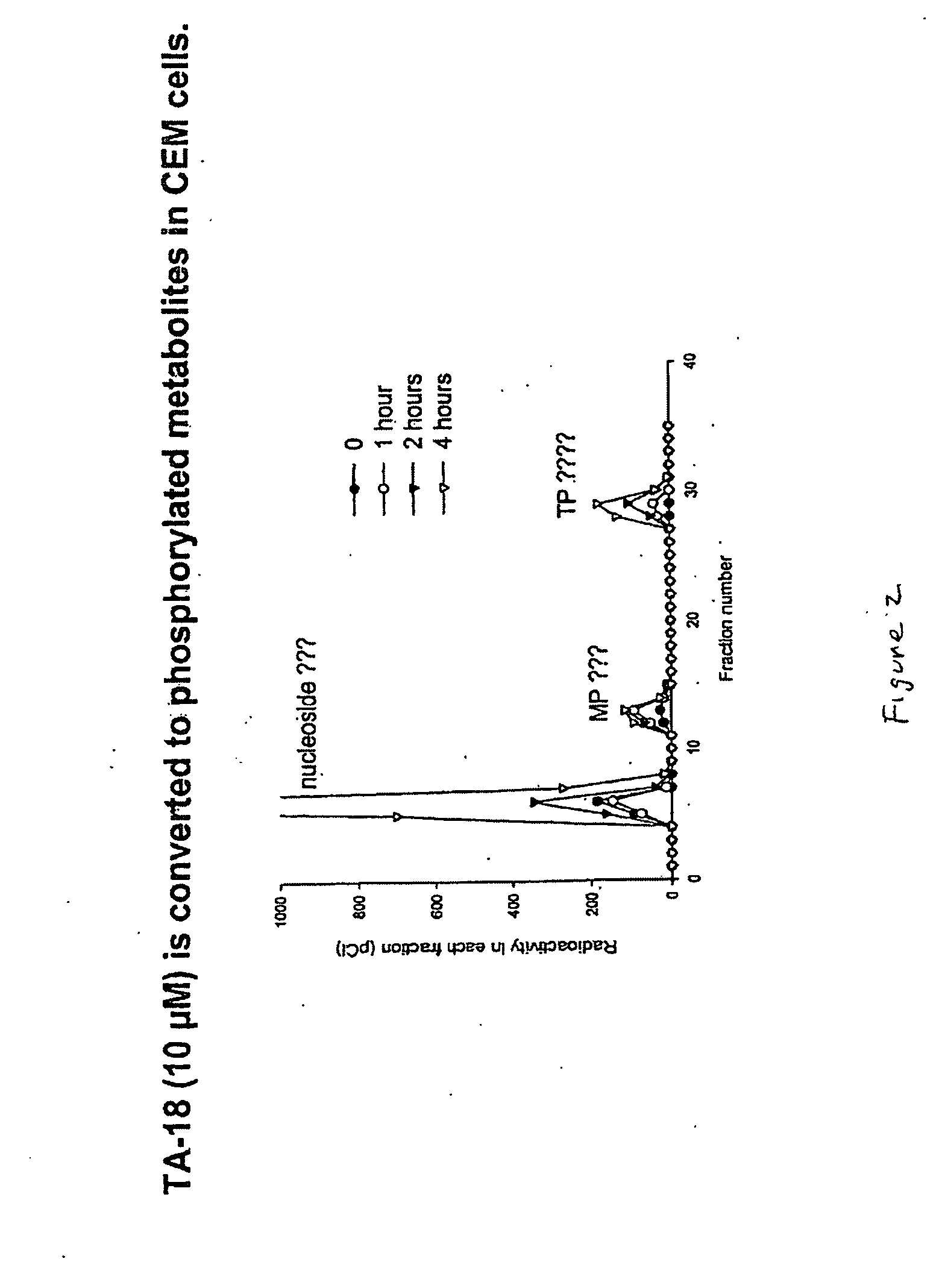
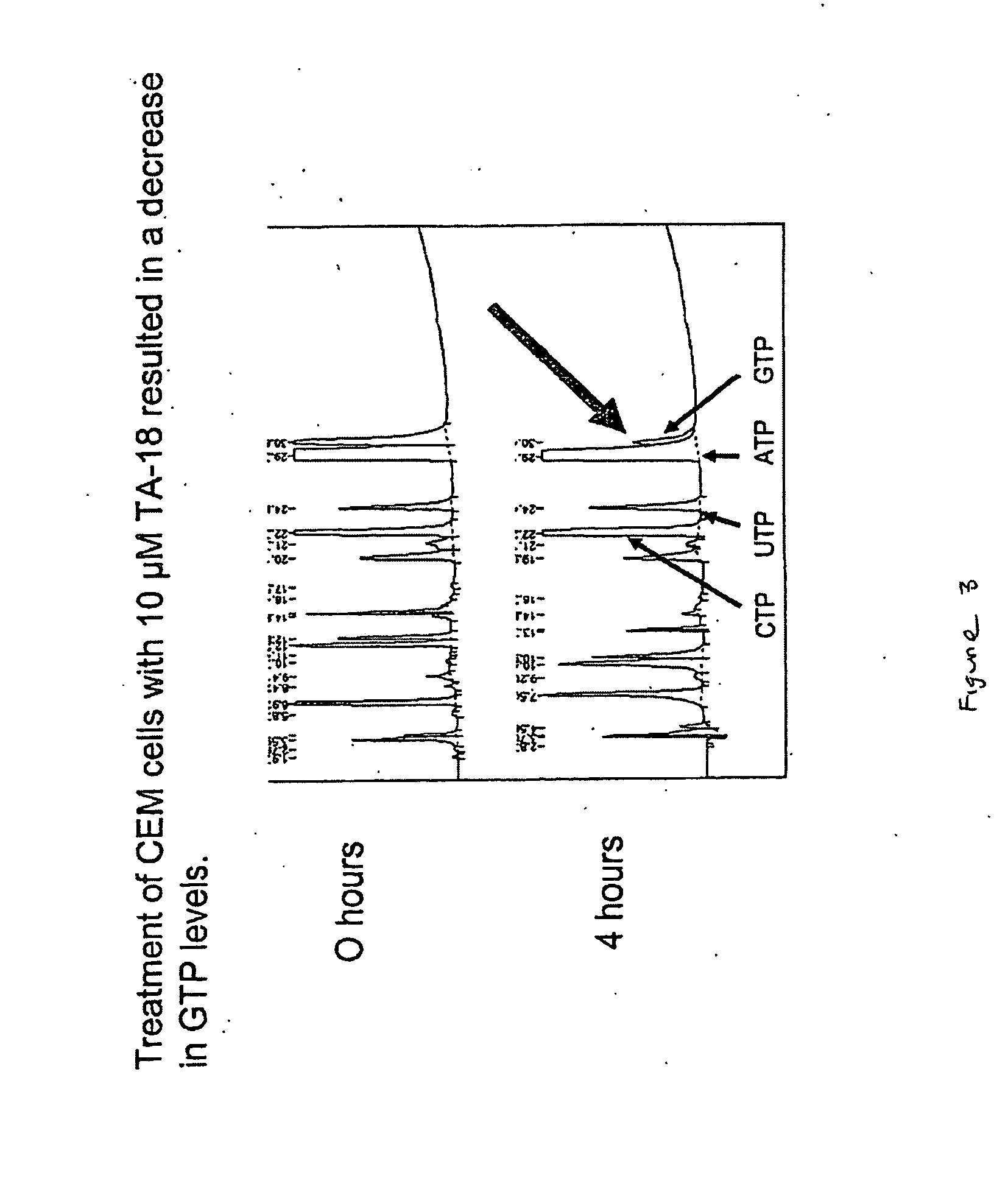
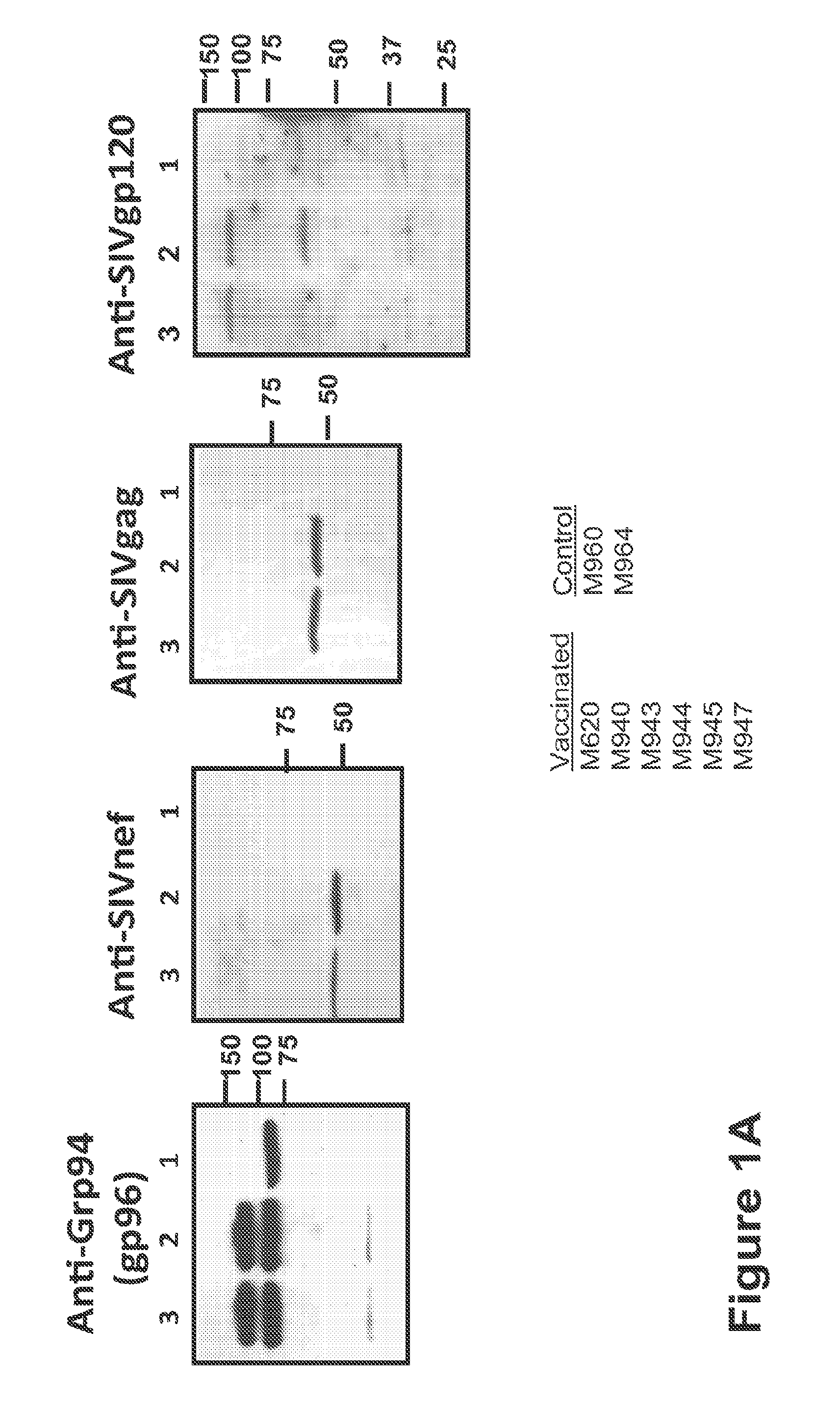
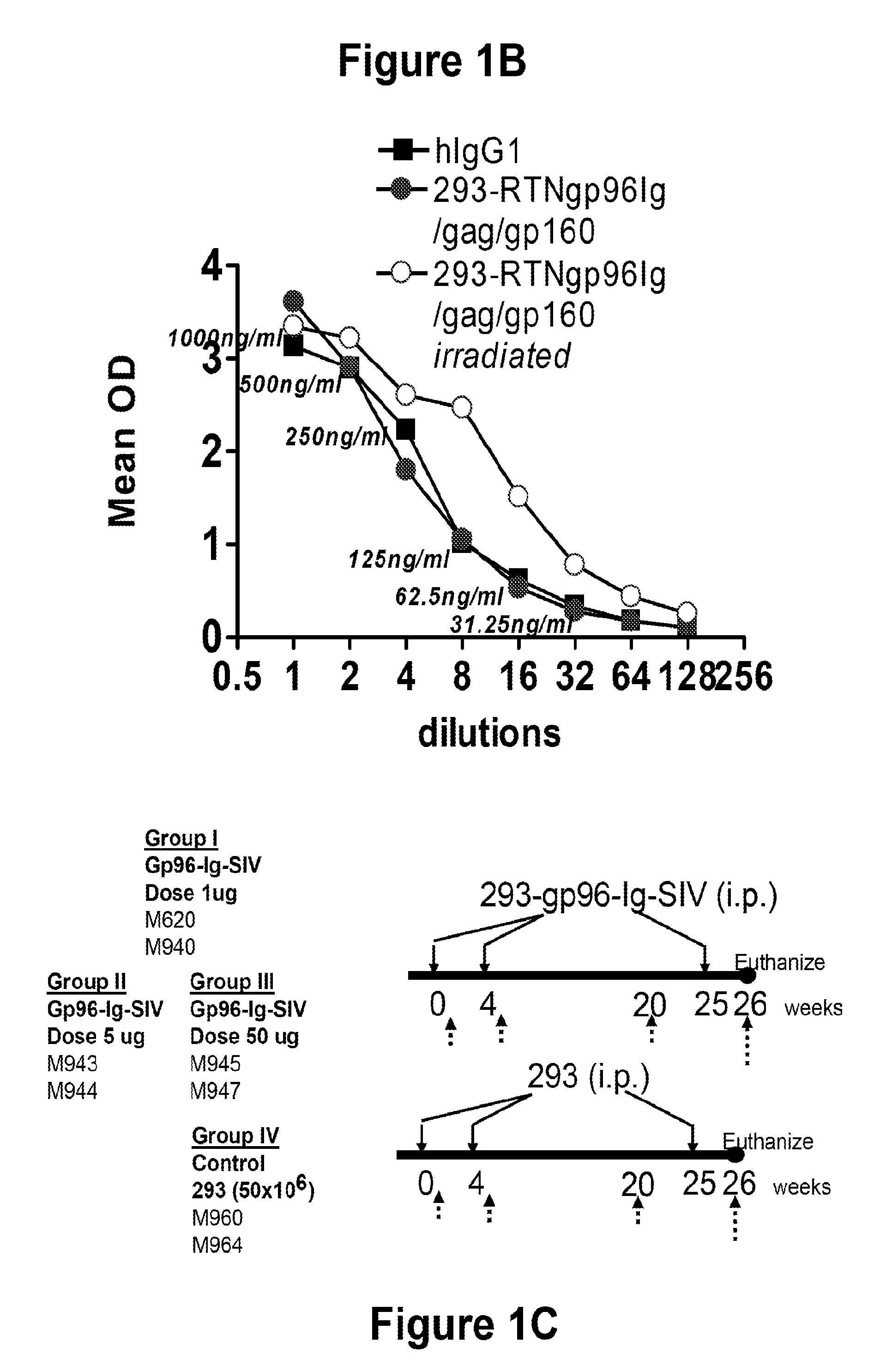
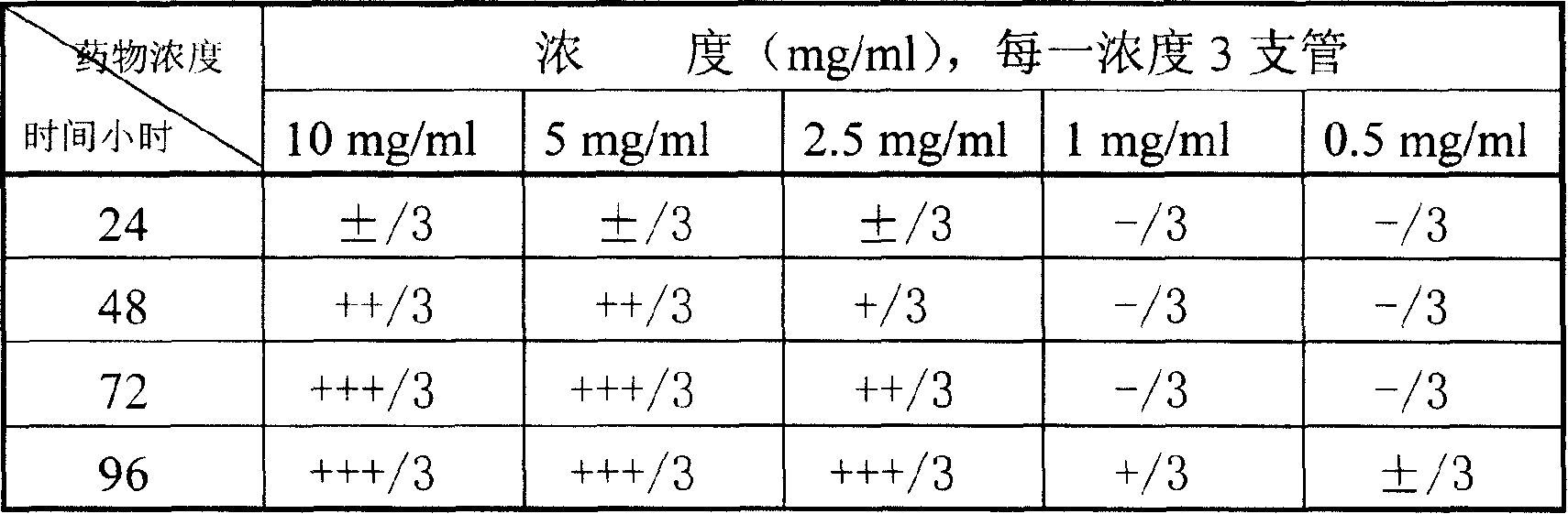
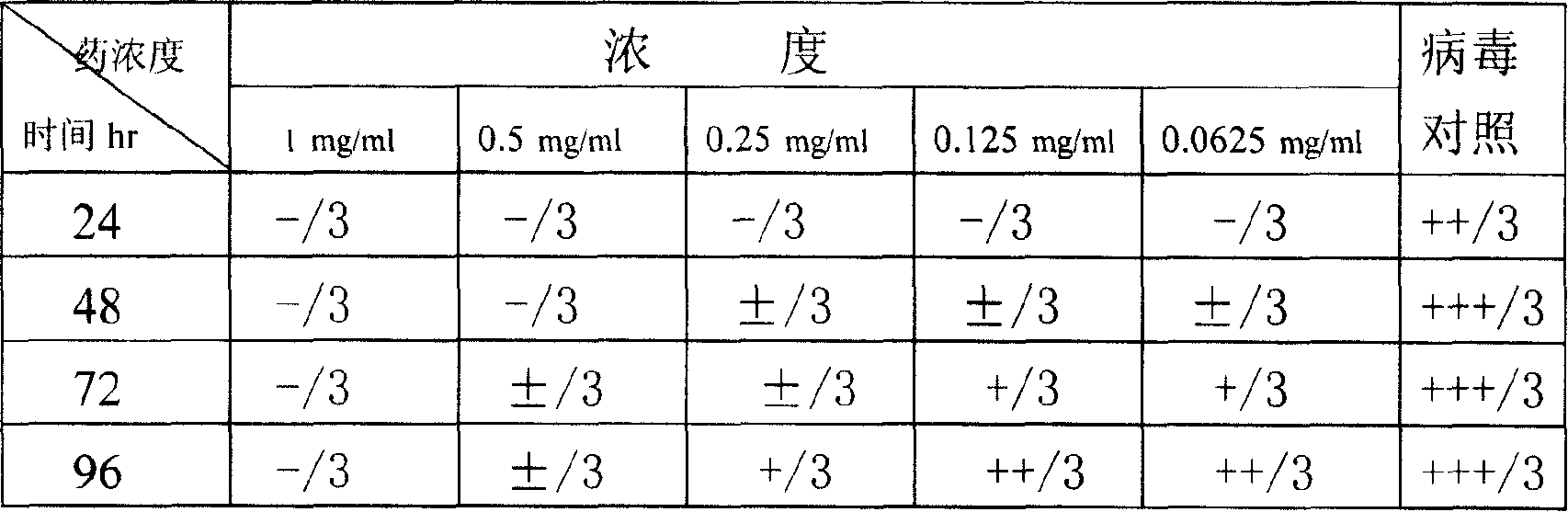
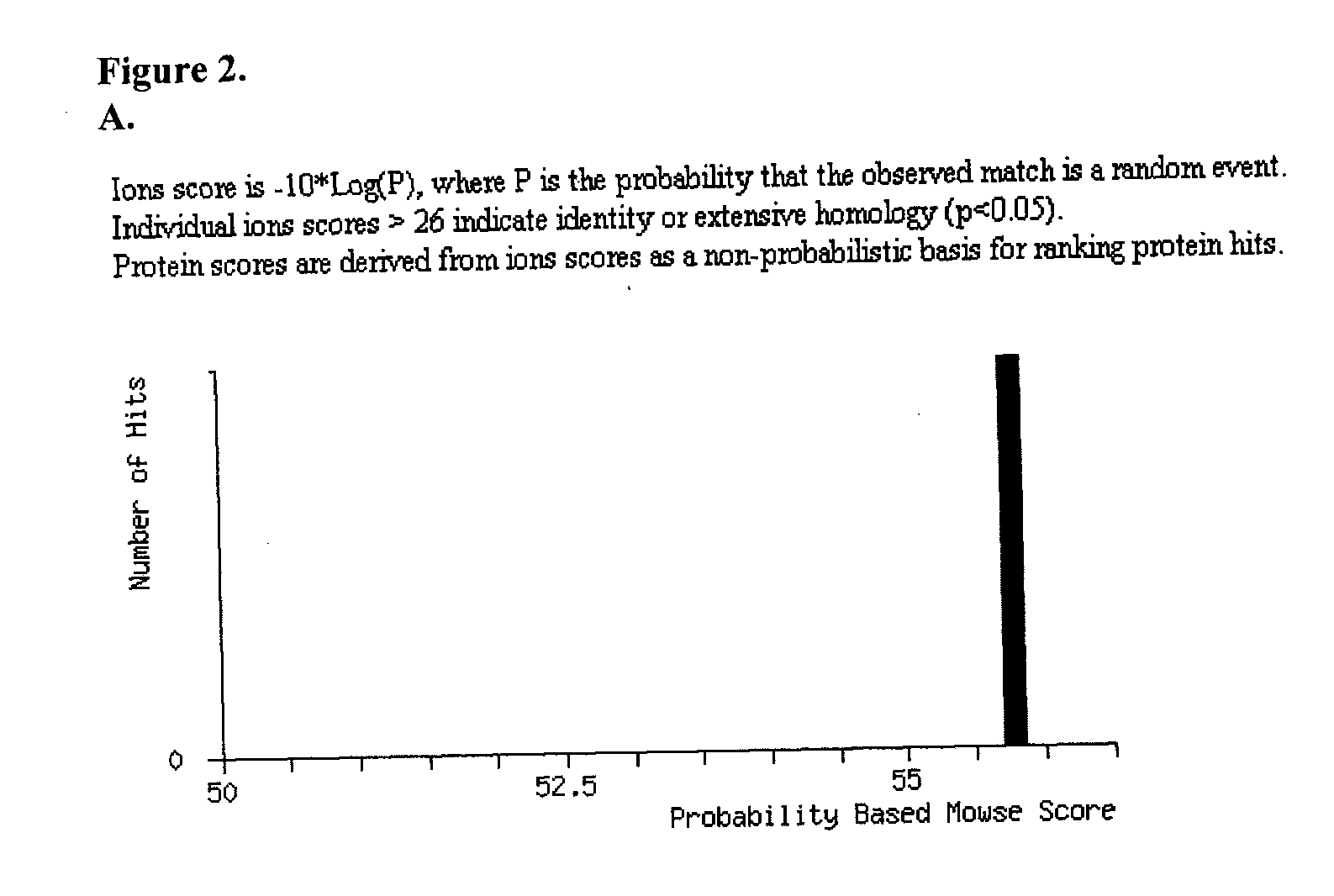
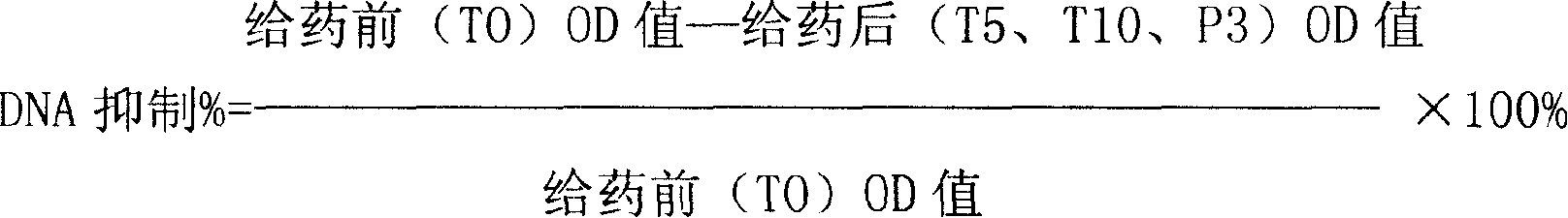Patents
Literature
32 results about "Hiv hcv coinfection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coinfection of HIV and hepatitis C (HIV/HCV coinfection) is relatively common. In people who contracted HIV from intravenous drug use, the coinfection rate is 50 to 90 percent. People are most likely to contract it from blood that contains the virus.
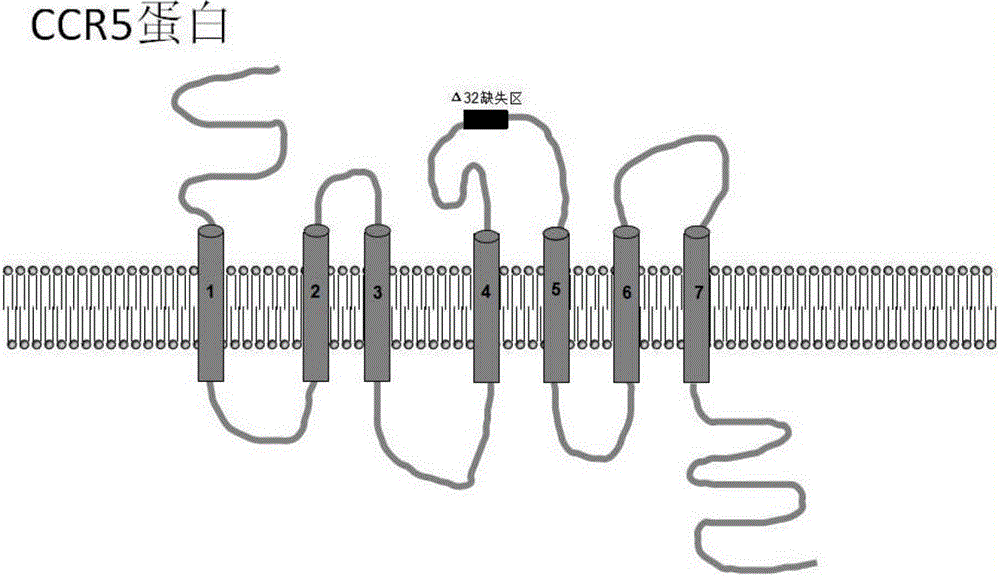
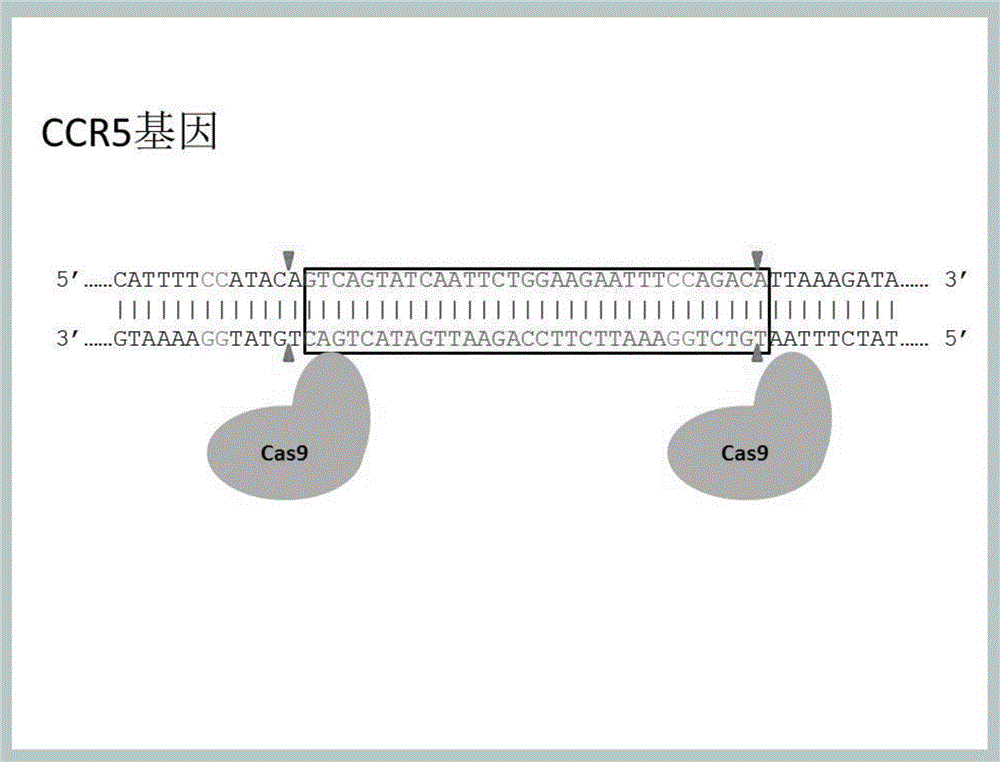
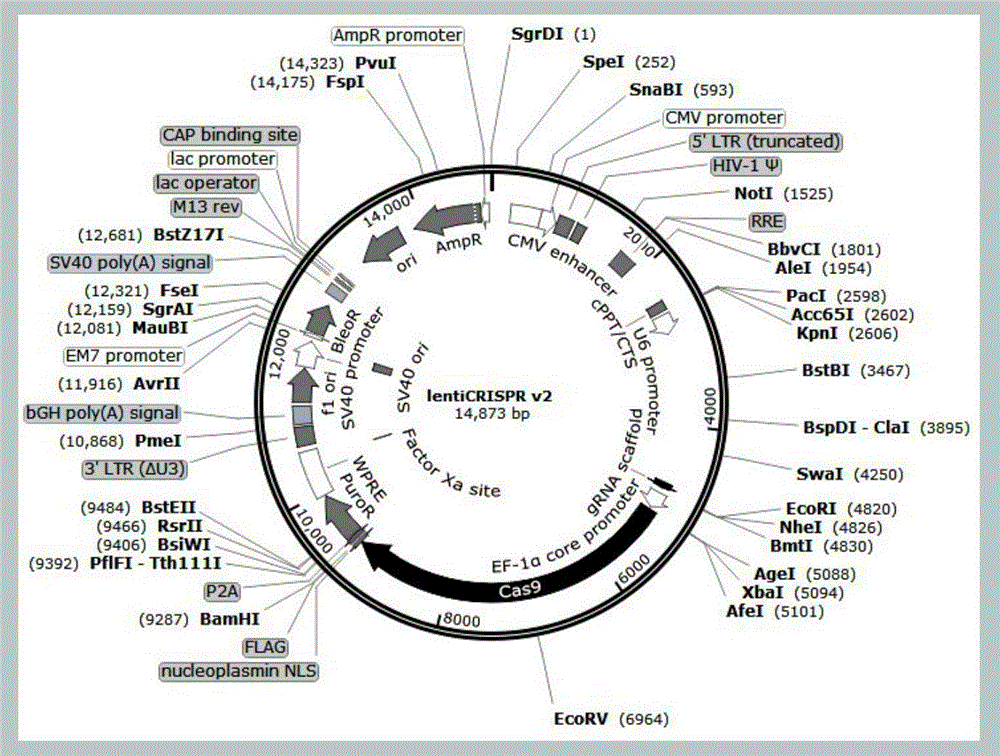
Method for inducing CCR5-delta32 deletion with genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9
The invention relates to a method for successfully inducing cell chemokine receptor CCR5 genes to be mutated into CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes with a new genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9. CCR5 is an important receptor for human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) to invade personal host cells. CCR5-delta32 deletion means deletion of 32 basic groups occurs in a CCR5 coding region, so that the sequence after the 185th amino acid is changed, and early termination occurs. CCR5-delta32 biallelic-gene homozygous deletion has natural resistance to HIV infection, and can not be infected by HIV. By means of the method, a slow virus packaging system and the CRISPR technology are used at the same time; as the slow virus infecting host range is wide, the method can be applied to cells such as bone marrow stem cells and CD4T cells, and the CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes hopefully become medicine for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome or other diseases.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Combined therapy for treatment of HIV infection
InactiveUS7094413B2Good curative effectReduce resistanceBiocideSugar derivativesImmunodeficiency virusGastrointestinal complications
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical preparations and methods for treating individuals infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The pharmaceutical preparations comprise an immunomodulating agent and a anti-retroviral compound. The pharmaceutical preparations are used to treat HIV infected patients, particularly for gastrointestinal complications arising from viral infection. In addition, the pharmaceutical preparations of the present invention have the effect of raising the levels of CD4+ single positive and CD4+ and CD8+ double positive T cells, thus promoting restoration and normalization of the immune system following HIV infection.
Owner:SANGSTAT MEDICAL +1
Immunological adjuvant, and its application in preparing vaccine and medicine for anti-virus
InactiveCN1718243AImprove immune activityReach clearAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsAnti virusDisease
An immunoadjuvant used to prepare the antiviral vaccine or medicine for increasing the immune activity of the antigens for HBV, HCV, SARS coronavirus, fowl influenza virus, etc is a kind of human or animal's novel heat shock proteins gp96, hsp108 and hsp70.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compositions and methods for generating an immune response
InactiveUS20070048861A1Increase typeSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunodeficiency virusEukaryotic plasmids
The present invention relates to novel plasmid constructs useful for the delivery of DNA vaccines. The present invention provides novel plasmids having a transcription cassette capable of directing the expression of a vaccine nucleic acid insert encoding immunogens derived from any pathogen, including fungi, bacteria and viruses. The present invention, however, is particularly useful for inducing in a patient an immune response against pathogenic viruses such as HIV, measles or influenza. Immunodeficiency virus vaccine inserts of the present invention express non-infectious HIV virus-like particles (VLP) bearing multiple viral epitopes. VLPs allow presentation of the epitopes to multiple histocompatability types, thereby reducing the possibility of the targeted virus escaping the immune response. Also described are methods for immunizing a patient by delivery of a novel plasmid of the present invention to the patient for expression of the vaccine insert therein. Optionally, the immunization protocol may include a booster vaccination that may be a live vector vaccine such as a recombinant pox virus or modified vaccinia Arbora vector. The booster live vaccine vector includes a transcription cassette expressing the same vaccine insert as the primary immunizing vector.
Owner:ROBINSON HARRIET L +11
Cranesbill total flavonoid extract and use in preparation of anti-virus medicine
InactiveCN1434052APromote absorptionGood effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAnti virusHepatitis B virus
The present invention relates to a cranesbill total flavone extract and its application in preparation of anti-virus medicine. The external and internal tests show that it has the action of inhibit herpes virus, influenza virus, hepatitis B virus and AIDS virus. Said invented cranesbill total flavone extract and its extract effective component quercetin-3-O-beta-D-galactopyranose and added auxiliary material can be made into the dosage forms of capsule, tablet, grnaules and injection for curing viral hepatitis, viral influenza, herpes virus infection and AIDS virus infection.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Enhanced method and composition for the treatment of hiv+ tuberculosis patients with Anti-retroviral drugs and liposomal encapsulation for delivery of reduced glutathione
InactiveUS20120244212A1Increase intracellular and extra cellular antioxidantsReduced glutathioneAntibacterial agentsBiocideNucleoside Reverse Transcriptase InhibitorDisease
The invention is the use of a therapeutically effective amount of glutathione (reduced) in a liposome encapsulation for oral administration to improve symptoms of illnesses that are related to tuberculosis and HIV and more generally viruses and for the treatment and prevention of virus, particularly HHV-6 and EBV, which liposomal encapsulation of glutathione (reduced) is referred to as liposomal glutathione. The application references specifically reduced glutathione and its importance, and how to stabilize it effectively so it can be taken orally, and need not be refrigerated. New uses for tuberculosis are discussed. The combination is proposed of reduced glutathione and Highly Active Anti-Retroviral Therapy having at least one pharmaceutical composition selected from the group of Nucleoside / tide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs), Protease Inhibitors (PIs), and Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NnRTIs), and further anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Owner:GUILFORD FREDERICK TIMOTHY
Azole nucleosides and use as inhibitors of RNA and DNA viral polymerases
InactiveUS20100129317A1Inhibition is effectivePrevent slippingBiocideSugar derivativesCrimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virusPolymerase L
Azole nucleosides represented by the formulae (I) and (II); wherein A=C or N B═C or N X═H; C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, heterocyclo, halogen such as F, Cl, Br and I; OH, NH2, NH—(C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heterocyclo); Z═H; C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkynyl, aryl, heterocyclo, halogen such as F, Cl, Br, I; OH NH2, NH—(C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heterocyclo; E=(CH2)HONHR; n is an interger from 0-6 and more typically 0-3; R1= aryl or heterocyclo; each of W, Y, R is individually selected from the group consisting of H; C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, alkenyl, cycloalkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, heterocyclo, halogen such as F, Cl, Br, and I; O, OH, Oalkyl, Oaryl, NH2, NH(C1-C6 alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl or heterocyclo); provided that at least one of W, Y, and R is other than H and wherein both W and Y together can be ═O; and each D individually is OH, Oalkyl, Oaryl, FL and H; pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, prodrugs thereof and mixtures thereof are provided. Compounds of this disclosure are useful as inhibitors of viral RNA and DNA polymerases such as, but not limited to, Influenza, hantaan Virus, Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, Polio, Coxsackie A and B, Rhino, Echo, orthopoxvirus (small pox), HIV, Ebola, and West Nile virus polymerases; and especially orthopoxvirus, HIV, and hepatitis B.
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP +1
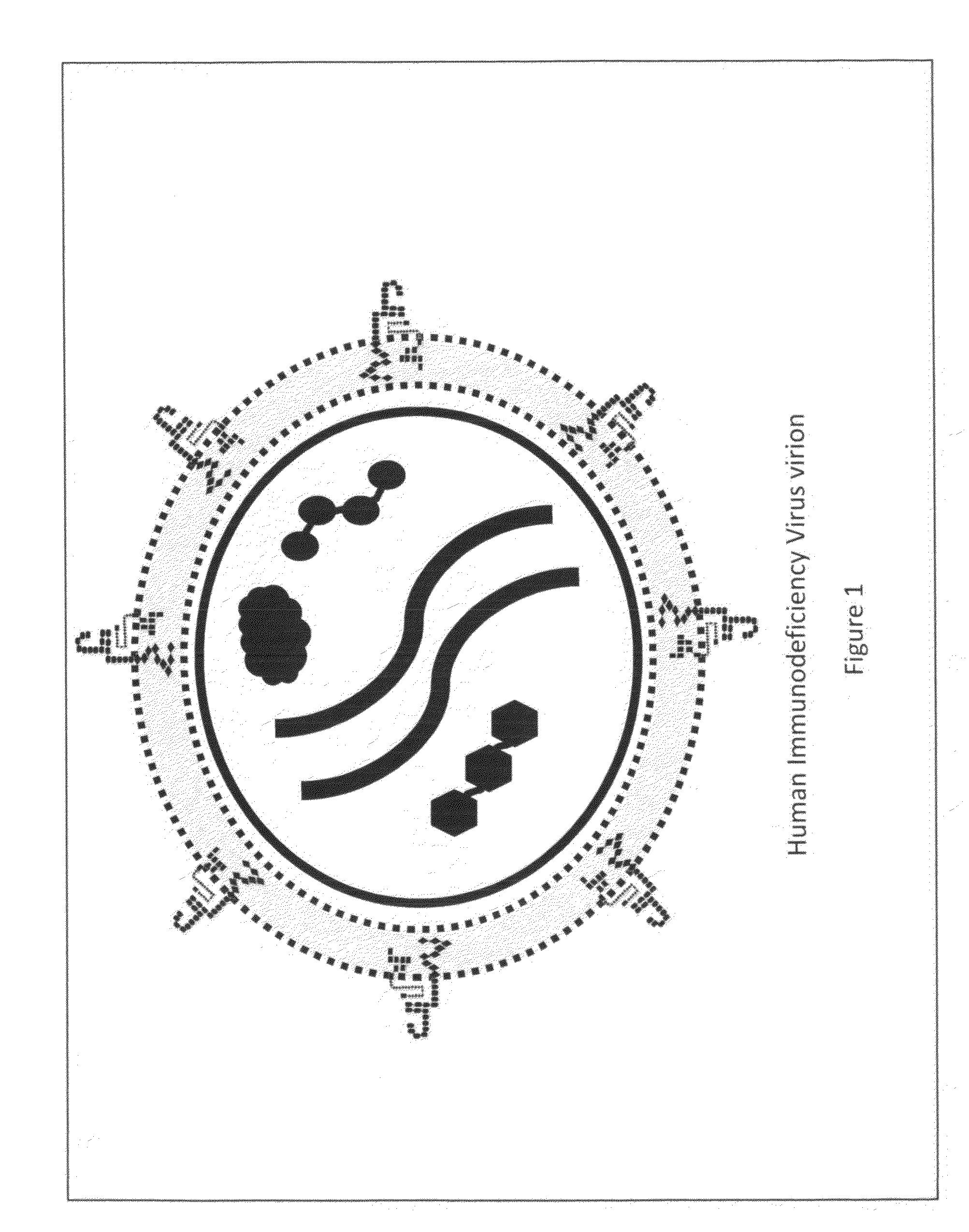
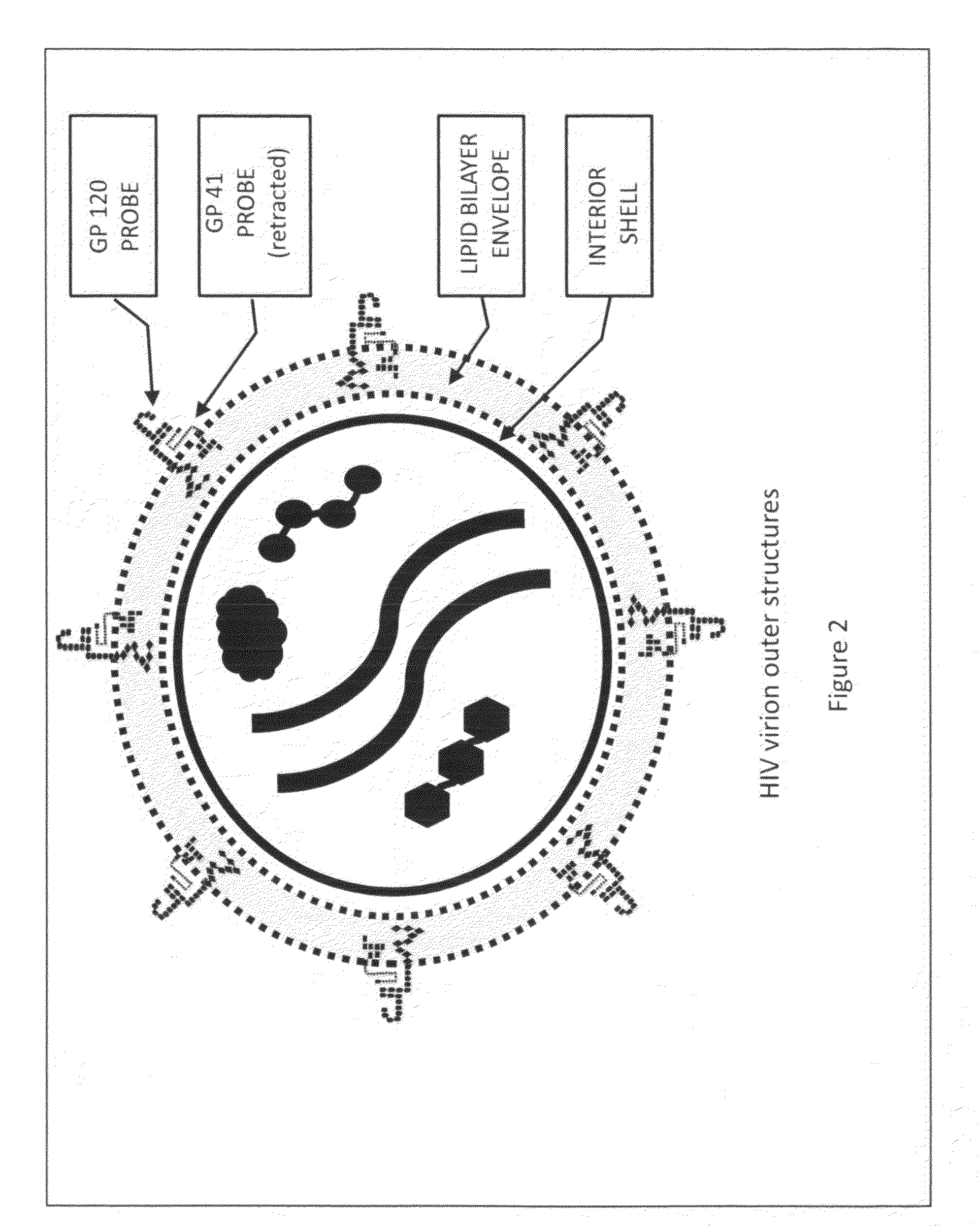
Anti-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Surrogate Target Agent Technology Filter Intended to Neutralize or Remove Human Immunodeficiency Virus Virions From Blood
InactiveUS20090281473A1Effectively averting AIDSHaemofiltrationMedical devicesImmunodeficiency virusHuman immunodeficiency virus disease
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus posses a significant threat to the world's population. Current strategies utilized to treat infectious agents have not been adequate to contain and eradicate this deadly viral infection. HIV seeks out its host, a T-Helper cell, by utilizing glycoprotein 120 probes to engage a CD4 cell-surface receptor located on the surface of a T-Helper cell. Developing blood filtering techniques that incorporate filter mediums that offer HIV virion's probes the opportunity to engage the cell-surface receptors they are seeking offers a means of neutralizing and removing HIV. Filtering the blood of a patient with filter mediums comprised of T-Helper cells, sheets of lipid bilayer or virus-like structures with each type of medium possessing cell-surface receptors intended to attract and engage HIV virions provides an effective strategy to prevent and treat AIDS.
Owner:SCHEIBER LANE BERNARD +1
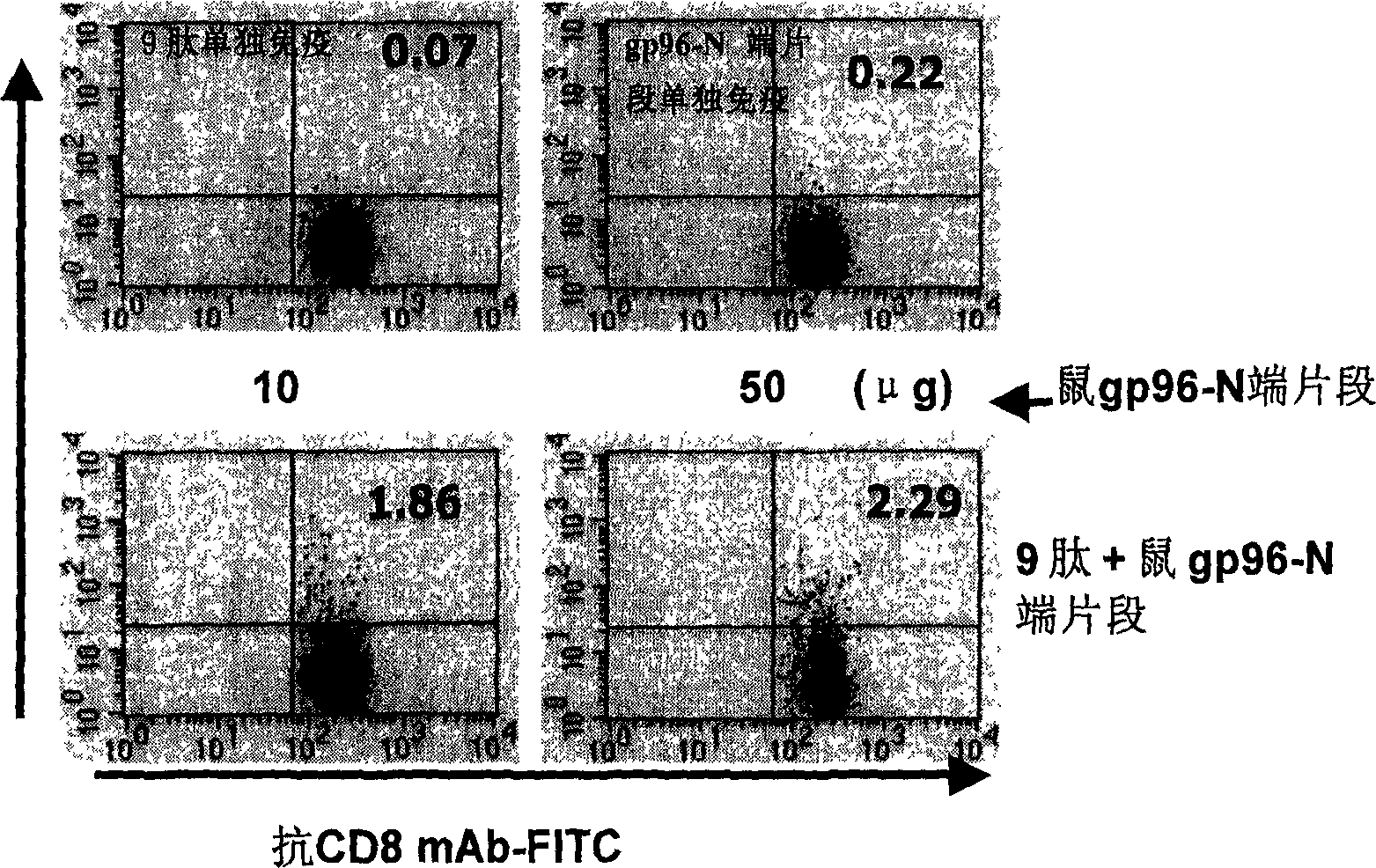
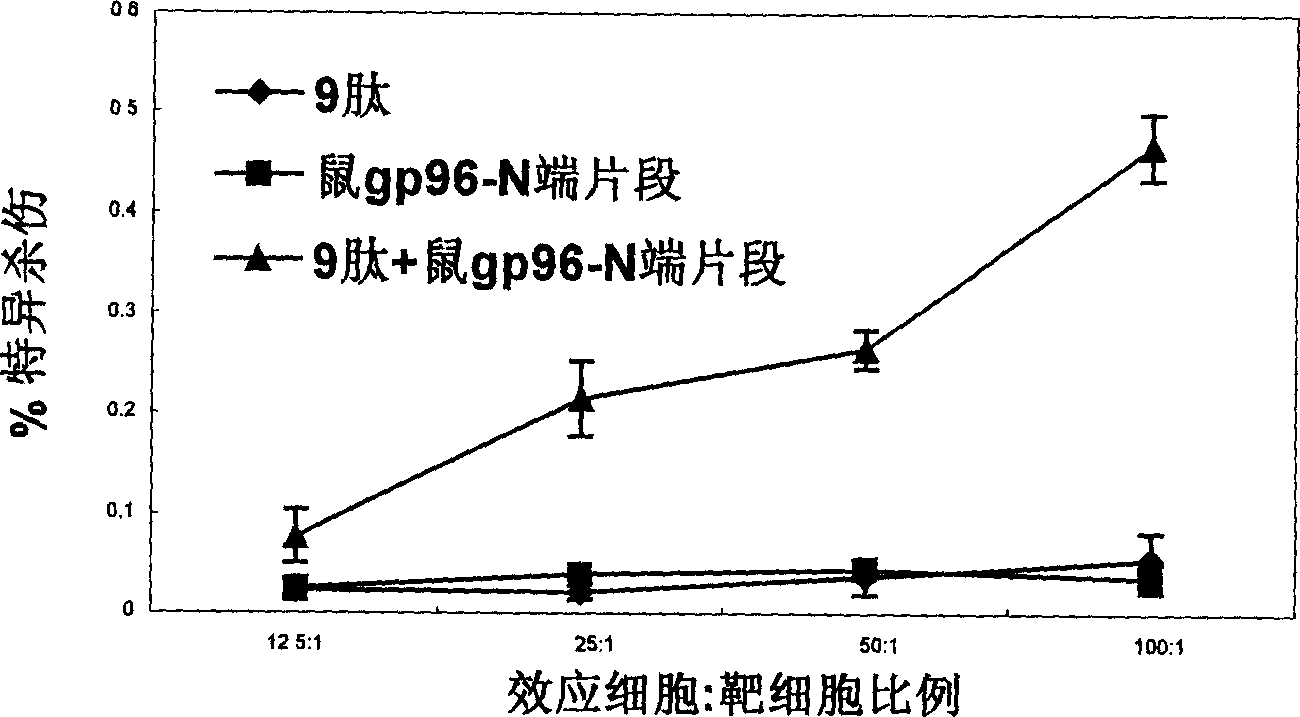
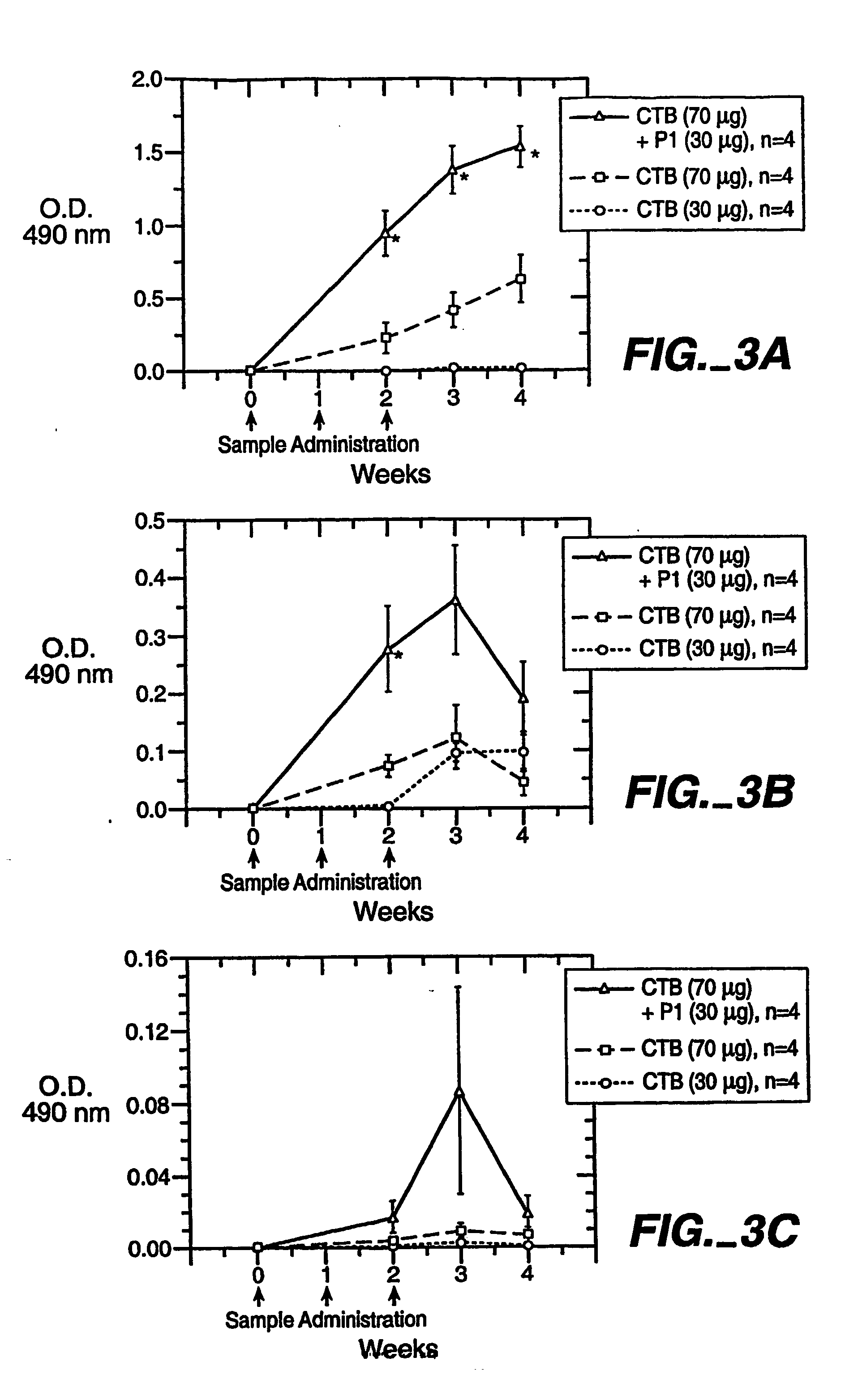
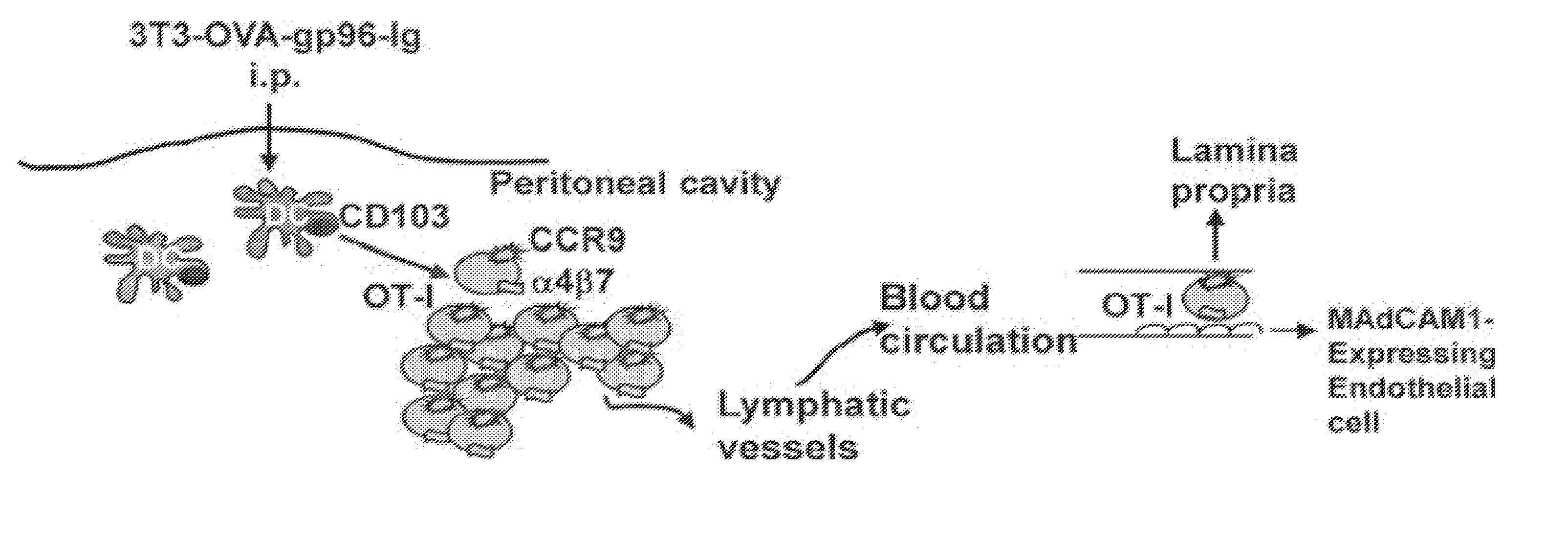
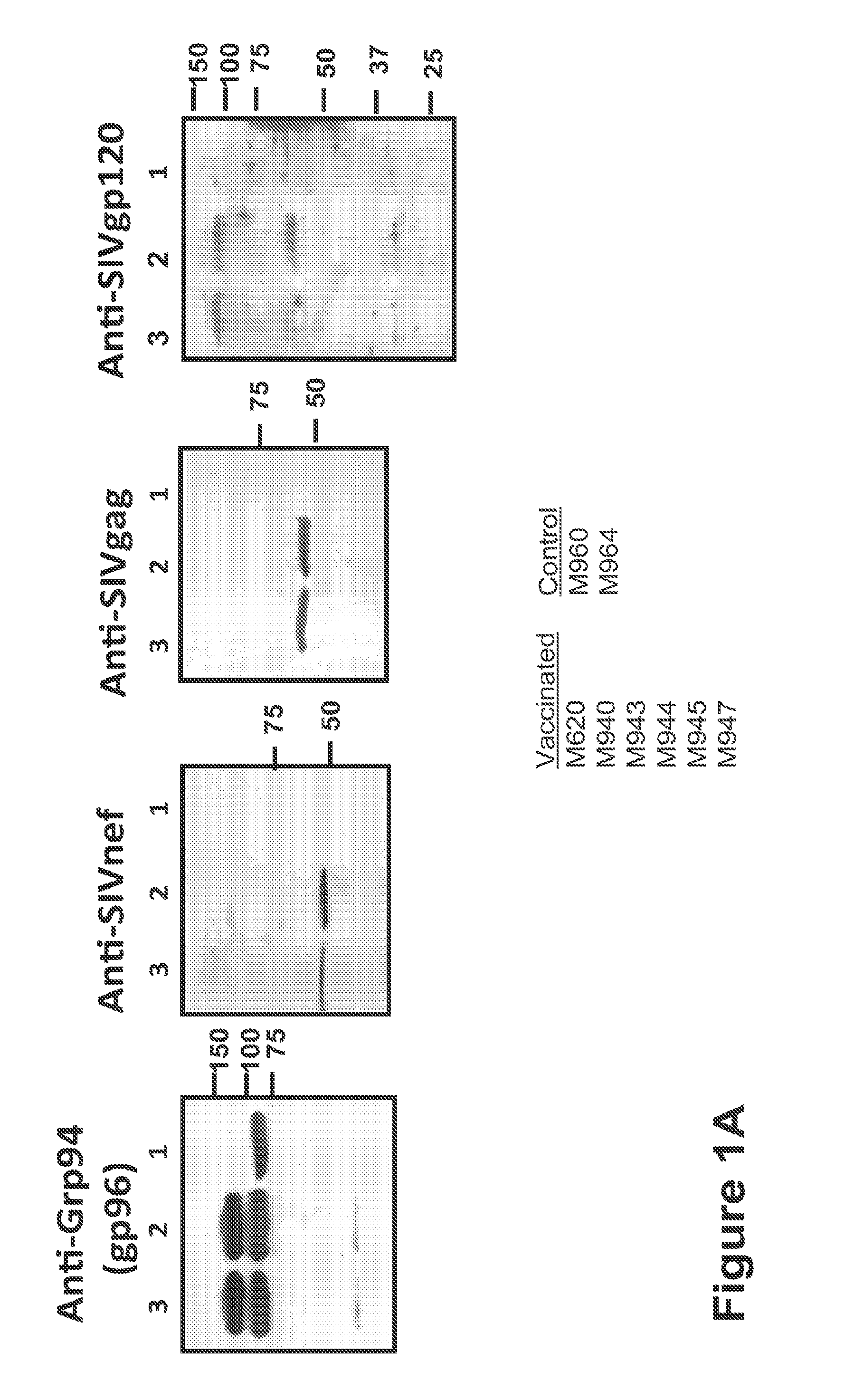
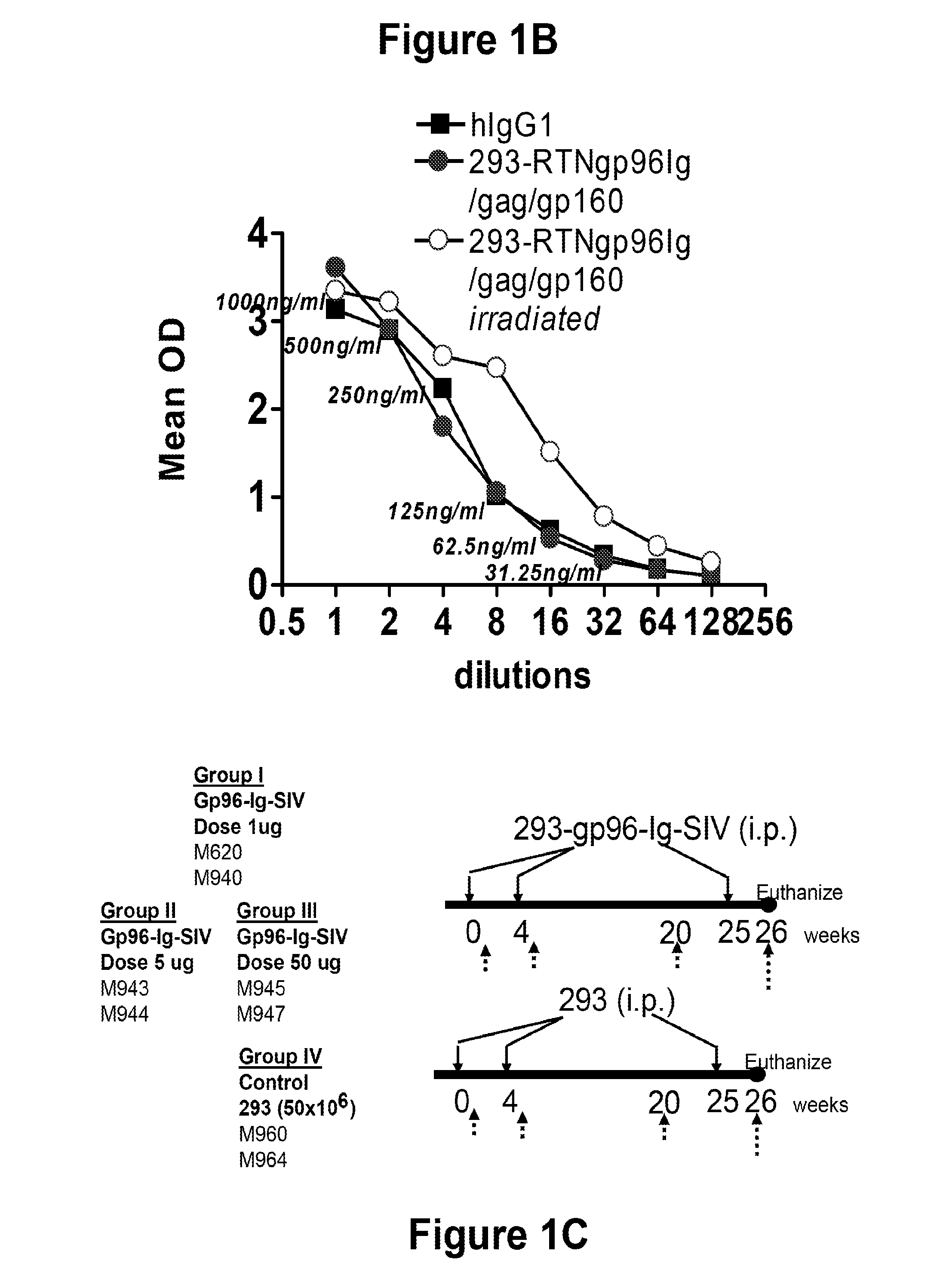
Hiv/siv vaccines for the generation of mucosal and systemic immunity
Compositions of genetically engineered, secreted gp96 (gp69-Ig) induced strong mucosal and systemic immune responses and CD8 expansion that was independent of CD4 help. Immunization of patients with gp96-Ig immunization is especially attractive for induction of mucosal and systemic immunity to SIV / HIV and other diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
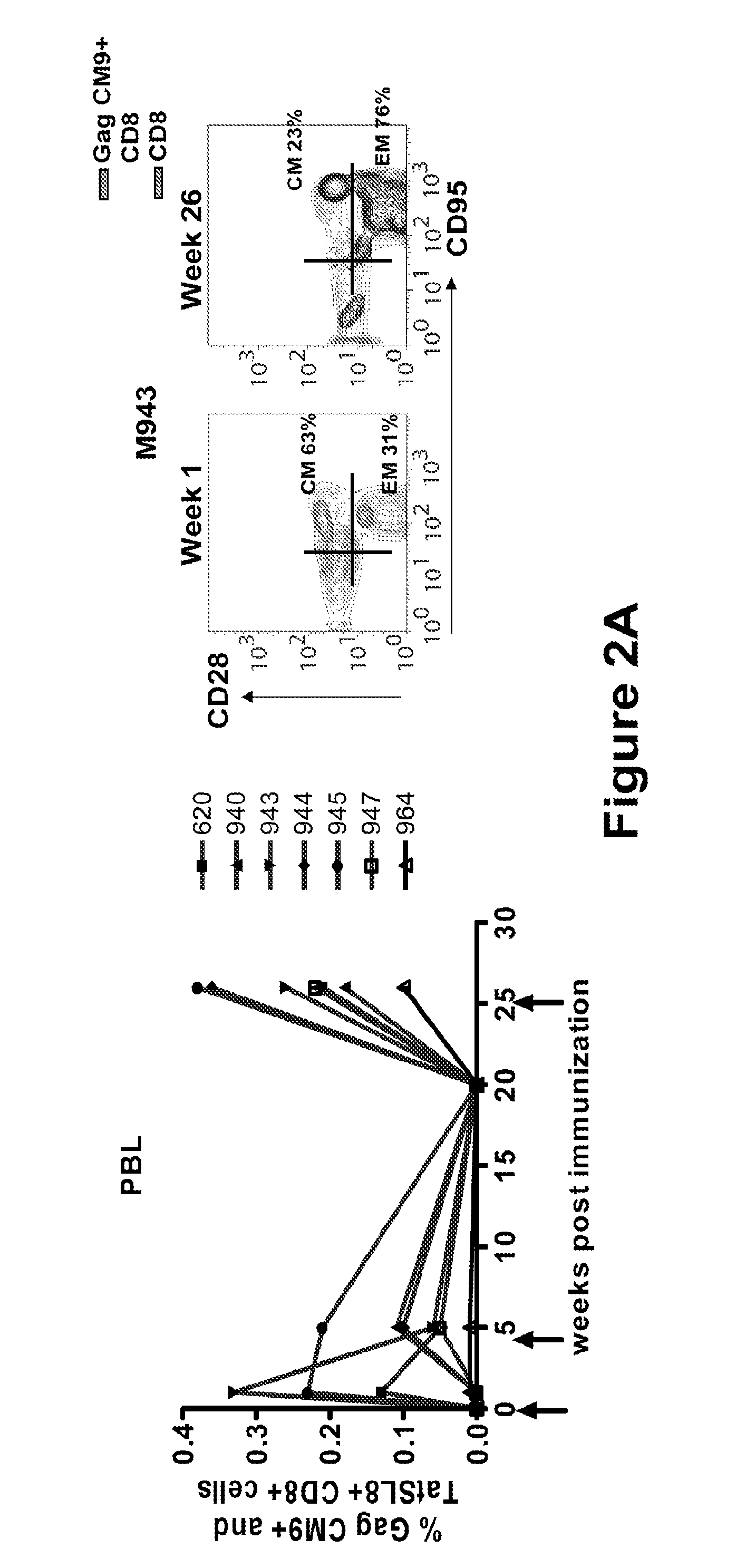
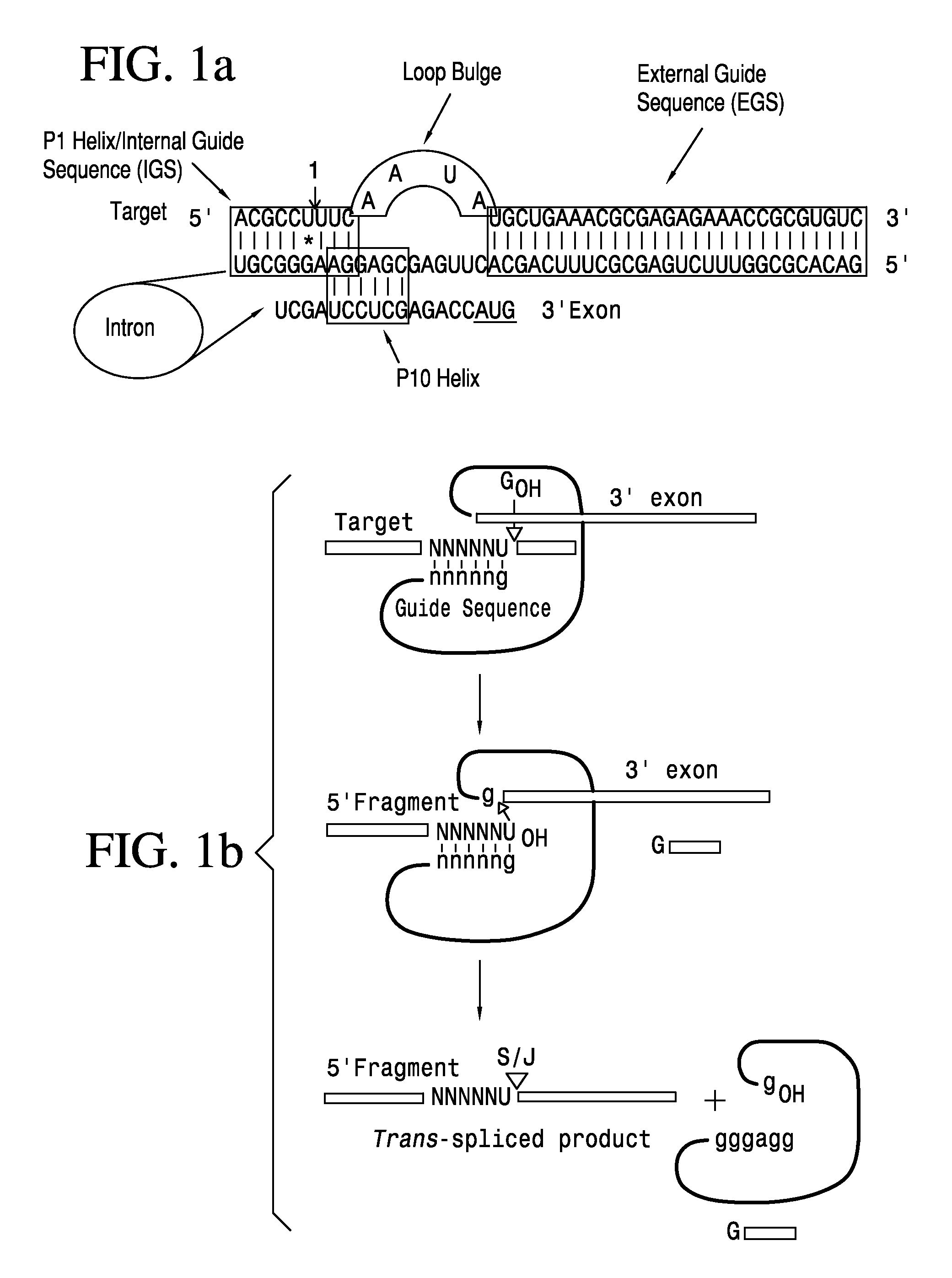
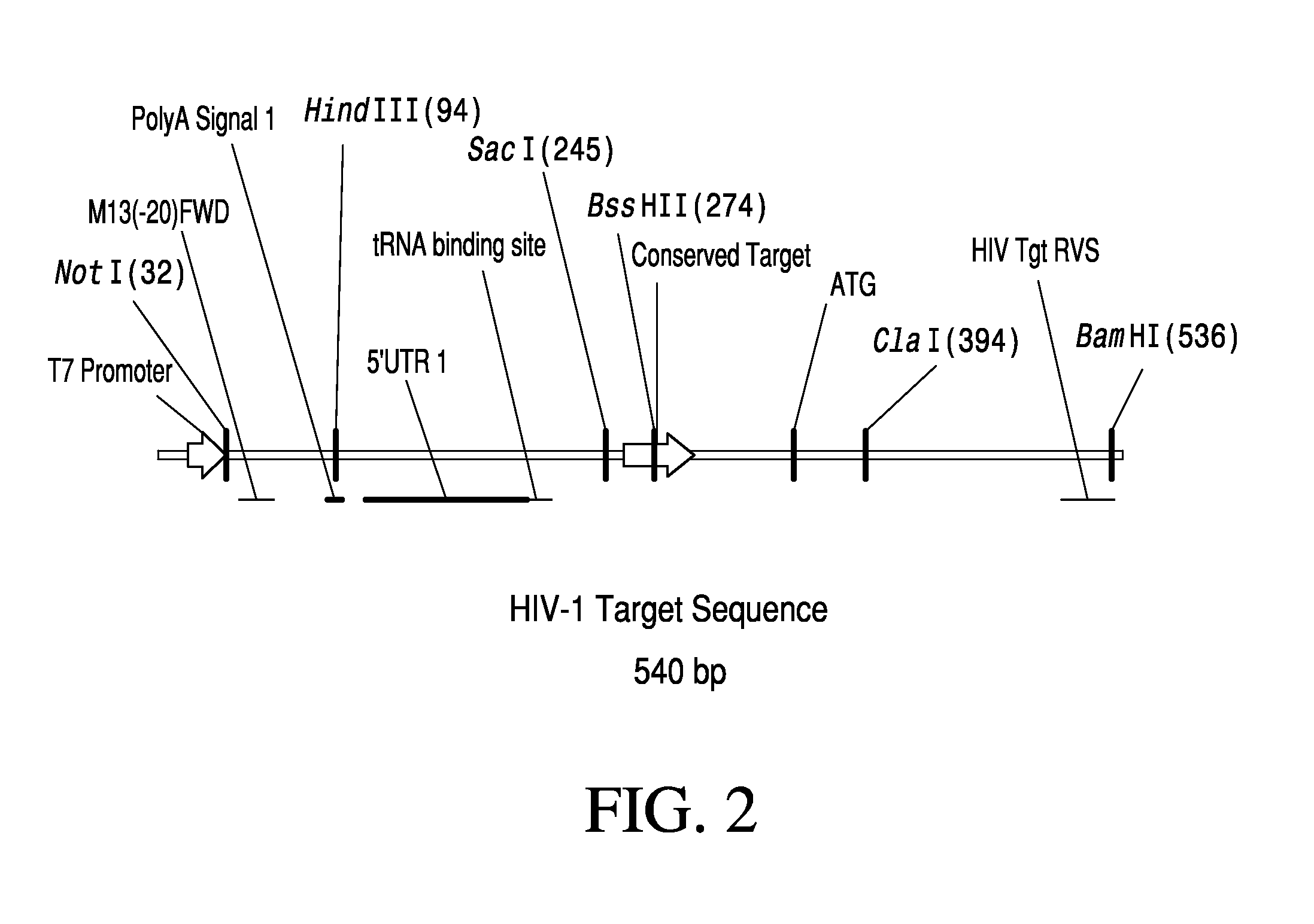
Anti-HIV Group I Introns and Uses Thereof in Treating HIV Infections
ActiveUS20120276071A1Reduce probabilityReduce viral loadBiocideSugar derivativesAbnormal macrophageIntein
Described is a unique class of antiviral molecule that can be applied to control and eliminate HIV infection in patients using myeloablation therapies and replenishment with transformed bone marrow stem cells programmed to express the antiviral molecule. These anti-viral molecules target the HIV genome in a highly conserved domain, and when expressed in cells prior to infection will cause the cell to die upon infection with HIV. Cell death insures no proliferation of new virus. Reconstituting the immune system with cells expressing these antivirals prevents re-establishment of HIV infection from reservoirs in the re-established lymphocyte and macrophage populations. Over time, reservoirs will be depleted entirely, effectively eliminating the virus. In effect, this new type of antiviral can be used to cure HIV infections.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Application of triptolide in preparation of medicament for treating or preventing human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV)
InactiveCN102755335AEnhanced inhibitory effectWide variety of sourcesOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsPeripheral blood mononuclear cellHuman immunodeficiency
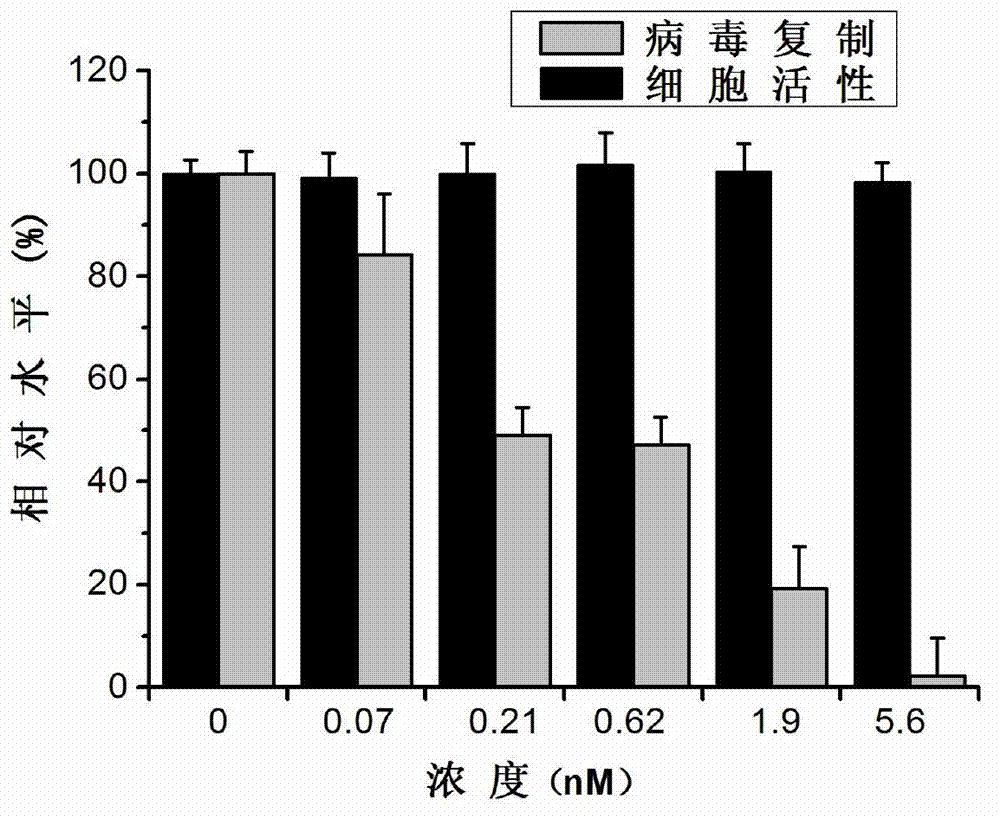
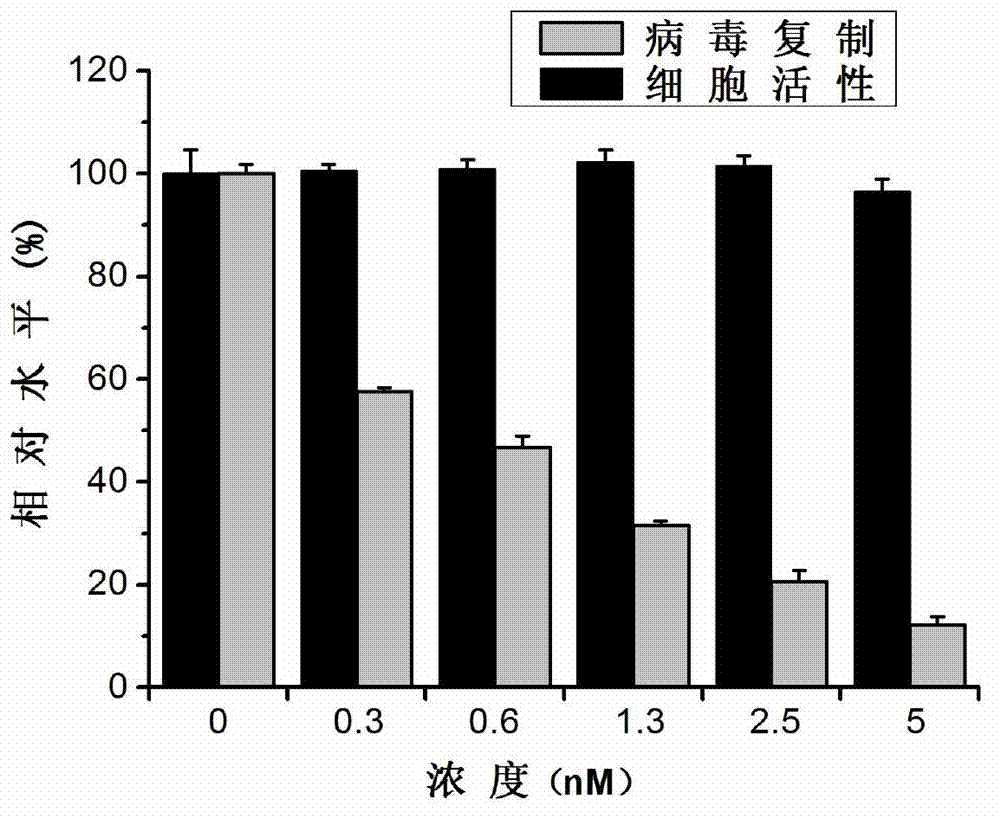
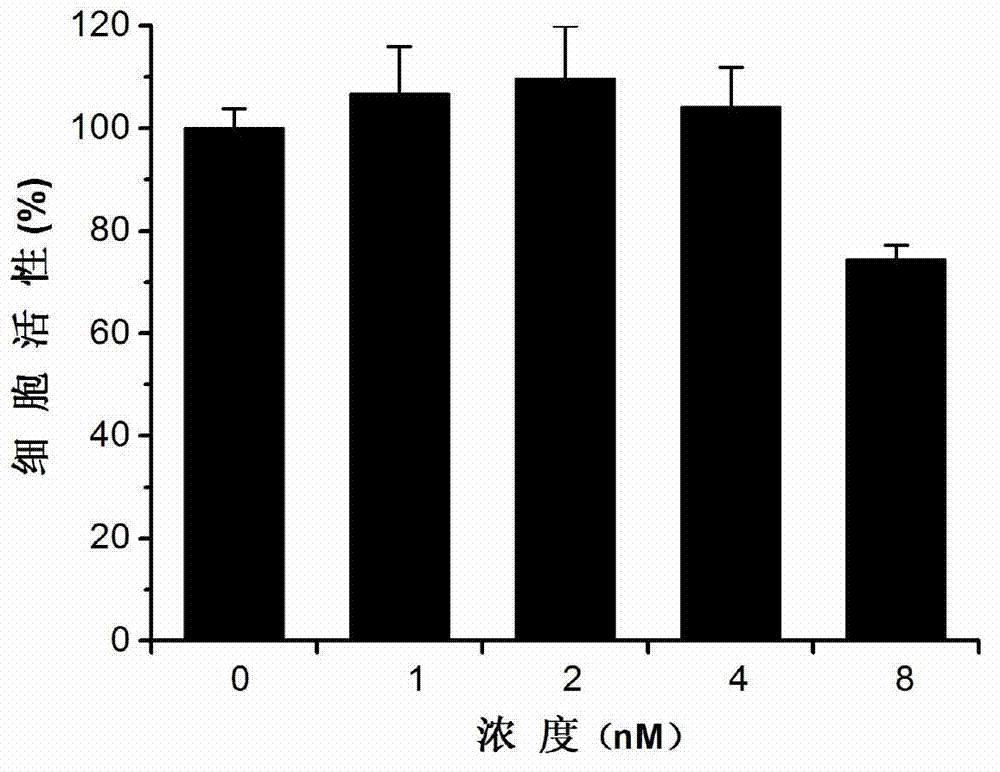
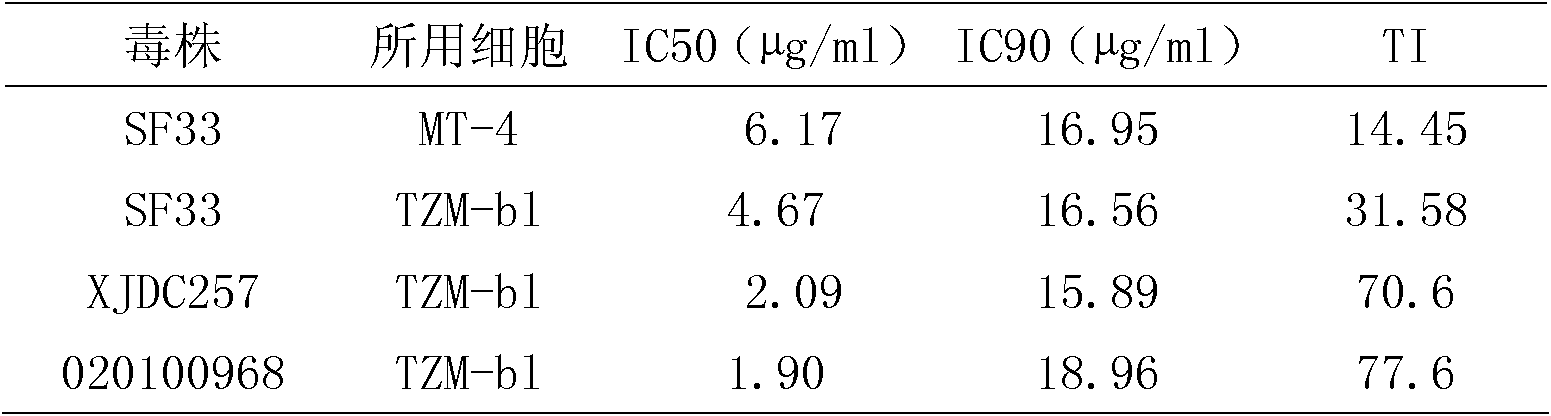
The invention discloses an application of triptolide in preparation of a medicament for treating or preventing human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV). The triptolide is diterpenoid naturally existing in roots of tripterygium wilfordii hook, and can dose-dependently inhibit replication of I type HIV (HIV-1) in cells in vitro. The half inhibitory concentrations on HIV-1 inhibition in TZM-b1 cells, JurkatT lymphocytes and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells are respectively 0.32nM, 0.45nM and 1.1nM. The triptolide has a remarkable inhibiting effect on the replication of the HIV-1 in the TZM-b1 cells, the JurkatT lymphocytes and the human peripheral blood mononuclear cells; and the triptolide is an active ingredient in Chinese medicinal tripterygium wilfordii hook, so the triptolide is wide in source. The compound has a broad prospect for developing anti-HIV-1 medicaments.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Antiretroviral drug formulations for treatment of children exposed to hiv/aids
InactiveUS20110117193A1Reduce morbidityDissolve fastPowder deliveryBiocideImmunodeficiency virusMother to child transmission
The present disclosure provides fast disintegrating formulations for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) in patients such as neonatal, perinatal and pediatric children. Neonatal and perinatal formulations provide for the prevention or reduction of incidence of mother to child transmission of HIV. Also provided are formulations and methods for treating pediatric children having HIV / AIDS. The orally administered fast disintegrating formulations are in granule and tablet form and are specially formulation for children to increase adherence to treatment protocols.
Owner:DUQUESNE UNIVERSITY
Composition and method for enhancing immune response
InactiveUS20060013831A1Decreasing nicotine useBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsBiological bodyAntigen
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Composition of starwort total glycopeptides and total flavone and preparation method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101390921ASafe broad-spectrum antiviral drug actionHigh-efficiency broad-spectrum antiviral drugsBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAlkaneDisease
Disclosed is a dark brown combination with the molecular of 1,000-100,000, which is composed of total glycopeptides ingredient and total flavonoid ingredient, and extracted from stellaria through three methods and used as safer and more efficient natural broad-spectrum anti-viral medicine. The total peptide part accounts for 15%-25% and is composed of 17 types of amino acids respectively according to the proportions, such as by proportion, such as aspartic acid, methionine and isoleucine; the total sugar accounts for 15%-30% and is composed of glucose, galactose and arabinose; the total flavonoid which is mainly apigenin glycoside accounts for 10%-40%; Oxygenated alkane which contains alcohols accounts for 25%-40%. The combination can be used as the medicines for the treatment of the diseases, including HIV, hepatitis viruses, influenza virus such as Highly-pathogenic avian influenza virus, condyloma virus, herpes virus and mumps virus, and have no toxicity after application; the combination can be made into more than 10 types of medicinal preparations and health care products, and avoid environmental pollution during the production process.
Owner:朱耕新
Hiv/siv vaccines for the generation of mucosal and systemic immunity
Compositions of genetically engineered, secreted gp96 (gp69-Ig) induced strong mucosal and systemic immune responses and CD8 expansion that was independent of CD4 help. Immunization of patients with gp96-Ig immunization is especially attractive for induction of mucosal and systemic immunity to SIV / HIV and other diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Application of bodinerin for preparing medicine to treat viral influenza and AIDS
InactiveCN1903249AEnhance pharmacological effectsAntiviralsPlant ingredientsDiseaseHiv hcv coinfection
Owner:YUNNAN INST OF MATERIA MEDICA
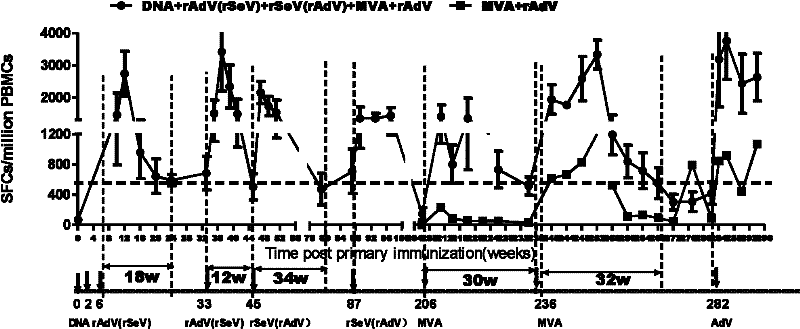
Sequential and repeated application of four or more HIV vector gene vaccines
ActiveCN102258779AIncrease sequential useInduce cross immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHIV ProteinsVector vaccine
The invention relates to a sequential and repeated application strategy of four or more HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) vector gene vaccines, capable of maintaining high-level specific immune response for a long time. The combined AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) vaccine for preventing and / or treating AIDS is capable of activating broad-spectrum anti-AIDS virus cellular immune response, and is composed of four or more AIDS vaccines. The different AIDS vaccines can contain the same HIV protein gene, one kind of AIDS vaccine is inoculated once, and each kind of vaccine can be inoculated twice continuously. After the four or more kinds of different vector vaccines are sequentially applied, the vector vaccines can be repeatedly and sequentially applied.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
Application of silverweed cinquefoil root extract to preparation of anti-AIDS medicament
InactiveCN102204970AInhibition of replication activityAntiviralsPlant ingredientsIn vitro cytotoxicityInhibitory effect
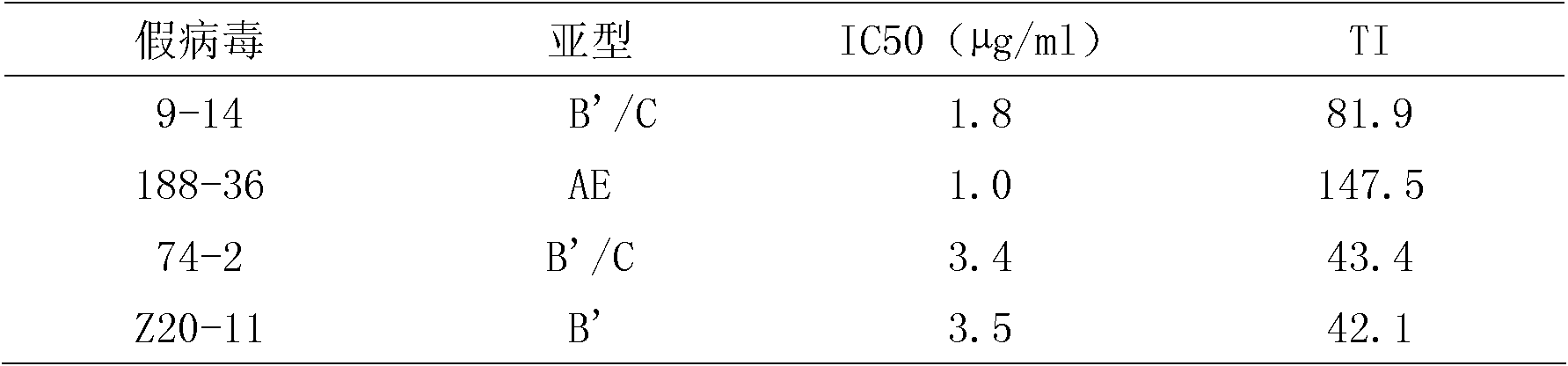
The invention discloses application of a silverweed cinquefoil root extract to the preparation of an anti-AIDS medicament. The anti-AIDS virus function of the silverweed cinquefoil root extract is observed by performing an in-vitro cytotoxicity test and an HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) in-vitro suppression test. As proved by test results, the silverweed cinquefoil root extract has certain suppression effects on HIV-1 standard strains, clinical strains and pseudo-viruses and has HIV replication suppression activity.
Owner:LOGISTICS UNIV OF CAPF +1
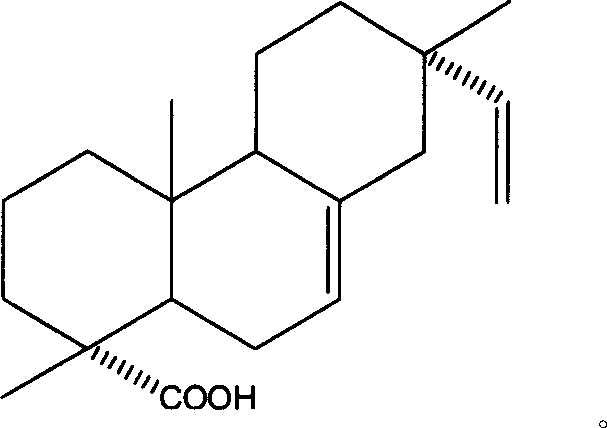
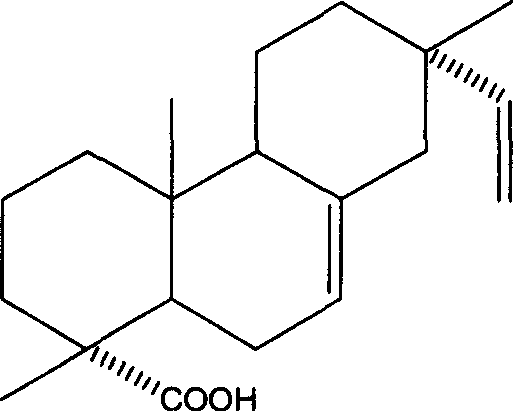
Use of 7,16-pimaric dienoic acid for preparing Anti-AIDS medicine
InactiveCN1977833AStrong inhibitory activityAntiviralsAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsMedicineIntegrase activity
The present invention belongs to the field of medicine technology, and it relates to an application of 7,16-pimaradiene acid for preparing medicine for resisting AIDS. Its external active detection for resisting AIDS virus proteinase or integral proteinase shows that its median effective inhibition concentration IC50 for AIDS virus HIV-1 proteinase is 33.68 m g / ml, and the median effective inhibition concentration IC50 for AIDS virus HIV-1 integral proteinase is 45.79 mu g / ml, so that it can be used for preparing medicine for resisting AIDS.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
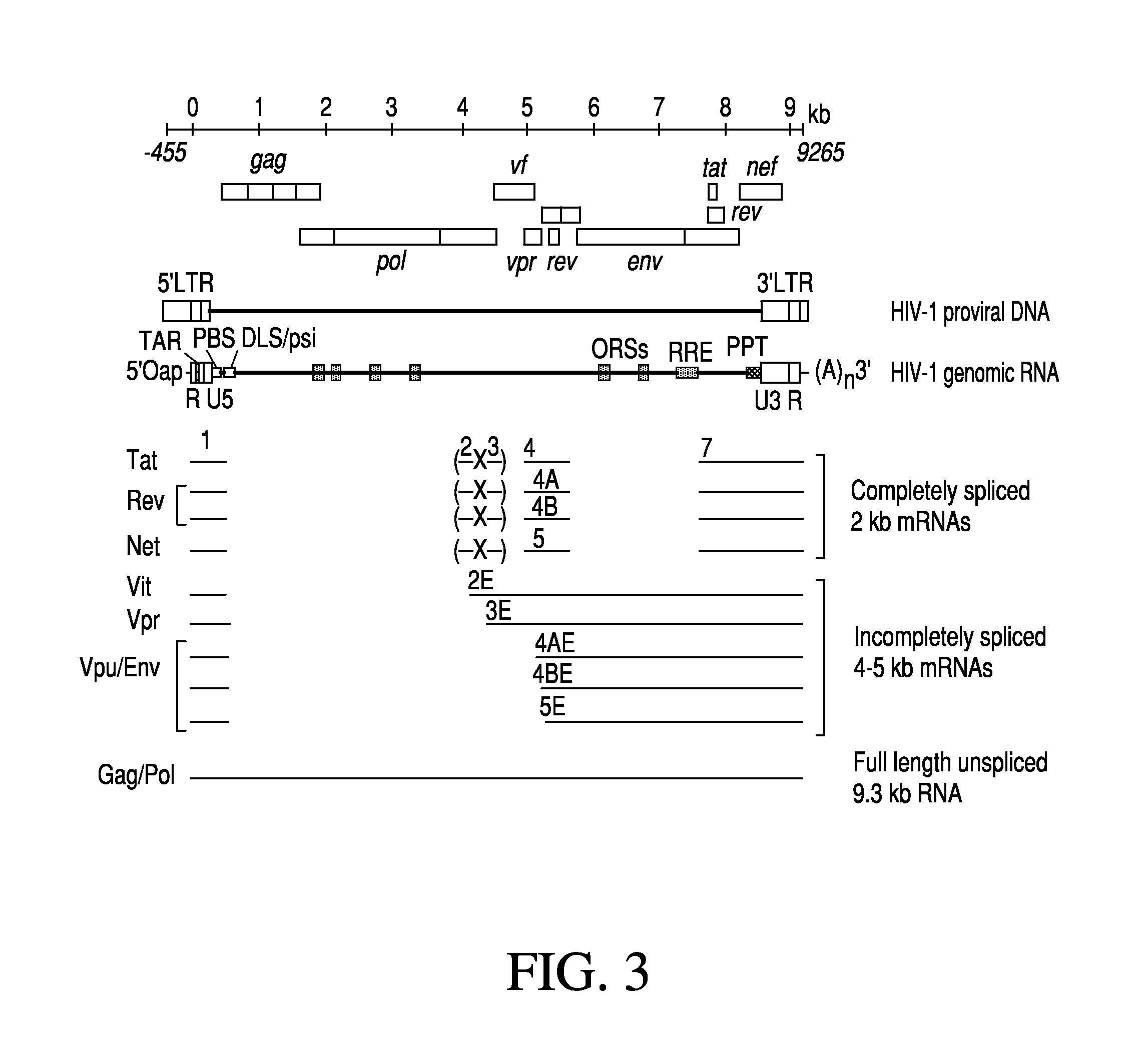
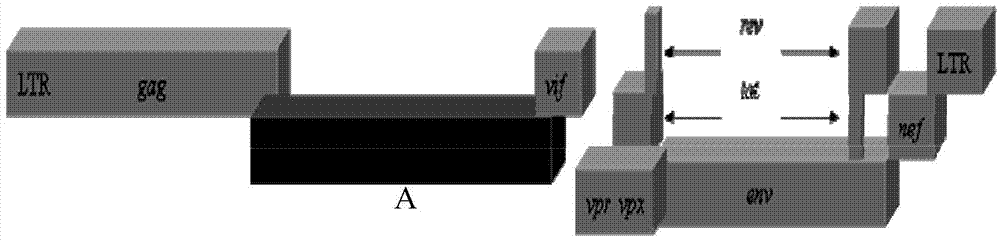
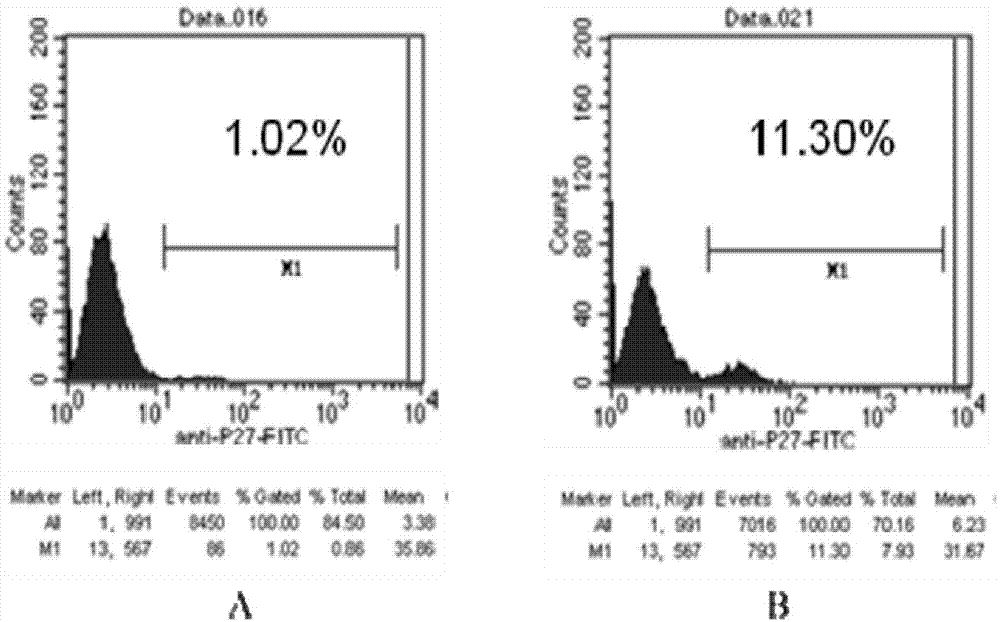
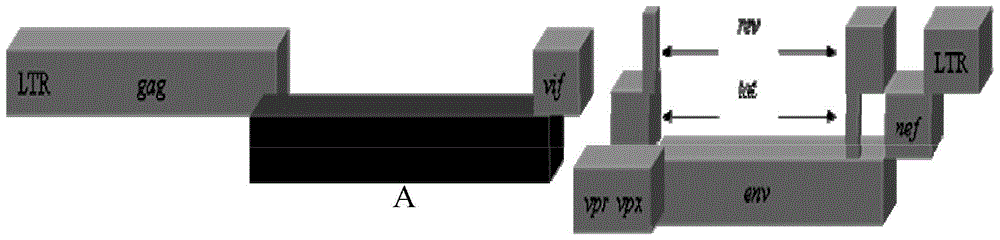
Recombinant immunodeficiency plasmid and virus and application thereof
ActiveCN104263745AEfficient replication capabilityViruses/bacteriophagesVector-based foreign material introductionFeline immunodeficiency virusImmunodeficiency virus
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a recombinant immunodeficiency plasmid and virus and application thereof. The immunodeficiency plasmid comprises LTR, gag gene, nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID No.1, vif gene, vpr gene, vpx gene, tat gene, rev gene, env gene and nef gene. The nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1 is introduced to the pathogenic SIVmac239 full-length plasmid frame to construct the immunodeficiency plasmid comprising a plurality of drug target spots, and packaging is performed in the 293T cell to generate immunodeficiency virus. The virus has the capacity for infecting target cells and the capacity of efficient replication, and is applicable to researching human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in-vivo infection process, pathogeny characteristic, pathogenesis and immunoreaction and screening anti-HIV drugs and anti-HIV drug application strategies.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of castanapetmine in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs
The invention discloses application of castanapetmine in preparation of anti-AIDS drugs. By virtue of an in vitro cytotoxicity test and an HIV in vitro inhibit assay, anti-HIV effects of the chestnut seed spectabiline are observed, and the results indicate that the c castanapetmine has a certain inhibiting effect for HIV-1 standard strain, clinical strain and pseudovirus, has activity for inhibiting HIV-1 virus replication. The castanapetmine and the medically acceptable auxiliaries are prepared into an anti-HIV drug, wherein a dosage form of the drug is one of injection, capsule, tablet, granule, pill, mixture and oral liquid.
Owner:NANJING ZELANG MEDICAL TECH
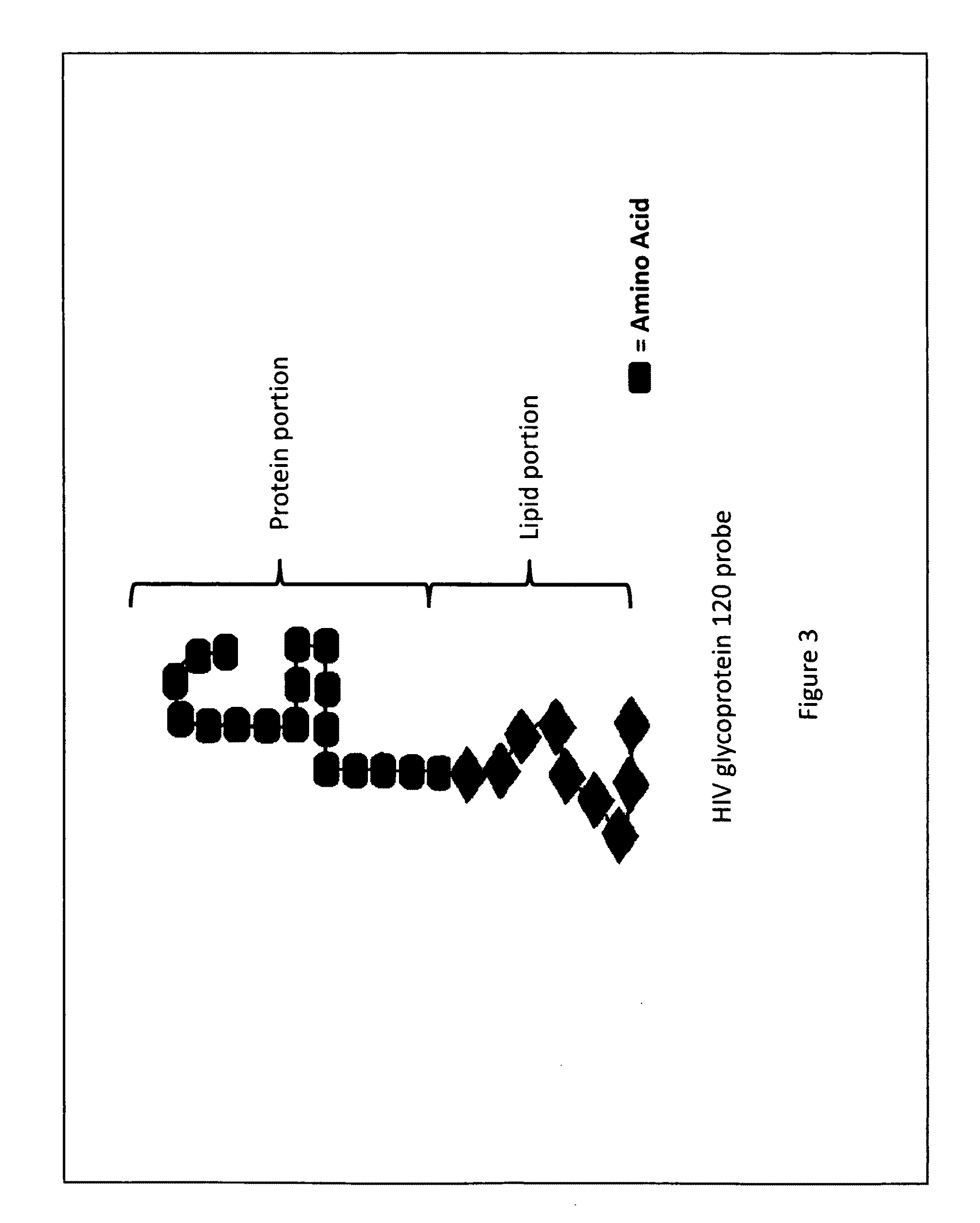
Vaccine comprised specifically of protein subunits of human immunodeficiency virus's glycoprotein 120 probe to prevent and treat an infection caused by the human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS20090220542A1Safe and practical and effective vaccinePractical, convenient and safeViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsImmunodeficiency virusHuman immunodeficiency
The human immunodeficiency virus poses a significant threat to the health and well being of the world's population. Current strategies utilized to eradicate this deadly pathogen have not been effective. A vaccine comprised solely of protein subunits of the glycoprotein 120 probe as the active ingredient, can be effective in stimulating an individual's immune system to repel an HIV infection. The protein subunit of the glycoprotein 120 probe extends from the surface of HIV and is the unique identifier of an HIV virion. When protein subunits of HIV's glycoprotein probe are exclusively presented to the immune system, the antibodies generated will neutralize the glycoprotein 120 probes located on the surface of HIV virions, such that the virus's virions then are incapable of engaging a T-Helper cell and thus the infectious threat posed by HIV is averted.
Owner:SCHEIBER LANE BERNARD +1
Application of castanospermine in preparation of anti-AIDs drug
InactiveCN104188965AReduce energy consumptionLarge amount of separationOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsCastanospermineOral solutions
The invention discloses an application of castanospermine in the preparation of an anti-AIDs (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) drug. The AIDs virus resisting effect of the castanospermine is observed through in-vitro cytotoxicity tests and HIV virus in-vitro inhibiting tests. The result shows that the castanospermine has certain inhibiting effect on HIV-1 standard strains, clinic strains and pseudoviruses and has the activity of inhibiting HIV-1 virus replication. The anti-AIDs drug is jointly prepared from the castanospermine and a medicinal acceptable auxiliary material. The form of the drug can be an injection, a capsule, a tablet, a granule, a pill, a mixture or an oral solution.
Owner:NANJING ZELANG MEDICAL TECH
Phenolic glycosides composition of starwort undersaturation polyoses and antiviral application method of preparing the same
The invention relates to a kind of natural medicine of broad spectrum antibiotic. At present, the broad spectrum antibiotic medicine with high effect and safety is at shortage all round the world. The invention is intended to extract unsaturated polyoses, polyoses alcohol or phenolic compounds with the main formula weight under 4,000 and with the content of hydrosulphonyl, thioalcohol, alkene and / or alkane radicals, from plant chickweed or other chickweed plant with two resin adsorption methods or a water extraction and alcohol precipition method, especially the compound with flavonoid compound and total phenolic glycoside ingredients. Therefore, the compound in the invention can be applied to cure ADIS virus, hepatitis virus, influenza virus and parainfluenza virus comprising SARS, adenovirus, verruca acuminate virus, enterovirus, mumps virus, herpes simplex virus, herpes zoster virus and varicella. No toxic effect has been found in the application. What is more, the invention can be made into 10 sorts of formulation, disinfector and health-improving products.
Owner:朱耕新
A kind of recombinant immunodeficiency plasmid and virus and application
ActiveCN104263745BViruses/bacteriophagesVector-based foreign material introductionImmunodeficiency virusImmunodeficiency
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a recombinant immunodeficiency plasmid and virus and application thereof. The immunodeficiency plasmid comprises LTR, gag gene, nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID No.1, vif gene, vpr gene, vpx gene, tat gene, rev gene, env gene and nef gene. The nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1 is introduced to the pathogenic SIVmac239 full-length plasmid frame to construct the immunodeficiency plasmid comprising a plurality of drug target spots, and packaging is performed in the 293T cell to generate immunodeficiency virus. The virus has the capacity for infecting target cells and the capacity of efficient replication, and is applicable to researching human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in-vivo infection process, pathogeny characteristic, pathogenesis and immunoreaction and screening anti-HIV drugs and anti-HIV drug application strategies.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
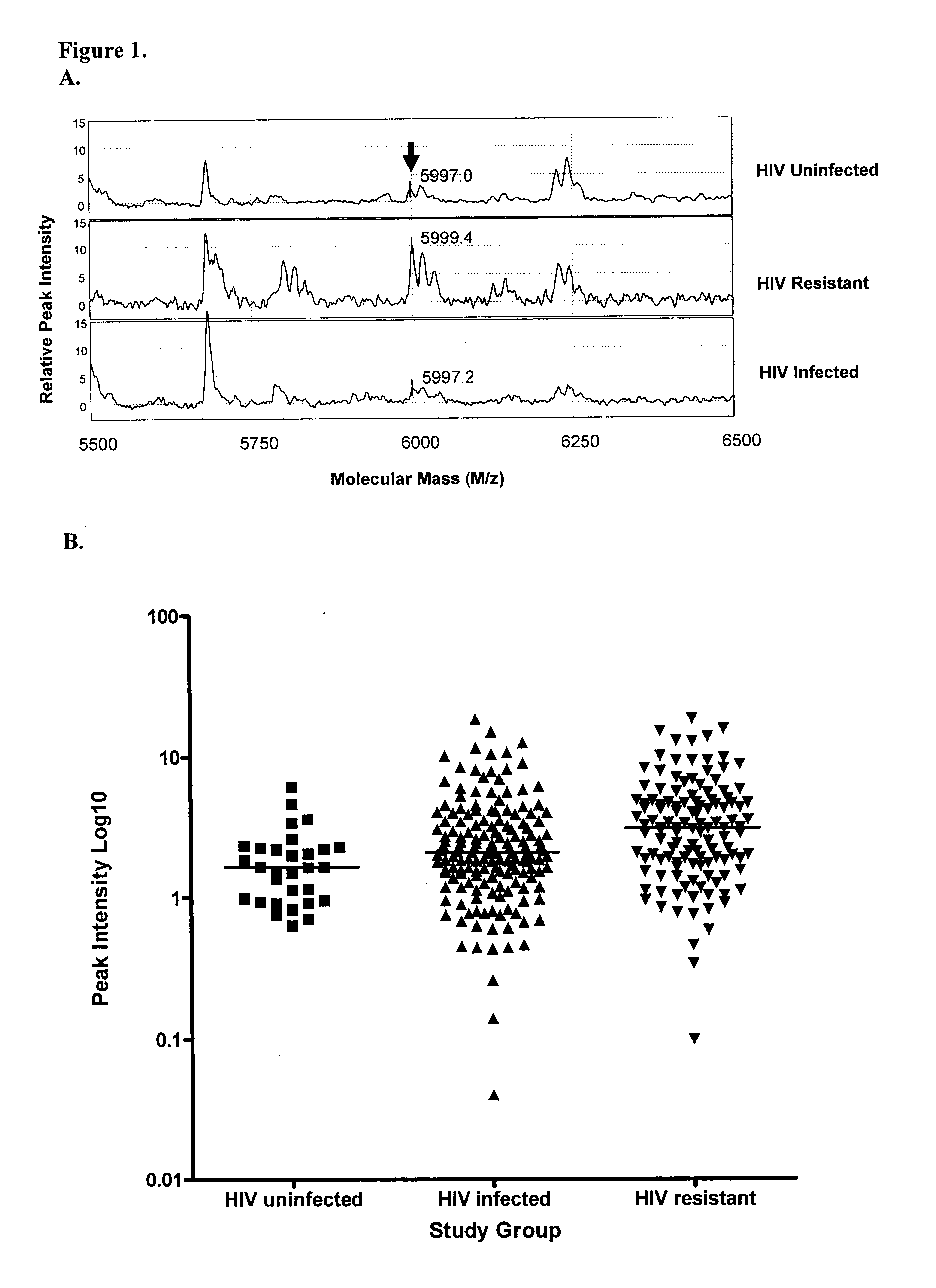
Trappin-2 (elafin) inhibits HIV
In sub-Saharan Africa, the vast majority of HIV transmission occurs through heterosexual contact, therefore, the initial site of HIV infection occurs within the genital tract. In a cohort of HIV-highly exposed sex workers we have identified a select group of individuals who epidemiologically and clinically appear to be HIV-resistant. Studies of these women indicate a strong correlation of HIV-specific immune responses within the genital tract to protection from infection. We hypothesized that a characteristic immune phenotype is present within the genital tract of the HIV-resistant women when compared to susceptible controls. To test this we used SELDI-TOF mass spectrometry to profile the proteome of genital tract secretions from the HIV-resistant women and found a number of potential biomarkers (differentially expressed proteins) which correlated to HIV-resistance. Purification and tandem mass spectrometry resulted in the identification of a particular biomarker, namely trappin-2 (elafin). This protein was tested for HIV inhibitory activity in vitro and found to be a potent inhibitor of T tropic viral infection.
Owner:BALL T BLAKE +2
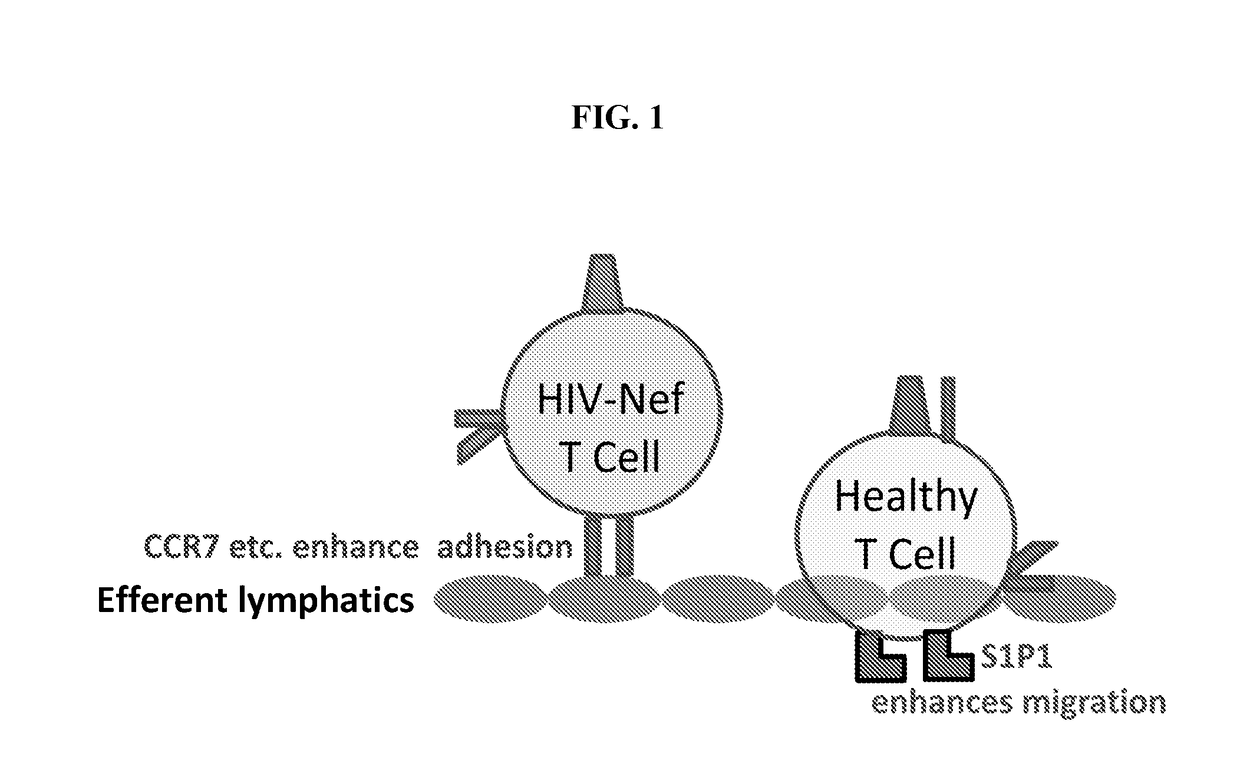
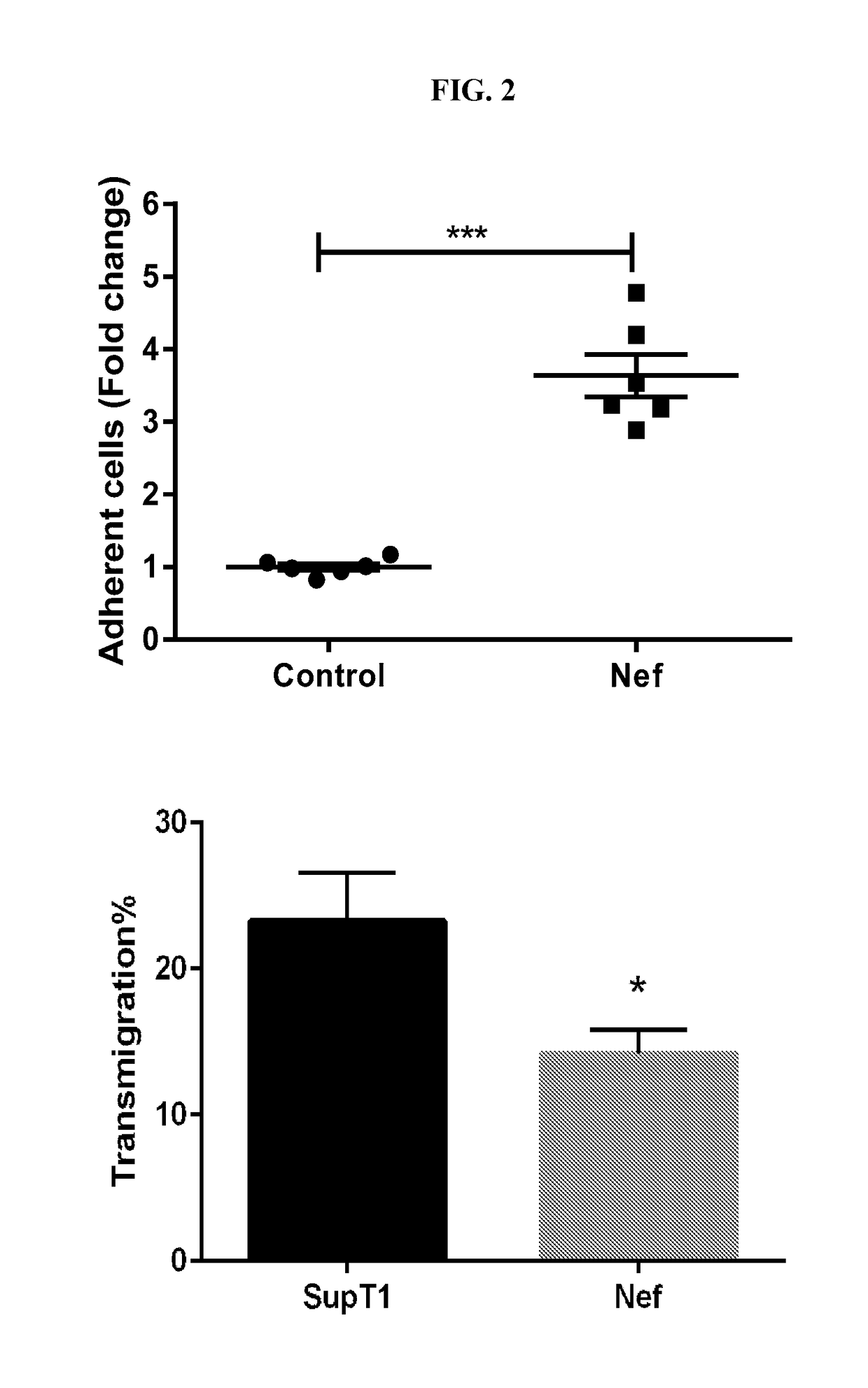
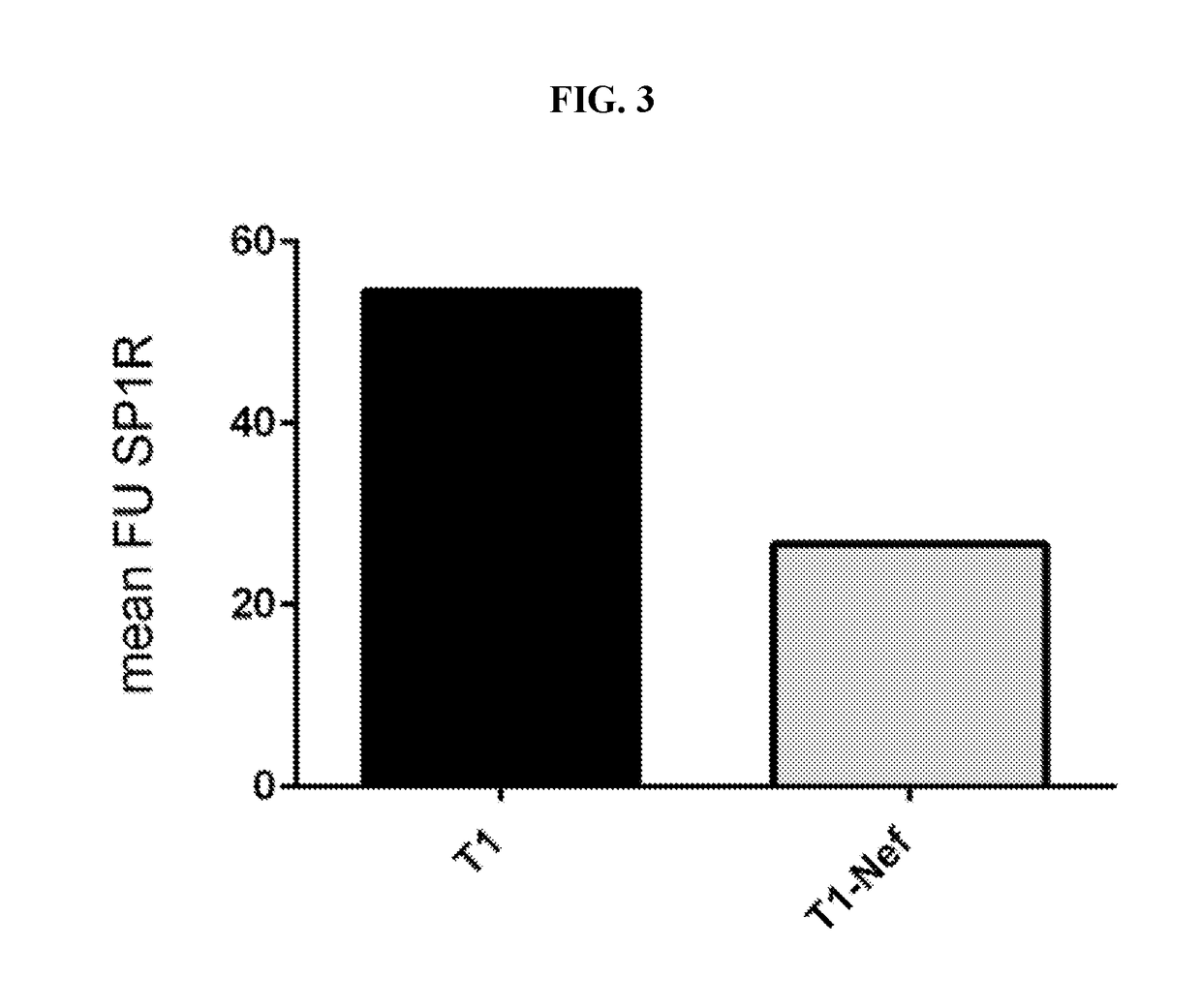
Mobilizing hiv-infected cells from lymphatic reservoirs
InactiveUS20190010217A1Reduce retentionPromote sportsImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsT cellVirus
Provided herein are methods of treating HIV infection, including retention of HIV+ T cells in viral reservoirs such as lymph nodes. More particularly, provided herein are methods in which an effective amount of a HIV Nef pathway inhibitor (e.g., anti-Nef agent) is administered to a subject in need thereof, whereby administration of the inhibitor treats HIV infection in the subject, decreases retention of HIV+ T cells in lymph nodes, and increases migration of HIV+ T cells from lymph nodes.
Owner:U S DEPT OF VETERAN AFFAIRS AS REPRESENTED BY THE TECH TRANSFER PROGRAM +1
Application of caulis flavone A in preparation of anti-HIV drug
The invention discloses application of caulis flavone A in preparation of an anti-HIV drug; the anti-HIV effect of caulis flavone A is observed through in-vitro cytotoxicity tests and in-vitro HIV inhibition tests; and the results show that caulis flavone A has a certain inhibiting effect on HIV-1 standard strains, clinical strains and pseudovirus and has the activity of inhibiting HIV-1 virus replication. Caulis flavone A is prepared into the anti-HIV drug together with pharmaceutically acceptable auxiliary materials; and the dosage form of the drug is one of injection, capsules, troches, granules, pills, mixture and oral liquid.
Owner:NANJING BIAOKE BIO TECH
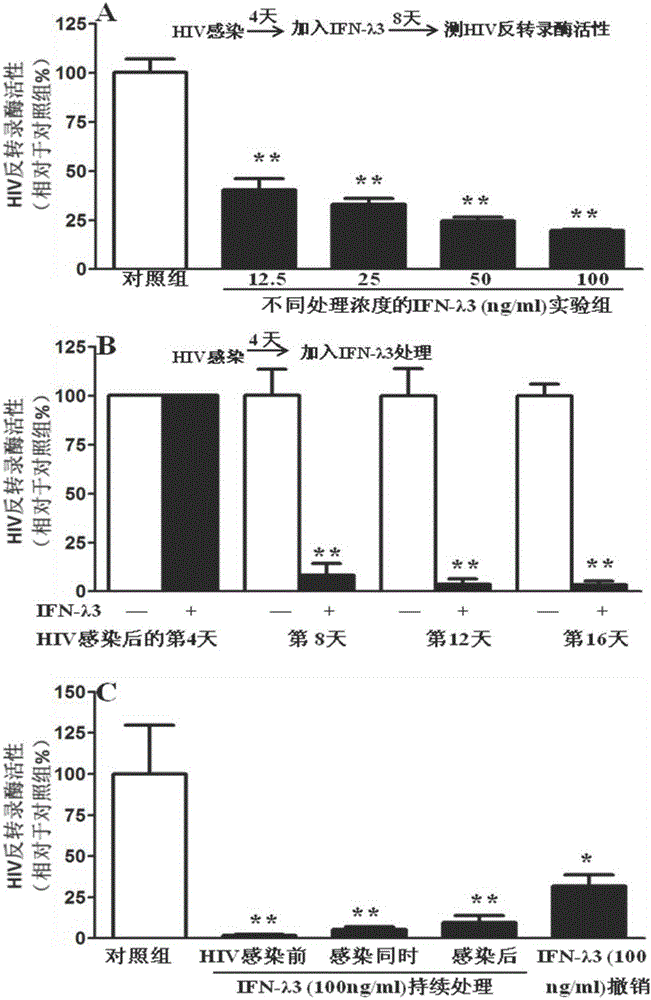
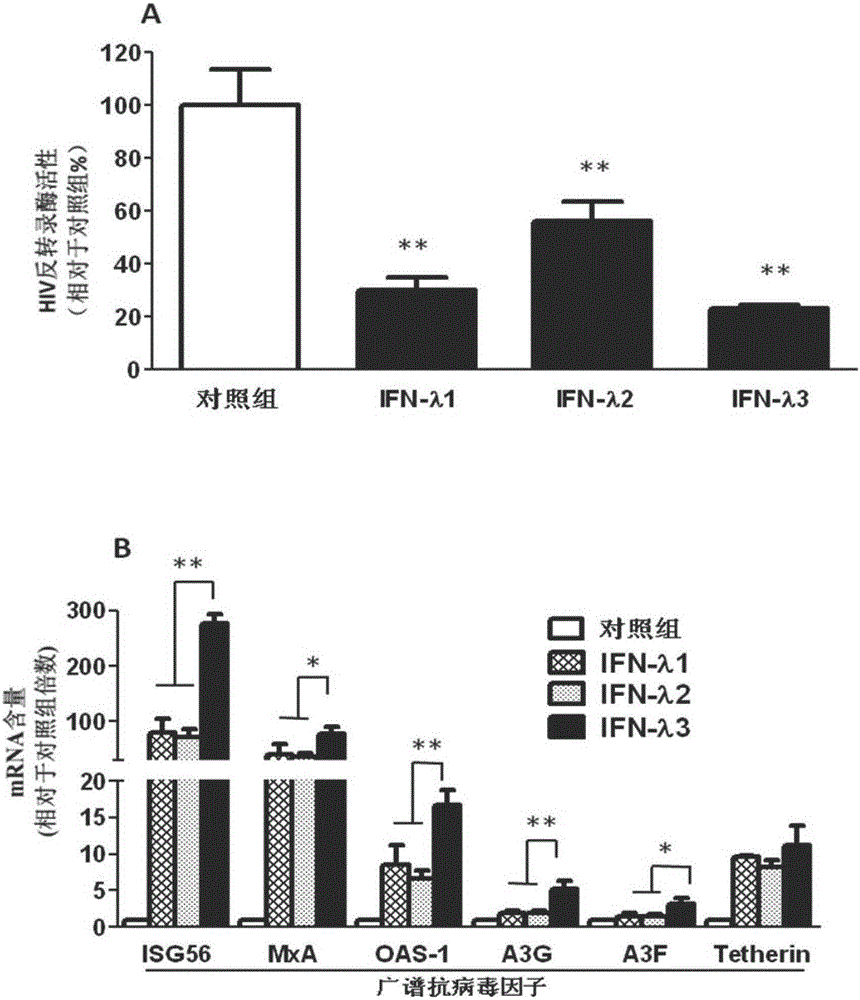
Application of IFN (Interferon)-lambda3 to preparation of medicine for preventing or treating acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
InactiveCN106729635ANo side effectsEnhanced inhibitory effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsAnti virusTherapy HIV
The invention relates to application of IFN (Interferon)-lambda3 to preparation of a medicine for preventing or treating acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy. The medicine prepared from IFN-lambda3 can be used for effectively inhibiting the activity of human immunodeficiency virus infected human macrophage, the expression of anti-virus genes is induced, and the effect of inhibiting the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is good.
Owner:武汉市疾病预防控制中心
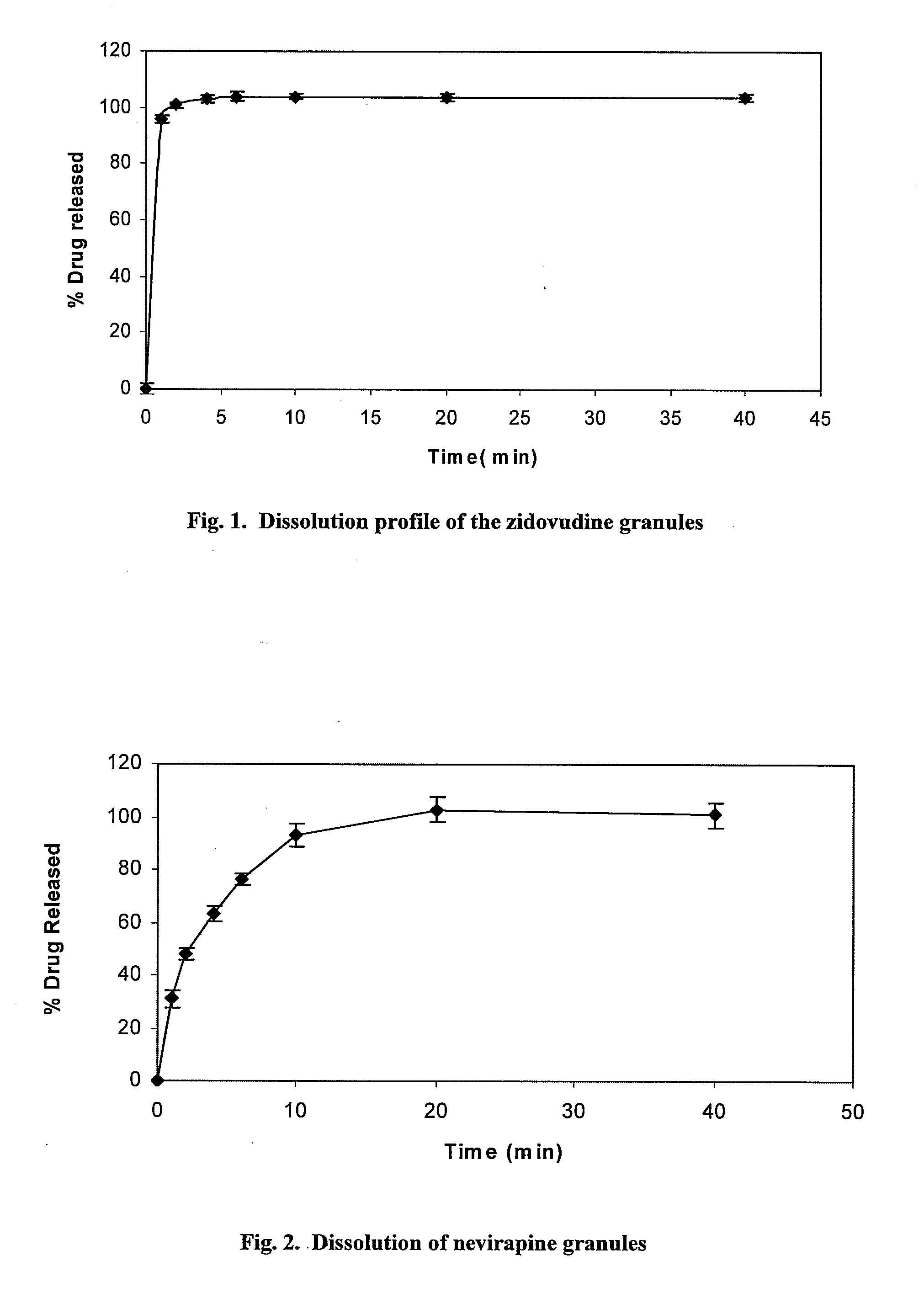
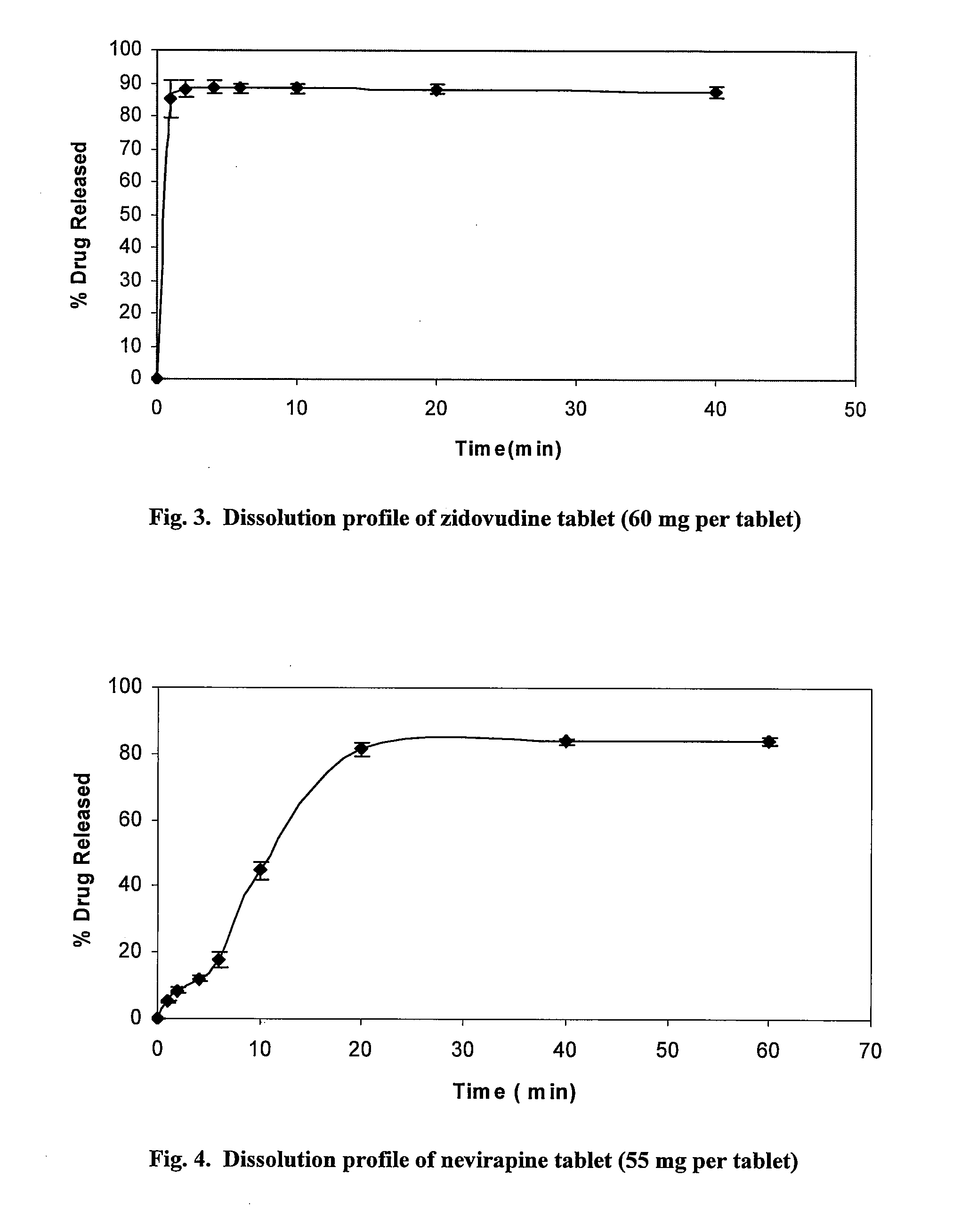
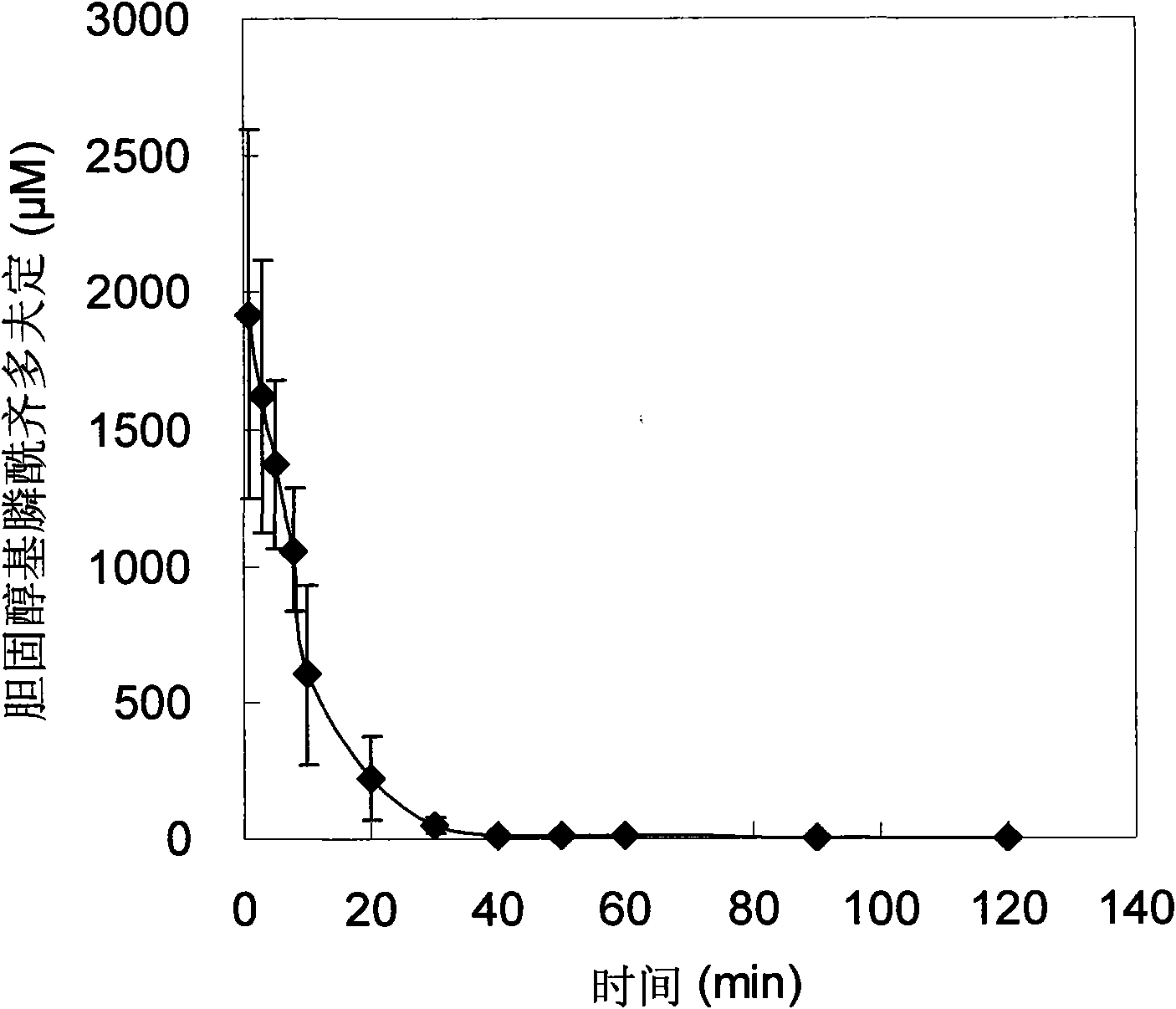
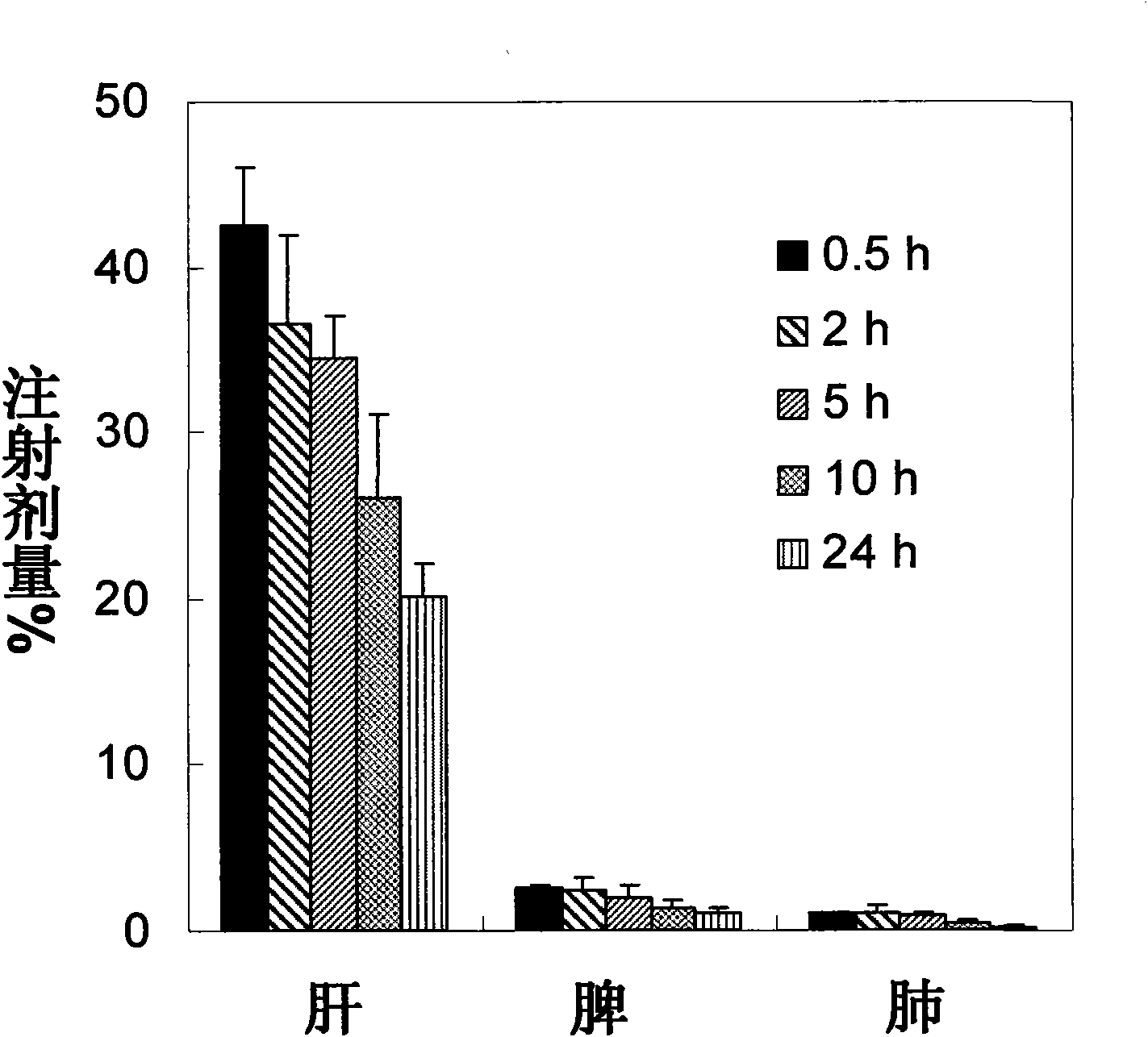
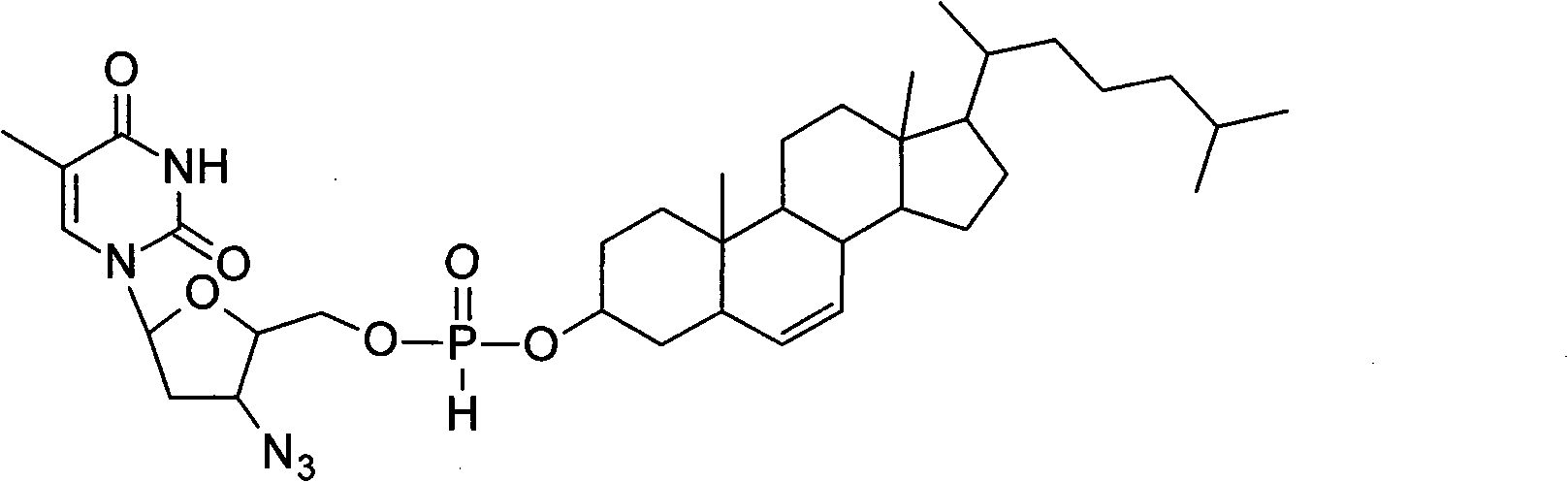
Application of zidovudine lipid derivative in medicaments for treating virus associated diseases
The invention discloses application of zidovudine lipid derivative in medicaments for treating virus associated diseases. The zidovudine lipid derivative comprises cholesteryl phosphono zidovudine and cholesteryl phosphinylidyne zidovudine which are amphipathic zidovudine lipid derivatives and can form a nano-scale dispersed self-assembly transmission system in water; the zidovudine lipid derivative has strong anti-HIV function in vitro and the efficacy of the derivative is 5 to 50 times that of zidovudine; moreover, the zidovudine lipid derivative is mainly distributed in a mononuclear macrophage system after in vivo medication and plays a role in treating virus infection within macrophage.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com