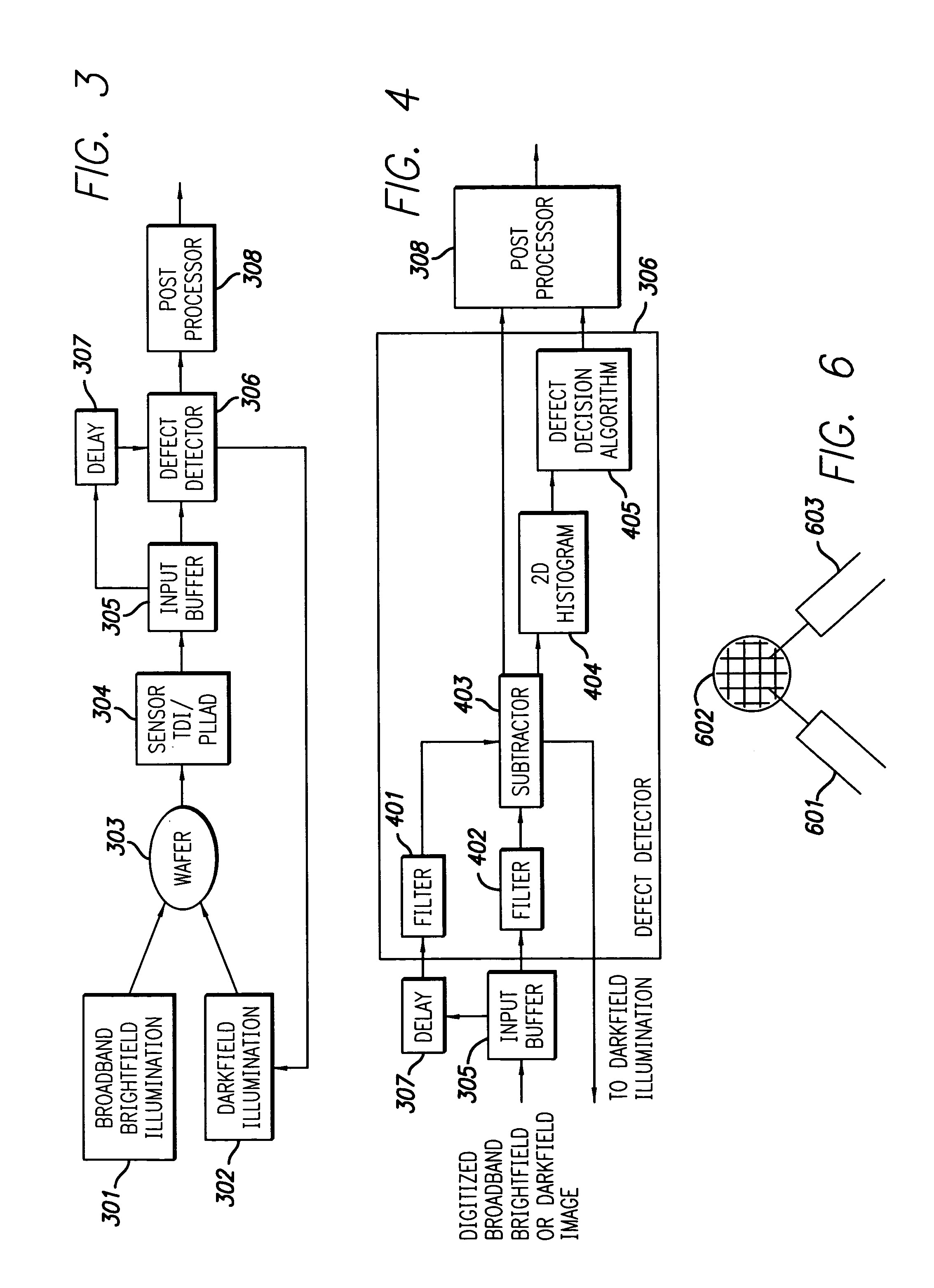
InactiveUS20050062962A1Great level of detectionImprove the level ofPolarisation-affecting propertiesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDual modePost processor
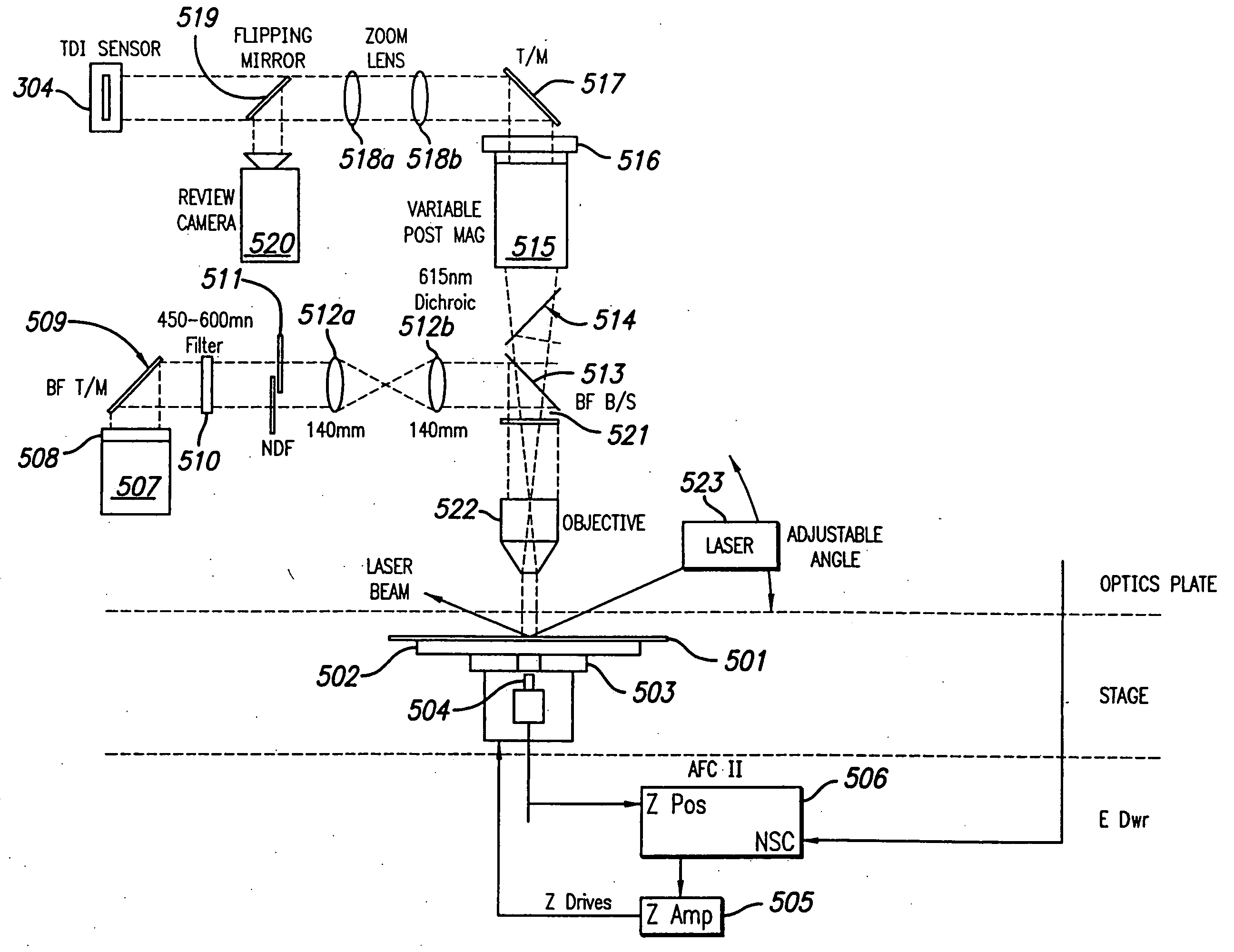
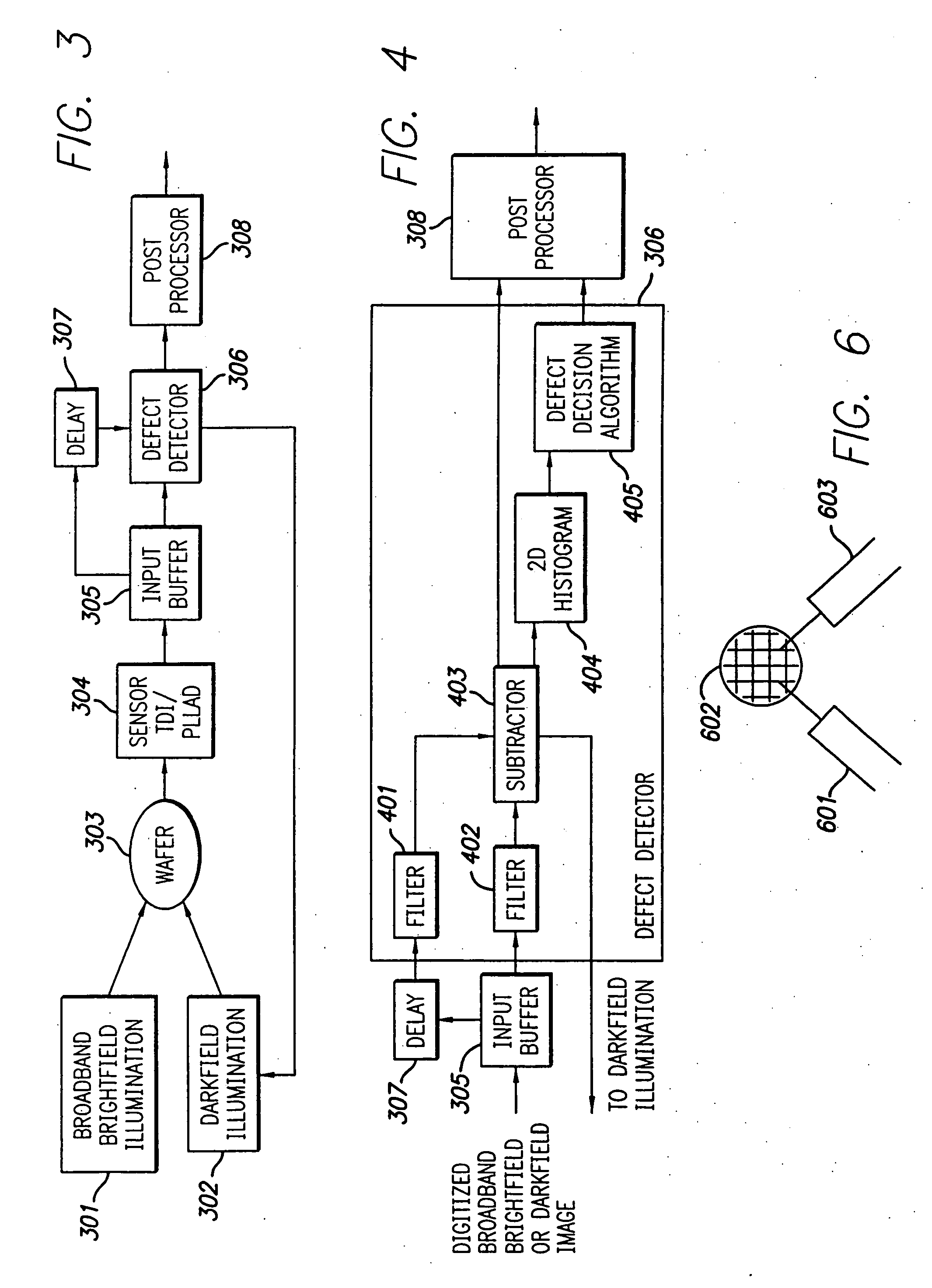
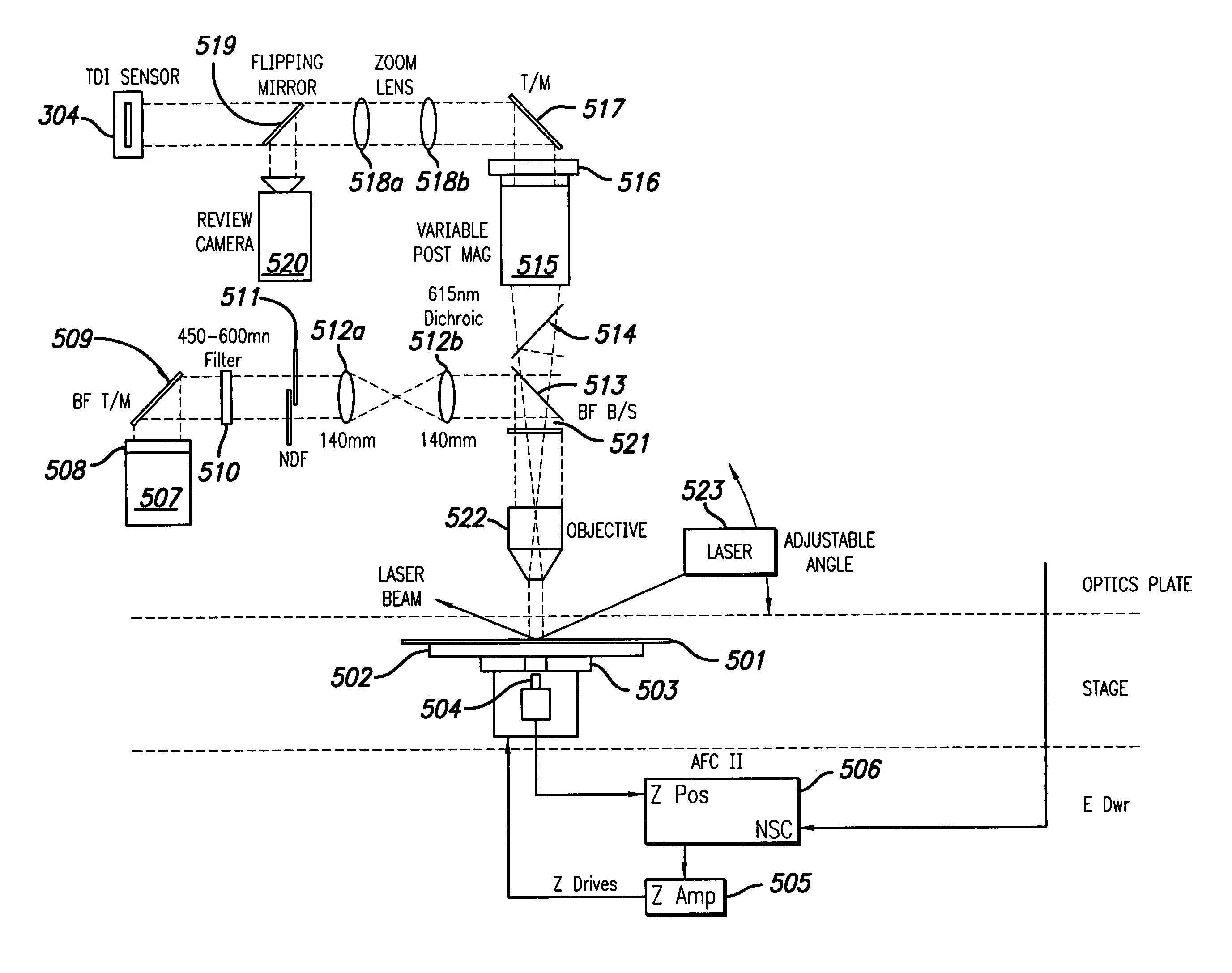
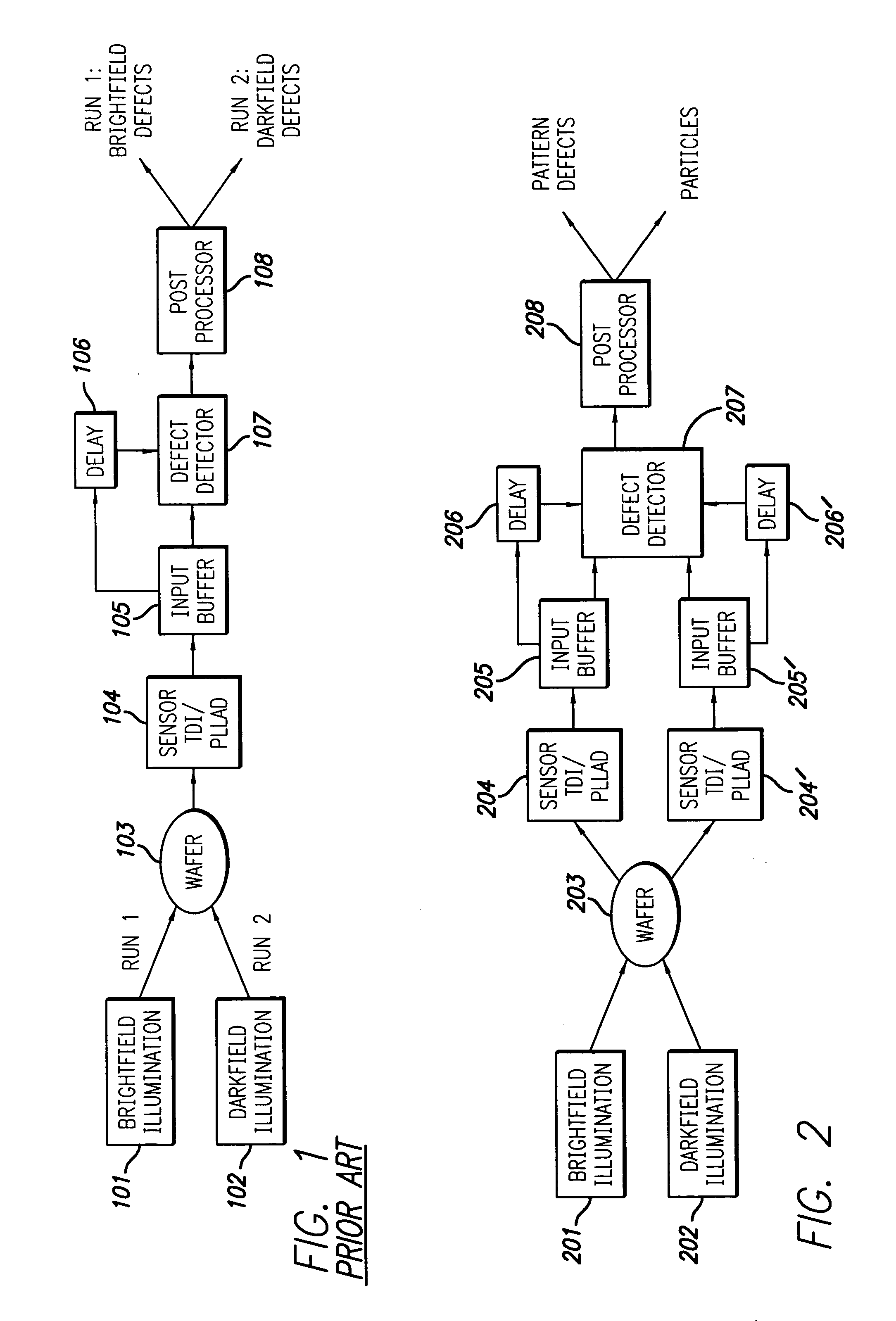
The broadband brightfield / darkfield wafer inspection system provided receives broadband brightfield illumination information via a defect detector, which signals for initiation of darkfield illumination. The defect detector forms a two dimensional histogram of the defect data and a dual mode defect decision algorithm and post processor assess defects. Darkfield radiation is provided by two adjustable height laser beams which illuminate the surface of the wafer from approximately 6 to 39 degrees. Each laser is oriented at an azimuth angle 45 degrees from the orientation of the Manhattan geometry on the wafer, and 90 degrees in azimuth from one another. Vertical angular adjustability is provided by modifying cylindrical lens position to compensate for angular mirror change by translating an adjustable mirror, positioning the illumination spot into the sensor field of view, rotating and subsequently moving the cylindrical lens. A brightfield beamsplitter in the system is removable, and preferably replaced with a blank when performing darkfield illumination. Light level control for the system is provided by a dual polarizer first stage. Light exiting from the second polarizer passes through a filter which absorbs a portion of the light and comprises the second stage of light control. The beam then passes through a polarizing beamsplitter. The second channel is further reflected and polarized and both beams thereafter illuminate the substrate.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Braced microscope
A novel microscope and method of obtaining images includes a combination of the conventional darkfield illuminations technique with electronic image inversion (converting a positive to a negative image) and other improvements to further enhance the contrast and resolution of the final image. The microscope and method are referred to herein as Inverted Darkfield Contrast (IDC) and are believed to be particularly suitable for viewing live cells in real time with no staining or preparation.
Owner:1192062 ALBERTA
Automated protein crystallization imaging
An apparatus that automatically captures, stores and analyzes images of crystallization experiments contained in a number of crystallization plates. The apparatus includes a plate nest capable of accommodating protein crystallization plates of a plurality of different types, image acquisition optics, including an objective lens and an image capturing device, for focusing an image of a crystallization well, a light source including a bright field illumination device and a dark field illumination device, a nest positioning controller for moving the position of the plate nest with respect to the image acquisition optics to align various selected wells with said objective lens for imaging of the content of the wells. A database stores experiment information associated with each of the crystallization plates, the experiment information including identification of specific crystal forming parameter values, each of the crystallization plates is identified in said database by a unique identification code. A crystallization imaging controller controls crystallization imaging by retrieving the experiment information for each crystallization plate inserted into the apparatus, and controlling the nest positioning controller and the image acquisition optics in accordance with the retrieved experiment information. The apparatus captures multiple images of each crystal site using different light source and polarization conditions, and processes the multiple images to form extended fused images of each crystal site.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI ASHEVILLE
Device and method for dark field illumination
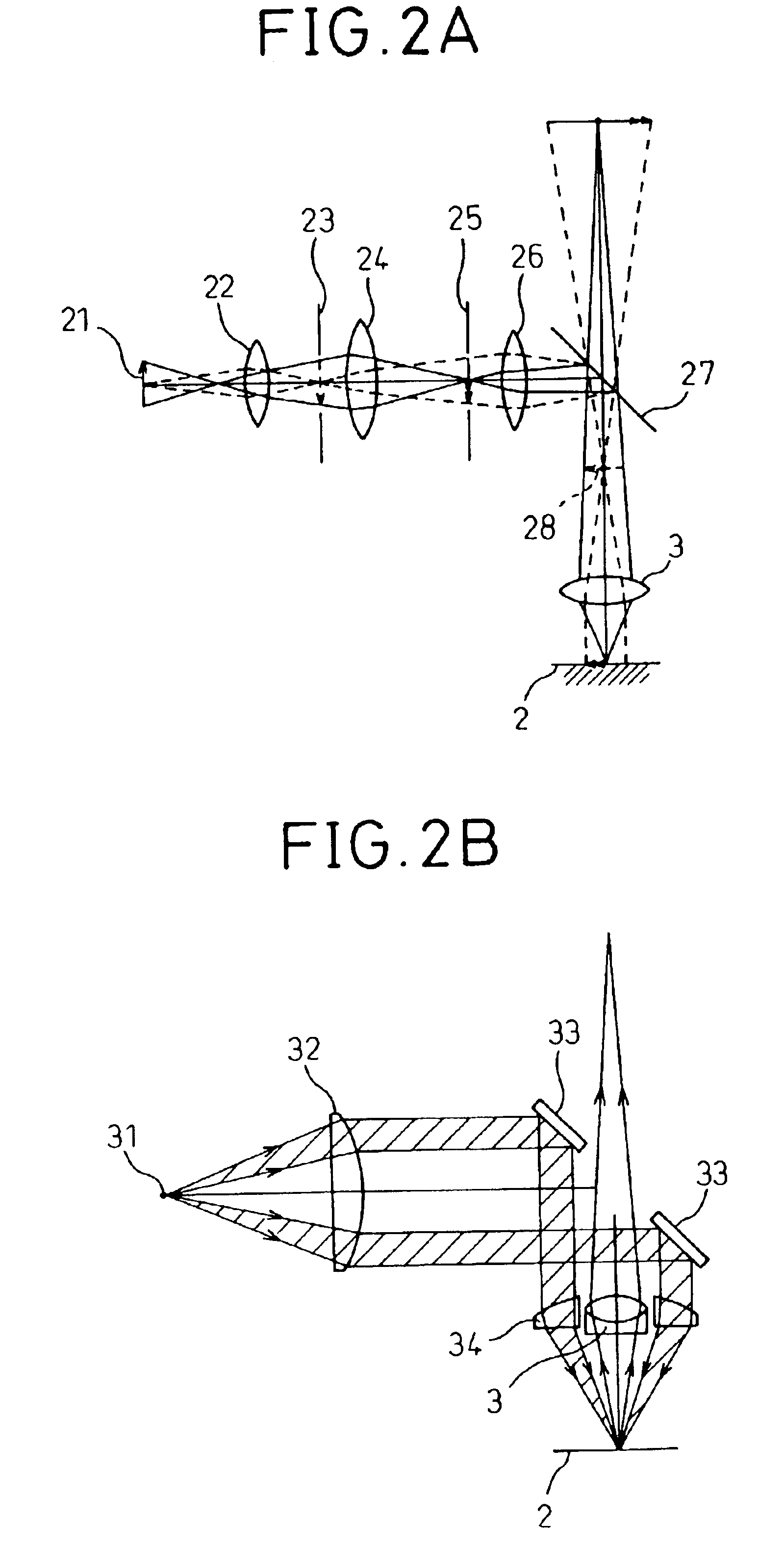
Disclosed is a dark field illumination apparatus which is capable of performing a dark field illumination which exhibits a sufficient brightness and a sufficiently suppressed unevenness in brightness. The apparatus comprises a shaping system for shaping a light beam from a light source into approximately parallel beam having a ring- shaped section; a fly-eye optical device for forming a plurality of light source images in the vicinity of its exit plane based on the approximately parallel beam, the light source images being arranged circularly; and a light collection optical system for collecting light beams from the light source images and superposing them on an object plane.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Light pipe illumination system and method
InactiveUS7823783B2Easy to aimOvercome disadvantagesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical axisLight pipe
A system and method is provided for illuminating a subject using a light pipe that transmits light from a source, such as an LED ring illuminator to an outlet that directs the light appropriately as either bright field illumination, dark field illumination or both. The light pipe can include concentric cylinders, typically with a bright field illuminator nested within a dark field illuminator. The tip of the dark field illuminator may be angled so as to internally reflect light inwardly toward the central optical axis of a camera at a low angle. The tip can be located near the focal plane of the camera for the desired field of view. The field of view of the camera sensor can be modified to reject data outside of a illumination field of a particular shape. This illumination field can be created by shaping the light pipe in a predetermined form that projects the modified illumination field. Likewise, a set of aiming illuminators (in, for example, a noticeable color) can be provided around the perimeter of the light pipe to delineate outer boundaries of the illumination field or area of interest. These approaches facilitate better aiming of the sensor into the desired area of interest so that it is illuminated and / or acquired most-fully.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
Reflected dark field method and apparatus
Owner:GEMOLOGICAL INST OF AMERICA INC
Hand held symbology reader illumination diffuser
ActiveUS7617984B2Coupling light guidesSensing by electromagnetic radiationDiffuse illuminationHand held
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
Lighting system and method used for dark field detection of defect in spherical optical element surface
ActiveCN103293162AImplement dark field illuminationIncrease contrastOptically investigating flaws/contaminationOptical elementsMicro imagingImaging processing
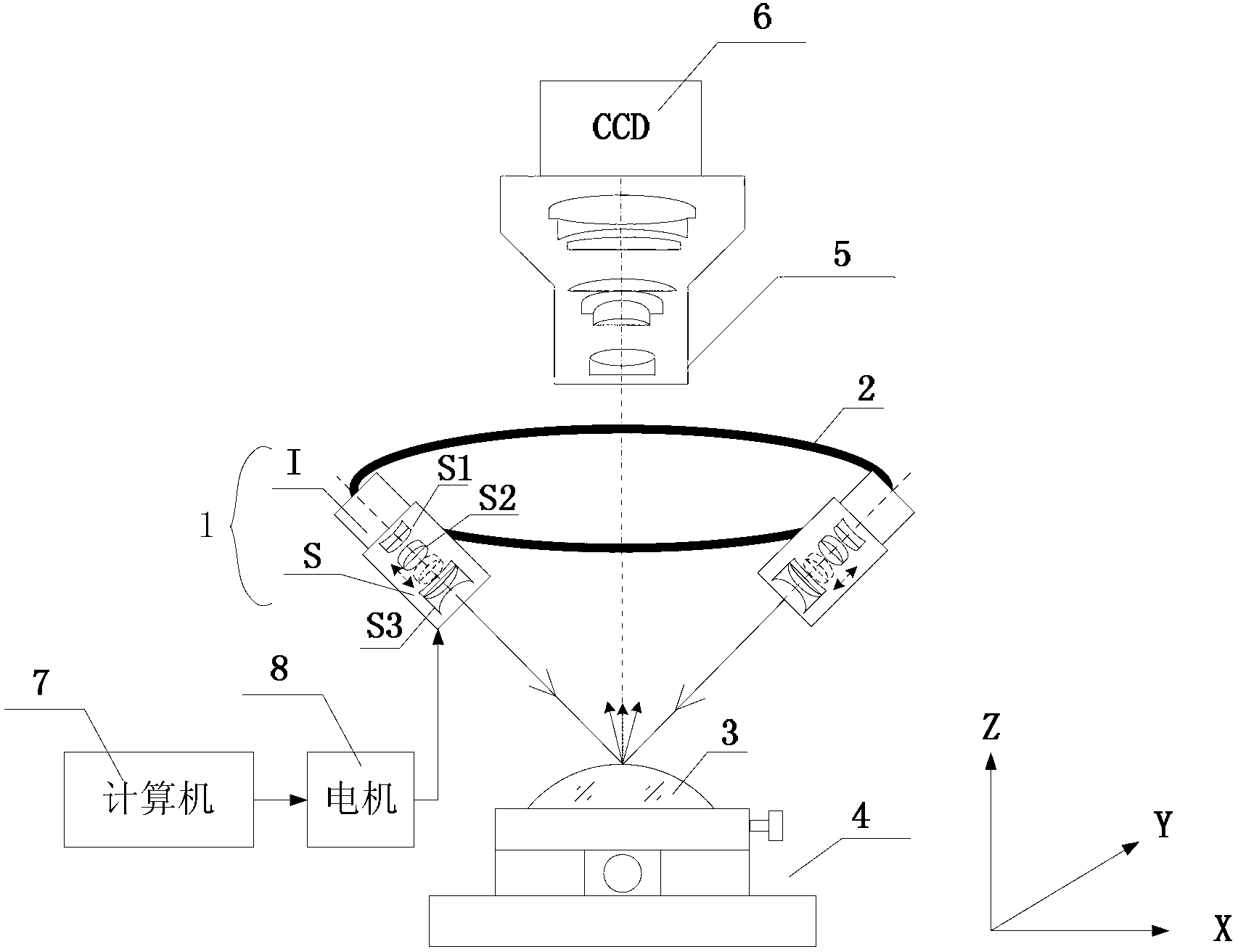
The invention discloses a lighting system and method used for dark field detection of a defect in a spherical optical element surface. The lighting system comprises a spherical light source, a light source support, an optical element to be detected, an optical element multidimensional holding device, a microscopic imaging system, a charge coupling element, a computer and a motor, wherein the spherical light source comprises a uniform face light source and a zoom lens group lens barrel, a plurality of spherical light sources are circlewise arranged on the light source support at equal intervals, a zoom adjusting component comprises a zoom lens group lens barrel, a front lens fixing group, a zoom lens group, a back lens fixing group, a zoom lens barrel, a gear and a sliding rail; the optical element to be detected and the holding device are arranged below the light source support, the microscopic imaging system and the charge coupling element are arranged above the light source support, and the light axis of the microscopic imaging system, the circle centre of a circular surface formed by a plurality of light sources, and the sphere centre of the optical element to be detected are coaxial. According to the dark field lighting for defect detection in the spherical optical element surface, an imaging is a bright defect image in the dark background, the contrast ratio is good, thus being easy for subsequent image processing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
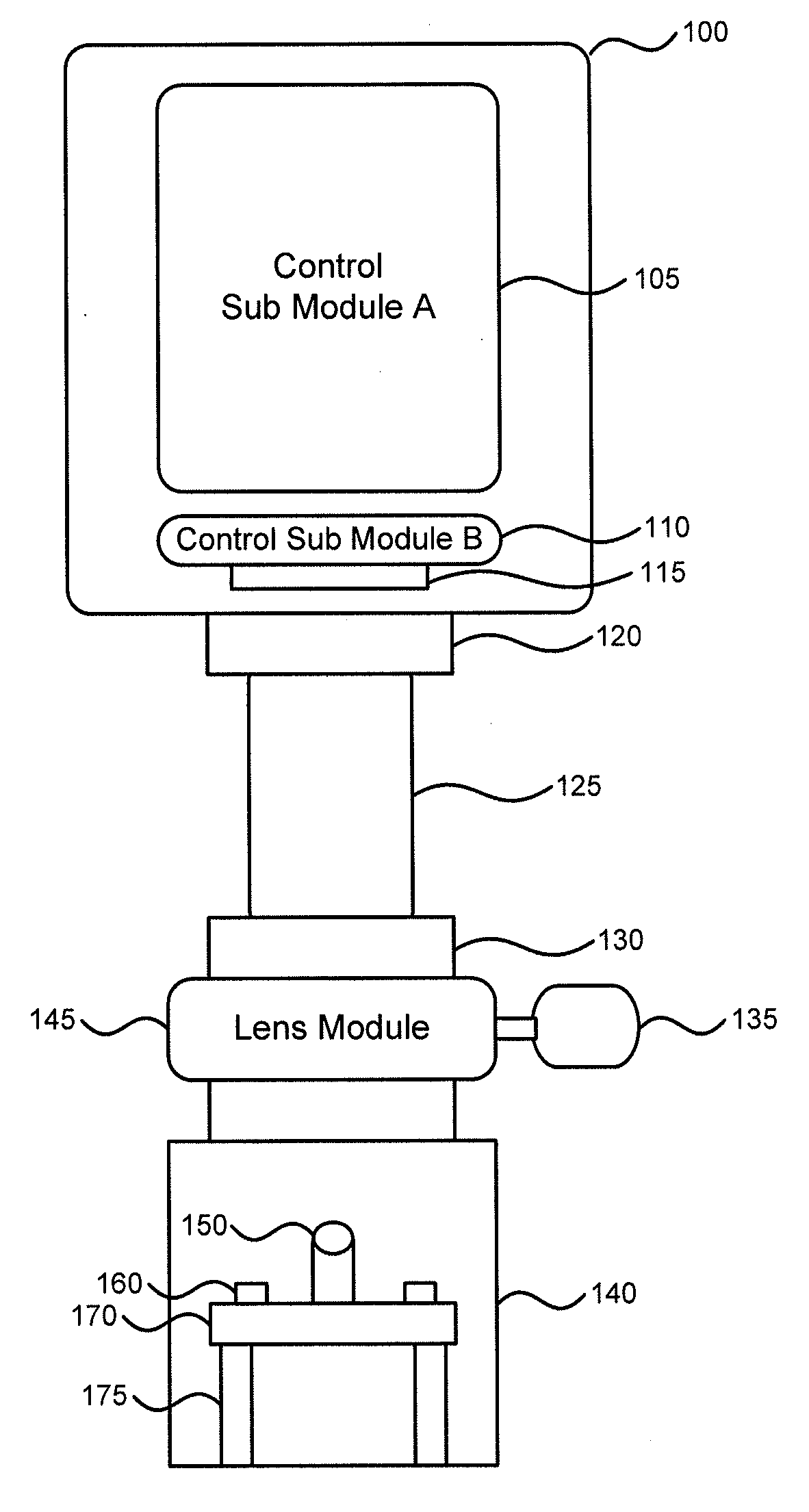
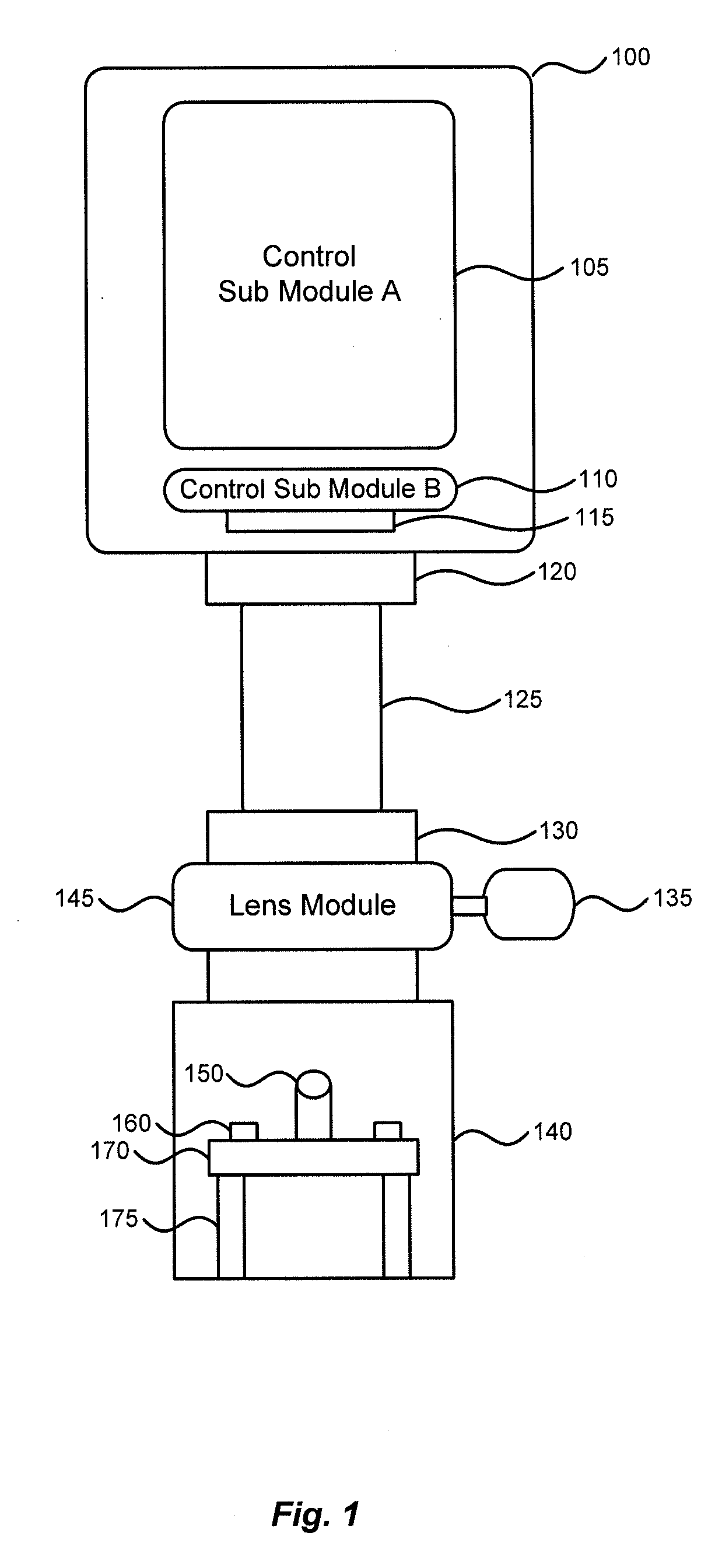
Modular microscope construction
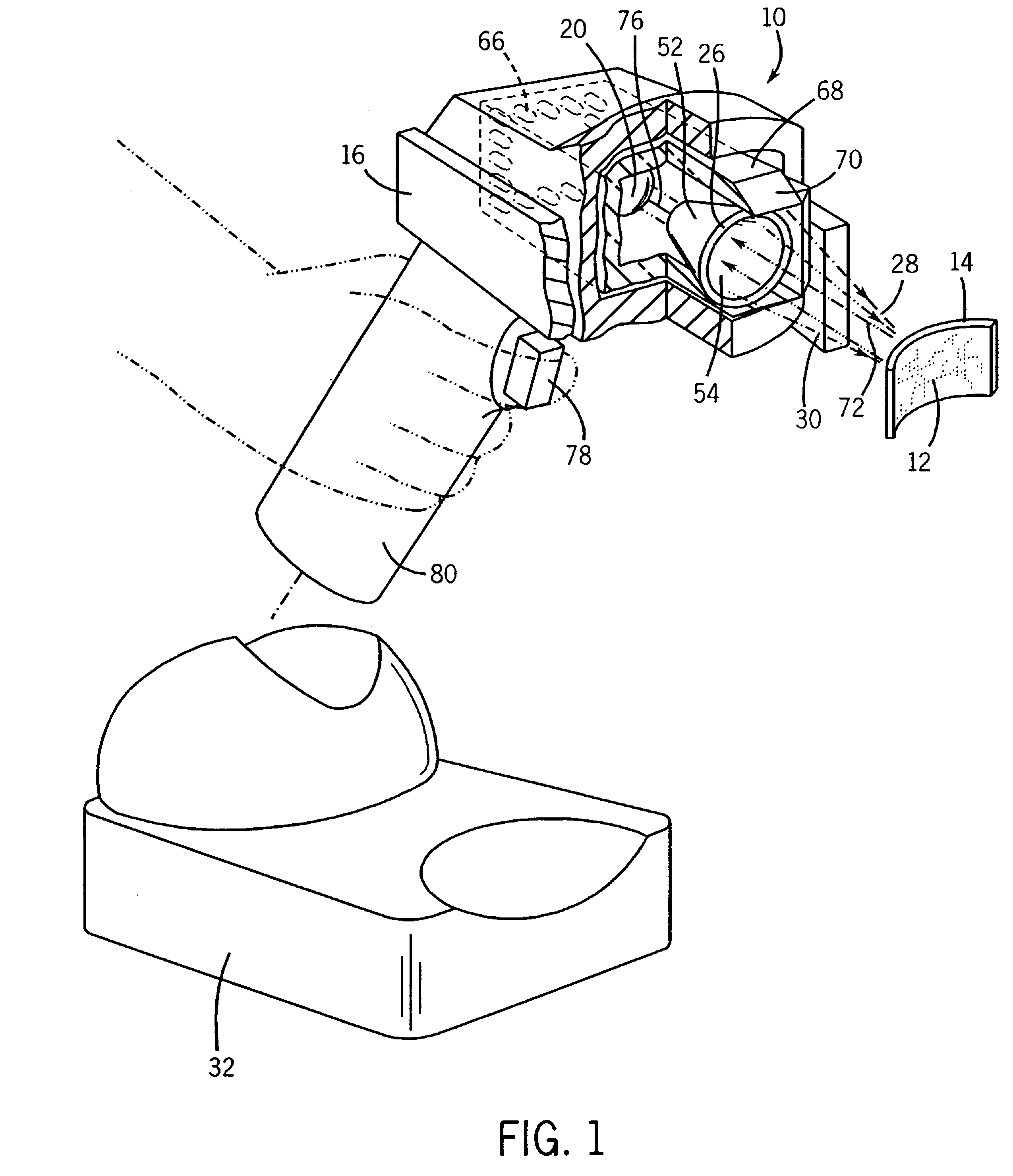
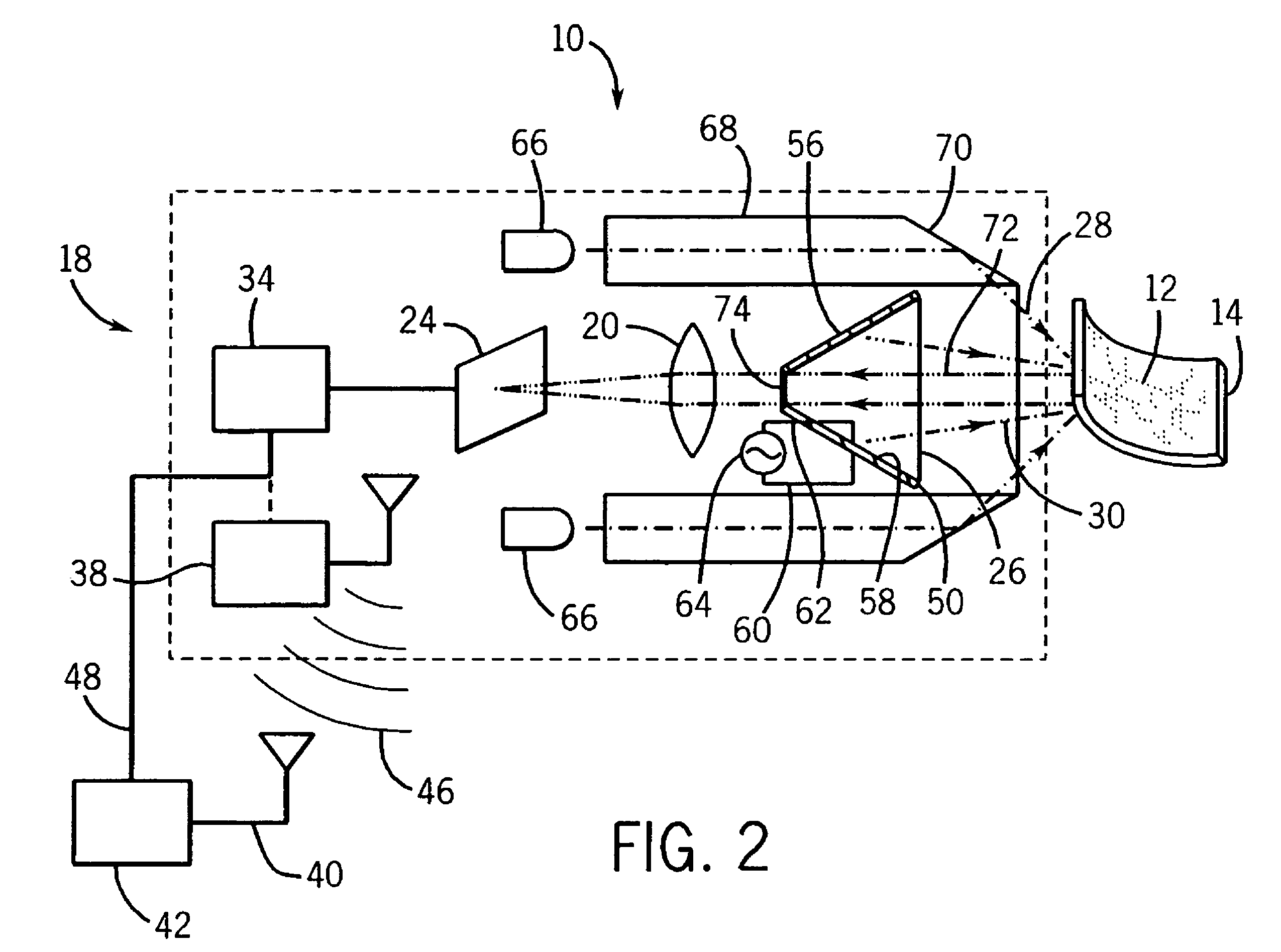
A system, apparatus and method for using modular microscopes is disclosed. Connecting the housings of the individual microscope modules provide the structural framework of the modular microscope. Furthermore, the modular microscope can include specialized software, the distribution and use of which can be controlled using security keys or identifiers stored on one or more of the microscope modules. The security keys and identifiers can be based on calibration data associated with the physical, electrical, or optical properties of one of more of the modules. The illumination modules disclosed provide for selectable wavelengths and controllable levels of output illumination for both bright field and dark field illumination.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
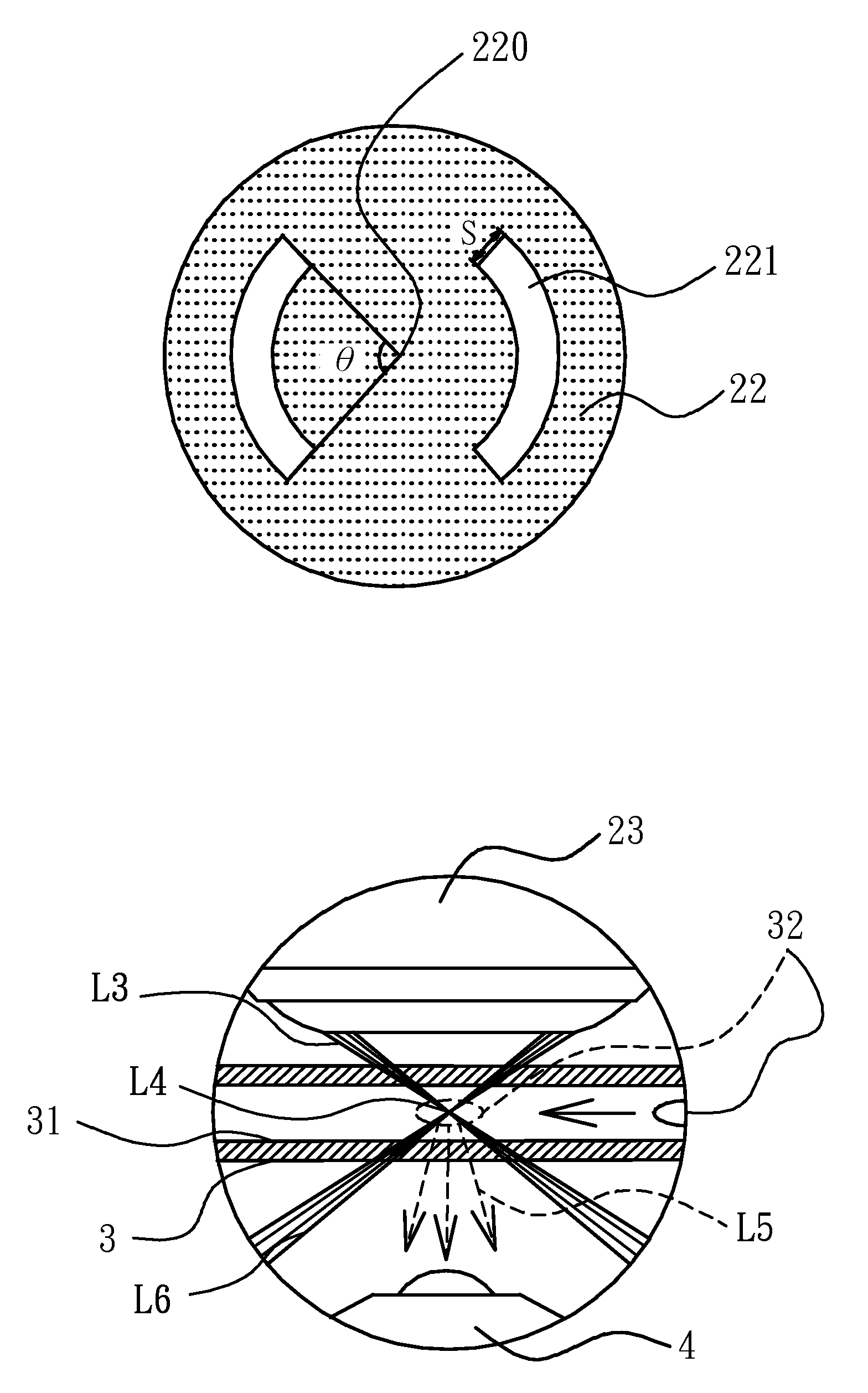
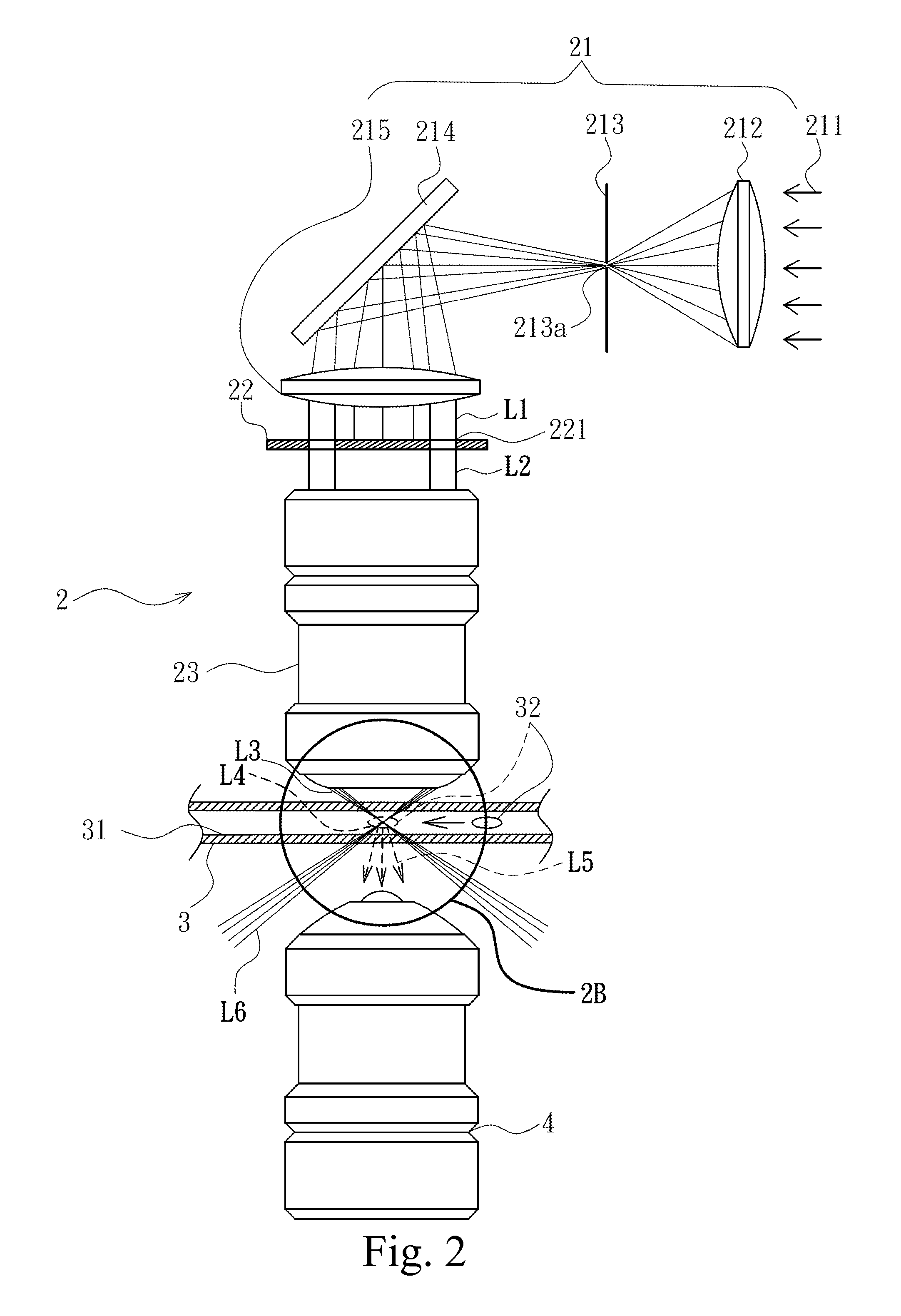
Objective-type dark-field illumination device for microfluidic channel
InactiveUS20110157692A1Conveniently and rapidly adjustedReduce image contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesFluorescenceImage contrast
An objective-type dark-field illumination device for a microfluidic channel is provided and includes an optical stop having a pair of symmetric curved slits used to adjust the optical path and inner numerical aperture of a dark-field light source generated by the device. The dark-field illumination can focus on a smaller spot to illuminate a sample in the microfluidic channel by matching a pin-hole combined with a transmitter objective lens. The optical path and smaller spot is advantageous to solve the problem of a traditional dark-field illumination that may generate background light noise scattered from inner walls of the microfluidic channel to lower the image contrast. Therefore, the signal or image resolution of capturing the scattered light and / or emitted fluorescent light emitted from the sample in the microfluidic channel can be enhanced. Meanwhile, the device can simultaneously excite and detect multiple fluorescent samples with different excited wavelengths in the microfluidic channel.
Owner:NAT SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Dark field illumination method based on total internal reflection
InactiveCN104568886AAchieve lightingSimple structureFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiological cellMicro nanoparticles
The invention discloses a dark field illumination method based on total internal reflection. The dark field illumination method can be applied to optical microscopic imaging studies on micro / nano-particles, biological samples and the like. Dark field illumination on the sample is achieved on the basis of total internal reflection of illuminating light; scattered light or fluorescent light of the sample is utilized as a signal for optical imaging and detection, thus observation and measurement on micro / nano-scale samples are achieved; and the dark field illumination method has good applicability and compatibility on existing imaging devices such as microscopes. The illuminating light is subjected to total internal reflection for once or a plurality of times in a total internal reflection prism or a sample pool by the total internal reflection to form total internal reflection dark field illumination; and the dark field illumination method can be applied to the fields of studies on nano materials, biological cells, interaction between light and materials, and the like.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
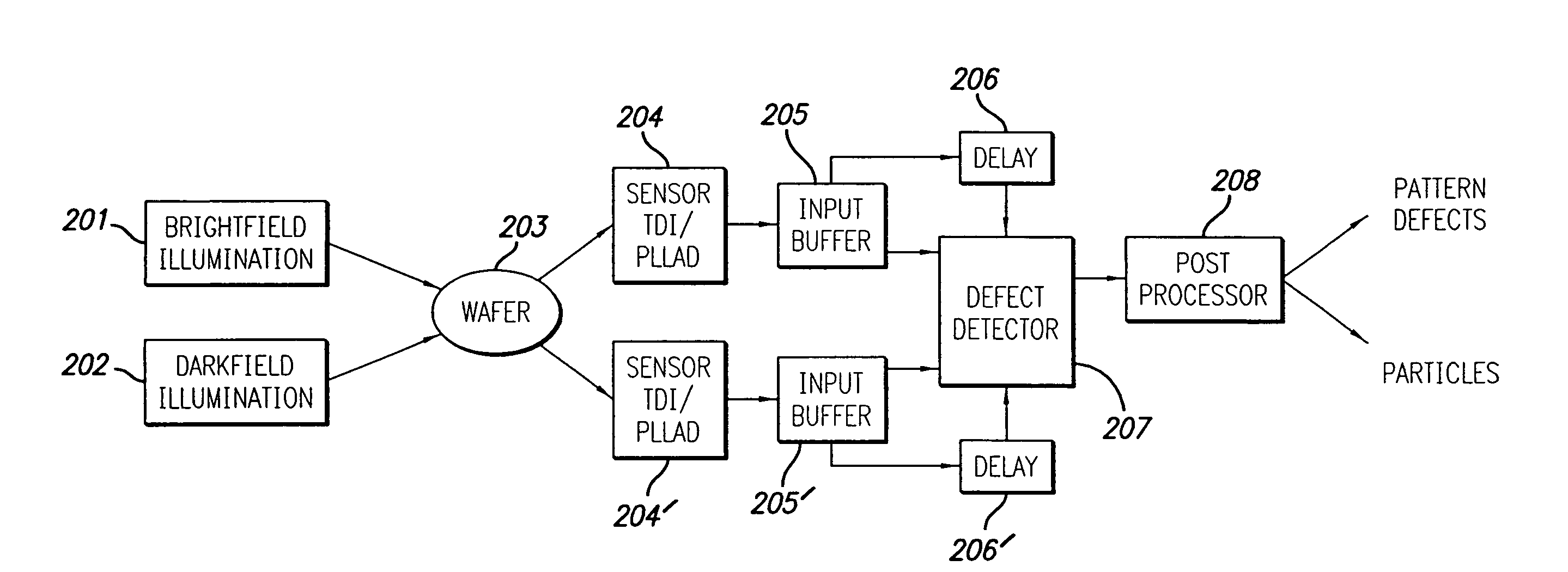
Wafer defect inspection machine having a dual illumination system
InactiveUS6867424B2Low costBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOptical axisLighting system
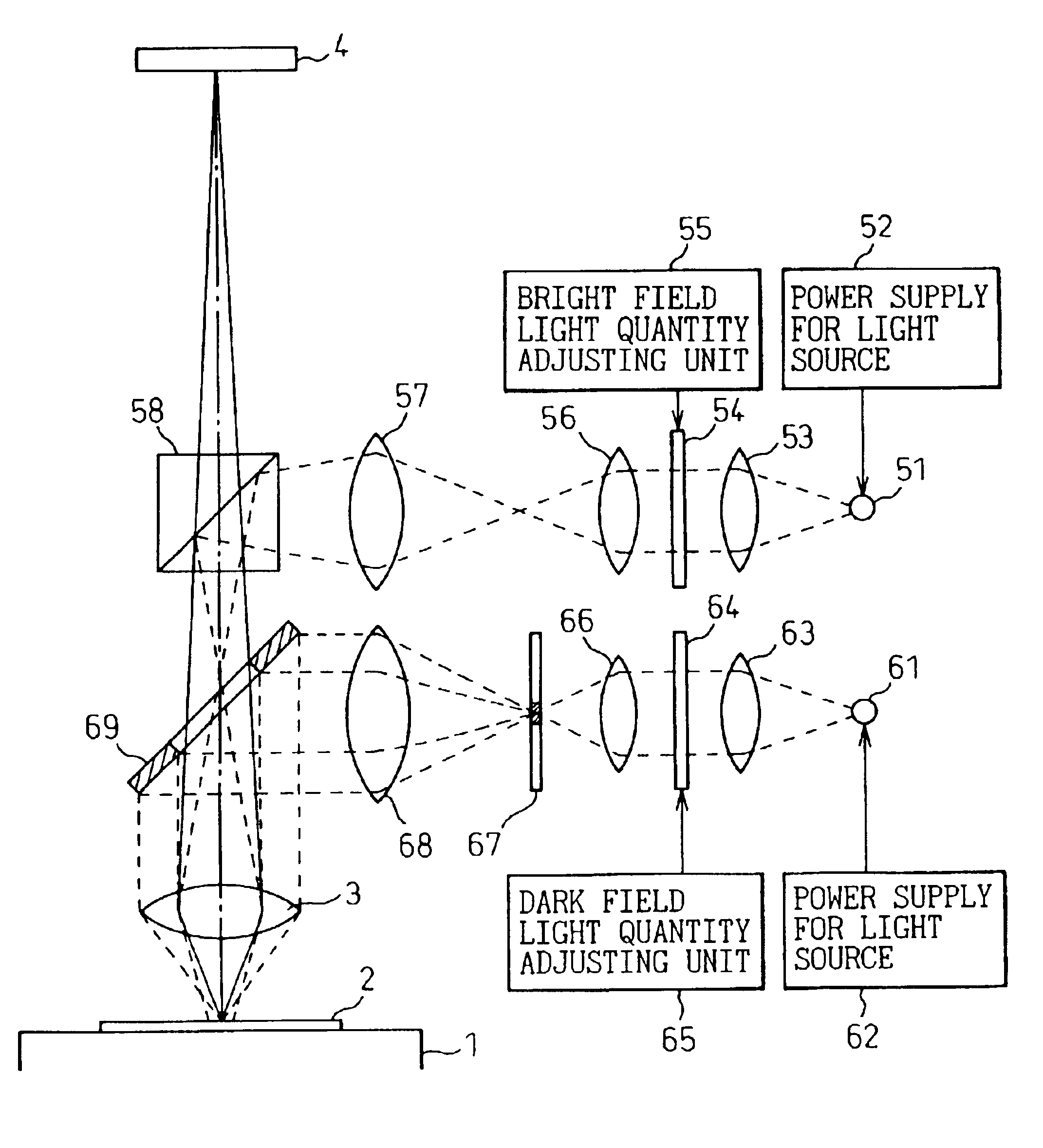
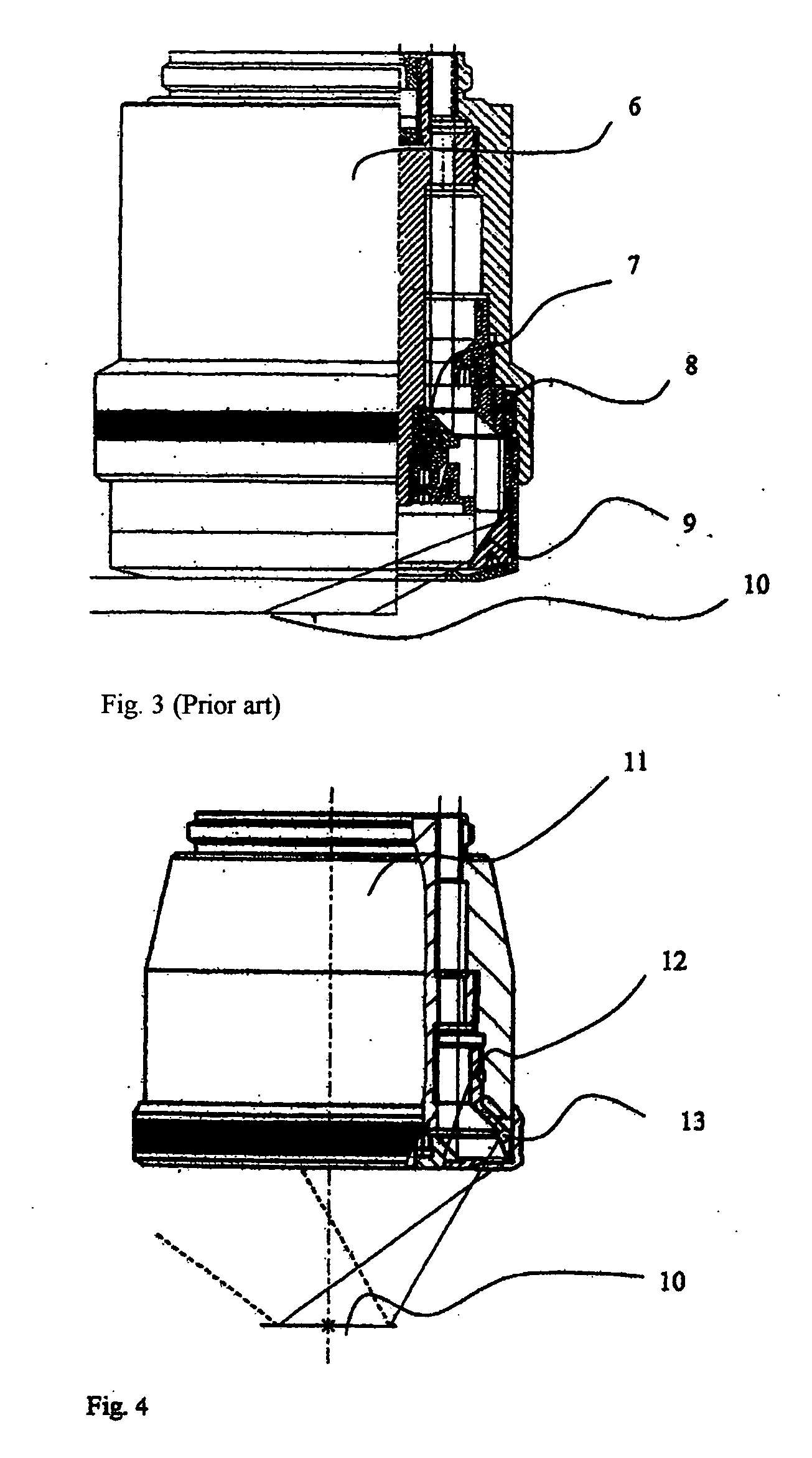
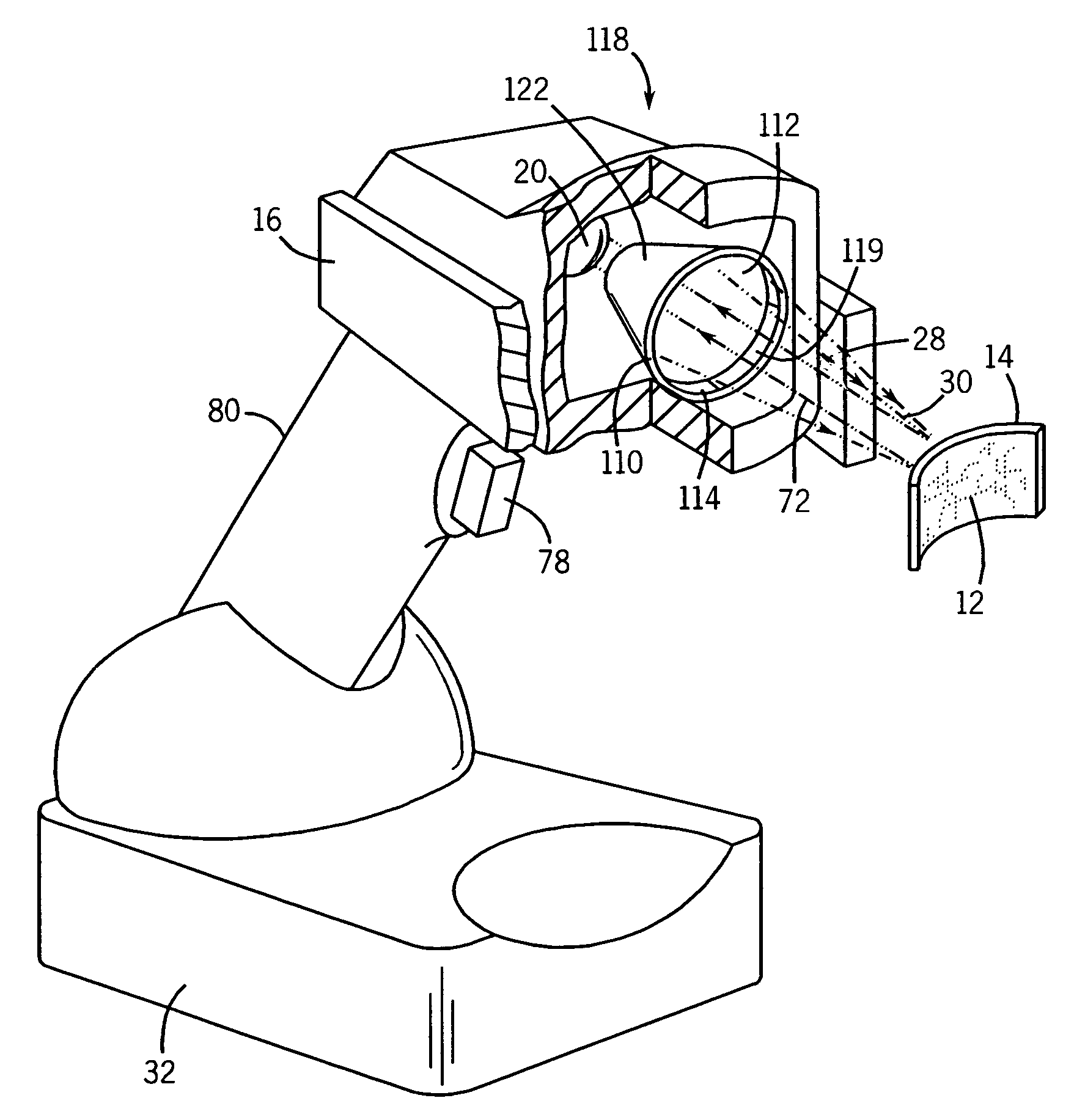
A low-cost defect inspection machine for semiconductor wafers that can detect various defects has been disclosed and comprises an optical system that projects a pattern image, an image sensor and a processing circuit that processes the image signal and detects defect portions, wherein the optical system comprises an objective lens, a bright field illumination system that has a semi-transparent mirror and irradiates a specimen through the objective lens with the illumination light reflected by the semi-transparent mirror in the range that includes the optical axis of the objective lens, and a dark field illumination system that has a reflecting mirror provided in the portion except for the projection path of the objective lens and irradiates a specimen through the objective lens with the illumination light reflected by the reflecting mirror.
Owner:TOKYO SEIMITSU
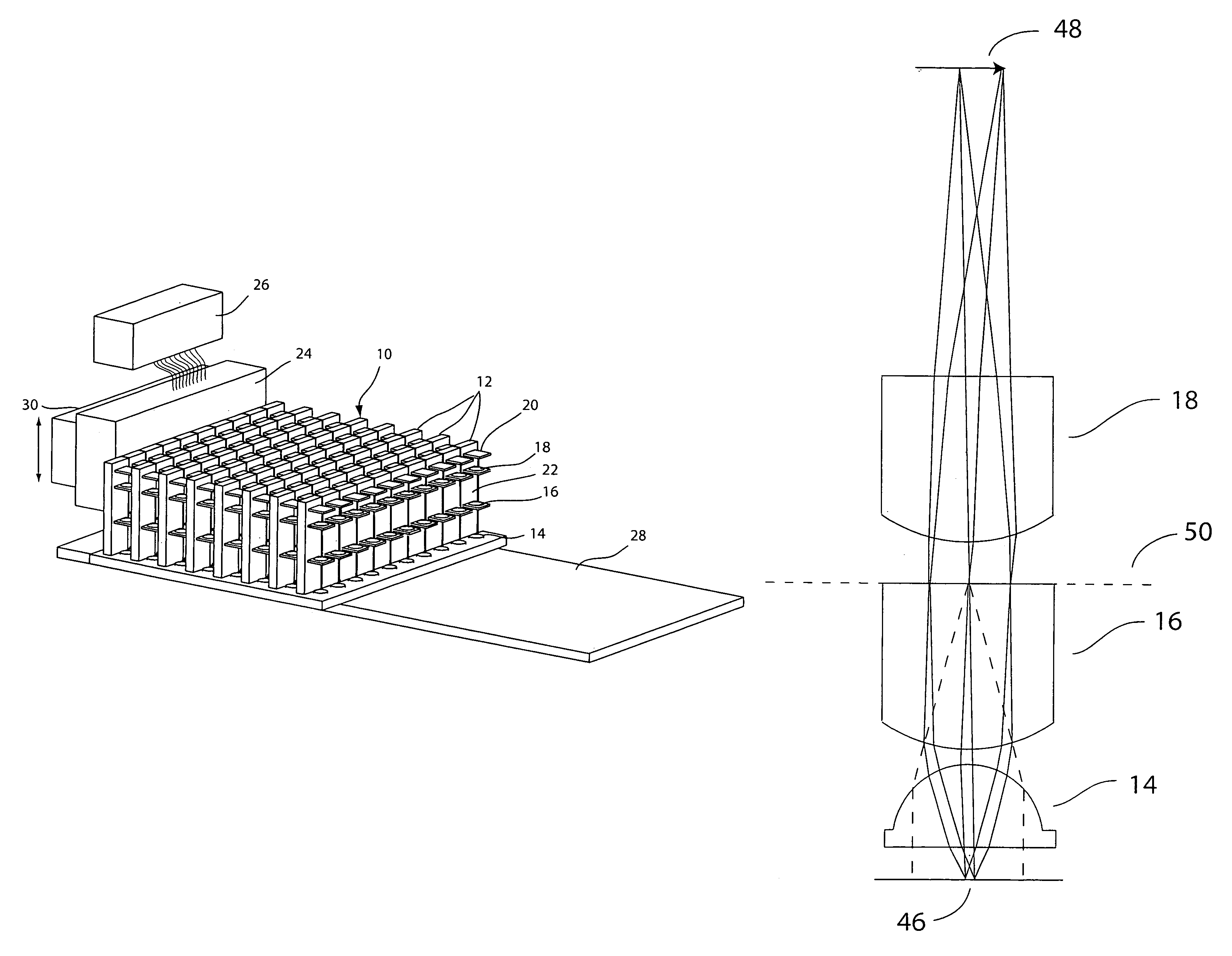
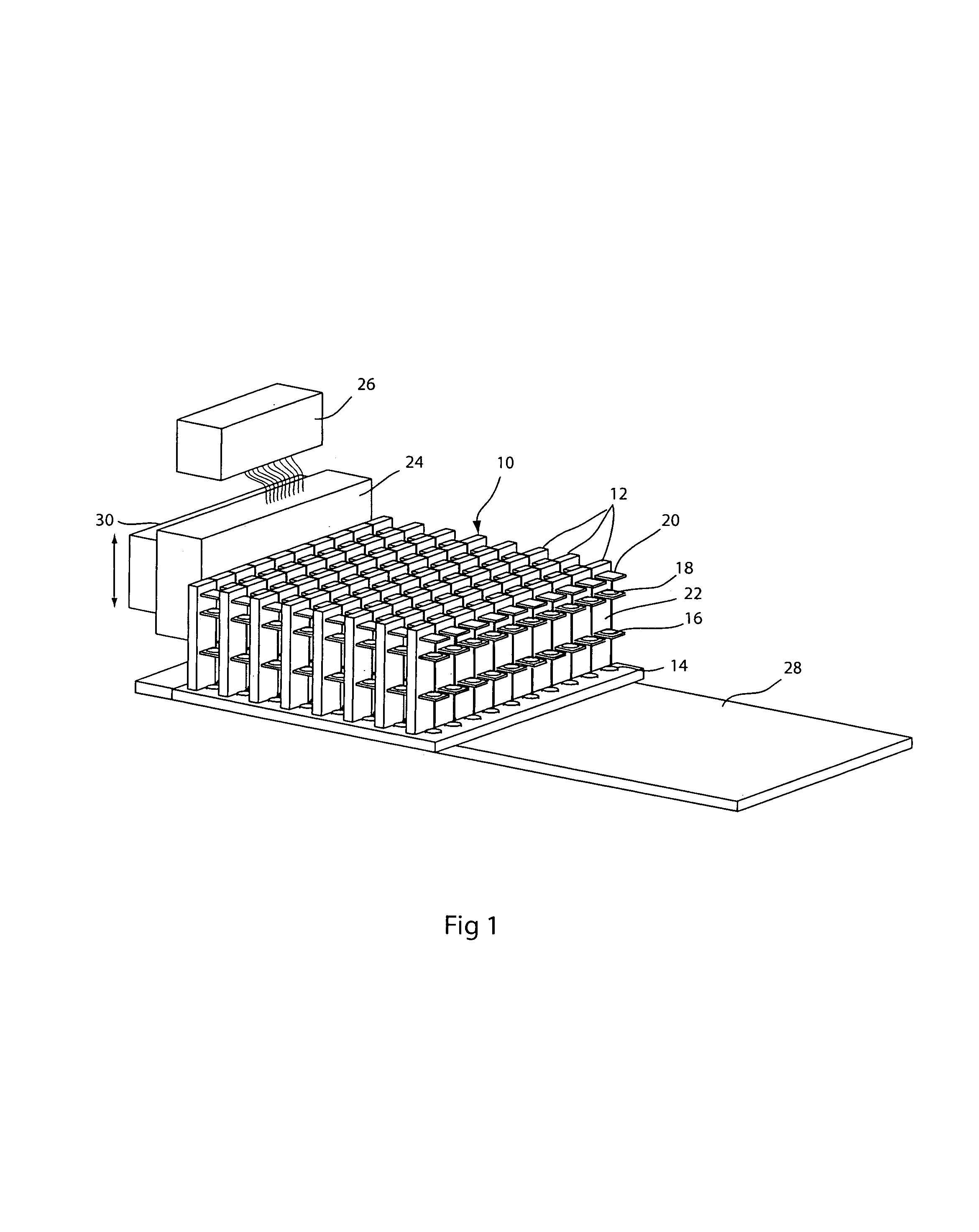
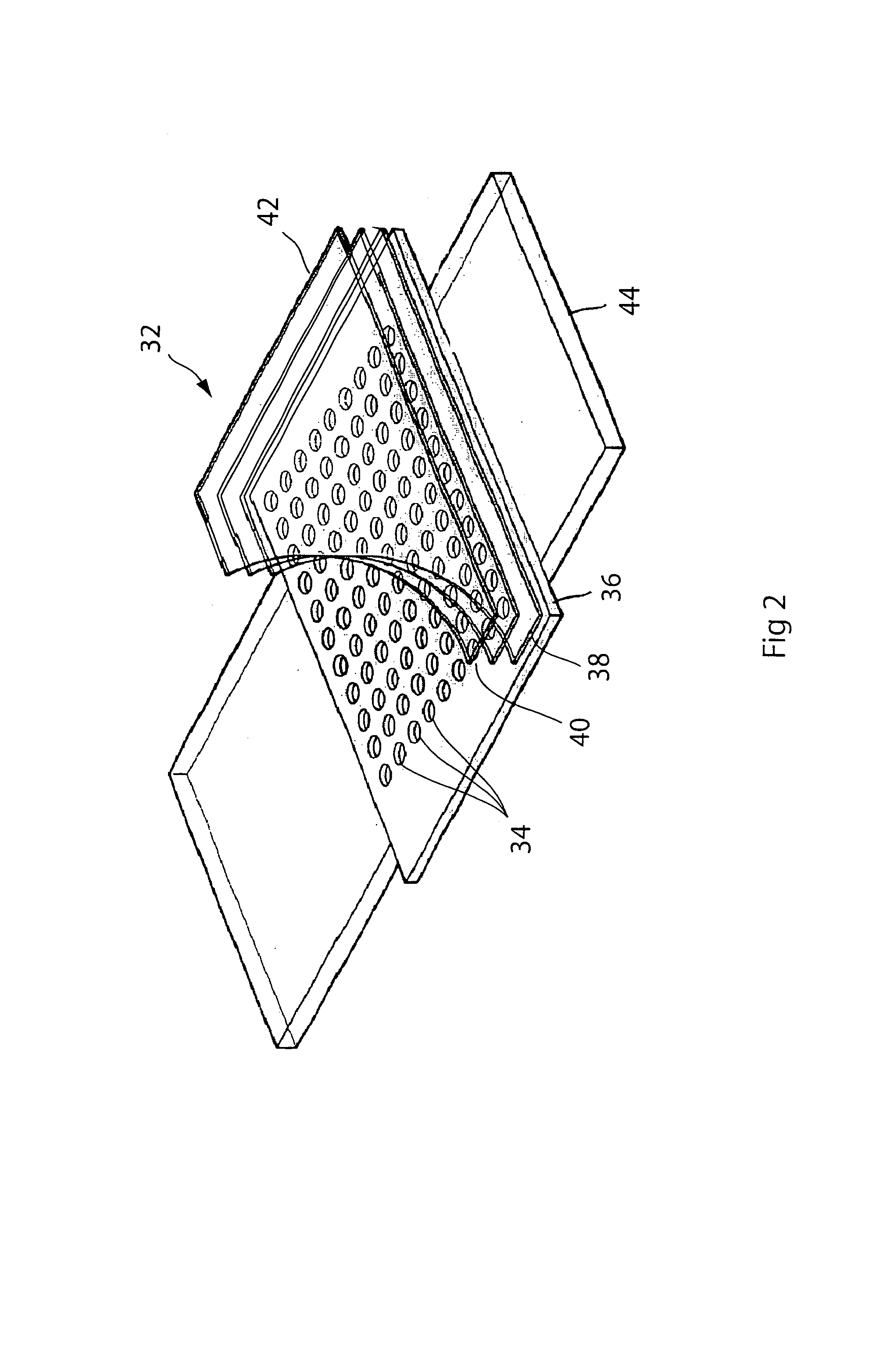
EPI-illumination system for an array microscope
An epi-illumination system for an array microscope. For Kohler illumination, illumination light sources are placed, actually or virtually, at the pupils of respective individual microscope elements of an array microscope. In one Kohler illumination embodiment, the light source is a point source comprising the tip of an optical fiber placed on the optical axis at the pupil of its corresponding microscope element. In another Kohler illumination embodiment, the illumination light is provided by a reflective boundary placed on the optical axis of a corresponding microscope element. For critical illumination the light sources are placed at locations conjugate with their respective object planes so as to image the light sources thereon. For dark-field illumination, the support material around a microscope element lens, which is used to support an array of lenses, is fashioned to form an illumination optical element so that light from an off-axis source is directed by the illumination element toward the object plane at an angle such that light will not be reflected into the field of view of the imaging system, but scattered or fluorescence light will be within that field of view. The illumination optical element may be refractive element, a Fresnel element, a reflective element, a diffractive element, or some combination of one or more of these elements. An array of pinhole apertures may be provided to operate the array microscope in a confocal mode. All of the embodiments may be used for epi-fluorescence microscopy.
Owner:DMETRIX INC
Apparatus For Inspecting Defects
InactiveUS20100208249A1Raise the ratioHigh sensitivityPolarisation-affecting propertiesAnalysis by material excitationIrradiationField of view
A defect inspection apparatus and method includes a darkfield illumination optical system which conducts darkfield illumination upon the surface of a sample with irradiation light having at least one of wavelength band, a darkfield detection optical system which includes a reflecting objective lens for converging the light scattered from the surface of the sample that has been darkfield-illuminated with the irradiation light having the at least one wavelength band, and imaging optics for imaging onto a light-receiving surface of an image sensor the scattered light that the reflecting objective lens has converged, and an image processor which, in accordance with an image signal obtained from the image sensor of the darkfield detection optical system, discriminates defects or defect candidates present on the surface of the sample.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Single axis illumination for multi-axis imaging system
InactiveUS7312432B2Improved telecentricityModify spatialBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSolid-state devicesPhase maskCritical illumination
A single-axis illumination system for a multiple-axis imaging system, particularly an array microscope. A single-axis illumination system is used to trans-illuminate an object viewed with an array of imaging elements having multiple respective axes. The numerical apertures of the imaging elements are preferably matched to the numerical aperture of the illumination system. For Kohler illumination, the light source is placed effectively at the front focal plane of the illumination system. For critical illumination, the light source is effectively imaged onto the object plane of the imaging system. For dark field illumination, an annular light source is effectively provided. For phase contrast microscopy, an annular phase mask is placed effectively at the back focal plane of the objective lens of the imaging system and a corresponding annular amplitude mask is provided effectively at the light source. For Hoffman modulation contrast microscopy, an amplitude mask is placed effectively at the back focal plane of the objective lens of the imaging system and a slit is provided at a source of light of the illumination system. Structured illumination and interferometry, and a secondary source, may also be used with trans-illumination methods and apparatus according to the present invention.
Owner:DMETRIX INC
High throughput brightfield/darkfield wafer inspection system using advanced optical techniques
InactiveUS7164475B2Improve the level ofPolarisation-affecting propertiesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDual modePost processor
The broadband brightfield / darkfield wafer inspection system provided receives broadband brightfield illumination information via a defect detector, which signals for initiation of darkfield illumination. The defect detector forms a two dimensional histogram of the defect data and a dual mode defect decision algorithm and post processor assess defects. Darkfield radiation is provided by two adjustable height laser beams Vertical angular adjustability is provided by modifying cylindrical lens position to compensate for angular mirror change by translating an adjustable mirror, positioning the illumination spot into the sensor field of view, rotating and subsequently moving the cylindrical lens. A brightfield beamsplitter in the system is removable, and preferably replaced with a blank when performing darkfield illumination. Light level control for the system is provided by a dual polarizer first stage.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
High throughput brightfield/darkfield water inspection system using advanced optical techniques
InactiveUS20080225298A1Improve the level ofScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDual modeWater quality
The broadband brightfield / darkfield wafer inspection system provided receives broadband brightfield illumination information via a defect detector, which signals for initiation of darkfield illumination. The defect detector forms a two dimensional histogram of the defect data and a dual mode defect decision algorithm and post processor assess defects. Darkfield radiation is provided by two adjustable height laser beams which illuminate the surface of the wafer from approximately 6 to 39 degrees. Each laser is oriented at an azimuth angle 45 degrees from the orientation of the manhattan geometry on the wafer, and 90 degrees in azimuth from one another. Vertical angular adjustability is provided by modifying cylindrical lens position to compensate for angular mirror change by translating an adjustable mirror, positioning the illumination spot into the sensor field of view, rotating and subsequently moving the cylindrical lens. A brightfield beamsplitter in the system is removable, and preferably replaced with a blank when performing darkfield illumination. Light level control for the system is provided by a dual polarizer first stage. Light exiting from the second polarizer passes through a filter which absorbs a portion of the light and comprises the second stage of light control. The beam then passes through a polarizing beamsplitter. The second channel is further reflected and polarized and both beams thereafter illuminate the substrate.
Owner:KLA CORP
Optimizing use and performance of optical systems implemented with telecentric on-axis dark field illumination
InactiveUS20090219518A1Aberration correctionAvoid lightAngle measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementCamera lensTelecentric lens
Systems and methods are provided for imaging a planar specular object such as a semiconductor wafer. In one embodiment, an imaging system for imaging a defect on a planar specular object includes a telecentric lens having a sufficiently aspherical surface such that the telecentric lens is substantially corrected for an optical aberration. The imaging system also includes a telecentric stop including an aperture therein to block light reflected from the planar specular object while allowing light reflected from the defect to pass through the aperture. The imaging system further includes a lens group having a system stop positioned between the telecentric stop and the lens group. The lens group is substantially corrected for the optical aberration independent of the telecentric lens.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Patterned illumination method and apparatus for machine vision systems
This application relates to an apparatus and method for providing patterned illumination fields for use within process control and article inspection applications. More specifically, it pertains to the use of patterned illuminators to enable visual surface inspection of polished objects such as ball bearings. The use of patterned illuminators properly disposed in relation to a polished part under inspection allows small surface imperfections such as scratches and pits to become visible against the normal surface background. The use of carefully engineered illuminators facilitates advantageous defect-site scattering from generally dark field sources. The patterned nature of the illuminators defined by this invention allows the complete surface of three-dimensional parts to be effectively highlighted using dark field illumination fields.
Owner:PRESSCO TECH INC
System and method for employing infrared illumination for machine vision
InactiveUS20070125863A1Visual representatino by photographic printingCharacter and pattern recognitionResistBeam splitter
This invention provides a machine vision device adapted to read inscribed symbology on the surface of an object, such as a wafer, covered in photoresist that employs both bright field and dark field illumination in the infrared region. Using illumination with light in this spectral band, an inscribed symbol can be read by a camera sensor substantially unaffected by the presence of and / or number of layers of photoresist covering the symbol. The camera sensor is tuned to receive such illumination, and is thereby provided with an image that distinguishes the symbol's scribe lines on the underlying wafer surface from the surrounding specular wafer surface. The device includes a housing that supports the imager and imager lens below an array of IR LEDs. The sensor has an optical axis that is reflected from horizontal to vertical by a mirror and then back to horizontal by a beam splitter that is aligned with two spherical lenses and an outlet window at the front of the housing. The array is located in line with lenticular arrays behind the beam splitter, along the central optical axis of the lenses and window.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
Method and apparatus for performing failure analysis with fluorescence inks
InactiveUS20050018898A1Easy to watchEasy to identifySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialFluorescence
A method for performing failure analysis on a semiconductor device under inspection includes preparing of a device sample using an encapsulation material containing a dye, the prepared device sample possibly including a failure area having wicked in encapsulation material containing the dye. The prepared device sample is then sectioned to facilitate viewing a cross section face of the device under inspection. Lastly, a dark field analysis on the prepared device sample is performed with the use of dark field illumination. Responsive to at least one failure area containing wicked in encapsulation material with dye occurring on the cross section face of the device under inspection, the failure area can be readily identified as well as a contrast and perspective of remaining portions of the cross section face being maintained.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Optimizing use and performance of optical systems implemented with telecentric on-axis dark field illumination
InactiveUS20070009257A1Stay focusedAberration correctionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsDarkfield illuminationImage system
Systems and methods are provided for imaging a planar specular object such as a semiconductor wafer. In one embodiment, an imaging system for imaging a defect on a planar specular object includes a telecentric lens having a sufficiently aspherical surface such that the telecentric lens is substantially corrected for an optical aberration. The imaging system also includes a telecentric stop including an aperture therein to block light reflected from the planar specular object while allowing light reflected from the defect to pass through the aperture. The imaging system further includes a lens group having a system stop positioned between the telecentric stop and the lens group. The lens group is substantially corrected for the optical aberration independent of the telecentric lens.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Darkfield illumination system
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
High throughput brightfield/darkfield water inspection system using advanced optical techniques
InactiveUS7554655B2Improve the level ofScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDual modePost processor
Owner:KLA CORP
Illumination devices for image acquisition systems
InactiveUS8016199B2Uniform bright field illuminationLess componentsMirrorsCharacter and pattern recognitionElectricityComputer science
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Mobile molecular diagnostics system with wireless communication
ActiveUS9901923B2Low costLow setHeating or cooling apparatusNanoparticle analysisPoint of careProtein detection
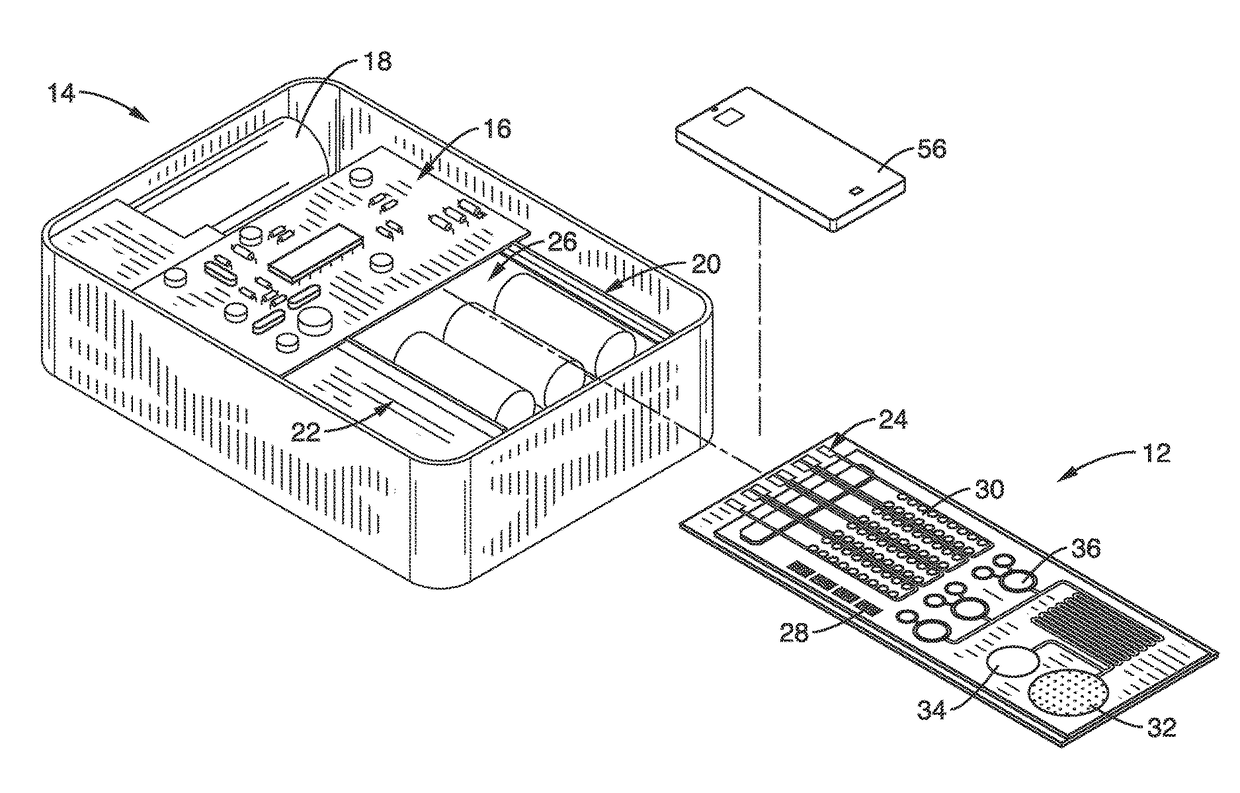
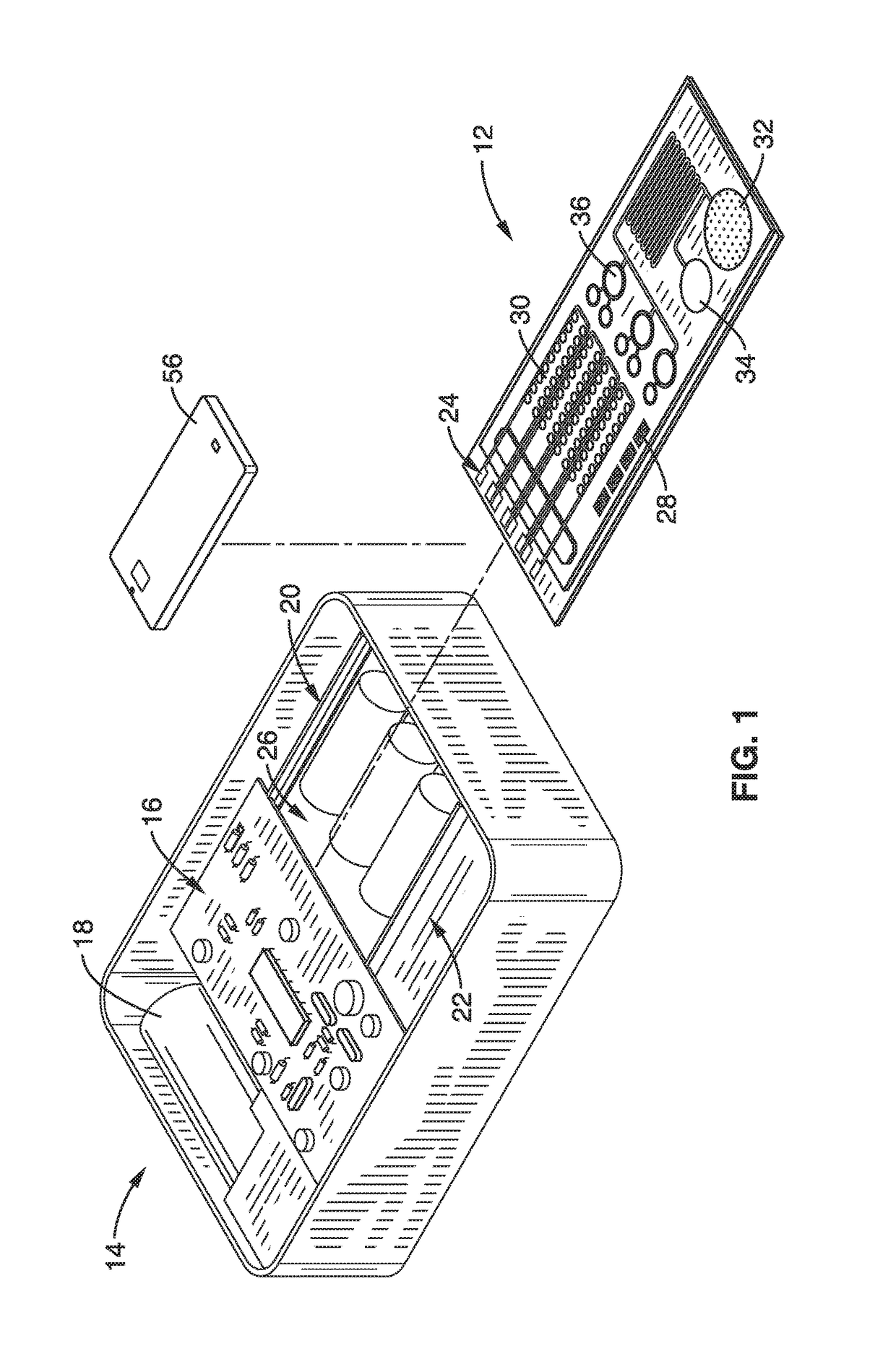
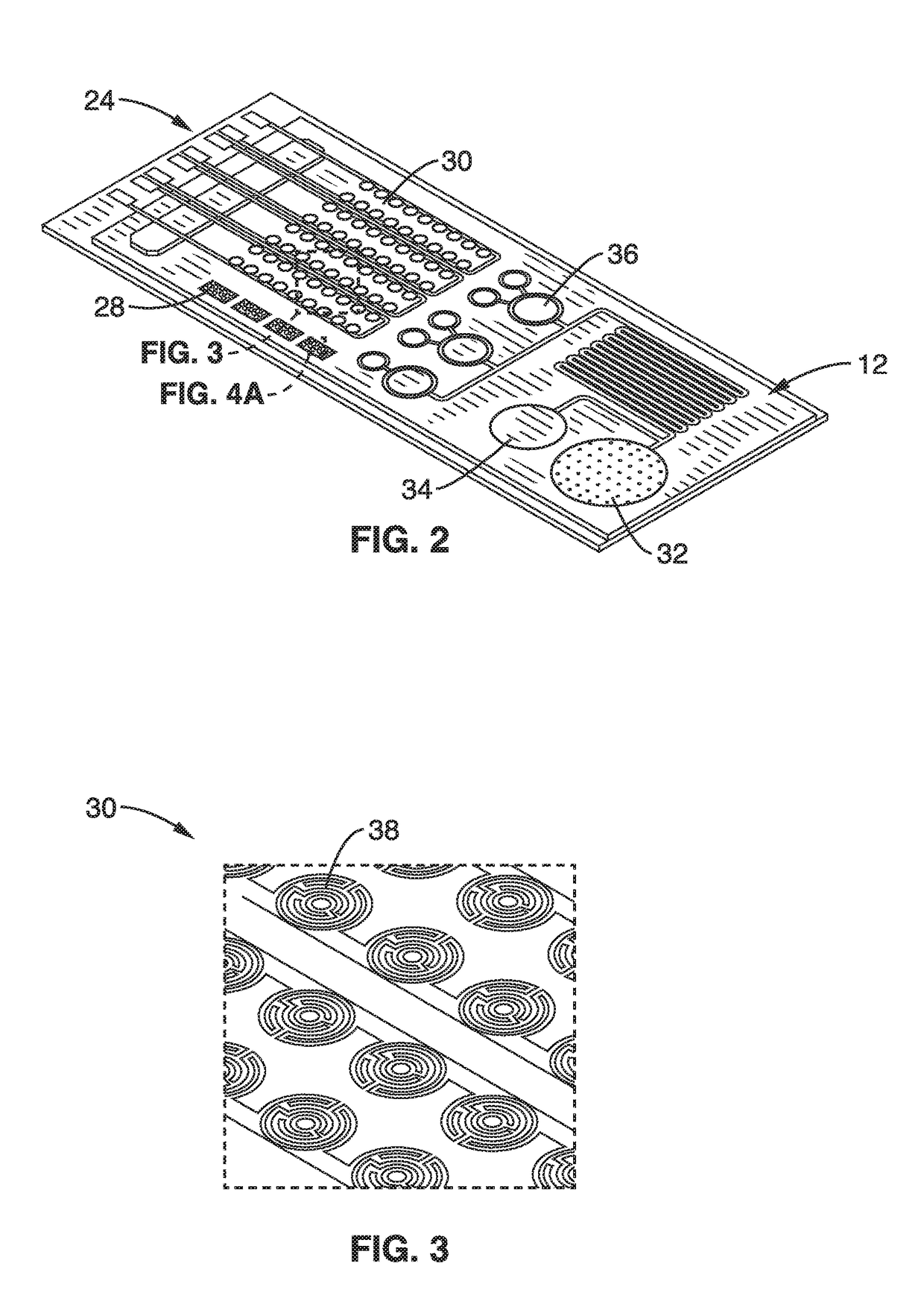
A mobile, self contained molecular diagnostics system is provided with a microfluidic chip, detection apparatus and an integrated or wireless control interface and imager. The system provides automated sample preparation and rapid optical detection of multianalyte nucleic acids and proteins. On chip PCR may be performed to improve the optical fluorescence signal for nucleic acid detections. Plasmonic protein detection is performed using a dark field smartphone microscope. Dark field illumination is based on an evanescent field generated by LED total internal reflection. The smartphone element may also be used as an interface to control the detection apparatus, acquire images, process data and for wireless communications with remote computers. The handheld automated system has low power requirements and is particularly suited for point of care and on demand diagnostics in resource limited settings.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
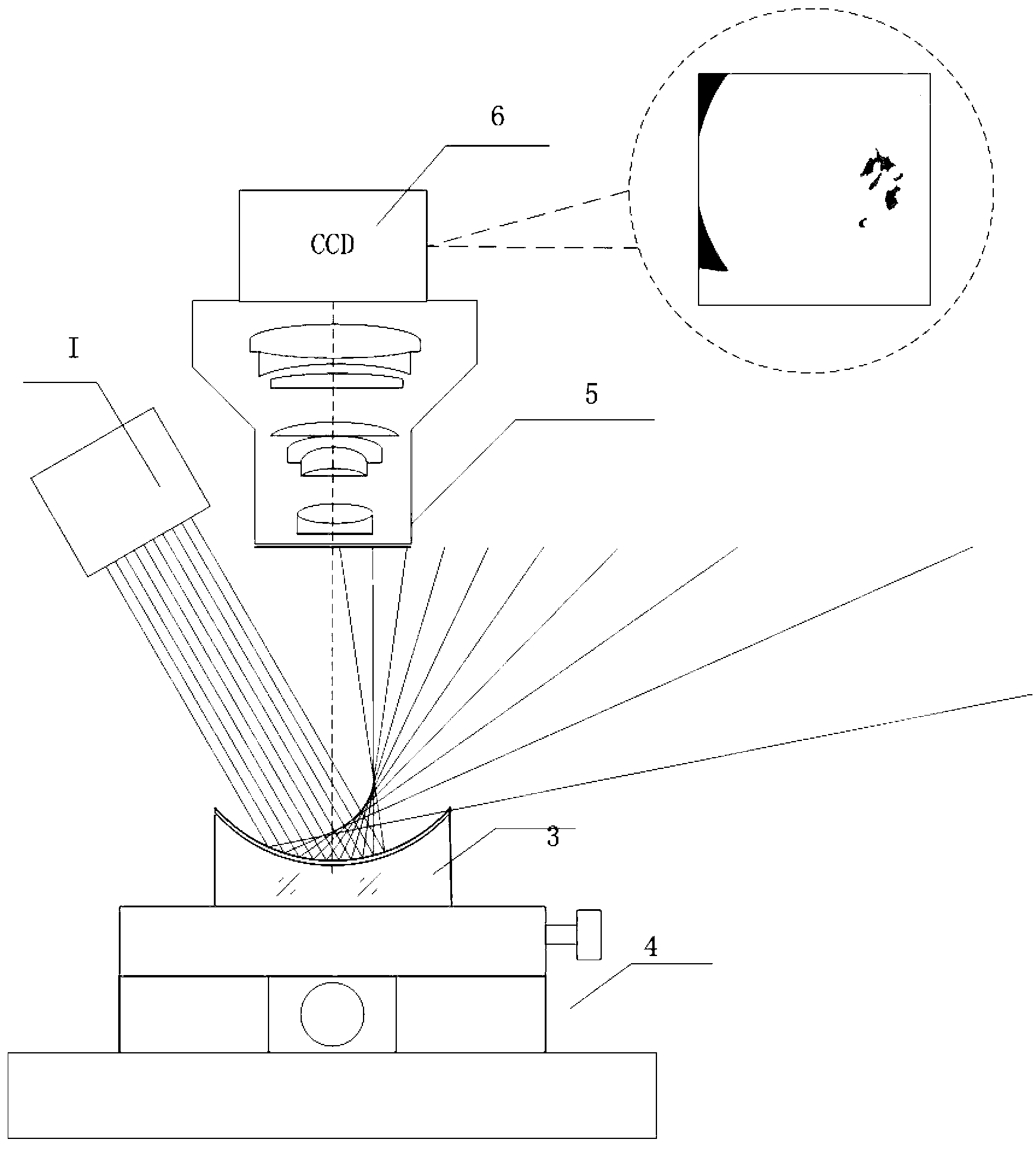
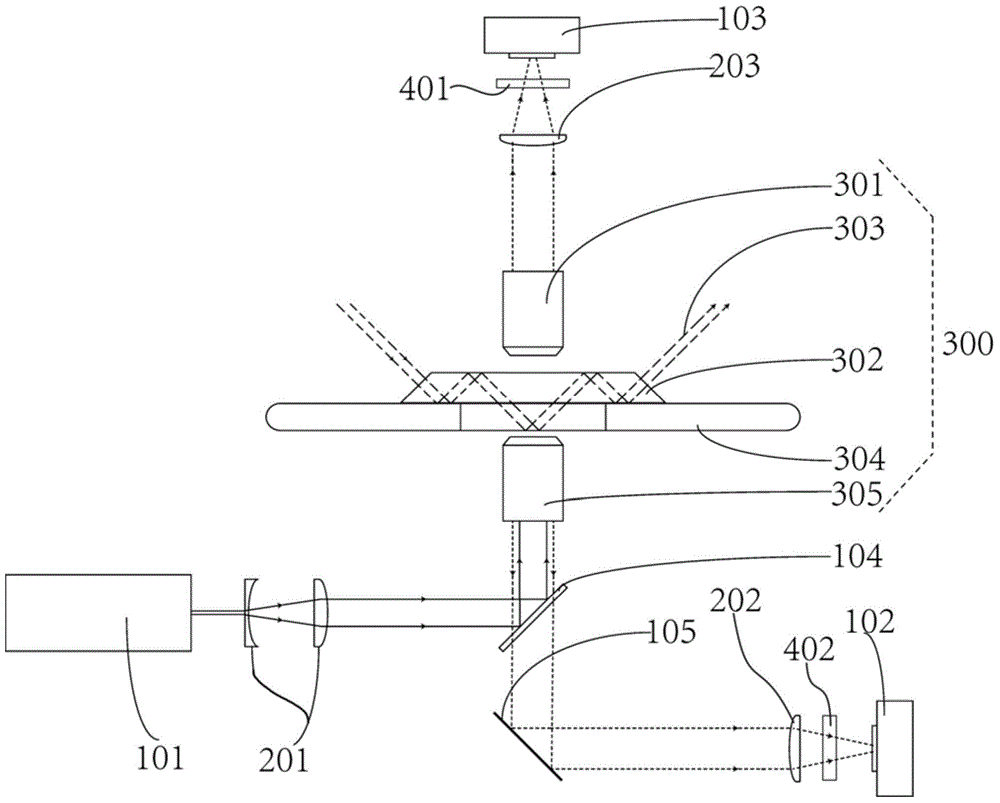
Corneal contact lens comprehensive detector and focusing evaluating algorithm thereof
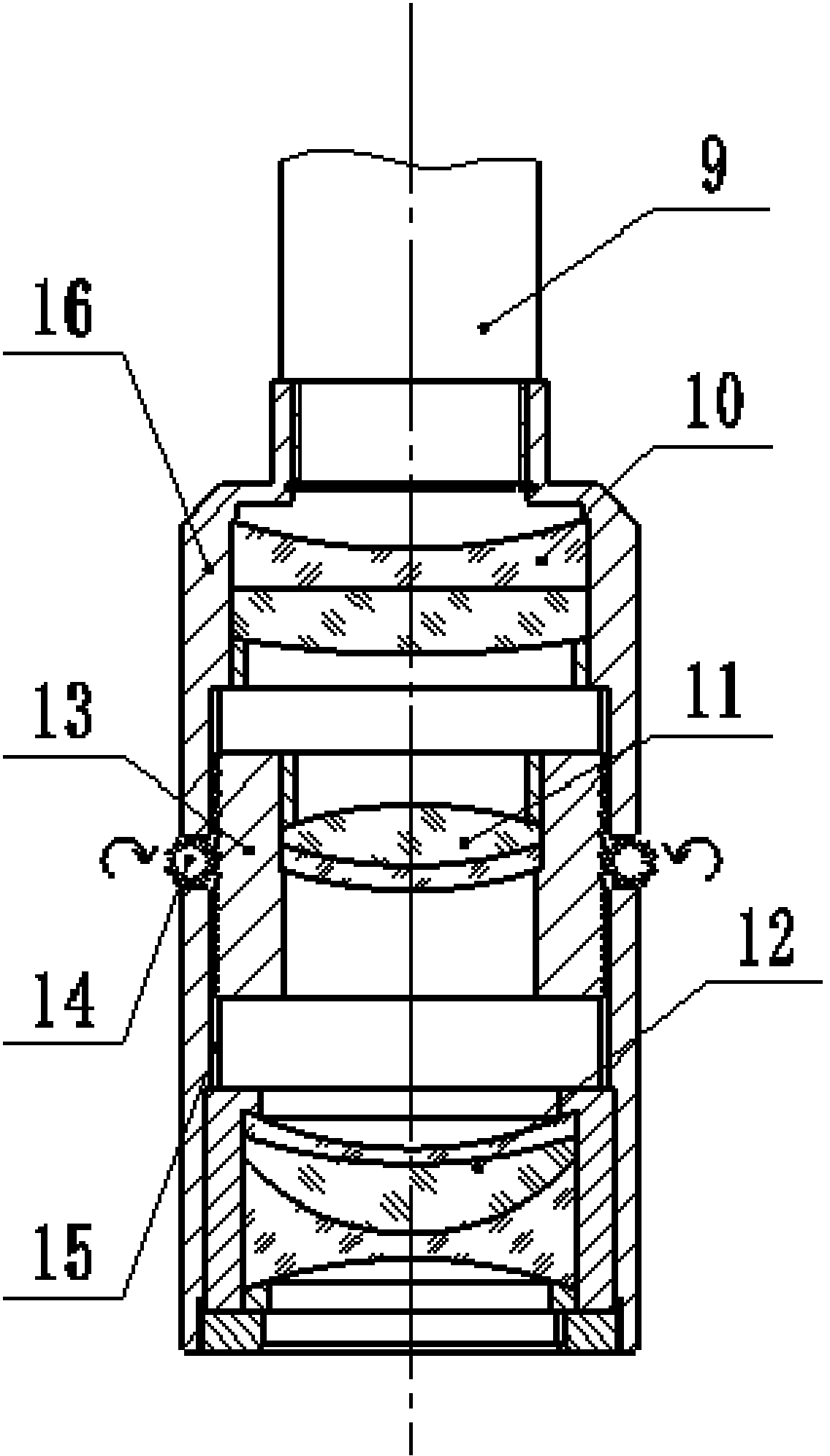
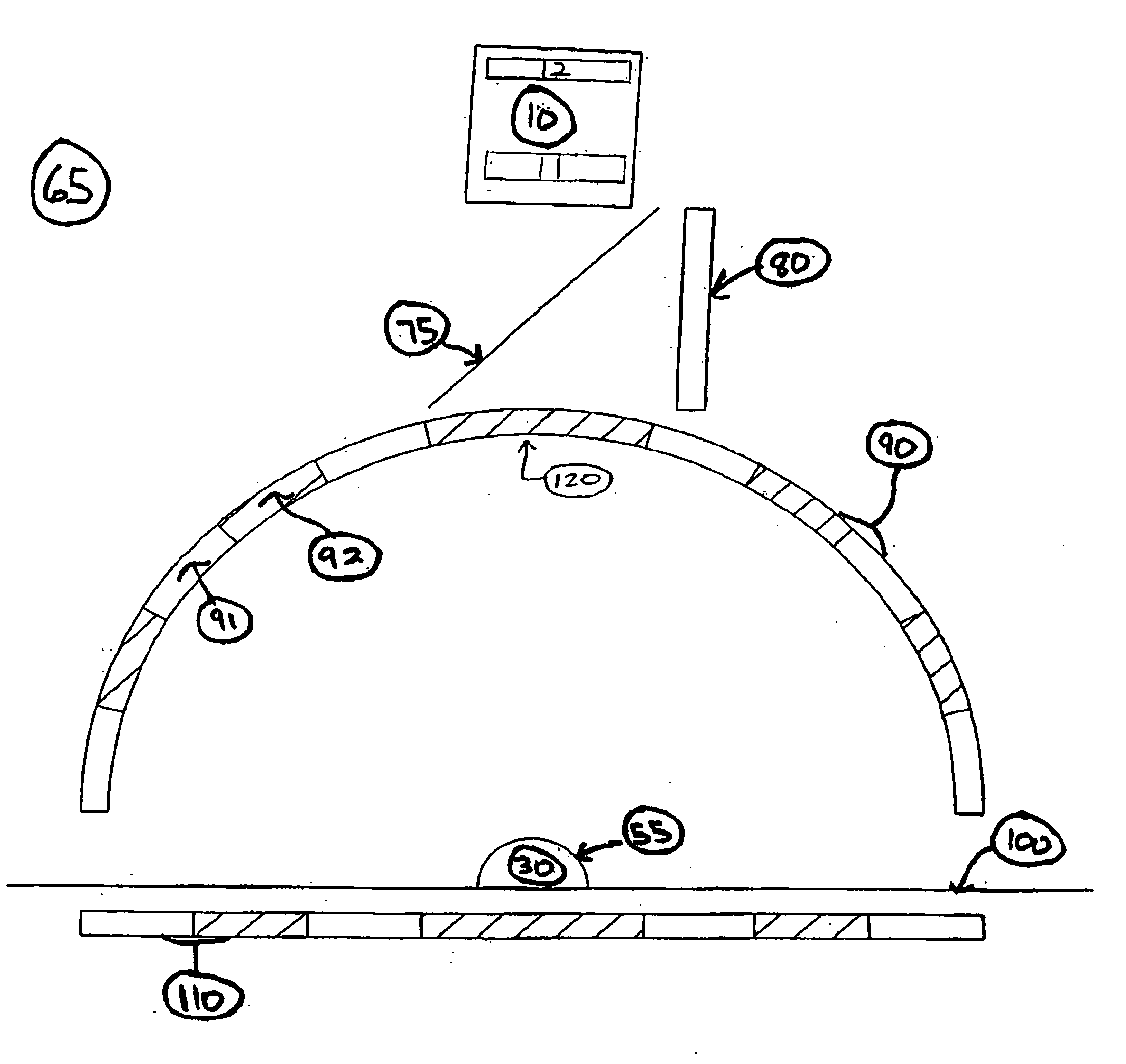
ActiveCN103792686AGo digitalFully automatedSpectales/gogglesTesting optical propertiesEyepieceLight pipe
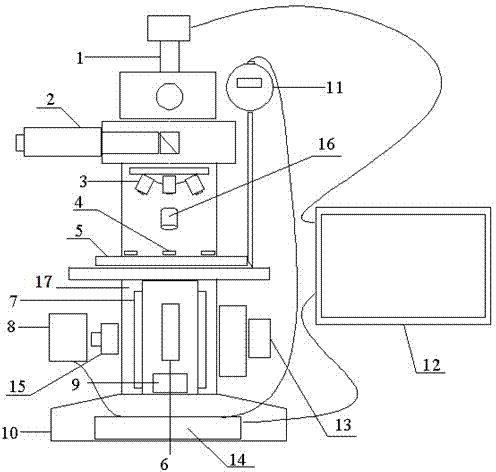
The invention relates to a corneal contact lens comprehensive detector and a focusing evaluating algorithm of the corneal contact lens comprehensive detector. The corneal contact lens comprehensive detector comprises an optical imaging device, an electronic ocular, an objective table, a lifting device, a digital dial indicator, a singlechip and a tablet personal computer and corresponding measuring control software, wherein a collimation light pipe is arranged between the ocular and an objective lens; an LED (light-emitting diode) oblique incidence lighting device and a dark filed lighting device are also respectively arranged above and below the objective table; a digital dial indicator probe is contacted with the objective table, and a digital signal is output to a controller; the lifting device comprises a vertical arm fixed on a base, guide rails and a stepping motor arranged on the vertical arm, and a gear and rack transmission device which realizes the variable speed lifting by switching an electromagnetic clutch, and the stepping motor and the electromagnetic clutch are controlled by a controller. The corneal contact lens comprehensive detector and the focusing evaluating algorithm of the corneal contact lens comprehensive detector provided by the invention have the advantages that a lens surface quality detection function and a lens diameter measuring function are also integrated, the intelligent measurement of a lens is realized, and the detection efficiency and measurement accuracy are improved.
Owner:AUTEK CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com