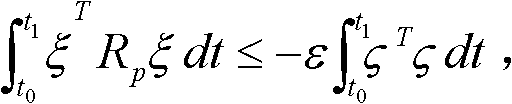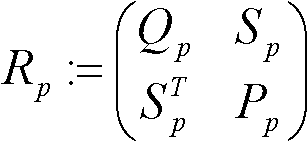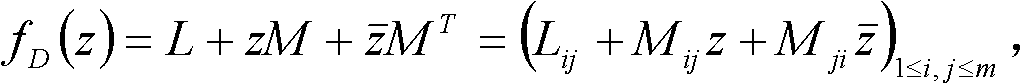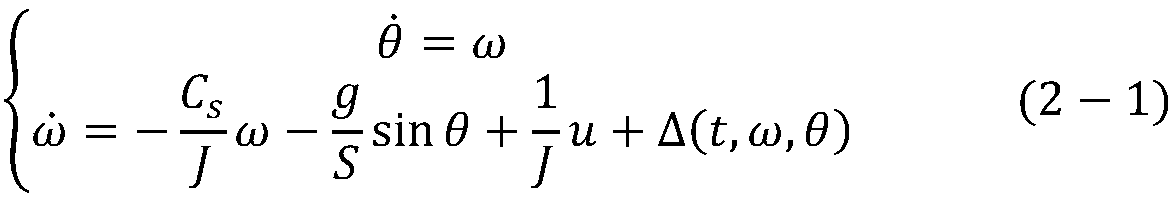Patents
Literature
94 results about "Gain scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In control theory, gain scheduling is an approach to control of non-linear systems that uses a family of linear controllers, each of which provides satisfactory control for a different operating point of the system.
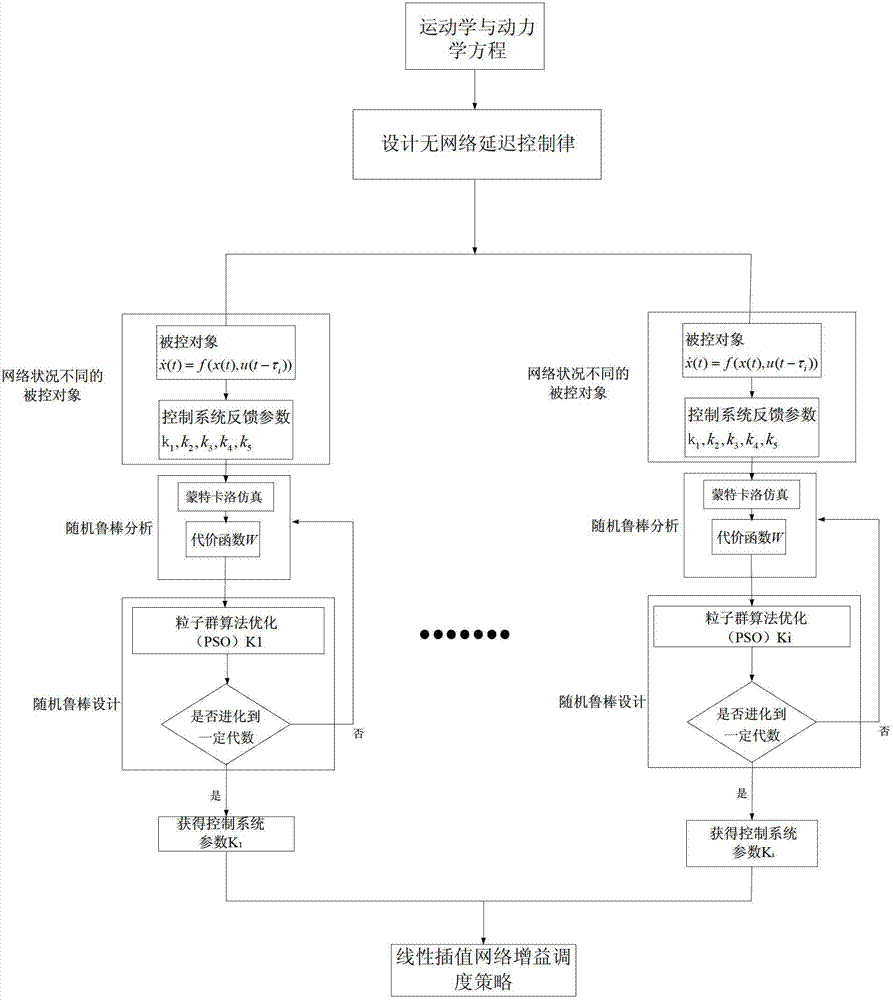
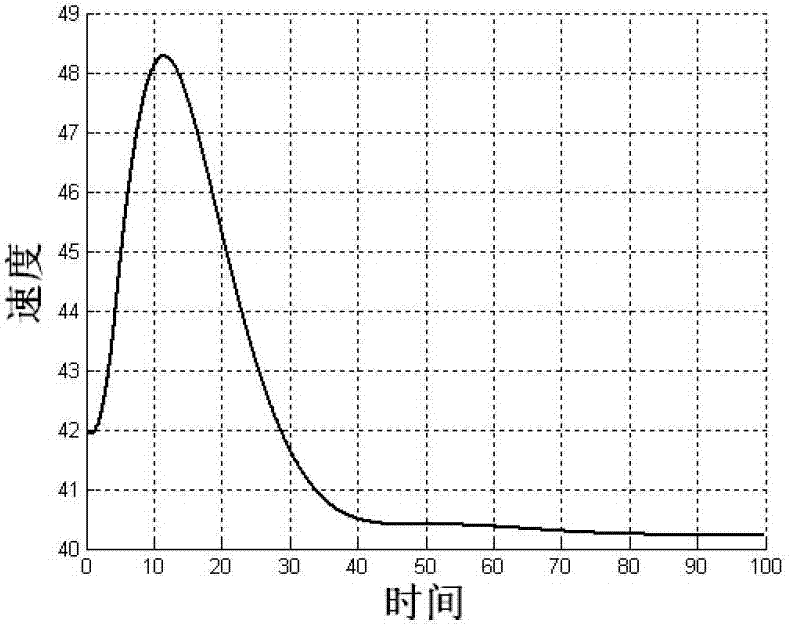
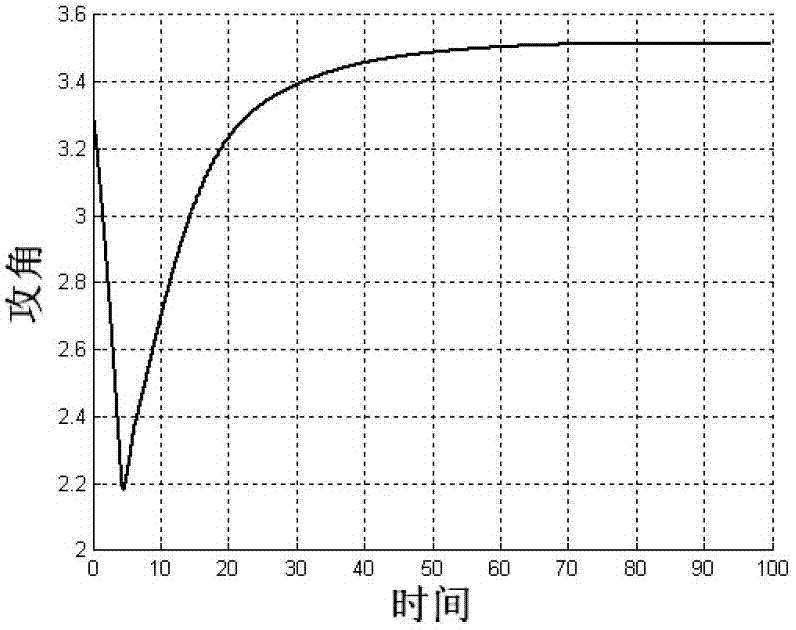
Microminiature unmanned aerial vehicle longitudinal control method with random delay of distributed network
ActiveCN103116280AAlleviate quality deteriorationImprove stabilityAdaptive controlClosed loopEngineering
The invention discloses a microminiature unmanned aerial vehicle longitudinal control method with random delay of a distributed network, and belongs to the field of flying control technology. The method includes firstly setting up an unmanned aerial vehicle longitudinal system model and designing a flying control system without network delay, secondly carrying out random robustness analysis and design on the flying control system on the condition of different network random delay, ensuring a gain scheduling strategy of the flying control system, and lastly carrying out closed-loop six-free-degree freedom nonlinear Monte-Carlo simulation verification. According to the control method, deterioration of quality of the flying control system due to network delay is relieved, and stability of the distributed type system can be strengthened. Through utilization of the random robust analysis and design method and the gain scheduling strategy based on linear interpolation, the obtained control has the advantages of being simple, and facilitating engineering realization. Control quality of an original system can be well maintained on the condition of changes of large network delay.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
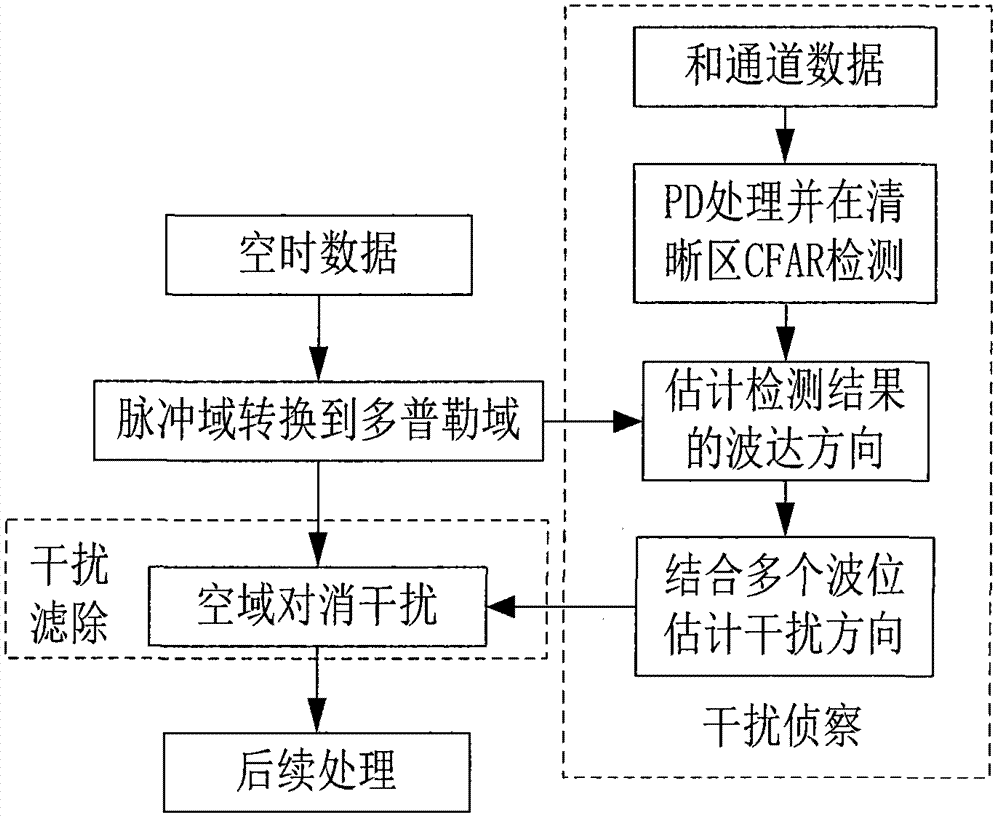
Method and system for resisting dense forwarding type defraud interference of airborne radar
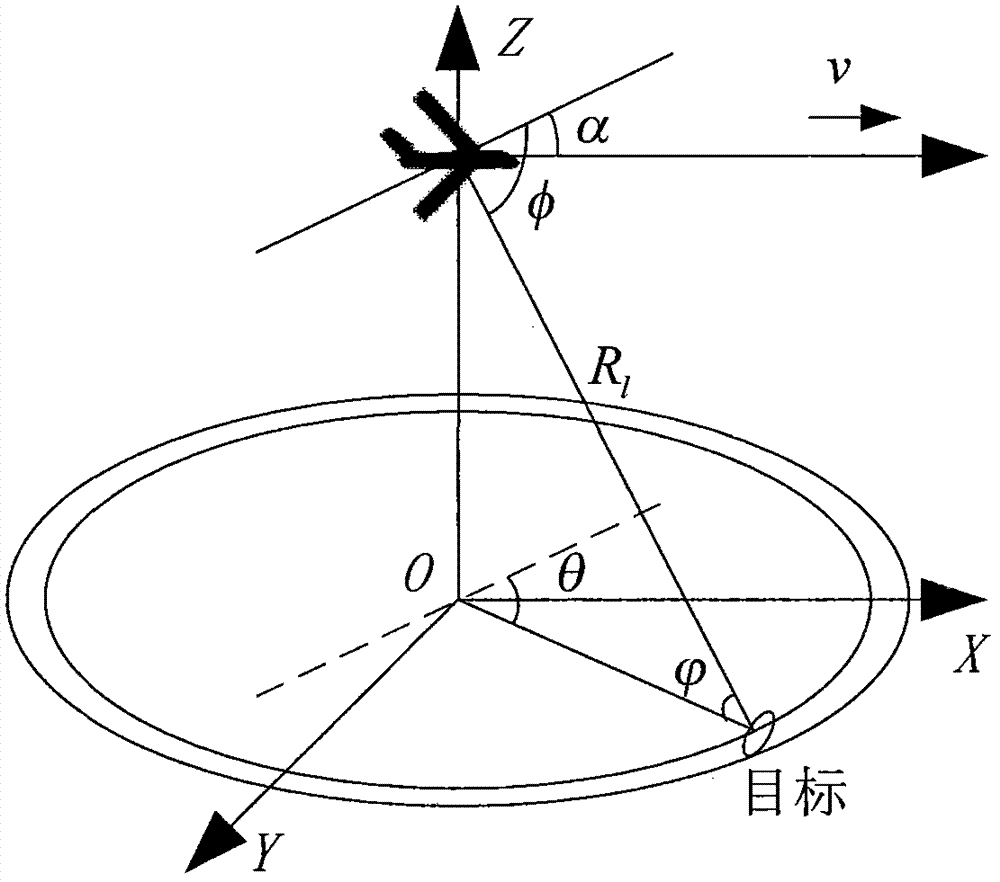
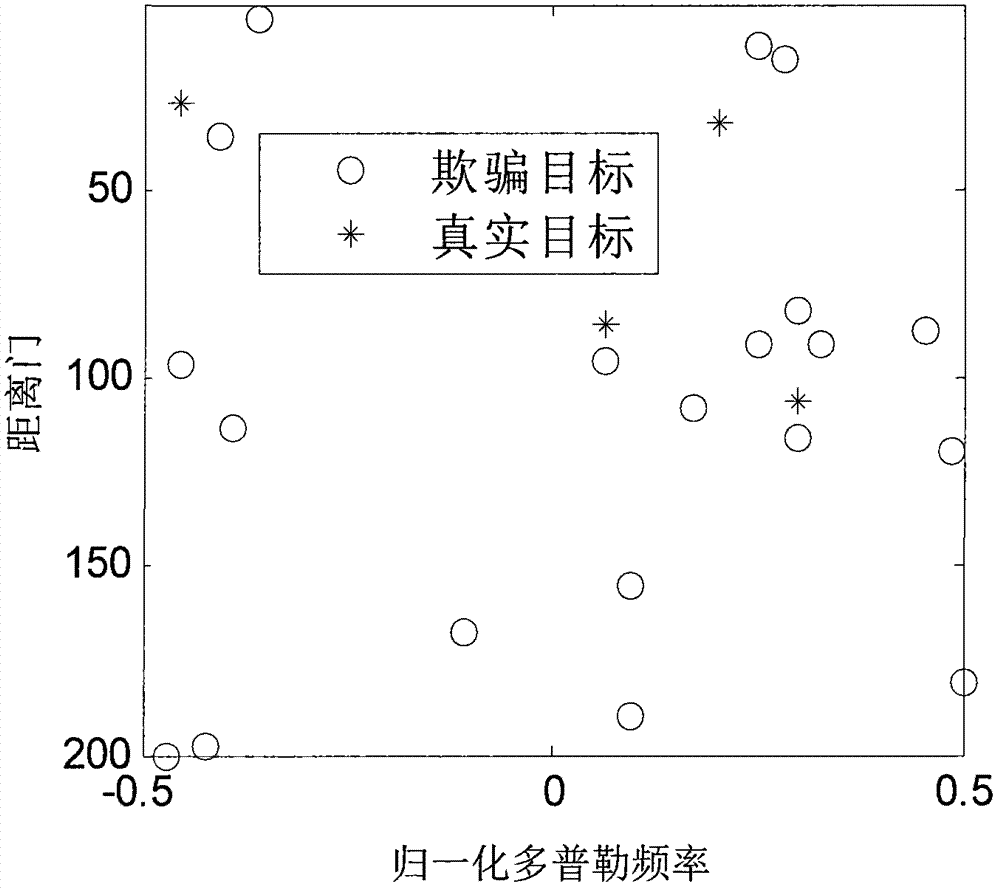
ActiveCN103399303AImprove object detection performanceAddress issues that adversely affect performanceWave based measurement systemsFalse alarmCovariance matrix
The invention discloses a method and a system for resisting dense forwarding type defraud interference of an airborne radar, and the resistance of dense forwarding type defraud interference is realized through an interference scout module and an interference filter and elimination module. Interference scout is used for carrying out the PD (probability of defraud) treatment on data received by a radar; the CFAR (constant false alarm rate) detection is carried out on data in a clear area; a detection result direction of arrival is estimated; an interference direction of arrival is estimated with combination of the detection result of a plurality of wave positions. In the interference filter and elimination treatment, a sum beam pointing to the interference direction is formed according to an interference scout result; the sum beam pointing to the interference direction is used as an auxiliary passageway, an existing space passageway is used as a main passageway, the method of GSC (gain scheduling control) is adopted to filter and eliminate interference, and the channel covariance matrix of the interference is estimated according to an interference sample selected from the clear area. By adopting the method and the system, the difficult problem of inhibition on dense forwarding type defraud interference is solved, the dense forwarding type interference is fundamentally filtered and eliminated, false alarms caused by the dense forwarding type interference are reduced, adverse effects on a CRAR detection threshold and the STAP (space time adaptive processing) performance are eliminated, the detection performance of a radar target is improved, the system is simple and easy to realize, and an engineering application value is provided.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
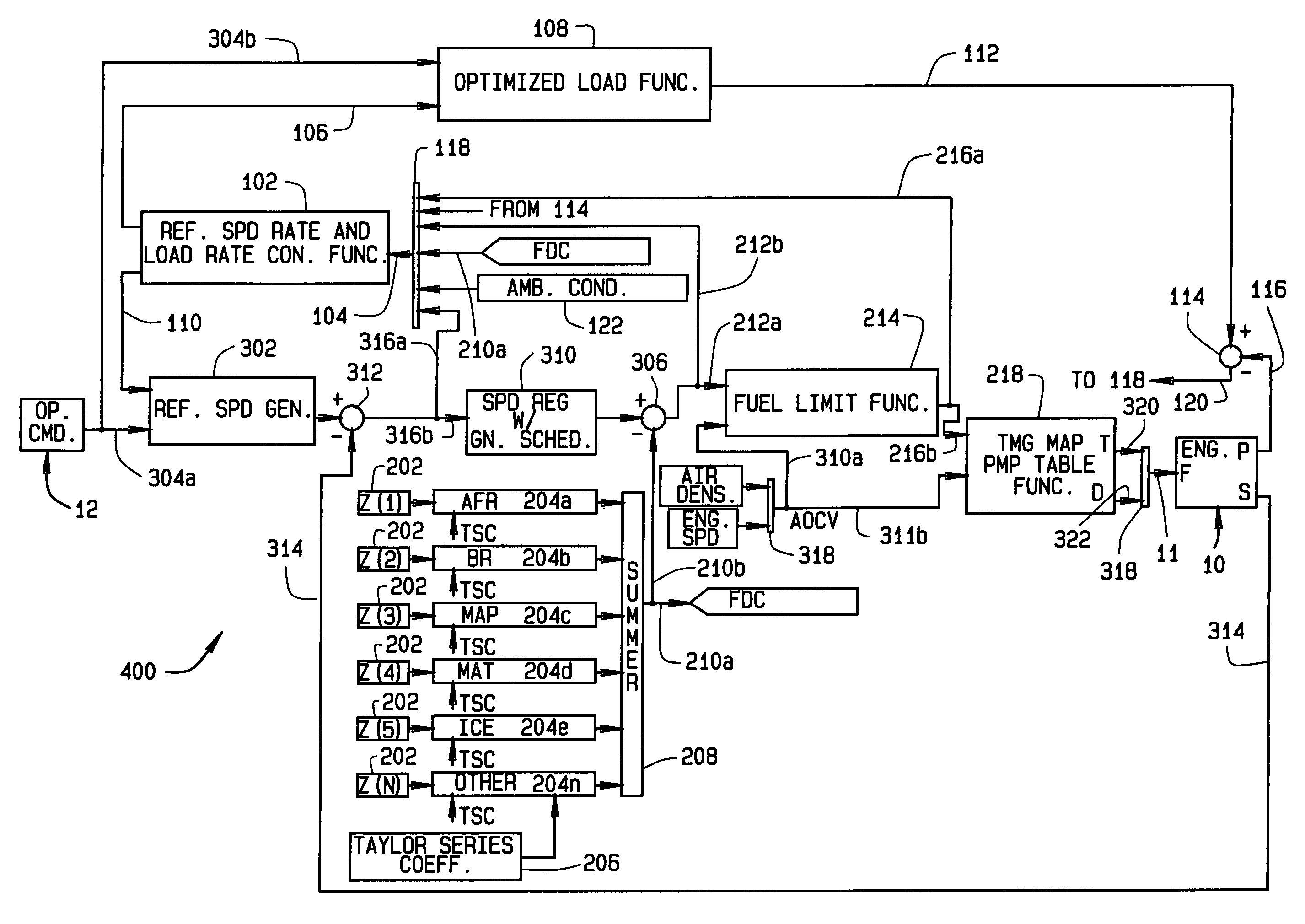
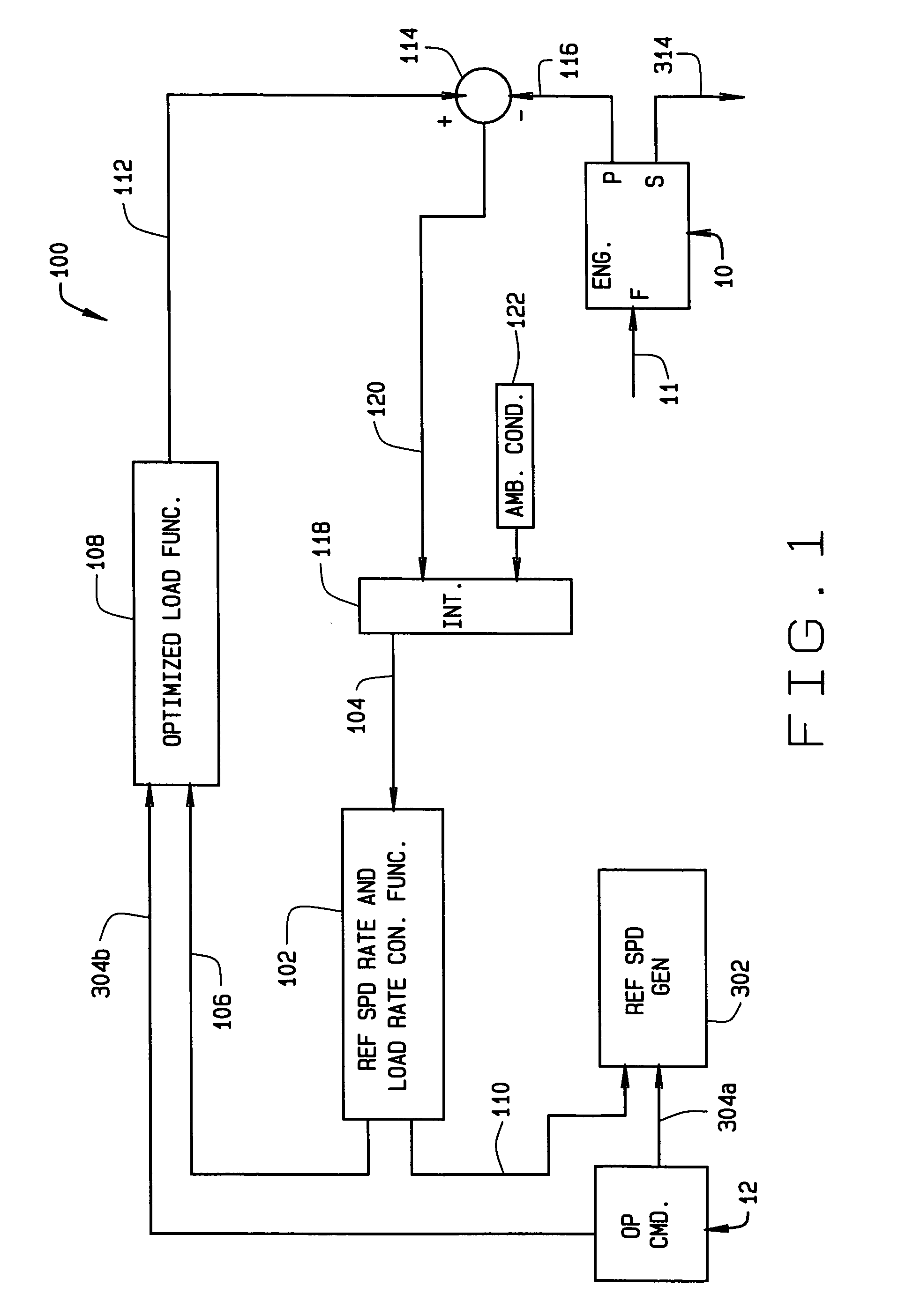
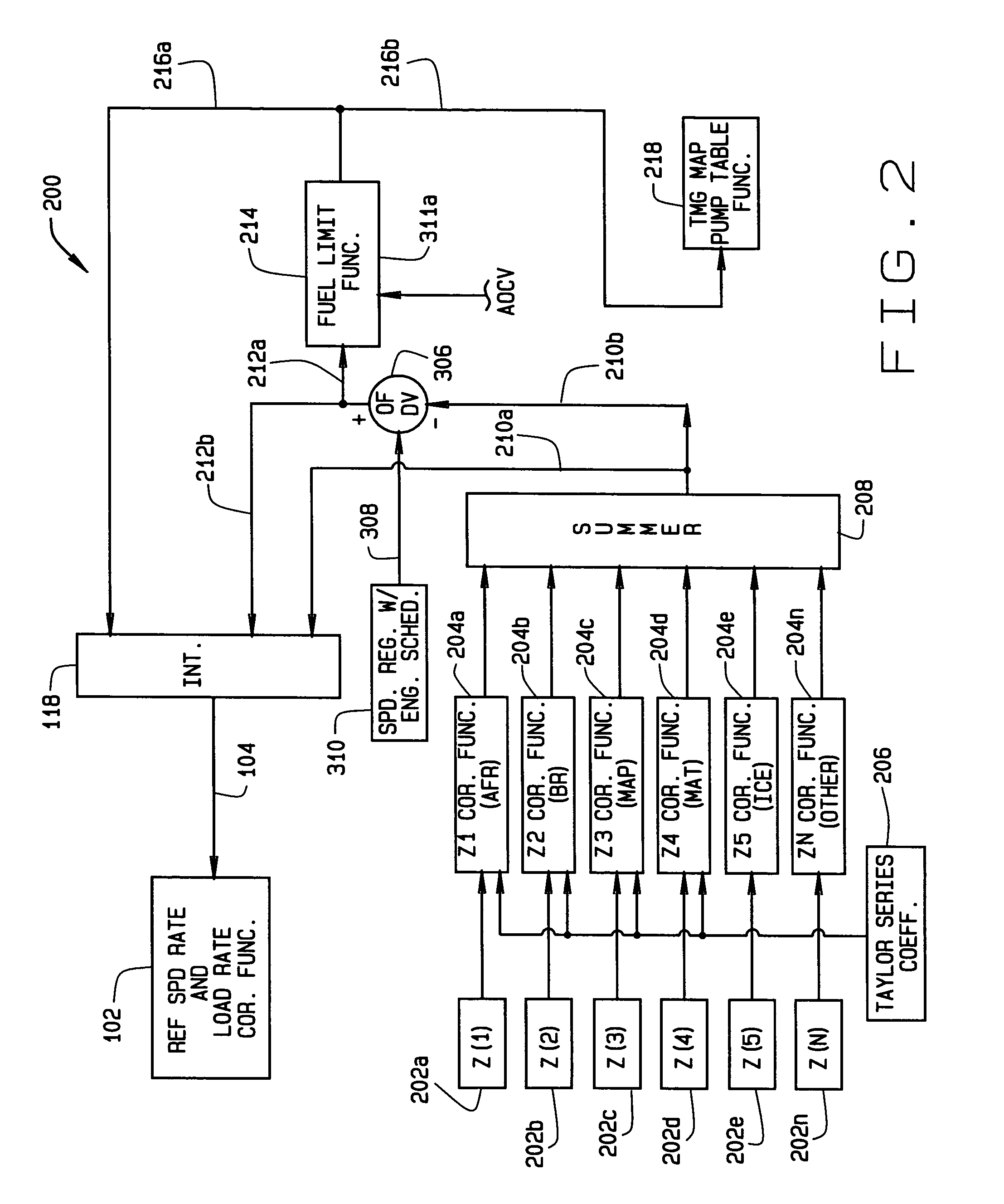
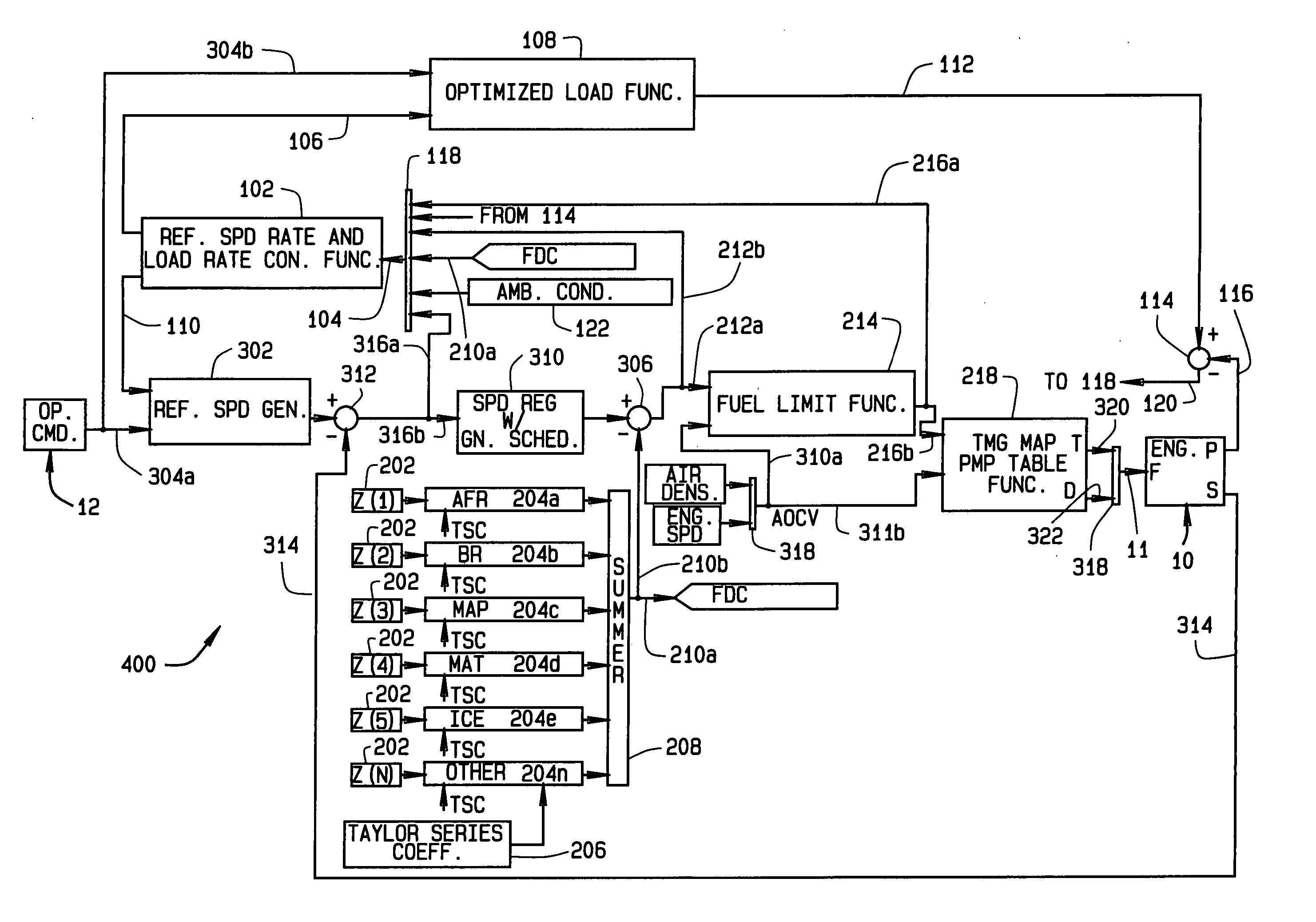
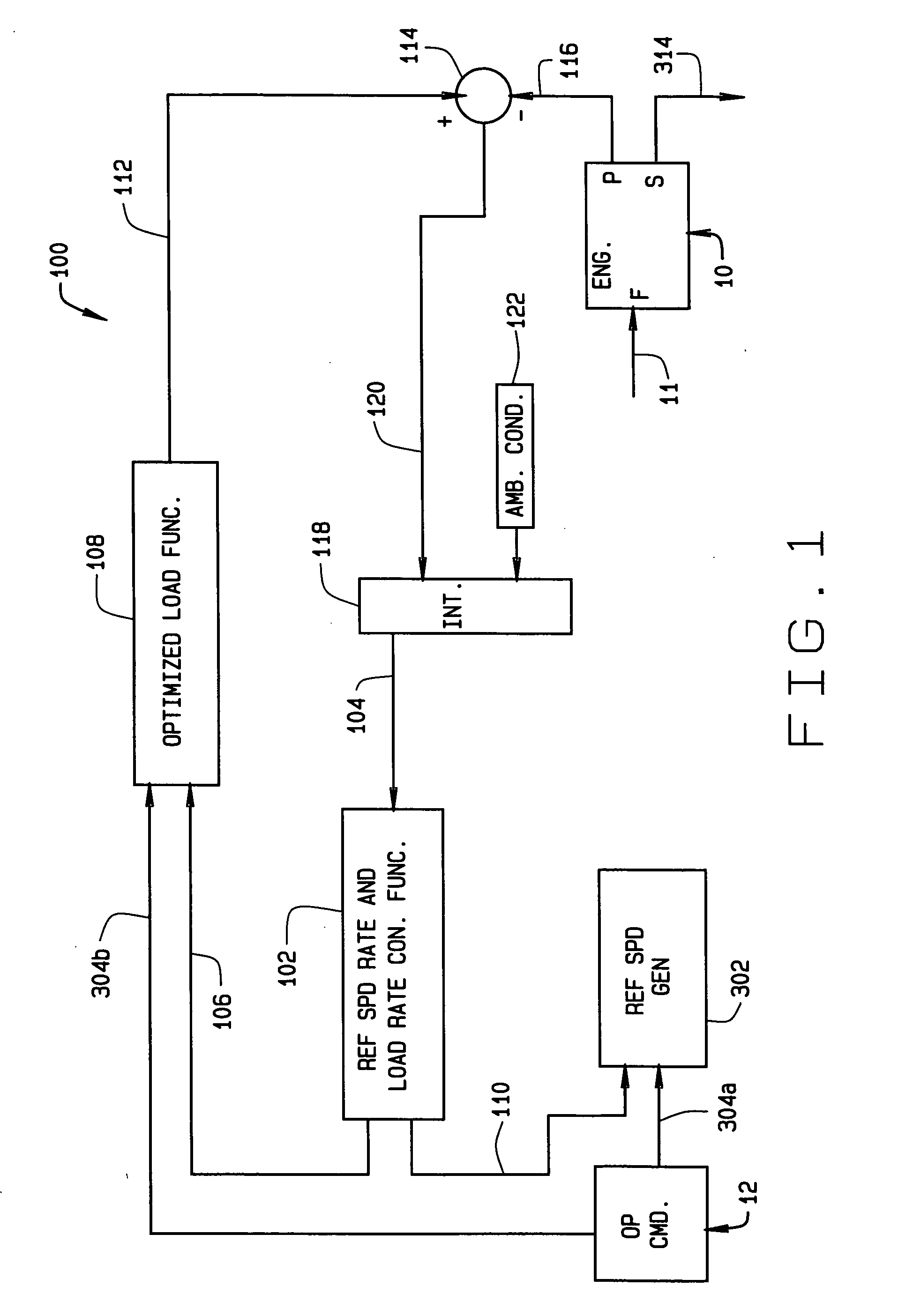
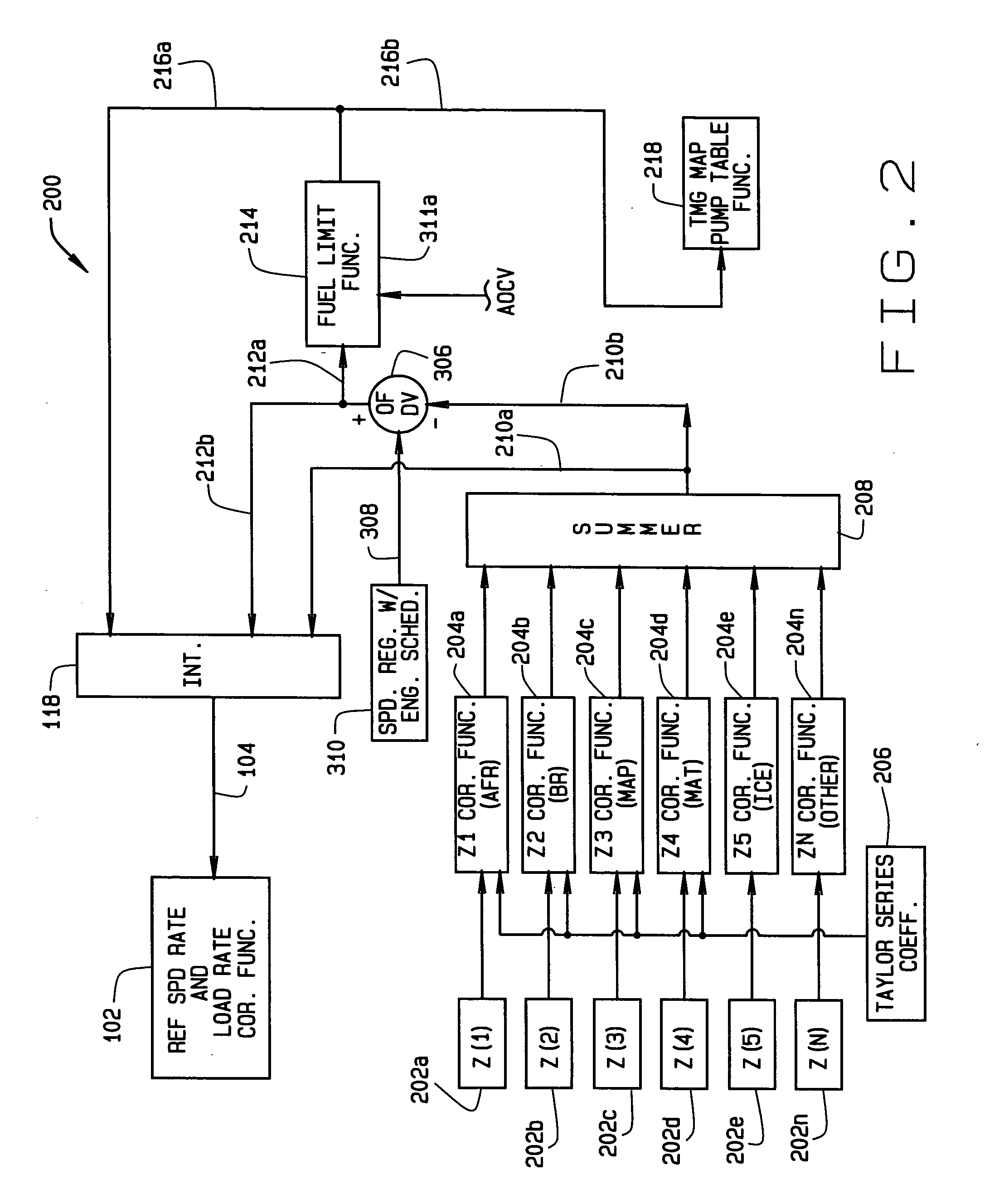
Diesel engine control system with optimized fuel delivery
InactiveUS7047938B2Promotes efficient combustionReduce deliveryElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsEngineeringSlew rate
A system (400) and method of determining fuel demands of a locomotive engine (10) based upon engine speed and power produced by the engine at a given time, so to optimize the engine's power output for a load while reducing engine emissions. The engine control architecture comprises three interrelated control loops (100–300). A primary feedback control loop (100) employs integral type control with gain scheduling to regulate engine speed to commanded slew rated based upon the locomotive's operator commands. A second control loop (200) provides an active, feed forward or predictive control consisting of a plurality of correction functions each utilizing a Taylor series having coefficients for each term in the series, the coefficients being modified to adapt the system to the engine with which it is used. A control third loop (300) optimizes reference speed slew rates and engine load rates by providing feedback of nominal engine fuel requirements or fuel demand, corrections to fuel demand based upon outputs from the second control loop, speed error values, and ambient conditions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Diesel engine control system with optimized fuel delivery
InactiveUS20050171655A1Optimize fuel deliveryPromotes efficient combustionElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsEngineeringSlew rate
A system (400) and method of determining fuel demands of a locomotive engine (10) based upon engine speed and power produced by the engine at a given time, so to optimize the engine's power output for a load while reducing engine emissions. The engine control architecture comprises three interrelated control loops (100-300). A primary feedback control loop (100) employs integral type control with gain scheduling to regulate engine speed to commanded slew rated based upon the locomotive's operator commands. A second control loop (200) provides an active, feed forward or predictive control consisting of a plurality of correction functions each utilizing a Taylor series having coefficients for each term in the series, the coefficients being modified to adapt the system to the engine with which it is used. A control third loop (300) optimizes reference speed slew rates and engine load rates by providing feedback of nominal engine fuel requirements or fuel demand, corrections to fuel demand based upon outputs from the second control loop, speed error values, and ambient conditions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
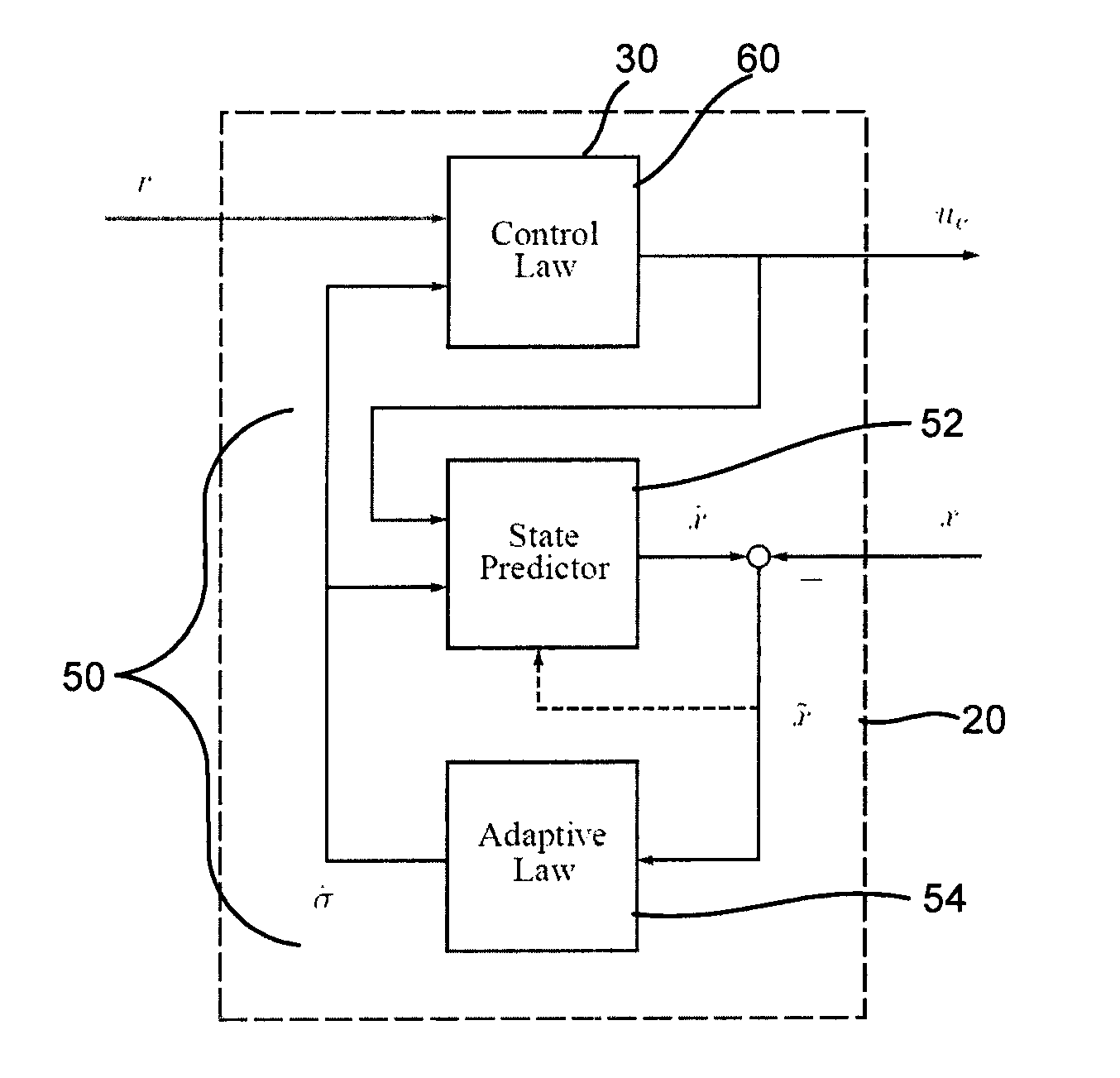
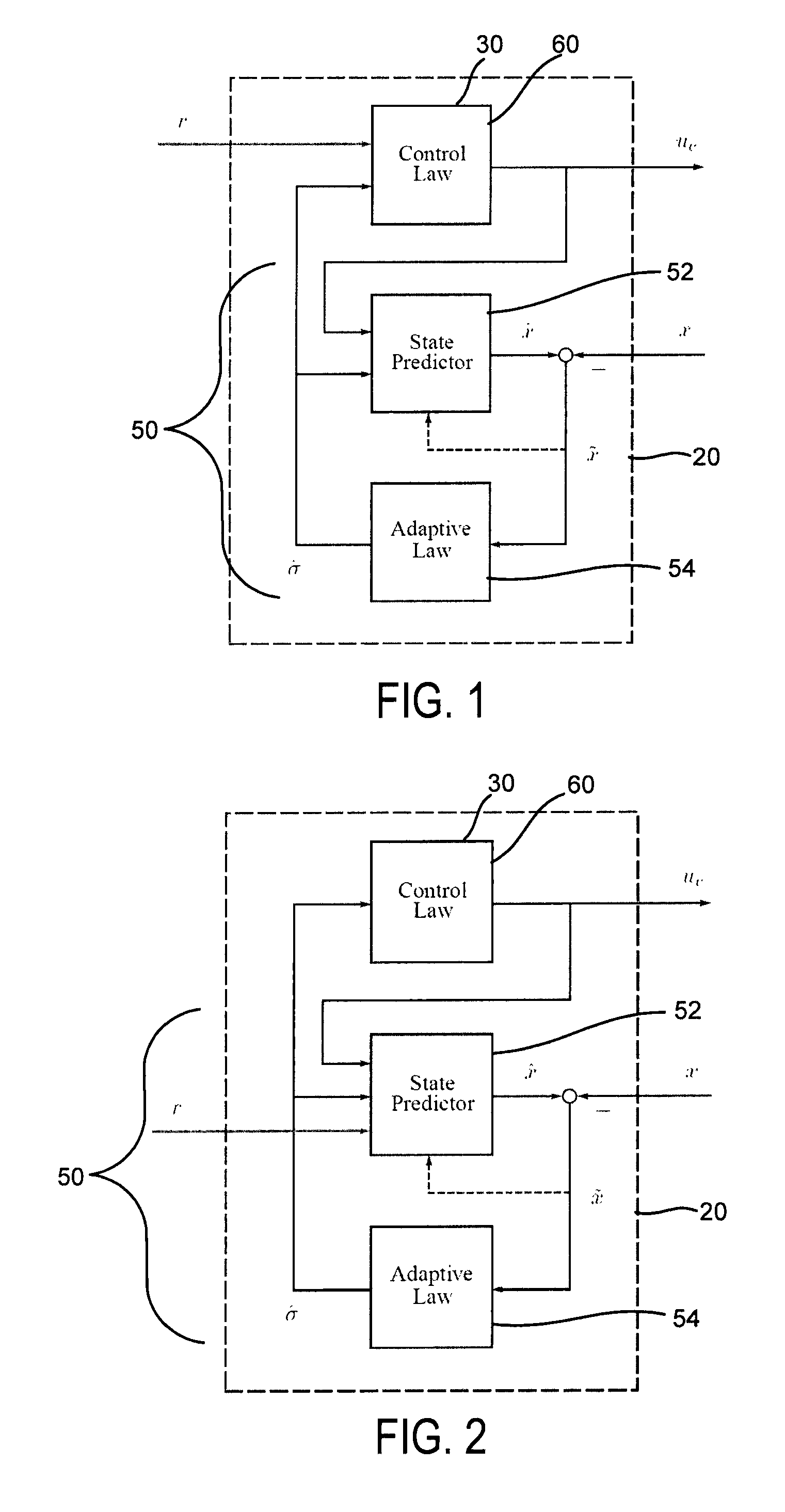
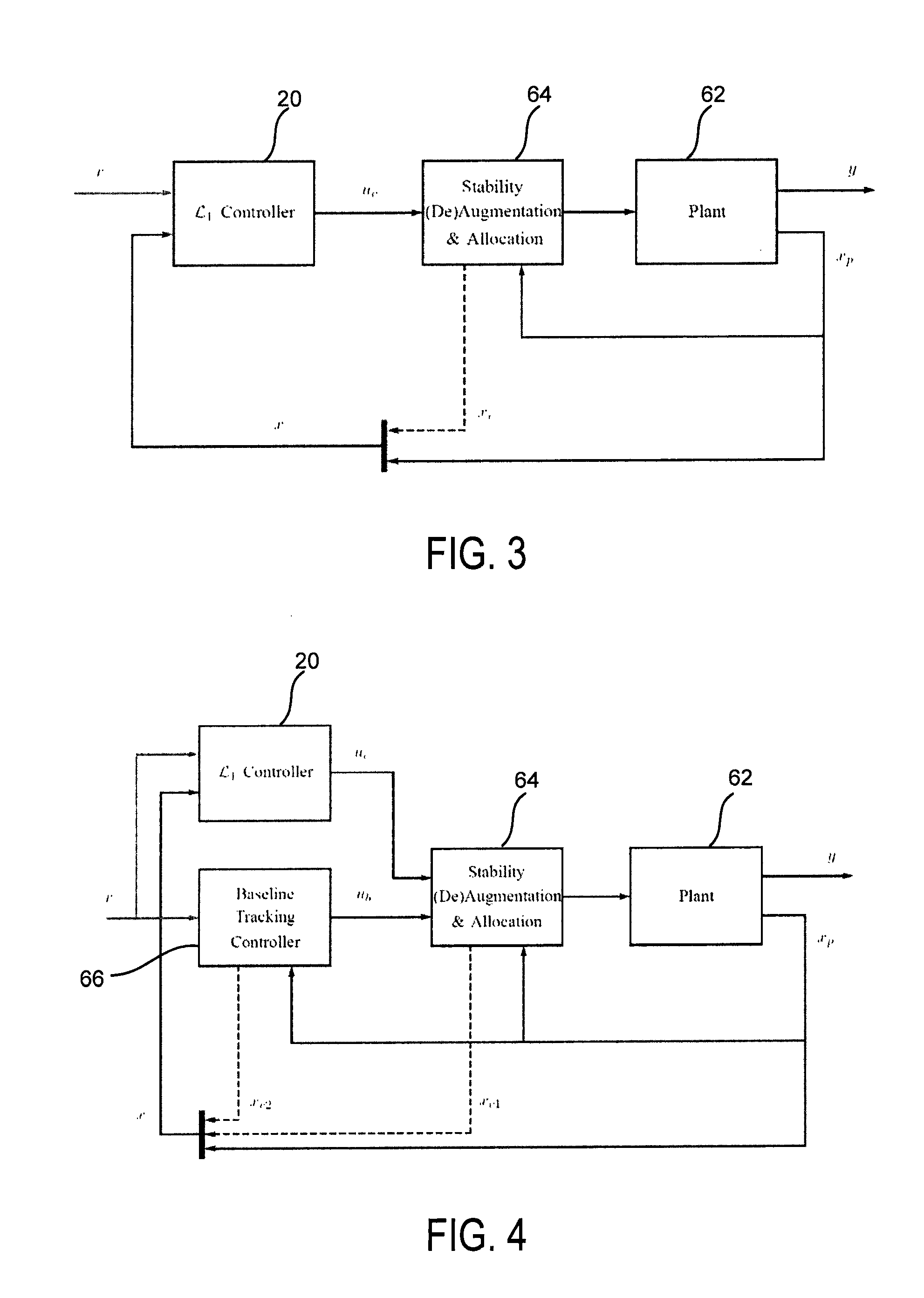
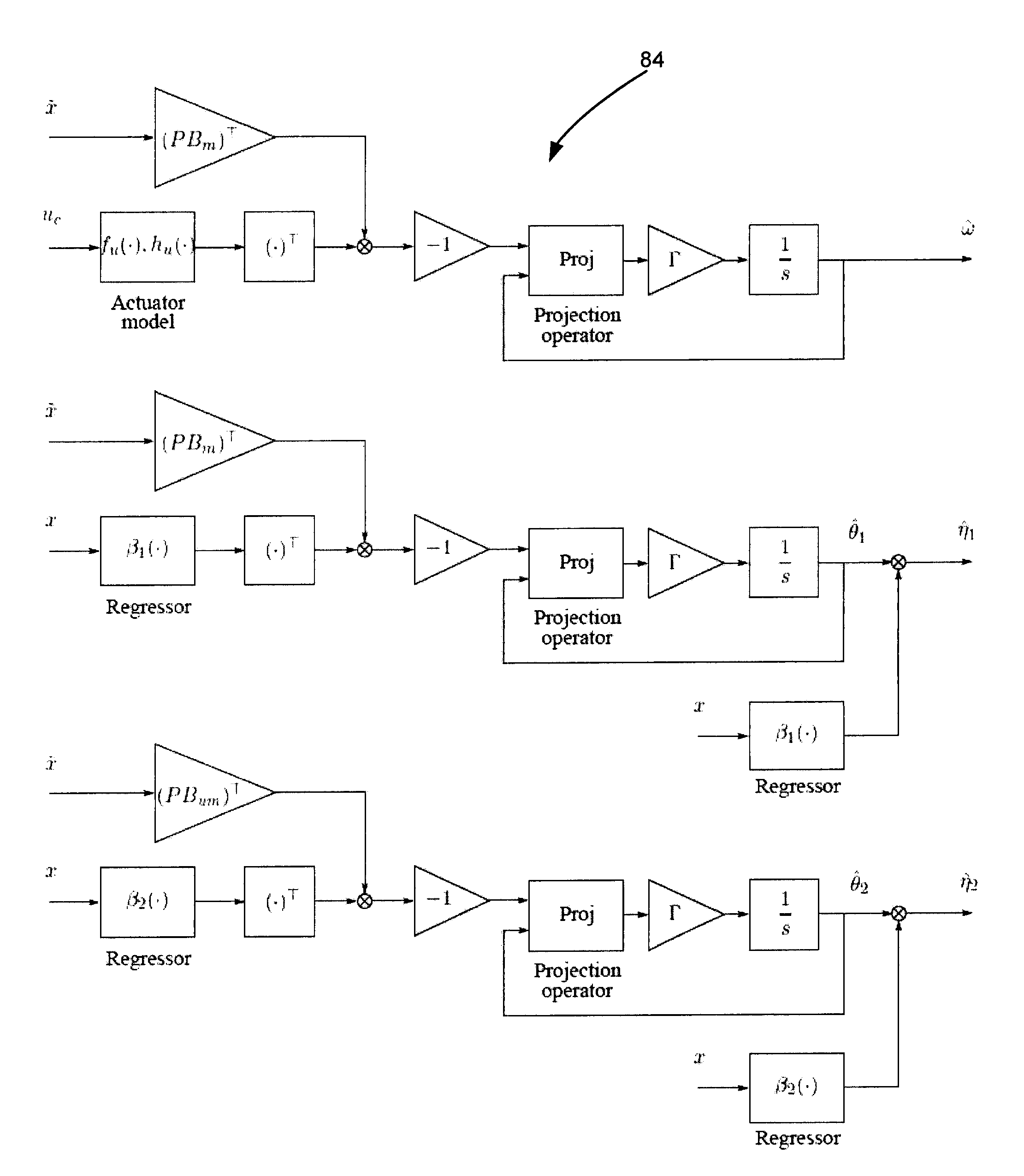
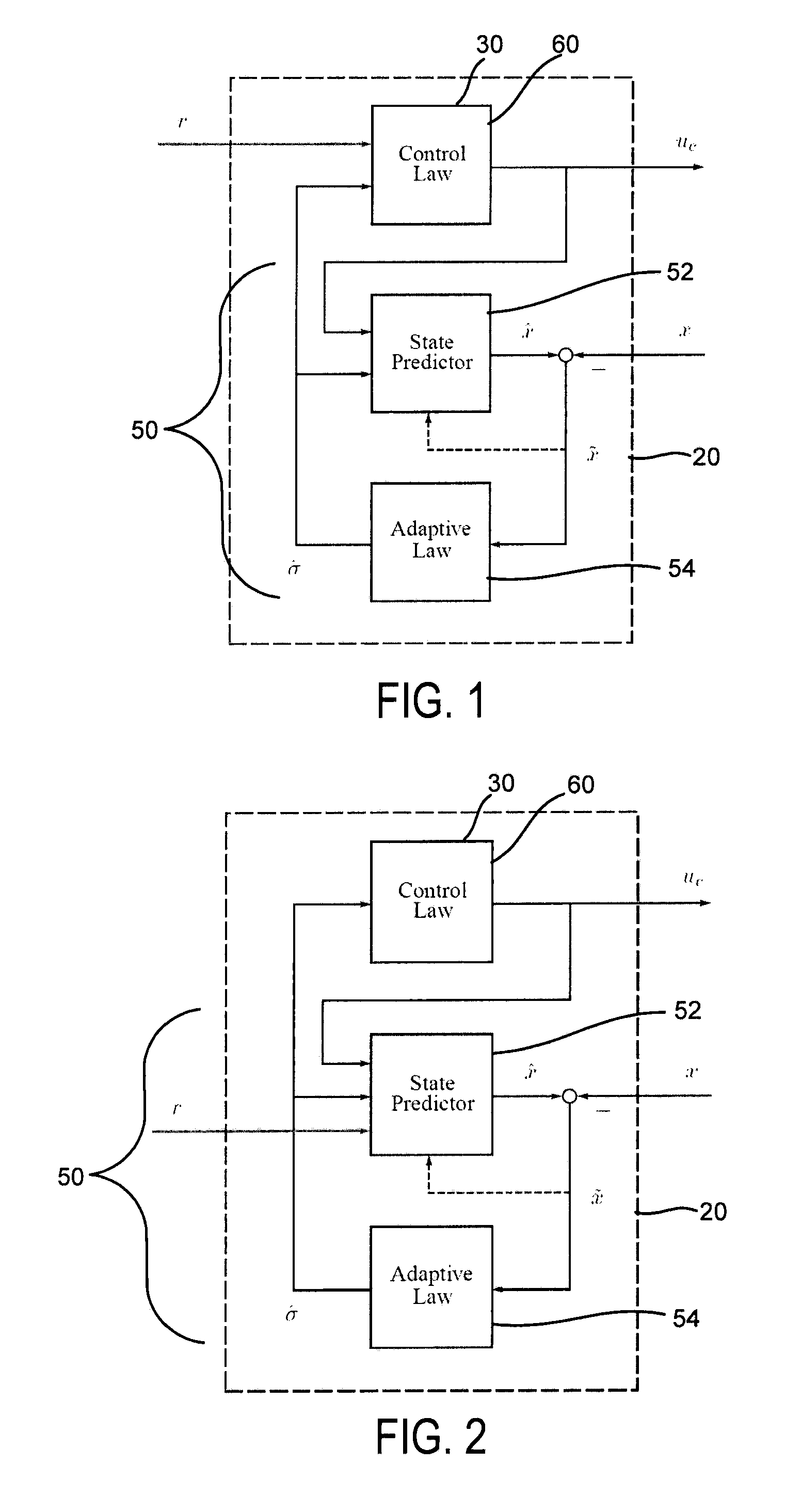
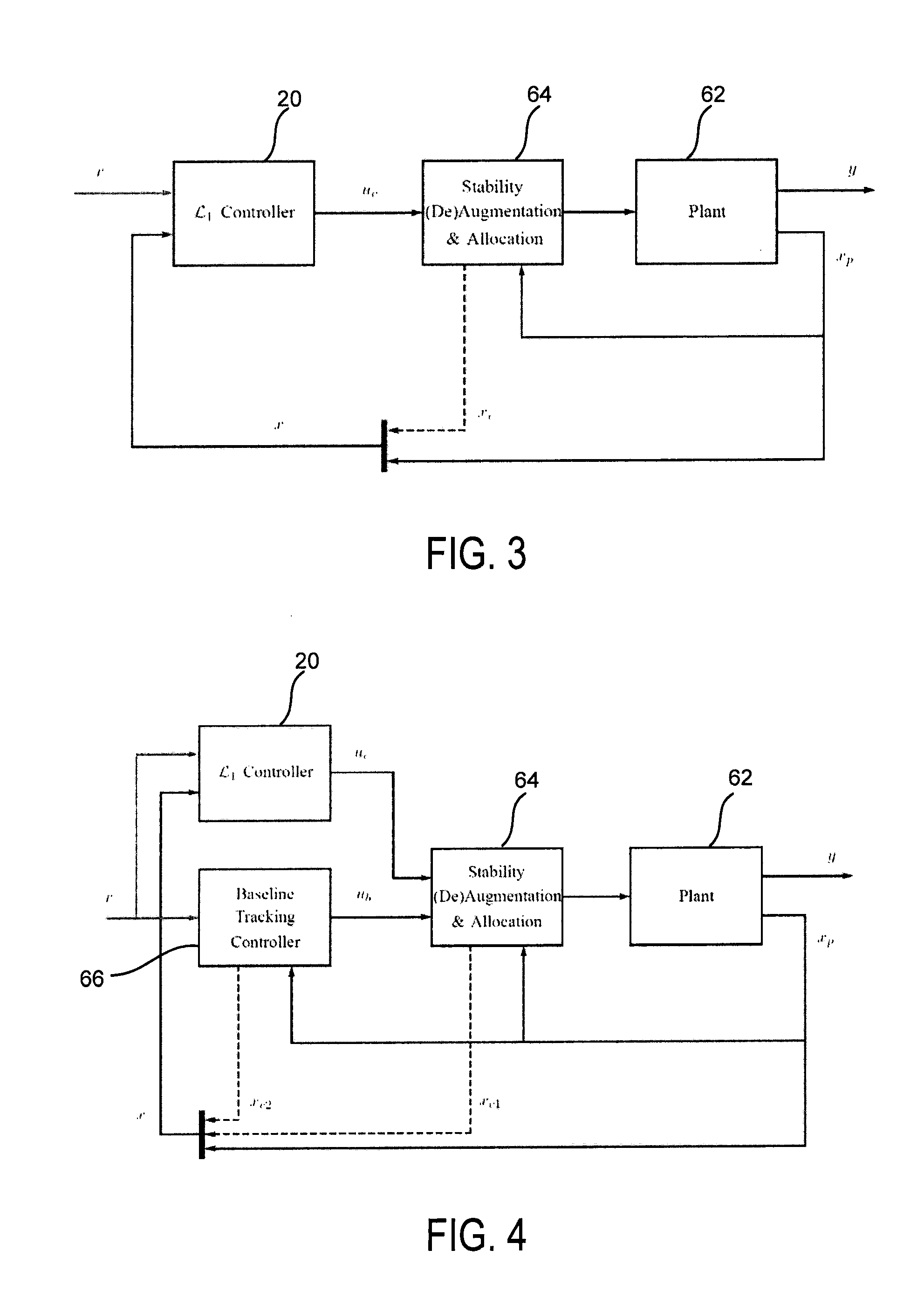
Adaptive control for uncertain nonlinear multi-input multi-output systems
ActiveUS20110196514A1Fast adaptive controlGuaranteed performanceAdaptive controlMulti inputHigh frequency power
Systems and methods of adaptive control for uncertain nonlinear multi-input multi-output systems in the presence of significant unmatched uncertainty with assured performance are provided. The need for gain-scheduling is eliminated through the use of bandwidth-limited (low-pass) filtering in the control channel, which appropriately attenuates the high frequencies typically appearing in fast adaptation situations and preserves the robustness margins in the presence of fast adaptation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
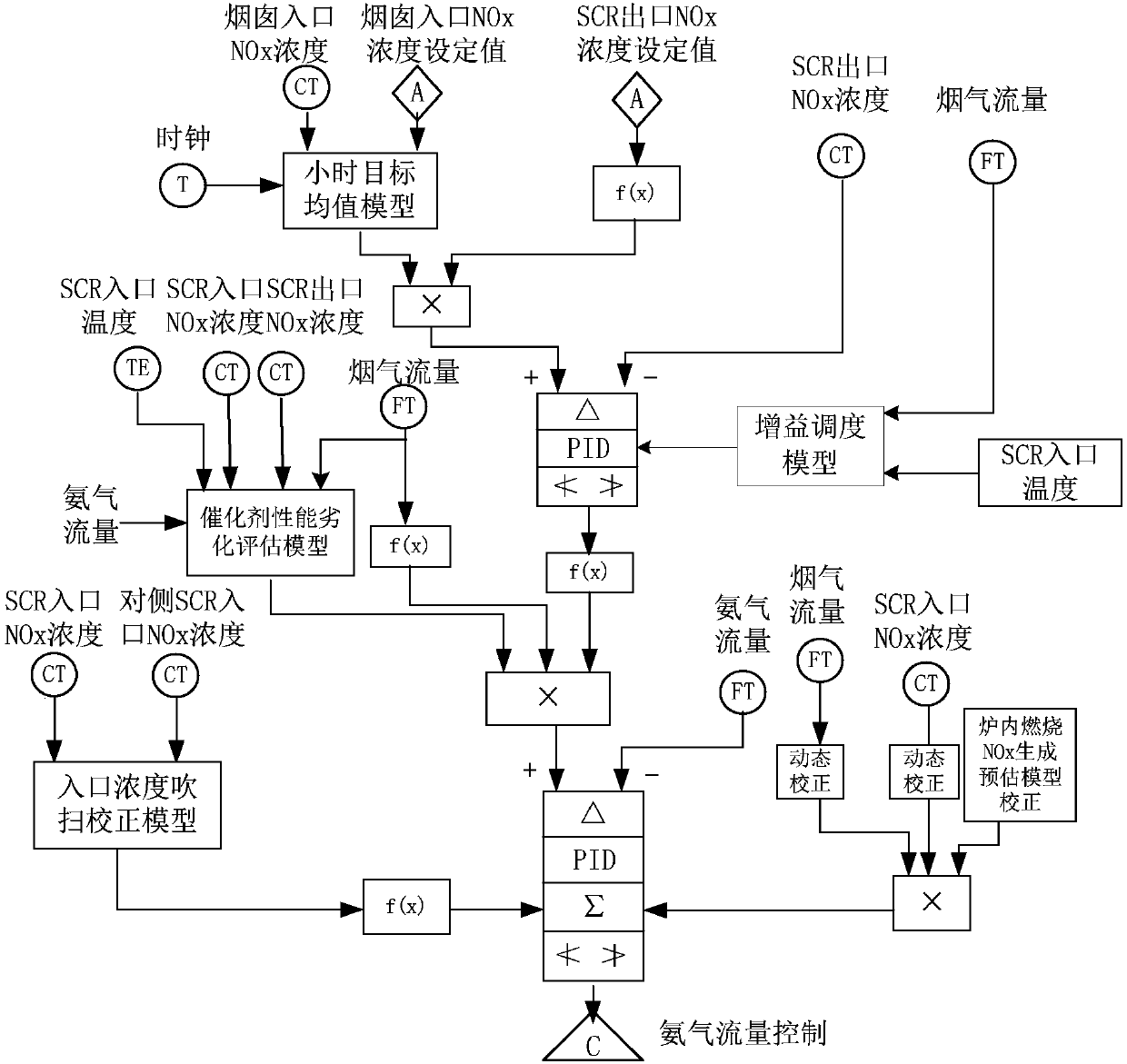
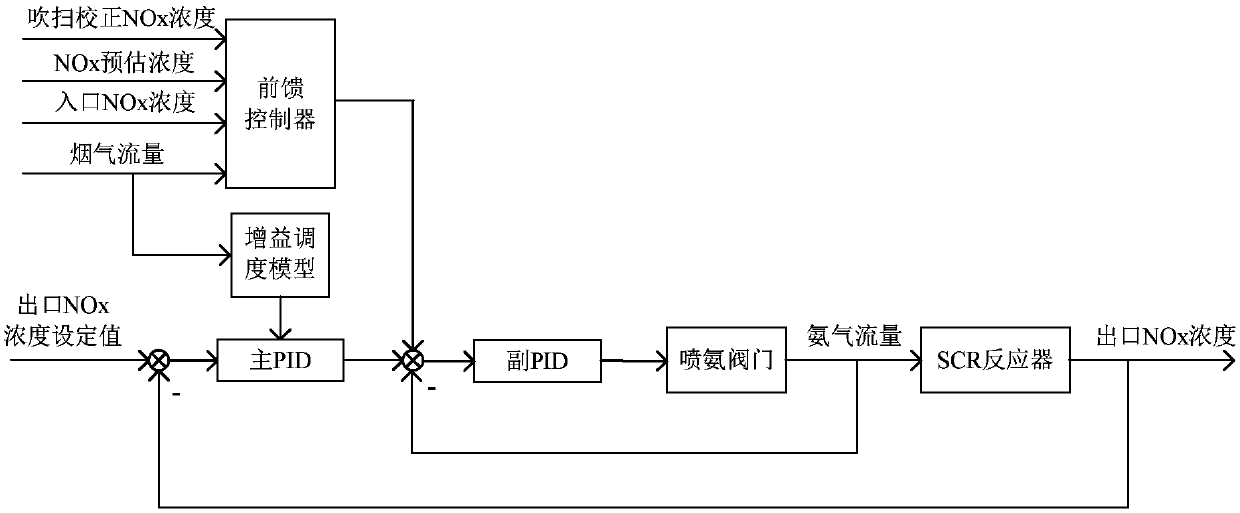
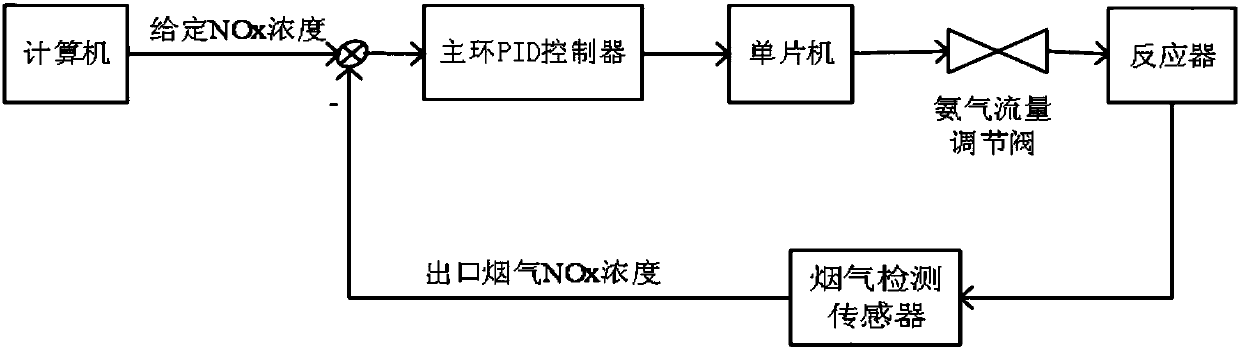
All working condition standard emission control method for thermal power unit denitration system
ActiveCN107561941AImprove stabilityImprove anti-disturbance abilityAdaptive controlAutomatic controlControl signal
The invention provides an all working condition standard emission control method for a thermal power unit denitration system. The method comprises the steps that a main ring PID controller, a sub-ringPID controller and a feedforward controller are arranged in a denitration control system; the main ring PID controller calculates an ammonia injection control signal according to an outlet NOx concentration set value and an outlet NOx concentration feedback signal; the feedforward controller calculates an ammonia injection feedforward control signal according to the purge correction NOx concentration, the NOx estimated concentration, the inlet NOx concentration and the flue gas flow; and the sub-ring PID controller controls the opening of an ammonia injection valve according to the ammonia injection control signal, the ammonia injection feedforward control signal and an ammonia flow feedback signal. According to the invention, a gain scheduling model and an hour mean model are added intoa main ring to realize automatic control of the variable working condition of the denitration system; an inlet concentration purge correction model is introduced into a sub-ring to realize dynamic ammonia injection correction; the ammonia injection is accurately controlled; and a technical support is provided for whole process robustness and all working condition standard emission.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
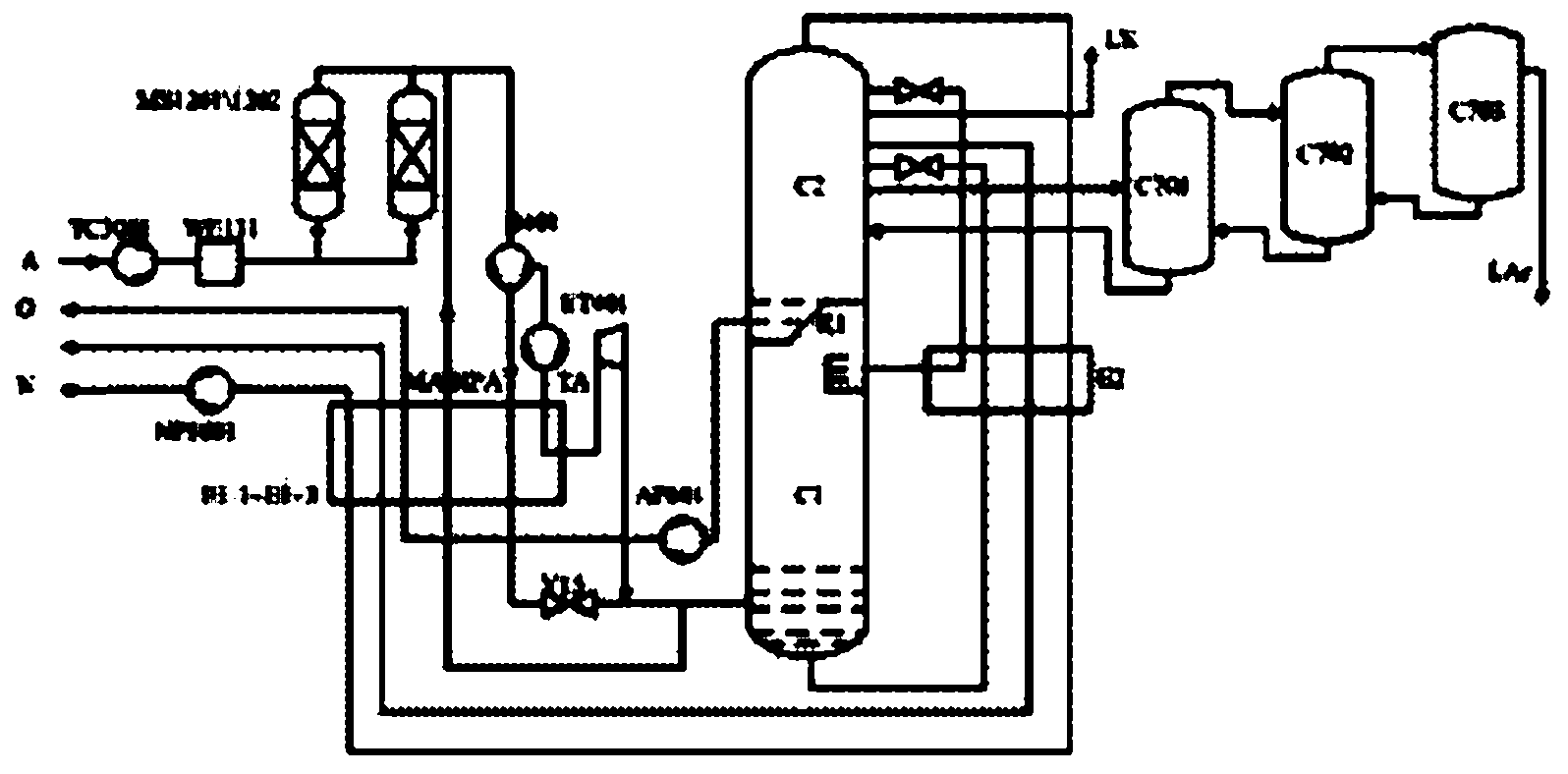
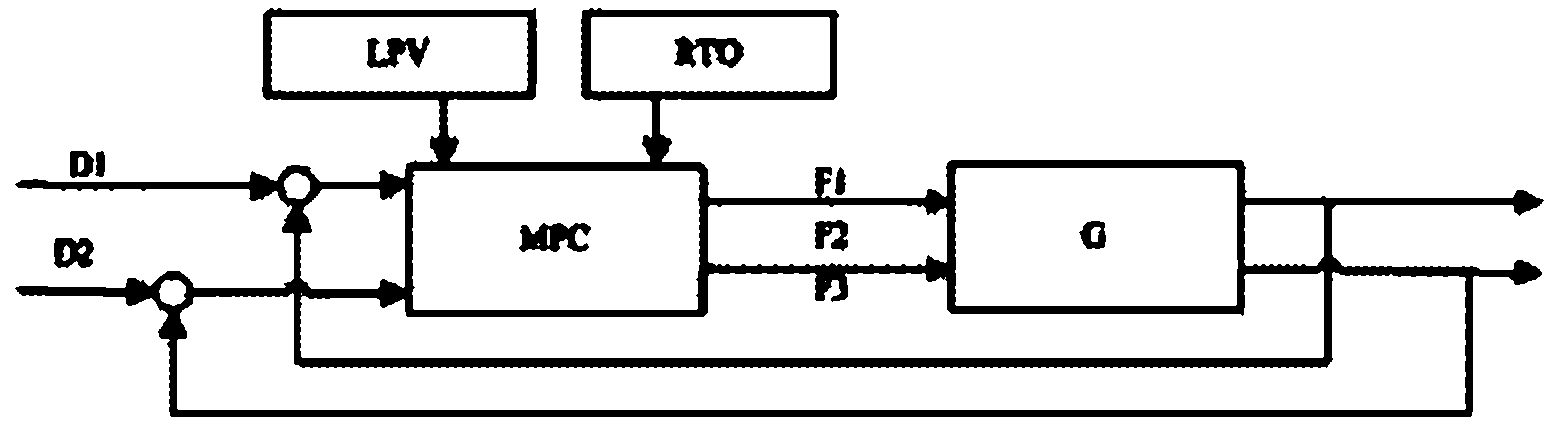
Automatic load-variable multi-variable control method for air separation device
InactiveCN102520615ARealize decoupling controlRealize dynamic compensationAdaptive controlAir separationNonlinear control
The invention discloses an automatic load-variable multi-variable control method for an air separation device. According to the method, a module 1, namely a gain scheduling module, a module 2, namely a dynamic multi-variable model prediction control module, and a module 3, namely a process real-time optimization module are involved. The method comprises the following steps that: the module 3 calculates the optimal steady state value of a process variable related to load change according to the load-variable requirement of the device and sends the optimal steady state value to the module 2; the module 1 determines a prediction model adopted by a controller of the module 2 at the moment according to the current value of a scheduling variable; and the module 2 gradually pushes the device to the optimal steady state working point which is calculated by the module 3 on the premise of ensuring product quality and not going against equipment constraints. By the method, the problems of mutual decoupling of energy and a material, nonlinear control and the like in the wide-range load-variable process of the air separation device can be radically solved, smooth and quick transition among different working conditions is realized, and the load-variable operation quality and speed of the air separation device are ensured.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD +1
Magnetically levitated transporter
InactiveUS6871597B1Eliminates static instabilityReduce instabilityRailway vehiclesElectric propulsionComputer control systemBogie
A magnetically levitated transporter comprising a plurality of bogies attached thereto and traveling over a track comprising a plurality of rails, and a method for operating such transporter, comprising a plurality of magnets attached to each bogie, a plurality of the magnets being offset outboard with respect to the rails and a plurality of the magnets being offset inboard with respect to the rails, and a computer control system employing gain scheduling to control current provided to each of the magnets.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for aero engine
ActiveCN111271181AImprove performanceReduce perturbation rangeSustainable transportationGas turbine plantsControl engineeringGain scheduling
The invention provides a conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for an aero engine. The conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controllerfor the aero engine comprises a conservation-reducing two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller group solving module and a degradation parameter estimation loop. According to the conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for the aero engine, the degradation parameter estimation loop is additionally arranged, a gain scheduling controller group is improved to obtain the conservation-reducing two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller group solving module, reduces the perturbation range of an uncertainty model is reduced, and the conservatism of a robust gain schedulingcontroller is reduced. The degradation parameter estimation loop realizes the reliable estimation of degradation parameters, and then traditional scheduling parameters are combined to realize the gainscheduling control when the engine performance is degraded, the control accuracy of the gain scheduling is improved to the greater extent when the engine performance is degraded, the control system transition time is shortened, the dynamic deviation and static deviation are reduced, high robustness and low conservation are achieved, and the performance of an engine is given to full play.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Design method of robust pitch controller above rated wind speed for wind turbine
InactiveCN102269125AEnhanced inhibitory effectSave energyWind motor controlMachines/enginesControl signalControl theory
The invention introduces a design method and control method of a robust pitch controller above the rated wind speed of a wind power generator. The pitch controller design method first establishes the blade load model, performs vector transformation to achieve decoupling, and linearizes the decoupling model in the vertex set of the scheduling parameter convex set; secondly, converts the model into an LPV system, and uses H The ∞ theory standardizes the model as a standardized augmented control object containing performance indicators, uses the linear matrix inequality method to design the controllers on the vertex set of the convex set of scheduling parameters, and uses the gain scheduling principle to obtain the global pitch controller, and finally uses the vector The inverse of the transform yields the actual control signal.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
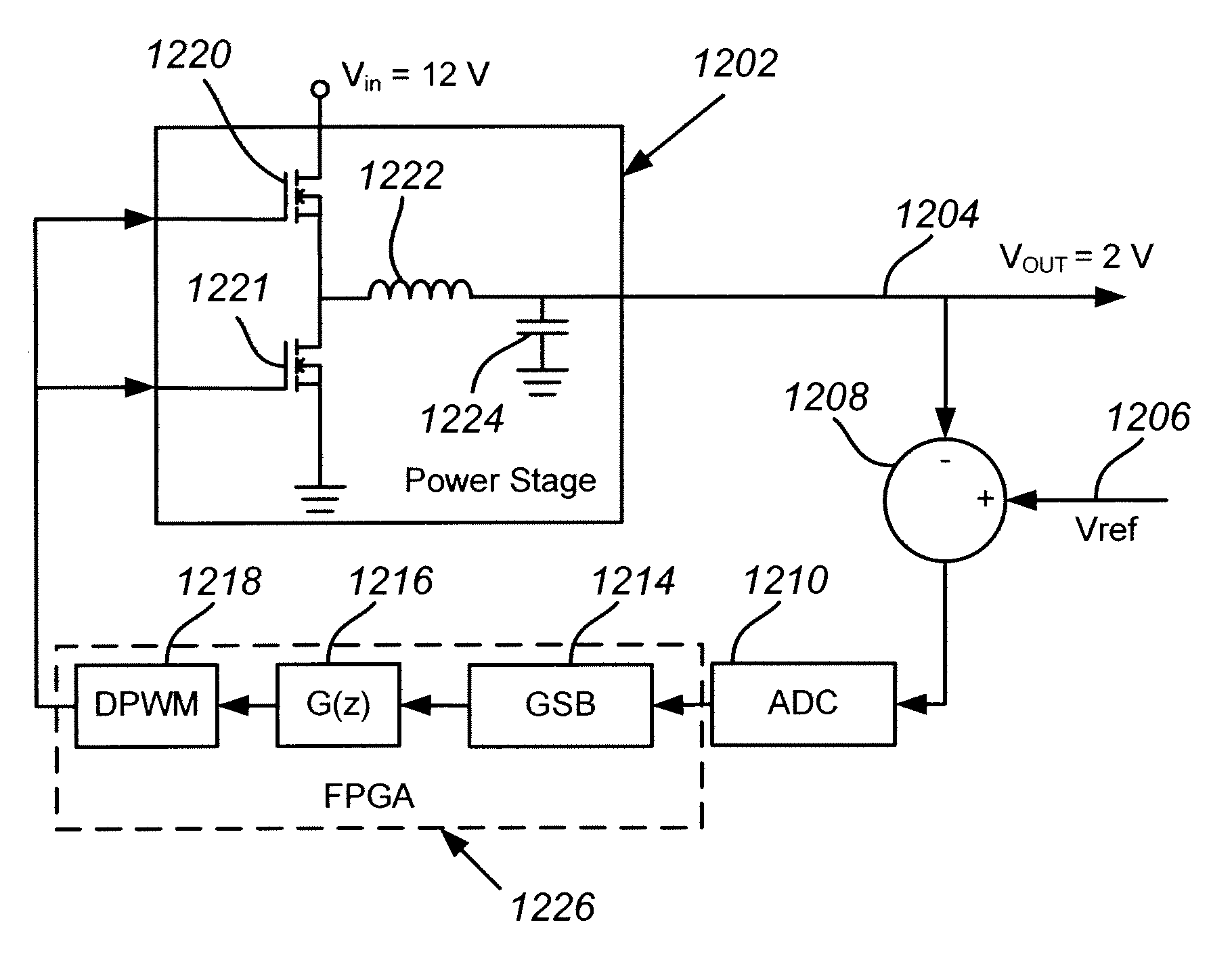
Digital control of pwm converters with nonlinear gain scheduling
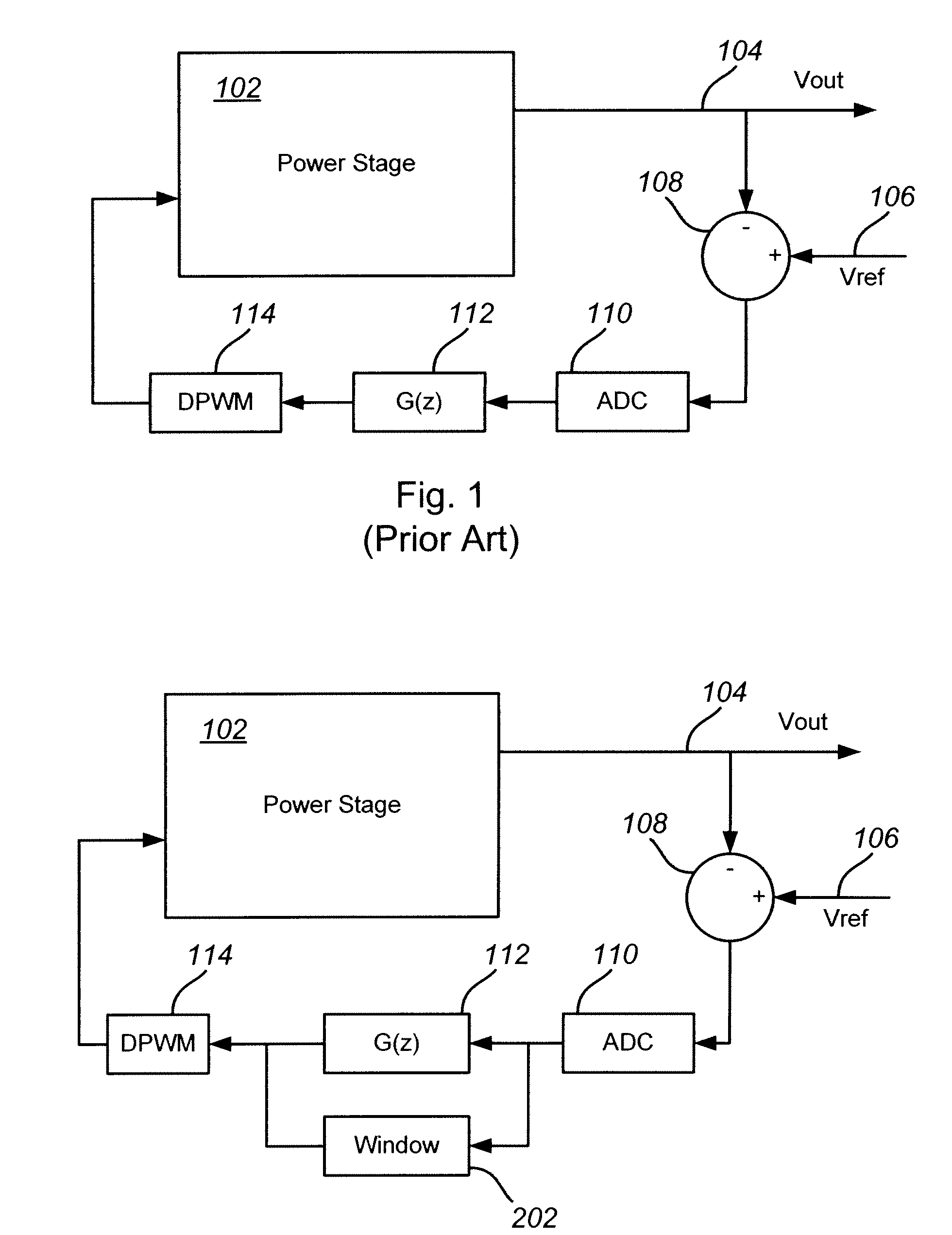
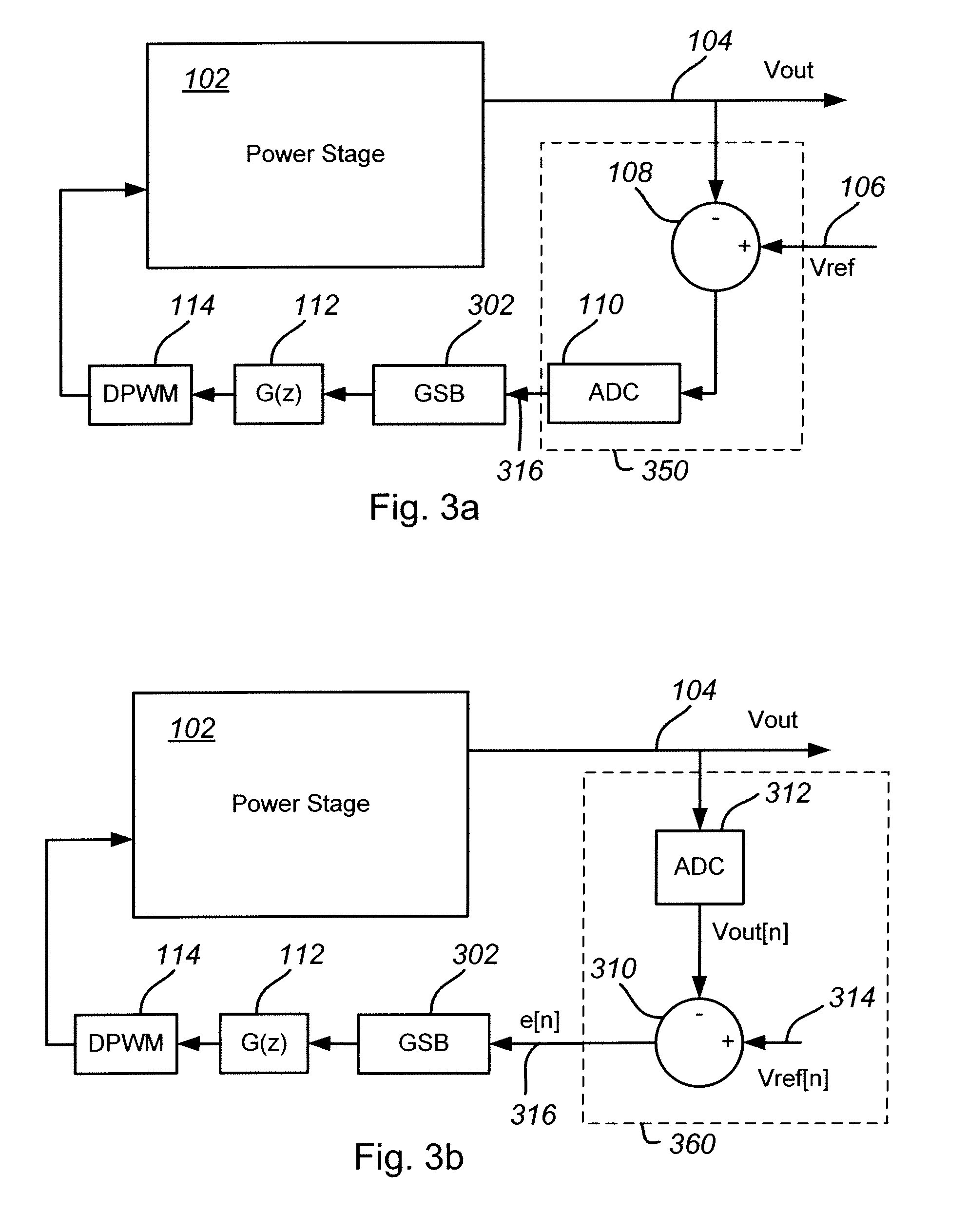
A system and method for controlling a digital pulse-width modulated power converter achieves a fast large-signal transient response while maintaining a slow response near the steady-state operating point in order to assure stability and to reduce the system's susceptibility to noise. Digital output error samples are processed through a gain scheduling block that applies a non-linear gain function to produce a weak loop response when the system is near its steady-state equilibrium point and a strong loop response when large transients are encountered. The resulting system maintains a fast transient response to large error signals while reducing noise and loop jittering and assuring loop stability.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
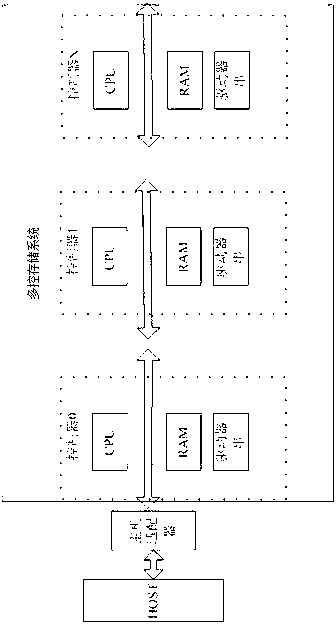
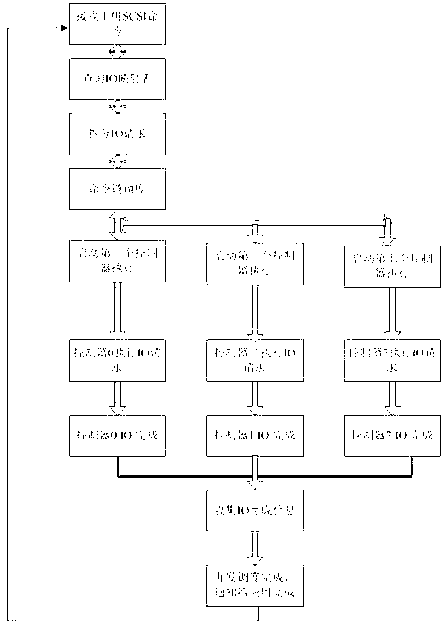
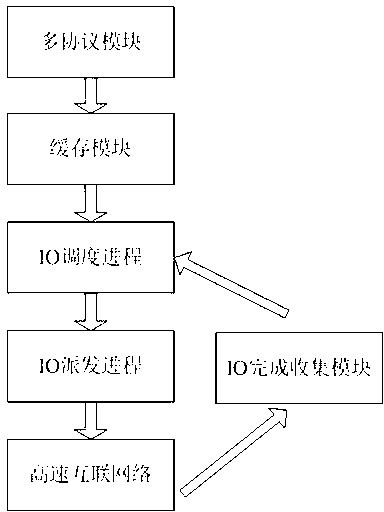
Self-adaptive IO (Input Output) scheduling method of multi-control storage system
ActiveCN103135943AImprove load statusLoad balancingInput/output to record carriersController architectureNetwork connection
The invention provides a self-adaptive I / O (Input / Output) scheduling method of a multi-control storage system. The self-adaptive I / O scheduling method of the multi-control storage system has the advantages of being capable of achieving load balance of a multiple controller architecture and among controllers; avoiding risk and performance choke points caused by single controller failure; supporting a plurality of host connecting interfaces; supporting an ISCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface), an FC (Fibre Channel), an InfiniBand and 10 gigabit network connection; being capable of providing high bandwidth IB (InfiniBand) and the 10 gigabit network connection for users at the same time; and meeting the differentiation requirements of customers for high bandwidth and high performance. The invention relates to I / O scheduling of the multi-control storage system and provides the I / O scheduling method among multiple controllers. When the multi-control storage system accepts an I / O request from an application layer, the self-adaptive I / O scheduling method of the multi-control storage system can be utilized to schedule the I / O request to the multiple controllers to perform simultaneous concurrent execution, not only allocates unallocated I / O requests to low load controllers, but also reschedules I / O requests to lower load controllers from overload controllers, so that the load state of every controller in a system is improved, I / O load scheduling and balance on multi-control nodes are achieved, potentials of equipment are fully scheduled, and the performance of the system is improved.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
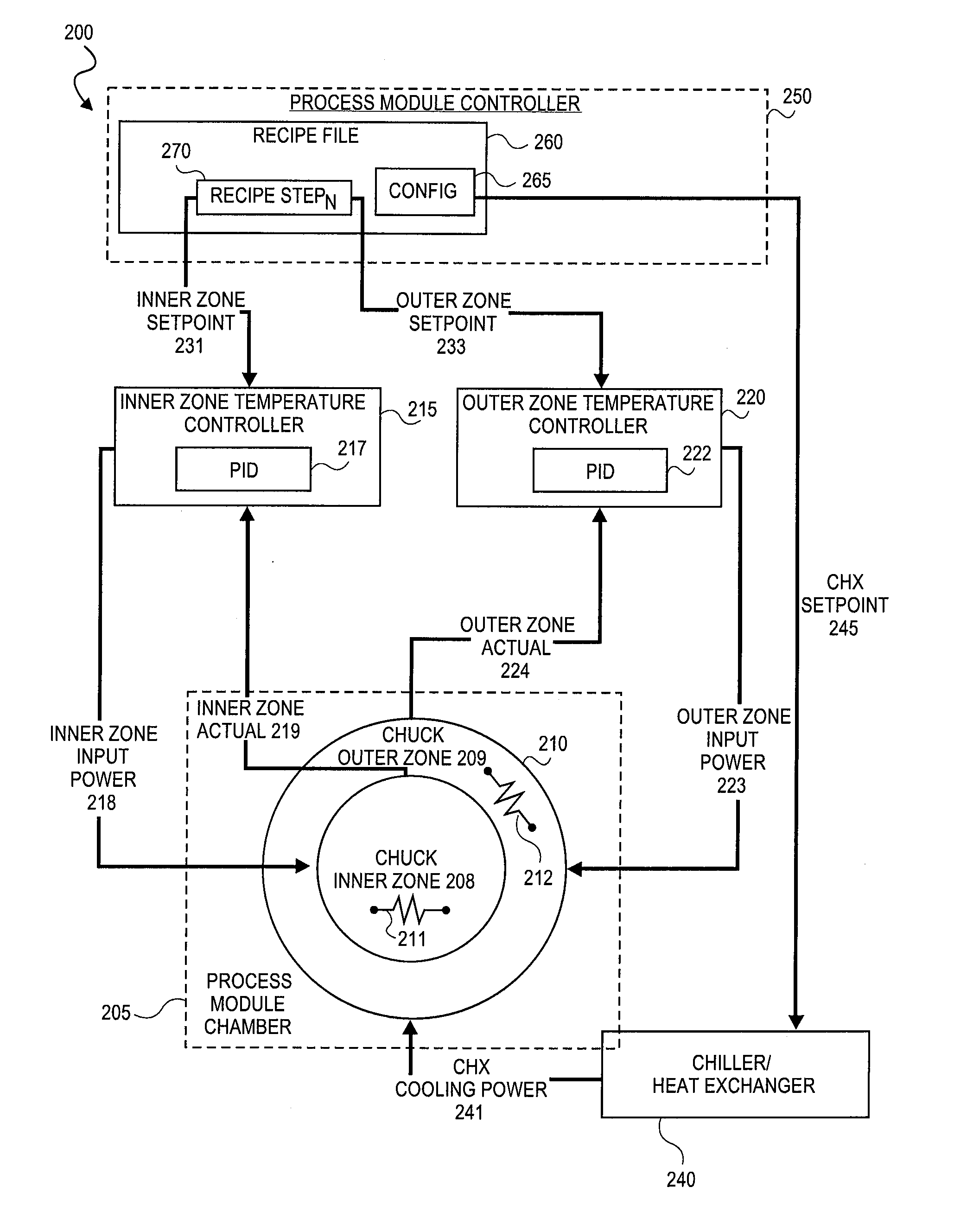
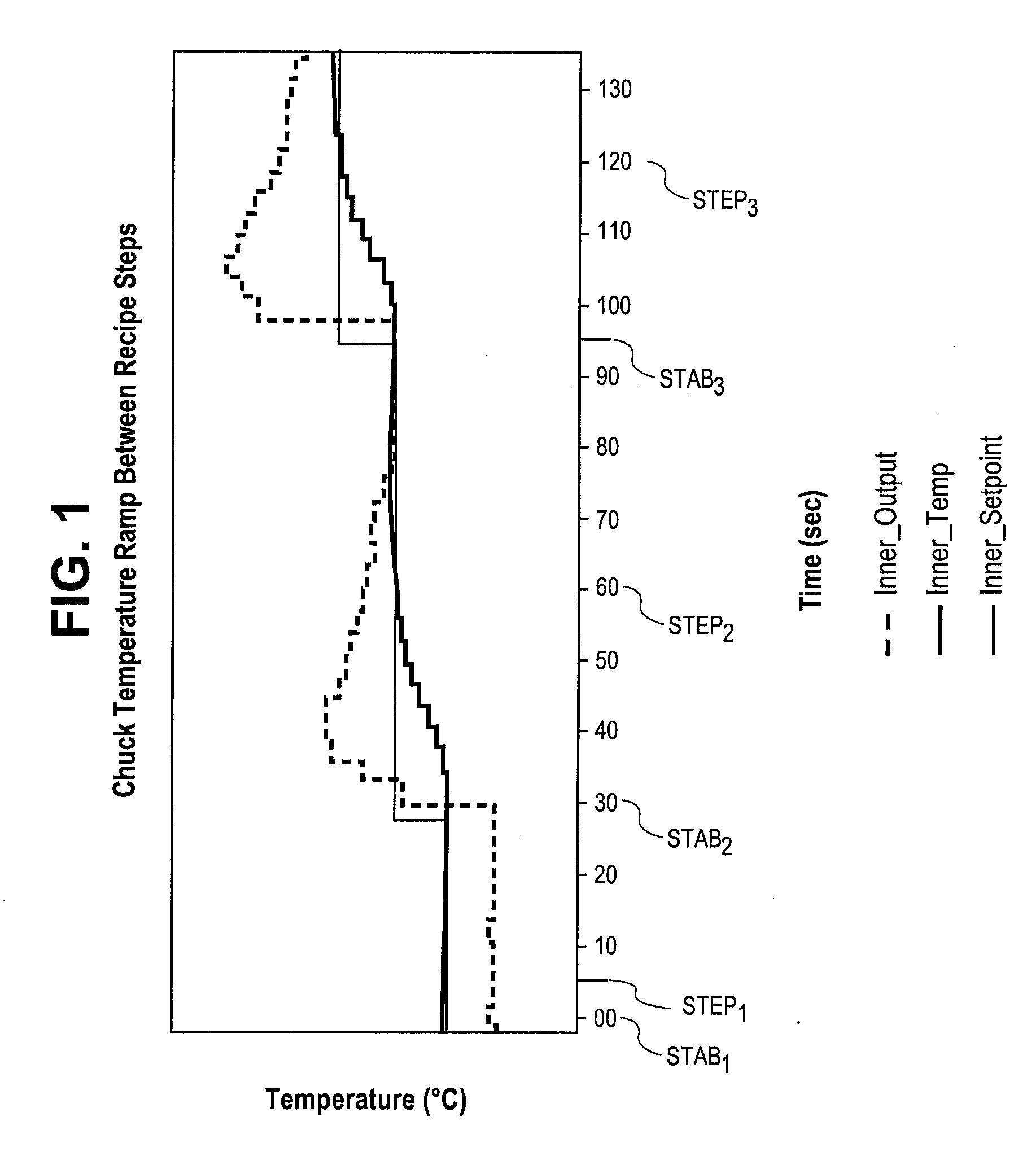
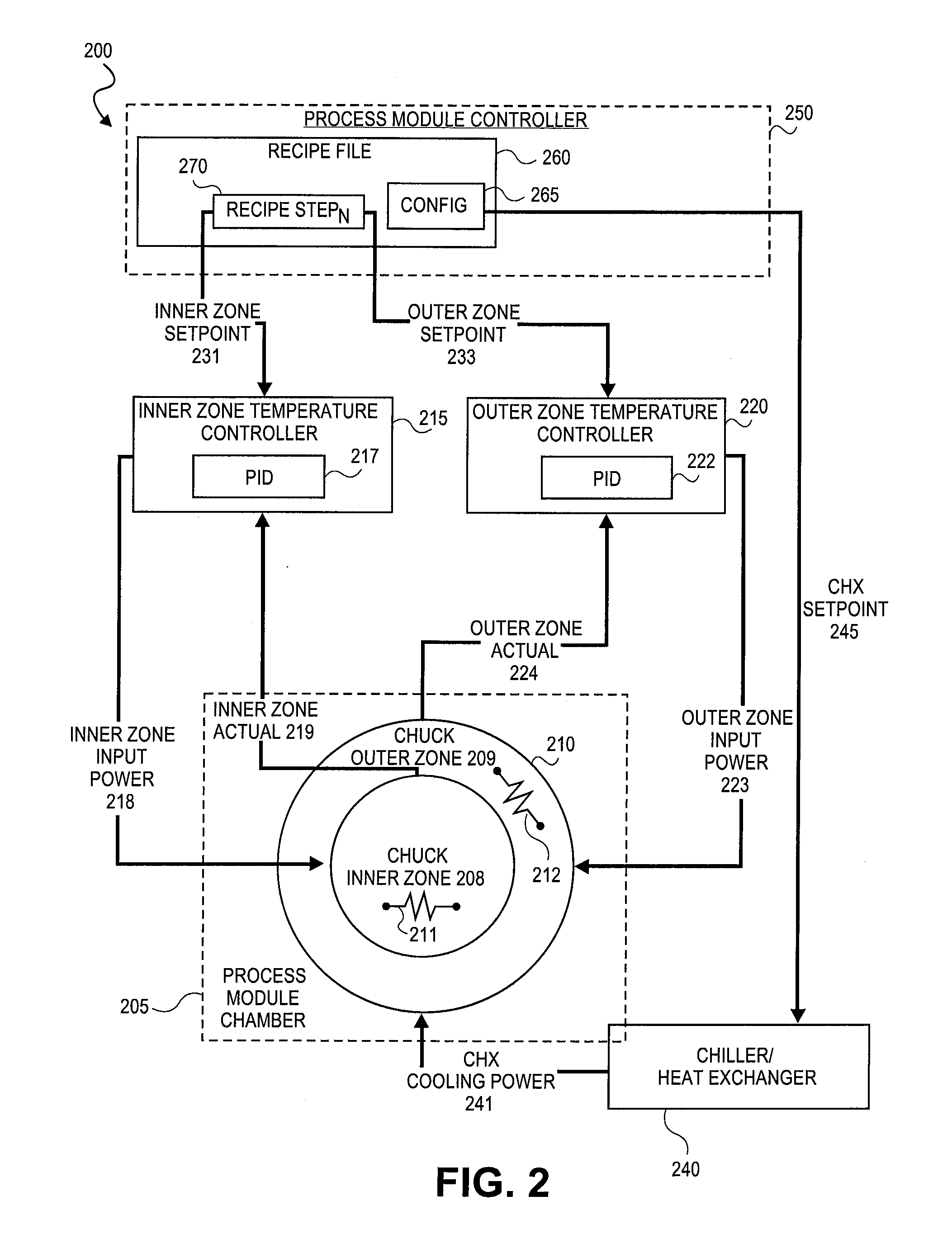
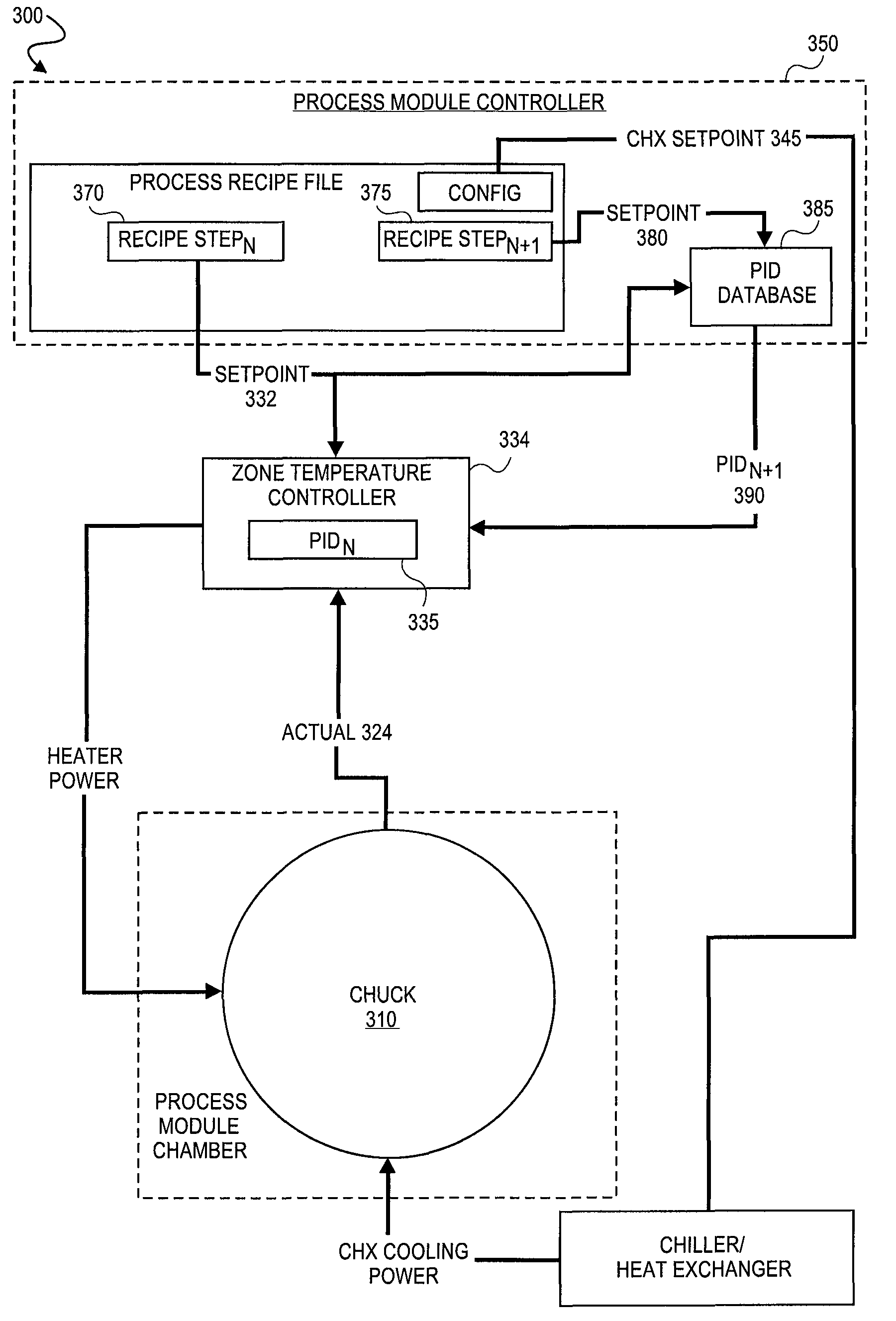
Method of controlling process parameters for semiconductor manufacturing apparatus
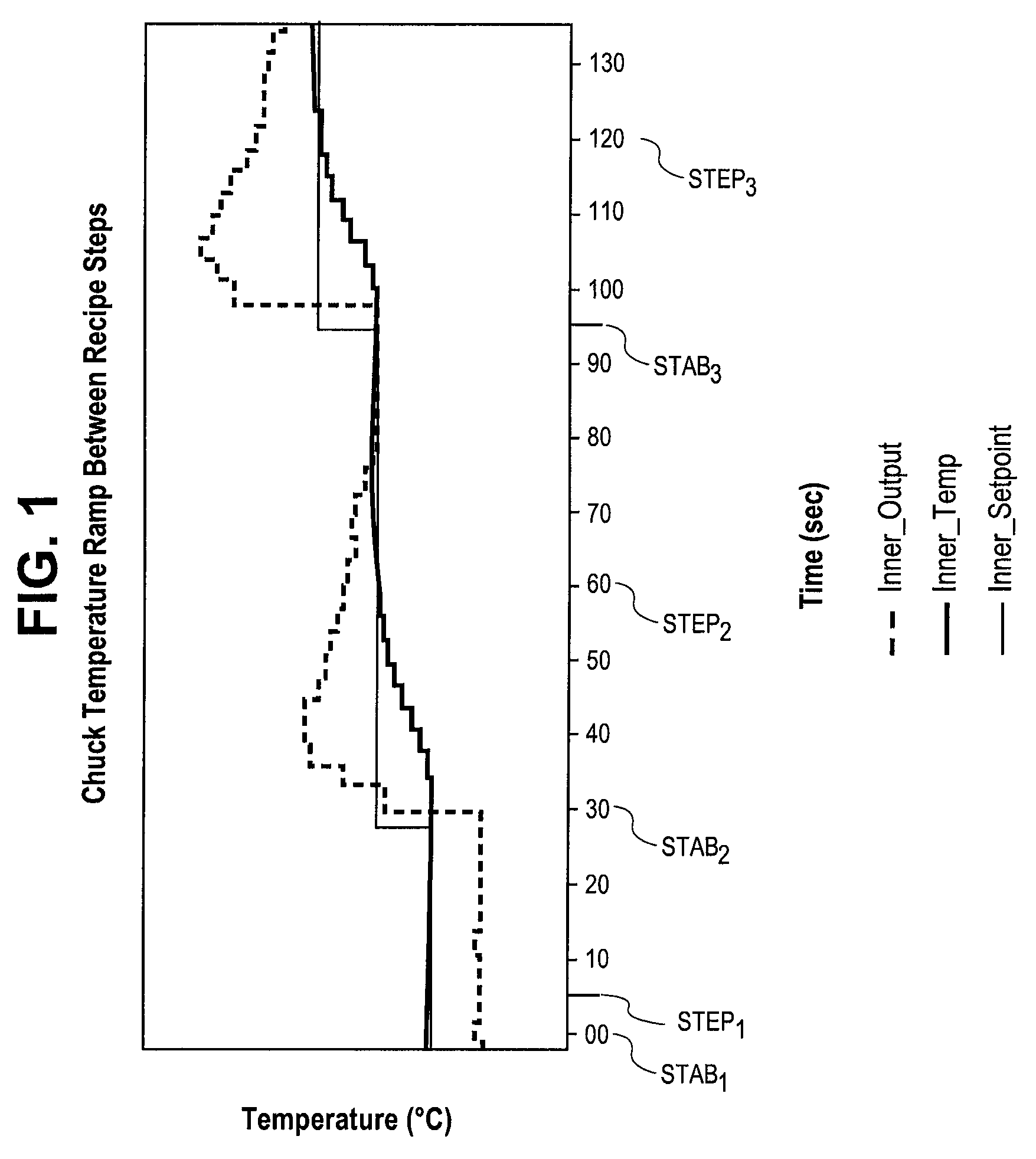
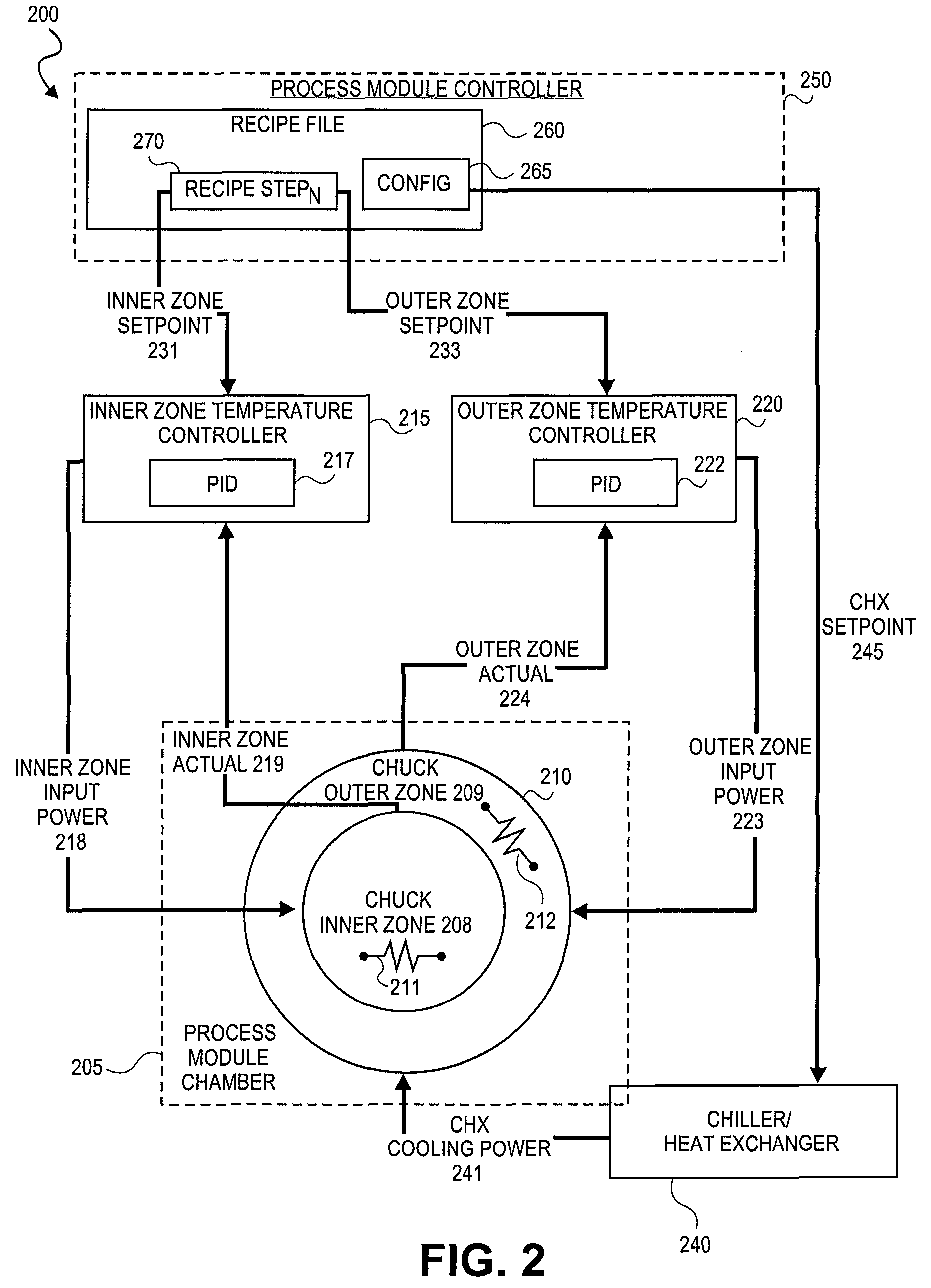
InactiveUS20090177310A1Short response timeShort stabilization timeAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTemperature controlSelf adaptive
Methods and systems for adaptively controlling process parameters in semiconductor manufacturing equipment. An embodiment provides for gain scheduling of PID controllers across recipe steps. One embodiment provides a method for controlling a chuck temperature during a semiconductor manufacturing process, the method employing a first set of proportional-integral-derivative (PID) values in a PID controller to control the chuck temperature at a first setpoint in a first step of a process recipe and employing a second set of PID values in the PID controller to control the chuck temperature at a second setpoint, different than the first setpoint, in a second step of the process recipe. The methods and systems provide reduced controller response times where process parameter setpoint between steps of a process recipe span a wide range.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
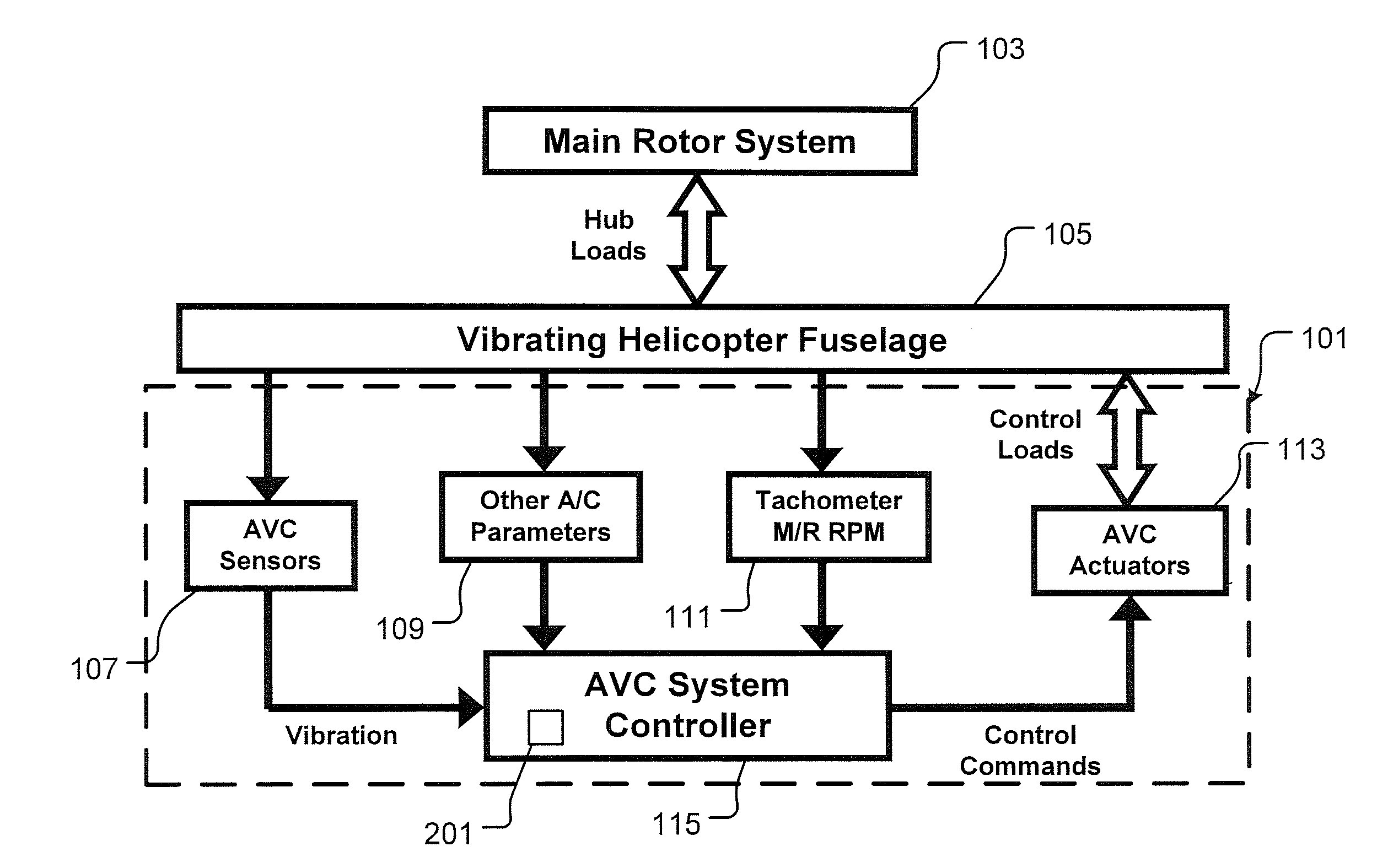
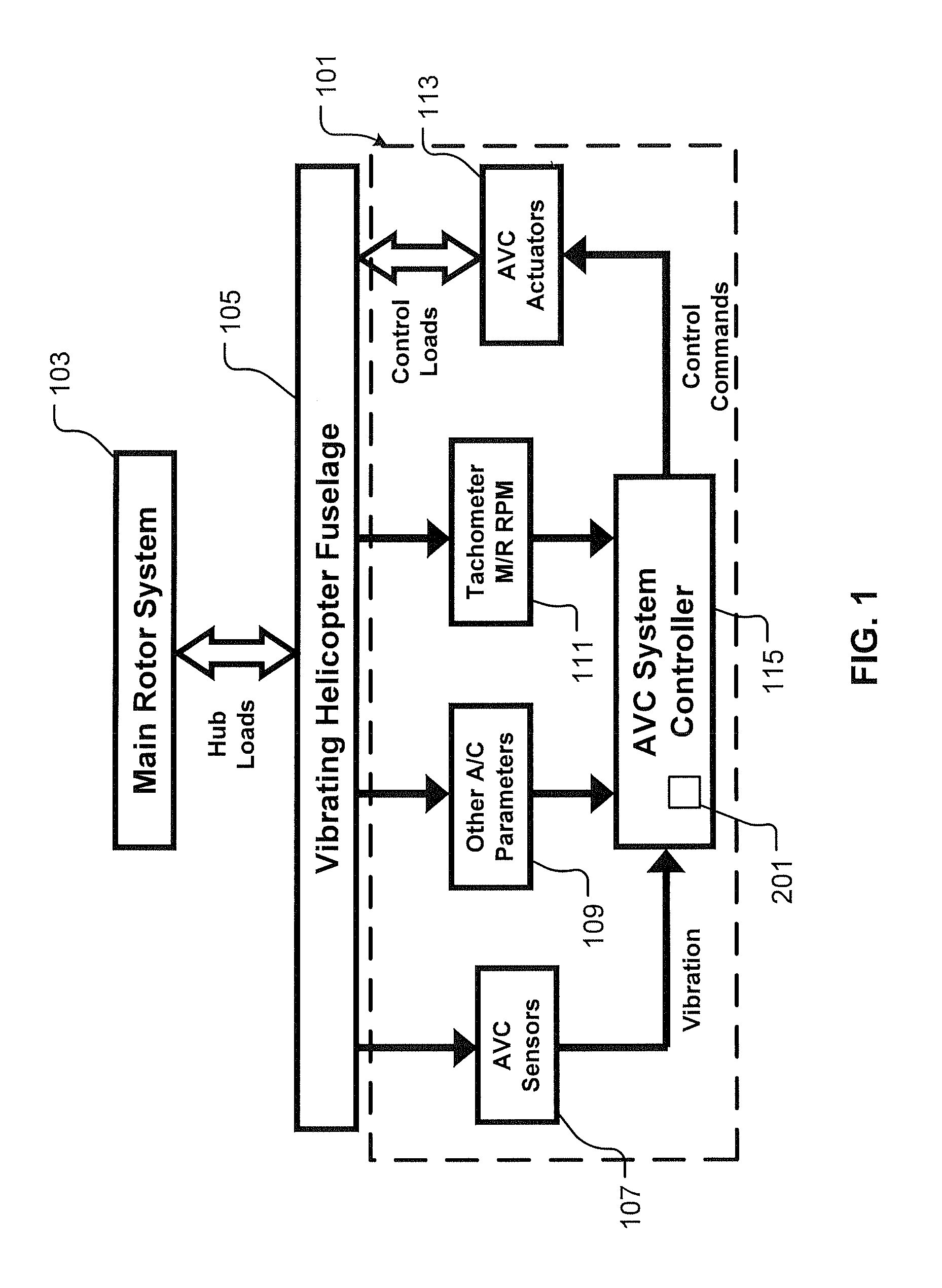
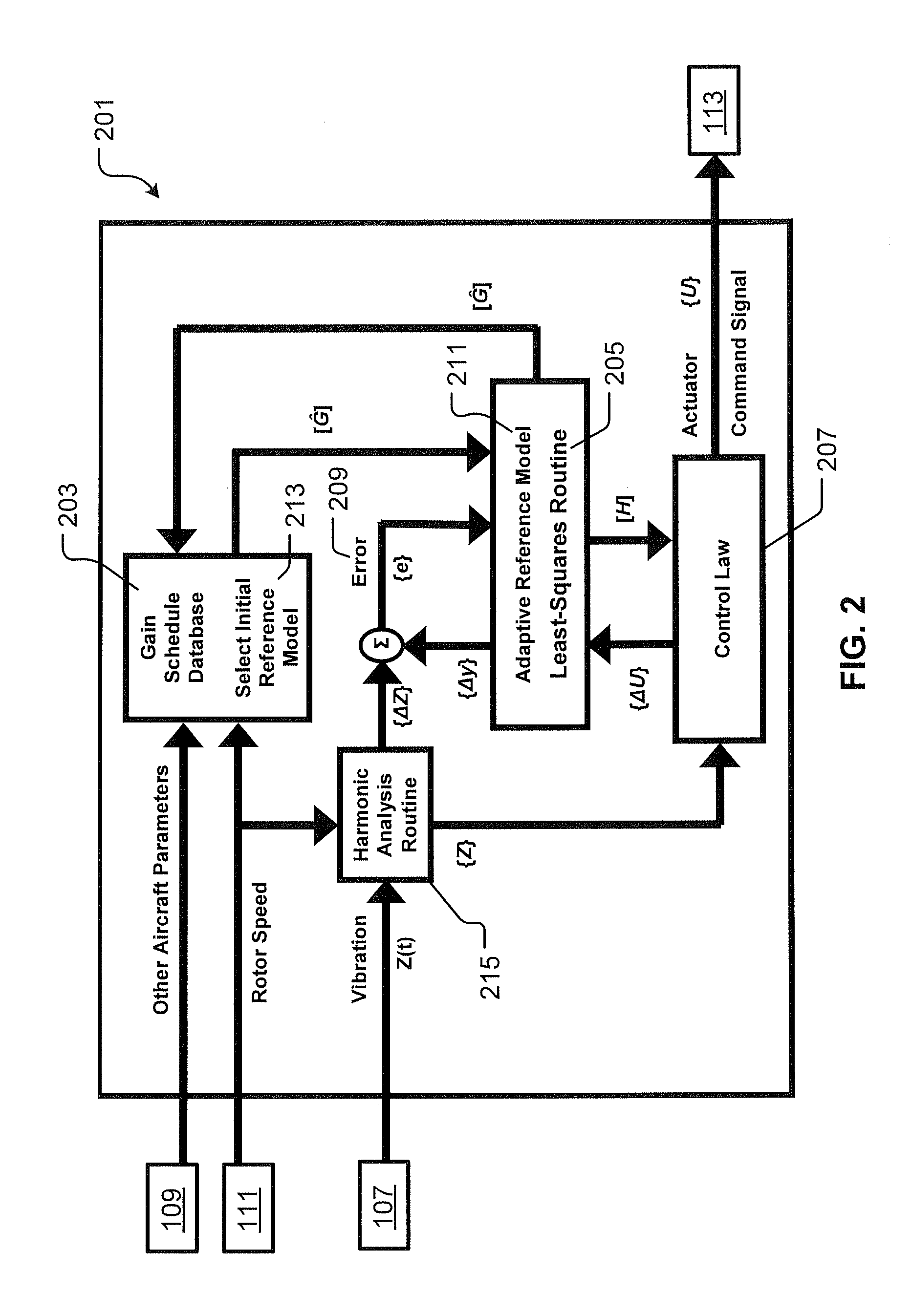
System and Method for Vibration Control in a Rotorcraft Using an Adaptive Reference Model Algorithm
The adaptive reference model algorithm uses a gain scheduling feature combined with a customized Least-Squares routine as an adaptive method for adjusting feedback control so as to account for variations in Transfer Function (G), thereby optimizing the effectiveness of the Active Vibration Control (AVC) System. The Least-Squares routine identifies the transfer function in a background process without interruption of closed loop vibration control. This identification approach is accomplished without intentional interrogation of the AVC actuators and without intentional vibration level changes. For this adaptive control logic, the dynamic relationship between AVC actuators and AVC sensors is represented by a mathematical model of Transfer Function (G). The mathematical model of Transfer Function (G) is continuously updated by the Least-Squares routine. A feedback gain (H) is computed from the mathematical model of Transfer Function (G), and the feedback gain (H) is updated each time the mathematical model of Transfer Function (G) is updated.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
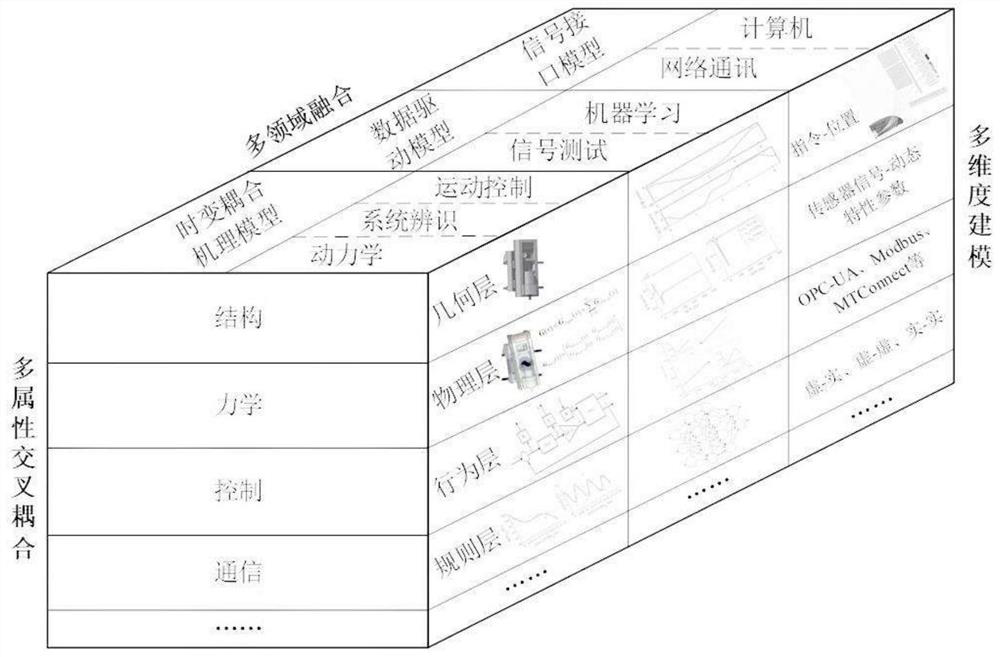
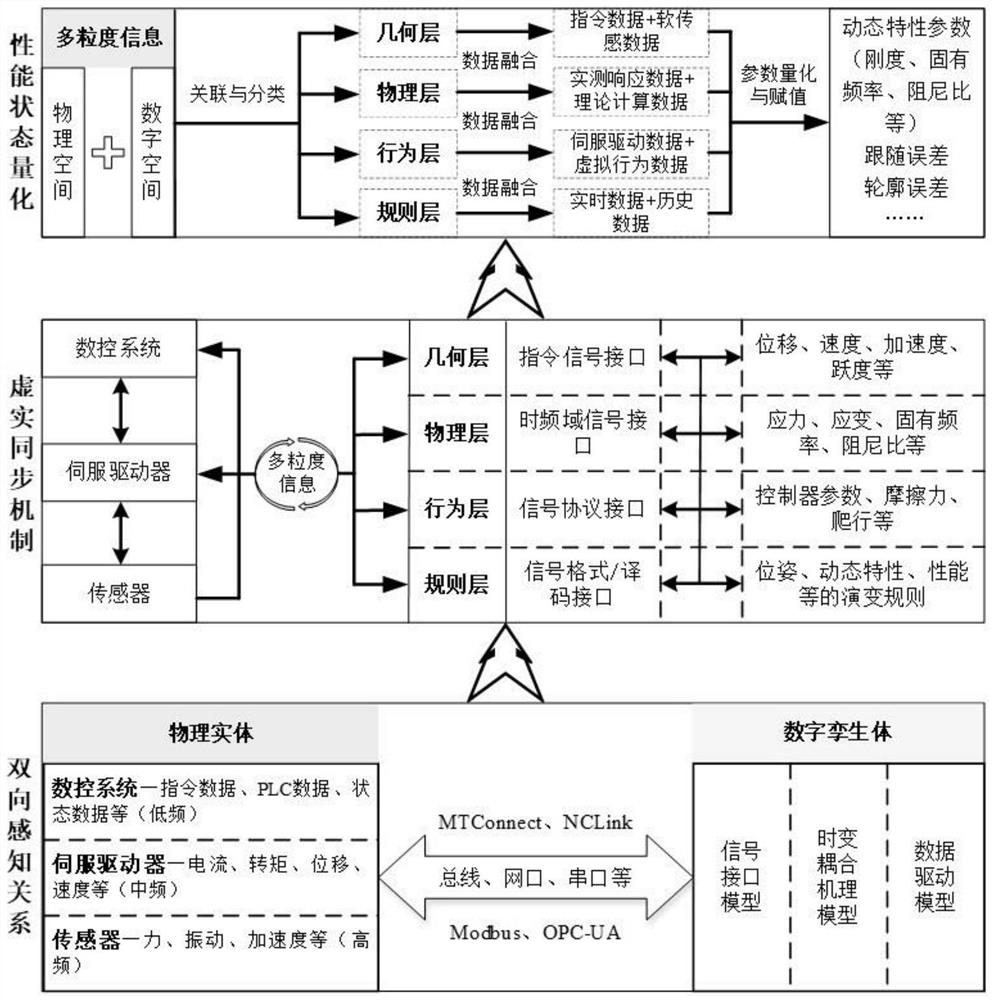
Contour error suppression method for digital twin-driven multi-axis numerical control machine tool
ActiveCN112859739AAchieve inhibitionProgramme controlComputer controlMulti objective optimization algorithmMotor control
The invention relates to the field of numerical control machine tools, and particularly discloses a contour error suppression method for a digital twin-driven multi-axis numerical control machine tool. The method comprises the steps of S1 establishing a virtual model of a digital twinborn body corresponding to a physical entity, and adopting a multi-parameter gain scheduling control strategy based on a global task coordinate system, so as to obtain a time-varying coupling mechanism model of a multi-axis feeding system; establishing a data driving model of the multi-axis feeding system by using signal testing and machine learning; S2 performing virtual-real synchronization, and establishing a bidirectional sensing relationship between the digital twinborn body and the physical entity through a communication protocol with strong compatibility; S3 dynamically estimating a contour error; and S4 contour error suppression: according to the pre-estimation model, adopting a multi-objective optimization algorithm to obtain an optimal motion control parameter and a track maximum limiting speed corresponding to the optimal motion control parameter. By adopting the technical scheme of the invention, the contour error can be effectively reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
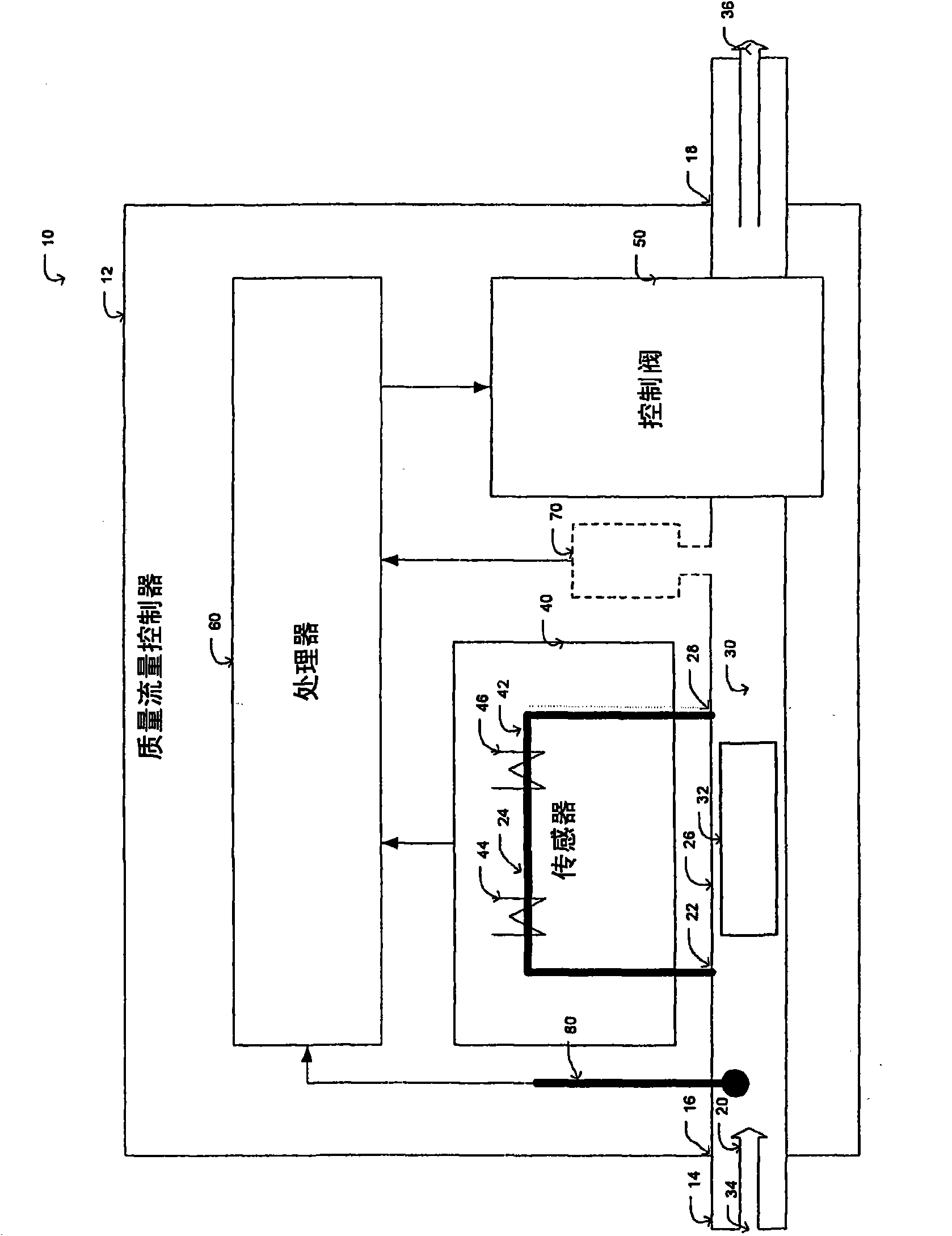
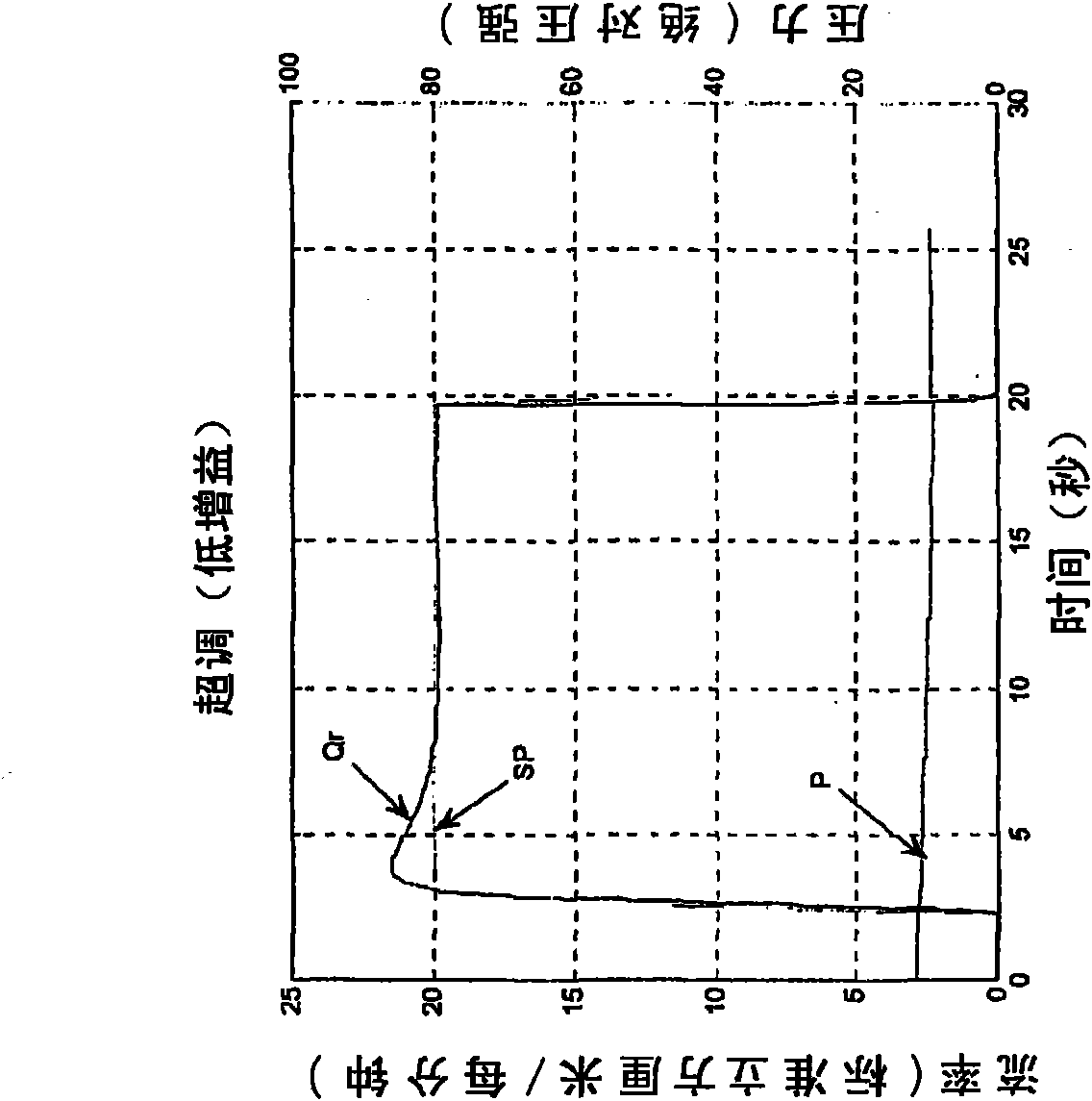
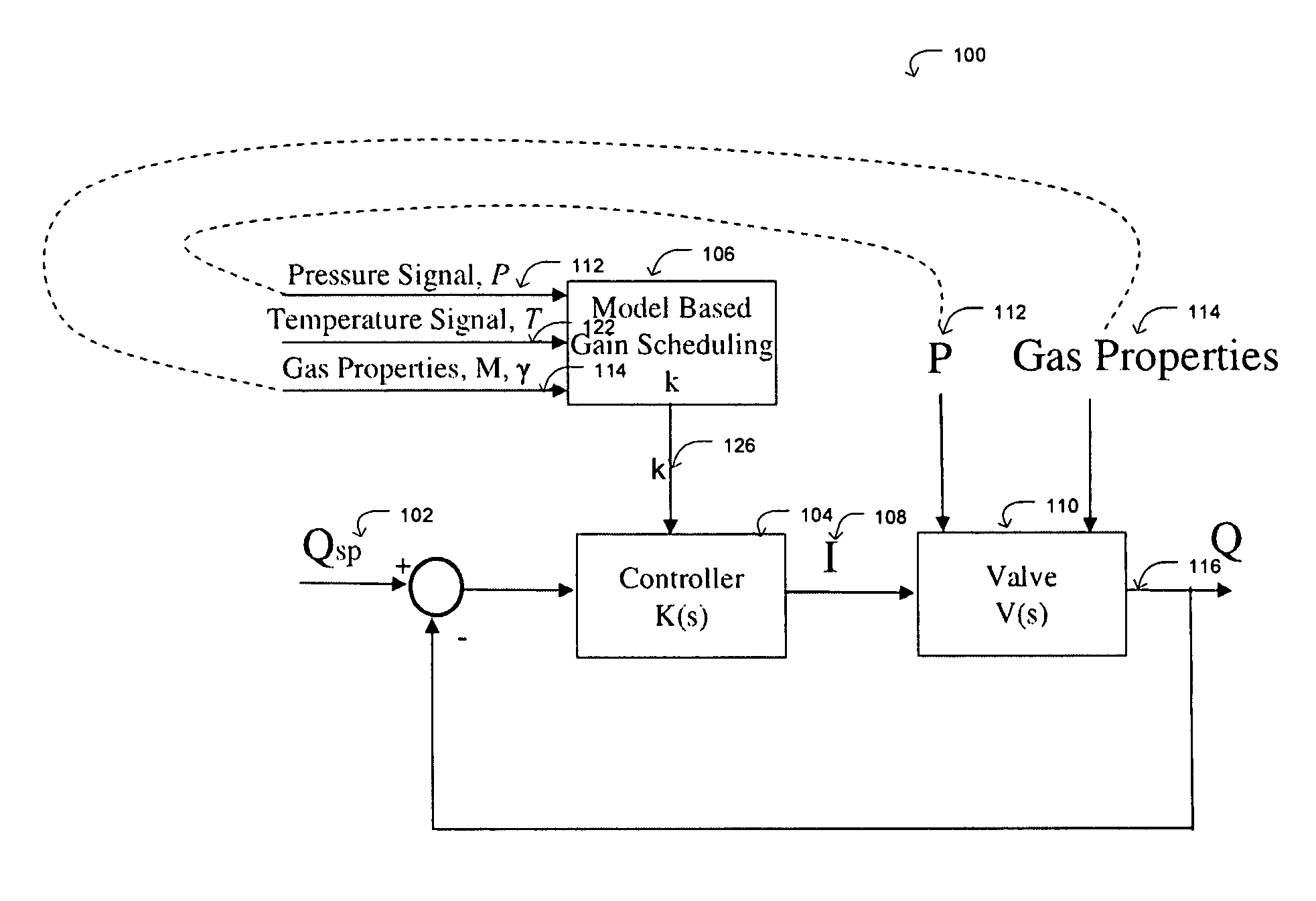
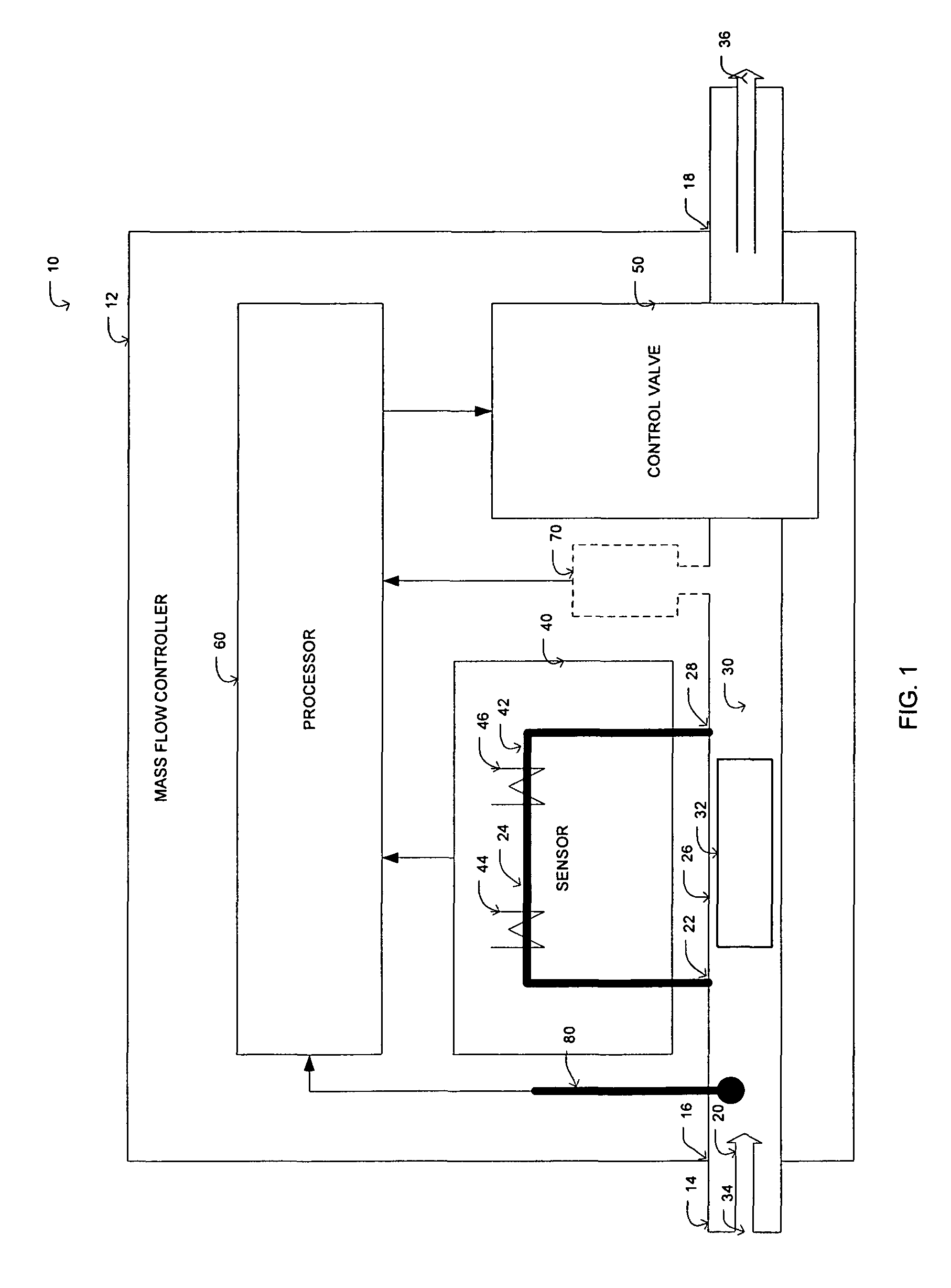
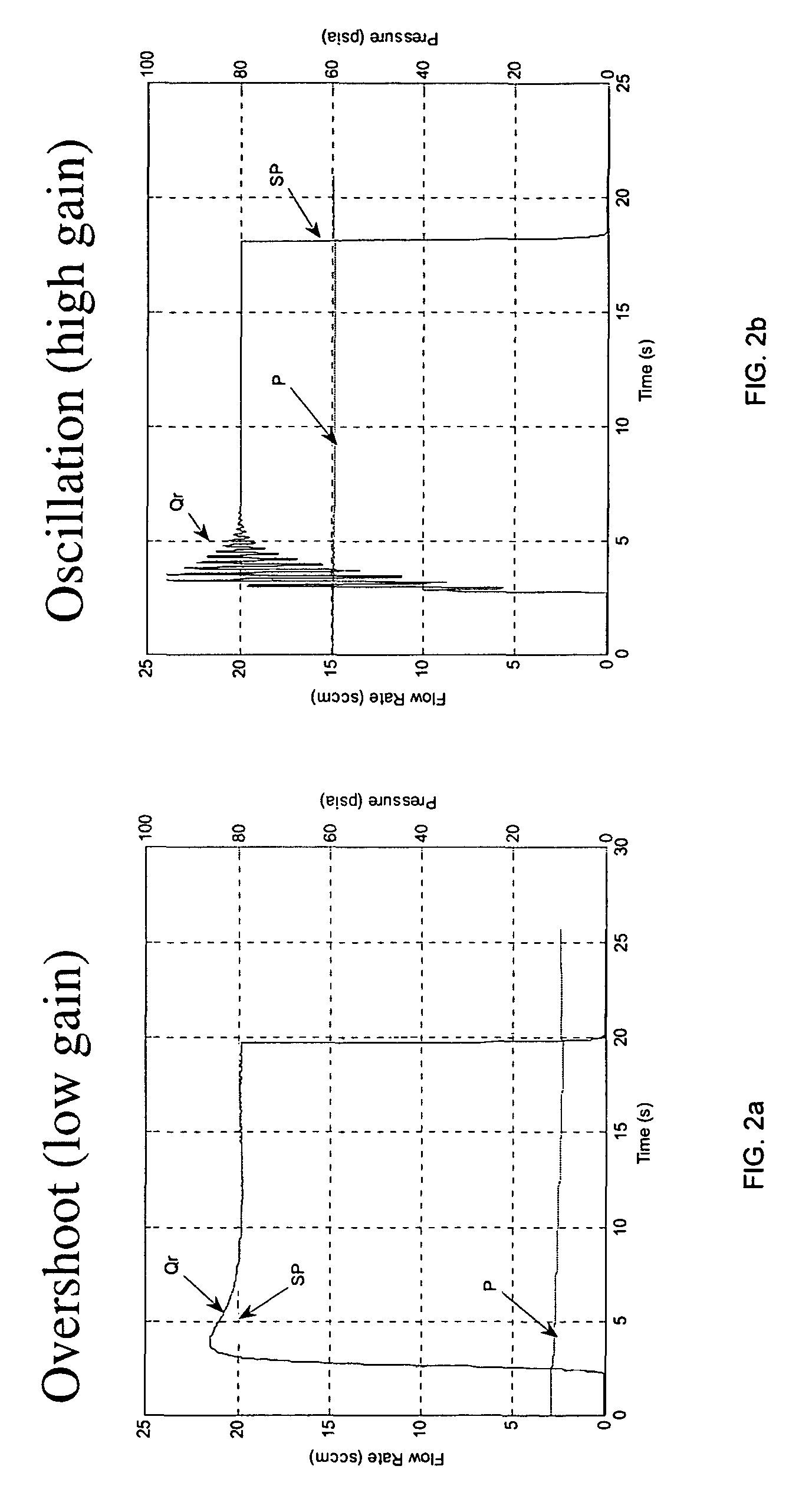
Controller gain scheduling for mass flow controllers
ActiveCN101636641AVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFlow control using electric meansCalibration gasFeedback controller
A mass flow controller having a feedback controller gain, comprises: a sensor configured so as to sense the flow of fluid through controller; a valve arranged so as to adjust the flow of fluid through the controller; and a processor configured so as to controlling the valve as a function of the flow of fluid sensed by the sensor. The sensor and valve are arranged within a feedback system, and the processor updates the feedback controller gain in real time based on the ratio of at least one calibration gas parameter to at least one operating gas parameter, such that the closed loop transfer function of the feedback system remains substantially constant regardless of operating conditions so as to have a consistent control performance at different operation conditions from the calibration condition.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
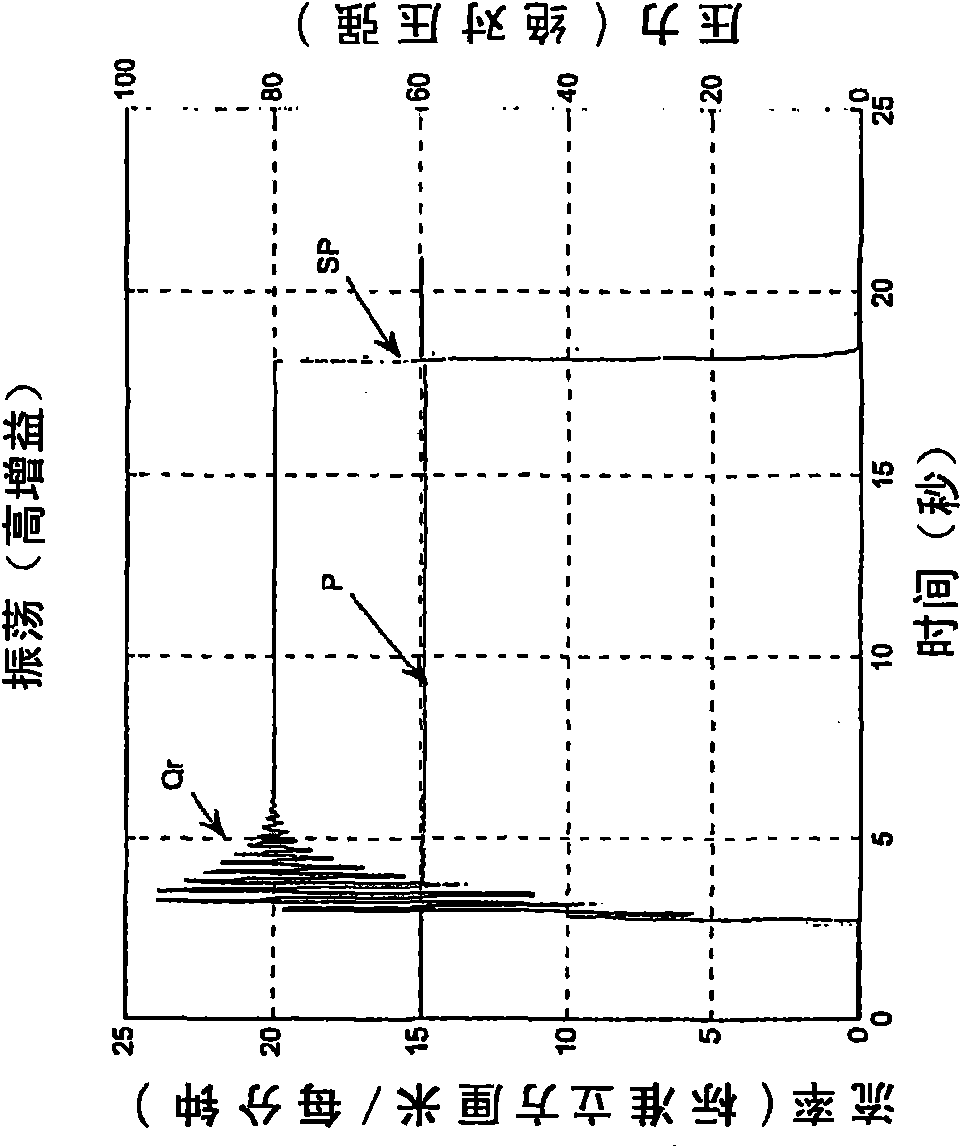
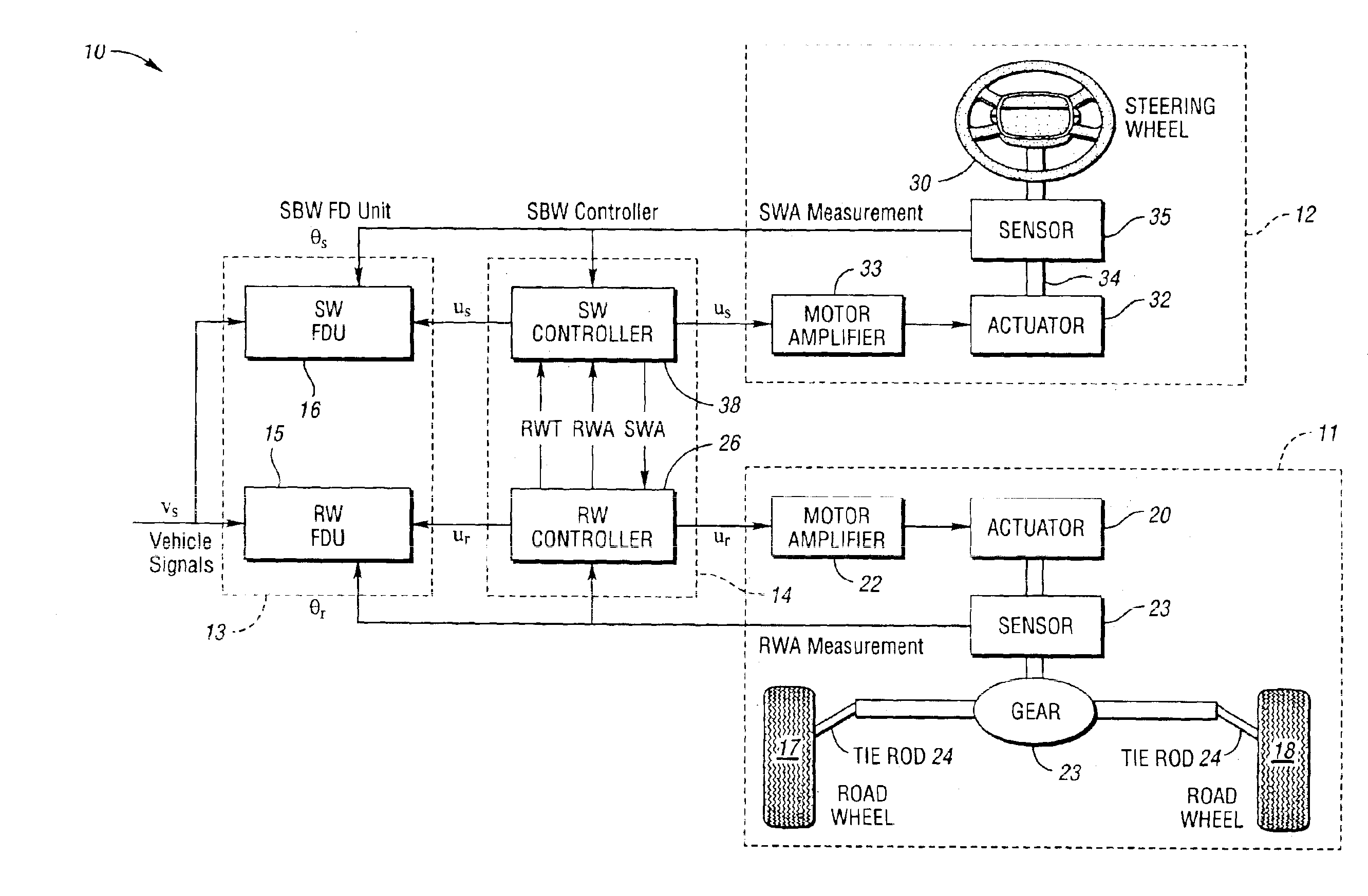
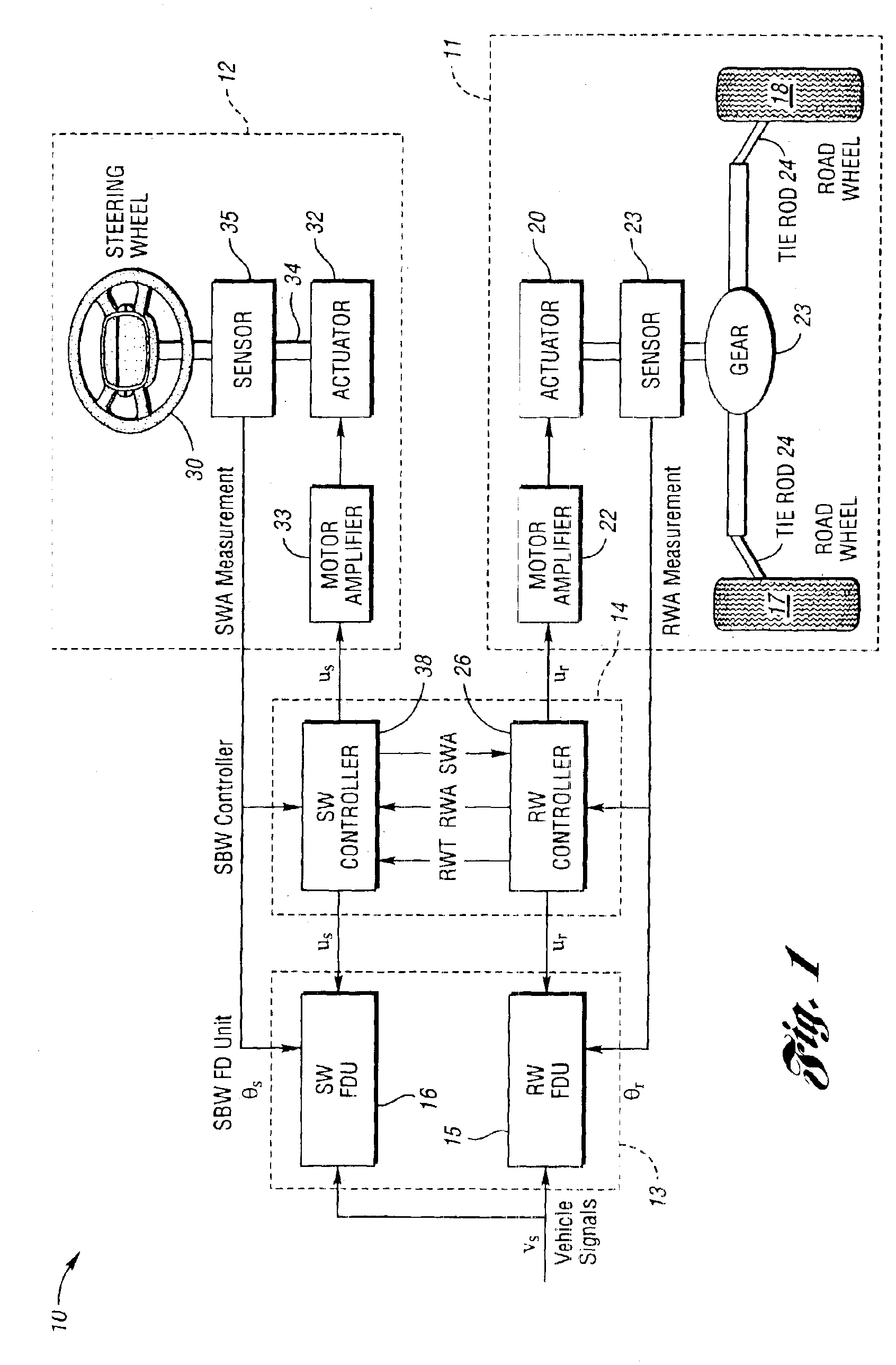
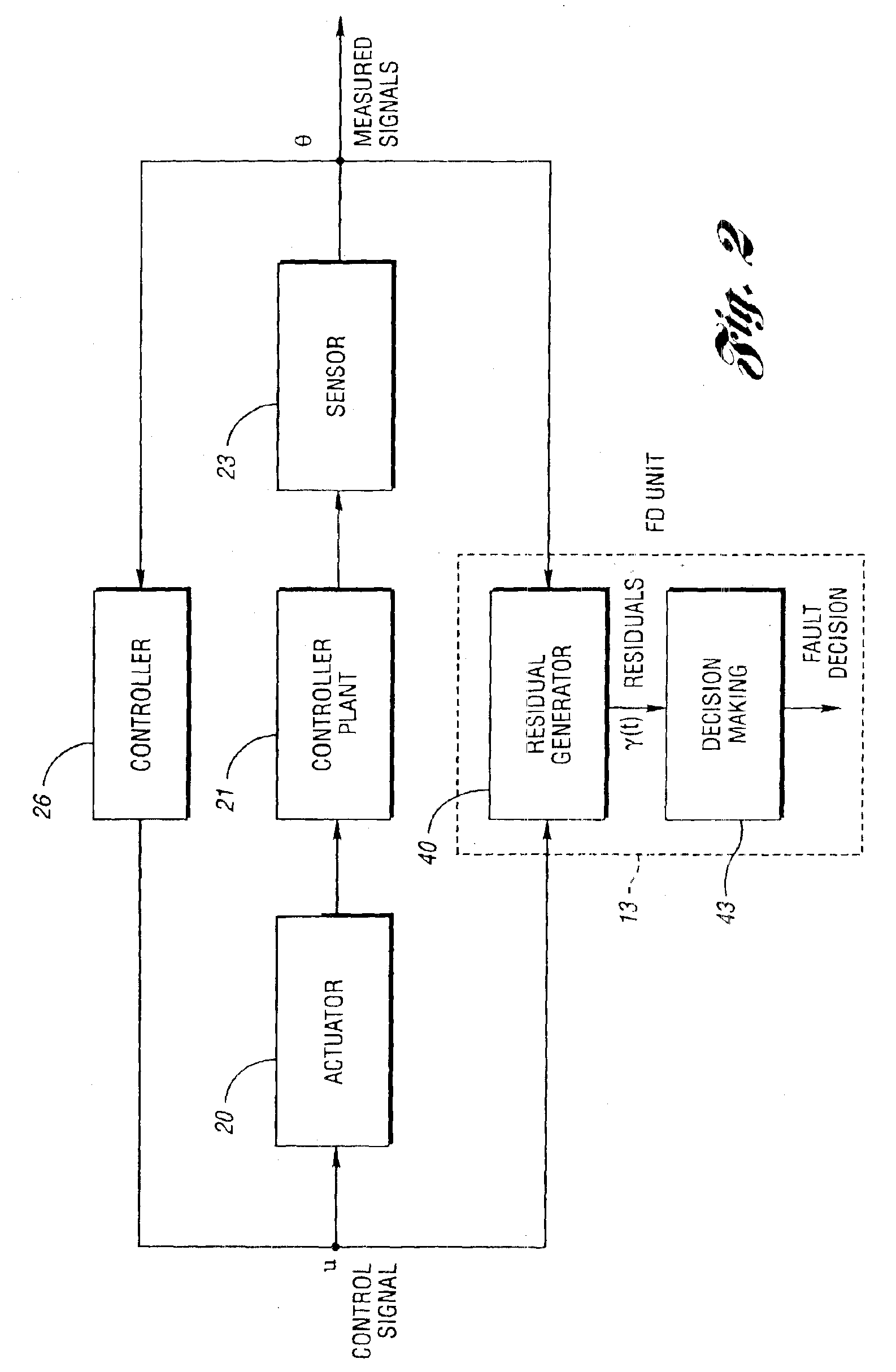
System and method of robust fault detection for a vehicle steer-by-wire system
InactiveUS6885922B2Low costImprove reliabilityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMathematical modelSteering control
The present invention involves a system and method of model-based fault detection for a vehicle steer-by-wire system. The method includes providing a steer-by-wire fault detection unit to implement fault detection for the fault occurrence in sensors, actuators, and the controlled plant. The steer-by-wire fault detection unit is composed of a residual generator and decision-making unit. The residual generator generates a series of residual signal which are difference between the estimation signals based on a steer-by-wire controlled plant mathematical model and the actual measurement signals of steer-by-wire controlled plant. The decision making unit determines whether any faults have occurred by applying a fault test rule for residual signals. The fault detection for the steer-by-wire system includes the influence of system uncertainty and nonlinearity, A robust gain scheduling H∞ fault detector is implemented to generate residual signals to reduce the effect of system uncertainty and nonlinearity for the residual signals. Therefore, the fault detection system is robust with respect to the model uncertainty, external noise and dynamic gain change, and is sensitive to faults occurrence in the steer-by-wire controlled plant.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
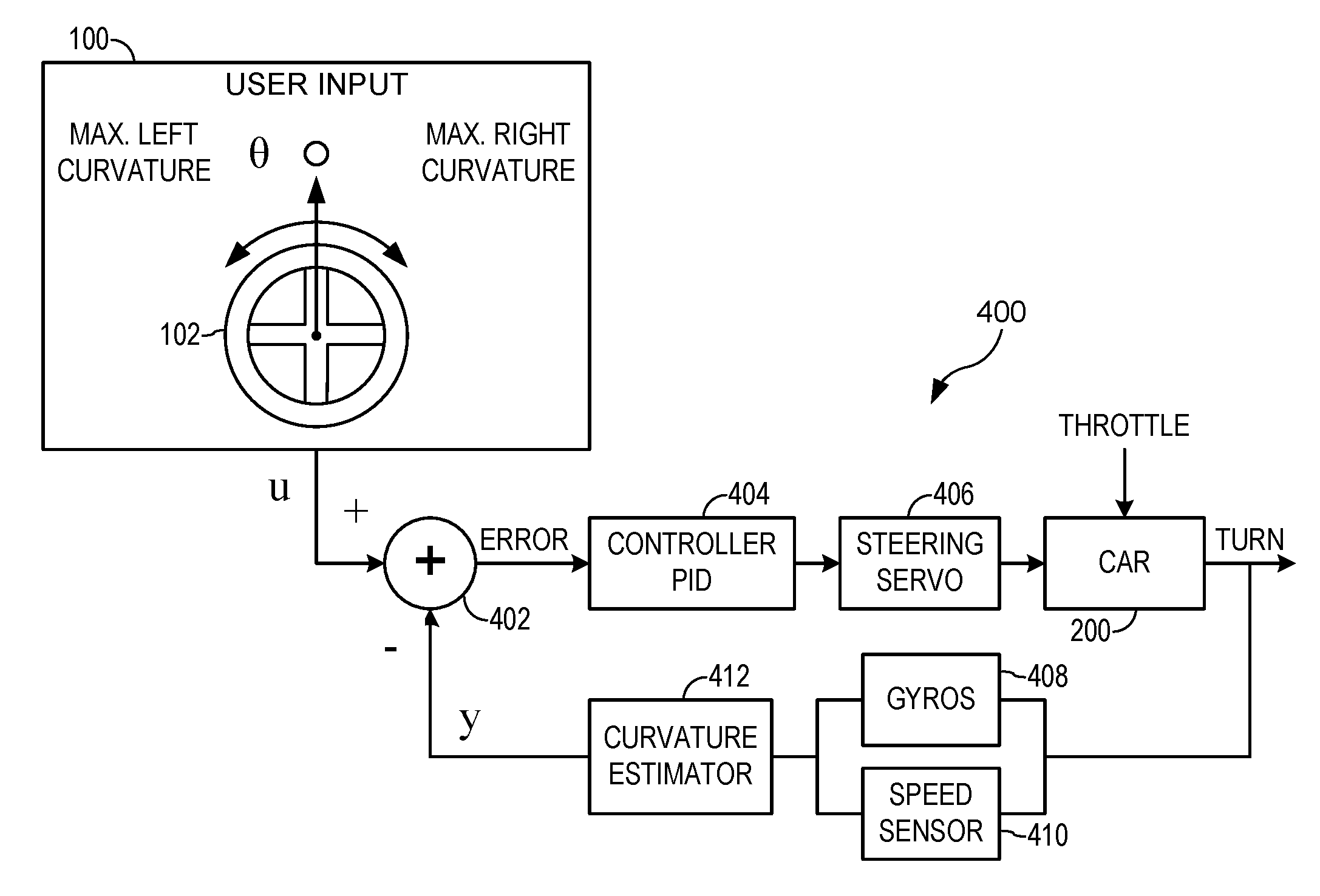
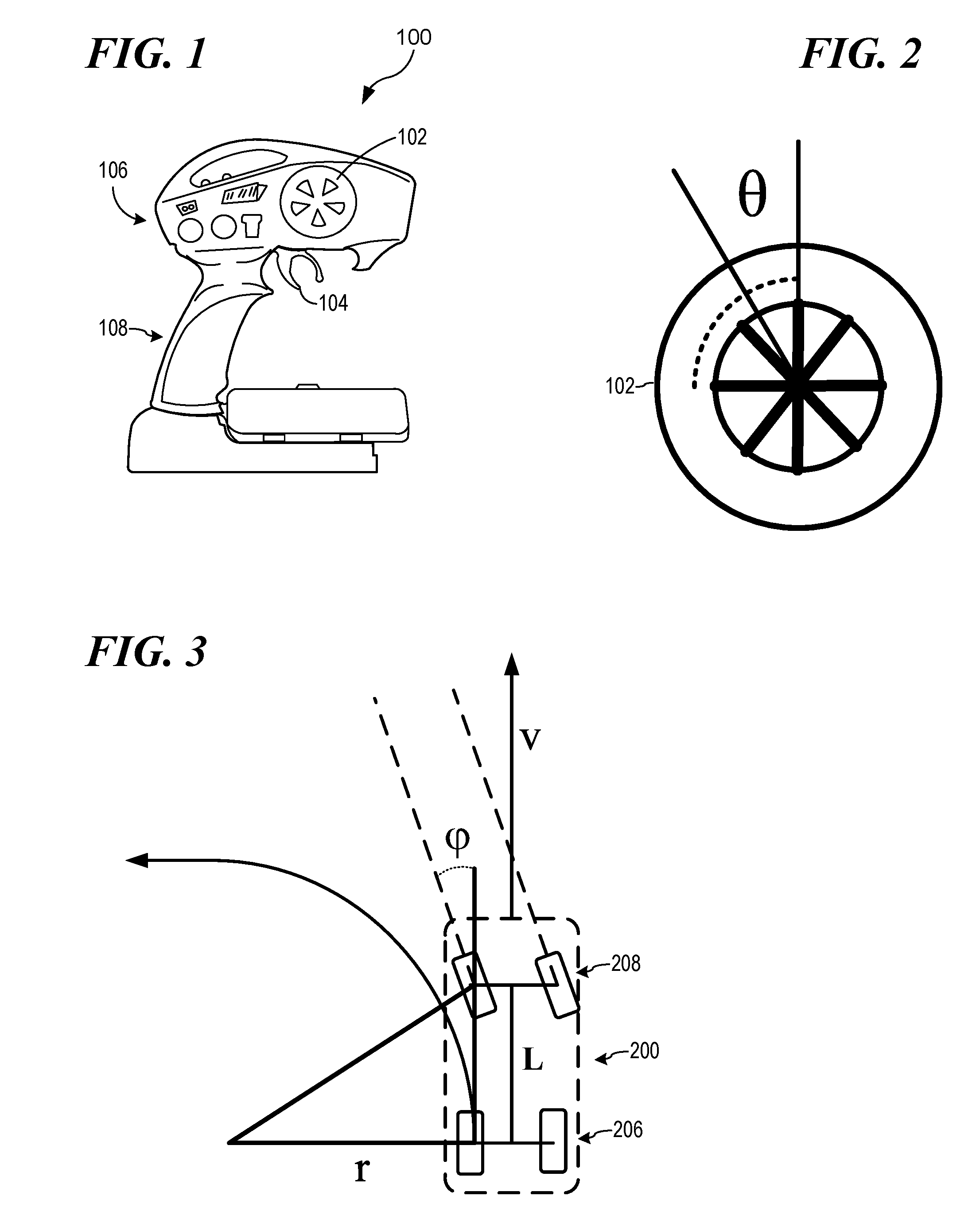
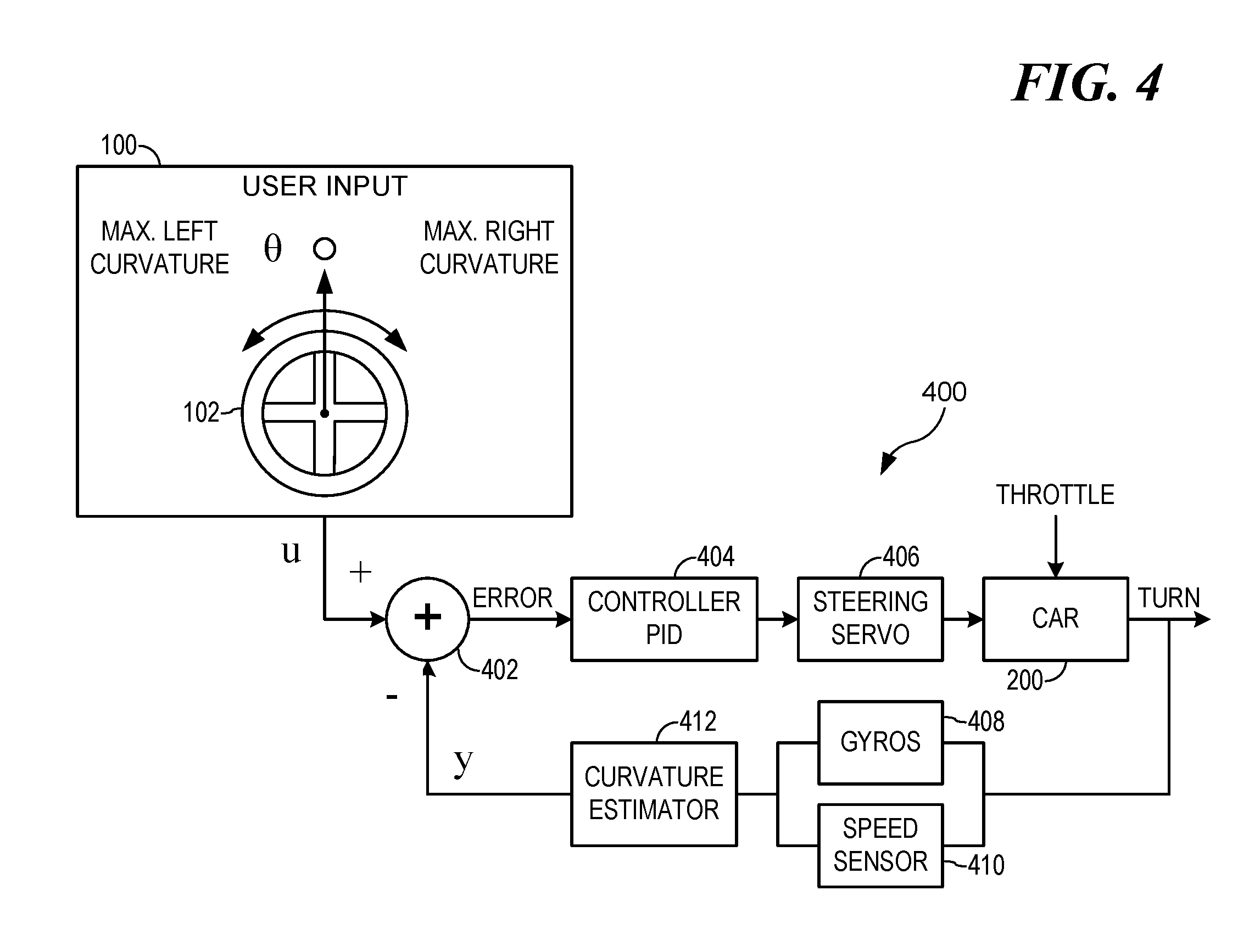
Steering stabilizing apparatus for a model vehicle
ActiveUS20160303485A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesAutomatic steering controlElectronic systemsSteering control
An electronic system for stabilizing steering of a model vehicle may provide a curvature steering control of an RC vehicle. The approximate curvature control of the RC vehicle determined using error integration to achieve full steering. Application of a leaky integrator may be used to minimize steering memory. The leak factor may be based off gain scheduling of the steering input.
Owner:TRAXXAS
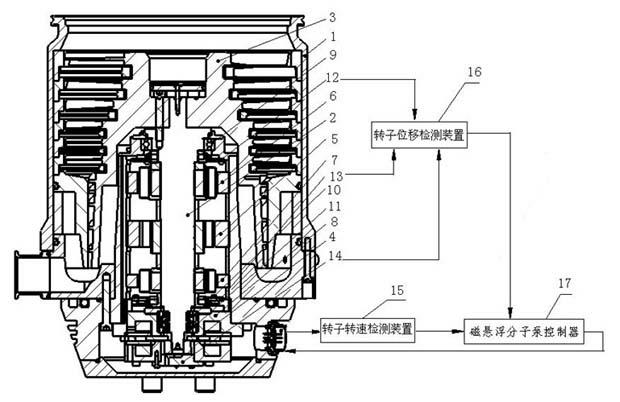
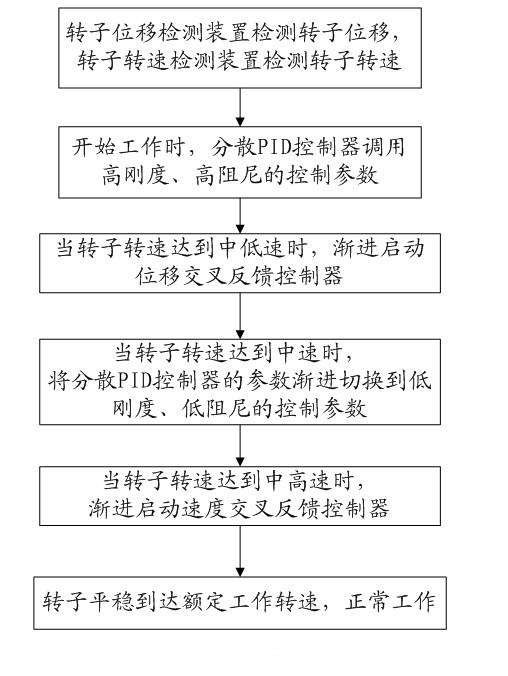
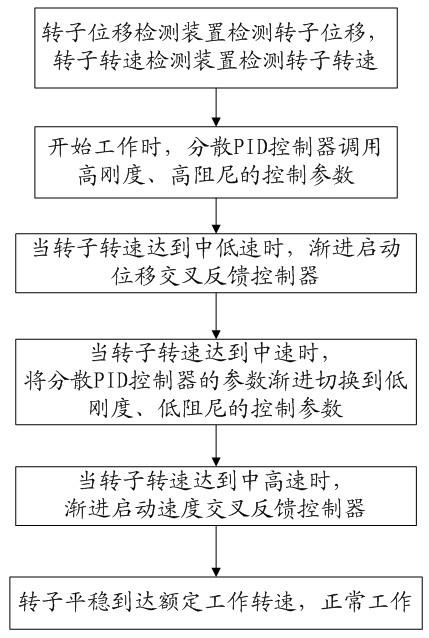
Gain scheduling control method for magnetic suspension molecular pump
ActiveCN102425554AEnsure stabilityGuaranteed to workPump controlAxial flow pumpsNutationProportion integration differentiation
The invention discloses a gain scheduling control method for a magnetic suspension molecular pump. The method comprises the following steps of: calling a high-rigidity and high-damping control parameter to control the magnetic suspension molecular pump by using a dispersion PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) controller when a rotor rotates at a low rotating speed, and gradually starting a displacement cross feedback controller when the speed of the rotor rises to a medium-low speed to effectively suppress rotor precession in the rotating process of the rotor and vibration caused by the structural mode of a system; when the rotating speed of the rotor reaches a medium speed, gradually switching the parameter of the dispersion PID controller to a low-rigidity and low-damping control parameter; and when the rotating speed of the rotor reaches a medium-high speed, gradually starting a speed cross feedback controller to suppress rotor nutation in the rotating process of the rotor and ensure that the rotor can stably reach a rated working rotating speed. Due to the adoption of the method, the technical problem of vibration caused by the rotor gyroscopic action in the working process of the molecular pump and the structural mode of the system is solved, the rotor vibration can be effectively suppressed in the working process of the molecular pump, and stable running of the magnetic suspension molecular pump can be ensured.
Owner:KYKY TECH +1
Robust gain scheduling control method based on regional pole assignment
InactiveCN102323754ASimple design methodGuaranteed stabilityAdaptive controlClosed-loop poleClosed loop
The invention provides a robust gain scheduling control method based on regional pole assignment. The realization principle is as follows: the controlled object is divided into a linear time invariant part and a parameter module by the method, wherein the parameter module is used for reflecting the nonlinear characteristic, time variant characteristic and certain uncertainty of the object; the nominal part is linear time invariant and the parametric variation part varies along with variation of the parameter module of the controlled object, thus ensuring the closed-loop system to satisfy the robust stability and robustness and have specified dynamic characteristics; the performance indexes are written into integral quadratic constraints under a unified framework according to the index requirements; in particular, the dynamic characteristics can be directly reflected by closed-loop poles on the position of the complex plane; therefore the index requirements of the dynamic characteristics are realized through regional pole constraints; and the constraints given by the performance index requirements are transformed into linear matrix inequality (LMI) systems and a solver in an LMI toolbox provided by a matrix laboratory (MATLAB) is utilized for solving, thus finally obtaining the controller satisfying the requirements.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
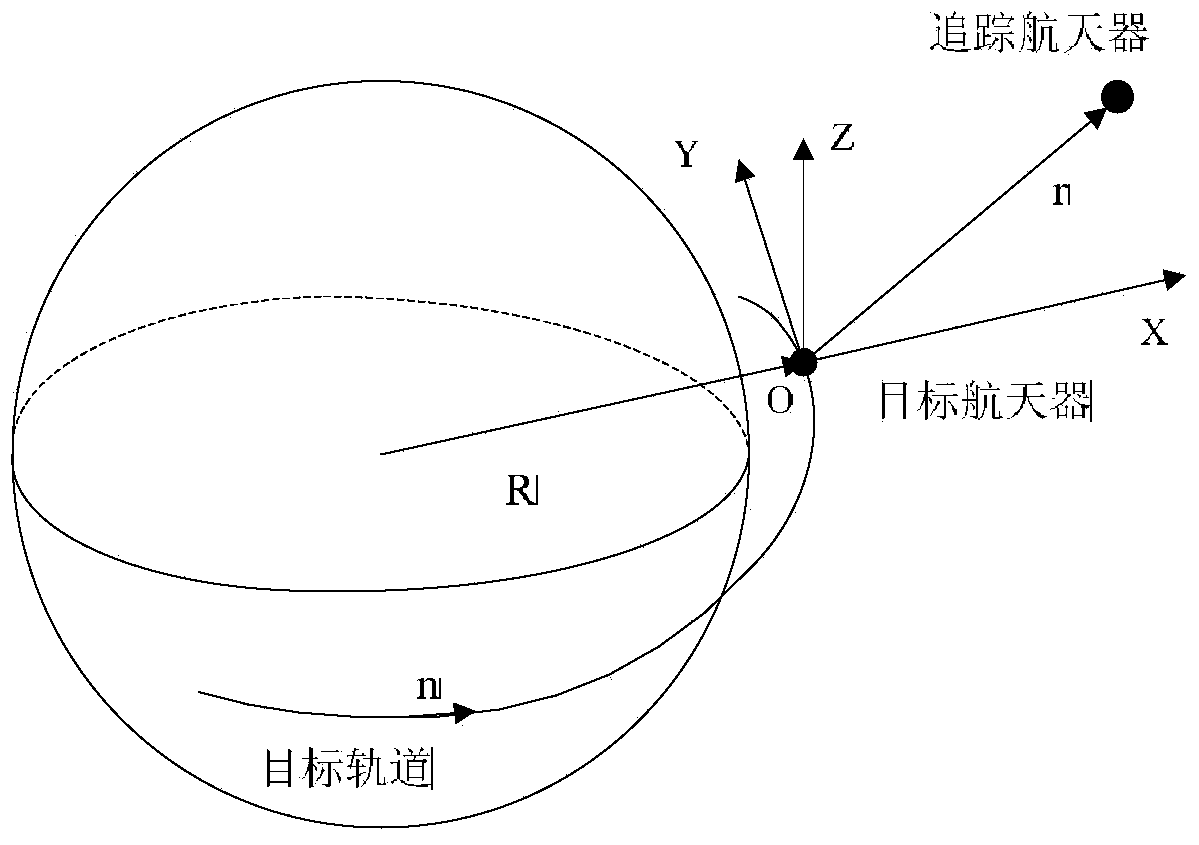
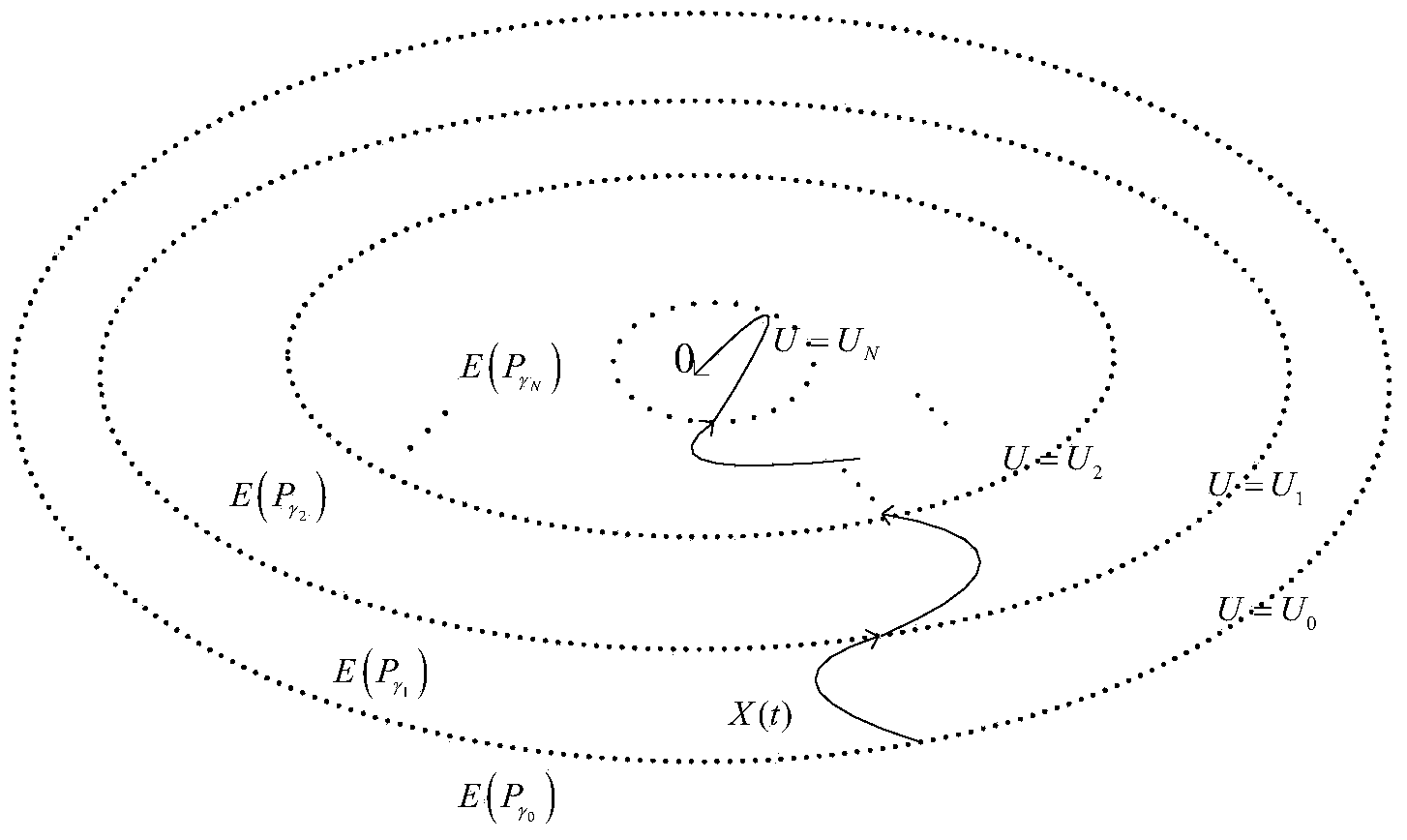
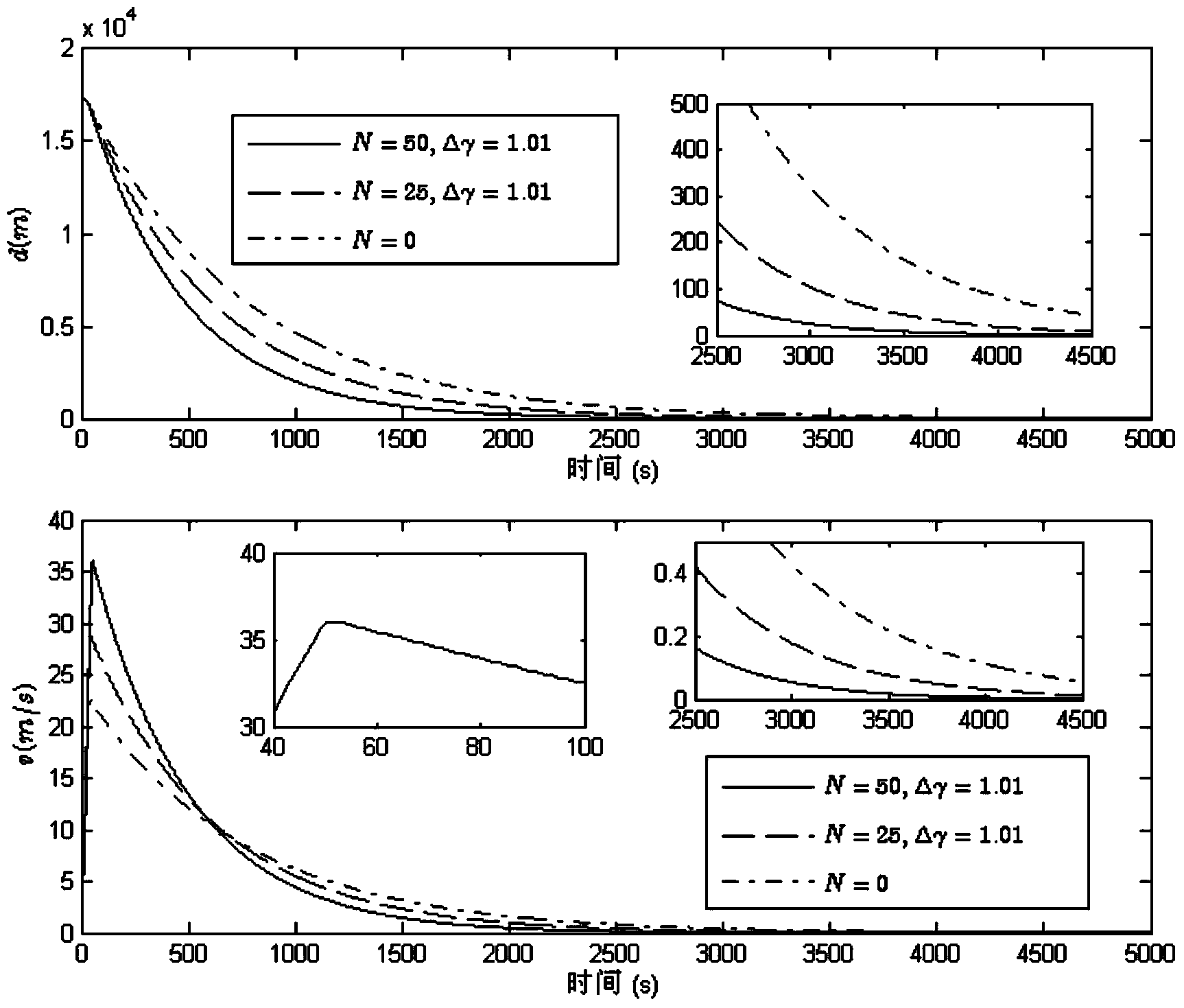
Space rendezvous system gain scheduling control method with linearization errors taken into consideration
ActiveCN104076818AFast convergenceShorten the timePosition/course control in three dimensionsAdaptive controlSpace rendezvousLinearization error
The invention provides a space rendezvous system gain scheduling control method with linearization errors taken into consideration, and relates to a spacecraft orbit rendezvous gain scheduling control method. The space rendezvous system gain scheduling control method solves the problem that due to the fact that according to an existing aircraft orbit rendezvous control method, input saturation and parameter uncertainty caused by the linearization errors are ignored, time consumption is high when an aircraft orbit rendezvous task is completed. According to the space rendezvous system gain scheduling control method, the parameter uncertainty caused by the linearization errors is taken into consideration and endowed with exact meanings, an aircraft orbit rendezvous relative movement model is established, a gain scheduling controller of an aircraft orbit rendezvous is then designed, the aircraft orbit rendezvous is controlled through the gain scheduling controller, and the rendezvous task is completed. The space rendezvous system gain scheduling control method is mainly used for controlling the aircraft orbit rendezvous.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学人工智能研究院有限公司
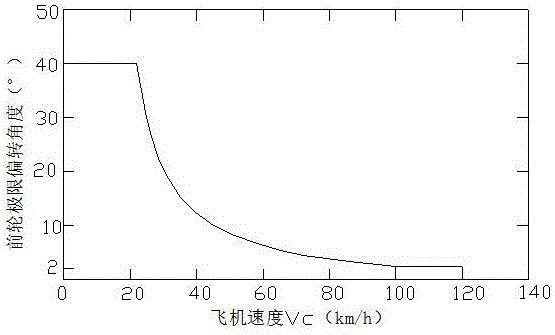
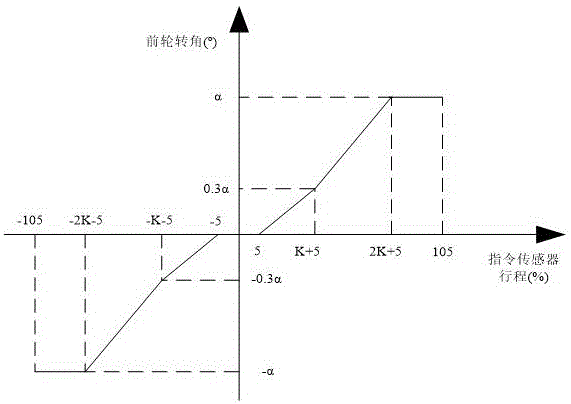
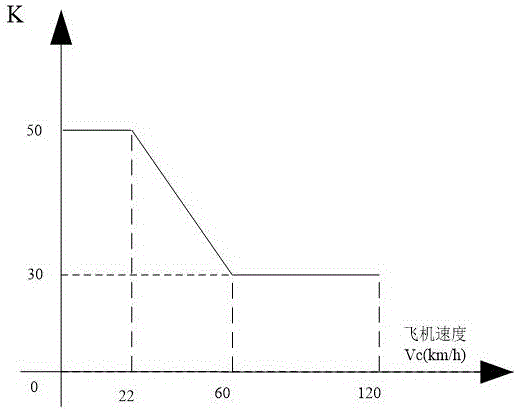
Front wheel turning anti-swing system with medium speed correction function
ActiveCN105905284ASafe manipulationLighten the manipulation burdenProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersWheel arrangementsMan machineAutomated control system
The invention discloses a front wheel turning anti-swing system with a medium speed correction function. The system comprises an instruction sensor, a hydraulic valve, a turning actuator, a feedback sensor and a front wheel turning control box. The system is normally at an anti-swing state; the hydraulic valve is at a power-off state, and when a front airplane wheel sways, oil is forced to flow the other cavity from one cavity of the turning actuator through a two-way damping valve of the hydraulic valve; when a nose landing gear of an airplane is put down and a power switch is connected, an on-plane power supply supplies power for the front wheel turning control box, and the front wheel turning control box automatically controls the system to be switched into a turning state from the anti-swing state when receiving the instruction value of the instruction sensor. The medium speed correction function of the front wheel turning anti-swing system is fulfilled, the maximum autonomous manipulation ability of a pilot is rendered under the premise of ensuring the manipulation safety of the airplane, and the ground maneuver performance of the airplane is improved; automatic switching of the system states and gain scheduling manipulation of turning are realized, the manipulation load of the pilot is decreased, and man-machine comfort is enhanced.
Owner:JIANGXI HONGDU AVIATION IND GRP
Controller gain scheduling for mass flow controllers
ActiveUS8079383B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsCalibration gasFeedback controller
A mass flow controller having a feedback controller gain, comprises: a sensor configured so as to sense the flow of fluid through controller; a valve arranged so as to adjust the flow of fluid through the controller; and a processor configured so as to control the valve as a function of the flow of fluid sensed by the sensor. The sensor and valve are arranged within a feedback system, and the processor updates the feedback controller gain in real time based on the ratio of at least one calibration gas parameter to at least one operating gas parameter, such that the closed loop transfer function of the feedback system remains substantially constant regardless of operating conditions so as to have a consistent control performance at different operation conditions from the calibration condition.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Automatic gain scheduling method for wind power plants distributed as priority level according to blower involvement
InactiveCN104124715AIncrease power generationLow failure rateSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationPeaking power plantElectric power system
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
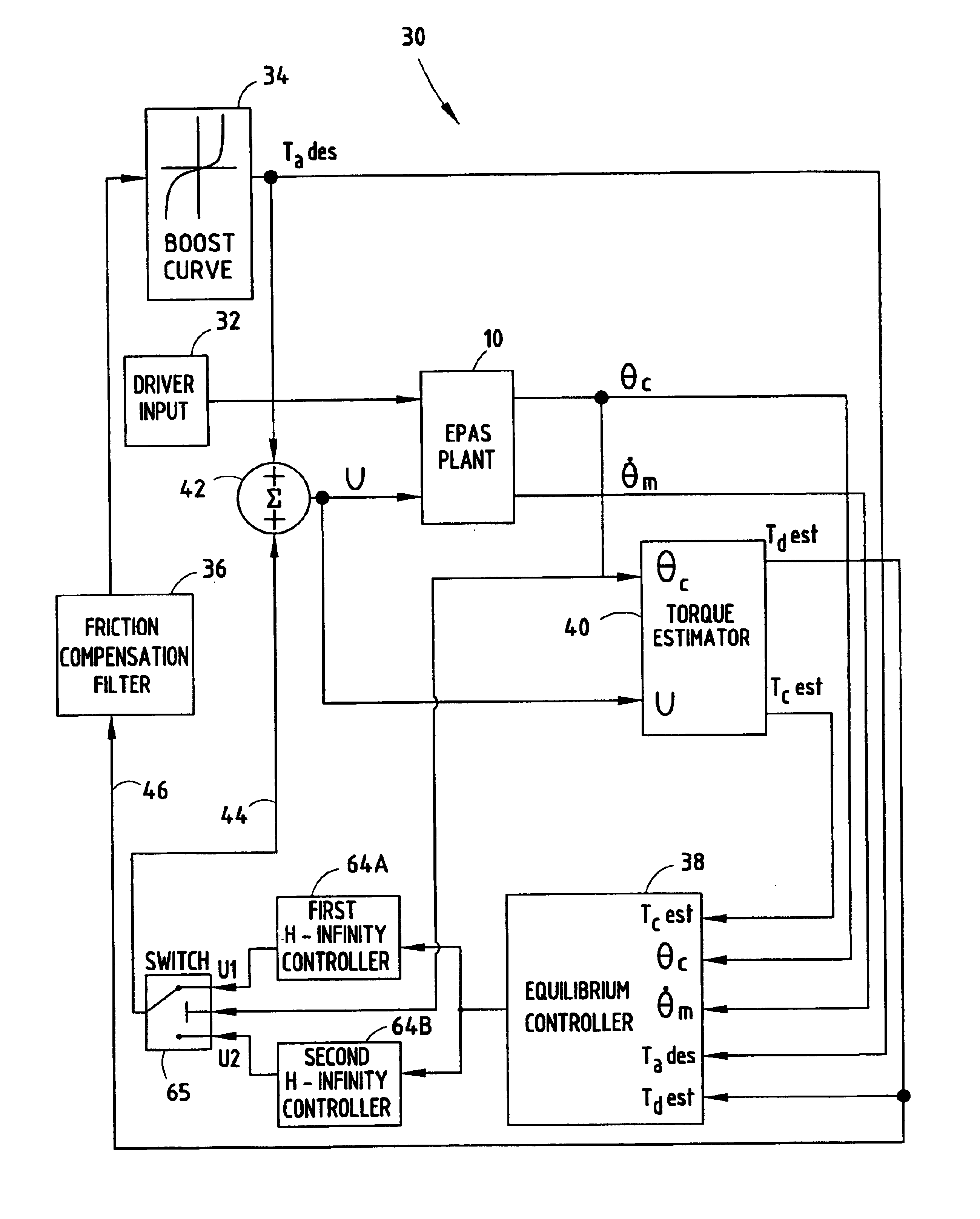
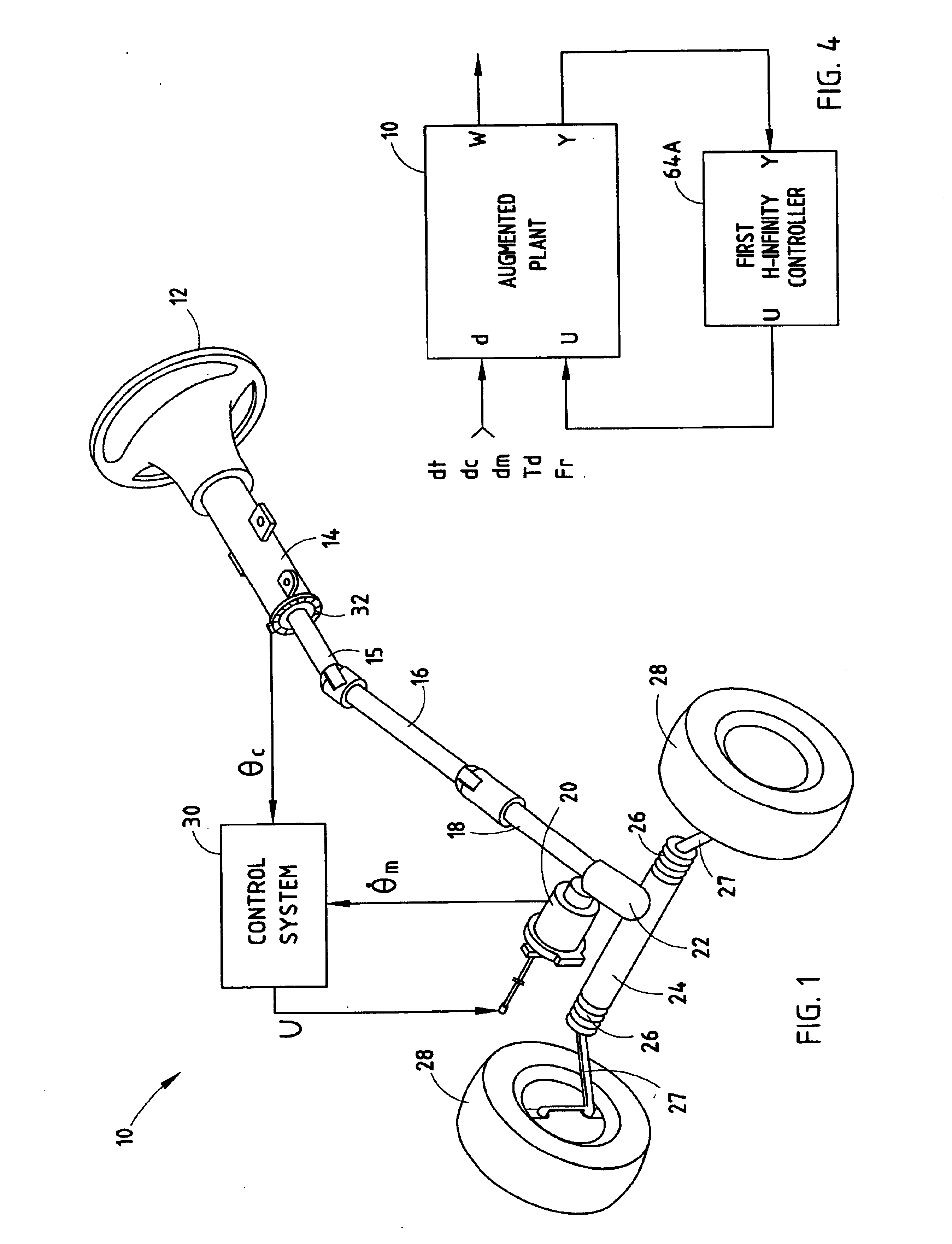
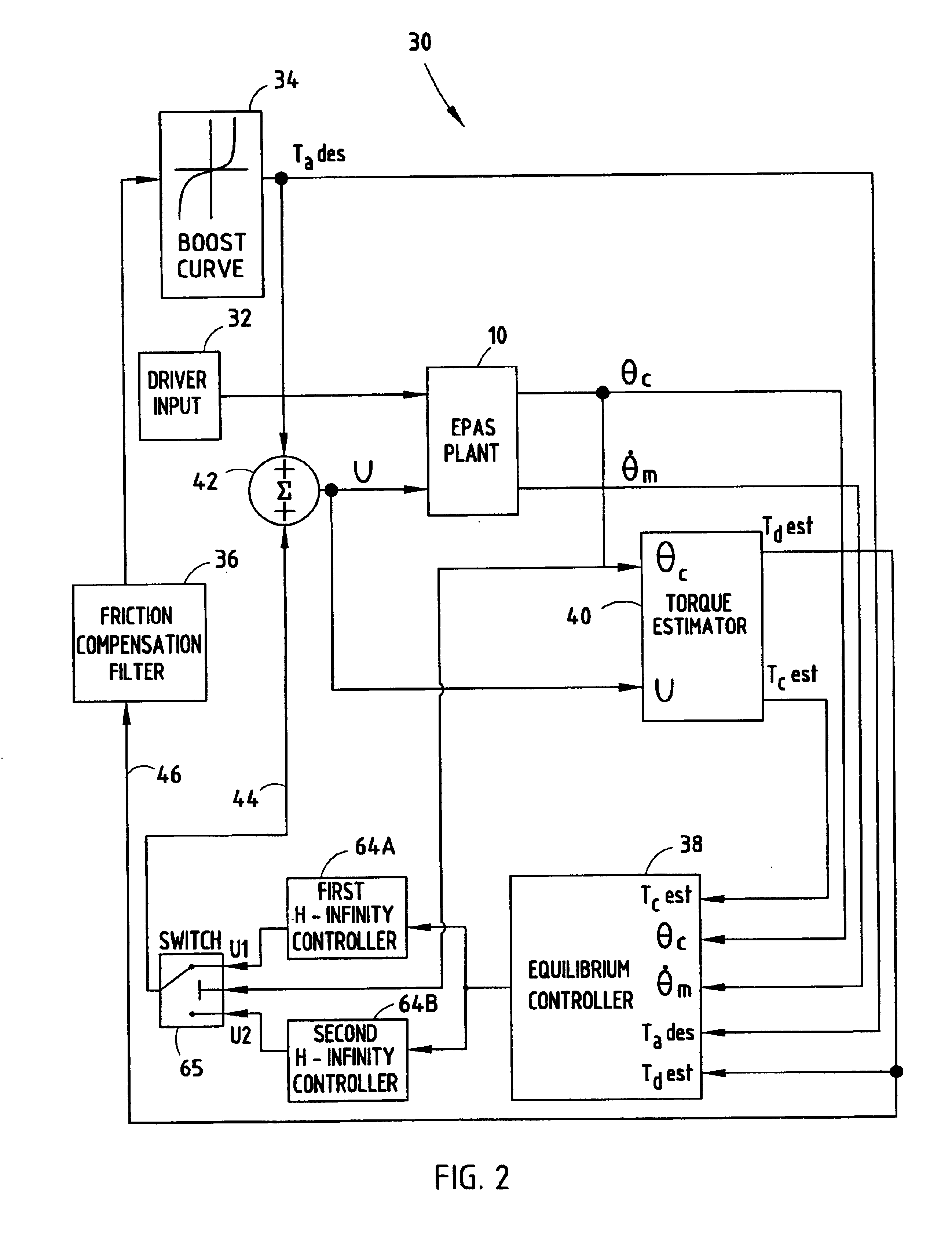
H-infinity control and gain scheduling method for electric power assist steering system
InactiveUS6896094B2Stable and robustImproved on-centerSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringH-infinity methods in control theory
A steering system (10) and method (70) for controlling the steering of a vehicle having a steering assembly including a steering wheel (12), a steering column (14) connected to said steering wheel (12), and an electric motor (20) operatively engaged with the steering assembly for supplying torque assist. A steering angle sensor (32) is employed for sensing an angular position θc of the steering column (14). The steering system has first and second H-infinity controllers (64A and 64B) coupled in a feedback path (44) for generating first and second feedback signals as a function of the driver torque and first and second characteristics (JC and KC) of the steering system. One of the first and second feedback signals is selected and the selected feedback signal is combined with a feedforward signal to generate a motor control signal (U) as a function of the estimated torque.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
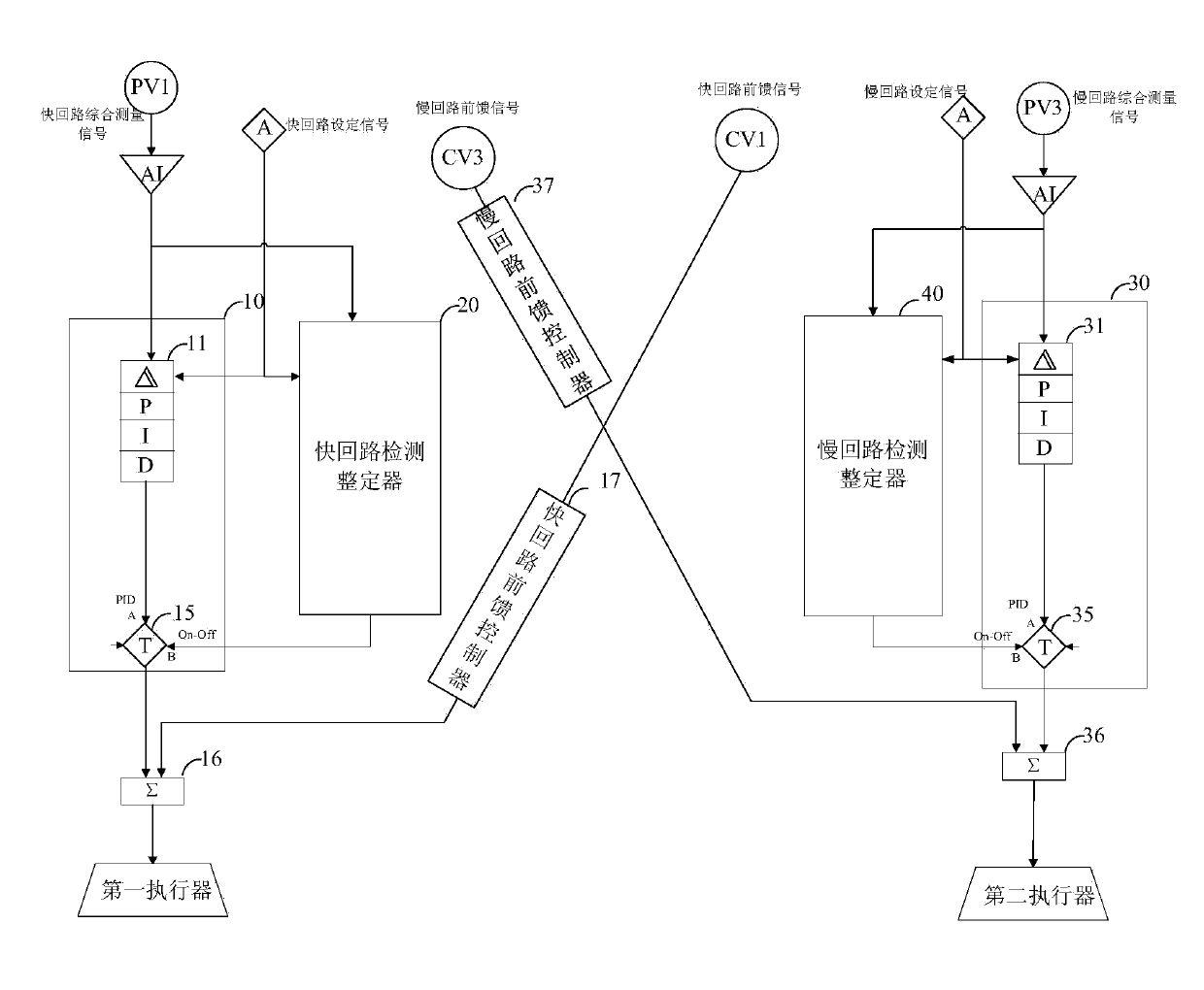
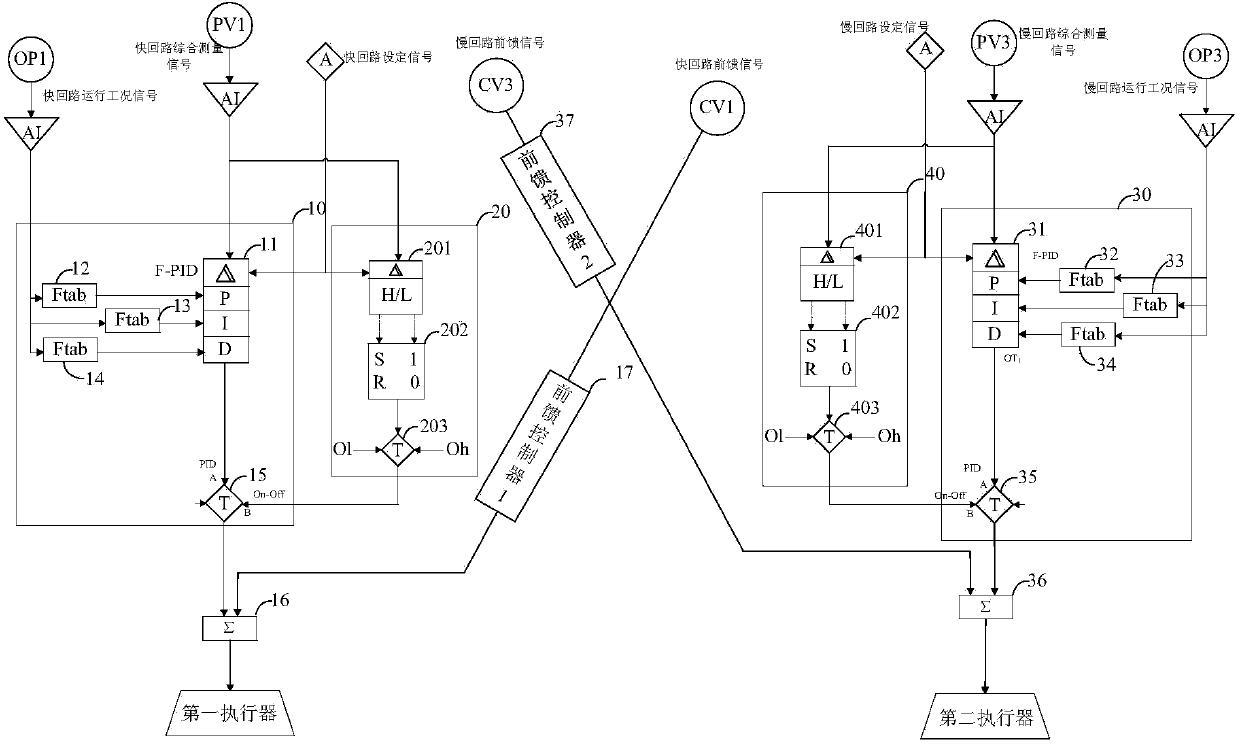
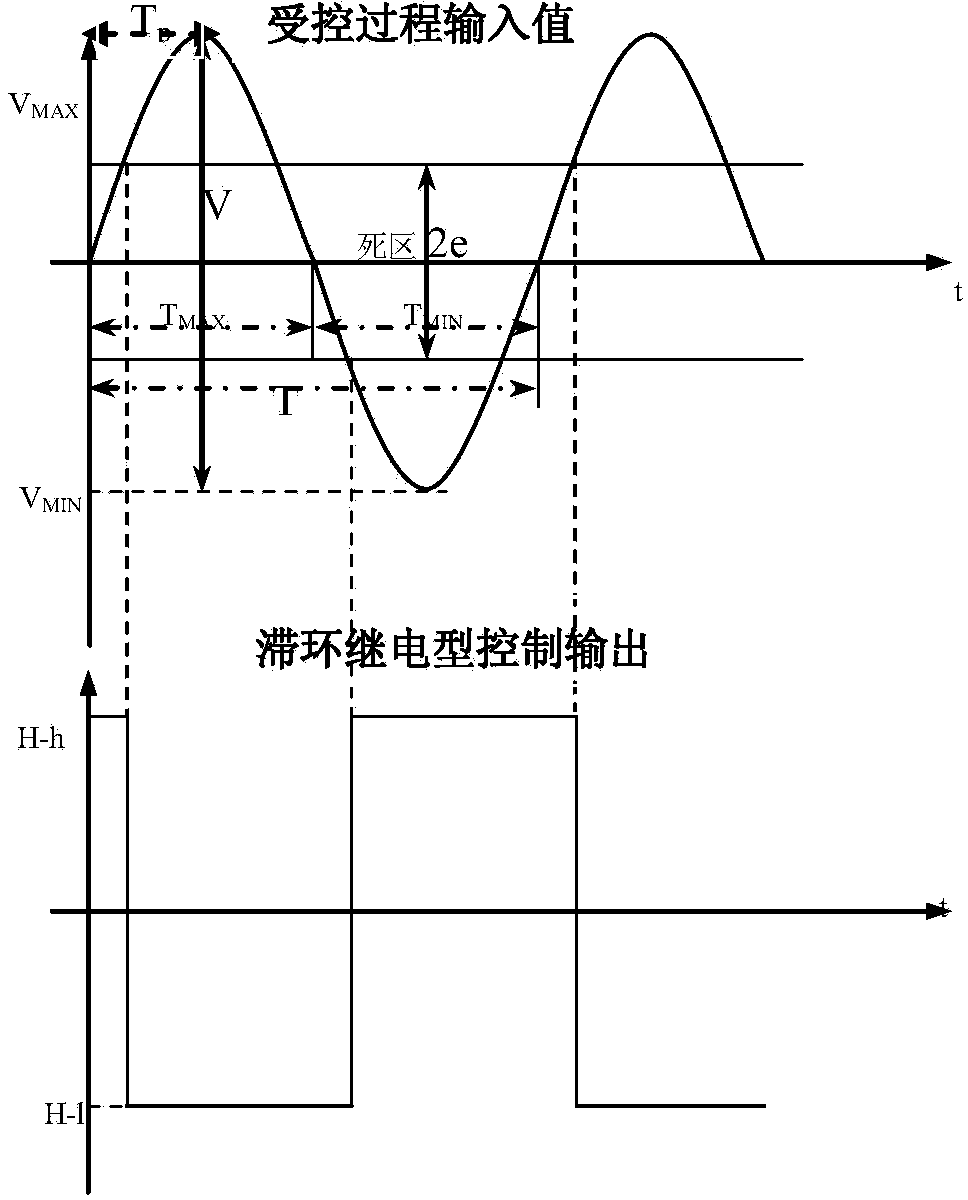
Self-gain-scheduling PID (proportion integration differentiation) controller of double-in double-out system of heat-engine plant
The invention provides a self-gain-scheduling PID (proportion integration differentiation) controller of a double-in double-out system of a heat-engine plant. Through a quick / slow loop detection setter, a quick / slow loop control mode switch, quick and slow loop feedforward controllers and quick and slow loop feedforward-feedback comprehensive arithmetic units, and through lap joint of proper modules, relay feedback control of a general double-in double-out system loop is realized, critical vibration information of the process is measured, and under the condition that a controlled system mathematic model is not known, P, I and D parameters of the double-in double-out system loop can be automatically set in closed-loop control according to stability margin as required; according to changes of actually-measured operation condition signals and deviation signals, optimal P, I and D parameters of quick and slow loops are automatically inferred in real time, transition time of a control system is reduced to the utmost, and dynamic and static deviations of the control system are reduced. By the self-gain-scheduling PID controller, parameter setting of the multivariable control system becomes more quick and scientific, and the control system has high robustness.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Adaptive control for uncertain nonlinear multi-input multi-output systems
ActiveUS8712559B2Quick controlGuaranteed performanceSpecial data processing applicationsAdaptive controlMulti inputControl channel
Systems and methods of adaptive control for uncertain nonlinear multi-input multi-output systems in the presence of significant unmatched uncertainty with assured performance are provided. The need for gain-scheduling is eliminated through the use of bandwidth-limited (low-pass) filtering in the control channel, which appropriately attenuates the high frequencies typically appearing in fast adaptation situations and preserves the robustness margins in the presence of fast adaptation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Method of controlling process parameters for semiconductor manufacturing apparatus
InactiveUS7848840B2Short stabilization timeShort response timeTemperatue controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf adaptiveControl theory
Methods and systems for adaptively controlling process parameters in semiconductor manufacturing equipment. An embodiment provides for gain scheduling of PID controllers across recipe steps. One embodiment provides a method for controlling a chuck temperature during a semiconductor manufacturing process, the method employing a first set of proportional-integral-derivative (PID) values in a PID controller to control the chuck temperature at a first setpoint in a first step of a process recipe and employing a second set of PID values in the PID controller to control the chuck temperature at a second setpoint, different than the first setpoint, in a second step of the process recipe. The methods and systems provide reduced controller response times where process parameter setpoint between steps of a process recipe span a wide range.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Magnetic suspension flywheel buffeting weakening method based on sliding mode variable structure control
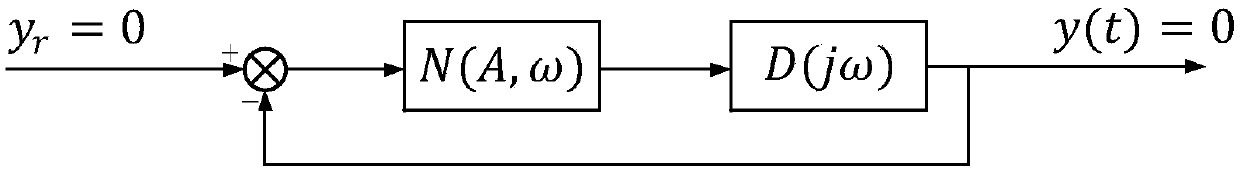
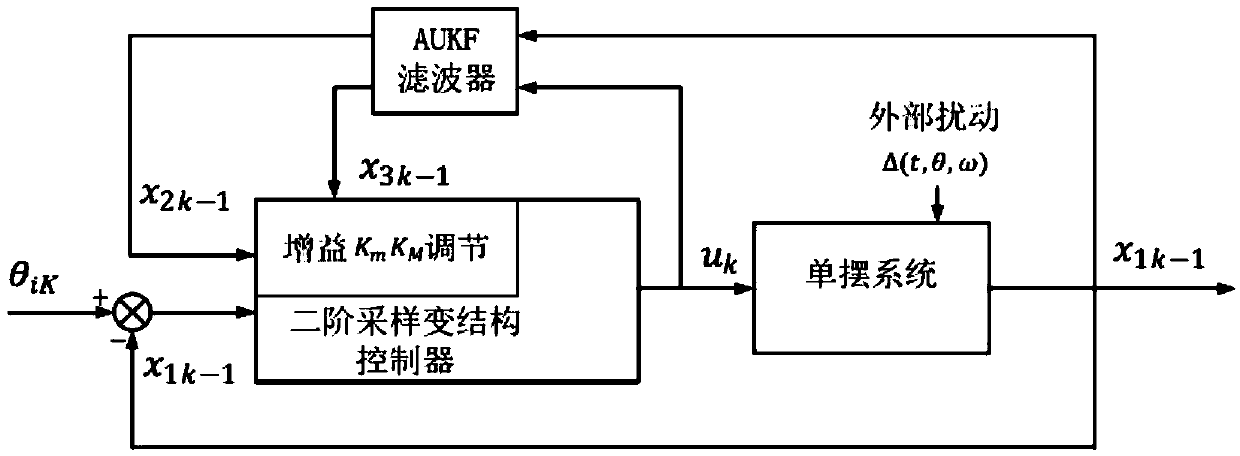
InactiveCN108681255AAvoid shockReduce buffetingAdaptive controlResearch ObjectVariable structure control systems
The invention discloses a magnetic suspension flywheel buffeting weakening method based on sliding mode variable structure control; the method uses a generalized description function method of a sliding mode variable structure control system and an adaptive unscented Kalman filtering algorithm to weaken signal buffeting, takes buffeting imported by the variable structure control and the system stability design as research objects, starts from variable structure control buffeting inhibition and present conditions and existing problems of a DF method applied in a non-linear system, emphasizes onstability analysis of a frequency correlation description function N (A, [omega]) and a variable structure switching gain adaptive adjusting method, proposes the adaptive unscented Kalman filtering (AUKF) algorithm, and designs a H[delta] sliding mode controller based on gain scheduling, thus verifying the validity of the proposed buffeting adjusting and inhibition method. The method ensures thesliding mode variable structure control method not to be sensitive to extraneous disturbances, can ensure an excellent robustness, and can effectively weaken system buffeting caused by continuously switching of the flywheel structure.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
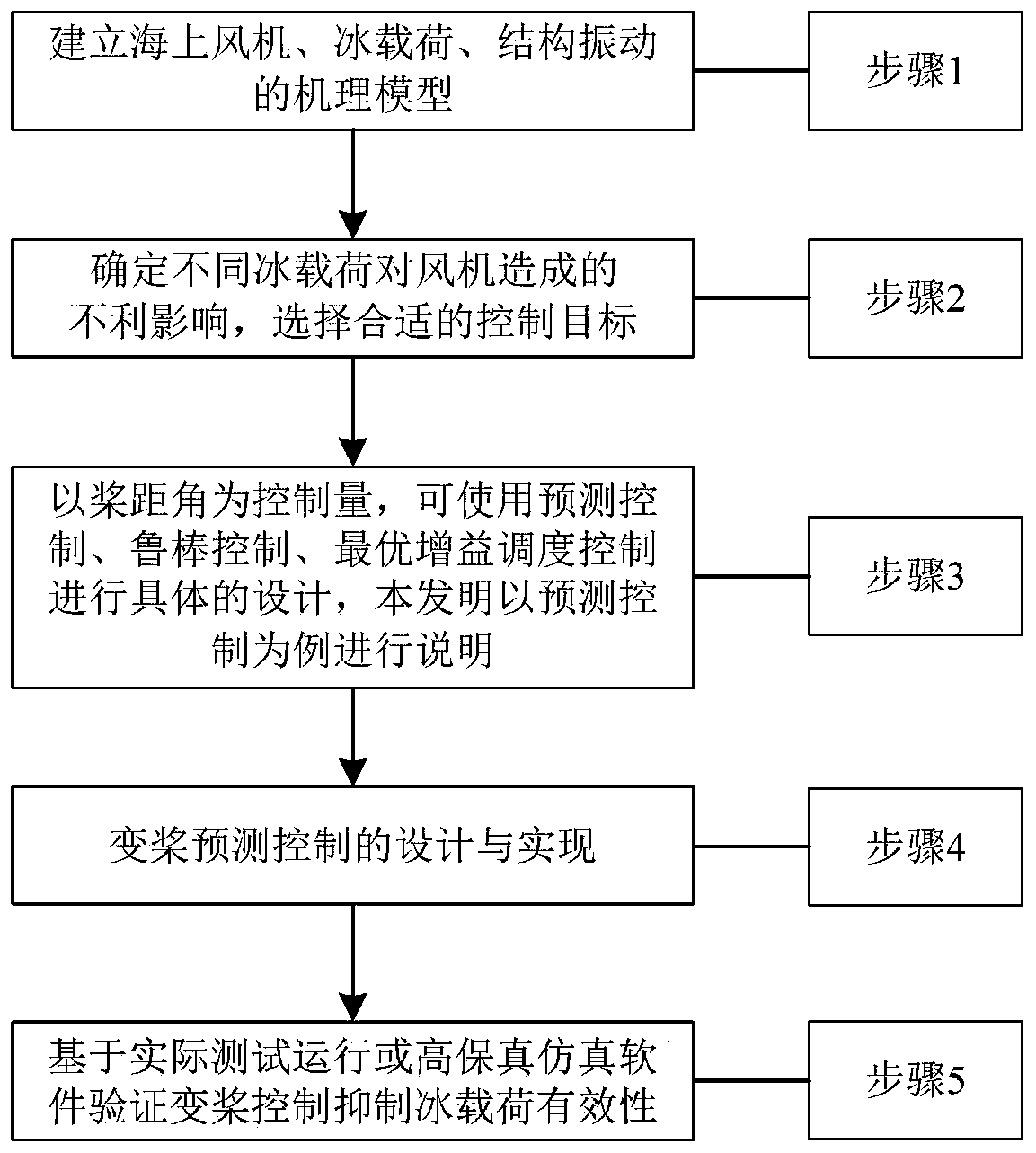
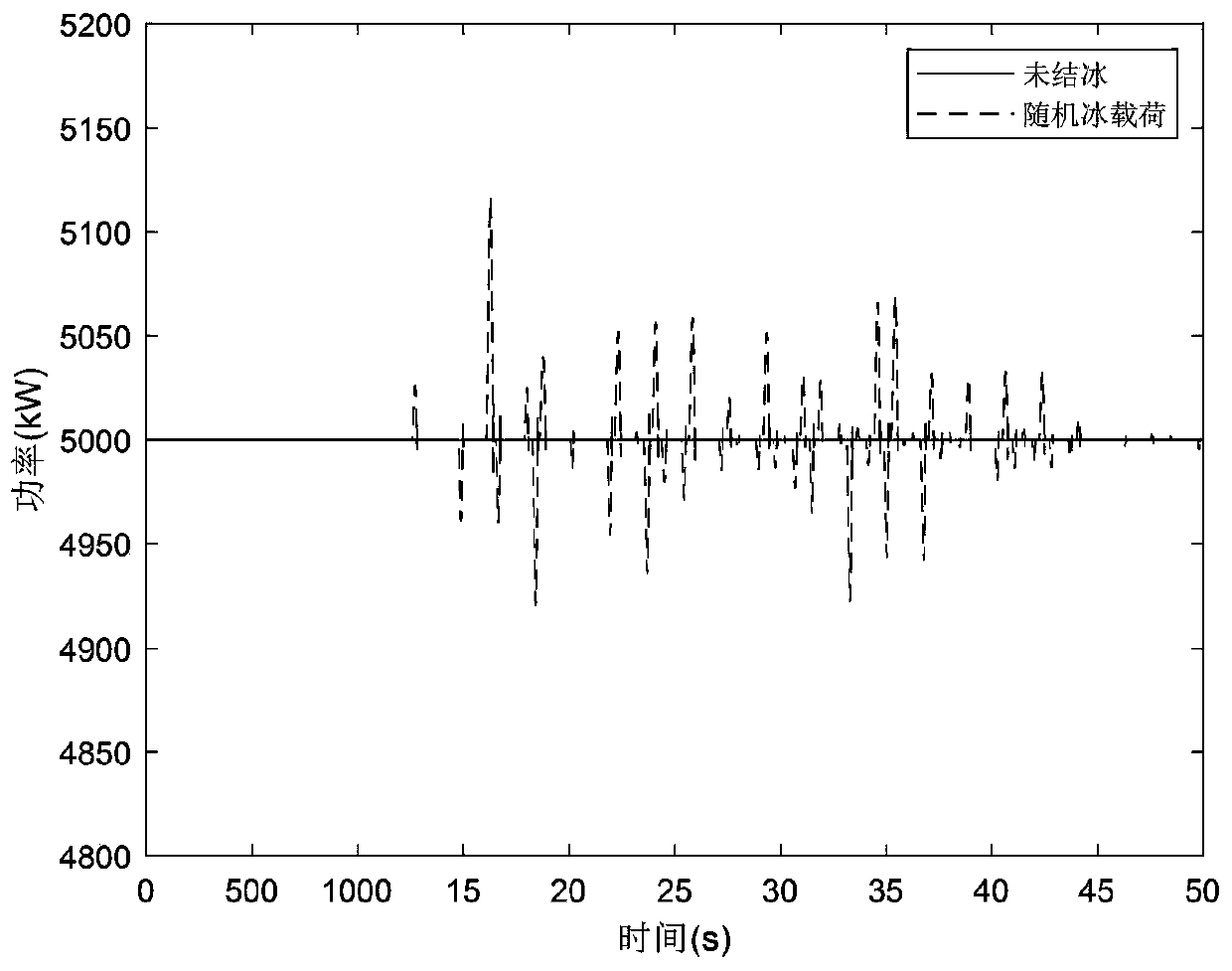
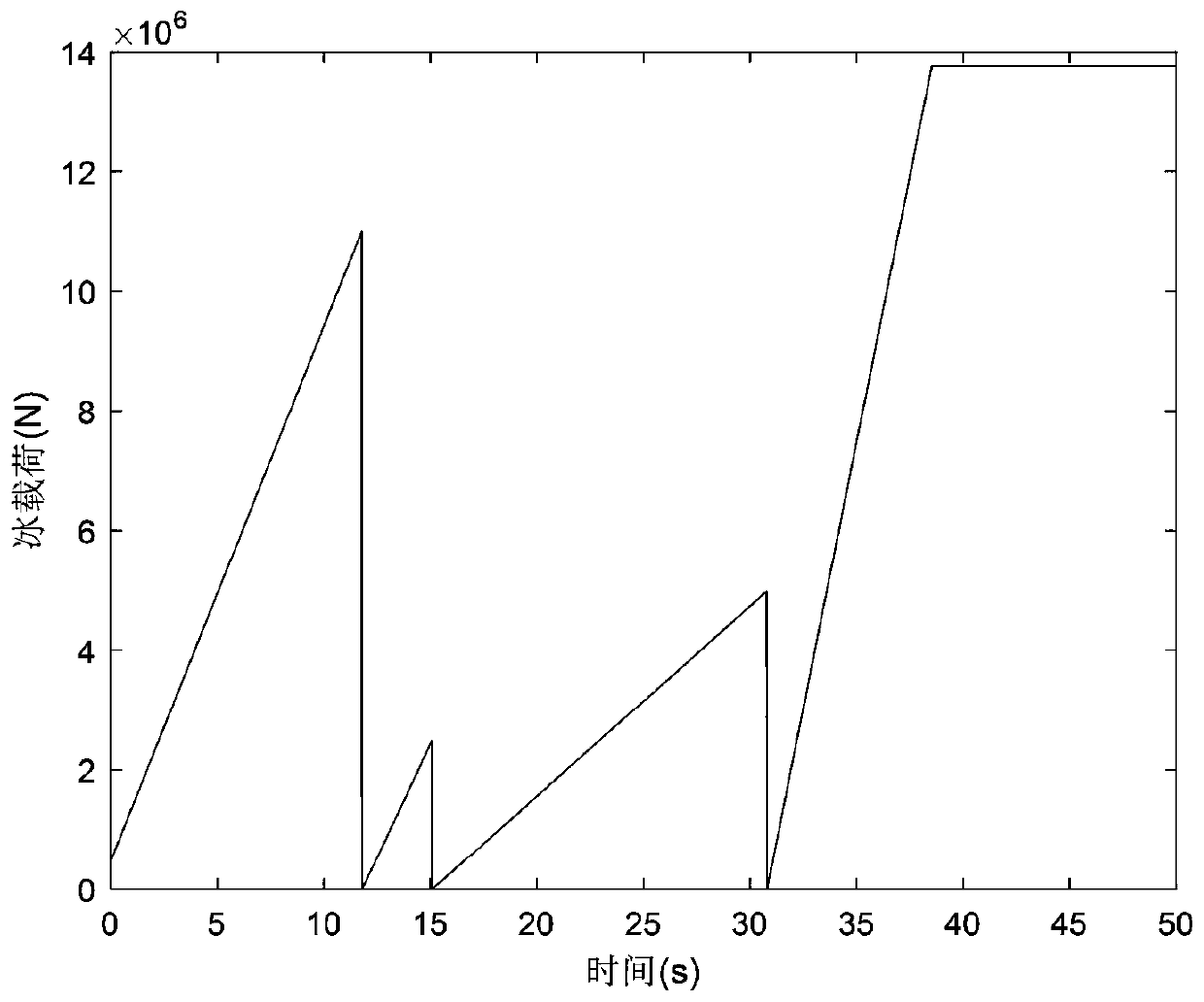
Method for inhibiting ice load of offshore wind turbine based on variable pitch control
ActiveCN111327239AVerify suppression effectWind motor controlGeneration protection through controlControl mannerField tests
The invention discloses a method for inhibiting ice load of an offshore wind turbine based on variable pitch control. The method comprises that: firstly, a wind turbine mechanism model, an ice load mechanism model and a structural vibration mechanism model are established for qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing the influence of the ice load on the wind turbine; then, the influence of different types of ice loads on the draught fan is determined through field testing or simulation, the influence comprises power fluctuation and mechanical fatigue load increase, and a proper control targetis selected according to the influence of the ice loads on the draught fan; then, the pitch angle is used as a controlled variable, and the ice load of the offshore wind turbine is restrained througha variable pitch control mode of predictive control or robust control or optimal gain scheduling control; preferably, a predictive control mode is adopted; and finally, based on field fan actual testing or high-fidelity simulation software, the inhibiting effect of variable pitch control on the ice load is verified.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for aero engine Conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for aero engine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f263fdf4-1038-407d-8e33-bd08857a8b46/HDA0002439601400000011.png)
![Conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for aero engine Conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for aero engine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f263fdf4-1038-407d-8e33-bd08857a8b46/HDA0002439601400000012.png)
![Conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for aero engine Conservation-reducing gain scheduling two-degree-of-freedom [mu] controller for aero engine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f263fdf4-1038-407d-8e33-bd08857a8b46/HDA0002439601400000013.png)